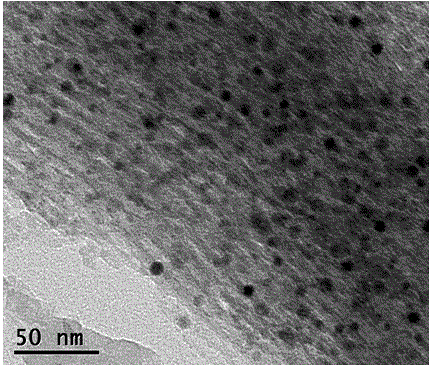
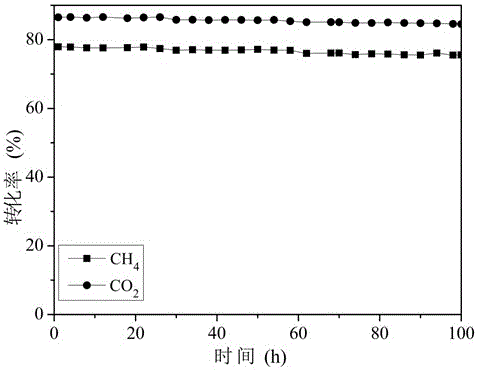
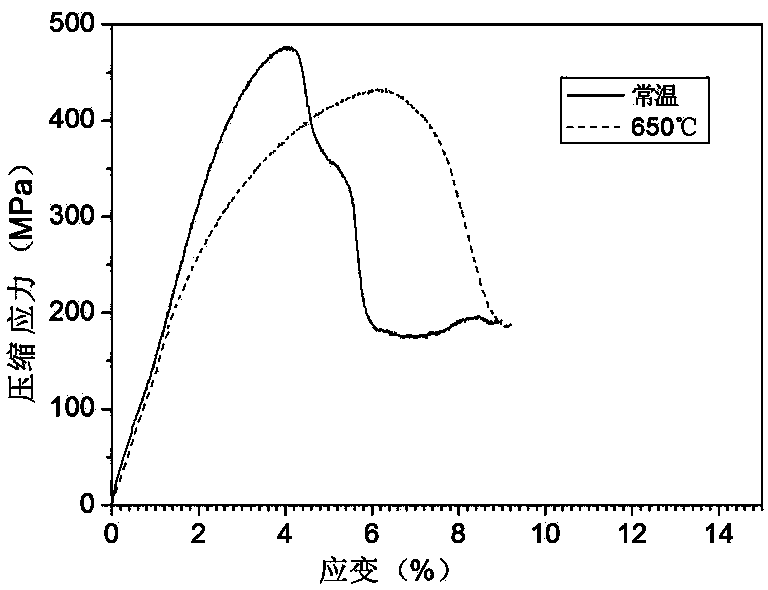
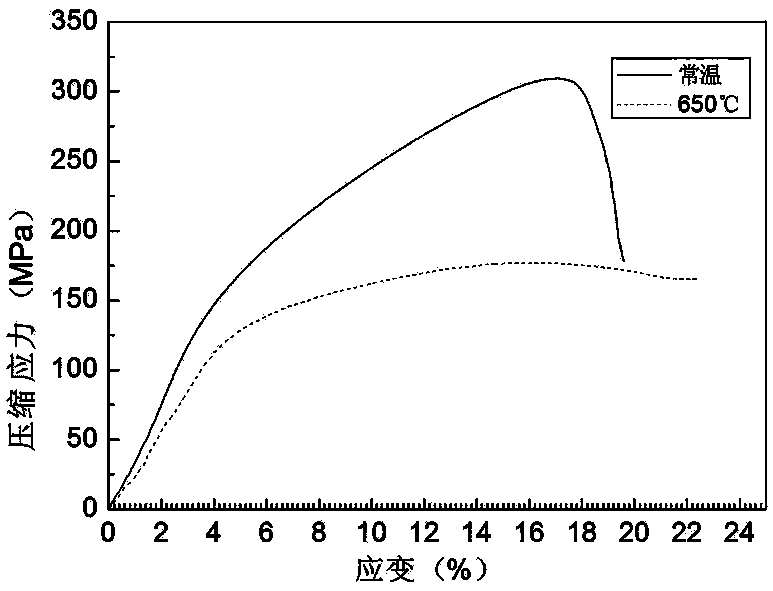
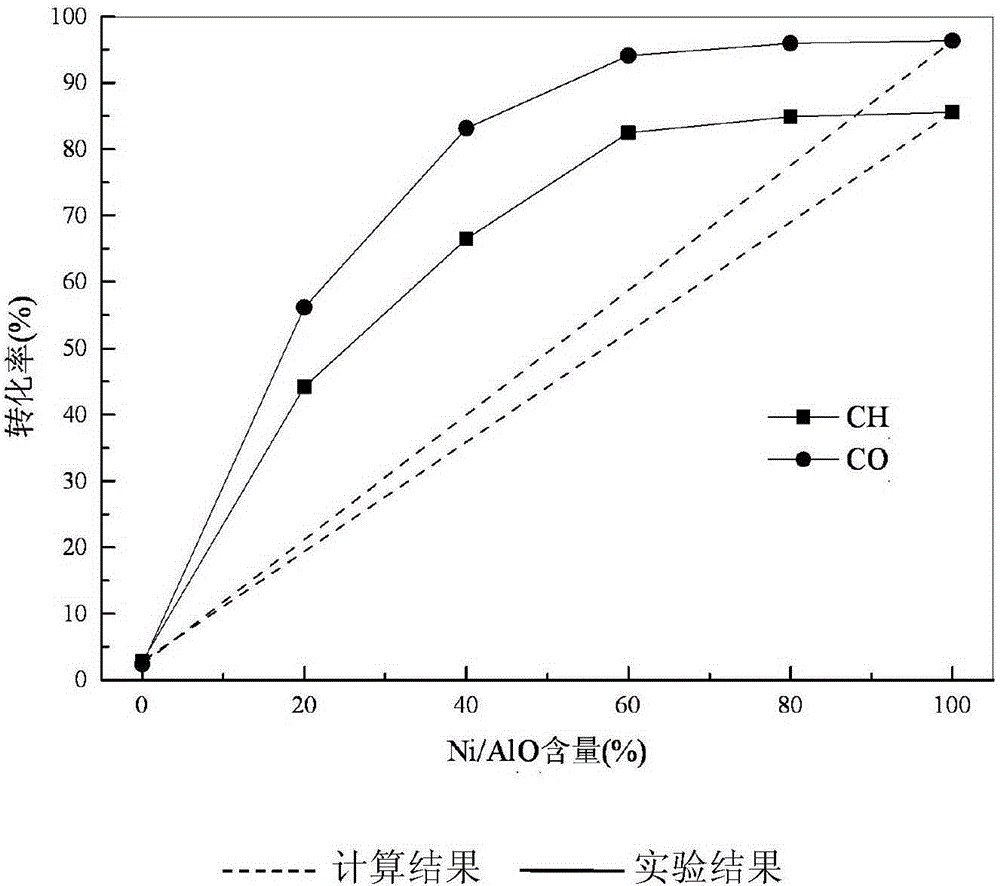
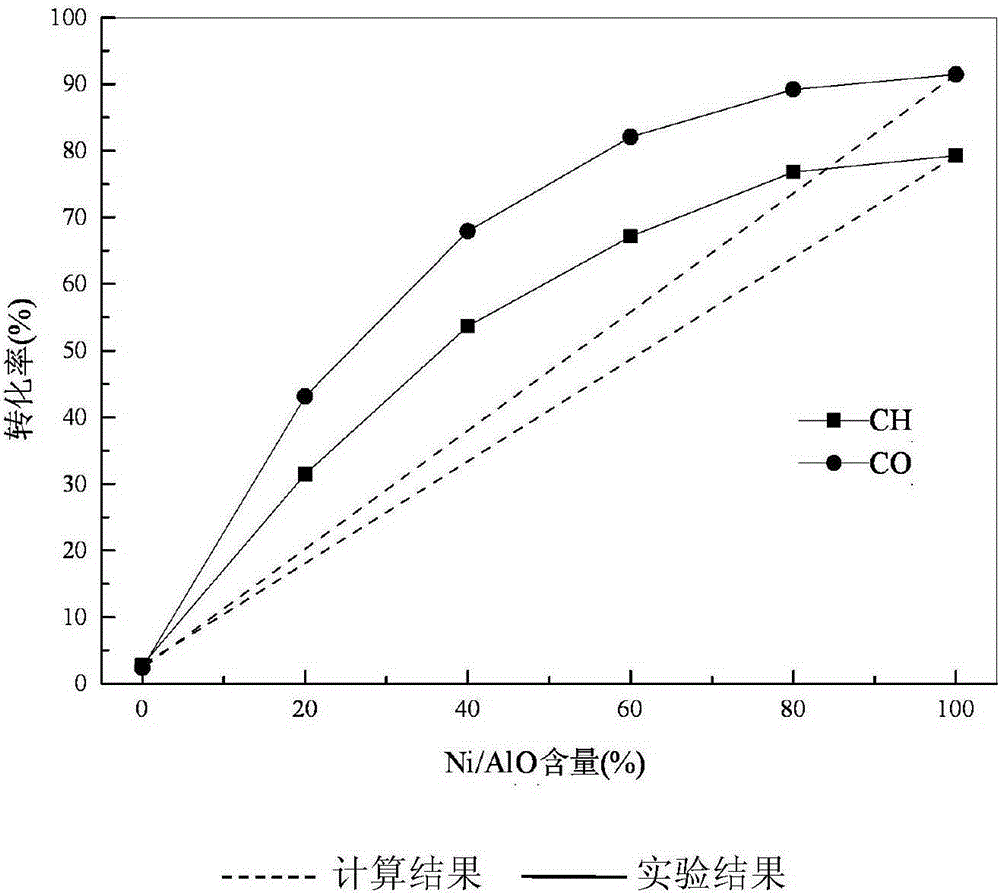
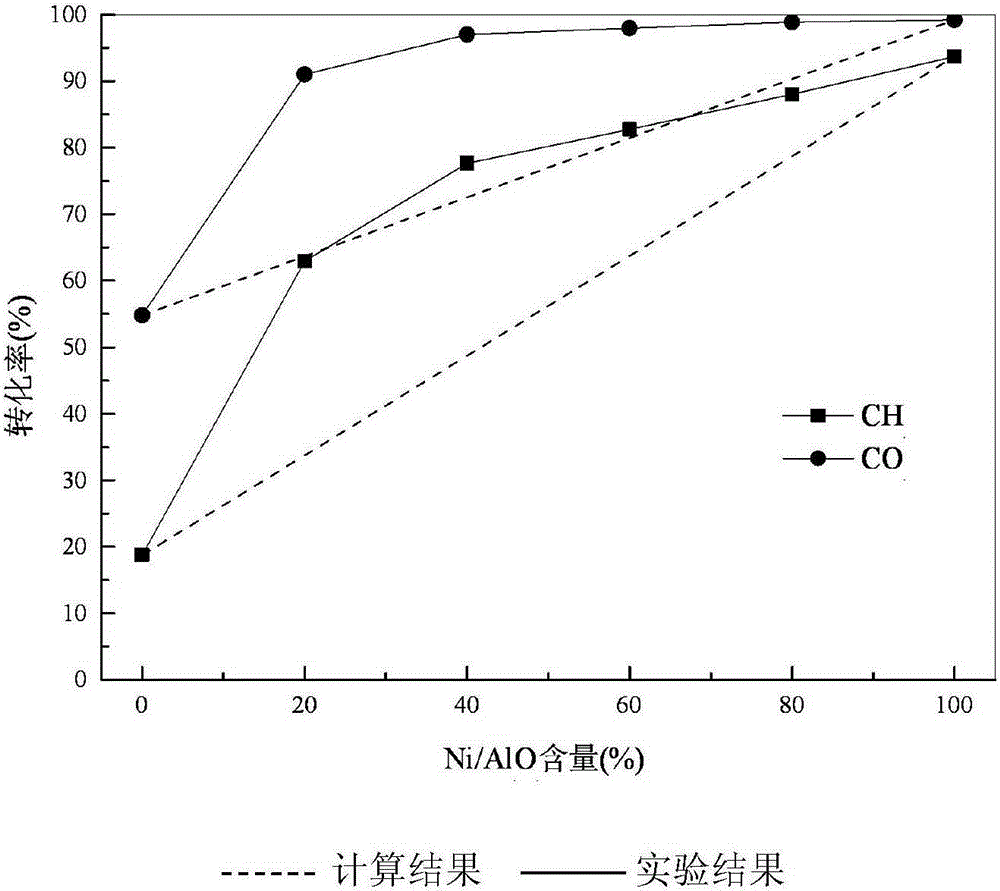
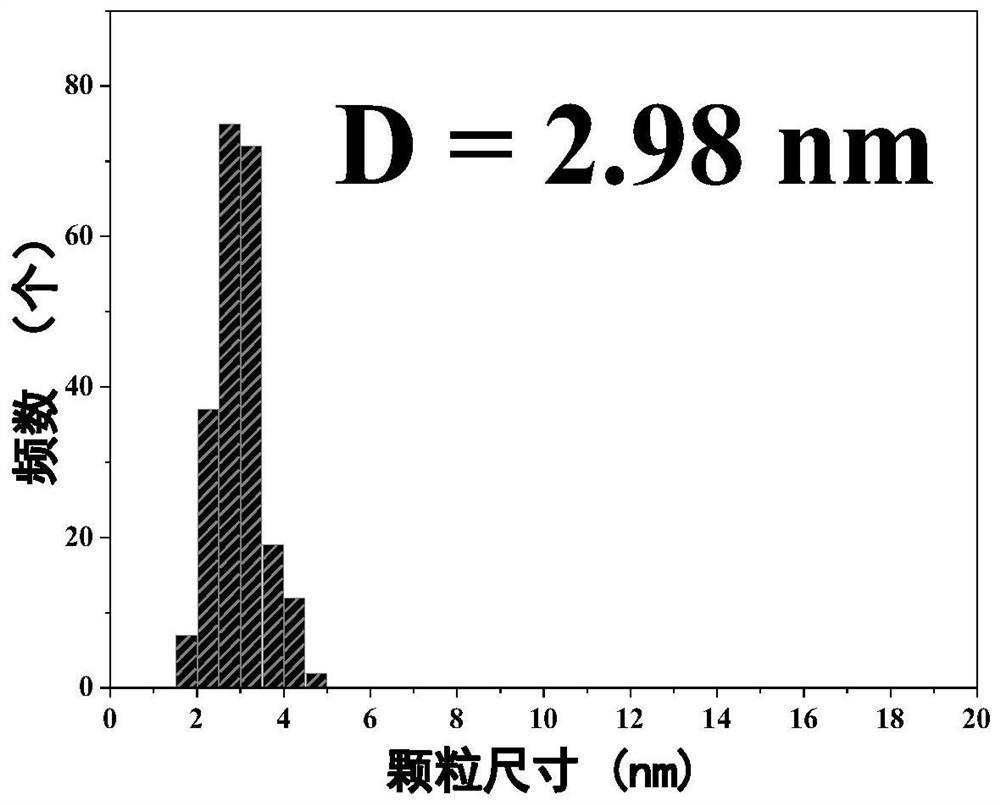
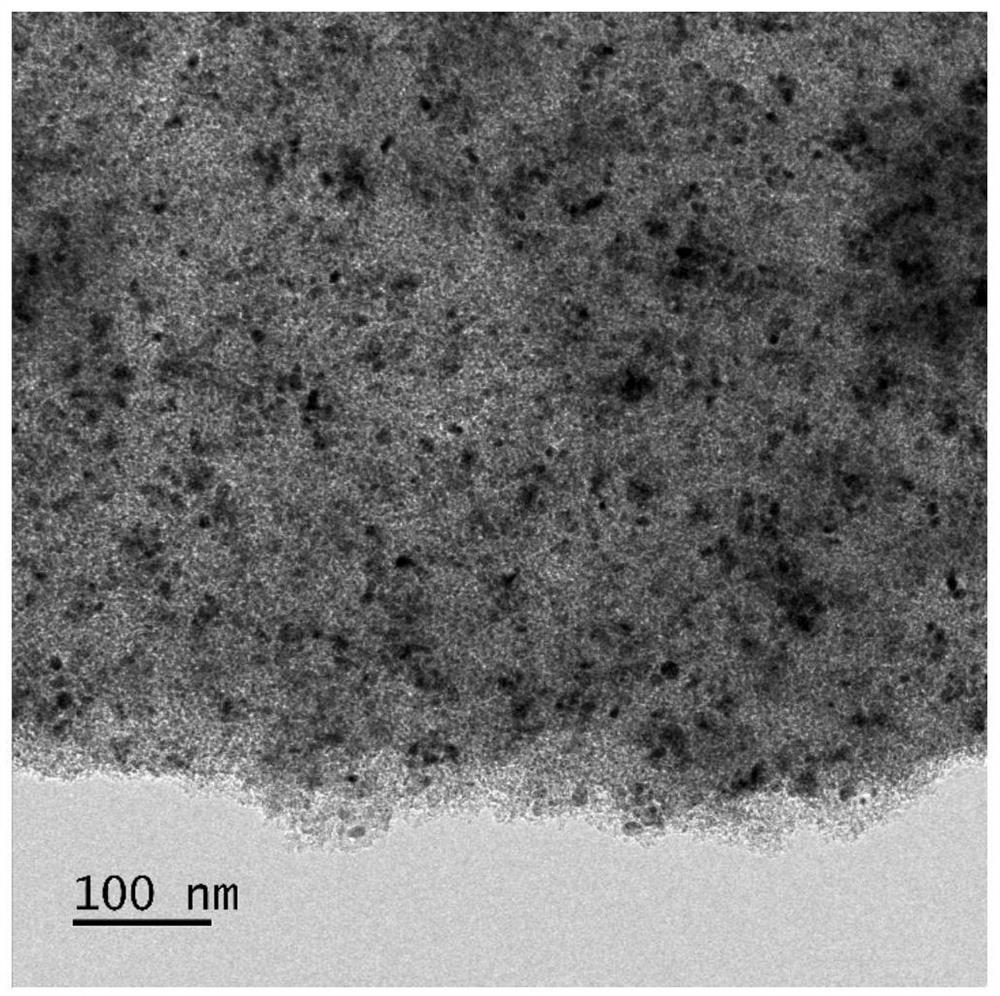
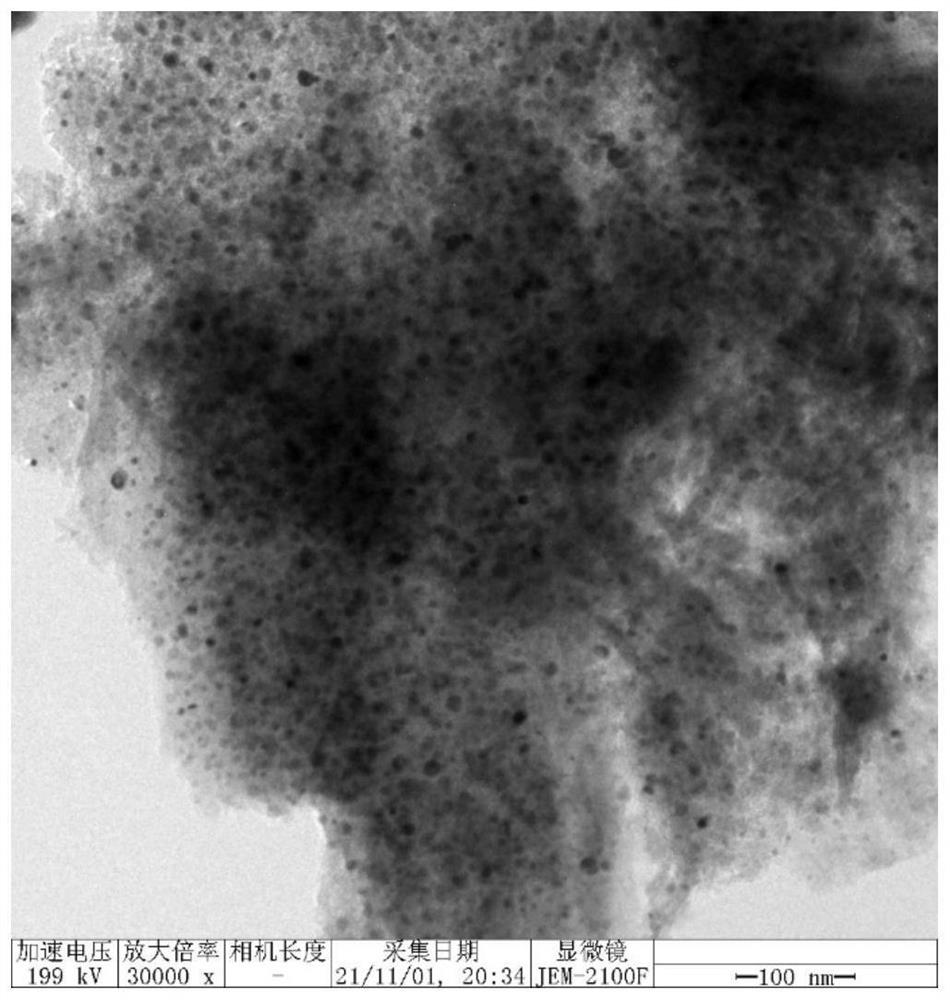
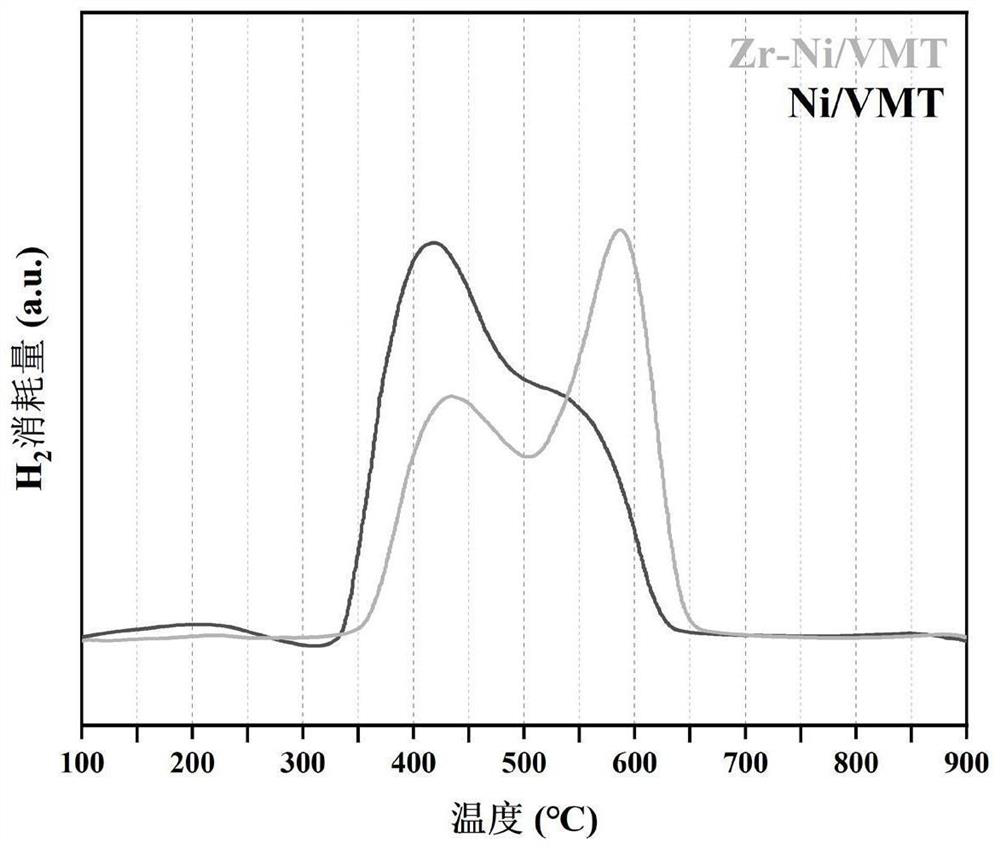
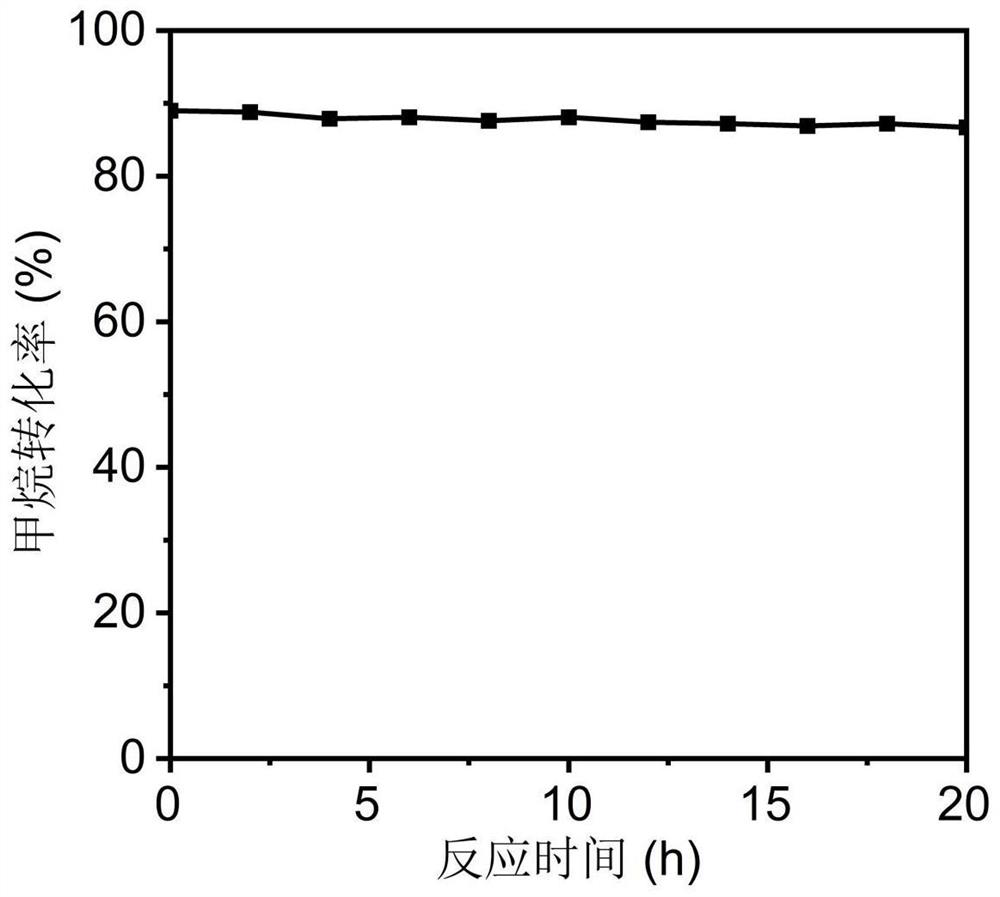
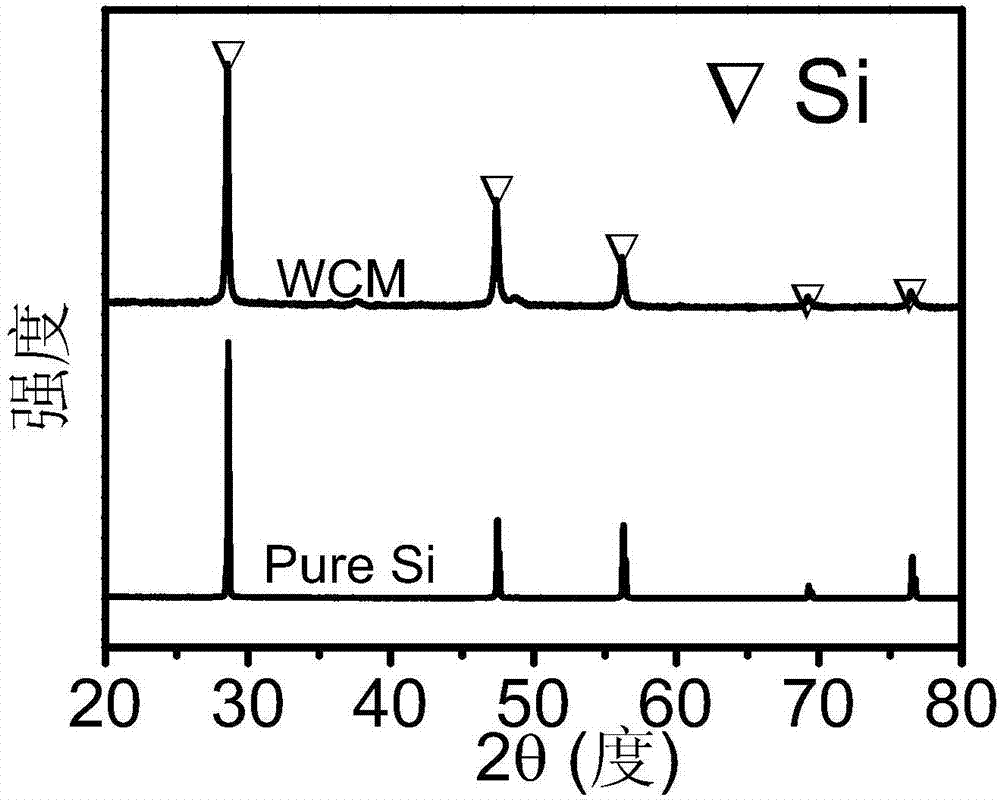
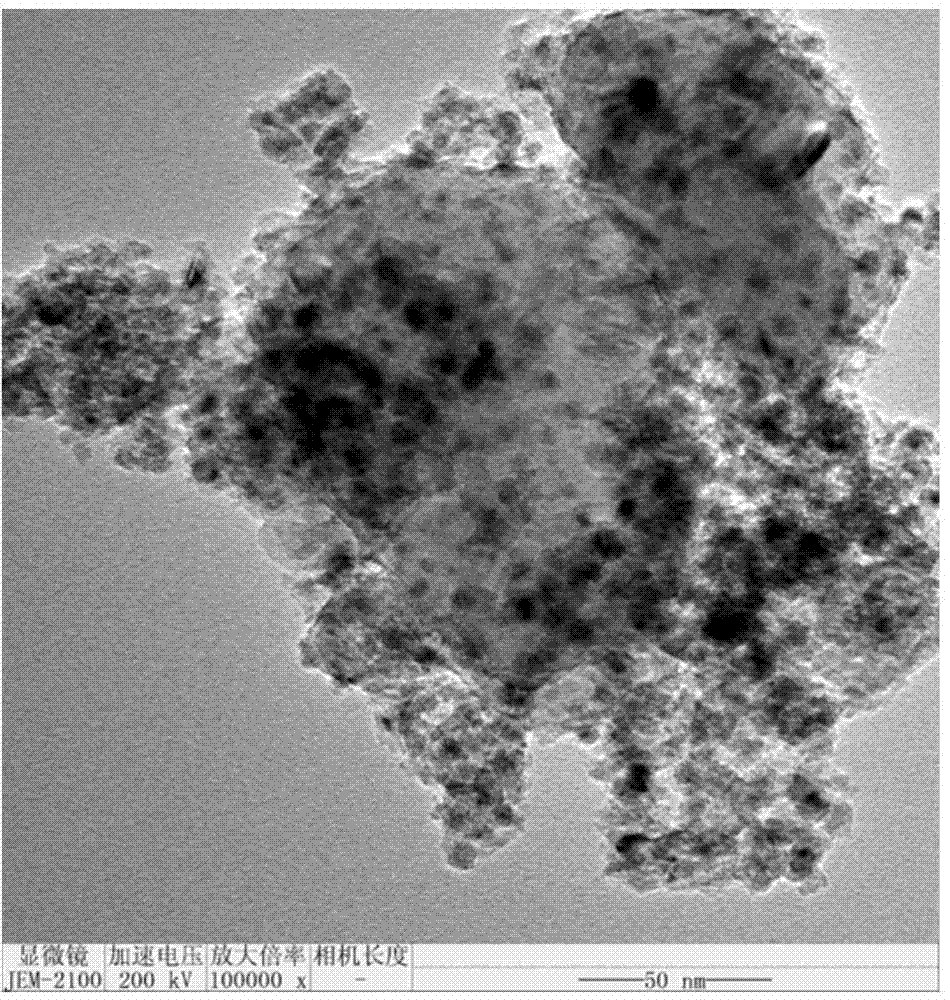
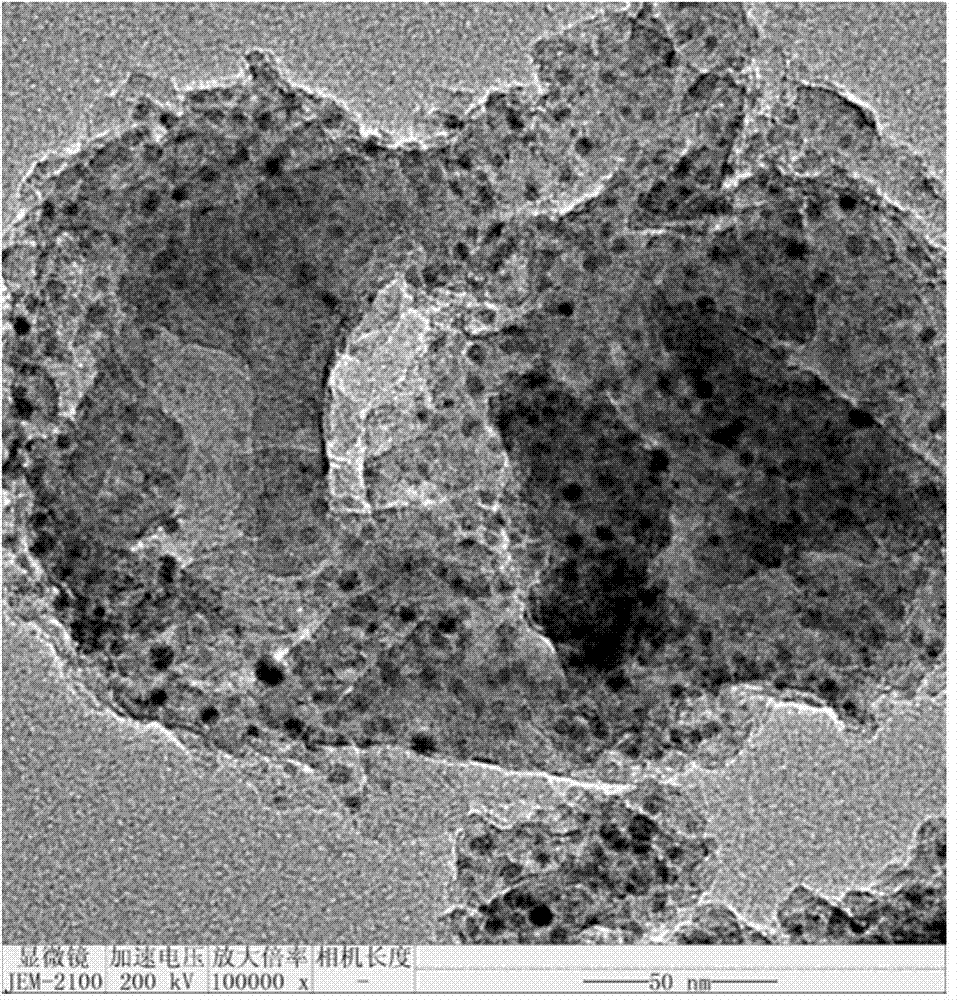
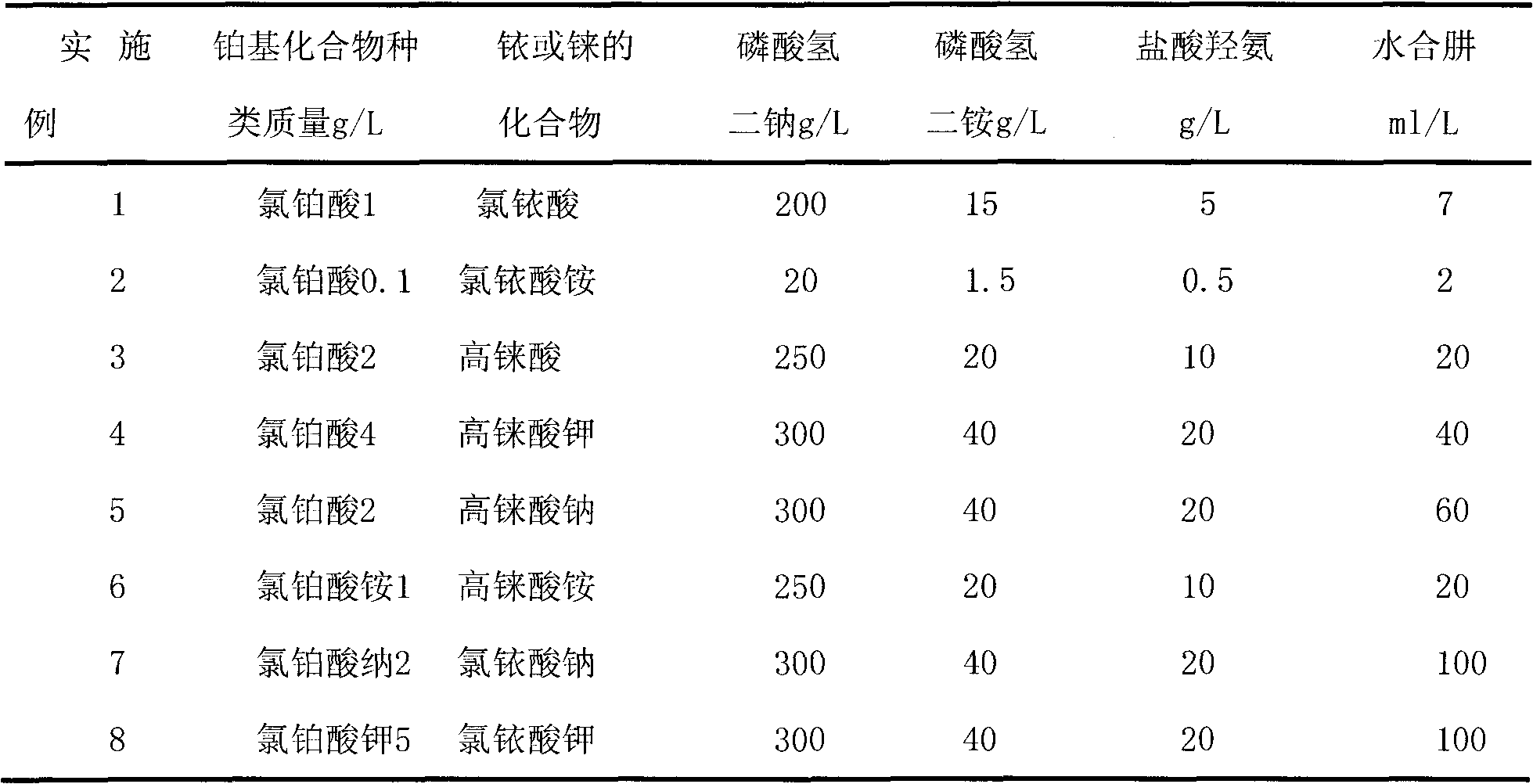
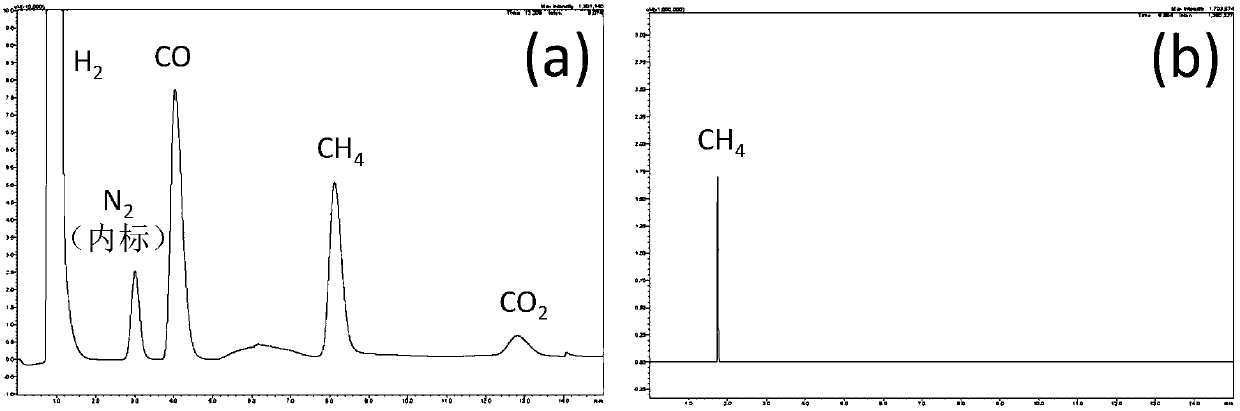
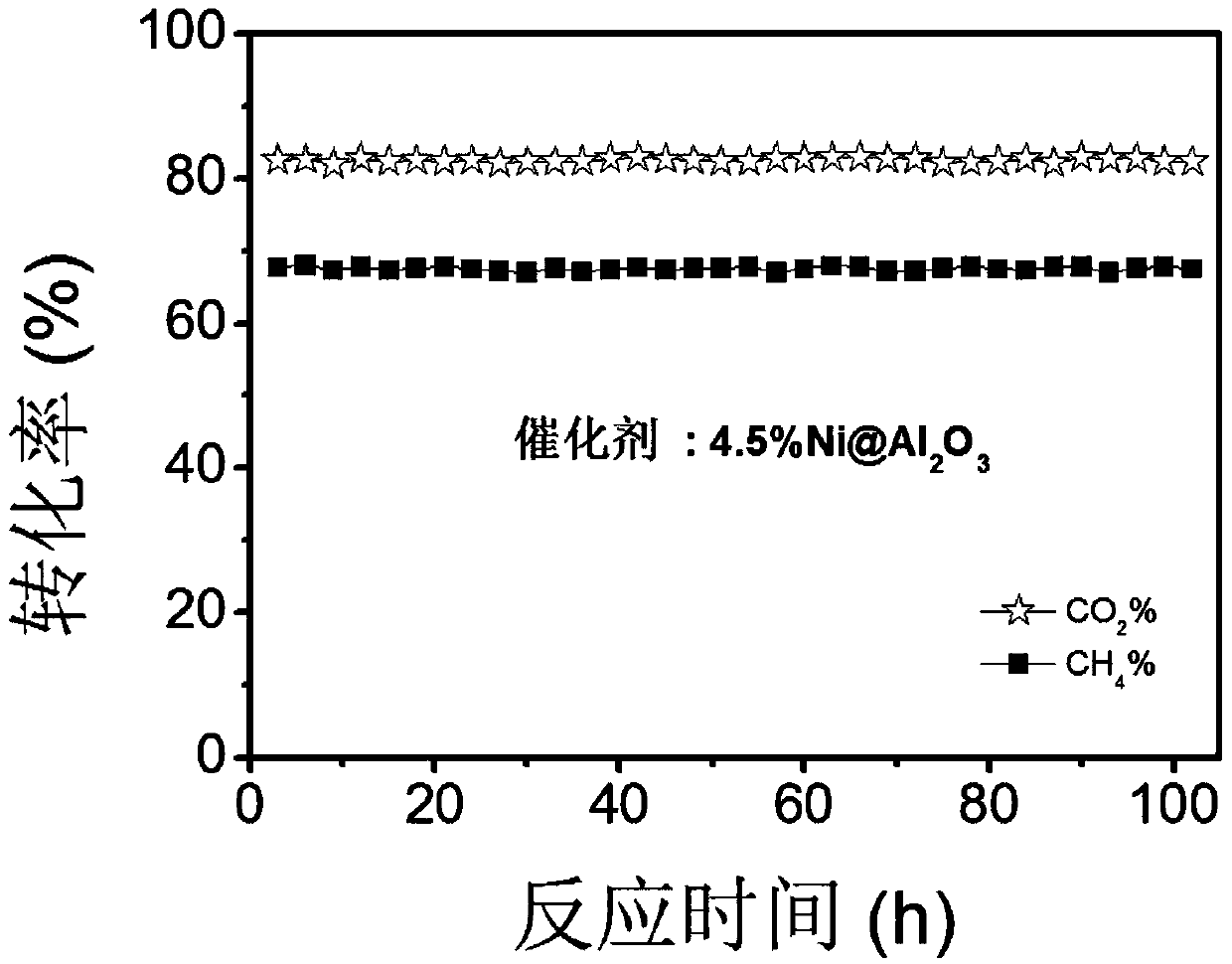
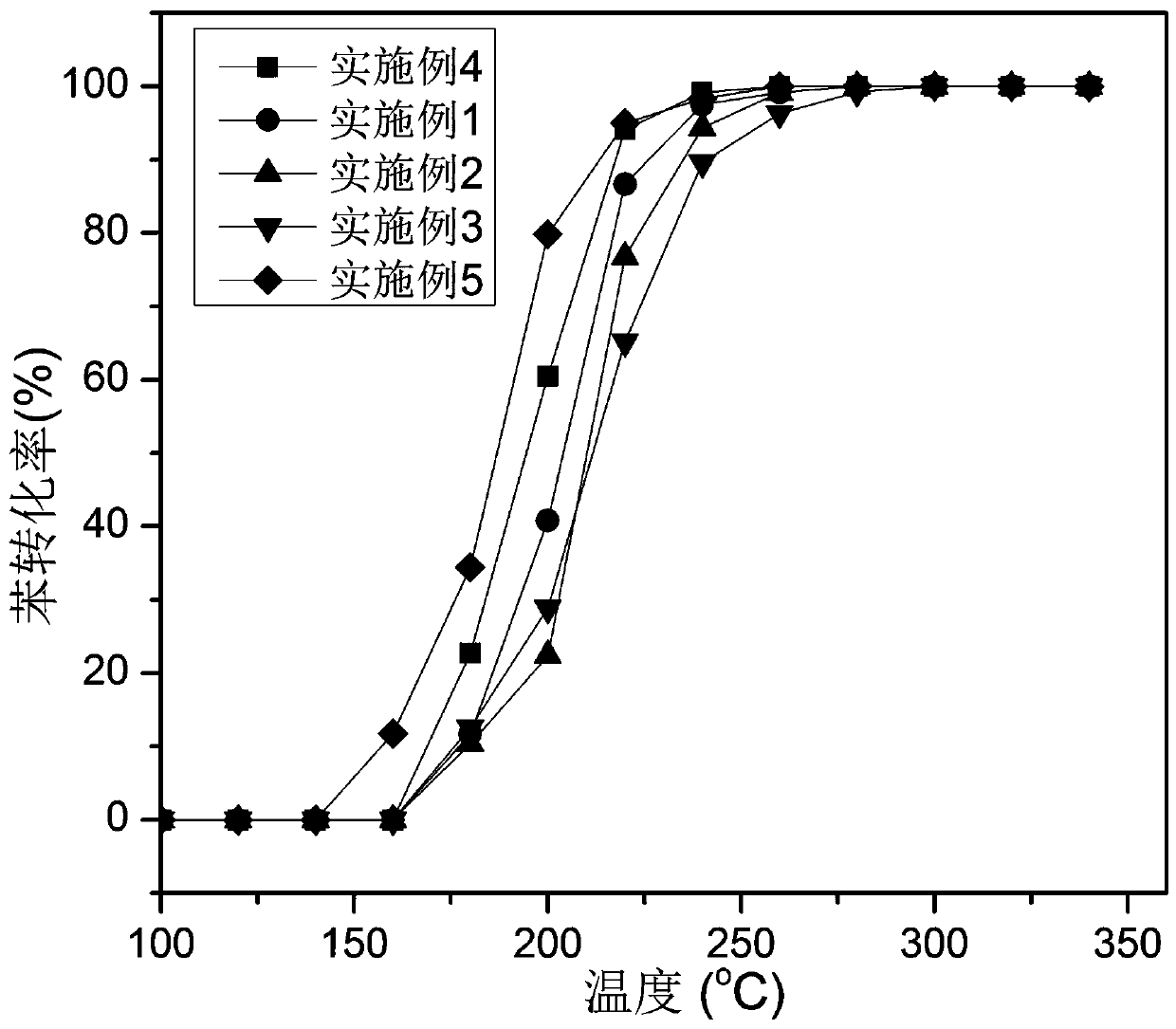
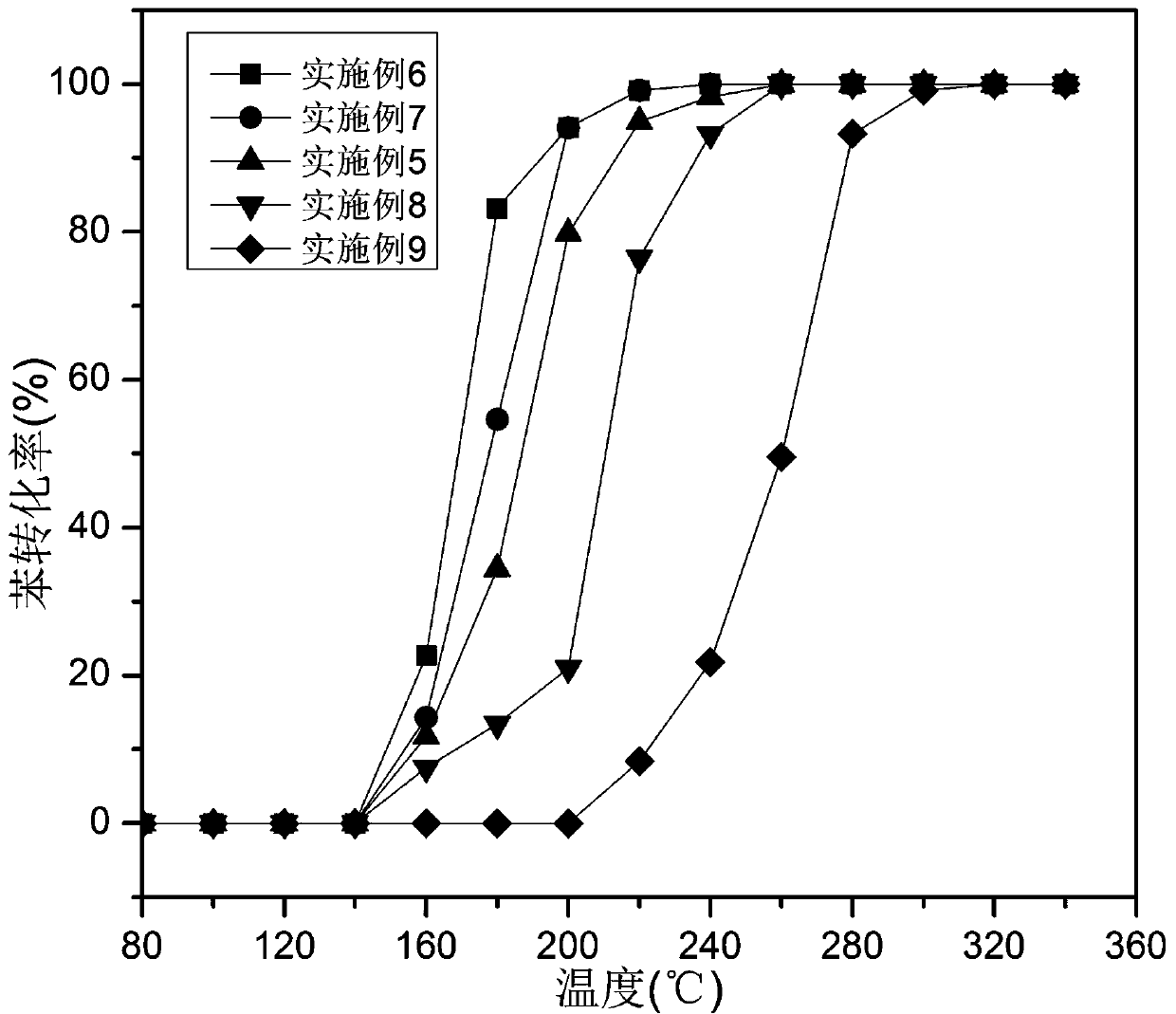
Patents
Literature
40results about How to "Improve anti-sintering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ni-based catalyst adopting core-shell structure and used in DRM (dry reforming of methane) and preparation method
InactiveCN107552054AImprove anti-sinteringImprove anti-carbon performanceHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGas compositionReaction temperature
The invention discloses a Ni-based catalyst adopting a core-shell structure and used in DRM (dry reforming of methane) and a preparation method. A Ni-MOx@SiO2 (M is Zr, La and Ce) multi-core core-shell material is prepared with a reversed-phase microemulsion method with nickel nitrate, zirconium nitrate and the like as precursor salt. The additive amount of metal oxide in the catalyst is 1%-5% ofthe weight of the catalyst and the additive amount of nickel is 5%-10% of the weight of the catalyst. The sintering resistance and carbon deposit resistance of the catalyst are remarkably enhanced dueto addition of the metal oxide. The catalyst shows high activity, high stability and extremely high carbon deposit resistance and sintering resistance under the reaction conditions of normal pressure, reaction gas composition CH4:CO2 being 1.05:1, the air speed being 1,8000 ml.gcat<-1>.h<-1> and the reaction temperature being 800 DEG C. The catalyst has the advantages of being simple to prepare,free of secondary pollution to the environment, low in cost, high in catalytic efficiency and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Biomass pyrolysis gasification multifunctional iron-based catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103394356AImprove stabilityImprove anti-sintering and anti-carbon abilityGas purification with selectively adsorptive solidsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMuffle furnacePyrolysis
A biomass pyrolysis gasification multifunctional iron-based catalyst and a preparation method thereof are disclosed. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) carrier pretreatment: placing CaO in a muffle furnace for calcining, then grinding and screening to prepare CaO carrier particles; (2) introduction of a main active component: mixing the CaO carrier particles with a Fe(NO3)3.9H2O solution, stirring and immersing, drying, calcining and grinding; (3) introduction of an auxiliary active component: mixing the sample prepared by the step (2) with a Ce(NO3)3.6H2O solution, stirring, immersing, drying, placing the obtained sample in a muffle furnace for calcining, placing the calcined sample in a dryer to cool to room temperature, grinding, then mixing the obtained powder with a Zr(NO3)4.5H2O solution, stirring, immersing, drying, then placing the sample in a muffle furnace for calcining, then placing the calcined sample in a dryer to cool to room temperature, and then grinding; and (4) shaping of the catalyst: performing shaping on the obtained catalyst, and screening to obtain the catalyst finished product.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Carried by CeO2 based composite oxides coated carrier Pd catalyst, its prepn. method
InactiveCN1903428AStrong combinationNot easy to fall offDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationCordieriteComposite oxide
A catalyst for catalytic combustion features that a coated composite oxide layer based on CeO2 is carried by cellular ceramic carrier. It contains the cellular cordierite ceramic matrix, coated composite oxide layer based on CeO2, and Pd. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Catalyst for producing synthesis gas by catalytic partial oxidation of methane and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101279271AHigh selectivityReduce manufacturing costHydrogenCarbon monoxideNickel catalystPartial oxidation
The present invention provides a catalyst for preparing a compound gas by methane catalyzing partial oxidation and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst relates to a loading type catalyst which is added with a cerium oxide-based compound accessory ingredient and a noble metal ruthenium; wherein, the content of nickel is 5 to 15 percent (weight percent, the same below), the content of the cerium oxide-based compound accessory ingredient is 0.1 to 5 percent, the content of ruthenium is 0.1 to 0.2 and the rest is the content of a carrier. The catalyst has excellent reaction property; the methane converting rate as well as the selectivity of CO and H2 is all higher than 95 percent; besides, the stability is excellent.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Electrocatalyst for proton exchange film fuel cell
ActiveCN1990101AImprove stabilityImprove electrocatalytic activityCatalyst carriersCell electrodesConductive materialsTitanium oxide
An electric catalyst used for proton exchange membrane fuel cells, active component is Pt or PtRu, auxiliary component is titanium oxide; the atom ratio of platinum and titanium is 0.01-99, the atom ratio of platinum and ruthenium is 0.01-99, the particle size of the active component is 1-20nm. The active component can be impregnated in the titanium oxide modified porous conductive material, gained support-type electric catalyst, which contained activity group sharing percentage for the quality of 1-99%, the atom ratio of platinum and titanium is 0.01-99. Active components can be added as a percentage of 0-99% of the auxiliary components, become a multi-component catalysts; adding auxiliary components was transition metal or a transition metal oxides or several. Preparation methods can be used colloidal law or impregnation - Reduction Act. The invention of the electric catalyst can be used in proton exchange membrane fuel cells.
Owner:中科军联(张家港)新能源科技有限公司
Hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106000405AIncreased diffusion and mass transfer ratesGood anti-sintering and anti-coking propertiesHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationChemistryCarbon dioxide
The invention discloses a hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst, a preparation method and application of the catalyst to a carbon dioxide methane reforming reaction. The hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst is prepared from a carrier and an active ingredient dispersed on the carrier. The catalyst is characterized in that the carrier is selected from at least one of inorganic oxides and contains macropore with the average pore size larger than 50 nm and mesopore with the average pore size of 1 nm-50 nm, and nickel is adopted as the active ingredient. The hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst is used for the carbon dioxide methane reforming reaction, has the excellent sintering resistance and carbon deposition resistance and has the important realistic significance on promoting industrialization of the carbon dioxide methane reforming reaction.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for rapidly preparing highly-dispersed nickel-based catalyst for methane reforming with carbon dioxide
InactiveCN106000444ASimple preparation processShorten evaporation timeHydrogenMolecular sieve catalystsNickel catalystHigh carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method for rapidly preparing a highly-dispersed nickel-based catalyst for methane reforming with carbon dioxide. A high-temperature-resistant mesoporous material with a large specific surface area and ordered mesoporous passages is adopted as a carrier of the catalyst, a nickel precursor salt and the mesoporous material are ground and stirred to uniformly disperse the nickel precursor salt on the surface of the mesoporous material carrier which is not de-molded by adopting a solid-state grinding method, and during drying, the nickel precursor salt enters the passages to obtain a nickel catalyst with highly-dispersed active ingredients and high carbon deposition resistance and sintering resistance by calcination and H2 reduction. The preparation method has the advantages of simple preparation process, high catalysis efficiency, energy saving (calcination is not required during preparation of the carrier), uniform distribution of the active ingredients and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy and a preparation method thereof. The porous alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 25%-35% of Ni, 10%-15% of Al, 2%-4% of Ce and the balance of Cu. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) heating Cu, Ni, Al and Ce to a molten state so as to obtain Cu-Ni-Al-Ce alloy liquid; (2) carrying out atomization and pulverization on the alloy liquid to obtain Cu-Ni-Al-Ce atomized powder; (3) sending the atomized powder into an atmosphere sintering furnace for high-purity hydrogen gas reduction; (4) carrying out hot pressed sintering on the reduced and atomized powder, so as to obtain the Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy. The Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy disclosed by the invention has the advantages of uniform chemical components and high alloy purity, and better high-temperature compression property and high-temperature creep resistance at a relatively-high porosity. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process and low cost.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Biomass pyrolysis gasification multifunctional iron-based catalyst
ActiveCN104148081APrevent sinteringInhibit carbon depositionCoke ovensMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentRoom temperature
The invention relates to a multifunctional iron-based catalyst pyrolyzed and gasified by biomass, which comprises the following ingredients by weight: 5-15 parts of iron oxide, 8-13 parts of cerium oxide, 7-12 parts of zirconia and 60-80 parts of calcium oxide. A method for the catalyst comprises the following steps: (1)pretreating a carrier; (2) introduction of a main active component: mixing the CaO carrier particles with a Fe(NO3)3.9H2O solution, stirring and immersing, drying, calcining and grinding; (3) introduction of an auxiliary active component: mixing the sample prepared by the step (2) with a Ce(NO3)3.6H2O solution, stirring, immersing, drying, placing the obtained sample in a muffle furnace for calcining, placing the calcined sample in a dryer to cool to room temperature, grinding, then mixing the obtained powder with a Zr(NO3)4.5H2O solution, stirring, immersing, drying, then placing the sample in a muffle furnace for calcining, then placing the calcined sample in a dryer to cool to room temperature, and then grinding; and (4) shaping of the catalyst.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Ordered mesopore scheelite loaded nickel-based bio-oil reforming catalyst
InactiveCN109078640AImprove orderGood dispersionHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionActive componentActive ingredient
The invention relates to an ordered mesopore scheelite loaded nickel-based bio-oil reforming catalyst which comprises catalyst active ingredients and a catalyst carrier. The catalyst active ingredients include, by weight, 10-30wt% of Ni and the balance of mesopore scheelite catalyst carrier. The catalyst has the advantages that scheelite large in specific surface area, low in cost and easy to getis adopted as the catalyst carrier, catalytic active component is nickel, and bio-oil molecules are enabled to be cracked and chain-broken to form high-quality synthesis gas of low molecular hydrocarbon and high-content hydrogen. The catalyst is simple to prepare, high in mechanical strength and catalytic activity and reproducible, can be used for bio-oil reforming hydrogen production and can be applied to biomass direct catalytic gasification hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hydrocalumite derived cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid
ActiveCN109718785AImprove anti-sintering performanceImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAcetic acidActive component
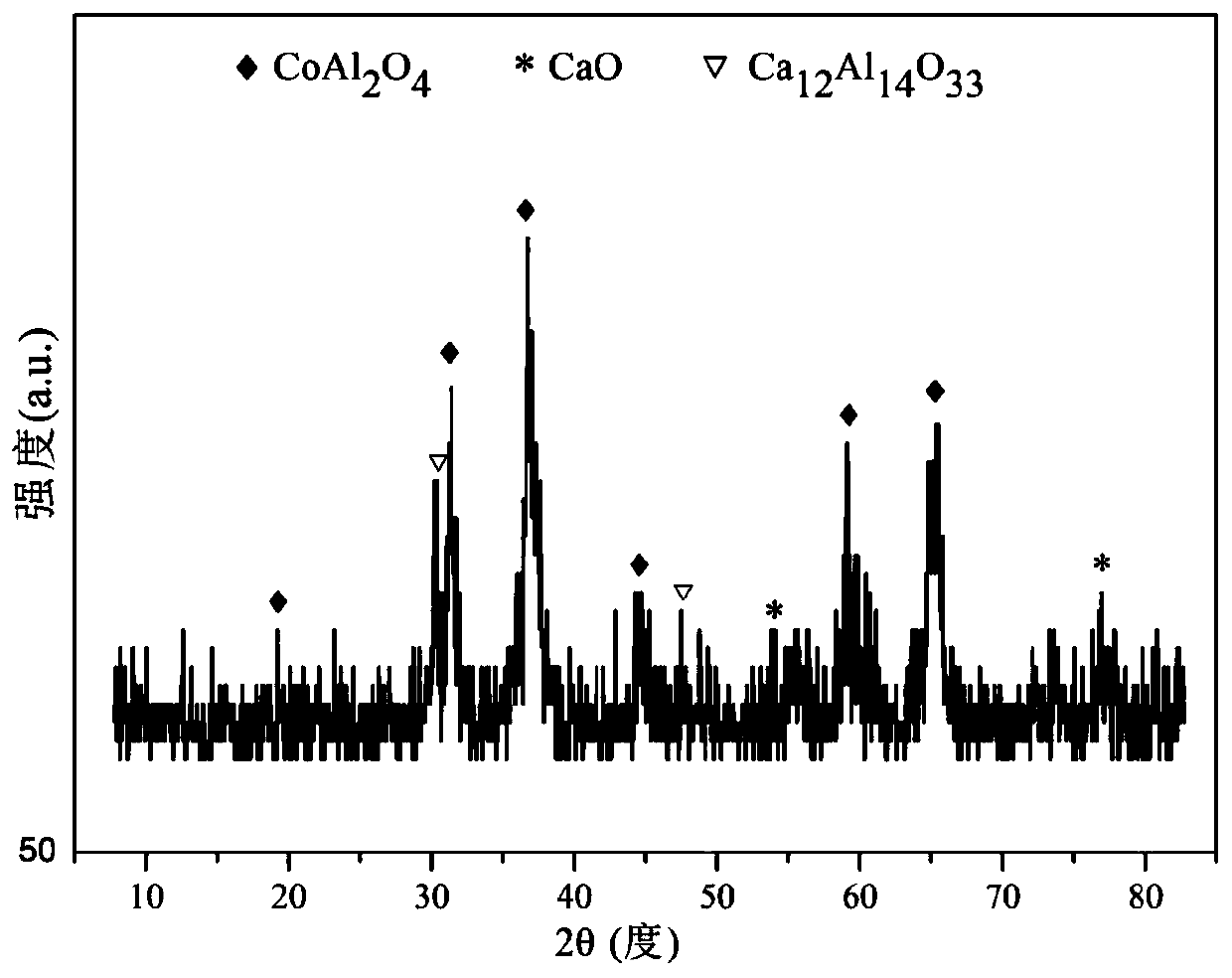
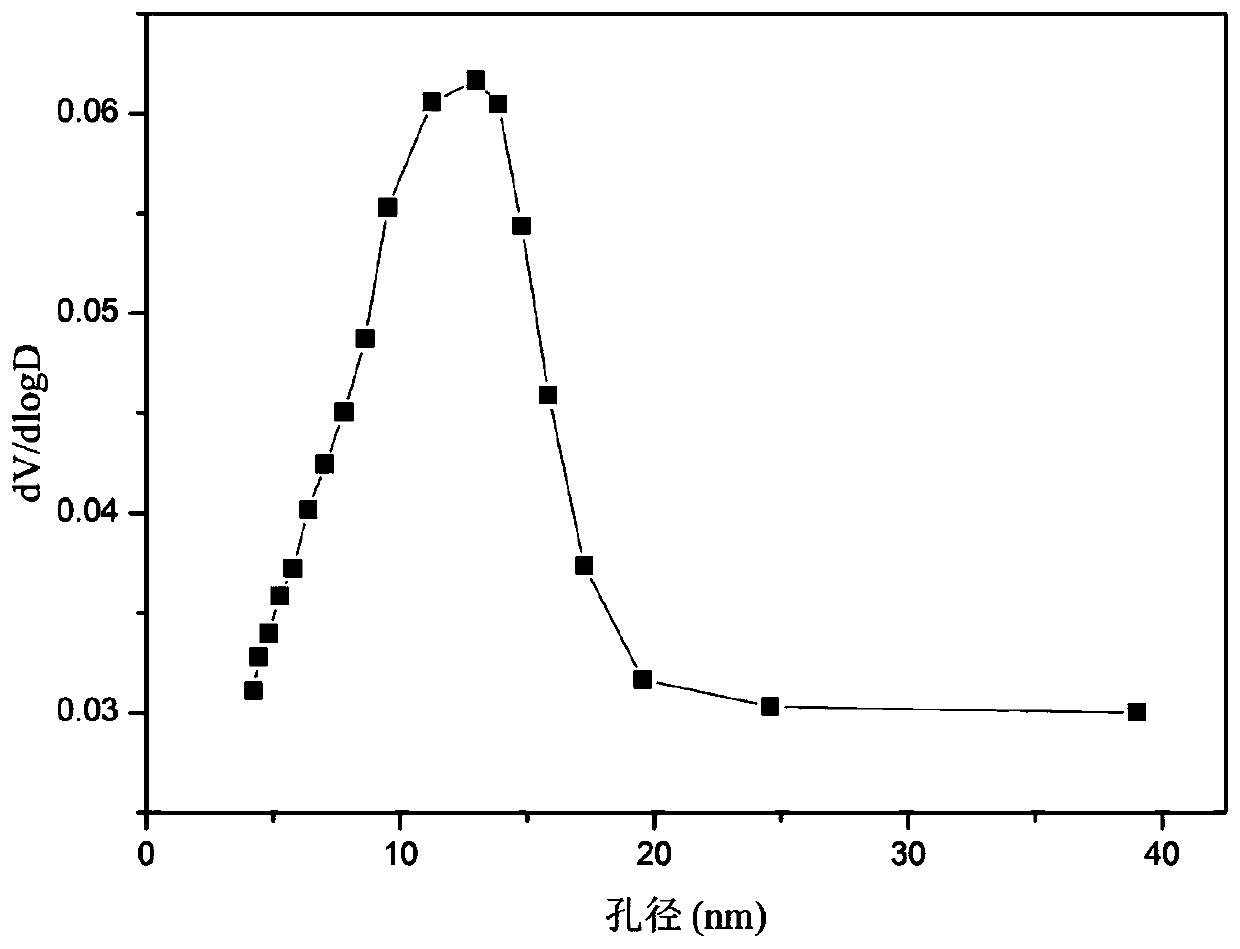
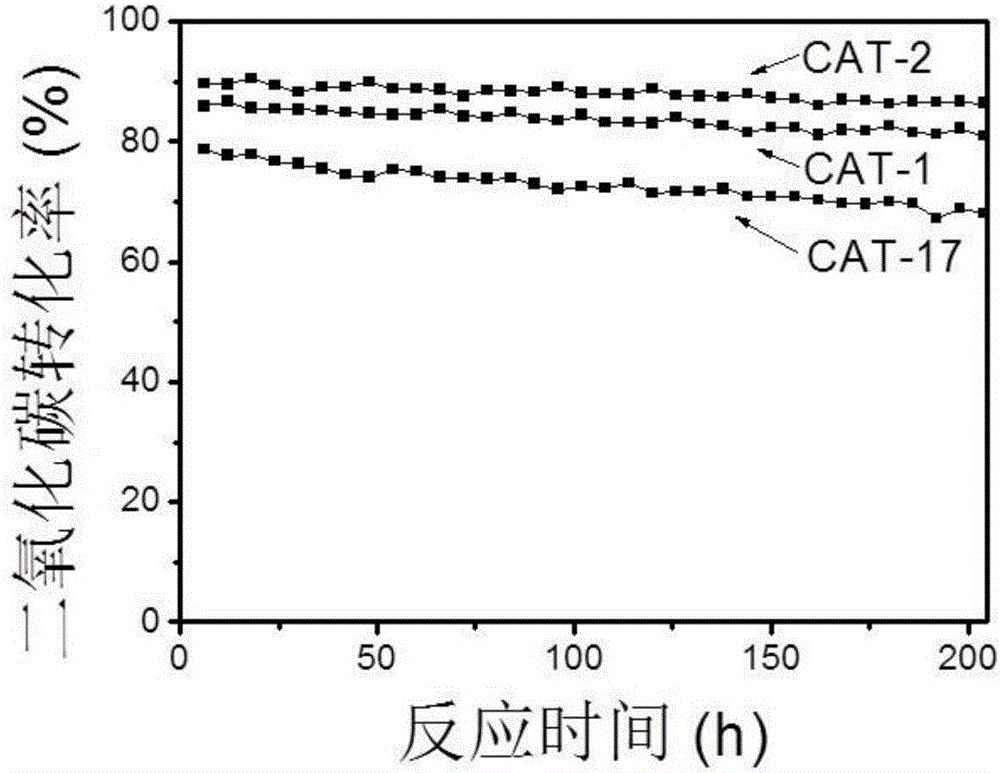
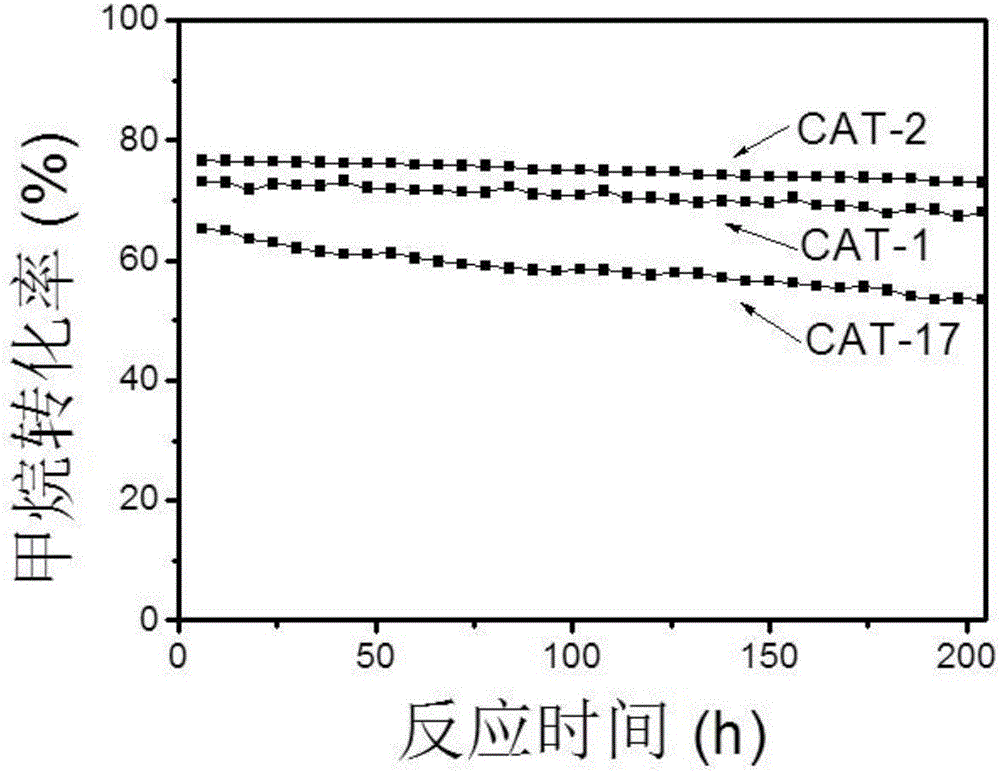
The invention relates to a hydrocalumite derived cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Directed at the problem that catalyst structure change and the oxidation and sintering of active components can cause catalyst deactivation in existing catalysts during the autothermal reforming reaction of acetic acid, the invention provides a new catalyst characterized by stable structure, sintering resistance, oxidation resistance, carbon deposition resistance, and high activity. The molar composition of the catalyst is (CaO)a(CoO)b(AlO1.5) c, wherein a is1.66-5.19, b is 0.34-0.81 and c is 1.0. The invention adopts coprecipitation method to prepare a catalyst precursor, and then roasting is carried out to obtain the Ca-Co-Al-O mesoporous composite oxide. The catalyst takes calcium oxide as the framework, contains cobalt-alumina spinel phase and a small amount of Ca12Al14O33, inhibits the acidity of the catalyst, improves the carbon deposition resistance and sintering resistance of the catalyst, and improves the activity of hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Catalyst, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106807375AAchieve emission reduction and recyclingExcellent comprehensive catalytic performanceHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionCarbon dioxideMacropore
The invention discloses a catalyst which comprises a carrier and an active component dispersed over the carrier and is characterized in that the carrier is selected from at least one of inorganic oxides; the carrier comprises macropores and mesoporouses; the active component comprises an active element; the active element comprises a ferrum element; the ferrum element is ferrum and / or cobalt. The catalyst, as a high-temperature stable catalyst of a carbon dioxide reforming methane reaction, can produce synthetic gas and achieves emission reduction and recycling of carbon dioxide. Under a reaction condition of normal atmosphere and 800 DEG C, the multilevel pore loading metal catalyst shows excellent comprehensive catalytical performance and has very good stability, sintering resistance and carbon deposit resistance in addition to high activity and good selectivity.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for producing synthesis gas by catalytic partial oxidation of methane and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101279271BHigh selectivityReduce manufacturing costHydrogenCarbon monoxideNickel catalystPartial oxidation
The present invention provides a catalyst for preparing a compound gas by methane catalyzing partial oxidation and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst relates to a loading type catalyst which is added with a cerium oxide-based compound accessory ingredient and a noble metal ruthenium; wherein, the content of nickel is 5 to 15 percent (weight percent, the same below), the content of the cerium oxide-based compound accessory ingredient is 0.1 to 5 percent, the content of ruthenium is 0.1 to 0.2 and the rest is the content of a carrier. The catalyst has excellent reaction property; the methane converting rate as well as the selectivity of CO and H2 is all higher than 95 percent; besides, the stability is excellent.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
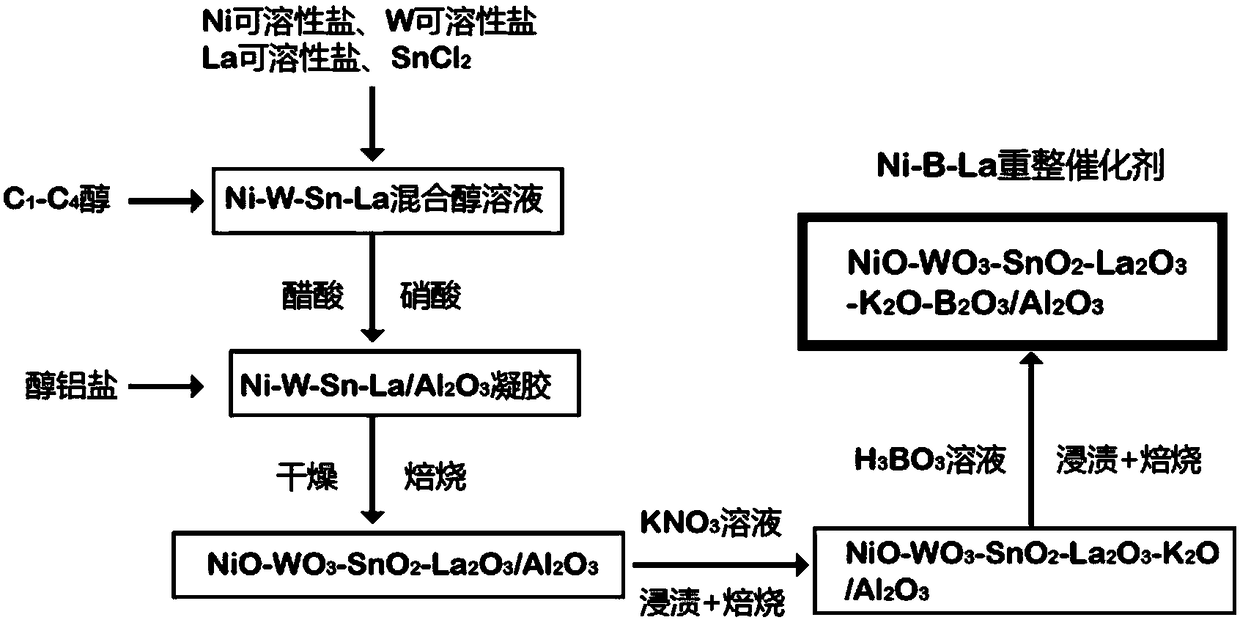
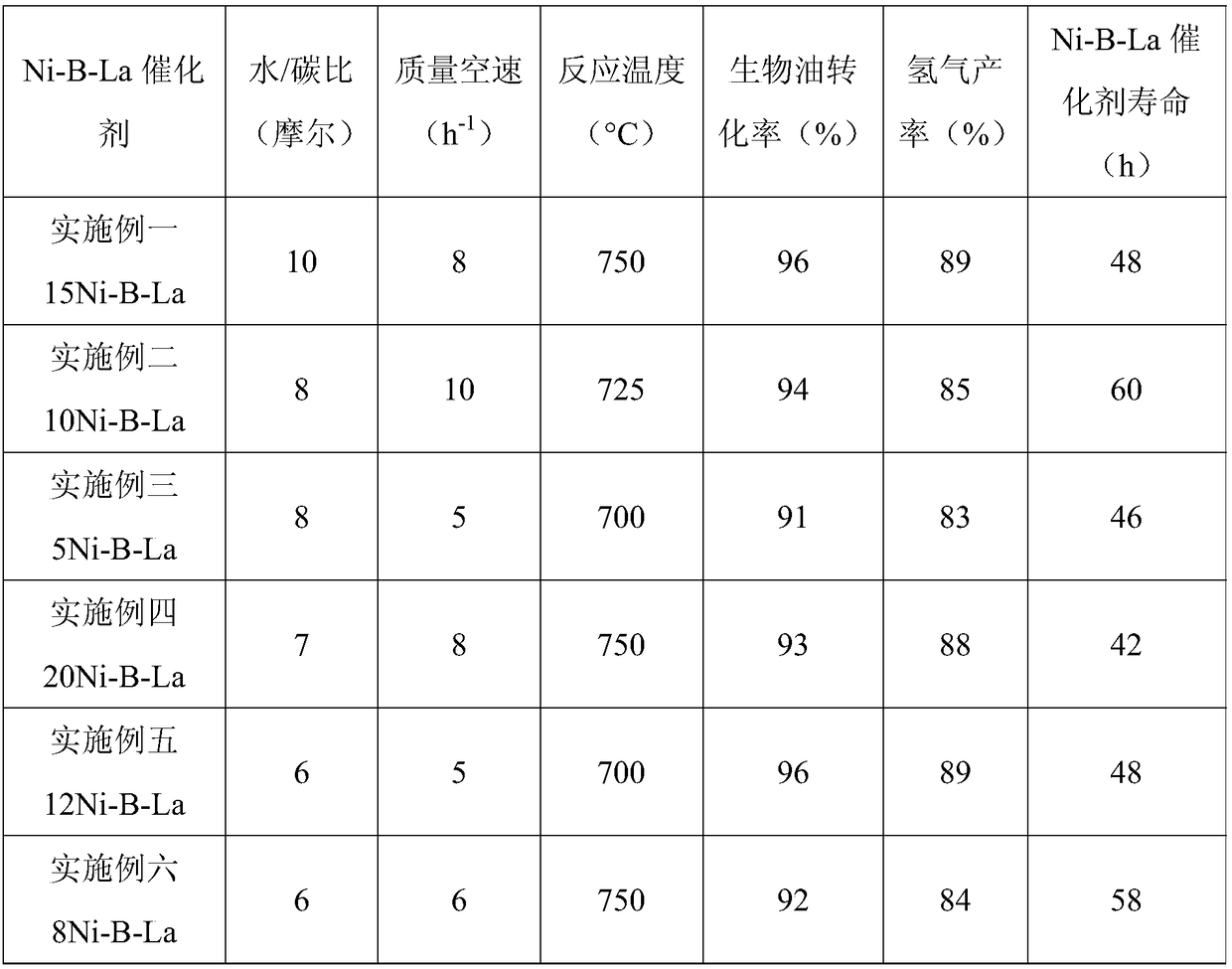
Ni-B-La catalyst for bio-oil catalytic reforming hydrogen production and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108554418AWide variety of sourcesLow priceHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationCatalytic reformingActive component
The invention discloses Ni-B-La catalyst for bio-oil catalytic reforming hydrogen production and a preparation method thereof. The Ni-B-La catalyst comprises a catalyst active component, a catalyst auxiliary agent and a catalyst carrier, the catalyst active component is Ni, and the weight is 5-20% of the total weight of the Ni-B-La catalyst; the catalyst auxiliary agent is La2O3, WO3, SnO2, K2O and B2O3, the weight of La2O3 is 5-15%, of the total weight of the Ni-B-La catalyst, the weight of WO3 is 1-5% of the total weight of the Ni-B-La catalyst, the weight of SnO2 is 0.5-2% of the total weight of the Ni-B-La catalyst, the weight of K2O is 0.1-0.5% of the total weight of the Ni-B-La catalyst, and the weight of the B2O3 is 0.5-3% of the total weight of the Ni-B-La catalyst; the catalyst carrier is Al2O3, and the weight is the balance; the catalyst has the advantages that the preparation process of the Ni-B-La catalyst is mature, reliable and easy to operate, selected raw materials arewidely available, the price is low, anti-sintering and anti-coking performance is good, stability is strong, reactivity is high, life is long, conversion rate of bio-oil is high, and the hydrogen yield is high.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Anti-sintering cavitation-damage-resistant copper alloy and processing method thereof
The invention discloses an anti-sintering cavitation-damage-resistant copper alloy and a processing method thereof; the anti-sintering cavitation-damage-resistant copper alloy comprises the followingcomponents by the mass percentage: 64.0%-72.0% of Cu, 1.0%-3.0% of Al, 2.5%-4.0% of Ni, 0.5%-2.0% of Si, 0.5%-2.0% of Mn, 0.2%-1.0% of Fe, and the balance Zn. The anti-sintering cavitation-damage-resistant copper alloy has the advantages of high strength, good sintering resistance, good cavitation damage resistance, environmental protection, wide application range, and quite high application and popularization value.
Owner:贝原合金(苏州)有限公司
Catalyst and preparation method for preparing synthesis gas through reforming reaction of CO<2> and CH<4>
InactiveCN105170154ALow costImprove anti-sinteringHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsDispersityCarbon deposit
The invention relates to a catalyst and preparation method for preparing synthesis gas through a reforming reaction of CO<2> and CH<4>. The catalyst is formed by mixing a nickel-base part, namely Ni / gamma-Al<2>O<3> (component I), with a carbon material part (component II). In the preparation process, organic solvent serves as impregnation liquid, and ultrasonic intensifying treatment is conducted in a matched mode so that active site points of the nickel-base part can be increased, and the dispersity of active components can be improved. The carbon material is utilized for replacing part of the nickel-base component, cost of the catalyst can be lowered, and meanwhile the carbon material serves as a modulation auxiliary agent and conducts regulation and control on the nickel-base part. In the reaction process, through the synergistic effect of the nickel-base part and the carbon material part, the activity and stability of the catalyst can be enhanced, and the anti-sintering performance and anti-carbon-deposit performance of the catalyst can be improved. The catalyst has the advantages that the cost is low, raw materials are easy to obtain, and catalytic activity is good.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Preparation method of acidified two-dimensional layered vermiculite loaded nickel-based catalyst
PendingCN114308043AGood metal dispersionSmall particle sizeHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMolecular sieveRoasting
The invention relates to a preparation method of an acidified two-dimensional layered vermiculite loaded nickel-based catalyst. According to the method, expanded vermiculite is adopted as a carrier, a vermiculite structure in which a layered molecular sieve with a large specific surface area is removed is obtained through treatment in an acid solution, washing and drying, and then the acidified two-dimensional layered vermiculite loaded nickel-based catalyst is prepared through a slightly excessive liquid-phase high-temperature roasting method. The catalyst has the advantages of simple composition, simple preparation process, easy operation, low production cost and the like, and the catalyst prepared without subsequent addition of auxiliaries has the advantages of uniform dispersion of metal particles, small average particle size, high sintering resistance at high temperature, high carbon deposition resistance and the like; the catalyst has a good industrial prospect when applied to methane and carbon dioxide reforming reaction for synthesis gas preparation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of zirconium dioxide modified layered porous vermiculite loaded nickel-based catalyst
PendingCN114272927AImprove stabilityGood dispersionHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of a zirconium dioxide modified layered porous vermiculite loaded nickel-based catalyst. According to the method, acid-treated two-dimensional layered porous vermiculite is taken as a carrier, and zirconium dioxide and nickel metal are anchored in a mesoporous structure of a layered molecular sieve at the same time through a co-initial wet immersion high-temperature reduction method, so that the zirconium dioxide modified layered porous vermiculite loaded nickel-based catalyst rich in Ni-Zr interfaces and a large number of oxygen vacancies is prepared. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation process is easy to operate, the process energy consumption is low, the preparation method is good in repeatability and the like, the prepared catalyst has the advantages of being small in metal particle, uniform in dispersion, high in reactant adsorption and activation capacity and the like, and the Ni-Zr interface effect and oxygen vacancies rich in the zirconium dioxide auxiliary play a synergistic effect; the prepared catalyst has the advantages of high sintering resistance and carbon deposition resistance at high temperature and the like. The method has a good prospect when being applied to the reaction for preparing the synthesis gas by reforming the methane and the carbon dioxide.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modified boron nitride loaded nickel-based methane dry reforming catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114192180AHigh activityImprove stabilityHydrogenPhysical/chemical process catalystsNickel catalystPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a modified boron nitride loaded nickel-based methane dry reforming catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, different stripping methods are used for modifying the boron nitride, then the modified boron nitride is used as a carrier for supporting the active metal Ni, and the excellent sintering resistance and carbon deposition resistance are achieved in the methane dry reforming reaction. According to the invention, the content of Ni is adjusted by using a simple impregnation method, and the modified boron nitride loaded nickel catalyst with high activity and high stability is obtained. The catalyst can be used for solving the problems of sintering and serious carbon deposition of active components in a methane dry reforming reaction. The catalyst has the advantages of simple preparation process, low cost and high catalytic efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Organic silicon waste contact body borne nickel-based methanation catalyst and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN104841448AHigh thermal conductivityImprove anti-sinteringHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh concentrationMethanation
The invention belongs to the field of methanation catalysis, and relates to an organic silicon waste contact body borne nickel-based methanation catalyst and a preparation method therefor. The catalyst comprises a carrier, an active component, a modifier and an auxiliary agent, wherein the carrier is an organic silicon waste contact body, the modifier is a porous inorganic oxide, the active component is Ni, and the auxiliary agent is a transition metal oxide. By using the porous inorganic oxide modifier in the invention, on one hand, the interacting force between the active component and the carrier is enhanced, and the dispersibility of the active component is improved; on the other hand, the inorganic oxide dispersed in the active component further serves as a physical barrier, and suppresses agglomeration and sintering of Ni particles. The catalyst obtained in the invention is high in catalytic activity, high in anti-carbon deposition and anti-sintering performance and low in cost, and particularly suitable for methanation reaction systems of high-concentration CO.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chemical composition plating method for preparing supported platinum bimetallic alloy composite material
InactiveCN101775595ALow costImprove anti-sinteringLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingRheniumIridium
The invention relates to a chemical composition plating method for preparing a supported platinum bimetallic alloy composite material, which belongs to the technical field of the preparation of the bimetallic alloy material. A chemical platinum plating layer prepared by using the single platinum chemical planting method has bad performance and higher cost. For improving the performance of the single platinum planting layer and reducing the usage of the noble platinum, the invention provides the chemical composition plating method for depositing a platinum bimetallic alloy, which comprises three steps of pretreatment of a matrix, activation of the matrix, chemical composition plating and heat treatment after planting. After being subjected to pretreatment and activation, inorganic oxides, composite oxides and a carbon carrier or a molecular sieve matrix are added into platinum-rhenium or platinum-iridium bimetallic chemical plating solution to carry out bimetallic chemical composition planting, and the obtained sample is subjected to heat treatment to obtain the supported platinum bimetallic alloy composite material. The platinum bimetallic alloy composite material prepared by the method has the characteristics of low cost, sintering resistance and excellent catalytic performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of organic-inorganic hybrid material coated nickel silicate nanotube catalyst
PendingCN114054065AImprove anti-carbon performanceInhibition of nucleationHydrogenPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganosiliconOrganic inorganic
The invention relates to a preparation method of an organic-inorganic hybrid material coated nickel silicate nanotube catalyst. According to the method, a modified Stober method is used, and a nickel silicate nanotube coated with an amino-functionalized organic-inorganic hybrid material is realized at normal temperature in one step, namely, an inorganic silicon source tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) is added, and meanwhile, an amino-carrying organic silicon source 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) is added; nickel nanoparticles with small sizes are obtained and are limited in a coating structure, and amino modification has a coordination effect, so that the catalyst sintering resistance is improved. The obtained organic-inorganic hybrid material coated nickel silicate nanotube catalyst has excellent catalytic performance, the sintering resistance and the carbon deposition resistance of the catalyst are improved, and a coupling enhancement effect is generated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of nickel-containing mesoporous catalyst
InactiveCN106732608ALarge specific surface areaImprove anti-sinteringHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsGaseous fuelsDispersityMethanation
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation and application of a catalyst for preparing synthetic natural gas from coke oven gas and coal and particularly relates to a preparation method of a nickel-containing mesoporous catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: taking aluminum oxide as a carrier, taking nickel oxide as a main active component and taking magnesium oxide and cobalt oxide as additives, preparing a catalyst precursor by using a method of coprecipitating nitrate and sodium aluminate, then roasting at the high temperature to prepare the catalyst. According to the nickel-containing mesoporous catalyst prepared by the method, all the components of the catalyst are uniformly dispersed, so that the dispersity of nickel which is used as the active component is improved; through the formed regular pores, the specific surface area of the catalyst is increased, so that the active site is in full contact with the raw material gas and rapidly carries out methanation; the magnesium oxide and the cobalt oxide which are used as the additives are added, the sintering resistance and the inhibition of carbon deposition of the catalyst in the high-temperature reaction environment are improved, and meanwhile, the selectivity is also improved. The catalyst has high low-temperature activity; the catalyst can be activated at 200 DEG C; the conversion ratio of CO can reach up to 98% at 230 DEG C; the selectivity of CH4 is greater than 96%.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Porous material and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111715202AUnique Si-O-Al structureHigh pore volumeCatalyst carriersAlkaline earth metalPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysts, and particularly relates to a porous material and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the porous materialprovided by the invention comprises the following steps: mixing and stirring silicon-containing slurry and an aluminum-containing compound to obtain silicon-aluminum slurry; adding a template agent and an alkali metal and / or alkaline earth metal compound into the silicon-aluminum slurry, carrying out stirring and aging to obtain aged slurry; and carrying out centrifugal separation on the aged slurry to obtain a solid crude product, and drying and roasting the solid crude product to obtain the porous material. According to the preparation method of the porous material provided by the invention, the pore diameter, specific surface area and pore volume of the material can be greatly improved, and the catalytic activity and stability of the material can also be improved.
Owner:SHENYANG SANJUKAITE CATALYST
Carried by CeO2 based composite oxides coated carrier Pd catalyst, its preparation method
InactiveCN100391599CHigh catalytic activityImprove thermal stabilityDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationCordieriteThermal stability
A catalyst for catalytic combustion features that a coated composite oxide layer based on CeO2 is carried by cellular ceramic carrier. It contains the cellular cordierite ceramic matrix, coated composite oxide layer based on CeO2, and Pd. Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of cu-ni-al-ce porous alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103710570BUniform chemical compositionHigh purityCell electrodesMolten stateChemical composition
The invention discloses a Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy and a preparation method thereof. The porous alloy comprises 25% to 35% of Ni, 10% to 15% of Al, 2% to 4% of Ce, the balance is Cu. The preparation method includes (1) heating Cu, Ni, Al, and Ce to a molten state to obtain Cu-Ni-Al-Ce alloy liquid; (2) atomizing the alloy liquid to obtain Cu-Ni-Al-Ce mist (3) sending the atomized powder into an atmosphere sintering furnace and reducing it with high-purity hydrogen; (4) hot pressing and sintering the reduced atomized powder to obtain a Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy. The Cu-Ni-Al-Ce porous alloy of the present invention has uniform chemical composition, high alloy purity, good high-temperature compression performance and high-temperature creep resistance under the condition of relatively high porosity, and the preparation method is simple in process and low in cost .
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Hydrocalumite-derived cobalt-based catalysts for autothermal reforming of acetic acid to produce hydrogen
ActiveCN109718785BImprove anti-sintering performanceImprove thermal stabilityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHigh activityCobalt
The invention relates to a hydrocalumite derived cobalt-based catalyst for hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid. Directed at the problem that catalyst structure change and the oxidation and sintering of active components can cause catalyst deactivation in existing catalysts during the autothermal reforming reaction of acetic acid, the invention provides a new catalyst characterized by stable structure, sintering resistance, oxidation resistance, carbon deposition resistance, and high activity. The molar composition of the catalyst is (CaO)a(CoO)b(AlO1.5) c, wherein a is1.66-5.19, b is 0.34-0.81 and c is 1.0. The invention adopts coprecipitation method to prepare a catalyst precursor, and then roasting is carried out to obtain the Ca-Co-Al-O mesoporous composite oxide. The catalyst takes calcium oxide as the framework, contains cobalt-alumina spinel phase and a small amount of Ca12Al14O33, inhibits the acidity of the catalyst, improves the carbon deposition resistance and sintering resistance of the catalyst, and improves the activity of hydrogen production by autothermal reforming of acetic acid.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Long-life steelmaking tundish dry material processing and using process
The invention discloses a long-life steelmaking tundish dry material processing and using process, which comprises a steelmaking tundish dry material processing process and a steelmaking tundish dry material using process, and the steelmaking tundish dry material processing process comprises formula determination, raw material selection, safe production, and delivery after production dates and batches are marked. The steelmaking tundish dry material using process comprises the steps that technicians are arranged on site to track construction; the technicians track the steel casting process and measure the temperature of the tundish shell at any time; the erosion thickness of a slag line and the sintering thickness of a tundish wall are measured after the tundish is used off line, the tundish is tracked and turned, and the difficulty of turning the tundish is observed; and test data is summarized. According to the dry material, the service time of the tundish can be greatly prolonged and can reach 50 hours or more, the erosion of an impact area and a slag line position is relatively shallow and is about 1 / 3 of the construction thickness, the tundish wall is basically not eroded, the temperature of a tundish shell is lower than 280 DEG C, the potential safety hazard of the tundish is solved, meanwhile, the cost of refractory materials per ton of steel is reduced, and the tundish runs safely.
Owner:本溪市众信冶金炉料有限公司
A kind of hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106000405BImprove anti-sinteringImprove anti-coking performanceHydrogenCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
This application discloses a hierarchical pore-supported nickel-based catalyst, a preparation method and its application in carbon dioxide methane reforming reaction. The hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst includes a carrier and active components dispersed on the carrier. It is characterized in that the carrier is selected from at least one inorganic oxide, and the carrier contains an average pore diameter greater than 50 nm. Macroporous and average pore diameters range from 1 nm to 50 nm mesopores; the active component is nickel. The hierarchical porous supported nickel-based catalyst is used in the carbon dioxide methane reforming reaction, has excellent sintering resistance and coke resistance, and has important practical significance in promoting the industrialization of the carbon dioxide methane reforming reaction.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of manganese-based catalyst for the treatment of volatile organic compounds and its preparation and application
ActiveCN106622212BEvenly distributedHigh purityHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsIncinerator apparatusOxalateBenzene
A manganese-based catalyst for use in the treatment of volatile organic compounds, consisting of manganese oxide and other transition metal oxides, wherein the mass fraction of manganese oxide is less than 60%, while the other transition metal oxides are greater than 40%, the other transition metal oxides being pure MxOy, M=Co, Ce, and Cr, or comprising Co3O4 and MxOy, M=Ce, and Cr, wherein 1≤x≤3 and 1≤y≤4. The method for preparing the manganese-based catalyst is an oxalate colloidal co-precipitation method. In the treatment of volatile organic compounds, the manganese-based catalyst exhibits high activity, a long life, high anti-sintering capacity, and like features in a benzene catalytic combustion reaction. The optimal catalyst may achieve the complete combustion of benzene, a representative model substrate having a stable structure in volatile organic compounds (VOCs), when below 230°C under the reaction conditions of normal pressure and a space velocity of 30000 mL / (g·h), which is comparable with the performance of noble metal catalysts.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com