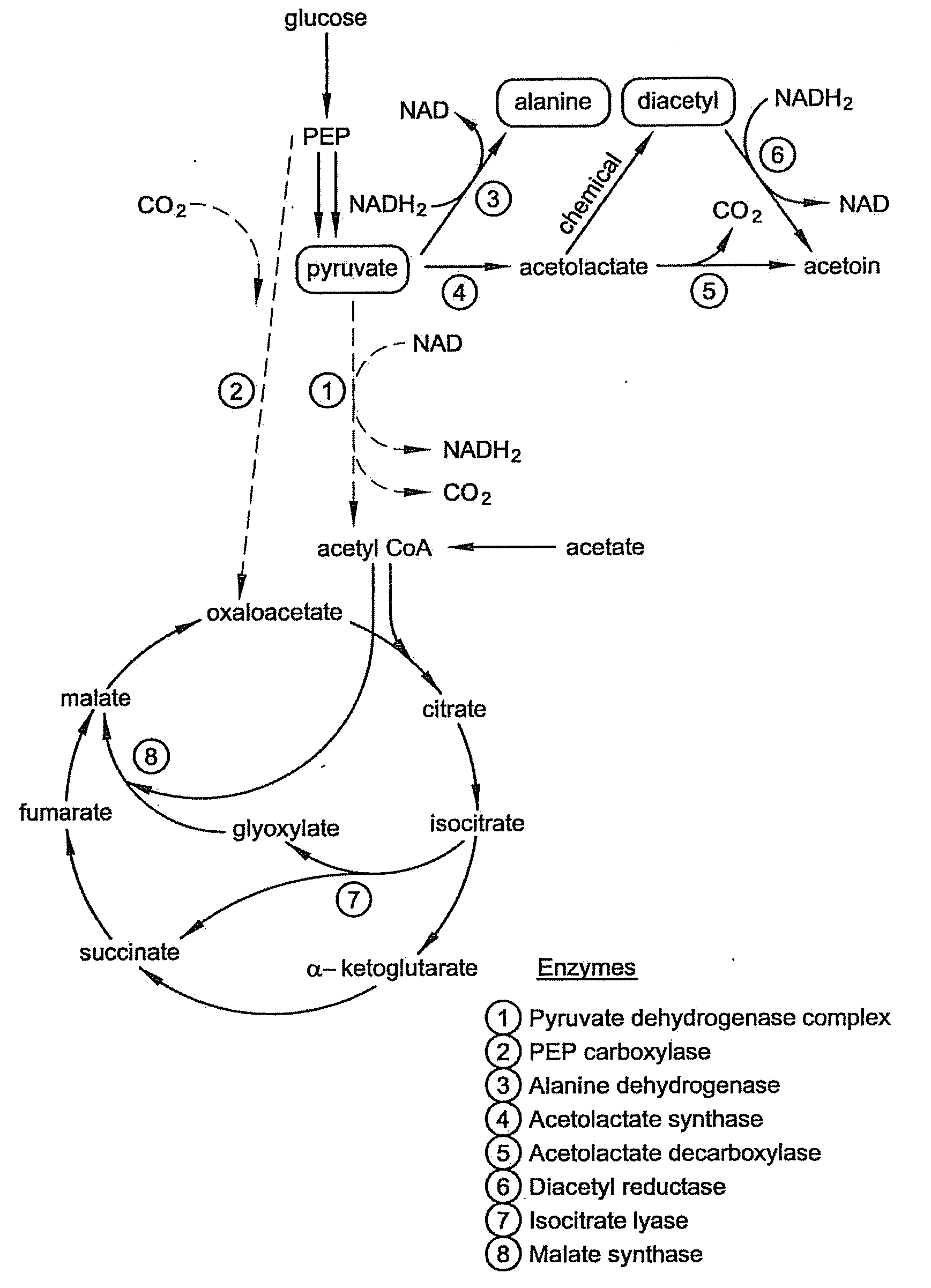
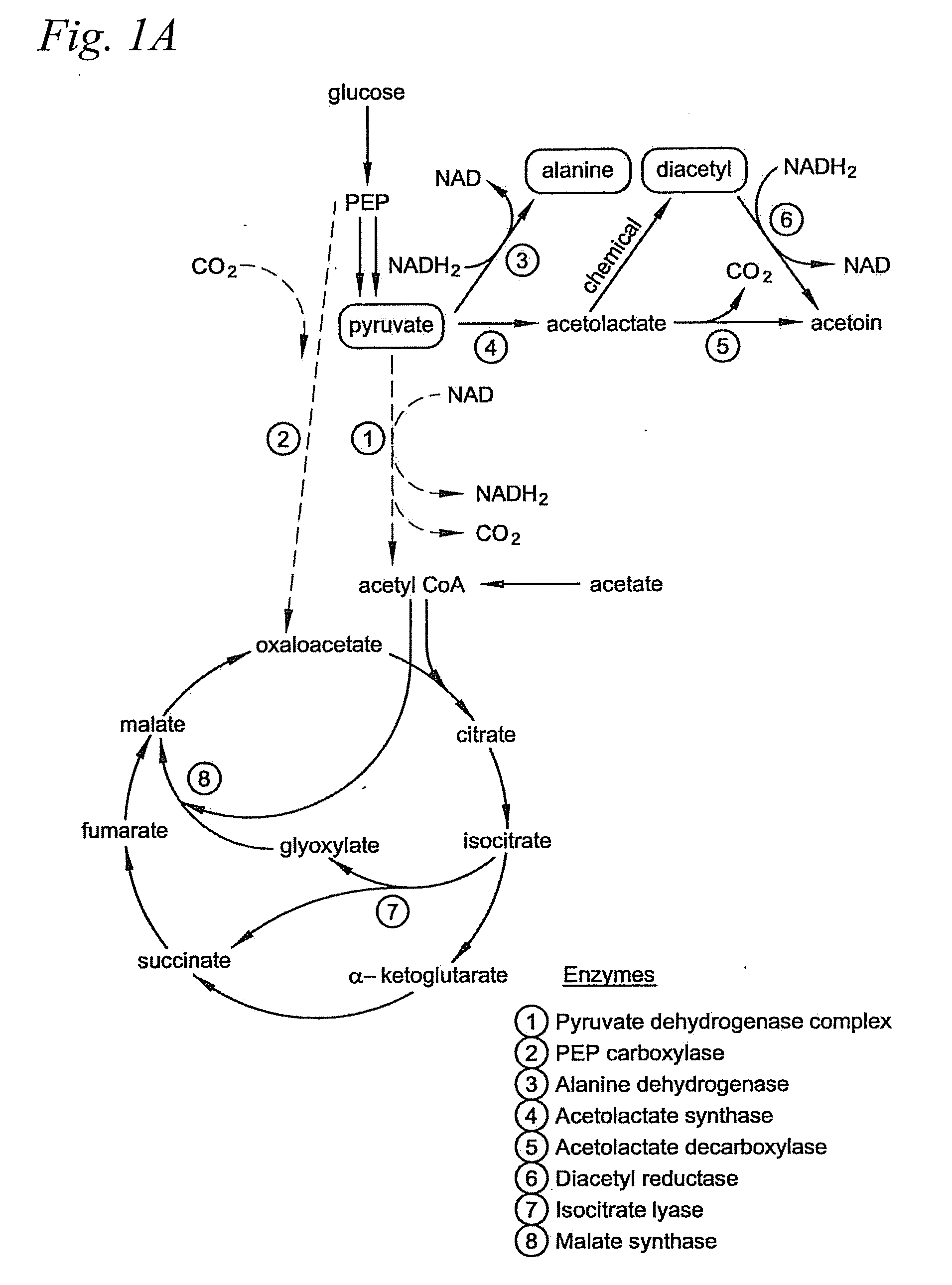
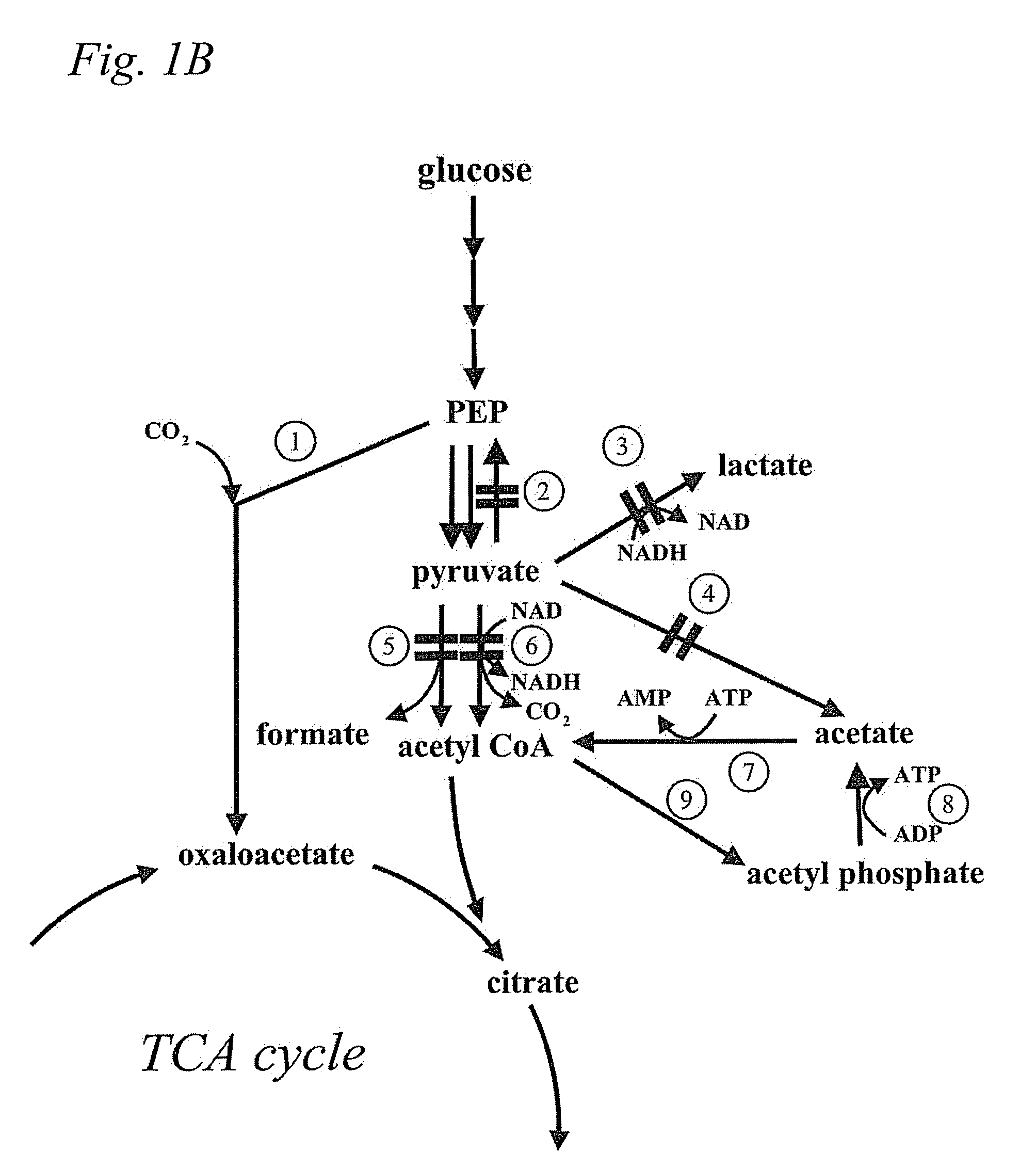
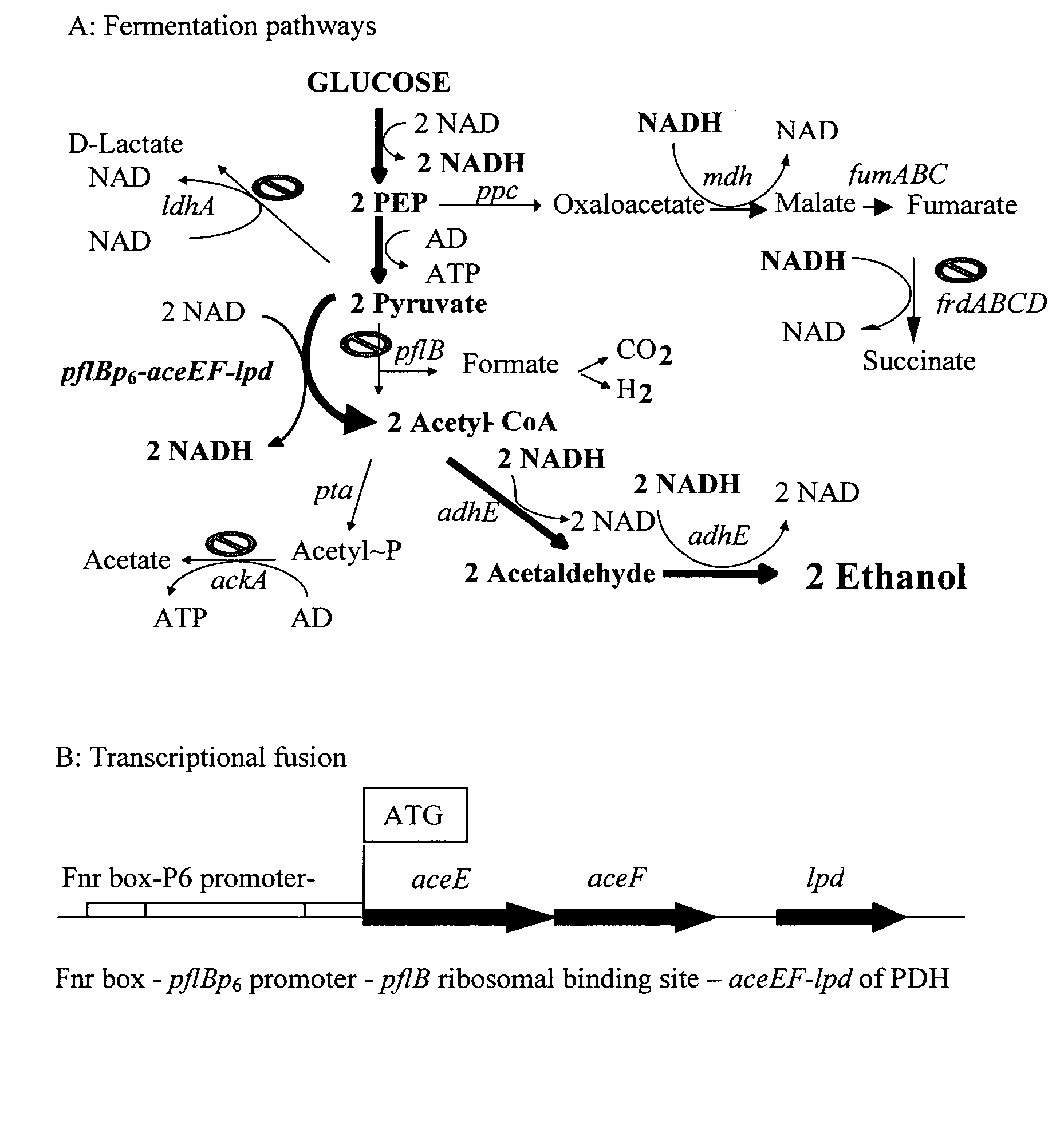
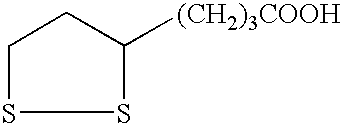
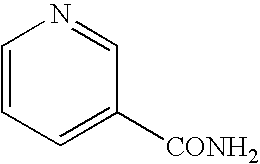
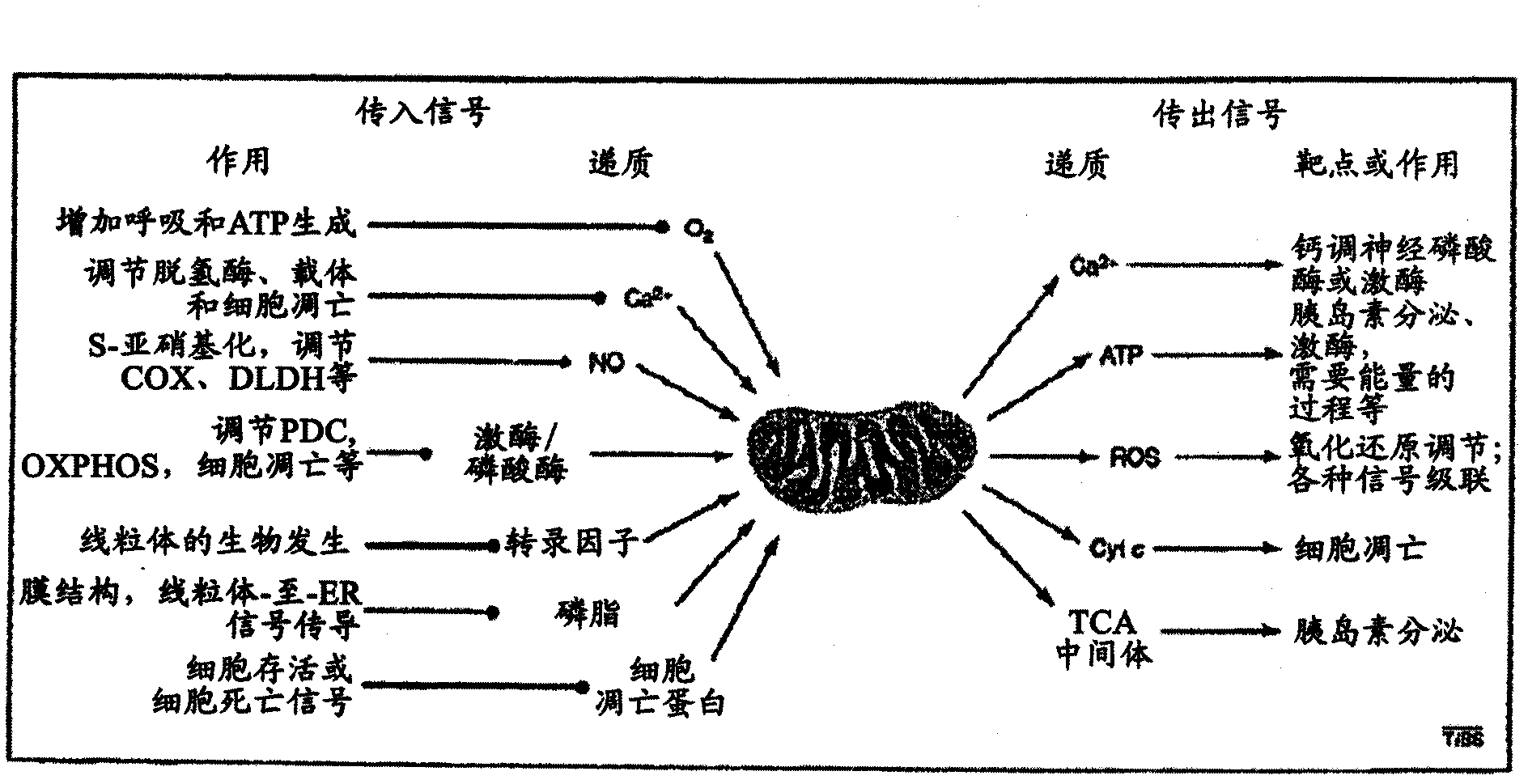
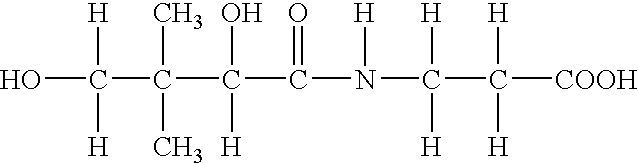Patents
Literature
155 results about "Pyruvic dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
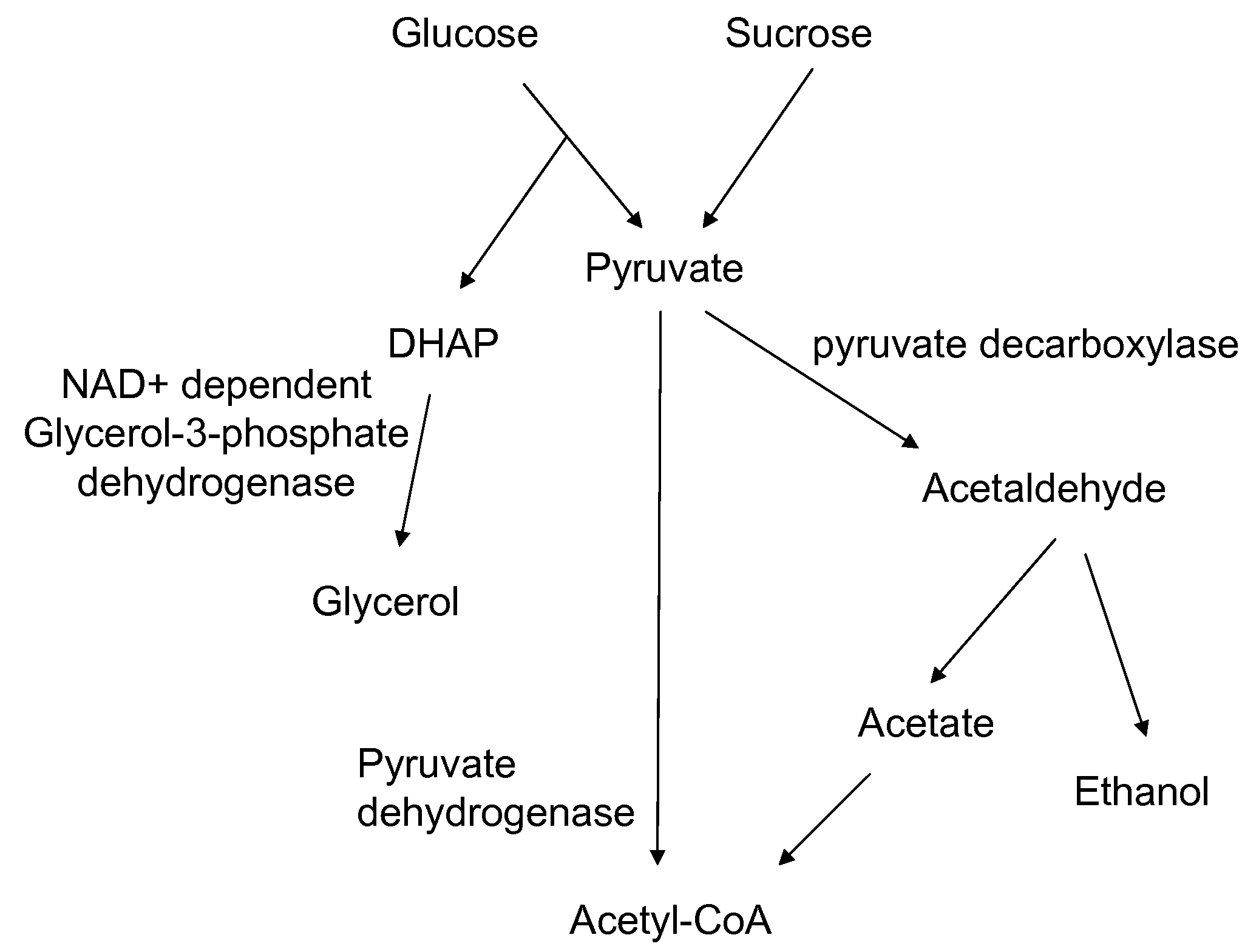
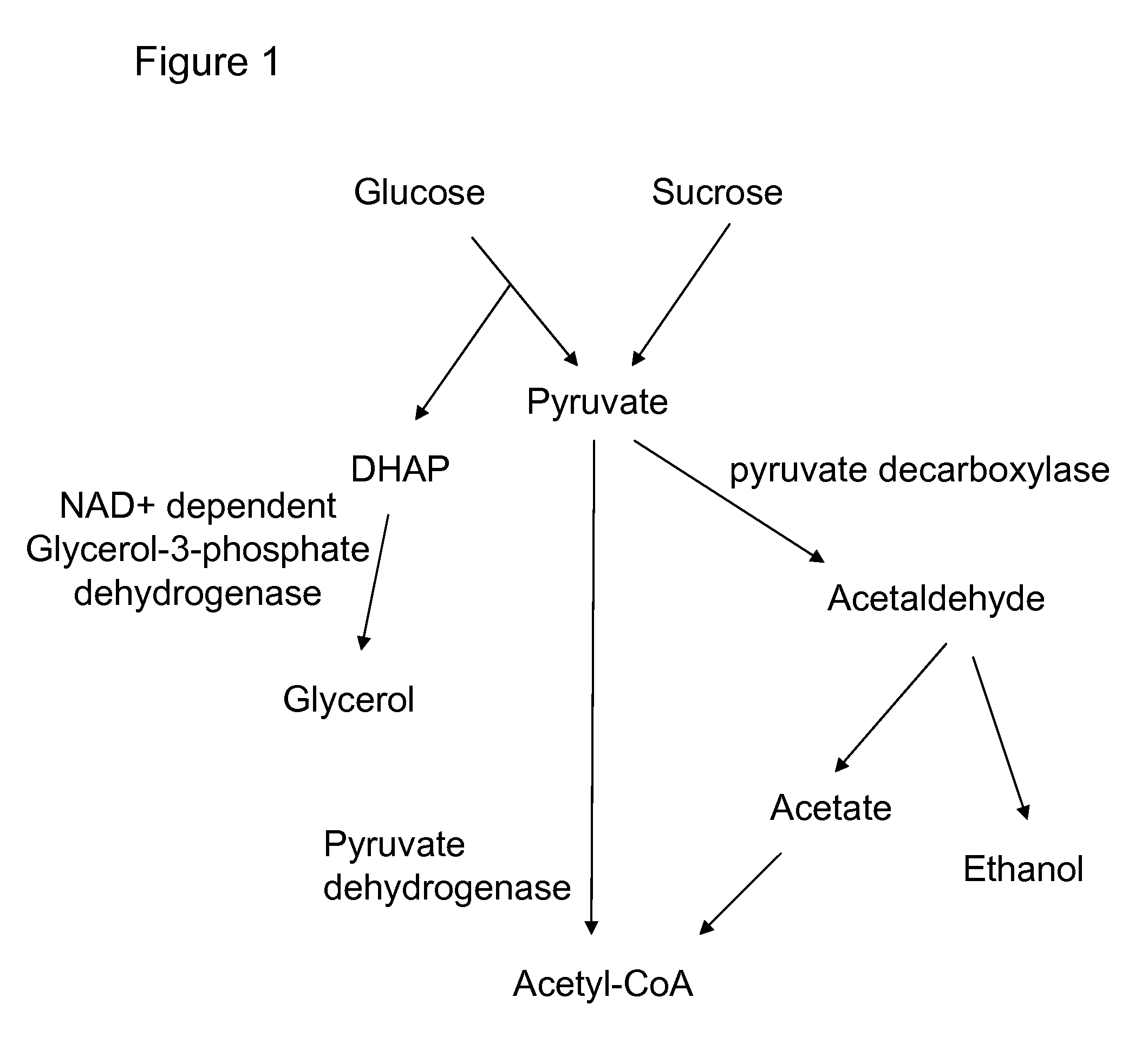
Enhanced pyruvate to acetolactate conversion in yeast
ActiveUS20090305363A1Improve throughputReduction of pyruvate decarboxylase activityFungiTransferasesYeastCytosol
A high flux in conversion of pyruvate to acetolactate was achieved in yeast through expression of acetolactate synthase in the cytosol in conjunction with reduction in pyruvate decarboxylase activity. Additional manipulations to improve flux to acetolactate are reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and reduced glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. Production of compounds having acetolactate as an upstream intermediate benefit from the increased conversion of pruvate to acetolactate in the described strains.
Owner:GEVO INC
Production of D-lactic acid with yeast
InactiveUS20070031950A1Increase productivityHigh yieldFungiOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyLactate dehydrogenase
A yeast strain, wherein the yeast strain is transformed with at least one copy of a gene coding for <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactate dehydrogenase functionally linked to a promoter sequence allowing the expression of the gene in the yeast strain and the yeast strain has undergone disruption of one or more pyruvate decarboxylase genes or pyruvate dehydrogenase genes. Also, a method of producing <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactic acid including culturing such a yeast strain in a medium and recovering <SMALLCAPS>D< / SMALLCAPS>-lactic acid.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
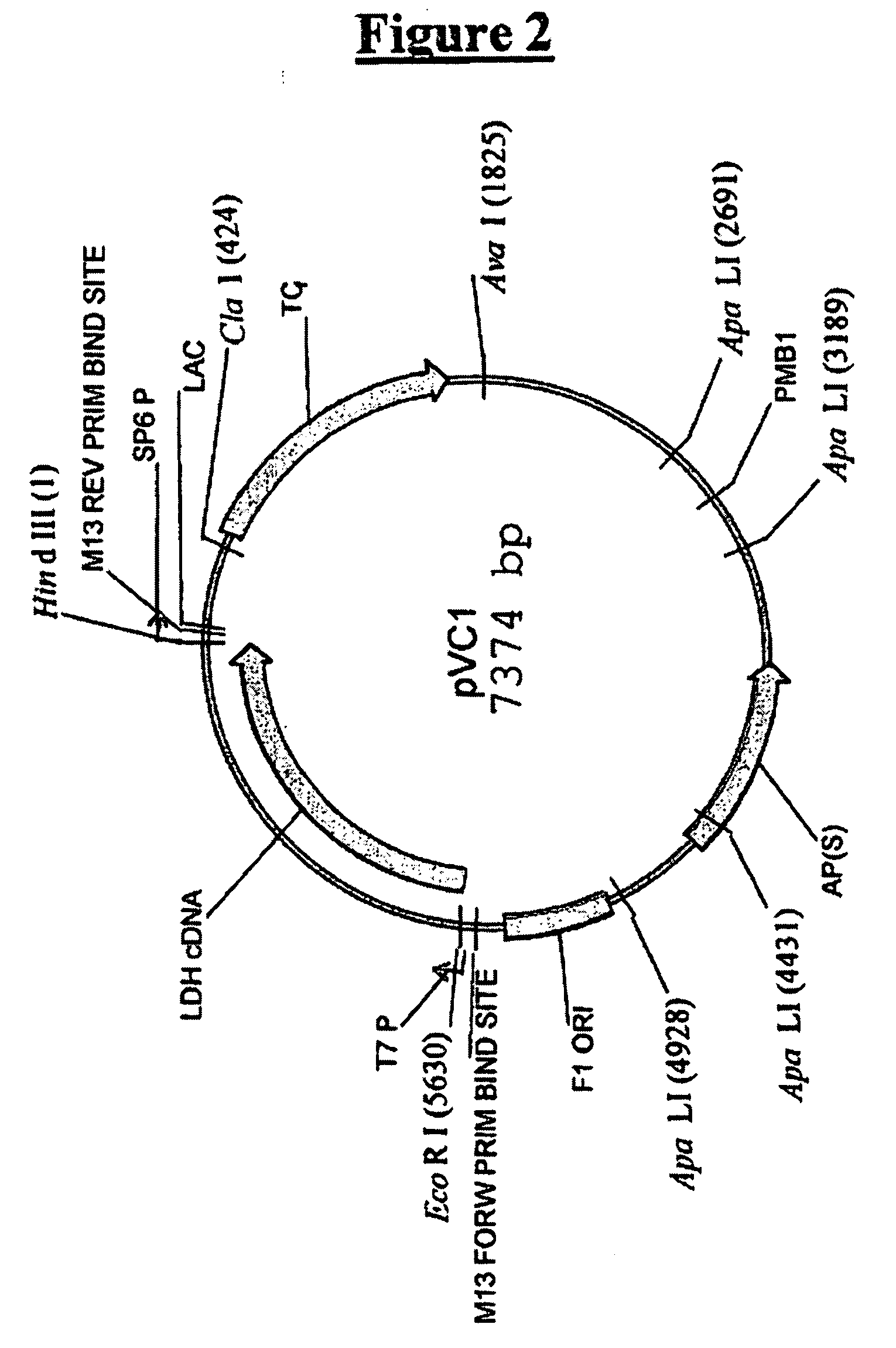
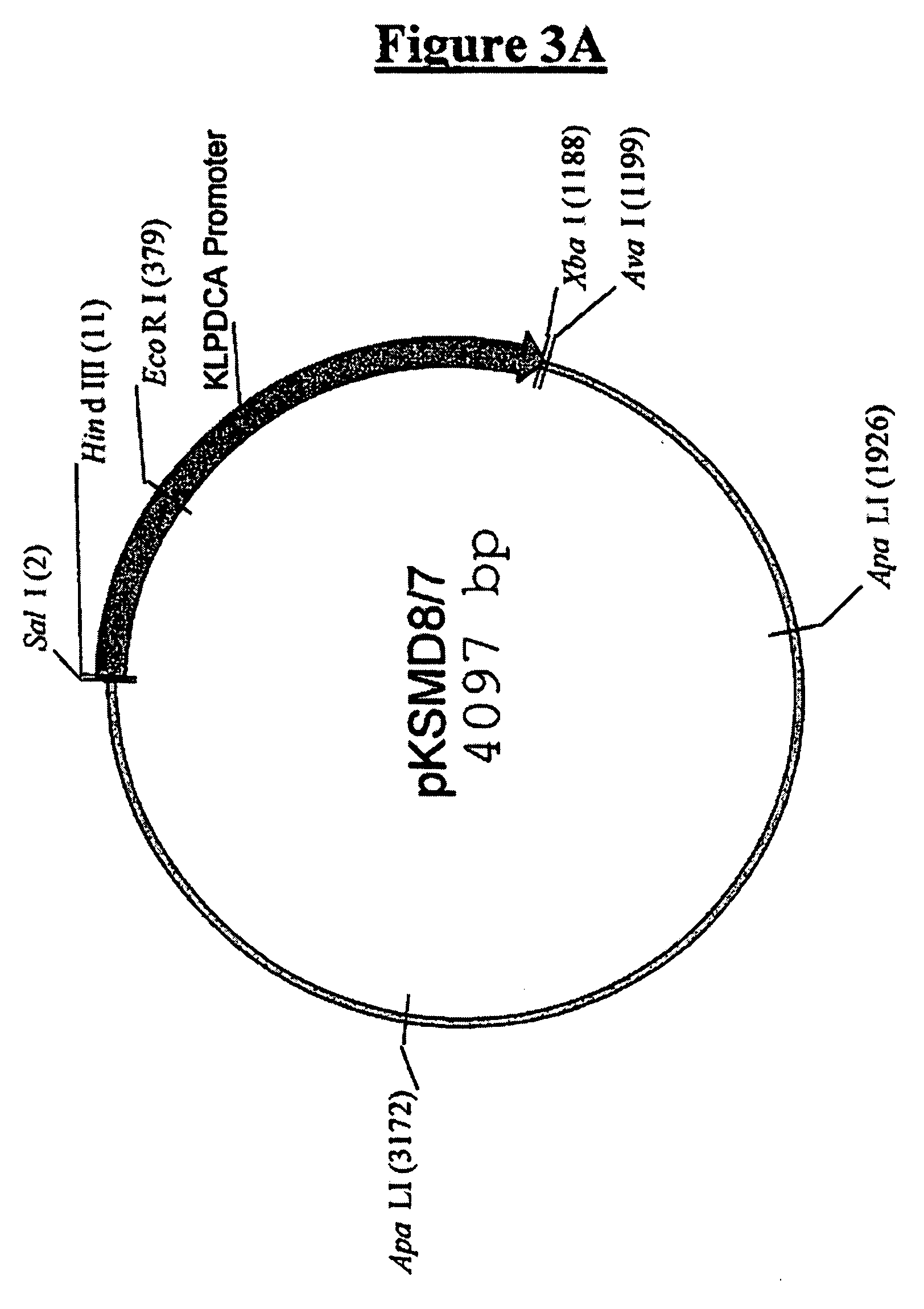
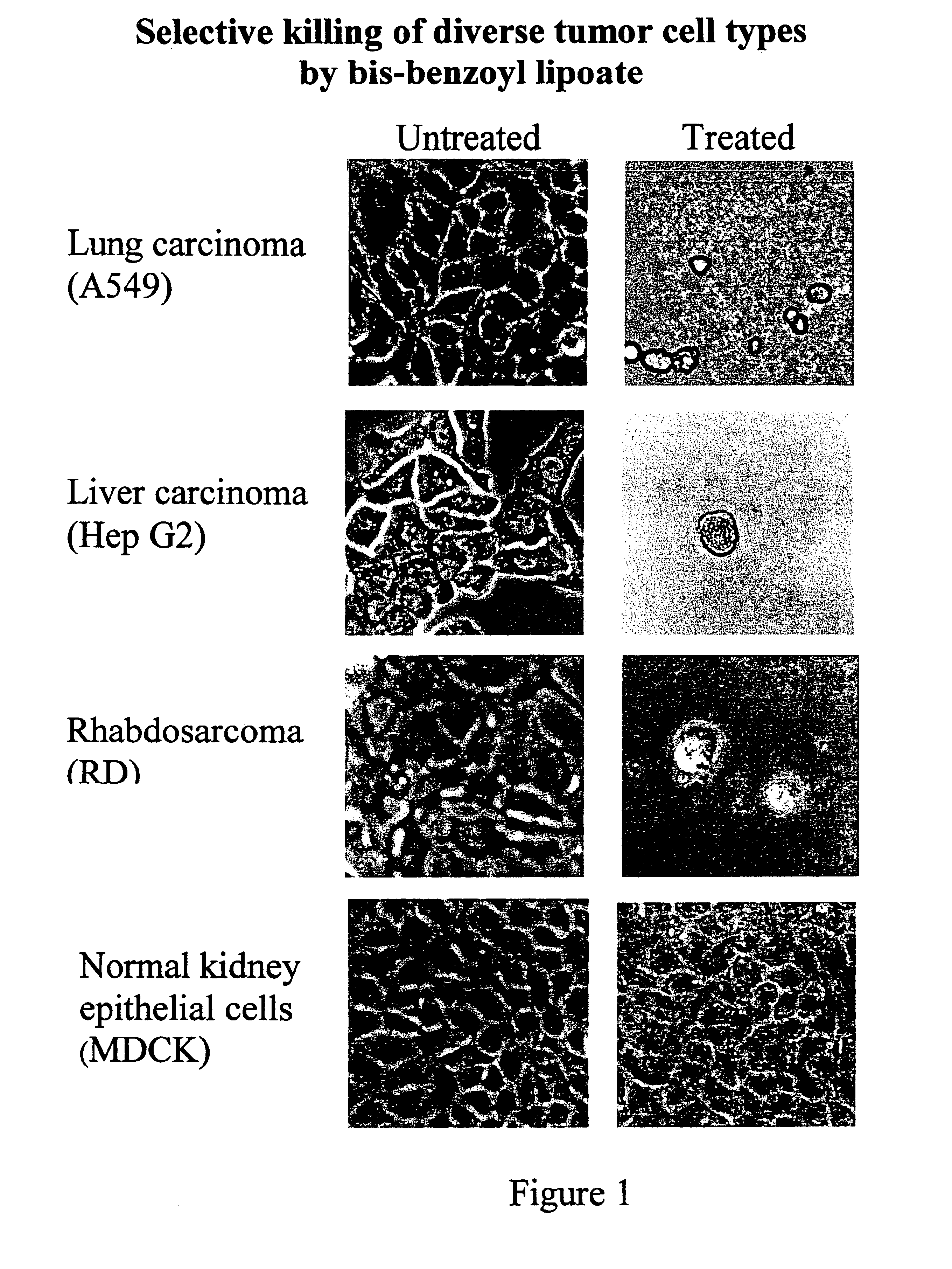
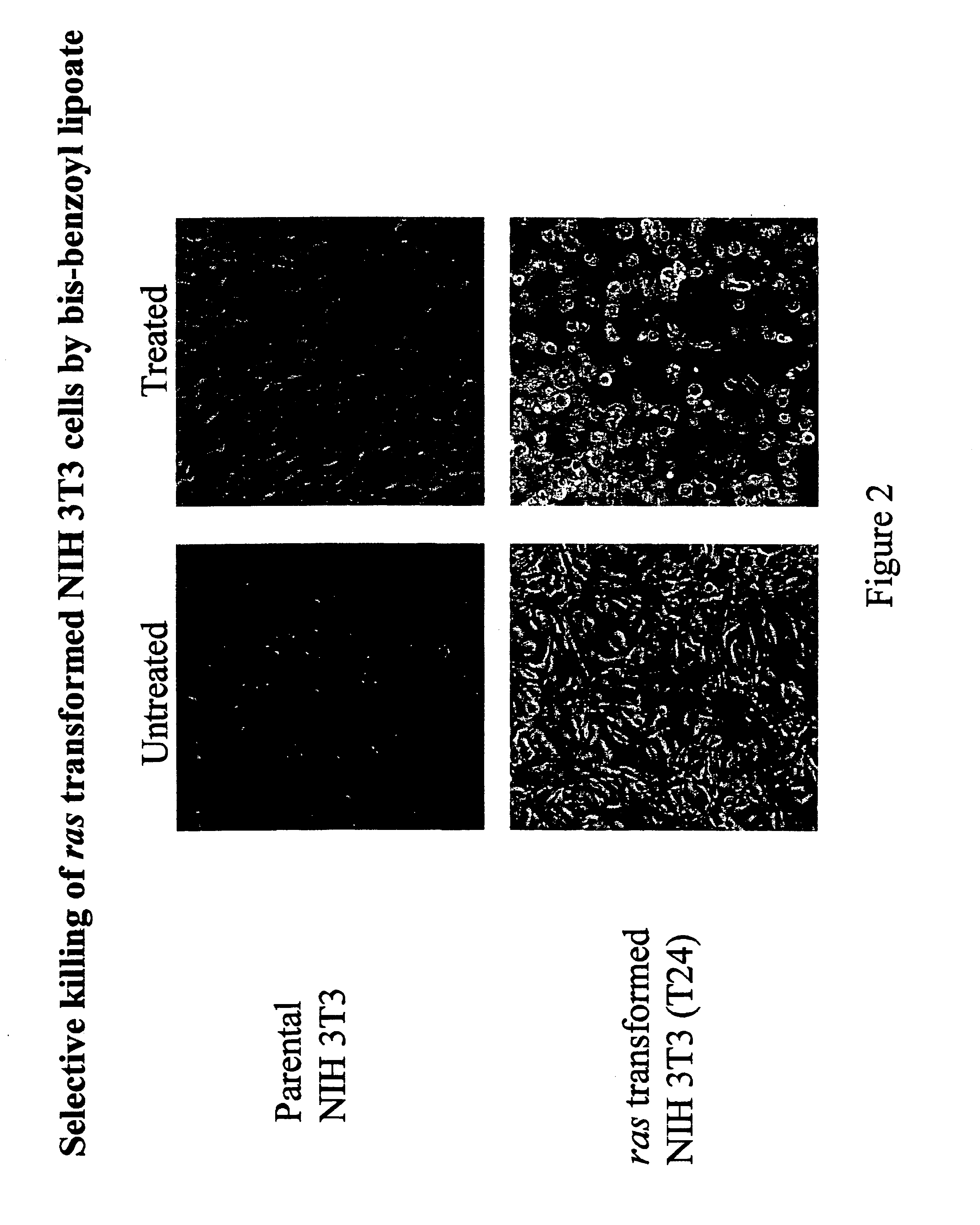
Lipoic acid derivatives and their use in treatment of disease
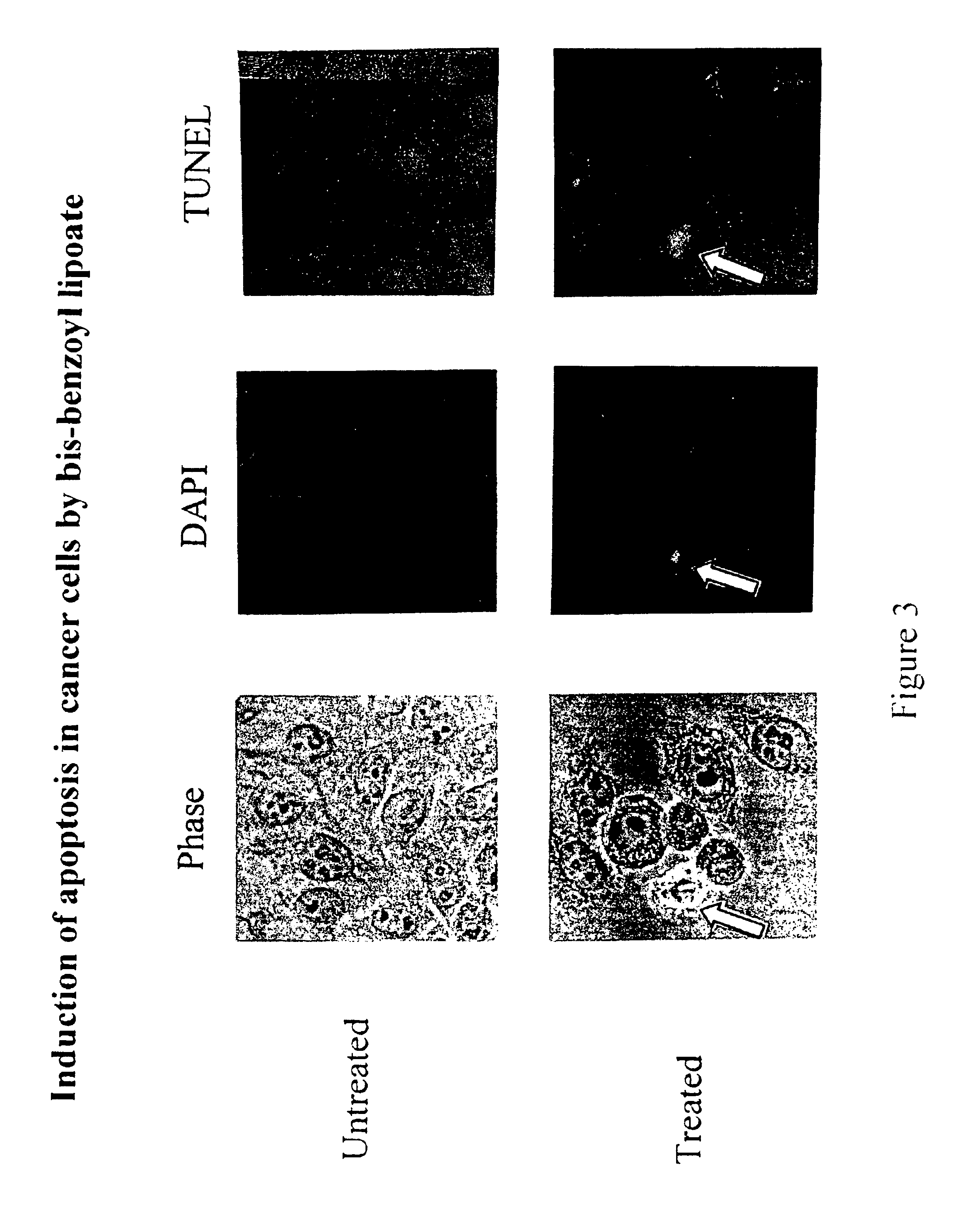
This invention relates to the identification of a novel class of therapeutic agents which selectively target and kill tumor cells and certain other types of diseased cells, and to compositions comprising lipoic acid derivatives which poison the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex specifically in such cells. This invention also provides for methods of using therapeutically effective amounts of the lipoic acid derivatives for the treatment of cancer and other diseases. The lipoic acid derivatives described herein have a wide range of preventive and therapeutic applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer and ischemic diseases
InactiveUS20090209618A1Treating and preventing neoplasiaReduced activityCompound screeningBiocideMedicinePyruvate dehydrogenase activity
The invention provides therapeutic and prophylactic compounds and methods for altering the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (e.g. PDK1, PDK2, PDK3, PDK4). Such therapies are useful for the treatment of neoplasia. The invention further provides therapeutic and prophylactic compounds and methods of altering pyruvate dehydrogenase activity to treat or prevent cell death related to ischemia.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Live attenuated mycoplasma strains
InactiveUS20090068231A1Reduce expressionReduced virulenceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesVaccination
The present invention provides live, attenuated Mycoplasma bacteria that exhibit reduced expression of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of pyruvate dehydrogenase, phosphopyruvate hydratase, 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase, and ribosomal protein L35, relative to a wild-type Mycoplasma bacterium of the same species. Also provided are vaccines and vaccination methods involving the use of the live, attenuated Mycoplasma bacteria, and methods for making live attenuated Mycoplasma bacteria.
Owner:WYETH LLC
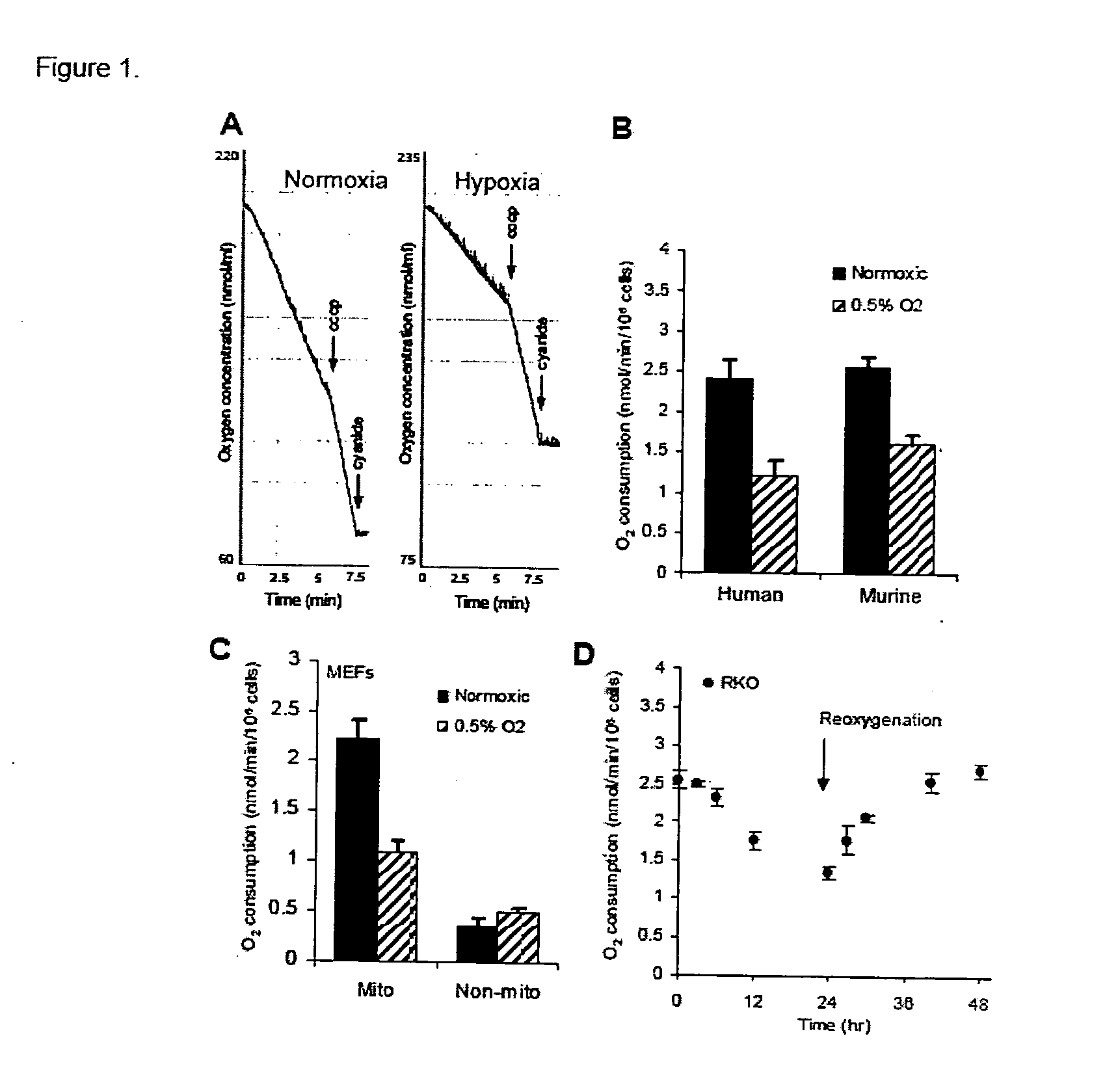
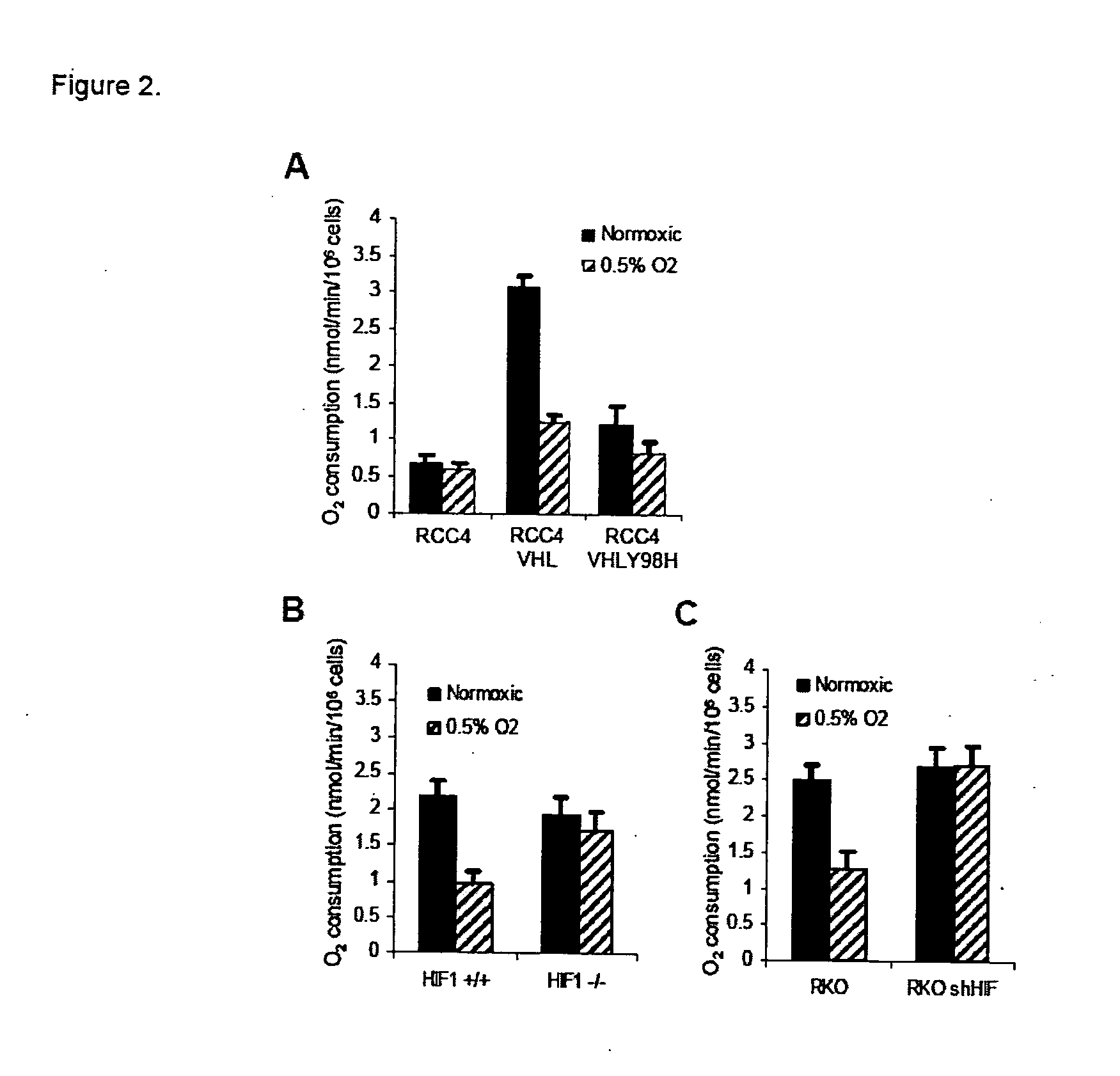
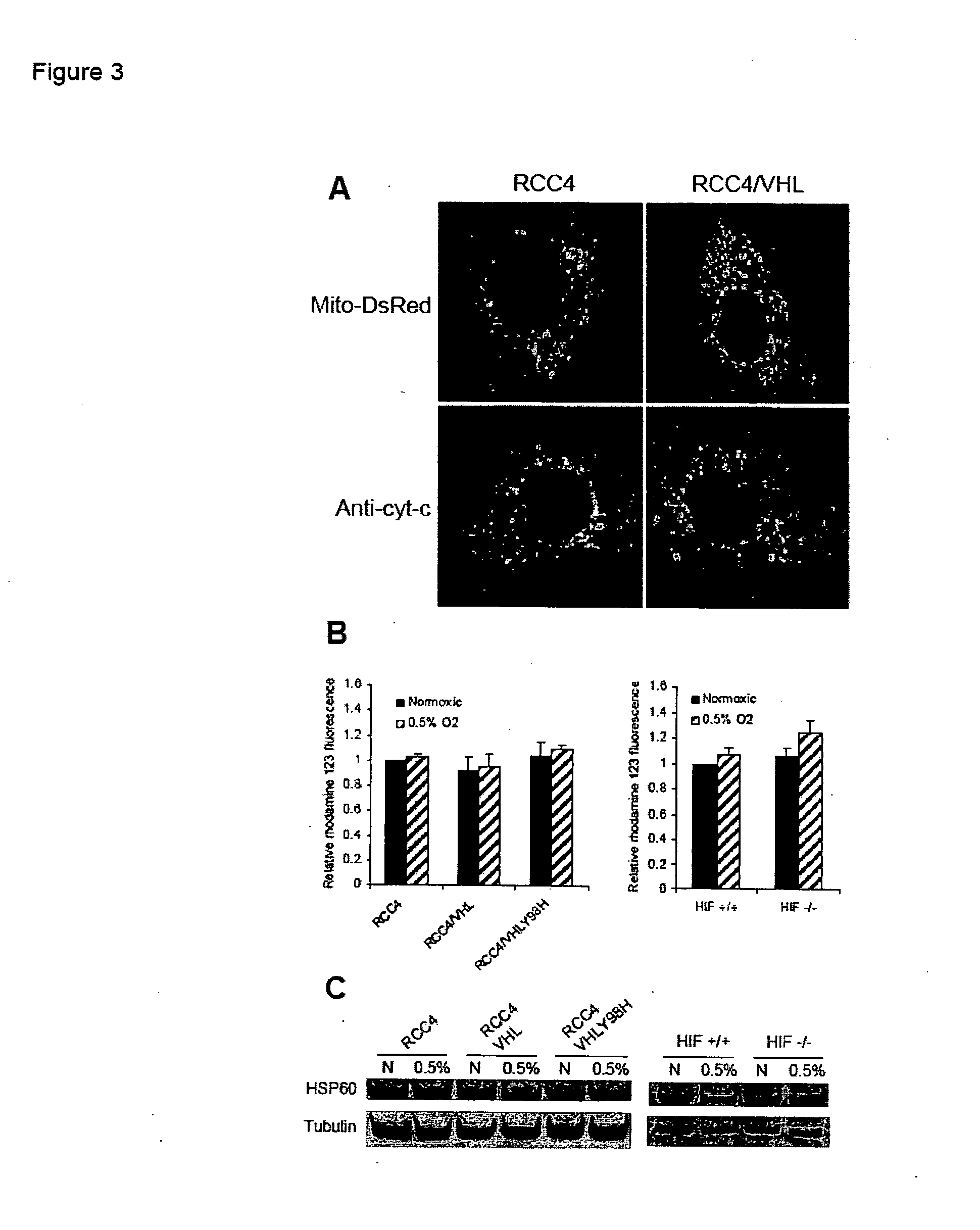
Modulation of mitochondrial oxygen consumption for therapeutic purposes
InactiveUS20070212360A1Increased blood vessel formationReduced activityBiocideAntibody ingredientsPhysiologyTherapeutic intent
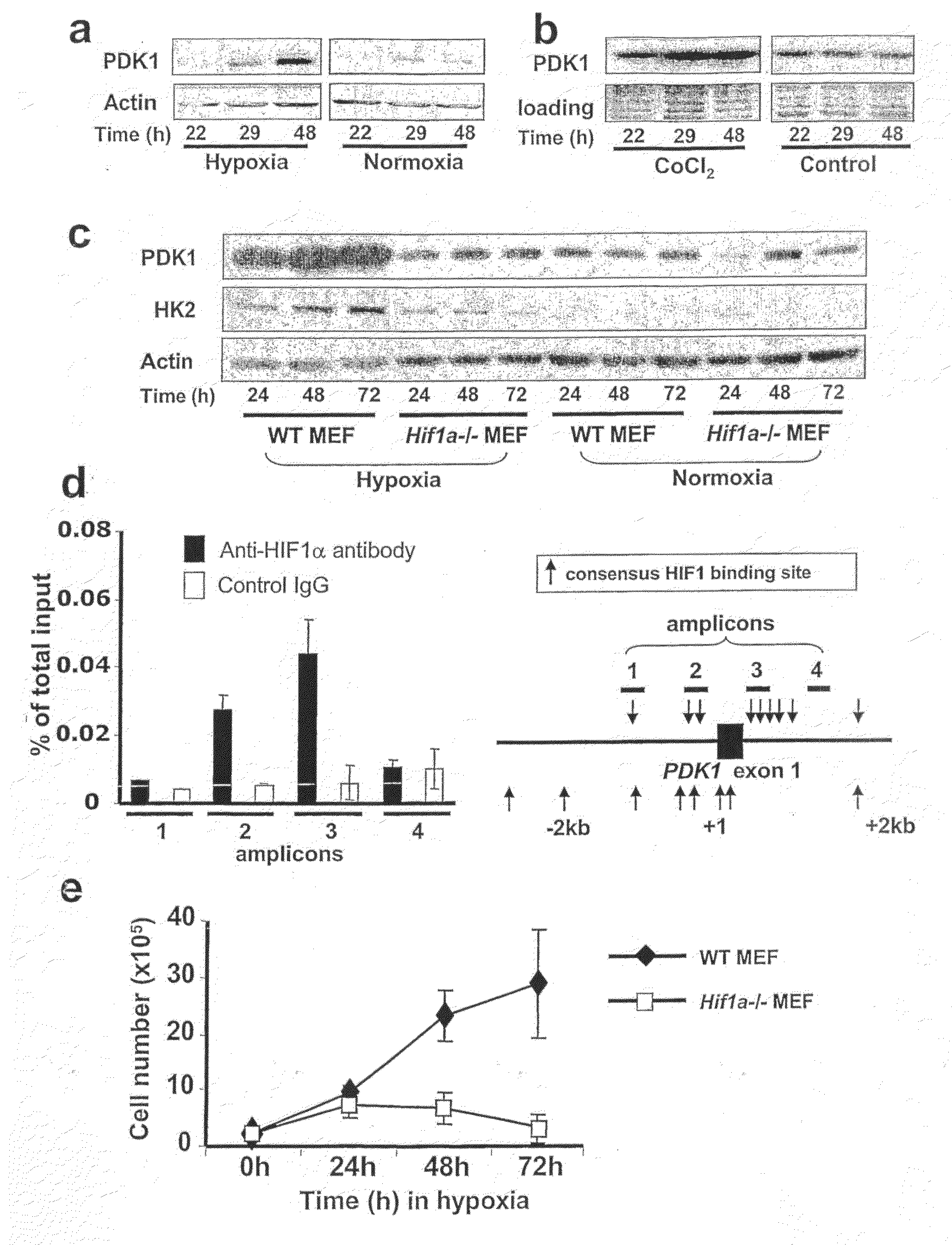
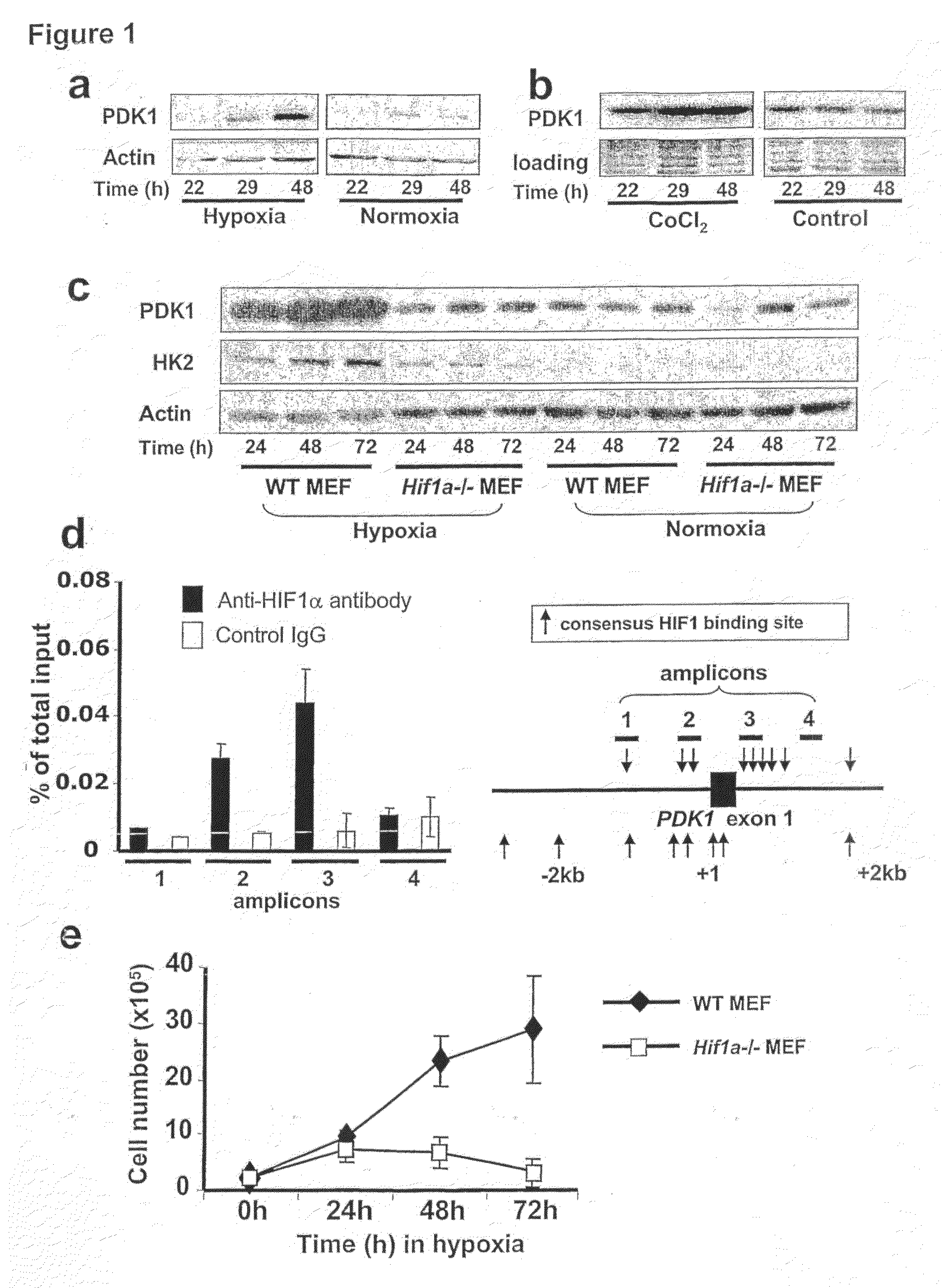
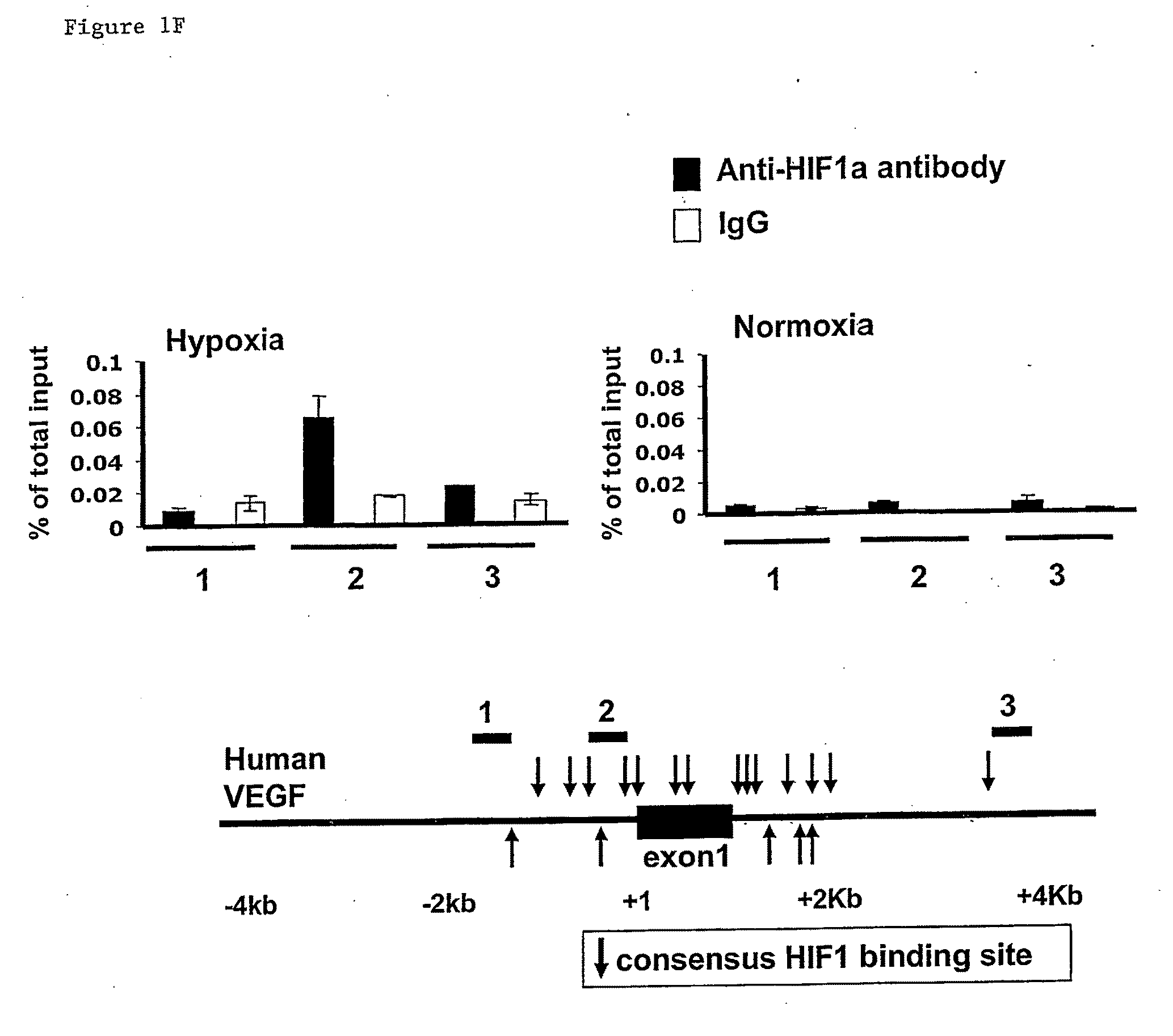
The HIF-1 transcription factor drives gene expression changes in hypoxia. While HIF-1 stimulates glycolysis, it also actively represses mitochondrial function and oxygen consumption by inducing pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1). PDK1 phosphorylates and inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase from converting pyruvate to acetyl-CoA to fuel the mitochondrial TCA cycle. This causes a drop in mitochondrial oxygen utilization and results in a relative increase in intracellular oxygen tension.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
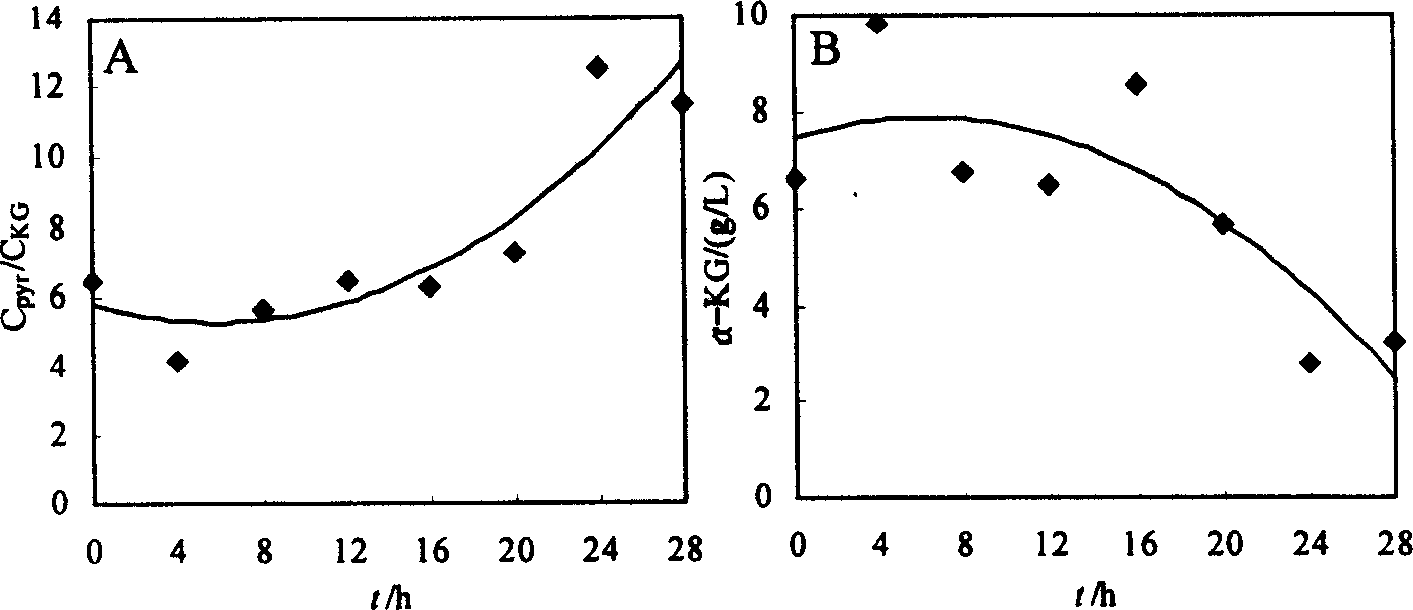
Method for microbial fermentation synthesis of ª‡- ketoglutaric acid
InactiveCN1544642AIncrease carbon molar ratioIncrease concentrationFermentationHigh concentrationIncreased biotin
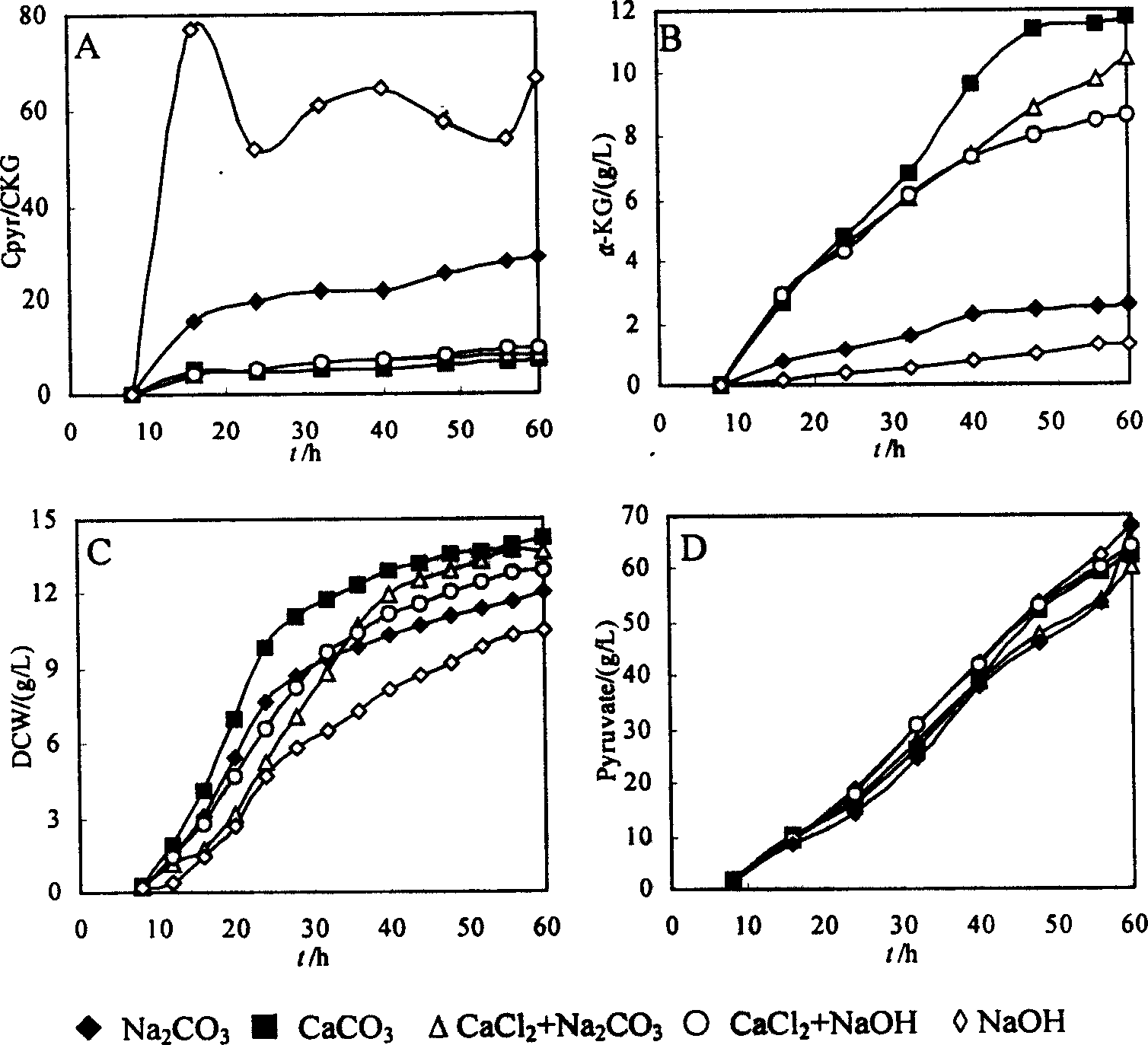
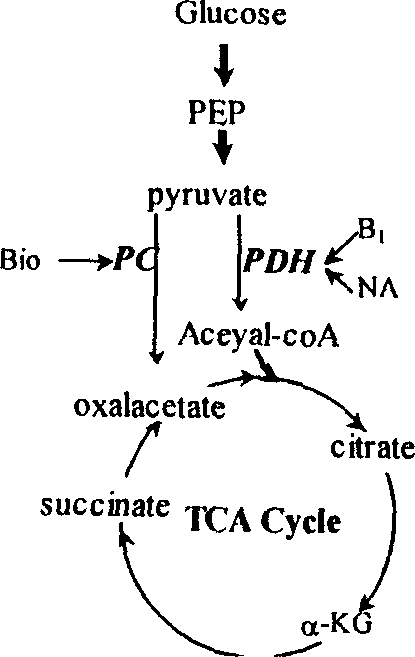
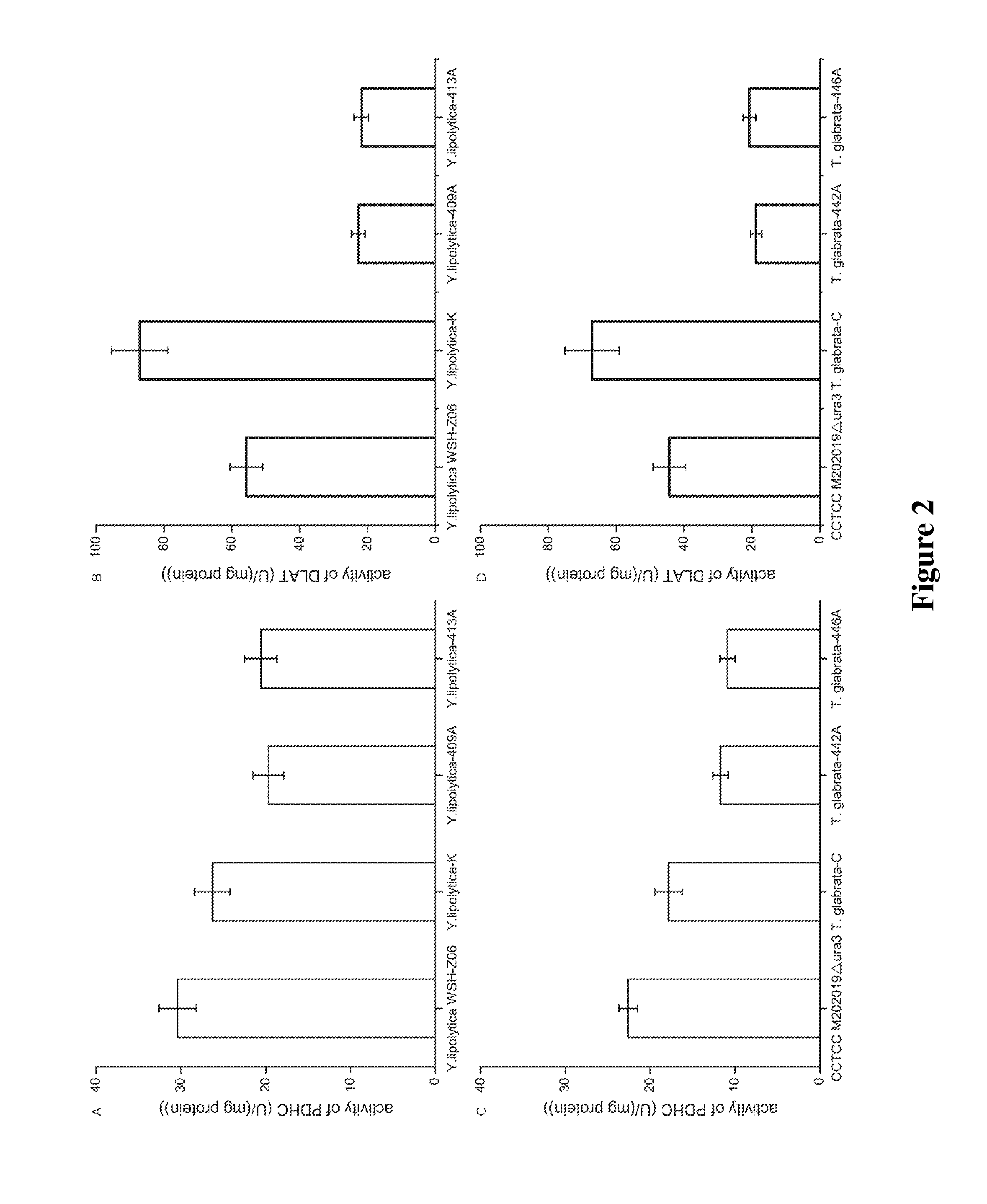
The invention is a method of synthesizing alpha-ketoglutarate by fermenting microbes, promoting to produce a large amount of alpha-ketoglutarate in fermenting course by adding CaCO3 to the culture medium and increasing biotin concentration. in the course of fermenting candida glabrata CCTCC M202019 to producing pyruvic acid, the delay of time of adding CaCO3 will inhibit the generation of alpha-ketoglutarate and increase the carbon mole ratio of pyruvic acid to alpha-ketoglutarate (CPYR / CKG), and increase of CaCO3 concentration in the culture medium will promote accumulation of a large amount of alpha-ketoglutarate, when the CaCO3 concentration is 40g / L, it is most beneficial to alpha-ketoglutarate generation. Keeping the CaCO3 concentration in the culture medium but increasing biotin concentration in the culture medium so as to promote the continuous increase of the alpha-ketoglutarate concentration but continuous decrease of CPYR / CKG value, and when biotin concentration is 60mum g / L, accumulated quantity of alpha- ketoglutarate is 23.5g / L. when Ca2+ exists, in-cell phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity can be increased by 40%, and the activity of pyruvic acid dehydrogenase system does not change obviously. The increase of the Ca2+ and biotin concentration can remarkably the activity of enhance pyruvic acid dehydrogenase, thus making T.glabrata transfer from production of pyruvic acid by fermenting to synthesis of high-concentration alpha-ketoglutarate.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Use of compounds for the elevation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity
InactiveCN101417964AEnhance PDH activityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryHydrogenPyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency
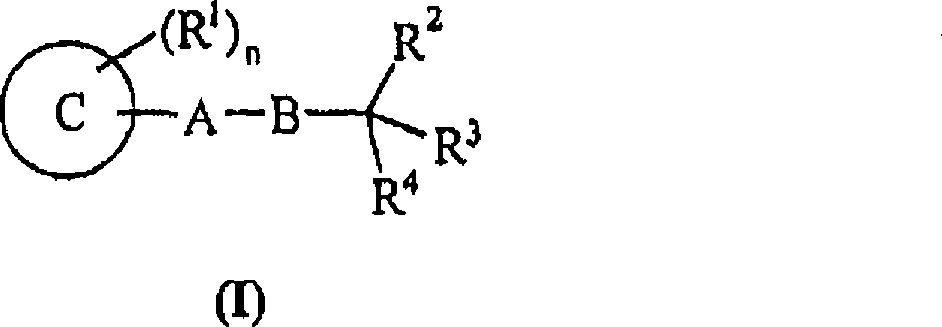
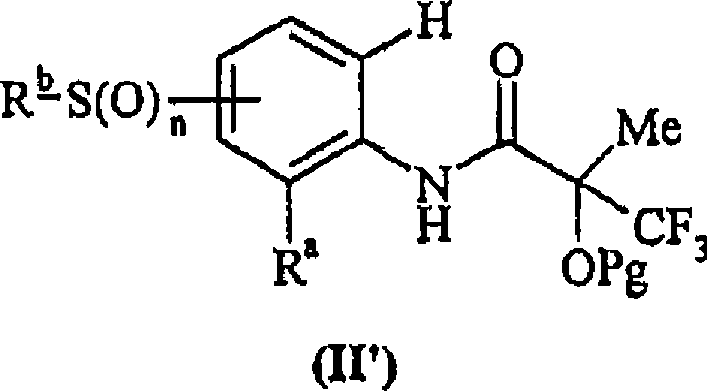
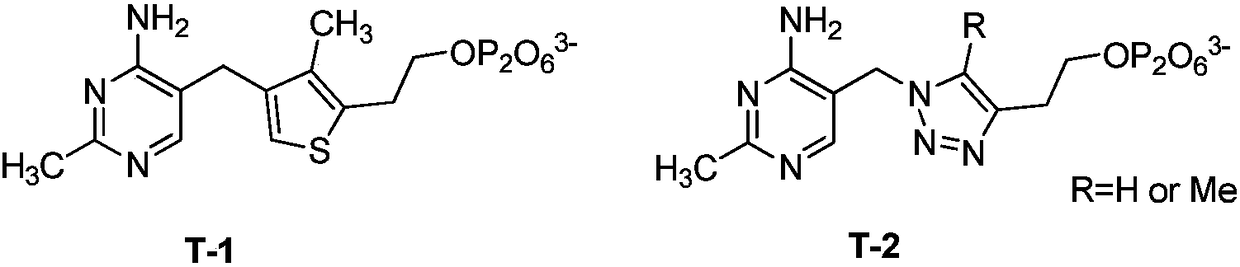
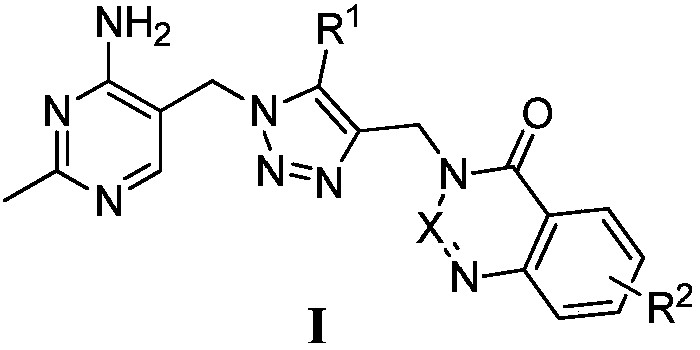
The use of compounds of formula (I), and salts thereof; and pharmaceutically acceptable in vivo cleavable prodrugs of said compound of formula (I); and pharmaceutically acceptable salts of said compound or said prodrugs; in formula (I), Ring C is phenyl or a carbon linked heteroaryl ring substituted as defined within; R<1> is an ortho substituent as defined within; n is 1 or 2; A-B is a linking group as defined within; R<2> and R<3> are as defined within; R<4> is hydroxy, hydrogen, halo, amino or methyl; in the manufacture of a medicament for use in the elevation of PDH activity in warm-blooded animals such as humans is described. Pharmaceutical compositions, methods and processes for preparation of compounds of formula (I) are also described.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Method for preparing high optical purity D-lactic acid by fermentation
InactiveCN101544992AHigh optical purityHigh yield and high optical purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationLactate dehydrogenaseGlucose polymers
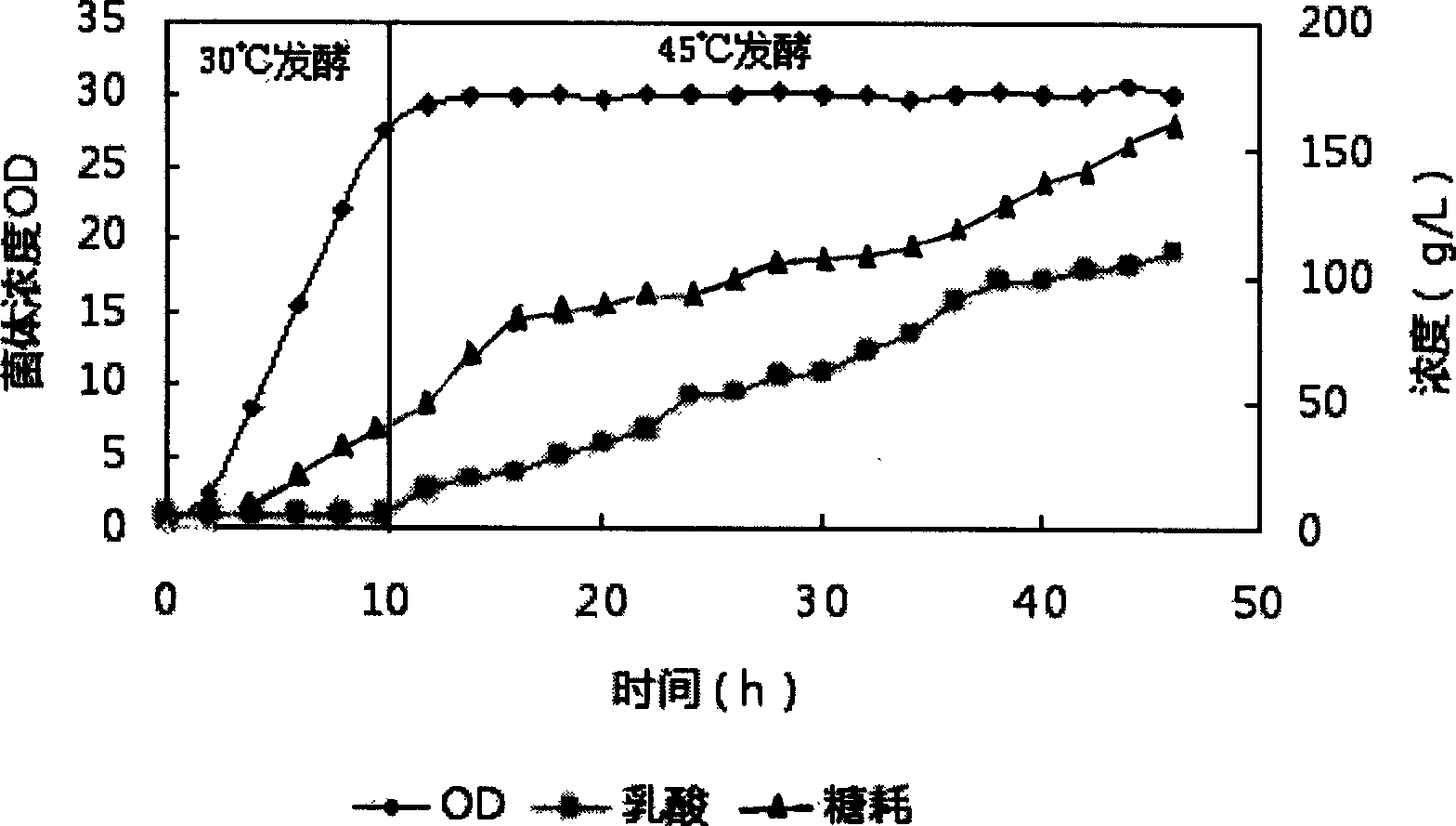
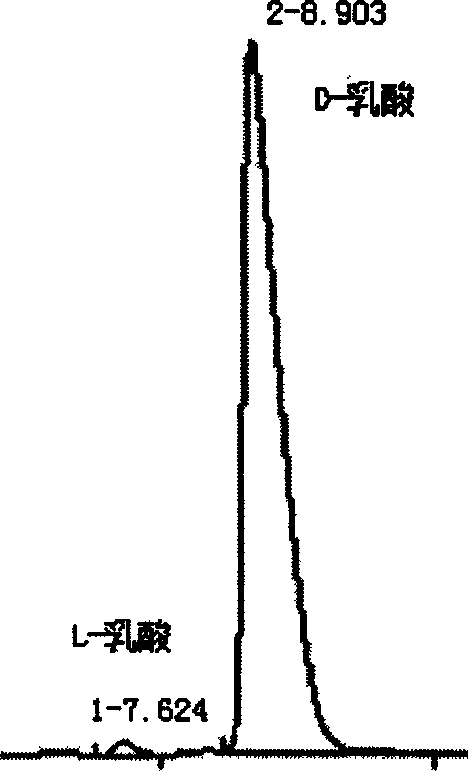
The invention provides a method for preparing high optical purity D-lactic acid by fermentation. The method is characterized in that D-lactic acid high-yield recombinant strain is fermented for 30 to 50 hours in stages at a temperature of between 20 and 45 DEG C to prepare the D-lactic acid with yield level reaching 12 percent and optical purity of the D-lactic acid reaching more than 99.5 percent. By expressing pyruvate dehydrogenase encoding gene and NAD dependency D-lactic acid dehydrogenase encoding gene of the D-lactic acid high recombinant strain under the control of fermentation parameter, the production process of the D-lactic acid can be controlled only by changing the fermentation temperature, so the aim and the effect of synthesizing optical purity D-lactic acid in high-efficiency by using glucose as a raw material are achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU PURIZYMES BIOTECH
Methods of selecting subjects for treatment with metabolic modulators
InactiveUS20170349949A1Reduce dosageReduce frequencyCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorylationActive agent
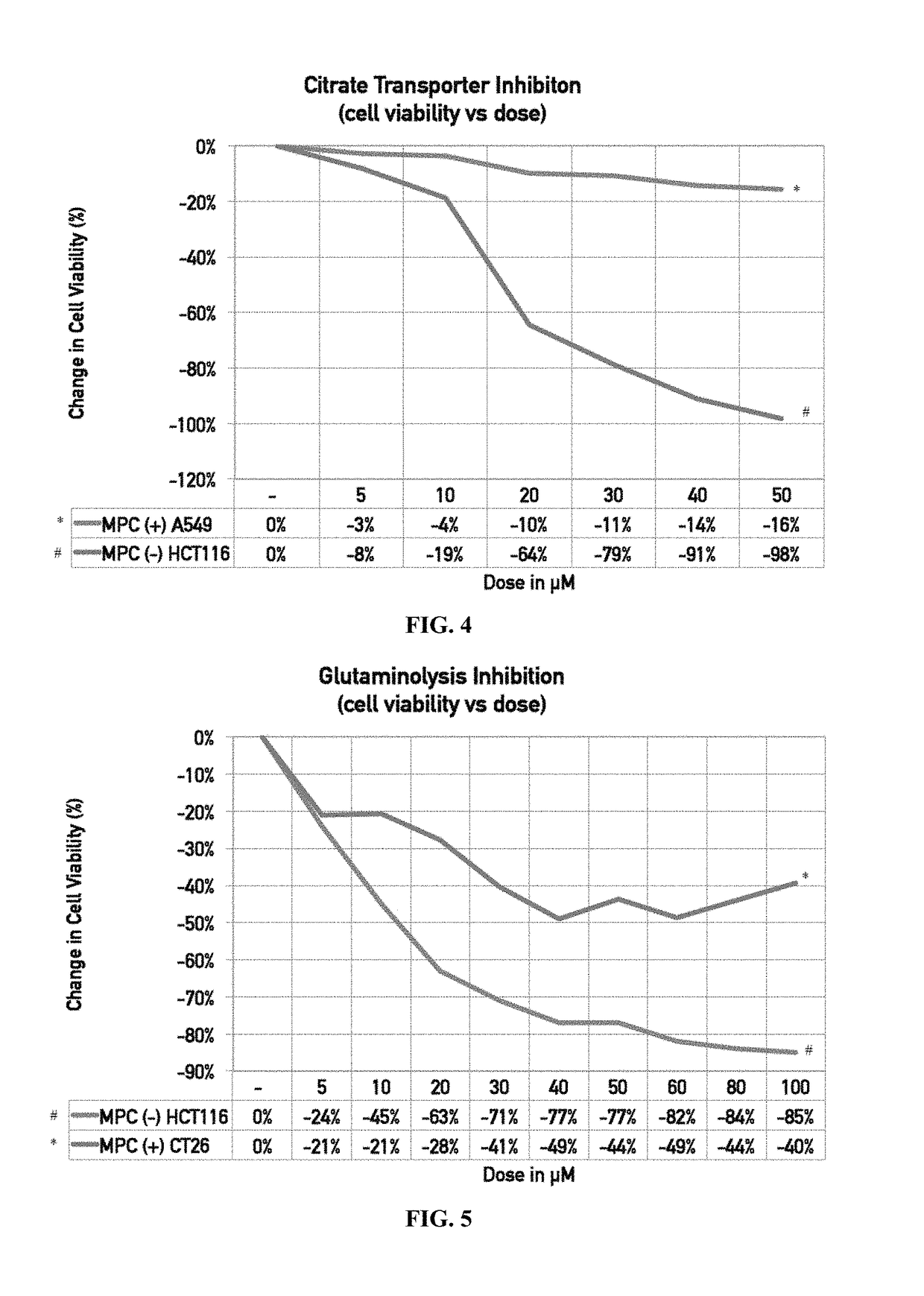
Methods of selecting a subject with cancer for treatment with an active agent that modifies pyruvate metabolism, the TCA cycle, or oxidative phosphorylation, as well as methods of treating the subject, determining the efficacy of the treatment, and adjusting the treatment dosage and frequency are provided. Methods of selecting and treating as subject typically include, (a) detecting the level of one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of one or more Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carriers (MPC), one or more components of the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDC), or mitochondrial glutamine transporter in diseased or disordered cells obtained from the subject; and (b) selecting the subject for treatment if the subject meets certain criteria and (c) administering the subject an effective amount of an active agent that modifies pyruvate metabolism, the TCA cycle, a related metabolic pathway, or oxidative phosphorylation to treat the disease or disorder.
Owner:CLARIA PARTIKULA LLC
Immunocapture-based measurements of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
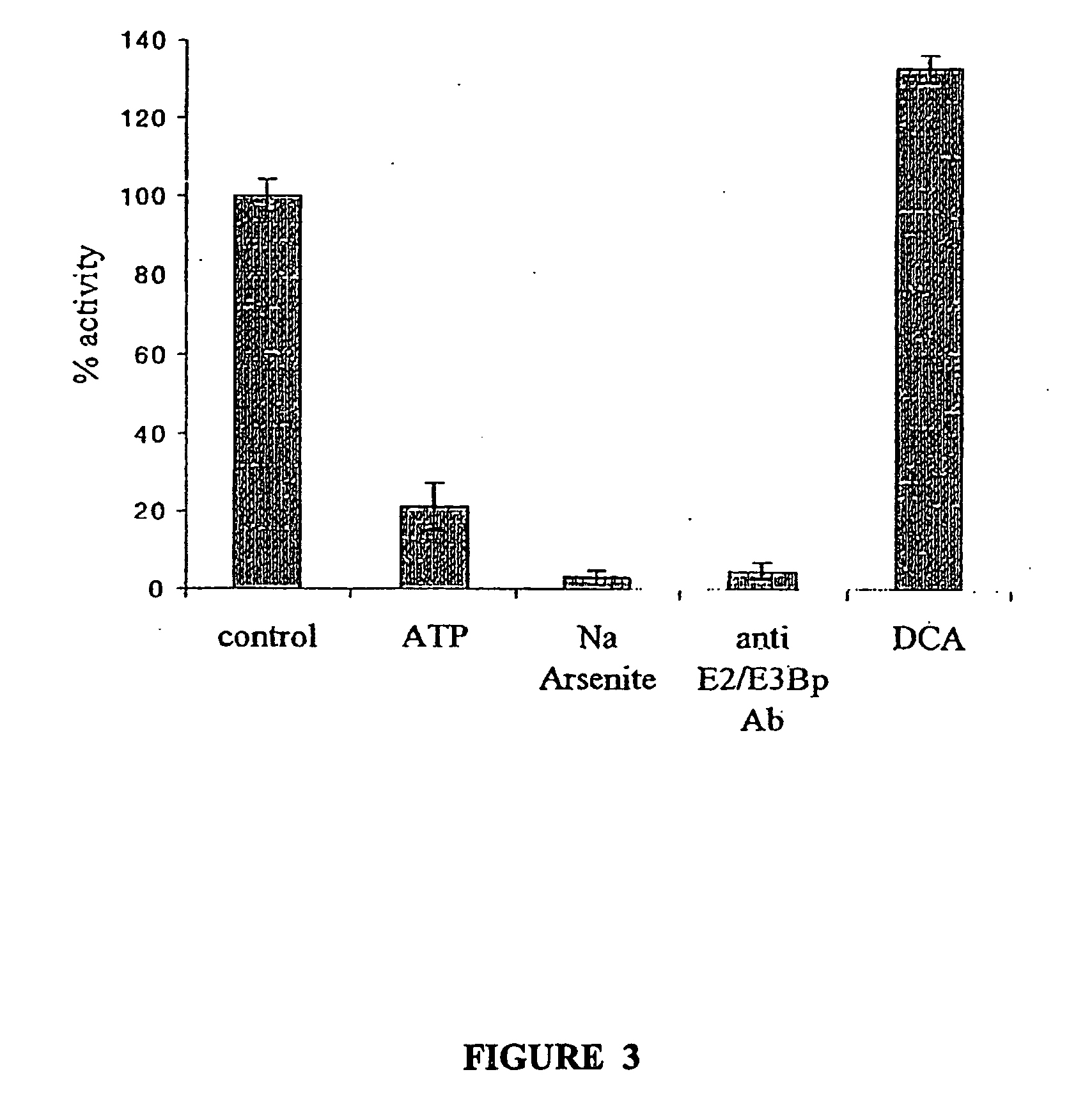
The present invention is based on the discovery that an antibody specific for PDH complex can be used to immunoprecitate PDH complex from the patient sample in an active state. Therefore the anti-PDH complex specific antibody can be used to determine the amount of and / or active state of PDH in a patient sample. The invention immunoassay methods for determining the amount and / or active state of PDH complex present in a patient sample are useful for screening to identify individuals having symptoms indicating malfunction of PDH complex. For example, the invention methods can be used to screen individuals for symptoms of onset of the diabetic state, such as insulitis, and for diagnosing late onset diseases, such as diabetes, Alzheimer's and the like.
Owner:MITOSCI
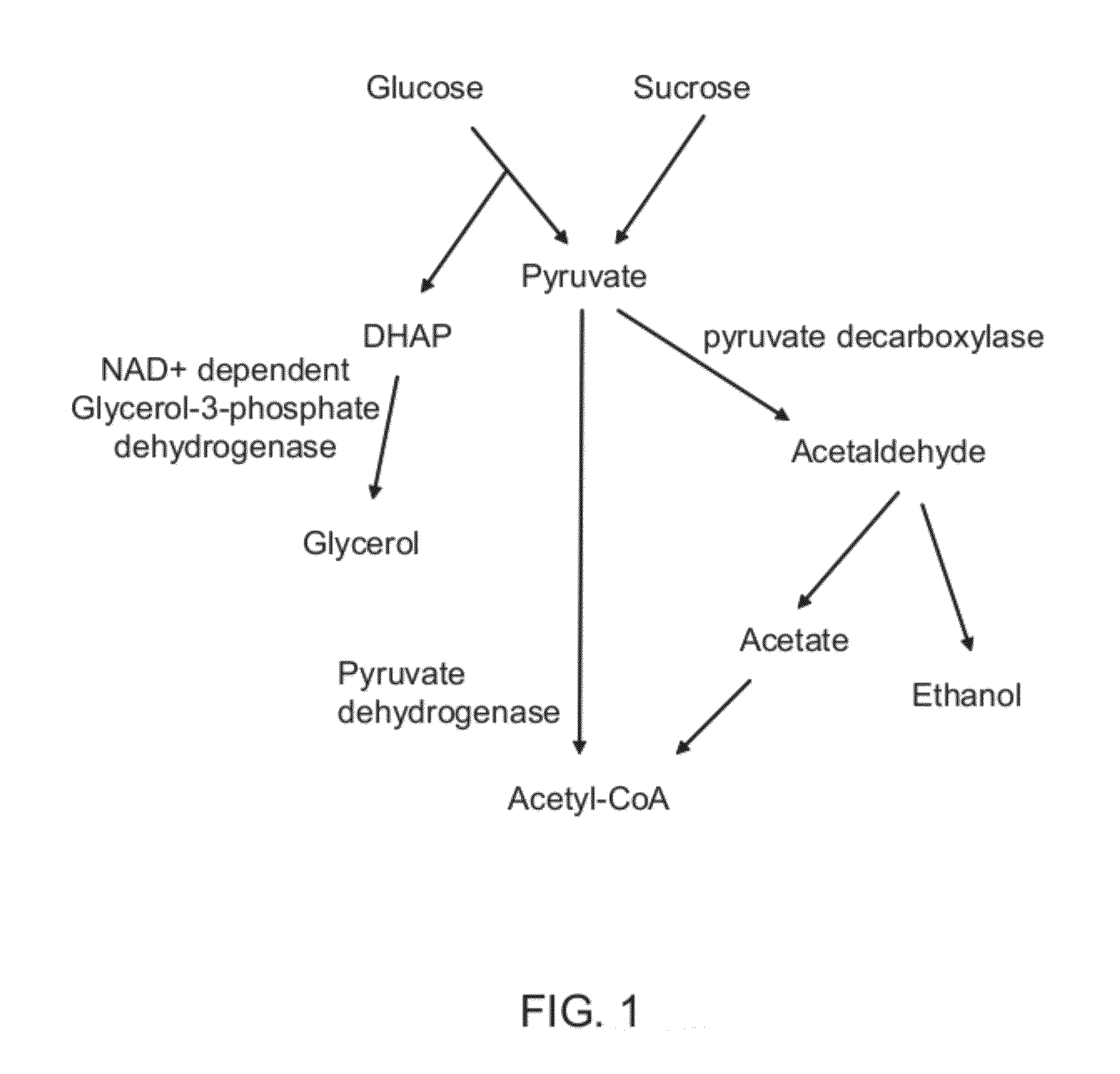
Microbial production of pyruvate and pyruvate derivatives
InactiveUS20100304450A1Redox balancedIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismMetabolite
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
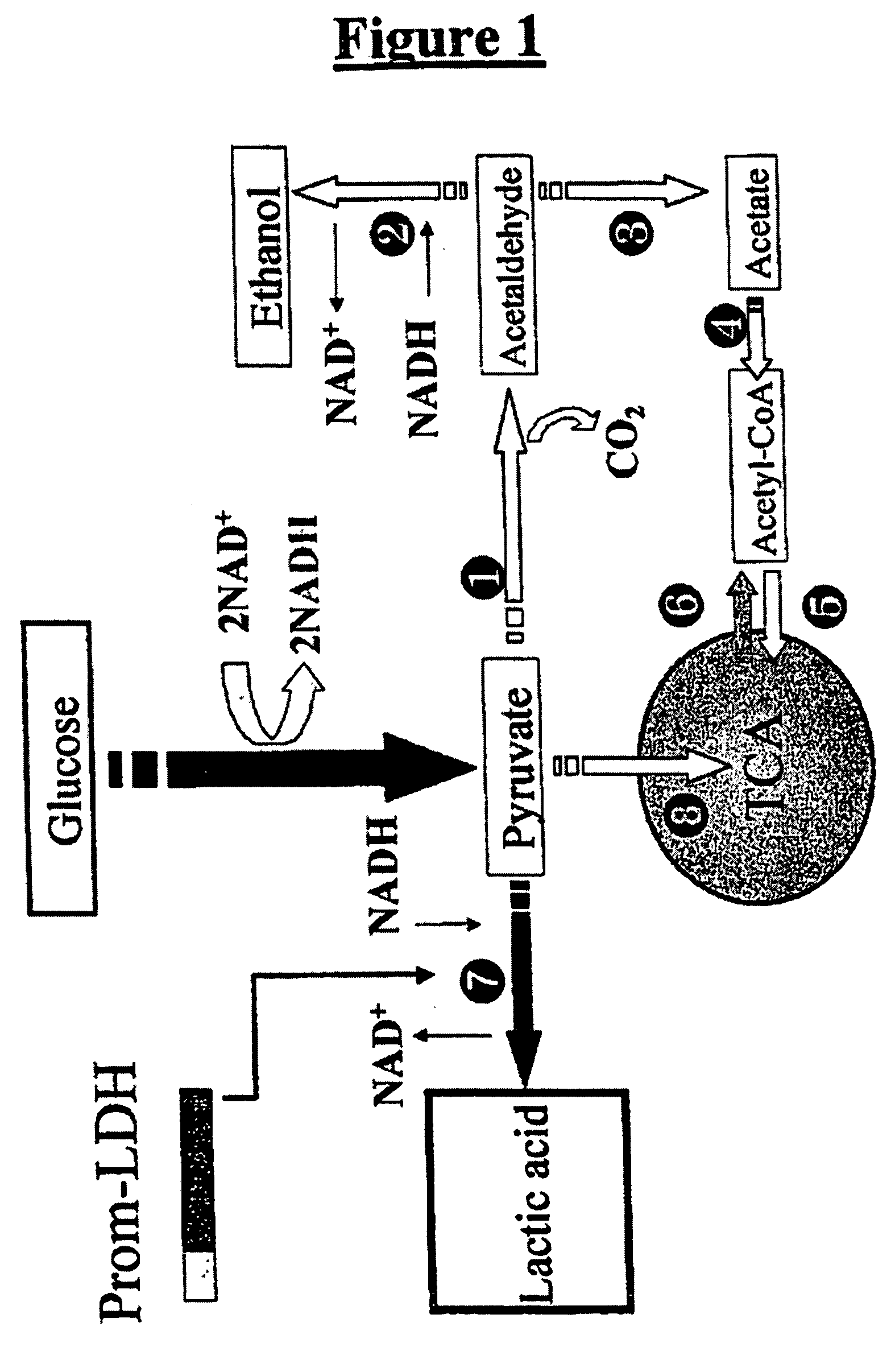
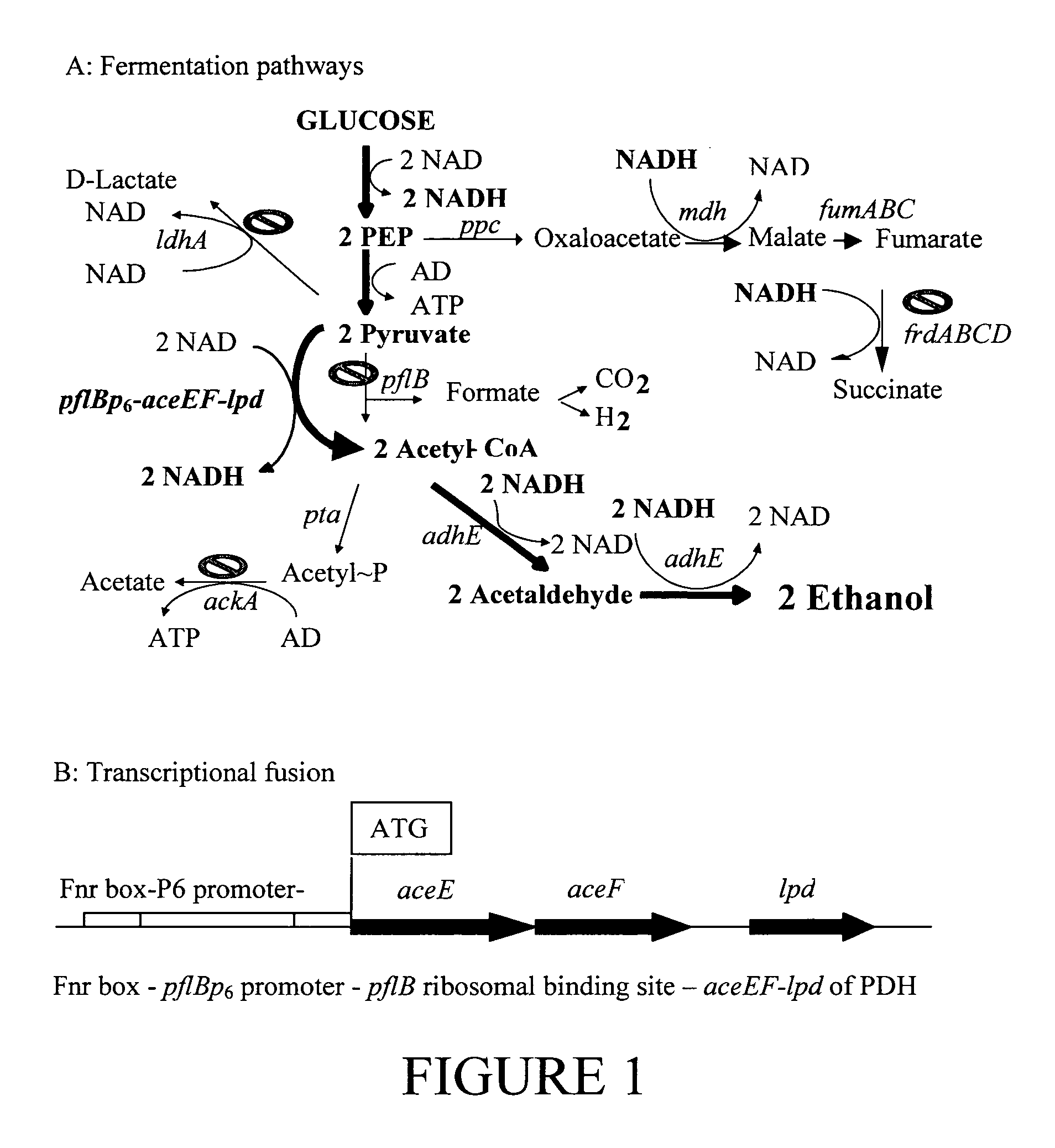
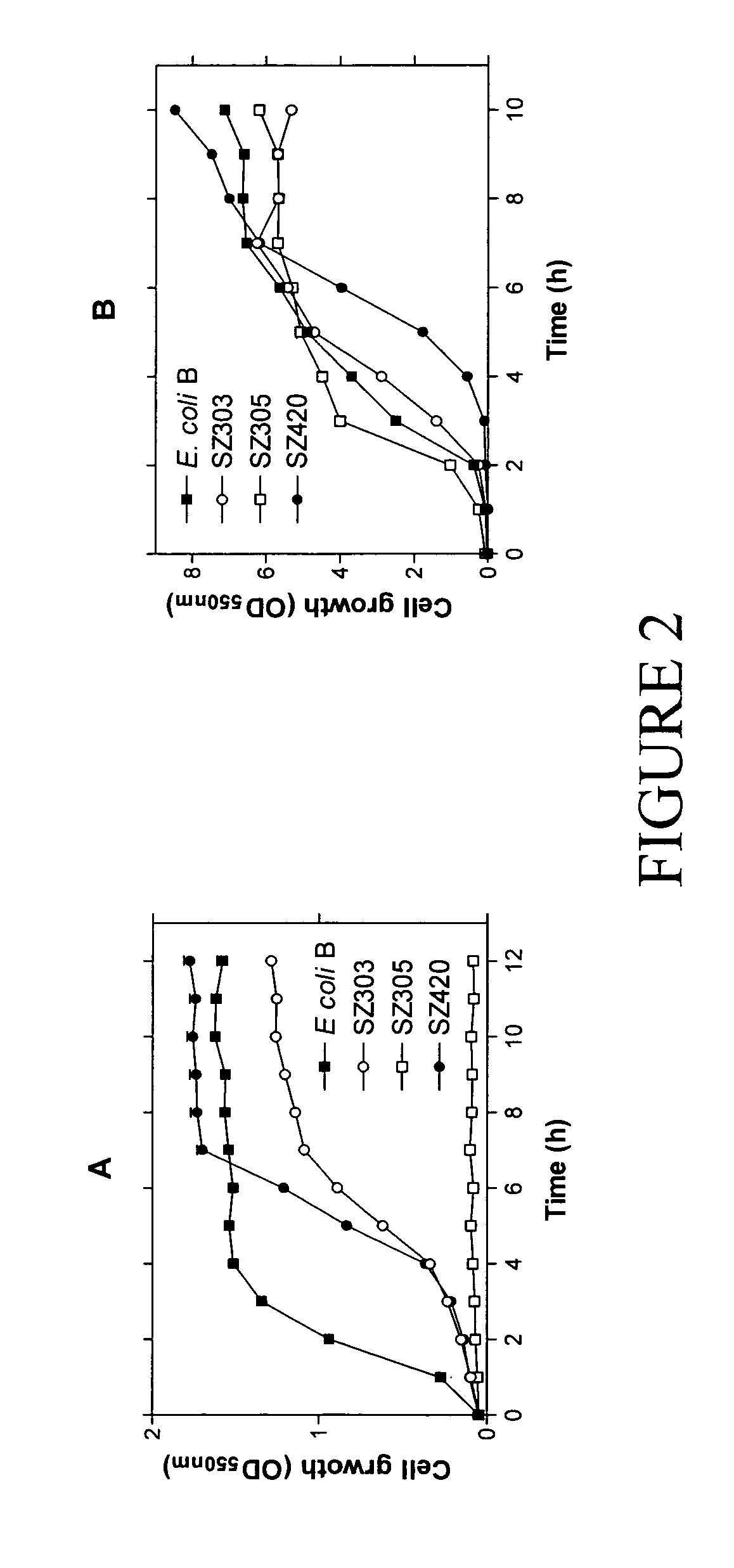
Native homoethanol Pathway for ethanol production in E. coli
InactiveUS20090082600A1Promote cell growthIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaOrganic compound preparationEscherichia coliOperon gene
A native homoethanol pathway including chromosomal deletions of genes that are competitive with the native homoethanol pathway, and a highly anaerobically expressed pyruvate dehydrogenase operon. Bacteria including the native homoethanol pathway. A method of making a bacteria derivative including a native homoethanol pathway by deleting genes that are competitive with ethanol production pathways, and performing transcriptional gene fusion and highly anaerobically expressing pyruvate dehydrogenase operon. A method of producing ethanol by fermenting bacteria including the native homoethanol pathway with biomass, and producing ethanol. Ethanol produced by the above method.
Owner:NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Fermentation technology of 3Ec nano enzyme
Owner:EIN INTL
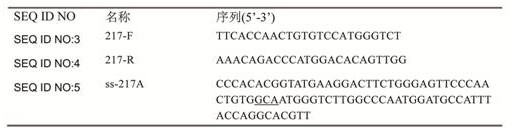
Pyruvate dehydrogenase mutant and method for producing L-amino acid by using mutant
ActiveCN113249347AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvic acidAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention provides a pyruvate dehydrogenase mutant, on the basis of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the 217 site of the sequence is mutated into any one of alanine, aspartic acid, glutamate, leucine and proline. The mutant can improve the yield and conversion rate of L-amino acids in a strain, growth of the strain is not inhibited while the yield is improved, a new way is provided for large-scale production of the L-amino acids, and the mutant has high application value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
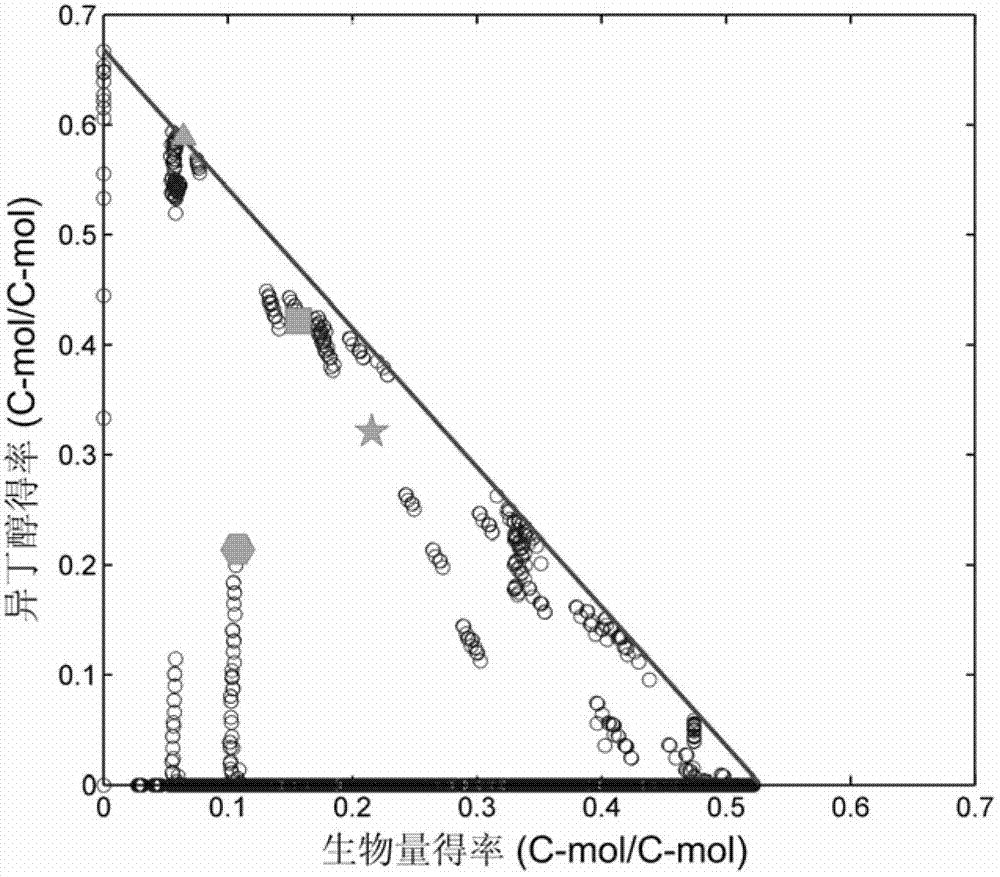
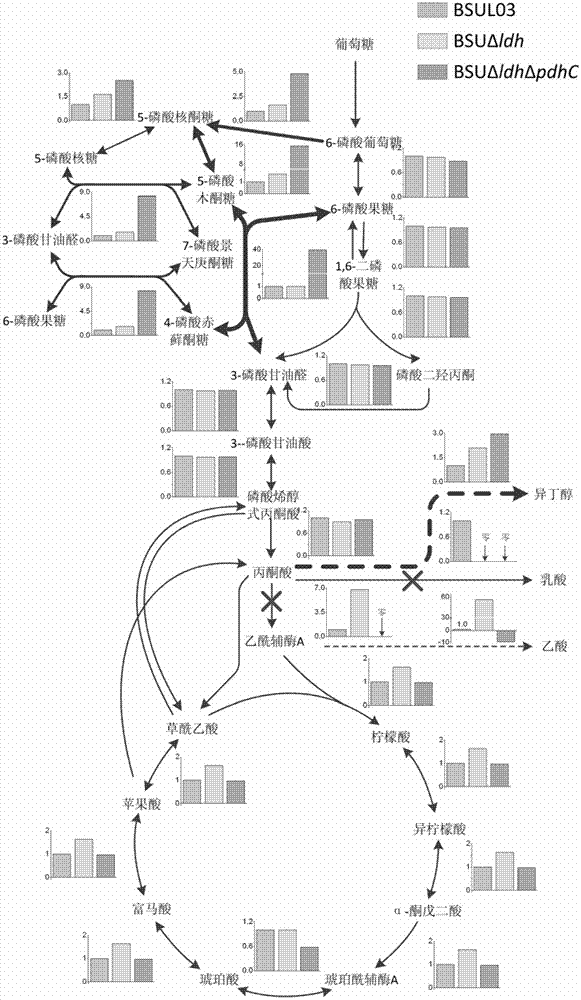
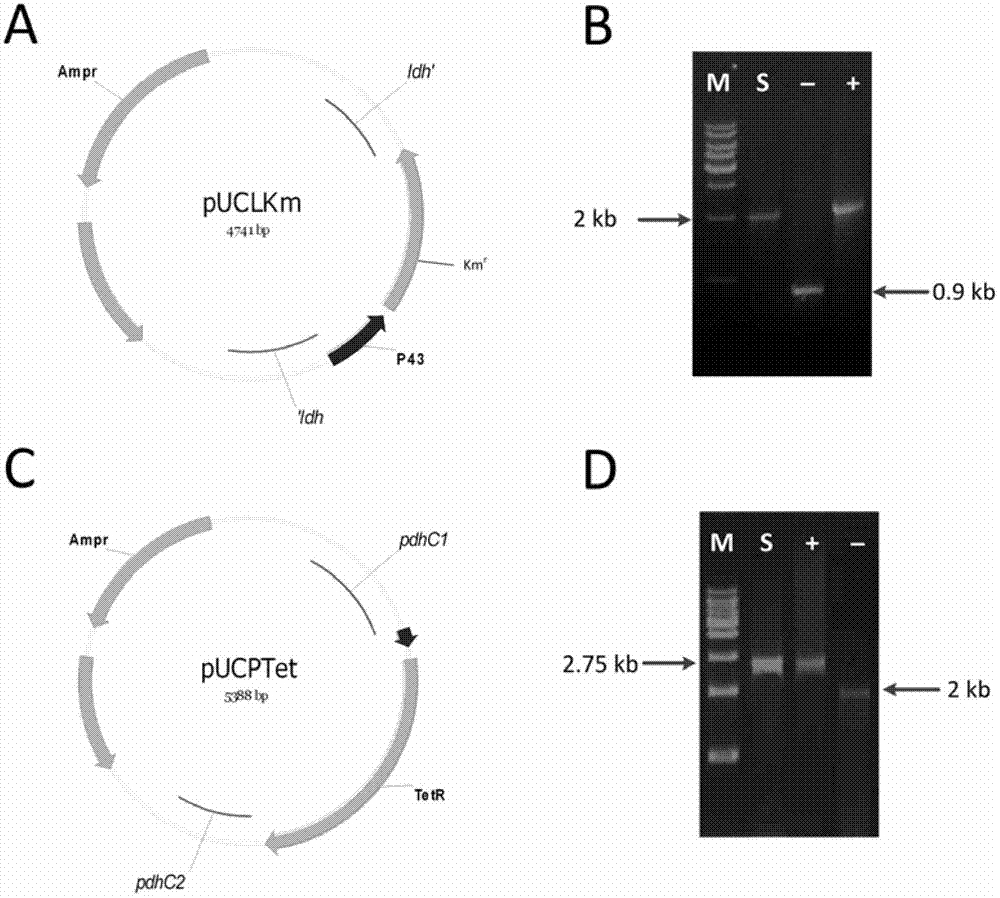
Isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and molecular modification method
InactiveCN102768713ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseIsobutanol synthesis
The invention relates to an isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and a molecular modification method. According to the method, the necessary path for the thallus growth and the isobutanol synthesis is calculated by a network module, the metabolic network model is subjected to the element mode analysis, the standard deviation coefficient of each gene is calculated, and the isobutanol biosynthesis yield of different genes is determined; the two key genes including an L-lactate dehydrogenase gene 1dh and a pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2 subunit coding gene pdhC which are most important to the isobutanol biosynthesis are predicted according to a principle that the standard deviation coefficient is smaller than 0.35, the standard deviation coefficients of the two genes are respectively 2.5 to 3 and 1.5 to 2; and through the determination of the two genes, the isobutanol yield can be improved, and 0.5-0.6C-mol / C-mol glucose can be reached. The key genes which are most important to the isobutanol biosynthesis are obtained through utilizing the relative flux value and are used as modification target spots, the molecular modification of the isobutanol synthetic bacterium is guided, and the isobutanol yield is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
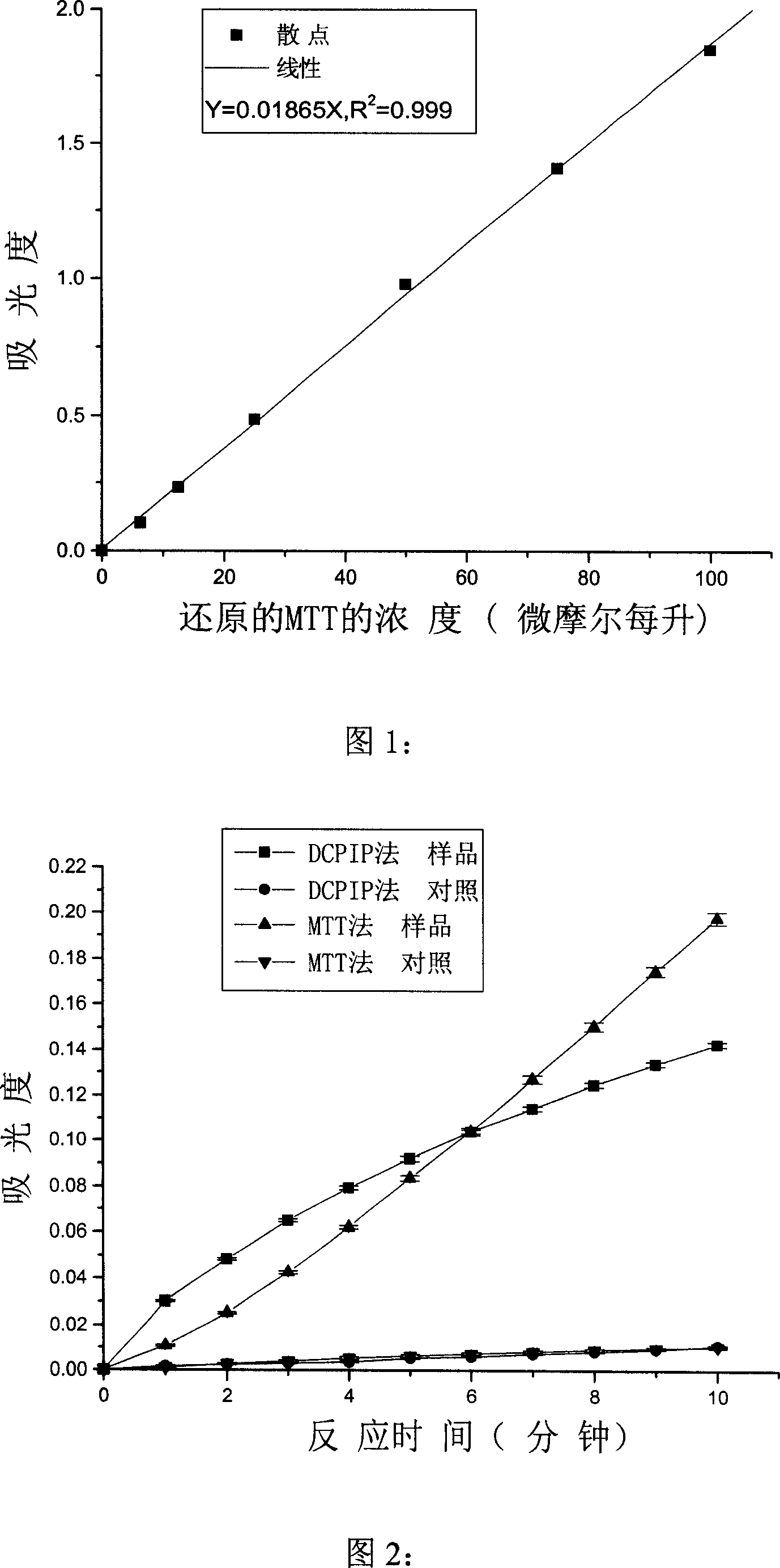
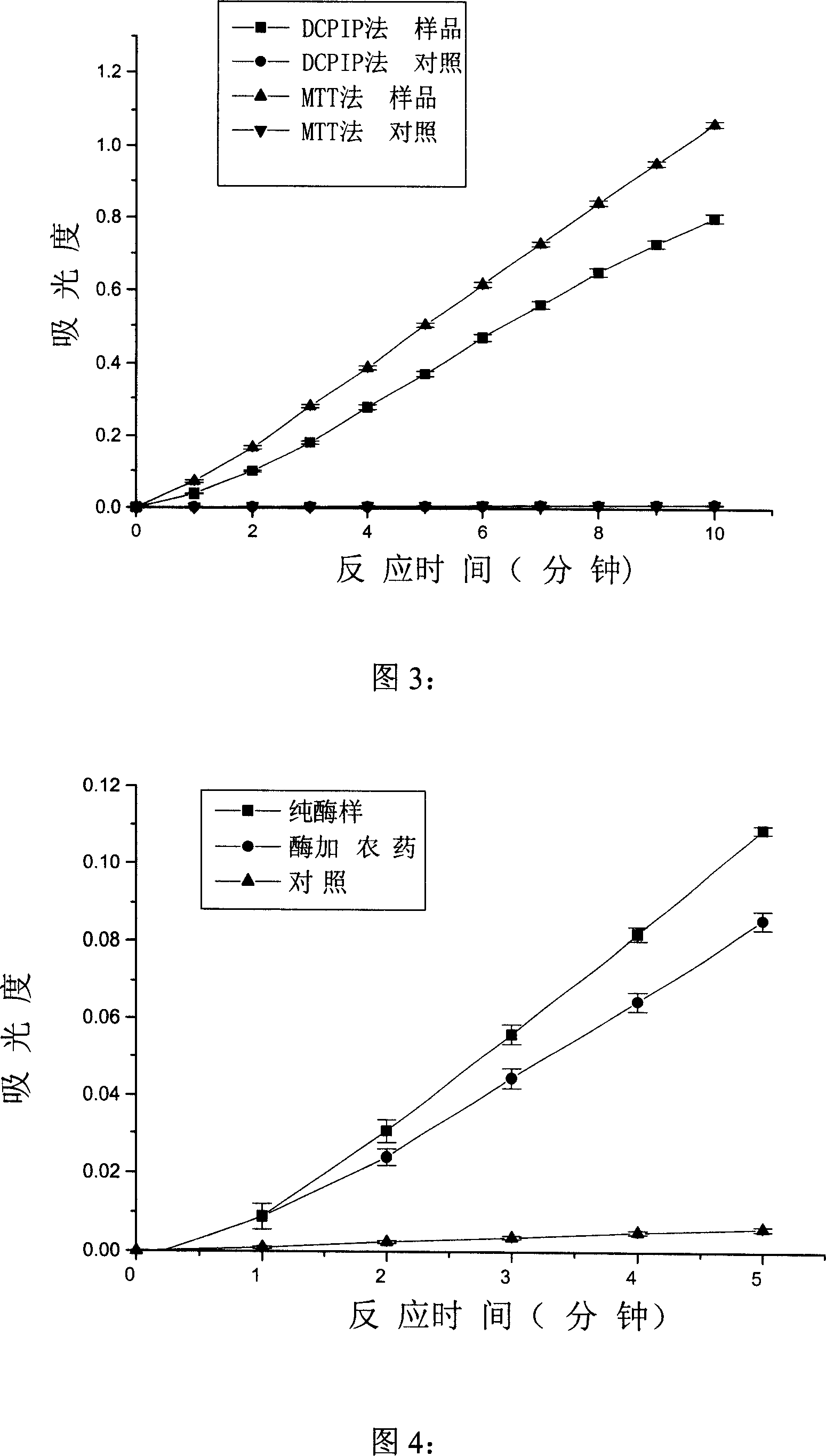
Spectrophotometry for testing activity of pyruvic acid dehydrogenase system
InactiveCN101017134ALow priceSmall standard errorMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsWavelengthMitophagy
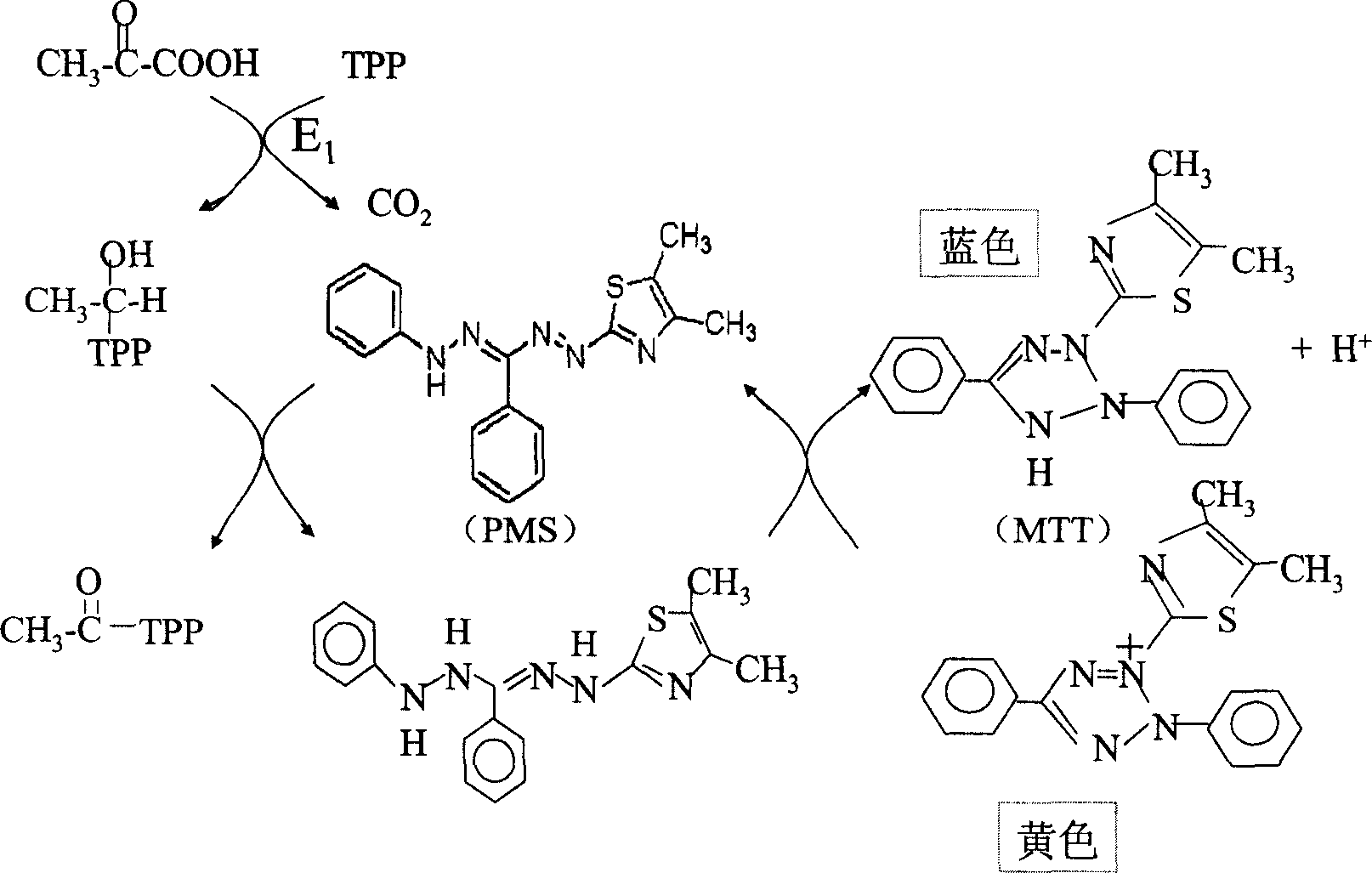
This invention relates to one splitting photometry to test pyruvate dehydrogenase enzyme activity, which comprises the following steps: using splitting meter under situation of underlay of sodium ketopropionate and aid factor magnesium chloride and cocarboxylase using phenazine methyl ester sulfate as electron deliver part and thiazole blue as electron receiver restored by the product of pyruvate dehydrogenase through hydroxyethylation-cocarboxylase with maximum absorptive peak from length for 400 to 430 nanometer into 540 to 640 nanometer; through testing wave length for 540 to 640 nanometer absorptive add volume to determine the restore volume and defining enzyme activity.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Detection method and reagent of enzyme activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
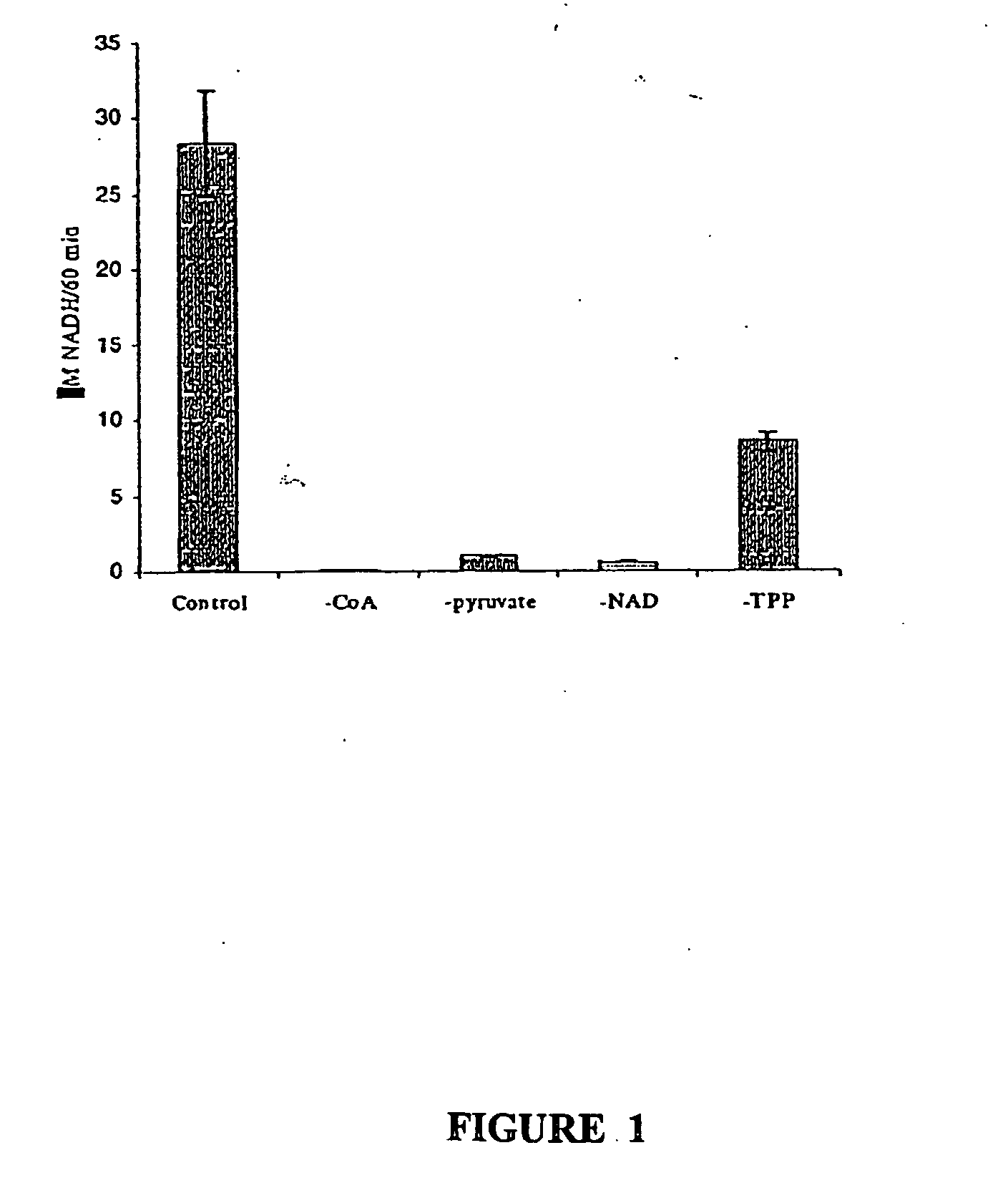
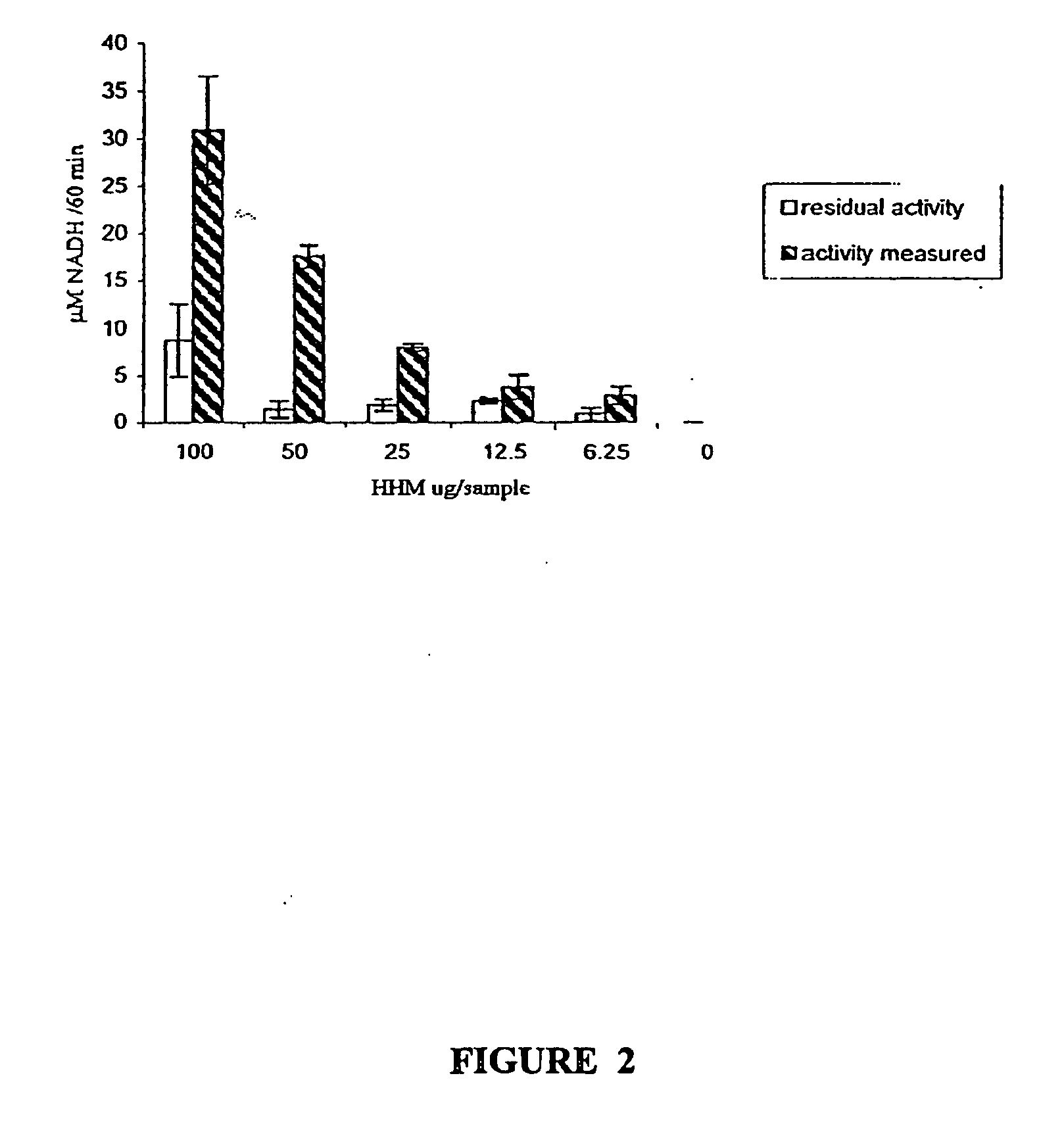
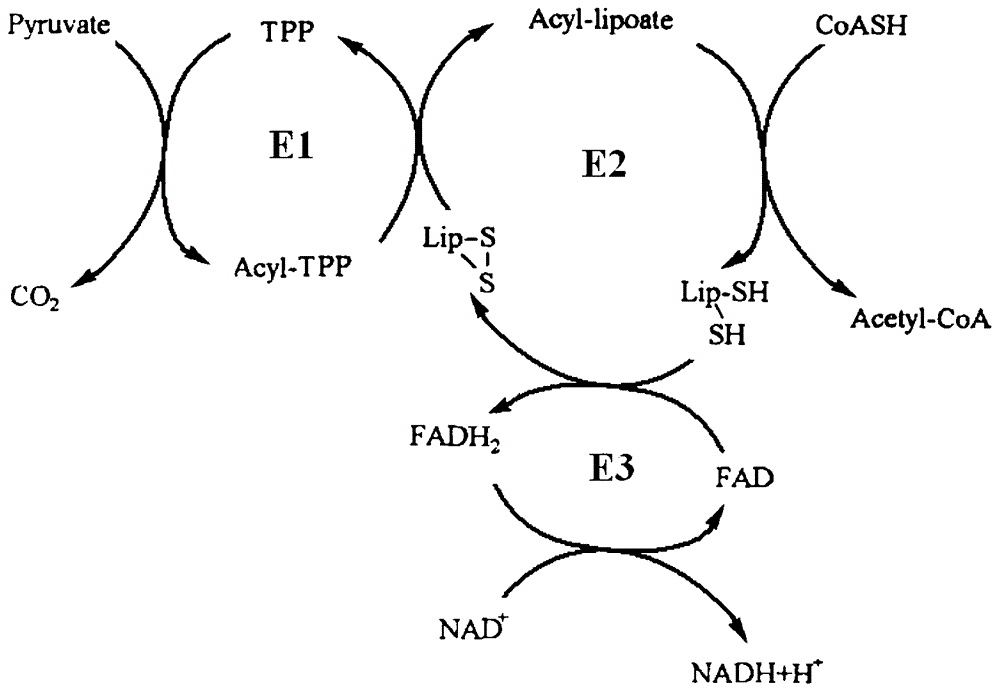
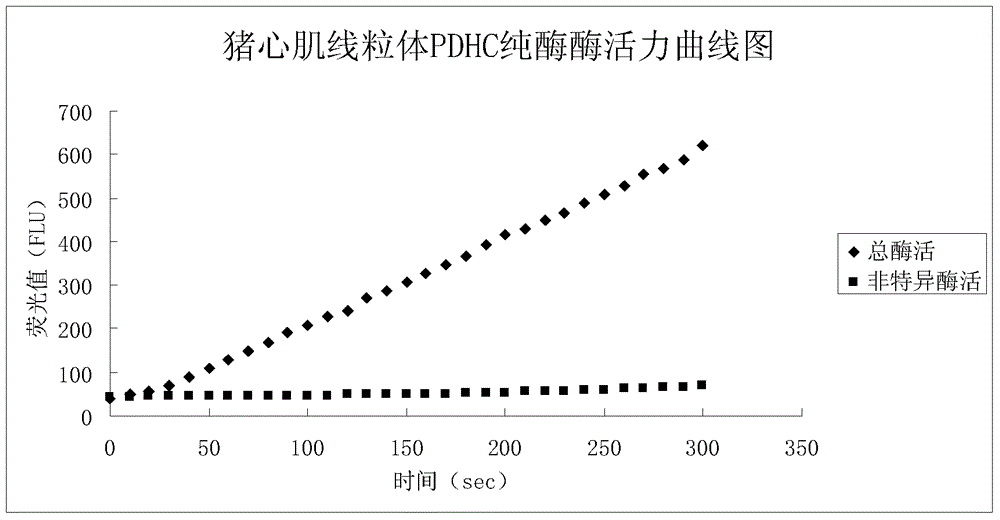
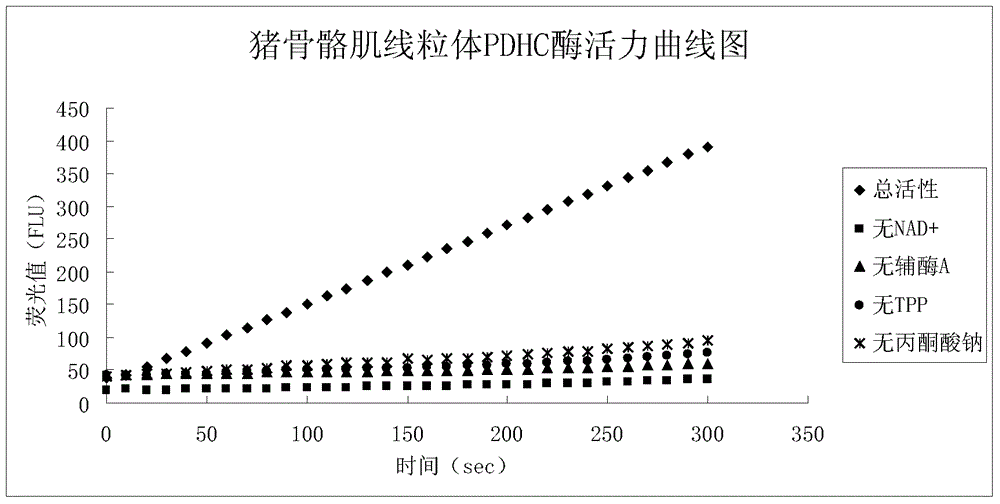
The invention provides a method for enzyme activity analysis and detection of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH complex, PDHC), and the invention also provides a reagent for determining the enzyme activity of PDHC. The method and the agent can be used for analysis and determination of the enzyme activity of PDHC in samples, and thus can be used for analysis, examination and diagnosis of clinical diseases. The principle of the invention is that: PDHC can orderly perform catalytic decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to generate products of CO2, acetyl coenzyme A, and NADH. Therefore, detection of the generation of the final product NADH means the detection of the enzyme activity of PDHC. NADH can emit fluorescence at a specific excitation wavelength, and the reaction rate is in direct proportion to the product fluorescence intensity, so the enzyme activity of PDHC in a sample can be calculated by detecting the fluorescence value change. The detection method of the enzyme activity of PDHC provided in the invention can realize rapid, specific, and sensitive determination of the enzyme activity of PDHC in a sample. Based on the method, the reagent for determining the enzyme activity of PDHC provided by the invention has the characteristics of convenience, rapidness, and high sensitivity, and facilitates popularization and application.
Owner:北京中科非凡生物技术有限公司
Recombinant microorganisms for enhanced production of mevalonate, isoprene, and isoprenoids
ActiveUS20160032323A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesHeterologousCitrate synthase
The invention features compositions and methods for the increased production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids in microorganisms by engineering a microorganism for increased carbon flux towards mevalonate production in the following enzymatic pathways: (a) citrate synthase, (b) phosphotransacetylase, (c) acetate kinase, (d) lactate dehydrogenase, (e) malic enzyme, and (f) pyruvate dehydrogenase such that one of more of the enzyme activity is modulated. In addition, production of mevalonate, isoprene, isoprenoid precursor molecules, and / or isoprenoids can be further enhanced by the heterologous expression of the mvaE and mvaS genes (such as, but not limited to, mvaE and mvaS genes from the organisms Listeria grayi DSM 20601, Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus gallinarum EG2, and Enterococcus casseliflavus).
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
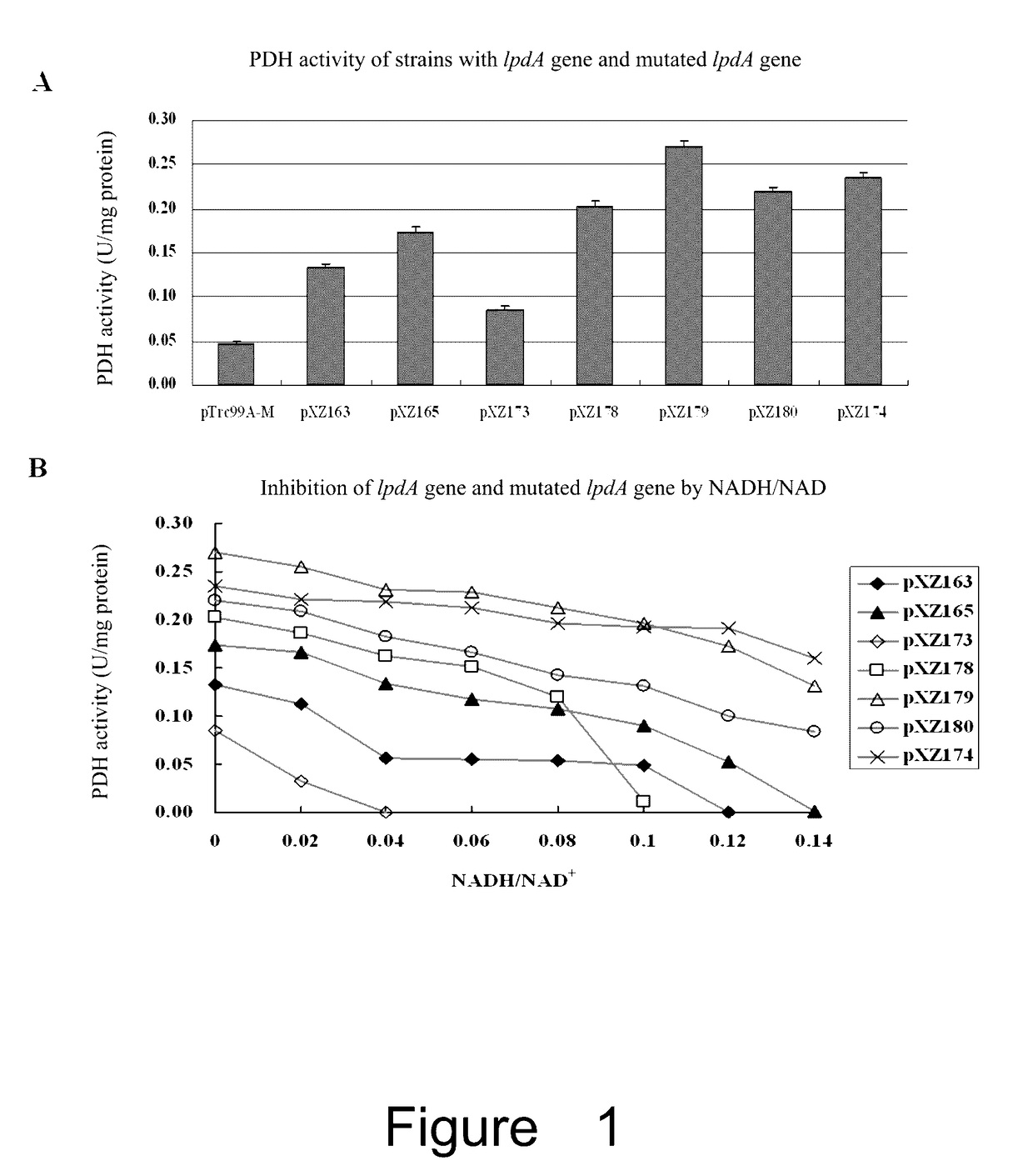
Escherichia coli containing mutated lpdA gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of modifying E. coli through genetic engineering. Specifically, the invention provides an E. coli containing a mutated lpdA gene. The invention also relates to use of the E. coli in the production of chemical material such as ethanol, and succinate etc. The invention also provides a method of producing chemical materials such as ethanol and succinate etc. by using the E. coli, as well as a method for increasing the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase in E. coli by introducing a mutated lpdA gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Microbial production of pyruvate and other metabolites
InactiveUS20050255572A1Redox balancedIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaAcetic acidMicroorganism
Microbial production of pyruvate and metabolites derived from pyruvate in cells exhibiting reduced pyruvate dehydrogenase activity compared to wild-type cells. Acetate and glucose are supplied as a carbon sources.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Application of Chinese yarn glycoprotein in improvement of activities of oxidative metabolism enzymes of mitochondria of brain cell
ActiveCN102920998AHigh activitySimple extraction methodNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsYarnKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to an application of Chinese yarn glycoprotein in improvement of the activities of an oxidative metabolism enzymes of mitochondria of a brain cell. Selection and verification are carried out by an animal test so as to prove that the Chinese yarn glycoprotein can obviously improve the activities of key enzymes namely pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase used for oxidative metabolism in the mitochondria of the brain cell, so that brain cell deterioration and damage diseases, such as senile dementia, vascular dementia, cerebral infarction and cerebral palsy, accompanying with oxidative metabolism efficiency reduction caused by reduction of the activities of the enzymes can be effectively treated.
Owner:新乡博凯生物技术有限公司
Staphylococcus aureus mutant strain, and preparation method and applications thereof
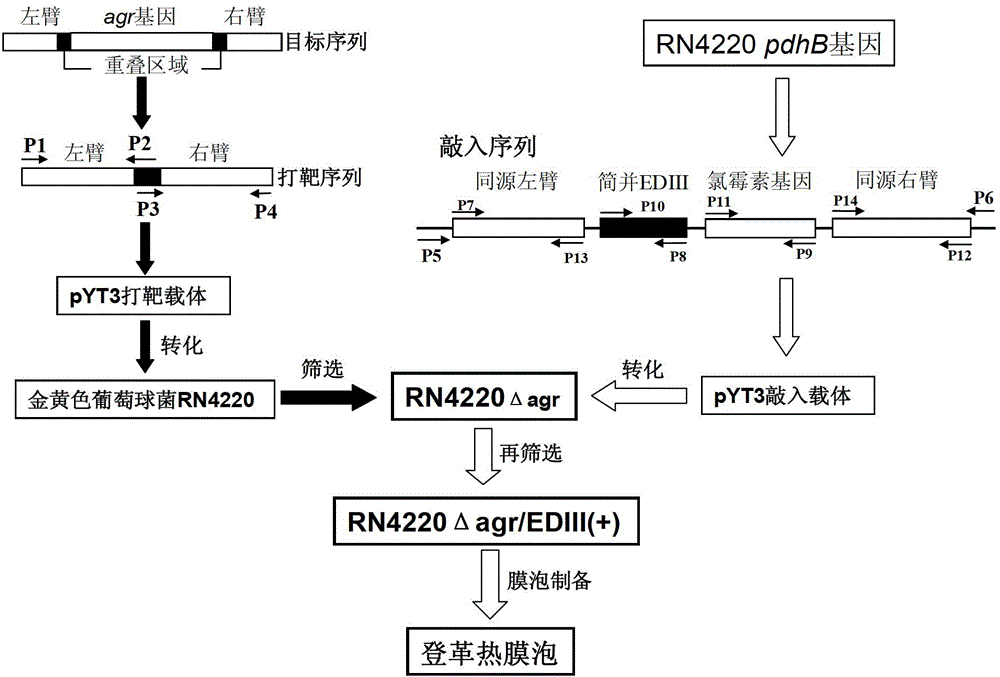
ActiveCN103333849ABiological properties are stableLow toxicityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses a staphylococcus aureus mutant strain, and a preparation method and applications thereof in general. The preservation number of the mutant strain is CGMCC No.7583. The preparation method comprises following steps: performing gene knockout of agr gene, which is used for encoding a global regulatory factor (Agr) and is in staphylococcus aureus RN 4220 strain chromosomes, by application of homologous recombination; implanting a degenerate sequence used for encoding dengue virus envelope E protein EDIII region to 3' terminal of RN4220 pdhB gene, which is used for encoding pyruvate dehydrogenase beta-subnit ,by application of homologous recombination; implanting chloramphenicol resistant encoding gene at the back of EDIII; and then performing nucleotide sequencing for identification. The mutant strain of the invention is taken as engineering bacteria, and after fermentation, bacterial membrane vesicles containing dengue virus EDIII recombinant protein are purified from obtained fermentation supernatant. The dengue virus membrane vesicles produced by bacteria are used as a vaccine in prevention of infectious disease caused by dengue virus.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
System for treating eye and nerve diseases in diabetic and non-diabetic patients
The present invention is a system capable of increasing retinal and neural glucose oxidation by enhancing pyruvate dehydrogenase activity and therefore treats retinopathy and central nervous system disorders in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients. The current invention is a system of the treating of eye and nerve diseases using insulin pulses to a patient utilizing Chronic Intermittent Intravenous Insulin Therapy to achieve an increase in retinal and neural glucose oxidation by enhancing pryuvate dehydrogenase activity, therefore treating retinopathy and central nervous system disorders in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
Owner:AOKI THOMAS T
Enzyme cofactor combination for supplementing pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha ketogluterate dehydrogenase complexes
The present invention provides a method and pharmaceutical composition for preventing or treating the development of syndromes related to dysfunctional energy metabolism, such as neuropathy, spontaneous nocturnal muscle cramps associated with neuropathy, seizuring, diabetes mellitus; pediatric hypoglycemia; myopathy; muscle fatigue; muscle spasms; somnolence; reduced mental acuity; exercise intolerance and myocardial insufficiency, which are due to cofactor deficiencies associated with the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and the alpha-ketogluterate dehydrogenase (a-ketogluterate dehydrogenase) complex in humans or other mammals in need thereof. In particular, a method of preventing or treating at least one syndrome related to defective glucose metabolism in humans or other mammals is provided comprised of administering a combination of enzyme cofactors containing therapeutically effective amounts of thioctic acid, niacinamide, pantothenate, riboflavin and thiamine. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprised of a carrier and the combination of cofactors.
Owner:HOWARD JAMES R
Pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN102056605AMinimize side effectsAntineoplastic agentsAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsMetabolitePhosphorylation
A pharmaceutically-acceptable modulator of the regulation or perturbation of the structure, expression, and / or activity of at least one enzyme and / or enzyme complex, or subunit thereof, such as via the altered mitochondrial energy metabolism of the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex of warm-blooded animals, including humans, and methods of use thereof, comprises an effective amount of at least one lipoic acid derivative and at least one pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier thereof to affect the complex's phosphorylation state. By increasing PDH kinase activity and / or decreasing PDH phosphatase activity, the modulator prevents the detoxification anaerobic glycolytic toxic metabolites through inhibition of the activity of the PDH complex's El a subunit, obliging increased mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation activity. As cells characterized by hyperproliferation, such as tumor cells, cannot also generate acetyl-CoA and NADH because of the modulator's additional action in inhibiting the action of the PDH complex's E2 subunit, the mitochondrial membrane polarization is lost, facilitating cell death.
Owner:罗伯特・绍尔 +1
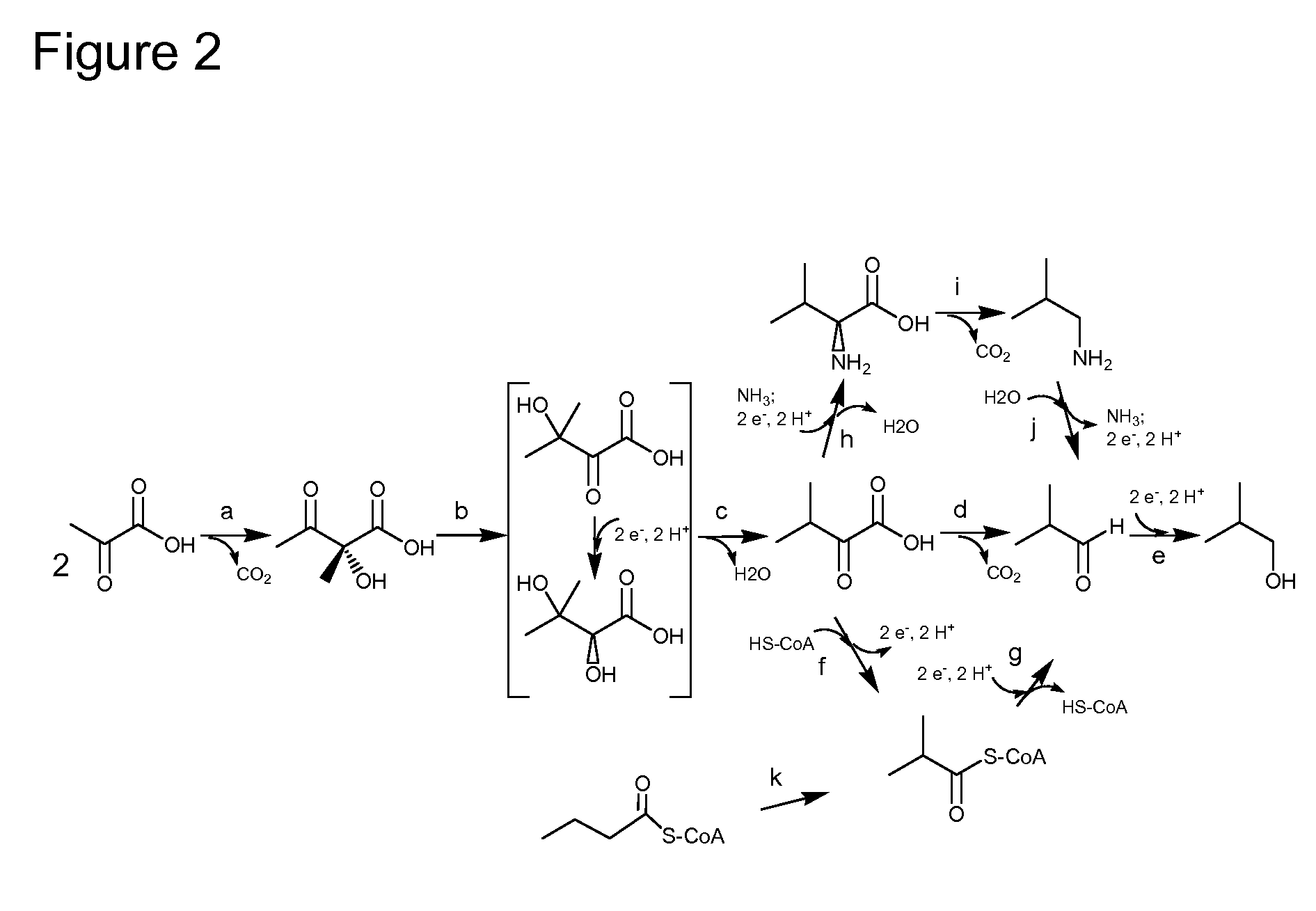
Branched-chain alpha-keto-acid dehydrogenase system inhibitor and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108976214AThorough responseSimple post-processingPlant growth regulatorsBiocideHalogenGeometric isomer
The invention provides a compound and a preparation method and an application thereof, in particular a compound as shown in a formula I or a stereisomer, a geometrical isomer, tautomer, a despinner, anitric oxide, a hydrate, a solvate and pharmaceutical acceptable salt, wherein R1 is hydrogen or halogen and X is C or N; and R2 is a mono-substituent or a poly-substituent in any positions of a benzene ring, and the substituents can be same or different. The compound can be used for inhibiting growth of algae. The formula I is as shown in the description.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
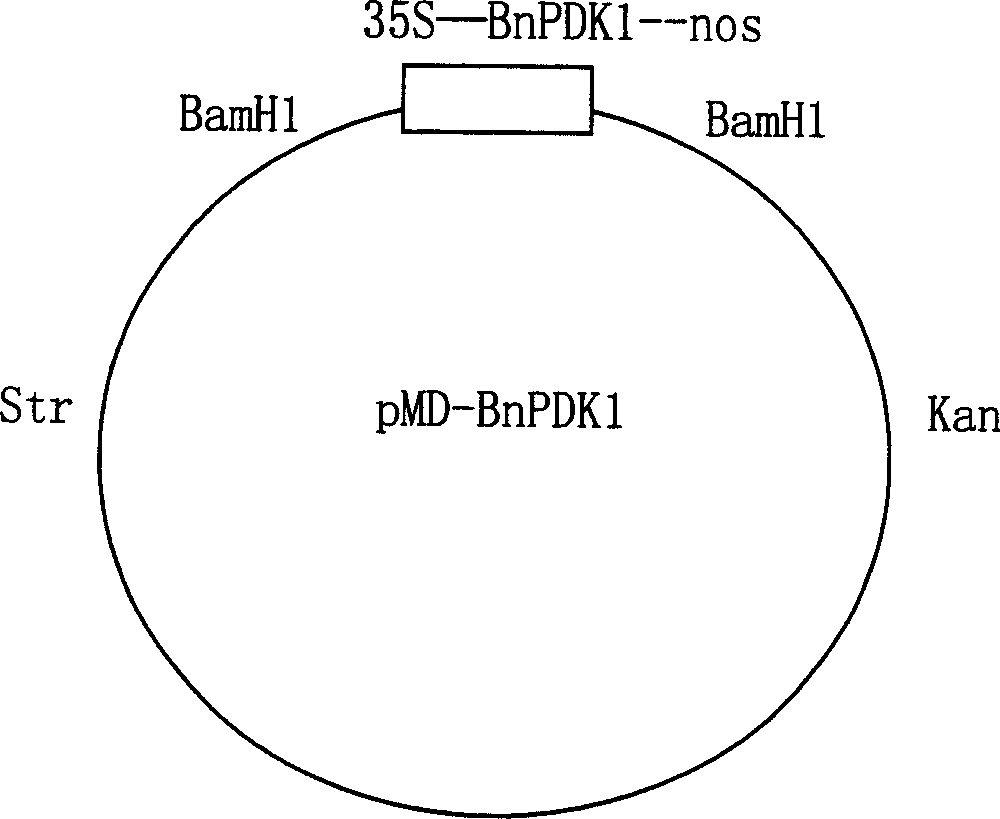
Rape pyruvic dehydrogenase kinase gene and its application in rape
InactiveCN1772906AShortened growth periodIncrease productionOxidoreductasesFermentationNucleotidePlant cell
The present invention discloses one kind of rape pyruvic dehydrogenase kinase gene and its application in rape, and relates to gene engineering technology. The gene has nucleotide sequence coding the protein kinase catalysis area and mitochondrion locating sequence SEQ ID No. 1. The application of the gene in rape includes: 1. providing one kind of vector including proper promoter and translation controlling part; 2. providing one kind of host bacteria capable of being expressed in plant; 3. providing one method of introducing the vector to the plant cell; 4. providing one kind of plant transformed with the vector containing pyruvic dehydrogenase kinase gene; and 5. providing one transgenic rape capable of inhibiting the expression of rape pyruvic dehydrogenase kinase gene. The transgenic rape exhibits early blooming character, shortened growth period, and increased seed yield and oil bearing rate.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Enhanced Pyruvate to Acetolactate Conversion in Yeast
Owner:GEVO INC
Method for Decreasing Pyruvate Catabolism and Increasing the Accumulation of Pyruvate in Microbes
ActiveUS20160138054A1Accelerate the accumulation processDecreasing pyruvate catabolismFungiAcyltransferasesPyruvate catabolismMicroorganism
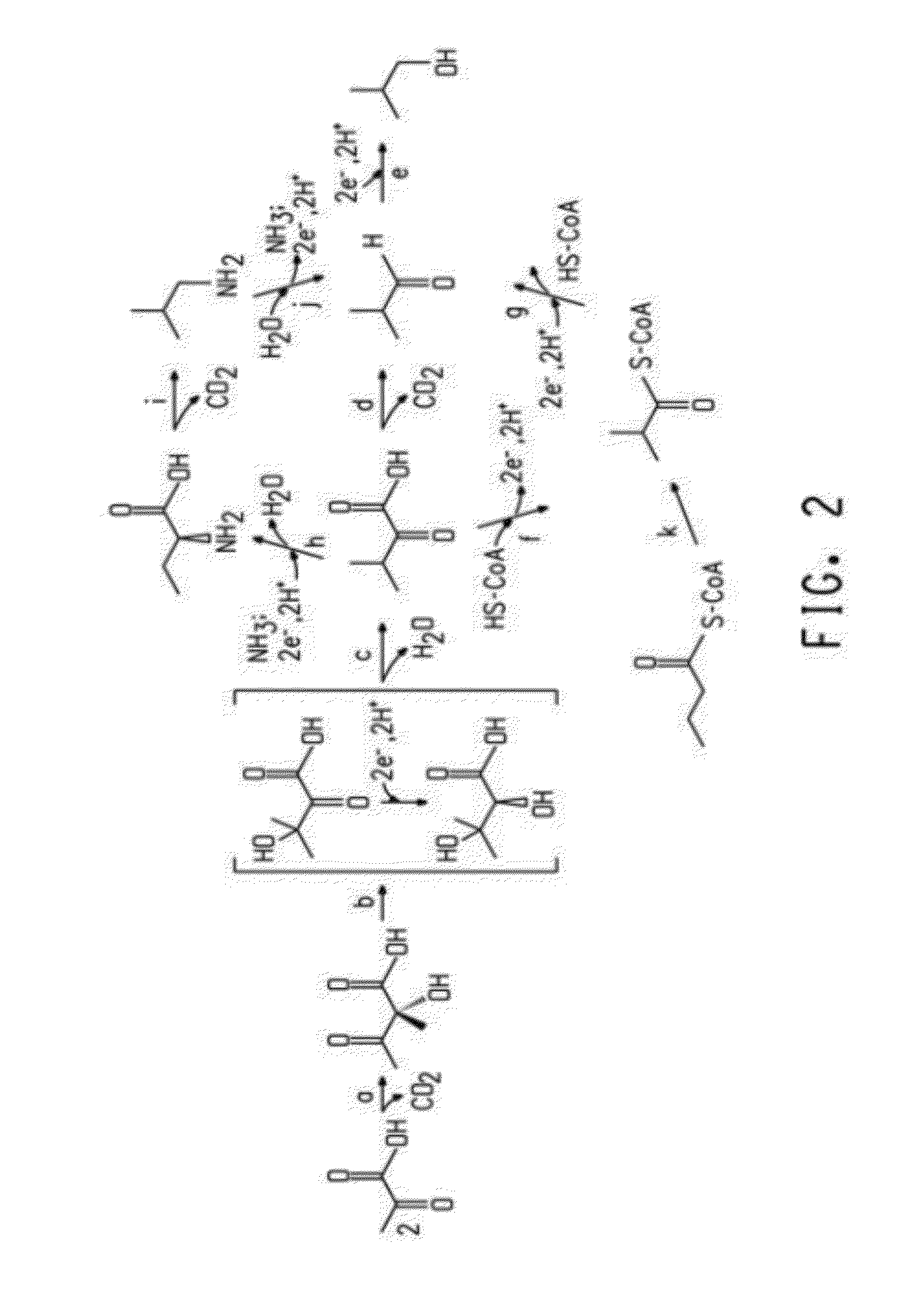
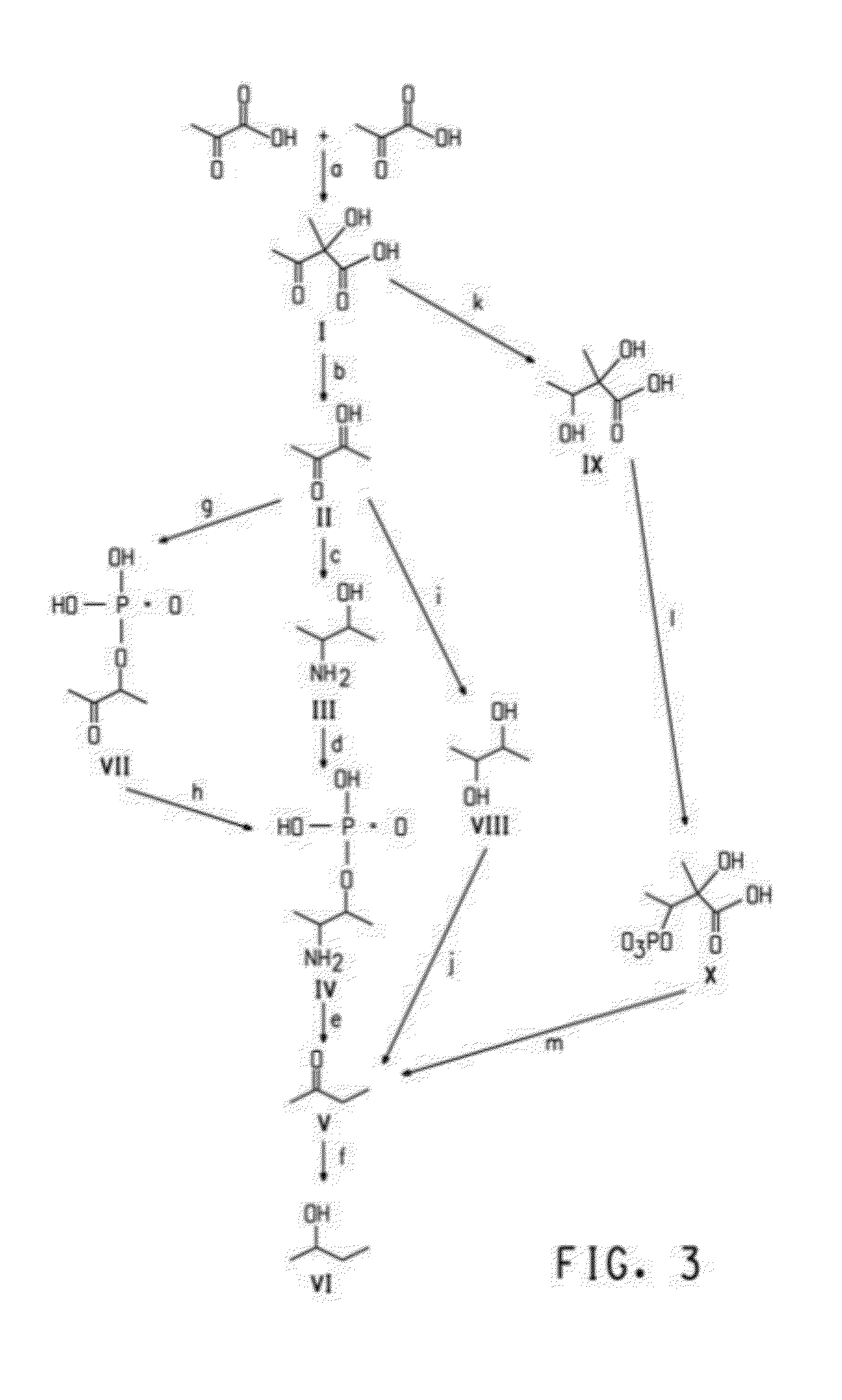
The present invention provides a method for decreasing pyruvate catabolism and increasing the accumulation of pyruvate in microbes. By overexpressing wild type dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase or dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase mutants which have mutations at conservative active sites, the present invention provide a method to decrease overall activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and pyruvate catabolism, and thus increase the accumulation of extracellular pyruvate without killing the pyruvate-producing microbes. Overexpressing dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase mutants is an effective way to increase pyruvate accumulation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com