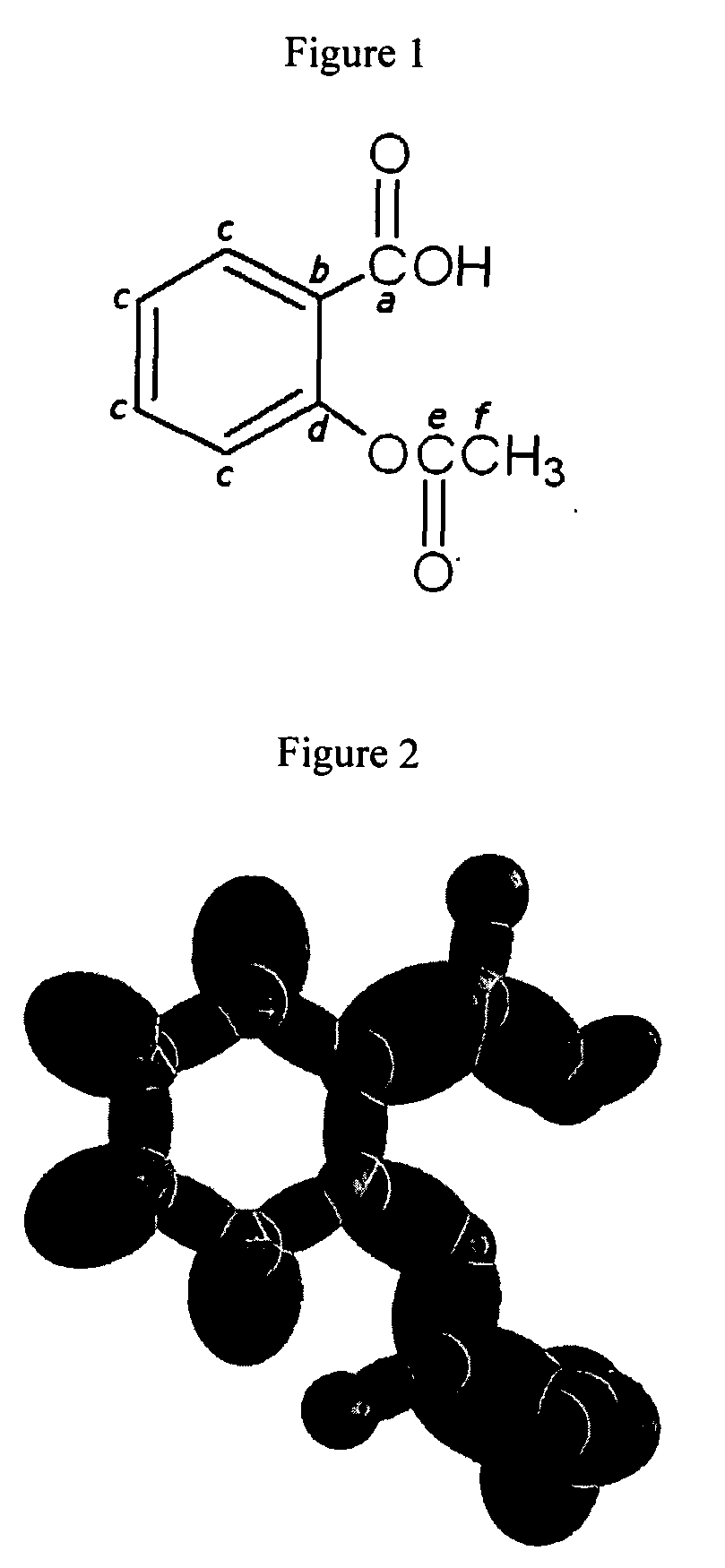
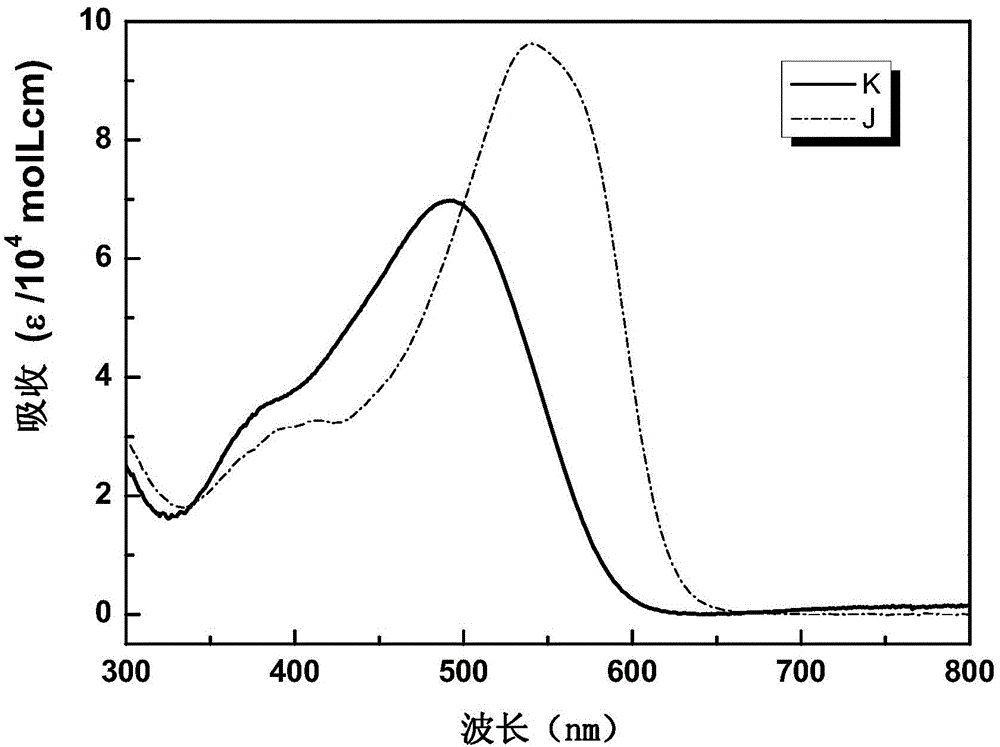
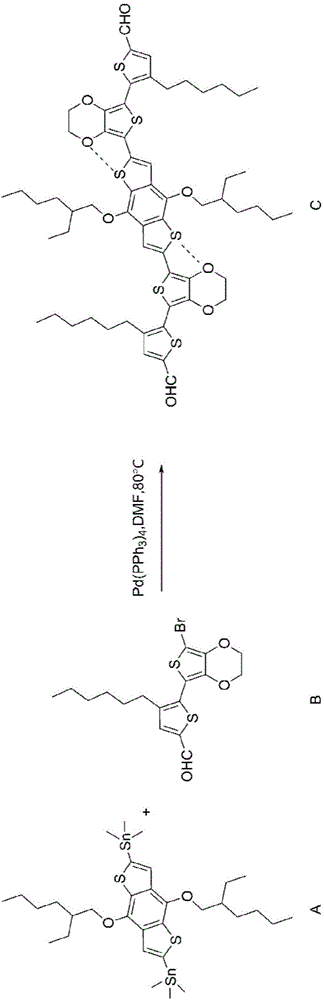
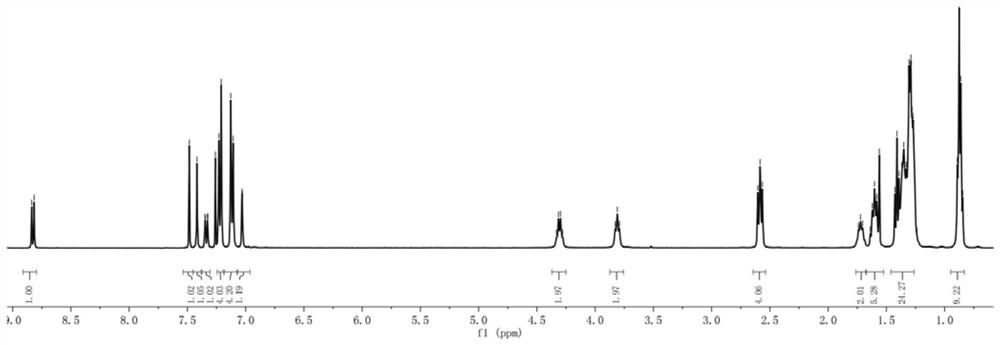
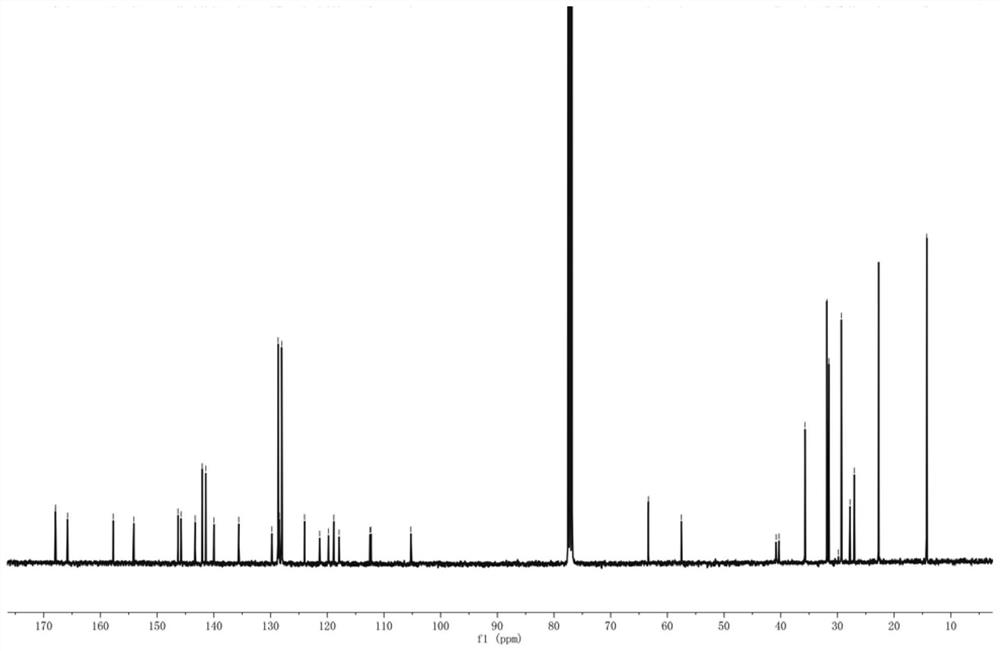
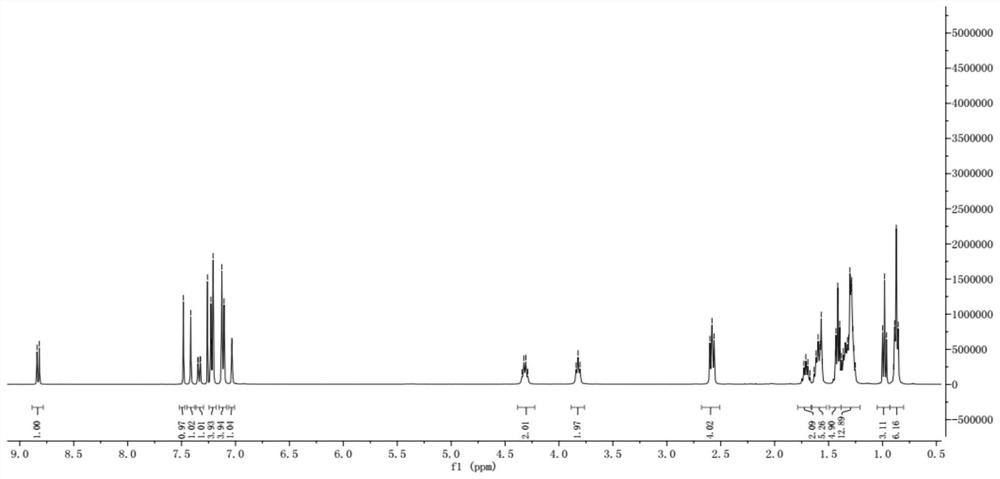
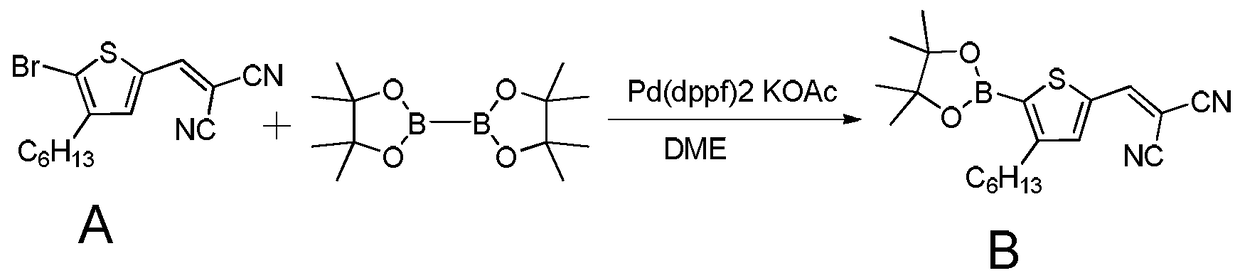
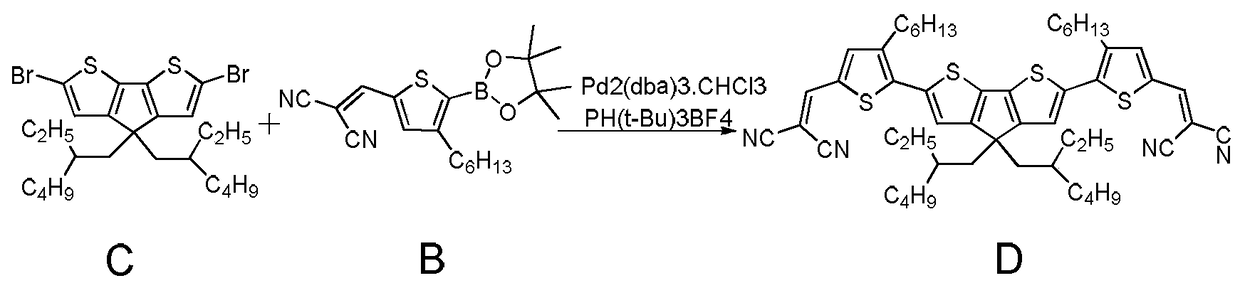
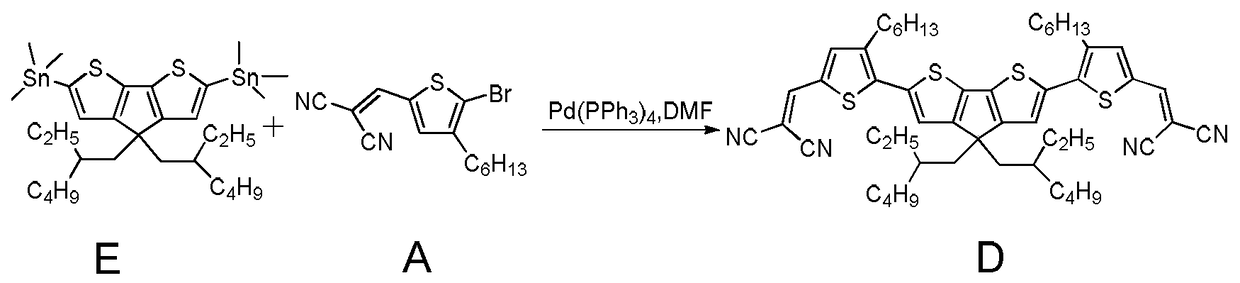
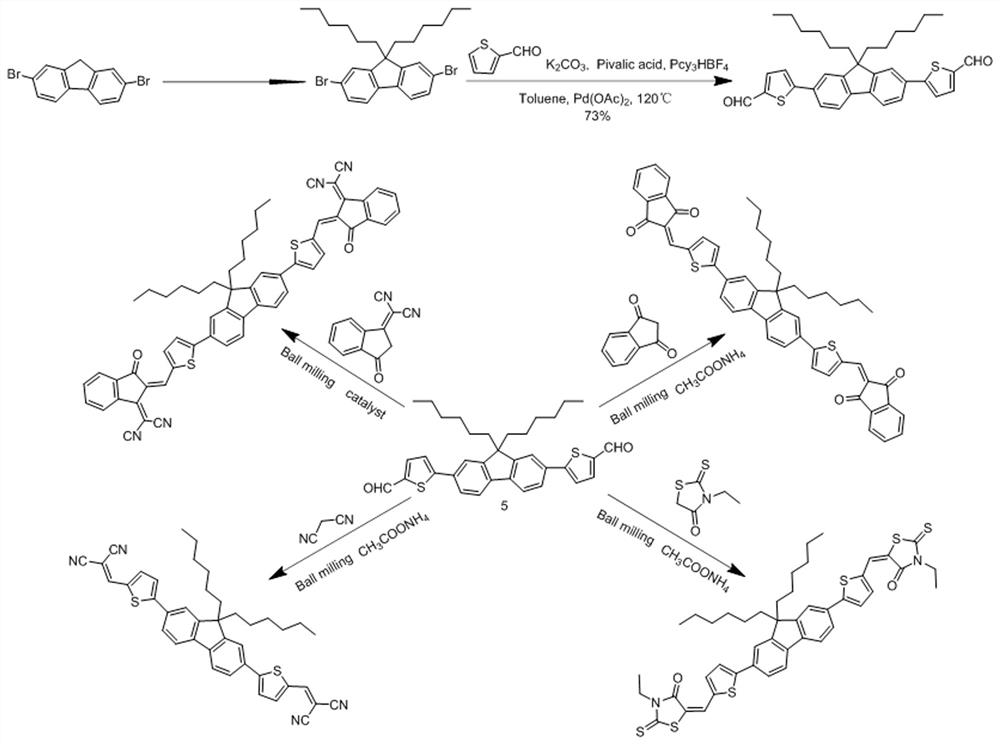
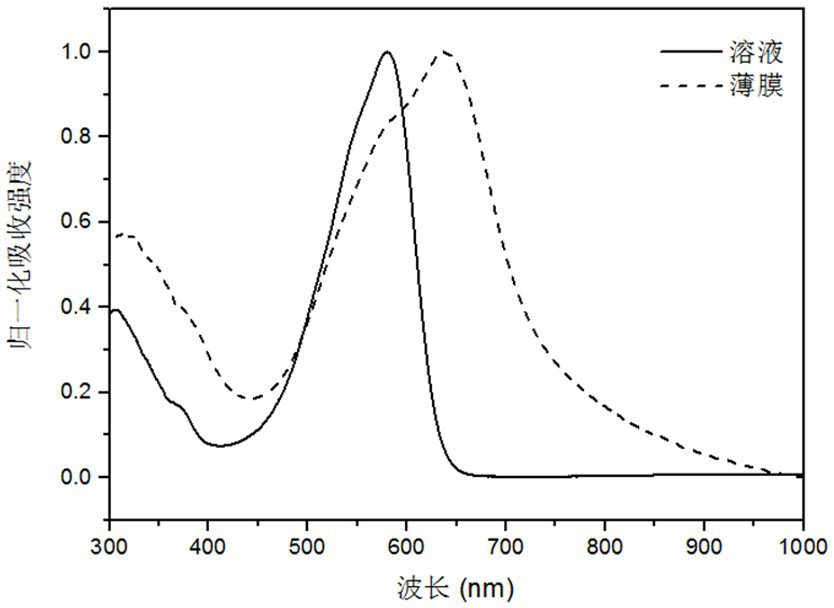
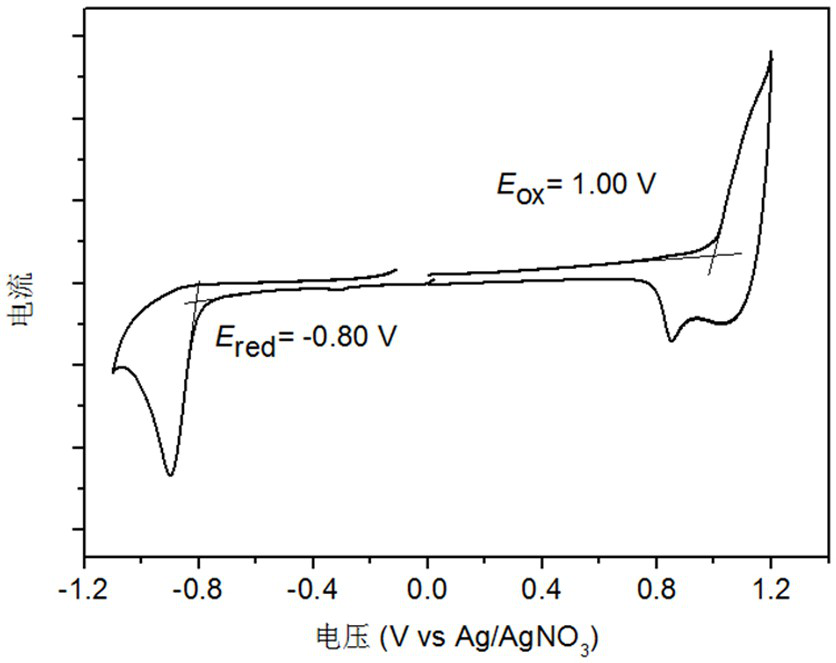
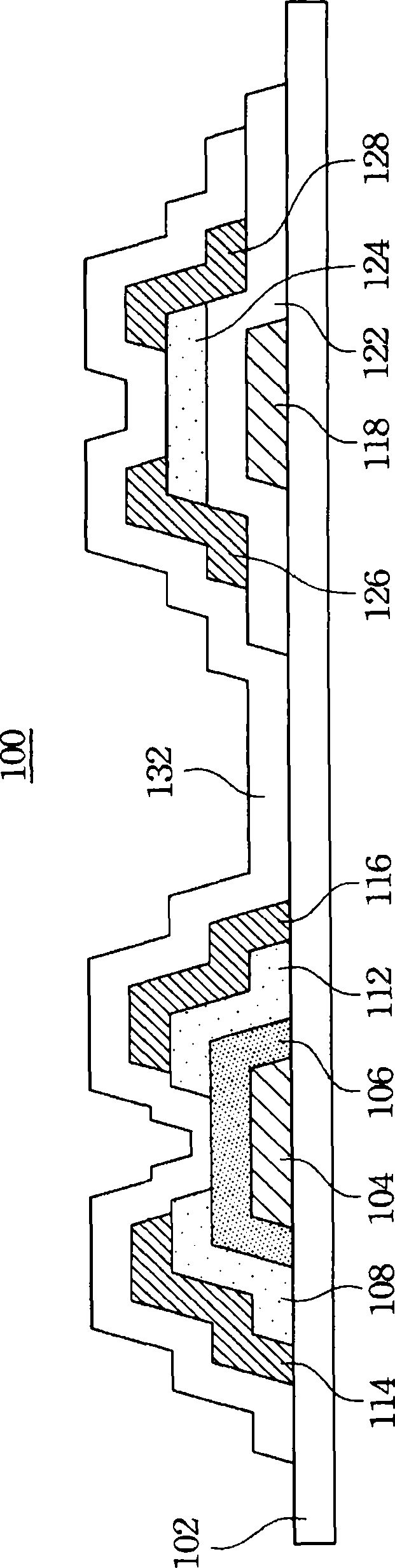
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Molecular semiconductor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
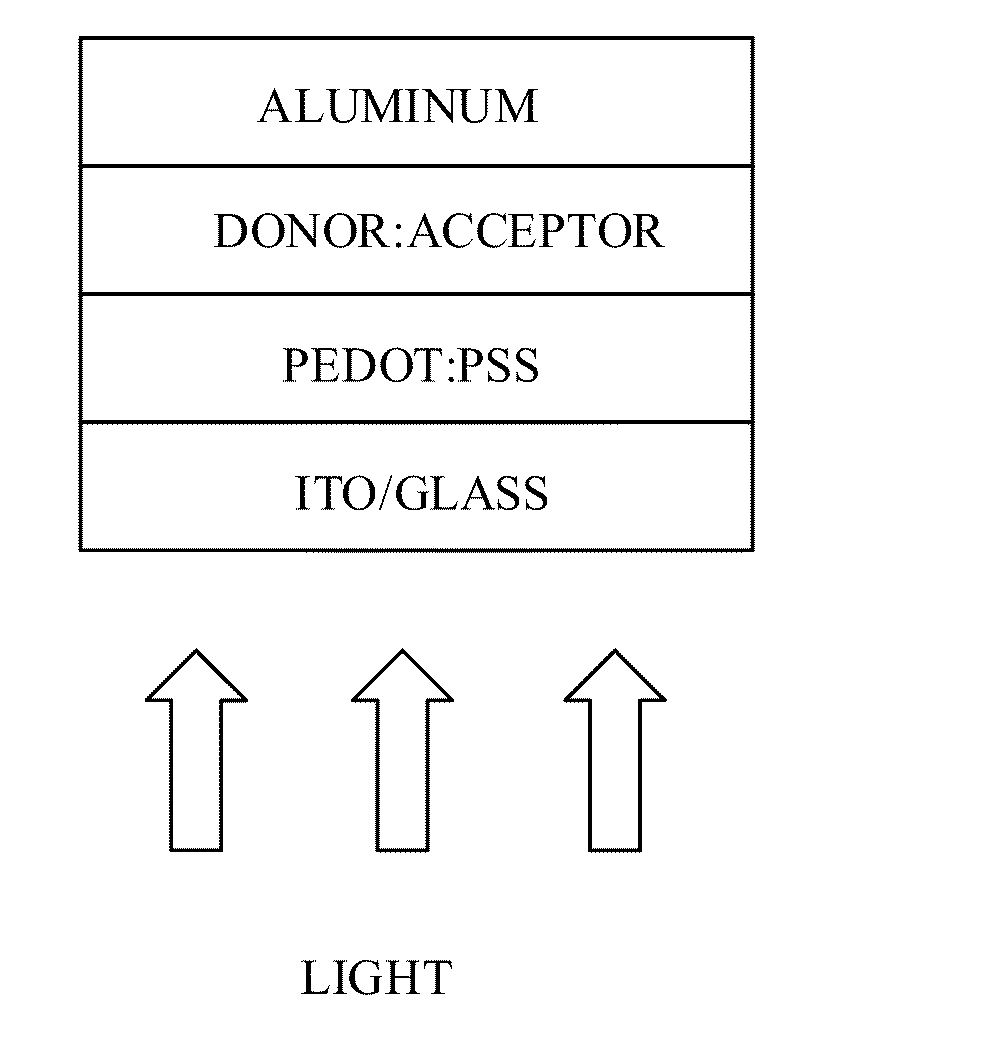
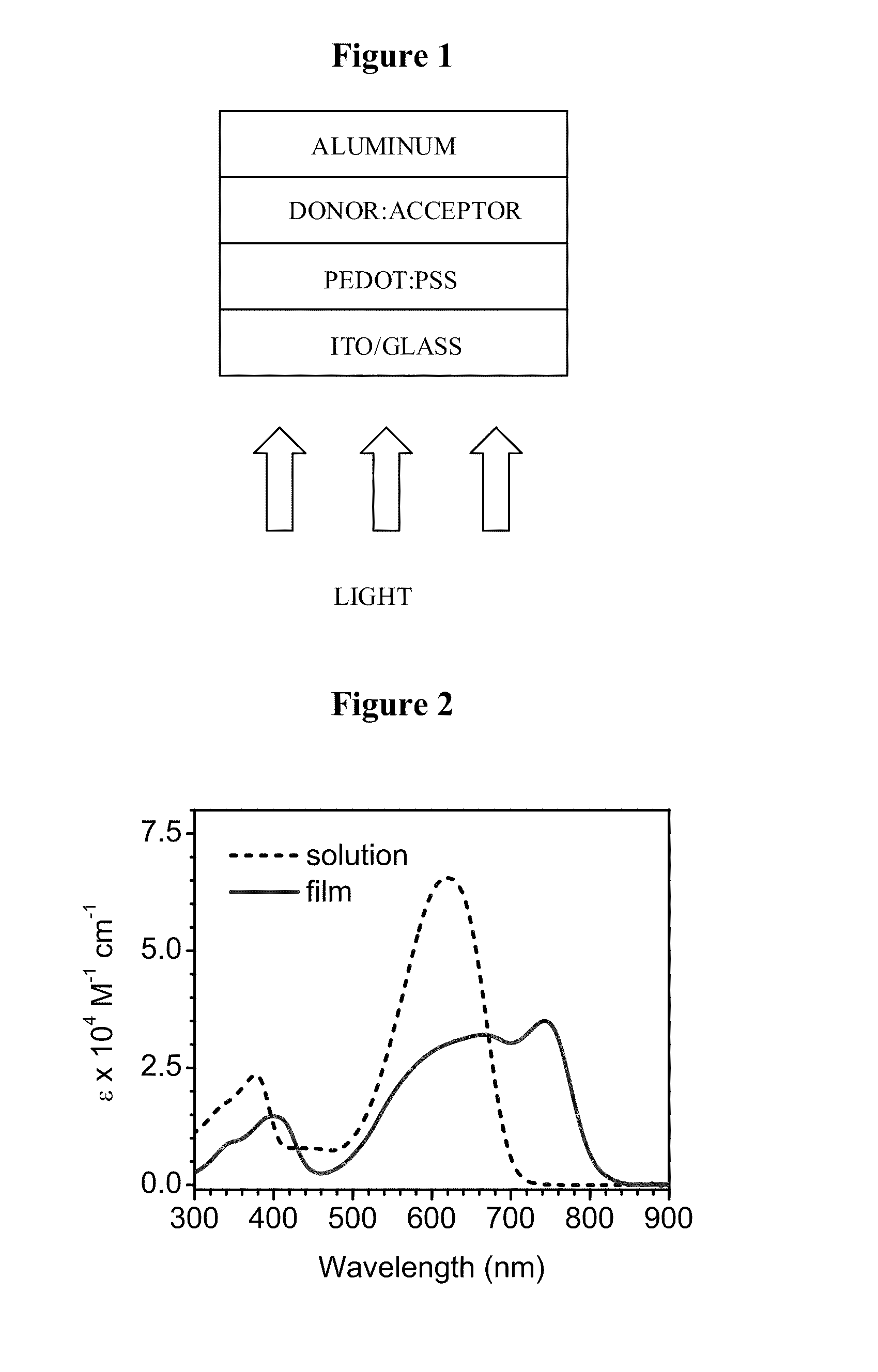
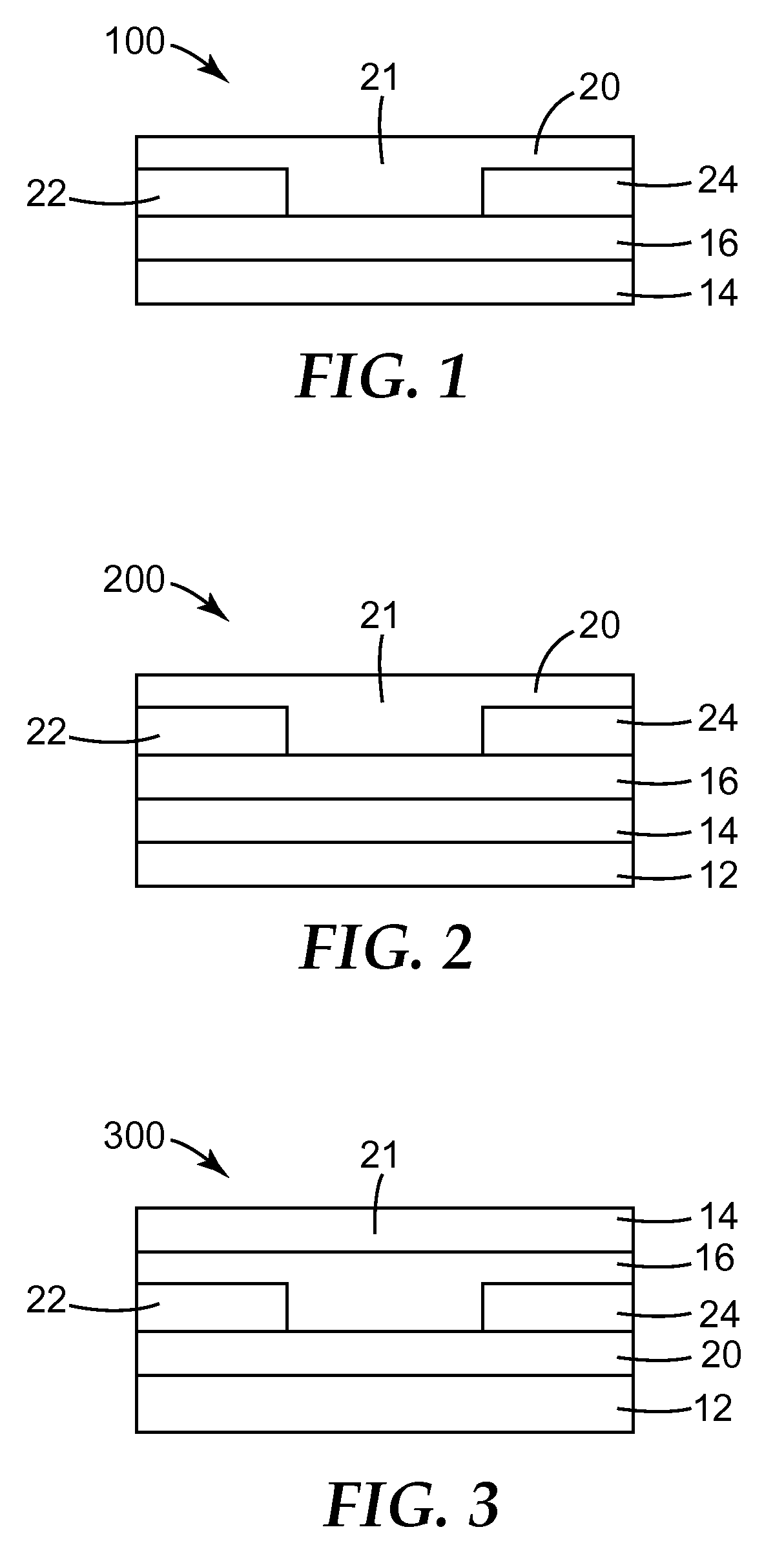
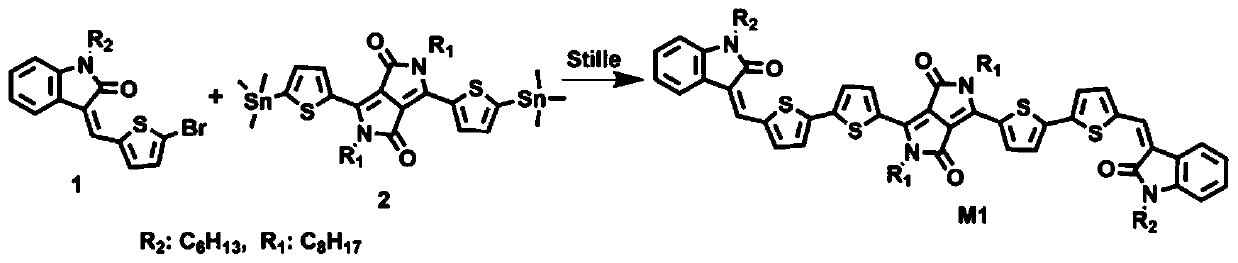
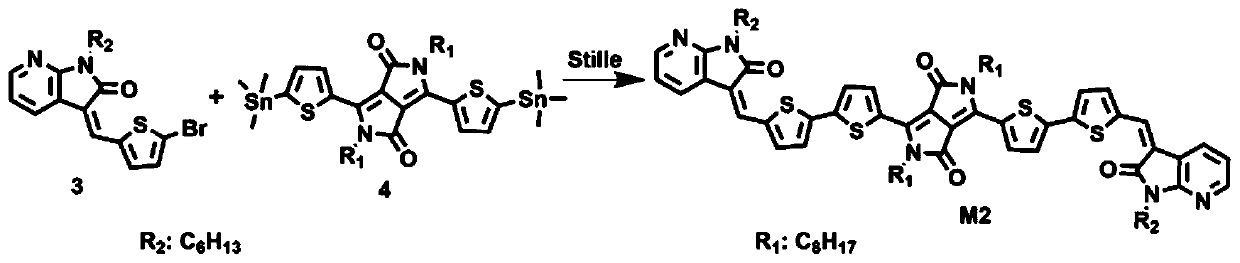
Molecular semiconductors containing diketopyrrolopyrrole and dithioketopyrrolopyrrole chromophores for small molecule or vapor processed solar cells
Optoelectronic devices, such as photovoltaic devices, comprising a low band gap, solution processable diketopyrrolopyrrole or dithioketopyrrolopyrrole chromophore core or cores are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of fabricating such optoelectronic devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Solution Processable Organic Semiconductors
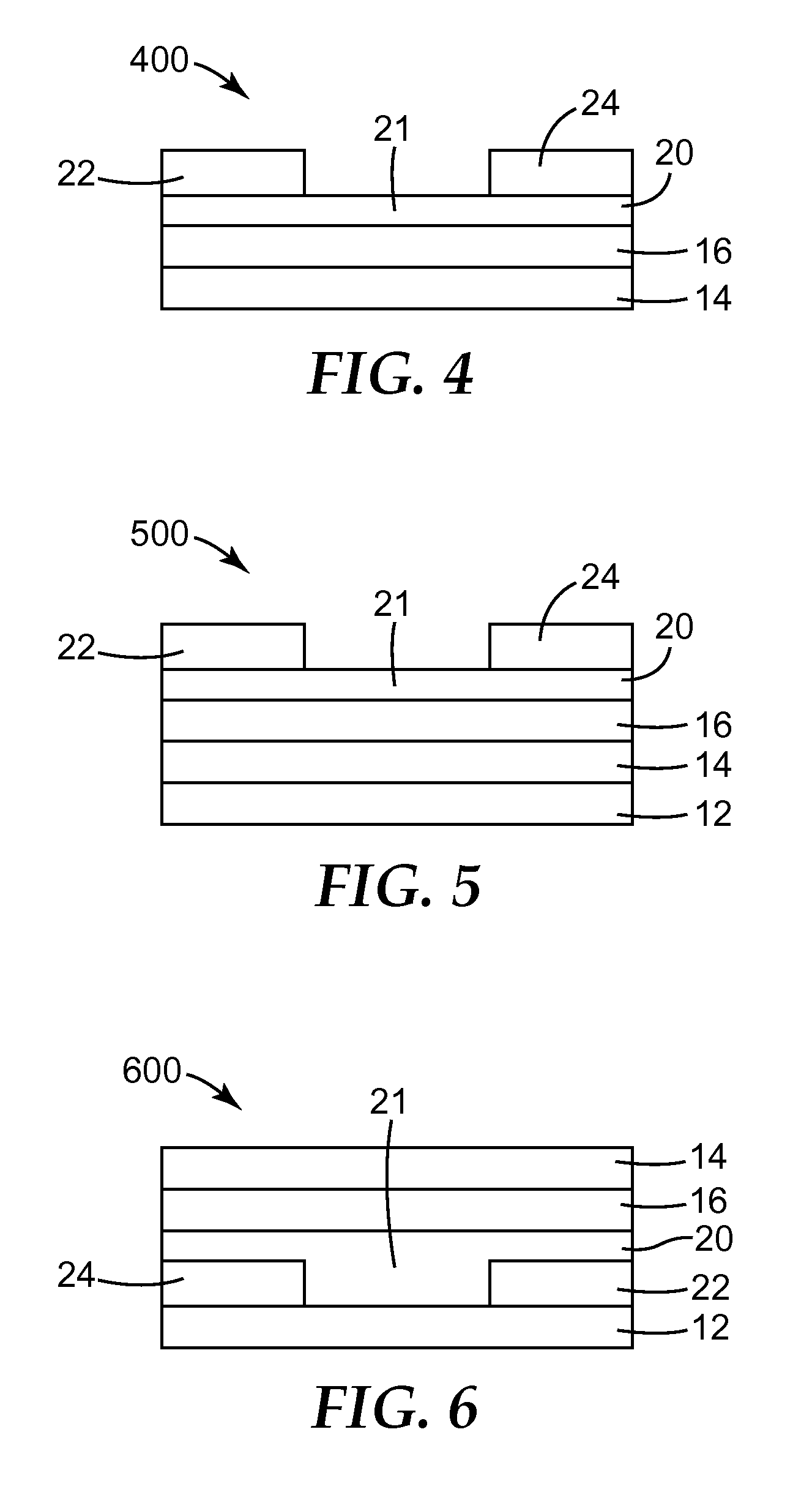
InactiveUS20100270542A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnthraceneSilylene
Semiconductor devices, methods of making semiconductor devices, and coating compositions that can be used to provide a semiconductor layer within a semiconductor device are described. The coating compositions include a small molecule semiconductor, an insulating polymer, and an organic solvent that can dissolve both the small molecule semiconductor material and the insulating polymer. The small molecule semiconductor is an anthracene-based compound (i.e., anthracene derivative) substituted with two thiophene groups as well as with two silylethynyl groups.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Preparation method of organic film transistor
ActiveCN102637825AFlexibleImprove mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmNanostructure
The invention discloses a method for preparing an organic film transistor. An active layer and an insulating layer consist of small-molecular semiconductors / insulating polymer crosslinking films, wherein the small-molecular semiconductor / insulating polymer crosslinking film consists of a one-dimensional Internet-shaped nano-structure formed by the small-molecular semiconductor material in an insulating polymer / solvent system. The organic film transistor provided by the invention has the characteristics of solubilization preparation, flexibility and high migration rate; and meanwhile, the preparation method provided by the invention can realize simple solubilization preparation of the active layer and insulating layer of the transistor, reduces the preparation cost, and has important application values in the preparation of a flexible, large-area and low-cost organic film transistor.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
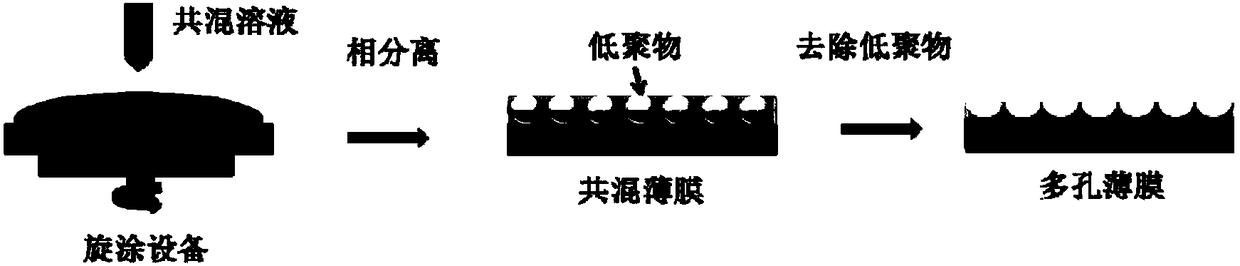
Method for preparing porous organic semiconductor film by using solution method and application thereof
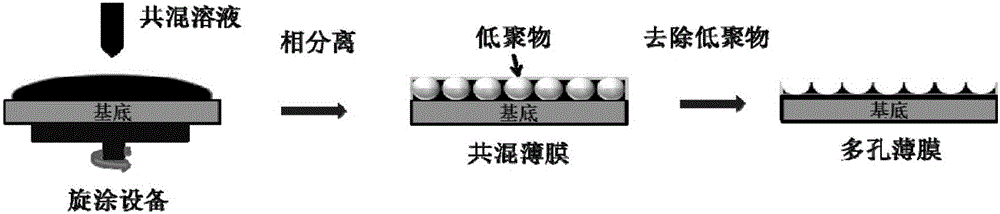
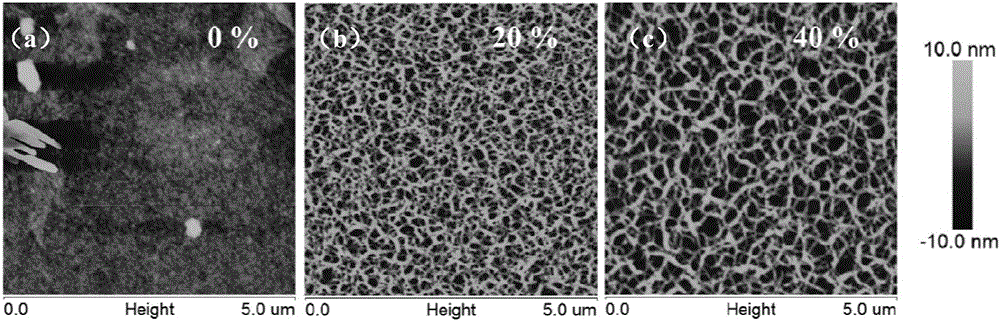
ActiveCN105842302ASolve problems that are not suitable for evaporation processesSimple methodMaterial resistanceOligomerMolecular semiconductor
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous organic semiconductor film by using a solution method and application thereof. The method is characterized by including: dissolving organic semiconductor with high molecular weight and oligomer with low molecular weight in an organic solvent to obtain a blending solution; spin-coating the blending solution on the substrate to form a blending film by a solution spin-coating method, and using an appropriate solvent to dissolve and remove the oligomer with low molecular weight in the blending film to obtain the porous organic semiconductor film. The porous film is prepared by the solution method, and the method is simple, has good repeatability, has low requirements of the device and technology condition, and is suitable for preparing most of the high-molecular semiconductor porous films. The porous organic semiconductor film prepared by the invention can be used for the gas phase sensor, and can significantly improve the detection effect of the organic semiconductor material on the corresponding gas analyte by means of providing an effective gas dispersion channel.
Owner:黄山市开发投资集团有限公司
Novel organic polymer semiconductor compounds, methods of forming organic polymer semiconductor thin film using the same, and organic thin film transistors using the same
ActiveUS20060255334A1Improve solubilityLeakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic filmSide chain
Disclosed herein is an organic polymer semiconductor compound, a method of forming an organic polymer semiconductor thin film using the same, and an organic thin film transistor using the same. Example embodiments of this invention pertain to an organic polymer semiconductor having a side chain including a removable substituent, and to an organic thin film transistor using the organic polymer semiconductor for an organic active layer, which has lower leakage current, higher charge mobility, and / or a higher on / off ratio.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Double-parameter and high-sensitivity organic small molecular semiconductor film magnetic sensor
InactiveCN101858961AReduce power consumptionImprove efficiencyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesElectronic transmissionData acquisition
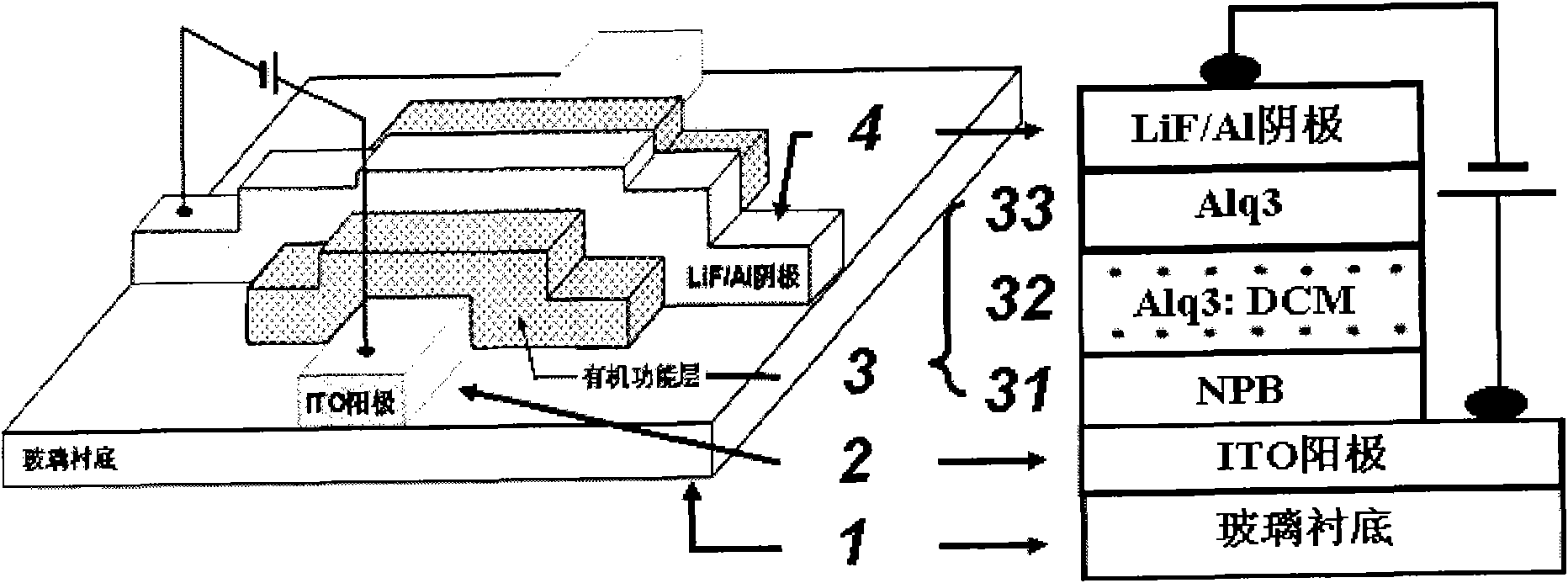
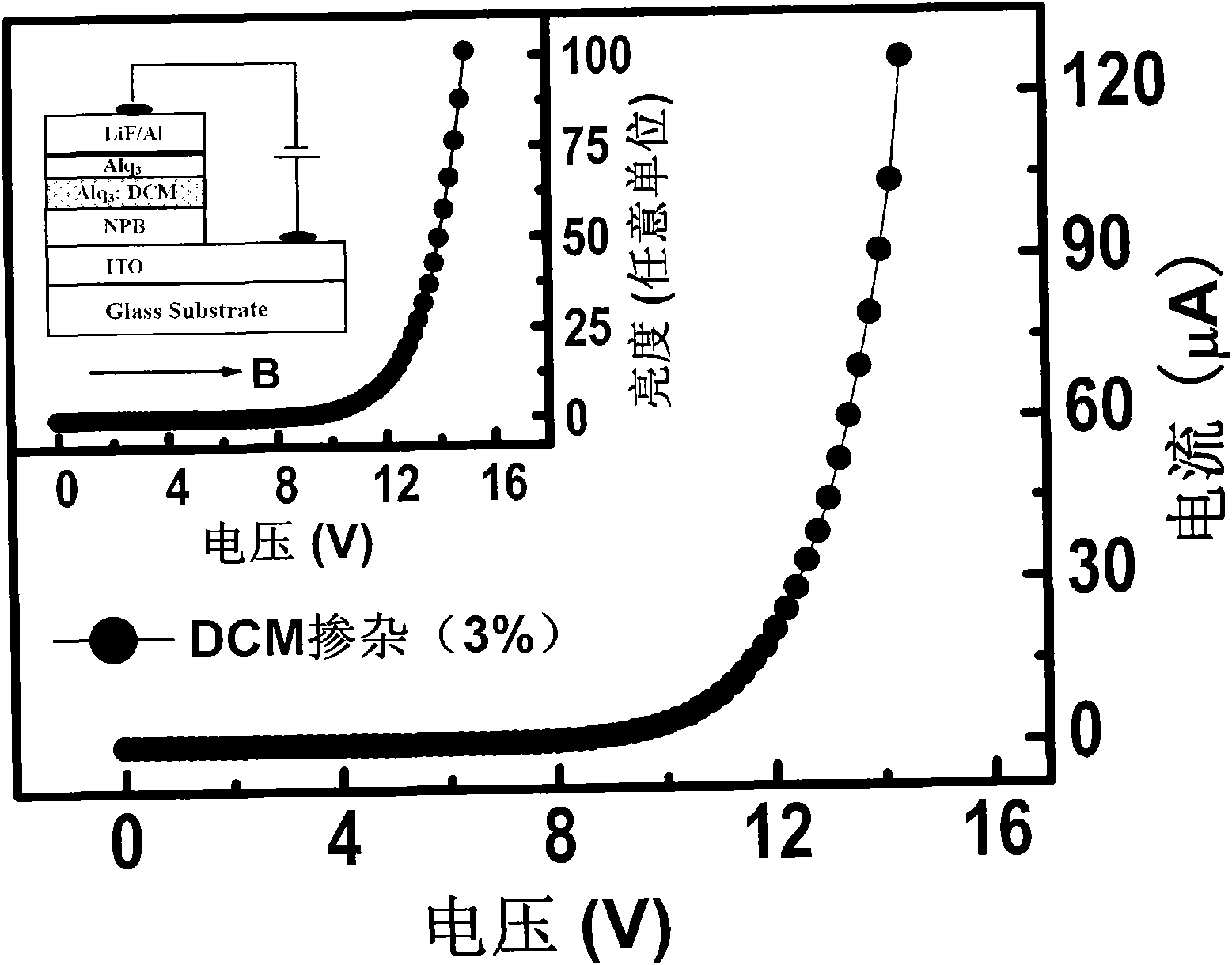
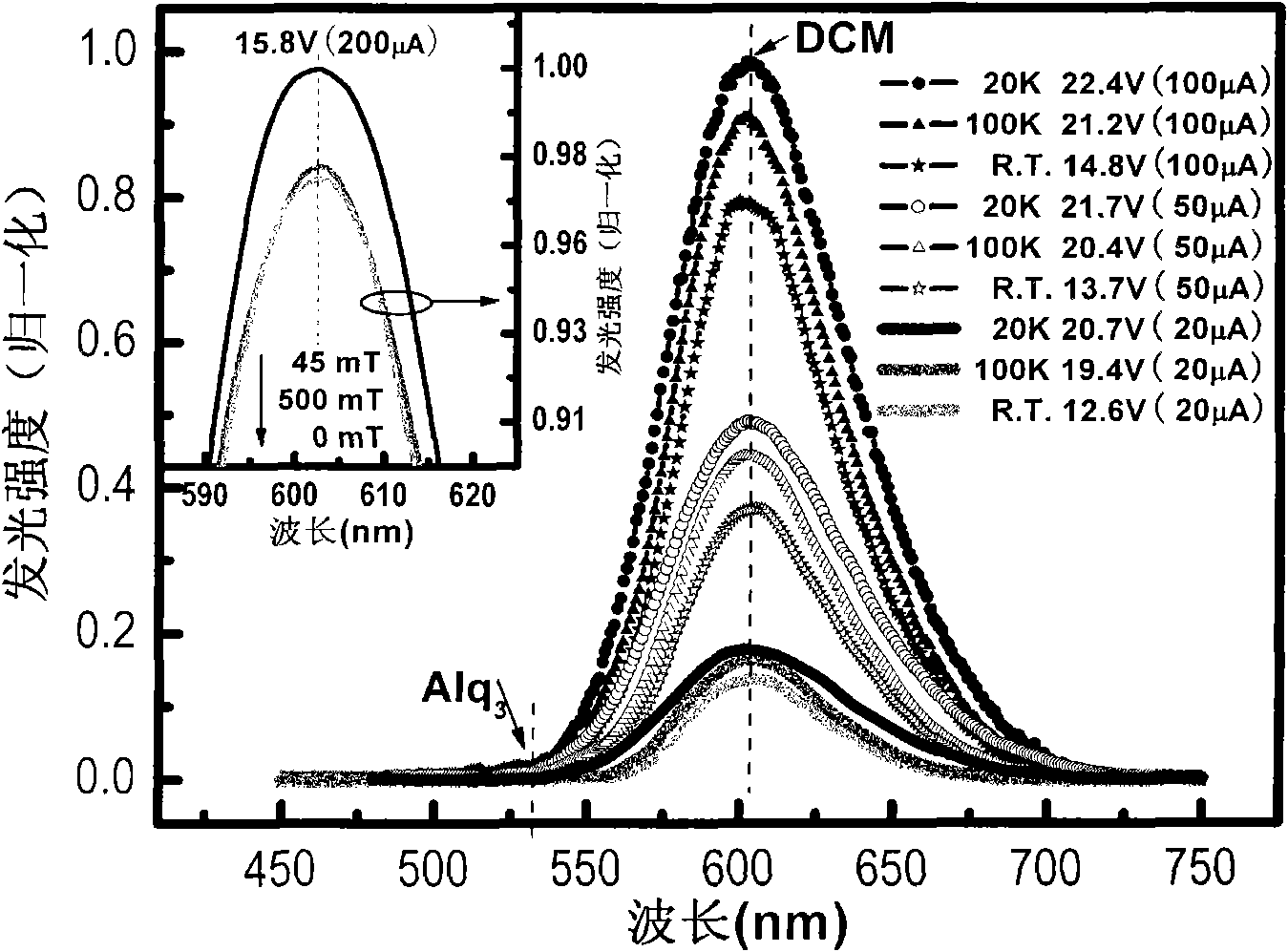
The invention provides a double-parameter and high-sensitivity organic small molecular semiconductor film magnetic sensor, which is an organic electroluminescence material Alq3-based organic semiconductor film device. The magnetic sensor has a laminated film structure, and the structure comprises a substrate, a conductive transparent anode ITO, an organic material functional layer and a LiF / Al cathode from the bottom to the top; the organic material functional layer consists of a hole transmission layer NPB, a sensing layer Alq3: 3 percent doping agent DCM and an electronic transmission layer Alq3; and the electroluminescence intensity of the magnetic sensor is measured by a silicon photoelectric probe and output through a digital universal meter, and the obtained signal is finally acquired by a computer through a data acquisition module. The magnetic sensor also has the advantages of the current popular MR sensor such as low power consumption, high sensitivity, small size and the like, can realize double-parameter (namely magnetic resistance and magnetic luminescence) response, and has good thermal stability at the same time; and the reliability of the sensor is greatly enhanced.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
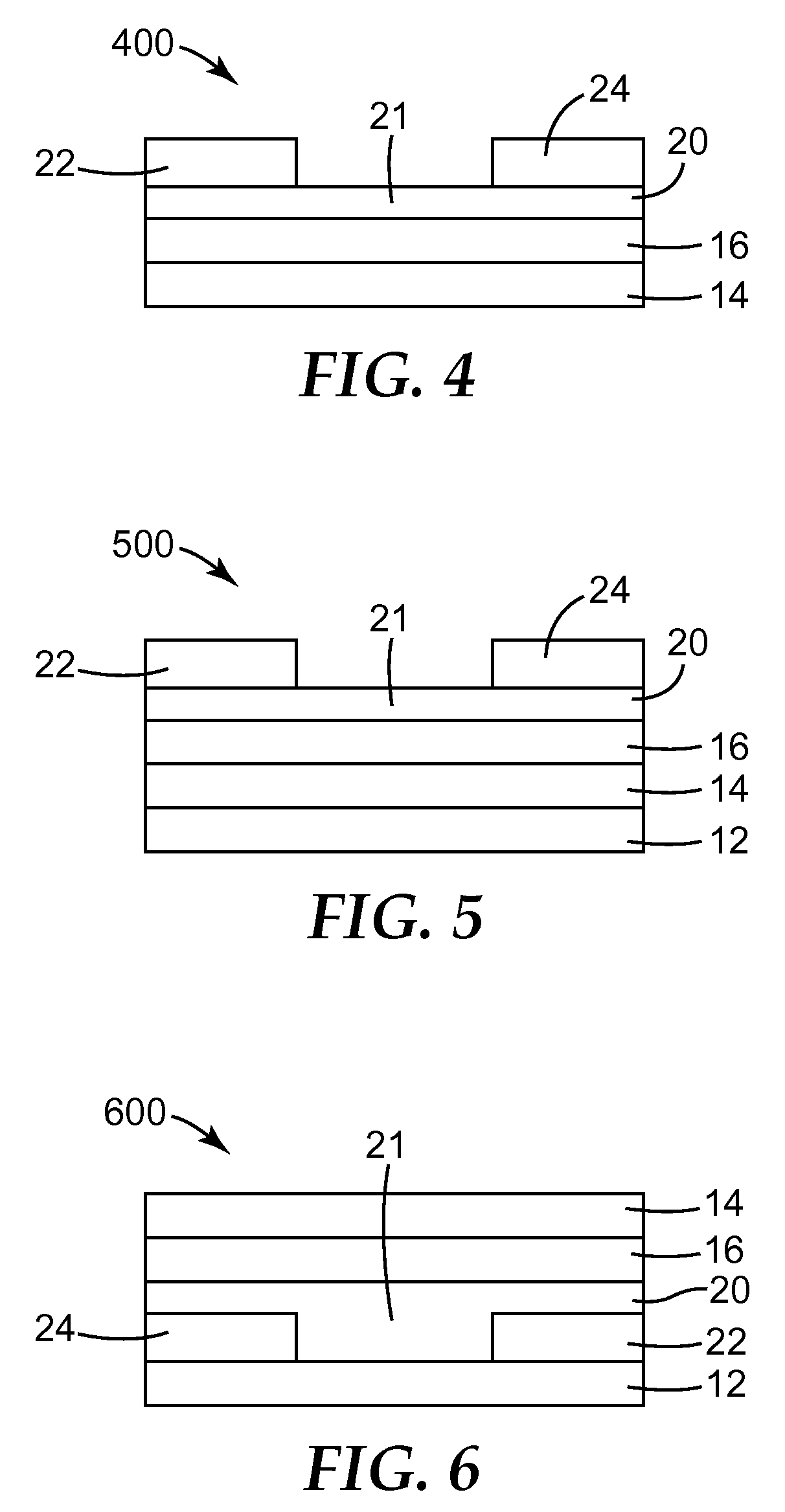
Low contact resistance organic thin film transistors
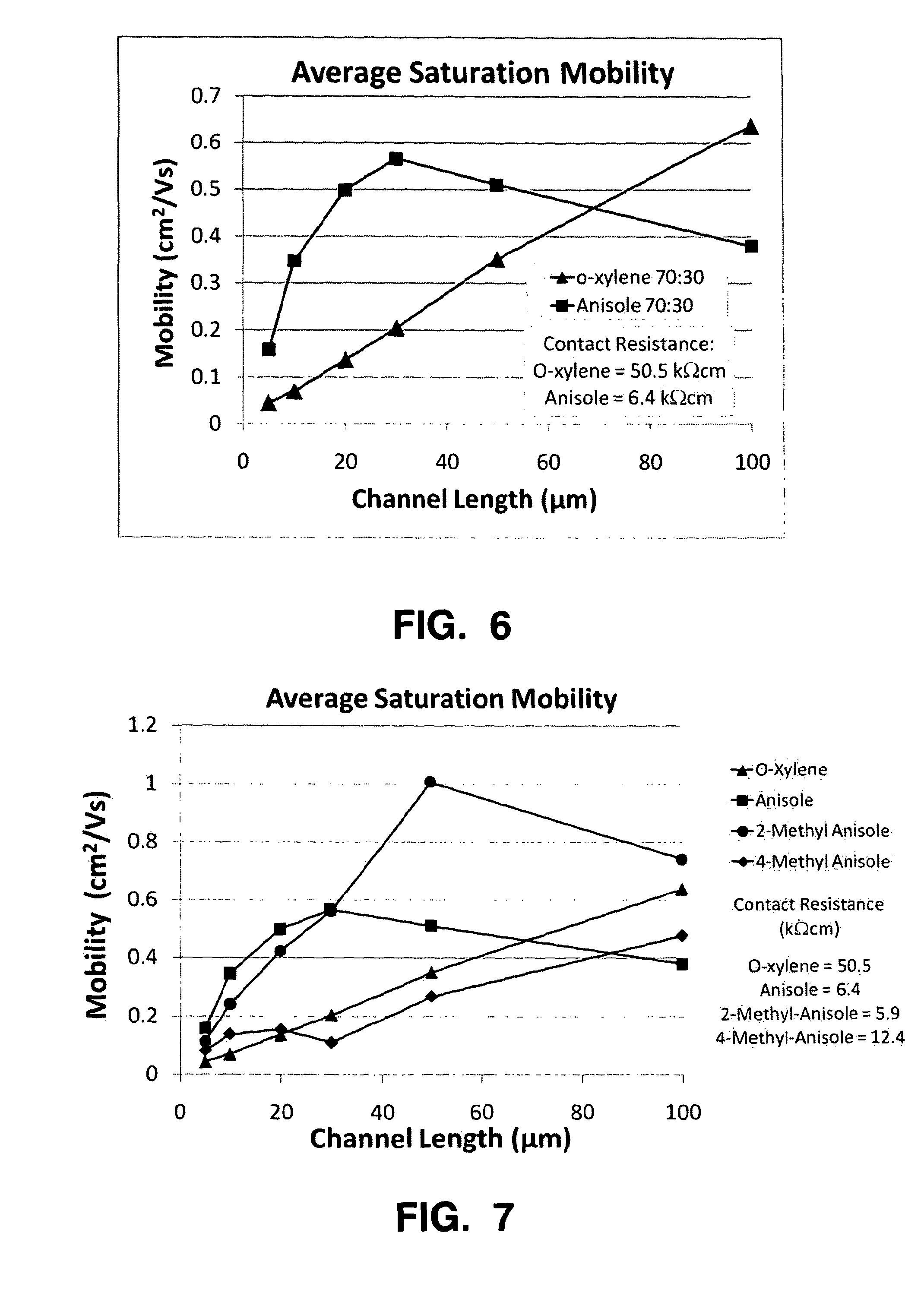
ActiveUS20130149812A1Reduce contact resistanceReduce biasConductive materialSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsSolvent
The invention provides the use of a solvent selected from the group consisting of alkoxybenzenes and alkyl substituted alkoxybenzenes in reducing the contact resistance in an organic thin film transistor comprising a semiconductor layer comprising a blend of a small molecule semiconductor material and a polymer material that is deposited from a solution of said small molecule semiconductor material and said polymer material in said solvent and novel semiconductor blend formulations that are of particular use in preparing organic thin film transistors. Said solvents yield devices with lower absolute contact resistance, lower absolute channel resistance, and lower proportion of contact resistance to the total channel resistance.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
Novel thiophene-thiazole derivatives and organic thin film transistors using the same
InactiveUS20060151779A1High carrier mobilityReduce leakage currentOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic filmSemiconductor materials
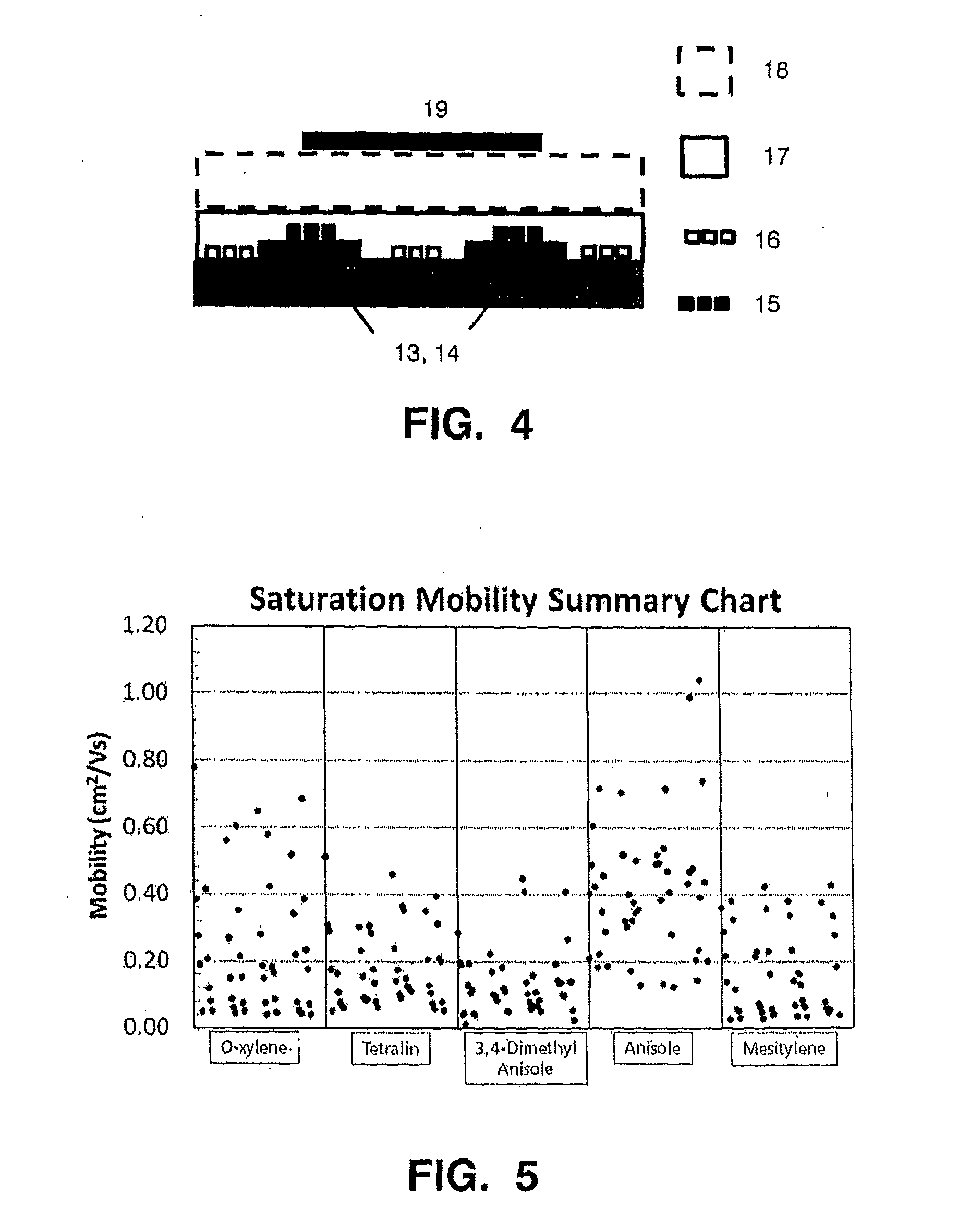
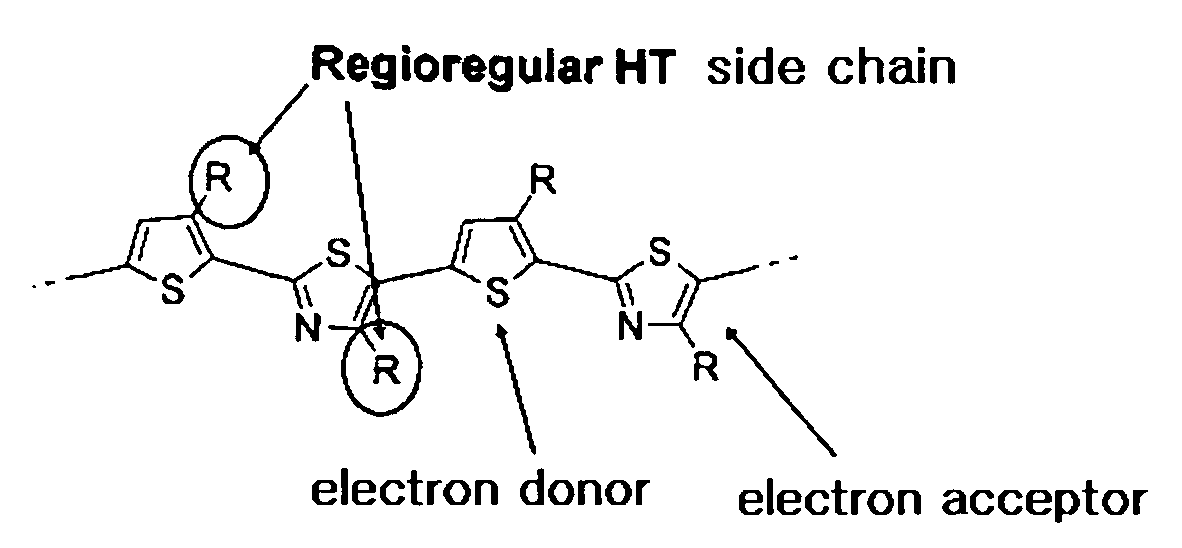
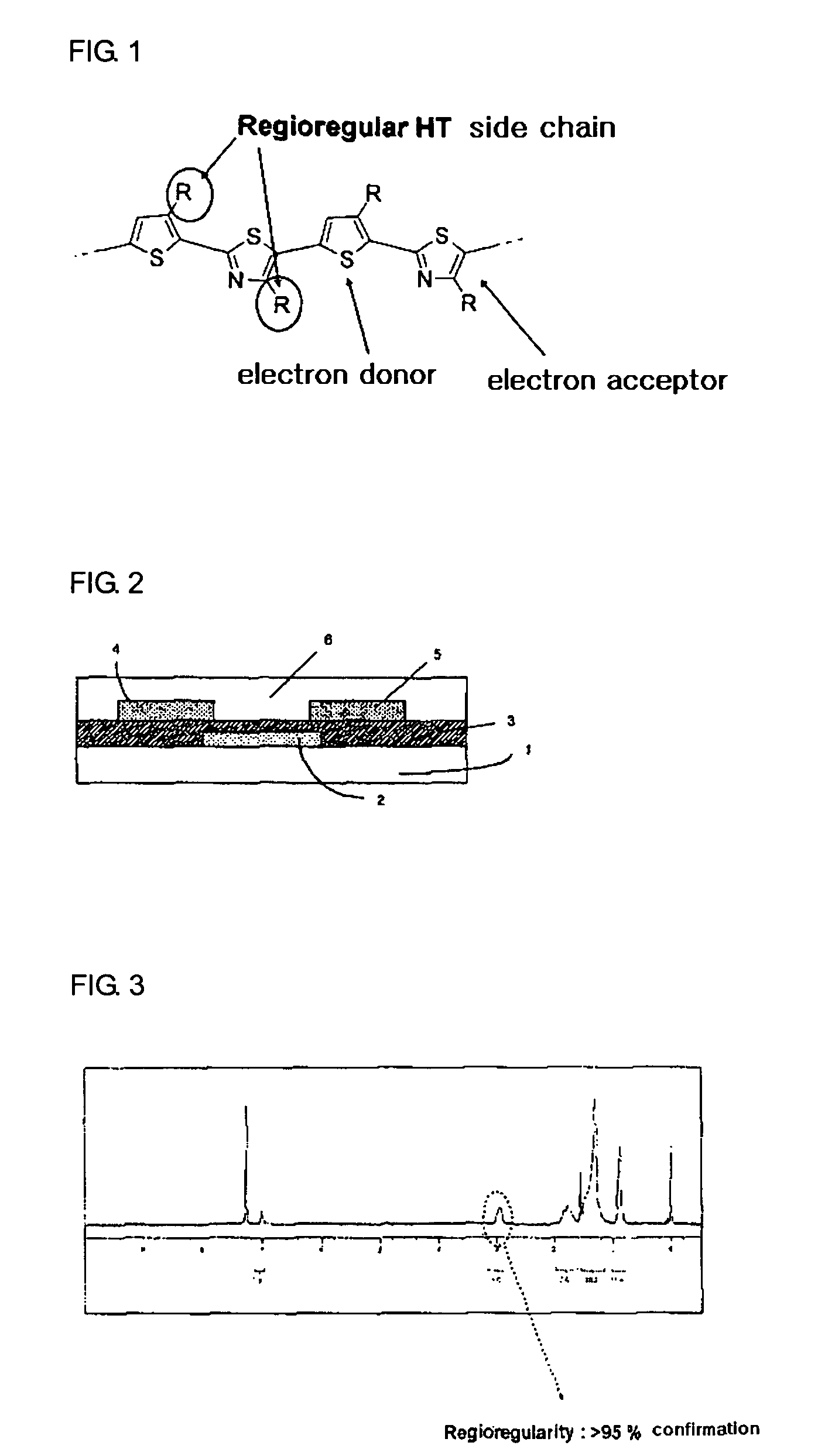
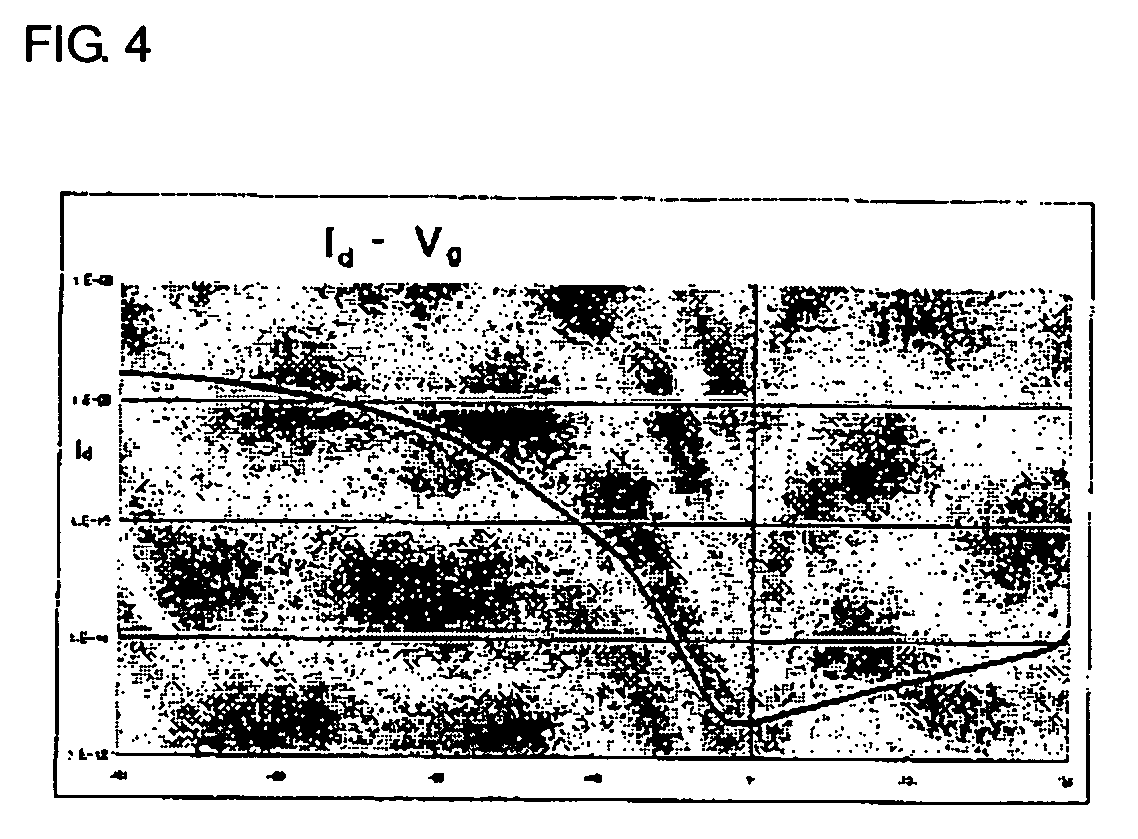
Novel thiophene-thiazole derivatives and organic thin film transistors using the derivatives. The thiophene-thiazole derivatives are organic polymer semiconductor materials in which a thiophene having p-type semiconductor characteristics is joined to a thiazole having n-type semiconductor characteristics in an alternating manner to have a head-to-tail structure. The use of the thiophene-thiazole derivatives as materials for an organic active layer enables fabrication of organic thin film transistors with low leakage current, high charge carrier mobility and high on / off current ratio.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fast ferroelectric transistor memory based on two-dimensional organic molecular semiconductors and preparation thereof
InactiveCN107275483AFast operationEasy to makeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFerroelectric polymersEvaporation
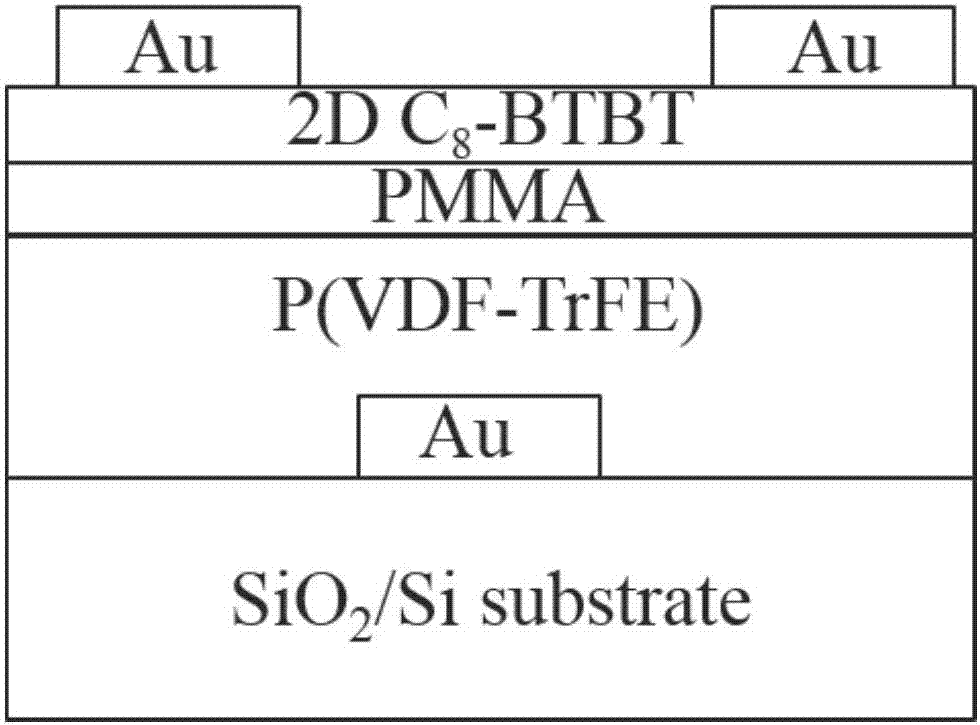
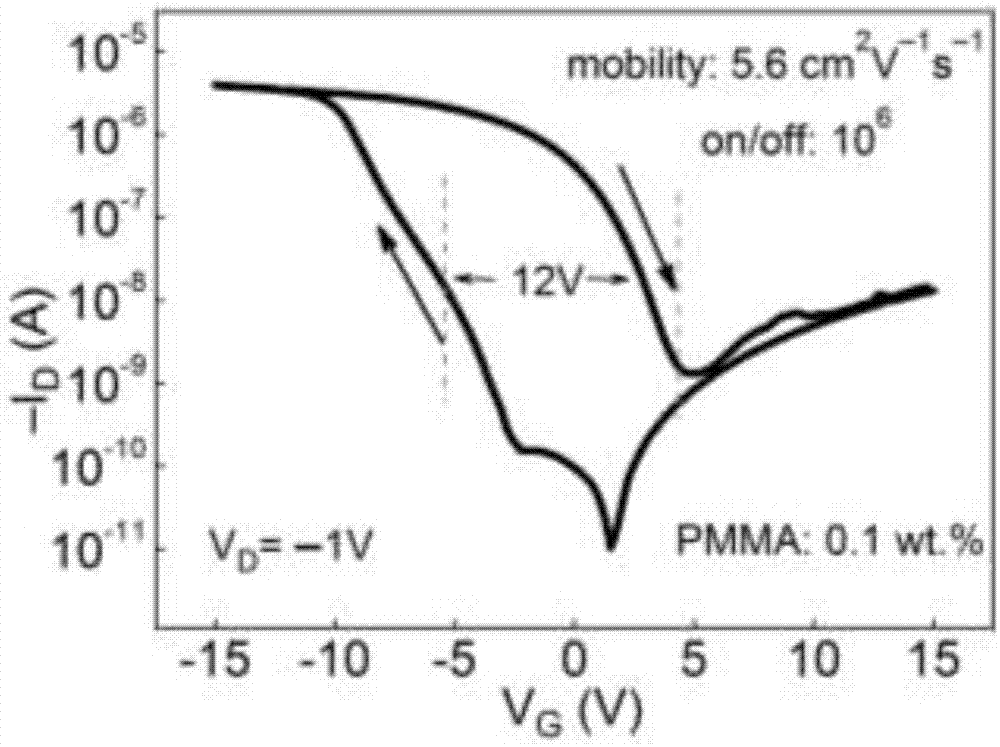
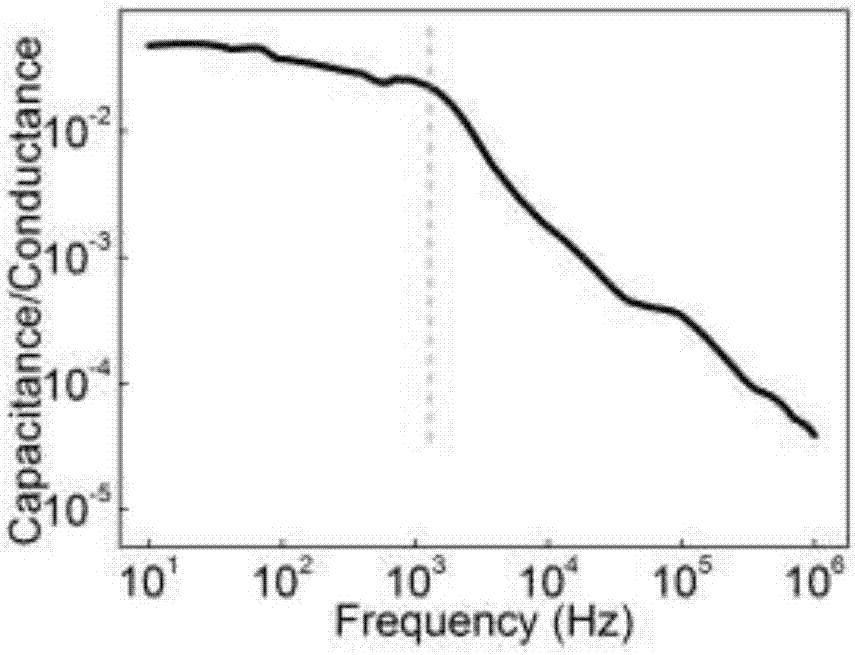
A fast ferroelectric transistor memory based on two-dimensional organic molecule semiconductors is prepared in a way that heavily doped p-type silicon is taken as a substrate and 50-250 nm silicon dioxide is grown and used as an insulating layer; a layer of 20-50 nm gold is prepared on the silicon dioxide by thermal evaporation and used as the gate, and then a layer of ferroelectric polymer material, poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene), is spin-coated on the gate; and a layer of untrathin polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) with thickness of 2-10 nm and a dioctyl benzothiophene benzothiophene semiconductor layer (C8-BTBT) with thickness of 5-10 nm are grown respectively on P (VDF-TrFE) by the floating coffee effect and the phase separation method, wherein the passivation layer PMMA is under the two-dimensional semiconductor layer C8-BTBT, gold is deposited on the semiconductor layer as a source and a drain to prepare a two-dimensional organic molecular semiconductor ferroelectric transistor memory having a bottom gate top contact structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Organic small molecular semiconductor material containing anthracene dithiophene as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108117563AGood light capture abilityHigh electron mobilityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOxygenStructural formula
The invention discloses an organic small molecular semiconductor material containing anthracene dithiophene as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The structural formula of the material is as shown in a formula I, wherein the unit A is an electron deficient group; R1 is hydrogen or alkyl with 1-30 carbon atoms or a group in the alkyl with 1-30 carbon atoms, one or more of which are replaced by halogen atoms, oxygen atoms, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, hydroxyl, amino, carboxyl, ester groups, cyan or nitryl. The material has unique advantages of relatively good light capturing ability, proper electronic energy level, relatively high electronic mobility and the like, and is applied to organic solar battery apparatuses as an electron acceptor material to obtain good apparatus performances.
Owner:东莞伏安光电科技有限公司
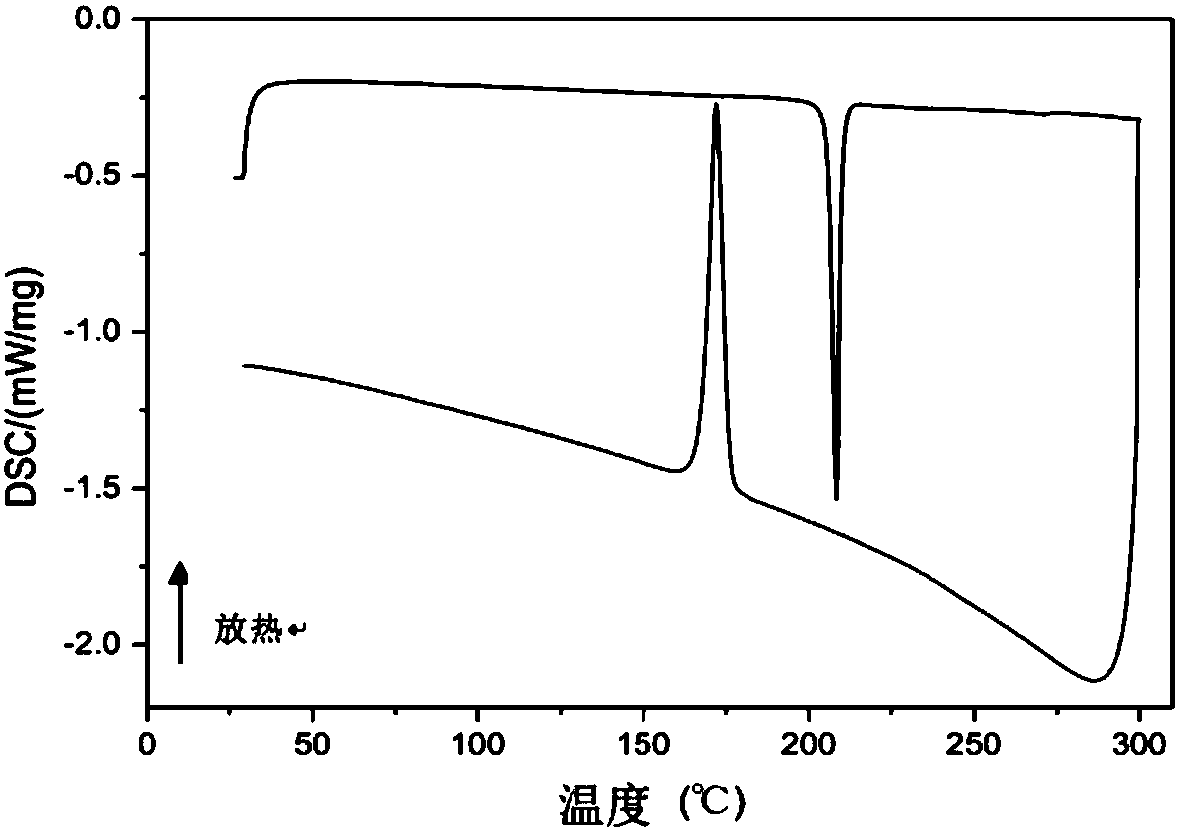
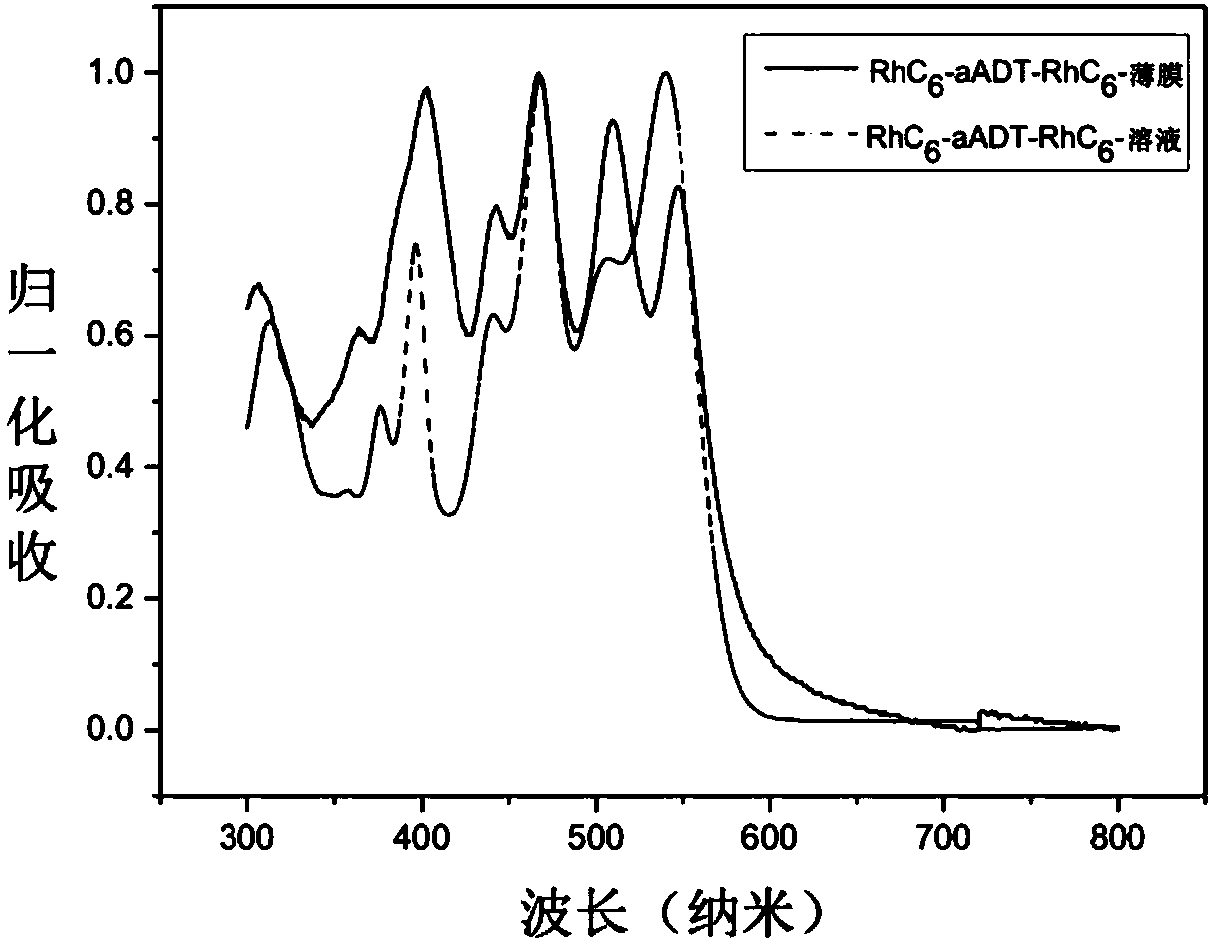
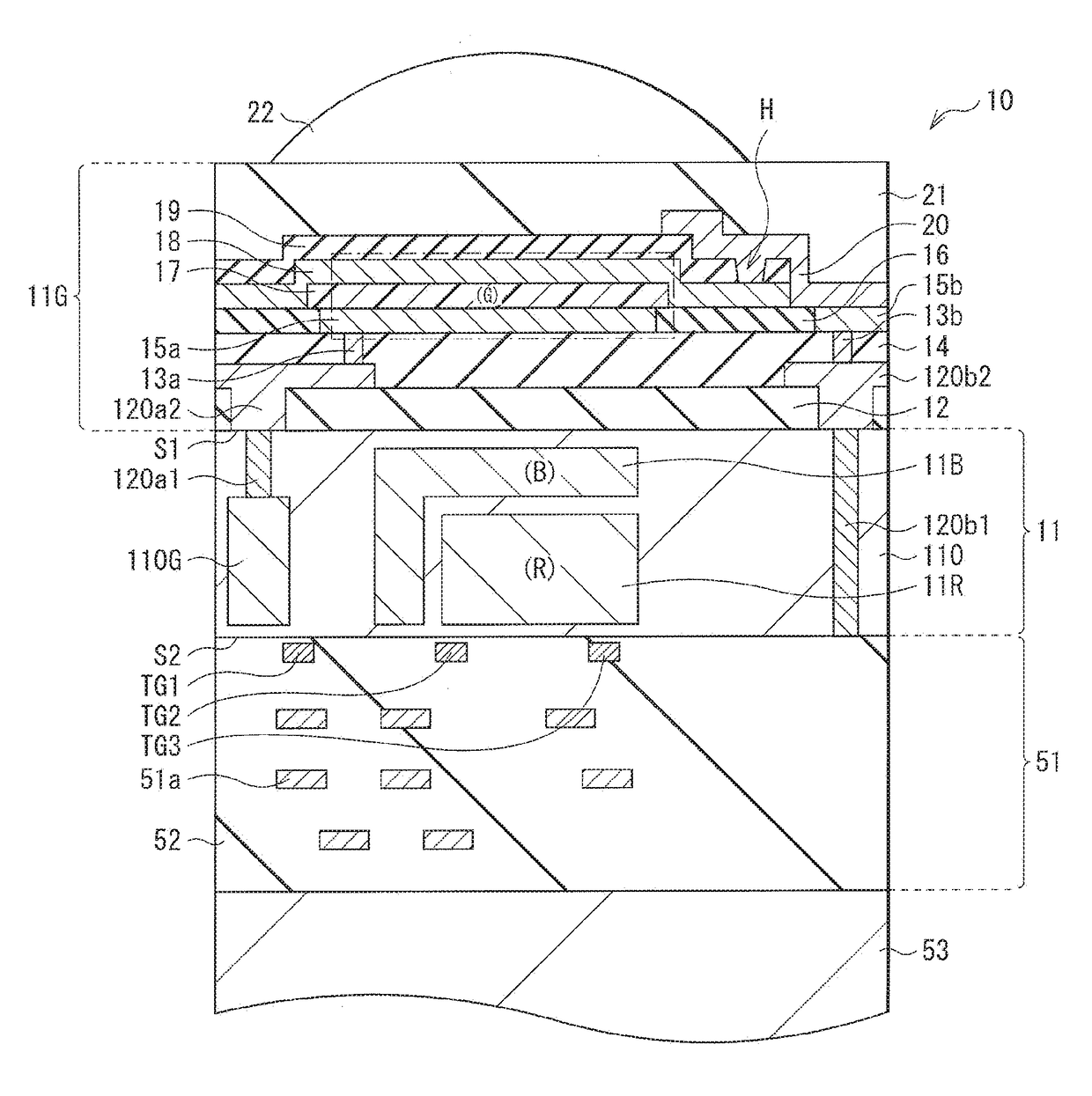
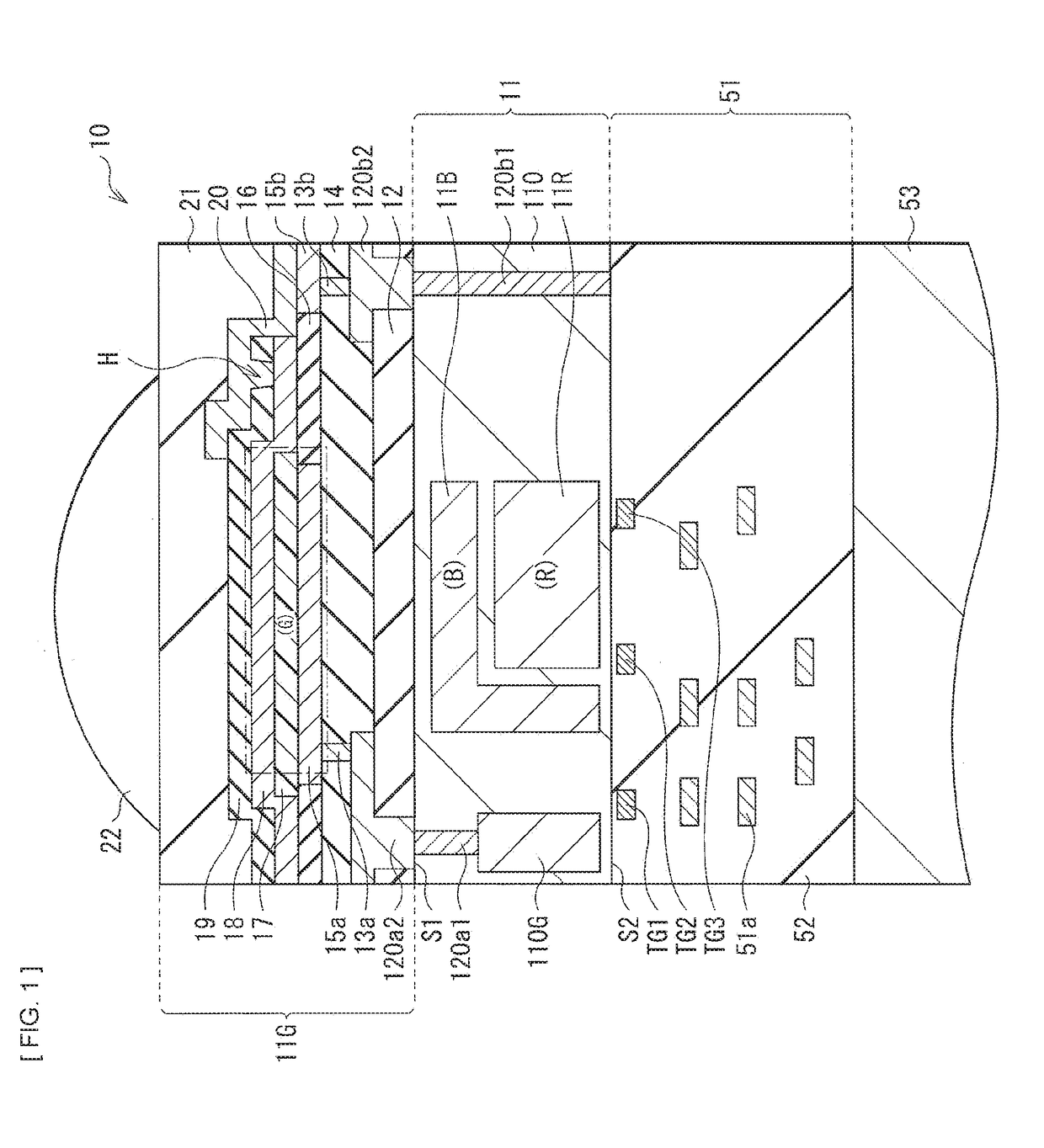
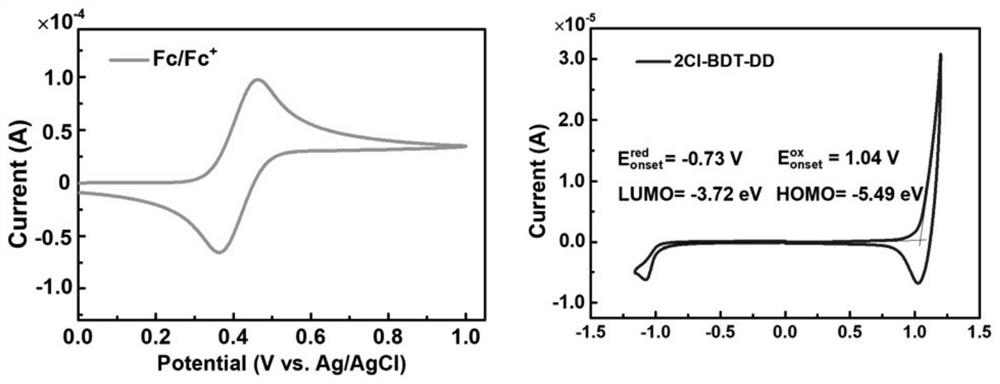
Photoelectric conversion element, imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20180233540A1High selectivityQuick responseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesMolecular materialsPhotoelectric conversion
A photoelectric conversion element according to one embodiment of the disclosure includes: a first electrode and a second electrode that are oppositely disposed; and a photoelectric conversion layer that is provided between the first electrode and the second electrode, and includes a high-molecular semiconductor material and a low-molecular material. The high-molecular semiconductor material has an absorption coefficient in a visible light region of 50000 cm−1 or less. The low-molecular material includes an absorption peak in a wavelength range corresponding to one color in the visible light region.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Low contact resistance organic thin film transistors
InactiveUS9159926B2Reduce contact resistanceReduce biasSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSemiconductor package
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
System and Method of Computing and Rendering the Nature of Molecules,Molecular Ions, Compounds and Materials
InactiveUS20110066414A1Data visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesDisplay deviceMaxwell's equations
A method and system of physically solving the charge, mass, and current density functions of pharmaceuticals, allotropes of carbon, metals, silicon molecules, semiconductors, boron molecules, aluminum molecules, coordinate compounds, and organometallic molecules, and tin molecules, or any portion of these species using Maxwell's equations and computing and rendering the physical nature of the chemical bond using the solutions. The results can be displayed on visual or graphical media. The display can be static or dynamic such that electron motion and specie's vibrational, rotational, and translational motion can be displayed in an embodiment. The displayed information is useful to anticipate reactivity and physical properties. The insight into the nature of the chemical bond of at least one species can permit the solution and display of those of other species to provide utility to anticipate their reactivity and physical properties.
Owner:MILLS RANDELL L
Solution processable organic semiconductors
InactiveUS8178873B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnthraceneSemiconductor materials
Semiconductor devices, methods of making semiconductor devices, and coating compositions that can be used to provide a semiconductor layer within a semiconductor device are described. The coating compositions include a small molecule semiconductor, an insulating polymer, and an organic solvent that can dissolve both the small molecule semiconductor material and the insulating polymer. The small molecule semiconductor is an anthracene-based compound (i.e., anthracene derivative) substituted with two thiophene groups as well as with two silylethynyl groups.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Improvements in thin film production
InactiveCN101243560ABroaden prospects for commercial developmentImprove stabilitySpecific nanostructure formationMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon nanotubeThin membrane
The present invention discloses a method of manufacturing a film comprising uniformly dispersed carbon nanotubes, the method comprising the steps of: modifying a molecular semiconductor to render it soluble; modifying the molecular semiconductor to promote a high degree of molecular order; and Frontier orbital overlap between adjacent molecules; modifying carbon nanotubes to make them soluble; combining the soluble carbon nanotubes with the soluble molecular semiconductor in a solvent to form a solution; making the described film.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SURREY
A kind of method and application of solution method for preparing porous organic semiconductor thin film
ActiveCN105842302BSolve problems that are not suitable for evaporation processesSimple methodMaterial resistanceGas phaseSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing porous organic semiconductor film by using a solution method and application thereof. The method is characterized by including: dissolving organic semiconductor with high molecular weight and oligomer with low molecular weight in an organic solvent to obtain a blending solution; spin-coating the blending solution on the substrate to form a blending film by a solution spin-coating method, and using an appropriate solvent to dissolve and remove the oligomer with low molecular weight in the blending film to obtain the porous organic semiconductor film. The porous film is prepared by the solution method, and the method is simple, has good repeatability, has low requirements of the device and technology condition, and is suitable for preparing most of the high-molecular semiconductor porous films. The porous organic semiconductor film prepared by the invention can be used for the gas phase sensor, and can significantly improve the detection effect of the organic semiconductor material on the corresponding gas analyte by means of providing an effective gas dispersion channel.
Owner:黄山市开发投资集团有限公司
Transistor structure
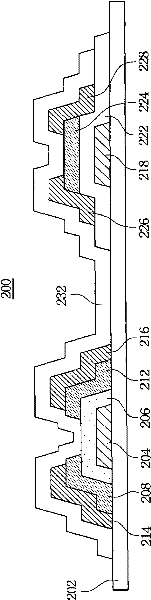
ActiveCN102447062ASolve the problem of low carrier mobilitySolve the costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionMolecular semiconductor
The invention relates to a transistor structure which comprises a patterning N-type transparent oxide semiconductor layer and a patterning P-type organic high molecular semiconductor layer. The patterning N-type transparent oxide semiconductor layer is formed on a baseplate to serve as a base electrode. The patterning P-type organic high molecular semiconductor layer is formed on the patterning N-type transparent oxide semiconductor layer and comprises a first part and a second part so that the patterning N-type transparent oxide semiconductor layer respectively forms heterojunction interfaces with the first part and the second part of the patterning P-type organic high molecular semiconductor layer, wherein the first part of the patterning P-type organic high molecular semiconductor layer serves as an emitting electrode, and the second part of the patterning P-type organic high molecular semiconductor layer serves as a collecting electrode.
Owner:E INK HLDG INC
Low-loss fluorine-containing polymer multilayer dielectric film and preparation method and application thereof
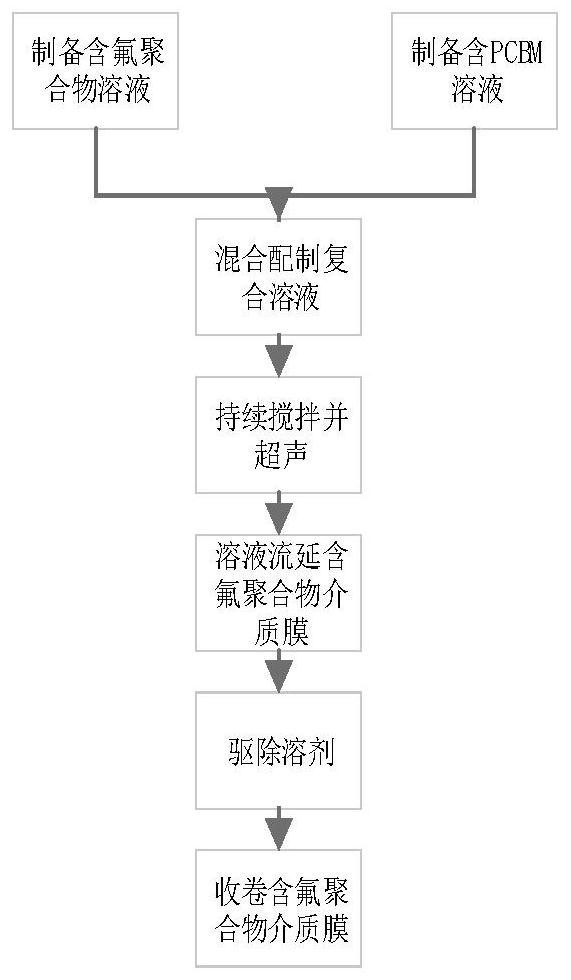
PendingCN114121490AImprove charge and discharge efficiencySuppress leakage currentThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricDielectricDischarge efficiency
The invention discloses a low-loss fluorine-containing polymer multilayer dielectric film as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Belongs to the technical field of polymer films. The method comprises the following specific steps: 1, preparing an organic molecule semiconductor solution and a fluorine-containing polymer solution; mixing the two solutions according to the ratio of (0.5-1.5): (98.5-99.5), stirring, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment for 24 hours to obtain a mixed solution of the fluorine-containing polymer / organic molecule semiconductor; casting the obtained fluorine-containing polymer / organic molecule semiconductor mixed solution on two sides of a low-loss polymer, and heating to remove the solvent to obtain a low-loss fluorine-containing polymer multilayer dielectric film; and metal electrodes are evaporated on the two sides of the obtained low-loss fluorine-containing polymer multilayer dielectric film. The interlayer composite dielectric film is widely applied to a thin-film capacitor, the loss of the low-loss fluorine-containing polymer multilayer dielectric film is obviously reduced, meanwhile, relatively good energy storage density and charge-discharge efficiency are kept, and the interlayer composite dielectric film is a dielectric film with excellent performance.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of few-layer organic crystalline state film and organic field effect transistor
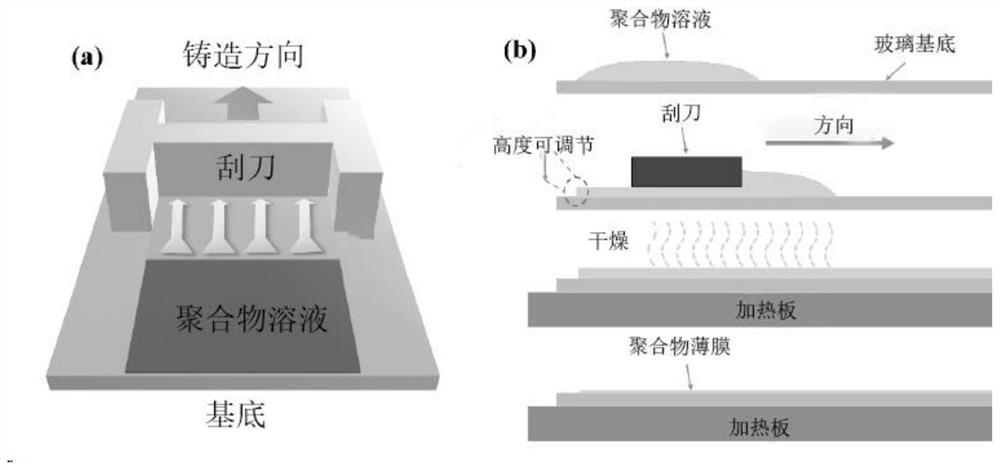
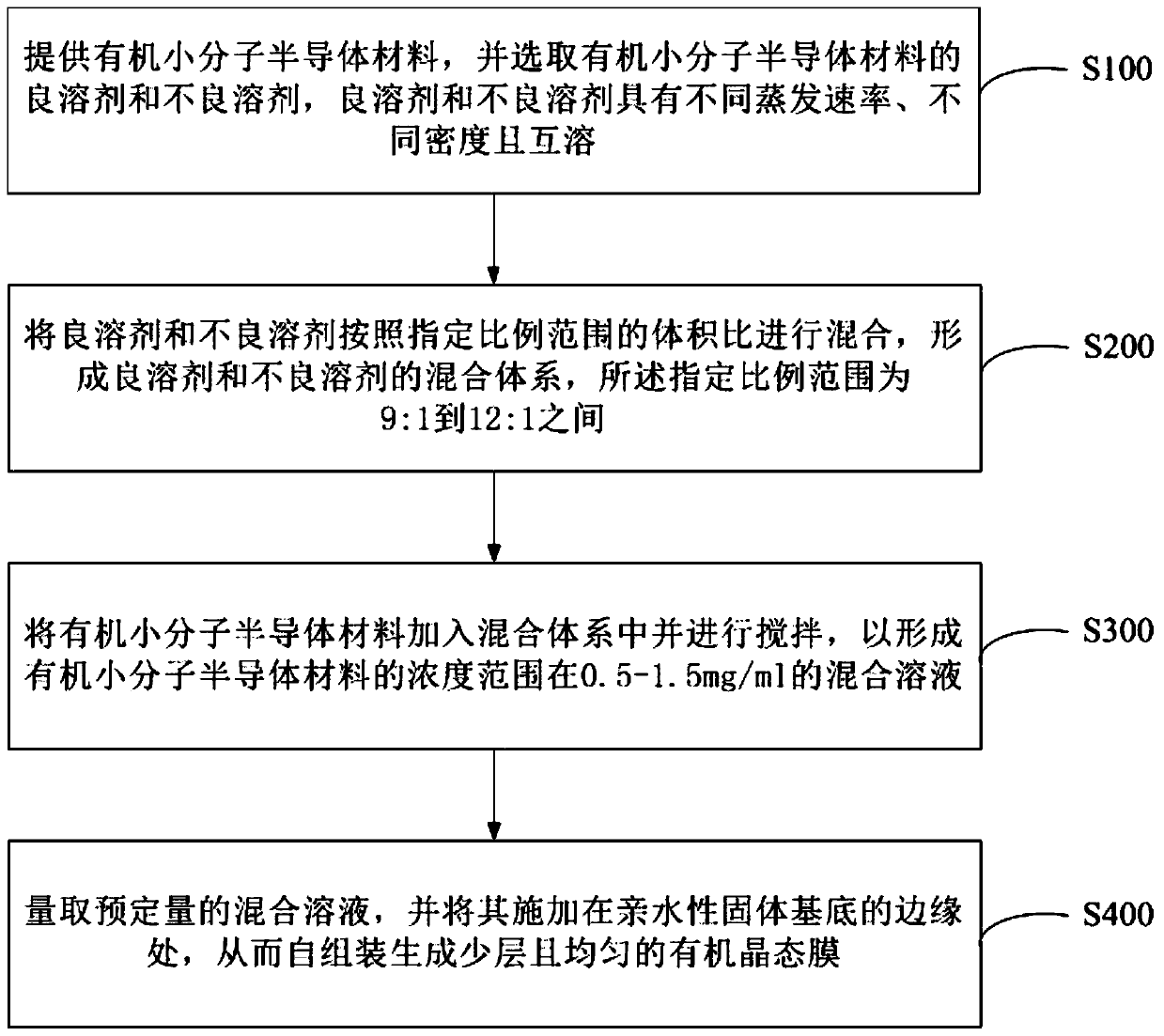
ActiveCN110265549AStrong convective depositionWith smoothnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic field-effect transistorSolvent
The invention provides a preparation method of a few-layer organic crystalline state film and an organic field effect transistor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: providing an organic small molecular semiconductor material, and selecting a good solvent and a bad solvent of the organic small molecular semiconductor material, wherein the good solvent and the poor solvent have different evaporation rates and different densities and are mutually soluble; mixing the good solvent and the poor solvent according to a volume ratio of a specified proportion range to form a mixed system of the good solvent and the bad solvent, wherein the specified proportion range is 9:1-12:1; adding the organic small molecular semiconductor material into the mixed system and carrying out stirring to form a mixed solution of the organic small molecular semiconductor material, wherein the concentration of the mixed solution is 0.5-1.5mg / ml; and weighing a predetermined amount of the mixed solution, and applying the mixed solution to the edge of a hydrophilic solid substrate, thereby generating the few-layer and uniform organic crystalline state film by self-assembly. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a one-step method can be used for directly and rapidly obtaining a high-uniformity few-layer organic crystalline state film structure ordered in a long-range surface.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Organic small-molecular semiconductor material containing anthracene tetrathiophene and application of material
ActiveCN108003176AGood light capture abilitySuitable electronic energy levelOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesStructural formulaOxygen
The invention discloses an organic small-molecular semiconductor material containing anthracene tetrathiophene and application of the material. The structural formula of the material is the formula I(the formula can be seen in the description), wherein a unit A is an electron-deficient group, and R1 and R2 are hydrogen, or alkyl groups with 1-30 carbon atoms, or groups formed by substituting oneor more carbon atoms in the alkyl groups with 1-30 carbon atoms with halogen atoms, oxygen atoms, alkenyl groups, alkynyl groups, aryl groups, hydroxyl groups, amino groups, carbonyl groups, carboxylgroups, ester groups, cyano groups or nitryl groups. The material has four active sites, can be connected with four electron withdrawing groups, and is high in chemical modification property; the organic semiconductor material has good light capturing capacity, is beneficial for obtaining high electronic mobility due to the large conjugate plane, and can be used as an electron acceptor material inthe field of organic battery devices. The material is used as the electron acceptor material in organic solar battery devices, and good device performance is obtained.
Owner:东莞伏安光电科技有限公司
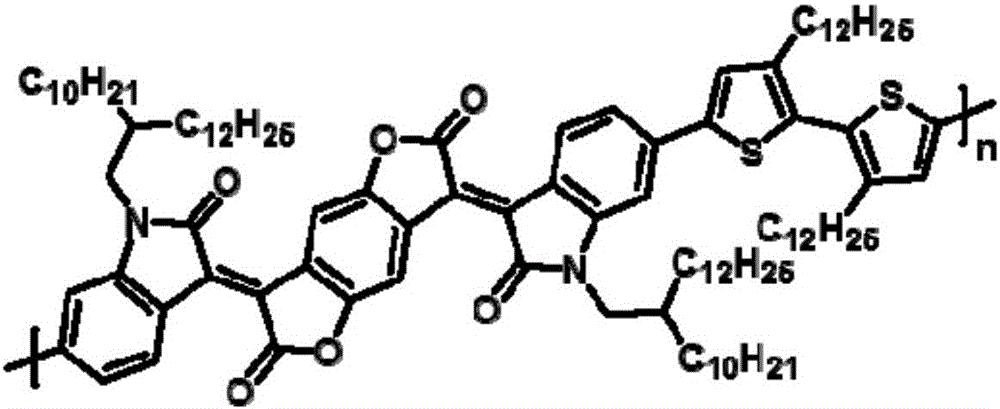
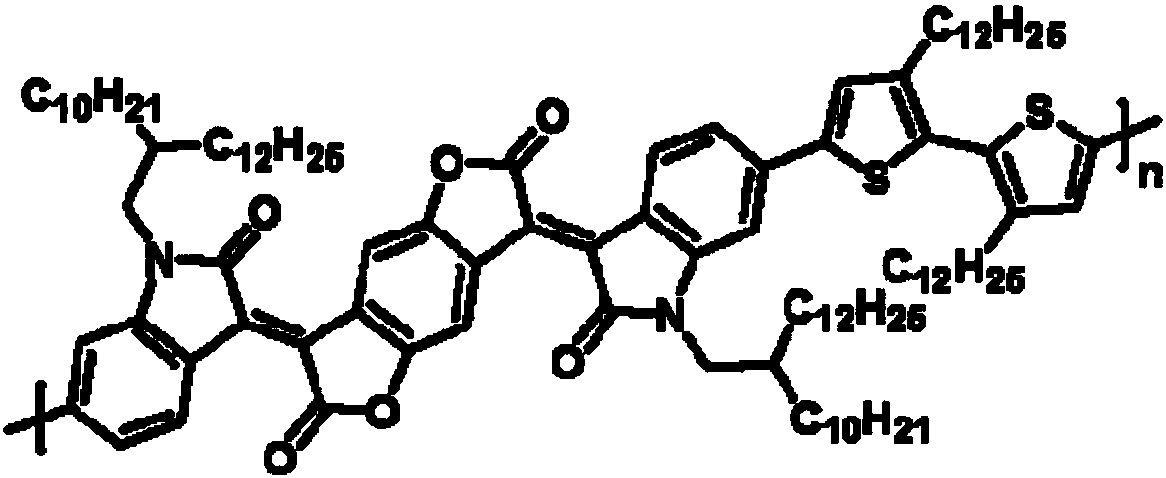
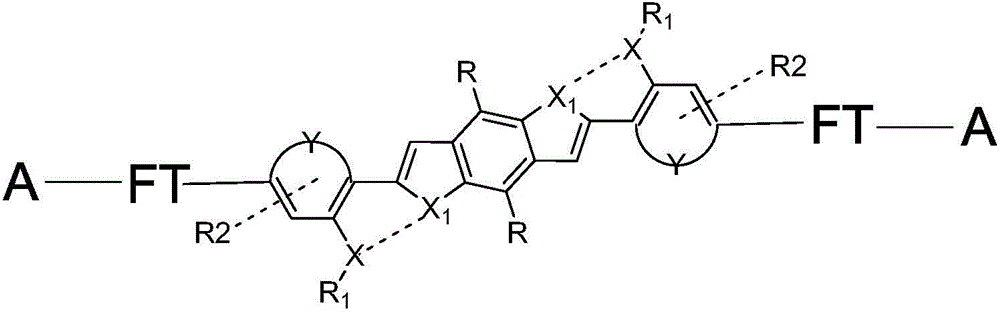
Solution-processible conjugated micro-molecular semiconductor materials based on thiophene pyrrolopyrroledione and semi-indigo
InactiveCN110818730AImprove solubilityGuaranteed processing effectOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic filmMolecular semiconductor
The invention discloses novel A2-D-A1-D-A2 type conjugated micro-molecular semiconductor materials taking pyrrolopyrroledione and a semi-indigo unit as acceptors (A1 and A2) and a bithiophene bridge as a donor (D). The novel conjugated micro-molecular semiconductor materials have the advantages of clear molecular structure and molecular weight, no batch difference, solution processing characteristic and good film-forming property. Organic thin film transistor devices show that semiconductors with the structure have an electron transmission characteristic, and the spectrum absorption covers visible light and extends to the near-infrared field, so that the materials can be processed by a solution, and have wide application prospects in the organic electronic fields of organic thin film transistors, organic photovoltaics, organic thermoelectricity and the like.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
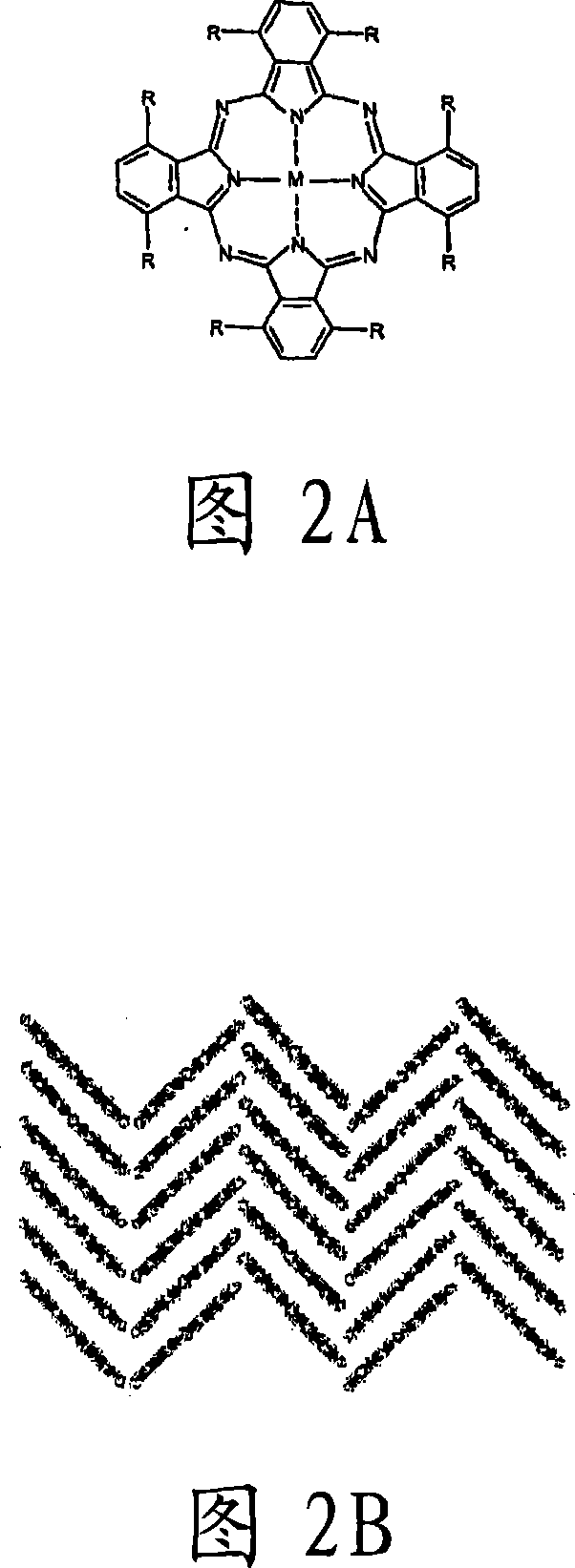
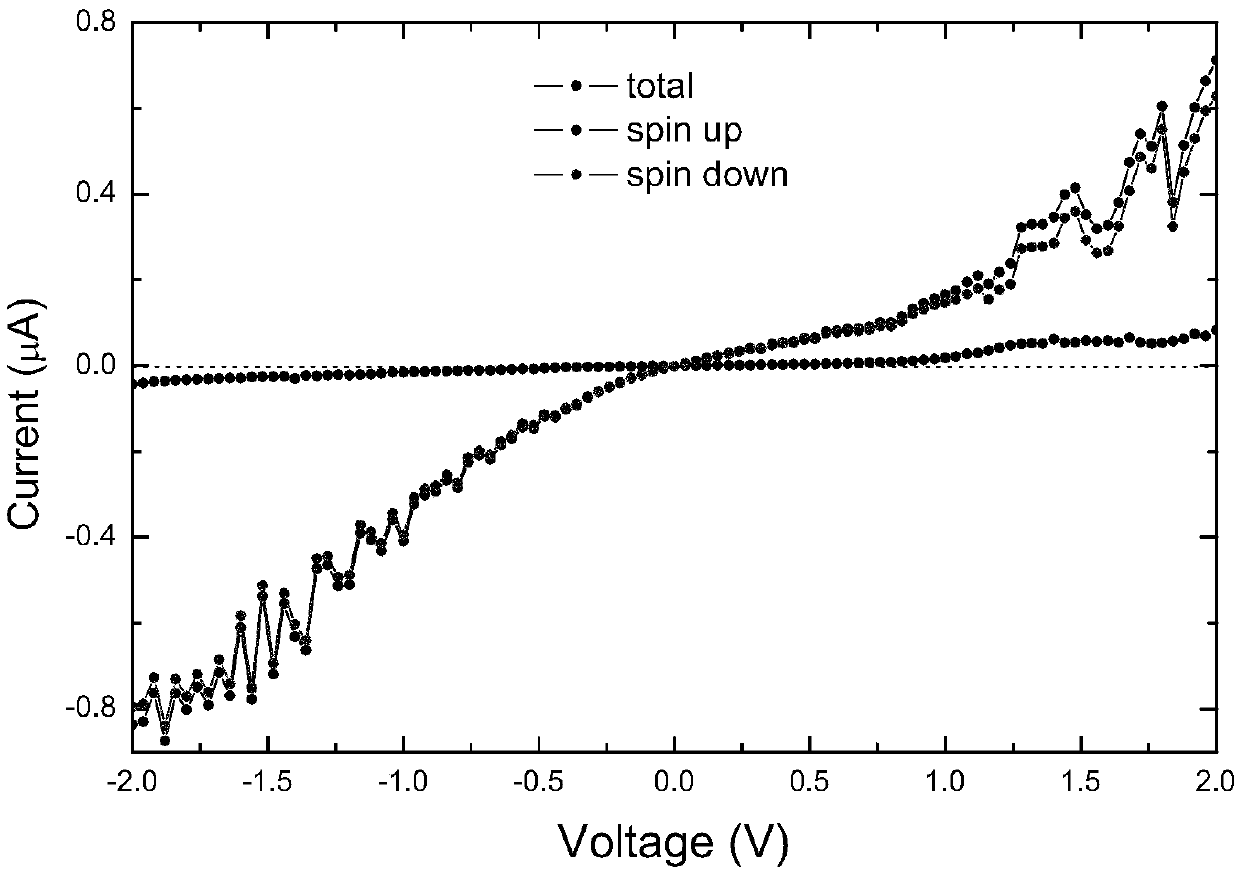
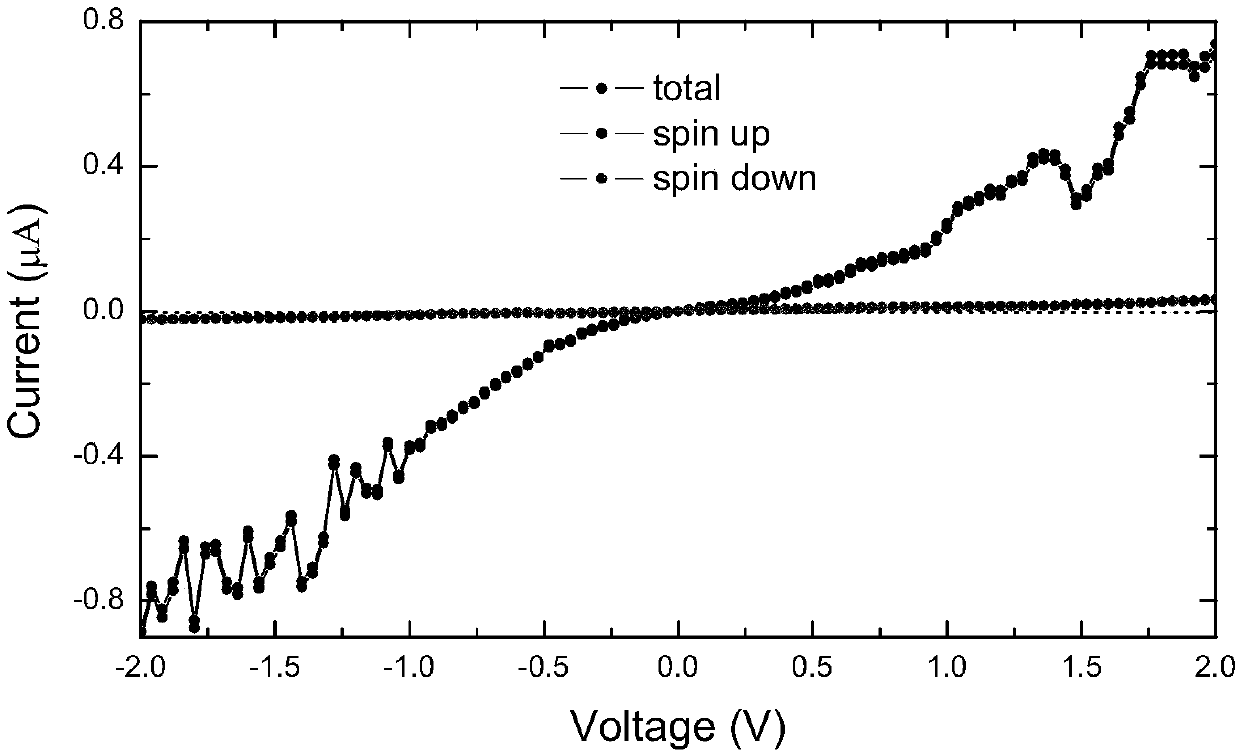
Cobalt-molecular multiferroic material based spin filtering heterojunction device and preparation thereof
ActiveCN108206204AEasy to manufactureInteresting spin filter effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionMetallic materials
The invention relates to a cobalt-molecular multiferroic material based spin filtering heterojunction device and preparation thereof. The spin filtering heterojunction device comprises two cobalt electrodes as source and drain electrodes respectively, a molecular multiferroic material (NH4)3Cr2O8 forming a thin material layer of an intermediate scattering area between the two cobalt electrodes, and grids connected to the two sides of the molecular multiferroic material (NH4)3Cr2O8; and the two cobalt electrodes include thin layers formed by metal materials cobalt respectively. Compared with the prior art, The molecular multiferroic material (NH4)3Cr2O8 makes contact with the surfaces of the Co electrodes to form a unique spin filtering effect due to spin interaction between 3d tracks of chromium ions (Cr5+) in the magnetic center of the molecular multiferroic material (NH4)3Cr2O8; and in addition, the spin filtering effect is sound and stable and is irrelevant to the type of a semiconductor substrate of a device, and the device is easy to realize, and can be widely applied to molecular semiconductor electronic devices.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Device for registration of optical holograms on the amorphous molecular semiconductor films
InactiveUS6998197B2Lowering of dark conductivityEliminate bulkyPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansZeroth orderLight beam
This invention relates to the field of holography, in particular to a method and a device for recording optical holograms by means of amorphous molecular semiconductor (AMS) films deposited on a glass substrate pre-covered with a transparent electric conducting sub-layer. More precisely, the invention relates to a method and device for registering optical holograms on AMS-films which operates in such a way that the AMS-films possess the maximum achievable information parameters: Holographic sensitivity, optimal spatial frequency of the transmitted characteristic, band parameters for the spatial frequencies of the transmitted characteristic, “signal-to-noise” ratio in the restored holographic image, reference and object beam intensities ratio during hologram registration, and cycling ability. It is also an advantage that the device provides optimal operation efficiency of the registering media based on AMS-films, and restricts the development and erasing of the hologram upon reaching the pre-set value of the diffraction efficiency measured in the zeroth order of diffraction. The latter makes the device a universal device.
Owner:AGELLIS GROUP
Organic small-molecular semiconductor material
ActiveCN104974178AGood planaritySmall spectral absorption wavelengthOrganic chemistryHydrogenLength wave
An organic small-molecular semiconductor material includes a benzo-diheterocyclic ring derivative [pi] conjugated unit and a composite structure, which is composed of an aromatic ring unit or an aromatic diheterocyclic ring derivative unit, being connected directly to the benzo-diheterocyclic ring derivative [pi] conjugate unit. The organic small-molecular semiconductor material has a structure formula as follows, wherein X and X1 includes S or O, Y includes a structural unit which can form a five-membered aromatic ring unit or a six-membered aromatic ring unit with an adjacent butadiene unit, R includes hydrogen, a substituted or non-substituted C1-C20 alkyl group or hetero alkyl group or a substituted or non-substituted modified aromatic or hetero-aromatic [pi]-conjugated unit derivative, R1 includes a substituted or non-substituted C1-C20 alkyl group or hetero alkyl group, which is connected to the X, R2 is substituted groups which are distributed on selected positions of the five-membered aromatic ring unit or the six-membered aromatic ring unit, and the T includes an electron acceptor group unit which is directly connected to a position 1 and an oligothiophene short-chain unit which is mainly formed by combining 1-12 modified or non-modified thiophenes. The organic small-molecular semiconductor material, compared with a linear oligothiophene material, is lower in spectral bandwidth and is longer in spectral absorption wavelength.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
A kind of organic small molecule semiconductor material containing rhodanine fused isatin and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN111349104BImprove stabilityAvoid photochemical reactionsSilicon organic compoundsSolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellMolecular orbital energy
The invention relates to a small organic molecule semiconductor material containing rhodanine fused (like) isatin and its preparation method and application. The general structural formula of the material is shown in Formula I. The invention has excellent solubility, is soluble in common organic solvents, and can be used for solution processing to prepare organic optoelectronic devices; it has good response to the solar spectrum and good frontier molecular orbital energy levels, and the molecules have good planarity. It has high electron mobility and can be used as a small molecule acceptor material in the active layer material of organic solar cells.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Organic small molecule semiconductor materials, their synthesis methods and applications
ActiveCN105315297BSmall electron accepting abilitySmall molecule semiconductor materials have strong electron accepting abilityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesMolecular orbital energySemiconductor materials
Disclosed are an organic small molecular semiconductor material, and a synthetic method therefor. The semiconductor material comprises a diaromatic ring pentalene π-conjugate unit and an aromatic group, and has the following structural formula (I), wherein X1 and X2 are independently selected from O, S or Se; X3 is selected from O, S, Se, NR2, C(R2)2 or Si(R2)2; R2 is selected from a linear or branched alkyl group comprising 1-20 carbon atoms, and a linear or branched modified alkaryl or heterocyclic aryl comprising 7-20 carbon atoms; R1 is selected from a hydrogen atom, a linear or branched alkyl group comprising 1-20 carbon atoms, and a linear or branched modified alkaryl or heterocyclic aryl comprising 7-20 carbon atoms; and A is an electron-withdrawing unit. The semiconductor material can be synthesised by a transition metal catalysed condensation reaction. The semiconductor material of the present invention has a small spectrum band gap, a long spectrum absorption wavelength, a relatively low highest occupied molecular orbital and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital energy level, and can be used as a photoelectric material, especially as a receptor material in an organic photovoltaic device, and it also has advantages such as a simple preparation process, a low cost, etc.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Fluorenyl small-molecule semiconductor acceptor material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113698381AShort reaction timeHigh atomic economyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic solar cell acceptor materials, and particularly relates to a fluorenyl small-molecule semiconductor acceptor material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: under the condition of an inorganic catalyst, carrying out Knoevenagel condensation reaction on a compound with active methylene and aldehyde in a mechanical ball milling manner; and after the reaction is finished, purifying and drying in vacuum to obtain the fluorenyl small-molecule semiconductor. The semiconductor has wide and strong absorption in a visible-near infrared region, the flexible side chain provides good solubility for the material, and allows solution processing. As a semiconductor active layer acceptor material, the semiconductor has a potential application prospect in organic solar cells. Use of harmful and high-toxicity catalysts is avoided, the use of organic solvents is reduced, and the method conforms to the green chemical principle of environmental protection and economy.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Transistor structure
ActiveCN102447062BSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionMolecular semiconductor
Owner:E INK HLDG INC
A conjugated small molecule semiconductor material containing halogen modified core group and its preparation and application
ActiveCN111848649BLimit generationSmooth steeringOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesOrganic solar cellSemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a conjugated small molecular semiconductor material containing a halogen-modified core group and its preparation and application. The small-molecule semiconductor material includes a halogenated two-dimensional thienothiophene core, a bridging unit and a hexylthiophene end group, and its preparation method is to recycle an organotin reagent reaction and Still coupling to obtain a target molecule, a total of seven steps of reaction: tin reagent Reaction, Still coupling reaction, tin reagent reaction, Still coupling reaction, tin reagent reaction, Still single-sided coupling reaction and Still double-sided coupling reaction, the three-step tin reagent reaction in the seven-step reaction all yields a crude product that does not need to go through the column Directly put into the next reaction, efficient and easy to operate. The small molecule semiconductor material of the present invention has a longer range of ultraviolet-visible absorption, deeper electron highest occupied orbital and lowest empty orbital, has good solubility and light absorption performance, and can be used as an electron donor material for small molecule organic solar cells .
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Photoelectric conversion element, imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS10879314B2High selectivityQuick responseTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesMolecular materialsEngineering
A photoelectric conversion element according to one embodiment of the disclosure includes: a first electrode and a second electrode that are oppositely disposed; and a photoelectric conversion layer that is provided between the first electrode and the second electrode, and includes a high-molecular semiconductor material and a low-molecular material. The high-molecular semiconductor material has an absorption coefficient in a visible light region of 50000 cm−1 or less. The low-molecular material includes an absorption peak in a wavelength range corresponding to one color in the visible light region.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com