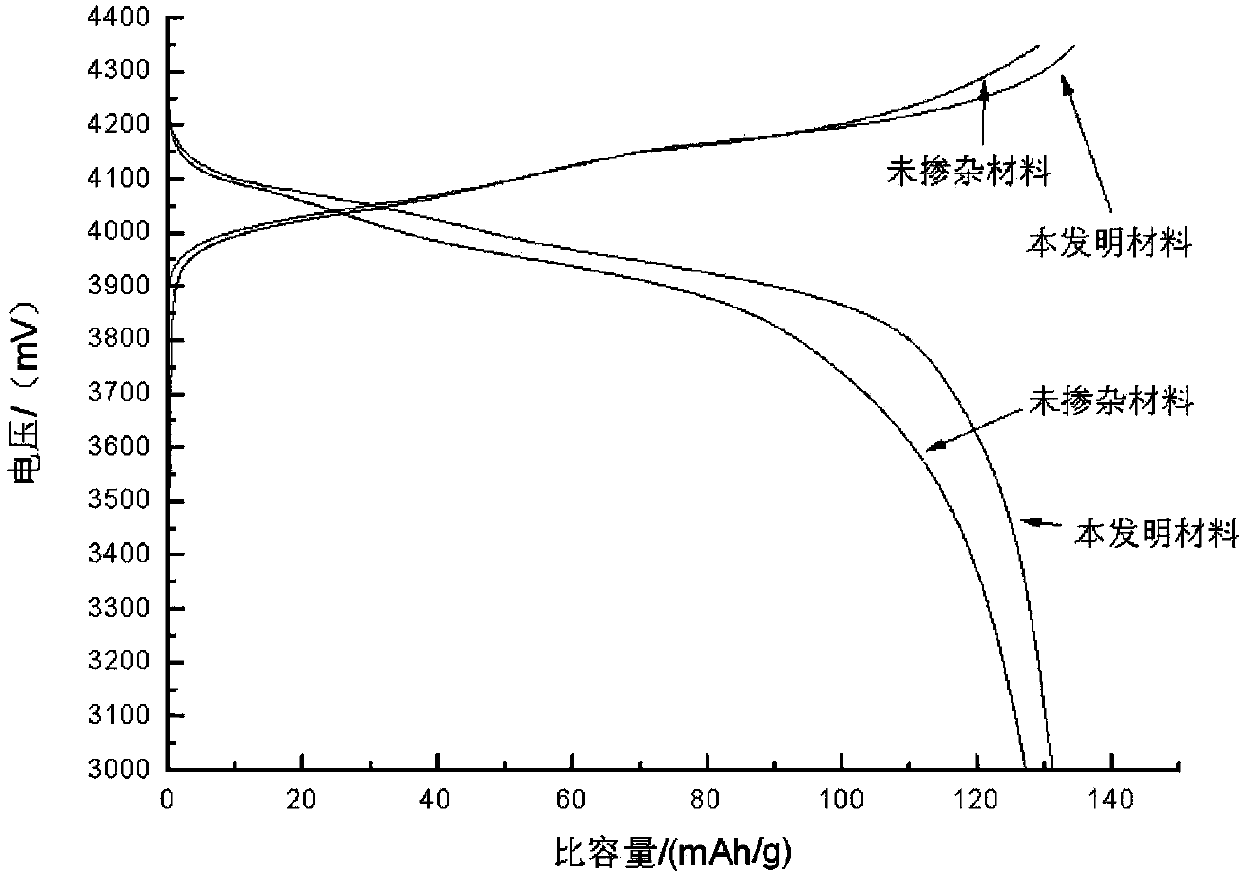
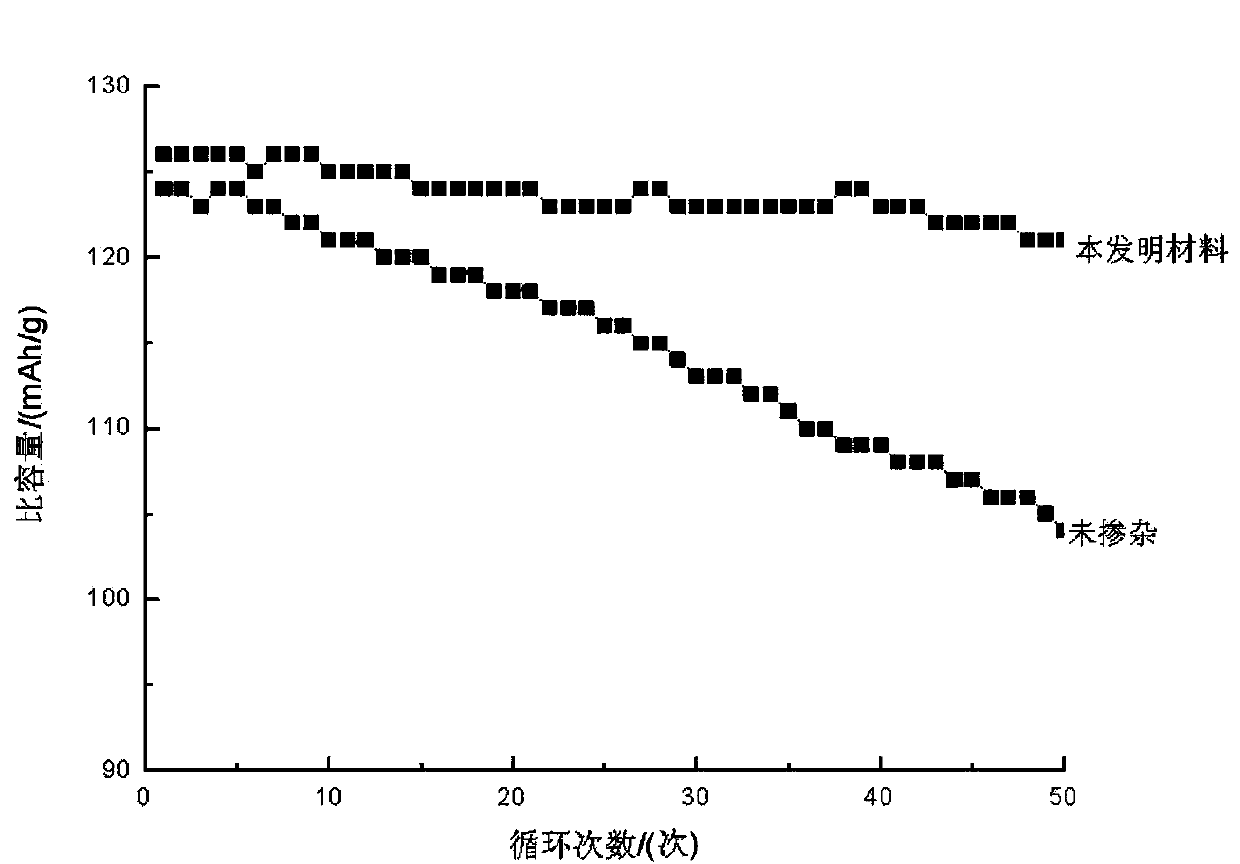
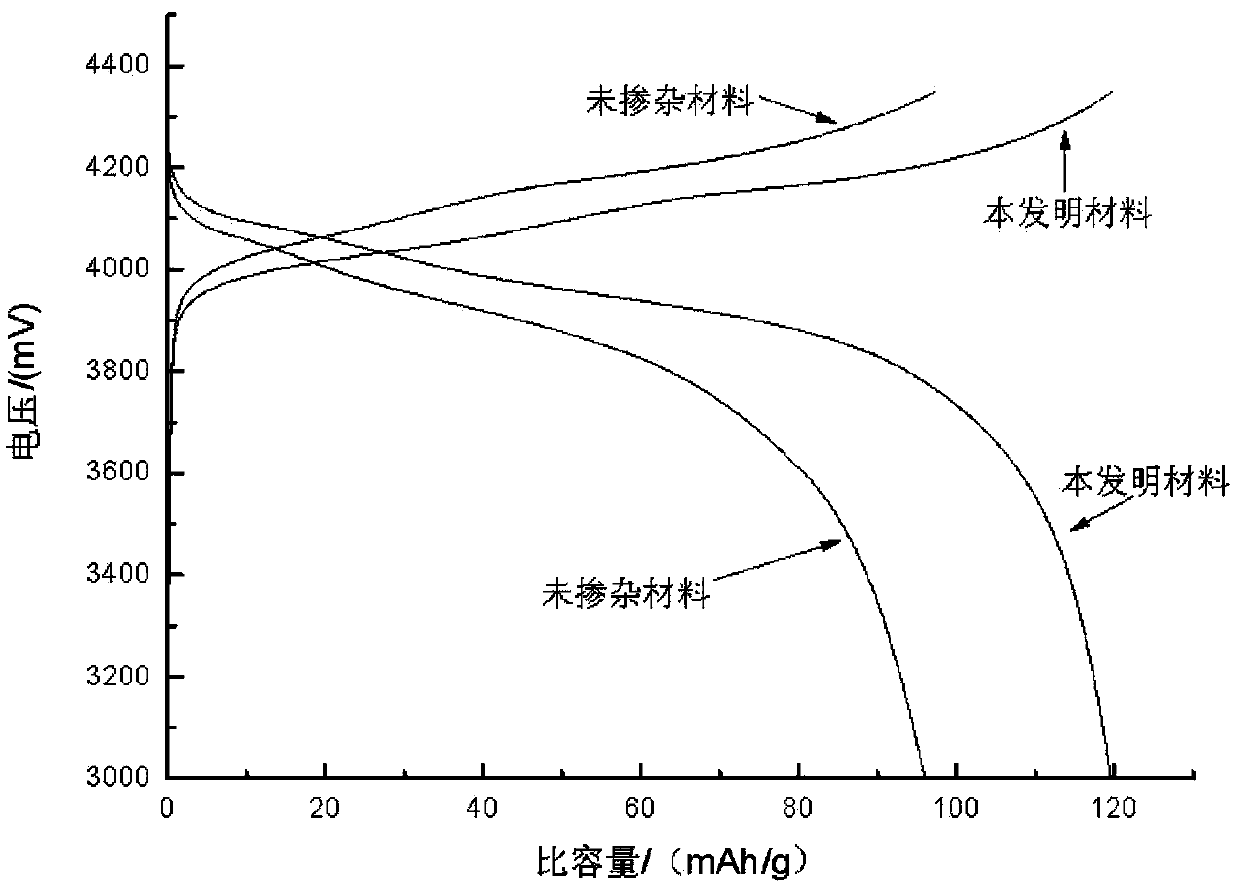
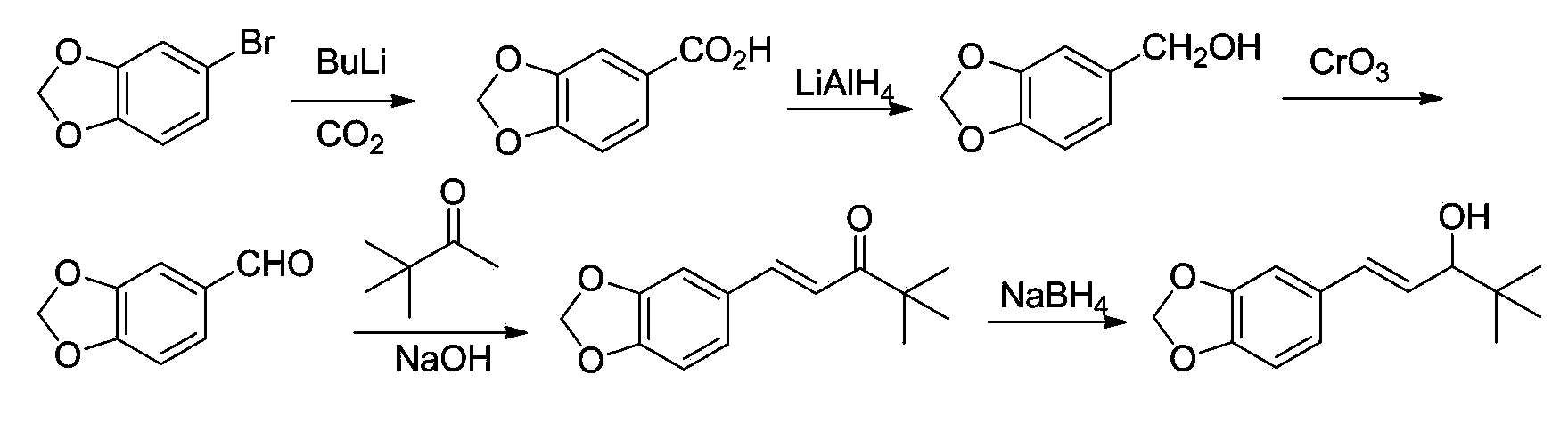
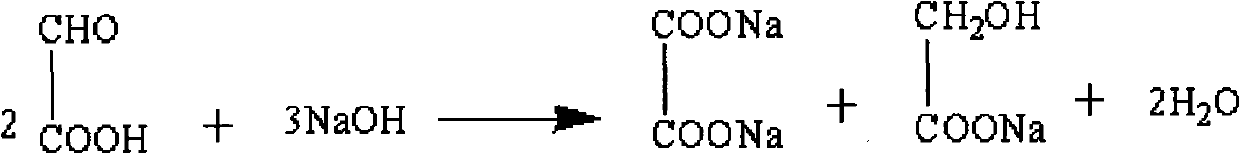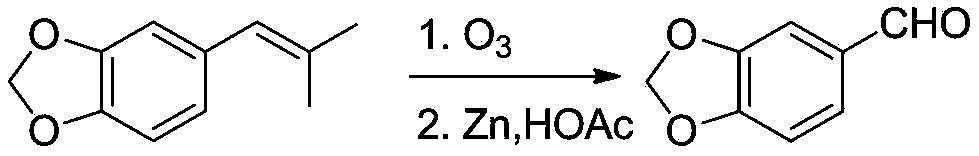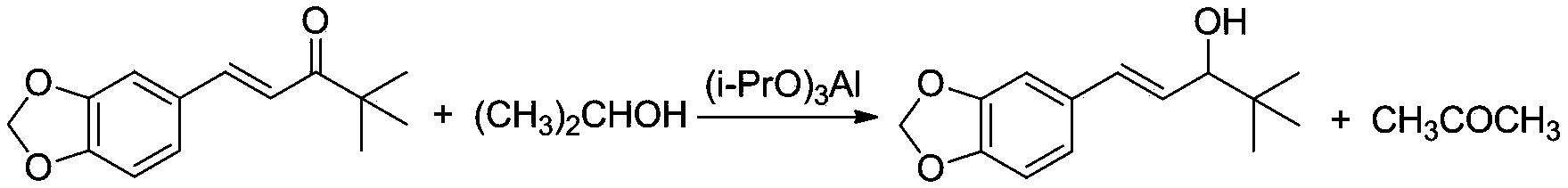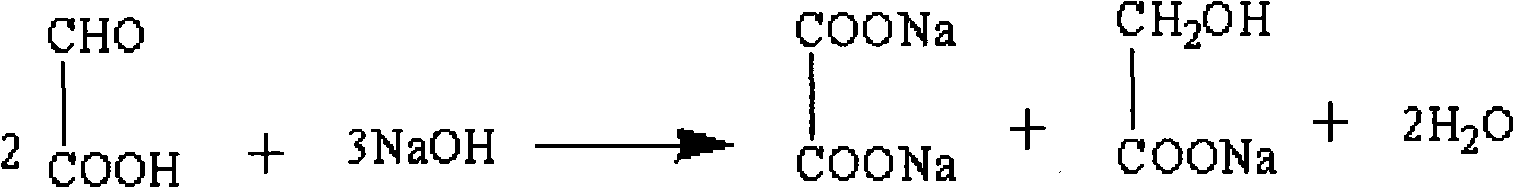Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Avoid disproportionation reactions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing monofluoromethane by Pd-M alloy supported catalyst
ActiveCN109824473AModerate pHImprove stabilityPreparation by dehalogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNanoparticleAlloy catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing monofluoromethane by using a Pd-M alloy supported catalyst. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following steps: firstly, loading metalM nanoparticles on a carrier, then mixing and stirring a Pd precursor aqueous solution, preparing monodisperse Pd atoms on metal M through displacement reaction, and combining the Pd atoms with the Mmetal through roasting to form a Pd-M alloy to obtain the monodisperse Pd-M alloy supported catalyst, wherein the metal M can be Cu, Zn, Ni, Ru, Sn or Fe. Compared with single, double and multi-component non-alloy catalysts, the Pd-M alloy supported catalyst has higher selectivity to monofluoromethane (HFC-41) when used for catalyzing hydrogenation dechlorination of chloro-monofluoromethane to prepare monofluoromethane, can reach about 95%, is not prone to carbon deposition, and has longer service life (within 10% of activity reduction and within 5% of selectivity reduction within 1000h); andmoreover, the process route for preparing the monofluoromethane is simple, environment-friendly and safe.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
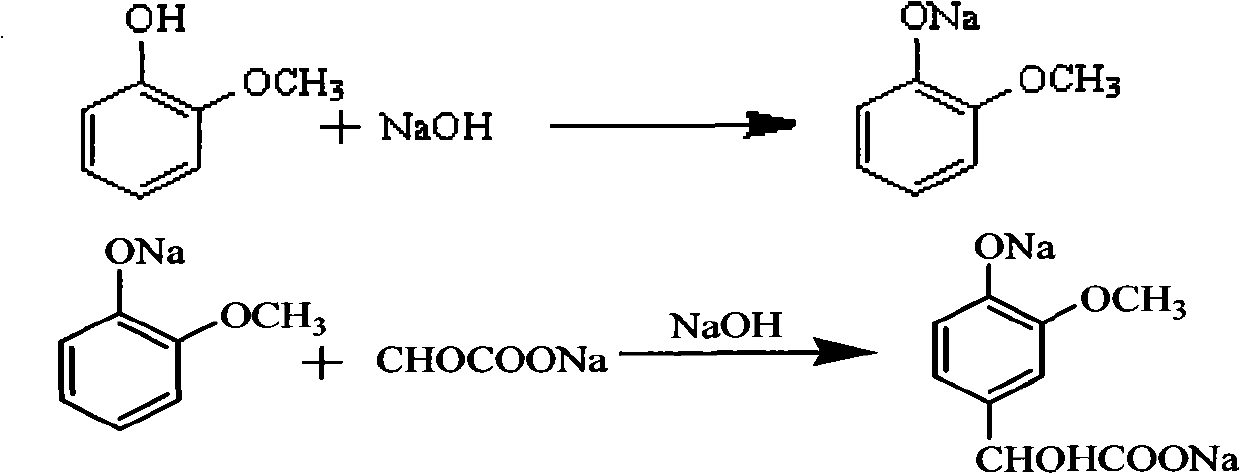
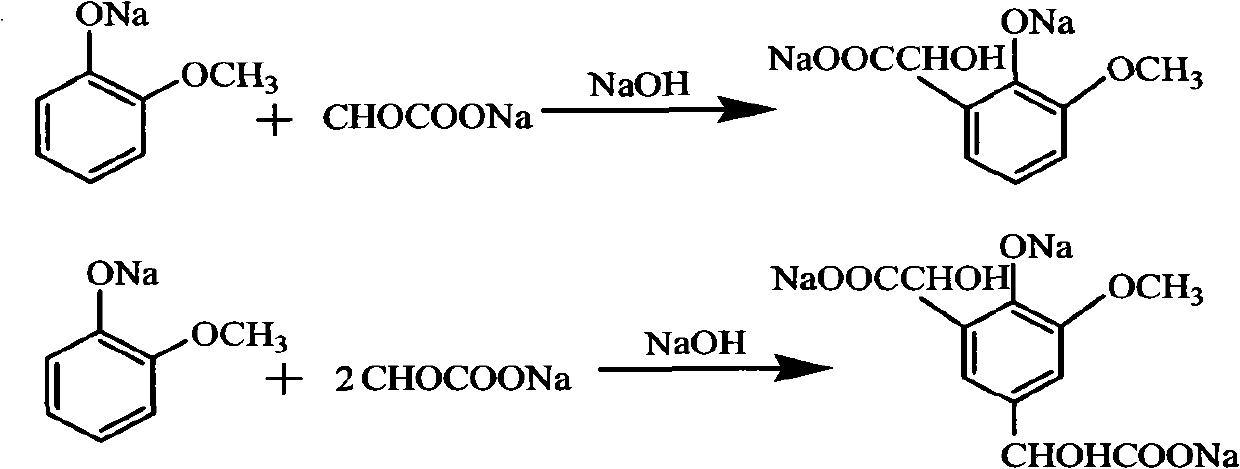
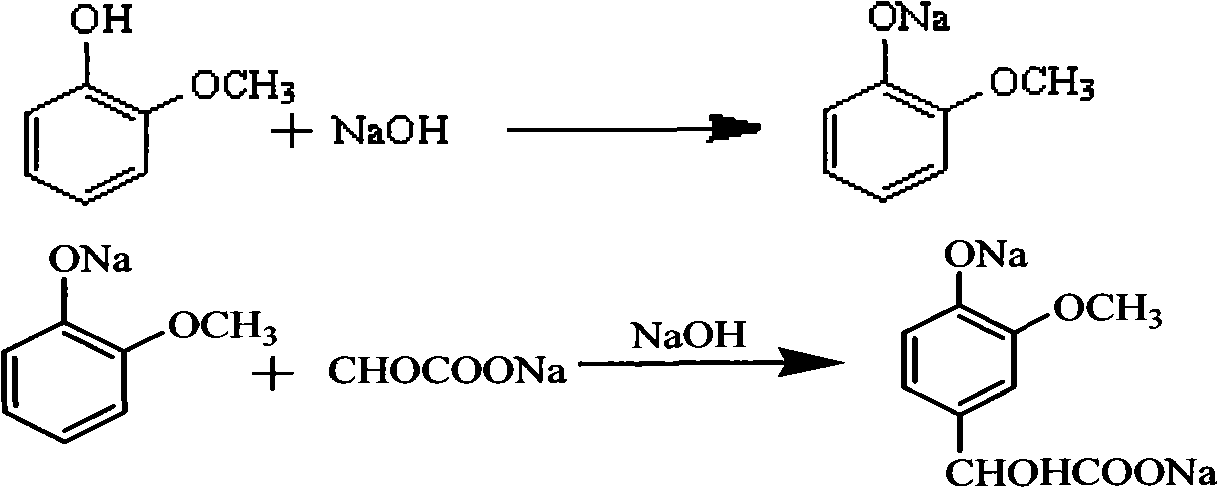
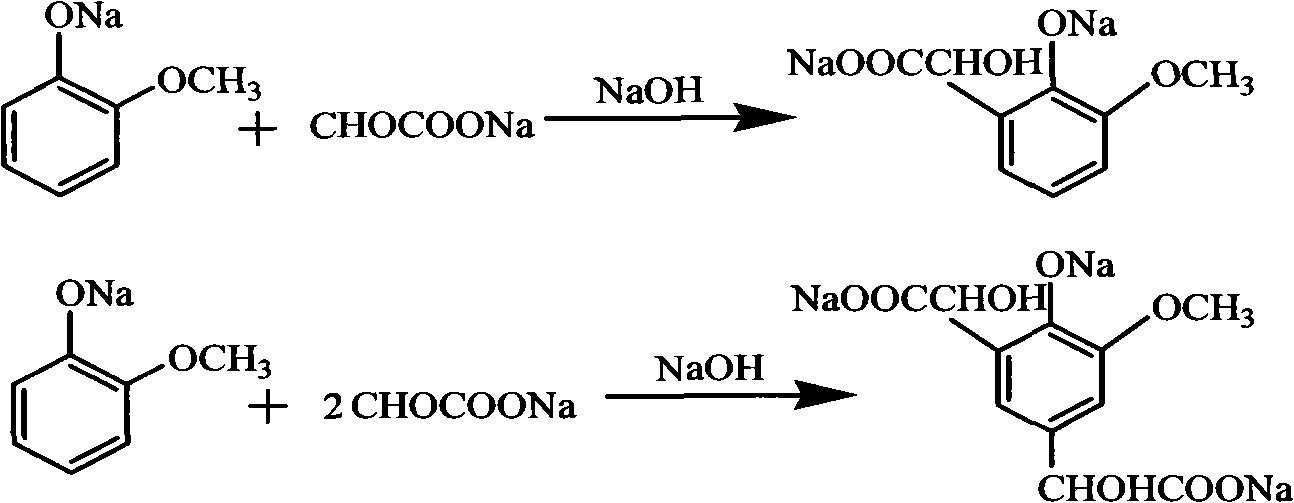
Method for preparing 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy mandelic acid
ActiveCN102086151APrevent oxidationIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationReaction temperatureGuaiacol
A method for preparing 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy mandelic acid adopts guaiacol and glyoxylic acid as raw materials, and comprises the following steps: slowly adding a 30 wt% sodium hydroxide solution into the glyoxylic acid solution with stirring, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-50 DEG C and a pH value of 1-7 to obtain a sodium glyoxylate solution; adding the guaiacol into water with stirring and under the protection of nitrogen gas, slowly adding the 30 wt% sodium hydroxide solution, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-50 DEG C and a pH value of 11-12 to obtain guaiacol sodium; slowly and dropwisely adding the sodium glyoxylate solution into the guaiacol sodium solution with stirring and under the protection of nitrogen gas, with the mole ratio of the sodium glyoxylate and the guaiacol sodium being 1:1.2-2, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-20 DEG C and a pH value of 11-12, 30-90 min afterthe dropwise addition, stirring the mixed solution for 1-3 hours, stopping the reaction at the reaction temperature for 24-36 hours, then acidifying the reaction solution by a 50 wt% sulfuric acid solution to control the pH value to be 4-5. The yield of the reaction is above 95 wt%.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for preparing nano-grade rutile phase RuO2-SnO2 oxide
The invention provides a method for preparing RuO2-SnO2 oxide completely composed of nanoscale rutile phase by using RuCl3, SnCl2 and SnCl4 as precursors. The ratio of RuO2:SnO2 in the titanium anode coating prepared by the invention is 1:4-4 : 1, the surface coating of the titanium substrate is entirely composed of nanoscale rutile phase RuO2-SnO2 oxide or solid solution, and its specific surface area exceeds 460m2·g-1; and the raw materials are easy to obtain and the method is simple.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
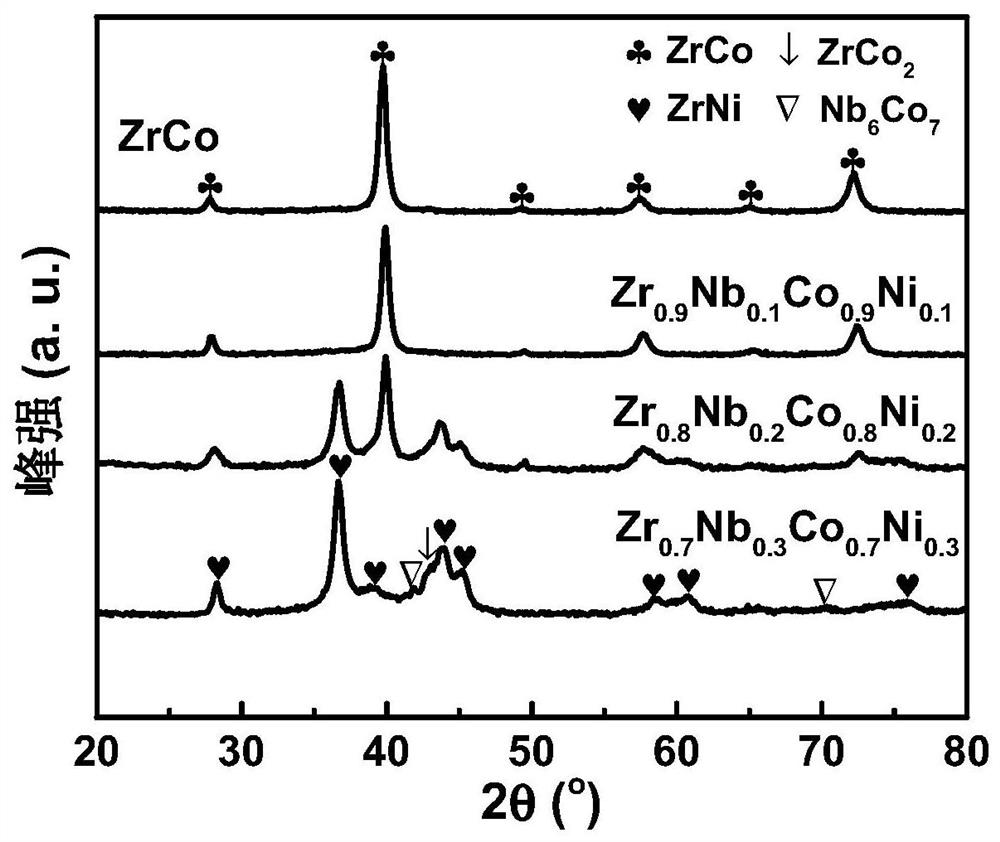
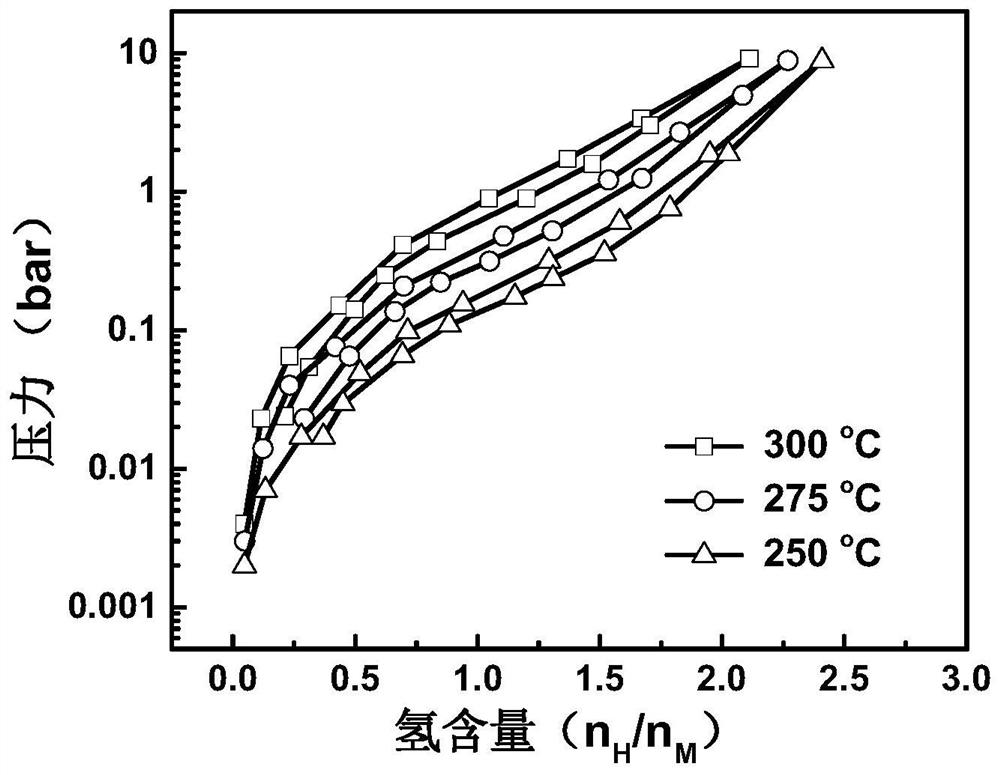
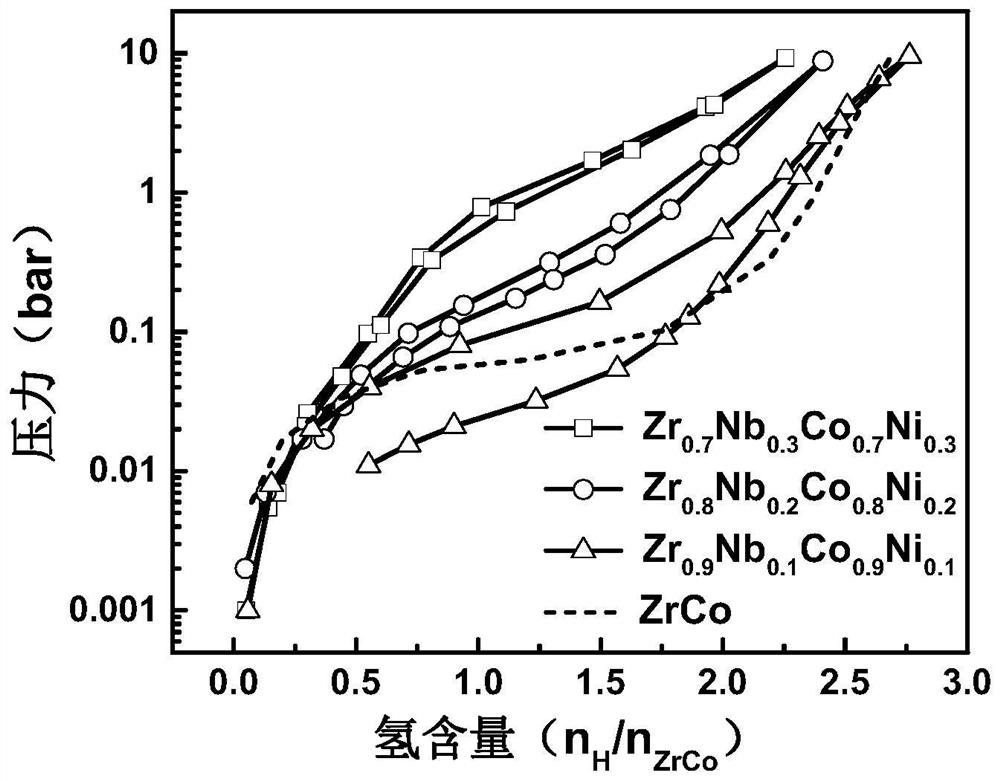
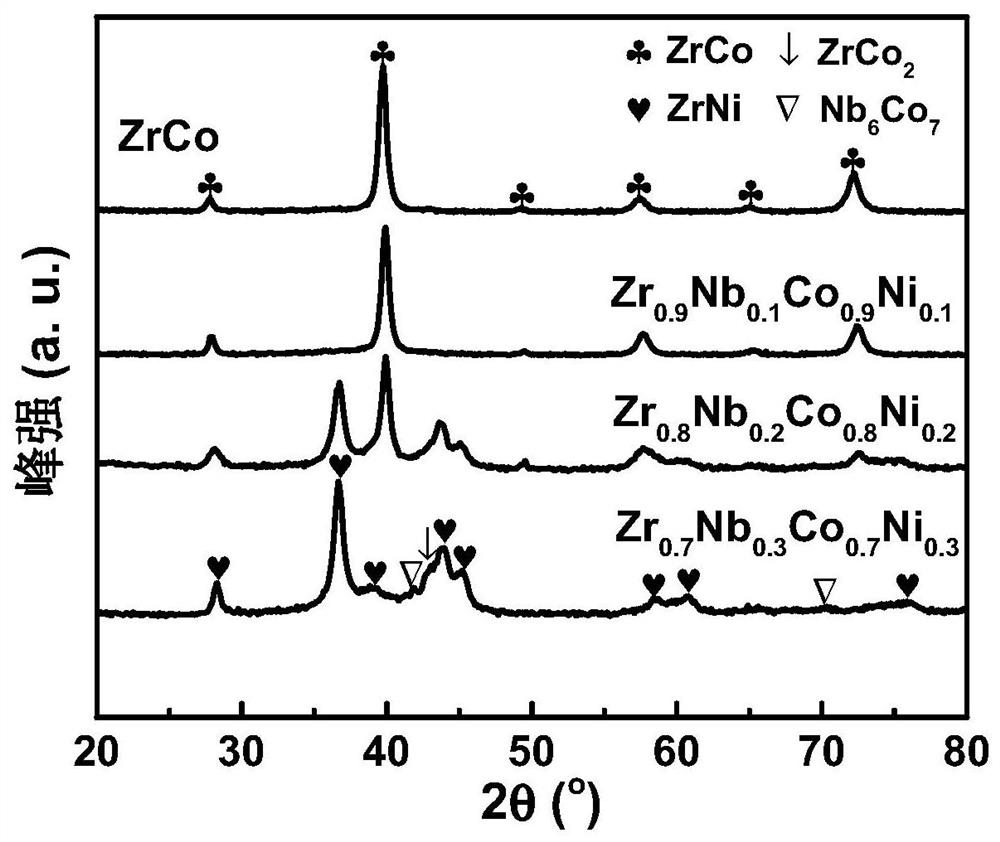
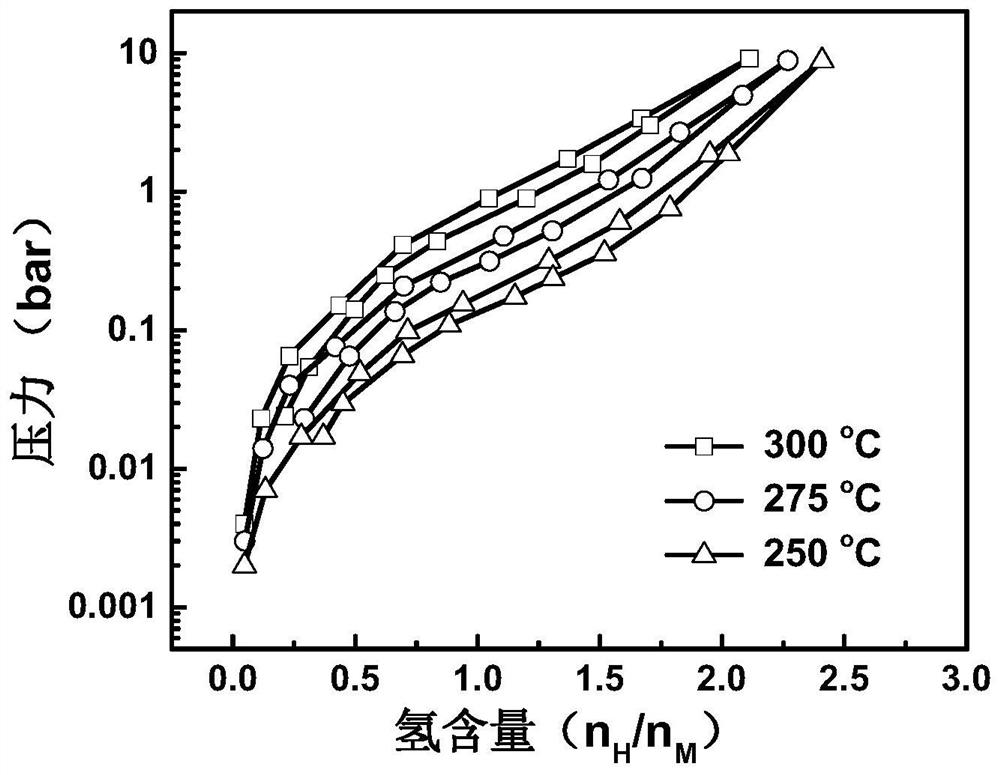
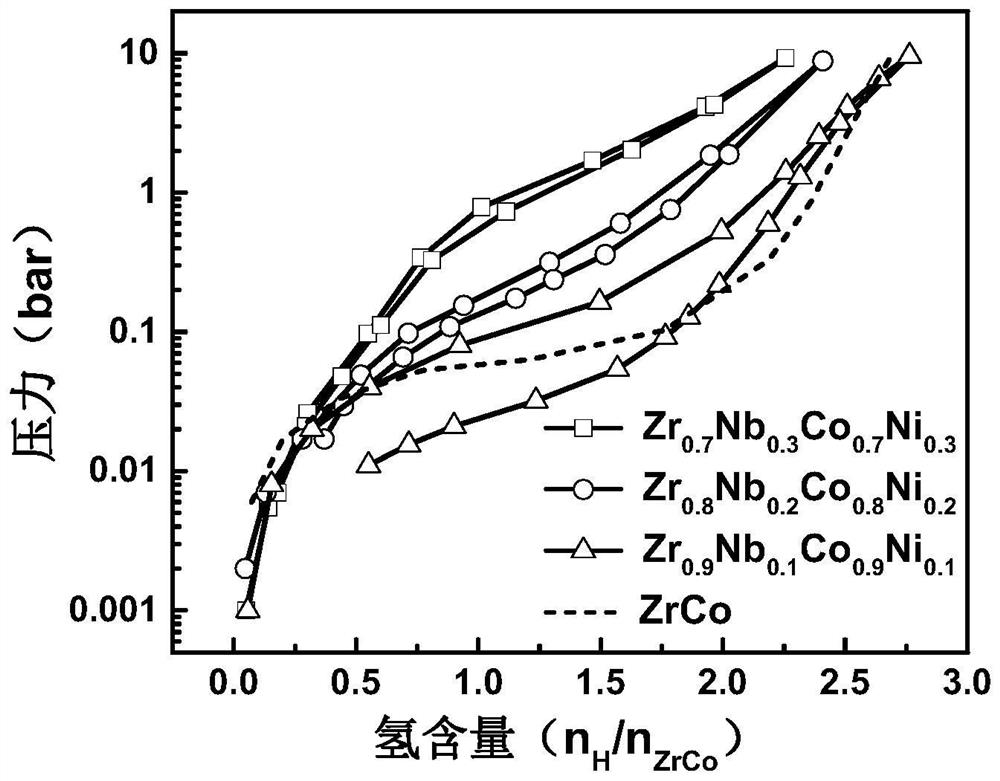
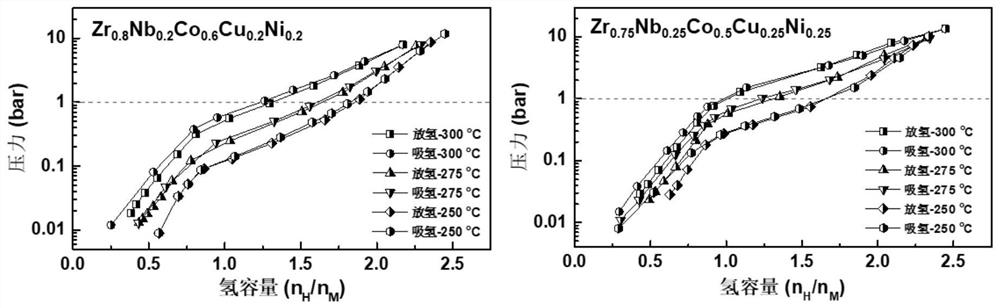
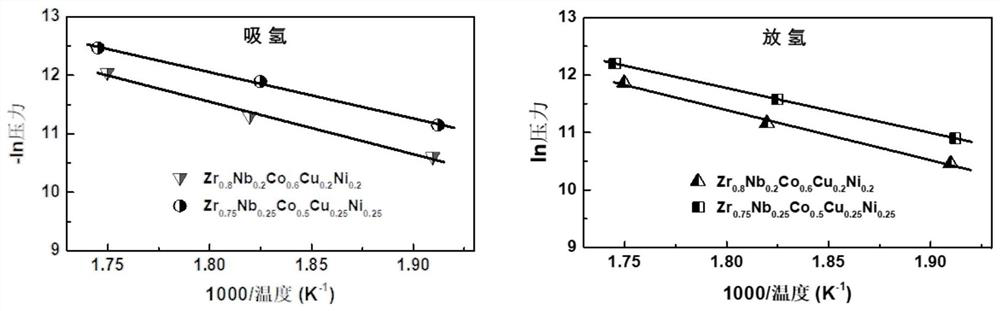
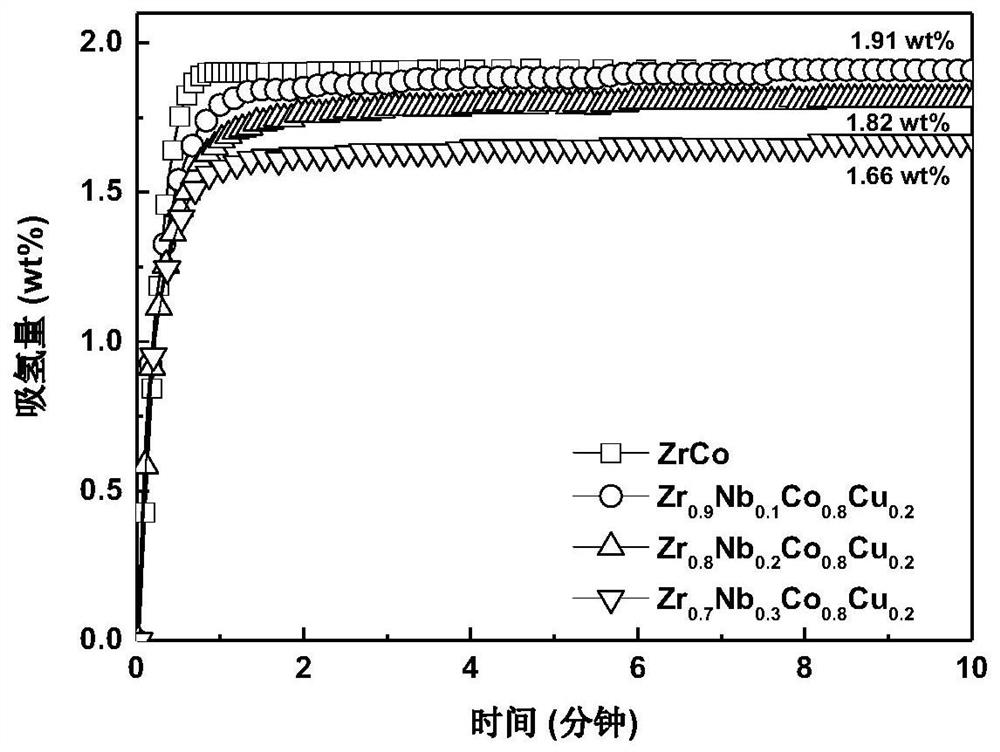
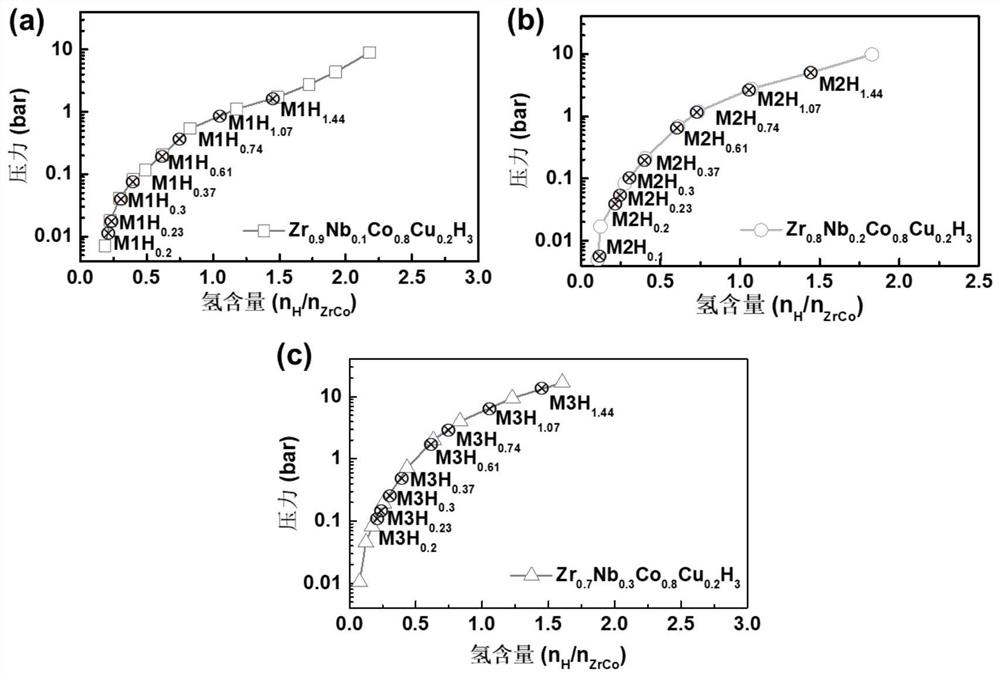
High-cycling-capacity ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy as well as preparation and application thereof
The invention discloses a high-cycling-capacity ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy, preparation of the alloy and application of the alloy to storage, supply and recovery of hydrogen isotopes. The chemical general formula of the high-cycling-capacity ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy is Zr(1-x)NbxCo(1-y)Niy, wherein x is larger than 0 but smaller than or equal to 0.5, and y is largerthan 0 but smaller than or equal to 0.5. A preparation method of the alloy includes the following steps that (1) Zr, Nb, Co and Ni elementary substance raw materials are mixed according to the proportion in the chemical general formula and then are placed into a magnetic suspension induction smelting furnace; and (2) smelting, cooling and solidifying are performed under the protection of an argonatmosphere to prepare the high-cycling-capacity ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy. The method is simple in step and high in safety, the prepared hydrogen isotope storage alloy is not requiredto be subjected to vacuum operation in the circulation process, the method is still applicable in complex hydrogen isotope scenes, and the method has long-term significance in promoting application and popularization of the ZrCo-based alloy in the field of hydrogen isotope storage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
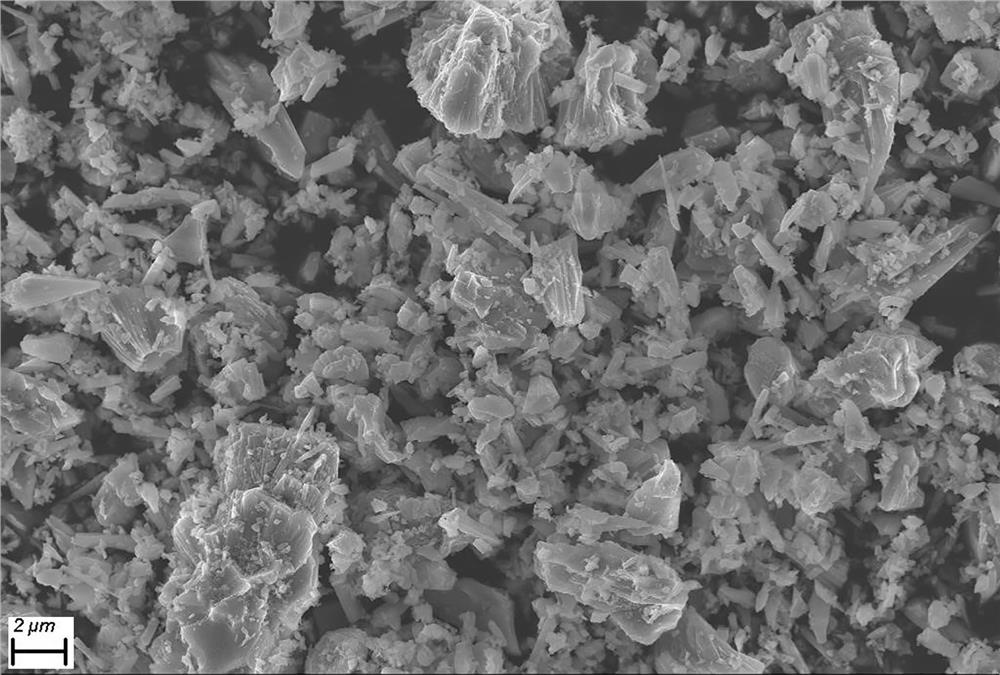
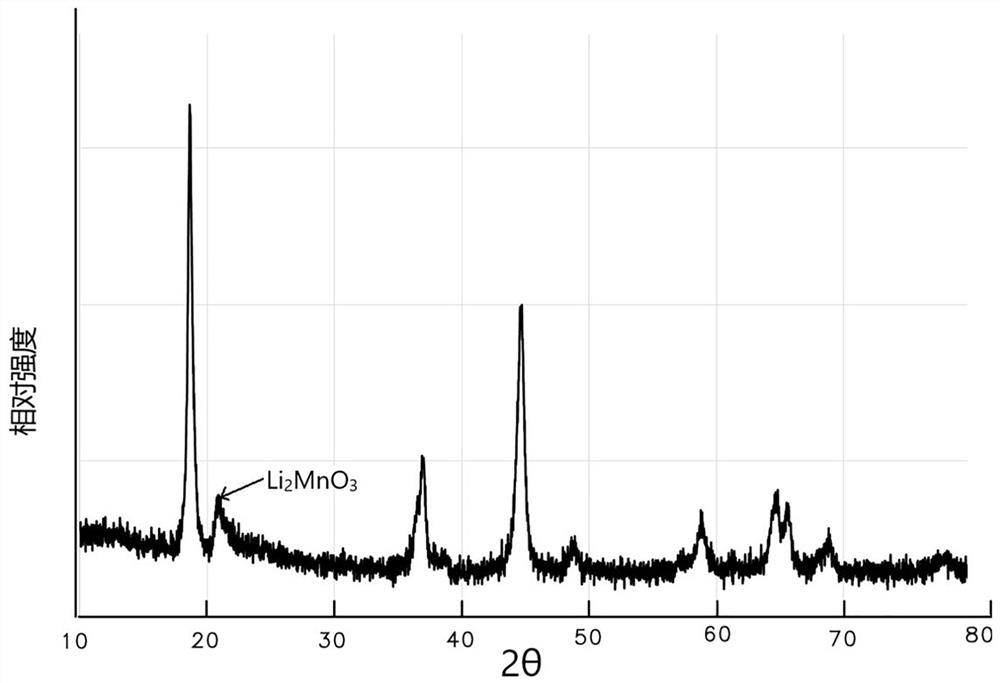
Cobalt-free nickel-free positive electrode material and preparation method thereof and battery
ActiveCN113078308ASuppress generationPromote generationAlkali titanatesPositive electrodesElectrode materialMaterials science
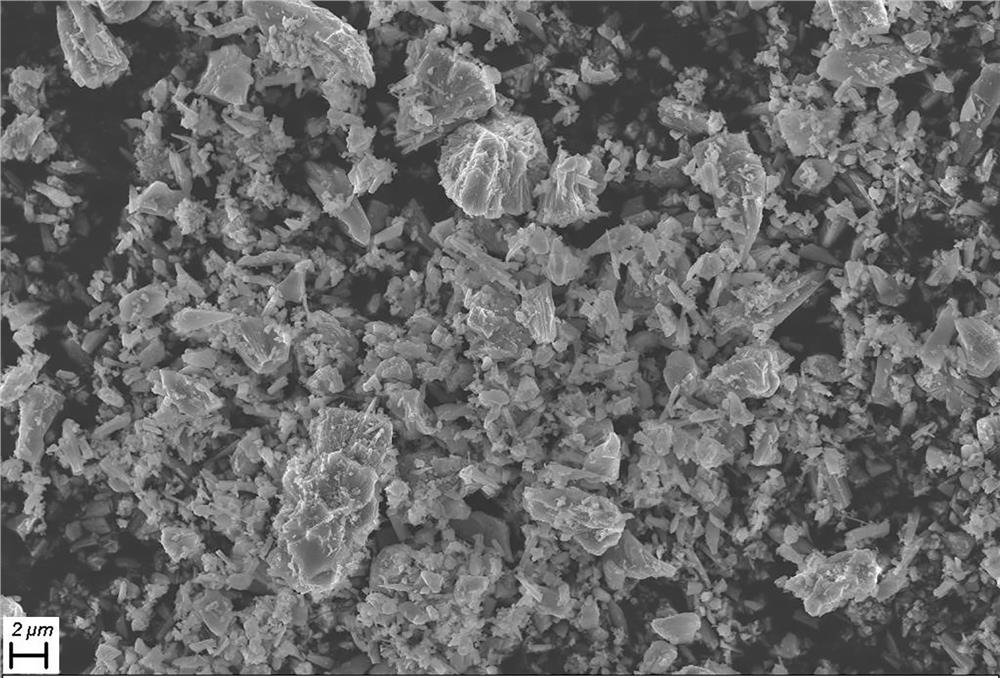
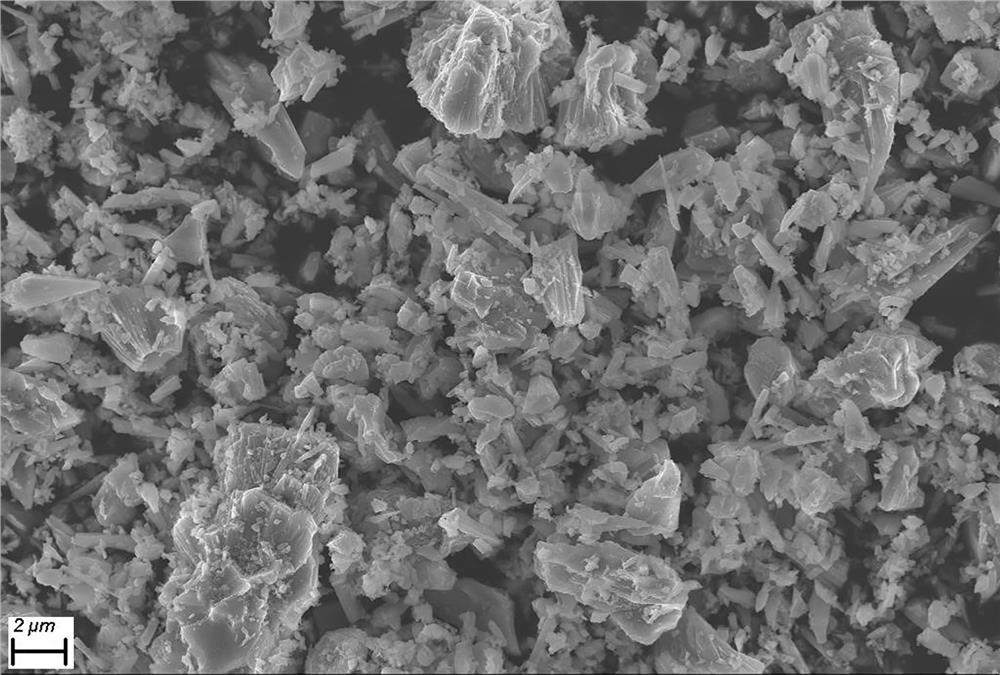
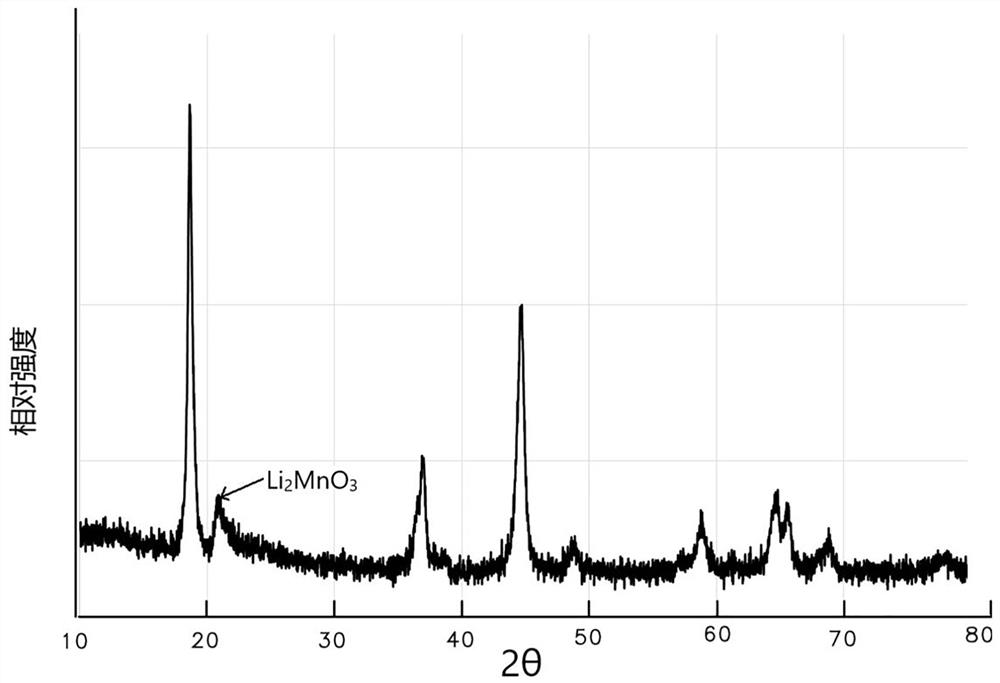
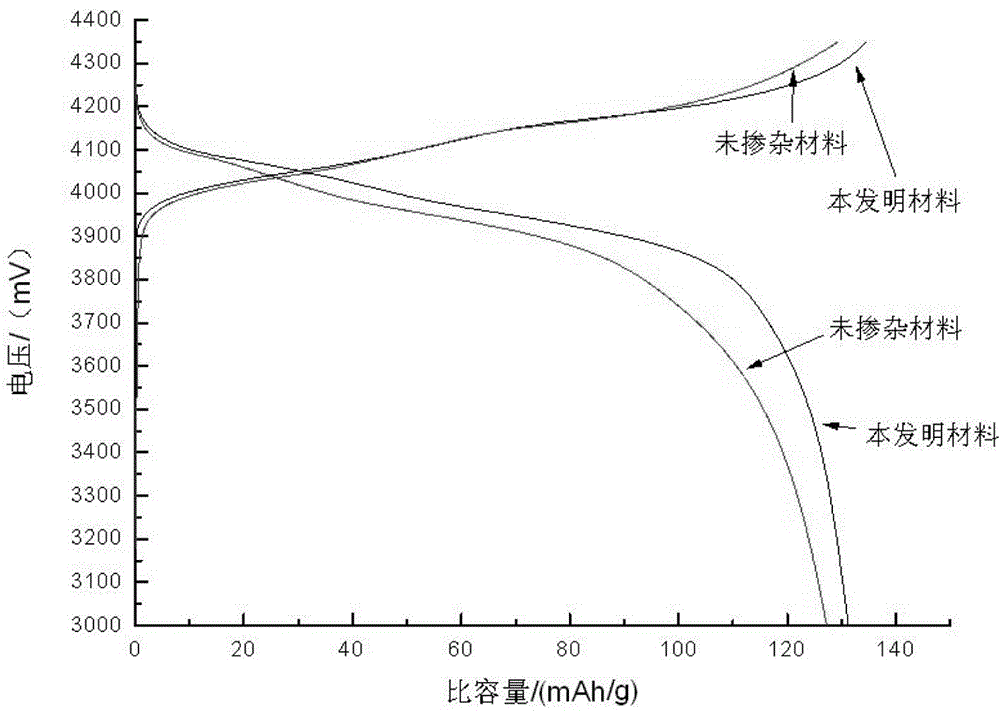
The invention provides a cobalt-free and nickel-free positive electrode material and a preparation method thereof and a battery. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a cobalt-free and nickel-free matrix material, mixing the cobalt-free and nickel-free matrix material, a lithium source and a bivalent manganese compound, and carrying out a reaction to prepare the cobalt-free and nickel-free positive electrode material. According to the invention, the bivalent manganese compound is added in the preparation process, so that generation of layered LiMnO2 and generation of spinel LiMn2O4 are effectively inhibited, generation of layered Li2MnO3 is promoted, and the cycle performance is improved in the cycle process; and the preparation method has the advantages of being simple in preparation process, low in cost, small in pollution, high in cycle performance and the like.
Owner:SVOLT ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Novel process for reducing consumption of formaldehyde in production of neopentyl glycol
ActiveCN103012059AAvoid disproportionation reactionsReduce consumptionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationIsobutyraldehydeNeopentyl glycol
The invention provides a novel process for reducing the consumption of formaldehyde in the production of neopentyl glycol, comprising the following steps of: adding recycled diluted formaldehyde into a condensation kettle; starting agitating, and adding formaldehyde with the concentration of 37% to enable formaldehyde total amount in the condensation kettle to be 24 Kmol; adding 8 Kmol of isobutyraldehyde with the concentration of 97-98% and adding 4.12 Kmol of an NaOH solution with the concentration of 30%, which is one half of the total amount, at a room temperature; controlling the temperature in the kettle to 30-35 DEG C, the pH to 9-11 and the time to 2 hours in a process of adding alkali; then, improving the pH to 12-13 and adding the residual half of 4.12 Kmol of the NaOH solution with the concentration of 30% at a constant speed; controlling the temperature of the system to 40-45 DEG C and controlling time to 2 hours; raising the temperature to 45-50 DEG C and keeping for 3-4 hours; adding formic acid to neutralize a condensed solution until the pH is 7-8; recycling superfluous formaldehyde in a condensation reaction by pressurized distilling; and dehydrating an aldehyde removing solution from an aldehyde removing tower and carrying out pre-fractionation, rectification and flaking to obtain a neopentyl glycol finished product. According to the novel process provided by the invention, the utilization rate of formaldehyde in a production process of neopentyl glycol is improved, the quality of neopentyl glycol is improved and the consumption of sodium hydroxide is reduced.
Owner:大庆三聚能源净化有限公司
ABS chromium-free coarsening solution, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN110172684AImprove stabilityGood coarsening effectLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processChromium freeElectrolysis
The invention provides an ABS chromium-free coarsening solution. The coarsening solution is an aqueous solution containing manganese sulfate, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid and methanesulfonic acid. The invention further provides a coarsening method of the chromium-free coarsening solution for ABS plastic. The prepared chromium-free coarsening solution is electrolyzed by an electrolysis device, the ABS plastic is placed in the coarsening solution for chemical coarsening, and the chromium-free coarsening solution needs to be connected with evaporation equipment so as to maintain the specific gravity of the solution. According to the coarsening solution, the environmental pollution caused by conventional chromium acid coarsening and the use of explosive raw materials such as potassium permanganate are avoided, the coarsening method improves the stability of coarsening liquid and coarsening capability, and the ABS chromium-free coarsening solution has good coarsening effect and industrialapplication value.
Owner:南通柏源汽车零部件有限公司
Method for preparing trifluoromethyl-1,2,2-trifluoro-1,2-dichloroethyl ether
ActiveCN102001919AEasy to control temperatureEasy temperature controlEther preparation by compound additionLiquid-gas reaction processesGas phaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing trifluoromethyl-1,2,2-trifluoro-1,2-dichloroethyl ether, which comprises the following steps of: 1) continuously introducing gaseous fluoroxy trifluoromethane thinned by using nitrogen from the lower part of a reaction tower, wherein the content of the fluoroxy trifluoromethane is 5 to 50 volume percent; 2) introducing quantitative liquid 1,2-difluoro-1,2-dichloroethylene from the upper part of the reaction tower to countercurrent contact and react with the gaseous fluoroxy trifluoromethane, controlling the reaction temperature to be between 110 DEG C below zero and 5 DEG C below zero through a heat exchange device, generating the trifluoromethyl-1,2,2-trifluoro-1,2-dichloroethyl ether, and discharging the un-reacted incoagulable gas from the top of the reaction tower for neutralization treatment; and 3) when the tail gas discharged from the top of the reaction tower contains the fluoroxy trifluoromethane or the 1,2-difluoro-1,2-dichloroethylene content of the sampled analysis liquid phase is less than 1 volume percent by detection, terminating the reaction, and stopping introducing the gaseous fluoroxy trifluoromethane. The method has the advantages of low metering requirement, convenience of operation, long service life of equipment and high yield.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
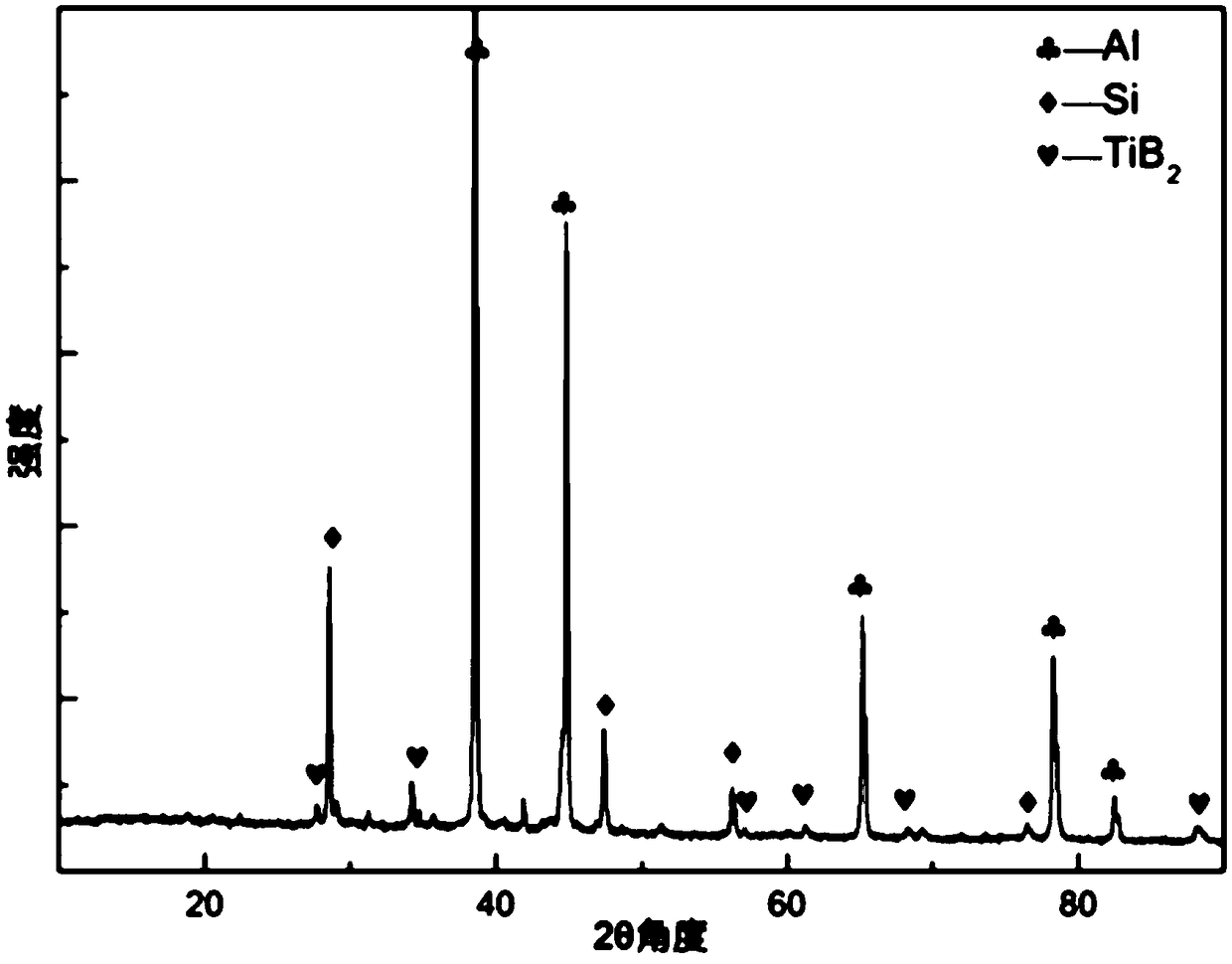
In-situ synthesized TiB2 particle-reinforced Al matrix composite and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of composites, and discloses an in-situ synthesized TiB2 particle-reinforced Al matrix composite and a preparation method thereof. The in-situ synthesized TiB2 particle-reinforced Al matrix composite comprises an Al alloy and submicron TiB2 particles, wherein the Al alloy is adopted as a matrix; and the submicron TiB2 particles are formed inside the matrix in anin-situ manner. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an Al3Ti / Al intermediate composite; (2) preparing an AlB2 / Al intermediate composite; and (3) preparing a TiB2 / Al composite. The preparation method is simple in process and easy to operate; and the particles of the prepared AlB2 / Al intermediate composite are small and distributed more uniformly.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Carbon nano tube-loaded bimetallic catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104549259AReduce economic costsLow priceCatalyst carriersOrganic compound preparationChemistryCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a carbon nano tube-loaded bimetallic catalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The catalyst comprises a first metal, a second metal and a carrier component, wherein the first metal is VIII element, the second metal is a main group metal in IV, V or IIB, the first metal accounts for 1-5wt% of the carrier, the atomic ratio of the second metal to the first metal is 0.01-0.5, and the carrier is a vulcanized multiwalled carbon nanotube. The catalyst provided by the invention has the advantages that (1) raw materials are low in prices and easily available and the economical cost is low; (2) the reaction condition is mild, the energy consumption is low and the process is simple and easy to operate; (3) the reaction is environmentally friendly and green and pollution-free; and (4) the reaction conversion ratio is high, the selectivity is good and the product purity is high.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preserving quality of nitric oxide
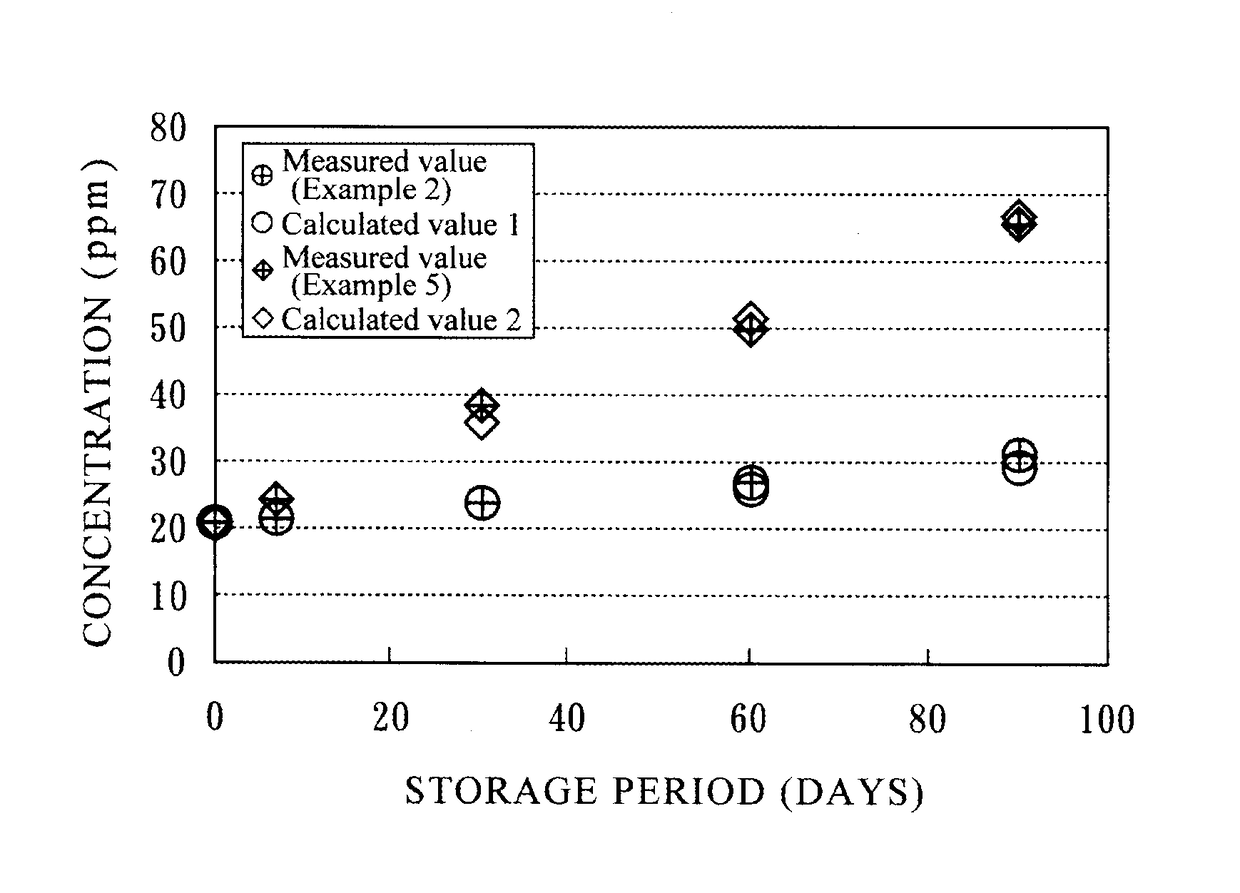
ActiveUS20160003414A1Maintain qualityAvoid disproportionation reactionsVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeGas handling applicationsGas cylinderNitrogen dioxide
A method provide high-purity nitric oxide by preserving quality of the nitric oxide by suitably inhibiting the disproportionation reaction of the nitric oxide that is transported in a state of being stored in a high-pressure gas cylinder, and decreasing the amount of nitrous oxide and nitrogen dioxide that are produced during the transportation. When the nitric oxide is transported in a state of being stored in the high-pressure gas cylinder, the nitric oxide is filled into the high-pressure gas cylinder at a gauge pressure between 1.96 MPa to 3.5 MPa to be stored, and is transported in a state in which the exterior surface temperature of the high-pressure gas cylinder is held in a range from −15° C. to 5° C.
Owner:SUMITOMO SEIKA CHEM CO LTD
Preparation method of stiripentol
InactiveCN102690252AEasy to separateAvoid disproportionation reactionsOrganic chemistryChemistryCondensation reaction
The invention relates to a method for preparing stiripentol disclosed as a chemical structural formula II from 4-(2-methylallyl)-1,2-phenyldiphenol disclosed as a chemical structural formula I, which comprises the following steps: etherifying 4-(2-methylallyl)-1,2-phenyldiphenol, isomerizing, and carrying out oxidation reaction, condensation reaction and reduction reaction to obtain the stiripentol. The stiripentol is a new drug for treating epilepsy.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
A method for preparing spherical tin oxide nanomaterials
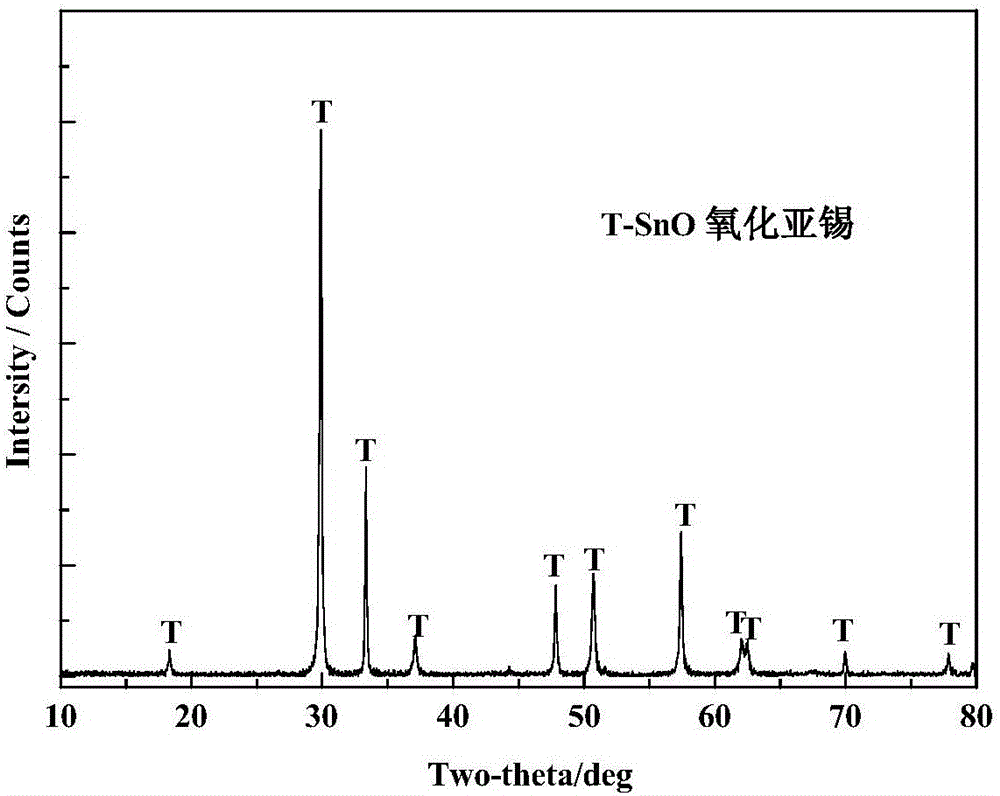
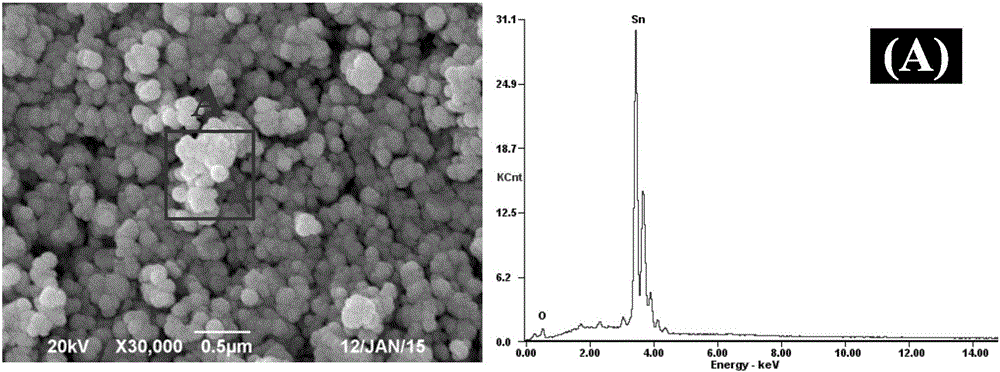
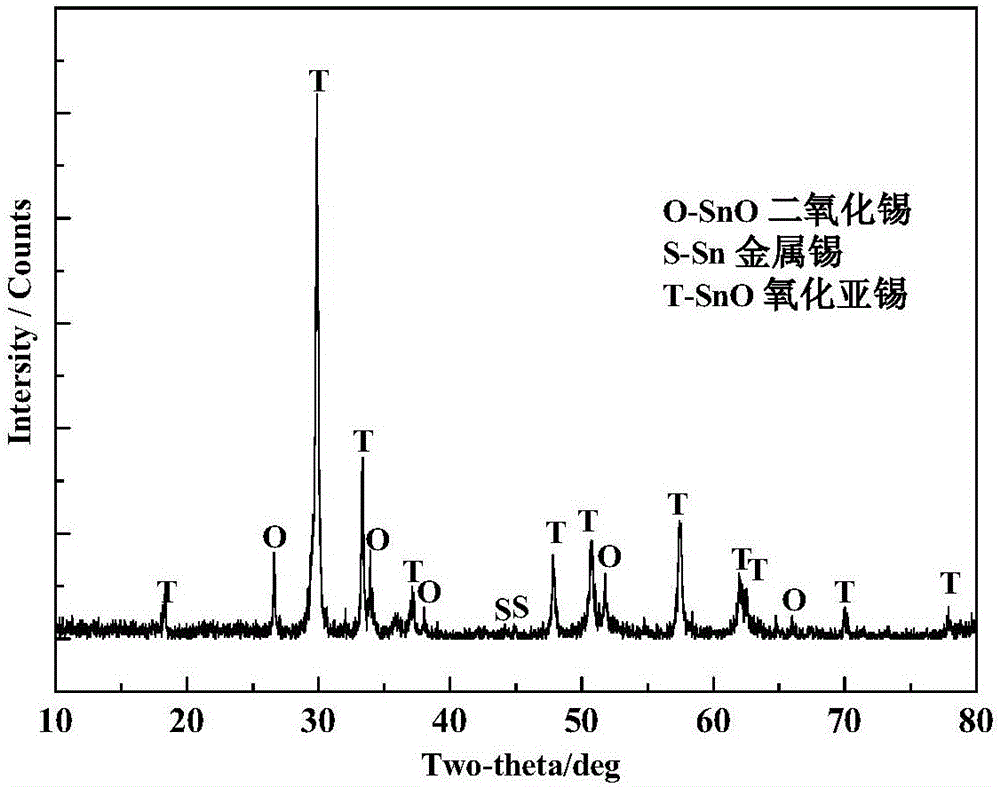
ActiveCN105540651BUniform particle size distributionAvoid disproportionation reactionsNanotechnologyTin oxidesTin dioxideSTANNOUS OXIDE
The invention discloses a method for preparing a spherical stannous oxide nanomaterial. According to the method, stannic oxide, silicon dioxide and sodium humate are ground, mixed, put in a CO / (CO+CO2) atmosphere and calcined at a high temperature, smoke produced during calcination is introduced to water at the temperature under 10 DEG C, and the spherical stannous oxide nanomaterial is obtained through separation in water. The prepared stannous oxide nanomaterial has a regular spherical shape in appearance, uniform particle sizes and high purity, the method is simple and convenient to operate and environment-friendly and facilitates industrial production, and the production cost is low.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Zrco-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy with high cycle capacity and its preparation and application
The invention discloses a ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy with high circulation capacity, its preparation and application in storage, supply and recovery of hydrogen isotope. The general chemical formula of the high cycle capacity ZrCo-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy is Zr 1‑x Nb x co 1‑y Ni y , where 0
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
The high nickel copper anode adopts the process of periodic reverse current electrolysis
ActiveCN113652716BEvenly dispersedHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEElectrolytic agent
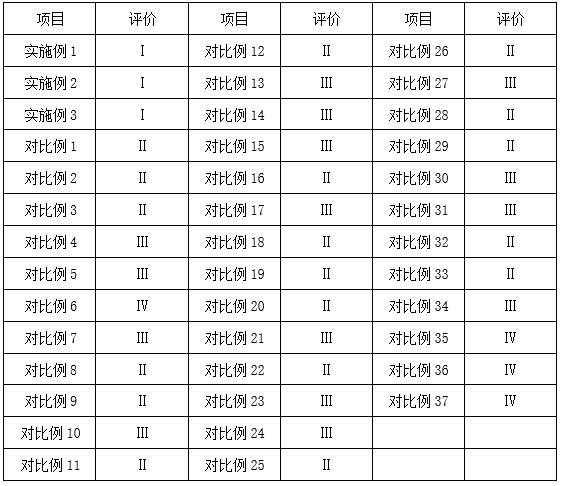
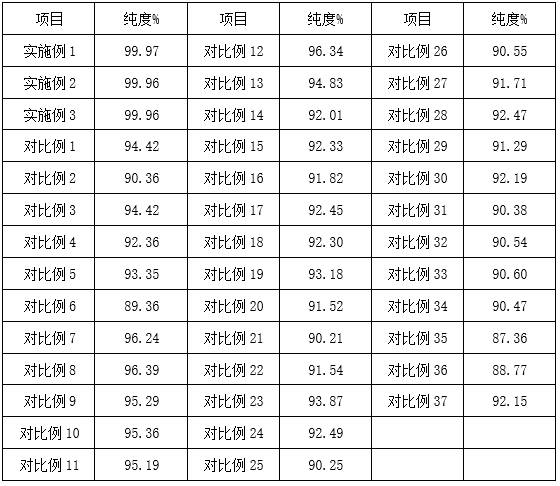
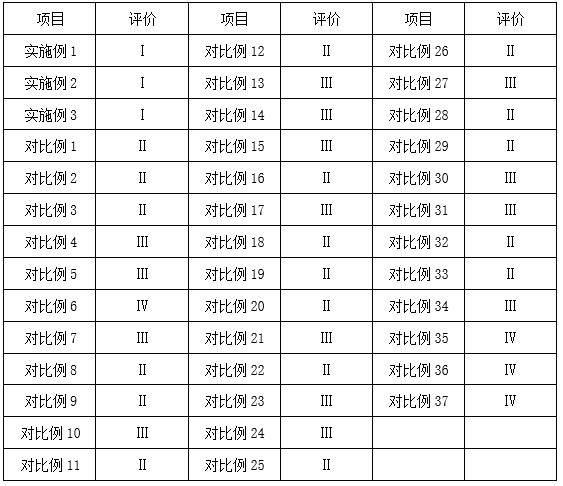
The invention provides a process for electrolysis of high nickel copper anode by periodic reverse current. Among them, the periodic reverse current can ensure the maximum use efficiency of electrolytic copper. By modifying the cathode copper sheet, the impurities and oxide film on the surface of the copper sheet are reduced. The treatment agent contains oxalic acid, which can be complexed by nickel ions. , reduce the concentration of nickel ions in the solution, improve the purity of the cathode copper after electrolysis, and purify the circulating electrolyte to reduce the waste of resources. The leveling agent can control the growth of grains, refine the grains, and make the surface of the cathode copper produced more flat. At the same time, it can effectively promote the reduction of copper ions and speed up the progress of electrolysis. The brightener can improve the brightness of the cathode copper electrode plate and effectively promote the shedding of anode slime, avoid the occurrence of anode polarization, speed up electrolysis, and improve production efficiency.
Owner:江西新金叶实业有限公司
A kind of preparation method of rhenium hexafluoride
ActiveCN110589893BAvoid disproportionation reactionsPrevent restoreRhenium compoundsHexafluoridePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method of rhenium hexafluoride, which belongs to the technical field of fluorine chemical industry. In this method, the rhenium powder and nitrogen trifluoride mainly generate a mixture of rhenium hexafluoride and rhenium heptafluoride by adjusting the fluorination reaction conditions, and the disproportionation reaction of other valence rhenium fluorides can be basically avoided; The reaction conditions are such that rhenium heptafluoride reacts with rhenium powder to form rhenium hexafluoride, preventing rhenium heptafluoride and rhenium hexafluoride from being reduced to rhenium fluoride in a lower valence state. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, safety and economy, high synthesis conversion rate, and the prepared rhenium hexafluoride has a purity higher than 90 wt%.
Owner:PERIC SPECIAL GASES CO LTD
Process for electrolyzing high nickel-copper anode by adopting periodic reverse current
ActiveCN113652716AEvenly dispersedHigh purityPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEElectrolytic agent
The invention provides a process for electrolyzing a high nickel-copper anode by adopting periodic reverse current, wherein the periodic reverse current can guarantee the maximum use efficiency of electrolytic copper, a cathode copper sheet is modified, impurities and an oxidation film on the surface of the copper sheet are reduced, a treatment agent contains oxalic acid components, nickel ions can be complexed through oxalic acid, the concentration of the nickel ions in a solution is reduced, the purity of the electrolyzed cathode copper is improved, and a circulated electrolyte is circularly purified, so that the waste of resources is reduced. A leveling agent can control the growth of crystal grains, so that the crystal grains are refined, and the surface of the produced cathode copper is smoother. Meanwhile, the reduction effect of copper ions can be effectively promoted, and the electrolysis progress is accelerated. A brightening agent can improve the brightness of a cathode copper electrode plate and effectively promote anode mud to fall off, the anode polarization phenomenon is avoided, the electrolysis speed is increased, and the production efficiency is improved.
Owner:江西新金叶实业有限公司
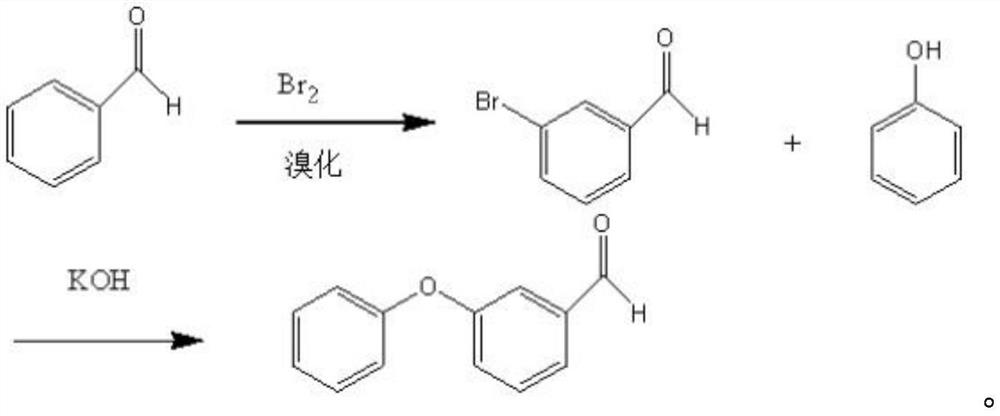
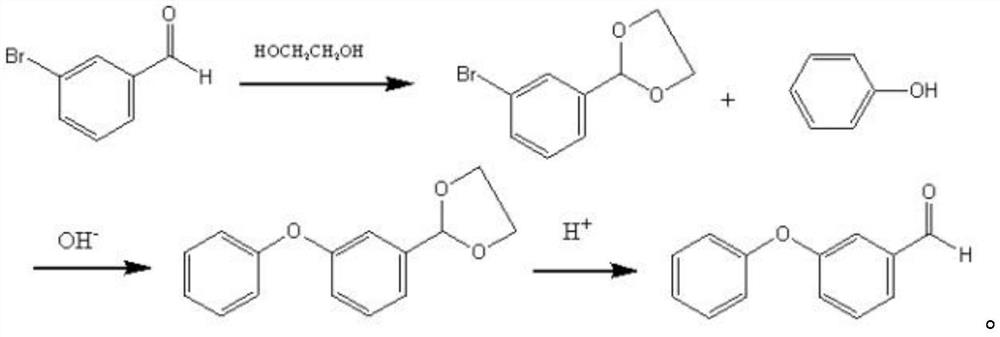
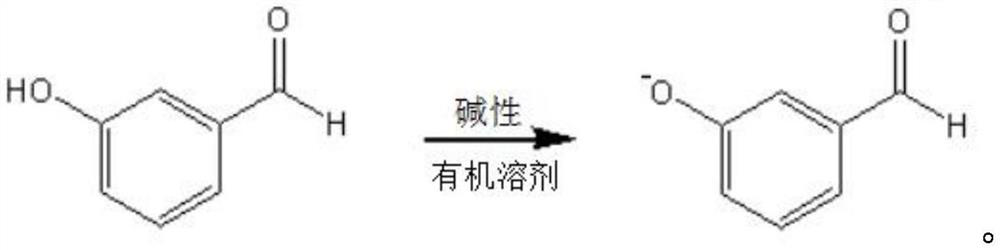
Preparation method of m-phenoxy benzaldehyde
ActiveCN112661624ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getThe process is easy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound separation/purificationM-hydroxybenzaldehydeBenzaldehyde
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, and particularly relates to a preparation method of m-phenoxy benzaldehyde. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, m-hydroxybenzaldehyde is salified by phenolic hydroxyl under an alkaline anhydrous condition, and then is subjected to substitution reaction with halobenzene to obtain m-phenoxy benzaldehyde, so that disproportionation reaction of aldehyde groups during reaction in an alkaline aqueous solution is avoided, the utilization rate of raw materials is increased, and side reactions are reduced. The purification of the m-phenoxybenzaldehyde product and the improvement of the yield are facilitated. The test result of the embodiment shows that the yield of m-phenoxybenzaldehyde obtained by the preparation method provided by the invention is 79.9-81%, and the yield is high; the gas phase content of m-phenoxy benzaldehyde is 98.9%-99.3%, and the purity of m-phenoxy benzaldehyde is high.
Owner:锦州三丰科技有限公司
A kind of cobalt-free nickel-free cathode material, its preparation method and battery
ActiveCN113078308BSuppress generationPromote generationAlkali titanatesPositive electrodesNickel substratePhysical chemistry
The invention provides a cobalt-free and nickel-free positive electrode material, a preparation method thereof and a battery. The preparation method comprises: preparing a cobalt-free nickel-free base material, mixing the cobalt-free nickel-free base material, a lithium source and a divalent manganese compound After the reaction, the cobalt-free and nickel-free cathode material is prepared. The present invention effectively inhibits layered LiMnO by adding a divalent manganese compound in the preparation process 2 Generation and spinel LiMn 2 o 4 Generates, promotes layered Li 2 MnO 3 In the process of circulation, the cycle performance is improved, and the invention has the characteristics of simple preparation process, low cost, little pollution and high cycle performance.
Owner:SVOLT ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A kind of positive electrode material of battery and its high-temperature solid phase synthesis method
InactiveCN103730650BIncrease capacityAvoid breakingCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsElectrical batterySynthetic materials
The invention discloses a battery cathode material of which the chemical formula is LiLa0.1 Co0.1 Mn1.8 O4. The spinel structure of the battery cathode material LiLa0.1 Co0.1 Mn1.8 O4 provided by the invention has low probability of being damaged after the mixing of Co ions, the electrical conductivity of a synthetic material is enhanced, a diffusion coefficient is increased to 2.4*10<-12> - 1.4*10<-11> m<2> / s from 9.2*10<-14> - 2.6*10<-12> m<2> / s, so as to be convenient for lithium-ion taking off and embedding, after the addition of LA ions, part of Mn ions can be replaced, in a later period of slight discharging, the concentration of Mn<+3> ions is lower, disproportionation reaction is prevented, dendritic crystal forming on the surface of a positive pole is avoided, a diaphragm is pierced, and the safety performance is improved. The synthetic material adopts a spinel structure. The synthetic material is more superior in cycle performance.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A method for preparing monofluoromethane with PD-M alloy supported catalyst
ActiveCN109824473BModerate pHImprove stabilityPreparation by dehalogenationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for preparing monofluoromethane with a Pd-M alloy supported catalyst. The preparation method of the catalyst of the present invention is as follows: first load the metal M nanoparticles on the carrier, then mix and stir the Pd precursor aqueous solution, prepare monodispersed Pd atoms on the M metal through a displacement reaction, and combine the Pd atoms with the M metal by roasting. The metals are combined to form a Pd-M alloy to obtain the monodisperse Pd-M alloy supported catalyst, wherein the metal M can be Cu, Zn, Ni, Ru, Sn or Fe. Compared with single, double and multi-component non-alloy catalysts, when the Pd-M alloy supported catalyst of the present invention is used to catalyze hydrodechlorination of chlorofluoromethane to prepare monofluoromethane, it is more effective for monofluoromethane (HFC-41 ) has a higher selectivity, which can reach about 95%, and the catalyst is not easy to deposit carbon, and has a longer life (within 1000h, the activity decreases within 10%, and the selectivity decreases within 5%). The process route of fluoromethane is simple, environmentally friendly and safe.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A New Process for Reducing Formaldehyde Consumption in Neopentyl Glycol Production
ActiveCN103012059BAvoid disproportionation reactionsReduce consumptionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationProcess engineeringNeopentyl glycol
The invention provides a novel process for reducing the consumption of formaldehyde in the production of neopentyl glycol, comprising the following steps of: adding recycled diluted formaldehyde into a condensation kettle; starting agitating, and adding formaldehyde with the concentration of 37% to enable formaldehyde total amount in the condensation kettle to be 24 Kmol; adding 8 Kmol of isobutyraldehyde with the concentration of 97-98% and adding 4.12 Kmol of an NaOH solution with the concentration of 30%, which is one half of the total amount, at a room temperature; controlling the temperature in the kettle to 30-35 DEG C, the pH to 9-11 and the time to 2 hours in a process of adding alkali; then, improving the pH to 12-13 and adding the residual half of 4.12 Kmol of the NaOH solution with the concentration of 30% at a constant speed; controlling the temperature of the system to 40-45 DEG C and controlling time to 2 hours; raising the temperature to 45-50 DEG C and keeping for 3-4 hours; adding formic acid to neutralize a condensed solution until the pH is 7-8; recycling superfluous formaldehyde in a condensation reaction by pressurized distilling; and dehydrating an aldehyde removing solution from an aldehyde removing tower and carrying out pre-fractionation, rectification and flaking to obtain a neopentyl glycol finished product. According to the novel process provided by the invention, the utilization rate of formaldehyde in a production process of neopentyl glycol is improved, the quality of neopentyl glycol is improved and the consumption of sodium hydroxide is reduced.
Owner:大庆三聚能源净化有限公司
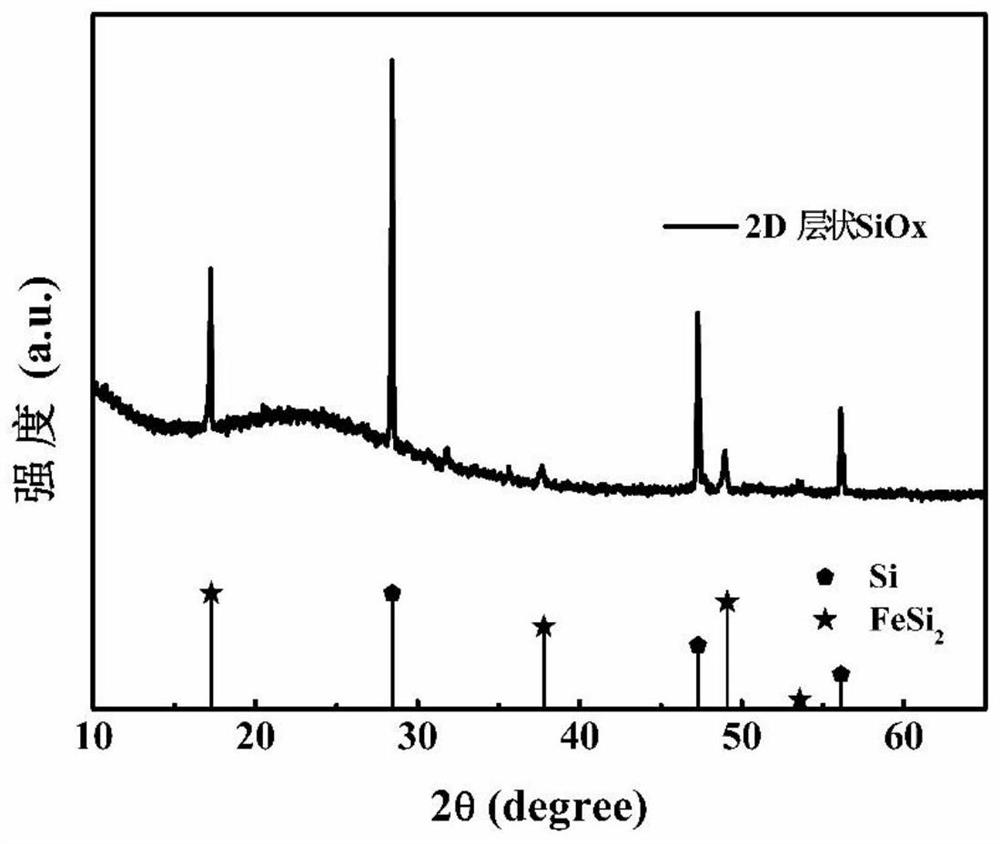
A kind of layered siox material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112194138BPlay an etching roleEtching and dissolution process is slow and gentleNegative electrodesSecondary cellsMicron scalePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a layered SiOx material, which is an accordion-shaped layered micron-scale particle. The particle size of the SiOx material is 0.5-20 μm, and there are slits and gaps with a nanometer-scale width between any adjacent layers. The width of the slit gap is 1-50nm, and the thickness of a single sheet is 30-40nm; the preparation method is: dissolving CaSi 2 The Ca in the layered siloxene material is obtained; the hydrogen bond and hydroxyl group on the surface of the siloxene are removed by high-temperature calcination to obtain a SiOx material. The preparation process of the present invention is simple, the process is less, the requirements for equipment are not high, and it is easy to industrialize mass production, and the obtained 2D layered SiOx material can be directly used as the negative electrode material of lithium ion battery without coating, showing excellent electrochemical performance .
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
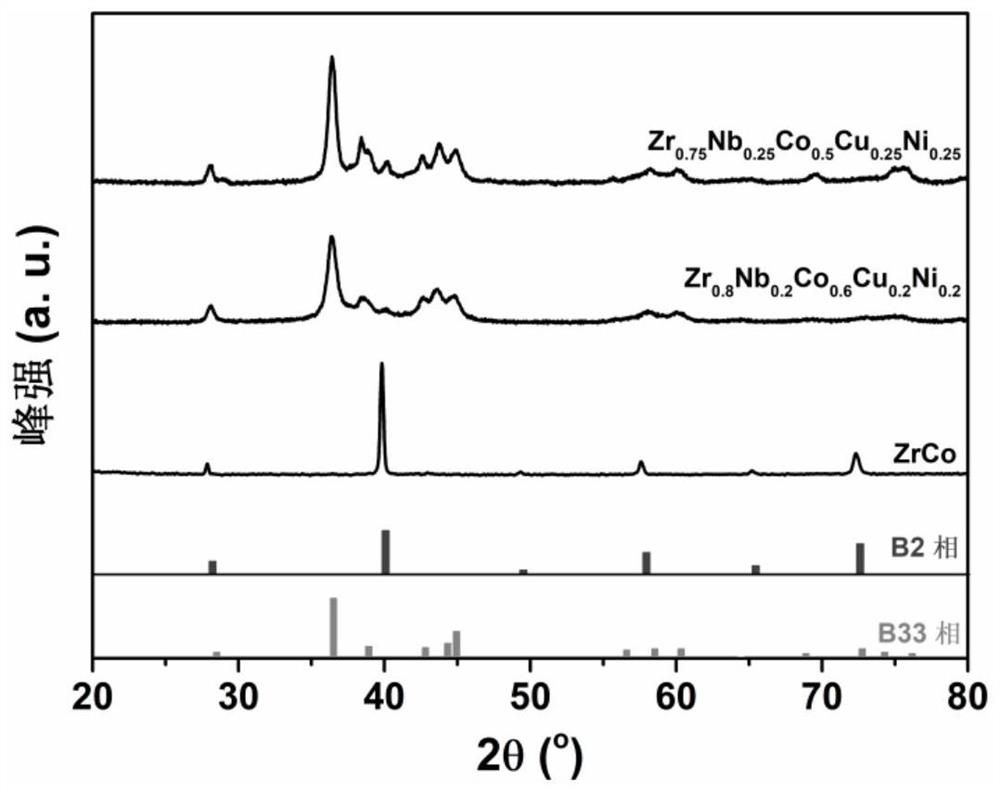
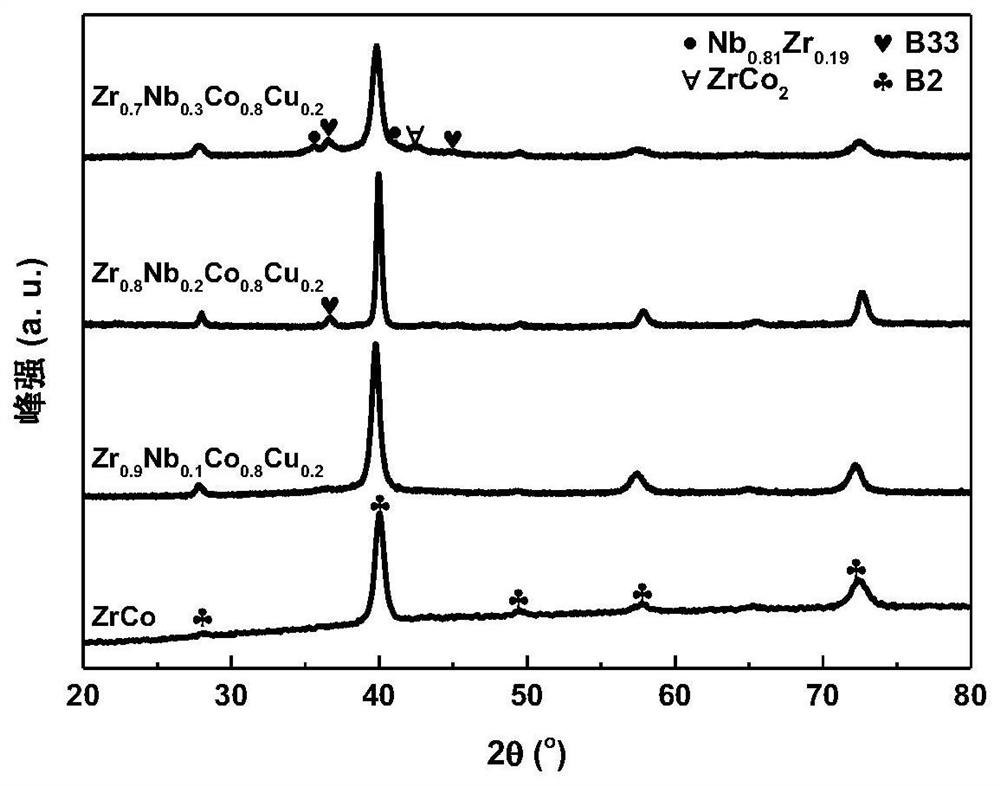
ZrCO-based high-entropy intermetallic compounds with stable isomorphic hydrogen absorption/desorption reactions and their preparation and application
The present invention discloses a stable ZRCO base high -entropy metal intervertebral compound with stable -type crystalline -type suction / hydrogen reactions and its preparation methods and applications in hydrogen isotope storage, supply, and recycling.The chemical general formula of the ZRCO base high entropy metal compound is ZR 1‑ x NB x CO 1‑2x CU x NI x Among them, 0 <x ≤0.3; the intervertebral metal compound of the ZRCO high entropy metal has a structural orthogonal crystal B33 phase and a cubic crystal type B2;Orthogonal crystal B33 phase and orthopedic crystal ZRCOH 3 The phase and cubic crystal type B2 phase is related to the cubic crystal ZRCO (H) phase.The method of preparation includes: prepare zr 1‑x NB x CO 1‑ 2x CU x NI x The alloy ingot, the room temperature is damaged by the hydrogen absorption, and the hydrogen absorption powder is obtained, and then the air is dehydrated at 500 ° C. The ZRCO base high entropy metal intervertebral compound with an orthogonal crystal B33 is obtained at 500 ° C.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Battery cathode material and high temperature solid phase synthesis method
InactiveCN103730650AIncrease capacityAvoid breakingCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsSolid phasesSolid-phase synthesis
The invention discloses a battery cathode material of which the chemical formula is LiLa0.1 Co0.1 Mn1.8 O4. The spinel structure of the battery cathode material LiLa0.1 Co0.1 Mn1.8 O4 provided by the invention has low probability of being damaged after the mixing of Co ions, the electrical conductivity of a synthetic material is enhanced, a diffusion coefficient is increased to 2.4*10<-12> - 1.4*10<-11> m<2> / s from 9.2*10<-14> - 2.6*10<-12> m<2> / s, so as to be convenient for lithium-ion taking off and embedding, after the addition of LA ions, part of Mn ions can be replaced, in a later period of slight discharging, the concentration of Mn<+3> ions is lower, disproportionation reaction is prevented, dendritic crystal forming on the surface of a positive pole is avoided, a diaphragm is pierced, and the safety performance is improved. The synthetic material adopts a spinel structure. The synthetic material is more superior in cycle performance.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of stiripentol
InactiveCN102690252BWith industrial productionEasy to separateOrganic chemistryNew medicationsIsomerization
The invention relates to a method for preparing stiripentol disclosed as a chemical structural formula II from 4-(2-methylallyl)-1,2-phenyldiphenol disclosed as a chemical structural formula I, which comprises the following steps: etherifying 4-(2-methylallyl)-1,2-phenyldiphenol, isomerizing, and carrying out oxidation reaction, condensation reaction and reduction reaction to obtain the stiripentol. The stiripentol is a new drug for treating epilepsy.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for preparing 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy mandelic acid
ActiveCN102086151BAvoid disproportionation reactionsPrevent oxidationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationReaction temperatureGuaiacol
A method for preparing 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy mandelic acid adopts guaiacol and glyoxylic acid as raw materials, and comprises the following steps: slowly adding a 30 wt% sodium hydroxide solution into the glyoxylic acid solution with stirring, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-50 DEG C and a pH value of 1-7 to obtain a sodium glyoxylate solution; adding the guaiacol into water with stirring and under the protection of nitrogen gas, slowly adding the 30 wt% sodium hydroxide solution, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-50 DEG C and a pH value of 11-12 to obtain guaiacol sodium; slowly and dropwisely adding the sodium glyoxylate solution into the guaiacol sodium solution with stirring and under the protection of nitrogen gas, with the mole ratio of the sodium glyoxylate and the guaiacol sodium being 1:1.2-2, allowing the mixed solution to react at a reaction temperature of 0-20 DEG C and a pH value of 11-12, 30-90 min after the dropwise addition, stirring the mixed solution for 1-3 hours, stopping the reaction at the reaction temperature for 24-36 hours, then acidifying the reaction solution by a 50 wt% sulfuric acid solution to control the pH value to be 4-5. The yield of the reaction is above 95 wt%.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Carbon nanotube-supported bimetallic catalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104549259BReduce economic costsCheap and easy to getCatalyst carriersOrganic compound preparationCarbon nanotubeHigh selectivity
The invention relates to a bimetallic catalyst supported by carbon nanotubes and its preparation method and application, comprising a first metal, a second metal and a carrier component, wherein the first metal is a Group VIII element, and the second metal is IV, V or IIB The main group metal, the amount of the first metal in the carrier is 1-5wt%, the atomic ratio of the second metal to the first metal is 0.01-0.5, and the carrier is a vulcanized multi-walled carbon nanotube . The invention has the following advantages: 1) The raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, and the economic cost is low. 2) The reaction condition is mild, the energy consumption is low, the process is simple and easy to operate. 3) The reaction is environmentally friendly, green and pollution-free. 4) The reaction conversion rate is high, the selectivity is good, and the product purity is high.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Zrco-based hydrogen isotope storage alloy with high cycle stability and orthorhombic crystal structure and its preparation and application
ActiveCN112251647BAvoid disproportionation reactionsImprove structural stabilityHydrogenPhysical chemistryIngot
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preserving quality of nitric oxide
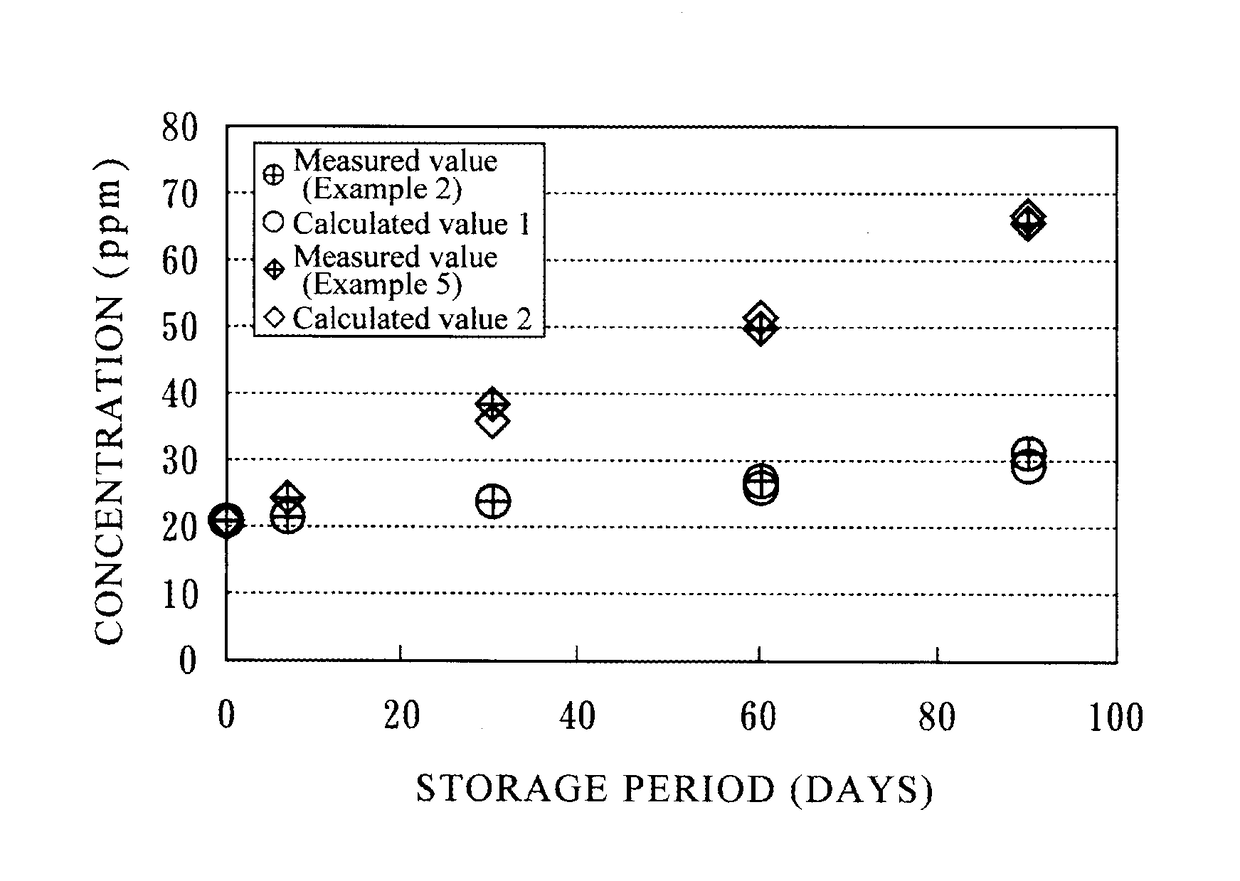
ActiveUS9945516B2Maintain qualityAvoid disproportionation reactionsVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeGas handling applicationsGas cylinderNitrogen dioxide
A method provide high-purity nitric oxide by preserving quality of the nitric oxide by suitably inhibiting the disproportionation reaction of the nitric oxide that is transported in a state of being stored in a high-pressure gas cylinder, and decreasing the amount of nitrous oxide and nitrogen dioxide that are produced during the transportation. When the nitric oxide is transported in a state of being stored in the high-pressure gas cylinder, the nitric oxide is filled into the high-pressure gas cylinder at a gauge pressure between 1.96 MPa to 3.5 MPa to be stored, and is transported in a state in which the exterior surface temperature of the high-pressure gas cylinder is held in a range from −15° C. to 5° C.
Owner:SUMITOMO SEIKA CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com