Patents
Literature
137 results about "Lung cancer cell line" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
SK-MES-1 is a human lung cancer cell line that displays epithelial morphology and grows as monolayers in tissue culture. These cells exhibit a cytokeratin expression pattern typical of simple epithelia (i.e., CK7, CK8, CK18, and CK19), and similar to that found in adenocarcinomas.
RUNX3 gene showing anti-tumor activity and use thereof
InactiveUS7368255B2Reduce selection requirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthCancers diagnosis
The present invention relates to a RUNX3 gene showing anti-tumor activity which is essentially involved in TGF-β dependent-programmed cell death (apoptosis) and use thereof. In addition, the present invention finds that the RUNX3 gene expression is suppressed in the various gastric cancer and lung cancer cell lines. The suppression of the RUNX3 gene expression is due to hyper-methylation of CpG island located around RUNX3 exon (1). The RUNX3 gene and its gene product of the present invention can be used effectively for the development of anti-cancer agents. CpG island around RUNX3 exon (1) could also be used not only for the development of anti-cancer agents which regulate the abnormal DNA methylation and there by induce RUNX3 expression but also for the development of methods for cancer diagnosis by measuring the abnormal DNA methylation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
MiR-126 full-length gene knockout kit based on CRISPR-Cas9 technology and application thereof
ActiveCN106566838AOvercoming the drawbacks of studying microRNA functionHigh knockout efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionSingle strandCell strain
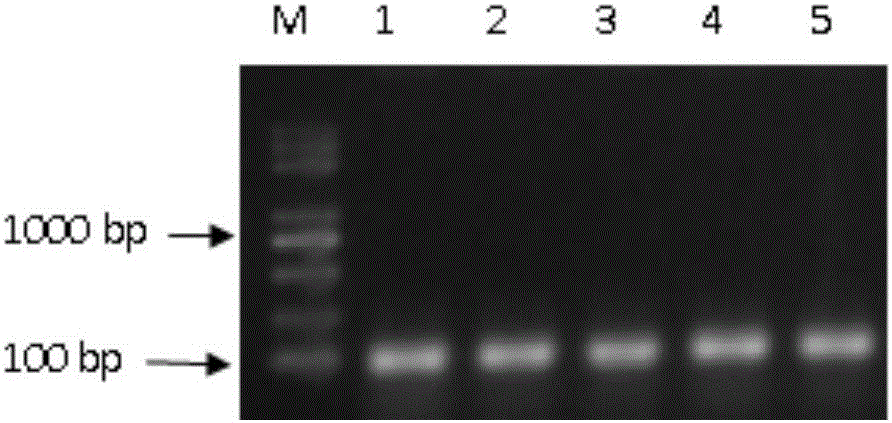
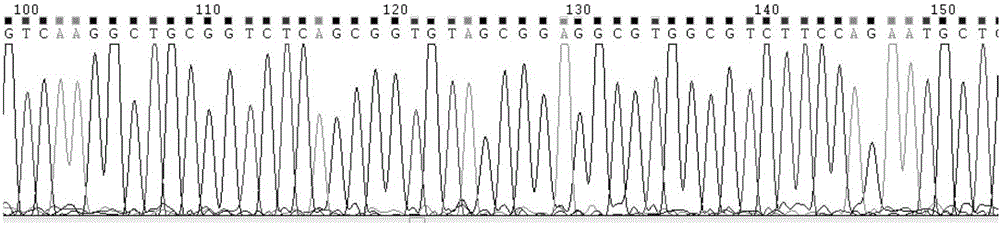
The invention discloses a MiR-126 full-length gene knockout kit based on a CRISPR-Cas9 technology and an application thereof. CRISPR-Cas9 target sequences upstream and downstream a MiR-126 gene are preferably selected, and sgRNA single strands are designed and synthesized for the target sequences and built into a carrier. Through 293T cell strain transfection, sgRNA and trRNA constitute a specific recognition structure. Thus, Cas9 enzyme is guided to specifically shear the corresponding sequences at the two ends of the MiR-126 gene. Drug sieving is carried out constantly to get a MiR-126 full-length gene knockout cell strain. An optimal upstream and downstream sgRNA combination is obtained through drug sieving cell strain sequencing verification. The knockout efficiency of the combination is as high as 90% above. The kit built based on the combination can be used to carry out specific MiR-126 full-length gene knockout on a variety of cell lines such as 293T, a lung cancer cell line A 549 and a vascular endothelial cell HUVEC line.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
Lung cancer organ model and application thereof in tumor research
PendingCN109554346AFast and efficient buildPreserve genetic informationMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug screeningAbnormal tissue growthCell-Extracellular Matrix
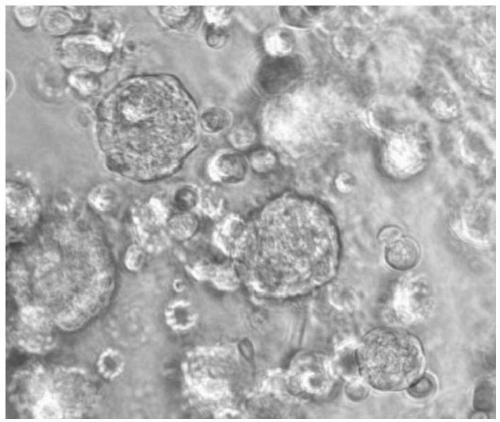
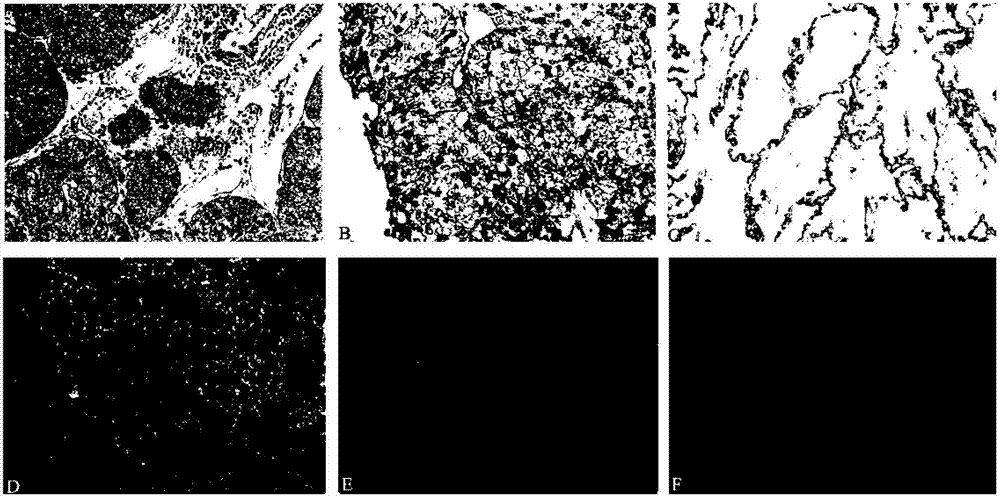
The invention discloses a lung cancer organ model and an application thereof in tumor research. An establishment method of the lung cancer organ model comprises the steps as follows: (1) lung cancer tumor cells are added to a three-dimensional culture medium for culture, and the lung cancer tumor cells are added to a culture medium to be continuously cultured after a tumor layer is formed, whereinthe culture medium contains growth factors and extracellular matrix suitable for growth lung cancer tumor cells; (2) a system obtained through culture in step (1) forms single cell after protease enzymolysis, resuspension is performed by the culture medium after separation, and then, the lung cancer organ model is obtained. By use of the method, a specimen library containing a large number of lung cancer organ models can be established, heterogeneity and diversity of lung cancer are greatly covered, the defect of insufficient representativeness of traditional lung cancer cell lines is effectively overcome, and the lung cancer organ model becomes an efficient platform for research of occurrence and development mechanisms of lung cancer.
Owner:BEIJING CHEST HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
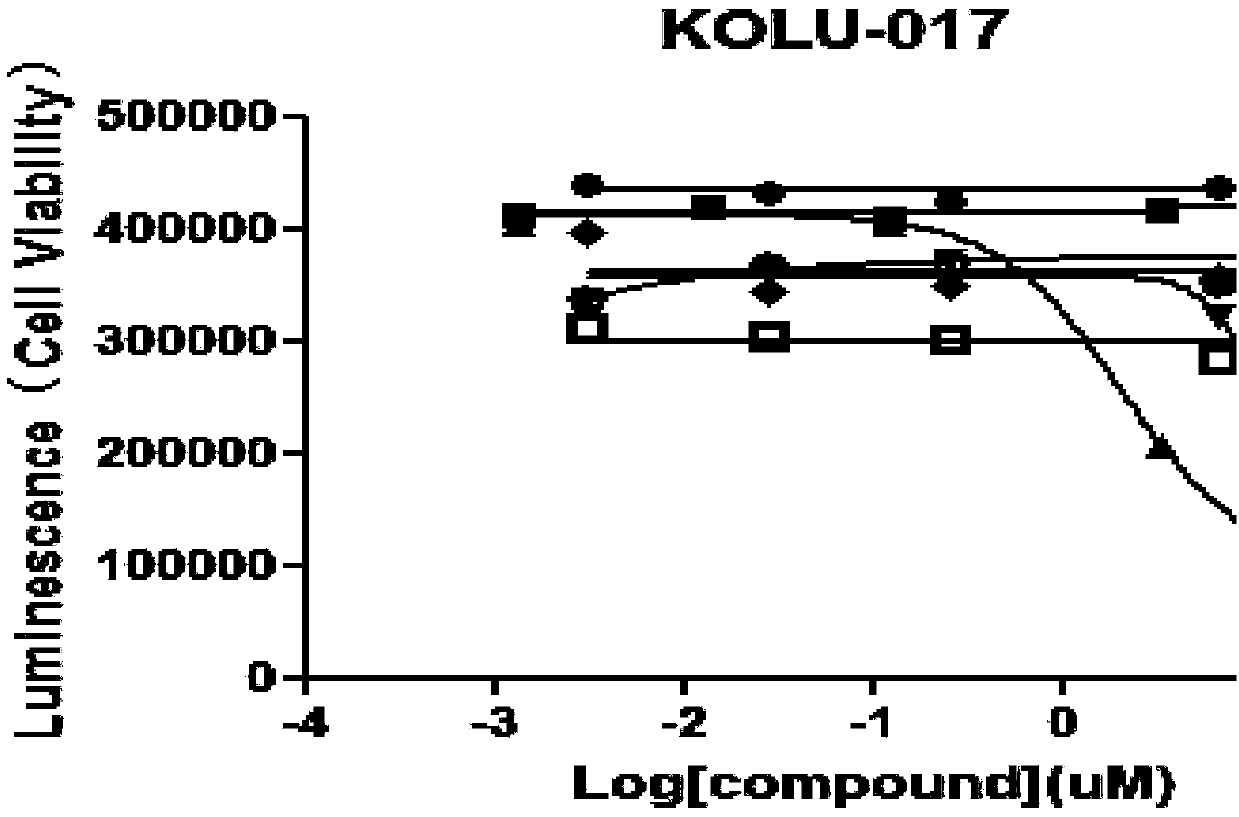
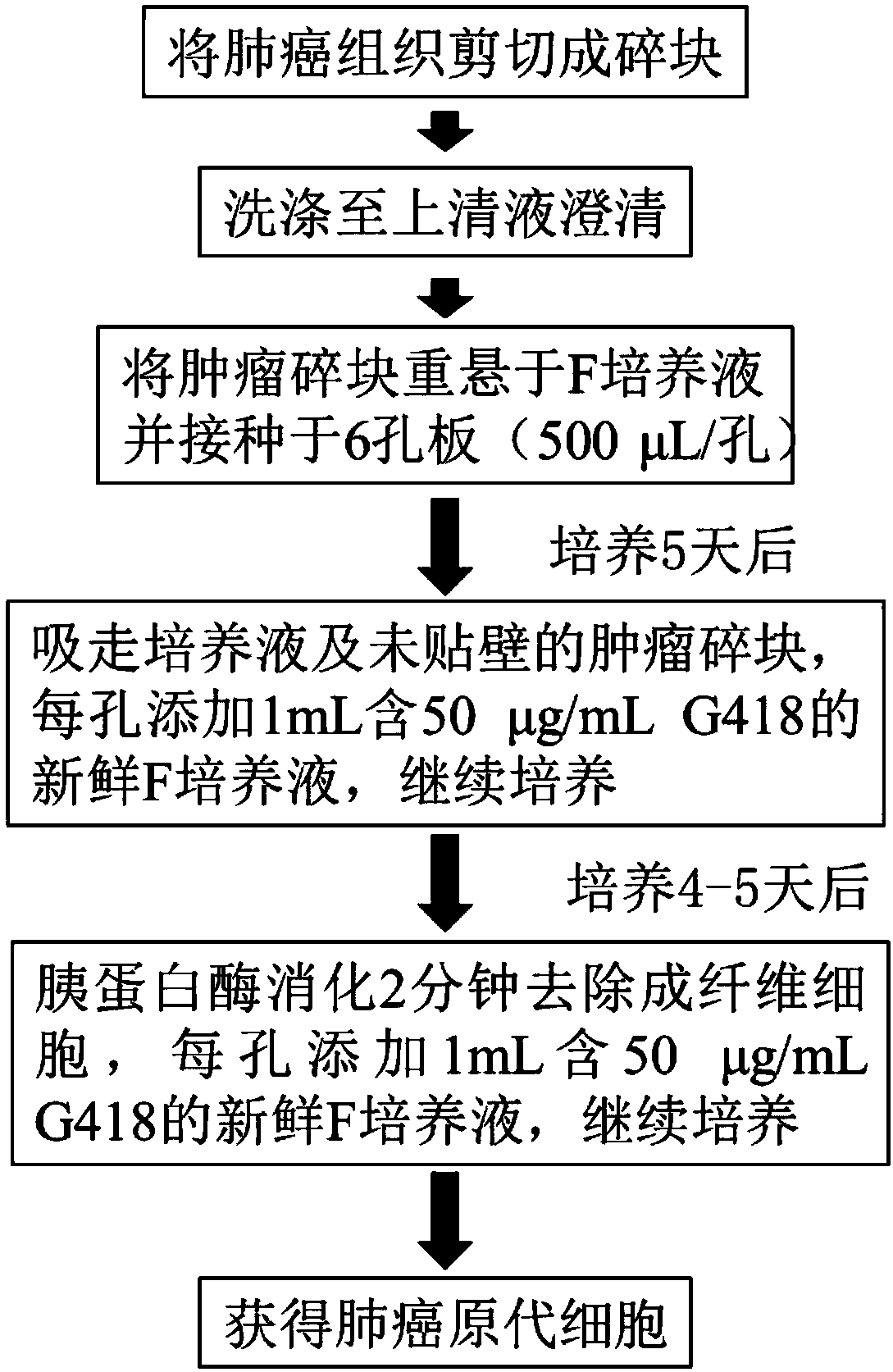
Cell culture solution and establishment method of human primary lung cancer cell line
InactiveCN108486059AExcellent adhesionPromote growthCulture processCell culture active agentsCulture fluidBasic research
The invention discloses a cell culture solution. The cell culture solution is characterized in that fetal bovine serum, kinase inhibitor Y-27632, GlutaMAX, insulin, hydrocortisone, epidermal growth factors and adenine are added into an F-12 medium and DMEM mixture. By using the F culture solution, cell attachment and growth in tissue blocks can be promoted, and meanwhile the growth of fibroblastscan be promoted; by adopting the cell culture method, the human primary lung cancer cells can be established with a high success rate, the culture time is short, and multiple times of passage and proliferation of the cells can be realized. An important material source is provided for basic research in lung cancer and related translational medicine application. The cell culture solution has great practical significance and practical value.
Owner:深圳市因诺转化医学研究院 +1
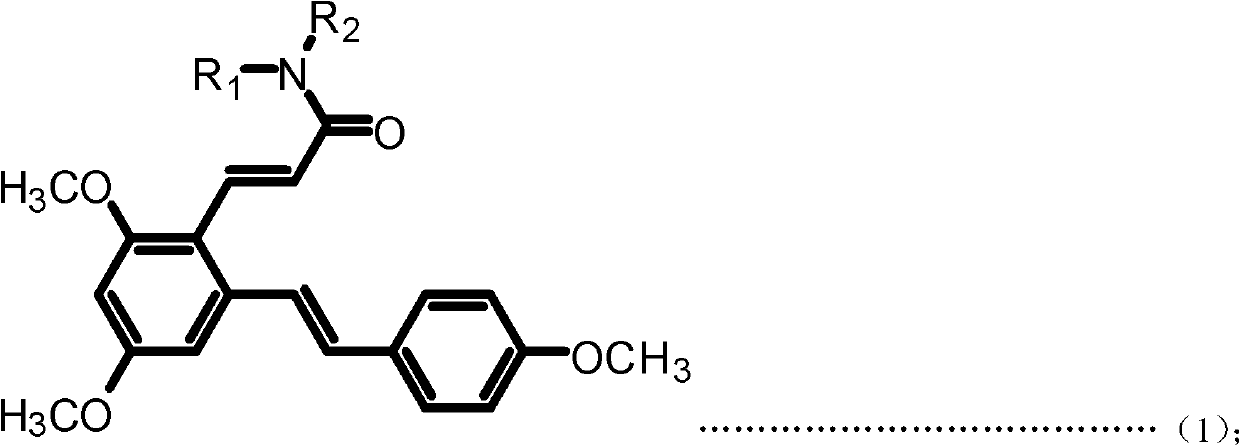
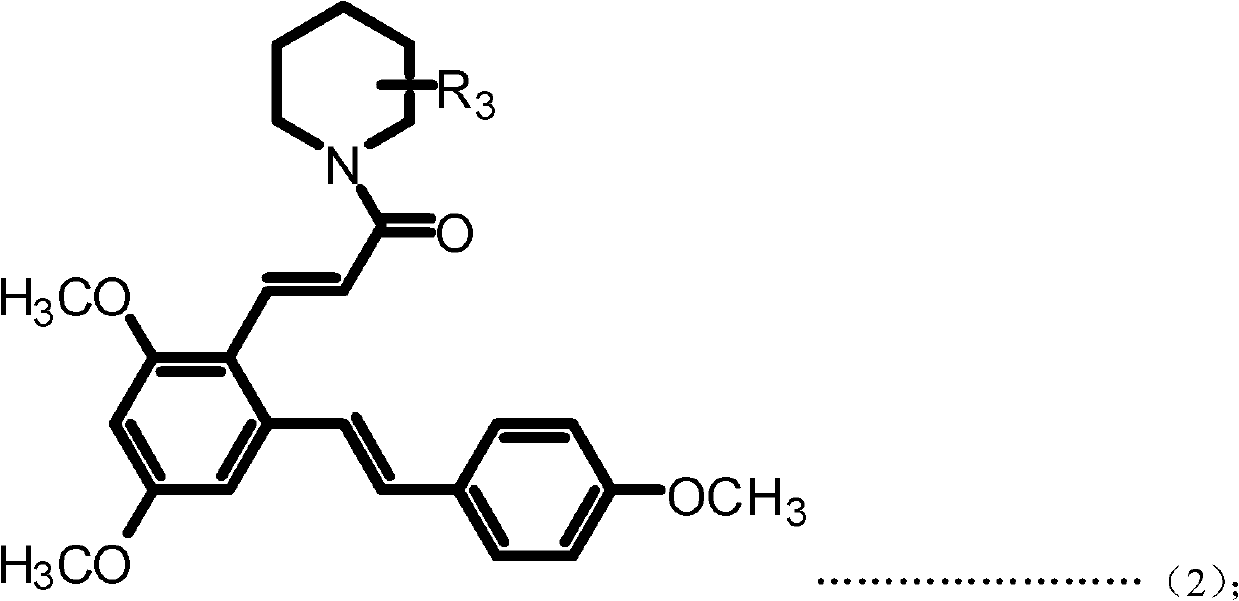
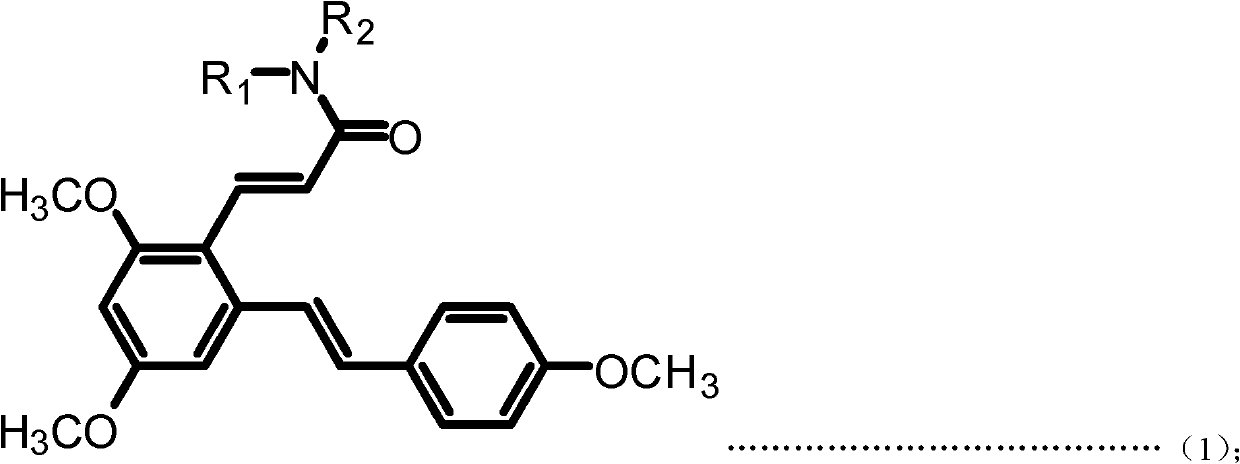
Resveratrol benzene acrylamide derivative, preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN102617391AStrong growth inhibitory effectOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationBenzeneWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a resveratrol benzene acrylamide derivative, a preparing method and an application thereof. The resveratrol benzene acrylamide derivative has a structure shown in general formula (1) and general formula (2): the resveratrol benzene acrylamide derivative has an obvious effect of growth inhibition for a human body breast cancer cell line (MCF-7), a human body lung cancer cell line (A549) and a human body melanoma cell line (B16-F10), thereby the resveratrol benzene acrylamide derivative can be used for preparing antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:黄山市开发投资集团有限公司
Human non-small cell lung cancer cell line, and establishment method and application thereof
PendingCN104694476ARandom combinationBest practiceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCancer cellOncology
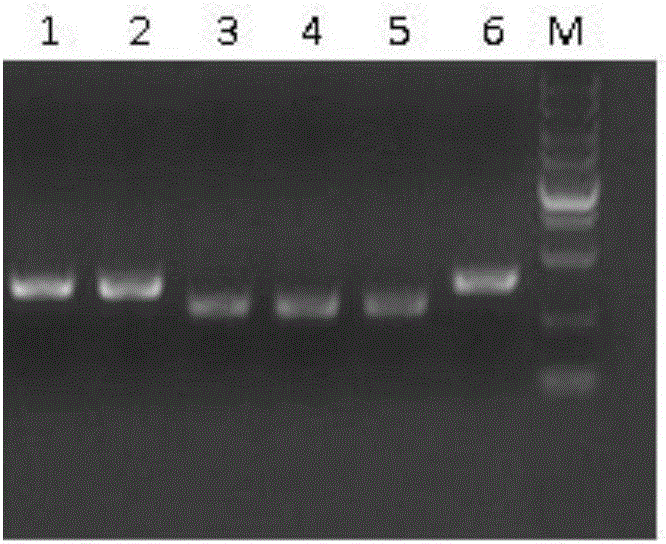
The invention discloses a non-small cell lung cancer cell line, and an establishment method and application thereof. The human non-small cell lung cancer cell line is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with an accession number of CCTCC NO: C2012128. The establishment method comprises the following steps: step 1, acquiring a fresh clinical human non-small cell lung cancer surgical specimen, cutting the specimen into small blocks with a size of 20 to 50 mg and inoculation mammals with the block through subcutaneous puncture; and step 2, in 70 to 90 days after the puncture-inoculation, killing a tumor-bearing animal, taking tumor tissue out of the tumor-bearing animal and carrying out primary culture and subculture of cancer cells. According to the invention, the human non-small cell lung cancer cell line has the advantages of stable properties, capability of realizing stable multiple passage, a high tumor formation rate, a short latent period and good homogeneity; meanwhile, the human non-small cell lung cancer cell line has acquired drug resistance to gefitinib, can be used to analyze correlation between in-vitro and in-vivo drug sensibilities and drug resistance and is the ideal cell line for basic research on and preclinical application of human non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEMPARTNER CO LTD +1
L-OddC prodrugs for cancer
ActiveCN101534835AImprove bioavailabilityUnique activityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemAnticarcinogenWilms' tumor
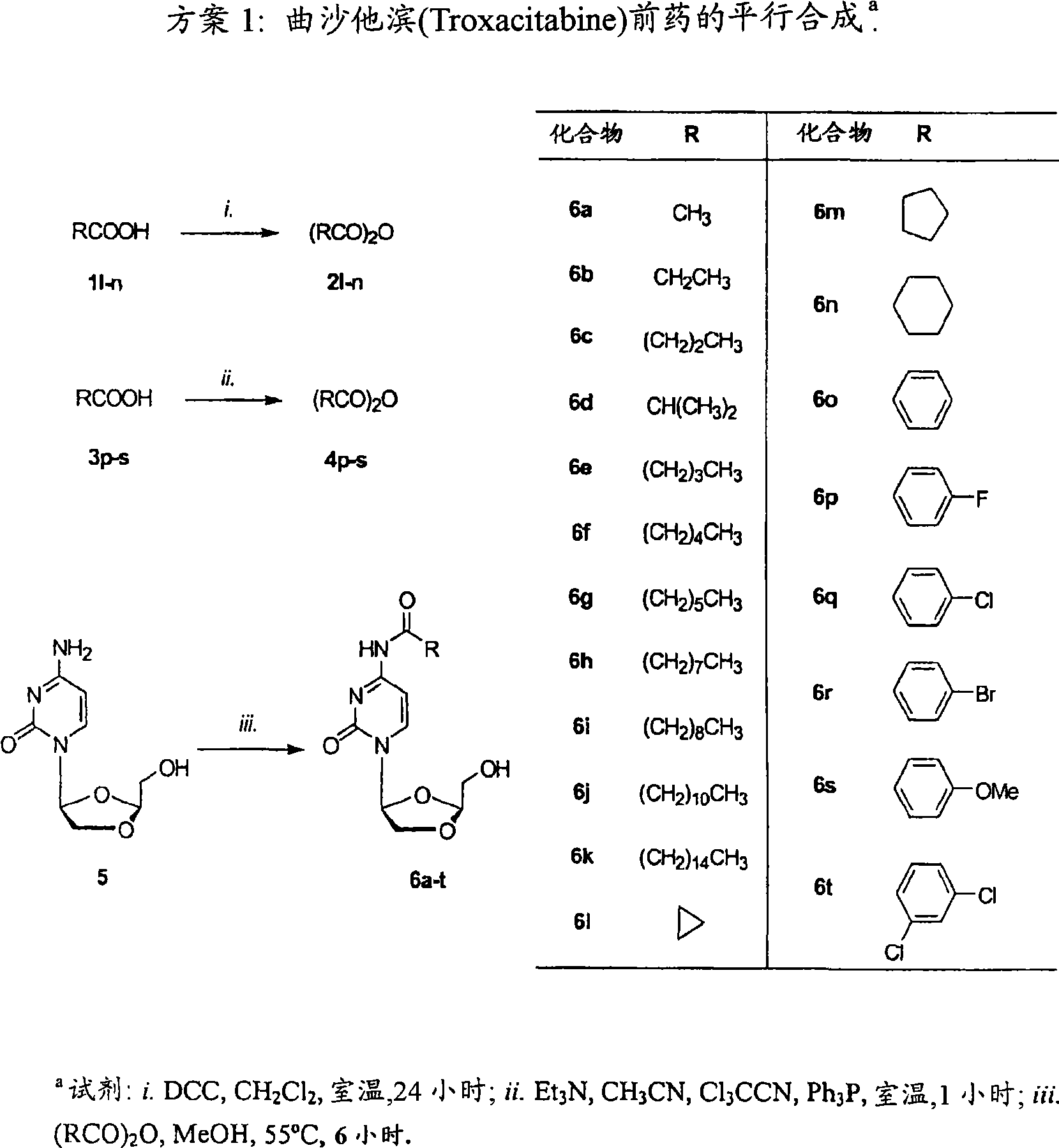
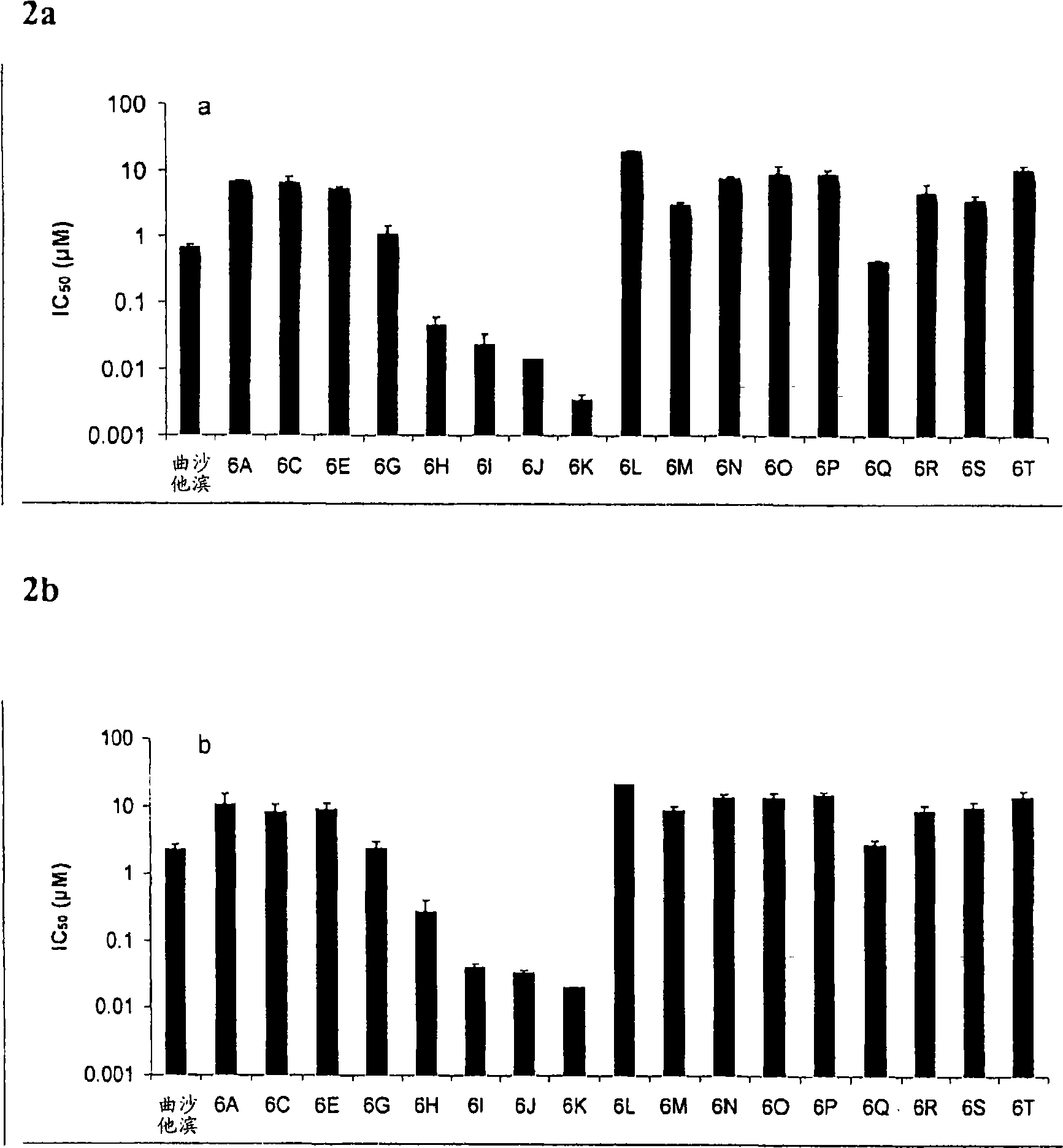
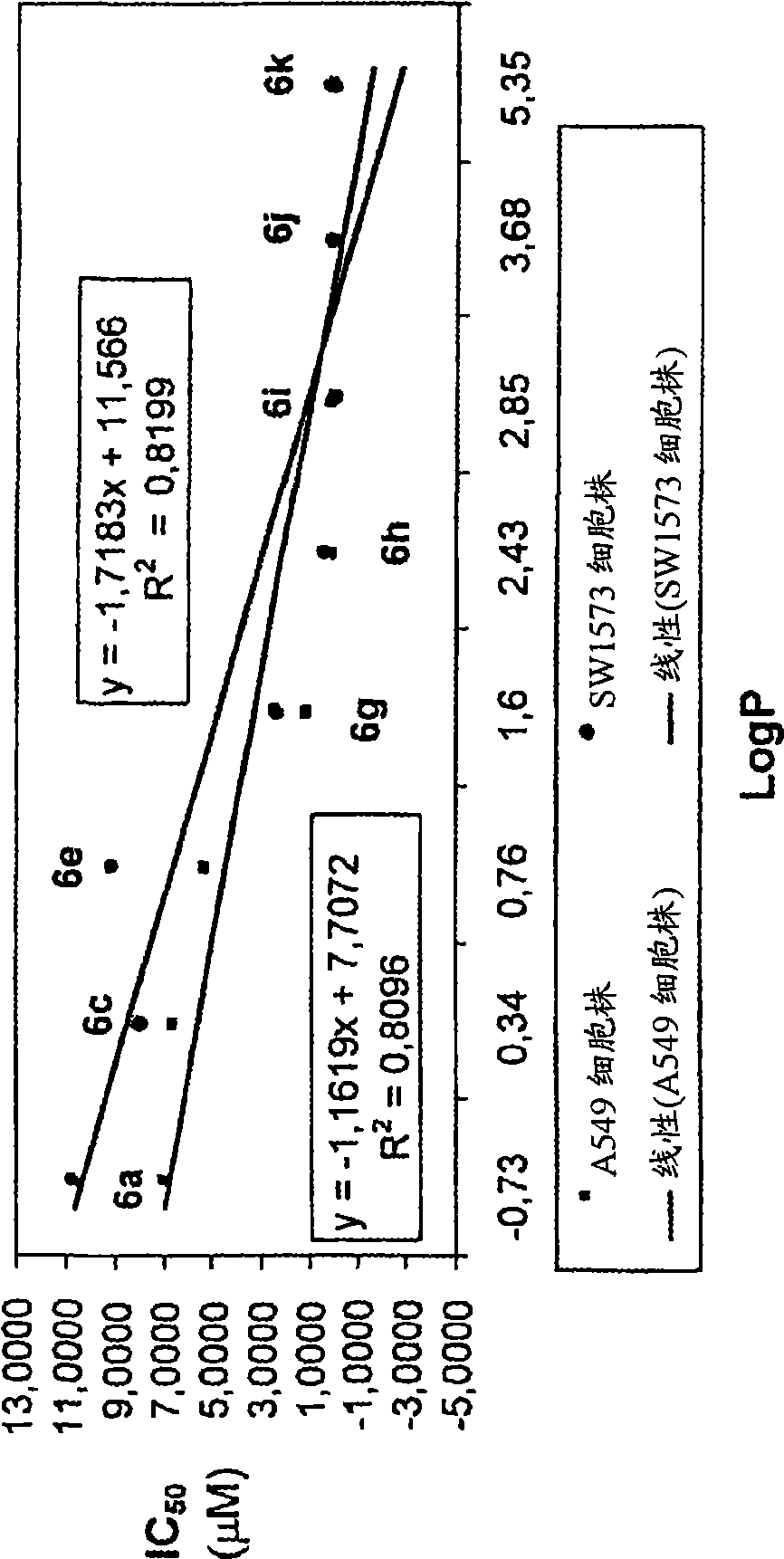
The main drawback in the use of most nucleoside anticancer agents originates from their hydrophilic nature, of which property requires a high and frequent dosage for an intravenous administration. Unlike other nucleoside anti-tumor agents, troxacitabine appears to predominantly enter tumor cells by passive diffusion rather then by using nucleoside transporters, although this may be model dependent. Accordingly, in the present work, a small library of twenty troxacitabine prodrugs has been synthesized using a parallel approach in order to evaluate the relationship between the lipophilicity of the prodrugs and their antitumor activity. Biological evaluation of the prodrugs on two non-small cell lung cancer cell lines (A549 and SW1573) and in pancreatic cell lines clearly showed better antitumor activity than that of troxacitabine, with IC50 values in the nanomolar range.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
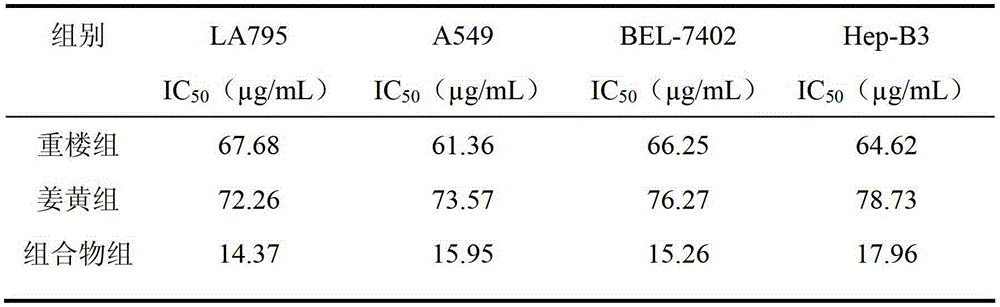
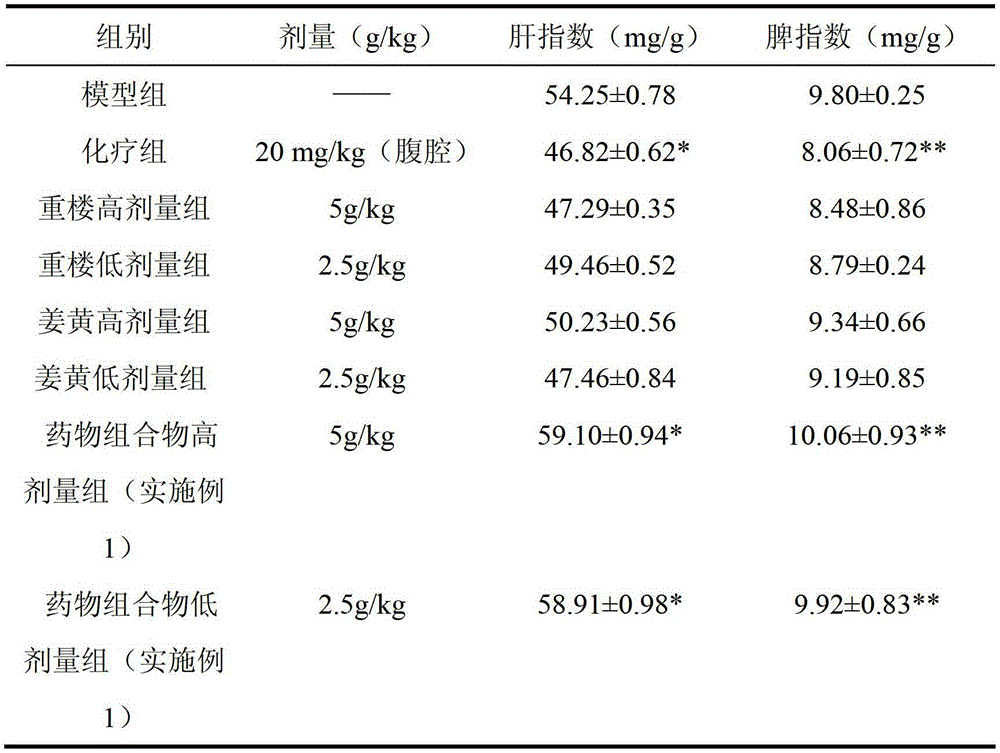
Traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating lung cancer and liver cancer
ActiveCN103142934AGrowth inhibitionHigh activityDigestive systemRespiratory disorderSpleenLung cancer cell line
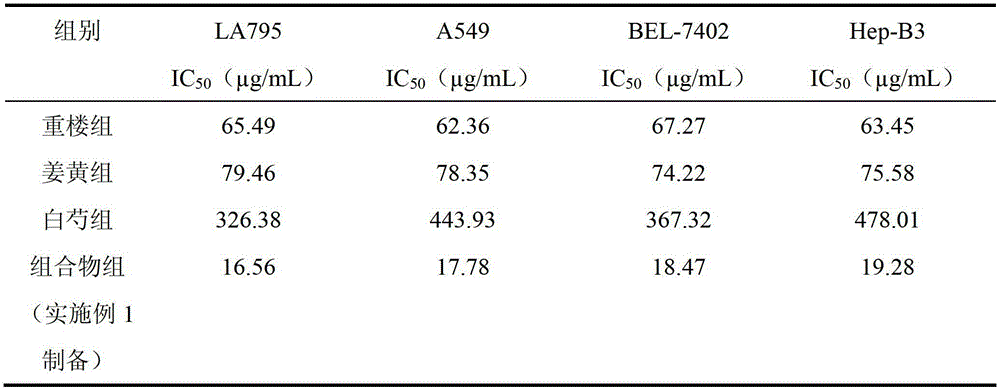
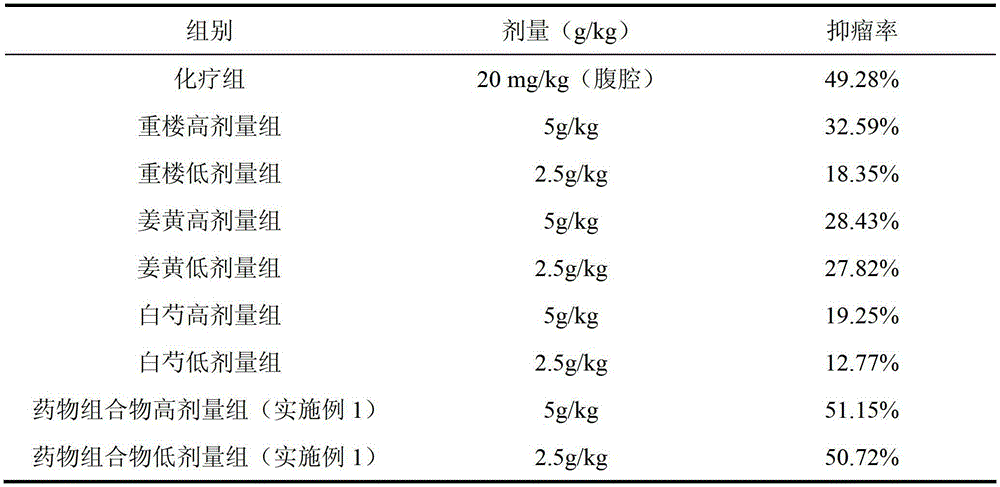
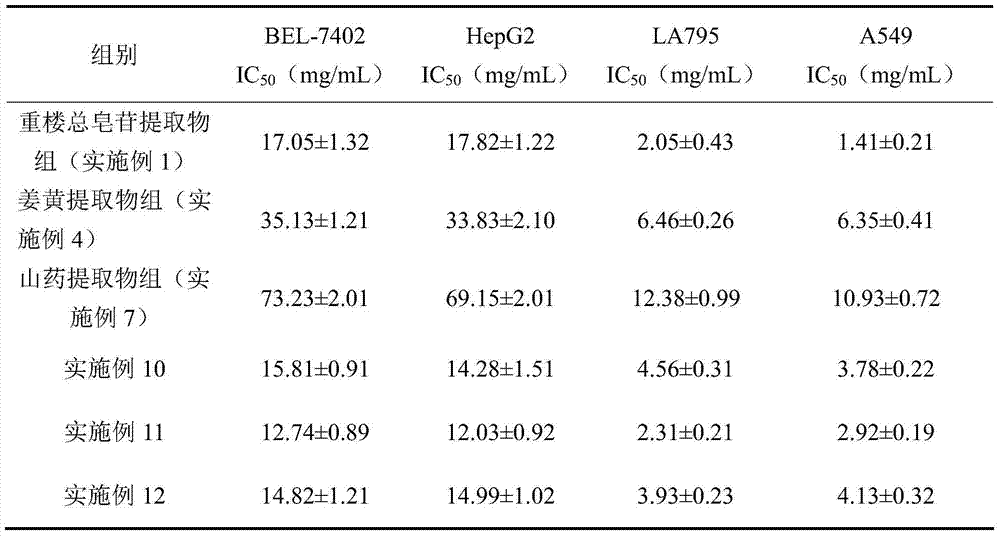
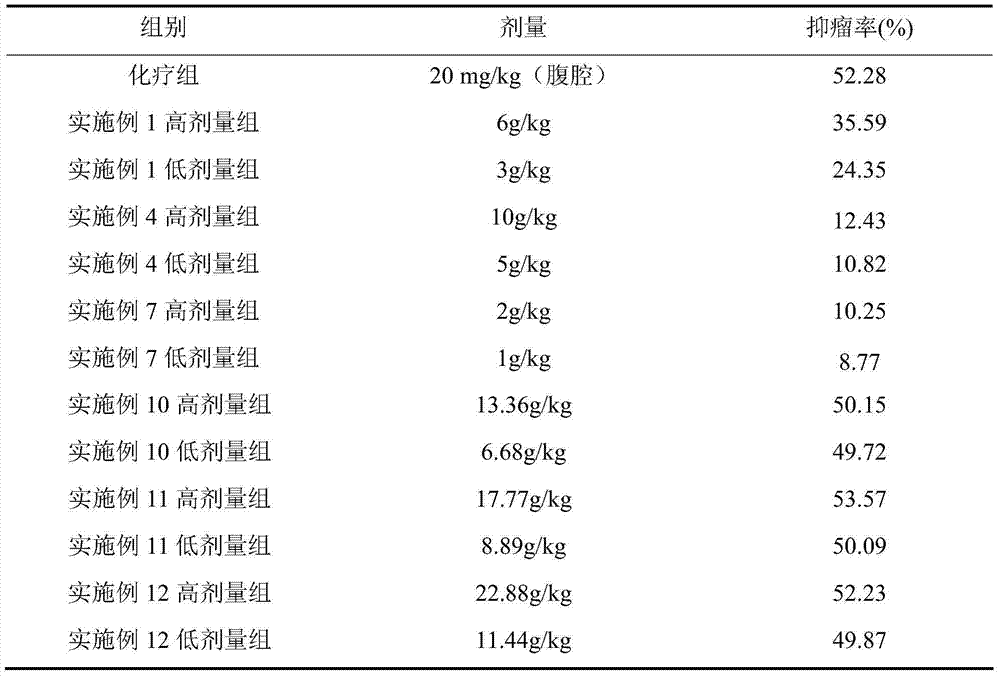
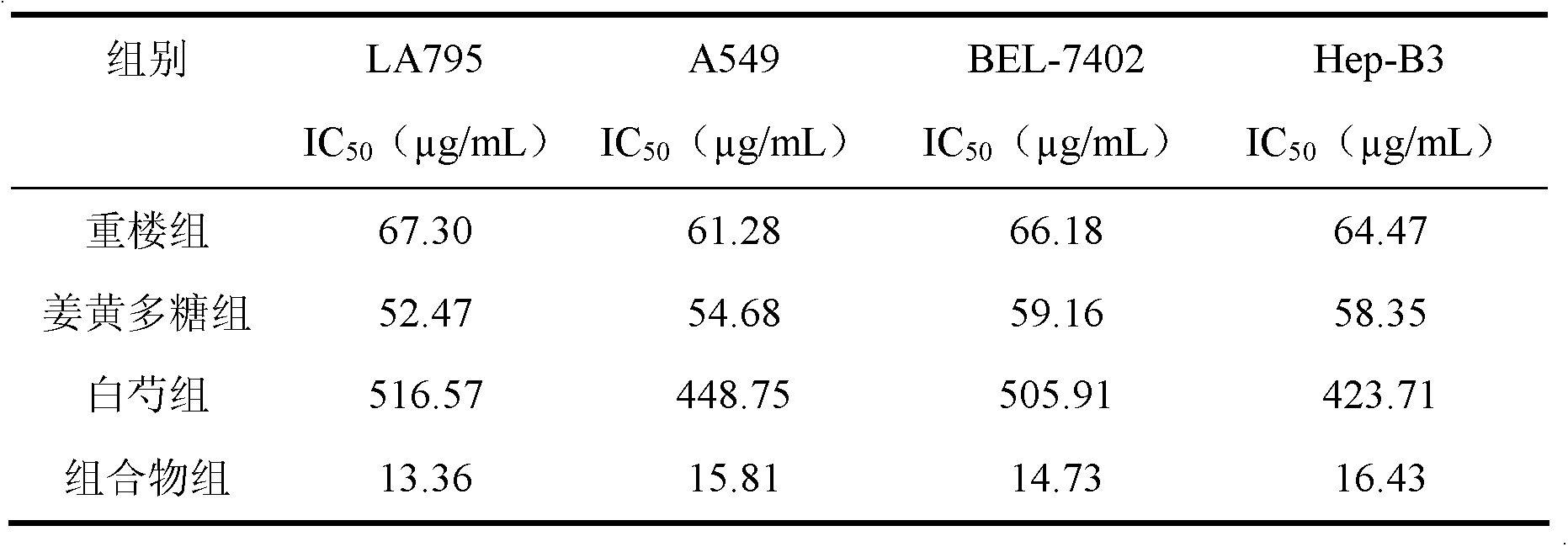
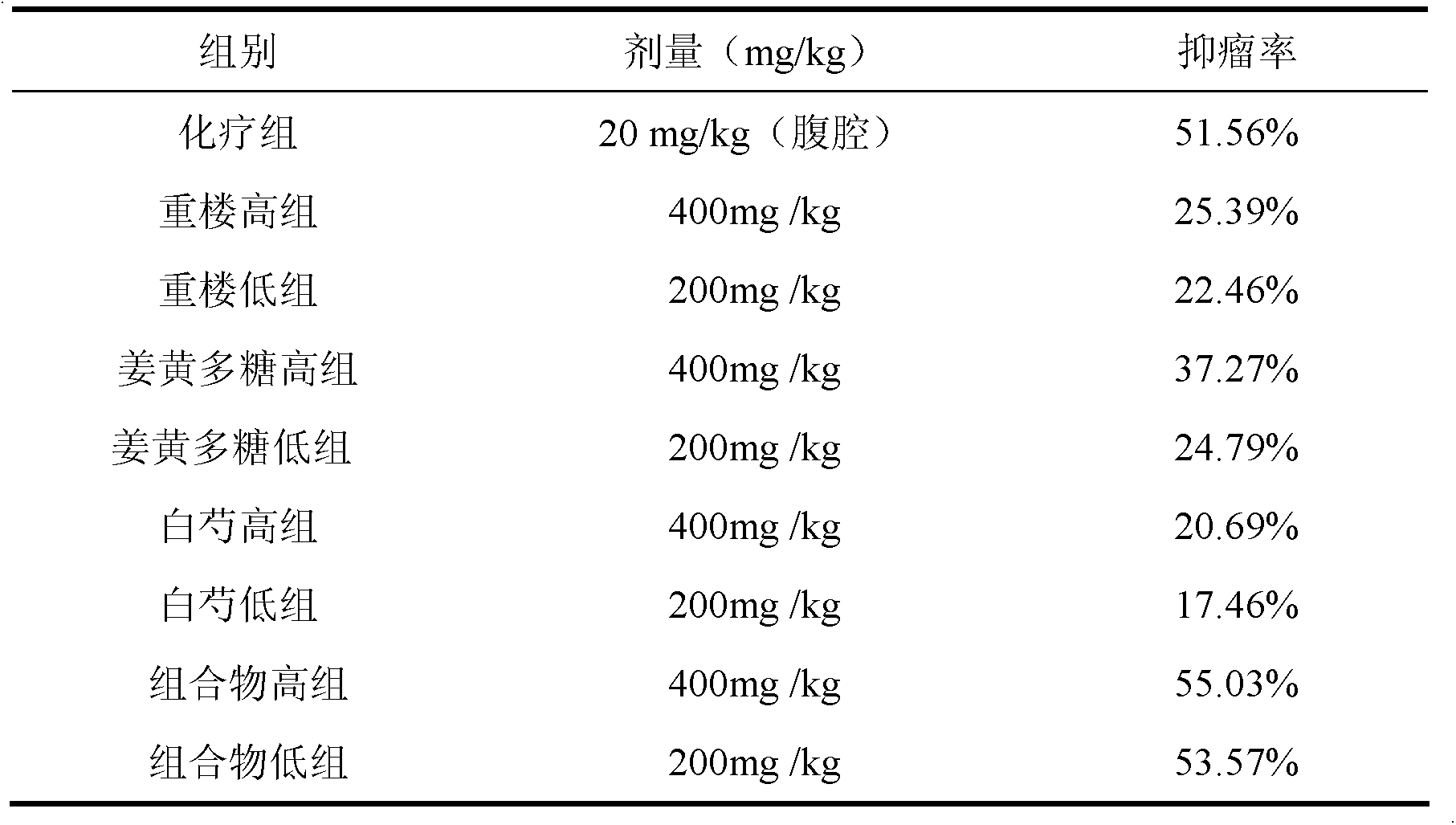
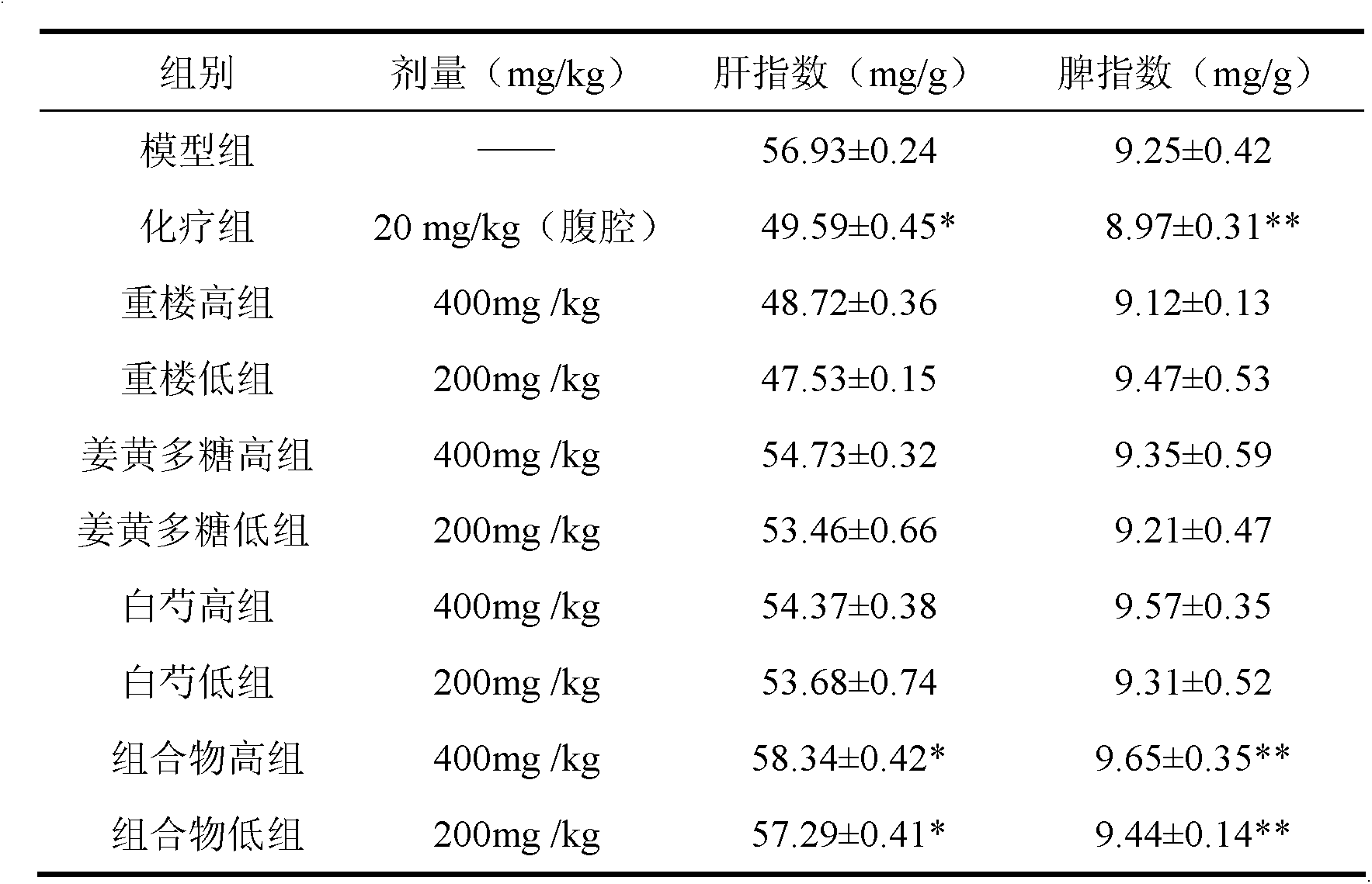
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating lung cancer and liver cancer. The composition consists of rhizoma paridis yunnanensis extract, rhizoma curcumae longae extract and white paeony root extract according to a mass ratio of 1:(15-25):(5-15). Experiments prove that the traditional Chinese medicinal composition can obviously inhibit lung cancer cell lines such as LA795 and hepatoma cell lines such as Hep-B3 from growing, the half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of the lung cancer cell lines and the hepatoma cell lines can respectively reach below 20 micrograms / milliliter; tests on mouse models bearing lung adenocarcinoma and liver cancer tumors show that the lung adenocarcinoma and liver cancer inhibition rates are respectively above 50%, and the spleen index and liver index of mice are increased; and compared with raw medicinal materials which are separately applied, the medicinal composition has high anti-lung cancer and anti-liver cancer activities, an exact effect and a good inhibition effect on lung cancer and liver cancer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
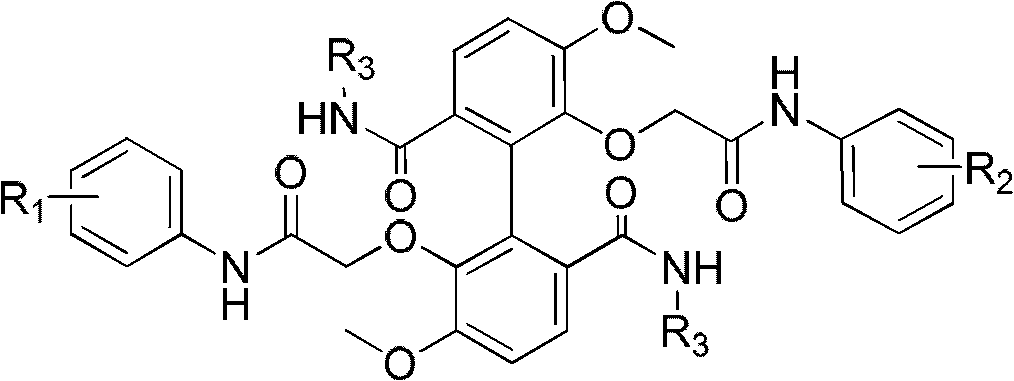
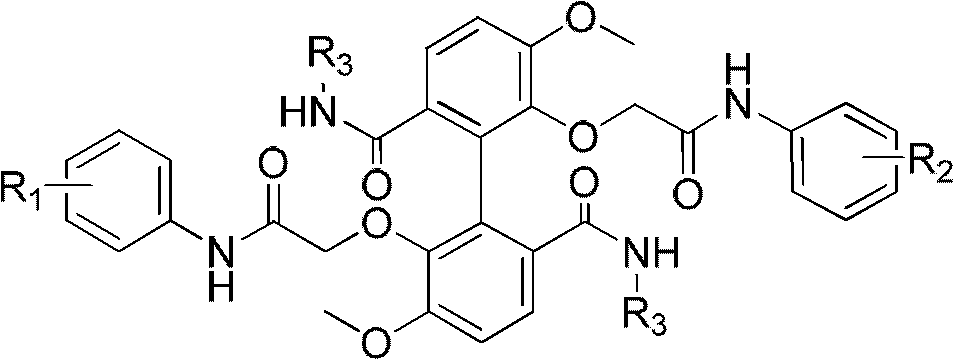
Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles
A large number of aziridinyl quinones represented by Series 1-9 were studied with respect to their DT-diaphorase substrate activity, DNA reductive alkylation, cytostatic / cytotoxic activity, and in vivo activity. As a result generalizations have been made with respect with respect to the following: DT-diaphorase substrate design, DT-diaphorase-cytotoxicity QSAR, and DNA reductive alkylating agent design. A saturating relationship exists between the substrate specificity for human recombinant DT-diaphorase and the cytotoxicity in the human H460 non-small-cell lung cancer cell line. The interpretation of this relationship is that reductive activation is no longer rate limiting for substrates with high DT-diaphorase substrate specificities. High DT-diaphorase substrate specificity is not desirable in the indole and cylopent[b]indole systems because of the result is the loss of cancer selectivity along with increased toxicity. We conclude that aziridinyl quinones of this type should possess a substrate specificity (VMAX / KM )<10x10-4 s-1 for DT-diaphorase in order not to be too toxic or nonselective. While some DNA alkylation was required for cytostatic and cytotoxic activity by Series 1-9, too much alkylation results in loss of cancer selectivity as well as increased in vivo toxicity. Indeed, the most lethal compounds are the indole systems with a leaving group in the 3a-position (like the antitumor agent EO-9). We conclude that relatively poor DNA alkylating agents (according to our assay) show the lowest toxicity with the highest antitumor activity.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
MiRNA in-situ hybridization probe, its detection kit and its application
ActiveCN102732619ALow priceStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHybridization probeCancer cell lines
The invention provides an miRNA in-situ hybridization probe, its detection kit and its application. A fluorine atom is modified by a 2-carbon atom of the base five-carbon ring of the hybridization probe. The preferable sequence of the probe is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, wherein fluorine atoms are modified by 2-carbon atoms of third, sixth, fifteenth and twentieth base five-carbon rings. The other preferable sequence of the probe is represented by SEQ ID NO:2, wherein the fluorine atoms are modified by 2-carbon atoms of third, eighth, thirteenth and twenty-first base five-carbon rings. Digoxin is modified by 5' and 3' terminals of the probe. The invention also provides an in-situ hybridization detection kit of the hybridization probe. The probe of the invention can be applied to the preparation of miRNA in-situ hybridization detection kits for lung cancer cell lines or lung cancer tissues, and the preparation of miRNA in-situ hybridization detection kits for esophageal cancer cell lines or esophageal cancer tissues. The kit of the invention has the advantages of low price and good specificity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU EXONS BIOLOGICAL TECH
Biphenyl compound serving as antitumor medicament and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102010347ARaw material source is easy to getConvenient sourceOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationAbnormal tissue growthApoptosis
The invention discloses a biphenyl compound serving as an antitumor medicament and a preparation method thereof. The biphenyl compound has antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo, has the effects of inducing apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation on colorectal cancer cell lines, lung cancer cell lines, liver cancer cell lines, breast cancer cell lines or pancreatic cancer cell lines in vitro and has the effects of inhibiting tumors on liver cancers and colorectal cancers in vivo. The biphenyl compound can be applied to preparation of the antitumor medicament. The preparation method of the biphenyl compound has the advantages of readily available raw materials, mild reaction conditions, easily operated reaction processes and cheap and readily available reagents.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
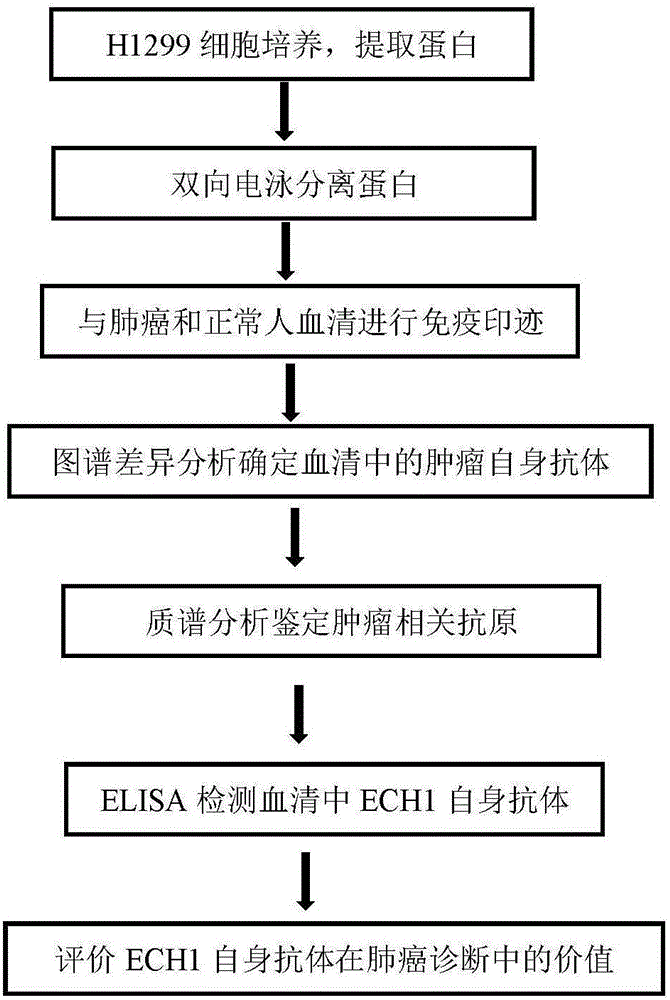
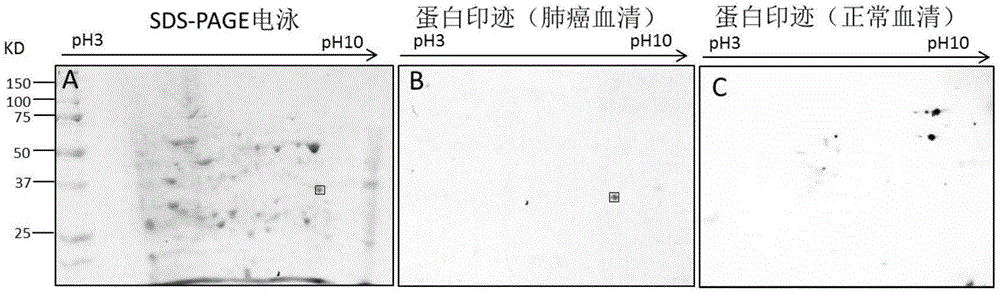
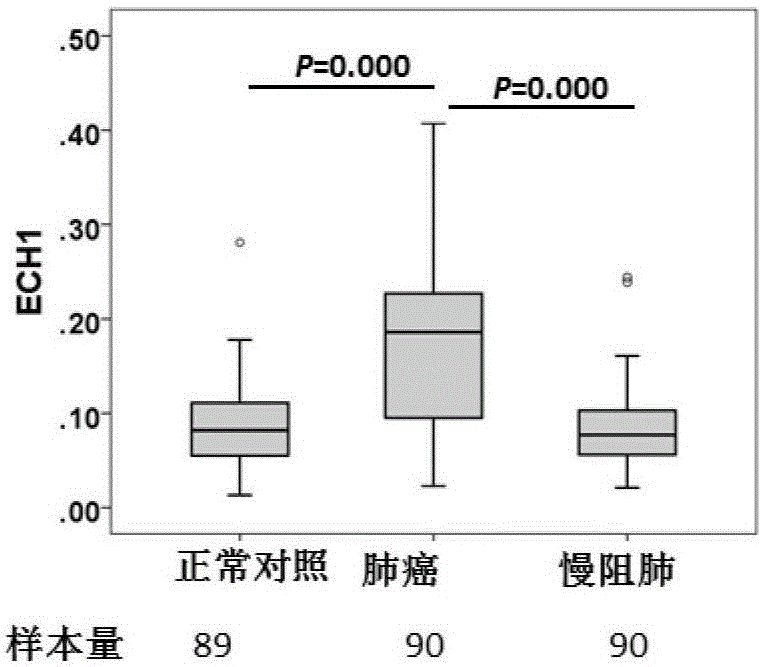
Method for screening and identifying ECH1 autoantibody and application thereof
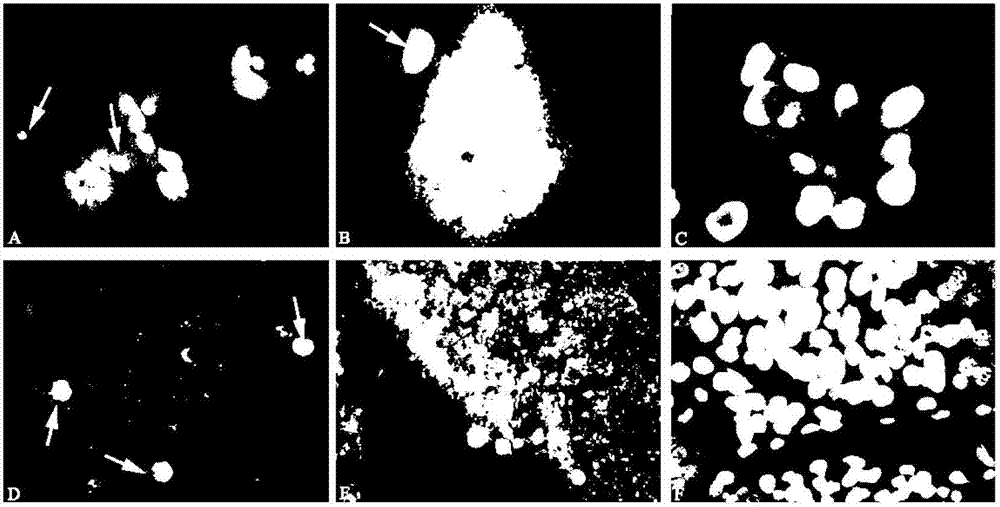
The invention discloses a method for screening and identifying an ECH1 autoantibody and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: adopting a lung cancer cell line H1299 holoprotein extractive for performing two-dimensional electrophoresis; adopting a western blot method for processing the serum of 5 patients with lung cancer and serum of 5 normal people, screening the significant tumor autoantibody, and after comparative analysis, only further analyzing the protein spots appearing in the serum of the patients; cutting and digesting the interesting protein spots on SDS-PAGE gelatin, and then adopting a LG-MS / MS mass spectrometry method for analyzing the protein spots, detecting and identifying as ECH1; and further verifying if the ECH1 autoantibody can be used as a lung cancer diagnosis marker. Through research, the invention finds that the detection for the serum ECH1 autoantibody according to an ELISA method can be used for more accurately identifying the patients with lung cancer from the normal people, identifying the patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases and early diagnosing the lung cancer.
Owner:郑州臻合生物科技有限公司
Human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance lung cancer cell line and establishing method and application thereof
ActiveCN108866000AHigh tumorigenic activityLow tumor formation rateCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The invention relates to a human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance lung cancer cell line and an establishing method and application thereof. The establishing method comprises the following steps: collecting and confirming precipitates containing cancer cells from pleural fluid of a lung cancer patient with human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance, culturing in vitro, inoculating to mouse underarm, taking tumor tissue after tumor formation, carrying out primary culture, and confirming drug-resistance tumor cells with purity being more than 90%, thereby establishing the human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance lung cancer cell line with preservation number of CCTCC NO: C2018121. The cell line keeps main clinical biological characteristics, can reflect a drug resistance mechanism more truly, has a high tumor formation rate, stable biological characteristics and strong vitality, and is an ideal cell line material for basic research and preclinical testing of human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI PULMONARY HOSPITAL
Lung cancer marker SBP-1 and its application
The invention relates to the molecular biology and tumor medicine fields, and relates to an application of a lung cancer marker SBP-1 in lung cancer diagnosis, and a method for detecting lung cancer by taking SBP-1 as the marker. According to the invention, a comparative proteomics method is employed for comparative analysis of protein expression profile of a lung cancer cell line / tissue and normal control cell / tissue, and a mass spectrum identifies the partial difference protein points. SBP-1 protein is a difference point, and enables high expression in cancer cells by comparing with that of the normal cells, and the difference is obvious. The invention employs RT-PCR and an immunohistochemical technology to respectively detect mRNA of SBP-1 and expression level of protein expression in normal tissue, the result displays that the expression of SBP-1 in the lung cancer tissue is obviously higher than that of its paired normal tissue, so that SBP-1 can be taken as a diagnosis marker of lung cancer. The invention also provides a lung cancer diagnostic kit and a detection method used for lung cancer.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102204974AGood effectHas a tumor suppressive effectAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsActinidiaHep G2
The invention discloses a compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines. The Chinese medicinal composition is characterized by comprising the following traditional Chinese medicines in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of Chinese actinidia root, 20-40 parts of salvia chinensis, 20-40 parts of herba scutellariae barbatae, 20-40 parts of herba oldenlandiae and 20-40 parts of giant knotweed. The compound Chinese actinidia root Chinese medicinal composition has remarkable proliferation inhibition effects on various cancer cells such as a hepatoma cell line Hep-G2, a lung cancer cell line NCI-H460, a gastric cancer cell line MGC-803, a breast cancer cell line MCF-7, a colon cancer cell line HCT-116 and the like, and can be used for reducing physical and psychological pains of a cancer patient in the chemo-treatment process and solving the problems of difficult and expensive administration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SIXIAN PHARMA
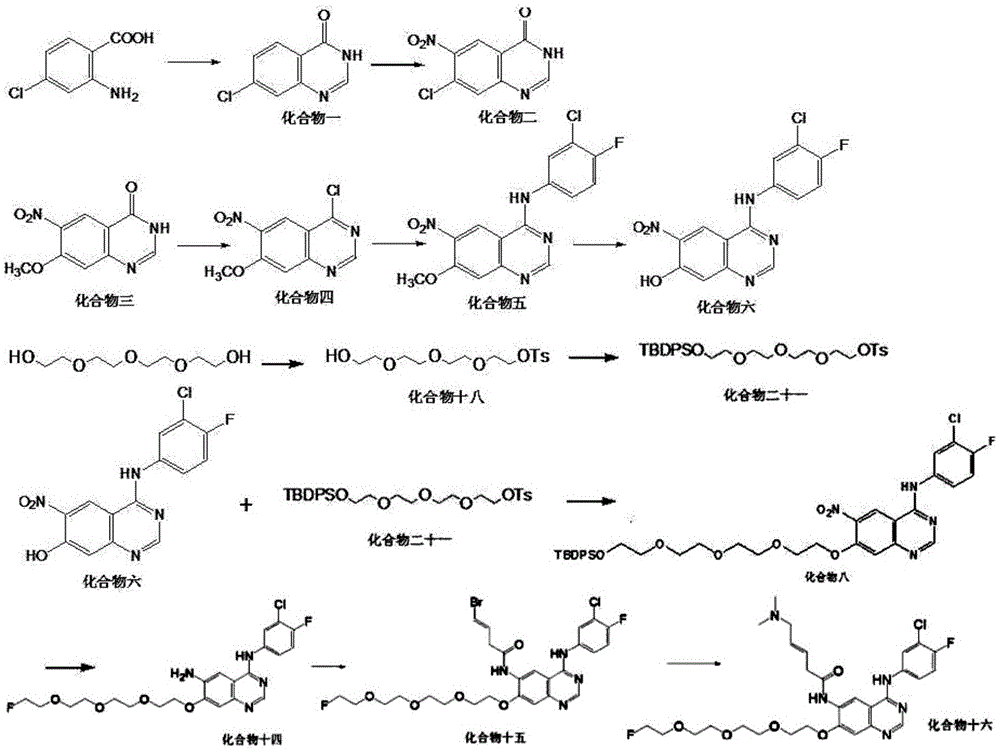
Quinazoline derivatives and quinazoline complex protein kinase inhibitor for inhibiting multiplicaiton of tumor cells and preparation method thereof
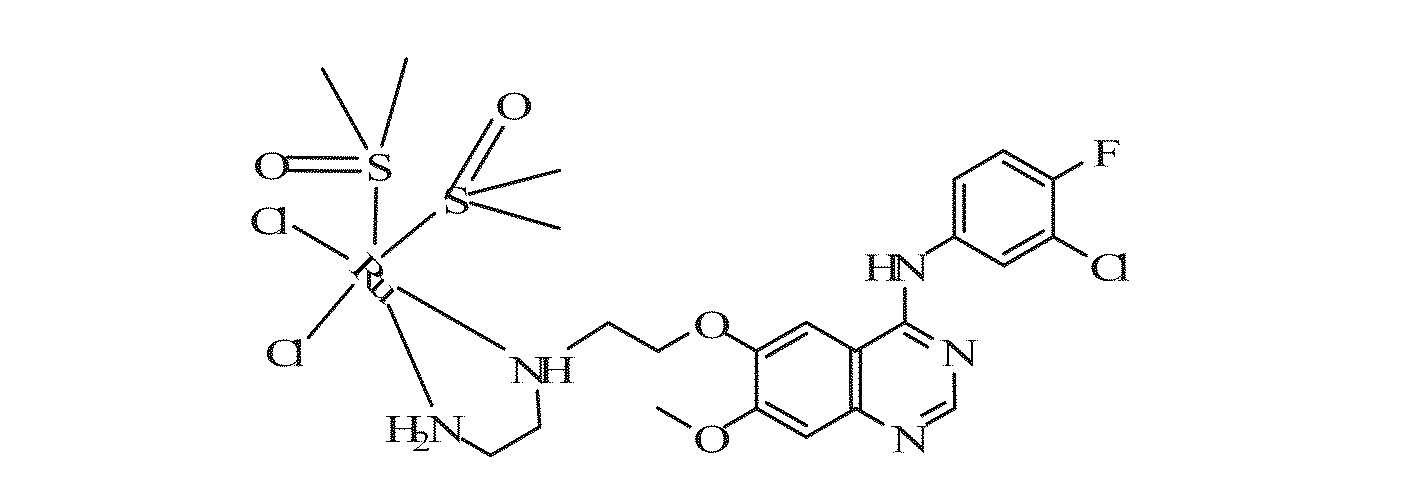
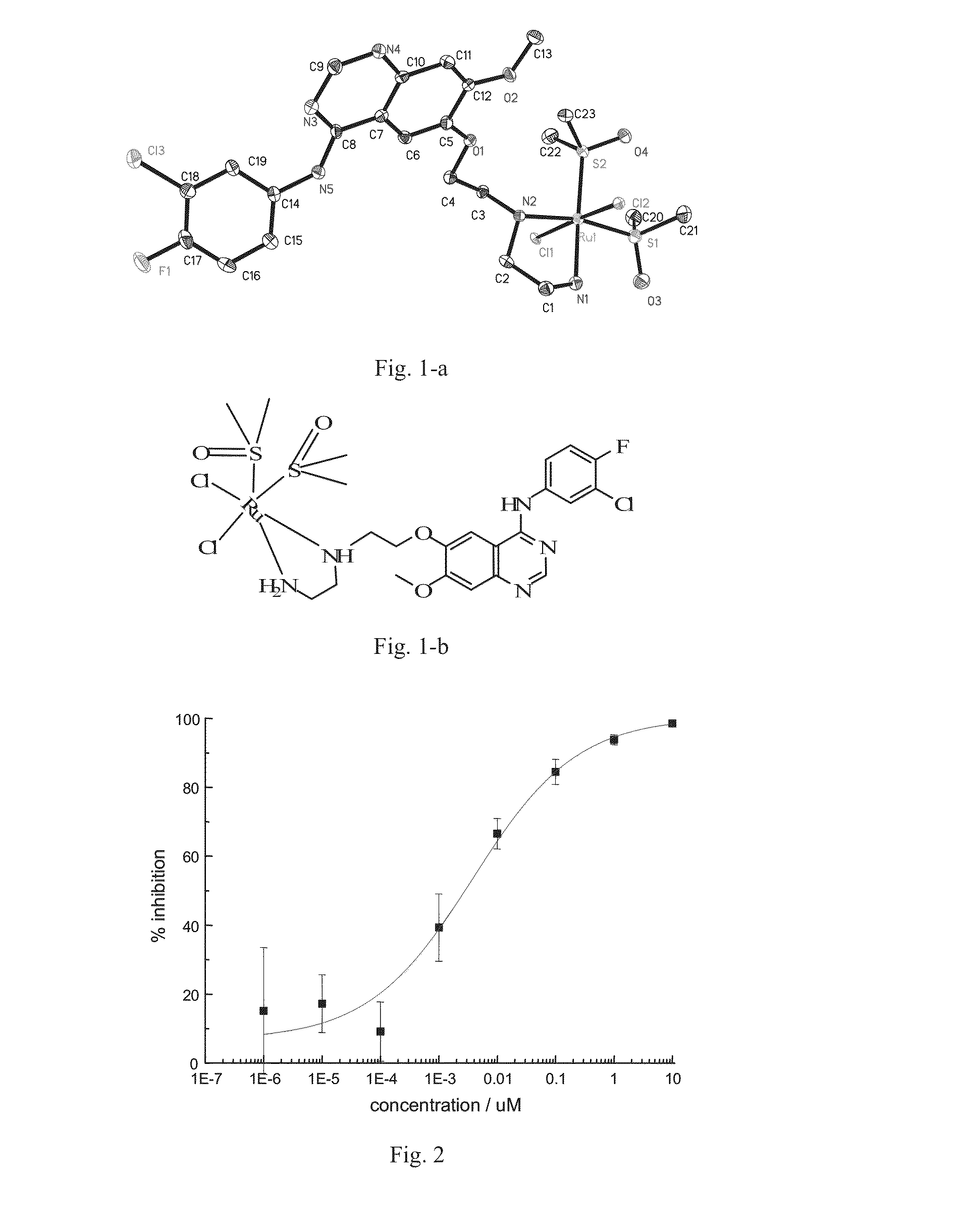
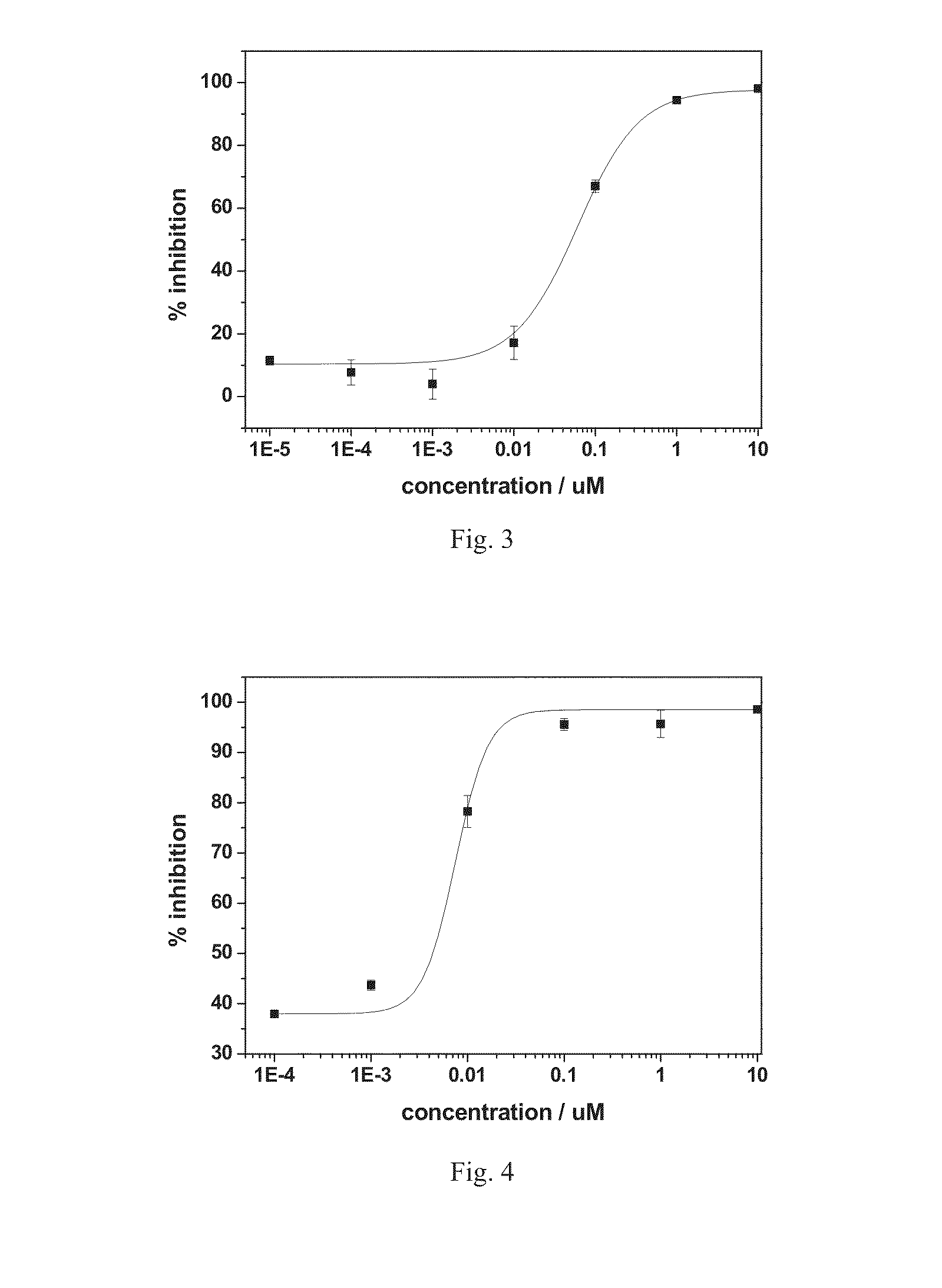
ActiveUS20130225811A1Strong inhibitory activityEnhanced inhibitory effectRuthenium organic compoundsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsProstate cancer cellPTK Inhibitors
Quinazoline derivatives represented by general formula (1) and quinazoline complexes as protein kinase inhibitors, and their preparation methods are provided. Wherein, in general formula (1), at least one of R and R′ is a group containing an atom capable of coordinating with noble metals, m and n are either the same or different and are integers from 0 to 5. Said quinazoline complex as protein kinase inhibitor is formed by coordination compound containing noble metal and said quinazoline derivative ligand capable of coordinating with noble metal in the coordination compound. Used as tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors, Quinazoline derivatives and quinazoline complexes as protein kinase inhibitors provided by the present invention have exhibited good inhibitory effect on proliferation of various tumor cells including human breast cancer cells line (drug-resistant) MCF-7 / A, human breast cancer cell line (sensitive) MCF-7 / S, prostate cancer cell PC-3, keratinocytes Colo-16, human non-small cell lung cancer cell line A549, etc.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
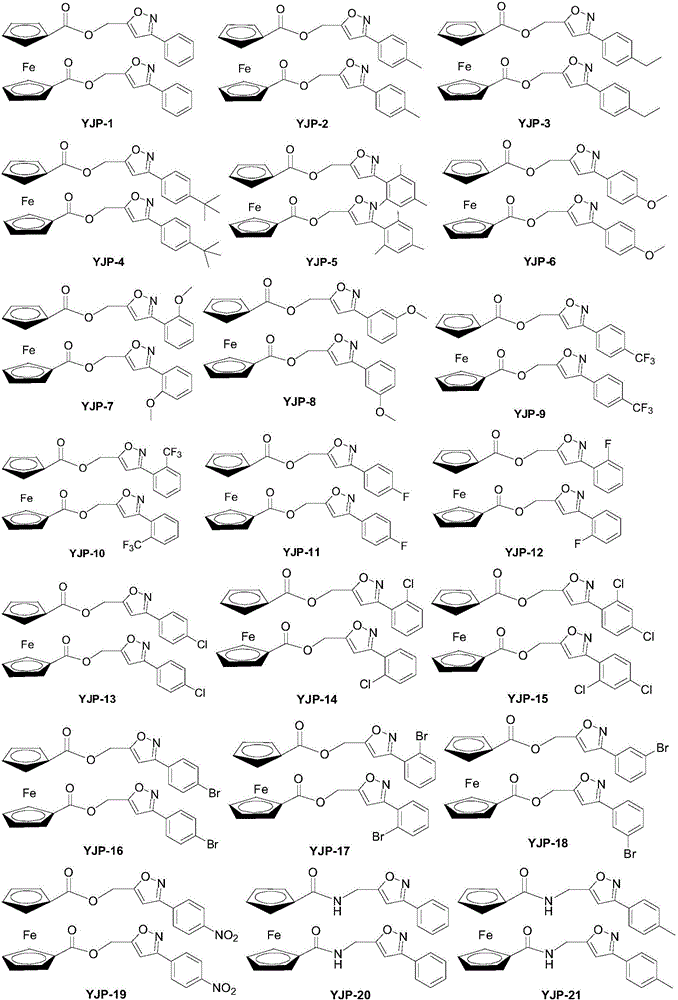
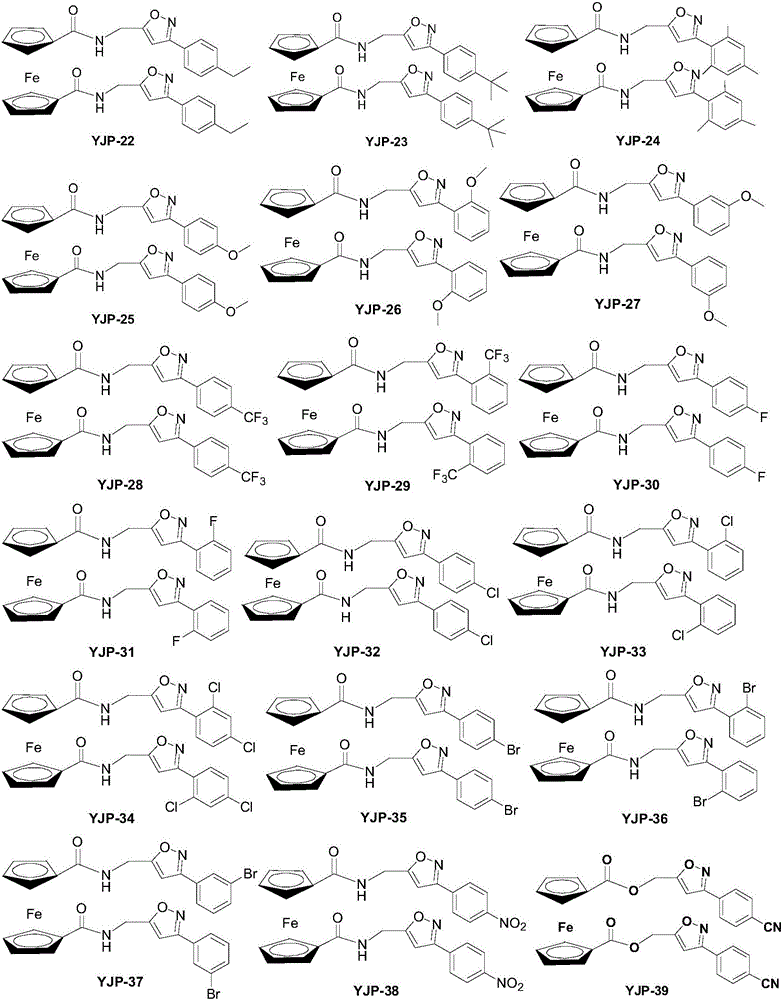
Ferrocene derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106518933AStrong inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseCarcinoma cell line
The invention relates to a ferrocene derivative shown as a formula (IA) or a formula (IB) or a pharmaceutically-acceptable salt or a solvate and a medicinal composition thereof. In the formula, R is independently selected from hydrogen, halogen, a cyano-group, a nitro-group, alkyl with 1 to 6 carbon atoms, alkoxy with 1 to 6 carbon atoms, hydroxyl-alkyl with 1 to 6 carbon atoms, halogenated alkyl with 1 to 6 carbon atoms, halogenated alkoxy with 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or alkoxy with 1 to 6 carbon atoms; Z is selected from O, S or NR1; R1 is hydrogen or alkyl with 1 to 6 carbon atoms independently; n is an integer of 0 to 5. The invention further provides a preparation method and medical application of the compound shown as the formula (IA) or the formula (IB) or the pharmaceutically-acceptable salt thereof. The compound has very high restraining activity specific to a lung cancer cell line A549, a colorectal carcinoma cell line HCT116 and / or a breast cancer cell line MCT-7, has broad-spectrum anti-cancer activity, and can be taken as a candidate compound or a lead compound for treating tumor diseases or cancer diseases. The derivative is shown in the description.
Owner:XIAMEN INST OF RARE EARTH MATERIALS
Traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating lung cancer and liver cancer
InactiveCN103142935AGrowth inhibitionHigh activityDigestive systemRespiratory disorderSpleenLung cancer cell line
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal composition for treating lung cancer and liver cancer. The composition consists of rhizoma paridis yunnanensis extract and rhizoma curcumae longae extract according to a mass ratio of 1:(5-25). Experiments prove that the traditional Chinese medicinal composition can obviously inhibit lung cancer cell lines such as LA795 and hepatoma cell lines such as Hep-B3 from growing, the half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of the lung cancer cell lines and the hepatoma cell lines can respectively reach below 20 micrograms / milliliter; tests on mouse models bearing lung adenocarcinoma and liver cancer tumors show that the lung adenocarcinoma and liver cancer inhibition rates are respectively above 50%, and the spleen index and liver index of mice are increased; and compared with raw medicinal materials which are separately applied, the medicinal composition has high anti-lung cancer and anti-liver cancer activities, an exact effect and a good inhibition effect on lung cancer and liver cancer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
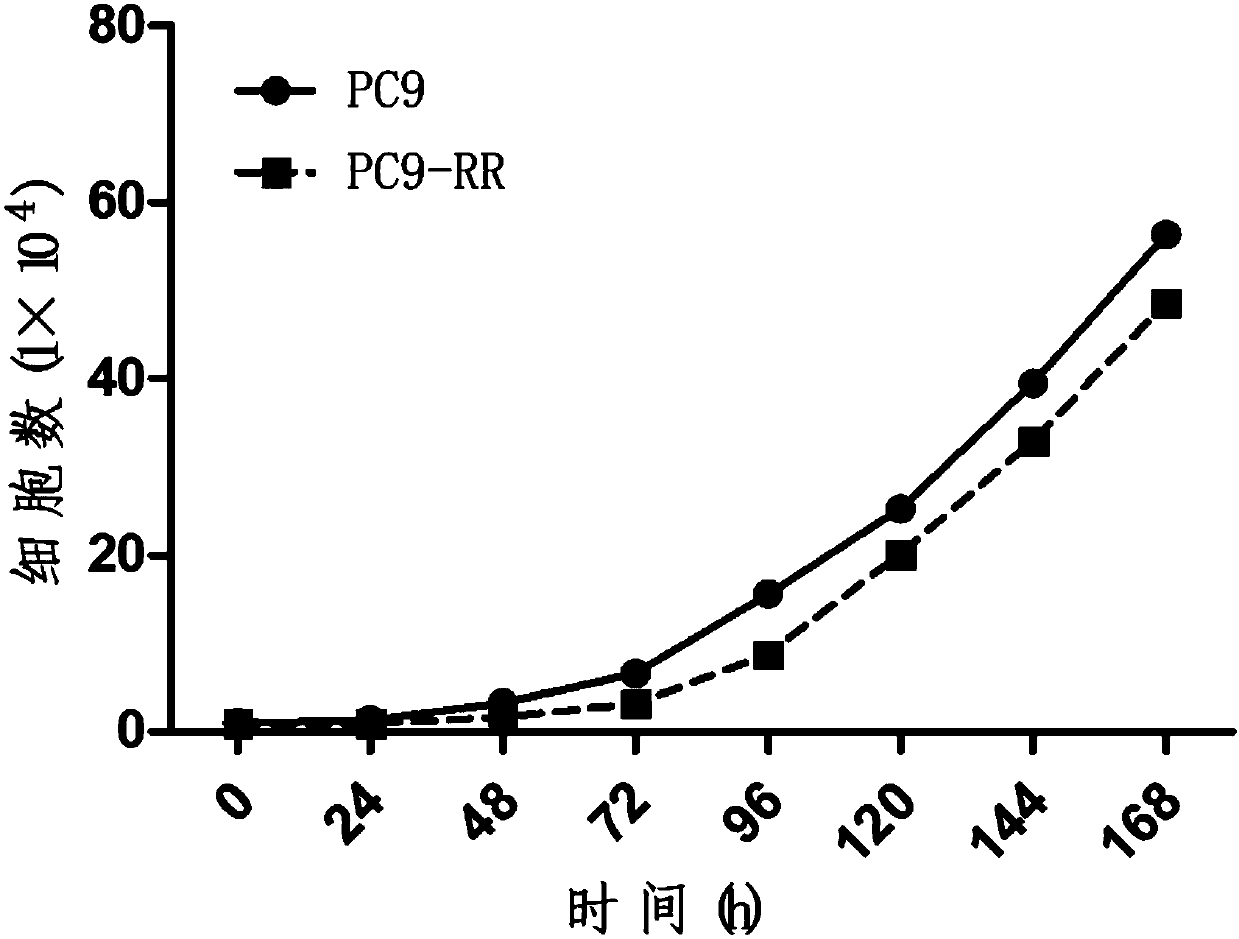
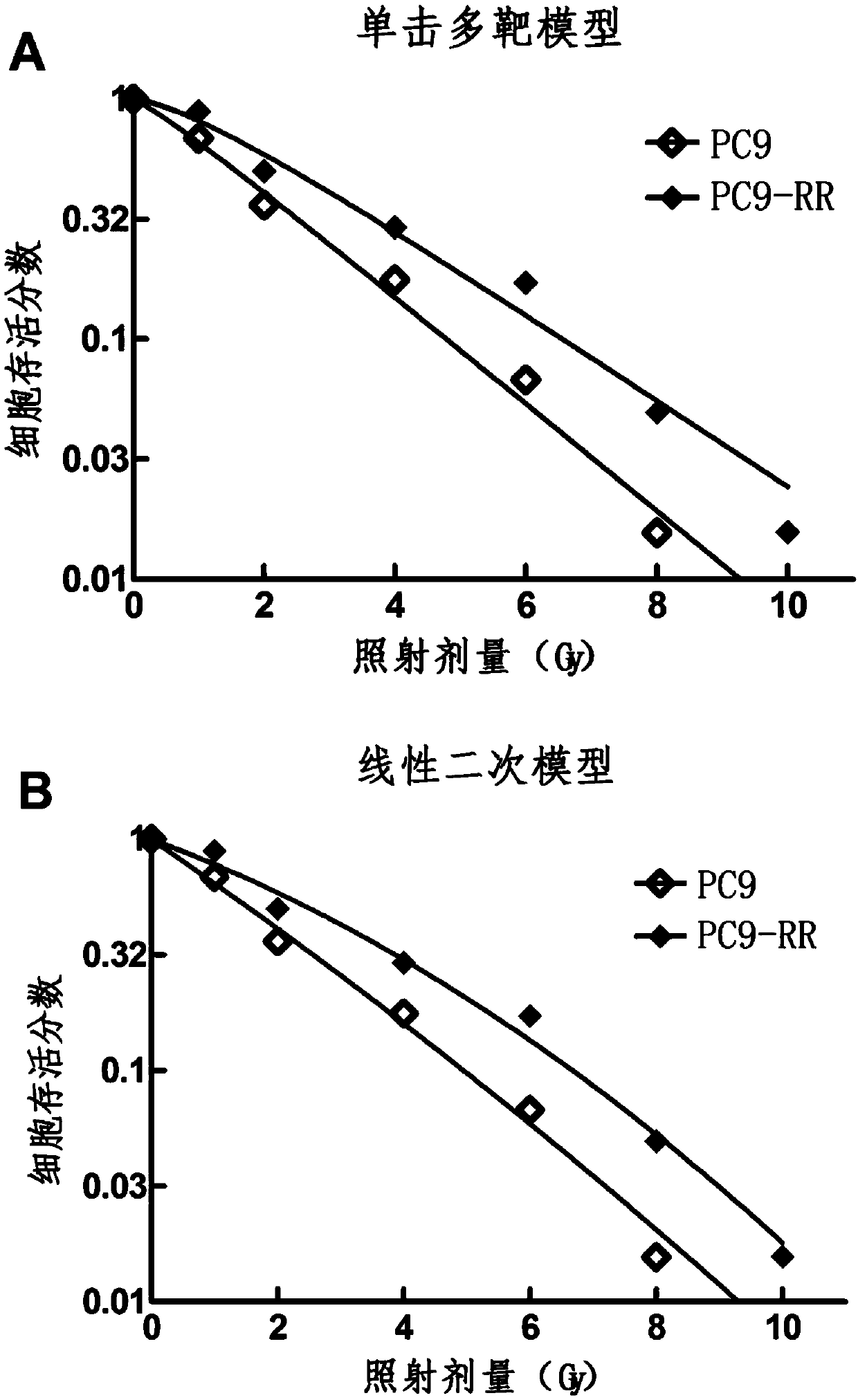
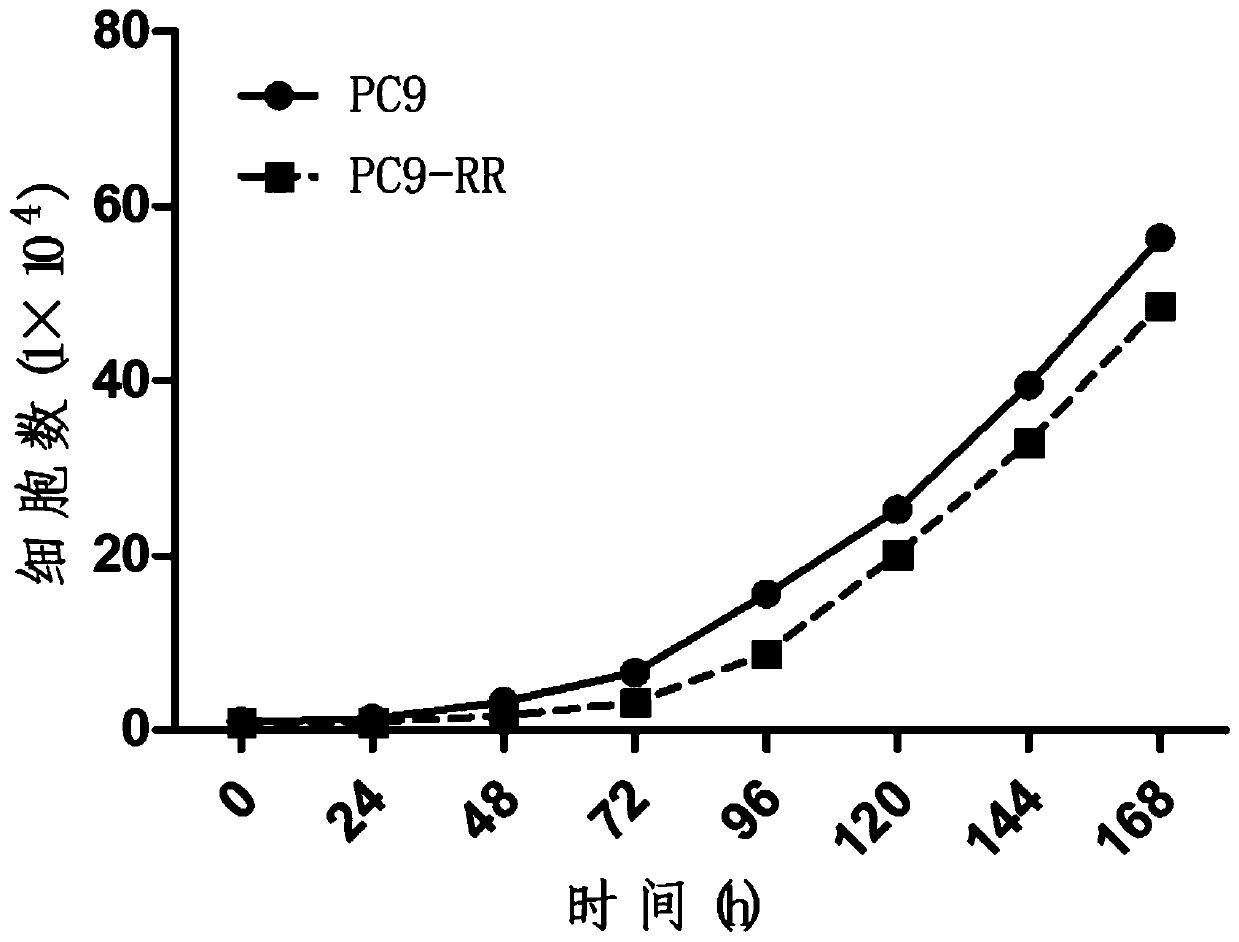
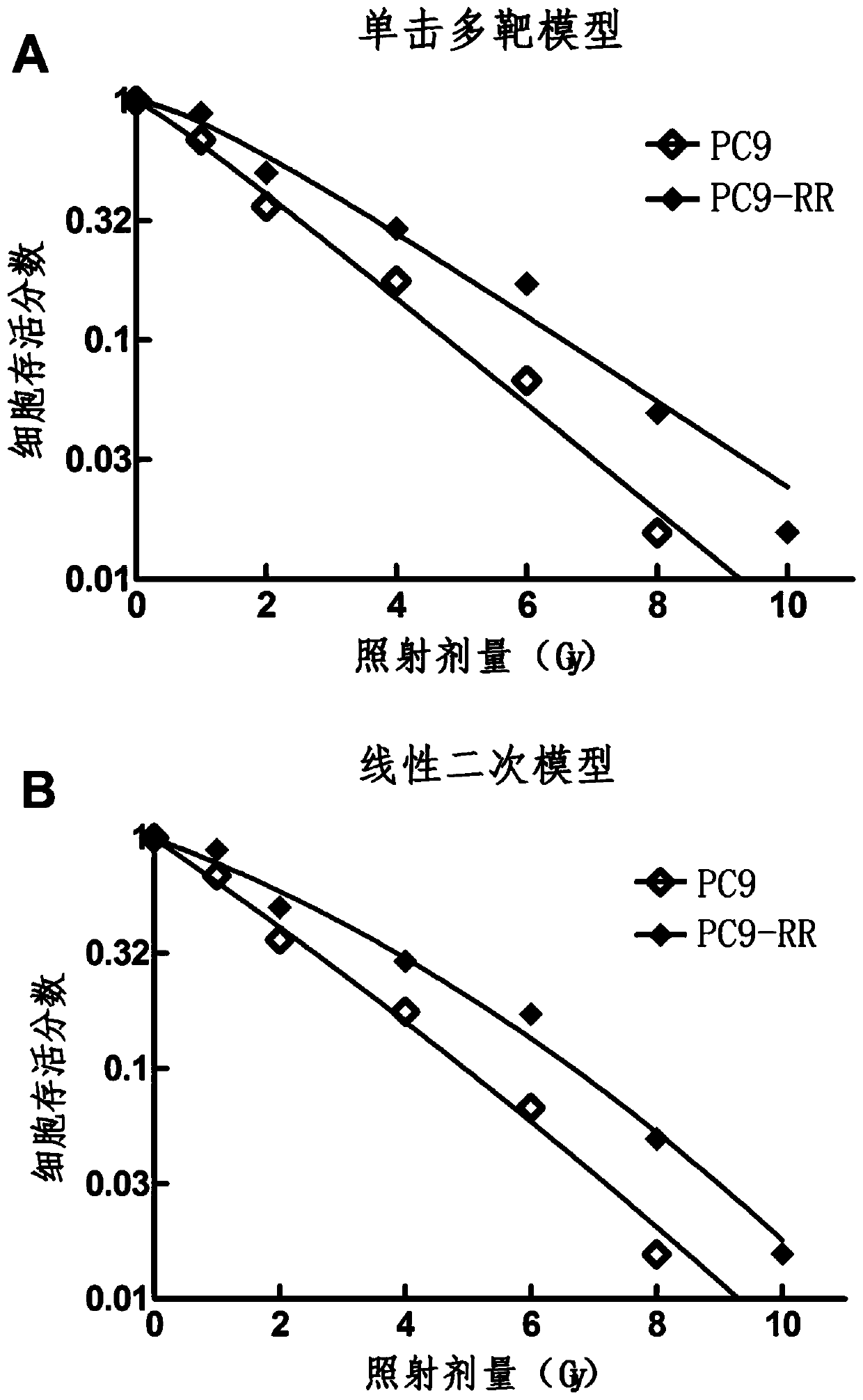
Radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line, construction method thereof and application of cell line
ActiveCN107779438ARadiotherapy is well tolerated and stableCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAdenocarcinoma lung cancerRadiation tolerance
The invention discloses a radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line, a construction method thereof and an application of the cell line. The radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line is named asa human lung adenocarcinoma radiation tolerance cell strain PC9-RR, and the collection number is CGMCC No. 14314. The radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line comprises radiotherapy tolerance cells acquired by performing repeated X-ray irradiation and culture on a human lung adenocarcinoma cell strain PC9, is strong and stable in radiotherapy tolerance and has a good application prospect in terms of serving as a cell model for lung cancer radiotherapy resistance mechanism research and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
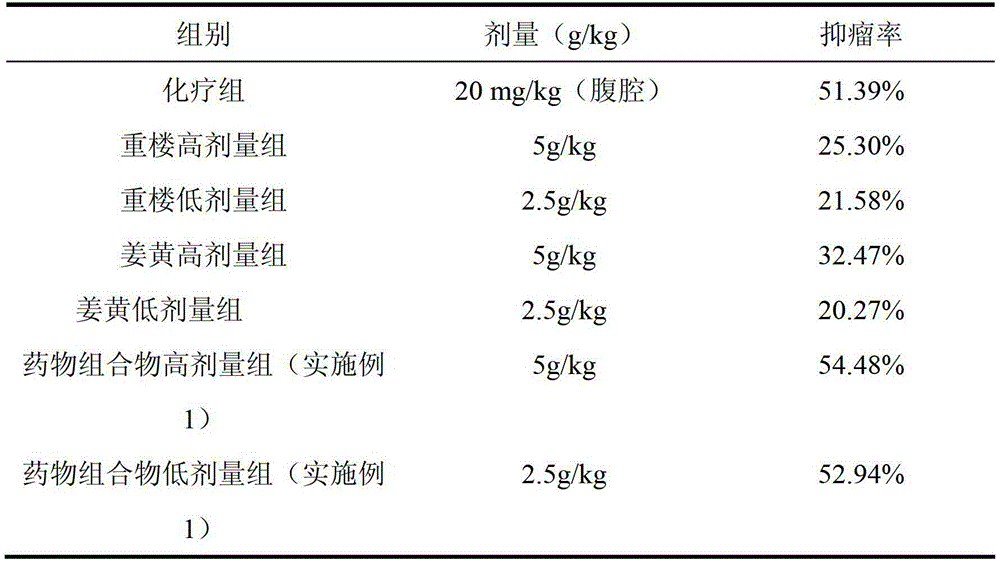
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for resisting liver cancer and lung cancer
ActiveCN103933472AGrowth inhibitory effectSynergisticAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsWilms' tumorRhizome
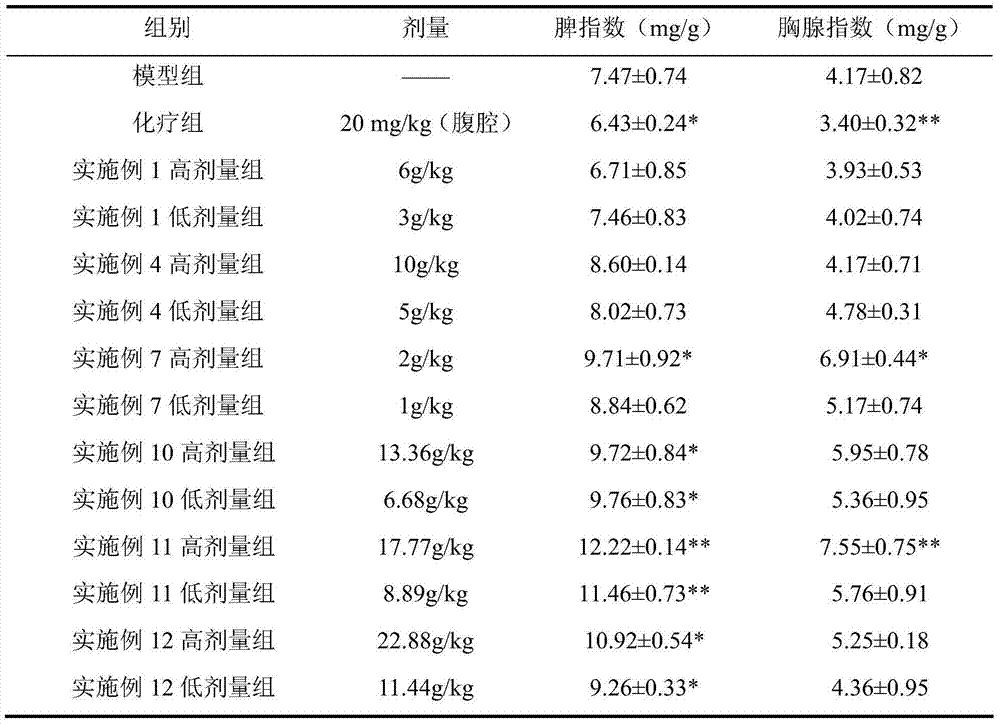
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for resisting a liver cancer and a lung cancer. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from a rhizoma paridis total saponin extract, a curcuma extract and a dioscorease rhizome extract of which the mass ratio is 1:(10-20):(1-10). An in-vitro MTT process activity test proves that the traditional Chinese medicine composition disclosed by the invention has a growth inhibition effect on an LA795 lung cancer cell line and an HepG2 hepatoma cell line; IC50 respectively can be up to below 20mg / mL (dose). An in-vivo experiment proves that the traditional Chinese medicine composition disclosed by the invention has a significant growth inhibition effect on mice T739 lung cancer metastasis in mice, an HepA liver cancer and an H22 lung cancer, and the tumor control rates respectively can be up to 53%, 55% and 57%. Compared with component administration of components forming the composition, the tumor control effect of the composition disclosed by the invention has a synergistic enhancement effect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors NXGF and NXGH with antineoplastic activity and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105646375APrevent proliferationGood antitumor activityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsChemical structureTumor therapy
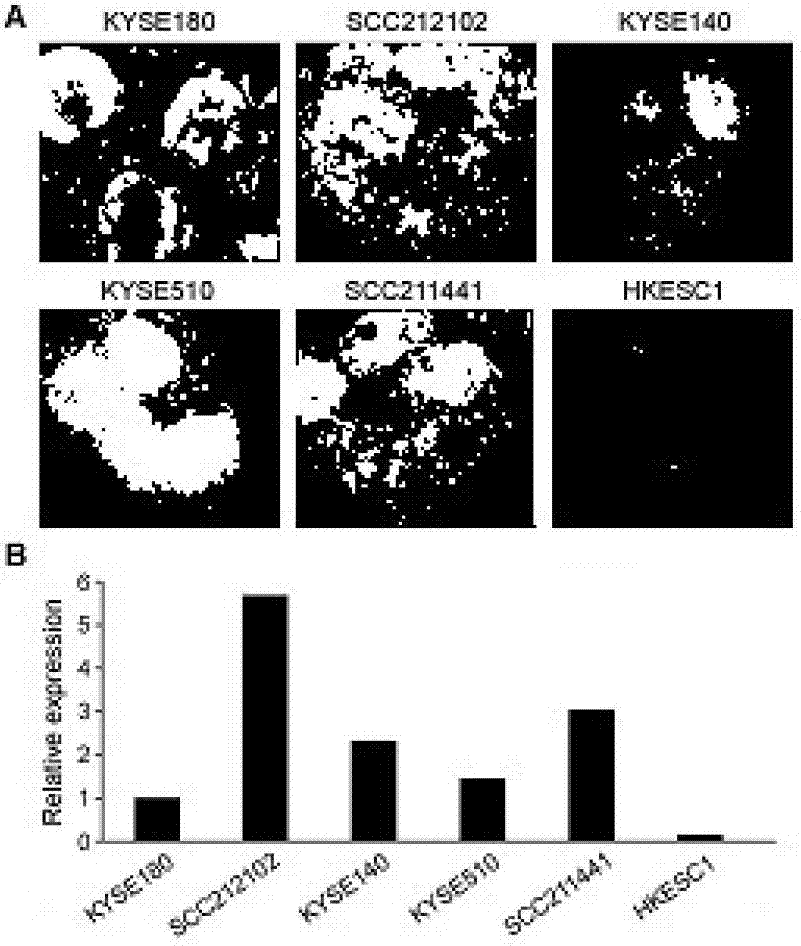
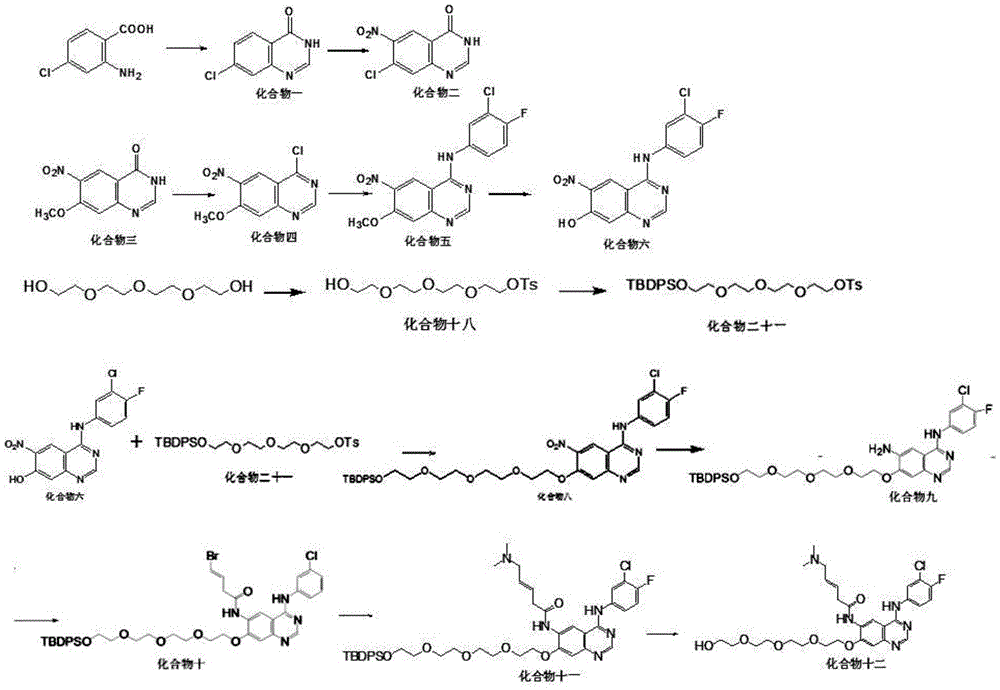
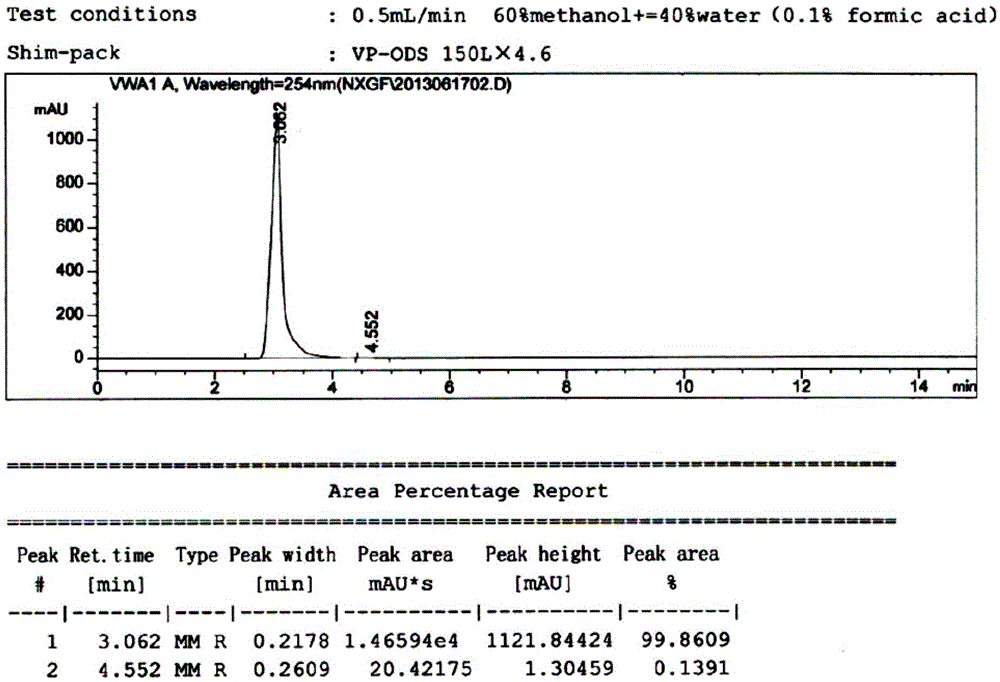
The invention discloses epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR TKI) NXGF and NXGH with antineoplastic activity and a preparing method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of biological medicine. The brand new EGFR TKI are obtained by optimizing and improving the chemical structure of Pelitinib and named NXGF (the formula I) and NXGH (the formula II) respectively. It is shown through research that the synthesized EGFR TKI-NXGF and the synthesized EGFR TKI-NXGH can effectively inhibit proliferation of tumor cells, have a higher proliferation inhibiting effect on the mutation EGFR lung cancer cell line HCC827 compared with Pelitinib, and thus can be clinically applied as an antineoplastic agent. The invention further discloses the preparing method of the EGFR TKI NXGF and NXGH with antineoplastic activity. By proposing the EGFR TKI NXGF and NXGH with antineoplastic activity, and the preparing method and application thereof, an effective technical means is provided for treating tumors and especially non-small cell lung cancer.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Traditional Chinese medicine composition having anti-lung cancer and anti-liver cancer effects
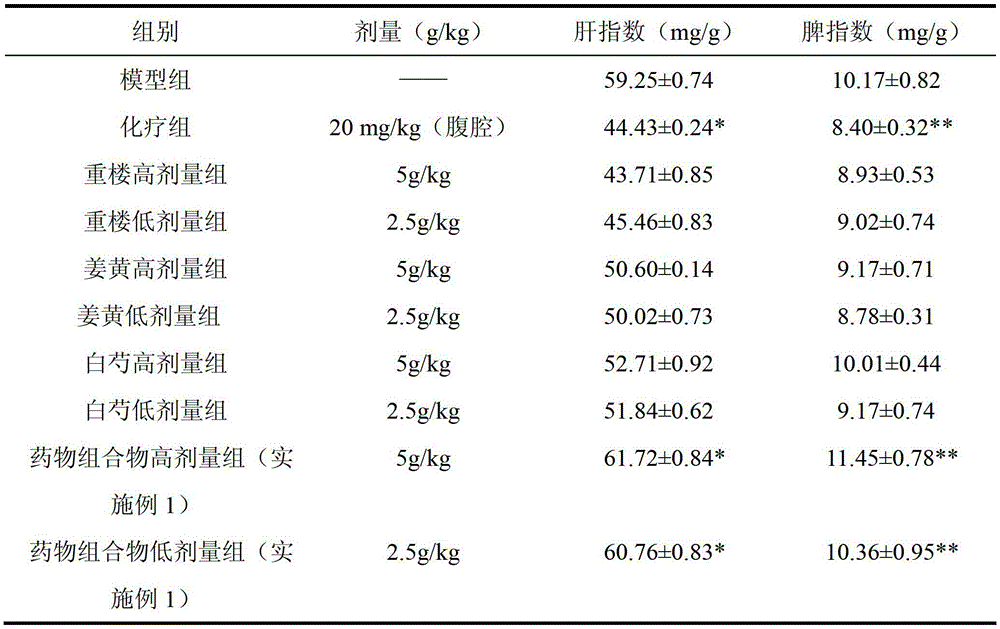
ActiveCN103169844AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectApoptosis
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition having anti-lung cancer and anti-liver cancer effects. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is composed of a paris polyphylla extract, turmeric polysaccharides and a radix paeoniae alba extract in a weight ratio of 1: (0.1-5): (1-10). The in-vitro MTT (Methylthiazolyl Tetrazolium) assay activity tests proves that traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention is capable of obviously inhibiting the growth of lung cancer cell lines such as LA795 and liver cancer cell lines such as Hep-B3; and lung adenocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma-bearing mice model tests show that the anti-tumor rates of the traditional Chinese medicine composition both are more than 50%, and the traditional Chinese medicine composition is capable of improving the spleen index and the liver index of the mice, and obviously inhibiting pulmonary metastasis of subcutaneously transplanted tumors of the mice and causing apoptosis of tumor cells without any obvious toxic and side effects. Compared with single use of each raw material, the medicine composition is higher in anti-lung cancer and anti-liver cancer activity and clear in action, and has excellent inhibition effect on the lung cancer and the liver cancer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A radiotherapy-resistant lung cancer cell line and its construction method and application
ActiveCN107779438BRadiotherapy is well tolerated and stableCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer cellPulmonary adenocarcinoma
The invention discloses a radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line, a construction method thereof and an application of the cell line. The radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line is named asa human lung adenocarcinoma radiation tolerance cell strain PC9-RR, and the collection number is CGMCC No. 14314. The radiotherapy tolerance lung cancer cell line comprises radiotherapy tolerance cells acquired by performing repeated X-ray irradiation and culture on a human lung adenocarcinoma cell strain PC9, is strong and stable in radiotherapy tolerance and has a good application prospect in terms of serving as a cell model for lung cancer radiotherapy resistance mechanism research and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
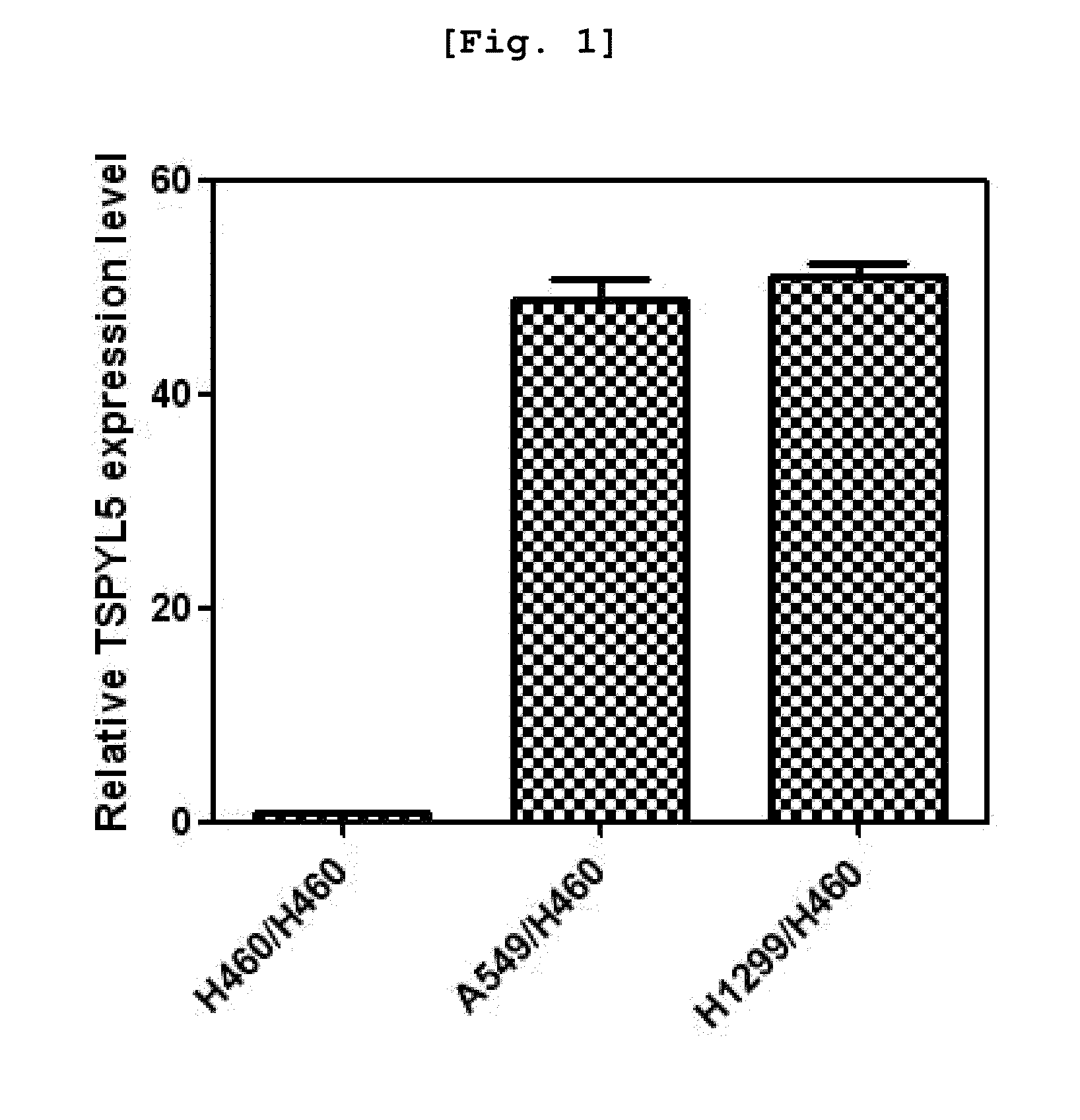
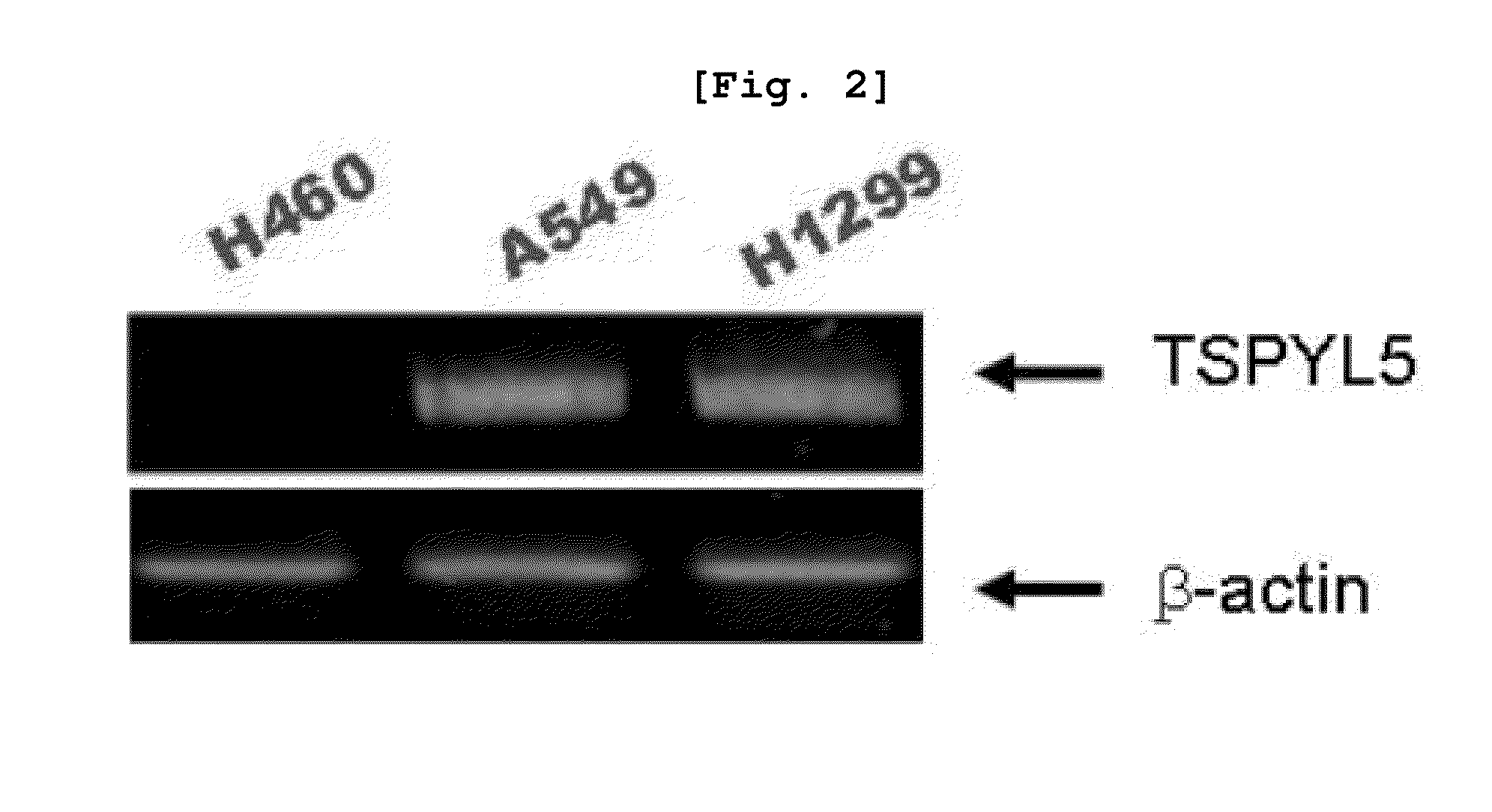
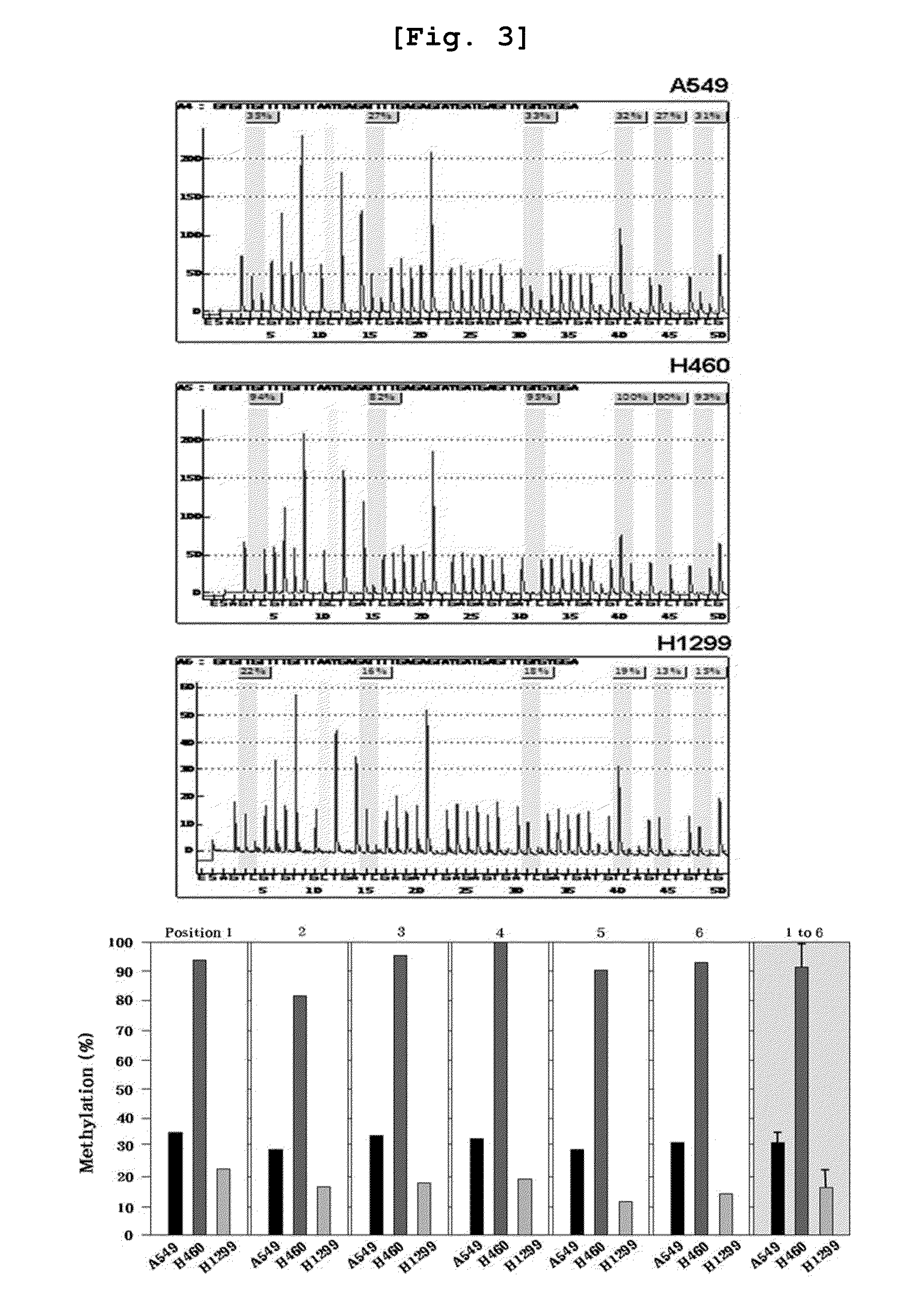
Method for enhancing chemical sensitivity or radiosensitivity of cancer cells by inhibiting expression of tspyl5
ActiveUS20110111400A1Enhancing apoptotic effectHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnticarcinogenCancer cell
Disclosed herein is a method for enhancing sensitivity of cancer cells to compounds or radiation by inhibiting the expression of testis-specific protein, Y-encoded like 5 (TSPYL5). More specifically, because methylation of TSPYL5 protein expressed in lung cancer cell line was inhibited to increase the expression level of the gene, resistance to stress such as radiation or anticancer agents was increased. Because the sensitivity of cancer cells to stress such as radiation or anticancer agents was increased by inhibiting the expression of the TSPYL5 gene to promote the apoptosis of the cells, an anticancer supplement agent containing an inhibitor of the expression or activity of the TSPYL5 gene of the present invention inhibits the growth of cancer cells and enhances the sensitivity to various stresses to maximize the apoptosis. Thus, when used in combination with radiotherapy or chemotherapy, the anticancer supplement agent may be used very usefully for anticancer treatment.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
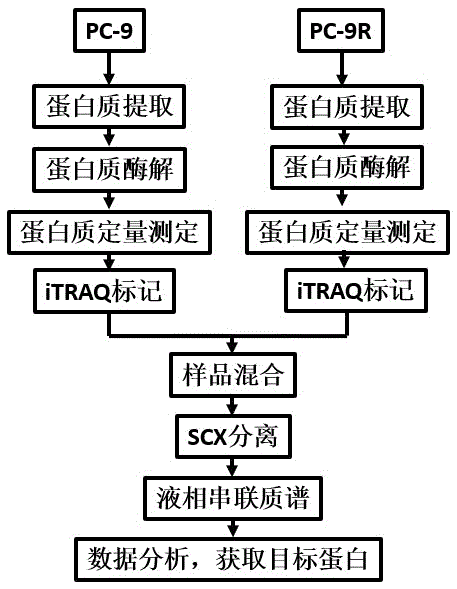
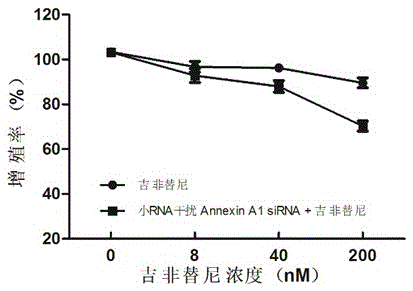
Method for detecting drug-resistant mechanism of gefitinib
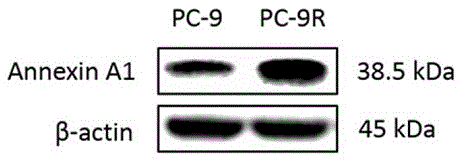
InactiveCN105510603ATo achieve the purpose of reversing the basis of gefitinib resistanceElectrophoretic profilingBiological testingHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a method for detecting a drug-resistant mechanism of gefitinib and belongs to the field of medicines. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing high throughput screening on protein signaling molecules participating in gefitinib drug resistance by adopting iTRAQ quantification (isotope labeling relative or absolute quantification) proteomics technology; (2) screening to obtain differential expression protein signaling molecules of gefitinib sensitive lung cancer cell lines and gefitinib rug-resistant cell lines by adopting western blot (western immunoblotting test) technical identification; and (3) proving expression of the protein signaling molecules discovered by interference by adopting MTT (MTT cytotoxicity assay). The sensitivity of gefitinib can be improved, so that the expression level change of the newly discovered protein signaling molecules is proved to be a drug-resistant mechanism of gefitinib. The method contributes to detecting new protein signaling molecules participating in gefitinib drug resistance, and tolerance-resistant drugs are designed by virtue of the new detected protein signaling molecules.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
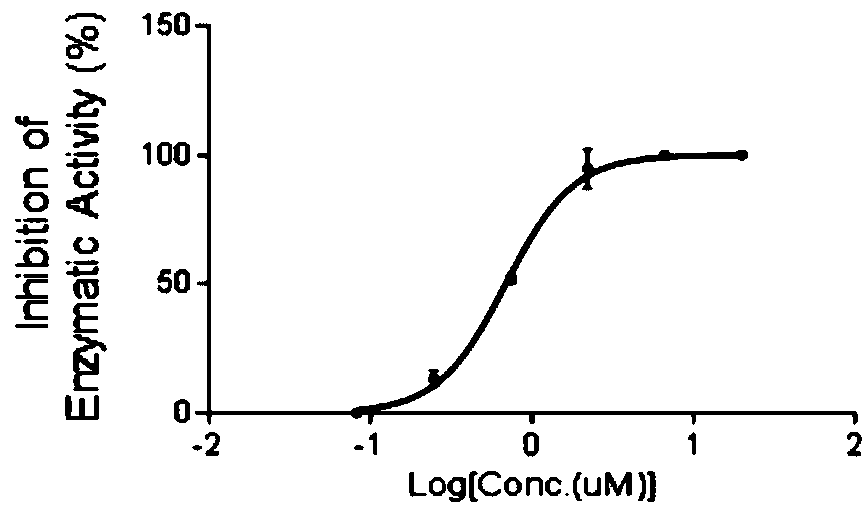
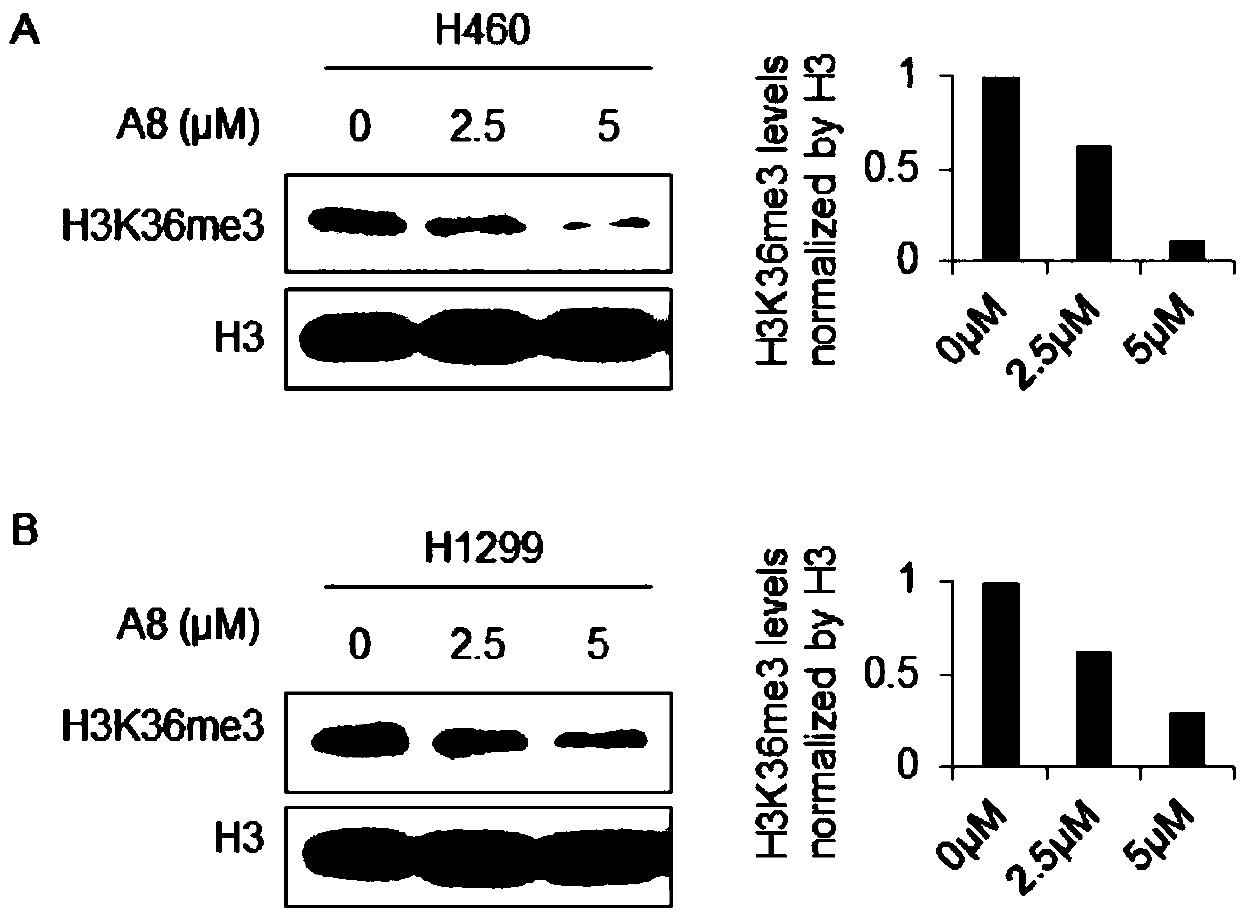
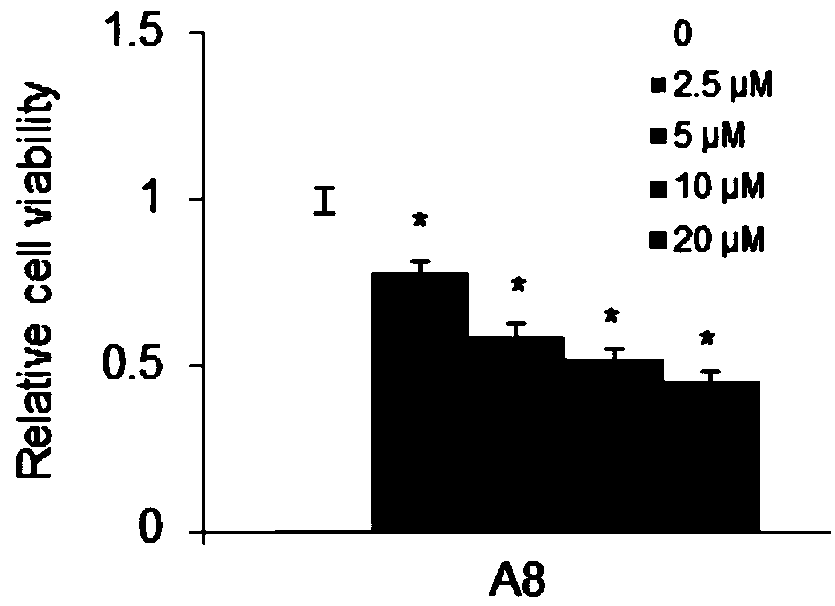
Compound A8 used as histone transmethylase NSD3 activity inhibitor and application thereof
ActiveCN108853110AValidation of antitumor activityEnhanced inhibitory effectAntineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsChemical structurePurine
The invention discloses a compound A8 used as a histone transmethylase NSD3 activity inhibitor and a medicine purpose thereof. The compound A8 has a chemical structure shown as a formula I in description, and the chemical name is 6-amino-9-(2-(p-tolyloxy)ethyl)-9H-purine-8-thiol. The medicine purpose refers to the preparation of anti-tumor medicine by using at least one of the compound A8 or hydrates, pharmaceutically acceptable salt, dynamic isomers, stereoisomers and precursor compounds as active ingredients. Experiments show that the compound A8 can effectively inhibit the NSD3 enzyme activity; the enzyme level IC50 value is 0.69+ / -0.06mumol / L; the growth and proliferation of a non-small-cell lung cancer cell line H460 can be obviously inhibited. The compound has the effect of inhibiting the tumor cell proliferation, is hopeful to being used as an active ingredient for preparing the anti-tumor medicine and has medicine prospects.
Owner:普美瑞(常州)生物科技有限公司
Application of cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP combined PD1 antibody (Nivolumab) in preparation of antitumor drugs
InactiveCN106692967AGrowth inhibitionImprove anti-tumor effectOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsColon cancer cellWilms' tumor
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, and relates to application of cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP combined PD1 antibody (Nivolumab) in preparation of antitumor combined drugs. Studies indicate that the cGAMP combined Nivolumab can significantly inhibit the growth of a variety of tumor cells, has obvious anti-tumor effect, and can be used for preparing the antitumor combined drugs. A C57BL / 6 mouse subcutaneous transplantation tumor model shows that the cGAMP combined Nivolumab has obvious inhibition effect on adenocarcinoma cell line MC38, lung cancer cell line LLC, breast cancer cell line EO771, melanoma cell line B16-F10 and colon cancer cells MC38, and the obvious inhibition effect is superior to single drug use effect, so that the cGAMP can be combined with the Nivolumab for the treatment of tumors.
Owner:LIAOCHENG CITY ORIENT BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
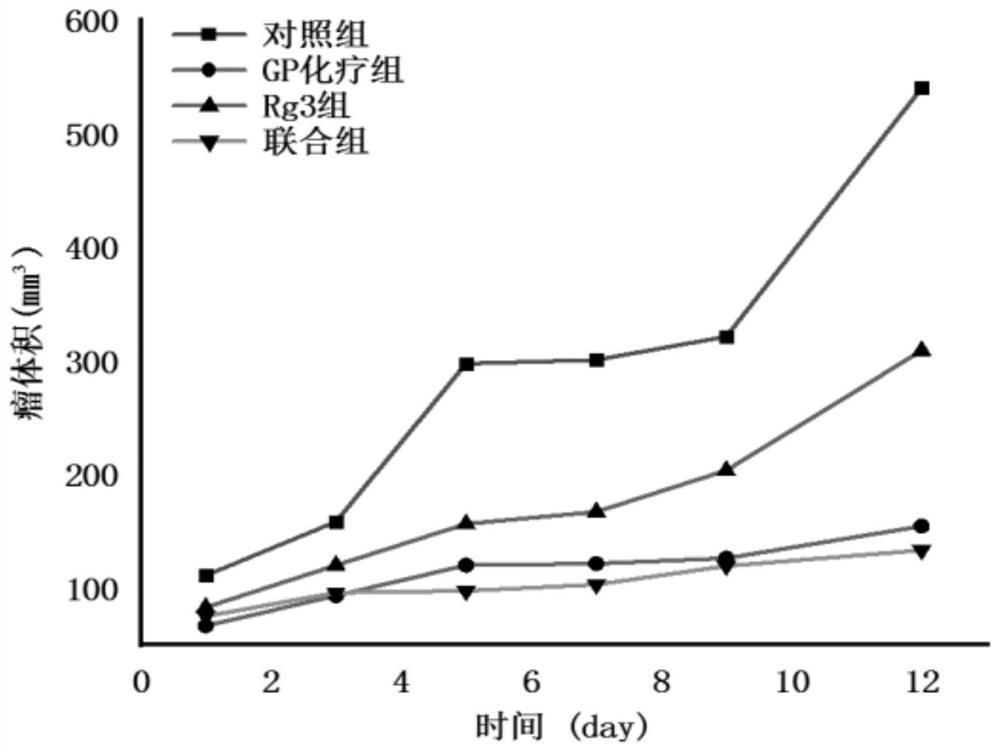
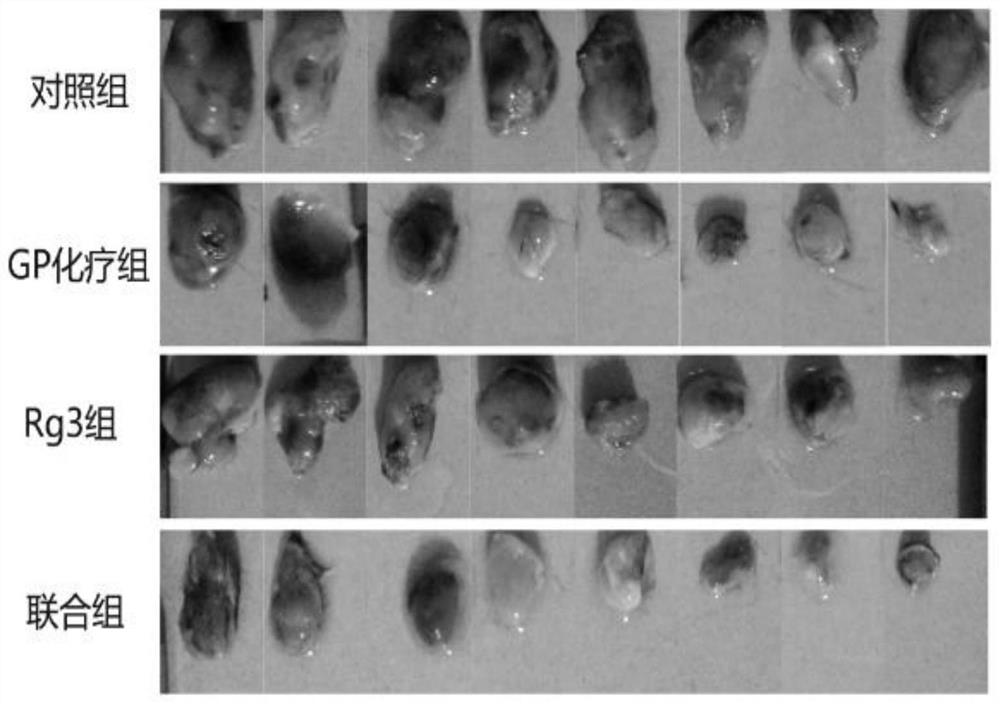
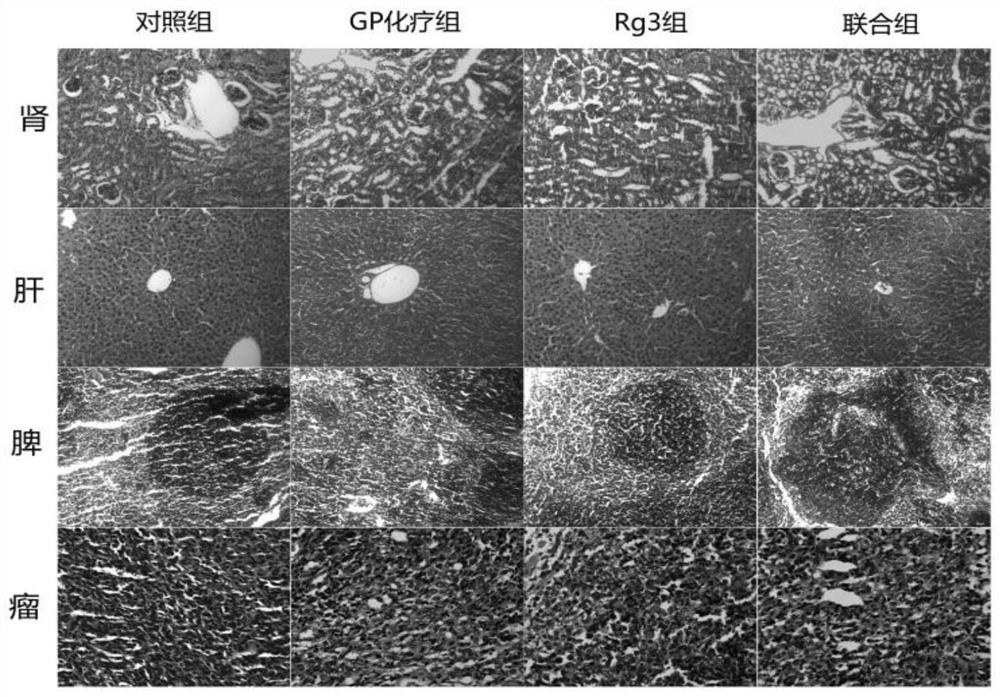
Application of ginsenoside Rg3 in combination with GP
InactiveCN112057464AStrong growth inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsMouse tumorEosin
The invention discloses application of ginsenoside Rg3 in combination with GP as an antitumor drug. A mouse Lewis lung cancer cell line (LLC) is selected and inoculated to the right armpit of a C57BL / 6N mouse, and the influence of ginsenoside Rg3 and Rg3 in combination with GP on Lewis lung cancer is observed; hematoxylin-eosin staining is performed on the liver, kidney, spleen and tumors, and pathological changes of ginsenoside Rg3 in combination with GP on the liver, kidney, spleen and tumors of mice with the Lewis lung cancer are detected; and tumor tissues are subjected to immunohistochemical staining, and the density of blood vessels in tumors and the expression of tumor platelet surface activation markers are detected. The conclusion is that the ginsenoside Rg3 in combination with GPcan enhance the effects of ginsenoside Rg3 of inhibiting the tumor growth of the mice with the Lewis lung cancer and inhibiting tumor angiogenesis, and the tumor inhibition effect of the ginsenosideRg3 is possibly and closely related to CD62P expression reduction; and the ginsenoside Rg3 in combination with GP can achieve the synergistic and toxicity-reducing effects.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative
ActiveCN111848631AHighly toxicEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTyrosine-kinase inhibitorTyrosine
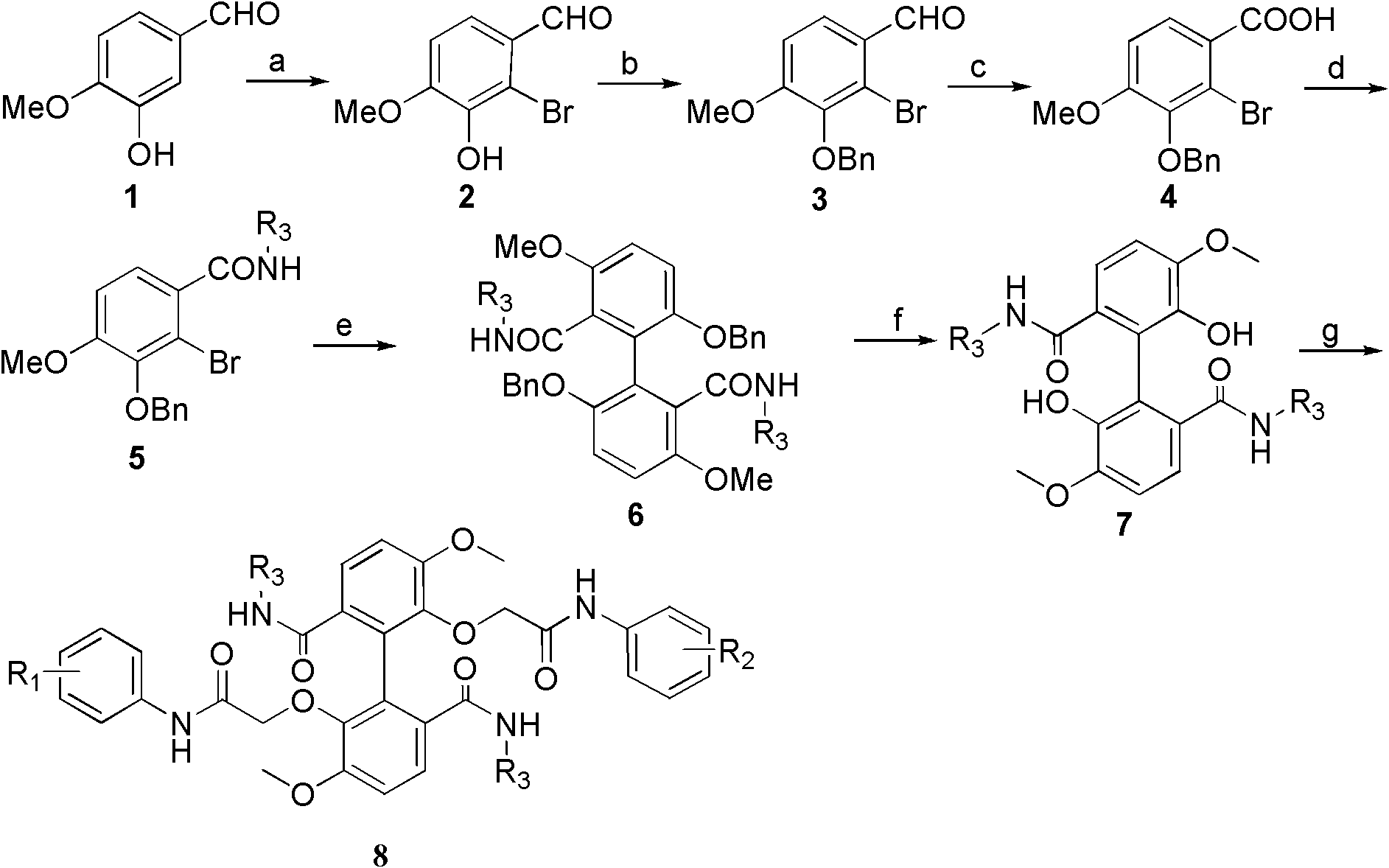
The invention provides a pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of chemical medicines. The derivative is a compound shown as a formula I, or a salt thereof, or a stereoisomer thereof. The compound disclosed by the invention is low in toxicity to normal cells, has an obvious inhibition effect on a lung cancer cell line, particularly has good selectivity on EGFR mutant cells HCC827, and has an obvious inhibition effect; meanwhile, the compound provided by the invention can effectively inhibit phosphorylation of EGFR. In addition, the compound provided by the invention has good inhibitory activity and selectivity on mutant EGFR. The compound disclosed by the invention can be used for treating lung cancer, particularly non-small cell lung cancer, has a relatively strong inhibition effect on EGFR mutant lung cancer, and is relatively low in toxicity; the compound can also be used for preparing tyrosine kinase inhibitors, especially EGFR phosphorylation inhibitors, and has good application prospects.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV +1
Multiple medicine-resistant cell line for lung cancer
A multi drug resistance of the lung cancer cell line relates to a multi drug resistance cell line. The invention is to analyze the morphology and biological ethology change of tumour cells after chemotherapy drug resistance, screen the chemotherapy drugs and decide the sensitivity of the chemotherapy drugs, analyze the multi drug resistance mechanism of tumour chemotherapy and screen multidrug resistance reversal agents in vitro, which provides a multi drug resistance of the lung cancer cell line. The establish of the multi drug resistance of the lung cancer cell line includes: (1) placing the Anip973 cells into culture solution containing foetal bovine serum, penicillin and streptomycin and laying them in a environment with a temperature of 37 DEG C and 5% of carbon dioxide concentration; (2) when the Anip973 cells cover 70%-90% of the incubator inwall area, continuing to culture the Anip973 cells in NVB solution with 0.01-0.02 mug / mL for 24h; (3) throwing the NVB solution and adding culture solution with the same volumes, after the generation of the survival Anip973 cells then entering the logarithmic growth phase, continuing to culture for 24h in NVB solution with an increased concentration; (4) repeating the step (3) until the concentration of NVB reach 2.0-2.2 mug / mL, then the Anip973 / NVB cell line is prepared.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d3d26f69-9bf8-4af9-97bf-bf399977eec9/US20030139609A1-20030724-C00001.png)
![Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d3d26f69-9bf8-4af9-97bf-bf399977eec9/US20030139609A1-20030724-C00002.png)
![Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles Aziridinyl quinone antitumor agents based on indoles and cyclopent[b]indoles](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d3d26f69-9bf8-4af9-97bf-bf399977eec9/US20030139609A1-20030724-C00003.png)



![Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2b00021a-28bf-42d2-9f8c-30f3ab145e3c/HDA0002656190280000011.png)
![Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2b00021a-28bf-42d2-9f8c-30f3ab145e3c/HDA0002656190280000012.png)
![Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative Pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative targeting EGFR mutation as well as preparation method and application of pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivative](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2b00021a-28bf-42d2-9f8c-30f3ab145e3c/HDA0002656190280000021.png)


