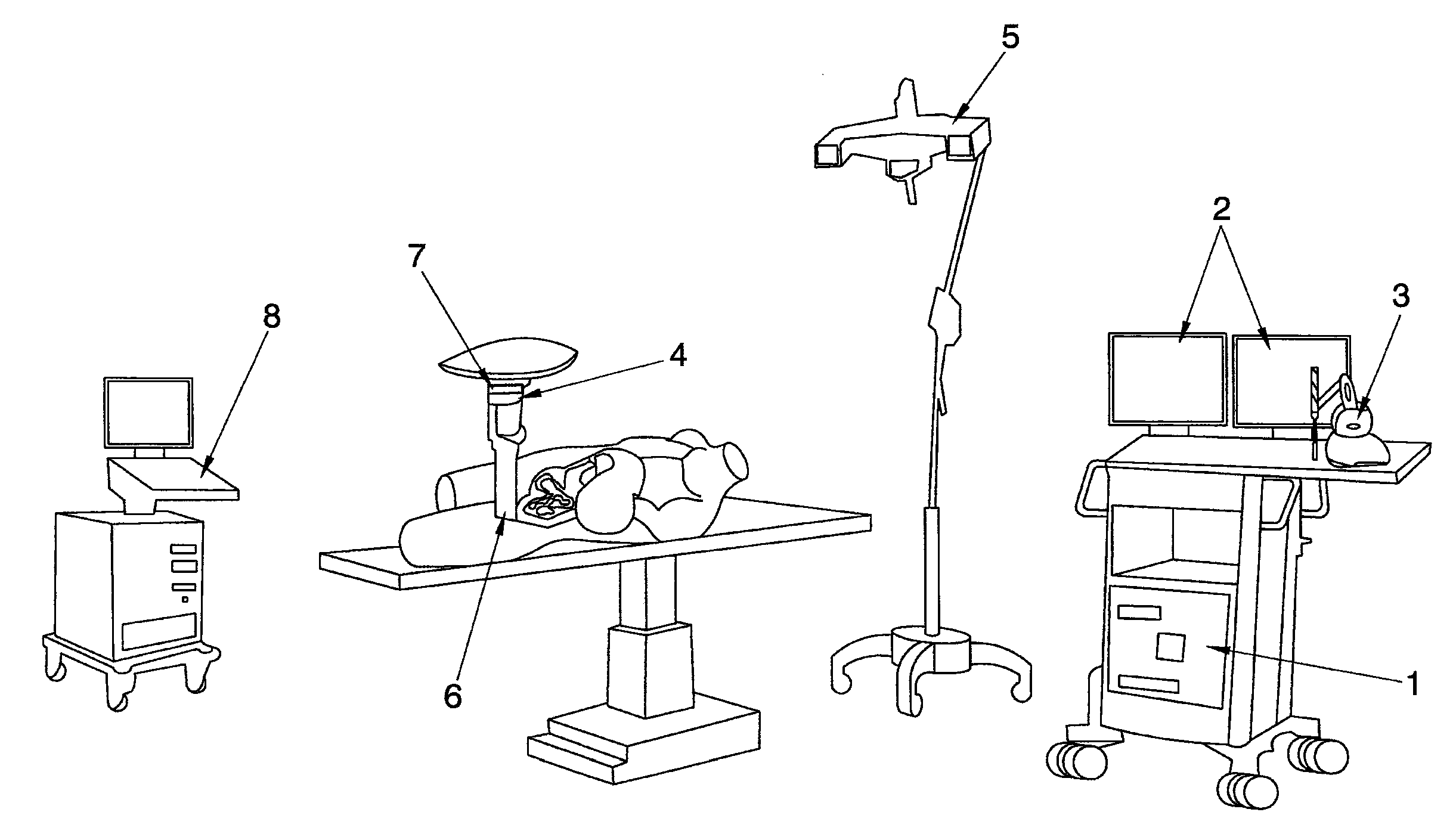
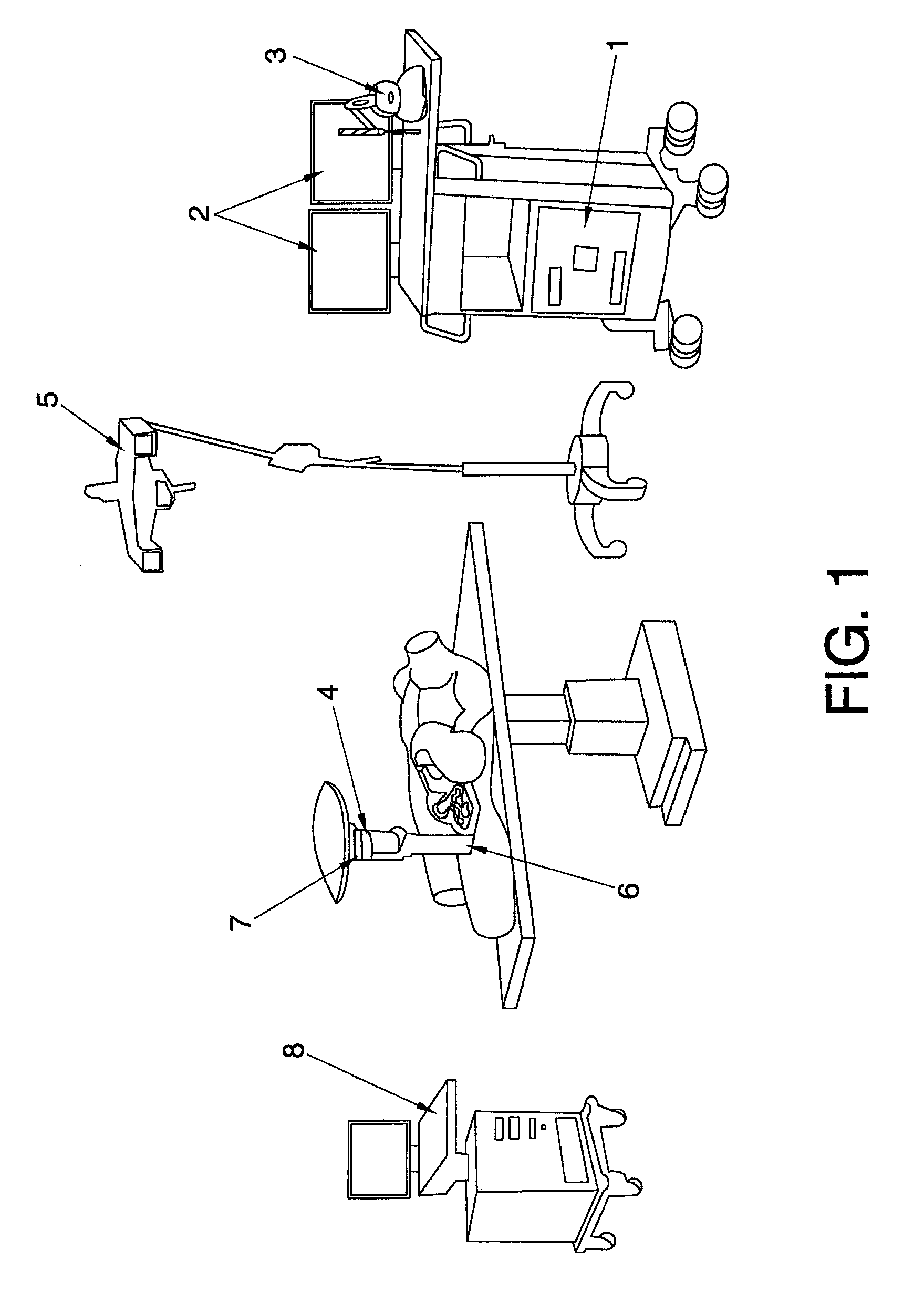
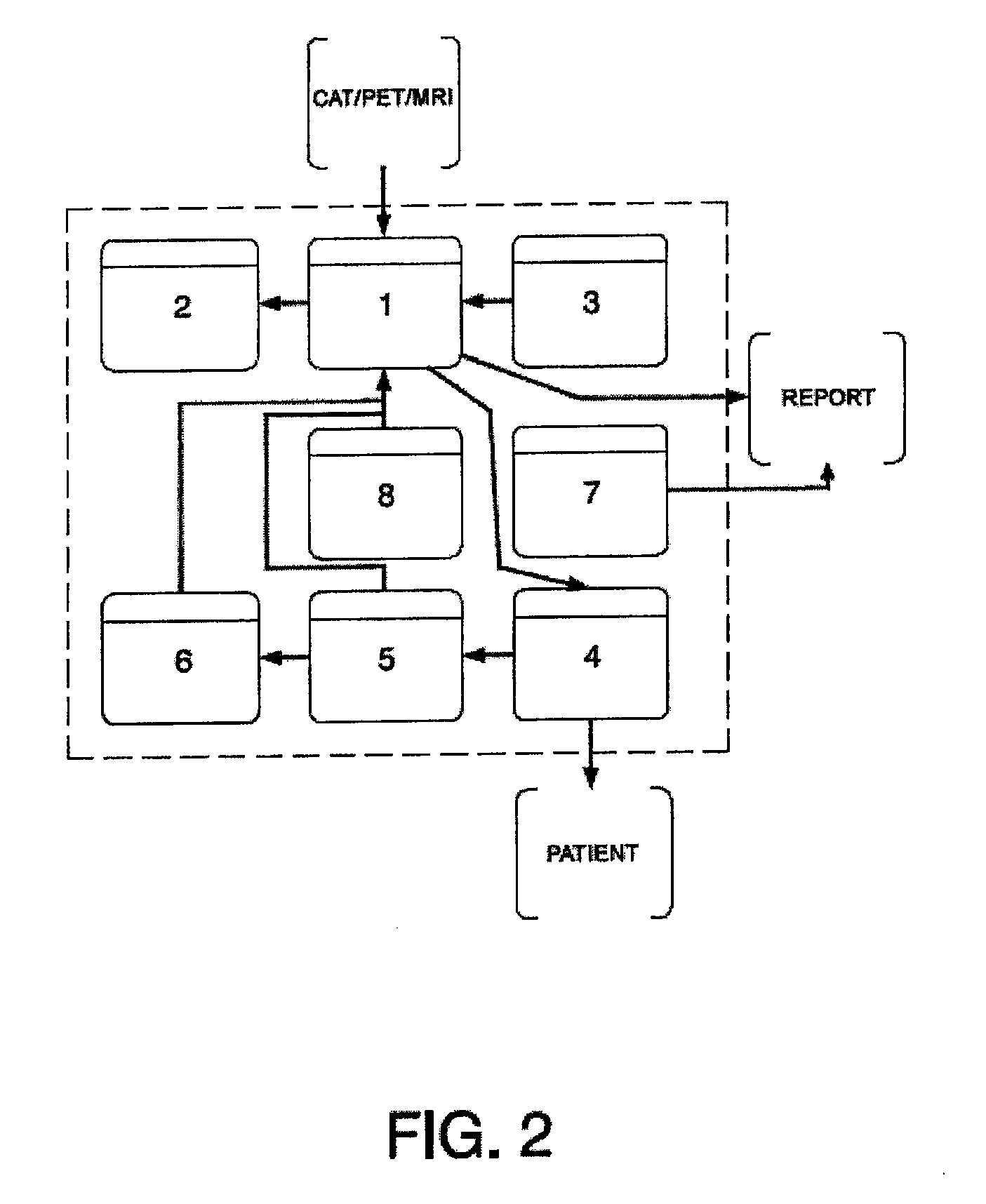
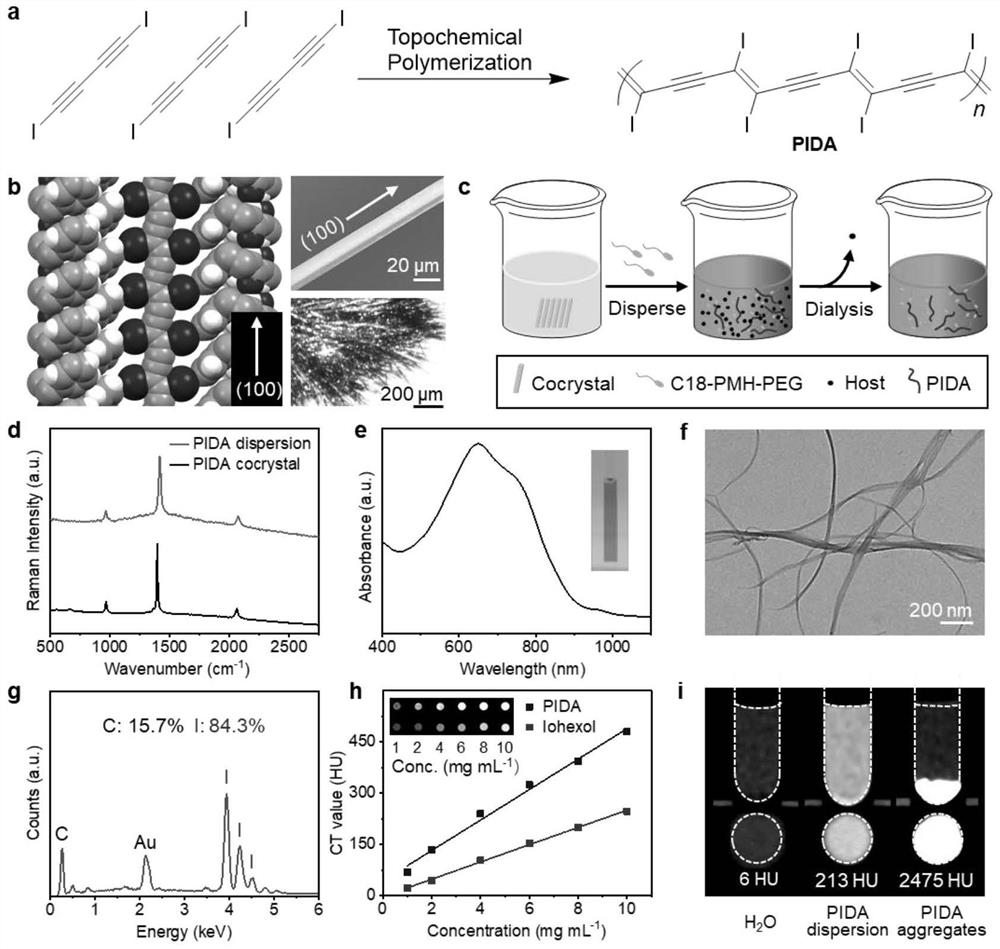
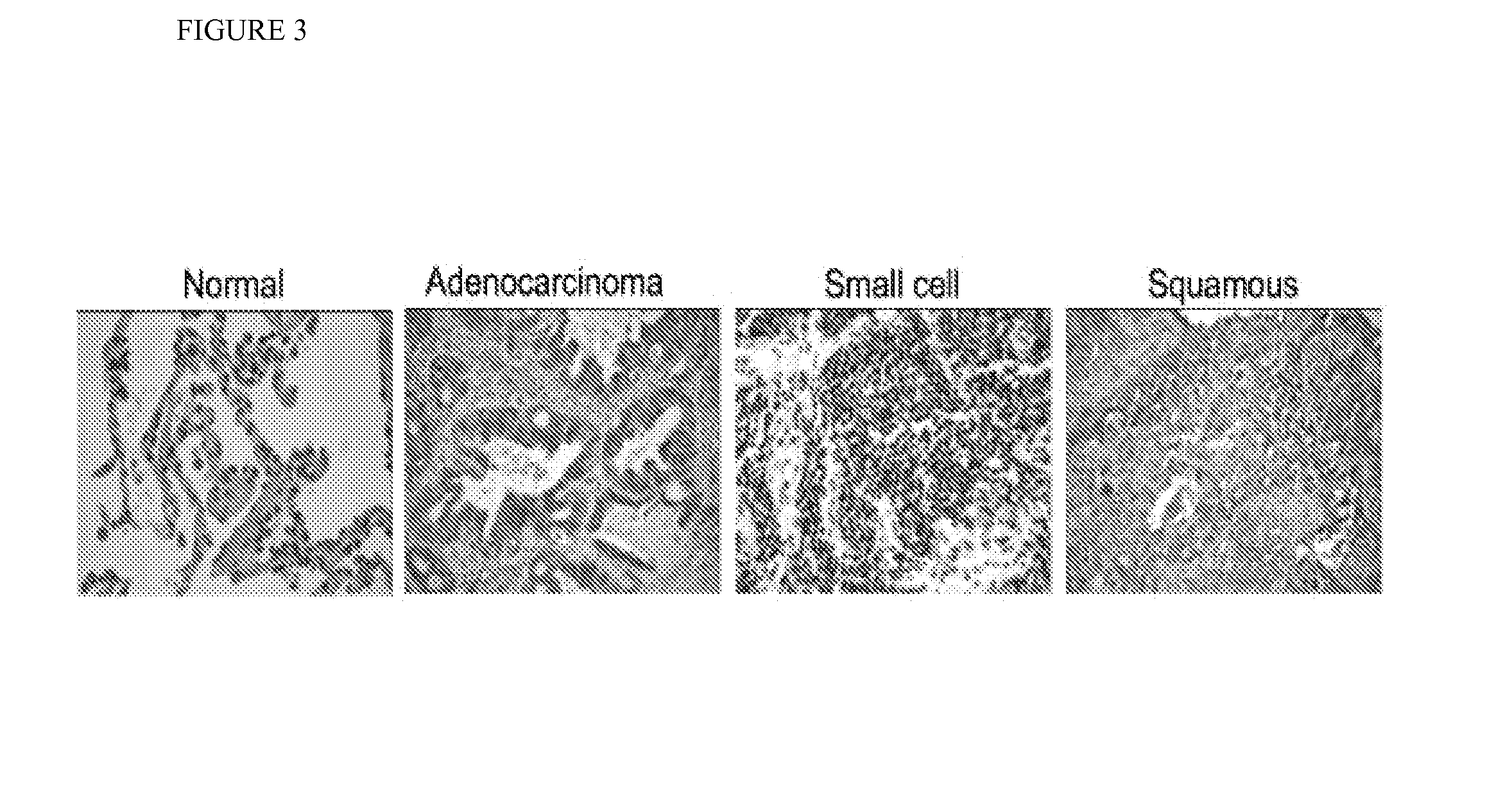
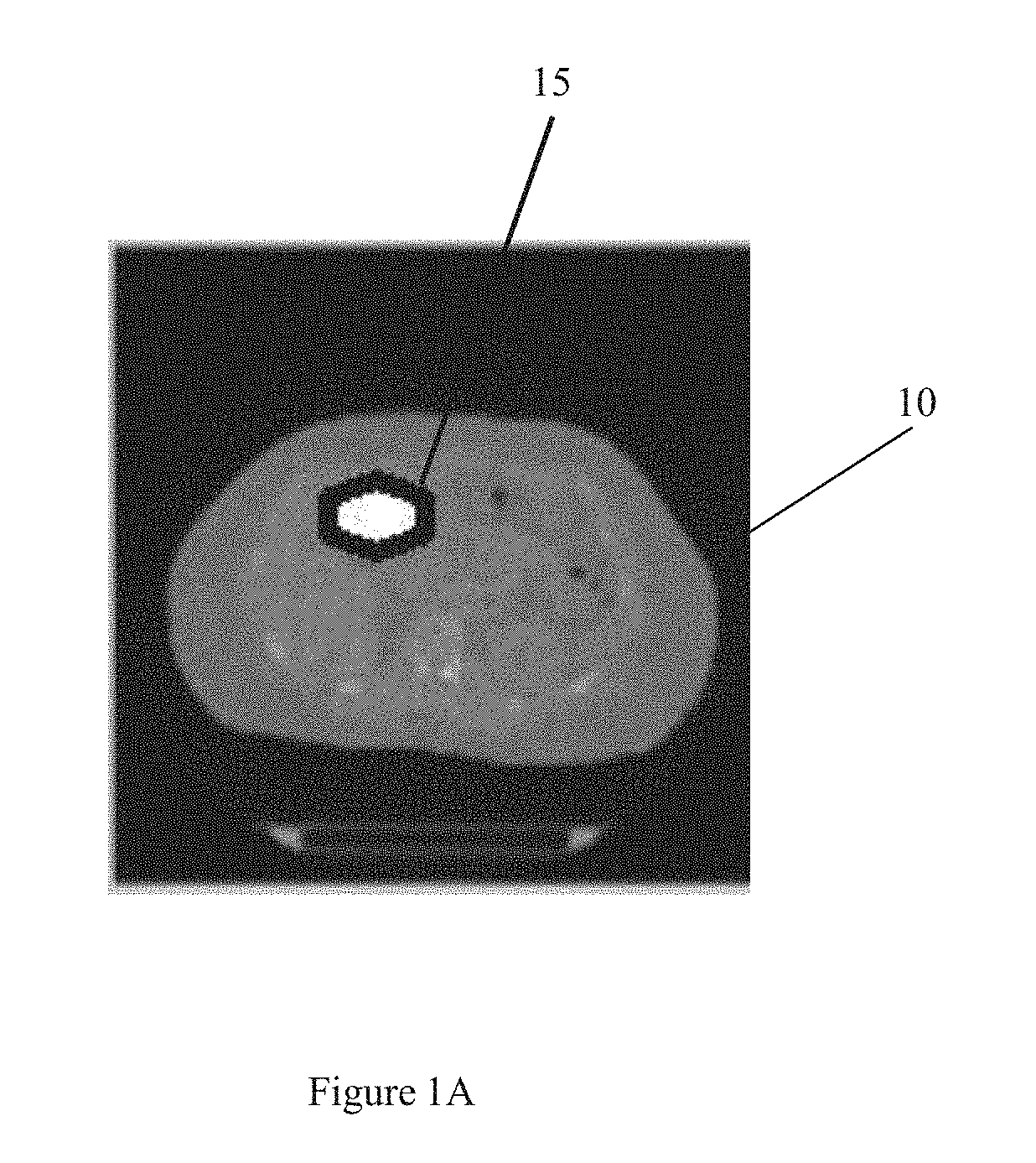
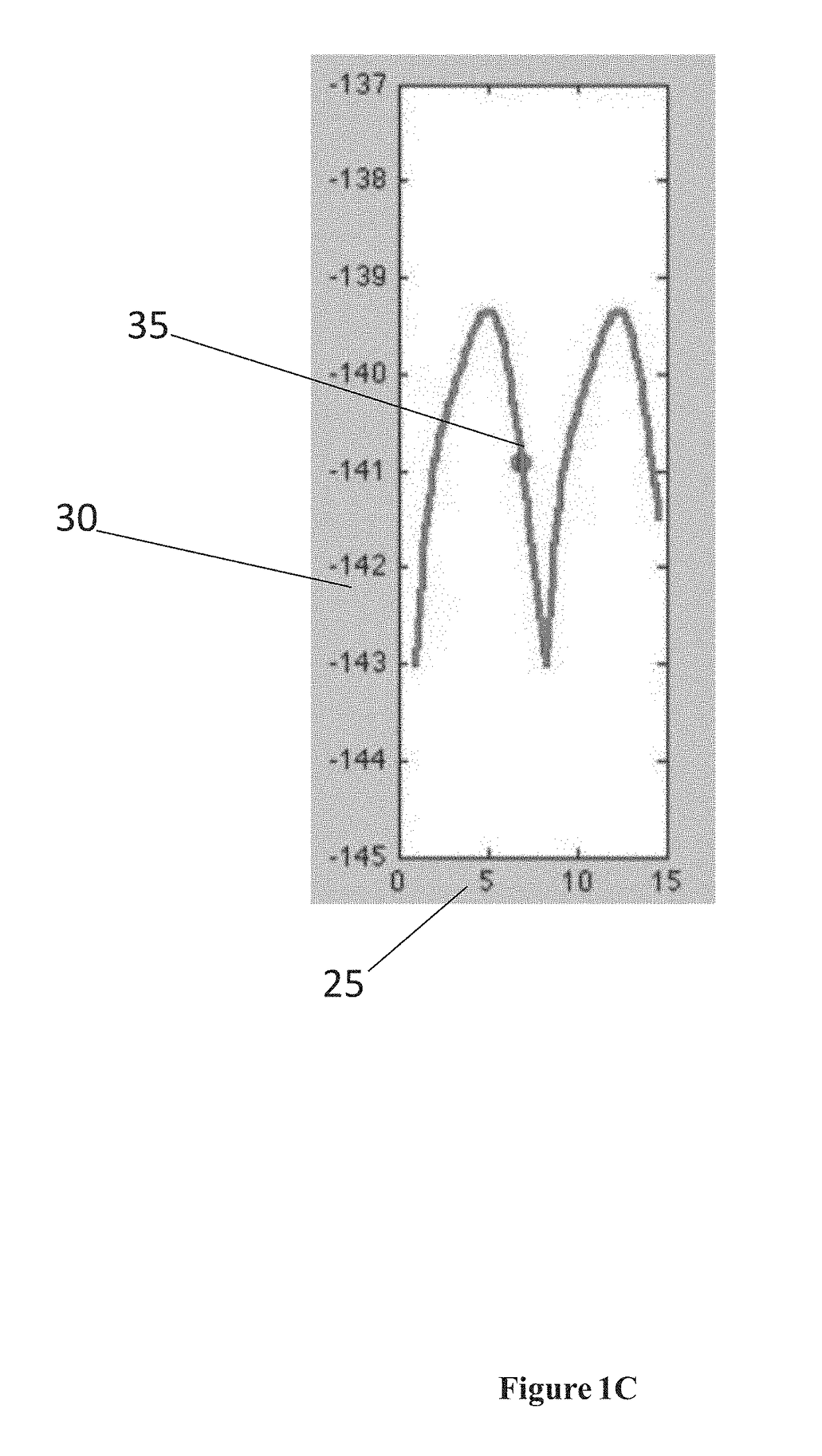
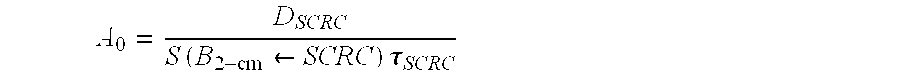Patents
Literature
69 results about "Delivered radiation dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
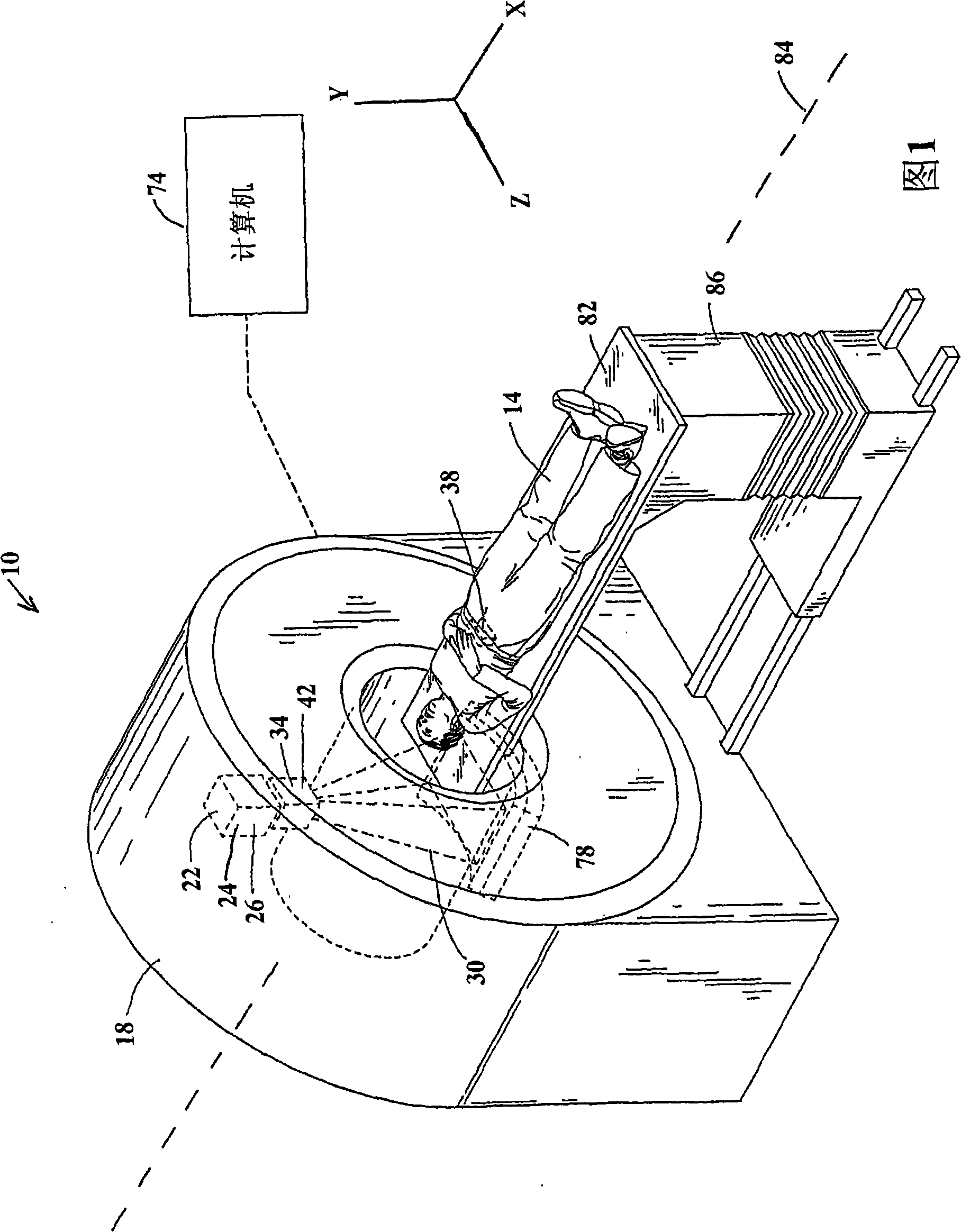
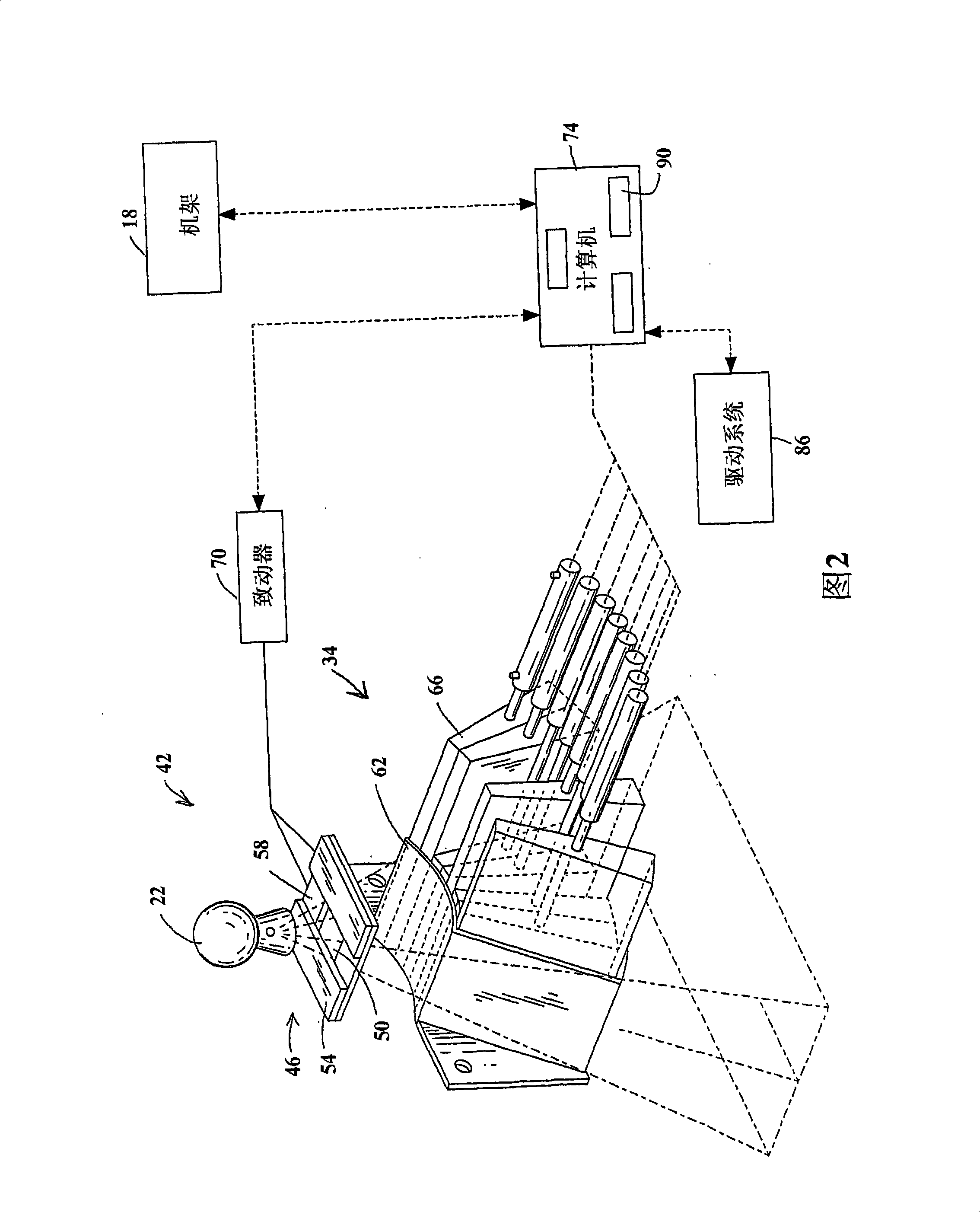
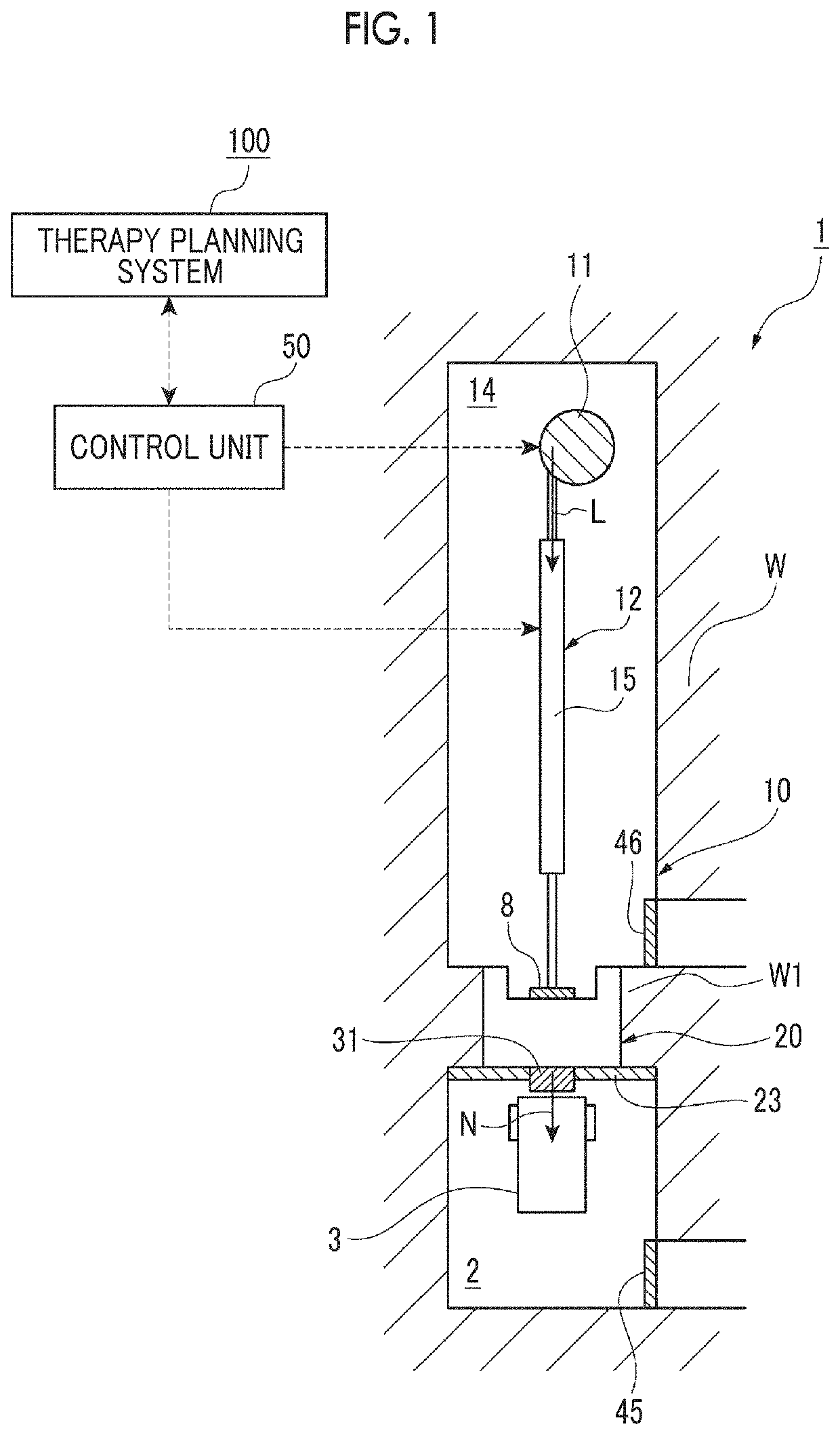
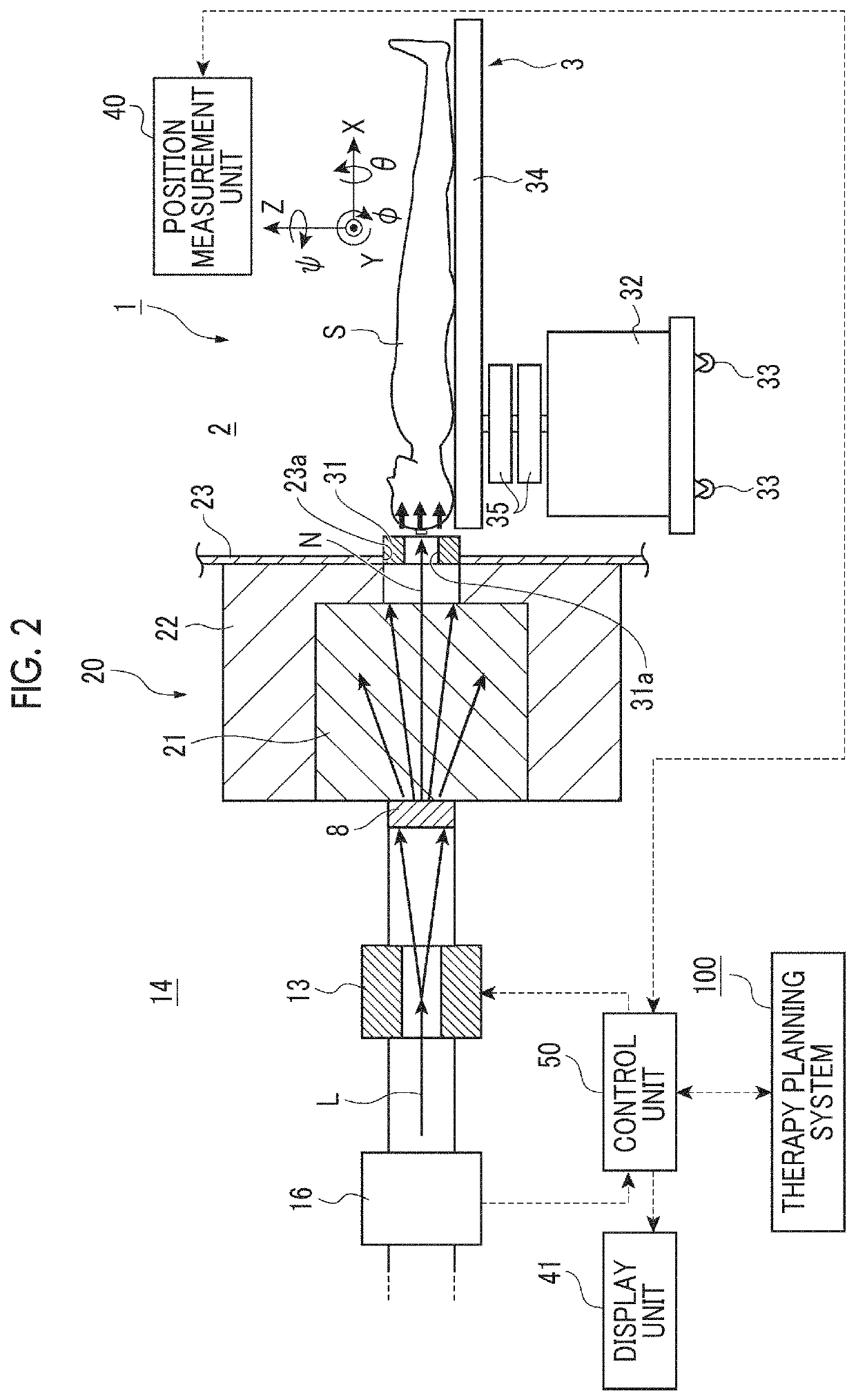
Method and system for processing data relating to a radiation therapy treatment plan
InactiveCN101268476ACharacter and pattern recognitionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyImage basedMedical physics
The invention provides a system and method of automatically processing data relating to a radiation therapy treatment plan. The method includes the acts of acquiring image data of a patient, generating a treatment plan for the patient based at least in part on the image data, the treatment plan including a calculated radiation dose to be delivered to the patient, acquiring an on-line image of the patient in substantially a treatment position, delivering at least a portion of the calculated radiation dose to the patient, and automatically recalculating the radiation dose received by the patient.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Method for reconstruction of super-resolution coronary sagittal plane image of lung 4D-CT image based on motion estimation
InactiveCN103440676AIncrease brightnessImprove clarityImage analysis2D-image generationPulmonary parenchyma3d image
The invention discloses a method for reconstruction of a super-resolution coronary sagittal plane image of a lung 4D-CT image based on motion estimation. The method for reconstruction of the super-resolution coronary sagittal plane image of the lung 4D-CT image based on the motion estimation comprises the sequential steps of (1) reading data of the lung 4D-CT image which is formed by a plurality of lung 3D images, wherein the phase positions of the lung 3D images are different; (2) extracting coronary sagittal plane images, corresponding to the same position of the lung, from all the phase positions according to the data of the lung 4D-CT image; (3) estimating motion vector fields between the lung coronary sagittal plane images with different frames based on the full search block matching algorithm; (4) reconstructing the super-resolution lung 4D-CT coronary sagittal plane image by means of the iteration back projection method and based on the motion vector fields obtained in the step (3). According to the method for reconstruction of the super-resolution coronary sagittal plane image of the lung 4D-CT image, the resolution ratio of the reconstructed super-resolution lung 4D-CT coronary sagittal plane image obtained with the method is improved obviously, the brightness and definition of blood vessels and peripheral tissue in the lung parenchyma are improved obviously in a partial enlarged image, the limitation of low resolution caused by the collection time and radiological dose is eliminated, and accurate radiotherapy of lung cancer can be effectively guided.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Planning system for intraoperative radiation therapy and method for carrying out said planning
ActiveUS20110052036A1Surgical navigation systemsAnalogue computers for chemical processesDosimetry radiationProgram planning
The invention relates to a simulation and planning system for intraoperative radiation therapy and to a method allowing said system to be used for treatment studies, simulation, planning, training and recording, which system generally comprises a central processing unit or computer (1) for management and control and software-based communication with the rest of the devices and the user; one or several monitors or screens (2) for displaying images and peripherals responsible for gathering data relating to the actions performed by said user, a deformation simulation module for the virtual simulation of the deformation produced in the organs and tissues during the process; algorithms for instantly calculating the radiation dose applied during the radiation therapy treatment simulation and means for recording all the activities carried out and generating a full dosimetry report.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
Conjugated carbon-iodine polymer and preparation thereof, and application of conjugated carbon-iodine polymer in preparation of positioning marker
ActiveCN114149569AStrong absorption capacityPrecise resectionX-ray constrast preparationsPhotovoltaic energy generationMetal ArtifactImaging quality
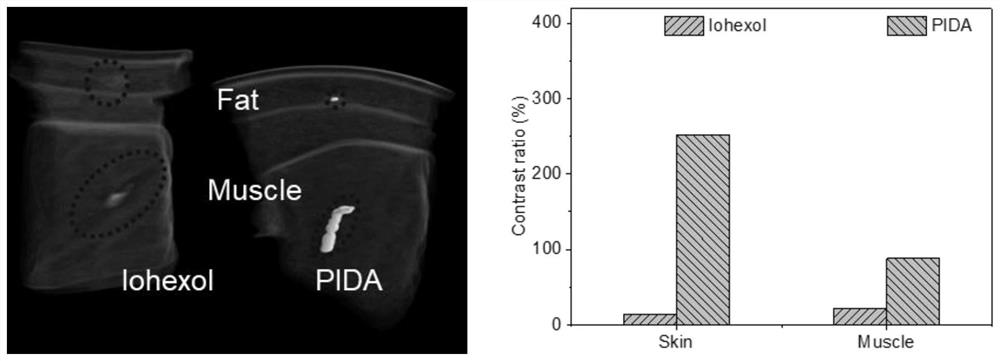
The invention relates to a conjugated carbon-iodine polymer, preparation thereof and application of the conjugated carbon-iodine polymer in preparation of a positioning marker, and belongs to the technical field of imaging markers. According to the brand-new imaging marker based on the conjugated carbon-iodine polymer disclosed by the invention, due to the conjugated structure, the polymer has very strong absorption in a visible light region, and the iodine content up to 84.1% corresponds to the superstrong imaging capability of the polymer. In the tumor operation process, based on double guidance of polymer image marking and naked eye observation, the marking can better assist in determining the cutting edge of the tumor, so that accurate cutting of the tumor is achieved, and damage to surrounding normal tissue is reduced as much as possible. In the tumor cyber knife treatment process, the polymer can replace a clinical gold mark to provide ray marking guidance, the ray imaging quality and more accurate radiation dose distribution are improved due to no metal artifacts, the relative stability of the marking position is improved due to good biocompatibility, and the radiotherapy side effect can be further reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
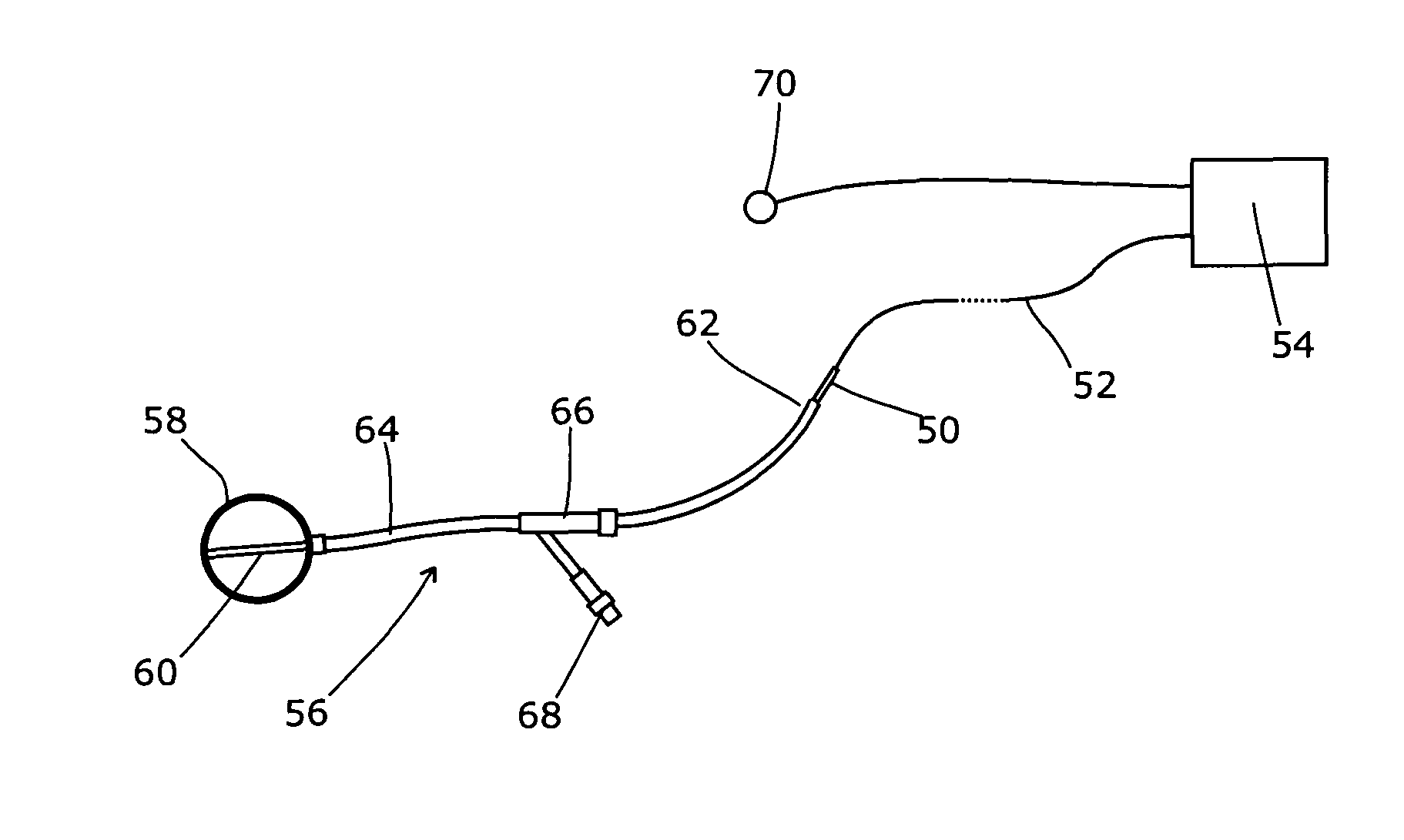
Apparatus for respiration state gated brachytherapy
ActiveUS8270568B2Prevent excessive penetrationDose lessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLeft breastBrachytherapy
During treatment by brachytherapy, radiation passes beyond the target volume and delivers radiation dose to adjacent tissue such as the lungs and, especially in the case of treatment of the left breast, to the heart. The heart is particularly vulnerable to radiation; to minimise the dose it receives in such circumstances, we propose an apparatus for treatment by brachytherapy comprising an X-ray source sized for insertion into a patient, a respiration state monitor, and a control apparatus adapted to receive respiration state information from the respiration state monitor and control the output of the X-ray source; the control apparatus being arranged to operate the X-ray source at a first output level when the respiration state monitor indicates a degree of lung inflation above a first preset threshold and operate the X-ray source at a second and lower output level when the respiration state monitor indicates a degree of lung inflation below a second preset threshold.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
The radioactive nanometer coating compound rack and its preparation method
InactiveCN1943805AHigh bonding strengthImprove wear resistanceSurgeryBiliary tumorPercent Diameter Stenosis
The invention relates to medical equipment and technology, especially the radioactive nano-coated steadier for the treatment of esophageal, airway and biliary tumors and its preparation method. The radioactive metal steadier applied in clinic at present are mainly used for the prevention of vascular restenosis after benign expansions, in the prevention and cure against the narrow cavity diseases caused by malignant tumor, there are still many problems. The invention develops radioactive nano-coated compound steadier by advanced nuclear and nano-technology technology. The original medical steadier was coated with a layer containing the isotope 125I nano composite film, with 300 to 900 radiation dose, less than 300 nm coating thickness. The invention not only has a supporting effect, but also has fistula prevention and radiation therapy effect. In a fairly long period of time to maintain the vascular flow, which not only improves the quality of life of patients but also prolong the patient's life.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Edentulous jaw oral implant guide plate retaining device, implant guide plate, preparation method and fixation method thereof
InactiveCN109223212AReduce mistakesImprove repair effectDental implantsLess invasiveEdentulous patient
The invention discloses an edentulous jaw oral implant guide plate retaining device, an implant guide plate, a preparation method and a fixation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of oral implants. Through the cooperation between the retention pin and the retention cap, the position of the retention pin in the oral cavity can be re-engraved in the mold through the retention cap when the mold is taken out, according to the position of the retention pin in the model, the position of the one-way retention hole of the positioning retention pin is determined on the implant guide plate, The implant guide plate is positioned and fixed through a one-way retention hole and a retention nail after the implant guide plate is put into the oral cavity, thereby playing the role of fixingthe implant guide plate, ensuring that the position of the implant guide plate in place during the operation is consistent with the position designed before the operation, reducing the error caused bythe position deviation of the implant guide plate, and improving the repair effect. Compared with the traditional edentulous patient, the invention reduces the steps of photographing the CBCT in theinitial diagnosis, and reduces the radiation dose accepted by the patient. Retention devices are less invasive, less costly, and more easily accepted by the majority of patients.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
System and method for patient-specific radiotherapy treatment verification and quality assurance
A radiotherapy treatment verification and quality assurance method may include receiving at least one set of first medical images of at least a portion of a patient. A three-dimensional model of the portion of the patient may be created based on the at least one set of first medical images. At least one dosimeter may be inserted into at least a portion of the model. The dosimeter is configured to measure exposure to radiation. The model may be irradiated in accordance with a radiotherapy treatment plan created by a treatment planning system. A readout of the model may be taken or performed to measure in three-dimensions a delivered radiation doses distribution.
Owner:E·T·帕帕斯 +1
Radiation parameter determination method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
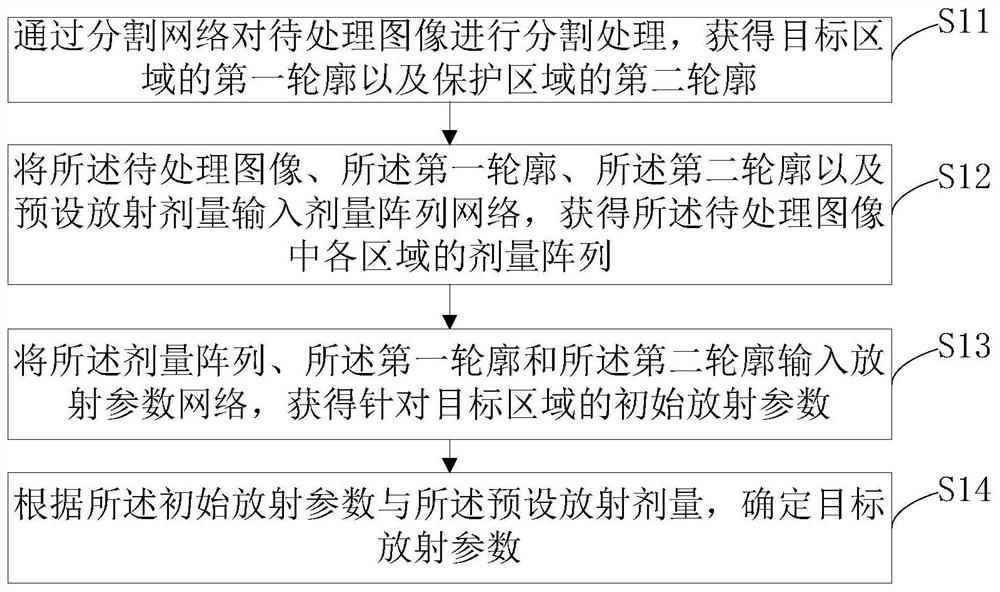
PendingCN111833988AReduce manual interventionReduce mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisRadiation doseElectronic equipment
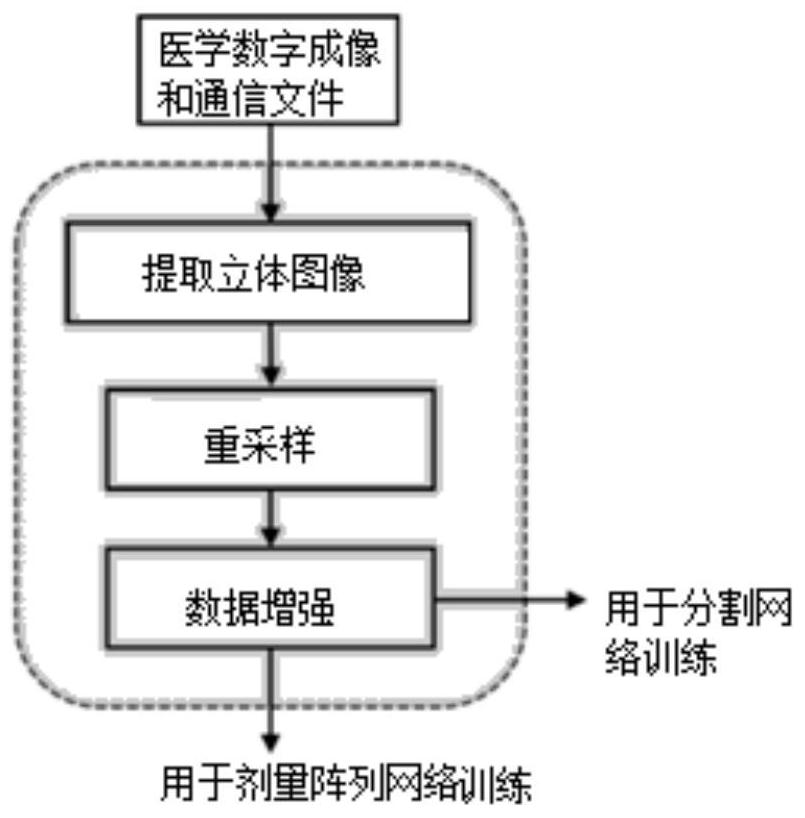
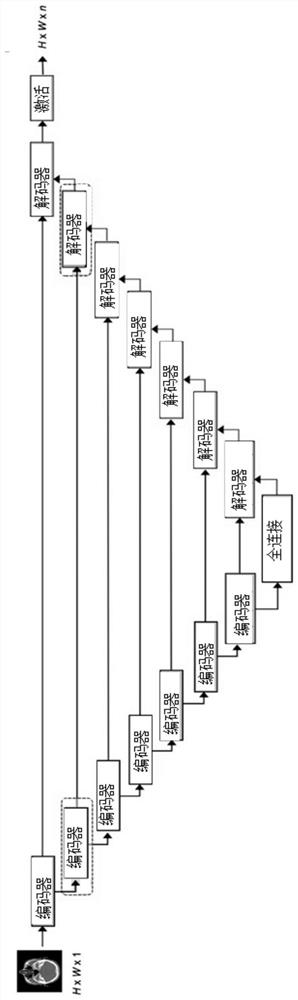
The invention relates to a radiation parameter determination method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of performing segmentation processing on a to-be-processed image through a segmentation network to obtain a first contour of a target area and a second contour of a protection area; inputting the to-be-processed image, the first contour, the second contour and a preset radiation dose into a dose array network to obtain a dose array; inputting the dose array, the first contour and the second contour into a radiation parameter network to obtaininitial radiation parameters; and determining a target radiation parameter according to the initial radiation parameter and a preset radiation dose. According to the radiation parameter determinationmethod provided by the embodiment of the invention, a target area and a protection area in the image are automatically segmented through the segmentation network, and errors of manual intervention are reduced. The initial radiation parameters of the medical instrument are determined through the dose array network and the radiation parameter network, so that the target radiation parameters are determined, the process of determining the radiation parameters can be automatically realized, and the working efficiency and the accuracy of the scheme are improved.
Owner:BEIJING ANDE YIZHI TECH CO LTD
Method for Fiducial-less Real-time Tracking in Radiation Treatment of Abdominal Tumors
InactiveUS20140343345A1Improve accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAbdominal tumorTumor location
A method for fiducial-less real-time motion tracking of abdominal tumors based on the correlation between the patient's breathing pattern and the diaphragm / lung border during treatment delivery. This invention utilizes an edge detection technique to delineate the diaphragm / lung border on radiographic images in order to calculate or determine tumor locations in the abdomen. The position of the diaphragm / lung border is synchronized with the breathing pattern obtained from continuous optical monitoring of a patient's respiratory cycle. The real-time optical breathing pattern obtained from monitoring is used to determine or calculate the position of the diaphragm / lung border during treatment delivery. The position of the diaphragm / lung border is then used to determine the tumor location in real-time. The target tumor coordinates generated through this process are used by the treatment delivery system to adjust the radiation beam geometry of the treatment delivery system to follow the tumor in real-time and accurately deliver radiation dose.
Owner:WU XIAODONG +1
Equal-difference dose gradient radiation lung cancer surviving or resisting cell model as well as construction and application
PendingCN110878284AHelp to findAccurate researchElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentTumor/cancer cellsDose gradientCancer cell
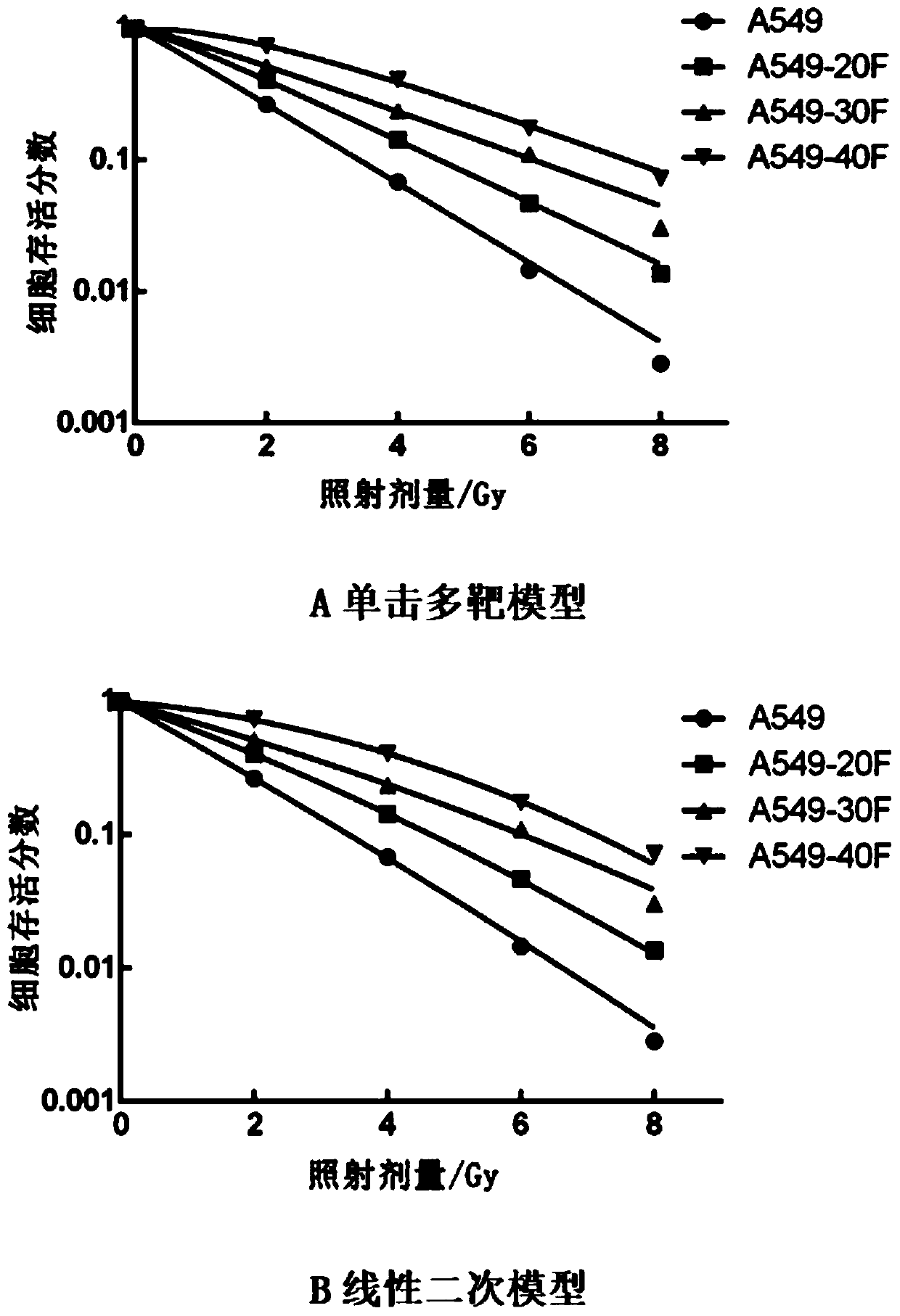
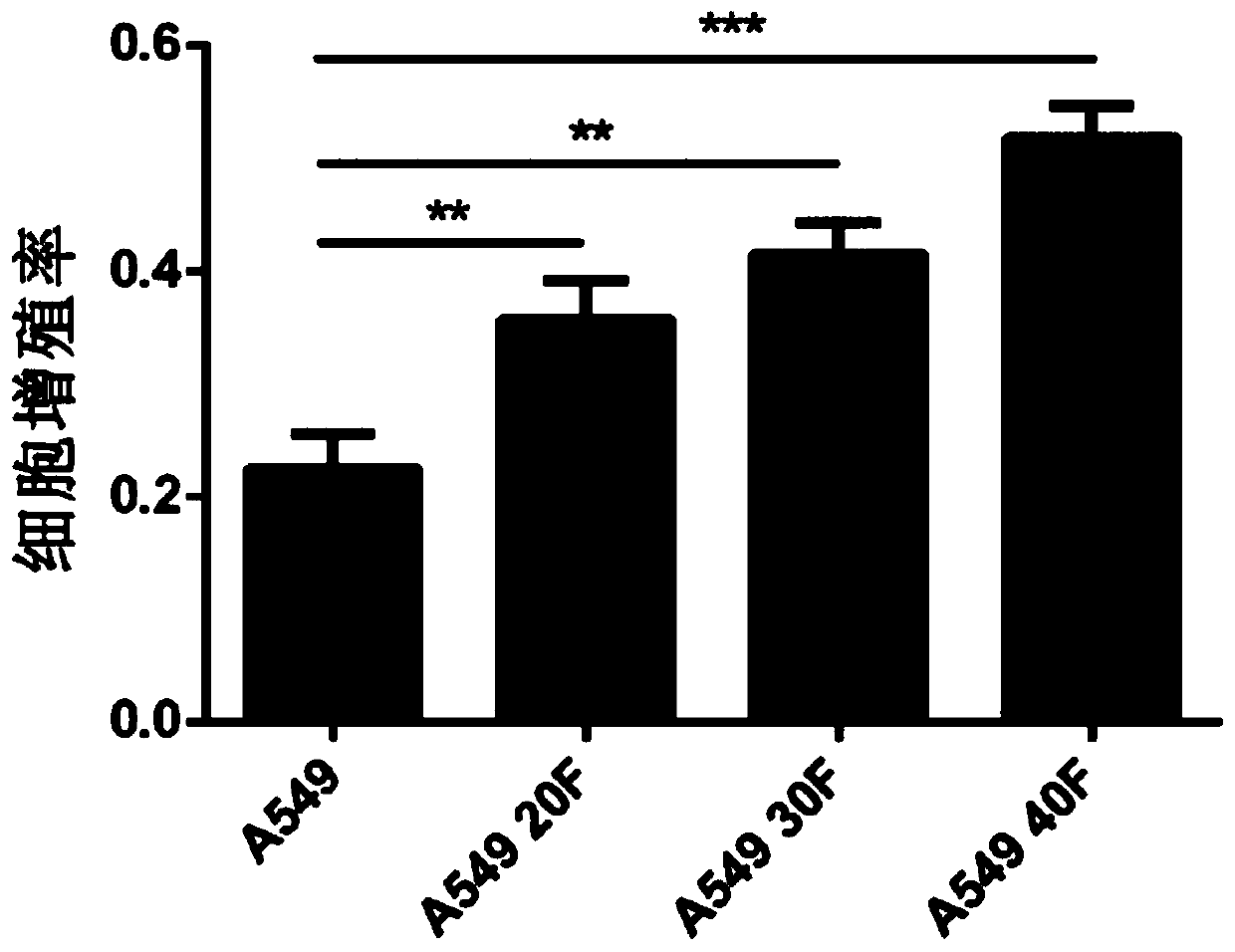
The invention discloses a lung cancer resisting cell strain for radiotherapy, and a construction method and an application of the cell strain, and particularly discloses an application of the cell strain in preparation of the equal-difference dose gradient radiation human lung cancer surviving or resisting cell model. The lung cancer cell resisting line for radiotherapy is selected from three radiation resistant cell lines derived from a human lung cancer cell line A549, the strain is named as a human lung cancer cell radioactive ray resistant strain A549-20F, A549-30F and A549-40F respectively, and the preservation numbers of the strains are CGMCC No. 18161, CGMCC No. 18163 and CGMCC No. 18162 respectively. The cell model provided by the invention is closer to a clinical dose segmentationmodel, the radiation effect is more closely observed and researched dynamically according to the radiation dose in clinical practice; a series of continuous specific changes caused by progressive increase of the radiotherapy dosage in a lung cancer patient can be better simulated, key biomarkers for promoting lung cancer radiation survival / resistance can be found, a radiation resistance generation mechanism can be clarified, and the model has important significance for clinically optimizing a radiotherapy scheme and realizing accurate radiotherapy.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Compounds and methods of use in ablative radiotherapy
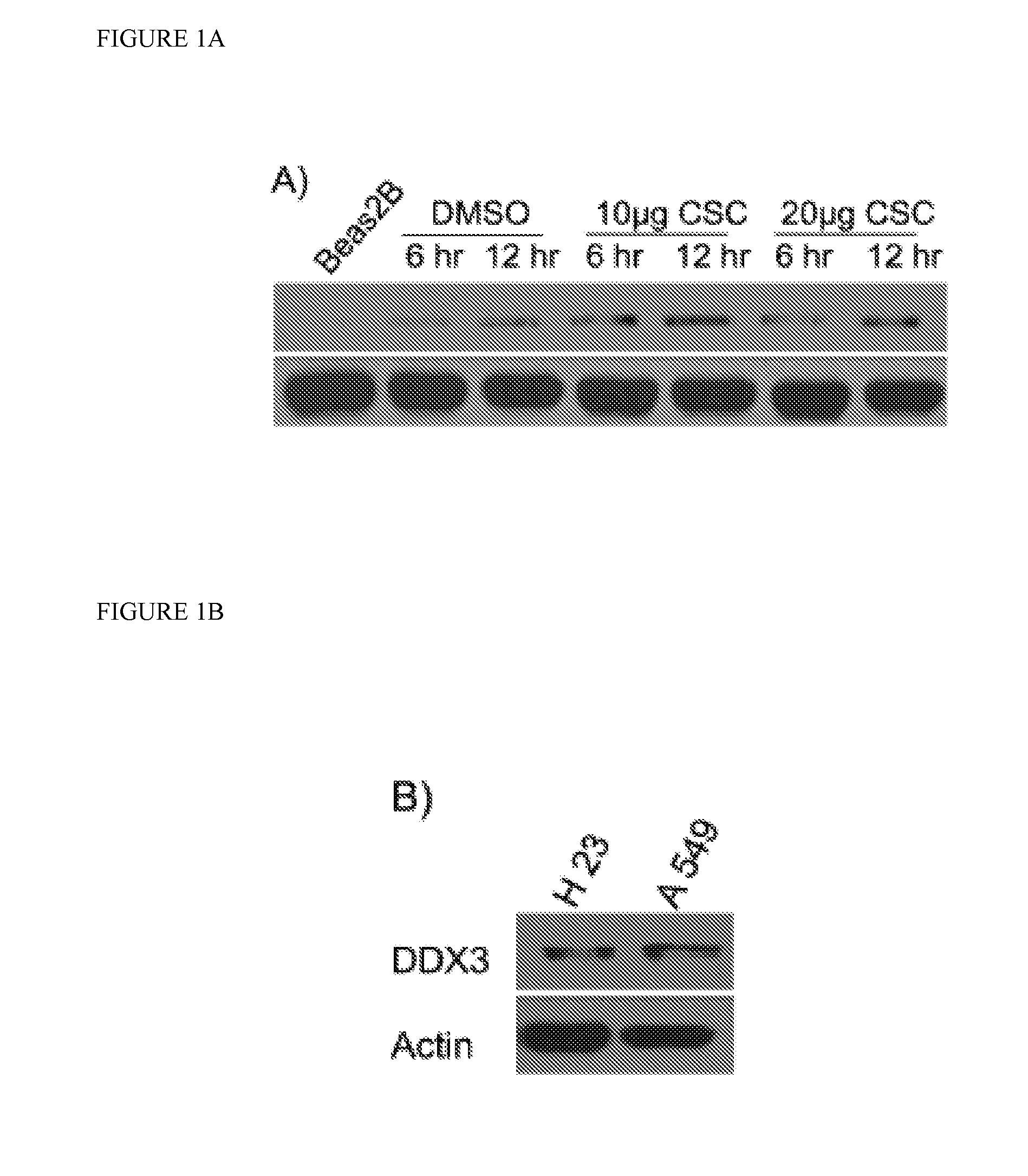
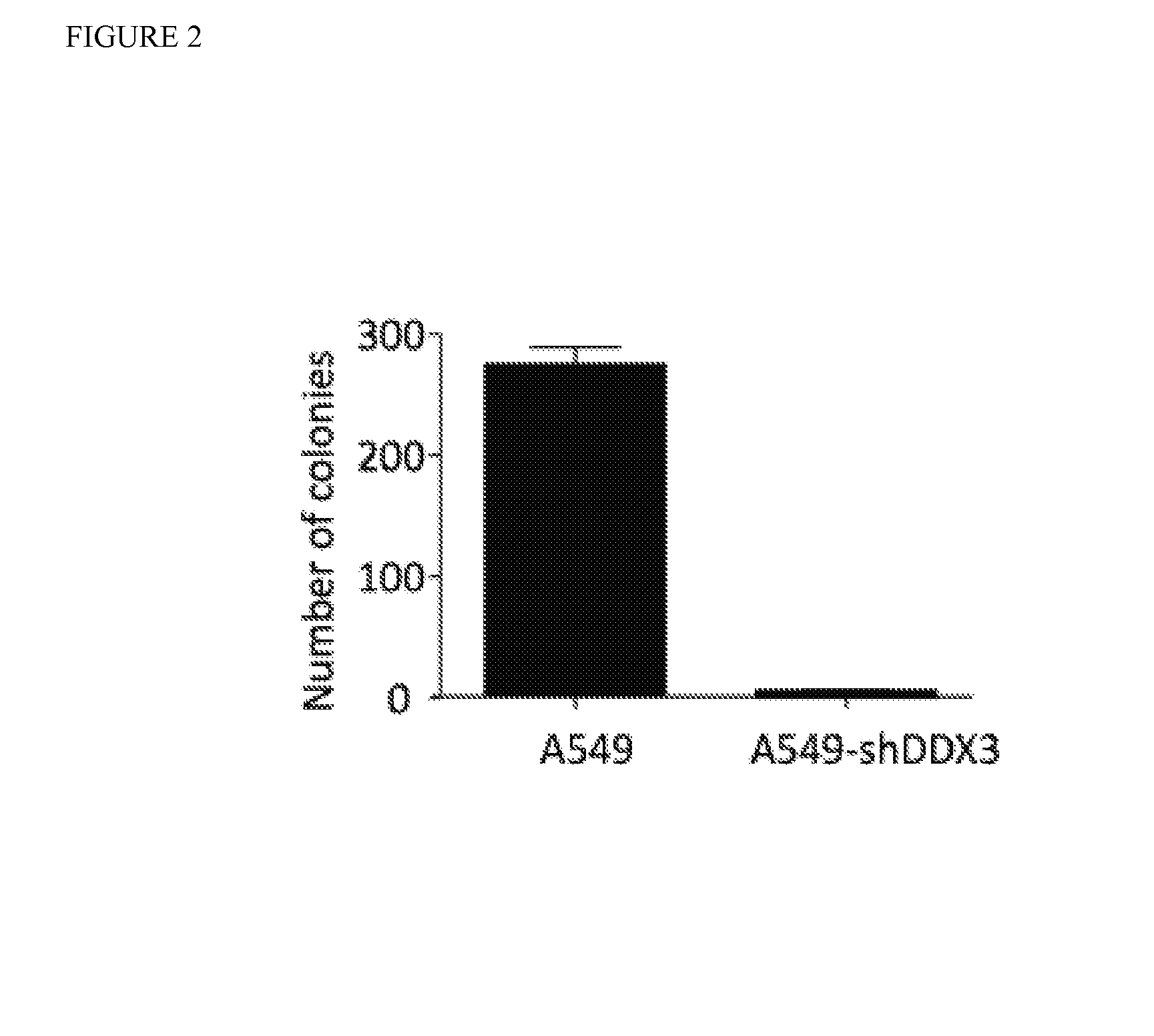
ActiveUS20140018606A1Reduce lung tumor burdenImprove efficiencyBiocideOrganic chemistryDead box helicaseRadical radiotherapy
Provided herein is the compound RK-33, or a salt, solvate, stereoisomer, or derivative thereof, which is shown to be an inhibitor if the DEAD box helicase DDX3, in mammalian cells. RK-33 is also provided herein for use as a radiation dose sensitizer in a subject suffering from a proliferative disease and undergoing radiation therapy. Methods of treatment of proliferative diseases, such as cancer with a combination of RK-33 and radiotherapy methods such as stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
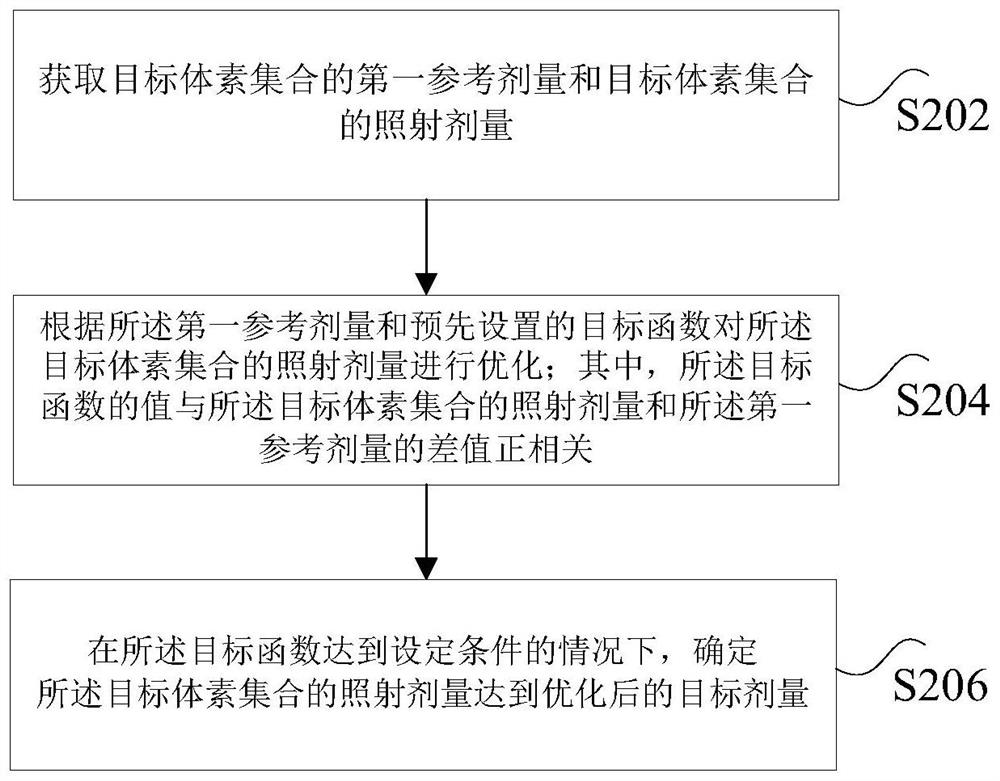
Radiotherapy dose optimization method and device
PendingCN114496161AImprove optimization efficiencySolve the technical problem of low optimization efficiencyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesHealth-index calculationVoxelRadiology
The invention discloses a radiotherapy dose optimization method and device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first reference dose of a target voxel set and an irradiation dose of the target voxel set; optimizing the irradiation dose of the target voxel set according to the first reference dose and a preset target function; wherein the value of the target function is in positive correlation with the difference between the irradiation dose of the target voxel set and the first reference dose; and determining that the irradiation dose of the target voxel set reaches the optimized target dose under the condition that the target function reaches a set condition. The technical problem of low radiation dose optimization efficiency caused by excessive dependence on manual debugging is solved.
Owner:MANTEIA TECH CO LTD
Sensitizer for radiotherapy and application thereof
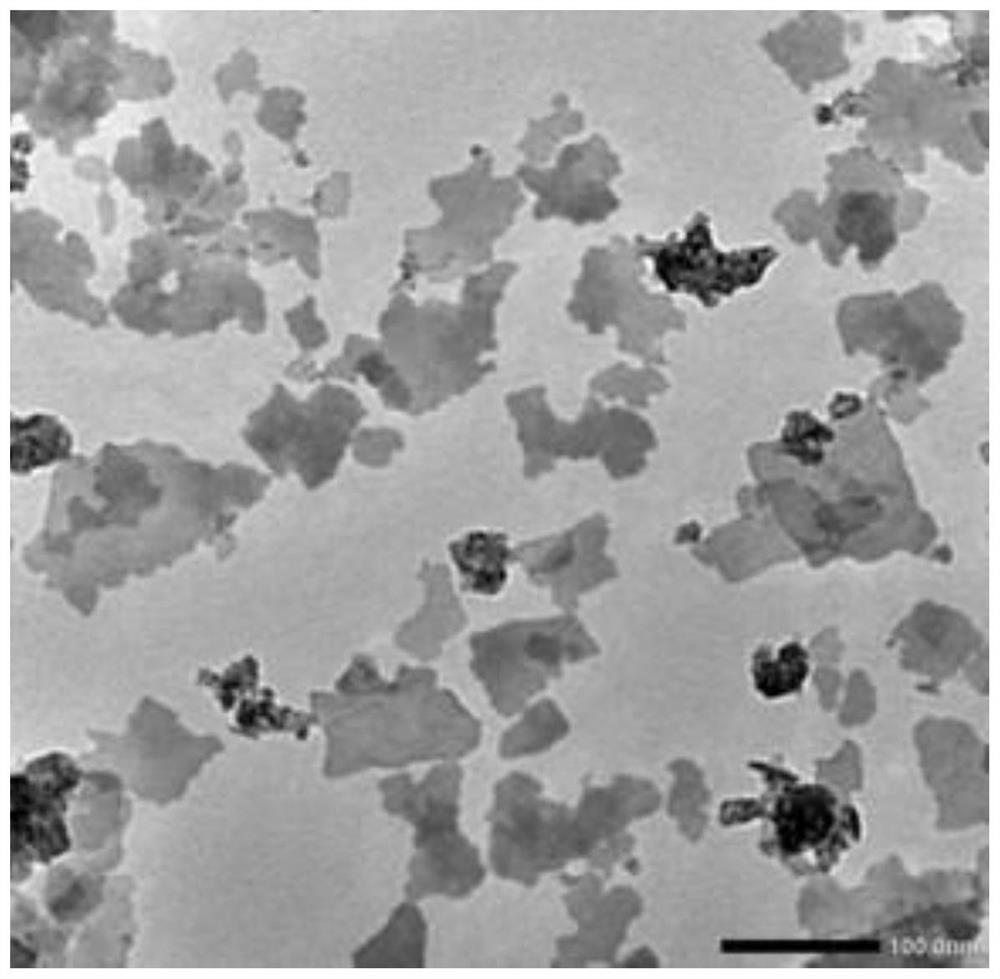
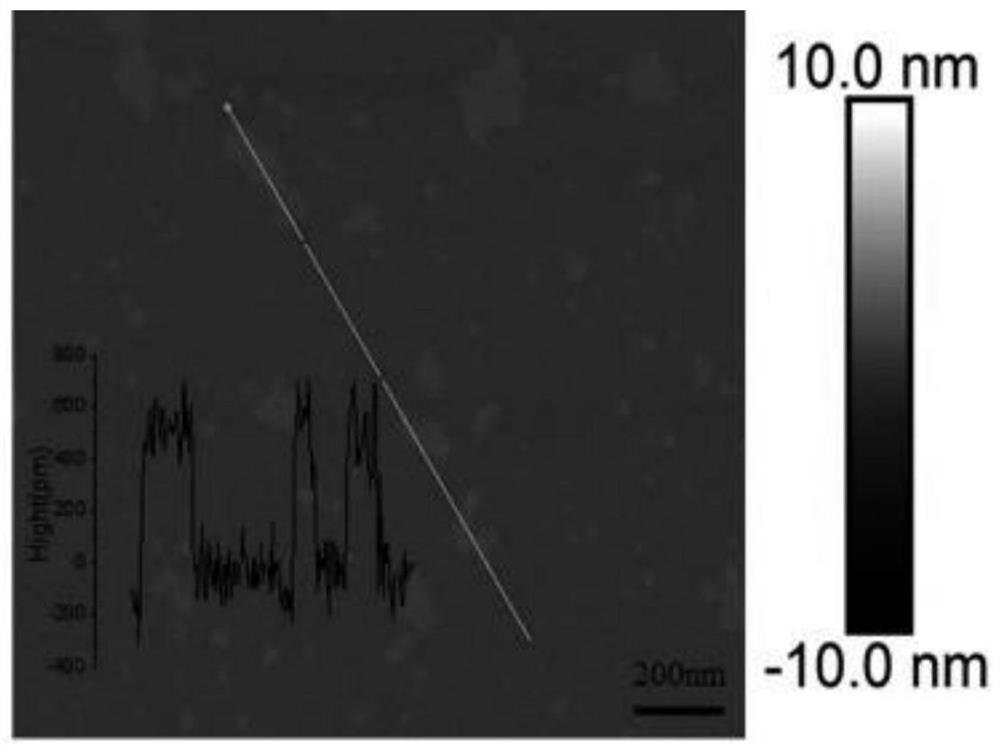
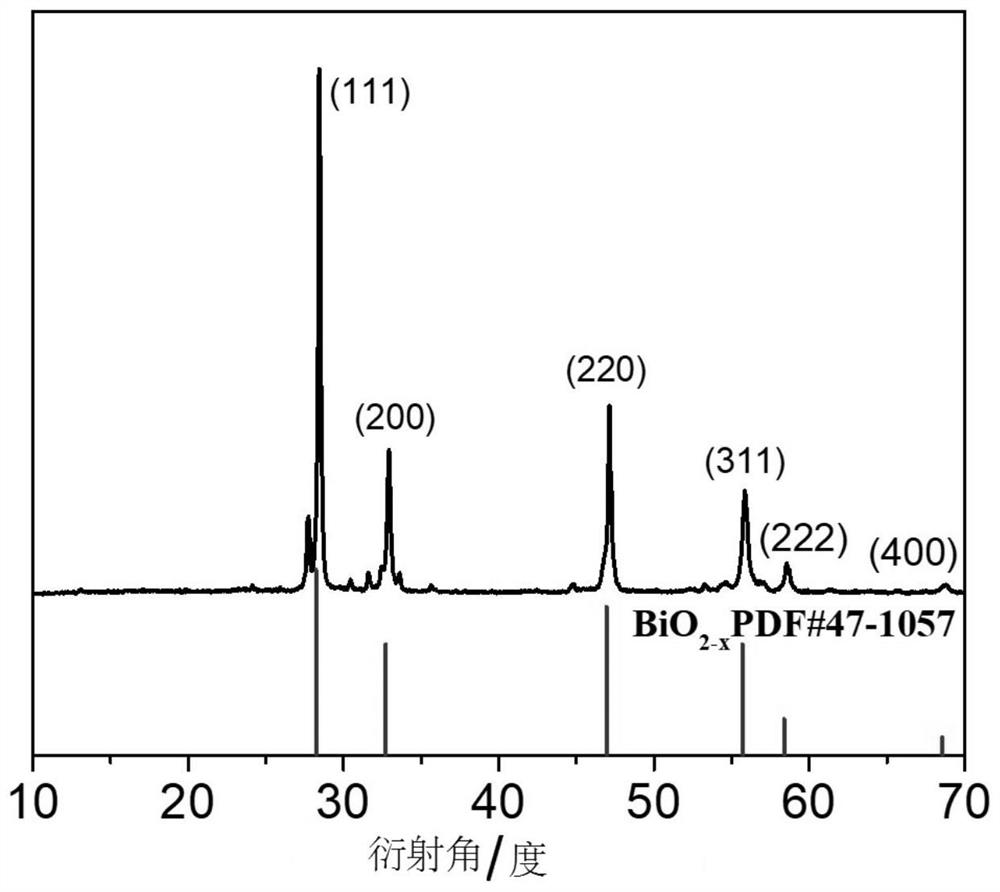
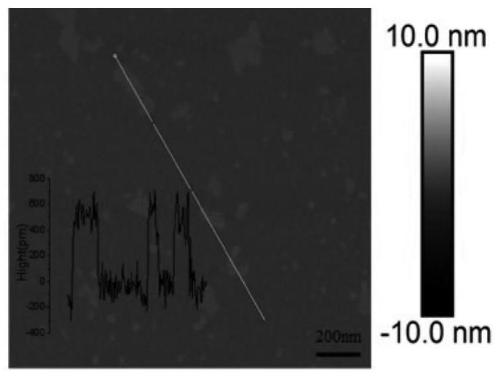
ActiveCN114712500AGood biocompatibilityLow toxicityInorganic active ingredientsNanomedicineRadioactive agentOxygen deficiency
The invention relates to a sensitizer for radiotherapy and application thereof, belongs to the field of nanomaterial chemistry and biochemistry, and solves the problems that an existing radiotherapy sensitizer cannot improve the hypoxic state in a tumor microenvironment, radiotherapy is insensitive, the dosage of a radioactive agent is large, and damage to normal tissues is large. The sensitizer for radiotherapy comprises BiO2-x nanosheets, the molecular structure has oxygen deficiency, and the sensitizer is prepared from the following raw materials: hydroxide of alkali metal and bismuthate; and x ranges from 0.15 to 0.6. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving hydroxide of alkali metal and bismuthate, and stirring to obtain a solution; transferring the solution into a reaction container, heating, and reacting for a period of time; and cooling to room temperature, washing with deionized water, and drying at 60-100 DEG C for 2-8 hours to obtain BiO2-x. The BiO2-x disclosed by the invention can be used as a sensitizer to be applied to radiotherapy sensitization of tumors, and a very good inhibition effect on the tumors under a relatively low radiation dose is realized.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Radiation dosimetry and blocking antibodies and methods and uses therefor in the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20060127311A1Less costlyLong half-lifeNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSurgically-Created Resection CavityWilms' tumor
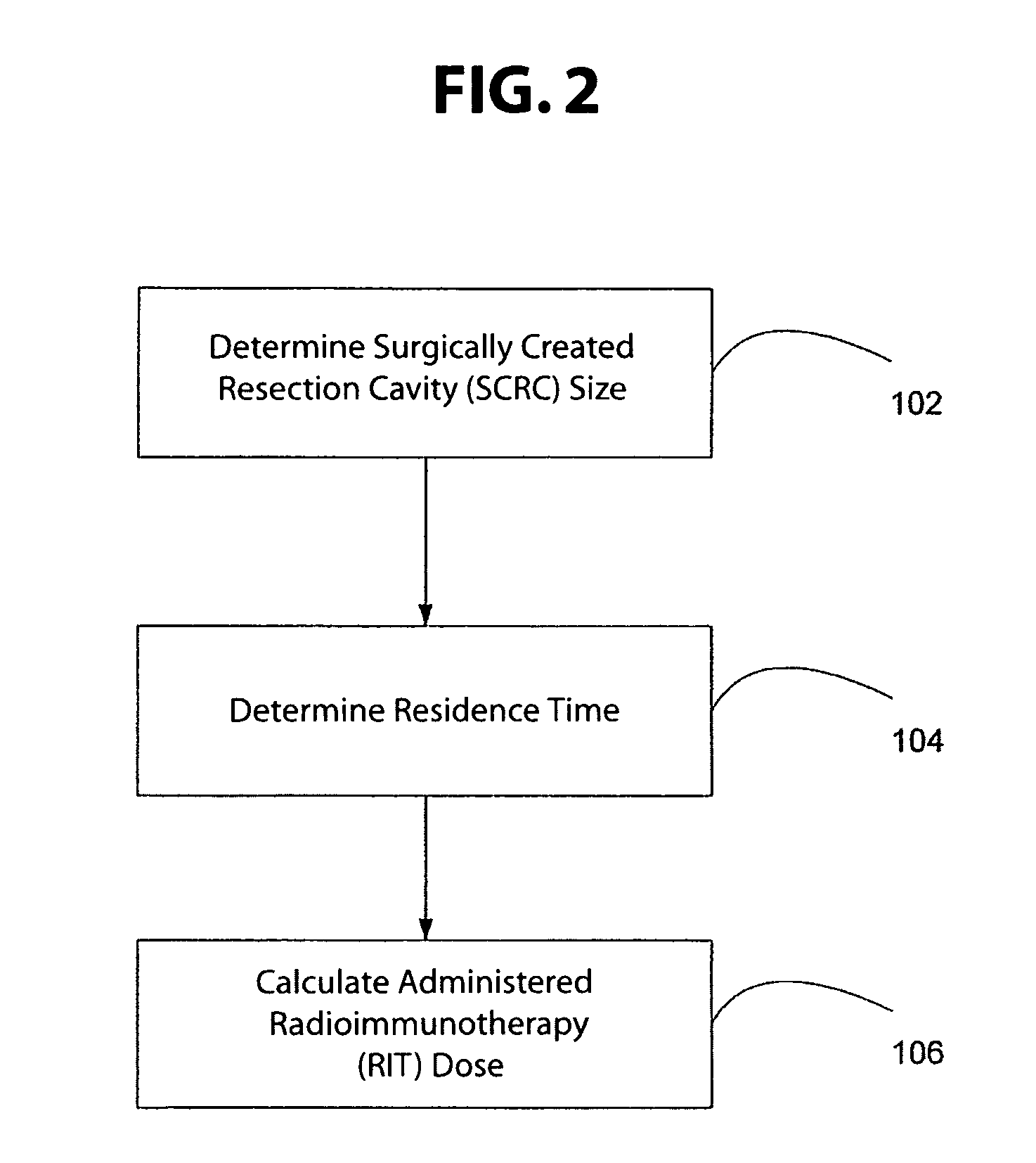
Disclosed is a method for dosimetry estimation for a region of interest at or around a surgically created resection cavity in a subject. These methods enable medical practitioners to estimate the amount of administered Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) agent needed to safely and effectively achieve a final Radiation Absorbed Dose (RAD). Furthermore, computer hardware and software are provided herein, so that the methods according to the invention may be automated for more efficient use. Also disclosed is a method of enhancing delivery of therapeutic antibodies that specifically bind to an extracellular stromal constituent of a tumor in a mammalian subject. The method comprises administering to a subject an effective dosage of a blocking antibody, said blocking antibodies specifically binding to said extracellular stromal constituent and blocking the binding of therapeutic antibodies to non-target tissue.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Thin film transistor array substrate, pixel circuit, X-ray detector and driving method thereof
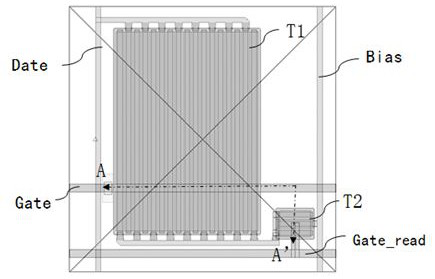
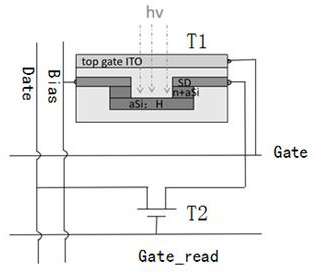
ActiveCN112002721AReduce blinking frequencyIncrease refresh rateTransistorTelevision system detailsTransistor arrayScan line
The invention provides a thin film transistor array substrate, a pixel circuit, an X-ray detector and a driving method thereof and relates to the technical field of photoelectricity. The thin film transistor array substrate comprises scanning lines, reading scanning lines, data lines and bias lines, wherein the scanning lines and the reading scanning lines are horizontally arranged, and the data lines and the bias lines are vertically arranged. The plurality of pixel units are defined by the scanning lines and the data lines in a crossed manner; each pixel unit comprises a photoconductive thinfilm transistor positioned in the photoconductive region and a reading thin film transistor positioned at the reading end. The photoconductive effect of the aSi thin film transistor is utilized to integrate the photocurrent and control the magnification times, so that the signal amplification in the pixel is realized, and the precise control of the magnification times can be realized while the radiation dose is reduced; meanwhile, the pixel structure and the process structure are simplified.
Owner:NANJING DETECH FUTURE TECH CO LTD
Dose calculation system, dose quality assurance system and storage medium
PendingCN112133440ARealize automatic modelingCalculation speedMedical simulationCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmSimulation
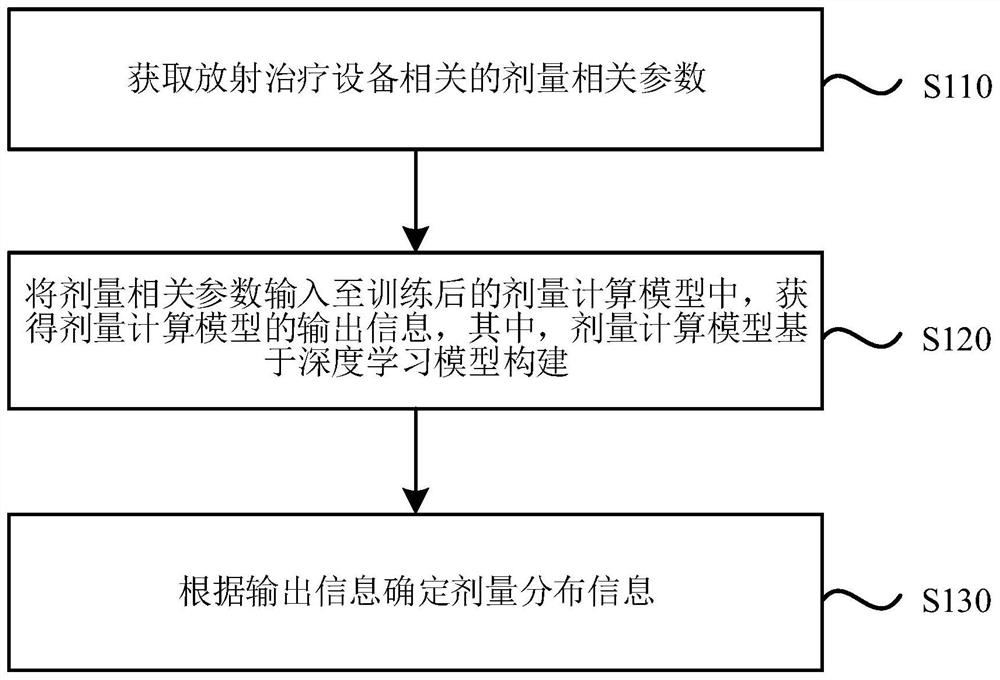
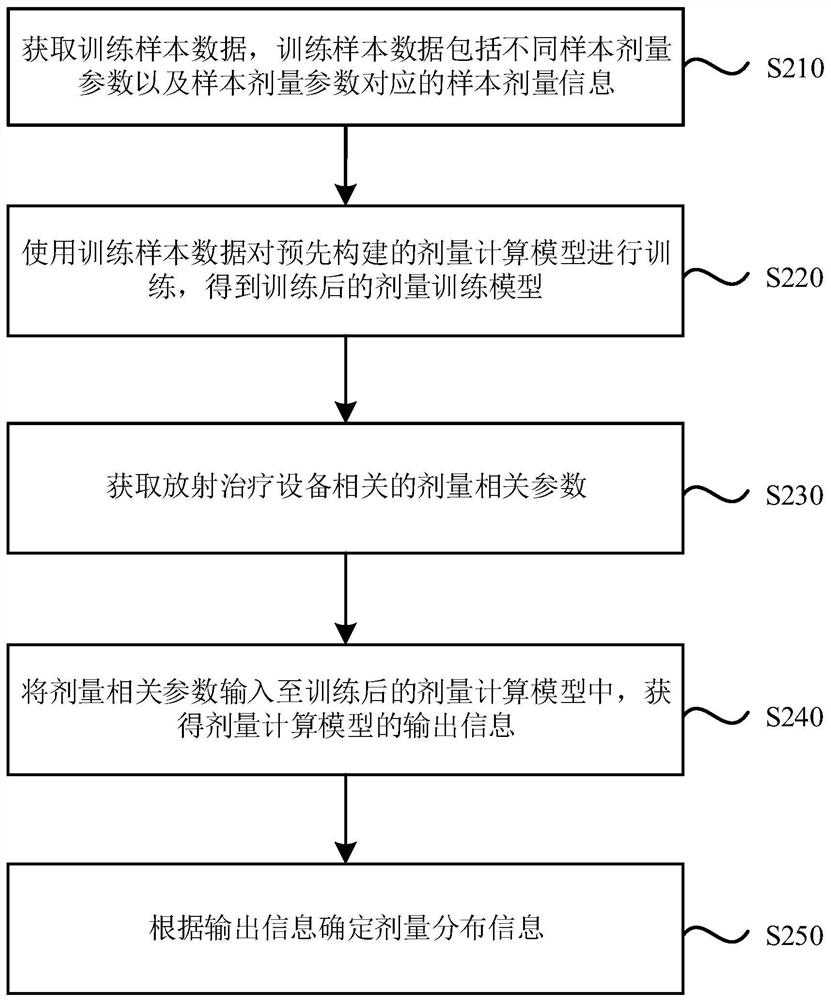
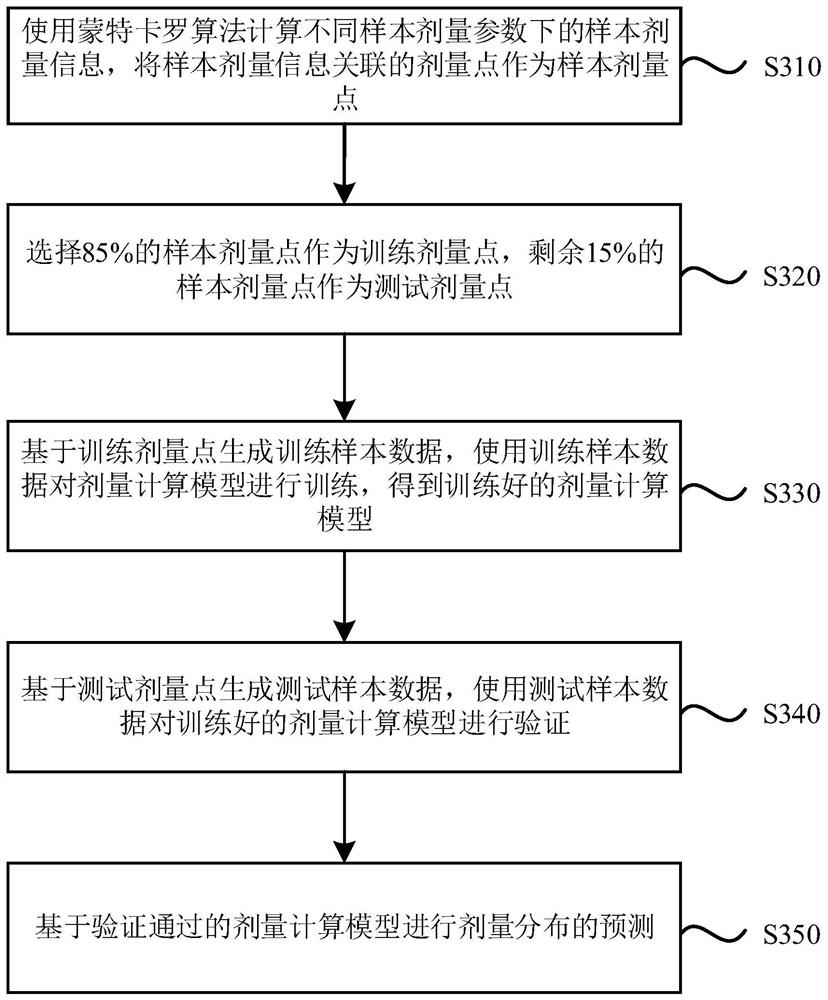
The embodiment of the invention discloses a dose calculation system, a dose quality assurance system and a storage medium. The dose calculation system comprises a processor, and the processor is configured to process the following steps: acquiring dose-related parameters related to radiotherapy equipment; inputting the dose-related parameters into a trained dose calculation model to obtain outputinformation of the dose calculation model, wherein the dose calculation model is constructed based on a deep learning model; and determining dose distribution information according to the output information. According to the embodiment of the invention, the dose calculation model is constructed and trained based on the deep learning model, automatic modeling is realized, a user does not need to manually adjust parameters, the calculation speed is high, the calculation efficiency of dose distribution prediction is improved, and the modeling process of rapid Monte Carlo dose calculation in a radiotherapy system is accelerated; and moreover, the dose calculation model can be used for guaranteeing the quality of the radiation dose, improves the calculation efficiency, and is high in accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Triazolopyrimidine compound, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111333655AHigh selectivityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellPharmacophore
The invention discloses a triazolopyrimidine compound, a preparation method and application thereof. The triazolopyrimidine compound is an mTOR inhibitor with a novel structure, the lead compound hasa new compound skeleton found by using a virtual screening and pharmacophore method, and targeted design is carried out according to different PI3K and mTOR protein structures. Therefore, the lead compound has the characteristics of high activity and high selectivity. Moreover, the compound is creatively used as a radiosensitizer for cancer treatment, so that the sensitivity of cancer cells to radiotherapy can be improved, the radiation dose in radiotherapy is greatly reduced, the side effect is reduced, and the radiotherapy effect is improved.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
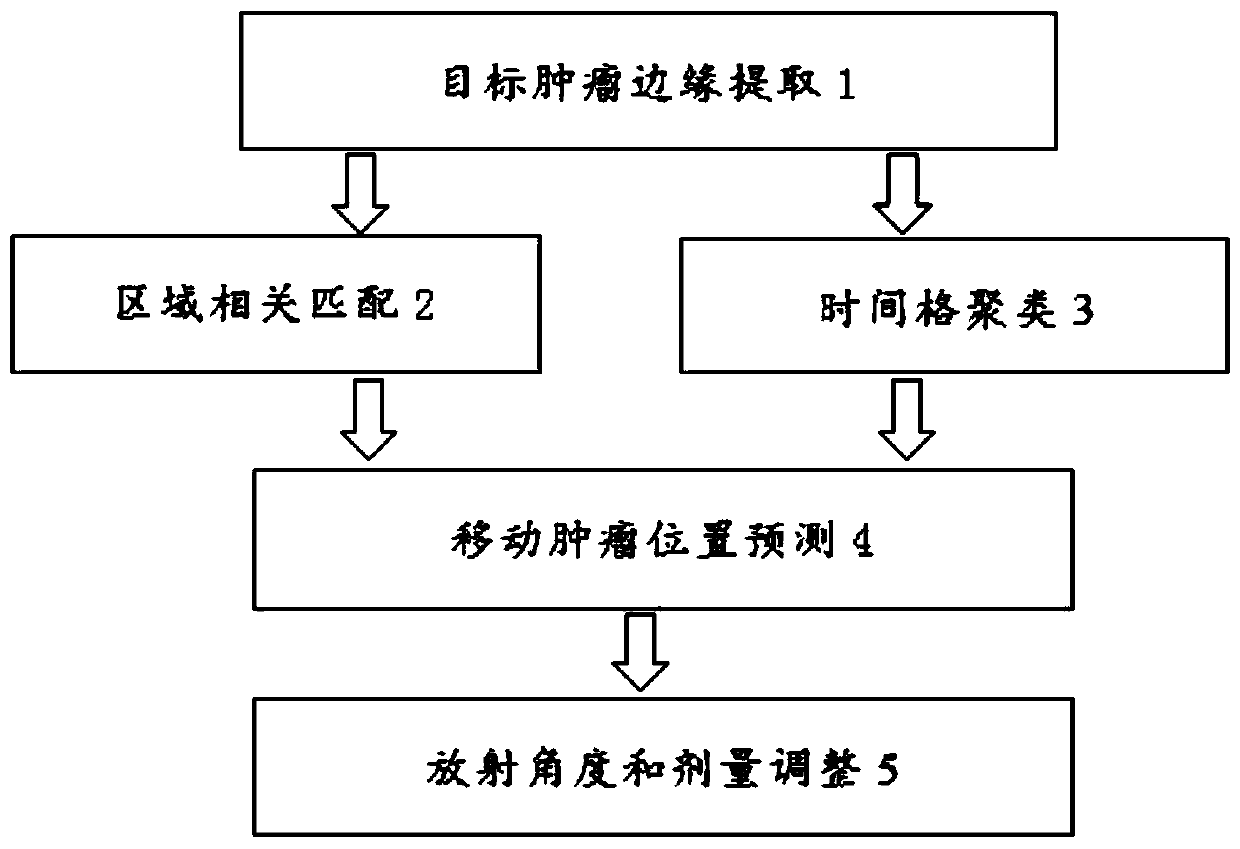
Method for dynamically adjusting radioactive angle and dosage according to movement of tumor
ActiveCN111388882AImprove accuracyHigh precisionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTumor marginTreatment targets
The invention provides a method for dynamically adjusting the radioactive angle and dosage according to the movement of a tumor. According to the method, the moving position and spreading area of a dynamic tumor are precisely predicted and tracked, and the deflection of a radioactive angle is adjusted in time, and the radioactive dosage of a treatment target can be accurately controlled. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting the edge of a target tumor; (2) performing area related matching; (3) performing time grid clustering; (4) predicting the moving tumor position; and (5)adjusting the radioactive angle and dosage.
Owner:SHANDONG RES INST OF TUMOUR PREVENTION TREATMENT +2
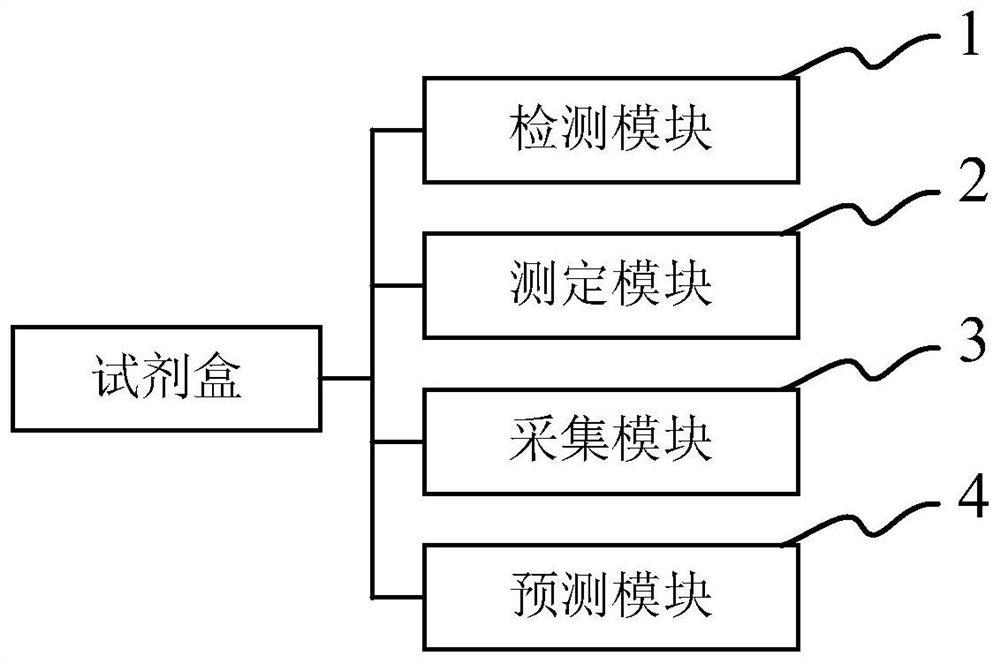
Kit for predicting lung injury clinical progress of patient with chest tumor after radiotherapy
PendingCN111912973AEffective clinical interventionBiological testingInterleukin 6Pulmonary infection
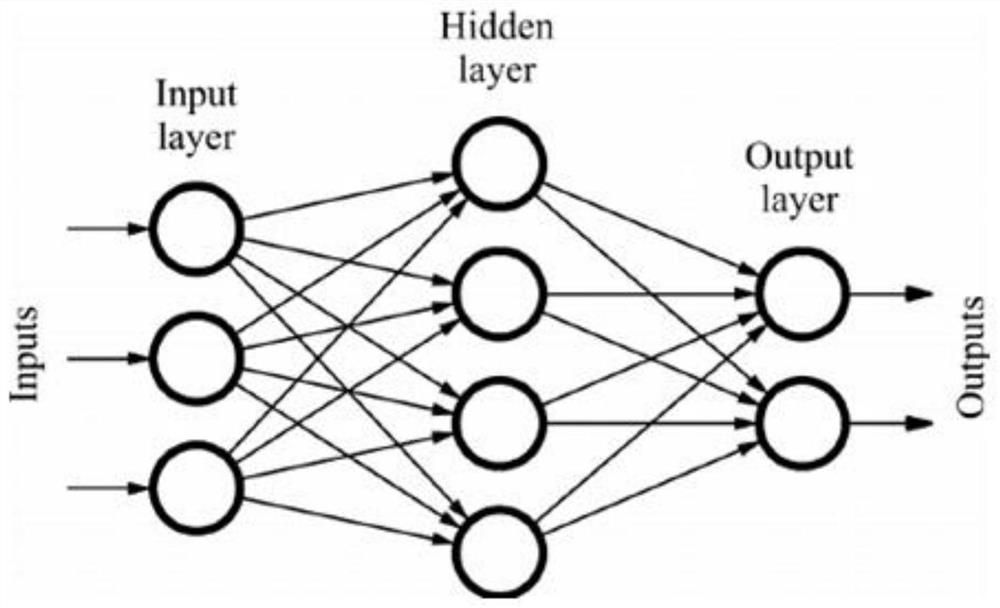
The invention discloses a kit for predicting the lung injury clinical progress of a patient with chest tumor after radiotherapy. A detection module detects the number and proportion of seven immune cells in peripheral blood of the patient with chest tumor, and the seven immune cells comprise NK cells, lymphocytes, granulocytes, monocytes, DC cells, T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes; a measuring module is used for measuring the concentrations of five cytokines in peripheral blood, and the five cytokines comprise interleukin 4, interleukin 6, interleukin 8, interleukin 13 and gamma interferon; anacquisition module acquires the clinical information of the patient withchest tumor, and the clinical information comprises age, gender, weight, hypertension, diabetes, pulmonary infection, radiationfield and radiation dose; and a prediction module inputs the number and proportion of the seven immune cells, the concentrations of the five cell factors and the clinical information into a feedforward neural network for prediction, and predicts the probability of occurrence and severity of lung injury at different stages after radiotherapy of the patient with chest tumor .
Owner:上海焕一生物科技有限公司
Neutron capture therapy system and therapy planning system for neutron capture therapy
ActiveUS10568964B2Precision therapyEnergy modified materialsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMedicineNeutron capture
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD +1
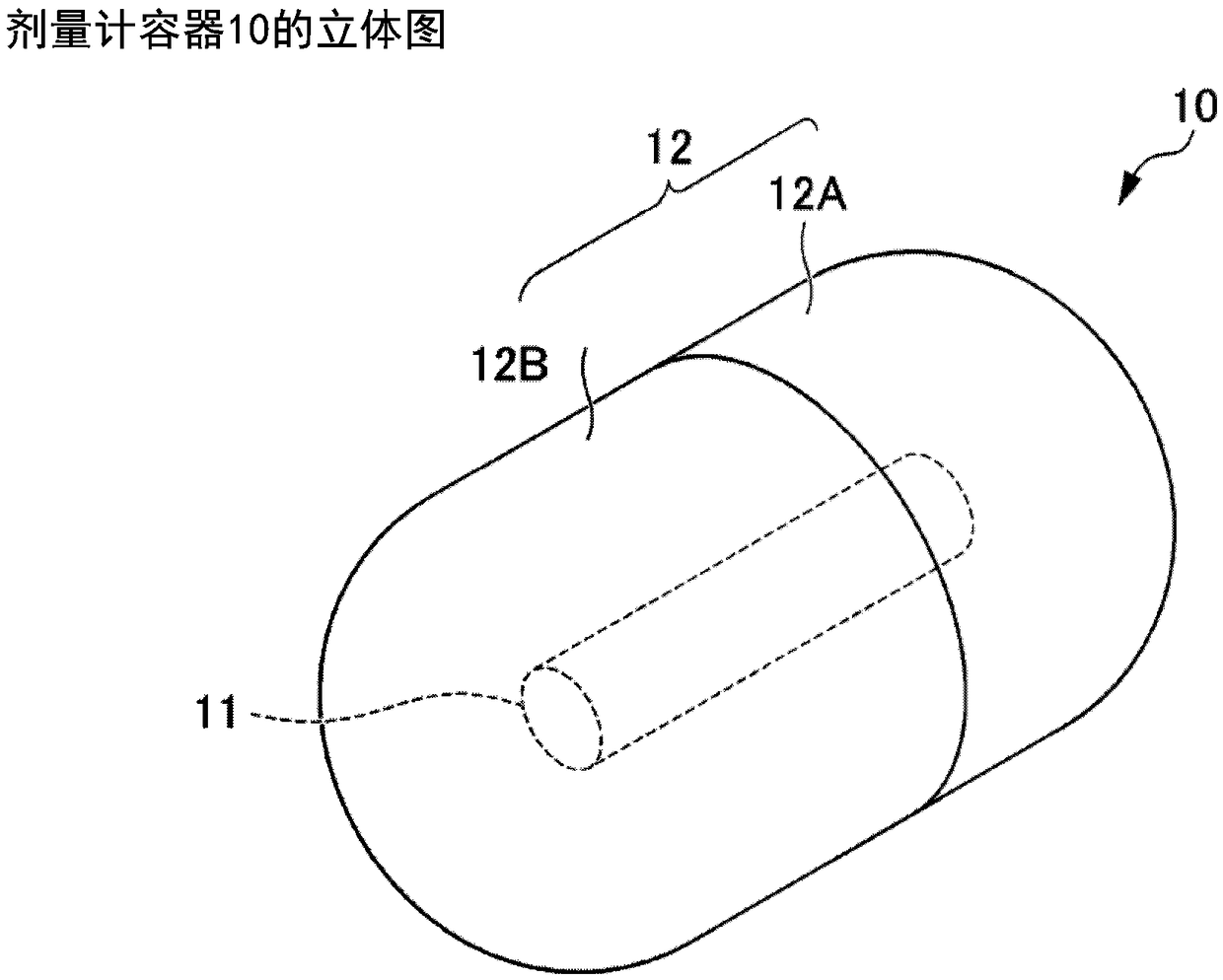
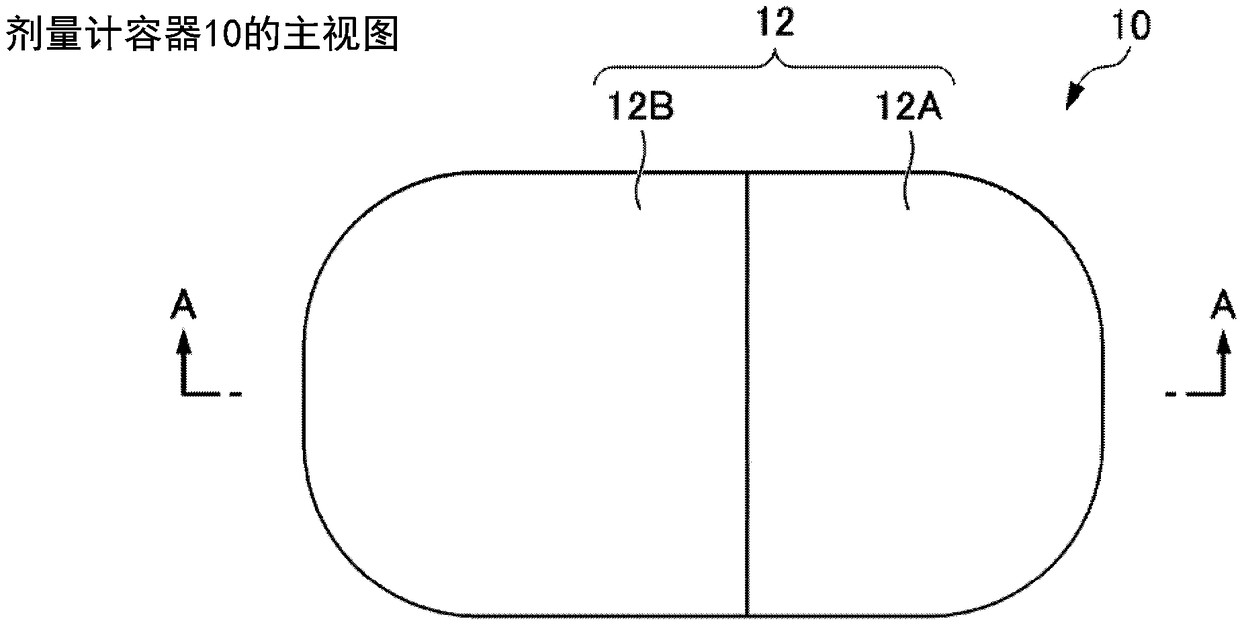
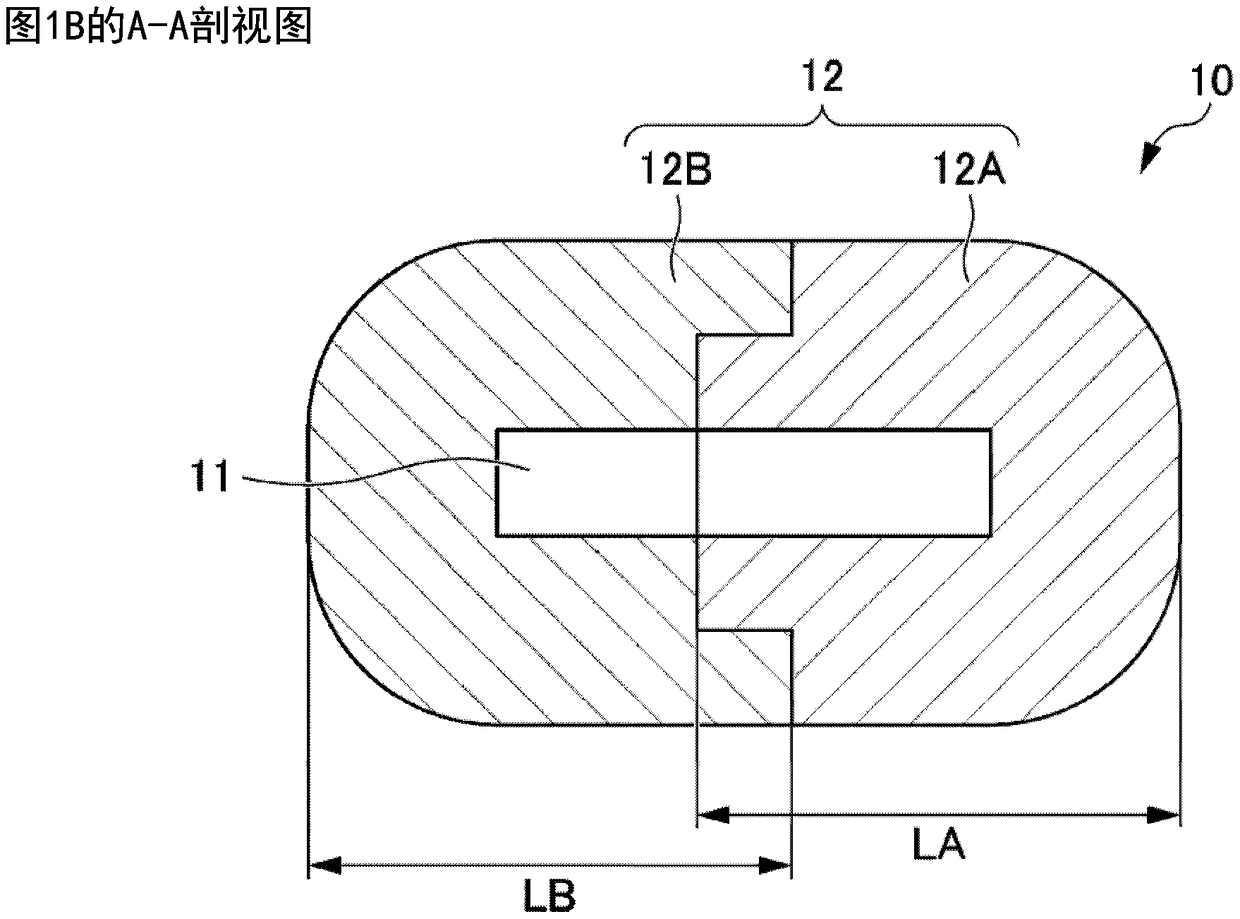
Dosimeter container and dose measuring body
The objective of the present invention is to provide a dosimeter container which contributes both to an increase in radiation dose measurement accuracy and a reduction in the size of a measuring device. The dosimeter container (10) of the present invention is provided with an accommodating portion (11) and a shielding portion (12) surrounding the accommodating portion (11). The accommodating portion (11) accommodates a radiation dose measuring instrument which measures a dose of prescribed radiation other than neutron beams. The shielding portion (12) comprises a member of a material which transmits the abovementioned prescribed radiation and shields neutron beams. The shielding portion (12) is preferably a sintered body of LiF, in particular a sintered body of 6LiF. The shielding portion(12) has at least two shielding portion constituent members (a main body portion (12A) and a lid portion (12B)), and adjacent members are capable of abutting one another, and more preferably capable of mating with one another. The size of the accommodating portion (11) is substantially the same as or larger than the size of the radiation dose measuring instrument, and the accommodating portion (11) extends through all the constituent members. The dosimeter container (10) is suitable for use as a dose measuring body (1) in which a radiation dose measuring instrument (51) is accommodated in theaccommodating portion (11).
Owner:NIPPON LIGHT METAL CO LTD
Polymeric polyglycolide-polylactide radioactive seed source thin-layer tablet and it spreparing method
InactiveCN1709518AGood antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effectIncrease elasticityRadioactive preparation carriersYarnLactide
The present invention discloses a high-molecular polyglycolide-lactide radioactive seed source thin-layer sheet and its preparation method. The yarn made up by using high-molecular polyglycolide-lactide can be woven into gauze fabric, on the fabric the radioactive seed source is placed, and two surfaces of said fabric are respectively coated with chitosan layer whose thickness is 0.25-0.35mm. Said invention adopts high-molecular medical material chitosan to make coating and after-processing, so that the PGLA degradation can be implemented under the controllable state, and the new type collating layer PGLA with special biological degradability can be used as carrier and thin-layer support, and can be used for curing tumor bed residue, and can ensure uniformity of radio logical dose distribution.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Sensitizer for radiotherapy and preparation method and application of sensitizer
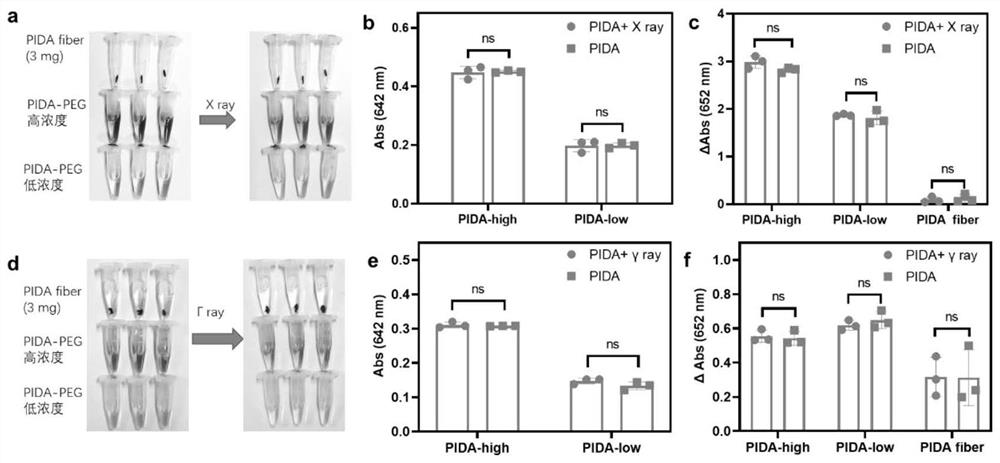
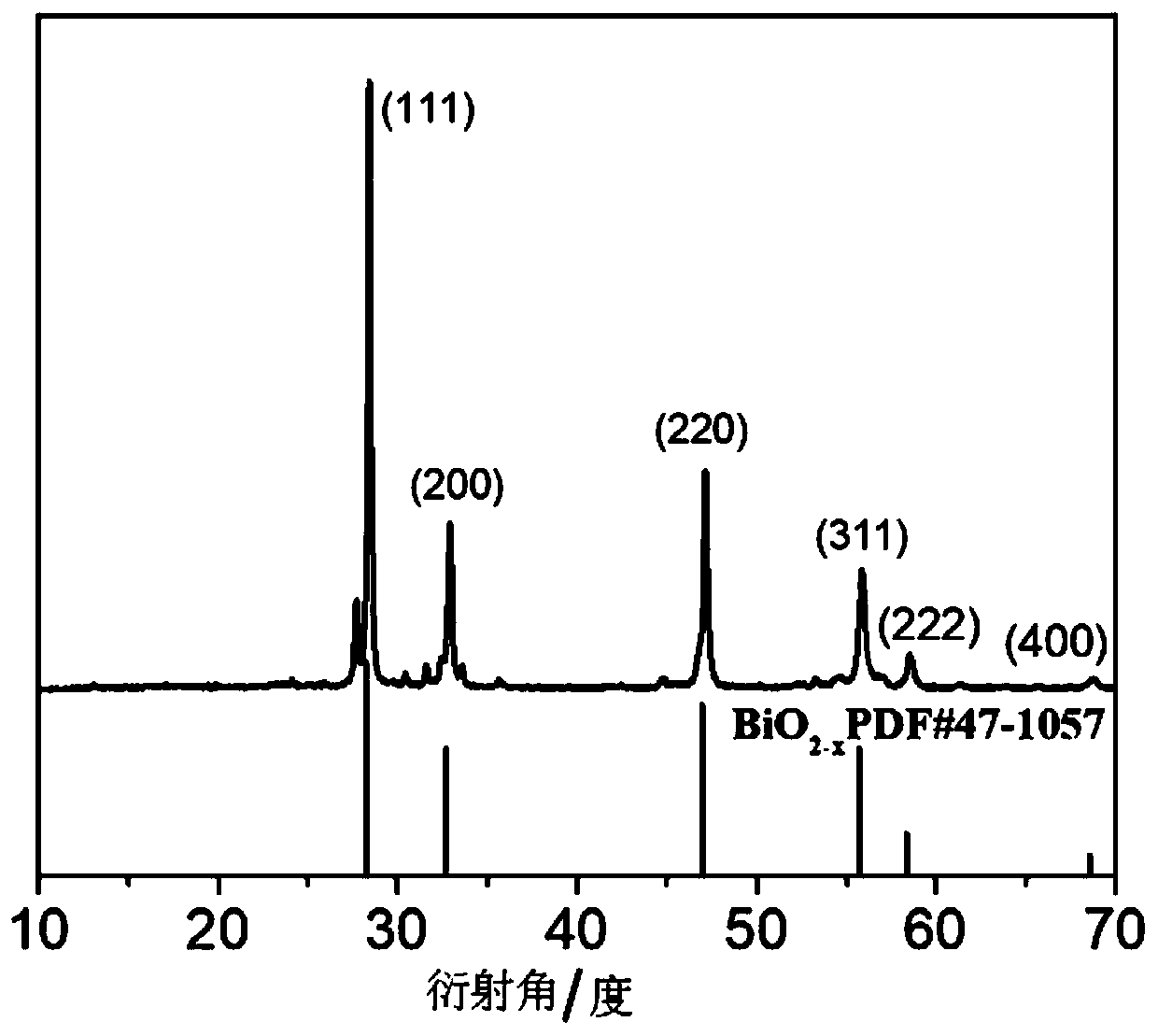
ActiveCN111035761AHigh-efficiency catalytic productionImprove hypoxiaInorganic active ingredientsNanomedicineOxygen vacancyDelivered radiation dose
The invention relates to a sensitizer for radiotherapy and a preparation method and application of the sensitizer, belongs to the field of nano material chemistry and biochemistry, and solves the problems that the existing radiotherapy sensitizer cannot improve the hypoxic state in a tumor microenvironment, is insensitive to radiotherapy, large in dosage of a radiation agent and large in damage tonormal tissues. The molecular formula of the sensitizer for radiotherapy is BiO2-x, the molecular structure has oxygen vacancy, and the preparation raw material of the sensitizer comprises hydroxideof alkali metal and bismuthate. The preparation method of the sensitizer comprises the following steps: dissolving the hydroxide of alkali metal and the bismuthate, and stirring to obtain a solution;transferring the solution into a reaction container, heating, and reacting for a period of time; the BiO2-x provided by the invention can be used as the sensitizer to be applied to radiotherapy sensitization of tumors, and has a very good inhibition effect on tumors under a relatively low radiation dose.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
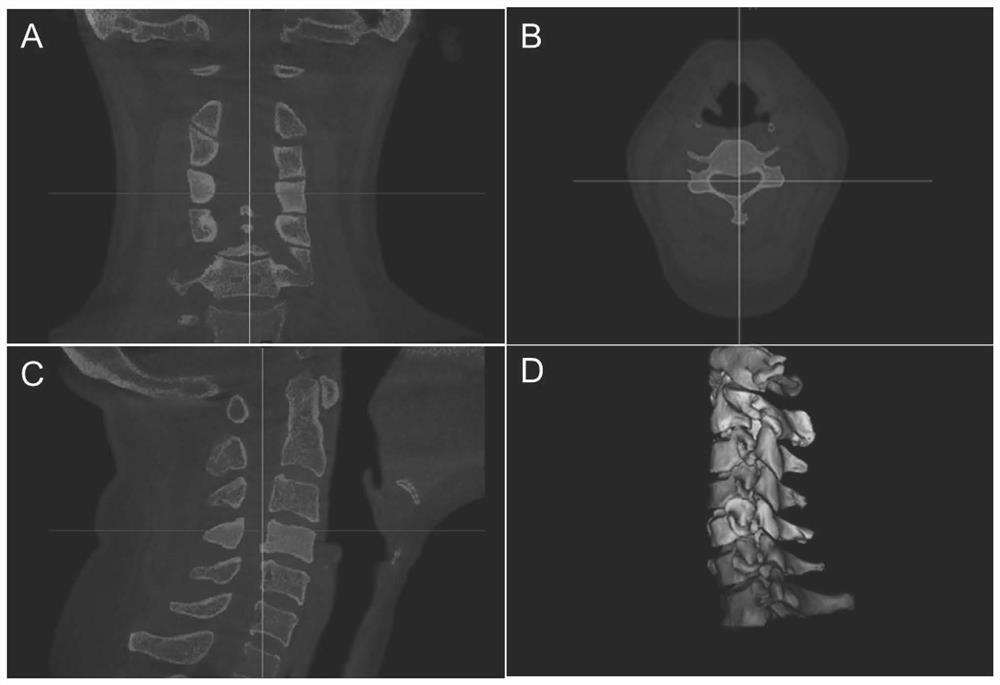
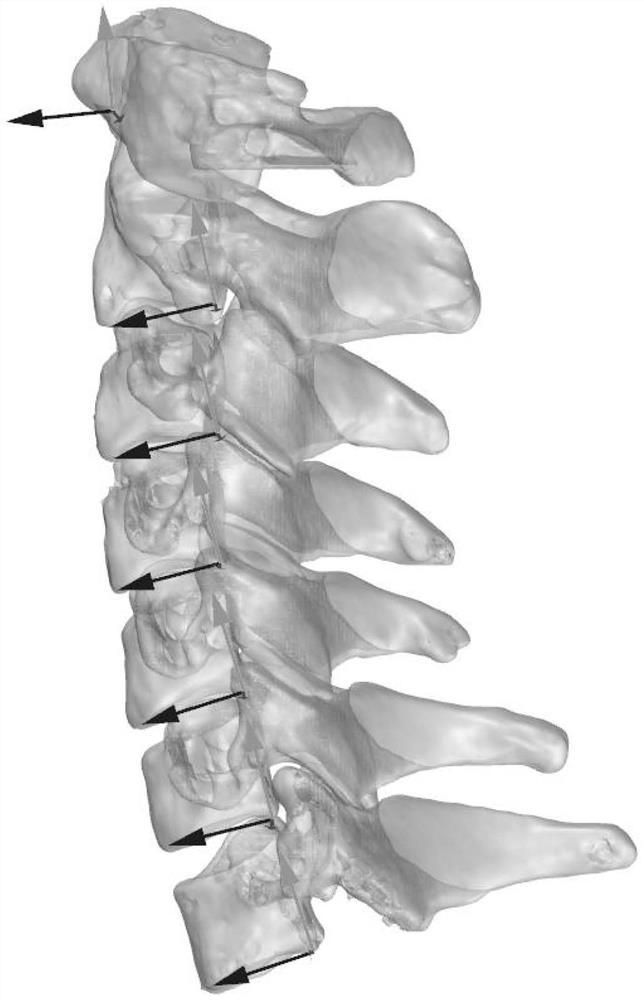
Cone beam CT and image fusion combined cervical vertebra in-vivo three-dimensional motion analysis method
ActiveCN112085833AHigh speedReduce radiation doseImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyImage segmentation
The invention discloses a cone beam CT and image fusion combined cervical vertebra in-vivo three-dimensional motion analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, enabling a cone beam CT machine to shoot images of different cervical vertebra function positions; S2, importing to carry out image segmentation and 3D modeling; S3, for the 3D cervical vertebra model at the neutral position, determining a local coordinate system according to the anatomical orientation of the human body; S4, performing image fusion and recording spatial position parameter change on each segment of cervical vertebra model at different functional positions relative to the neutral position; S5, performing threshold judgment on the precision of image fusion to determine whether the image fusion is successful or not; and S6, further calculating the spatial position parameter change between different sections to obtain the relative change of the two sections, and the invention relates to the technical field of CT influence. According to the invention, the problem of unclear imaging caused by conventional X-ray fluoroscopy shooting is solved; nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) is adopted, so that dynamic motion abnormity cannot be seen; MRI is long in scanning time and inconvenient in 3D modeling; and CT also has the problems of large radiation dose and the like.
Owner:南昌大学第一附属医院
Method for Fiducialless Real-time Tracking in Radiation Treatment of Abdominal Tumors
InactiveUS20170209713A1Improve accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyAbdominal tumorTumor location
A method for fiducial-less real-time motion tracking of abdominal tumors based on the correlation between the patient's breathing pattern and the diaphragm / lung border during treatment delivery. This invention utilizes an edge detection technique to delineate the diaphragm / lung border on radiographic images in order to calculate or determine tumor locations in the abdomen. The position of the diaphragm / lung border is synchronized with the breathing pattern obtained from continuous optical monitoring of a patient's respiratory cycle. The real-time optical breathing pattern obtained from monitoring is used to determine or calculate the position of the diaphragm / lung border during treatment delivery. The position of the diaphragm / lung border is then used to determine the tumor location in real-time. The target tumor coordinates generated through this process are used by the treatment delivery system to adjust the radiation beam geometry of the treatment delivery system to follow the tumor in real-time and accurately deliver radiation dose.
Owner:WU XIAODONG +1
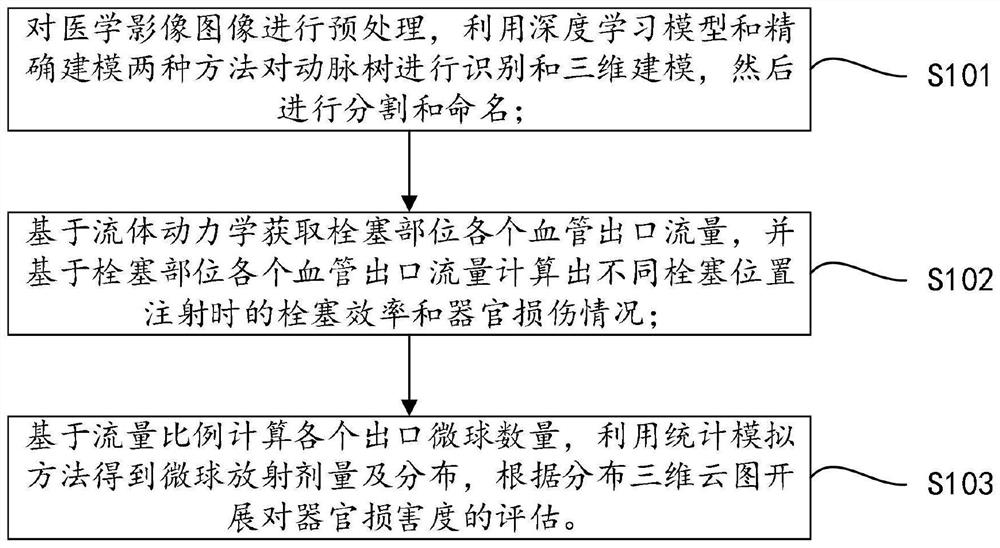
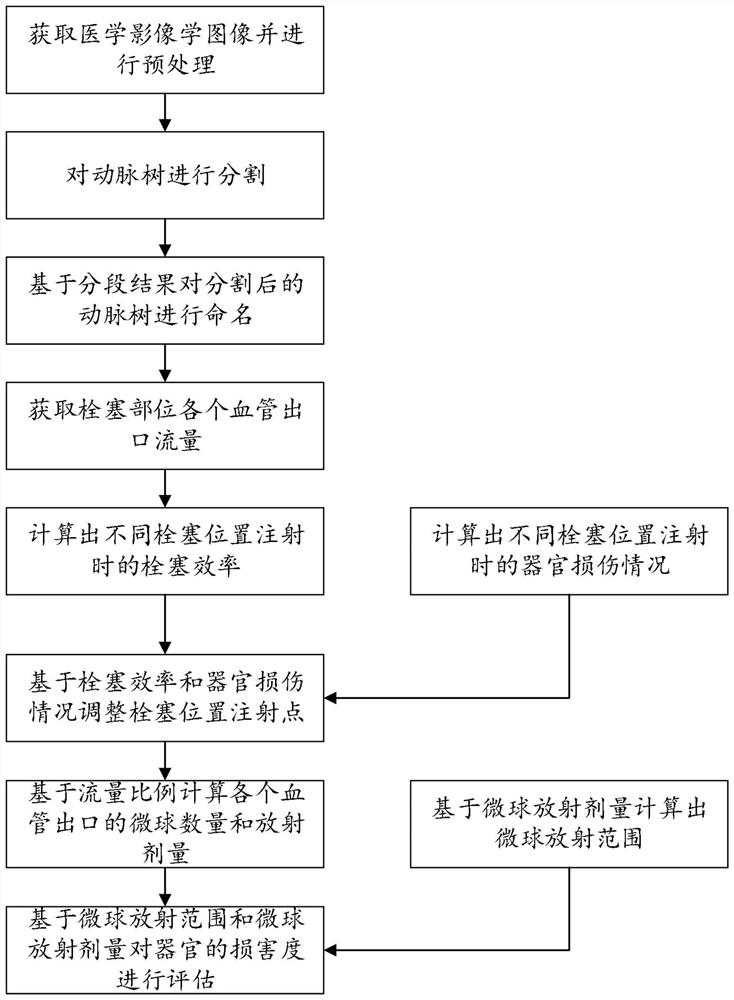
Radioembolism dose and injection position evaluation method based on fluid dynamics
PendingCN114880960AGuaranteed therapeutic effectDesign optimisation/simulationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyArterial treeOrgan damage
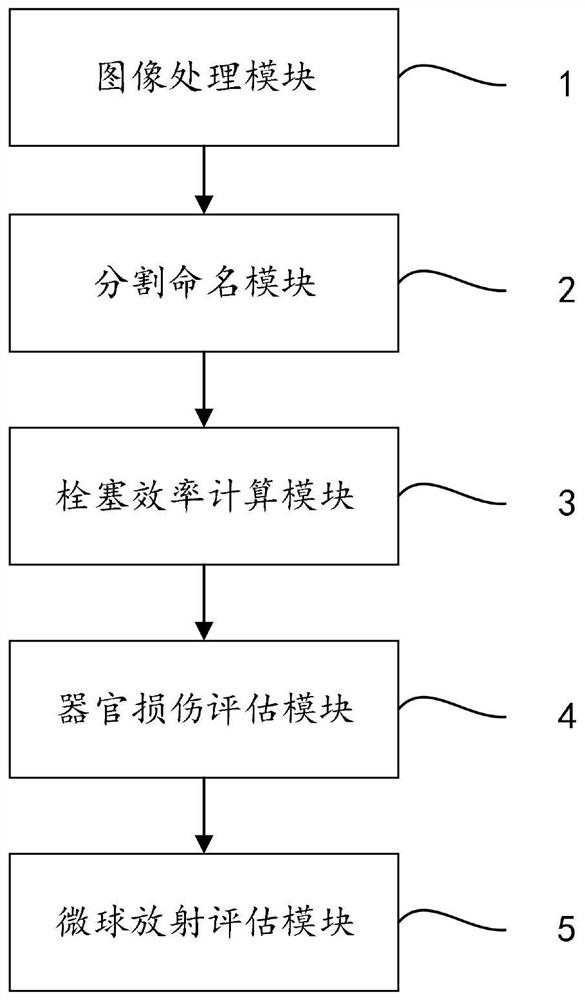
The invention relates to the technical field of interventional radiology arterial embolism, and discloses a radioembolism dose and injection position evaluation method based on fluid dynamics. Medical imaging images are acquired and preprocessed, and an artery tree is subjected to recognition and three-dimensional reconstruction by using the trained deep learning model and an accurate modeling method; segmenting and naming the reconstructed blood vessel; obtaining the flow of each blood vessel outlet of the embolism part based on fluid dynamics, and calculating embolism efficiency and organ injury conditions during injection at different embolism positions based on the flow of each blood vessel outlet of the embolism part; the method comprises the following steps: calculating the microsphere radiation quantity of each blood vessel outlet based on a flow ratio, then analyzing the radiation dose and distribution of the microspheres by using a statistical simulation method, drawing a radiation dose distribution three-dimensional cloud chart, and evaluating the damage degree of organs based on the radiation dose of the microspheres to ensure the treatment effect on tumors.
Owner:青岛埃米博创医疗科技有限公司
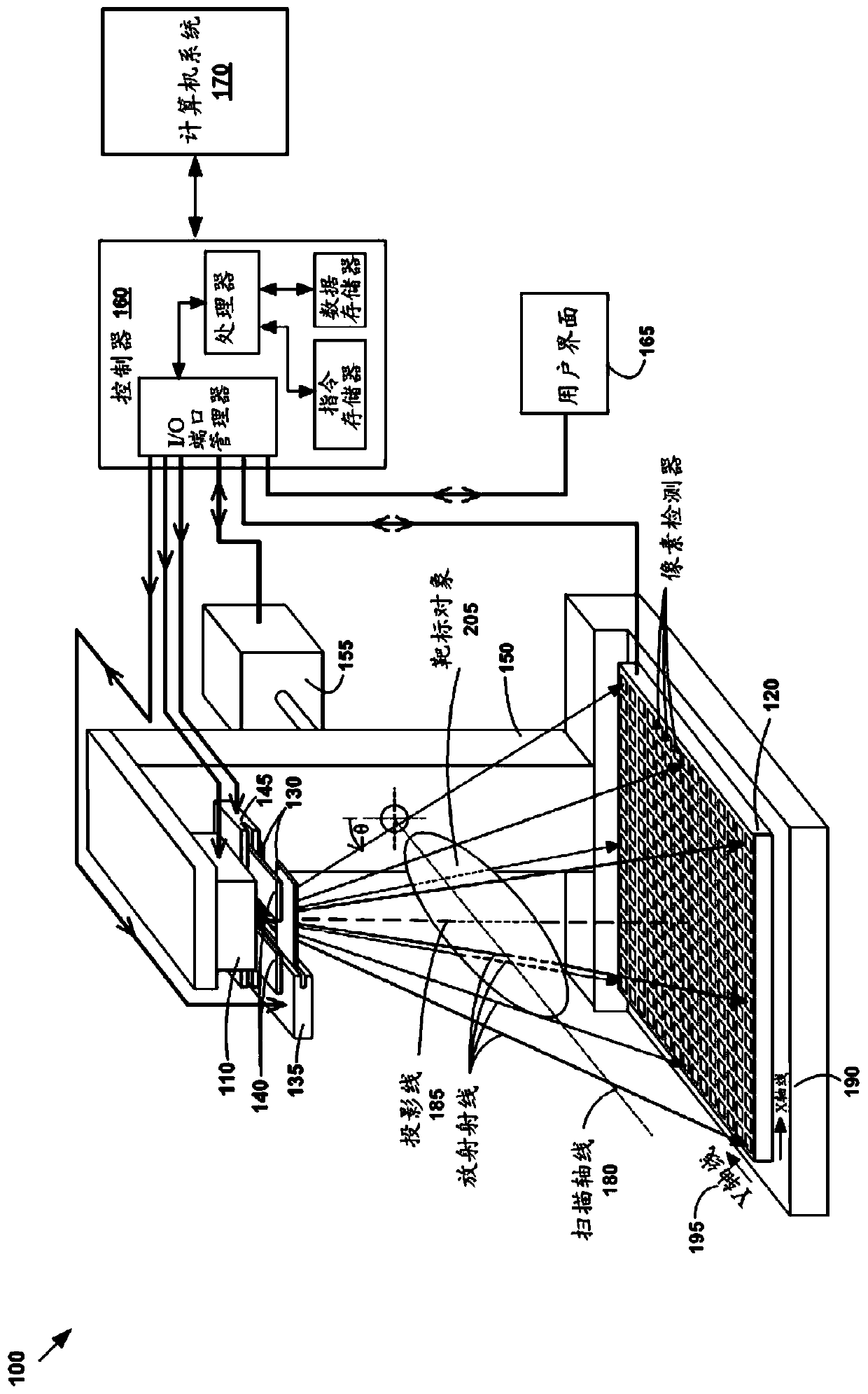
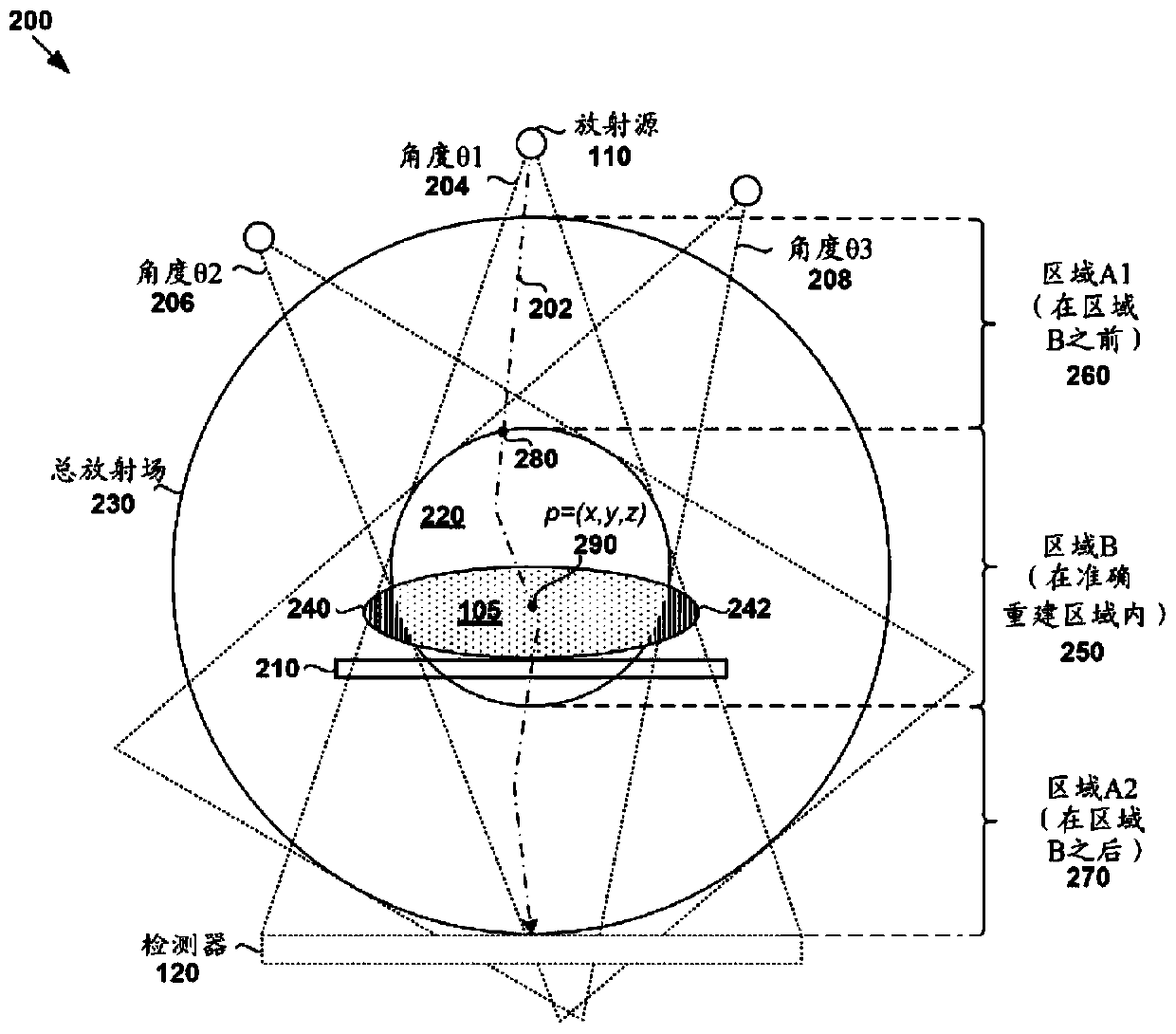
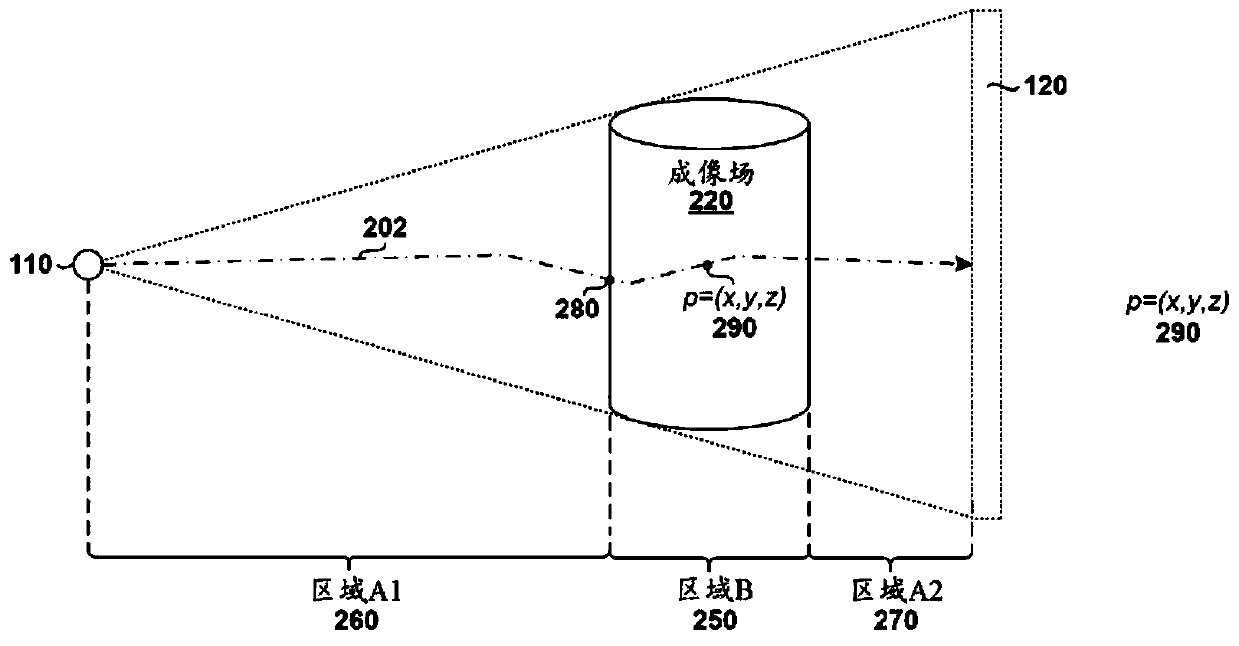
Method and system for radiation dose estimation
Example methods and systems are provided for performing radiation dose estimation on a target subject. In one example, radiation dose estimation may include obtaining projection image data acquired using an imaging system, generating partially reconstructed volumetric image data based on the projection image data, and generating partitions of the projection image data. Partially reconstructed volumetric image data may be associated with the first region of the total radiation field. The subregions may be associated with a second region of the total radiation field which is located in front of the first region from the direction of the radiation source. Radiation dose data for the target object may be estimated based on partially reconstructed volume image data associated with the first region and the partition associated with the second region.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Carbon material dosimeter
Radiation dosimeters that are based on carbon materials such as carbon powder, carbon fibers, carbon nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes are developed. The dosimeter may contain a singular element or multiple sensing elements that are arrayed in 1-D, 2-D and 3-D formations. Each sensing element is made up of two electrodes with carbon materials deposited between the electrodes. The sensing elements may be deposited on flexible substrates to create flexible dosimeters. In addition, the carbon sensing materials may be deposited onto transparent substrates to achieve a transparent dosimeter. Transparent and / or flexible dosimeters can be fabricated with the carbon materials. The sensing elements are connected to external power sources. As the elements are exposed to radiation beams, the change in resistivity or conductance of the carbon materials is measured by current detection circuitry.
Owner:约翰·T·W·姚
Calculation equipment, device and storage medium for radiation dose
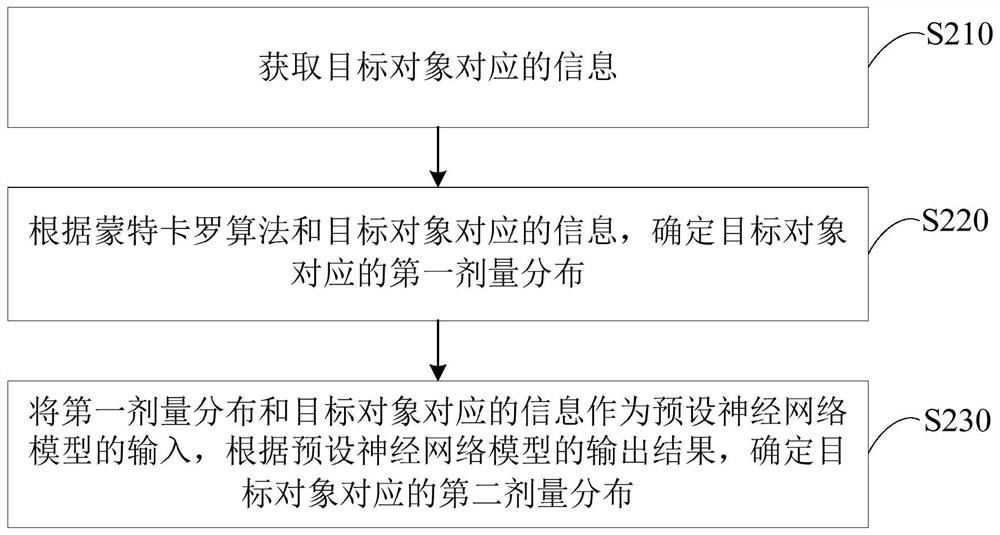
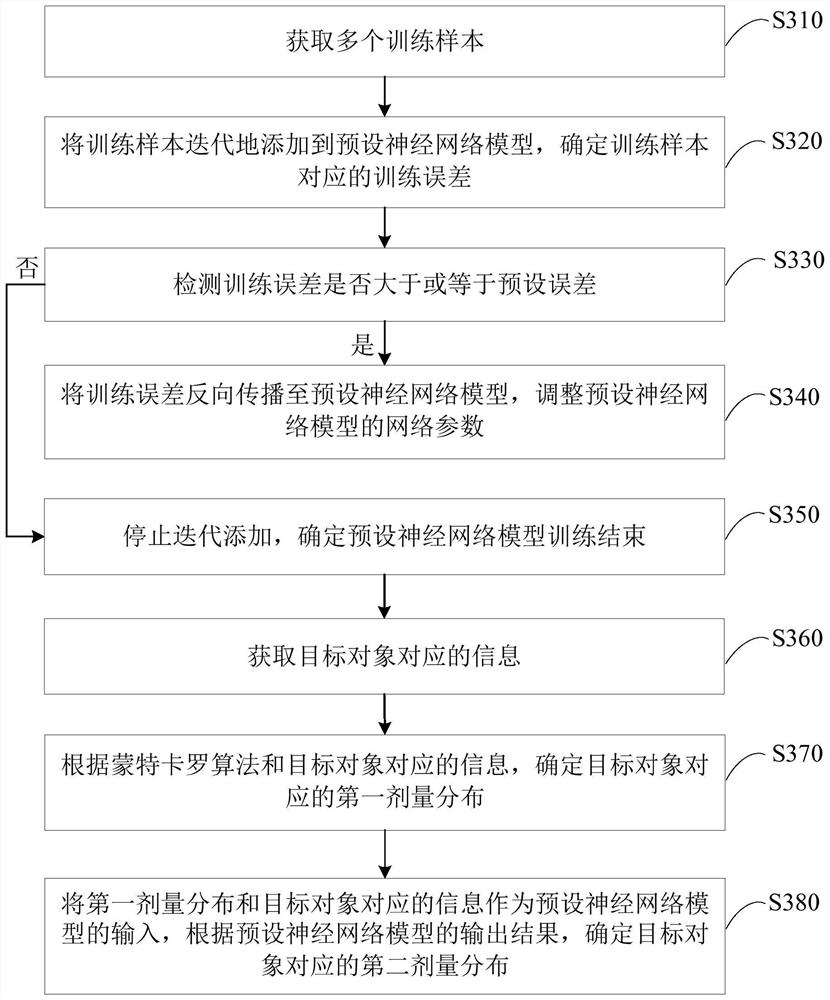
ActiveCN109621228BReduce precisionQuick fixLight therapyMachine learningComputational scienceNetwork model
The embodiment of the invention discloses a radiation dose calculation device, device and storage medium. The device includes: one or more processors; a memory for storing one or more programs; when the one or more programs are executed by the one or more processors, the one or more processors perform the following operations: obtain the target The information corresponding to the object; according to the Monte Carlo algorithm and the information corresponding to the target object, determine the first dose distribution corresponding to the target object; use the first dose distribution and the information corresponding to the target object as the input of the preset neural network model, according to the preset The output result of the neural network model determines the second dose distribution corresponding to the target object; wherein, the accuracy of the second dose distribution is higher than the accuracy of the first dose distribution. Through the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention, faster calculation speed and higher calculation accuracy can be ensured to meet clinical needs.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com