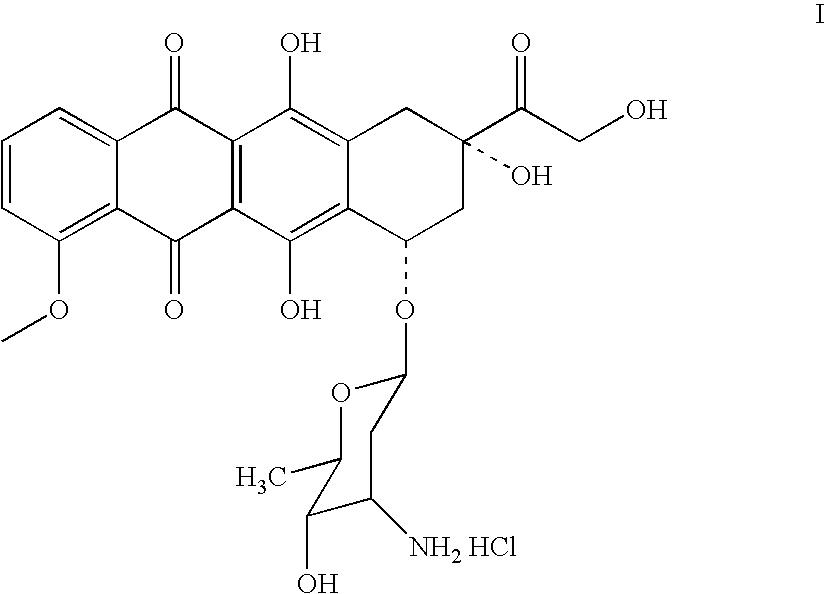
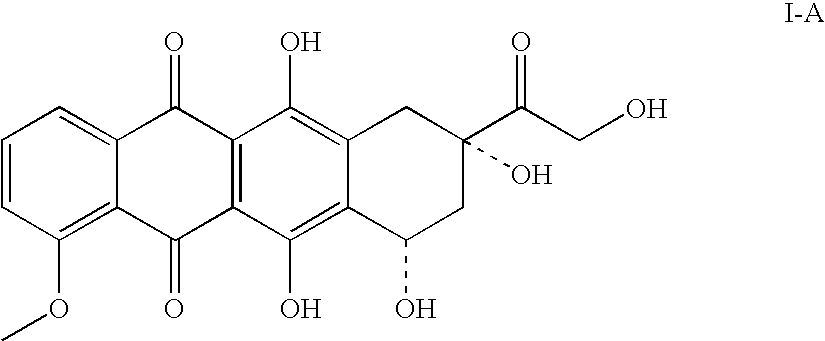
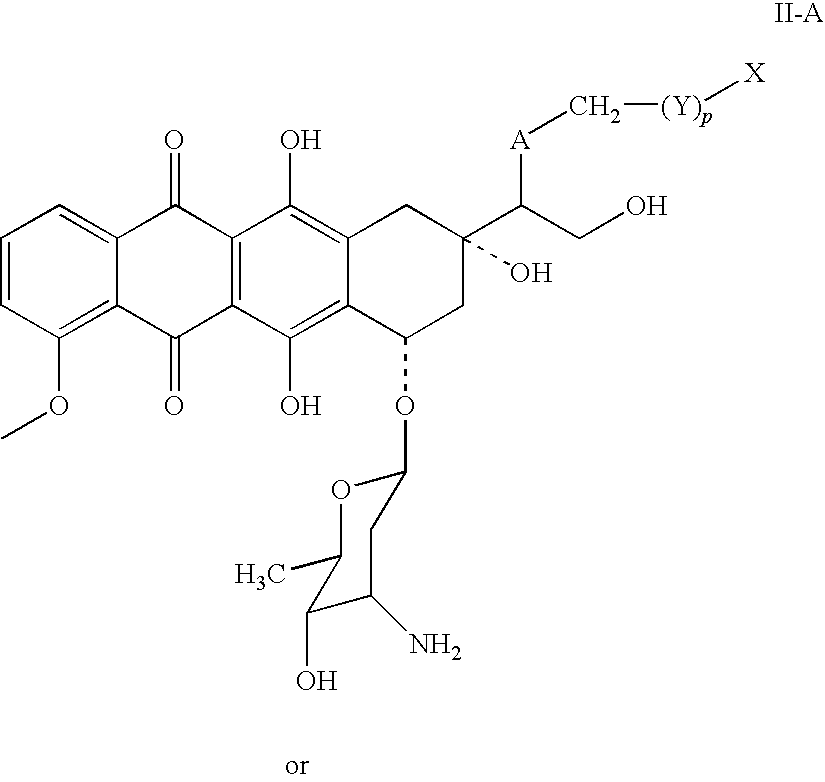
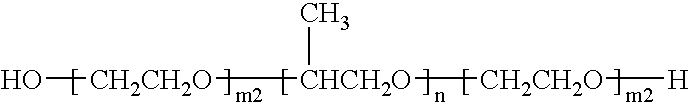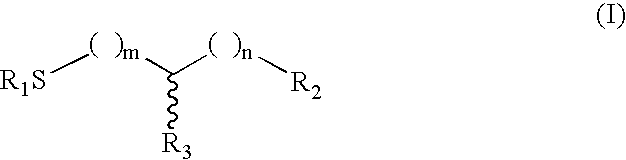Patents
Literature
95 results about "Doxorubicinone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
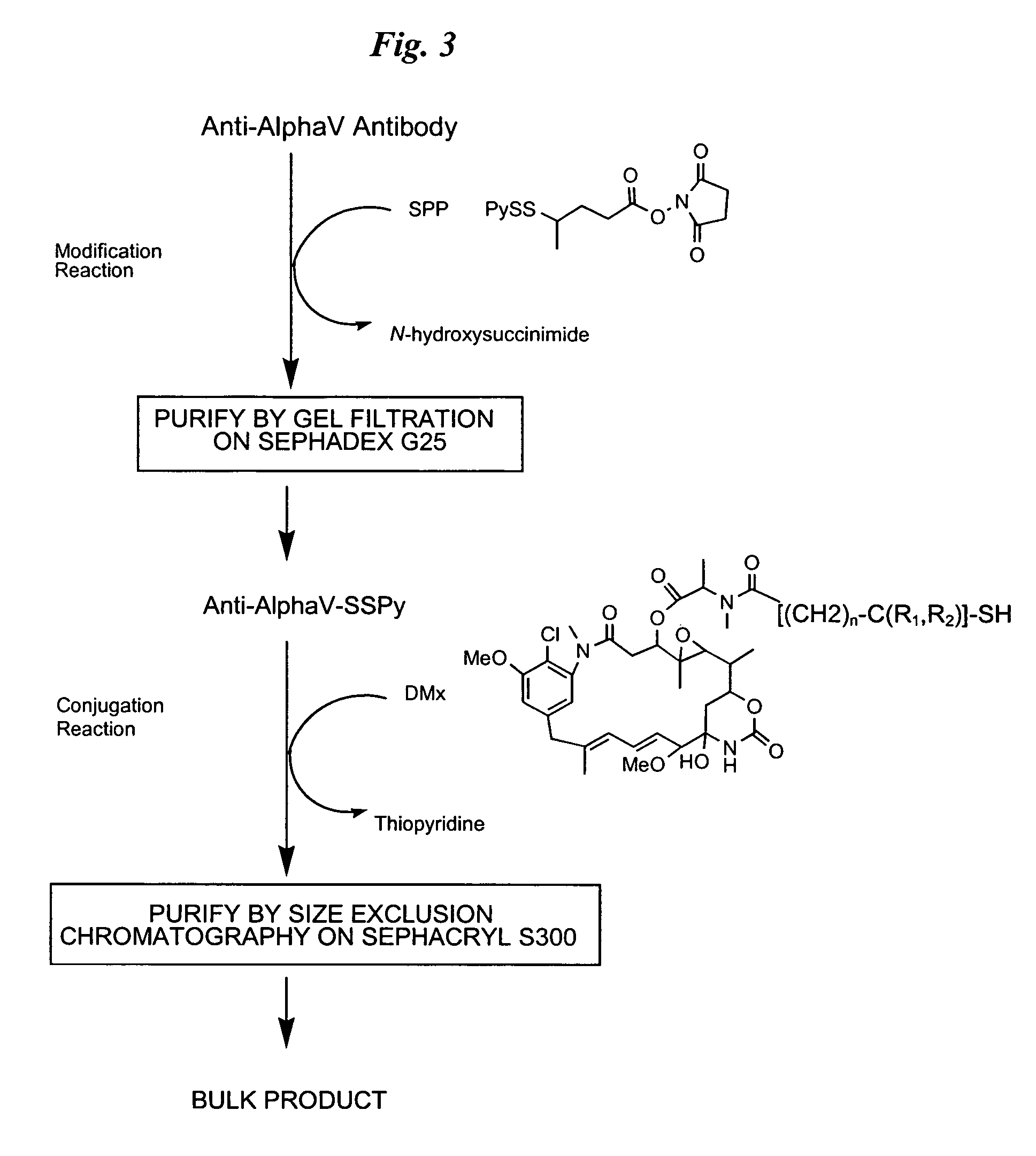
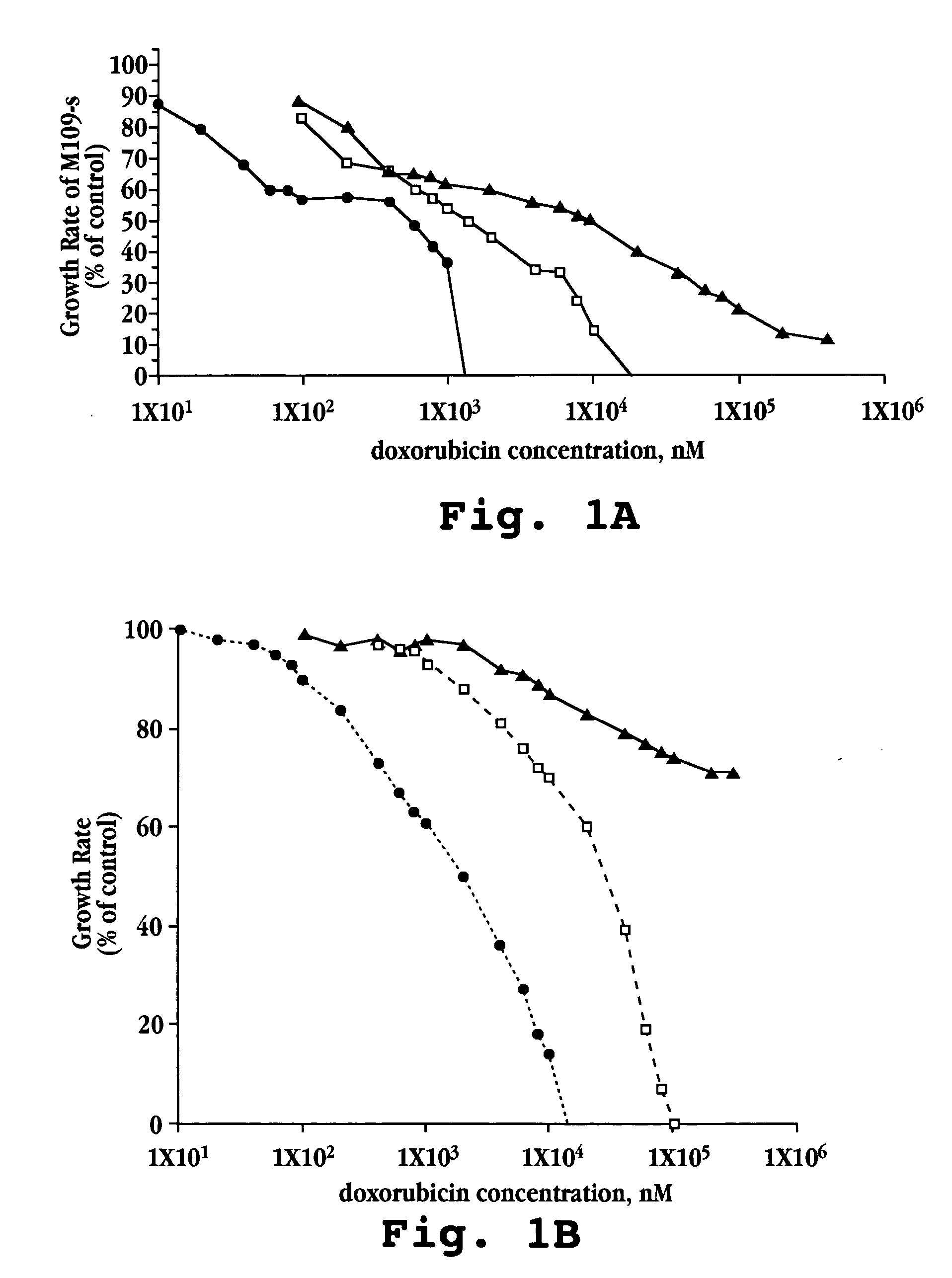
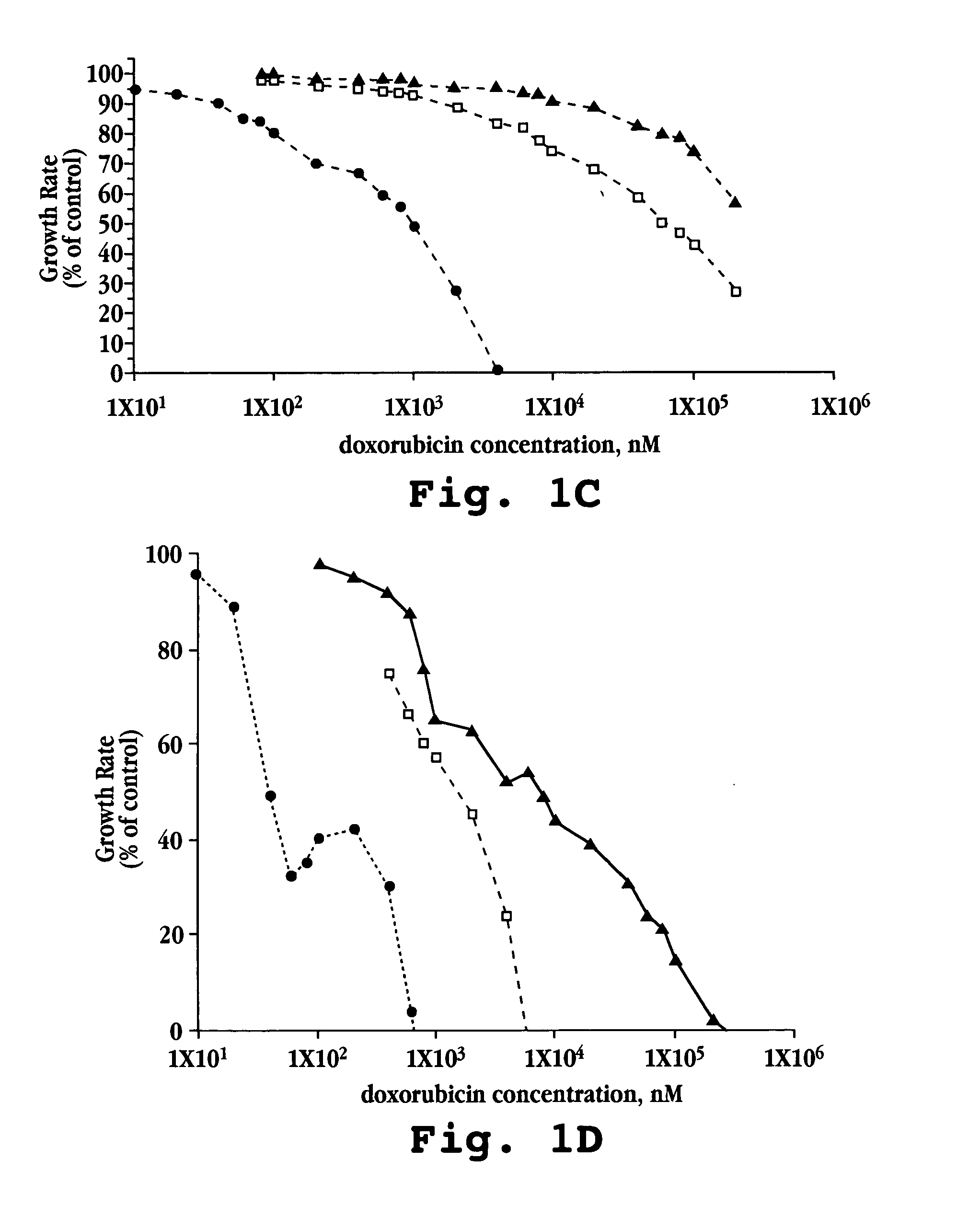
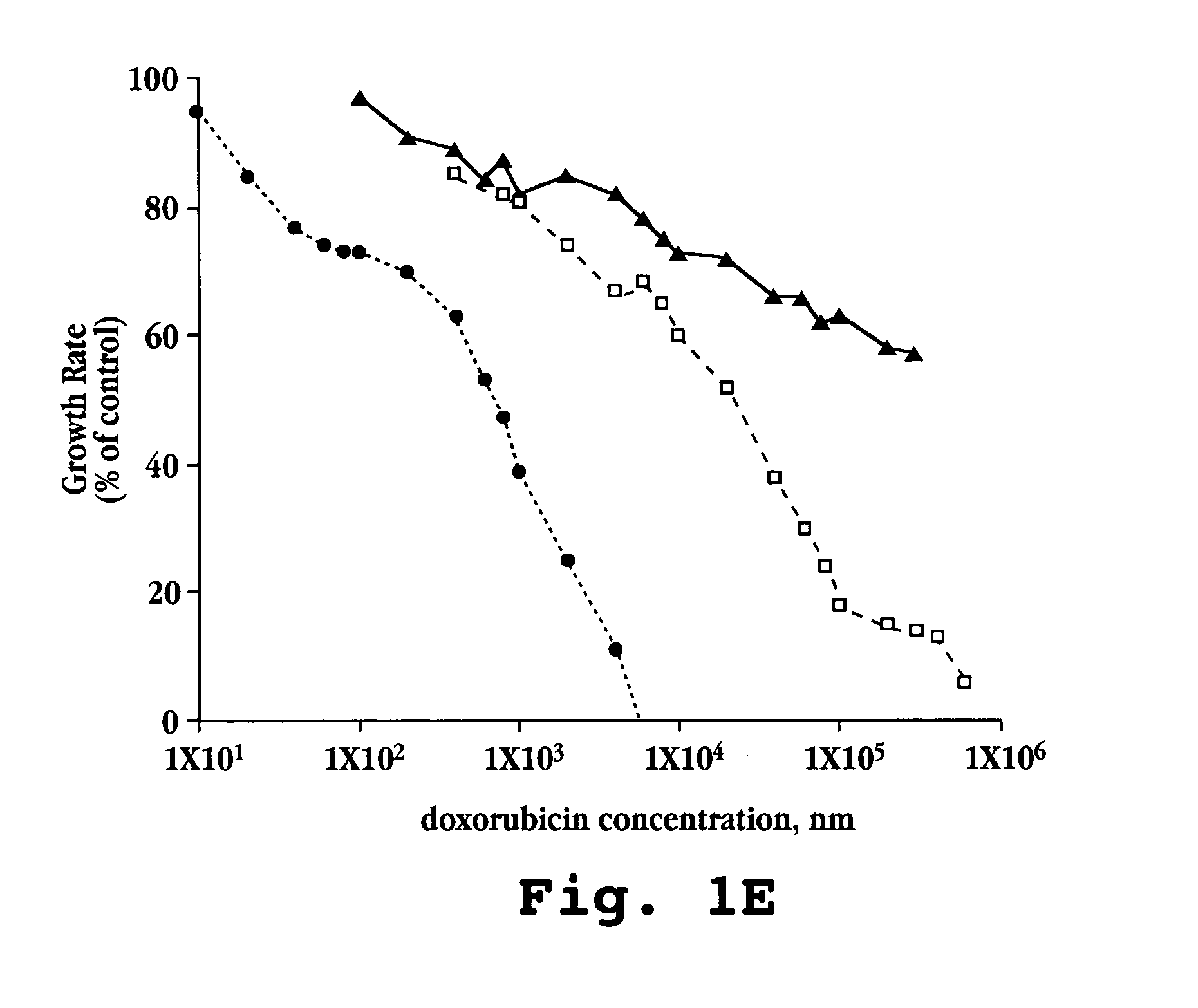
Anti-integrin immunoconjugates, methods and uses
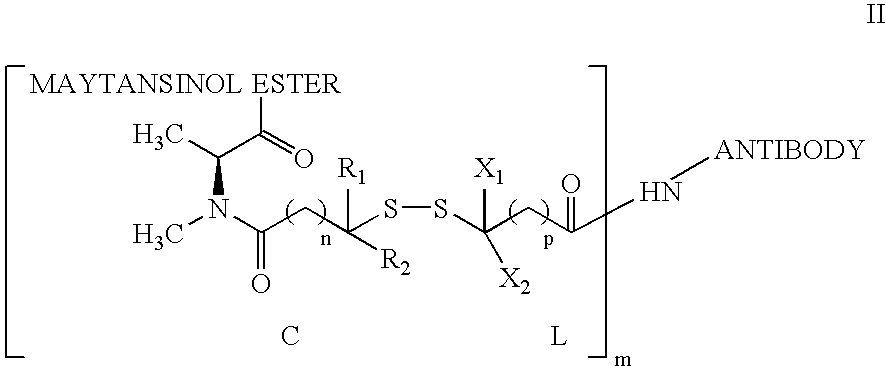
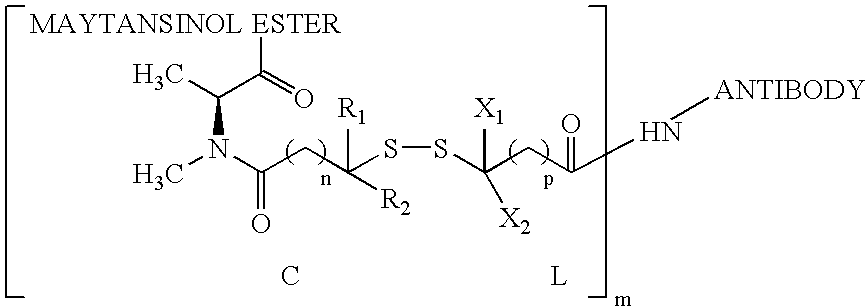
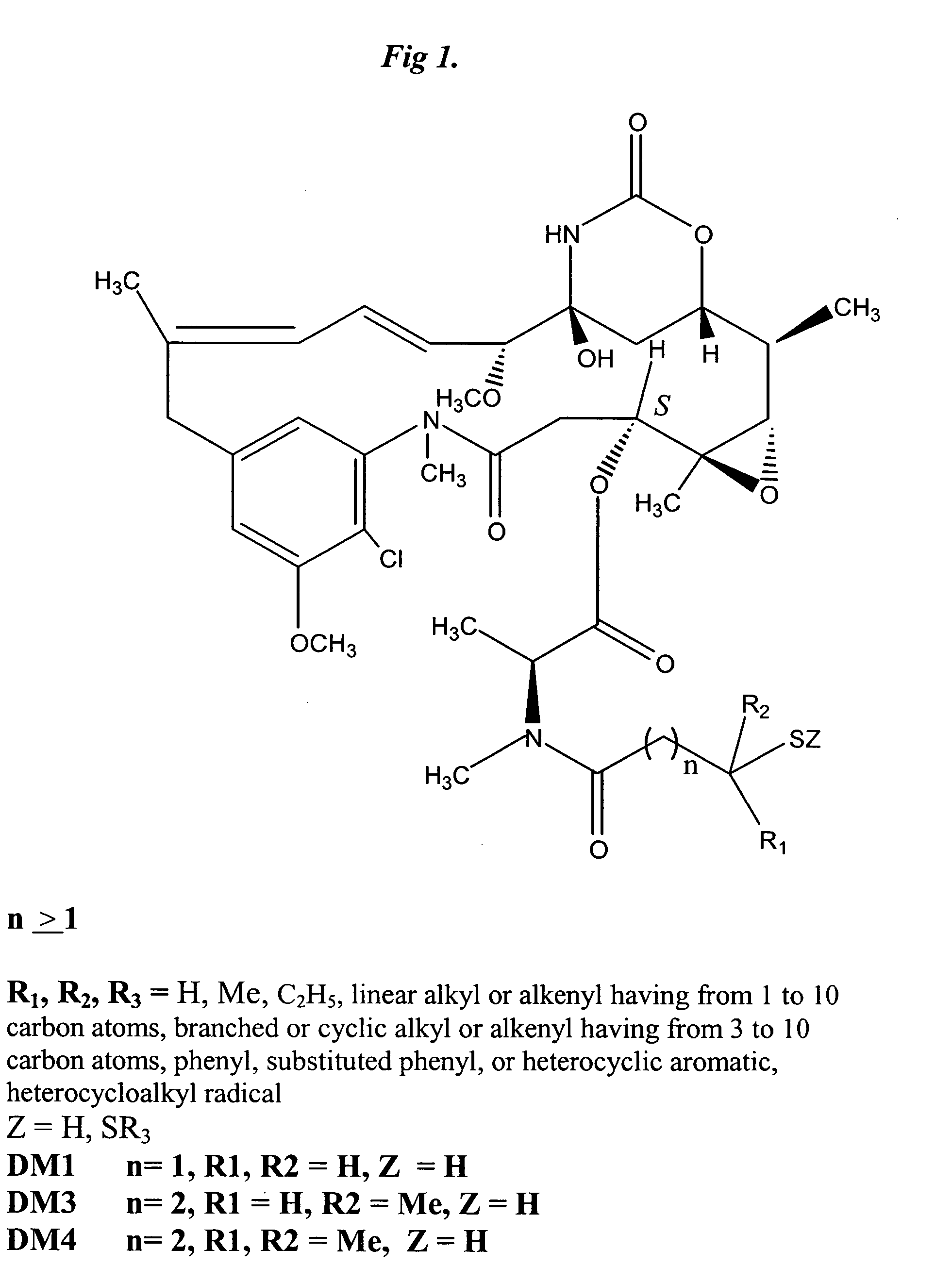
The invention relates to conjugates of anti-integrin specific antibodies with cytotoxic compounds, the synthesis, selection, and use of such conjugates for use in cancer therapy or other diseases mediated by cell proliferation, cell migration, or inflammation and which pathology involves angiogenesis or neovascularization of new tissue. In addition the invention relates to combination therapy of such diseases wherein the treatment comprises use of said conjugates in combination with one or more other treatment modalities including but not limited to: chemotherapy, surgery or radiation therapy. The preferred conjugates contain maytansinoid compounds linked to the antibody by a disulfide linkage, and preferred chemotherapeutic agents are doxorubicin, a taxane, a camptothecin, a podophyllotoxin, a nucleoside analog, or a pyrimidine analog.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC +1
Anti integrin antibodies linked to nanoparticles loaded with chemotherapeutic agents
InactiveUS20120263739A1Enhance efficacyCytotoxic effect be even enhancePowder deliveryNanomedicineDoxorubicinAntibody
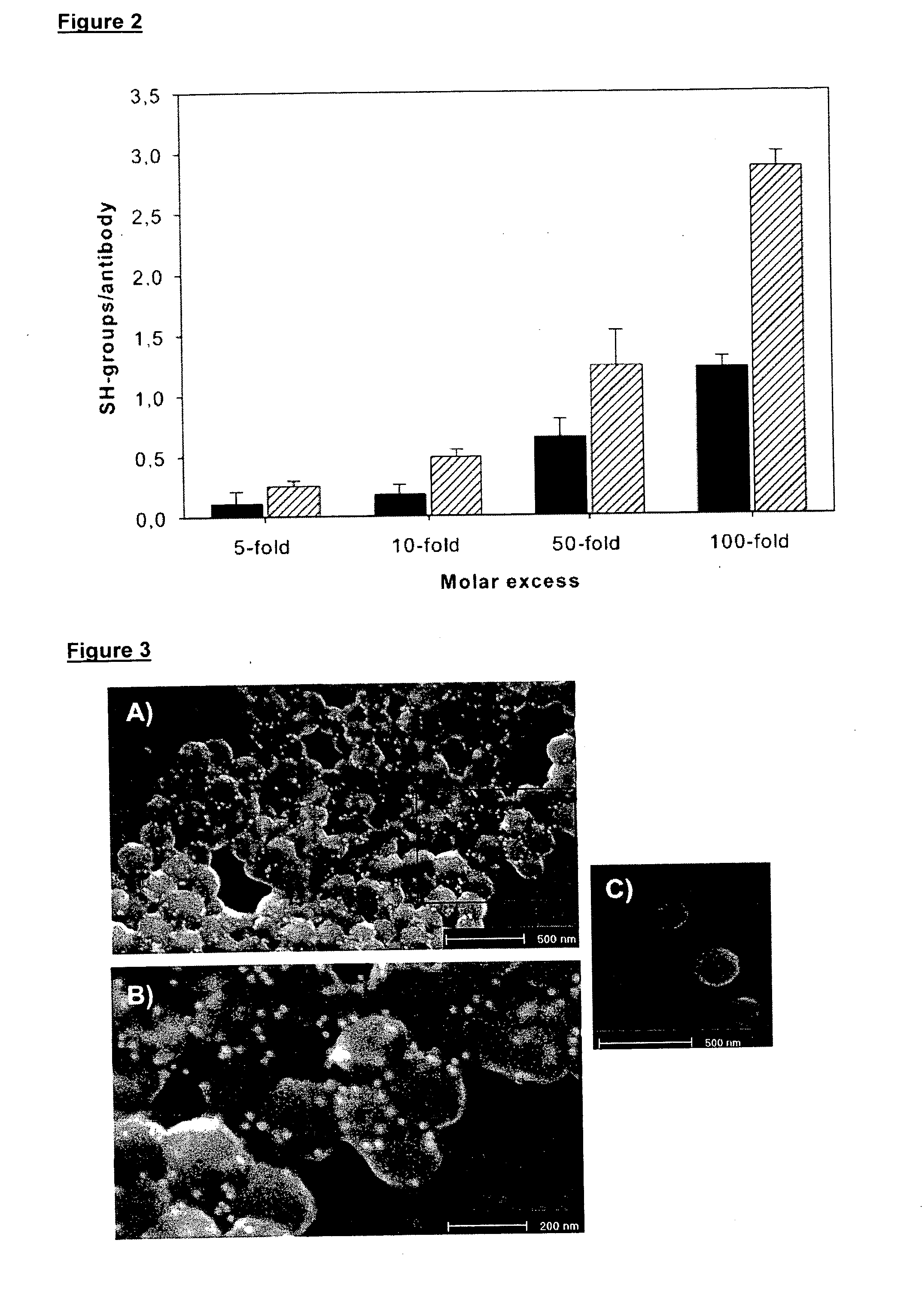
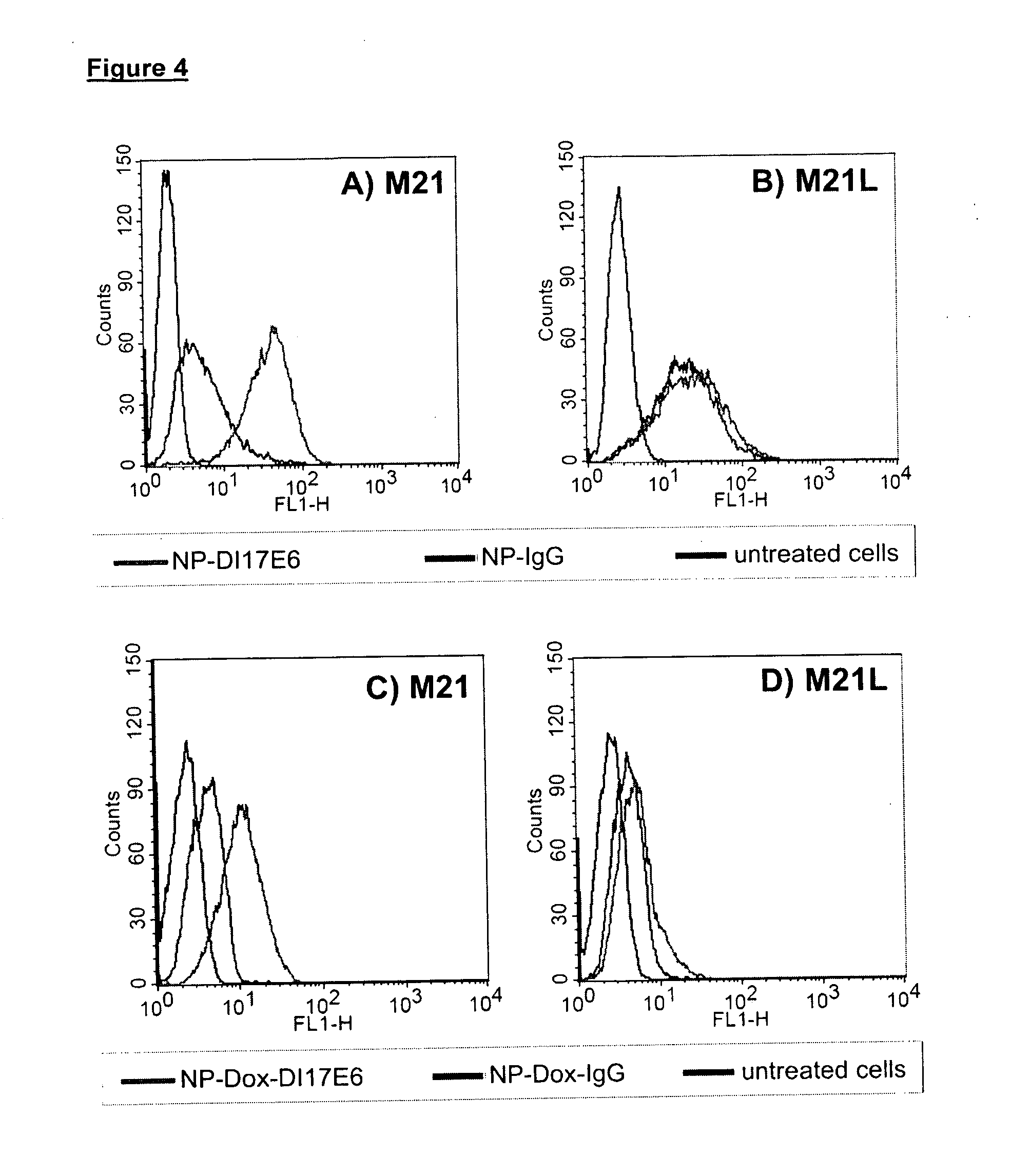
The invention relates to anti-integrin antibodies which are covalently linked to nanoparticles, wherein these nanoparticles were prior loaded with chemotherapeutic / cytotoxic agents. The antibody-chemotherapeutic agent-nanoparticle conjugates according to the invention, especially wherein the antibody is MAb DI17E6 and the cytotoxic agent is doxorubicin show a significant increase of tumor cell toxicity.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Doxorubicin formulations for anti-cancer use
Doxorubicin block copolymer formulations for use in preparing injectable compositions for treating cancer patients which contain lactose for solubilizing the doxorubicin and block copolymers in said formulations and methyl paraben for stabilizing these formulations, as well as a method of preparing and using these injectable compositions.
Owner:SOFTKEMO PHARMA CORP
Doxorubicin immunoassay
Novel conjugates of doxorubicin and novel doxorubicin immunogens derived from the 13 and 14 positions of doxorubicin and antibodies generated by these doxorubicin linked immunogens all of which are useful in immunoassays for the quantification and monitoring of doxorubicin in biological fluids.
Owner:SALADAX BIOMEDICAL INC
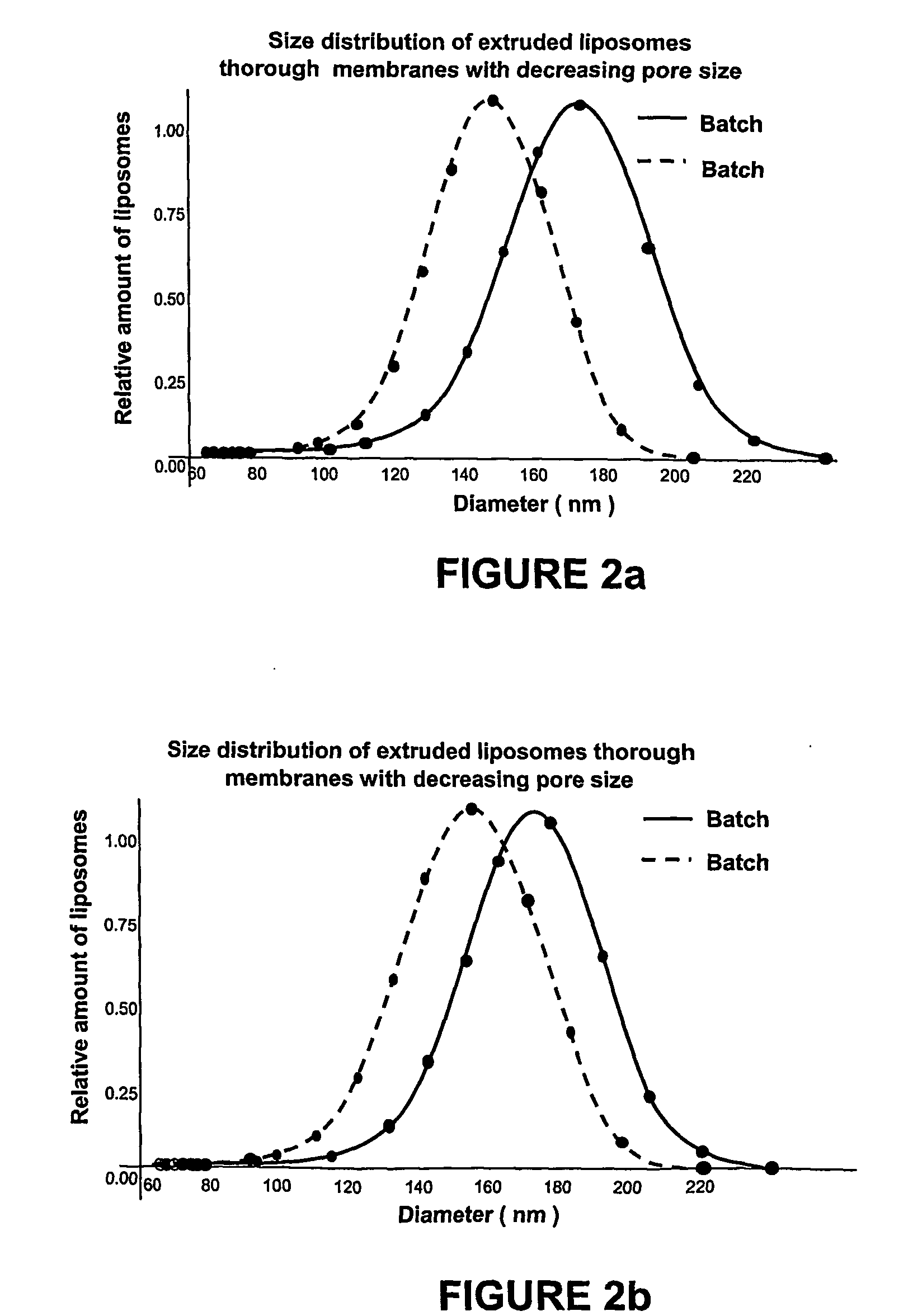
Process for producing liposome suspension and product containing liposome suspension produced thereby
A process for the large scale production of a liposome suspension, in which three selected lipid compounds in a predetermined ratio are dissolved in an alcohol solvent to form a mixture, which, in turn, is directly admixed with an aqueous ammonium sulfate solution in a predetermined ratio. The resultant mixture is subjected to a pore-extrusion treatment, followed by dialyzing the pore-extruded mixture with a 5% to 15% sucrose aqueous solution, such that a liposome suspension containing liposome particles suspended in the liposome suspension is obtained. The thus obtained liposome suspension can be used to encapsulate a selected drug, in particular doxorubicin.
Owner:TTY BIOPHARM
Preparation method and application of temperature and oxidant dual stimuli responsive nano-aggregate
InactiveCN105175656AAchieve graded and controlled releaseAchieving the role of passive targetingOrganic active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryBiocompatibility TestingCytotoxicity
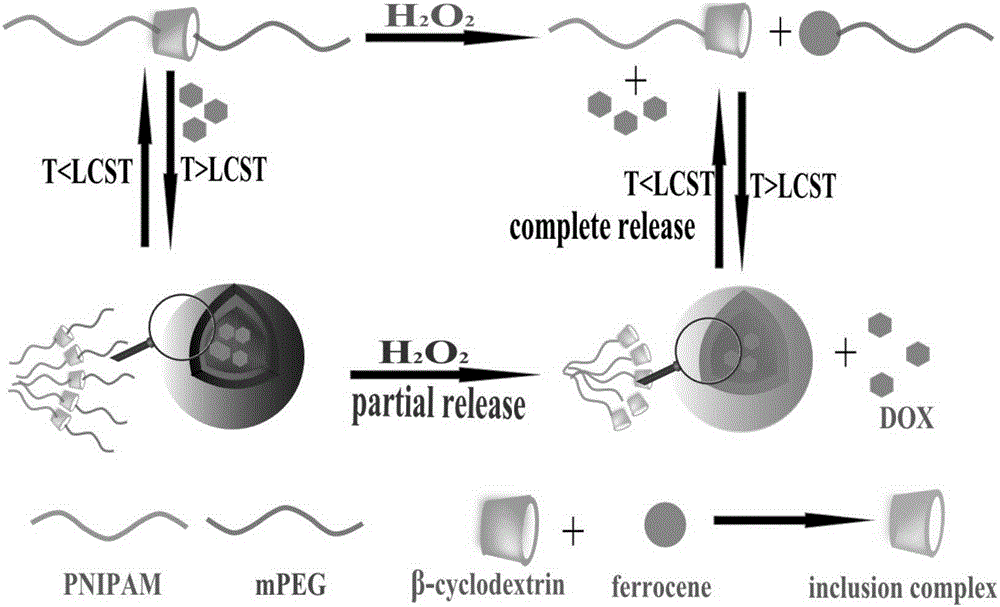
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a temperature and oxidant dual stimuli responsive nano-aggregate. According to the invention, the redox inclusion principle of beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) and ferrocene (Fc) and the temperature sensitive properties of the polymer poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) are utilized to connect PNIPAM-beta-CD with the end containing a beta-CD host group to hydrophilic polyethylene glycol (mPEG-Fc) with the end modified by an Fc guest group in a water solution through a host-guest recognized noncovalent bond, thus forming a supramolecular complex mPEG-Fc / PNIPAM-beta-CD. When the temperature is higher than the LCST (lower critical solution temperature) of PNIPAM, the macromolecular adduct can further gather in water to form a micellar structure. Micelle formation and disintegration can be realized by adjusting the solution temperature and adding an oxidant. cytotoxicity assessment experiments find that the supramolecular complex has very good biocompatibility. The supramolecular micelle packing the anticancer drug doxorubicin has very good effect in inhibiting A549 tumor cell growth. The preparation method of the nano-aggregate is simple, environment-friendly and economical, and the nano-aggregate has great application value in the field of biological medicine.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Model for studying the role of genes in chemoresistance
InactiveUS20090186839A1Increased chemosensitivityReduce cancer progressionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDoxorubicinPatient population
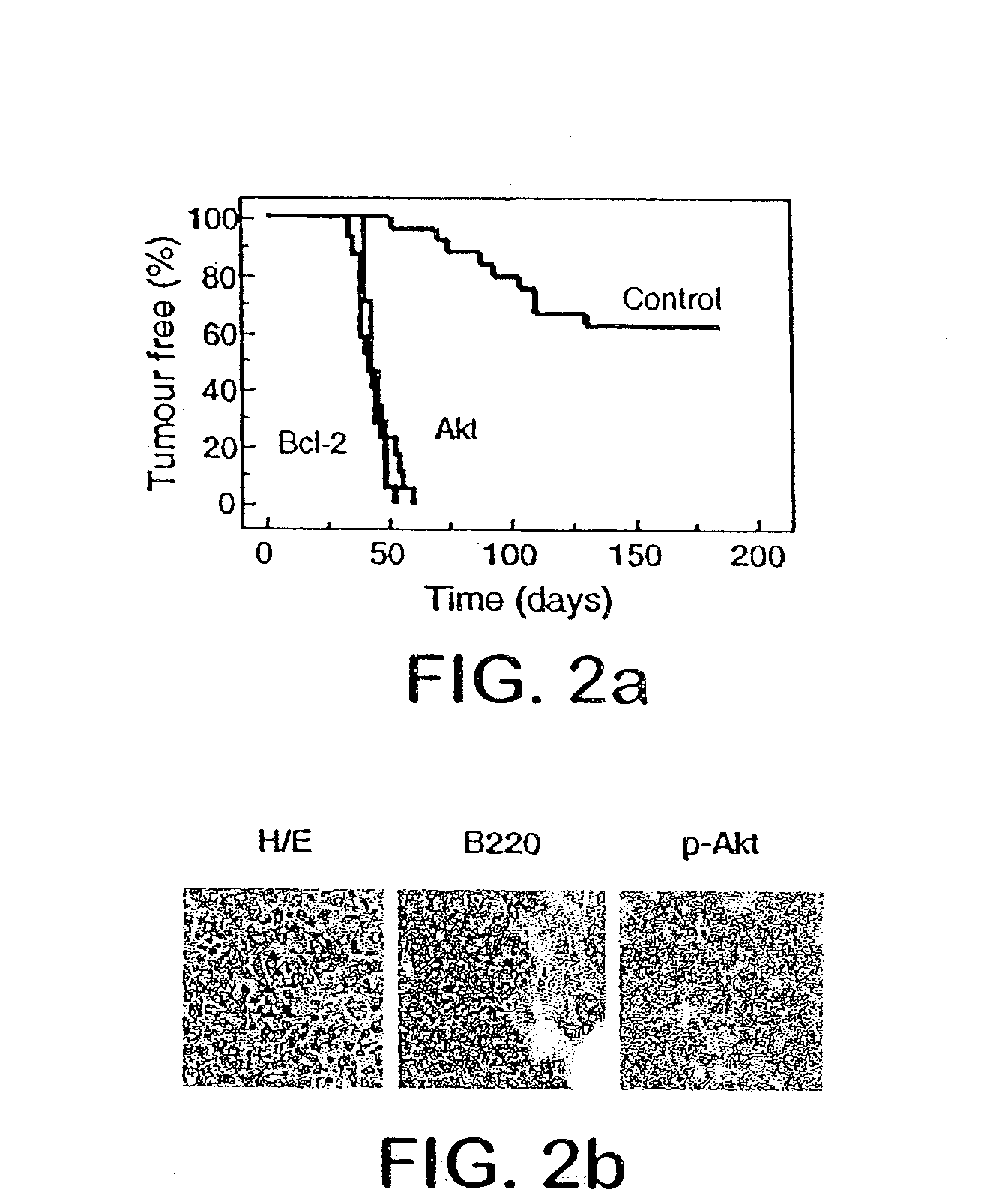
The invention provides novel inhibitors of protein translation initiation and inhibitors of eIF4F activity that can increase chemosensitivity or diminish or reverse chemoresistance in growth transformed cells and thereby reduce hyperproliferative conditions, such as cancer progression, in select patient populations having particular tumor genotypes. The invention also provides methods which target translation initiation controls in growth-transformed cells, such as tumor subtypes with altered expression of a gene activity, including the human akt, bcl-2, eIF4E, eIF4A or PTEN activities, to restore drug sensitivity in vivo in a genotype selective manner. In one aspect, the inhibitors of translation initiation of the invention are rocaglates, i.e., cyclopenta[b]benzofurons, which increases chemosensitivity or diminishes or reverses chemoresistance either alone or in combination, additively or synergistically, with other agents that alter growth or death. Preferably, the rocaglate is silvestrol, which is used alone or in combination with doxorubicin to reverses chemoresistance in PTEN-deficient lymphomas or eIF4E-over-expressing lymphomas and to promote cancer remission.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
Multi drug response markers for breast cancer cells
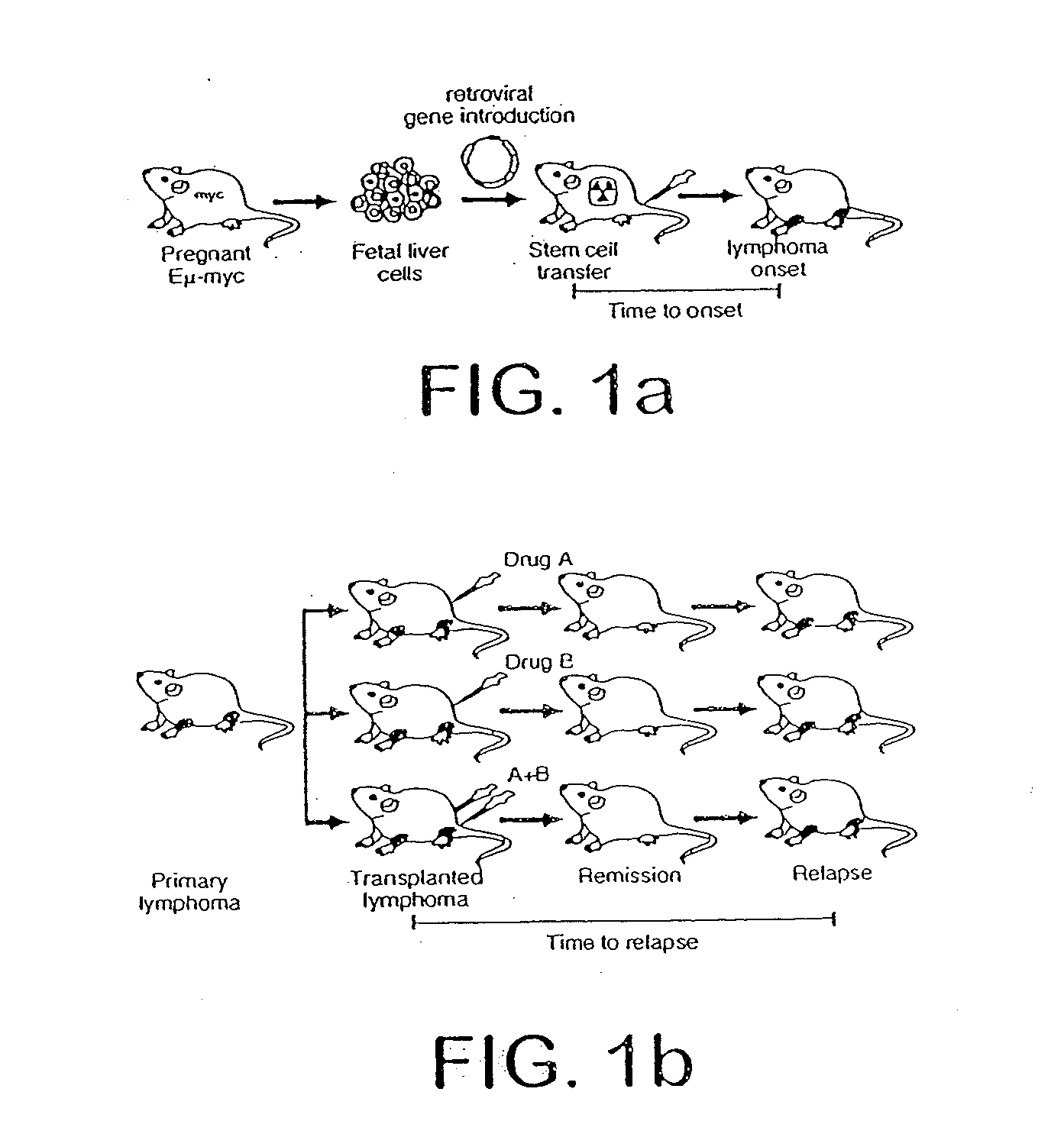
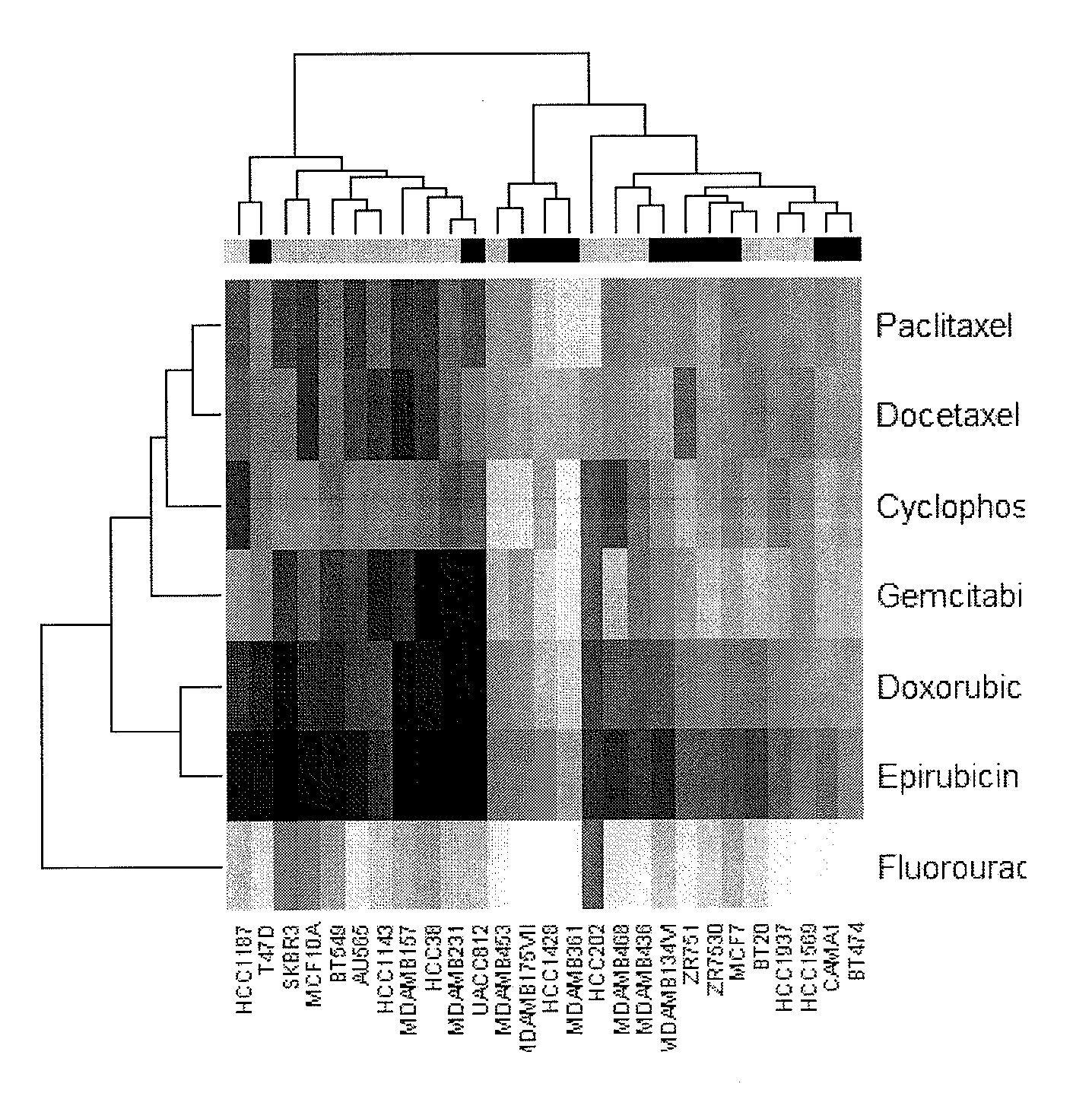
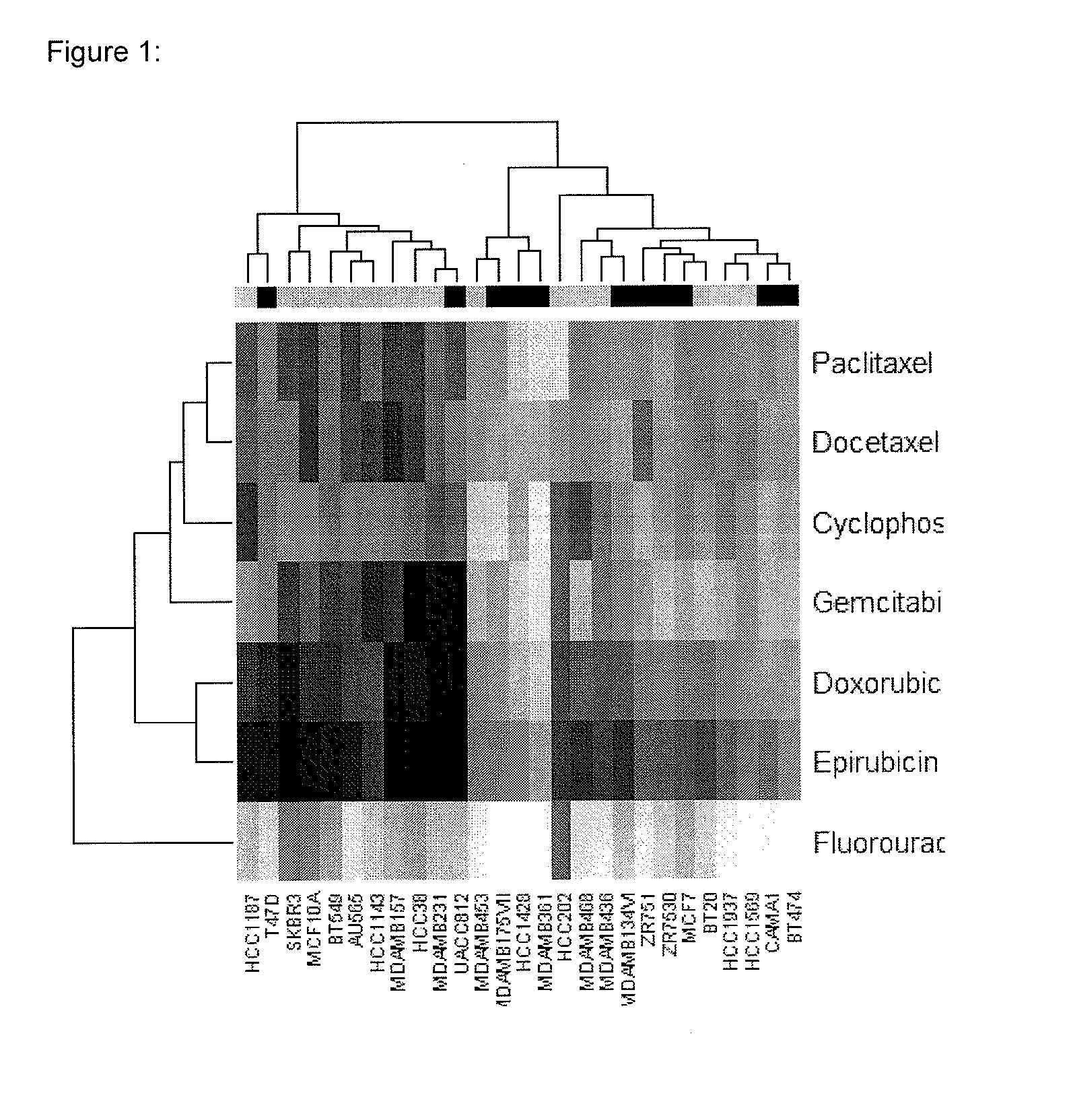
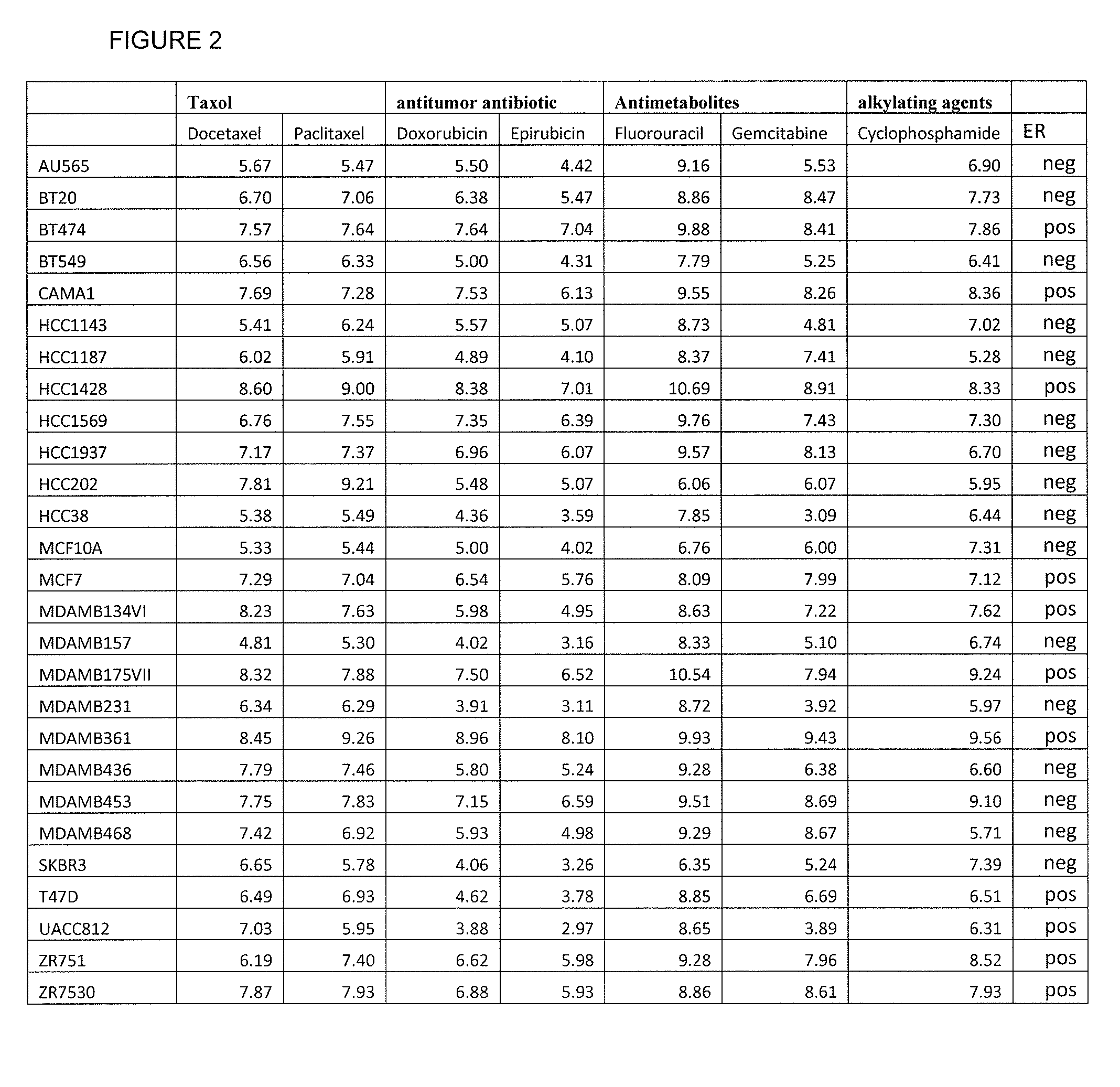
The present invention provides methods for preparing a gene expression profile of a breast cancer cell, tumor, or cell line, where the gene expression profile may be evaluated for one or more gene expression signatures indicative of multidrug resistance. The signature may be indicative of resistance to one or more chemotherapeutic agents selected from a Taxol (e.g., Docetaxel or Paclitaxel), an antibiotic (e.g., Doxorubicin or Epirubicin), an antimetabolite (e.g., Fluorouracil and / or Gemcitabine), and an alkylating agent (e.g., Cyclophosphamide). Generally, the gene expression profile contains the level of expression for a plurality of genes listed in FIGS. 3, 4, and / or 5. Gene expression profiles for evaluating multidrug resistance for ER positive and ER negative breast cancers are also provided.
Owner:PRECISION THERAPEUTICS
Pharmaceutical composition of small-sized liposomes and method of preparation
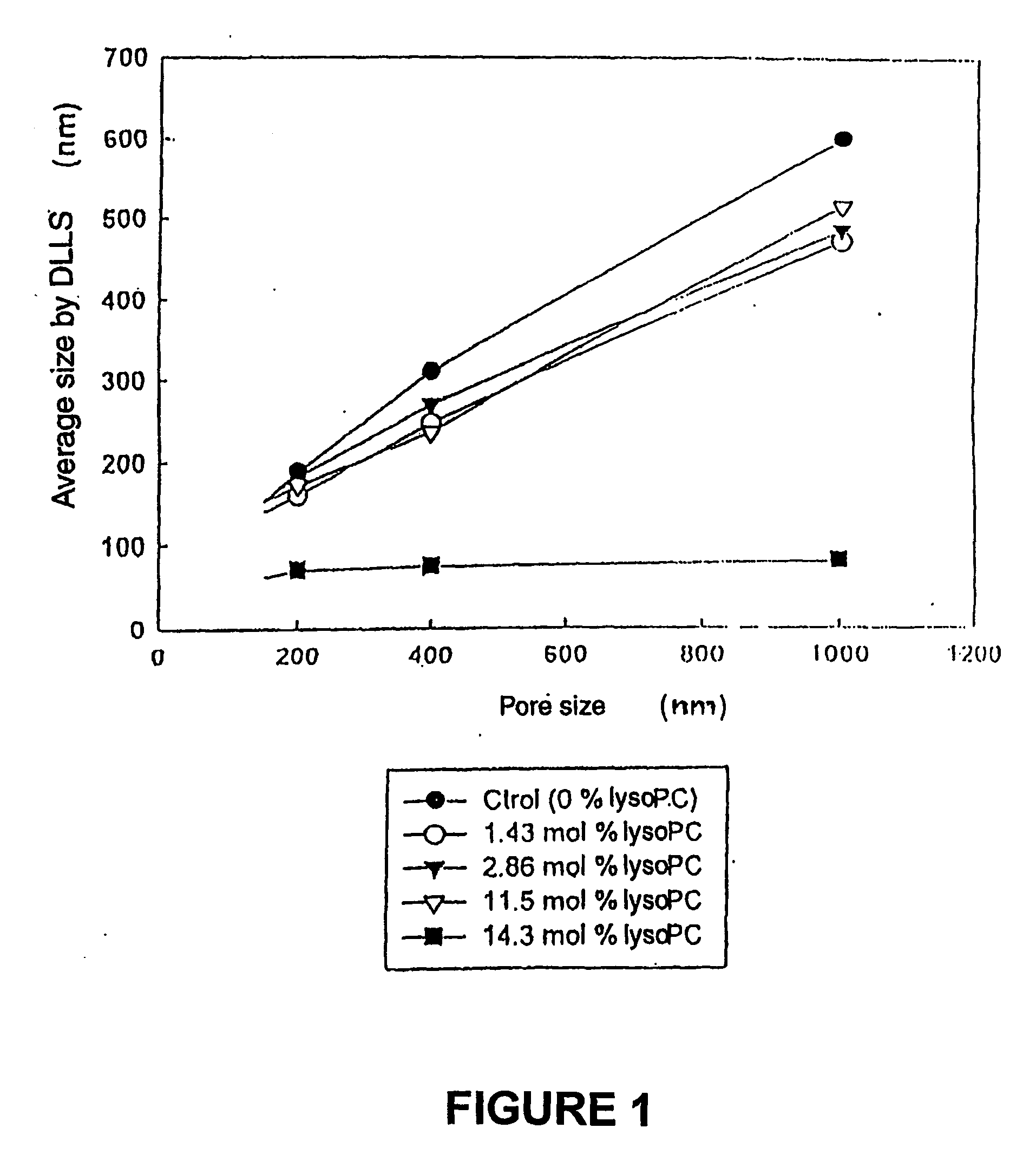
InactiveUS20060078605A1Simple procedureIncrease volumeBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsLipid formationAtherion elymus
A pharmaceutical composition of small sized unilamellar liposomes for the supply active principles by injection, with an improved permanency in the blood flow, where the unilamellar membrane contains a mixture of saturated lipids encompassing at least one lysophospholipid in a quantity from about 0.5 mol % to about 6.0 mol % with reference total lipids and the production method. Additionally, liposomes of high encapsulation efficiency of an active principle like doxorubicine are prepared through the adding of a solution of calcium ions.
Owner:MAMMARELLA CARLOS ALBERTO GENARO
Retinol derivatives, their use in the treatment of cancer and for potentiating the efficacy of other cytotoxic agents
A group of new compounds, N-(all-trans-Retinoyl)-L-cysteic acid, N-(13-cis-Retinoyl)-L-cysteic acid, N-(all-trans-Retinoyl)-L-cysteinesulfinic acid, N-(13-cis-Retinoyl)-L-cysteinesulfinic acid, N-(all-trans-Retinoyl)-L-homocysteic acid, N-(13-cis-Retinoyl)-L-homocysteic acid, and sodium salts of these compounds, including sodium salts of their esters and amides, is shown to exhibit therapeutic effects per se, and which compounds in combination with cytotoxic compounds, such as docetaxel, paclitaxel, doxorubicin and mitoxantrone, exhibit a synergistic effect. These compounds make it possible to manufacture new formulations of poorly soluble pharmaceutical compounds, and the present invention discloses a process of manufacturing water-soluble formulations of such compounds, exemplified by docetaxel, and paclitaxel, exhibiting enhanced pharmacological activity, and formulations of water-soluble pharmaceuticals exemplified by doxorubicin and mitoxantrone, exhibiting improved therapeutic efficacy.
Owner:OASMIA PHARMA AB
Synergistic pharmaceutical combination for the treatment of cancer
A novel pharmaceutical combination comprising a cytotoxic antineoplastic agent selected from a the group consisting of paclitaxel, docetaxel, doxorubicin and gemcitabine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and at least one cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor; wherein the said combination exhibits synergistic effects when used in the treatment of cancer. The invention also relates to a method for the treatment of cancer, using a therapeutically effective amount of the said combination.
Owner:PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD
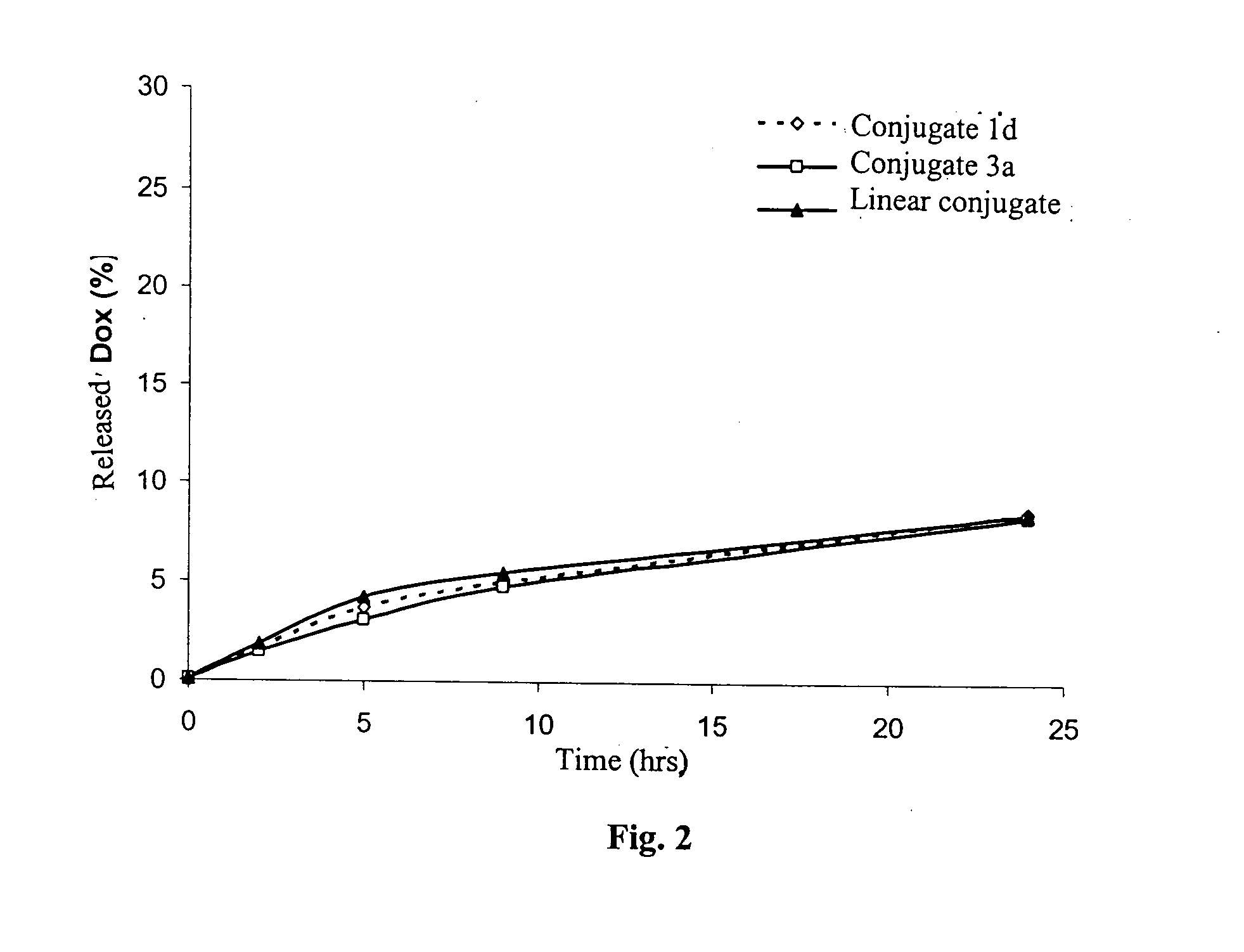
Grafted macromolecular conjugates of doxorubicin with anticancer activity and method of their preparation
A polymeric drug, in which a cancerostatic connected via spacers containing hydrolytically cleavable hydrazone bonds is bound to a water-soluble polymeric carrier prepared on the basis of a N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymer, wherein the structure of the polymeric drug consists of the main chain of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide carrying the cancerostatic and another chain of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide—a graft, which may also carry a cancerostatic, said grafts being bound to the main chain by a bond that is stable in the body and / or by a bond cleavable in the body, especially by an oligopeptide spacer selected from the series of GlyLeuGly, GlyPheGly, GlyPheLeuGly and GlyLeuPheGly, and a method of its preparation.
Owner:ZENTIVA AS
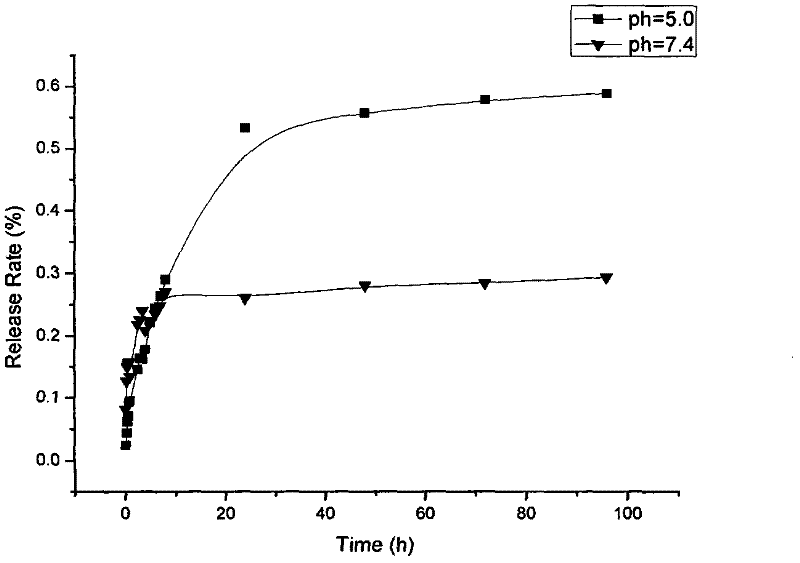
Ph sensitive doxorubicin nanoliposome modified by folic acid-carboxymethyl chitosan
InactiveCN102225051AReduce pollutionPH sensitiveOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCholesterolTumor targeting
The invention relates to pH sensitive doxorubicin nanoliposome modified by folic acid-carboxymethyl chitosan and its preparation method. The liposome provided in the invention comprises doxorubicin, phosphatide, cholesterol, vitamin E, folic acid-carboxymethyl chitosan. The prepared liposome has pH sensitivity, tumor targeting performance and long cyclic active targeting drug delivery functions.
Owner:上海微纳科技有限公司
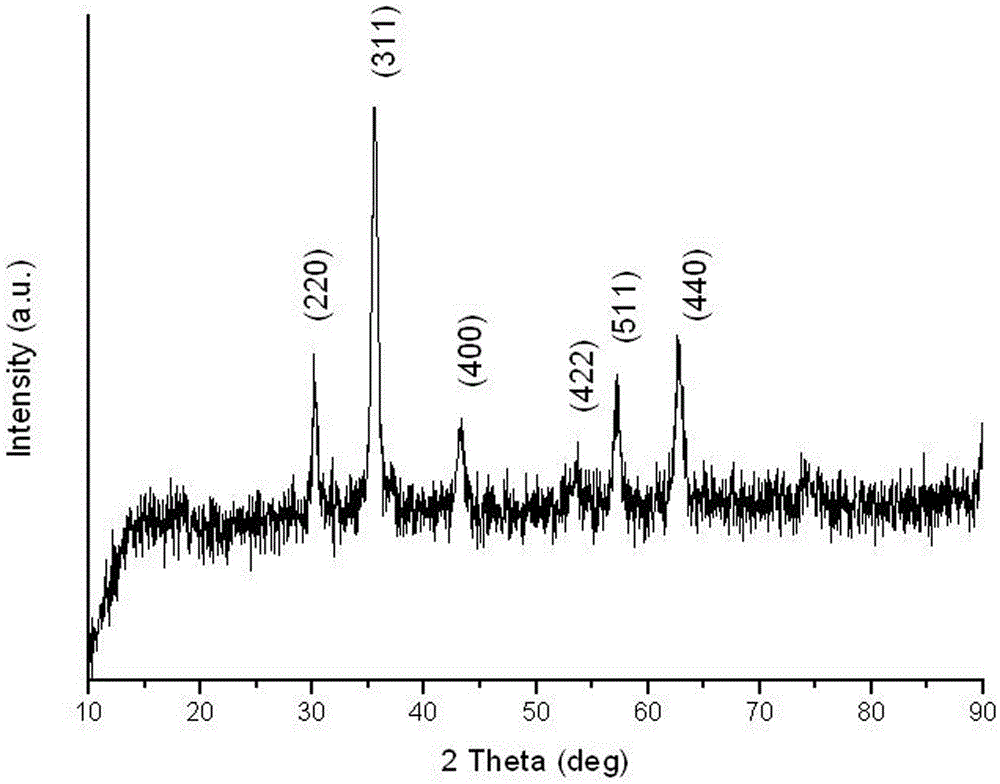
Preparation method and application of Fe3O4@CA-beta-CD nano microspheres
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of Fe3O4@CA-beta-CD nano microspheres. By adopting an ultrasonic-assisted coprecipitation method, citric acid modified Fe3O4@CA nanoparticles are synthesized. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding Fe3O4@CA into distilled water, thereby obtaining a Fe3O4@CA solution; adding beta-cyclodextrin into the Fe3O4@CA solution, uniformly stirring, drying, washing, and separating by using a strong magnet, thereby obtaining the Fe3O4@CA-beta-CD nano microspheres; performing ultrasonic dispersion on Fe3O4@CA-beta-CD nano microspheres in deoxidated distilled water, adding doxorubicin, performing ultrasonic treatment by using an ultrasonic cell cracker, separating, washing, and drying, thereby obtaining doxorubicin-supported ferroferric oxide nano microspheres Fe3O4@CA-beta-CD-DOX. The microspheres are slow-released in a phosphate buffer at the pH value of 7.4, the release time is 12 hours, and a slow release effect is achieved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
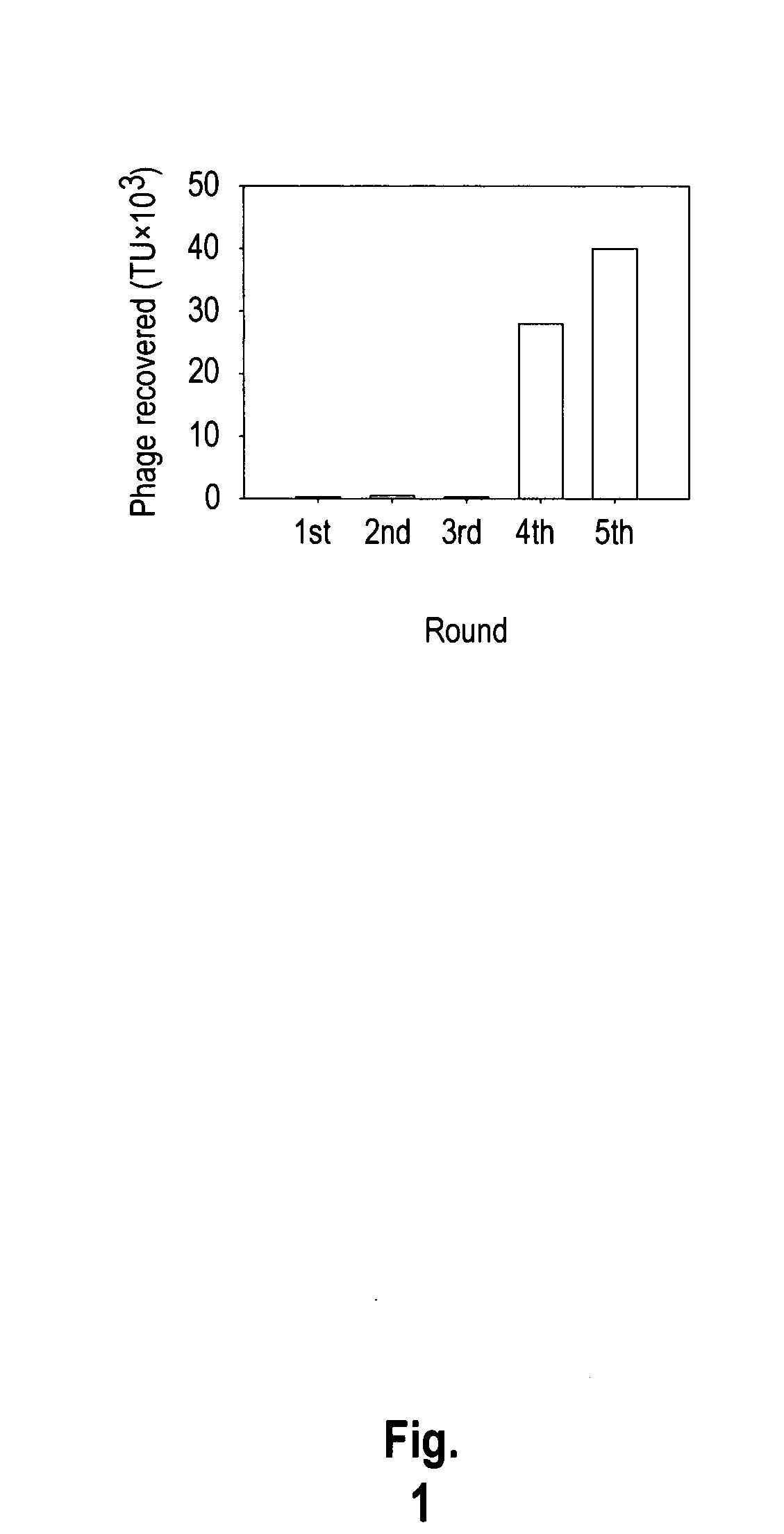
Lung cancer-targeted peptides and applications thereof
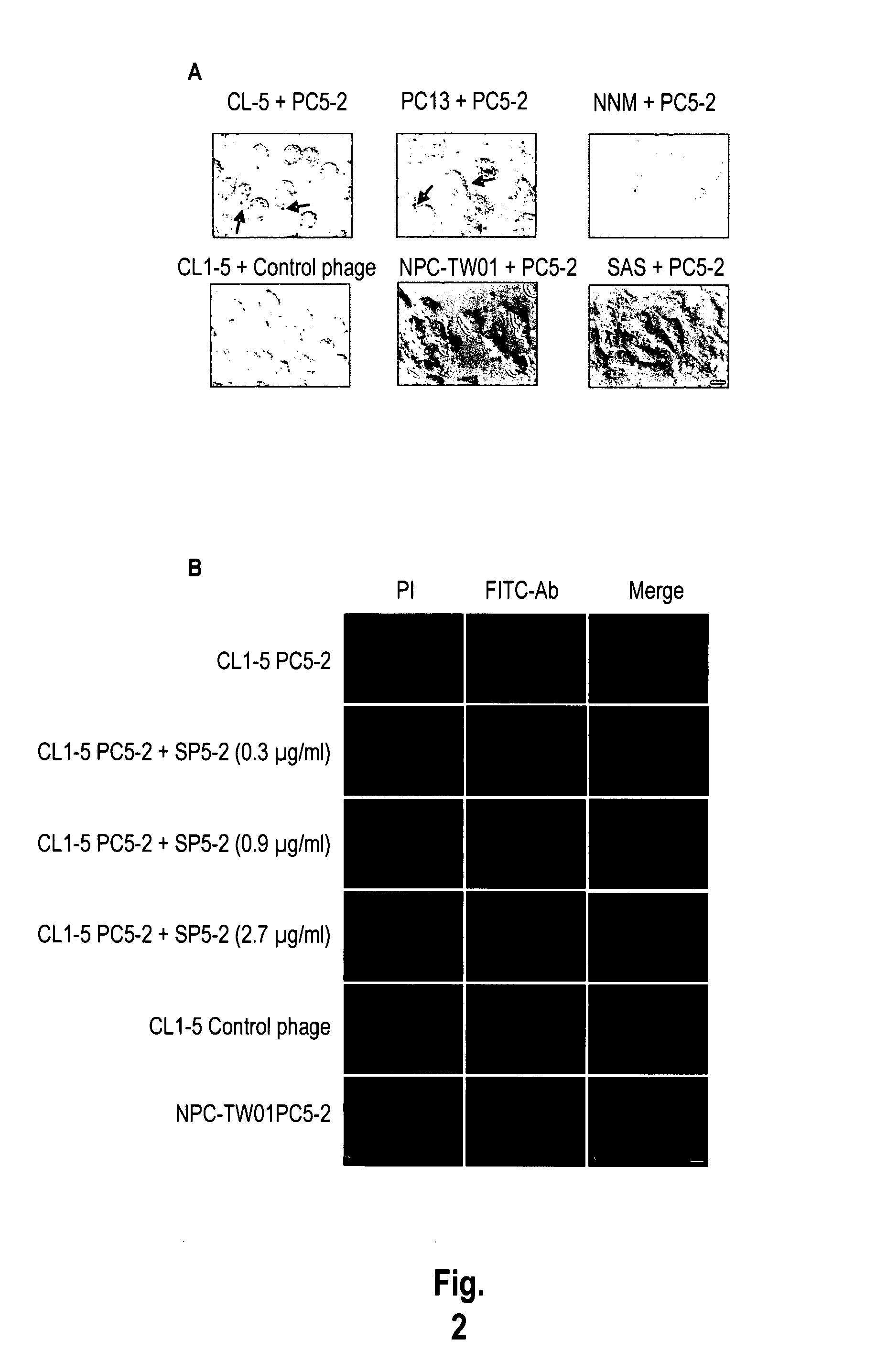
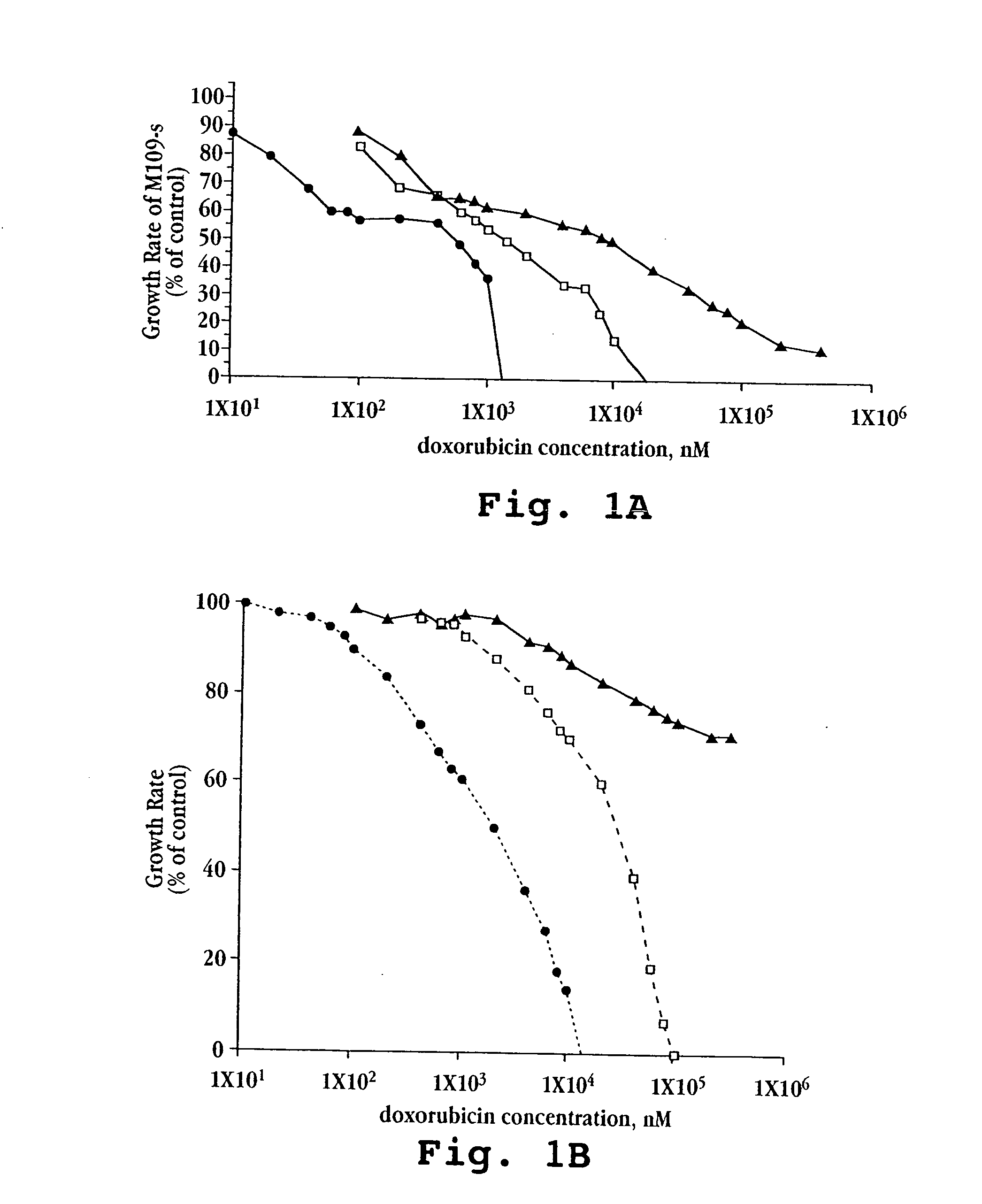
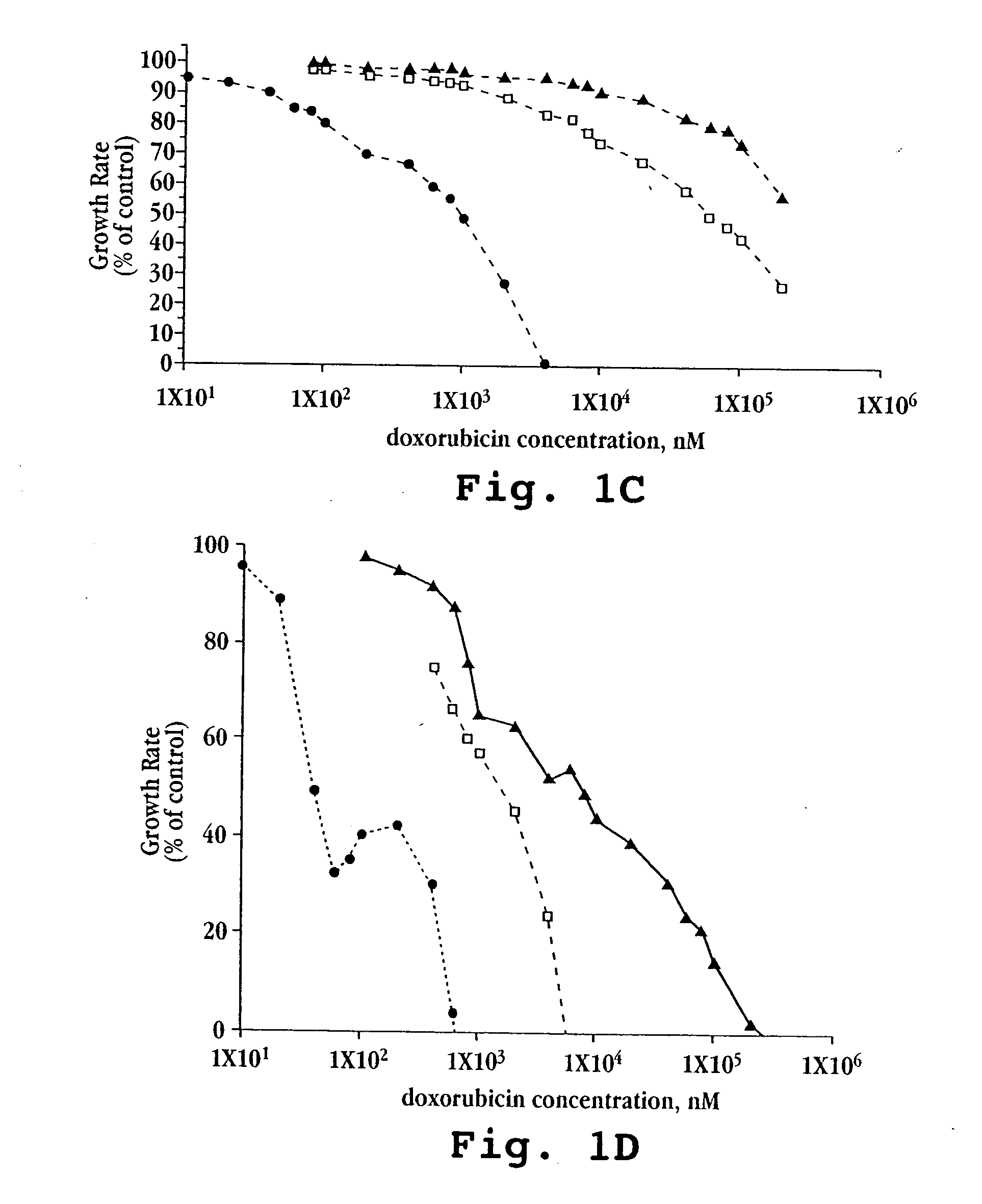
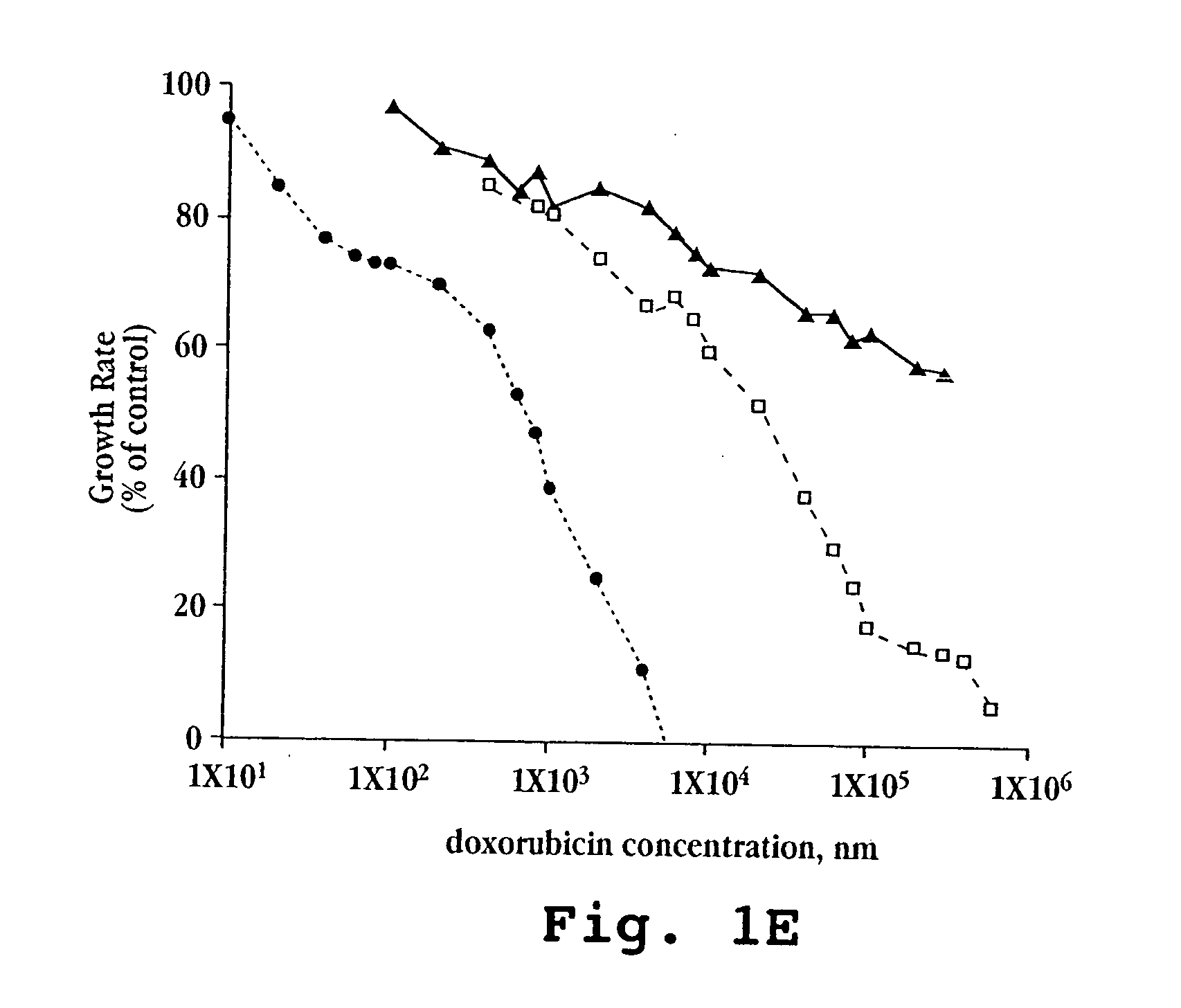
The invention provides nucleic acids, peptides, and antibodies for use in applications including diagnosis and therapy. The peptides target lung cancer and were identified by phage display. Targeting phage PC5-2 and synthetic peptide SP5-2 were both able to recognize human pulmonary tumor specimens from lung cancer patients. In SCID mice bearing NSCLC xenografts, the targeting phage was able to target tumor masses specifically. When the peptide was coupled to liposomes containing the anti-cancer drugs vinorelbine or doxorubicin, the efficacy of these drugs against human lung cancer xenografts was improved, the survival rate increased, and the drug toxicity was reduced.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
Method for drug loading in liposomes
A liposome composition having a protonatable therapeutic agent entrapped in the form of a salt with a glucuronate anion is disclosed. Methods for preparing the composition using an ammonium ion transmembrane gradient having glucuronate as the counterion are also disclosed. In one embodiment where the protonatable agent is doxorubicin, the method of the invention has comparable loading efficiency, faster release rate, without compromising the therapeutic efficacy compared to loading with an ammonium ion gradient having sulfate as the counterion.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Compositions and methods of reducing tissue levels of drugs when given as orotate derivatives
ActiveUS20090131344A1Low toxicityToxic effectsSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideSide effectTissue toxicity
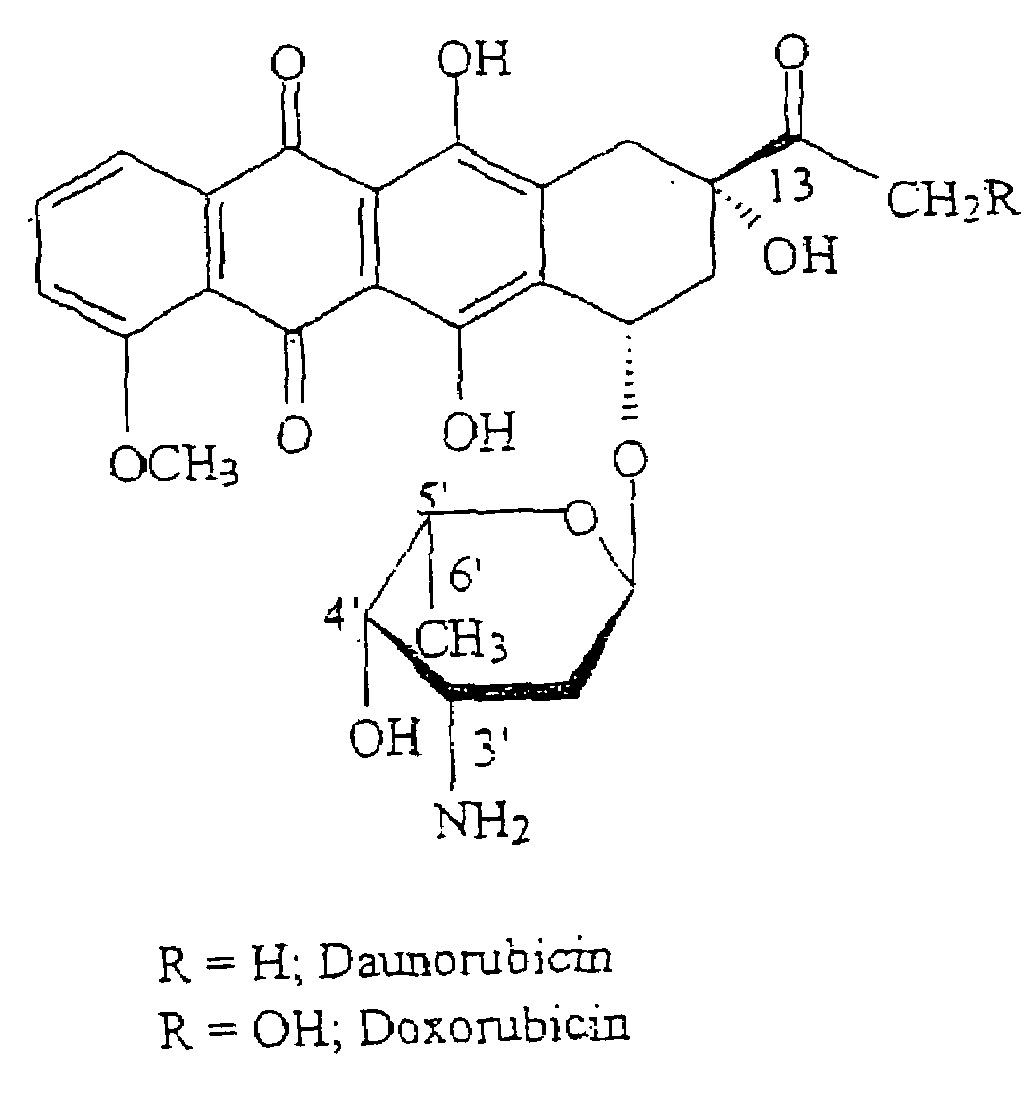
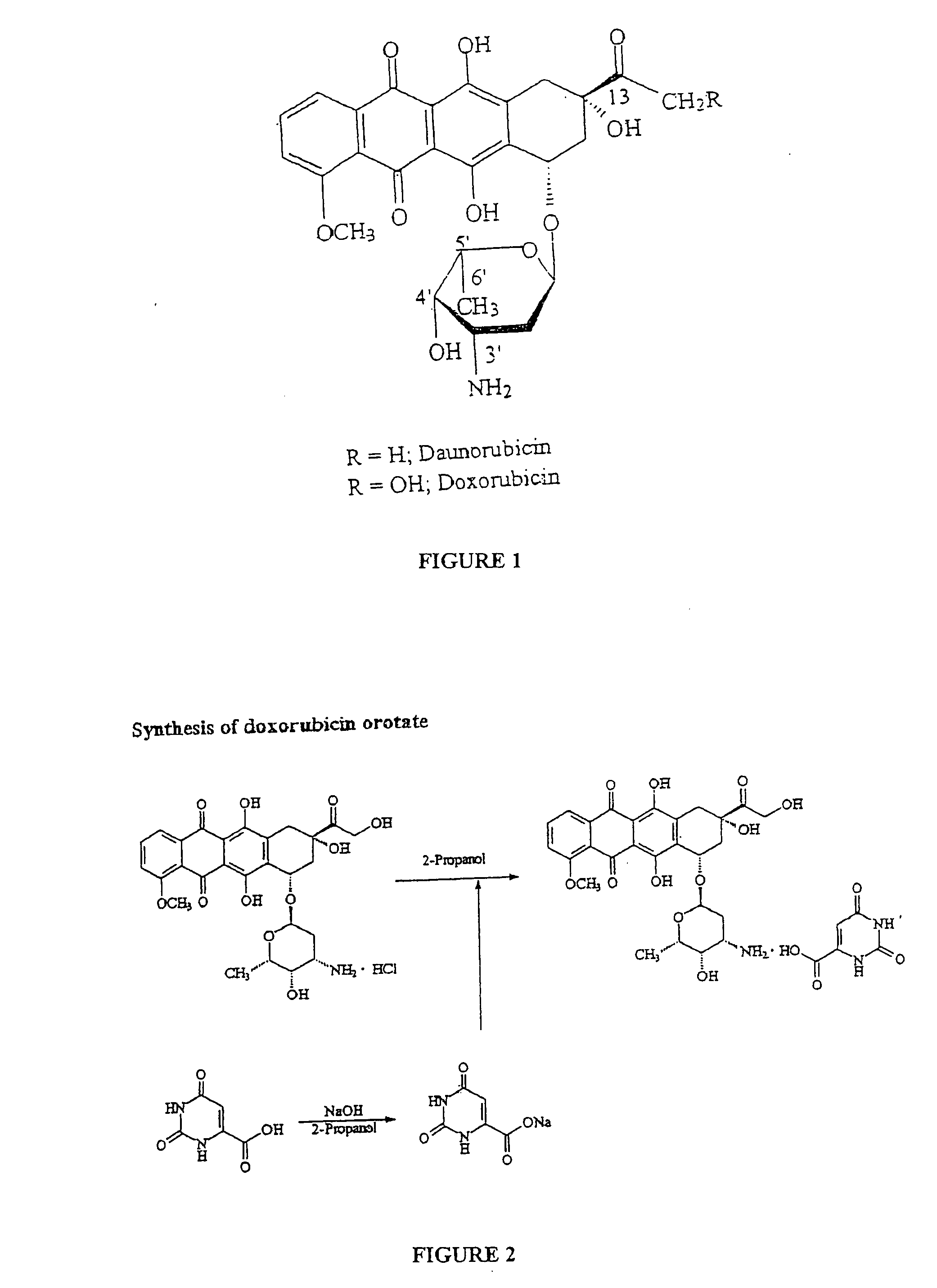
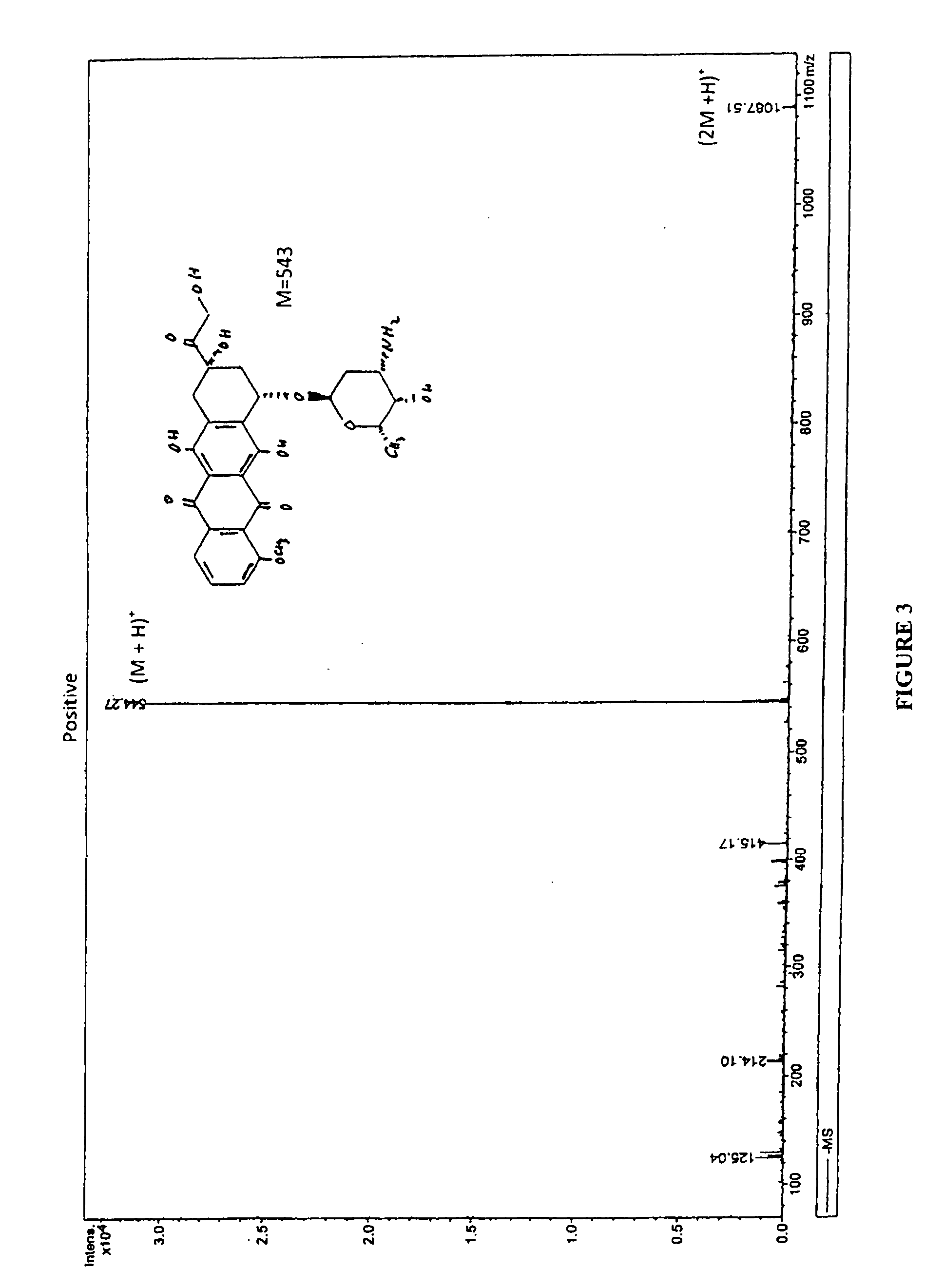
This invention is in the field of chemical restructuring of pharmaceutical agents known to cause tissue toxicity as a side effect, by producing their orotate derivatives. More particularly, it concerns orotate derivatives of the anthracyclines, doxorubicin and daunorubicin, that are found to reduce levels of the pharmaceutical agent in noncancerous tissues. These orotate derivatives are equally efficacious in inhibiting the SCCAKI-1 kidney tumor in animals and the reduction in the heart tissue of doxorubicin compared with doxorubicin HCl suggests a reduction in toxicity induced by free radical generation by the anthracyclines.
Owner:SAVVIPHARM INC
Compound recipe anti-cancer drugs slow release agent comprising anticancer antibiotics and booster thereof
Disclosed is a compound anticancer slow release agent which comprises slow release microspheres and dissolvent, wherein the slow release microballoons comprise anti-cancer active constituents and slow release auxiliary materials, the dissolvent being specific dissolvent containing suspension adjuvant. The anticancer effective ingredients include Aclarubicin, Idarubicin, Doxorubicin, Epirubicin, Valtaxin, Pirarubicin, Losaxantrone, Losoxantrone and / or anticancer antibiotic synergistic agents selected from phosphoinositide-3-kinase inhibitor, pyrimidine analogues and / or DNA restoration enzyme inhibitor, the slow release auxiliary materials are selected from polylactic acid copolymer EVAc, or sebacic acid copolymer, the viscosity of the suspension adjuvant is 100-3000cp (at 20-30 deg C). The slow release microspheres can also be prepared into slow release implanting agent for lowering down the whole body toxicity reaction of the medicament when locally dispensing on the tumor, and for selectively increasing the tumor local medicinal concentration.
Owner:SHANDONG LANJIN PHARMA
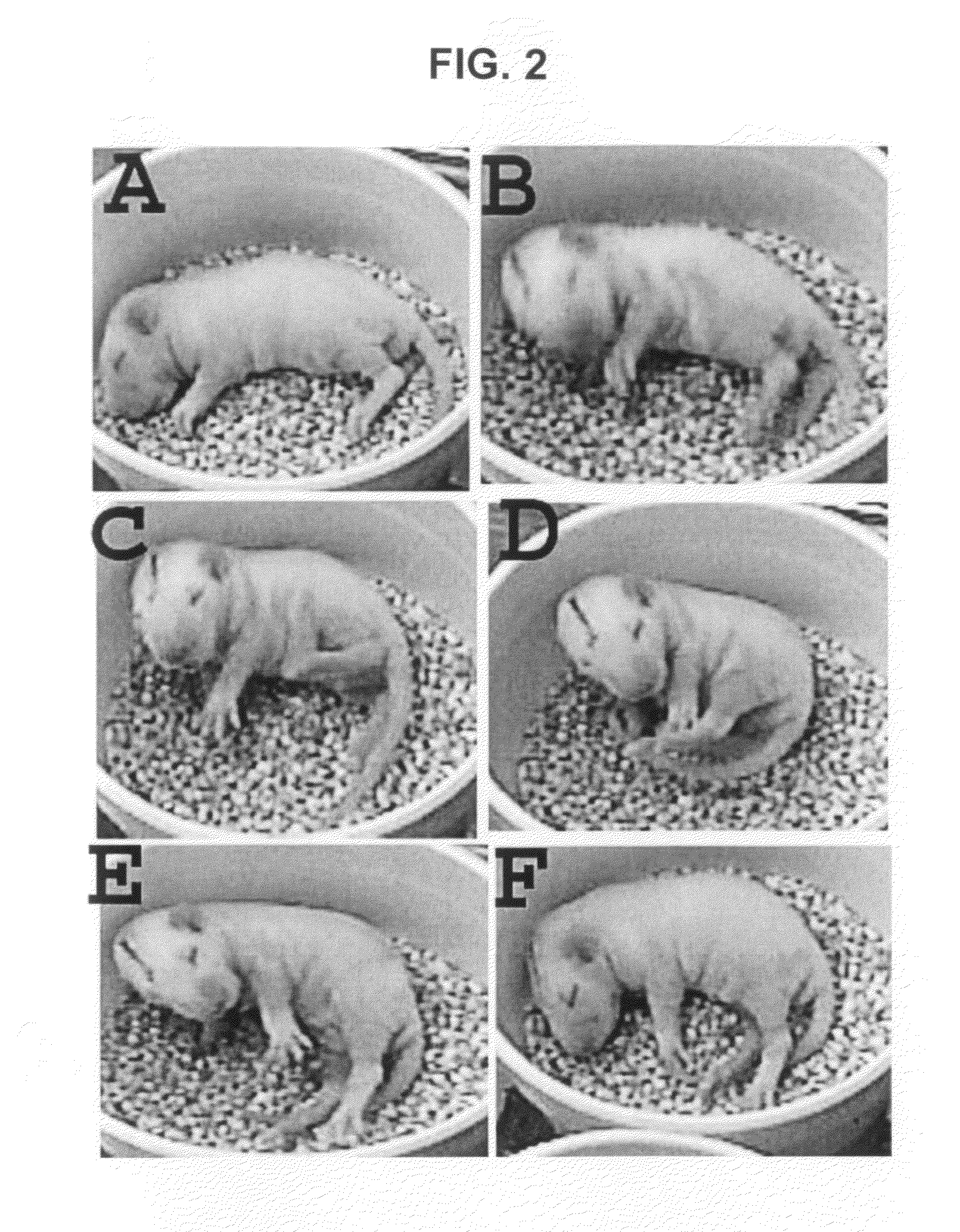
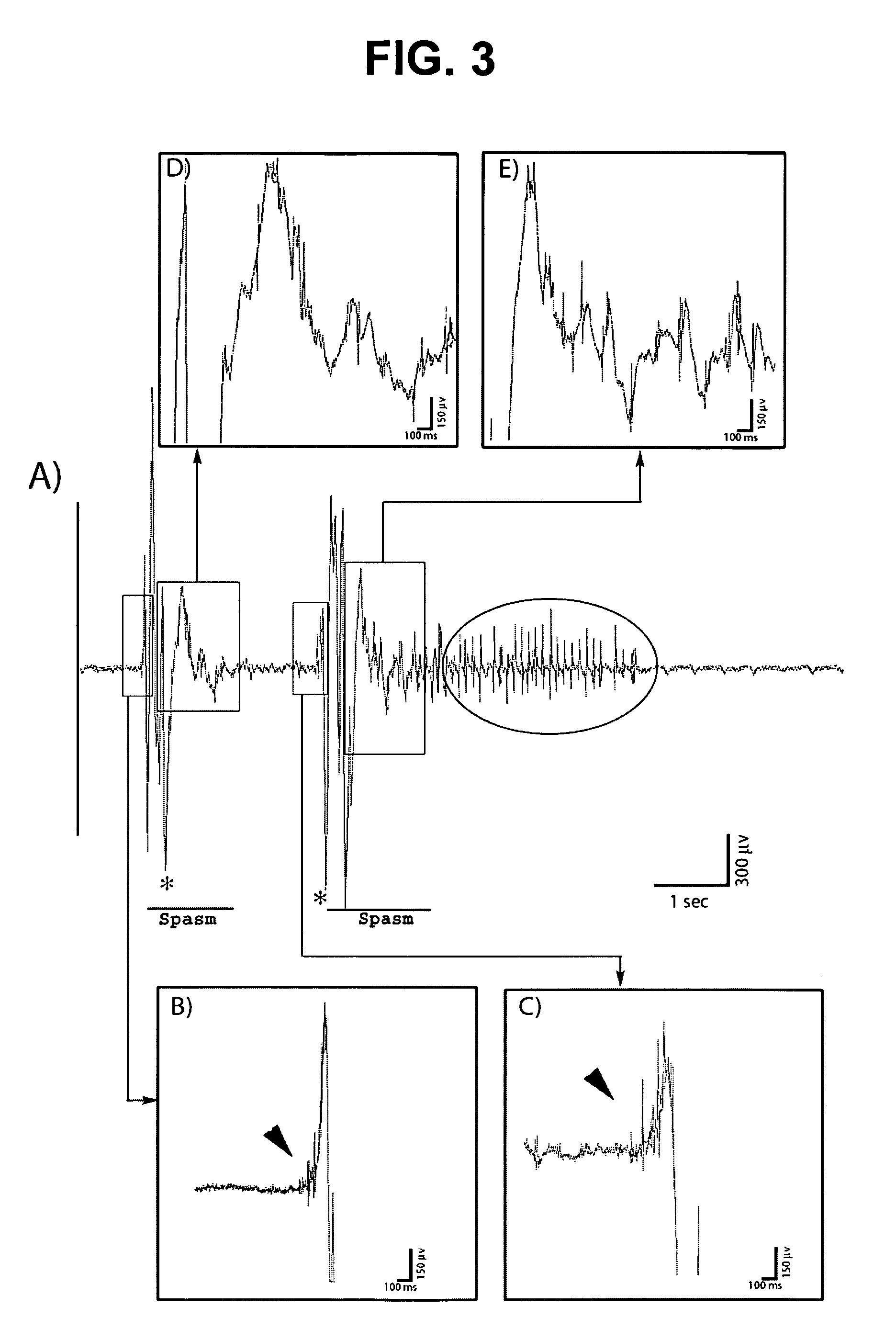
Model of infantile spasm syndrome
InactiveUS7863499B2In-vivo testing preparationsAnimal husbandryP chlorophenylalanineChemical compound
Provided are non-human mammals treated with doxorubicin, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA), where the mammal exhibits a symptom characteristic of infantile spasms. Also provided are methods of making a non-human mammal exhibit a symptom of infantile spasms. Additionally, methods are provided for screening a compound for the potential to attenuate a symptom of infantile spasms.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
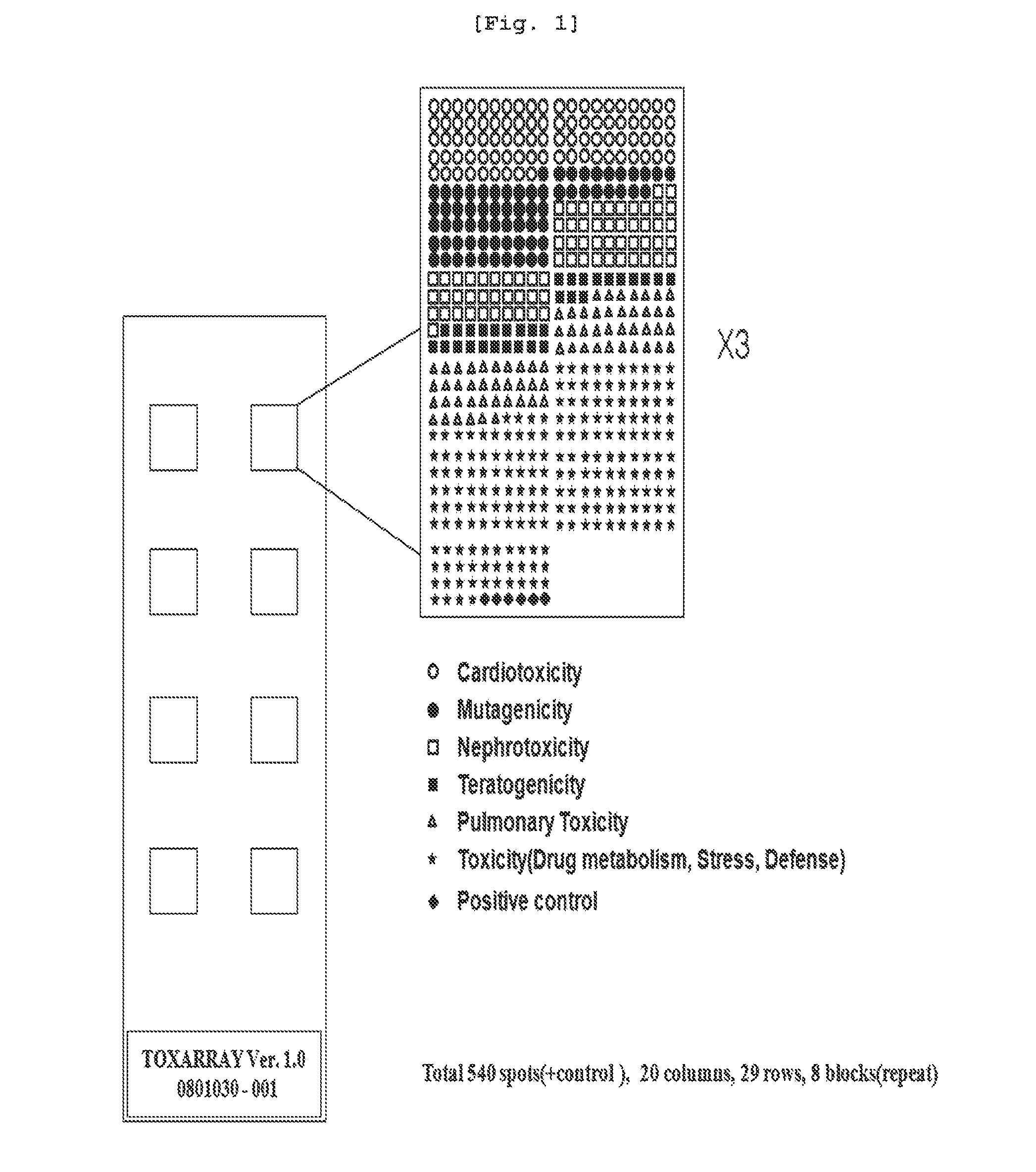
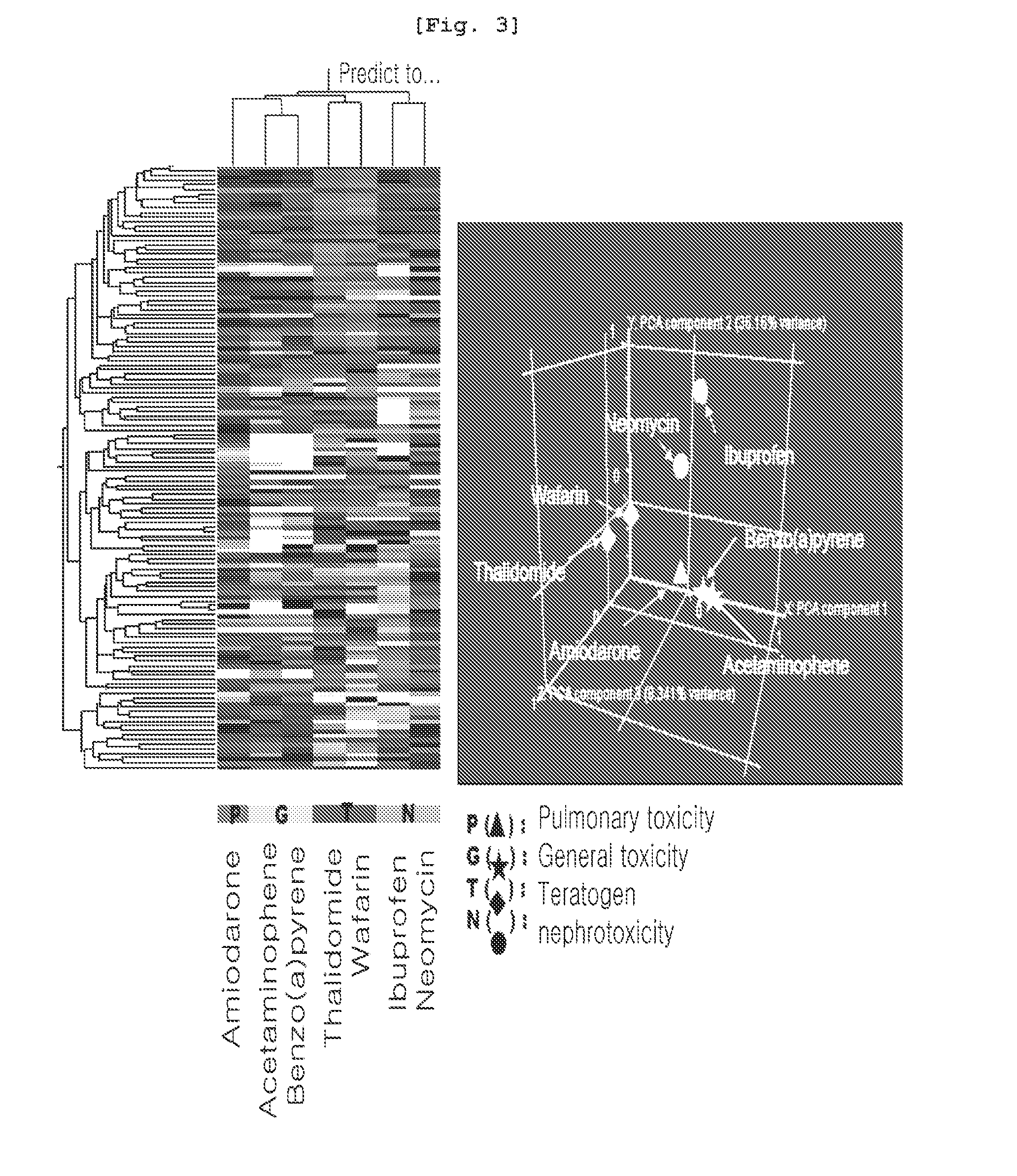
Marker genes for screening of drug-induced toxicity in human cells and screening method using the same
InactiveUS20110118127A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDrug induced toxicityCardiotoxicity
The present invention relates to a marker gene for screening a drug inducing toxicity in human and a screening method using the same. More precisely, the invention relates to a microarray on which marker genes up-or down-regulated specifically by 16 drugs inducing pulmonary toxicity, teratogenicity, nephrotoxicity, cardiotoxicity or mutation (Methotrexate, Nitrofurantoin, Amiodarone, Carbamazepine, Valproic acid, Thalidomide, Cisplatin, Gentamycin, Amphotericine, Furylfuramide, N-nitroso-N-methylurea, methylmethanesulfonate, 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide, 2-nitrofluorene, Doxorubicin and Daunorubicin) are integrated, a kit comprising the said microarray, and a screening method of a drug inducing toxicity in human using the same. The DNA microarray containing the marker gene of the present invention facilitates the construction of Toxtarget Array for screening a drug inducing toxicity in human using drug-specific genes, suggesting that this chip can be effectively used for monitoring drugs or chemicals carrying toxicity to human or determining risks thereof and also it can be used as a tool for examining mechanisms of toxicity / side effects caused by the drugs.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
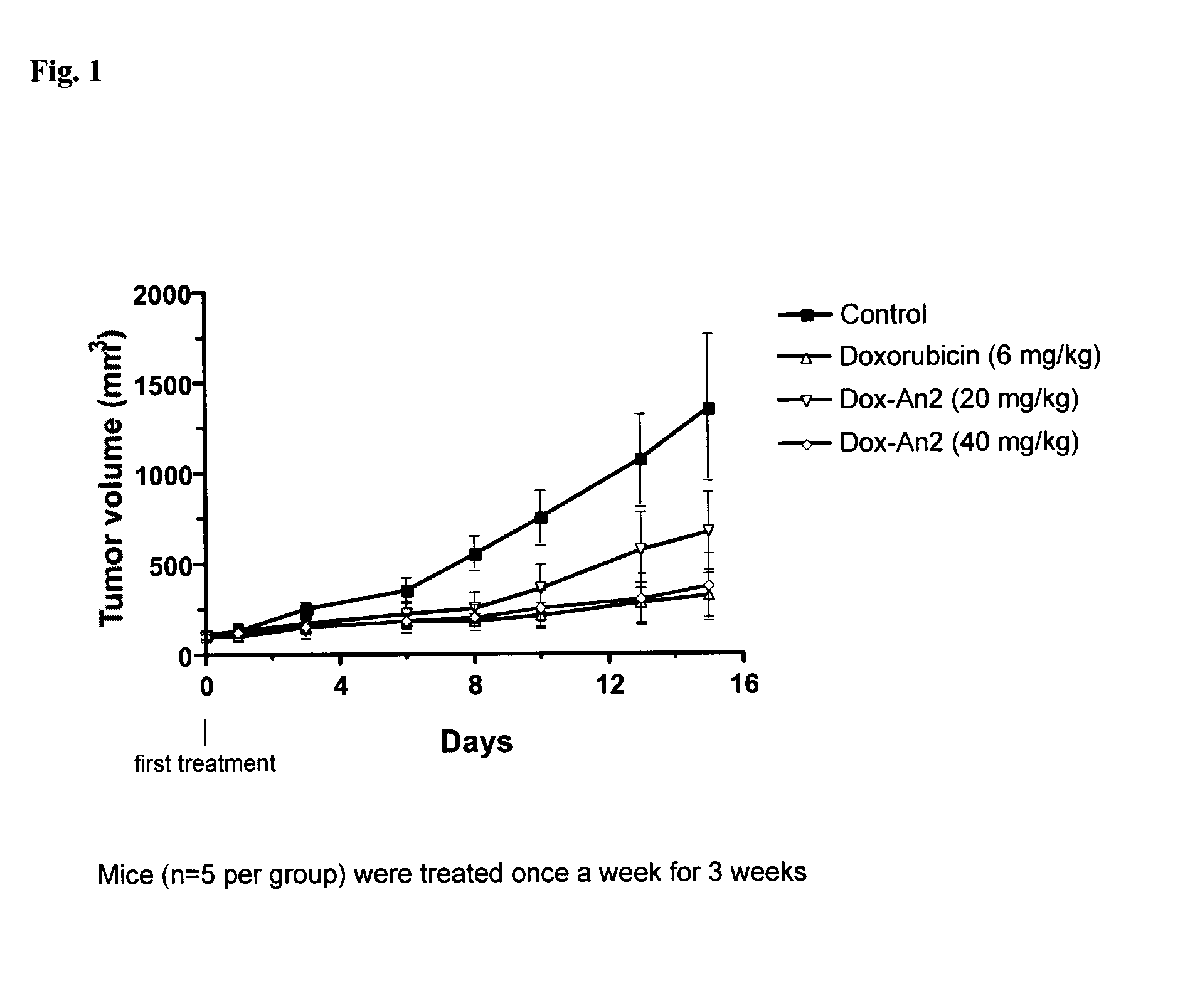
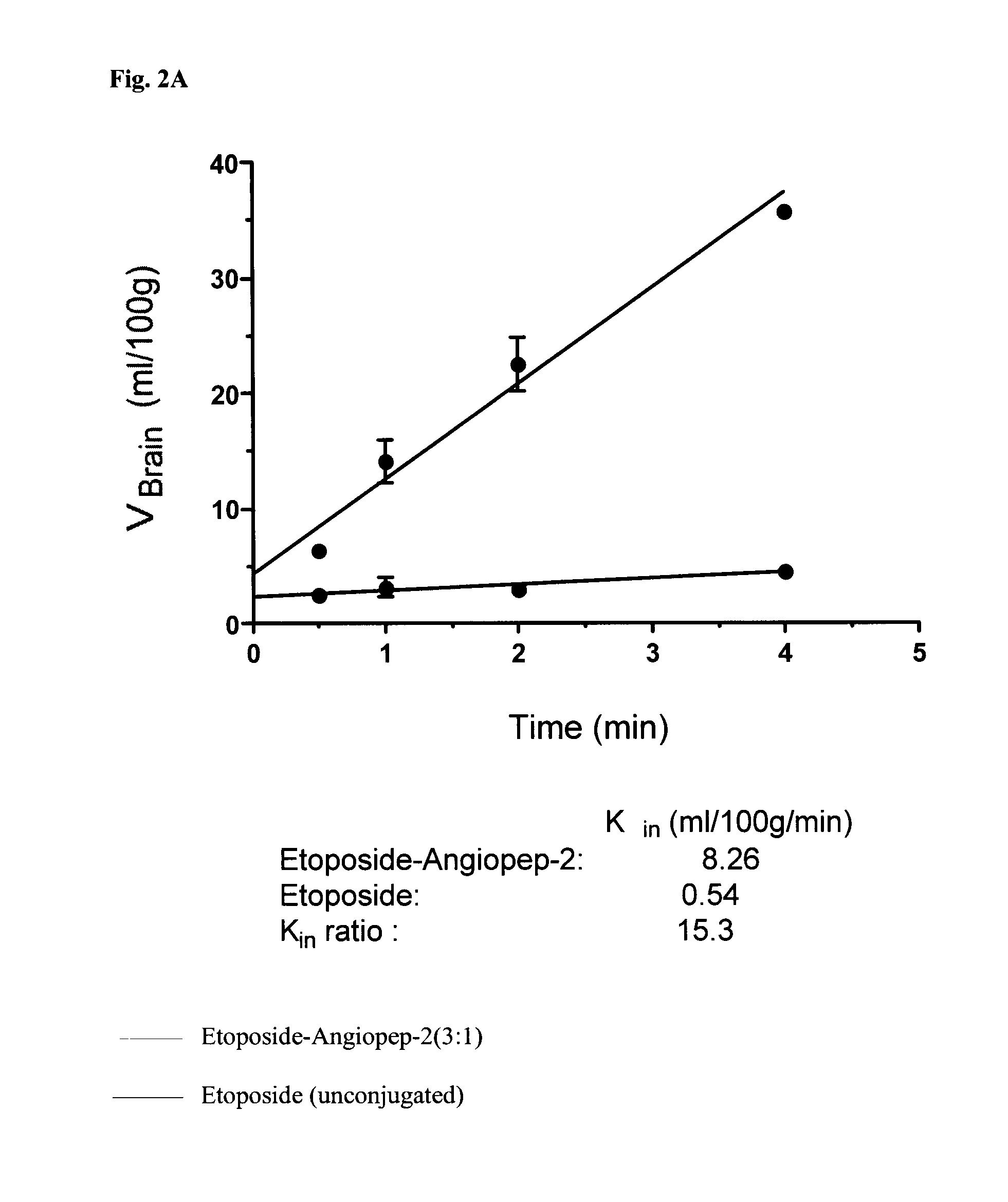
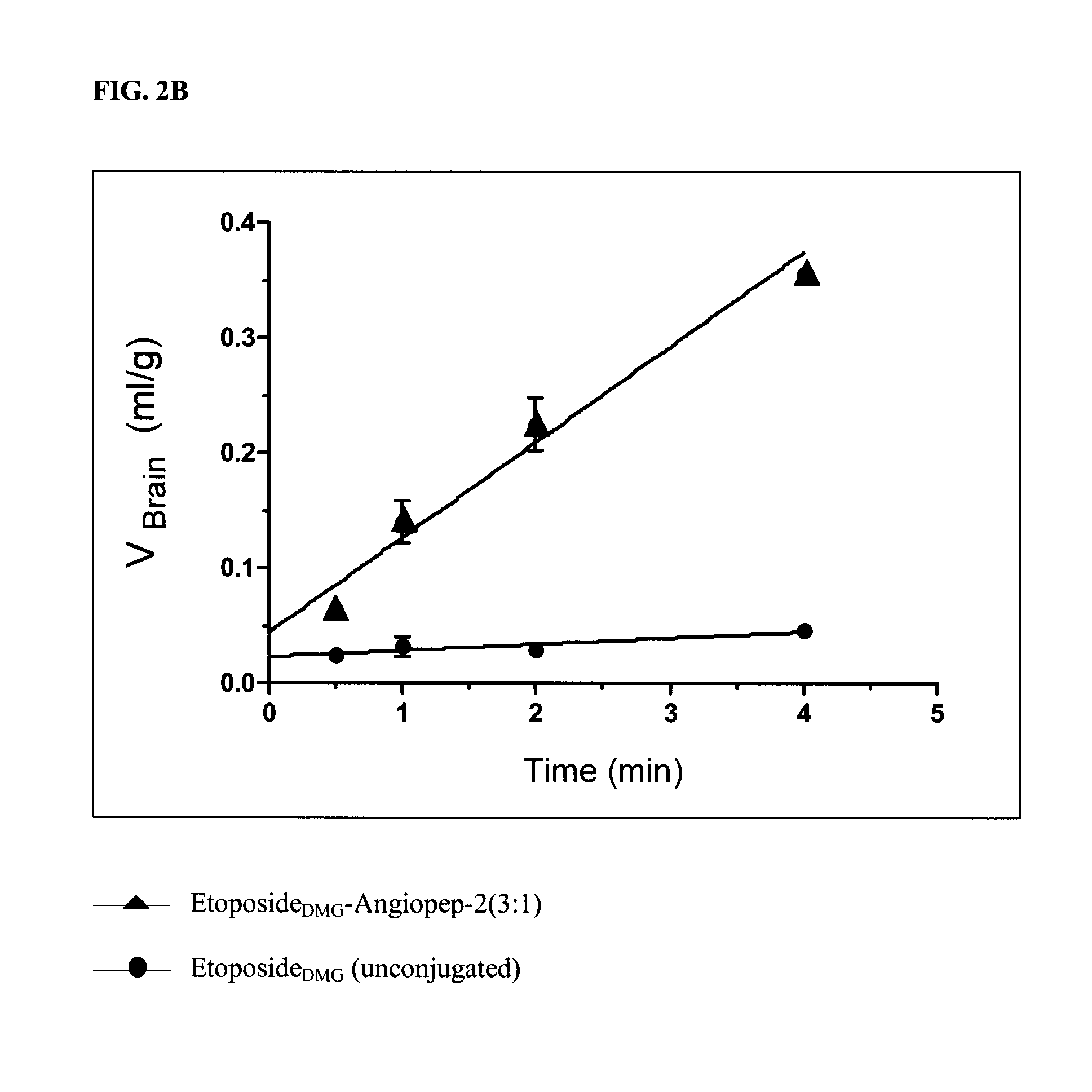
Etoposide and doxorubicin conjugates for drug delivery
ActiveUS8828925B2Improve propertiesReduce frequencySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsCell type specificKidney
The invention relates to improvements in the field of drug delivery. More particularly, the invention relates to polypeptides having a hydrolyzable covalent bond to a therapeutic agent that includes, etoposide, etoposide 4′-dimethylglycine or doxorubicin. These polypeptide conjugates can be used as vectors to transport the podophyllotoxin derivative across the blood brain barrier (BBB) or into particular cell types such as ovary, liver, lung, or kidney. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions that include the compounds of the invention and to uses thereof in methods of treatment.
Owner:ANGLACHEM INC
Method of treating multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20040038904A1Toxic effect is reduced and minimizedConvenient for patientBiocideNervous disorderPharmaceutical drugProtective Agents
The present invention provides for use of an anthracycline, such as doxorubicin, alone or in combination with a protective agent, such as dexrazoxane, for treating multiple sclerosis.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO
Antineoplastic conjugates of transferin, albumin and polyethylene glycol
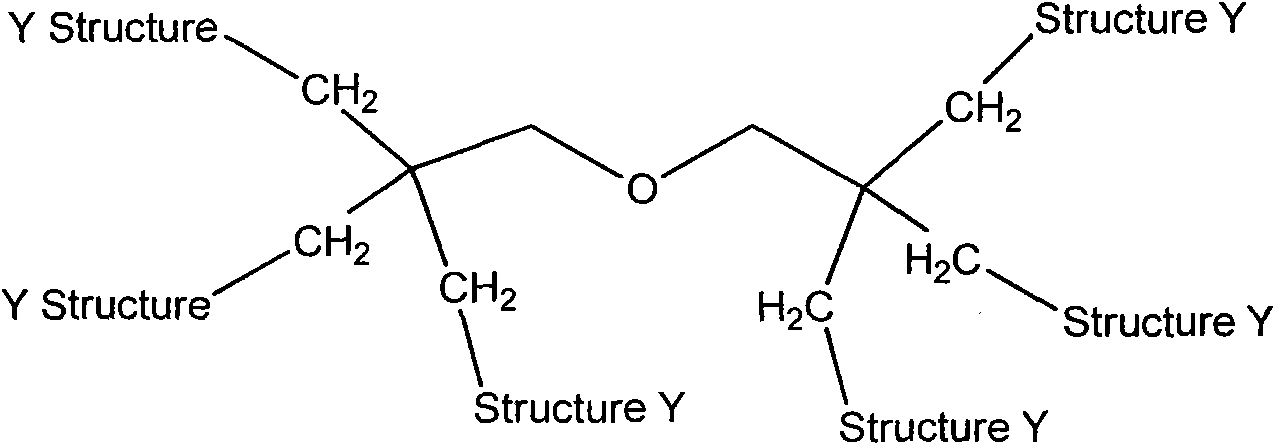
Conjugates of transferrin, albumin and polyethylence glycol consisting of native or thiolated transferrin or albumin or of polyethylene glycol (MW between approximately 5,000 and 20,0000) with at least one HS-, HO- or H2N group and cytostatic compounds derived through maleinimide or N-hydroxysuccinimide ester compounds, such as doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin, mitoxandrone, chloroambucil, melphalan, 5-fluorouracyl, 5'-desoxy-5-fluorouridine, thioguanine, methotrexate, paclitaxel, docetaxel, topotecan, 9-aminocamptothecin, etoposide, teniposide, mitopodoside, vinblastine, vincristine, vindesine, vinorelbine or a compound of general formula A, B, C or D, where n=0-6, X=-NH2, -OH, -COOH, -O-CO-R-COR*, -NH-CO-R-COR*, where R is an aliphatic carbon chain with 1-6 carbon atoms or a substituted or unsubstituted phenylene group and R*H, phenyl, alkyl with 1-6 carbon atoms.
Owner:KRATZ FELIX
Preparation method of polyethylene glycol modified nano-micelle or vesicle with pH (potential of hydrogen) responsivity and high drug loading capacity
ActiveCN108078924AFacilitated releaseHigh drug loadingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor therapyDrug loading dose
The invention belongs to the field of high polymer materials and biomedical engineering and particularly relates to a preparation method of a polyethylene glycol modified nano-micelle or a vesicle with pH (potential of hydrogen) responsivity and high drug loading capacity. The method comprises the steps of allowing polyethylene glycol and cis-aconitic acid anhydride modified doxorubicin to give areaction to generate an amphipathic segmented copolymer, and obtaining the nano-micelle or the vesicle with the pH responsivity and the high drug loading capacity by taking an anticancer drug, namelydoxorubicin as a hydrophobic chain segment and polyethylene glycol as a hydrophilic chain segment. The nano-micelle or the vesicle takes the anticancer drug as the hydrophobic chain segment, and therefore, has the higher drug loading capacity; at the same time, cis-aconitic acid anhydride is sensitive to acid; and therefore, the prepared nano-micelle or the vesicle has the pH responsivity, is applicable to the field of tumor therapy, can improve chemotherapy efficiency and reduces toxic and side effects of the anticancer drug on normal tissues.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Anti-integrin immunoconjugates, methods and uses
InactiveUS8603483B2Effective rate of releaseSenses disorderAntipyreticDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to conjugates of anti-integrin specific antibodies with cytotoxic compounds, the synthesis, selection, and use of such conjugates for use in cancer therapy or other diseases mediated by cell proliferation, cell migration, or inflammation and which pathology involves angiogenesis or neovascularization of new tissue. In addition the invention relates to combination therapy of such diseases wherein the treatment comprises use of said conjugates in combination with one or more other treatment modalities including but not limited to: chemotherapy, surgery or radiation therapy. The preferred conjugates contain maytansinoid compounds linked to the antibody by a disulfide linkage, and preferred chemotherapeutic agents are doxorubicin, a taxane, a camptothecin, a podophyllotoxin, a nucleoside analog, or a pyrimidine analog.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC +1
Method for drug loading in liposomes
A liposome composition having a protonatable therapeutic agent entrapped in the form of a salt with an glucuronate anion is disclosed. Methods for preparing the composition using an ammonium ion transmembrane gradient having glucuronate as the counterion are also disclsoed. In one embodiment where the protonatable agent is doxorubicin, the method of the invention has comparable loading efficiency, faster release rate, without compromising the therapeutic efficacy compared to loading with an ammonium ion gradient having sulfate as the counterion.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
FAP-Activated Therapeutic Agents, and Uses Related Thereto
ActiveUS20170128476A1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFibrosisAnthracycline
Disclosed are prodrugs of anthracyclines (such as doxorubicin) and derivatives thereof that are selectively cleaved and activated by fibroblast activating protein (FAP). The prodrugs are useful for targeted delivery of “warhead” anthracycline or anthracycline derivative to FAP-expressing tissues, including cancer (e.g., solid tumors). Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the prodrugs, as well as methods of using the prodrugs to treat a disorder characterized by FAP upregulation, e.g., cancer, undesirable fibrosis, and undesirable inflammation.
Owner:BACH BIOSCI LLC
Nonlinear polymer having doxorubicin structure, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103910867AImprove solubilityExtended half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicinePolymer
The invention discloses a nonlinear polymer having a doxorubicin structure, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The doxorubicin coupled nonlinear polymer has better effects on treatment of age-related macular degeneration compared with other forms of drugs or medicaments.
Owner:张雅珍
Nonlinear polymer having doxorubicin structure, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103910868AImprove solubilityExtended half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicinePolymer
The invention discloses a nonlinear polymer having a doxorubicin structure, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The doxorubicin coupled nonlinear polymer has better effects on treatment of age-related macular degeneration compared with other forms of drugs or medicaments.
Owner:张雅珍
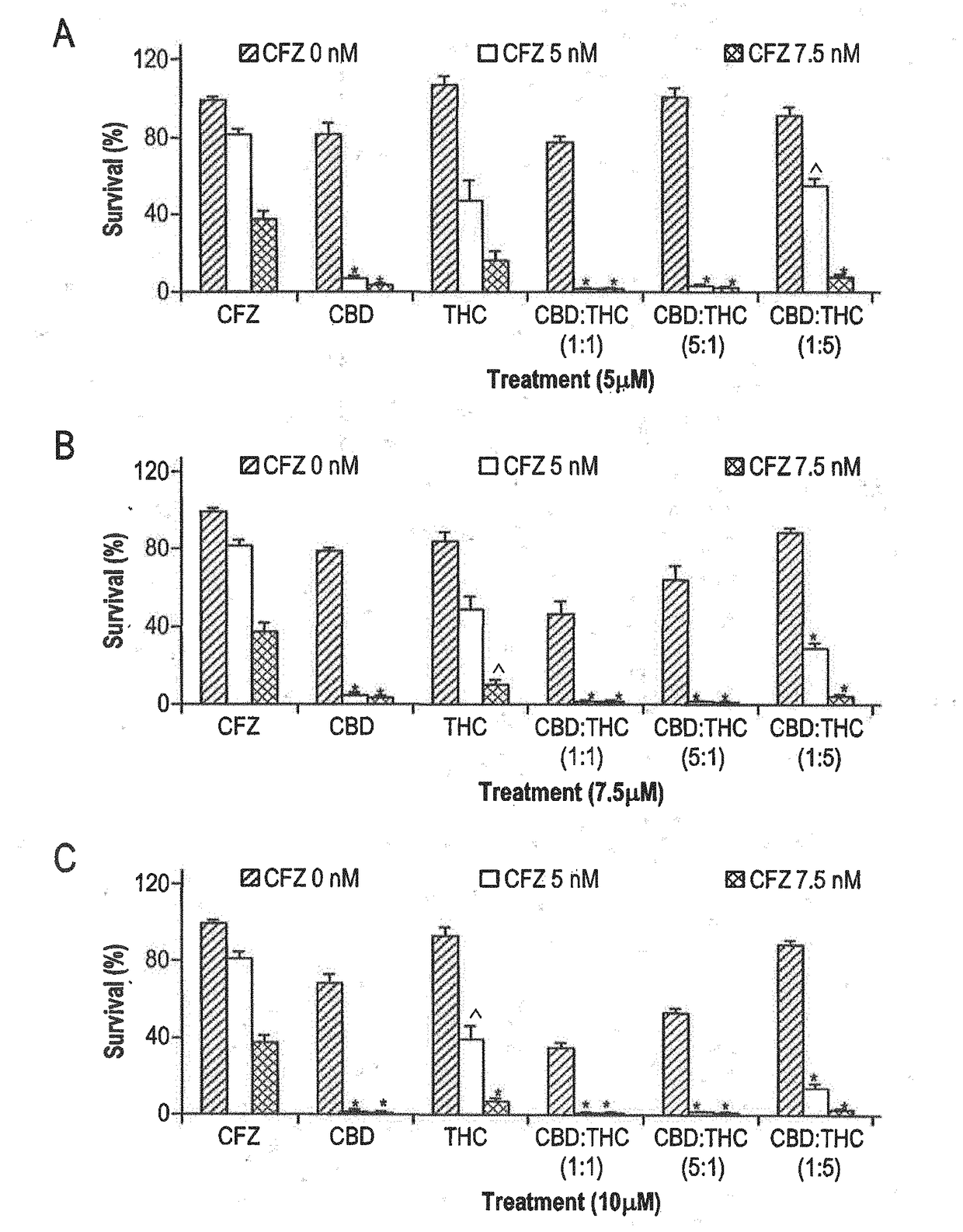
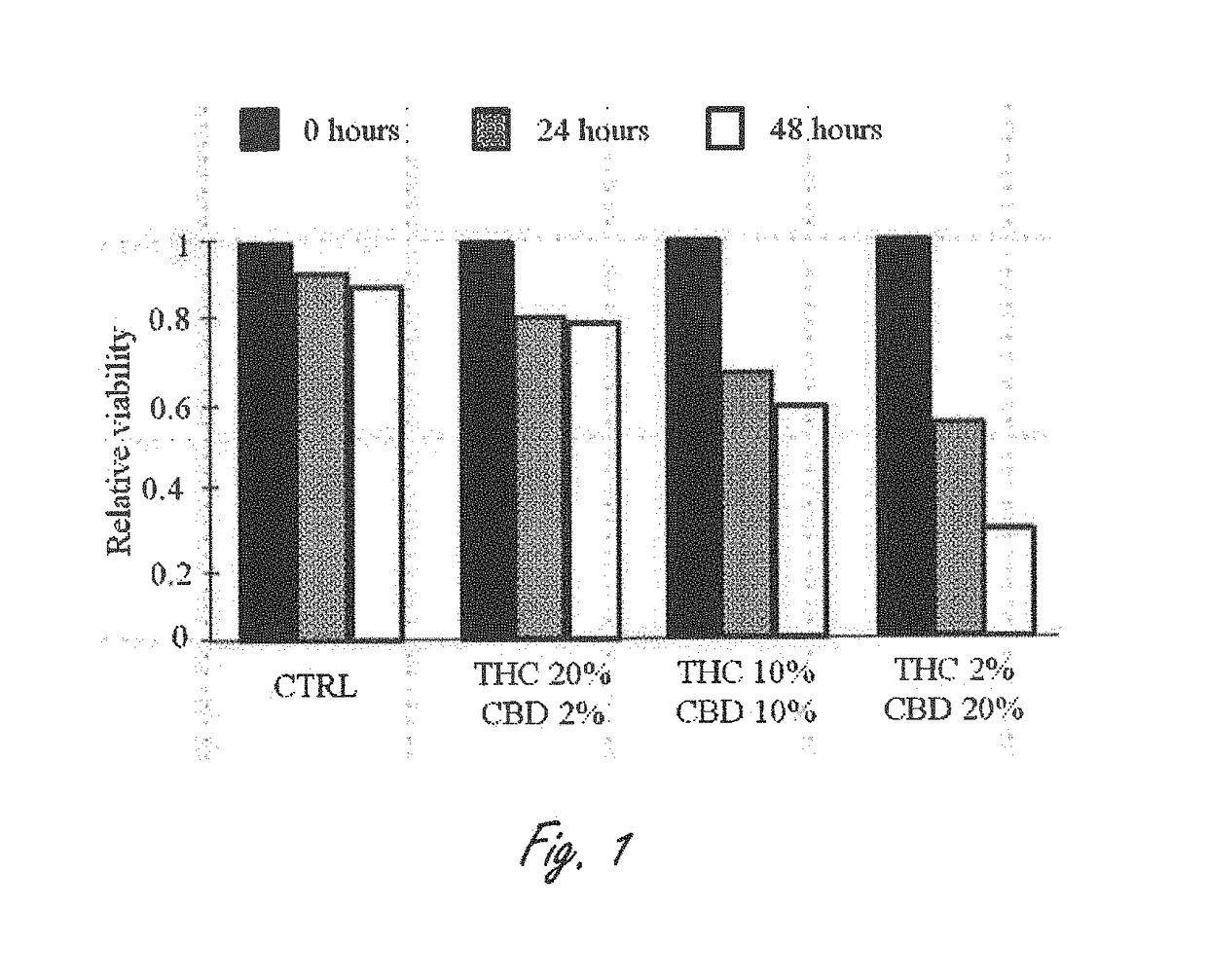
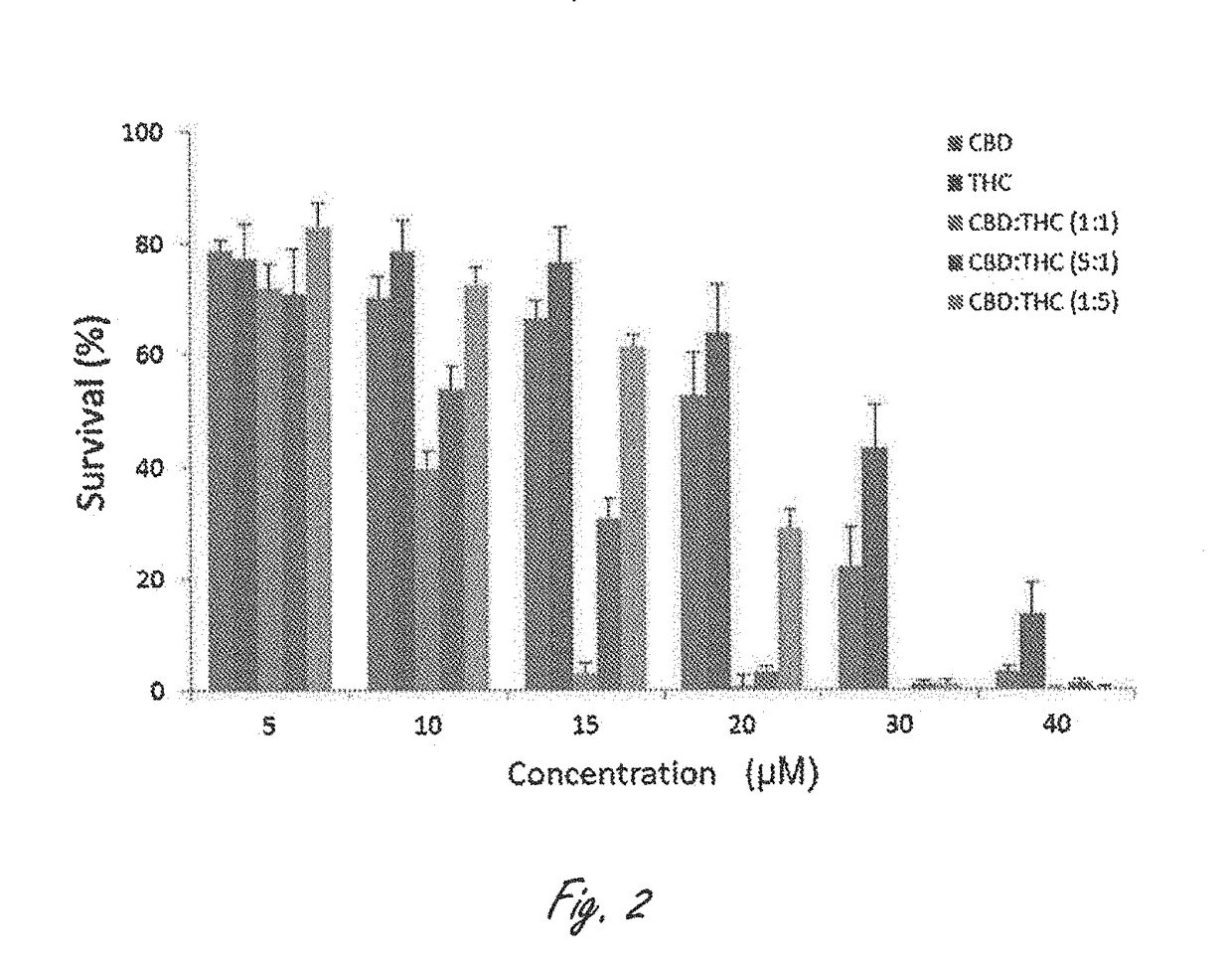
Novel cannabinoid combination therapies for multiple myeloma (MM)
InactiveUS20180185324A1Strong cytotoxicityReduced viabilityHydroxy compound active ingredientsBoron compound active ingredientsCannabinoidCytotoxicity
The present invention discloses a cytotoxic cocktail comprising; (a) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one cannabinoid selected from the group consisting of: cannabidiol (CBD) or a derivative thereof, Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or a derivative thereof, and any combination thereof; and (b) at least one therapeutic agent selected from the group consisting of: bortezomib (BTZ), carflizomib (CFZ), lenalidomide (LEN), dexamethasone (DEX), melphalan (MEL) and doxorubicin (DOXO). In a core embodiment the cocktail is conferring a synergistic effect with respect to inhibition or cytotoxicity of multiple myeloma (MM) cells, relative to said at least one therapeutic agent selected from the group consisting of: BTZ, CFZ, LEN, DEX, MEL, DOXO and said CBD and THC, administered separately in a similar concentration.
Owner:ONE WORLD CANNABIS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com