Patents
Literature
80results about How to "Reduce magnetization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
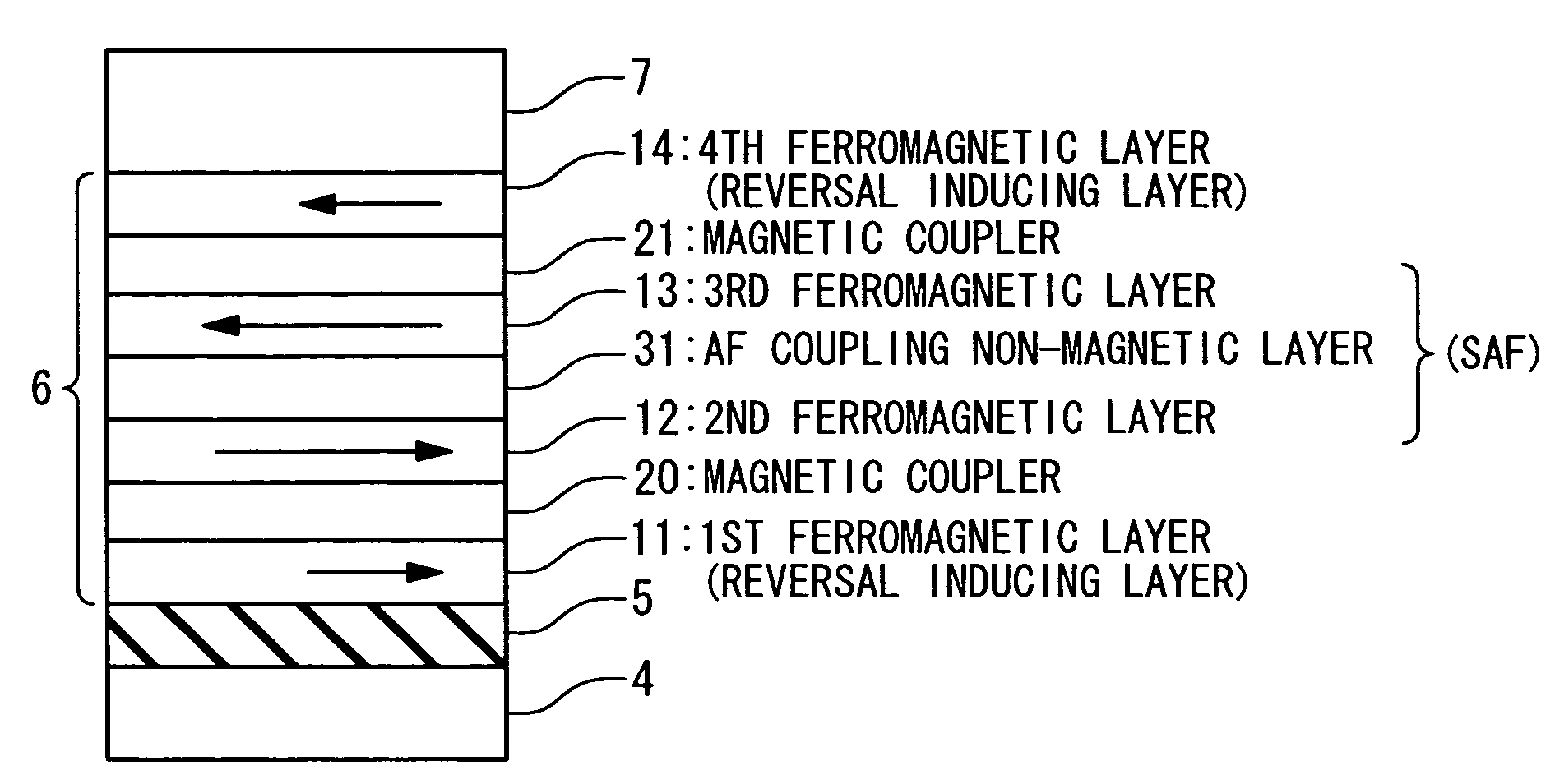
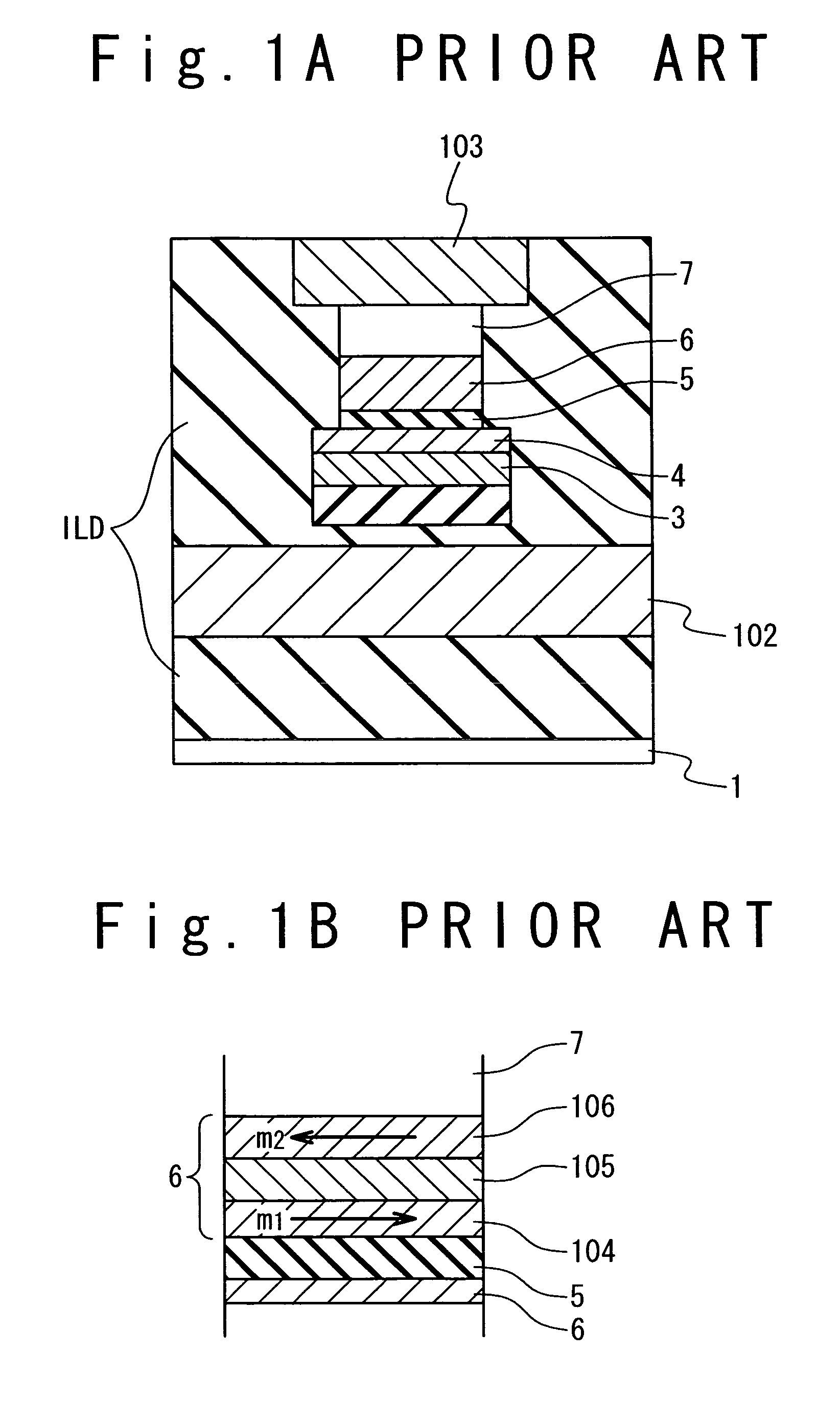
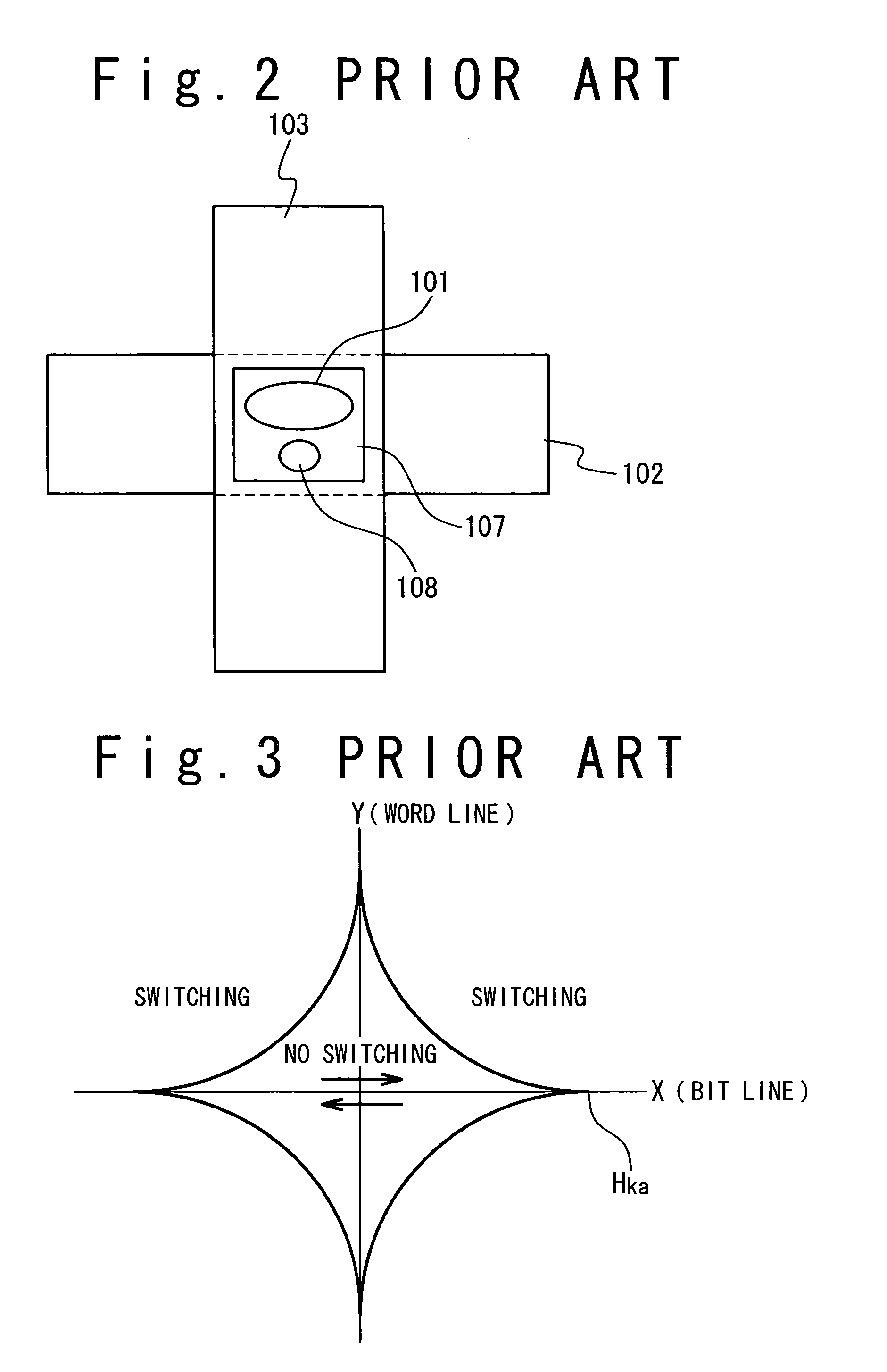
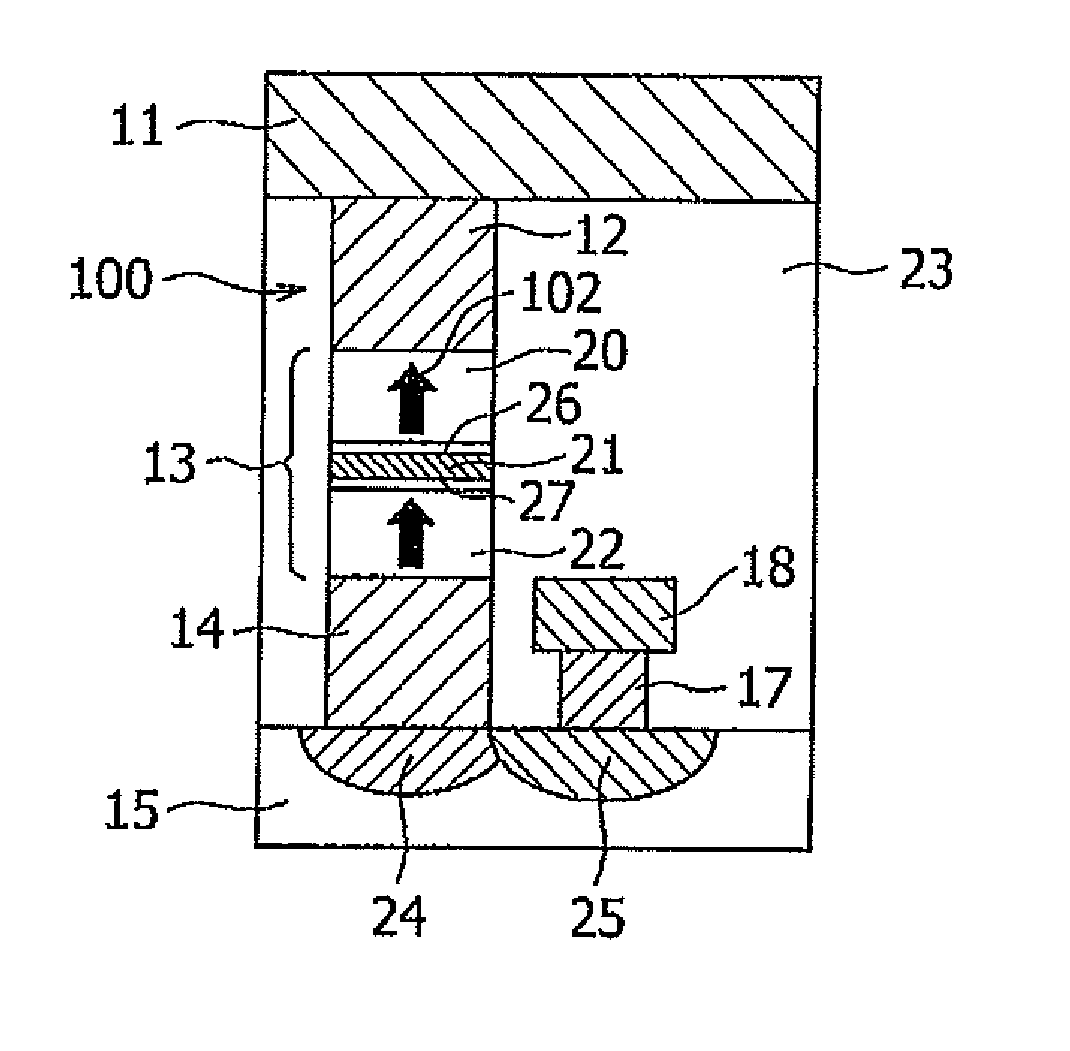
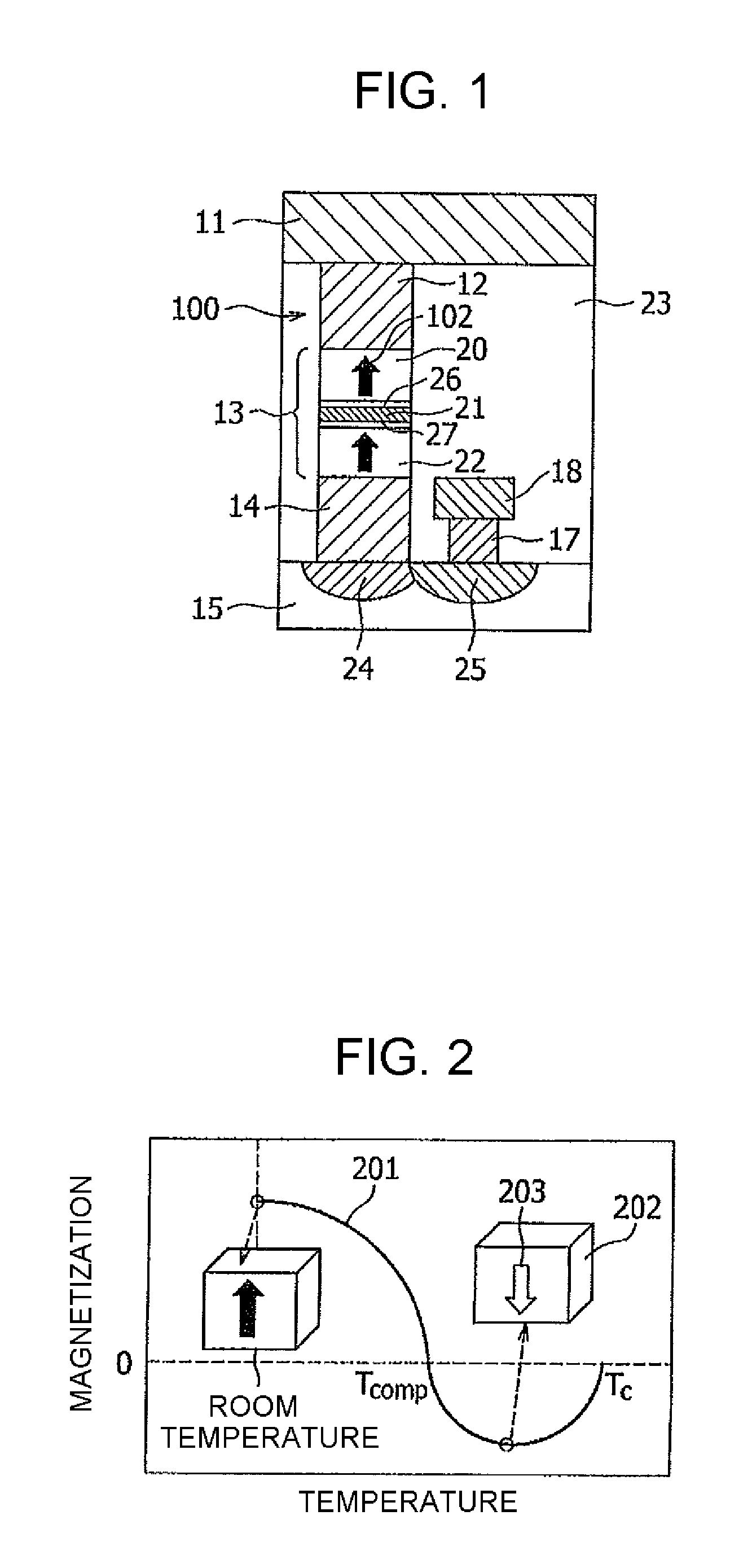
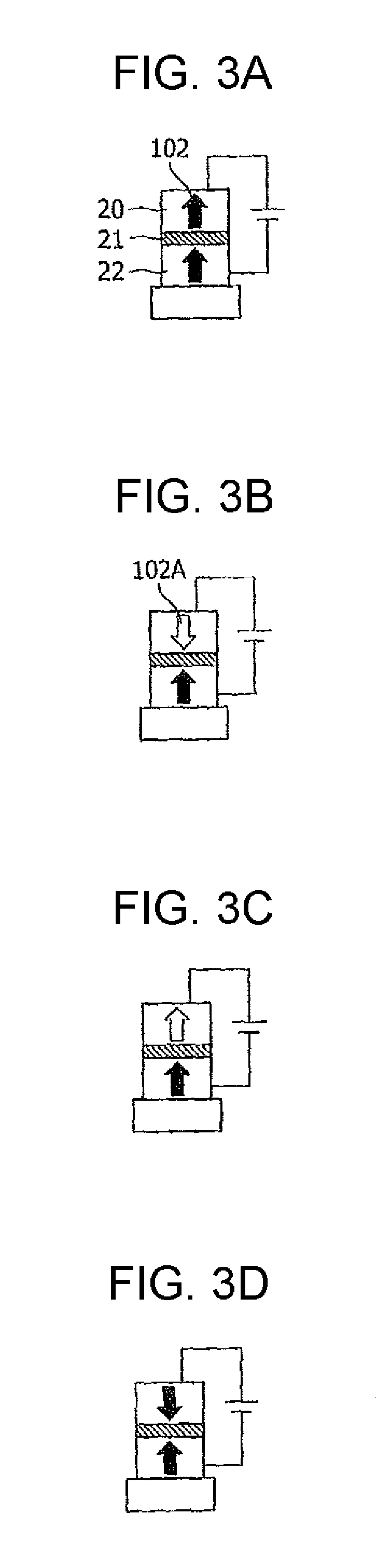
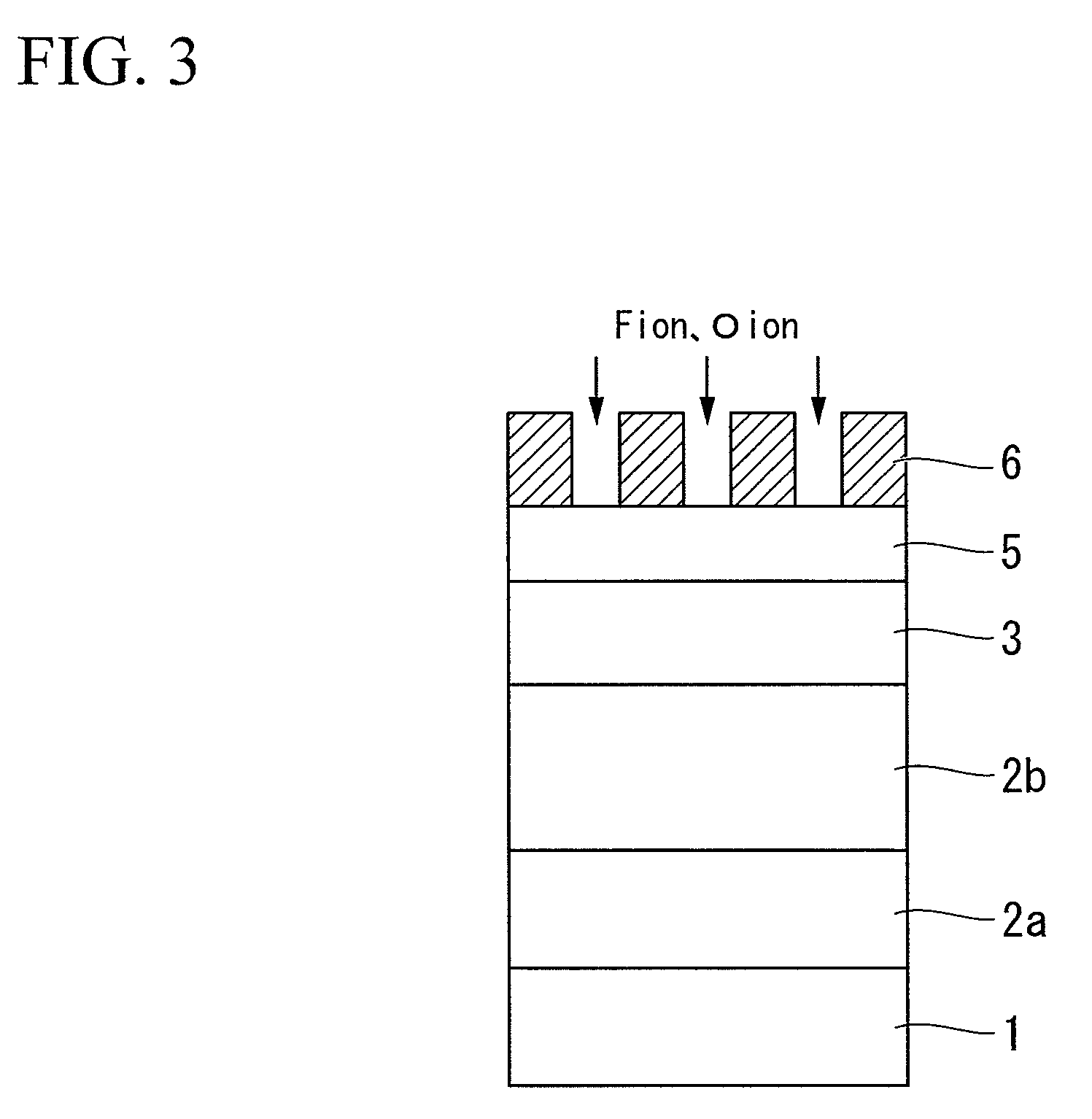
Magnetoresistive device and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS20060262594A1Reducing a magnetic field necessaryIncreased writing marginNanomagnetismDigital storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic memory
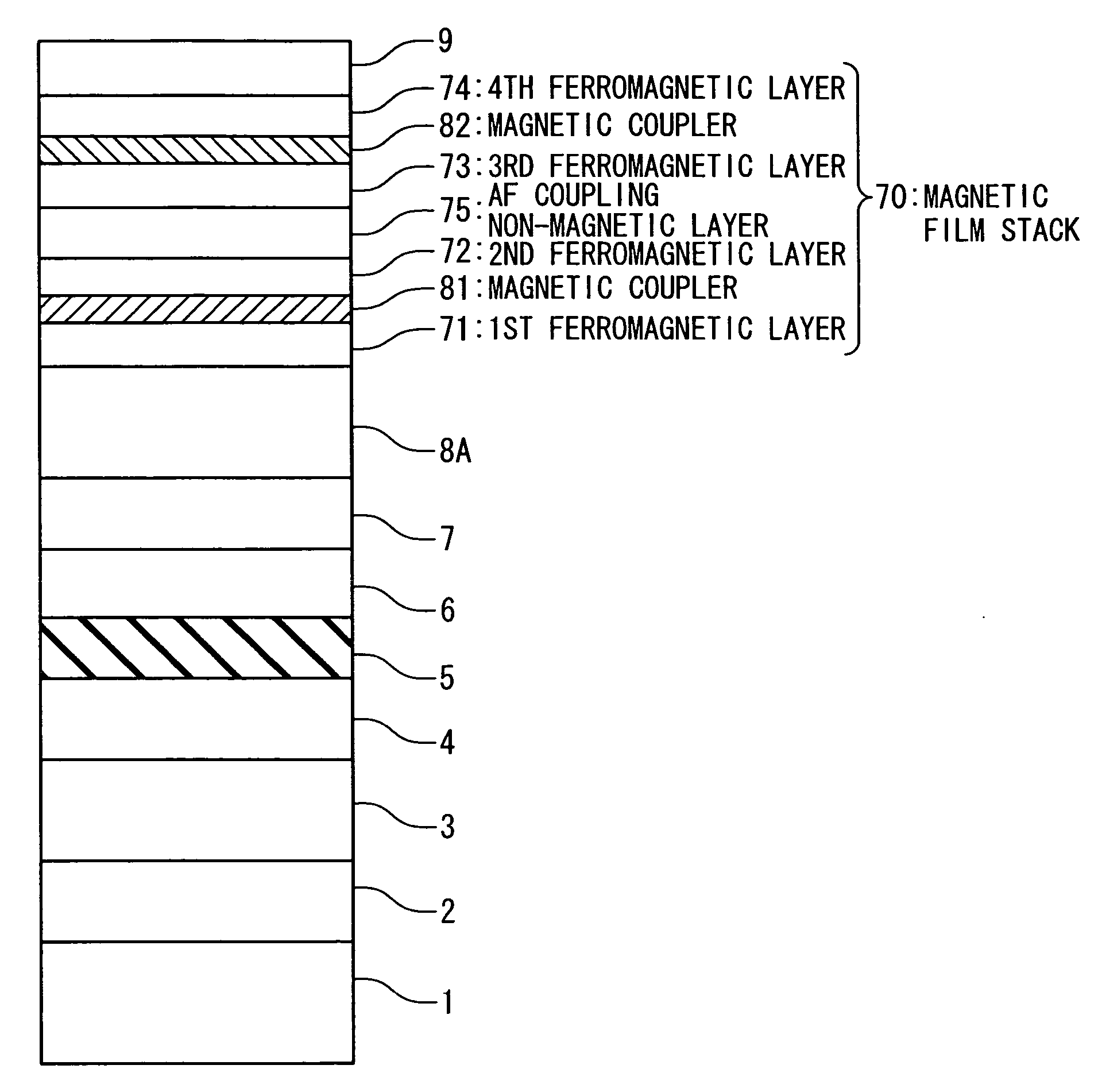
A magnetic film stack is composed of a synthetic antiferromagnet including a plurality of ferromagnetic layers, adjacent two of which are antiferromagnetically coupled through a non-magnetic layer; and a reversal inducing layer exhibiting ferromagnetism. The reversal inducing layer is ferromagnetically coupled to the synthetic antiferromagnet, and designed to have a coercive field smaller than a magnetic field at which antiferromagnetic coupling within the synthetic antiferromagnet starts to be decoupled.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetic memory with a magnetic tunnel junction written in a thermally assisted manner, and method for writing the same
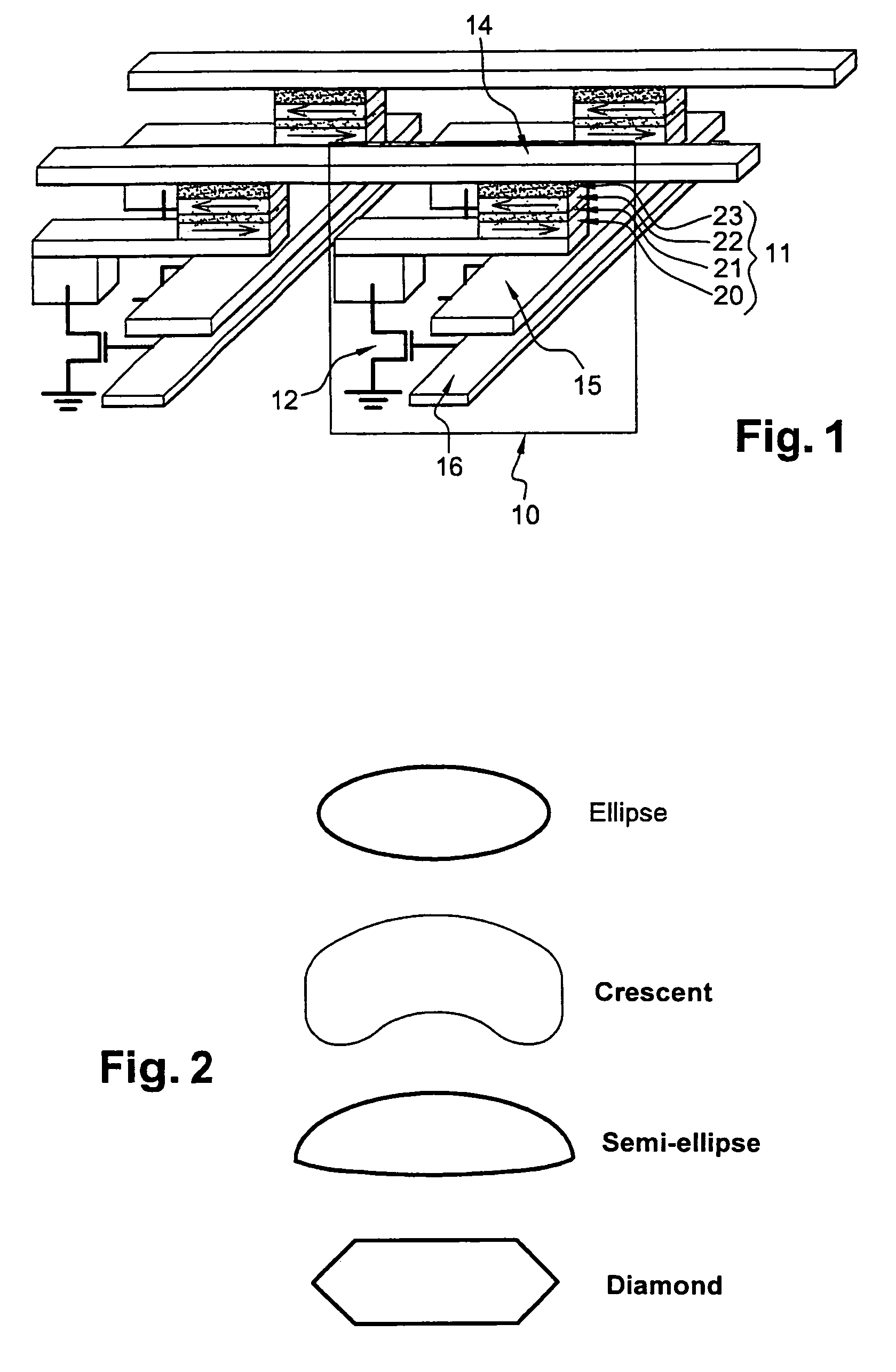
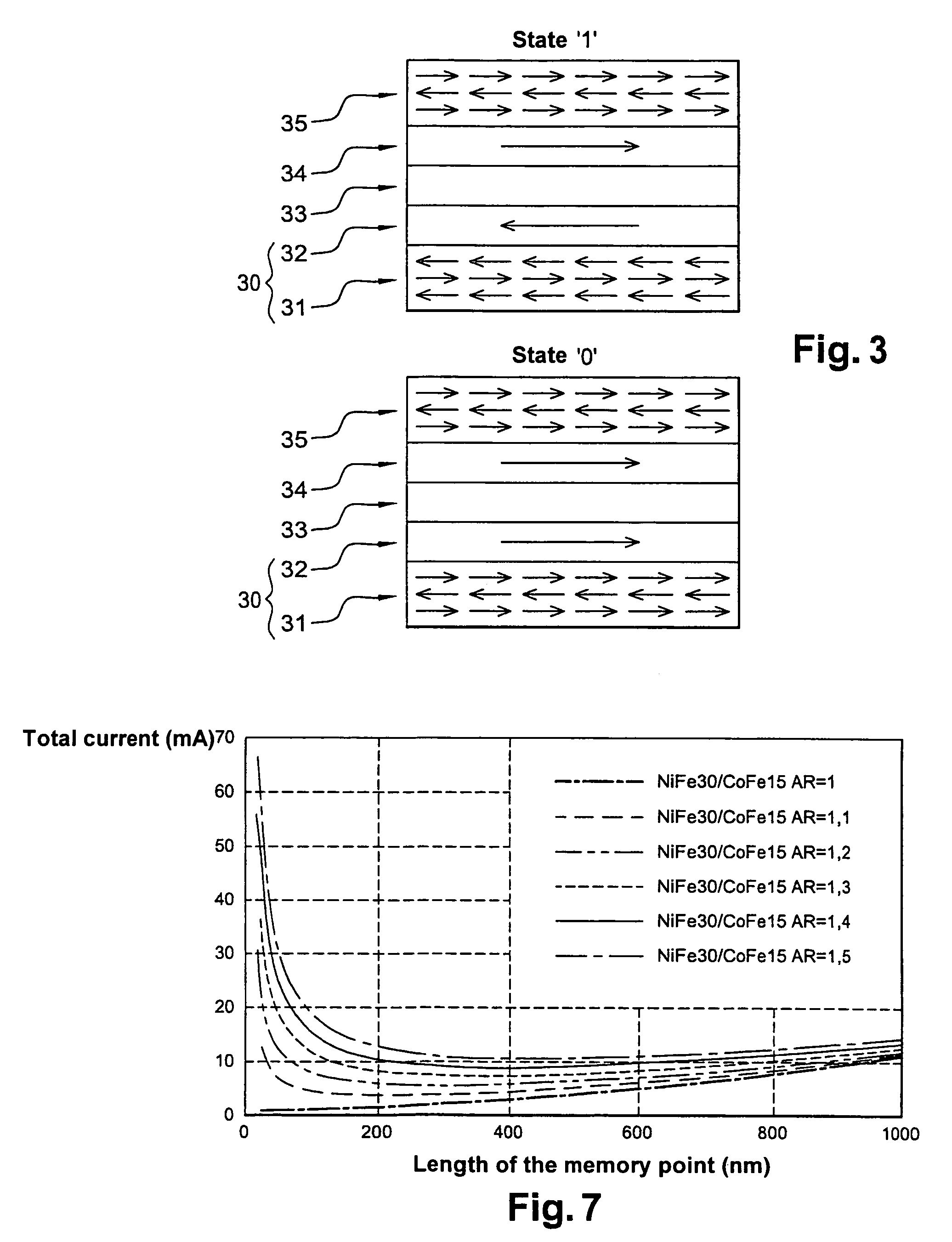
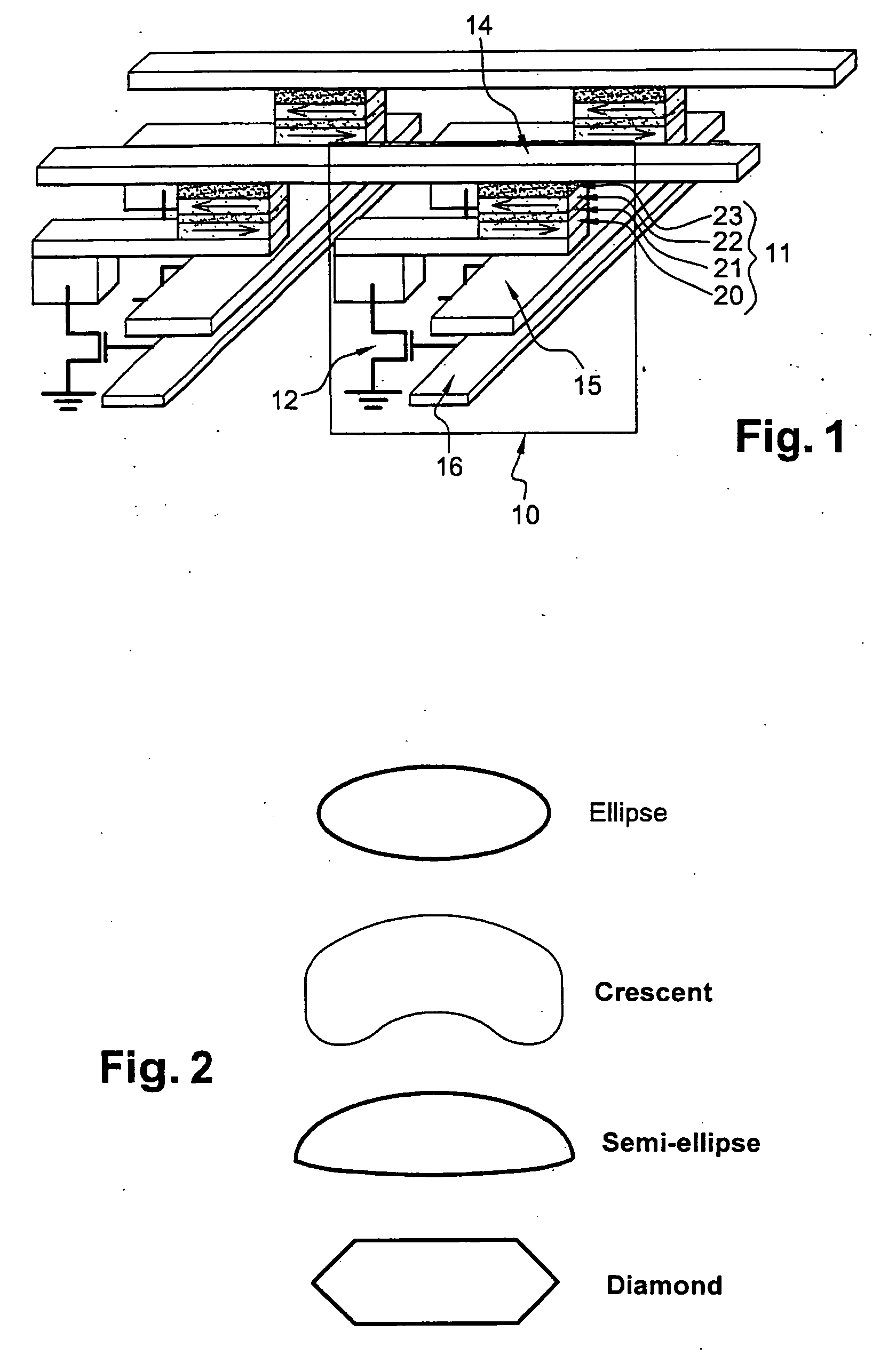
ActiveUS7411817B2Reduce magnetizationElectric power required to effect the writing of a memory point may be loweredDigital storageMagnetic memoryOperating temperature
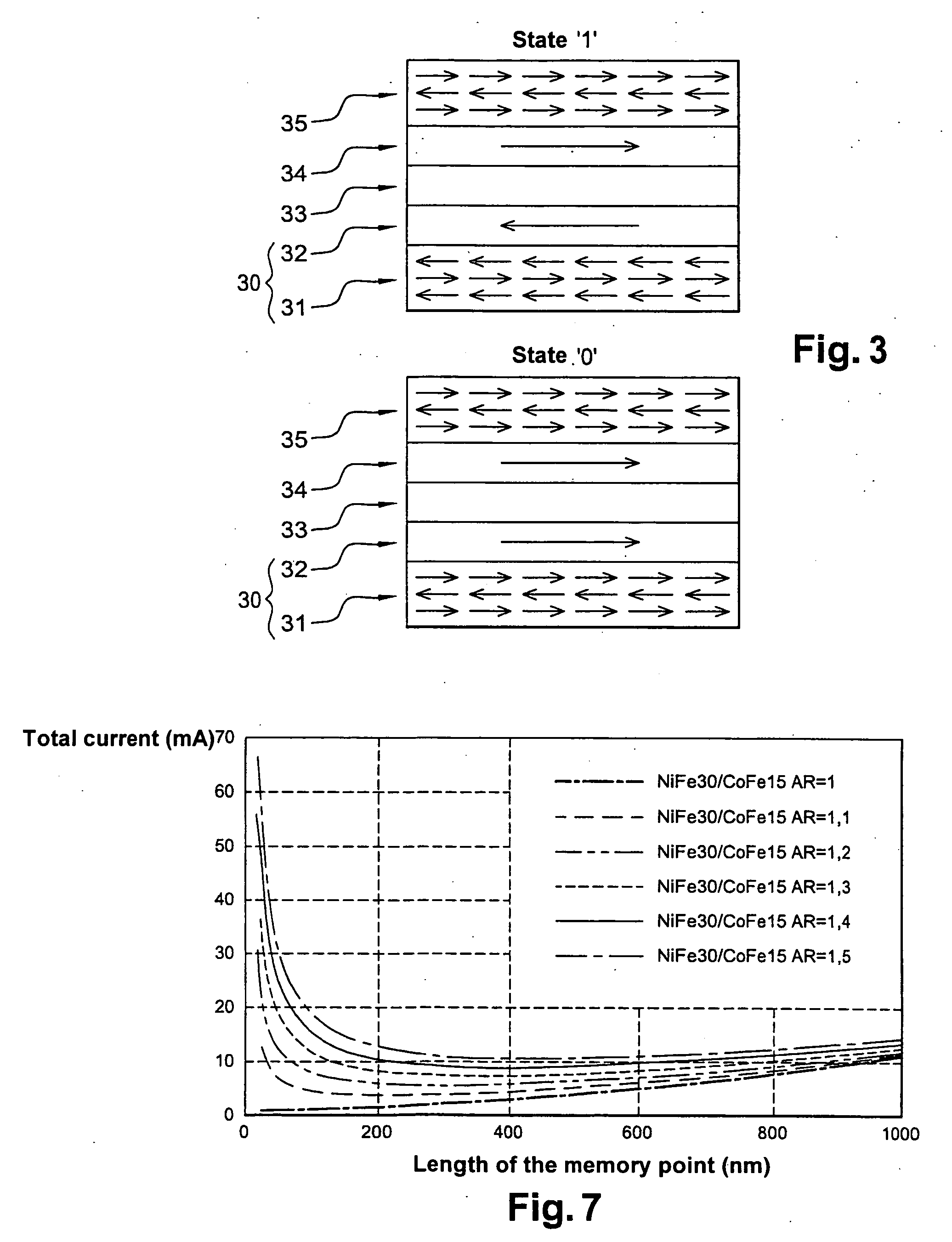
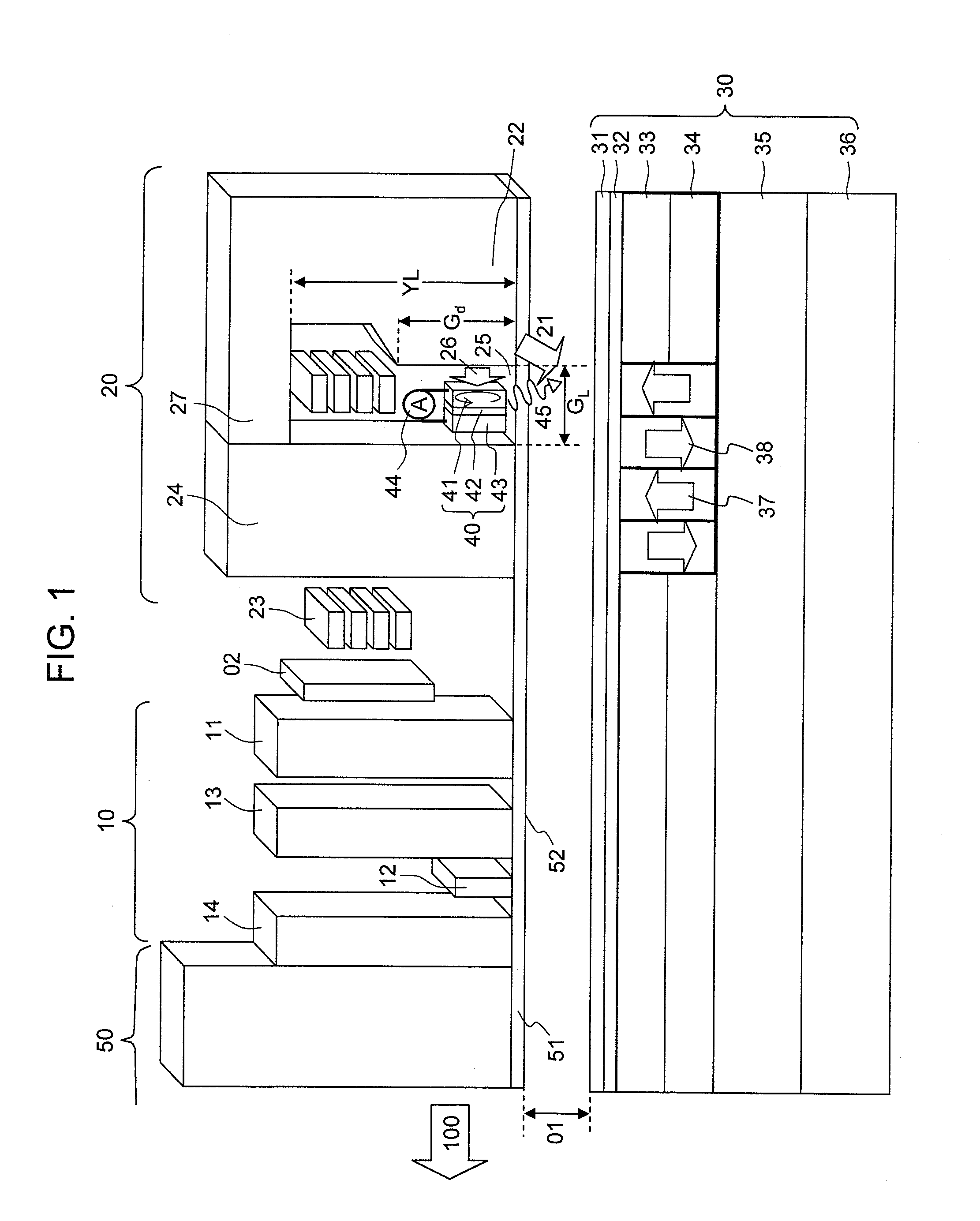
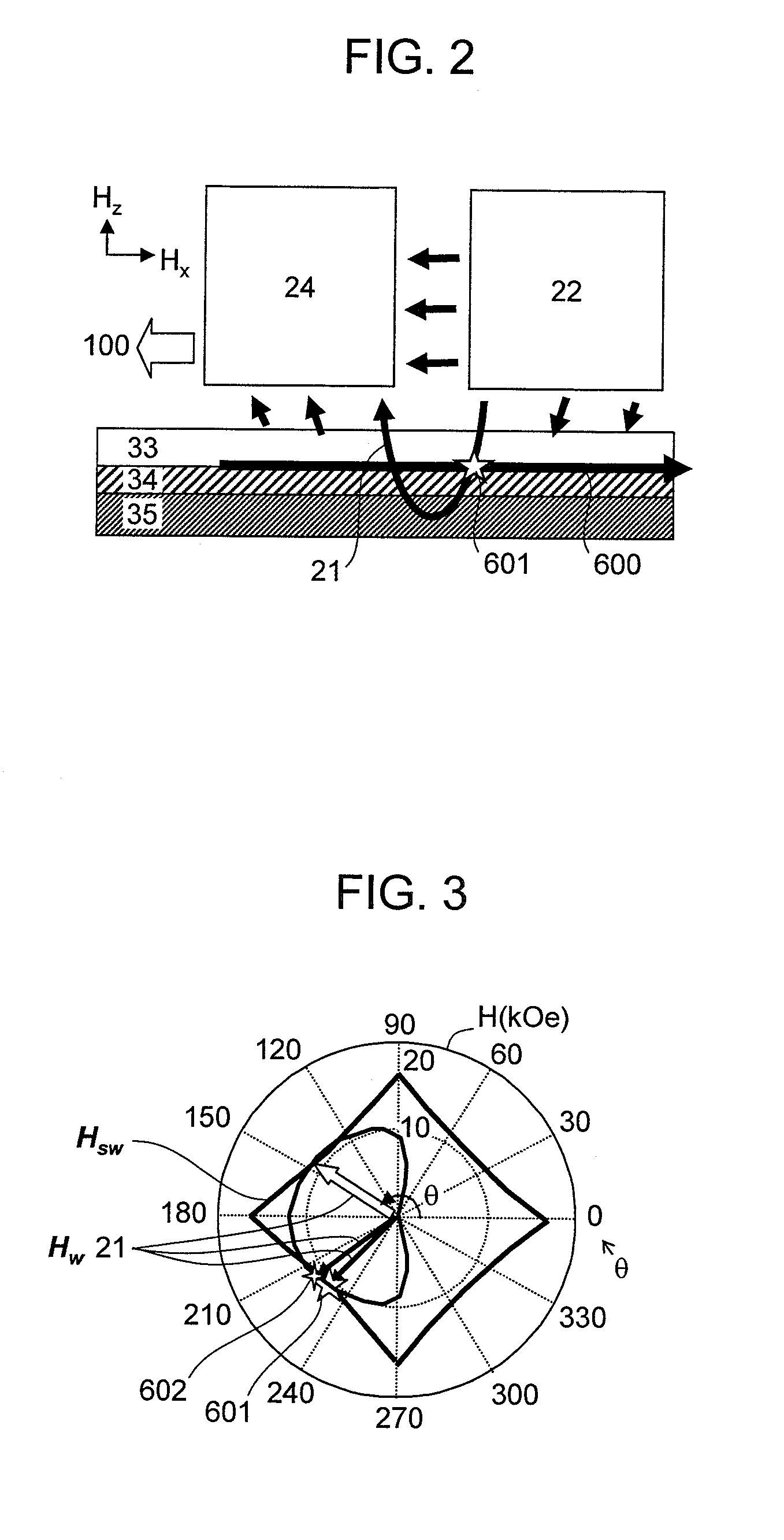
A system and method for writing to a magnetic memory written in a thermally assisted manner, each memory point formed by a magnetic tunnel junction, and having a substantially circular cross-section of the memory which is parallel to the plane of the layers forming the tunnel junction. The tunnel junction includes at least a trapped layer with a fixed magnetisation direction, a free layer with a variable magnetisation direction with an insulating layer arranged there between. The free layer is formed from at least one soft magnetic layer and a trapped layer, with the two layers being magnetically coupled by contact. During read operations and at rest, the operating temperature of the memory is lower than the blocking temperature of the free and trapped layers, respectively.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Magnetic memory with a magnetic tunnel junction written in a thermally assisted manner, and method for writing the same
ActiveUS20060291276A1Reduce magnetizationElectric power required to effect the writing of a memory point may be loweredDigital storageMagnetic memoryOperating temperature
The invention relates to a magnetic memory written in a thermally assisted manner, each memory point (40) consisting of a magnetic tunnel junction, and the cross-section of the memory parallel to the plane of the layers forming the tunnel junction being circular or essentially circular. Said tunnel junction comprises at least one trapped layer (44) with a fixed magnetisation direction, a free layer (42) with a variable magnetisation direction, and an insulating layer (43) arranged between the free layer (42) and the trapped layer (44). According to the invention, the free layer (42) is formed from at least one soft magnetic layer and a trapped layer (41), said two layers being magnetically coupled by contact, and the operating temperature of the reading memory or resting memory is selected in such a way that it is lower than the blocking temperature of the respectively free and trapped layers.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Magnetic head, magnetic recording method and apparatus for controlling magnetic head with spin torque oscillator in a disk drive
ActiveUS20130229895A1Improve recording densityThe implementation process is simpleManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
A microwave assisted magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole unit that produces a recording field for writing to a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, and a high-frequency magnetic field oscillator that produces a high-frequency magnetic field. The recording magnetic pole unit includes a magnetic core with a write gap portion at which a main recording field component is concentrated, and the high-frequency magnetic field oscillator is disposed in the write gap.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Low power consumption magnetic memory and magnetic information recording device
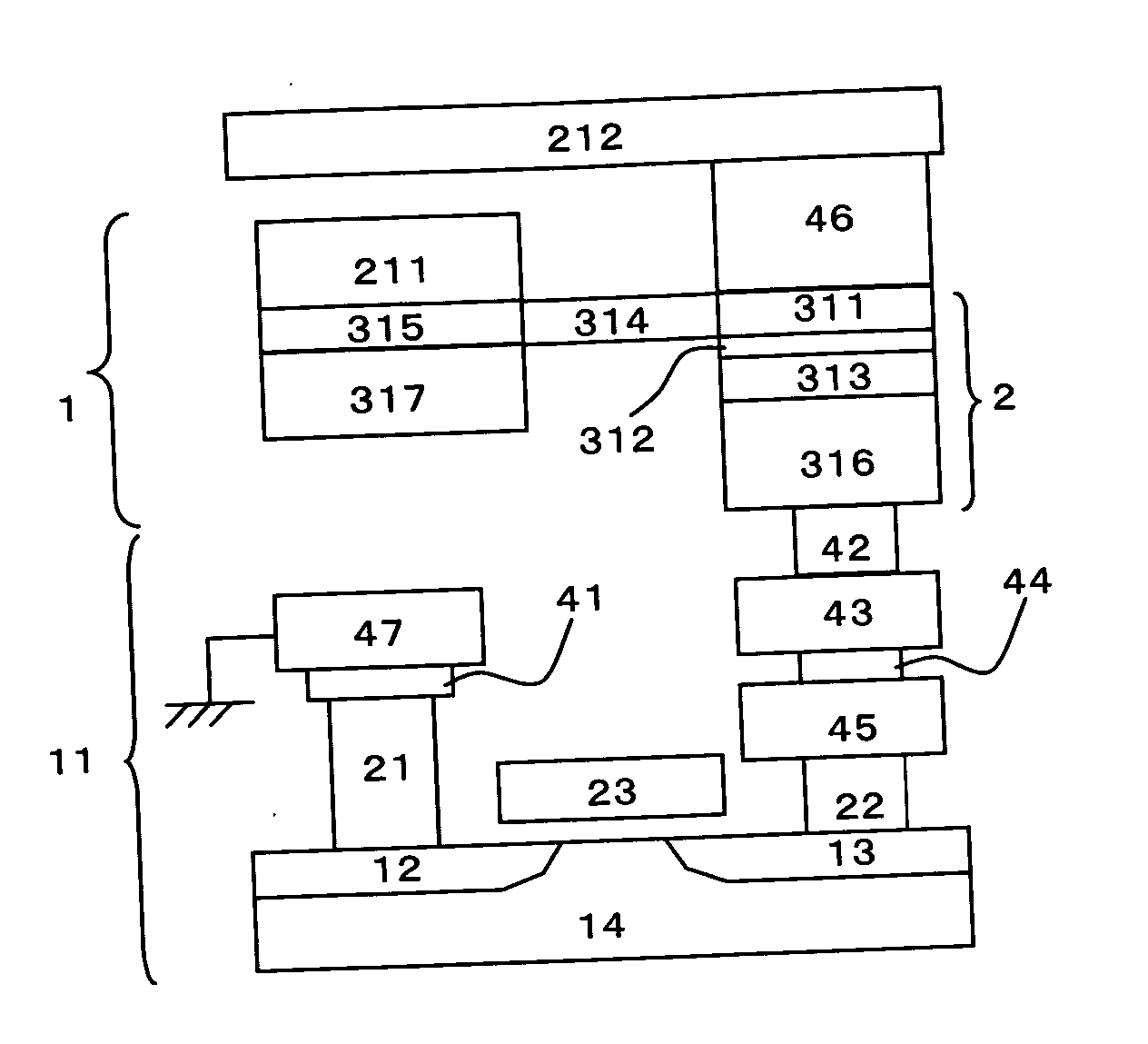
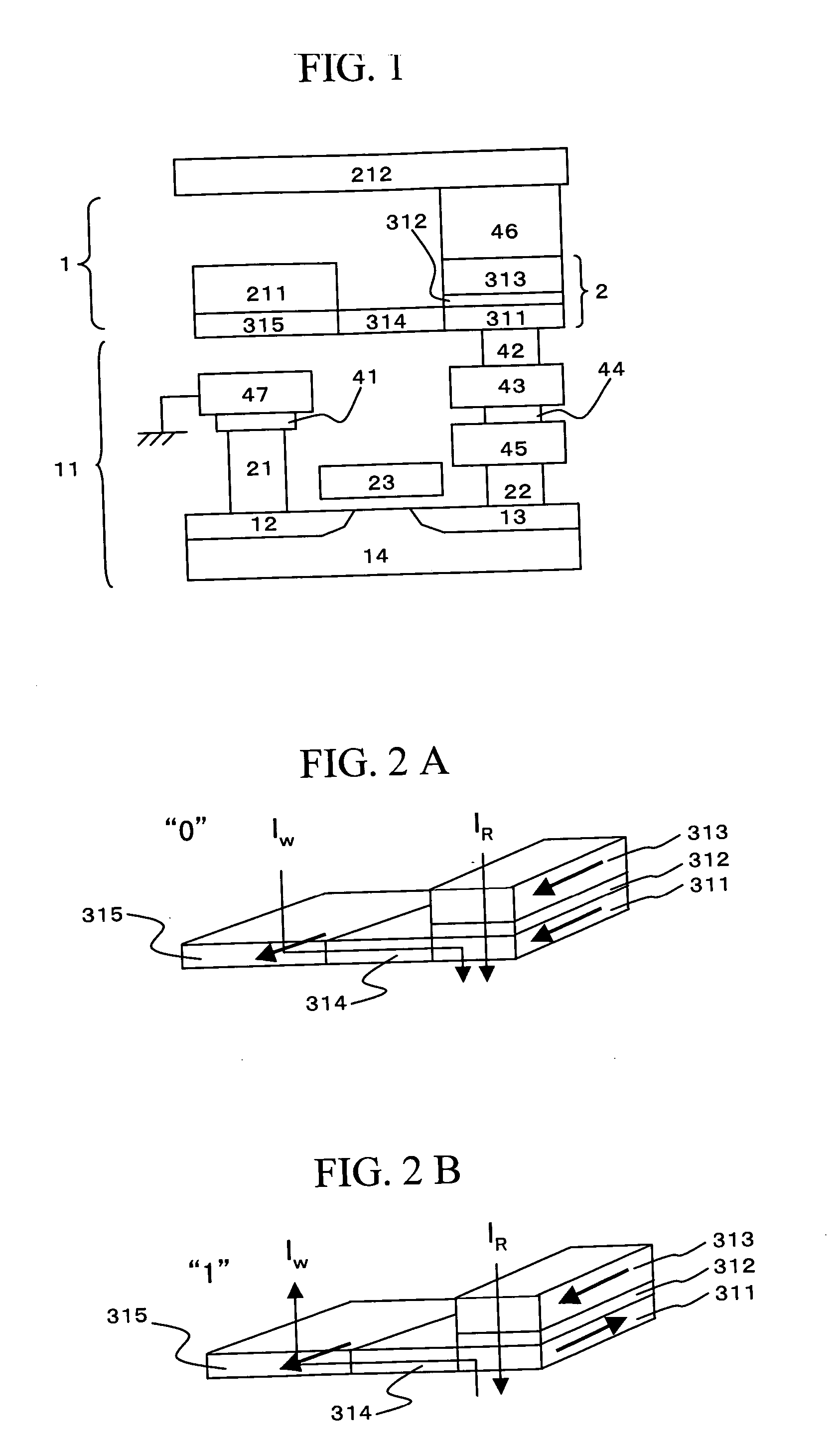
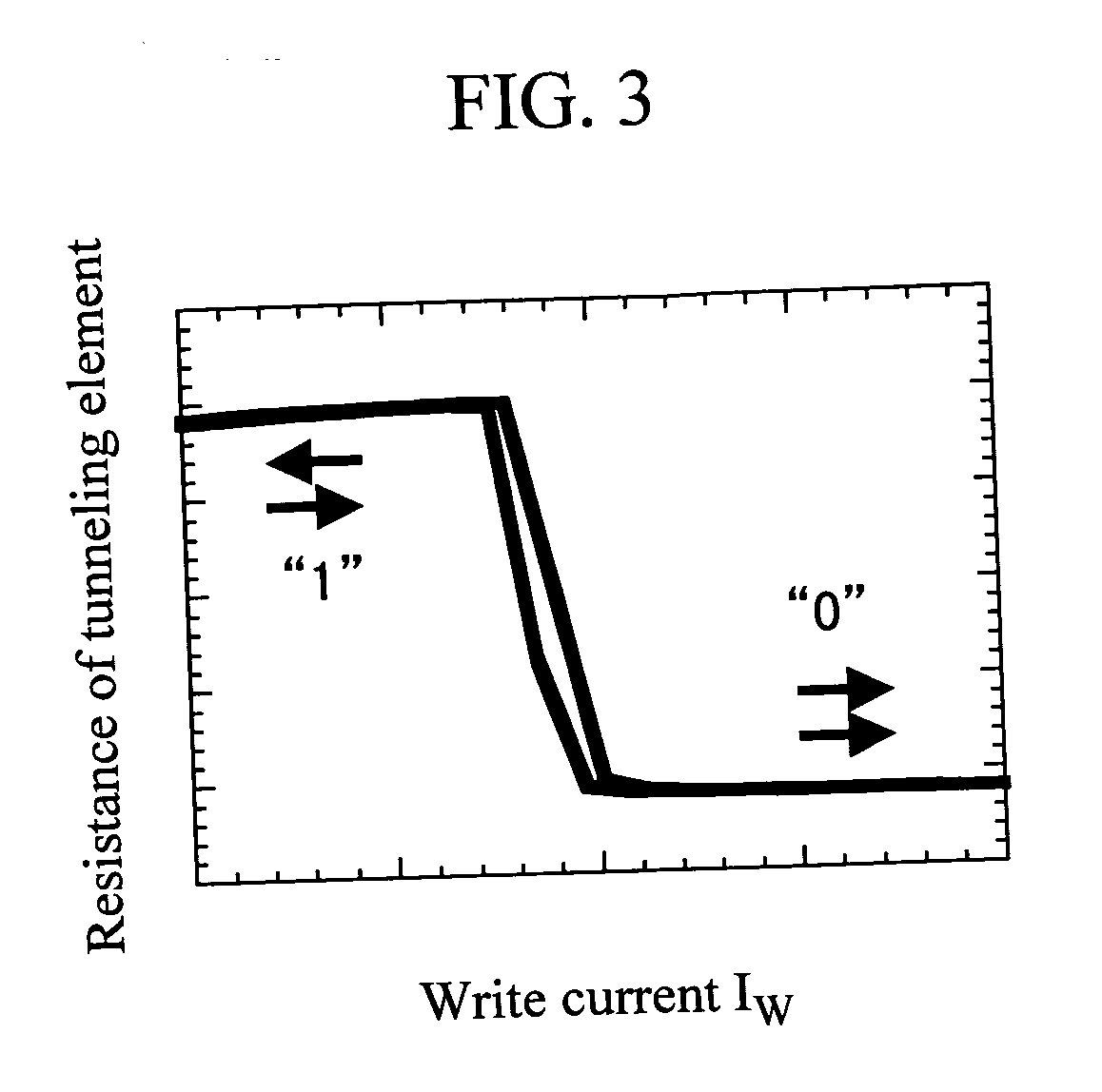
ActiveUS20060067116A1Reduce power consumptionReduce magnetizationTransistorSolid-state devicesMagnetic memoryNon magnetic
A highly integrated magnetic memory with low power consumption is provided. A first element portion which has a free layer, a first pinned layer formed in the film thickness direction of the free layer, and an insulation barrier layer formed between the free layer and the first pinned layer, and a second element portion which has the aforementioned free layer, a second pinned layer formed in the film surface direction of the free layer, and a non-magnetic layer formed between the free layer and the second pinned layer are provided. A current IW flows in the film surface direction of the second element portion for writing the magnetic information and a current IR flows in the film thickness direction of the first element portion for reading the magnetic information.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
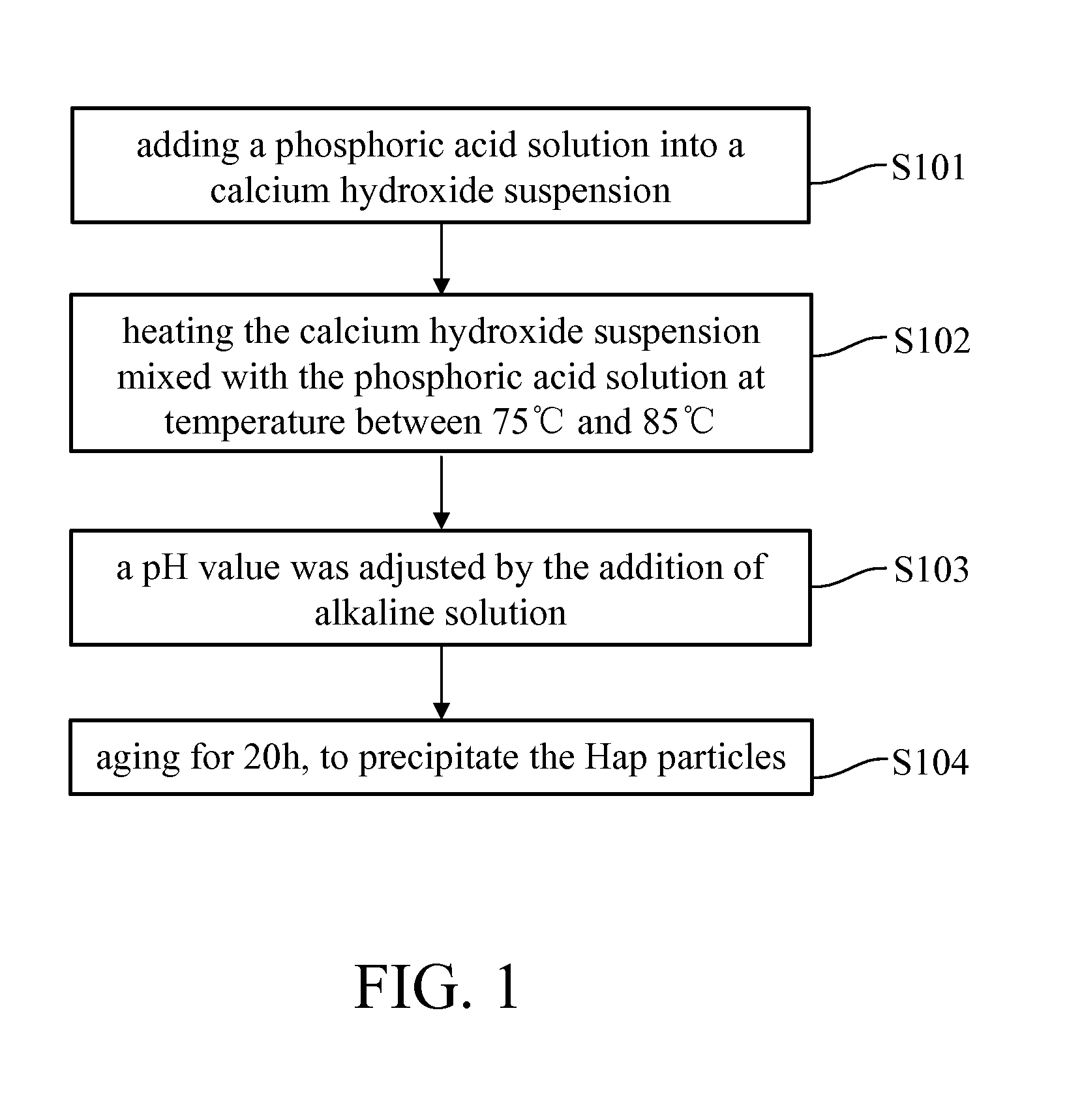
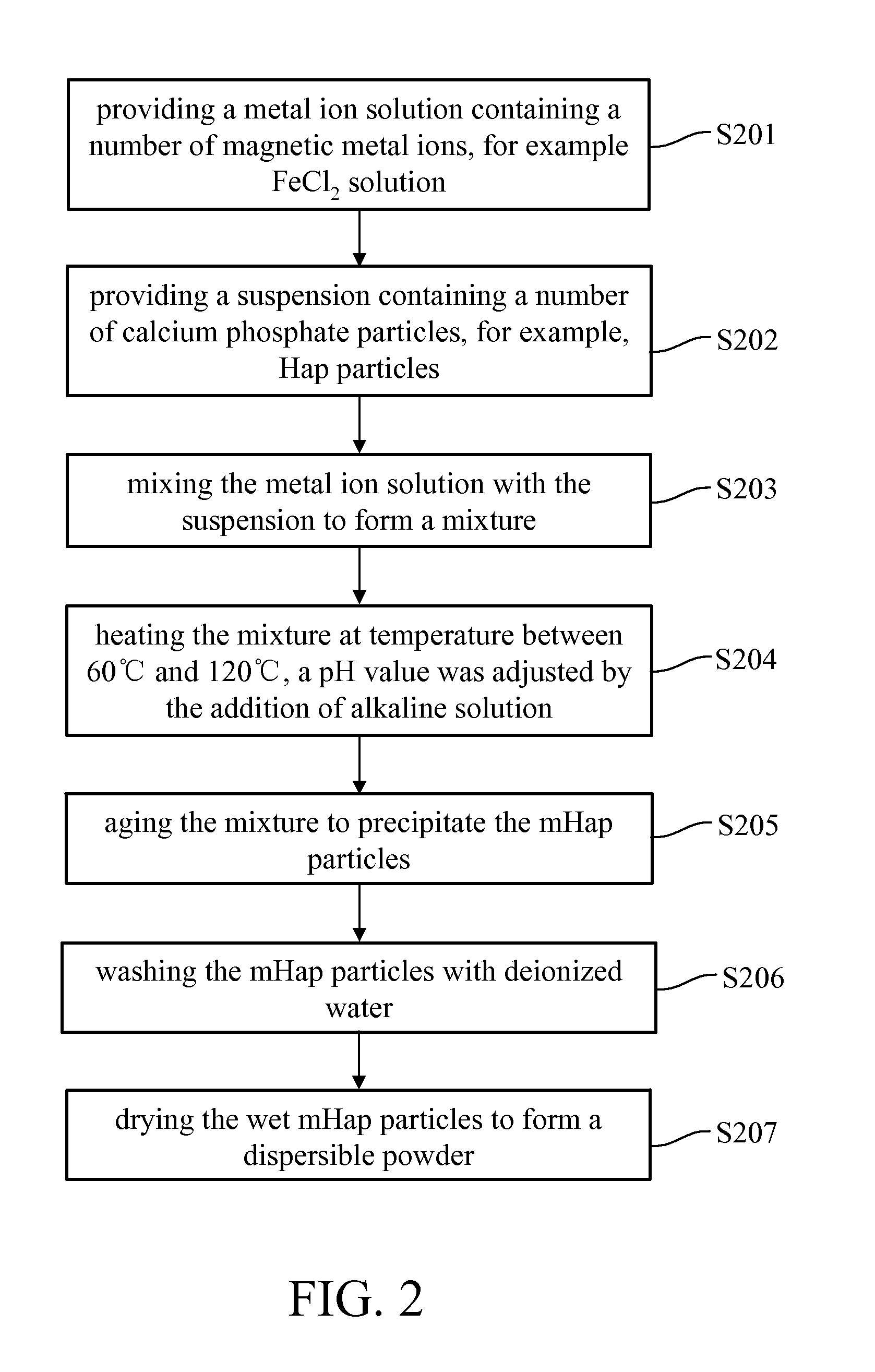
Superparamagnetic nanoparticles IN MEDICAL THERAPEUTICS and manufacturing method THEREOF
InactiveUS20110135577A1Safe and effectiveAvoid problemsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelivery vehicleMagnetite
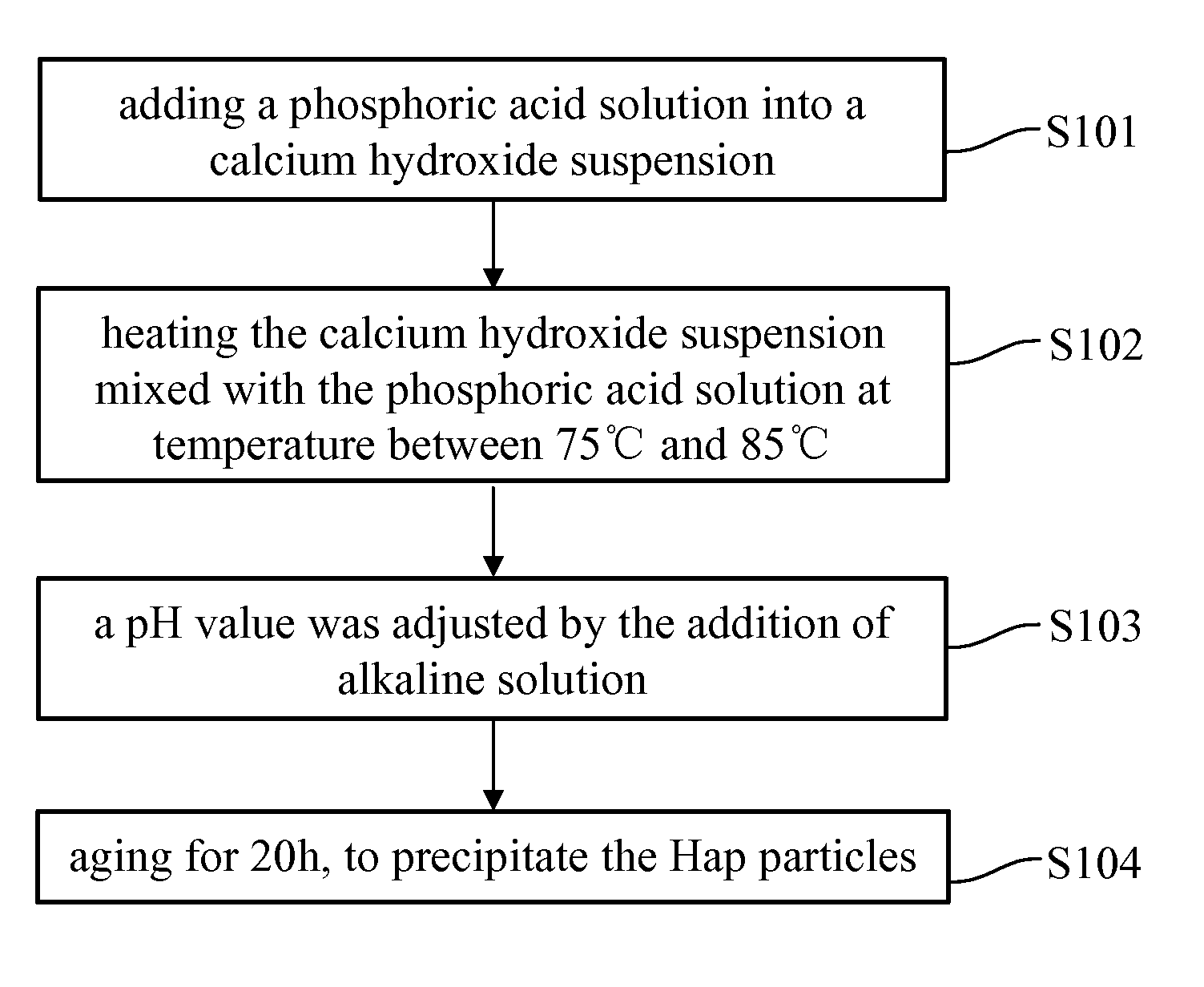
The successful transfer of therapeutic agents such as genetic materials (e.g. nucleic acid) or drug into living cells is the most important issue depending on the development of the delivery carrier. A method for manufacturing superparamagnetic nanoparticles in medical therapeutics is described to develop nano-sized calcium phosphate (CaP) mineral was rendered magnetic as delivery vehicle. The CaP-based magnetized nanoparticles (NPs) were possessed superparamagnetic property by hetero-epitaxial growth of magnetite on the CaP crystallites and also showed no harm to the cultured cells and elicited no cytotoxicity. The magnetized CaP was demonstrated to have good plasmid DNA binding affinity or drug carrying capacity. It significantly increased the expression of gene transfection and efficiency in delivery to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) under exogenous magnetic field. According to the above facts, this newly-synthesized magnetized CaP NPs has great potential as a novel non-viral targeted delivery vehicle to be applied for medical applications.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Magnetoresistive device and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7538402B2Reducing a magnetic field necessaryIncreased writing marginNanomagnetismDigital storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic memory
Owner:NEC CORP
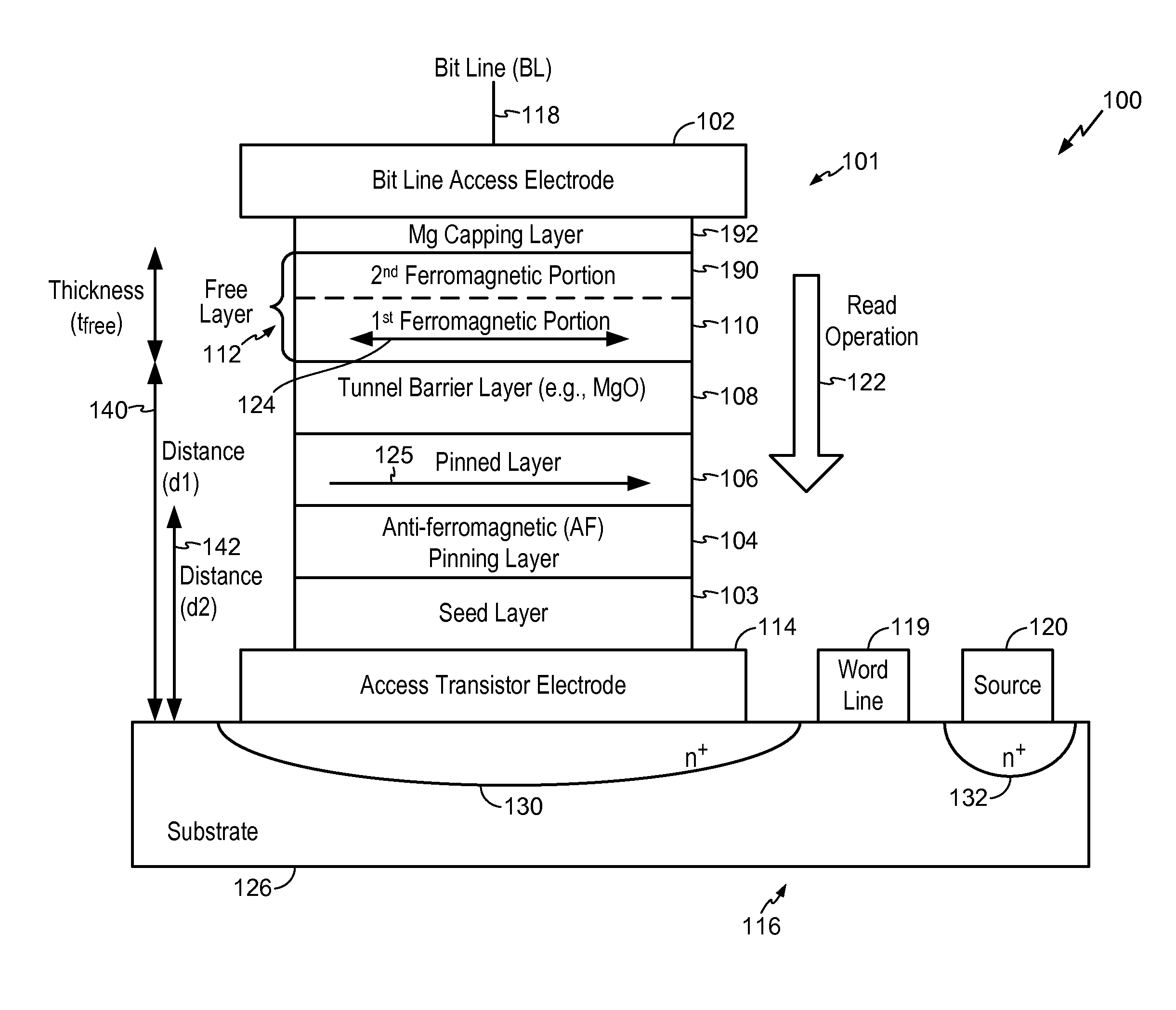
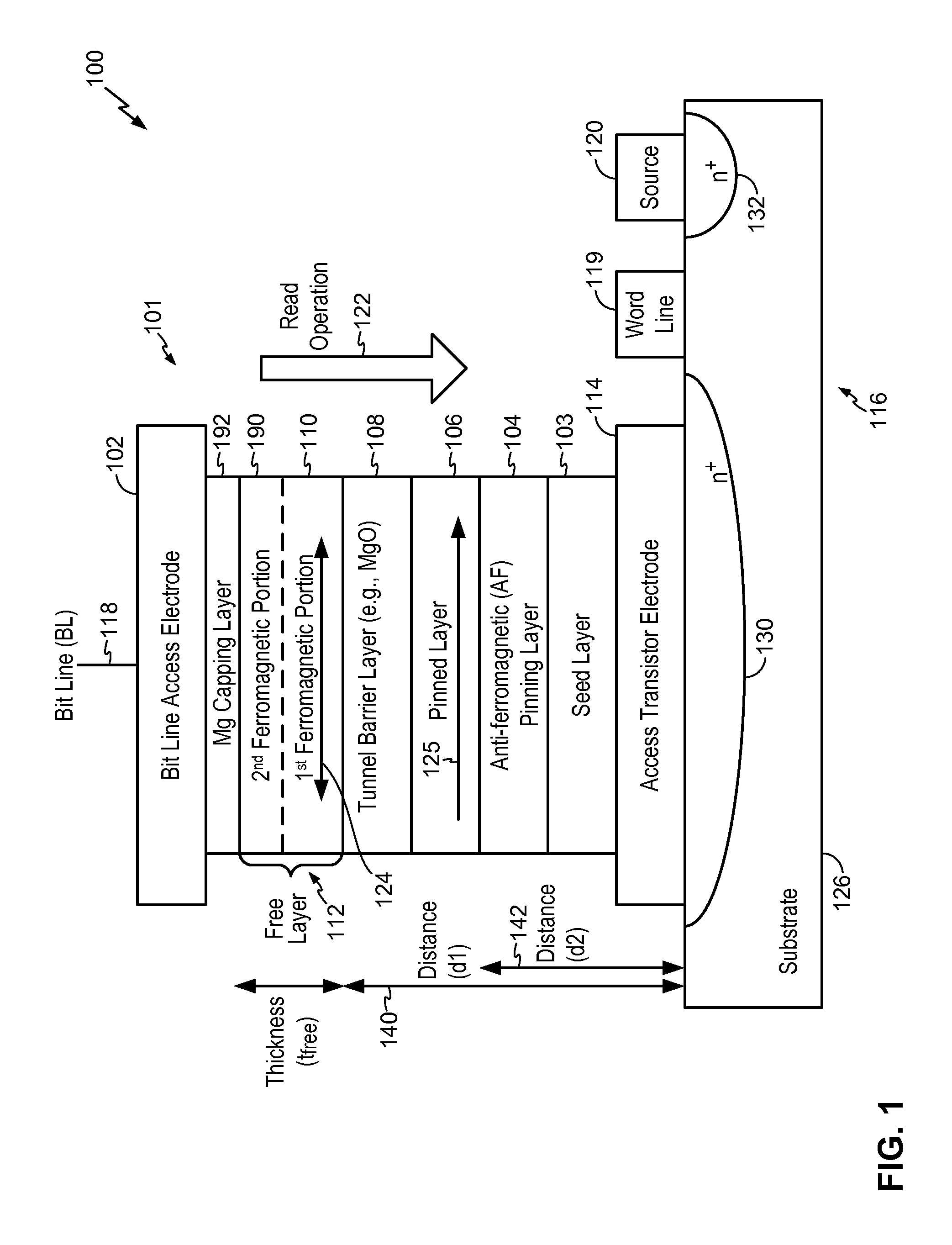
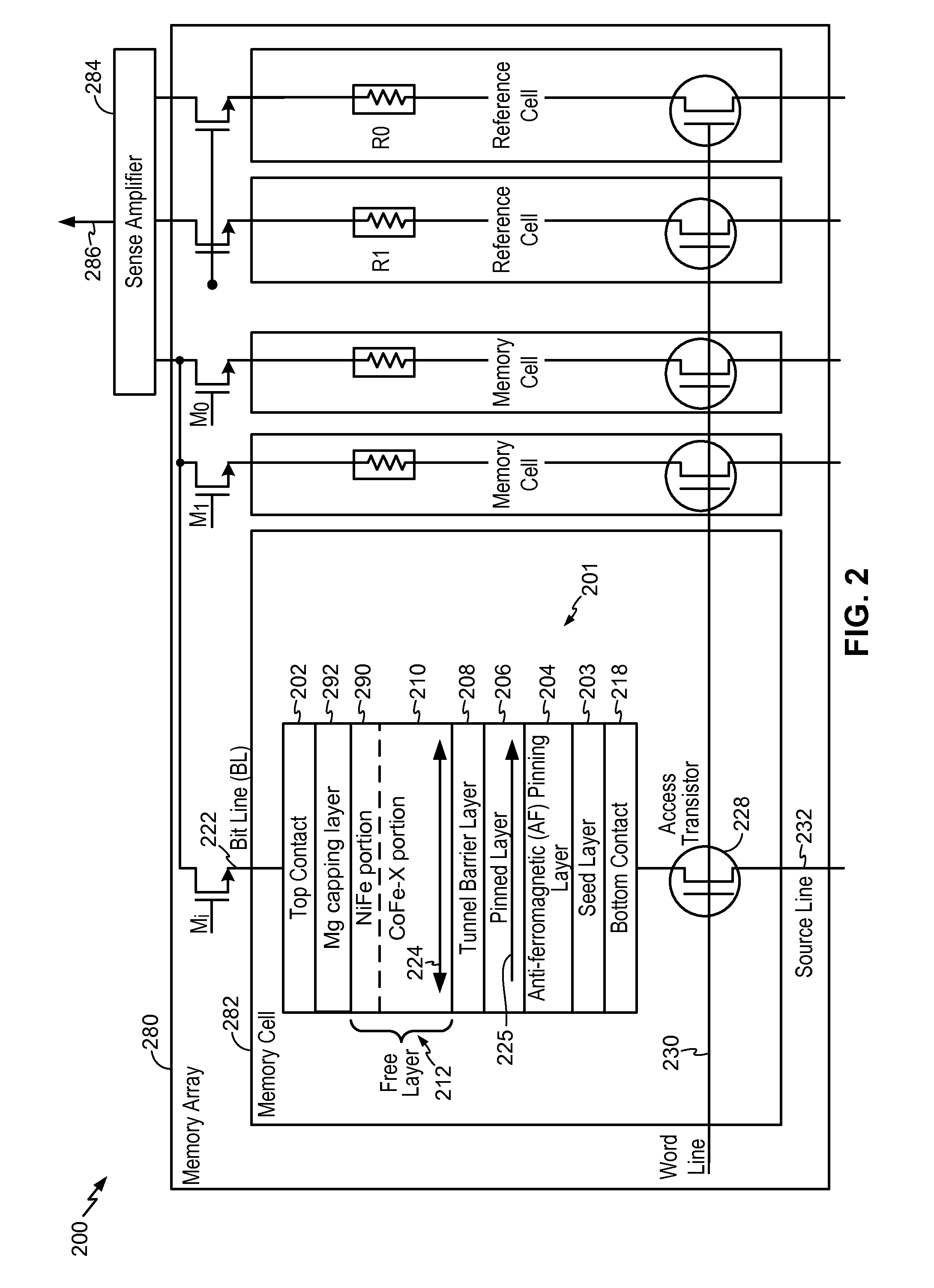
Magnetic Tunnel Junction Device and Fabrication
InactiveUS20110141796A1Improve crystallizationImprove thermal stabilityGalvano-magnetic material selectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringTunnel junction
A magnetic tunneling junction (MTJ) device and fabrication method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, an apparatus is disclosed that includes an MTJ device. The MTJ device includes a barrier layer, a free layer, and a magnesium (Mg) capping layer. The free layer is positioned between the barrier layer and the magnesium (Mg) capping layer.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Magnetoresistance element and storage device using the same
ActiveUS20110310660A1Easy to operateIncrease the number ofNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic memoryNon magnetic
A magnetic memory element having a memory cell of size 4F2 is provided that realizes a crosspoint-type memory. In the magnetic memory element, a first magnetic layer, a third magnetic layer (spin polarization enhancement layer), an intermediate layer, a fourth magnetic layer (spin polarization enhancement layer), and a second magnetic layer are stacked in order. The intermediate layer is made of an insulating material or a nonmagnetic material. The second magnetic layer is composed of a ternary alloy of gadolinium, iron and cobalt, a binary alloy of gadolinium and cobalt, or a binary alloy of terbium and cobalt. Alternatively, the first magnetic layer is composed of a ternary alloy of terbium, iron and cobalt, or a binary alloy of terbium and cobalt.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Soft magnetic underlayer with exchange coupling induced anisotropy for perpendicular magnetic recording media
InactiveUS7241516B1Reduction of domain noiseReducing pulse widthRecord information storageMagnetic recordingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Coupling
An improved soft underlayer structure for perpendicular magnetic recording. The structure includes at least two soft underlayers separated by a non-magnetic spacer layer. The soft underlayer structure incorporates exchange coupling induced anisotropy for improved perpendicular magnetic recording properties, including an improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and reduced adjacent track erasure.
Owner:MAXTOR
Method of producing magnetic recording medium, and magnetic recording and reading device
ActiveUS20100165504A1Maintain good propertiesExcellent high recording-density propertyDriving/moving recording headsVacuum evaporation coatingReactive plasmaNon magnetic
The present invention aims to provide a method of producing a magnetic recording medium which is a method of producing a magnetic recording medium having a magnetically-separated magnetic recording pattern, the method including: forming a magnetic layer on a non-magnetic substrate; then exposing a surface of the magnetic layer partially to reactive plasma, or a reactive ion generated in the plasma to amorphize the portion of the magnetic layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Magneto-resistance effect element, magnetic head, magnetic recording/reproducing device and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20080080098A1Remarkable effectLower resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
A magneto-resistance effect element includes: a first magnetization layer of which a magnetization is substantially fixed in one direction; a second magnetization layer of which a magnetization is rotated in accordance with an external magnetic field; an intermediate layer which contains insulating portions and magnetic metallic portions and which is provided between the the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer; and a pair of electrodes to flow current in a direction perpendicular to a film surface of a multilayered film made of the first magnetic layer, the intermediate layer and the second magnetic layer; wherein the magnetic metallic portions of the intermediate layer contain non-ferromagnetic metal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
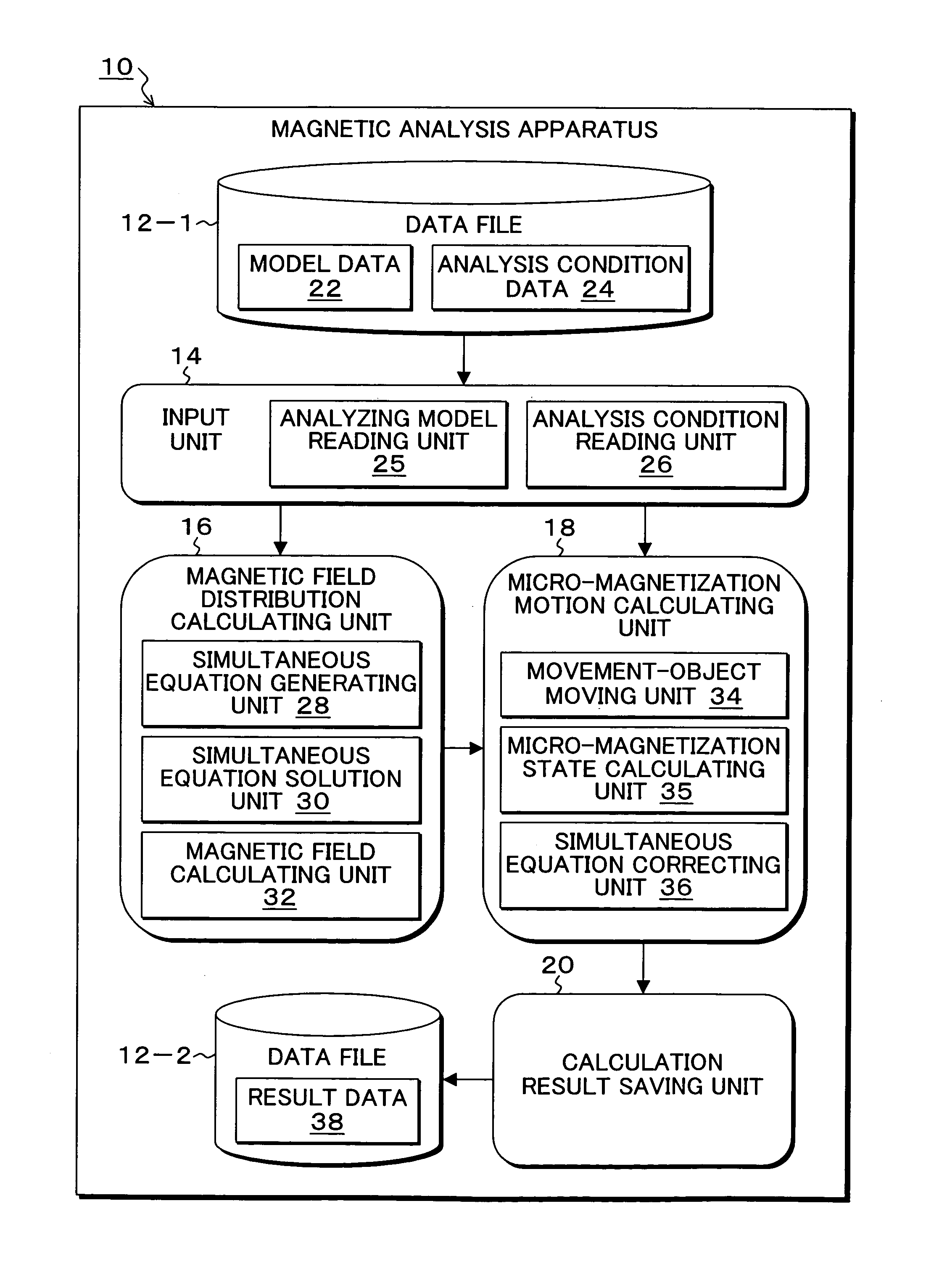
Micro-magnetization analysis program, method, and apparatus
InactiveUS7236899B1Reduce generationReduce magnetizationSpectral/fourier analysisMagnetic measurementsSimultaneous equationsMagnetization
A micro-magnetization analysis program, method, and apparatus which can analyze transitional change of a micro-magnetization state while one of a plurality of magnetic substances such as a recording medium and a recording head is moved in an arbitrary direction. An input unit reads an analysis object model in which merely regions of a magnetic substance fixed in a space and a magnetic substance to be moved are subjected to mesh-division into minute elements and analysis conditions. A magnetic field distribution calculating unit generates a first magnetic field equation, generates a second magnetic field equation, and solves the simultaneous equations thereof.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
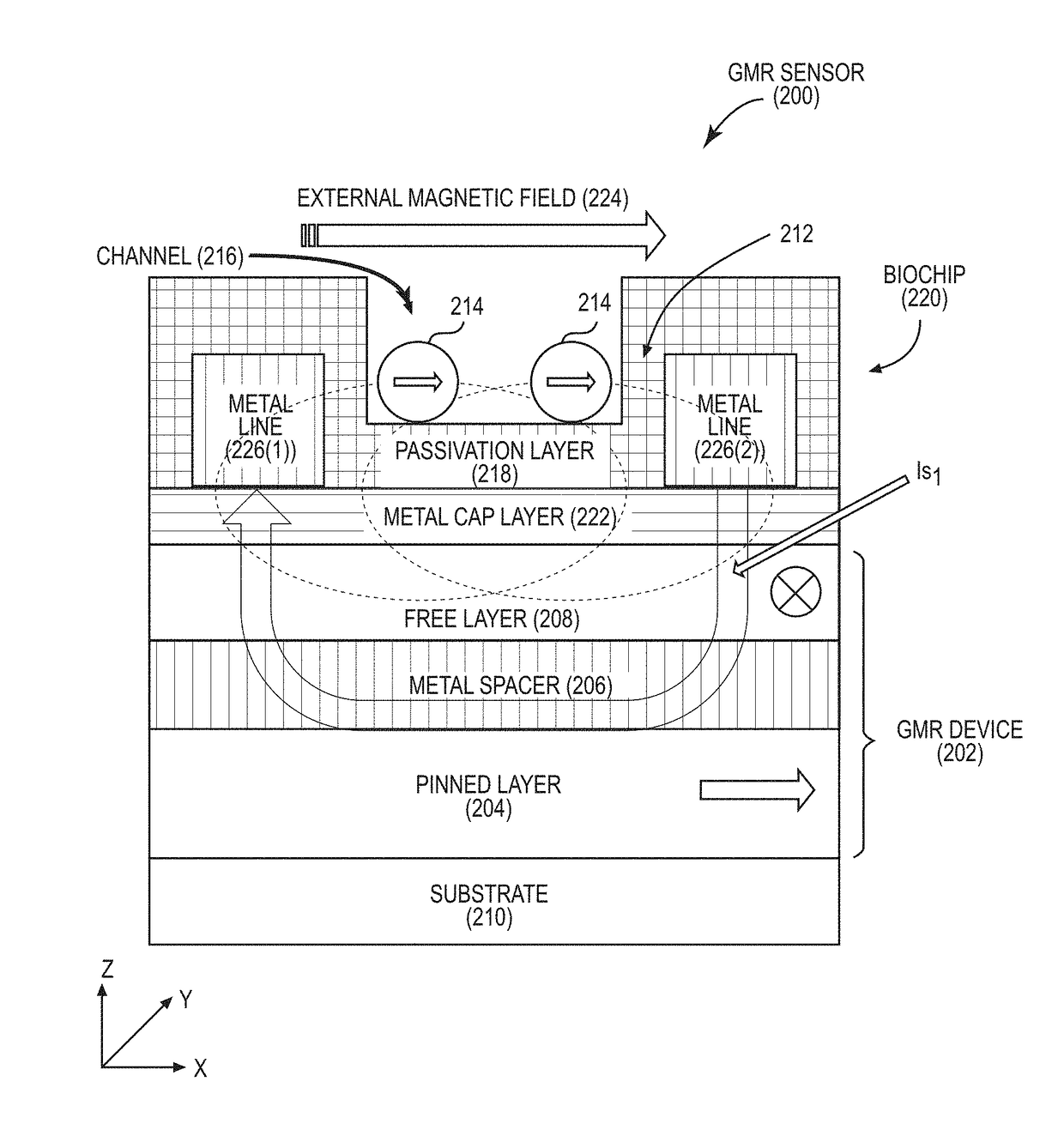
Tunnel magneto-resistive (TMR) sensors employing tmr devices with different magnetic field sensitivities for increased detection sensitivity
ActiveUS20180284200A1Easy to changeReduce magnetization angleMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic anisotropy
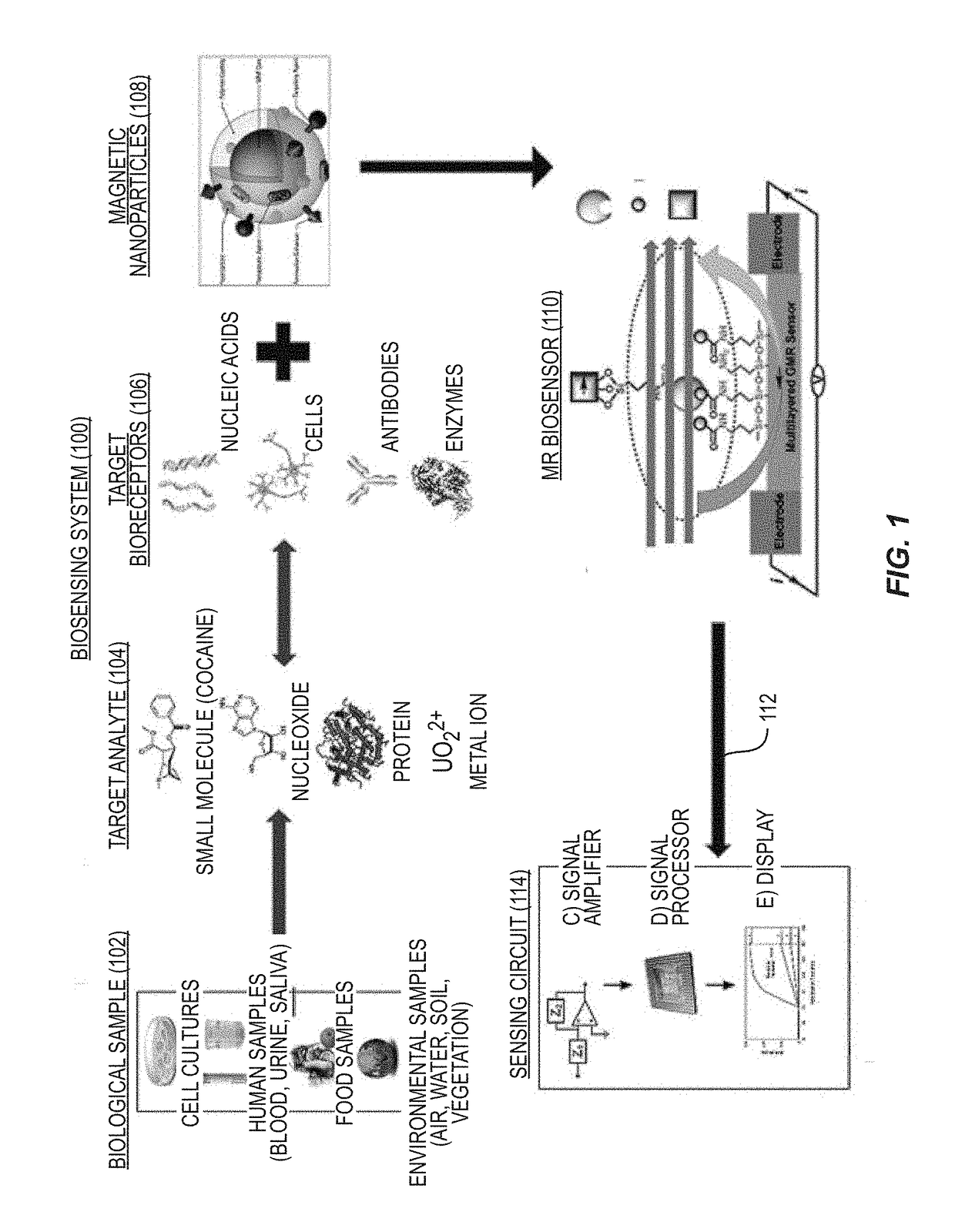
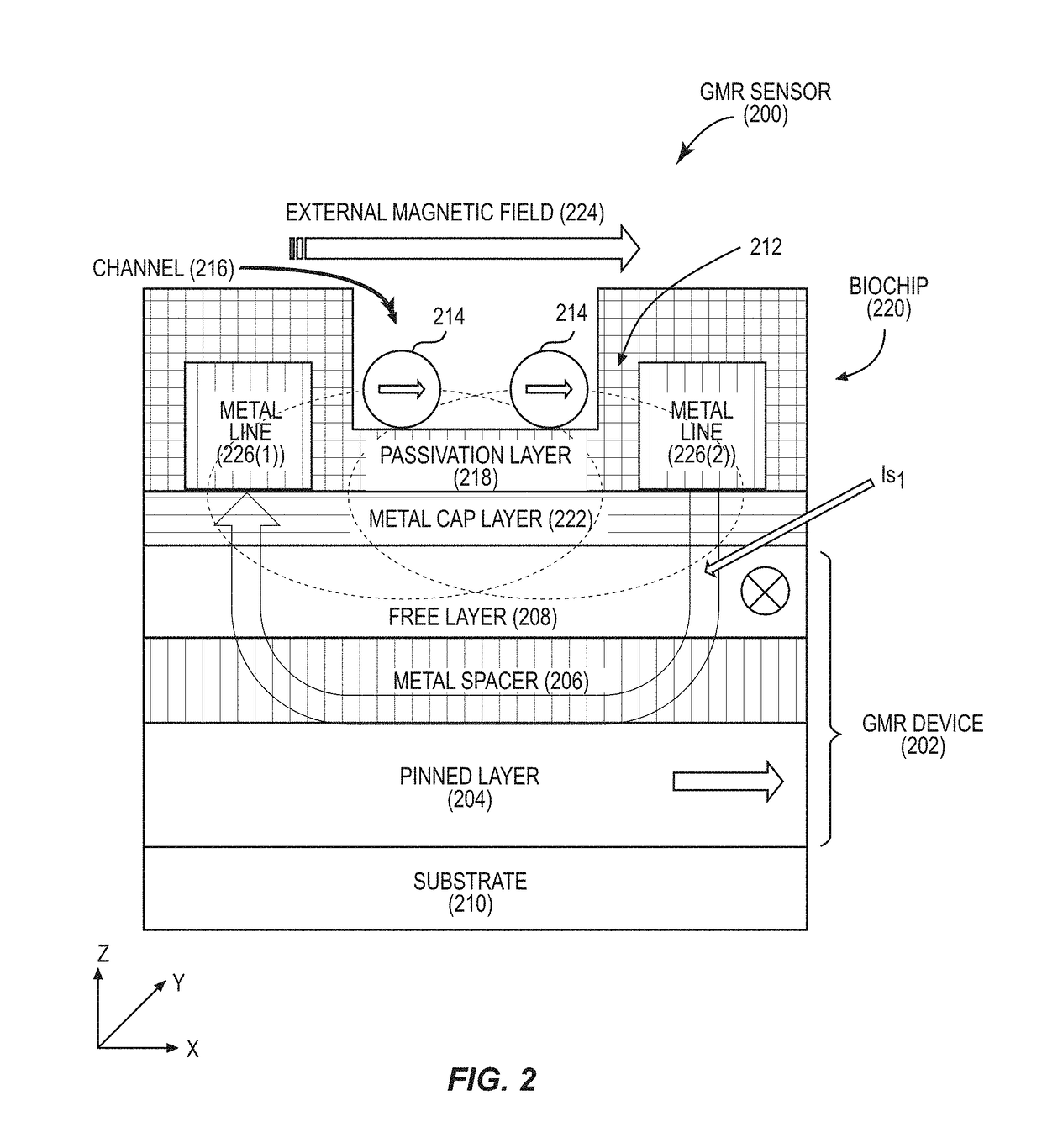
Tunnel magneto-resistive (TMR) sensors employing TMR devices with different magnetic field sensitivities for increased detection sensitivity are disclosed. For example, a TMR sensor may be used as a biosensor to detect the presence of biological materials. In aspects disclosed herein, free layers of at least two TMR devices in a TMR sensor are fabricated to exhibit different magnetic properties from each other (e.g., MR ratio, magnetic anisotropy, coercivity) so that each TMR device will exhibit a different change in resistance to a given magnetic stray field for increased magnetic field detection sensitivity. For example, the TMR devices may be fabricated to exhibit different magnetic properties such that one TMR device exhibits a greater change in resistance in the presence of a smaller magnetic stray field, and another TMR device exhibits a greater change in resistance in the presence of a larger magnetic stray field.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
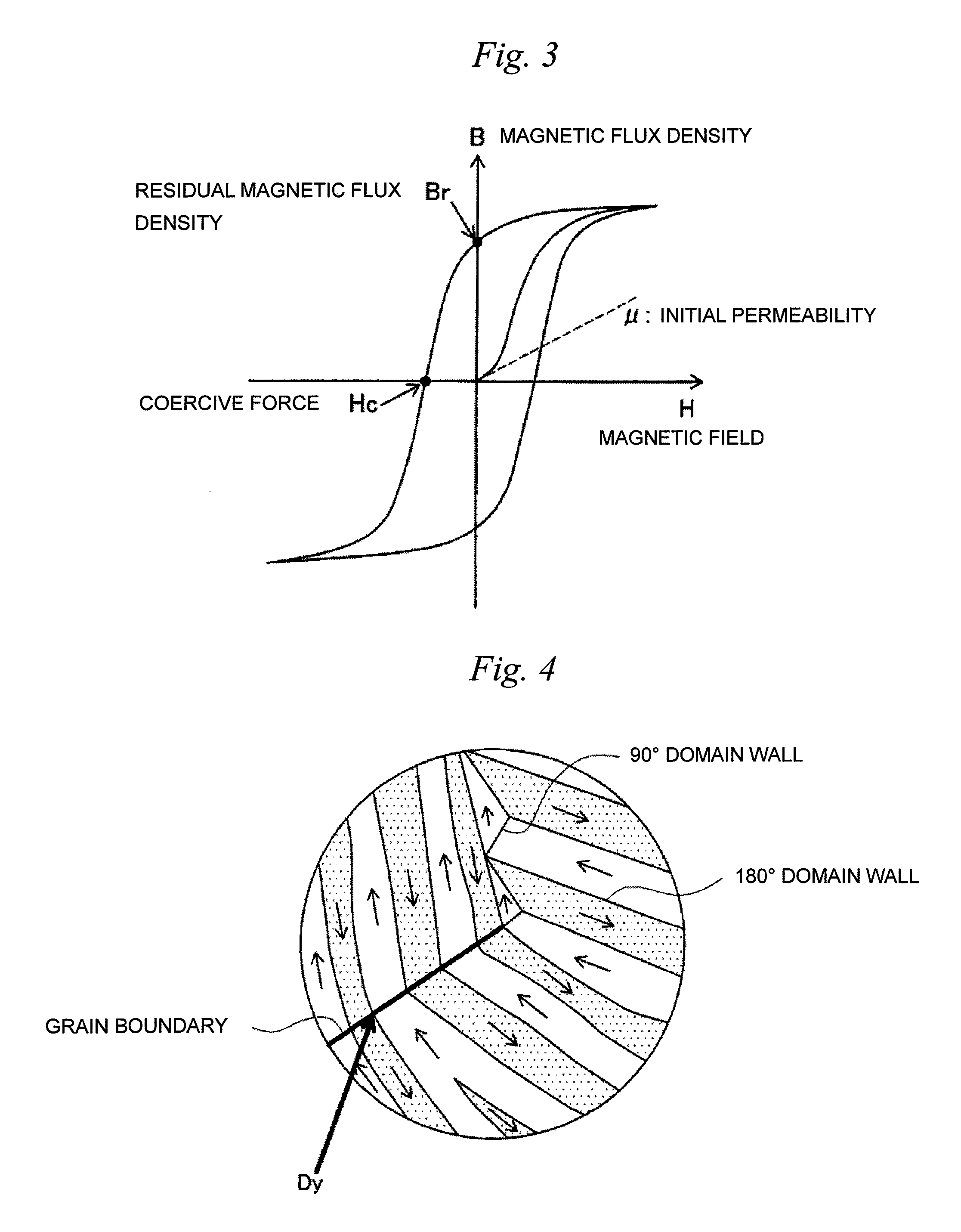
Permanent magnet and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110018664A1Improve coercive forceDecrease residual magnetizationPermanent magnetsCeramic shaping apparatusMagnetMetallurgy
The present invention relates to a permanent magnet obtained by wet-mixing a Dy compound or a Tb compound with a magnet raw material to coat a surface of the magnet raw material with the Dy compound or the Tb compound, and sintering a green sheet obtained by mixing the resulting magnet raw material with a resin binder and molding the resulting mixture. Since the present invention has the above-mentioned constitution, it becomes possible to sufficiently improve coercive force by Dy or Tb while decreasing the amount of Dy or Tb used. Further, it can be prevented that Dy or Tb is solid-solutionized in magnet particles to decrease residual magnetization.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Apparatus and method for recording information
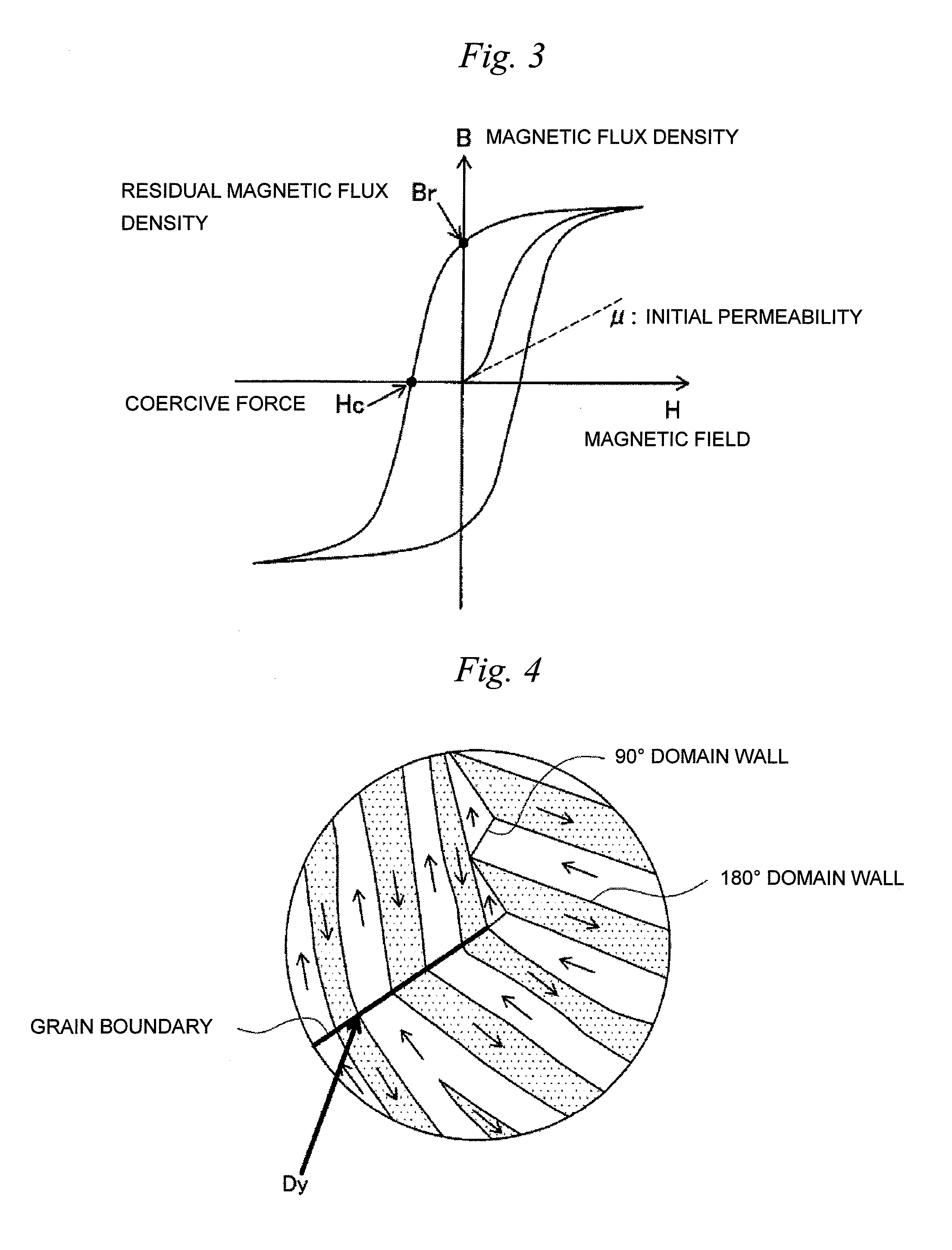
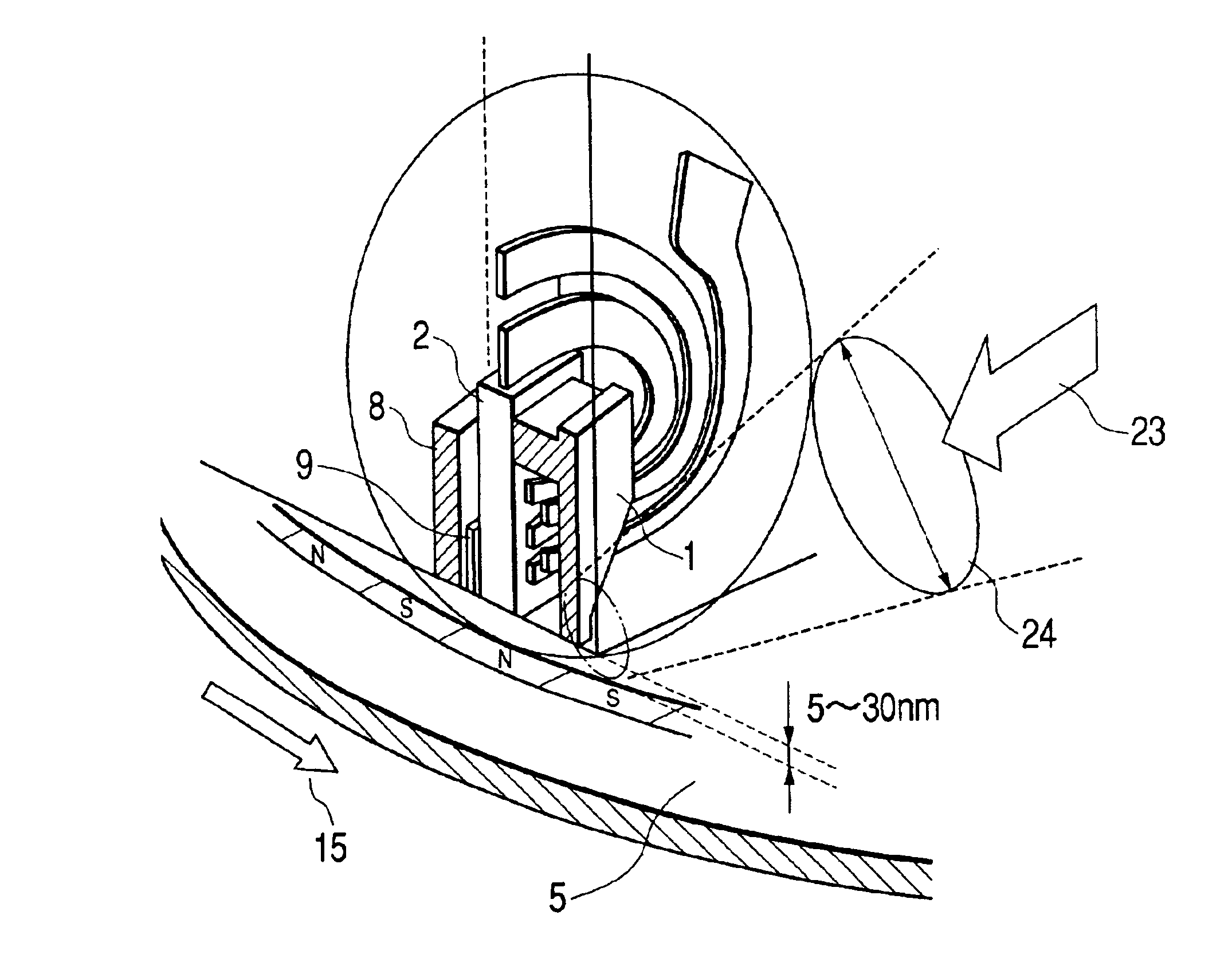
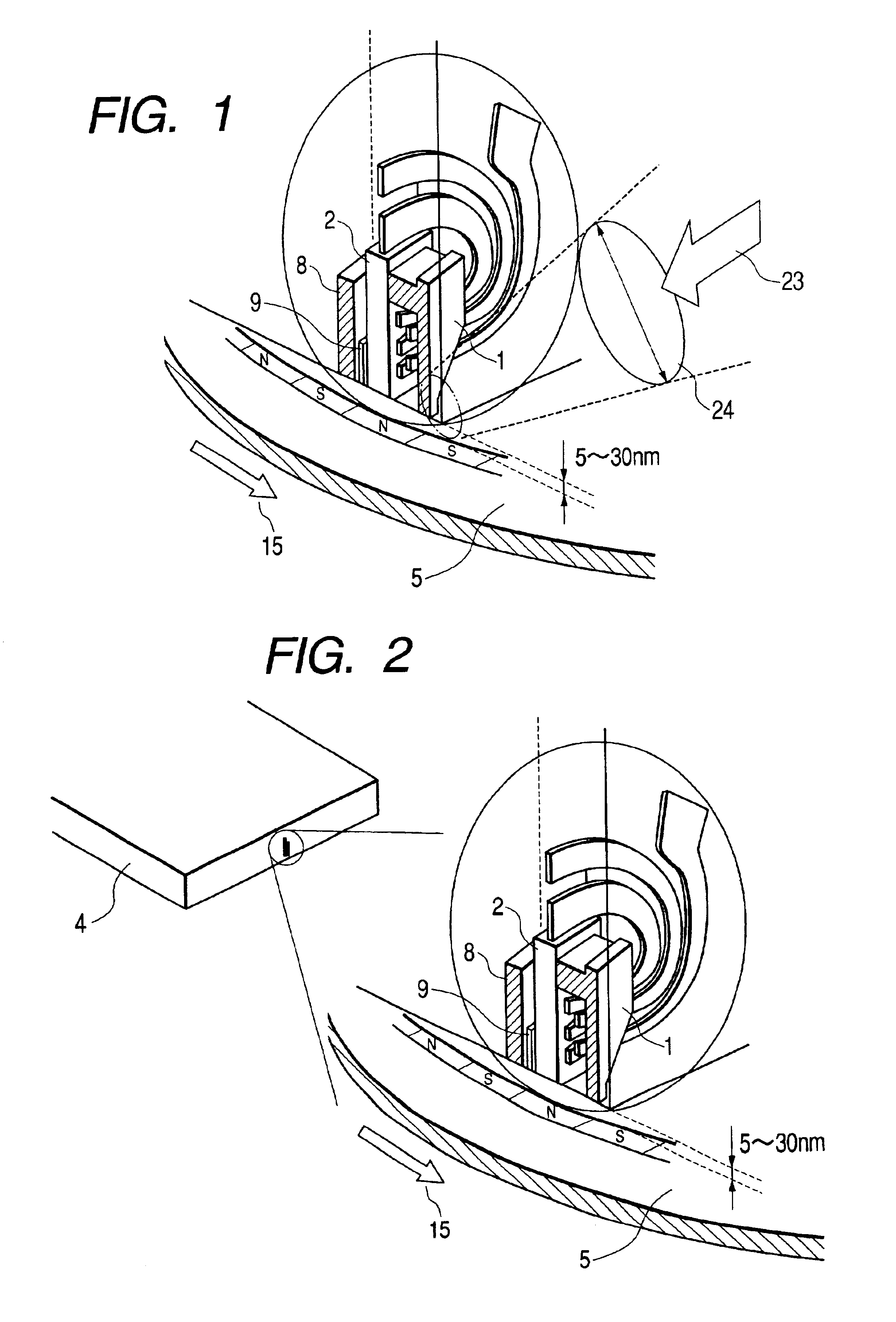
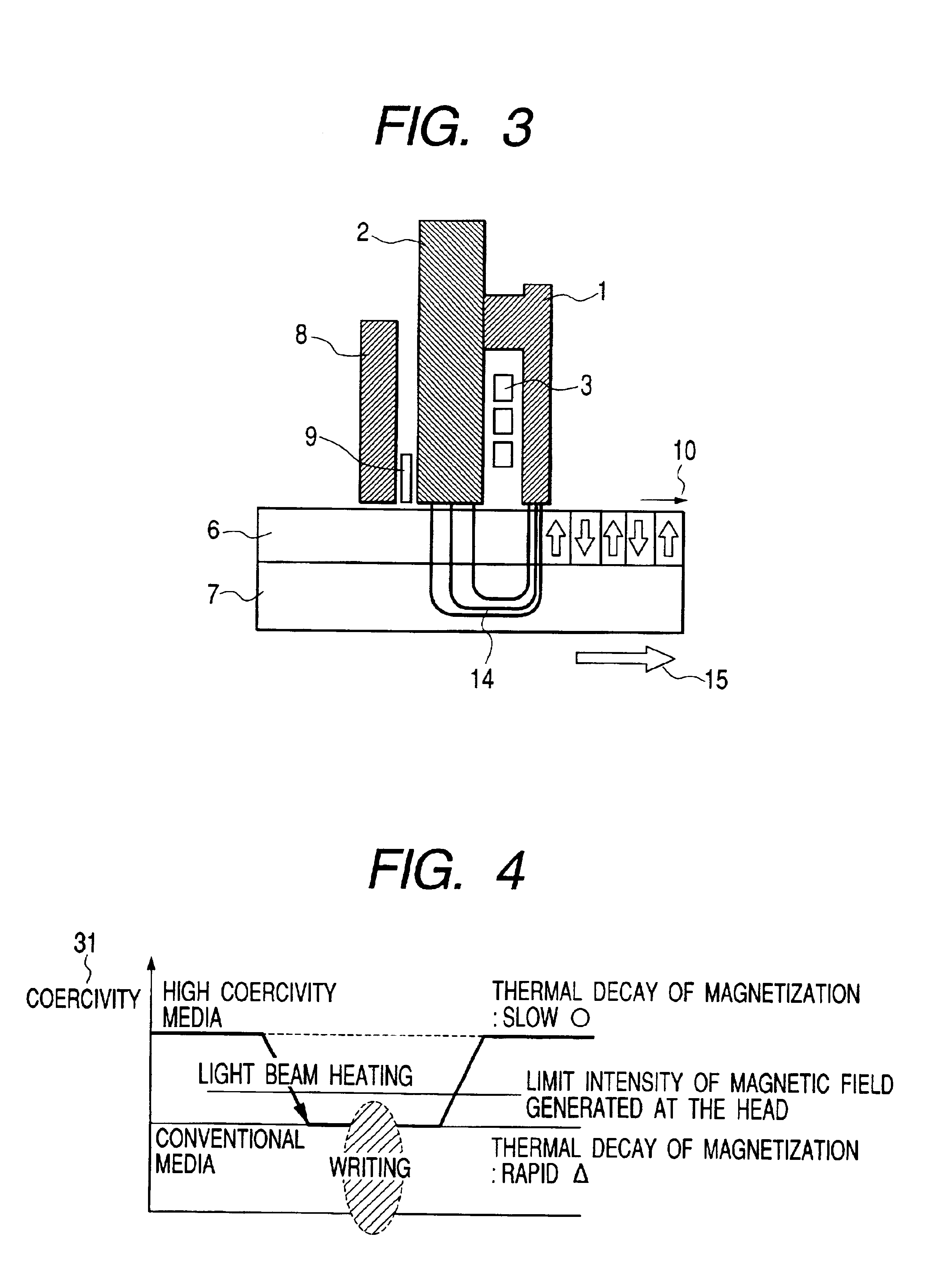
ActiveUS6952380B2Reduce magnetizationImprove reliabilityRecording by magnetic meansRecord information storageRoom temperatureThermal decay
A vertical magnetic recording apparatus is provided which can diminish thermal decay of magnetization to ensure a high reliability of the life of recorded information and which can stably effect the write of magnetic information. Light assist is performed by obliquely applying light to a gap between a main pole of a vertical recording head and a medium. The light is radiated from the head side of the apparatus with respect to the medium. Utilizing the present invention, the thermal decay of magnetization at room temperature is diminished, the life of the recorded information is increased, and the storage reliability of the disk is increased.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Perpendicular magnetic recording head
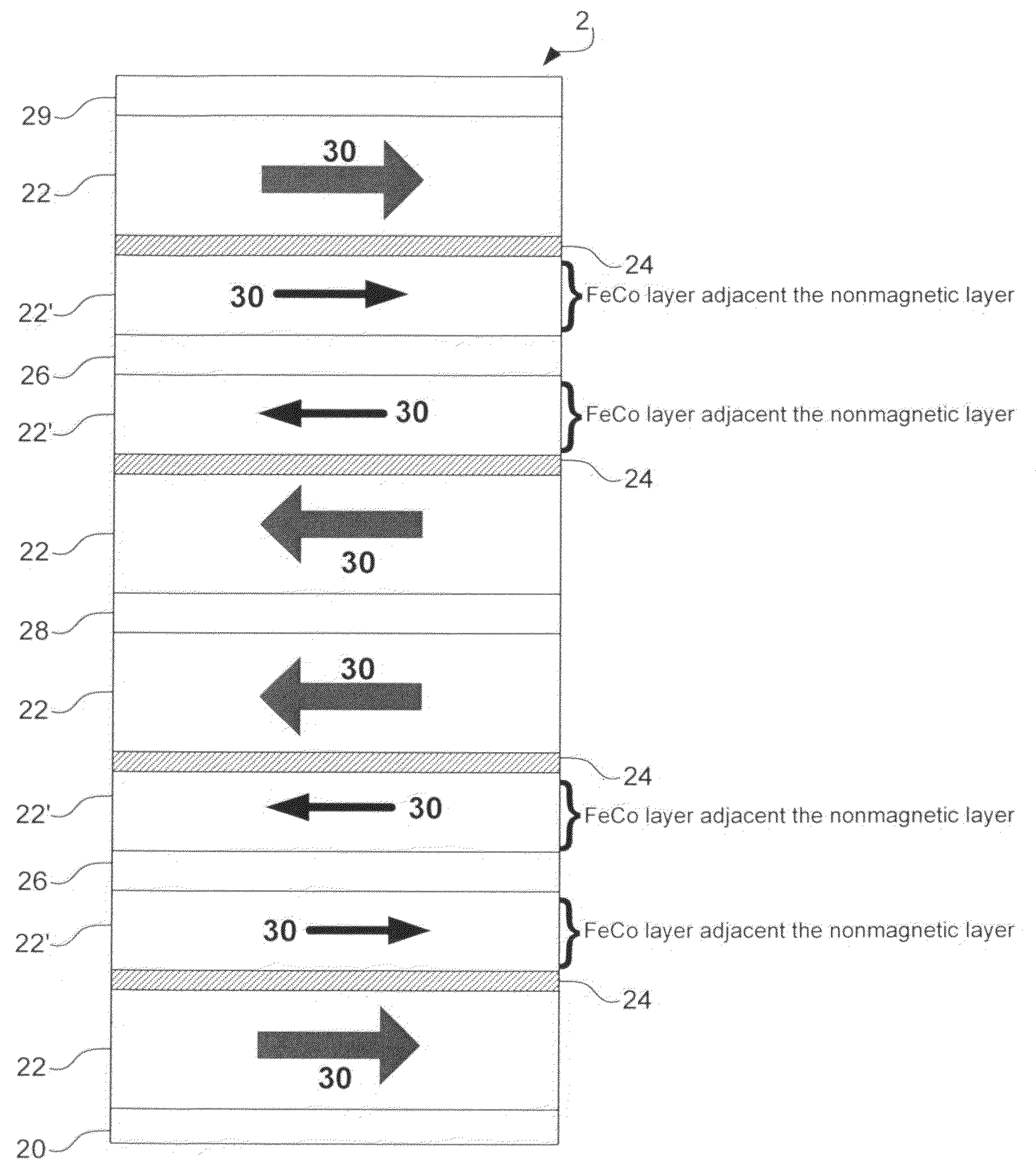
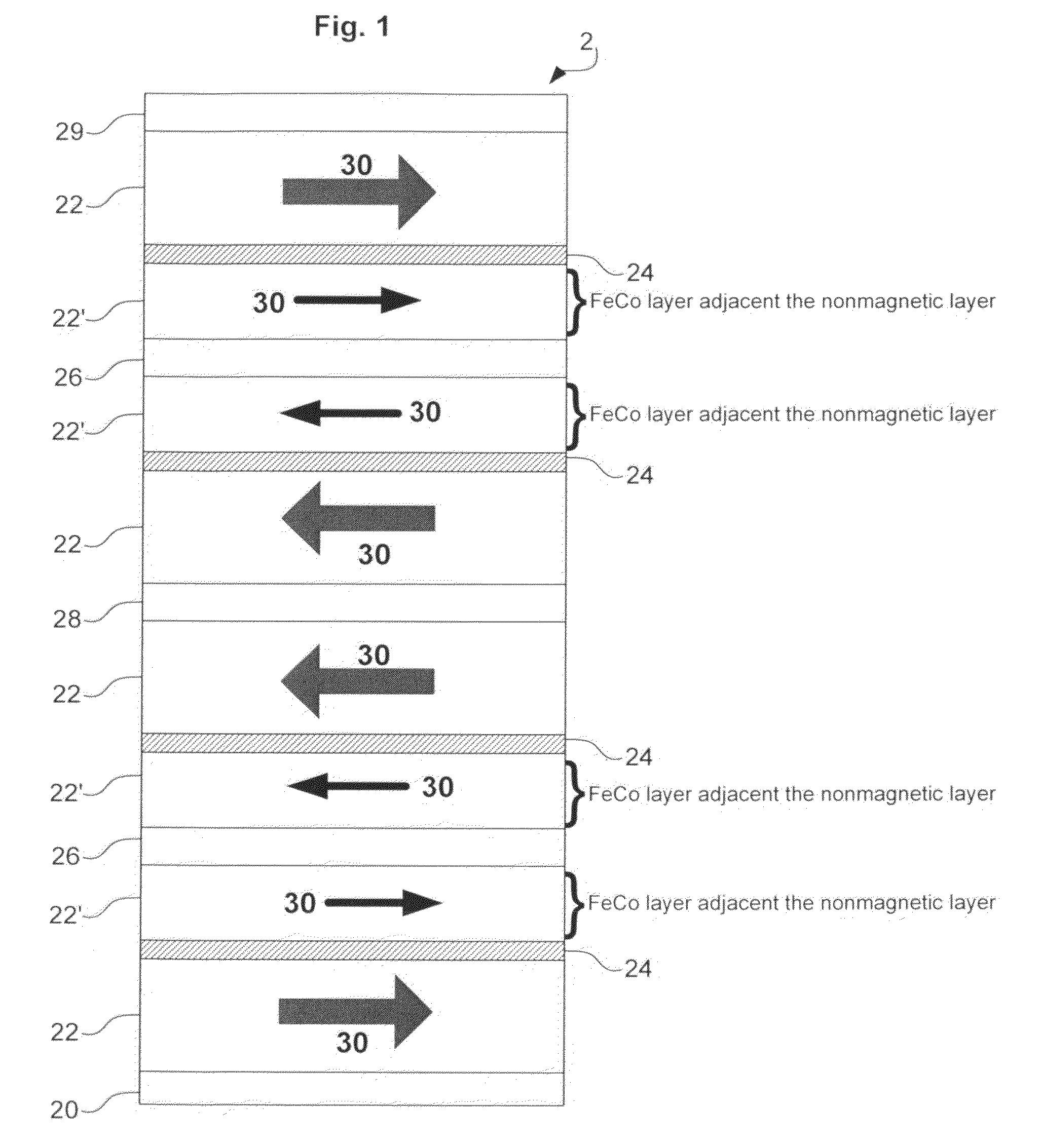
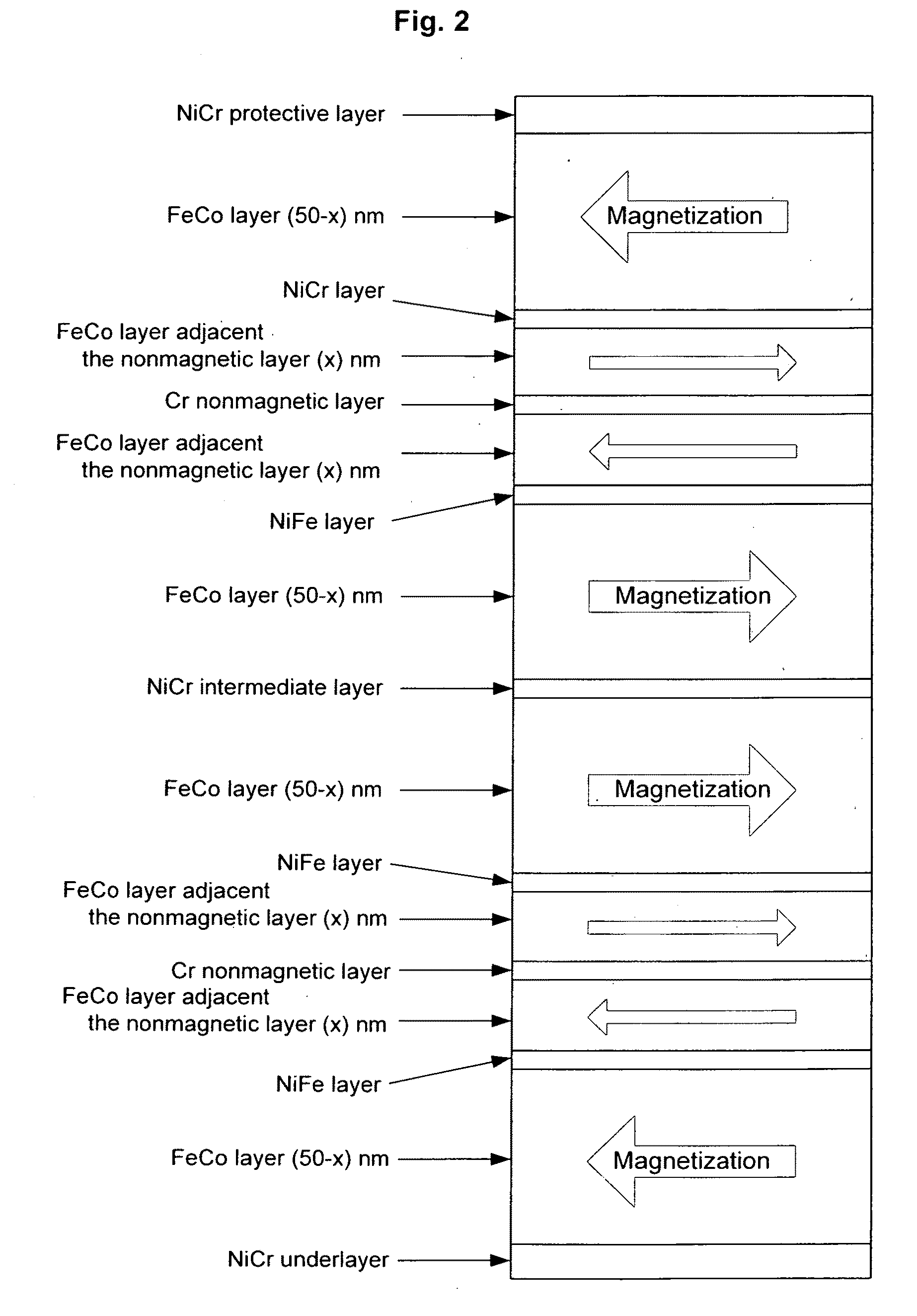
InactiveUS20090073608A1Suppresses erasureReducing remanent magnetization MrRecord information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsHigh densityMagnetization
Embodiments of the present invention provide a perpendicular magnetic recording head suitable for high density recording that suppresses erasure after recording by reducing the remanent magnetization Mr of the main magnetic pole and thereby decreasing the squareness S. Accordingly to one embodiment, a main magnetic pole piece of a perpendicular magnetic recording head includes a FeCo ferromagnetic layer, into which a NiFe soft magnetic layer is inserted. Inserting the NiFe soft magnetic layer in a position in the FeCo ferromagnetic layer 1 to 7 mm away from a nonmagnetic layer allows a remanent magnetization Mr to be decreased without changing the number of layers of the nonmagnetic layer or a film thickness of the FeCo ferromagnetic layer. This helps suppress erasure after recording.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Flux guide type device, head having the same, and drive
InactiveUS6961222B2Reduce decreaseEffectively miniaturizeNanomagnetismElectrical transducersMagnetizationMagnetic reluctance
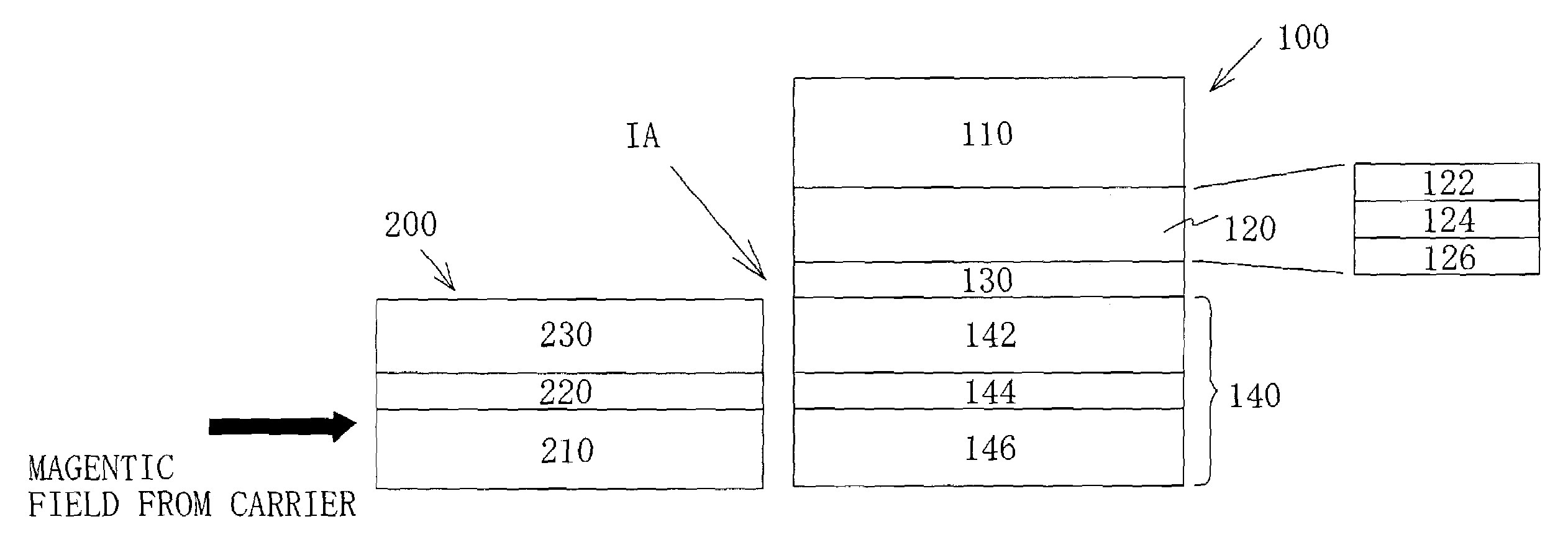
A flux guide type includes a magnetoresistive device for reading a signal flux, and a flux guide for transmitting the signal flux to the magnetoresistive device. The flux guide includes a laminated film that includes a ferromagnetic layer, a non-magnetic layer and a ferromagnetic layer in this order, and the two ferromagnetic layers in the flux guide have antiparallel directions of magnetization with respect to the non-magnetic layer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Magnetic metal powder suitable for use in magnetic recording media and method of manufacturing the powder
InactiveUS20070227302A1Reduce the amount requiredReducing thickness of oxide layerMaterials with ironMaterials with cobaltRare-earth elementMagnetic phase
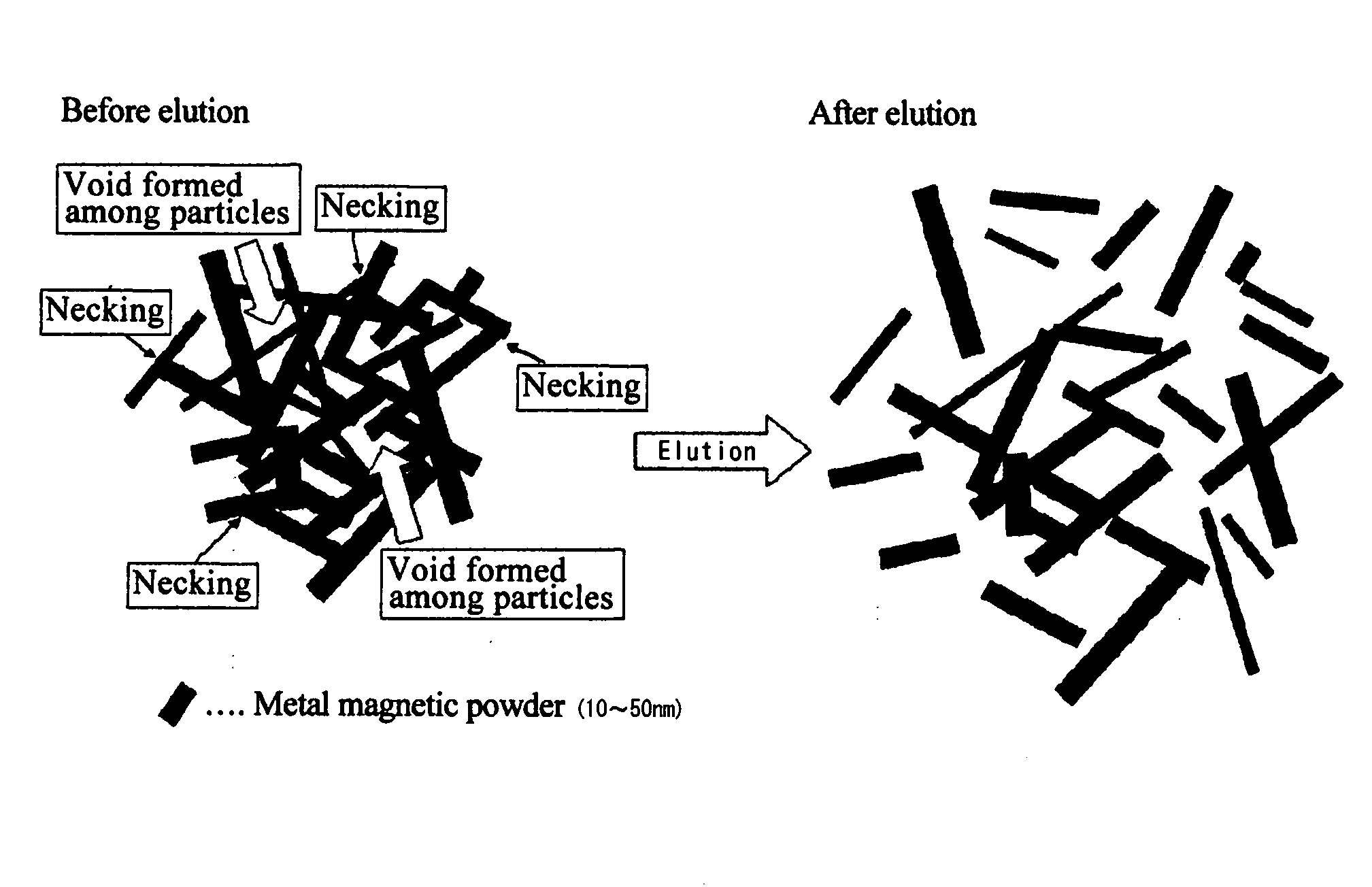
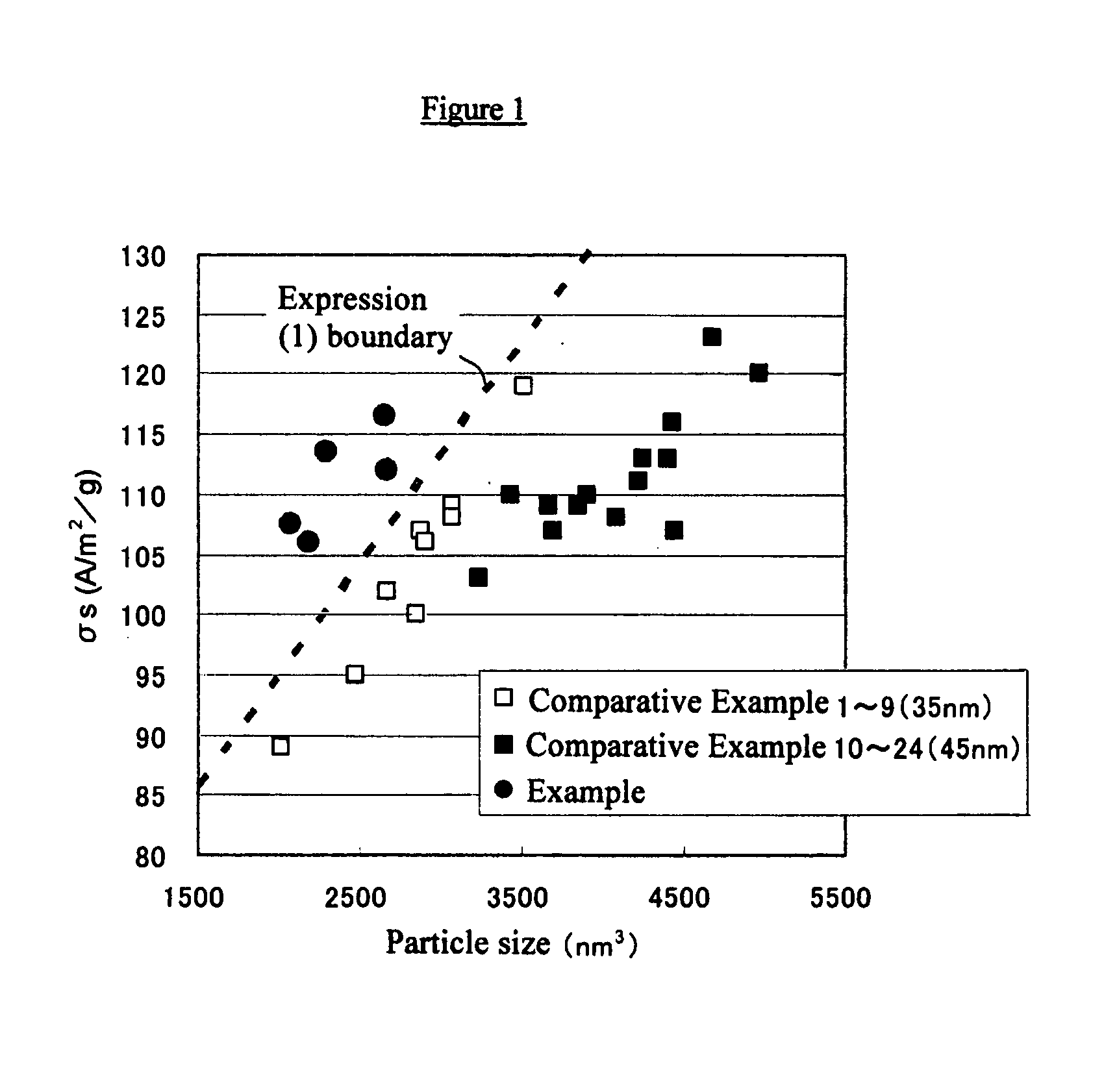
A metal magnetic powder for a magnetic recording medium is provided whose particles have a metal magnetic phase, composed mainly of Fe or Fe plus Co, and an oxide layer, wherein the average major axis length of the powder particles is 10-50 nm, the average particle volume including the oxide layer is 5,000 nm3 or less, the atomic ratio (R+Al+Si) / (Fe+Co) calculated using the content values (at. %) of the elements contained in the powder particles is 20% or less, where R is rare earth element (Y being treated as a rare earth element). The metal magnetic powder is obtained by using a complexing agent and a reducing agent to elute nonmagnetic constituents after firing. The metal magnetic powder exhibits a large saturation magnetization σs for its particle volume while maintaining weatherability comparable to the conventional level and is suitable for a coated-type magnetic recording medium.
Owner:DOWA ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CO LTD
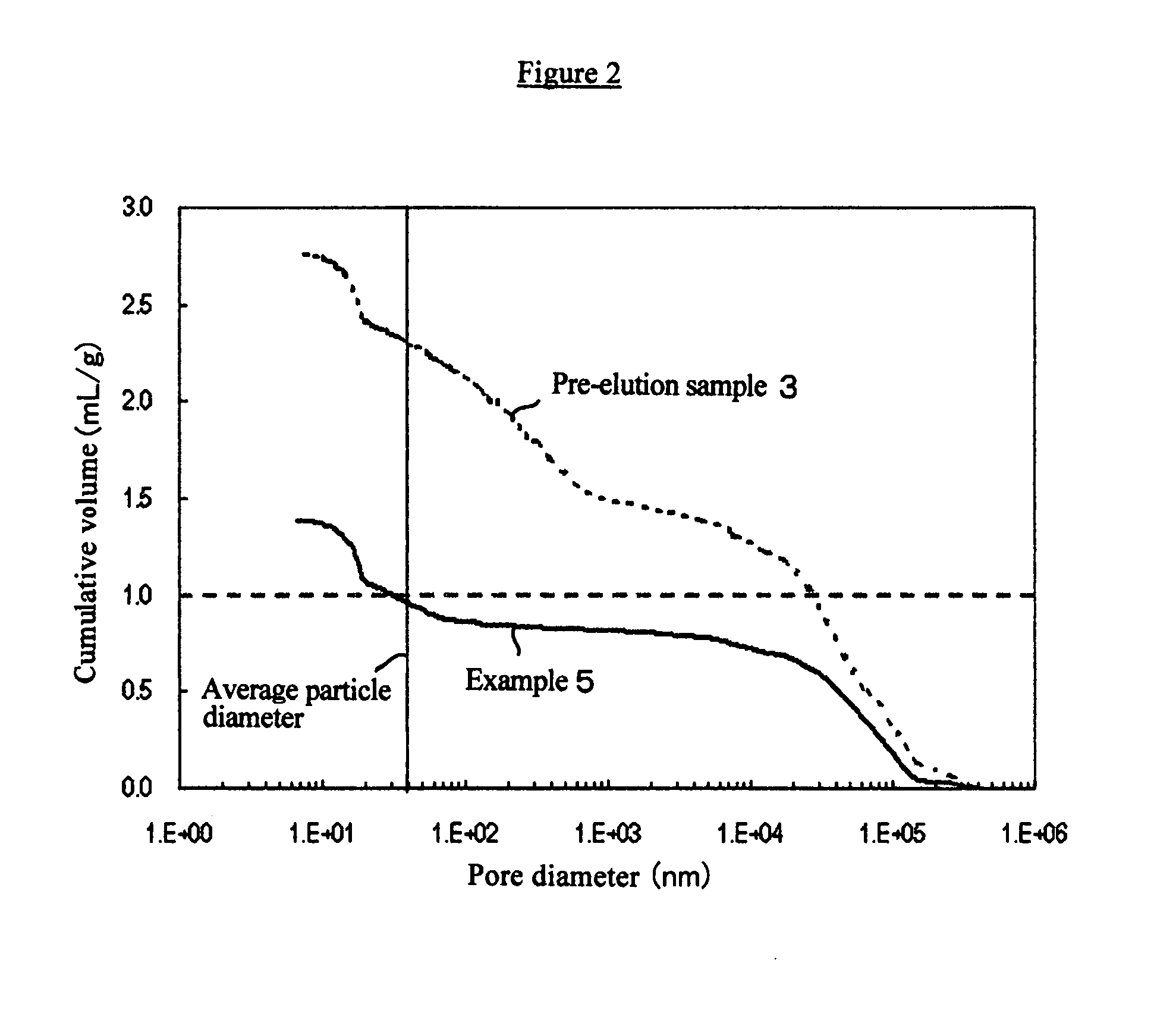
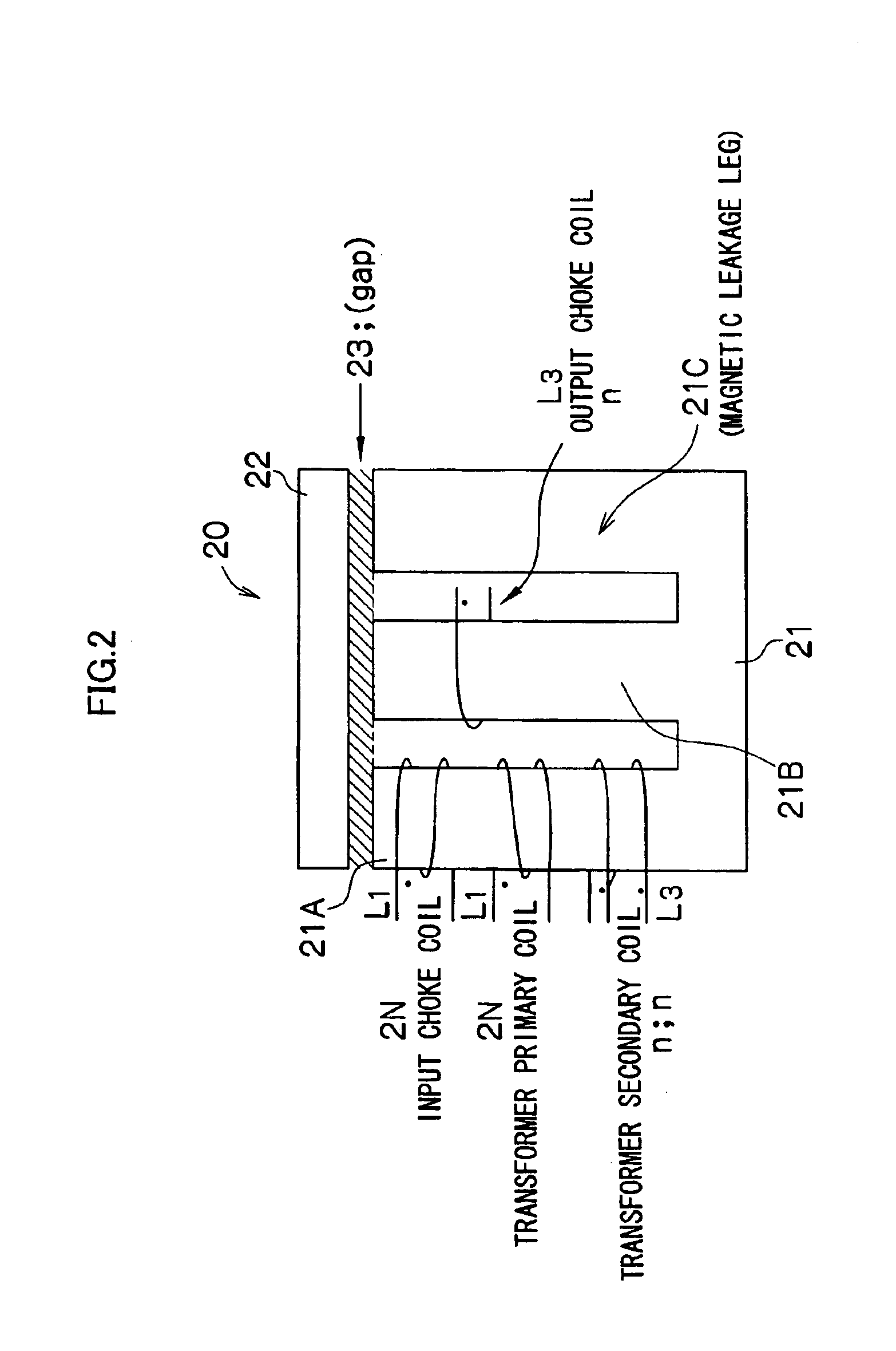
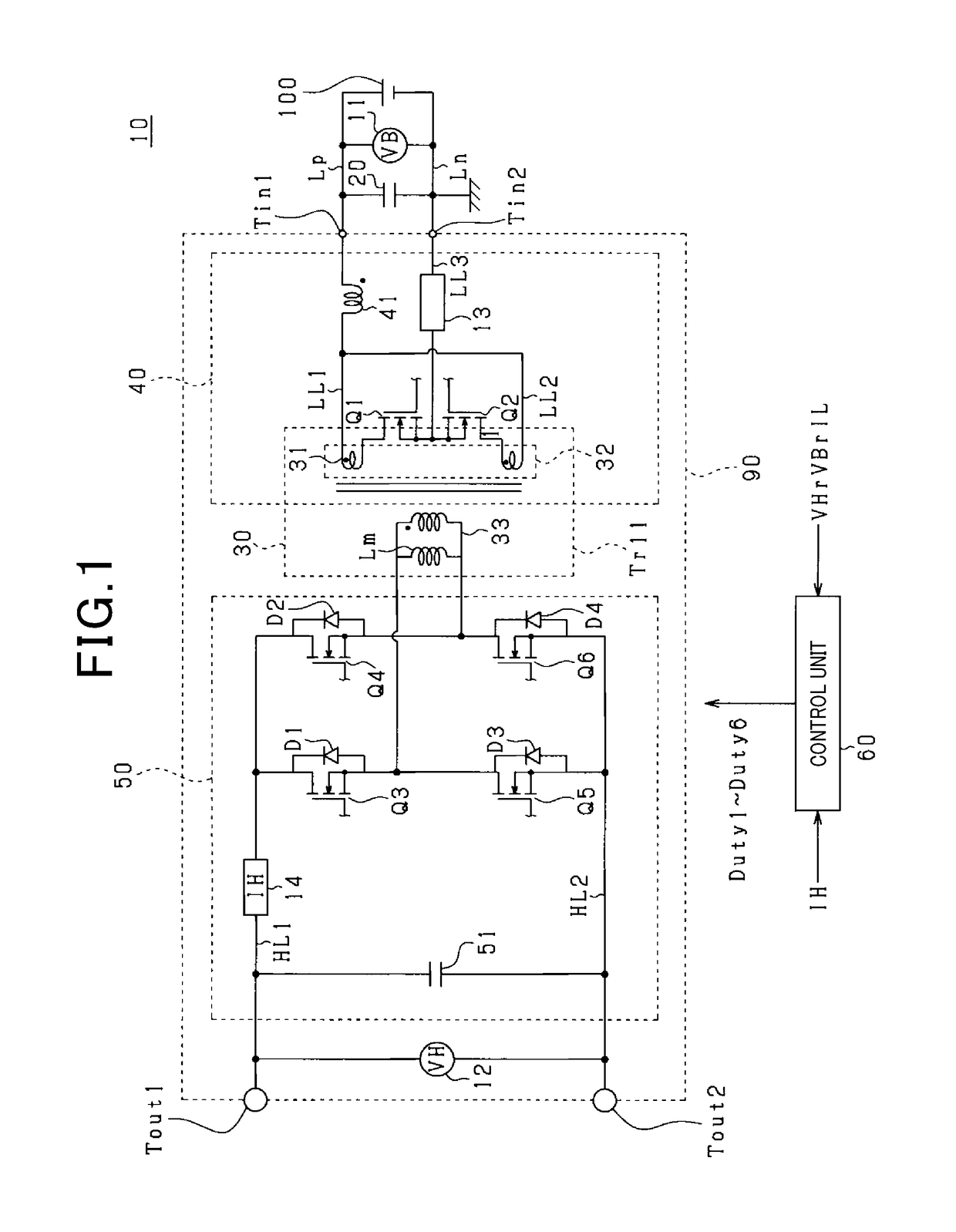
Insulating switching DC/DC converter
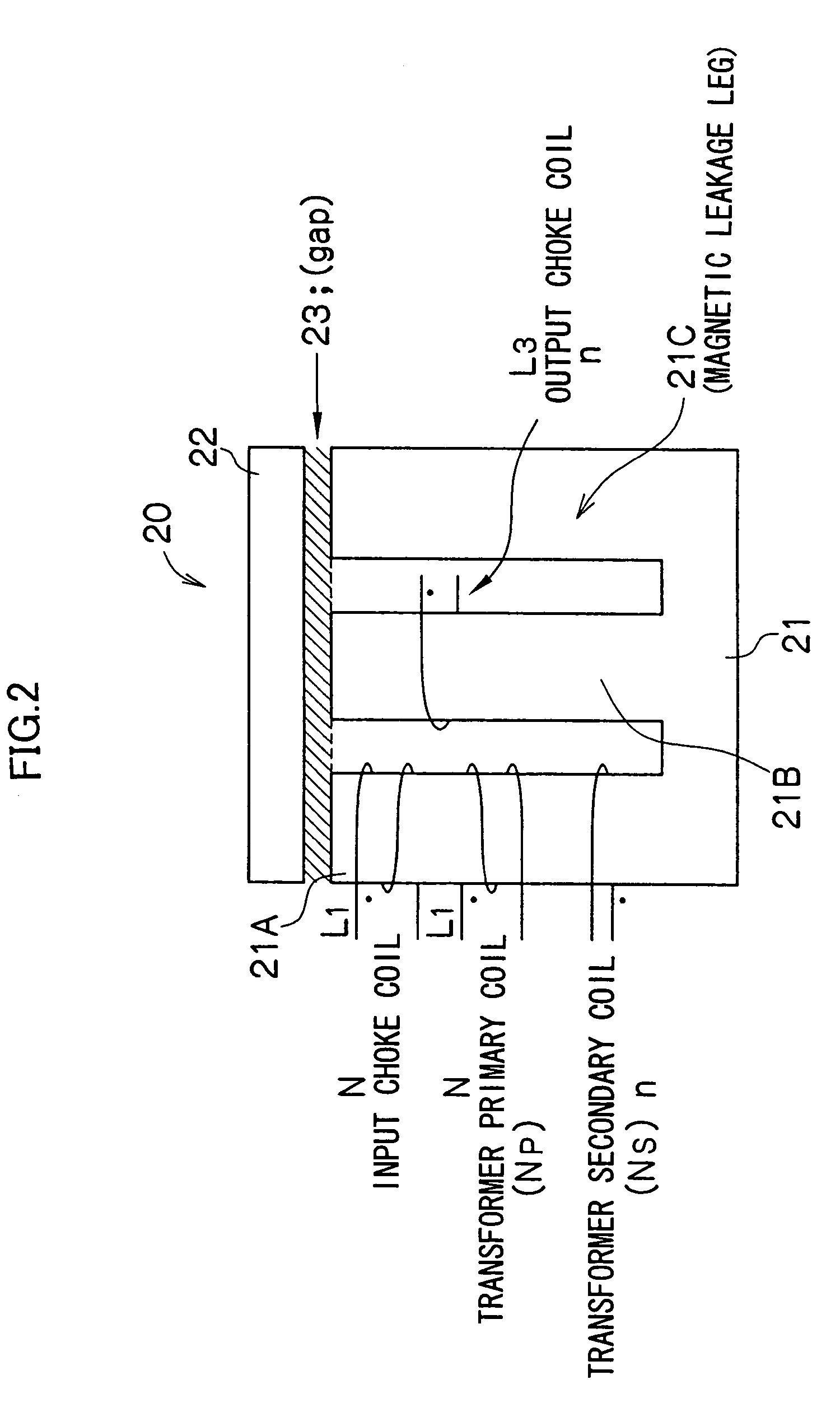
InactiveUS6961254B2Reduces core volume and core lossImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcMagnetizationSecondary side
In a DC / DC converter using an insulating transformer Tr having a center tap on the secondary side, an input choke coil L1 and an output choke coil L3 are integrated with the insulating transformer Tr, a primary coil (number of turns: 2N) and a secondary coil (number of turns: n+n) of the transformer, the input choke coil L1 (number of turns: 2N), and the output choke coil L3 (number of turns: n) are wound around a common core (magnetic core), and the coils are arranged in directions of canceling DC fluxes generated by the coils, so that the DC bias magnetization is considerably reduced.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Manufacturing method of magnetic recording medium, the magnetic recording medium, and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20090273861A1Reduce magnetizationImprove performanceDisposition/mounting of recording headsVacuum evaporation coatingMagnetizationEngineering
A magnetic recording medium includes a substrate; and a recording film formed on the substrate and including a main magnetic film, the main magnetic film where a recording area and a guard area are formed by local ion doping, the guard area having saturation magnetization smaller than saturation magnetization of the recording area. A primary layer is provided at a substrate side of the main magnetic film. A main ingredient of the primary layer is at least one kind of atom selected from a group consisting of Cr, B, Mo, Al, Si, and C.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
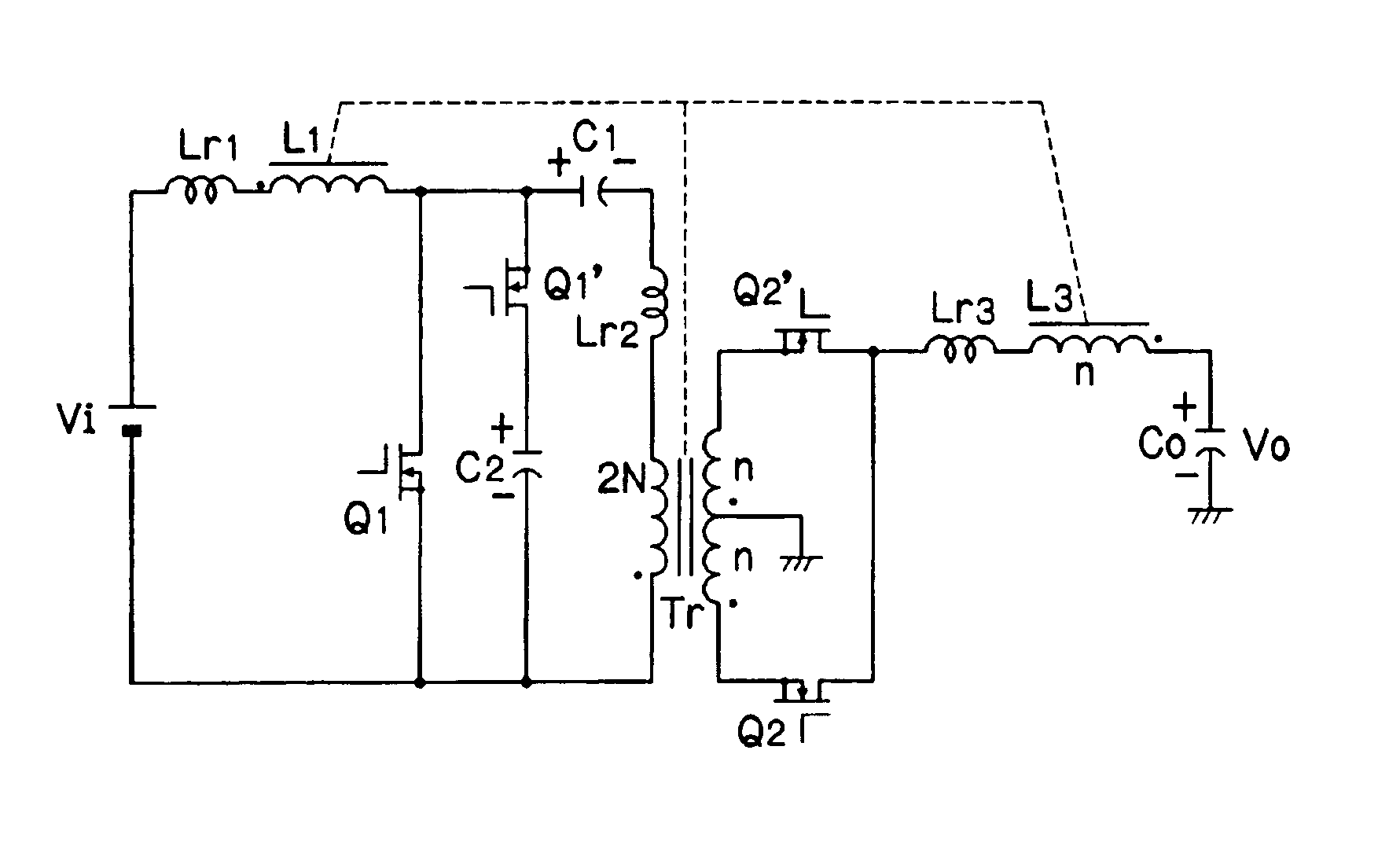
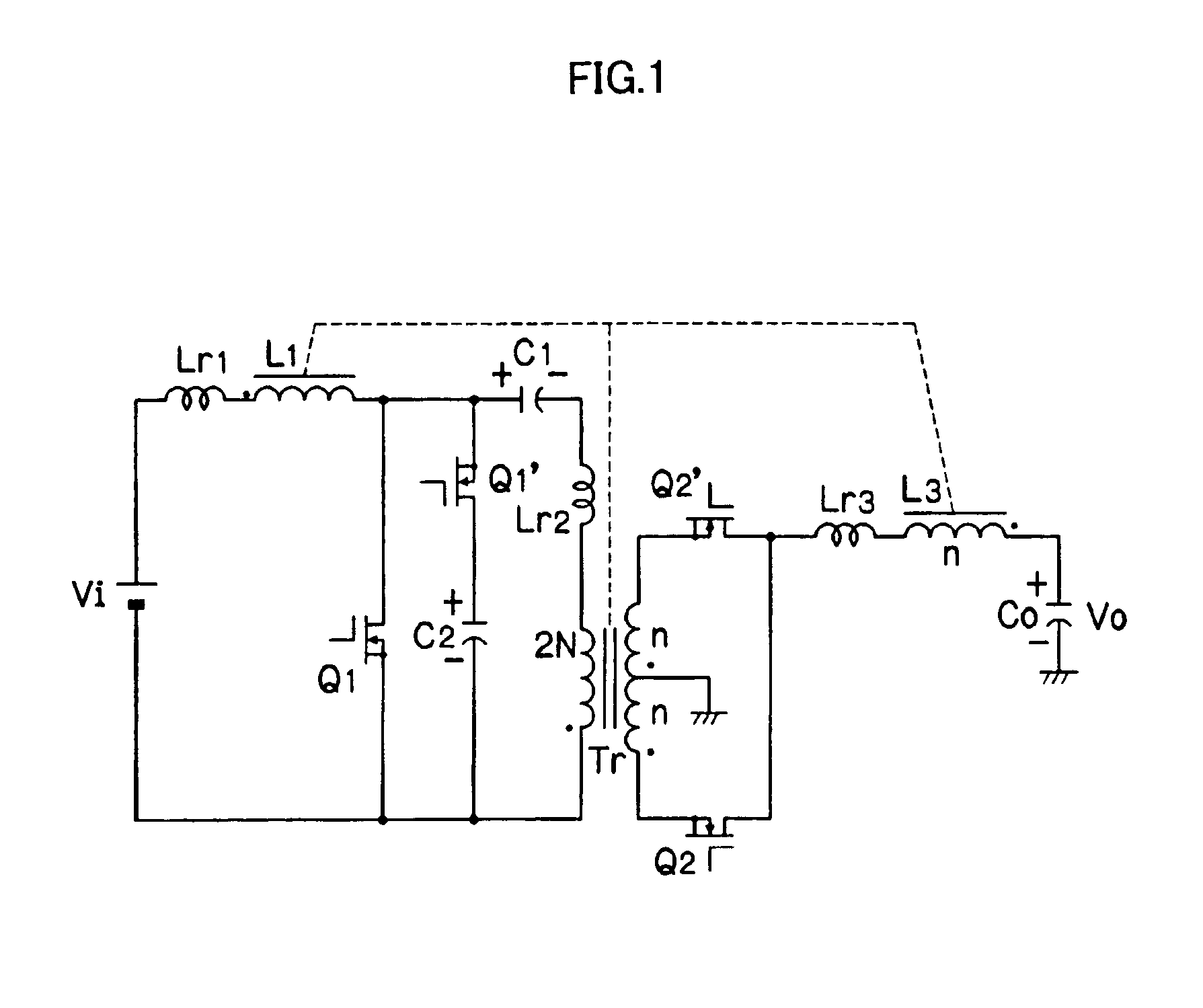
Insulating switching DC/DC converter
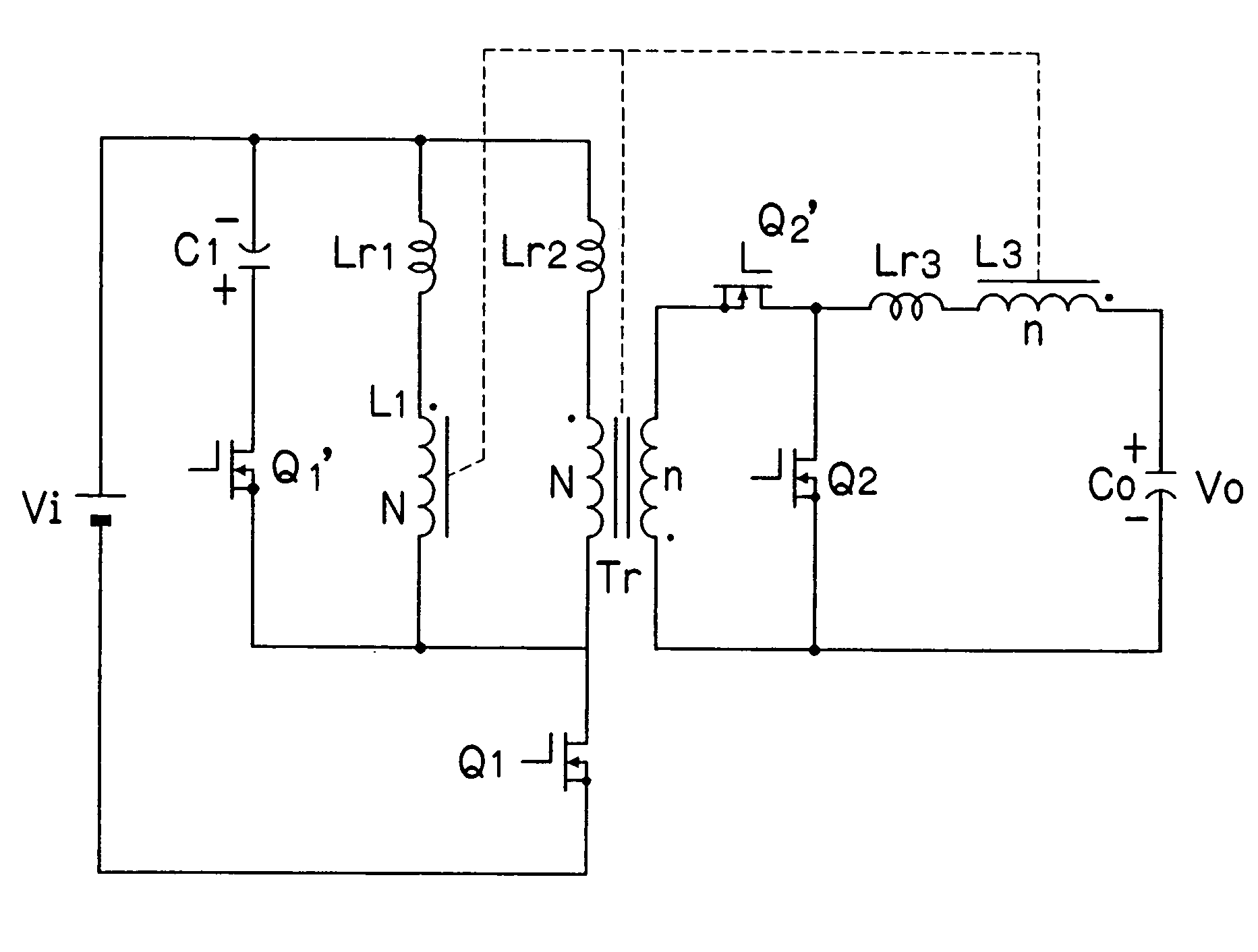
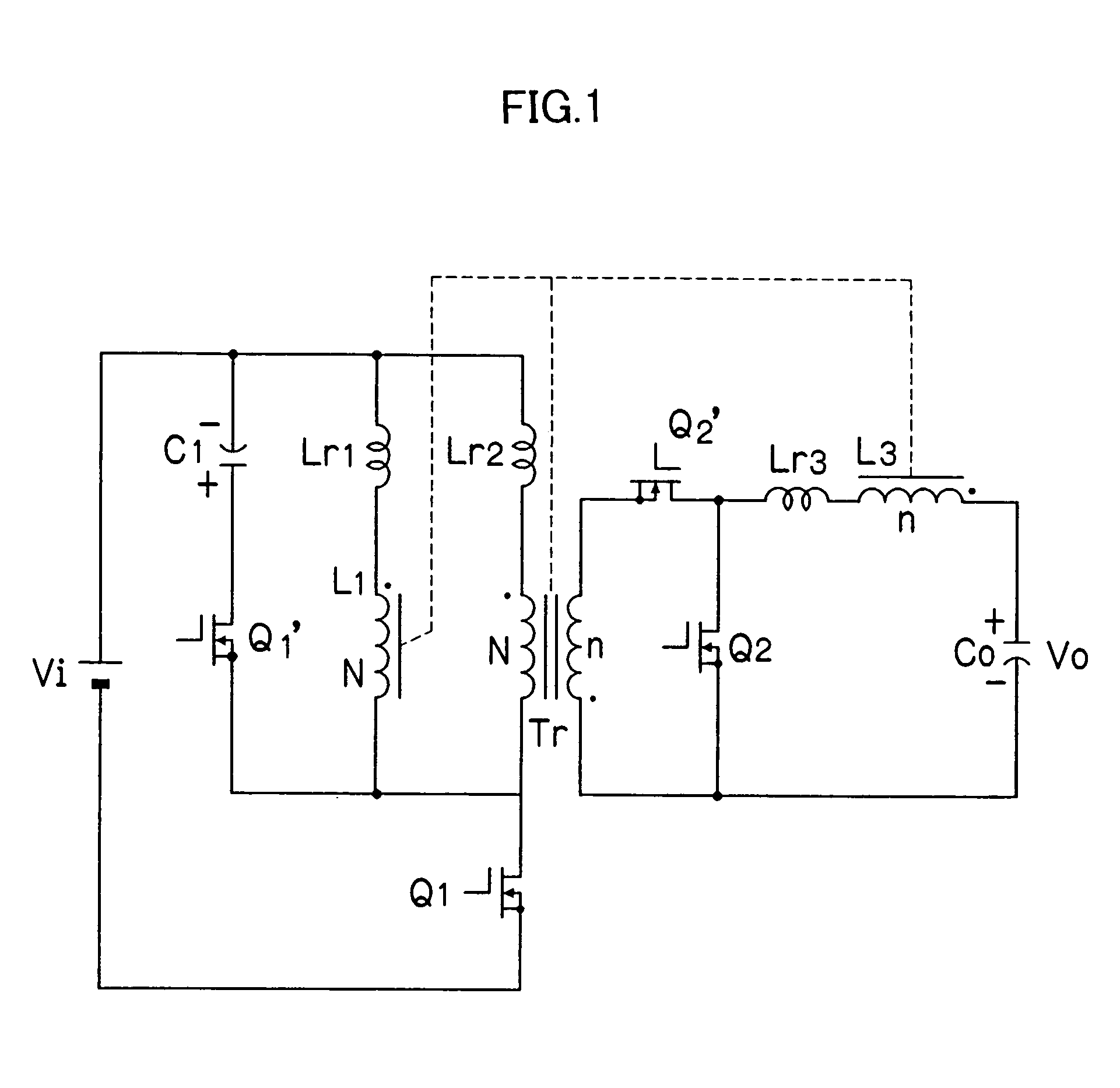
ActiveUS7057906B2Prevent DC bias magnetizationFirmly connectedAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionClamp capacitorMagnetization
In a switching DC / DC converter using an insulating transformer Tr, a primary coil and a secondary coil of the transformer Tr, an input choke coil L1, and an output choke coil L3 are wound around a common core and are formed into a single component. A primary circuit of the transformer Tr includes a switching device Q1 connected in series with the primary coil, an input choke coil L1 connected across the terminals of the primary coil, and a series circuit of a clamp capacitor C1 and a switching device Q1′ which are connected across the terminals of the primary coil. A secondary circuit of the transformer Tr includes rectifying switching devices Q2 and Q2′ connected to the secondary coil, the output choke coil L3, and an output smoothing capacitor C0. Further, a series circuit of the switching device Q1′ and the clamp capacitor C1 may be connected across the terminals of the switching device Q1. The coils are arranged in directions of canceling DC fluxes generated by the coils, so that it is possible to greatly reduce the DC bias magnetization of the core, the volume of the core, and core losses, thereby achieving higher efficiency in the overall apparatus.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Magnetic sensor and current sensor
InactiveUS20170371006A1Reduce exchangeReduce detectionThin magnetic filmsMagnetic measurement environmental aspectsCurrent sensorMagnetization
A magnetic sensor includes a magnetoresistive effect element having a sensitivity axis in a specific direction. The magnetoresistive effect element has on a substrate, a laminate structure in which a fixed magnetic layer and a free magnetic layer are laminated with a nonmagnetic material layer interposed therebetween and includes at a side of the free magnetic layer apart from the nonmagnetic material layer, a first antiferromagnetic layer which generates an exchange coupling bias with the free magnetic layer and aligns a magnetization direction thereof in a predetermined direction in a magnetization changeable state. The free magnetic layer includes a first ferromagnetic layer in contact with the first antiferromagnetic layer to be exchange-coupled therewith and a magnetic adjustment layer at a side of the first ferromagnetic layer apart from the first antiferromagnetic layer. The magnetic adjustment layer contains at least one iron group element and at least one platinum group element.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Composite transformer
ActiveUS20120062349A1Avoid energy lossReduce lossesTransformers/inductances magnetic coresFixed transformersTransformerInductor
A composite (combined type of) transformer includes: a transformer core including a plurality of transformer magnetic leg portions, a transformer magnetic leg portion, and a pair of transformer bases; a plurality of inductor cores each including an inductor magnetic leg portions, inductor outer magnetic leg portions, and a pair of inductor bases; and a plurality of windings wound around the transformer magnetic leg portion and the inductor magnetic leg portions. The windings are wound to generate magnetic fluxes in such directions as to be cancelled out in a magnetic closed circuit in the transformer core.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Magnetic recording disk
InactiveUS20020197516A1Improve performanceLittle noiseBase layers for recording layersVacuum evaporation coatingSilicon oxideTitanium oxide
The magnetic recording medium includes an underlayer 12 formed of an inorganic compound layer, and a magnetic layer 13 formed over the underlayer 12. The inorganic compound layer as the underlayer 12 has crystal grains and at least one kind of oxide, the crystal grains having as main elements at least one of cobalt oxide, chromium oxide, iron oxide and nickel, the at least one kind of oxide lying as a non-crystalline phase in grain boundaries between the crystal grains and selected from among silicon oxide, aluminum oxide, titanium oxide, tantalum oxide and zinc oxide.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Permanent magnet and process for producing permanent magnet
InactiveUS20110043311A1Improve coercive forceReduce amountTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusCompression moldingSlurry
The present invention relates to a permanent magnet manufactured by steps of: pulverizing a magnet raw material; mixing the pulverized magnet raw material with a rust preventive oil in which a Dy compound or a Tb compound is dissolved, thereby preparing a slurry; compression molding the slurry to form a molded body; and sintering the molded body.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Magnetic recording device
ActiveUS8670201B2Exhibit some effectLow coercivityRecord information storageAlignment for track following on disksElectrical currentMicrowave assisted
In a magnetic recording device adopting a microwave assisted recording method, a microwave frequency on a positive polarity side and a microwave frequency on a negative polarity side are adjusted to be optimal.The magnetic recording device of the invention supplies to a magnetic head a write current of which a current waveform on the positive polarity side and a current waveform on the negative polarity side are asymmetric.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Perpendicular magnetic recording head and perpendicular magnetic recording and reproducing system
InactiveUS7145750B2Inhibit deteriorationImproves overwrite erase ratioManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic polesMagnetization
There is provided a perpendicular magnetic recording and reproducing system in which the overwrite erase ratio of a perpendicular magnetic head has been improved to prevent the deterioration of an overwrite property. In the perpendicular magnetic head, a third magnetic pole composed of a soft magnetic layer is formed on the leading side of a recording magnetic pole via a non-magnetic layer, thereby reducing magnetic interference from magnetization on a medium with the recording magnetic pole and preventing the deterioration of the overwrite property.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD +1
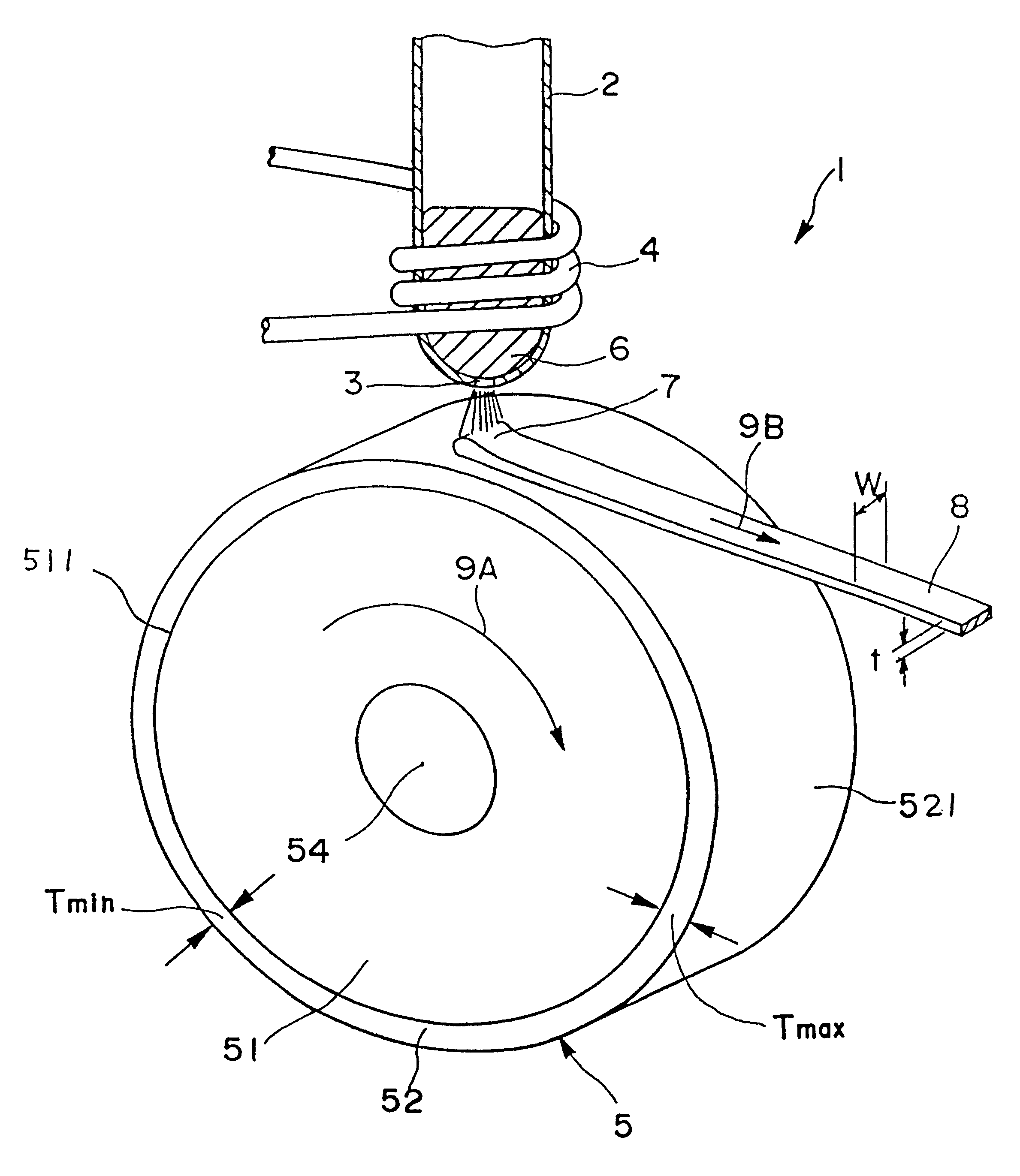
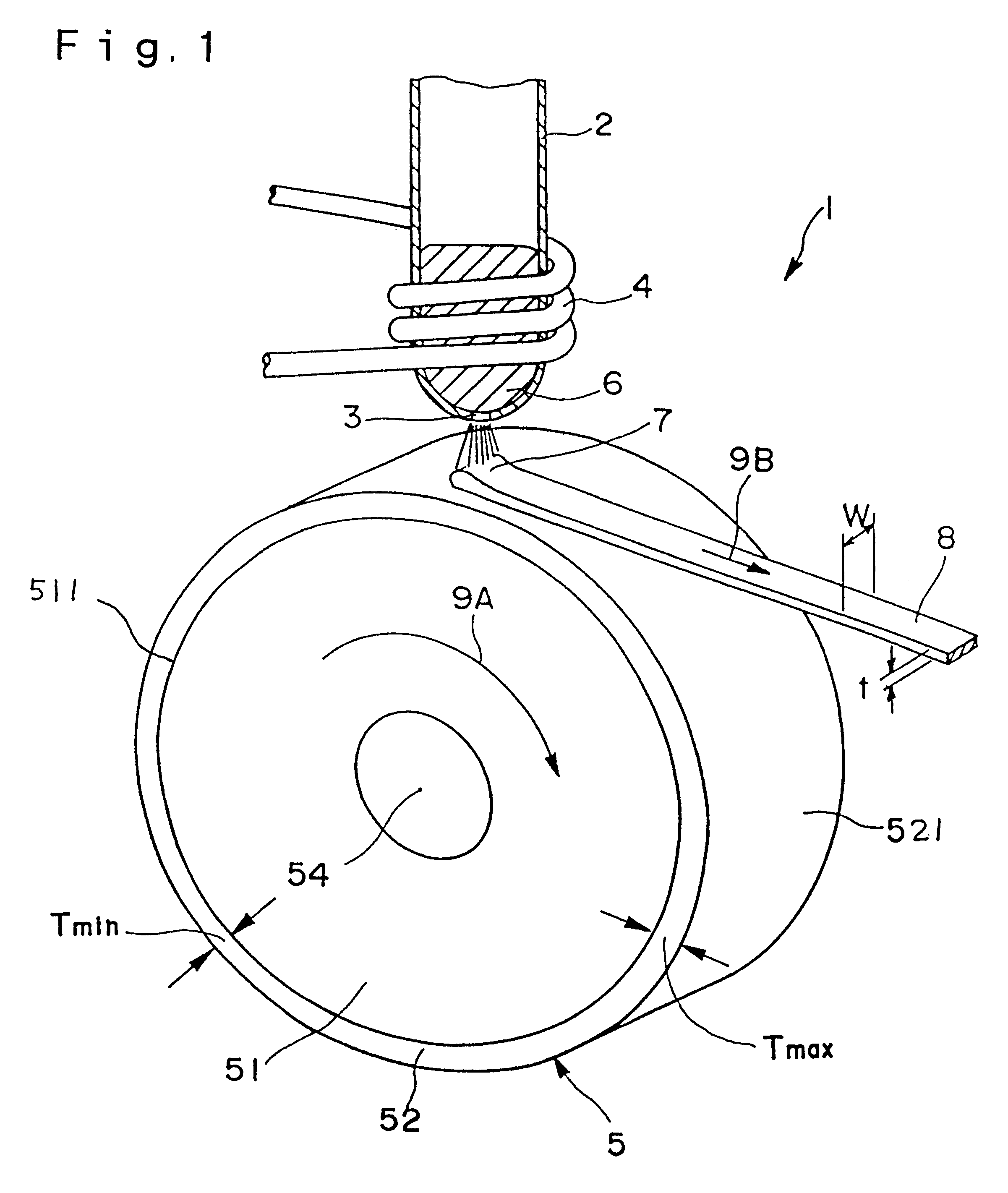
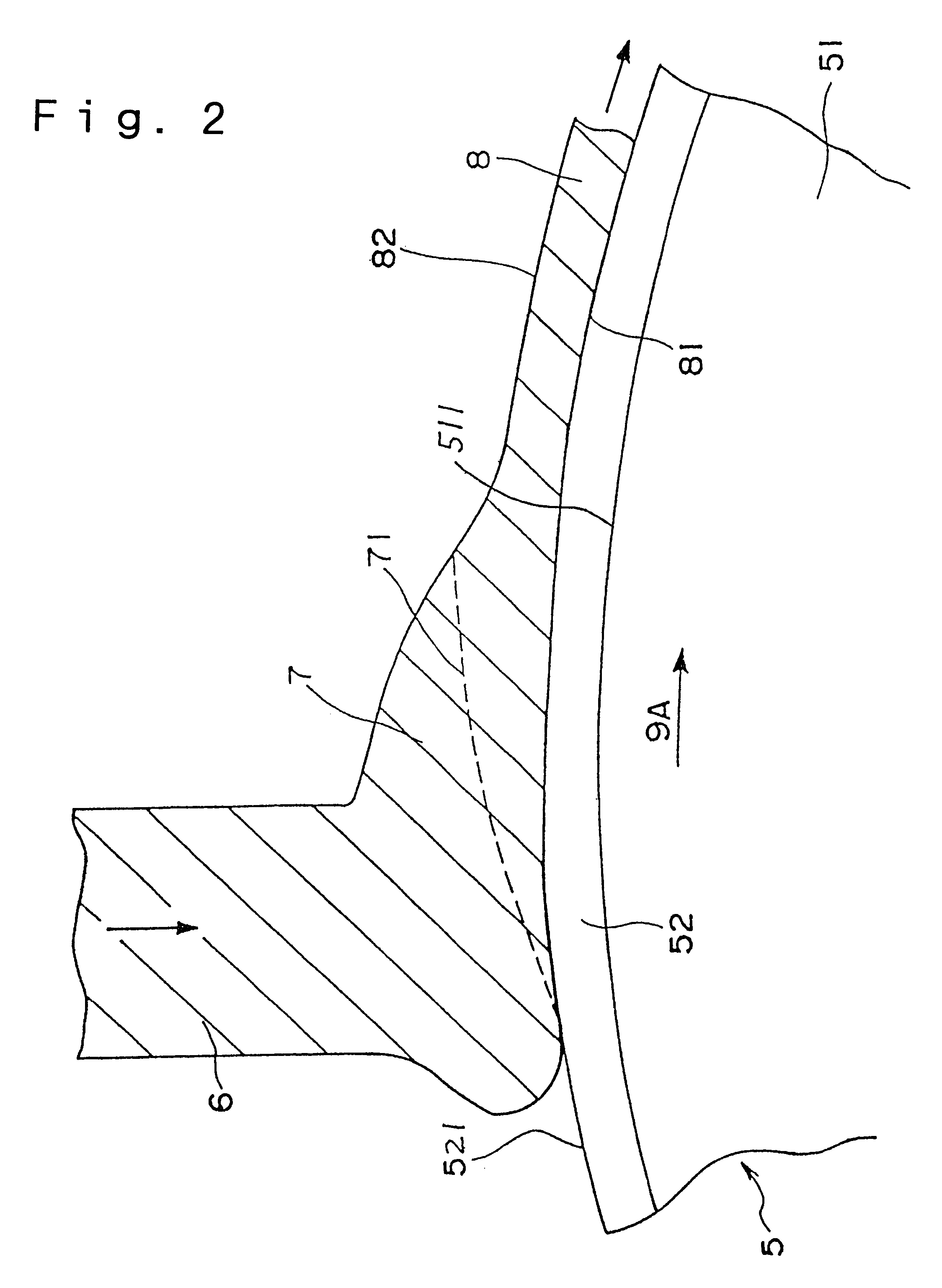
Cooling roll, method for manufacturing magnet material, ribbon shaped magnet material, magnetic powder and bonded magnet
InactiveUS6536507B1Improve conductivityIncreased durabilityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureSurface layerBand shape
A cooling roll (5) for producing magnet materials, comprising a roll base material (51) and a surface layer (52) covering the outer periphery of the material, wherein the roll base material (51) is preferably formed of a metal material of a high heat conductivity, and the surface layer (52) is formed of a material lower in heat conductivity than the roll base material (51) and preferably formed of ceramics. The surface layer (52) satisfies the relation, 1.01<=Tmax / Tmin<=3, where Tmax is the maximum thickness of the surface layer (52), and Tmin the minimum thickness. The peripheral surface (511) of the roll base material (51) has a surface roughness Ra of 0.03 to 8 mum.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
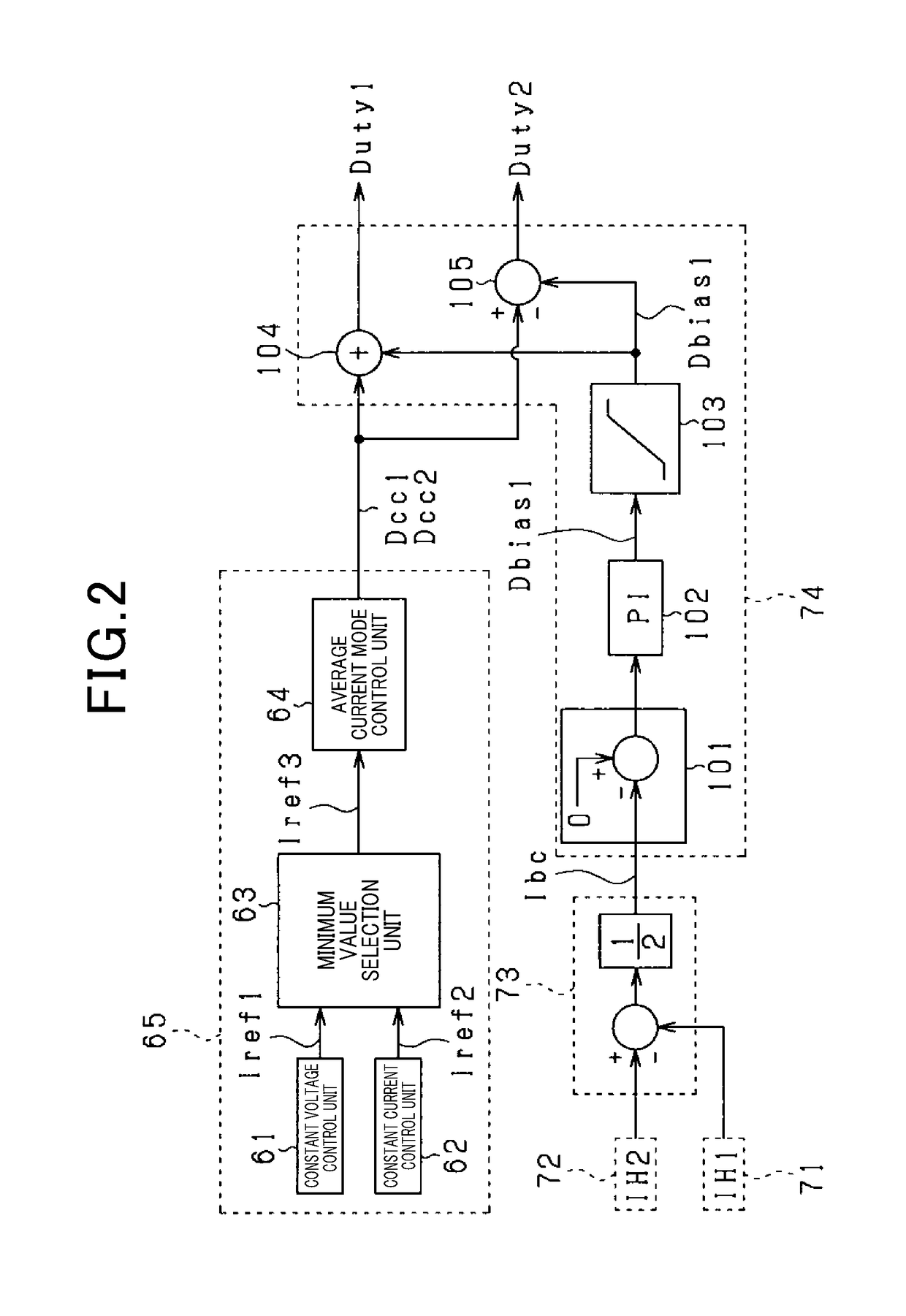
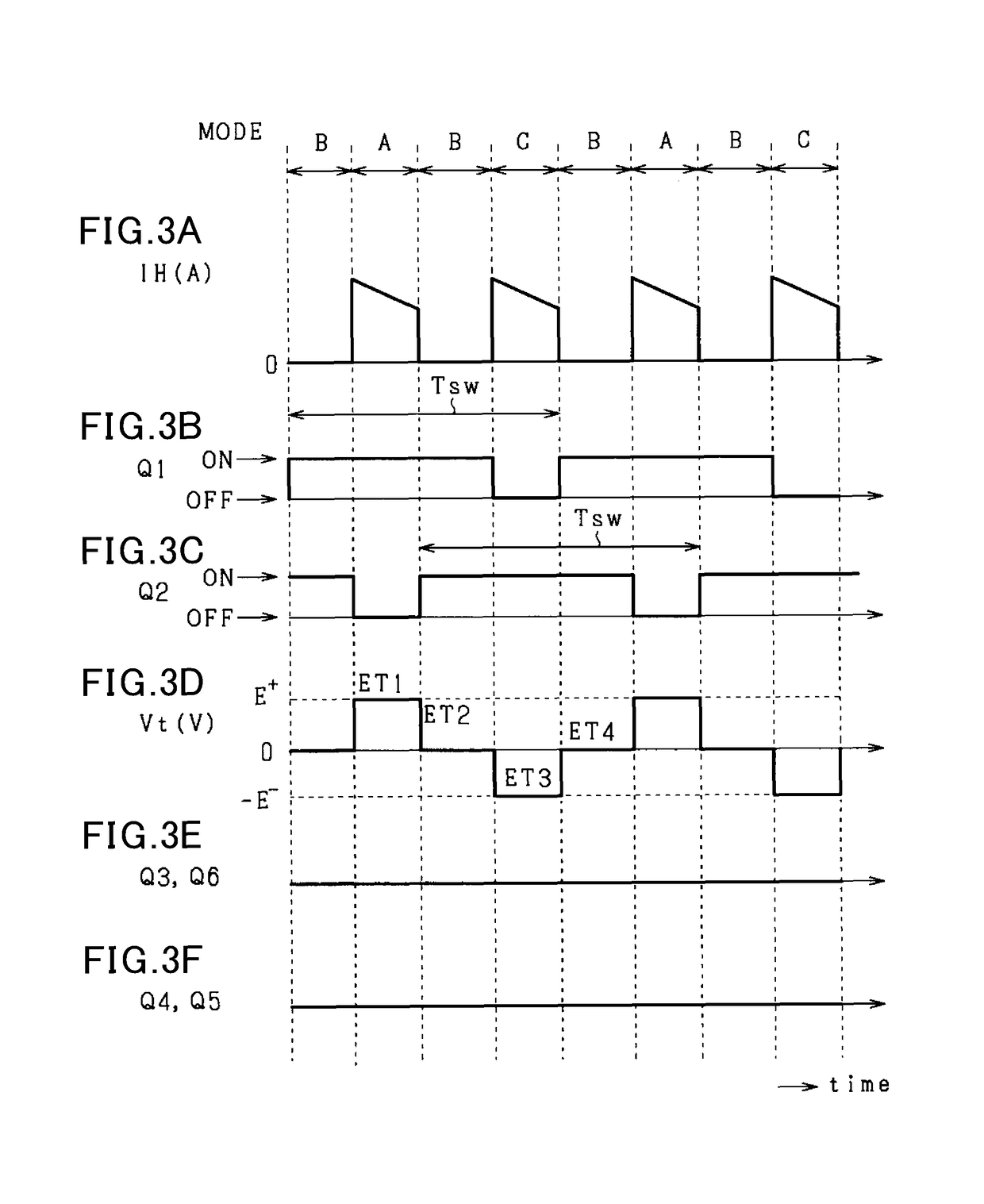
Control apparatus determining transformer magnetization in a DC/DC converter based on difference between primary and secondary currents
ActiveUS10224826B2The right amountSuppressing magnetizationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTransformerExcitation current
A control unit capable of accurately calculating a magnetization bias of a transformer is provided, thereby appropriately reducing the magnetization bias. The control unit acquires first and second currents that flow through a transformer during a period where either first or second switches individually turn ON. The control unit predicts an amount of magnetization bias in either positive side or negative side of the excitation current that flows through the transformer. The control unit reduces the magnetization bias of the transformer based on the predicted amount of magnetization bias.
Owner:SOKEN CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com