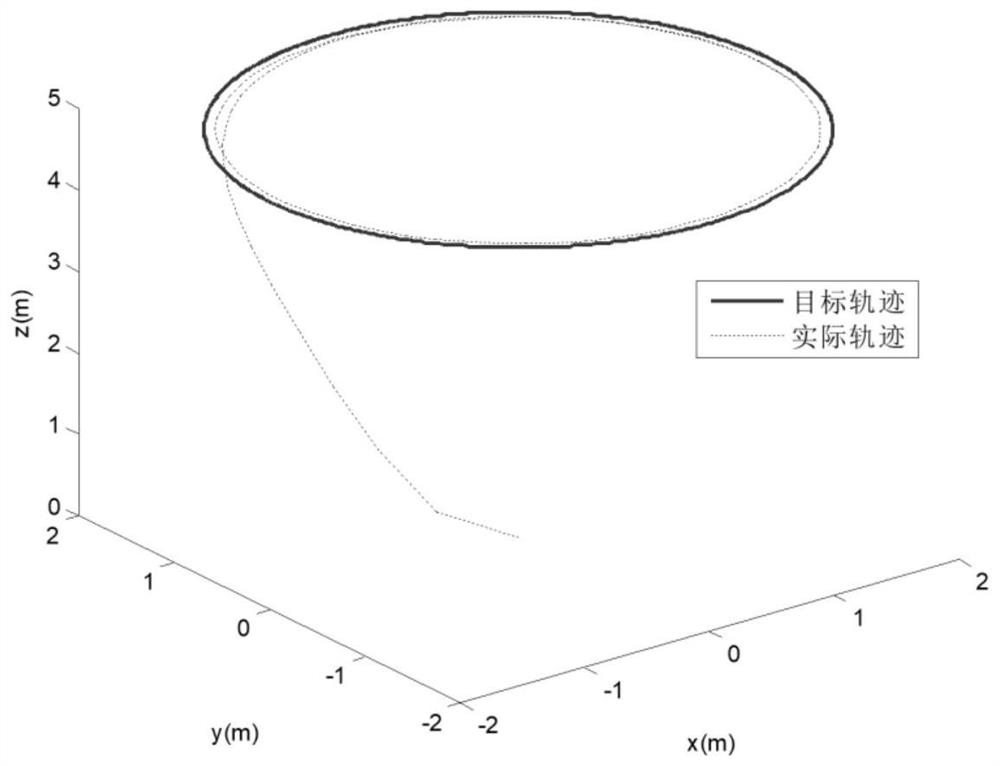
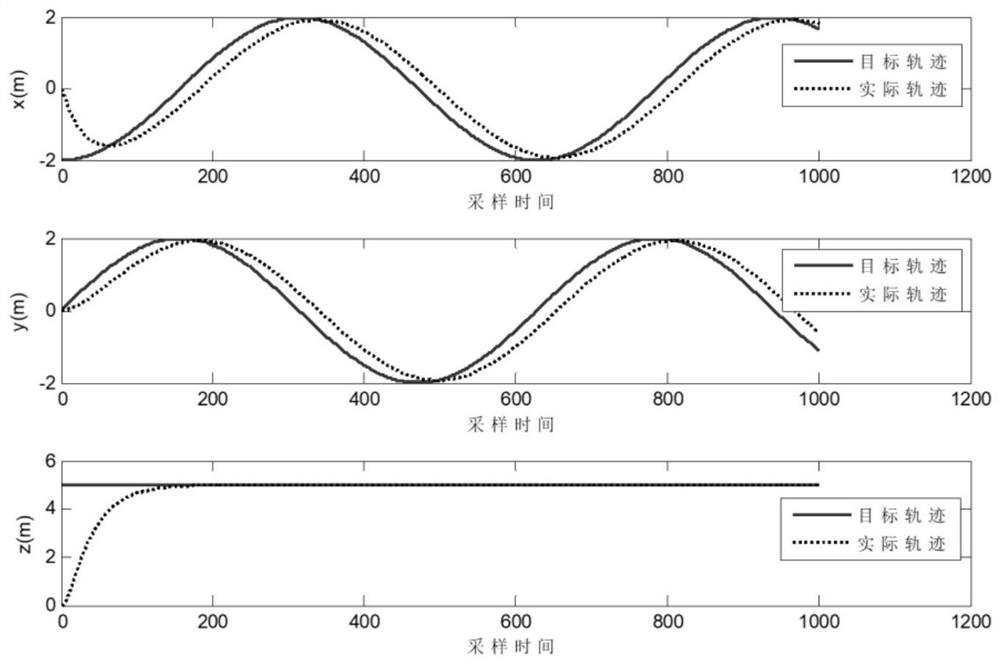
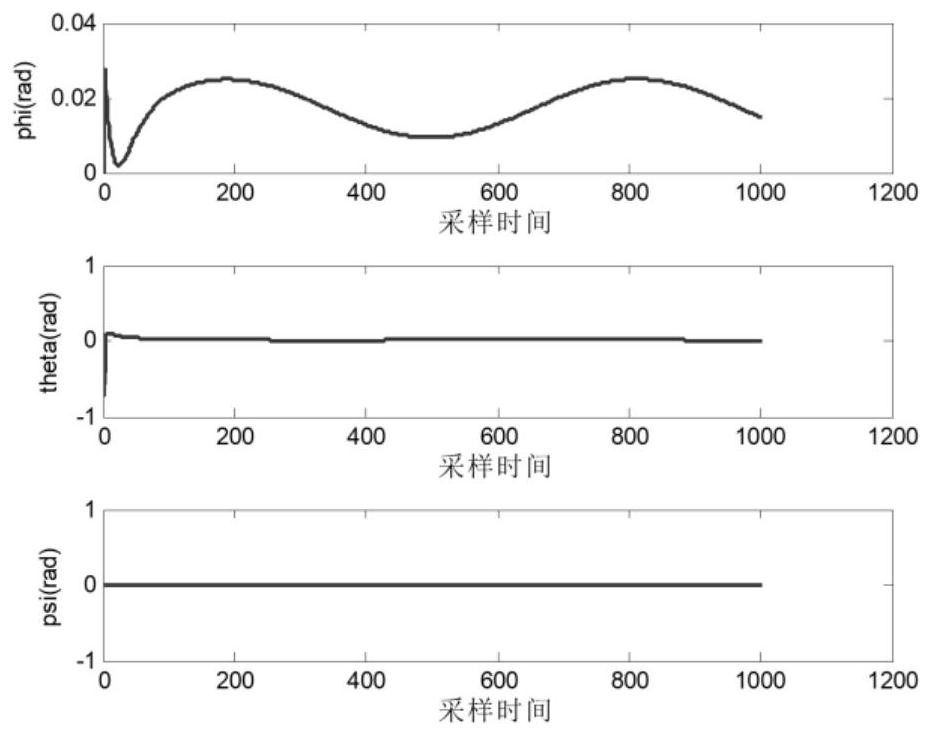
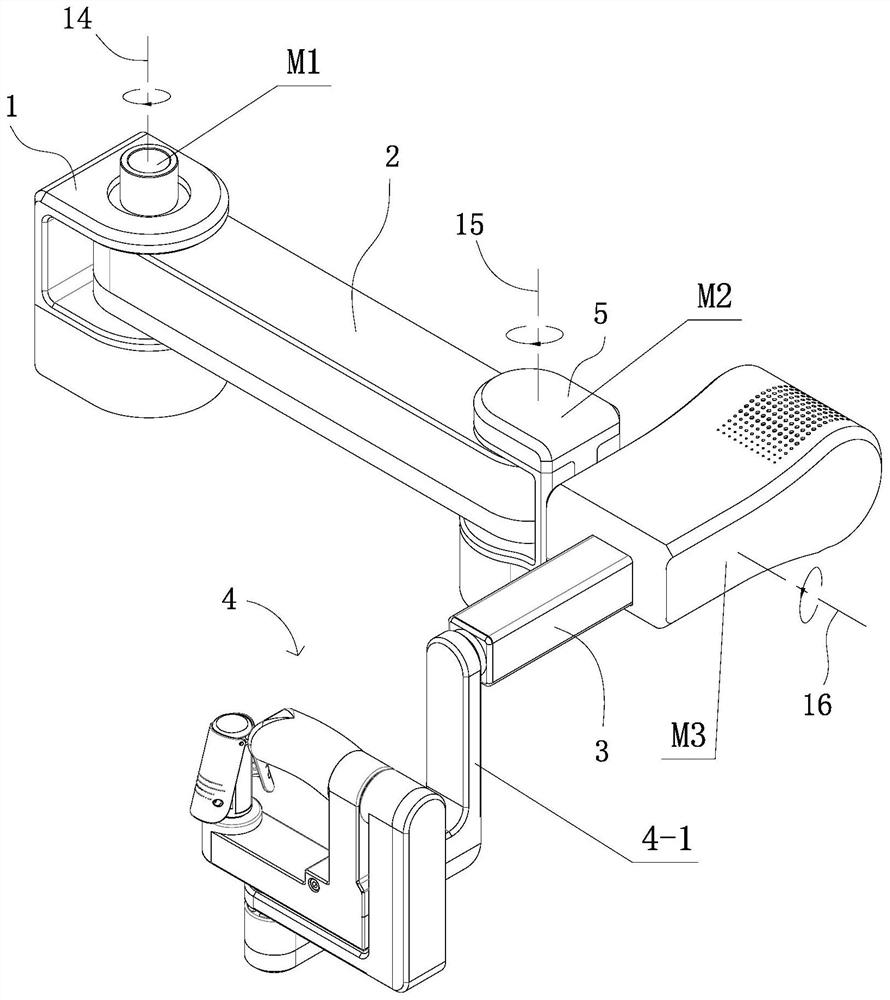
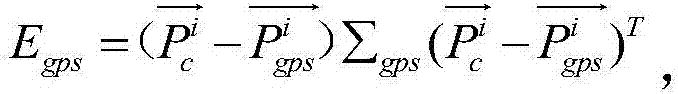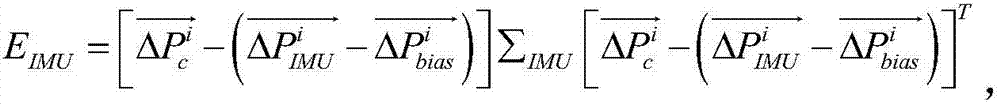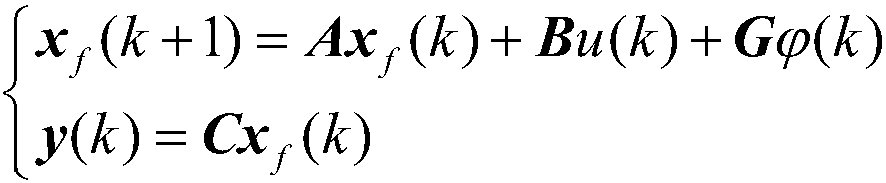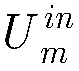Patents
Literature
110 results about "Kinematic modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
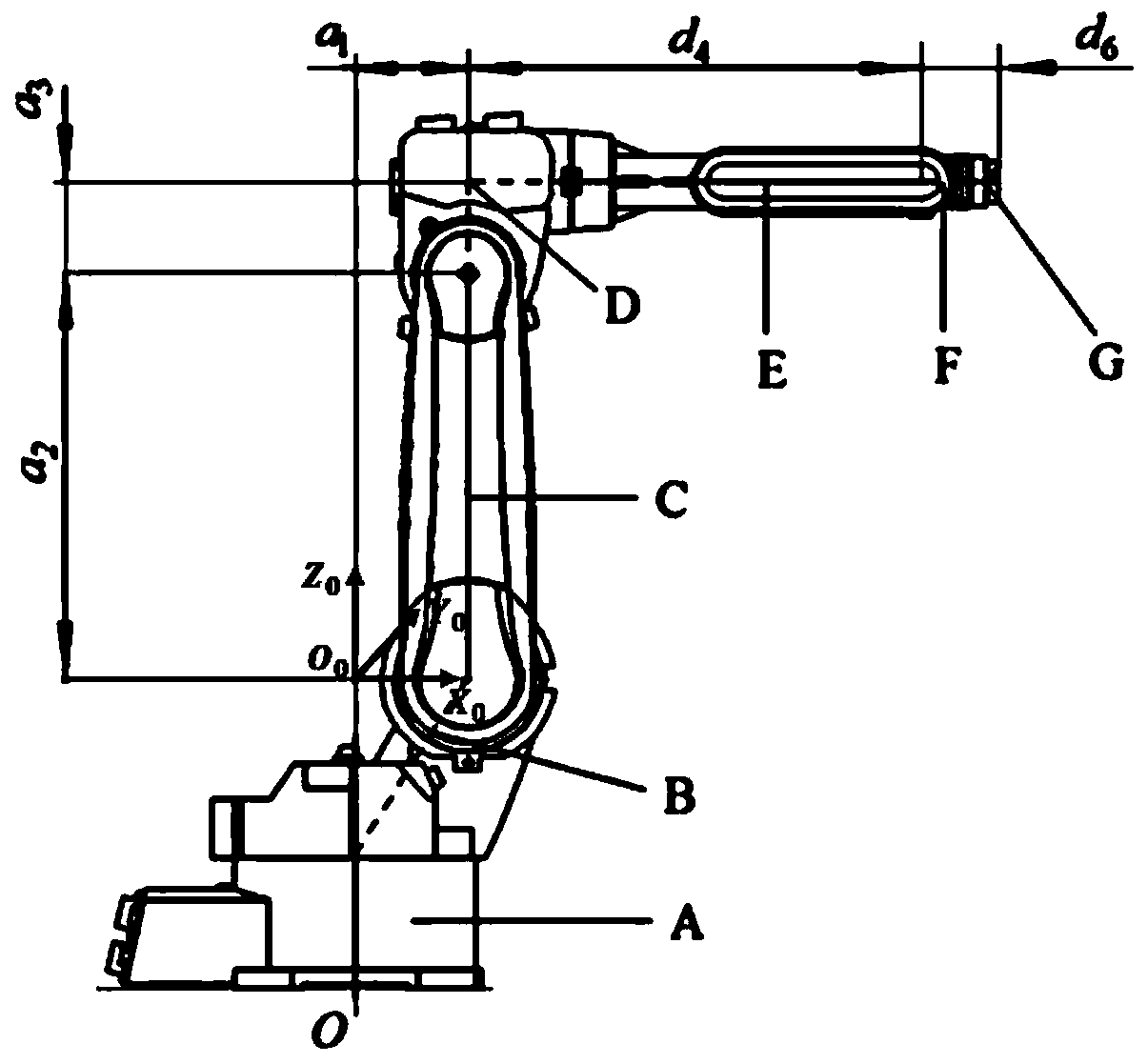
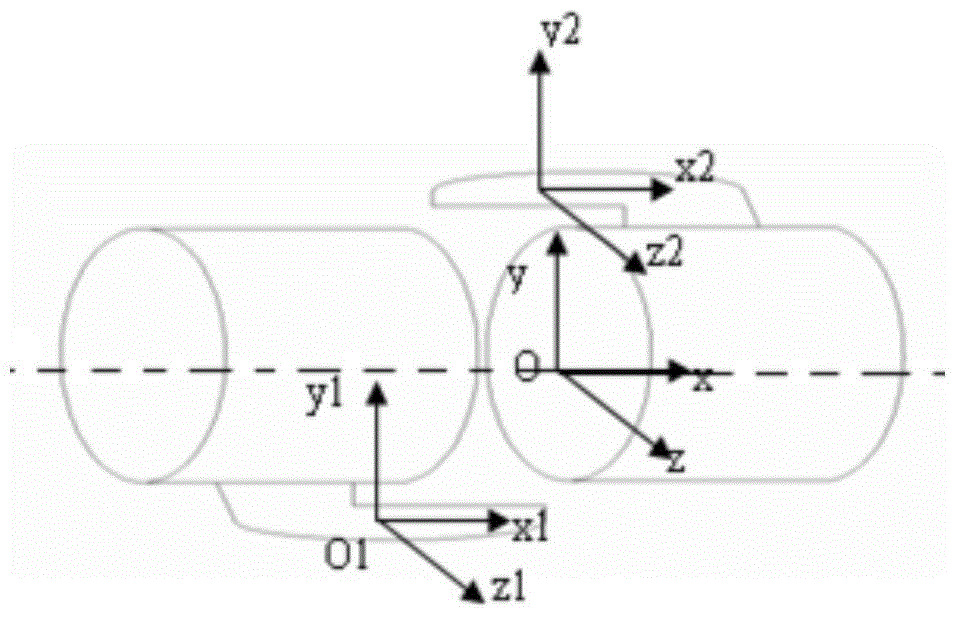
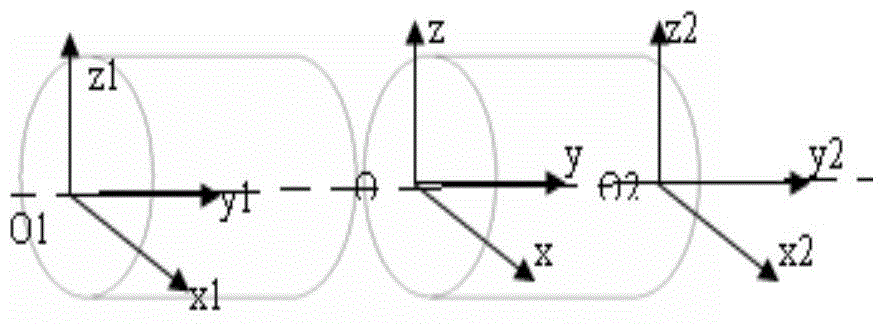
Kinematic Models. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, physical models were widely used by mathematics educators to depict a wide range of mathematical ideas in three dimensions. Most models were constructed in Europe, in particular Germany, for use in school and college instruction.
Cooperative navigation and localization system and method
ActiveCN107246868AReasonable designHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingLocalization systemGlobal optimization
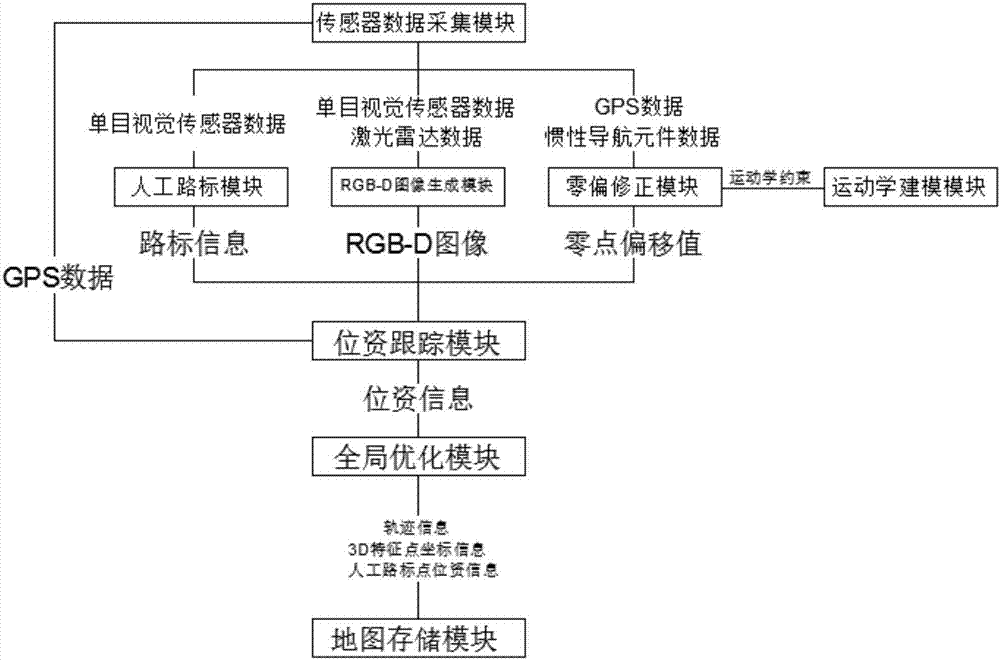
The invention discloses a cooperative navigation and localization system and method. The cooperative navigation and localization system comprises a sensor data collecting module, an RGB-D image generation module, a kinematic modeling module, a zero-deflection correction module, a position tracking module, a global optimization module and a map storage module. The cooperative navigation and localization system and method have the advantages that the system is provided with four sensors, namely the GPS, the monocular vision sensor, the inertial navigation element and the laser radar, the advantages of the sensors are combined, the precision and the application range of the sensors are improved, the cooperative navigation and localization system can normally work in various complex environments, and the cooperative navigation and localization system and method have the advantages of being quick in localization speed, high in localization precision, high in robustness, wide in application range and the like.
Owner:上海舵敏智能科技有限公司
Robot cartesian space trajectory planning method
ActiveCN104965517AGuaranteed SolvableEasy to operateAttitude controlAdaptive controlGeometric propertyKinematics equations
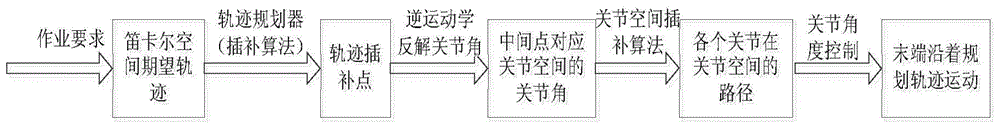
The invention discloses a robot cartesian space trajectory planning method. The method includes establishing a connecting rod coordinate system and obtaining a forward kinematic equation through a kinetic modeling analysis method; solving the rotating angles of a master control joint and a middle joint according to the vector geometric property and trajectory planning requirement of the robot; seeking a relation equation including introduced variables and solving the rotating angle of the corresponding joint by means of the kinetic modeling analysis method and the solved joint rotating angle; determining whether the pose position can be reached through a vector geometric method when the trajectory planning is carried out in a task space with obstacles; and planning the continuous time variant attitudes of coupled position information to complete the planning tasks. According to the method, extraneous roots can be prevented, efficient solutions can be screened and matched, strange paths can be effectively avoided, and meanwhile, the defects of complex end trajectory planned by the joint space can be prevented and optimized.
Owner:张耀伦
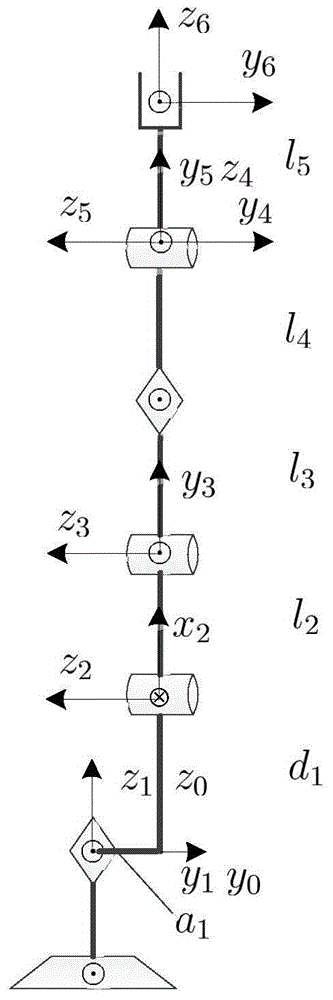
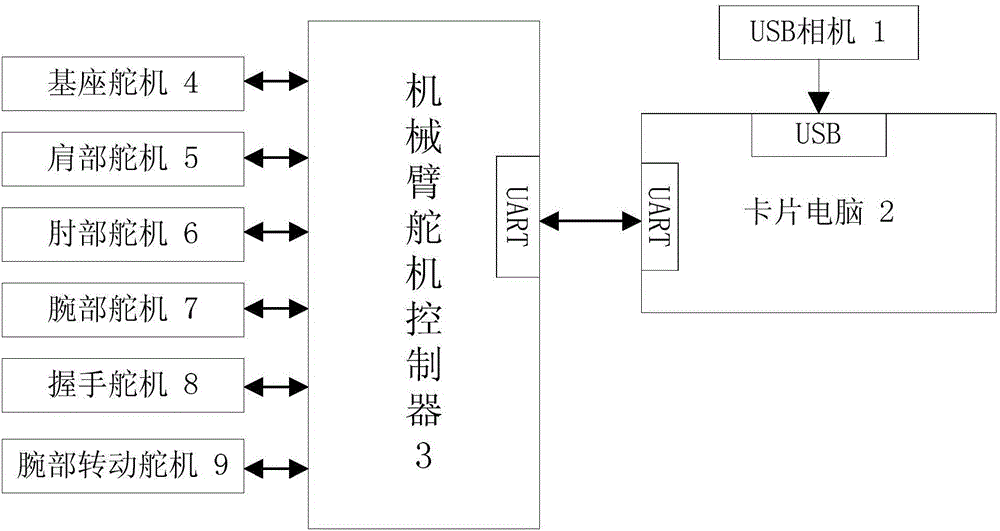
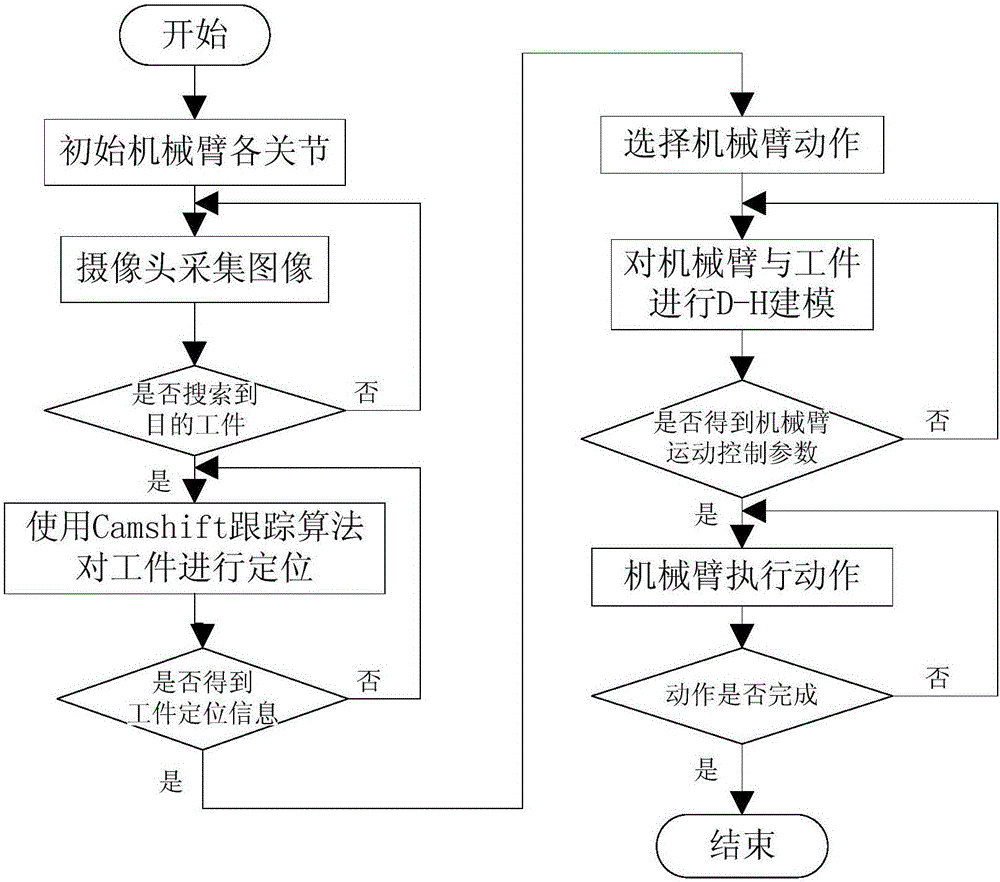
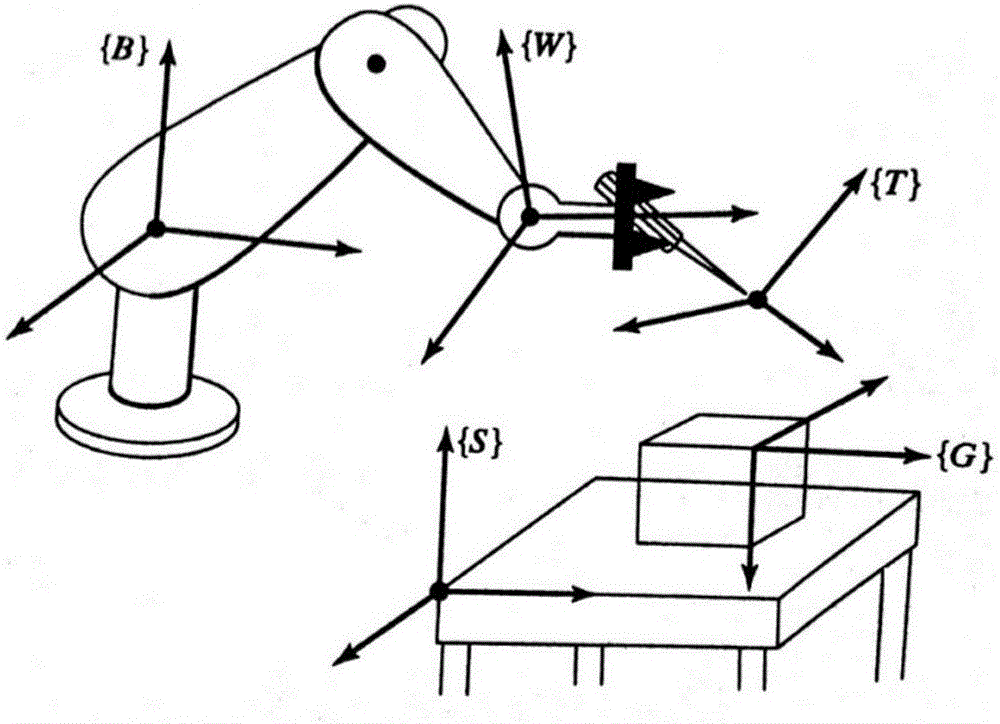
Visual mechanical arm control device and method based on Camshift visual tracking and D-H modeling algorithms
The invention discloses a visual mechanical arm control device based on Camshift visual tracking and D-H modeling algorithms. Image information acquired by a USB camera on a mechanical arm is analyzed by using a Camshift visual tracking algorithm to obtain precise positioning information of a workpiece to be grabbed and assembled; accurate positioning of such multiple targets as a visual mechanical arm, a target workpiece and a worktable is realized by using a robot forward kinematics D-H modeling algorithm; then, a multi-coordiate-system descriptive model with each steering engine joint as a coordinate system origin is built for the visual mechanical arm; and a closed analytic solution is derived through inverse dynamic calculation for different actions of the mechanical arm to determine unique control parameter of multiple steering engine joint movements of the mechanical arm, so that the precise control of the visual mechanical arm is realized, and such multiple actions as workpiece grabbing, machining, assembly and transportation by the mechanical arm are finished.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
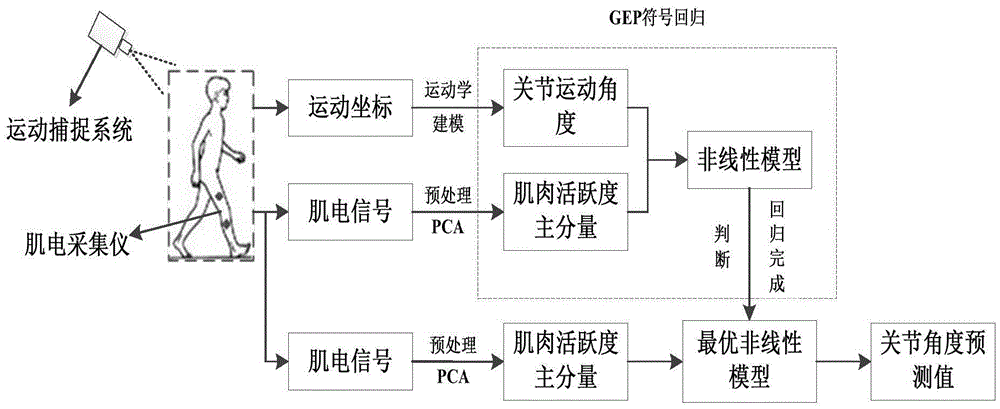
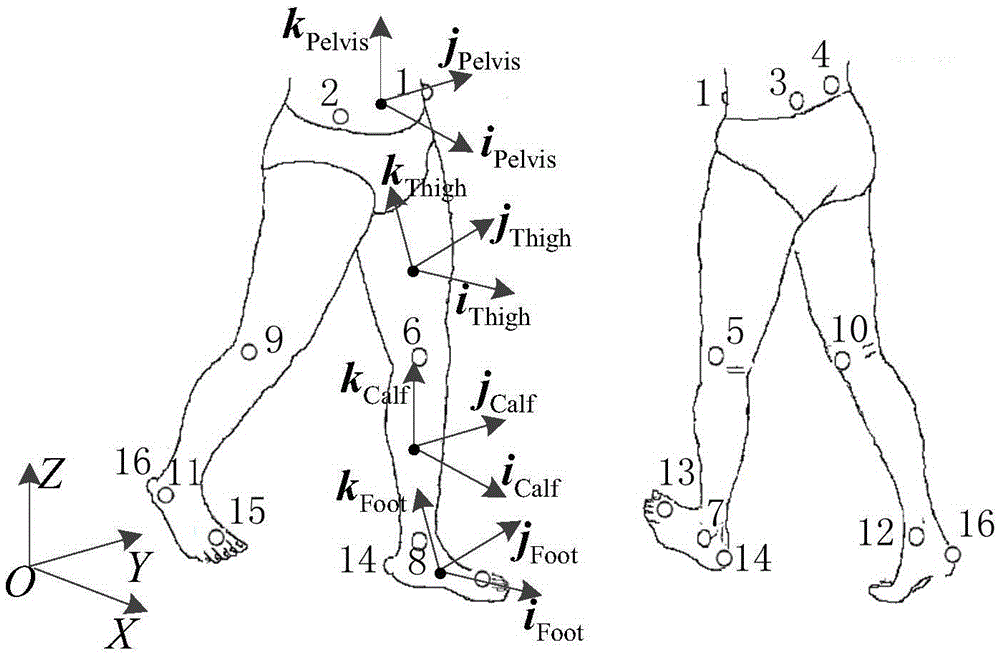
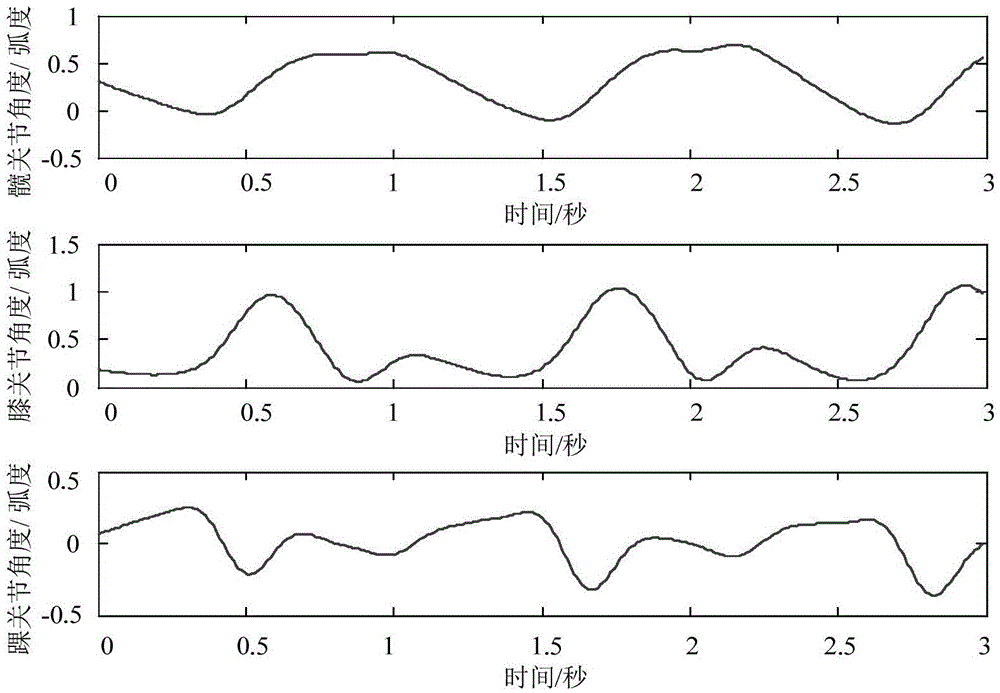
Angle and myoelectricity continuous decoding method for human body lower limb walking joint
ActiveCN105615890AControl the purpose of active trainingAccurate implementation of forecast angleDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVertical planePrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses an angle and myoelectricity continuous decoding method for a human body lower limb walking joint. The movement track of a lower limb body surface optical marking point in the human body walking process is recorded through an optical movement capture system, and the movement angle of the lower limb joint is precisely calculated through the human body lower limb kinematical modeling; surface electromyogram signals of eight main muscles related to lower limb movement in the human body walking process are synchronously acquired, the activity intensity information of the signals is extracted through filtering and rectifying preprocessing, and the optical independent feature vector set describing the intensity of the surface electromyogram signals is extracted through the principle component analysis method; a nonlinear regression model from surface electromyogram signal features (independent variables) to the vertical plane joint movement angles (dependent variables) is established through the gene expression programming symbol regression analysis method, and the lower limb movement track is predicted. The method is mainly applied to design and manufacture of medical rehabilitation machines.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
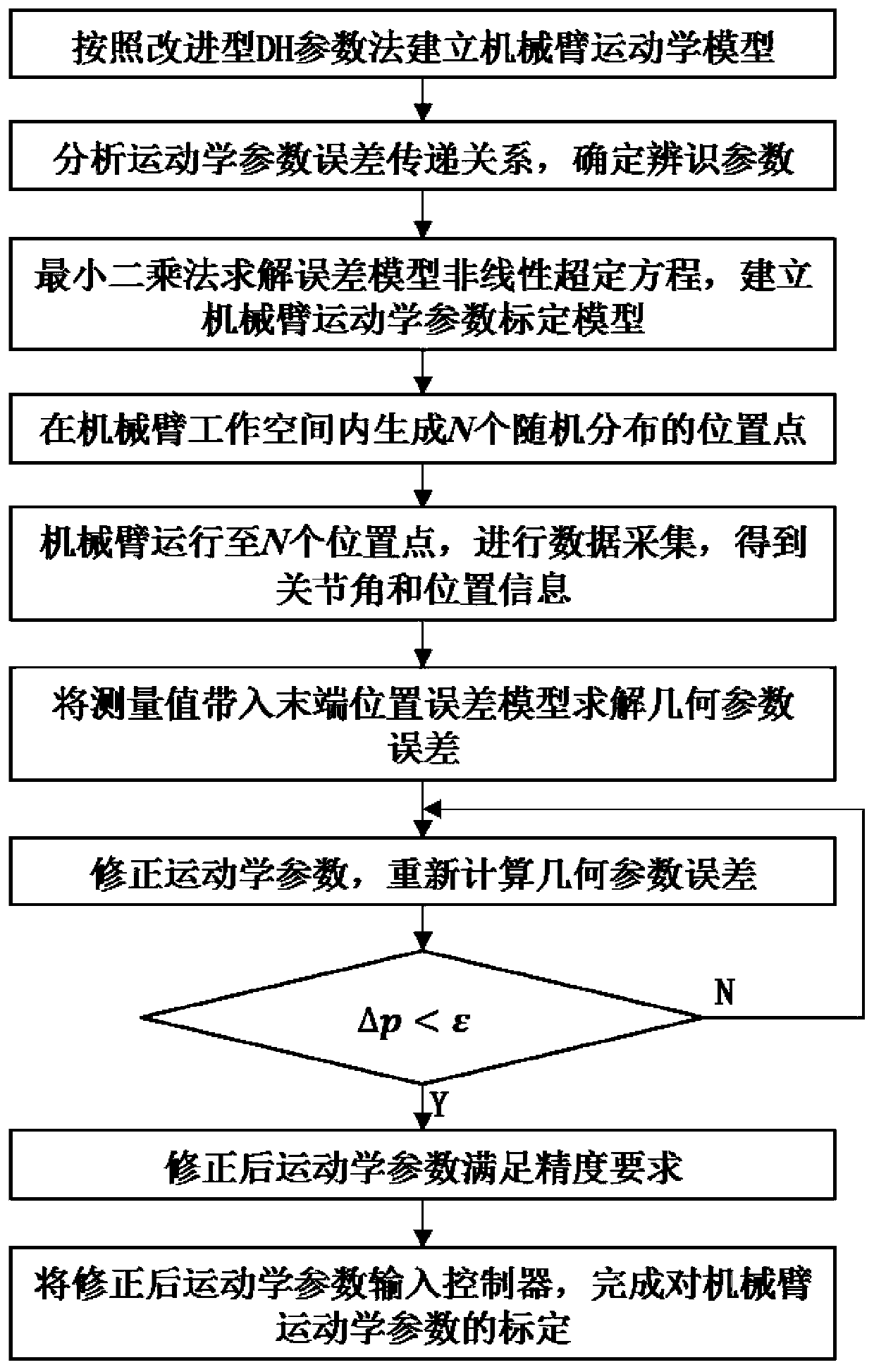
Mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method based on measuring of laser tracker
InactiveCN110281241ARealize offline calibrationImprove robustnessProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
The invention discloses a mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method based on measuring of a laser tracker, and belongs to the field of industrial mechanical arm kinematics, and relates to the mechanical arm kinematics parameter calibration method based on measuring of the laser tracker. The method is based on the mechanical arm joint construction. An improved DH parameter method is adopted for building a mechanical arm kinematics model, a kinematics modeling result is used for building a mechanical arm kinematics parameter error calibration model, in consideration with the mechanical arm three-dimensional space work range, the laser tracker is adopted for measuring N absolute position coordinates of the tail end of the mechanical arm, on the basis of the kinematics parameter error calibration model, through repeated iteration, the mechanical arm kinematics parameter error is solved, a corrected kinematics parameter is input into a mechanical arm controller, and offline calibration of the mechanical arm is achieved; the mechanical arm tail end position measuring method is high in robustness, high in speed, and high in process automation degree, the adopted error solving method is high in speed, high in precision and simple in process, and the high-precision rapid calibration of joint type mechanical arm kinematics parameters can be achieved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
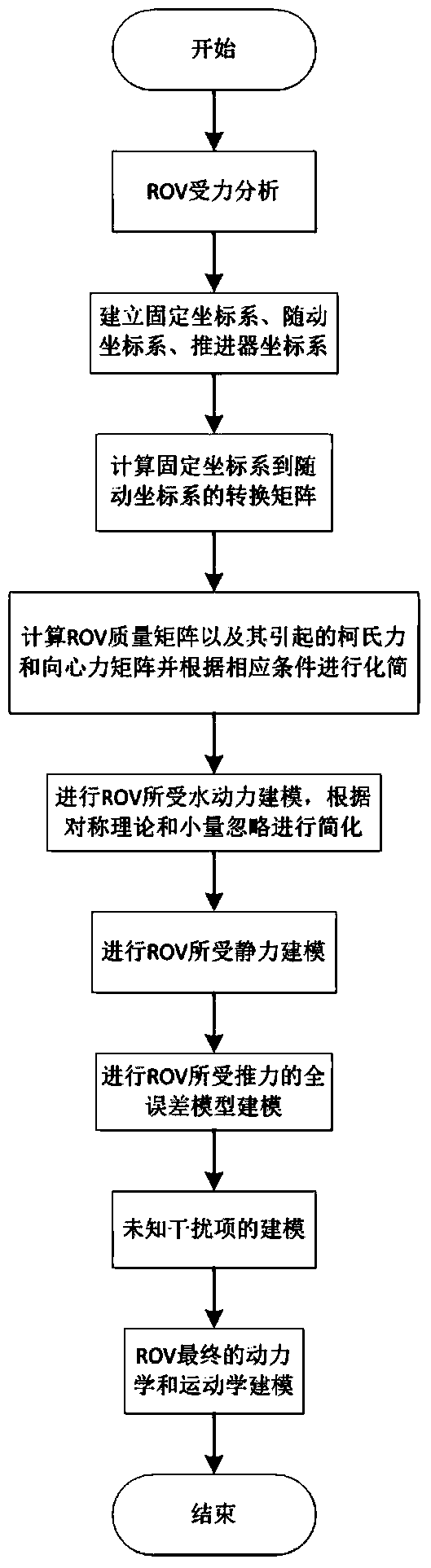
Dynamics and kinematics estimation method for deep sea operation type ROV
ActiveCN103942383AReduce difficultyAccurate calculationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of deep sea operation type ROVs, in particular to a dynamics and kinematics estimation method for a deep sea operation type ROV. The method comprises the steps of establishing a fixed coordinate system, a body coordinate system and a propeller coordinate system, and estimating a matrix for coordinate transform in six freedom degrees; estimating the mass matrix of the operation type ROV and a caused coriolis force and centripetal force matrix; estimating water power borne by the operation type ROV; estimating the static force borne by the operation type ROV; estimating the thrust of the operation type ROV; estimating unknown disturbance terms; determining the ultimate dynamic and kinematic model of the operation type ROV. According to the dynamics and kinematics estimation method for the deep sea operation type ROV, dynamic and kinematic modeling of the deep sea operation type ROV is carried out on the basis of dynamics, fluid mechanics, submarine maneuverability and other theories, aiming at complex mathematic models of underwater vehicles, the symmetry theory and the method of neglecting small magnitudes are utilized to simplify the mathematic models of the deep sea operation type ROV, and the established models can be used for estimating the stress situations of the ROV more accurately.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Error model predictive control method based on kinematics modeling of omnidirectional mobile robots
ActiveCN109885052ASolve the speed constraint problemFull rangePosition/course control in two dimensionsPosition/direction controlPredictive controllerOmnidirectional mobile robot
The invention discloses an error model predictive control method based on kinematics modeling of omnidirectional mobile robots. The error model predictive control method comprises the following stepsthat S11, a velocity constraint kinematics model is established between FM-OMR four Mecanum wheels; S12, a tracking error kinematics model of a FM-OMR is established; S13, aiming at the trajectory tracking problem of the FM-OMR and the tracking error kinematics model, an error model predictive controller combined with a velocity constraint equation is designed; and S14, according to the error model predictive controller, effective trajectory tracking parameters between the omnidirectional mobile robots are controlled so as to enable tracking errors between the omnidirectional mobile robots toremain unchanged. According to the error model predictive control method based on the kinematics modeling of the omnidirectional mobile robots, the error model predictive control method based on the trajectory tracking error kinematics modeling is provided aiming at the omnidirectional mobile robots with the four Mecanum wheels, the non-holonomic constraint problem of the effective trajectory tracking control is solved, and the accuracy and the validity are realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot motion analysis modeling and rapid solving method
ActiveCN110815180AThe principle of the method is simpleThe principle is simpleProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsControl engineeringMotor control
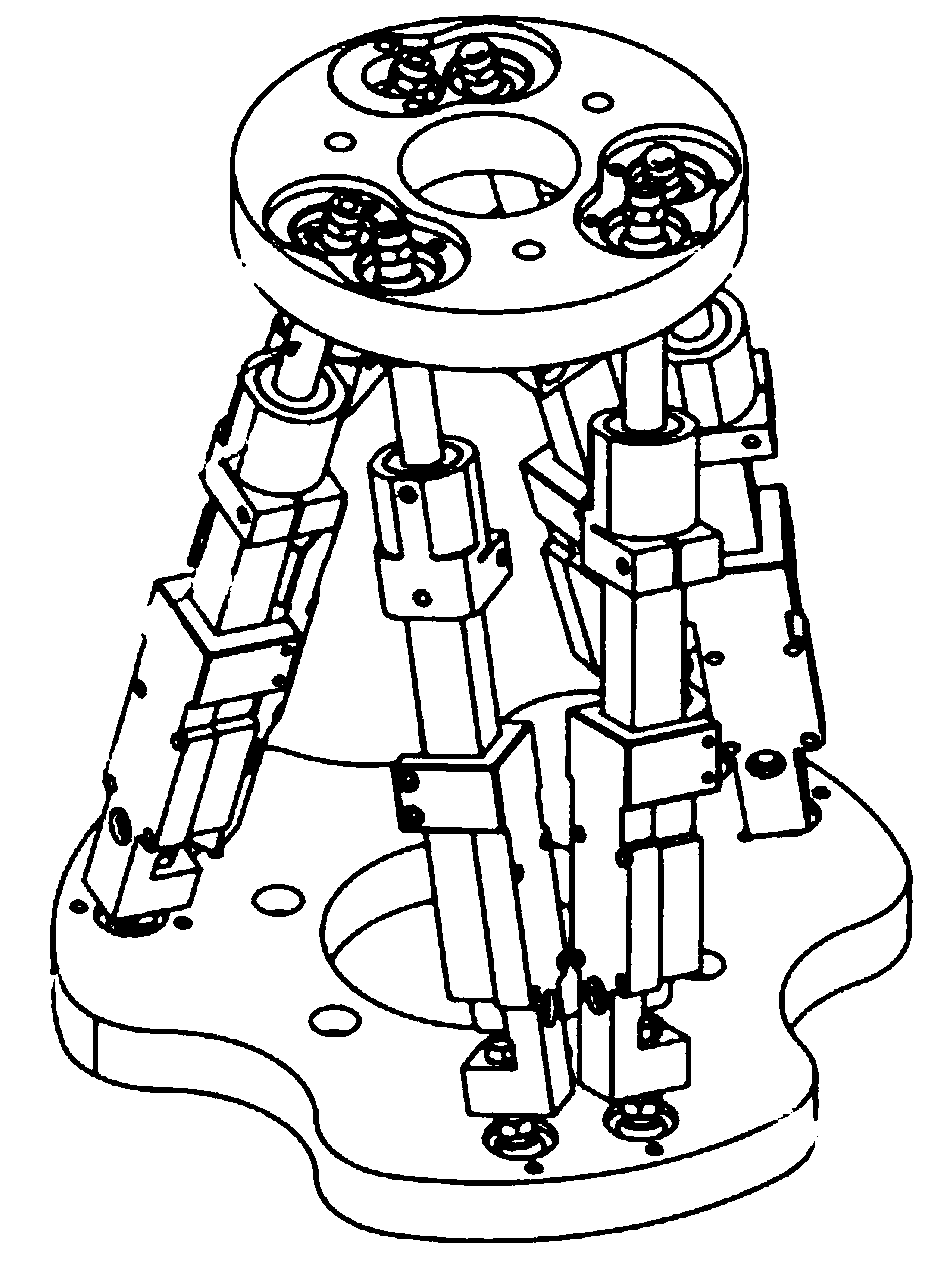
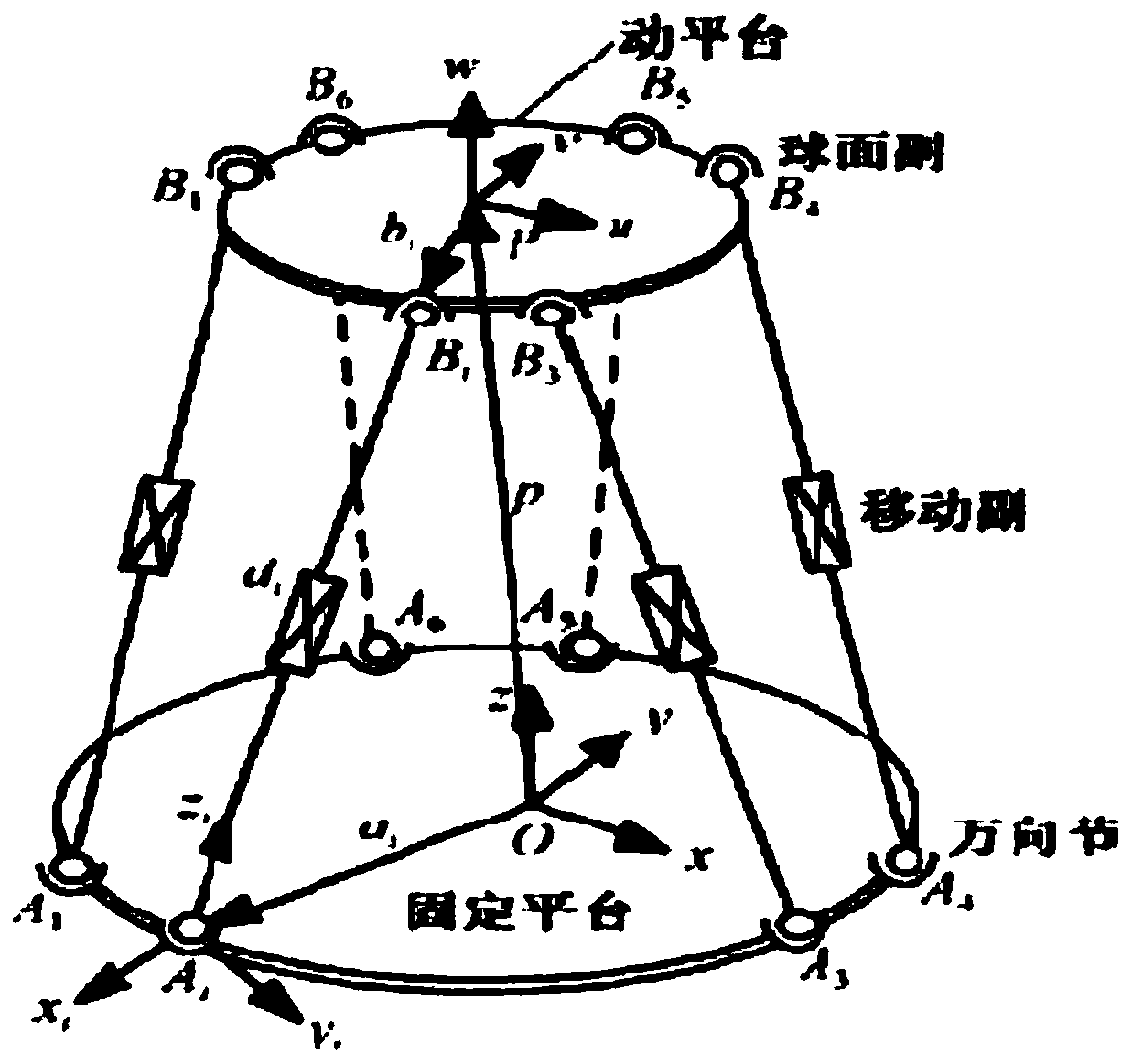
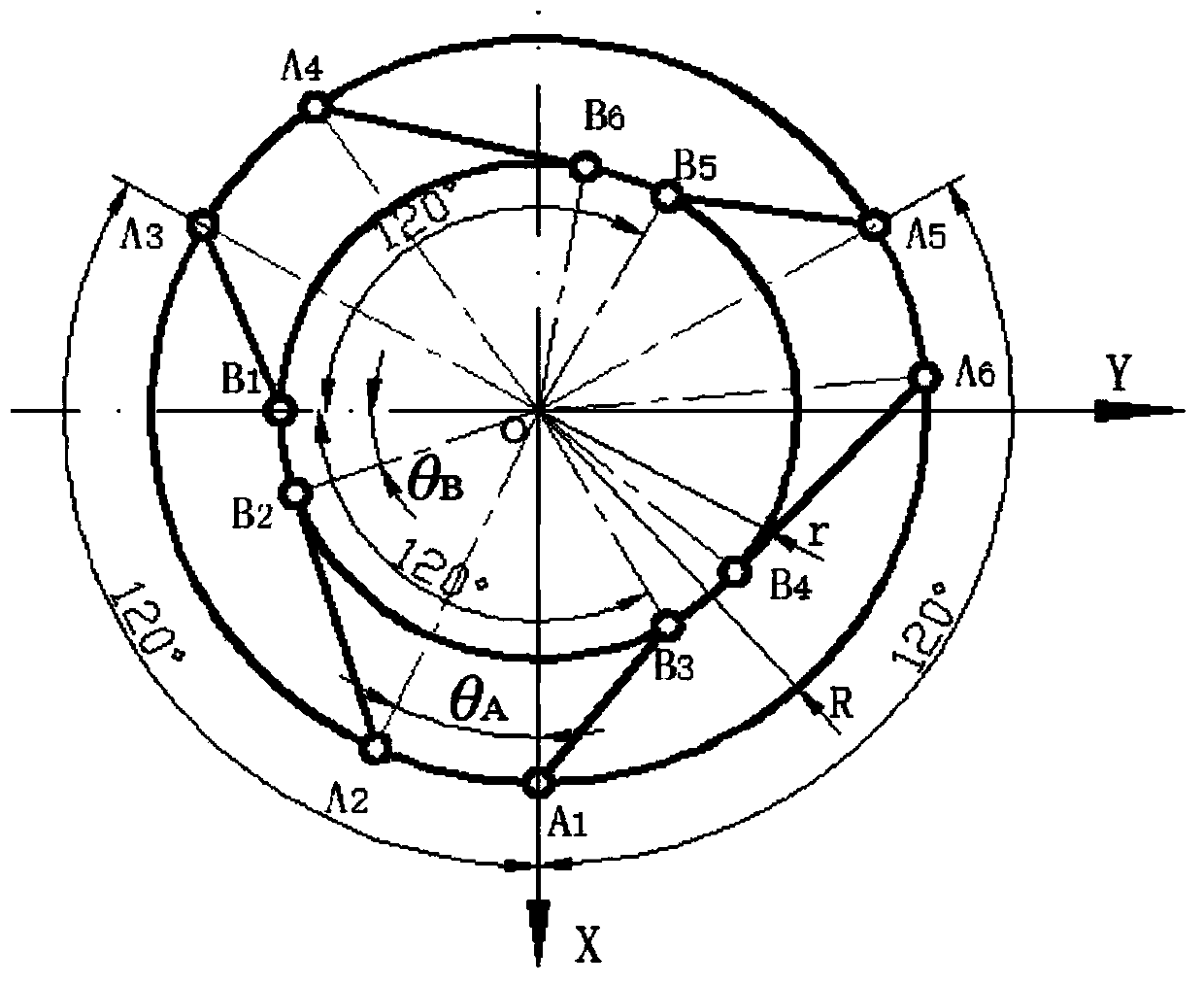
The invention discloses a six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot motion analysis modeling and rapid solving method. A six-degree-of-freedom mechanical platform is composed of six supporting rods with linear actuators, an upper platform, a lower platform and steering devices, wherein six steering devices are correspondingly arranged on the upper part and the lower part, the lower platform is fixed onan infrastructural facility, and the upper platform is controlled to move in the space by six degrees of freedom through telescopic motion of the six supporting rods. The mechanical platform has a parallel structure, namely six drivers jointly act on one platform, and the six-degree-of-freedom mechanical platform specifically comprises the following steps of kinematic modeling and solving and motion controlling, wherein the kinematic modeling and solving comprise the following steps of moving coordinate transformation, rotating coordinate transformation and composite posture; and the motion controlling comprises the following steps of establishing a mechanical system model, numerical simulation results are calculated according to the established model, and finally better control of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot is achieved. The six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot motion analysis modeling and rapid solving method is used for helping the kinematic modeling of the six-degree-of-freedom parallel robot to be solved quickly and controlled accurately.
Owner:WUHAN HUAZHONG AERONAUTICS M&C TECH CO LTD
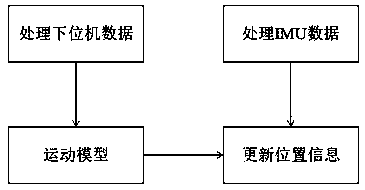
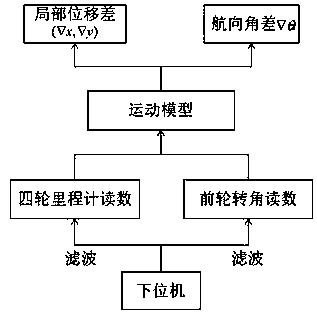
Four-wheel independent drive based IMU (inertial measurement unit) combined mileage calculation method
InactiveCN108036797ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDistance measurementTurn angleGyroscope
The invention relates to the technical field of positioning of four-wheel independent drive based unmanned vehicles, in particular to a four-wheel independent drive based IMU (inertial measurement unit) combined mileage calculation method. In order to realize positioning and navigation of the unmanned vehicles under the conditions of limited time and resources, four hub motor encoders are adoptedfor transmitting mileage data and tire turning angle data to an upper computer, IMU gyroscope data are read, then an eulerian angle is calculated, and local positioning information of the unmanned vehicles is obtained after calculation through establishing of a vehicle kinematic model. In traditional mileage calculation, the local positioning information is obtained according to accelerometer dataintegrals obtained by adoption of only one IMU, but over time, low precision is caused due to error accumulation. Therefore, by kinematic modeling of the unmanned vehicles and combination of IMU course angles for positioning and navigation, high-precision positioning information is obtained in short time.
Owner:深圳市隐湖科技有限公司
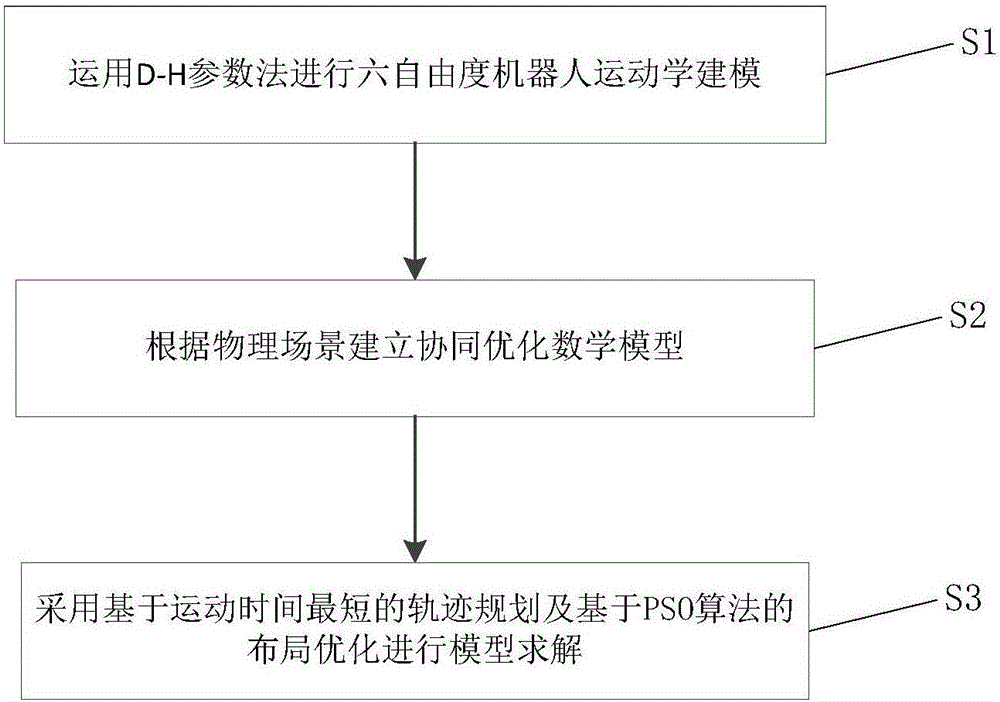
Station layout and motion time cooperative optimization method for six-freedom-degree robot
ActiveCN105676642AImprove work efficiencyEfficient solutionAdaptive controlMathematical modelSimulation
The invention relates to a station layout and motion time cooperative optimization method for a six-freedom-degree robot. The method comprises: S1, kinematical modeling is carried out on a six-freedom-degree robot; S2, according to physical scenes of the six-freedom-degree robot, a starting device, and a target device, a cooperative optimization mathematics model of station layout and motion time is established; and S3, in a space right-angle coordinate system, time of movement of an end effector of the six-freedom-degree robot from the starting device to the target device is used as a fitness value of a PSO algorithm and station layout of the starting device and the target device is used as a particle of the PSO algorithm to carry out processing based on the PSO algorithm so as to obtain an optimal solution of a cooperative optimization mathematics model and station layout corresponding to the optimal solution. Compared with the prior art, the provided method enables station optimization of the six-freedom-degree robot to be realized and the working efficiency of the robot to be improved substantially.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Engine oil seal assembly and detection automatic complete equipment based on visual technology
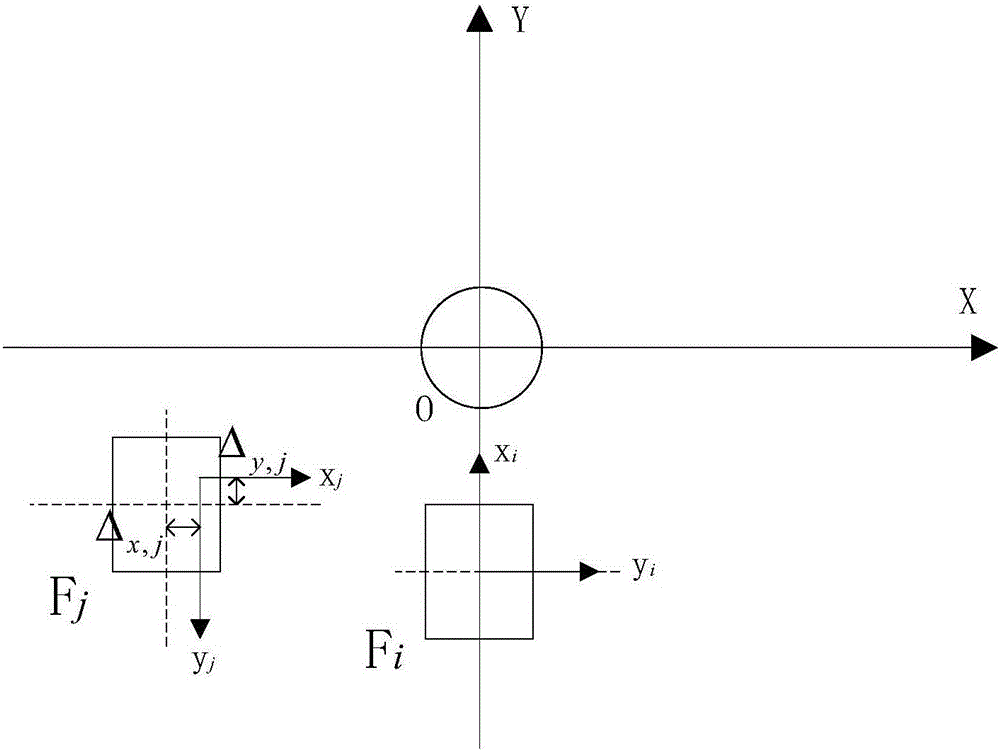
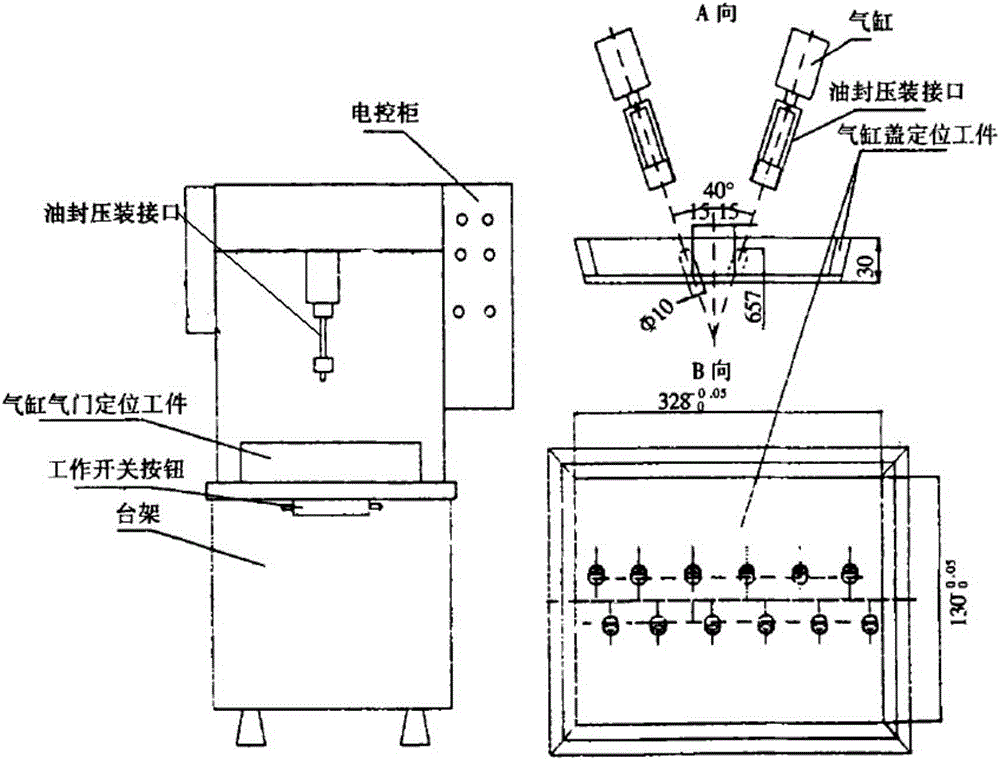
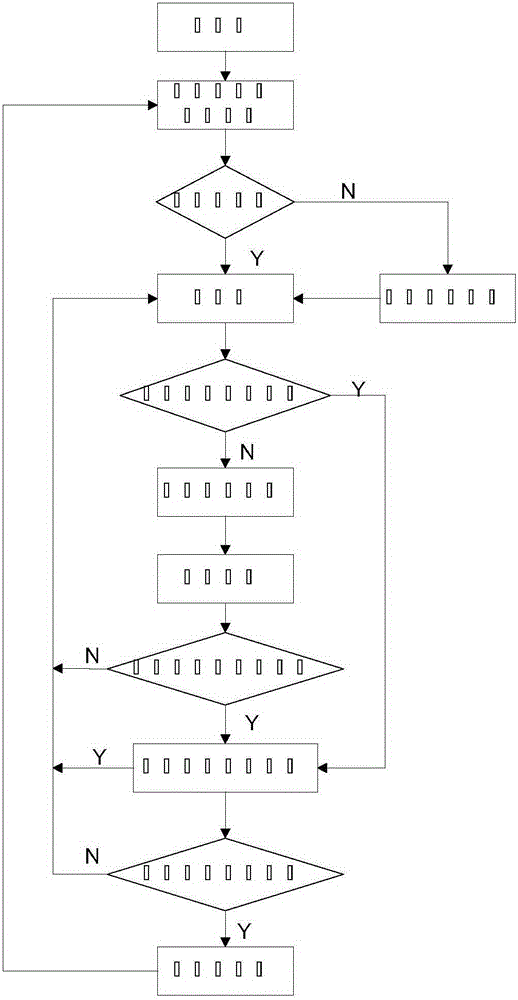
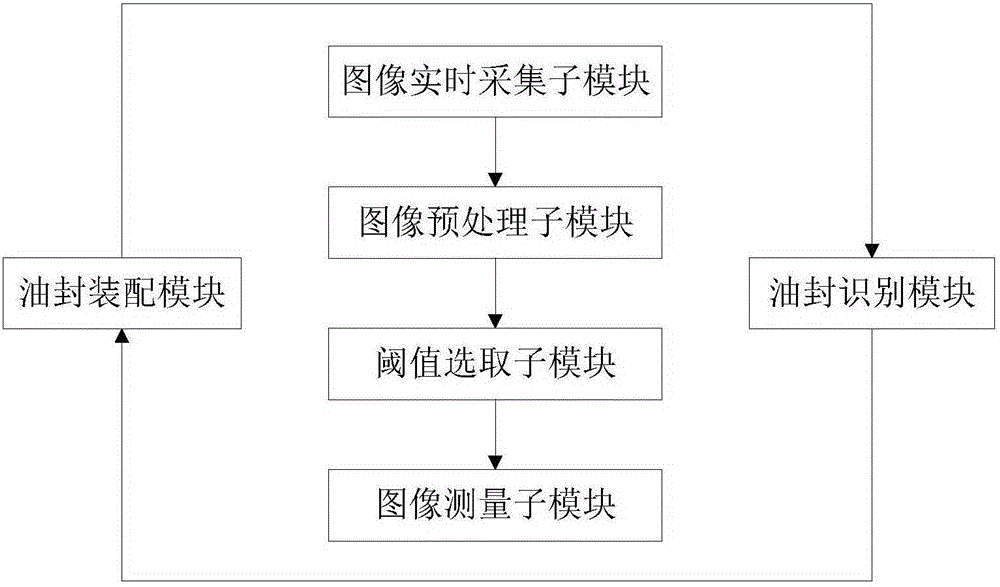
InactiveCN105171375APrecise positioningImprove versatilityUsing optical meansMetal working apparatusVisual technologyDynamic models
The invention relates to engine oil seal assembly and detection automatic complete equipment based on a visual technology. A multi-degree-of-freedom tandem type manipulator is adopted; an intelligent detection system based on machine vision is built, automatic detection on the positions of a cylinder cover and an oil seal is achieved before assembly, and automatic detection on assembly quality of the oil seal is also achieved after assembly; a compliant control system model is established based on a kinematic and dynamic model of a robot, accurate movement track planning based on vision information feedback is achieved, the key technologies like smart tooling design, machine vision, an intelligent control algorithm, kinematical modeling and accurate route planning are broken through, and practicability and commercialization of the engine oil seal assembly and detection automatic complete equipment based on the machine vision are achieved.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
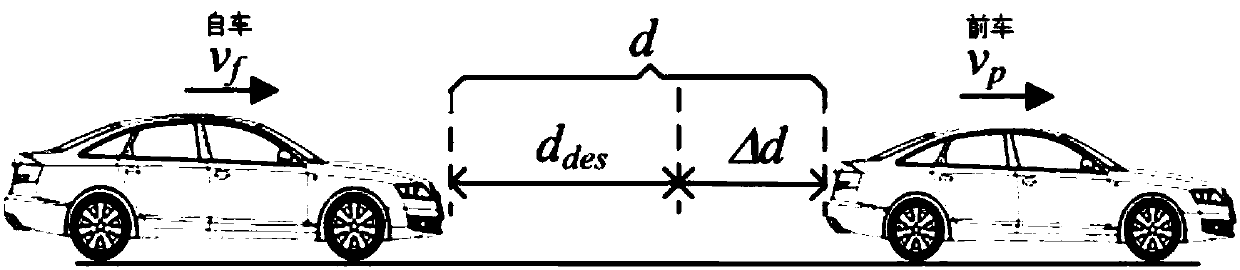
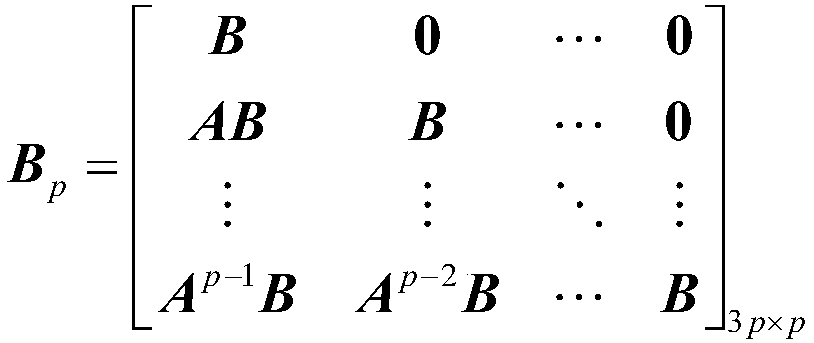
ACC longitudinal kinematical modeling method based on relative motion relation
ActiveCN107832517AImprove accuracyImprove forecast accuracyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDelta-vState parameter
The invention discloses an ACC longitudinal kinematical modeling method based on a relative motion relation. When ACC longitudinal kinematical modeling is carried out, self vehicle state parameters and front vehicle state parameters are comprehensively considered, the state quantity xf(k) is set to be [delta d(k), delta v(k), af(k)]T, a system disturbance quantity ap (k) and an expected vehicle distance ddes are introduced, and by means of a fixed time interval strategy, a variable time interval strategy or a quadratic regression model fitting driver following behaviors, the relative motion relation between a self vehicle and a front vehicle and influences of environment parameters are brought into the ACC longitudinal kinematical modeling process. The accuracy of model calculation is improved, prediction errors are reduced, and then the prediction precision and the anti-interference capacity of a following vehicle prediction model are improved.
Owner:合肥哈工焕一新能源技术有限公司
Turbine blade air film cooling hole self-adaptive compensation machining method
ActiveCN111708326AImprove machining accuracyImprove robustnessProgramme controlComputer controlPoint cloudTurbine blade
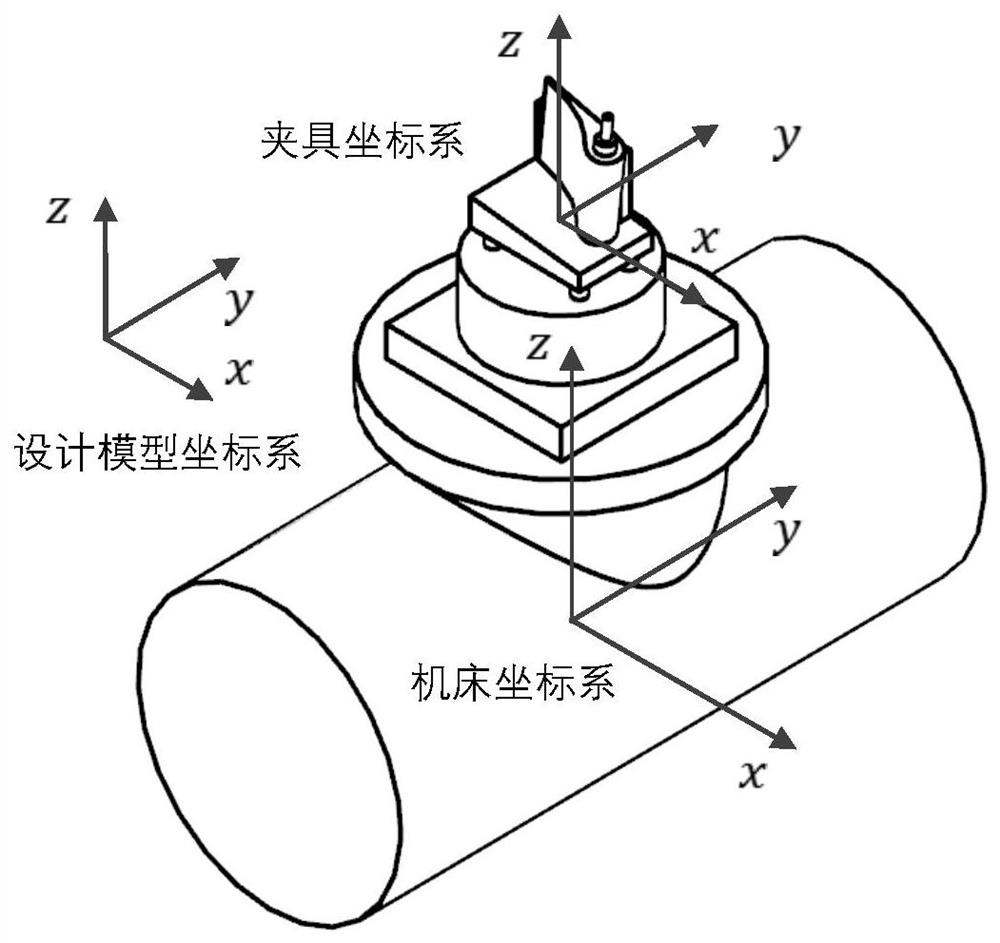
The invention discloses a turbine blade air film cooling hole self-adaptive compensation machining method. The method comprises the following steps: installing a turbine blade on a follow fixture; performing online measurement on the curved surface profile of the turbine blade to obtain an actual measurement point cloud; extracting a fine and uniform standard attitude point cloud of the curved surface profile area from a design model; establishing a design model coordinate system, a machine tool coordinate system and a clamp coordinate system, and deriving a transfer matrix; converting an attitude point cloud into a clamp coordinate system, and converting the actual measurement point cloud into the clamp coordinate system; deriving a pose deviation; extracting hole position coordinates ofair film cooling holes, and converting the hole position coordinates into a machine tool coordinate system; establishing real hole site mapping; carrying out kinematic modeling; calculating coordinateparameters of all shafts of the machine tool to obtain the machining attitude of the air film cooling hole; and inputting the compensated air film cooling hole machining program into the machine tool. Due to the application of the method, the machining precision of the turbine blade air film cooling hole can be improved, and the robustness for the profile error and the pose error of the turbine blade is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
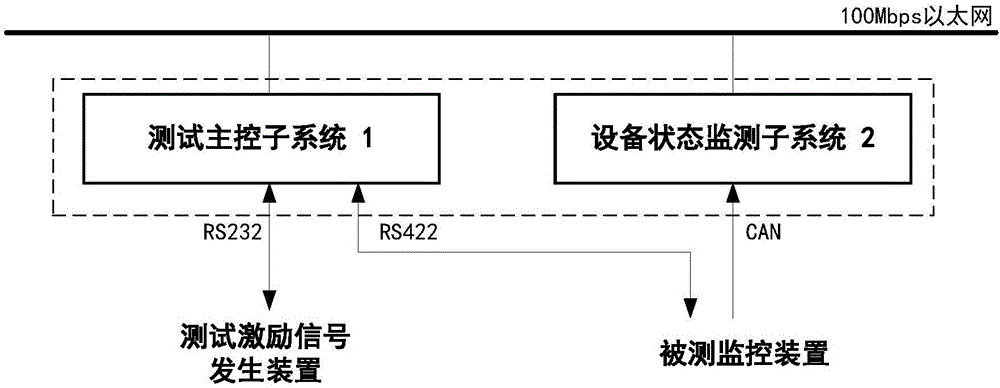
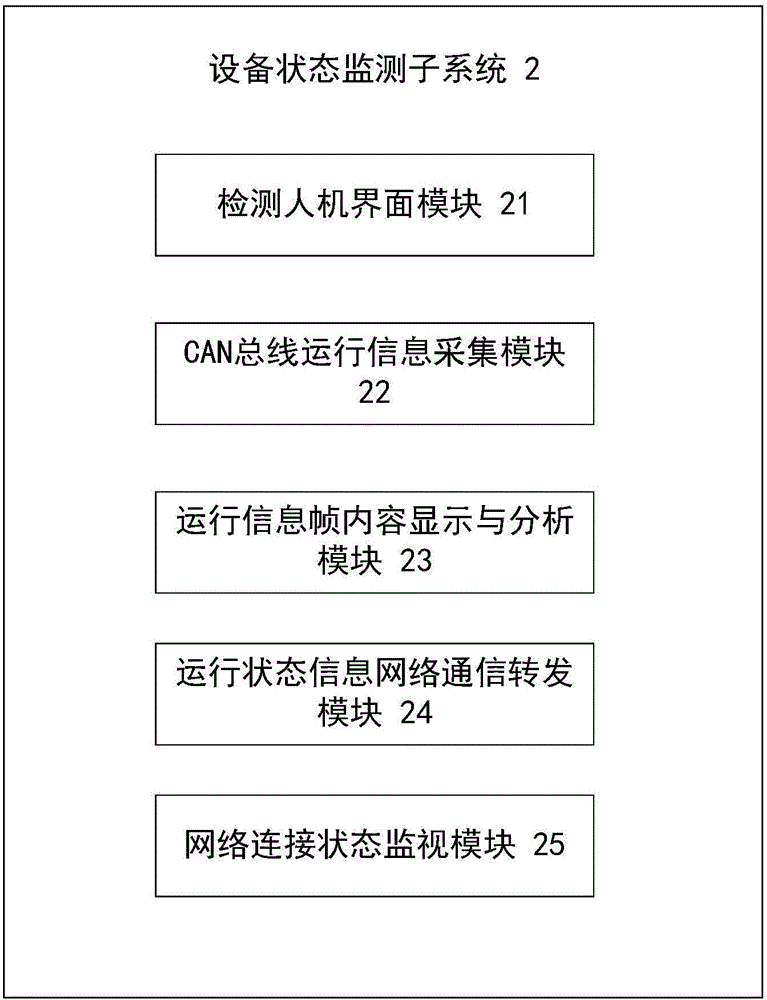
Test system and method of control function of visual train operation monitoring device
ActiveCN106774275ARealize closed-loop testingEasy to buildSimulator controlElectric testing/monitoringInformation networksNetwork communication
The invention discloses a test system and method of a control function of a visual train operation monitoring device. Simulation test operation scenes such as a line and a train are combined with a semi-physical signal simulation device, a finished control function test environment of the train operation monitoring device is formed, an automated test and a manual intervention test which are based on the scenes are achieved and are convenient to construct, and therefore a test process is more visual and efficient. According to the technical scheme, the test method of the control function of the visual train operation monitoring device comprises the steps that human-computer interface testing, ground line and device data loading, virtual train kinematical modeling, train running position operation, train simulation running scene graphical display, controlling and collecting of a test excitation signal generator, spot responder messaging, tested device feedback information displaying and network communication are achieved by a test main control subsystem; operation information collection, operation information frame content displaying and analysis, operation state information network communication forwarding of a monitored device CAN bus under test are achieved by a device state monitoring subsystem.
Owner:HUNAN CRRC TIMES SIGNAL & COMM CO LTD
Solving method of kinematics of underwater mechanical arm based on configuration plane
The invention provides a solving method of kinematics of an underwater mechanical arm based on a configuration plane. The calculation method comprises steps of inputting joint parameters of the underwater mechanical arm by carrying out analysis for mechanical arm joints, resolving the known working configuration of a robot according to types of joint modules, resolving the robot joints into corresponding types of basic joints according to movement types and inputting position arrays of target points of the robot; and modeling the basic joints by carrying out kinematical modeling for basic moving joints forming the space mechanical arm, and normalizing the kinematical modeling to form a unified modeling method. According to the invention, disadvantages are solved that solving is complex and it is hard to remove incorrect solution from multiple solutions in a traditional analytic method; problems of poor real-time performance and low precision of the common iteration method are solved; solving for inverse kinematics of the robot can be quickly and precisely achieved; and actual application requirements of the underwater mechanical arm are met.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Moveable robot movement high-precision control method
InactiveCN101116969AMatch Speed ResponseShorten speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorCommand and controlCoupling
The invention relates to a motion control method of high precision for a mobile robot. The prior control method can not control the motion precisely when wheels of the mobile robot generate instant fluctuation. The invention adopts a high speed digital processor TMS320LF2407A as a multi-axis servo motion controller. The detailed realization method is that initializing the processor; completing a control closed loop specific to the position and the speed of a single servo motor inside the processor; conducting kinematics modeling for the mobile robot and obtain the coordination relation between two wheels of the robot; using cross-coupling technology and fuzzy logic technology to obtain tuning control volume to modify speed control command and control line speed nu and angular speed omega. The invention does not need accurate control object model, compared with the previous single closed loop control, has practical characteristics and obvious progress, and based on the original system equipment, is easy to improve and realize.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
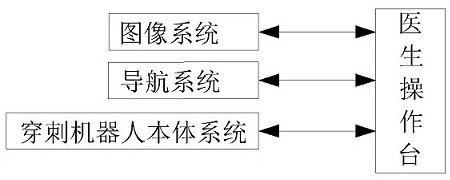
Space registration and real-time navigation method for minimally invasive mammary gland interventional surgical robot
InactiveCN113288429AMeet the requirements of biopsy punctureRealize visualizationSurgical navigation systemsSurgical manipulatorsMotion captureMammary gland structure
The invention discloses a space registration and real-time navigation method for a minimally invasive mammary gland interventional surgical robot. The method comprises the steps that S1, kinematics modeling and simulation of the robot are carried out; s2, positioning and registering by a navigation system; s3, coordinate scale calculation and spatial registration of an ICP registration algorithm; s4, the position and posture of the puncture needle are positioned in real time, kinematics modeling can be carried out on the puncture device, and forward and inverse kinematics solution is carried out; the degree of freedom, configuration and geometric parameters of the designed robot can meet the requirements of mammary gland biopsy puncture through preliminary verification, and the problem of inconsistent coordinate space scales is solved through an ICP iterative registration algorithm based on coordinate scale calculation and a registration algorithm simulation experiment; a navigation experiment platform is built based on an OptiTrack motion capture system and 3ds Max three-dimensional animation software, passive positioning probe calibration and image space registration are completed, and visualization and positioning tracking of the position and posture of a puncture needle are achieved.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF COMMERCE & TECH
Axis-invariant-based multi-axis robot system forward kinematics modeling and solving method
ActiveCN108983705AEfficient calculation methodImprove computing efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlMultiplexingSimulation
The invention provides an axis-invariant-based multi-axis robot system forward kinematics modeling and solving method. The axis-invariant-based multi-axis robot system forward kinematics modeling andsolving method realizes inherently compact, real-time, function-multiplexing, concise hierarchical and full-parameter modeling and real-time solution, has the functions of pseudo code and symbol analysis, can be set as circuits and codes, and can be executed in the multi-axis robot system directly or indirectly, partially or wholly. Besides, the invention also includes an analysis verification system constructed on the above principle for designing and verifying the multi-axis robot system.
Owner:居鹤华
AGV path tracking method based on inversion sliding mode control
ActiveCN111103798ARealize automatic adjustmentSuppress chatterAdaptive controlControl objectivePerformance index
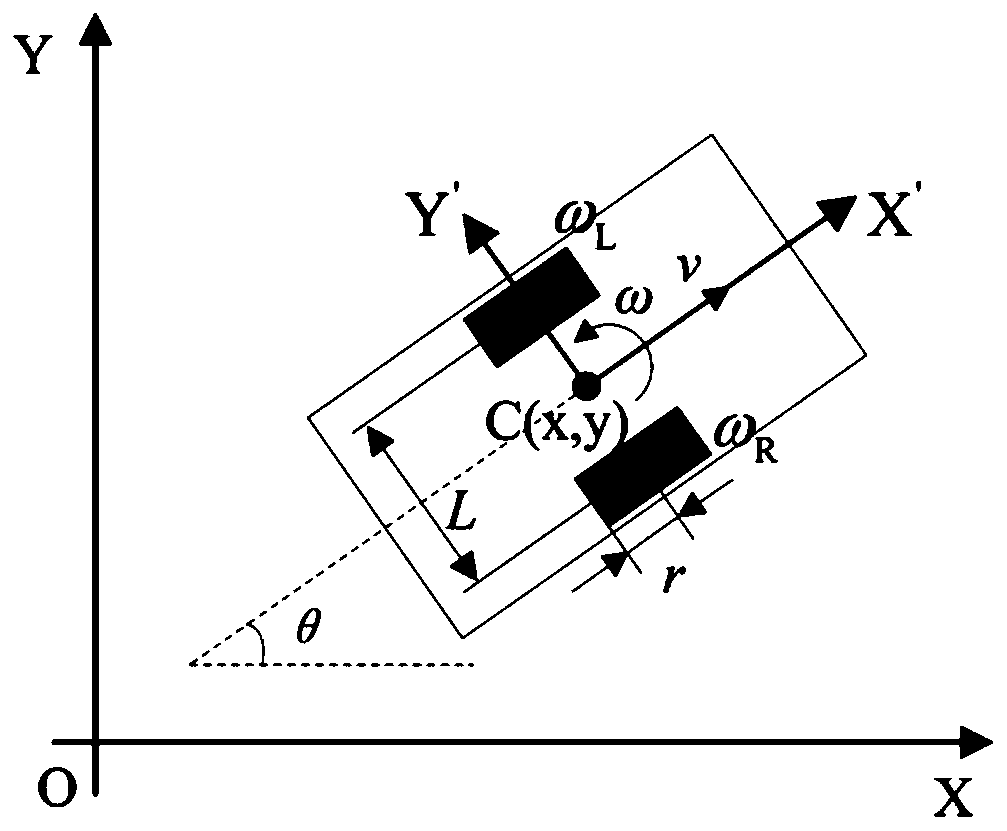
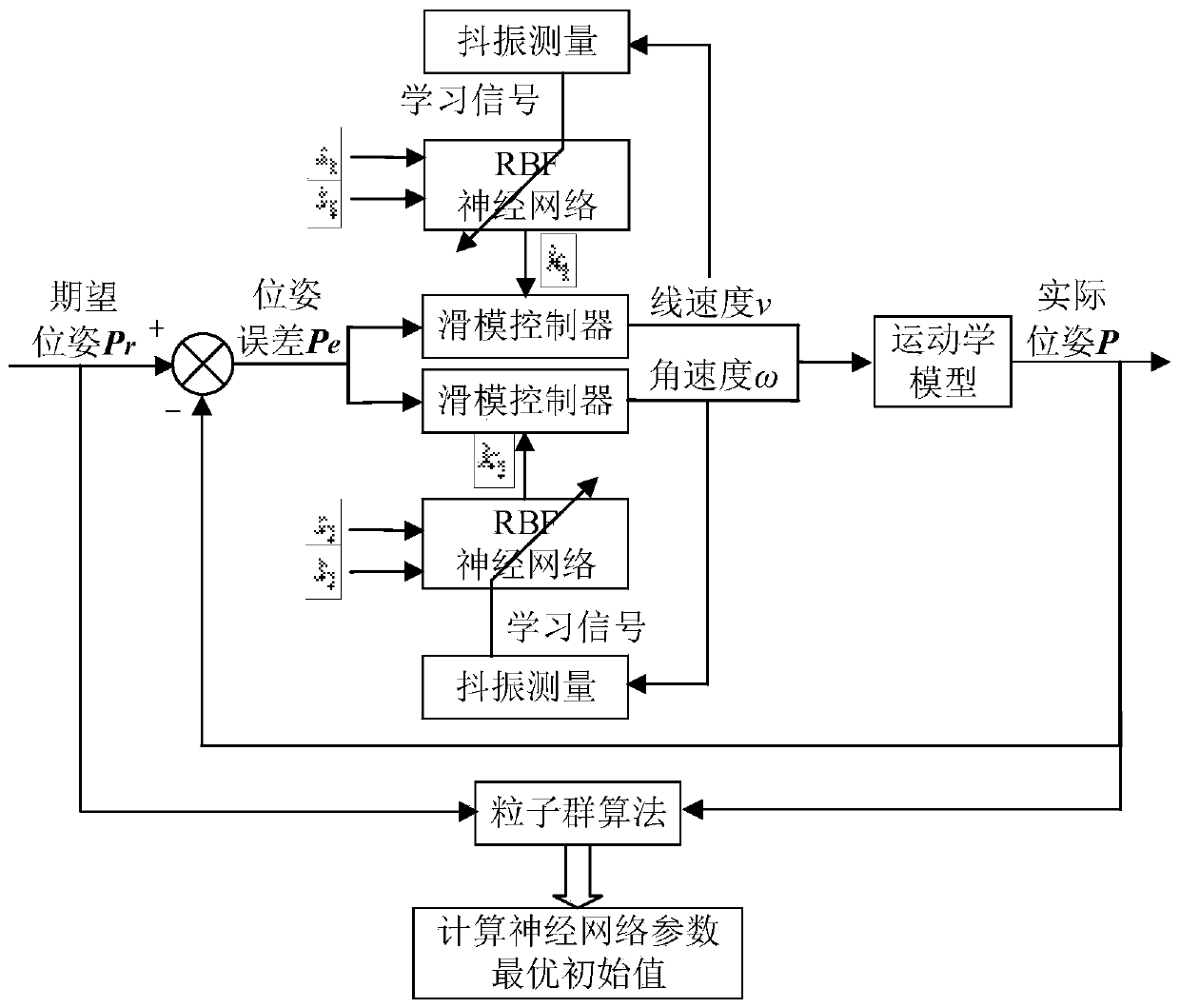
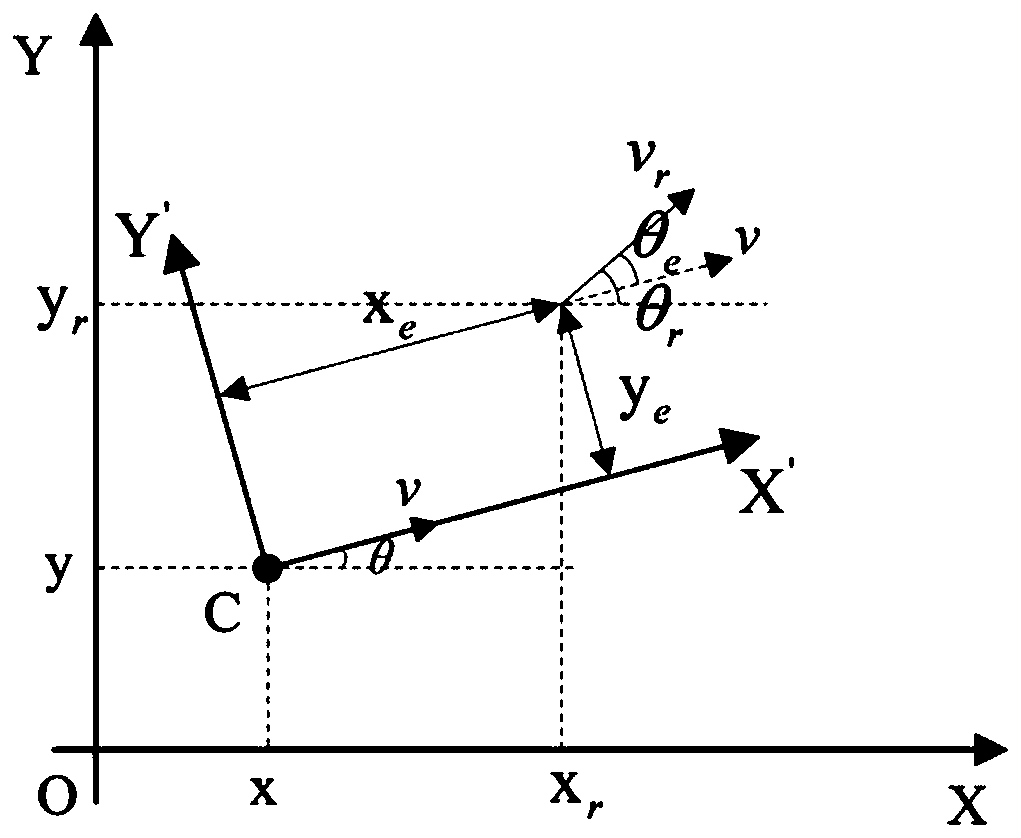
The invention belongs to the field of AGV motion control, and relates to an AGV path tracking method based on inversion sliding mode control. The AGV path tracking method comprises the following steps: determining a control target and a control quantity of an AGV system through kinematics modeling, designing an inversion sliding mode controller for the control quantity, and adding a constant-speedreaching law to obtain a system control law containing sliding mode control switching item gain; designing a performance index function of a RBF neural network by taking the buffeting amount as a learning signal, and dynamically adjusting the sliding mode control switching item gain; and optimizing the initial values of the iteratively updated control parameters in the RBF neural network by using a particle swarm algorithm. The buffeting amount is used as the learning signal of the neural network, system buffeting is suppressed more directly and effectively, and the particle swarm algorithmis utilized to calculate the optimal initial value of the parameters so as to accelerate convergence of the AGV system. The stability and the robustness of sliding mode control are fully utilized, buffeting of the AGV system is directly and effectively restrained and accurate and rapid path tracking of the AGV system is achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Zero-disturbance optimization control method for base of space manipulator
The invention discloses a zero-disturbance optimization control method for a base of a space manipulator. The method comprises the following steps that S1, a kinematic model is established for the space manipulator; S2, the kinematic model of the space manipulator is fixed equivalently; S3, a joint track of the space manipulator is parameterized through a seven-variable septic polynomial, the posture of the base of the space manipulator is represented through a quaternion equation, and a system state equation is established according to the position and posture of the base of the space manipulator; S4, an objective function of an optimization algorithm is established, and the objective function is simplified according to solution of the system state equation and limitation of joint speed parameters and angular acceleration parameters of the manipulator; S5, motion planning problems are solved through the optimization algorithm. According to the zero-disturbance optimization control method for the base of the space manipulator, the probability of finding the optimal base zero-disturbance space manipulator path is increased, calculating time for evaluation of the objective function through the particle swarm algorithm is saved, optimization is conducted on parallel computing, and calculating speed is multipled through parallel computing.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
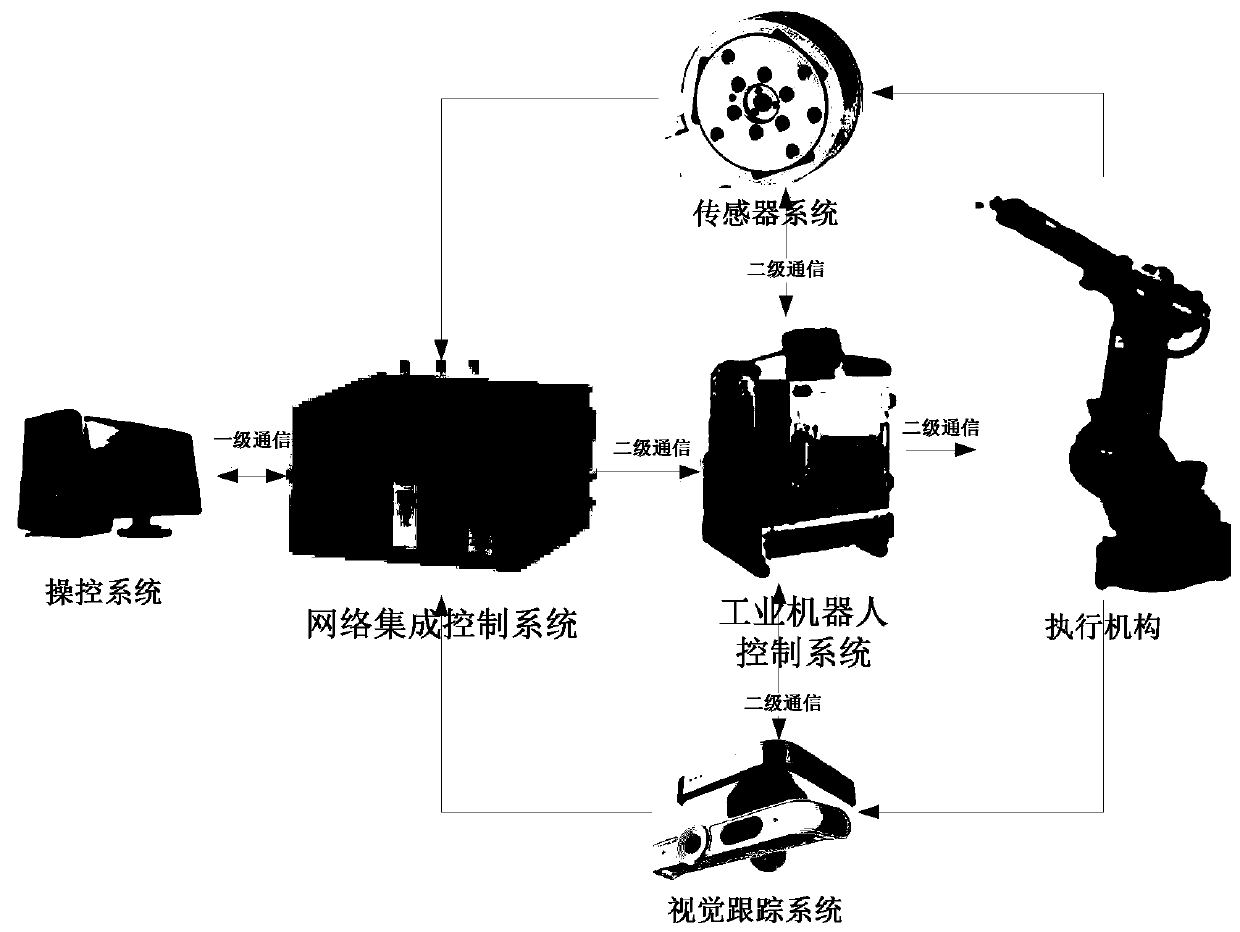
Industrial robot platform with dual-core motion controller
InactiveCN110666802AAchieve precise and stable controlImprove reliabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorDual coreMotion controller
The invention relates to an industrial robot platform with a dual-core motion controller. The industrial robot platform comprises an industrial robot control system, a sensor system, a control system,a network integrated control system, a visual tracking system and an actuating mechanism, wherein the sensor system is connected to the industrial robot control system; a processor is a system on chip and comprises an interface layer, an algorithm control layer and a fault tolerant control layer; the interface layer is of an FPGA structure and is responsible for information exchange with a motorcontrol module and controlling a servo device; the algorithm control layer is of an ARM and DSP dual-core structure, the ARM core is responsible for various peripheral drives, and the DSP end is responsible for a large number of matrix floating point class calculation such as kinematic modeling, trajectory planning; and the fault-tolerant control layer uses a 32-bit controller, carries out real time monitoring on the interface layer and the algorithm control layer, and carries out fault-tolerant planning on faults according to feedback and operating commands, so that the safe and reliable operation of a system is ensure, the fault-tolerant control layer uses a servo calibration method, and meanwhile, a visual feedback interface is expanded, so that secondary correction of the later visualfeedback is realized.
Owner:张焕焕
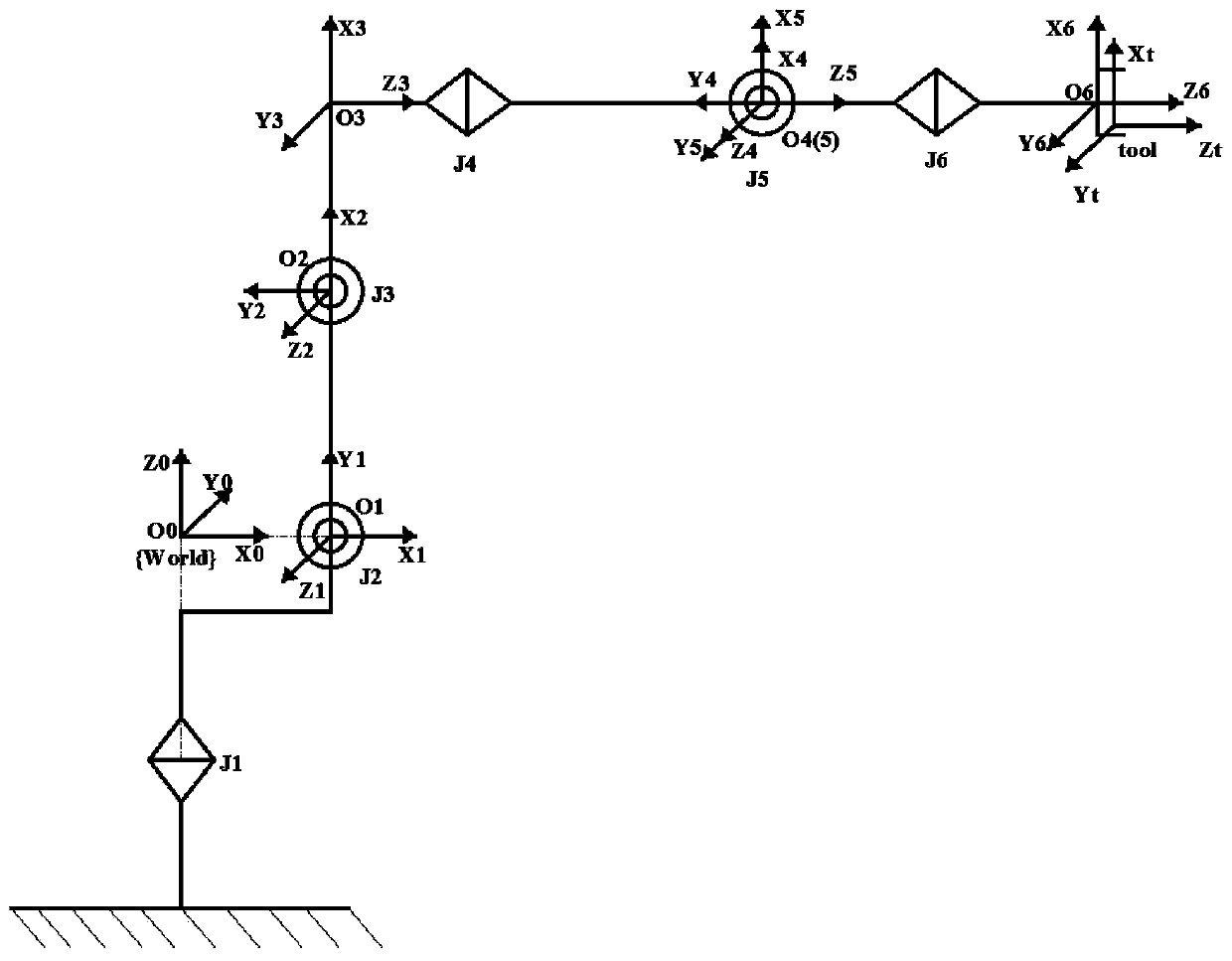
Industrial robot kinematic modelling method and system
InactiveCN105598957AImprove general performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationModel parameters
The invention relates to an industrial robot kinematic modelling method and an industrial robot kinematic modelling system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, encapsulating basic model parameters of an industrial robot according to attribute by adopting an object-oriented method so as to obtain different classes; S2, acquiring the initial position type of the industrial robot and a reference coordinate system and a tail end coordinate system of the industrial robot set by a user; S3, calculating the transformation relation between the reference coordinate system and the tail end coordinate system of the industrial robot at the initial position type according to the determined reference coordinate system and tail end coordinate system; S4, establishing a kinematic model of the industrial robot according to the classes obtained by encapsulating, the transformation relation between the reference coordinate system and the tail end coordinate system when the industrial robot is at the initial position type, and the number of joints, and obtaining the transformation relation between the tail end coordinate system and the reference coordinate system of the robot. According to the method and the system, the problem of insufficient universality of the existing kinematic modelling method is solved.
Owner:国机智能科技有限公司
Dual-mechanical arm synergic movement method and system
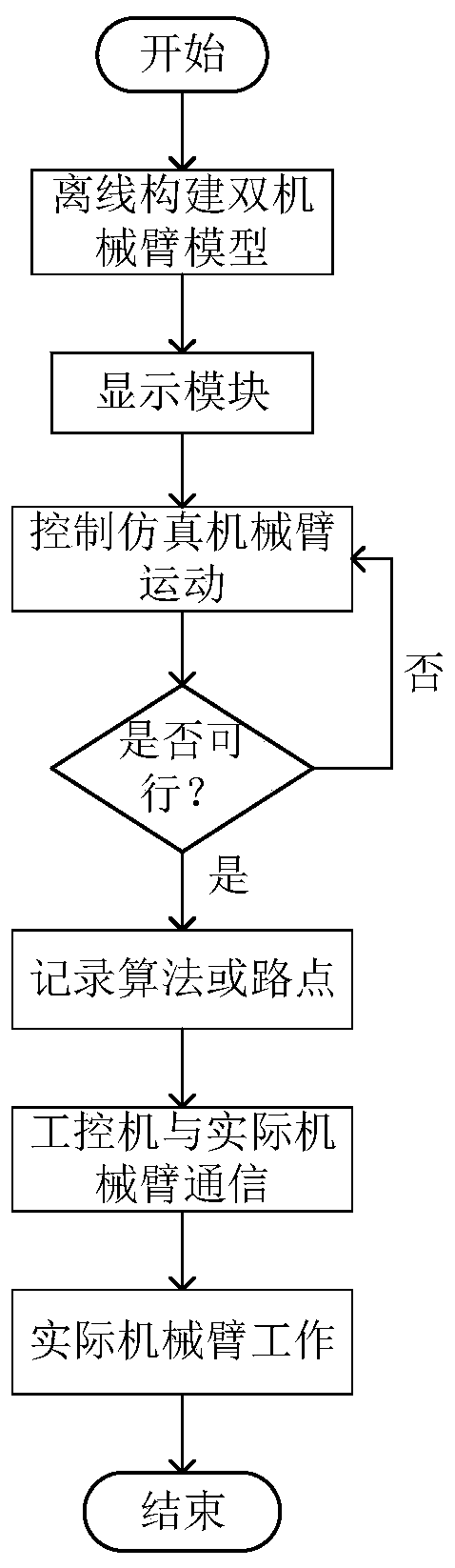
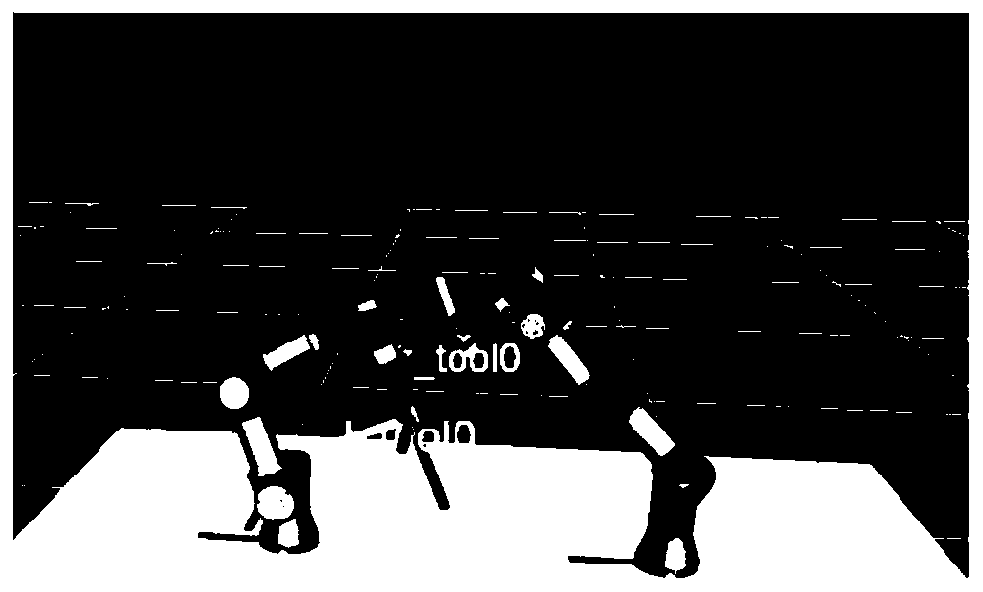
InactiveCN110695988AImprove work efficiencySimulation is accurateProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree-dimensional spaceCollision detection
The invention discloses a dual-mechanical arm synergic movement method and system. The method includes the steps of constructing a virtual dual-mechanical arm three-dimensional space model according to solid dual-mechanical arms; performing kinematics modeling on the mechanical arms; determining a synergic range of the dual-mechanical arms; controlling the virtual dual-mechanical arms to move to target poses according to actual needs, performing path planning and collision detection in real time in the movement process in cooperation with the synergic range, and saving feasible way points in adatabase of an industrial personal computer; building communication between the industrial personal computer and the actual dual-mechanical arms; and loading the feasible way points in the database to the actual dual-mechanical arms through the industrial personal computer, and controlling the dual-mechanical arms to move to the target poses. The system includes an industrial personal computer module, a communication module and a display module. By means of the dual-mechanical arm synergic movement method and system, the virtual dual-mechanical arms are controlled to do synergic motion, the preferred way points avoiding problems like mechanical arm collision are recorded, the actual dual-mechanical arms are controlled to move to the target poses according to the way points, damage to theactual dual-mechanical arms can be avoided, and very good application values are achieved in the fields of robot reaching and practical training.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
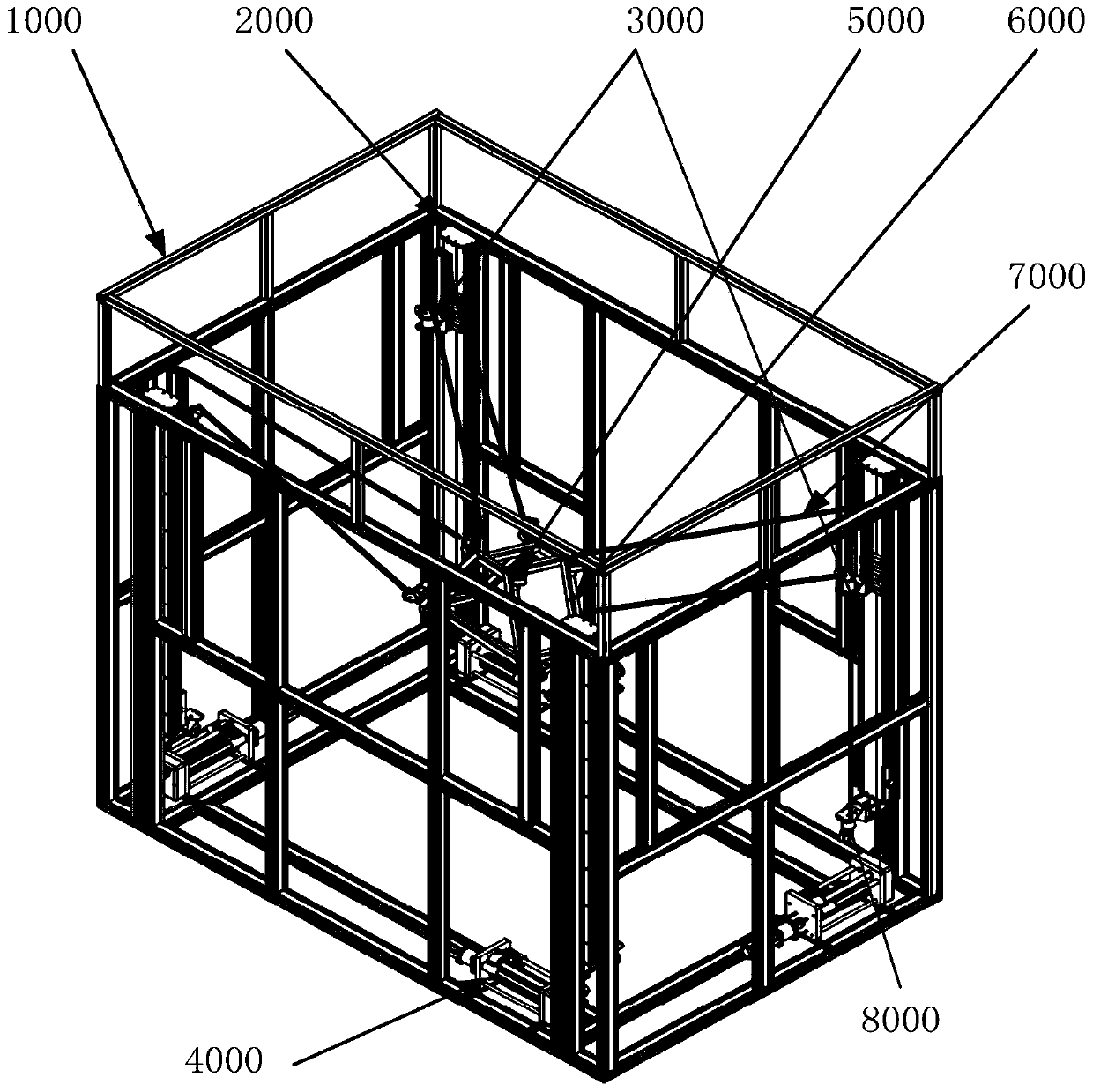
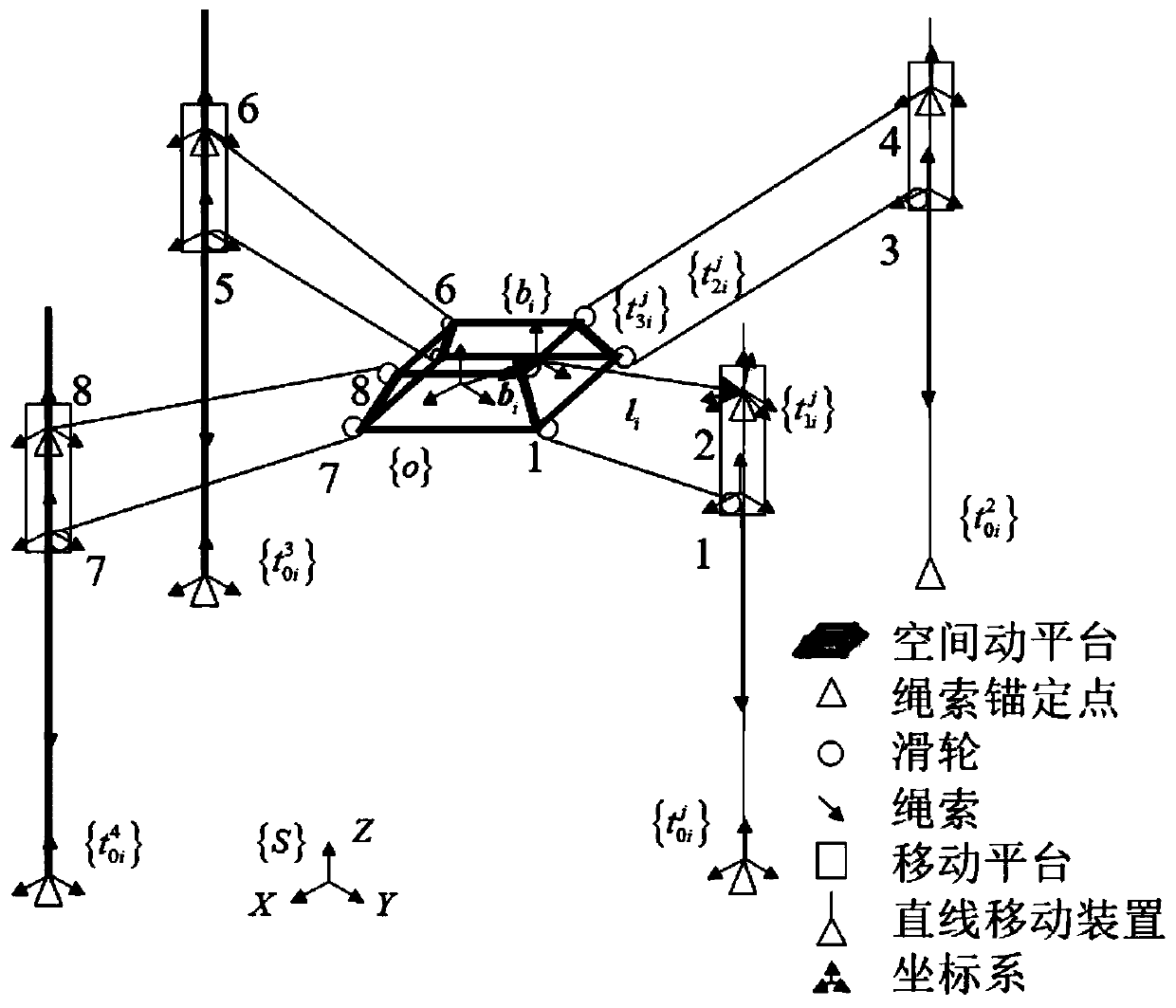
Kinematics speed solving method of cable-driven parallel robot with variable structure
The invention discloses a cable-driven parallel robot with a variable structure. The cable-driven parallel robot comprises a structural frame, a high-precision cable traction device, a linear moving device, a universal guiding device, a spatial mobile platform, universal traction devices, a cable and other parts. According to the cable-driven parallel robot with the variable structure, cable length and tension are changed through the high-precision cable traction device, so that the spatial mobile platform is controlled to move in a working space, and therefore object carrying, hoisting, maintaining and spraying work and other work are completed; spatial structure deformation is achieved through the linear moving device, and the spatial configuration can be adjusted according to the environment to meet different task requirements; and in addition, the plurality of universal traction devices are further arranged on the spatial mobile platform, and the load capacity and the system rigidity of the robot are improved through the traction force amplification effect of spatial movable pulley blocks. The invention further discloses a kinematics speed solving method of the cable-driven parallel robot with the variable structure, the method belongs to the field of robot motion control, kinematics modeling is performed on the cable-driven parallel robot with the variable structure basedon the screw theory, and a mapping model about the cable length and the spatial mobile platform pose is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
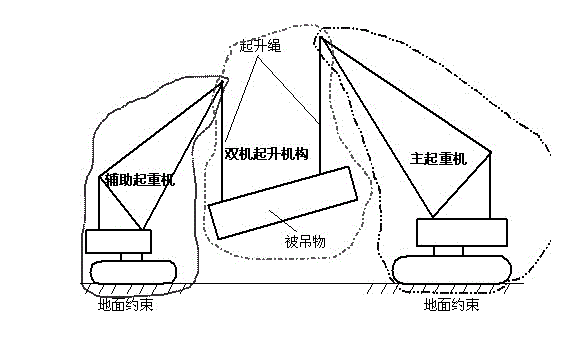
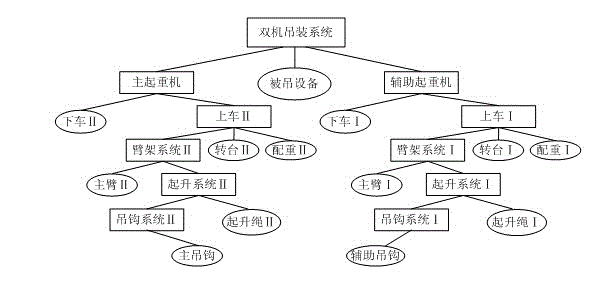
Double mobile crane cooperative hoisting simulation method based on kinematics and dynamics
InactiveCN103064297AIncrease the difficultyWill not affect the simulation effectSimulator controlThree dimensional simulationCollision detection
The invention belongs to the technical fields of hoisting techniques and three-dimensional simulation, and discloses a double mobile crane cooperative hoisting simulation model based on kinematics and dynamics. A double-crane system is divided into three parts, wherein hoisted objects and slings of the two cranes are one part which is called double-crane hoisting subsystem, one of the two cranes is one part which is called main crane subsystem, and the other crane is one part which is called assisting crane subsystem. The hoisting subsystem of two cranes adopts dynamics modeling, and the main crane subsystem and the assisting crane subsystem adopt kinematics modeling. The double mobile crane cooperative hoisting simulation method based on the kinematics and the dynamics has the advantages that hoisting processes of the swing effect, collision detection and the like of the two cranes can be factually simulated, hidden dangers can be found before hoisting in reality through simulation, and safety and efficiency of hoisting can be improved finally. In addition, kinematic models simplify the modeling of motion of the two cranes, parameters which need to be set are less, achievement is easier, and control is easier at the same time.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
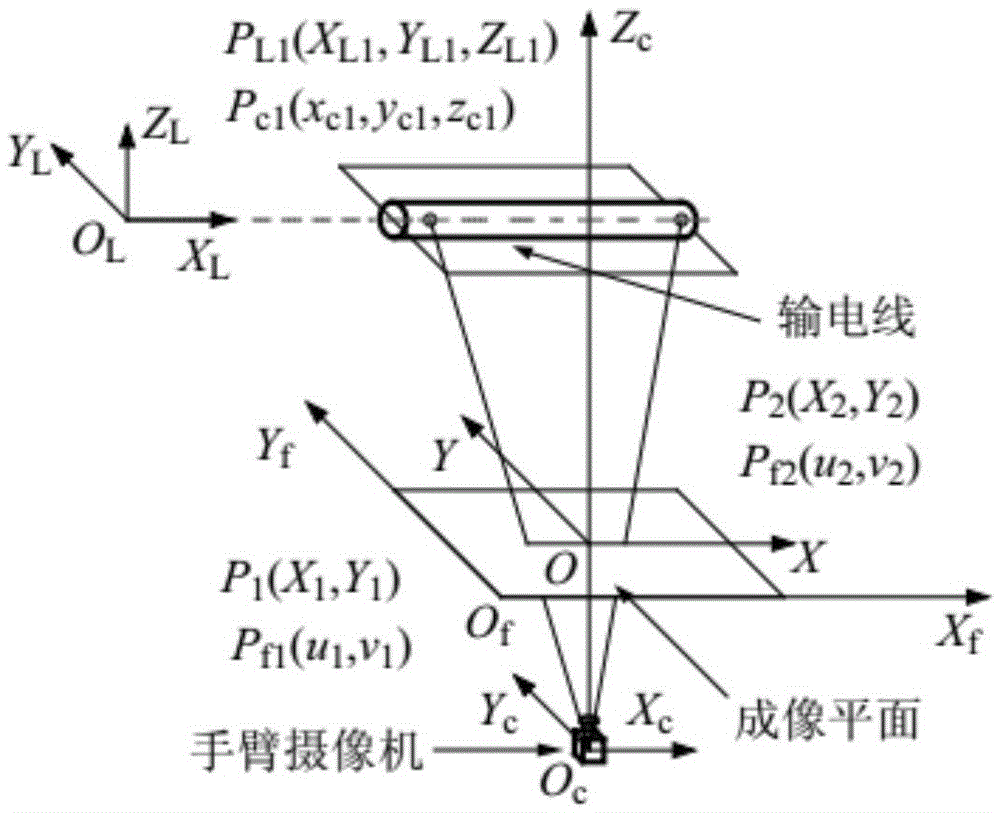
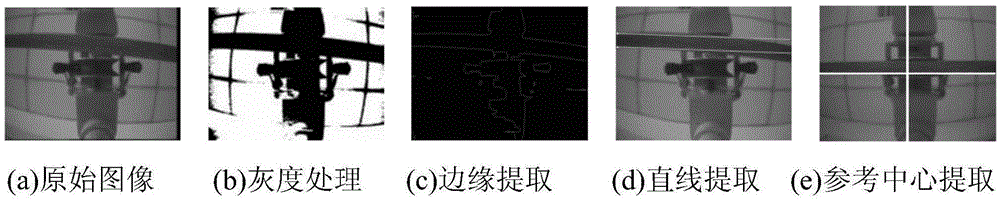
Visual servo line-grasping control method for electric transmission line inspection robot
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking method based on differential flatness characteristics
ActiveCN112241125AEasy to trackReduce the computational complexity of online optimizationAdaptive controlComputation complexityFlight vehicle
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking method based on differential flatness characteristics, which comprises the following steps: performing dynamics and kinematics modeling on a four-rotor aircraft, performing differential flatness attribute judgment on a model of the four-rotor aircraft, and converting an underactuated four-rotor model into a full-drive system through nonlinear change on the basis of the property. And setting a virtual control quantity, decoupling the highly coupled system, and converting the highly coupled system into a linear system. The flight path tracking control problem of a constrained system is processed through model prediction control, a polyhedron description system is constructed for the time-varying characteristics of the system and comprises an original time-varying system, the online optimization calculation complexity is reduced, and a real-time terminal penalty value enabling the system to be stable is deduced according to the online optimization calculation complexity. The model prediction control method for the time-varying system is designed, constraints and system time-varying characteristics in the unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking process are processed, the unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory tracking task can be effectively completed, the nonlinear characteristics of the unmanned aerial vehicleare well processed, the calculation complexity is low, and the tracking speed is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
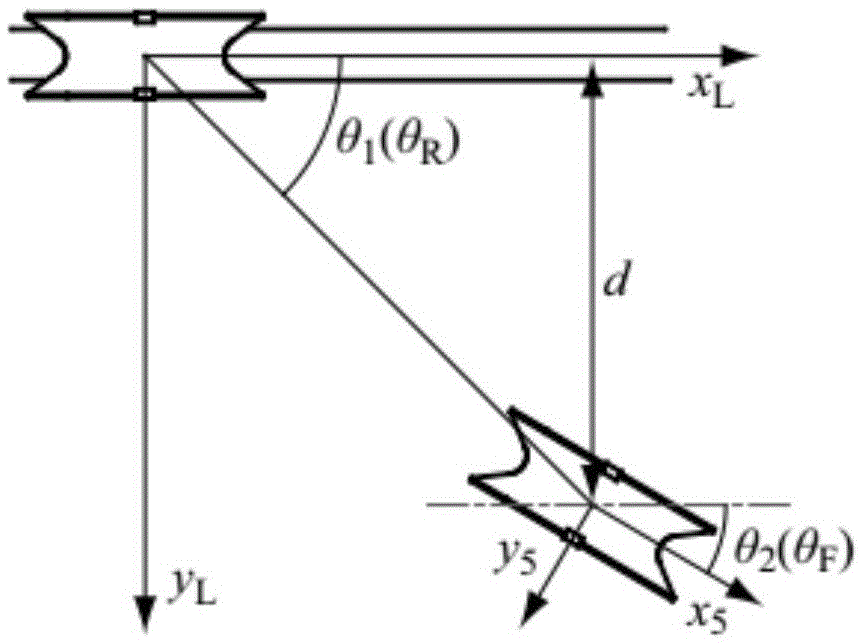
Master-slave tracking control method for minimally invasive surgery robot
ActiveCN112716608AImprove real-time performanceImprove accuracyMedical simulationSurgical manipulatorsMinimal invasive surgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention relates to a master-slave tracking control method for a minimally invasive surgical robot, solves the technical problems of poor real-time performance, poor accuracy and low precision of a master-slave tracking control method of an existing minimally invasive surgical robot system, and discloses a simplified kinematics modeling method combining a heterogeneous mapping mode and an isomorphic mapping mode. A master-slave manipulator positioning part adopts a heterogeneous mapping mode, and the master-slave manipulator posture part adopts an isomorphic mapping mode. The robot is widely applied to minimally invasive surgery robots.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIGAO SURGICAL ROBOT CO LTD
Three-freedom-degree pneumatic horizontal moving parallel mechanism
ActiveCN110653797AIncrease stiffnessStable three-dimensional translationProgramme-controlled manipulatorProduction lineEngineering
The invention discloses a three-freedom-degree pneumatic horizontal moving parallel mechanism, and belongs to the field of parallel robots. The three-freedom-degree pneumatic horizontal moving parallel mechanism comprises a fixing platform, an upper spherical hinge, a drive air cylinder, a lower spherical hinge, a moving platform, a cylinder pair, a circular sliding rail, a front baffle, a rear baffle, a left moving pair, a right moving pair and a rotation pair. A drive branch chain is composed of the upper spherical hinge, the drive air cylinder and the lower spherical hinge. An auxiliary branch chain is composed of the cylinder pair, the circular sliding rail, the front baffle, the rear baffle, the left moving pair, the right moving pair and the rotation pair. The drive air cylinder telescopically drives the moving platform to move. The auxiliary branch chain moves along with the movement of the moving platform. The auxiliary branch chain is adopted for restraining rotation of the moving platform, the stable three-dimension horizontal movement of the moving platform is achieved, and meanwhile the rigidity of the mechanism is improved through the auxiliary branch chain. The three-freedom-degree pneumatic horizontal moving parallel mechanism does not include a rotation driving mechanism, the kinematics positive solution is simple, and control is convenient. The three-freedom-degree pneumatic horizontal moving parallel mechanism has the advantages that kinematical modeling is simple, work space is large, positioning precision is high and rigidity is large; and the three-freedom-degree pneumatic horizontal moving parallel mechanism can be used for grabbing, sorting and other operation of an automatic production line.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Flexible control method for mechanical arm based on dynamics
InactiveCN110450154ARelieve pressureThe torque formula is simpleProgramme-controlled manipulatorLow speedHigh acceleration
Owner:佛山哨马智能装备科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com