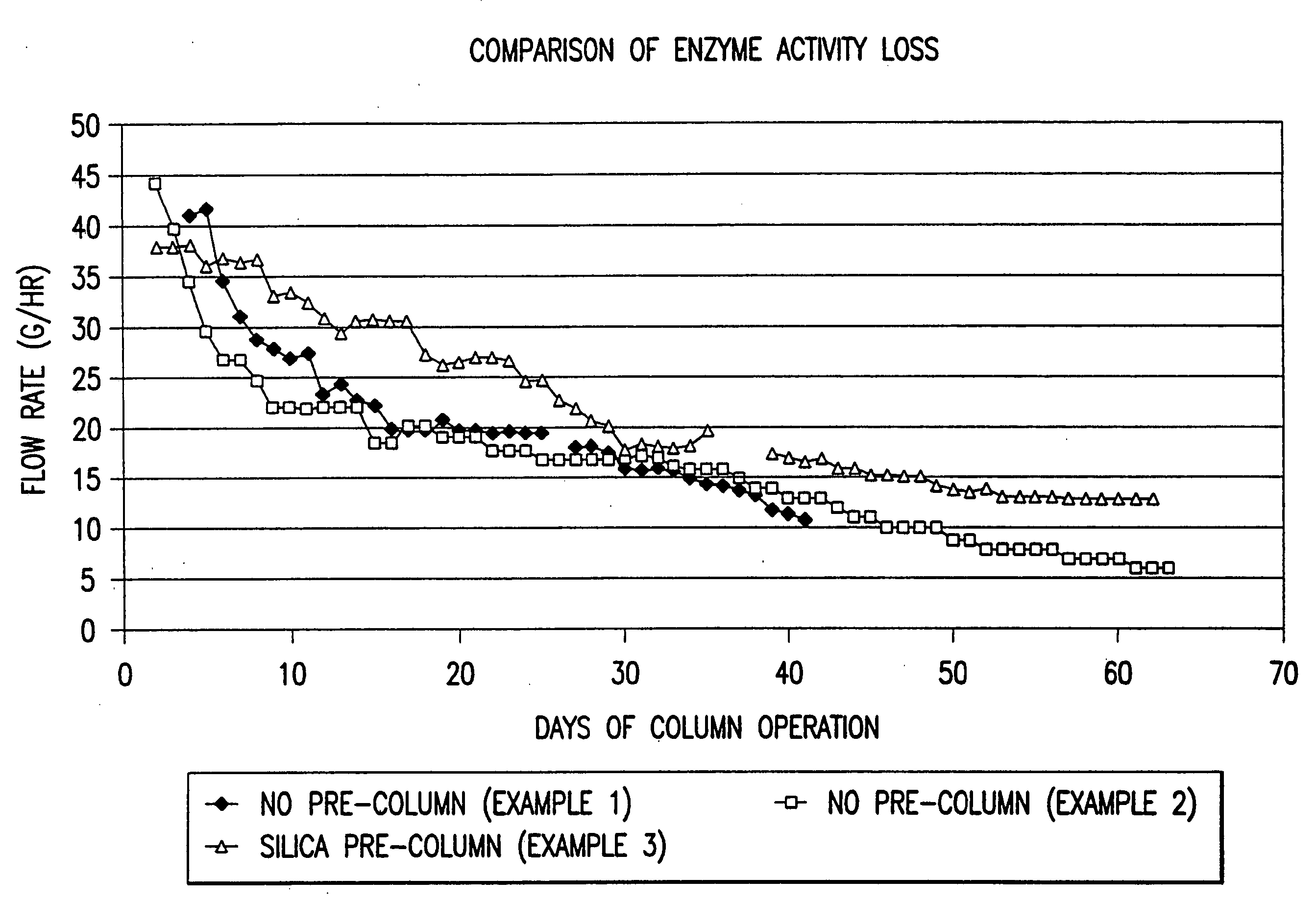
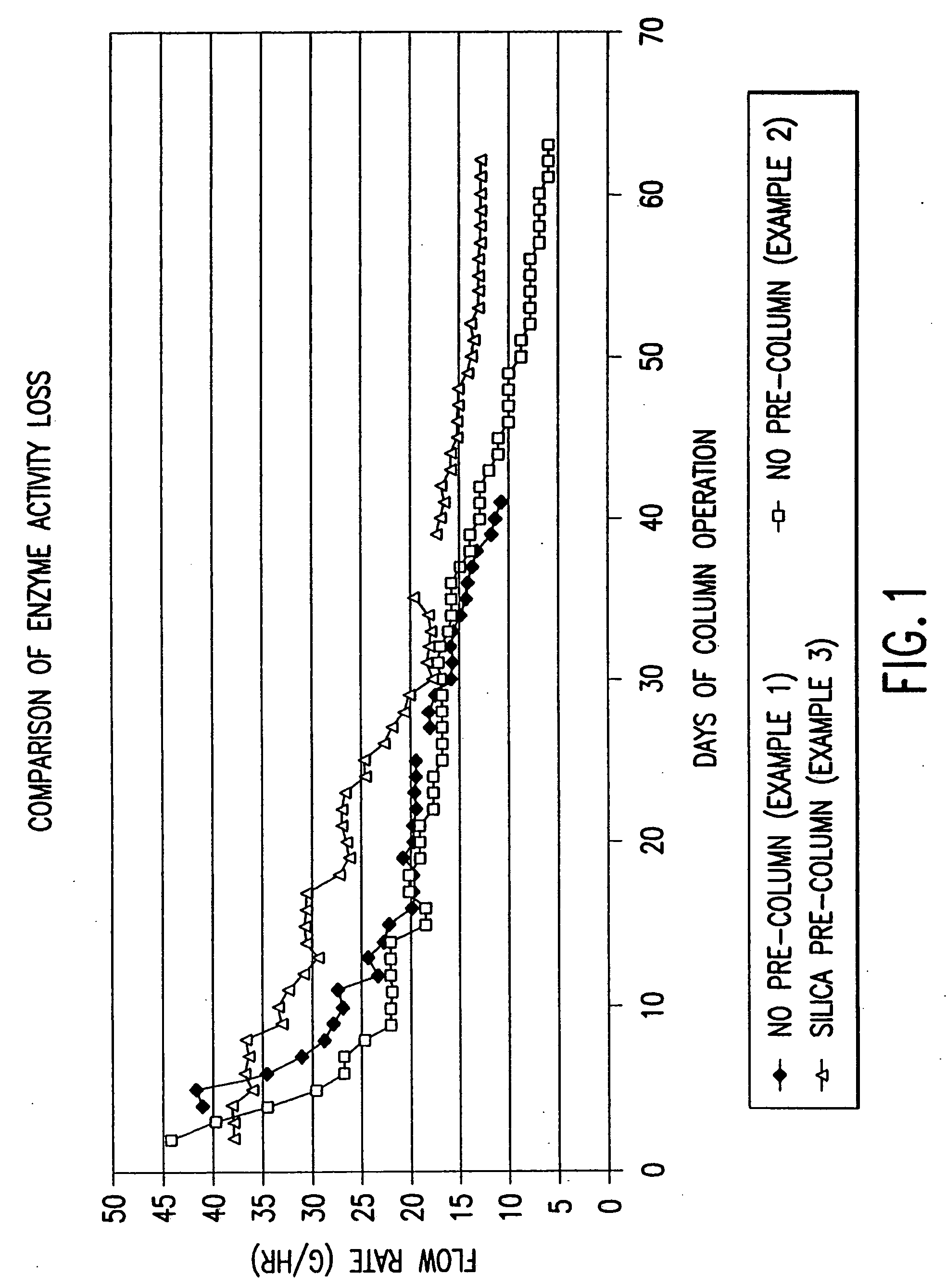
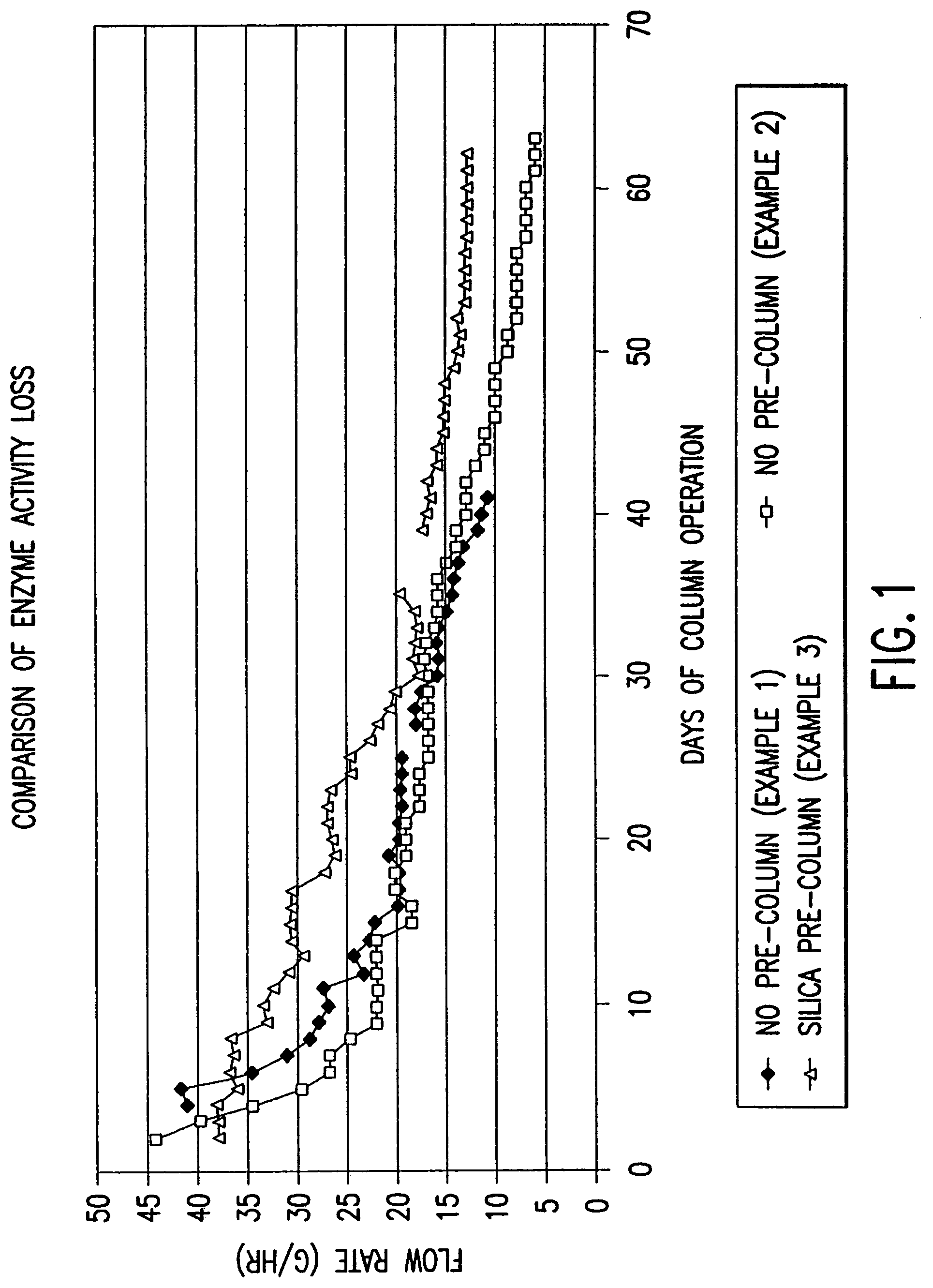
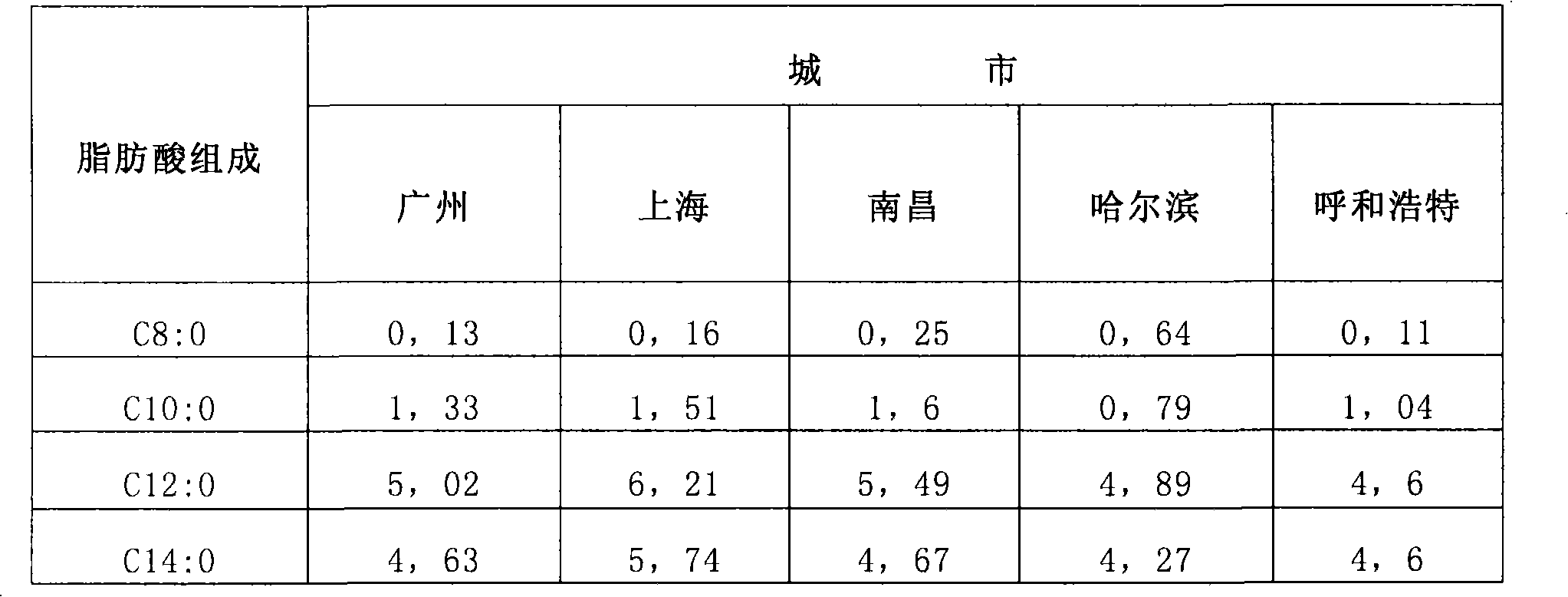
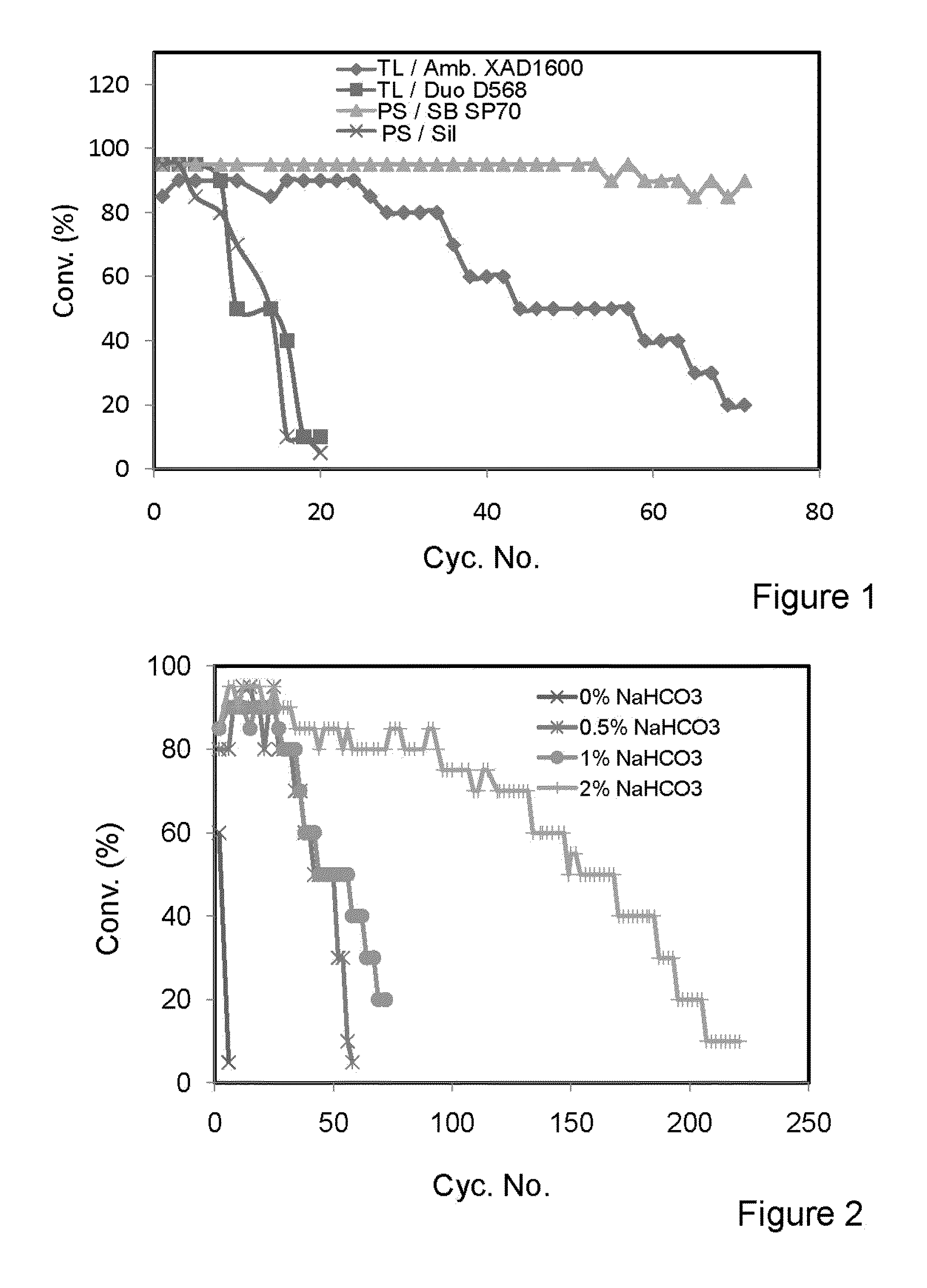
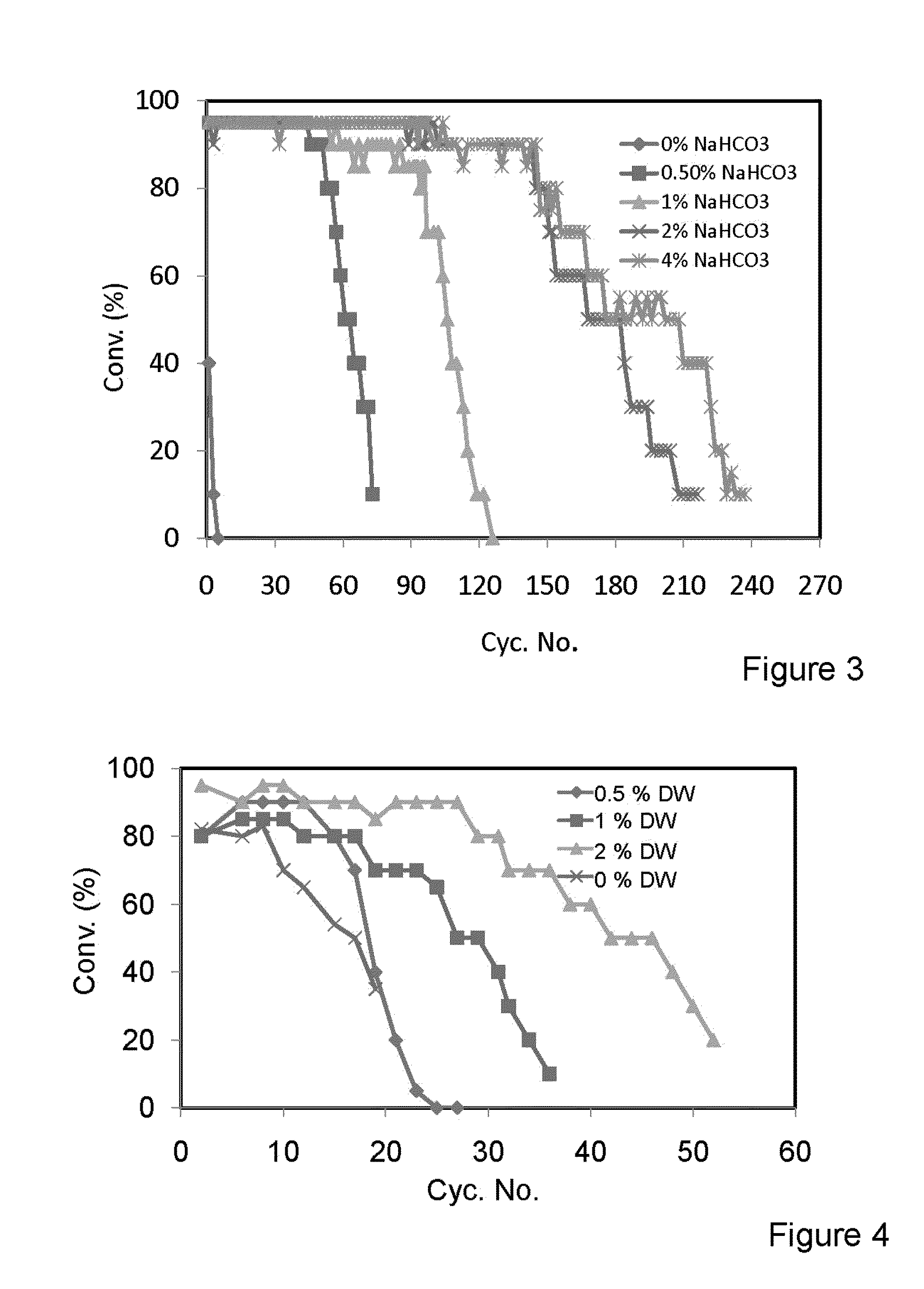
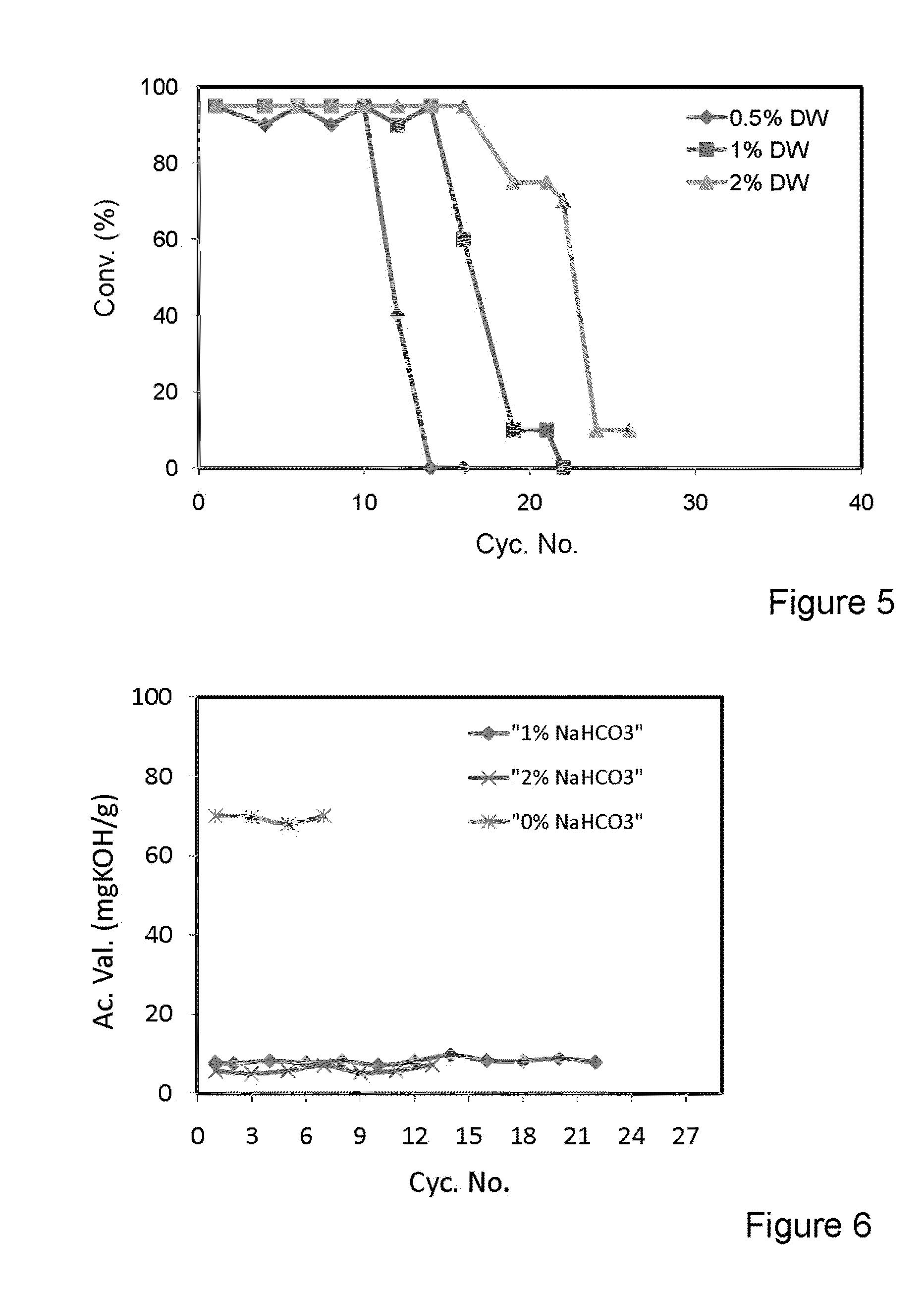
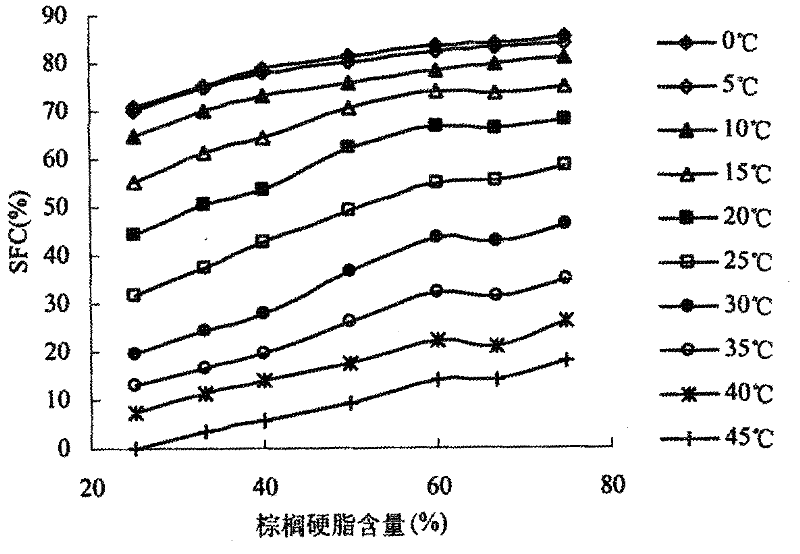
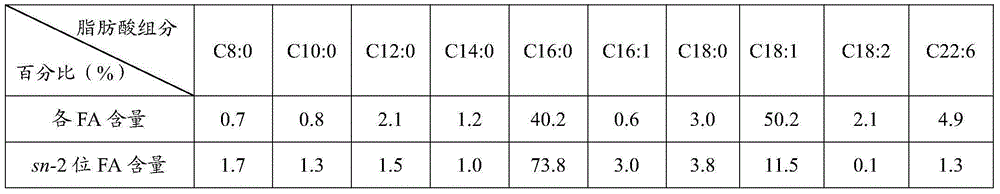
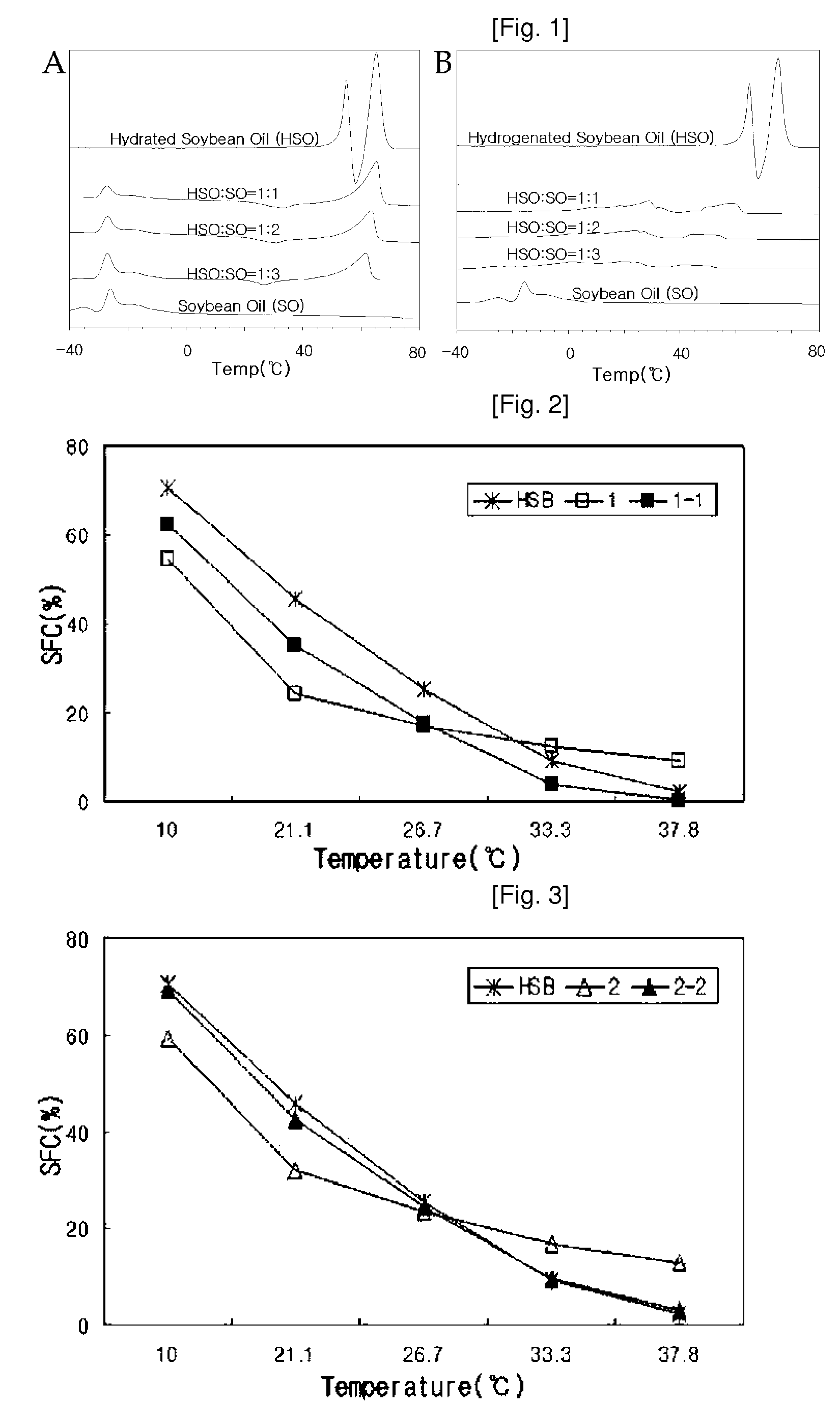
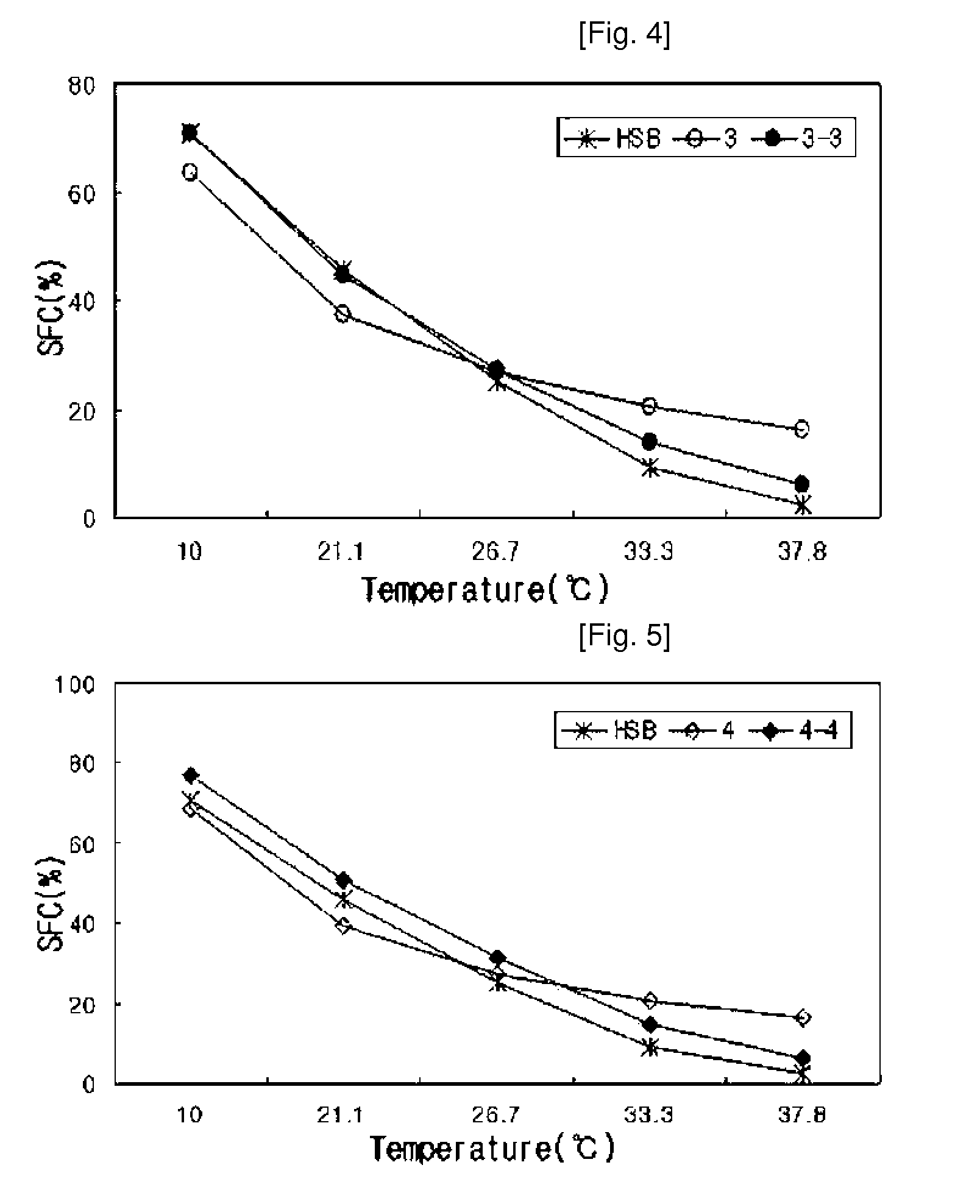
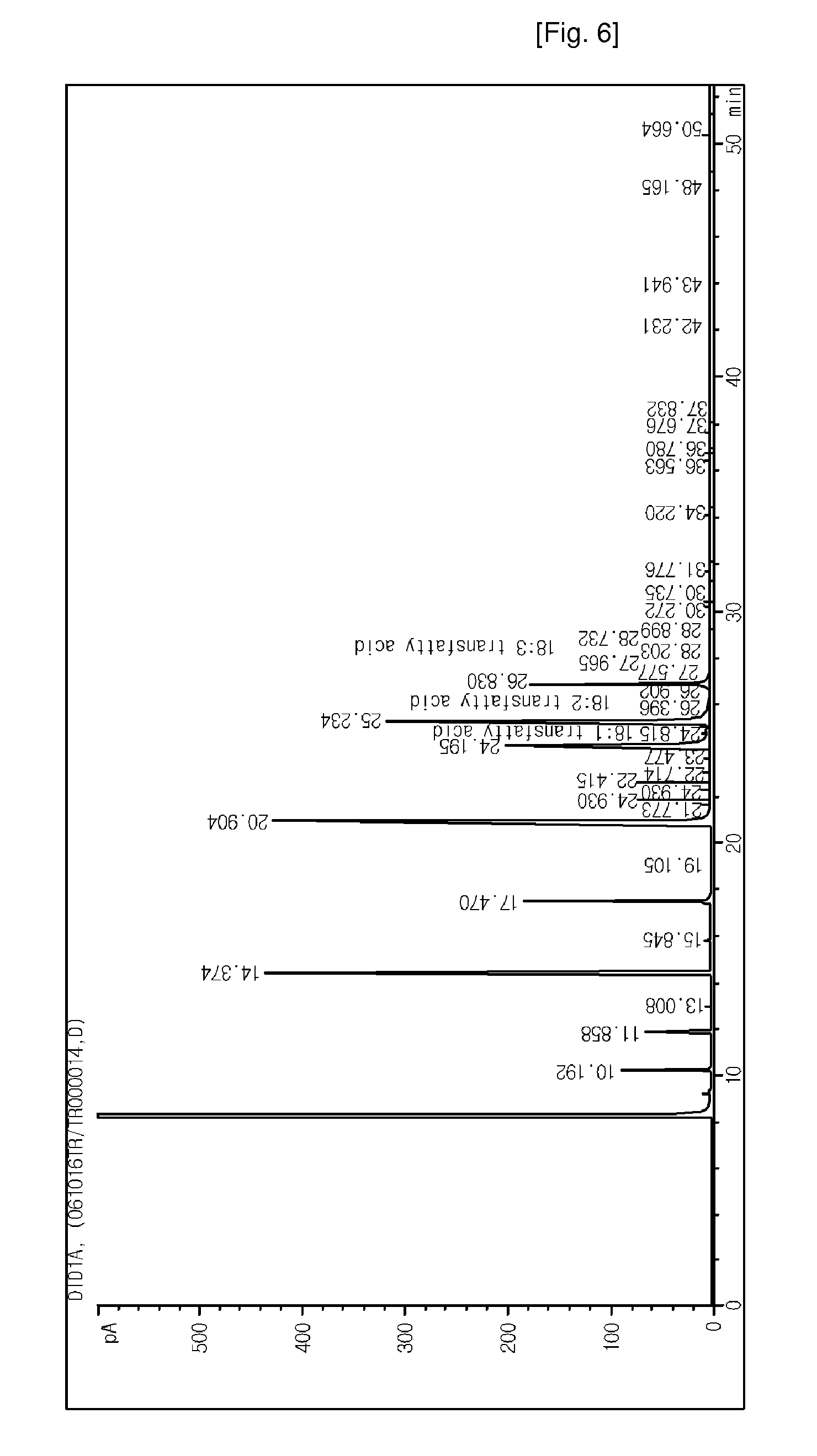
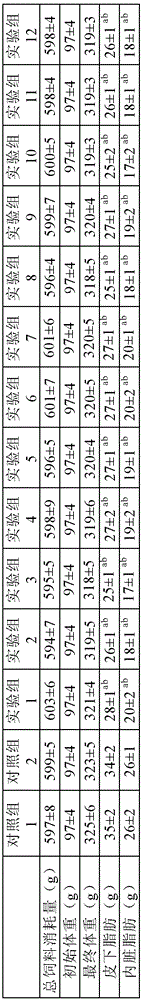
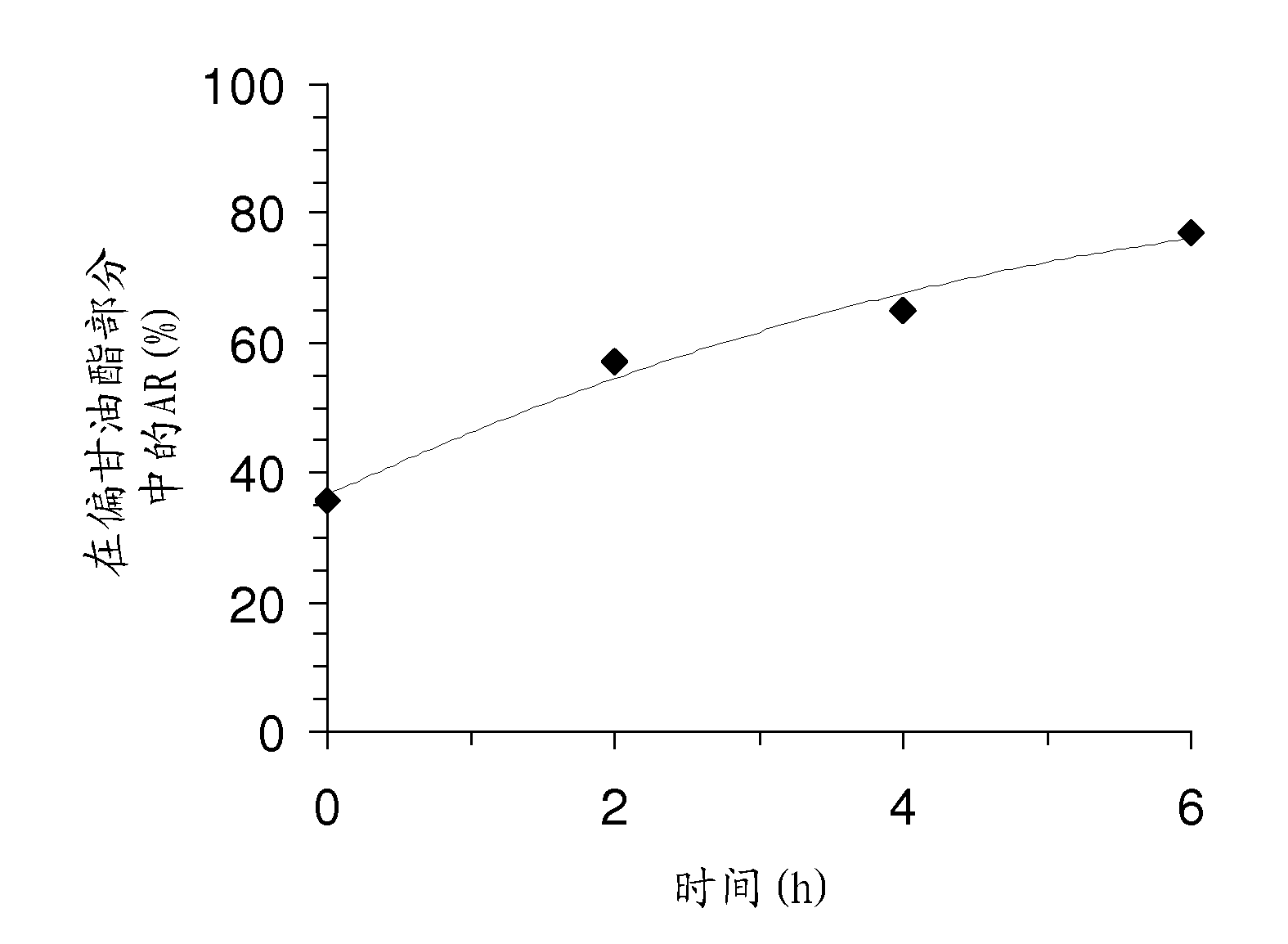Patents
Literature
62 results about "Enzymatic interesterification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymatic Interesterification (EIE) is the catalytic reaction that occurs when an enzyme is introduced into oil and rearranges the fatty acids on the glycerol backbone of a triglyceride. Triglycerides are either liquid or solid at room temperature. The rearrangement of the fatty acids that occurs with enzymatic interesterification provides structure and functionality to triglycerides at room temperature. This process adjusts the melting properties, increasing functionality and plasticity in food production applications. One of five different ways of altering melting property profiles, enzymatic interesterification is unlike the more widely used partial hydrogenation method in that it produces no trans fatty acids and lowers saturated fat content.
Method for producing fats or oils
ActiveUS20050014237A1Extended half-lifeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationEnzyme
The present invention is directed to improving productivity of an enzymatic method for making esterified, transesterified or interesterified products. Specifically, a method that can greatly improve the productivity of enzymatic transesterification or esterification by deodorization alone, or by deodorization and purification of the initial substrate to extend the useful life of the enzyme is disclosed.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Method for producing fats or oils
ActiveUS7452702B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationTransesterificationEnzyme
The present invention is directed to improving productivity of an enzymatic method for making esterified, transesterified or interesterified products. Specifically, a method that can greatly improve the productivity of enzymatic transesterification or esterification by deodorization alone, or by deodorization and purification of the initial substrate to extend the useful life of the enzyme is disclosed.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Preparation method of oil grease composite for infant food
The invention discloses oil grease composite for infant food, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The preparation method of the oil grease composite comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing fatty acid mixture, and / or fatty acid ethyl ester mixture, and fish oil so as to obtain a mixture 1; secondly, contacting the mixture 1 with lipase, and then conducting enzymatic interesterification so as to obtain a mixture 2; and thirdly, distilling the mixture 2, removing fatty acid ethyl ester and fatty acid in the mixture 2 so as to obtain the oil grease composite. The invention also discloses applications of the fish oil on preparing the oil grease composite for the infant food.
Owner:嘉里特种油脂(上海)有限公司
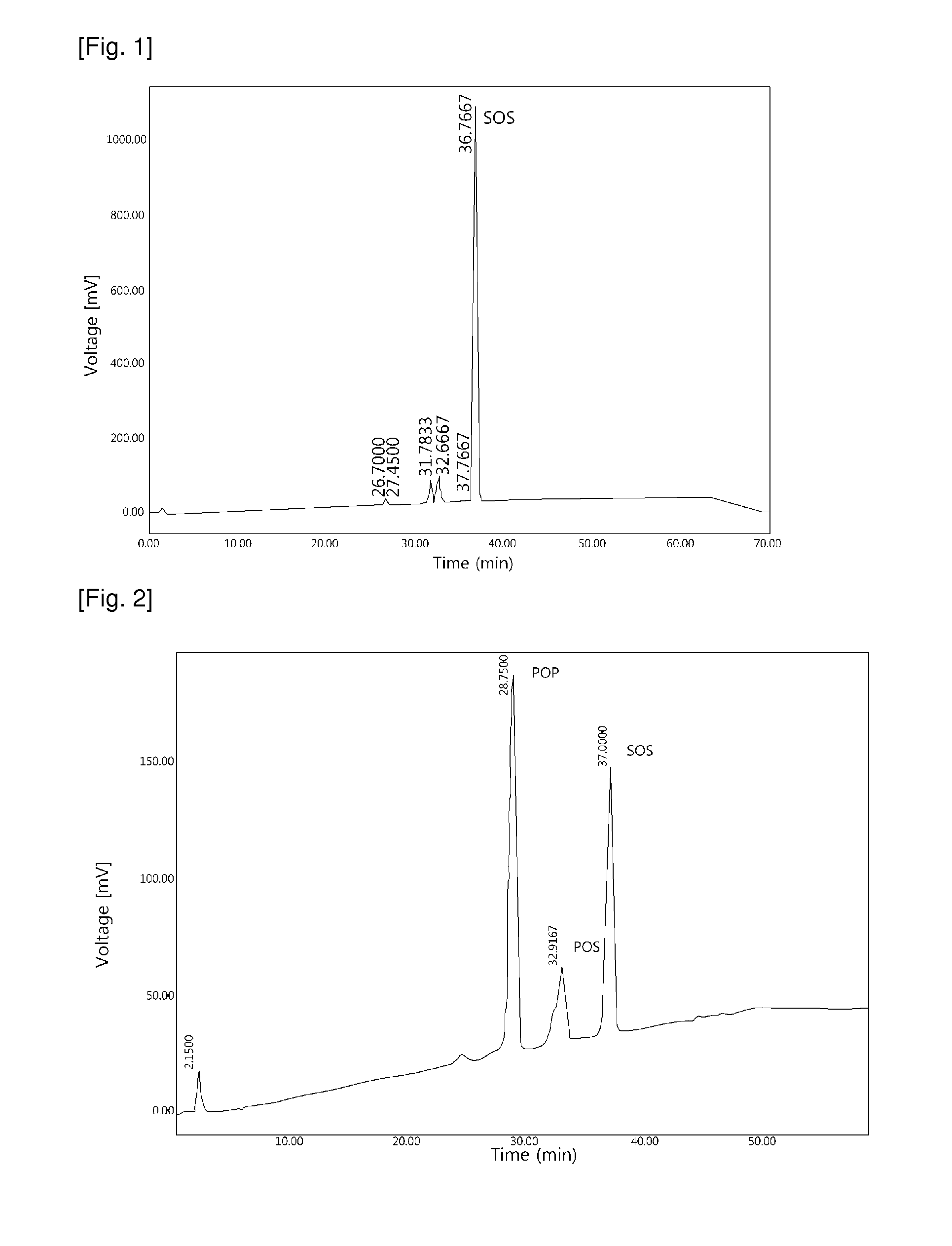
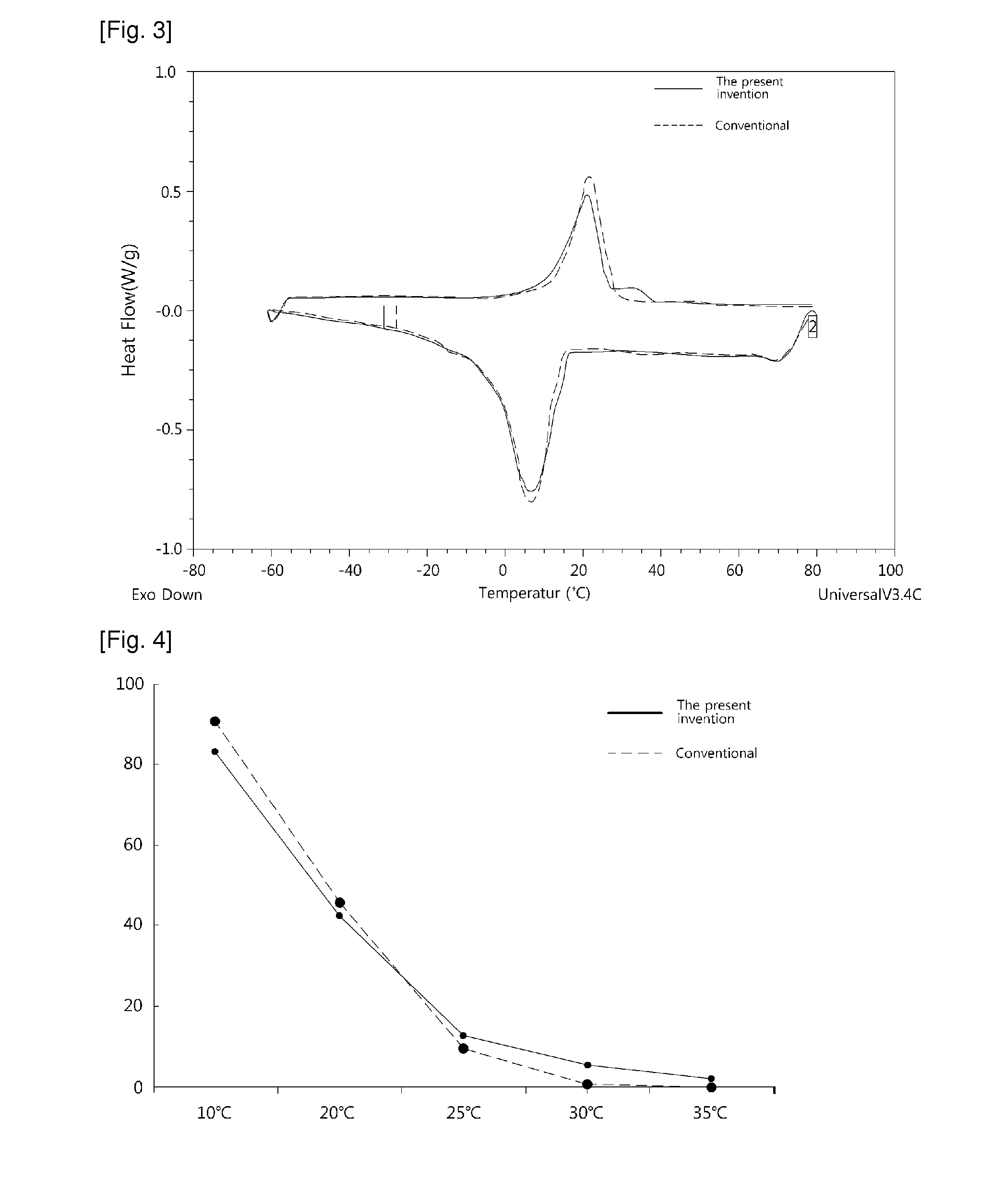
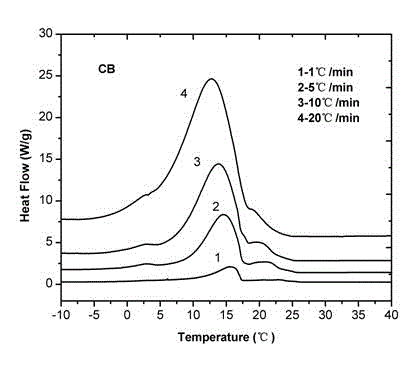
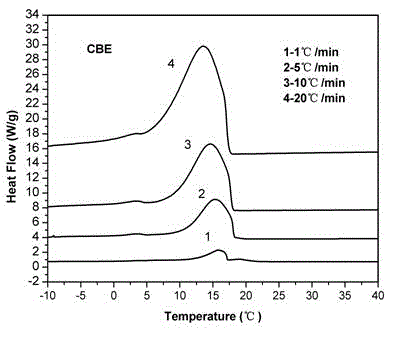
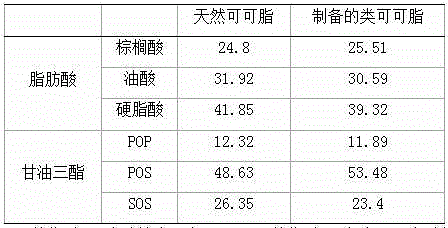
Cocoa butter equivalents produced by the enzymatic interesterification process and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN102215696ALow in trans fatty acidsFatty acid esterificationFatty-oils/fats refiningButter cocoaMonoglyceride
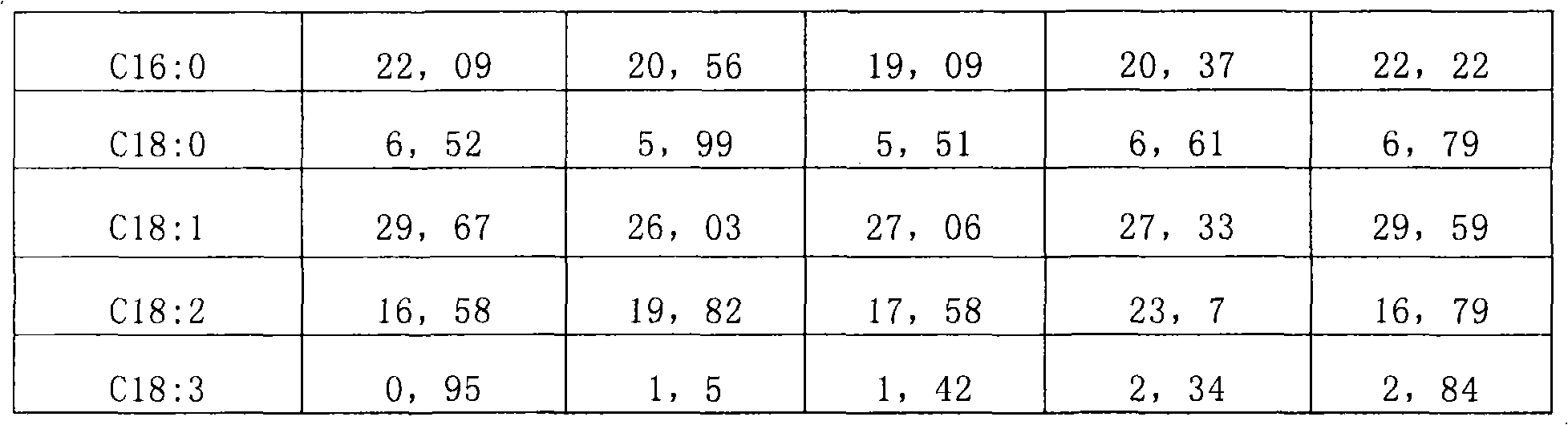
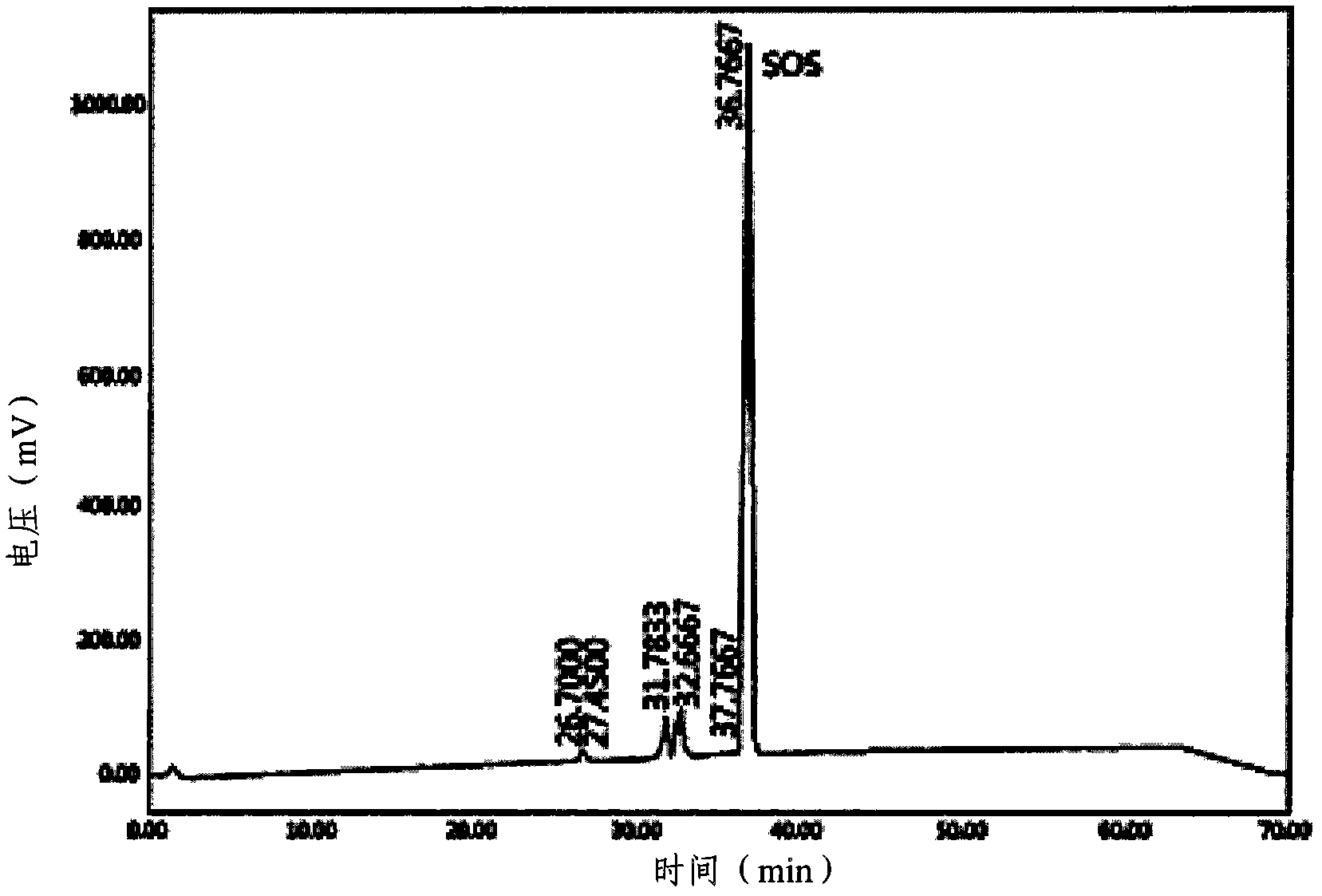
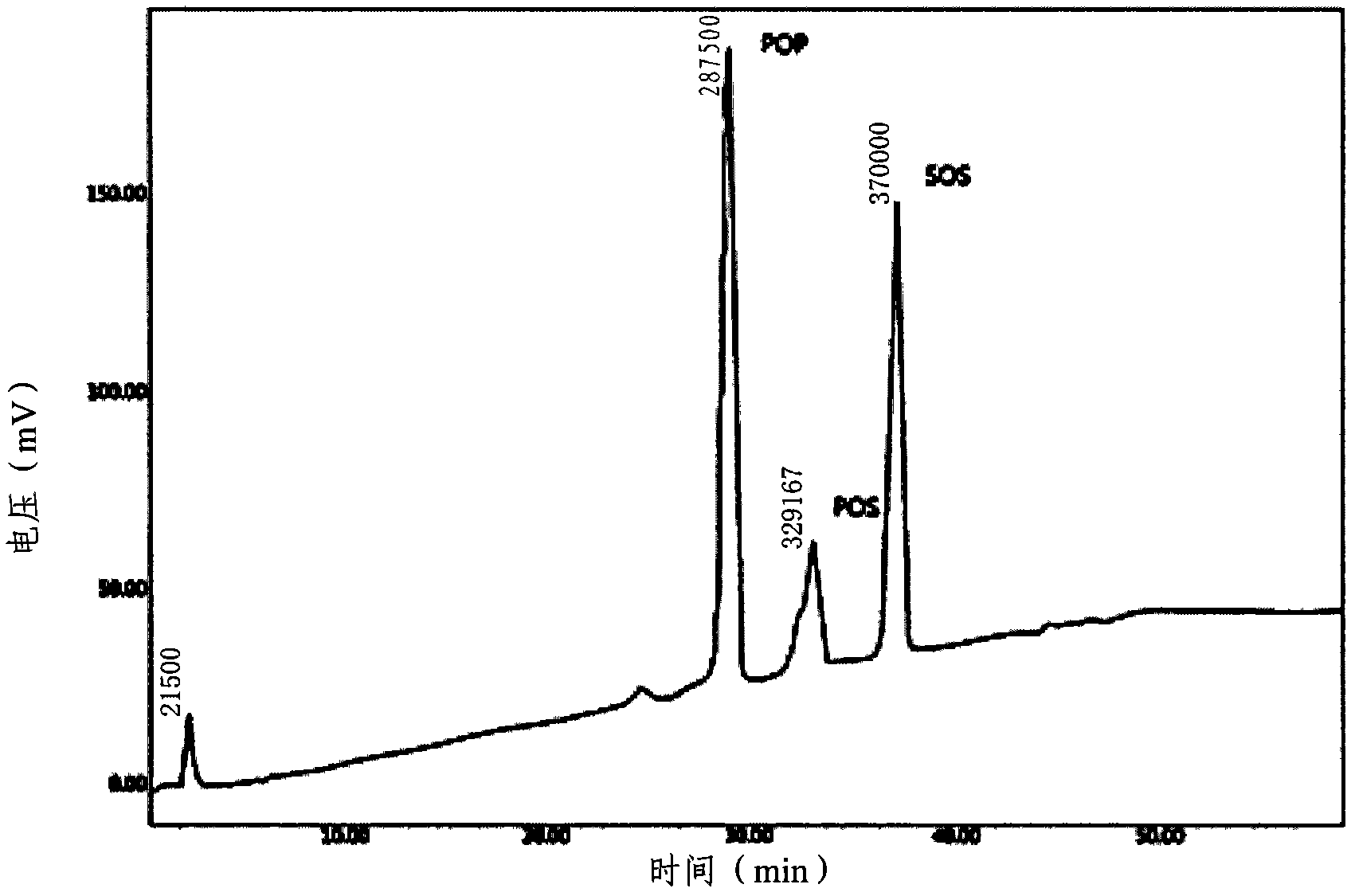
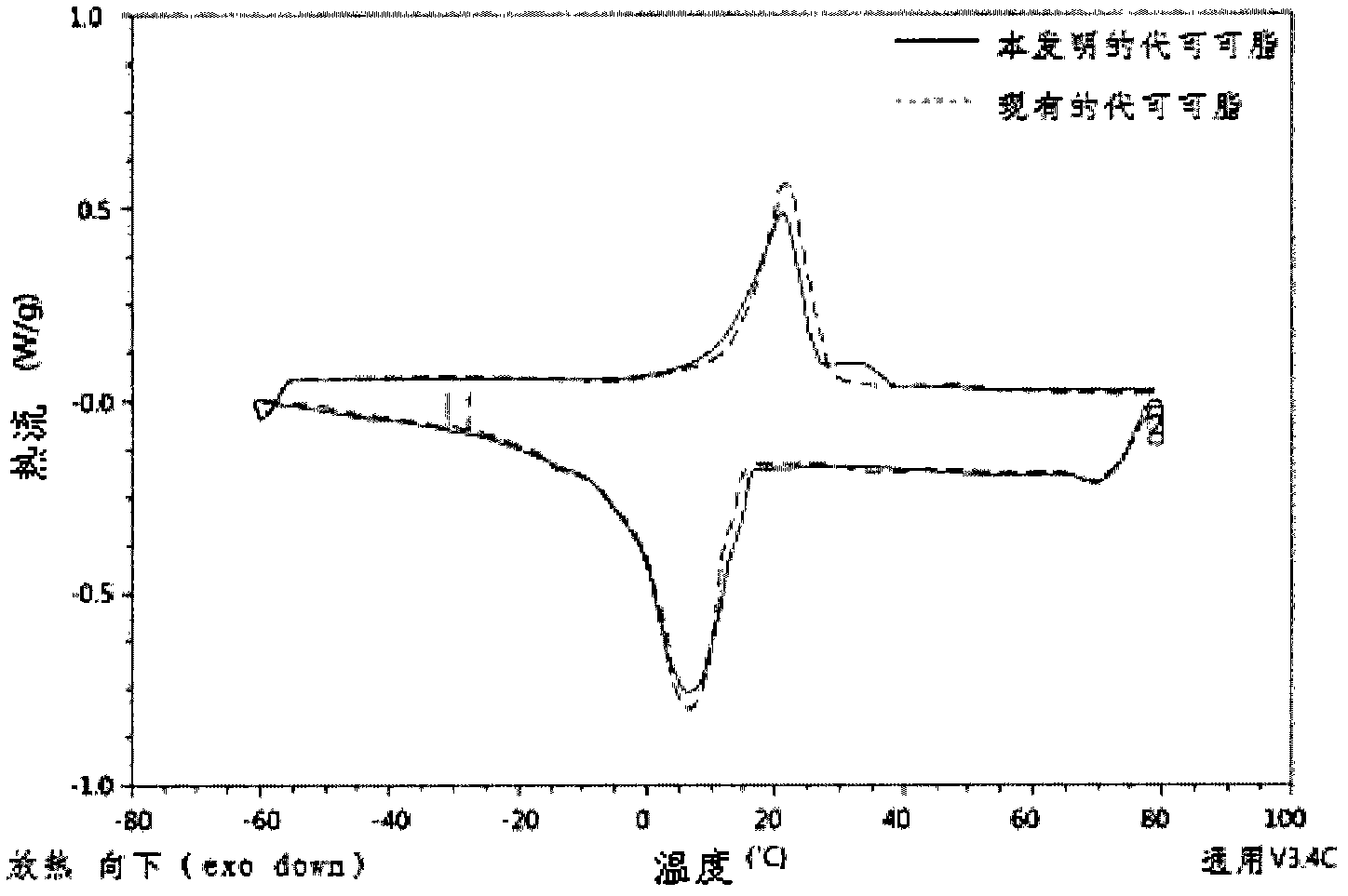
The present invention relates to a process for preparing hard butter having high SOS content by mixing oil for preparing butter with fatty acid or fatty acid ester, adding 1,3 regio-specific enzymes to the obtained mixture to carry out interesterification, distilling the obtained reactants to remove fatty aicd, ethyl ester, and monoglyceride and diglyceride formed after the reaction and fractionally extracting the obtained reactants to separate a solid phase, and to cocoa butter equivalents prepared by the hard butter and a process for preparing the same in which the cocoa butter equivalents can replace existing import cocoa butter equivalents with 1 : 1 because of its equivalent chemical properties, and have no difference in taste and properties with natural cocoa butter and also have lower trans fatty acid. Hard butter according to the present invention can make desired triglyceride structure in oil based on the reaction conditions and have a improved purity and yield in the whole process by recycling all of byproduct other than major product in the distillation and fractional distillation process and is eco-friendly matter by using the enzymatic interesterification reaction, and also cocoa butter equivalents made by the hard butter is characterized in replacing existing import cocoa butter equivalents with 1 : 1 because of its equivalent chemical composition and properties in the production of chocolate with no difference in taste.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
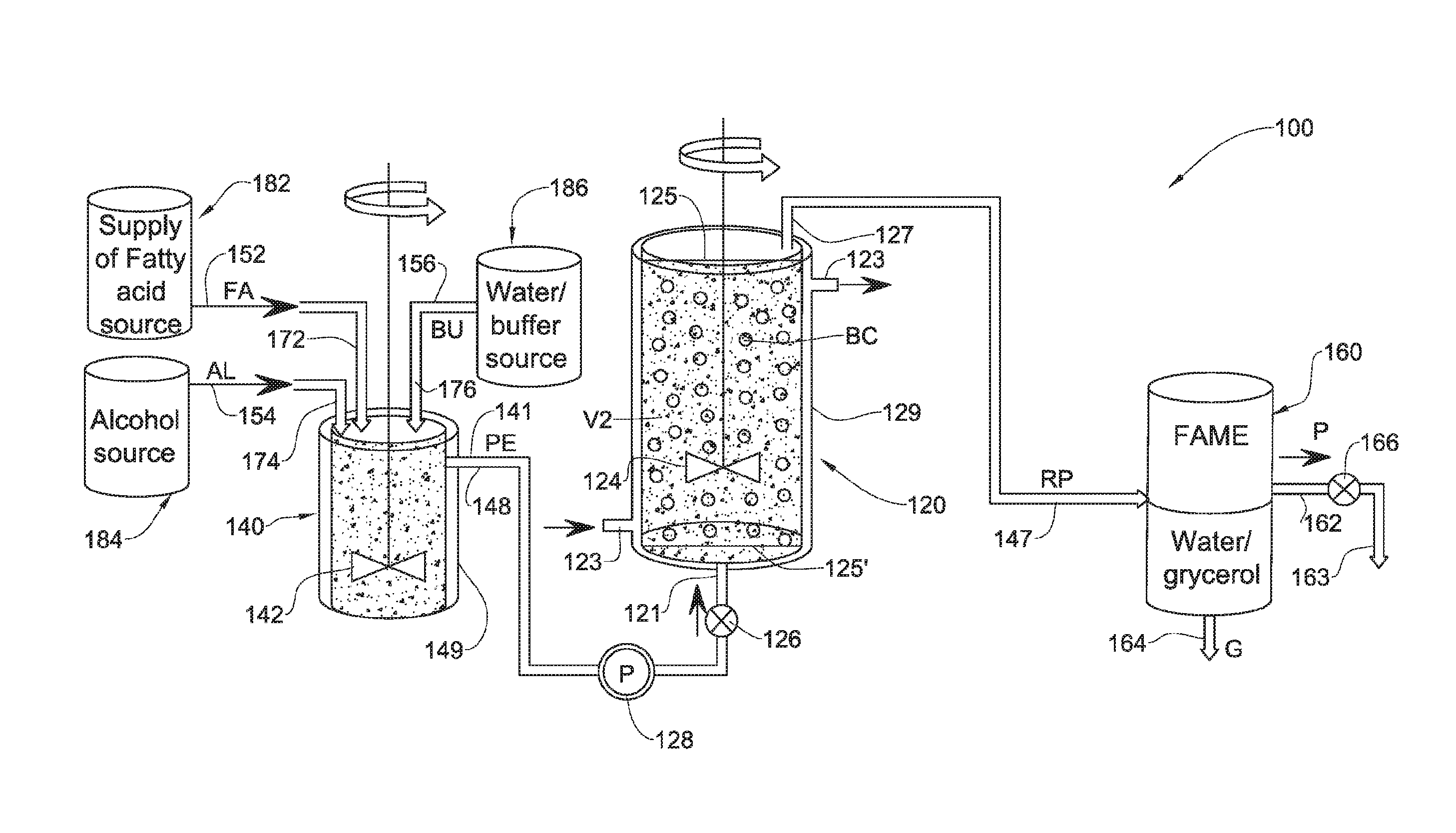
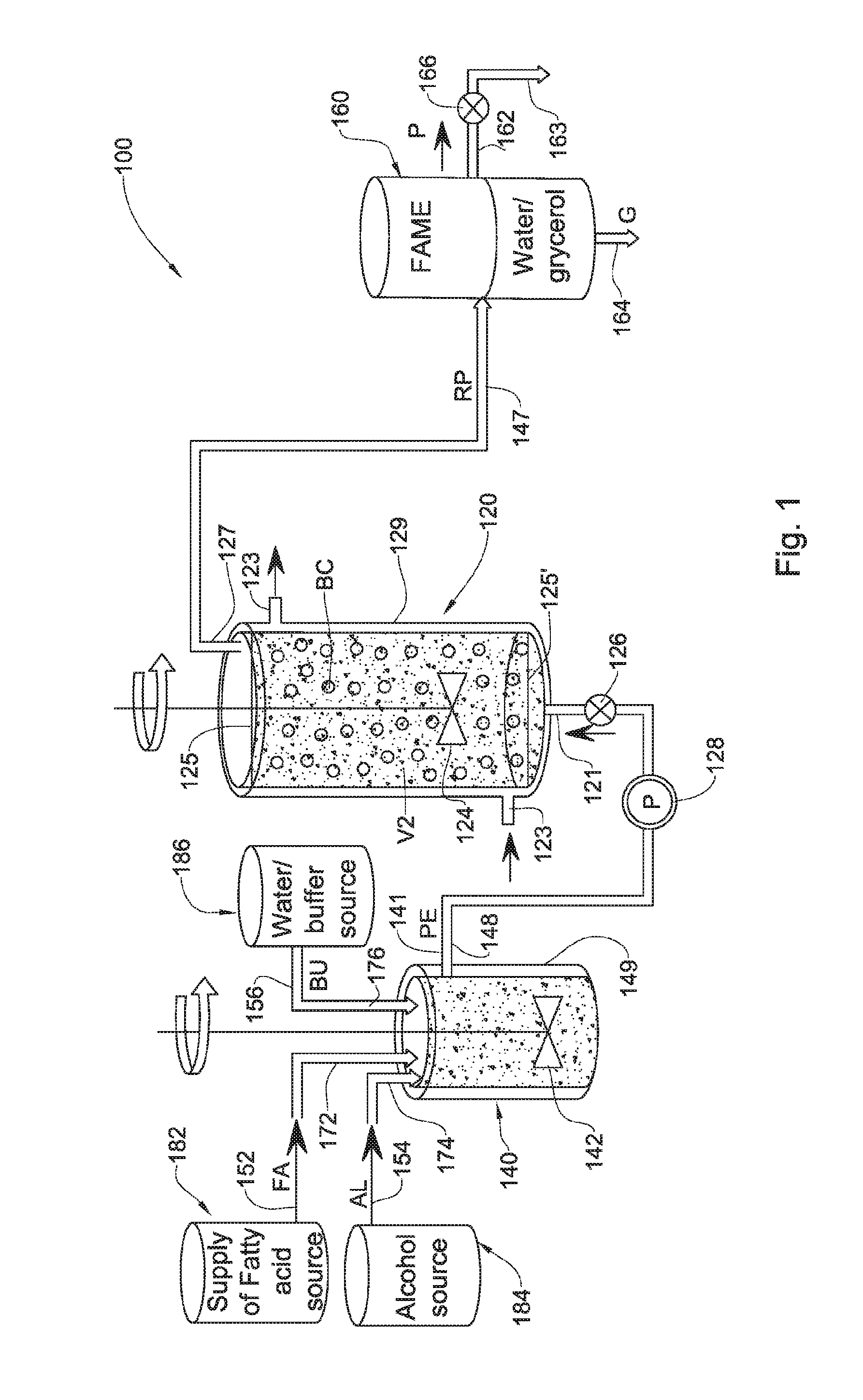
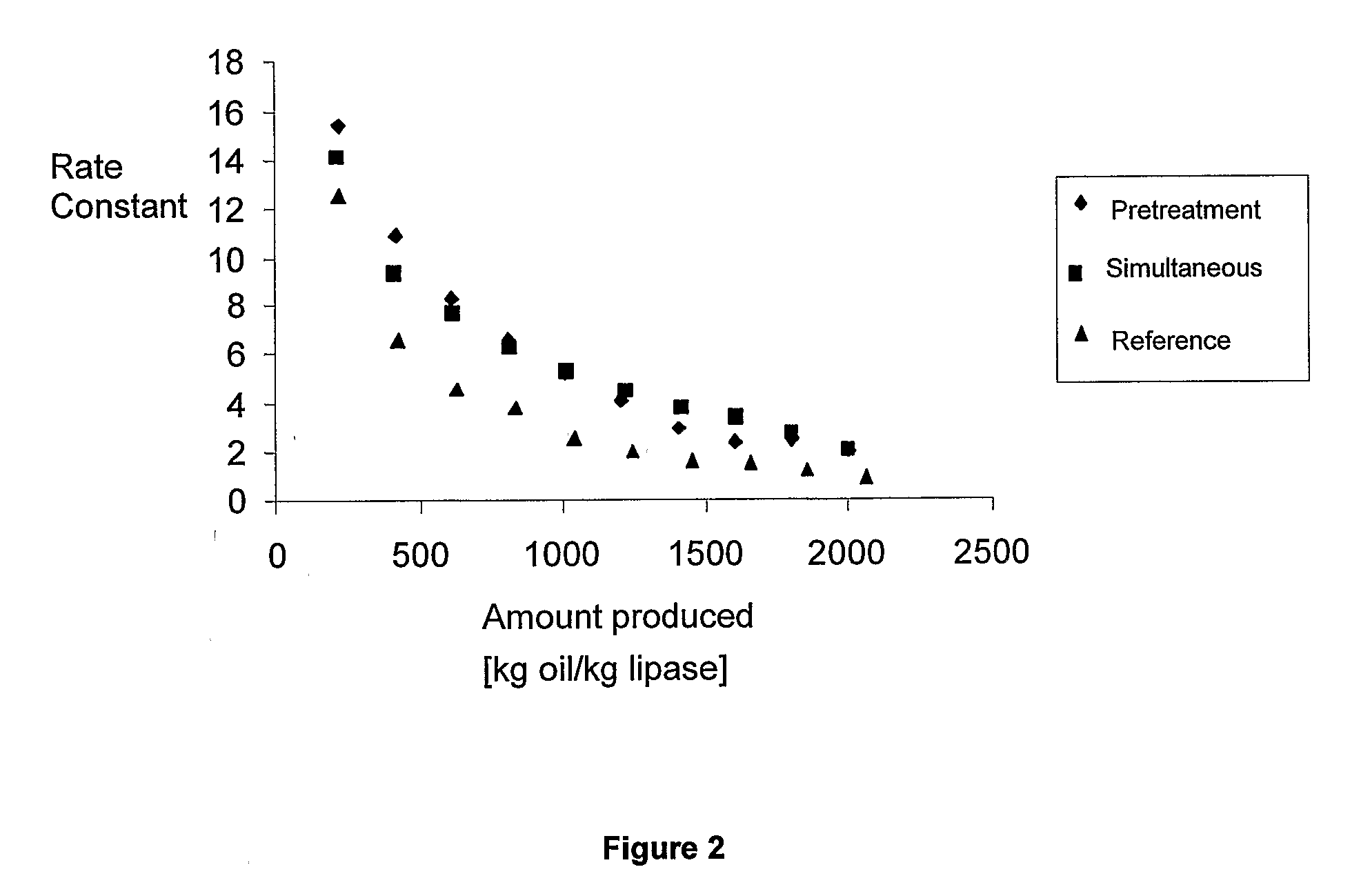
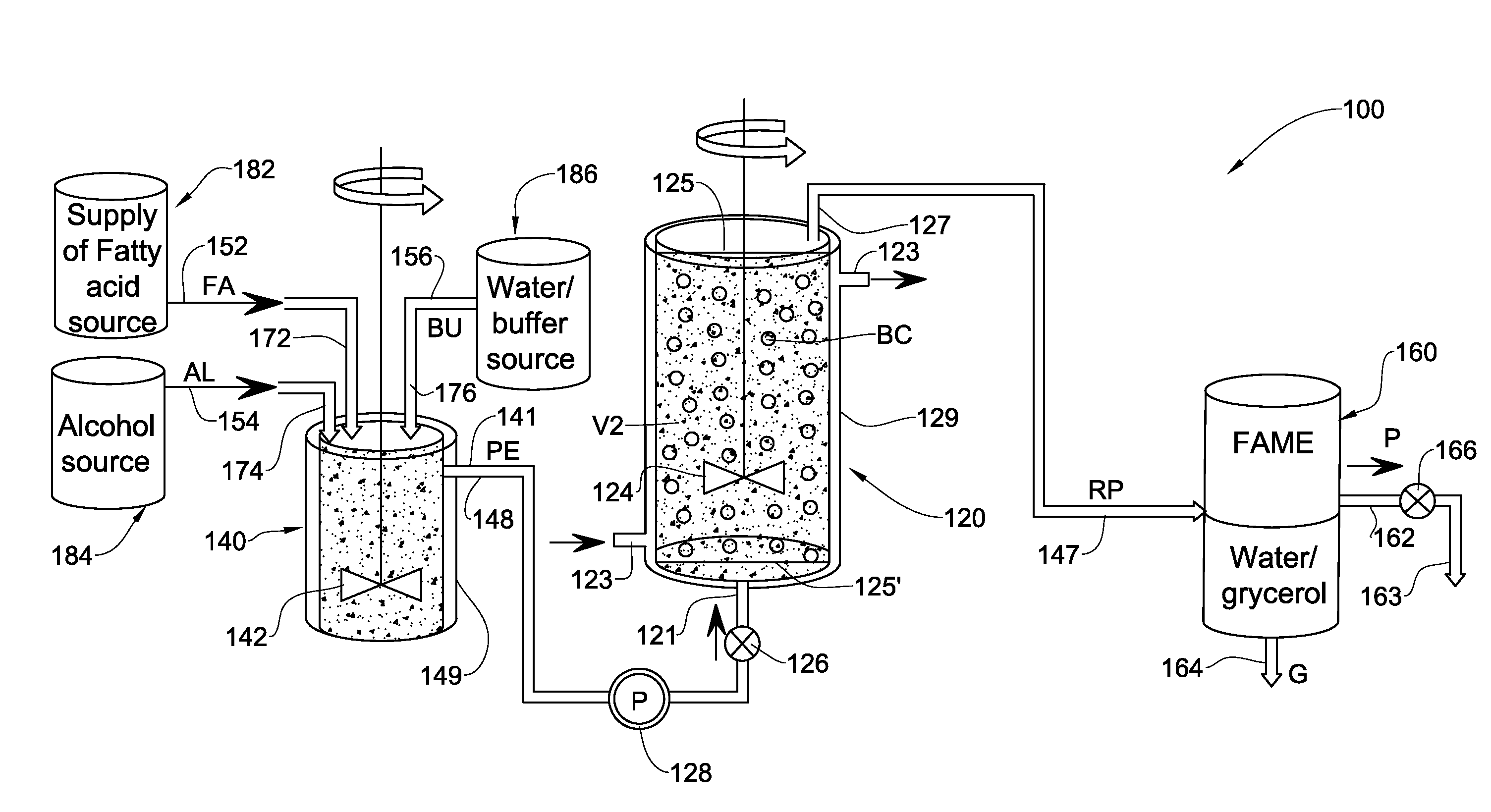
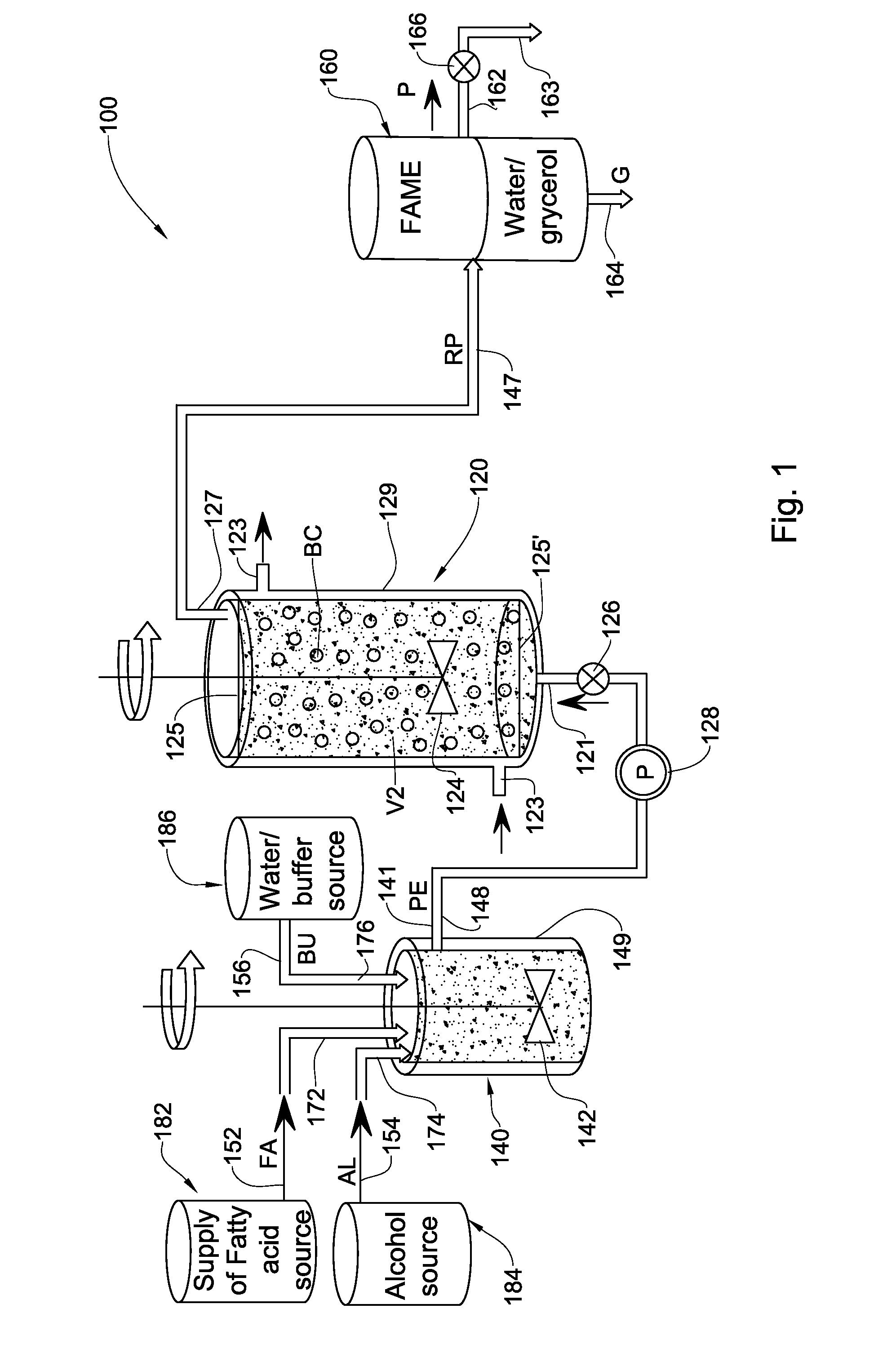
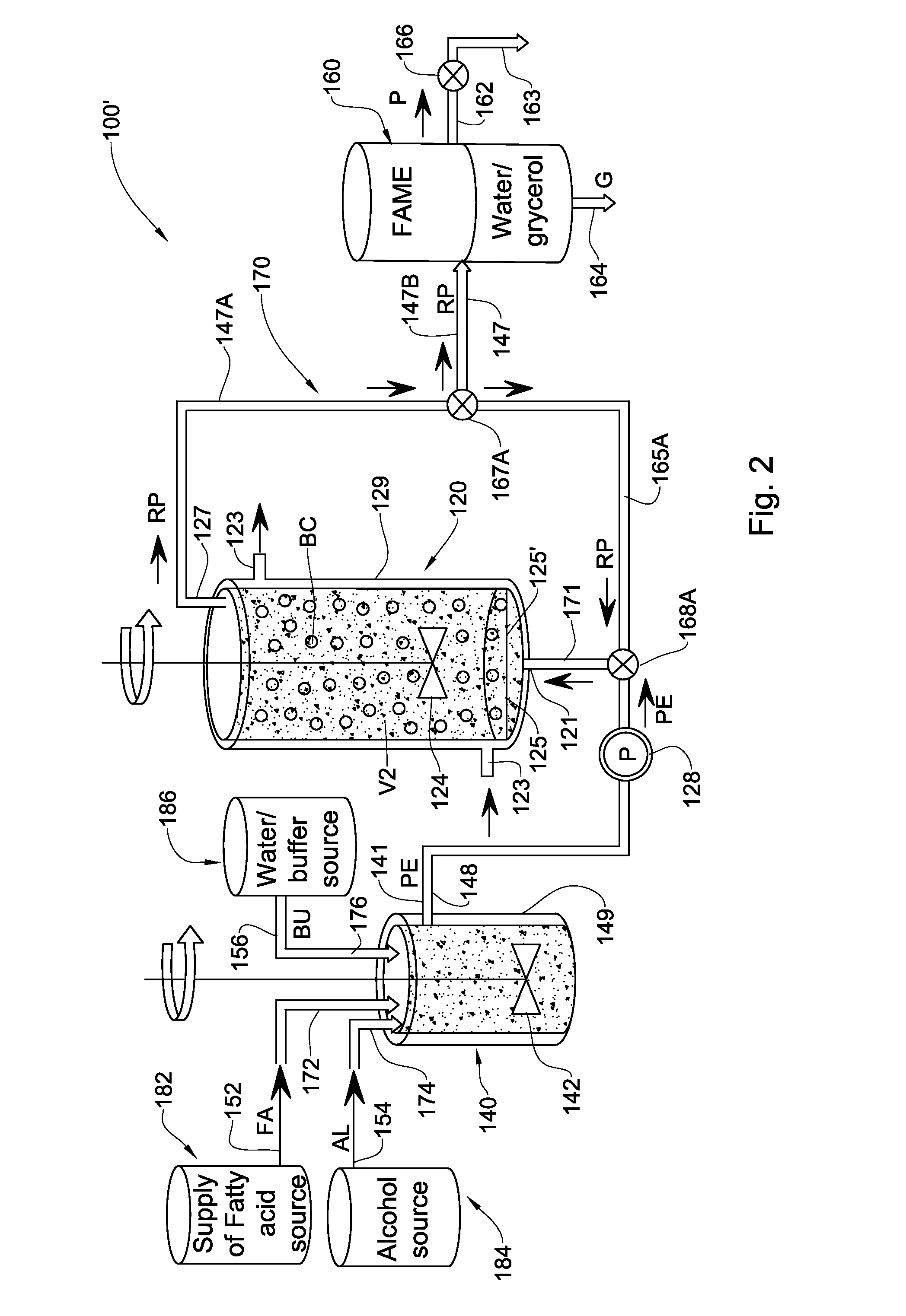
Enzymatic transesterification/esterification processes employing lipases immobilized on hydrophobic resins in the presence of water solutions
ActiveUS20130052701A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlcoholAqueous buffer
Disclosed are an enzymatic batchwise or continuous process for the production of fatty acid alkyl esters for use in the biofuels, food and detergent industries and a system therefor. The process utilizes enzymes immobilized on a hydrophobic resin mixed with a fatty acid source and an alcohol or alcohol donor in the presence of an alkaline or mild alkaline aqueous buffer, or in the presence of water or aqueous solution. The production process for fatty acid alkyl esters is carried out by transesterification or esterification simultaneously or sequentially. The biocatalyst activity is maintained with no significant activity losses in multiple uses and also avoids the accumulation of glycerol and water by-products or other hydrophilic compounds on the biocatalyst.
Owner:ENZYMOCORE LTD
Method for preparing low/zero-trans fatty acid shortening by enzymatic interesterification
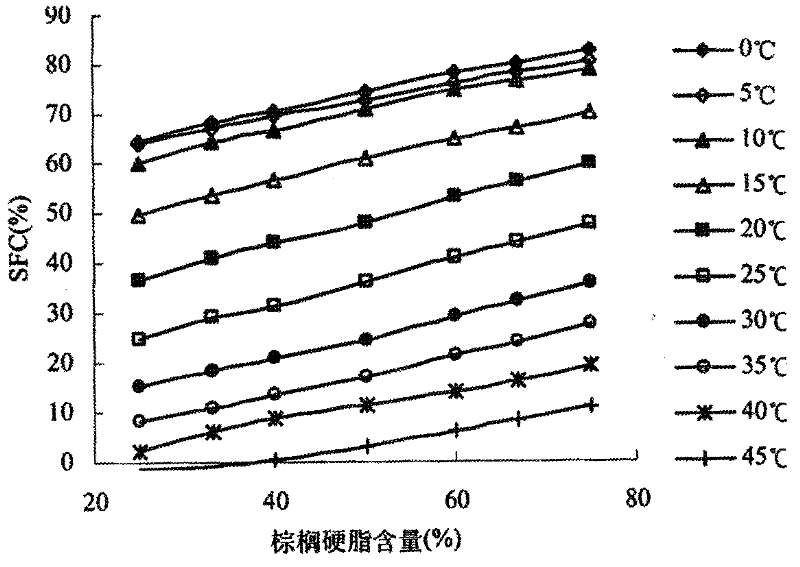
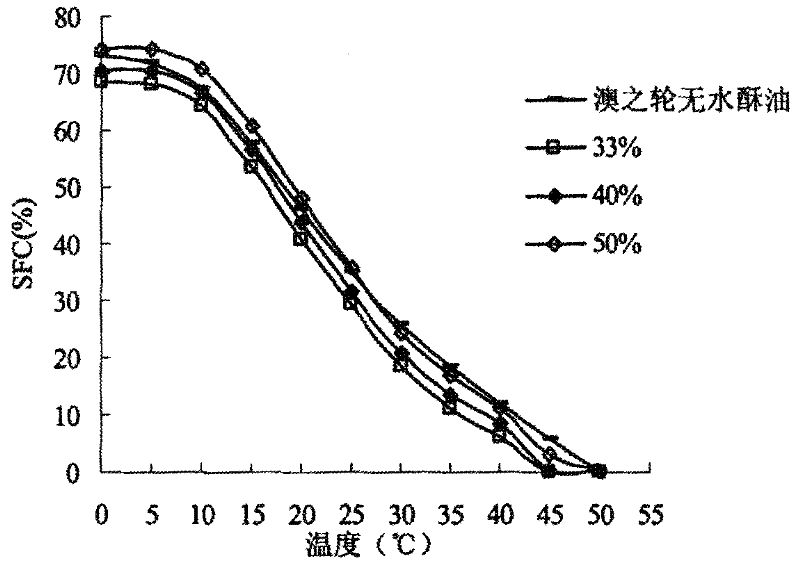
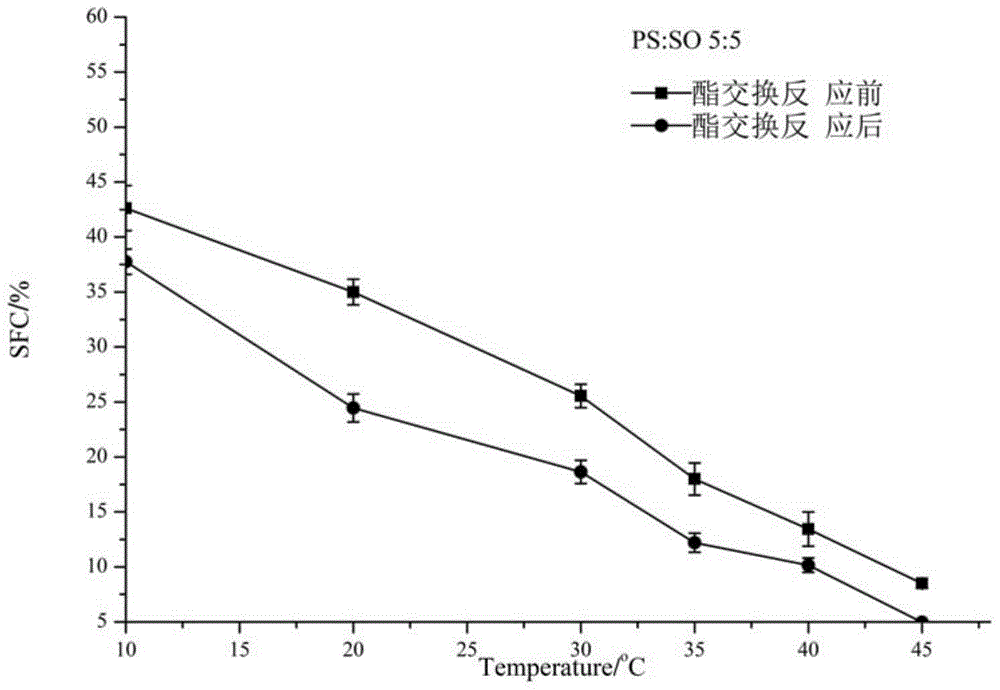
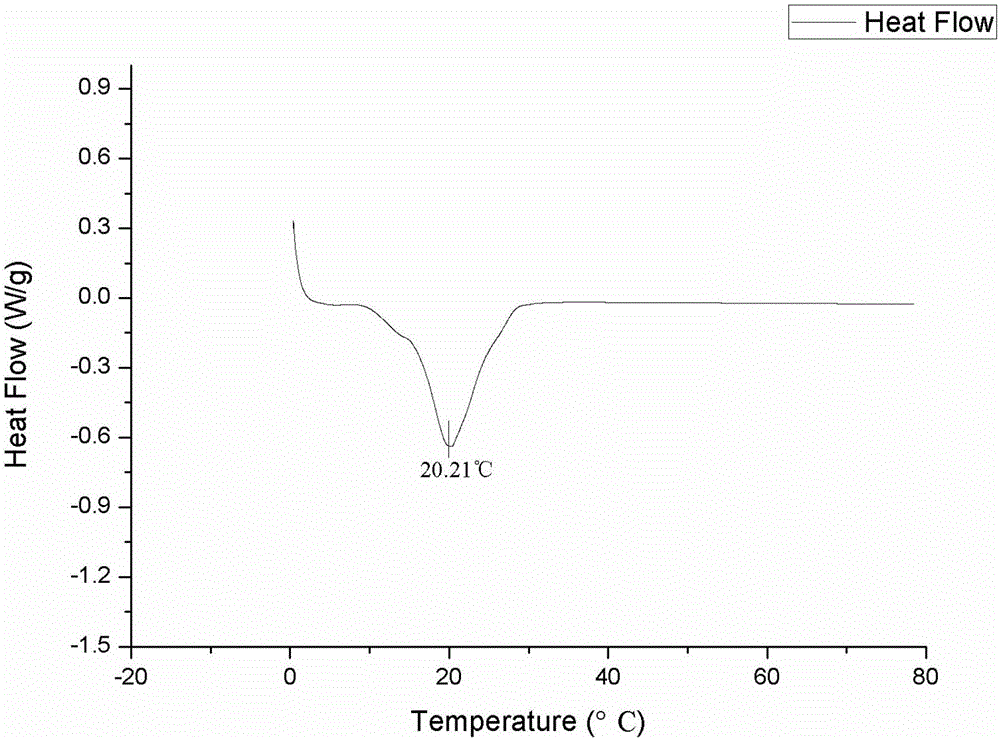
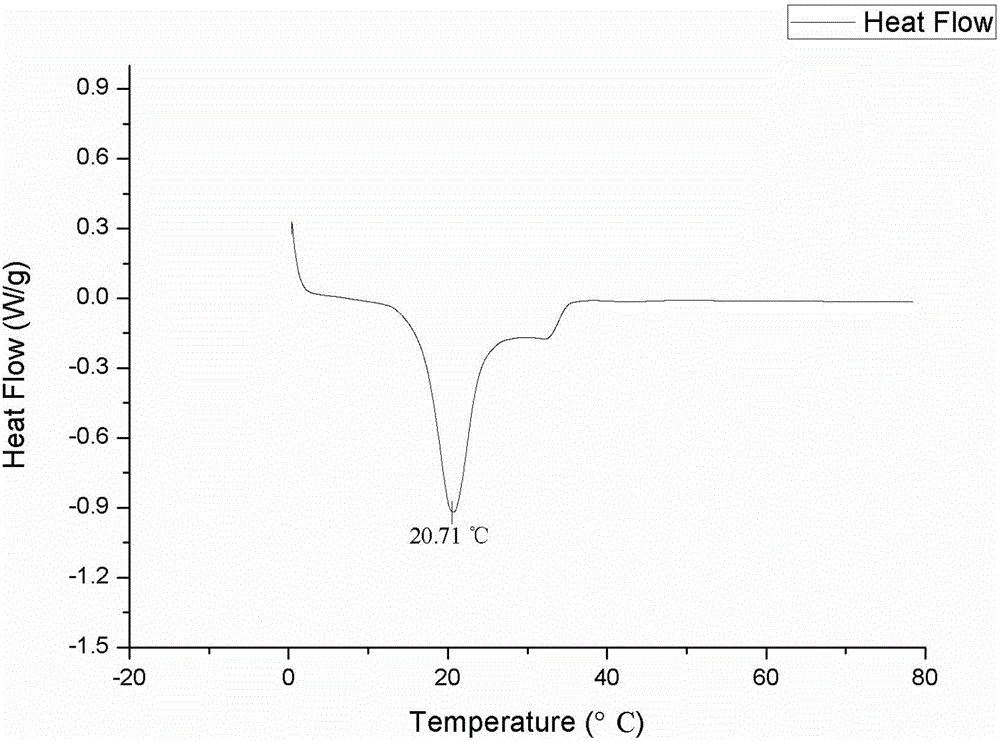
Belonging to the technical field of edible oil processing, the invention relates to a method for preparing low / zero-trans fatty acid shortening by enzymatic interesterification. The method of the invention adopts an immobilized lipase Lipozyme RM IM to catalyze lard and palm stearin or extremely hydrogenated oil (including extremely hydrogenated soybean oil, extremely hydrogenated canola oil, extremely hydrogenated palm oil and extremely hydrogenated cottonseed oil) for interesterification so as to prepare shortening. The solid fat content (SFC) of a reaction product under a temperature of 20DEG C is taken as an index, and by systematically studying the influences of temperature, adding amount of enzyme and time on an interesterification reaction, obtaining ideal technical parameters: a reaction temperature of 60-90DEG C, an enzyme adding amount of 6%-12%, and a reaction period of 1h-3h. In the invention, the compatibility and crystal form of a mixture system before and after an interesterification reaction are studied through an isothermal curve and an X-ray diffraction technology. Results indicate that: after interesterification, the compatibility of the mixture system is obviously improved, the crystal form is converted from beta type into beta' type, and the shortening prepared in the invention is superior to the market shortening in terms of application in bread baking. Widening the range of lard application, the method of the invention brings the abundant lard resources in our country into full play.
Owner:无锡食赫兹未来食品科技有限公司
Method for producing functional grease containing rich phytosterin ester from high-acid-value vegetable oil
ActiveCN104178531ARealize the processing effectRealize high-value utilizationFermentationOil and greaseVegetable oil
The invention relates to a method for producing functional grease containing rich phytosterin ester from high-acid-value vegetable oil. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) addition of reaction raw materials: adding phytosterin, high-acid-value grease and molecular sieve into a reaction kettle, adding 100-200ppm of antioxidant, heating to 45-60 DEG C, stirring and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a premixture, wherein the mole ratio of the phytosterin to free fatty acids in the high-acid-value grease is 1:1-5:1; (2) enzymatic ester exchange reaction: adding 5-40 g / L lipase into the premixture, and stirring to react at 45-60 DEG C under normal pressure for 6-12 hours; and (3) carrying out after-treatment on the product to obtain the functional grease containing rich phytosterin ester. The method can obviously lower the acid value of the high-acid-value vegetable oil and generate the new functional active component phytosterin ester, and the product is simple for separation and purification; and thus, the method can easily implement large-scale amplification.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cocoa butter equivalents produced by the enzymatic interesterification process and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20110262592A1Convenient in reaction processHigh yieldFatty acid esterificationFatty-oils/fats refiningButter cocoaMonoglyceride
The present invention relates to a process for preparing hard butter having high SOS content by mixing oil for preparing butter with fatty acid or fatty acid ester, adding 1,3 regio-specific enzymes to the obtained mixture to carry out interesterification, distilling the obtained reactants to remove fatty acid, ethyl ester, and monoglyceride and diglyceride formed after the reaction and fractionally extracting the obtained reactants to separate a solid phase, and to cocoa butter equivalents prepared by the hard butter and a process for preparing the same in which the cocoa butter equivalents can replace existing import cocoa butter equivalents with 1:1 because of its equivalent chemical properties, and have no difference in taste and properties with natural cocoa butter and also have lower trans fatty acid. Hard butter according to the present invention can make desired triglyceride structure in oil based on the reaction conditions and have a improved purity and yield in the whole process by recycling all of byproduct other than major product in the distillation and fractional distillation process and is eco-friendly matter by using the enzymatic interesterification reaction, and also cocoa butter equivalents made by the hard butter is characterized in replacing existing import cocoa butter equivalents with 1:1 because of its equivalent chemical composition and properties in the production of chocolate with no difference in taste.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Grease composition for margarine and shortening and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN104247783AReduce accumulationLow in trans fatty acidsEdible oils/fatsTriglycerideCompound (substance)
The invention relates to a medium-carbon-chain triglyceride fatty acid, long-carbon-chain triglyceride fatty acid and / or medium- and long-carbon-chain triglyceride fatty acid containing grease composition for margarine and shortening and a preparing method thereof. Relative to the total weight of the composition, the grease composition contains more than 80 wt% of triglycerides; relative to the total weight of all the fatty acids forming the grease composition, the medium-carbon-chain fatty acid accounts for 8-15 wt%; the grease composition is obtained through physical mixing or an ester exchange reaction, wherein the ester exchange reaction can be a chemical ester exchange reaction or an enzymatic ester exchange reaction.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Method for enzymatic preparation of 1,3-dioleoyl 2-palmitoyl triglyceride in subcritical system
ActiveCN105219813ALower Diffusion LimitsImprove solubilityFermentationTrans esterificationSolvent free
The invention relates to a method for the enzymatic preparation of 1,3-dioleoyl 2-palmitoyl triglyceride in a subcritical system, which comprises the following steps: (1) raw materials preparation: selecting lard oil with a cholesterol content of less than 0.05% as a raw material A, or selecting recombinant palm oil with a sn-2 palmitic acid mass content of not less than 60% as a raw material A; and selecting at least one of an oleic acid and oleate as a raw material B; and (2) subcritical enzyme-catalyzed ester exchange reaction: in a subcritical system, under the catalysis of lipase, enabling the raw materials A and B to have a selective enzyme-catalyzed ester exchange reaction in a reaction solvent, so that 1,3-dioleoyl 2-palmitoyl triglyceride is obtained. The method has the characteristics of rapid reaction rate, high selectivity, less dosage application, no solvent residue, and easiness for large-scale continuous production.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Modified cocoa butter and functional chocolate containing linolenic acid and preparation method of modified cocoa butter and functional chocolate
The invention discloses modified cocoa butter and functional chocolate containing linolenic acid and a preparation method of the modified cocoa butter and the functional chocolate. Firstly, cocoa butter and flaxseed oil are subjected to enzymatic transesterification to obtain the modified cocoa butter; and then the functional chocolate containing linolenic acid is prepared with the modified cocoa butter. The functional chocolate comprises the following components: 38-48 percent of the modified cocoa butter, 15-17 percent of cocoa powder, 30-38 percent of white granulated sugar as well as lactose, lecithin and vanillin. Compared with the traditional chocolate variety, the product disclosed in the invention contains an increased amount of linolenic acid and has better functions of nutrition and health. In addition, the prepared chocolate is smooth in surface, is fine and smooth in taste, and has a unique fragrance of the cocoa and the flaxseed oil. The shelf life of the chocolate at 20 DEG C is 428 days, about 61 weeks, so that the storage performance of the chocolate is well.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Technological process of fish oil low-temperature the smell of fish removing
InactiveCN101253952AThe inner structure is not destroyedSolve the problem of destroying the inner structure of fish oilEdible oils/fatsFood preparationHazardous substanceFish oil
The invention provides a method for removing a fishy smell from fish oil at a low temperature, belongs to the animal oil finery processing technology field, and aims to solve the problem that the prior method for removing the fishy smell from the fish oil at a high temperature can destroy the inner structure of the fish oil. The method for removing the fishy smell from the fish oil at a low temperature comprises the steps of mixing ethyl ester fish oil, glycerin and lipase in a hermetically sealed reaction vessel; subjecting the mixture to enzyme catalyzed interesterification; adding a fragrant fishy smell removing agent, the weight of which accounts for 0.1%-0.2% of that of ethyl ester; stirring for reaction for 24-33hr with pressure of 100-11300Pa in the vessel at the temperature of 60-80 DEG C; terminating the reaction; nitrogen filled packing after inspection; and refining to get the fish oil free of fishy smell. The method with significant effect of removing the fishy smell does not produce trans-fatty acid and polymerized hazardous substances, such as ketone and aldehyde, is applicable to manufacturing triglyceride fish oil by removing the fishy smell from the ethyl ester fish oil, and processing and refining other fish oil by removing the fishy smell.
Owner:河北康睿达脂质有限公司
Preparation method for natural flavor fatty acid ester
The invention discloses a method for continuous preparation of natural flavor fatty acid ester. Grease is converted into flavor fatty acid ester through enzymatic transesterification with lipase used as a catalyst and one or more selected from the group consisting of coconut oil rich in low and medium carbon chain fatty glyceride (no more than C14), natural cream, Brazilian palm oil and palm kernel oil as a substrate. Alcohol used in transesterification is micro-molecular alcohol like ethanol, butanol, isobutanol and isoamyl alcohol; immobilized lipase is filled in a packed-column reactor; under the condition of continuous operation, the reaction substrate and the micro-molecular alcohol continuously flow through the lipase packed-column reactor to synthesize fatty acid ester; and an obtained reaction mixture is purified by using molecular distillation technology so as to obtain high-purity flavor fatty acid ester, i.e., mixed low and medium carbon chain fatty acid ester.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FLOWER FLAVOURS & FRAGRANCES
Special oil for quick-frozen food and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105695522AAvoid breakingHigh catalytic efficiencyEdible oils/fats ingredientsFermentationOil and greaseNutritive values
The invention discloses a special oil for quick-frozen food and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out lipase catalytic ester exchange on palm stearin and liquid vegetable oil by using a fluidized bed reactor to prepare ester exchange oil; (2) adding an emulsifier into ester exchange oil, heating, uniformly mixing, cooling to 60 DEG C, adding an antioxidant, uniformly mixing, adding water, emulsifying, carrying out precooling-quenching kneading, and finally, cooking to obtain the special oil for quick freezing. The ester exchange oil contains abundant unsaturated fatty acids and certain amounts of essential fatty acids; the solid fat content (SFC) of the special oil product for quick-frozen food varies slowly at certain temperature; the special oil for quick-frozen food has a certain plastic range; and the oil crystals are fine and compact, and are mainly composed of beta- crystal form. The special oil for quick-frozen food has certain nutritive value and smooth mouthfeel, and provides mild stable production conditions for oil preparation by enzymatic ester exchange reaction in a fluidized bed reactor.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for enzymatic transesterfication preparation of cocoa butter equiralent by using 33-DEG C palm oil
The invention discloses a method for enzymatic transesterfication preparation of a cocoa butter equiralent by using 33-DEG C palm oil, and belongs to the technical field of enzymatic transesterfication preparation of cocoa butter equiralent. The 33-DEG C palm oil with high food safety and wide source of raw material is used as a raw material, lipase having the advantages of good Sn-1,3 site selectivity, high catalytic efficiency, broad reaction conditions and low price is adopted for enzymatic transesterfication preparation of the cocoa butter equiralent, especially, a scientific-compounding natural antioxidant is added in an enzyme catalysis process, an acid value of the cocoa butter equiralent can be significantly reduced, and the shelf life of the product is prolonged. The physicochemical properties of the finally prepared cocoa butter equiralent component and product are extremely similar to those of natural cocoa butter, the acid value is low, the ester exchange rate is high, the acyl transfer rate is low, the shelf life is long, and the cost is low. The acid value of the prepared cocoa butter equiralent is 0.5-0.8 mg KOH / g, the ester exchange rate is 82.68-88.76%, and the acyl transfer rate is 4.41-6.61%.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
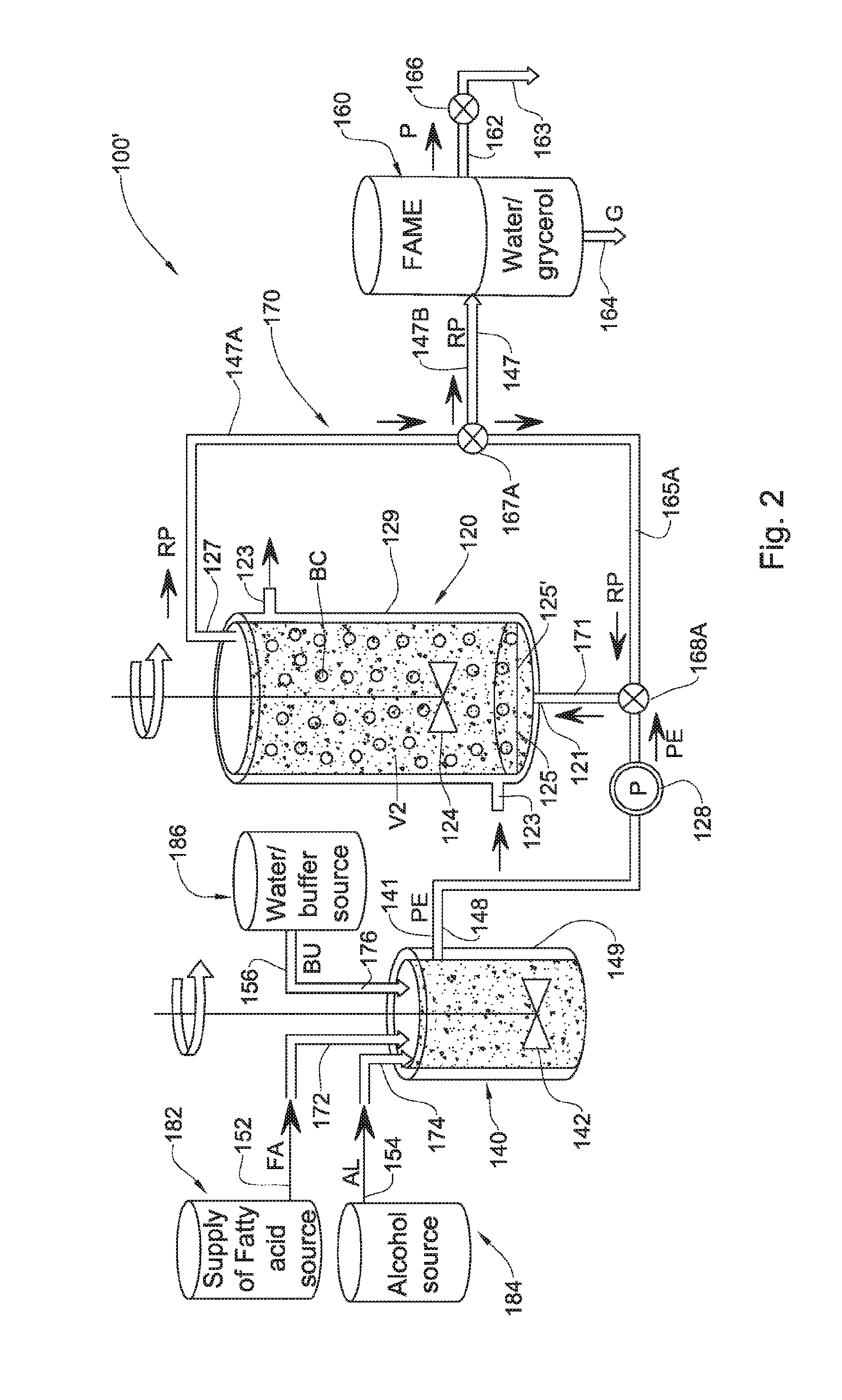
Enzymatic transesterification/esterification processing systems and processes employing lipases immobilzed on hydrophobic resins
InactiveUS20150353970A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProcess systemsTransesterification
Disclosed are processing systems and processes for carrying out enzymatic batchwise or continuous process for the production of fatty acid alkyl esters for use in the biofuels, food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and detergents industries.
Owner:TRANS BIO DIESEL LTD
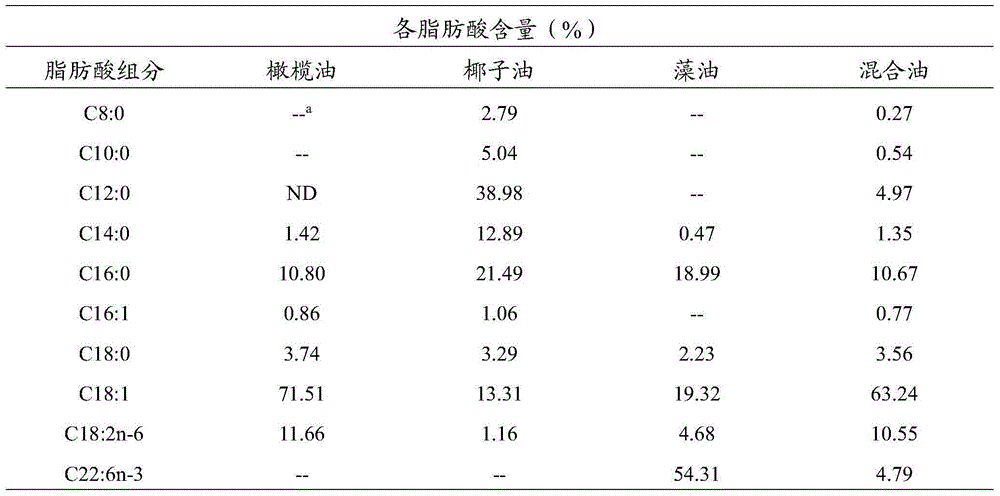
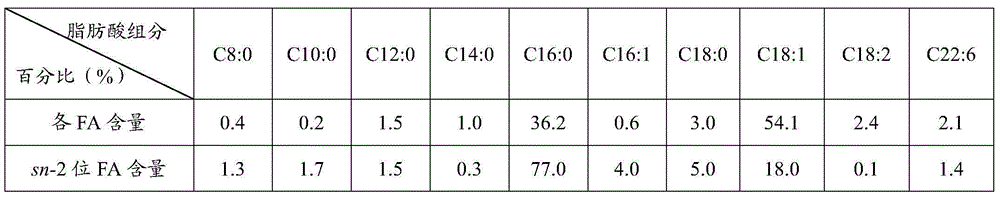
Synthesized breast milk fat substitute product from mixed fatty acid under enzymatic condition in microwave and method for preparing breast milk fat substitute product
The invention discloses a synthesized breast milk fat substitute product from mixed fatty acid under an enzymatic condition in microwave and a method for preparing the breast milk fat substitute product. The method includes respectively arranging molecular sieves and saturated salt solution in closed containers to control the activity of water; mixing olive oil with free fatty acid, coconut oil and algae oil with one another, mixing the olive oil with the free fatty acid, the coconut oil, the algae oil and triacylglycerol of palmitic acid with one another in the same reaction flasks and respectively arranging the reaction flasks and filter paper with lipase in the various closed containers and balancing the reaction flasks and the filter paper at the room temperatures; arranging substrates and the lipase in screwed glass bottles, closing the screwed glass bottles, carrying out enzymatic transesterfication reaction in constant-temperature water area shaking tables and microwave reactors, separating reaction grease by means of reduced-pressure distillation and refining the grease to obtain the breast milk fat substitute product. The olive oil with the free fatty acid is purified by the aid of a urea adduction process. The olive oil with the free fatty acid, the coconut oil, the algae oil and the triacylglycerol of the palmitic acid are used as the fatty enzymatic transesterfication substrates. The breast milk fat substitute product and the method have the advantages that the final reaction product contains abundant DNA (docosahexenoic acid), and the content of the palmitic acid on sn-2 sites of the breast milk fat substitute product is relatively high and can be assuredly equivalent to the content of palmitic acid on sn-2 sites of natural breast milk fat.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Trans fatty acid free fat for margarine produced by enzymatic interesterification and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20100151079A1Easy to useIncrease nutritionSpread compositionsFatty acid esterificationMonoglyceridePartial hydrogenation
The present invention can provide margarine oil with the enzymatic interesterification reaction, in which trans fatty acid, different from the existing partially hydrogenerated oil, is not formed in the process, and it has solid fat value profile and melting point corresponding to that of partially hydrogenerated oil and contains less than 1% of trans fatty acid, less than 27% of palmitic acid, more than 99% of triglyceride, less than 1% of diglyceride and monoglyceride, less than 1% of trans fatty acid and based on total fatty acid content. Accordingly, the margarine oil of the present invention is eco-friend and has lower trans fatty acid compared to the existing partially hydrogenerated oil and is easily to use for substituting in the ratio of 1:1 because of its physical properties corresponding to that of partially hydrogenerated oil for margarine oil and is also nutritionally excellent since it has lower palmitic acid content than natural palm oil which is usually used as a substitute for the existing margarine oil such as partially hydrogenerated oil.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for preparing cocoa butter equivalent by utilizing palm oil intermediate fractionation product enzymatic transesterfication
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cocoa butter equivalent by utilizing palm oil intermediate fractionation product enzymatic transesterfication. The method comprises the following steps: mixing a palm oil intermediate fractionation product with stearic acid according to a certain mass ratio, carrying out an esterification reaction by virtue of specific lipase to prepare the cocoa butter equivalent, and purifying the product by virtue of two-step crystallizing fractionation. By utilizing the method for preparing the cocoa butter equivalent disclosed by the invention, the produced cocoa butter equivalent is high in similarity with natural cocoa butter and is low in cost and high in safety.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Grease composition for formula milk powder as well as preparation method and application of grease composition
InactiveCN104413147AKeep the scentKeep the tasteMilk preparationSeed preservation by heatingCarbon numberMedium chain fatty acid
The invention relates to the field of deep processing of grease. Specifically, the invention relates to a grease composition for formula milk powder as well as a preparation method and application of the grease composition. More specifically, the grease composition is a transesterification product of crude grease through physical mixing, chemical transesterification or enzymatic transesterification, wherein in terms of the total weight of all fatty acids forming the grease composition, medium-chain fatty acid accounts for 5-25wt% and long-chain saturated fatty acid accounts for less than 15wt%; the weight ratio of n-6 series polyunsaturated fatty acid to n-3 series polyunsaturated fatty acid is (4-6) to 1, wherein the medium-chain fatty acid is fatty acid with carbon number of 6-12, and the long-chain fatty acid is fatty acid with carbon number of above 14.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
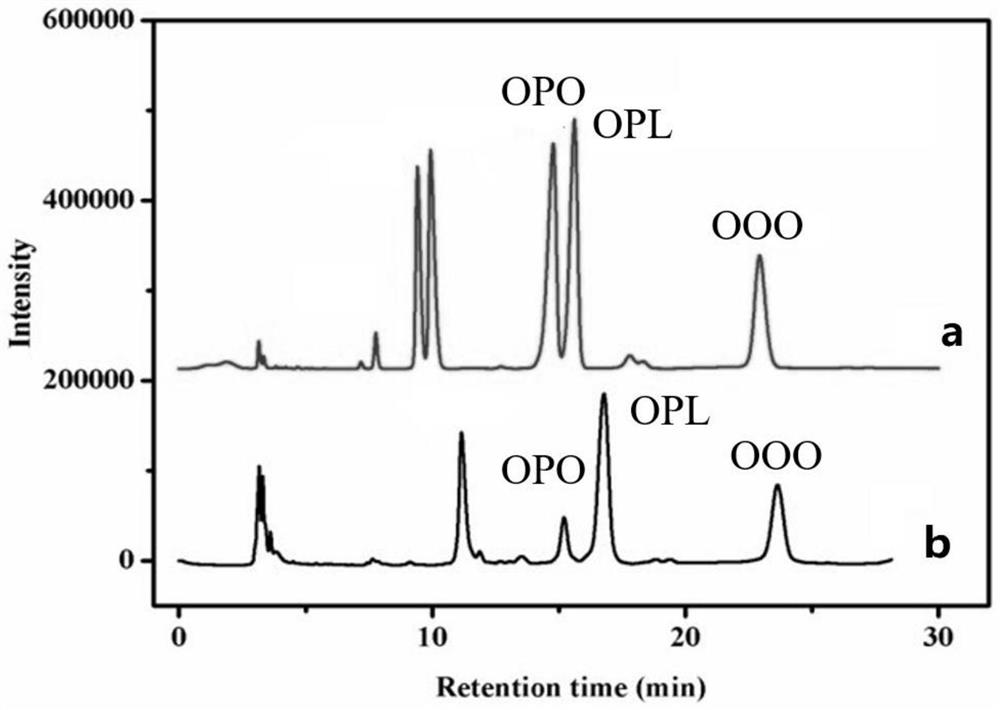
Preparation method of grease rich in OPL and OPO and product thereof
PendingCN112841313AAvoid generatingIncrease contentMilk preparationOrganic compound preparationTransesterificationSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of grease rich in OPL and OPO, wherein the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing OPO or LPL: mixing a PPP raw material and oleic acid / linoleic acid according to the ratio of PPP to oleic acid / linoleic acid of 1:3-1:5, adding lipase and a solvent, stirring or continuously flowing at a certain temperature for a certain time to carry out enzymatic transesterification, and purifying to remove fatty acid to obtain the grease rich in OPO / LPL; and (2) preparing grease rich in OPO and OPL: mixing the grease rich in OPO / LPL with linoleic acid / oleic acid according to a certain proportion, adding lipase and a solvent, stirring or continuously flowing at a certain temperature to carry out enzymatic transesterification, and purifying to remove fatty acid to obtain the grease rich in OPO and OPL. Cheap and easily available glycerol, palmitic acid, oleic acid and linoleic acid are used as raw materials, the intermediate product OPO / LPL is prepared, the grease rich in OPO and OPL can be obtained at the same time, and the method has the advantages that components of the synthetic product are relatively simple, and the content of the target product is controllable.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
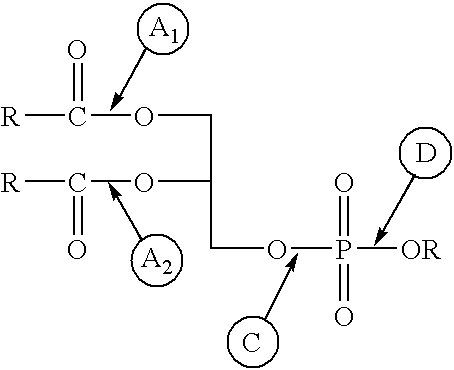
Enzymatic transesterification or hydrolysis of phospholipids in aqueous media
Methods of conducting phospholipase-catalyzed transesterification or hydrolysis of phospholipids present in aqueous liposomal suspensions, in the absence of detergents and organic solvents, are described. The method, which employs a water / solid particle interface, gives high conversions, particularly when the solid particle is silica gel having a small particle size and is present at a level at least four times the weight of the reacting lipid. The reaction is useful for the preparation of a variety of differently substituted phospholipids, as well as diacyl glycerols and ceramides.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Method for preparing squid liver oil
The invention relates to a method for preparing squid liver oil. A molecular distillation process is employed for removing free fatty acids in low-acid-value squid liver oil and further for reducing the acid value, neutral grease loss caused by acid removal in a caustic-soda neutralization method is avoided, and also astaxanthin is prevented from being converted into astacene under an alkali condition. Additionally, through an enzyme-promoted transesterification reaction and by utilizing the selectivity of immobilized lipase, saturated fatty acids and low-unsaturation-degree fatty acids are preferentially reacted with anhydrous ethanol, and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are relatively enriched on glycerin skeleton. The reaction conditions are mild, efficiency is high and speed is fast. Simultaneous enriching of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and astaxanthin in squid liver oil is realized, and the method possesses good popularization application prospect.
Owner:威海博宇食品有限公司
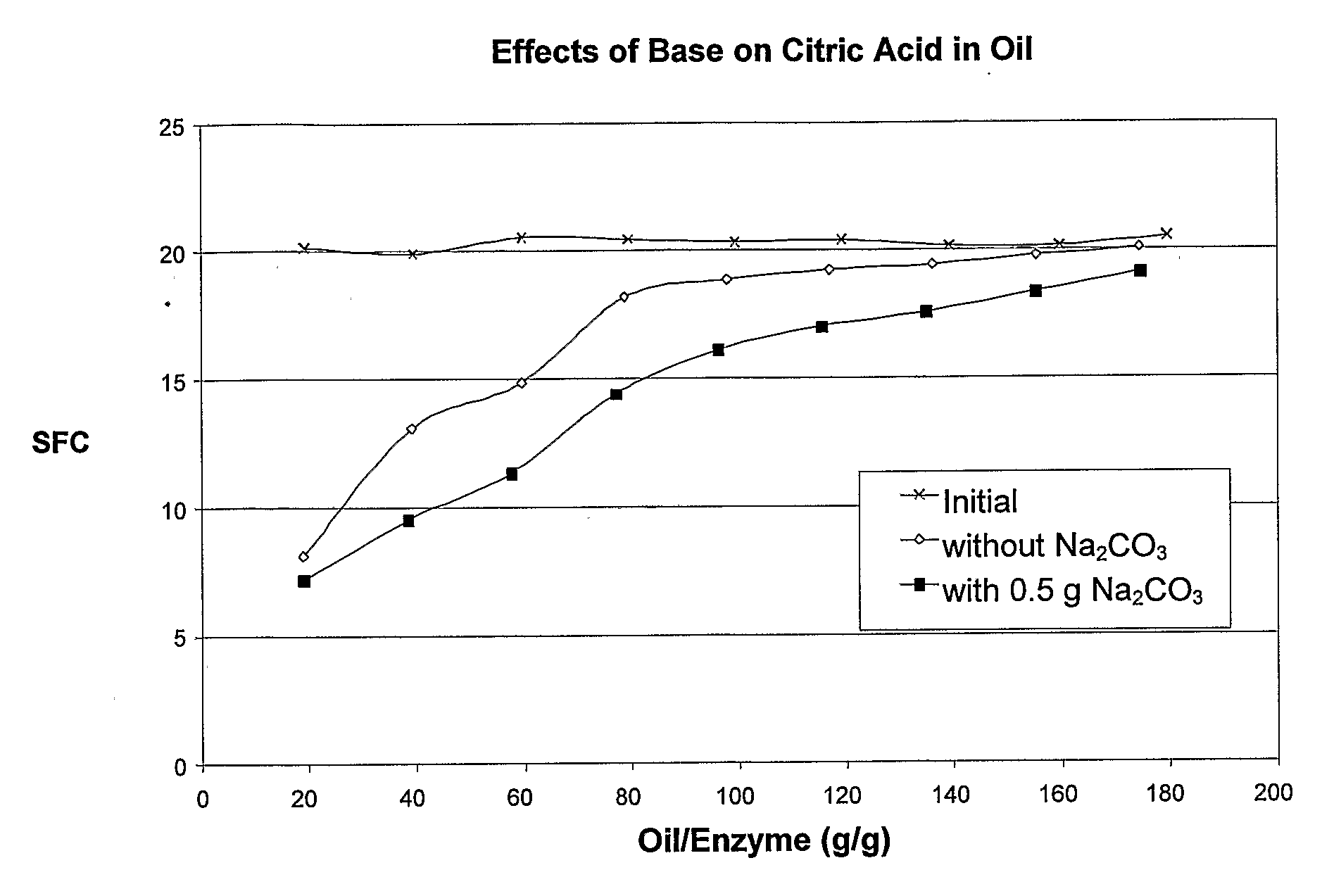
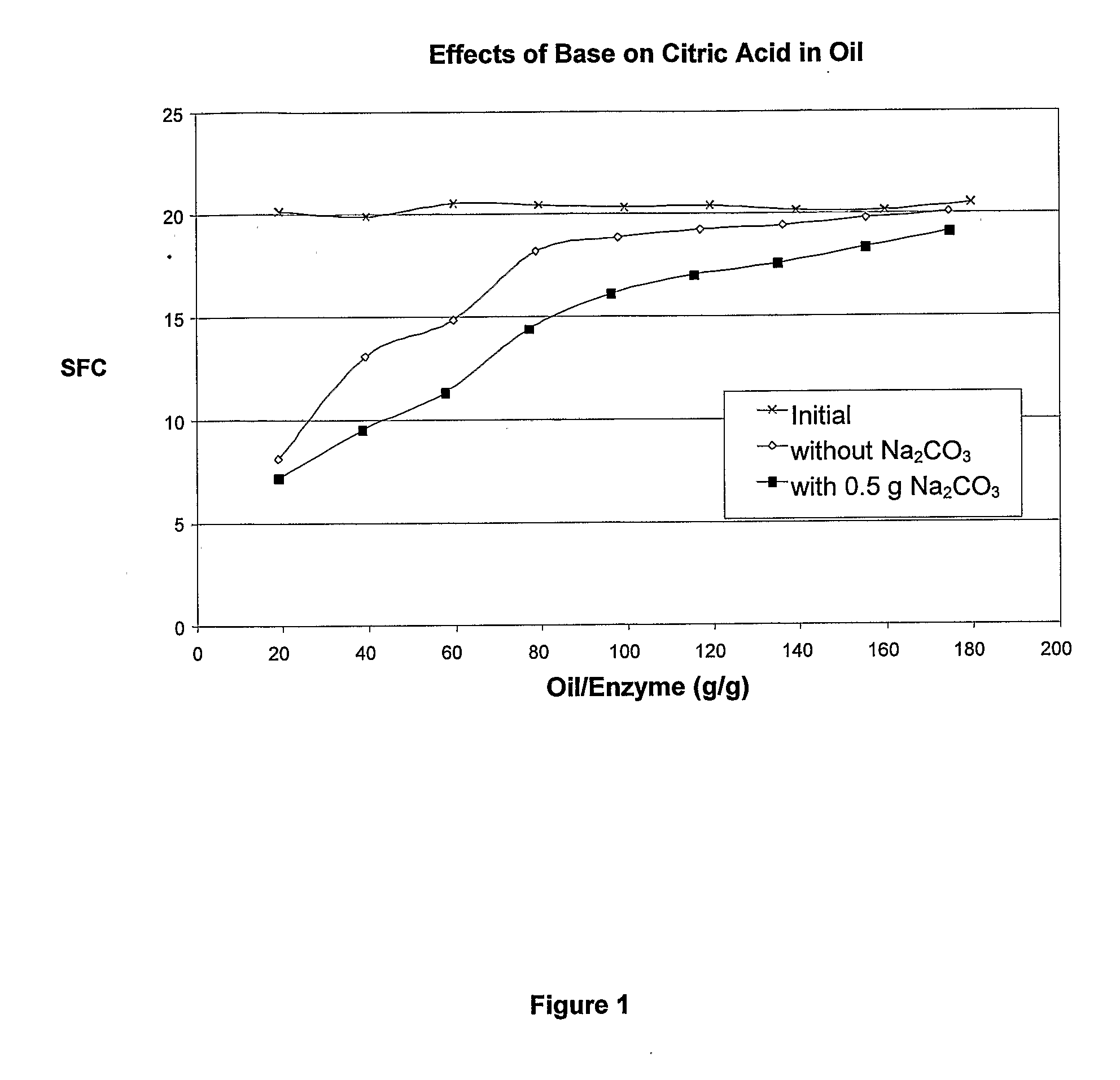
Enzymatic Oil Interesterification
An improved process for enzymatic interesterification of oil containing a chelating agent with a base and a lipase.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Structured lipid mixtures
The invention relates to structured lipid mixtures corresponding to formula (I): characterized in that R1CO, R2CO and R3CO independently of one another represent (i) linear saturated acyl groups containing 6 to 12 carbon atoms or (ii) the acyl group of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and / or an omega-3 or omega-6 fatty acid (OF), with the proviso that the quantity of CLA acyl groups amounts to 3 to 50 mol-% and the quantity of OF acyl groups to 5 to 25 mol-%, based on the quantity of acyl groups. The mixtures are preferably made by subjecting a mixture of component (a) a medium-chain triglyceride; and component (b) a CLA, an (OF), a TG-CLA (TG-OF) or a mixture thereof to enzymatic transesterification in the presence of a vegetable, marine or microbial oil.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Enzymatic transesterification/esterification processes employing lipases immobilized on hydrophobic resins in the presence of water solutions
Disclosed are processing systems and processes for carrying out enzymatic batchwise or continuous process for the production of fatty acid alkyl esters for use in the biofuels, food and detergent industries.
Owner:TRANS BIO DIESEL LTD
Frost-resistant oil and preparation method thereof, chocolate and preparation method of chocolate
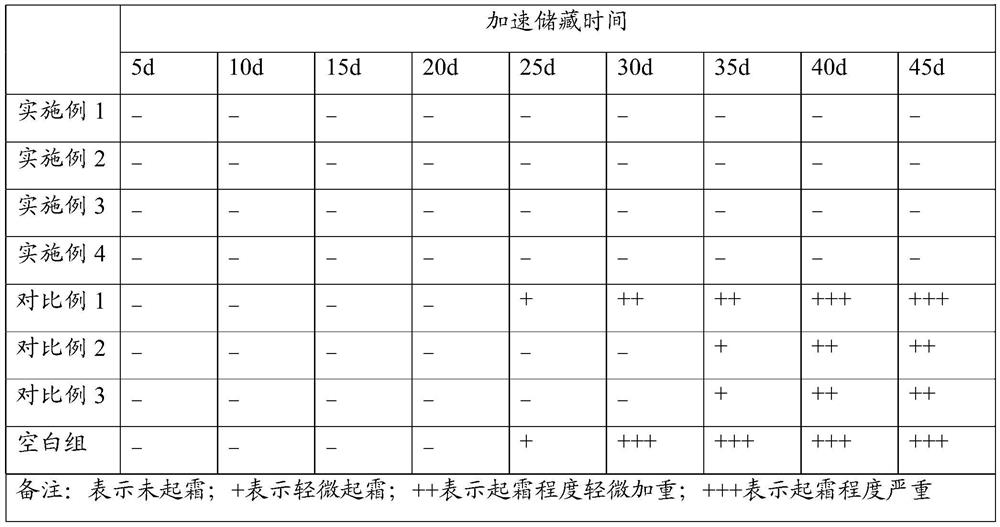
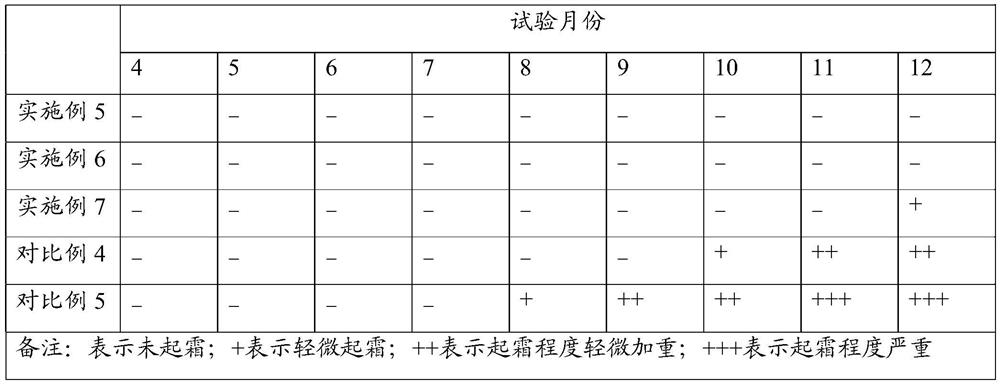
The invention is suitable for the technical field of food processing, and provides frost-resistant oil and a preparation method thereof, chocolate and a preparation method of the chocolate. The preparation method of the frost-resistant oil comprises the steps of: carrying out tertiary fractionation treatment on shea butter by taking an organic solvent as a medium to obtain shea butter tertiary stearin; mixing the shea butter tertiary stearin with oil-soluble tea polyphenols, solid palm oil and a cocoa butter substitute evenly, wherein the mass ratio of the shea butter tertiary stearin to the oil-soluble tea polyphenols to the solid palm oil to the cocoa butter substitute is (26-37):(2-4):(3-5):(11-21); and adding 1.5-5.5% by mass of candida rugosa lipase, and carrying out enzymatic transesterification to obtain frost-resistant oil. The prepared frost-resistant oil is added to an existing chocolate food system, so that production of frost flowers in the chocolate food system can be effectively inhibited, and meanwhile, the color, taste and texture of the chocolate can also be improved to a certain extent.
Owner:汕头市甜甜乐糖果食品有限公司
Method for preparing wheat germ pastry margarine by employing enzymatic interesterification under supercritical CO2 condition
The invention relates to a method for preparing a wheat germ pastry margarine by employing enzymatic interesterification under a supercritical CO2 condition. In traditional production of special oil for foods such as pastry margarine, a great number of trans-fatty acids are generated by a hydrogenation process, so that an interesterification technology can be used as an effective method for producing the special oil for zero-trans fatty acids instead of a traditional hydrogenation process. Catalysis of interesterification reaction in the supercritical state by immobilized lipase is achieved through the following steps: 1. drying in vacuum for 2 hours, and adding immobilized lipase and a trochanter to a reaction kettle; 2. carrying out sealed reaction, introducing CO2 to replace air in the reaction kettle, testing leakage, and finally introducing a certain amount of CO2 to reach appointed pressure; 3. heating, and carrying out stirring timing reaction; and 4. stopping reaction, and carrying out suction filtration while hot condition exists. Wheat germ oil and extremely hydrogenated wheat germ oil are subjected to interesterification by the method disclosed by the invention; compared with conventional interesterification, the method has the advantages that the time is relatively short; and the relatively esterification activity of the immobilized lipase is kept over 90%.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Enzymatic synthesis method for fenpyroxim
InactiveCN102181496BHigh yieldEfficientFermentationBulk chemical productionEnzymatic synthesisSec-Butanol
Owner:安徽安生生物化工科技有限责任公司
Method for producing ricinoleic acid ester by selective enzymatic transesterification
InactiveCN102341503AFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningVegetable oilTransesterification reaction
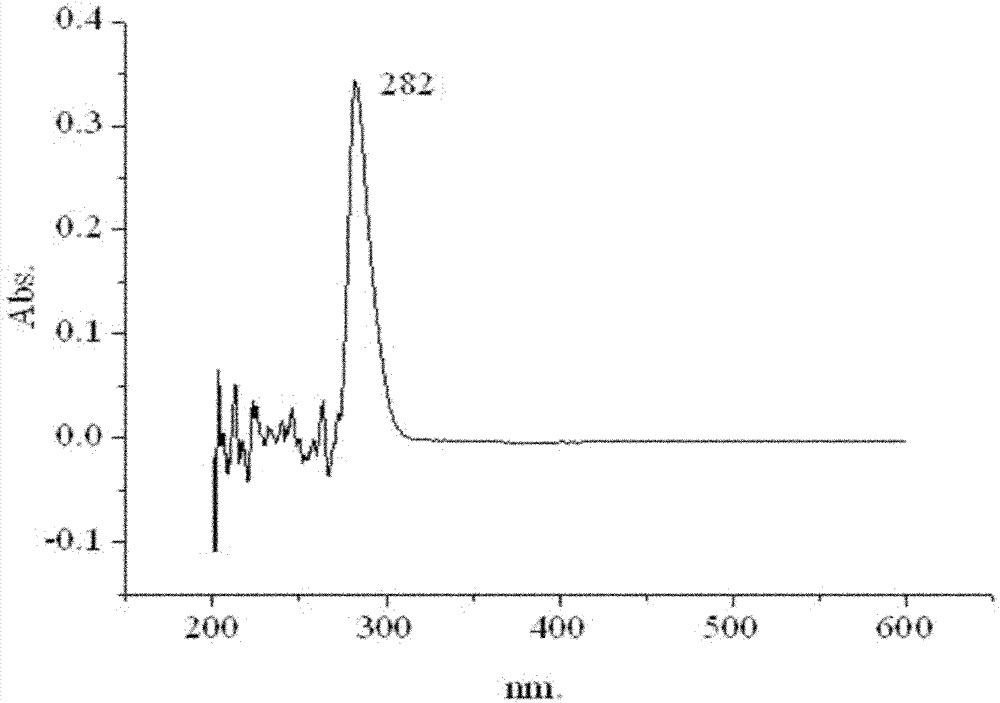
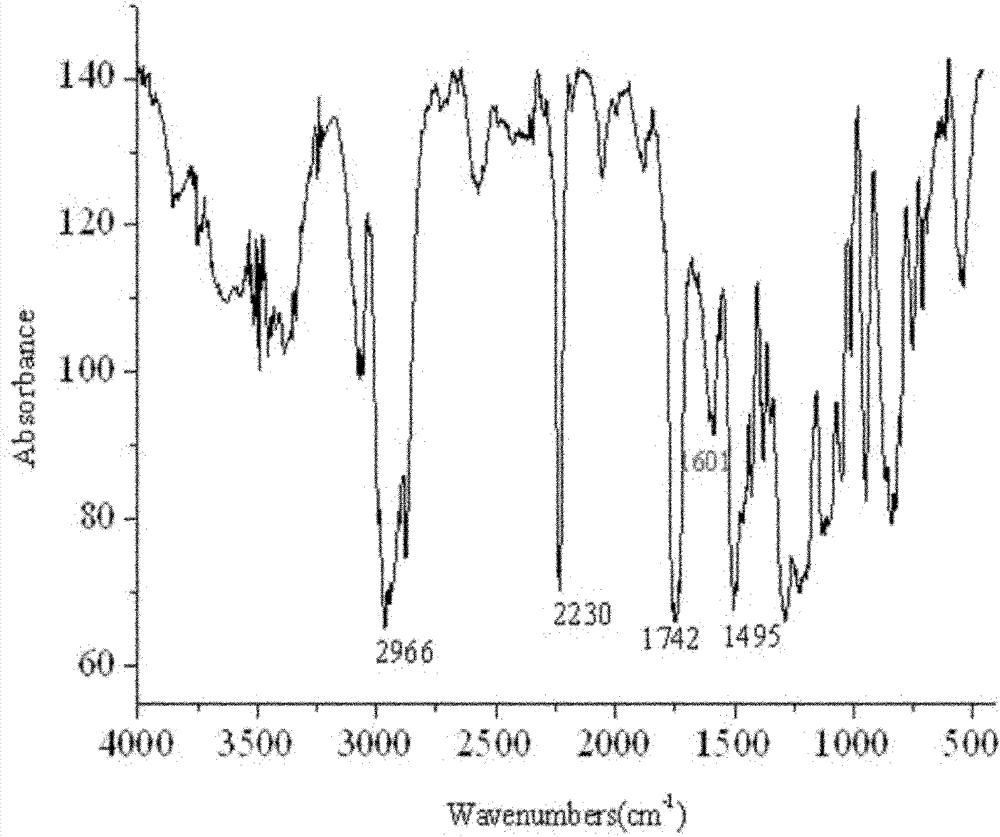
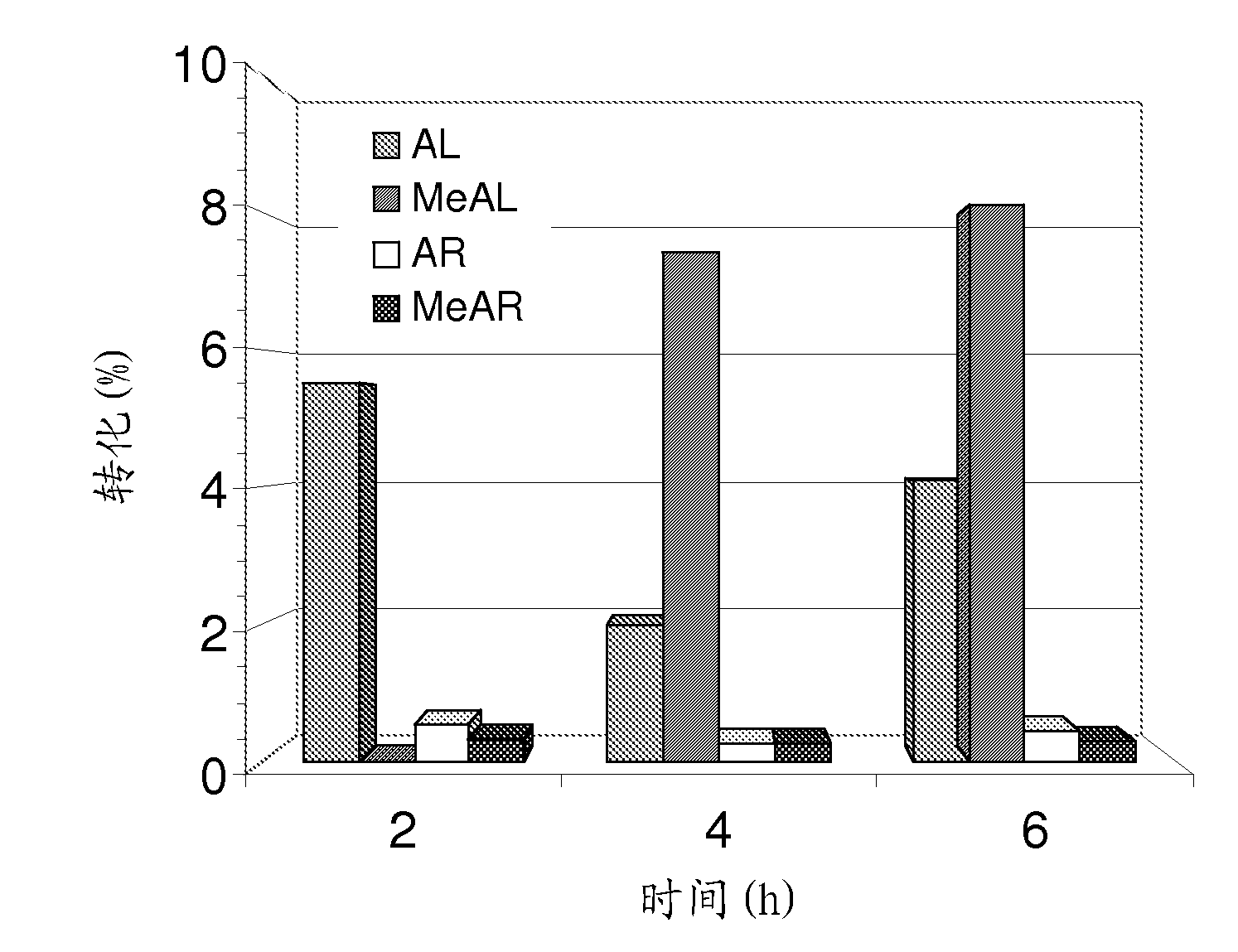
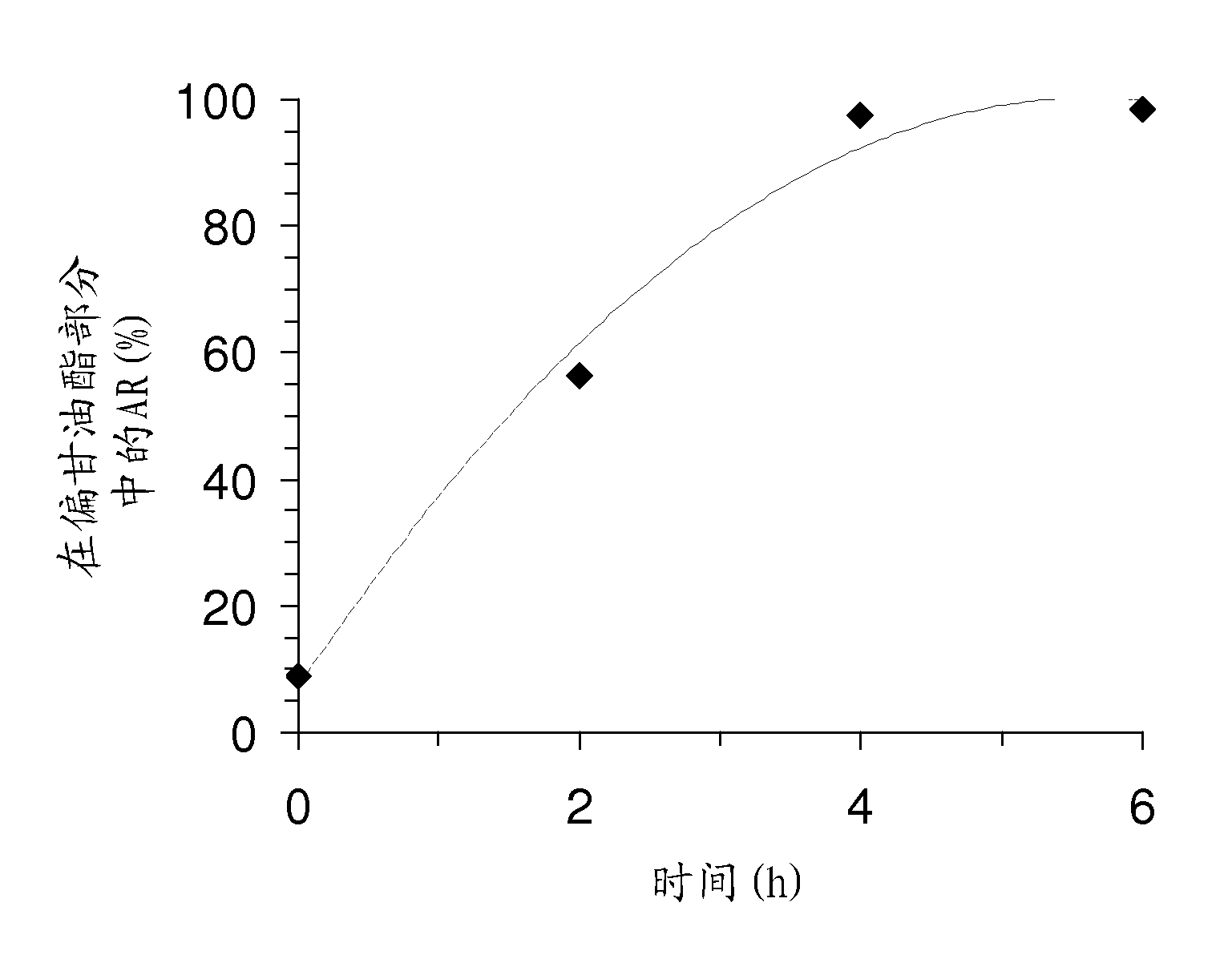
The present invention relates to a method for preparing ricinoleic acid ester from a pure or mixed vegetable oil, in particular castor oil, wherein said method includes at least the step of enzymatic transesterification in the presence of a light alcohol and using a typo-selective lipase in order to obtain a fraction enriched with ricinoleic acid ester. The method according to the invention for producing ricinoleic acid ester includes the following steps: i) a first transesterification reaction in the presence of a light alcohol and a lipase extracted from Geotrichum candidum, in order to obtain a mixture M containing AR mono-, di- and triglycerides, fatty acid esters other than AR, alcohol; ii) the step of separating said mixture M into at least two fractions, including a fraction A enriched with AR glycerides and a fraction B enriched with fatty acid esters other than AR; iii) the step of converting said AR glycerides into AR esters consisting of a fraction C rich in AR esters and a fraction rich in alcohol.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com