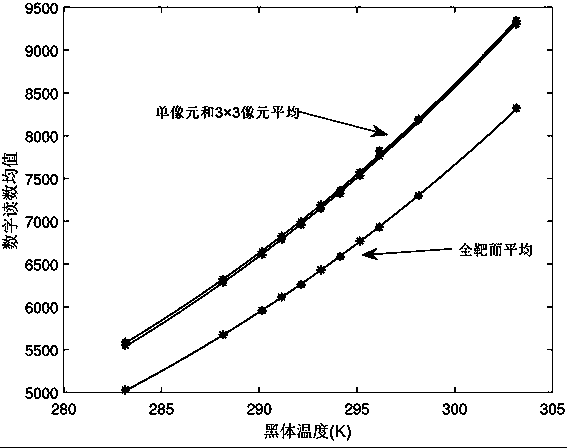
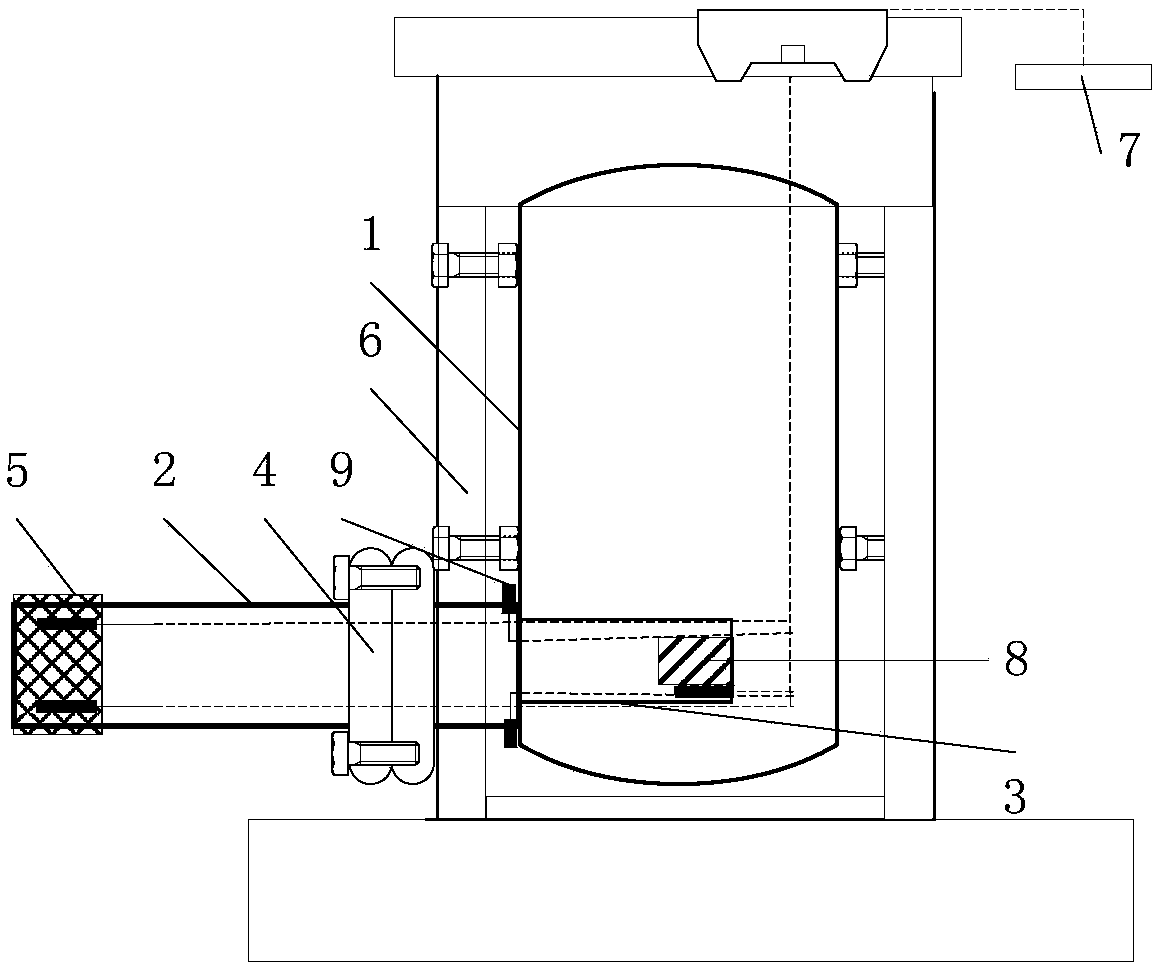
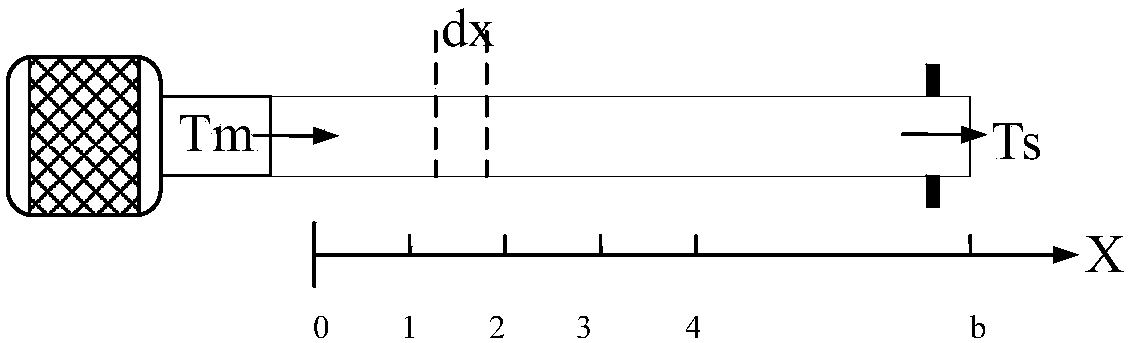
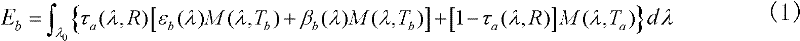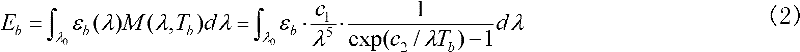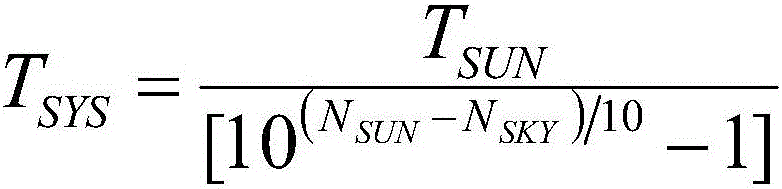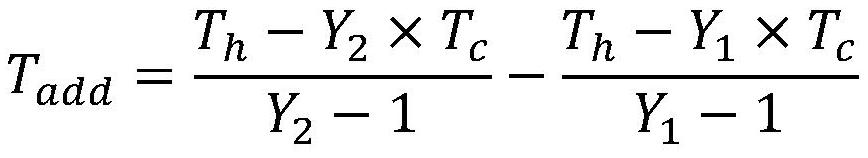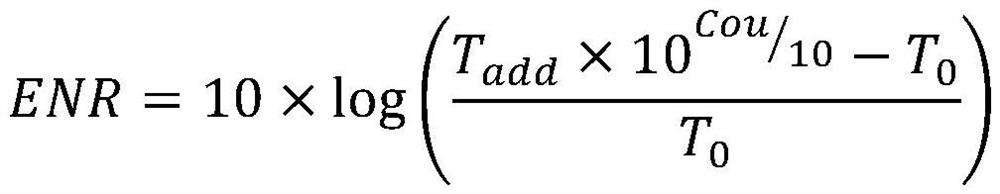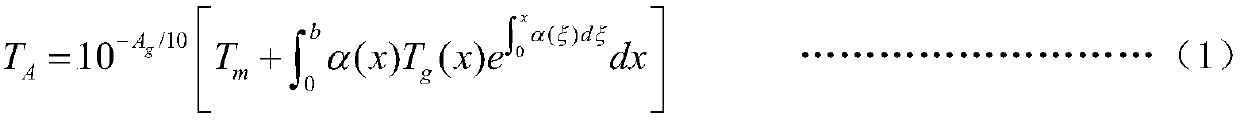Patents
Literature
41 results about "Noise-equivalent temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Noise-equivalent temperature (NET) is a measure of the sensitivity of a detector of thermal radiation in the infrared, terahertz or microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is the amount of incident signal temperature that would be needed to match the internal noise of the detector such that the signal-to-noise ratio is equal to one. Often the spectrum of the NET is reported as a temperature per root bandwidth. A detector that measures power is often interested in the analogous noise-equivalent power (NEP). If a relation between intensity and temperature is well defined over the pass band, as in the case of a blackbody, then the NET simply scales with the NEP.
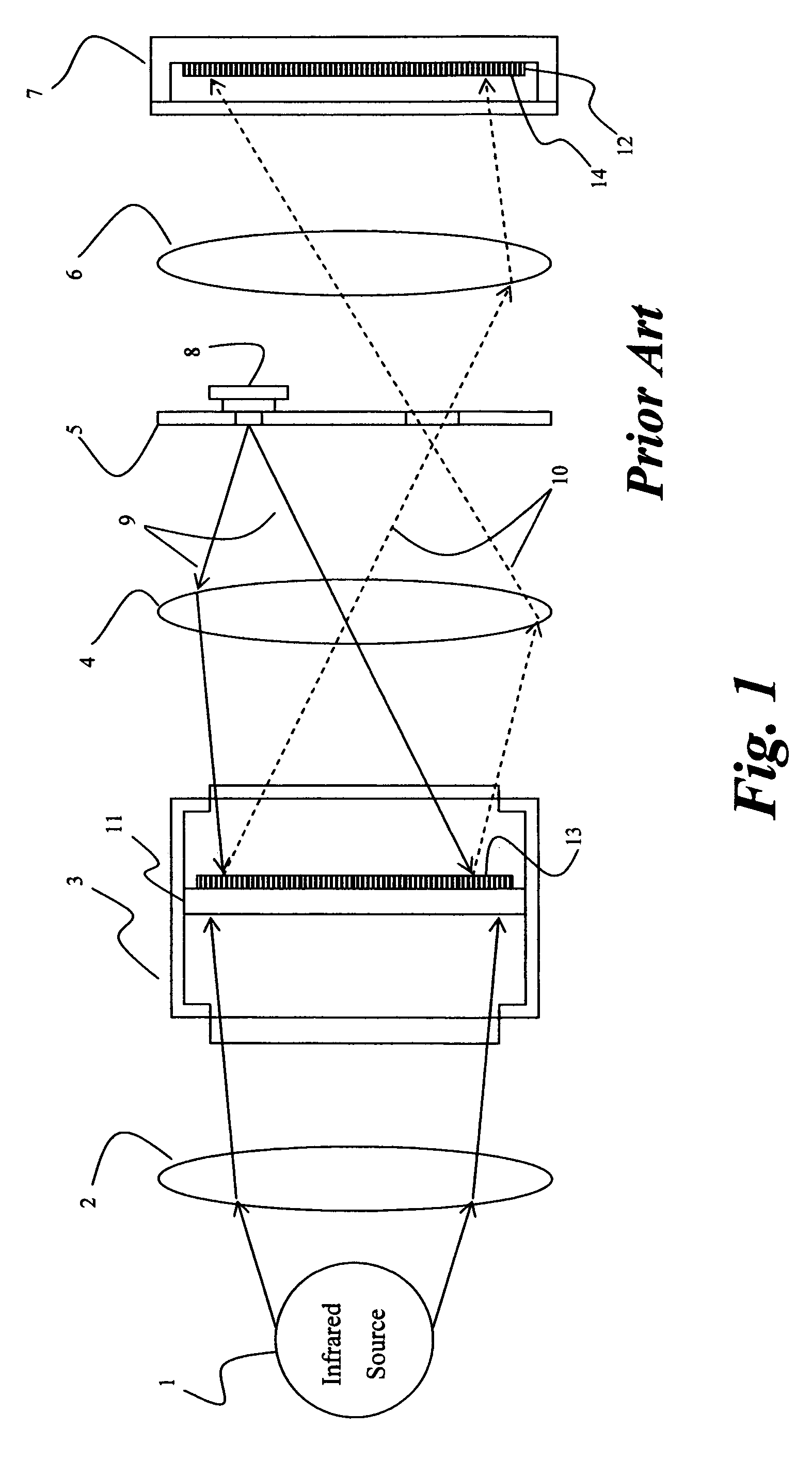
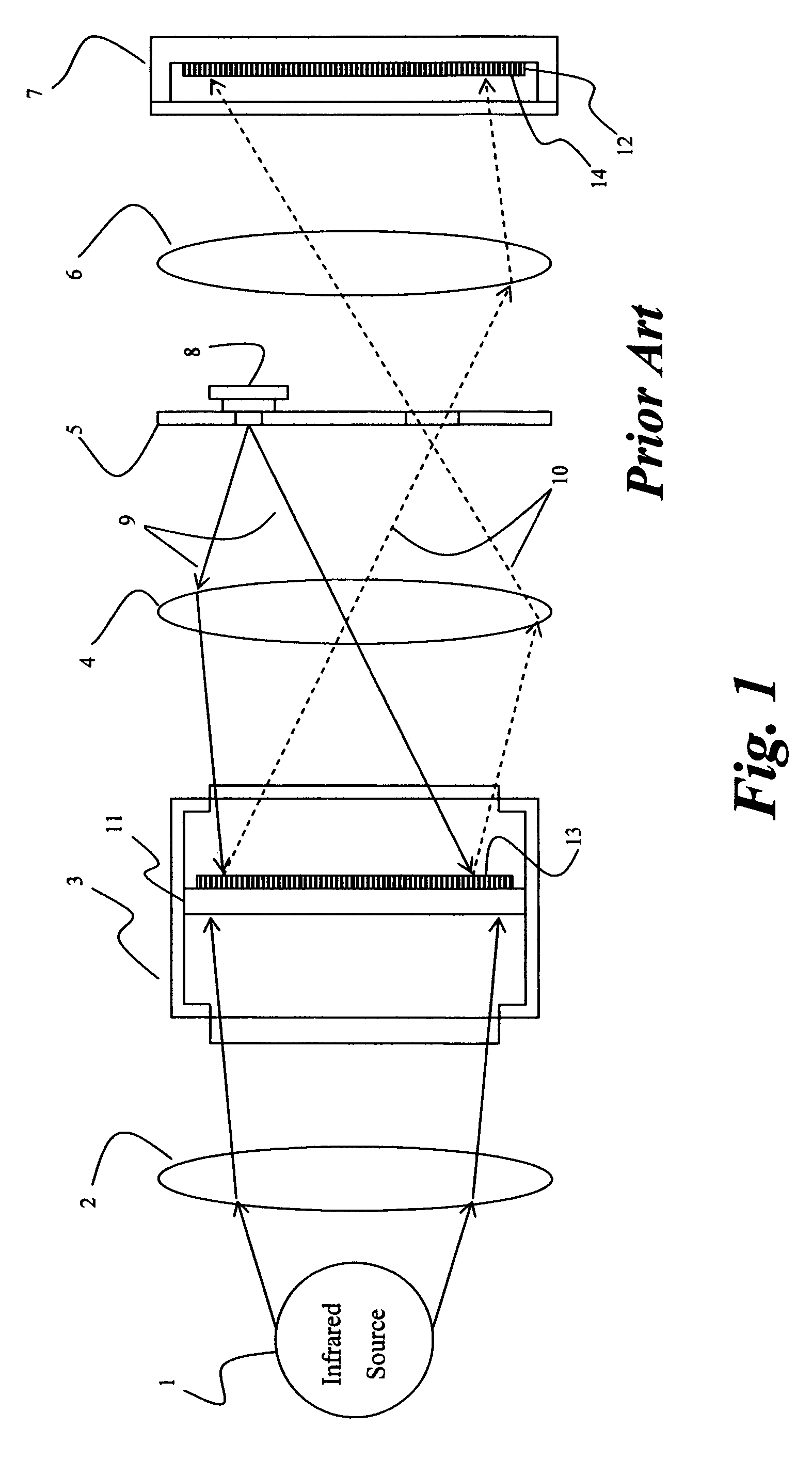
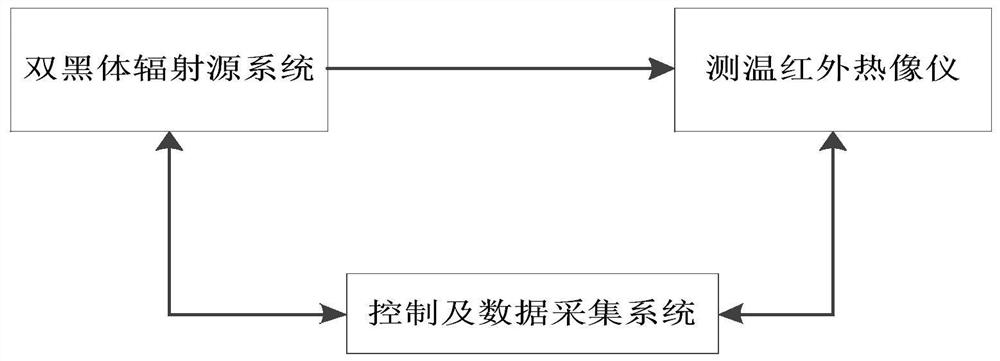
Method of searching for a thermal target
ActiveUS20090321636A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryGoal systemSignal-to-noise ratio
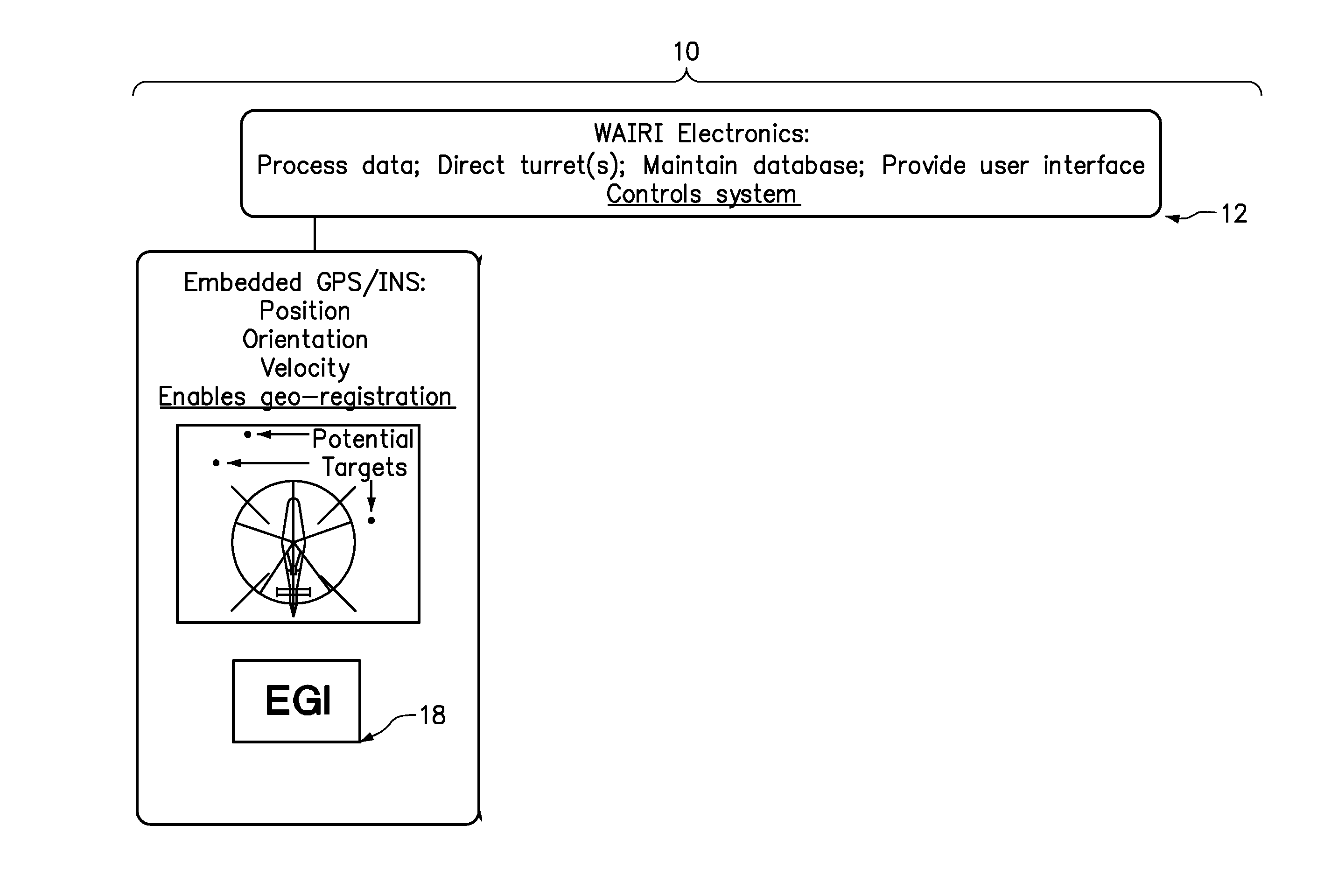
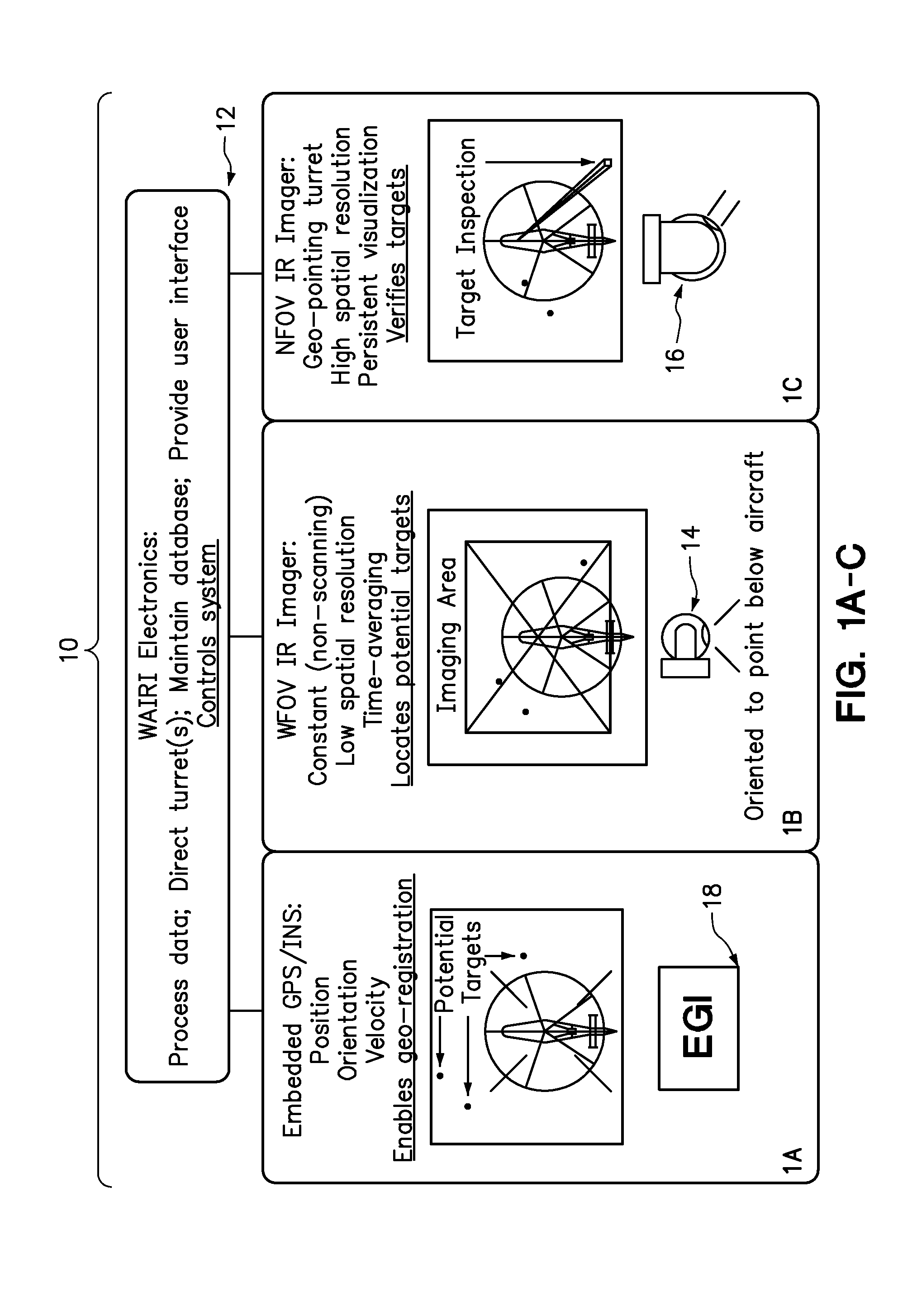
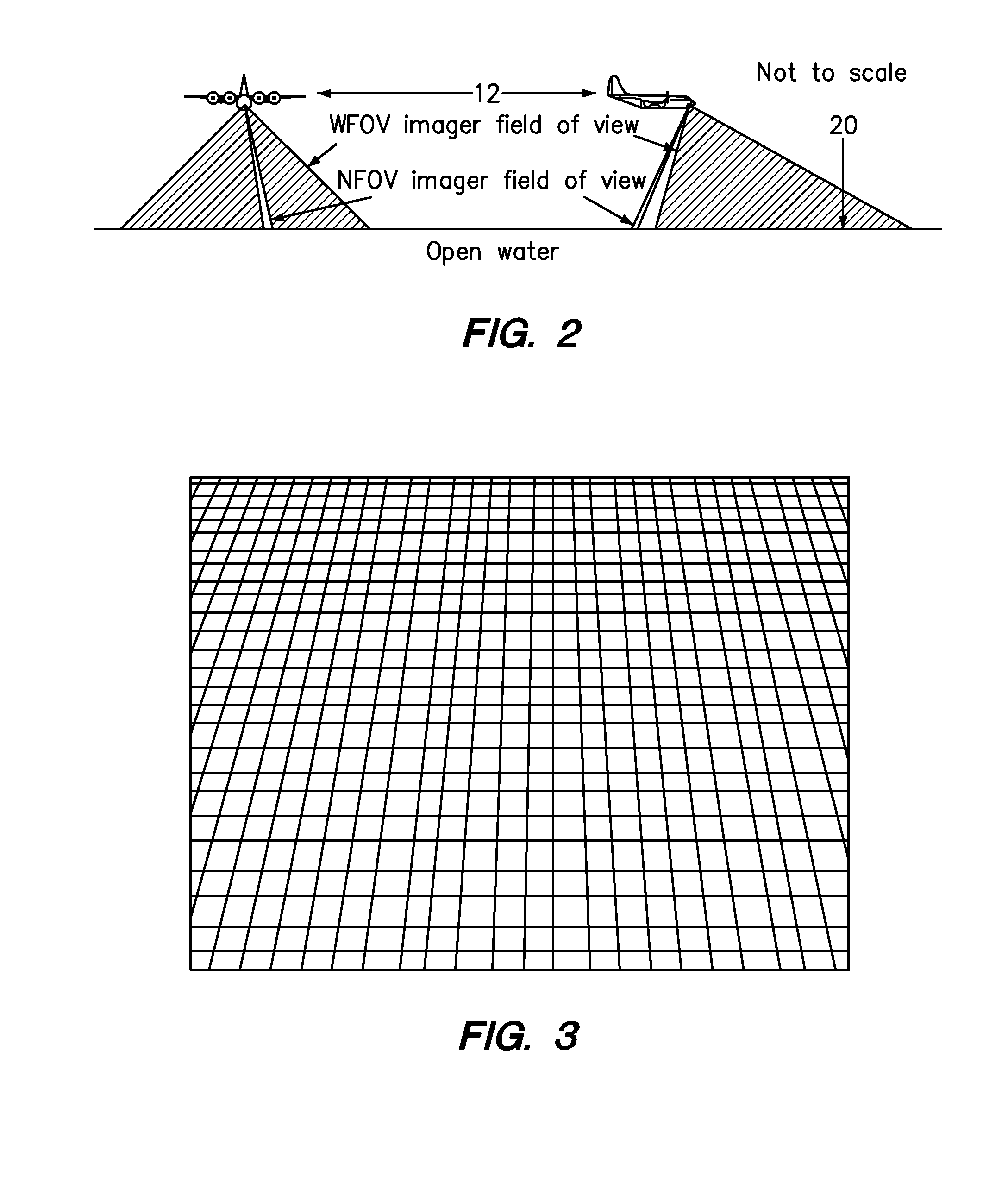
In one embodiment, an efficient method is presented for aerial searching for a small thermal target in a search area, such as a single person in open water, using two thermal imagers or “cameras” coupled with a computer which presents data from the system to a human user for inspection. One of the two thermal imagers has a very wide field of view (WFOV) fixed forward of or below the aircraft. The other, narrow field-of-view (NFOV) imager has a high zoom capability but its field of view can be reoriented to geo-point to a location on command. The WFOV thermal imager collects images rapidly so that no individual image is blurred due to changes in the field of view (FOV) on the time-scale of the image capture. The images are geo-registered using information from a global positioning receiver as well as the current altitude, roll, pitch, yaw, and velocity of the aircraft. As the aircraft moves and the FOV in the WFOV thermal imager changes, the computer averages the amplitude of the thermal radiation detected from each geo-registered position on the water below using the captured images continuously and in real time. The signal from a thermal target in the water is integrated while the background is relatively suppressed, enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio for the target as the square root of the number of images collected in which the target appears. A target which is much smaller than the area covered by a single pixel or that even has a thermal contrast below the noise equivalent temperature difference of the WFOV thermal imager can be detected. Thermal anomalies which have a signal commensurate in amplitude and spatial extent to the object of the search are selected by the system and their coordinates are relayed to the NFOV thermal imager. The NFOV thermal imager zooms into these locations sequentially and presents the image information to the human user who can then either reject or verify that the subject being imaged is the object of the search.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Scaling method of foundation microwave radiometer
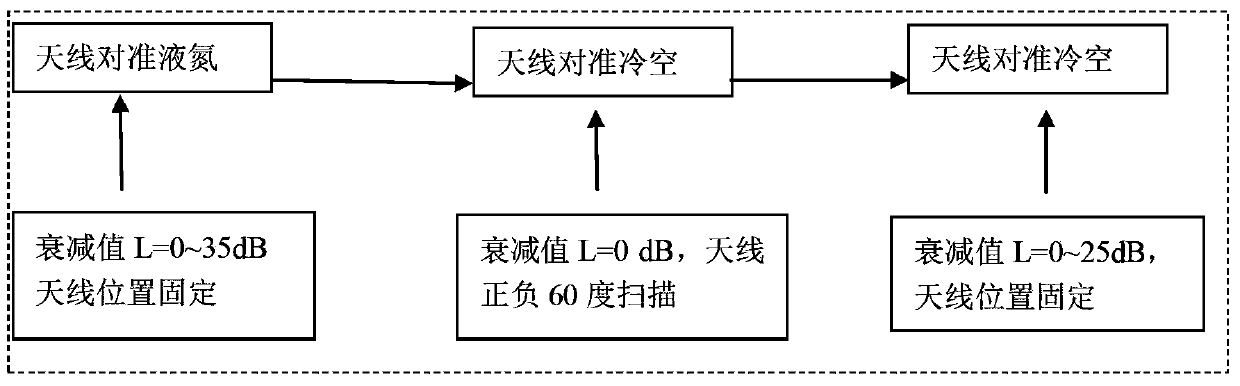
InactiveCN104181511AImprove inversion accuracyReduce calibration errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationCold airData matching
The invention relates to a scaling method of a foundation microwave radiometer. The scaling method comprises: obtaining voltage values output through each channel in different attenuation values, calculating corresponding equivalent brightness temperature values through attenuation values, calculating system non-linear factors and noise source injection noises according to corresponding relation between each equivalent brightness temperature value and the output voltage of each channel, and completing preliminary scaling; according to sounding profile data matching with time and place, establishing a corresponding relation of atmosphere optics thickness and atmosphere quality, substituting scaling parameters, obtaining a scaling relation curve, determining the scaling parameters according to the scaling relation curve; observing cold air and cold air coupling noises at each attenuation value, obtaining voltage values output through each channel at different attenuation values and fitting the attenuation values and the voltage values; calculating the equivalent noise temperature when an antenna aligns with the cold air through the relation of the attenuation values and the output voltage values of the attenuator, and determining the brightness temperature values corresponding to the cold air observed by the foundation microwave radiometer in different time and places.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Infrared thermal imager calibration method
InactiveCN103453995AQuickly judge whether it is qualifiedCalibration is fast and more standardizedRadiation pyrometryThermodynamicsBlack body
The invention relates to an infrared thermal imager calibration method. The infrared thermal imager calibration method comprises the following steps that 1 an infrared thermal imager is installed on a calibration working platform and aligned to the center of a standard black body, the infrared thermal imager and the center of the standard black body are made to be arranged coaxially, temperature measuring is conducted multiple times, and a basic error is calculated according to temperature measuring results; 2 the set temperature of the standard black body is adjusted to enable a target image to occupy more than one tenth of a whole view field, a level signal and a noise voltage are measured respectively, and the noise equivalent temperature difference is calculated; 3 an image of the infrared thermal imager is divided into a plurality of regions, the temperature of each region is measured independently and the temperatures are compared so as to detect the temperature uniformity of the regions; 4 the infrared thermal imager is placed at the position of a preset working distance, measuring values of the infrared thermal imager are read continuously at a certain period, and reading continues for a period of time so as to detect the continuous stable working performance of the infrared thermal imager. Compared with the prior art, the infrared thermal imager calibration method is quick in calibration process, and accurate and standard in calibration result.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
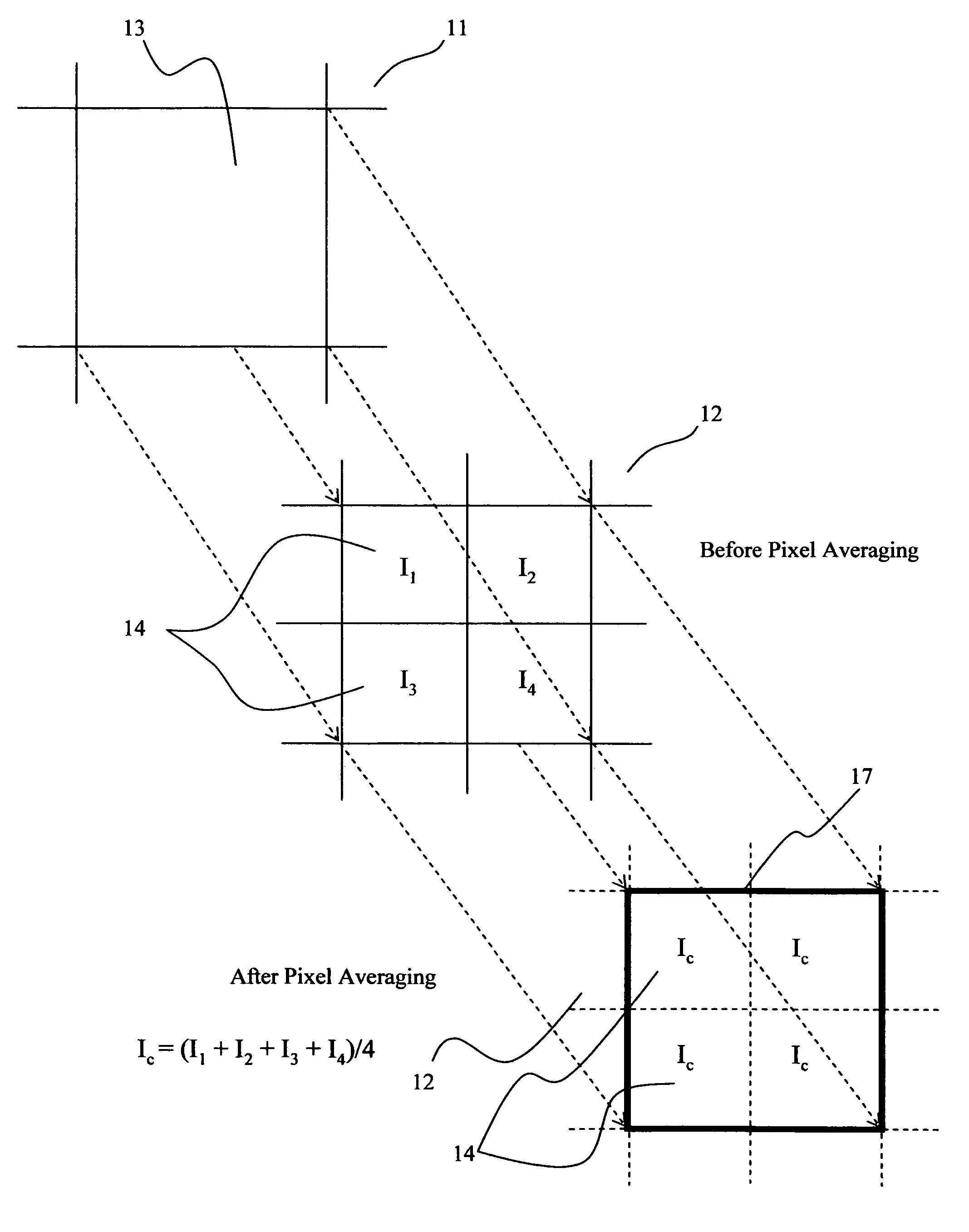
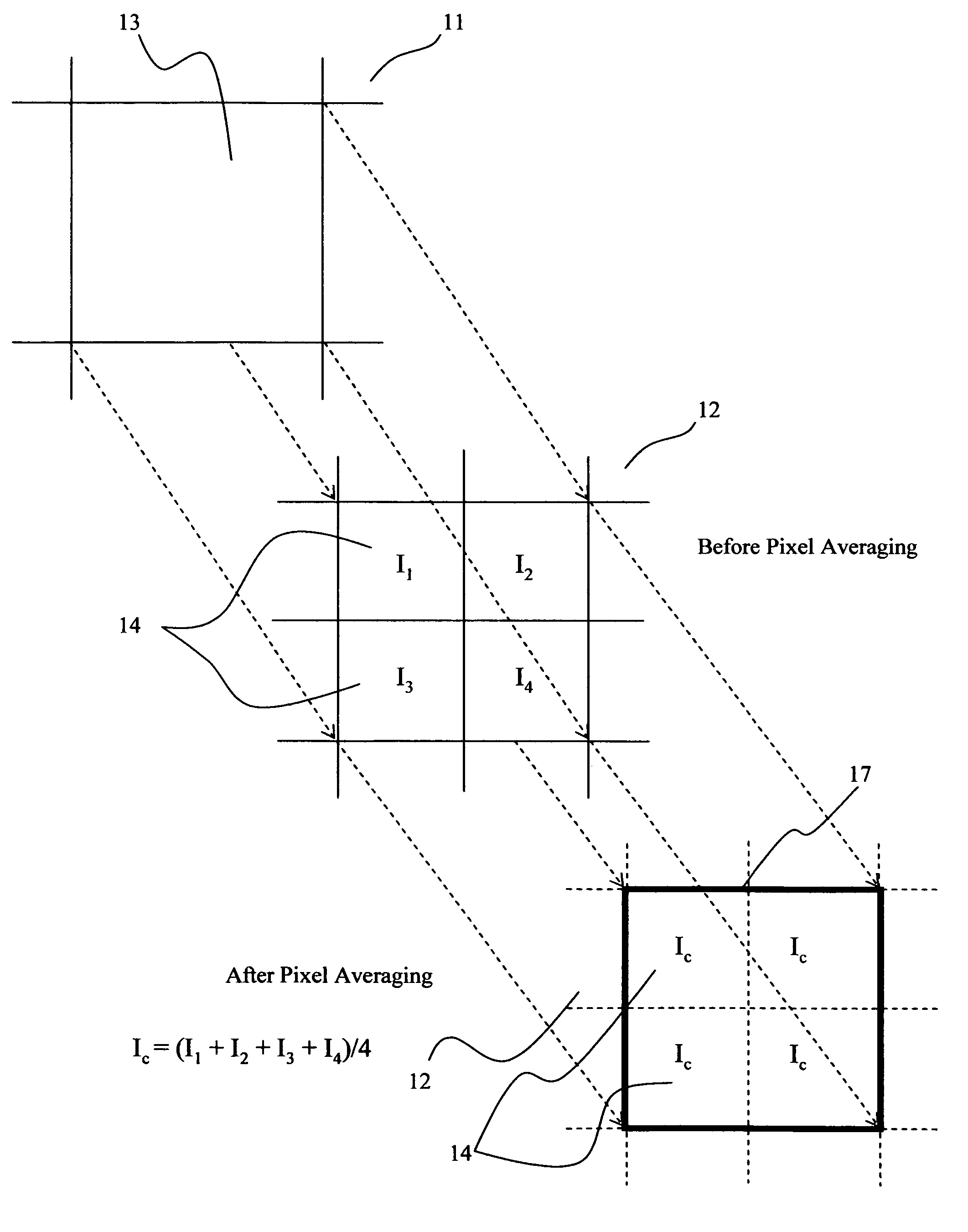
Noise reduction method for imaging devices
InactiveUS20070296838A1Reduce temperature differenceWithout qualityTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPresent methodImage resolution
A method for reducing the noise equivalent temperature difference associated with imaging devices having a detection array including micro-cantilevers and a charged-coupled device or a complementary metal oxide semiconductor imager is presented. The method includes calculating horizontal and vertical pixel ratios based upon the number of receptor pixels and micro-cantilever pixels, defining composite pseudo-pixels comprised of at least two receptor pixels, capturing at least one frame of an image, calculating the composite intensity for each composite pseudo-pixel based on the intensities of the receptor pixels therein, and reconstructing each frame so that receptor pixels within each composite pseudo-pixel are displayed with the appropriate composite intensity. While the present method lowers pixel resolution, the composite pseudo-pixels maintain image resolution within the reconstructed image.
Owner:FLIR COMML SYST
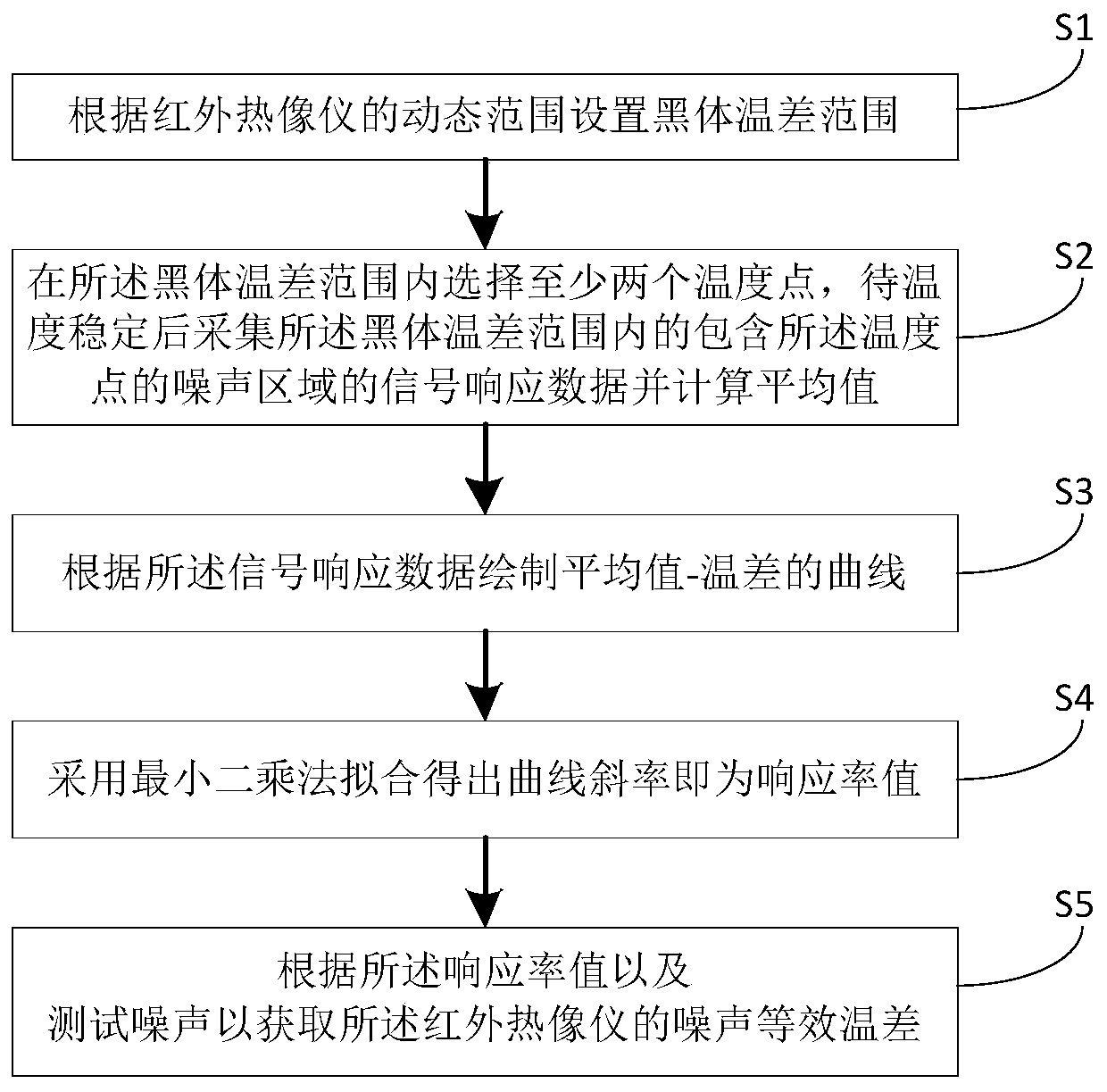
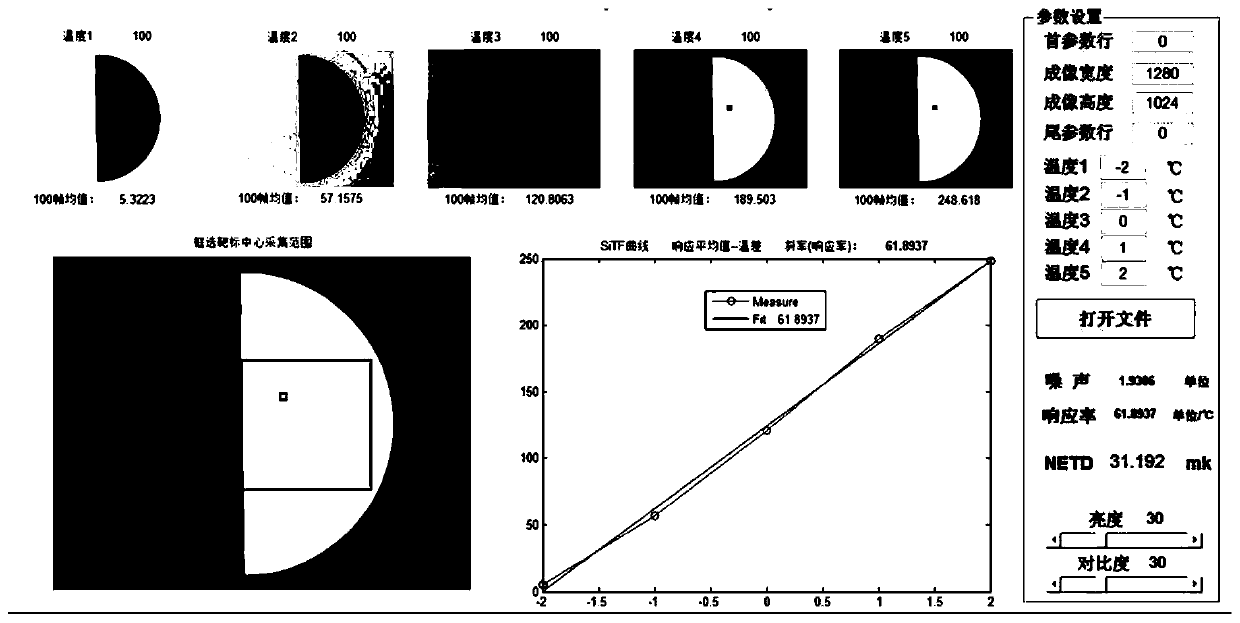
Noise equivalent temperature difference test method and system of infrared thermal imager
ActiveCN110095193AAccurate measurementAccurately reflectRadiation pyrometrySignal responseThermodynamics
The invention provides a noise equivalent temperature difference test method and system of an infrared thermal imager, and belongs to the technical field of optical detection. A blackbody temperaturedifference scope is set according to the dynamic range of the infrared thermal imager, at least two temperature points are selected in the blackbody temperature difference scope, signal response dataof a calculation area including the temperature points with the blackbody temperature difference scope is collected after that the temperature is table and a mean value is calculated, a mean value andtemperature difference curve is drafted according to the signal response data, a curve gradient, namely the responsivity value, is fit by a least square method, and the noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD) of the infrared thermal imager is obtained according to the responsivity value and test noise. Thus, the NETD of an infrared product is measured accurately, the real NETD level of theinfrared product is reflected more accurately, a unified NETD test system platform is formed, and real and reliable data reference is provided for test aimed at knowing the real situation at the early stage of bidding.
Owner:WUHAN GAOXIN TECH
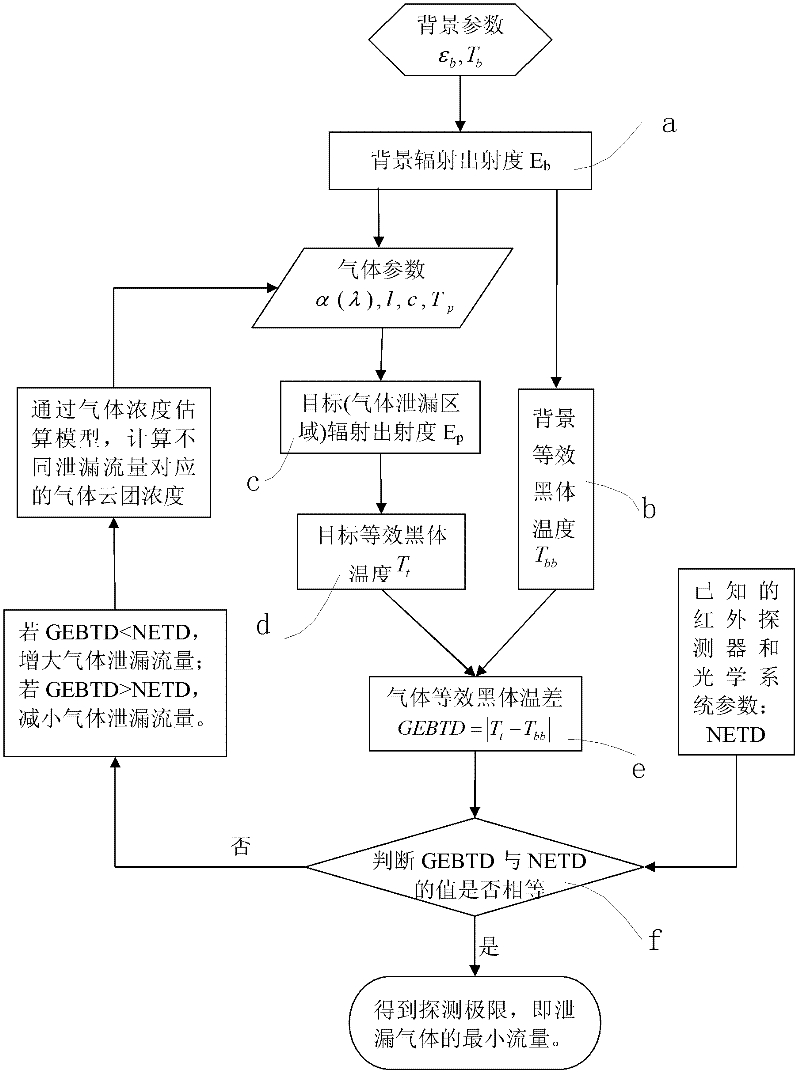
Calculation method for detection limit in gas-leakage infrared imaging
InactiveCN102589815ASimple designEase of performance evaluationDetection of fluid at leakage pointRadiation pyrometryImage detectionRadiant exitance
The invention relates to a calculation method for detection limit in gas-leakage infrared imaging, and belongs to the field of gas leakage detection. The calculation method comprises the following steps of: firstly calculating the background radiant exitance when no gas leaks, and taking the background radiant exitance as background radiant exitance for imaging detection; calculating equivalent blackbody temperature of the imaging detection background by the background radiant exitance for imaging detection; secondly, when gas leaks, calculating the radiant exitance after the background radiation is absorbed by gas according to a gas parameter in the background radiant exitance for imaging detection, namely a target radiant exitance for imaging detection; calculating target equivalent blackbody temperature for imaging detection by the target radiant exitance for imaging detection; then calculating an absolute value of the difference between the imaging detection background and the target equivalent blackbody temperature, and defining the absolute value as a gas equivalent blackbody temperature difference; and finally comparing gas equivalent temperature difference with a noise equivalent temperature difference of comprehensive performance parameters of an infrared detector and an optical system, and determining gas-leakage detection limit value, namely, a minimum flow of leaked gas.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
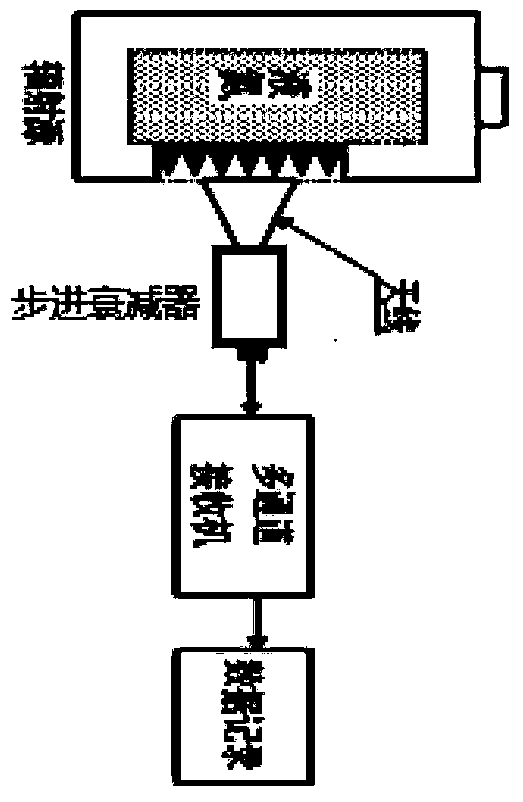
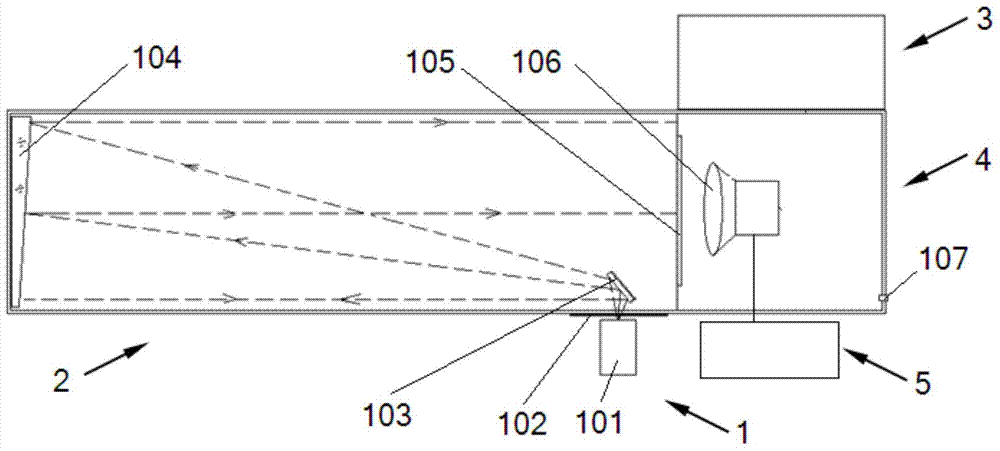
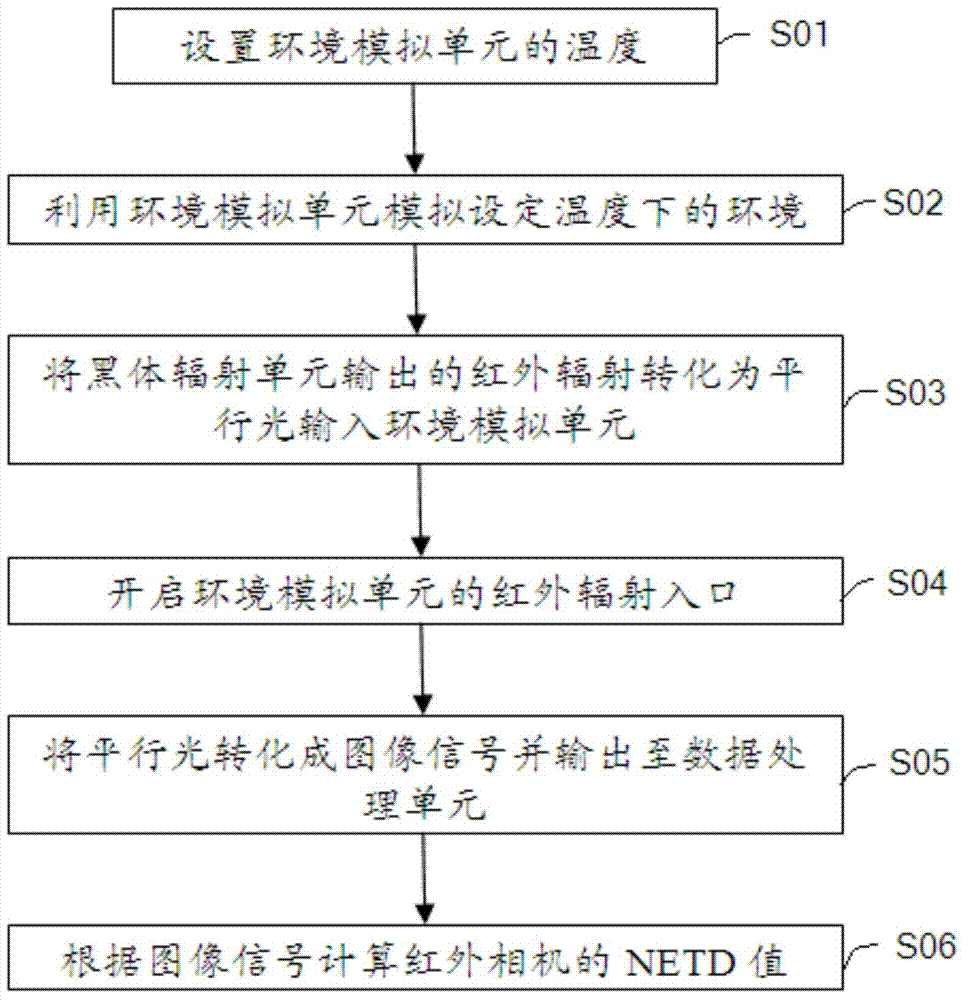
Measuring device and method for noise equivalent temperature differences of infrared camera in different environments
InactiveCN104713699AImprove measurement accuracyAccurate measurementOptical apparatus testingTemperature controlMeasurement device
The invention relates to a measuring device and method for noise equivalent temperature differences (NETD) of an infrared camera in different environments. The measuring device comprises a black-body radiation unit, an image transformation unit, a temperature control unit, an environmental simulation unit and a data processing unit. The temperature control unit communicates with the environmental simulation unit and controls the environment temperature of the environmental simulation unit; air holes in the environmental simulation unit are connected with a high-purify argon gas source. By means of the measuring device for noise equivalent temperature differences (NETD) of the infrared camera in different environments, different temperature environments in a field environment can be simulated for conducting NETD tests, NETD measuring results of different temperature environments are obtained, so that the effective action distance of the infrared camera is measured and calculated accurately, and the measuring accuracy of the infrared camera in the field environment is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
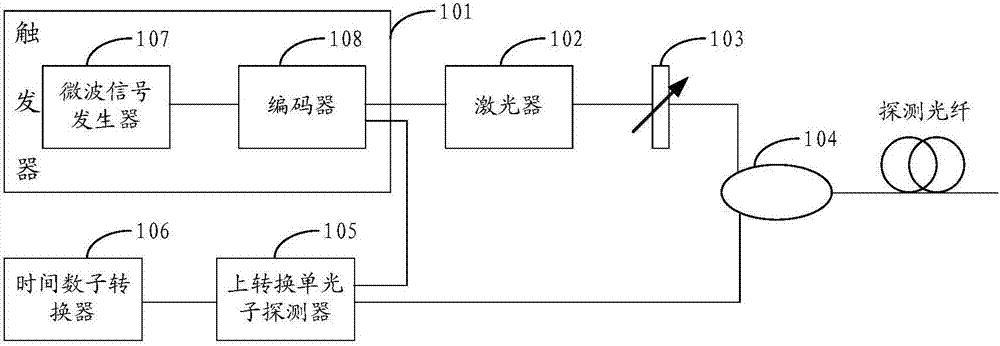
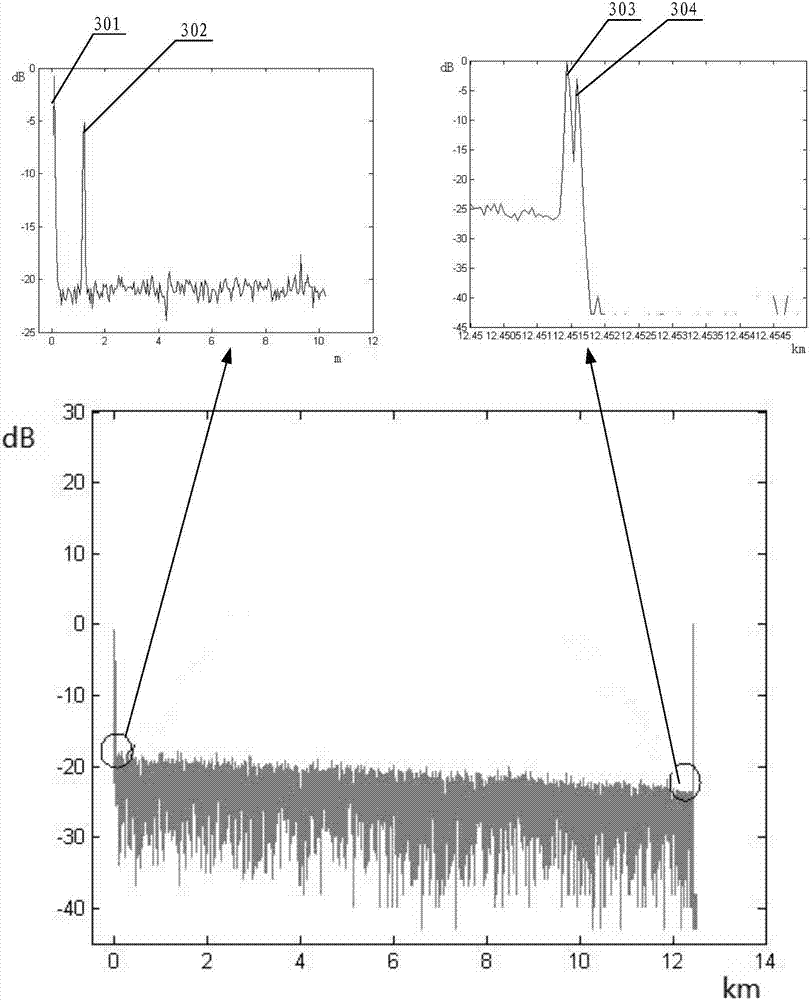
Optical time-domain reflectometer
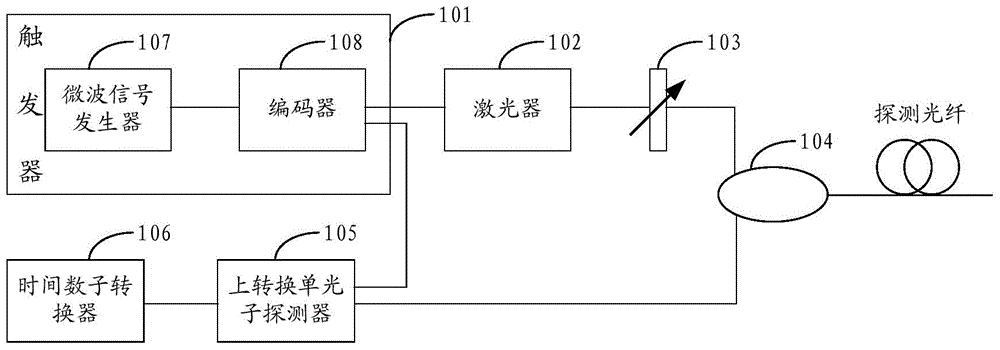
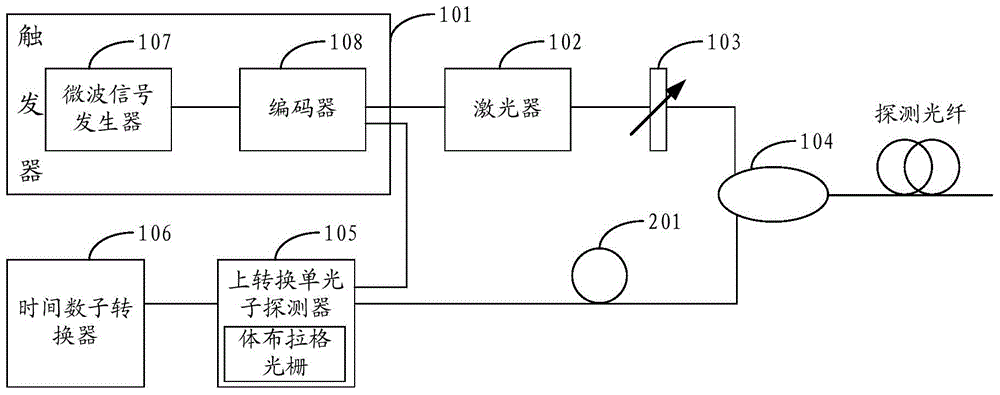
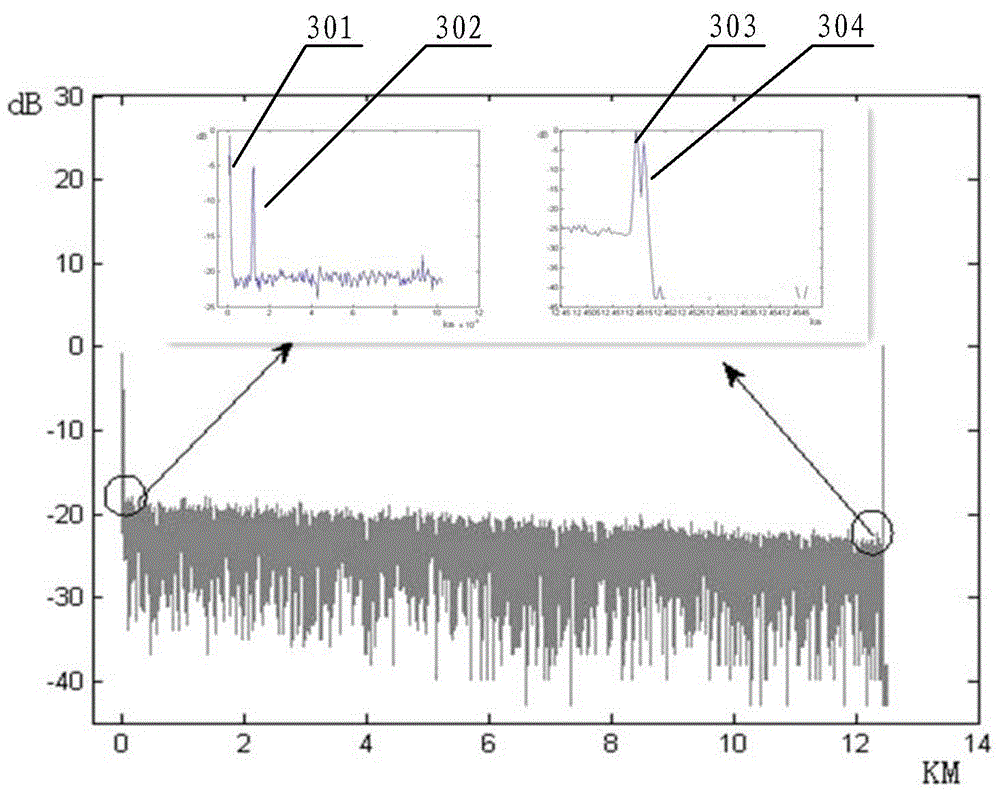
ActiveCN104426602ALarge dynamic rangeHigh-resolutionElectromagnetic transmissionTime-domain reflectometerUp conversion
The invention discloses an optical time-domain reflectometer comprising a trigger, a laser, an attenuator, a circulator, an up-conversion single-photon detector and a time-to-digital converter. The optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) of the invention employs the up-conversion single-photon detector. The up-conversion single-photon detector employs a pump light wavelength of 1900 nm to 2000 nm to carry out narrowband filtering on sum frequency light, a noise equivalent power (NEP) lower than the NEP of a classic detector is obtained under the same quantum efficiency, and the NEP value can reach -140dbm. The lower the NEP value is, the larger the detected dynamic range is. Therefore, the up-conversion single-photon detector effectively increases the detectable dynamic range of the OTDR, the detection resolution is improved, the measuring time is reduced, and dead zones after a Fresnel reflection peak are effectively prevented.
Owner:张强
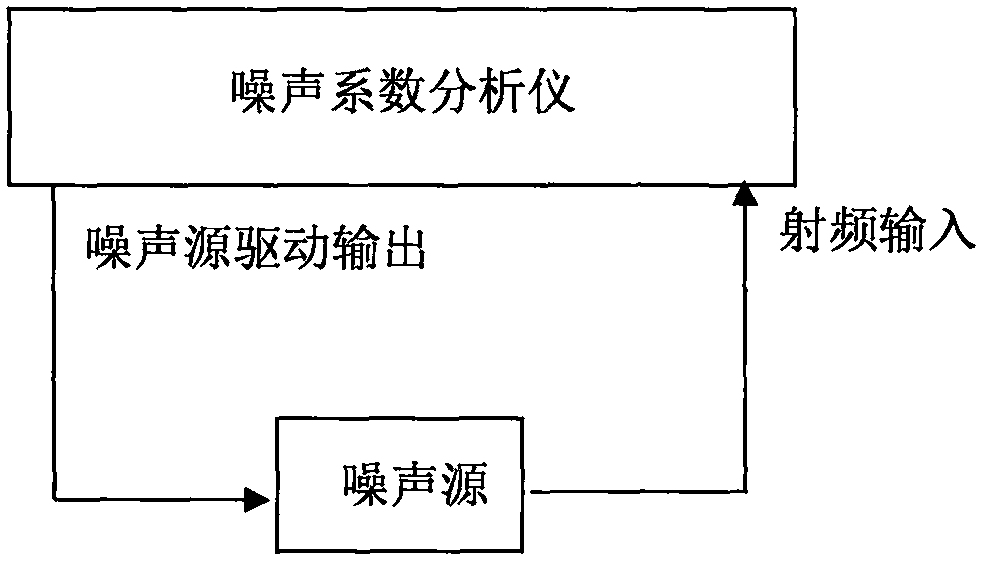
Noise coefficient scanning measurement method
ActiveCN107276695ARealize continuous scanning measurementFast measurementReceivers monitoringContinuous scanningEngineering
The invention provides a noise coefficient scanning measurement method. The method comprises the steps that a noise coefficient analyzer controls a noise source to be powered off and finishes single scanning measurement, thereby obtaining a group of cold noise power values P <cold > corresponding to scanning frequency points; the noise coefficient analyzer controls the noise source to be powered on and finishes the single scanning measurement, thereby obtaining a group of hot noise power values P <hot > corresponding to the scanning frequency points; and operating and displaying Y factors, equivalent noise temperature and noise coefficients according to the cold and hot noise power values of the corresponding scanning frequency points. According to the noise coefficient scanning measurement method provided by the invention, the continuous scanning measurement of the noise coefficients can be realized, the measurement speed of the noise coefficients is clearly improved, the noise coefficients of tested pieces can be measured precisely in real time, the operation of carrying out noise source power-on and power-off, channel presetting and response waiting needs to be carried out repeatedly at each measurement frequency point in the existing Y factor method is avoided, and the measurement efficiency of the noise coefficients is improved.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Noise reduction method for imaging devices
InactiveUS7652250B2Reduce temperature differenceWithout qualityTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPresent methodNoise reduction
A method for reducing the noise equivalent temperature difference associated with imaging devices having a detection array including micro-cantilevers and a charged-coupled device or a complementary metal oxide semiconductor imager is presented. The method includes calculating horizontal and vertical pixel ratios based upon the number of receptor pixels and micro-cantilever pixels, defining composite pseudo-pixels comprised of at least two receptor pixels, capturing at least one frame of an image, calculating the composite intensity for each composite pseudo-pixel based on the intensities of the receptor pixels therein, and reconstructing each frame so that receptor pixels within each composite pseudo-pixel are displayed with the appropriate composite intensity. While the present method lowers pixel resolution, the composite pseudo-pixels maintain image resolution within the reconstructed image.
Owner:FLIR COMML SYST
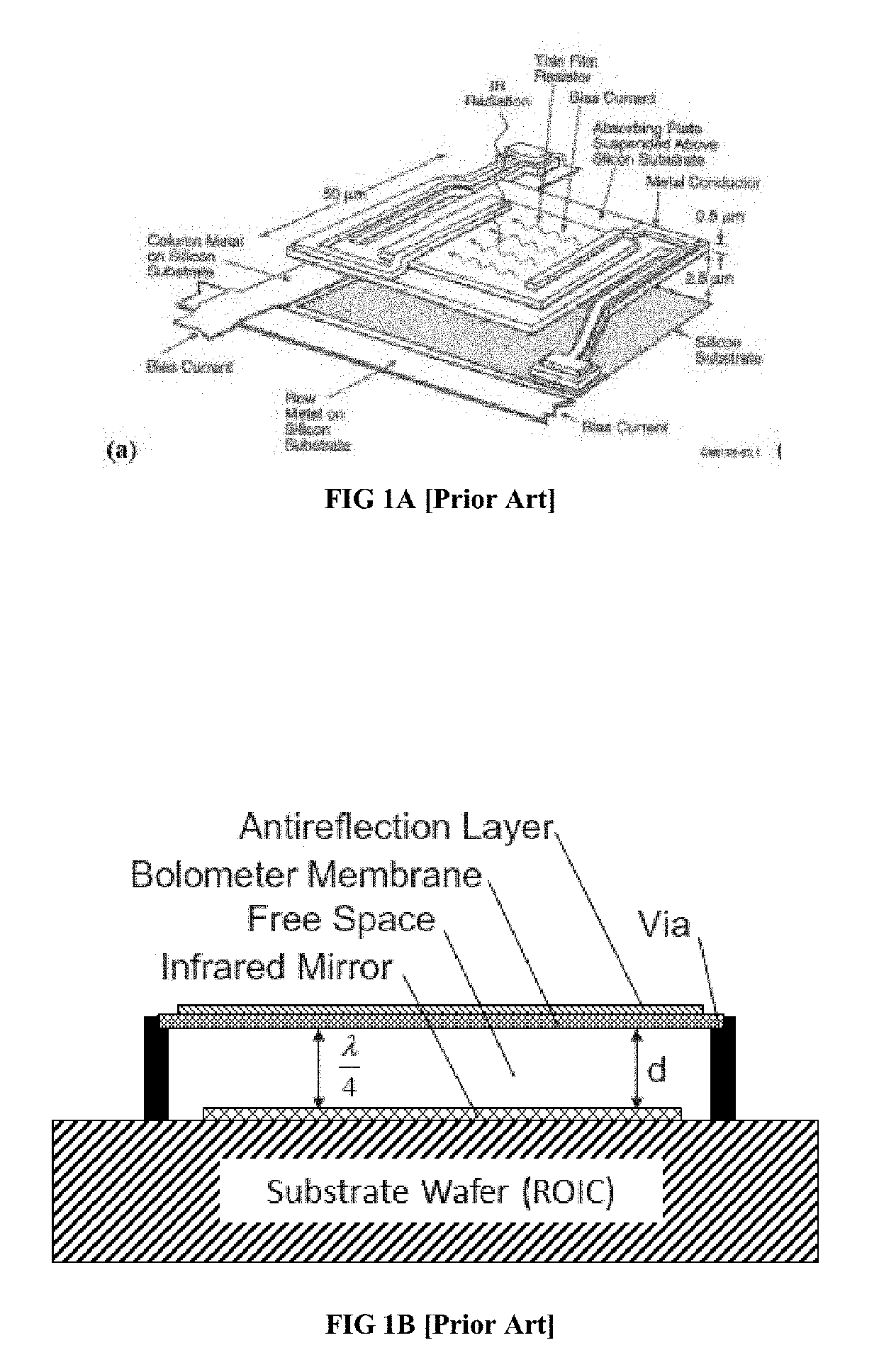
Medium Wave Infrared (MWIR) and Long Wavelength Infrared (LWIR) Operating Microbolometer with Raised Strut Design
ActiveUS20190123214A1Minimizes the thermal conductance of the device—allowingMinimizing thermal conductancePyrometry using electric radation detectorsSemiconductor devicesHeat fluxMicrobolometer
A semiconducting microbolometer sensor for detecting electromagnetic waves in the medium wavelength infrared (MWIR) and long-wavelength infrared (LWIR) is provided. A preferred embodiment provides a substrate layer, a bottom and top support structure with a strut-based mesh design, a meandered electrode layer that follows the top support structure design, a bolometer sensing material with a high TCR, and a disk-shaped absorber on top of the sensing material to maximize the heat flux absorption on the sensor. The bottom support of the sensor suspends the top support mesh, creating an air cavity. This air cavity along with the strut based mesh design and optimized thickness, dimension and shape of the layers contributed towards minimizing the thermal conductance of microbolometer and hence improved the figures of merits—responsivity, detectivity, noise equivalent power and noise equivalent temperature difference of microbolometer.
Owner:RANA MUKTI +1
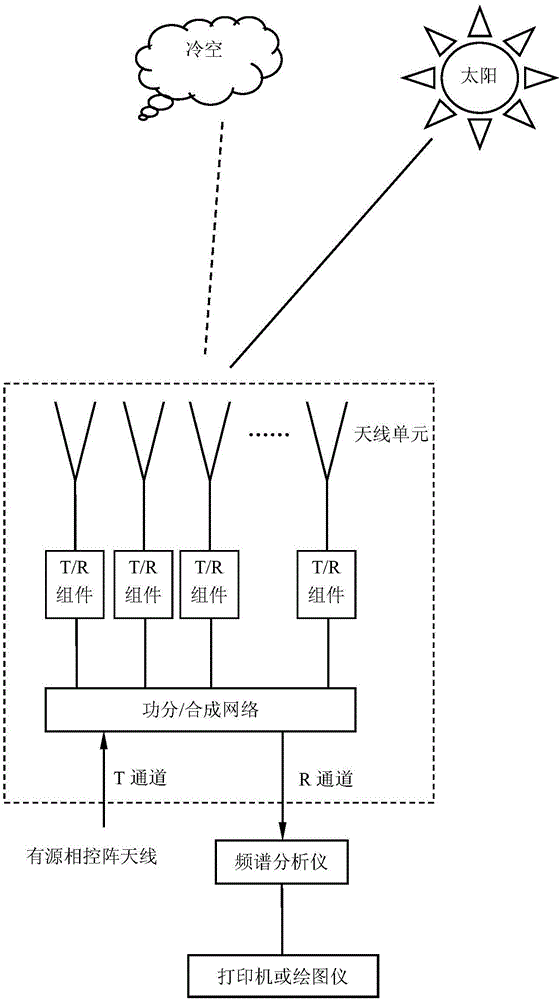
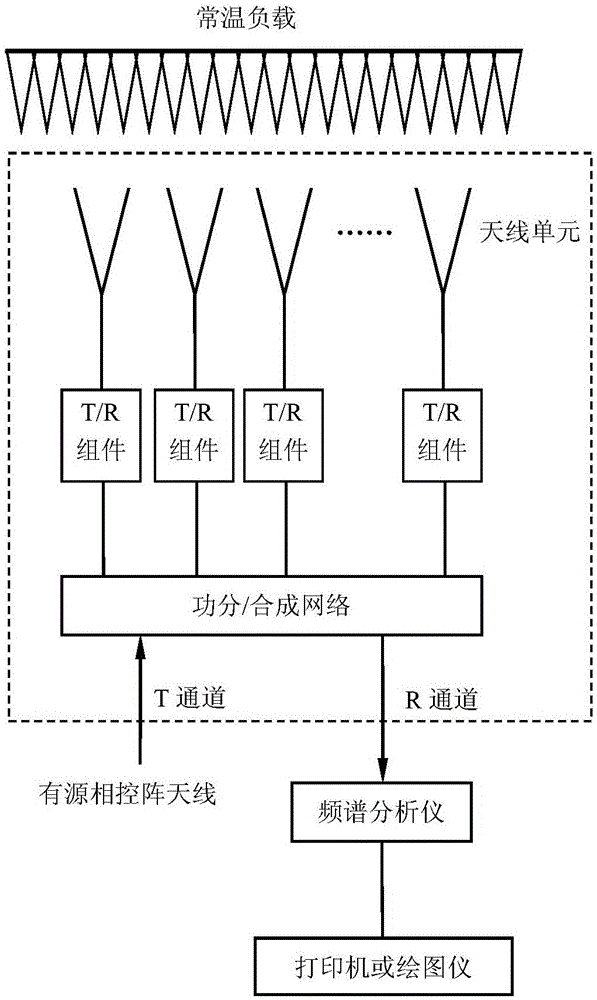
Method for measuring active phased-array antenna noise temperature
ActiveCN106100759ASimple test systemImprove measurement repeatabilityTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringRoom temperatureActive phase
The invention discloses a method for measuring active phased-array antenna noise temperature. The method comprises the following steps: respectively measuring noise power of each of the beam pointing alignment sun of the active phased-array antenna and the beam pointing deviation sun of the active phased-array antenna, thereby computing the noise temperature of the active phased-array antenna system; and then upwardly pointing the beam of the active phased-array antenna, and placing the room temperature load at the aperture surface of the antenna to measure the noise power output by the system, computing the equivalent noise temperature of an active phased-array antenna receiver; and finally, computing the noise temperature of the active phased-array antenna according to the noise temperature of the active phased-array antenna system and the equivalent noise temperature of the receiver. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and applicable, and has promotion and application value.
Owner:NO 54 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH GRP
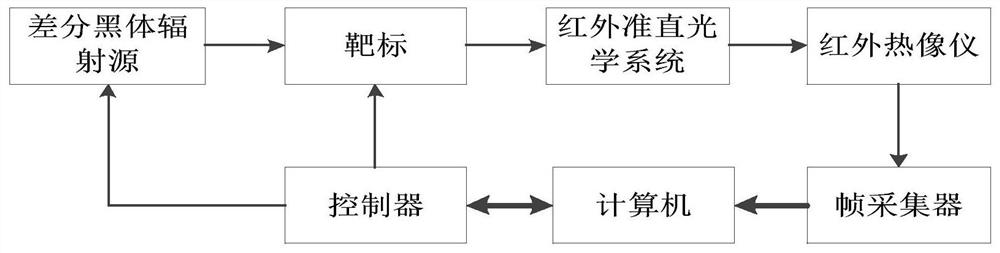
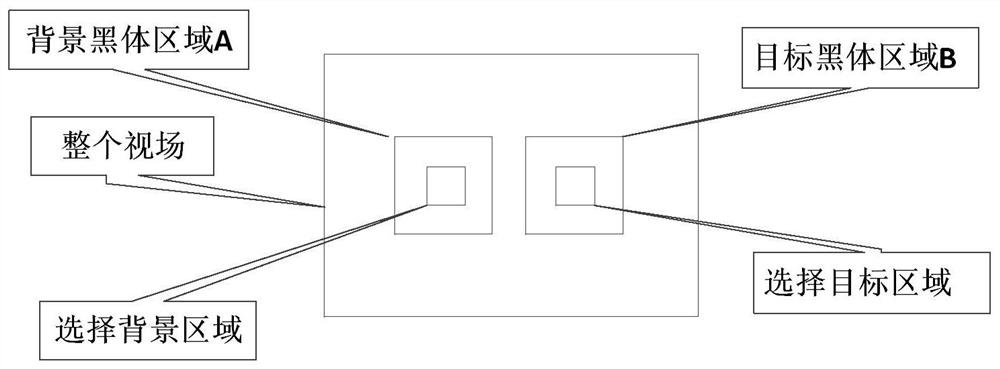
Noise equivalent temperature difference calibration method for temperature measurement thermal infrared imager
InactiveCN111947785AMeeting Calibration NeedsEasy to useRadiation pyrometryBlack-body radiationEmissivity
The invention discloses a noise equivalent temperature difference calibration method for a temperature measurement thermal infrared imager, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, enabling the emissivity and other parameters of a to-be-measured thermal infrared imager to be consistent with those of a target blackbody radiation source; 2, respectively selecting two temperature points for calculation, and taking the two temperature points as calculation areas; and 3, setting a double-blackbody radiation source, enabling the target radiation blackbody to be higher than the background temperature and stabilized at the differential temperature of the target radiation blackbody and the background radiation blackbody, and calculating the noise equivalent temperature difference on the selected calculation area according to a certain formula. The double-blackbody radiation source is adopted to calibrate the noise equivalent temperature difference of the temperature measurement thermalinfrared imager, field calibration is facilitated, disassembly and reassembly are convenient and rapid, the overall measurement system is simple, and the field calibration requirement of the temperature measurement thermal infrared imager can be met.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Thermopile infrared detector and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107990989AImprove response rateImprove the detection ratePyrometry using electric radation detectorsThermopileOptical pathlength
The invention provides a thermopile infrared detector and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of thermopile infrared detectors. The thermopile infrared detector includes aprocessed silicon substrate, an infrared absorption layer disposed on the processed silicon substrate, and a back cavity which is formed by patterning and etching the middle portion of the processedsilicon substrate and is provided with a downward opening. A metal reflective layer is disposed in the back cavity. A cavity is defined by the processed silicon substrate, the metal reflective layer and the infrared absorption layer and is namely an optical resonant cavity. Infrared rays are focused by a lens to the infrared absorption layer, and infrared rays reaching the infrared absorption layer and infrared rays reflected by the metal reflective layer form an about 1 / 2 optical path difference in the infrared absorption layer, thereby forming a standing wave effect, so that the infrared rays focused to the hot end infrared absorption layer are absorbed as much as possible. The infrared absorption rate is greatly increased, thereby increasing the response rate and detection rate of the thermopile infrared detector are increased, and the noise equivalent temperature difference of the thermopile infrared detector is greatly reduced.
Owner:南京方旭智芯微电子科技有限公司
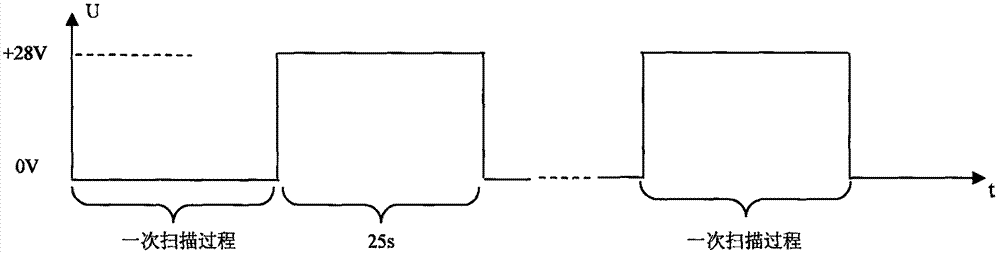
Method for testing refrigeration type infrared detector of infrared body temperature screening system
ActiveCN111623879ALow priceSensing radiation from moving bodiesThermometer testing/calibrationResponsivityBlack body
The invention discloses a method for testing a refrigeration type infrared detector of an intelligent infrared body temperature screening system. A test module comprises a surface source black body (1), optics (2), a detected detector (3), a detector driving circuit (4) and a test computer (5). The driving circuit (4) provides bias voltage for the detected detector, converts an analog voltage signal output by the detector into a Camera Link format digital image and transmits the Camera Link format digital image to the test computer (5). The test computer processes a digital image, calculates indexes of noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD), blind pixel rate, response rate and non-uniformity of the detector, has a median filtering function, conducts targeted screening on the detector through a fixation method according to the environment and the black body (target) temperature required for body temperature testing and screening, and uploads image data of the detector qualifiedin troubleshooting to an upper computer of the body temperature screening system. The method has the advantages of being convenient to operate and capable of effectively screening and testing the detector, the testing speed can be increased, and the cost of the refrigeration type infrared detector is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF REMOTE SENSING EQUIP
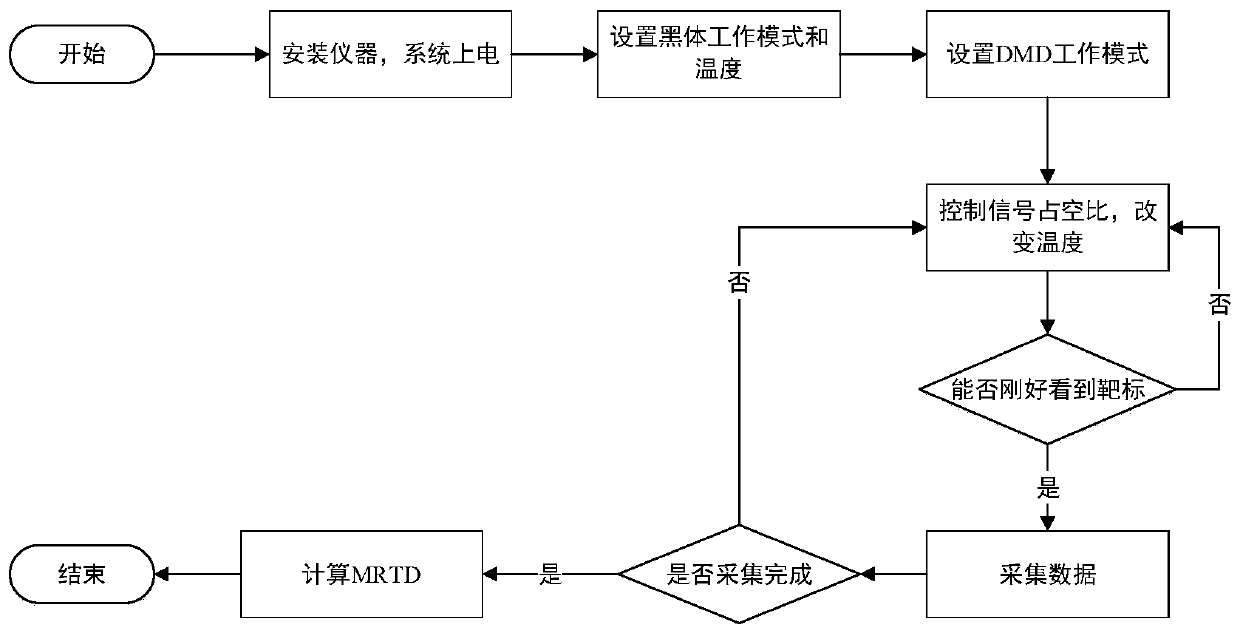
Infrared thermal imager NETD (noise equivalent temperature difference) and MRTD (minimum resolvable temperature difference) rapid testing device and method
ActiveCN110470404AReduce waiting timeImprove computing efficiencyRadiation pyrometryPrismRapid testing
The invention discloses an infrared thermal imager NETD (noise equivalent temperature difference) and MRTD (minimum resolvable temperature difference) rapid testing device and method. According to theinfrared thermal imager NETD (noise equivalent temperature difference) and MRTD (minimum resolvable temperature difference) rapid testing device and method of the invention, an upper computer controls the on-off time of a prism in a DMD chip through a DMD controller through adopting a pulse width modulation technology, so that the duty ratio of radiation signals reflected into a parallel light tube by the DMD chip is changed; a corresponding relation between blackbody temperature and the duty ratio of the radiation signal entering the parallel light tube is established; the duty ratio of theradiation signal entering the parallel light tube is adjusted, so that the detector output signal voltages of a to-be-detected infrared thermal imager which are corresponding to different duty ratiosare measured; and NETD and MRTD are calculated according to the measured detector output signal voltages of the to-be-detected infrared thermal imager. According to the method of the invention, the duty ratio of the radiation signal entering the parallel light tube is controlled, so that final radiation energy is changed; and therefore, the waiting time of a blackbody temperature change process isshortened, and the calculation efficiency of the NETD and the MRTD is improved.
Owner:成都盈盛源电气科技有限公司
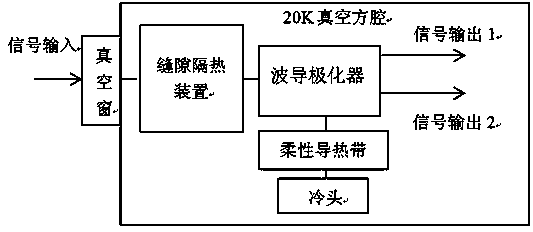
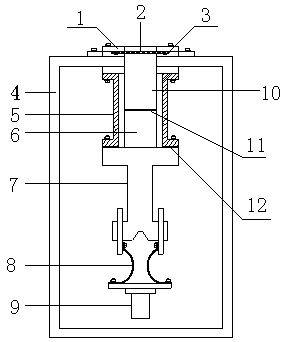
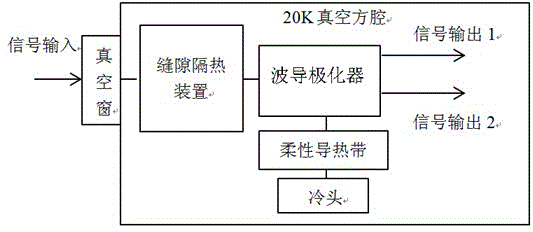
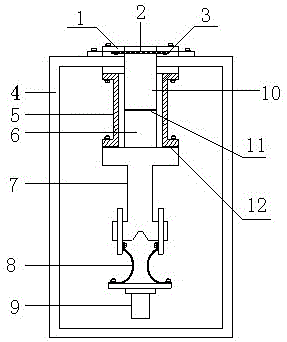
X-waveband refrigeration polarizer cooling structure device
ActiveCN103730710ALower Equivalent Noise TemperatureQuality factor G/T value increasesWaveguide type devicesSlot-waveguideSignal quality
The invention relates to an X-waveband refrigeration polarizer cooling structure device which comprises a polarizer, an upper waveguide cavity and a lower waveguide cavity. One end of the polarizer is connected with the cold end of a refrigerating machine through heat conducting strips, and the other end of the polarizer is connected with the end, not opposite to the upper waveguide cavity, of the lower waveguide cavity. A slot waveguide, the polarizer and the cold end of the refrigerating machine are located inside a vacuum cavity. The end, not opposite to the lower waveguide cavity, of the upper waveguide cavity is connected with the vacuum cavity. The heat conducting strips are a plurality of copper foils, wherein the ends of the copper foils are welded in a pressure mode. The vacuum cavity comprises a cavity body and a cover plate fixedly connected with the cavity body. A thermal insulation cylinder is arranged on the periphery of the slot waveguide, one end of the thermal insulation cylinder is fixedly connected with the inner wall of the cavity body, and the other end of the thermal insulation cylinder is fixedly connected with the end, connected with the lower waveguide cavity, of the polarizer. The upper waveguide cavity is fixedly connected with the cover plate, a sealing film is arranged between the upper waveguide cavity and the cover plate, and a gasket is arranged between the thermal insulation cylinder and the polarizer. According to the X-waveband refrigeration polarizer cooling structure device, due to the fact that the polarizer works under the vacuum and low-temperature environment, the equivalent noise temperature of the polarizer is reduced, and the quality of received signals is improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP NO 16 INST
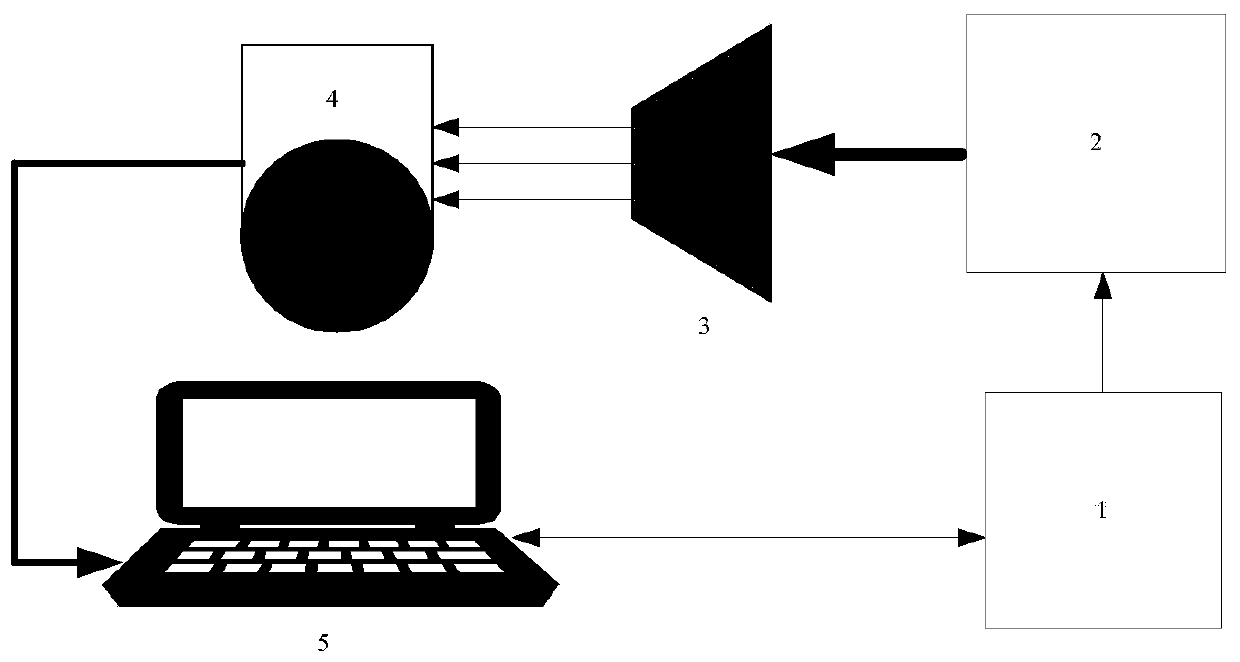
Noise equivalent temperature difference device of thermal infrared imager with ultra-large field of view and test method
ActiveCN111076819ASolve the untestableMeets linearity error requirementsRadiation pyrometryTemperature controlImaging processing
The invention provides a noise equivalent temperature difference device of a thermal infrared imager with an ultra-large field of view and a test method. A blackbody controller is connected with a blackbody radiation source, the blackbody radiation source provides the radiation energy; a light source incident from a black body is converted into a parallel light source through a collimating light tube to enter an infrared imaging system; the infrared imaging system is aligned with the center of the view field of the collimating light tube and transmits test data to an industrial personal computer; the industrial personal computer collects gray scale data from the infrared imaging system; and temperature control is conducted on the black body radiation source through the black body controller. According to the invention, the problem that the equivalent temperature difference of the infrared noise with the ultra-large field of view cannot be tested is solved and a test result meeting theprecision requirement is obtained; a three-dimensional noise model is introduced and time noise and space noise are subdivided into seven components, so that the noise of the infrared imaging system is comprehensively evaluated. According to the invention, the original gray scale data are sampled without being influenced by an image processing algorithm, so that the test accuracy is effectively improved.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Infrared imaging system and correction method
ActiveCN103308184BImprove uniformityImprove response non-uniformityPyrometry using electric radation detectorsElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses an infrared focal plane array detector unit with a non-uniform correction function, an infrared imaging system and a non-uniform correction method thereof. The infrared focal plane array detector unit comprises a pixel and a blind pixel which are made of the same thermistor material; the pixel responds to incident infrared radiation, while the blind pixel does not respond to the incident infrared radiation; the pixel and the blind pixel are connected in series, and are electrically connected with the inverted input end of an integrated amplifier, and the other end of the blind pixel, which is opposite to the end electrically connected with the pixel, is electrically connected with a compensating blind pixel; like the blind pixel, the compensating pixel does not respond to the incident infrared radiation; and the compensating pixel is used for compensating the blind pixel and indirectly compensating and correcting the nonuniformity of the corresponding pixel. The invention can effectively compensate the nonuniformity of the resistance of the pixel, thus broadening the dynamic range of the effective output of a focal plane array and decreasing noise-equivalent temperature difference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DALI TECH
Uncooled infrared detector and automatic gain correction circuit thereof
The invention provides an uncooled infrared detector and an automatic gain correction circuit thereof. The automatic gain correction circuit comprises a responsivity stabilizing unit which is connected to a sensitive pixel of the uncooled infrared detector and is used for compensating deviation caused by responsivity change of a pixel resistor at different temperatures; and the reference voltage correction unit is connected to the response rate stabilization unit and is used for correcting the reference voltage to compensate for deviation caused by non-uniformity of the resistance of the sensitive pixel on the chip. Through the automatic gain correction circuit provided by the invention, the influence of non-uniformity of pixel resistance is suppressed; meanwhile, the response rate is no longer inversely proportional to the pixel resistance value, the stability of the response rate and the noise equivalent temperature difference at high and low temperatures is ensured, and the use of a user is facilitated.
Owner:北方广微科技有限公司
Infrared detector, camera module and electronic equipment
PendingCN113990888ASolve cost pain pointsImprove absorption rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides an infrared detector, a camera module and electronic equipment. The infrared detector comprises an optical window, a thin film layer, a reflecting layer and a reading circuit layer which are stacked in sequence; the thin film layer comprises an absorption layer and a conversion layer, and the absorption layer is located between the optical window and the conversion layer; the optical window is used for incidence of infrared light, the absorption layer is used for absorbing the infrared light and converting the infrared light into heat energy, and the conversion layer is used for converting the heat energy into electric signals; the reflecting layer is used for reflecting the infrared light so as to increase the infrared light absorbed by the absorbing layer; the reading circuit is used for processing the electric signal, and the processed electric signal is used for forming a thermal infrared image; and the infrared detector further comprises a metasurface layer arranged on at least one of the optical window and the thin film layer, the metasurface layer comprises a plurality of microstructures arranged periodically, and the metasurface layer can improve the absorptivity of the absorption layer. According to the embodiment of the invention, the absorption rate of infrared light is improved, the noise equivalent temperature difference is reduced, and the sensitivity is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Thermal infrared detector performance testing method
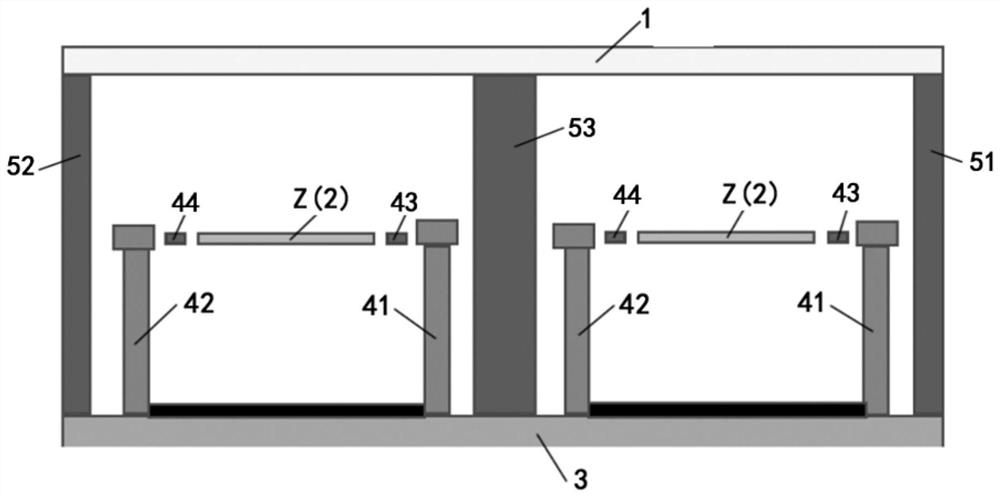
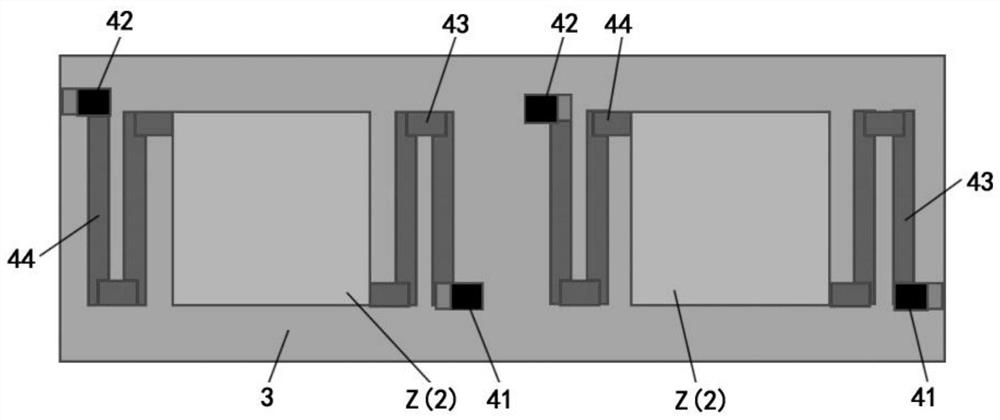
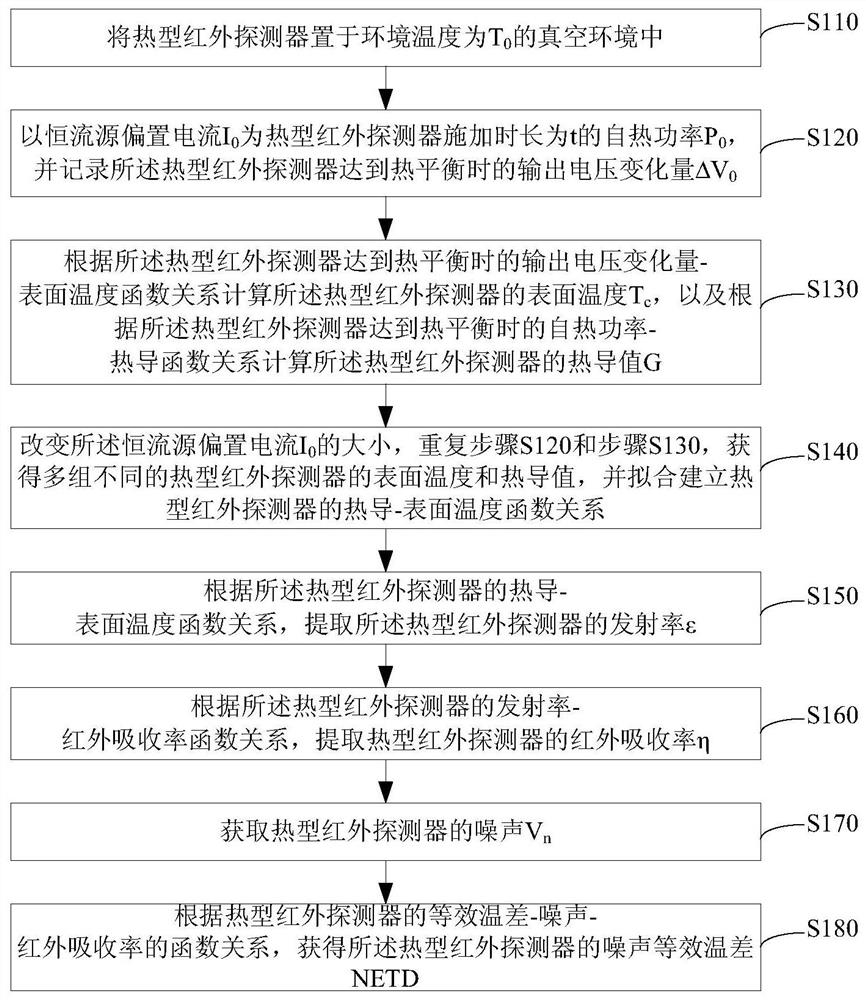
ActiveCN113091918ARealize the test of noise equivalent temperature differenceReduce testing costsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsIr absorptionThermal infrared
The invention relates to the technical field of thermal infrared detector testing, and particularly discloses a thermal infrared detector performance testing method, which comprises the following steps of: placing a thermal infrared detector in a vacuum environment with the environment temperature of 50 DEG C; constant current source bias current is used for applying self-heating power of the duration to the detector, and the output voltage variation when the thermal infrared detector reaches thermal balance is recorded; the surface temperature of the thermal infrared detector is calculated according to the output voltage variation-surface temperature function relation, and the thermal conductivity value of the thermal infrared detector is calculated according to the self-heating power-thermal conductivity function relation; a thermal conductivity-surface temperature function relationship is established; the emissivity of the thermal infrared detector is obtained, and the infrared absorptivity is obtained according to the emissivity; the noise of the thermal infrared detector is obtained; and the noise equivalent temperature difference is measured according to the function relationship of equivalent temperature difference-noise-infrared absorptivity. The thermal infrared detector performance test method provided by the invention is simple in test, and performance self-test is carried out by utilizing pure electrical excitation.
Owner:WUXI INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Low-temperature vacuum radiation temperature parameter calibration system and calibration method
PendingCN114353967AAchieve calibration traceabilityEnsure consistencyRadiation pyrometryMinimum resolvable temperature differenceRadiation temperature
The invention provides a low-temperature vacuum radiation temperature parameter calibration system and method, and the system comprises a vacuum cold cabin which is used for simulating a low-temperature vacuum environment; the infrared temperature difference radiation emission device is arranged in the vacuum cold cabin corresponding to the infrared temperature difference radiation emission device and is used for emitting first infrared radiation with a set temperature difference; and the collimation optical device is arranged in the vacuum cold cabin and is used for receiving the first infrared radiation, collimating the first infrared radiation and then transmitting the first infrared radiation to a target infrared load, so that noise equivalent temperature difference calibration and / or minimum distinguishable temperature difference calibration and / or minimum detectable temperature difference calibration are / is carried out on the target infrared load. The problems that radiation temperature parameters of an in-orbit space are difficult to calibrate, the accuracy of test data cannot be evaluated, and hidden dangers are generated in an infrared load low-temperature infrared target detection performance test are solved.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENXING METROLOGY & TEST INST
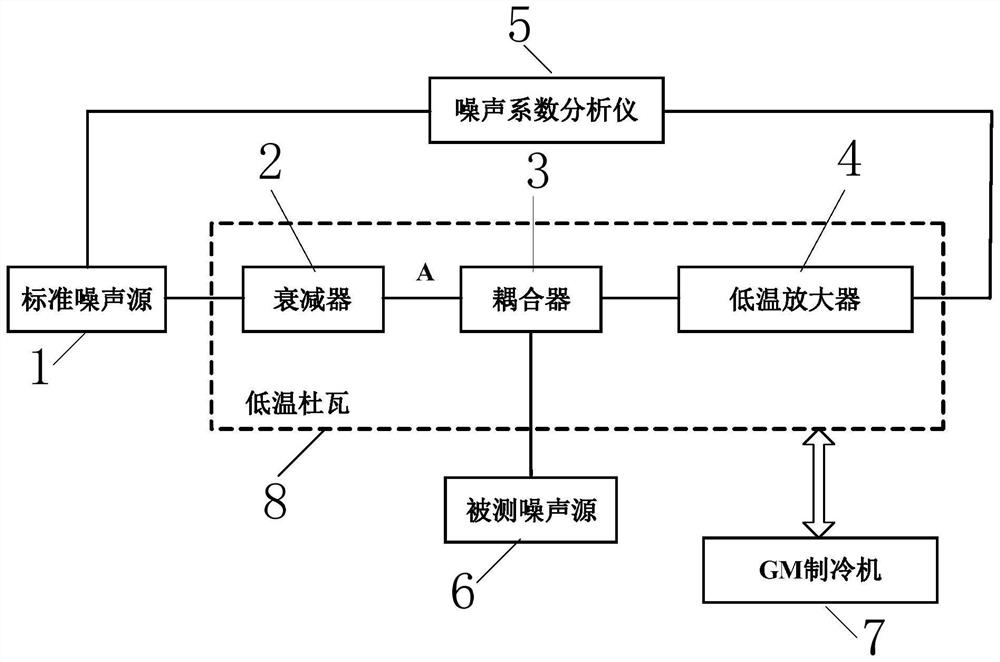
Noise source excess noise ratio test system and test method thereof
PendingCN112255470AReduce Mismatch EffectImprove test efficiencyNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementMicrowaveNoise
The invention relates to a noise source excess noise ratio test system and a test method thereof. The test system comprises a standard noise source, an attenuator, a coupler, a low-temperature amplifier, a tested noise source, a GM refrigerator, a noise coefficient analyzer, a temperature sensor and a temperature controller. According to the invention, a change of an output Y factor of a low-temperature microwave link in the power supply and non-power supply states of the tested noise source is measured by constructing a test system, an increment of an equivalent noise temperature of the low-temperature microwave link composed of the coupler and the low-temperature amplifier is calculated, and then the excess noise ratio of the noise source is determined. Compared with the prior art, by using the system and the method of the invention, adverse effects of physical switch switching on a test process and a test result during a traditional test are eliminated, and the system and the methodare stable in test system, high in test precision, easy and convenient to operate and the like.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP NO 16 INST
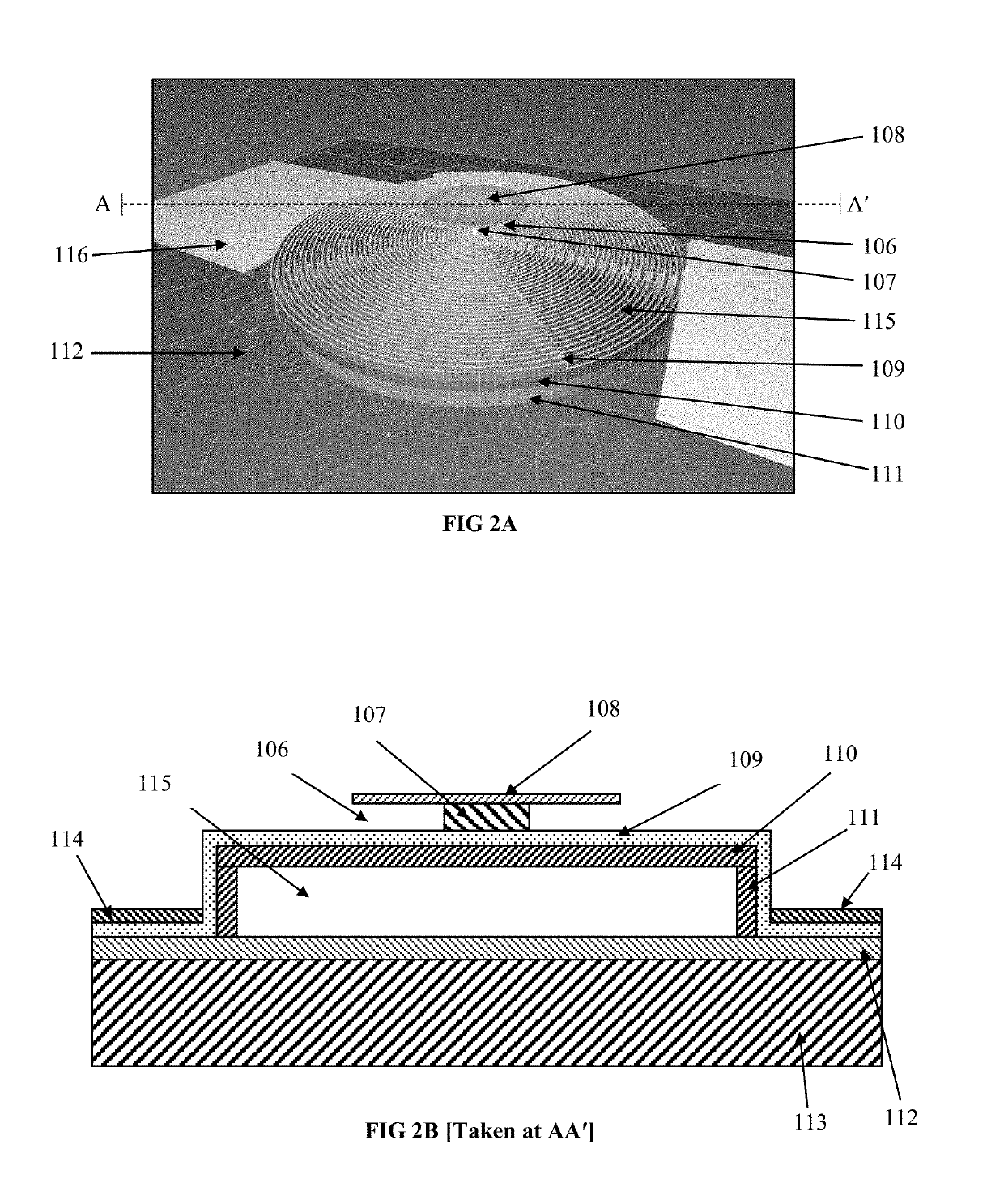
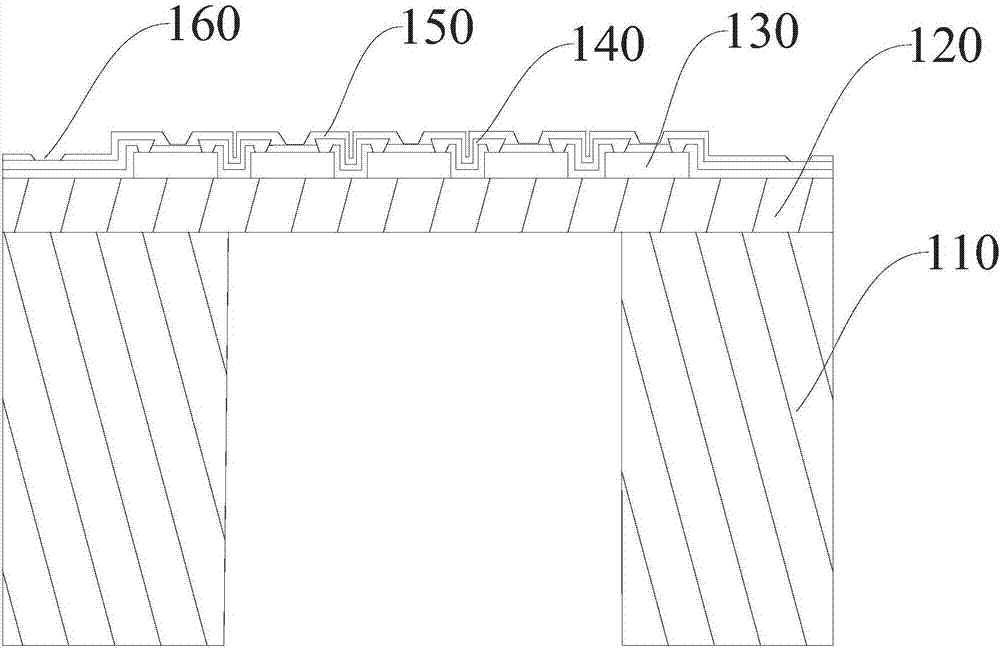
MEMS structure and processing method thereof, pyroelectric sensor and infrared detector
InactiveCN110823386AImprove optical absorption propertiesReduce noise equivalent temperature differenceTelevision system detailsImpedence networksFerroelectric thin filmsTitanium nitride
The invention discloses an MEMS (Micro-ElectroMechanical Systems) structure and a processing method thereof, a pyroelectric sensor and an infrared detector, and belongs to the technical field of MEMStechnology and infrared detection. The MEMS structure includes a substrate provided with a read-out integrated circuit, and includes: a thermal sensitive layer which is suspended on one side of the substrate and is a lanthanum lead titanate ferroelectric film; and a supporting structure used for supporting the thermal sensitive layer, wherein the supporting structure is connected with the substrate through a plurality of groups of anchor posts, an optical resonant cavity is formed between the supporting structure and the substrate, the supporting structure sequentially comprises a first silicon carbide layer, an electrode layer and a second silicon carbide layer, and the electrode layer is a titanium film and / or a titanium nitride film. The MEMS structure of the invention has the beneficial effects that: the lanthanum lead titanate ferroelectric film is used as the thermal sensitive layer, and the thermal sensitive layer is suspended on one side of the substrate through the supportingstructure, thus the optical absorption characteristic of the MEMS structure can be improved, and the noise equivalent temperature difference of the MEMS structure can be reduced.
Owner:RUZHOU YUFENG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multispectral noise equivalent temperature difference testing device and method
ActiveCN110987191AFulfill test requirementsSuppression of thermal radiation direct to the detectorRadiation pyrometryBlack bodyEngineering
The invention discloses a multispectral noise equivalent temperature difference testing device. The multispectral noise equivalent temperature difference testing device comprises a surface source black body, a circular variable optical filter wheel is arranged in the radiation light transmission direction of the surface source black body, an off-axis hyperboloid reflector is arranged on one side of the circular variable optical filter wheel in the light transmission direction, and an off-axis parabolic reflector is arranged on one side of the off-axis hyperboloid reflector in the light transmission direction; the surface source black body coincides with the focal point of the off-axis parabolic mirror through the virtual image point of the off-axis hyperboloid mirror. A Fourier spectrometer is arranged on one side of the off-axis parabolic mirror in the light transmission direction. The invention also discloses a test method. The device provided by the invention has a self-calibrationfunction, can correct the transmittance and background radiation of the optical element of the test system at any time, and eliminates system errors. According to the device and method, the Planck function is used for replacing a polynomial to fit the data, the physical significance is clearer, the influence of random errors in the testing process is restrained, and the device and method has the advantages in NETD testing of a small-dynamic-range system.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Coaxial standard low-temperature noise source
InactiveCN107727267ACorrection errorImprove accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsElectrical resistance and conductanceMatched load
The invention discloses a coaxial standard low-temperature noise source which comprises a matching load, a heat insulation transmission line, a heat preservation container, platinum resistor temperature sensors and a temperature measuring assembly, wherein the heat insulation transmission line penetrates through and is fixed on the side wall of the heat preservation container, a normal-temperatureconnector is connected to one end , outside the heat preservation container, of the heat insulation transmission line, one end of the heat insulation transmission line in the heat preservation container is connected with one end of the matched load, a matched load absorbing body is arranged in the other end of the matched load; at least two openings are formed in the two ends of the heat insulation transmission line; the platinum resistor temperature sensors are arranged in the openings and on the matched load absorbing body, the temperature measuring assembly is arranged outside the heat preservation container and is connected with the platinum resistor temperature sensor. The coaxial standard low-temperature noise source has the advantages of being convenient to use and high in precision, wide in the working frequency range and low in the output equivalent noise temperature.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
An x-band refrigeration polarizer cooling structure device
ActiveCN103730710BLower Equivalent Noise TemperatureQuality factor G/T value increasesWaveguide type devicesSlot-waveguideThermal insulation
The invention relates to an X-waveband refrigeration polarizer cooling structure device which comprises a polarizer, an upper waveguide cavity and a lower waveguide cavity. One end of the polarizer is connected with the cold end of a refrigerating machine through heat conducting strips, and the other end of the polarizer is connected with the end, not opposite to the upper waveguide cavity, of the lower waveguide cavity. A slot waveguide, the polarizer and the cold end of the refrigerating machine are located inside a vacuum cavity. The end, not opposite to the lower waveguide cavity, of the upper waveguide cavity is connected with the vacuum cavity. The heat conducting strips are a plurality of copper foils, wherein the ends of the copper foils are welded in a pressure mode. The vacuum cavity comprises a cavity body and a cover plate fixedly connected with the cavity body. A thermal insulation cylinder is arranged on the periphery of the slot waveguide, one end of the thermal insulation cylinder is fixedly connected with the inner wall of the cavity body, and the other end of the thermal insulation cylinder is fixedly connected with the end, connected with the lower waveguide cavity, of the polarizer. The upper waveguide cavity is fixedly connected with the cover plate, a sealing film is arranged between the upper waveguide cavity and the cover plate, and a gasket is arranged between the thermal insulation cylinder and the polarizer. According to the X-waveband refrigeration polarizer cooling structure device, due to the fact that the polarizer works under the vacuum and low-temperature environment, the equivalent noise temperature of the polarizer is reduced, and the quality of received signals is improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP NO 16 INST
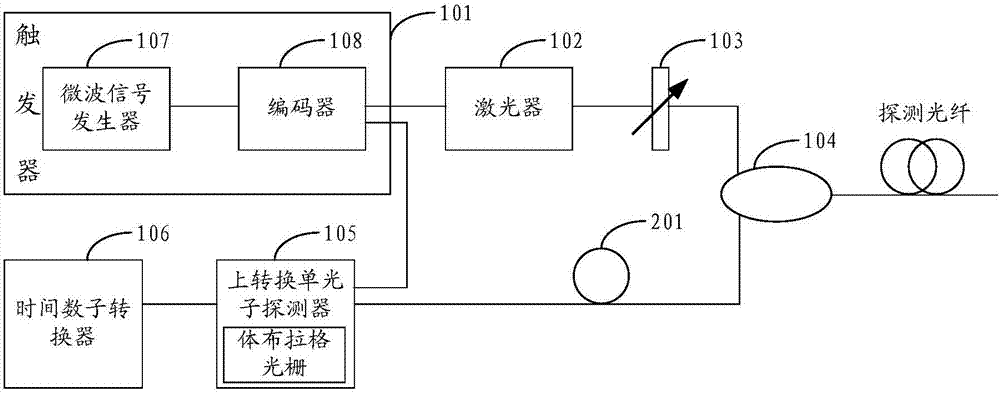
A fiber optic time domain reflectometer
ActiveCN104426602BLarge dynamic rangeHigh-resolutionElectromagnetic transmissionTime-domain reflectometerUp conversion
The invention discloses an optical time-domain reflectometer comprising a trigger, a laser, an attenuator, a circulator, an up-conversion single-photon detector and a time-to-digital converter. The optical time-domain reflectometer (OTDR) of the invention employs the up-conversion single-photon detector. The up-conversion single-photon detector employs a pump light wavelength of 1900 nm to 2000 nm to carry out narrowband filtering on sum frequency light, a noise equivalent power (NEP) lower than the NEP of a classic detector is obtained under the same quantum efficiency, and the NEP value can reach -140dbm. The lower the NEP value is, the larger the detected dynamic range is. Therefore, the up-conversion single-photon detector effectively increases the detectable dynamic range of the OTDR, the detection resolution is improved, the measuring time is reduced, and dead zones after a Fresnel reflection peak are effectively prevented.
Owner:张强
A processing system and method for infrared imaging system netd
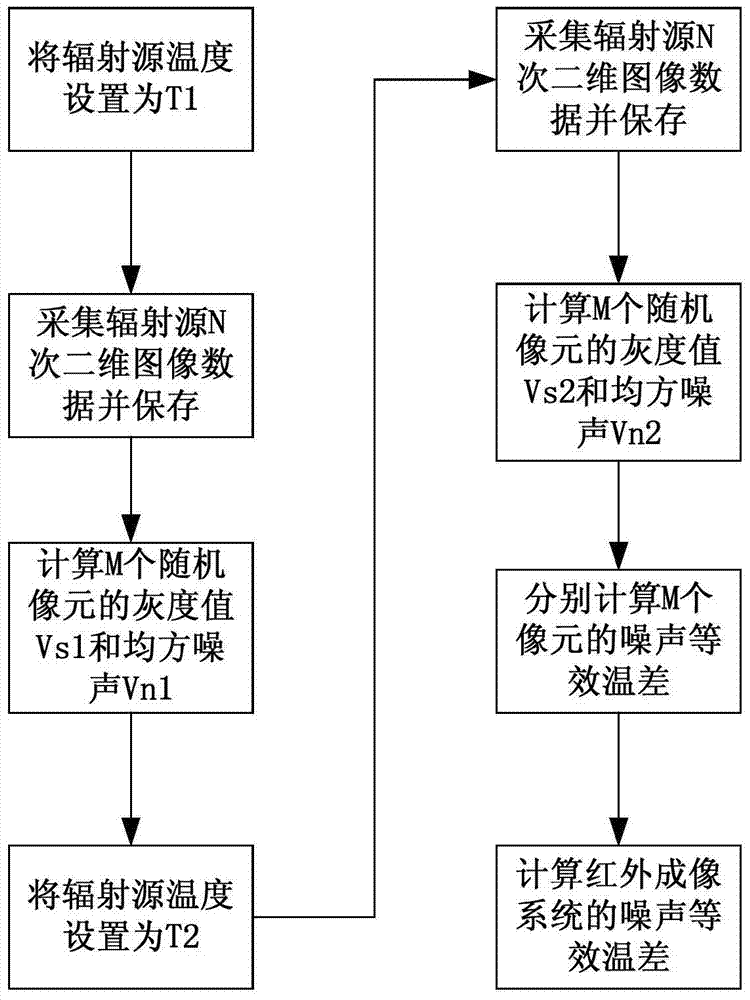
ActiveCN104729718BIncreased cost of testingReduce mistakesRadiation pyrometryMean squareData acquisition
The invention relates to a processing system and method for an infrared imaging system NETD, the method includes a parameter setting module, a data acquisition module, an image display module, a status display module, a NETD calculation module, a storage module, etc., and the parameter setting module is used to set The temperature value of the standard radiation source, the number of acquisitions N and the number of random pixels M, the data acquisition module and the storage module are used to complete the data acquisition and storage functions, and the calculation module mainly completes the acquisition data gray average value, mean square noise, NETD calculation, the state display module is used to display the current operating state, and the image display module is used to display the current grayscale image. The present invention avoids the use of complicated NETD test equipment and professional operators, and can obtain the infrared imaging system. Noise equivalent temperature difference.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com