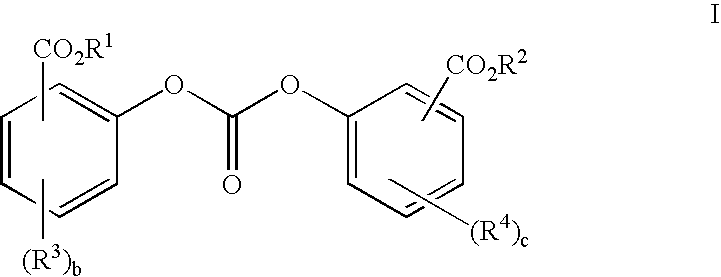
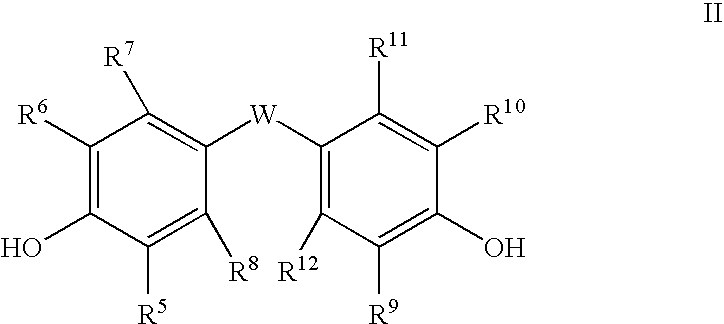
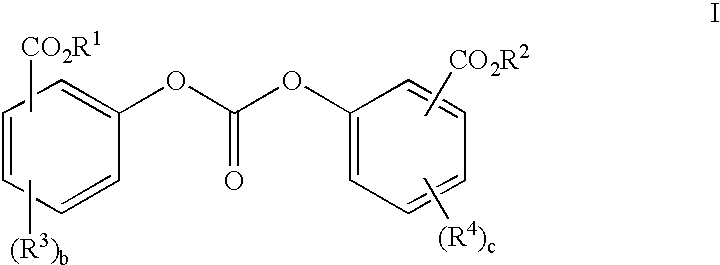
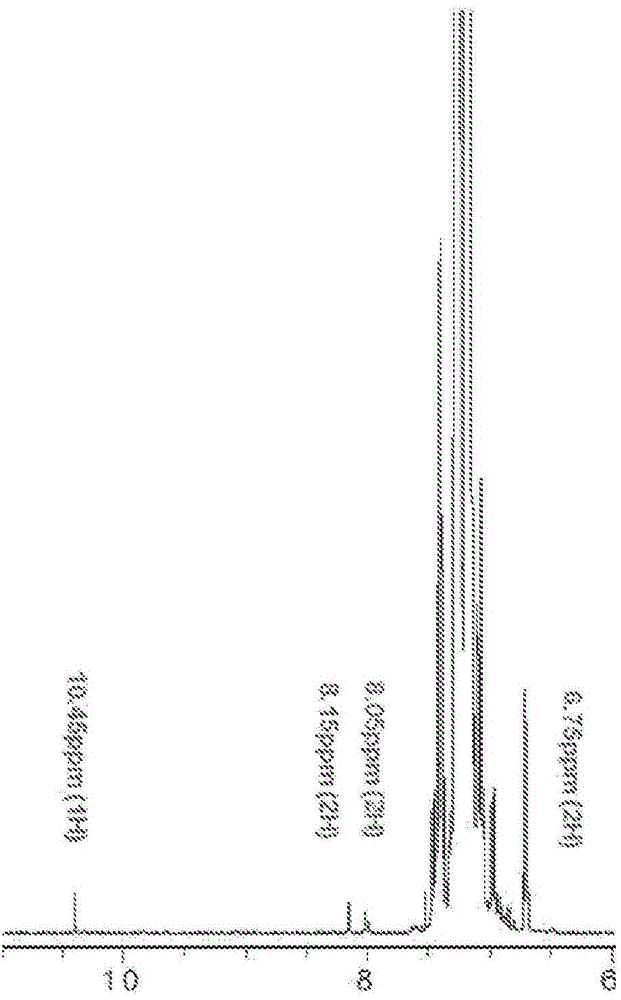
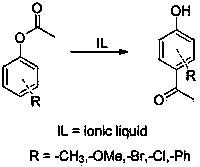Patents
Literature
77 results about "Fries rearrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
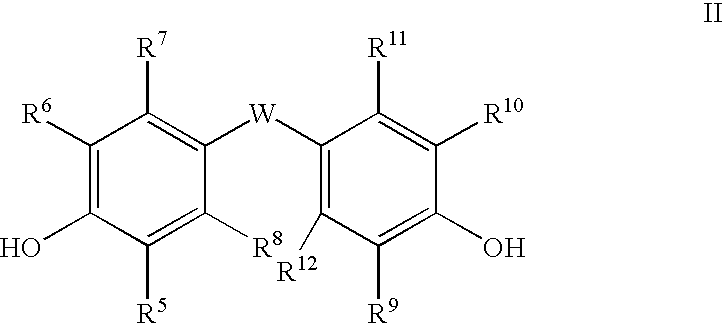
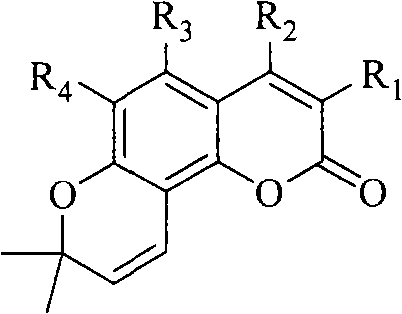
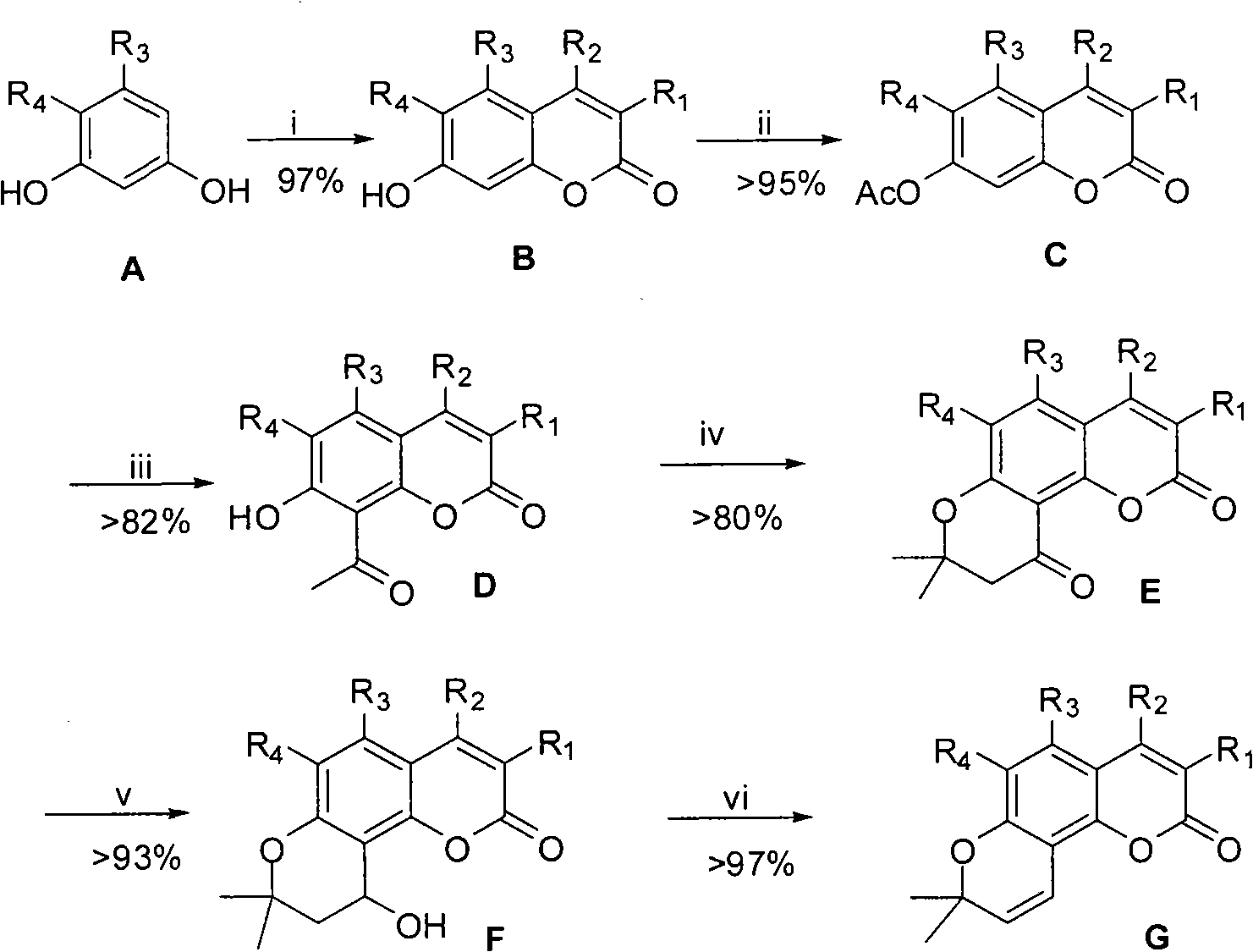
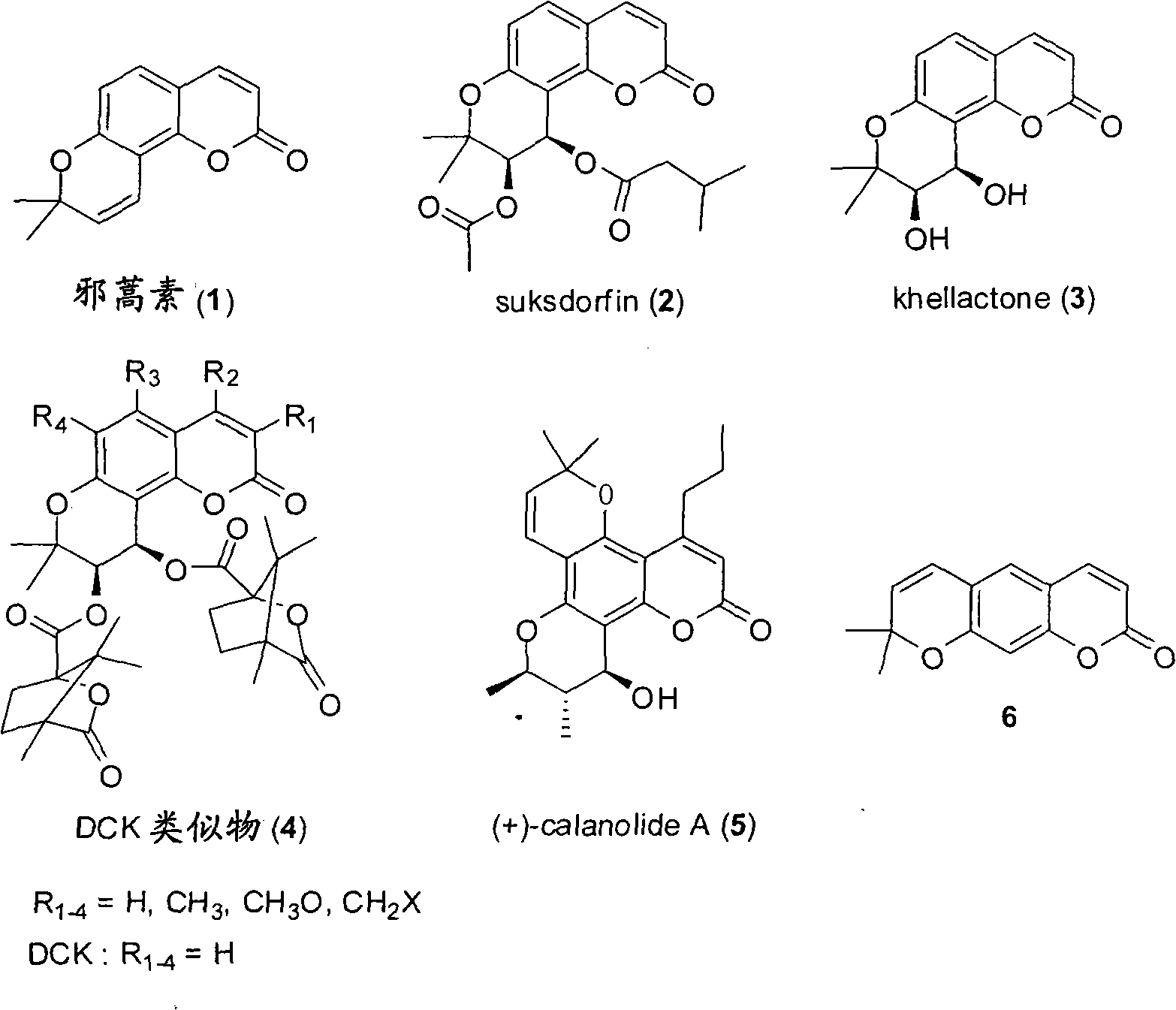
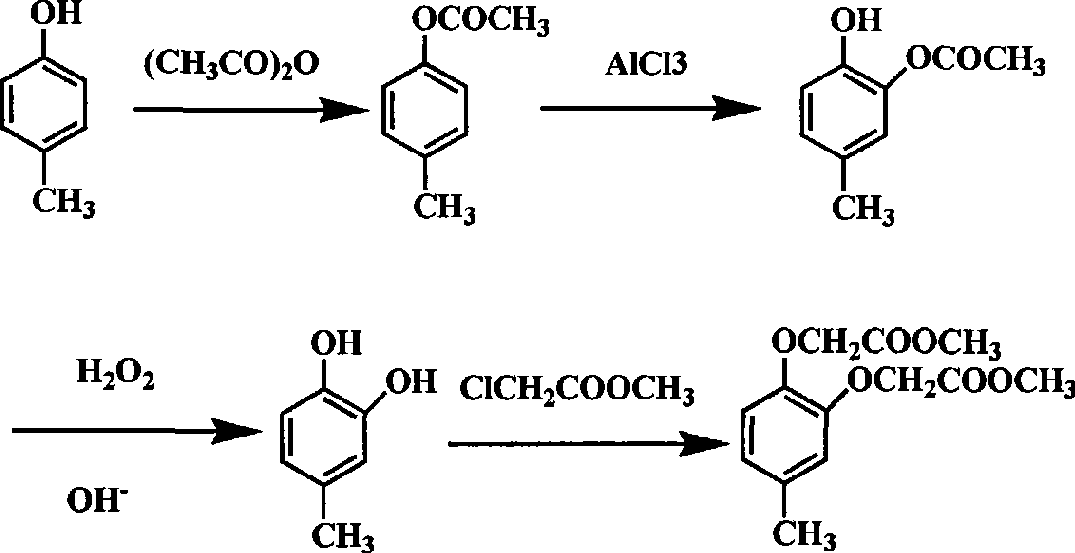
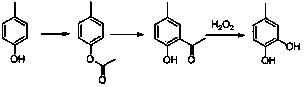
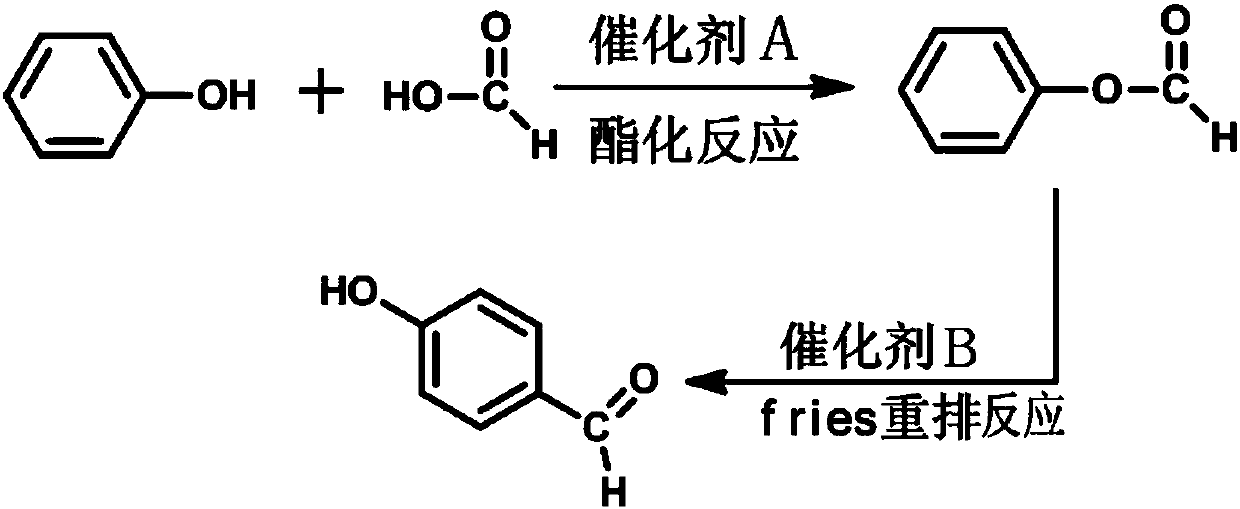
The Fries rearrangement, named for the German chemist Karl Theophil Fries, is a rearrangement reaction of a phenolic ester to a hydroxy aryl ketone by catalysis of Lewis acids. It involves migration of an acyl group of phenol ester to the aryl ring. The reaction is ortho and para selective and one of the two products can be favoured by changing reaction conditions, such as temperature and solvent.
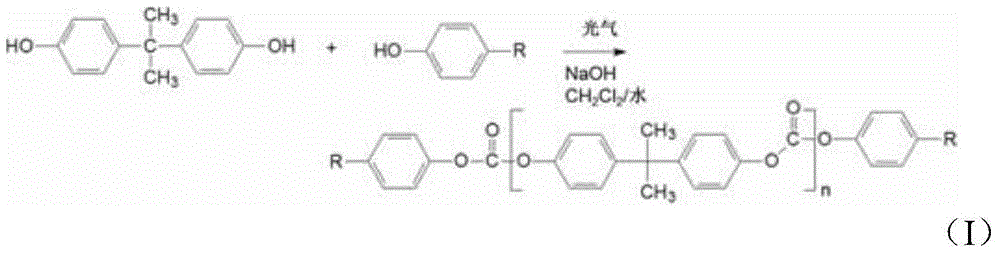
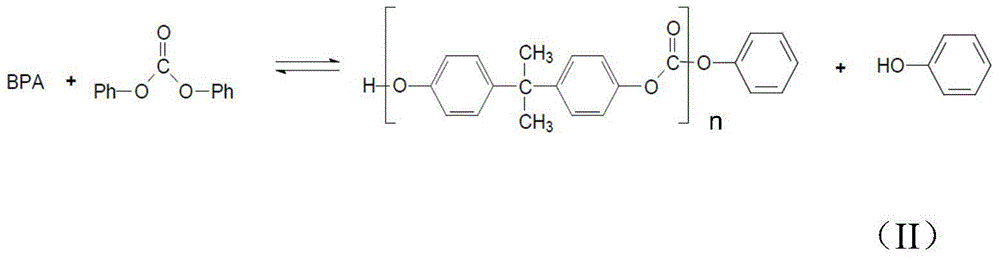
Method of polycarbonate preparation
InactiveUS20050261460A1Low levelImprove the level ofCeramic shaping apparatusFries rearrangementHydroquinone Compound
Polycarbonates containing low or undetectable levels of Fries rearrangement products and comprising repeat units derived from one or more of resorcinol, hydroquinone, methylhydroquinone, bisphenol A, and 4,4′-biphenol have been prepared by the melt reaction of one or more of the aforementioned dihydroxy aromatic compounds with an ester-substituted diaryl carbonate such as bis-methyl salicyl carbonate. Low, or in many instances undetectable, levels of Fries rearrangement products are found in the product polycarbonates obtained as the combined result of a highly effective catalyst system which suppresses the Fries reaction and the use of lower melt polymerization temperatures relative to temperatures required for the analogous polymerization reactions using diphenyl carbonate.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Method of polycarbonate preparation
InactiveUS6870025B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolycarbonate4,4'-Biphenol
Polycarbonates containing low or undetectable levels of Fries rearrangement products and comprising repeat units derived from one or more of resorcinol, hydroquinone, methylhydroquinone, bisphenol A, and 4,4′-biphenol have been prepared by the melt reaction of one or more of the aforementioned dihydroxy aromatic compounds with an ester-substituted diaryl carbonate such as bis-methyl salicyl carbonate. Low, or in many instances undetectable, levels of Fries rearrangement products are found in the product polycarbonates obtained as the combined result of a highly effective catalyst system which suppresses the Fries reaction and the use of lower melt polymerization temperatures relative to temperatures required for the analogous polymerization reactions using diphenyl carbonate.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Fluorescent polymeric articles fabricated from U.V. light absorbing polymer
InactiveUS6972147B1Excellent fluorescence protectionEliminate light absorptionSynthetic resin layered productsRecord information storageFluorescent polymerFries rearrangement
A fluorescent article is disclosed comprising a polymer matrix comprising a polymer having in its backbone repeating units of a U.V. light absorbing moiety, or a moiety capable of being transformed by photo-Fries rearrangement into a U.V. light absorbing moiety, the matrix further comprising a fluorescent dye. The matrix affords surprisingly improved fluorescence protection as compared to prior fluorescent articles having only U.V. light absorbing additives.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Triazine ring based polymers for photoinduced liquid crystal alignment, liquid crystal alignment layer containing the same, liquid crystal element using the alignment layer and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20040039150A1Easy alignmentImprove stabilityLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryCrystallographyPhotoisomerization
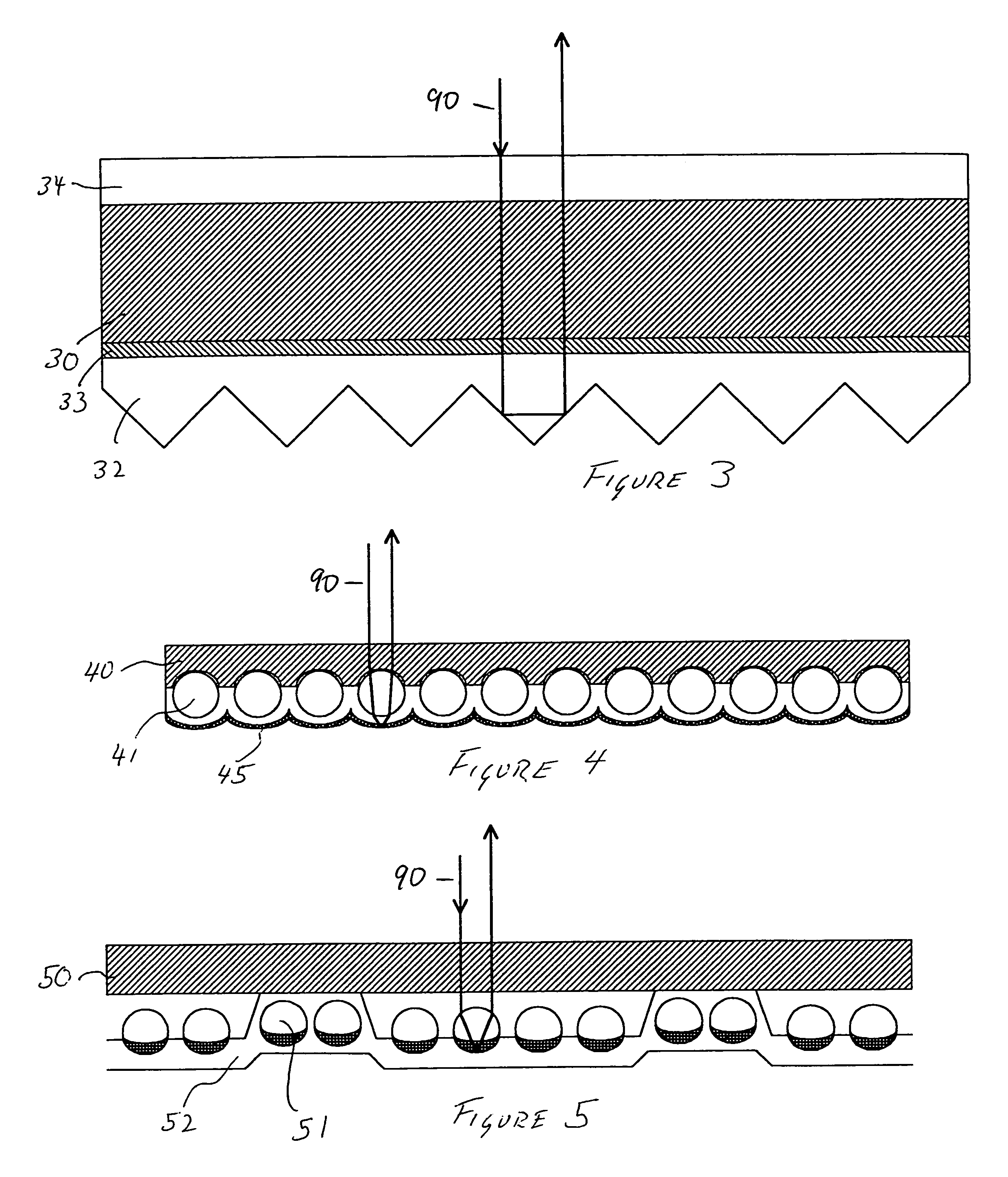
Triazine ring based polymers for photoinduced liquid crystal alignment introduces photoactive groups for inducing, reinforcing, improving and preserving liquid crystal alignment, for example photoreactor such as cinnamate, coumarin, chalcone and maleimide, as a chain to have at least one photoactive group. One of the photoactive groups can experience Fries rearrangement which induces liquid crystal alignment, and other groups can experience photodimerization, photoisomerization, photocrosslinking or photodegradation to reinforce, change or preserve the generated alignment.
Owner:LS MTRON LTD
Preparation method of benzoic acid herbicide dicamba
InactiveCN102516072AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationBenzoic acidFries rearrangement
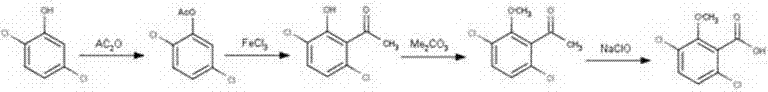
A preparation method of a benzoic acid herbicide dicamba relates to the technical filed of pesticide production. The invention employs 2,5-dichlorophenols as a raw material and carries out esterification, Fries rearrangement, etherification and oxidation to obtain 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid. The synthetic method has simple technology, easily available raw material, low cost, generates little "three wastes (waste gas, waste water and industrial residue)" and is more environment-friendly and more suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGQING AGROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Thermoplastic compositions, methods of manufacture, and articles thereof
A laser weldable composition made from a process of melt blending a combination of a partially crystalline thermoplastic polyester component such as poly(butylene terephthalate), an amorphous thermoplastic polycarbonate having a Fries rearrangement of greater than 150 to 10,000 ppm, and a filler such as glass fiber. The laser weldable composition has a polycarbonate aryl hydroxy end-group content of at least 300 ppm and provides improved near infrared transmission at 960 nanometers. A method welding components made from the weldable composition and welded articles made therefrom are also disclosed.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
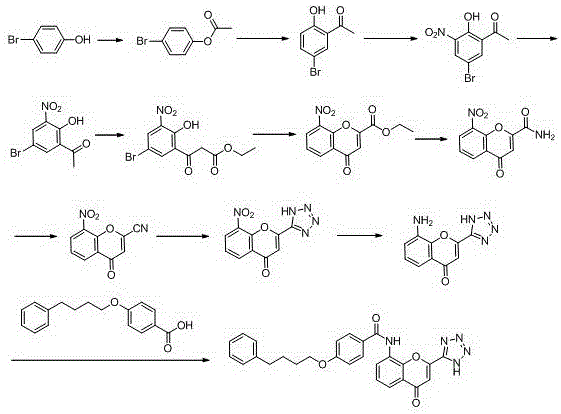
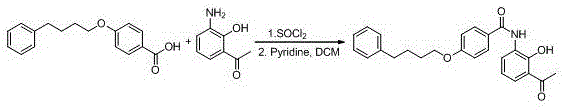
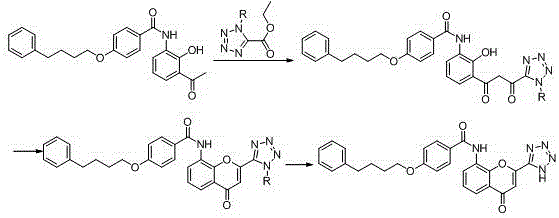
New preparation method of Pranlukast
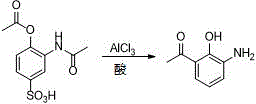
The invention provides a new preparation method of drug Pranlukast for treating asthma. The new preparation method includes the specific steps that with 2-aminophenol-4-sulfonic acid as a starting material, a key intermediate 3-amino-2-hydroxyacetophenone is prepared by means of acylation, Fries rearrangement and deprotection, then reacts with 4-(phenylbutoxy)benzoic acid, and then is subjected to condensation with ethyl 1H-tetrazole-5-acetate, and finally preparation is achieved through ring closing under the acidic condition. Compared with the prior art, the raw material used for the new preparation method is low in price and easy to obtain, industrialization of a process can be achieved easily, and the obtained final product is high in purity; and no dangerous process exists, equipment is simple, and the route is novel.
Owner:上海微巨实业有限公司
Method for preparing p-hydroxy phenyl ethyl ketone compound through rearrangement reaction under catalysis of acidic ionic liquid
ActiveCN103360225AImprove stabilityHigh catalytic activityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationOrganic solventOligomer
The invention provides a method for preparing a p-hydroxy phenyl ethyl ketone compound through Fries rearrangement reaction under catalysis of an acidic ionic liquid. The method comprises the following steps of: directly adding phenyl acetate to the ionic liquid, wherein the dosage of the ionic liquid is 10%-40% of the mole number of oligomers; next, reacting for 12-18 hours at a temperature ranging from 60 to 120 DEG C, thus obtaining p-hydroxy phenyl ethyl ketone without o-hydroxy phenyl ethyl ketone type product through extraction, drying and reduced pressure distillation. The ionic liquid applied to the method is used as a solvent and a catalyst, and is high in catalytic activity and selectivity; the dosage of the catalyst is low and the reaction yield is high; the use of other organic solvent and toxic catalyst is reduced, so that the corrosivity of the catalyst to equipment is reduced; the aftertreatment is simple and convenient.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Latent epoxy resin curing agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111423347AGood compatibilitySuitable for useOrganic chemistryPolymer scienceFries rearrangement
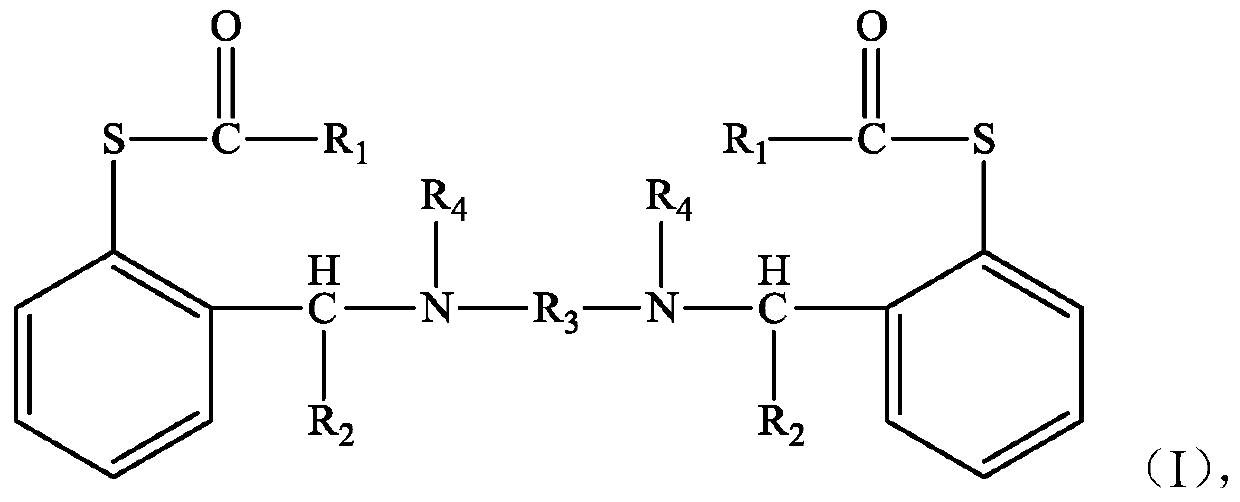
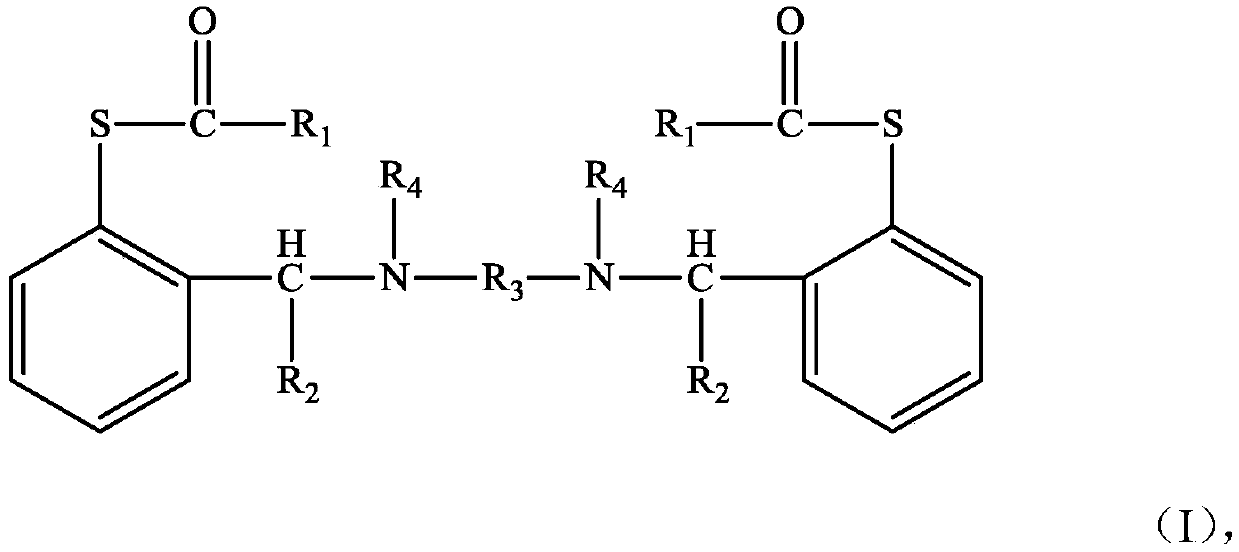
The invention discloses a compound shown as a structural formula (I) as a latent epoxy resin curing agent. The structure of the latent epoxy resin curing agent is phenolic aldehyde phenyl mercaptan ester. The preparation raw materials comprise phenylmercaptan, a carboxyl compound, an aldehyde compound and aromatic secondary amine. The curing agent is a low-viscosity liquid at normal temperature, after being matched with epoxy resin, the curing agent has a long working life, after the temperature is raised, the phenyl mercaptan ester is subjected to Fries rearrangement so as to dissociate an active group thiol, and the active group thiol can quickly react with the epoxy resin under the catalytic action of a tertiary amine group, so that the curing agent is particularly suitable for the field of prepregs with requirements on long operation time.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
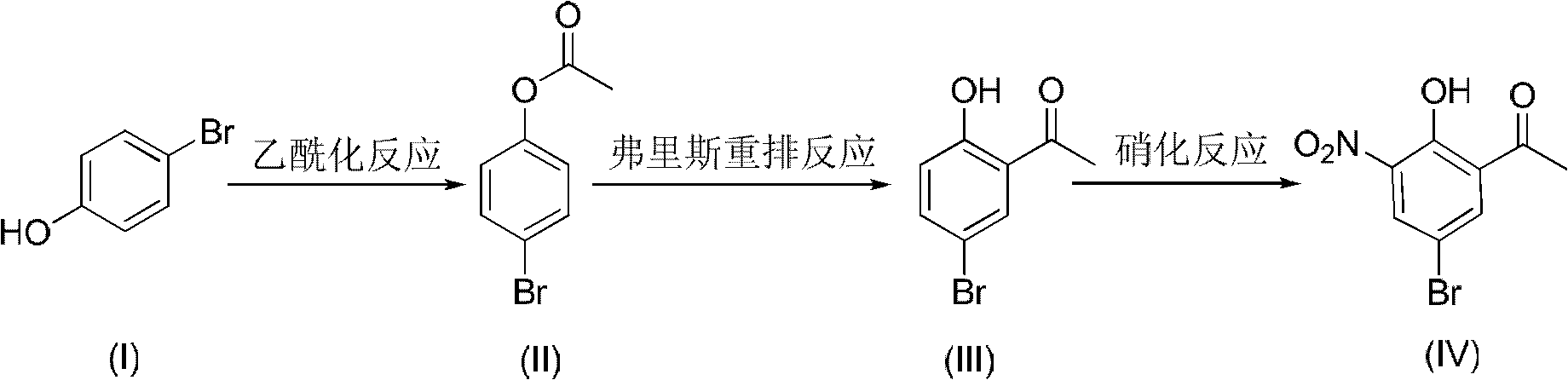
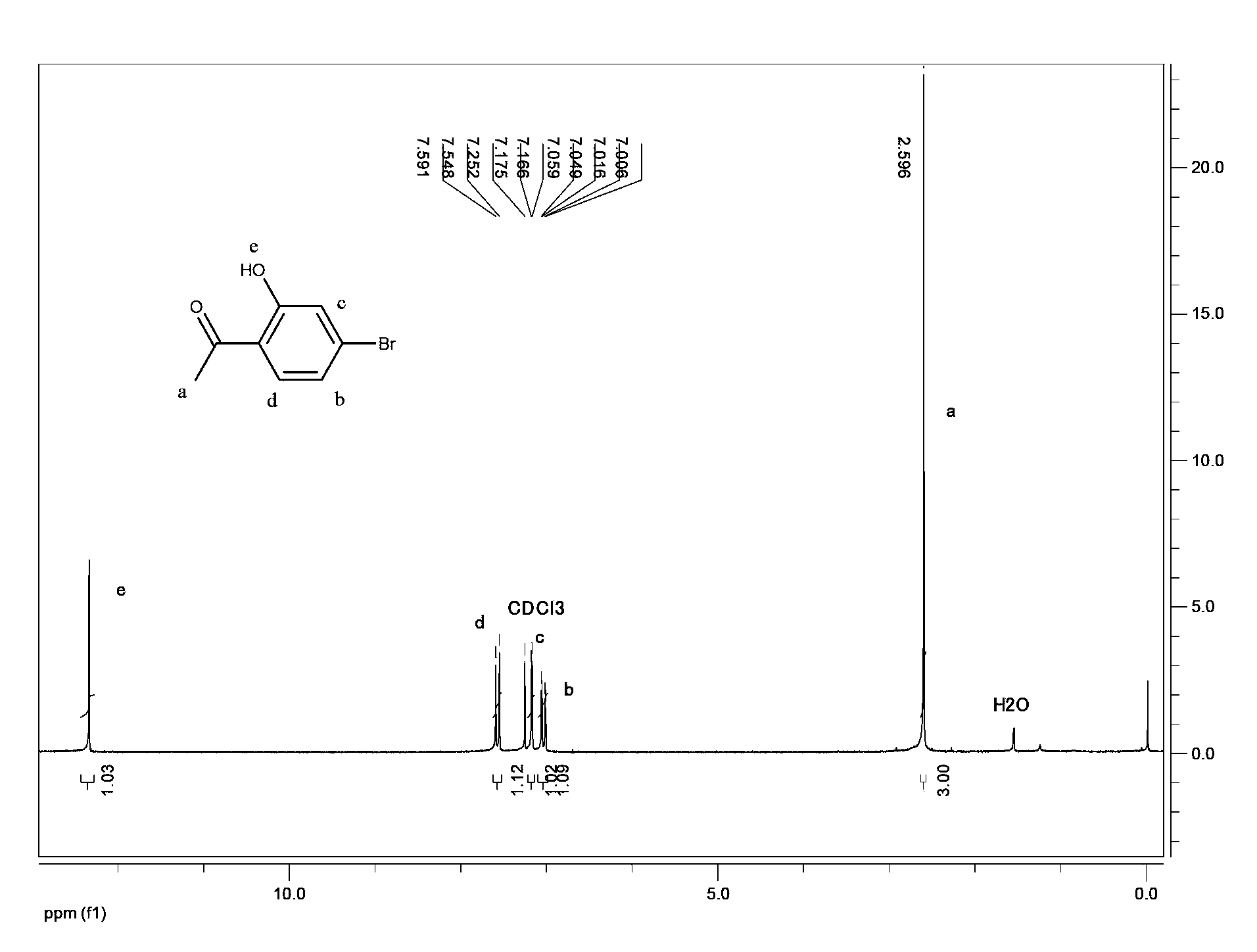
Method for preparing 5-bromo-2-hydroxy-3-nitroacetophenone
The present invention discloses a method for preparing 5-bromo-2-hydroxy-3-nitrophenylethanone. The method comprises that: (1) in the presence of an alkali, tetrachloroethylene is adopted as a reaction solvent, bromophenol completesly reacts with an acetylation reagent to obtain a tetrachloroethylene solution of bromoacetic acid phenolester; (2) Lewis acid is added to the resulting solution from the step (1) to completely carry out a Fries rearrangement reaction to obtain a tetrachloroethylene solution of 5-bromo-2-hydroxy acetophenone; (3) a nitration reagent is added to the resulting solution from the step (2) in a dropwise manner to completely carry out the reaction to obtain the 5-bromo-2-hydroxy-3-nitroacetophenone. According to the preparation method provided by the present invention, the three-step reaction is adopted, the tetrachloroethylenes having the same batch are adopted for purifying the final product, such that the solvent consuming is reduced, the cost is reduced, the post-processing time is shortened and the operation steps are simplified; the toxicity of the tetrachloroethylene is far less than the toxicities of chloroform and carbon tetrachloride, such that the hazards on the human body and the environment are less; the tetrachloroethylene is easy to reclaim; the industrialization is easy to realize.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
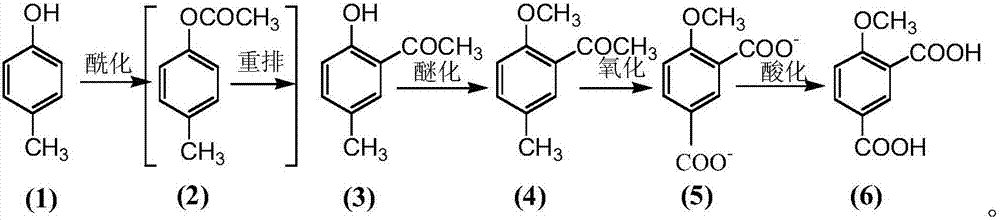
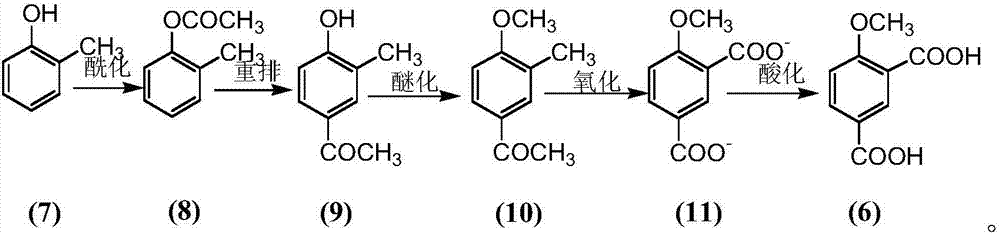
Preparation method for 4-methoxy-1,3-phthalic acid
InactiveCN107337596AReduce pollutionLess investmentPreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationFries rearrangementAnti platelet
The invention provides a preparation method for 4-methoxy-1,3-phthalic acid. 4-methoxy-1,3-phthalic acid is key intermediate for preparation of an anti-platelet aggregation drug picotamide (with a trade name of plactidil). According to the preparation method, 4-methoxy-1,3-phthalic acid is prepared from the starting raw material p-methylphenol or o-methylphenol through esterification, Fries rearrangement, methylation, oxidation and acidification. Compared with traditional preparation methods, the preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of low equipment investment, simple operation, quick reaction, high yield, low synthesis cost, greatly reduced environmental pollution and the like, and is particularly suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of 2-hydroxyl-4-substituted arone compound
ActiveCN103408414AHigh catalytic activityHigh activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsQuaternary ammonium cationSulfate radicals
The invention discloses a preparation method of a 2-hydroxyl-4-substituted arone compound. A Bronsted-Lewis dual acidic ionic liquid is taken as a catalyst to catalyze 3-substituted phenolic ester to undergo a Fries rearrangement reaction. The Bronsted-Lewis dual acidic ionic liquid catalyst is a quaternary ammonium salt ionic liquid containing dual acidity, contains a Lewis acid site of copper ions or zinc ions and a Bronsted acid site of a sulfonic group. The Bronsted acid site of the sulfonic group takes the quaternary ammonium salt as a cation and adopts a sulfate radical as an anion. The dual acidic ionic liquid catalyst has strong catalytic activity, high reaction selectivity, and an ortho product with high yield and high purity can be obtained. The reaction aftertreatment is simple and safe, has less pollution, and the catalyst can be used repeatedly. Specifically, the raw material 3-substituted phenolic ester of the Fries rearrangement reaction can be obtained by reaction of 3-substituted phenol with an acylation reagent acyl chloride.
Owner:BEIJING GREENCHEM TECH
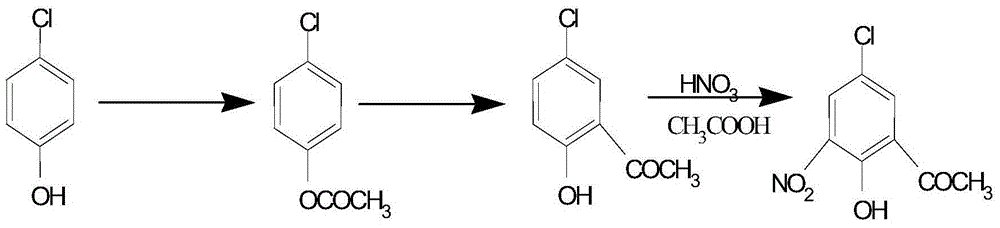
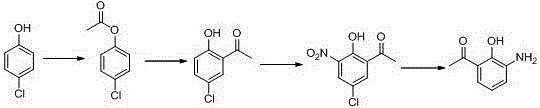
Preparation method for 5-chlorine-2-hydroxyl-3-nitroacetophenone
InactiveCN104402728AReduce usageReduce manufacturing costNitro compound preparationDistillationSolvent free
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of medical intermediates, and particularly relates to a preparation method for 5-chlorine-2-hydroxyl-3-nitroacetophenone. The preparation method comprises the steps: under the existence of a catalyst, reacting parachlorophenol with an acetylation reagent in a solvent-free condition, and performing decompression distillation to obtain acetic acid parachlorophenol and glacial acetic acid serving as a byproduct; adding lewis acid into acetic acid parachlorophenol to perform Fries rearrangement reaction, adding water into a system after the reaction is completed, stirring the mixture to obtain solid sediments, performing recrystallization by using methyl alcohol to obtain 5-chlorine-2-hydroxyacetophenone, adding glacial acetic acid for dissolving, then dropping a nitration reagent, and stirring and filtering to obtain 5-chlorine-2-hydroxyl-3-nitroacetophenone. According to the preparation method, the production cost is lowered, the reaction period is short, the purity is high, the yield is high, the operation is simple and convenient, and industrialization is easily realized.
Owner:SHANDONG JINCHENG PHARMA & CHEM
Method for manufacturing liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20160178969A1Improve display qualityAvoid failureTube/lamp screens manufactureNon-linear opticsPhotoisomerizationIn plane
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device including a photo-alignment film and capable of sufficiently improving the display quality. The method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device of the present invention is a method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device including a photo-alignment film. The method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device successively includes a step (1) of forming on a substrate a film from a photo-alignment-film material that contains a solvent and a polymer including a photo-functional group that is capable of causing at least one chemical reaction selected from the group consisting of photodimerization, photoisomerization, and photo-Fries rearrangement; a step (2) of pre-heating the film to evaporate the solvent; a step (3) of irradiating the pre-heated film with polarized light; and a step (4) including an operation of main-heating the polarized-light-irradiated film at multiple temperatures from a lower temperature to a higher temperature. The liquid crystal display device is of an in-plane switching mode or a fringe field switching mode in each of which a pre-tilt angle is substantially 0°.
Owner:SHARP KK
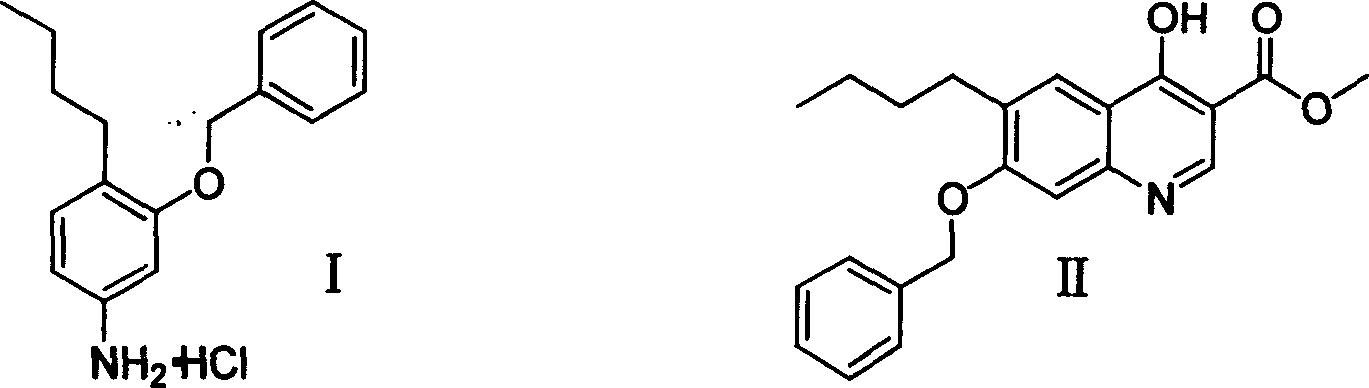
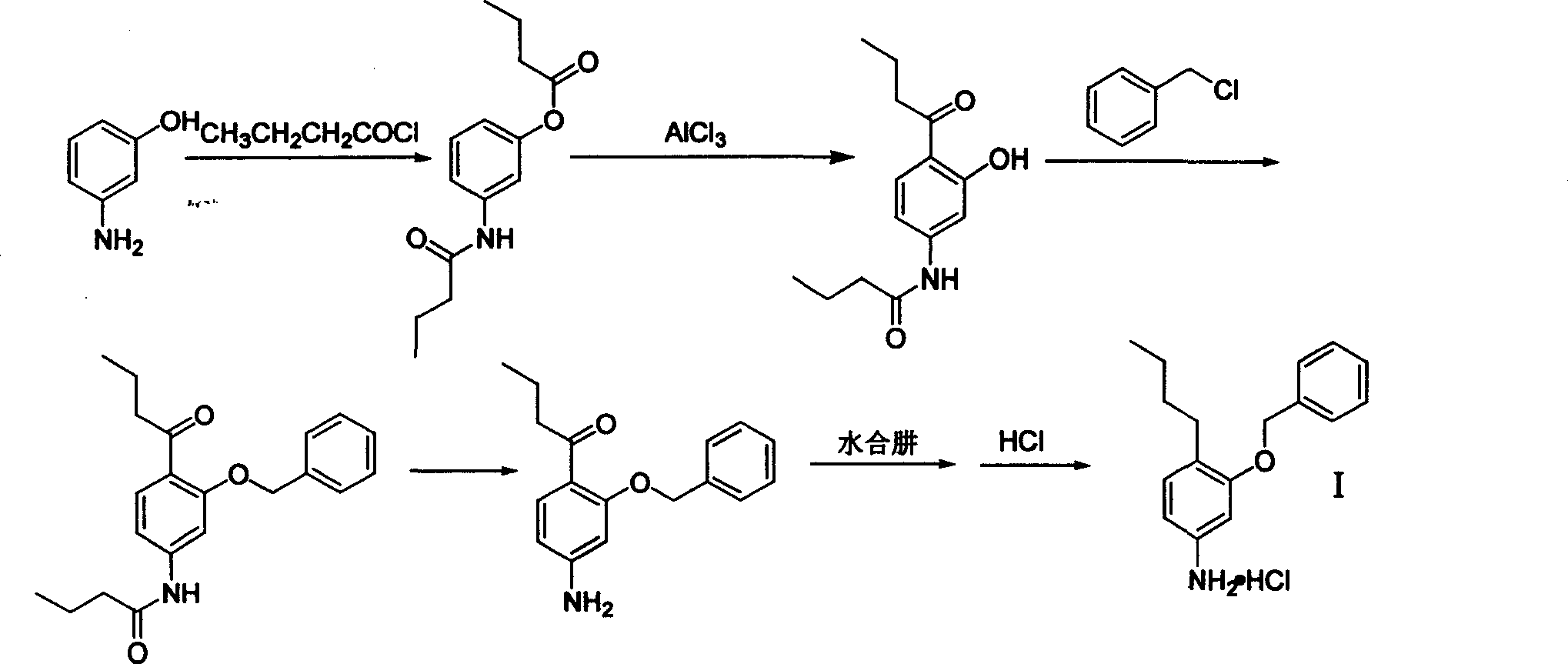
3-benzyloxy-4-butylaniline hydrochloride preparation method
InactiveCN1733703AReduce stirringStir wellOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationM-aminophenolFries rearrangement
The invention provides a process for preparing 3-benzyloxy-4-butylaniline hydrochlorides, which comprises using m-aminophenol as raw material, carrying out butanoylation reaction and Fries rearrangement, obtaining 2-butyryl-5-butyramidophenol, under the action of alkali, reacting 2-butyryl-5-butyramidophenol with benzyl halides, obtaining 2-butyryl-5-butyramidophenyl benzyl ether, hydrolyzing to obtain 3-benzyloxy-4-butyryl benzeneamine, finally carrying out Huangminglong reduction reaction to obtain 3-benzyloxy-4-butylaniline hydrochlorides.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Fluorescent polymeric articles having screening layer formed from U.V. light absorbing polymer
InactiveCN1473169AProtectReduce or eliminate dissolutionSynthetic resin layered productsElectrographic process apparatusFluorescent polymerFries rearrangement
A flurorescent article is disclosed in which a U.V. light screening layer comprising a polymer having in its backbone repeating units of a U.V. light absorbing moiety, or a moiety capable of being transformed by Photo-Fries rearrangement into a U.V. light absorbing moiety, is disposed in operative screening relation to a layer containing a fluorescent colorant. The U.V. light screening layer affords surprisingly improved fluoresence protection as compared to prior U.V. light screening layers having only U.V. light absorbing additives.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Synthetic method for ultraviolet absorbent namely 4,4'-dihexyloxybenzophenone
ActiveCN107129432AImprove conversion rateConducive to labor protectionPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesOrganic compound preparationUltravioletPotassium
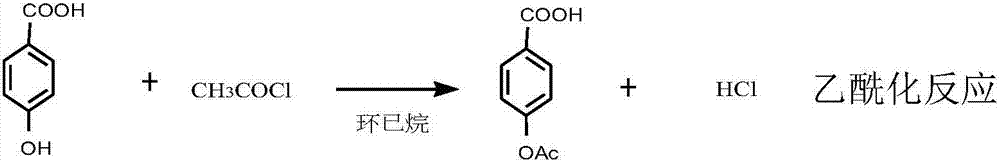
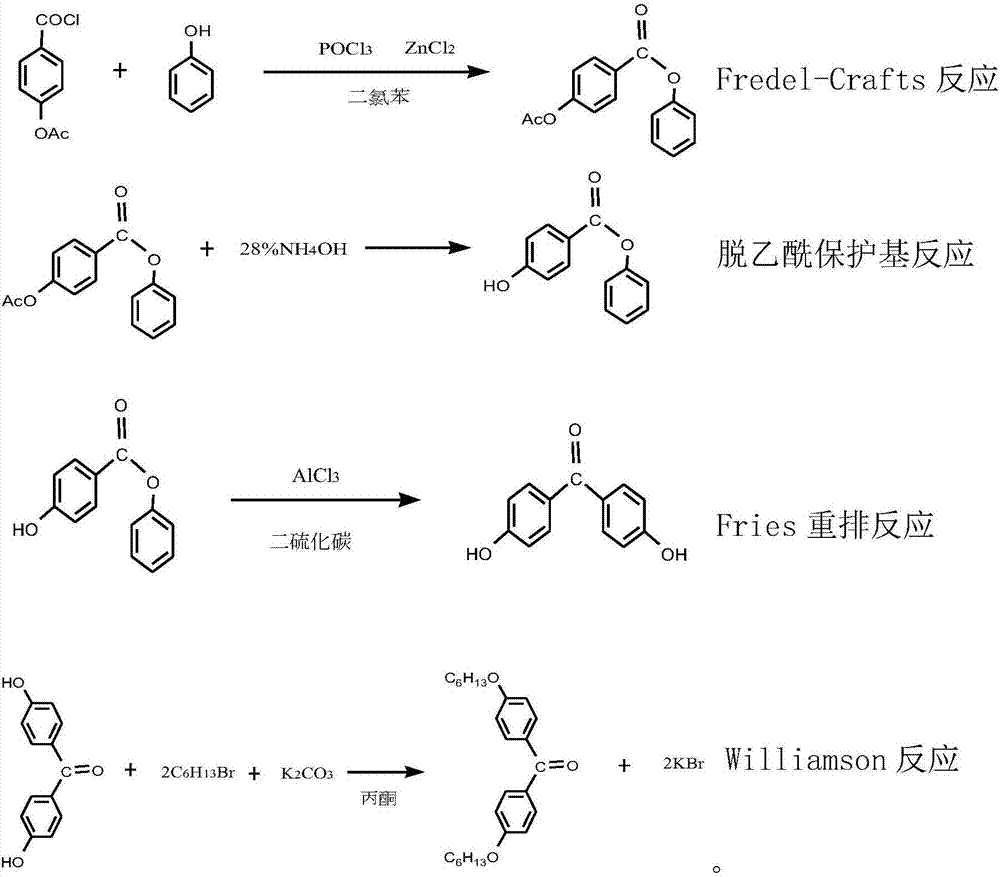
The invention discloses a synthetic method for an ultraviolet absorbent namely 4,4'-dihexyloxybenzophenone. The method comprises the following steps: with p-hydroxybenzoic acid as a starting material, carrying out acetylation to protect hydroxy; carrying out a Fredel-Crafts reaction of p-acetoxybenzoic acid and phenol under the catalysis of zinc chloride and phosphorus oxychloride so as to synthesize an intermediate namely phenyl p-hydroxybenzoate; then carrying out deacetylation to remove the protective group, and carrying out Fries rearrangement so as to prepare an intermediate namely 4,4-dihydroxybenzophenone; and forming a salt with 4,4-dihydroxybenzophenone and potassium carbonate, and carrying out a Williamson reaction of 1-bromohexane and the potassium salt of 4,4-dihydroxybenzophenone through catalysis of tetrabutylammonium bromide so as to synthesize the 4,4'-dihexyloxybenzophenone. The synthetic method provided by the invention has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, normal pressure, medium and low temperature, stable quality control, high raw material conversion rate, effective inhibition of side reactions, fewer three wastes, light pollution, and facilitation of protecting the environment and labor of a producer.
Owner:RUDONG JINKANGTAI CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method for 5-fluorin-2-hydroxyacetophenone
InactiveCN102557909AOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationFries rearrangementClaisen rearrangement
The invention provides a preparation method for 5-fluorin-2-hydroxyacetophenone. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing double esterification on amino groups and phenolic hydroxy in one step by taking amino-phenol as a raw material; performing Fries rearrangement under the condition of aluminum chloride / sodium chloride; heating a hydrolyzate after performing fluorine diazotization to obtain finished 5-fluorin-2-hydroxyacetophenone. The preparation method has the advantages of low prices of raw materials, relatively mild reaction conditions, total yield of up to 54.5 percent and industrial production application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOFLUORO SCI
New preparation method of 3-amino-2-hydroxyphenylacetone
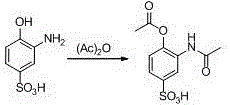
ActiveCN106831457ACheap and easy to getHigh purityOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid preparationState of artFries rearrangement
The invention discloses a new preparation method of a key intermediate, namely 3-amino-2-hydroxyphenylacetone, for preparation of Pranlukast. The new preparation method comprises the following main steps: taking 2-aminophenol-4-sulfonic acid as a starting raw material, and carrying out acylation, Fries rearrangement, hydrolysis and deprotection, so that 3-amino-2-hydroxyphenylacetone is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the new preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the used raw materials are cheap and easily available, technology can easily realize industrialization, and the obtained final product is high in purity; no danger technology is adopted, and equipment is simple; and route is novel, and synthesis route is short.
Owner:上海微巨实业有限公司
Preparation of amyrolin and derivatives thereof
InactiveCN101407522ASimple purification methodSuitable for industrial productionOrganic chemistryAnti-HIV AgentFries rearrangement
The invention relates to a synthesizing method and preparing process for seselin and the derivatives. The method takes substituted hydroxyphenol as a raw material, and after Pechmann reaction, acetylation, Fries rearrangement, cyclization, reduction and dehydration, the seselin compound can be obtained. The method has the advantages of simple operation of each step, controllable conditions, easily obtained reagent, convenient purification, single product and high yield. The synthesizing route overcomes the defects of low yield and being difficult to remove isomers of the existing methods. The seselin and the derivatives which are taken as the important bioactive substance and medical intermediate have good application prospect in anti-inflammatory, anti-fungus and anti-tumor aspects, particularly playing a key role in synthesizing candidate anti-HIV agents. The synthesizing route and the method have high application value and wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Chemical synthetic method for para-methyl catechol diacetoxyl dimethyl ester
InactiveCN101544564ARaw materials are easy to getMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationChemical synthesisAcetophenone
The invention relates to a synthetic method for para-methyl catechol diacetoxyl dimethyl ester. The method uses paracresol as an initial raw material to synthesize the para-methyl catechol diacetoxyl dimethyl ester into a target compound through acetylation reaction catalyzed by acid, Fries rearrangement reaction of phenolic ester, Dakin oxidation reaction of 2-hydroxy-5-methyl acetophenone and direct etherification reaction of para-methyl catechol. The total yield of the whole reaction is more than 70 percent, and the purity of the product is more than 98 percent. The method of the invention has the characteristics of easily-obtained raw materials, mild reaction condition, low equipment requirement, simple operation, low production cost, little side reaction, simple post treatment, and the like. Therefore, the synthetic method of the invention is a method suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:杭州浙大泛科化工有限公司
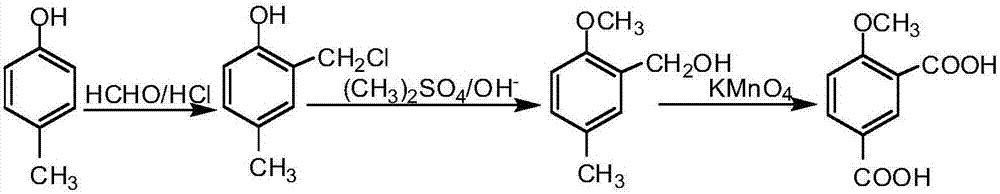
Method for preparing 4-methyl catechol
InactiveCN104030893AReduce pollutionSolving Operational Security IssuesPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesOrganic compound preparationCresolBoiling point
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing 4-methyl catechol. The method comprises the steps of carrying out acylation reaction on p-cresol as a starting materia to obtain p-cresyl acetate, carrying out Fries rearrangement reaction in a high-boiling-point inert solvent to obtained 2-hydroxy-5-methyl acetophenone, alkalifying, forming a salt, oxidizing at a low temperature, after the reaction is completed, reducing the reaction solution, acidifying, extracting and concentrating to obtain a crude product and distilling the crude product to obtain the pure 4-methyl catechol. The method disclosed by the invention is environmental friendly, available in raw materials, mild reaction conditions, low requirements on equipment, simple operation, low production cost, less side effects and high yield and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for manufacturing liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20160178968A1Improve display qualityAvoid failureTube/lamp screens manufactureCoatingsPhotoisomerizationIn plane
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device including a photo-alignment film and capable of sufficiently improving the display quality. The method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device of the present invention is a method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device including a photo-alignment film. The method for manufacturing a liquid crystal display device successively includes a step (1) of forming on a substrate a film from a photo-alignment-film material that contains a solvent, a polymer including a photo-functional group that is capable of causing at least one chemical reaction selected from the group consisting of photodimerization, photoisomerization, and photo-Fries rearrangement, and a polymer including a polyamic acid backbone and free from the photo-functional group; a step (2) of pre-heating the film to evaporate the solvent; a step (3) of irradiating the pre-heated film with polarized light; and a step (4) of main-heating the polarized-light-irradiated film. The liquid crystal display device is of an in-plane switching mode or a fringe field switching mode in each of which a pre-tilt angle is substantially 0°.
Owner:SHARP KK
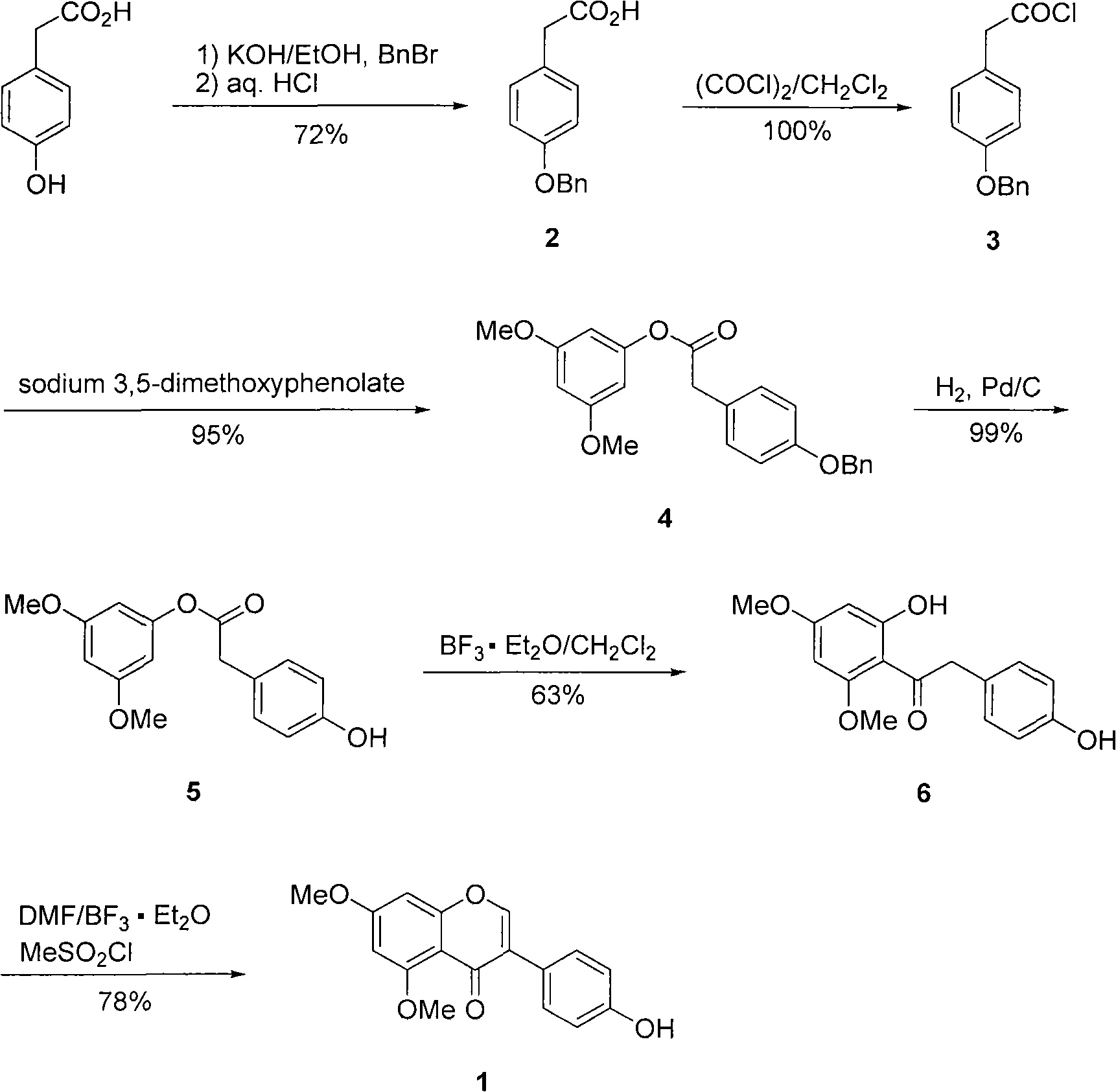
Natural product 5,7-dimethoxy-4'-hydroxyisoflavone preparation method
InactiveCN101613335AFacilitate the cyclization reactionHigh yieldOrganic chemistryN dimethylformamideNatural product
The invention relates a natural product 5,7-dimethoxy-4'-hydroxyisoflavone preparation method, comprising the following steps: adopting 4-hydroxylphenylacetic acid and 3,5-dimethoxyphenol as starting materials to perform Fries rearrangement reaction to generate hydroxydeoxybenzoin compound 1-(2,4-dimethoxy-6-hydroxylphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxylphenyl)ethanone; adopting N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as formylation reagent and solvent and adding methanesulfonyl chloride at the same time to promote Vilsmeier-Haack formylation reaction and consecutive cyclization reaction and increase the yield of 5,7-dimethoxy-4'-hydroxyisoflavone (1). The invention is simple and practical, the raw materials are cheap and accessible and the yield is high so that the preparation method is applicable to industrialized production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Liquid crystal display element and liquid crystal composition
ActiveCN110268314AReduce manufacturing costGood compatibilityLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsDielectric anisotropyLight irradiation
Owner:JNC CORP +1
Method for preparing 2,3-dihydroxytoluol
ActiveCN102010300AWide range of usesSave raw materialsOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationChemical synthesisFries rearrangement
The invention relates to the field of organic chemical synthesis, and discloses a method for preparing 2,3-dihydroxytoluol serving as a medicinal intermediate. In the method, the 2,3-dihydroxytoluol as the medicinal intermediate is synthesized by using o-cresol as a raw material and by three fine processing steps of esterification, Fries rearrangement and Dakin reactions. The 2,3-dihydroxytoluol is an important fine chemical engineering intermediate, and has the wide applications in medicinal industry; and at present, there are fewer reports on synthetic methods, and the synthetic methods arenot suitable for industrial production. In the method, the total yield of the process is 30 percent. In the method, the raw material is cheap, and the reaction conditions are mild. Thus, a process for synthesizing the 2,3-dihydroxytoluol is developed.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Synthesis method for raw material drugs of dicamba
InactiveCN107501089AReduce pollutionSimple processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSynthesis methods2-methoxybenzoic acid
The invention relates to a synthesis method for raw material drugs of dicamba. The synthesis method for the raw material drugs of dicamba comprises the following steps: taking 2,5-dichlorophenol as a starting material, carrying out esterification under the actions of an organic solvent and an organic esterification reagent to generate 2,5-dichlorophenol acetate; dissolving 2,5-dichlorophenol acetate in the organic solvent and adding a catalyst to generate Fries rearrangement, thus generating 3,6-dichloro-2-hydroxyacetophenone; making 3,6-dichloro-2-hydroxyacetophenone react with a methylating reagent under the action of an acid-binding agent to obtain 3,6-dichloro-2-methylacetophenone; synthesizing dicamba (3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoic acid) under the action of 3,6-dichloro-2-methylacetophenone. The synthesis method for the raw material drugs of dicamba disclosed by the invention is simple in process, highly available in raw materials and the catalyst, low in cost, simple in post-treatment operation, low in environmental pollution, high in safety of reaction operation, high in reaction yield, good in product quality and favorable for industrialization.
Owner:HENAN HDF CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of lorlatinib intermediate compound
InactiveCN110922315AReduce manufacturing costLow unit priceOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound separation/purificationPhotocatalytic reactionPtru catalyst
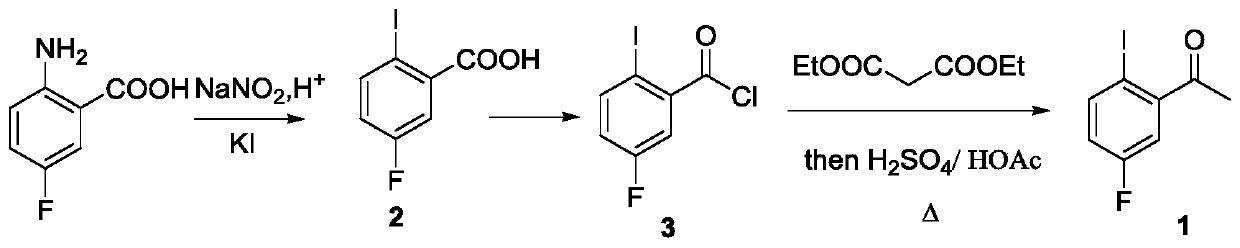
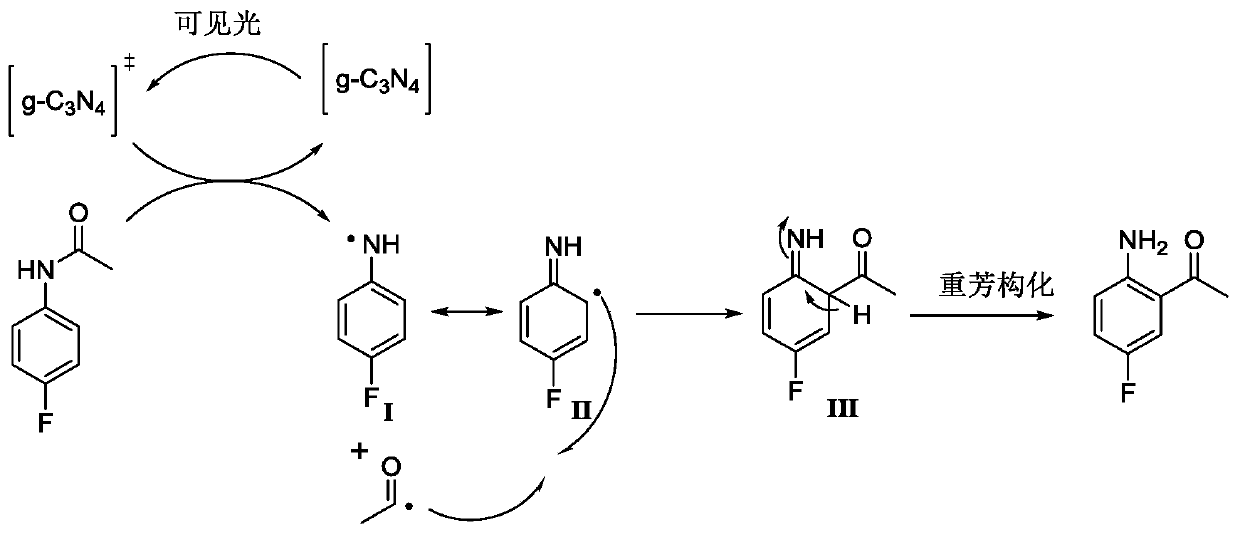
The invention relates to a preparation method of a lorlatinib intermediate compound. 4-fluoroacetanilide is taken as a raw material and carry out visible light Fries rearrangement in the presence of avisible light catalyst and visible light to obtain an intermediate product (2-amino-5-fluoroacetophenone); and the intermediate product can directly carry out diazotization-iodination reactions without purification to obtain the lorlatinib intermediate compound (3-fluoro-6-iodoacetophenone). The raw materials are cheap and easily available. The post treatment has simple steps. The using amounts of chemical reagents in rearrangement reactions are only catalytic amounts. The energy source of the reactions is the visible light. The preparation method is green and environmentally friendly. A continuous flowing type photocatalytic reaction system is formed. The purification method and post treatment are simple and convenient. No extra production cost or environmental protection cost is generated. The novel preparation method of 3-fluoro-6-iodoacetophenone can be applied to the industry and generates economical benefits.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
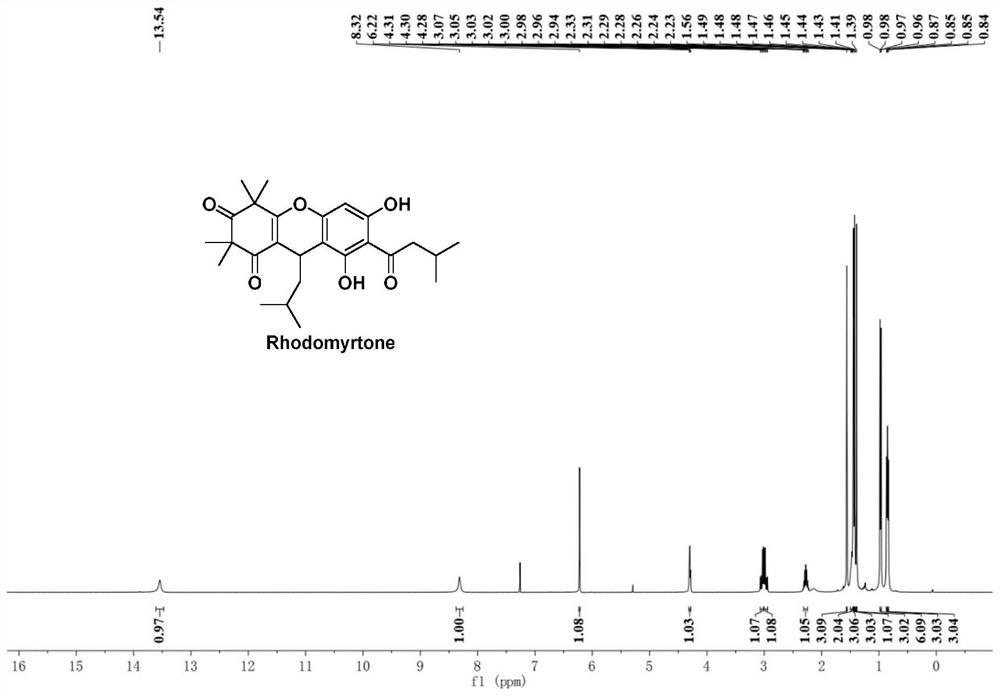
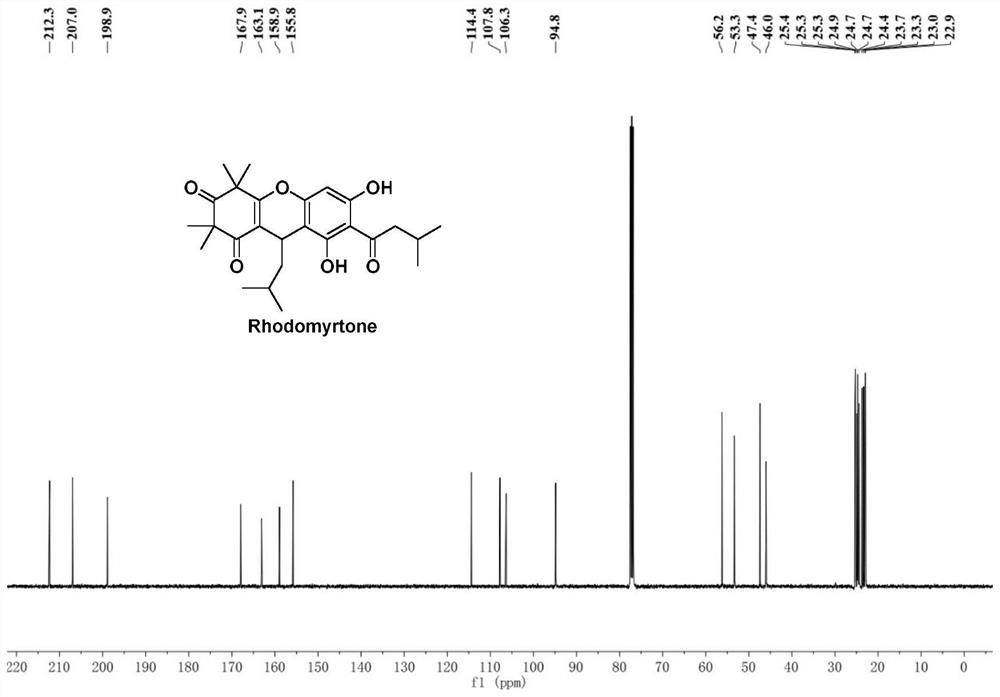
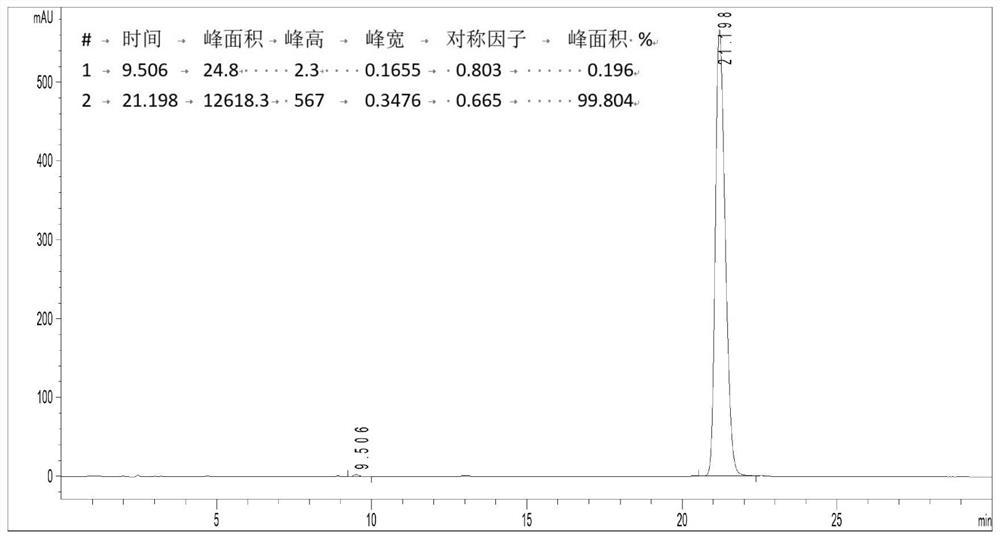
Improved preparation method of Rhodomyrtone
PendingCN114524795AEasy to operateHigh synthetic yieldOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisRhodomyrtone
The invention discloses an improved Rhodomyrtone preparation method, and relates to the technical field of chemical synthesis, the improved Rhodomyrtone preparation method effectively optimizes each reaction condition and post-treatment mode in the Friedel-Crafts acylation, methylation, reduction reaction, Michael addition and acid-mediated cyclization reaction, and Fries rearrangement reaction processes, and improves the yield of Rhodomyrtone. The problems that silica gel column chromatography separation needs to be used, a large number of explosive and toxic solvents are used, the total yield is low, and the method is only suitable for preparation on the scale of dozens or hundreds of milligrams in an existing synthesis method are solved, the obtained Rhodomyrtone does not need silica gel column chromatography separation, the total yield is high (34.6%), the purity is high (99.8%), and the method is suitable for amplified-scale preparation.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Synthetic method for p-hydroxybenzaldehyde
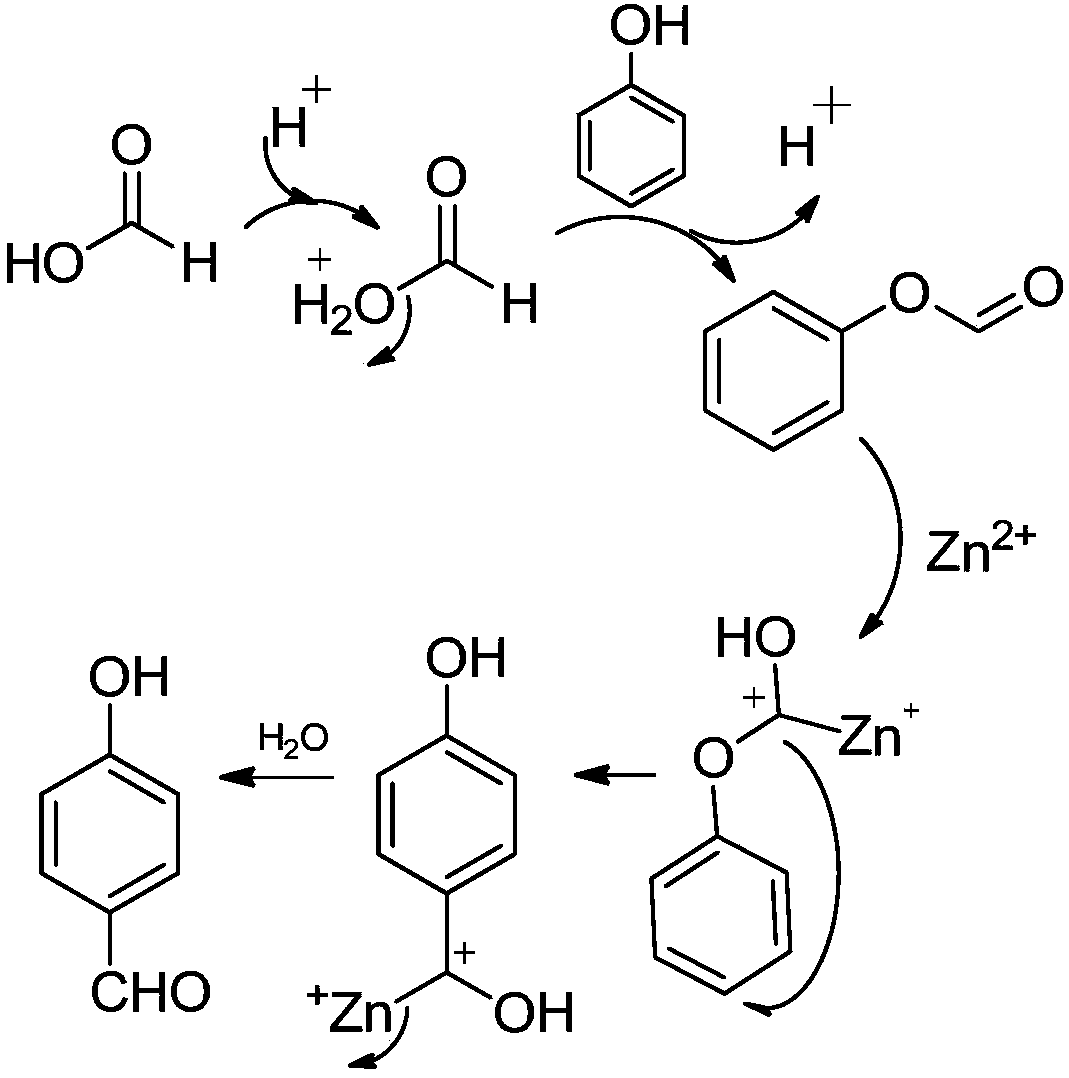
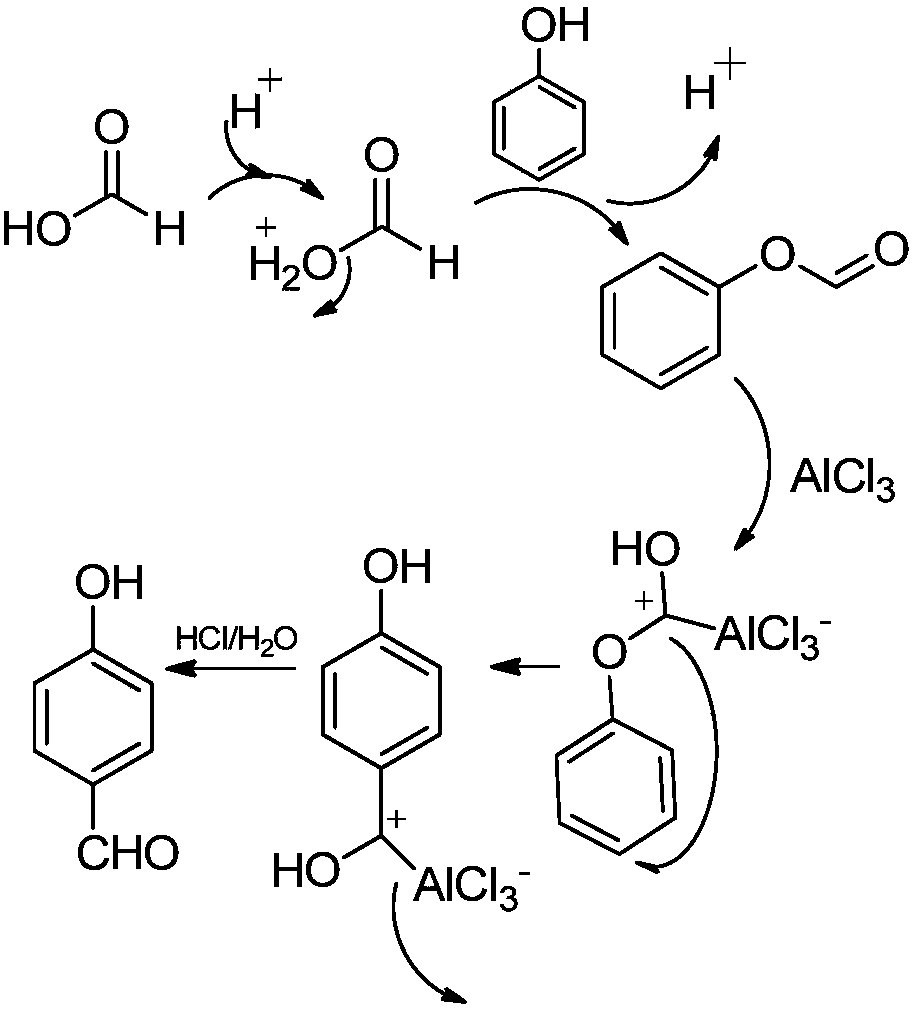
ActiveCN107935834ARaw materials are easy to getShort reaction timeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationFries rearrangementP-hydroxybenzaldehyde
The invention discloses a synthetic method for p-hydroxybenzaldehyde. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: with phenol and formic acid as raw materials, subjecting the raw materials toan esterification reaction under the action of a catalyst A so as to produce phenyl formate; and subjecting phenyl formate to a Fries rearrangement reaction under the action of a catalyst B so as to produce p-hydroxybenzaldehyde. According to the invention, the conversion rate of the raw materials is high, product yield is high, and the method is novel method for preparing p-hydroxybenzaldehyde from phenol and formic acid; and phenol and formic acid undergo the esterification reaction under the action of the catalyst A so as to produce phenyl formate, phenyl formate undergoes the Fries rearrangement reaction under the action of the catalyst B so as to produce p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, and then recrystallization and purification are carried out, so product purity can reach 99% or more, and overall product yield is as high as 95%. The method uses widely available raw materials and cheap and easily available catalysts, and is simple in reaction process, free of severe requirements on production equipment, low in equipment investment and convenient for industrial application.
Owner:THE NORTHWEST RES INST OF CHEM IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com