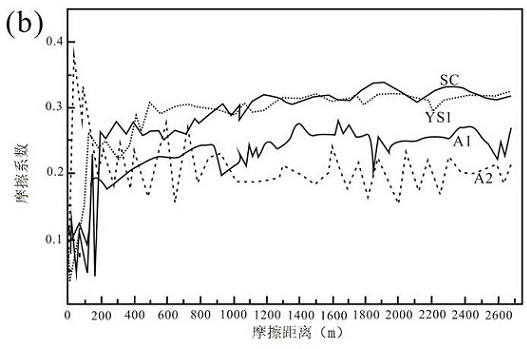
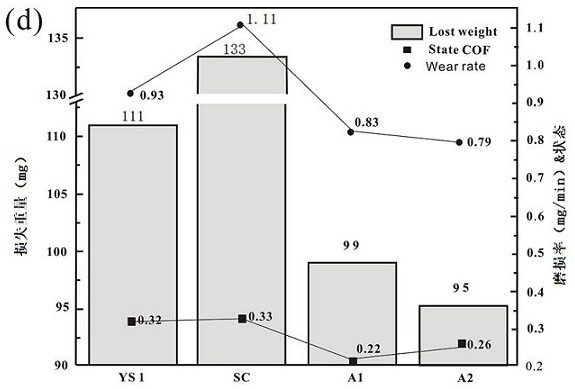
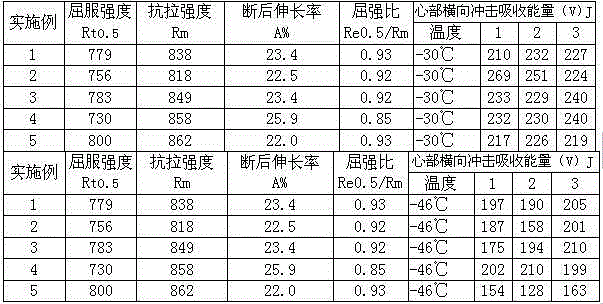
Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Toughness does not decrease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
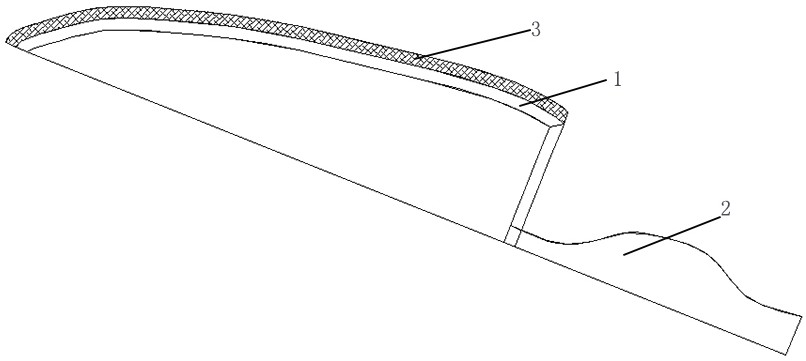
Tool for strengthening blade through laser cladding technology
ActiveCN106119838ASmall and uniform tissueLow dilution rateMetallic material coating processesMetal working apparatusAlloyLaser
The invention discloses a tool for strengthening a blade through the laser cladding technology. The tool comprises a tool body and a handle. The position of a cutting edge line of the tool body is provided with a cladding layer in a cladding manner, wherein the cladding layer is formed by abrasion-resisting hard alloy mixed powder. The hard alloy mixed powder is formed by mixing nickel-base alloy powder and tungsten carbide powder according to the proportion. By mass percent, the nickel-base alloy powder accounts for 40%-70%, and the tungsten carbide powder accounts for 30%-60%. The nickel-base alloy powder comprises, by mass percent, 18%-23% of Cr, 4%-7% of Fe, 2%-4.5% of Nb, 8%-11.5% of Mo, 0.2%-0.4% of Al, 1%-2.5% of Ti, 0.1%-0.6% of C, 0.2%-0.5% of Si, 0.2%-0.6% of Mn, 1.5%-2.5% of V and the balance Ni. The tool has the beneficial effects that the cladding layer and the tool body are in well metallurgy combination, the structure of the cladding layer is fine and uniform, and the dilution rate is low; after the tool body is sharpened, the hardness, sharpness, abrasion resistance and corrosion resistance of a blade part are greatly improved, cost is low, the hardness of the blade part is improved, and meanwhile tenacity cannot be reduced.
Owner:YANGJIANG KNIFESCISSOR HARDWARE RES INSTITUTION OF IND TECH +1
High-ductility steel for hot-bending bends and production method for hot rolled plates thereof
InactiveCN101161847AReasonable design of ingredientsReduce manufacturing costTemperature control deviceHeat treatment process controlHeating temperatureImpurity
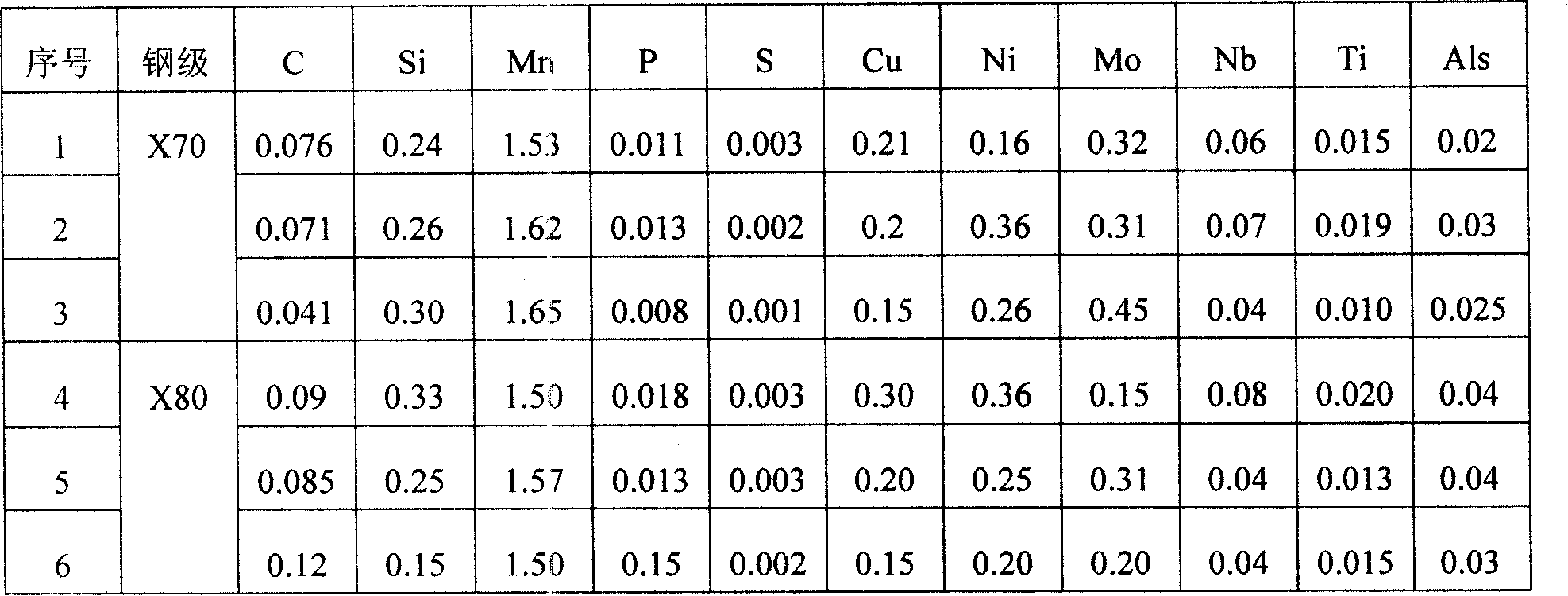
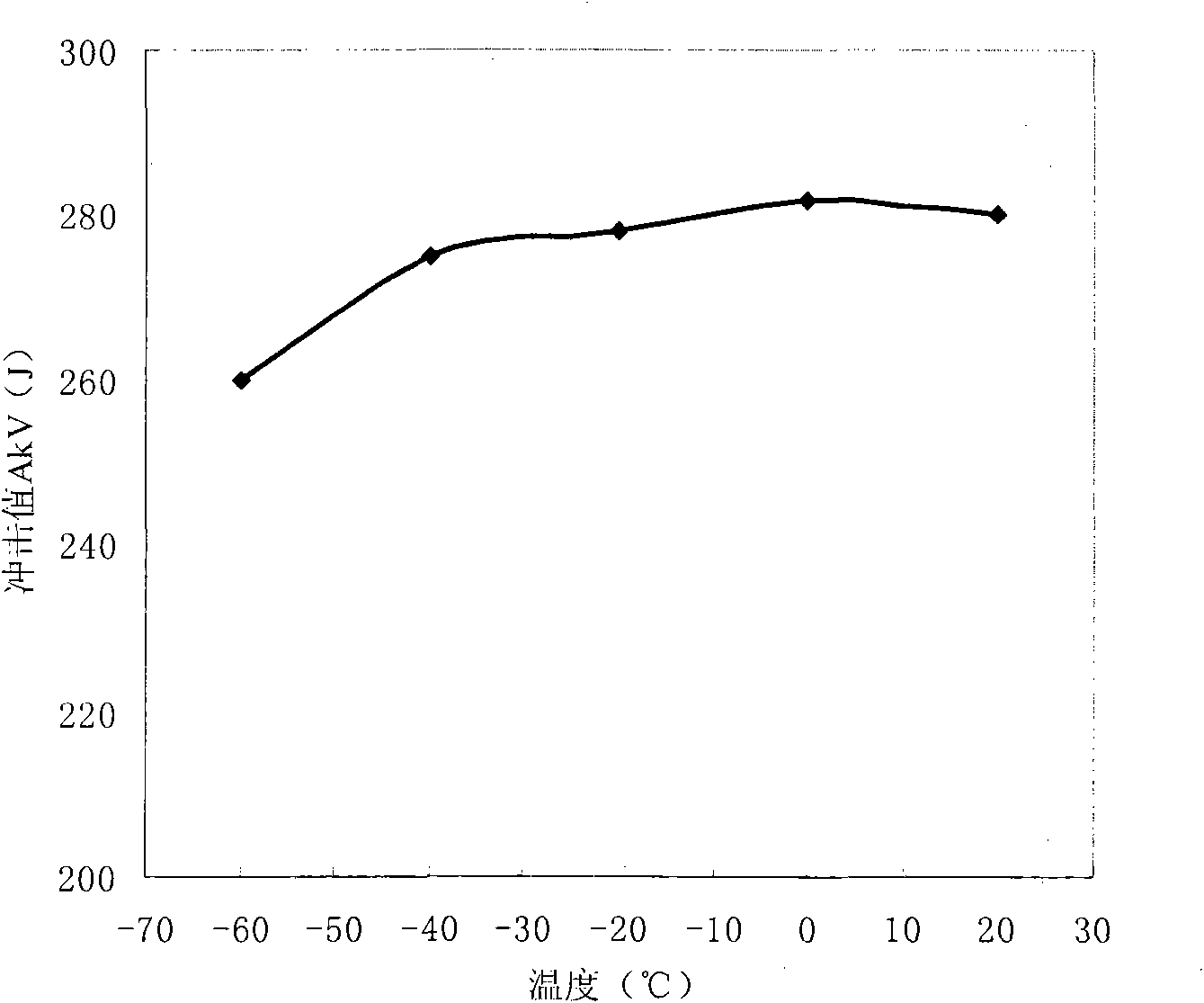
The invention provides a high toughness steel for hot bending bent steel and a production method of hot rolling flat plate thereof. The chemical compositions of the steel (weight percentage) comprise: C of 0.04 percent to 0.12 percent, Si of 10 percent to 0.30 percent, Mn of 1.50 percent to 1.65 percent, Nb of 0.04 percent to 0.08 percent, Ti of 0.008 percent to 0.025 percent, Ni of 0.15 percent to 0.36 percent, Mo of 0.15 percent to 0.30 percent, remaining iron and unavoidable impurities. The production method of the hot rolling flat plate comprises smelting, refining outside the hearth and continuous casting. Steel rolling is adopted a controlled rolling controlled cooling technics. The heating temperature of plate blank is ranged from 1160 DEG C to 1220 DEG C. Rough rolling temperature is ranged from 1010 DEG C to 1150 DEG C. Precision rolling temperature is ranged from 800 DEG C to 950 DEG C. Controlled cooling speed after rolled is ranged from 15 DEG C / s to 30 DEG C / s. Terminal cooling temperature is ranged from 450 DEG C to 600 DEG C. The invention has reasonable ingredient design. The production cost of the invention can be reduced about 15 percent compared to the prior art. The hot rolling steel plate of the invention can get composite organization with bainite as main part and has good low temperature toughness. The ballistic power is larger than 220 J in 20 DEG C below zero and the shearing area of DWTT at 15 DEG C below zero reaches up to 90 percent. The yield strength of the product reaches up to 520MPa and the tension resistance reaches up to 570MPa. The hot rolling steel toughness of the invention is not reduced after treatment and has better obdurability.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Duplex stainless steel with pitting corrosion resistance and favourable cold temperature flexibility and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101684542AImprove solubilityDecreased low temperature toughnessChemical compositionRoom temperature
The invention discloses a duplex stainless steel with pitting corrosion resistance and favourable cold temperature flexibility and a manufacturing method thereof. The duplex stainless steel comprisesthe following components in mass percentage: 0.01-0.10% of C, 0.2-1.0% of Si, more than 0% and less than 1.5% of Mn, 20.0-22.0% of Cr, 1.8-4.0% of Ni, 0.08-0.2% of N, more than 0% and less than 0.5% of Mo, less than or equal to 1.0% of one or more than one of W and Cu and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The invention controls Mn content below 1.5% until zero and simultaneously adjusts the content of elements of N, Ni and the like to ensure that steel has high strength, favourable corrosion resistance and favourable impact toughness at room temperature and low temperature when steel contains no or small amount of noble element Mo; meanwhile, the duplex stainless steel has low cost and small hot working difficulty, can be largely applied in the fields of buildings along the coast,petrochemical industry and the like and can replace 304 austenitic stainless steel of which the nickel content is above 8% at room temperature and lower temperature.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Compound film enhanced by inclusion complex of ring molecule and polymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101462388AStrong specificityGood controllabilitySynthetic resin layered productsSolventSelf assemble
The invention discloses a composite membrane reinforced by an inclusion complex of ring molecules and a polymer. The composite membrane is mainly formed by a polymer layer consisting of a linear polymer or a branch polymer and an inclusion complex layer formed by serially sleeving the ring molecules on partial chain links of the polymer which are compounded and accumulated layer by layer. The preparation of the composite membrane mainly comprises the following steps: a polymer component and a ring molecule component are dissolved into a solvent respectively to be prepared into a solution; and a substrate material is alternately immersed into the solution prepared by the polymer component and the ring molecule component, is kept stand for a period of time, and is taken out to remove excessive adhesive substances, and a multi-layer membrane system can be obtained by circulating the process. Compared with the prior art, a supermolecular multi-layer membrane greatly strengthens the mechanical property and the friction-resistant performance of the multi-layer membrane by introducing a self-assembling inclusion component of the polymer and the ring molecules, and has broad varieties of selectable polymers and broad application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
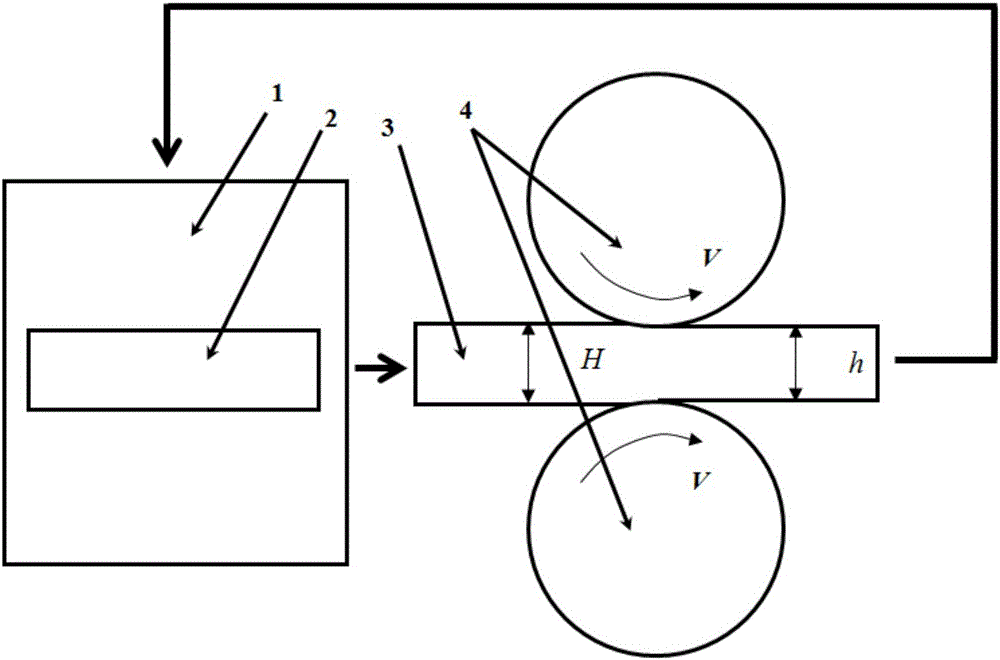
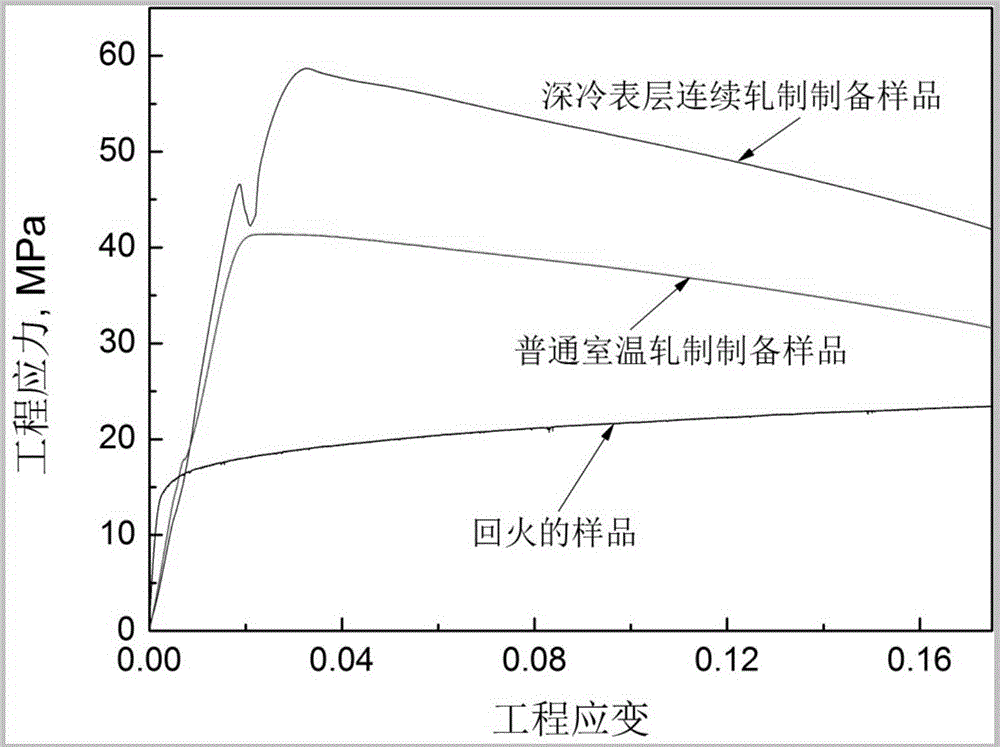
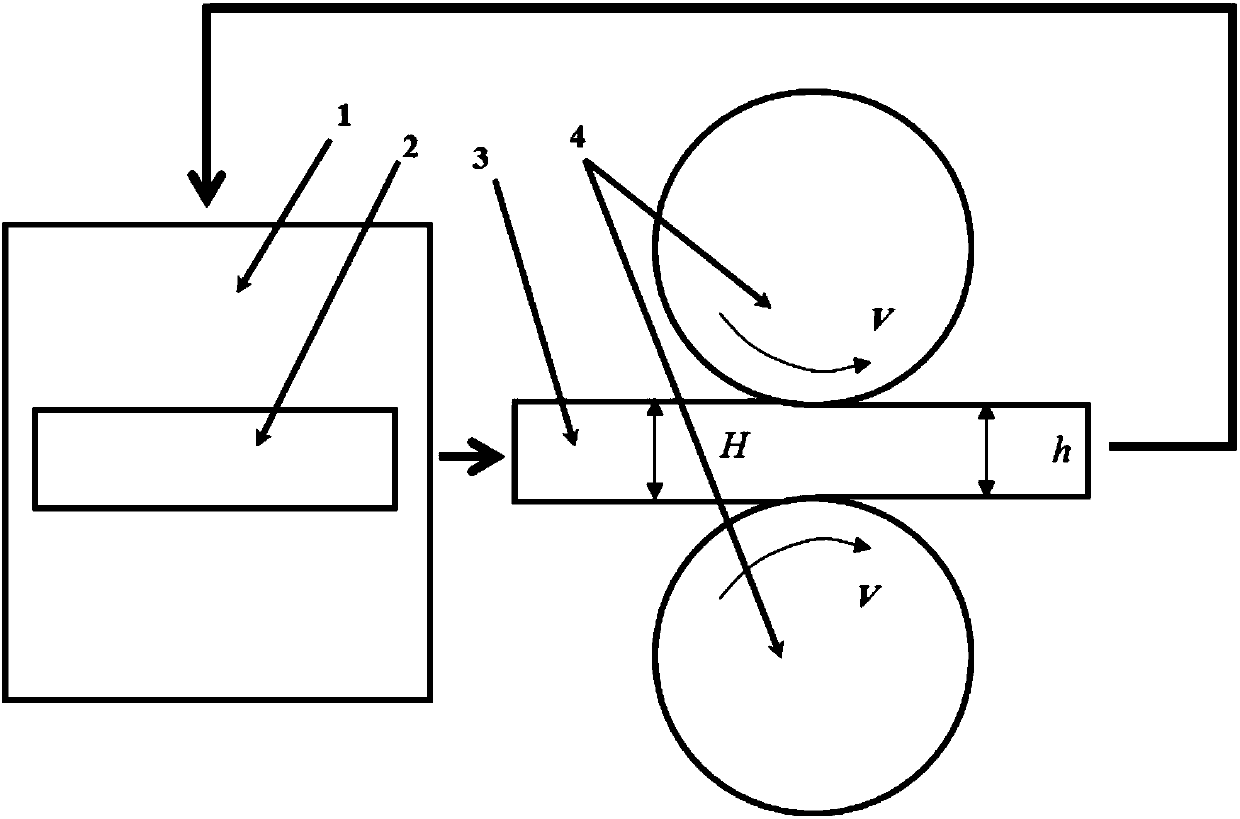
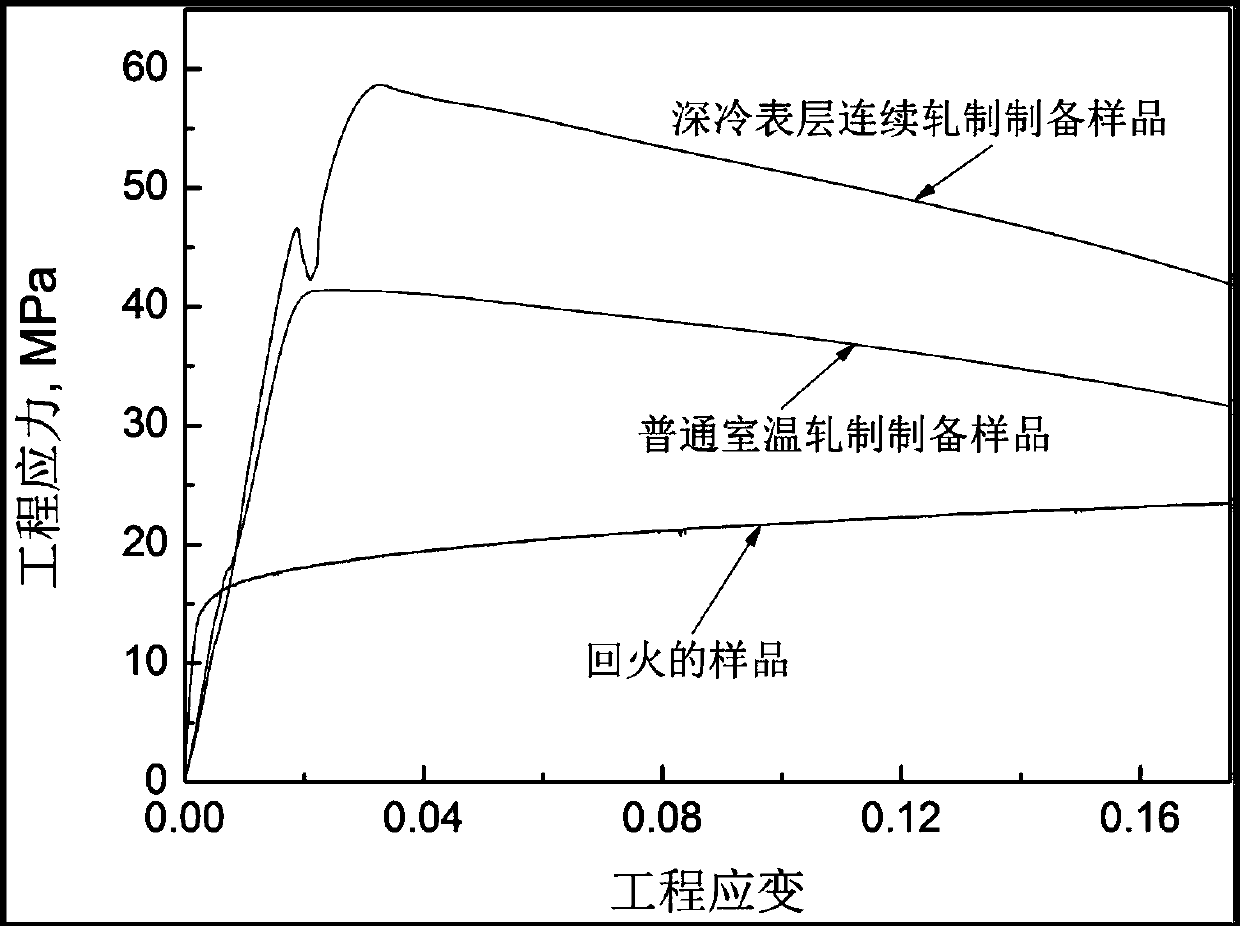
Deep-cooling surface-layer continuous-rolling preparation method for gradient strip
The invention provides a deep-cooling surface-layer continuous-rolling preparation method for a gradient strip. Grains in the surface-layer area are promoted to be refined through plastic deformation of the surface layer of a material, and meanwhile, recrystallization of ultra-fine grains in the plastic deformation process is restrained through ultralow-temperature deformation, so that a nano-structure is formed on the surface of the material; through multi-pass deep-cooling surface-layer rolling, the strip of a gradient structure is formed through a rolled piece, the surface layer of the material is of an ultra-fine grain structure, and coarse grains are located on the central area of the material; and compared with a material which is prepared through traditional cold rolling, the strength of the material is greatly improved under the condition that the material has better plasticity. Compared with the prior art that deep-cooling surface-layer rolling is only suitable for pure aluminum and aluminum alloy materials currently, through the technique, the tenacity of the material is hardly reduced, and the strength of the material can be improved by 30% or over.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for improving properties of H13 die steel by adding nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for improving properties of H13 die steel by adding nitrogen and belongs to the field of metal materials. In the method, chemical compositions of conventional H13 steel are improved, the strength, hardness and abrasive resistance of the die steel are improved by adding solid solution nitrogen element, and the toughness is not reduced. The nitrogen element is added by a method of adding a chromium nitride preliminary alloy, and other elements are added by a conventional method. In order to ensure yield of the nitrogen element during smelting, and reduce overflowing in the process of smelting and air bubbles during solidification, a smelting temperature is strictly controlled to be higher than a melting point within 50 DEG C, and the casting is quickly performed after the alloys completely smelt. The nitrogenous H13 die steel comprises the following chemical compositions by percentage: 0.28 to 0.40 percent of carbon, 0.8 to 1.2 percent of silicon, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of manganese, 4.75 to 5.5 percent of chromium, 1.10 to 1.75 percent of molybdenum, 0.8 to 1.2 percent of vanadium, 0.02 to 0.08 percent of nitrogen, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of phosphorus, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of sulfur and the balance of Fe. A forge piece after thermal treatment has the following properties: the hardness value is 53 to 55HRC, the tensile strength is over 1,800MPa, the yield strength is over 1,480MPa, the impact absorption power value is between 15 and 16 J, the strength and hardness are higher than those of the H13 steel, and the toughness is not lower than that of the H13 steel.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Low-alloy steel plate and heat treatment method for steel plate
The invention discloses a low-alloy steel plate and a heat treatment method for the steel plate. The strong-strength low-alloy steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.12 to 0.20 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.60 percent of Si, 1.20 to 1.80 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.030 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.030 percent of S, 0.020 to 0.080 percent of Nb, less than or equal to 0.050 percent of V, 0.010 to 0.060 percent of Ti, 0.015 to 0.045 percent of Al and the balance of Fe and trace impurities. According to the low-alloy steel plate and the heat treatment method for the steel plate, the strength loss of the steel plate after heat treatment can be effectively reduced, the yield strength and the tensile strength of the steel plate are strengthened by more than 30MPa compared with those of a conventional normalized steel plate, the alloy element content of the normalized steel plate can be effectively reduced, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:LAIWU STEEL YINSHAN SECTION CO LTD
Medium-carbon alloy cast steel shots and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to medium-carbon alloy cast steel shots and a manufacturing method thereof. Each medium-carbon alloy cast steel shot comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.35 to 0.45 percent of carbon, 0 to 0.2 silicon, 0.45 to 0.5 percent of manganese, 0.8 to 1.2 percent of chrome, 0 to 0.015 percent of sulfur, 0 to 0.020 percent of phosphor and the balance of iron and inevitable impurities. The manufacturing process comprises the following steps of: mixing and smelting, namely, smelting the raw material composition mixed proportionally into liquid steel, pouring the liquid steel into a tundish and performing deoxygenation by adopting an deoxidant; preparing shots by a centrifugally forming method, namely, pouring deoxygenized liquid steel into a centrifugal disc which rotates at a high speed, throwing out the liquid steel under the action of a centrifugal force to make the liquid steel fall into a cooling water pool, and taking the liquid steel out and drying the cooled steel to obtain formed cast steel shots; and performing heat treatment, namely, heating the formed cast steel shots until the temperature reaches 860 to 880 DEG C, performing cold quenching after keeping the temperature for 20 to 40 minutes, tempering for 40 to 80 minutes at the temperature of between 350 and 500 DEG C, and after tempering, cooling rapidly by a steel plate vibrating screen water cooling method to produce the medium-carbon alloy cast steel shots. The medium-carbon alloy cast steel shots and the manufacturing method thereof have the advantages of guaranteeing the high rigidity of the steel shots, avoiding crack generated in the centrifugally forming process and the heating tempering process, improving the toughness and the like.
Owner:淄博大亚金属科技股份有限公司
Steel plate for Ni-Mo low-temperature high-ductility X100 pipe fittings and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a steel plate for Ni-Mo low-temperature high-ductility X100 pipe fittings. The steel plate is prepared from the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.09-0.12% of C, 1.5-1.9% of Mn, 0.1-0.3% of Si, less than or equal to 0.003% of S, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, 0.04-0.065% of Nb, 0.008-0.003% of Ti, 0.02-0.10% of V, less than or equal to 0.06% of Alt, less than or equal to 0.010% of N, less than or equal to 0.006% of O, 0.40-0.50% of Mo, less than or equal to 0.35% of Cu, 0.51-0.65% of Ni, less than or equal to 0.35% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.01% of Ca and the balance of Fe. The manufacturing process of the steel plate comprises liquid steel smelting, external refining, plate blank reheating, TMCP process and quenched-tempered heat treatment; the finished product has high strength and high low-temperature ductility, and is welded and matched with an X100 main body pipeline; the process window of the heat treatment is widened by the ratio of the components Ni and Mo, and therefore, the yield and the percent of pass of the steel products are increased.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
High-alloy tool steel plate and production method thereof
InactiveCN110055457AToughness does not decreaseHigh strengthQuenching agentsChemical compositionSheet steel
The invention discloses a high-alloy tool steel plate and a production method thereof. The steel plate is prepared from the chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.5 to 0.6 percent of C, 0.15 to0.35 percent of Si, less than or equal to 0.025 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.025 percent of S, 1.5 to 1.8 percent of Mn, 0.25 to 0.35 percent of Mo, 0.07 to 0.12 percent of V, and the balanceFe and inevitable impurities. The production method comprises the processes of heating, rolling and heat-treating. According to the high-alloy tool steel plate and the production method thereof provided by the invention, by adopting the composition design without Cr and Ni adding and with low Mo, and through optimizing the heat treatment process, the performance of the steel plate is ensured, theimpact toughness is improved, and a greater benefit is brought for the manufacturing and using departments; and the produced high-alloy tool steel plate has favorable mechanical property and processability, has an excellent pressure casting performance, and meets the production needs of large die molds requiring high hardness such as pressure casting dies, supporting tools and die holders.
Owner:WUYANG IRON & STEEL
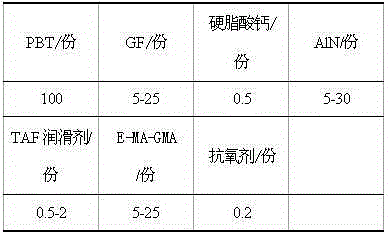
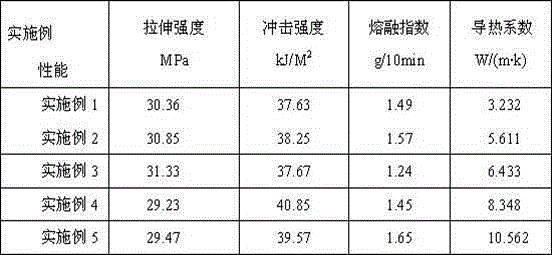
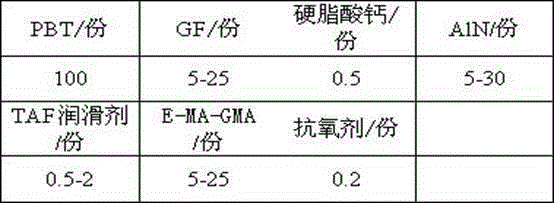
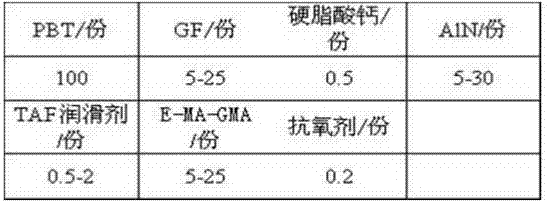
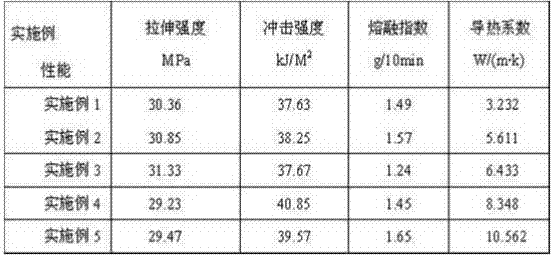
Heat-conduction heatproof PBT material for LED lamp holders, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105237967AGuaranteed StrengthToughness does not decreaseGlycidyl methacrylatePlastic materials
The invention relates to a heatproof plastic material and a preparation method thereof, and concretely relates to a heat-conduction heatproof PBT material for LED lamp holders, and a preparation method thereof. The heat-conduction heatproof PBT is mainly composed of a resin matrix, a reinforcing system, a heat conduction system, a lubrication system and an anti-oxidation system, wherein the resin matrix is PBT; the reinforcing system is glass fibers; the lubrication system is a TAF lubricant and calcium stearate; and the anti-oxidation system is an antioxidant 1010. The heat-conduction heatproof PBT material prepared in the invention adopts the glass fibers as a reinforcing skeleton, ethylene-methyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer (E-MA-GMA) as a compatibilizer and filled AlN as a heat conduction factor, so good strength and toughness are maintained on the premise of guaranteeing of the high heat conductivity of the PBT material; and the advantages of workability and low batch production cost of the PBT plastic make the heat conduction plastic be applied in LED lamp holder related fields.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Medium-carbon niobium-vanadium microalloying high-speed wheel steel and wheel preparation method
InactiveCN111961963AHigh strengthIncreased hardness levelFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesNiobiumUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses medium-carbon niobium-vanadium microalloying high-speed wheel steel and a wheel preparation method, and belongs to the field of railway wheel preparation. The medium-carbon niobium-vanadium microalloying high-speed wheel steel aims to solve the problems of poor adaptability and low strength and hardness of high-speed wheel steel in the prior art. The medium-carbon niobium-vanadium microalloying high-speed wheel steel comprises the following components of, by weight, 0.52%-0.56% of C, 0.15%-0.40% of Si, 0.50%-0.80% of Mn, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.015% of S, 0.01%-0.03% of Nb, 0.10%-0.20% of V and the balance Fe and inevitable impurity elements. According to the medium-carbon niobium-vanadium microalloying high-speed wheel steeland the wheel preparation method, Nb and V elements are added to form a brand new component design system, and a corresponding heat treatment process is matched, so that the strength and hardness levels of a wheel are improved by more than 5% compared with those of an ER8 wheel on the premise that the toughness index of the wheel is not reduced, the contact fatigue resistance and the wear resistance are also improved, and the adaptability of the wheel is stronger.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A kind of PBT heat-conducting, heat-resistant material for LED lamp holder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105237967BGuaranteed StrengthToughness does not decreaseGlycidyl methacrylatePlastic materials
A PBT heat-conducting and heat-resistant material for LED lamp holders and a preparation method thereof, relating to a heat-resistant plastic material and a preparation method thereof, the heat-conducting and heat-resistant PBT mainly consists of a resin matrix, a reinforcement system, a heat conduction system, and a lubrication system , Composition of antioxidant system. Among them, the resin matrix is PBT; the reinforcement system is glass fiber; the lubrication system is TAF lubricant and calcium stearate; the antioxidant system is antioxidant 1010. The thermally conductive and heat-resistant PBT material prepared by the present invention uses glass fiber as a reinforcing skeleton, uses ethylene-methyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate terpolymer (E-MA-GMA) as a compatibilizer, and is filled with AlN. The thermal conductivity factor maintains good strength and toughness while ensuring the high thermal conductivity of the PBT material. At the same time, the advantages of PBT plastics such as easy processing and low mass production cost can make the thermal conductive plastic used in LED lamp holders and other related fields.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
High-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of alloy materials, and particularly relates to a high-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging and a preparation method thereof. The high-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging is composed of the following elements in percentage by mass: 0.78 percent to 0.84 percent of Si, 1.18 percent to 1.24 percent of Mg, 0.38 percent to 0.42 percent of Cu, 0.20 percent to 0.25 percent of Fe, 0.12 percent to 0.15 percent of Mn, 0.23 percent to 0.26 percent of Cr, 0.01 percent to 0.05 percent of Ti, 0.01 percent to 0.03 percent of Sc and the balance Al. According to the high-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging and the preparation method thereof provided by the invention, by optimizing alloy components, assisting in adding silicon nitride powder and adopting the optimized aluminum bar heating process, solid solution process and aging process after die forging, the comprehensive performancerequirement of the aluminum alloy die forging is met, and the prepared aluminum alloy die forging is good in surface quality, good in performance of finished forgings in industrial production and excellent in comprehensive mechanical property.
Owner:山东骏程金属科技有限公司
Method for improving properties of H13 die steel by adding nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for improving properties of H13 die steel by adding nitrogen and belongs to the field of metal materials. In the method, chemical compositions of conventional H13 steel are improved, the strength, hardness and abrasive resistance of the die steel are improved by adding solid solution nitrogen element, and the toughness is not reduced. The nitrogen element is added by a method of adding a chromium nitride preliminary alloy, and other elements are added by a conventional method. In order to ensure yield of the nitrogen element during smelting, and reduce overflowing in the process of smelting and air bubbles during solidification, a smelting temperature is strictly controlled to be higher than a melting point within 50 DEG C, and the casting is quickly performed after the alloys completely smelt. The nitrogenous H13 die steel comprises the following chemical compositions by percentage: 0.28 to 0.40 percent of carbon, 0.8 to 1.2 percent of silicon, 0.2 to 0.5 percent of manganese, 4.75 to 5.5 percent of chromium, 1.10 to 1.75 percent of molybdenum, 0.8 to 1.2 percent of vanadium, 0.02 to 0.08 percent of nitrogen, less than or equal to 0.03 percent ofphosphorus, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of sulfur and the balance of Fe. A forge piece after thermal treatment has the following properties: the hardness value is 53 to 55HRC, the tensile strength is over 1,800MPa, the yield strength is over 1,480MPa, the impact absorption power value is between 15 and 16 J, the strength and hardness are higher than those of the H13 steel, and the toughness is not lower than that of the H13 steel.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Steel for in-situ nano reinforced and toughened crankshaft
ActiveCN113755760ASuppress generationReduce formationProcess efficiency improvementStress concentrationNanowire
The invention relates to steel for an in-situ nano reinforced and toughened crankshaft. The steel is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 0.40 to 0.42 percent of carbon, 0.23 to 0.27 percent of silicon, 0.70 to 0.74 percent of manganese, 1.08 to 1.18 percent of chromium, 0.21 to 0.23 percent of molybdenum, 0.005 to 0.015 percent of titanium, 0.02 to 0.04 percent of vanadium, 0.010 to 0.040 percent of aluminum, 0.014 to 0.025 percent of sulfur and less than or equal to 0.015 percent of phosphorus. According to the steel, trace alloy elements vanadium and rare earth nanowires are added in the refining process, and a series of operations of refining steps are improved, so that a large number of in-situ nano-particles which are dispersively distributed are formed in the processes of steel melt, solidification and the like, the particle size is 2-30 nanometers, the distance between the nano-particles is 20-100 nanometers, 109-1012 nano-particles are contained in each crystal grain, a large number of in-situ nano-particles are dispersed and distributed, so that the generation of columnar crystals is inhibited, fine isometric crystals are formed, macrosegregation is improved, the formation and size of brittle phases are reduced, and the strength and plasticity of the crankshaft steel are improved; the in-situ nanoparticles and the matrix are in a coherent or semi-coherent relationship, dislocation is not easy to accumulate, stress concentration is reduced, so that the toughness is not reduced, and the contradictory problem of strengthening and toughening is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Anti-carburizing construction process for casting cooling water pipe in blast furnace cooling wall
ActiveCN102367498AGuaranteed uniformityGuaranteed confidentialityMolten spray coatingCooling devicesWater basedChemical combination
The invention discloses an anti-carburizing construction process for casting a cooling water pipe in a blast furnace cooling wall, belonging to the technical field of the preparation of the metallurgical machinery. The invention provides an anti-carburizing construction process for casting the cooling water pipe in the blast furnace cooling wall without carburizing on the outer surface of the cooling water pipe and forming a carburizing layer. The anti-carburizing construction process comprises the following steps: bending the cooling water pipe, and derusting the bended cooling water pipe; then spraying an Al2O3 layer of which thickness is no more than 0.10-0.15mm on the outer surface of the cooling water pipe; then painting a water-based zircon powder paint layer of which thickness is no more than 0.2mm on the outer surface of the qualifiedly sprayed cooling water pipe, and drying; and finally embedding the cooling water pipe in a casting mould cavity, assembling the mould and casting the cooling wall, wherein the Al2O3 coating is directly formed through the chemical combination of the molten Al wire and oxygen in air during the spraying process.
Owner:SICHUAN HONGJIAN HEAVY MACHINERY MFG
Polyurethane foam based on graphene modification and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112920364AHigh mechanical strengthPlay an antibacterial and antibacterial rolePolyesterPolymer science
The invention discloses a polyurethane foam based on graphene modification, and particularly relates to the technical field of polyurethane foam. The polyurethane foam is prepared from the following raw materials: polyether polyol, polyester polyol, isocyanate, modified graphene, a foaming agent, a catalyst and a foam stabilizer. Graphene is modified by utilizing isocyanate and doxorubicin hydrochloride, an isocyanate group is introduced to the surface of graphene, the isocyanate group can react with polyether polyol, the purpose of modifying polyurethane foam by graphene polymerization is achieved, doxorubicin hydrochloride is loaded on graphene by utilizing an ultrasonic oscillation mode, a hydrogen bond can be formed between graphene and doxorubicin hydrochloride, the mechanical strength of the polyurethane foam can be effectively improved under the action of an isocyanate group and the hydrogen bond, and doxorubicin hydrochloride contained in the polyurethane foam can effectively achieve antibacterial and bacteriostatic effects, so that the use requirements of people can be met.
Owner:江苏威久科技发展有限公司
PBT heat conducting and heat resisting material for LED lamp holder
InactiveCN108219387AGuaranteed StrengthToughness does not decreaseHeat-exchange elementsPolymer scienceGlycidyl methacrylate
The invention discloses a PBT heat conducting and heat resisting material for an LED lamp holder and a preparation method of the PBT heat conducting and heat resisting material and relates to a heat resisting plastic material and a preparation method thereof. The heat conducting and heat resisting PBT mainly comprises a resin matrix, a reinforcing system, a heat conducting system, a lubricating system and an antioxidant system; the resin matrix is PBT; the reinforcing system is glass fibers; the lubricating system comprises a TAF lubricant and calcium stearate; the antioxidant system is an antioxidant 1010. According to the heat conducting and heat resisting PBT material prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the glass fibers are used as a reinforcing framework, anethylene-methyl acrylate-glycidyl methacrylate (E-MA-GMA) terpolymer is used as a compatibilizer, and AIN is filled as a heat conducting factor; better strength and toughness are kept under the condition of ensuring high heat conductivity of the PBT material; meanwhile, the PBT plastic has the advantages of easiness in processing, batch production, low cost and the like, so that the heat conducting plastic is applied to the related fields of LED lamp holders and the like.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG XINDA ENTERPRISE GRP
Compound film enhanced by inclusion complex of ring molecule and polymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101462388BGuaranteed CompatibilityAvoid Interface SeparationSynthetic resin layered productsSolventChain link
The invention discloses a composite membrane reinforced by an inclusion complex of ring molecules and a polymer. The composite membrane is mainly formed by a polymer layer consisting of a linear polymer or a branch polymer and an inclusion complex layer formed by serially sleeving the ring molecules on partial chain links of the polymer which are compounded and accumulated layer by layer. The preparation of the composite membrane mainly comprises the following steps: a polymer component and a ring molecule component are dissolved into a solvent respectively to be prepared into a solution; anda substrate material is alternately immersed into the solution prepared by the polymer component and the ring molecule component, is kept stand for a period of time, and is taken out to remove excessive adhesive substances, and a multi-layer membrane system can be obtained by circulating the process. Compared with the prior art, a supermolecular multi-layer membrane greatly strengthens the mechanical property and the friction-resistant performance of the multi-layer membrane by introducing a self-assembling inclusion component of the polymer and the ring molecules, and has broad varieties of selectable polymers and broad application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method of slurry pump cylinder sleeve
ActiveCN114164318AIncreased inner surface hardnessReduce toughnessPositive displacement pump componentsFurnace typesWear resistanceMachining
The invention relates to the technical field of cylinder sleeve machining, in particular to a slurry pump cylinder sleeve manufacturing method which comprises the steps that firstly, a cylinder sleeve inner container is subjected to rough machining; secondly, the cylinder sleeve inner container obtained after rough machining is subjected to heat treatment; thirdly, the cylinder sleeve inner container subjected to magnetic field heat treatment in the second step is machined and polished; and fourthly, after the cylinder sleeve outer sleeve is heated to 400-500 DEG C, the cylinder sleeve outer sleeve and the polished cylinder sleeve inner container are subjected to embedding and machining, and then the slurry pump cylinder sleeve is obtained. The surface hardness and wear resistance of the prepared inner container are improved, the hardness of the double-metal cylinder sleeve is improved from 58-61 HRC to 63-64 HRC, and meanwhile the toughness and other mechanical properties of the prepared cylinder sleeve are improved.
Owner:东营天工石油工程技术有限公司
A kind of steel plate for ni-mo low-temperature high-toughness X100 pipe fittings and its manufacturing method
The invention discloses a Ni-Mo steel plate for low-temperature high-toughness X100 pipe fittings. The chemical composition of the steel plate is C: 0.09-0.12%, Mn: 1.5-1.9%, Si: 0.1-0.3%, and S: ≤0.003%, P: ≤0.015%, Nb: 0.04~0.065%, Ti: 0.008~0.03%, V: 0.02~0.10%, Alt: ≤0.06%, N:≤0.010%, O: ≤0.006%, Mo : 0.40~0.50%, Cu: ≤0.35%, Ni: 0.51~0.65%, Cr: ≤0.35%, Ca: ≤0.01%, and the rest is Fe. The manufacturing process includes molten steel smelting-external refining-slab reheating-TMCP process-quenching and tempering heat treatment. The finished product has high strength and high low-temperature toughness, which matches the welding of X100 main pipeline. The process window improves the yield and qualification rate of steel products.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Medium-carbon medium-silicon niobium microalloyed high-speed wheel steel and wheel preparation method
ActiveCN111996444AImprove adaptabilityHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesPearliteUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses medium-carbon medium-silicon niobium microalloyed high-speed wheel steel and a wheel preparation method, and belongs to the field of railway wheel preparation. Aiming at the problems that in the prior art, high-speed wheel steel is poor in adaptability and low in strength and hardness, the invention provides medium-carbon medium-silicon niobium microalloyed high-speed wheelsteel. The steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.50%-0.58% of C, 0.50%-0.80% of Si, 0.50%-0.90% of Mn, 0.02%-0.04% of Nb, no greater than 0.015% of P, no greater than 0.015% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurity elements. The niobium element is added into the components of the wheel steel; niobium and carbon are combined to form niobium carbide, the effect of refining pearlite groups is achieved during steel rolling and heat treatment, meanwhile, it is guaranteed that a certain amount of ferrite is separated out, the strength and toughness matching of the wheel steel is improved, the strength and hardness level is improved by 5% or above compared with an ER8 wheel, and the contact fatigue resistance and wear resistance are also improved. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, heat treatment is subjected to process optimization, so that the adaptability of the wheel is further improved, and the wheel has relatively high strength and hardness.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of mud pump cylinder liner
ActiveCN114164318BIncreased inner surface hardnessToughness does not decreasePositive displacement pump componentsFurnace typesThermodynamicsEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of cylinder liner processing, in particular to a method for preparing a mud pump cylinder liner. Step 1: Roughly process the cylinder liner liner; Step 2: Perform heat treatment on the rough-processed cylinder liner liner; Step 3 1. Process and polish the cylinder liner liner after the magnetic field heat treatment in step 2; step 4, heat the cylinder liner coat to 400-500°C and install and machine the polished cylinder liner liner to obtain the mud pump cylinder liner. The surface hardness and wear resistance of the liner prepared by the present invention are improved, and the hardness of the bimetallic cylinder liner is increased from the existing 58-61HRC to 63-64HRC. At the same time, the toughness and other mechanical properties of the cylinder liner prepared by the present invention are improved. .
Owner:东营天工石油工程技术有限公司
A kind of heat treatment method of low-alloy steel plate and steel plate
The invention discloses a low-alloy steel plate and a heat treatment method for the steel plate. The strong-strength low-alloy steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.12 to 0.20 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.60 percent of Si, 1.20 to 1.80 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.030 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.030 percent of S, 0.020 to 0.080 percent of Nb, less than or equal to 0.050 percent of V, 0.010 to 0.060 percent of Ti, 0.015 to 0.045 percent of Al and the balance of Fe and trace impurities. According to the low-alloy steel plate and the heat treatment method for the steel plate, the strength loss of the steel plate after heat treatment can be effectively reduced, the yield strength and the tensile strength of the steel plate are strengthened by more than 30MPa compared with those of a conventional normalized steel plate, the alloy element content of the normalized steel plate can be effectively reduced, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:LAIWU STEEL YINSHAN SECTION CO LTD
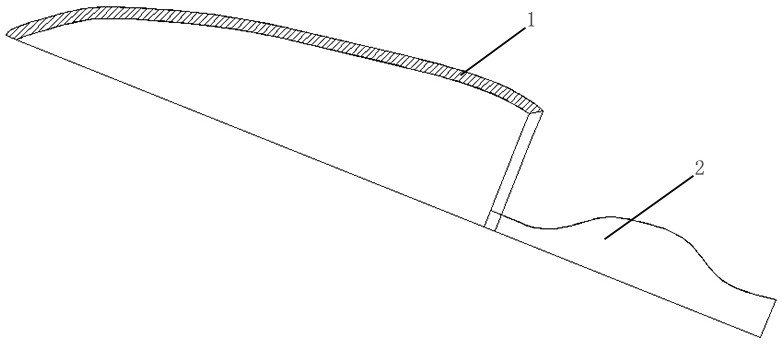
A knife that uses laser cladding technology to strengthen the blade
ActiveCN106119838BSmall and uniform tissueLow dilution rateMetallic material coating processesMetal working apparatusAlloyCemented carbide
The invention discloses a cutting tool which utilizes laser cladding technology to strengthen the cutting edge. Including the cutter body and the handle body, the cutting edge line position of the cutter body is clad with a layer of cladding layer formed by wear-resistant cemented carbide mixed powder, and the cemented carbide mixed powder is composed of nickel-based alloy powder and tungsten carbide powder The mass percentage of nickel-based alloy powder is 40%-70%, and the mass percentage of tungsten carbide powder is 30%-60%. The nickel-based alloy powder is composed of Cr: 18%-23%, Fe : 4%~7%, Nb: 2%~4.5%, Mo: 8%~11.5%, Al: 0.2%~0.4%, Ti: 1%~2.5%, C: 0.1%~0.6%, Si: 0.2 %~0.5%, Mn: 0.2%~0.6%, V: 1.5%~2.5%, the balance is Ni. The advantages of the present invention are that the cladding layer and the cutter body achieve good metallurgical bonding, the cladding layer structure is fine and uniform, and the dilution rate is low; after the cutter body is sharpened, the hardness, sharpness, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the blade are improved. Both have been greatly improved, the cost is low, and the toughness will not be reduced while increasing the hardness of the blade.
Owner:YANGJIANG KNIFESCISSOR HARDWARE RES INSTITUTION OF IND TECH +1
A high-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging and its preparation method
The invention belongs to the technical field of alloy materials, and in particular relates to a high-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging and a preparation method thereof. The high-strength and high-toughness aluminum alloy wheel die forging is composed of the following elements by mass percentage: Si: 0.78-0.84%, Mg: 1.18%-1.24%, Cu: 0.38%-0.42%, Fe: 0.20%-0.25%, Mn: 0.12% to 0.15%, Cr: 0.23% to 0.26%, Ti: 0.01% to 0.05%, Sc: 0.01% to 0.03%, and the balance Al. The present invention optimizes the alloy composition, assists in adding silicon nitride powder, and adopts optimized aluminum rod heating process, solid solution and aging process after die forging to meet the comprehensive performance requirements of aluminum alloy die forgings, and the prepared aluminum alloy die forgings The surface quality is good, the performance of finished forgings in industrial production is good, and the comprehensive mechanical properties are excellent.
Owner:山东骏程金属科技有限公司
A kind of deep-cooling surface layer continuous rolling preparation method of gradient strip
The invention provides a deep-cooling surface-layer continuous-rolling preparation method for a gradient strip. Grains in the surface-layer area are promoted to be refined through plastic deformation of the surface layer of a material, and meanwhile, recrystallization of ultra-fine grains in the plastic deformation process is restrained through ultralow-temperature deformation, so that a nano-structure is formed on the surface of the material; through multi-pass deep-cooling surface-layer rolling, the strip of a gradient structure is formed through a rolled piece, the surface layer of the material is of an ultra-fine grain structure, and coarse grains are located on the central area of the material; and compared with a material which is prepared through traditional cold rolling, the strength of the material is greatly improved under the condition that the material has better plasticity. Compared with the prior art that deep-cooling surface-layer rolling is only suitable for pure aluminum and aluminum alloy materials currently, through the technique, the tenacity of the material is hardly reduced, and the strength of the material can be improved by 30% or over.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
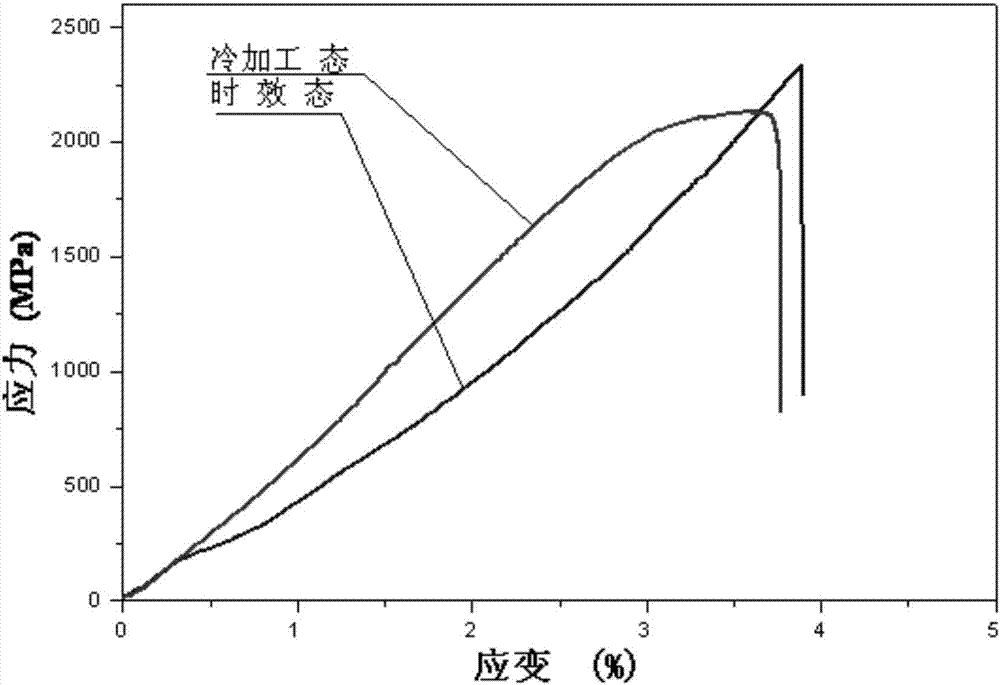
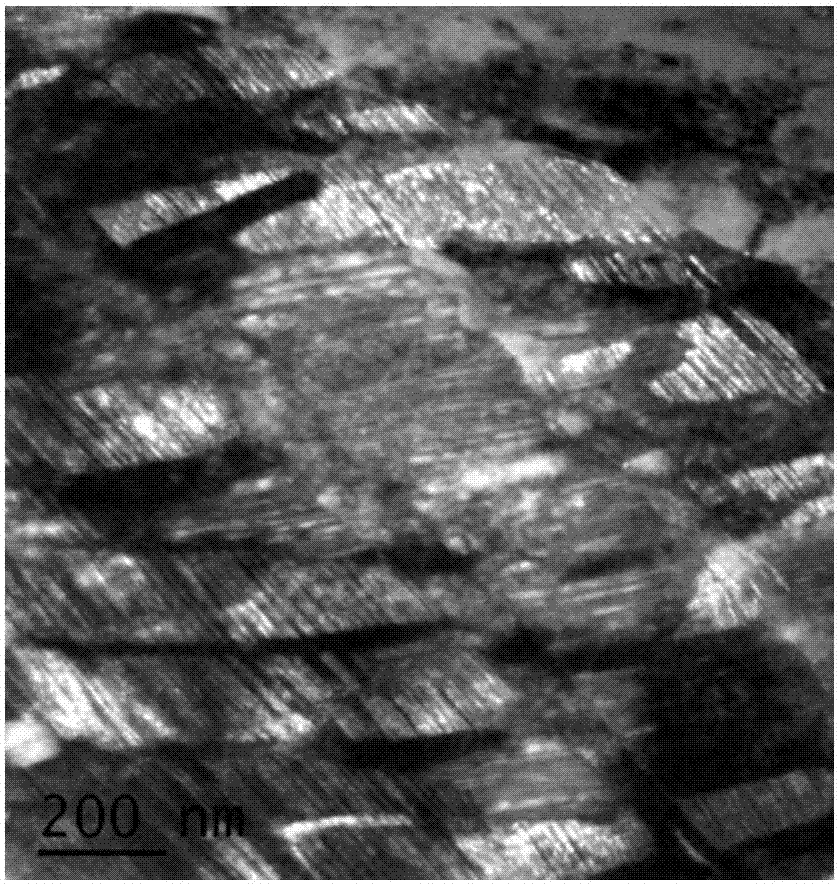
A kind of aging treatment method of cobalt-based alloy wire
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com