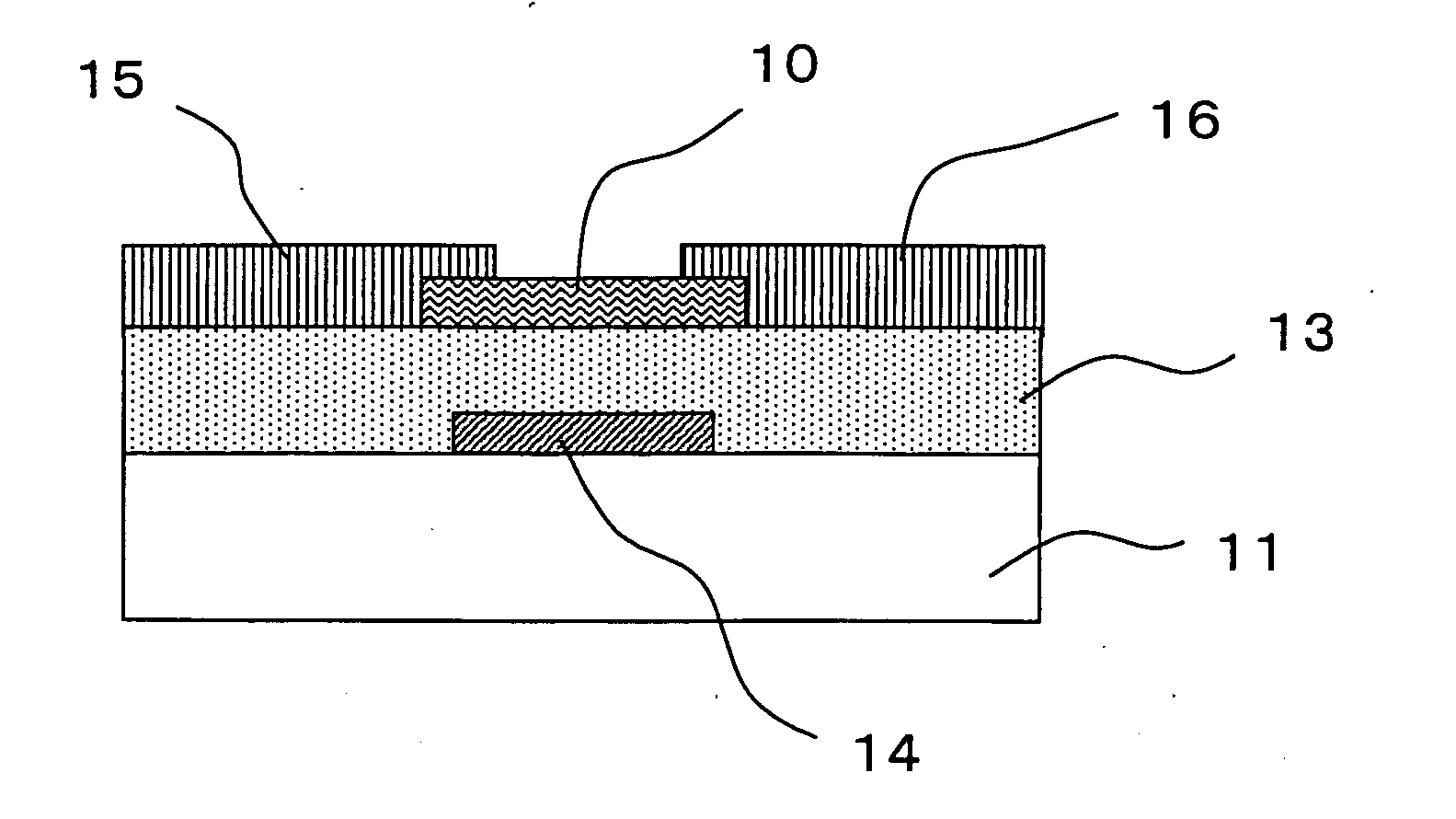
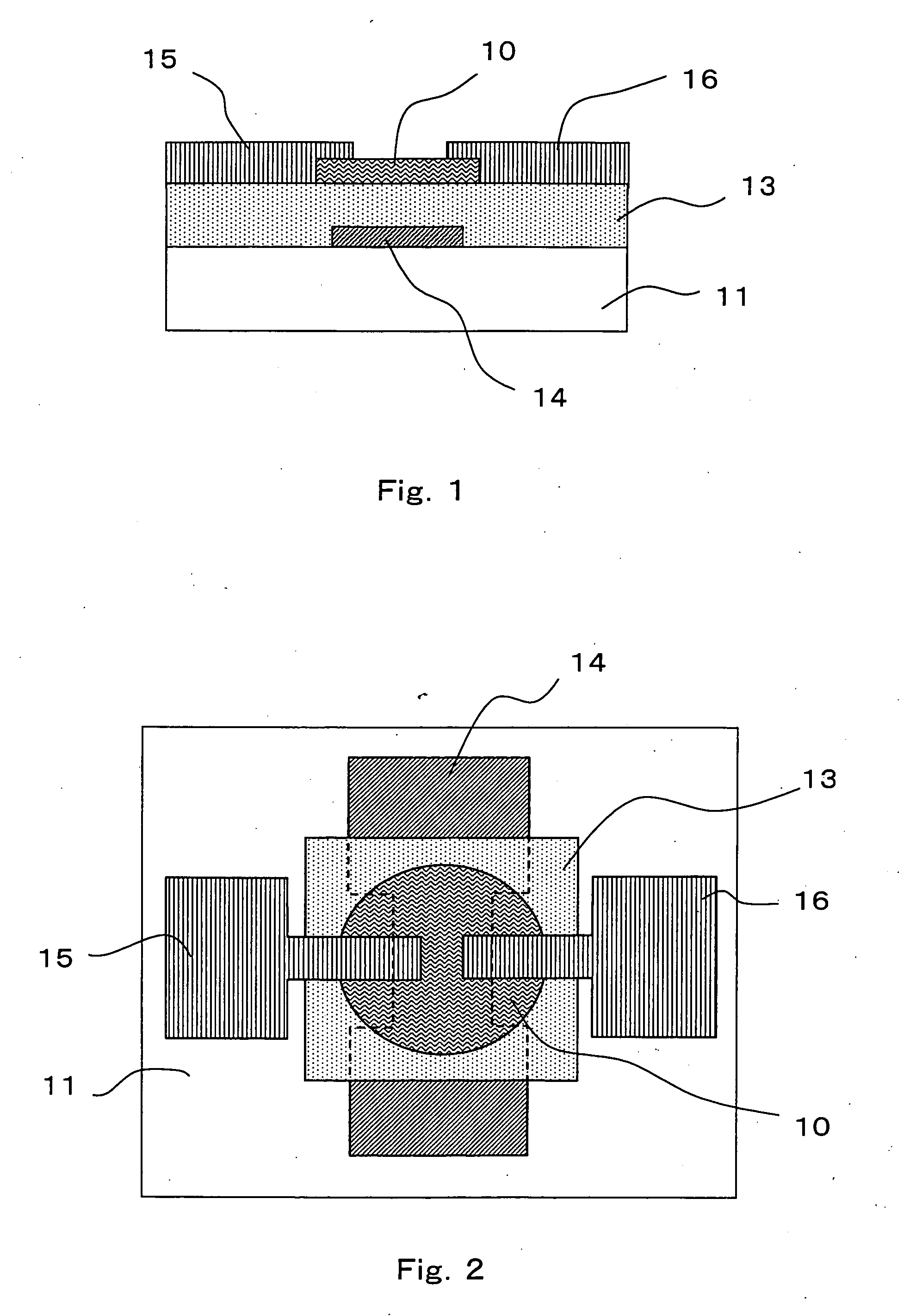
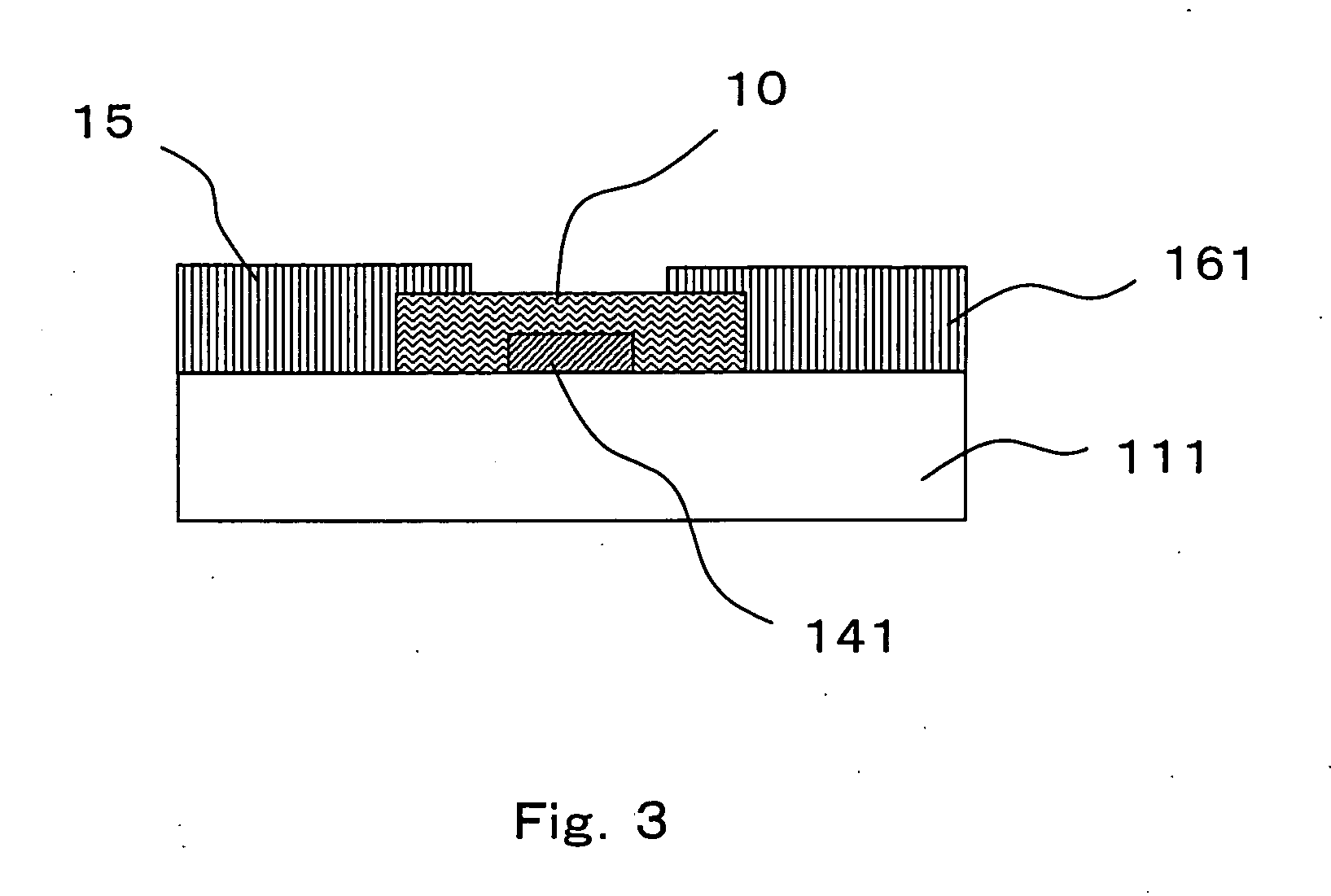
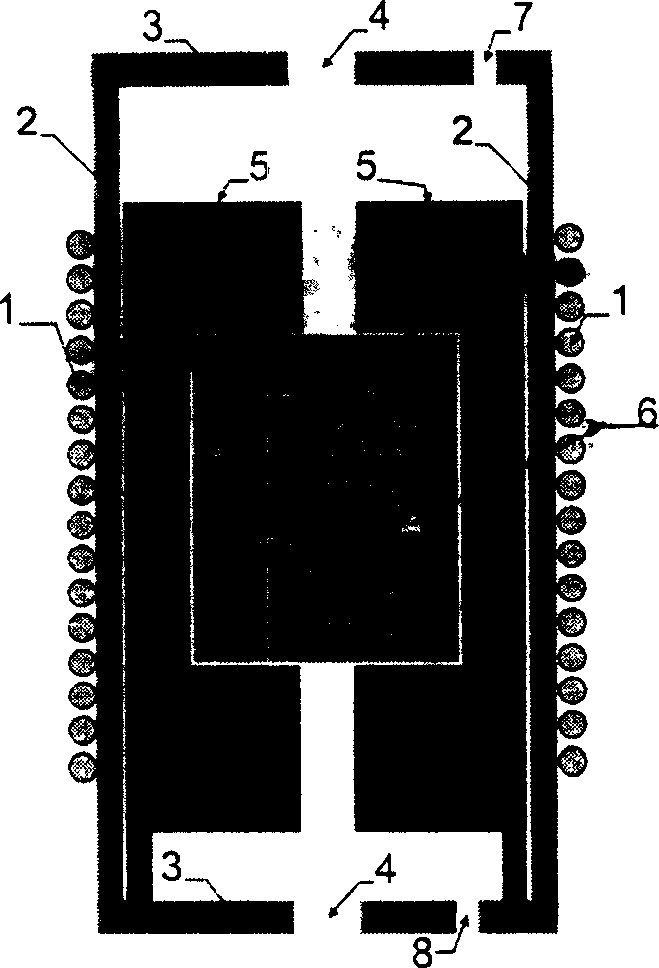
Patents
Literature
476 results about "Semiconductor properties" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Answer Wiki. The properties of semiconductor lies between conductors and insulators. They are conductive but not as much as conductors but also not as bad as insulators. Semi conductors have negative temperature of coeficients i.e their resistance increases as we increase the temperature which is just opposite of conductors(metals).
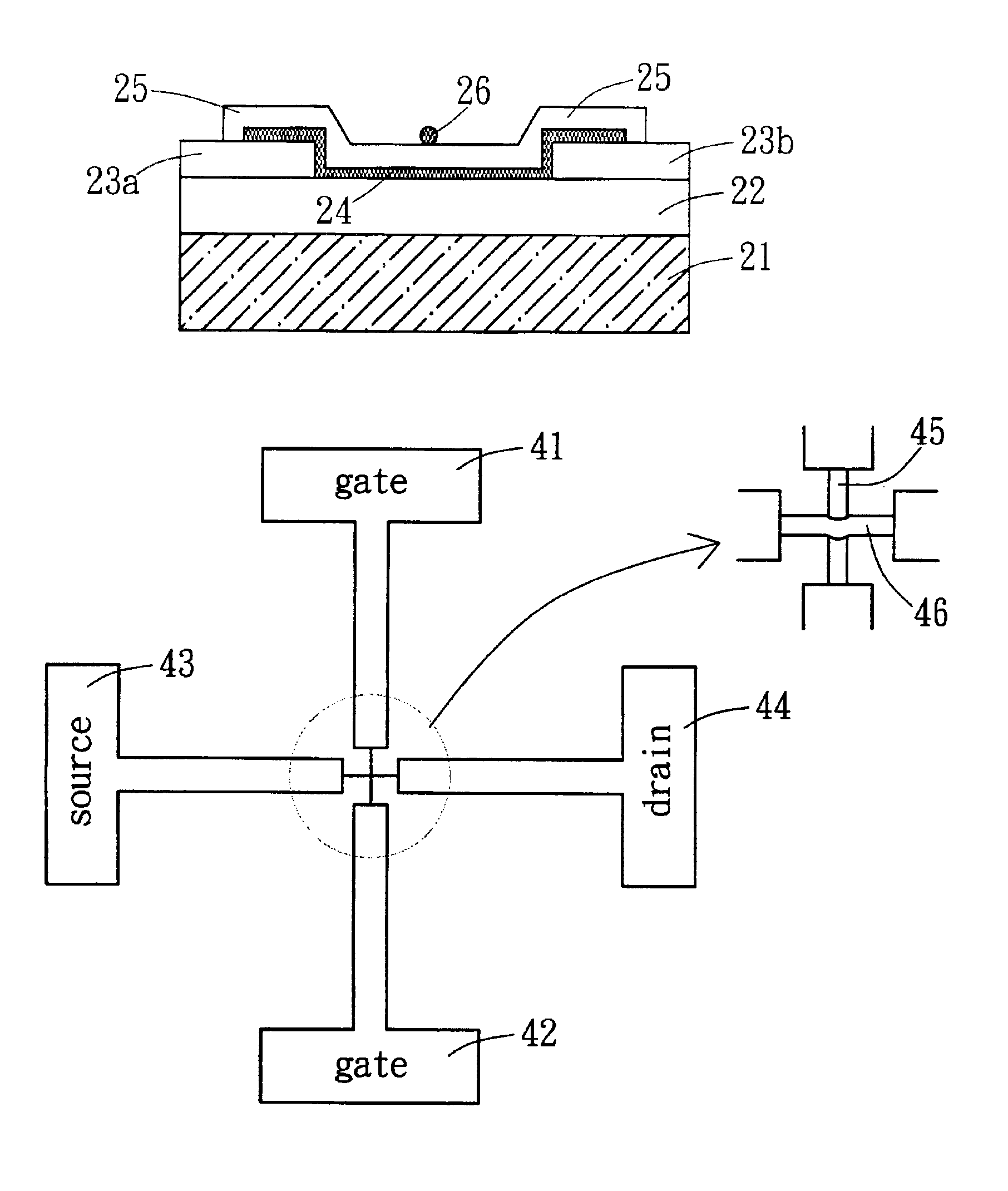
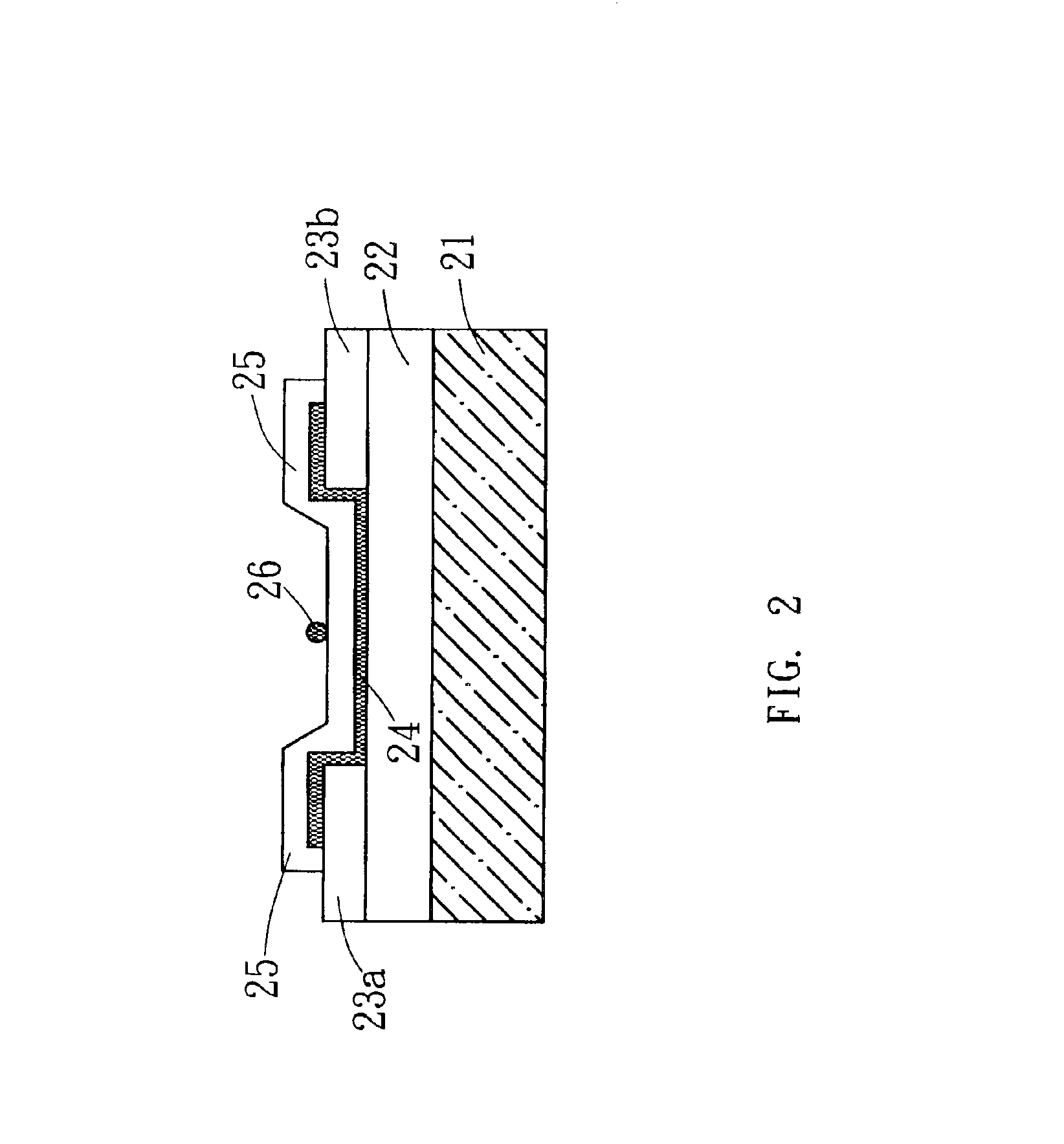
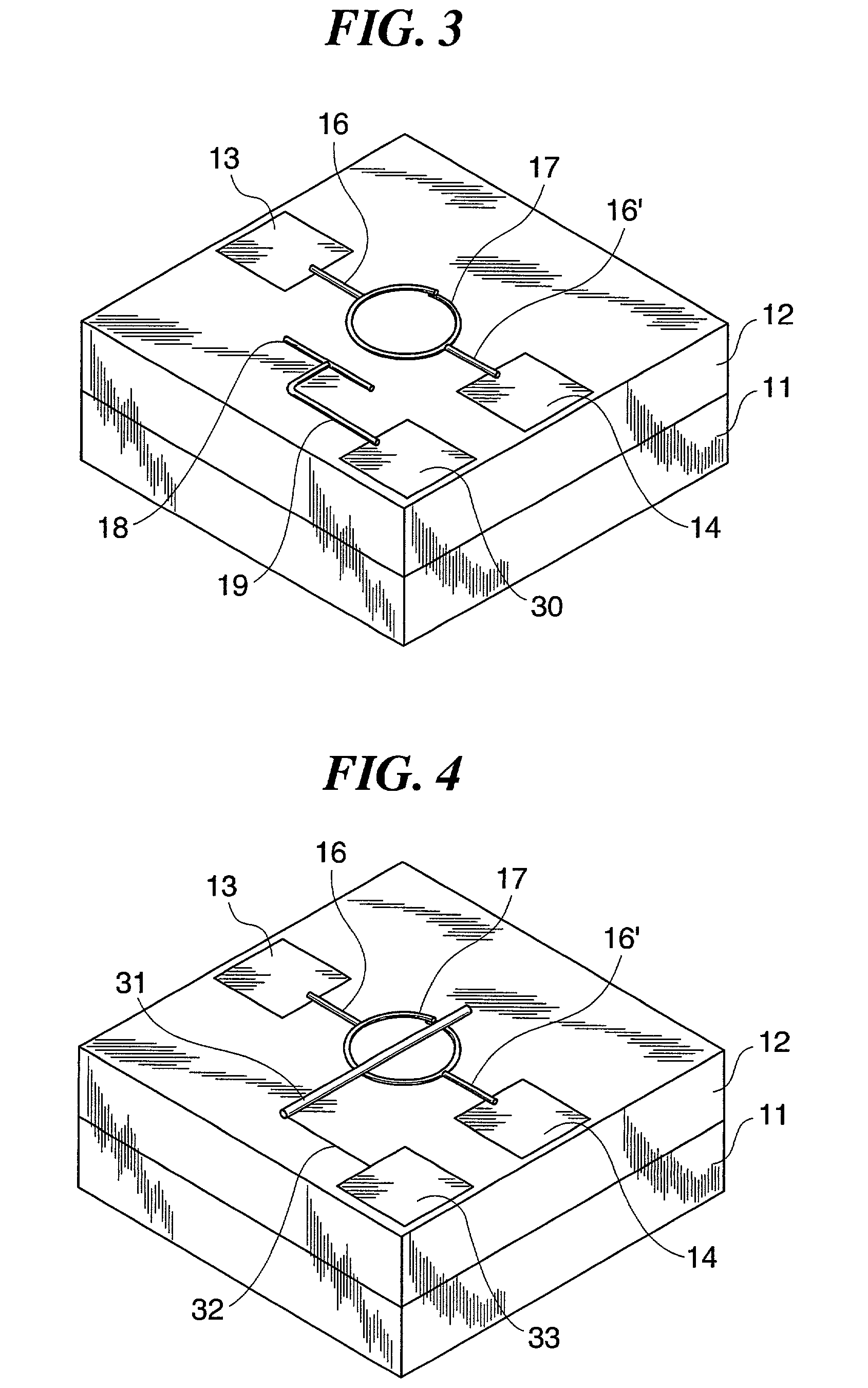
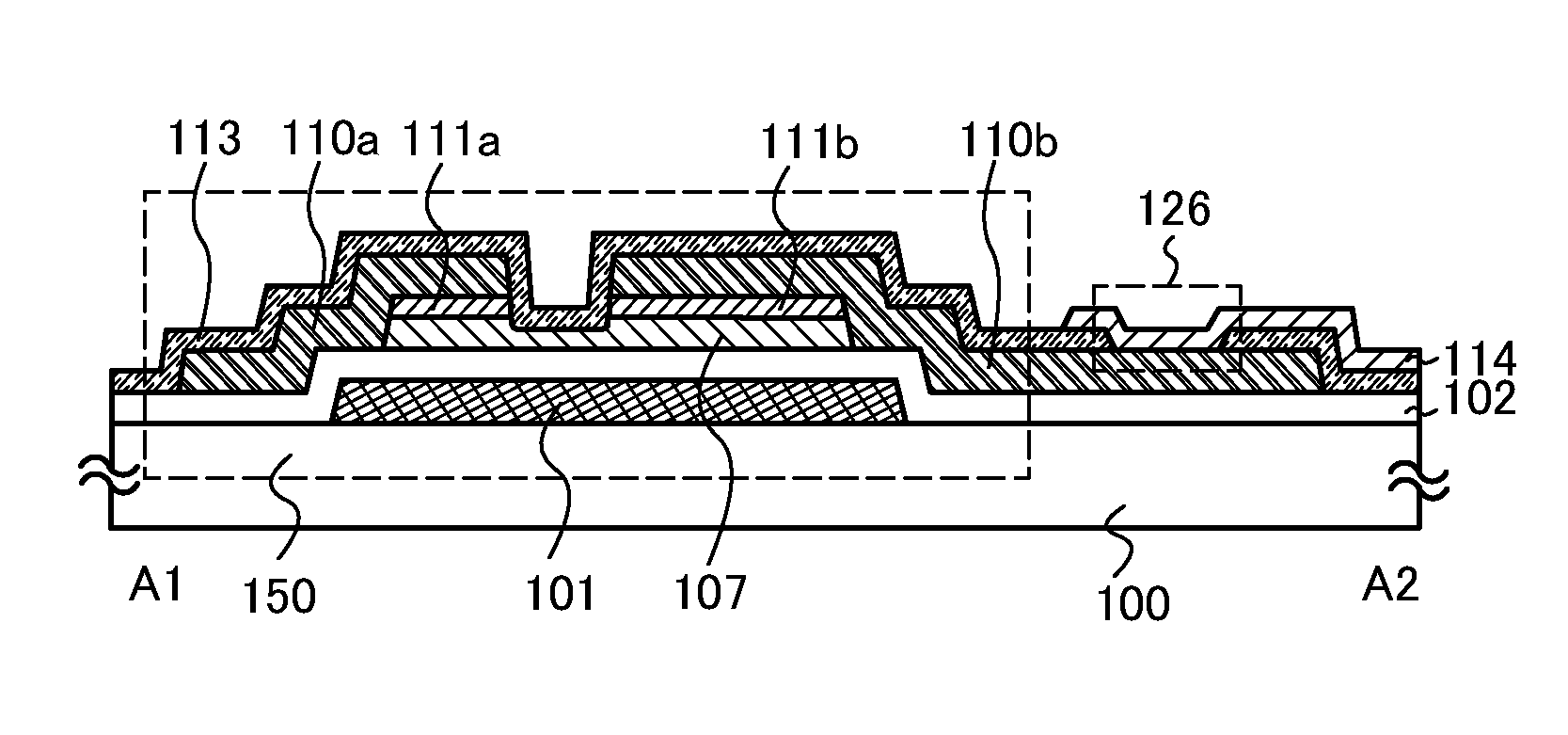
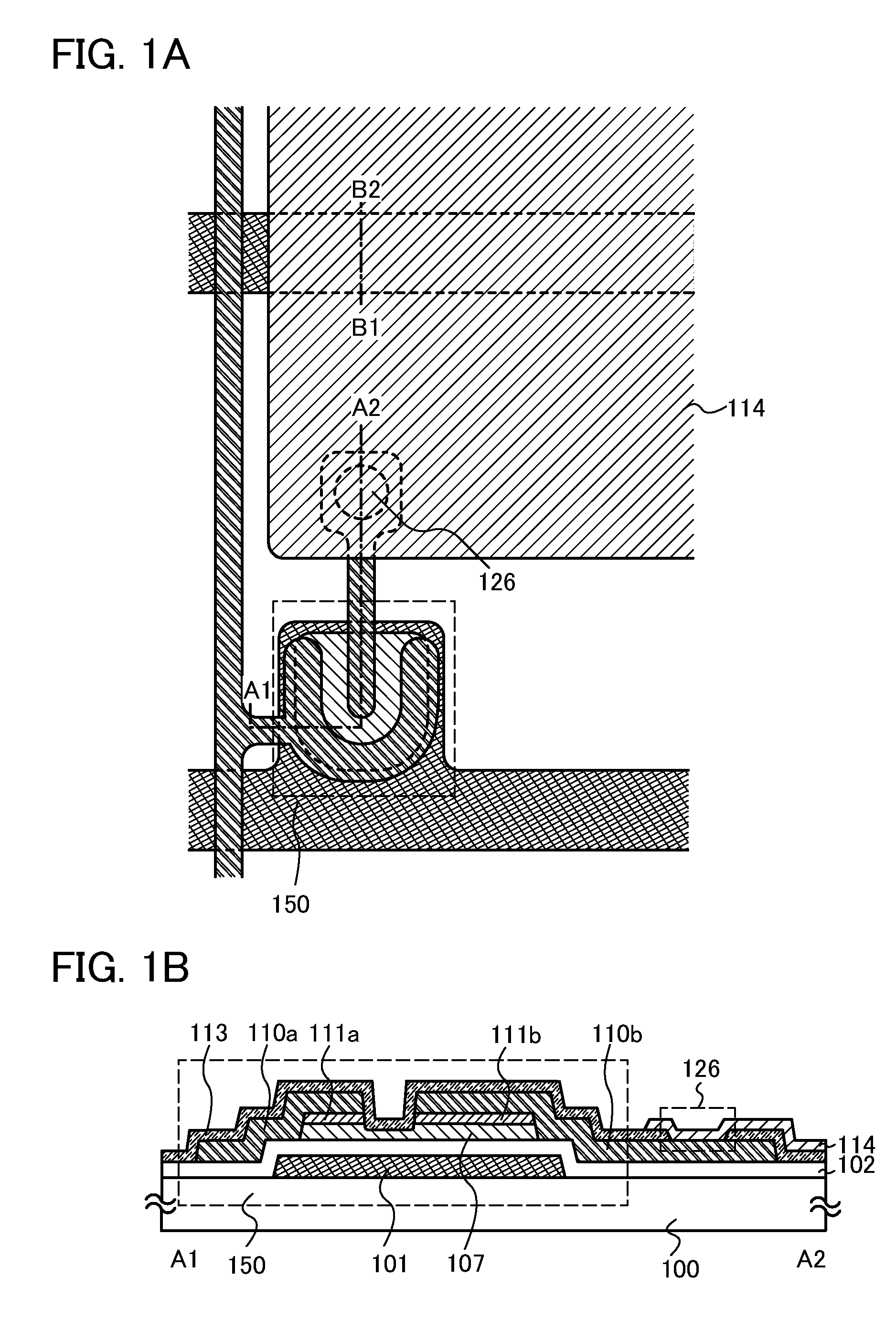
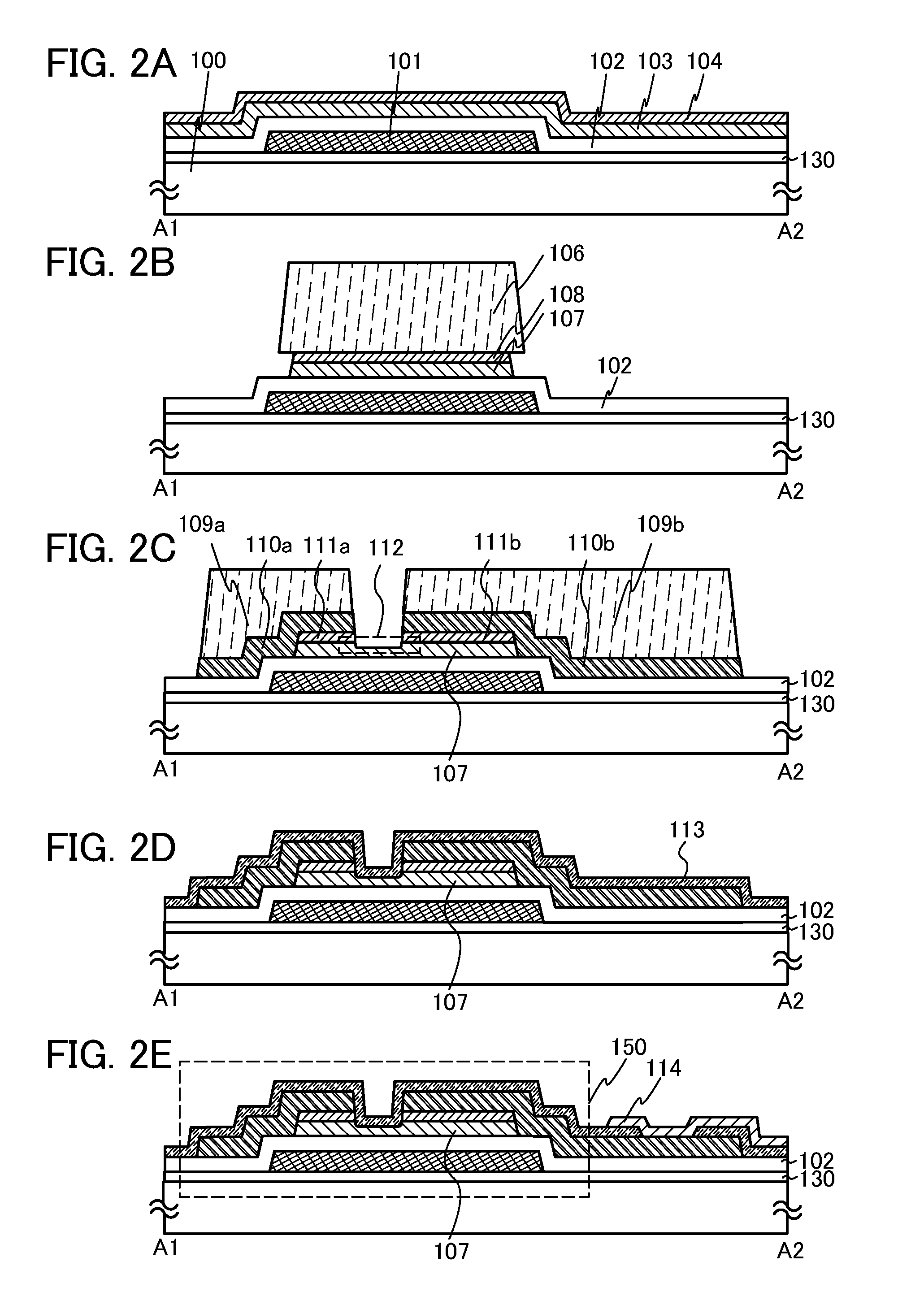
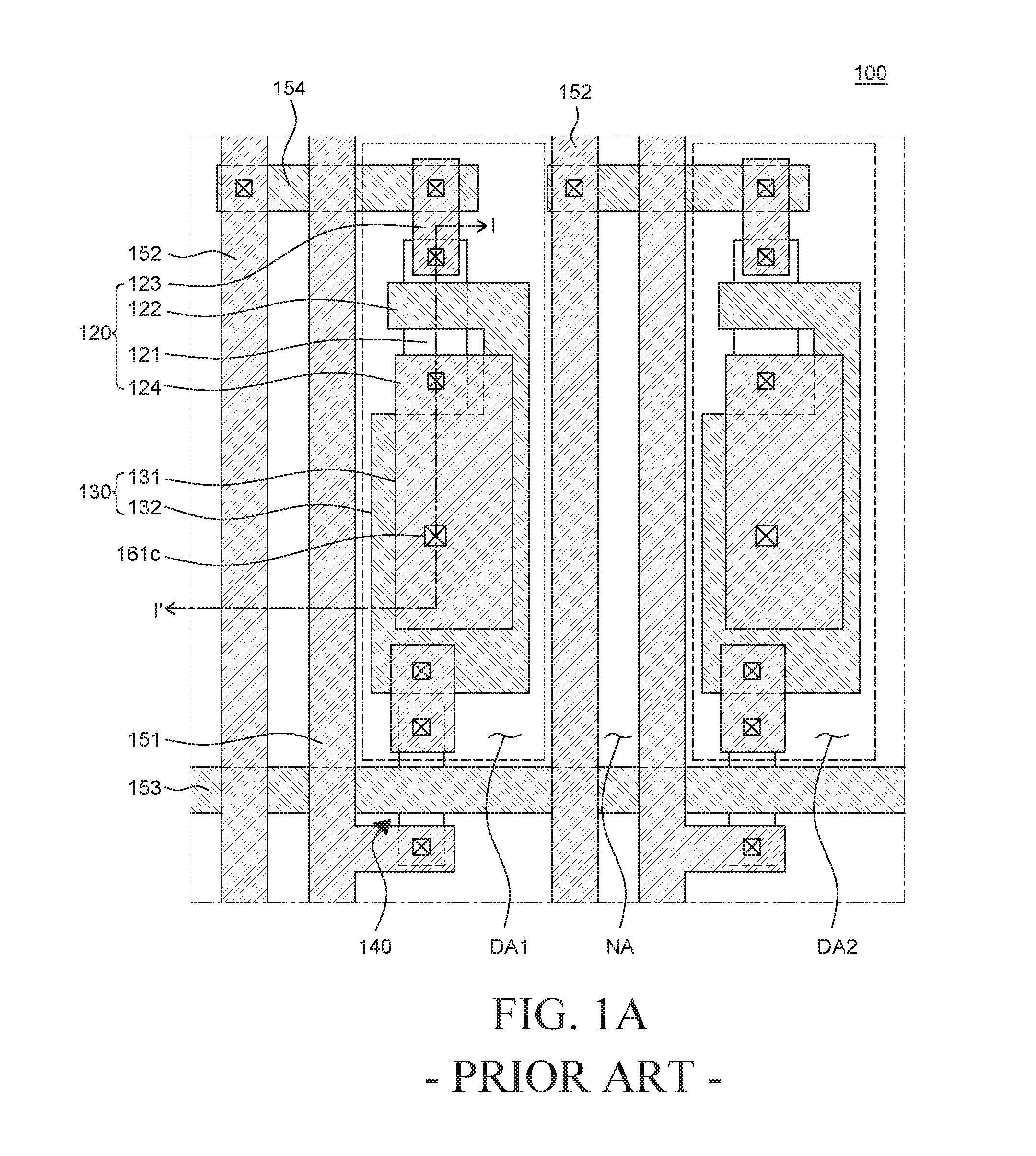
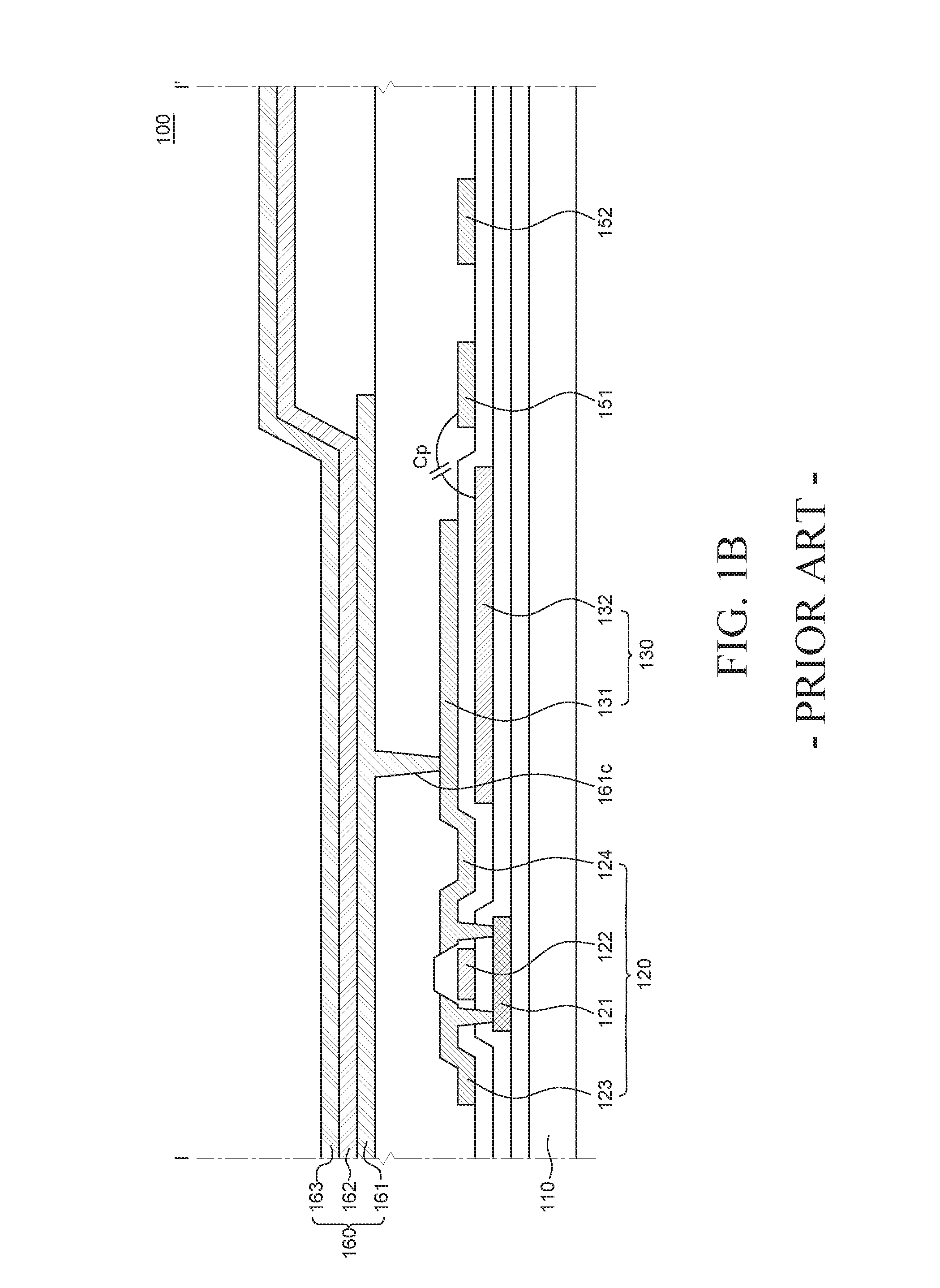
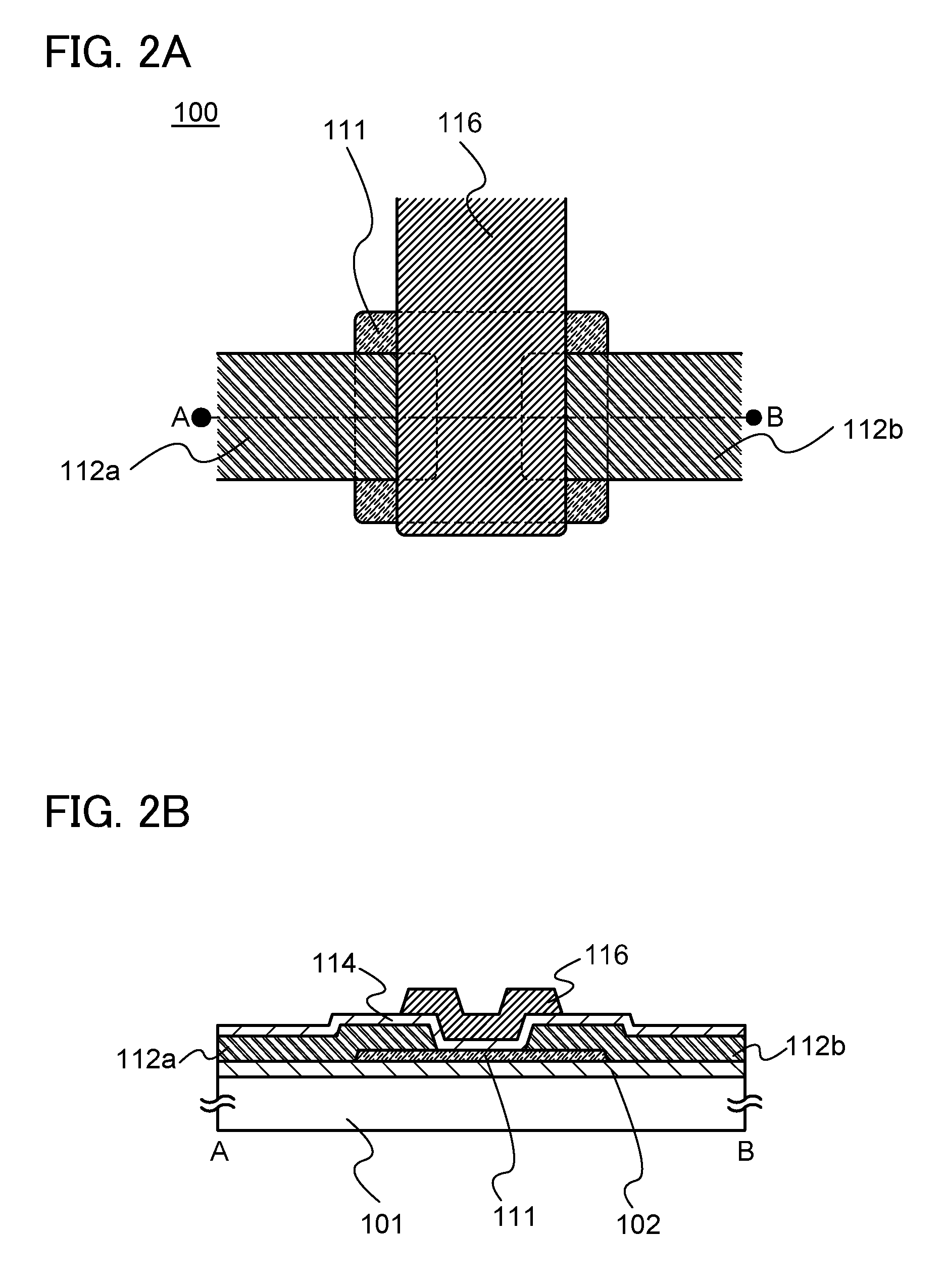
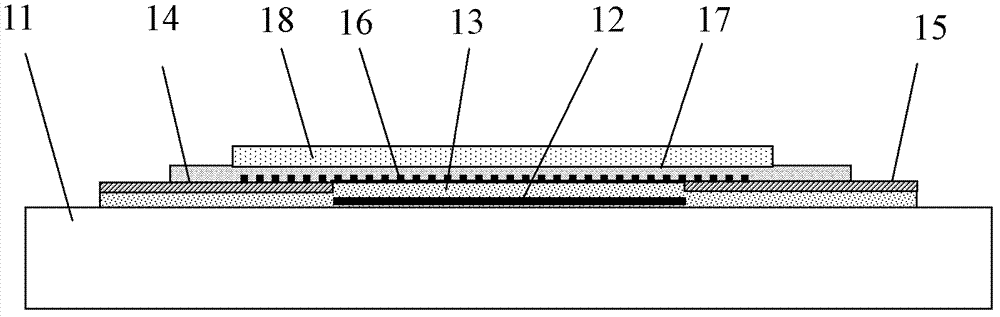
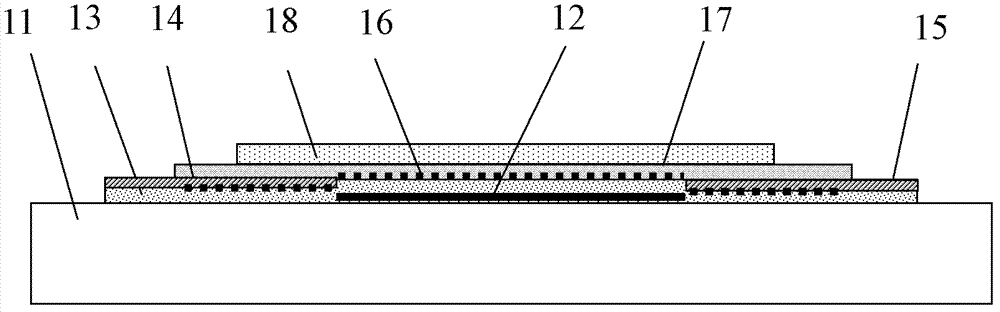
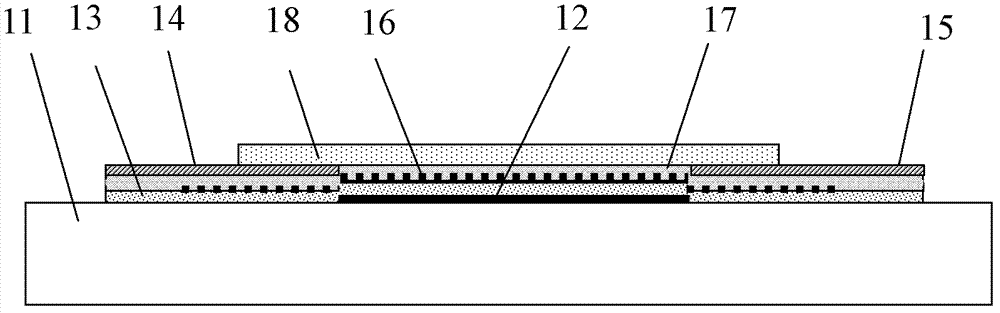
Semiconductor device
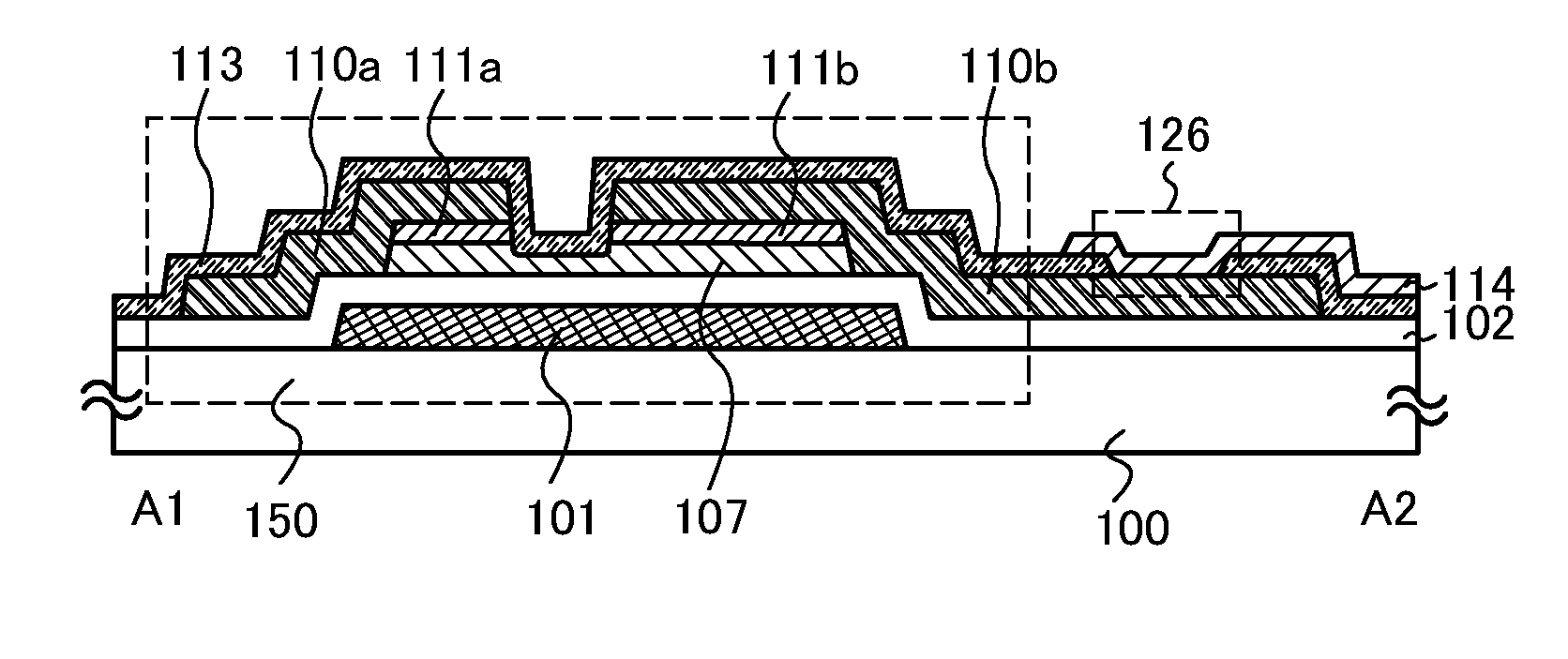
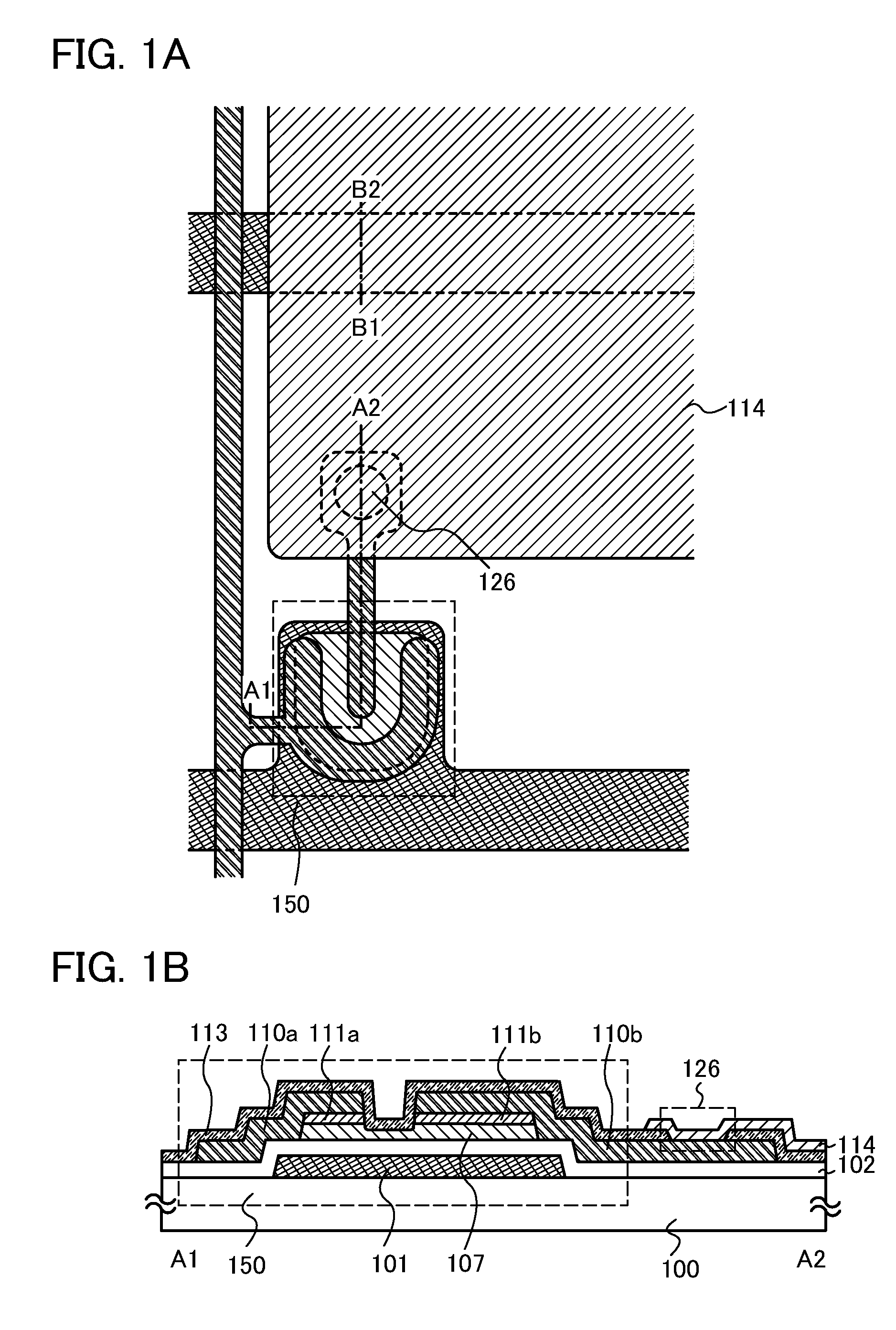
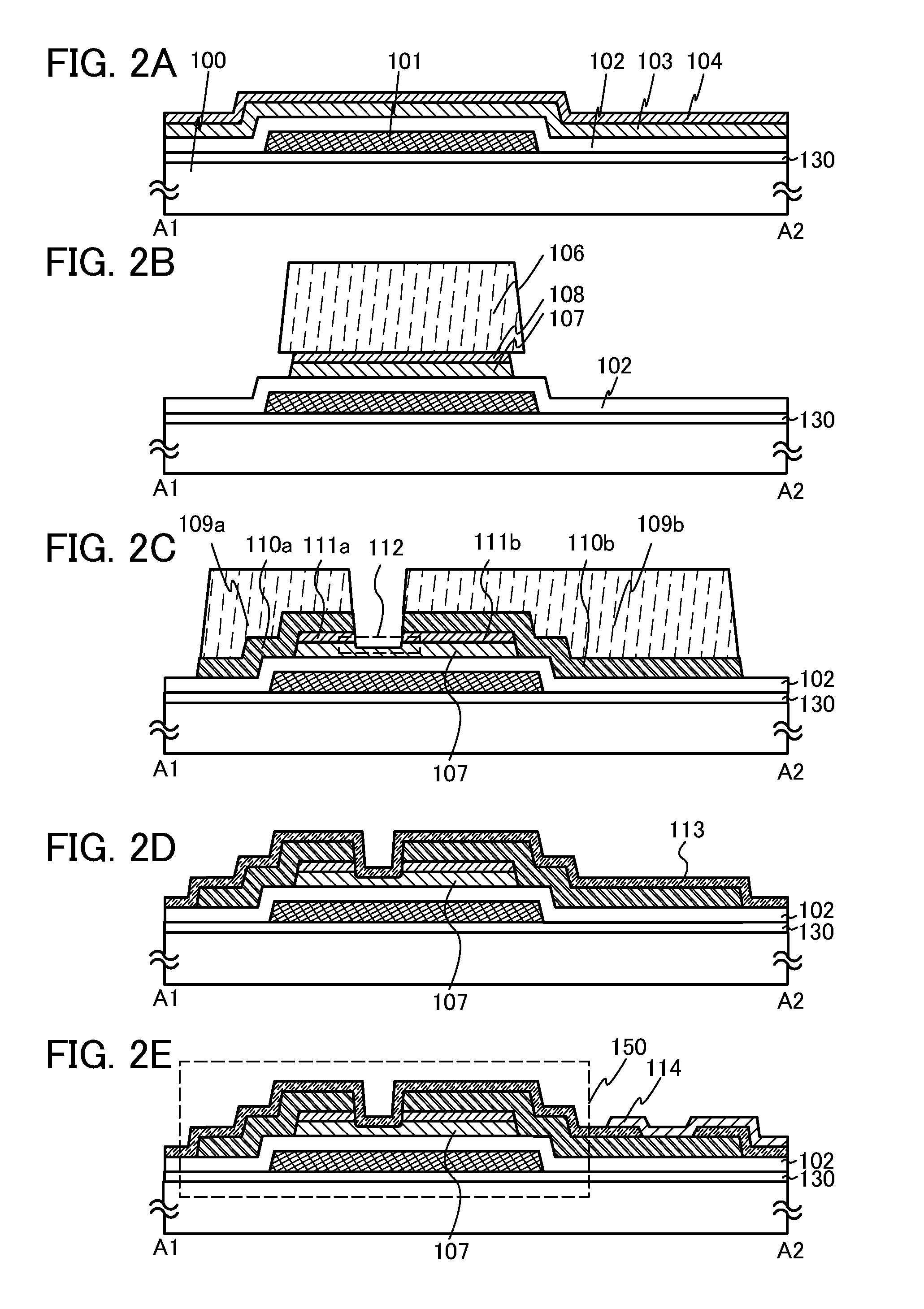
ActiveUS20100117075A1Improve barrier propertiesImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialOxygen
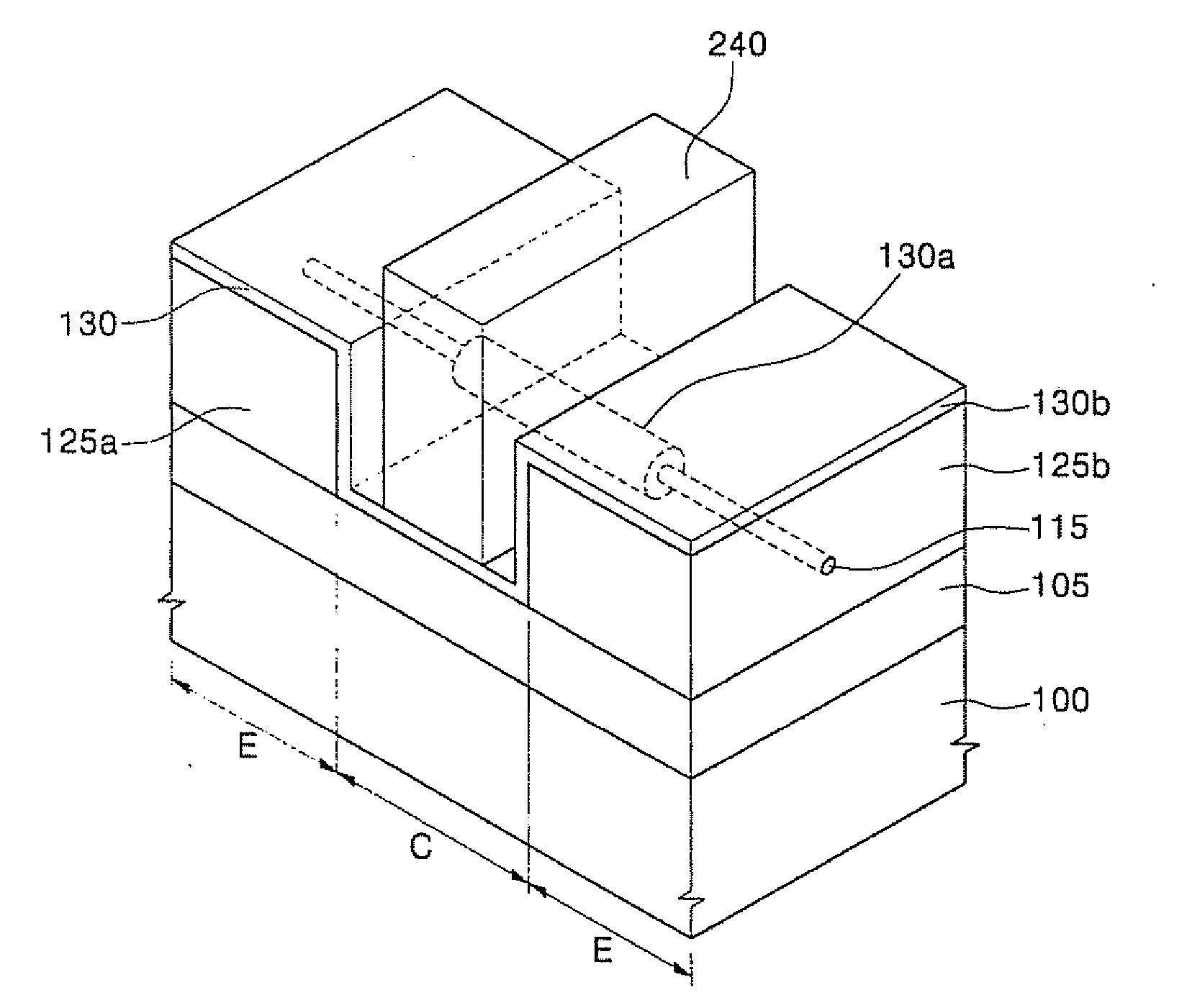
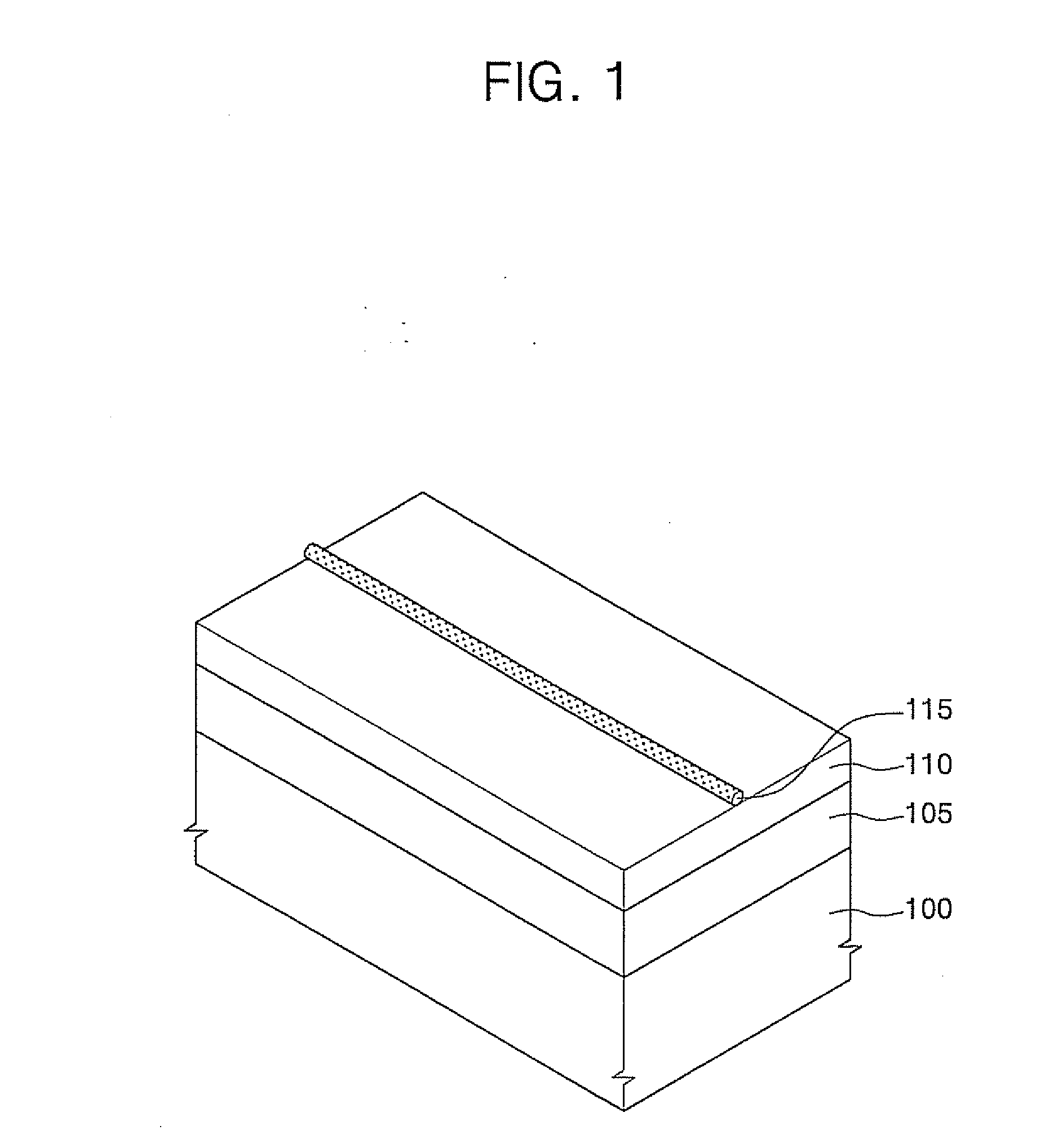
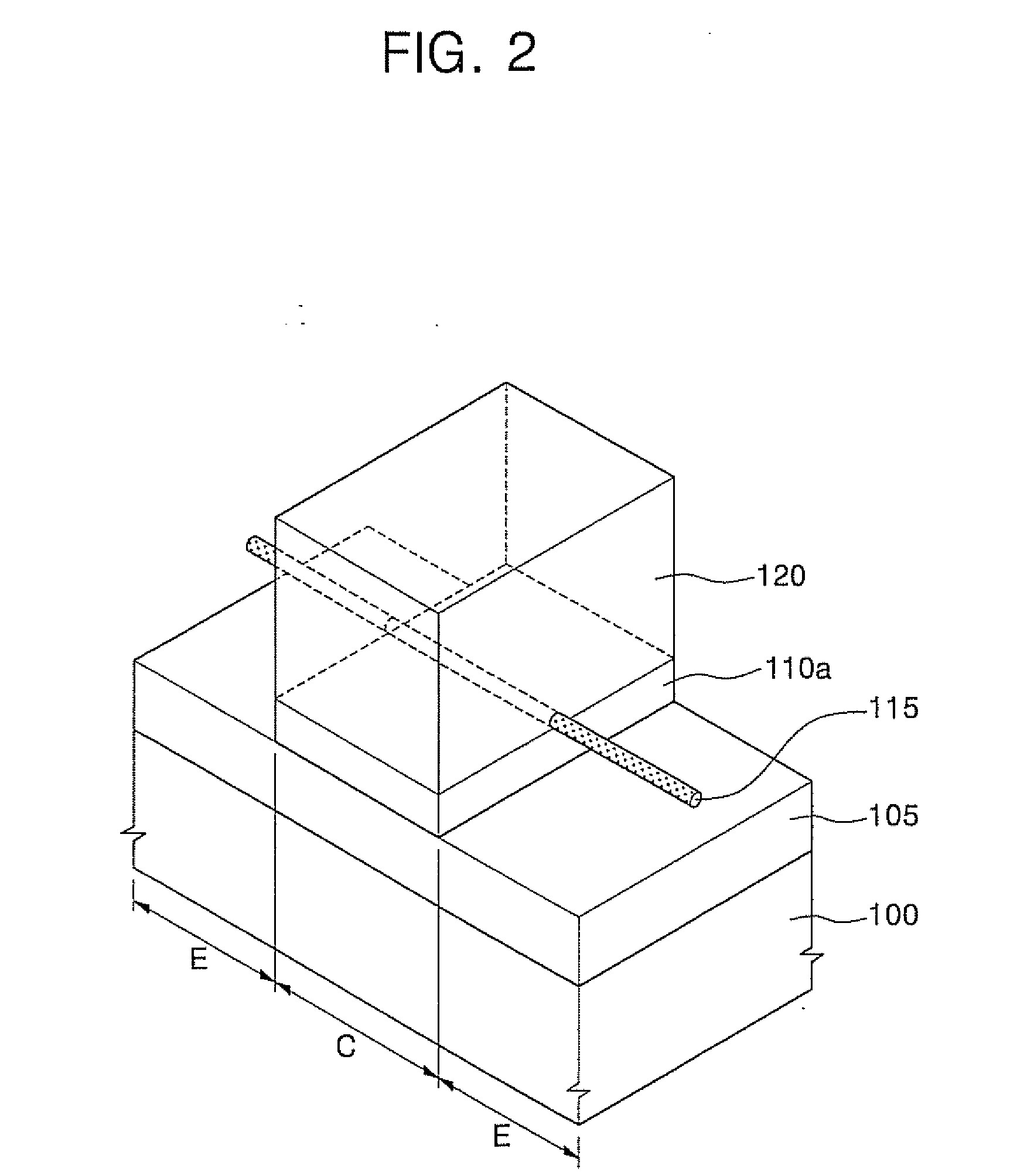
An object is to prevent an impurity such as moisture and oxygen from being mixed into an oxide semiconductor and suppress variation in semiconductor characteristics of a semiconductor device in which an oxide semiconductor is used. Another object is to provide a semiconductor device with high reliability. A gate insulating film provided over a substrate having an insulating surface, a source and a drain electrode which are provided over the gate insulating film, a first oxide semiconductor layer provided over the source electrode and the drain electrode, and a source and a drain region which are provided between the source electrode and the drain electrode and the first oxide semiconductor layer are provided. A barrier film is provided in contact with the first oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductive metal oxide thin film ferroelectric memory transistor
InactiveUS20060038242A1Simplify the manufacturing processHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention discloses a novel transistor structure employing semiconductive metal oxide as the transistor conductive channel. By replacing the silicon conductive channel with a semiconductive metal oxide channel, the transistors can achieve simpler fabrication process and could realize 3D structure to increase circuit density. The disclosed semiconductive metal oxide transistor can have great potential in ferroelectric non volatile memory device with the further advantages of good interfacial properties with the ferroelectric materials, possible lattice matching with the ferroelectric layer, reducing or eliminating the oxygen diffusion problem to improve the reliability of the ferroelectric memory transistor. The semiconductive metal oxide film is preferably a metal oxide exhibiting semiconducting properties at the transistor operating conditions, for example, In2O3 or RuO2. The present invention ferroelectric transistor can be a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductive metal oxide FET having a gate stack of a top metal electrode disposed on a ferroelectric layer disposed on a semiconductive metal oxide channel on a substrate. Using additional layer of bottom electrode and gate dielectric, the present invention ferroelectric transistor can also be a metal-ferroelectric-metal (optional)-gate dielectric (optional)-semiconductive metal oxide FET.
Owner:SHARP KK
Nanotube junctions
The present invention comprises a new nanoscale metal-semiconductor, semiconductor-semiconductor, or metal-metal junction, designed by introducing topological or chemical defects in the atomic structure of the nanotube. Nanotubes comprising adjacent sections having differing electrical properties are described. These nanotubes can be constructed from combinations of carbon, boron, nitrogen and other elements. The nanotube can be designed having different indices on either side of a junction point in a continuous tube so that the electrical properties on either side of the junction vary in a useful fashion. For example, the inventive nanotube may be electrically conducting on one side of a junction and semiconducting on the other side. An example of a semiconductor-metal junction is a Schottky barrier. Alternatively, the nanotube may exhibit different semiconductor properties on either side of the junction. Nanotubes containing heterojunctions, Schottky barriers, and metal-metal junctions are useful for microcircuitry.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semiconductive metal oxide thin film ferroelectric memory transistor
InactiveUS7378286B2Simplify the manufacturing processHigh densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention discloses a novel transistor structure employing semiconductive metal oxide as the transistor conductive channel. By replacing the silicon conductive channel with a semiconductive metal oxide channel, the transistors can achieve simpler fabrication process and could realize 3D structure to increase circuit density. The disclosed semiconductive metal oxide transistor can have great potential in ferroelectric non volatile memory device with the further advantages of good interfacial properties with the ferroelectric materials, possible lattice matching with the ferroelectric layer, reducing or eliminating the oxygen diffusion problem to improve the reliability of the ferroelectric memory transistor. The semiconductive metal oxide film is preferably a metal oxide exhibiting semiconducting properties at the transistor operating conditions, for example, In2O3 or RuO2. The present invention ferroelectric transistor can be a metal-ferroelectric-semiconductive metal oxide FET having a gate stack of a top metal electrode disposed on a ferroelectric layer disposed on a semiconductive metal oxide channel on a substrate. Using additional layer of bottom electrode and gate dielectric, the present invention ferroelectric transistor can also be a metal-ferroelectric-metal (optional)-gate dielectric (optional)-semiconductive metal oxide FET.
Owner:SHARP KK
Carbon nanotube gate field effect transistor
The present invention generally relates to an apparatus and method of carbon nanotube (CNT) gate field effect transistor (FET), which is used to replace the current metal gate of transistor for decreasing the gate width greatly. The carbon nanotube has its own intrinsic characters of metal and semiconductor, so it can be the channel, connector or next-level gate of transistor. Furthermore, the transistor has the structure of exchangeable source and drain, and can be defined the specificity by outside wiring.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
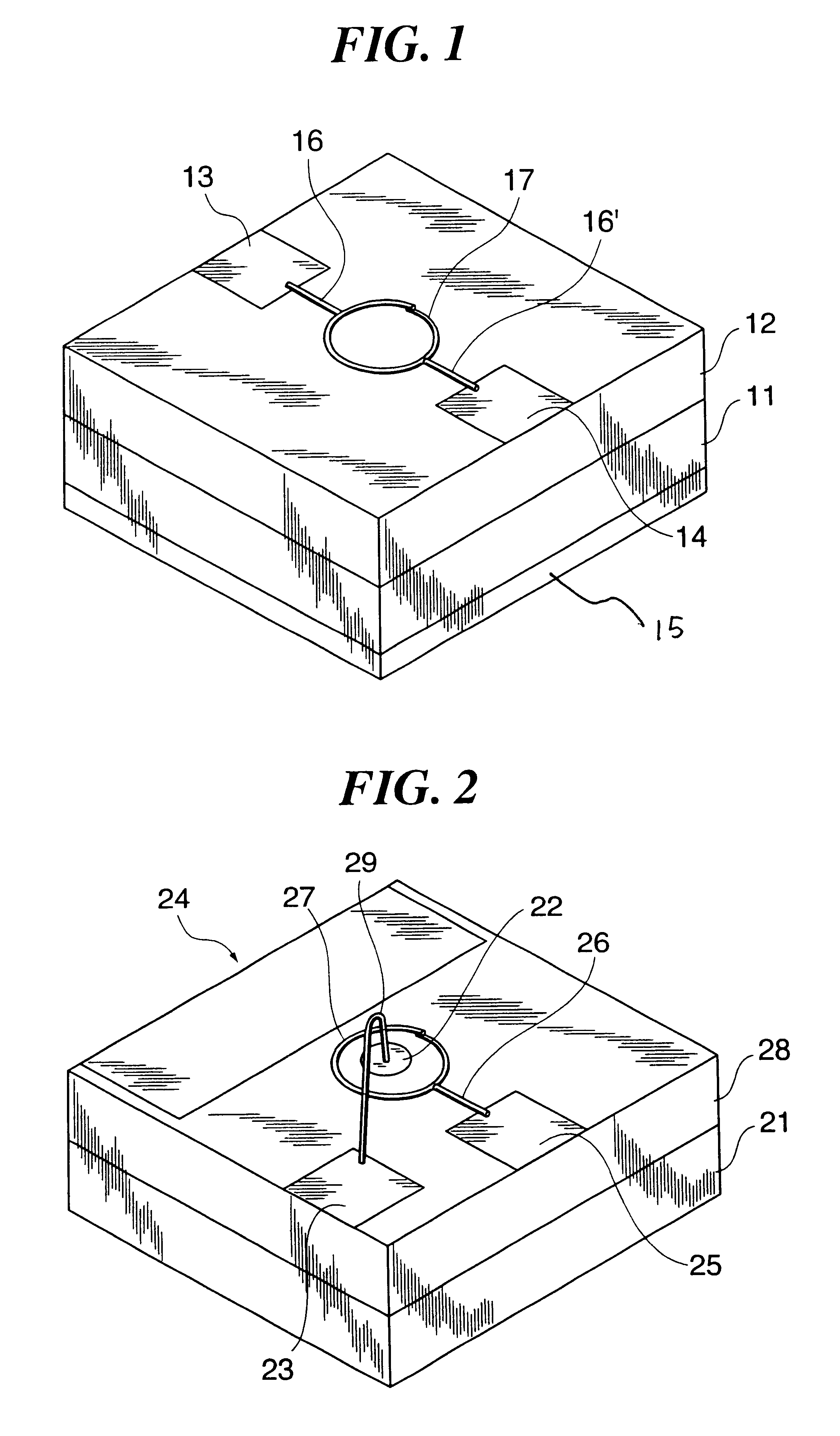
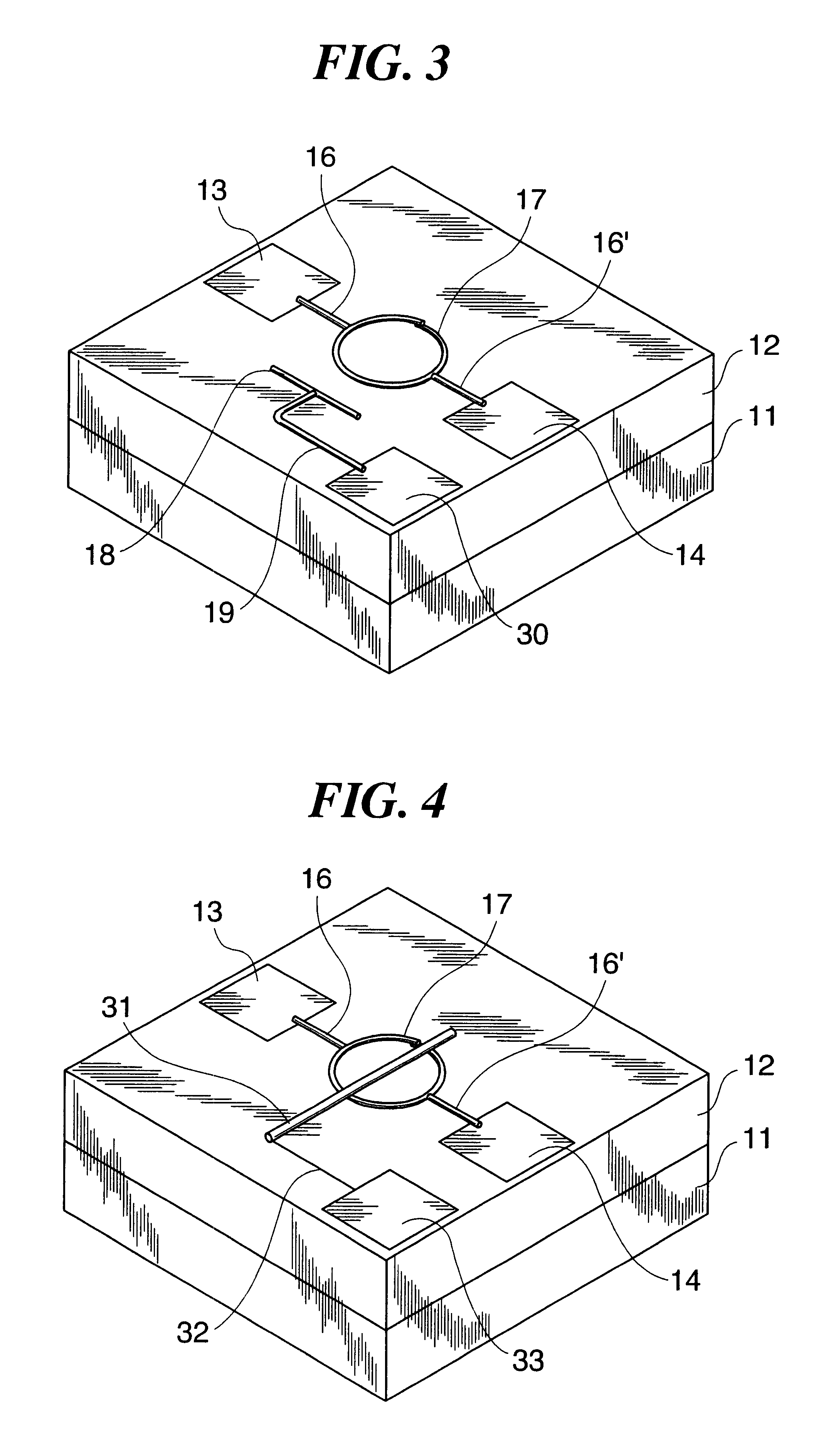
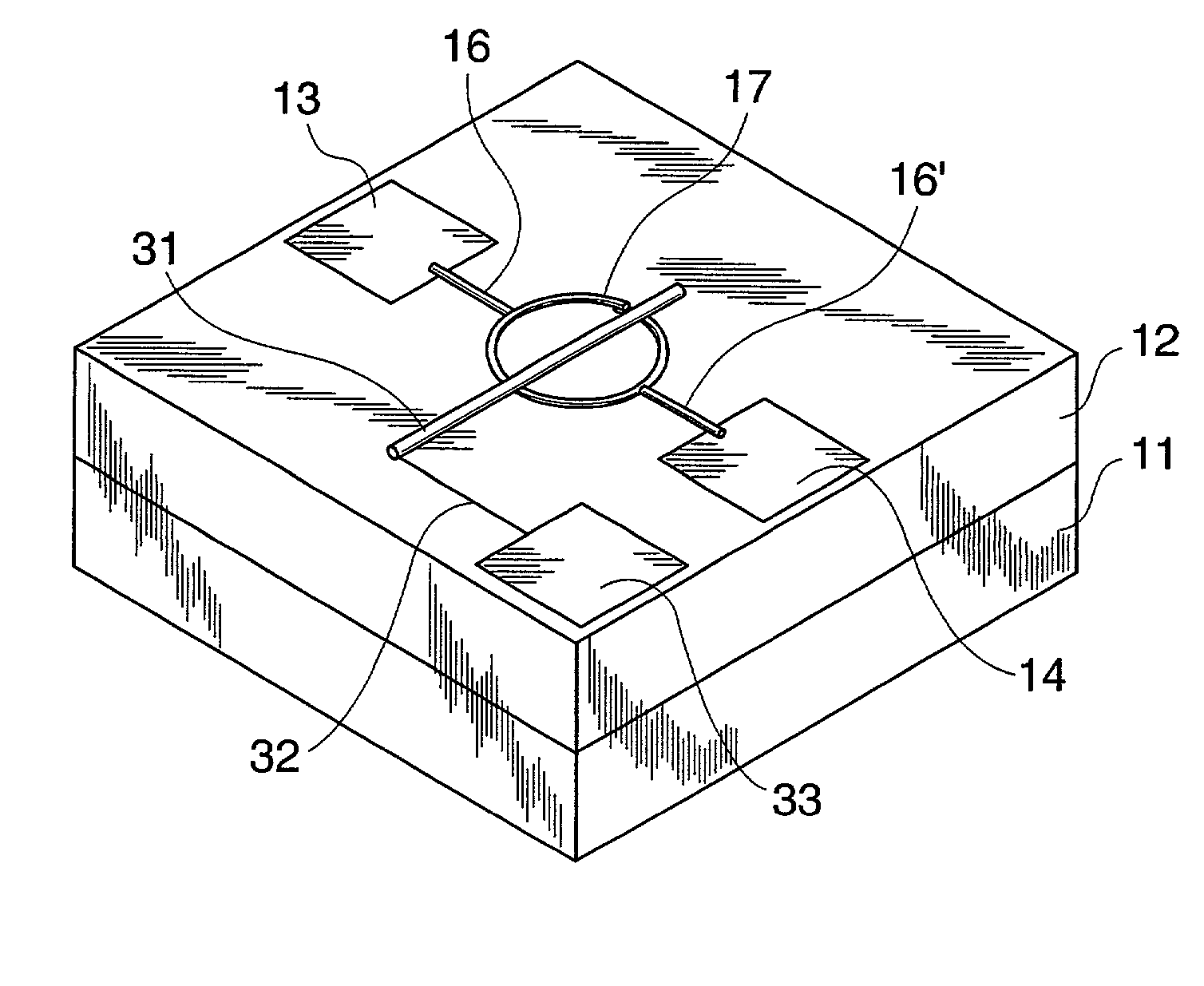
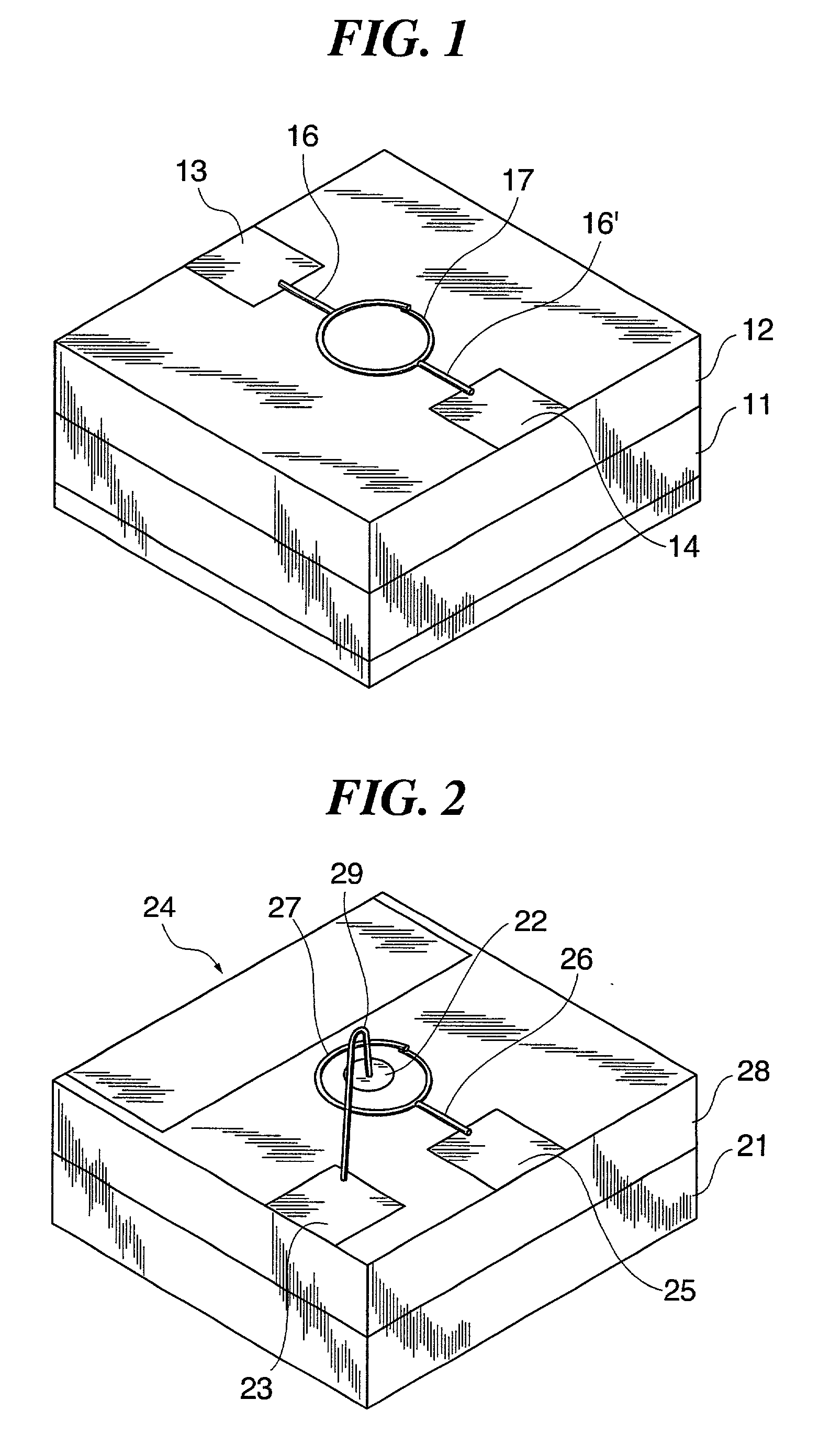
Transistor that uses carbon nanotube ring
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Transistor
A transistor of nanometer size is provided, which is capable of high-speed operation and operates at room temperatures by using carbon nanotubes for semiconductor devices. The transistor uses a carbon nanotube ring having semiconductor characteristics as a semiconductor material, or a carbon nanotube ring having conductivity or semiconductor characteristics as an electrode material.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
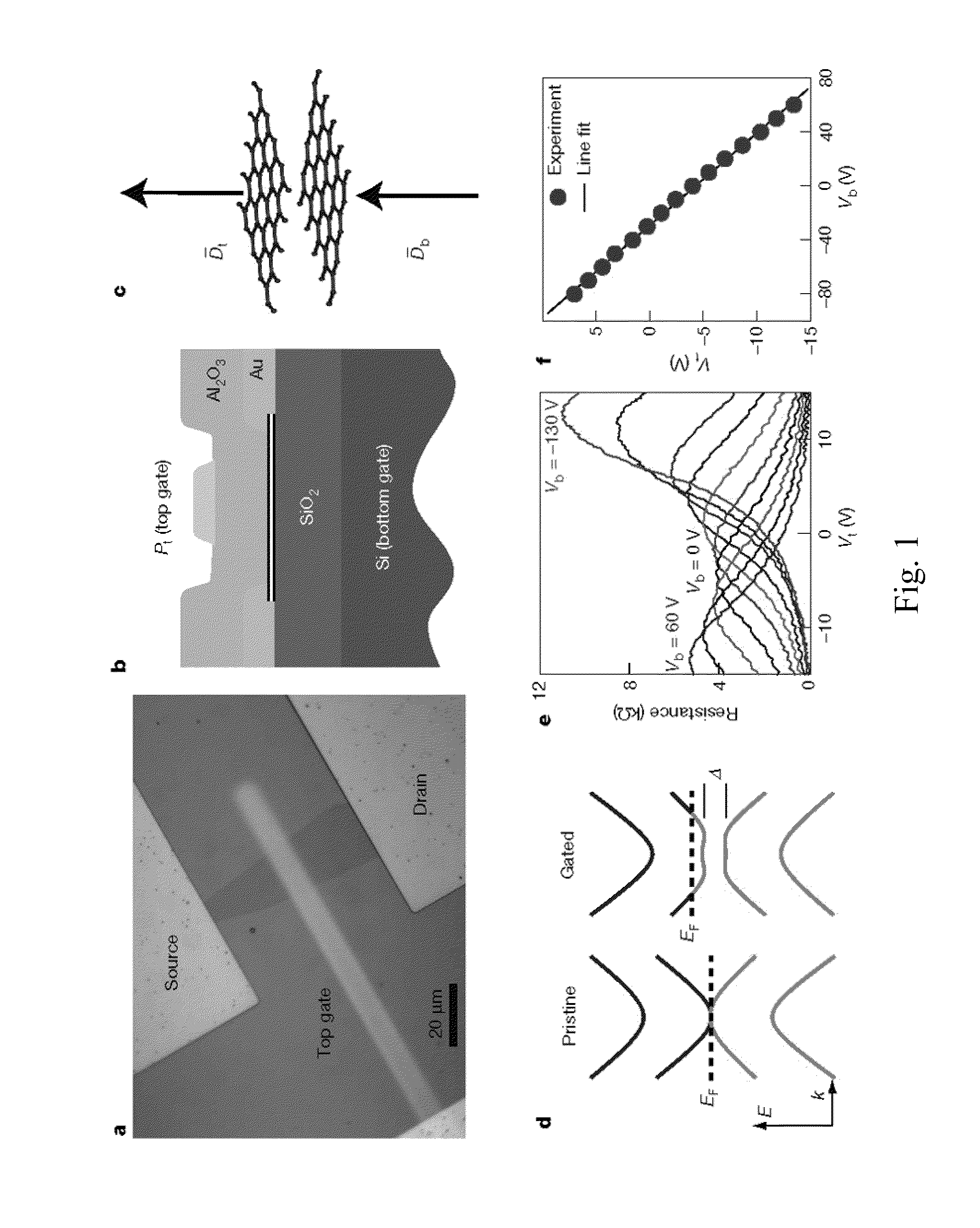
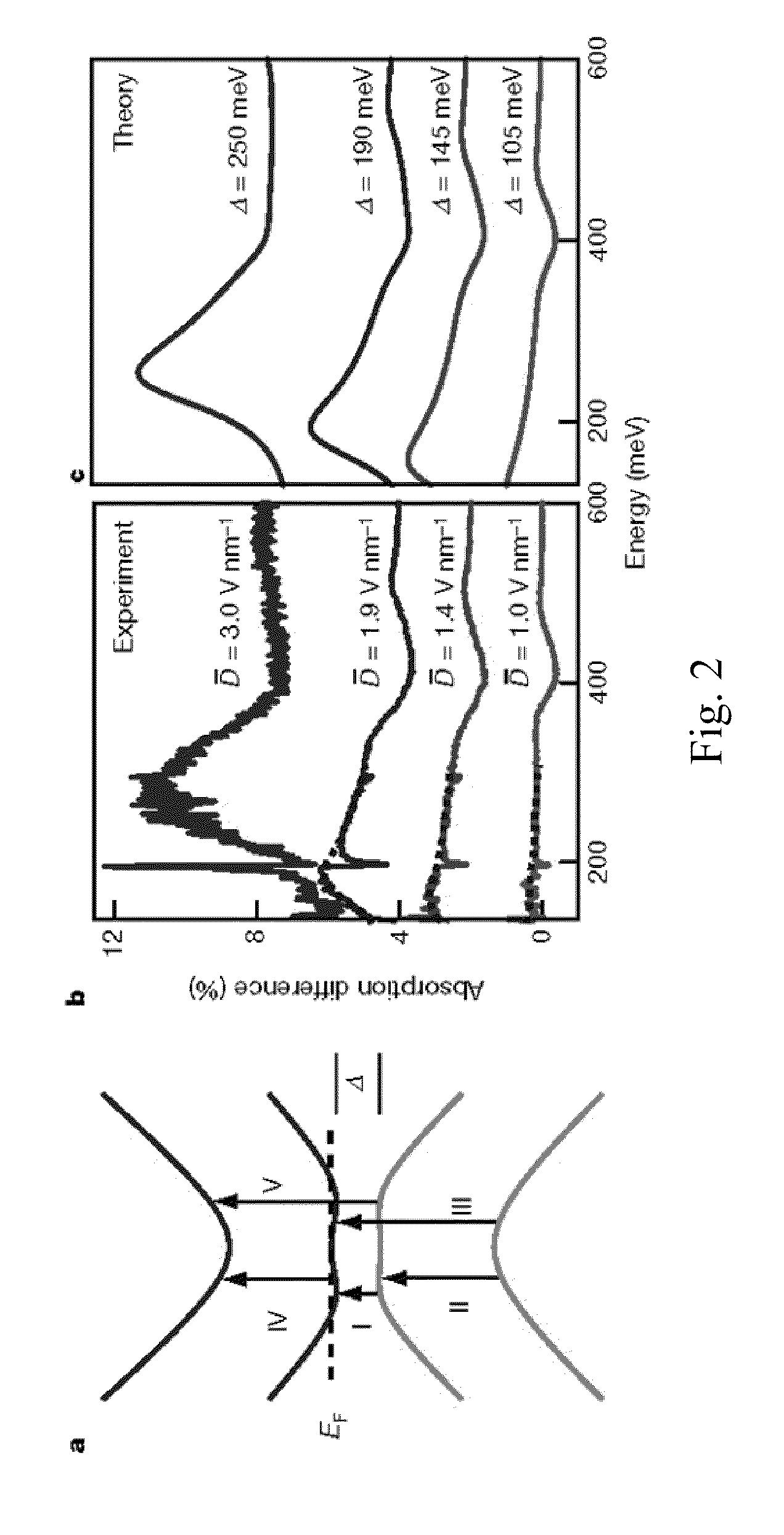
Graphene Device, Method of Investigating Graphene, and Method of Operating Graphene Device
InactiveUS20110006837A1Material analysis by optical meansElectric variable regulationBilayer grapheneSemiconductor properties
The present invention provides for a graphene device comprising: a first gate structure, a second gate structure that is transparent or semi-transparent, and a bilayer graphene coupled to the first and second gate structures, the bilayer graphene situated at least partially between the first and second gate structures. The present invention also provides for a method of investigating semiconductor properties of bilayer graphene and a method of operating the graphene device by producing a bandgap of at least 50 mV within the bilayer graphene by using the graphene device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for fabricating a biochip using the high density carbon nanotube film or pattern
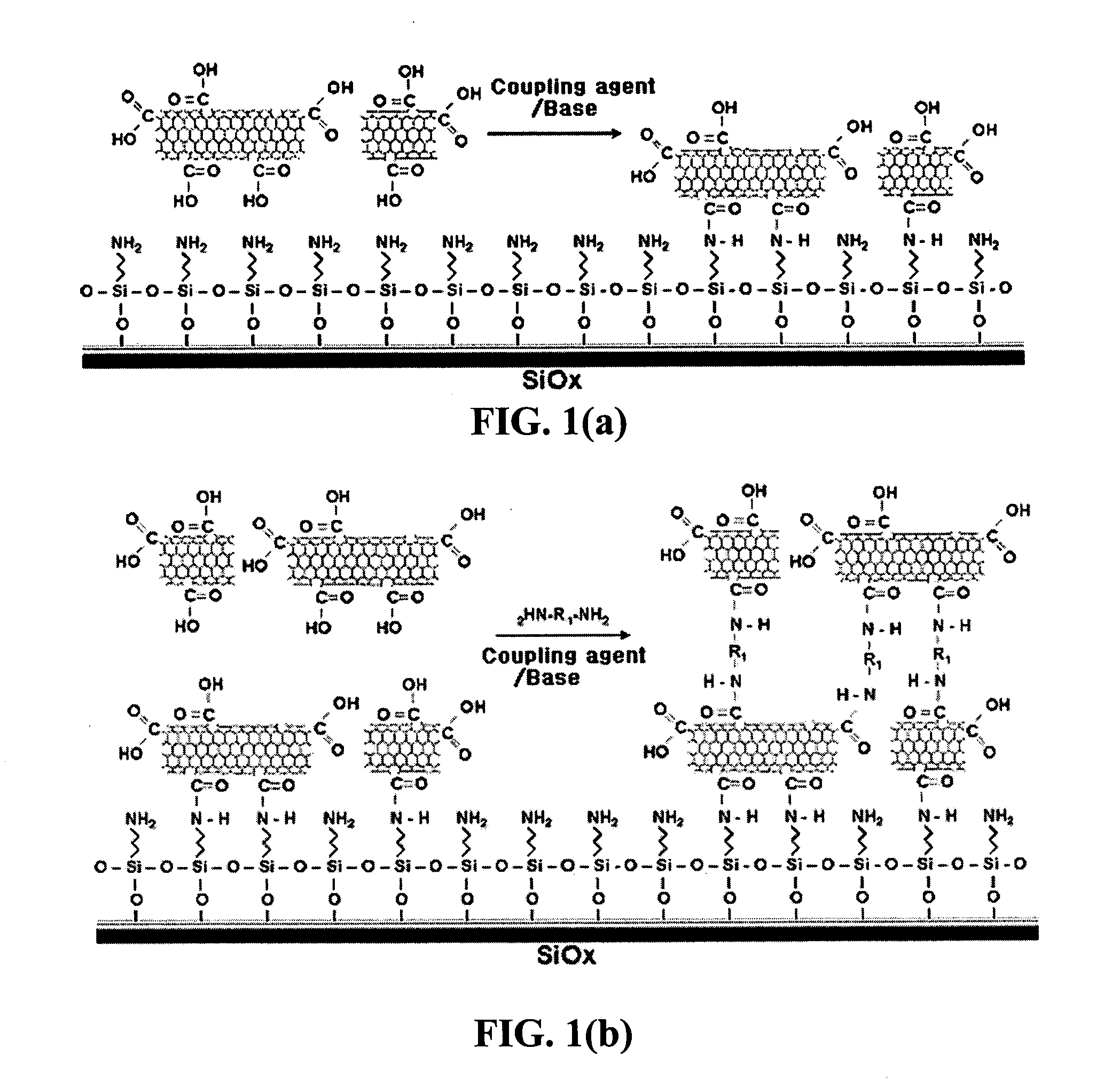
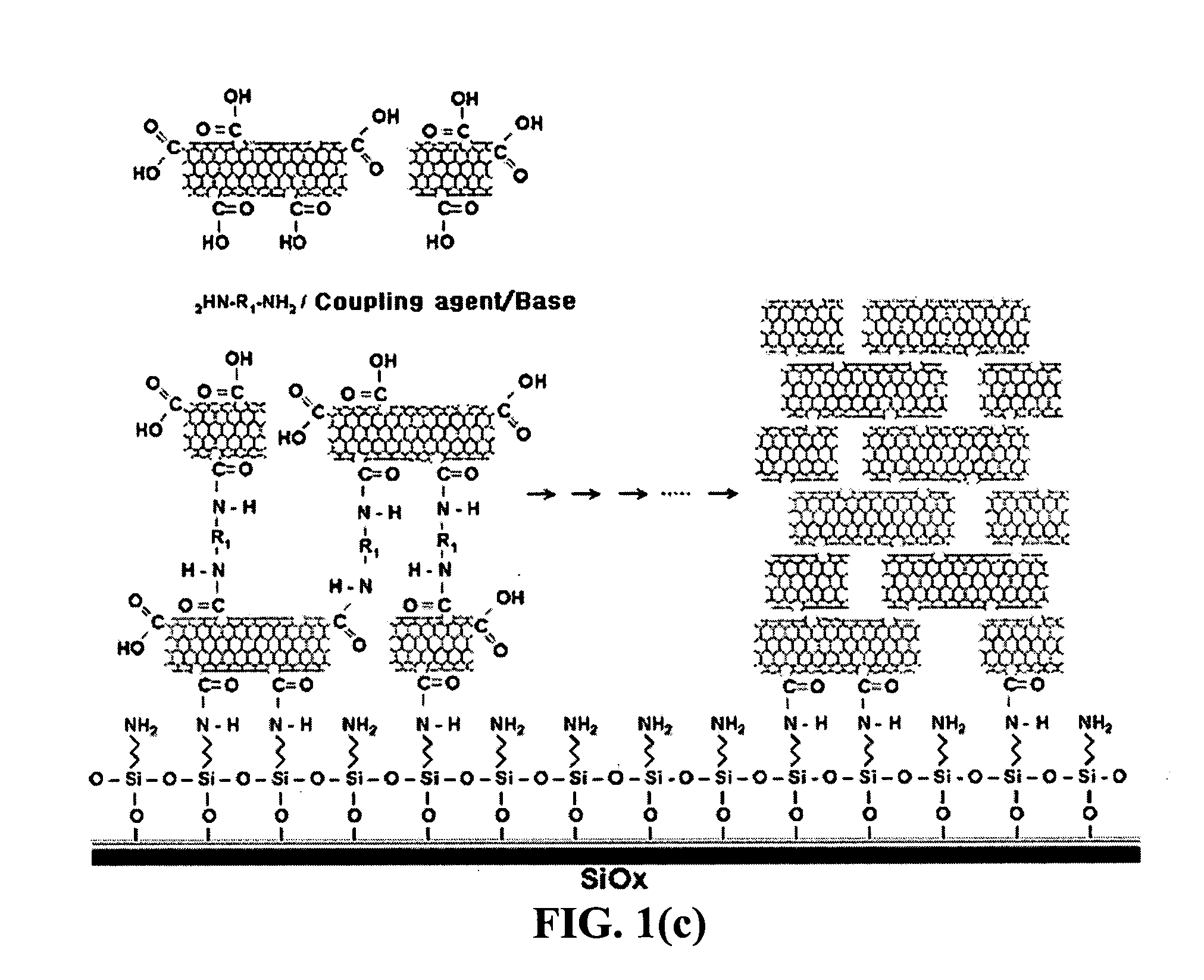
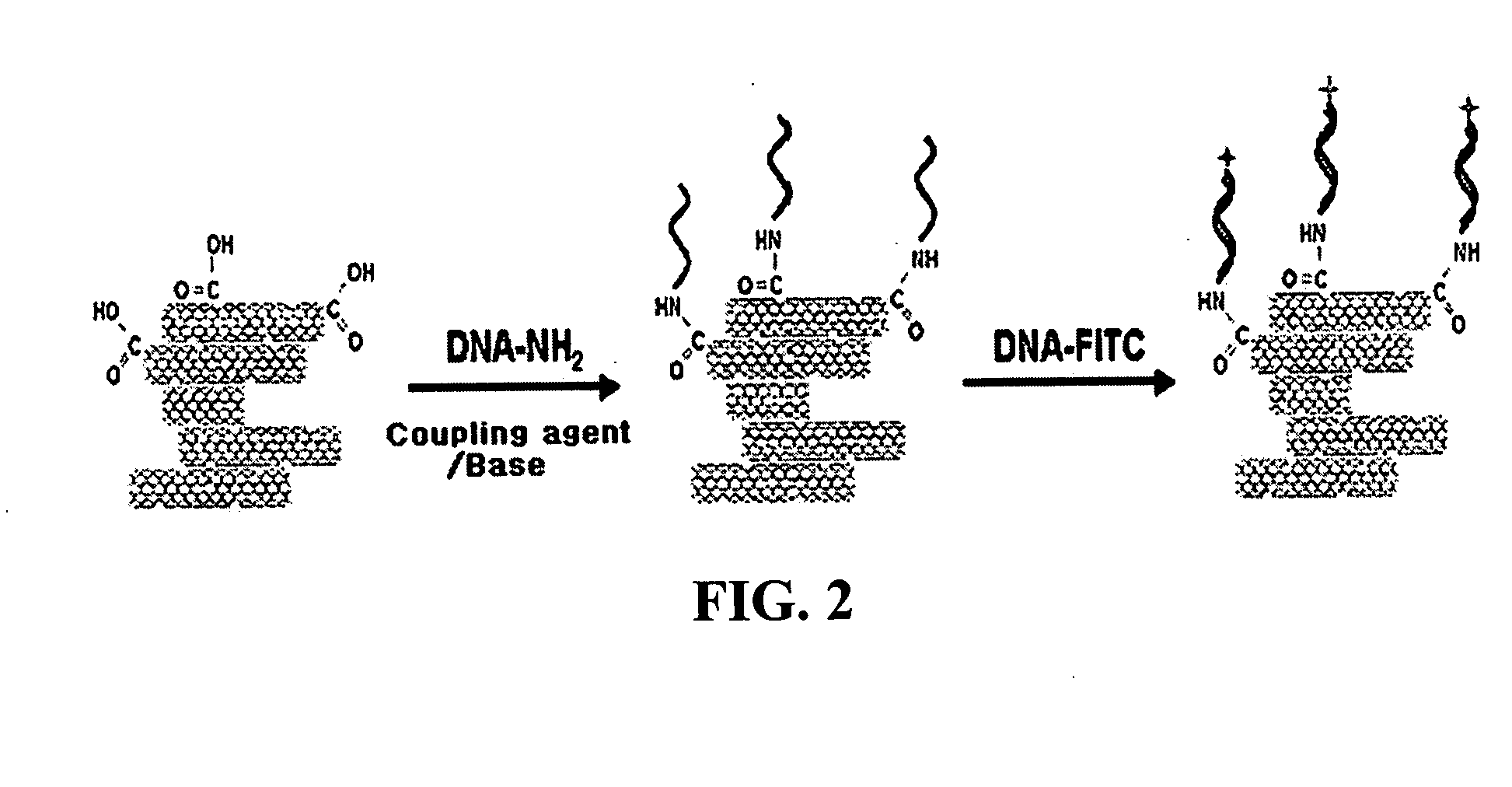
InactiveUS20050019791A1Improve defectsUtility and advantageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyElectrical conductorFluorescence
The present invention relates to a CNT-biochip comprising a bio-receptor which is attached by means of an exposed chemical functional group on a surface of a high density CNT film or pattern which is produced by laminating repeatedly carbon nanotubes (CNT) by chemical bond on the substrate modified with amine groups, and a method for fabricating the same. According to the present invention, it is possible to fabricate various types of CNT-biochips by chemical or physicochemical bonding of various bio-receptors to a CNT pattern (or film) containing exposed carboxyl groups or a CNT pattern (or film) modified by various chemical functional groups. Also, it is possible to fabricate a CNT-biochip comprising bio-receptors attached evenly with high density on a surface of a CNT film where chemical functional groups are abundant and present evenly. Further, the CNT-biochip is applicable to next generation biochips which measure an electrical or electrochemical signal using both conductor and semiconductor properties of the CNT, thereby not needing labeling. Particularly, upon fluorescent measurement of DNA hybridization using the CNT-DNA chip according to the present invention, it is possible to show more distinct signals, thereby producing excellent results. The CNT-DNA chip is useful for genotyping, mutation detection, pathogen identification and the like.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
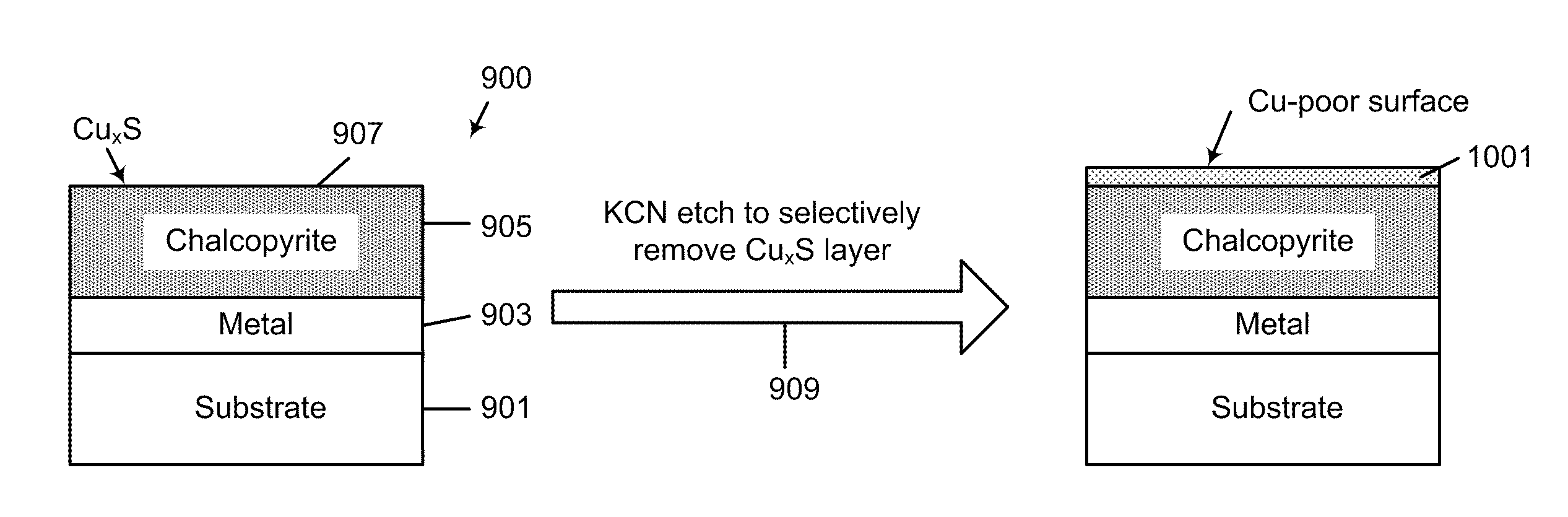
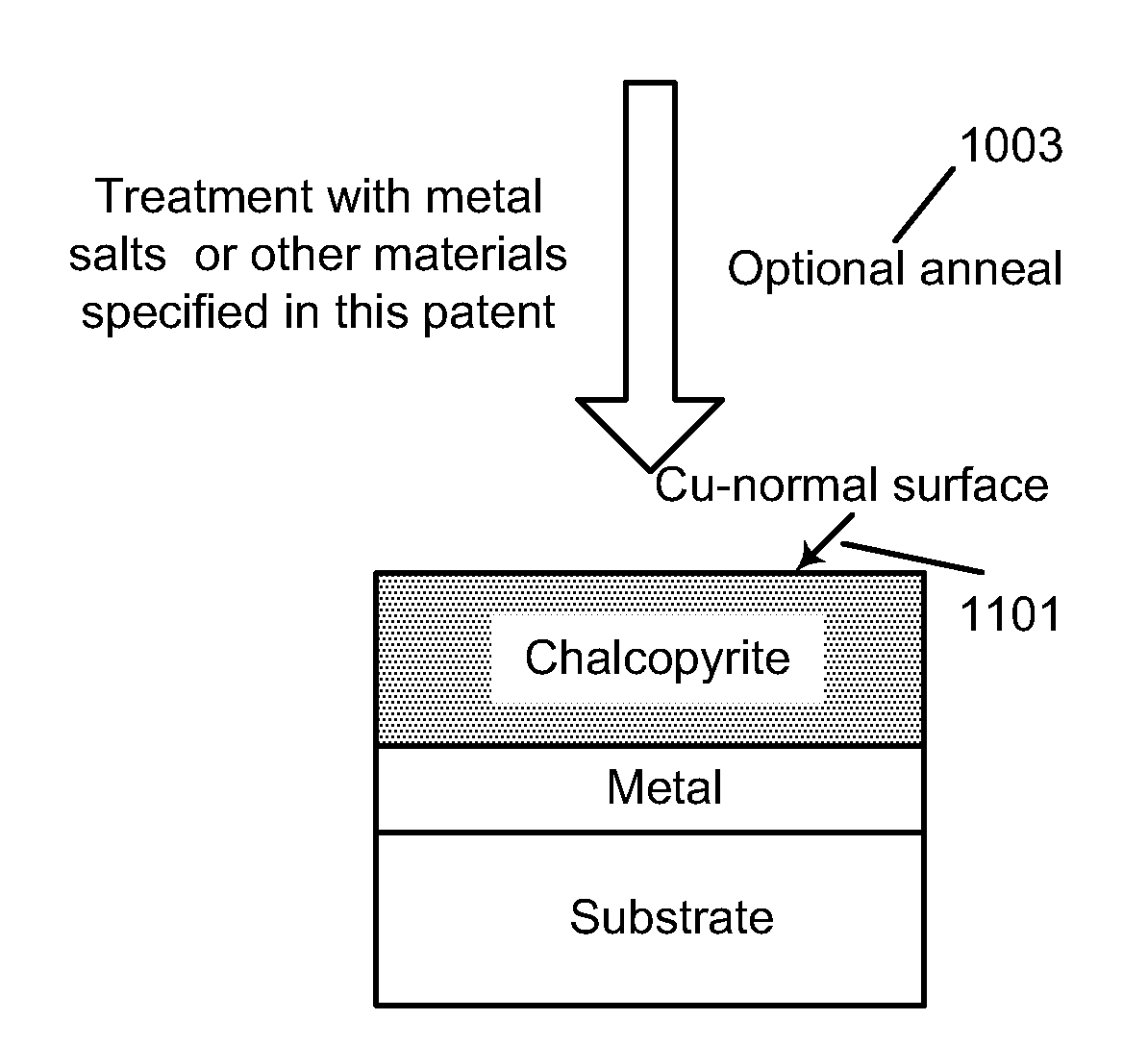
Sulfide species treatment of thin film photovoltaic cell and manufacturing method
ActiveUS8003430B1Toxic reductionAchieve benefitsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationIndiumSulfur
A method for forming a thin film photovoltaic device. The method includes providing a transparent substrate comprising a surface region, forming a first electrode layer overlying the surface region, forming a copper layer overlying the first electrode layer and forming an indium layer overlying the copper layer to form a multi-layered structure. The multi-layered structure is subjected to a thermal treatment process in an environment containing a sulfur bearing species to forming a copper indium disulfide material. The copper indium disulfide material comprising a copper-to-indium atomic ratio ranging from about 1.2:1 to about 2:1 and a thickness of substantially copper sulfide material having a copper sulfide surface region. The thickness of the copper sulfide material is selectively removed to expose a surface region having a copper poor surface comprising a copper to indium atomic ratio of less than about 0.95:1. The method subjects the copper poor surface to a sulfide species to convert the copper poor surface from an n-type semiconductor characteristic to a p-type semiconductor characteristic. A window layer is formed overlying the copper indium disulfide material.
Owner:CM MFG
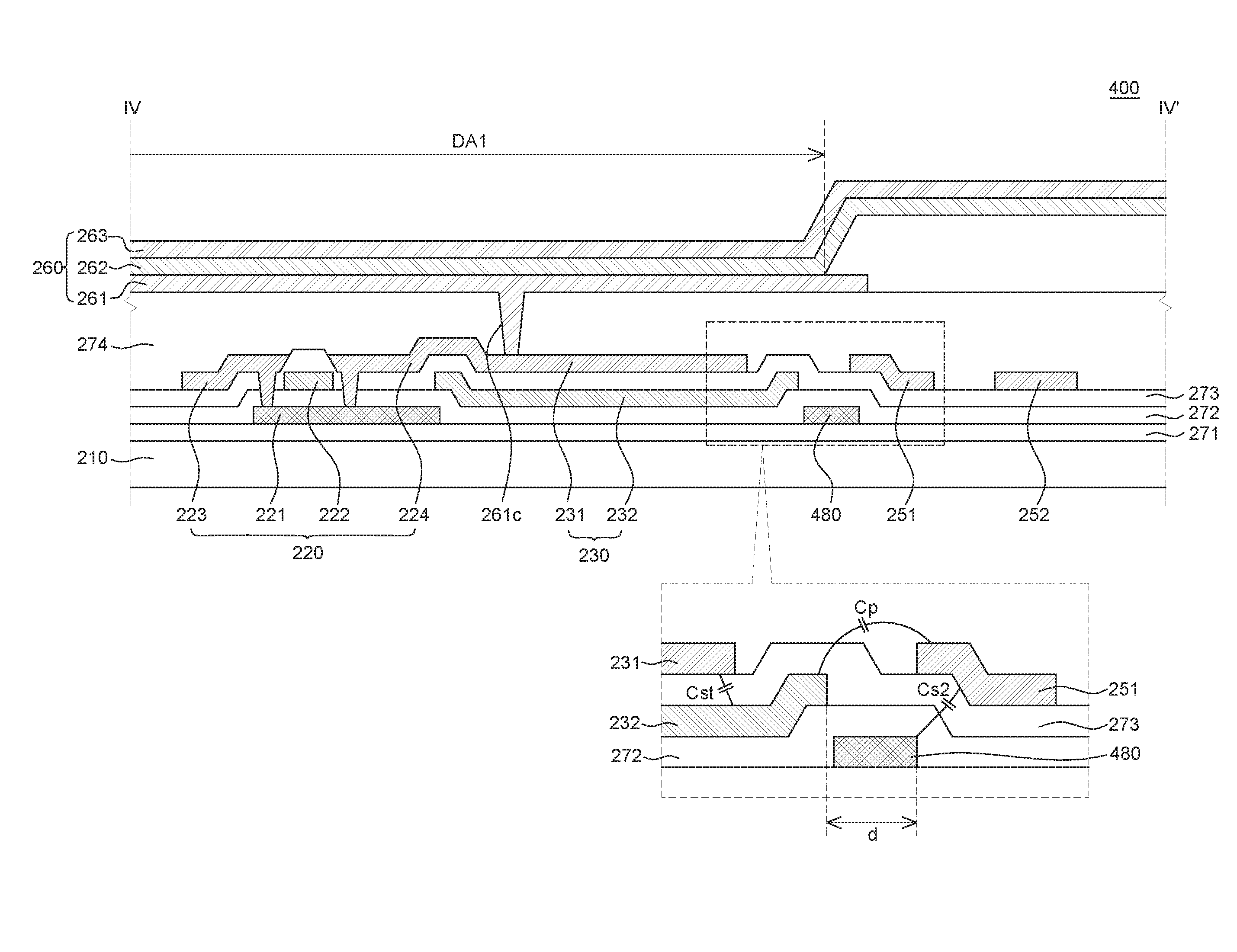
Array substrate and manufacturing method thereof as well as display equipment
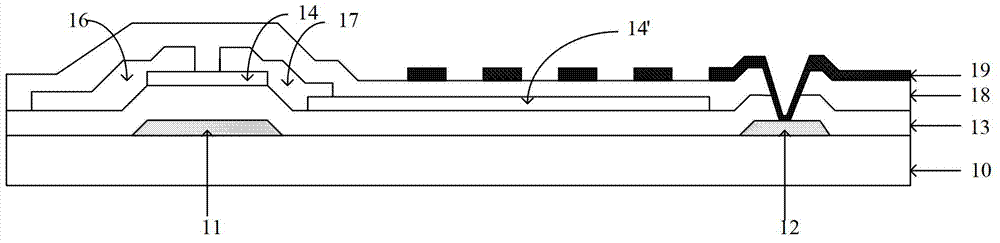
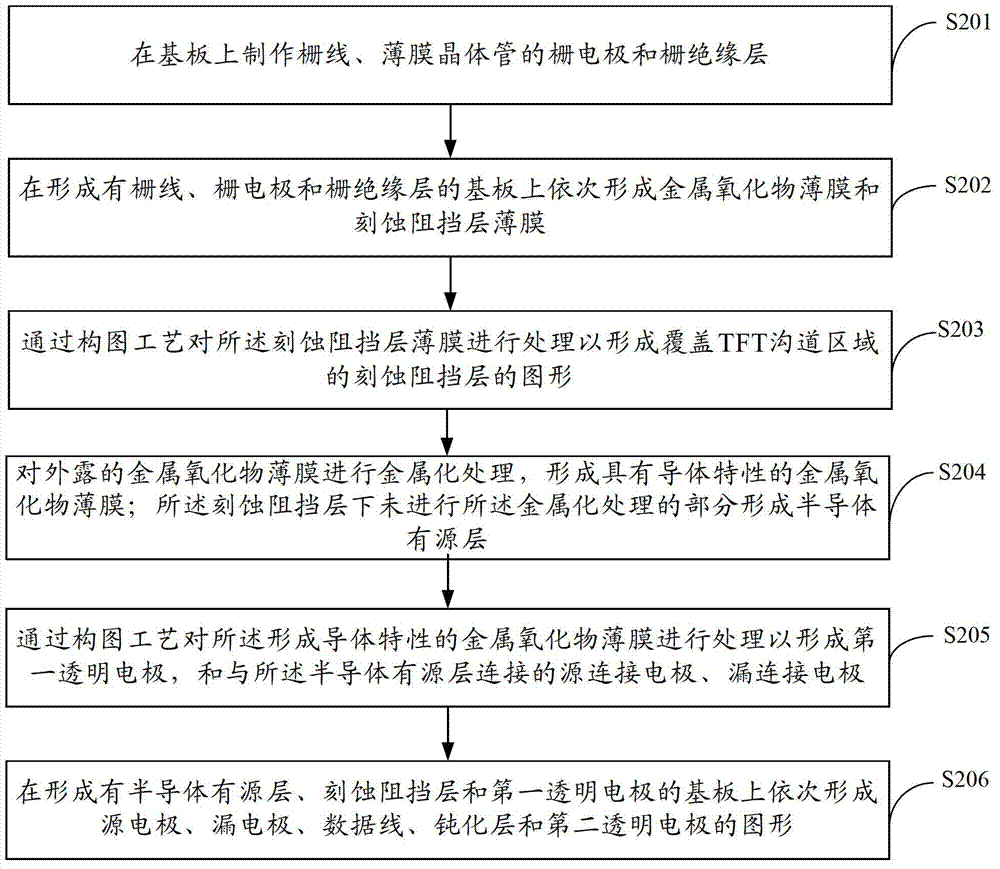
InactiveCN102790012AOmit stepsReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displayMulti dimensional
The embodiment of the invention discloses an array substrate and a manufacturing method thereof as well as display equipment, which belong to the technical field of liquid crystal displays and are used for lowering manufacturing cost. The manufacturing method comprises manufacturing processes of a film transistor, a first transparent electrode and a second transparent electrode; the first and the second transparent electrodes generate a multi-dimensional electric field; the manufacturing process of the first transparent electrode comprises formation of a metallic oxide film which has characteristics of a semiconductor; and the first transparent electrode is formed via a metalizing process of a part of the metallic oxide film, a semi-conductor active layer is formed by the rest of the metallic oxide film, which is executed for metalizing process. The manufacturing method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention is applicable to manufacturing of the liquid crystal displays.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
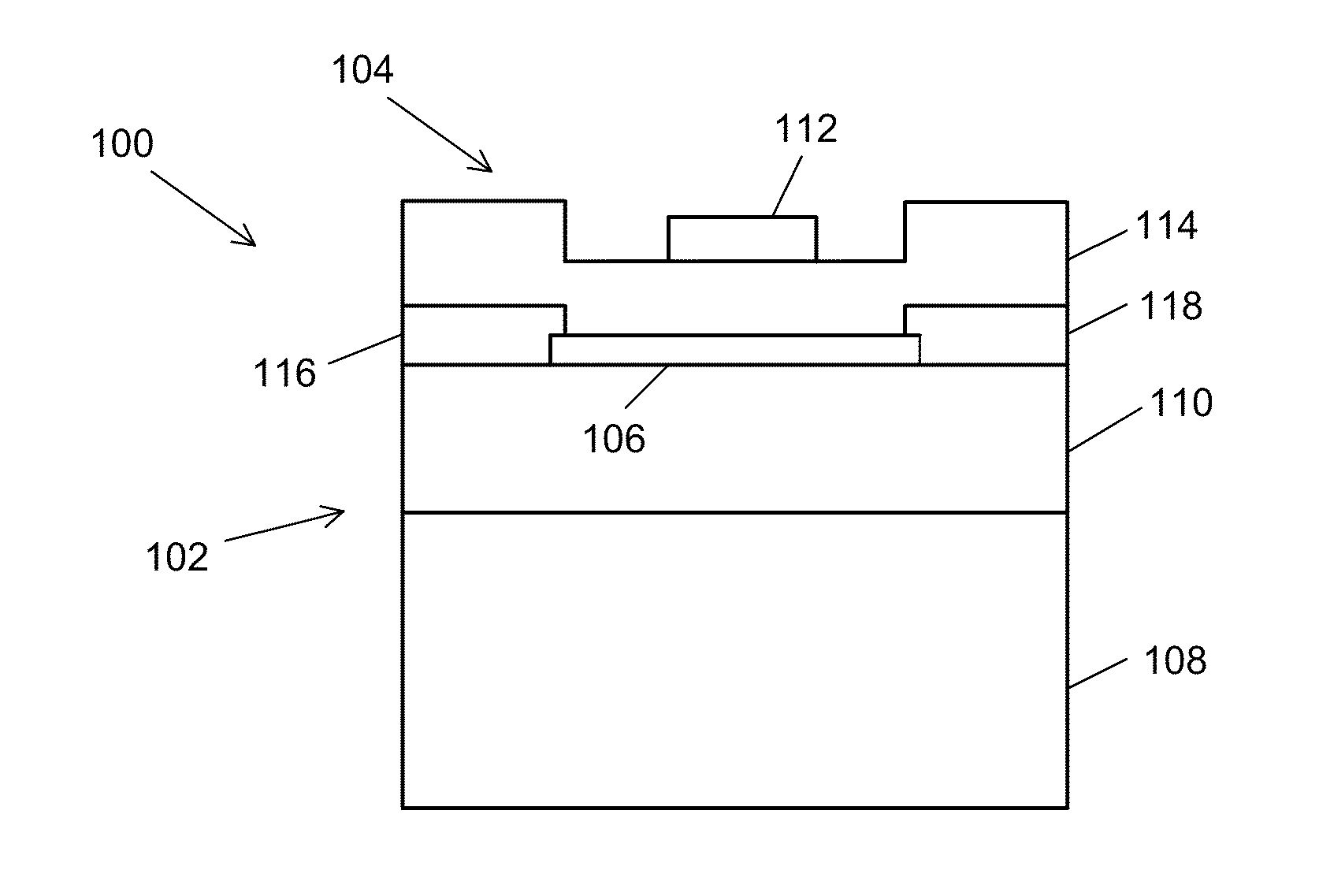
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS8502216B2Suppress mutationSuppress oxidation-reduction reactionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenMoisture
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
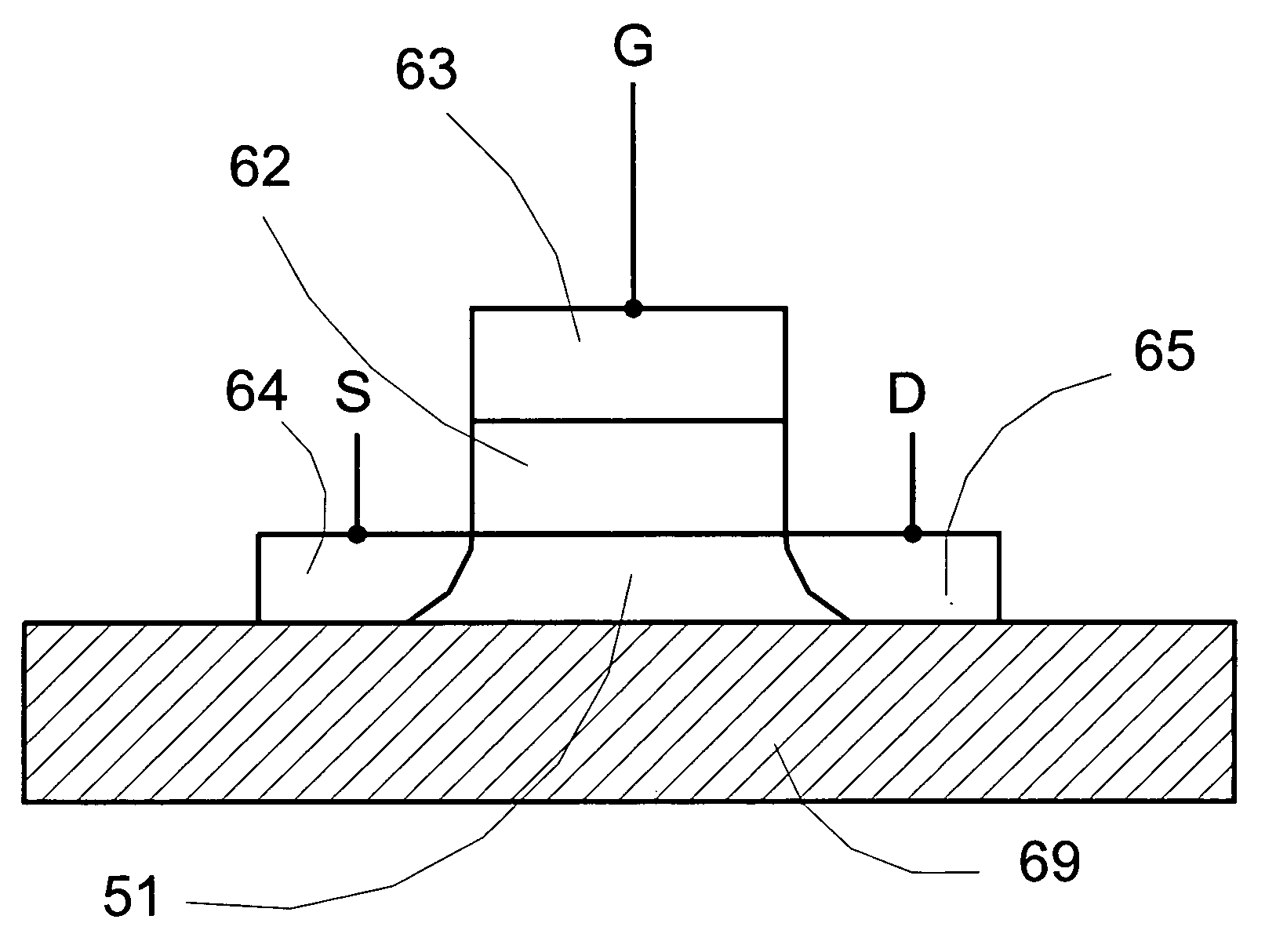
Semiconductor Devices Having Nano-Line Channels and Methods of Fabricating the Same
A semiconductor device includes a substrate, a gate electrode on the substrate and source and drain electrodes disposed at respective sides of the gate electrode. The device further includes a nano-line passing through the gate electrode and extending into the source and drain electrodes and having semiconductor characteristics. The nano-line may include a nano-wire and / or a nano-tube. A gate insulating layer may be interposed between the nano-line and the gate electrode. The source and drain electrodes may be disposed adjacent respective opposite sidewalls of the gate electrode, and the gate insulating layer may be further interposed between the source and drain electrodes and the gate electrode. Fabrication methods for such devices are also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Core/shell nanoparticles suitable for(f)ret-assays
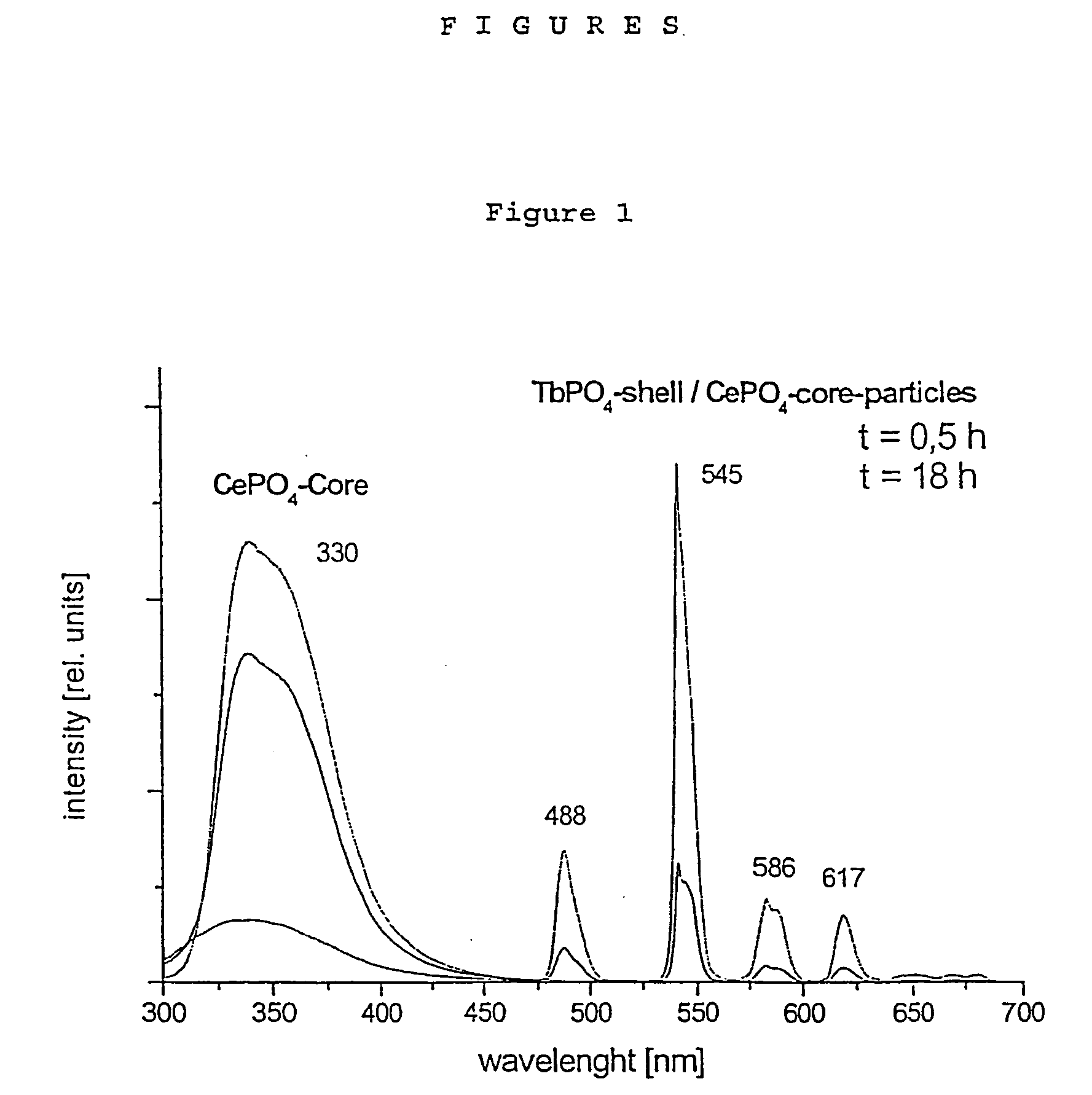
The present invention relates to luminescent inorganic nanoparticles comprising (a) a core made from a first metal salt or oxide being surrounded by (b) a shell made from a second metal salt or oxide being luminescent and having non-semiconductor properties. These particles can be advantageously used in (fluorescence) resonance energy transfer ((F)RET)-based bioassays in view of their higher (F)RET efficiency.
Owner:CENT FUR ANGEWANDTE NANOTECH
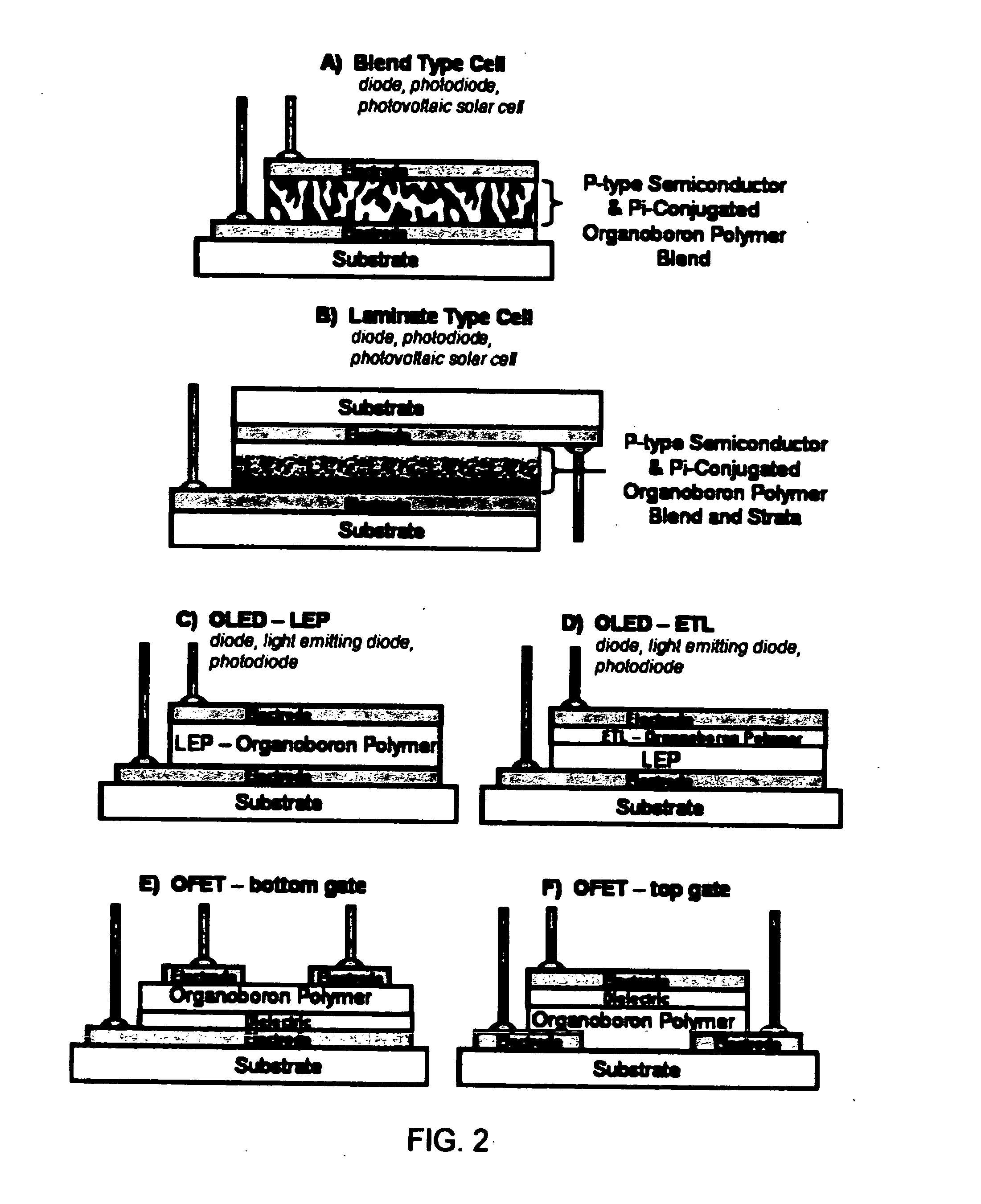
Use of pi-conjugated organoboron polymers in thin-film organic polymer electronic devices
InactiveUS20070215864A1Improve propertiesImproved propertyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotoluminescenceOrganic field-effect transistor
Pi-conjugated organoboron polymers for use in thin-film organic polymer electronic devices. The polymers contain aromatic and or unsaturated repeat units and boron atoms. The vacant p-orbital of the boron atoms conjugate with the pi-conjugated orbital system of the aromatic or unsaturated monomer units extending the pi-conjugation length of the polymer across the boron atoms. The pi-conjugated organoboron polymers are electron-deficient and, therefore, exhibit n-type semiconducting properties, photoluminescence, and electroluminescence. The invention provides thin-film organic polymer electronic devices, such as organic photovoltaic cells (OPVs), organic diodes, organic photodiodes, organic thin-film transistors (TFTs), organic field-effect transistors (OFETs), printable or flexible electronics, such as radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags, electronic papers, and printed circuit elements, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs), and energy storage devices employing the pi-conjugated organoboron polymers. In OLED and PLED applications these materials are used as the electron transport layer (ETL) to improve device efficiency. The polymers which exhibit photo- and electroluminescence are also useful as light-emitting material in PLEDs.
Owner:TDA RES
Method for reducing dielectric overetch using a dielectric etch stop at a planar surface
ActiveUS20060216937A1Prevent excessive dielectric overetchReducing dielectric overetchSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeDielectricNitride
A substantially planar surface coexposes conductive or semiconductor features and a dielectric etch stop material. A second dielectric material, different from the dielectric etch stop material, is deposited on the substantially planar surface. A selective etch etches a hole or trench in the second dielectric material, so that the etch stops on the conductive or semiconductor feature and the dielectric etch stop material. In a preferred embodiment the substantially planar surface is formed by filling gaps between the conductive or semiconductor features with a first dielectric such as oxide, recessing the oxide, filling with a second dielectric such as nitride, then planarizing to coexpose the nitride and the conductive or semiconductor features.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Electroric device, integrated circuit, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060118777A1Improve productivityFirm patternTransistorIndividual molecule manipulationCross-linkTransport layer
The present invention provides an electronic device including a transporting layer which involves a low environmental load and which is excellent in semiconductor characteristics by means of a configuration having, on the surface of a base body, at least a transporting layer constituted by a carbon nanotube structure layer having a network structure in which a plurality of carbon nanotubes mutually cross-link. Also, provided is a method of manufacturing the same.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Device and method for growng large diameter 6H-SiC monocrystal with semiconductor property
ActiveCN1554808ALarge crystalsFor the purpose of dopingPolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsEngineeringSingle crystal
The present invention relates to apparatus and method of growing great diameter 6H-SiC monocrystal with semiconductor characteristic and belongs to the field of crystal growing technology. The apparatus includes growing chamber, water cooler on the side wall of the growing chamber, graphite crucible, heat insulating material, induction heating system, cylindrical vapor guiding plate of Ta inside the crucible, and cylinder. Regulating the position of the crucible relative to the inducing coil can minimize the temperature at the crystal seed inside the crucible and increase the temperature field distribution in the growing direction. Altering the atmosphere composition or material compounding can obtain great diameter SiC monocrystal with n-type, p-type or semi-insulating type semiconductor characteristic. By means of selecting the Si plane of the crystal seed and growing temperature, the crystal form may be controlled and 6H-SiC may be obtained.
Owner:SICC CO LTD
Transparent multi-tactile sensor
InactiveUS20100117974A1Increase manufacturing costEasy to implementInput/output processes for data processingTouch SensesElectrical battery
The disclosure relates to a transparent multi-tactile sensor including a transparent semi-conducting active layer provided between two transparent conducting layers arranged as an array of cells formed by the intersection of rows and columns, characterised in that it comprises a control circuit successively supplying each semi-conducting portion corresponding to a cell, said control circuit including a means for analyzing the variation in the electrical characteristics due to the deformation of one or more sensor areas, each area including one or more cells, the semi-conducting characteristic of said intermediate layer making said cells independent from the measuring circuit.
Owner:STANTUM
Crystalline semiconductor film, plate-like body and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20170200790A1Maintain good propertiesAvoid leakage currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumSemiconductor structure
A semiconductor film, a sheet like object, and a semiconductor device are provided that have inhibited semiconductor properties, particularly leakage current, and excellent withstand voltage and heat dissipation. A crystalline semiconductor film or a sheet like object includes a corundum structured oxide semiconductor as a major component, wherein the film has a film thickness of 1 μm or more. Particularly, the semiconductor film or the object includes a semiconductor component of oxide of one or more selected from gallium, indium, and aluminum as a major component. A semiconductor device has a semiconductor structure including the semiconductor film or the object.
Owner:FLOSFIA
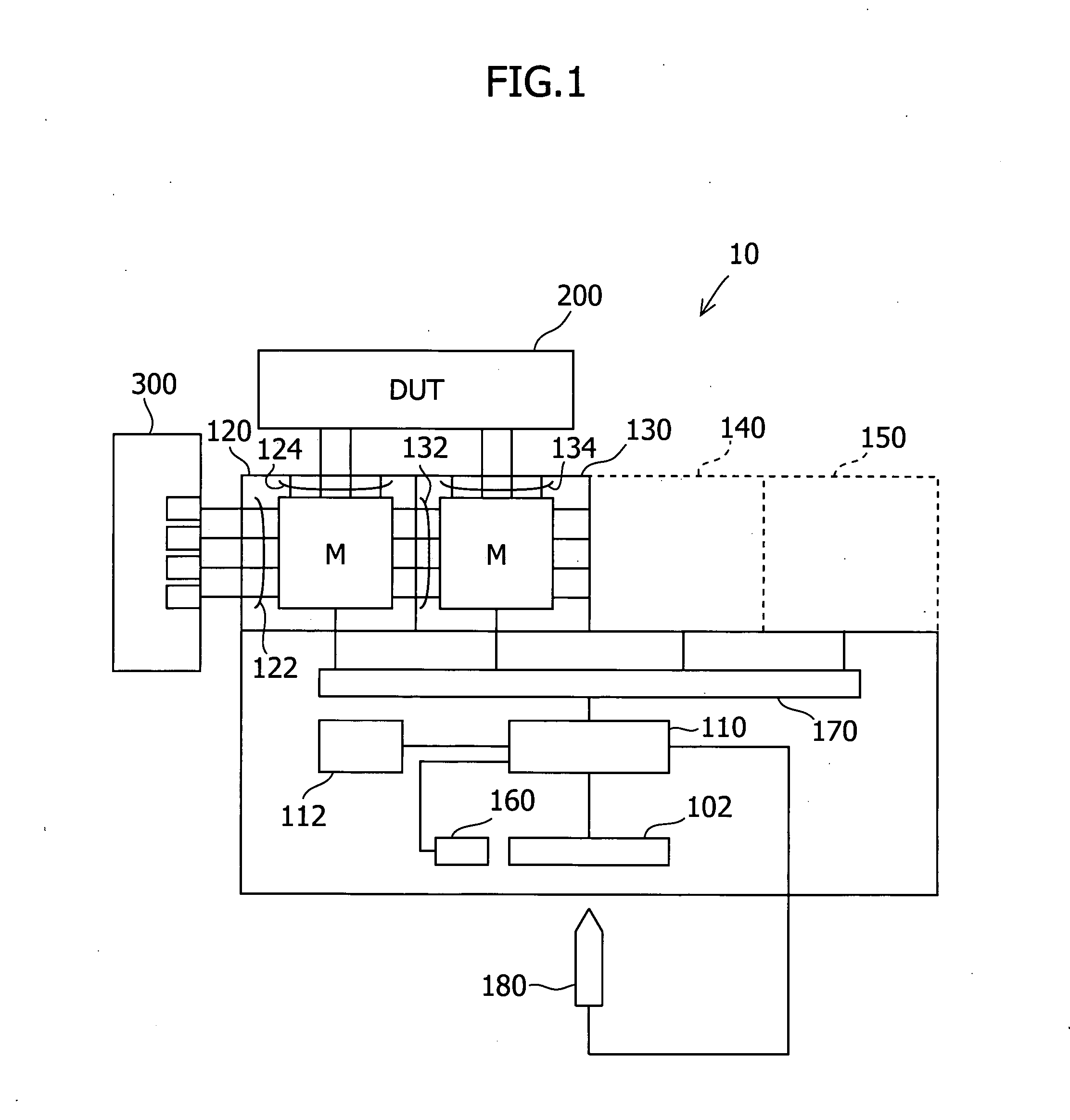
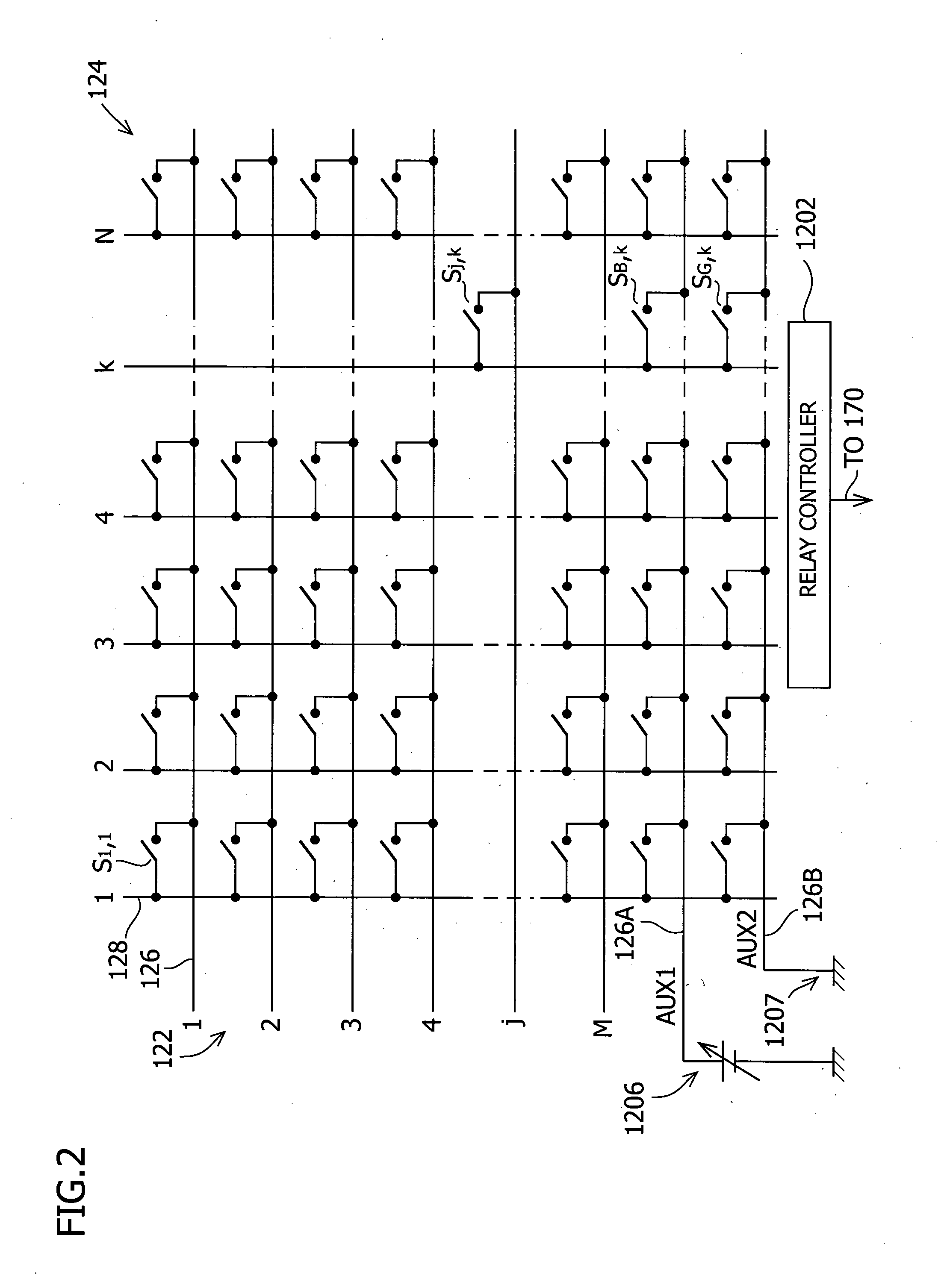
Switching matrix apparatus for semiconductor characteristic measurement apparatus
InactiveUS20060114243A1Shorten the overall cycleAddressing slow performanceElectrical testingCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectricityElectrical connection
The switching matrix apparatus is provided with a plurality of relay switches for opening and closing the electrical connections between a plurality of input terminals and a plurality of output terminals, and a display unit in which a plurality of light-emitting portions are arranged in a matrix in correspondence with the respective relay switches and in which indicators indicating the positions of the light-emitting portions in at least multiple columns and rows are displayed along at least two sides of the light-emitting portions arranged in a matrix. In order to facilitate confirmation of the position of a light-emitting portion that is about to be selected or has been selected with a light pen on the display unit, light is emitted by at least one other light-emitting portion relating to the light-emitting portion that is about to be selected or has been selected.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
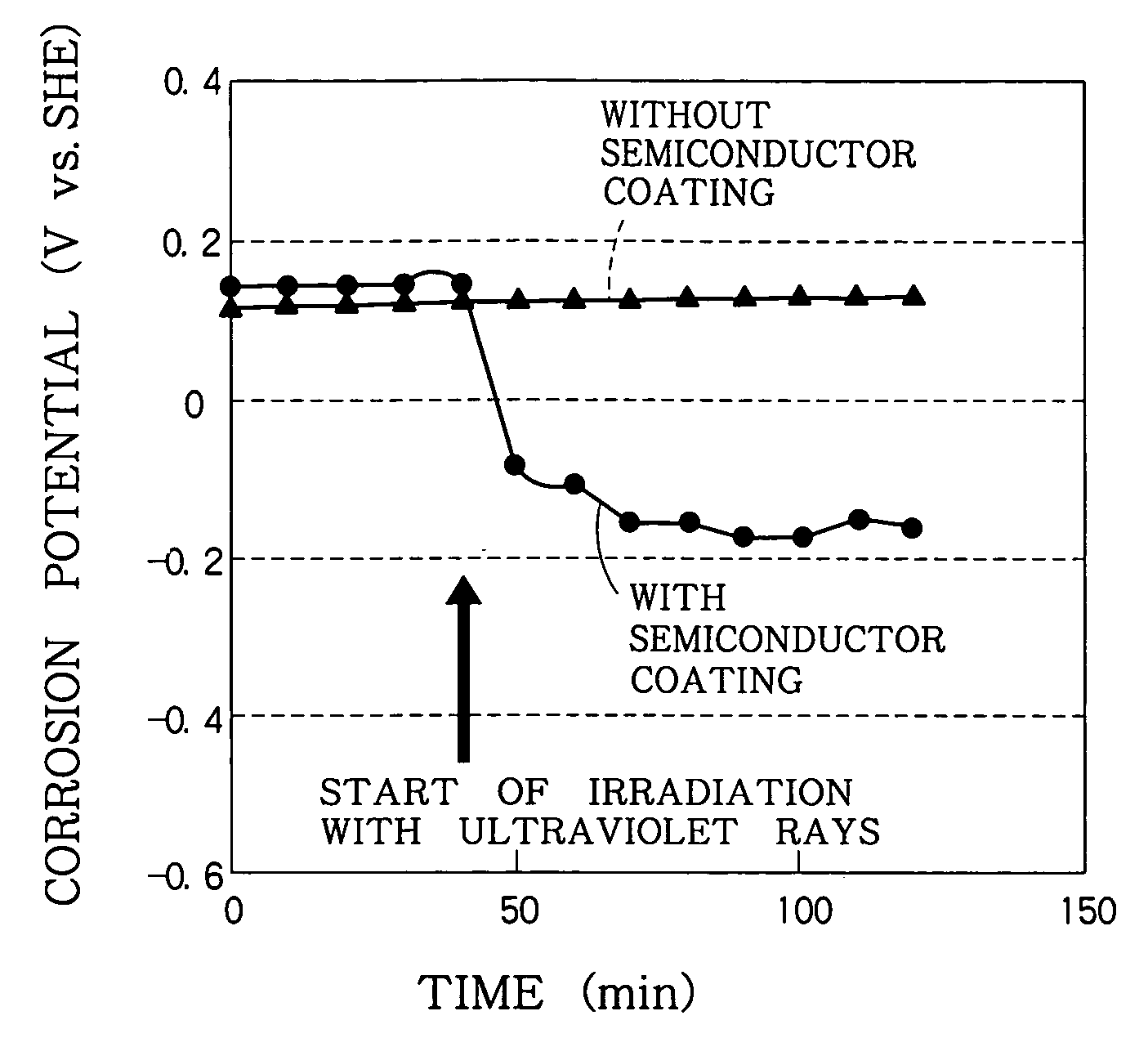
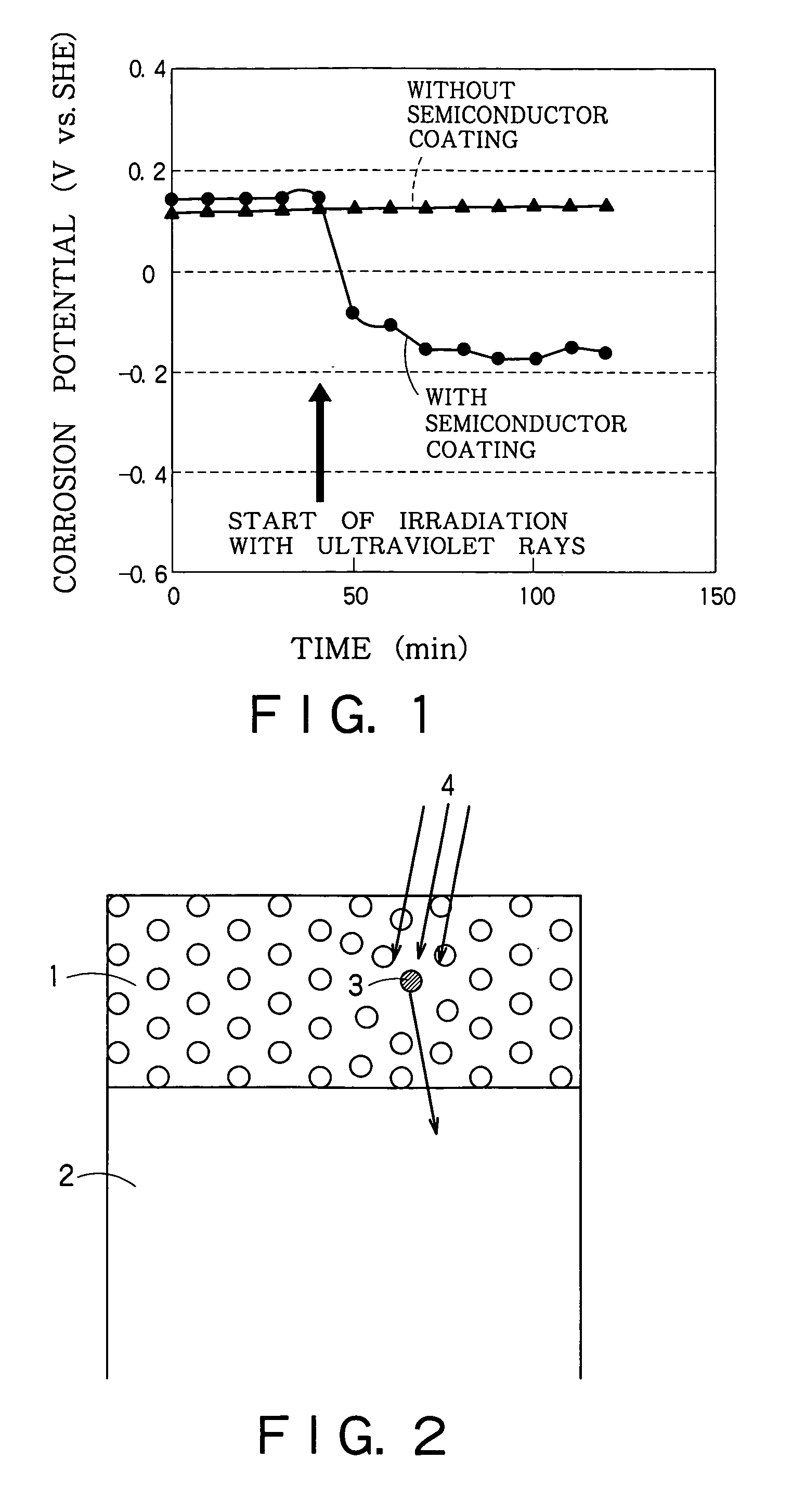
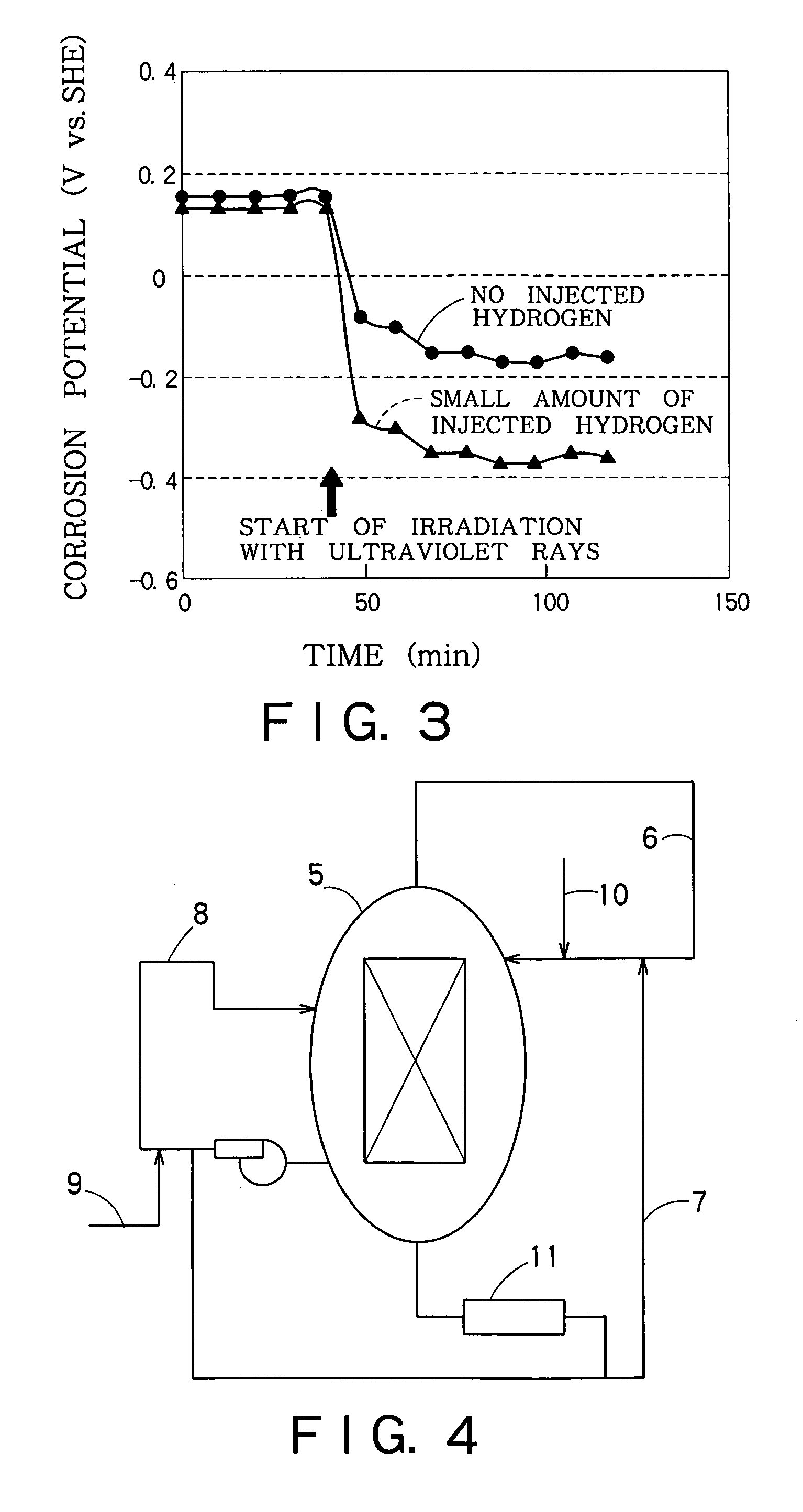
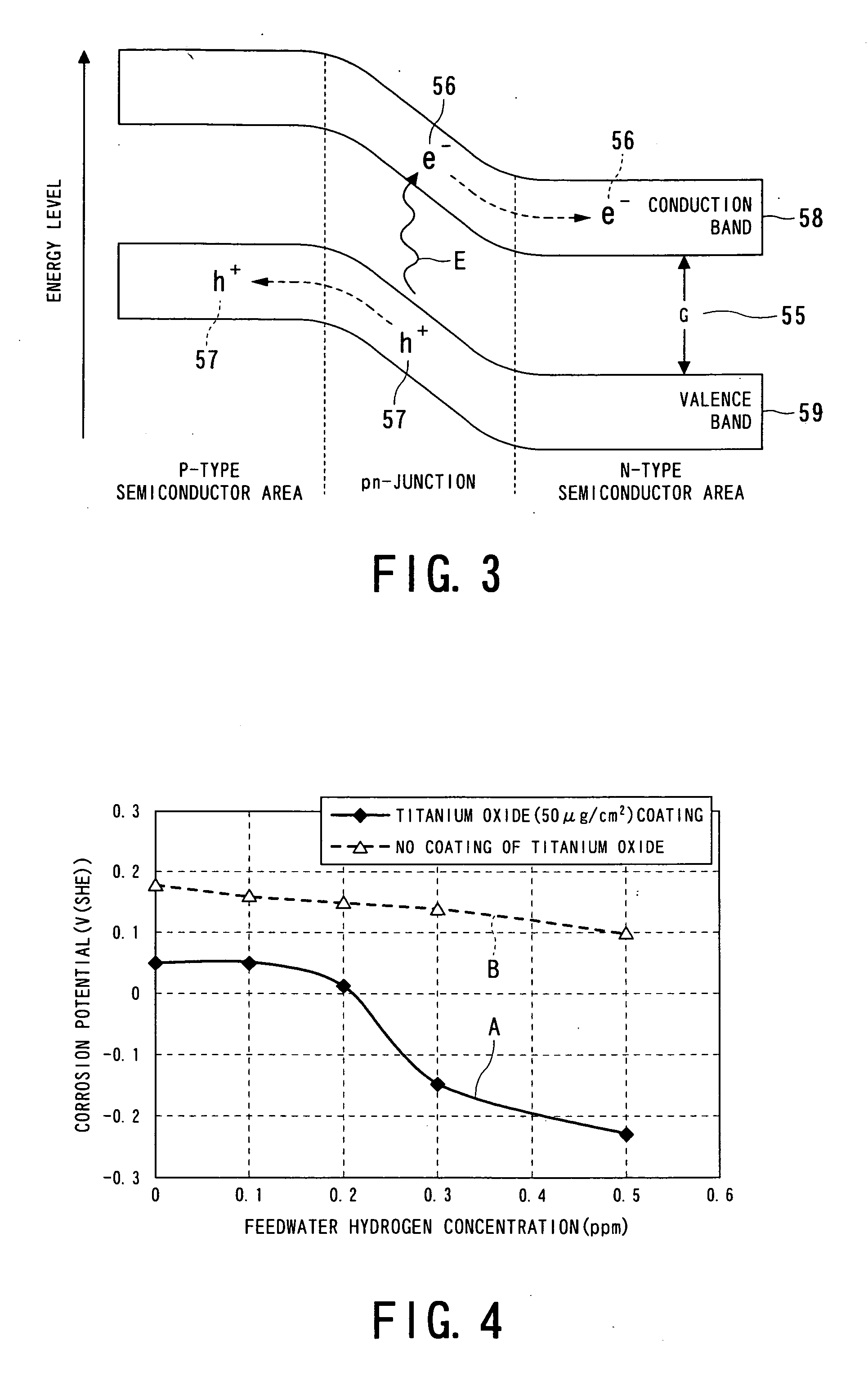
Reactor structural member and method of suppressing corrosion of the same
InactiveUS6940939B1Increase the concentration of hydrogenEffective preventionNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringHydrogen concentrationNuclear reactor
A photocatalytic substance having the properties of an n-type semiconductor is deposited on a surface of a metal base made of a stainless steel or Inconel. When necessary, the hydrogen concentration of the reactor water is increased. A current produced by the photocatalytic substance when the same is irradiated with light or radioactive rays in a nuclear reactor flows through the metal base to reduce corrosion current. When necessary, the photocatalytic substance is provided on its surface with at least one of Pt, Rh, Ru and Pd.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Organic polymer semiconductor, method of preparing the same, and ambipolar organic thin film transistor using the same
ActiveUS20080099758A1Electroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPolymer semiconductorOrganic semiconductor
Disclosed are an organic polymer semiconductor, an ambipolar organic thin film transistor using the same, an electronic device comprising the ambipolar organic thin film transistor and methods of fabricating the same. Example embodiments relate to an organic polymer semiconductor, which may include an aromatic ring derivative having p-type semiconductor properties and a heteroaromatic ring having n-type semiconductor properties in the main chain thereof, and which thus may exhibit both p-type transistor properties and n-type transistor properties when used in the organic active layer of an electronic device, e.g., an organic thin film transistor, an ambipolar organic thin film transistor using such an organic polymer semiconductor, an electronic device comprising the ambipolar organic thin film transistor and methods of fabricating the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Metal species surface treatment of thin film photovoltaic cell and manufacturing method
A method for forming a thin film photovoltaic device. The method includes providing a transparent substrate including a surface region. A first electrode layer is formed overlying the surface region. A copper layer is formed overlying the first electrode layer and an indium layer overlying the copper layer to form a multi-layered structure. The method subjects at least the multi-layered structure to a thermal treatment process in an environment containing a sulfur bearing species and form a copper indium disulfide material. The copper indium disulfide material includes a thickness of substantially copper sulfide material. The thickness of the copper sulfide material is removed to expose a surface region having a copper poor surface characterized by a copper to indium atomic ratio of less than about 0.95:1. The method subjects the copper poor surface to a metal cation species to convert the copper poor surface from an n-type semiconductor characteristic to a p-type semiconductor characteristic. A window layer is formed overlying the copper indium disulfide material.
Owner:CM MFG
Organic light emitting display device
ActiveUS20160163780A1Reduce coupling effectReduce parasitic capacitanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceActive layer
An organic light emitting display device is discussed. The organic light emitting display device includes a driving thin film transistor including an active layer and a gate electrode; a storage capacitor including a first electrode and a second electrode; a first pattern electrode including the gate electrode and the first electrode; an anode disposed on the driving thin film transistor and the storage capacitor; a second pattern electrode connected with an anode contact part which connects an output electrode connected with the active layer and the anode; and a patterned semiconductor layer including the active layer having a semiconductive characteristic and a shield unit having a conductive characteristic.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
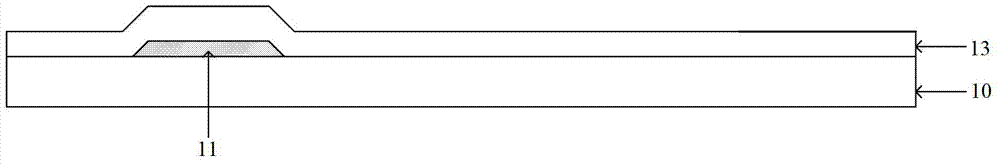
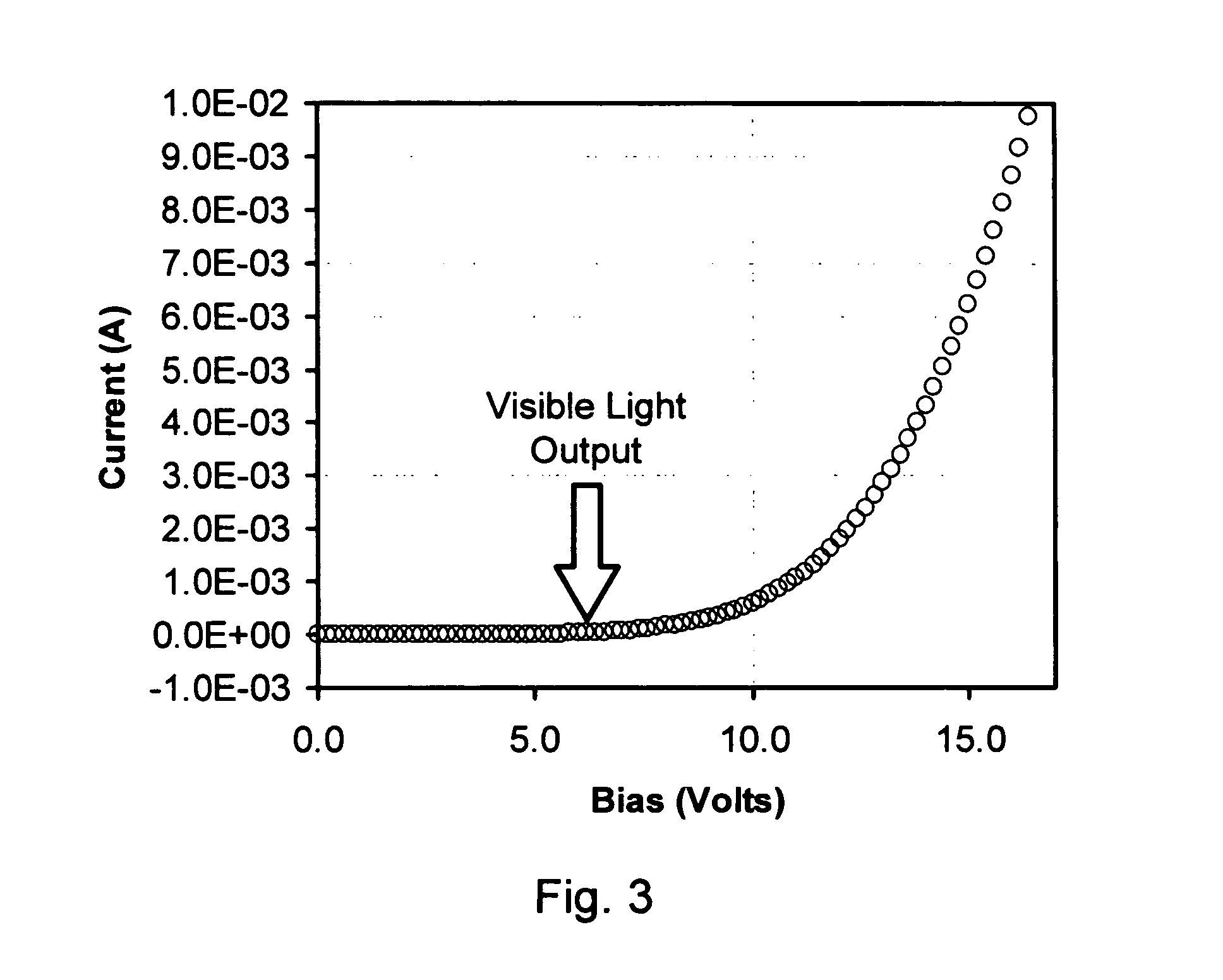
Method for forming oxide semiconductor film and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120244659A1Excellent semiconductor propertiesReduce the amount requiredSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHydrogenEngineering
A method for forming an oxide semiconductor film having favorable semiconductor characteristics is provided. In addition, a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having favorable electric characteristics, with use of the oxide semiconductor film is provided. A method for forming an oxide semiconductor film including the steps of forming an oxide semiconductor film, forming a hydrogen permeable film over and in contact with the oxide semiconductor film, forming a hydrogen capture film over and in contact with the hydrogen permeable film, and releasing hydrogen from the oxide semiconductor film by performing heat treatment. Further, in a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device, the method for forming an oxide semiconductor film is used.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Graphene field effect transistor
The invention discloses a graphene field effect transistor, and belongs to the technical field of electronics and graphene. A basic structure of the graphene field effect transistor comprises a grid, a source, a drain, an insulation layer and an active layer, wherein the active layer is formed by compositing single-layer or multi-layer graphene with the insulator or semiconductor characteristic after passivation and other semiconductor materials. The graphene field effect transistor successfully overcomes the fatal defects of the existing graphene field effect tube, has the higher performance compared with the conventional semiconductor field effect tube, and can promote an application of the graphene in the technical field of the electronics.
Owner:李德杰
Preparation method of nickel ion modified covalent organic framework material and application thereof
ActiveCN108794756AHigh selectivityFair priceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbon monoxideMaterials preparationBipyridine
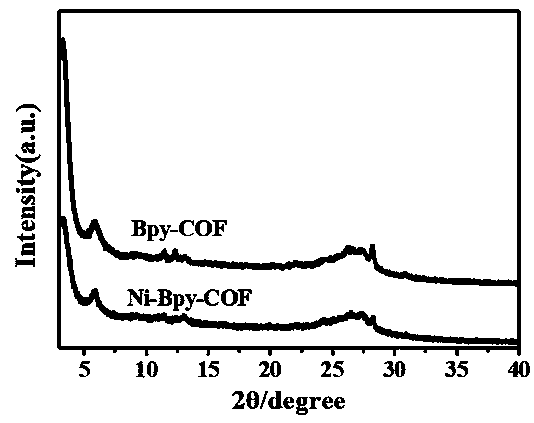
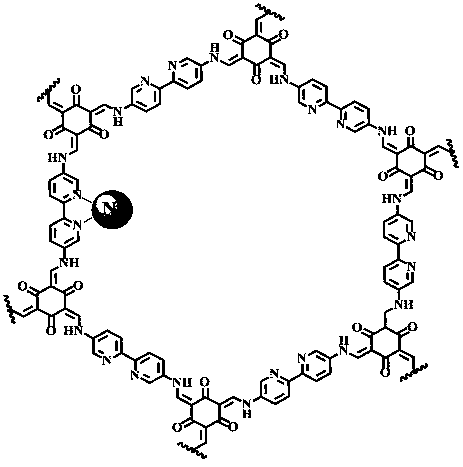
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nickel ion modified covalent organic framework material and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of material preparation and environment.The preparation method includes utilizing 5,5'-diamido-2,2'-bipyridine and 2,4,6-trihydroxy-1,3,5-benzenetrialdehyde to synthesize a covalent organic framework Bpy-COF by Schiff base condensation; conducting nickel ion post modification to obtain the nickel ion modified covalent organic framework material Ni-Bpy-COF. The principle and a method of the coordination chemistry are utilized to combinethe advantages of a metal complex molecular catalyst in high-selectivity photocatalytic conversion of CO2 with COFs having semiconductor properties, and the obtained Ni-Bpy-COF photocatalytic materialexhibits photocatalytic activity and has high efficiency and high selectivity photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to produce CO under visible light, the selectivity to CO2 photocatalytic reduction reaches 94%, and the problem of low selectivity of products in the existing photocatalytic reduction of CO2 of a semiconductor is solved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Nuclear power plant, method of forming corrosion-resistant coating therefor, and method of operating nuclear power plant
ActiveUS20060146975A1Good effectImprove efficiencyNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringSemiconductor propertiesMaterials science
In a nuclear power plant, a corrosion-resistant oxide film on a surface of the metal component of a reactor structure is exposed to a high-temperature water, the corrosion-resistant oxide film containing an oxide having a property of a P-type semiconductor, and a catalytic substance having a property of an N-type semiconductor is deposited on the oxide film. The oxide film maintains the property of the P-type semiconductor.
Owner:TOSHIBA ENERGY SYST & SOLUTIONS CORP +1
Organic semiconductor polymer for organic thin film transistor containing quinoxaline ring in the backbone chain
ActiveUS7030409B2High carrier mobilityLow off-state leakageTransistorSolid-state devicesSolubilityQuinoxaline
Disclosed herein is a composite-structured organic semiconductor polymer for an organic thin film transistor which contains quinoxaline rings in the backbone of the polymer. According to the organic semiconductor polymer, since quinoxaline rings having n-type semiconductor characteristics, such as high electron affinity, are incorporated into a polythiophene having p-type semiconductor characteristics, the organic semiconductor polymer simultaneously exhibits both p-type and n-type semiconductor characteristics. In addition, the polythienylquinoxaline derivative exhibits high solubility in organic solvents, co-planarity and stability in air. Furthermore, when the polythienylquinoxaline derivative is used as an active layer of an organic thin film transistor, the organic thin film transistor exhibits a high charge carrier mobility and a low off-state leakage current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com