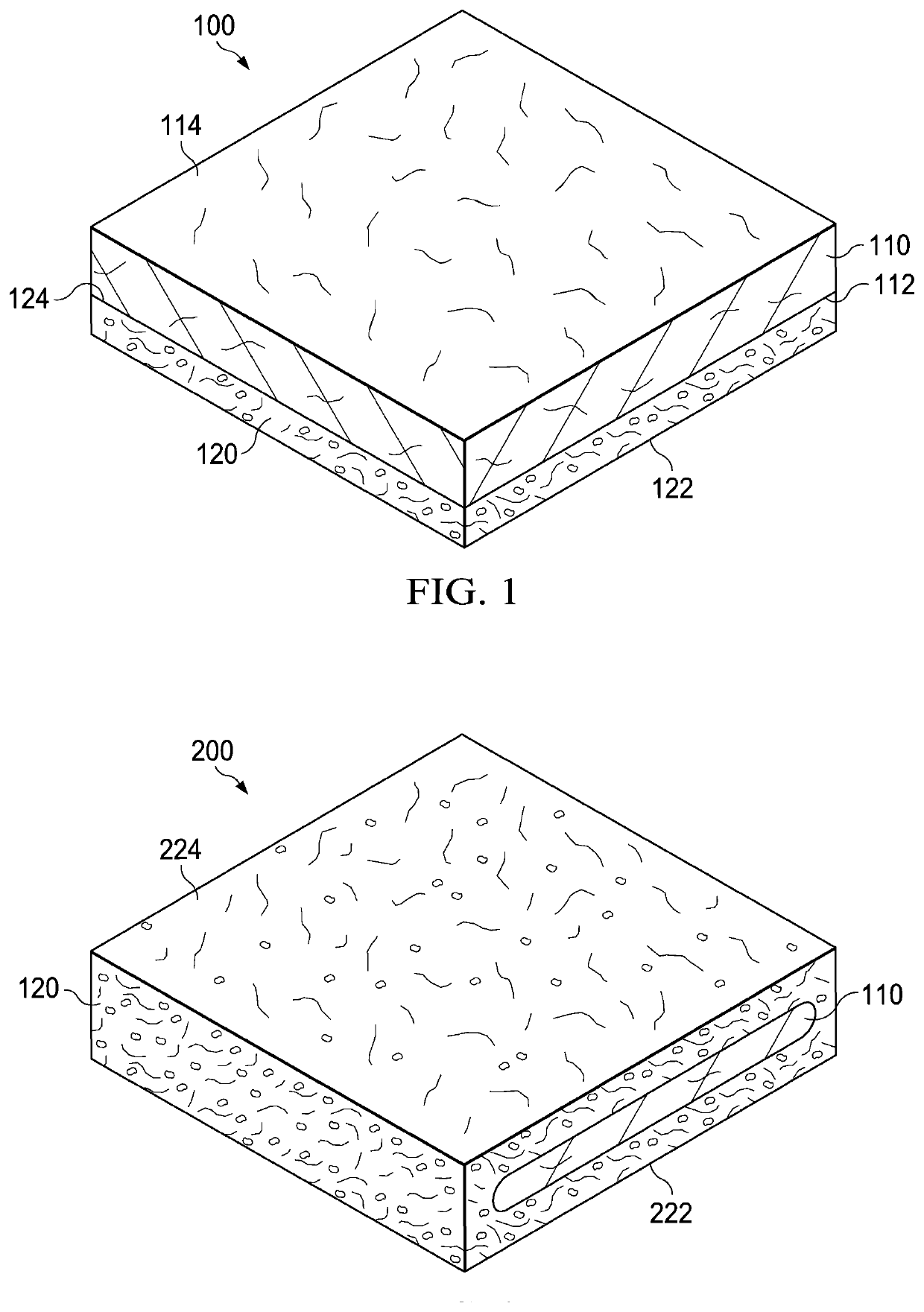
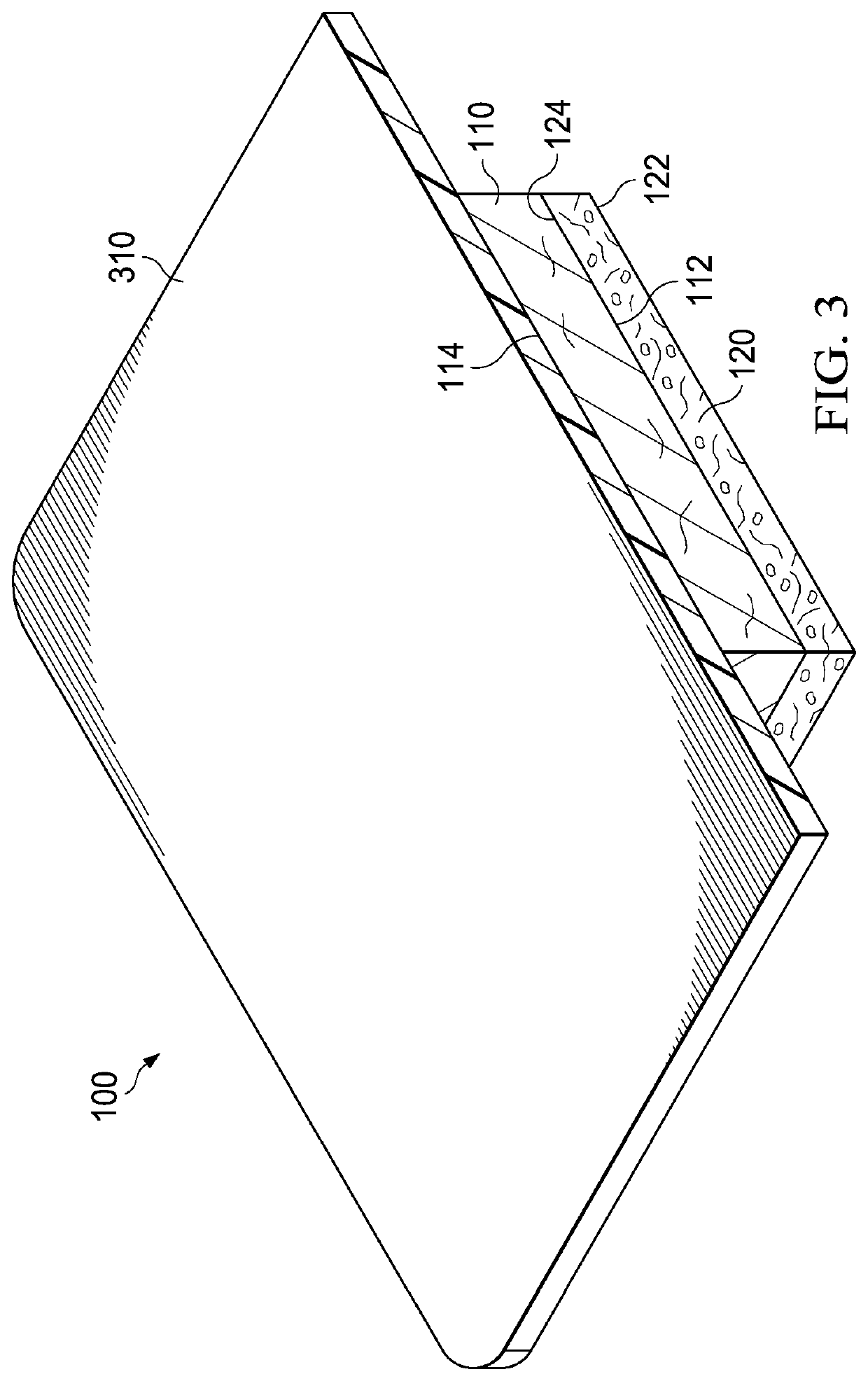
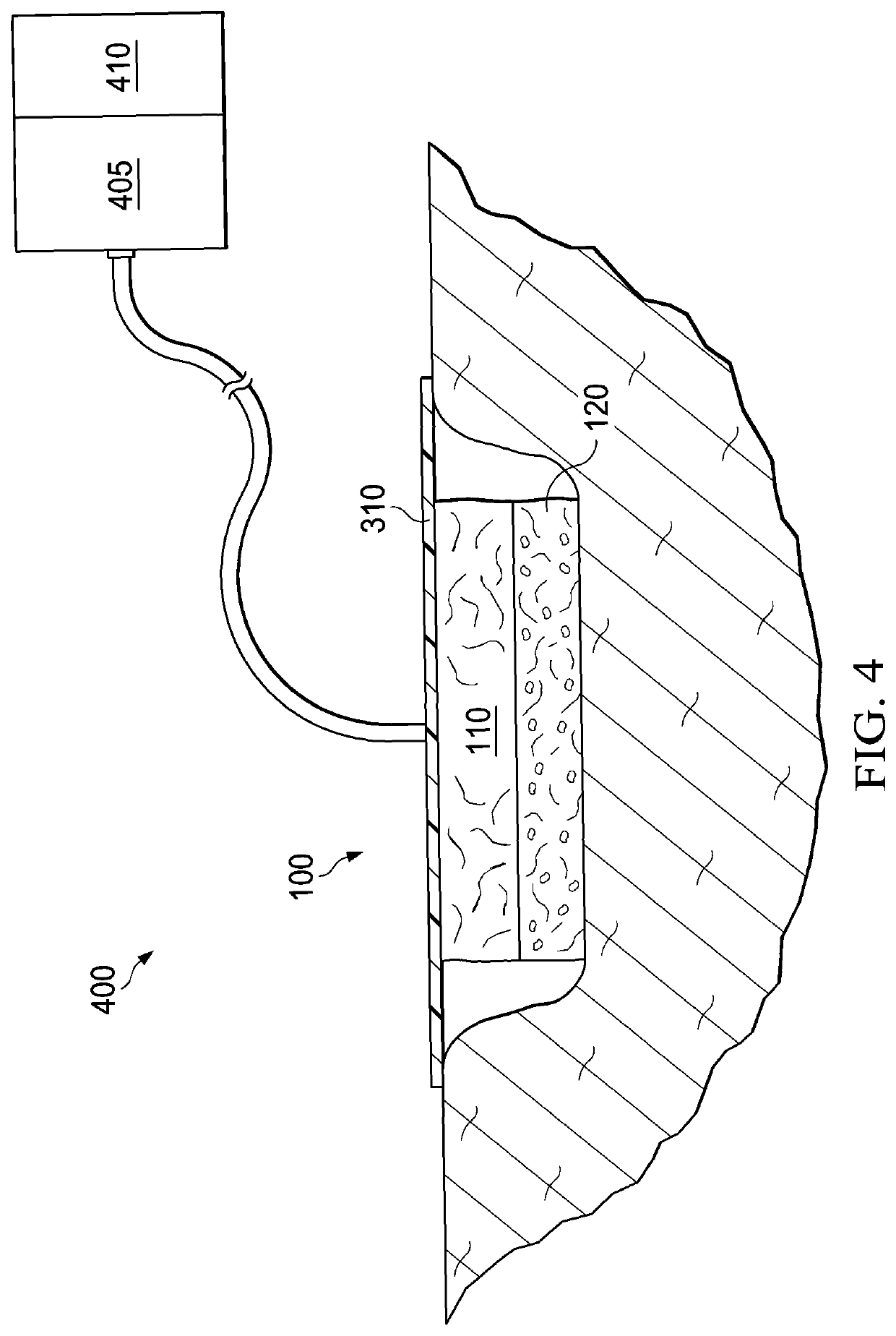
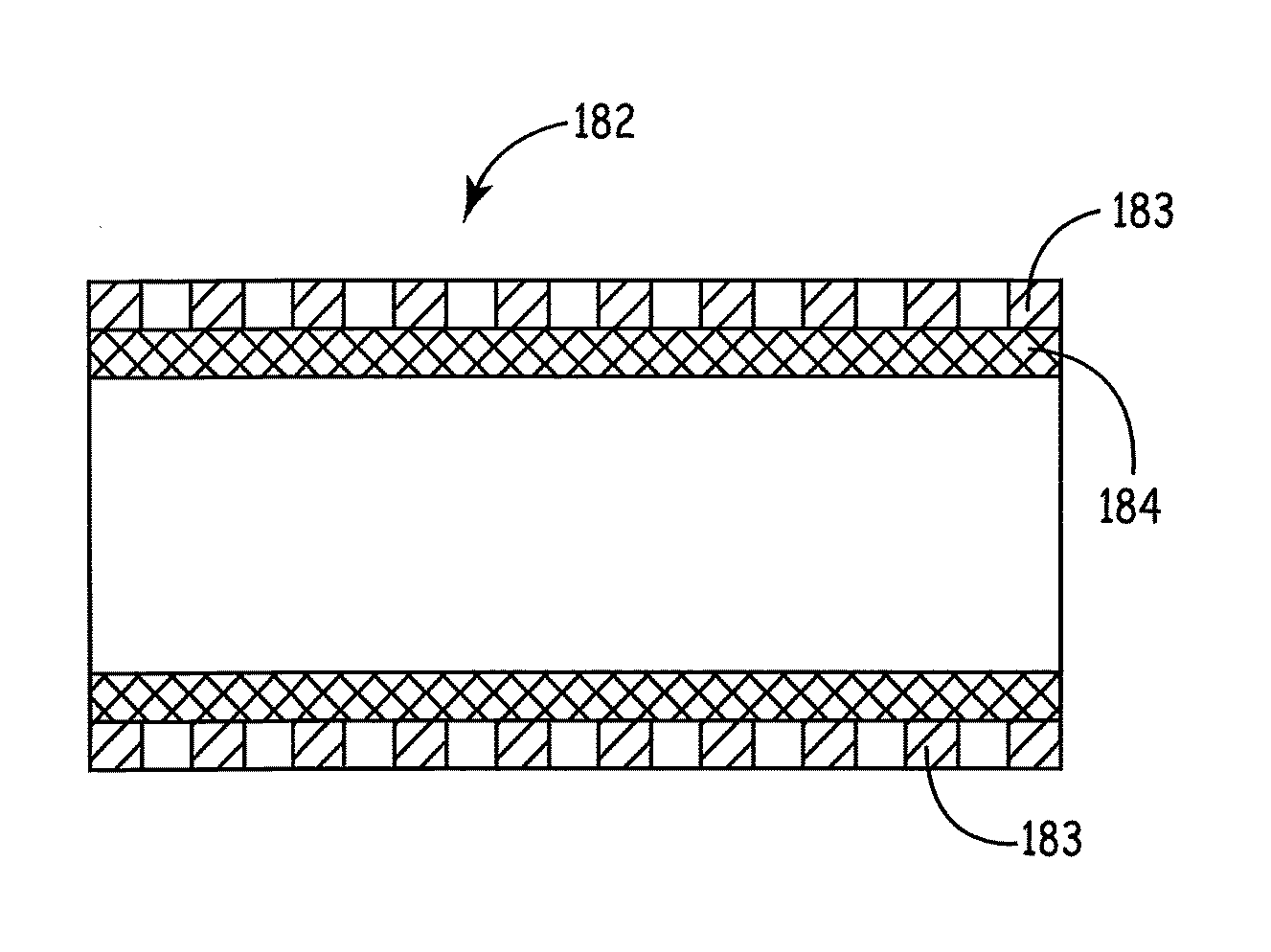
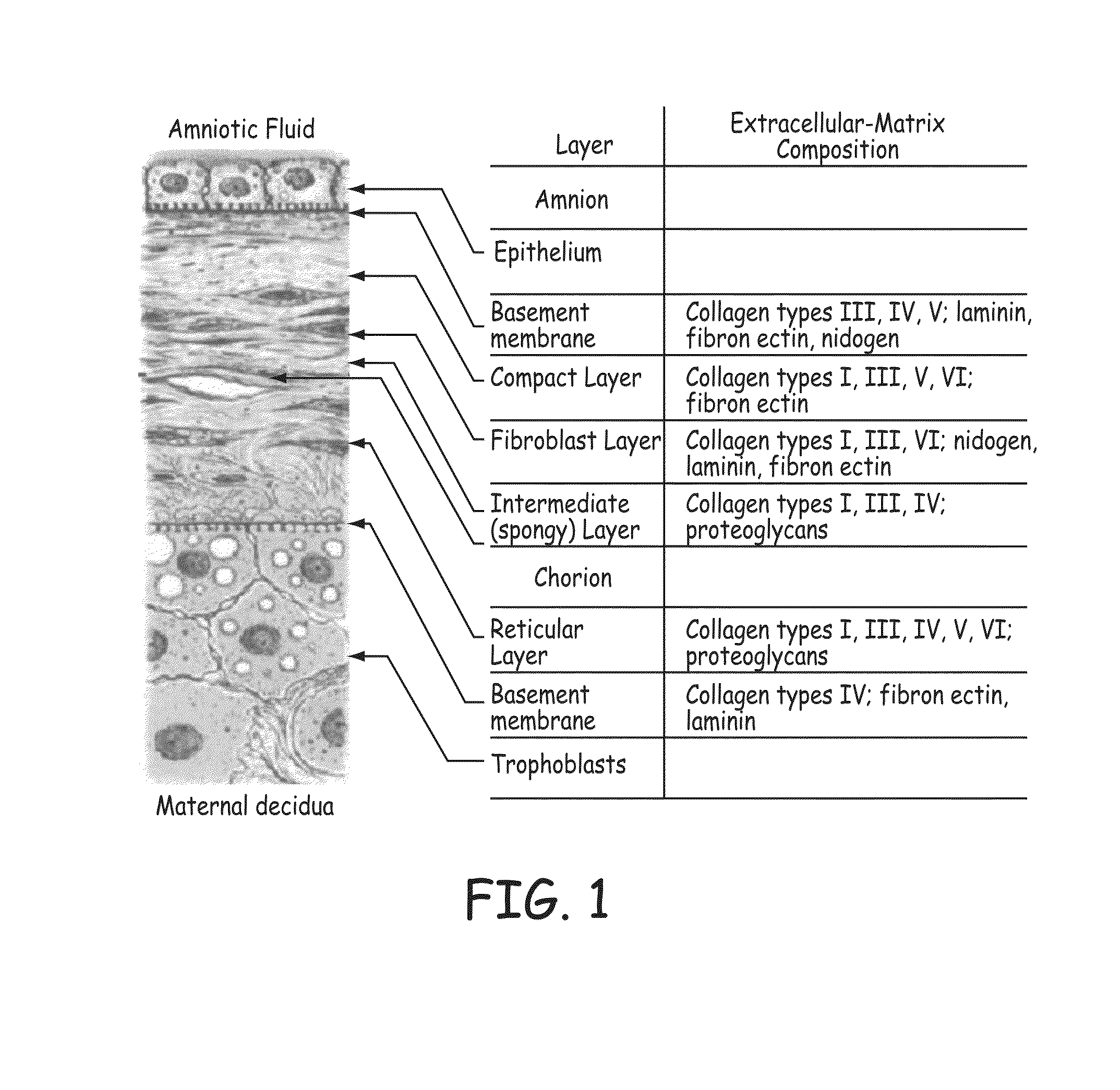
Patents
Literature
187 results about "Amniotic Sheet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
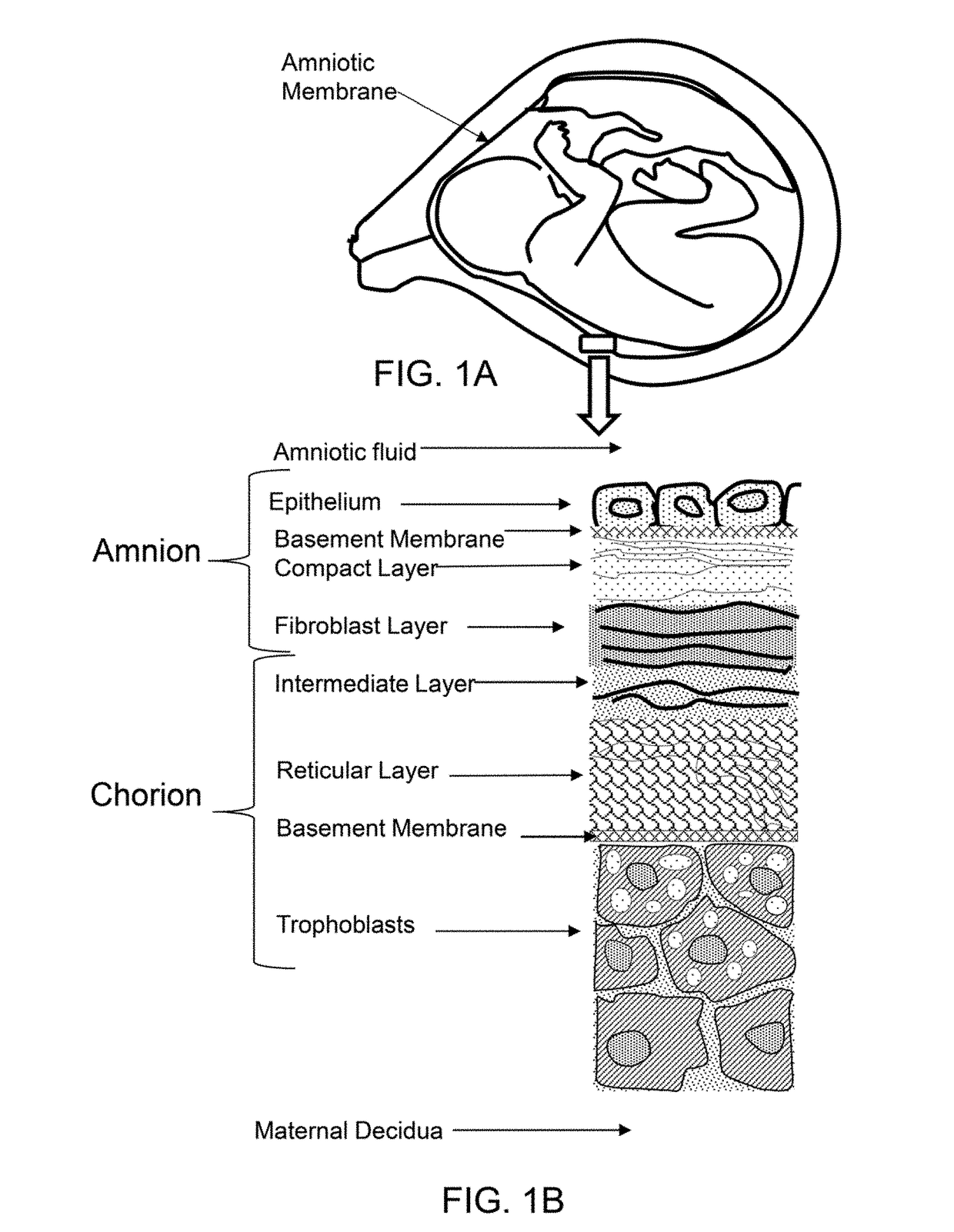
A sheet like projection that can result from uterine synechiae that has been encompassed by the expanding chorion and amnion. [] {comment=UToronto:chum}
Multipotent amniotic fetal stem cells
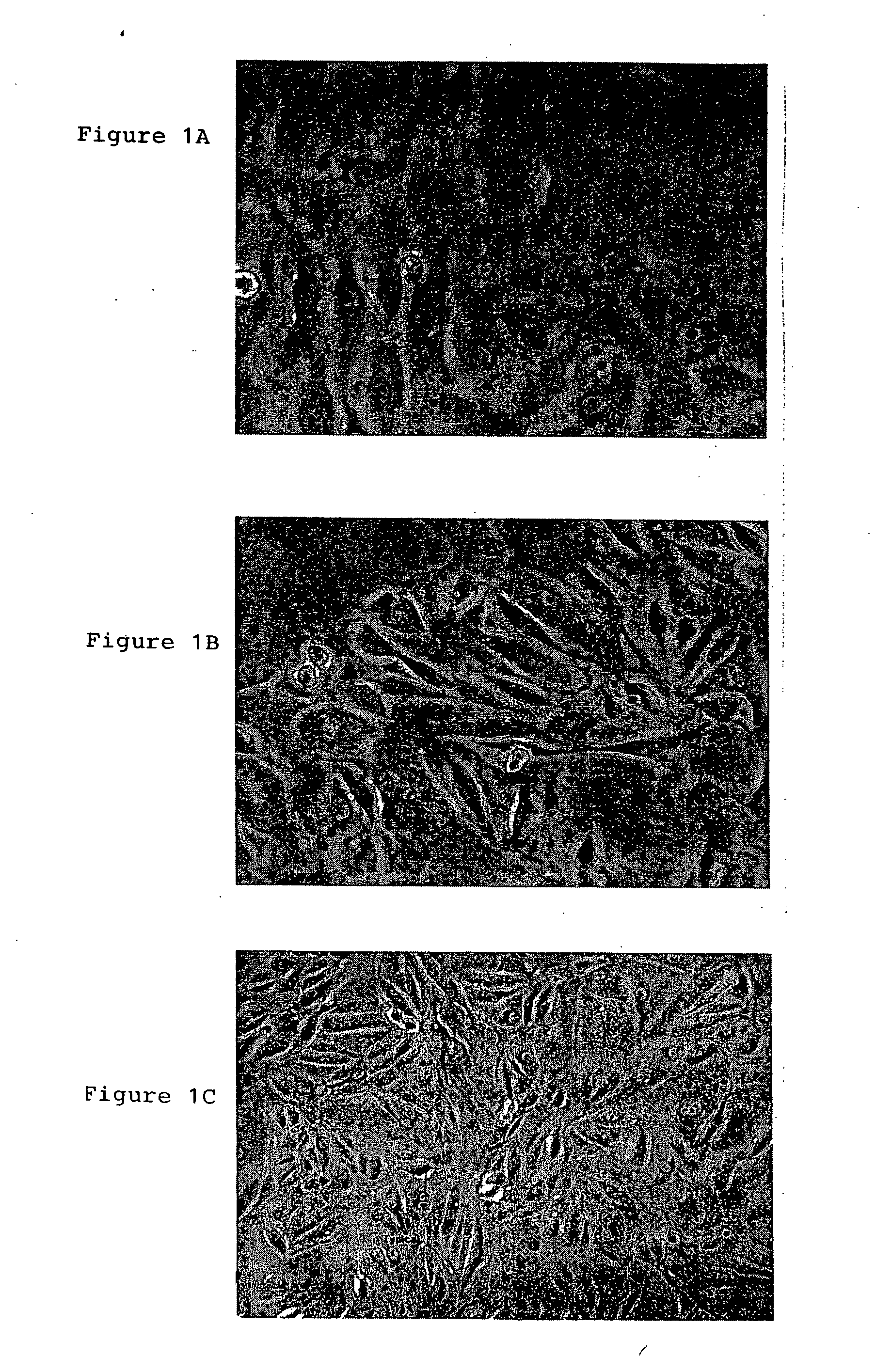
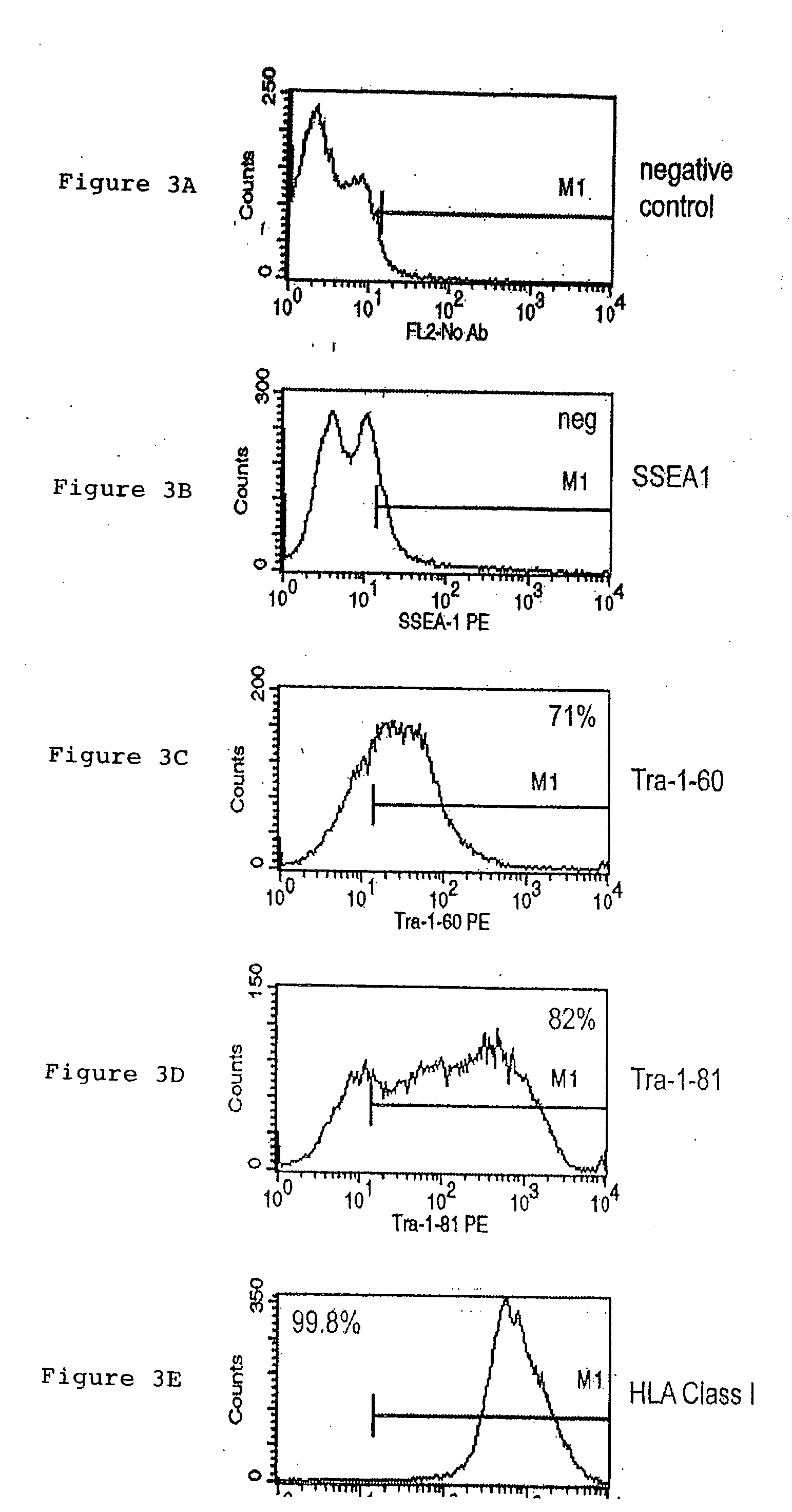
A source of multipotent amniotic fluid / fetal stem cells (MAFSCs) is disclosed. MAFSC are of fetal origin and have a normal diploid karyotype. These cells are characterized by the following cell surface markers: SSEA3, SSEA4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81, Tra-2-54, HLA class I, CD13, CD44, CD49b, CD105 and are distinguished by the absence of the antigen markers CD34, CD45, and HLA Class II, but are distinguished from mouse embryonic stem cells in that these cells do not express the cell surface marker SSEA1. MAFSC express the stem cell transcription factor Oct-4. MAFSC cells can be propagated for an indefinite period of time in continuous culture in an undifferentiated state. The MAFSCs have the ability to differentiate in culture in a regulated manner, into three or more subphenotypes. Cells can then be differentiated into endodermal, mesodermal and ectodermal derived tissues in vitro and in vivo. A method for isolating, identifying, expanding and differentiating MAFSCs is disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing contact lens-shaped amniotic dressing
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a contact lens-shaped amniotic dressing and a contact lens-shaped amniotic dressing prepared therefrom for treating ocular surface diseases, which does not require the use of sutures or an adhesion material. The inventive contact lens-shaped amniotic dressing is capable of solving the problems associated with suturing an amniotic membrane, e.g., highly delicate surgical techniques of suturing, long surgery time, stitch abscess, granuloma formation, tissue necrosis, and discomfort of patients; and the problems associated with the use of a support, e.g., the elimination of the support by eye blinking, breaking of the support, and discomfort.
Owner:SK BIOLAND CO LTD
Stents modified with material comprising amnion tissue and corresponding processes
A stent scaffold combined with amniotic tissue provides for a biocompatible stent that has improved biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. The amnion tissue can be variously modified or unmodified form of amnion tissue such as non-cryo amnion tissue, solubilized amnion tissue, amnion tissue fabric, chemically modified amnion tissue, amnion tissue treated with radiation, amnion tissue treated with heat, or a combination thereof. Materials such as polymer, placental tissue, pericardium tissue, small intestine submucosa can be used in combination with the amnion tissue. The amnion tissue can be attached to the inside, the outside, both inside and outside, or complete encapsulation of the stent scaffold. In some embodiments, at least part of the covering or lining comprises a plurality of layers of amnion tissue. The method of making the biocompatible stent and its delivery and deployment are also discussed.
Owner:PEYTANT SOLUTIONS INC
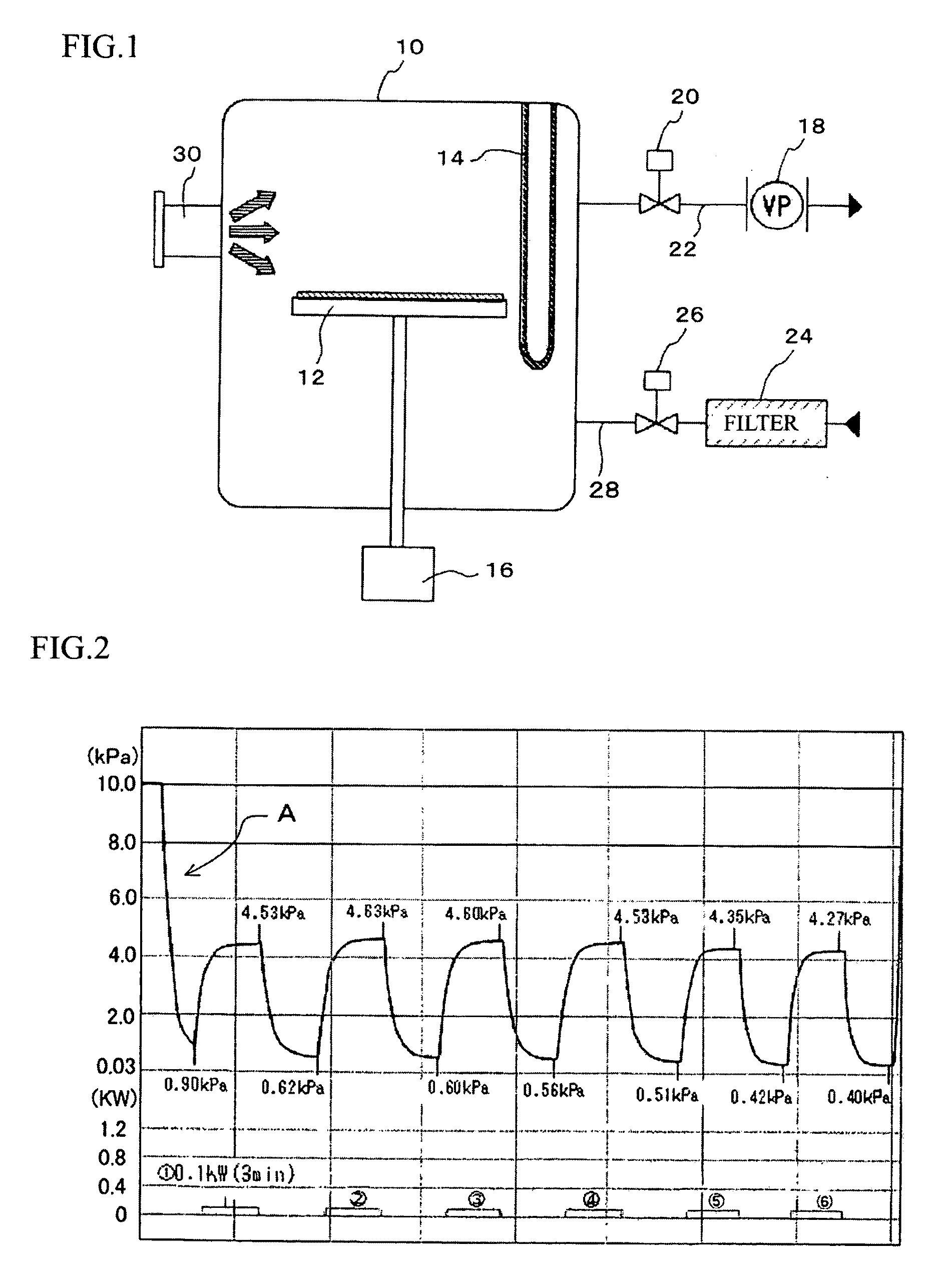
Dried amnion and method for drying teatment of amnion
ActiveUS20090258082A1Reduce pointsAvoid overall overheatingSenses disorderDead animal preservationBasementMicrowave
The present invention provides a dried amnion which is dried with maintaining tissues of a raw amnion and can be easily stored for a prolonged period of time. An amnion which is dried with maintaining cells and tissues of a raw amnion can be produced by repeating a pressure-reducing operation and a pressure-recovery operation several times, the pressure-reducing operation comprising continuously heating a raw amnion placed in a treatment vessel by a far-infrared heater provided in the treatment vessel and reducing the pressure of the inside of the treatment vessel, and the pressure-recovery operation comprising recovering the reduced pressure of the inside of the treatment vessel with heating the amnion by microwaves irradiated from a microwave heating apparatus provided outside of the treatment vessel, and the amnion is characterized by retaining basement membranes and connective tissues which are constituents of the raw amnion.
Owner:AMNOS
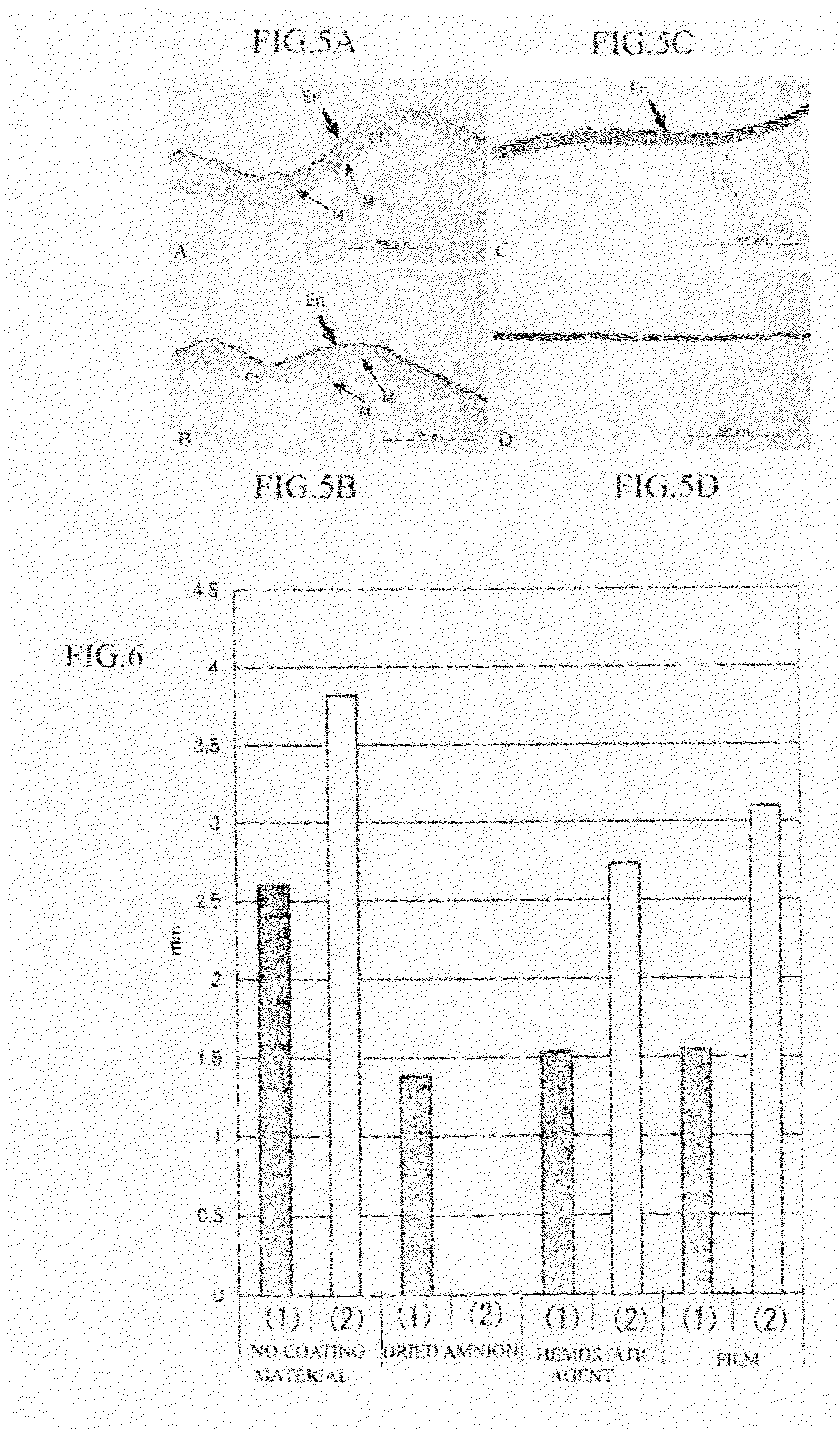
Amnion and chorion constructs and uses thereof in sport injury surgeries
Improved methods for sport injury surgeries are described. The improvement includes covering a damaged site of fascia with at least one of an amniotic fluid and a construct for use in surgical repair of the sport injury prior to wound closing. The construct contains an allograft comprising at least one layer of human amnion and chorion tissues and the construct has a size and shape suitable for covering the damaged site of fascia. The method improves fascial membrane repair, reduces complications and recovery time of sport injury surgeries.
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
Method for expansion of epithelial stem cells
InactiveUS7347876B2Expand the populationEye implantsTissue cultureComposite Tissue AllograftTissue biopsy
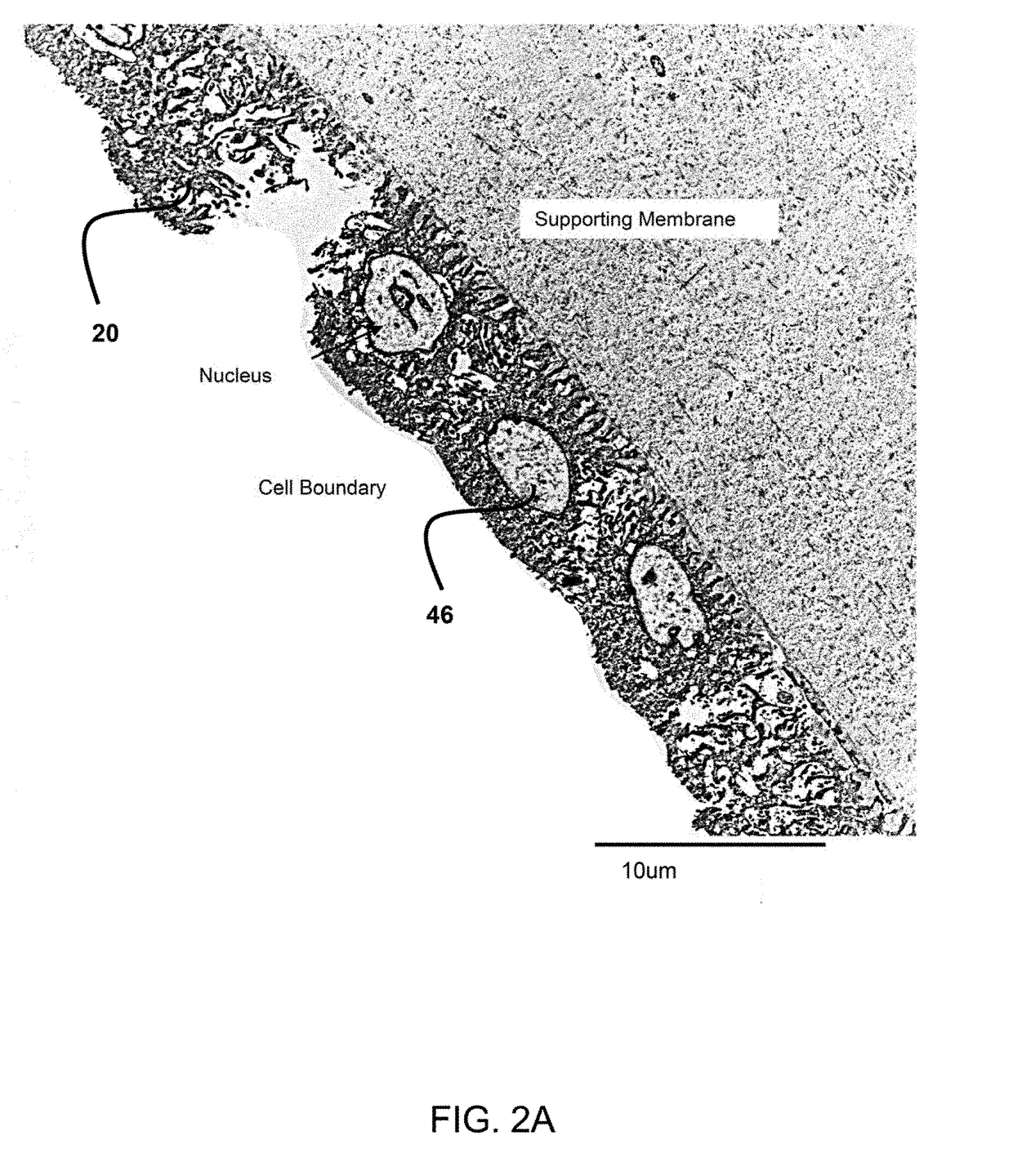
Transplantation of epithelial stem cells, cultured ex vivo on specifically treated amniotic membrane, yields, with that amniotic membrane, a surgical graft having expanded epithelial stem cells. The method of creating this graft and the graft itself are simple and effective to reconstruct damaged tissue, a preferred example being corneal tissue. The source of the epithelial stem cells can be a very small explant from healthy autologous and allogeneic tissue biopsy. The amniotic membrane is treated such that its extracellular matrix is maintained, but its cells are killed.
Owner:TSAI RAY JUI FANG
The preparation method of the radiant crosslink porous reticular cells amnionic hydro gel dressing and its preparation method
InactiveCN1943796AOvercome the shortcomings of low mechanical strength and poor complianceConvenient for clinical operationAbsorbent padsBandagesFreeze-dryingPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of an irradiative crosslink network cellular porous hydrogel dressing of amniotic membrane, the specific methods are: put the hydrogel solutions comprising of PVA, chitosan and acrylic acid-acrylamide copolymer on the porous stainless steel plate used to put the netty cellular amniotic membrane, add a small amount of agar, agitate uniformly, evacuate, and the hydrogel prototype was obtained; then press the hydrogel to film; then expose the membrane to 60Coy- ray irradiation in room temperature to crosslink, then dehydrate, freeze-dried, radiative sterilized, packed under aseptic conditions. The invention possesses good protection treatments, such as alleviate pain, resist to phlogosis and bacterium, and promote healing. It also has good hygroscopic properties, water retention, permeability and flexibility, further more we can have a selection of drugs according to sensitive bacteria of wound, pain, the need of arristing or activzte bleeding to and to help achieve sustained-release drug treatment purposes.
Owner:关志广
Amnion and chorion constructs and uses thereof in minimally invasive surgeries
A construct for use in a minimally invasive surgery is described. The construct contains an allograft having at least one layer of human amnion and chorion tissues, and is adapted for insertion into a small incision or a cannula employed in the minimally invasive surgery for access to the surgical site. The allograft has a shape appropriate for covering the surgical site. Methods of preparing the construct and using it in a minimally invasive surgery are also described. The products and methods improve the performance of the minimally invasive surgery, e.g., by reducing adhesions, scar formation while also reducing inflammation and risk of post-operative infection.
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
Preparing method and application of acellular amniotic membrane used for repairing skin wound difficult to heal
The invention relates to a preparing method and application of an amniotic membrane, in particular to a preparing method and application of an acellular amniotic membrane used for repairing skin wound difficult to heal. The preparing method specifically comprises the steps of isolating, cleaning and sterilizing an amniotic membrane tissue; arranging and drying the amniotic membrane tissue on a nitrocellulose membrane to manufacture an amniotic membrane paster; vibrating and digesting the amniotic membrane paster in mixed digestive fluid of 0.25%-0.5% of pancreatin and 0.2-0.5g / L EDTA.4Na for 10-30 minutes at a temperature of 37 DEG C; rinsing the amniotic membrane paster in TE buffer solution; vibrating overnight to fully remove amniotic membrane cells in TE-TritonX-100 solution; washing the amniotic membrane paster for three times in TE solution; vibrating and degrading the amniotic membrane paster for 2-4 hours in nucleic acid degrading solution at a temperature of 37 DEG C; washing the amniotic membrane paster for three times in the TE solution. The prepared acellular amniotic membrane paster can be stored for a long time after being refrigerated, dried, packed and sterilized by cobalt 60 irradiation and is a tissue engineering material which can be taken and used when needed. The acellular amniotic membrane paster can be easily separated from the nitrocellulose membrane to be used for repairing the skin wound after rewatered.
Owner:天晴干细胞股份有限公司
Amniotic membrane hydrogel and methods of making
ActiveUS10016464B2Mammal material medical ingredientsCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixCell free
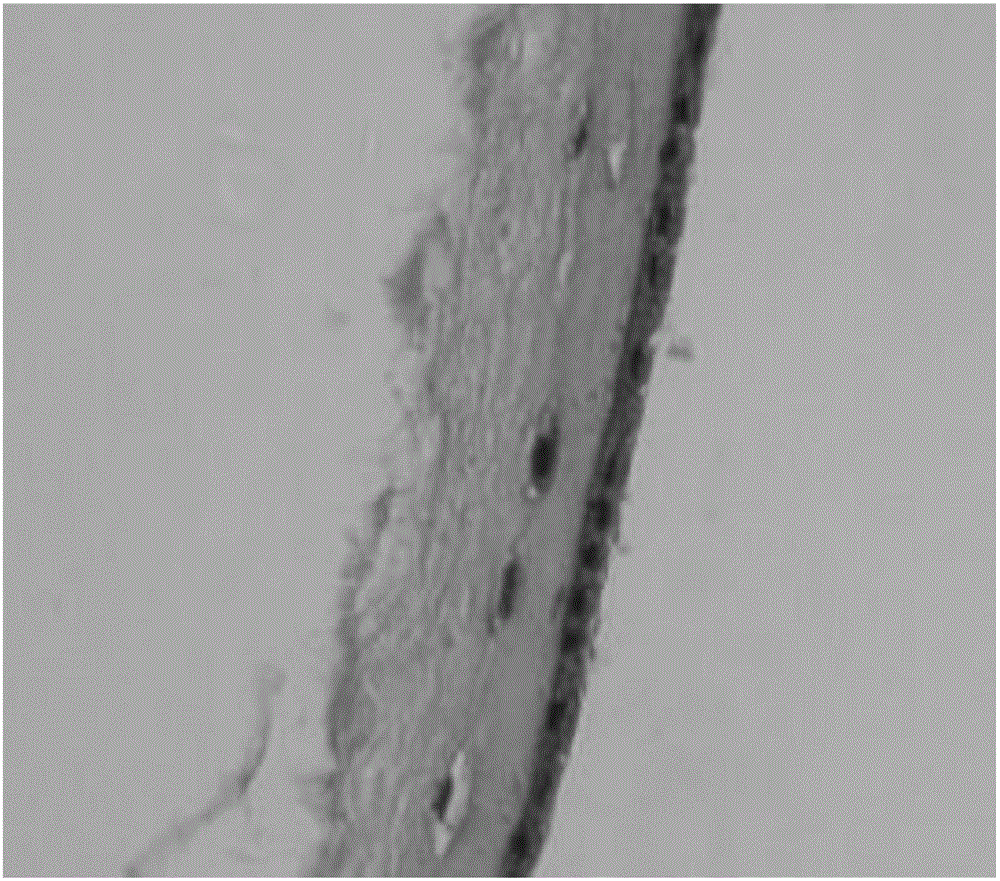
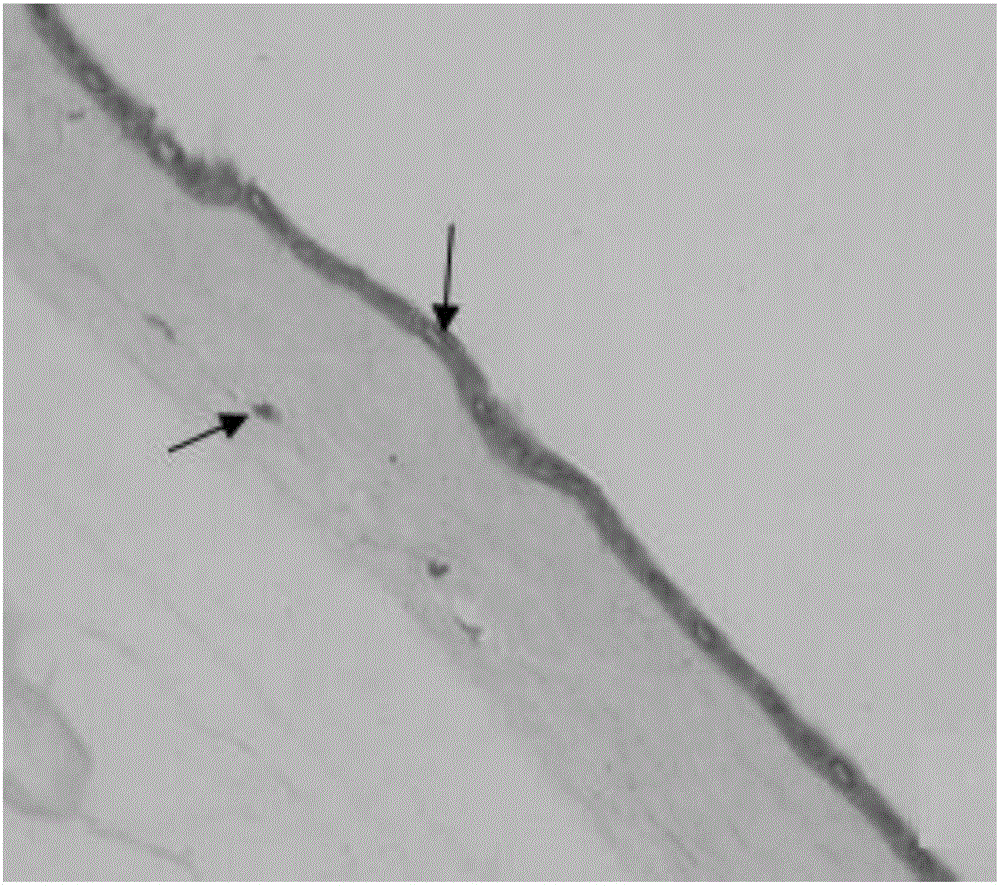
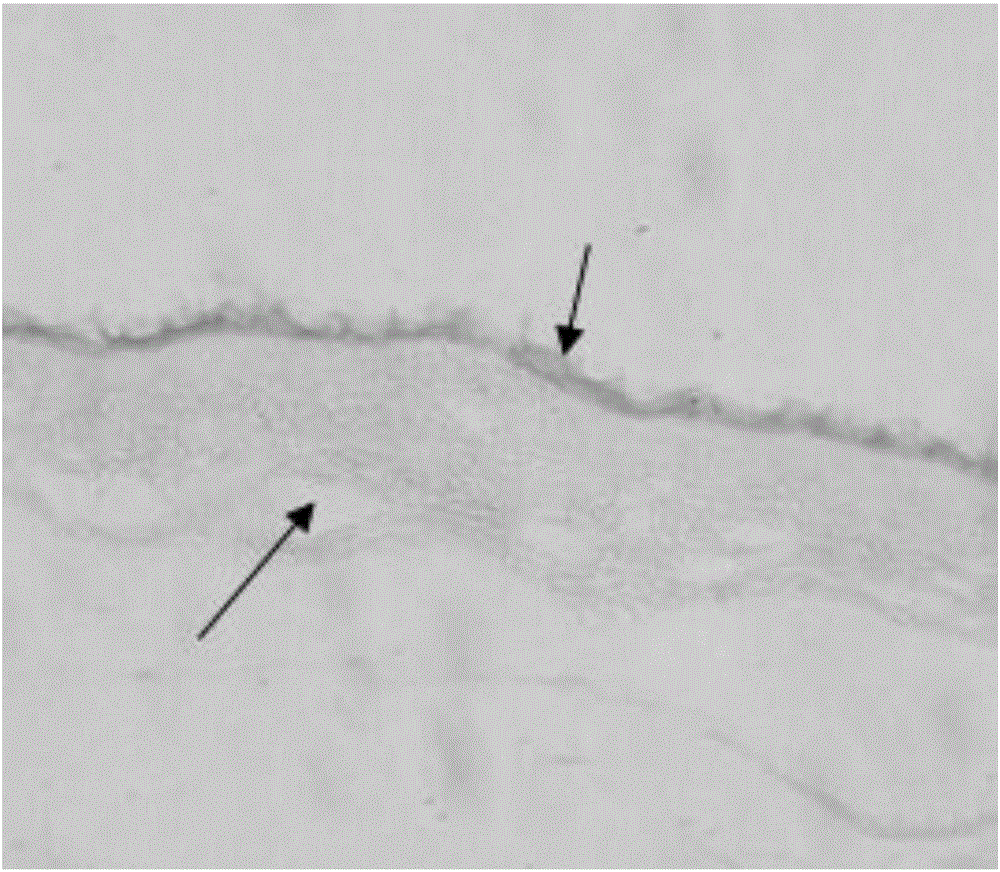
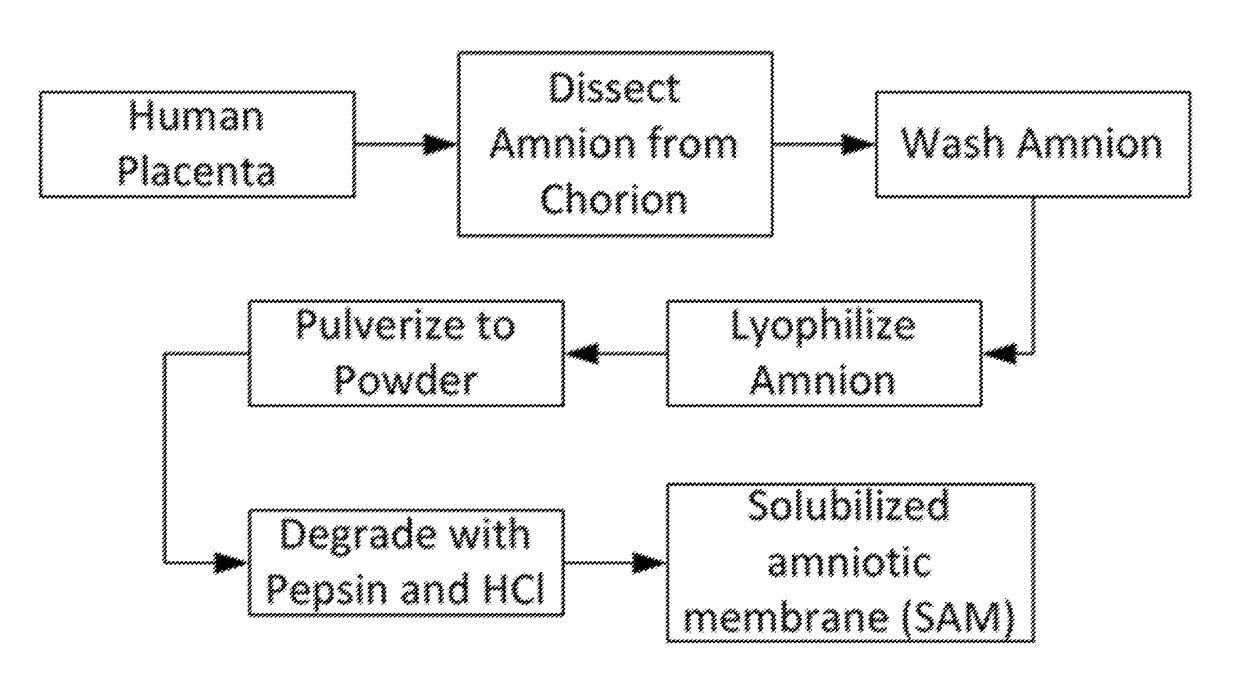
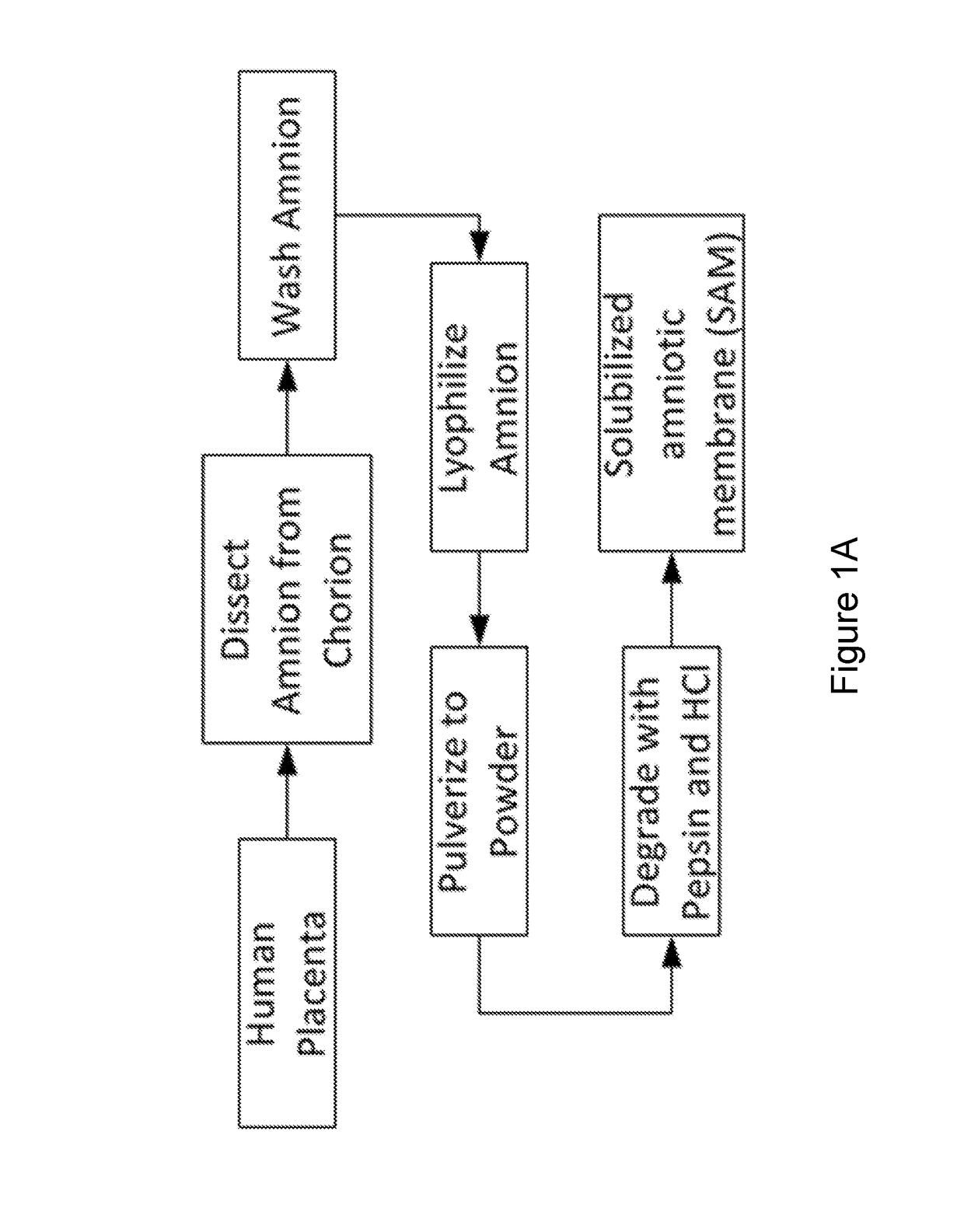
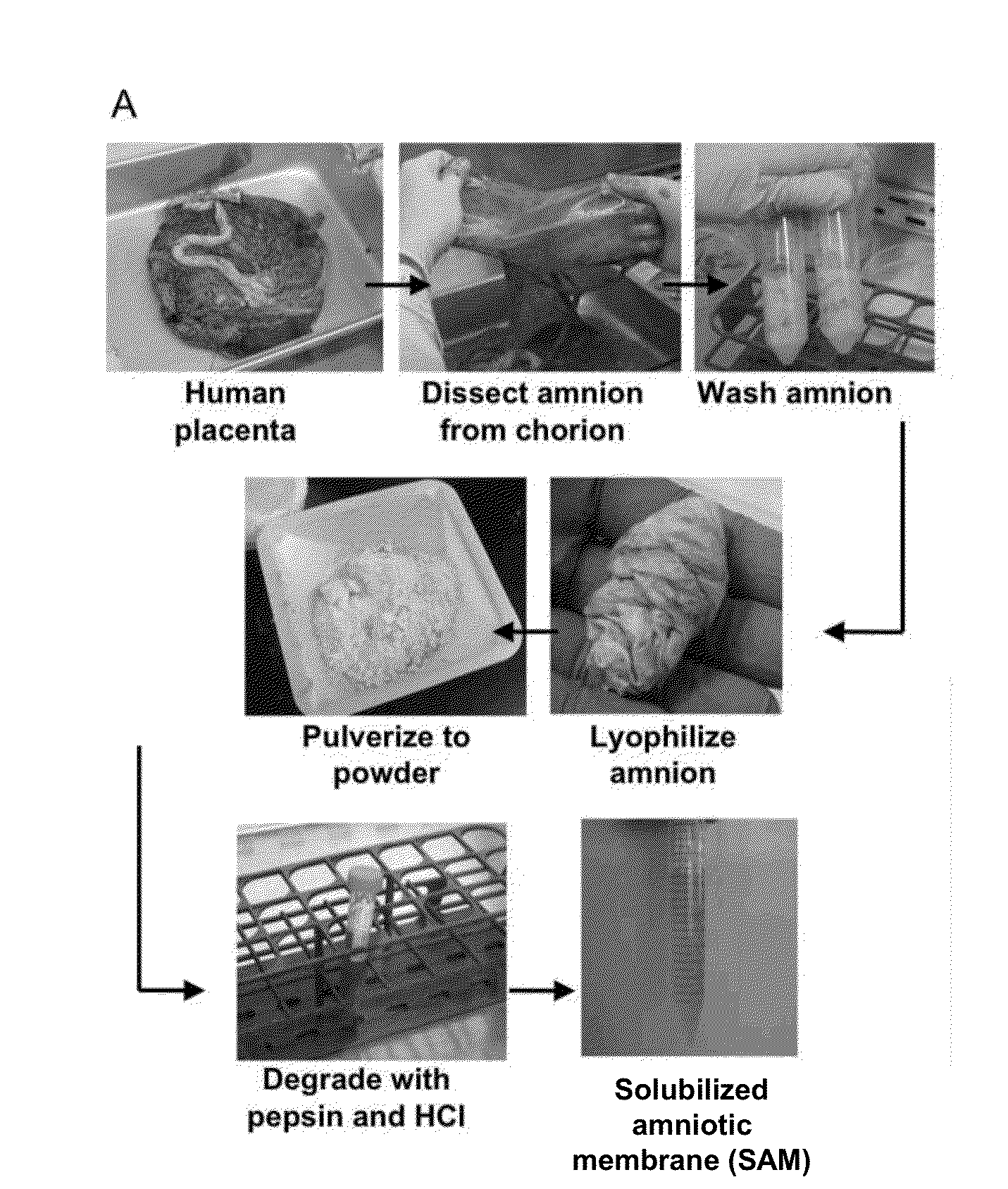
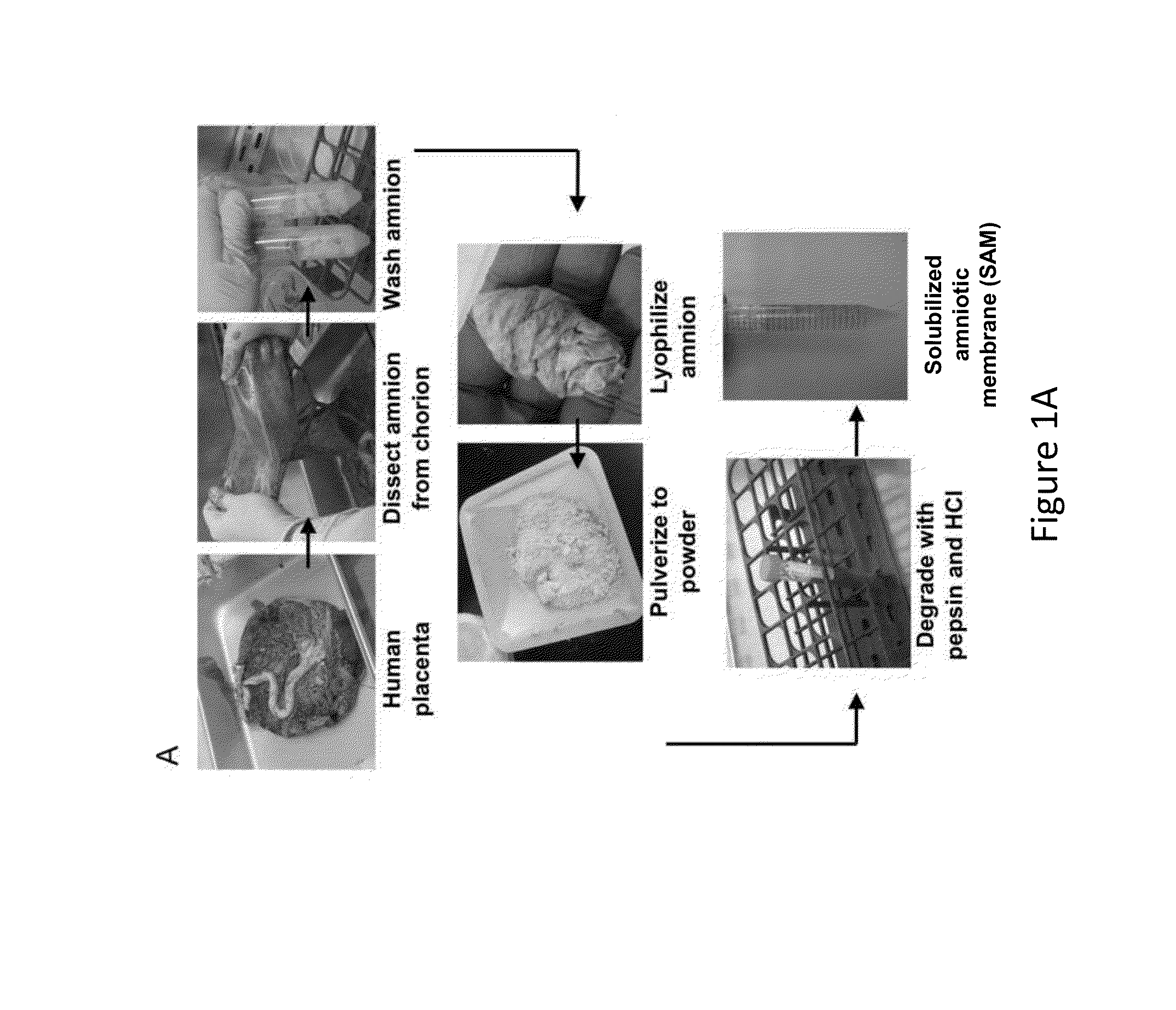
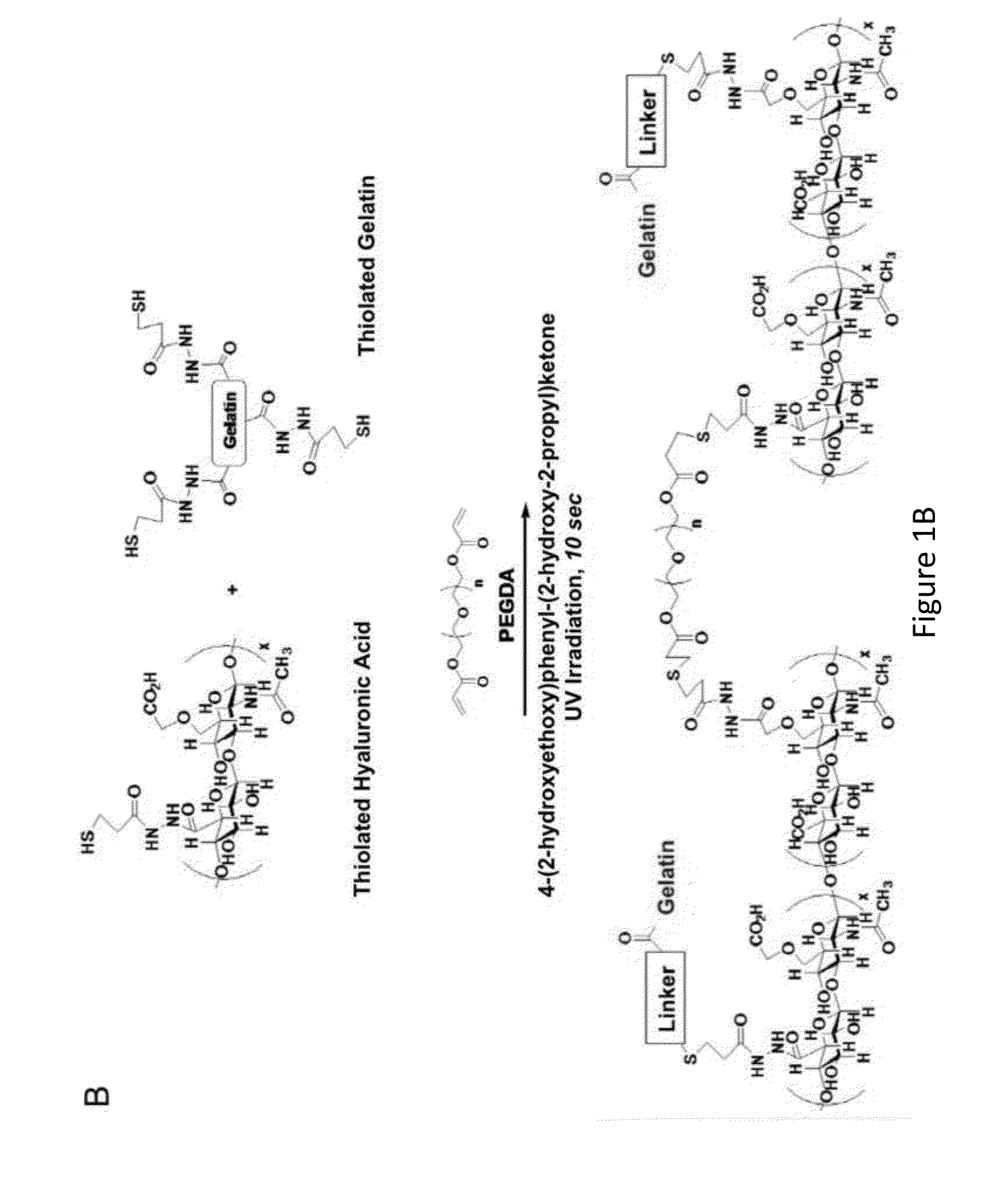
The present invention provides compositions and methods for wound healing and tissue regeneration. The compositions of the present invention comprise amniotic membrane of the placenta. In certain embodiments, the composition comprises amniotic membrane powder or solubilized amniotic membrane (SAM). In some aspects, the composition is cell-free and rich in cytokines, extracellular matrix proteins, and other components that improve tissue regeneration. In one aspect, the composition is a hydrogel scaffold that comprises amniotic membrane. The present invention reduces contraction and improves blood vessel development in regenerating tissue.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Single balloon ripening device with novel inserter and inflator
InactiveUS20060235461A1Avoid traumaEasy to disassembleStentsBalloon catheterIntrauterine pressure catheterExtra-amniotic
An improvement on the extra-amniotic balloon and technique of placement is disclosed. It involves a large capacity balloon, modified to efficiently place pressure on the cervix, and markers for ease and of placement. The malleable introducing stylet allows for safe and easy insertion, either manually or visually, through a cervix that is 0.5 cm or more in dilation. The optional traction collar can aid in more efficiently placing pressure on the cervix. The automatic pump for instillation of the fluid has a forward and reverse mode to allow for deflation and repositioning of the balloon if placement is less than optimal. This process can be performed by a physician or a nurse, already certified in the placement of fetal scalp electrodes or intrauterine pressure catheters. Additionally, the procedure can be performed by one person.
Owner:DESSERTSTORK INTERPRISES
Amniotic Membrane Hydrogel and Methods of Making
ActiveUS20140348940A1Mammal material medical ingredientsCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixRegeneration tissue
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Amnion stroma tectorial blood vessel internal branch and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1927413AOvercome the disadvantages of injuryTo achieve the purpose of skinStentsProsthesisIntravascular stentBioavailability
The invention relates to an amnion substrate covered blood vessel internal support and relative production. Wherein, it covers and decorates the blood vessel internal support and plants the endothelium cell, to avoid narrow condition; the support is formed by blood vessel internal support, amnion substrate covering the support, and the endothelium cell planted on the substrate. And the production comprises that removing cells of amnion, to be biological film with substrate film and dense layer; covering and decorating it on the blood vessel internal support, to form smooth and flat film on the inner surface; then planting the endothelium cell, to form a liner, as one inner layer of blood vessel sample, and approach the surface of support to the inner wall of vessel, to increase the bioavailability and blood compatibility.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Dressing including dehydrated placental tissue for wound healing
A dressing for wound healing is provided herein including dehydrated placental tissue, collagen, and oxidized regenerated cellulose. The dehydrated placental tissue may be present in a first layer and the collagen and the oxidized regenerated cellulose may be combined into a second layer. The dehydrated placental tissue may comprise amniotic membrane tissue, chorion tissue, or a combination thereof. The second layer including the collagen and the oxidized regenerated cellulose may comprise about 50% to about 60% collagen by weight and about 40% to about 50% ORC by weight.
Owner:SYSTAGENIX WOUND MANAGEMENT (US) INC
Method of using amnion allograft in heart valve repair surgery
InactiveUS20130211504A1Speed up the repair processSuitable shapeVenous valvesBlood vesselsHeart valve repairAnesthesia
Improved methods for heart valve repair surgery are described. The methods utilize an allograft comprising a layer of amnion to improve the performance and reduce complications of heart valve repair surgery and the allograft has a pre-made size and shape suitable for the application.
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
Stents modified with material comprising amnion tissue and corresponding processes
A stent scaffold combined with amniotic tissue provides for a biocompatible stent that has improved biocompatibility and hemocompatibility. The amnion tissue can be variously modified or unmodified form of amnion tissue such as non-cryo amnion tissue, solubilized amnion tissue, amnion tissue fabric, chemically modified amnion tissue, amnion tissue treated with radiation, amnion tissue treated with heat, or a combination thereof. Materials such as polymer, placental tissue, pericardium tissue, small intestine submucosa can be used in combination with the amnion tissue. The amnion tissue can be attached to the inside, the outside, both inside and outside, or complete encapsulation of the stent scaffold. In some embodiments, at least part of the covering or lining comprises a plurality of layers of amnion tissue. The method of making the biocompatible stent and its delivery and deployment are also discussed.
Owner:PEYTANT SOLUTIONS INC
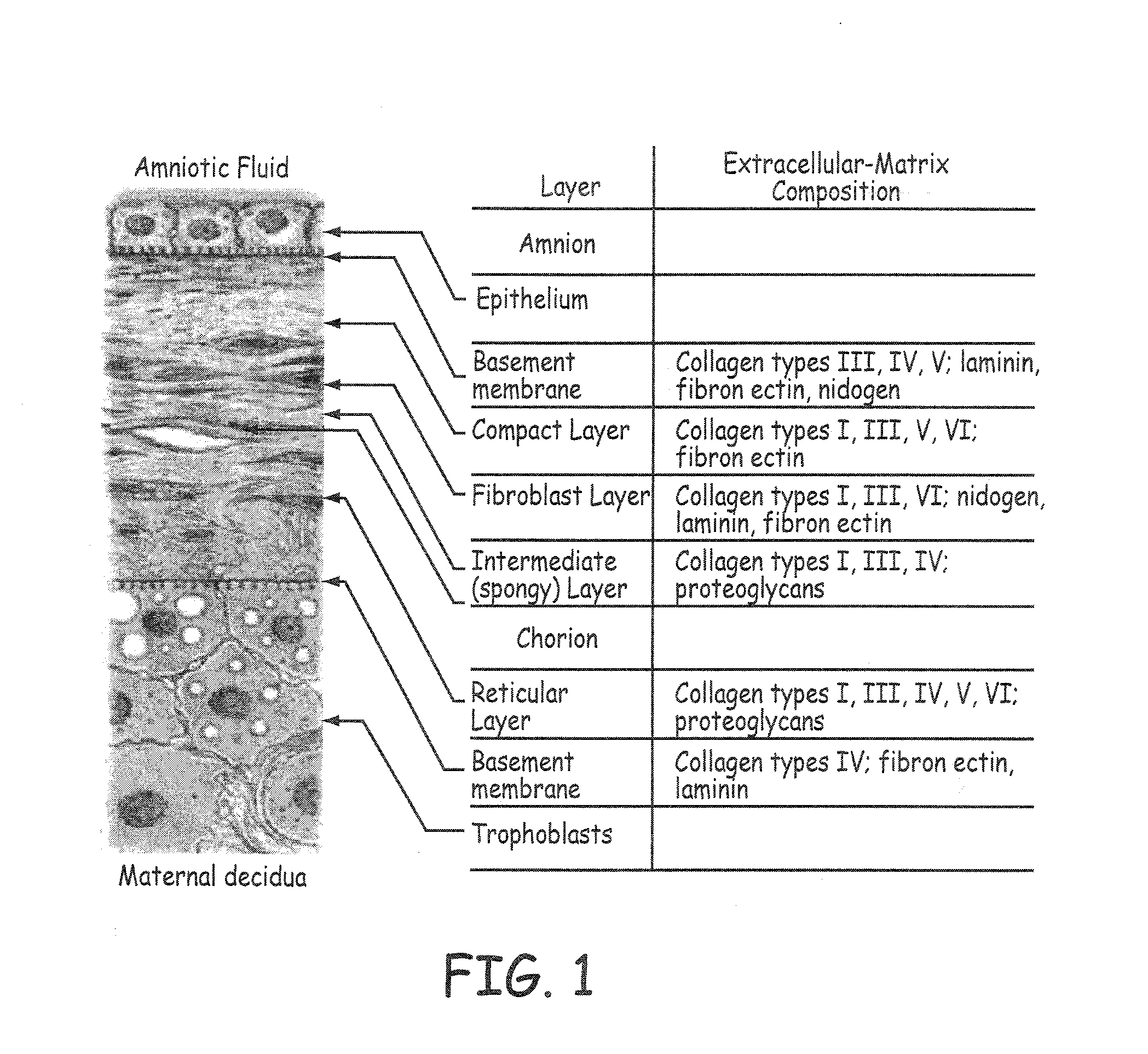
Collagen compositions and uses for biomaterial implants
InactiveUS20160263280A1Promote tissue regenerationReduce scarsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmniotic SheetImplant
Compositions containing purified collagen biomaterial derived from tissues, for example, insoluble amnion, soluble amnion, soluble chorion of the human placenta, are provided. The collagen compositions can be used to promote wound healing, promote tissue regeneration, prevent or reduce scarring, reduce local inflammation, minimize tissue rejection, promote graft integration. Methods for using the collagen composition as a biomaterial implant for dermal filling, skin grafting, and hair transplantation are also provided.
Owner:MAM HLDG OF WEST FLORIDA L L C
Method for preparing human amniotic membrane epithelial cells from human placenta amnion and application thereof
ActiveCN106520676APromote proliferationHigh purityCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsForcepsDigestion
The invention relates to a method for preparing human amniotic membrane epithelial cells from human placenta amnion and application thereof, in particular to the method for preparing human amniotic membrane epithelial cells from the placenta amnion. The method comprises the following steps that the surface of a placenta is flushed with a basic balanced salt solution repeatedly and the placenta is sterilized; a foetal membrane outer layer amnion is torn and taken into a glass dish by surgical forceps, the grimy blood on the surface of the foetal membrane outer layer amnion is flushed with the basic balanced salt solution, and then the foetal membrane outer layer amnion is sheared into small blocks; the small amnion blocks are evenly attached to a culture dish, the epithelial layer of the amnion faces downwards, and after drying, a complete medium is added for culture; fluid infusion is conducted two days later, and then culture is continued; when epithelial cells are seen to crawl out, a tissue is removed, and medium change is conducted to continue culture; after multiple typical epithelial cell masses occur, the local fusion rate reaches 90%, and continuous cell culture is conducted; and harvesting is conducted, specifically, digestion is conducted by pancreatic enzymes, counting and freezing storage are conducted, and the human amniotic membrane epithelial cells are obtained. The invention further relates to the prepared human amniotic membrane epithelial cells and the application thereof. The method has the advantages showing in the specifications.
Owner:BOYALIFE
Method of using amnion allograft in heart transplant surgery
InactiveUS20130209524A1Suitable shapeReduce sizeBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismHeart transplantationImproved method
Owner:LIVENTA BIOSCI
Method for extracting sub-totipotent stem cell from chorion of fetal surface of placenta
ActiveCN105200007AReduce processingReduce manpowerNervous disorderGenetic material ingredientsFiltrationMagnetic bead
The invention relates to a method for extracting sub-totipotent stem cells from a chorion of a fetal surface of a placenta. The method comprises the steps of removing an amnion and stagnated blood from the placenta, and then repetitively washing the surface of the placenta to perform sterilization; shearing the chorion of the fetal surface in a glass utensil, removing placenta lobule tissues remained on the surface as much as possible, and shearing the chorion into small blocks; washing small tissue blocks by using a screen and a great amount of normal saline, and removing residual blood cells; performing tissue digestion: performing oscillatory digestion in a constant temperature shaker by using mixed enzymes; adding a proper amount of FBS for termination after digestion, performing filtration through a filter screen, and adding a great amount of normal saline to wash filter residues to obtain cells as many as possible; performing centrifugation, abandoning supernatant, adding saline water for washing and performing centrifugation to obtain mononuclear cells; performing magnetic bead sorting (OCT-4 positive, Nanog positive and STRO-1 negative) to obtain target cells. The invention further relates to the sub-totipotent stem cells obtained by adopting the method and pharmaceutical use thereof. The sub-totipotent stem cells have excellent characteristics.
Owner:BOYALIFE
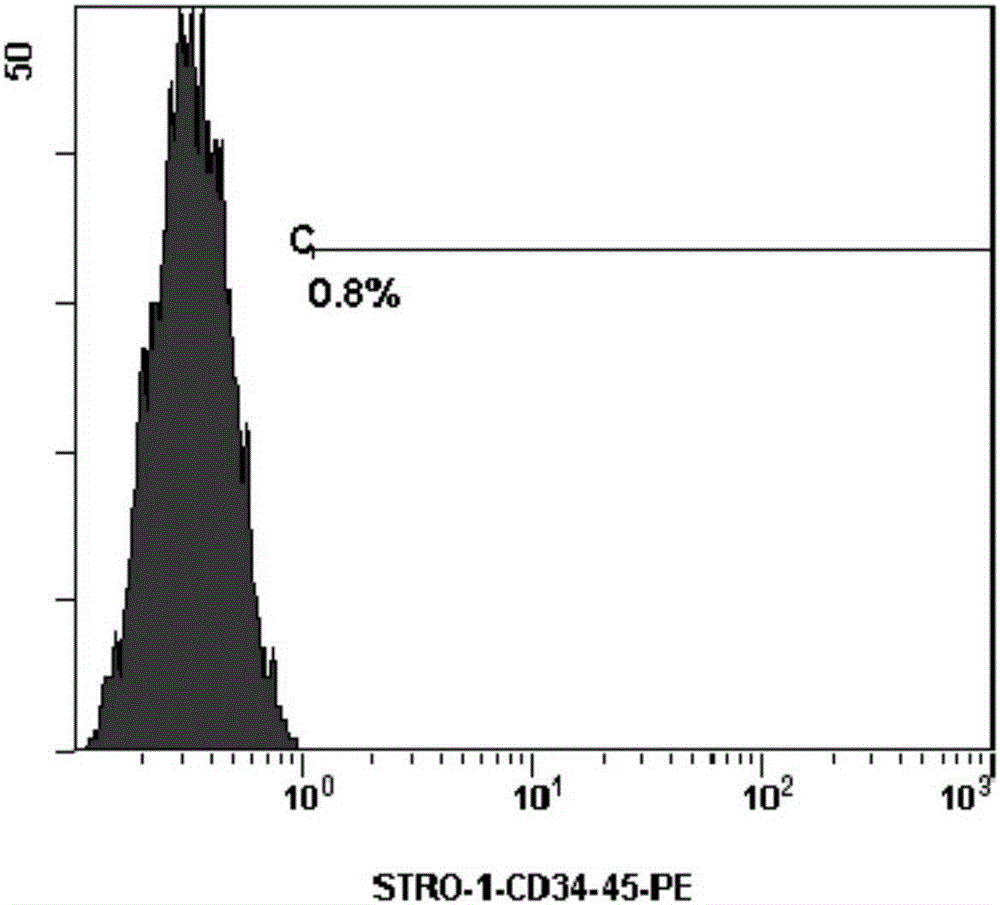
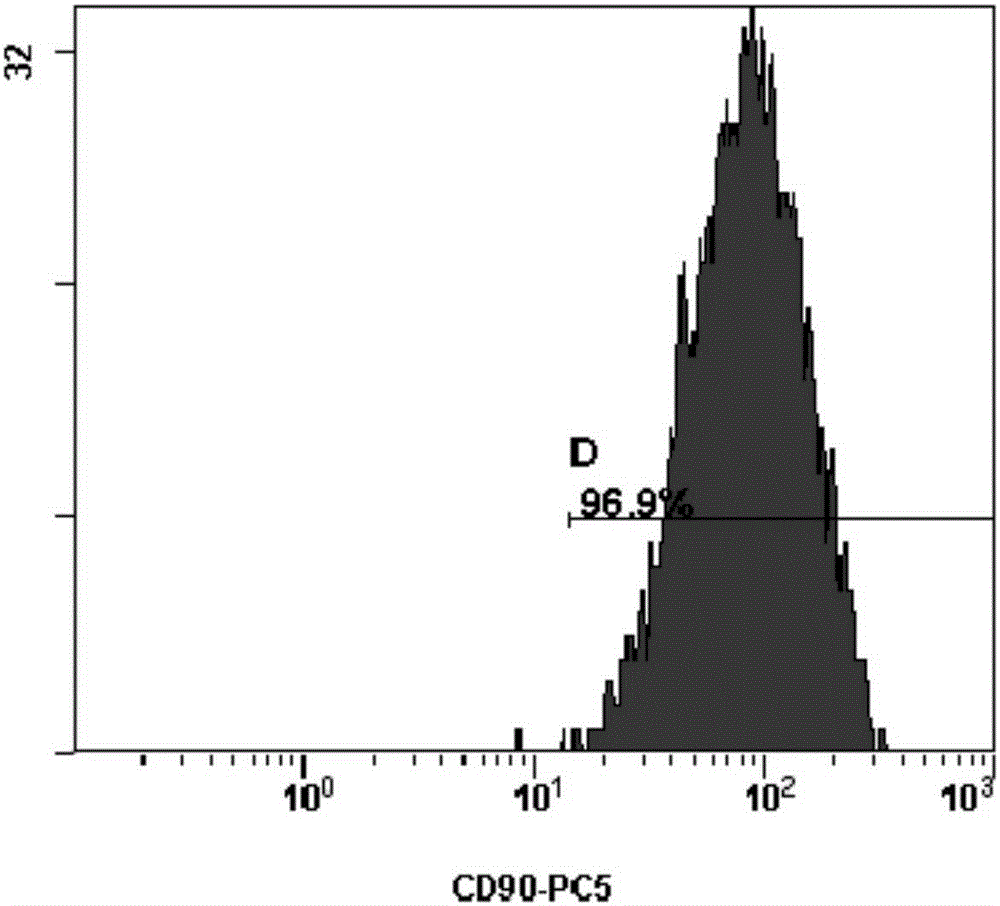
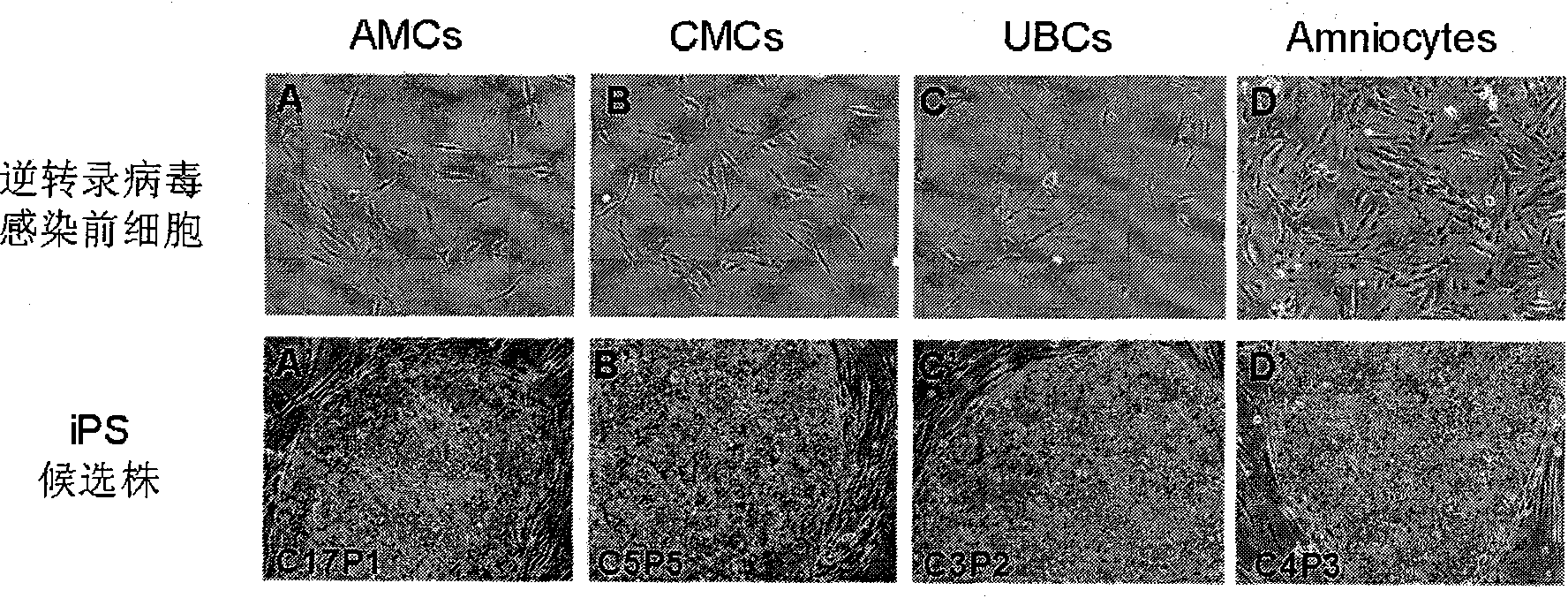
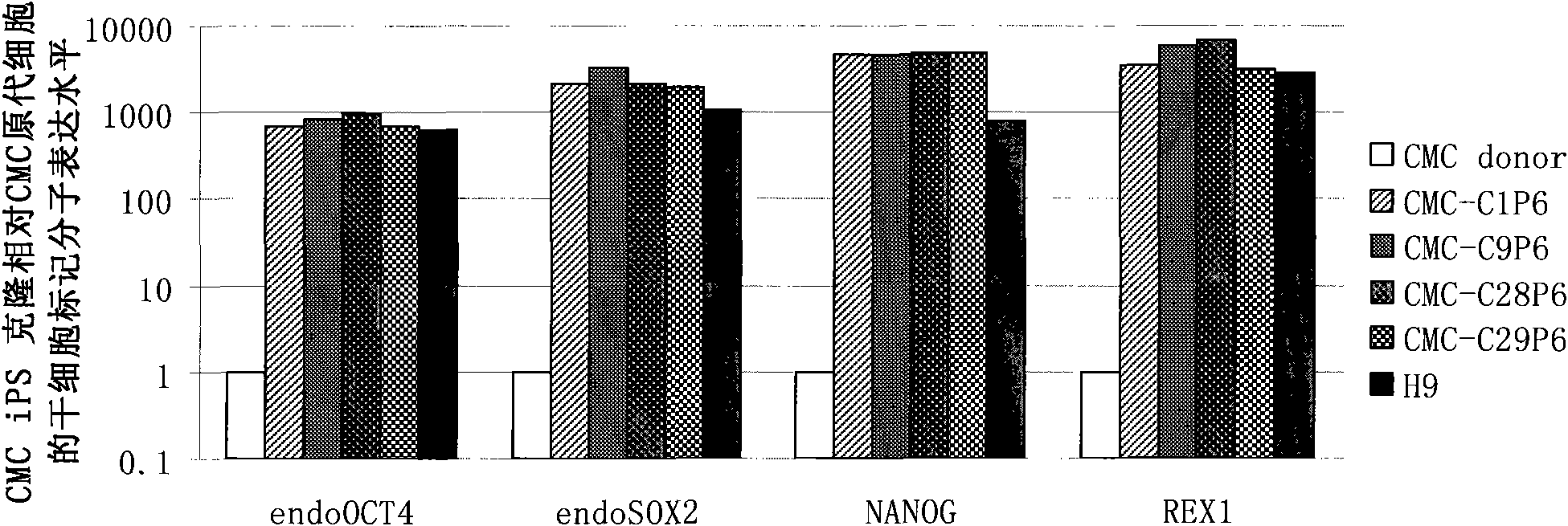
Cell type used for producing induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101984050AGreat therapeutic application prospectsGood pluripotencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionControl orientedDisease
The invention discloses four cell types which have wide heteroplastic transplantation application prospect and can be effectively induced into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells. The origins of three cell types are placental tissue, namely amnion mesenchymal cell, chorion mesenchymal cell and umbilical cord mesenchymal cell; and the origin of the other one is amniotic fluid cell. Besides, the invention also discloses an induction reprogramming method for producing cells capable of producing induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by efficient induction, including the following steps: cDNA containing pluripotent stem cell factor is respectively introduced into the four primary culture cells; the four primary cells in which cDNA is introduced are respectively cultured on appropriate culture mediums, primary iPS is obtained and then quality of iPS is optimized on appropriate culture mediums, and cloning of pluripotent stem cell can be primarily evaluated. In the invention, three mesenchymal cells of placenta origin and amniotic fluid cell all can be induced into iPS, wherein the chorion mesenchymal cell is compared with fibroblast, efficiency of induction reprogramming is improved by over 100 times, efficiency is about 2.3%, and the efficiency is slightly higher than that of horny cell; and a means which is more effective and more pertinent is provided for building disease model, screening drug and controlling oriented differentiation.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of treatment utilizing an acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition
ActiveUS9814746B2Reduce in quantityHigh cure rateCosmetic preparationsAerosol deliveryMedicineAmniotic fluid
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions are described having a number of various compositional embodiments. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition has essentially no live or active amniotic cells. The amniotic cells may be destroyed, and the cells and cell debris may be removed from the acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may comprise micronized placental tissue particles, and / or amniotic fluid. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be a dispersion of micronized amniotic membrane combined with a fluid, such as plasma, saline, amniotic fluid, combinations thereof and the like. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be combined with a matrix component to form a composite. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be used in conjunction with a composition comprising viable cells, such as stem cells.
Owner:AMNIO TECH
Preparation method and application of autologous mesenchymal stem cell-loaded human amniotic membrane cornea paster
InactiveCN103055348ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisBone marrow mesenchymal stem cellsMembrane configuration
The invention discloses a preparation method of an autologous mesenchymal stem cell-loaded human amniotic membrane cornea paster, wherein autologous sourced mesenchymal stem cells are planted onto an amniotic membrane to be taken as bearing carriers to treat the corneal injury. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating monocyte separated from bone marrow into an alpha-MEM culture medium, amplifying to a third generation to inoculate 2.5*10<5> cells onto the 1.2cm*1.2cm amniotic membrane, and tightly arranging the cells after 48 hours, wherein the cover area of the mesenchymal stem cell under an inverted microscope is greater than 80%, and the immunofluorescent staining shows that the positive rate of cells CD44 and CD90 is greater than 90%. The human amniotic membrane-loaded mesenchymal stem cell paster is free from dissolving and falling after being transplanted within one week, and new vessels can not be generated within eight months. The method is free from immunological rejection, an enough cell source can be provided, and the method can be used for the clinic treatment of the corneal injury.
Owner:北京清美联创干细胞科技有限公司
Alpha-thalassemia screening kit and application thereof in prenatal screening
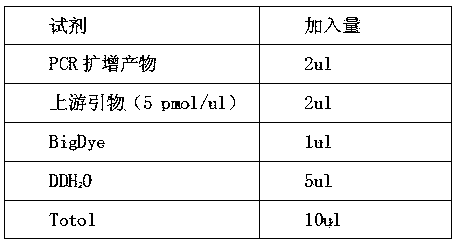
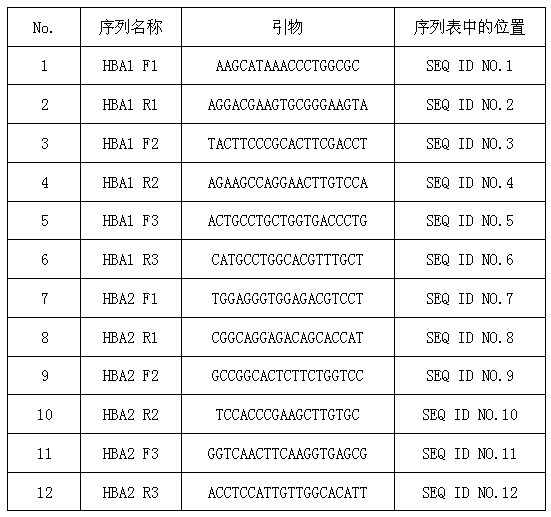
ActiveCN103421903AReasonable primer designAchieving Prenatal ScreeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseObstetrics
The invention discloses an alpha-thalassemia screening kit and application thereof in prenatal screening and belongs to the technical field of prenatal screening of alpha-thalassemia. The alpha-thalassemia screening kit comprises a negative control sample, a positive control sample, PCRmasterMIX, and a PCR primer. Application of the alpha-thalassemia screening kit includes: amplifying fetal DNA in maternal peripheral blood by the designed primer so as to perform prenatal screening on alpha-thalassemia. The maternal peripheral blood is collected for prenatal screening of alpha-thalassemia, with no need for puncturing the amnion cavity and inserting pile tissue and with no injury to fetus, and the alpha-thalassemia screening kit is safe and reliable; accuracy is up to 99.99%; the technical blank of noninvasive prenatal screening of alpha-thalassemia is filled, and fewer children with diseases are born.
Owner:邯郸市康业生物科技有限公司
Ectocornea-like sheet and method of constructing the same
InactiveUS20050003532A1Reduce differentiationHigh divisional potentialEye implantsArtificial cell constructsDiseaseOral mucosal epithelial cell
It is intended to provide a transplantation material applicable to ocular surface diseases with a need for ectocornea transplantation (i.e., an ectocornea-like sheet). Oral mucosal epithelial cells are inoculated onto an amnion and then cultured in the coexistence of supporter cells. When a layered structure of the oral mucosal epithelial cells is formed, the outermost layer is brought into contact with air, thereby inducing differentiation. Thus, an ectocornea-like sheet having an oral mucosal epithelial cell layer on the amnion is obtained.
Owner:AMNIOTEC +1
Method and kit for acquiring amniotic mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN106635976AHigh purityHigh activityCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDigestion TreatmentMesenchymal stem cell
The invention discloses a method and a kit for acquiring amniotic mesenchymal stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out first digestion treatment on an amniotic membrane by adopting a first enzymic preparation, and abandoning digestion liquid, thus obtaining a first digestion product; carrying out second digestion treatment on the first digestion product by adopting a second enzymic preparation, and abandoning digestion liquid, thus obtaining a second digestion product; and separating the amniotic mesenchymal stem cells from the digestion product, wherein the first enzymic preparation comprises a trypsin-EDTA mixed solution, the second enzymic preparation comprises collagenase and DNase I. With the adoption of the method and the kit for acquiring the amniotic mesenchymal stem cells provided by the invention, a number of amniotic mesenchymal stem cells with high purity and high activity can be obtained.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI +1
Amnion derived therapeutic composition and process of making same
ActiveUS20180271915A1Reduce harmMaintain their viabilityOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAmniotic fluidPlacental tissue
Acellular amnion derived therapeutic compositions are described having a number of various compositional embodiments. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition has essentially no live or active amniotic cells. The amniotic cells may be destroyed and the cells and cell debris may be removed from the acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may comprise micronized placental tissue particles, and / or amniotic fluid. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be a dispersion of micronized amniotic membrane combined with a fluid, such as plasma, saline, amniotic fluid, combinations thereof and the like. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be combined with a matrix component to form a composite. An acellular amnion derived therapeutic composition may be used in conjunction with a composition comprising viable cells, such as stem cells.
Owner:AMNIO TECH
Human amniotic epithelial cell separation method
ActiveCN104974980AHigh purityHigh differentiation potentialEmbryonic cellsEpithelium surfaceCell activity
Owner:CHONGQING CELL BIOENG TECH CO LTD
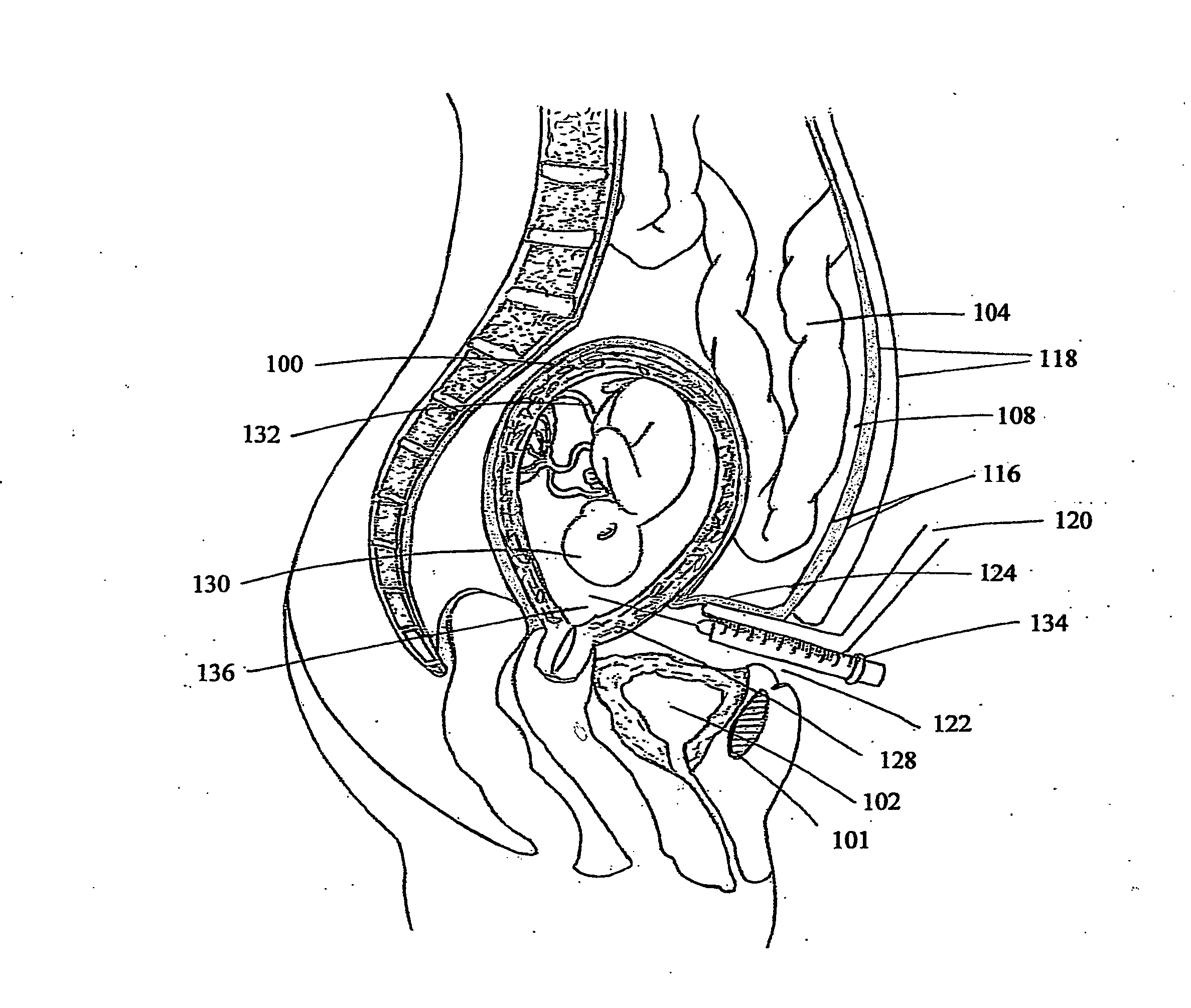
Intrauterine fetal growth restriction - The biochemical rationale of treatment modalities including extraperitoneal transamniotic fetal supplements
ActiveUS20140330246A1Decreases placental transfer of D-glucoseImproving fetal hypoglycemiaBiocideMedical devicesDiseaseMineral supplementation
Intrauterine fetal growth restriction (IUGR) is an affliction of a disparaging spectrum, placental insufficiency being the major inciting pathology. The resultant fetal hypoglycemia is alleviated by intravenous hypertonic D-glucose 25-50% maternal supplements, by improving the Vmax of placental transfer for D-glucose, in accordance with Michaelis-Menten model of substrate transfer. Fetal normoglycemia so restored in turn surprisingly improves fetal hypoxia, hypercapnia, hyperlacticemia, acidosis, hypertriglyceridemia, oliguria / hydromnios, and the fetal nutrient / mineral / vitamin acquisition. The list being phenomenal can only convince an inquiring reader by a biochemical sojourn into the aquatic world of the fetus, herein described. Maternal carbohydrate-predominant IUGR diet with maximal amounts of vitamin / mineral supplements are highly beneficial. Transamniotic isotonic D-glucose supplements via minimally invasive suprapubic extraperitonial pelvic approach and amniotomy (Sumathi Paturu's technique), with a subcutaneously implanted pregnancy port (SIPP) catheter is the additional therapy advocated.
Owner:PATURU SUMATHI
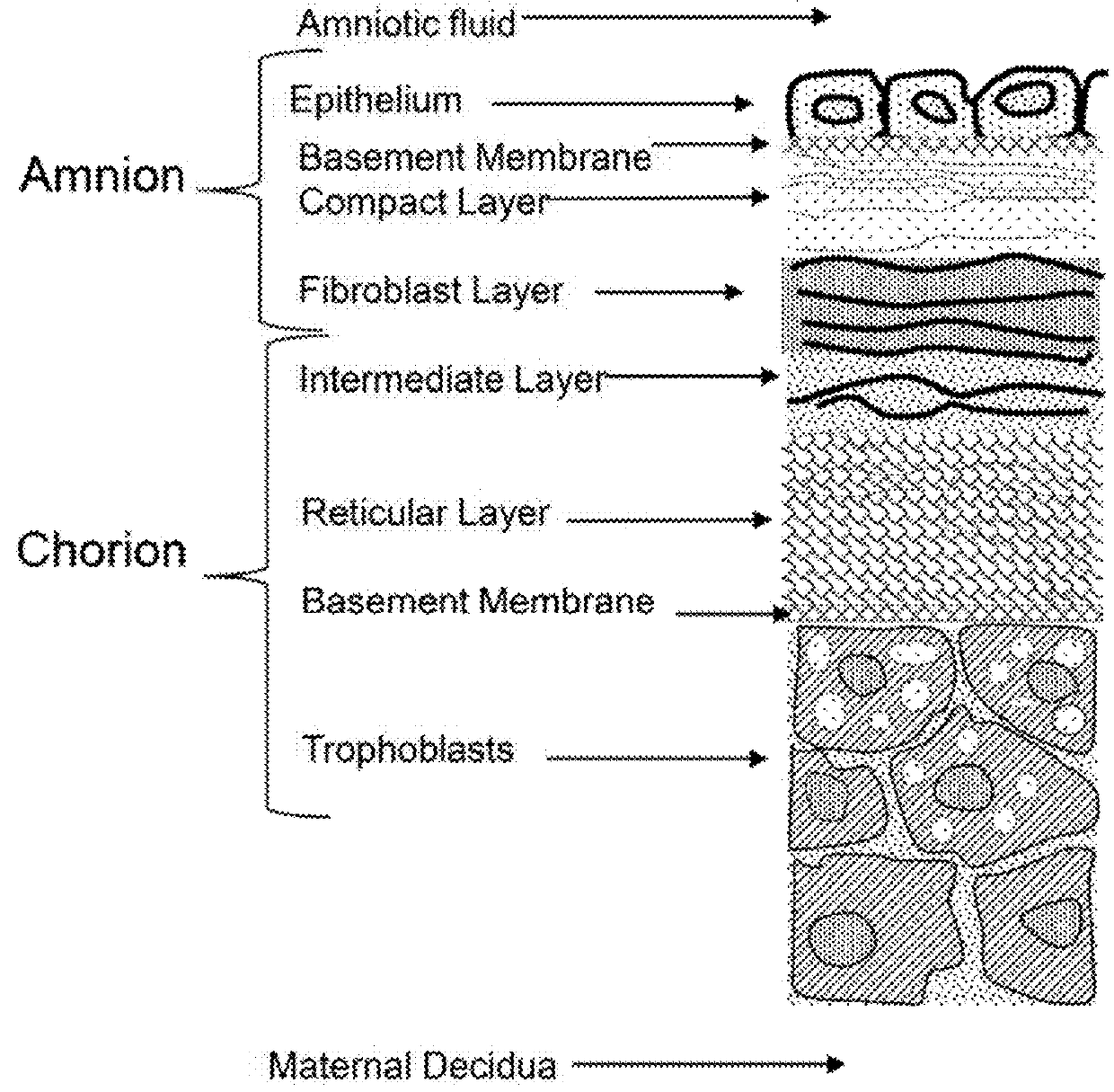
A composite membrane comprising a decellularized amniotic membrane and a method for preparing the same
ActiveCN110944654APreserve the physical support functionImprove mechanical propertiesSenses disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAmniotic SheetBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to the field of biomedical teclxnology, and relates to a composite membrane comprising a decellularized amniotic membrane, a use of the composite membrane, and a method for preparing the composite membrane.
Owner:WUHAN KANGCHUANG TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com