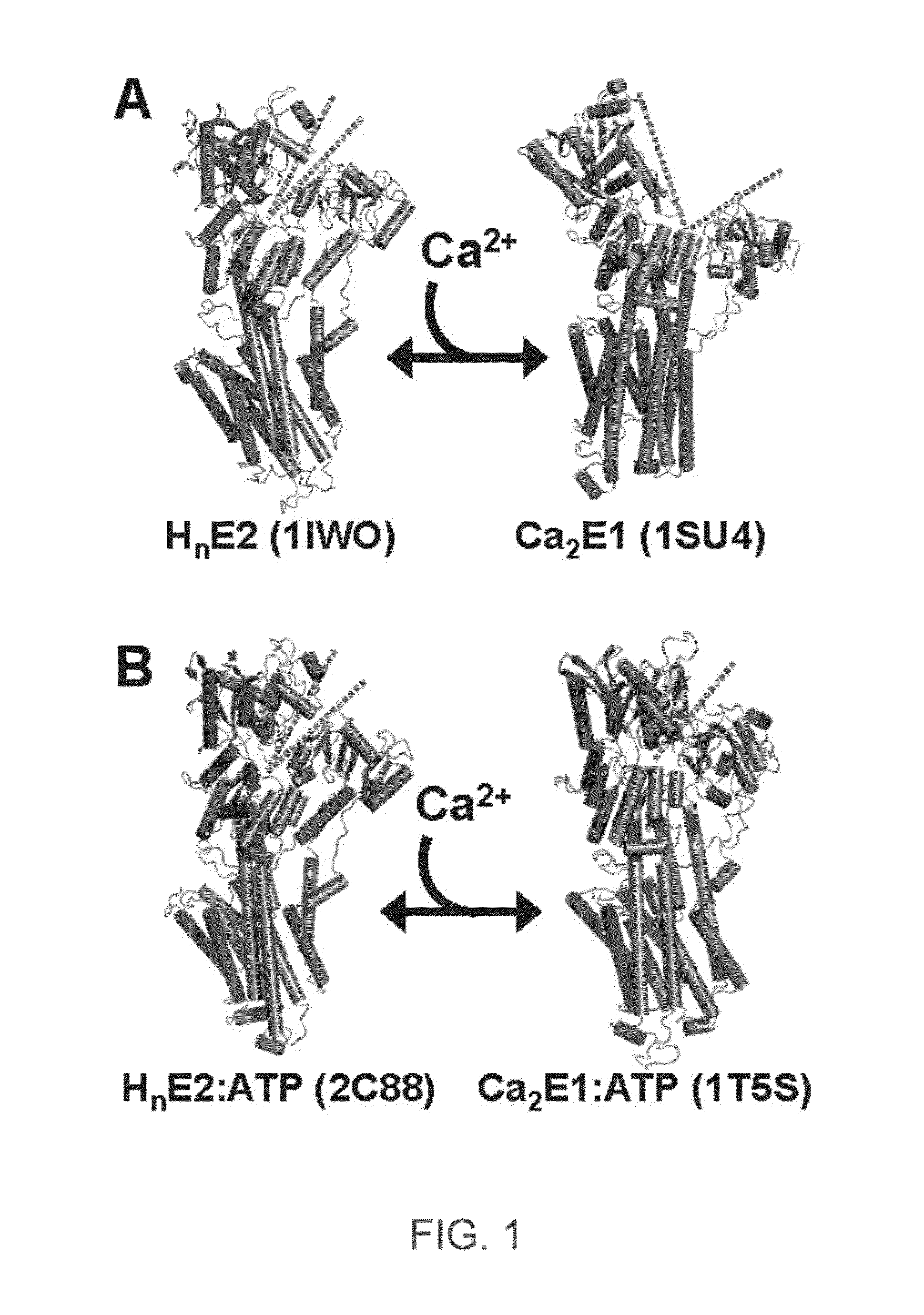Patents
Literature
129 results about "Calcium handling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
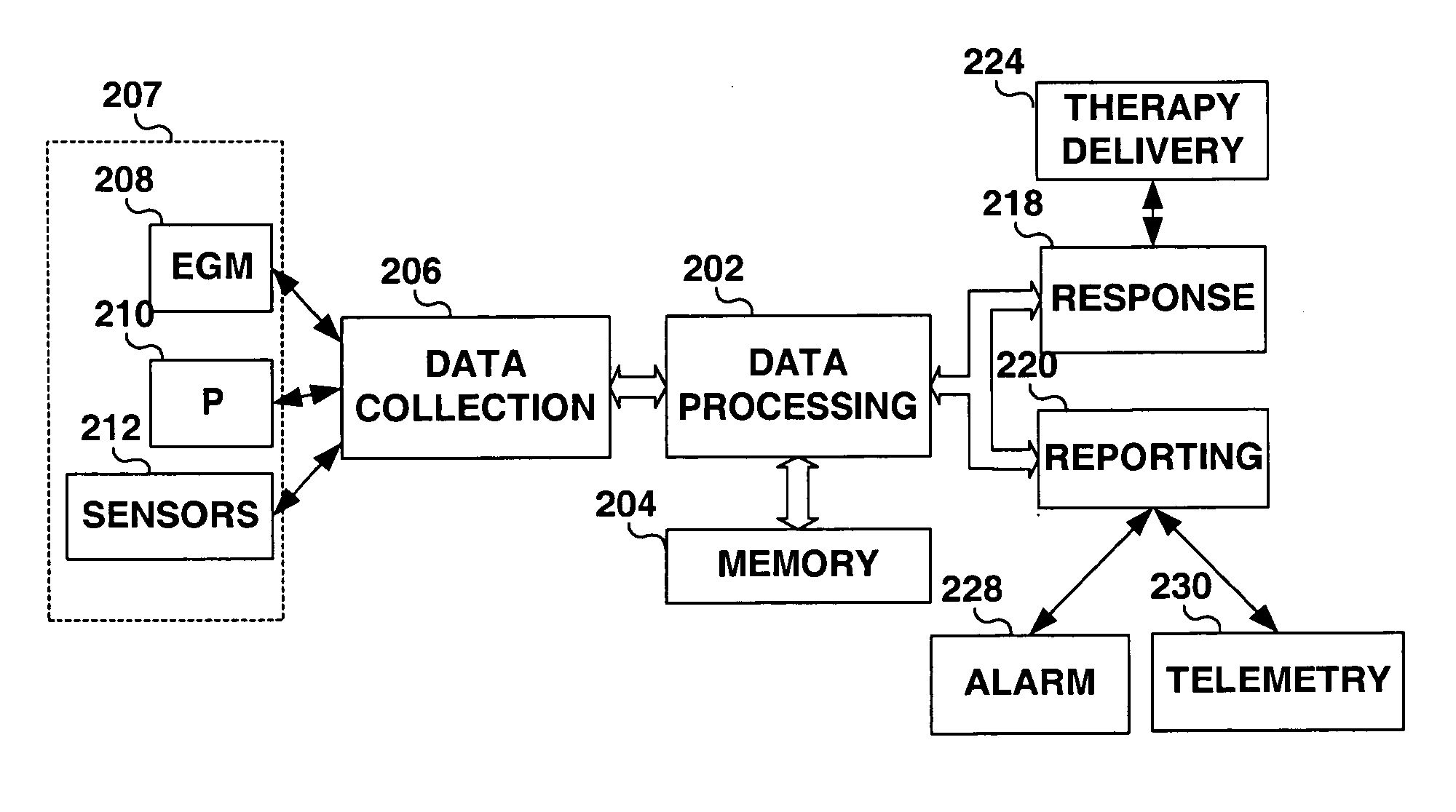
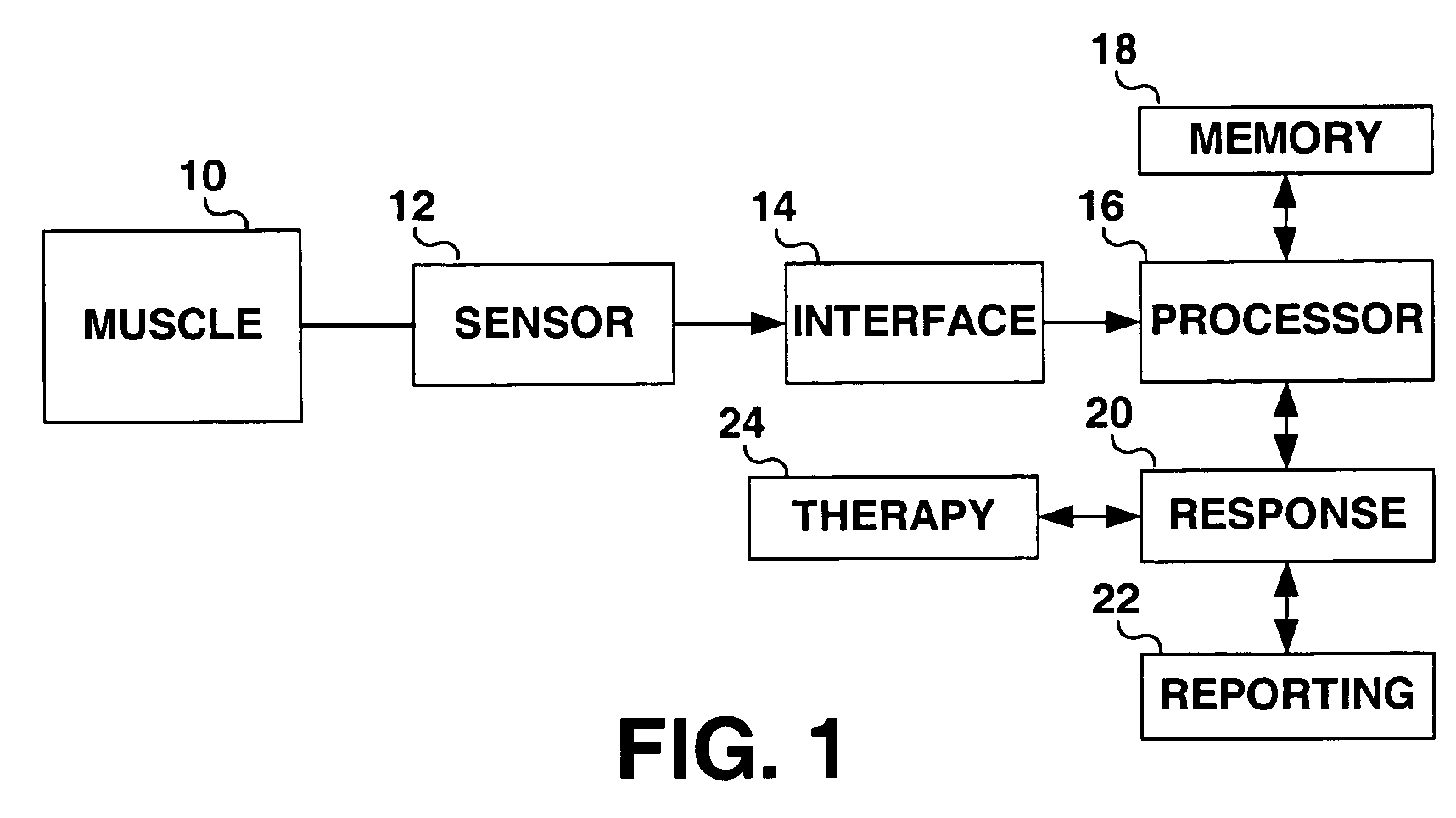
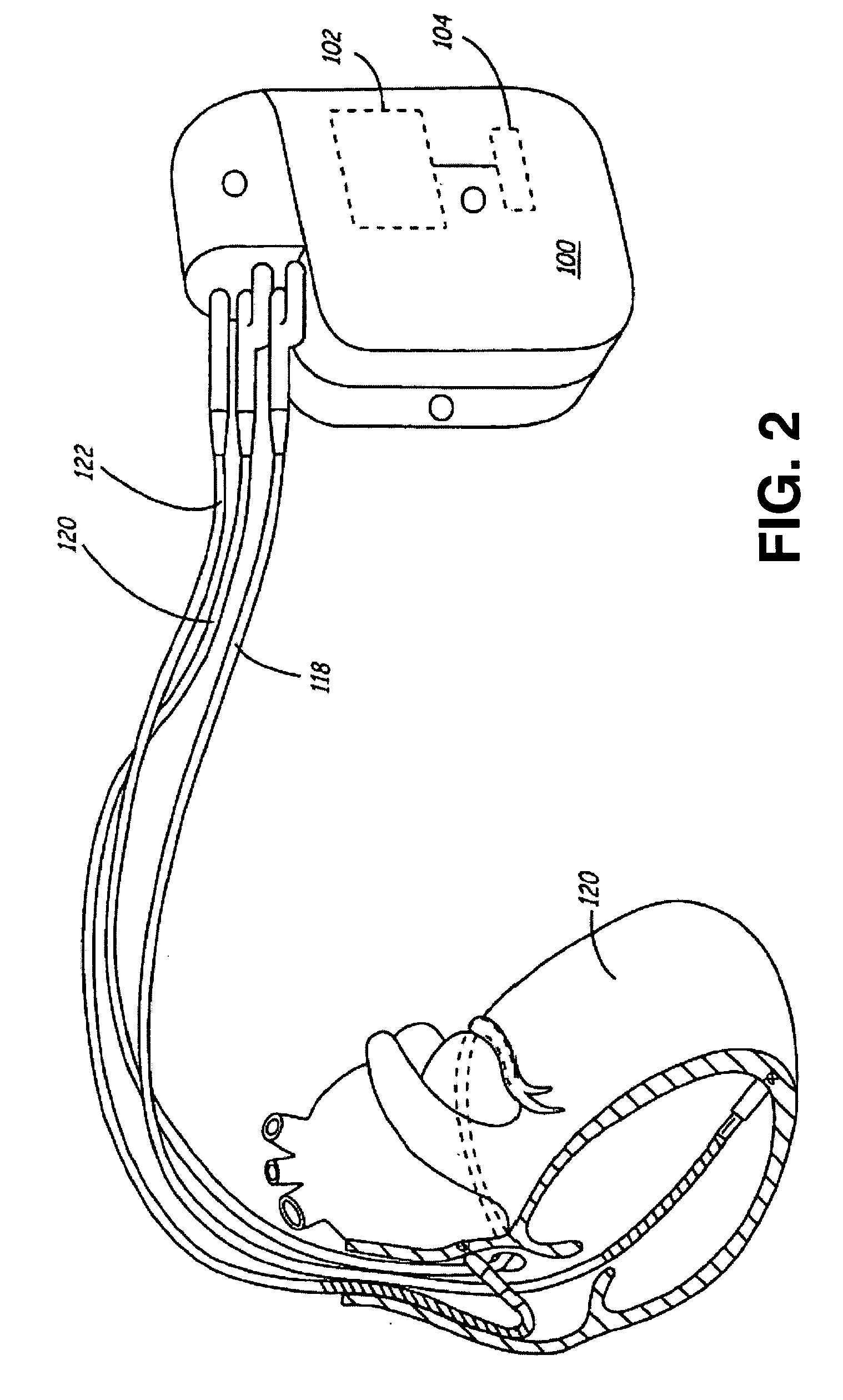
Method and apparatus for muscle function measurement
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for monitoring muscle function based on an index derived from a pressure or force signal. The muscle function index is derived from an instantaneous muscle stiffness ratio computed as the ratio of the first time derivative of the pressure or force waveform to the corresponding instantaneous pressure or force. The instantaneous stiffness ratio, {dot over (E)} / E(t), is in units of 1 / sec and relates to the rate of strong bond formation and will be influenced by calcium handling properties of the muscle fibers and the intracellular calcium concentration. As such, an index derived from {dot over (E)} / E(t) provides a measure of the inotropic status of the muscle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vehicle wheel steel and smelting method
The invention relates to a wheel steel and a smelting method thereof. The wheel steel comprises elements of carbon, silicon, manganese, niobium, phosphor, oxygen, sulfur and iron, etc. By adopting the steps of hot metal pretreatment, converter smelting, refining outside the converter and conventional rolling, the wheel steel is smelted. The components of the alloy are controlled by means of micro alloying and calcium treatment, etc. The indexes of the yield strength, the tensile strength and the bending fatigue life of the wheel made from the wheel steel are all higher than that of the existing wheel steel, furthermore, the wheel steel can be further thinned; therefore, cars adopting the wheel made from the wheel steel can achieve energy saving.
Owner:BENGANG STEEL PLATES
Non-quenched steel for camshafts and preparation method of non-quenched steel
InactiveCN110205547AMeet production needsImprove mechanical propertiesCalcium handlingContinuous casting
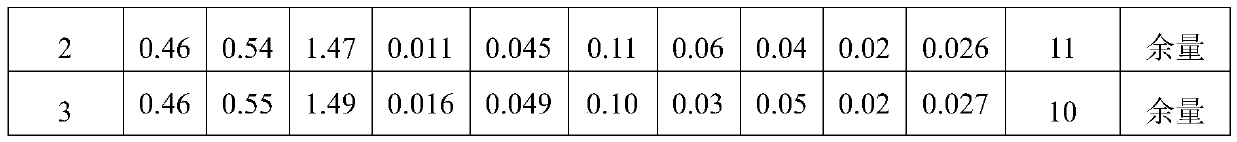
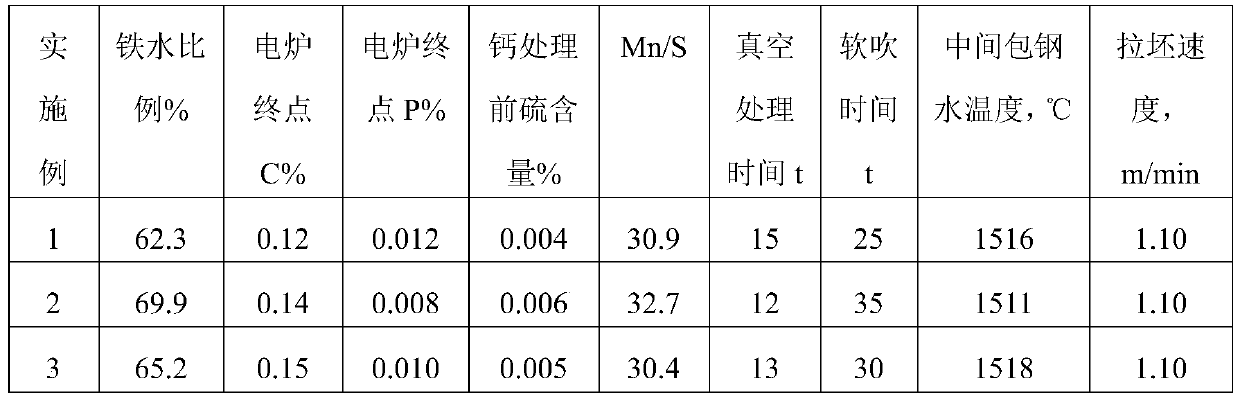
The invention belongs to the technical field of automobile steel and particularly relates to non-quenched steel for camshafts and a preparation method of the non-quenched steel. The steel is preparedfrom the chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.42%-0.49% of C, 0.30%-0.60% of Si, 1.00%-1.50% of Mn, 0.06-0.13% of V, 0.035%-0.075% of S, less than or equal to 0.035% of P, less than or equal to 0.30% of Cr, less than or equal to 0.30% of Ni, less than or equal to 0.30% of Cu, 0.010%-0.040% of Alt, less than or equal to 15 ppm of [O], and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities, specifically, C+Si / 6+Mn / 4.5+1.8*V is equal to 1-1.1. Electric furnace smelting and LF refining are adopted, desulfuration, then sulfuration and proper calcium treatment process are adopted in the refining process, and Mn / S is controlled. The vacuum treatment time of the steel is longer than or equal to 12 minutes, and the soft blowing time is longer than or equal to 20 minutes. A casting blank is cast through continuous casting, the pulling speed and the superheat degree are controlled, and the continuous casting of twelve furnaces or more is achieved. The heating and soaking temperature, the heating time, the initial rolling temperature, the final rolling temperature, the cooling speed and the like are controlled in the rolling process, and finally, peeling and flaw detection are carried out, so that high-quality round steel is obtained; and the round steel can meet the requirement for direct cutting processing.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Synchronous fluorine-calcium removal treatment process for reverse osmosis concentrated liquor of waste water from lead-zinc smelting
ActiveCN104445717ADestroy scale inhibitionEnsure reaction precipitation effectWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processCalcium handlingReverse osmosis
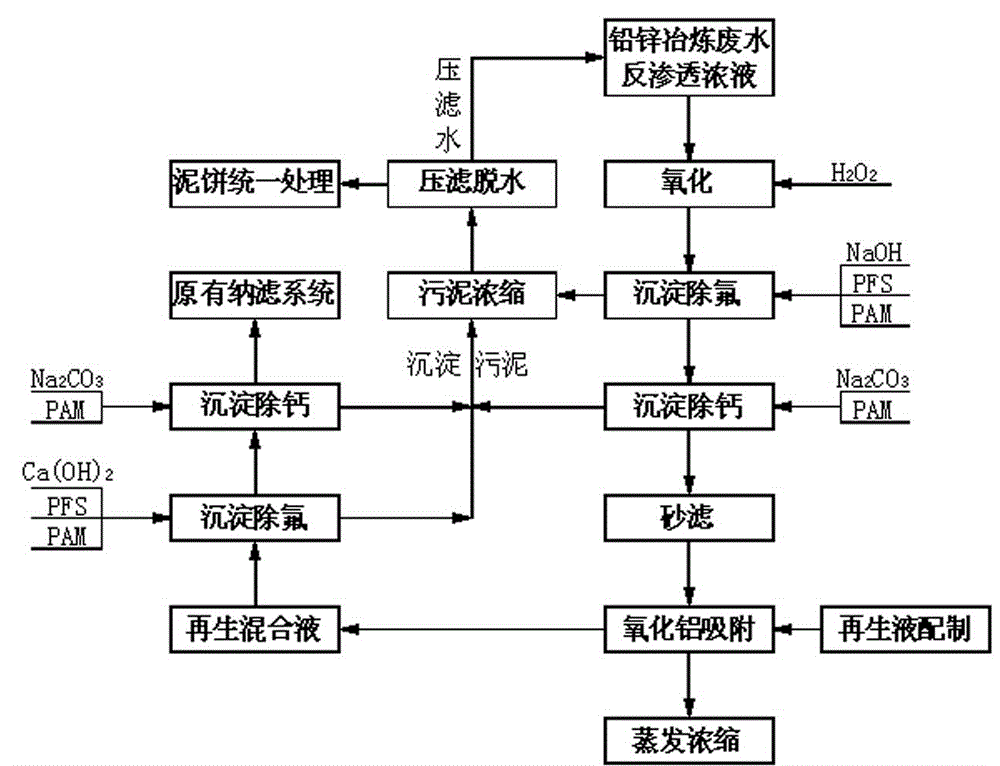
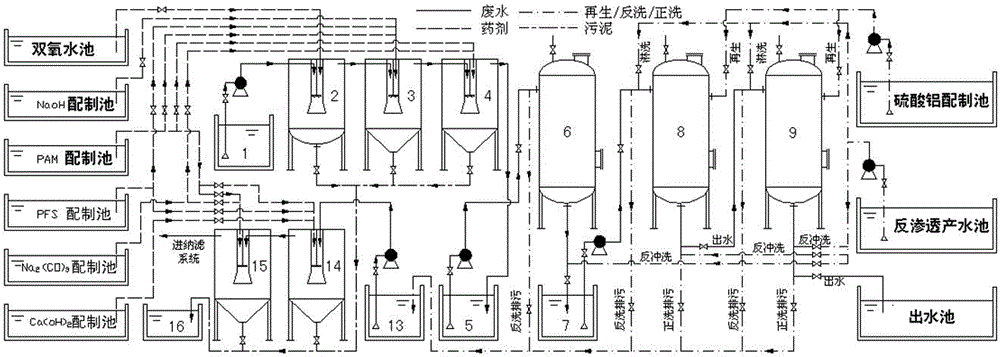
The invention relates to a synchronous fluorine-calcium removal treatment process for the reverse osmosis concentrated liquor of waste water from lead-zinc smelting. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, removing fluorine by virtue of oxidation and precipitation, secondly, removing calcium by precipitating, thirdly, removing fluorine by virtue of adsorption, next, sequentially regenerating activated aluminum oxide, removing fluorine from the generated mixed liquor, removing calcium from the generated mixed liquor and treating the generated mixed liquor, and finally, removing fluorine by precipitating, wherein the precipitation sludge generated in the calcium removal process is gathered and dehydrated by virtue of filter pressing, the water obtained by filter pressing is returned to a reverse osmosis concentrated liquor collecting tank for circular treatment, and the mud cake is subjected to unified disposal. After the oxidization, precipitation and adsorption treatment processes are adopted, the fluorine content and the calcium content of the reverse osmosis concentrated liquor are lower than 3mg / L and 50mg / L, respectively, and the problems of scaling and blockage caused by fluorine ions and calcium ions in the subsequent evaporation and concentration process of the reverse osmosis concentrated liquor are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGJIN LINGNAN NONFEMET COMPANY +1
Process for smelting low-cost X70 pipeline steel moderate-thickness plate blanks
The invention discloses a process for smelting low-cost X70 pipeline steel moderate-thickness plate blanks. The process comprises the steps of molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, LF furnace refining and plate blank continuous casting. In the process, C is 0.04%-0.08%, Mn is 1.40%-1.80%, Nb is 0.04%-0.08%, Cr is 0.2%-0.3%, P <= 0.015%, S <= 0.002%, N <= 60ppm, H <= 3.0ppm, and precious alloys Ni and Mo are not added. An RH (VD) vacuum treatment process is omitted, calcium treatment is performed after LF treatment, and inclusions are ensured to fully float upwards. The plate blank continuous casting step adopts a dynamitic soft-reduction process, and the center segregation of continuous casting blanks is controlled to be B-grade 1.0 or lower. The process for smelting the low-cost X70 pipeline steel moderate-thickness plate blanks is low in molten alloy cost and process cost and capable of achieving batch and industrial production of low-cost X70 pipeline steel moderate-thickness plates.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
LF refining method of titanium-containing austenitic stainless steel
The invention discloses an LF refining method of titanium-containing austenitic stainless steel. The LF refining method comprises the following steps: (1) tapping molten steel subjected to AOD treatment to a steel ladle; (2) hoisting the steel ladle to a slagging-off station to remove slag; (3) performing LF pull-in aluminum deoxidation and calcium treatment; (4) performing LF heightened titaniumrefining slag and lime slagging; (5) performing LF titanium alloying; (6) performing LF component and temperature confirming and performing weak blow and pull-out; (7) performing continuous casting. According to the method, the high-titanium refining slag is added in the LF refining process, TiO2 in the slag is saturated in advance, the activity of TiO2 in the slag is improved, and the oxidation reaction of titanium is inhibited. High-titanium refining slag and lime are adopted for slagging, so the slagging speed is high, and occupational hazards caused by fluorite are avoided. Meanwhile, an aluminum deoxidation-calcium treatment-titanium alloying process route is adopted, so formation of high-melting-point inclusions in the production process is prevented or inhibited, and the product quality is improved.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
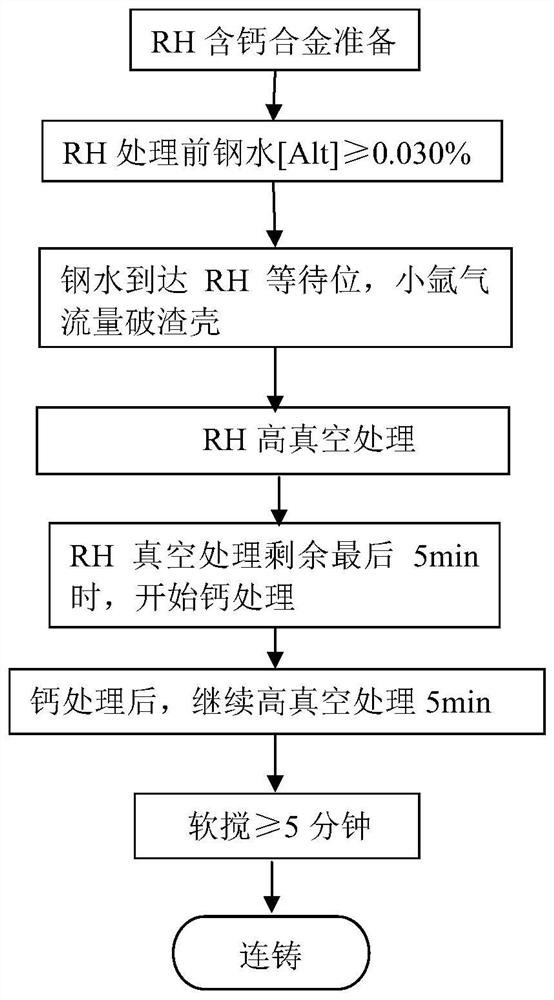
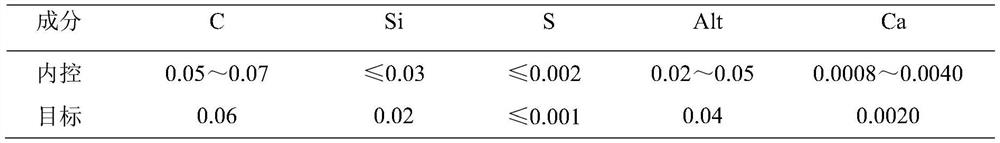
RH vacuum calcification furnace process treatment method
ActiveCN111575446AStable and efficient calcium treatment processImprove pouring effectCalcium handlingSlag
The invention discloses an RH vacuum calcification furnace process treatment method. The RH vacuum calcification furnace process treatment method comprises the following steps of KR molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, RH vacuum refining and slab continuous casting, wherein the RH vacuum refining comprises decarburization, deoxidation alloying and calcium treatment; in the decarburizationprocess, a slag surface deoxidizing agent is added to the surface of furnace slag in the middle and later periods of the decarburization, the adding amount is 1.0-2.0 kg per ton of steel, and the ladle slag is modified to enable the content of (T.Fe + MnO) in the slag to be less than or equal to 5 wt%; in the deoxidation alloying process, an alloy and carbon powder are added for the deoxidation alloying; in the calcium treatment process, a seamless pure calcium wire is started to be fed for calcium treatment 5 minutes after the deoxidation alloying is finished, and the pressure of a vacuum chamber is increased to 200 mbar or above during the calcium treatment; and after the calcium treatment is finished, the pressure of the vacuum chamber is reduced to 2 mbar or below, static circulationis conducted for 6 minutes, and then vacuum breaking tapping is conducted. According to the process method, the seamless calcium wire is fed after the deoxidation alloying, and meanwhile, the Ca element is uniformly distributed in molten steel by utilizing RH molten steel circular stirring, so that the modification of Al2O3 inclusion is realized, the Ca element oxidation amount is low, the calciumyield is increased, and the calcium treatment effect is stabilized.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE +2
Nitridation technique of supersupercritical high-pressure boiler tube billet steel
The invention relates to a nitridation technique, particularly a nitridation technique of supersupercritical high-pressure boiler tube billet steel. The nitridation technique comprises the following steps: electric furnace smelting, primary LF (ladle furnace) refinement, VD (vacuum degasser) vacuum degassing and secondary LF refinement, wherein in the electric furnace smelting process, the tapping components and temperature need to be controlled, and stirring with argon is also needed; in the primary LF refinement process, the mass percents of Cr and C need to be controlled; and in the secondary LF refinement process, calcium treatment is needed after the components are adjusted to a proper state, soft argon blowing treatment is performed after the temperature and all the components are adjusted, and the molten steel can be fed to a continuous casting process after the soft argon blowing is finished. In the nitridation technique, the nitrogen content is adjusted respectively by introducing nitrogen as a stirring gas into the ladle in the primary LF refinement process and VD vacuum degassing process and supplementing chromium nitride alloy in the secondary LF refinement process. According to the technique, the nitrogen content can be controlled at 0.030-0.070% by introducing nitrogen and adding chromium nitride in a scientific proportion; and after adding the nitrogen, no quality problems of the casting blank, such as surface pores, subsurface pores and the like, are produced.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A Calcium Treatment Method in the Vacuum Process of Rh Refining Furnace
ActiveCN110042202BImprove the qualified rate of flaw detectionSolve secondary oxidationCalcium handlingEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a calcium treatment method in the vacuum process of an RH refining furnace. Through the vacuum cycle treatment process of the RH vacuum refining furnace, the RH alloy silo is used to add a calcium-containing alloy to the molten steel circulating in a vacuum chamber to modify molten steel inclusions and calcium treatment. The process is stable and controllable. After the treatment, the calcium composition of molten steel is controlled stably and accurately. The calcium recovery rate reaches more than 20%. The molten steel inclusions are fully denatured. The invention successfully solves the problem of secondary oxidation caused by the tumbling and exposure of molten steel when the pure calcium wire is fed after the vacuum treatment of the RH refining furnace, stabilizes the calcium treatment effect, reduces the content of inclusions, improves the cleanliness of the molten steel and passes the flaw detection of the finished steel plate The production rate is reduced, and the economic benefit is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Smelting method for sulfur-containing and aluminum-containing steel
The invention discloses a smelting method for sulfur-containing and aluminum-containing steel. In the LF refining process, high-alkalinity slag is prepared from lime and pre-molten refining slag to assist in aluminum wire precipitation deoxidization and calcium carbide diffusion deoxidization, it is required that the sulfur content is not larger than 0.008% before LF station leaving, the content of sulfur in the steel is reduced, the content of sulfur entering VD / RH steel is stabilized, and it is avoided that Al2O3 and CaS impurities are generated during calcium treatment; and calcium treatment is performed ahead of VD / RH vacuum treatment. By means of the method, the Al2O3 impurities and calcium in the steel can react to generate low-melting-point liquid-state 12CaO.7Al2O3 and 3CaO.Al2O3;after vacuum breaking, sulfur feeding is performed, and since the time interval between the calcium feeding procedure and the sulfur feeding procedure is long, it can be avoided that the calcium and the sulfur react to generate CaS impurities. The method mainly has the advantages that the cleanliness of molten steel can be improved, the formation of the Al2O3 and CaS impurities is reduced, the cleanliness of the molten steel is improved, scaffolding of a continuous casting nozzle is reduced, the continuous casting and continuous pouring ratio is increased, and production cost is reduced.
Owner:DONGBEI SPECIAL STEEL GROUP
Calcium treatment method under special steelmaking process
ActiveCN103614513AReduce in quantityImprove purityProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingAluminate
The invention relates to a calcium treatment method implemented under a special steelmaking process. The calcium treatment method is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out desulfurization in a molten iron pretreatment process, namely, blowing CaO+Mg powder to desulfurize the molten iron until the sulfur content is 0.0018 to 0.0022 percent, and slagging off after the desulfurization; controlling the oxygen content at an end point of a converter within 650ppm in an converter process; ensuring the vacuum degree to be less than or equal to 300Pa in the RH (Ruhrstahl Heraeus) process, and maintaining the vacuum degree for 10 to 30 minutes; and secondarily returning the molten iron subjected to RH treatment to an LF (Ladle Furnace), adjusting the temperature, slagging after the RH treatment is completed, then conducting the calcium treatment, ensuring the feeding speed of a calcium line to be 180 to 200m / min, ensuring the feeding quantity of steel to be 1.4m / t, and controlling the bottom-blowing flow rate at 50 to 100 NL / min. By adopting the method, the impurities can be gradually converted from primary silicon manganate to calcium aluminosilicate, so that the quantity of the impurities per unit area of a steel plate can be remarkably reduced and is reduced from 87 to 100 / mm<2> to 12 to 25 / mm<2>. After the RH vacuum and calcium treatment, the type of the impurities is changed, and a product is deviated to the side of CaO-CaS; the size of the impurities in a tundish is relatively small, the impurities with the size being less than 10 micrometers account for 99.61 percent, and the impurity with the size being more than 30 micrometers is not found. By adopting the method, the molten steel purity and the steel plate flaw detection qualification rate can be improved, the calcium yield is stabilized at 20 percent or more, and the economic benefit is obvious.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Production method of low-phosphorous-content gear steel for automobile gearbox
The invention relates to a production method of low-phosphorous-content gear steel for an automobile gearbox. The production method comprises the process flow including converter smelting, LF+RH refining, continuous casting, hot rolling and rolling. According to a converter technology, dual-drag smelting is adopted, steel ladle slag is improved while the quantity of slag discharged out of a largeladle is decreased, and the content of FeO in large ladle slag is controlled to be equal to or lower than 1.5wt%. According to the LF refining working step, final slag is subjected to refining operation with the high alkalinity and the low calcium-to-aluminum ratio, and in the process, aluminum wire making precipitation deoxidation is used in cooperation with slag top calcium carbide diffusion deoxidation. According to RH, ferrotitanium is added in the later period of high-vacuum circulation, and the soft blow time after calcium treatment is longer than or equal to ten minutes. Protective casting is carried out in the whole process of the continuous casting step, the problems in tundish oxygenation and working procedure recarburization are solved by adopting a covering agent with the low content of ferrous oxide and a low-carbon slag absorbing agent, and a casting blank enters a pit for slow cooling after being discharged out of a production line. With the production method of low-phosphorous gear steel for the automobile gearbox, the technical problem that the gear steel for the automobile gearbox is relatively high in phosphorus content, unstable in ingredient, wide in bandwidthrange of hardenability, and the like is solved.
Owner:HANDAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
Preparation method of aluminum-calcium alloy used for vacuum refining molten steel deoxidation and device thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of aluminum-calcium alloy used for vacuum refining molten steel deoxidation and a device thereof; the high-purity aluminum and calcium are used as the raw material and are prepared according to the weight percent as follows: 70-90 percent of aluminum and 10-30 percent calcium; the calcium is added to the aluminum which is molten by a low-frequency sensing induction furnace, the aluminum and the calcium are molten for 30-40 minutes under the protection of argon gas and then cast into an ingot; after being cooled, the ingot is broken into blocks to prepare the aluminum-calcium alloy. The invention has the advantages that the alloy has high purity and high calcium content and is used for vacuum refining molten steel deoxidation; the deoxidation and calcium can be completed in one step; the O, C, N, S ingredients in the steel are ensured not to exceed the standard requirement; meanwhile, the Al2O3 inclusion content in the steel is greatly reduced, thereby having the obvious effects of reducing nodulation at a pouring water gap and improving steel quality.
Owner:郭庆成
Calcium treatment-free production process of low-carbon silicon-containing killed clean steel
The invention discloses a calcium treatment-free production process of low-carbon silicon-containing killed clean steel, and belongs to the technical field of iron and steel metallurgy. The process ischaracterized in that the production of the molded low-carbon low-aluminum killed clean steel is carried out under the condition that calcium treatment is not used, and the specific flow comprises the steps of processing molten iron, performing combined oxygen blowing to a converter from the top and the bottom, LF refining (adjusting the aluminum component of the molten steel, feeding aluminum for three times, and feeding aluminum-iron-rare earth core-spun yarn), performing argon soft blowing to the bottom of a ladle, continuous casting and continuous rolling. Compared with the prior art, a calcium treatment process is not adopted, so that the calcium treatment cost is saved, the problem that high-melting-point aluminate is prone to generate floccule flow is avoided, the forming performance of a steel sheet is improved, and the occurrence probability of cold bending cracking is reduced.
Owner:RIZHAO STEEL HLDG GROUP
Austenitic stainless steel for electronic products and preparation method of austenitic stainless steel
InactiveCN110819893AThe second phase is proportionally reducedIncrease contentSolution treatmentCalcium handling
The invention discloses austenitic stainless steel for electronic products and a preparation method of the austenitic stainless steel, and belongs to the field of stainless steel smelting. The problems that existing austenitic stainless steel is high in chromated nickel equivalent and poor in corrosion resistance are solved. The stainless steel comprises smaller than 0.03% of C, 0.5%-1.5% of Mn, smaller than 0.75% of Si, smaller than 0.04% of P, smaller than 0.01% of S, 15.0%-19.0% of Cr, 9.0%-15.0% of Ni, 2.0%-3.0% of Mo, smaller than 0.5% of Cu, smaller than 0.1% of N, smaller than 0.01% ofO and the balance Fe and other uncontrollable elements. The preparation method comprises the steps of smelting and casting, wherein a Si-Ca-Ba line is utilized for calcium treatment; hot rolling; hotline solution treatment and acid pickling; cold rolling; and degreasing. The stainless steel prepared through the method is low in chromated nickel equivalent, good in corrosion resistance, low in magnetic conductivity and high in hardness.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Treatment method of silico-calcareous collophanite
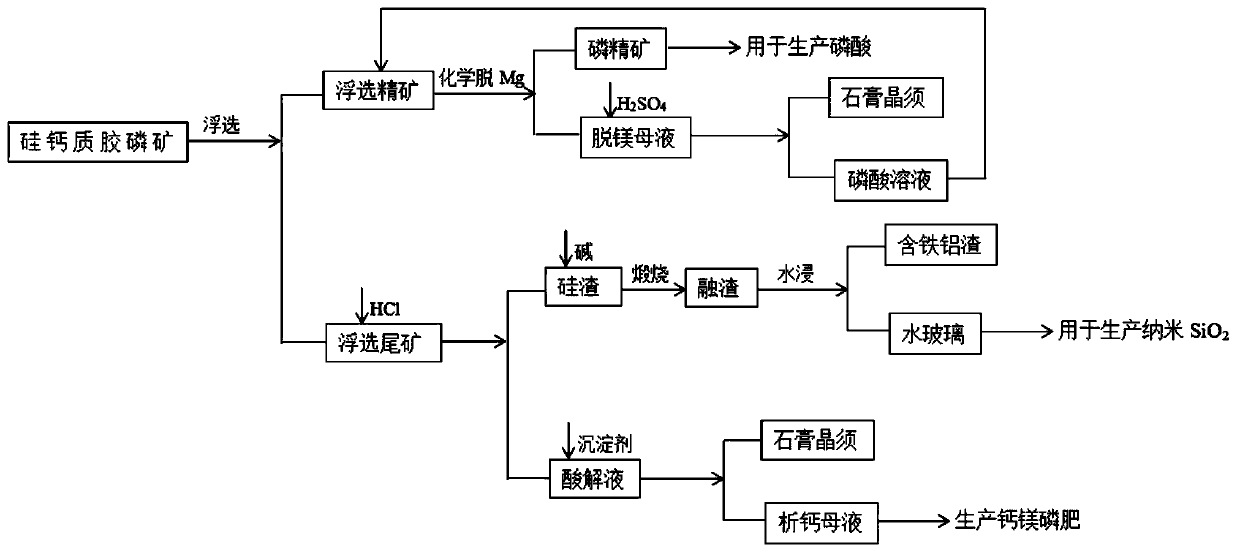
ActiveCN111422878AProcessing method advantagesIncrease profitPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsO-Phosphoric AcidCalcium handling
The invention provides a treatment method of silico-calcareous collophanite, which comprises the following steps: carrying out direct flotation on silico-calcareous collophanite to obtain flotation concentrate and flotation tailings, carrying out magnesium removal treatment on the flotation concentrate to obtain phosphate concentrate, carrying out calcium precipitation treatment on a magnesium removal mother liquor obtained by magnesium removal treatment to obtain gypsum whiskers and a phosphoric acid solution, carrying out acidolysis on flotation tailings, carrying out alkali fusion-water leaching treatment on silicon slag obtained through acidolysis so that water glass is obtained, and carrying out calcium precipitation treatment on an acidolysis liquid obtained through acidolysis so that gypsum whiskers are obtained. Phosphorus concentrate capable of being used for wet-process phosphoric acid is obtained through flotation-chemical method magnesium removal, sodium silicate is obtained through alkali fusion-water leaching to achieve recycling of silicon in tailings, and acidolysis liquid is comprehensively utilized to produce gypsum whiskers and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer. According to the method, a new utilization way of the silico-calcareous collophanite is opened up, and the utilization value of the collophanite is improved.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Composite cored wire for steelmaking and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a composite cored wire for steelmaking and a preparation method thereof, and aims to provide a deep slow-release deoxidization technology for clean steelmaking. Through the technology, impurities in molten steel and impurities in steel slag can be removed. The composite cored wire prepared according to certain component proportion and method steps has the advantages of high deoxidization efficiency and desulfurization efficiency, capability of reducing the calcium splashing probability, greatly improved yield in a calcium treatment process and reduced calcium treatment cost. Oxygen in the steel slag can be effectively removed, and oxygen in the steel slag is prevented from invading into the molten steel again after being saturated.
Owner:秦皇岛双轮环保科技股份有限公司
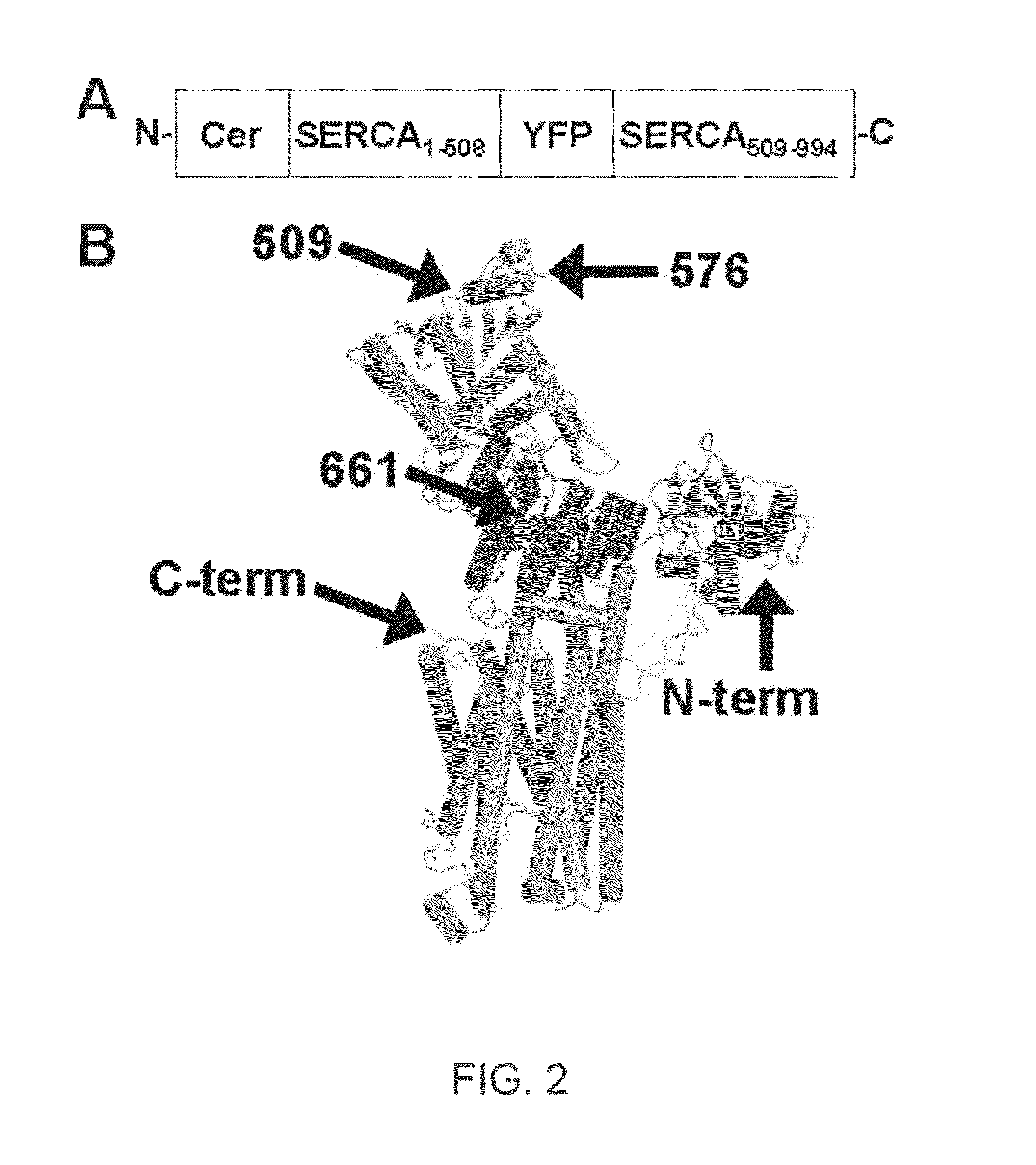
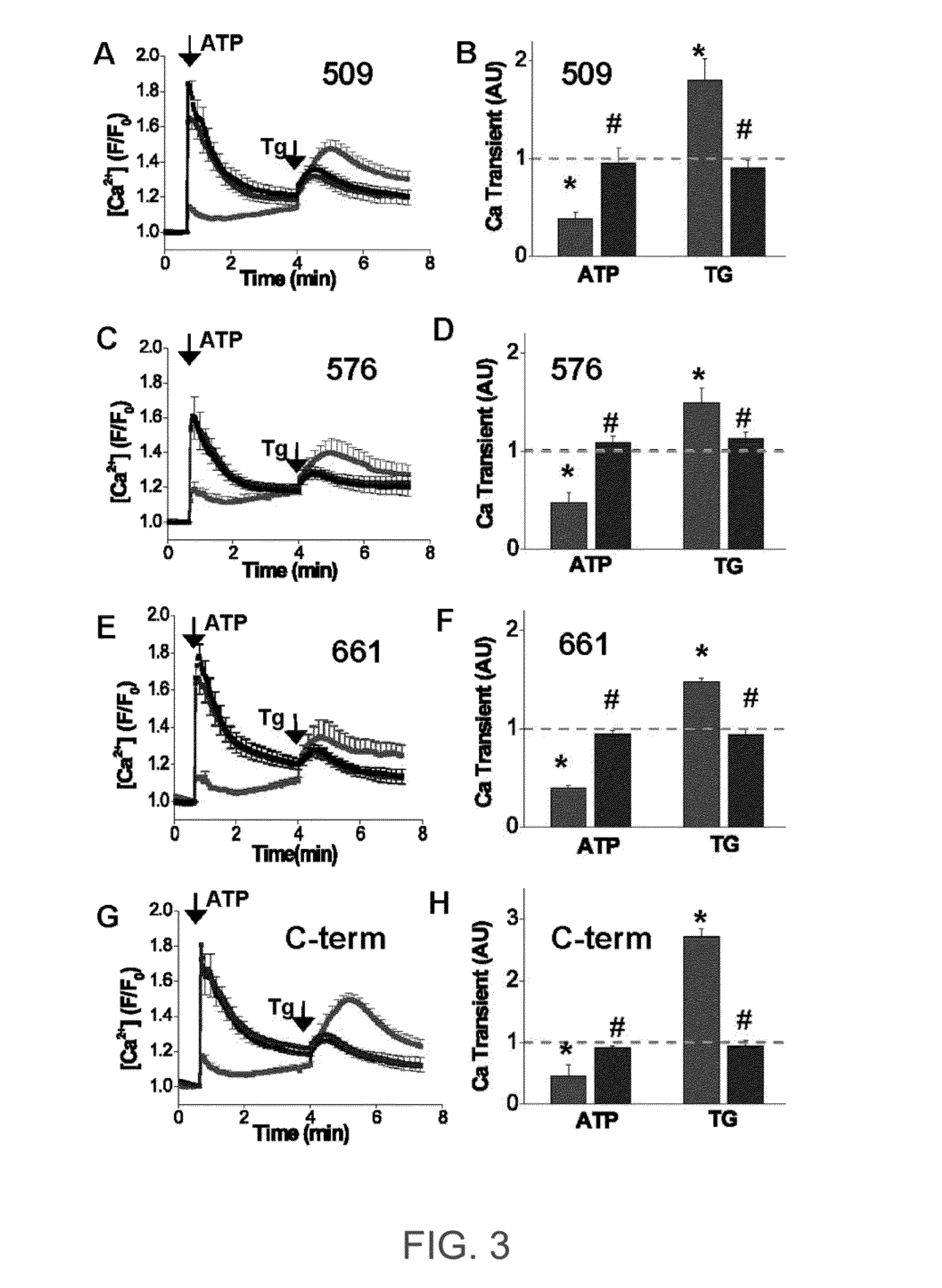
ENGINEERED PROTEIN: "2-COLOR SERCA", AN ION-MOTIVE ATPase FUSED TO CERULEAN AND YELLOW FLUORESCENT PROTEIN
A method and engineered proteins for use therewith suitable for studying SERCA that are capable of being used in vivo and do not require protein purification or chemical labeling of SERCA, or reconstitution into artificial membranes. The engineered protein for calcium handling within human cells includes a two-color SERCA construct having three component proteins fused together. The three component proteins include a blue fluorescent protein (cerulean), SERCA2a and a yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), or a red fluorescent protein (tagRFP acceptor), SERCA and a green fluorescent protein (GFP). The method of determining SERCA activity for optimization of cardiac function includes resolving structure changes of the two-color SERCA construct. The two-color SERCA constructs are catalytically active and able to pump calcium following the step of resolving structure changes.
Owner:LOYOLA UNIV OF CHICAGO
Aluminum deoxidation method for nitrogen-containing super stainless steel
The invention belongs to the field of ferrous metallurgy, and particularly relates to an aluminum deoxidation method for nitrogen-containing super stainless steel. The aluminum deoxidation method includes the following steps of: carrying out slagging-off after chromium reduction of the nitrogen-containing super stainless steel, adding lime, fluorite and aluminum blocks into molten steel to make new slag, carrying out desulfurization, and then transferring the molten steel to an LF refining station; mixing aluminum shots and silicon-calcium powder, subsequently dividing the mixture into two equal parts, and adding a first part of deoxidizer to carry out slag surface diffusion deoxidation; afterwards, sequentially adding an aluminum wire and a silicon-calcium wire into the molten steel for precipitation deoxidation and calcium treatment; adding a second part of deoxidizer to continue slag surface diffusion deoxidation; and continuing to carry out soft blowing, carrying out tapping afterthe temperature is qualified, and carrying out die casting or continuous casting. According to the aluminum deoxidation method, the content of aluminum in the nitrogen-containing super stainless steelcan be controlled to be 0.015% to 0.030%, the total oxygen content is controlled to be within 20 ppm, precipitation of aluminum nitride caused by the too high aluminum content in a thermal processingand heat treatment process is avoided, and therefore the cold / hot processing performance and the mechanical properties of the nitrogen-containing super stainless steel are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Smelting method capable of controlling gas valve steel inclusions
ActiveCN107090537ALess impuritiesImprove finished product qualityProcess efficiency improvementSlagMolten steel
The invention discloses a smelting method, particularly discloses a smelting method capable of controlling gas valve steel inclusions, belongs to the technical field of metallurgical processing technological design and provides the smelting method capable of controlling the gas valve steel inclusions. Impurities in molten steel of stainless steel can be effectively lowered, and accordingly the inclusions in a finished product stainless steel blank are reduced. The smelting method includes the several steps of adjusting slag by a slag modifier in an AOD smelting furnace, adjusting slag by a modifier in a refining furnace and conducting calcium treatment in an argon blowing environment after refining is completed.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Smelting preparation method of high-cleanliness titanium-containing steel
The invention discloses a smelting preparation method of high-cleanliness titanium-containing steel. The Ti content of the high-cleanliness titanium-containing steel is above 0.010%. The smelting preparation method comprises the following smelting steps of (1) carrying out converter smelting, (2) carrying out converter tapping, (3) carrying out deoxidation alloying, (4) carrying out LF treatment,(5) carrying out RH treatment, wherein the vacuum degree is controlled to be below 5 mbar, the high vacuum holding time of the vacuum degree below 2.5 mbar is 8-20 min, the mass percentage of N in molten steel is less than or equal to 50ppm, a ferrotitanium wire is fed according to the LF end point residual Ti content to adjust the Ti content, then calcium treatment is conducted, and soft blowingis conducted for above 10 min after calcium treatment; and (6) carrying out continuous casting. According to the smelting preparation method, in order to avoid the situation that TiN is formed due tothe fact that the N content in the molten steel is too high in the refining process, the process is adjusted, a titanium alloy is not added in the LF process to adjust the Ti component, a titanium wire is fed after N removal in RH treatment to adjust the component, and TiN inclusions generated in the steel smelting process are greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A production process for controlling large inclusions in acid-resistant pipeline steel
ActiveCN107099747BControl quantityDeterioration of mechanical propertiesProcess efficiency improvementCalcium handlingMetallurgy
The invention discloses a production process for controlling large inclusions in acid-resistant pipeline steel. Through systematic analysis on a pipeline steel inclusion control mechanism adopting a BOF-RH-LF production process, the component design is reasonably performed; the pipeline steel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.02-0.04 percent of C, 0.10-0.30 percent of Si, 1.00-1.30 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.013 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.0010 percent of S, 0.030-0.070 percent of Nb, 0.006-0.020 percent of Ti, 0.10-0.30 percent of Ni, 0.10-0.30 percent of Cr, 0.10-0.30 percent of Cu, 0.015-0.050 percent of Al and the balance of Fe. The production process disclosed by the invention has the benefits that the content of sulfurs in molten steel before calcium treatment is ensured to be less than 10 ppm; the quantitative calcium treatment is performed after the end of LF; the purpose of improving the purity of the molten steel is achieved, so that the internal quality of steels is improved, and the economic benefits are improved.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
530 MPa-grade thin galvanized band steel and production method thereof
ActiveCN106834937AGood formabilityReduce usageHot-dipping/immersion processesCalcium handlingMolten steel
The invention discloses 530 MPa-grade thin galvanized band steel and a production method thereof. The 530 MPa-grade thin galvanized band steel comprises, by weight, 0.08-0.12% of C, 0-0.06% of Si, 1.1-1.5% of Mn, 0-0.016% of P, 0-0.008% of S, 0.040-0.055% of Nb, 0.020-0.045% of Als, 0-0.007% of N, 0.015-0.030% of Ti, 0.0015-0.0045% of Ca, and the balance Fe. Converter and LF refining is conducted in a low nitrogen mode, LF refining, the acid-soluble aluminum content before LF refining calcium treatment is 0.025-0.045%, molten steel is clearly blown by bottom blowing argon after calcium treatment for 6-15 min, and refining is completed; and when refining is finished, the acid-insoluble aluminum content is less than or equal to 0.004 wt%, the ratio of the acid-insoluble aluminum content to the calcium content is less than or equal to 2.5, and in order to reach the ratio, calcium treatment is conducted. The 530 MPa-grade thin galvanized band steel meets the requirements of the surface quality level FB in GB2518 and EN10346.
Owner:HBIS COMPANY LIMITED HANDAN BRANCH COMPANY
Methods For The Selective Treatment Of Tumors By Calcium-Mediated Induction Of Apoptosis
InactiveUS20110098232A1Exceed capacityImprove leakageCyclic peptide ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCalcium handlingCalcium influx
Available evidence indicates that tumor cells exhibit consistent abnormalities in Calcium influx and intracellular storage of sequestered Calcium when compared to normal cells. The present invention provides clinical methods by which such differences are exploited to induce Apoptosis selectively in tumor cells while sparing normal cells. These methods are based upon employing drugs that, acting alone or in synergistic combinations, produce an increase in intracellular Calcium loading such that either or both of two major Apoptotic pathways are triggered to produce selective killing of malignant cells. Since the invention is based upon fundamental cell cycle requirements, to the extent that Calcium handling abnormalities are a general characteristic of the malignant state, the methods presented here are widely applicable regardless of tissue of origin and degree of cellular de-differentiation.
Owner:ZEILIG CHARLES E
Rolled steel and rolled steel inclusion control method
ActiveCN113604723APrevent getting involvedReduce aggregationManufacturing convertersCalcium handlingMolten steel
The invention relates to a rolled steel and rolled steel inclusion control method. The rolled steel is produced by the following control method of (1), converter smelting; (2), RH furnace refining; (3), LF furnace refining; and (4) continuous casting protection casting; in the LF furnace refining stage in the step (3), soft blowing and calcium treatment are carried out, the primary soft blowing is carried out for 3-5 min, the flow is 200-800 NL / min, the calcium treatment wire feeding amount is 160-220 m / furnace, it is ensured that the Ca content of out-of-station is 20-35 ppm or Ca / Als is larger than or equal to 0.08, the secondary soft blowing is carried out for 12-18 min after calcium treatment, the flow is 80-220 NL / min, aluminum, alloy and heating operations are forbidden in the soft blowing and calcium treatment process, and molten steel exposure is strictly forbidden in the soft blowing process. According to the control method, the quality of rolled steel products can be improved, the quality objection rate is reduced, and the purposes of reducing cost and improving efficiency are finally achieved.
Owner:RIZHAO STEEL HLDG GROUP
Production method for increasing continuous pouring times for calcium-free treatment of cold heading steel in furnace
InactiveCN112080608AAvoid nodules causing problemsAvoid it happening againManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementIron powderCalcium handling
The invention relates to a production method for increasing the continuous pouring times for calcium-free treatment of cold heading steel in a furnace. The production method comprises the following steps of: controlling the binary alkalinity of refining slag to be 9.0-13.0 when an LF furnace starts to heat; evenly scattering ferrosilicon powder is to the surface of the refining slag for slagging after 10-15 min of treatment of an LF furnace, where the added amount of the ferrosilicon powder is 0.8-1.4 kg per ton of steel, and the binary alkalinity of the refining slag is controlled to be 2.8-4.5; and after 5-15 min of treatment of the LF furnace, feeding an aluminum wire to control the aluminum content of molten steel to be 0.050% to 0.060%, controlling the aluminum content of a finished molten steel product to be 0.015% to 0.030%, and ensuring that the aluminum wire is fed before ferrosilicon powder is added; wherein final slag of the LF furnace comprises the following components in percentage: 48% to 58% of CaO, 13% to 17% of SiO2, 20% to 30% of Al2O3 and 4% to 8% of MgO. The production method provided by the invention prevents nodulation of a sprue in a pouring process of a steel billet and realizes 15-20 times of continuous pouring for calcium-free treatment of the molten steel in the furnace.
Owner:XINGTAI IRON & STEEL
Refining method of LF (ladle furnace) for producing steel for containers in CSP production line
ActiveCN107916319ALow revision rate for edge crack defectsReduce breakout rateProduction lineSteelmaking
The invention relates to a refining method of an LF (ladle furnace) for producing steel for containers in a CSP production line. Refining in the LF is performed after smelting in a convertor; one-timeheating is adopted, and one-time slagging, desulfurization and alloy addition is performed; calcium treatment is performed; and then soft blow is performed for 3 to 4 min, and then conventional subsequent procedures are implemented. According to the refining method, in the refining procedure of the steelmaking LF, the one-time heating and the one-time slagging, desulfurization and alloy additionare optimally controlled, so that the problems of low surface edge crack defect changing rate and component qualified rate, frequent interrupted steel casting and the like of an existing CSP production line for producing the steel for the containers can be obviously solved, the edge crack defect changing rate is reduced within 1.0%, the component qualified rate is increased to more than 98%, and the steel breakout rate is reduced within 0.3%.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Method for refining rare earth inclusions in super stainless steel
ActiveCN114058767AAdd calcium treatment processReduce oxygen contentProcess efficiency improvementAluminateYarn
The invention provides a method for refining rare earth inclusions in super stainless steel, and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy. According to the method, the molten steel of the super stainless steel is subjected to primary refining and refining operation, so that the sizes of rare earth inclusions in the super stainless steel can be effectively refined, and the total oxygen content is remarkably reduced. Wherein during primary refining, the contents of oxygen, sulfur and aluminum in tapping molten steel can be effectively controlled within a proper range; in the refining process, slag adjusting, diffusion deoxidation treatment, precipitation deoxidation treatment, calcium treatment for feeding a silicon-calcium wire and rare earth treatment for feeding a rare earth core-spun yarn are sequentially carried out, the total oxygen content of the molten steel can be further reduced, and the size of rare earth inclusions can be further refined. A calcium treatment process is added before rare earth treatment, and a feeding amount formula of a silicon-calcium line is designed, so that calcium aluminate inclusions are in a semi-liquid state, collision growth of the calcium aluminate inclusions is inhibited, and the situation that the sizes of the rare earth inclusions are too large due to genetic effects is avoided.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for solving blockage of pouring nozzle of billet caster producing high carbon chromium bearing steel
The invention discloses a method for solving blockage of a pouring nozzle of a billet caster producing high carbon chromium bearing steel. The method includes LF refining, RH refining and a casting process. According to the method, calcium treatment operation is carried out in the middle of the LF refining. Calcium line addition is 0.10-0.35 kg / t steel. The content of molten steel Ca is controlledwithin 0.0010-0.0025 wt %. The sulfur content of the molten steel is less than or equal to 0.010 wt % before calcium treatment, otherwise the calcium treatment is delayed. Aluminum products are not added into the molten steel in the later period of the LF refining and the RH process. A slab section of the billet caster is less than or equal to 260mm*260mm. A tundish nozzle is an immersion nozzle,and an argon blowing stopper with holes is not needed to be used. The method solves the technical problems troubling the billet caster producing high carbon chromium bearing steel for a long time that the immersion nozzle is likely to be plugged, causing the billet caster to have accidents to stop pouring, the molten steel to return to a furnace or falls to the ground. The method reduces the production cost, improves the benefit of an enterprise and has excellent promotion and application value.
Owner:HANDAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
Smelting method capable of improving heavy rail steel cleanliness
InactiveCN108796172AImprove cleanlinessImprove fatigue performanceManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSocial benefitsMolten steel
The invention discloses a smelting method capable of improving heavy rail steel cleanliness, and belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy. The problem that the cleanliness of existing heavy rail steel cannot meet the requirements of the high speed railway is solved. The smelting method comprises the following steps of molten iron pretreatment, converter smelting, LF refining, RH refining and continuous casting, wherein in the step of LF refining, iron calcium lines of 1-3m / t of molten steel are adopted for calcium treatment. According to the smelting method, through the steps, P inthe steel rail can be controlled to be 0-0.0060%, S in the steel rail can be controlled to be 0-0.0030%, O in the steel rail can be controlled to be 0-0.0010%, N in the steel rail can be controlled to be 0-0.0050%, H in the steel rail can be controlled to be 0-0.00015%, the sum of P, S, O, N and H is 0-160ppm, and the grade of all inclusions is 0-1.0. Through the smelting method, the cleanlinessof the heavy rail steel is remarkably improved, and the smelting method has a certain social benefit and is worthy of application and popularization.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com