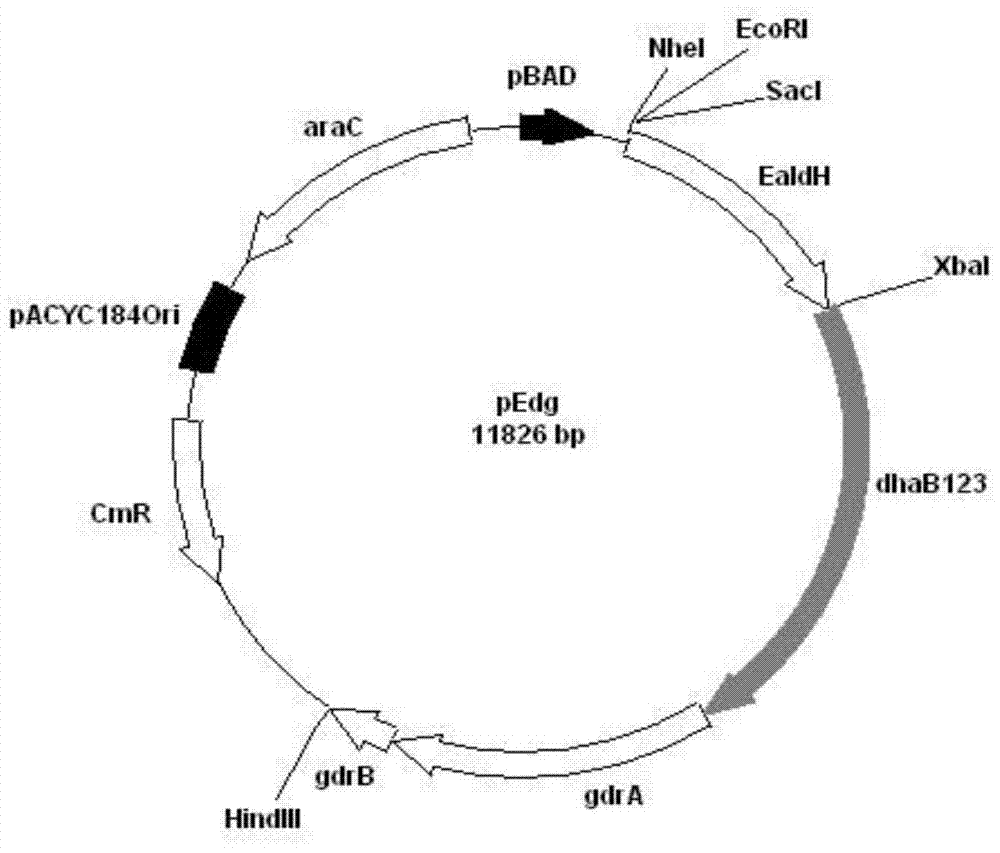
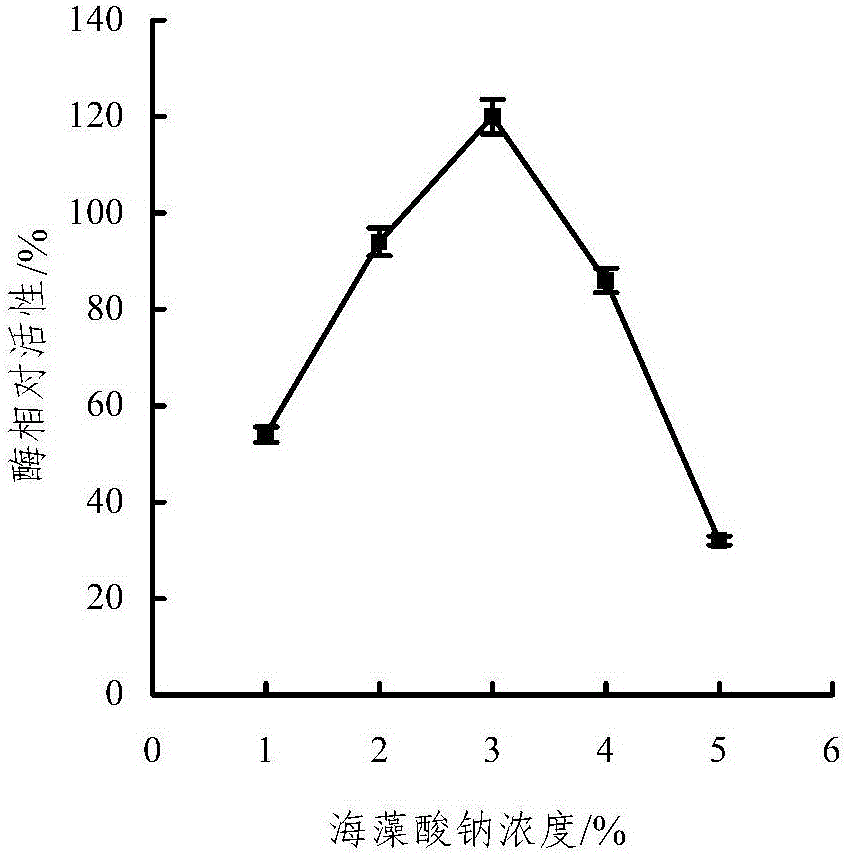
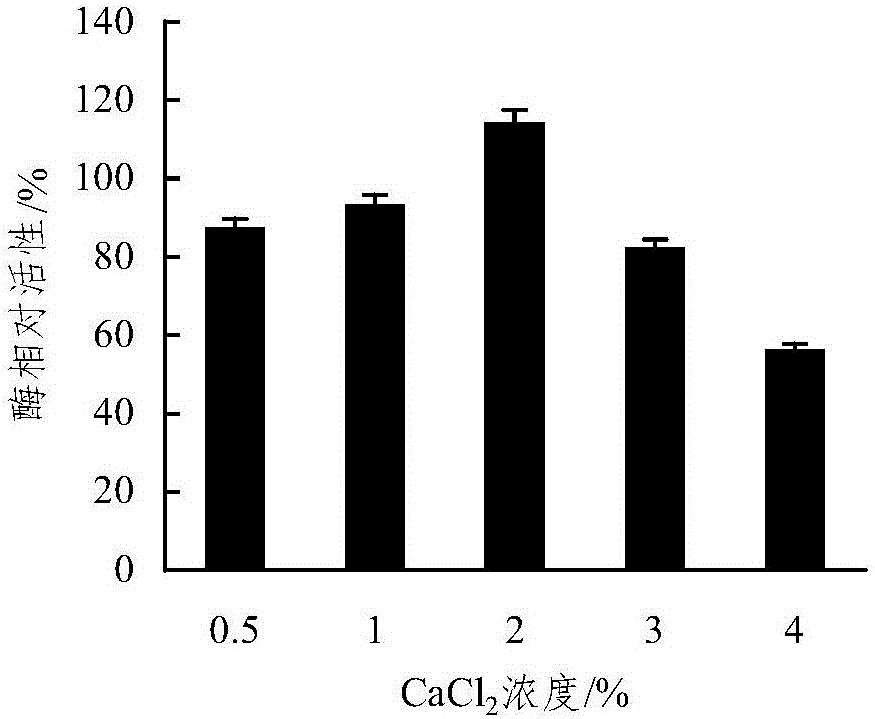
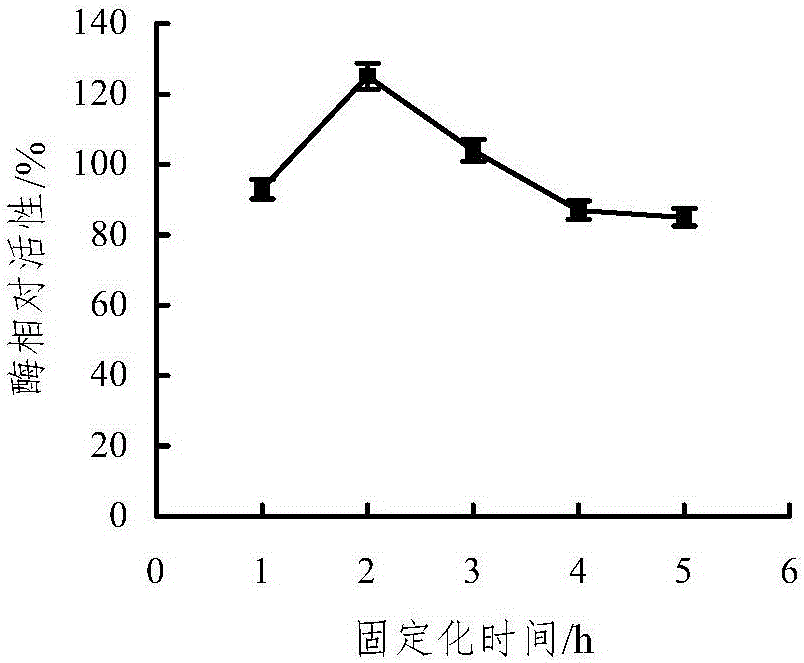
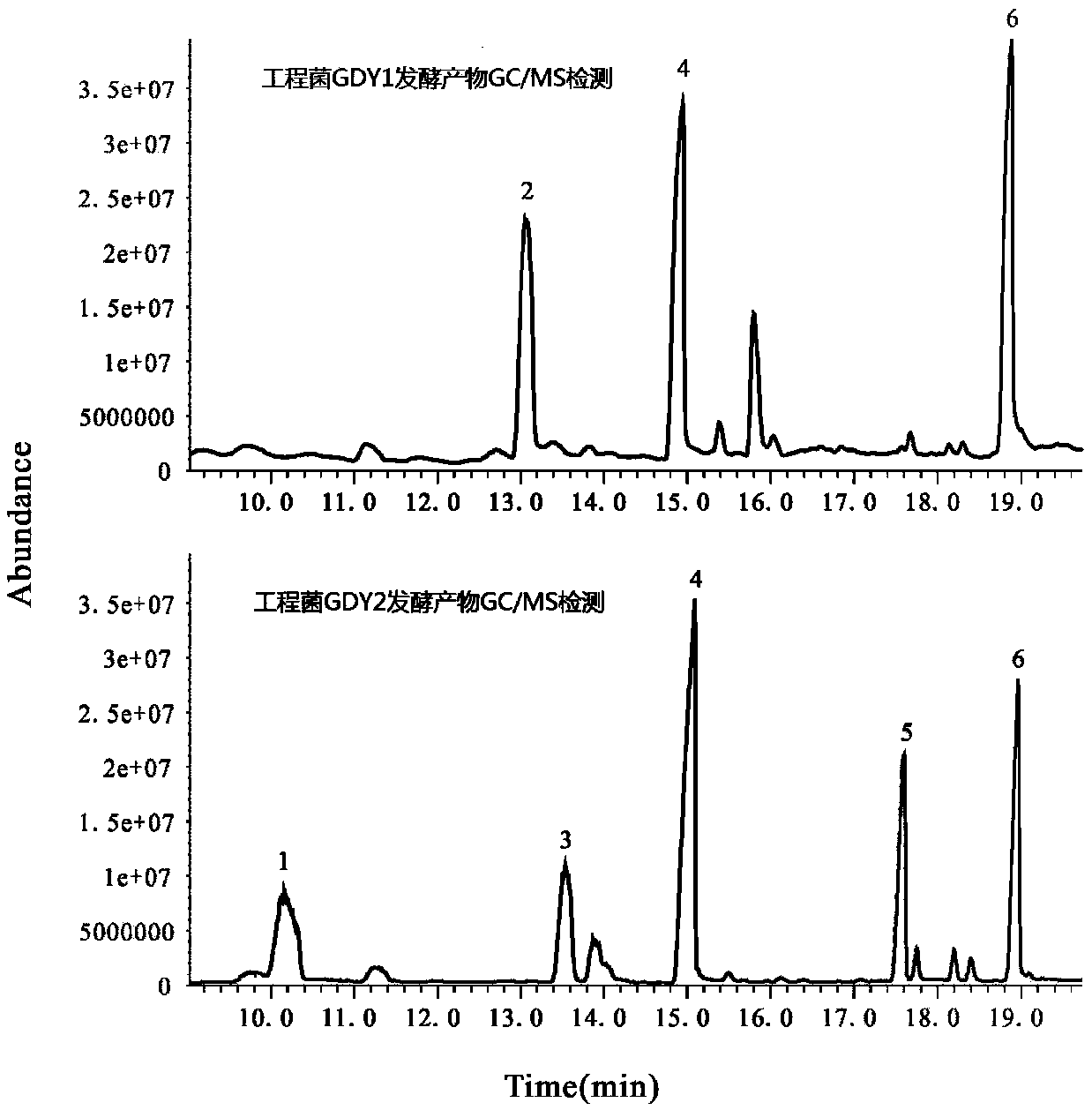
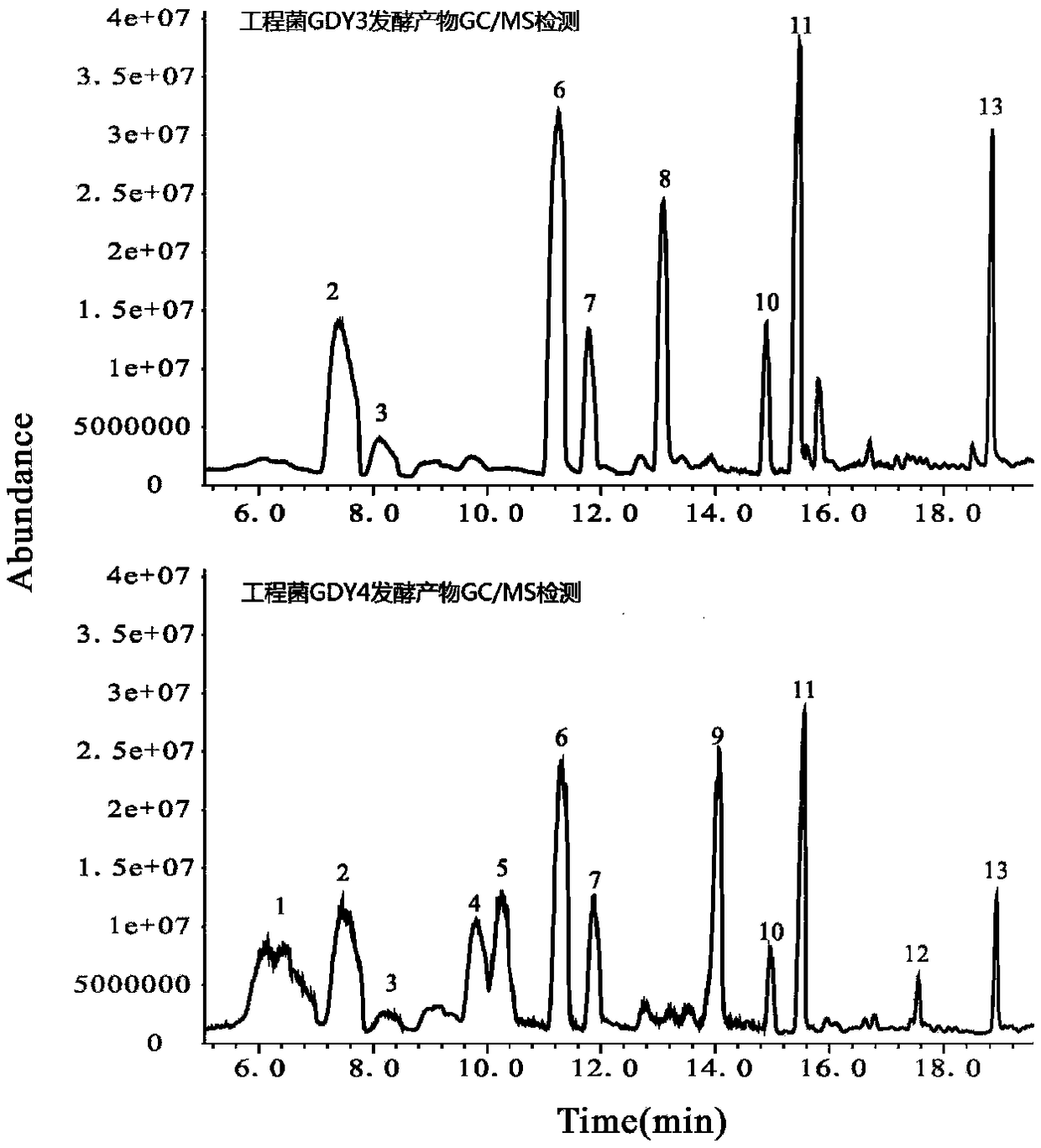
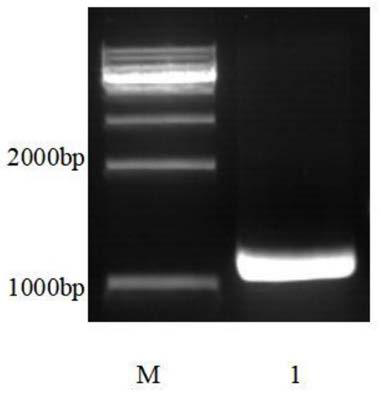
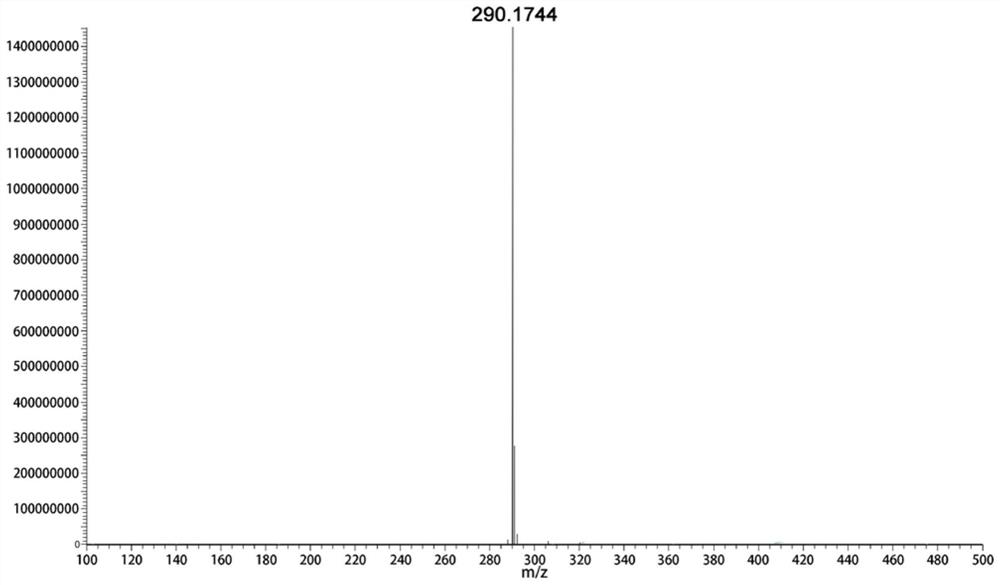
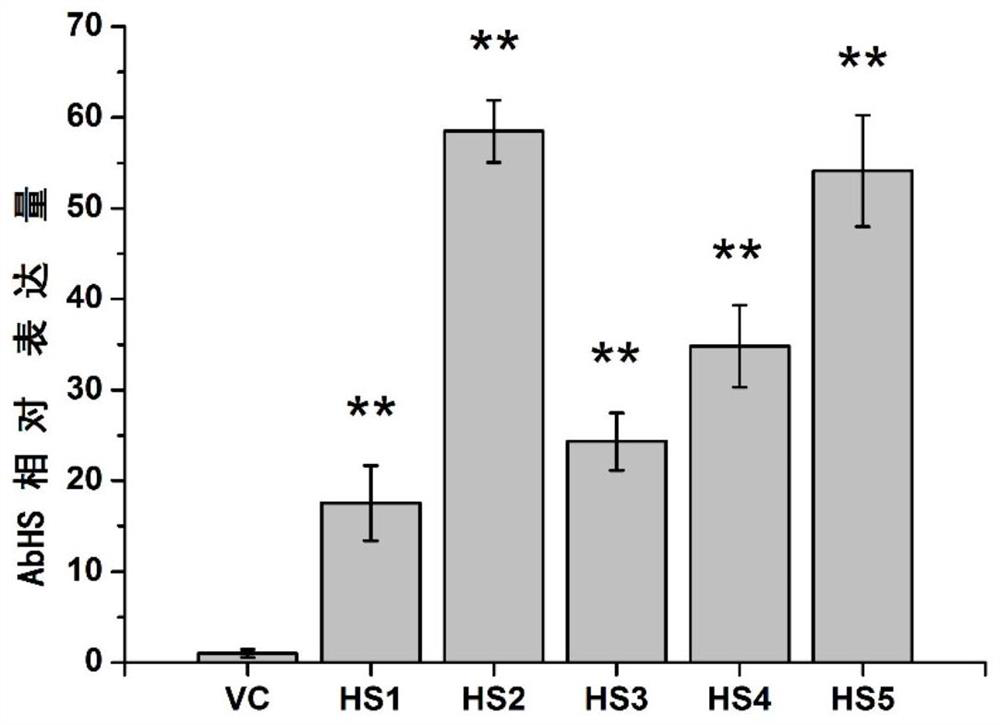
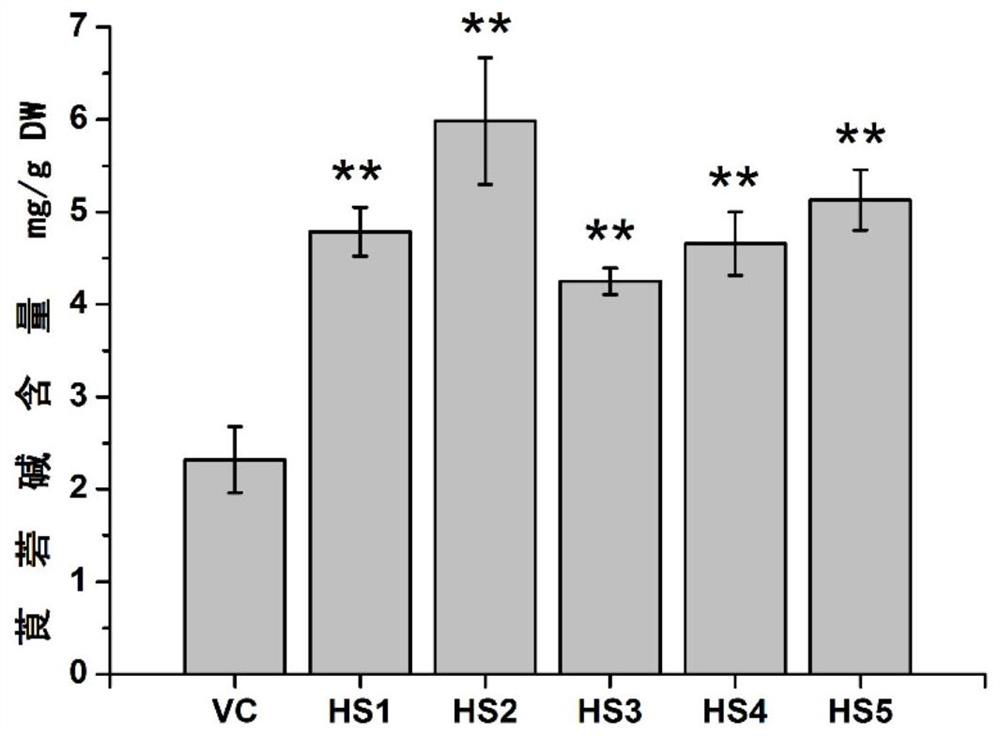
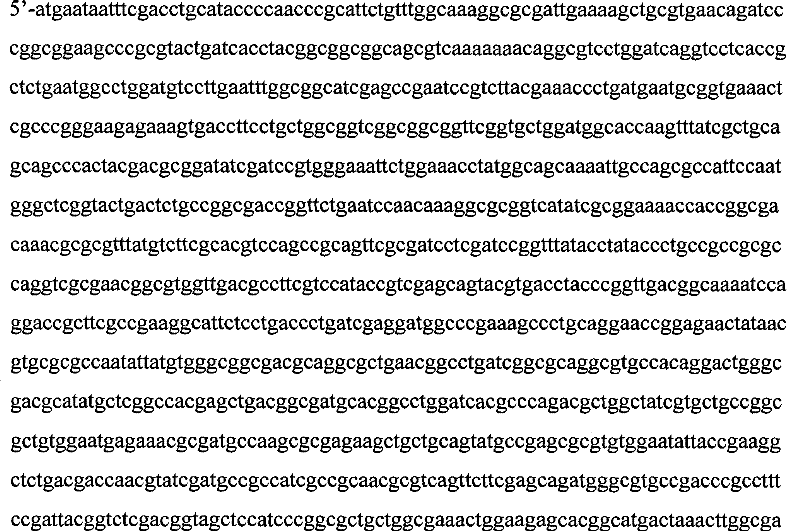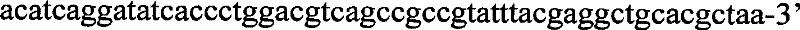Patents
Literature
35 results about "Aldehyde Reductase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
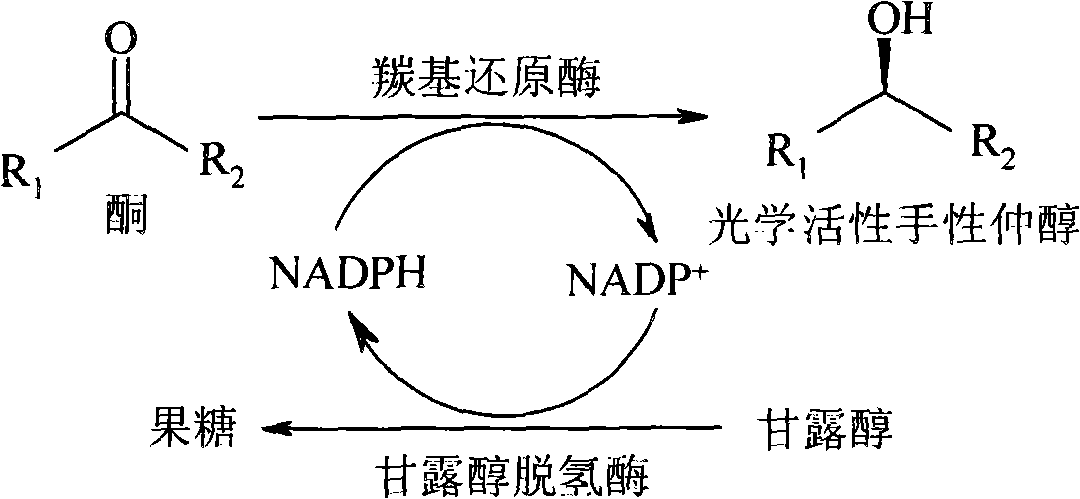
An enzyme that catalyzes reversibly the oxidation of an aldose to an alditol. It possesses broad specificity for many aldoses. EC 1.1.1.21.
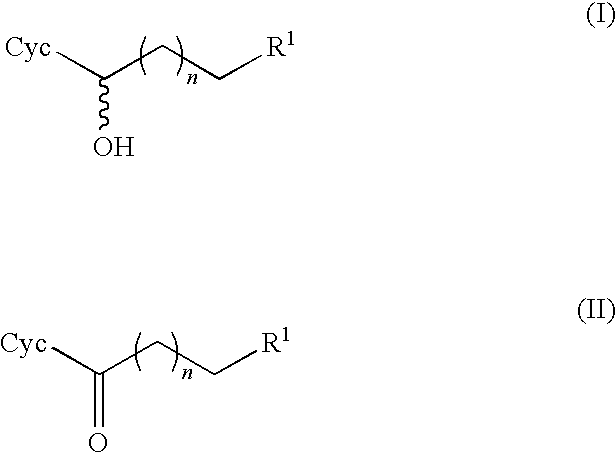
Method For Producing Optically Active Alcohols From Alkanones Using a Dehydrogenase of Azoarcus
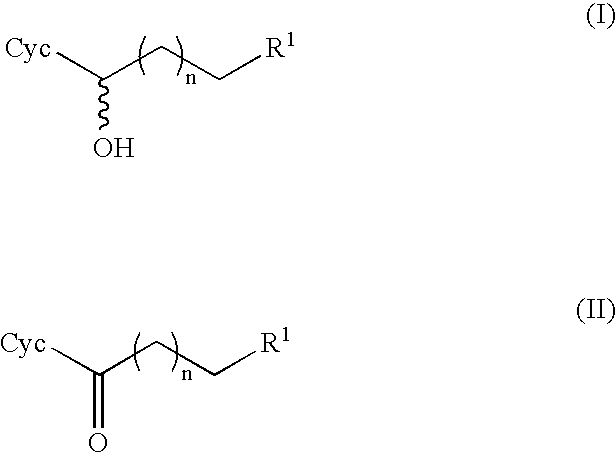
The invention relates to a method for producing the optically active alkanols of formula (I), wherein n is an integer of from 0 to 5; Cyc represents an optionally substituted, mononuclear or polynuclear, saturated or unsaturated, carbocylic or heterocyclic ring, and R1 represents halogen, SH, OH, NO2, NR2R3 or NR2R3R4+X−, wherein R2, R3 and R4 independently represent H or a lower alkyl or lower alkoxy group and X− represents a counterion. According to the invention, an enzyme (E) selected from the groups of dehydrogenases, aldehyde reductases and carbonyl reductases is incubated in a medium containing the alkanone of formula (II), wherein n, Cyc and R1 are defined as above, in the presence of reduction equivalents. The compound of formula (II) is enzymatically reduced to the compound of formula (I) and the reduction equivalents consumed during reaction are regenerated by reacting a sacrificial alcohol to the corresponding sacrificial ketone using enzyme (E) and at least partially removing the sacrificial ketone from the reaction medium, and then isolating the product (I) so produced.
Owner:BASF AG
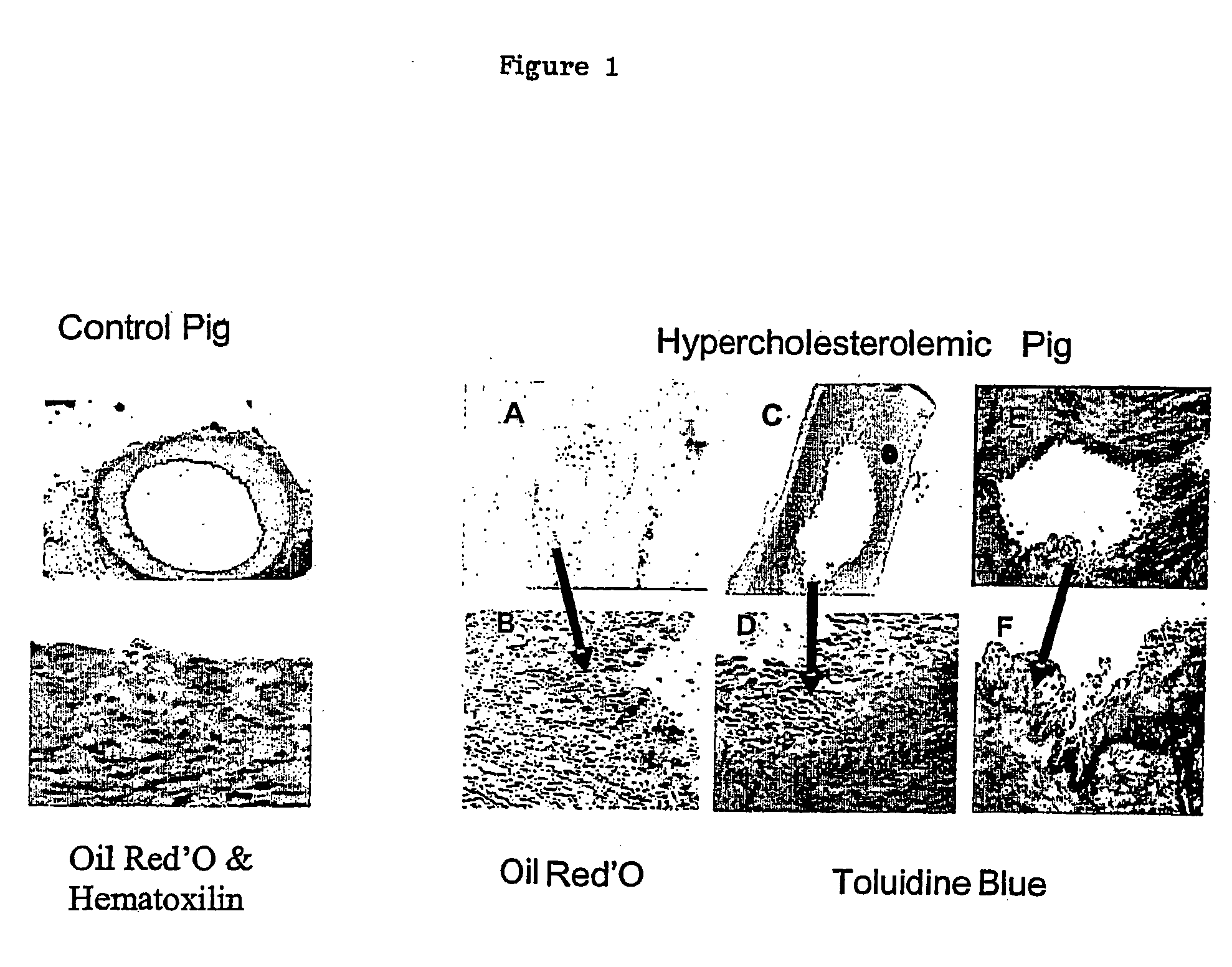
Methods and composition for identifying therapeutic agents of atherosclerotic plaque lesions
InactiveUS20060154252A1Reduce accumulationReducing and monitoring growthMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical active ingredientsPhospholipasePhosphate
The present invention relates to a method for identifying therapeutic agents for reducing and monitoring the growth, erosion, rupture or stability of an atherosclerotic plaque comprising the analysis of the differential expression of at least two genes coding proteins chosen among among Stearoyl CoA desaturase, Phosphatidic acid phosphate, and Phosphoinositide-specific-phospholipase-B1, eventually in association with the analysis of the differential expression of at least one gene coding a protein choosen in the group comprising Aldose reductase and aldehyde reductase, Sphingomyelinase, Acid ceramidase, Ceramide glucosyl transferase, Sphingosin phosphate liase, Thymosine beta 4, Aldehyde dehydogenase, ATPase Ca++ binding protein and CD163.
Owner:MARGUERIE GERARD +1
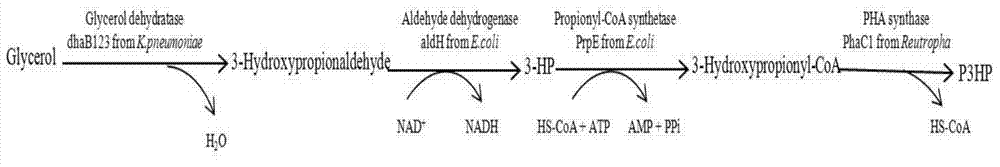
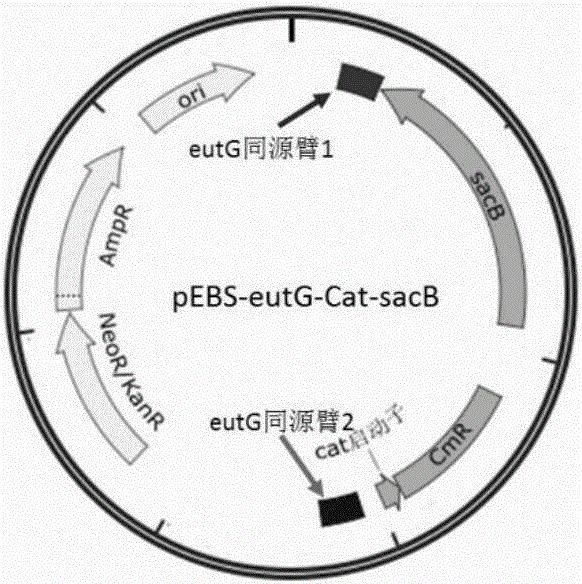
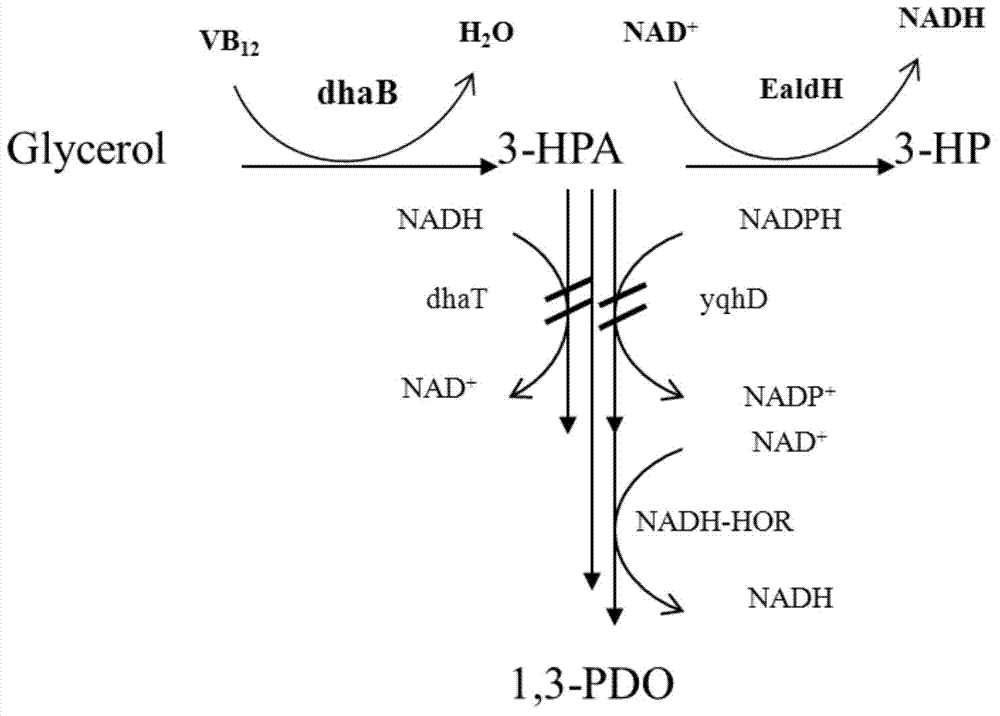
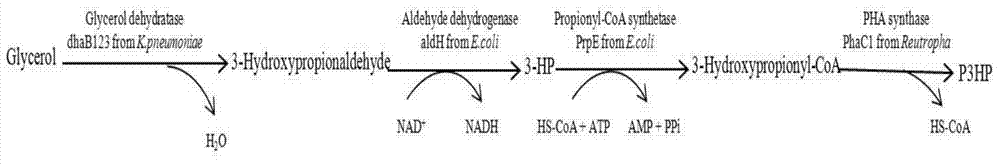
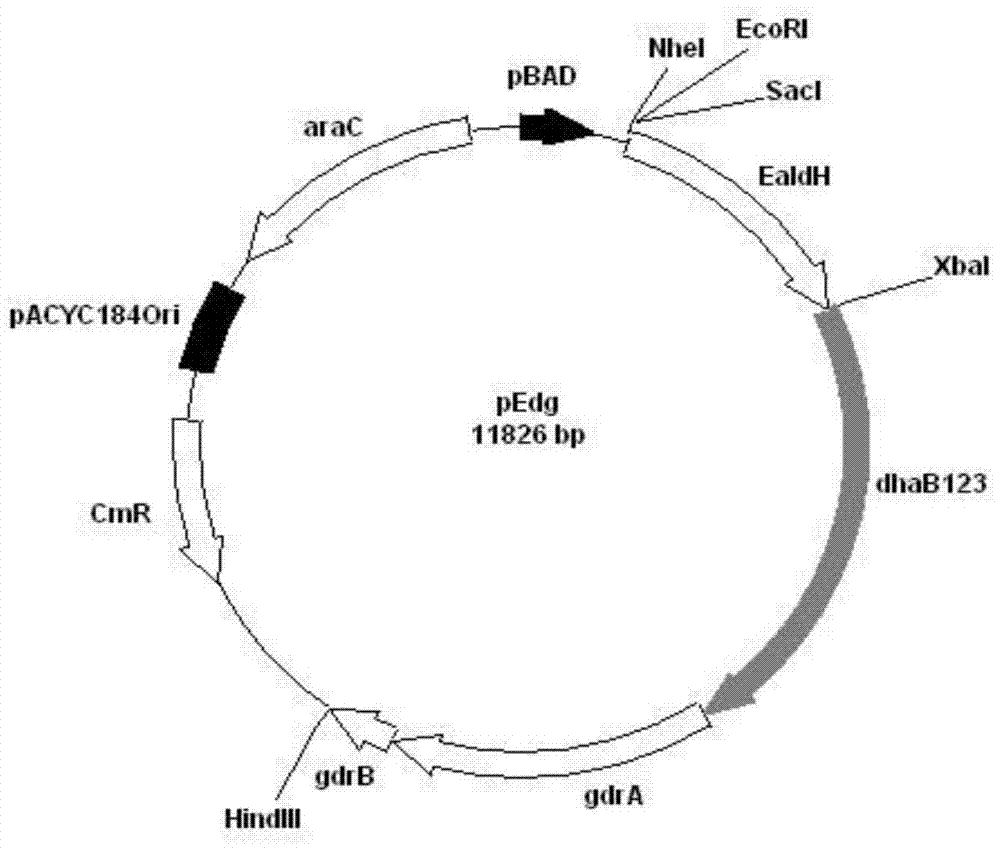
Recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497922AReduce synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidK pneumoniae
The invention discloses recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombination bacterium is obtained by introducing glycerol dehydratase gene, glycerol dehydratase reactivation enzyme gene, aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase gene into a host recombination klebsiella pneumonia in which 1, 3-propylene glycol oxidoreductase gene and aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene are knocked out. According to the technical scheme, the production cost of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) is reduced, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) can be synthesized at the same time by taking a same thallus as the host.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Embedding and co-immobilization method of aldehyde ketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveCN104988133AHigh catalytic activityImprove thermal stabilityOn/in organic carrierMulti-enzyme systemsFiltrationRefrigerated temperature
The invention discloses an embedding and co-immobilization method of aldehyde ketone reductase and glucose dehydrogenase. The method includes the steps that the aldehyde ketone reductase and the glucose dehydrogenase are mixed and then added to a sodium alginate aqueous solution to be stirred and mixed evenly, then the mixture is dropwise added to a Cacl2 aqueous solution, the mixture is made to stand in a refrigerator at the temperature of 4 DEG C, washing is conducted through distilled water, vacuum filtration is conducted, and immobilized particles are obtained. Compared with free aldehyde ketone reductase, the catalytic activity of the co-immobilized enzyme prepared through the method is increased by 1.32 times, the heat stability, the PH stability and other performance of the co-immobilized enzyme prepared through the method are improved as well, and meanwhile, the cost is lowered due to reuse of the co-immobilized enzyme.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
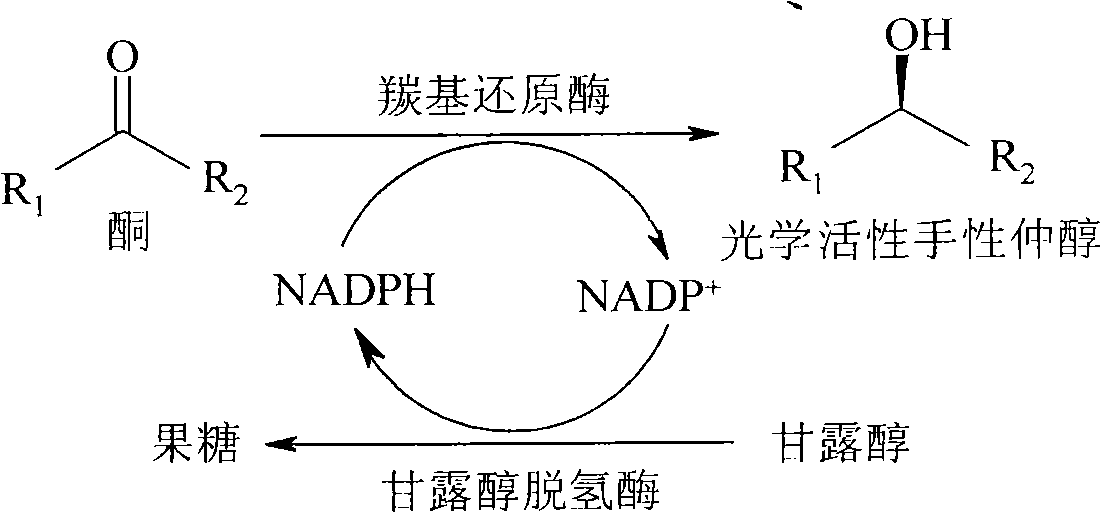
Method for preparing optical activity chirality secondary alcohol with rhodotorula reductase formulation
InactiveCN101314787AIncrease concentrationEasy extractionMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh concentrationChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for preparing optical activity chiral secondary alcohol by using a rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent. The rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent is extracted from a rhodotorula cell, and comprises aldehyde reductase and mannitol dehydrogenase. Through the coupled chemical reaction of the aldehyde reductase and the mannitol dehydrogenase, mannite which is low in price can be used as cosubstrate, so that the in-situ regeneration and the cyclic utilization of coenzyme NADPH are realized during the reducing reaction process of a carbonyl group. The complete and highly-selective reduction of the high-concentration carbonyl substrate can be realized only through adding the coenzyme with catalytic amount in a synthesized reaction system. The production process is simple, the product is easy to extract and purify, and the rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent can be used for preparing the chiral secondary alcohol with various high optical purity, in particular to (S)-aromatic secondary alcohol.
Owner:江苏华荣生物科技有限公司
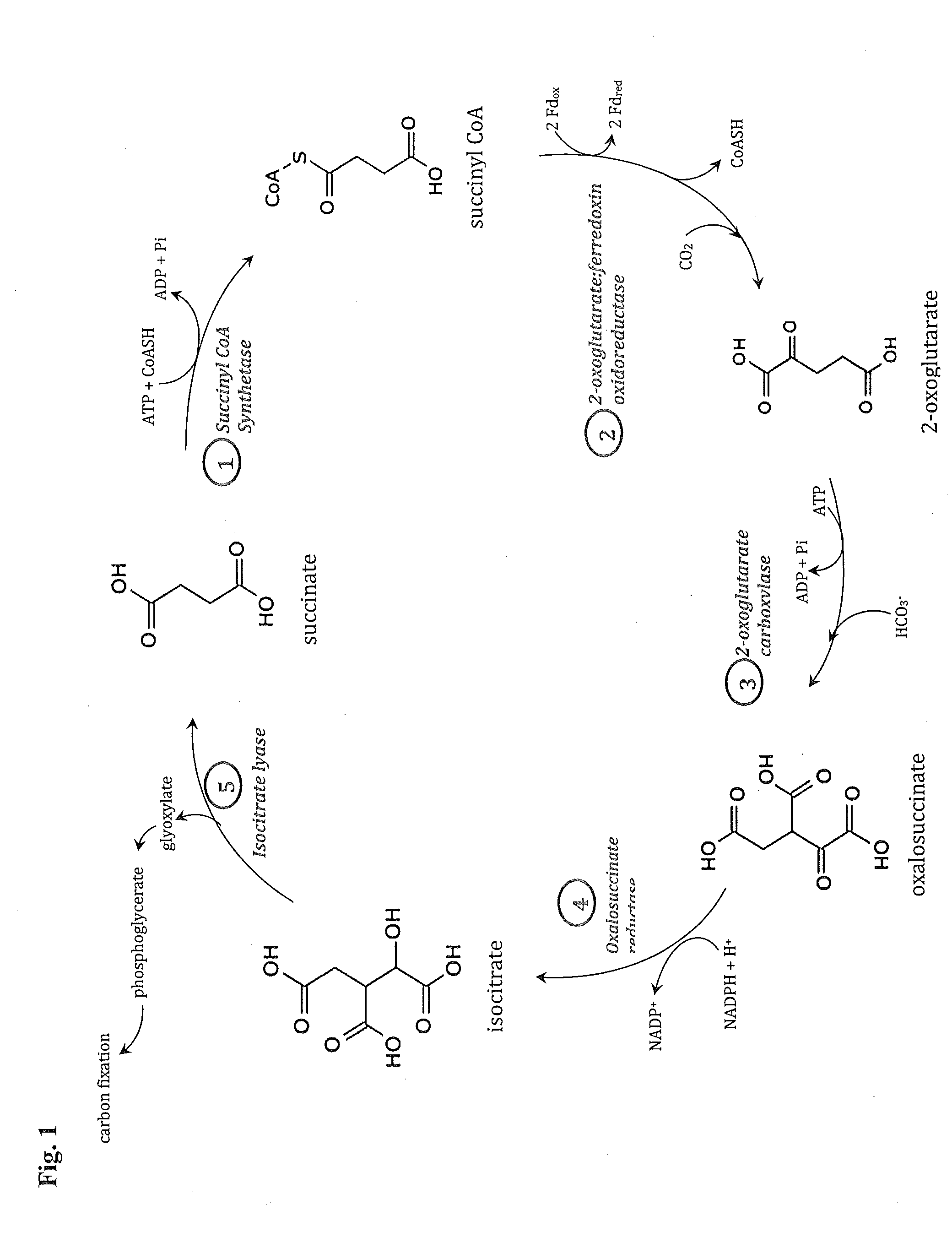
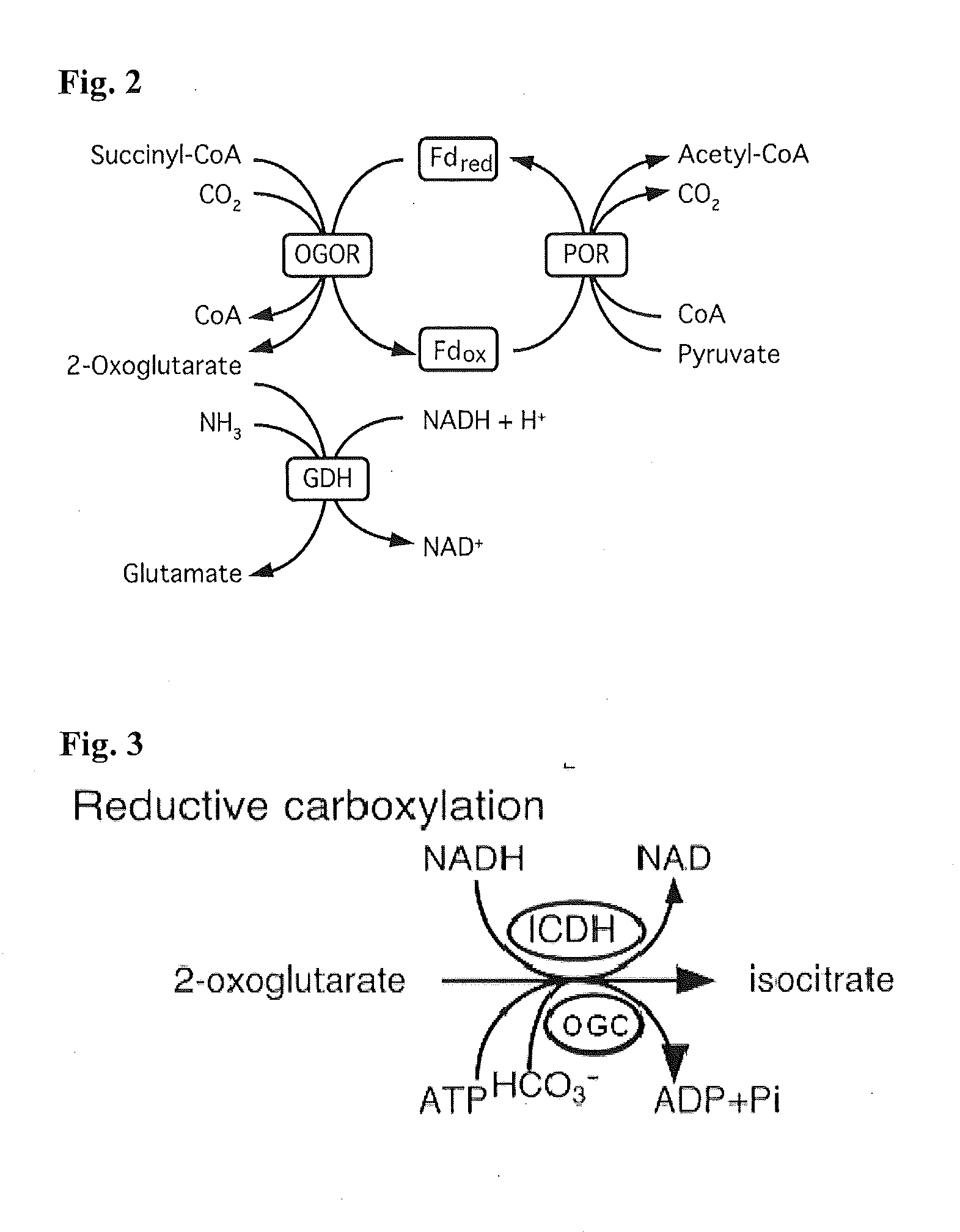
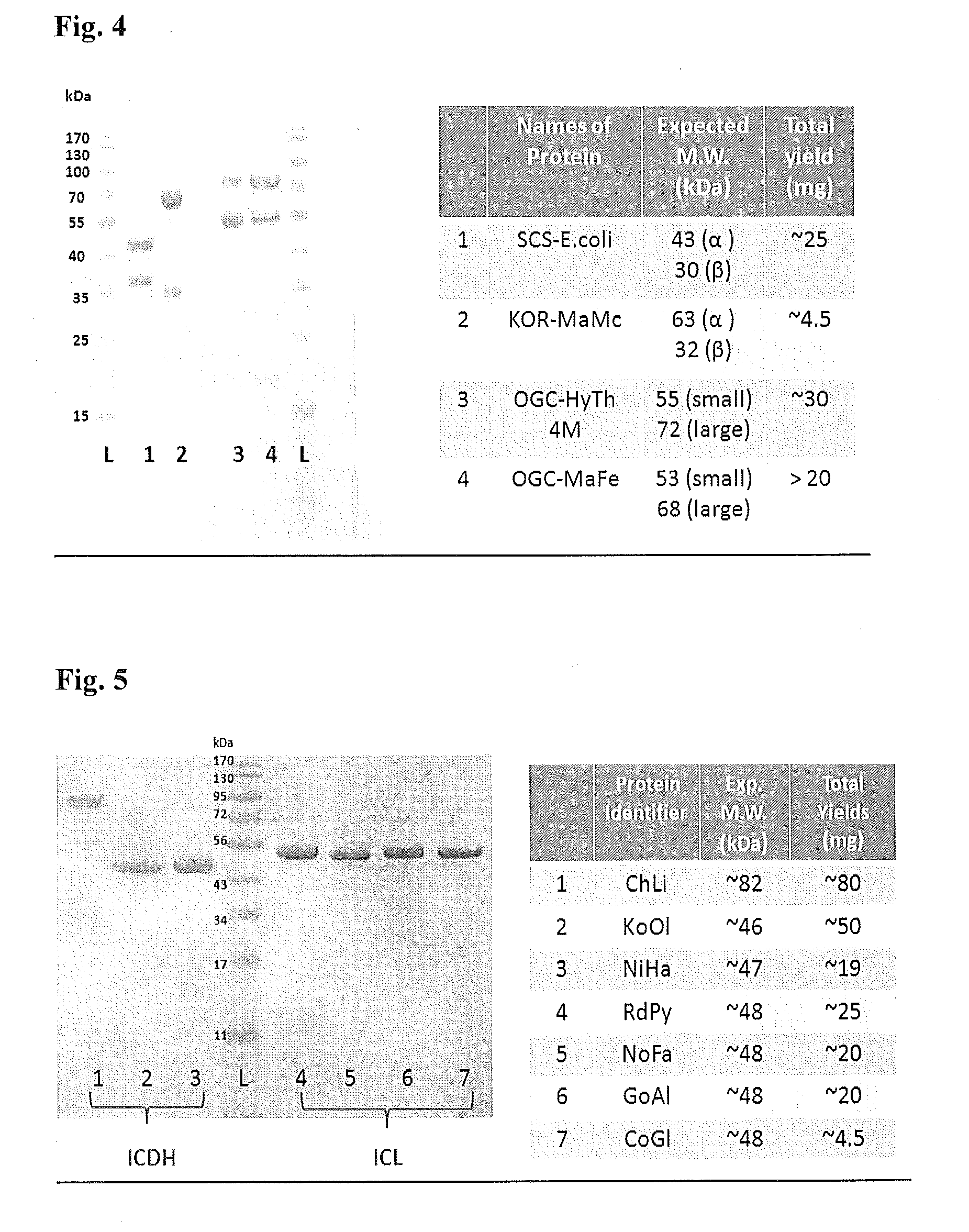
Synthetic Pathway for Biological Carbon Dioxide Sequestration
InactiveUS20140150135A1Improve efficiencyIncreased biomass productionBiocideOrganic chemistryHeterologousNucleotide
This invention relates to methods for increasing carbon fixation and / or increasing biomass production in a plant, comprising: introducing into a plant, plant part, and / or plant cell one or more heterologous polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the enzyme activity of succinyl CoA synthetase, 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase, oxalosuccinate reductase and isocitrate lyase to produce a stably transformed plant, plant part, and / or plant cell expressing the one or more heterologous polynucleotides. The methods further comprise introducing into a plant, plant part or plant cell heterologous polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the enzyme activity of glyoxylate carboligase and tartronic semialdehyde reductase, and / or heterologous polynucleotides encoding a superoxide reductase from an archaeon species, an aquaporin and / or an inhibitor of cell wall invertase inhibitor. Additionally, transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells are provided as well as products produced from the transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Rhodotorula reductase formulation, preparation and method for preparing optical activity chirality secondary alcohol with the same
InactiveCN101314768AIncrease concentrationEasy extractionOxidoreductasesFermentationHigh concentrationMANNITOL/SORBITOL
The invention discloses a rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent and a preparing method thereof, and a method for preparing optical activity chiral secondary alcohol by using the rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent. The rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent is extracted from a rhodotorula cell, and comprises aldehyde reductase and mannitol dehydrogenase. Through the coupled reaction of the aldehyde reductase and the mannitol dehydrogenase, mannite which has low price can be used as cosubstrate, so that the in-situ regeneration and the cyclic utilization of coenzyme NADPH are realized during the reducing reaction process of a carbonyl group. The complete and highly-selective reduction of the high-concentration carbonyl substrate can be realized only through adding the coenzyme with catalytic amount in a synthesized reaction system. The production process is simple, the product is easy to extract and purify, and the rhodotorula reducing enzyme preparation agent can be used for preparing the chiral secondary alcohol with various high optical purity, in particular to (S)-aromatic secondary alcohol.
Owner:江苏华荣生物科技有限公司
Leishmania antigens suitable for a diagnostic kit of Leishmania
A purified Leishmania infantum polypeptide comprising at least 10 consecutive amino acids of a protein is provided. The protein is mitochondrial integral ADP / ATP carrier protein, NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase, mitochondrial carrier protein, guanine nucleotide binding protein beta subunit (LACK), aldehyde reductase, ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase Rieske iron-sulfur protein, truncated elongation factor 1-alpha having a molecular weight as determined by SDS-PAGE of 36.4 kDa, truncated elongation factor 1-alpha having a molecular weight as determined by SDS-PAGE of 34.5 kDa, or truncated elongation factor 1-alpha having a molecular weight as determined by SDS-PAGE of 30.6 kDa. Methods for using the polypeptides for diagnosing MVL are disclosed.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
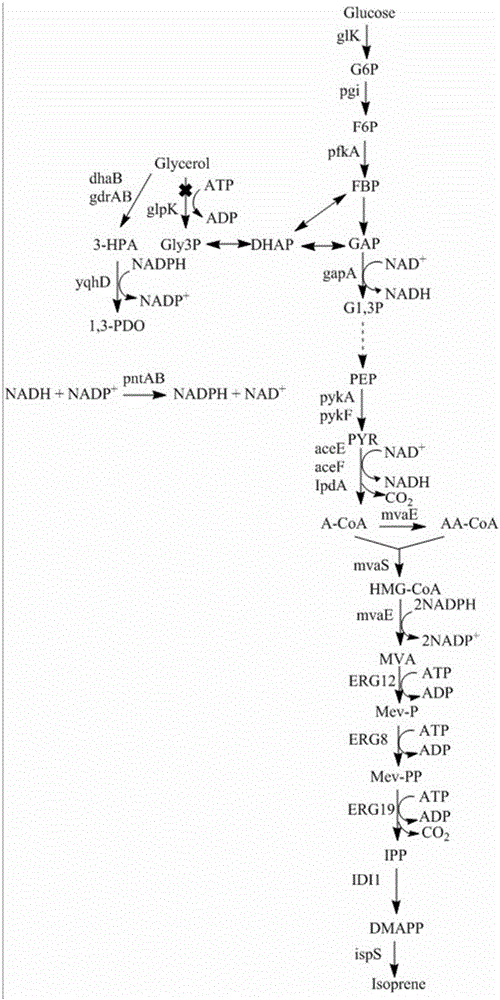
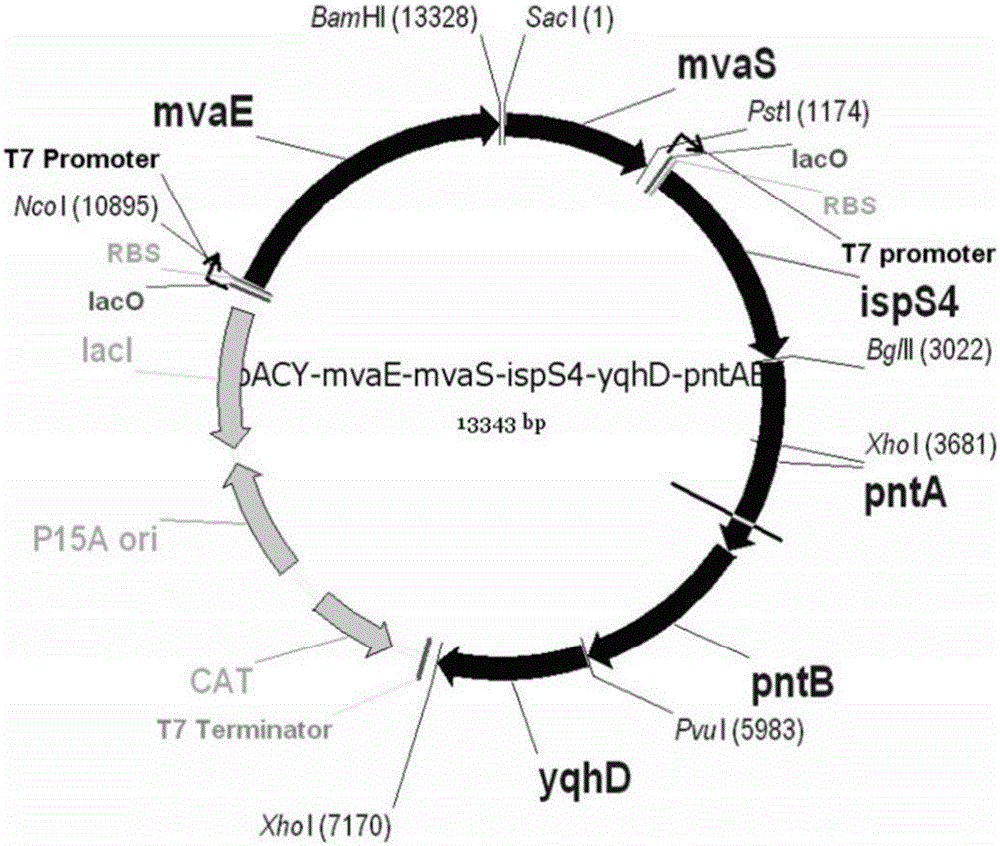
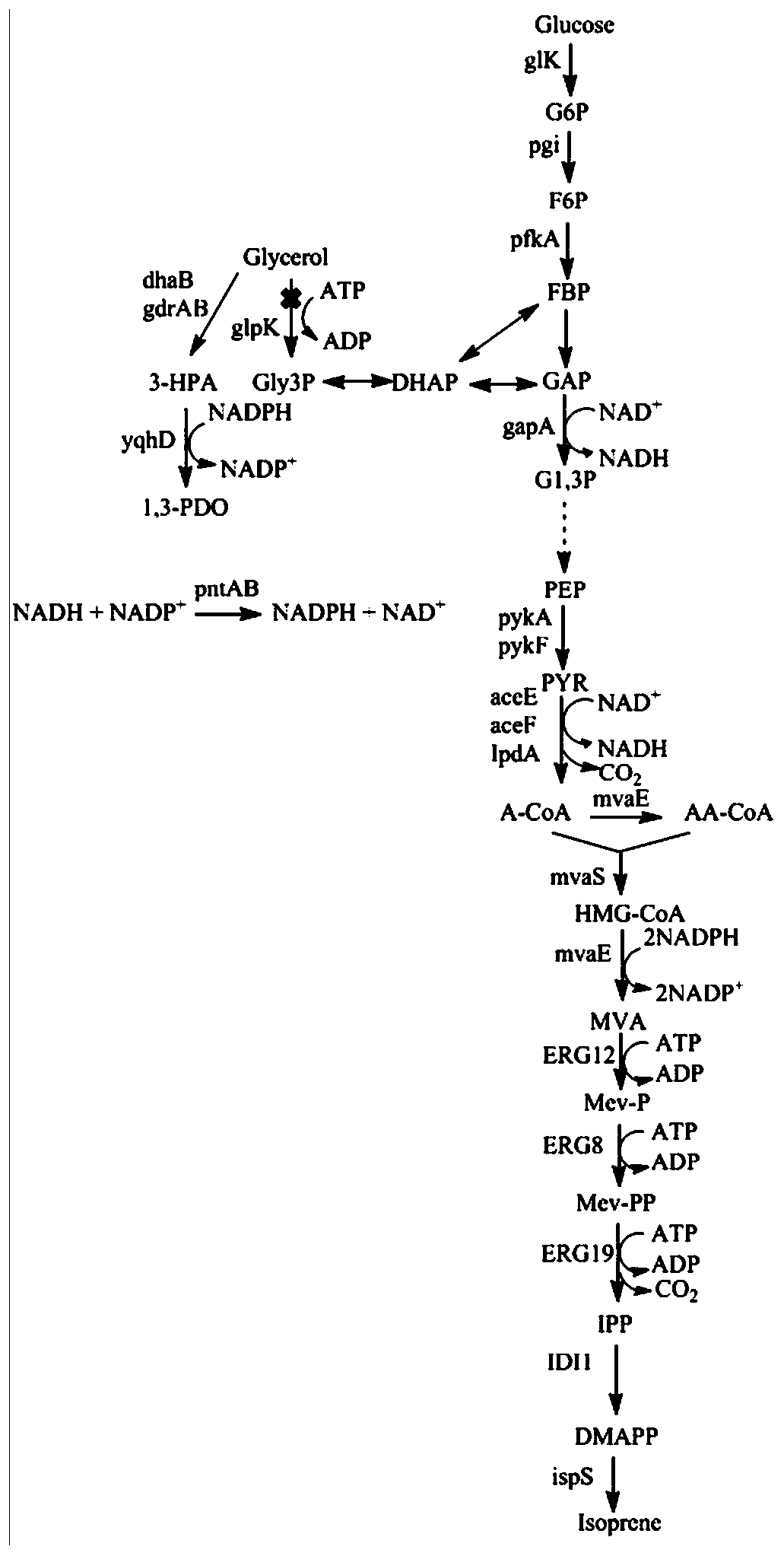
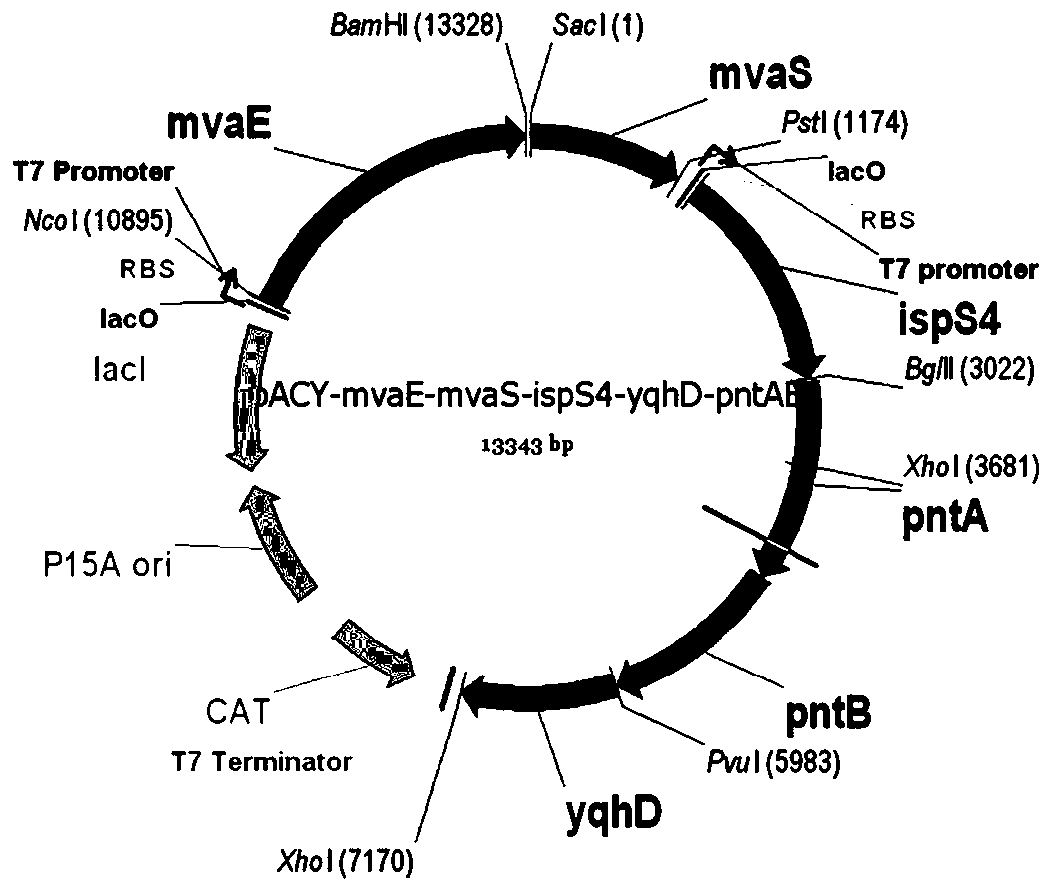
Genetic engineering strain capable of coproducing isoprene and 1,3-propylene glycol and establishment method and application thereof
ActiveCN106350476AReduce consumptionBalance metabolismBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHMG-CoA reductase
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain capable of coproducing isoprene and 1,3-propylene glycol and an establishment method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. In the genetic engineering strain, a glycerol dehydratase gene and a glycerol dehydratase gene reactivating enzyme gene are integrated, a glycerol kinase gene is knocked out, and HMG-CoA reductase, HMG-CoA synthetase, mevalonate kinase, phosphomevalonate kinase, pyrophosphomevalonate decarboxylase, IPP isomerase, isoprene synthetase, aldehyde reductase and transhydrogenase are overexpressed. According to the invention, through genetic engineering, a metabolic way capable of coproducing the isoprene and the 1,3-propylene glycol is successfully established in escherichia coli; by the establishment method, redox cofactors in cells of the genetic engineering strain are metabolized in a balanced way, and the yield in coproducing the isoprene and the 1,3-propylene glycol through glucose and glycerol fermentation is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing optically active alcohols from alkanones using a dehydrogenase of azoarcus
The invention relates to a method for producing the optically active alkanols of formula (I), wherein n is an integer of from 0 to 5; Cyc represents an optionally substituted, mononuclear or polynuclear, saturated or unsaturated, carbocylic or heterocyclic ring, and R1 represents halogen, SH, OH, NO2, NR2R3 or NR2R3R4+X−, wherein R2, R3 and R4 independently represent H or a lower alkyl or lower alkoxy group and X− represents a counterion. According to the invention, an enzyme (E) selected from the groups of dehydrogenases, aldehyde reductases and carbonyl reductases is incubated in a medium containing the alkanone of formula (II), wherein n, Cyc and R1 are defined as above, in the presence of reduction equivalents. The compound of formula (II) is enzymatically reduced to the compound of formula (I) and the reduction equivalents consumed during reaction are regenerated by reacting a sacrificial alcohol to the corresponding sacrificial ketone using enzyme (E) and at least partially removing the sacrificial ketone from the reaction medium, and then isolating the product (I) so produced.
Owner:BASF SE
Escherichia coli for synthesis of propane through pathway of valine and establishing method of escherichia coli
InactiveCN105296410ADecreased aldehyde reductase activityDoes not affect normal growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFormate
The invention discloses escherichia coli for synthesis of propane through the pathway of valine and an establishing method of the escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the escherichia coli, nine sorts of aldose reductase genes, a lactic dehydrogenase gene, a fumarate reductase gene, a formate-lyase gene and an overall transcription factor gene are eliminated. Meanwhile, overexpression of an acetolactate synthetase gene, a ketol-acid reductoisomerase gene, a DHAD gene, a 2-ketoacid decarboxylase gene and an aldehyde deformylating oxygenase gene is achieved. The invention provides the establishing method of the escherichia coli at the same time. Through overexpression of the propane synthesis pathway in an improved strain, the strain successfully achieves biosynthesis of propane.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium for selectively producing retinol as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN113265344ASynthetic participationIncrease productionFungiTransferasesCell factoryRetinol dehydrogenase
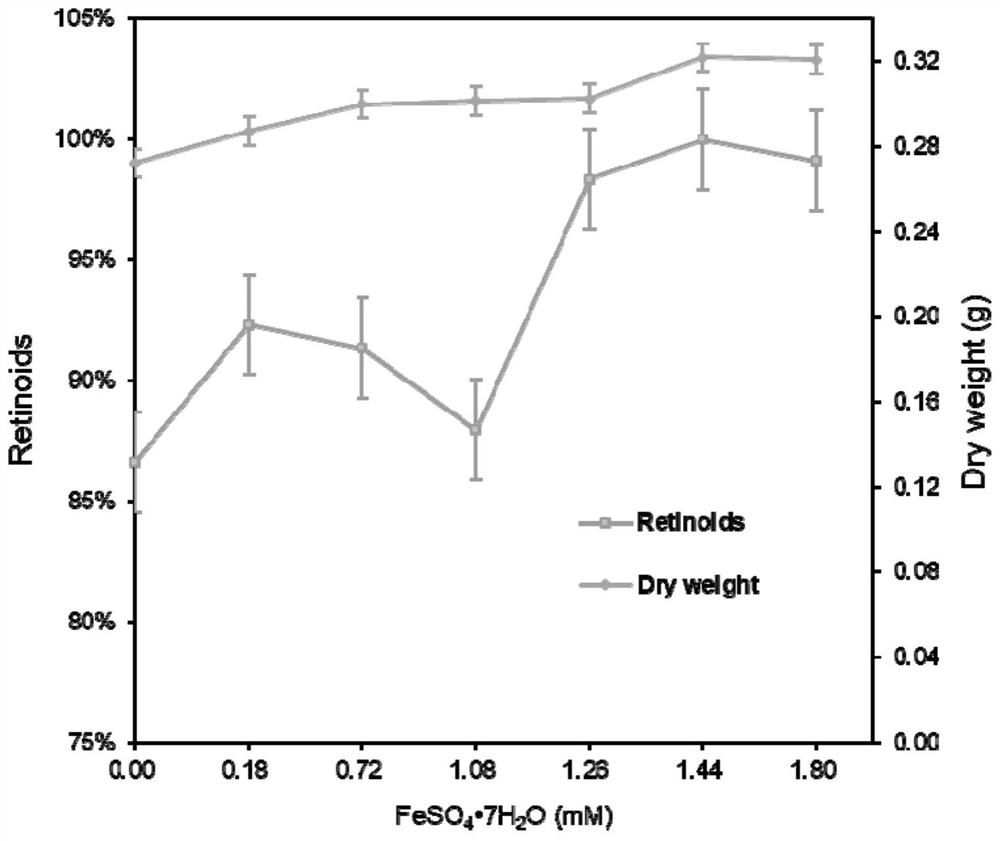
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for selectively producing retinol as well as a construction method and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the genetically engineered bacterium, an engineering strain for producing beta-carotene is taken as a starting bacterium, beta-carotene 15, 15'-dioxygenase coding genes and aldehyde reductase coding genes or / and retinol dehydrogenase coding genes are introduced, and selective production of retinol in a cell factory is realized. In order to further improve the yield of retinol, a geranyl-geranyl pyrophosphate synthase mutant encoding gene is further introduced into the genetically engineered bacterium, an NADH kinase encoding gene of an N-terminal mitochondrial positioning peptide is cut off, and meanwhile, a mevalonic acid pathway transcription inhibition factor gene is knocked out, so that the supply of precursors and coenzymes is increased. The invention also provides a method for producing retinol by using the genetically engineered bacterium, ferrous ions and an antioxidant are added in the fermentation process, so that the yield of retinol is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
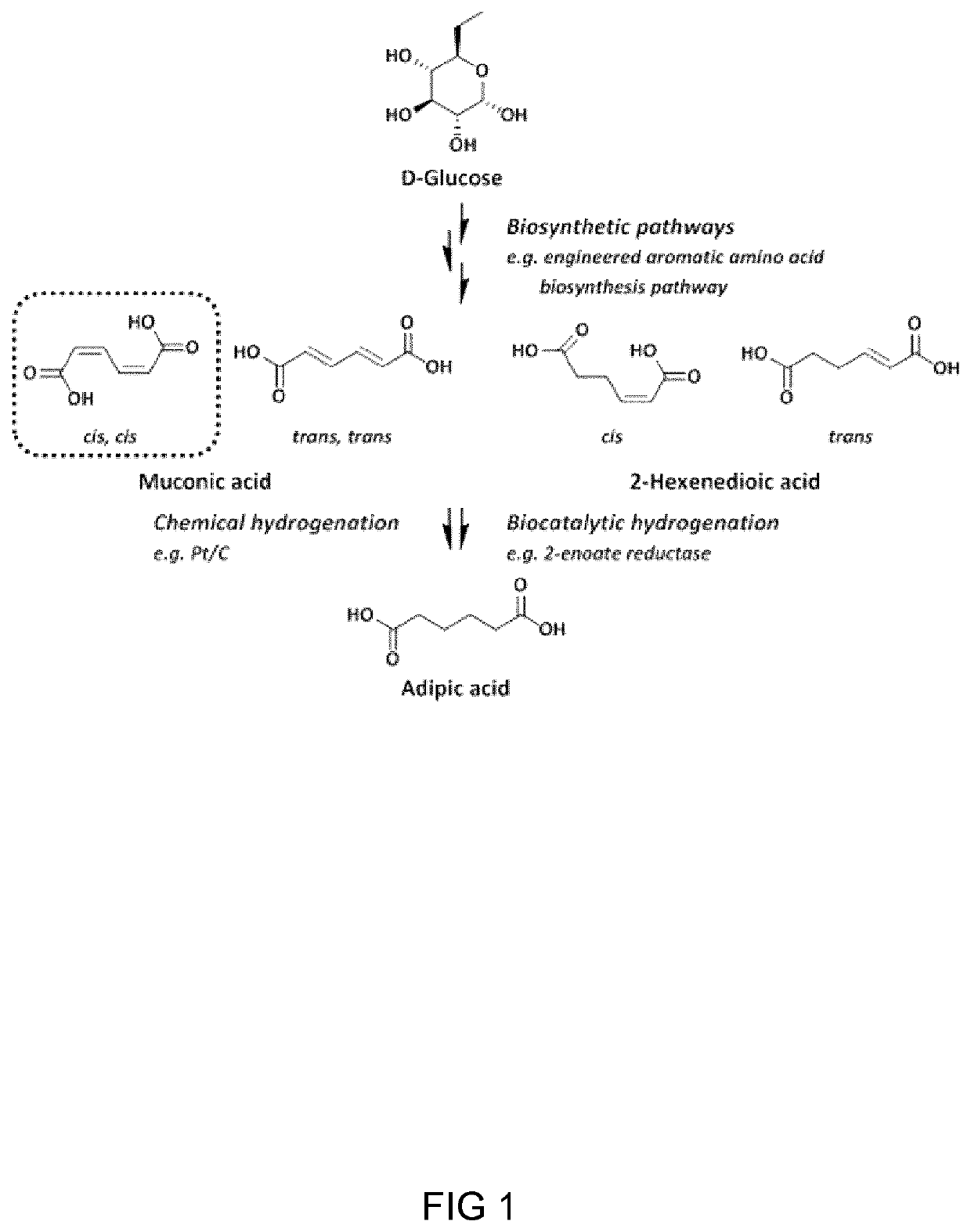
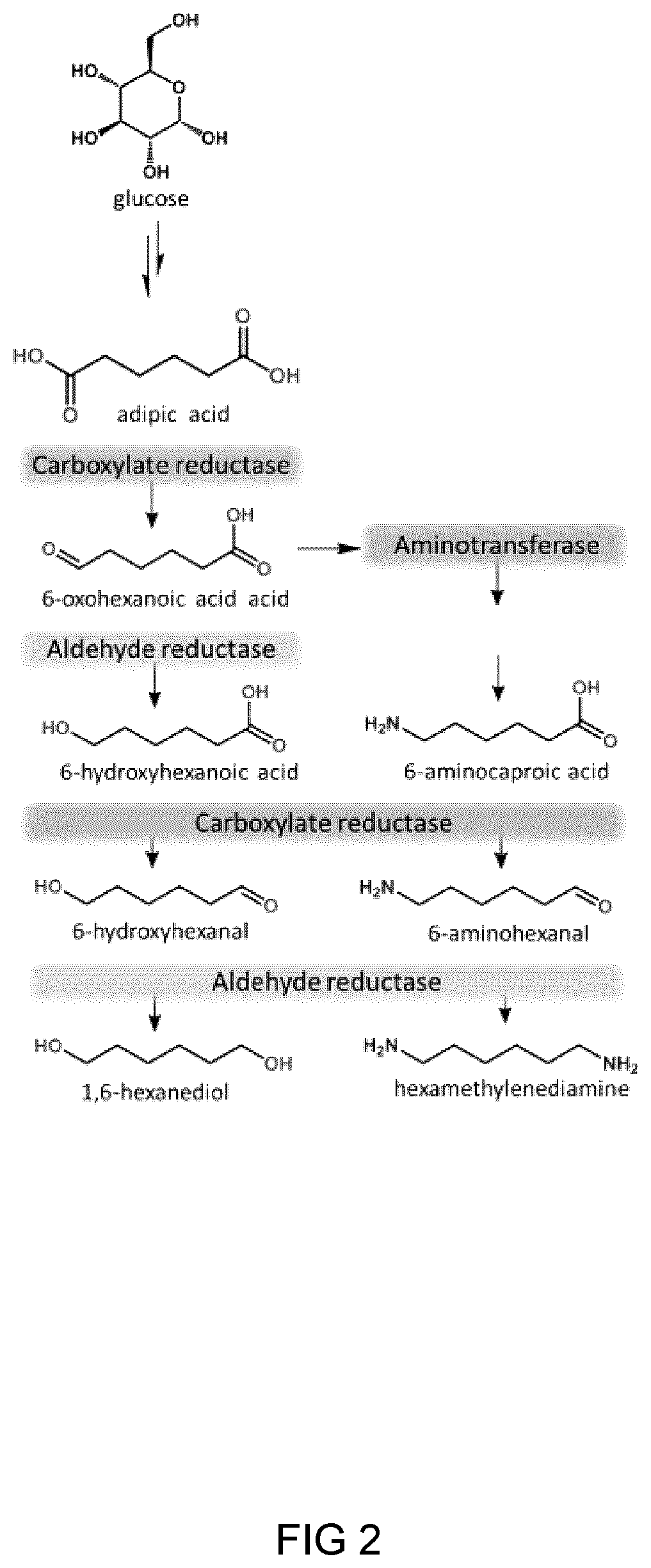
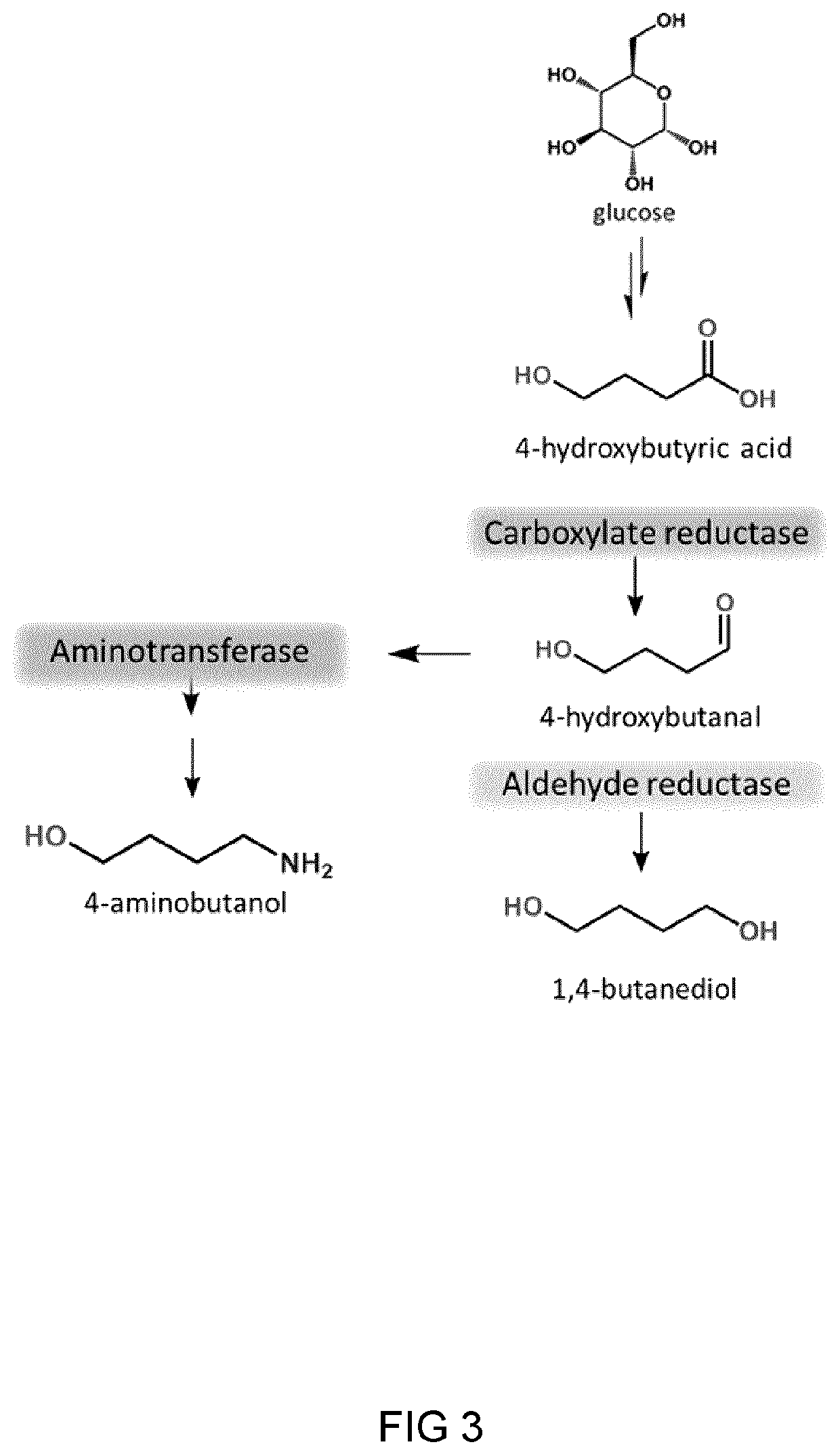
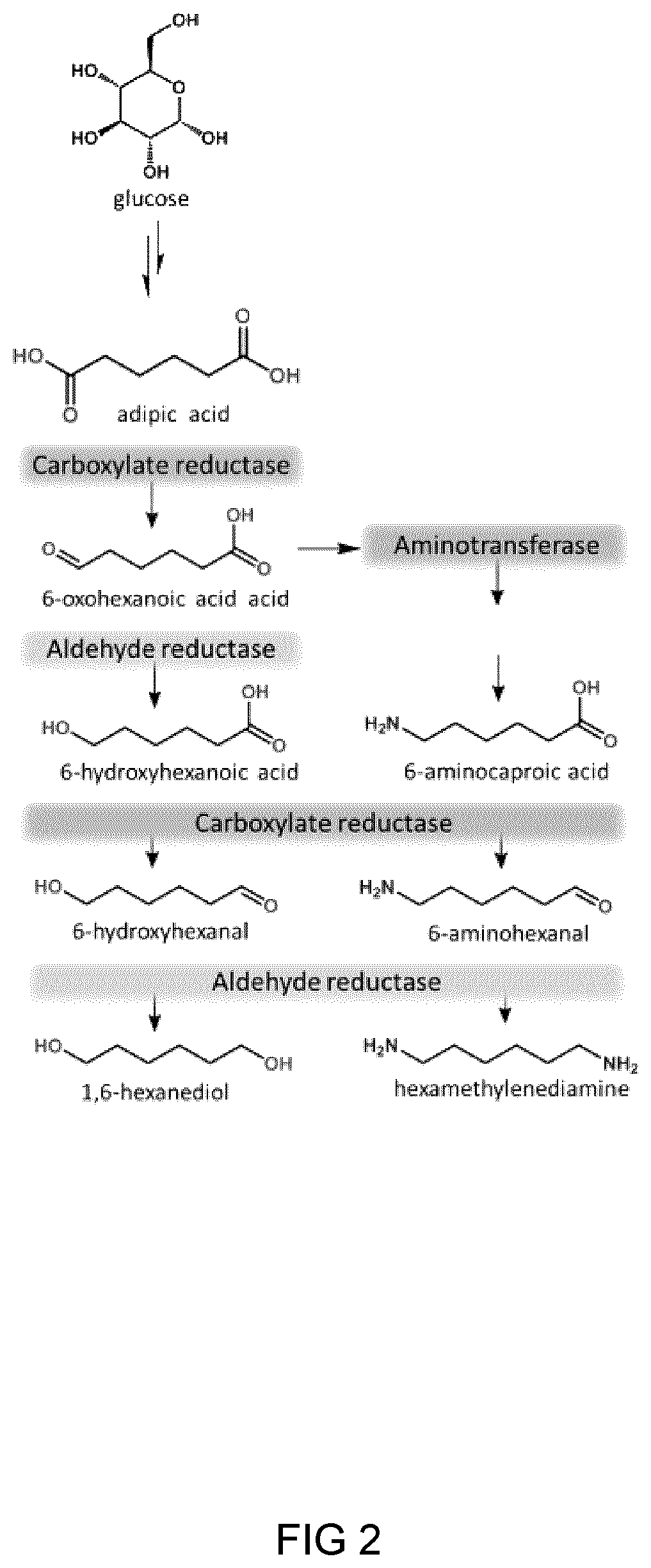
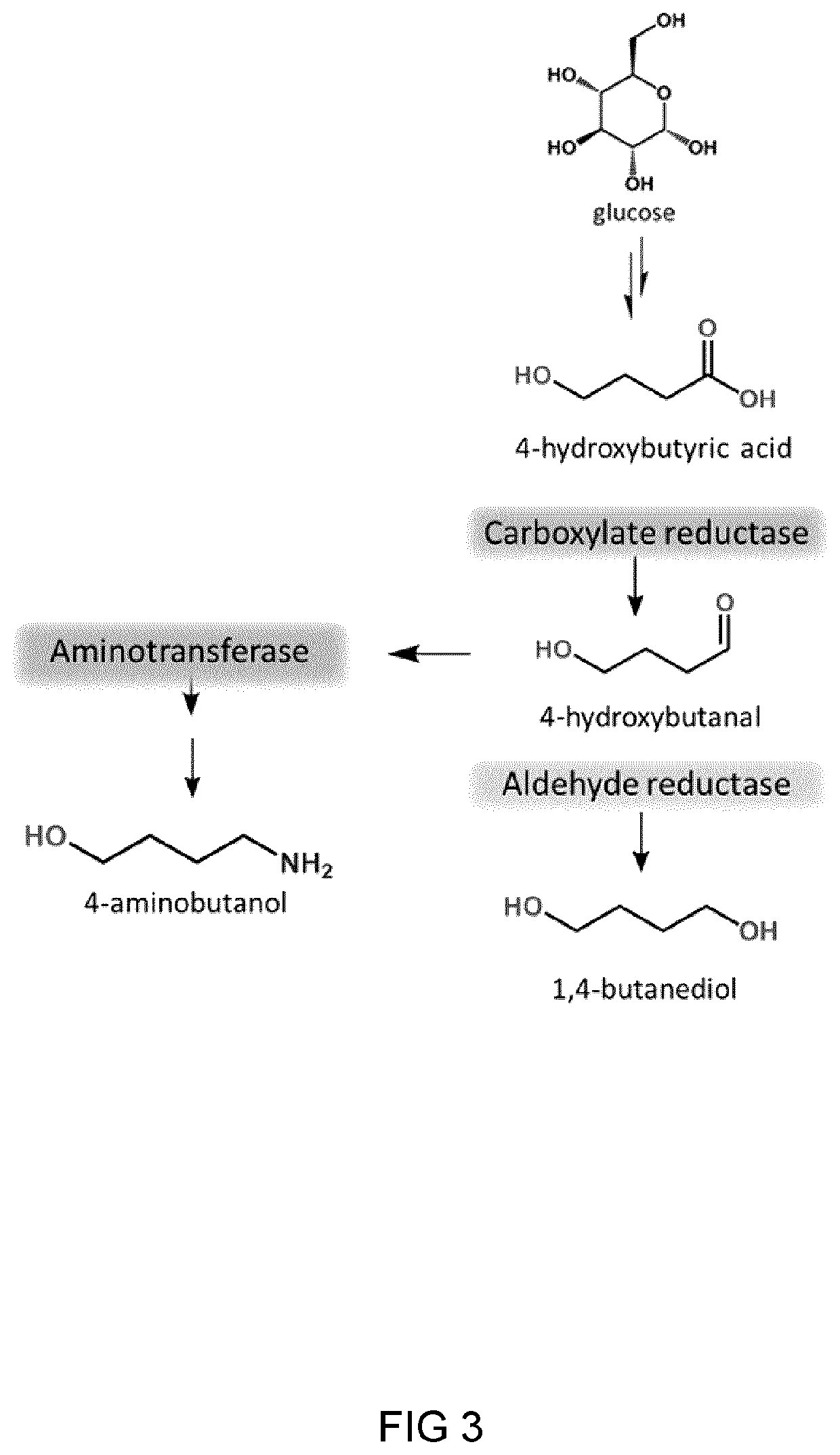
Process And Microorganism For Synthesis Of Adipic Acid From Carboxylic Acids
A method for biosynthesis of polymer precursors, including, adipic acid, 1,6-hexanediol, 6-hydroxyhexanoic and 6-aminocaproic acids from carboxylic acids is provided. A method for biosynthesis of adipic acid from six-carbon dicarboxylic acids having α, β-enoate reductase activity by treatment with an enzyme is provided. The biocatalytic conversion of aliphatic and hydroxycarboxylic acids to corresponding aldehydes, alcohols, and amines using novel carboxylate reductases, aldehyde reductases, and aminotransferases is described. Also provided are genetically engineered microorganisms for use in the biosynthetic processes.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
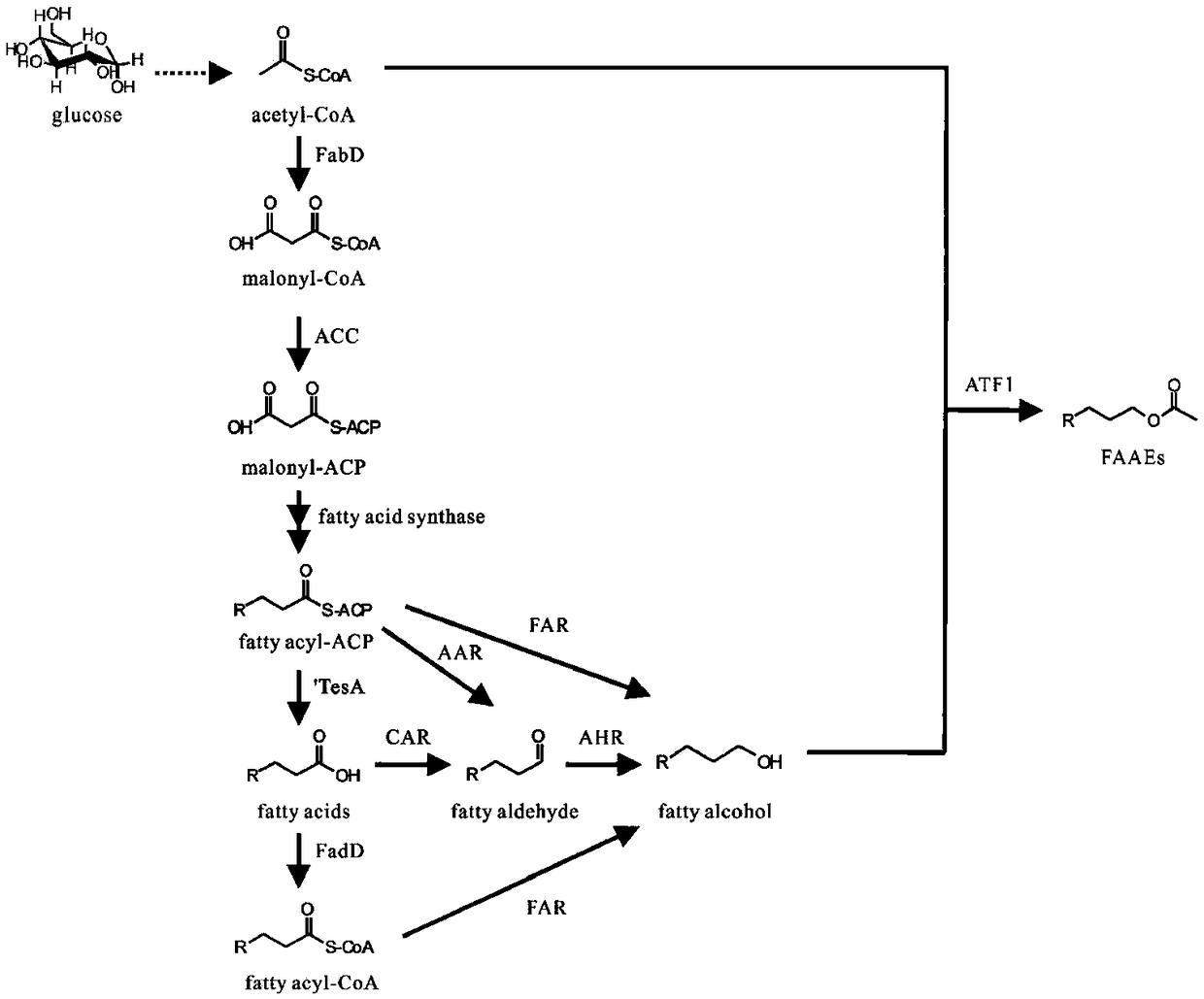
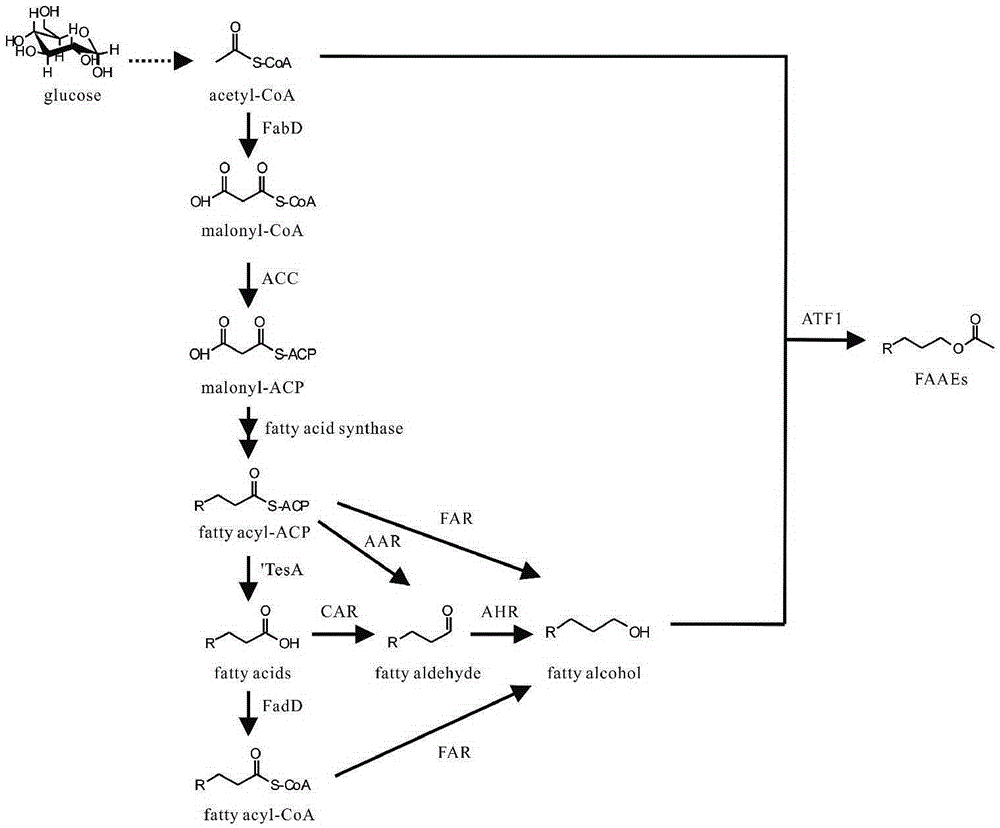
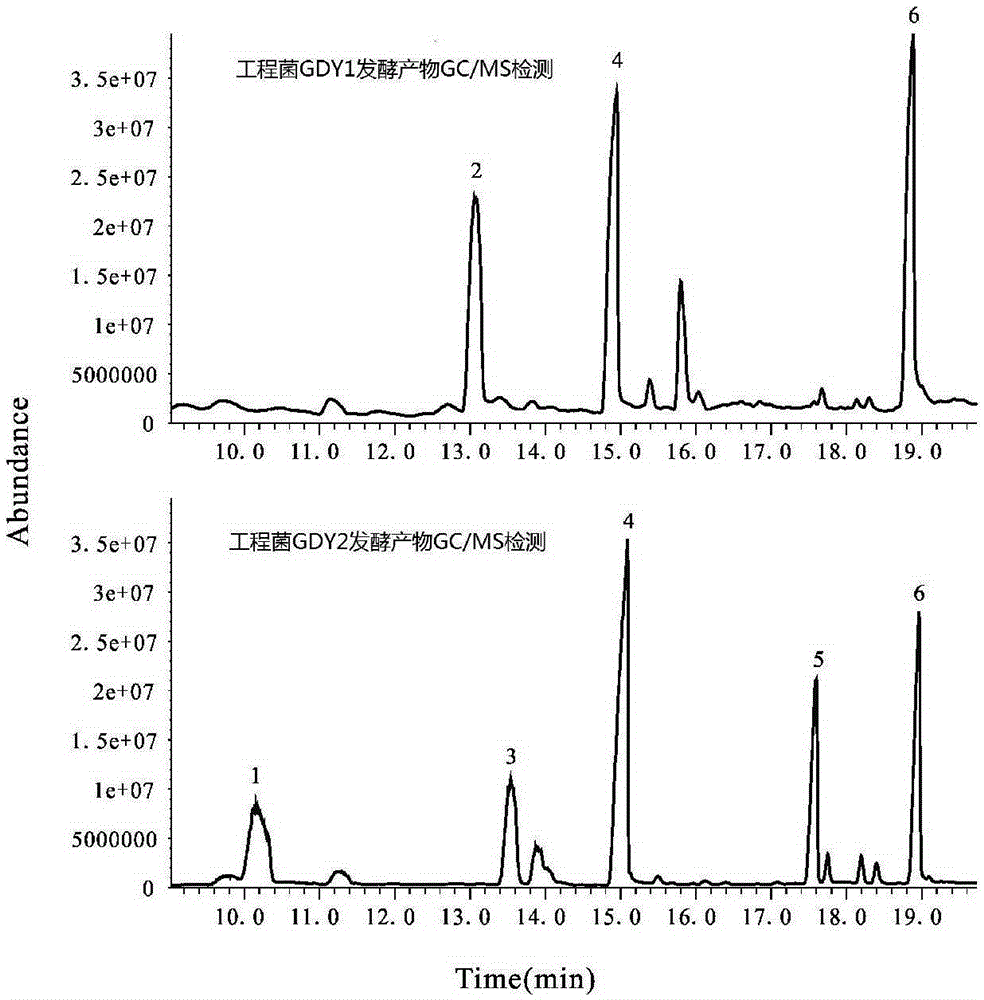
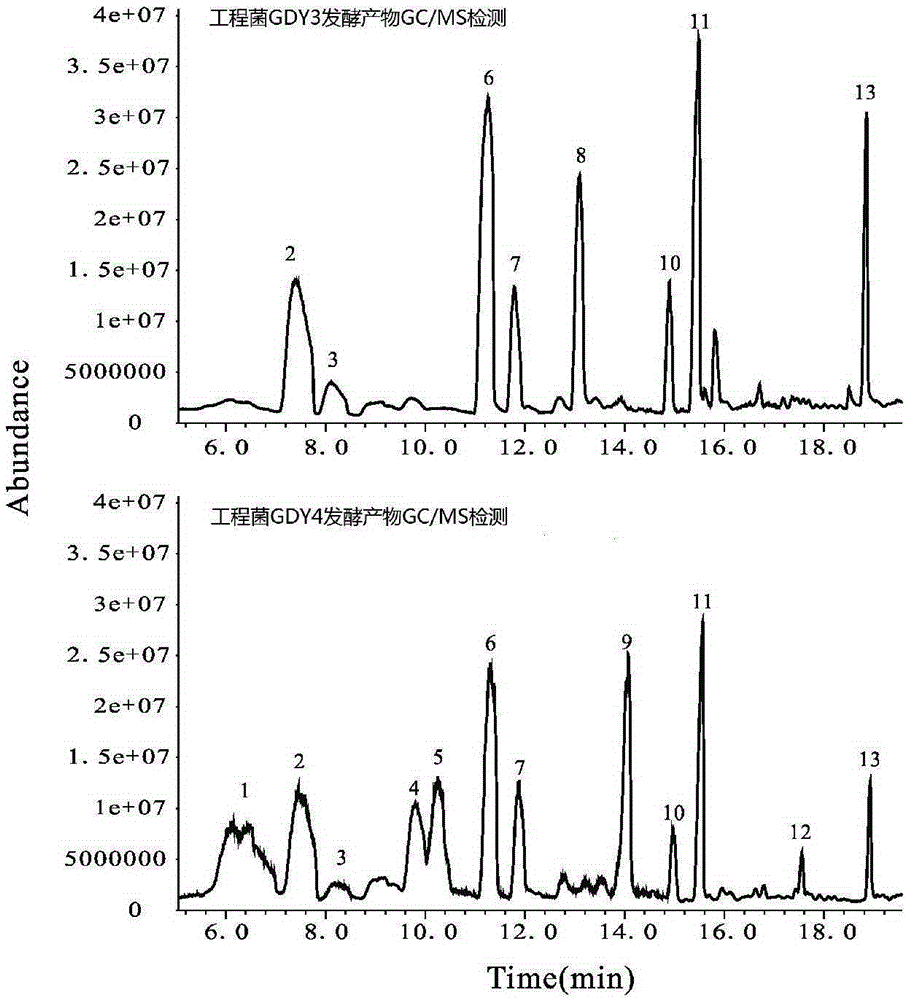
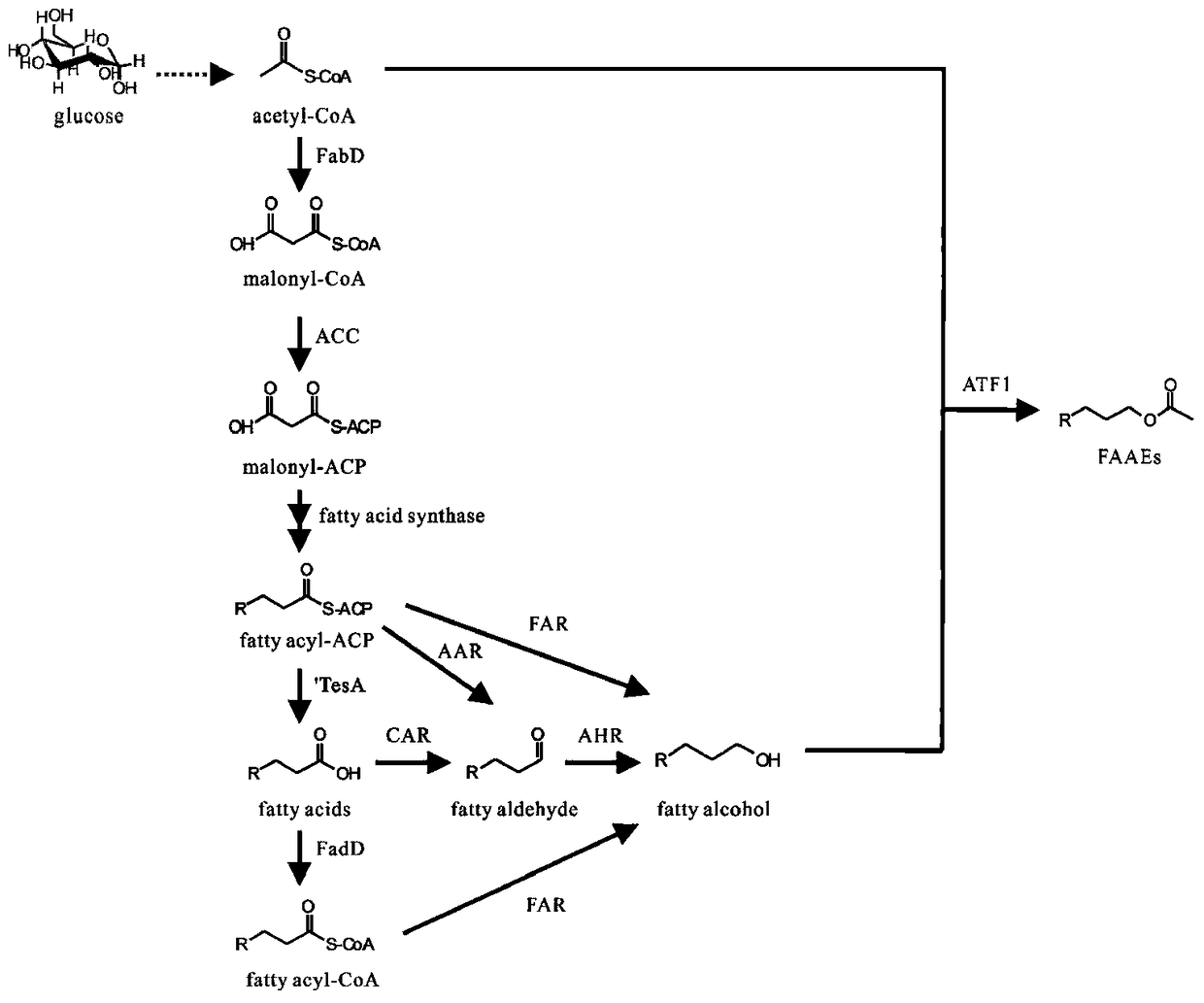
Method for synthesizing fatty alcohol acetates base on fatty acids in microorganisms in vivo
ActiveCN109234295AFast growthGenetic manipulation technology is matureBiofuelsFermentationMicrobial transformationIn vivo
A method for synthesize pheromone fatty alcohol acetate ester based on three intermediate product of fatty acid metabolism pathway in microorganism includes such steps as high expression of fatty acidacyl ester in microorganism, high expression of fatty acid acyl ester in microorganism, high expression of fatty acid acyl ester in microorganism, high expression of fatty acid acyl ester in microorganism, high expression of fatty acid acyl ester in microorganism, high expression of fatty acid acyl ester in microorganism, and high expression of fatty acid acyl ester in microorganism. ACP reductase AAR, carboxylic acid reductase CAR, acyl-CoA reductase FAR and aldehyde reductase AHR, respectively. ACP, fatty acid or acyl-CoA producing fatty alcohol. At last, the pheromone fatty alcohol acetatewas synthesized by the reaction of fatty alcohol and acetyl-CoA with high expression of alcohol acetyltransferase ATF1 in fatty alcohol-producing engineering bacteria. The invention can realize microbial conversion from glucose to fatty alcohol acetate, and provides a feasible path for large-scale biosynthesis of fatty alcohol acetate.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
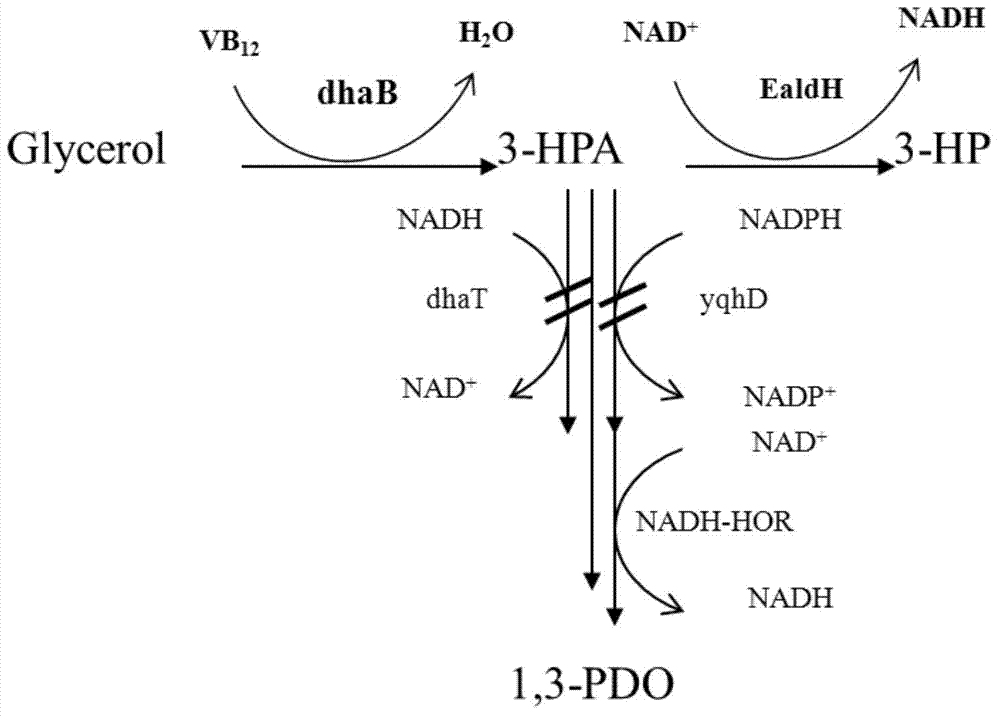
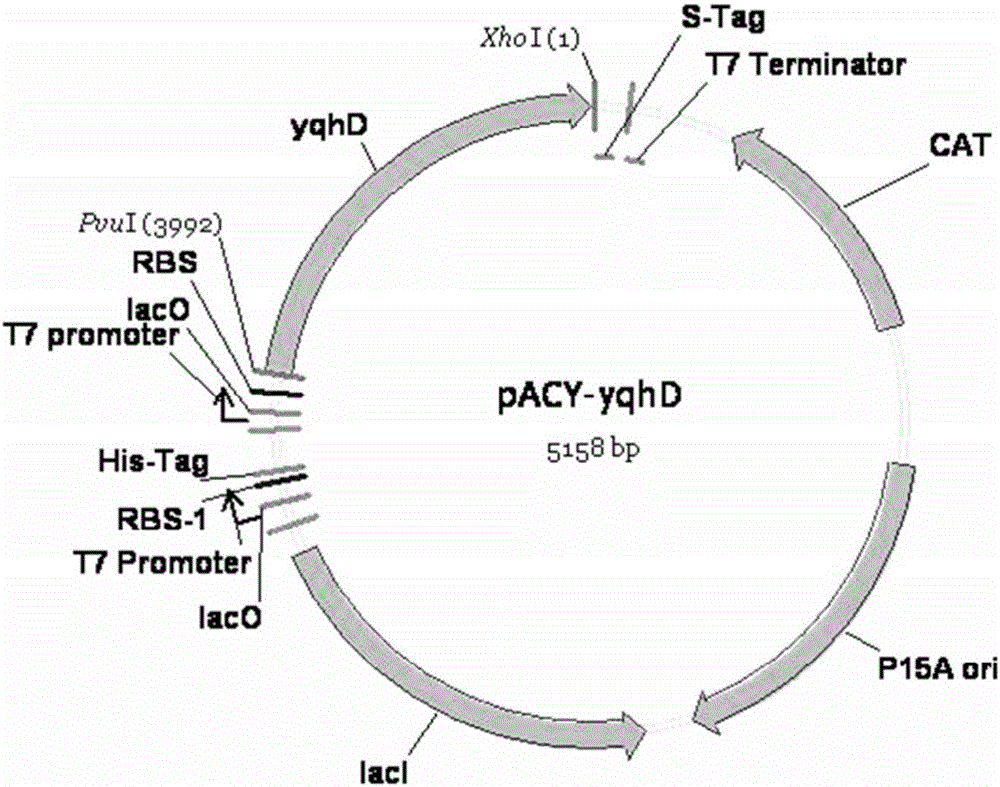
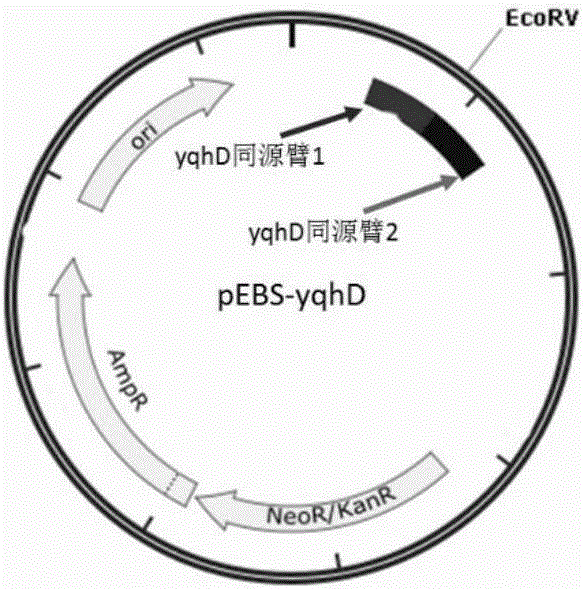
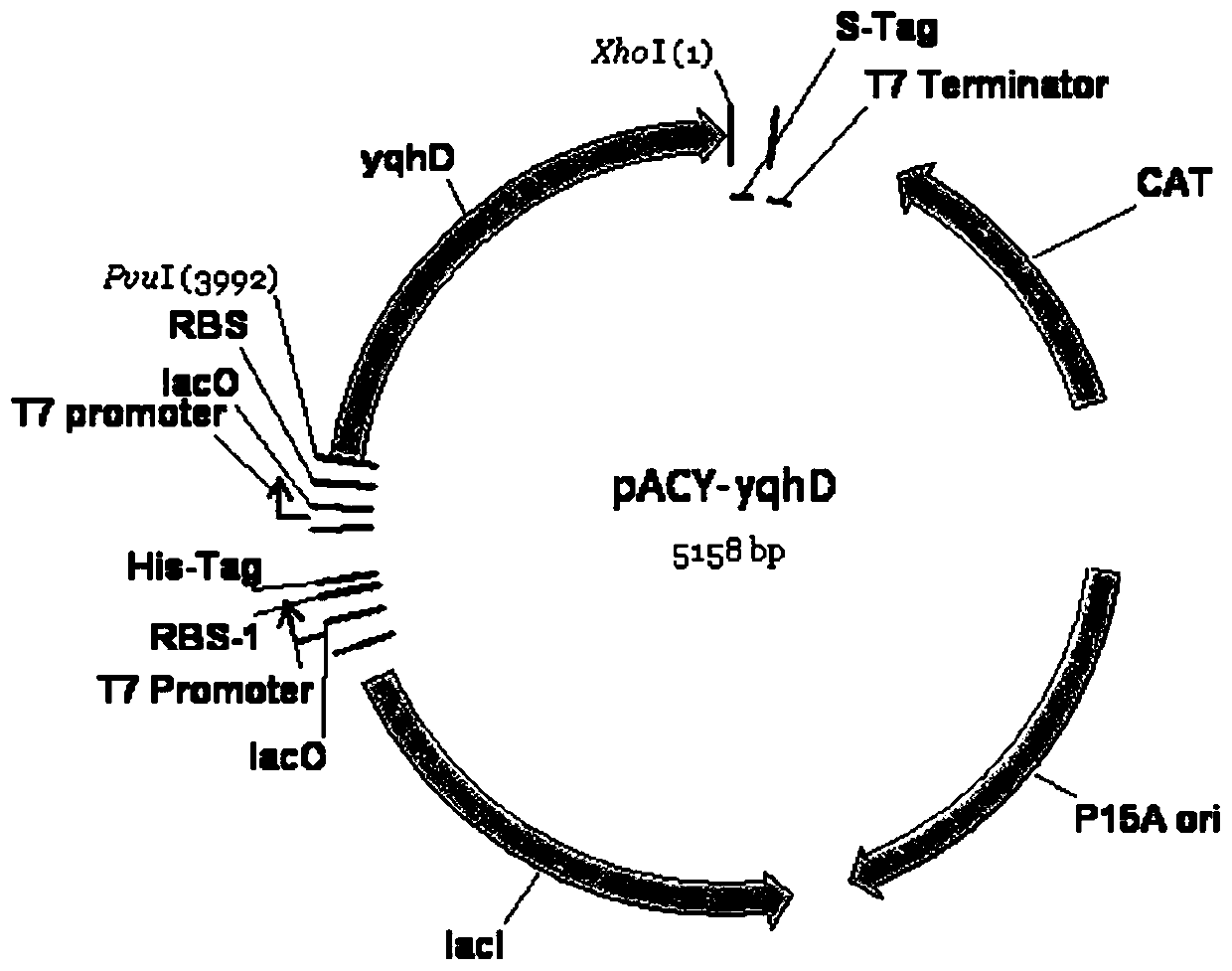
Recombinant expression of aldehyde reductase and application thereof in bioconversion of glycerol into 1,3-propylene glycol
InactiveCN101633928BIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processes1,3-PropanediolGenetically engineered
The invention discloses recombinant expression of aldehyde reductase and an application thereof in bioconversion of glycerol into 1, 3-propylene glycol, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention is characterized in that a recombinant expression vector containing aldehyde reductase gene sequence is used to express the enzyme to a host cell for preparing 1, 3-propylene glycol. The beneficial effects and benefits of the invention are that recombinant Klebsiella (Pdk-yqhD) takes glycol as substrate to ferment for 30h, and the concentration of 1, 3-propylene glycol in the fermentation liquor is improved by 17.1% in comparison with a comparison strain; compared with the original strain, by using the recombinant restrain in the invention for fermentation, the yield of 1, 3-propylene glycol is improved by 10-50%, which lays a foundation on constructing genetically engineered microorganism of the high yield of the 1, 3-propylene glycol taking glycol as substrate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103497922BReduce synthesisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniae3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention discloses recombination klebsiella pneumonia capable of co-producing 3-HP and P3HP, and a preparation method and application thereof. The recombination bacterium is obtained by introducing glycerol dehydratase gene, glycerol dehydratase reactivation enzyme gene, aldehyde dehydrogenase gene, propionyl coenzyme A synthetase gene and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthetase gene into a host recombination klebsiella pneumonia in which 1, 3-propylene glycol oxidoreductase gene and aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene are knocked out. According to the technical scheme, the production cost of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) is reduced, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and poly(3-hydroxypropionic acid) can be synthesized at the same time by taking a same thallus as the host.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing long-chain binary acid by using recombinant escherichia coli strain
InactiveCN107022513AHigh yieldOvercome the conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDegradation pathway
The invention discloses a method for producing long-chain binary acid by using a recombinant escherichia coli strain. The method comprises the following steps of knocking out or weakening a fatty acid beta-oxidation and degradation pathway gene in escherichia coli to establish the recombinant escherichia coli; using the recombinant escherichia coli to express fatty acid synthetase and a fatty acid synthesizing regulatory gene, and utilizing sustained carbon source glucose as a raw material to enable a cell to accumulate long-chain fatty acid; finally, expressing fatty acid hydroxylase, fatty alcohol, aldehyde reductase and the like on the basis, and gradually converting the accumulated long-chain fatty acid step by step, so as to obtain the long-chain binary acid. The method has the advantages that the defects of the prior art are overcome; in the whole preparation process, the reaction conditions are mild, the technology is simple, the environment-friendly effect is realized, and the product yield is higher.
Owner:河北美邦工程科技股份有限公司
Hyoscyamine aldehyde reductase and its application
The present invention discloses a hyoscyamine aldehyde reductase synthase(HAR) and its application, the hyoscyamine aldehyde reductase synthase has an amino acid residue sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 4, and a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 3; the catalyzed reaction product hyoscyamine aldehyde after the prokaryotic expression is hyoscyamine, the hyoscyamine aldehyde is used to transform atropa belladonna, which can increase the content of hyoscyamine in atropa belladonna cell line, and has important meaning to increase the content of tropane alkaloids in atropa belladonna.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for synthesizing fatty alcohol acetic acid ester in microorganism
ActiveCN105331647AFast growthGenetic manipulation technology is matureBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMicrobial transformationCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing pheromone fatty alcohol acetic acid ester in a microorganism, based on a fatty acid metabolic pathway and by using three intermediate products as precursor molecules. The method includes: highly expressing acyl-ACP reductase AAR, carboxylic acid reductase CAR, acyl-CoA reductase FAR and aldehyde reductase AHR in the microorganism to respectively obtain engineering bacteria capable of reducing acyl-ACP, fatty acid or acyl-CoA fat generating alcohol; highly expressing alcohol acetyltransferase ATF1 in the fat-generating alcohol engineering bacteria to catalyze reaction of fatty alcohol and acetyl coenzyme A to synthesize the pheromone fatty alcohol acetic acid ester. By the method, microbial conversion from glucose to the fatty alcohol acetic acid ester can be realized, and a feasible way is provided for biologically synthesizing the fatty alcohol acetic acid ester on a large scale.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
Genetically engineered bacteria for co-production of isoprene and 1,3-propanediol and its construction method and application
ActiveCN106350476BRealize joint productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant host cell for the biosynthesis of vanillin or vanillin beta-D-glucoside
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
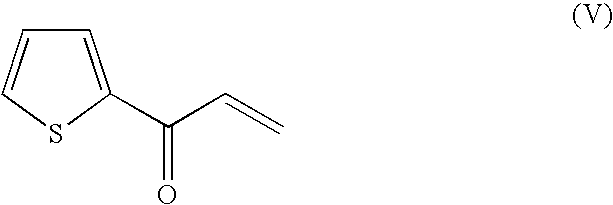
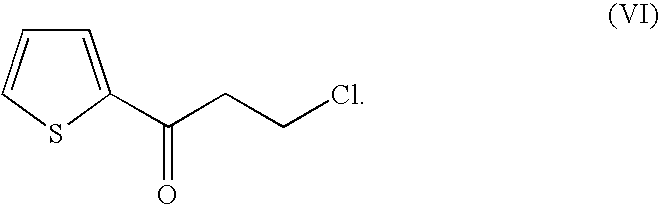
A method for synthesizing (s)-n,n-dimethyl-3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thiophene)-1-propanamine catalyzed by the recombinant bacterial crude enzyme system of aldehyde and ketone reductase
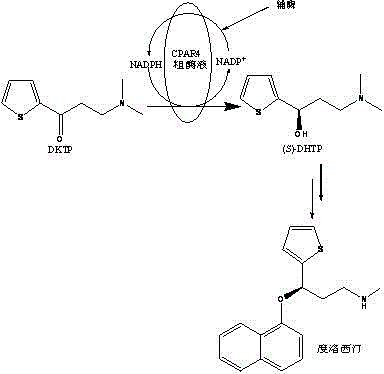
Aldehyde and ketone reductase crude enzyme system catalytic synthesis of recombinant bacteria ( S )‑N,N‑Dimethyl‑3‑hydroxy‑3‑(2‑thiophene)‑1‑propylamine (( S )‑DHTP), which belongs to the technical field of biocatalytic asymmetric transformation. The present invention is to add auxiliary substrate and initial amount of coenzyme NADP in recombinant bacterial crude enzyme system + Promote the regeneration cycle of the coenzyme NADPH in the system, the reaction substrate is N,N-dimethyl-3-ketone-3-(2-thiophene)-1-propanamine (DTKP), and the recombinant bacteria express the aldehyde and ketone reductase gene of E. coli BL21(DE3)(pETCPAR4), aldehyde and ketone reductase gene cpar4 from Candida parapsilosis ( Candida parapsilosis ) CCTCC NO: M 203011, the gene encodes aldehyde and ketone reductase CPAR4, which catalyzes the asymmetric reduction of DKTP to ( S )‑DHTP. The invention utilizes the cell-free system to catalyze the reaction without additionally adding coupling enzymes required for coenzyme regeneration in the reaction system, improves the efficiency of the direct action of the enzyme and the substrate, shortens the reaction time, and obtains better conversion effects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing 1, 6-hexanediol through whole-cell catalysis, recombinant microorganism and application of recombinant microorganism
ActiveCN114606169AIncrease productionShort reaction timeBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliCarboxylic acid reductase
The invention relates to the technical field of biochemical engineering, and particularly discloses a method for producing 1, 6-hexanediol through whole-cell catalysis, a recombinant microorganism and application of the recombinant microorganism. Compared with an original strain, the recombinant microorganism provided by the invention has the advantages that aldehyde reductase yahk is overexpressed, carboxylic acid reductase MpCAR and 4 '-phosphoric acid panthenyl aminotransferase sfp are expressed, and the original strain is escherichia coli. The recombinant Escherichia coli obtained by introducing exogenous carboxylic acid reductase and 4 '-phosphoric acid panthenotransferase into Escherichia coli and overexpressing aldehyde reductase is used for whole-cell catalysis, 1, 6-hexanediol can be produced from 1, 6-adipic acid under mild conditions, and the method has a very wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A method for synthesizing fatty alcohol acetate in microorganisms
ActiveCN105331647BFast growthGenetic manipulation technology is matureBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesMicrobial transformationFatty alcohol
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing pheromone fatty alcohol acetate in microorganisms based on three intermediate products of fatty acid metabolism pathway as precursor molecules. The reductase CAR, fatty acyl-CoA reductase FAR and aldehyde reductase AHR are used to obtain engineering bacteria that can reduce fatty acyl-ACP, fatty acid or fatty acyl-CoA to produce fatty alcohol, respectively. Finally, alcohol acetyltransferase ATF1 was highly expressed in fatty alcohol-producing engineering bacteria, which was used to catalyze the reaction of fatty alcohol and acetyl-CoA to synthesize pheromone fatty alcohol acetate. The invention can realize the microbial transformation from glucose to fatty alcohol acetate, and provides a feasible way for large-scale biosynthesis of fatty alcohol acetate.
Owner:GANNAN NORMAL UNIV
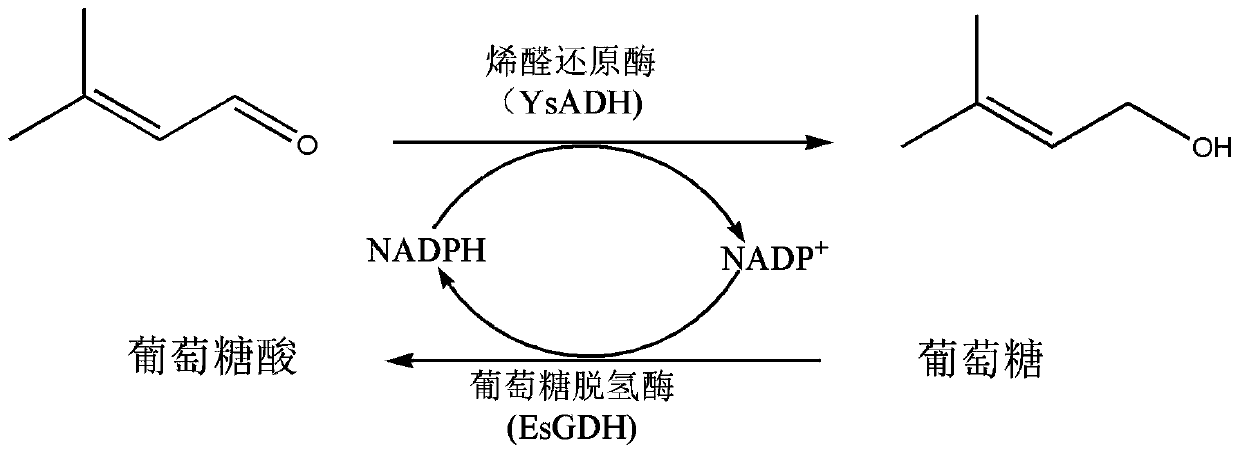
Recombinant genetically engineered bacterium of co-expressing olefine aldehyde reductase and glucose dehydrogenase and application of recombinant genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN110643556AHigh regional selectivityIncrease vitalityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRegioselectivityAllylic alcohol
The invention discloses a recombinant genetically engineered bacterium of co-expressing olefine aldehyde reductase and glucose dehydrogenase and application of the recombinant genetically engineered bacterium to catalyzes the synthesis of allylic alcohols with methylcrotonaldehyde. The genetically engineered bacterium is obtained by co-introducing olefine aldehyde reductase gene and D- glucose dehydrogenase into a host bacteria. A method has the advantages of being high in regioselectivity and high in activity. The 500mM substrate methylcrotonaldehyde is completely converted into the product of the allylic alcohols in 3.5h, no by-product saturated alcohol is detected during the reaction, and it is indicated that the method is efficient and specific in catalyzing the C=O hydrogenation of methylcrotonaldehyde to obtain the corresponding allylic alcohols. Meanwhile, the recombinant cells induce the production of D-glucose dehydrogenase, with glucose as a co-substrate, the glucose dehydrogenase can continuously convert NADP+ to NADPH, additional coenzymes do not need to be added in the reaction process, thus the production cost is greatly lowered, and the method is more suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae with detoxification function and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110452827AEthanol fermentation process is smooth and efficientFungiBiofuelsCelluloseBiotechnology
The invention relates to genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae with a detoxification function. The genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae contains an exogenous aldehyde reductase gene, and the exogenous aldehyde reductase gene is an aldehyde reductase gene of which the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The exogenous aldehyde reductase gene is obtained in a way that genome DNA of pichia stipitis is taken as a template for PCR amplification, and meanwhile, two enzyme digestion sites including Xho I and Not I are introduced into the terminal C and the terminal N respectively. A GRE2 gene segment is connected to a pYES2 / NTA plasmid vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid pYES2 / NTA-GRE2, and then the recombinant plasmid pYES2 / NTA-GRE2 is transformed into the saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain the genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae with the detoxification function. The saccharomyces cerevisiae can efficiently ferment pretreatment materials of lignocellulose to produce fuel ethanol; meanwhile, inhibitory or toxic aldehyde substances generated in the fermentation process can be removed, and detoxification of fermentation inhibiting substances in the pretreatmentmaterials of the lignocellulose is achieved, so that it is ensured that the process of producing the ethanol through fermentation of the cellulose is smooth and efficient.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
Hyospolamine reductase and its application
The present invention discloses hyoscyamine aldehyde reductase synthase (hyoscyamine aldehyde reductase synthase, HAR) and its application, which has the amino acid residue sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.4 and the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.3; The hyoscypolamine reduction reaction product catalyzed by prokaryotic expression is hyoscypolamine, and the hyoscypolamine content in belladonna cell lines can be increased after the hyoscypolaldehyde reductase is used to transform belladonna cell lines. Significance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
A gene recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae with detoxification function and its construction method and application
ActiveCN110452827BEthanol fermentation process is smooth and efficientFungiBiofuelsCelluloseEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae with a detoxification function. The genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae contains an exogenous aldehyde reductase gene, and the exogenous aldehyde reductase gene is an aldehyde reductase gene of which the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The exogenous aldehyde reductase gene is obtained in a way that genome DNA of pichia stipitis is taken as a template for PCR amplification, and meanwhile, two enzyme digestion sites including Xho I and Not I are introduced into the terminal C and the terminal N respectively. A GRE2 gene segment is connected to a pYES2 / NTA plasmid vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid pYES2 / NTA-GRE2, and then the recombinant plasmid pYES2 / NTA-GRE2 is transformed into the saccharomyces cerevisiae to obtain the genetic recombination saccharomyces cerevisiae with the detoxification function. The saccharomyces cerevisiae can efficiently ferment pretreatment materials of lignocellulose to produce fuel ethanol; meanwhile, inhibitory or toxic aldehyde substances generated in the fermentation process can be removed, and detoxification of fermentation inhibiting substances in the pretreatmentmaterials of the lignocellulose is achieved, so that it is ensured that the process of producing the ethanol through fermentation of the cellulose is smooth and efficient.
Owner:ZHONGRONG TECH CORP LTD
Process and microorganism for synthesis of adipic acid from carboxylic acids
A method for biosynthesis of polymer precursors, including, adipic acid, 1,6-hexanediol, 6-hydroxyhexanoic and 6-aminocaproic acids from carboxylic acids is provided. A method for biosynthesis of adipic acid from six-carbon dicarboxylic acids having α, β-enoate reductase activity by treatment with an enzyme is provided. The biocatalytic conversion of aliphatic and hydroxycarboxylic acids to corresponding aldehydes, alcohols, and amines using novel carboxylate reductases, aldehyde reductases, and aminotransferases is described. Also provided are genetically engineered microorganisms for use in the biosynthetic processes.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
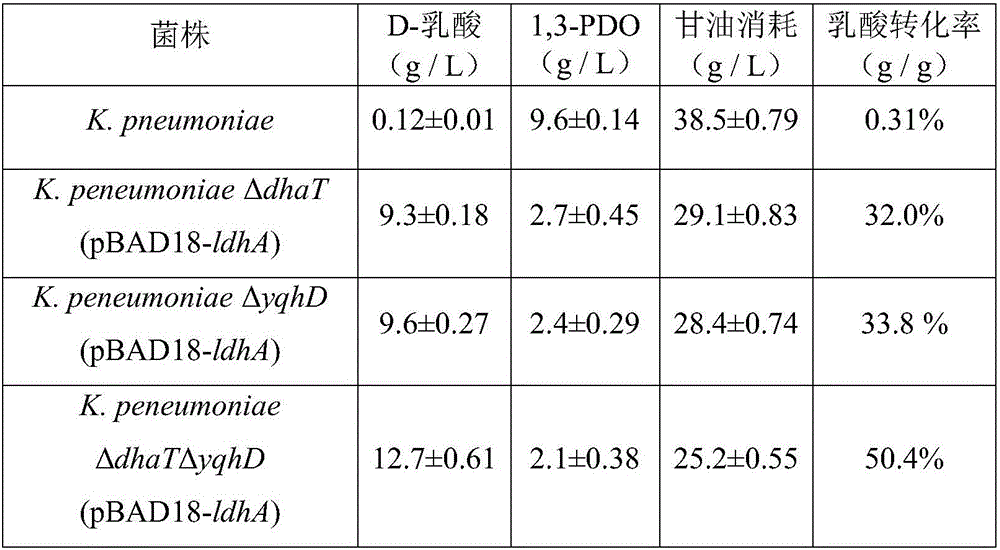
Recombinant bacterium for synthesizing D-lactic acid by adopting biodiesel by-product, namely, glycerol and applications of recombinant bacterium
InactiveCN106434505AImprove conversion rateCost advantageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeBiodiesel
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for synthesizing D-lactic acid by adopting the biodiesel by-product, namely, glycerol and applications of the recombinant bacterium, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. For the recombinant bacterium provided by the invention, the dehydrogenase gene of D-lactic acid, namely, ldhA is introduced into the host, namely, recombinant Klebsiella pneumoniae with the 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase gene dhaT and the aldehyde reductase / alcohol dehydrogenase gene yqhD knocked out, and thus the engineering strain is obtained. D-lactic acid is synthesized by taking the biodiesel by-product, namely, glycerol as the substrate, in the shake flask level, the yield and conversion rate respectively achieve 12.7g / L and 50.4%, the optical purity is 100%, and the recombinant bacterium has the advantages that the optical purity and conversion rate are high, and the production cost is low.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com