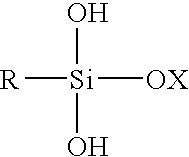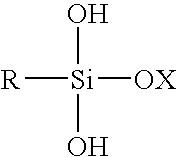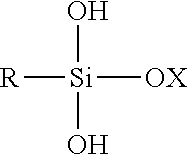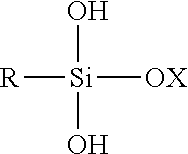Patents
Literature
49 results about "HYDROPHOBIC STARCH" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The starch esterification was carried out in two steps. In the first step, native starch was dispersed in an alkali reaction medium, and in the second step, it was treated for esterification. Finally, hydrophobic starch esters were obtained. The starch was dried at 100 °C for 2 h before reaction was accomplished.
Hydrophobic starch having near-neutral dry product pH
ActiveUS7375214B2Little and no corrosivityLow production costBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCombustionNeutral ph
A free-flowing, hydrophobic starch composition has a near-neutral dry product pH. Methods for making the hydrophobic starch composition by preparing an aqueous mixture comprising a starch, a siliconate, and an acid, where the aqueous mixture has a near-neutral pH, and drying the starch solids to obtain a hydrophobic starch. Novel fuel compositions comprise hydrophobic starch which can be used in internal combustion engines, such as diesel engines. Hydrophobic starch compositions may be used as fuels or fuel components. Novel methods of fueling and operating internal combustion engines use hydrophobic starch as fuel or fuel components.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Hydrophobic starch derivatives
InactiveUS7157573B2Maintain good propertiesHigh viscosityEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesPolymer scienceHydrophobe
The invention relates to a process for preparing a hydrophobic starch, comprising etherification, esterification or amidation of a root or tuber starch comprising at least 95 wt. % of amylopectin, based on dry substance of the starch, or a derivative thereof, with a substituent comprising an alkyl chain having from 4–24 carbon atoms. The invention further relates to a hydrophobic starch obtainable by said process.
Owner:COOP AVEBE U A
Preparation method and application of hydrophobic starch sulfate ester in cement water-reducing agent
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a hydrophobic starch sulfate ester in a cement water-reducing agent, and belongs to the fields of chemistry and chemical engineering. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a sulfamic acid, starch, urea, aliphatic tertiary alcohol or aryl methyl alcohol and water into a reactor under the conditions that the molar ratio of the sulfamic acid to the starch is (0.5-3.0):1, the molar ratio of the urea to the starch is (0.1-3.0):1, the molar ratio of the aliphatic tertiary alcohol or the aryl methyl alcohol to the starch is (0.1-1) and the adding amount of the water accounts for 10% to 30% of the dry weight of the starch; and reacting for 1 to 10 hours at a temperature of 80 DEG C to 150 DEG C, thereby obtaining the hydrophobic starch sulfate ester in which the sulfonyl substitution degree is between 0.04 and 0.89 as well as the alkyl substitution degree is between 0.01 and 0.2. The hydrophobic starch sulfate ester is applied to the cement water-reducing agent, wherein the mass percent of the hydrophobic starch sulfate ester accounts for 0.1% to 1.0% of that of cement. According to the method, a dry method and one-pot reaction are adopted, so that the environmental pollution caused by the application of an organic solvent is avoided. Thus, the production cost is decreased.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation methods of biodegradable yoghourt-cup material and product
InactiveCN108192303AOvercome barrierOvercome the disadvantage of high brittlenessCross-linkPolymer science
The invention provides preparation methods of a biodegradable yoghourt-cup material and a product, and belongs to the field of polymer materials. The biodegradable yoghourt-cup material is prepared from the following components: 55-75 parts of polylactic acid, 15-35 parts of thermoplastic hydrophobic starch, 5-10 parts of poly(butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate), 0.3-0.7 part of a nucleating agent,0.5-1 part of a chain extender, 0.1-0.3 part of a cross-linking agent and 0.1-0.15 part of a compatilizer. The material provided by the invention has the advantages that the polylactic acid are blended with the thermoplastic hydrophobic starch and the poly(butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate) for modification, and then the auxiliary agents such as the nucleating agent, the chain extender, the cross-linking agent, the compatilizer and the like are added, so that the defects of low barrier property and high brittleness of the polylactic acid are overcome, good mechanical strength and good flexibility are achieved, the product cost is reduced, the application field of a polylactic acid material is expanded, and the pollution to the environment is greatly reduced compared with the pollution of the petroleum-based plastic.
Owner:JILIN COFCO BIOCHEM +1
Starch-based degradable bioplastic and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106916372AImprove hydrophobicityImprove descriptiveBiodegradable plasticNatural environment
The invention relates to a starch-based degradable bioplastic and a preparation method thereof. The objective of the invention is mainly to overcomes the disadvantages of proneness to production of plastic garbage and pollution to environment of general-purpose plastics in the prior art and the disadvantage of high price of biodegradable plastics in the prior art. The starch-based degradable bioplastic is characterized by comprising a high-hydrophobicity starchy material, aliphatic acid, a nucleating agent, a modifier, an oxidation promoter and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the above-mentioned components, a high polymer material and other auxiliary materials with a mixer; then adding a mixture obtained in the previous step into a double-screw extruder; carrying out mixing, plasticization and granulation in the double-screw extruder; and carrying out blow molding, calendaring, vacuum molding and the like so as to obtain the starch-based degradable bioplastic or a film. The starch-based degradable bioplastic is free of toxicity and applicable to agricultural films, food packaging materials, disposable plastic products for daily life, etc. The starch-based degradable bioplastic can be degraded by light, water and microbes in natural environment, so the problem of environmental pollution caused by waste general-purpose plastics in the prior art is overcome.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG XINDA ENTERPRISE GRP
Fuels comprising hydrophobic starch and methods of fueling an engine
ActiveUS7374587B2Little and no corrosivityLow production costLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCombustionNeutral ph
A free-flowing, hydrophobic starch composition has a near-neutral dry product pH. Methods for making the hydrophobic starch composition by preparing an aqueous mixture comprising a starch, a siliconate, and an acid, where the aqueous mixture has a near-neutral pH, and drying the starch solids to obtain a hydrophobic starch. Novel fuel compositions comprise hydrophobic starch which can be used in internal combustion engines, such as diesel engines. Hydrophobic starch compositions may be used as fuels or fuel components. Novel methods of fueling and operating internal combustion engines use hydrophobic starch as fuel or fuel components.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Microsphere-type high-hydrophoby starch, as well as preparation method and application thereof
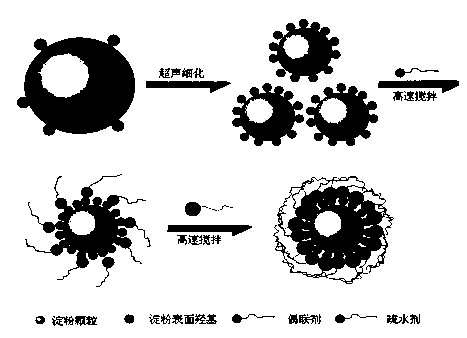
The invention belongs to the technical field of modification of natural polymer materials, and particularly relates to microsphere-type high-hydrophoby starch, as well as a preparation method and the application thereof. The adopted technical scheme is that the preparation method of the microsphere-type high-hydrophoby starch comprises the following steps: dry starch is subjected to ultrasonic oscillation processing firstly, a coupling agent and a hydrophobic agent are added separately in sequence under the condition of stirring with high speed, and the microsphere-type high-hydrophoby starch is obtained after drying. The hydrophobic starch can remedy shortages of chemical modification, physical modification and coupling agent modification in the prior art, and is small in particle size, large in specific surface area, high in the efficiency of being packaged by the coupling agent and the hydrophobic agent, strong in hydrophobic nature, good in mutual solubility with polyolefin resin, and excellent in physical and biological degradability of modified starch-based plastic.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Hydrophobic starch having near-neutral dry product pH
ActiveUS20060189801A1Reduces potential corrosivenessLittle and no corrosivitySugar derivativesLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCombustionNeutral ph
A free-flowing, hydrophobic starch composition has a near-neutral dry product pH. Methods for making the hydrophobic starch composition by preparing an aqueous mixture comprising a starch, a siliconate, and an acid, where the aqueous mixture has a near-neutral pH, and drying the starch solids to obtain a hydrophobic starch. Novel fuel compositions comprise hydrophobic starch which can be used in internal combustion engines, such as diesel engines. Hydrophobic starch compositions may be used as fuels or fuel components. Novel methods of fueling and operating internal combustion engines use hydrophobic starch as fuel or fuel components.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Microencapsulate and process for the manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20110171349A1Readily be dispersed into waterNot rapidly releaseMilk preparationWort preparationSolubilityMethacrylate
The present invention relates to a microencapsulate comprising microcapsules having a diameter of 0.1 μm to 25 μm, said microcapsules comprising: —a core particle having a diameter of 90 nm to 23 μm and containing at least 3% of the active component by weight of said core particle; and—a coating that fully envelops the core particle and containing at least 20 wt. % of a hydrophobic polymer selected from cellulosic ethers, cellulosic esters, zein, shellac, gluten, polylactide, hydrophobic starch derivatives, polyvinyl acetate polymers, polymers or copolymers derived from an acrylic acid ester and / or a methacrylic acid ester and combinations thereof; wherein the core particle contains a release trigger component and / or the coating contains a release trigger component, said release trigger component being selected from: —a water-swellable polymer having a water-uptake capacity at 37° C. and pH 7.0 of less than 20 wt. % and a water-uptake capacity at 37° C. and pH 2.0 of at least 50 wt. %; an—an edible salt having a water solubility at 37° C. and a pH of 7.0 of less than 1 mg / ml and a water solubility at 37° C. and a pH of 2.0 of at least 5 mg / ml; The microencapsulate of the present invention does not release the encapsulated active component when incorporated in water-containing foodstuffs, beverages, nutritional compositions or pharmaceutical compositions. Following ingestion, however, the active component is released rapidly.
Owner:FEYECON BV +1
Starch-base degradable bioplastic and preparing method thereof
The invention relates to starch-base degradable bioplastic and a preparing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biodegradable materials. The starch-base degradable bioplastic is prepared from 40-85% of commodity polymer plastic, 10-50% of a high-hydrophobicity starchiness material, 0.5-5% of aliphatic polyester and 0.1-5.5% of oxidation accelerator. The preparing method of the starch-base degradable bioplastic includes the following steps that starch is treated in a hydrophobization mode to obtain the high-hydrophobicity starchiness material, the raw material components are mixed by a ratio and prepared into master batch through a twin-screw extrusion machine, and after the master batch and the commodity polymer plastic are mixed, the starch-base degradable bioplastic is prepared through injection molding, flattening, blow molding, vacuumizing and forming. The product prepared through the method can be used repeatedly on the dry condition without perpendicular sunlight incidence, the strength is kept unchanged basically, an abandoned product is completely decomposed finally in wet soil, no harmful component is generated, and the environment is not polluted.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG XINDA ENTERPRISE GRP
Hyperbranched-starch-modified zinc oxide and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of rubber processing, in particular to hyperbranched-starch-modified zinc oxide and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the modified zinc oxide, hyperbranched hydrophobic starch-modified zinc oxide is adopted as the modified zinc oxide, and the zinc oxide is of a nano form, and is distributed on the surface of hyperbranched hydrophobic starch evenly and stably. The zinc oxide can be dispersed in a rubber matrix uniformly, and has stable properties without agglomeration, the problems of traditional zinc oxide are solved, and vulcanization activity, reinforcement and other effects can be developed better.
Owner:ZHONGCE RUBBER GRP CO LTD
Method for preparing hydrophobic starch
The invention provides a hydrophobic starch preparation method, relates to a preparation method for the hydrophobic starch, in particular to a wet preparation method for the hydrophobic starch. The invention aims to provide the preparation method for the hydrophobic starch. The preparation method comprises the following steps: brewing overcooked starch into starch milk with the mass concentration of between 25 and 40 percent by water or 80-95 mass percent ethanol aqueous solution, placing and stirring the starch milk in a reaction kettle; adding anhydrous sodium sulfate accounting for 3 to 15 mass percent of the overcooked starch, and keeping a constant temperature for 5 to 15 minutes; regulating the pH value of the emulsion to 8.5 to 11.0 by a 3 to 6 percent sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, starting to add hexamethyldisilazane accounting for 5 to 15 mass percent of the overcooked starch, keeping the constant pH value of the emulsion by 5 to 10 mass percent hydrochloric acid or the 3 to 6 mass percent sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and carrying out the reaction for 2 to 15 hours; and after the reaction is finished, regulating the pH value of the emulsion to 6.0 to 7.0 by 5 to 10 mass percent hydrochloric acid, and obtaining the product after filtrating, washing, drying and crushing the starch milk.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Hydrophobic starch-nanometer calcium carbonate compound and preparation method thereof
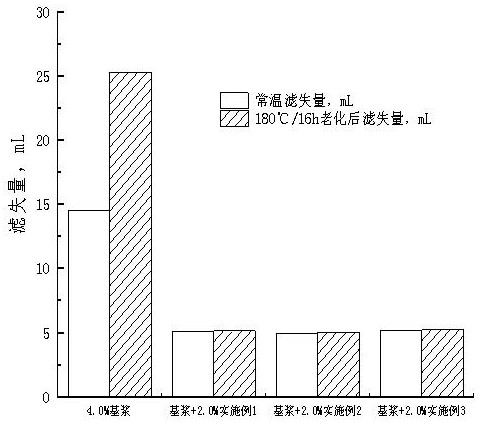
ActiveCN104629094AGood reservoir protection effectRelieve pressureDrilling compositionKneader reactorOrganosolv
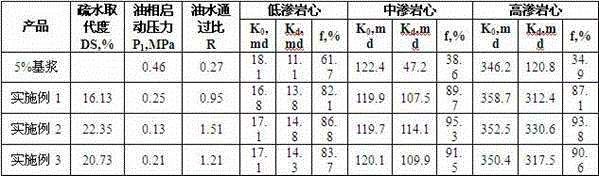
The invention relates to a hydrophobic starch-nanometer calcium carbonate compound and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical filed of hydrophobization temporary plugging. The preparation method of the compound comprises the following steps: placing 1000-2000g of starch in a kneader, sequentially adding 100-200g of sodium carbonate, 100-200mL of water and 125-250mL of ethanol, and carrying out a closed kneading reaction at a preset temperature; sequentially adding 125-250mL of ethanol and 150-300Ml of benzoyl chloride, and carrying out a closed kneading reaction at 30-40DEG C; slowly adding 500-1500g of nanometer calcium carbonate, and carrying out a closed kneading reaction at 30-50DEG C; and stopping stirring, cooling to room temperature, allowing the obtained material to stand for 3-6h, discharging the material, washing, drying, and crushing to obtain a product. The product has a same substitution value with products obtained through an organic solvent method, can effectively reduce the oil phase starting pressure, increases the oil water passing ratio, maintains high permeability restoration ratio, and has a good reservoir protection effect.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Hydrophobic starch-fiber composite foam material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a hydrophobic starch-fiber composite foam material which is prepared from 100 parts of starch, 10-50 parts of plant fibers, 10-30 parts of a plasticizer, 1-10 parts of a filler, 1-5 parts of a silane coupling agent and 0.5-2.5 parts of a hydrophobic agent. The material has the advantages of uniform pore distribution, high porosity, good resilience, low density, hydrophobicsurfaces and oil-water selectivity. Compared with extrusion and mould pressing process methods, the preparation method of the hydrophobic starch fiber composite foam material disclosed by the invention has the advantages that a freezing replacement method is adopted, the requirement on operation equipment is low, the operation is simple and safe, and the size, the dimension and the shape of a sample can be controlled.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
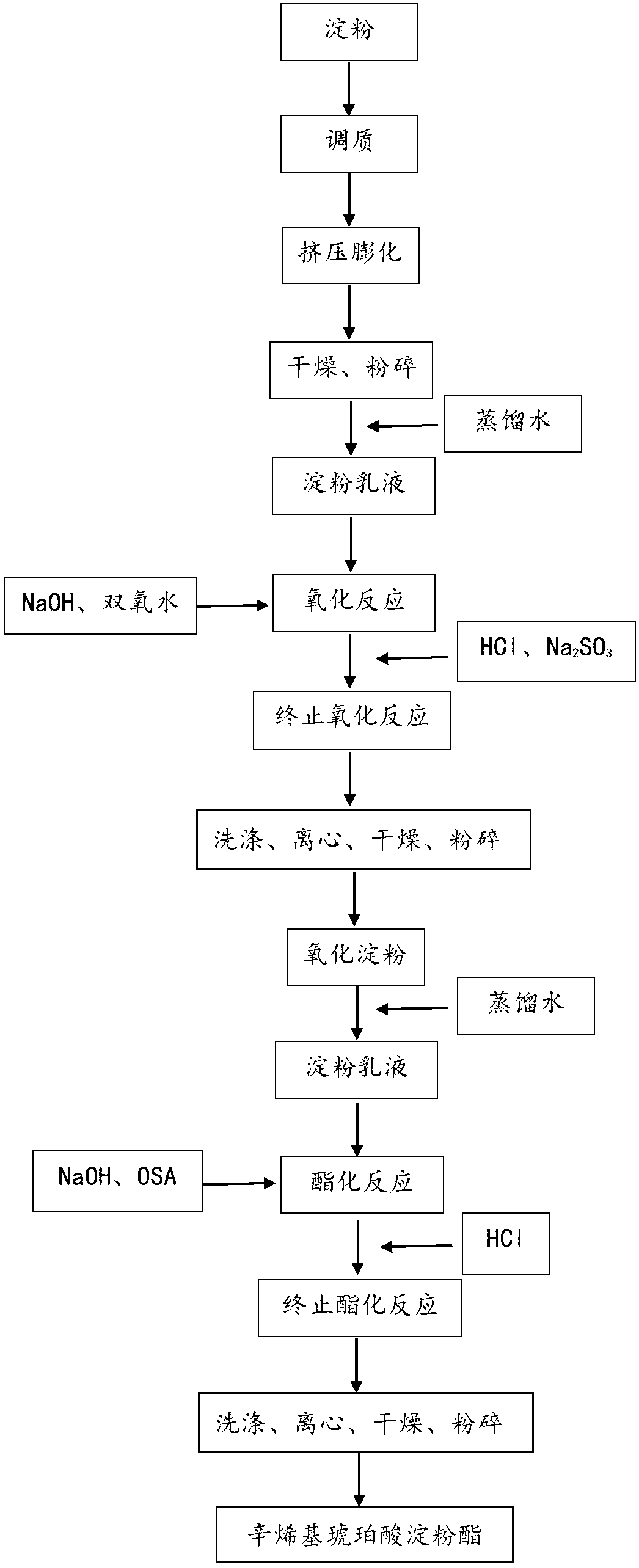
Starch octenylsuccinate, preparation method, and application thereof
The invention discloses a preparation method of low-viscosity and high-hydrophobic starch octenylsuccinate which is especially used for moisturizing emulsions. The preparation method includes steps of: 1) carrying out extrusion puffing to starch to prepare a starch emulsion, and preparing oxidized starch with H2O2 as an oxidant; 2) regulating pH with a NaOH solution and slowly adding the octenylsuccinic anhydride to the starch emulsion, and after a reaction is finished, regulating the pH of the starch emulsion with a HCl solution; 3) washing, centrifuging, drying and crushing the starch emulsion to obtain the low-viscosity and high-hydrophobic starch octenylsuccinate. With quinoa (corn and rice) starch as raw material, the starch is pre-treated through the extrusive puffing, so that reaction active sites are exposed, and reaction efficiency and substitution degree are increased. After the pressing activation pre-treatment and oxidization treatment, the hydrophobic group, octenylsuccinic anhydride, is introduced to increase the hydrophobicity of the surfaces of the starch granules, so that the starch octenylsuccinate has excellent emulsibility and emulsification stability, and can be extensively applied to moisturizing emulsions.
Owner:SHENYANG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method for hydrophobic starch calcium
The invention provides a preparation method for hydrophobic starch calcium; the preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out constant temperature stirring of native starch, modified starch or starch derivatives and water at a 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system to form a 30-40 wt.% starch emulsion; 2) in the 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system, adjusting the pH value of the emulsion to 7.5-8.5 with an alkaline solution; 3) in the 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system, adding anhydride; and constantly adding an alkaline solution or a calcium salt to maintain the pH value of the emulsion at 7.5-8.5, and continuing to carry out a reaction for a certain time; 4) in the 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system, adding an acid to adjust the pH value to 6.0; and 5) adding water, washing and filtering, drying at the temperature of 50 DEG C, crushing, and sieving to obtain white hydrophobic starch calcium. The hydrophobic starch calcium product belongs to adsorbent modified starch, has the advantages of good fluidity, good hydrophobicity and good safety, is an excellent adsorbent, and can be widely applied in cold spray products, such as adsorbents, talcum powders, prickly-heat powders and other skin-care products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY
Hydrophobic starch with high jetting property and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of starch modification and in particular relates to hydrophobic starch with a high jetting property and a preparation method thereof. According to the hydrophobic starch, fused silicon dioxide is used as a flowability modifier and the control on an adding amount of the fused silicon dioxide is combined; after fused silicon dioxide treatment is adopted,a hydrophobic coupling agent is used for treating; the control on a dosage of the hydrophobic coupling agent is combined and the limitation on conditions of a preparation technology is adopted, so that the hydrophobic property and the flowability of the starch are greatly improved and the energy consumption is reduced. Specifically, the repose angle of corn starch can be reduced to 20 degrees or lower; the activation index of the modified corn starch reaches 97 percent or more; the comprehensive performance including the flowability and the hydrophobic property of the corn starch is improved.
Owner:枣庄市东方变性淀粉有限公司
Low-migration hydrophobic starch-based nano-composite film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107722313AReduce rateReduced diffusion coefficient for long-term migrationAmylaseOrganic solvent
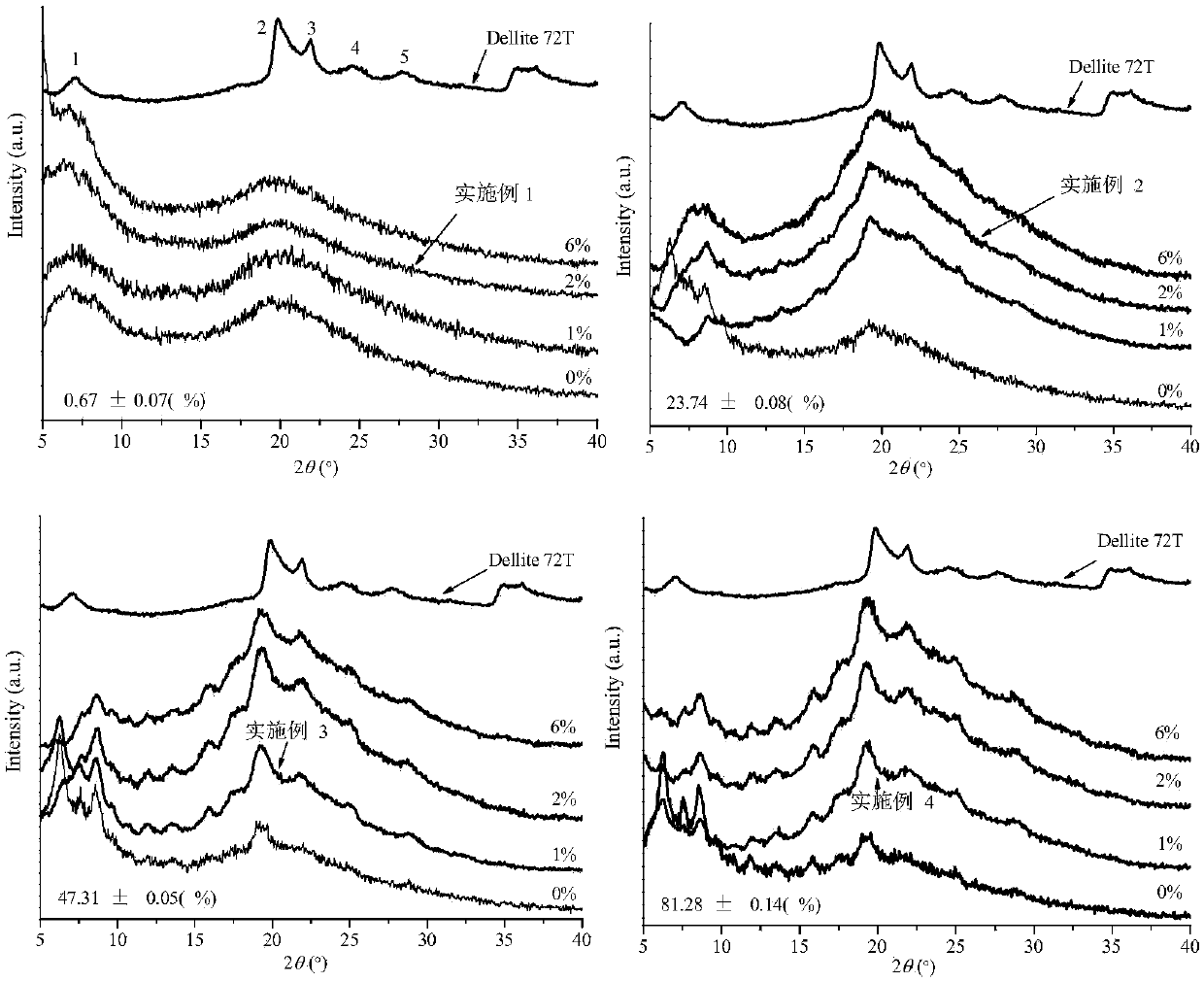
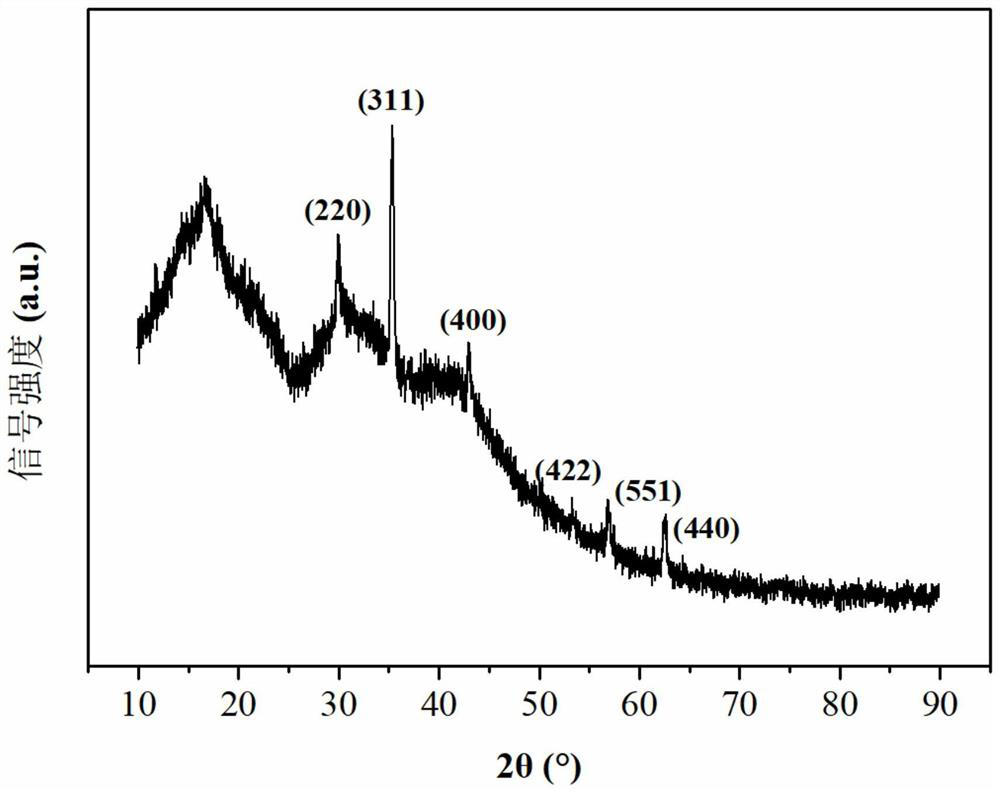
The invention relates to a low-migration hydrophobic starch-based nano-composite film. A preparation method of the composite film includes the steps: S1 dispersing starch into an organic solvent, stirring and activating the starch and then adding anhydride to prepare hydrophobic esterified starch; S2 dispersing the hydrophobic esterified starch and organically modified montmorillonite Dellite 72Tinto the organic solvent to form turbid liquid, adding plasticizers, uniformly stirring the plasticizers and the turbid liquid, pouring mixture into a mould, and drying the mixture to obtain the hydrophobic starch-based nano-composite film. In the S1, the content of amylase in the starch is 0.5-82%, and the esterification degree of the hydrophobic esterified starch is larger than 2.3. In the S2, the weight ratio of the hydrophobic esterified starch to the organically modified montmorillonite Dellite 72T is 100:(1-6). By regulating interaction of the hydrophobic esterified starch, the organically modified montmorillonite and the plasticizers and regulating a formed aggregation structure, the whole migration initial release rate and the long-term migration diffusion coefficient of the plasticizers in the prepared composite film are remarkably reduced, and migration of the plasticizers is effectively slowed down.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
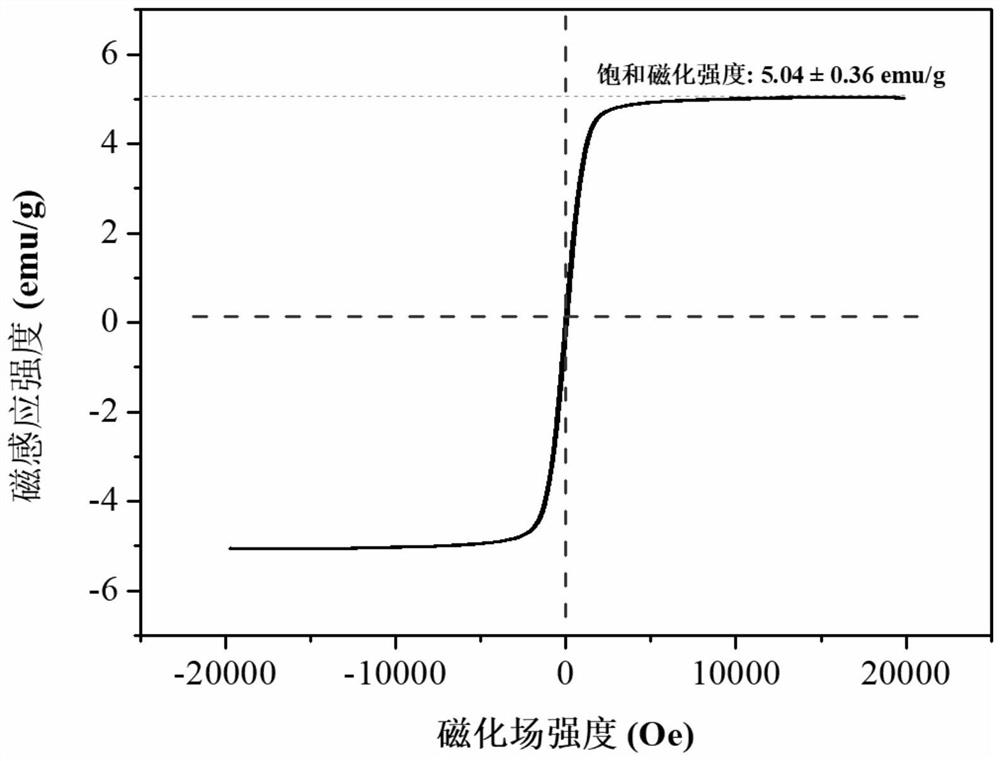
Preparation method of magnetic super-hydrophobic starch-based aerogel for oil-water separation
ActiveCN114272904ALow costLess prone to secondary pollutionFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesGeneral water supply conservationRetrogradation (starch)Silicic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of magnetic super-hydrophobic starch-based aerogel capable of being used for oil-water separation, and belongs to the field of oil-water separation. Nano starch prepared by an enzymolysis retrogradation method is modified by hexadecyltrimethoxysilane to serve as a super-hydrophobic coating, and then the surfaces of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles prepared by a rapid coprecipitation method are modified by tetraethoxysilane and a KH560 silane coupling agent in sequence; and compounding the shell-core structure magnetic nanoparticles formed after modification with starch to prepare magnetic starch-based aerogel, and finally spraying a super-hydrophobic coating suspension onto the surface of the aerogel to prepare the magnetic super-hydrophobic starch-based aerogel. The magnetic super-hydrophobic starch-based aerogel disclosed by the invention shows excellent water-oil selective absorbability, namely oil-water separation characteristic, can be used for remotely controlling floating oil absorption under the guidance of a magnetic field, can be adsorbed and recycled by a magnet after oil absorption is finished, and shows huge potential of being applied to ocean leaked oil cleaning.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A kind of starch-based degradable bioplastic and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to starch-base degradable bioplastic and a preparing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biodegradable materials. The starch-base degradable bioplastic is prepared from 40-85% of commodity polymer plastic, 10-50% of a high-hydrophobicity starchiness material, 0.5-5% of aliphatic polyester and 0.1-5.5% of oxidation accelerator. The preparing method of the starch-base degradable bioplastic includes the following steps that starch is treated in a hydrophobization mode to obtain the high-hydrophobicity starchiness material, the raw material components are mixed by a ratio and prepared into master batch through a twin-screw extrusion machine, and after the master batch and the commodity polymer plastic are mixed, the starch-base degradable bioplastic is prepared through injection molding, flattening, blow molding, vacuumizing and forming. The product prepared through the method can be used repeatedly on the dry condition without perpendicular sunlight incidence, the strength is kept unchanged basically, an abandoned product is completely decomposed finally in wet soil, no harmful component is generated, and the environment is not polluted.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG XINDA ENTERPRISE GRP
Fuels comprising hydrophobic starch and methods of fueling an enginge
ActiveUS20060185225A1Reduces potential corrosivenessLittle and no corrosivityLiquid carbonaceous fuelsCombustionNeutral ph
A free-flowing, hydrophobic starch composition has a near-neutral dry product pH. Methods for making the hydrophobic starch composition by preparing an aqueous mixture comprising a starch, a siliconate, and an acid, where the aqueous mixture has a near-neutral pH, and drying the starch solids to obtain a hydrophobic starch. Novel fuel compositions comprise hydrophobic starch which can be used in internal combustion engines, such as diesel engines. Hydrophobic starch compositions may be used as fuels or fuel components. Novel methods of fueling and operating internal combustion engines use hydrophobic starch as fuel or fuel components.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Preparation method of hydrophobic starch food packaging film
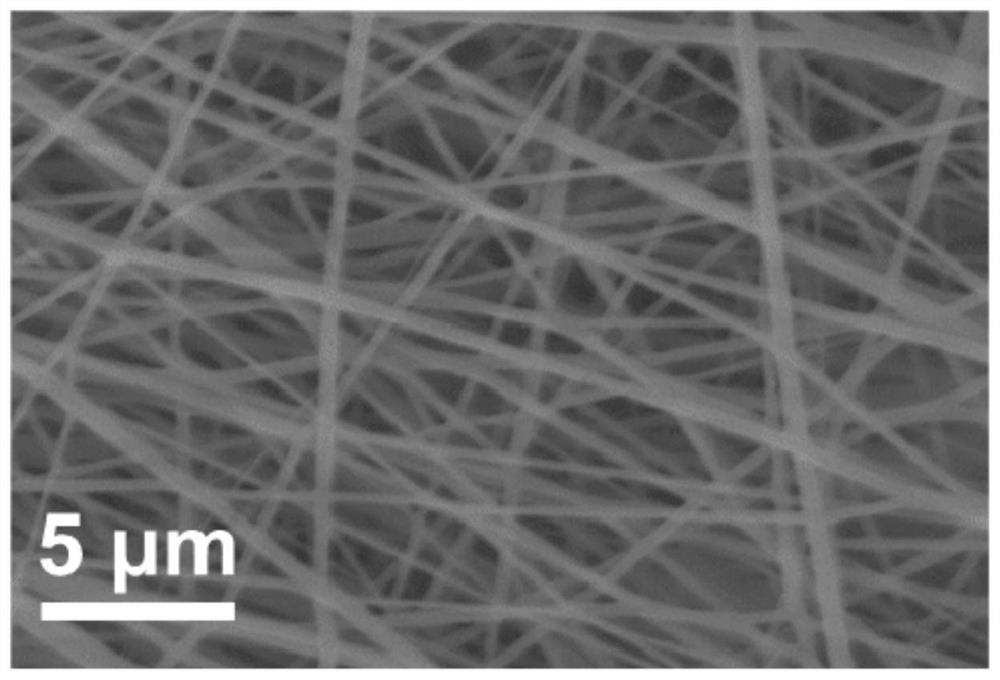
PendingCN113005771AImprove water resistanceEasy to operateLiquid repellent fibresNon-woven fabricsFiberSpinning
The invention discloses a preparation method of a hydrophobic starch food packaging film. The preparation method of the hydrophobic starch food packaging film comprises the following steps: dissolving starch in a dimethyl sulfoxide aqueous solution to form a spinning solution; performing electrostatic spinning on the spinning solution to prepare a starch nanofiber membrane; performing stearic acid modification on the starch nanofiber membrane to form a bionic hydrophobic coating on the surface of the membrane, and reacting to obtain the hydrophobic starch food packaging film. The starch nanofiber membrane is prepared by using an electrostatic spinning method, so that the operation is simple, the reaction is mild, the prepared nanofiber membrane has a smoother and more uniform fiber network compared with a common starch membrane, the membrane performance is improved, more reaction sites are provided for subsequent stearic acid modification, and the hydrophobicity is favorably improved; and the starch nanofiber membrane is stearic, so that a barrier is formed on the surface of the starch nanofiber membrane, water permeation is avoided, and the water blocking performance of the food packaging film is improved.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Hydrophobic starch-based nano biological latex as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108976343AImprove water resistanceHigh solid contentPaper coatingCoatingsPaper manufacturingPetroleum
The invention belongs to the technical field of papermaking light industry and particularly relates to a hydrophobic starch-based nano biological latex as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The hydrophobic starch-based nano biological latex is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-100 parts of starch or starch derivatives, 2-50 parts of hydrophobicannular acrylate monomers, 2-50 parts of carboxylic acrylate monomers, 0.1-10 parts of an emulsifying agent, 0.1-10 parts of an initiator, 0.5-10 parts of a plasticizer and 20-200 parts of water. According to the method, a hydrophobic monomer are introduced into the starch, so that the water resistance of the biological latex is improved. The hydrophobic monomer has an annular structure and multiple alkyls and can better isolate hydroxy in the starch. In addition, by virtue of adding the plasticizer, the obtained biological latex has the characteristics of high solid content and low viscosityand is beneficial to a coating process. Compared with a traditional bio-surfactant latex, the biological latex prepared by the method has excellent gluing effect and can partially or completely substitute for petroleum-base butadiene-styrene latex in the paper manufacturing industry field.
Owner:NANXIONG MATERIAL PRODION BASE OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI GUANGZHOU CHEM +4
Nanofiber-hydrophobic starch compound-based filtrate reducer for drilling fluid and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a nanofiber-hydrophobic starch compound-based filtrate reducer for a drilling fluid. The nanofiber-hydrophobic starch compound-based filtrate reducer comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 33-41% of cationic nano cellulose, 4.5-6.0% of a dispersing agent, 34-43% of hydrophobic modified starch, 11-13% of nano silicon dioxide and 6.5-7.1% of nano graphite.Sugarcane residues are dried, crushed, purified, dialyzed and cationized and are combined with hydrophobic modified starch on the basis to form a nanofiber-hydrophobic modified starch compound, and meanwhile, nano silicon dioxide is used as an auxiliary material, so that the temperature resistance and the nano pore filling capacity of the nanofiber-hydrophobic modified starch compound are enhanced, and the filtrate loss reduction effect of the nanofiber-hydrophobic modified starch compound is improved. The treating agent has strong filtration loss reduction and temperature resistance, is non-toxic, and has no adverse effect on the environment.
Owner:中石化石油工程技术服务有限公司 +2
Microencapsulate and process for the manufacture thereof
InactiveUS8637104B2Readily be dispersed into waterNot rapidly releaseMilk preparationWort preparationSolubilityMethacrylate
The present invention relates to a microencapsulate comprising microcapsules having a diameter of 0.1 μm to 25 μm, said microcapsules comprising: —a core particle having a diameter of 90 nm to 23 μm and containing at least 3% of the active component by weight of said core particle; and—a coating that fully envelops the core particle and containing at least 20 wt. % of a hydrophobic polymer selected from cellulosic ethers, cellulosic esters, zein, shellac, gluten, polylactide, hydrophobic starch derivatives, polyvinyl acetate polymers, polymers or copolymers derived from an acrylic acid ester and / or a methacrylic acid ester and combinations thereof; wherein the core particle contains a release trigger component and / or the coating contains a release trigger component, said release trigger component being selected from: —a water-swellable polymer having a water-uptake capacity at 37° C. and pH 7.0 of less than 20 wt. % and a water-uptake capacity at 37° C. and pH 2.0 of at least 50 wt. %; and—an edible salt having a water solubility at 37° C. and a pH of 7.0 of less than 1 mg / ml and a water solubility at 37° C. and a pH of 2.0 of at least 5 mg / ml; The microencapsulate of the present invention does not release the encapsulated active component when incorporated in water-containing foodstuffs, beverages, nutritional compositions or pharmaceutical compositions. Following ingestion, however, the active component is released rapidly.
Owner:FEYECON BV +1
Waterproof gypsum board core, preparation method thereof and waterproof gypsum board
The embodiment of the invention discloses a waterproof gypsum board core, a preparation method thereof and a waterproof gypsum board. The waterproof gypsum board core comprises calcined gypsum powder,starch, glass fibers, water and a processing aid, wherein the starch comprises hydrophobic starch and hydrophilic starch. The waterproof gypsum board comprises a waterproof gypsum board core and surface protection paper. By adopting a mode of compounding the hydrophobic starch and the hydrophilic starch, effective bonding among inorganic components in the gypsum board is guaranteed, and the surface protection paper attached to the surface can be effectively bonded, the density of the surface protection paper is not increased; meanwhile, the coverage of hydrophobic groups on the surface of thegypsum board can be enhanced, so that the water absorption performance of the gypsum board is effectively reduced, and the water resistance of the gypsum board is improved.
Owner:肇庆北新建材有限公司 +1
Preparation method of biological film mono non-staple-food composite modified hydrophobic starch
The invention discloses a preparation method of biological film mono non-staple-food composite modified hydrophobic starch. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cyclically drying starch with hot air; adding dry starch, triglyceride and succinate into a grinding machine together; grinding until the materials are uniformly mixed; dissolving the uniformly mixed starch into an ethanol solution; adjusting the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value and adding hexamethyldisilazane; heating and stirring to obtain a starch solution; carrying out starch molecule diffusion and transportation on the starch solution under the permeation effect of a biological film; and after finishing transportation, carrying out precipitation, filtering and vacuum drying treatment to obtain the composite modified hydrophobic starch. According to the preparation method of the biological film mono non-staple-food composite modified hydrophobic starch, disclosed by the invention, the used raw materials are simple and easy to obtain and the preparation method is simple; preparation conditions are moderate and the preparation method is safe and environmentally friendly and is suitable for industrialized production; the prepared composite modified hydrophobic starch has stable performances, a high hydrophobic capability, good dispersity and solubility and high reaction efficiency, and can be widely applied.
Owner:ANHUI RUIYAN NEW MATERIAL TECH RES INST
A kind of preparation method of hydrophobic starch calcium
The invention provides a preparation method for hydrophobic starch calcium; the preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) carrying out constant temperature stirring of native starch, modified starch or starch derivatives and water at a 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system to form a 30-40 wt.% starch emulsion; 2) in the 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system, adjusting the pH value of the emulsion to 7.5-8.5 with an alkaline solution; 3) in the 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system, adding anhydride; and constantly adding an alkaline solution or a calcium salt to maintain the pH value of the emulsion at 7.5-8.5, and continuing to carry out a reaction for a certain time; 4) in the 25 DEG C-40 DEG C reaction system, adding an acid to adjust the pH value to 6.0; and 5) adding water, washing and filtering, drying at the temperature of 50 DEG C, crushing, and sieving to obtain white hydrophobic starch calcium. The hydrophobic starch calcium product belongs to adsorbent modified starch, has the advantages of good fluidity, good hydrophobicity and good safety, is an excellent adsorbent, and can be widely applied in cold spray products, such as adsorbents, talcum powders, prickly-heat powders and other skin-care products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDICINE CO LTD XINCHANG PHAMACEUTICAL FACTORY
Single-phase preparation of hydrophobic starch product
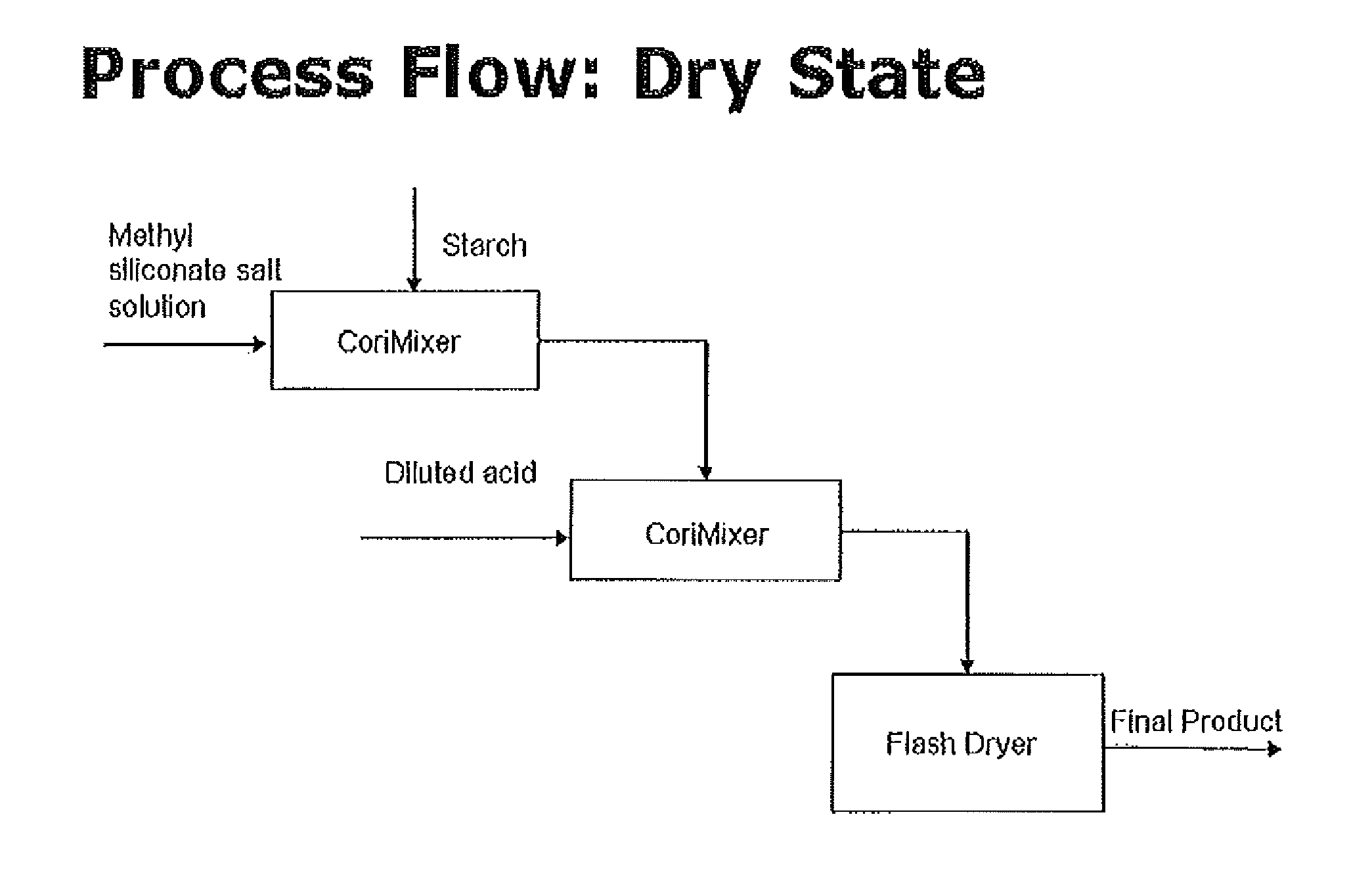
A single phase preparation of free flowing, hydrophobic starches which comprises a starch treated with a siliconate and an acid in a single phase process, is described herein.
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Preparation method of pollution-free potato suckercide based on novel hydrophobic material
InactiveCN113331193AReduce hydrophilicityPrevent facilitationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPesticide residueFood safety
The invention relates to the field of agricultural product medicament preparation, in particular to a preparation method of a pollution-free potato suckercide based on a novel hydrophobic material. The pollution-free potato suckercide comprises hydrophobic starch, hydrophobic inorganic nano powder and an ethanol solution, the two environment-friendly hydrophobic powder new materials are prepared from cheap materials, and the preparation method is very simple, so that the bud inhibition treatment cost of the suckercide for potatoes is not greatly different from that of the conventional common method, but the materials adopted by the suckercide prepared by the method are non-toxic environment-friendly materials, food safety risks do not exist, pesticide residues do not need to be detected, and the suckercide has wide application prospects.
Owner:金华市铨沥科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com