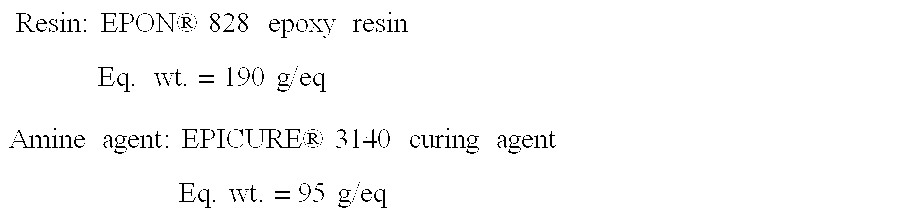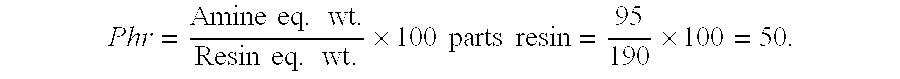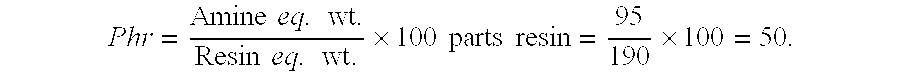Patents
Literature
119 results about "Ion selective membrane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
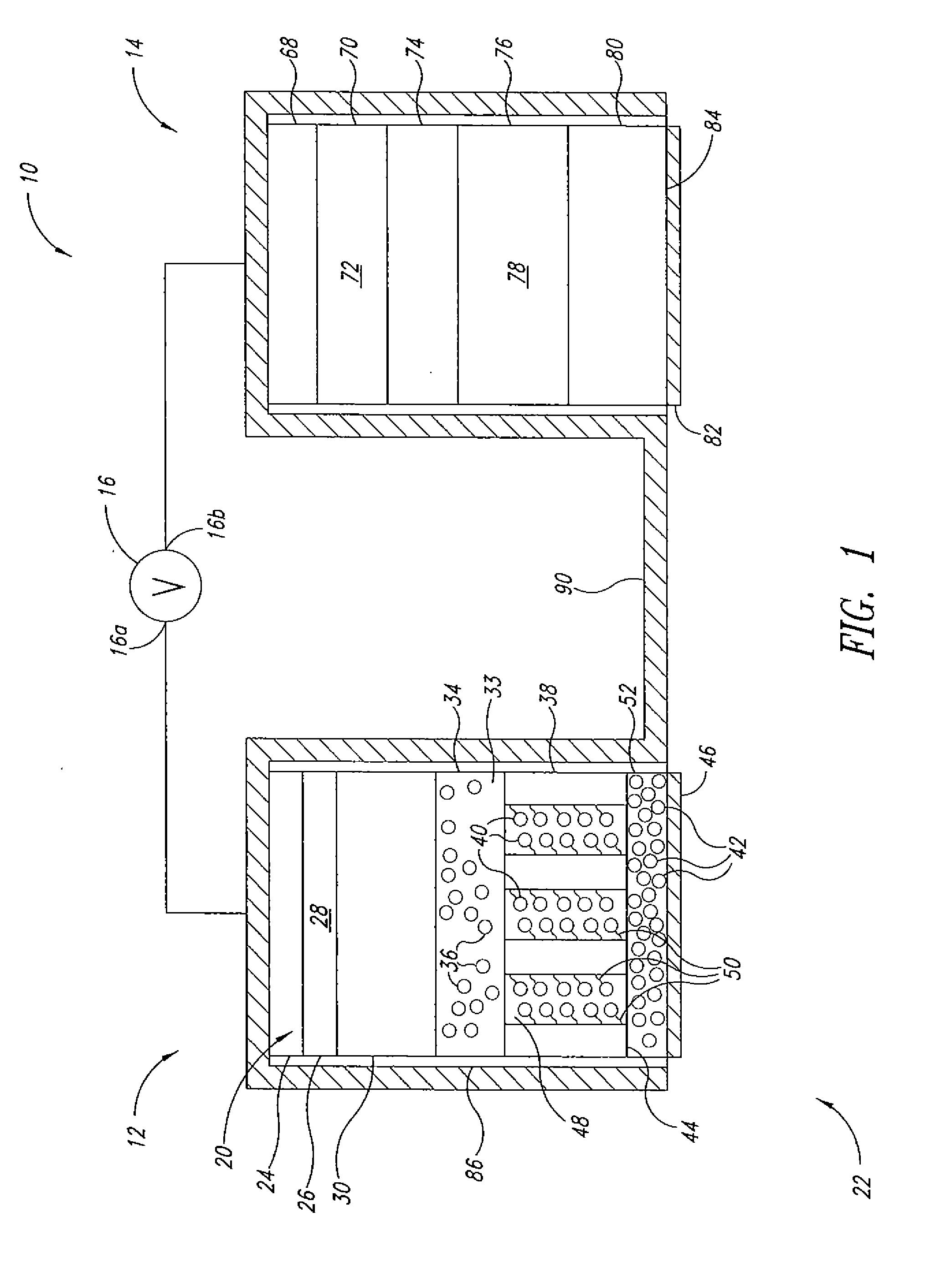
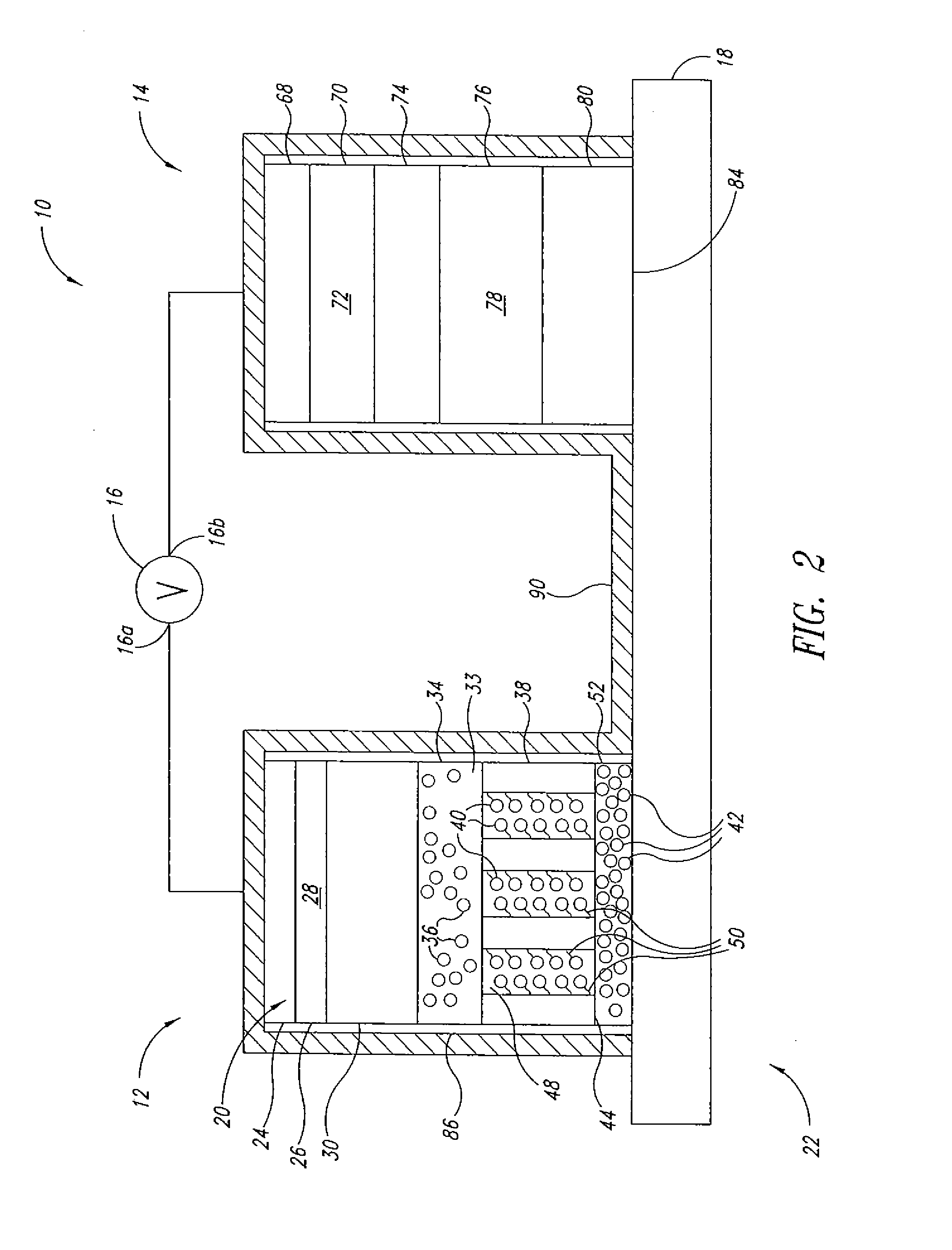
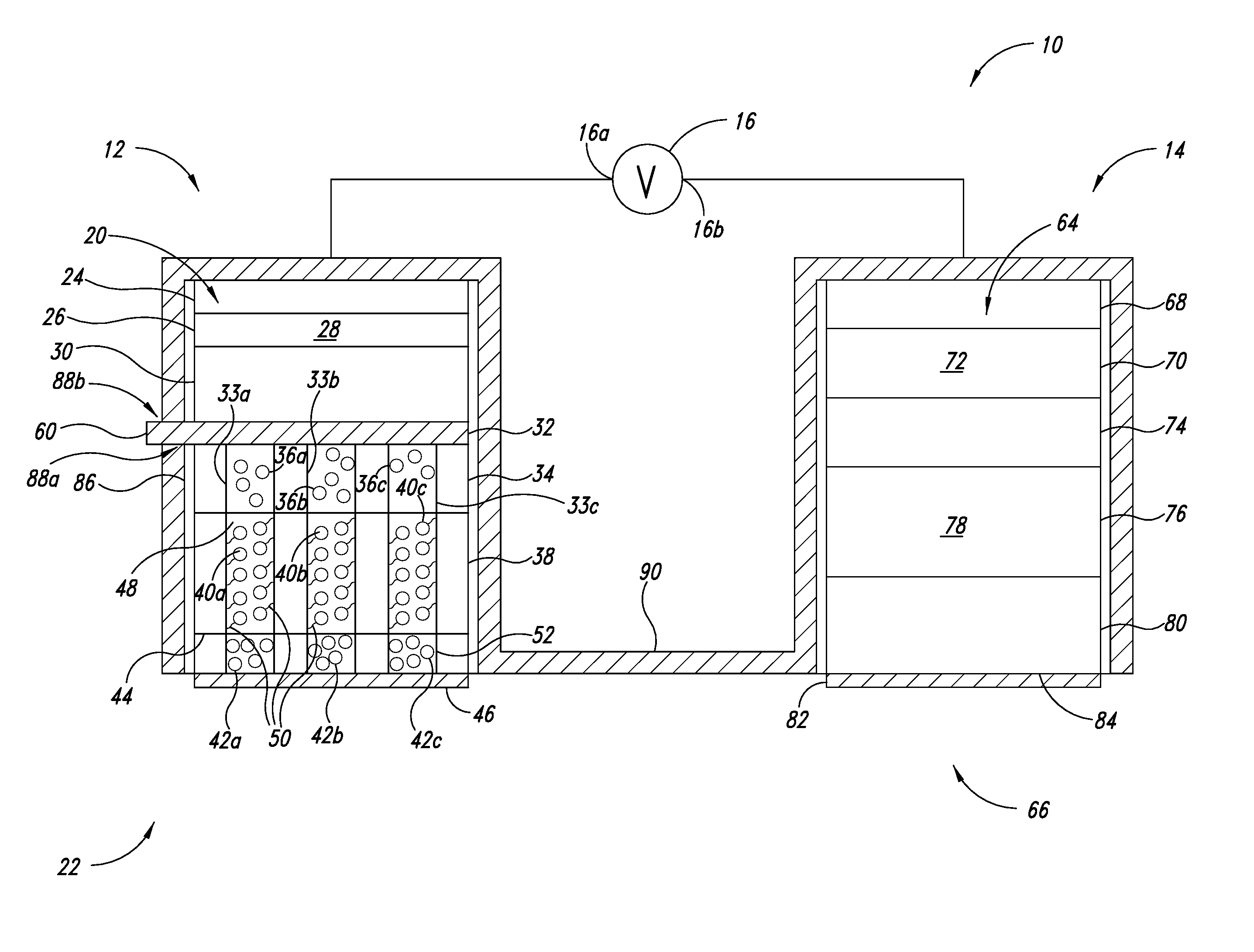
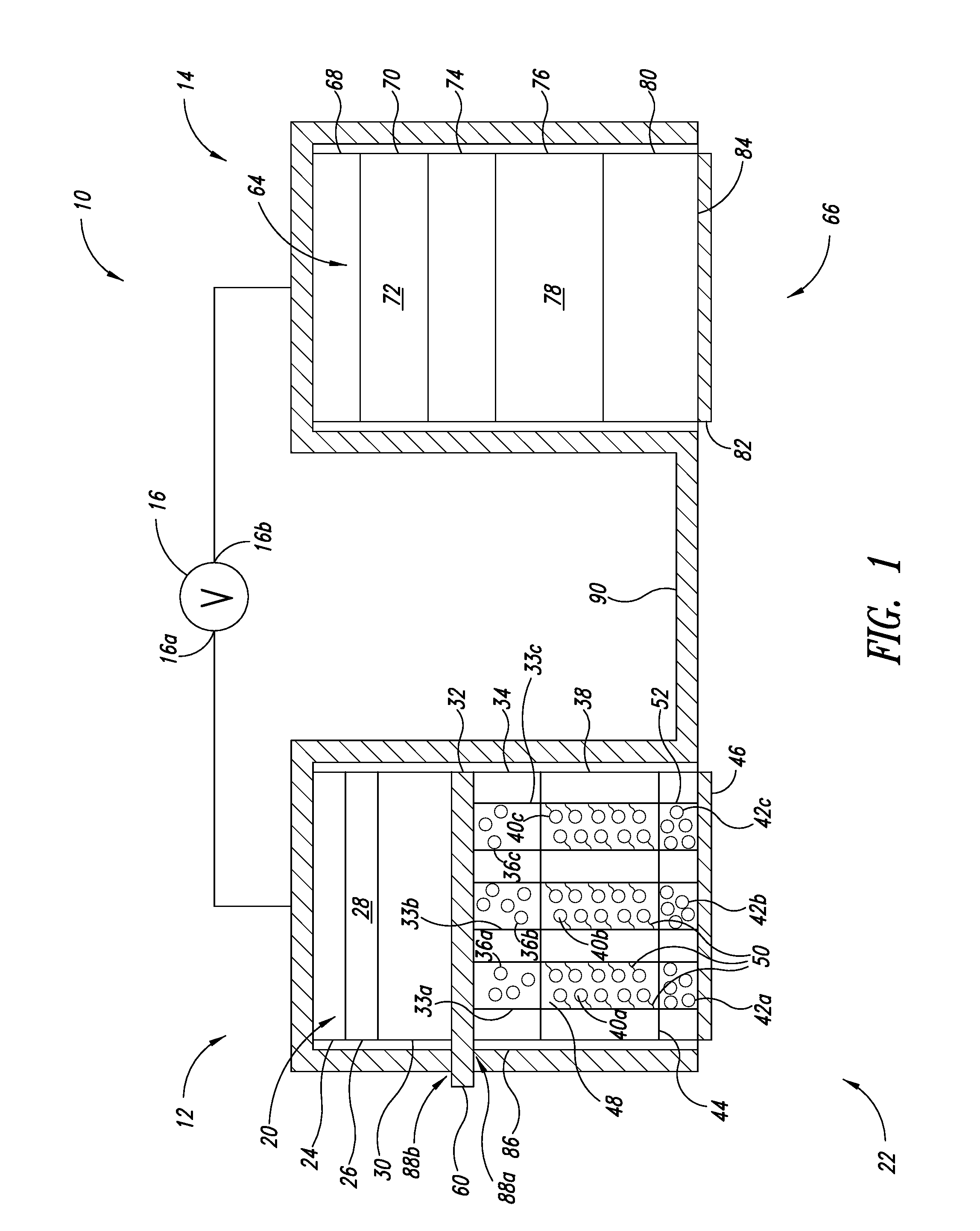
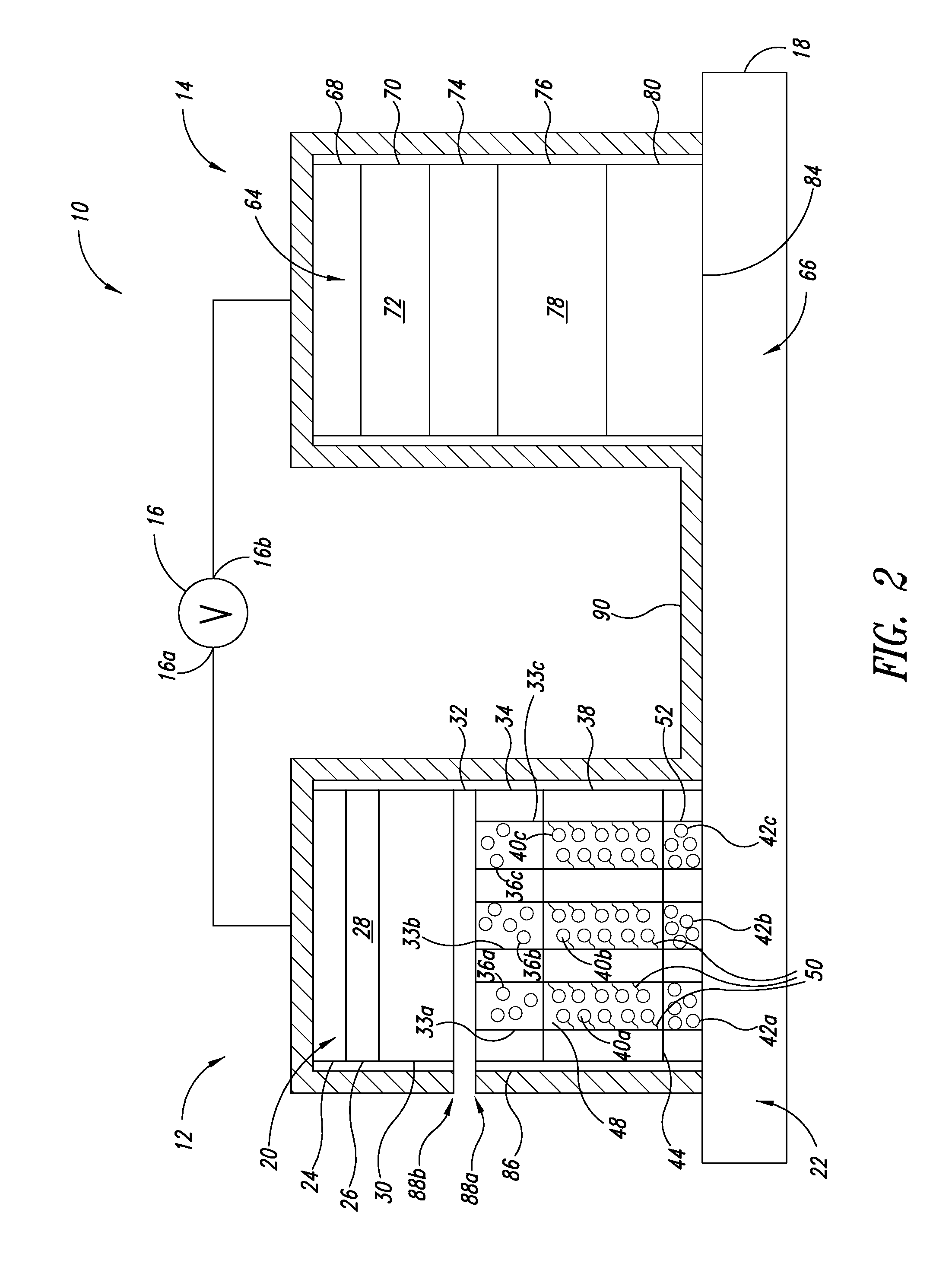
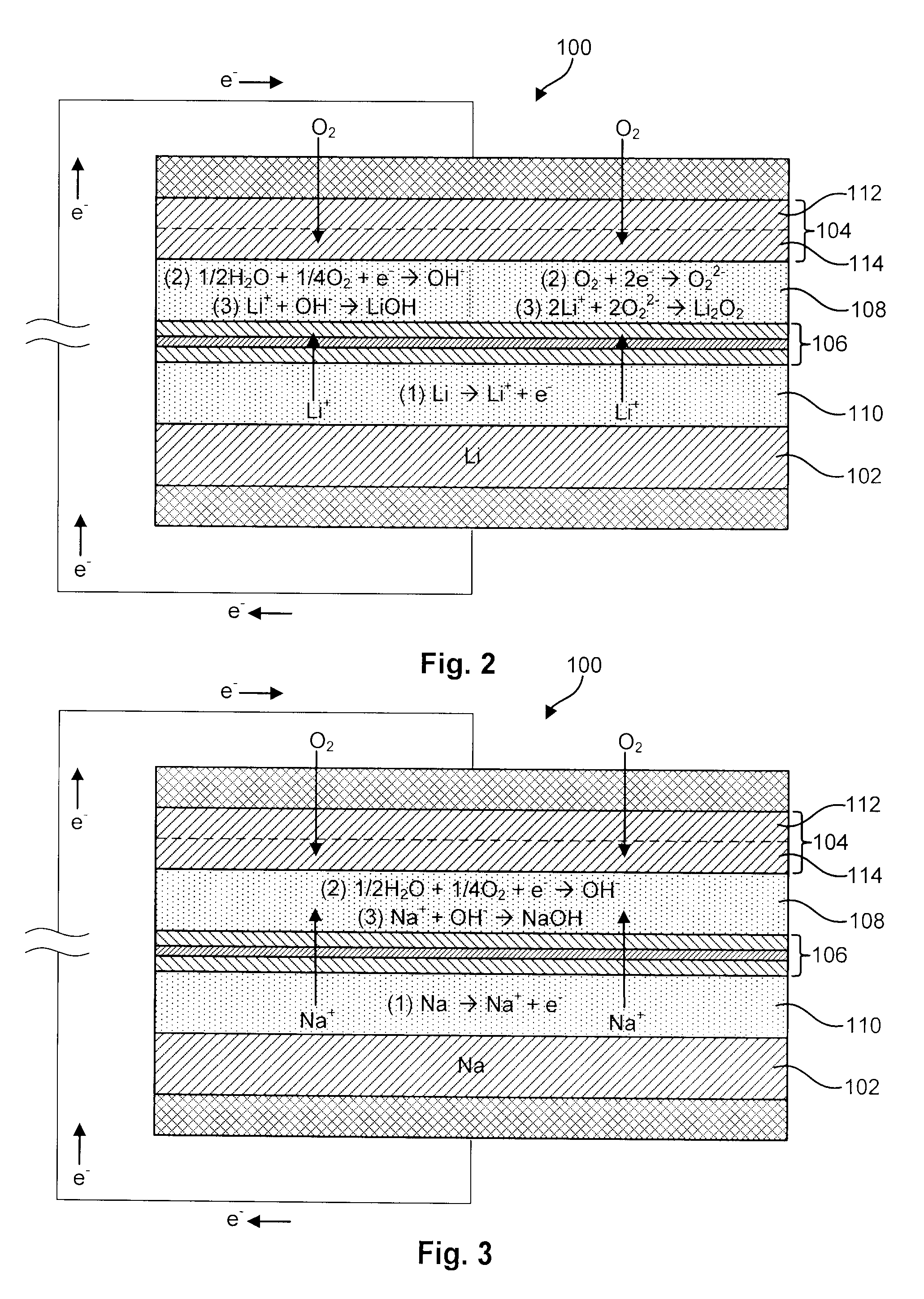
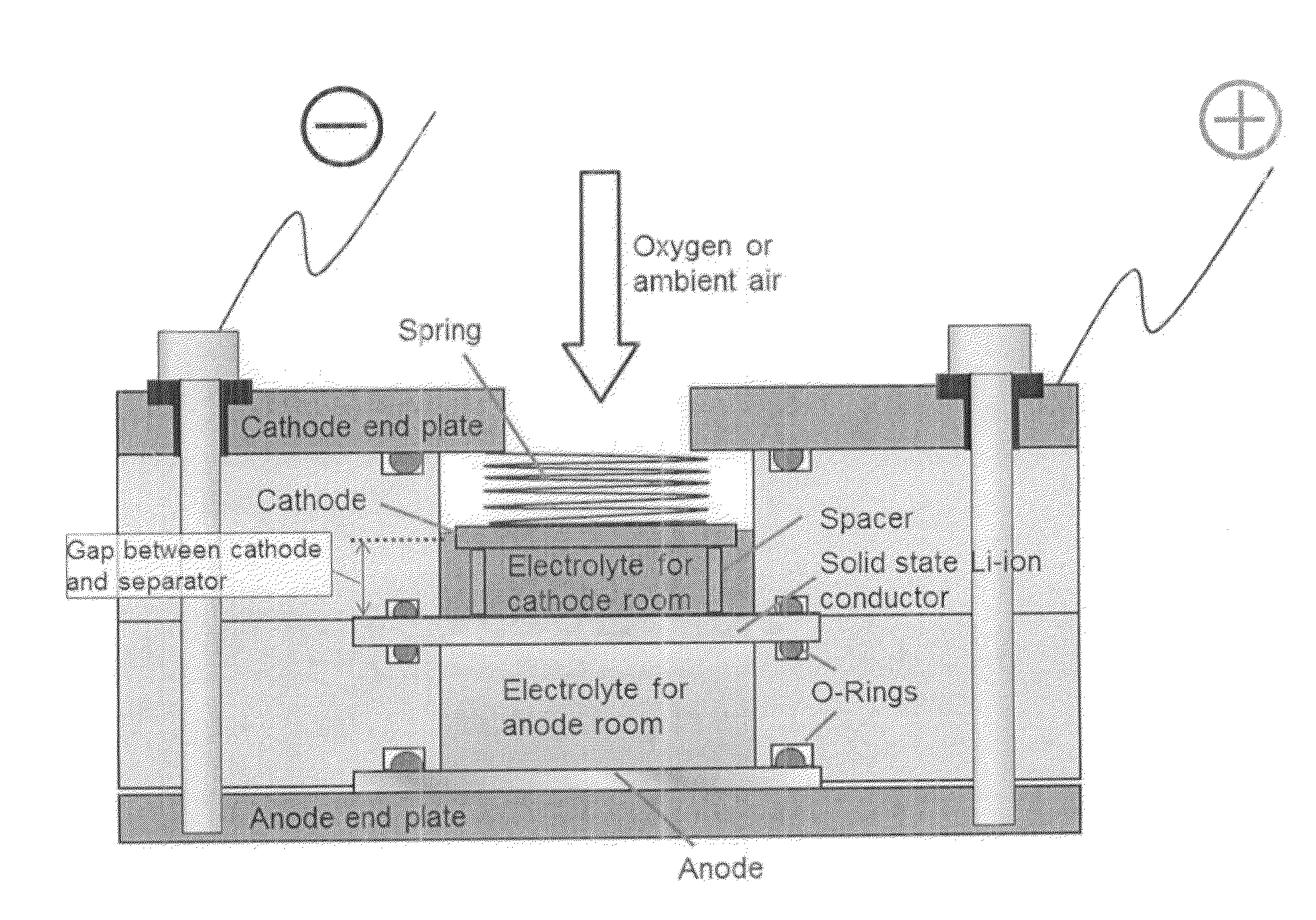
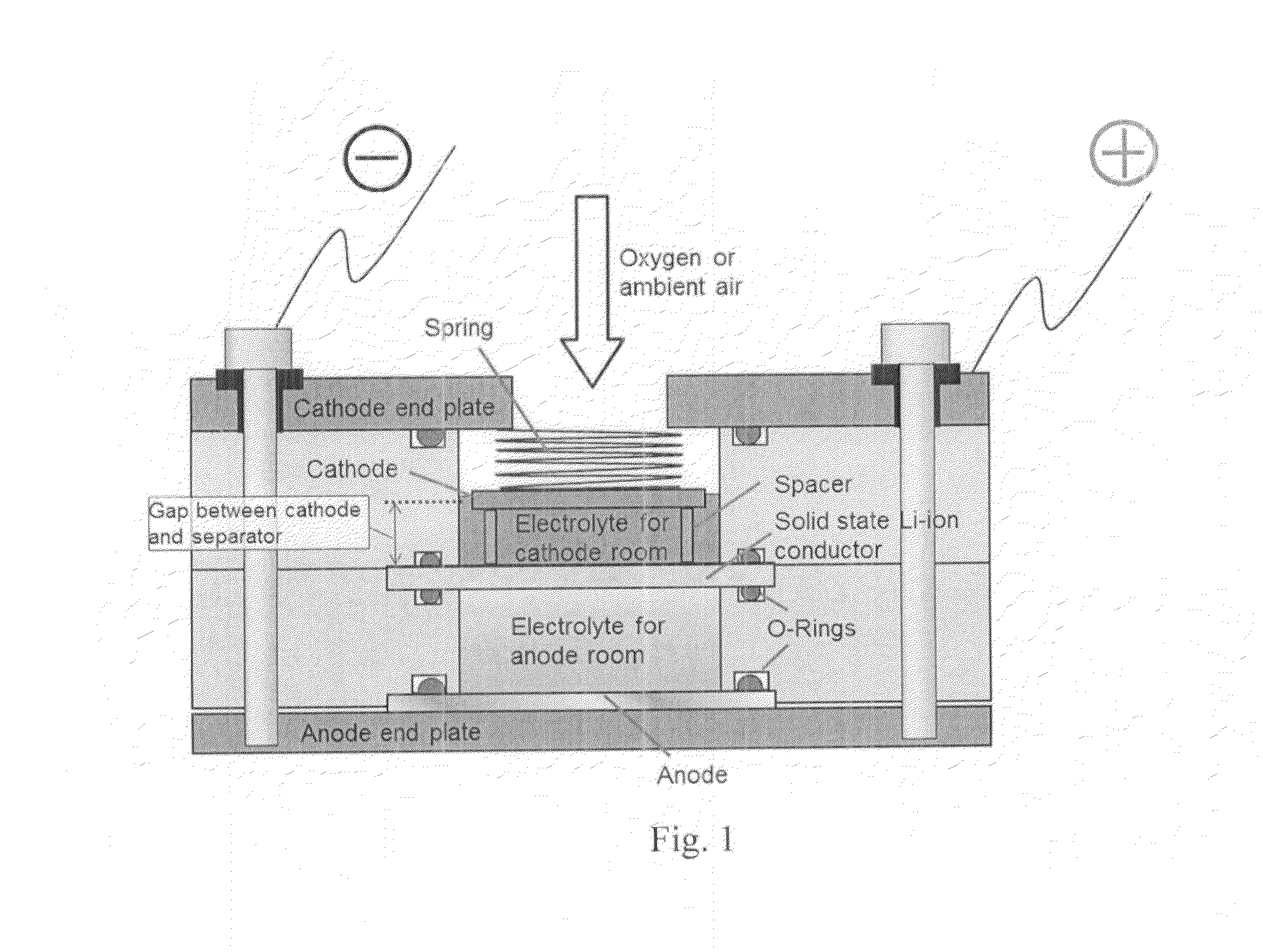
Advanced Metal-Air Battery Having a Ceramic Membrane Electrolyte Background of the Invention
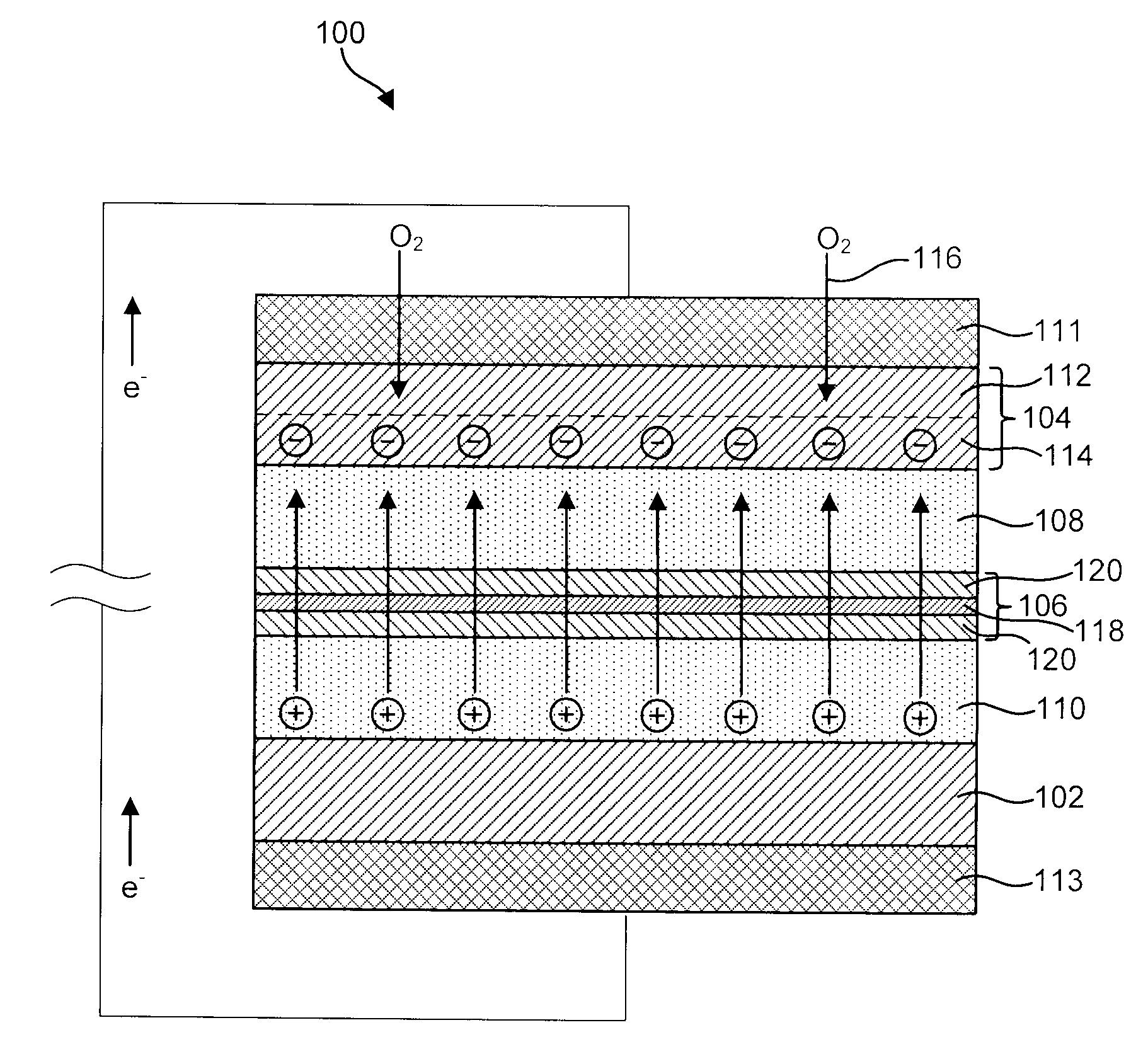
ActiveUS20080268327A1Reduce oxygenReduce layeringFuel and primary cellsSolid electrolytesOxygenCeramic membrane
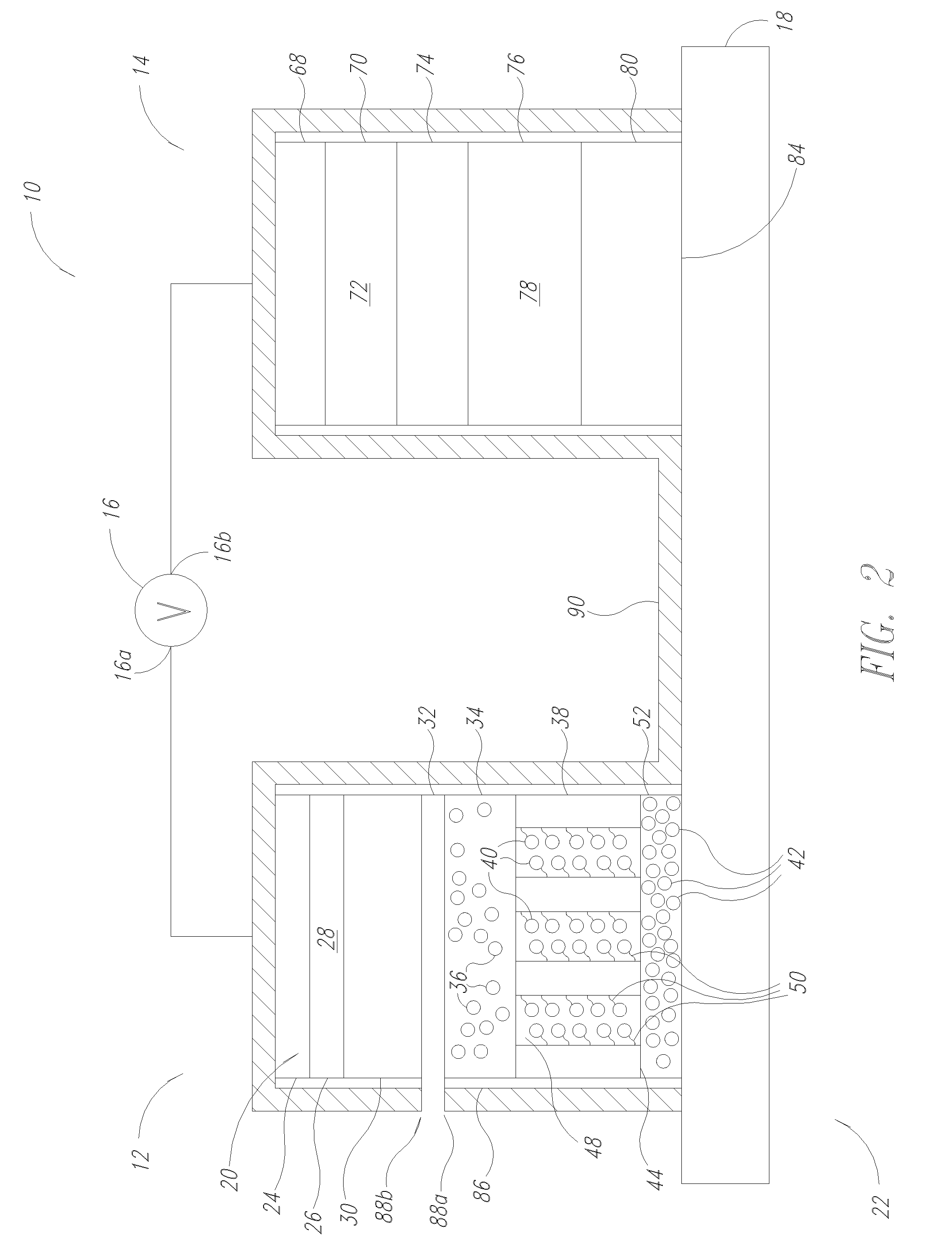
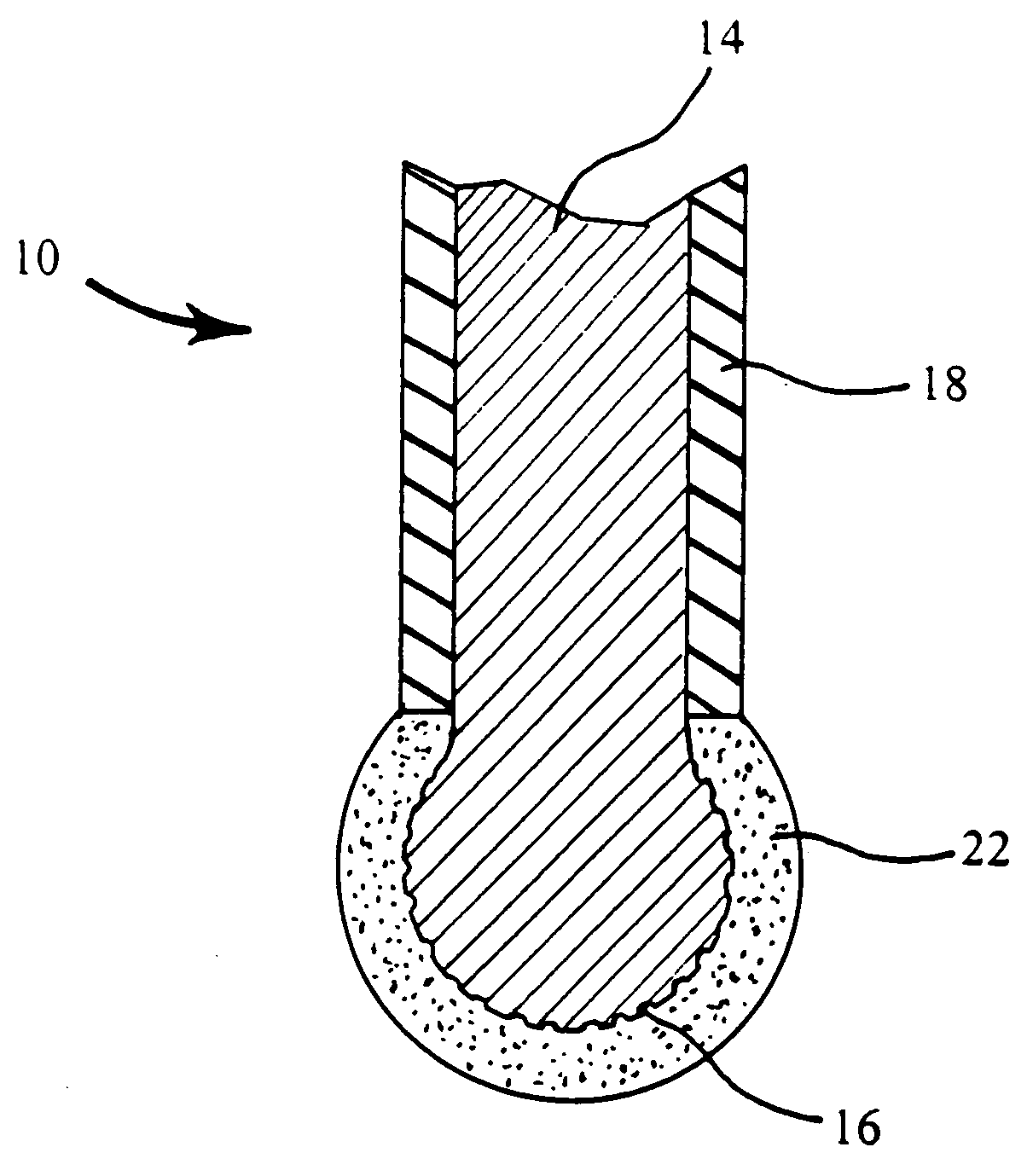
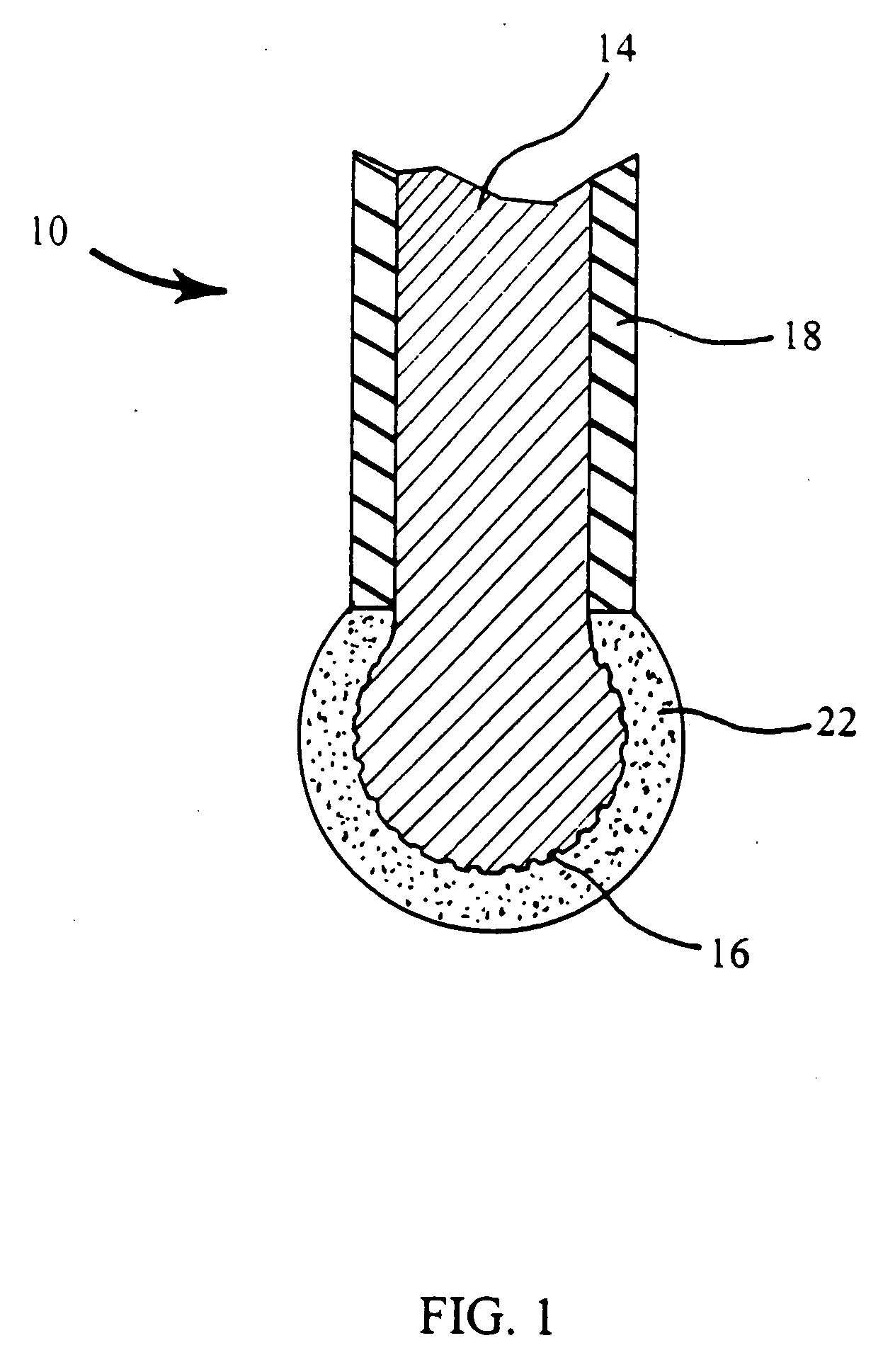
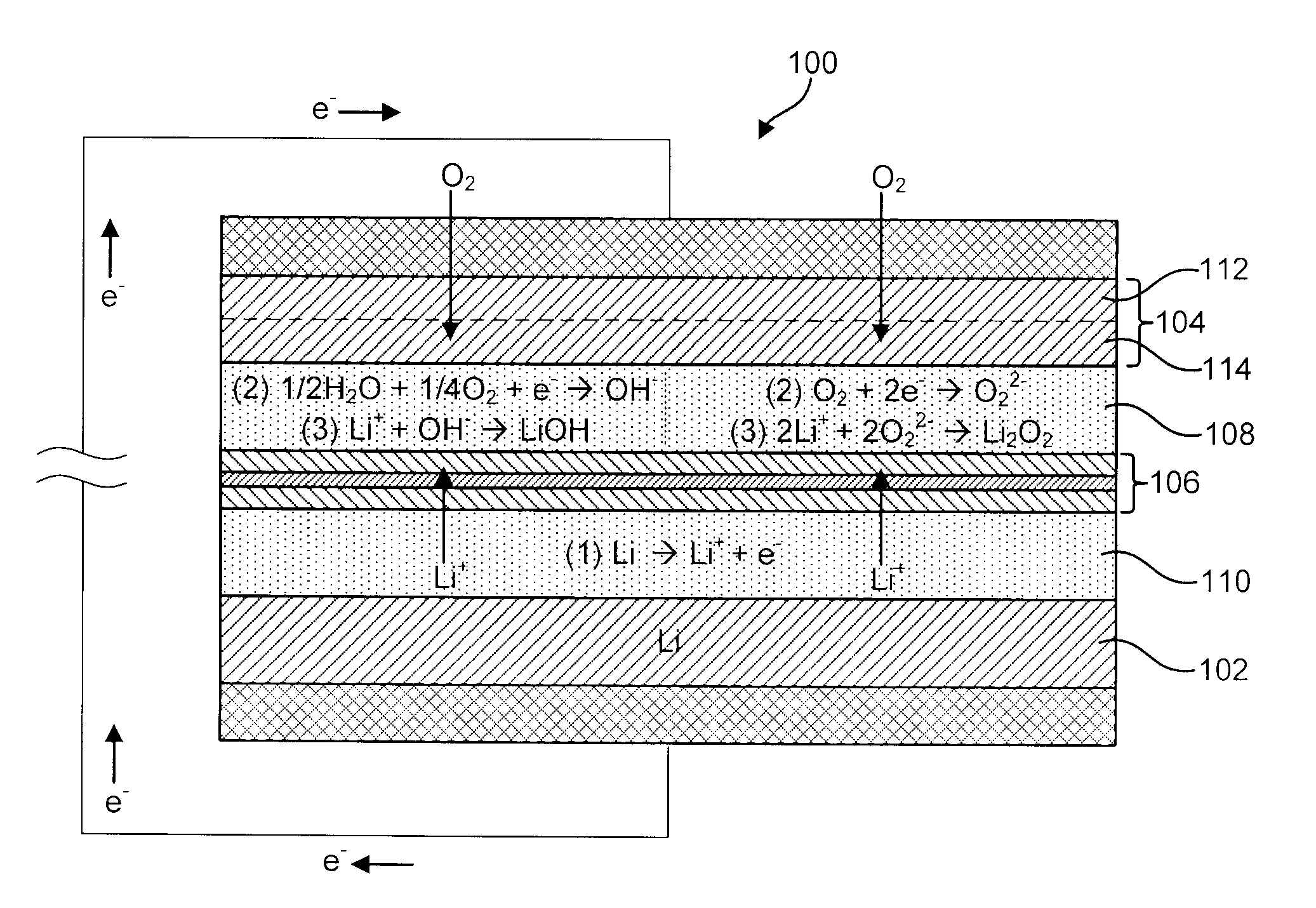
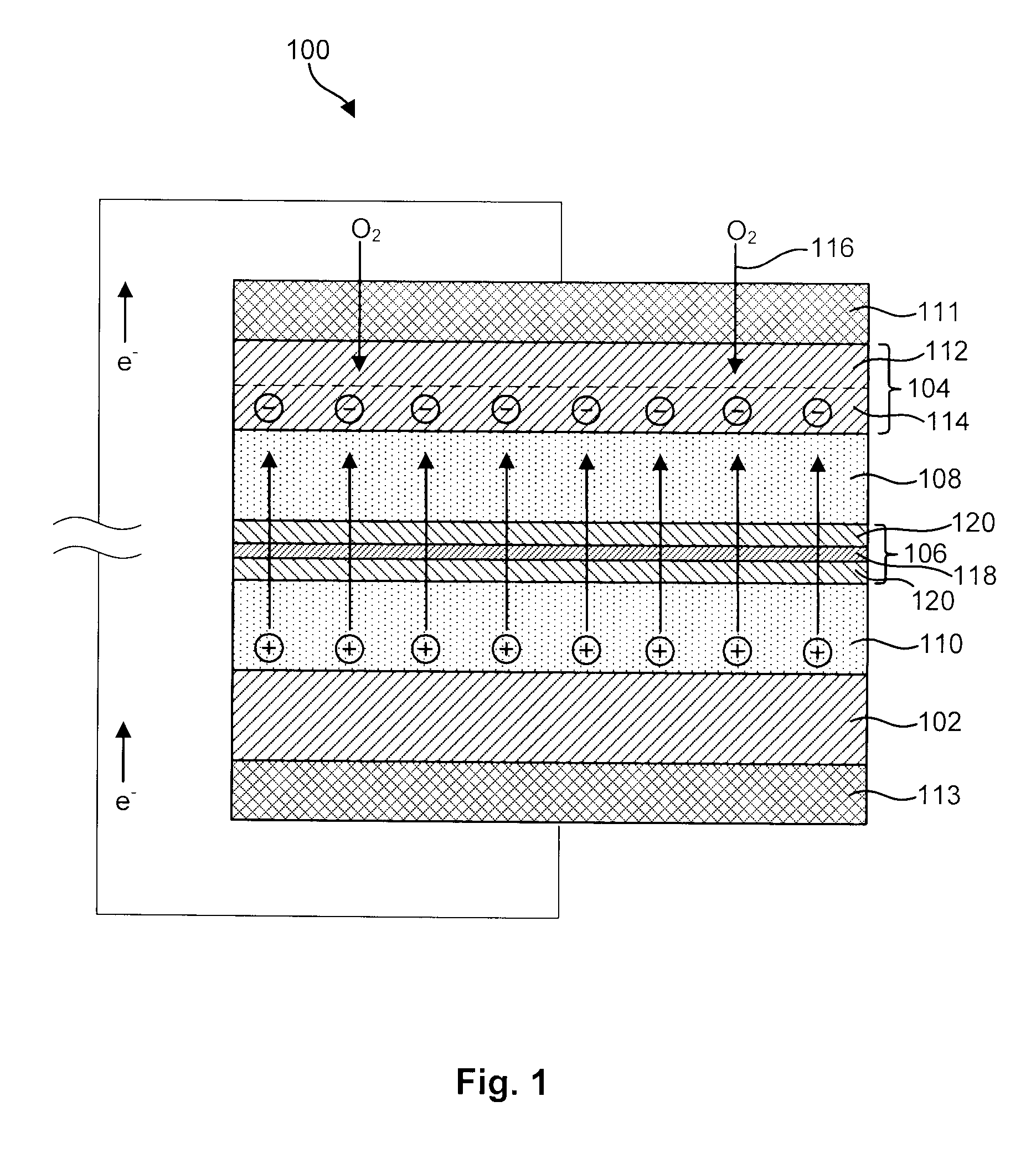
A metal-air battery is disclosed in one embodiment of the invention as including a cathode to reduce oxygen molecules and an alkali-metal-containing anode to oxidize the alkali metal (e.g., Li, Na, and K) contained therein to produce alkali-metal ions. An aqueous catholyte is placed in ionic communication with the cathode to store reaction products generated by reacting the alkali-metal ions with the oxygen containing anions. These reaction products are stored as solutes dissolved in the aqueous catholyte. An ion-selective membrane is interposed between the alkali-metal containing anode and the aqueous catholyte. The ion-selective membrane is designed to be conductive to the alkali-metal ions while being impermeable to the aqueous catholyte.
Owner:FIELD UPGRADING USA INC
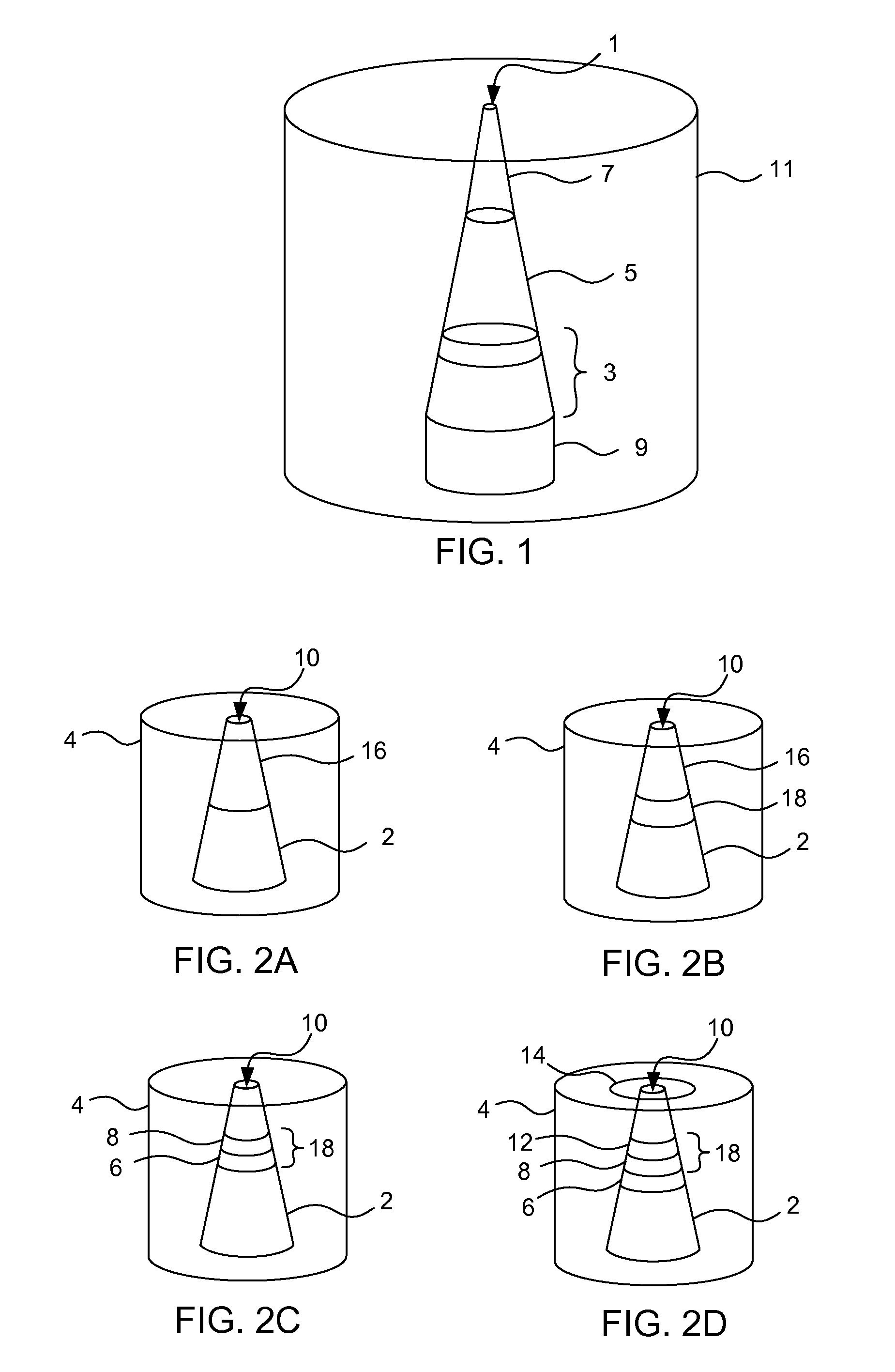
Iontophoretic device and method of delivery of active agents to biological interface
InactiveUS20070083185A1Increase loadImproved release characteristicElectrotherapyMedical devicesActive agentElectrolyte composition
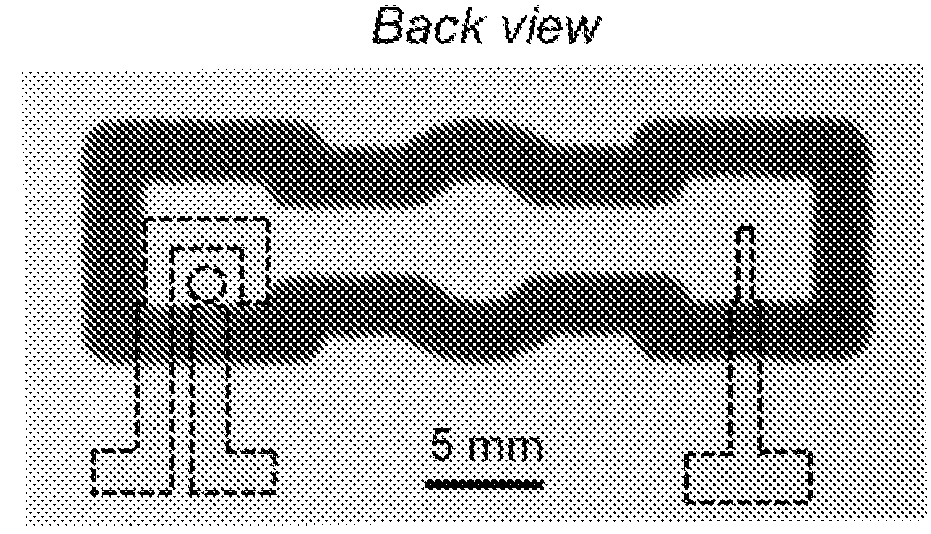
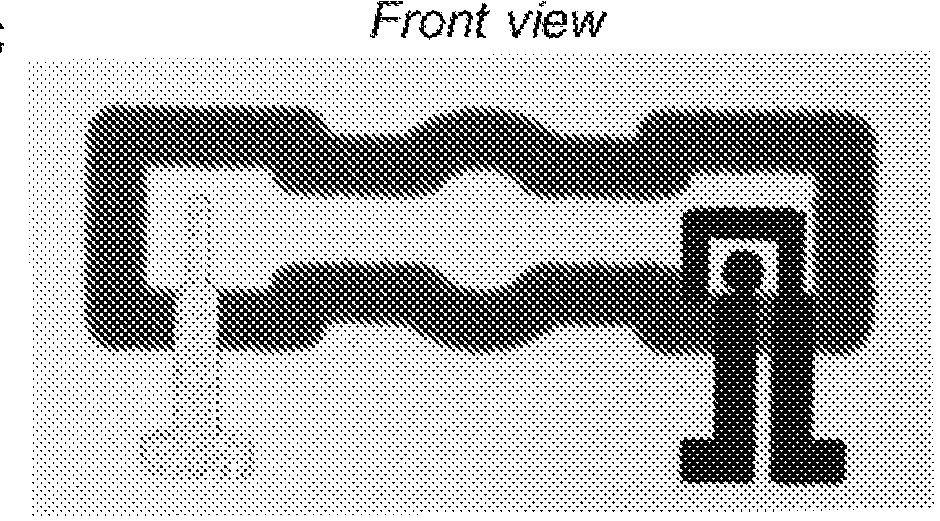
An iontophoresis device includes an active electrode element operable to provide an electrical potential; an electrolyte reservoir comprising an electrolyte composition; an inner active agent reservoir comprising a gel matrix and distributed in said gel matrix, a first positively charged active agent; an inner ion selective membrane deposed between said electrolyte reservoir and said inner active agent reservoir; and an outermost ion selective membrane having an outer surface, the outer surface being against the biological interface, wherein, the gel matrix comprises a hydrophilic polycarboxylated polymer having net negative charges.
Owner:TITI ELLEBEAU INC
Iontophoresis device to deliver multiple active agents to biological interfaces
An iontophoresis device includes active and counter electrode assemblies. The active electrode assembly includes an active electrode element and at least two laterally spaced active agent reservoirs. The active electrode assembly may also include an outermost ion selective membrane caching an active agent and a further active agent carried by an outer surface of the outermost ion selective membrane. The active electrode assembly may also include an electrolyte reservoir storing electrolyte and an inner ion selective membrane positioned between the electrolyte reservoir and the active agents. The active electrode may also include an inner withdrawable sealing liner between the electrolyte reservoir and the active agents. An outer release liner may protectively cover or overlay the further active agent and / or outer surface prior to use. The active electrode assembly may also include a blister pack of at least two hydrating agent blisters to selectively hydrate dehydrated active agent.
Owner:TITI ELLEBEAU INC
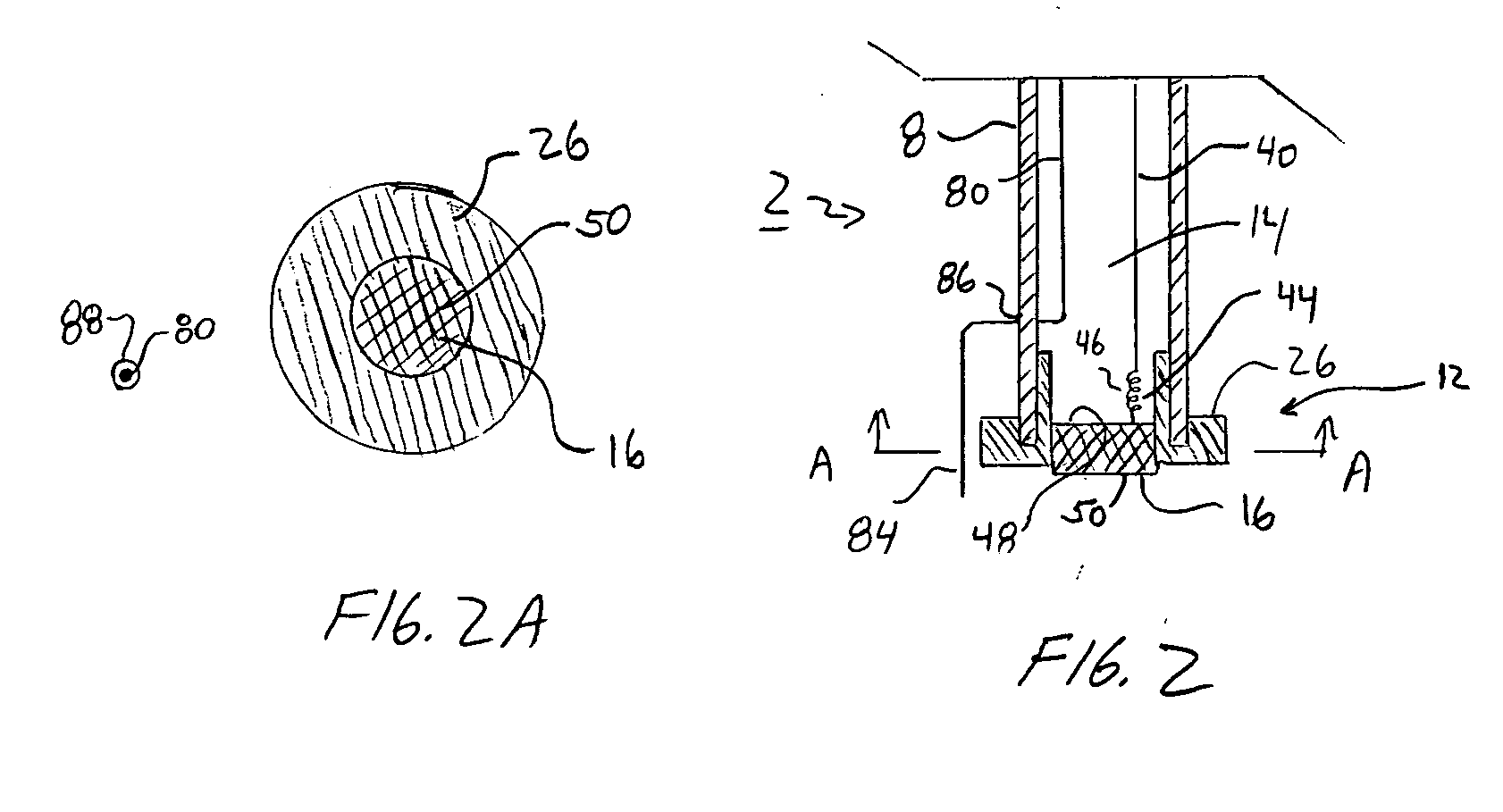
Sensor Apparatus
InactiveUS20140158536A1Coaxial cables/analogue cablesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPolyvinyl chlorideEngineering
In the present invention, the solid contacted ISE and the solid contacted reference are based on a conductive porous network with a solid contact and membrane disposed thereon. The porous networks are not only mechanically stable, but also provide pore structure for the solid contact and membrane to intercalate, which enhances the life time and stability of the sensors. The invention further incorporates a unique fluidic fitting sensor and sealing mechanism so that measurements can be taken at high pressures. The fitting design has many benefits, such as low cost and disposability, which allows them to be mass manufactured. These sensors can be produced for detection of many different kinds of ions by applying different types of ion selective membranes, including polyvinylchloride (PVC) based ion-selective membranes and fluorous matrixes based ion-selective membranes.
Owner:UNITED SCI LLC
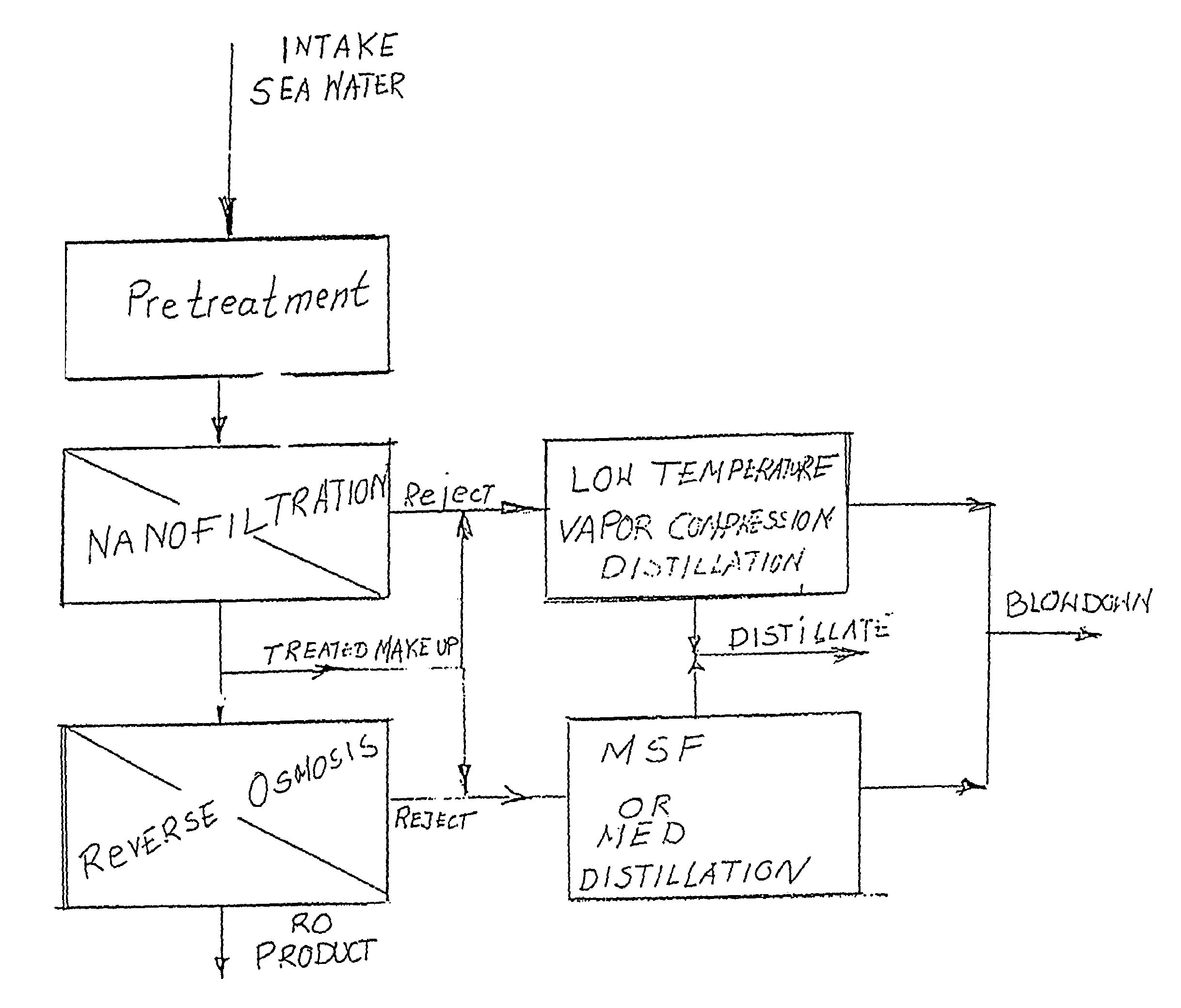
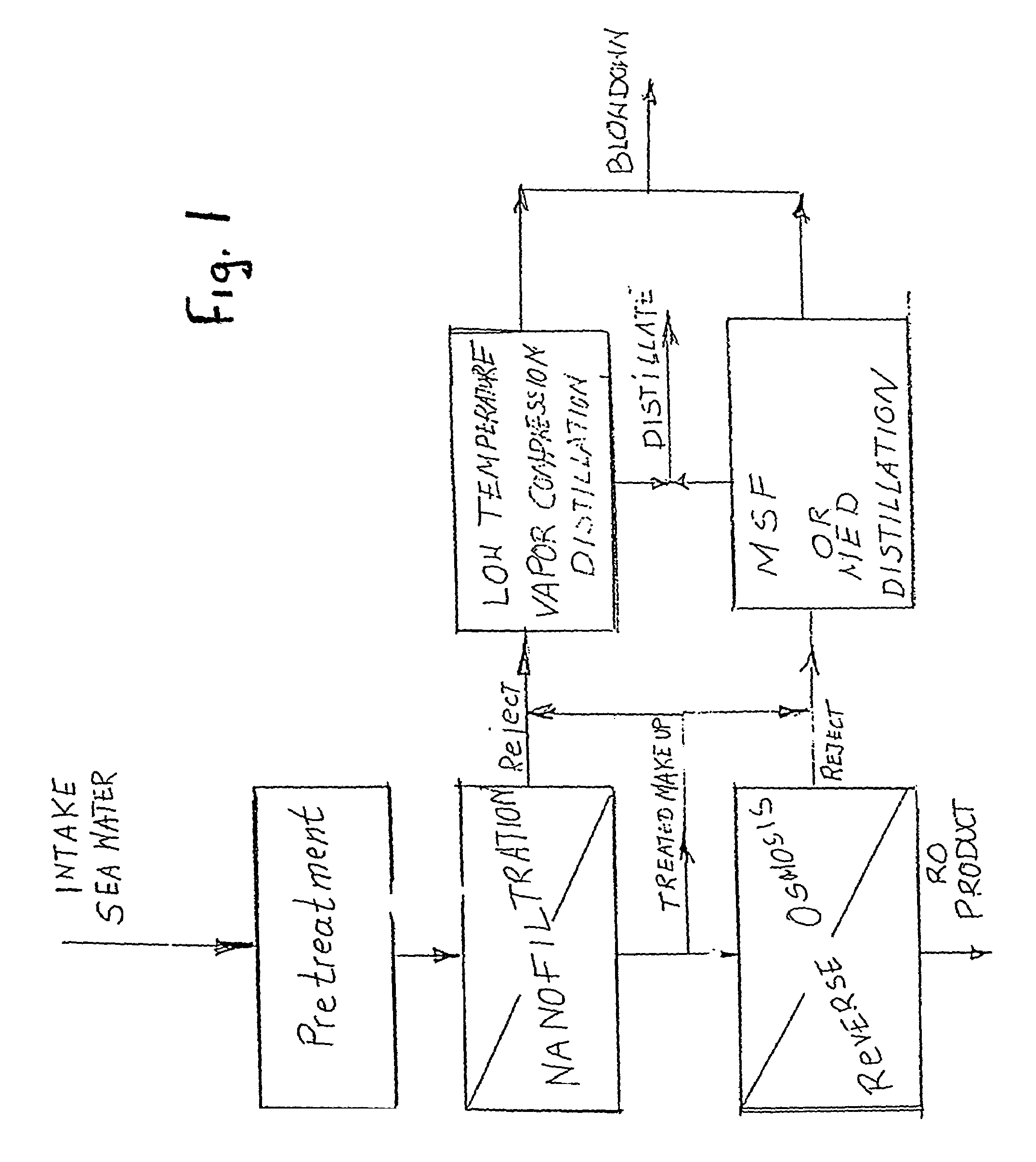
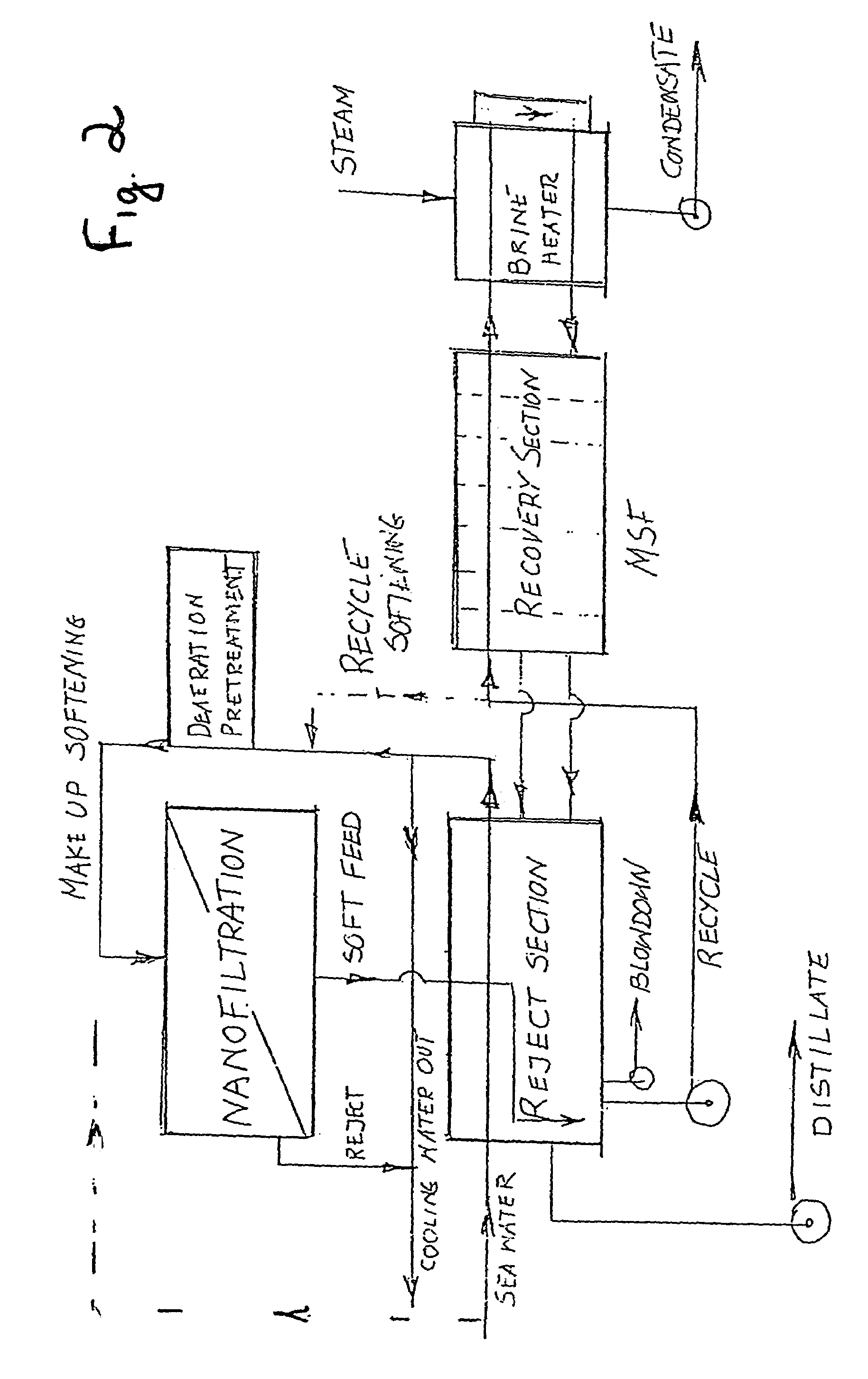
Water desalination process using ion selective membranes
InactiveUS6998053B2OperationReduce energy consumptionMembranesGeneral water supply conservationSaline waterWater desalination
The invention is directed to an improved desalination process to produce potable water. The process represents an improvement of hybrid of membrane and desalination technologies. The improvement of the invention comprises the operation of an ion selective membrane at a variable pressure as a function of the cost of electricity to form a softened salt water that is blended in variable proportions, to increase the top operating temperature of the desalination system and increase recovery of potable water, with untreated salt water.
Owner:L E T LEADING EDGE TECH LTD
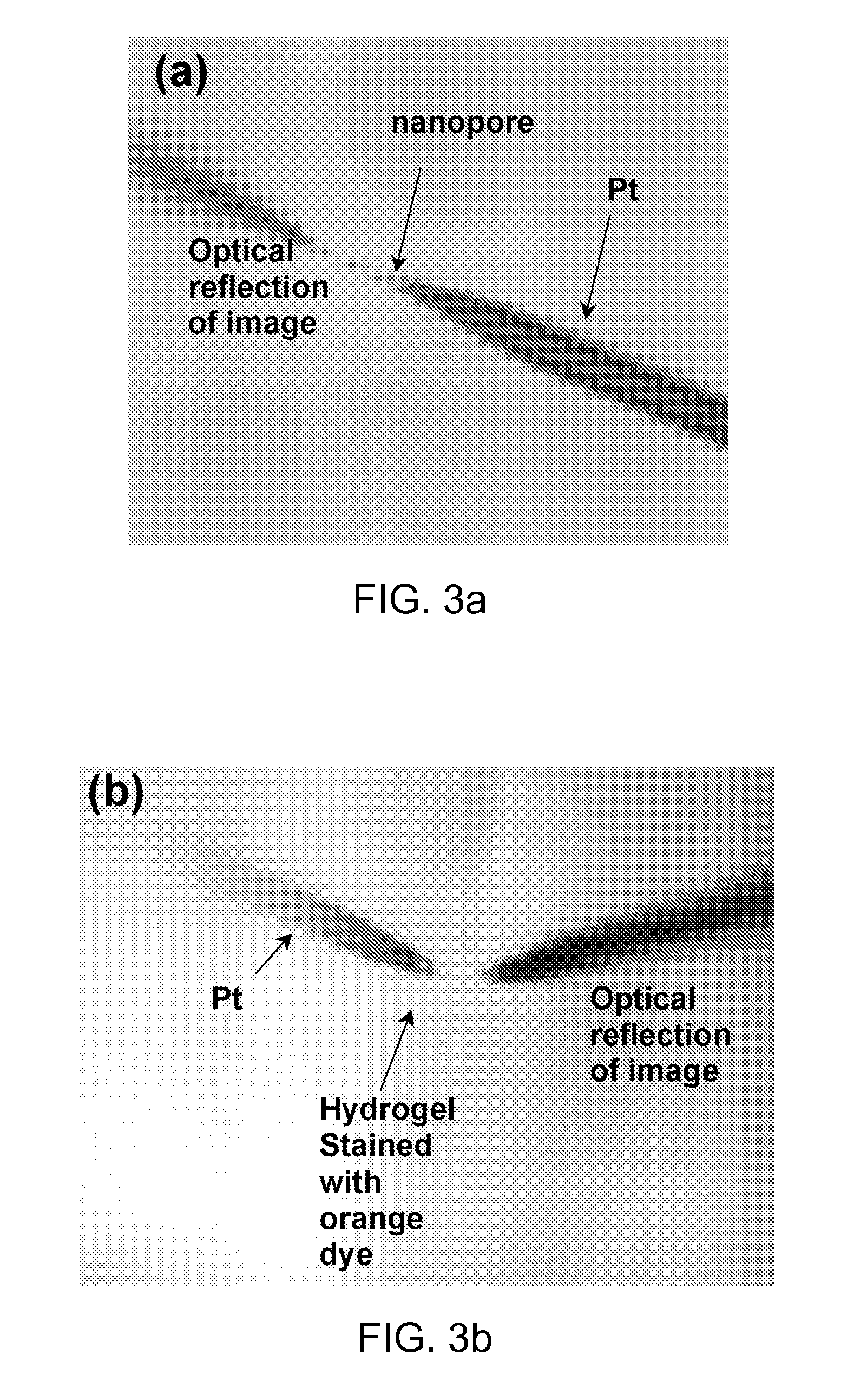
Nanopore based ion-selective electrodes
Nanopore based ion-selective electrodes and methods of their manufacture as well as methods for their use are disclosed and described. The nanopore based ion-selective electrode can include a pore being present in a solid material and having a nanosize opening in the solid material, a metal conductor disposed inside the pore opposite the opening in the solid material, a reference electrode material contacting said metal conductor and disposed inside the pore, a conductive composition in contact with the reference electrode and disposed in the pore, and an ion-selective membrane. The ion-selective membrane can be configured to isolate the metal conductor, reference electrode material, and conductive composition together within the pore.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Iontophoresis apparatus and method to deliver active agents to biological interfaces
An iontophoresis device includes active and counter electrode assemblies. The active electrode assembly includes an active electrode element, an outermost ion selective membrane caching an active agent and a further active agent carried by an outer surface of the outermost ion selective membrane. The active electrode assembly may also include an inner active agent reservoir storing additional active agent, an electrolyte reservoir storing electrolyte, an inner ion selective membrane positioned between the electrolyte reservoir and the active agents. The active electrode may also include an inner withdrawable sealing liner between the electrolyte reservoir and the active agents. An outer release liner may protectively cover or overlay the further active agent and / or outer surface prior to use.
Owner:TITI ELLEBEAU INC
Ion-selective solid-state polymeric membrane electrondes
InactiveUS20050006237A1Strengthen membraneMinimal and no failureWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementIon selective membraneElectron
An improved ion-sensing electrode for detecting ions or polyions is provided having an electrically conducting member sheathed or coated with a layer of insulation except at an exposed, uninsulated area, where the insulation free surface of the electrically conducting member is texturized, and a polymeric membrane coated on the insulation-free surface of the electrically conducting member, where the ion selective membrane includes an ionophore. The texturized surface improves the starting EMF stability and reproducibility of the ion-sensing electrodes, and further improves membrane adherence to the electrically conducting member.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Chloride ion selective membrane and sensor
ActiveUS7384523B2High sensitivityGood choiceWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementEpoxyPolyamide
Owner:RADIOMETER AS
Ion selective electrode
InactiveUS20070144919A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical conductorSalt bridge
An ion selective electrode (ISE) includes an electrode body or housing having an ion selective membrane located at one end thereof and an indicator electrode formed at or adjacent to the ion selective membrane. A sealed vessel is disposed inside the electrode body, the sealed vessel holding an electrically conductive solution and a reference electrode conductor, wherein a portion of the reference electrode conductor is submerged in the electrically conductive solution. The ISE includes a conductive member having a proximal end and a distal end, wherein the proximal end of the conductive member terminates inside the sealed vessel and the distal end terminates outside the housing. The construction of the ISE keeps the reference electrode separate from the indicator electrode. Electrons are passed to the reference electrode via the conductive member obviating the need for a salt bridge. Importantly, no reference electrode is needed that connects to the inner membrane surface. The ISE operates on the double capacitor mechanism which is fundamentally different from the conventional Nernst redox reactions described in the prior art.
Owner:KUANG LU CHENG TRUST
Solid-state ion selective electrodes and methods of producing the same
InactiveUS20020038762A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansPolymer scienceHydrophobic polymer
The present invention relates to solid-state ion selective electrodes (ISEs), methods of producing same and devices containing same. The electrodes include: (a) an internal reference element which includes a homogenous conducting body; (b) a solid contact which includes a hydrophobic polymer, an ionophore and particles of conductive material and (c) an ion selective membrane which includes a hydrophobic polymer and an ionophore. The particles of conductive material are dispersed throughout the hydrophobic polymer of the solid contact. The method includes a the steps of: (a) providing an internal reference element which includes a homogenous conducting body; (b) preparing an emulsion which includes a hydrophobic polymer, an ionophore, particles of conductive material, and an organic solvent; (c) applying emulsion to the reference element and allowing the organic solvent to evaporate thereby causing a residue of the emulsion to form a solid contact adhering the reference element; (d) preparing a solution which includes ahydrophobic polymer, an ionophore and an organic solvent; and (e) applying the solution the solid contact and allowing the organic solvent to evaporate to form an ion selective membrane adhering the solid contact.
Owner:ADVANED MONITORING SYST
Paper-Based Reference Electrode And Potentiometric Ion Sensing
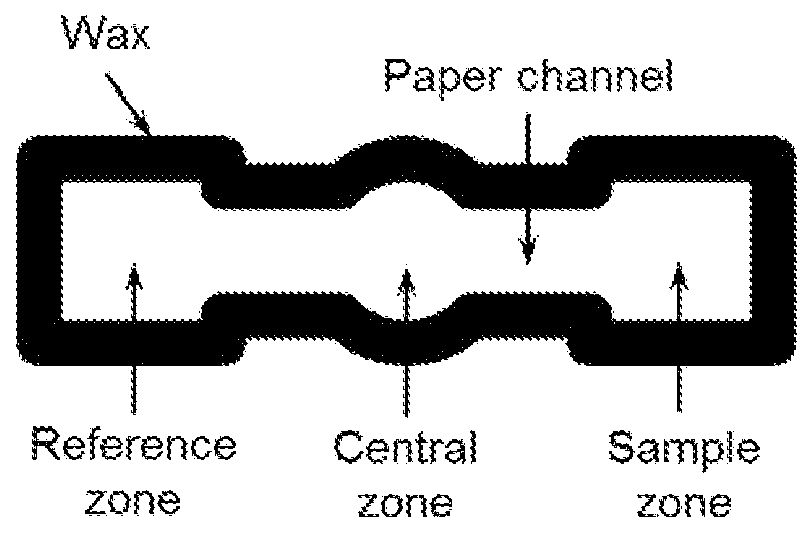
InactiveUS20160033438A1Low costSimple and affordable and disposableWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementPaper basedMicrofluidic channel
Microfluidic, electrochemical devices are described. The microfluidic, electrochemical device may include a sample zone on a first porous, hydrophilic layer, a reference zone and a microfluidic channel, wherein the microfluidic channel provides for predominantly diffusive fluid communication between the sample zone and the reference zone; (therefore realizing a similar function of a reference electrode), a fluid-impermeable material that defines each of the sample zone, reference zone and microfluidic channel, a first electrode in fluid communication with the sample zone and a second electrode in fluid communication with the reference zone. Also described are microfluidic, electrochemical devices containing an ion-selective membrane for potentiometric ion sensing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Desalination device using selective membranes and magnetic fields
ActiveUS20110147295A1Electrostatic separatorsGeneral water supply conservationDesalinationBrackish water
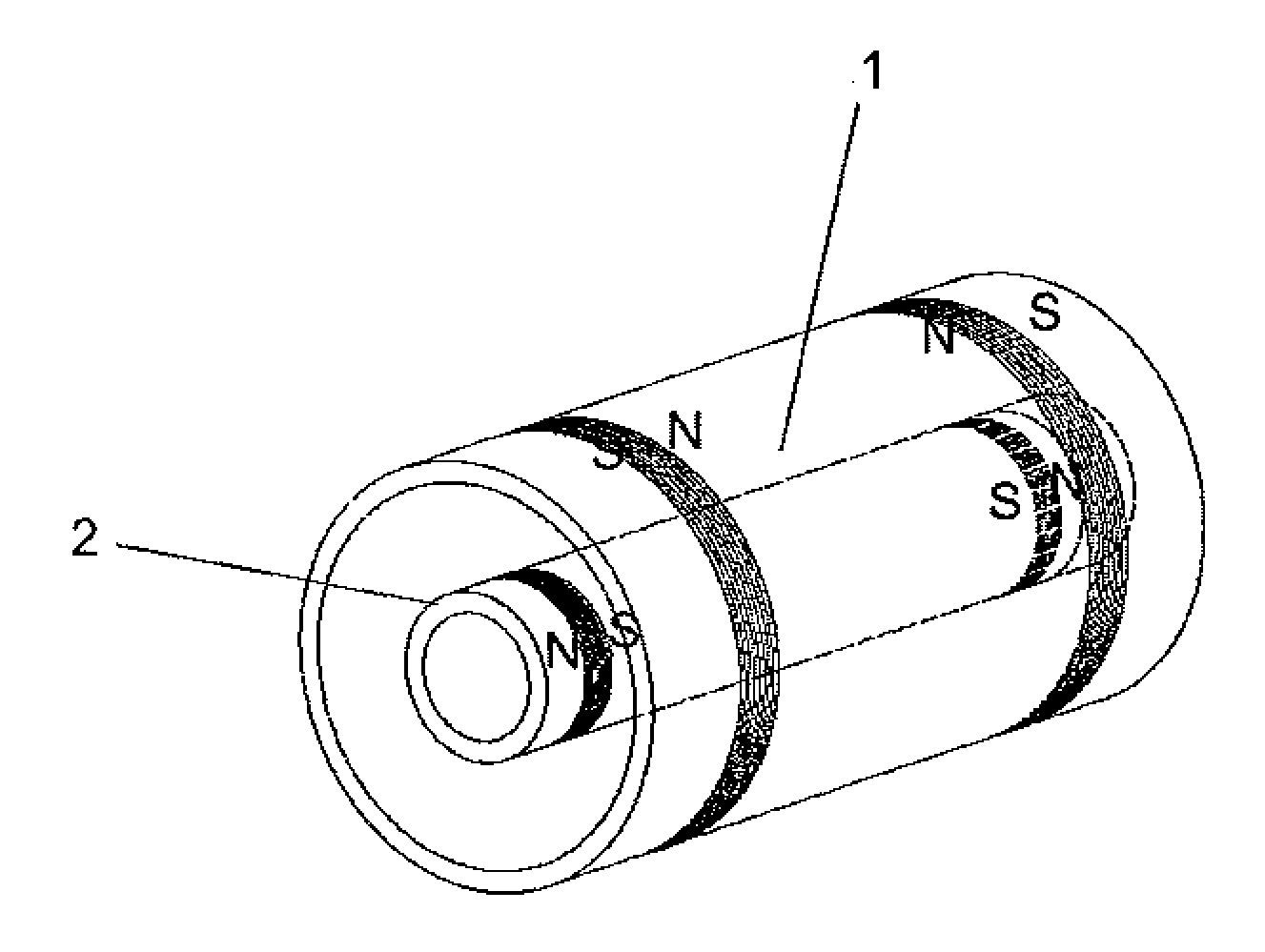
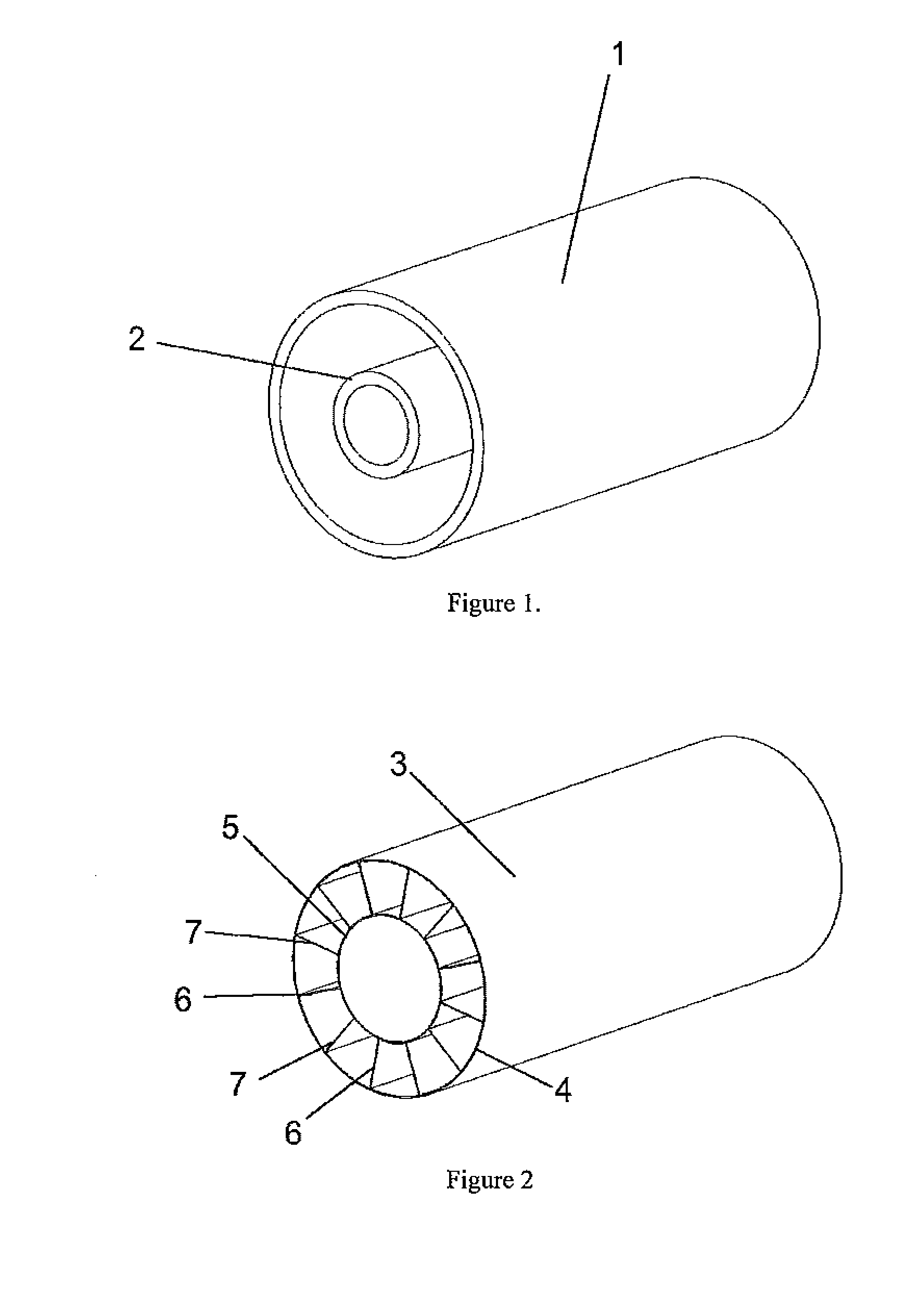
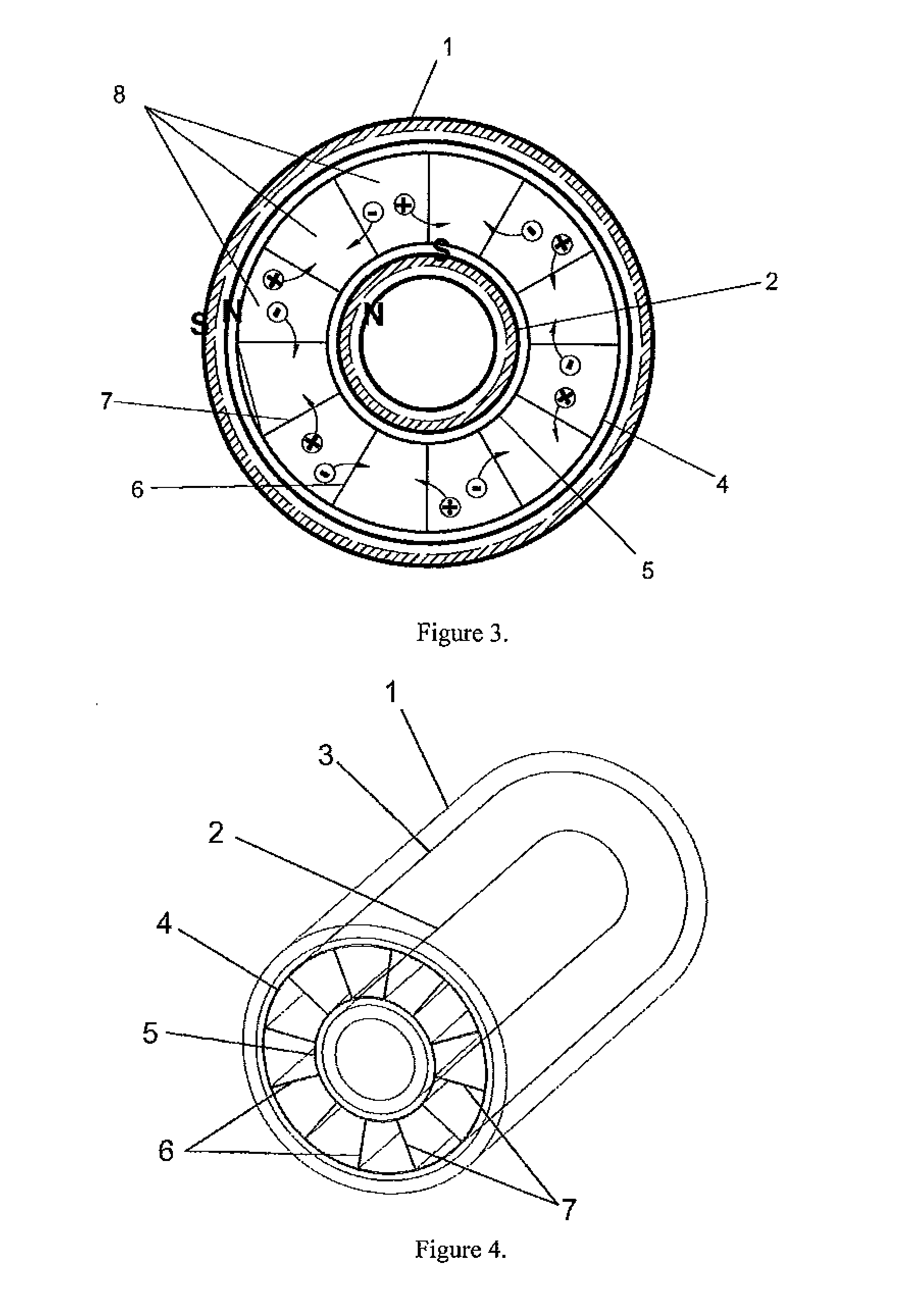
Device designed to desalinate brackish water which performs said function by the combined action of magnetic fields generated inside the device and ion-selective membranes, thus obtaining two separate water currents, one with a low salt concentration and the other reject current with a high salt concentration. It comprises an external cylindrical body of magnetized iron (1), an inner body also cylindrical and made of the same material (2) and an intermediate chamber (3) in which are placed a series of ion-selective membranes (6 and 7) arranged radially around the axle common to all of the bodies, and placed alternately such that each negative-ion selective membrane has a positive-ion selective membrane on either side.
Owner:PENAS BALLESTER PEDRO +1
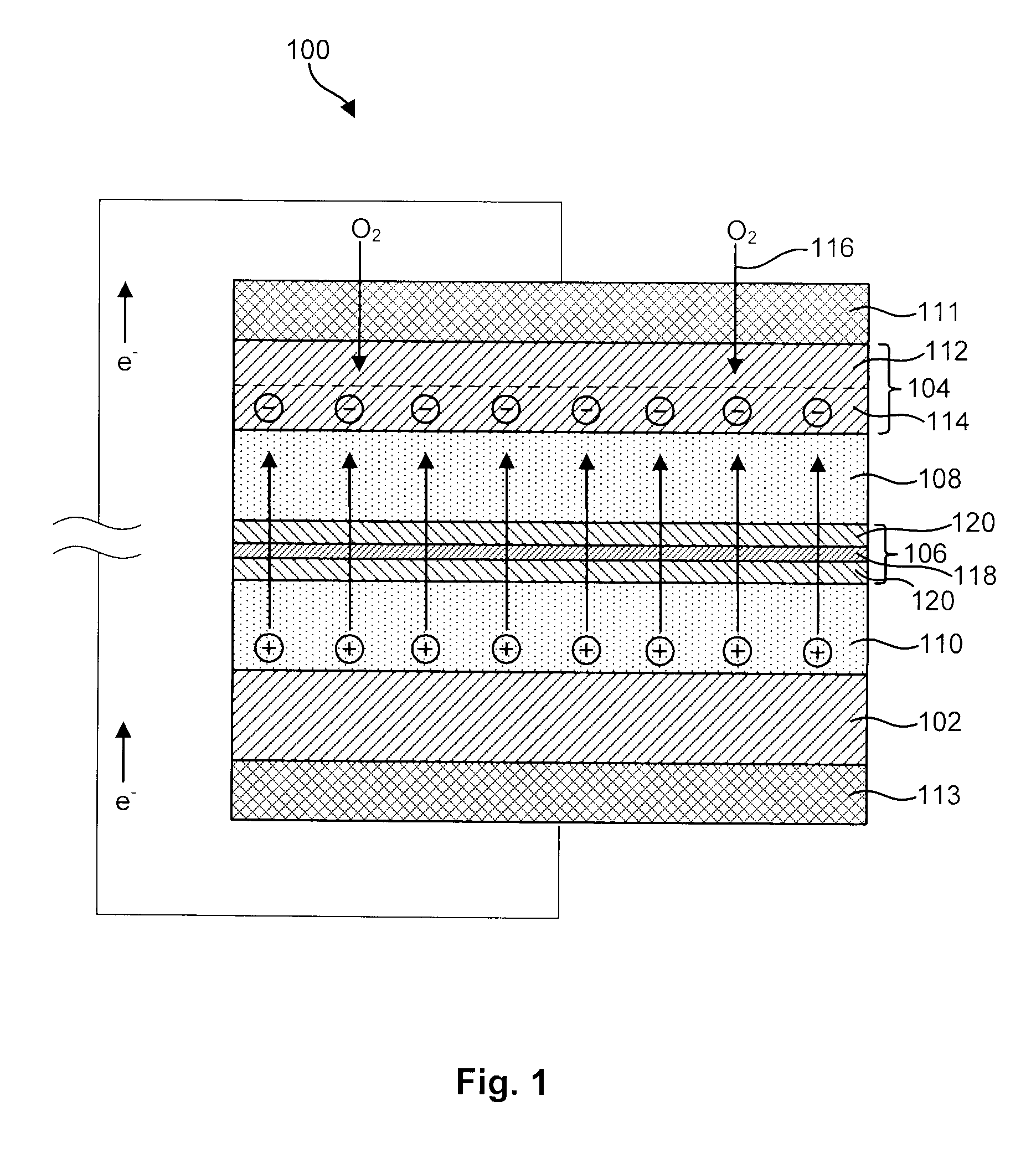
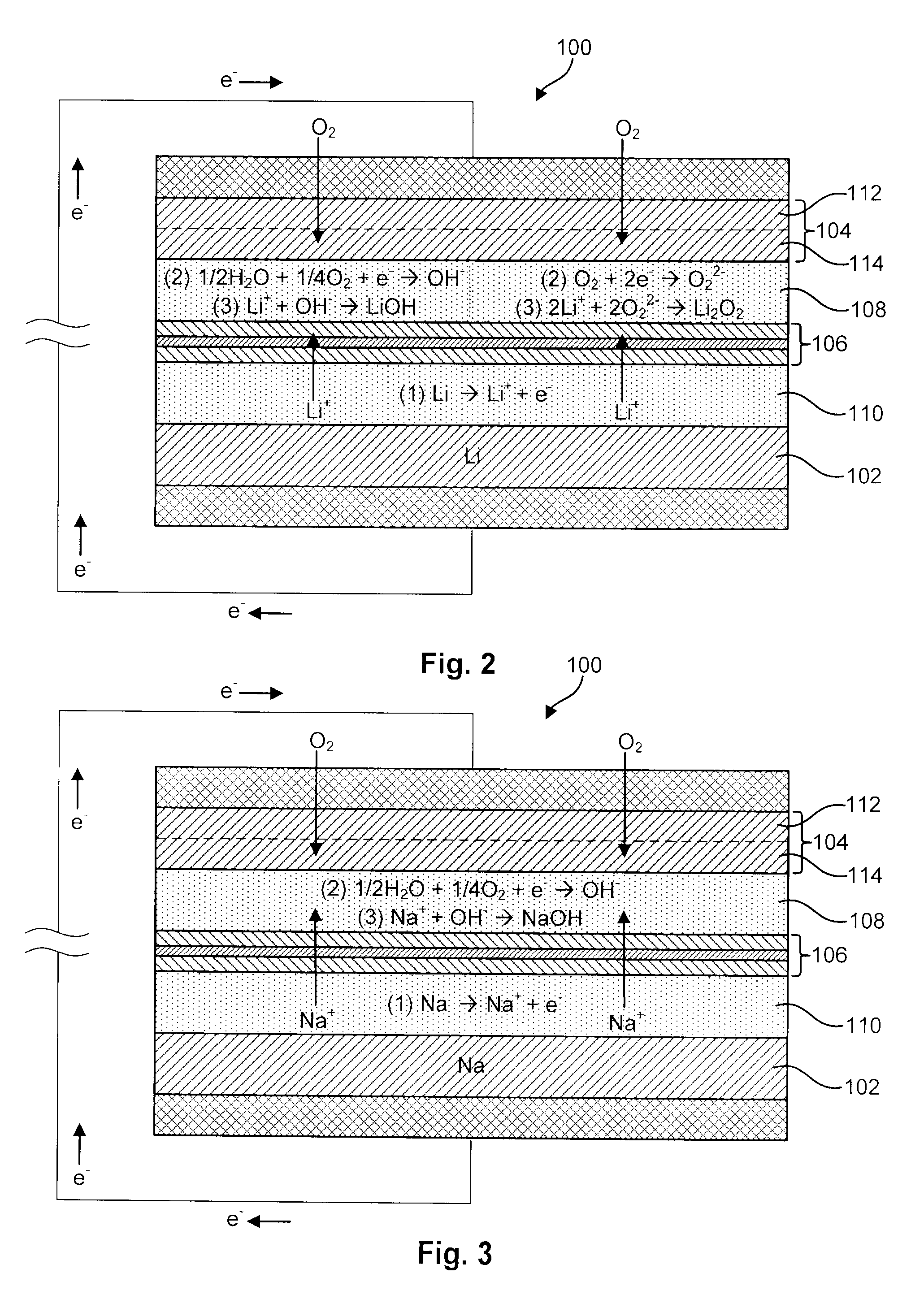
Advanced metal-air battery having a ceramic membrane electrolyte
ActiveUS8012633B2Reduce oxygenReduce layeringFuel and primary cellsSolid electrolytesOxygenCeramic membrane
A metal-air battery is disclosed in one embodiment of the invention as including a cathode to reduce oxygen molecules and an alkali-metal-containing anode to oxidize the alkali metal (e.g., Li, Na, and K) contained therein to produce alkali-metal ions. An aqueous catholyte is placed in ionic communication with the cathode to store reaction products generated by reacting the alkali-metal ions with the oxygen containing anions. These reaction products are stored as solutes dissolved in the aqueous catholyte. An ion-selective membrane is interposed between the alkali-metal containing anode and the aqueous catholyte. The ion-selective membrane is designed to be conductive to the alkali-metal ions while being impermeable to the aqueous catholyte.
Owner:FIELD UPGRADING USA INC
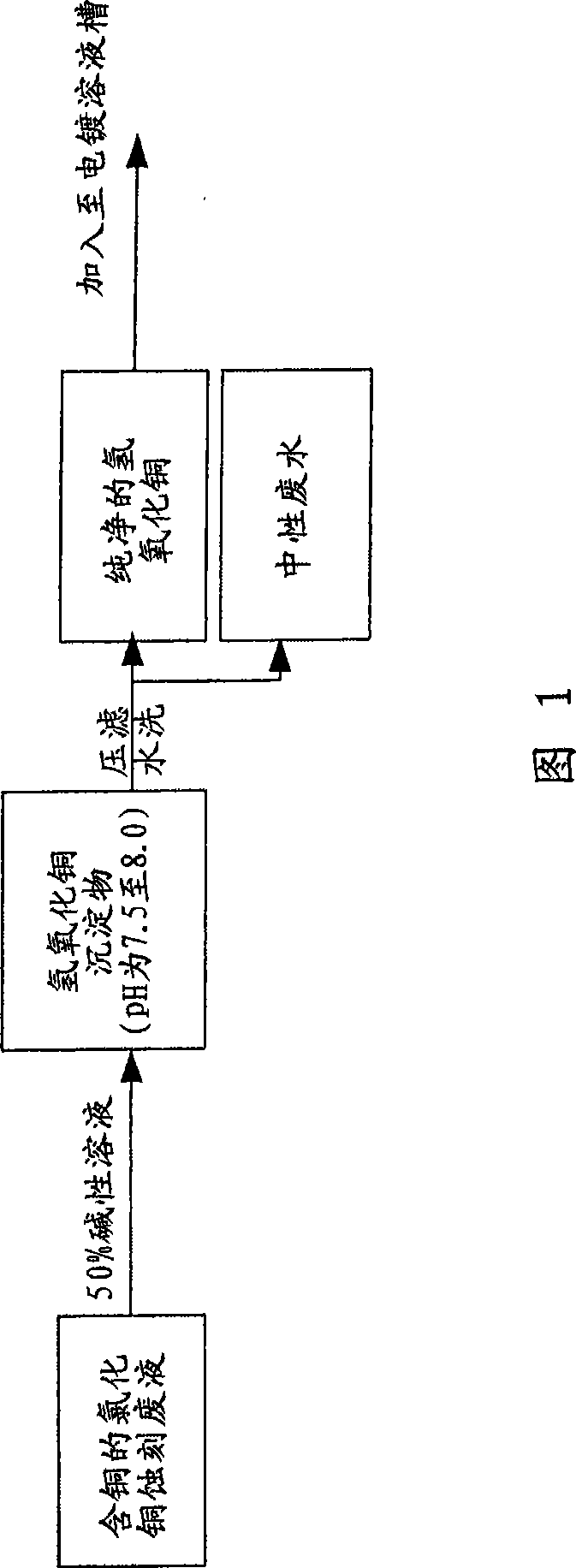
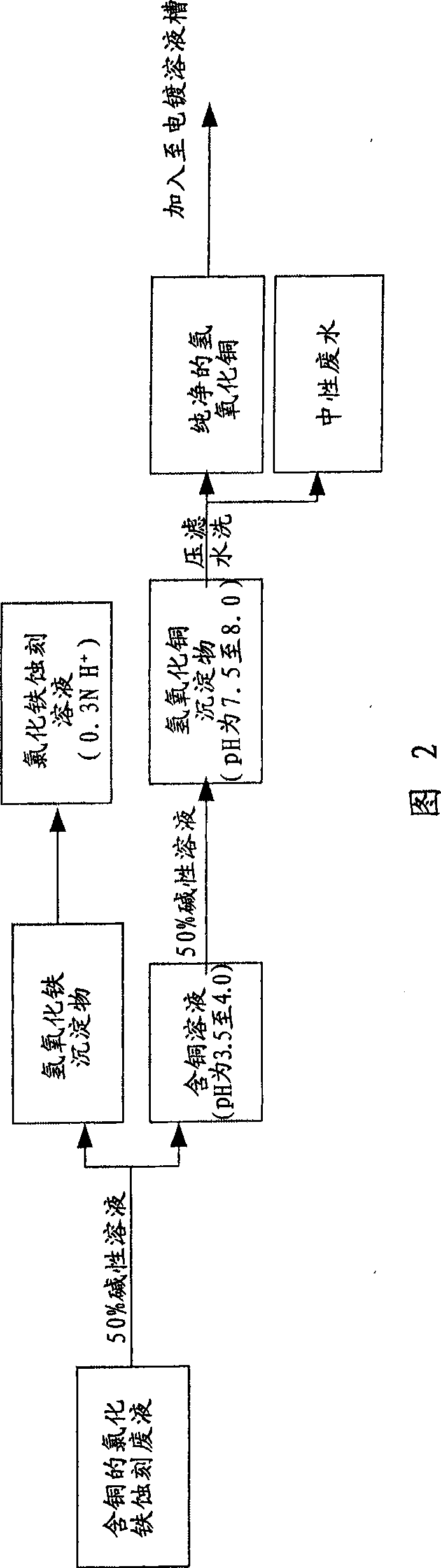
Copper resource cyclic regeneration method in manufacture process
The invention provides a method for cycling and regenerating copper resource in processing procedure. When acid etching waste liquid containing copper is generated during the processing procedure of etching, the acid etching waste liquid containing copper is mainly treated by alkaline solution to form electroplating solution containing copper for electroplating, and then the electroplating solution containing copper is put in the processing procedure of electroplating copper once again. As the method no longer reduces metal copper from the etching waste solution, so as to require no extracting solution which easily pollutes liquid medicine or no expensive ion selective membrane, no high-temperature copper melting and no electrical purification which consumes large amount of electricity, or no outsourcing treatment, therefore, the problems generated during delivering pollutants can be prevented.
Owner:TRINITY RESOURCES TECH HLDG
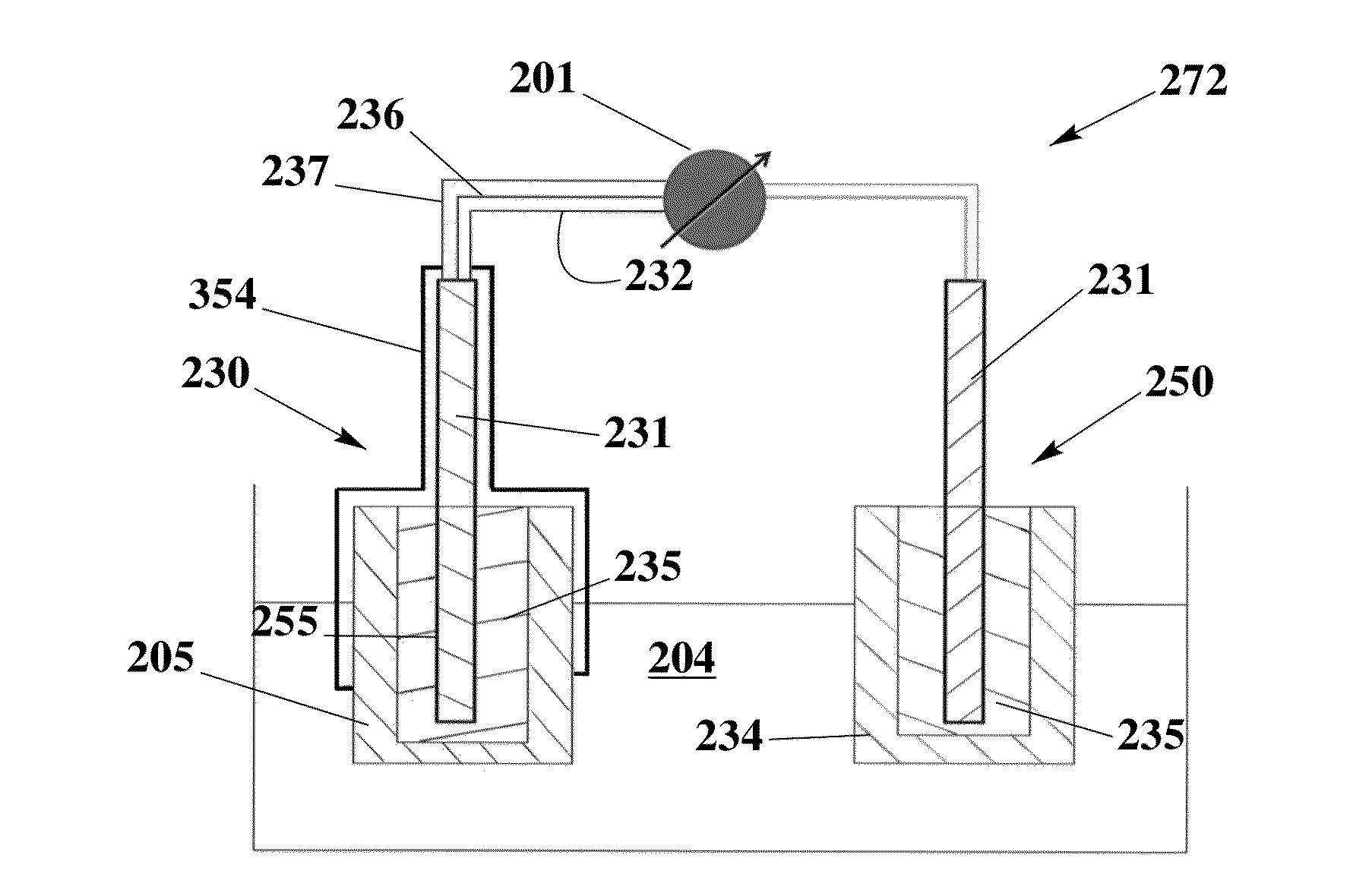
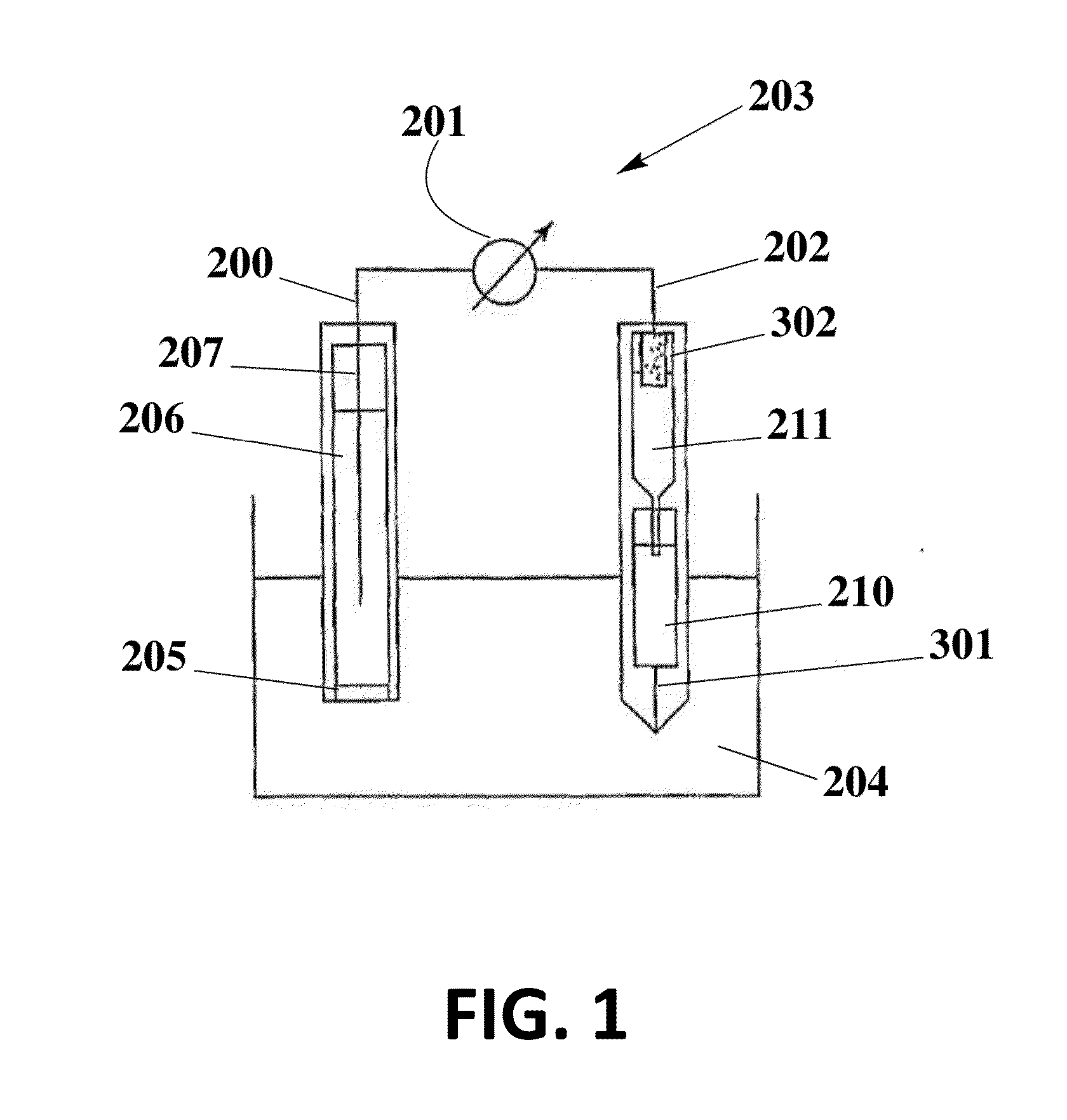
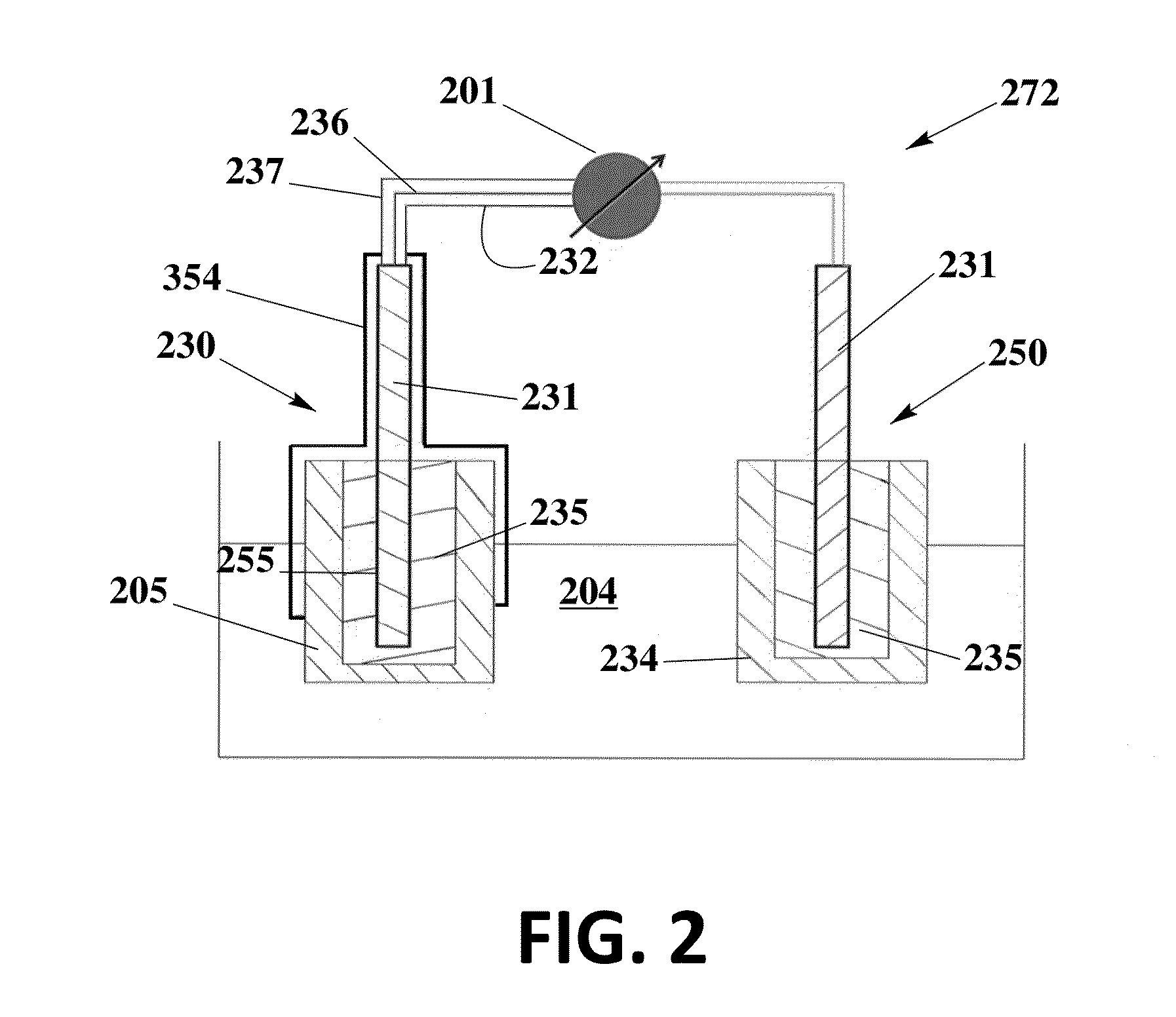
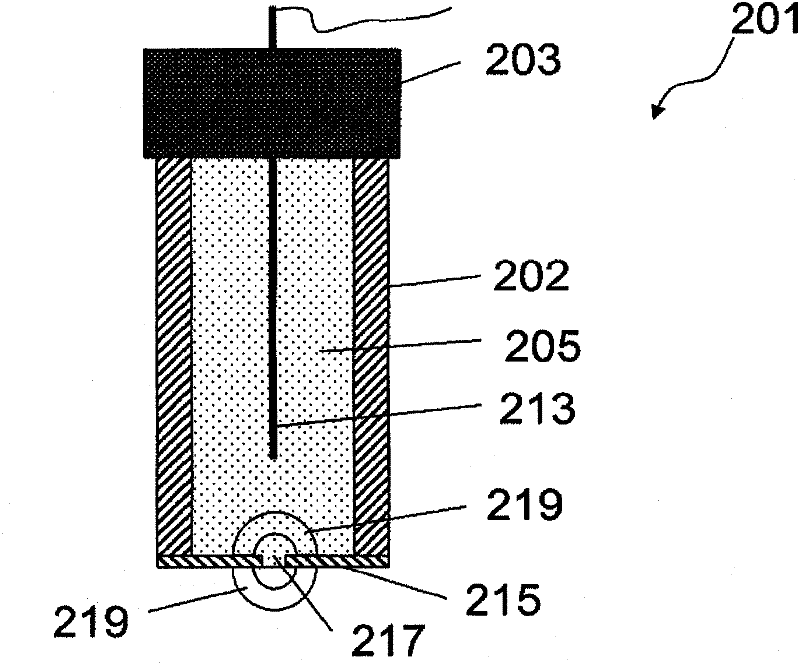
ion selective electrode
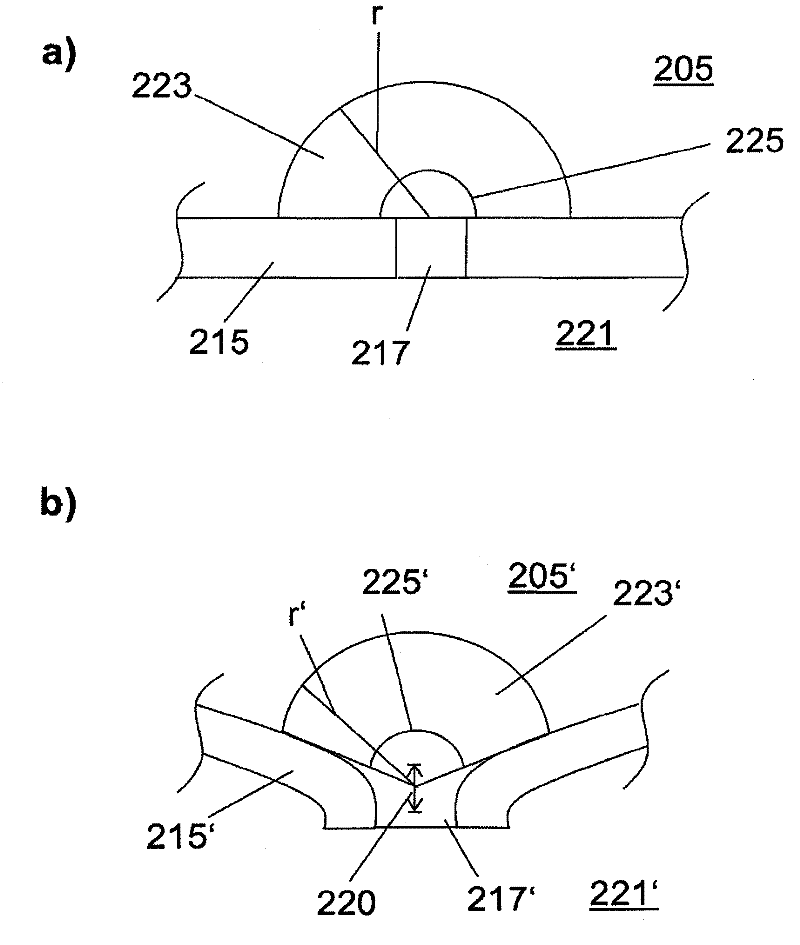
The invention relates to an ion-selective electrode (201) comprising: a housing (202, 215) which surrounds a housing internal space, an ion-selective membrane (203), in particular a polymer membrane, and a sensing system which is in contact with the ion-selective membrane and is intended to sense a potential of the ion-selective membrane, wherein the ion-selective membrane at least partially fills the housing internal space, and is in contact with a medium, which surrounds the housing, via at least one hole (217) which passes through a wall of the housing.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER CONDUCTA GESELLSCHAFT FUER MESS UND REGELTECHNIK MBH CO KG
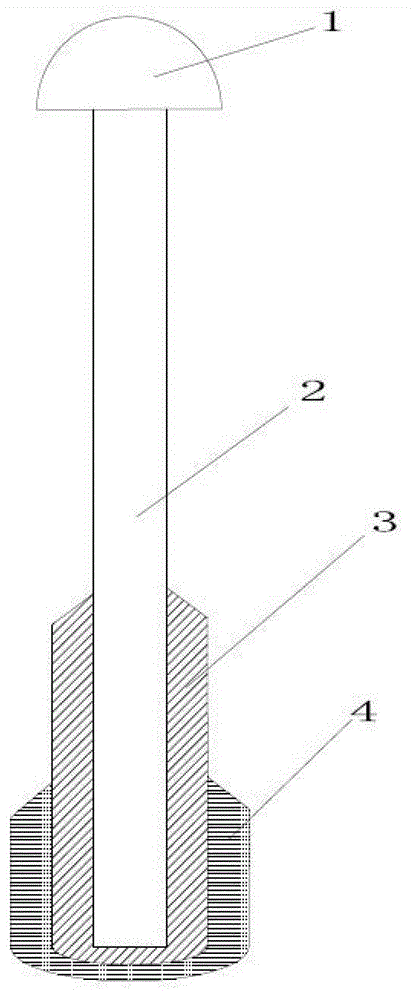
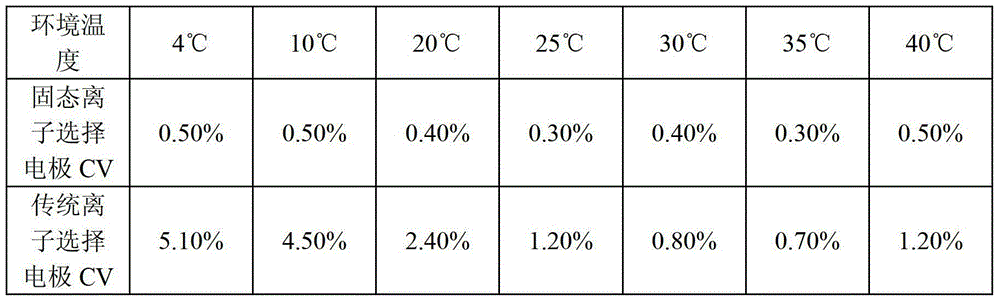
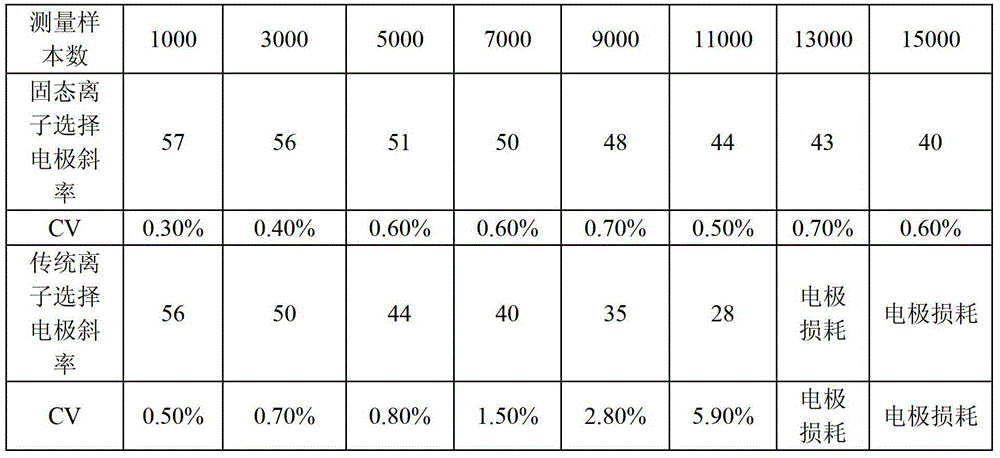
All solid-state ion selective electrode and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103336044AWide temperature adaptabilityMeasurement stabilityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAll solid stateConductive polymer
The invention discloses an all solid-state ion selective electrode comprising an electrode cap and an electrode core, wherein a conductive polymer layer covers the lower part of the electrode core, a layer of ion selective membrane covers the surface of the conductive polymer layer, the conductive polymer layer contains a conductive polymer and a lipophilic additive, and the thickness of the ion selective membrane is 0.5-2mm. The invention also discloses a preparation method and an application of the all solid-state ion selective electrode. The all solid-state ion selective electrode disclosed by the invention can contain such additional polymers suitable for biological sensors as polyvinyl chloride, polyurethane or silicone rubber and lipophilic or hydrophilic additives. The conductive polymer can bring stable potential performance and wide temperature adaptability. Compared with the traditional ion selective electrode, the all solid-state ion selective electrode has the advantages of no internal filling liquid, long service life, stable electrode measurement, wide temperature adaptability, less external disturbance, easiness and convenience for use, non-maintenance, etc.
Owner:NANJING PERLONG MEDICAL EQUIP
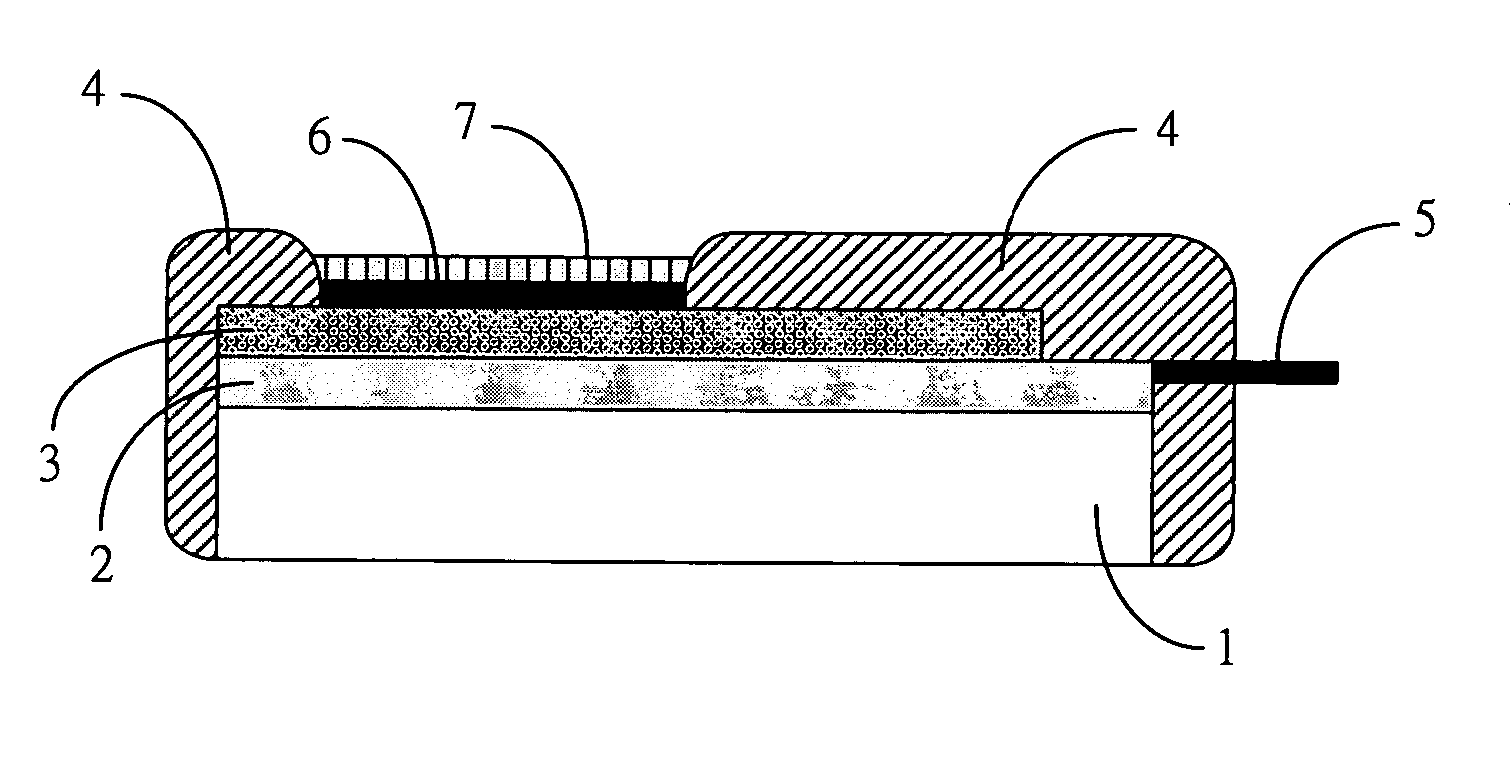
Microsensor with a well having a membrane disposed therein
ActiveUS7438851B2Function increaseSmall sizeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRing patternSolvent based
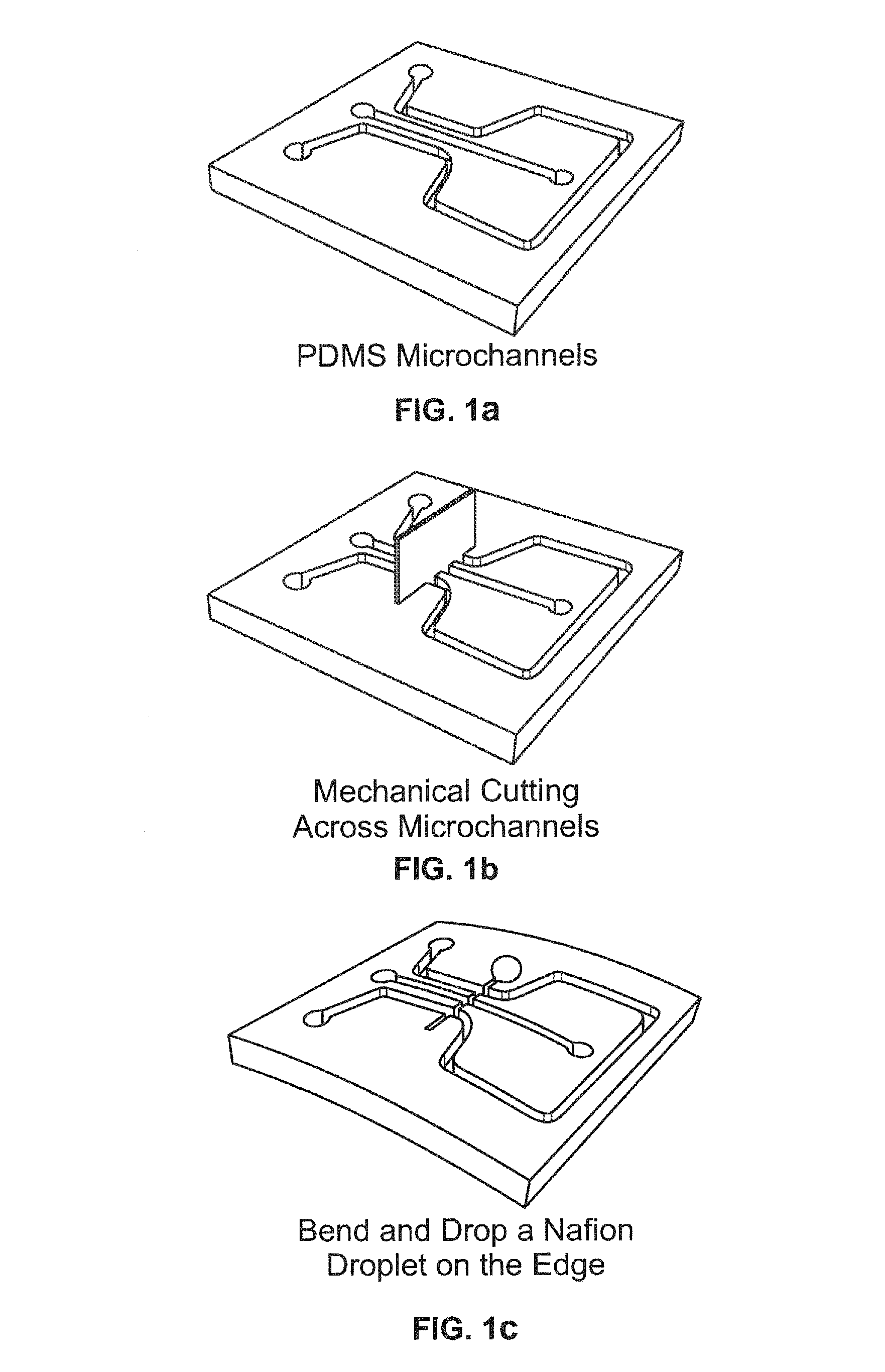
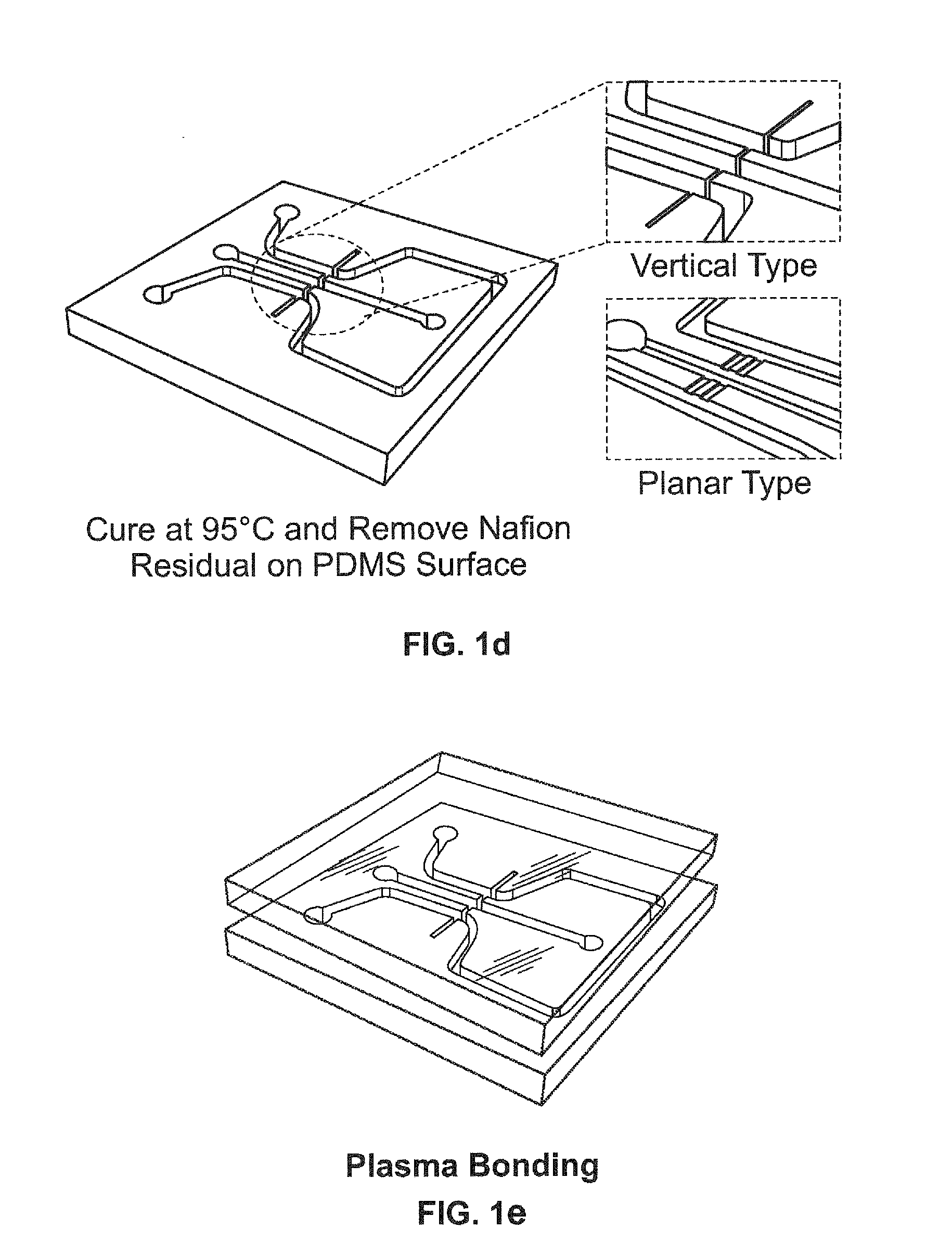
A micromachined device such as a solid-state liquid chemical sensor for receiving and retaining a plurality of separate liquid droplets at desired sites, a method of making the device and a method of using the device are provided. The technique works for both aqueous and solvent-based solutions. The device includes a substrate having an upper surface, and a first set of three-dimensional, thin film well rings patterned at the upper surface of the substrate. Each of the wells is capable of receiving and retaining a known quantity of liquid at one of the desired sites through surface tension. A method for patterning a membrane / solvent solution results in reproducibly-sized, uniformly-thick membranes. The patterning precision of this method allows one to place the membranes closer together, making the sensors smaller and less expensive, and the uniform film thickness imparts reproducibility to the sensors. The final film thickness can be controlled over a 3 to 50 micron range, and lateral dimensions can be as small as 20 microns using conventional materials. The simple patterning steps can be done on full wafers in a mass fabrication process. A second set of well rings may be photo-patterned at the same time as the first set of well rings to isolate functional groups on top of ion-selective membrane.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Ion selective membrane used by non-solid-state electrode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102569702AEasy to prepareLow costCell component detailsAlkaline earth metalPolyvinyl chloride
The invention relates to a diaphragm containing a non-solid-state electrode for a chemical power supply system. The diaphragm is characterized by being an intermolecular force type ion exchange membrane, which comprises two basic components including a matrix and molecules with ion exchange activity, wherein the two components are bonded by means of intermolecular force, the component of the matrix of the membrane is selected from organic polymer compounds, preferably one or some of PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate), PP (Propene Polymer), PE (Poly Ethylene), PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride), PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), PVA (Polyvinyl Acetate), PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), PAN (Polyacrylonitrile), PEO (Polyoxyethylene Oxide), CMC (Carboxy Methylated Cellulose), starch and polyacrylic acid, and the ion exchange active molecules are selected from micromolecular organic or inorganic acids, alkaline metal and alkali or salt of alkaline-earth metal. The diaphragm only allows alkaline metal ions, alkaline-earth metal ions or hydrogen ions and the like to pass through and doe not allow transition metal ions to pass through. The diaphragm is low in manufacturing cost and easy for industrialization realization, and has potential application values in the fields of flow batteries, air batteries and fuel batteries.
Owner:常州孚达新能源科技有限公司
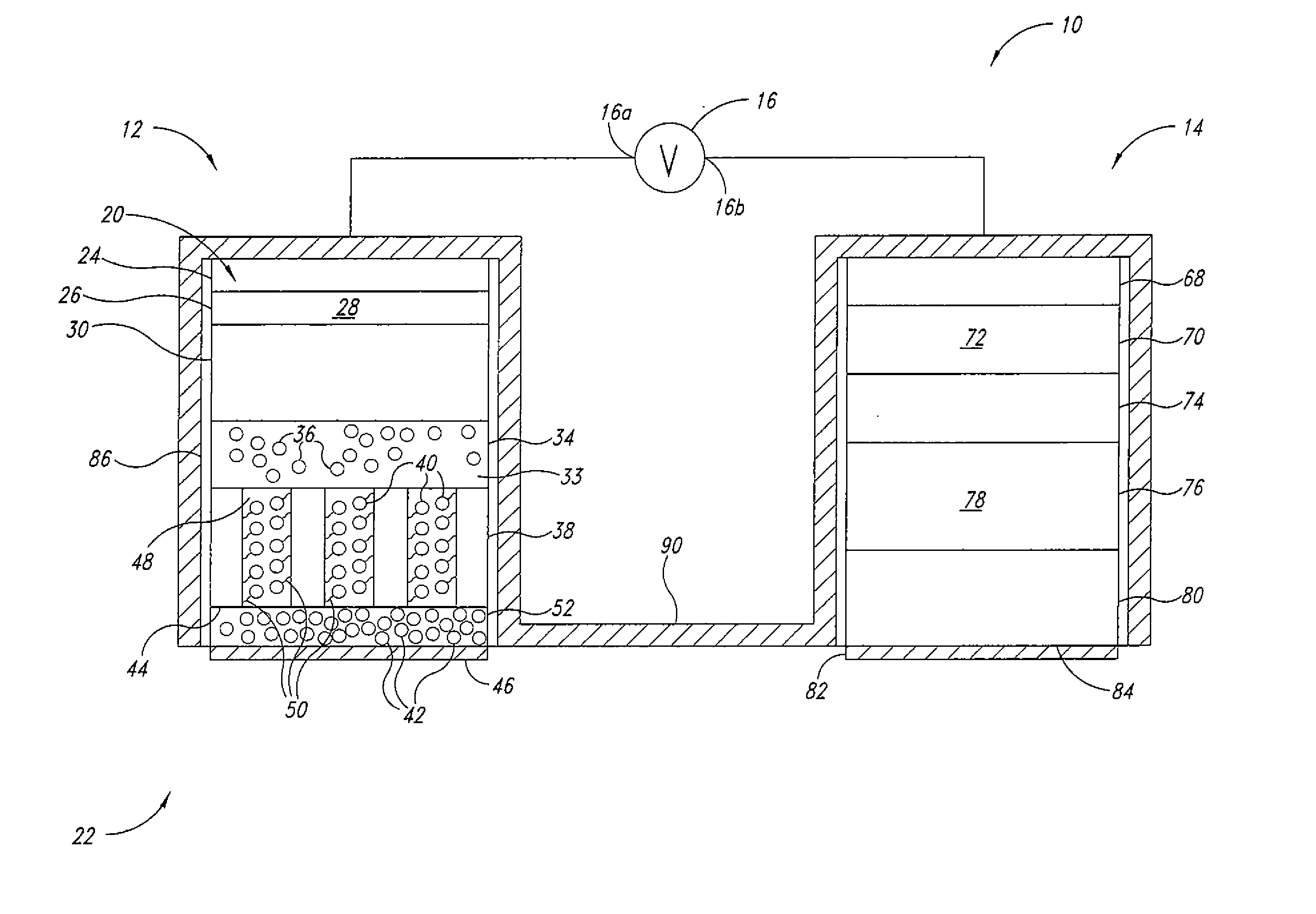
Lithium-air battery with cathode separated from free lithium ion
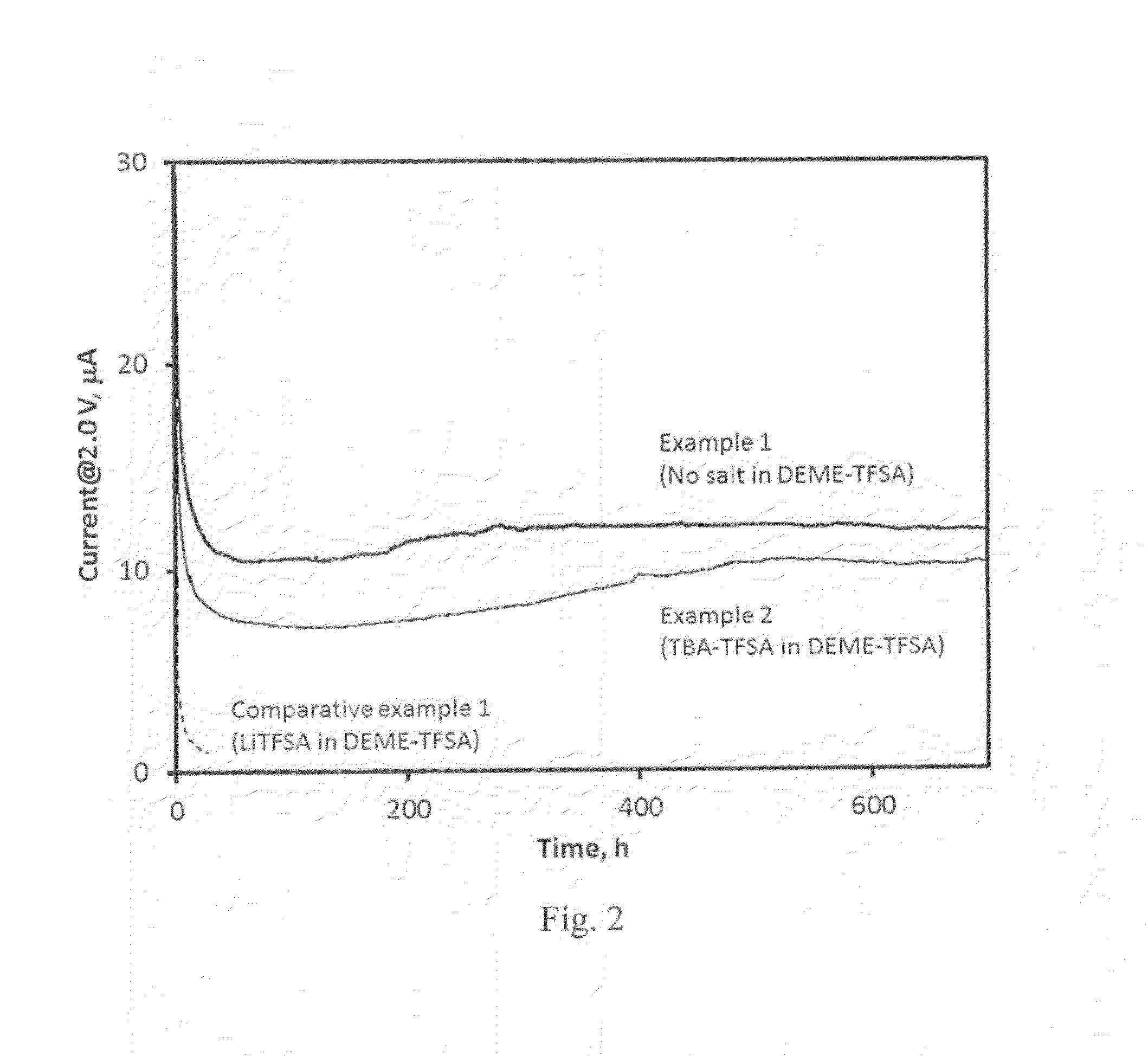
A lithium-air electrochemical cell is provided. The battery comprises: an anode compartment; a cathode compartment; and a lithium ion conductive membrane separating the anode compartment from the cathode compartment. The anode compartment comprises an anode having lithium or a lithium alloy as active metal and a lithium ion electrolyte, while the cathode compartment comprises an air electrode and an ionic liquid capable of supporting the reduction of oxygen. A lithium ion concentration in the cathode compartment is such that the lithium ion concentration is greatest at the lithium ion selective membrane and lowest at the cathode.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Chloride ion selective membrane
ActiveUS20050006253A1High sensitivityGood choiceWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementEpoxyPolyamide
A chloride selective electrode membrane comprises a polymeric matrix wherein the matrix comprises an epoxy resin, and an amine agent selected from the group consisting of polyamides, amidoamines and mixtures thereof. The amine agent is present in stoichiometric excess and functions as both curing agent and chloride selective agent.
Owner:RADIOMETER AS
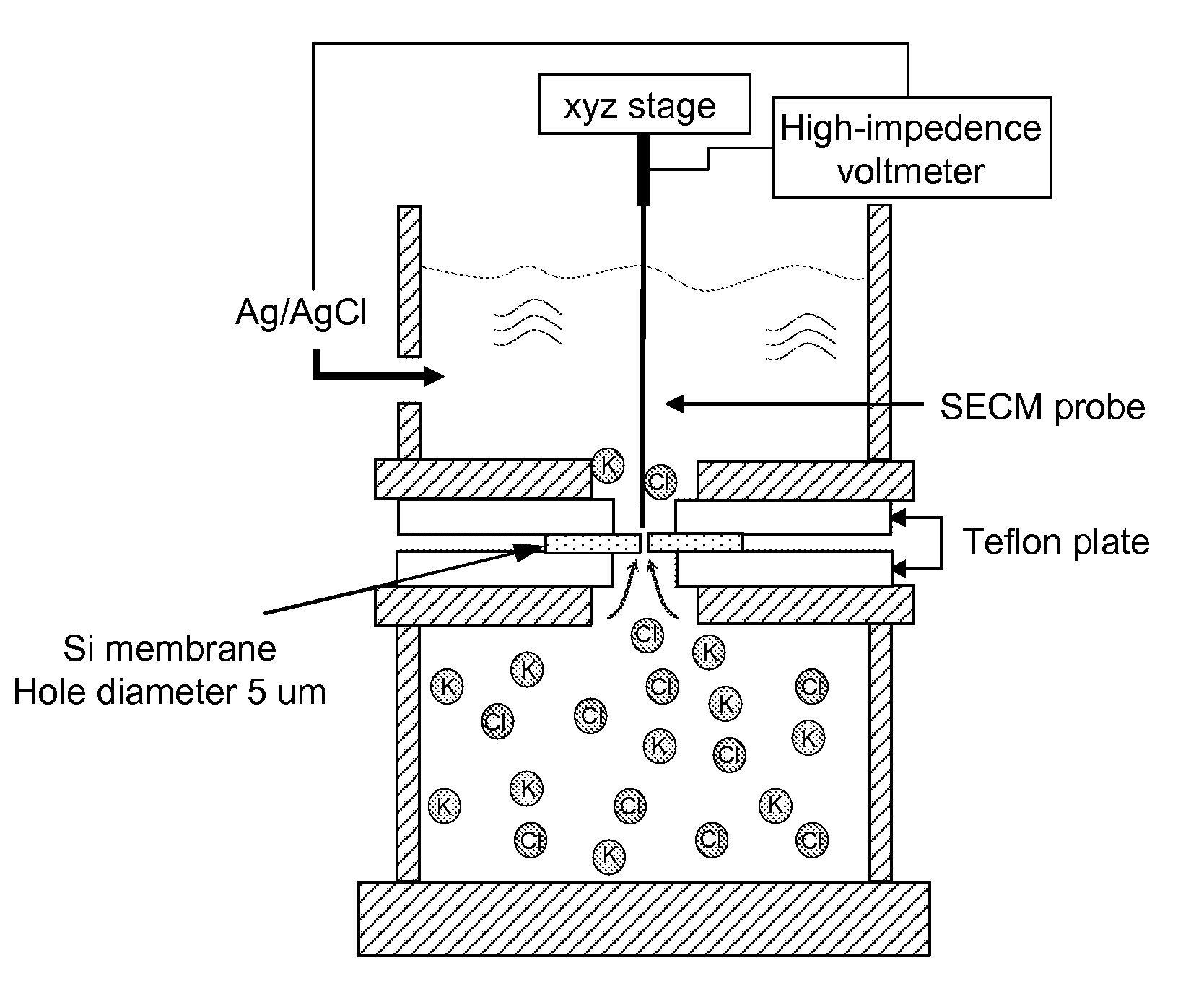
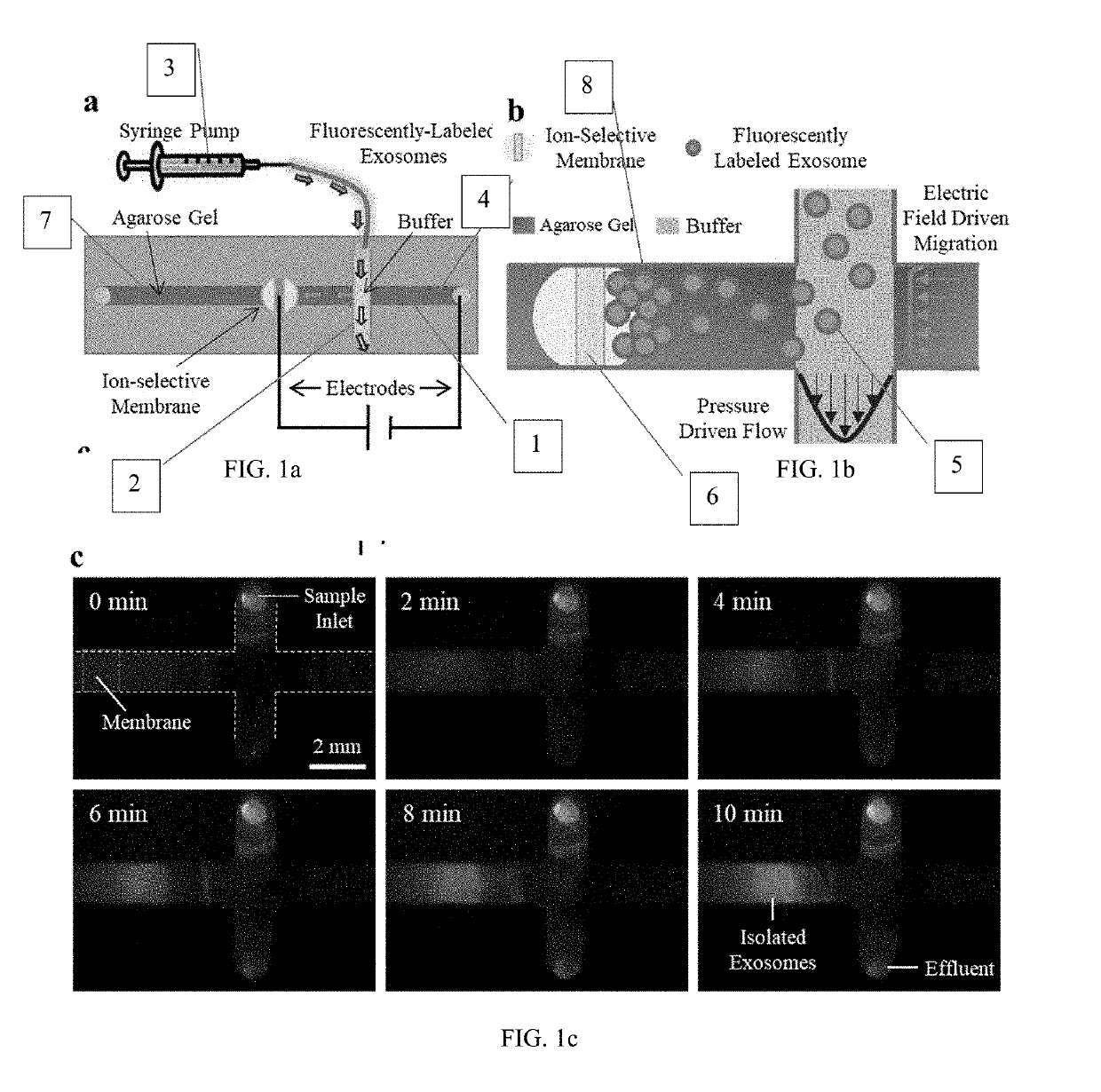
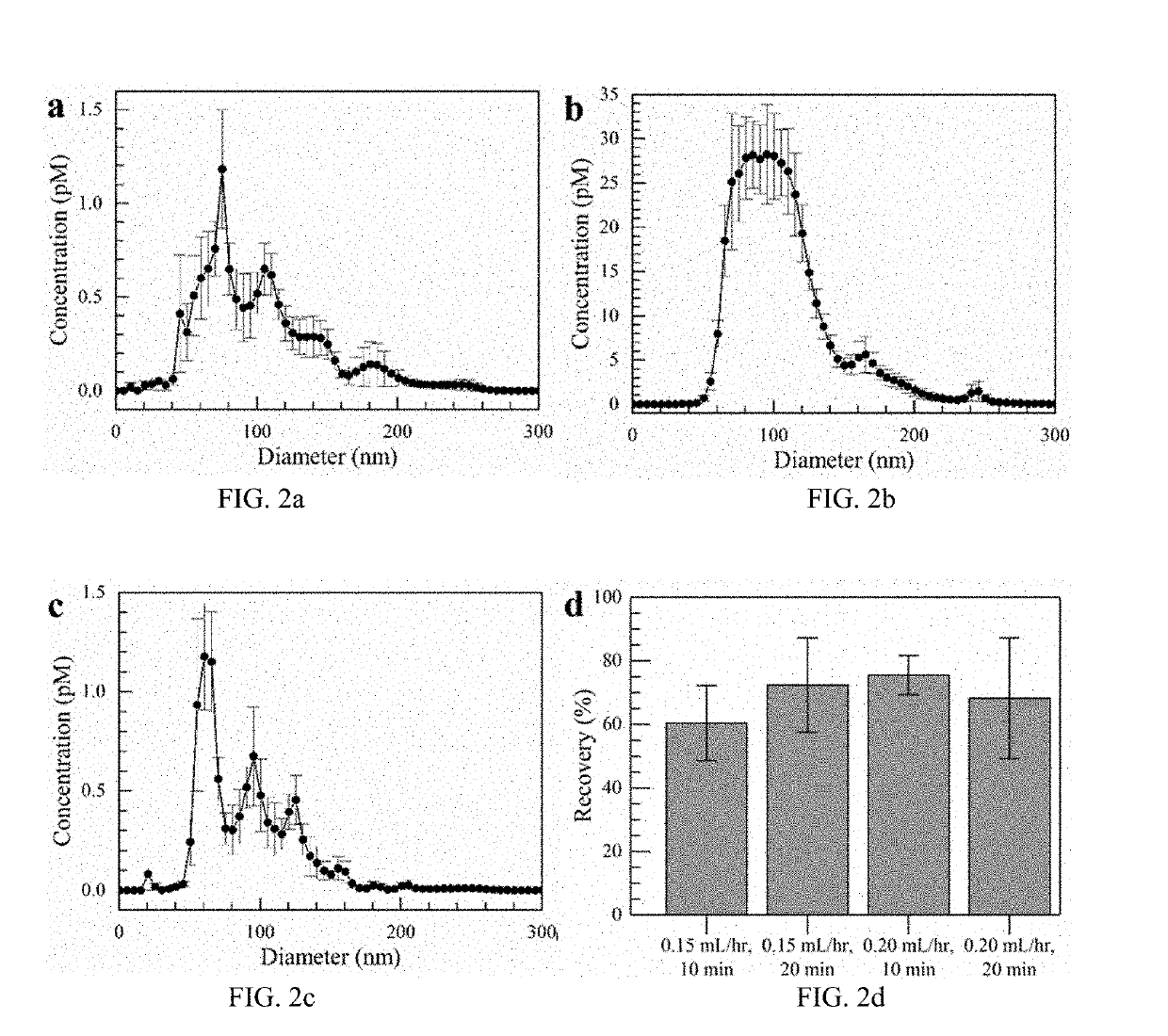
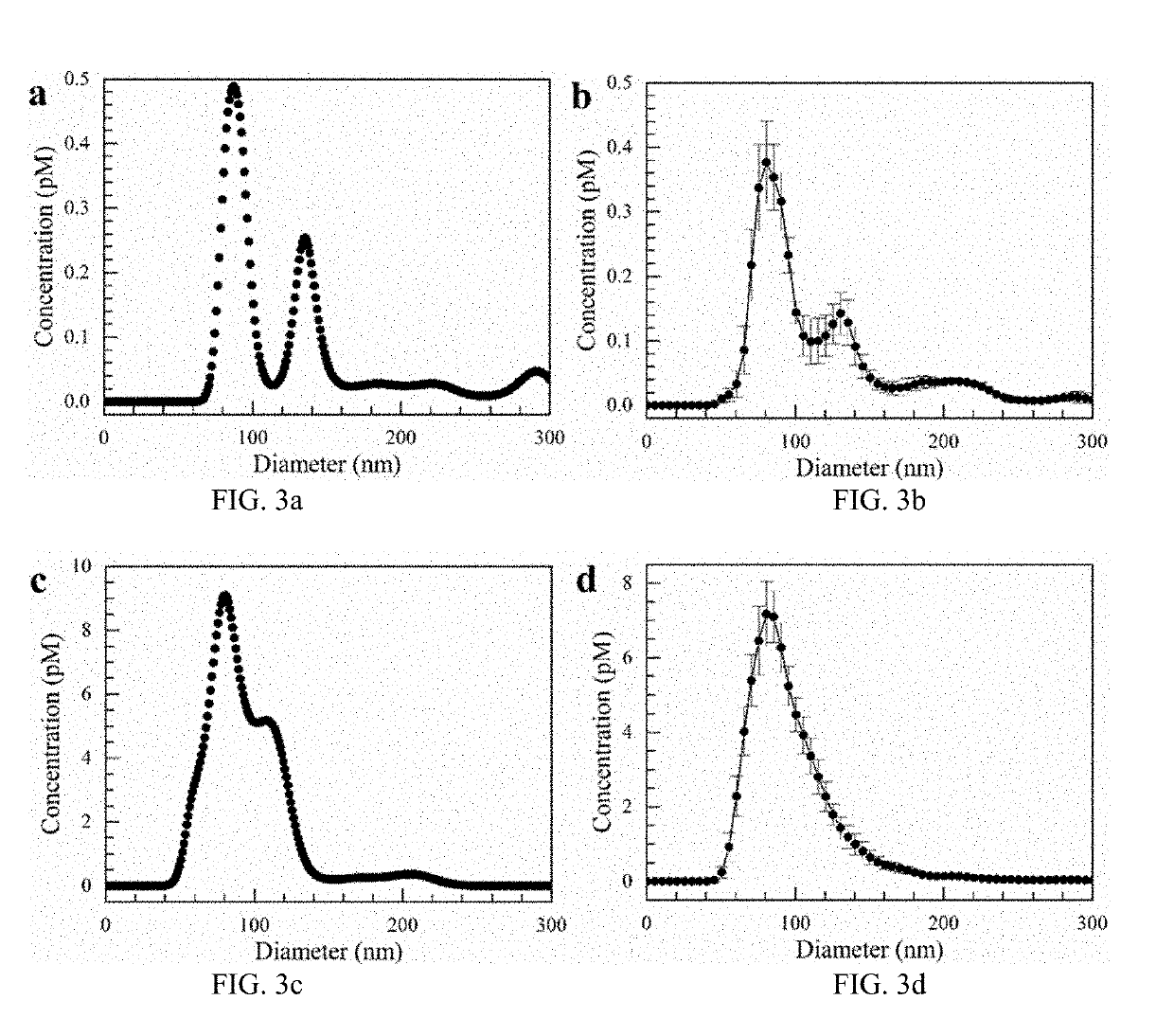
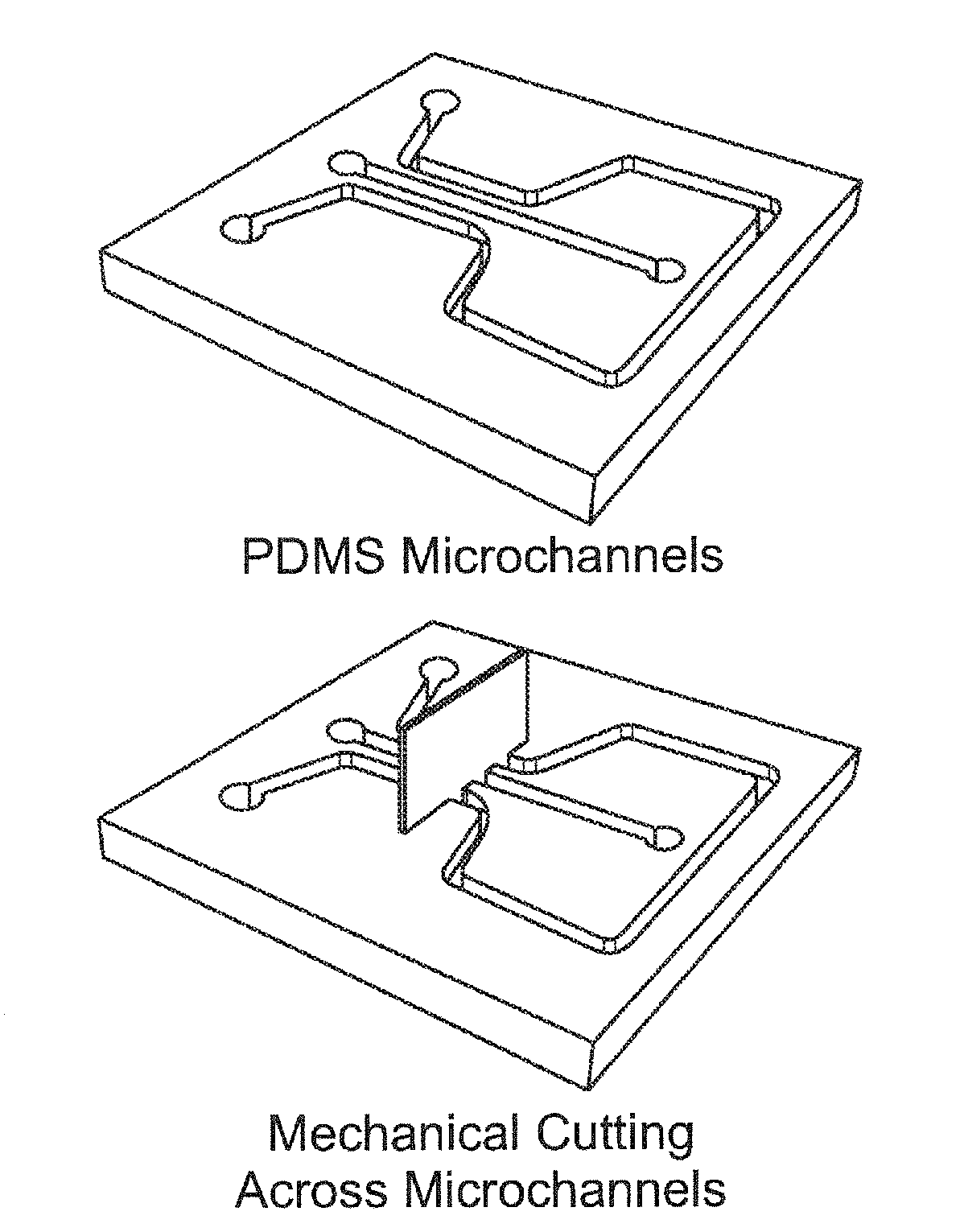
Simultaneous isolation and preconcentration of exosomes by ion concentration polarization method and apparatus
ActiveUS20190271619A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationNanoparticle tracking analysisCell culture media
Exosomes carry microRNA biomarkers, occur in higher abundance in cancerous patients than in healthy ones, and because they are present in most biofluids, including blood and urine, can be obtained non-invasively. Standard laboratory techniques to isolate exosomes are expensive, time-consuming, provide poor purity, and recover on the order of 25% of the available exosomes. We present a new microfluidic technique to simultaneously isolate exosomes and preconcentrate them by electrophoresis using a high transverse local electric field generated by ion-depleting ion-selective membrane. We use pressure-driven flow to deliver an exosome sample to a microfluidic chip such that the transverse electric field forces them out of the cross flow and into an agarose gel which filters out unwanted cellular debris while the ion-selective membrane concentrates the exosomes through an enrichment effect. We efficiently isolated exosomes from 1×PBS buffer, cell culture media and blood serum. Using flow rates from 150 μL / hr to 200 μL / hr and field strengths of 100 V / cm, we consistently captured between 60% to 80% of exosomes from buffer, cell culture media, and blood serum as confirmed by both fluorescence spectroscopy and nanoparticle tracking analysis. Our microfluidic chip maintained this recovery rate for more than twenty minutes with a concentration factor of 15 for ten minutes of isolation.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Electrokinetic concentration devices
InactiveUS8440063B2Enhance and reduce operation efficiencyReduce or enhance adsorption of said speciesSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringPressure-driven flow
The present invention provides a device and methods of use thereof in concentrating a species of interest and / or controlling liquid flow in a device. The methods make use of a device comprising a fluidic chip comprising a planar array of channels through which a liquid comprising a species of interest can be made to pass with at least one rigid substrate connected thereto such that at least a portion of a surface of the substrate bounds the channels, and a high aspect ratio ion-selective membrane is embedded within the chip, attached to at least a portion of the channels. The device comprises a unit to induce an electric field in the channel and a unit to induce an electrokinetic or pressure driven flow in the channel.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation method for selecting SPEEK/GO/TiO2 composite ion selection membrane in nanometer insertion layer
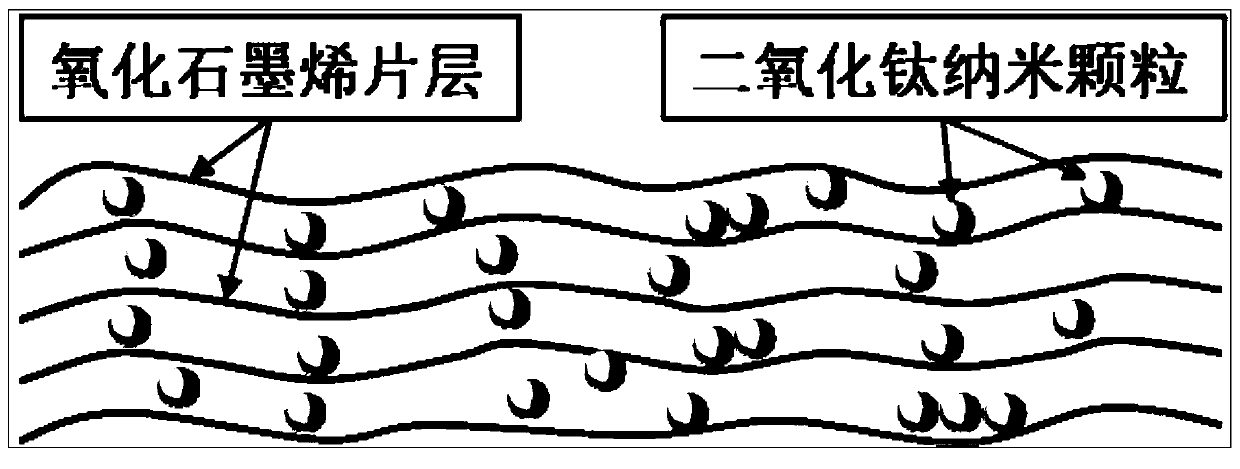
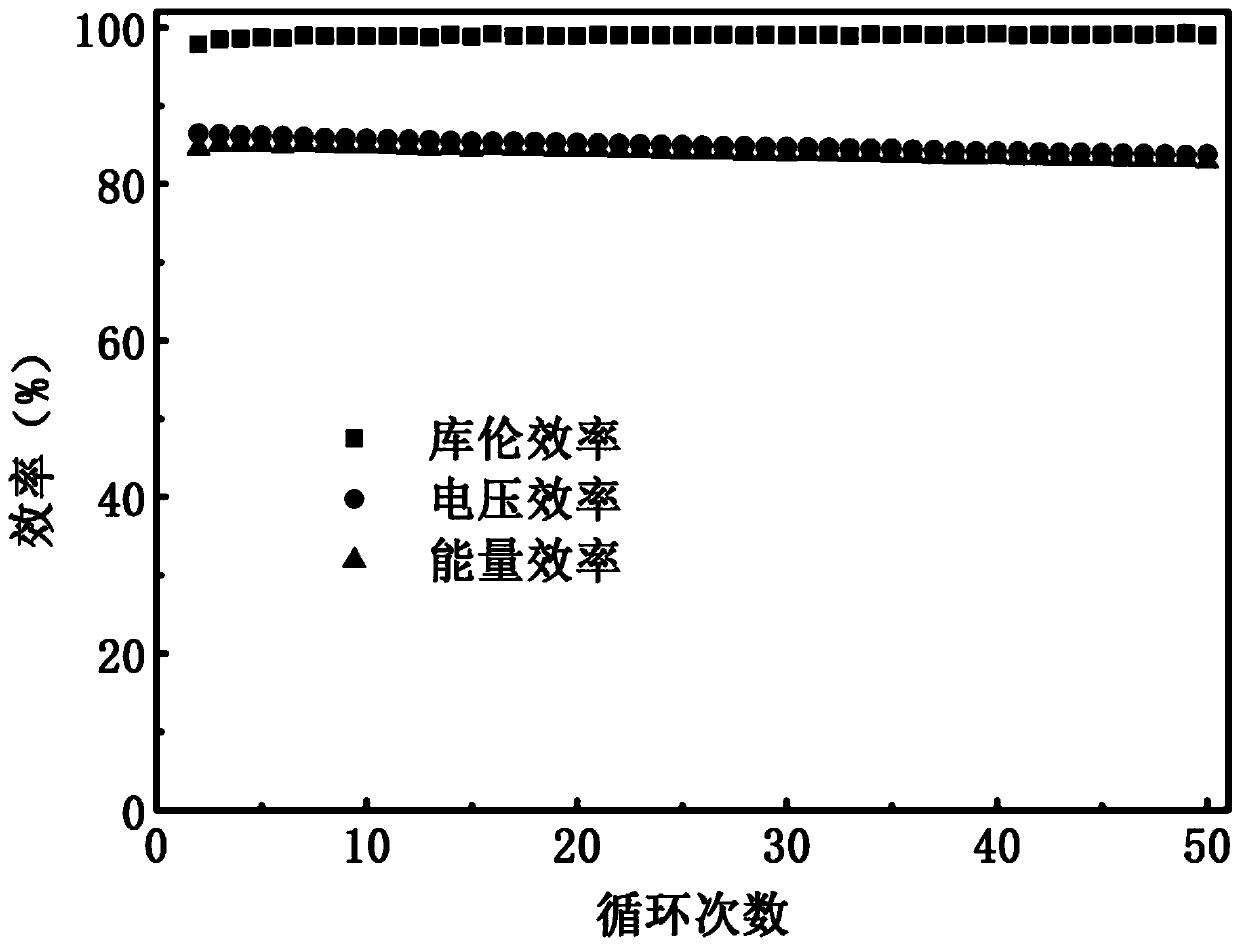
ActiveCN110350223AImprove conductivityImprove conduction abilityRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium redox batteryIon permeation
The invention relates to the field of a diaphragm for an all-vanadium oxygen-reduction redox flow battery, in particular to a preparation method for selecting a sulfonated polyetheretherketone / graphene oxide / titanium dioxide nanometer particle composite ion selection membrane in a nanometer insertion layer. By the preparation method, the problems of vanadium ion permeation seriousness, poor ion selectivity and high cost of a proton exchange membrane in an existing commercial diaphragm are solved. The low-cost sulfonated polyetheretherketone (SPEEK) is used as a base film, a graphene oxide / titanium dioxide nanometer particle (GO / TiO2) insertion layer composite material is used for controlling an ion selection conduction passage, and the SPEEK / GO / TiO2 composite ion selection membrane is prepared by a film formation method such as dispersion step by step and solution pouring. The composite ion selection membrane prepared by the invention has the advantages of favorable ion selection conductivity, excellent vanadium ion blocking performance, favorable mechanical property, chemical stability and excellent single VRB battery performance and the like and is widely applied to the field ofthe all-vanadium oxygen-reduction redox flow battery.
Owner:山东奥德储能科技有限公司
Electrokinetic concentration device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20090120796A1High mechanical strengthEnhance and reduce operation efficiencySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringPressure-driven flow
The present invention provides a device and methods of use thereof in concentrating a species of interest and / or controlling liquid flow in a device. The methods, inter-alia, make use of a device comprising a fluidic chip comprising a planar array of channels through which a liquid comprising a species of interest can be made to pass with at least one rigid substrate connected thereto such that at least a portion of a surface of the substrate bounds the channels, and an ion-selective membrane is attached to at least a portion of the surface of the substrate, which bounds said channels, or which bounds a portion of a surface of one of said channels. The device comprises a unit to induce an electric field in the channel and a unit to induce an electrokinetic or pressure driven flow in the channel.
Owner:HAN JONGYOON +2
Carbon dioxide biochemical analysis dry plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105319250AHigh measurement accuracyImprove long-term stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesSalt bridgePotassium
The invention relates to a carbon dioxide biochemical analysis dry plate and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of blood-gas biochemical sensors. The dry plate is used for detecting the concentration of carbon dioxide in a body fluid, and comprises a supporting layer, an insulating layer, a salt bridge, electrodes, a reference layer, a carbonate ion selective membrane and a buffering layer. According to the preparation method, metal / metal salt thin slice electrodes are prepared, the reference layer is attached onto the electrodes, the ratio of sodium chloride to potassium chloride in the reference layer and the water content of the reference layer are constant, the carbonate ion selective membrane and the buffering layer are sequentially attached onto the solid reference layer, carbon dioxide selective electrodes are prepared, and hydroxyl vinyl resin is utilized as a bonding agent for the carbonate ion selective membrane. The prepared dry plate provided by the invention overcomes the defects that the conventional ion selective electrode is complex to operate, high in use cost and maintenance cost, slow in response, not easy to carry, and the like, and has the advantages of being simple to operate, high in response speed, small in size, simple in preparation process, low in production cost, and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:吴国清
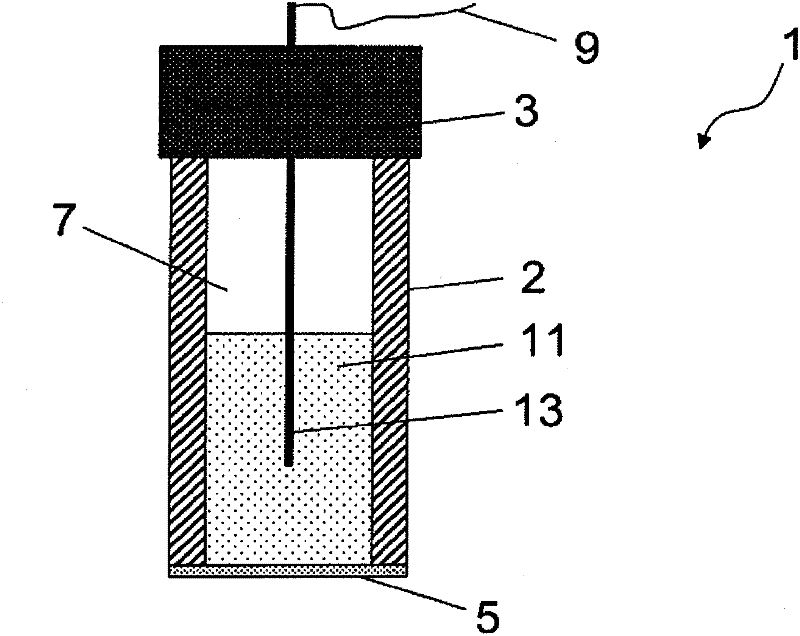
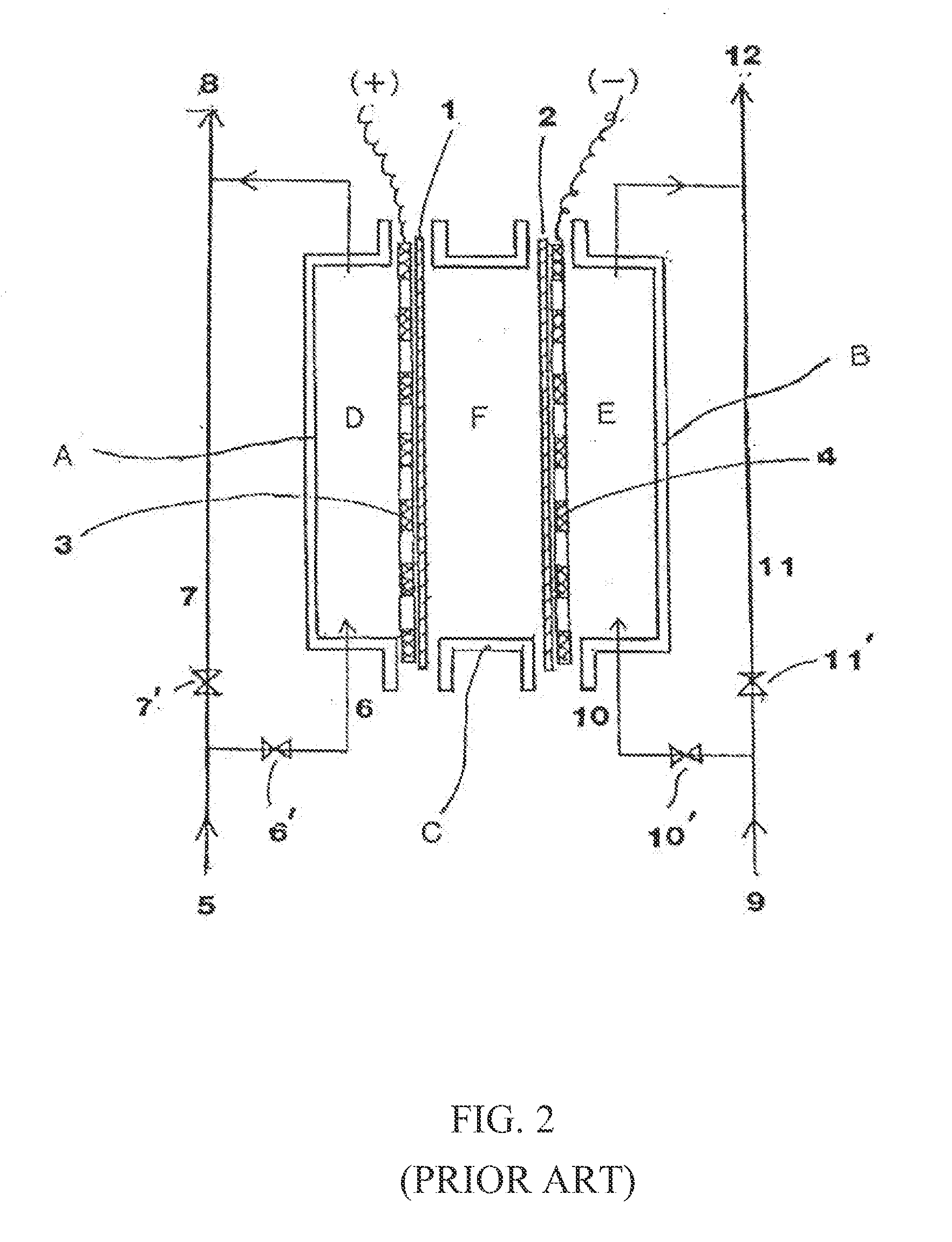
Dual Diaphragm Electrolysis cell assembly and method for generating a cleaning solution without any salt residues and simultaneously generating a sanitizing solution having a predetermined level of available free chlorine and PH
InactiveUS20150176142A1Improve cleanlinessHigh laminar flow rateCellsElectrode shape/formsPotassiumCell assembly
An electrolysis cell assembly to produce diluted Sodium Hydroxide solutions NaOH and diluted Hypochlorous Acid HOCl solutions having cleaning and sanitizing properties. The electrolysis cell consists of two insulating end pieces for a cylindrical electrolysis cell comprising at least two cylindrical electrodes with two cylindrical ion selective membranes arranged co-axially between them. The method of producing different volumes and concentrations of diluted NaOH solutions and diluted HOCl solutions comprises recirculating an aqueous sodium chloride or potassium chloride solution into the middle chamber of the cylindrical electrolytic cell and feeding softened filtered water into the cathode chamber and into the anode chamber of the cylindrical electrolysis cell.
Owner:AQUAOX
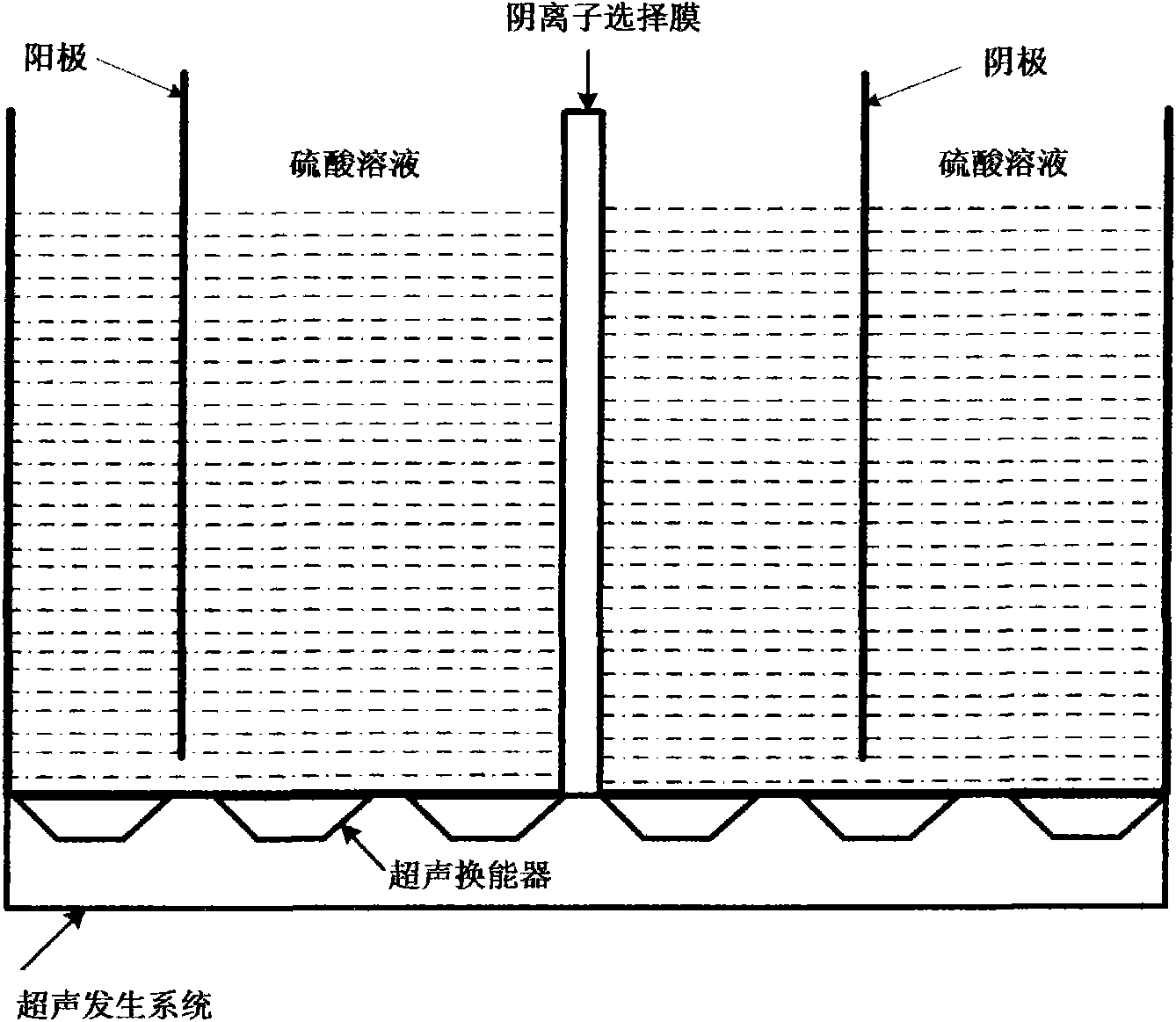
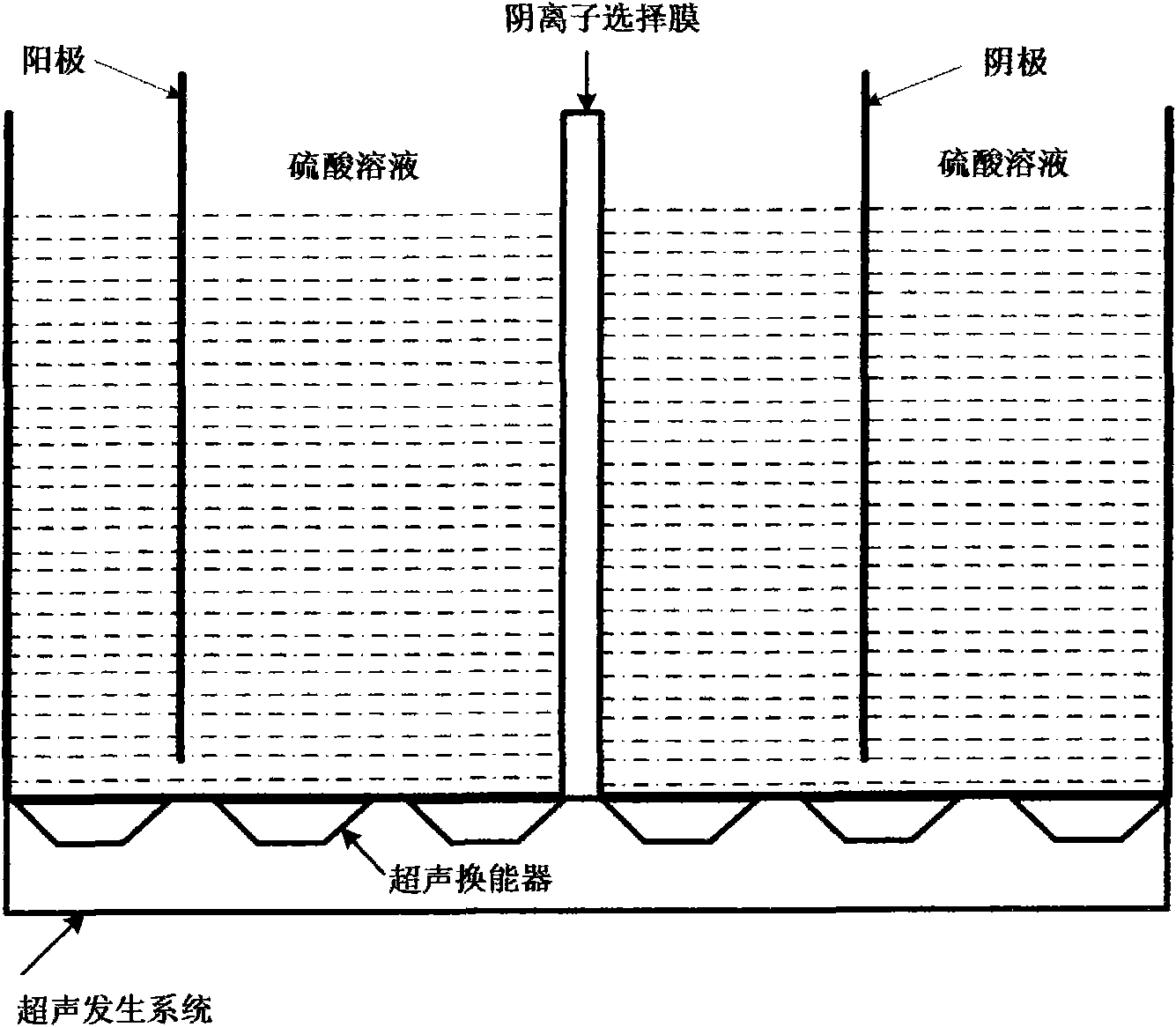
Method for preparing peroxysulfuric acid by sonoelectrochemical method
InactiveCN101864578ARaise the potentialHigh energyElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing peroxysulfuric acid by a sonoelectrochemical method, which is characterized in that in the method, a sulphuric acid solution is placed in an electrolyzer; pure platinum serves as an anode, and a lead board or thermal shock graphite serves as a cathode; the cathode and the anode are separated by a sulfonic group anion selecting membrane; an ultrasonic is added at the bottom of the electrolyzer; the electrolysis temperature is 0-40 DEG C, and the electrolysis voltage is kept between 3V and 7V, and the current density is 1000A / m<2>-6000A / m<2>; the frequency of the added ultrasonic is 20kHz-100kHz, the sound intensity of the ultrasonic is 5-20W / m<2>, and the electrolysis time of the ultrasonic is 1-5 hours; and sulfate radicals in the sulphuric acid solution at the anode zone is subject to an oxidation reaction to produce the peroxysulfuric acid. Compared with the conventional method for preparing peroxysulfuric acid by the high concentration synthesis method, the invention has the advantages of simple method, reduced energy consumption, shortened reaction time, higher activity of a generated oxidant and the like.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Potentiometric urea sensor based on ion-selective electrode
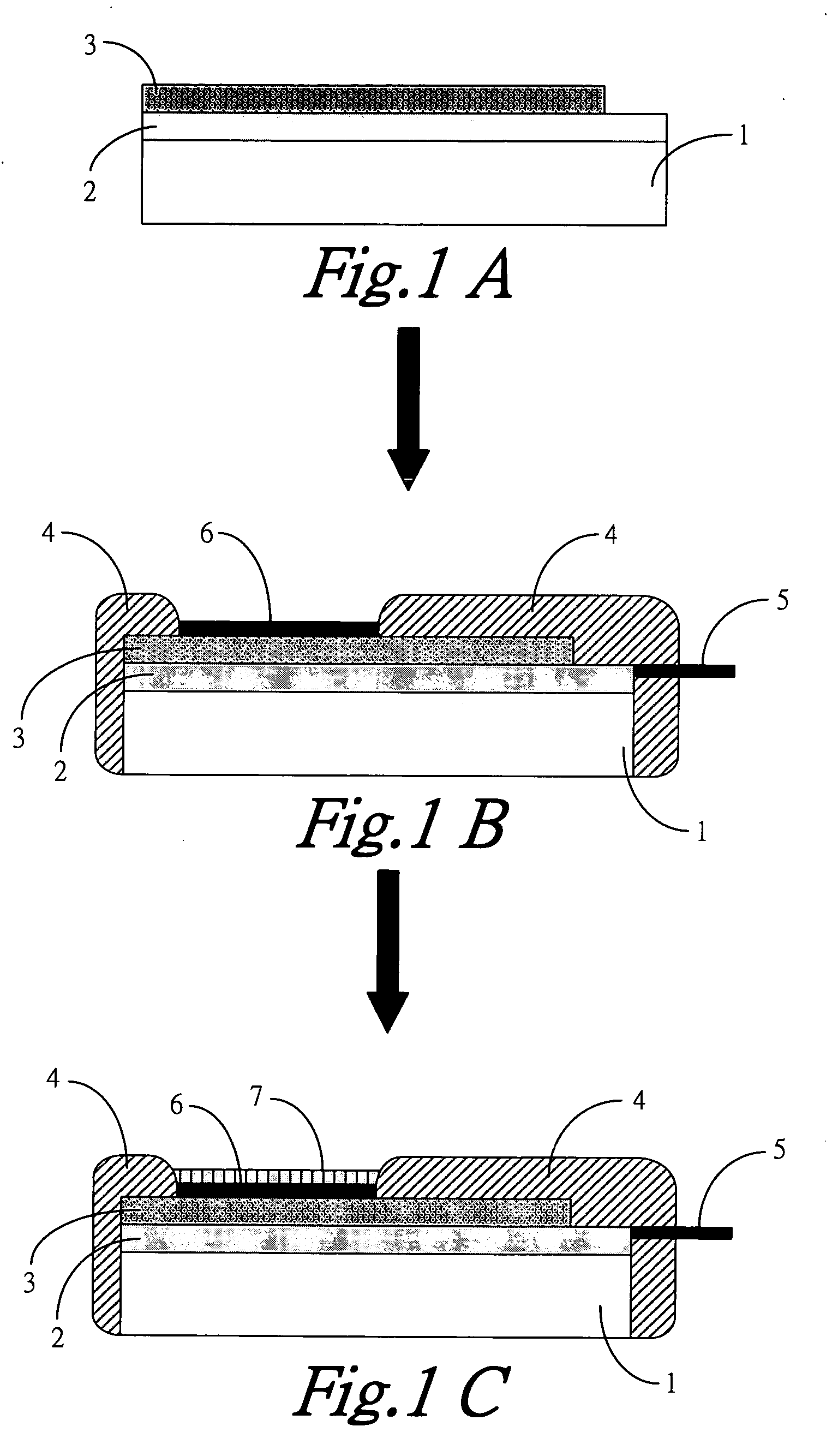
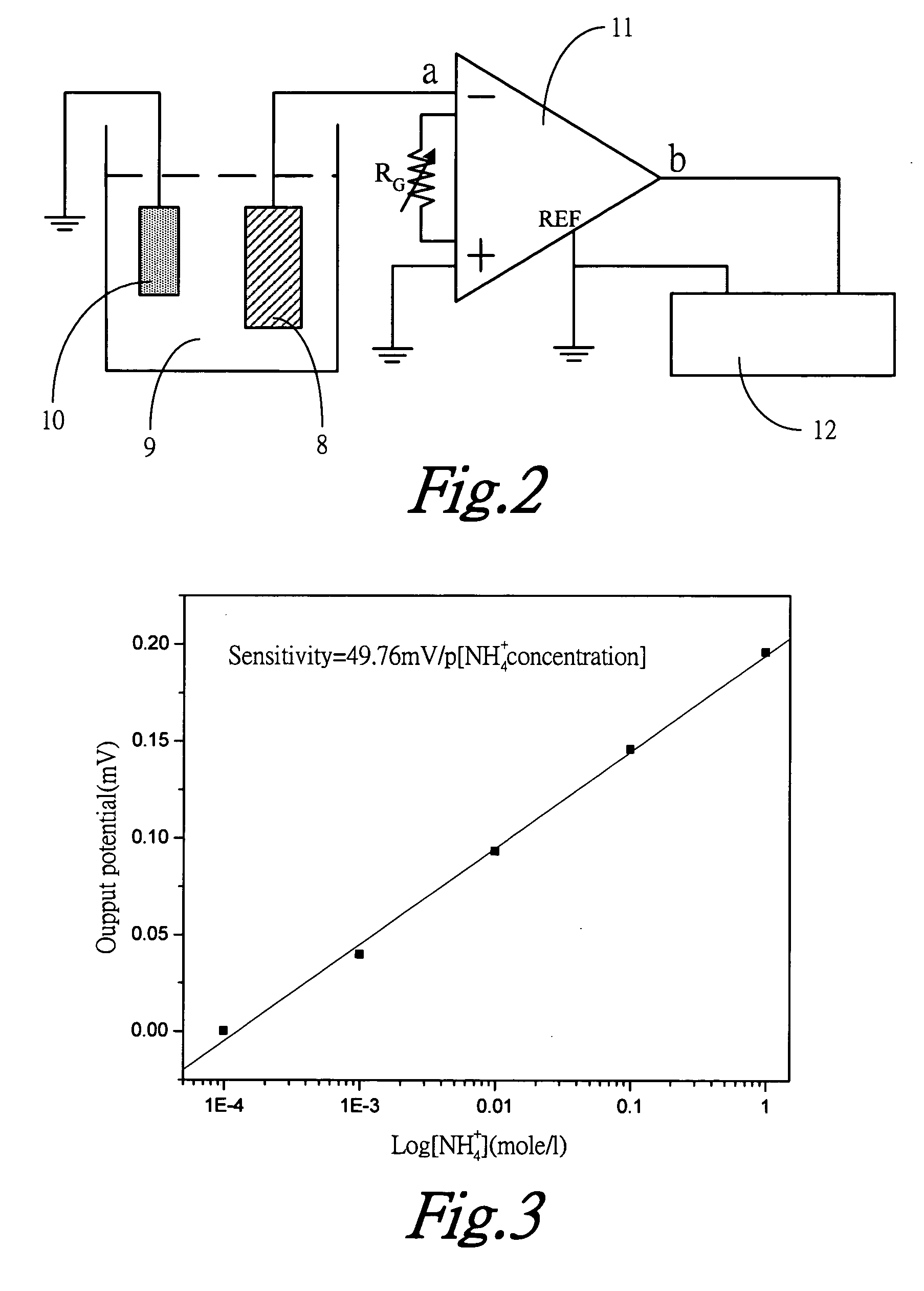
InactiveUS20060096858A1Low costEasy to packImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzymeIon selective membrane
The present invention is a sensor for detecting urea using a separating-style structure of ion-selective electrode, in which an ammonium ion-selective membrane is immobilized on a conductive layer on the surface of a substrate, said conductive layer has a sensing region and a non-sensing region after packaged, and a conductive line is used to retrieve a sensing signal from said conductive layer. In the end, employing the enzyme immobilization method to immobilize a urea enzyme onto ammonium ion-selective membrane, thus the fabrication of a potentiometric urea sensor is completed.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
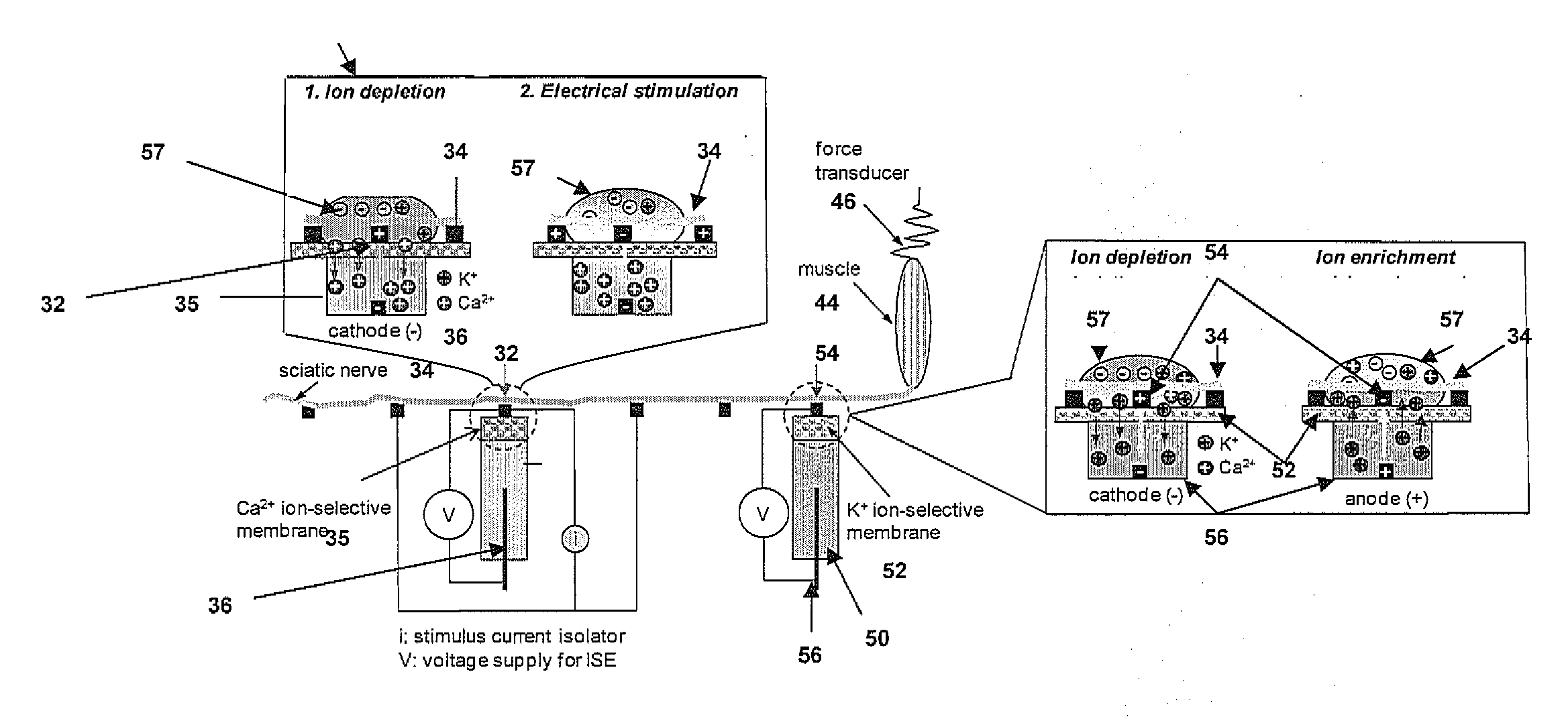
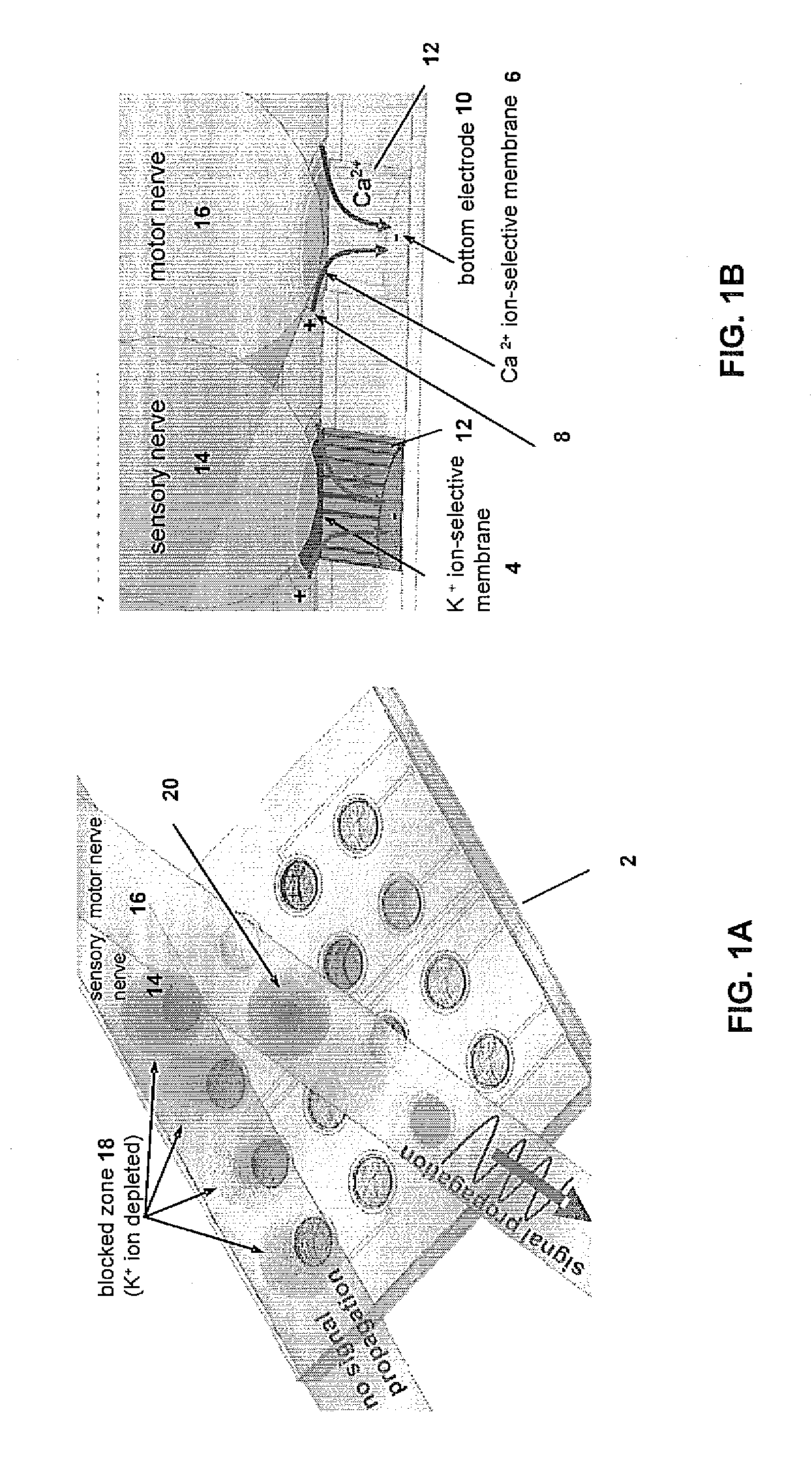
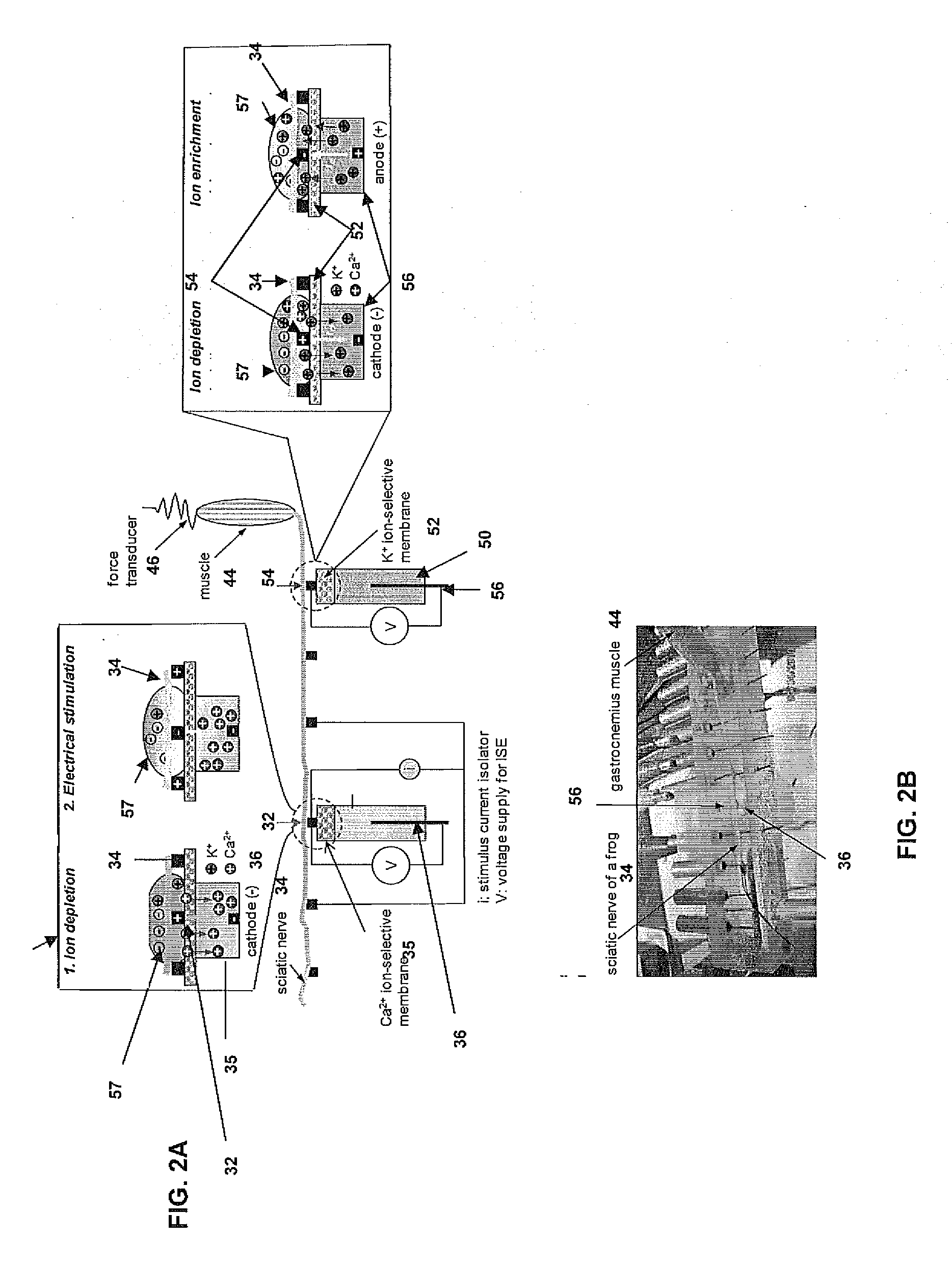
Microfabricated ion-selective electrodes for functional electrical stimulation and neural blocking
A neural prosthetic device is provided that includes one or more ion-selective membranes enabled by electrically-controlled local modulation of ion concentrations around a nerve so as to achieve different excitability states of the nerve for electrical stimulation or inhibition of nerve signal propagation. The local modulation is achieved by positioning the nerve in a bipolar perpendicular arrangement so as to modulate the ion concentrations of the one or more ion-selective membranes in situ to change the nerve excitability locally at the site of electrical stimulation or along the nerve for on-demand suppression of nerve propagation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com