Patents
Literature
95 results about "Cathode sputtering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
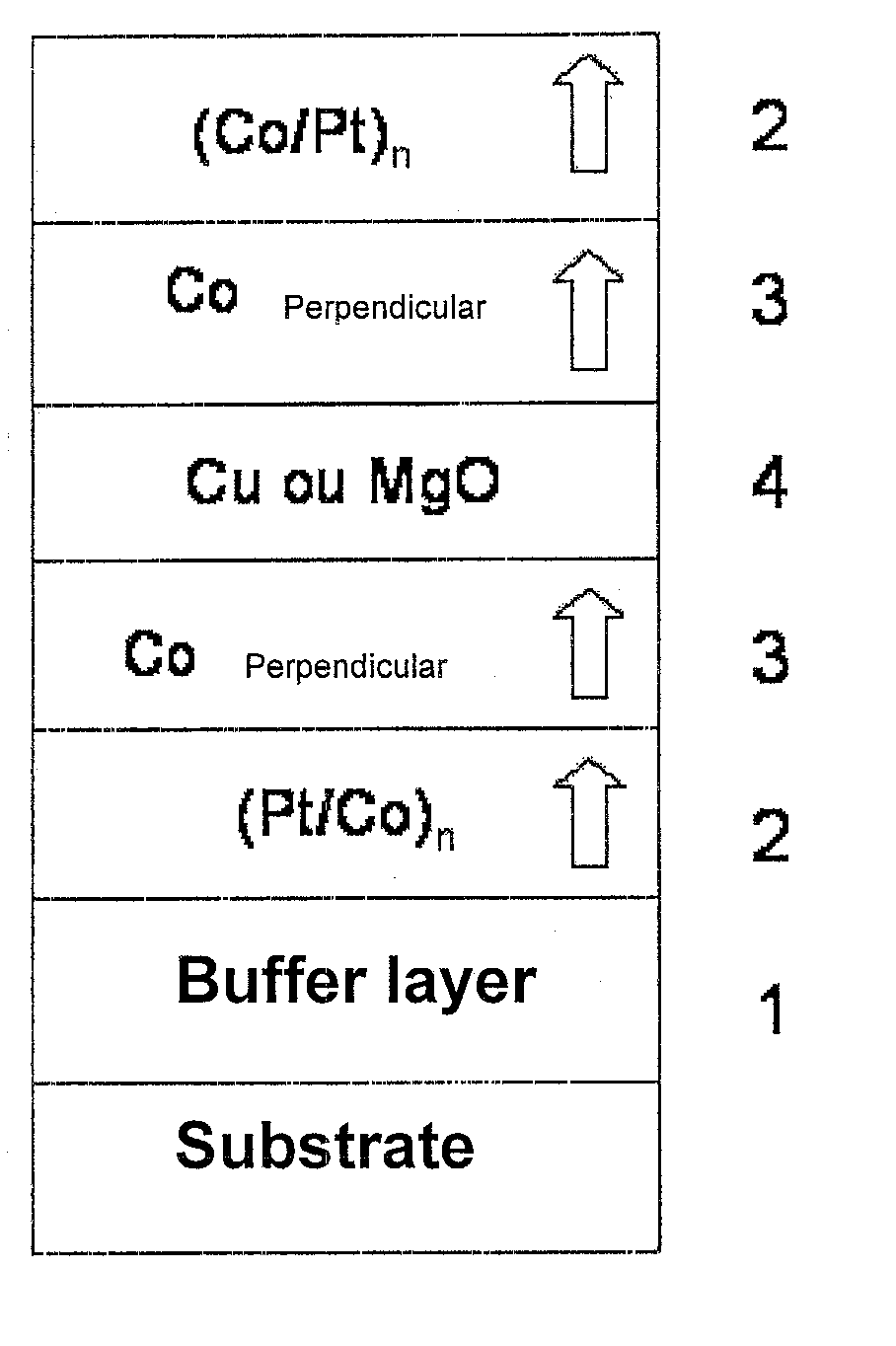
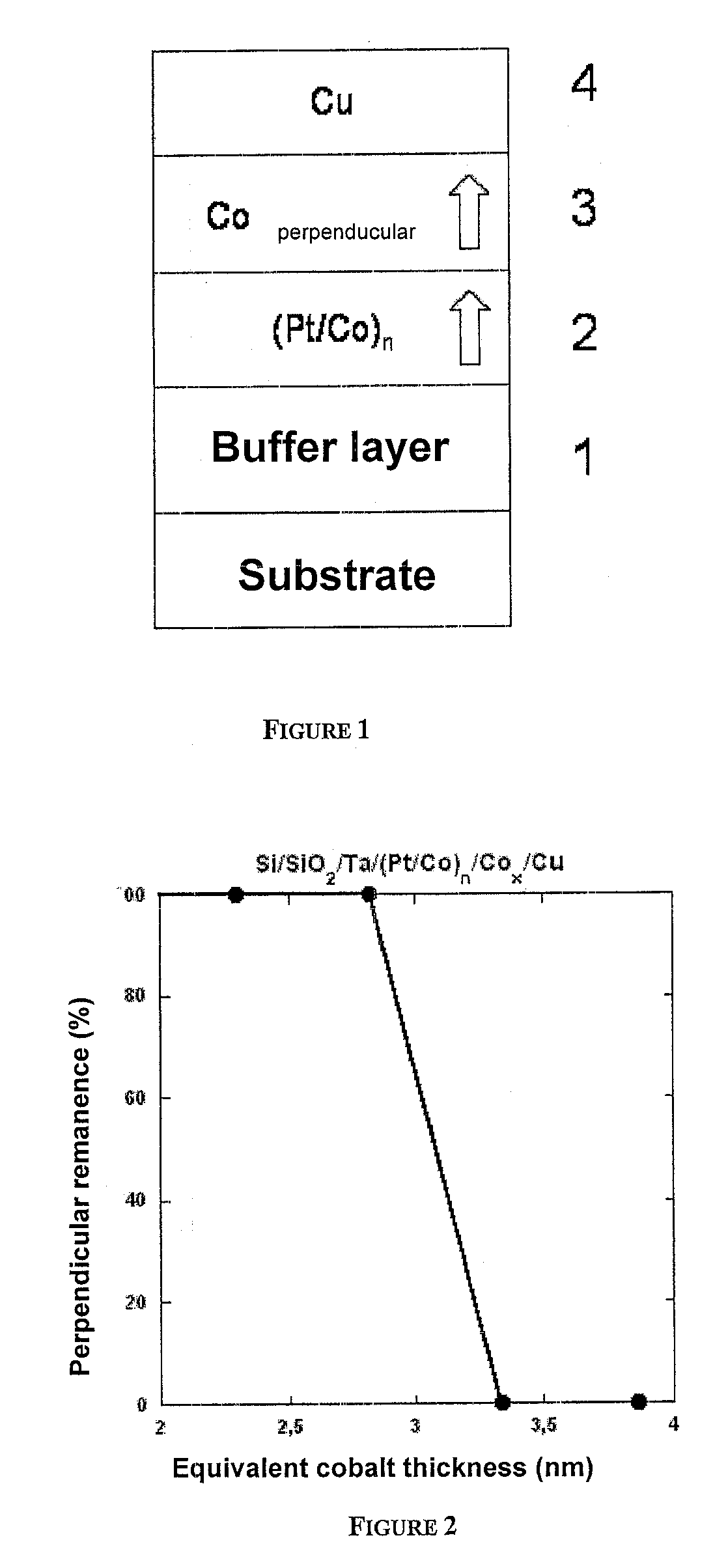
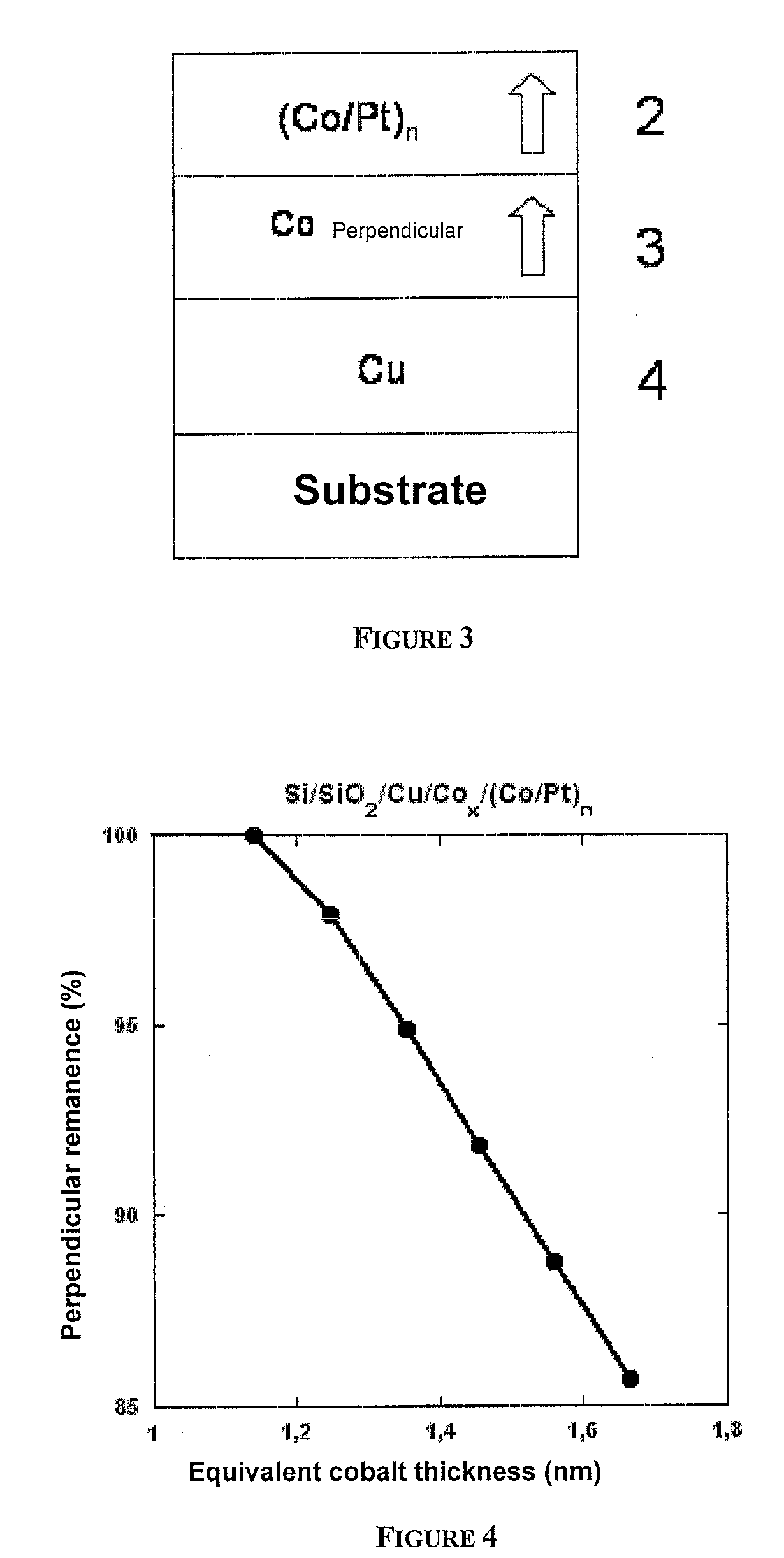
Thin-film magnetic device with strong spin polarisation perpendicular to the plane of the layers, magnetic tunnel junction and spin valve using such a device
ActiveUS20080031035A1Improve scalabilityImprove adhesionNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeHigh rate
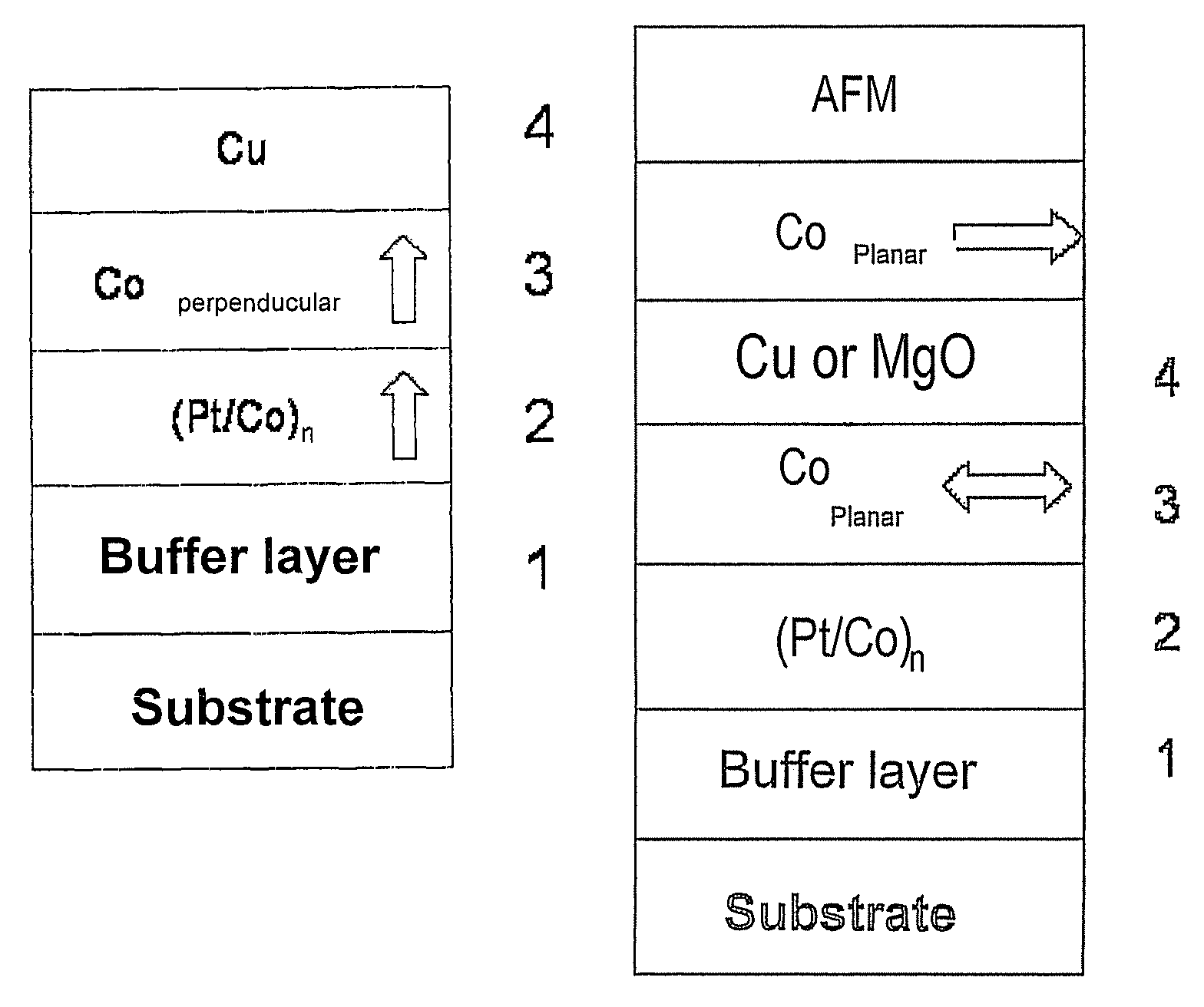
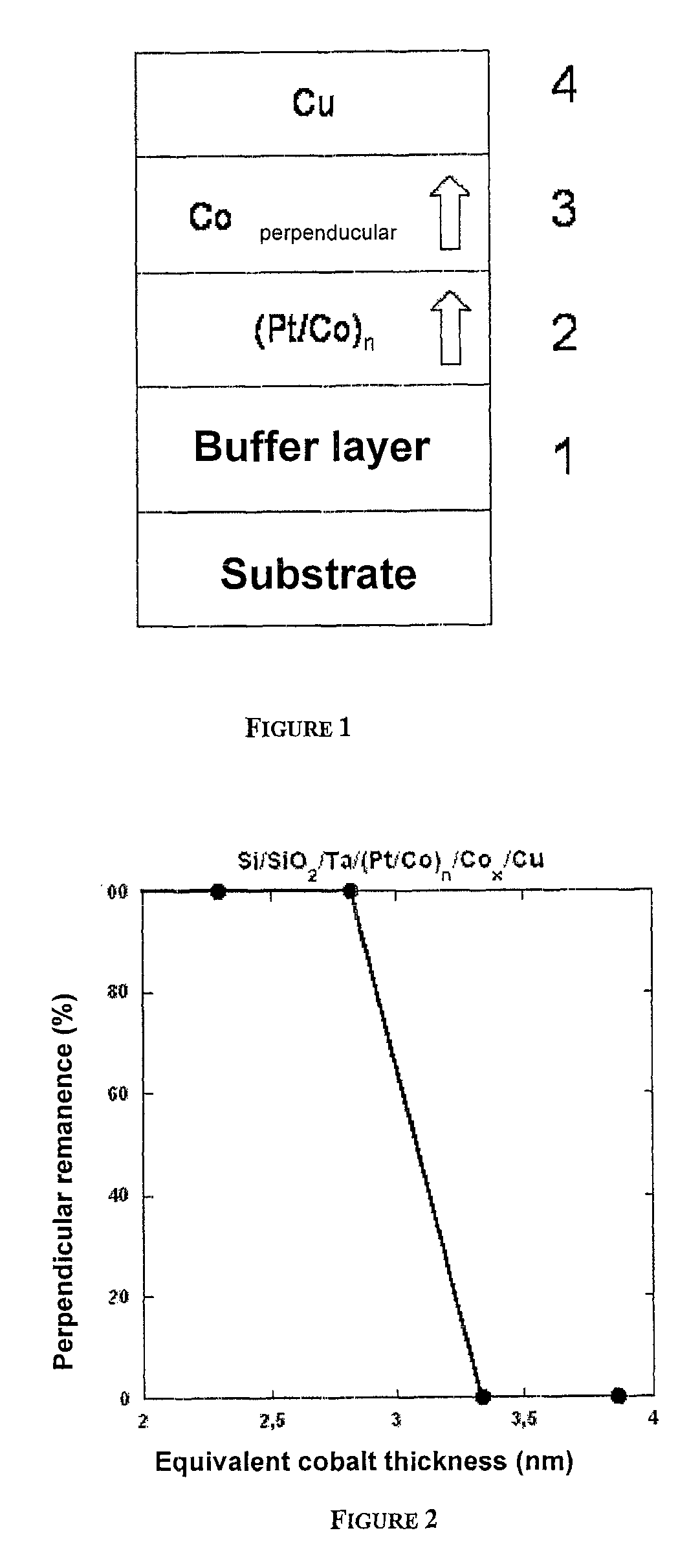
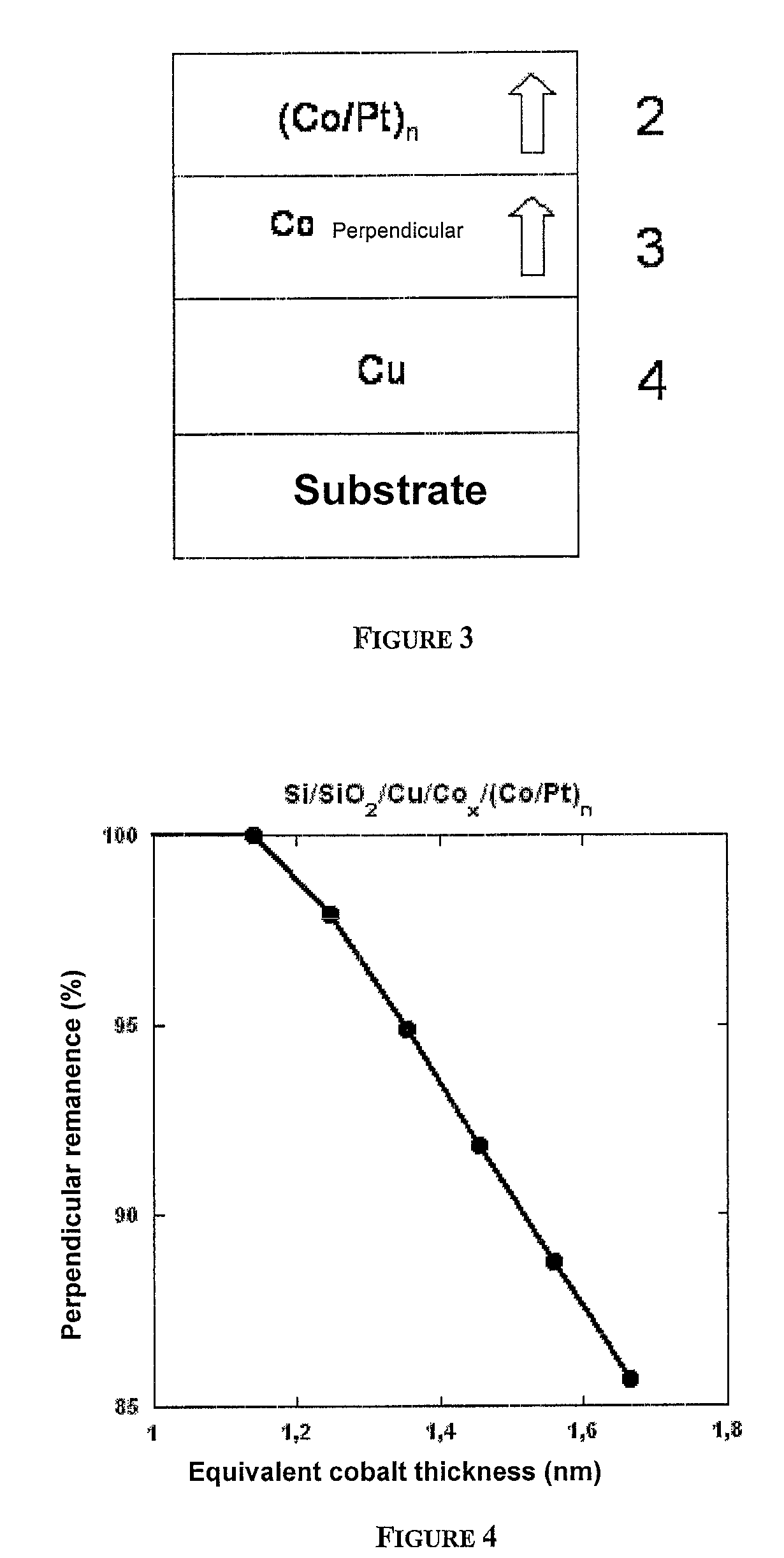
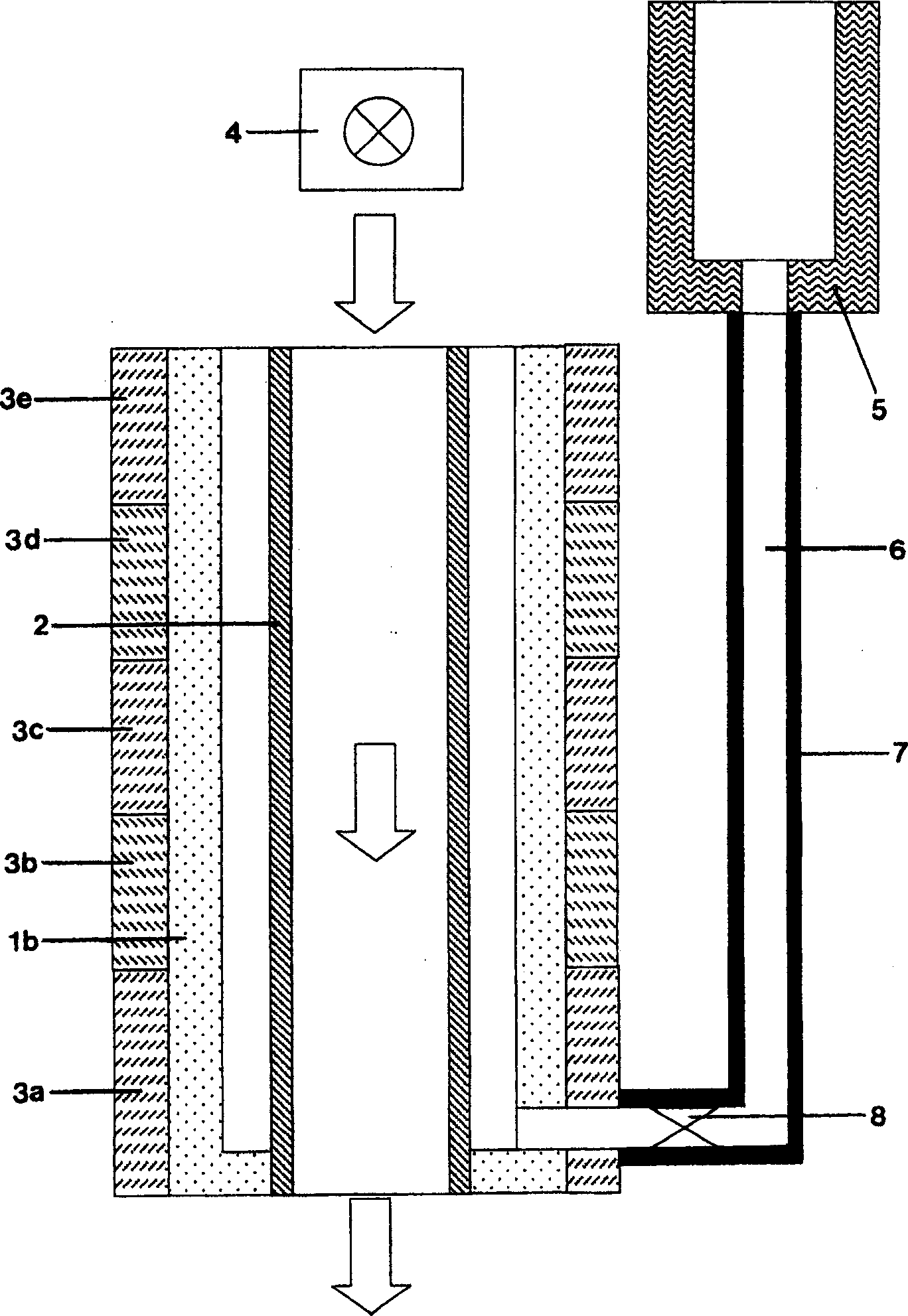
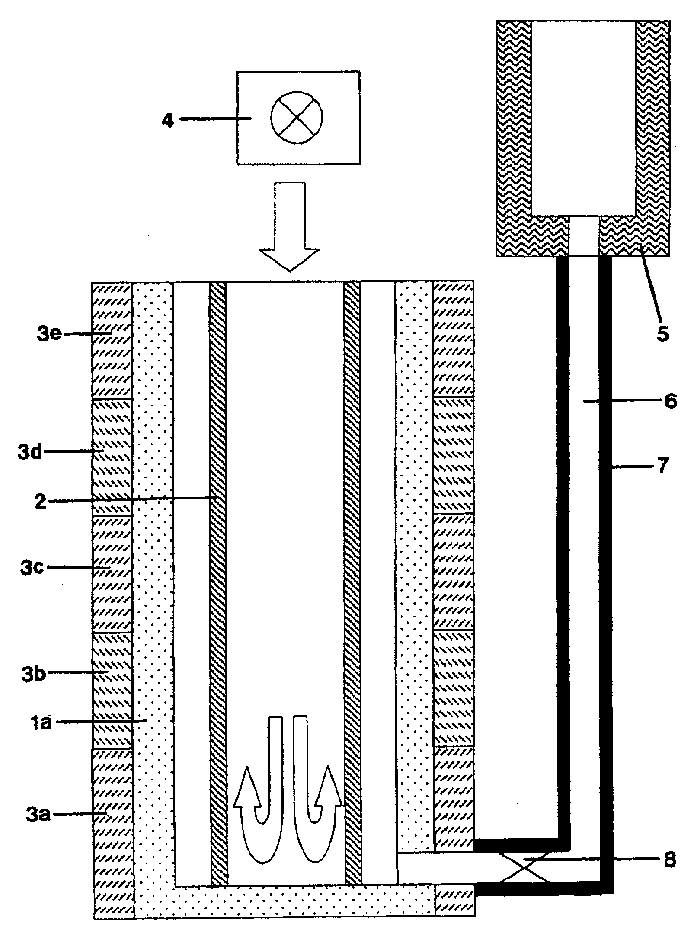
A thin-film magnetic device comprises, on a substrate, a composite assembly deposited by cathode sputtering and consists of a first layer made of a ferromagnetic material with a high rate of spin polarisation, the magnetisation of which is in plane in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, a second layer made of a magnetic material with high perpendicular anisotropy, the magnetisation of which is outside the plane of said layer in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, and coupling of which with said first layer induces a decrease in the effective demagnetising field of the entire device, a third layer that is in contact with the first layer via its interface opposite to that which is common to the second layer and made of a material that is not magnetic and not polarising for electrons passing through the device.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
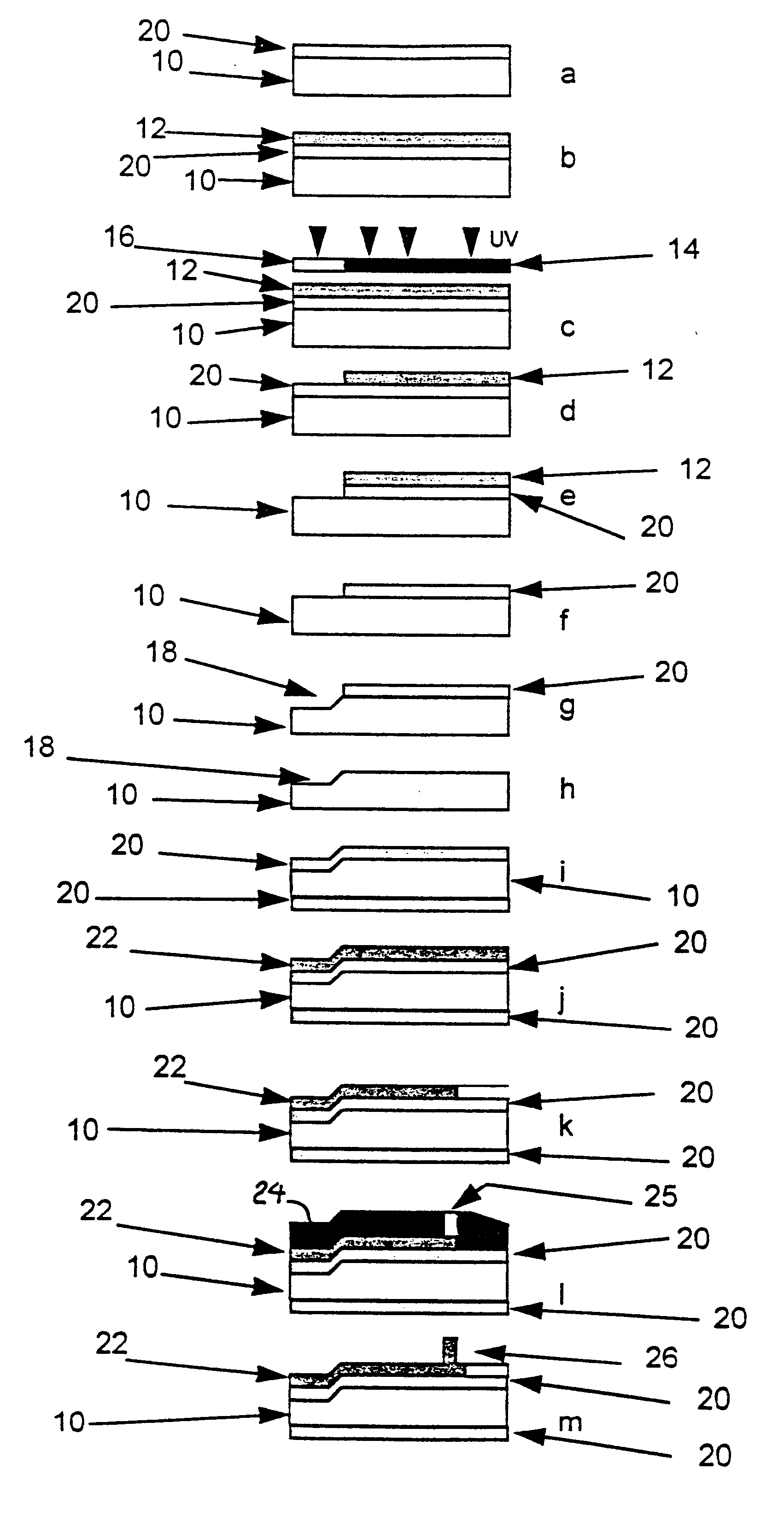
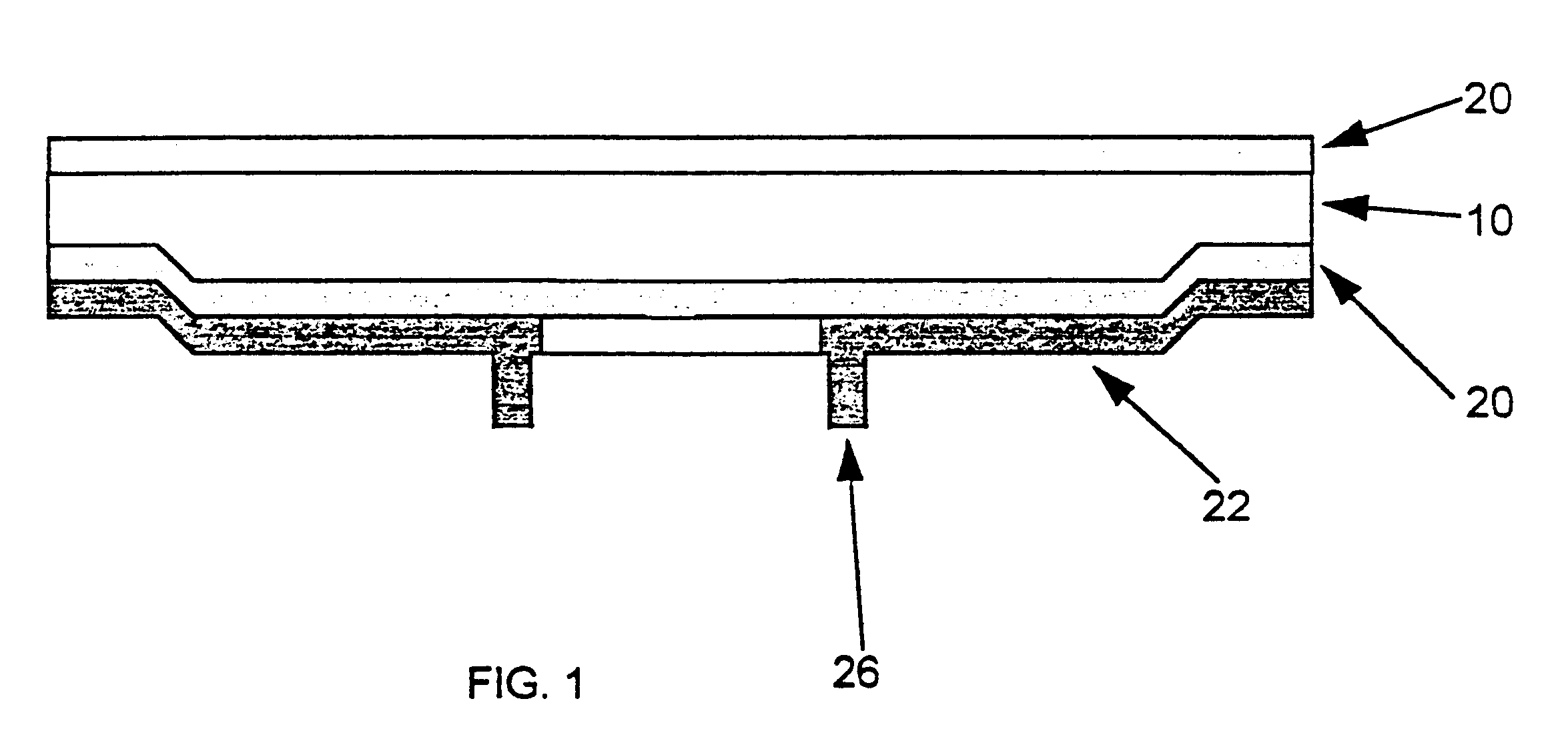
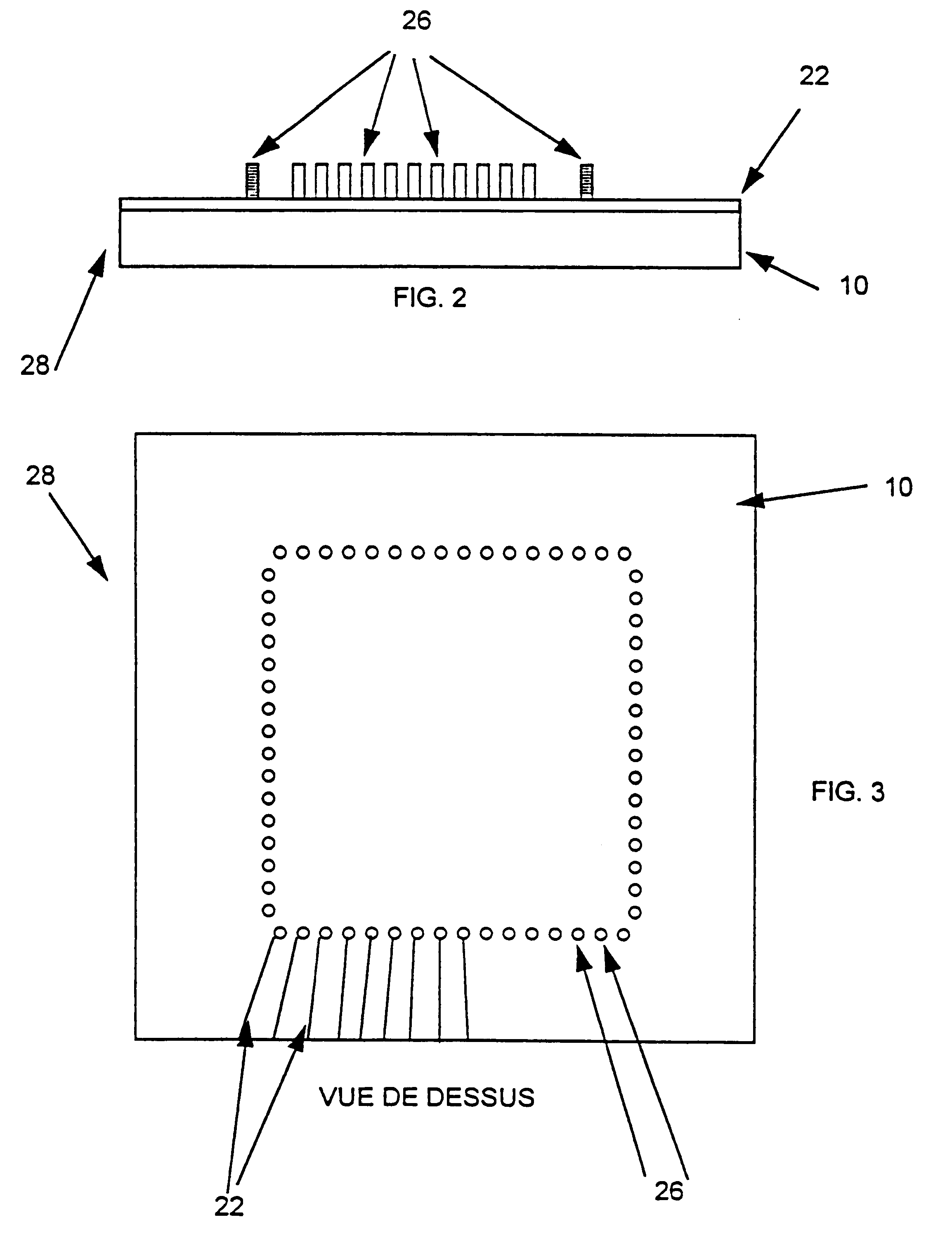
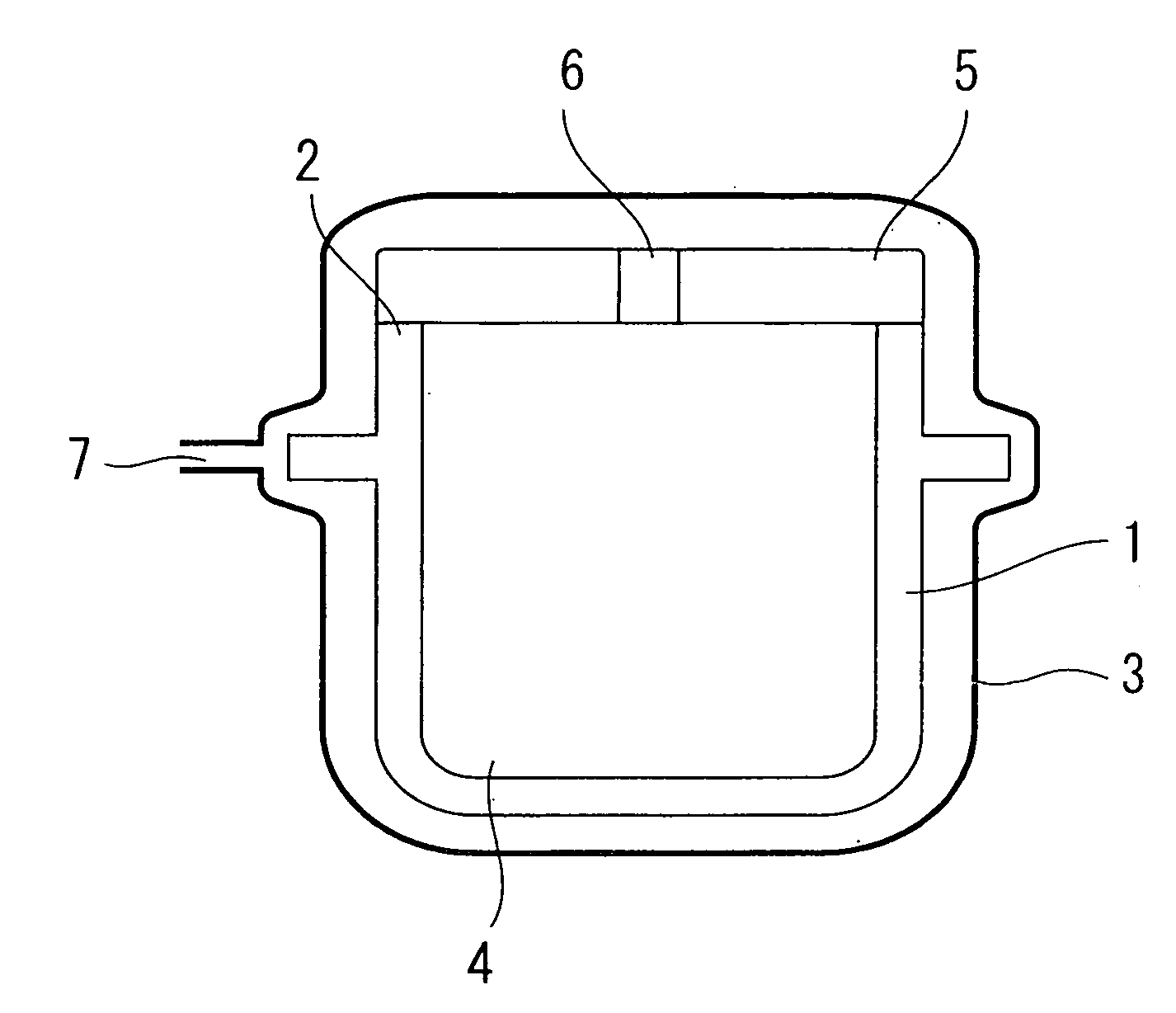
Method for making cards with multiple contact tips for testing semiconductor chips
InactiveUS6289583B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDecorative surface effectsGas phaseSemiconductor chip
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing a card with multiple tips, designed in particular for testing semiconductor chips or integrated circuits before encapsulation thereof and comprising an oxidised silicon substrate 10 on the two opposite surfaces, one of the surfaces being provided with conducting strips connected to contacts in the form of tips 26. A thin metal layer 22 is deposited by vapour deposition in a vacuum or by cathode sputtering on one of the insulated surfaces of the monolithic substrate 10, and the conducting strips are obtained by means of a UV photolithography operation making use of a photosensitive resin, followed by etching of the thin metal layer 22 according to the location and shape of the tips 26. Another UV photolithography operation is then performed consisting in depositing a thick layer 24 of photosensitive resin on the thin etched layer, the resin then being revealed with the drawing 25 of the tips. The tips 26 are finally obtained by electroforming by means of a bath containing metal ions enabling electroformed pads corresponding to the shape of the drawings 25 to be achieved.
Owner:MESATRONIC
Method and process for deposition of textured zinc oxide thin films
InactiveUS20080308411A1Large widthLow costVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingReactive gasZinc atom
A method for sputtering a textured zinc oxide coating onto a substrate by reactive-environment hollow cathode sputtering comprises providing a sputter reactor that has a cathode channel and a flow exit end. The cathode channel allows a gas stream to flow therein. This cathode channel is at least partially defined by a channel-defining surface that includes at least one zinc-containing target. A gas is flowed through the channel, such that the gas emerges from the flow exit. A plasma is then generated such that material is sputtered off the channel-defining surface to form a gaseous mixture containing zinc atoms that is transported to the substrate. A reactive gas is then introduced into the sputter reactor so that the reactive gas reacts with the zinc-containing gaseous mixture to form the textured zinc oxide coating.
Owner:NEW MILLENNIUM SOLAR EQUIP CORP
Thin-film magnetic device with strong spin polarization perpendicular to the plane of the layers, magnetic tunnel junction and spin valve using such a device
ActiveUS7813202B2Optimize spin polarizationImprove polarizationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeHigh rate
A thin-film magnetic device comprises, on a substrate, a composite assembly deposited by cathode sputtering and consists of a first layer made of a ferromagnetic material with a high rate of spin polarization, the magnetization of which is in plane in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, a second layer made of a magnetic material with high perpendicular anisotropy, the magnetization of which is outside the plane of said layer in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, and coupling of which with said first layer induces a decrease in the effective demagnetizing field of the entire device, a third layer that is in contact with the first layer via its interface opposite to that which is common to the second layer and made of a material that is not magnetic and not polarizing for electrons passing through the device.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Sputtered transparent conductive films
InactiveUS20060118406A1Readily availableAvoid difficult choicesCellsVacuum evaporation coatingDopantSputtering
A hollow cathode sputtering apparatus and related method for introducing dopants into a sputtered coating is provided. The method utilizes a sputter reactor which includes a cathode channel that allows a gas stream to flow therein and a flow exit end from which gases may flow out of and towards a substrate to be coated. The cathode channel as used in the invention is defined by a channel defining surface that includes at least one target material. The sputter reactor further includes a dopant target positioned to provide dopant atoms to the gas stream when the gas stream is flowed through the cathode channel.
Owner:NEW MILLENNIUM SOLAR EQUIP CORP
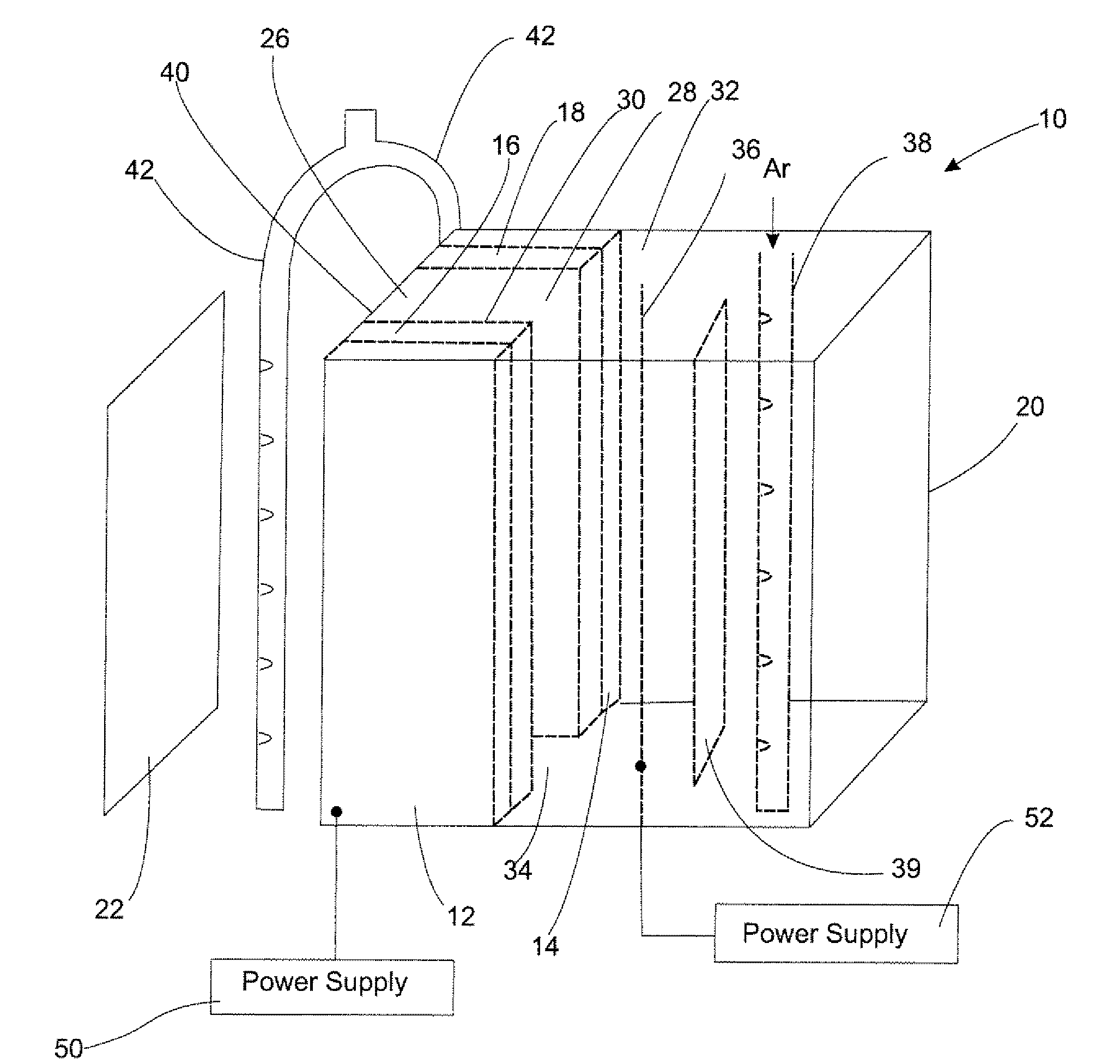
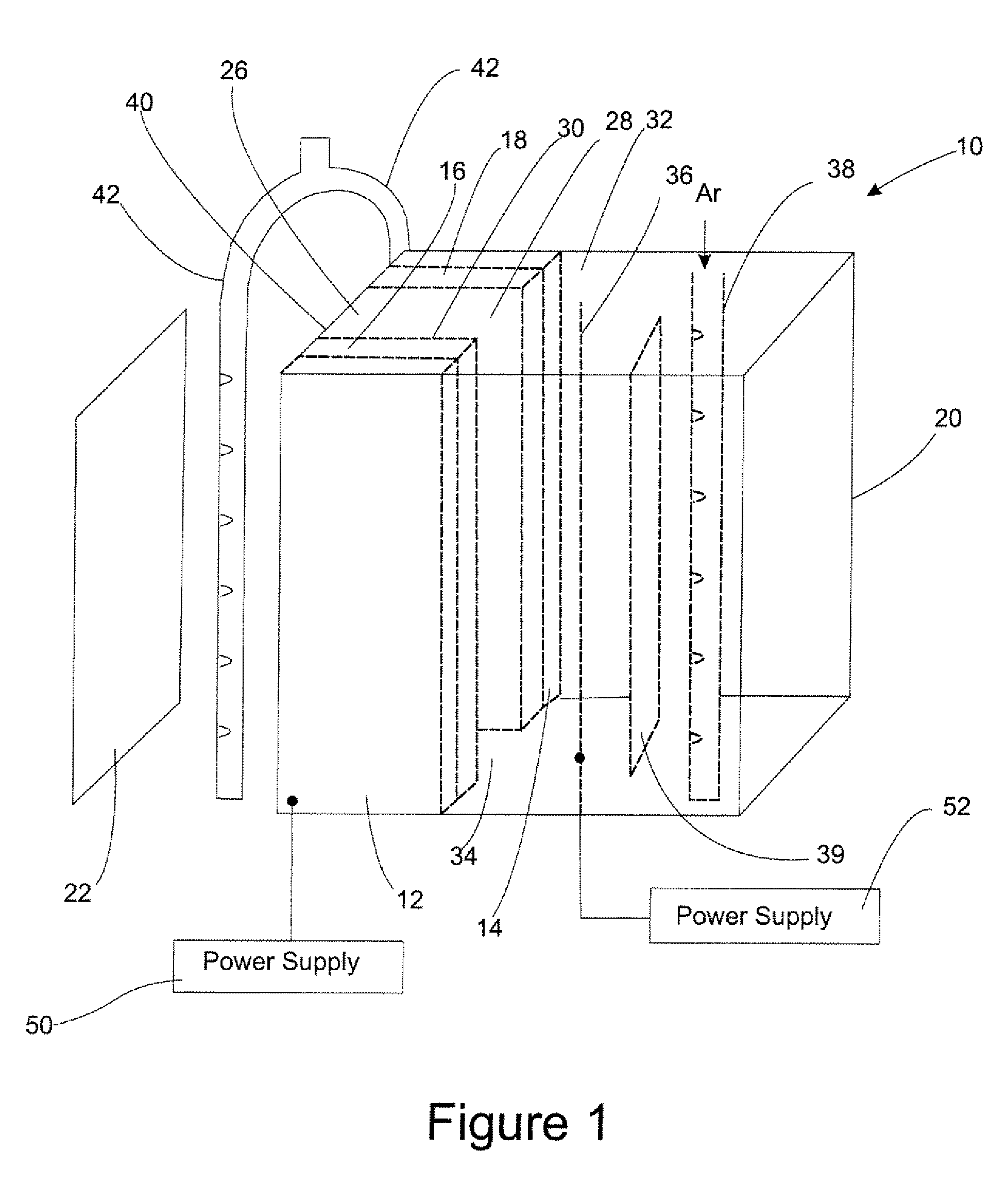
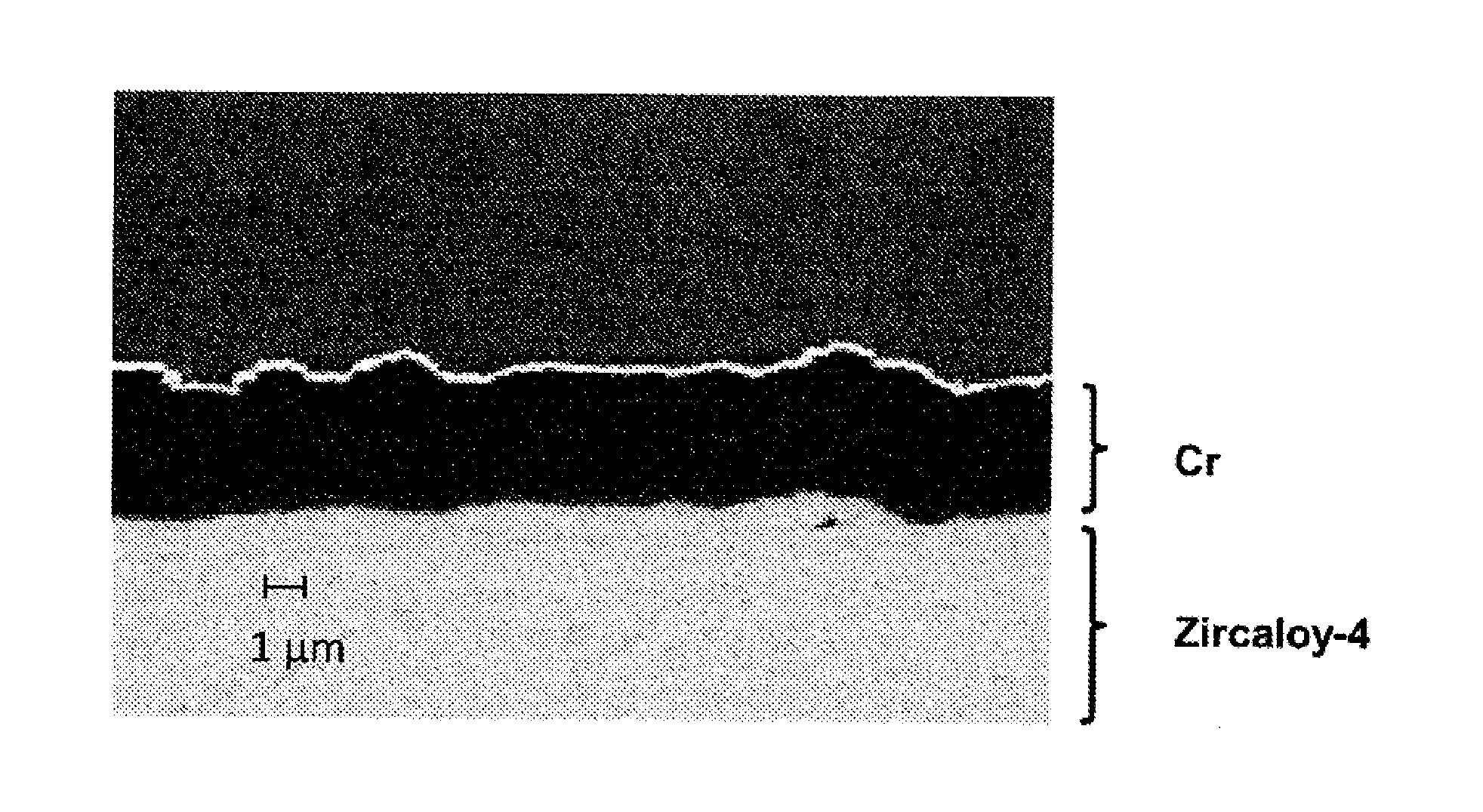
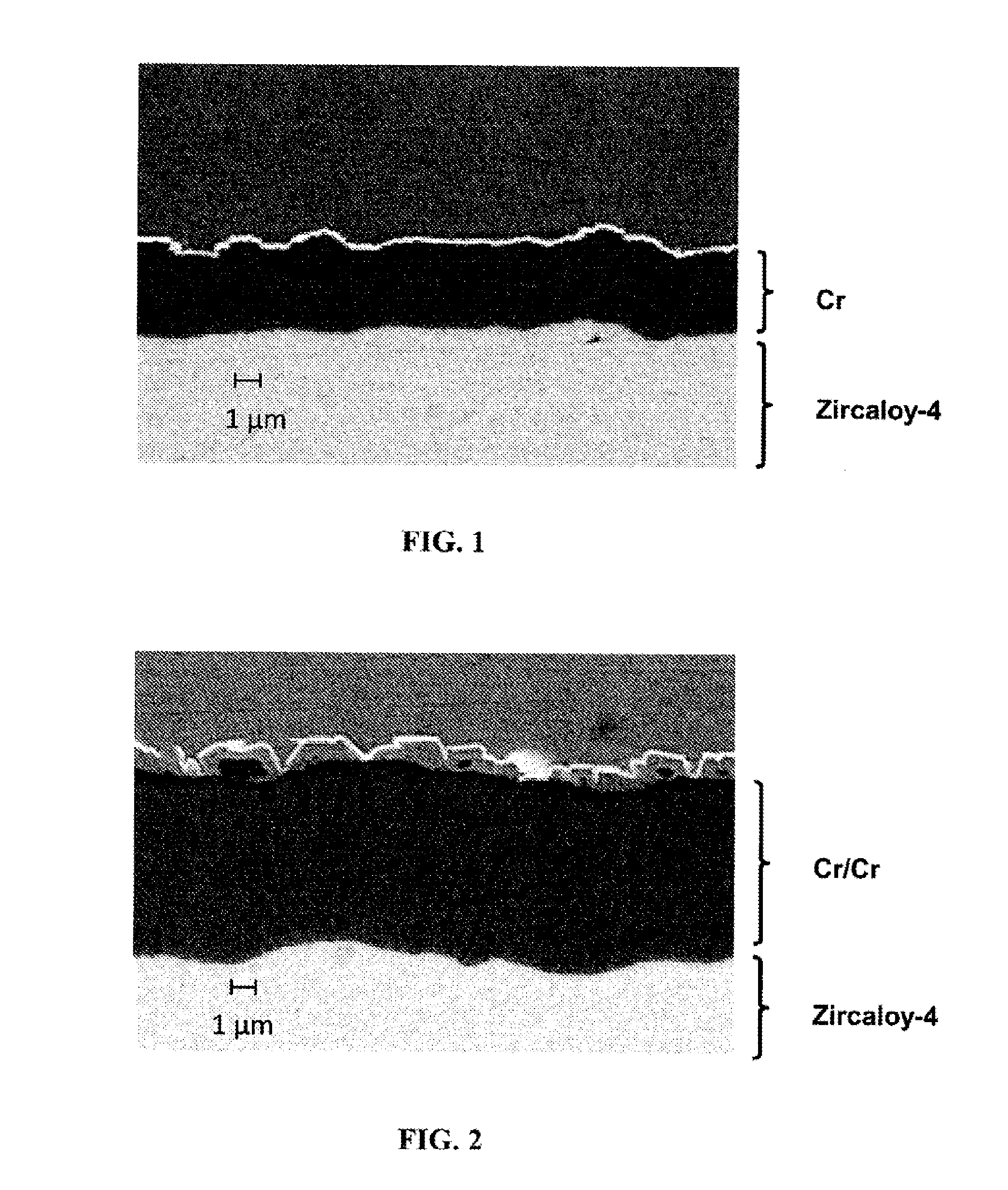
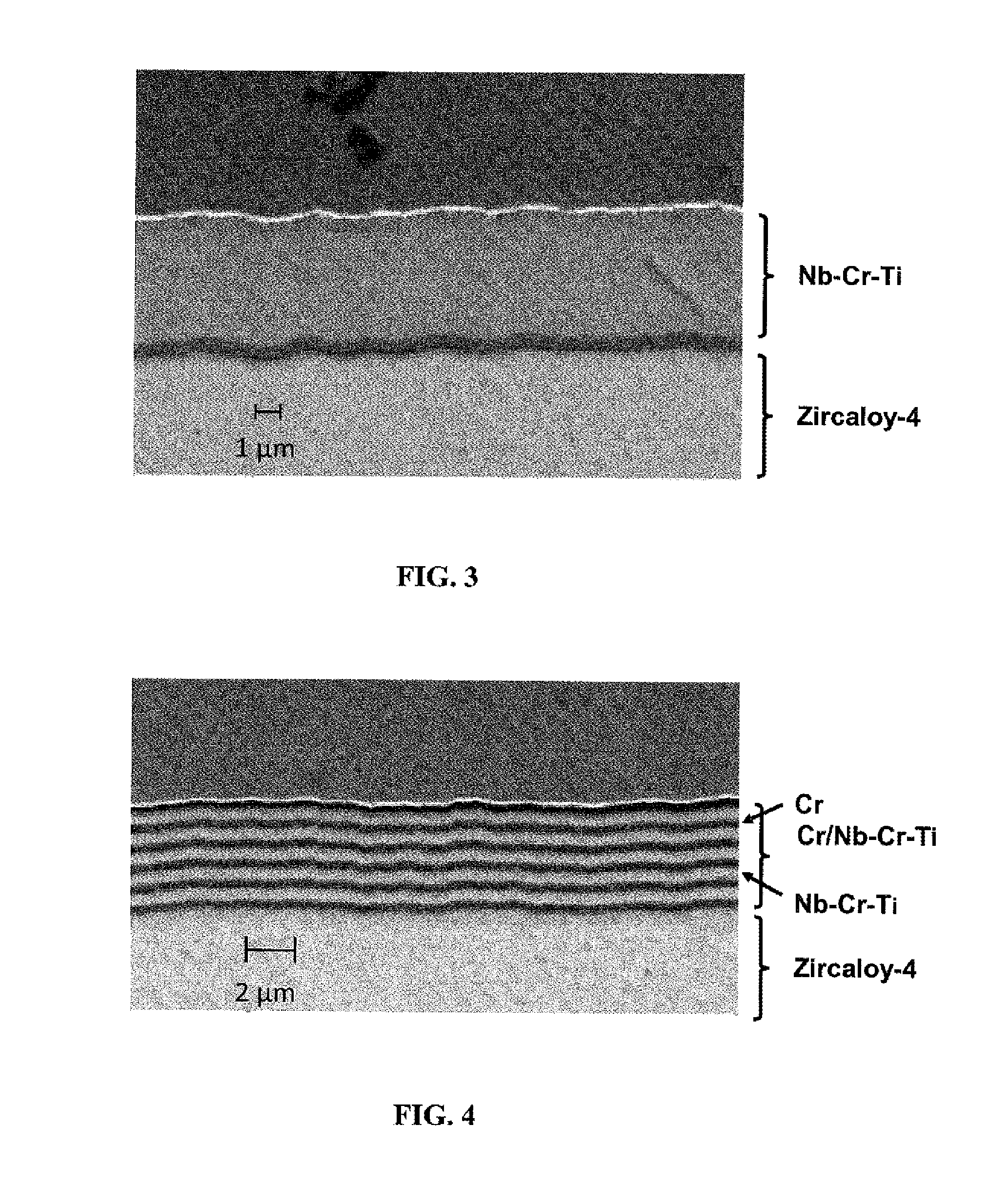
Multilayer material resistant to oxidation in a nuclear environment
ActiveUS20150050521A1Improve the immunityPromote oxidationFuel elementsNuclear energy generationNuclear reactorMetal
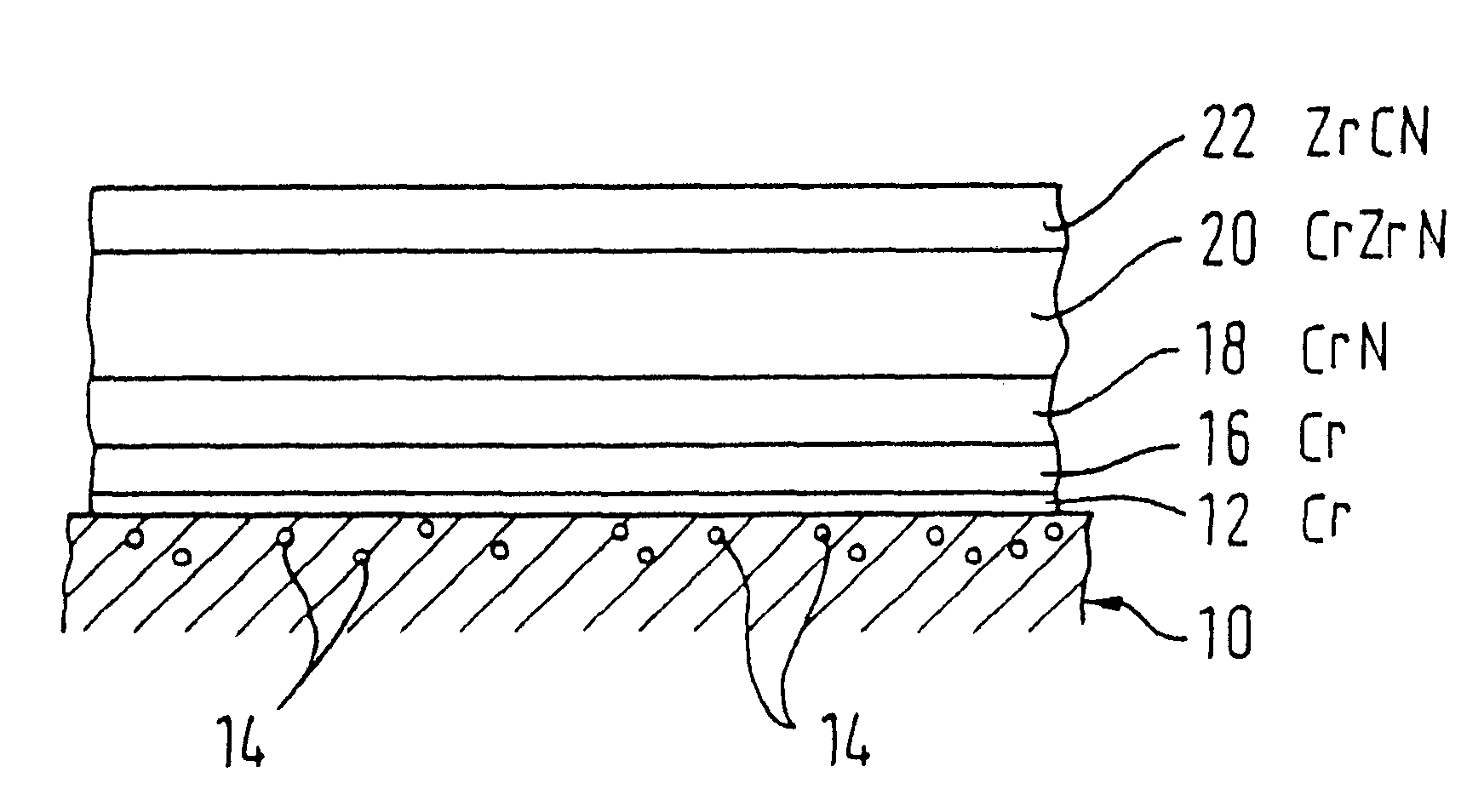
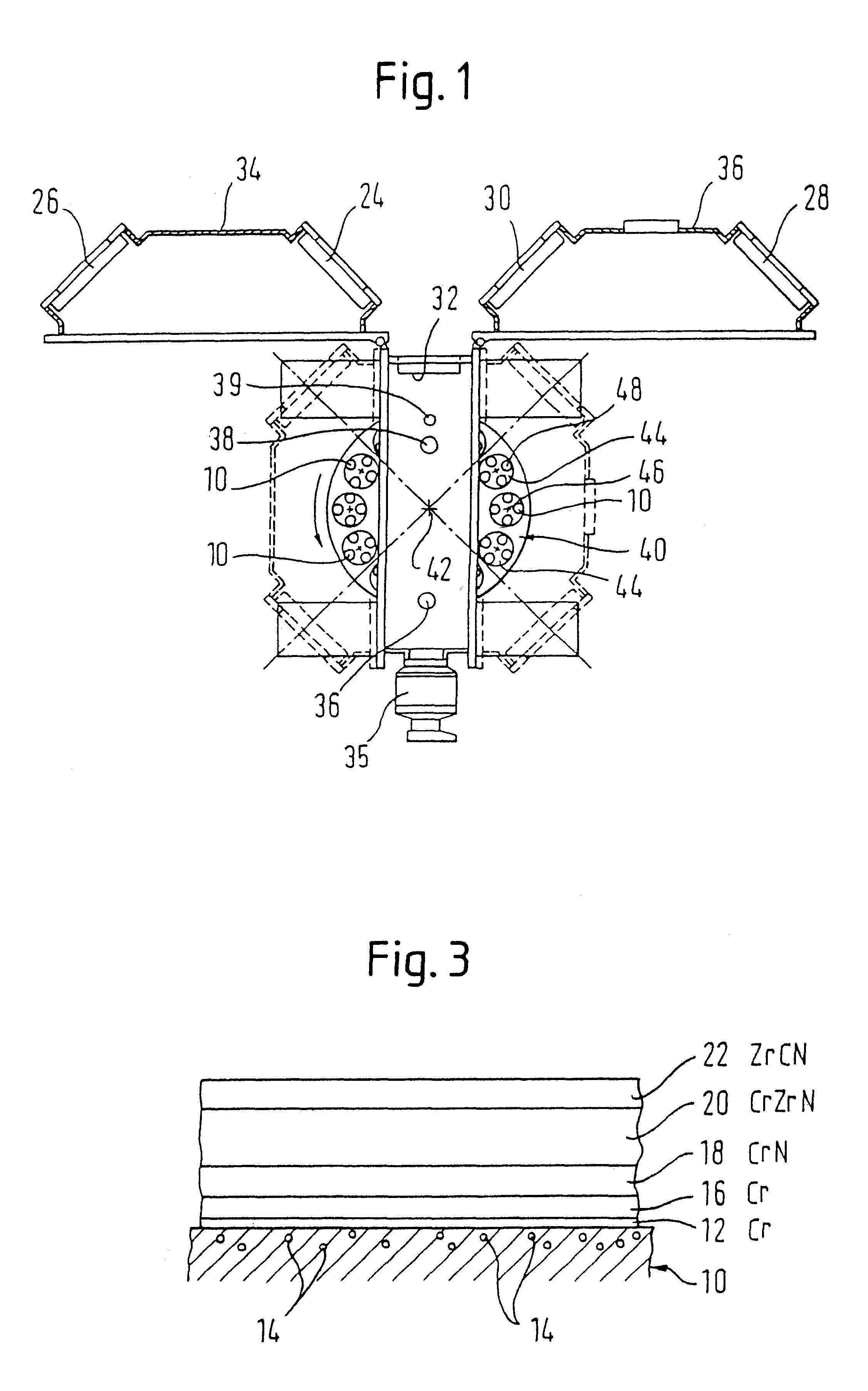
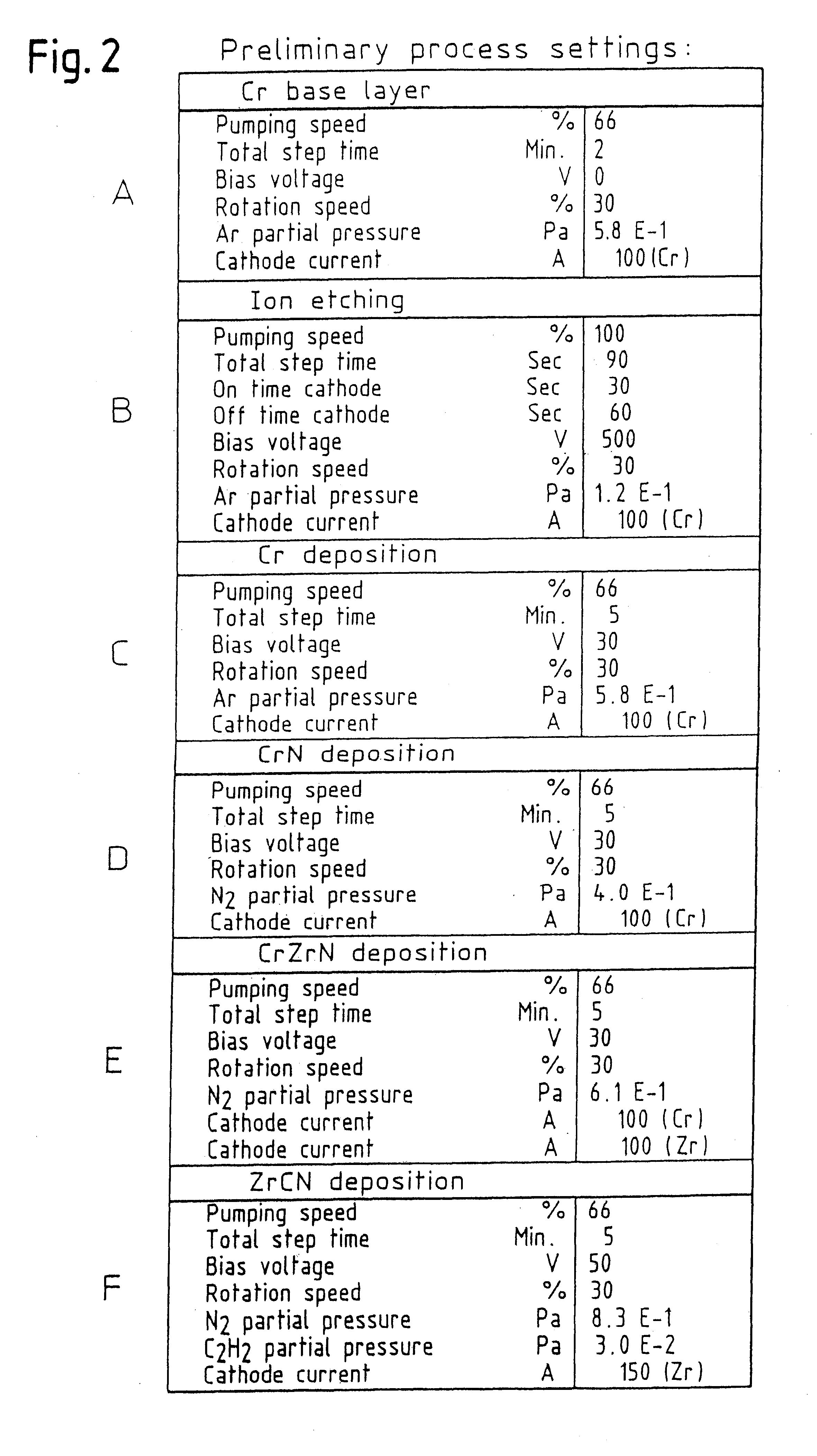
Multilayer material comprising a zirconium-based substrate covered with a multilayer coating, the multilayer coating comprising metallic layers composed of identical or different substances chosen from chromium, a chromium alloy or a ternary alloy of the Nb—Cr—Ti system. Such a material has improved resistance to oxidation in accident conditions of a nuclear reactor. The invention also relates to a multilayer coating, a part composed wholly or partly of the multilayer material or of the multilayer coating, as well as the method for manufacturing the multilayer material such as for example a magnetron cathodic sputtering process.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
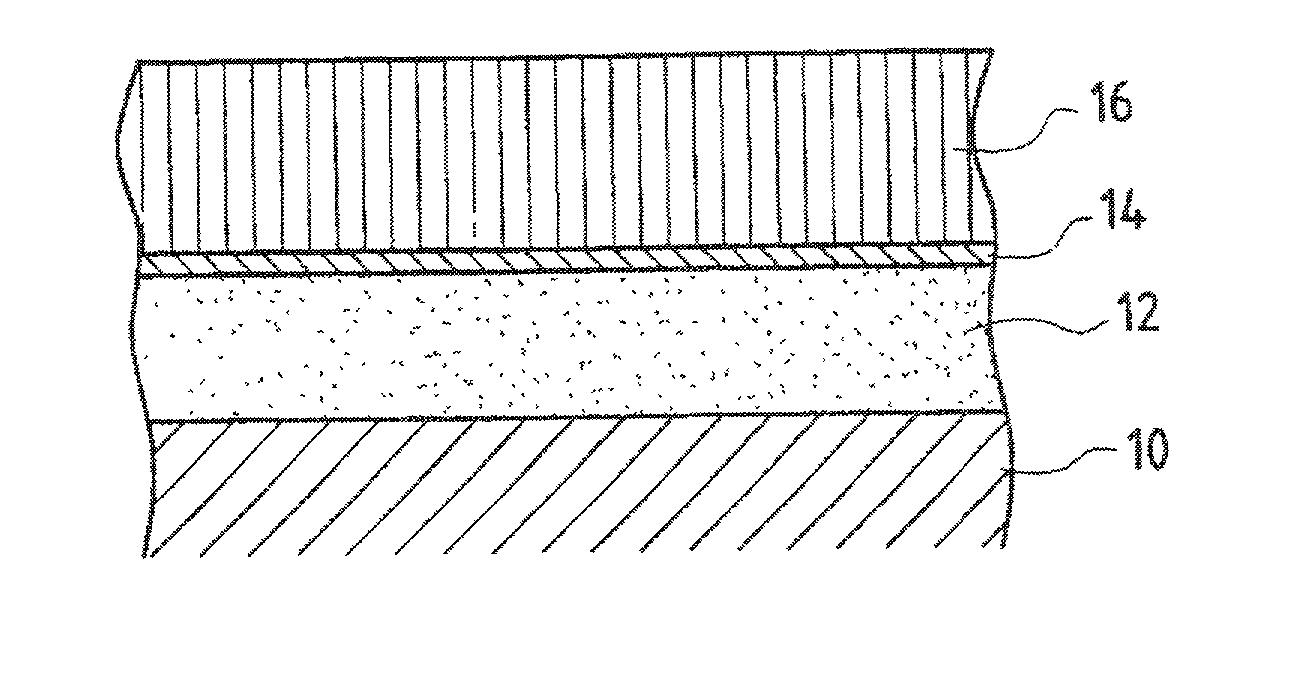
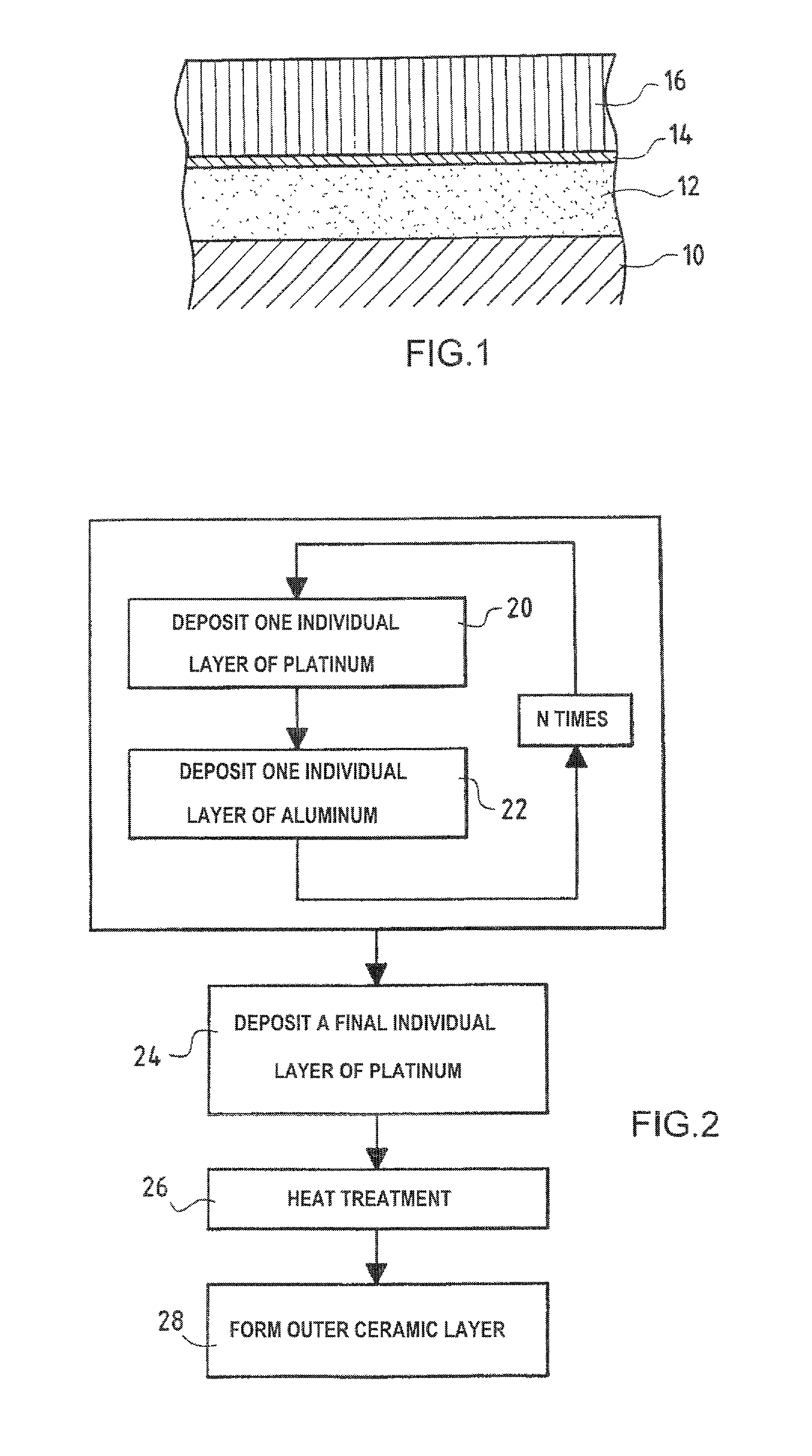
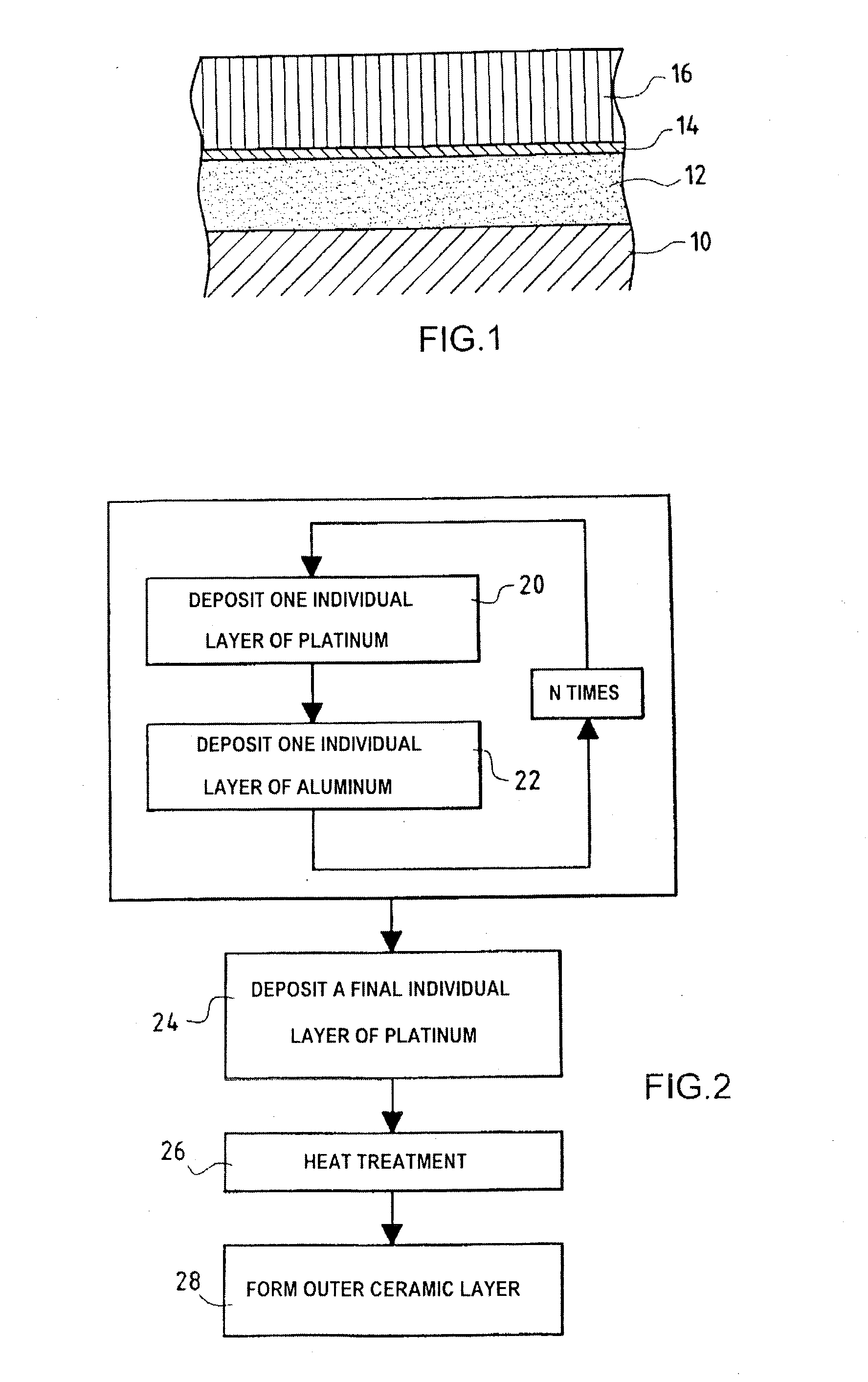
Method of making a protective coating forming a thermal barrier with a bonding underlayer on a superalloy substrate, and a part obtained thereby
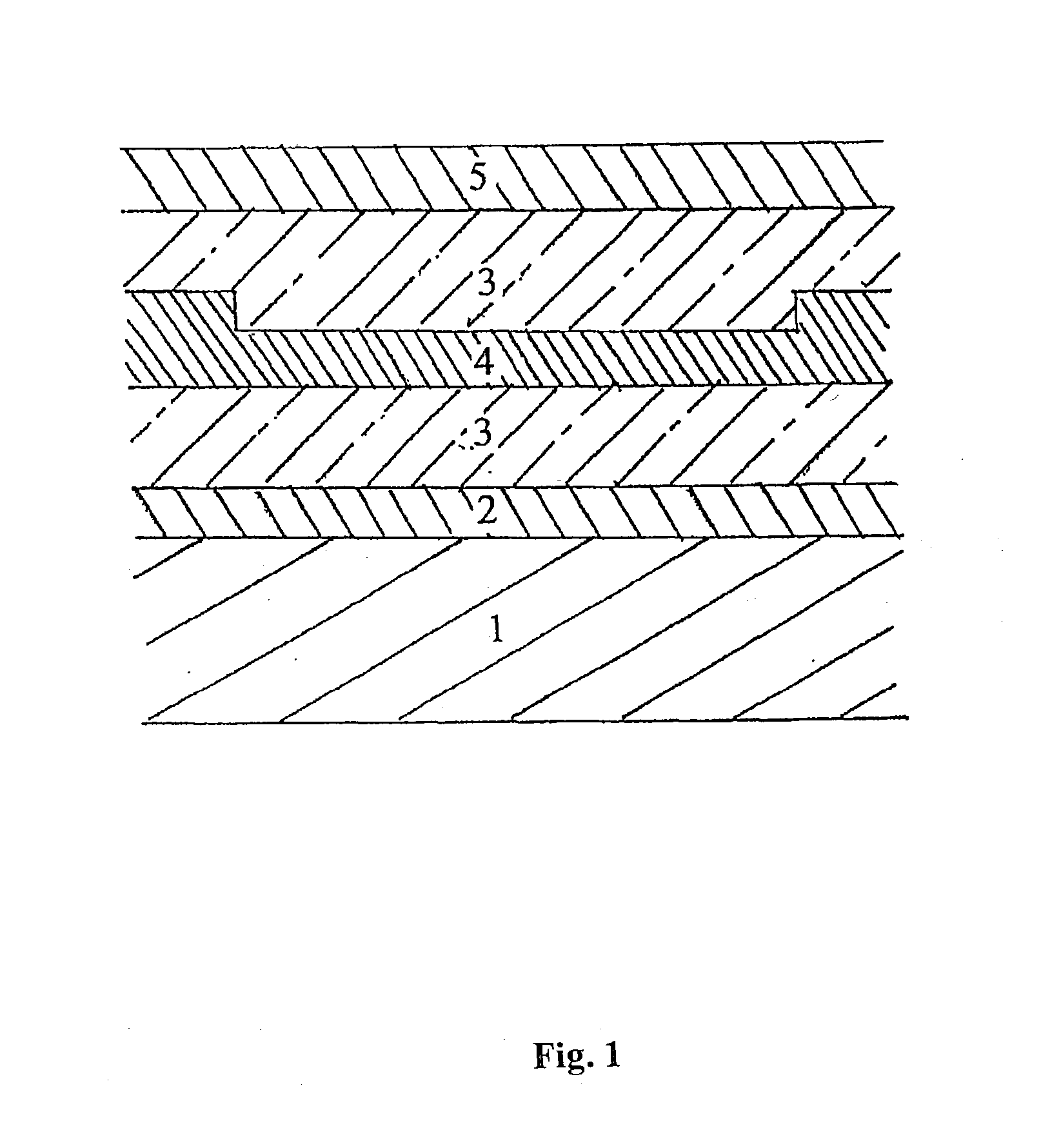
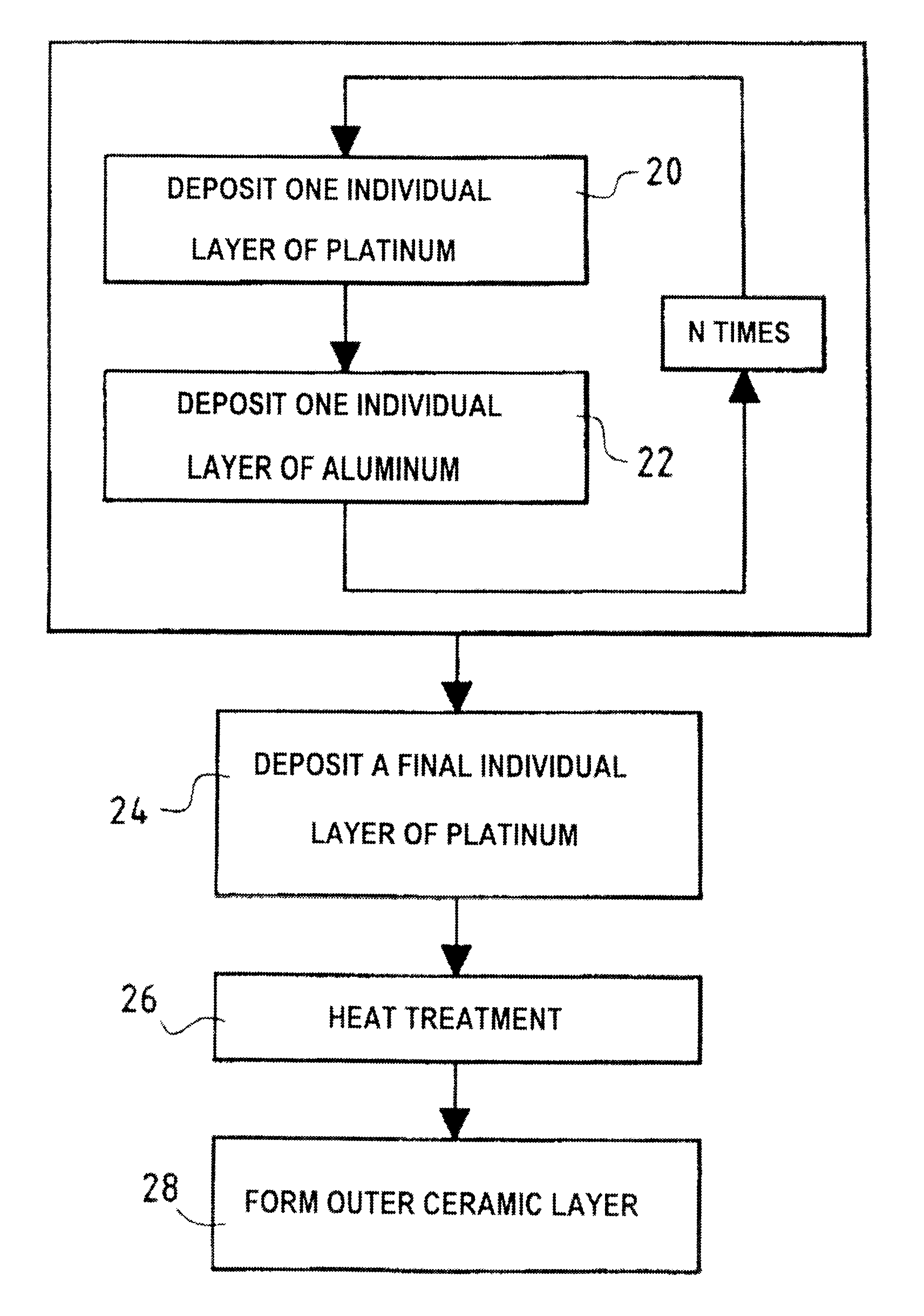
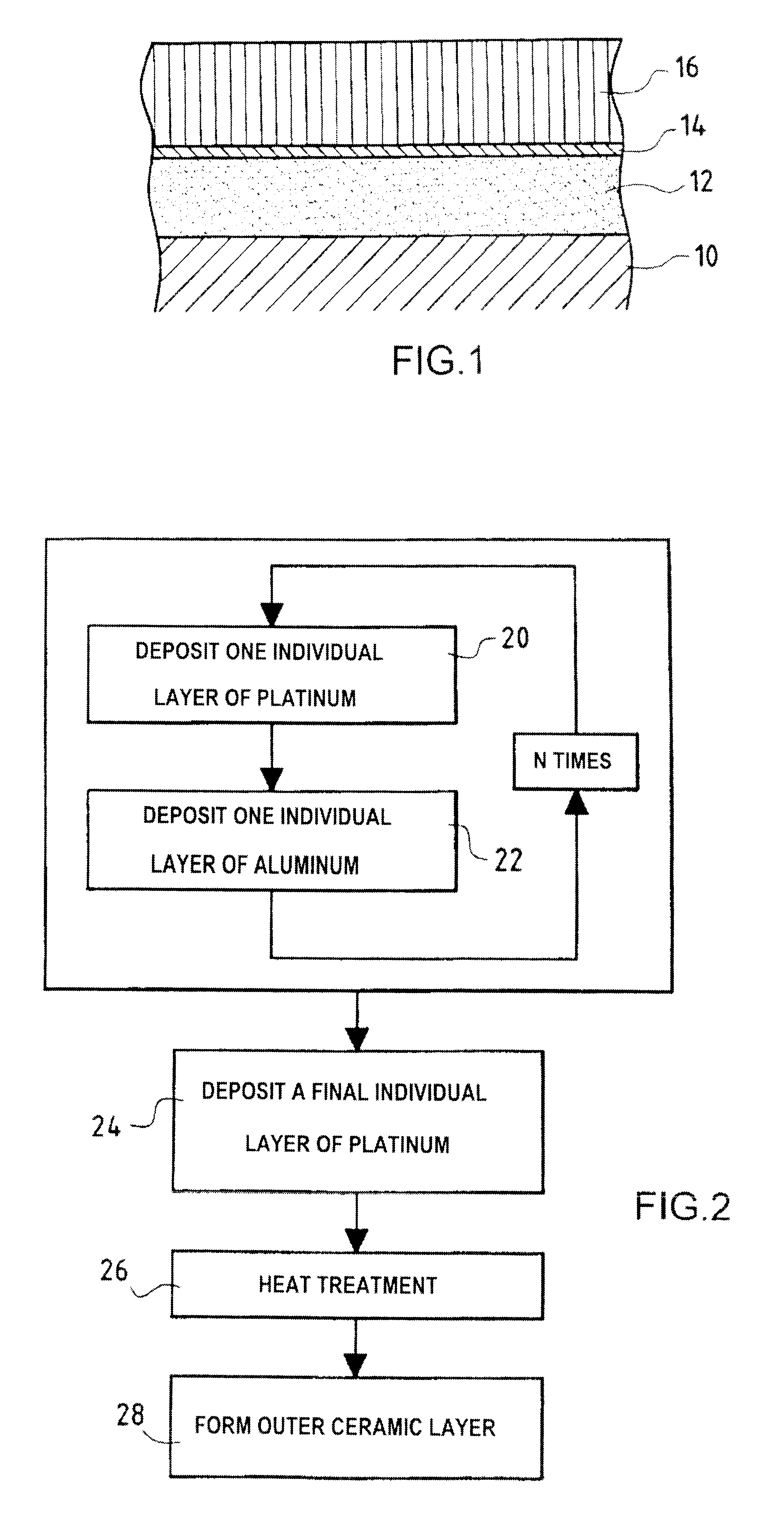
A protective coating forming a thermal barrier is made on a superalloy metal substrate by forming a bonding underlayer on the substrate, the bonding underlayer being constituted by an intermetallic compound comprising at least aluminum and a metal from the platinum group, and by forming a ceramic outer layer which is anchored on a film of alumina present on the surface of the bonding underlayer. The bonding underlayer preferably has a thickness of less than 50 mum and is made by using physical vapor deposition, e.g. by cathode sputtering, to deposit a plurality of individual layers alternately of aluminum and of a metal from the platinum group, and by causing the metals in the resulting layers to react together exothermally.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
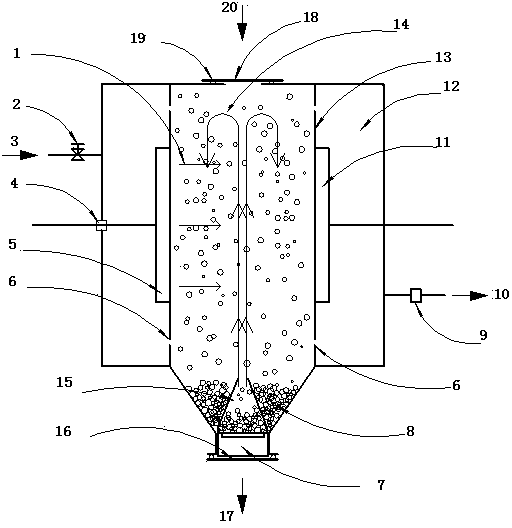
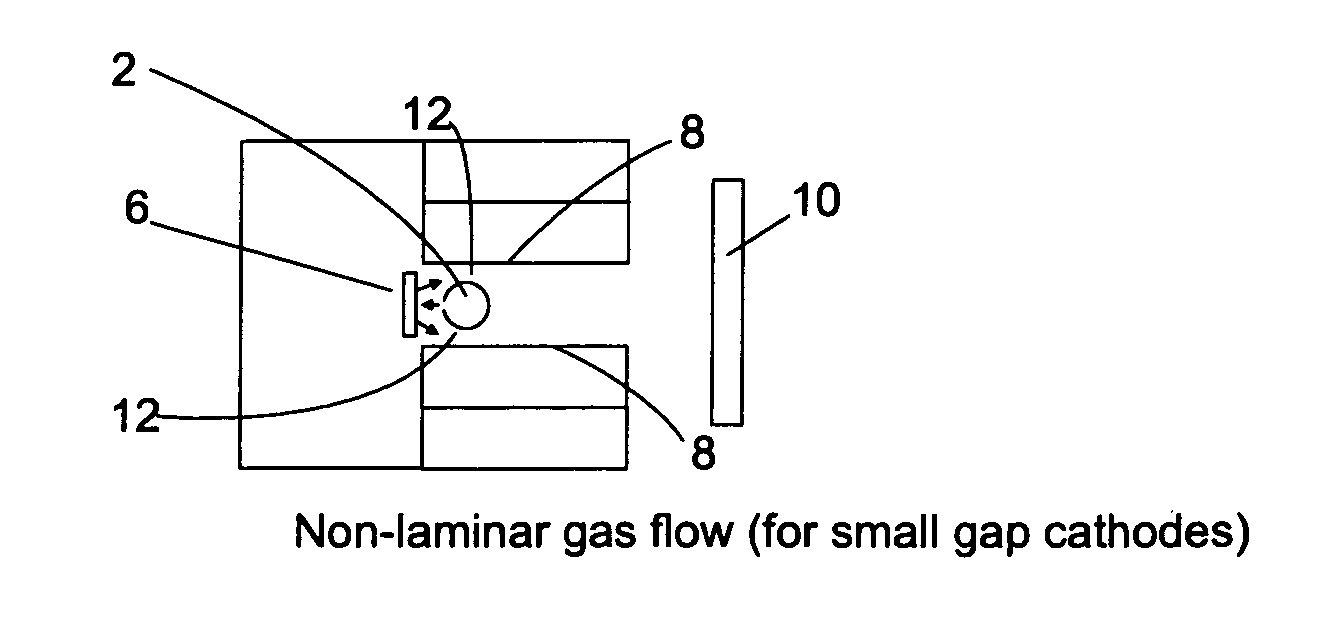
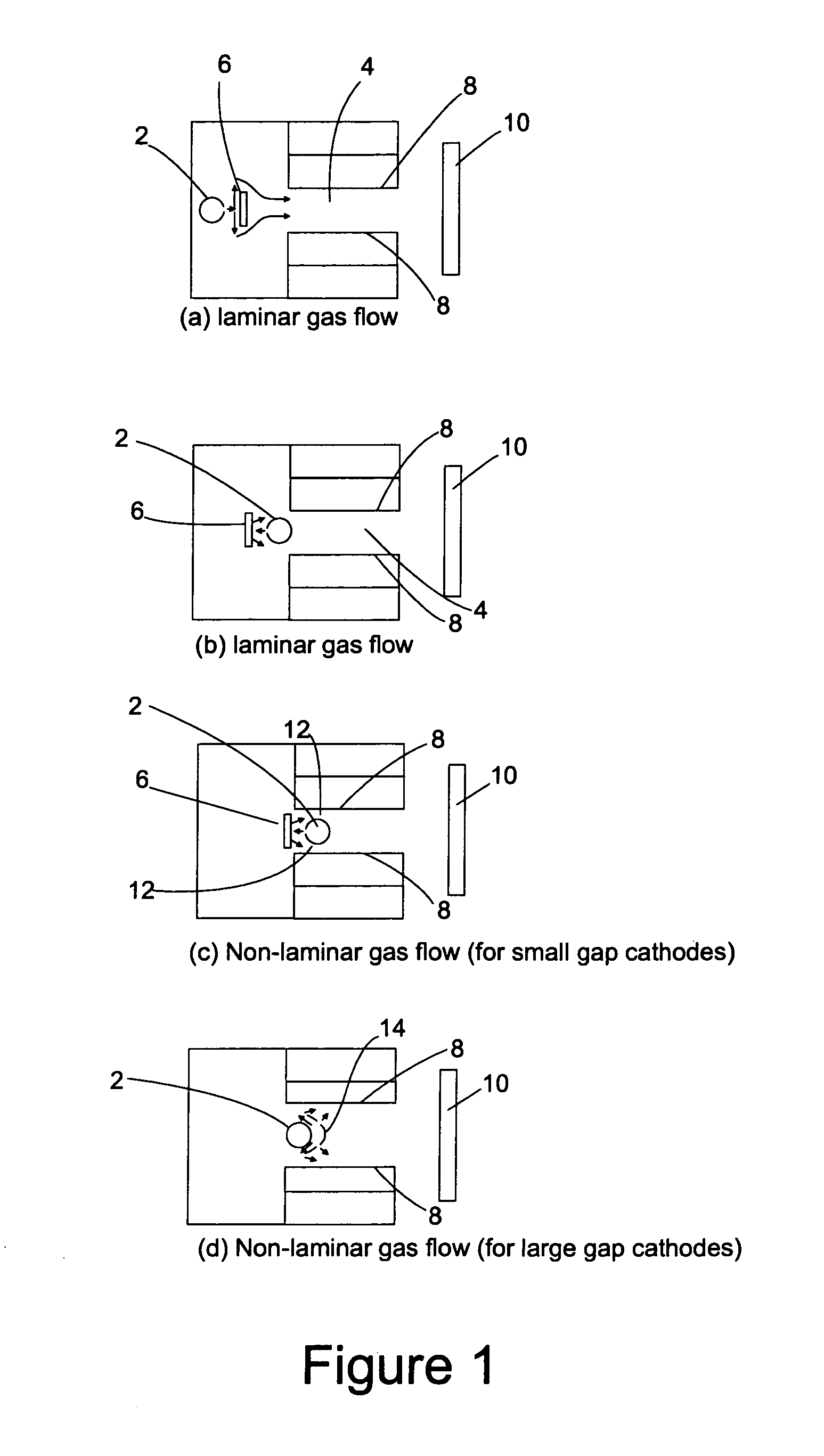
Hollow cathode sputtering apparatus and related method
The present invention provides an improved hollow cathode method for sputter coating a substrate. The method of the invention comprises providing a channel for gas to flow through, the channel defined by a channel defining surface wherein one or more portions of the channel-defining surface include at least one target material. Gas is flowed through the channel wherein at least a portion of the gas is a non-laminarly flowing gas. While the gas is flowing through the channel a plasma is generated causing target material to be sputtered off the channel-defining surface to form a gaseous mixture containing target atoms that is transported to the substrate. In an important application of the present invention, a method for forming oxide films and in particular zinc oxide films is provided.
Owner:NEW MILLENNIUM SOLAR EQUIP CORP
Method of applying a coating by physical vapour deposition
InactiveUS6503373B2Improve adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseTemperature resistance
The invention relates to a method of applying a coating by physical vapour deposition onto an article of organic material, in particular of non- conductive organic material such as plastic and / or epoxy material, especially ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene Copolymers) and polymers with high temperature resistance, or onto an article of another composition coated with such organic material, wherein a Cr layer is deposited on the article prior to deposition of said coating to form a diffusion barrier for water coming from said article, said Cr layer itself being deposited by a physical vapour deposition process comprising at least the following steps:a) depositing a first layer of Cr on said article in a physical vapour deposition apparatus using an arc evaporator or cathode sputtering source, or in a combined arc evaporator and cathode sputtering apparatus, using zero bias, andb) subsequently applying a negative bias voltage to said article having said first layer of Cr and depositing a further layer of Cr on said first layer using Cr ions in the same physical vapour deposition apparatus.
Owner:HAUZER TECHNO COATING EURO +1
Manufacture of tubular targets
InactiveCN1363716APrevent solidificationAvoid inhomogeneityVacuum evaporation coatingIngot casting plantsMolten stateHeater Rod
A process for producing a tube target for cathode sputtering plants, in which the tube target is formed from a metallic inner tube made of a first material with a first melting point of Ts1>=900 K and a metallic outer tube that concentrically surrounds the inner tube and that is made of a second material with a second melting point of Ts2<=800 K. The inside diameter of the outer tube and the outside diameter of the inner tube are proportioned in such a way that the two tubes fit together tightly and are mechanically firmly joined. The outer tube is formed by casting the second material in a molten state in a heated, vertical, A cylindrical permanent mold, which has a heated mandrel that constitutes the inner tube. After a space between the mold and the inner tube has been filled with the molten second material, a first thermal gradient develops between the inner tube and the mold, a second thermal gradient develops between the bottom and the top of the mold, and the outer tube is simultaneously cooled from the inside to the outside and from the bottom to the top.
Owner:MATERION ADVANCED MATERIALS GERMANY GMBH
Tube target
InactiveUS6793784B1Uniform and fine-grained structureSimple and low-costCellsElectric discharge tubesMaterials scienceFine grain
A tube target for cathode sputtering installations, and a process for producing a cylindrical hollow body for such a tube target and its use. The problem of providing a simple and low-cost process for producing a cylindrical hollow body for a tube target and of providing a cylindrical hollow body with a uniform, fine-grained structure is solved by the cylindrical hollow body being produced by centrifugal casting of a melt.
Owner:HERAEUS MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY GMBH & CO KG
Sputtering target and method for finishing surface of such target
ActiveUS7951275B2Improve evennessPrevent peelingCellsVacuum evaporation coatingSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
Provided is a hollow cathode sputtering target comprising an inner bottom face having a surface roughness of Ra≦1.0 μm, and preferably Ra≦0.5 μm. This hollow cathode sputtering target has superior sputter film evenness (uniformity), generates few arcing and particles, is capable of suppressing the peeling of the redeposited film on the bottom face, and has superior deposition characteristics.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
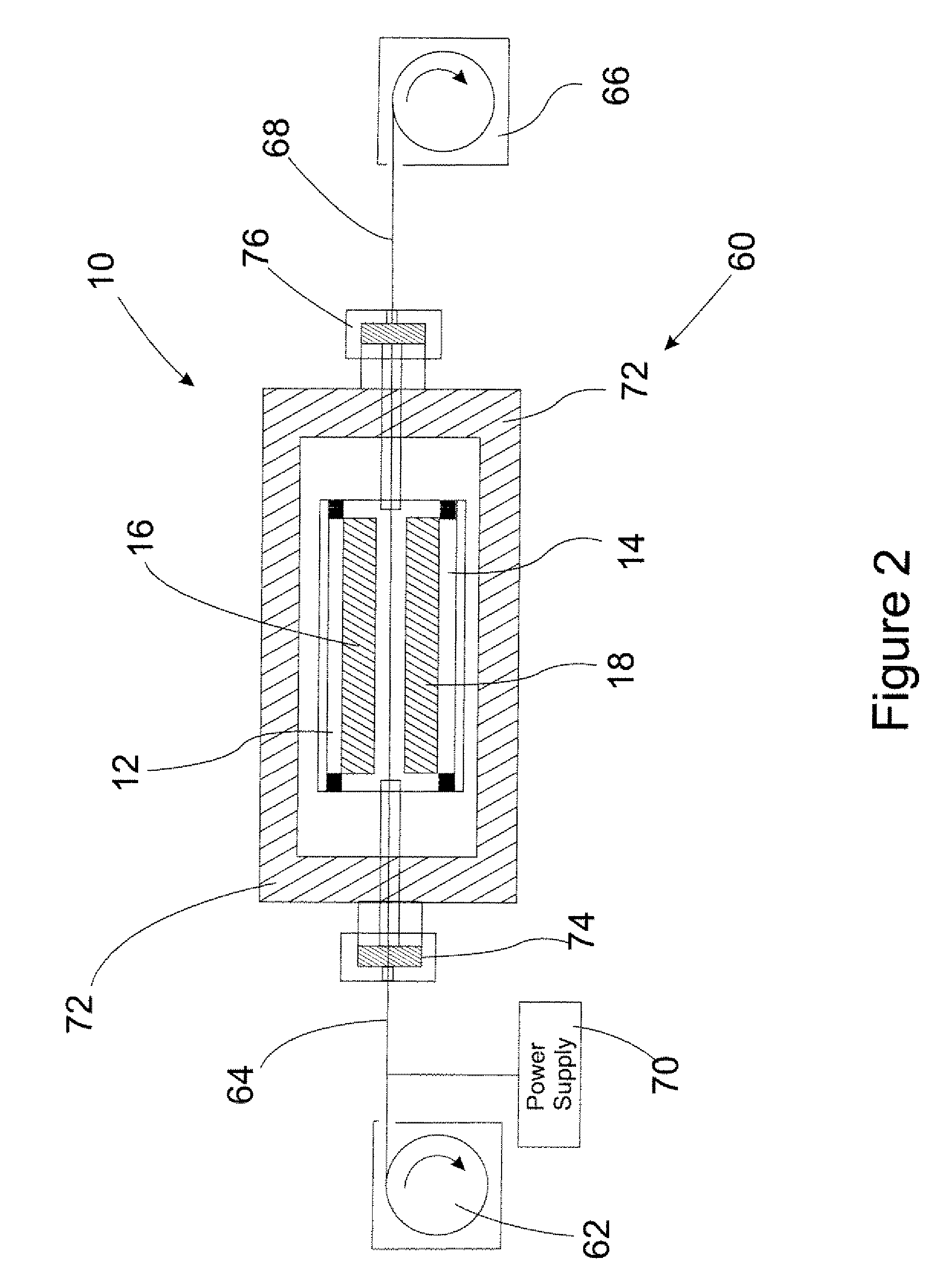
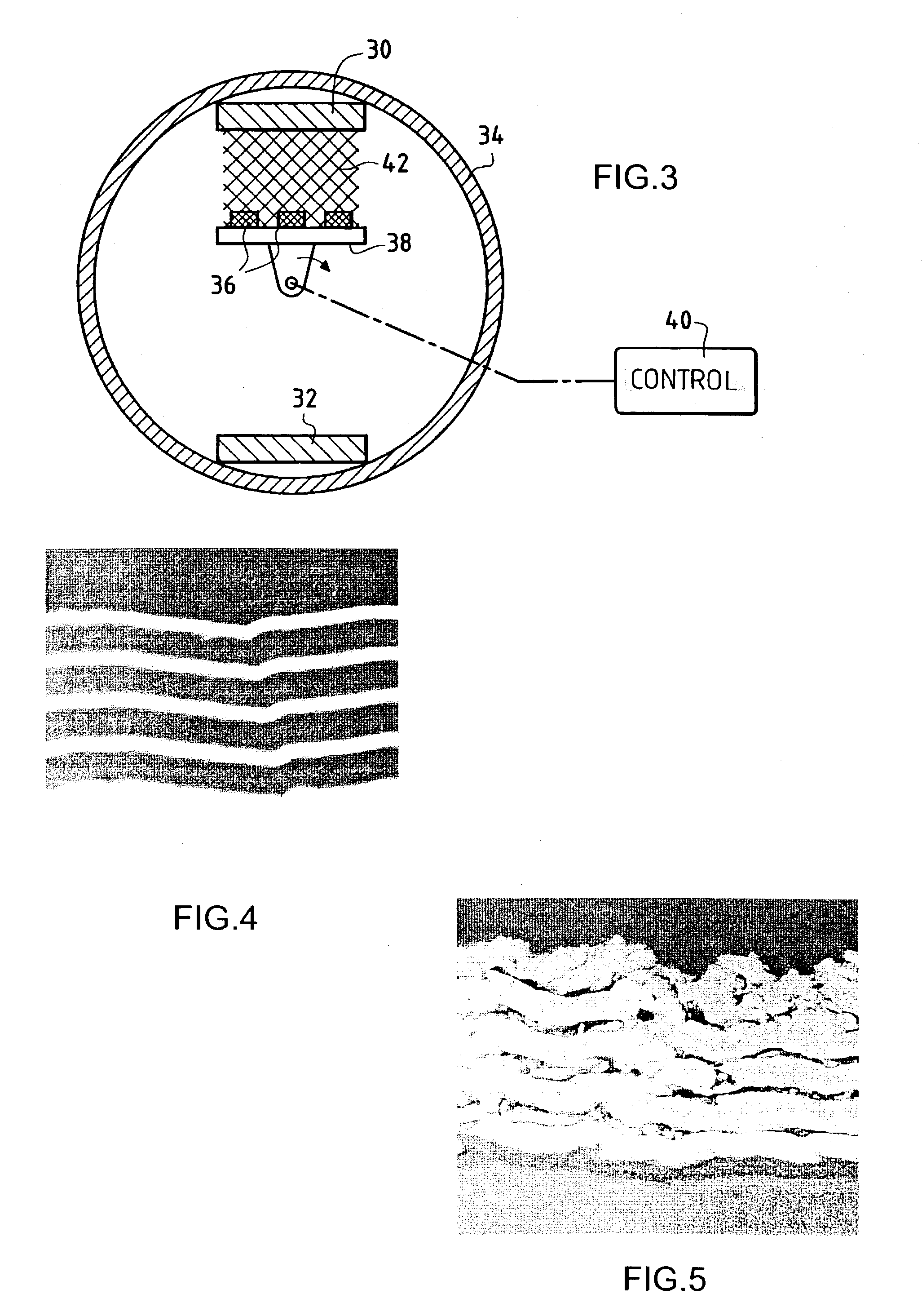
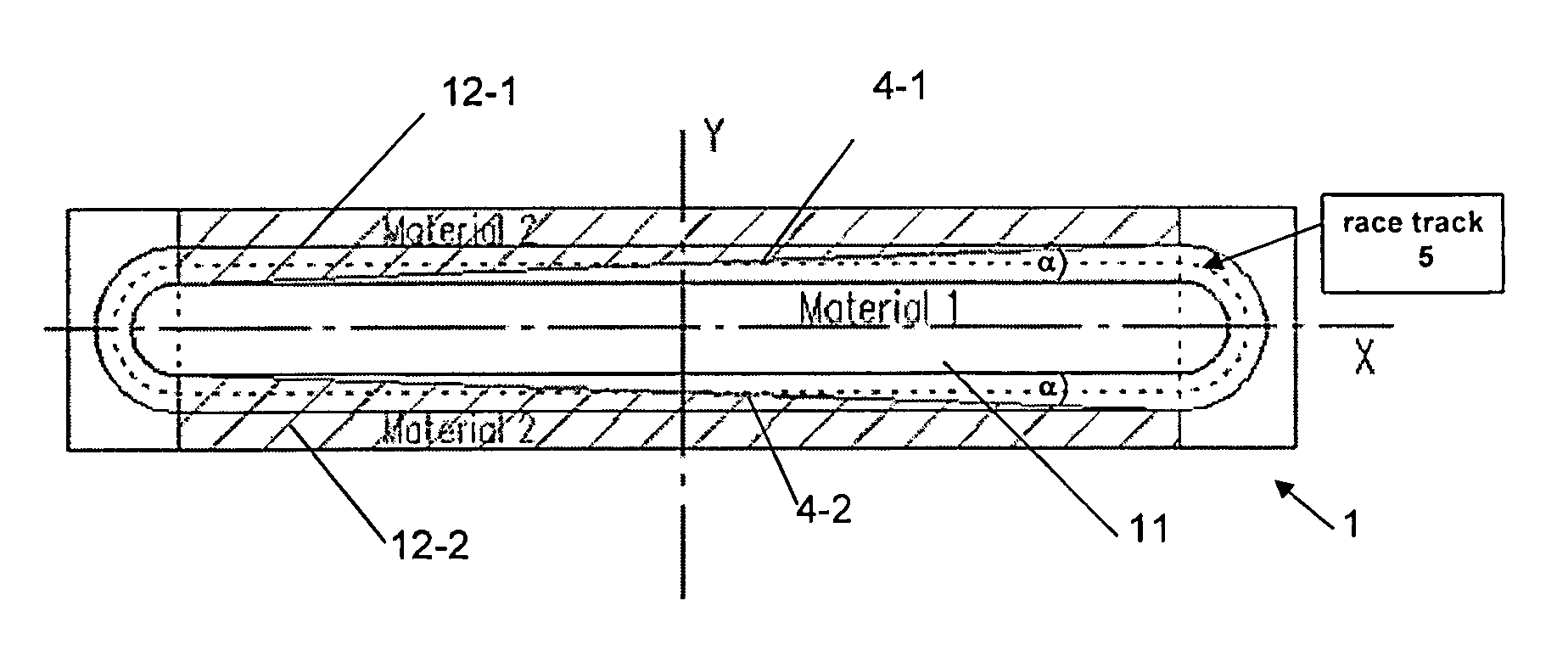
Method & apparatus for multi-stage sputter deposition of uniform thickness layers
ActiveUS20050178651A1Well formedSimple methodCellsVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringSputter deposition
A method of forming a uniform thickness layer of a selected material on a surface of a substrate comprises steps of: (a) providing a multi-stage cathode sputtering apparatus comprising a group of spaced-apart cathode / target assemblies and a means for transporting at least one substrate / workpiece past each cathode / target assembly, each cathode / target assembly comprising a sputtering surface oriented substantially parallel to the first surface of the substrate during transport past the group of cathode / target assemblies, the group of cathode / target assemblies adapted for providing different angular sputtered film thickness profiles; and (b) transporting the substrate past each cathode / target assembly while providing different sputtered film thickness profiles from at least some of the cathode / target assemblies, such that a plurality of sub-layers is deposited on the surface of the substrate / workpiece which collectively form a uniform thickness layer of the selected material.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Ceramic cylindrical sputtering target and method for producing same
ActiveCN104066700AHigh densityReduce arcingVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringHigh density
The present invention provides a ceramic cylindrical sputtering target characterized in being a single article having a length of 500 mm or longer and a relative density of 95% or greater. The ceramic cylindrical sputtering target is a single article having a high density and length of 500 mm or longer and therefore eliminates the need to use a stack of multiple sputtering targets in order to obtain a long target. Consequently, when the ceramic cylindrical sputtering target of the present invention is used in a magnetron rotary cathode sputtering target, and the like, there are no or few partitions in the target as a whole and therefore there is little arcing and particle generation during sputtering.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Method for manufacturing a resistive device for a memory or logic circuit
ActiveUS20170309497A1Low variabilitySolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingChemical speciesEngineering
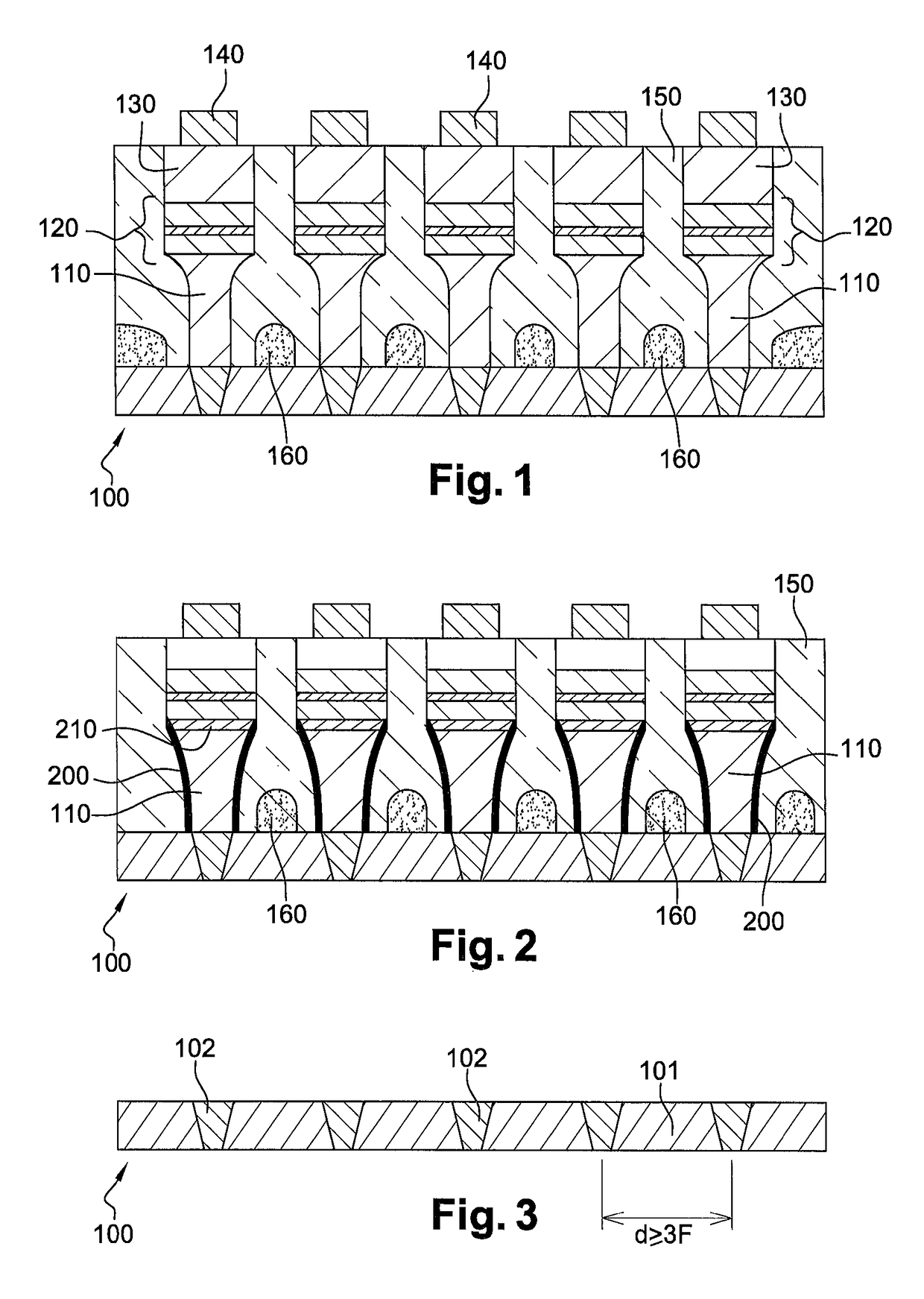
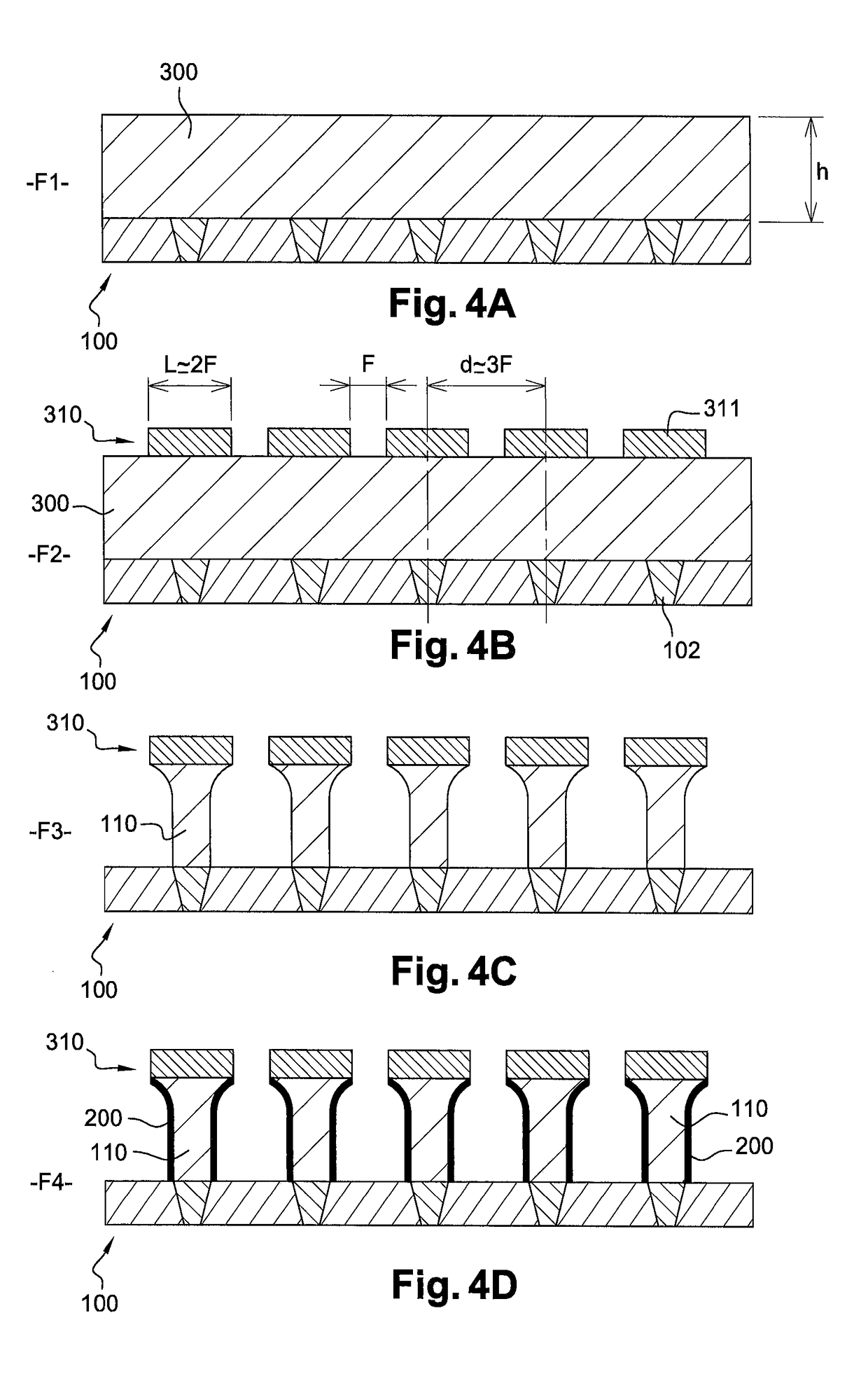
A method for manufacturing a resistive device, includes depositing a first electrically conductive layer on a substrate; forming an etching mask on the first conductive layer; etching the first conductive layer through the mask, such as to obtain a plurality of electrically conductive pillars separated from one another; and forming storage elements with variable electrical resistance at the tops of the electrically conductive pillars, such that each storage element is supported by one of the electrically conductive pillars, the step of forming the storage elements including the following operations depositing a first layer by non-collimated cathode sputtering at normal incidence relative to the substrate; and depositing a second layer on the first layer by cathode sputtering, the second layer including a first chemical species sputtered at an oblique incidence.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +2
Layer-by-layer analysis method for surface layer of copper alloy material
ActiveCN102539517ARealize Layer-by-Layer AnalysisLayer-to-layer resolution improvementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass spectrometrySpectrometer
The invention provides a layer-by-layer analysis method for a surface layer of a copper alloy material, comprising the steps of: selecting a glow discharge ion source and a mass spectrum analysis condition to carry out sample treatment and sample analysis; peeling an analyzed sample by utilizing the glow discharge ion source under the action of cathode sputtering; recording a continuous change signal of analyzed sample mass spectrum peak strength along with the time in a high-sensitivity mass spectrometer system in real time; and converting the continuous change signal into change of the chemical composition of the sample along with the depth by using a composition and depth double-calibration method so as to finish the layer-by-layer quantified analysis of the surface layer of an aluminum bronze membrane sample on a brass base material. In the invention, proper analysis parameters such as argon pressure, discharge voltage, sample sputtering spot surface diameter, sample measurement time and the like are selected to improve interlayer resolution to be thousands of nanometers, so that the ultrathin layer-by-layer analysis of the surface layer of bronze on the brass base material is realized.
Owner:GUOBIAO BEIJING TESTING & CERTIFICATION CO LTD
Method for producing a multi-functional, multi-ply layer on a transparent plastic substrate and a multi-functional multi-ply layer produced according to said method
InactiveUS20030104185A1Not to damageSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingOrganosiliconCathode sputtering
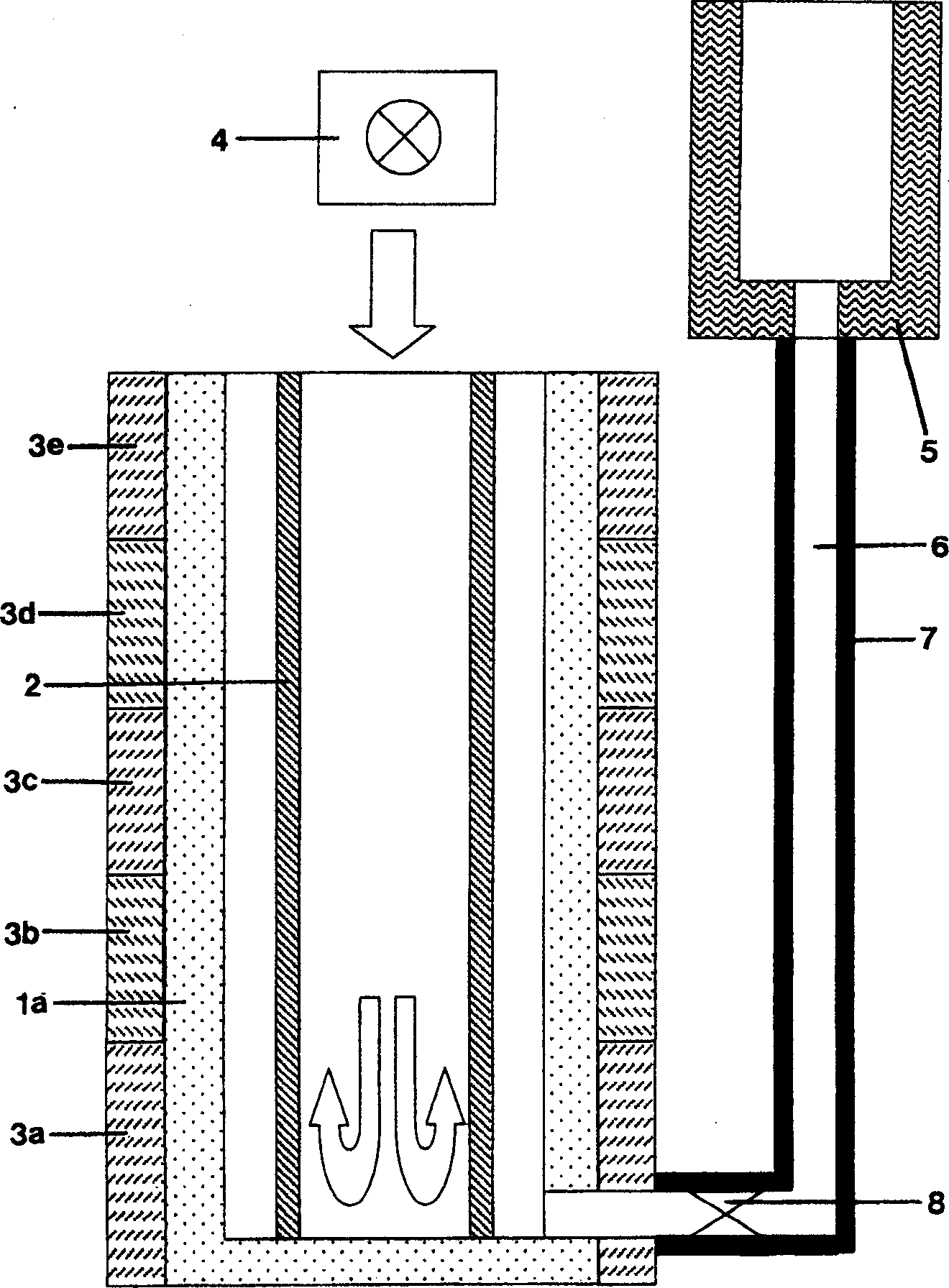
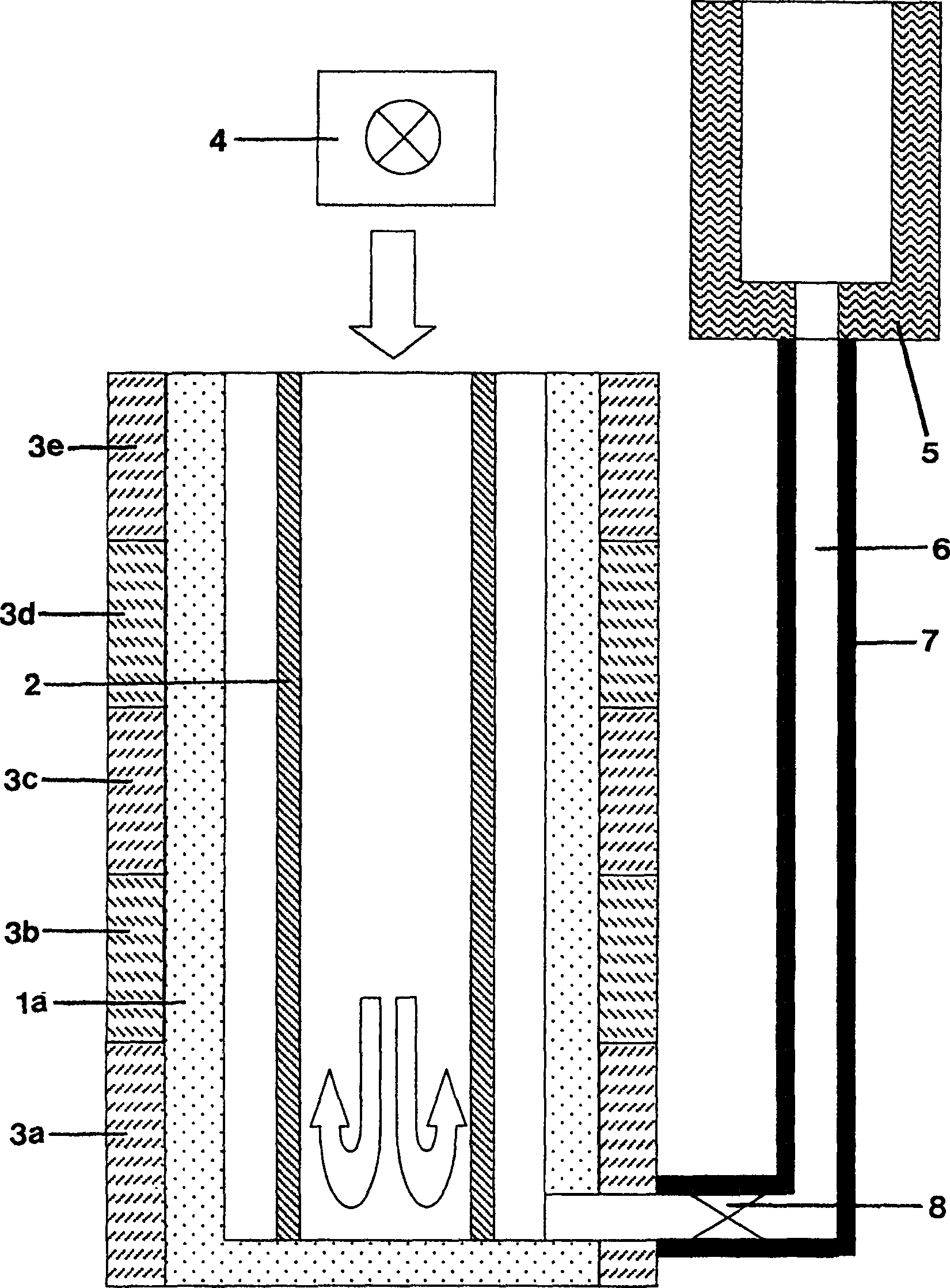
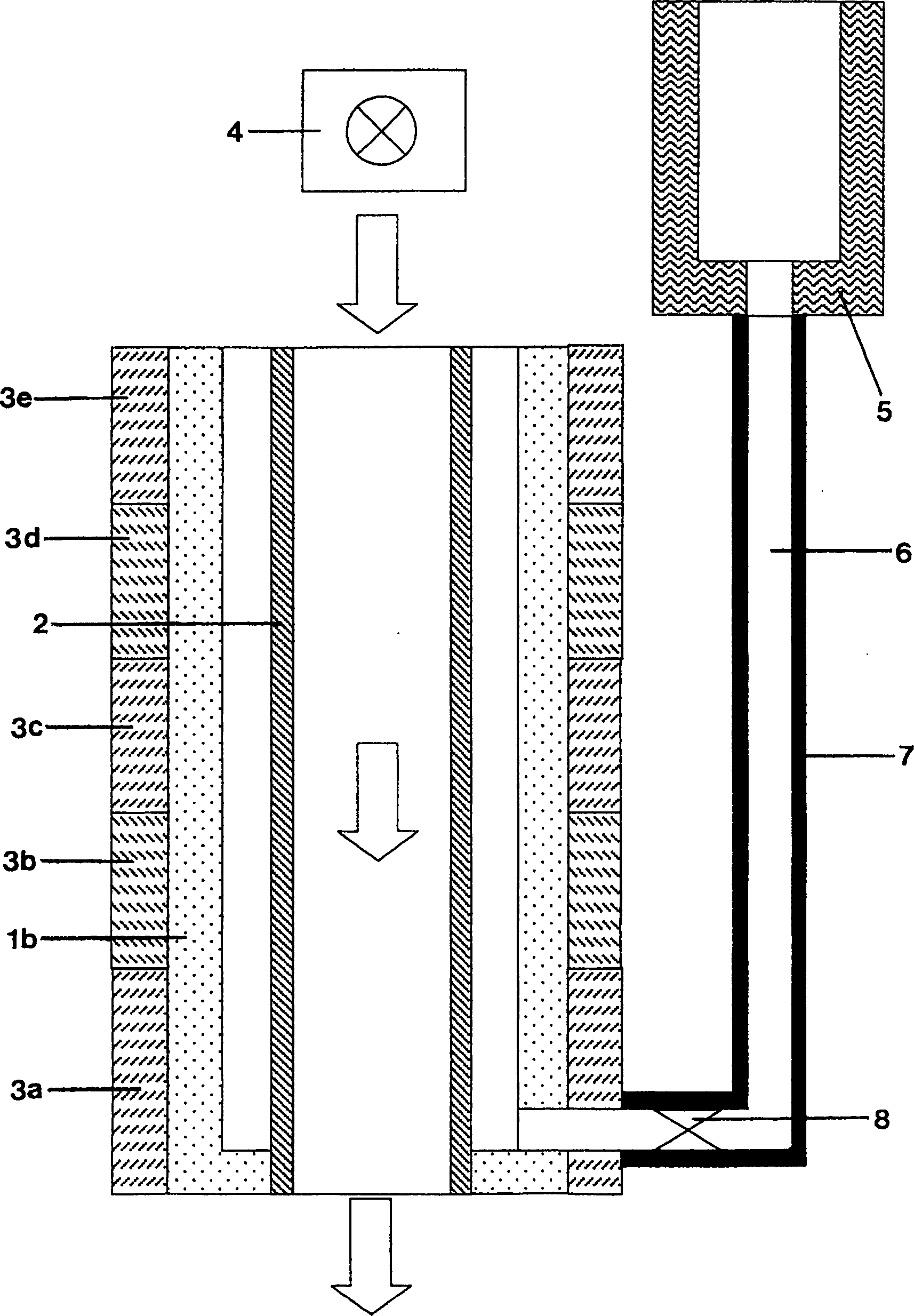
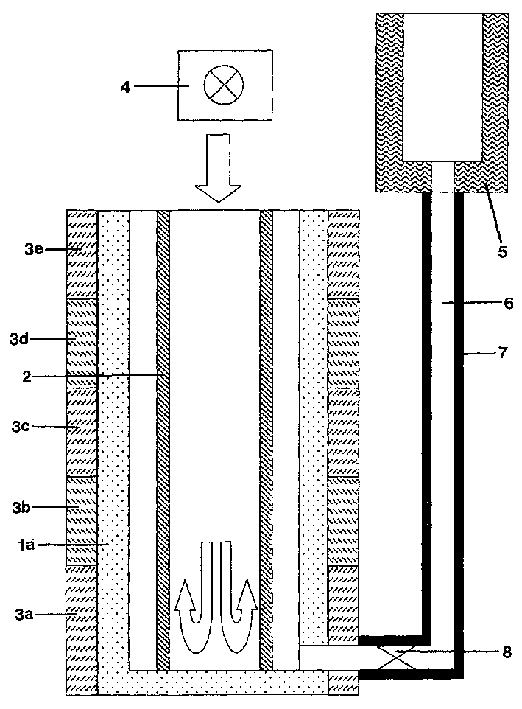
The invention relates to a process for producing a multifunctional multi-ply layer on a transparent plastic substrate and to a multifunctional multi-ply layer produced thereby. In the process, a multi-ply layer is constructed by a plasma-assisted method on a transparent plastics substrate (1) in an enclosed process by using a microwave plasma source to produce a plasma and continuously maintaining the plasma during the course of the process. A first adhesion-promoting organosilicon polymer layer (2) is subsequently deposited in the microwave plasma, and then cathode sputtering is used to deposit a first ITO layer (3), and a transparent layer of metal and / or of metal oxide and a second ITO layer (3). Finally, an organosilicon polymer layer (5) is deposited. The multifunctional multi-ply layer is composed of a first adhesion-promoting organosilicon polymer layer (2) with a thickness of from 50 to 300 nm, of a first ITO layer (3) with a thickness of from 50 from 300 nm, of at least one transparent layer with a thickness of from 10 to 30 nm of metal and / or of metal oxide, of a second ITO layer (3) with a thickness of from 50 to 300 nm, and of at least one final organosilicon polymer layer (5) with a thickness of from 300 nm to 6 000 nm.
Owner:ROTH & RAU B V
Method of making a protective coating forming a thermal barrier with a bonding underlayer on a superalloy substrate, and a part obtained thereby
A protective coating forming a thermal barrier is made on a superalloy metal substrate by forming a bonding underlayer on the substrate, the bonding underlayer being constituted by an intermetallic compound comprising at least aluminum and a metal from the platinum group, and by forming a ceramic outer layer which is anchored on a film of alumina present on the surface of the bonding underlayer. The bonding underlayer preferably has a thickness of less than 50 mum and is made by using physical vapor deposition, e.g. by cathode sputtering, to deposit a plurality of individual layers alternately of aluminum and of a metal from the platinum group, and by causing the metals in the resulting layers to react together exothermally.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
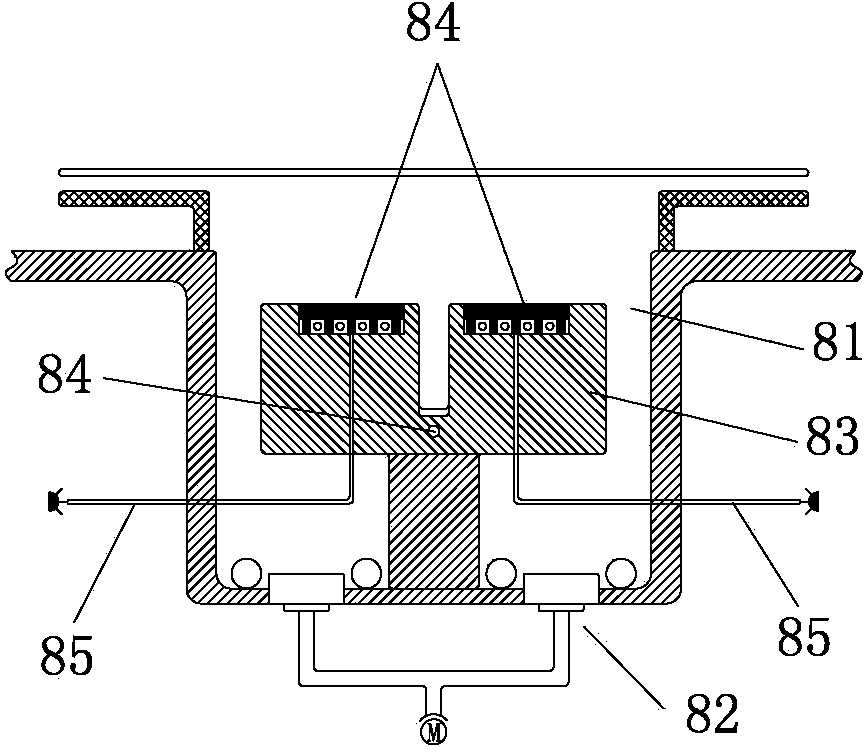
Packaging device and packaging method for hollow cathode type sputtering target
ActiveUS20070131545A1Avoid dirt adhesionAvoid dust adhesionCapsCap application using vaccuumEngineeringCathode sputtering
Provided are a packaging device and packaging method of a hollow cathode sputtering target which installs, in the hollow cathode sputtering target, a cover of a size capable of covering a void of the target; provides one or more through-holes to the cover; places a resin bag over them, and performs vacuum suction to the inside of the bag. This packaging device and packaging method of a hollow cathode sputtering target is capable of performing vacuum suction even to the inside of the hollow portion covered with the resin bag.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method of making a protective coating forming a thermal barrier with a bonding underlayer on a superalloy substrate, and a part obtained thereby
InactiveUS20040028938A1Small thicknessDecorative surface effectsOrnamental structuresGas phaseSuperalloy
A protective coating forming a thermal barrier is made on a superalloy metal substrate by forming a bonding underlayer on the substrate, the bonding underlayer being constituted by an intermetallic compound comprising at least aluminum and a metal from the platinum group, and by forming a ceramic outer layer which is anchored on a film of alumina present on the surface of the bonding underlayer. The bonding underlayer preferably has a thickness of less than 50 mum and is made by using physical vapor deposition, e.g. by cathode sputtering, to deposit a plurality of individual layers alternately of aluminum and of a metal from the platinum group, and by causing the metals in the resulting layers to react together exothermally.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Multi-magnetic field magnetron sputtering cathode
InactiveCN102586749AIncrease profitImprove uniformityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringMagnetic field coupling
The invention discloses a multi-magnetic field magnetron sputtering cathode. The cathode is characterized in that: a plurality of magnet units are arranged and combined to form a multi-magnetic field coupled planar sputtering cathode, and are arranged along the length direction of a rectangular cathode. Compared with the prior art, the cathode has the advantages that: effective sputtering time of a single rectangular planar cathode sputtering system is greatly prolonged, effective deposition distances of the system is greatly increased, and the uniformity of a planar cathode sputter coating and the utilization rate of a planar target are effectively improved. The whole cathode is simply designed and has a simple preparation process, so that a planar cathode coating mode has a wide application field in industrial production.
Owner:王正安
Manufacture of tubular targets
InactiveCN1196806CPrevent solidificationAvoid inhomogeneityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMolten stateHeater Rod
A process for producing a tube target for cathode sputtering plants, in which the tube target is formed from a metallic inner tube (target holder) made of a first material with a first melting point of Ts1>=900 K and a metallic outer tube (target) that concentrically surrounds the inner tube and that is made of a second material with a second melting point of Ts2<=800 K. The inside diameter of the outer tube and the outside diameter of the inner tube are proportioned in such a way that the two tubes fit together tightly and are mechanically firmly joined. The outer tube is formed by casting the second material in a molten state in a heated, vertical, cylindrical permanent mold, which has a heated mandrel that constitutes the inner tube. After a space between the mold and the inner tube has been filled with the molten second material, a first thermal gradient develops between the inner tube and the mold, a second thermal gradient develops between the bottom and the top of the mold, and the outer tube is simultaneously cooled from the inside to the outside and from the bottom to the top.
Owner:MATERION ADVANCED MATERIALS GERMANY GMBH
Coating device and coating method for winding type sputtering three-layer dielectric film
ActiveCN103805955ASmall footprintCompact structureVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringDielectric
The invention relates to a coating device and a coating method for a winding type sputtering three-layer dielectric film. The coating device comprises a cold roller, a main motor for driving the cold roller, a vacuum cavity wrapping the cold roller, an unwinding mechanism, a winding mechanism and five cathode chambers, wherein the middle three cathode chambers of the five cathode chambers have the same structure which is a dual-target cathode chamber; the cathode targets in the dual-target cathode chamber are two cathode sputtering targets; the two cathode chambers on the two sides in the five cathode chambers have the same structure which is a single-target cathode chamber; the cathode target of the single-target cathode chamber is a cathode sputtering target. By adopting the structure, the middle three dual-target cathode chambers perform sputtering on the middle dielectric film of the three-layer dielectric film by use of the same atmosphere, thus the film forming time of the middle dielectric film is prolonged, and the sputtering target range of the dual-target cathode is more accurate.
Owner:深圳市锦瑞新材料股份有限公司
Sputtering target and method for finishing surface of such target
ActiveUS20070108046A1Good effectFavorable target usabilityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingSurface roughnessOptoelectronics
Provided is a hollow cathode sputtering target comprising an inner bottom face having a surface roughness of Ra≦1.0 μm, and preferably Ra≦0.5 μm. This hollow cathode sputtering target has superior sputter film evenness (uniformity), generates few arcing and particles, is capable of suppressing the peeling of the redeposited film on the bottom face, and has superior deposition characteristics.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Ceramic preparation method, resulting ceramics and use thereof, particularly as a cathode sputtering target
ActiveCN101535210AIncrease charge mobilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDopantBoiling point
The invention relates to a method for preparing a ceramic from an inorganic base material in the form of a powder with a high boiling point, including a step in which the powder of the inorganic base material is mixed with a second inorganic component which is also in powder form and which serves as a dopant for the inorganic base material. The dopant comprises a single inorganic material or a mixture of at least two inorganic materials that have a dopant effect on the inorganic base material. The method also includes a sintering step performed at a high temperature. Owing to the high densitythereof, the resulting ceramics are suitable for use as a target element. The films and electrodes obtained from said ceramics have particularly beneficial properties.
Owner:加拿大魁北克电力公司 +1
Vacuum atomization suspension uniform sputtering coating method for spherical powder material
ActiveCN103436848ACorrosion resistance hasImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh energyMoisture resistance
The invention discloses a vacuum atomization suspension uniform sputtering coating method for a spherical powder material. Spherical powder is placed in a vacuum atomization tank; a cathode sputtering target and an anode body are arranged in the vacuum atomization tank; in the vacuum environment, when high-energy particles accelerated by an electric field or a magnetic field impact the surface of the cathode sputtering target, atomic molecules on the surface of the target carry out momentum exchange with the high-energy particles, so that atoms or molecules are splashed out of the surface of the target and have a certain energy; when the splashed atoms or molecules are collided with the spherical powder which is atomized and suspended in the vacuum, thin film deposition on the spherical powder is implemented. According to the invention, the high-performance spherical powder material which has functions of high and low temperature resistance, high-pressure resistance, moisture resistance, corrosion resistance, antioxidation and the like, has excellent performance, meets different requirements and has special functions can be produced; the antioxidant surface of the spherical metal powder can be subjected to functionalization processing.
Owner:(CNBM) BENGBU DESIGN & RES INST FOR GLASS IND CO LTD +1
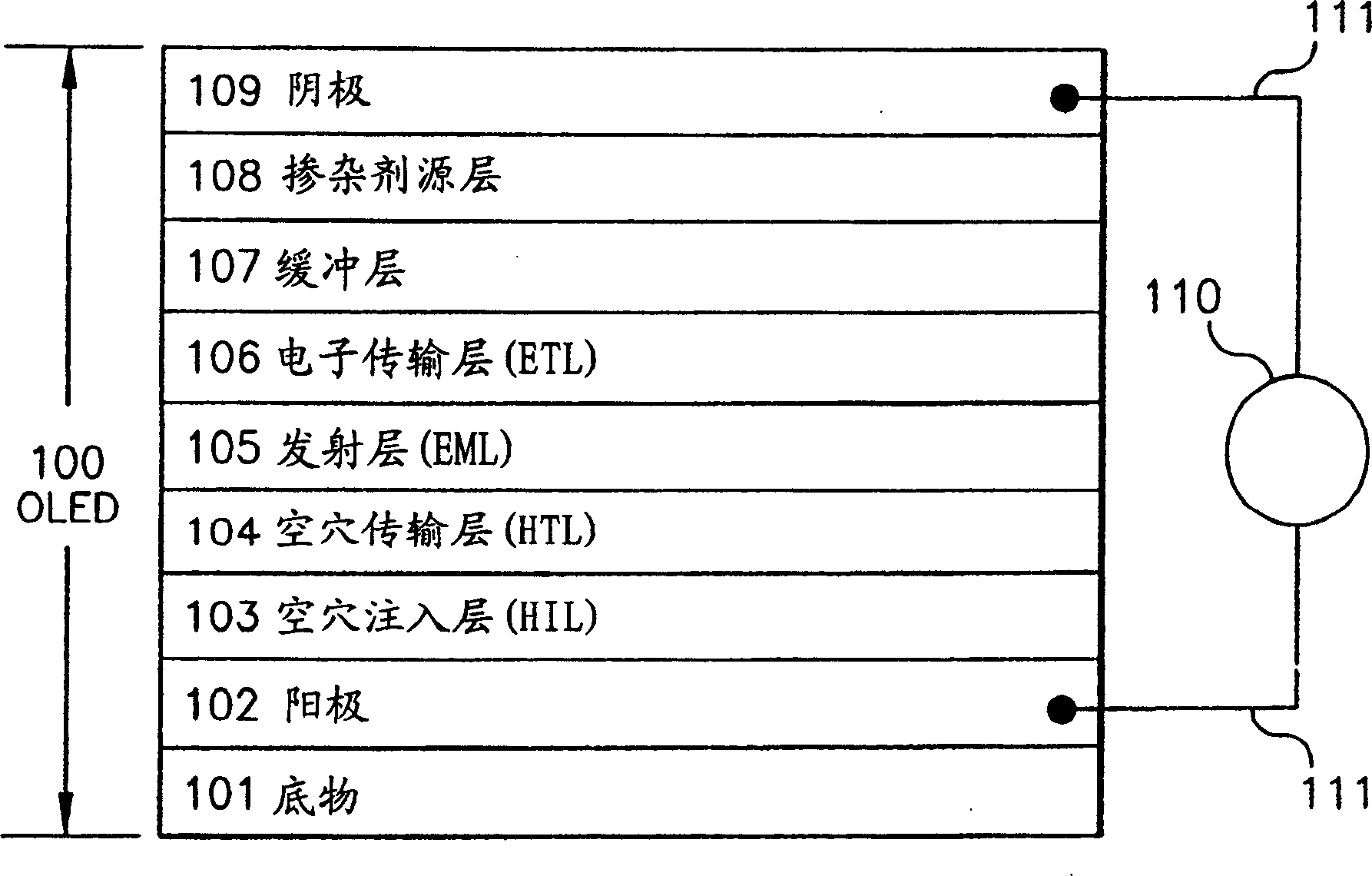
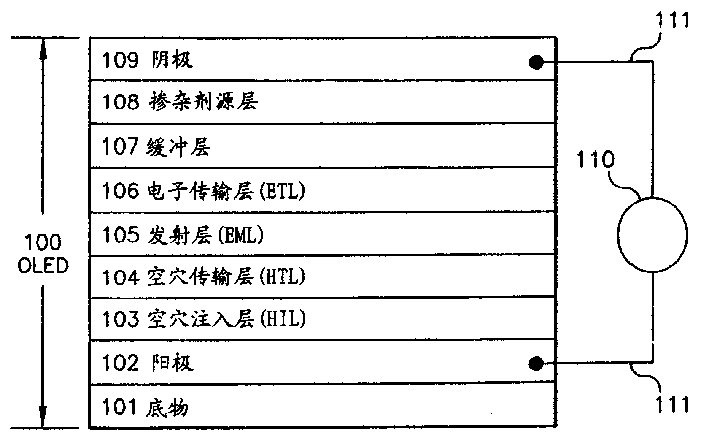
An organic light-emitting device structure using metal cathode sputtering
InactiveCN1467864AAvoid damageLarge manufacturing tolerancesElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDopantElectron injection
An OLED device, including a substrate, an anode formed of a conductive material disposed over the substrate, an emissive layer having an electroluminescent material provided over the anode layer, a buffer layer, provided over the emissive layer and including phthalocyanine or derivatives thereof, an electron injecting dopant source layer provided over the buffer layer and including a compound of an alkali metal or thermal decomposition products thereof; and a sputtered layer of a metal or metal alloy provided over the buffer layer and selected to function with the buffer layer to inject electrons into the emissive layer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Coating substrates with an alloy by means of cathode sputtering
Owner:SINGULUS TECHNOLGIES AG
Hollow cathode sputtering apparatus and related method
Owner:NEW MILLENNIUM SOLAR EQUIP CORP
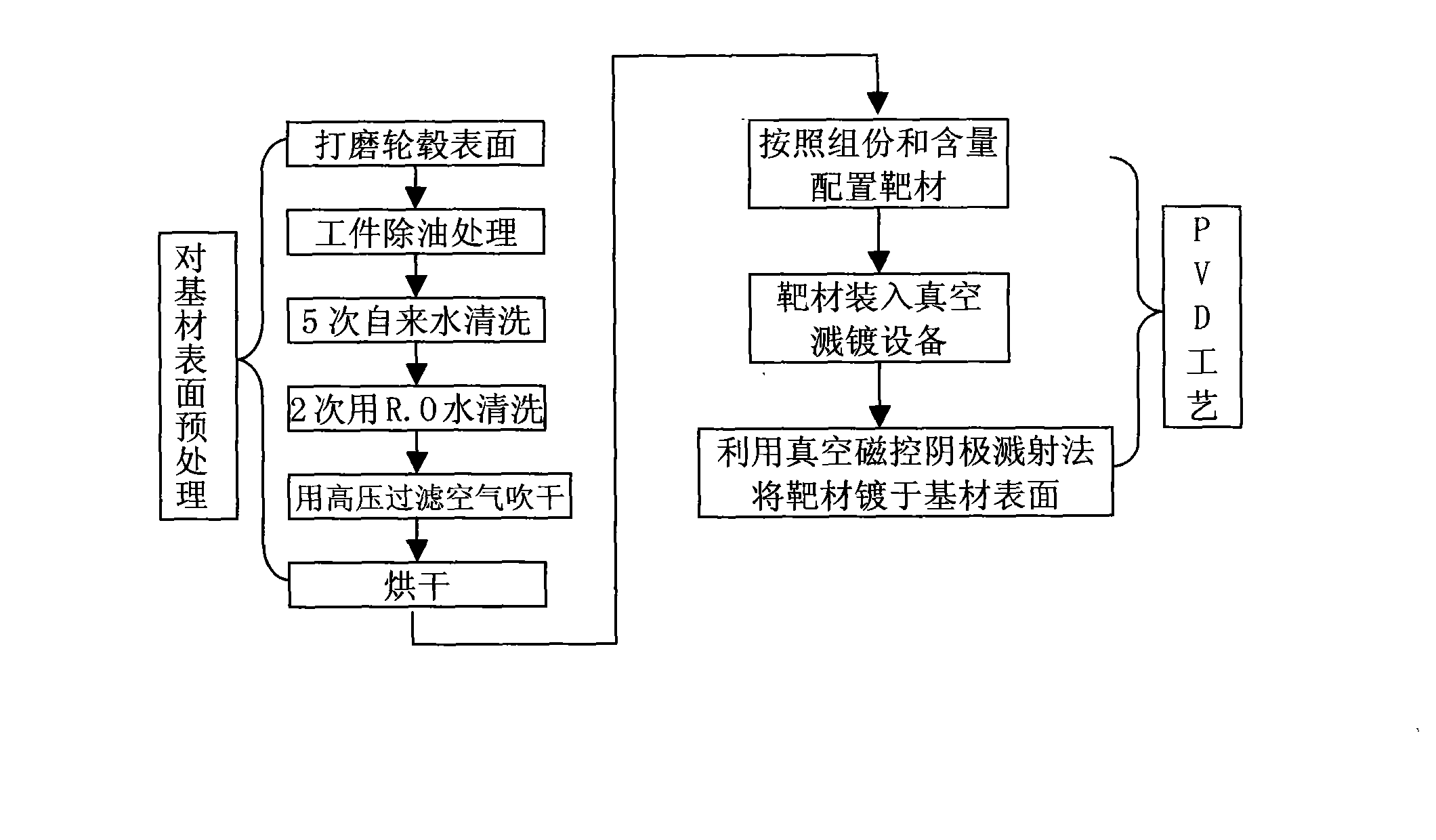
Target and process for utilizing same to plate film on aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate
InactiveCN102051532AReduce pollutionGood adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingManganeseAlloy substrate
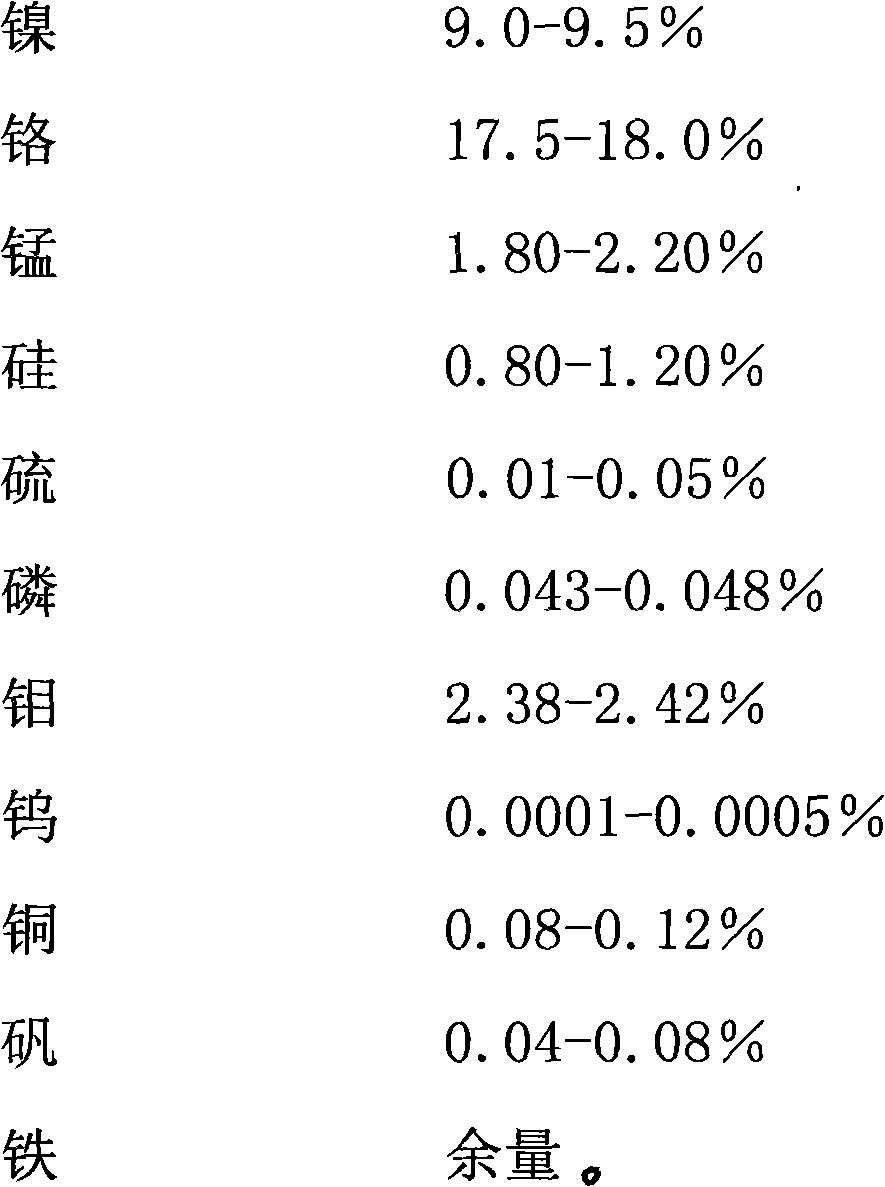
The invention relates to a process for plating a film on an aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate. The method comprises the following steps of: pretreating the surface of a substrate; preparing a target from the following components in percentage by weight: 0.06-0.10 percent of carbon, 9.0-9.5 percent of nickel, 17.5-18.0 percent of chromium, 1.80-2.20 percent of manganese, 0.80-1.20 percent of silicon, 0.01-0.05 percent of sulphur, 0.043-0.048 percent of phosphorus, 2.38-2.42 percent of molybdenum, 0.0001-0.0005 percent of tungsten, 0.08-0.12 percent of copper, 0.04-0.08 percent of vitriol and the balance of iron; loading the target into vacuum sputtering equipment; and finally, plating the target on the surface of the substrate by adopting a vacuum magnetic control cathode sputtering method, wherein before sputtering is carried out, the vacuum degree in a furnace is 3.0-4mTorr, the argon quantity used during sputtering is 25-60R, direct current is used for bombarding, the voltage is 180-200V, and the current is 10-15A. The process not only achieves the purpose of environmental protection but also meets the requirement on quality.
Owner:YULIN AUTOMOBILE FITTINGS KUNSHAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com