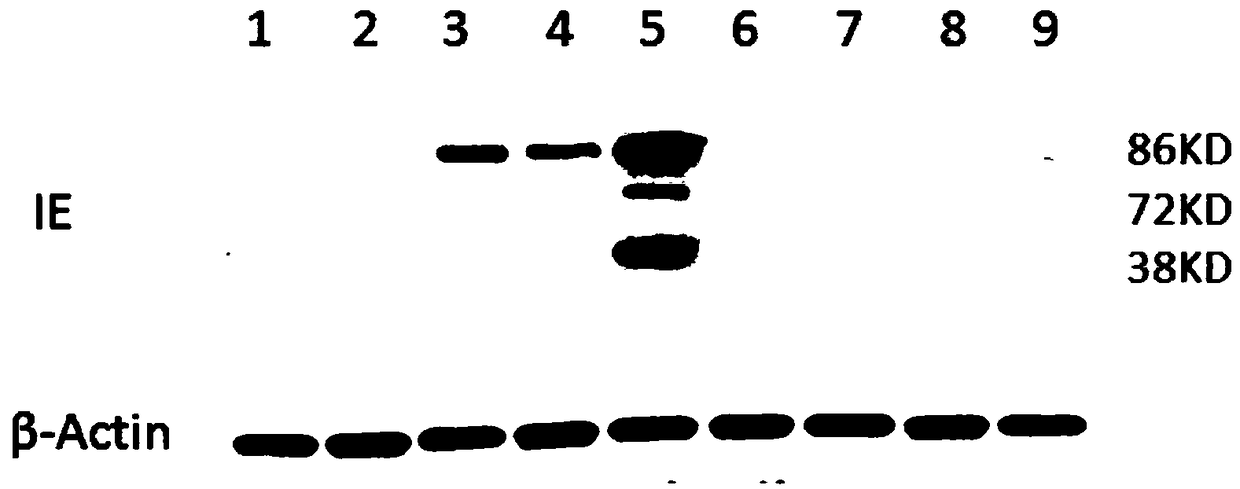
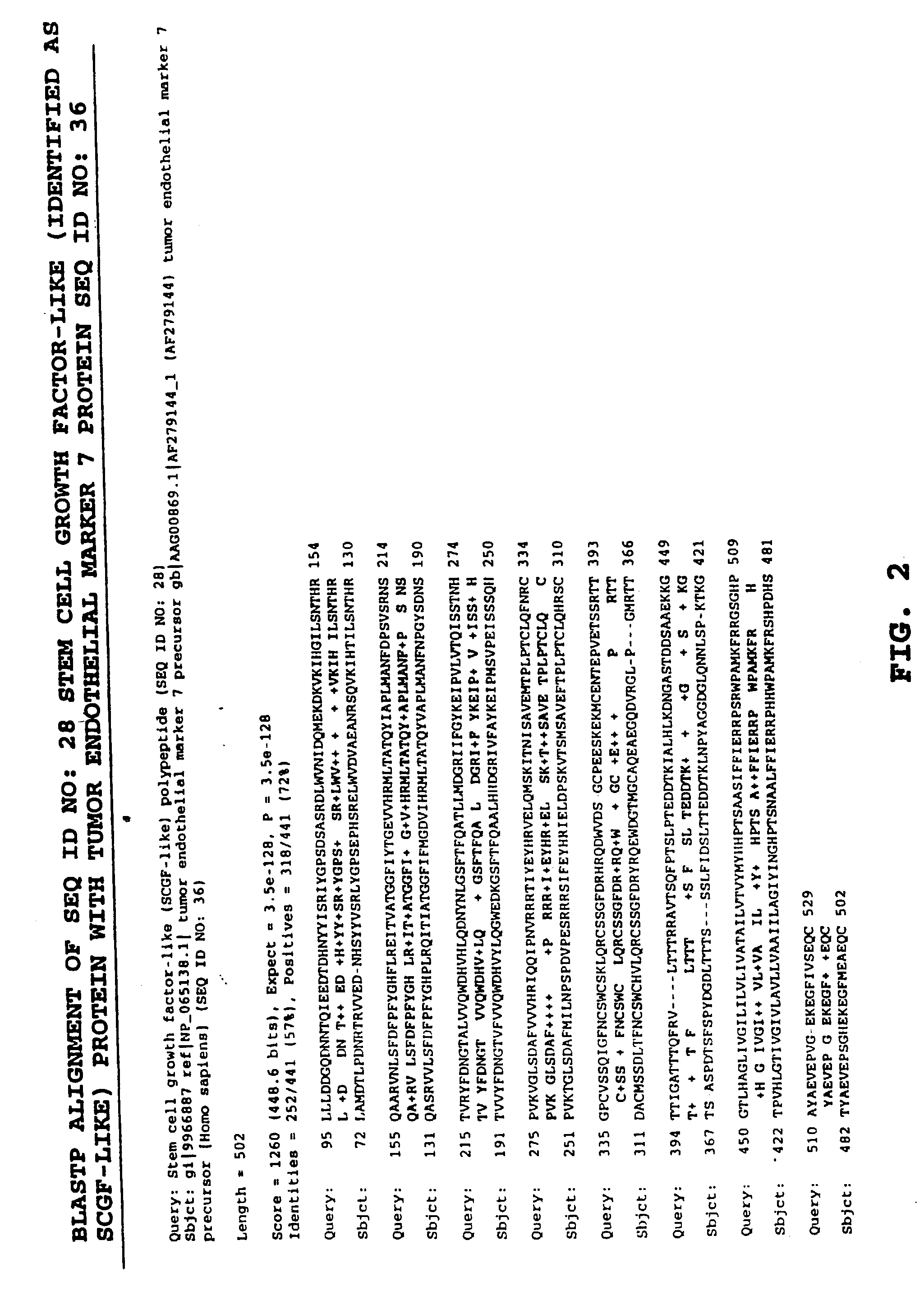
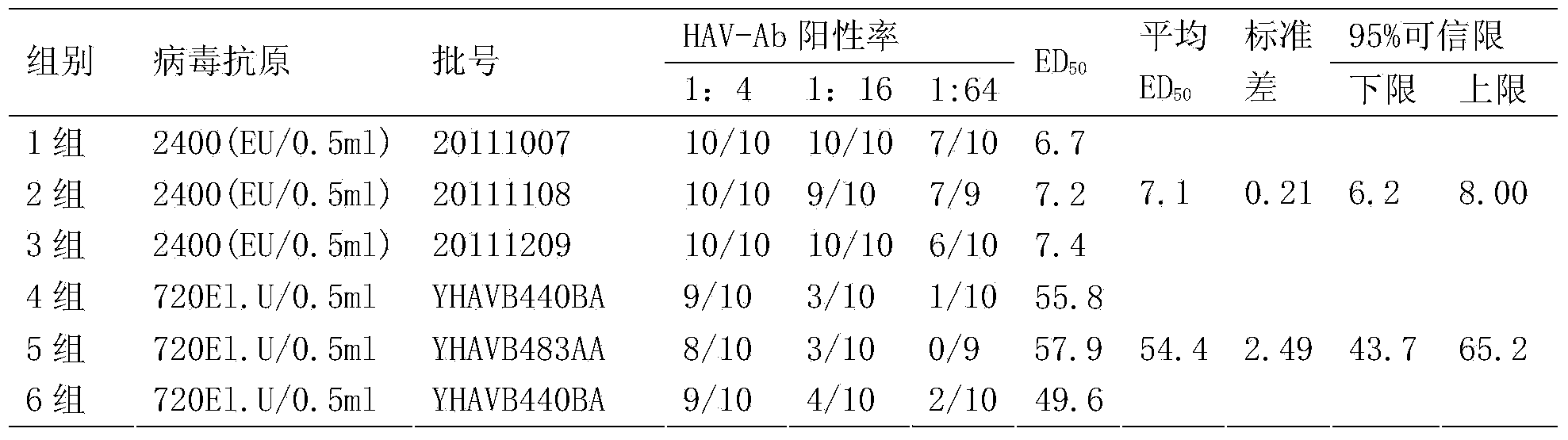
Patents
Literature
101 results about "Pulmonary myofibroblast" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides and mutants or variants thereof that correspond to a novel human and mouse secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptide. These polynucleotides comprise nucleic acid sequences isolated from cDNA libraries prepared from mouse bone marrow and human fetal liver spleen, ovary, adult brain, lung tumor, spinal cord, cervix, ovary, endothelial cells, umbilical cord, placental, lymphocyte, lung fibroblast, fetal brain, and testis. Other aspects of the invention include vectors containing processes for producing novel human secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides, and antibodies specific for such polypeptides.
Owner:KIRIN PHARMA +1
Novel proteins and methods for producing the proteins
InactiveUS20020051969A1Efficient productionSure easyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsCulture mediums
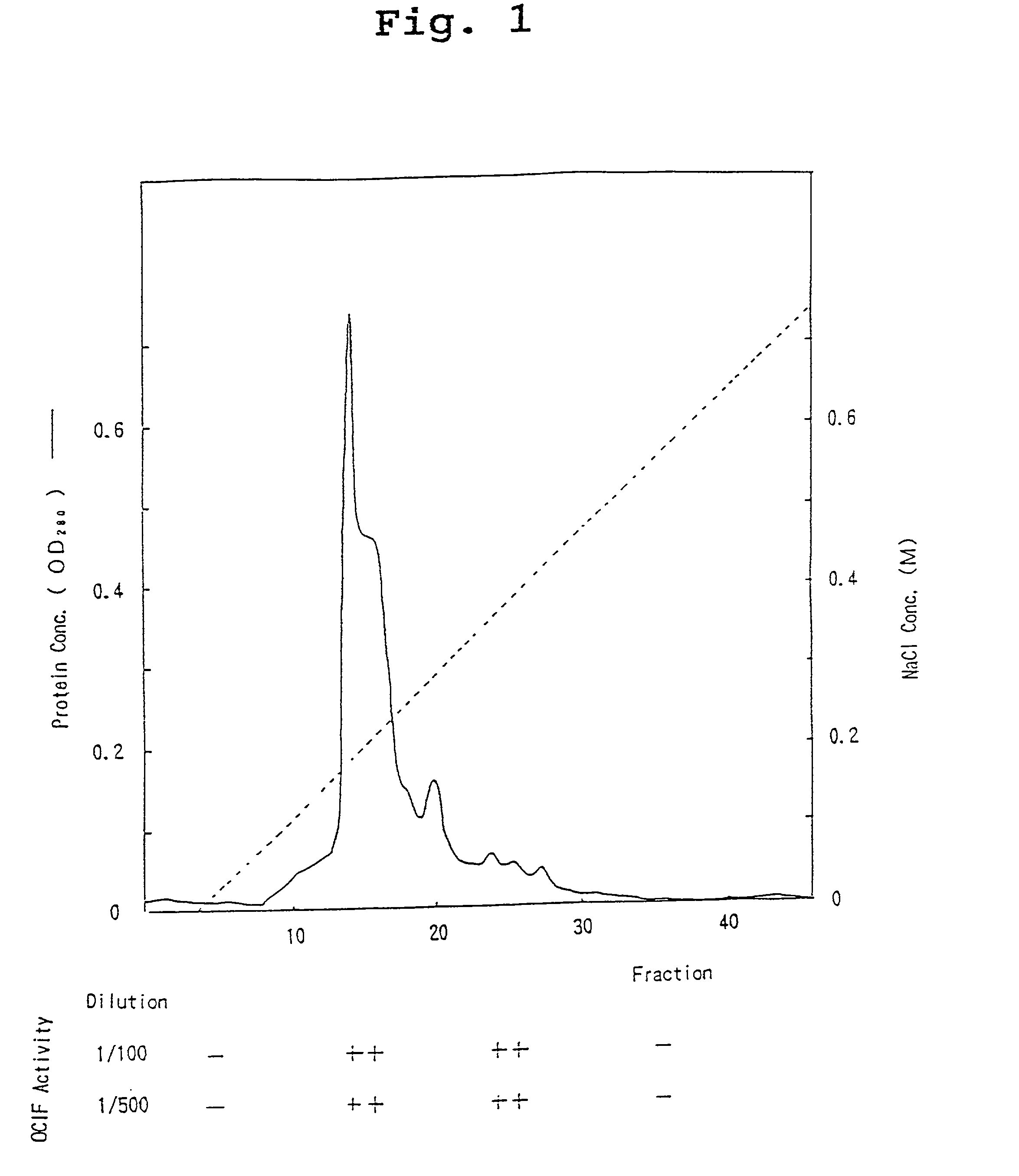
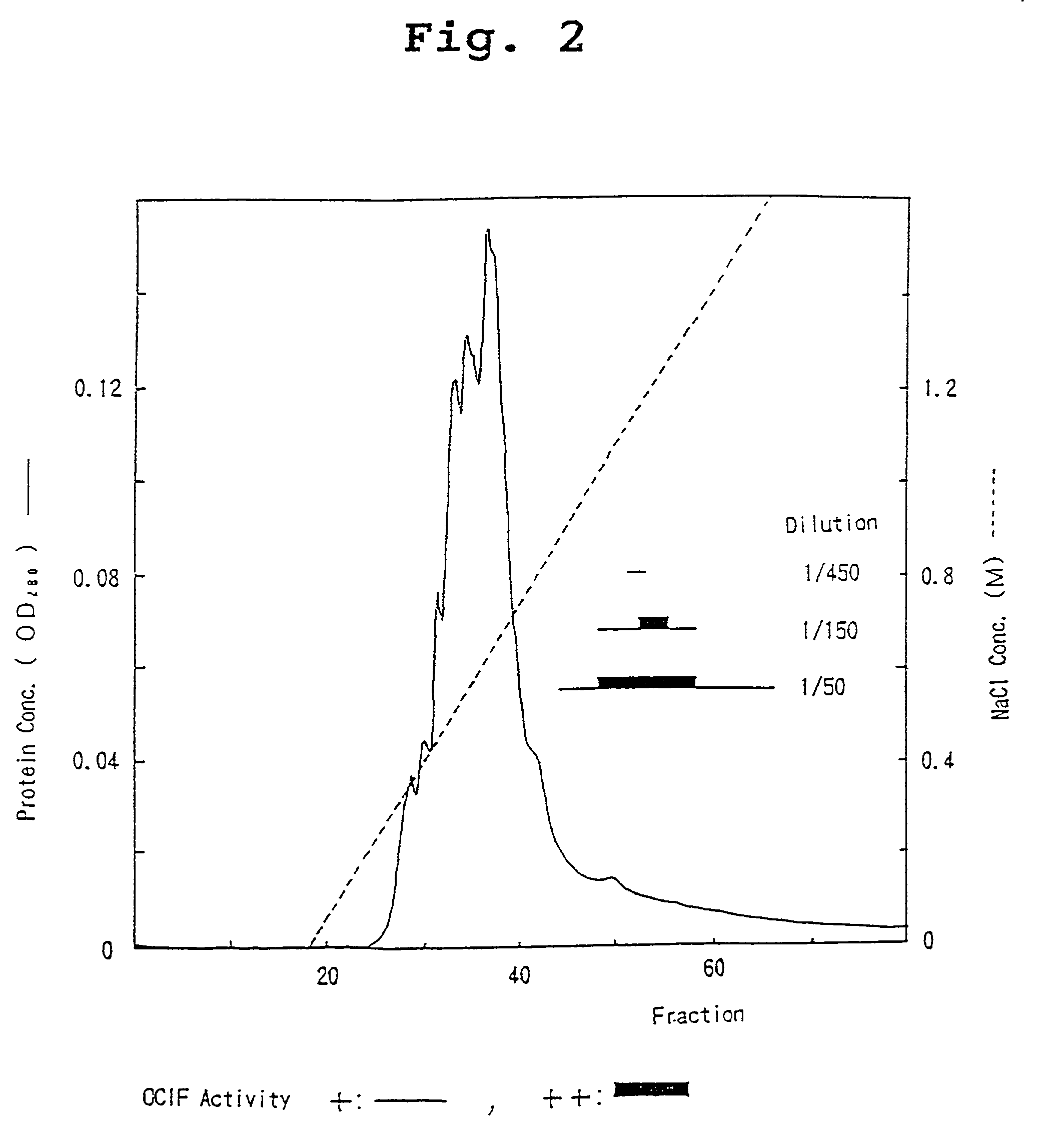
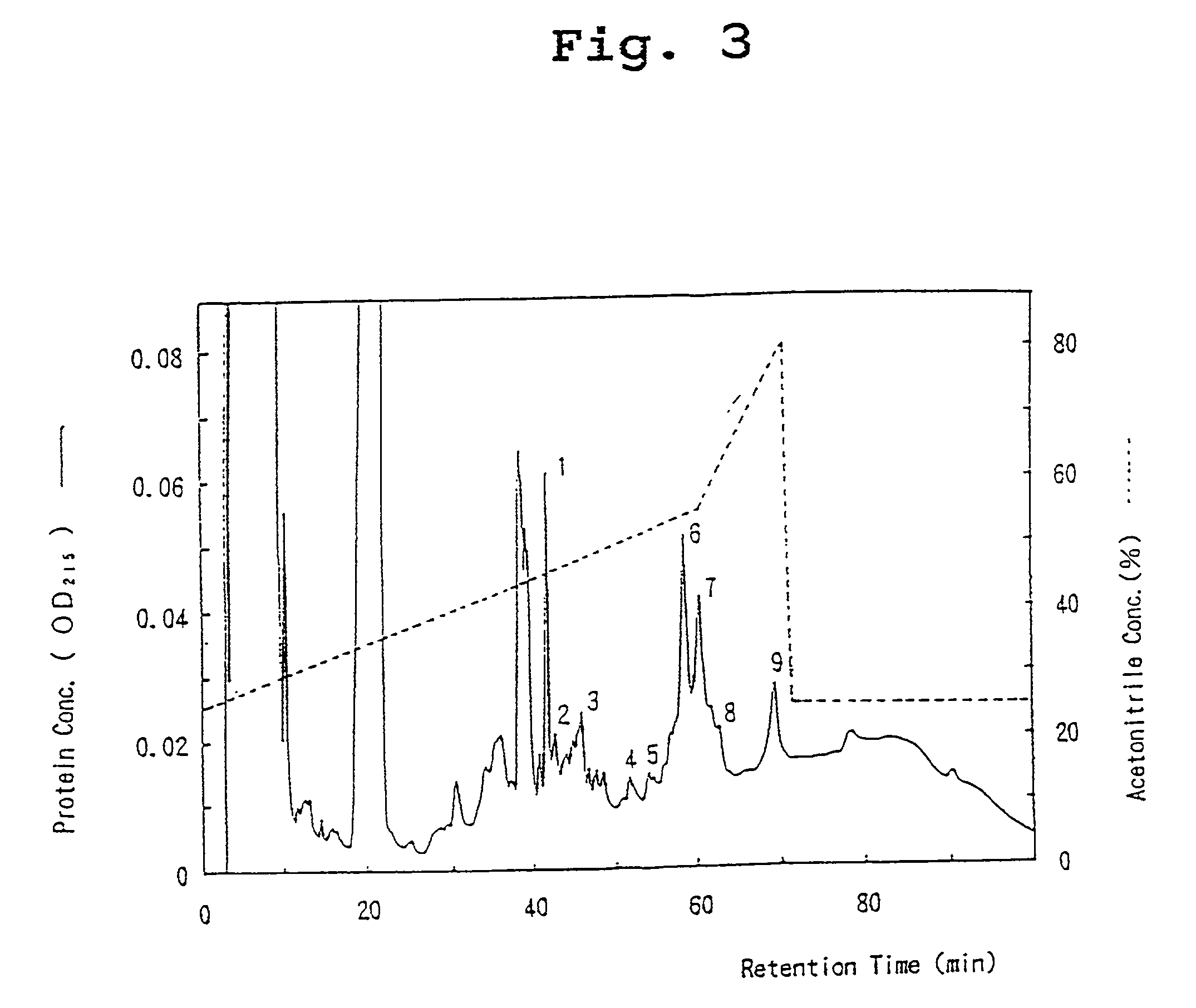
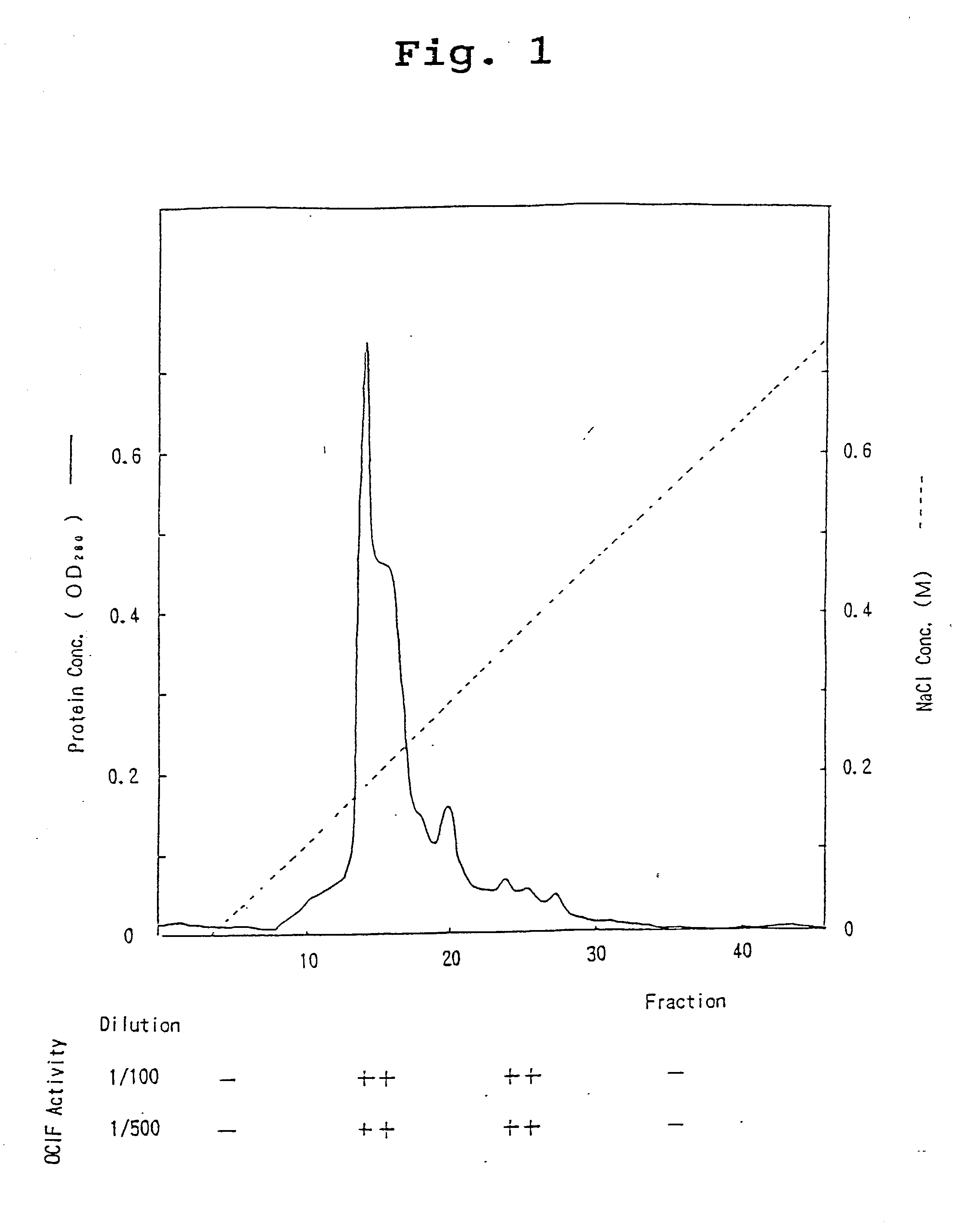
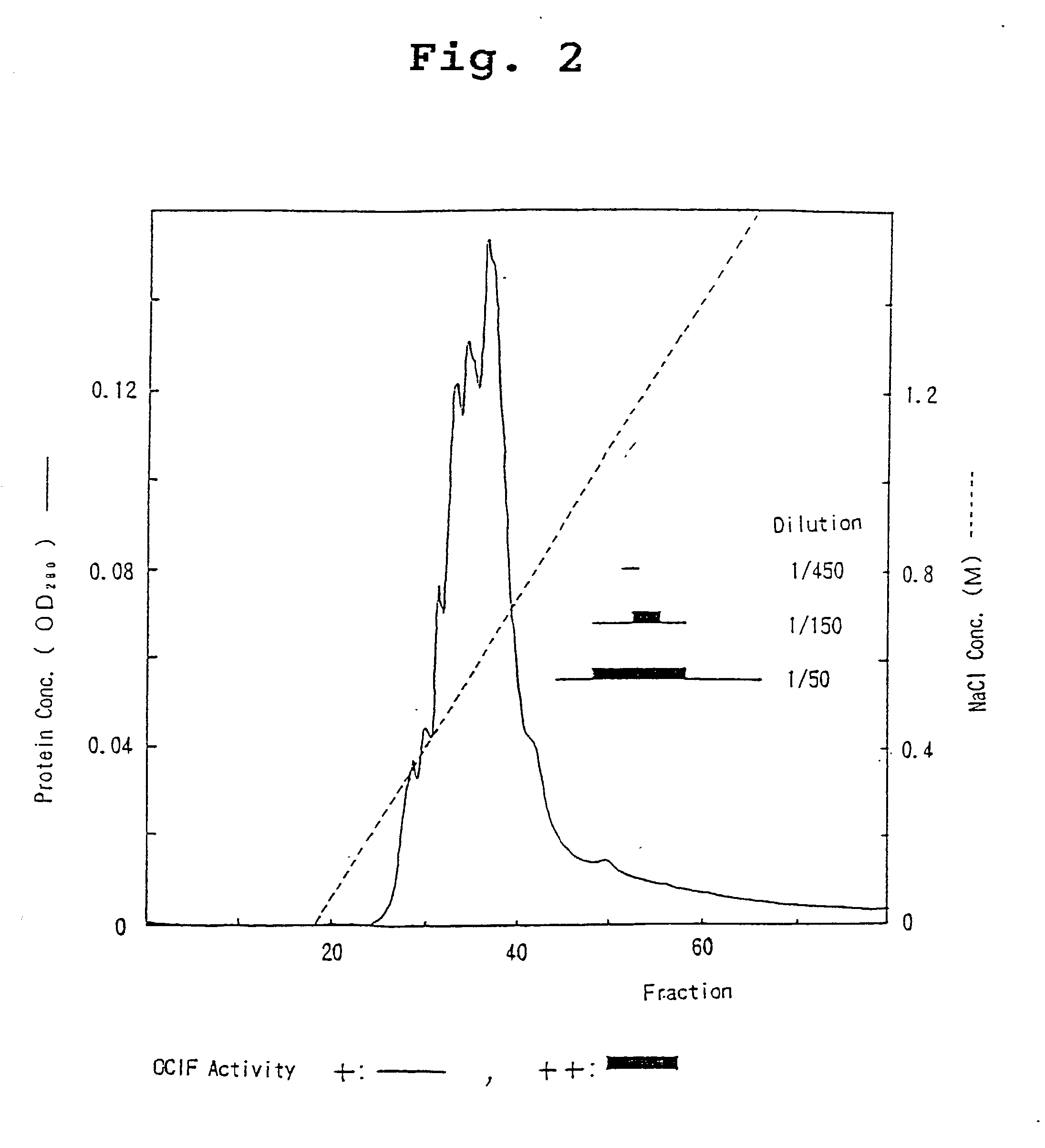
A protein which inhibits osteoclast differentiation and / or maturation and a method of production of the protein. The protein is produced by human embryonic lung fibroblasts and has molecular weight of about 60 kD and about 120 kD under non-reducing conditions and about 60 kD under reducing conditions on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, respectively. The protein can be isolated and purified from culture medium of the said fibroblasts. Furthermore, the protein can be produced by gene engineering. The present invention includes cDNA for producing the protein by gene engineering, antibodies having specific affinity to the protein or a method for determination of the protein concentration using the antibodies.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Pharmaceutical use of Graptopetalum and related plants
ActiveUS7364758B2No detectable side effectImprove survival rateBiocideAntipyreticDiseaseLiver fibrosis
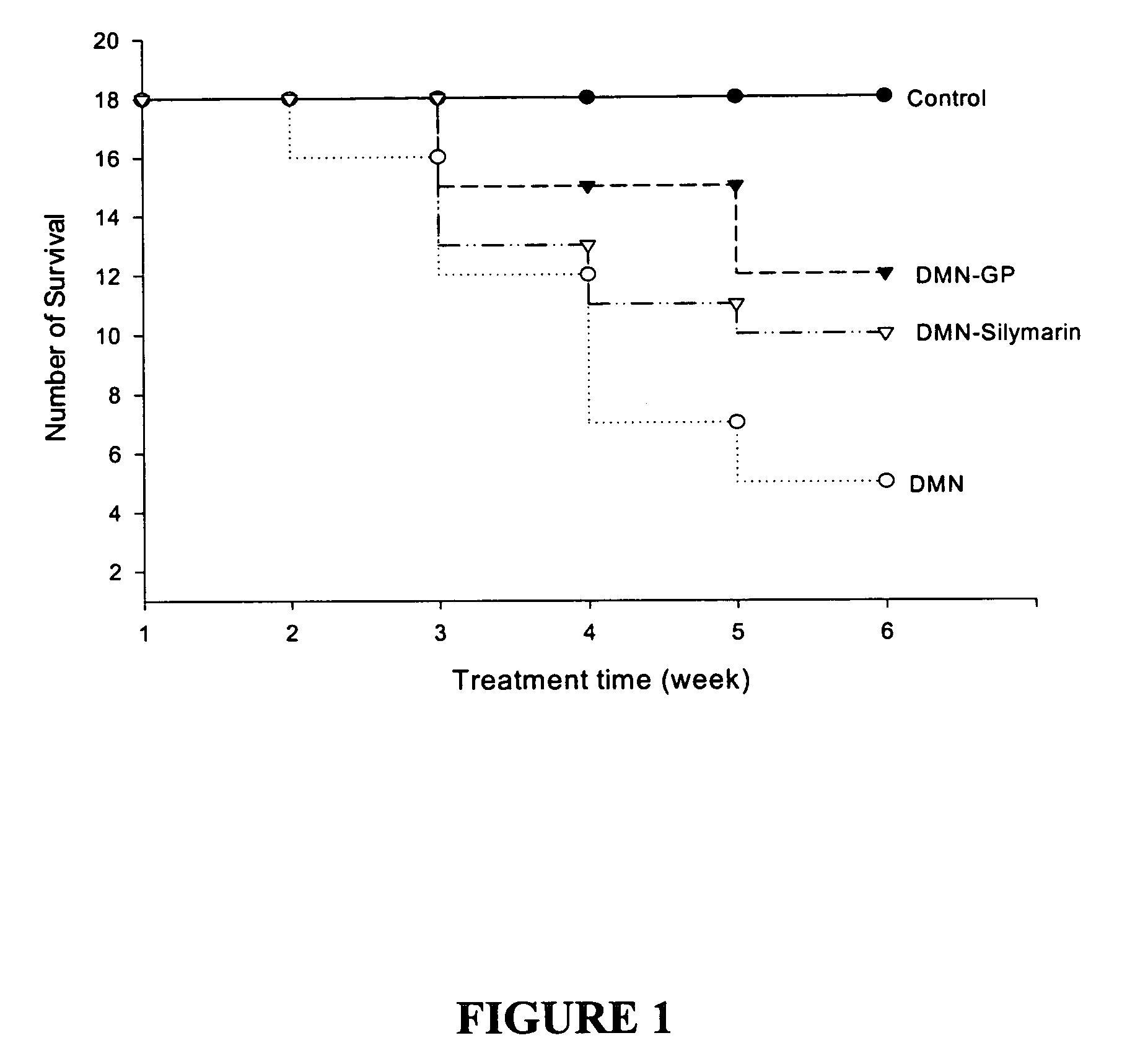
The present invention relates to compositions comprising Graptopetalum and uses thereof Graptopetalum can protect animals from liver diseases and medical conditions, such as inflammation, steatosis, and fibrosis. In particular, Graptopetalum inhibits proliferation of activated hepatic stellate cells, which play a pivotal role in liver fibrosis. Graptopetalum also has anti-fibrosis activities as well as inhibits proliferation of lung fibroblasts. Therefore, in addition to being a prophylactic and therapeutic agent for the liver, Graptopetalum is useful against fibrosis or inflammation of tissues or organs other than the liver, in particular lung, kidney, and bladder. Other plants in the family of Crassulaceae, particularly Echeveria, have similar effects as Graptopetalum.
Owner:TAICHUNG VETERANS GENERAL HOSPITAL +1
Beta-hydroxy protected didecyl quaternary ammonium salt with anticancer activity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101967105AEfficient killingOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationCancer cellPharmaceutical Substances
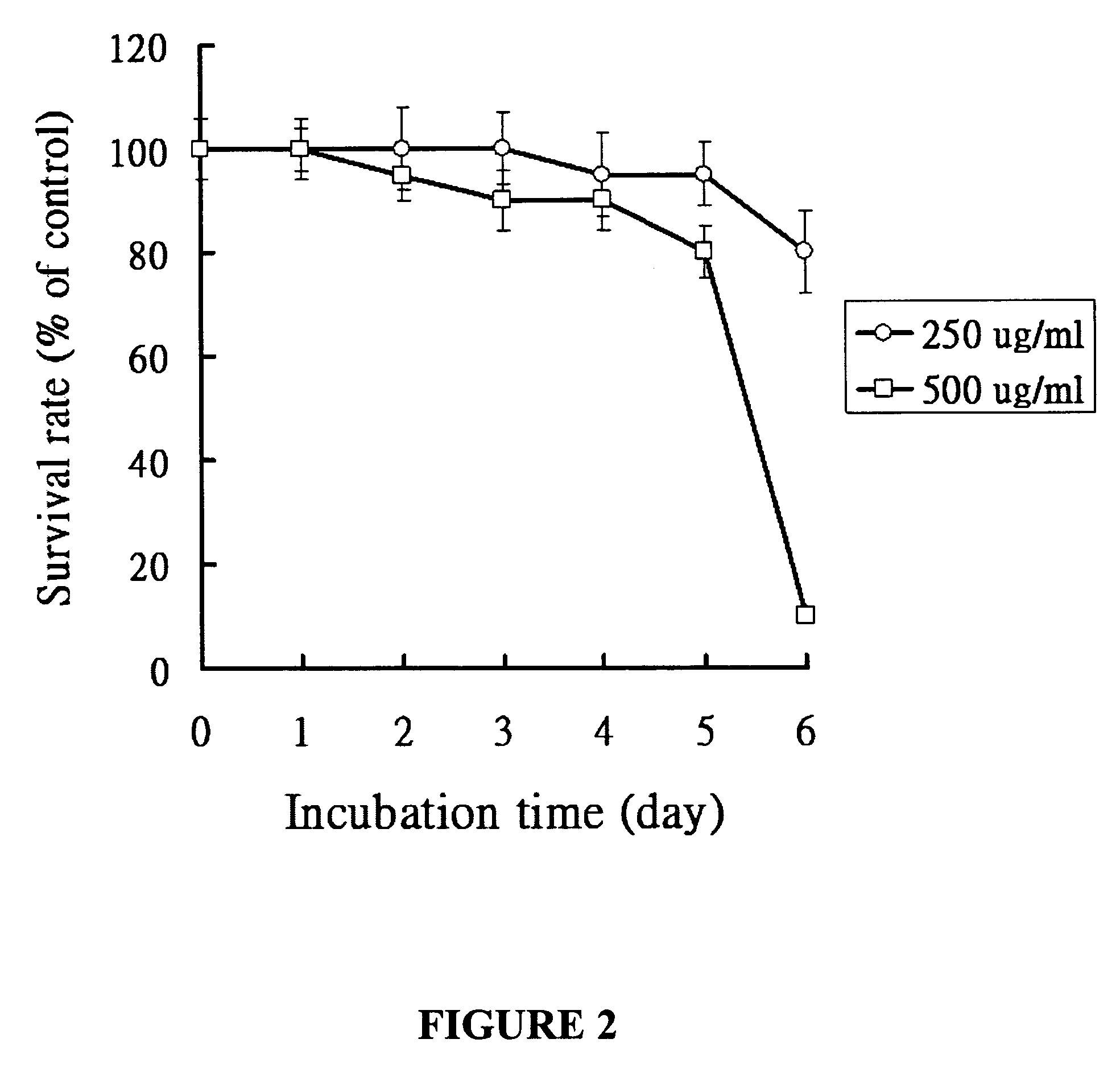
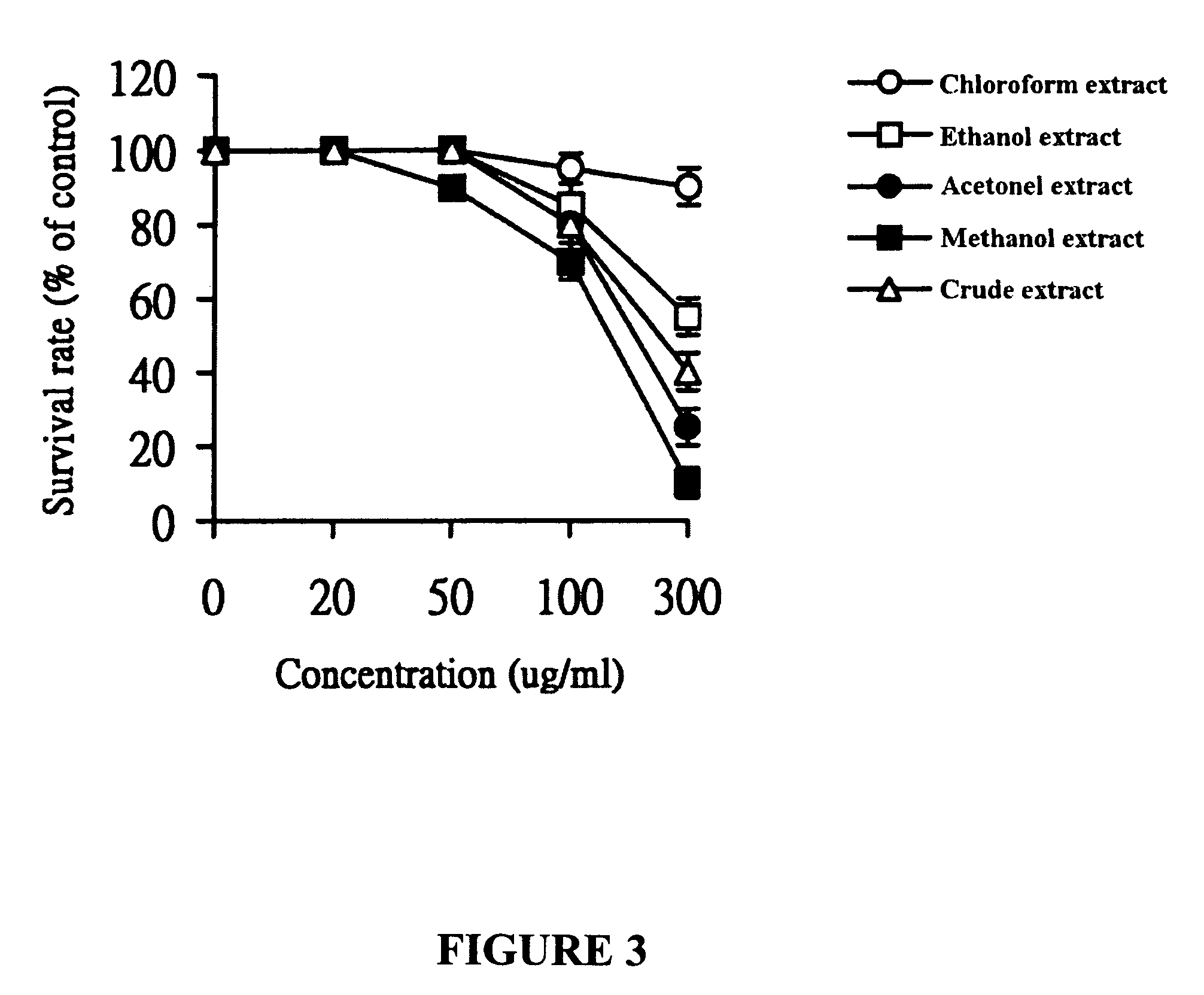
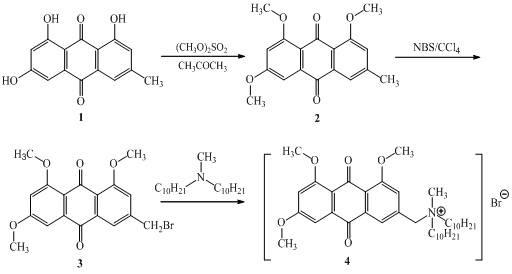
The invention relates to the synthesis of an emodin derivative with anticancer function, in particular to beta-hydroxy protected didecyl quaternary ammonium salt with anticancer activity and a preparation method thereof. The didecyl quaternary ammonium salt is methyl didecyl-[2-(4,5-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-9,10-anthraquinonyl)methyl] ammonium salt and is prepared from emodin serving as a raw materialthrough a series of synthetic reactions. In the invention, the emodin derivative has proliferation inhibiting functions with different degrees for five cancer cells such as liver cancer HepG2, gastric cancer BGC, neuroma SH-SY5Y, gastric cancer AGS and cervical cancer Hela and the normal human embryonic lung fibroblast HELF, and can be used for preparing medicaments for treating cancers.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
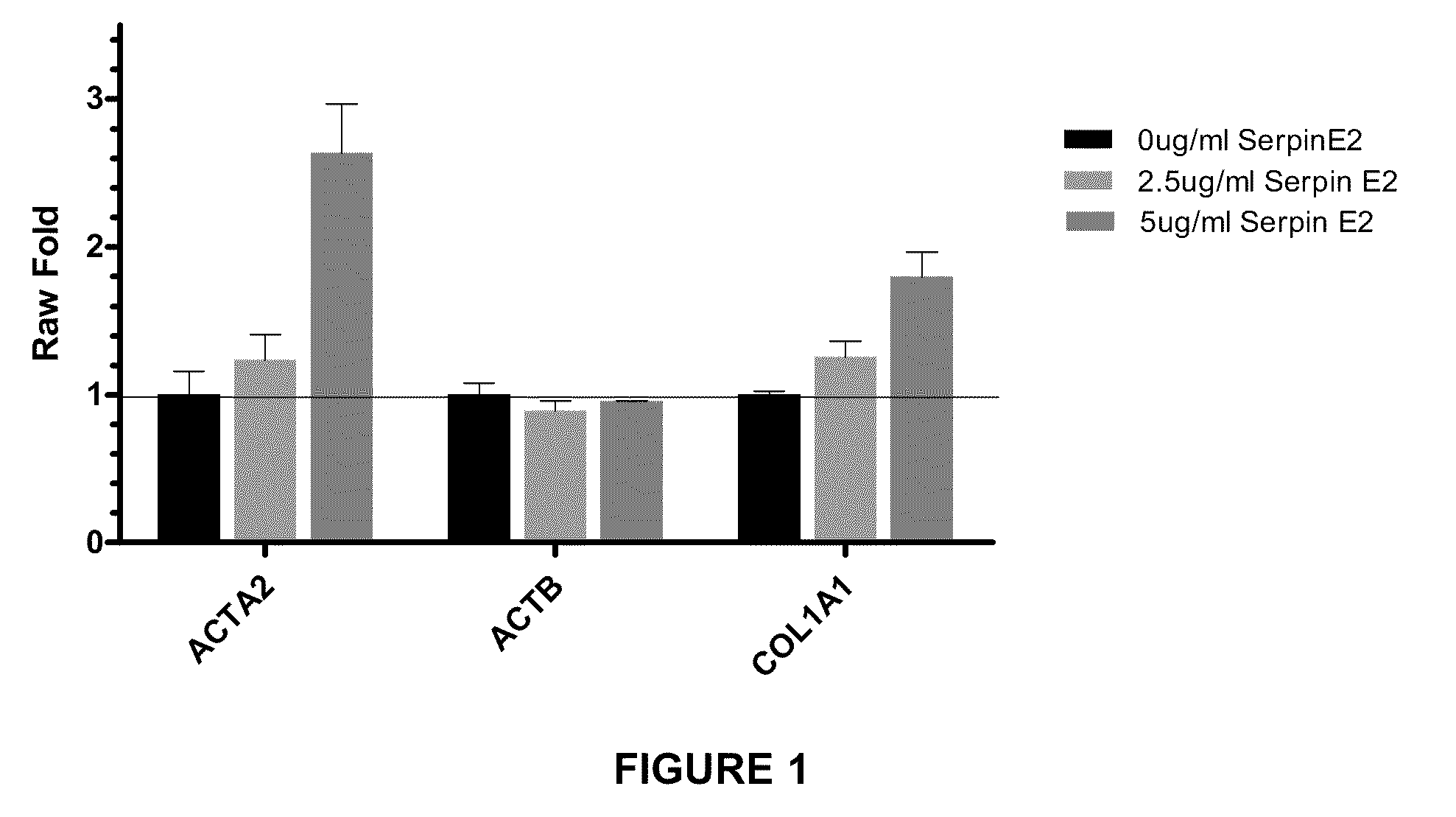
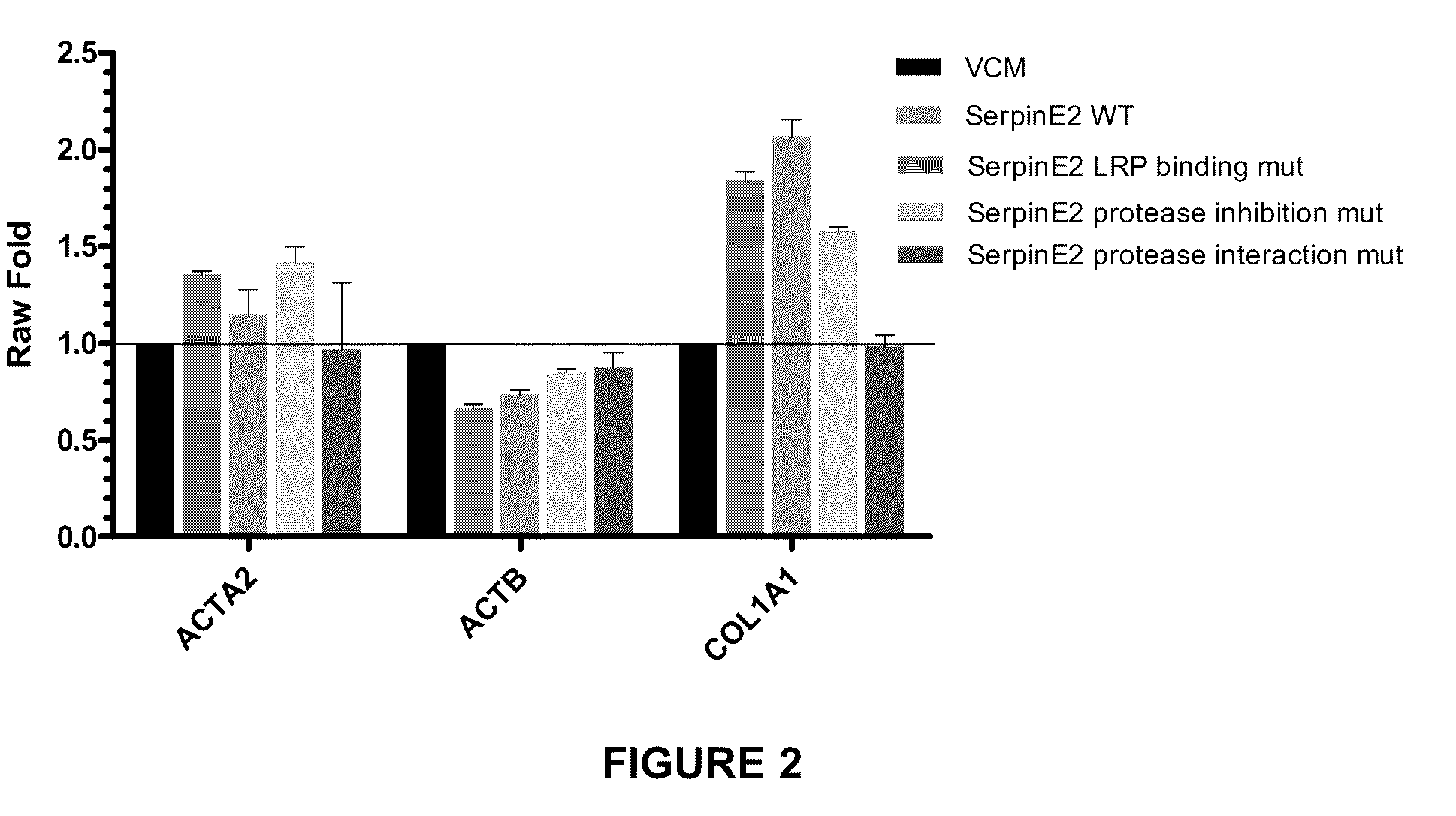
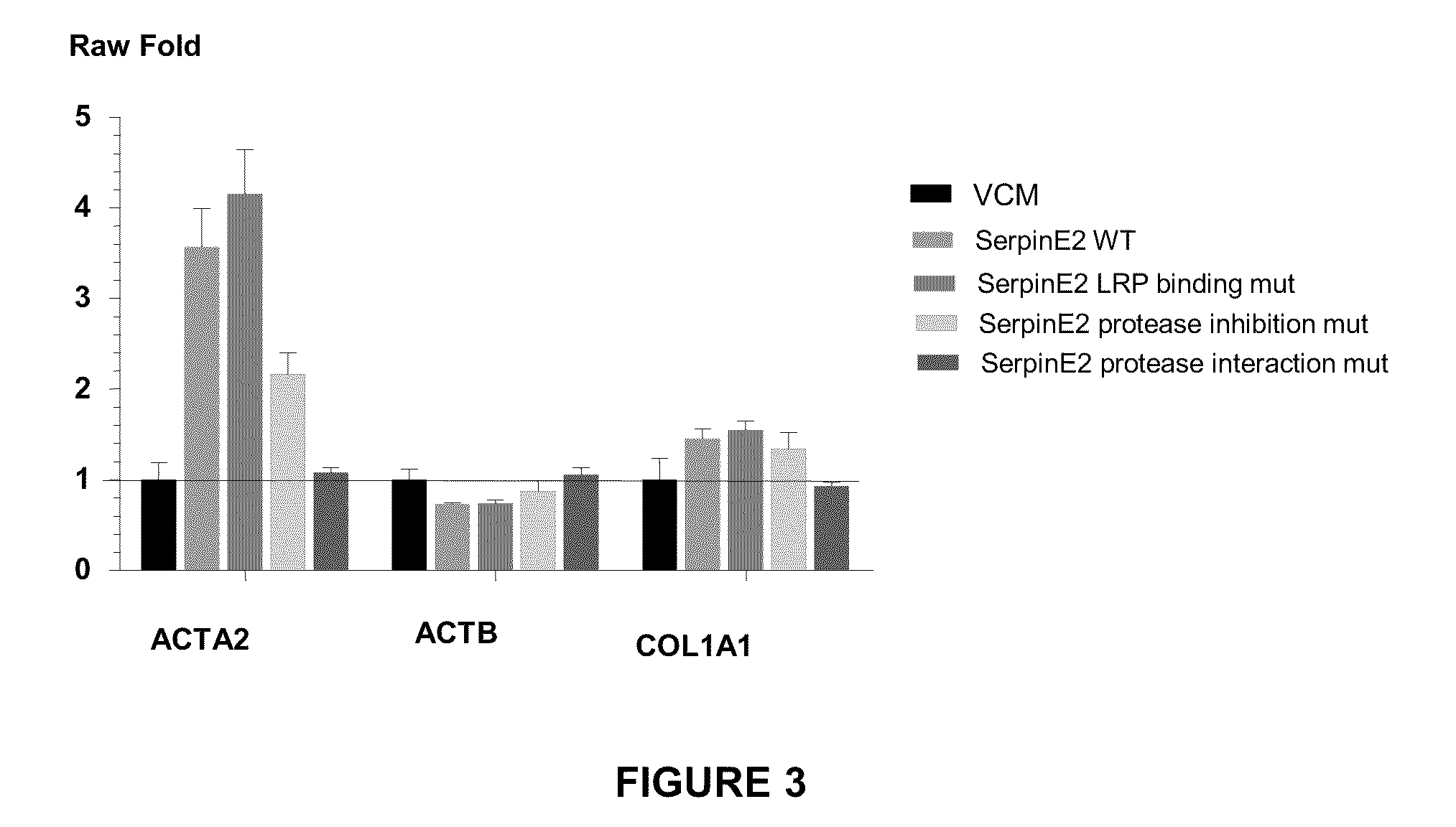
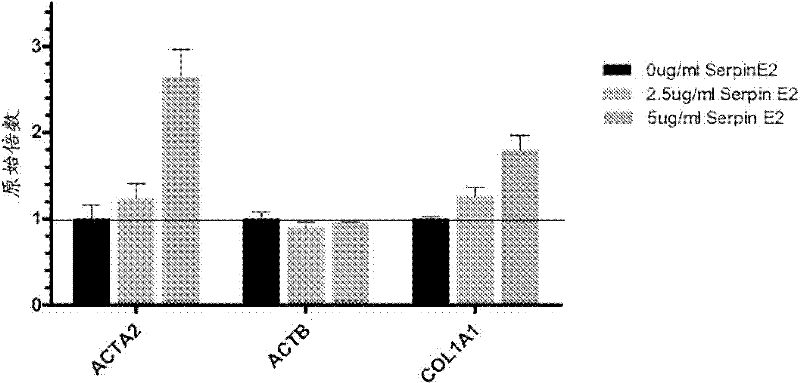
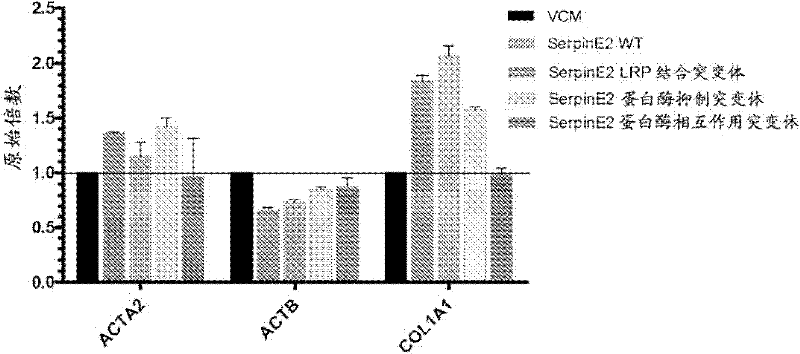
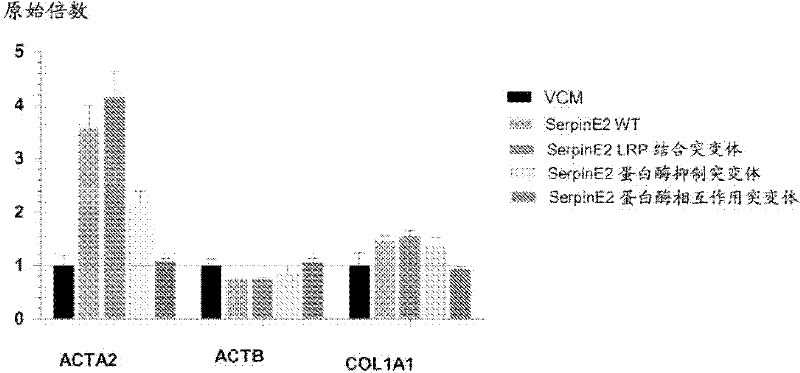
Compositions and methods for regulating collagen and smooth muscle actin expression by serpine2
InactiveUS20100183620A1Reduce expressionReduce formationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesActin
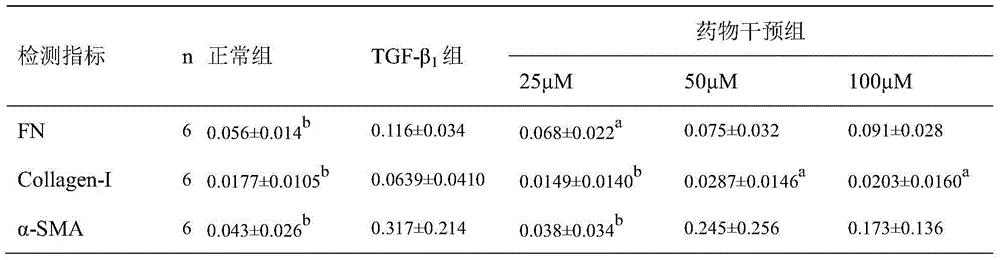
The invention encompasses methods and compositions for increasing or decreasing collagen 1A1 expression and / or α-smooth muscle actin expression in lung fibroblasts using SERPINE2 and antagonists of SERPINE2. The invention also encompasses methods and compositions for increasing or decreasing the formation of myofibroblasts. The invention further provides methods and compositions for treatment of lung diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC +1
Panax notoginseng saponins ST-4, and medicinal composition, preparation and use thereof
ActiveCN101323635AWith preventionTherapeuticOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsPANAX NOTOGINSENG ROOTMedicine
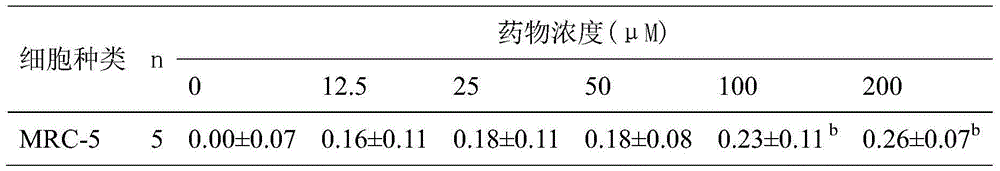
The invention discloses a notoginsenoside ST-4 which is a new dammarane type triterpenoid saponin compound shown in the structural formula (I), and a preparation method thereof. The invention also provides applications of the notoginsenoside ST-4 in the preparation of drugs against HSV-1. An HSV-1 strain and HELF (MRC-5) are used as cell experimental subjects to carry out the experiment of antiviral activity of the new compound which is the notoginsenoside ST-4. The results show that the notoginsenoside ST-4 has therapeutical effect for cells infected by HSV-1 and can reduce the infectivity of HSV-1 for MRC-5 cells and be applied to the preparation of drugs against HSV-1.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
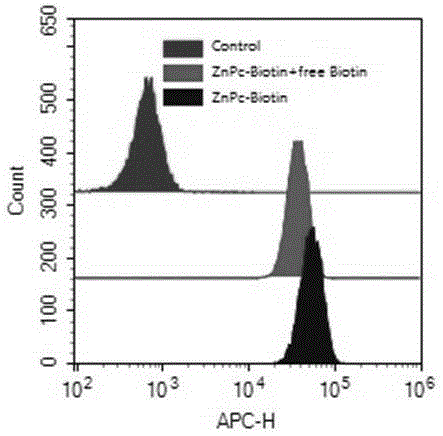
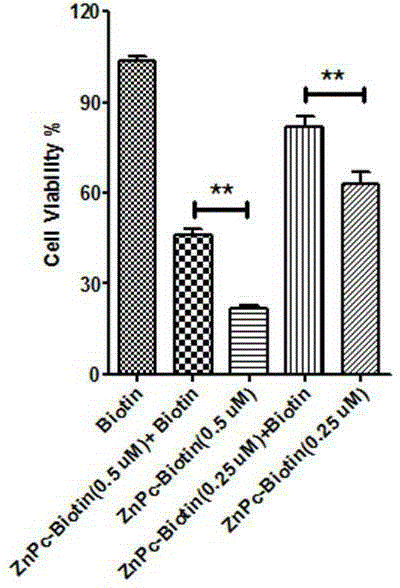
Bilateral biotin-phthalocyanine zinc conjugate as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105418643AEnhance targeted uptakeGood biocompatibilityOrganic chemistry methodsAntineoplastic agentsTarget therapyTargeting therapy
The invention discloses a bilateral biotin-phthalocyanine zinc conjugate as well as preparation and application thereof. According to the conjugate disclosed by the invention, a biotin-cell growth-promoting factor (which is a critical micronutrient for cells to maintain normal functions, growth and reproduction) is used as a tumor target and is covalently connected onto a phthalocyanine zinc photosensitizer capable of being used for a photodynamic therapy, thus obtaining a third-generation anti-cancer photosensitizer for targeted therapy. Meanwhile, according to the conjugate, the biotin instead of a phthalocyanine zinc derivative acts a research object, human breast cancer cell MCF-7 and human embryo lung inoblast HELF act as subject cell lines respectively, a research regarding the in-vitro anti-cancer activity of the biotin is developed, and a prodrug suitable for a molecular targeted therapy is screened out, and a foundation is laid for applying the biotin instead of the phthalocyanine zinc derivative to the targeted therapy of cancers. The compound, namely the conjugate disclosed by the invention, is relatively simple in synthesis method, easily available in raw materials, low in cost, fewer in side reactions, relatively high in yield, easy to purify and beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Human embryo lung fibroblast strain and method for using human embryo lung fibroblast strain for producing hand-foot-mouth viral vaccine
InactiveCN102911910AAvoid Residual EffectsReduced purification stepsAntiviralsEmbryonic cellsEmbryoViral Vaccine
The invention provides a novel human embryo lung diploid fibroblast strain Walvax-2, CCTCCC201055. The cell strain is sensitive to main epidemic disease viral strains-coxsackievirus 16-type COX.A16 in a group A and enterovirus 71-type EV71 second-strain virus of a hand-foot-mouth disease, and virus output is high. The invention further provides a method for preparing a divalent hand-foot-mouth virus inactivated vaccine and application of the human embryo lung diploid fibroblast strain in preparation of the hand-foot-mouth virus inactivated vaccine. The divalent inactivated vaccine produced by the human embryo lung diploid fibroblast strain can effectively prevent hand-foot-mouth disease.
Owner:云南沃森生物技术股份有限公司
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer
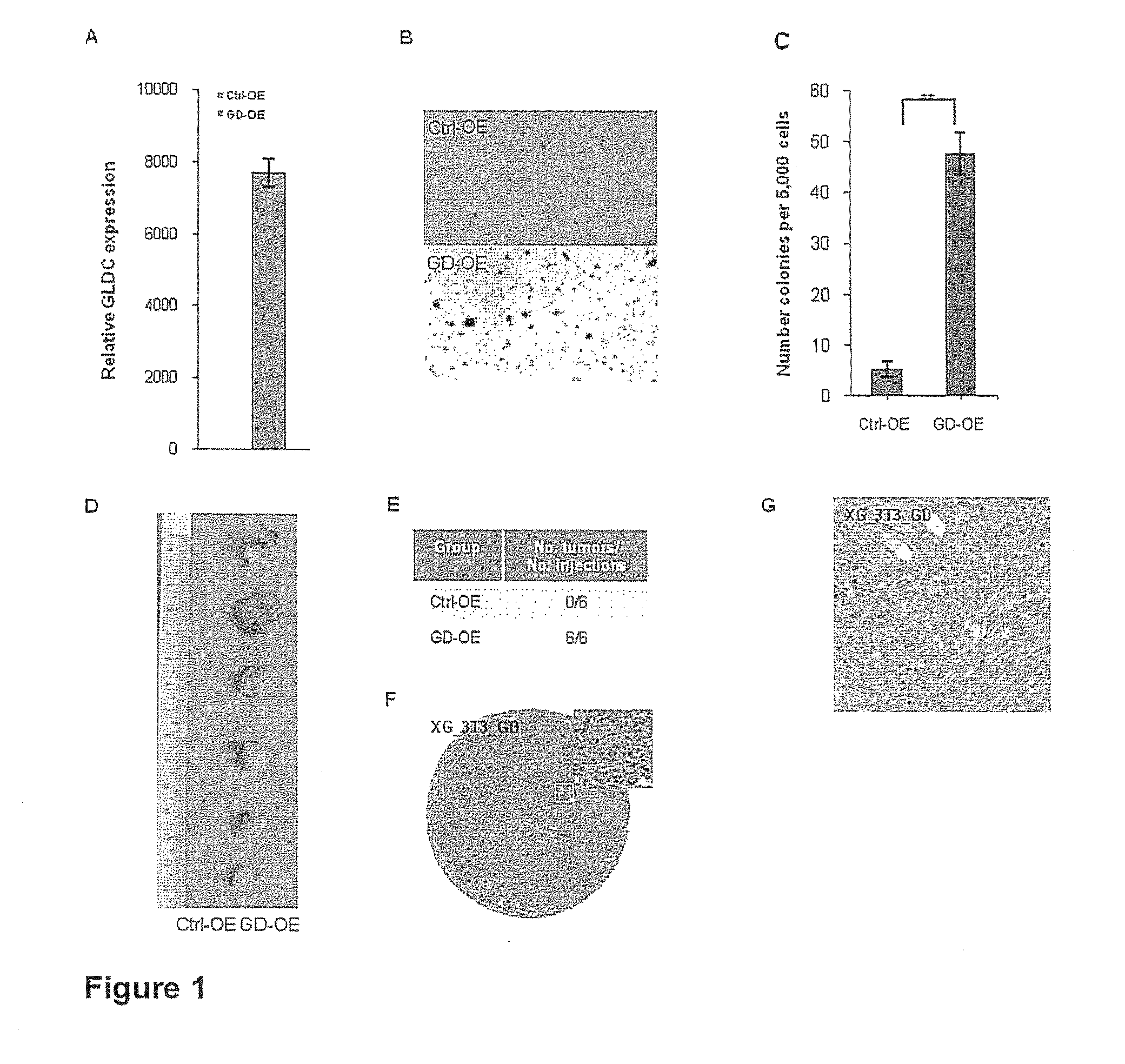
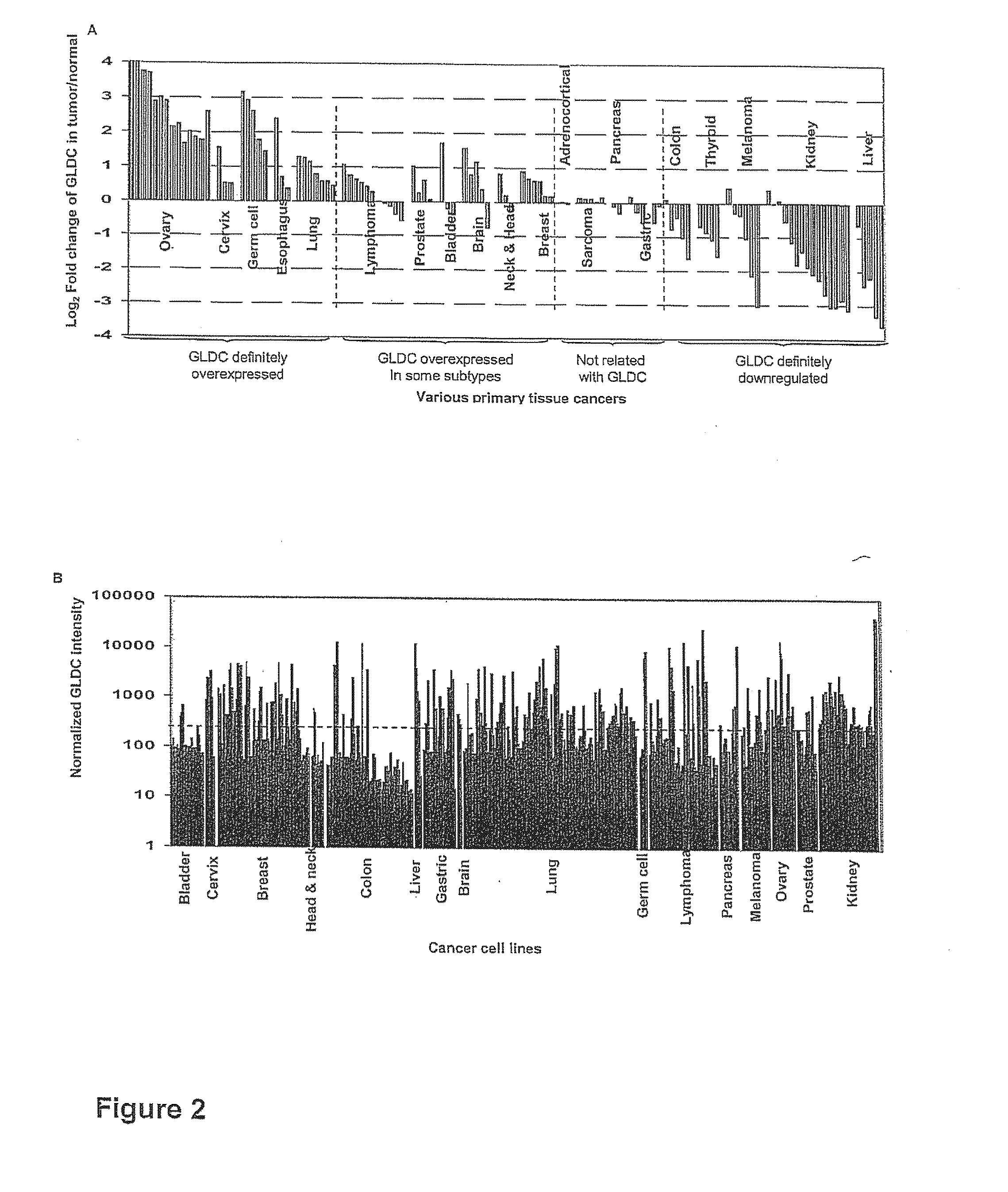
Targeting metabolic enzymes in human cancer Abstract Lung cancer is a devastating disease and a major therapeutic burden with poor prognosis. The functional heterogeneity of lung cancer (different tumor formation ability in bulk of tumor) is highly related with clinical chemoresistance and relapse. Here we find that, glycine dehydrogenase (GLDC), one of the metabolic enzyme involved in glycine metabolism, is overexpressed in various subtypes of human lung cancer and possibly several other types of cancers. GLDC was found to be highly expressed in tumor-initiating subpopulation of human lung cancer cells compared with non-tumorigenic subpopulation. By array studies we showed that normal lung cells express low levels of GLDC compared to xenograft and primary tumor. Functional studies showed that RNAi inhibition of GLDC inhibits significantly the clonal growth of tumor-initiating cells in vitro and tumor formation in immunodeficient mice. Overexpression of GLDC in non-tumorigenic subpopulation convert the cells to become tumorigenic. Furthermore, over-expression of GLDC in NIH / 3T3 cells and human primary lung fibroblasts can transform these cells, displaying anchorage-independent growth in soft agar and tumor-forming in mice. Not only is GLDC is expressed human lung cancer, it is also up-regulated in other types of cancer, such as colon cancer. RNAi knockdown of GLDC in colon cancer cell line, CACO-2 cells, can also inhibit the tumor formation in mice. Thus GLDC maybe a new metabolic target for treatment of lung cancer, and other cancers.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
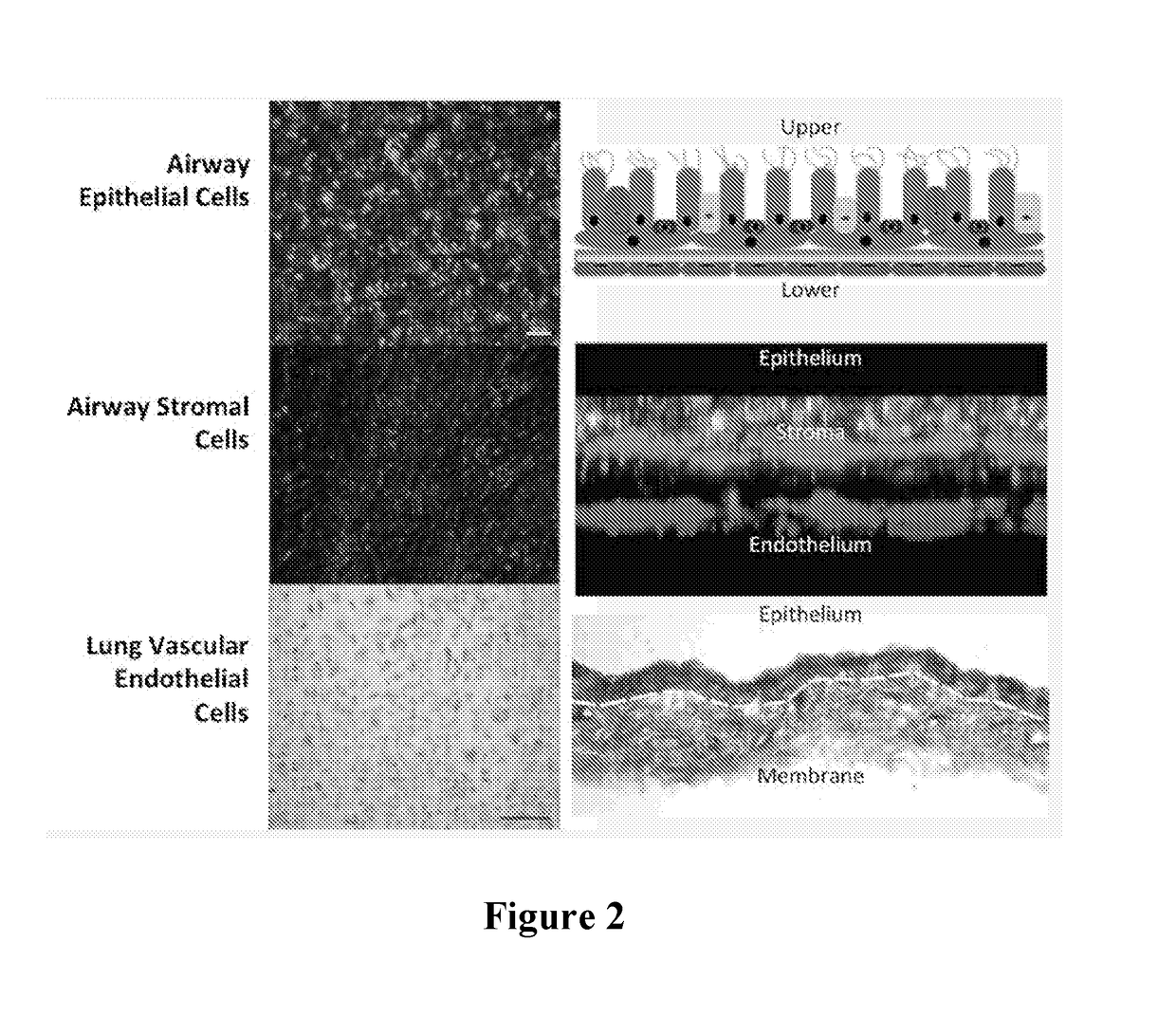
Multi-layer airway organoids and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20180291350A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell layerFibroblast
Provided herein are artificial lung organoids. The artificial lung organoids may include an epithelial cell layer comprising mammalian lung epithelial cells, a stromal cell layer comprising mammalian lung fibroblast cells and an endothelial cell layer comprising mammalian endothelial cells. The artificial lung organoids may optionally include a porous membrane between said epithelial cell layer and said stromal cell layer and / or between said stromal cell layer and said endothelial lung cell layer.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Japanese encephalitis vaccine prepared by human embryonic lung fibroblasts and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101524536AFully identifiedFully standardizedViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsImmune effectsJapanese encephalitis vaccine
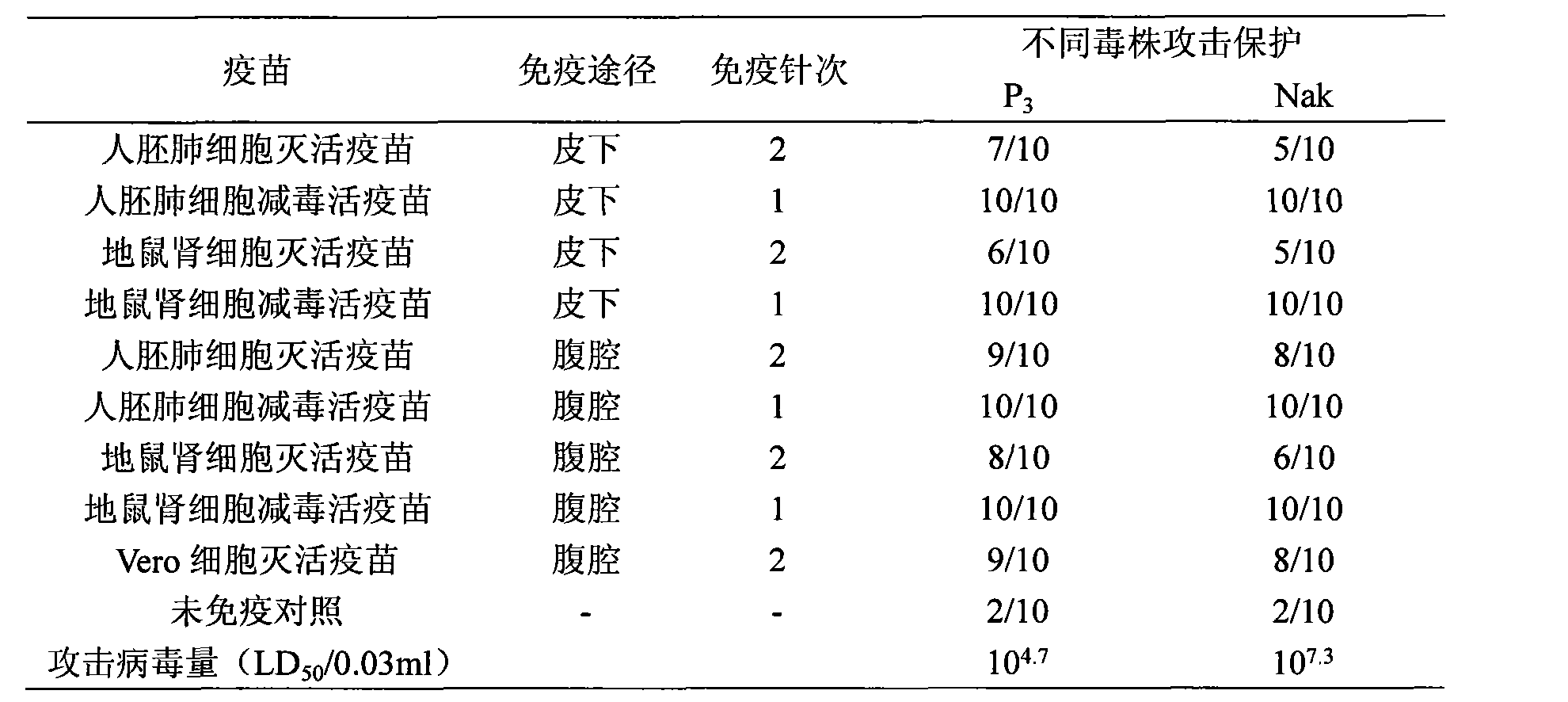
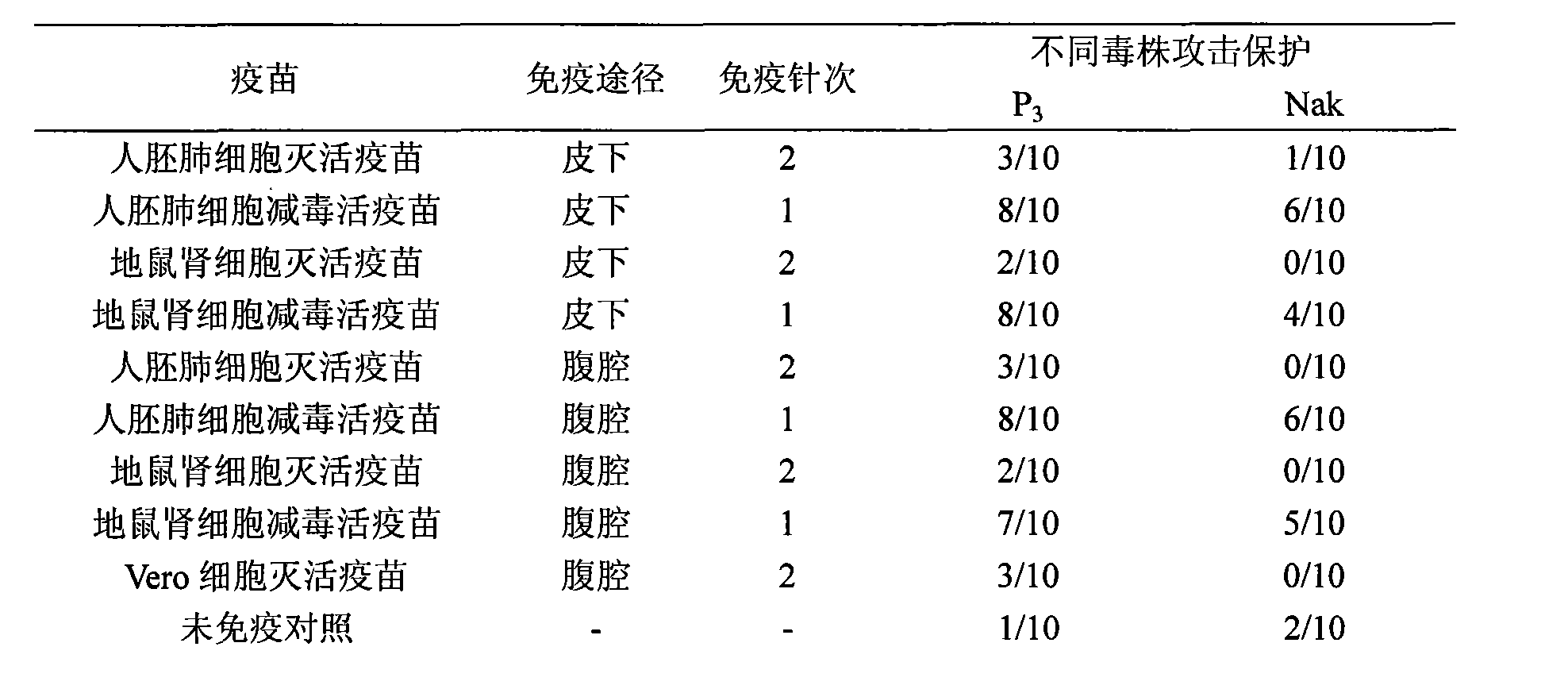
The invention discloses a Japanese encephalitis vaccine prepared by human embryonic lung fibroblasts and a preparation method thereof, comprising culture and expansion of the human embryonic lung fibroblasts. The method comprises the following steps: Japanese encephalitis virus strain P3, strain SA14-14-2 or strain Nakayama is naturalized and inoculated to fit the human embryonic lung fibroblasts, and the seeds of Japanese encephalitis viruses are prepared on the human embryonic lung fibroblasts; wherein, an inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine also comprises the steps of harvesting viruses, inactivating viruses, concentrating, purifying and the like; an attenuated live vaccine also comprises the steps of harvesting viruses, concentrating, purifying and the like. Due to being prepared by healthy human embryonic lung fibroblasts, the two kinds of Japanese encephalitis vaccines do not contain any adventitious pollution agent and tumorigenicity, has high purity after being purified and has the advantages of good immune effect and high security. The preparation method of the invention is suitable for large-scale industrial production and can meet the preparation processes of Japanese encephalitis vaccines required by domestic and abroad markets.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHUA BIOLOGICAL PROD
Ursolic acid derivative with anti-cancer activity and preparation method thereof
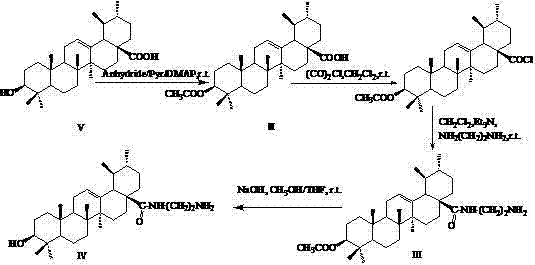
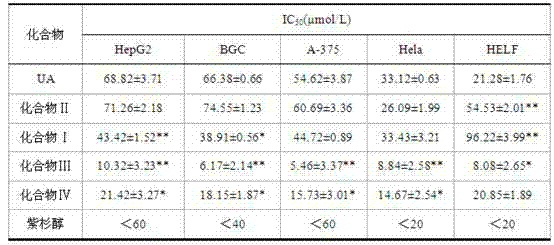
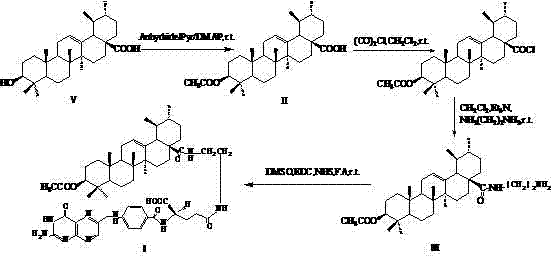
InactiveCN102516351AGood antitumor effect in vitroTargetedSteroidsAntineoplastic agentsUrsolic acidEthylenediamines
The invention provides an ursolic acid derivative, which is N-[3beta-acetoxy-ursa-12- alkene-28-acyl]-aminoethylenediamine-folic acid. A natural product ursolic acid is structurally transformed to obtain N-[3beta-acetoxy-ursa-12- alkene-28-acyl]-aminoethylenediamine-folic acid (I), N-[3beta-acetoxy-ursa-12-alkene-28-acyl]-aminoethylenediamine (III) and N-[3beta-acetoxy-ursa-12- alkene-28-acyl]-aminoethylenediamine (IV). The in vitro cell proliferation inhibition test shows that the proliferation inhibition effect of the compounds I, III and IV on tested tumor cell lines HepG2, of BGC823, A-375, Hela and the like is superior to that of the ursolic acid, and the toxic effect of the compounds I, III and IV on human embryonic lung fibroblasts (HELF) is lower than that of the ursolic acid. The in vitro anti-tumor effect of the compound III is the best, and the compound I has certain targeting.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Methods and materials relating to stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides and polynucleotides
InactiveUS20030022825A1Minimize side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymologyCDNA librarySpinal cord
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides and mutants or variants thereof that correspond to a novel human and mouse secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptide. These polynucleotides comprise nucleic acid sequences isolated from cDNA libraries prepared from mouse bone marrow and human fetal liver spleen, ovary, adult brain, lung tumor, spinal cord, cervix, ovary, endothelial cells, umbilical cord, placental, lymphocyte, lung fibroblast, fetal brain, and testis. Other aspects of the invention include vectors containing processes for producing novel human secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides, and antibodies specific for such polypeptides.
Owner:KIRIN PHARMA +1
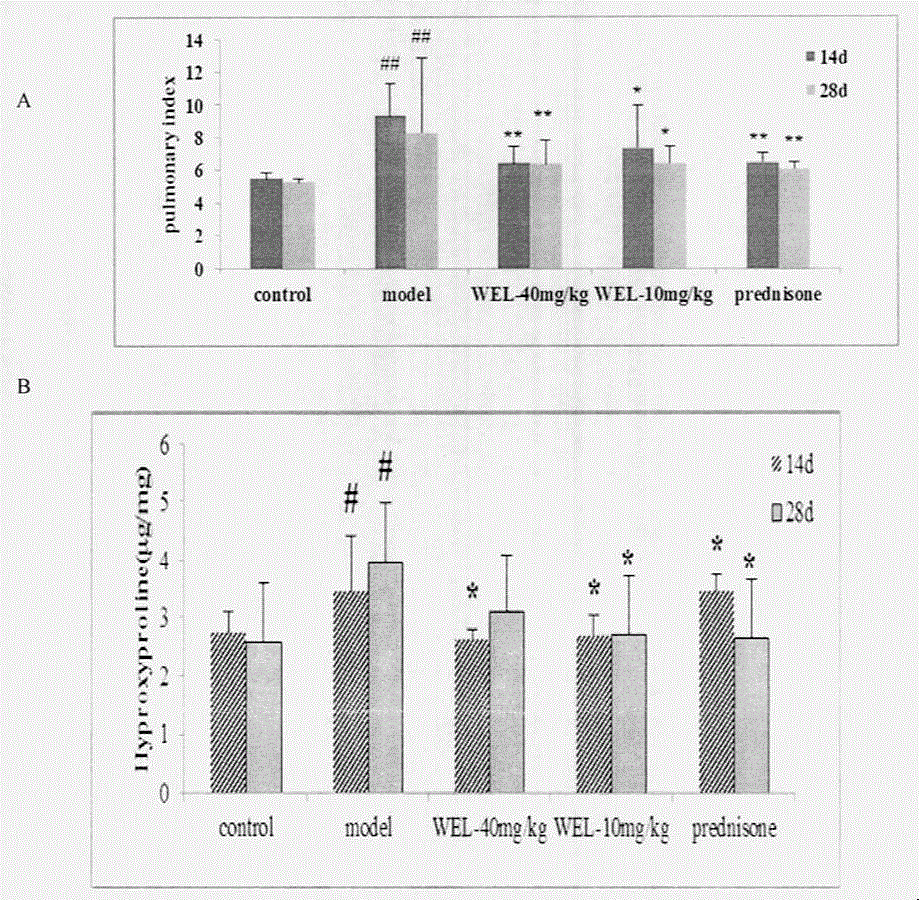
Application of wedelolactone in preparation of anti-pulmonary fibrosis drug
ActiveCN103816148AEnhance pharmacological effectsHas liver protectionRespiratory disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsWedelolactoneHydroxyproline
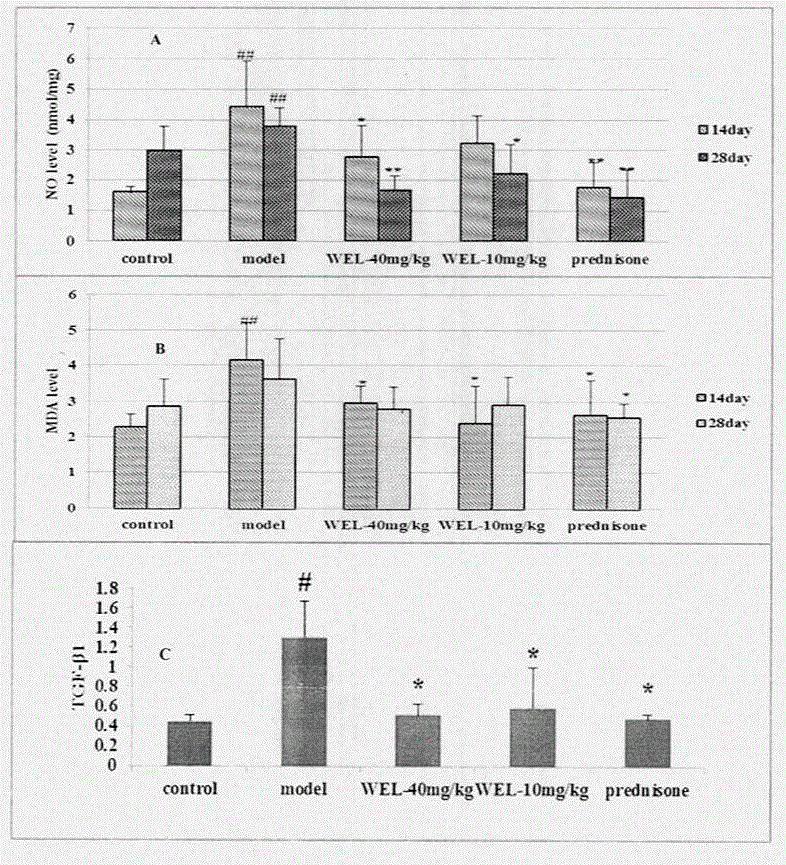
The invention relates to a drug application of a chemical substance wedelolactone for treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. The chemical substance wedelolactone is derived from a traditional Chinese medicine eclipta, and the structure is determined through spectral data; the wedelolactone can significantly improve the degree of model mouse lung tissue pulmonary fibrosis after intragastric administration, reduce NO (Nitrogen Oxide) and MDA (Methylene dioxyamphetamine) contents reflecting degree of lung injury, HYP (Hydroxyproline) content reflecting collagen deposition in the lung tissues, and cell factor TGF-beta 1 (Transforming Growth Factor) content causing pulmonary fibrosis, and inhibit human embryo lung fibroblast proliferation in vitro and HYP content of the human embryo lung fibroblast. In-vivo and in-vitro experiments show that wedelolactone can obviously improve bleomycin induced mouse pulmonary fibrosis, so that the wedelolactone can be taken as a novel drug for treating pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Application of hesperidin in preparation of medicament for preventing and/or treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases
InactiveCN104906120APrevent proliferationInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDiseaseBiological activation
The invention discloses an application of hesperidin in preparation of a medicament for preventing and / or treating pulmonary fibrosis diseases. By virtue of experimental verification, the hesperidin can achieve an effect of preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting lung fibroblast proliferation, inhibiting epithelium-mesenchyme conversion of alveolar epithelial cells and inhibiting lung fibroblast activation, so that the hesperidin can achieve a new application in preparation of the medicament for preventing and / or treating the pulmonary fibrosis diseases. The application relates to various medicament dosage forms such as capsules, drop pills, aerosol preparations, spraying agents, tablets, granules and injections prepared from the hesperidin. Moreover, the application also relates to a composition, which is formed by taking the hesperidin as a main component, for preventing and treating the pulmonary fibrosis.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Hydroxyl whole-protection didecyl quaternary ammonium with anti-tumor activity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101941914AEfficient killingOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBiologyMethyl palmoxirate
The invention relates to synthesis of an emodin derivant with an anti-tumor function, in particular to a hydroxyl whole-protection didecyl quaternary ammonium with anti-tumor activity and a preparation method thereof. The didecyl quaternary ammonium is decyldimethylchlorosilane-[2-(4,5,7-trimethoxy-9,10-anthraquinonyl)methyl]. The preparation method is characterized by taking emodin as a raw material to carry out a series of synthetic reaction. The emodin derivant of the invention has proliferation inhibition action of different degrees on liver cancer HepG2, gastric cancer BGC, neuroma SH-SY5Y, gastric cancer AGS, cervical cancer Hela and the like as well as normal human embryonic lung fibroblast HELP and can be used for preparing medicines for treating cancers.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Novel proteins and methods for producing the proteins
InactiveUS20030153048A1Efficient productionSure easyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsCulture mediums
A protein which inhibits osteoclast differentiation and / or maturation and a method of production of the protein. The protein is produced by human embryonic lung fibroblasts and has molecular weight of about 60 kD and about 120 kD under non-reducing conditions and about 60 kD under reducing conditions on SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, respectively. The protein can be isolated and purified from culture medium of the said fibroblasts. Furthermore, the protein can be produced by gene engineering. The present invention includes cDNA for producing the protein by gene engineering, antibodies having specific affinity to the protein or a method for determination of the protein concentration using the antibodies.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Application of human embryonic lung fibroblast strains in preparation of rabies inactivated vaccine
InactiveCN103468650ACharacteristics of typical human diploid cells cultured in vitroEasy to shapeMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsAntigenImmune effects
The invention discloses an application of human embryonic lung fibroblast strains Walvax-2 in the preparation of a rabies inactivated vaccine. The human embryonic lung fibroblast strains Walvax-2 are susceptible to rabies viruses, and when the human embryonic lung fibroblast strains are used for producing the rabies virus vaccine, the diploid cell rabies virus inactivated purified vaccine for people can be obtained, wherein the vaccine is high in antigen purity, good in immune effect, high in safety and low in price.
Owner:云南沃森生物技术股份有限公司
Application of danshinolic acid B in preparation of medicine of treating scleroderma
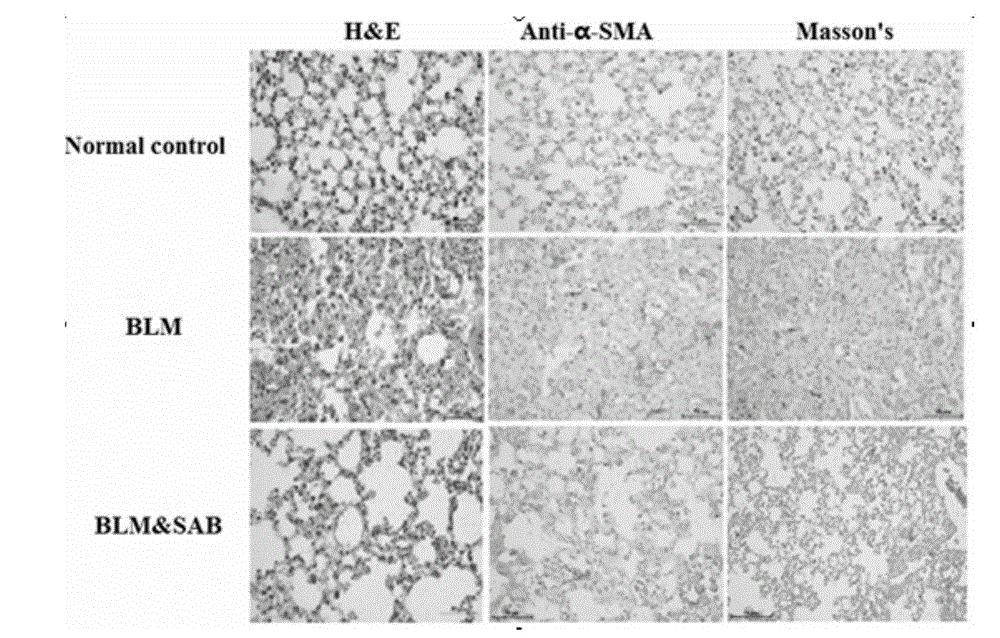
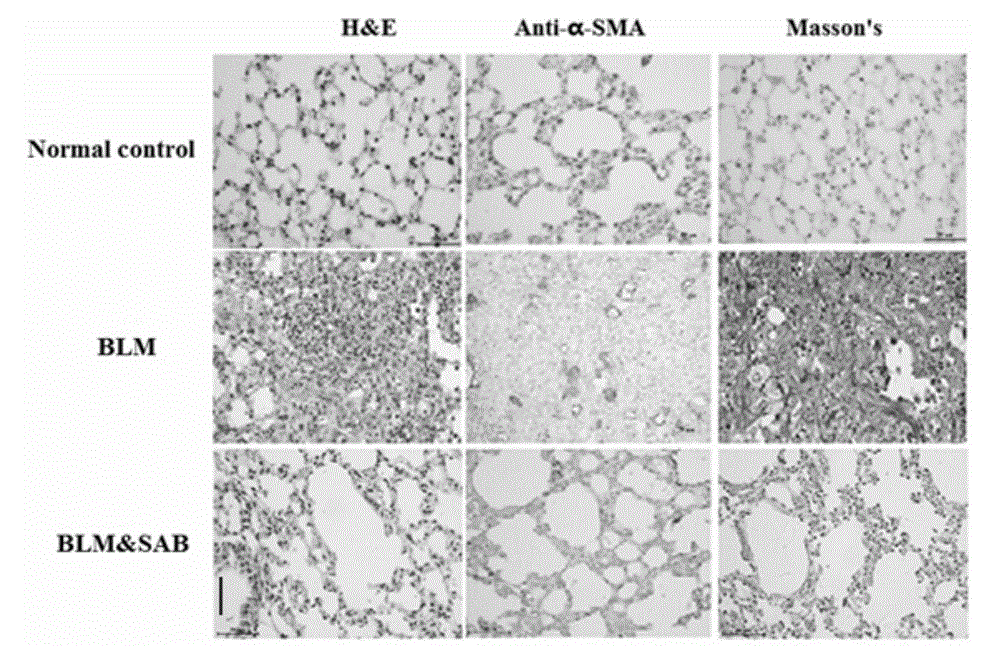
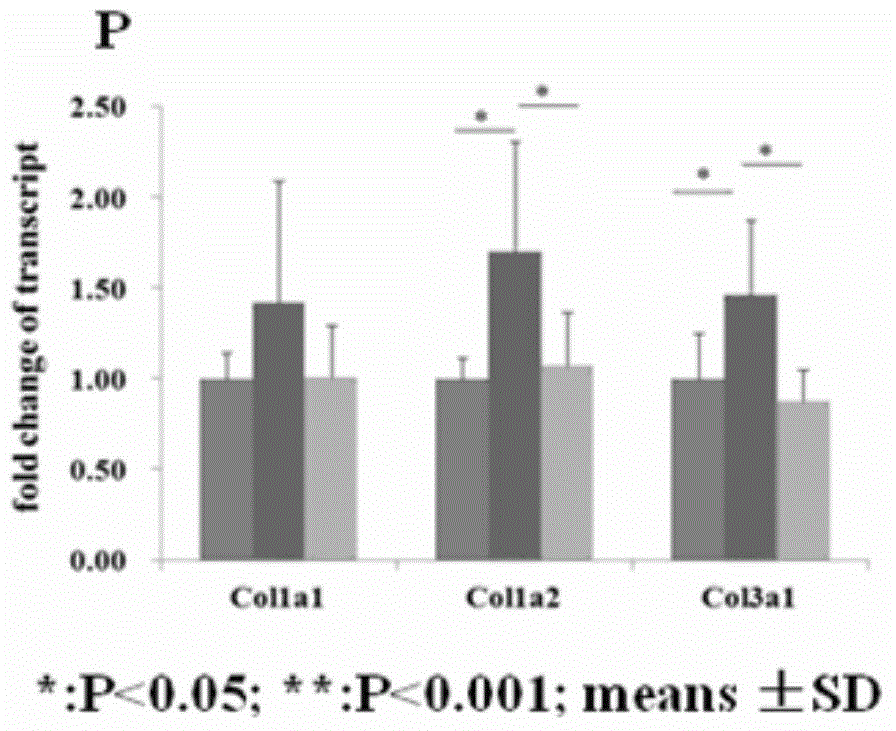
InactiveCN104546821AInhibit inflammationPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticSalvianolic acid BMedicine
The invention relates to the field of chemical engineering in a hospital, particularly relates to a new application of a small molecule compound, and further particularly relates to an application of a small molecule compound danshinolic acid B in preparation of a medicine of treating scleroderma. The invention provides an application of danshinolic acid B in preparation of a medicine of treating scleroderma, and further provides a corresponding medicine composition and a medicine preparation. The inventor of the invention makes an animal experiment, which shows that a compound SAB remarkably relieves the pulmonary fibrosis of a mice suffering from the scleroderma, and a further cell experiment indicates that the small molecule compound can inhibit cell inflammation induced by TNFalpha, and can inhibit the skin flbroblast of a patient suffering from the scleroderma cultured in vitro, human embryonic lung fibroblast proliferation and collagen expression, and inhibit transformation of pulmonary epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells. The application shows that the compound has a function of resisting fibrosis of the scleroderma, and has a good application prospect for preventing and treating the scleroderma.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Anti-human-cytomegalovirus drug screening method and application thereof
PendingCN108642121AIncrease the number ofEasy to storeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionFibroblastScreening method
The invention relates to an anti-human-cytomegalovirus (HCMV) drug screening method and application thereof. The anti-human-cytomegalovirus (HCMV) drug screening method is characterized in that mitochondrial content in human embryonic lung fibroblasts can be induced to increase using the HCMV, a significant correlation exists between increase of the mitochondrial content and amplification of the HCMV, an inhibition ratio of drugs to the mitochondrial increment induced by the HCMV is calculated by measuring a variation of the mitochondrial content, and the anti-HCMV effect of the drugs is effectively reflected. The anti-human-cytomegalovirus (HCMV) drug screening method has the characteristic of being easy to operate, flexible in detecting, sensitive in reaction and accurate in result.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HOSPITAL
Methods and materials relating to stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides and polynucleotides
InactiveUS20030211987A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCDNA librarySpinal cord
The invention provides novel polynucleotides and polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides and mutants or variants thereof that correspond to a novel human secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptide. These polynucleotides comprise nucleic acid sequences isolated from cDNA libraries prepared from human fetal liver spleen, ovary, adult brain, lung tumor, spinal cord, cervix, ovary, endothelial cells, umbilical cord, lymphocyte, lung fibroblast, fetal brain, and testis. Other aspects of the invention include vectors containing processes for producing novel human secreted stem cell growth factor-like polypeptides, and antibodies specific for such polypeptides.
Owner:KIRIN PHARMA
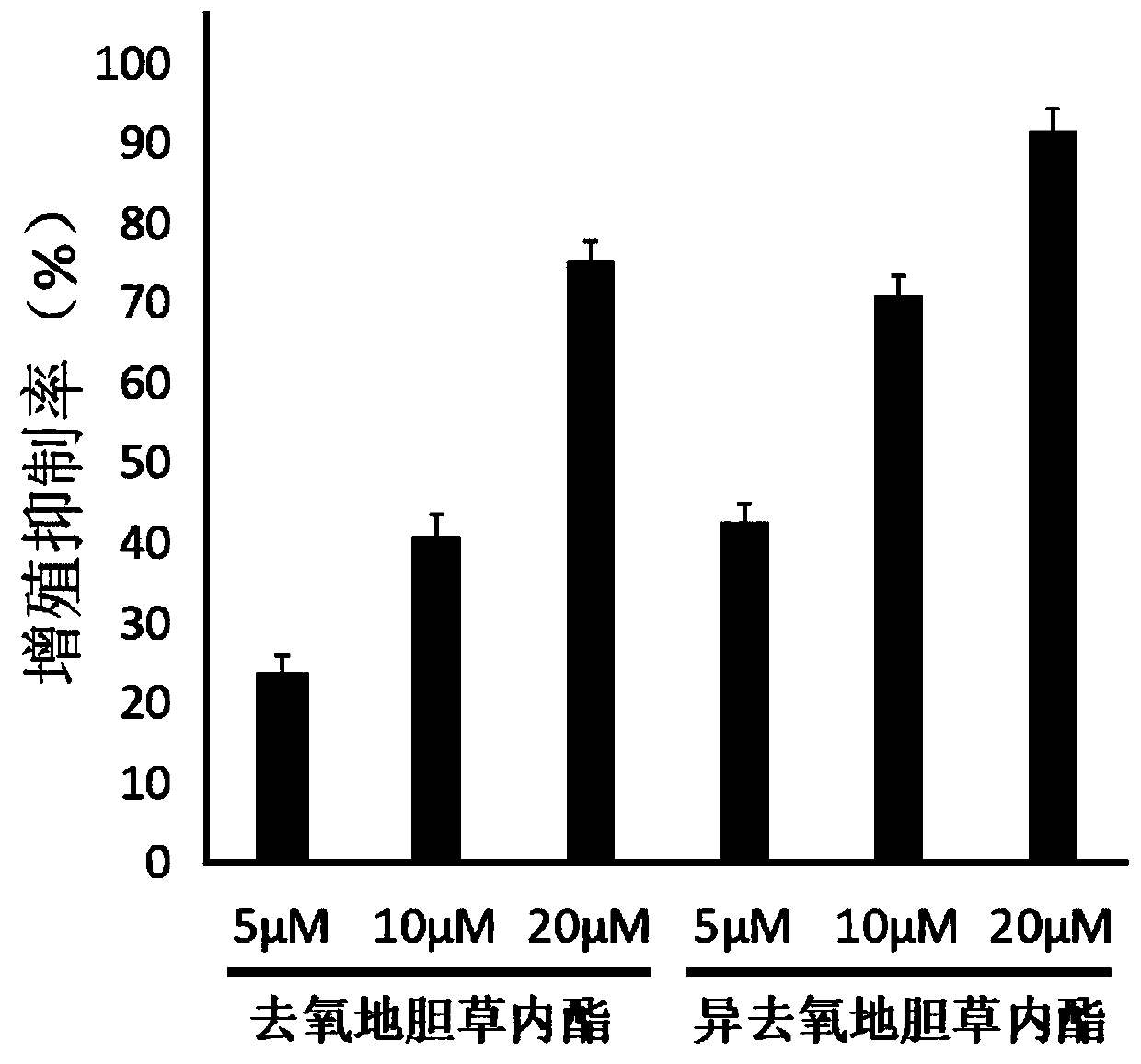
Application of deoxyelephantolide or isodeoxyelephantolide in preparation of a medicine used for resisting lung fibrosis
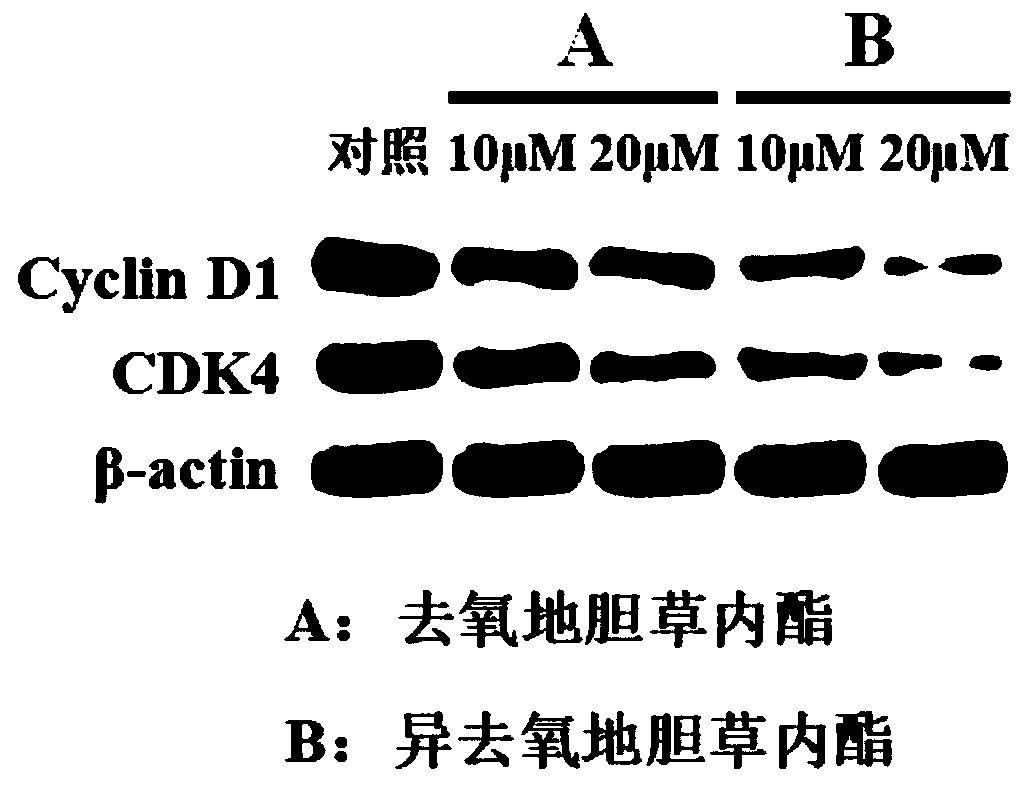
ActiveCN111084773ADivide and proliferateProliferation inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderCell divisionCyclin D1
The invention discloses an application of deoxyelephantolide or isodeoxyelephantolide in preparation of a medicine used for resisting lung fibrosis. Researches find that the deoxyelephantolide or theisodeoxyelephantolide can be used for effectively inhibiting the proliferation of human embryonic lung fibroblasts HFL1. Western Blot results show that the proliferation inhibition effect of the deoxyelephantolide or the isodeoxyelephantolide on human embryonic lung fibroblasts HFL1 is likely to be related with the situation that the human embryonic lung fibroblasts is blocked in a G1 phase and can not realize cell division and proliferation through down regulation of the expression of cyclin D1 and CDK4. Therefore, the deoxyelephantolide or the isodeoxyelephantolide has the prospect of beingdeveloped into the medicine used for resisting the lung fibrosis.
Owner:仁合熙德隆药业有限公司
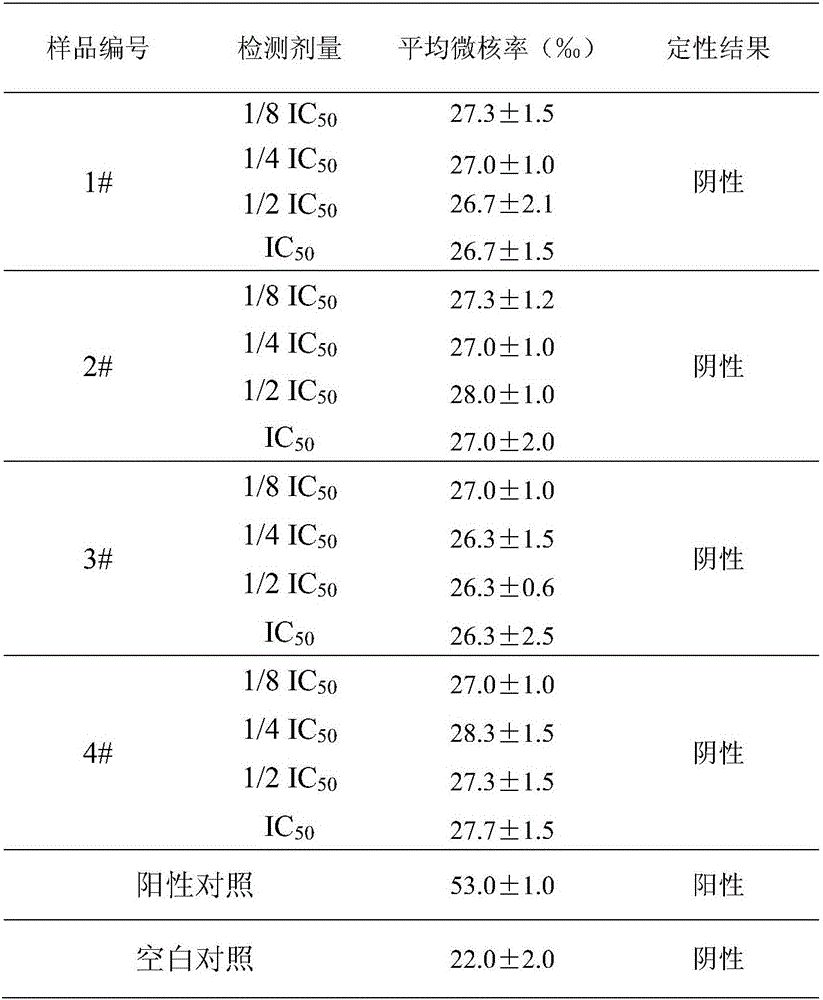
Method for detecting influence of electronic cigarette product on micronucleus rate of cells
ActiveCN106546722AEasy to handleAccurate and effective detectionBiological testingTest sampleFibroblast
The invention discloses a method for detecting the influence of an electronic cigarette product on the micronucleus rate of cells. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing test samples, preparing a human lung fibroblast single cell suspension fluid, calculating the concentration of the human lung fibroblast single cell suspension fluid, inoculating the human lung fibroblast single cell suspension fluid, dividing the test samples into groups, setting the detection dosages of the test samples, preparing a test sample culture medium, subjecting the test sample culture medium to low permeability, and preparing a droplet slice of the test sample culture medium. The using characteristics and effect modes of electronic cigarette products are taken into account, an electronic cigarette product sample preprocessing method is established; according to the electronic cigarette product acted target cells, human lung fibroblast is taken as the cell for the cytotoxicity tests of electronic cigarette products, the sample detection dosage is determined at the same time, and thus an in-vitro micronucleus test method suitable for the electronic cigarette products is established.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
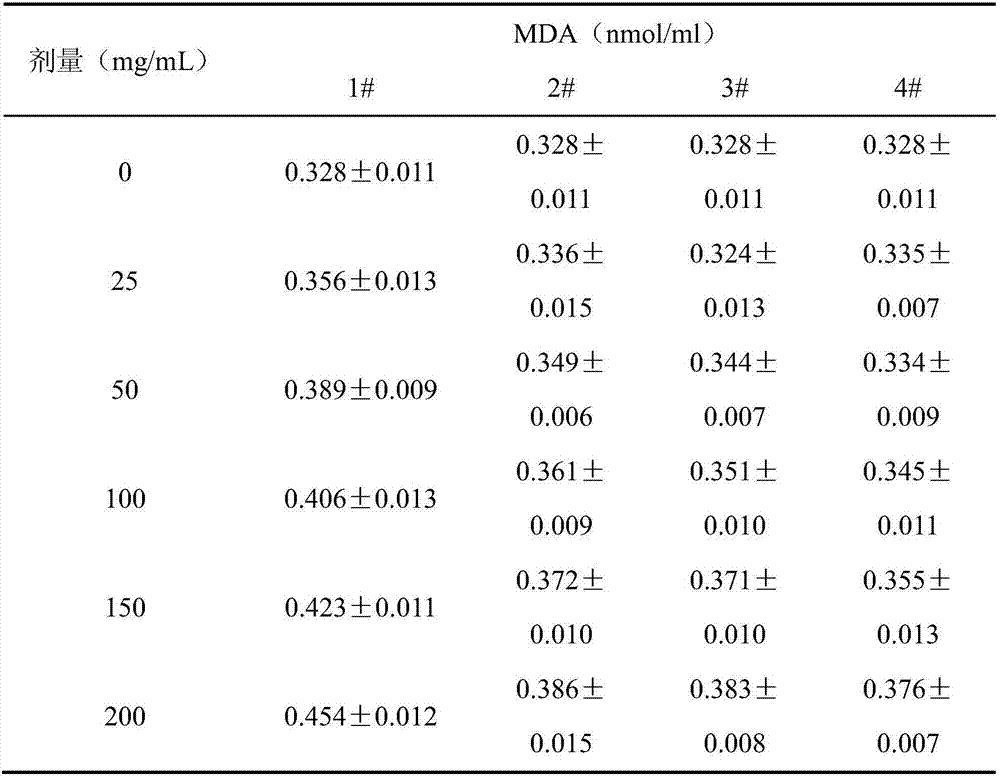
Method for detecting influence of electronic cigarette product to peroxidating of cell lipid
InactiveCN107460227AEasy to handleAccurate and effective peroxidation effectMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTest sampleSingle cell suspension
The invention discloses a method for detecting influence of an electronic cigarette product to peroxidating of cell lipid. The method comprises the following steps: pretreatment of test samples, preparation of human lung fibroblasts single-cell suspension, calculating of concentration of cells of the human lung fibroblasts single-cell suspension, cell inoculation of the human lung fibroblasts single-cell suspension, grouping of the test samples, setting of detection dosage of the test samples, preparation of cultured products of the test samples, incubation of the test samples, collection of incubated products of the test samples, cracking and centrifuging of the incubated products of the test samples, calculation of the content of malonyldialdehyde and the like. By effective treatment to samples, optimal setting on the detecting dosage and correct selection of target cells, the method can accurately and effectively detect the influence of the electronic cigarette product to peroxidating of the cell lipid.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
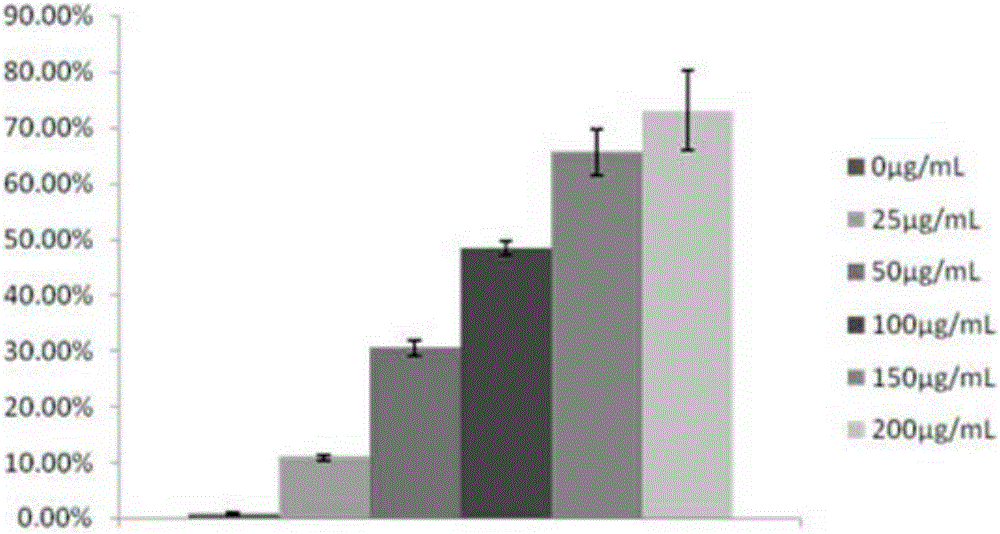
Method of detecting influence on early apoptosis of cells due to total particulate matters in cigarette smoke
InactiveCN106591413AAccurate and effective detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisCytotoxicitySingle cell suspension
The invention discloses a method of detecting influence on early apoptosis of cells due to total particulate matters in cigarette smoke. The method includes the steps of: 1) pre-treating to-be-detected substances; 2) preparing a human lung fibroblast single cell suspension liquid; 3) calculating cell concentration of the human lung fibroblast single cell suspension liquid; 4) performing cell inoculation to the human lung fibroblast single cell suspension liquid; 5) grouping the to-be-detected samples; 6) setting detection dose of the to-be-detected samples; 7) preparing a to-be-detected sample culture substance; 8) incubating the to-be-detected samples; 9) collecting incubated products of the to-be-detected samples; and 10) calculating influence ratio of early apoptosis of cells. Through optimization of sample detection dose and correct selection on target cells, the method can accurately and effectively detect the influence on early apoptosis of cells due to the total particulate matters in cigarette smoke. As a complementary method for cytotoxicity detection for the total particulate matters in cigarette smoke, the method distinguishes the influence between necrocytosis and cell apoptosis of the product.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Compositions and methods for modulating collagen and smooth muscle actin expression by serpine2
InactiveCN102292101APeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderSmooth muscleIdiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
The invention encompasses methods and compositions for increasing or decreasing collagen 1A1 expression and / or α-smooth muscle actin expression in lung fibroblasts using SERPINE2 and antagonists of SERPINE2. The invention also encompasses methods and compositions for increasing or decreasing the formation of myofibroblasts. The invention further provides methods and compositions for treatment of lung diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:五佳医疗股份有限公司 +1
Application of pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc in killing staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN102755647AAvoid damageEasy to makeAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityBacteroides
The invention relates to an application of pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc in killing staphylococcus aureus. The pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc are taken as the main component for killing staphylococcus, and a phosphate buffer solution and a medical surfactant are added as auxiliary agents to prepare a drug for killing staphylococcus aureus. The drug has the advantages that the main component has a definite structure with the purity reaching more than 98 percent, and has a good water solubility; the drug can be specially combined with cell membranes of bacteria, is low in use concentration, and has small toxicity on human embryonic lung fibroblast and skin; and when the concentration of the pentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc is greater than 5 mu M, as long as a light source with excitation wavelength of 670 nm is used to radiate for 2 minutes, more than 99.99 percent of staphylococcus aureus can be killed. Thepentamer lysinephthalocyanine zinc has a good application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of human fetal lung fibroblast line in preparation of hepatitis A vaccines
ActiveCN103525770AIncrease productionImproving immunogenicityMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsAntigenHepatitis A vaccine
The invention discloses an application of a human diploid fibroblast line Walvax-2 in the preparation of hepatitis A vaccines. The human diploid fibroblast line is susceptible to hepatitis A viruses. A human diploid cell hepatitis A virus purifying vaccine having the advantages of high antigen purity, good immunization effect, high security and low price can be obtained by adopting the Walvax-2 to produce the hepatitis A vaccines.
Owner:云南沃森生物技术股份有限公司
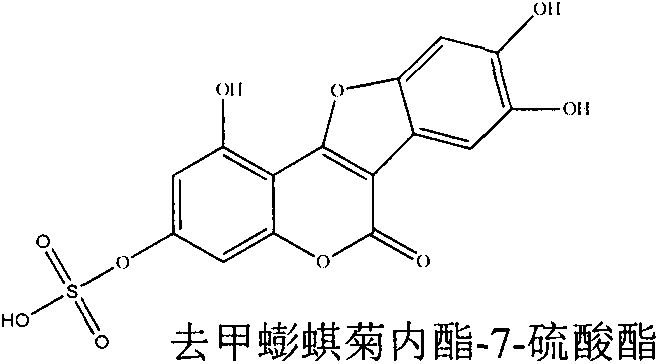
Application of demethylwedelolactone-7-sulfate in preparation of anti-pulmonary fibrosis drug
InactiveCN103919769AGood interventionClear pharmacological activityRespiratory disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsDiseaseHydroxyproline
The invention relates to application of demethylwedelolactone-7-sulfate in preparation of an anti-pulmonary fibrosis drug. The compound demethylwedelolactone-7-sulfate is obtained from traditional Chinese medicine herba ecliptae for the first time and the structure of demethylwedelolactone-7-sulfate is determined through NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) and other wave spectrum data, the in-vivo and in-vitro pharmacological experiments prove that the demethylwedelolactone-7-sulfate can obviously inhibit the proliferation of TGF-beta1 induced human embryo lung fibroblasts and the HYP (hydroxyproline) content, the inflammation and fibrosis degree of lung tissue in bleomycin induced mice pulmonary fibrosis model can be reduced after the anti-pulmonary fibrosis drug is orally taken at a dosage of the 5-30mg / kg, the content of MDA (methylene dioxyamphetamine) reflecting the lung injury degree in lung tissues is influenced, the content of HYP reflecting the collagen deposition of lung tissue can be reduced, the content of cell factor TGF-beta1 causing pulmonary fibrosis can be reduced, and the like, so that the pharmacological action for improving the pulmonary fibrosis degree can be achieved. The demethylwedelolactone-7-sulfate has new applications as a drug for treating or improving pulmonary fibrosis disease.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for detecting influence of total particulate matters in cigarette smoke on reactive oxygen secretion of cells
InactiveCN106520904AEasy to handleAccurate and effective detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnosticsPositive controlOxygen
The invention discloses a method for detecting the influence of total particulate matters in cigarette smoke on reactive oxygen secretion of cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment of to-be-detected total particulate matters in cigarette smoke; (2) preparation of monoplast suspension of human lung fibroblasts; (3) calculation of the cell concentration of the monoplast suspension of human lung fibroblasts; (4) cell inoculation of the monoplast suspension of human lung fibroblasts; (5) grouping of the to-be-detected total particulate matters in cigarette smoke; (6) setting of the detection dosages of the to-be-detected total particulate matters; (7) preparation of cultivated to-be-detected total particulate matters; (8) incubation of the to-be-detected total particulate matters; (9) addition of positive controls; (10) probe loading; (11) sample determination; and (12) calculation of reactive oxygen species. Through effective treatment of samples, optimization of the detection dosages and correct selection of target cells, the method is capable of accurately and effectively detecting the influence of the total particulate matters in cigarette smoke on reactive oxygen species in cells.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com