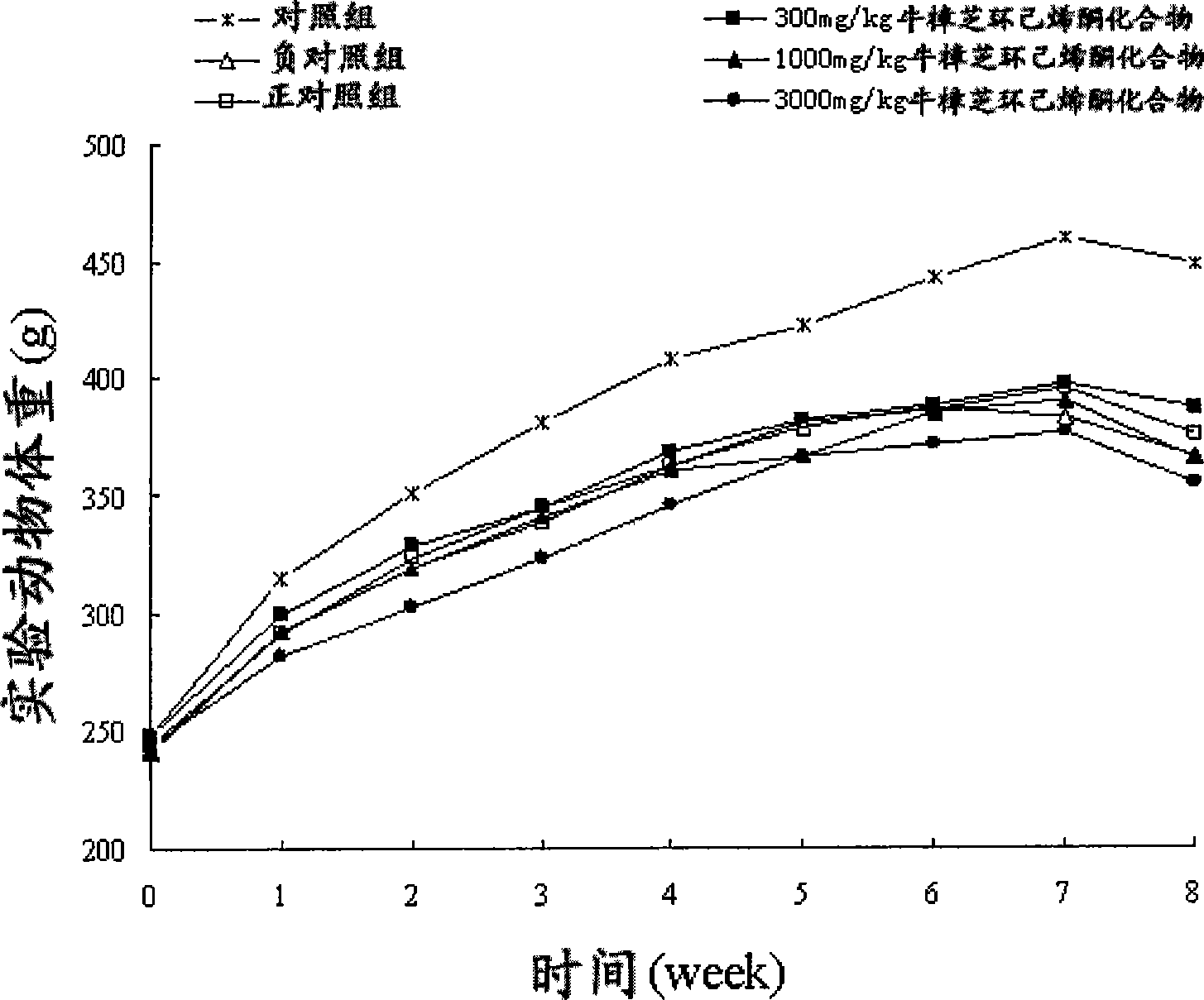
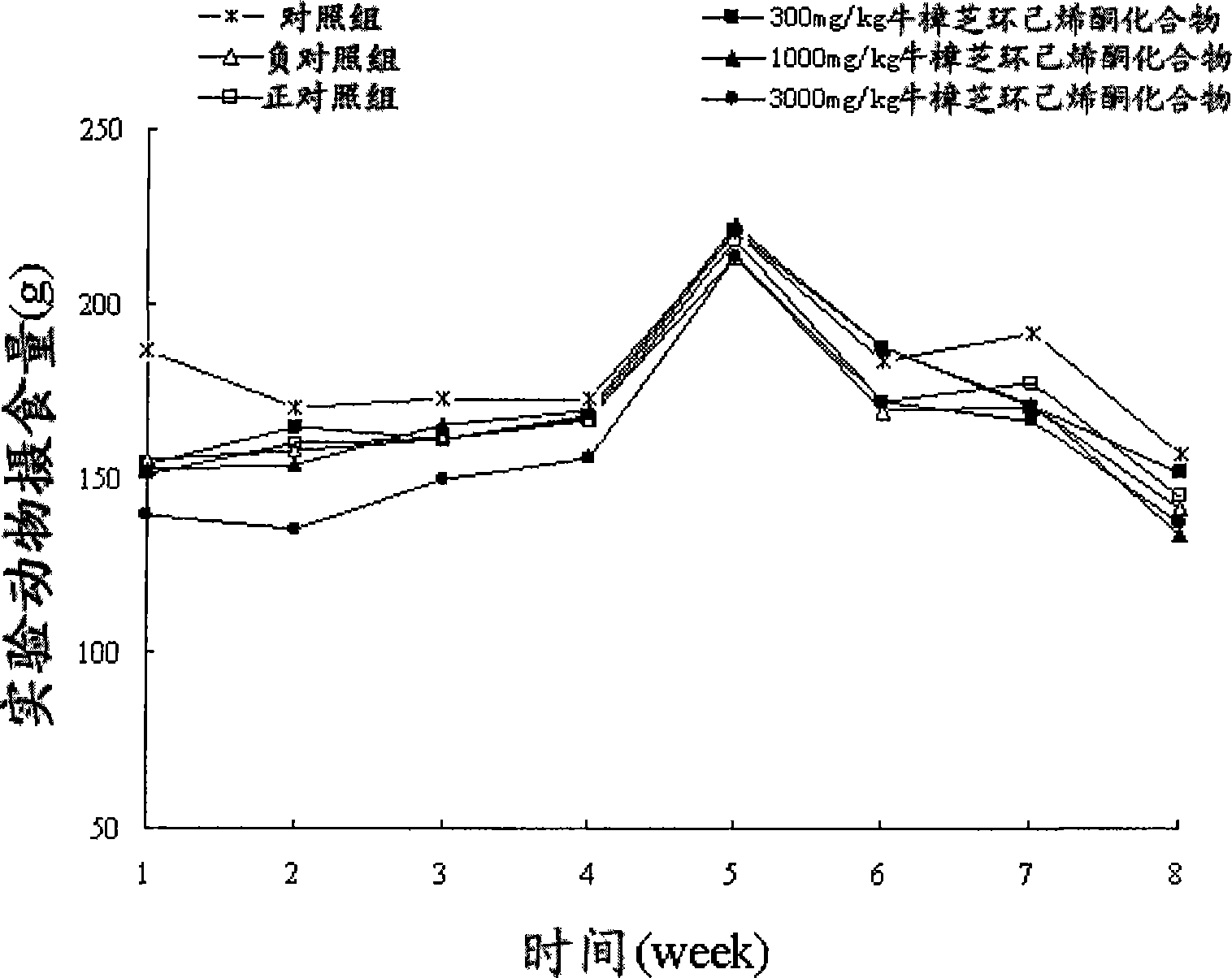
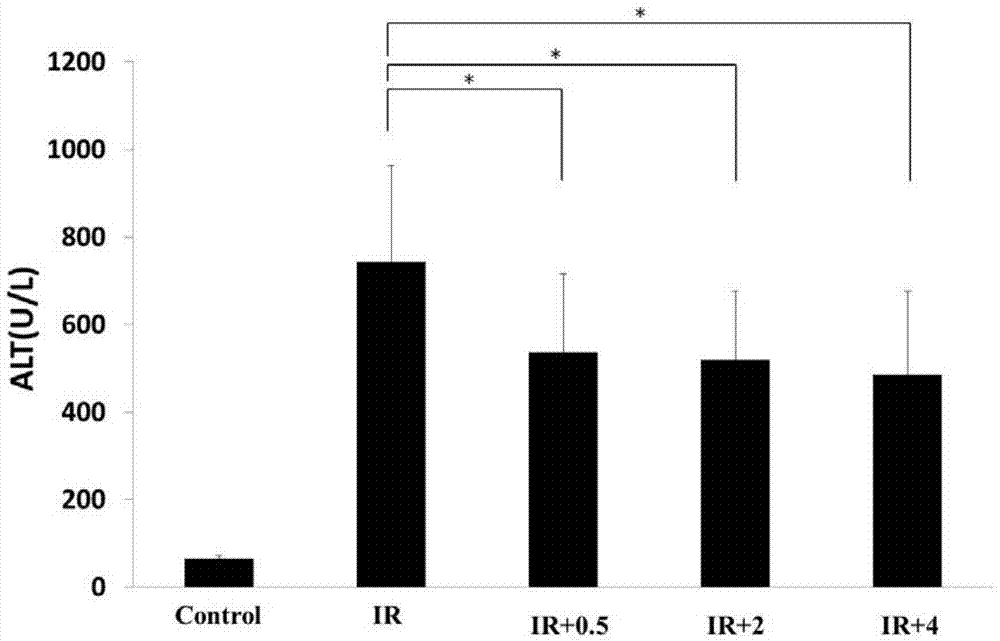
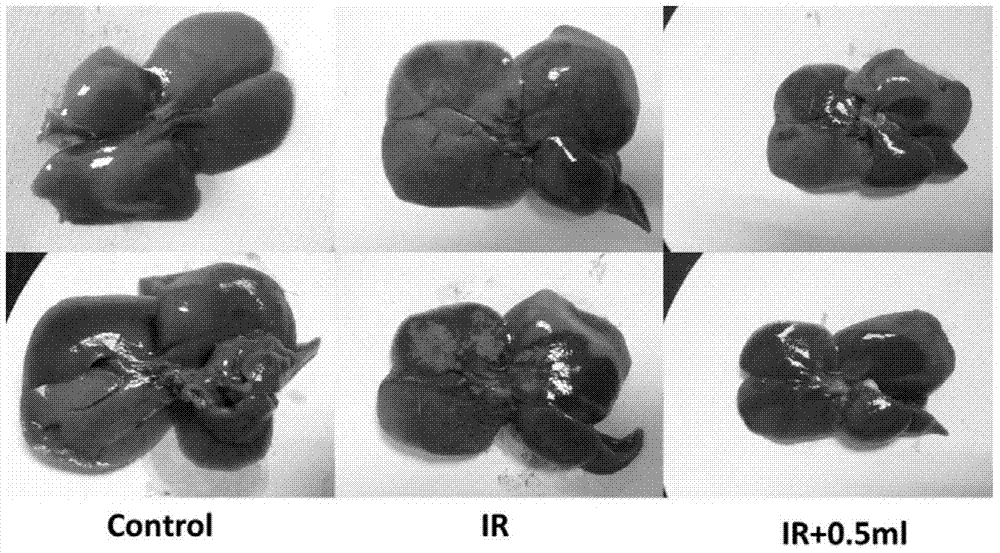
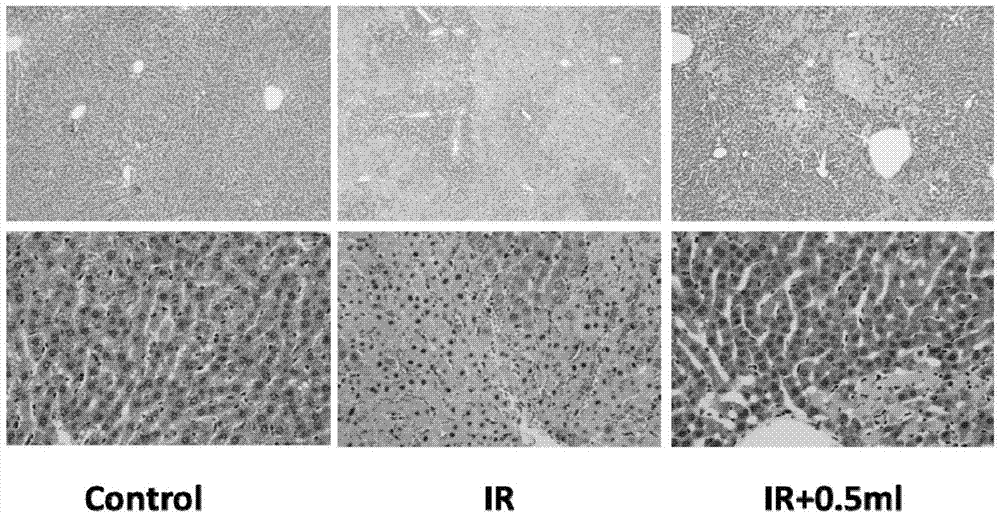
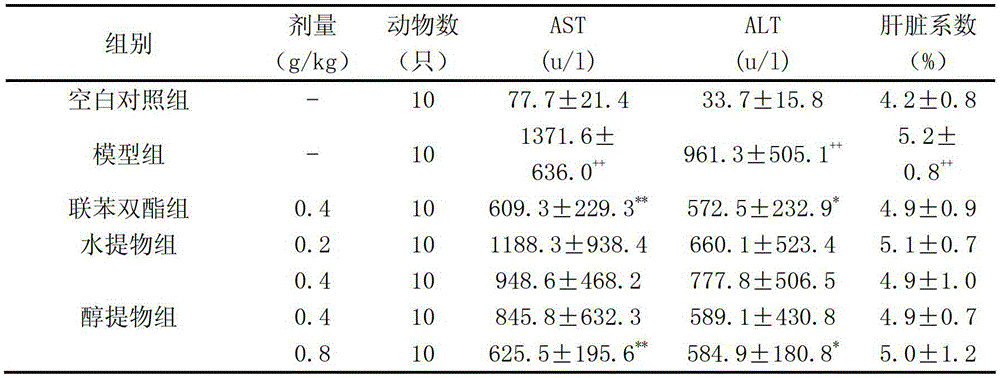
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Alanine transaminase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alanine transaminase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme (EC 2.6.1.2). It is also called alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) and was formerly called serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (SGPT) or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) and was first characterized in the mid-1950s by Arthur Karmen and colleagues. ALT is found in plasma and in various body tissues but is most common in the liver. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle. Serum ALT level, serum AST (aspartate transaminase) level, and their ratio (AST/ALT ratio) are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.
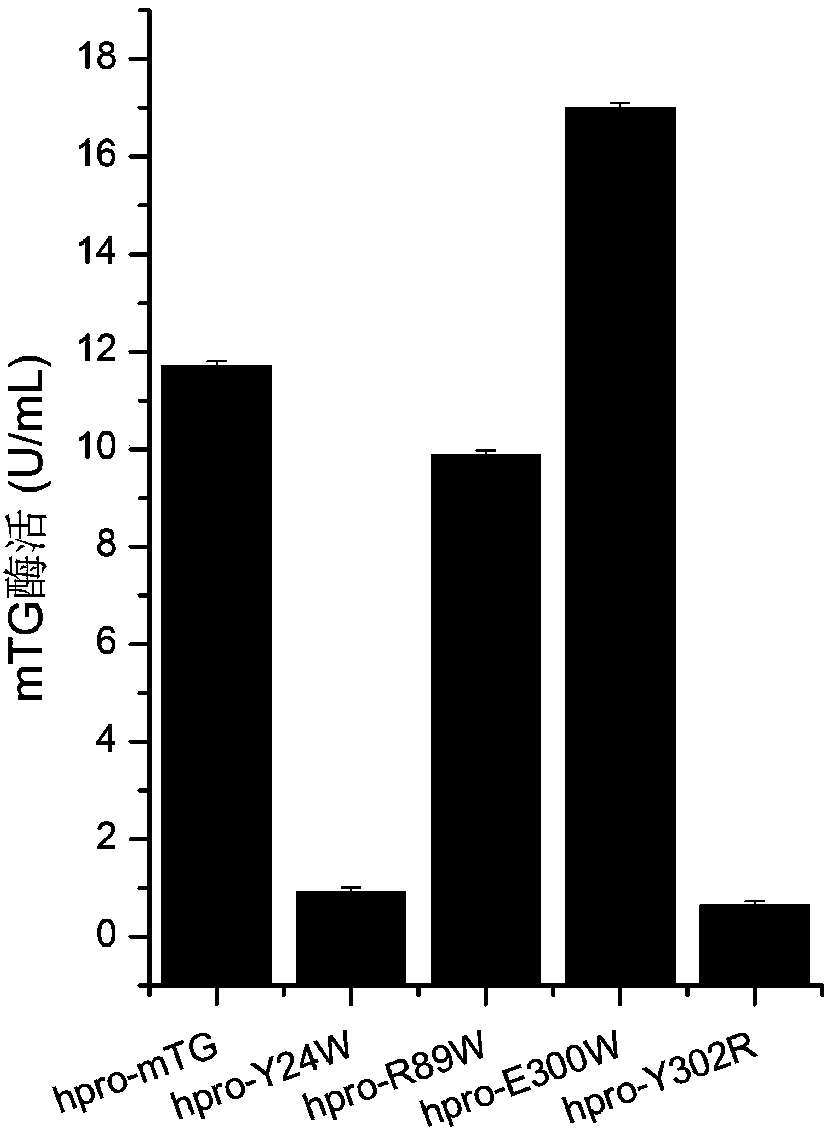
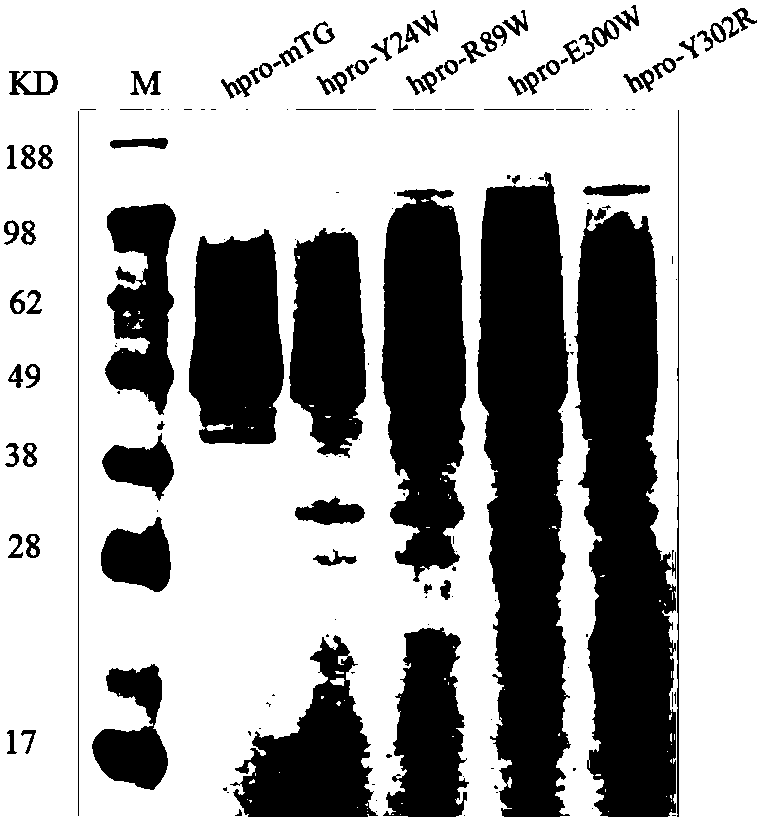
Glutamine transaminase mutant with improved enzymatic activity
ActiveCN107739734AEasy to separate and purifyEasy to trainFungiAcyltransferasesAmine transaminase activityReactive site
The invention discloses a glutamine transaminase mutant with improved enzymatic activity, which belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The site-specific mutagenesis is performed on glutamine transaminase, an amino acid residue close to an active site of the glutamine transaminase is changed, so that the catalytic efficiency of the glutamine transaminase is improved, and the enzymatic activityof the glutamine transaminase is further improved. Recombinant yarrowia lipolytica with improved enzymatic activity is established by the glutamine transaminase mutant, the enzymatic activity of theglutamine transaminase is improved by 1.45 times compared with an original strain, the enzymatic activity of the shake flask fermentation can reach 16.995U / mL, and the enzymatic activity of the fermenting tank fermentation can reach 59.85U / mL which is the highest fermentation value reported at present.
Owner:TAIXING DONGSHENG FOOD TECH
Blood-fat reducing composition and application thereof
ActiveCN104055773ALittle side effectsShort treatment cycleOrganic active ingredientsDough treatmentSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseVitamin b6
The invention belongs to the technical field of health-care products, food and medicine and discloses a blood-fat reducing composition and an application thereof. The composition comprises ornithine, aspartate and vitamin B6. The blood-fat reducing composition can adjust blood-fat, protect the liver, enhance the blood supply capacity of heart and cerebral vessels, lower triglyceride and cholesterol, improve the enzyme activity of alanine transaminase and glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, promote fatty acid metabolism, and recover the blood-fat reducing ability of the body; the blood-fat reducing composition can be used for preparing the medicine for reducing the blood fat, the health-care products, food additives or the food.
Owner:万红贵 +1
Compound medicament for treating chronic liver disease and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103127273ADigestive systemPlant ingredientsSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseAcute toxicity testing
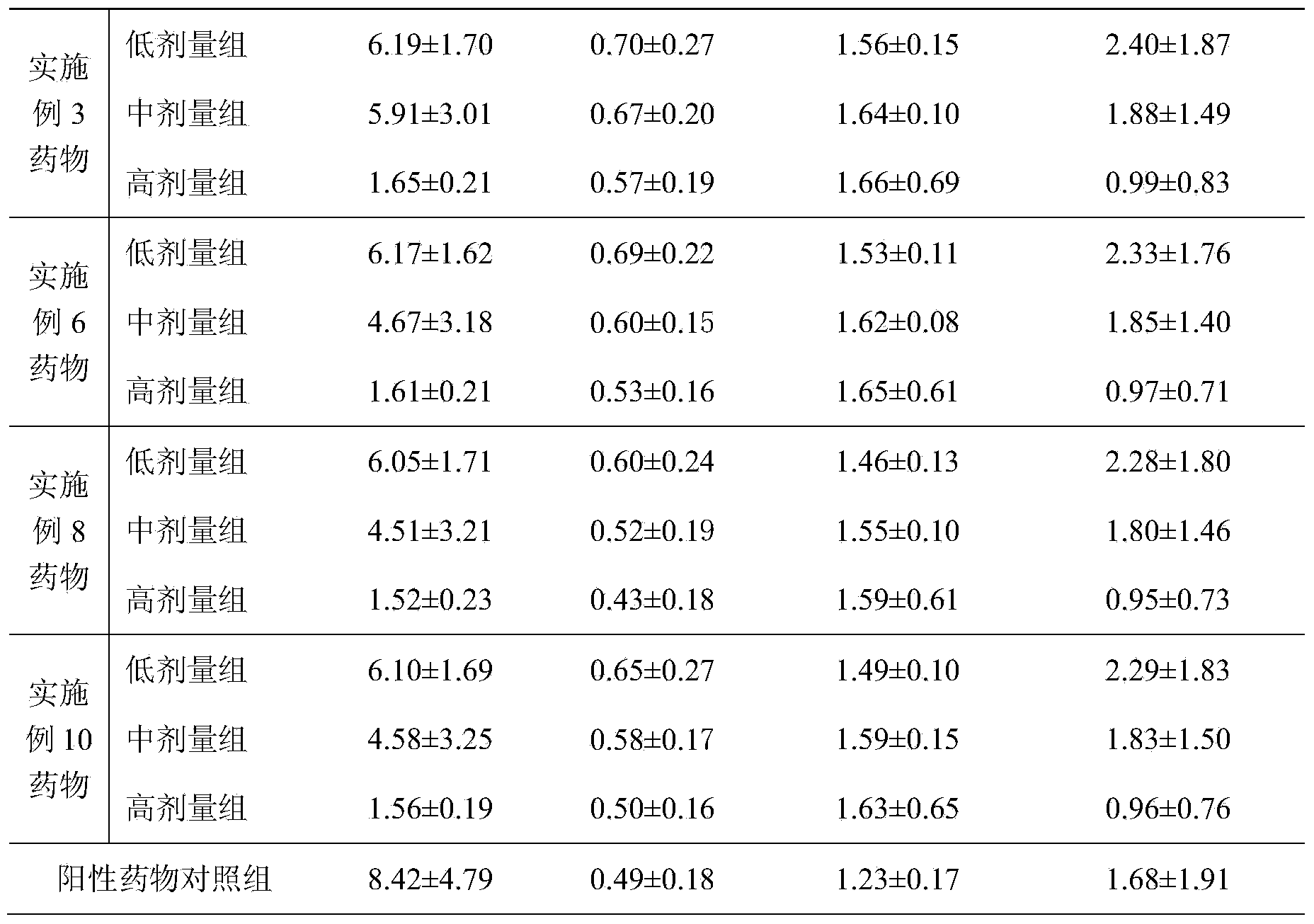
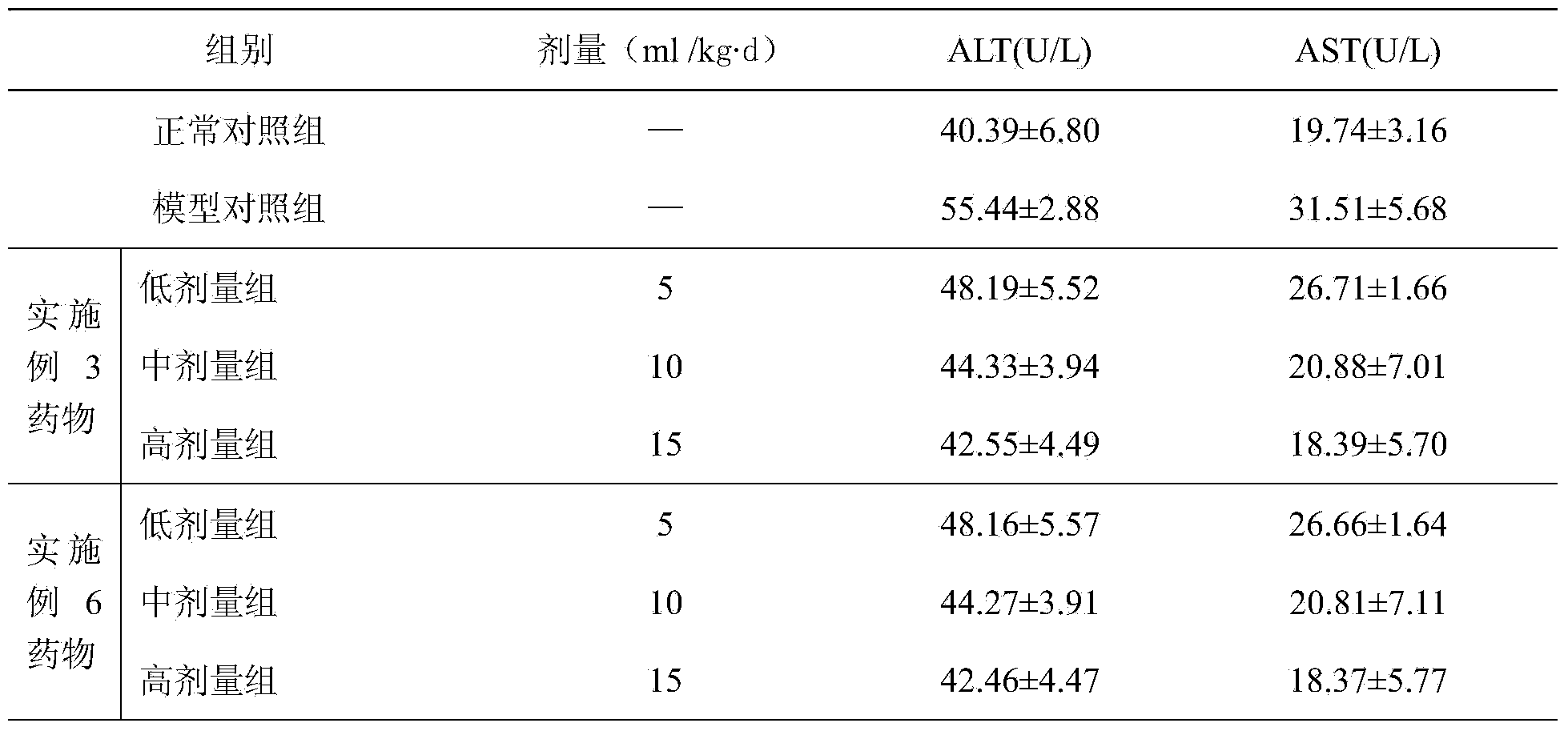
The invention relates to a compound medicament for treating a chronic liver disease and a preparation method thereof. The compound medicament is prepared from artemisia capillaries, artemisia rupestris, cichorium glandulosum boiss et huet, rose, rhubarb and licorice which are used as raw materials and medicinal accessories and prepared into an oral preparation, syrup granules, hard capsules and tablets by adopting a method of solvent extraction, impurity removal, concentration and drying. The active ingredients in the compound medicament are dissolved by adopting a reasonable extraction method according to the Uyghur medicinal theory, the characteristics of national medicine and the long-term folk clinical practice of the Uyghur nationality, so that the medicinal effects are enhanced, and the bioavailability is improved. Animal experiments prove that the compound medicament has a protective effect on liver injury. Pharmacodynamic experiments show that the extract obtained by the method can inordinately reduce the alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transferase (AST) levels in mouse serum of a liver injury model, the pathological symptoms in each medication administration team are relieved, and the liver injury is protected. Acute toxicity experiments show that the maximum dosage of the extract obtained by the method is equivalent to 337 folds of clinical human proposed dosage according to mouse intragastric single-time administration toxicity test, and the extract is nontoxic and safe.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel alanine transaminase enzyme and methods of use
InactiveUS20050214883A1Damage of in useSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseAlanine transaminase
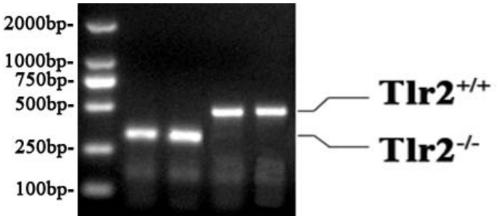
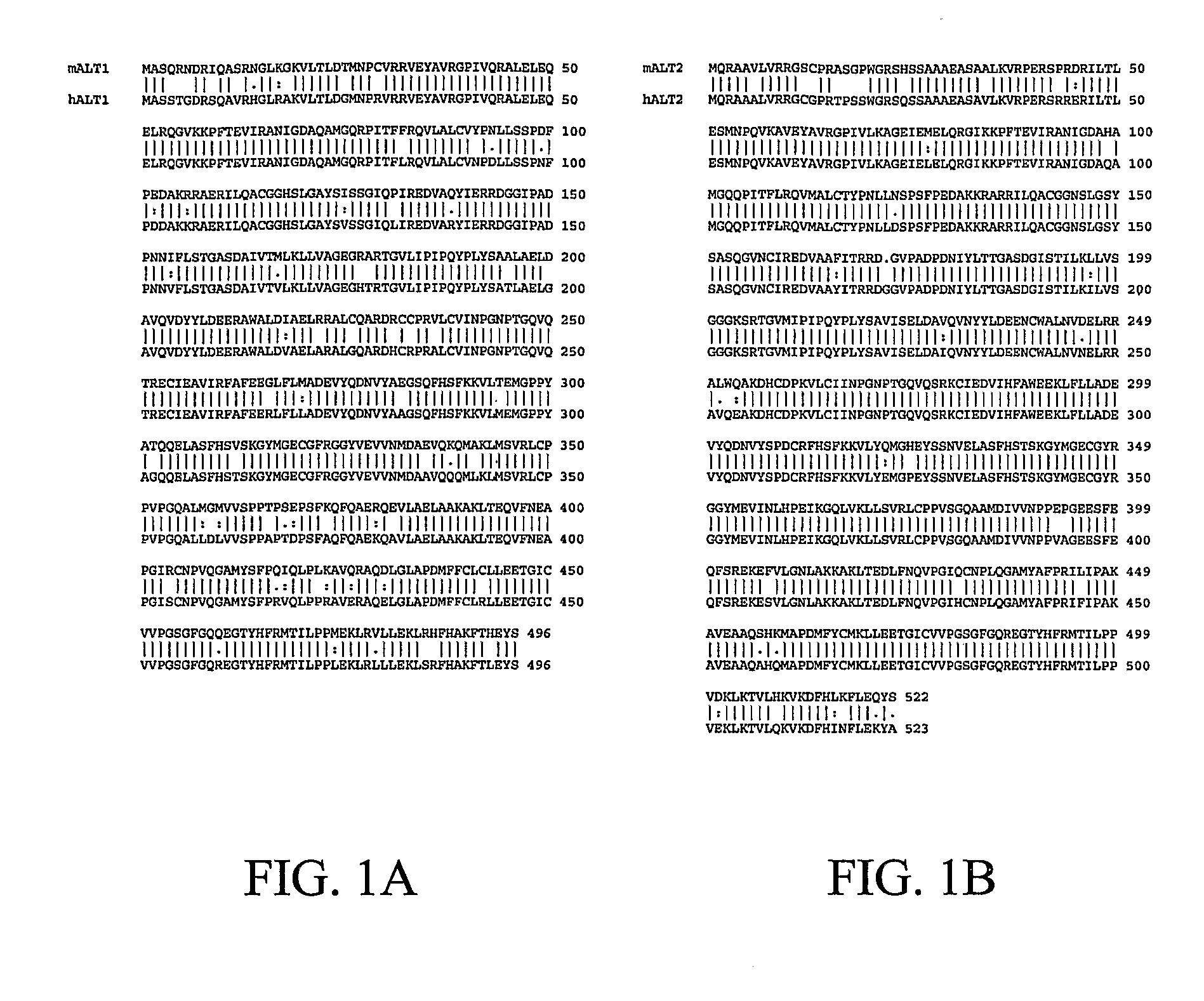
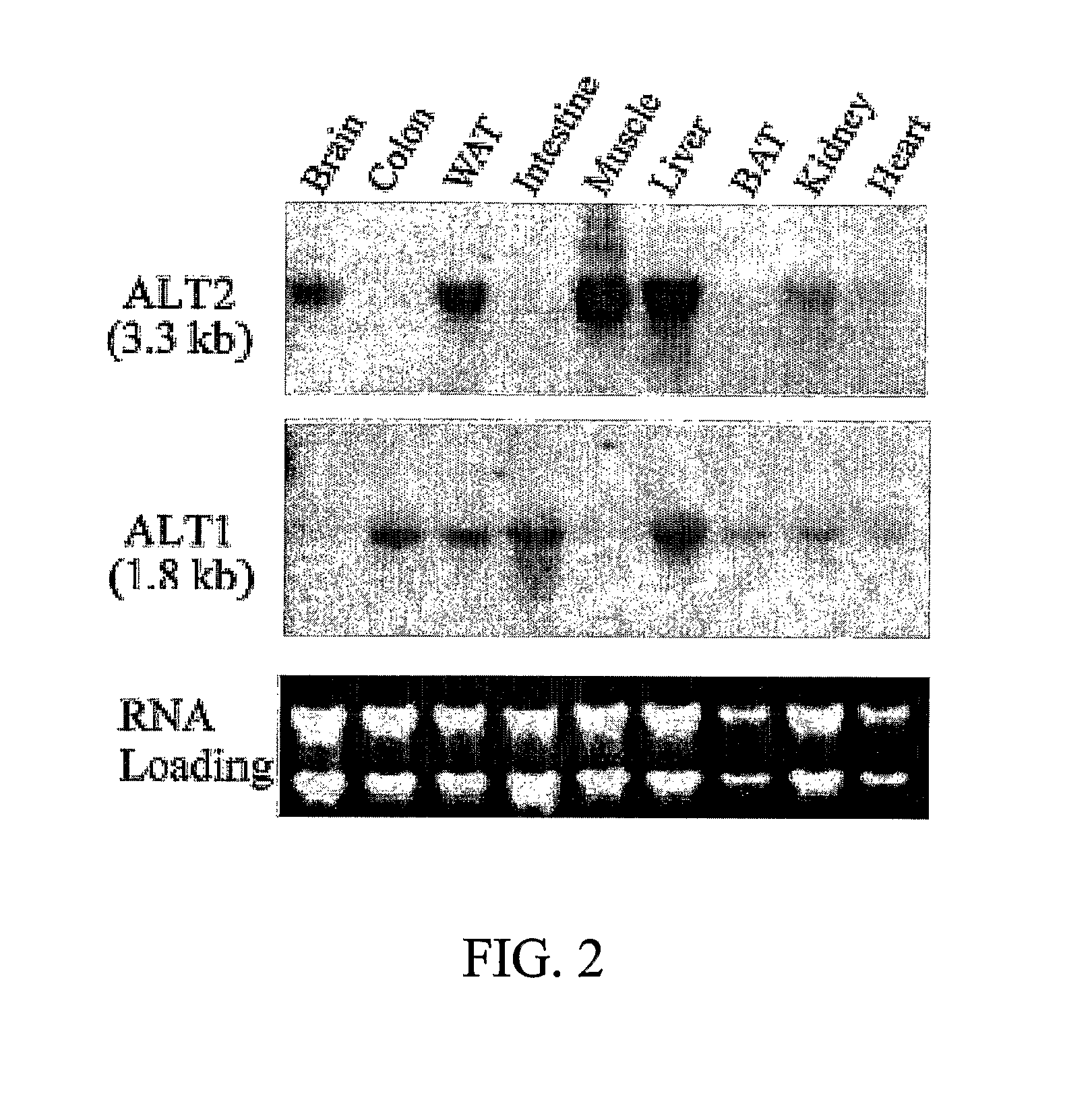
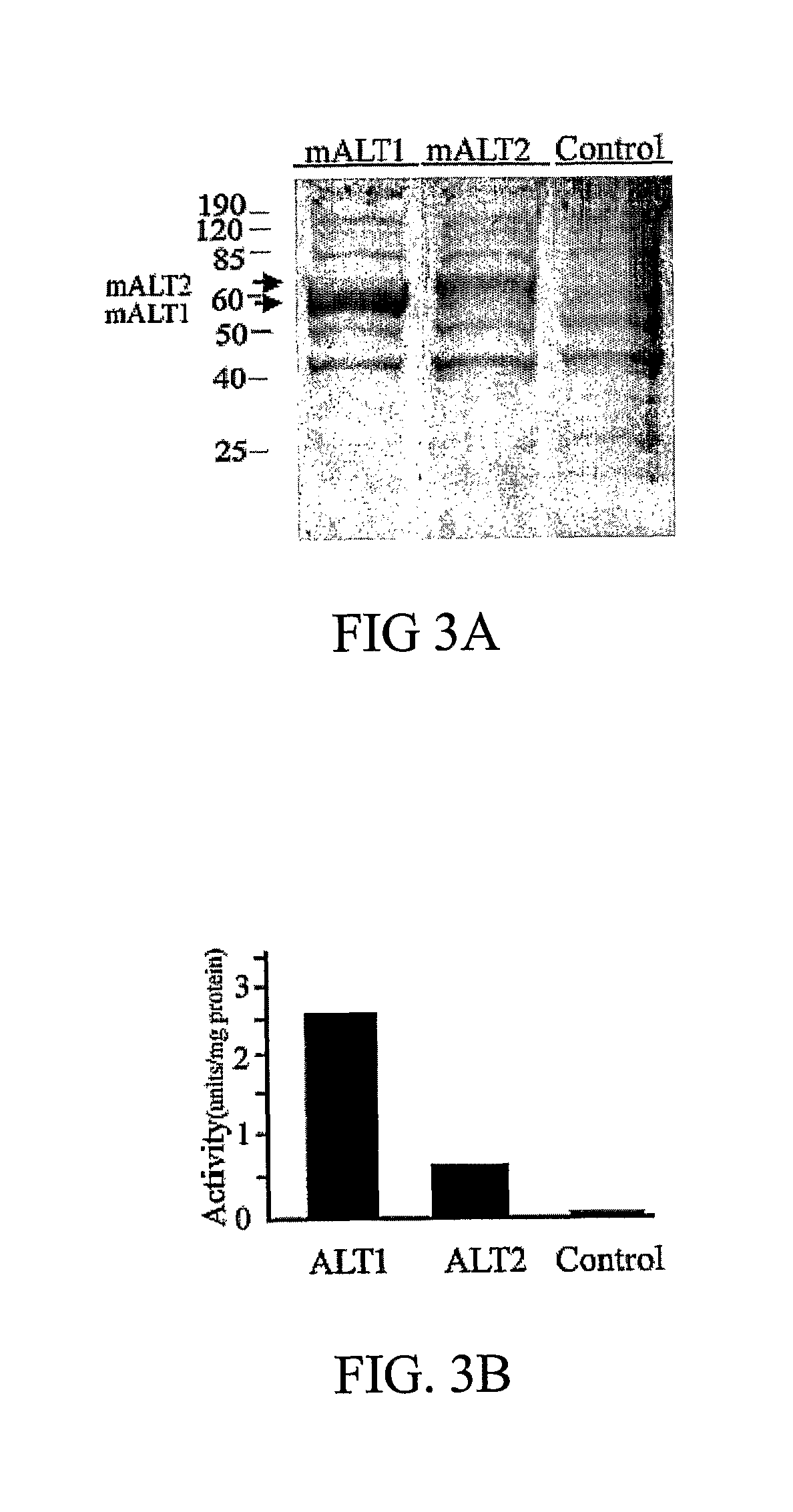
A novel alanine transaminase gene (ALT2) is isolated from human tissue. ALT2 specific polynucleotides, polypeptides, and antibodies are described. ALT2 is expressed predominately in liver, kidney, brain, muscle, and adipose tissue. ALT2 can be used to diagnose injury and diseases involving tissues expressing ALT2.
Owner:GONG DA WEI +2
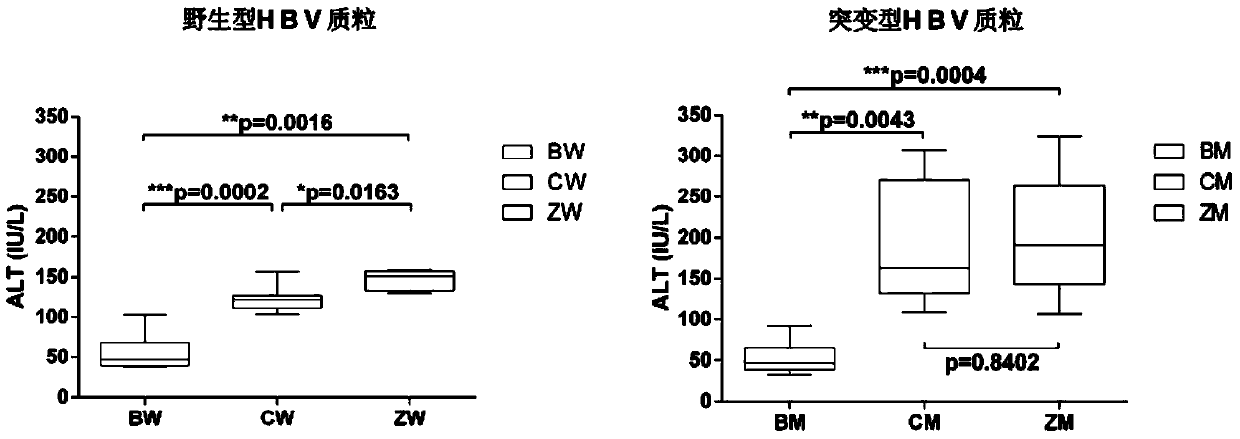
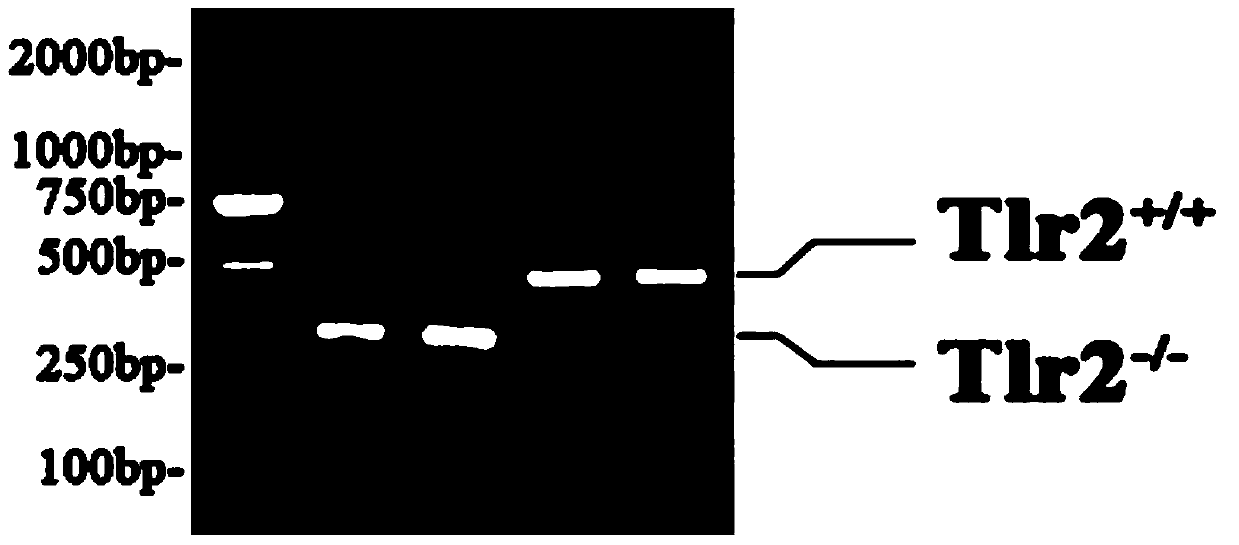
Method for constructing hepatitis B virus (HBV) infected mouse model
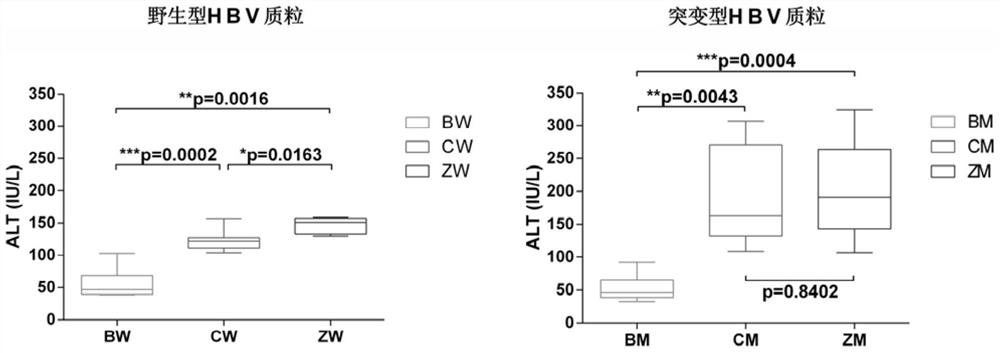
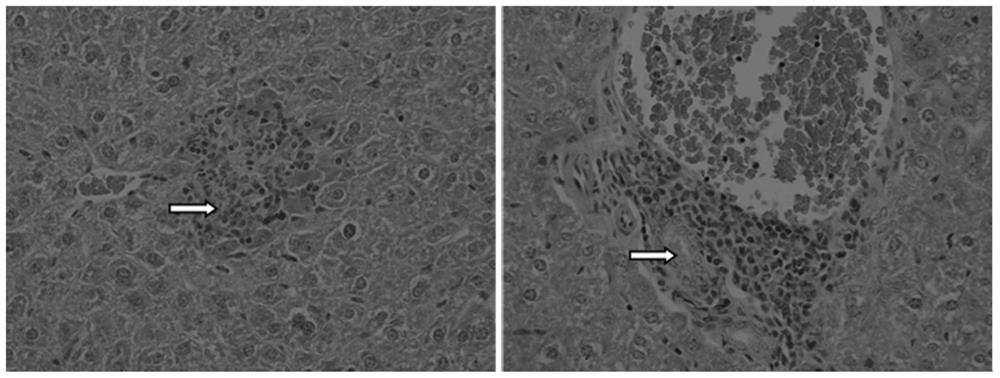
ActiveCN104212835ADoes not induce an immune responseSimplify the build processIn-vivo testing preparationsVector-based foreign material introductionSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseImmunodeficiency
Owner:张欣欣 +6
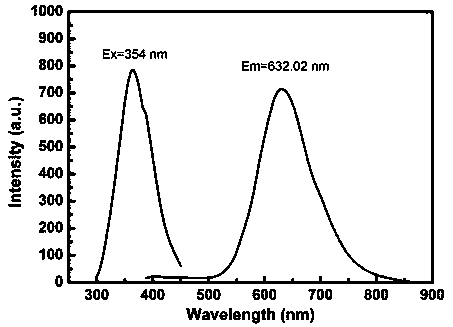
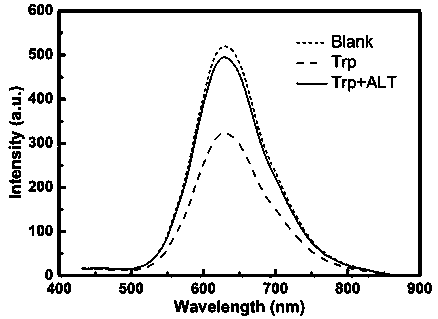
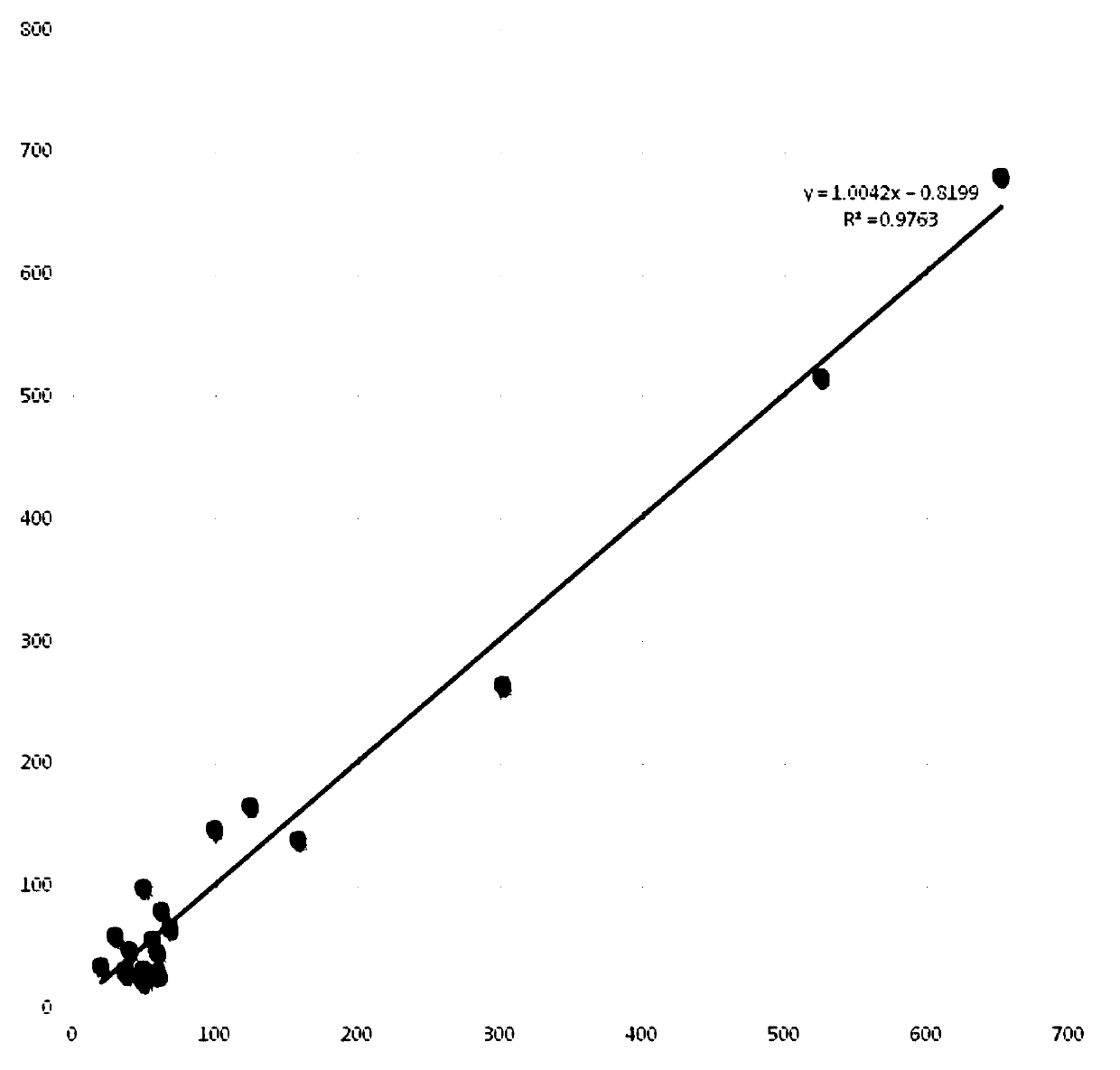
Method for quantitatively detecting alanine transaminase in solution based on copper nanocluster fluorescent probe
InactiveCN109596580AOptically stableSmall particle sizeFluorescence/phosphorescenceSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseSpecific detection
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting alanine transaminase in a solution based on a copper nanocluster fluorescent probe, wherein a copper nanocluster with glutathione as a protective agent is used as a fluorescent probe, and the content of alanine transaminase in the solution is specifically detected through a fluorescence "off-on" mode. The label-free, highly sensitive and selective detection of alanine transaminase is achieved by adopting the fluorescence "off-on" mode. The method is simple and rapid, the specific detection of alanine transaminase can be realized, the detection linear range is wide, and the detection limit is low. The method in the invention has good detection sensitivity and selectivity and has good application prospects in disease detection, clinical application and other aspects.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
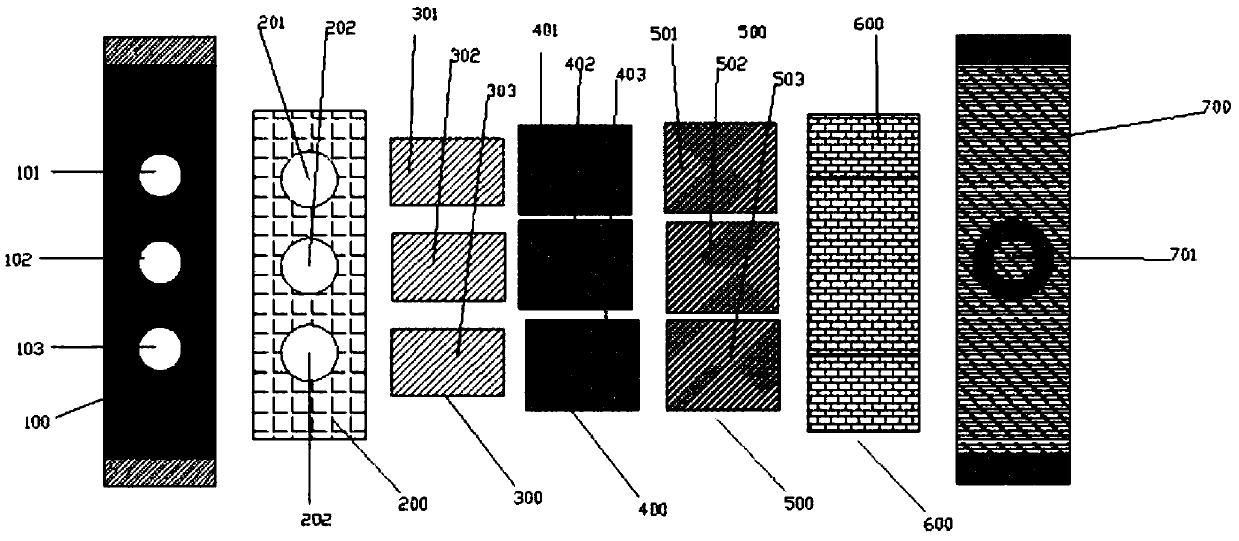
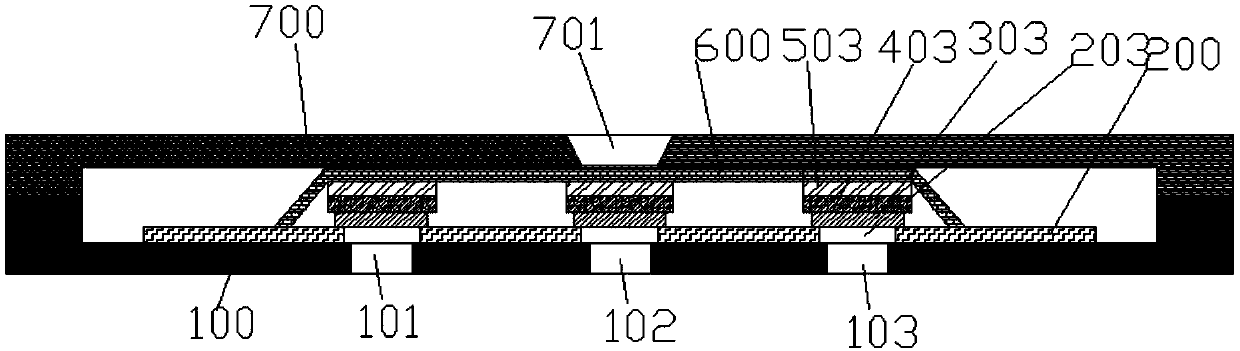
Test card for liver function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109580927AEasy to operateImprove matchBiological testingDiffusionSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminase
The invention discloses a test card for the liver function and a preparation method thereof. The test card comprises an upper shell, a lower shell, a sample adding hole formed in the upper shell, an alanine transaminase detecting unit, a total bilirubin detecting unit and a glutamic oxalacetic transaminase detecting unit, wherein the alanine transaminase detecting unit, the total bilirubin detecting unit and the glutamic oxalacetic transaminase detecting unit are disposed between the upper shell and the lower shell. The alanine transaminase detecting unit, a total bilirubin detecting unit anda glutamic oxalacetic transaminase detecting unit comprise a bottom plate disposed at the upper end of the lower shell, lower shell detecting holes formed in the lower shell, bottom plate detecting holes formed in the bottom plate, a diffusion film disposed at the lower end of the upper shell and connected to the bottom plate, a whole blood separation layer disposed under the diffusion film and areaction layer disposed between the whole blood separation layer and the bottom plate detecting holes. The test card is matched with a dry biochemical analyzer for use, the operation is simple, the content of alanine transaminase, total bilirubin and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase can be detected rapidly and simultaneously without the need of a professional, and the detecting results are well matched with hospital detecting results.
Owner:杭州联晟生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing DL-alanine and D-alanine
The invention discloses a method for preparing DL-alanine and D-alanine. Fumaric acid and ammonia react through aspartase in a coupling reactor to synthesize L-aspartic acid; the synthesized L-aspartic acid reacts with L-aspartate dacarboxylase to obtain L-alanine; L-alanine undergoes racemization through alanine racemase to obtain DL-alanine; and DL-alanine concentrated mother liquor undergoes splitting through L-alanine aminotransferase in a fermentation cylinder so as to obtain D-alanine. Production of DL-alanine or D-alanine requires no extraction of intermediate products. The final product is obtained directly by one step. Thus, usage of sulfuric acid required for electroextraction of L-aspartic acid and the like, labor for each extraction process, energy consumption and production loss such as dissipation in actual production process are reduced. Meanwhile, DL-alanine mother liquor is comprehensively utilized for production of D-alanine, and overall yield and economic benefit are raised.
Owner:宜兴市前成生物有限公司
Novel alanine transaminase enzyme and methods of use
InactiveCN1636058ASugar derivativesHydrolasesSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseAlanine transaminase
A novel alanine aminotransferase gene (ALT2) has been isolated from human tissues, and ALT2-specific nucleic acids, proteins and antibodies thereof have been described above. ALT2 is mainly expressed in liver, kidney, brain, muscle and adipose tissue. ALT2 can be used as a diagnosis of damage and disease of ALT2-producing tissues.
Owner:北京昭衍新药研究中心股份有限公司
Cinnamomum kanehirae Hayata pimelie kelone compound for liver protection
The invention relates to an Antrodia Camphorata cyclohexanone compound for protecting the liver, particularly 4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methy-5[3,7,11- trimethyl-dodeca-2,6,10-trienyl]-cyclohex-2-enone separated from an Antrodia Camphorata extract and capable of effectively protecting the liver. The Antrodia Camphorata cyclohexanone compound is conducive to alleviating the injury of the liver tissue due to the chemical liver injury and the fiberization extent, and can reduce the concentrations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartic acid (AST), increase the contents of glutathione peroxidase (GSHPx) and catalase (CAT) in the liver and reduce the injury of free radicals to liver cells so as to improve the oxidization resistance of the liver tissue and further protect the liver.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
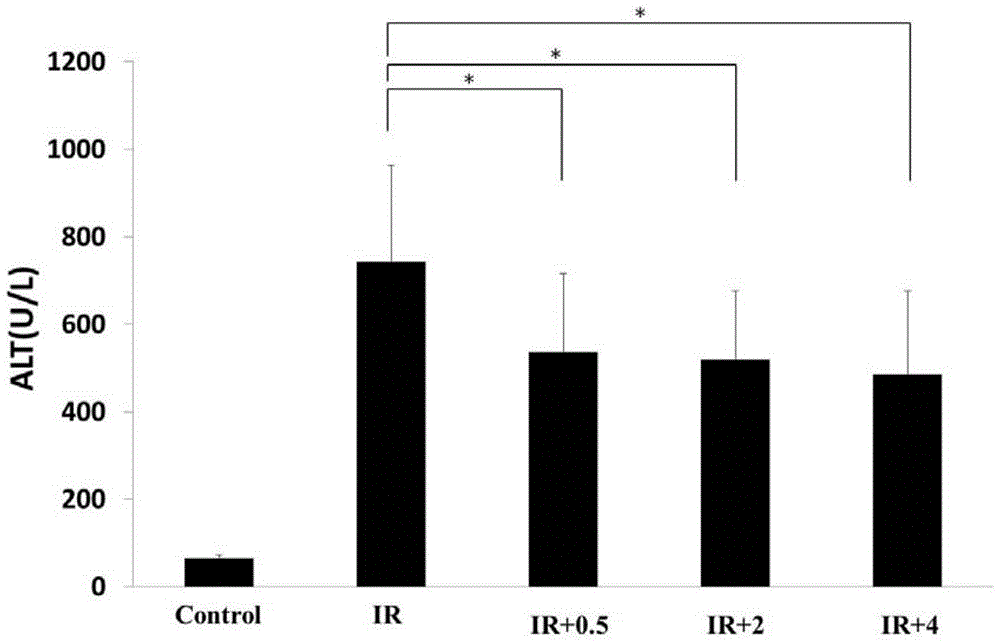
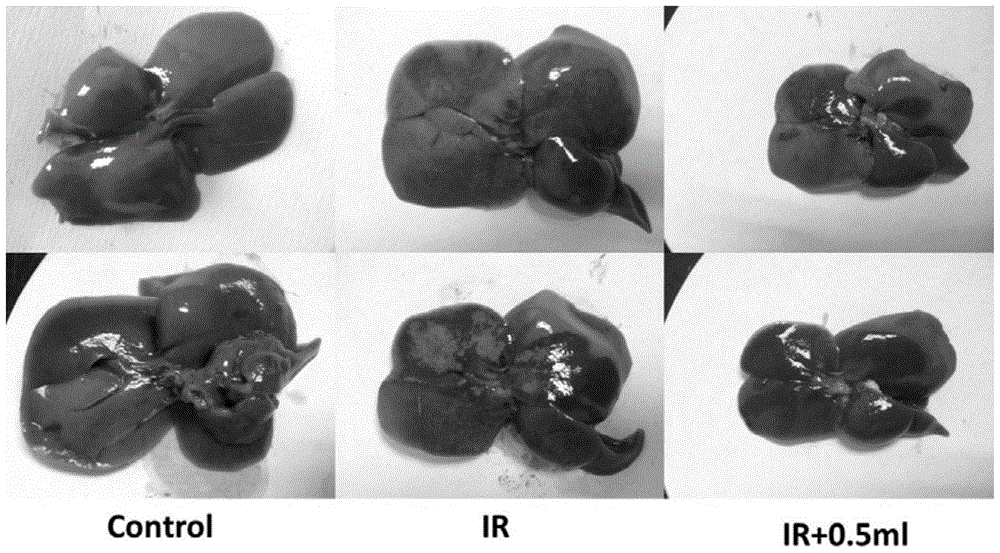
Application of methane injection in preparation of medicaments for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury
InactiveCN103690481AAvoid damageReduce deathHydrocarbon active ingredientsDigestive systemSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseRat liver
The invention discloses an application of methane injection in preparation of medicaments for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury, which comprises a preparation method of the methane injection. Animal experiments are performed on the methane injection, and the results prove that the methane injection can be used for obviously reducing the level of alanine transaminase, reducing liver injury and reducing hepatocyte apoptosis against a rat model with liver ischemia-reperfusion injury, so that the methane injection can be used for treating the liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Thus, the methane injection disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the medicaments for treating the ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for preparing alanine aminotransferase and application
InactiveCN103014033AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costTransferasesBiological testingAntigenThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a method for preparing alanine aminotransferase, which includes the following steps: modifying a whole-genome-synthesized humanized alanine aminotransferase encoding gene sequence, and removing rare codons of escherichia coli; inserting the modified alanine aminotransferase encoding gene sequence into an expression vector, and adopting bacterial strains of escherichia coli for transformation and expression; inoculating the transformed and expressed bacterial strains with an LB culture medium and performing IPTG (isopropyl-Beta-d-thiogalactoside) induction; and breaking the obtained thalli, performing centrifugal separation, and passing by the Ni-NTA columns for purification. The operation for preparing alanine aminotransferase is very simple, the preparation cost is low, the product yield is high, the purity is high, and high biological activity is obtained; the prepared alanine aminotransferase serving as antigenic substances can be used for animal immunization, related antibodies can be screened; and meanwhile, the method lays the foundation of quick establishment for a calibrator preparing platform imperative to the domestic clinical chemistry diagnosis as well as development and preparation for diagnostic reagent standard substances and references.
Owner:肖飞
Application of composition of micromolecular fucoidan and fucoxanthin to preparation of composition for improving nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
PendingCN112121056AHigh expressionImproving Impedance PerformanceOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseFucoxanthin
The invention relates to application of a composition of micromolecular fucoidan and fucoxanthin to preparation of composition for improving nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), in particular to application of the composition of the micromolecular fucoidan and the fucoxanthin to preparation of the composition for improving the NASH. The composition can achieve the purpose of improving the NASH byimproving the fatty liver coefficient and blood biochemical parameters of serum alanine transaminase (ALT), ante cibum glucose (AC) and glycosylated heme (HbAlc).
Owner:HI Q MARINE BIOTECH INT +1
Method for preparing D-alanine by microbial fermentation method
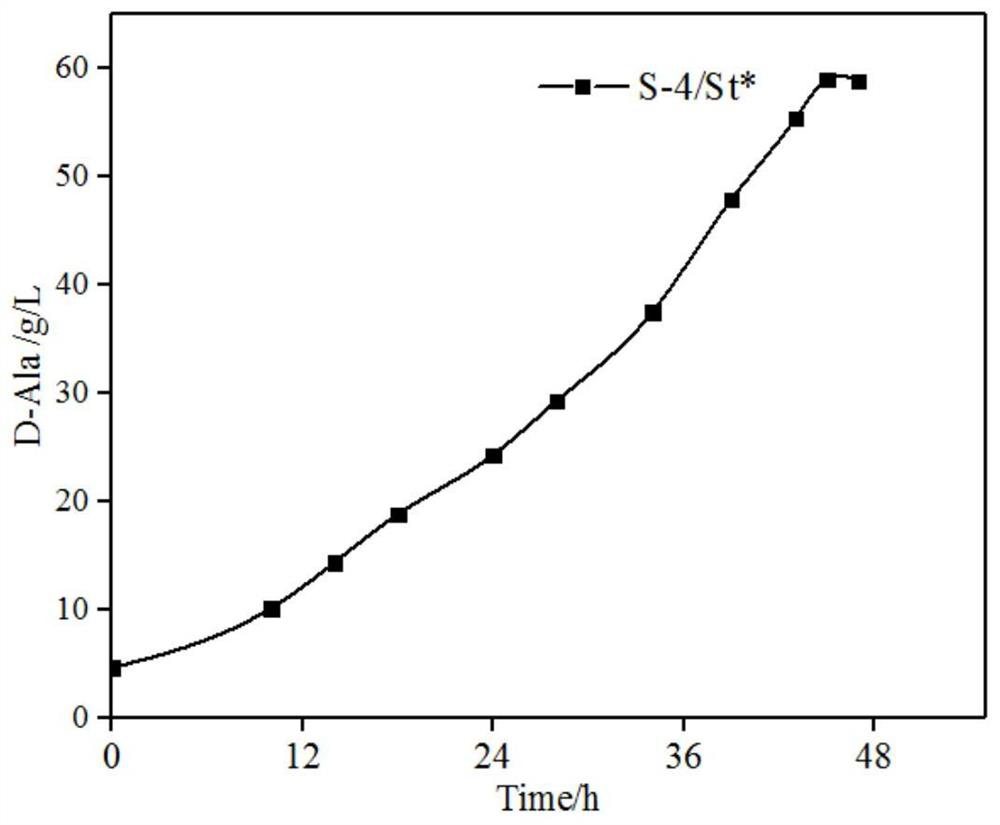
ActiveCN113462623AEfficient synthesisLow costBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminase
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and particularly relates to a method for preparing D-alanine by a microbial fermentation method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a genetically engineered bacterium for producing D-alanine, taking corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 as a starting strain of the genetically engineered bacterium, and knocking out an alanine racemase gene alr and L-alanine transaminase alaT; allowing meso-diaminopimelate dehydrogenase coding gene to be subjected to overexpression; knocking out an iolR repressor protein gene and simultaneously performing genome integration expression on a glucokinase gene glk1; and integrating edd and eda genes from Escherichia coli to obtain the gene. The strain uses glucose as a substrate to produce D-type amino acid through a direct fermentation method, the cost is low, the technology is simple, and the yield of D-alanine in a 5L fermentation tank can reach 50-60g / L. Besides, efficient synthesis of the D-type amino acid by a fermentation method belongs to creative research, and by means of the method, the fermentation method can be infinitely expanded, and various D-type amino acids can be efficiently synthesized at low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
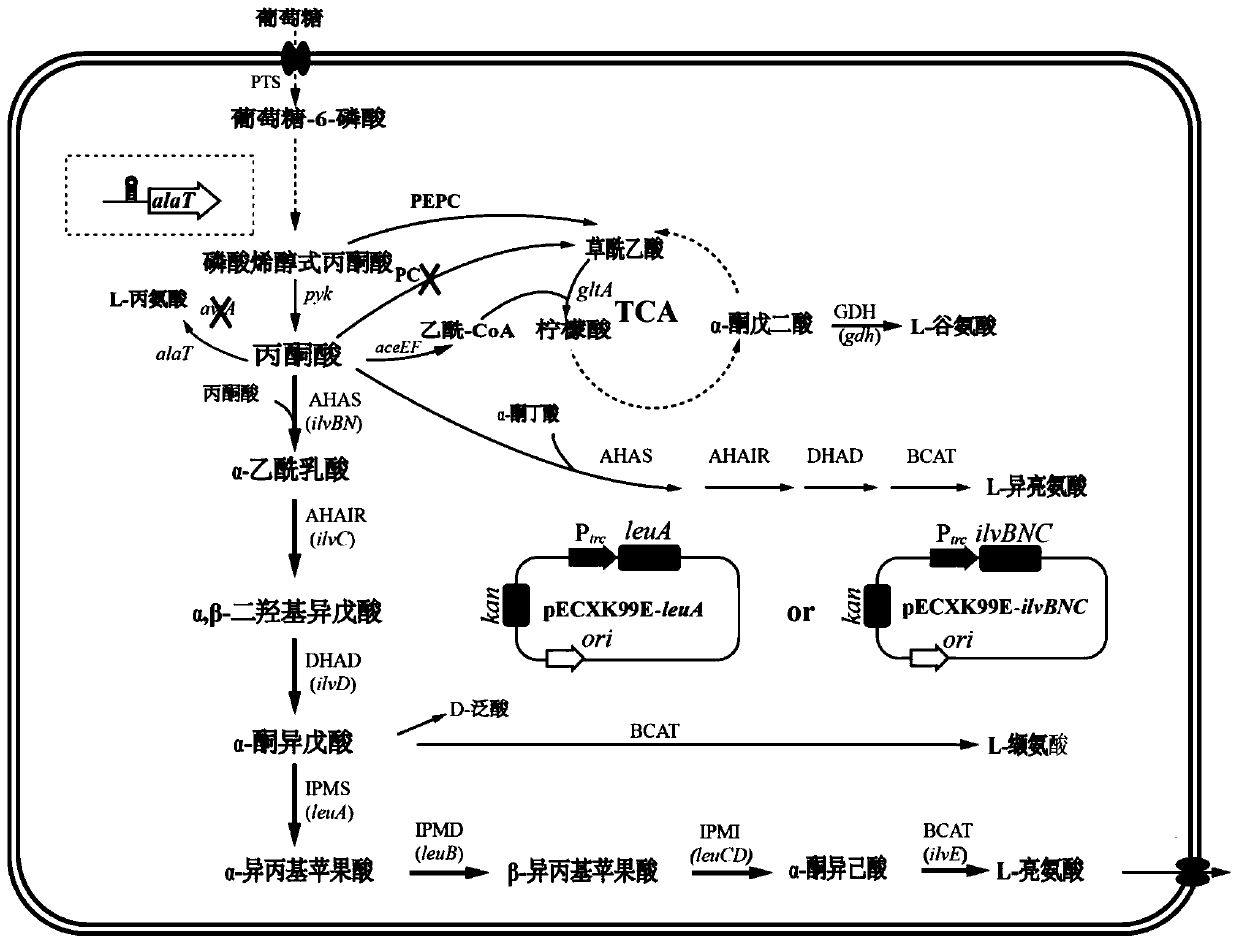
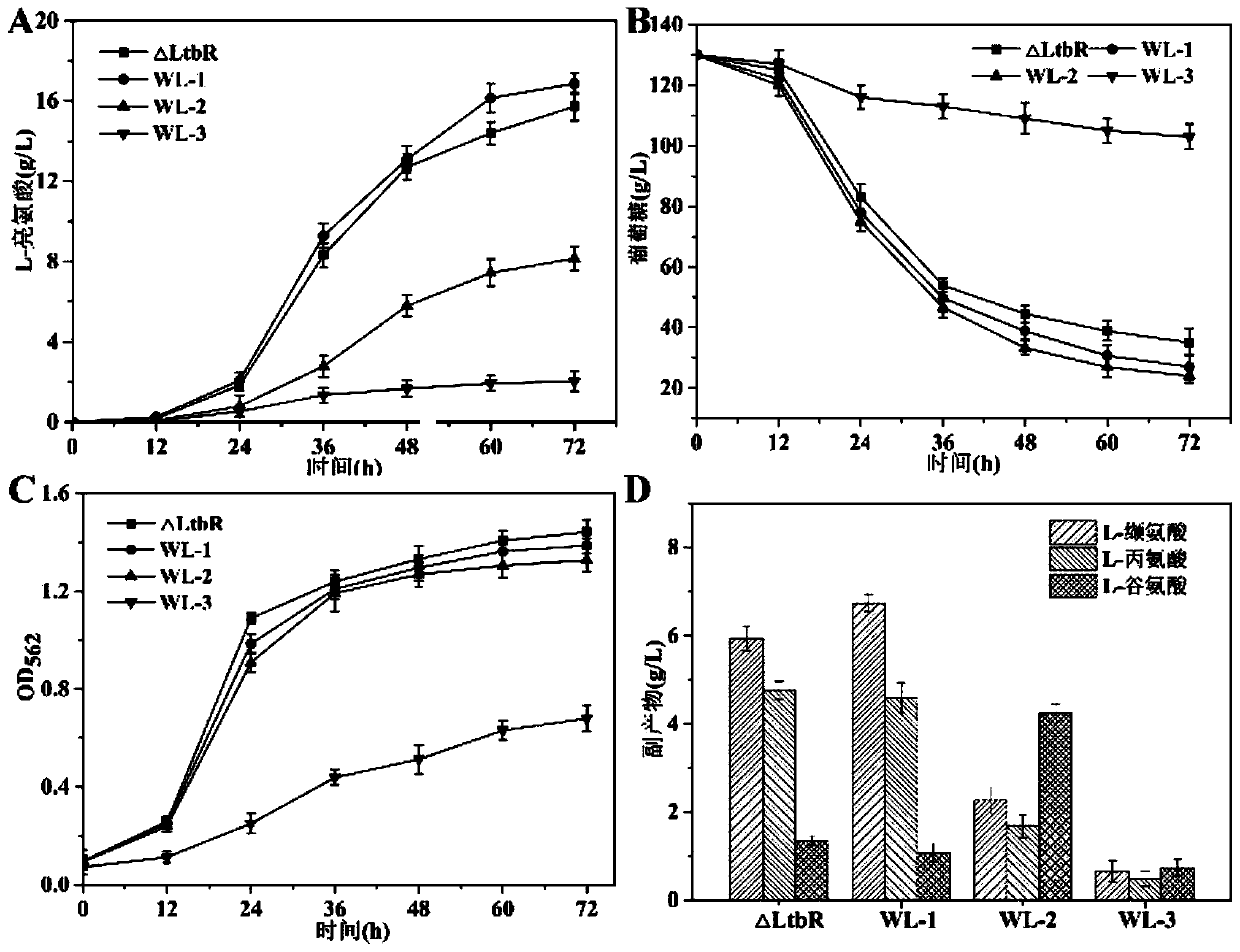
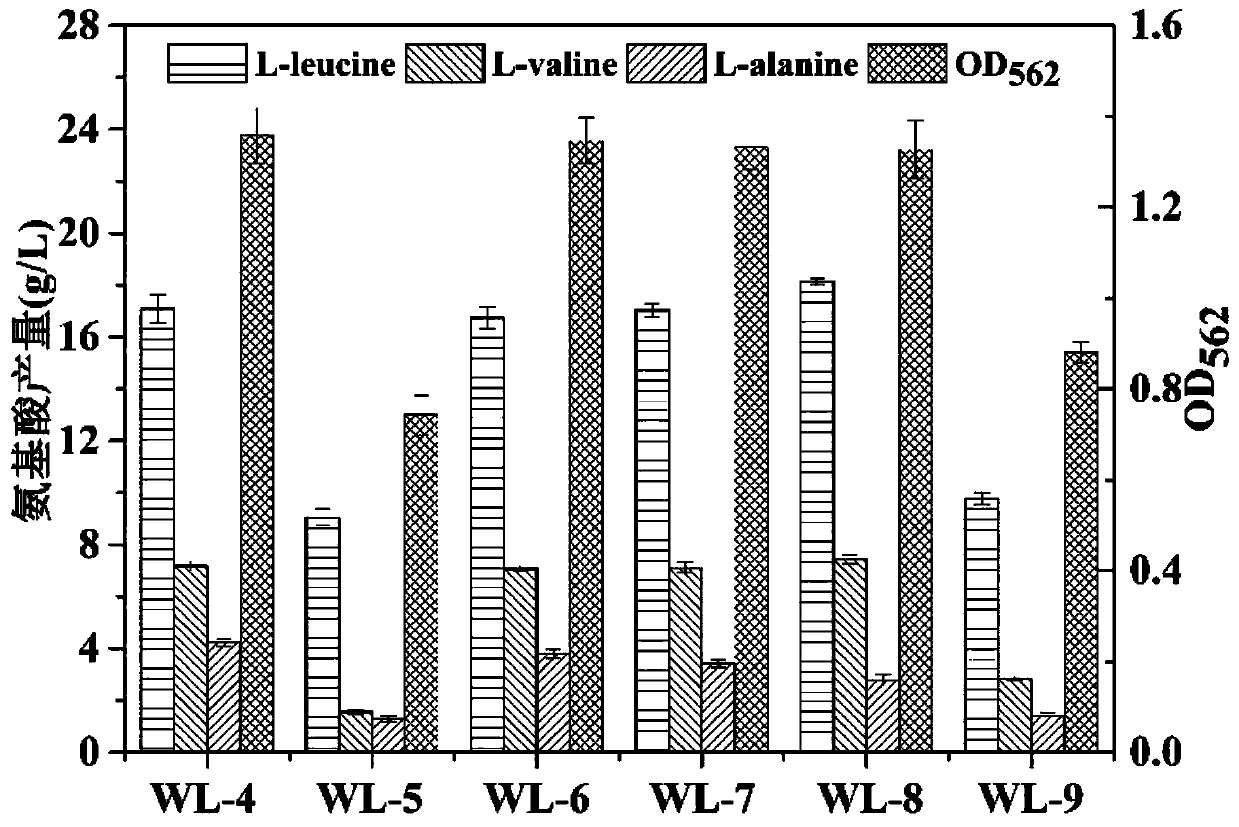
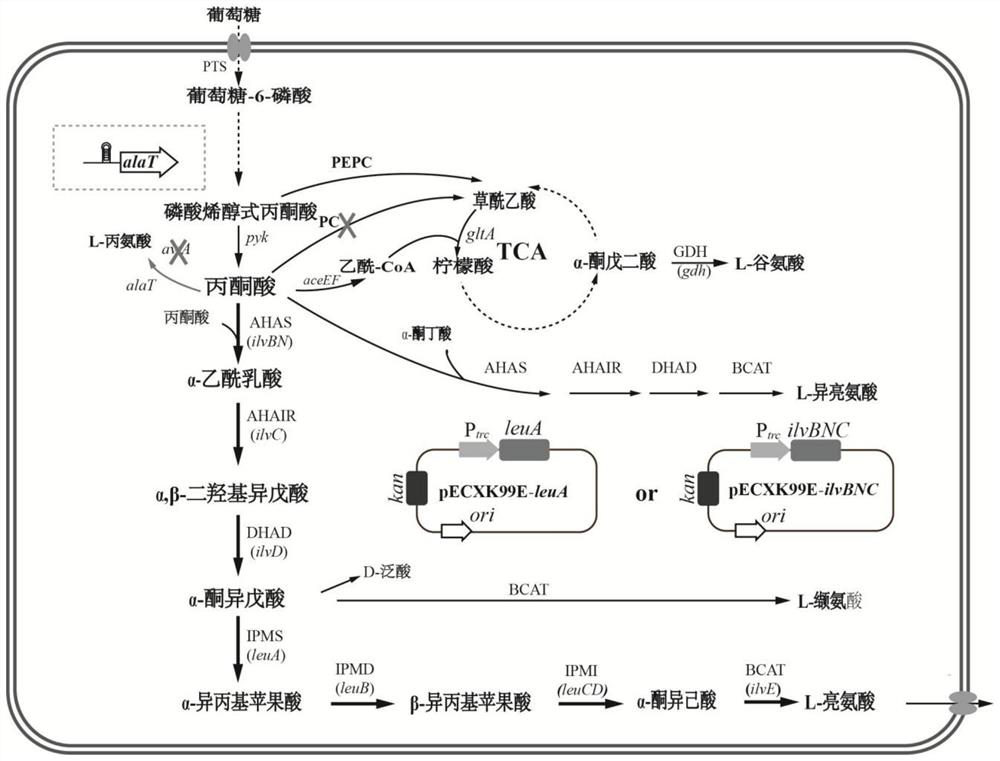
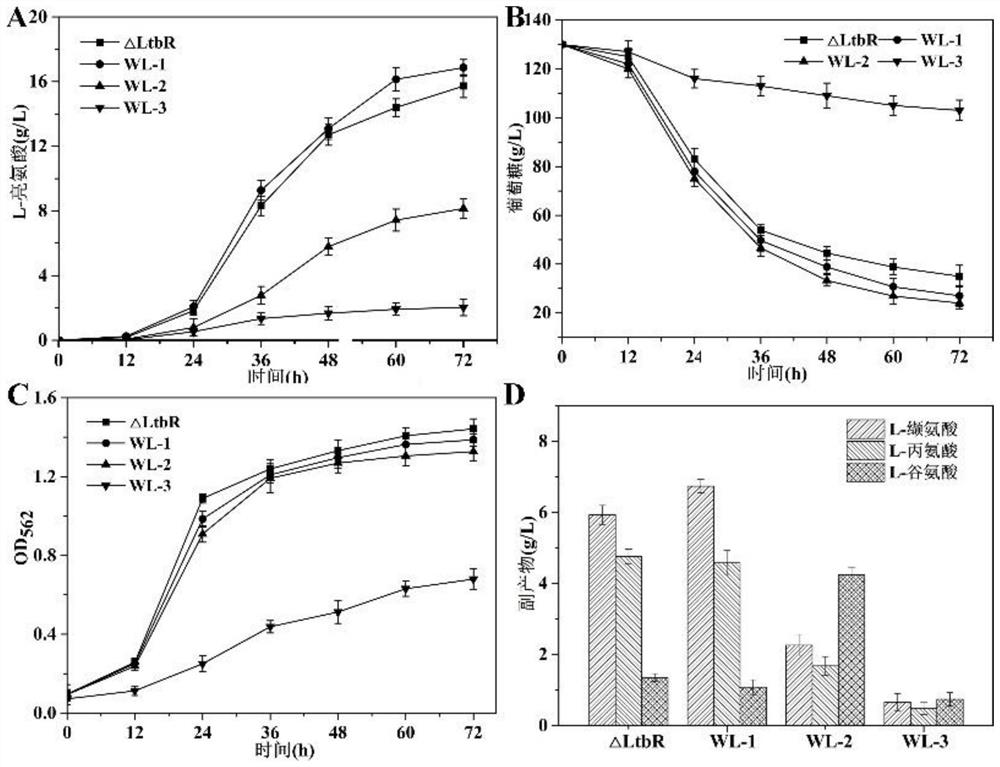
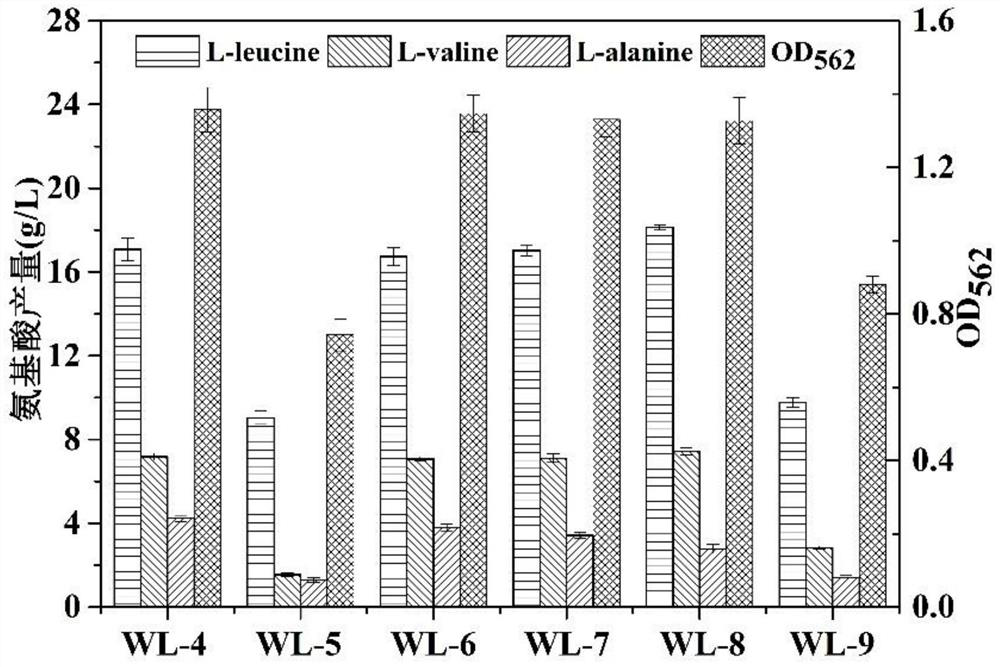
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant bacterium capable of effectively using pyruvic acid and construction method and application of corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant bacterium
ActiveCN110982769AEfficient use ofImprove utilizationBacteriaTransferasesSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminasePyruvate synthesis
The invention relates to a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant bacterium for enhancing effective utilization of pyruvic acid and improving the yield of leucine and a construction method of the corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant bacterium, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. According to the invention, a genetic engineering method is applied to knock out a pyruvate carboxylase genepyc participating in an intracellular oxaloacetic acid supplementing pathway and an alanine transaminase gene avtA participating in alanine synthesis in corynebacterium glutamicum; meanwhile, in order to weaken synthesis capacity of alanine in a competing branch, a T3 terminator is added in front of an alaT gene to weaken the expression level of the alaT gene, so that effective utilization of recombinant bacterial intracellular pyruvic acid is realized, and the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum with an improved L-leucine yield is obtained. The leucine yield of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is increased by 15.3% compared with an original strain. According to the invention, utilization of pyruvic acid is successfully strengthened, the synthetic flux of pyruvic acid to L-leucine is improved, and a new idea is provided for breeding pyruvic acid amino acid high-yield bacteria.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Aloe vera health care wine and production process thereof
ActiveCN108315132AHarm reductionQuality improvementAlcoholic beverage preparationSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseChain scission
The invention relates to a production process of health wine, in particular to an aloe vera health care wine and a production process thereof. The production process includes: by weight part, subjecting aloe vera leaf pulp, smashed steamed sorghum rice and wheat distiller's yeast in a ratio of 1:10:3 to solid state fermentation firstly, then conducting liquid state secondary fermentation, and finally using purified water for blending to a required alcohol content. As alcohol can kill microorganisms, the aloe vera health care wine provided by the invention can keep stable quality, and has highinhibition effect on vegetative forms of bacteria, spores, fungi and viruses. Additionally, because of the adding of aloe, under the combined action of bradykinin enzyme, catalase, alanine transaminase and other enzymes, ethanol can undergo enzymolysis, chain scission and dehydrogenation, and be decomposed into acetaldehyde substances that cannot be absorbed by the human body, thereby greatly reducing the harm of ethanol to the human body. At the same time, the aloe vera has the effects of expelling toxin and maintaining beauty, activating the cardiovascular system, dredging blood capillaries,and killing bacteria.
Owner:申世波
System for predicting liver inflammatory degree of chronic viral hepatitis B patient with alanine transaminase being less than two times of upper normal limit
ActiveCN106153923AExcellent diagnostic valueDisease diagnosisSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseNon invasive
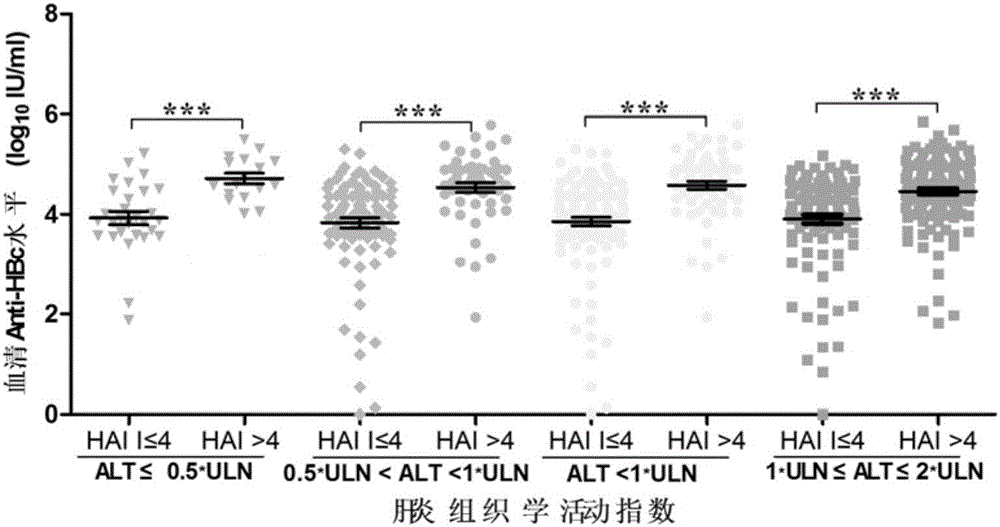
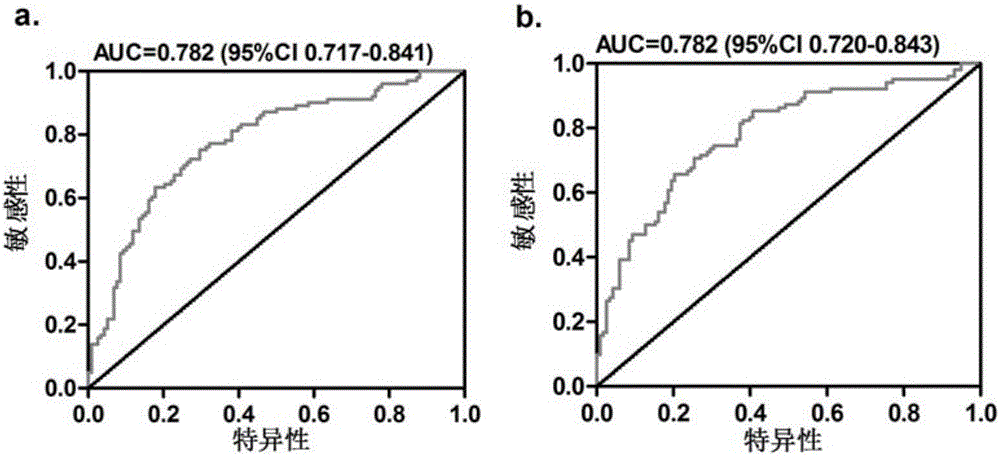
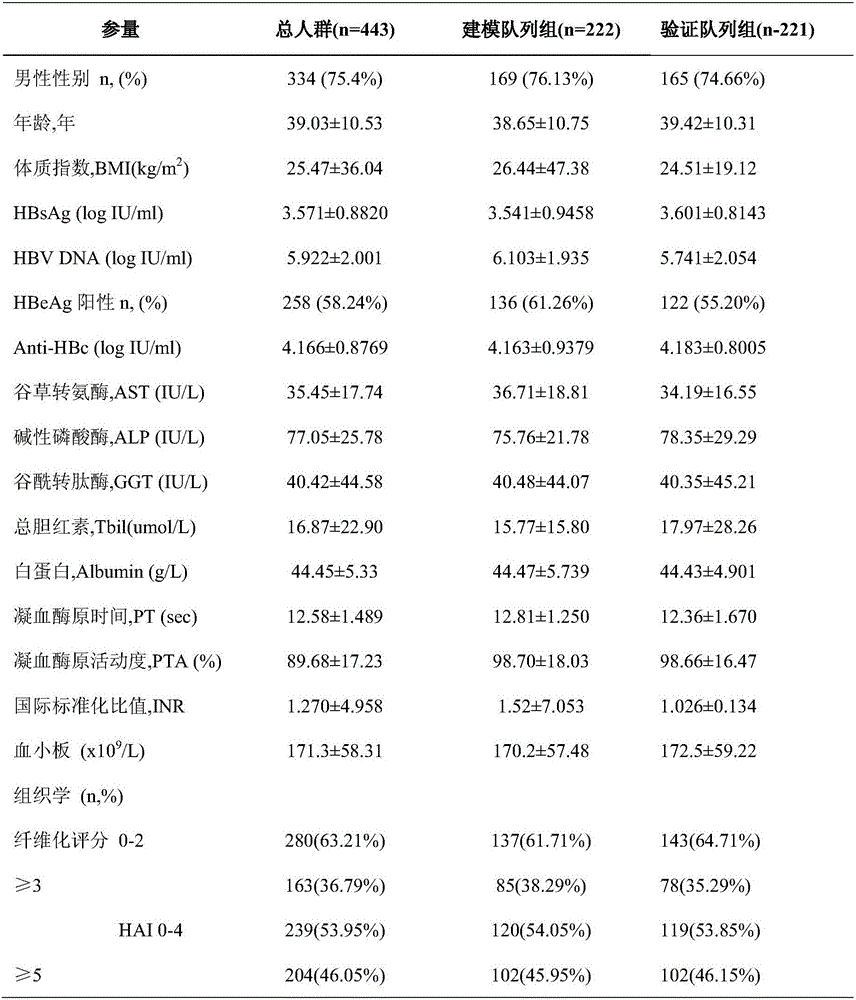
The invention aims to solve the problem that a non-invasive diagnosis method is hardly available for confirming the hepatic pathological state of people with alanine transaminase (ALT) being less than two times of an upper normal limit in the prior art, and provides a system for predicting a liver inflammatory degree of a chronic viral hepatitis B patient with alanine transaminase being less than two times of the upper normal limit. The system comprises a detection module, an Inf-index1 calculation module and a liver inflammatory degree prediction module, wherein the detection module is used for detecting hepatitis B core antibody content, glutamic oxalacetic transaminase content and albumin content in serum of the chronic viral hepatitis B patient with alanine transaminase being less than two times of the upper normal limit; the Inf-index1 calculation module is used for calculating Inf-index1 according to the hepatitis B core antibody content, the glutamic oxalacetic transaminase content and the albumin content; the liver inflammatory degree prediction module is used for predicting the liver inflammatory degree of the chronic viral hepatitis B patient with alanine transaminase being less than two times of the upper normal limit. As proved by clinical test, the system has high prediction accuracy on the inflammatory degree of the chronic viral hepatitis B patient with alanine transaminase being less than the double upper normal limit, and a novel method is provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FIRST HOSPITAL
Application of phosphorylated muramyl dipeptide for preparing medicine capable of constructing fulminant liver injury animal model
ActiveCN110652579AElevated serum ALT levelsOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseDipeptide
The invention relates to the technical field of animal model construction, in particular to application of phosphorylated muramyl dipeptide for preparing a medicine capable of constructing fulminant liver injury animal model. D-galactosamine and the phosphorylated muramyl dipeptide are adopted for jointly constructing the fulminant liver injury animal model, an animal serum ALT (Alanine transaminase) level can be induced to sharply rise under a situation that a proper dosage is given, and hepatic cells can be protected from massive necrosis. Since an injury phenomenon happens in short time after injection, a determination result shows that the fulminant liver injury animal model is successfully constructed.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum capable of effectively utilizing pyruvate and its construction and application
ActiveCN110982769BEfficient use ofImprove utilizationBacteriaTransferasesAlanine aminotransferasePyruvate synthesis
The invention relates to a recombinant bacterium of Corynebacterium glutamicum capable of enhancing the effective utilization of pyruvate and increasing the yield of leucine and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. The present invention applies the genetic engineering method to knock out the pyruvate carboxylase gene pyc and the alanine aminotransferase gene avtA involved in the synthesis of alanine in Corynebacterium glutamicum, which participate in the intracellular oxaloacetate replenishment pathway; The alanine synthesis ability of the branch, adding a T3 terminator before the alaT gene weakens its expression level, realizes the effective utilization of pyruvate in the recombinant bacteria, and obtains the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum with improved L-leucine production. The leucine yield of the recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum is 15.3% higher than that of the starting strain. This invention successfully strengthens the utilization of pyruvate and improves the synthesis flux from pyruvate to L-leucine, which also provides a new idea for breeding high-yielding bacteria of pyruvate family amino acids.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
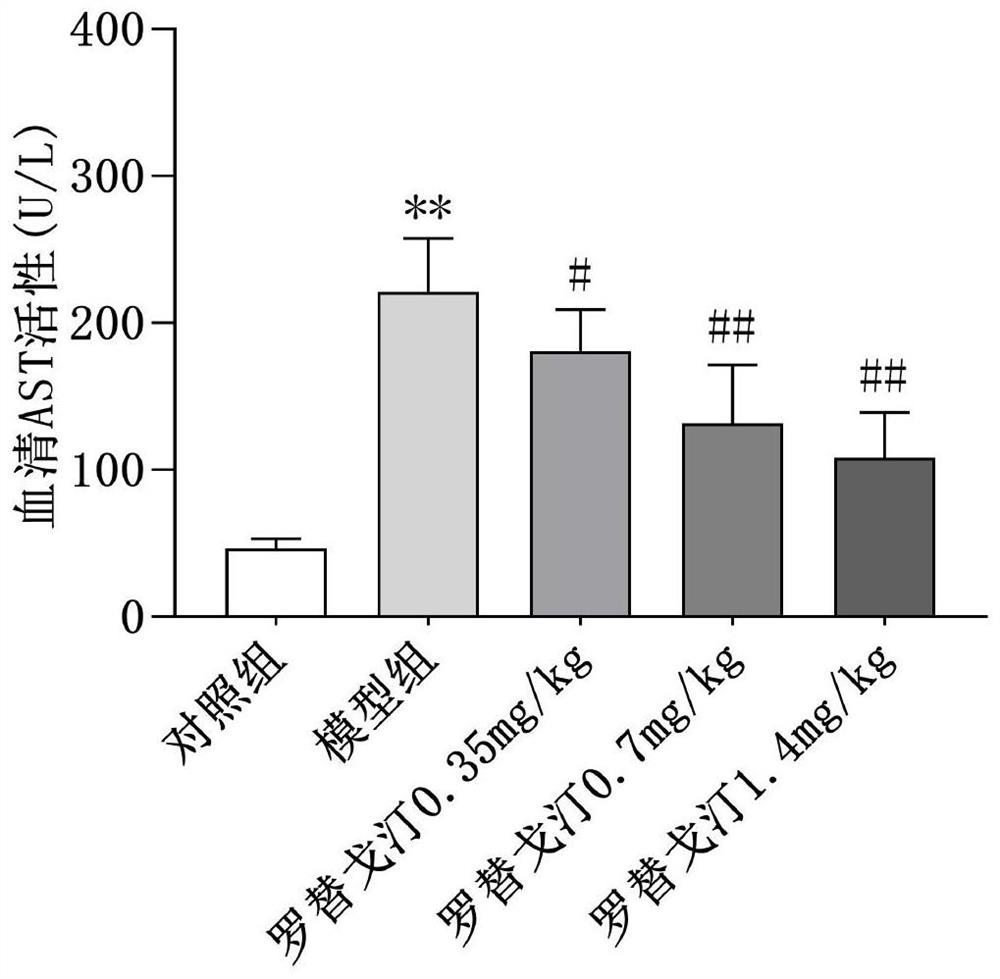
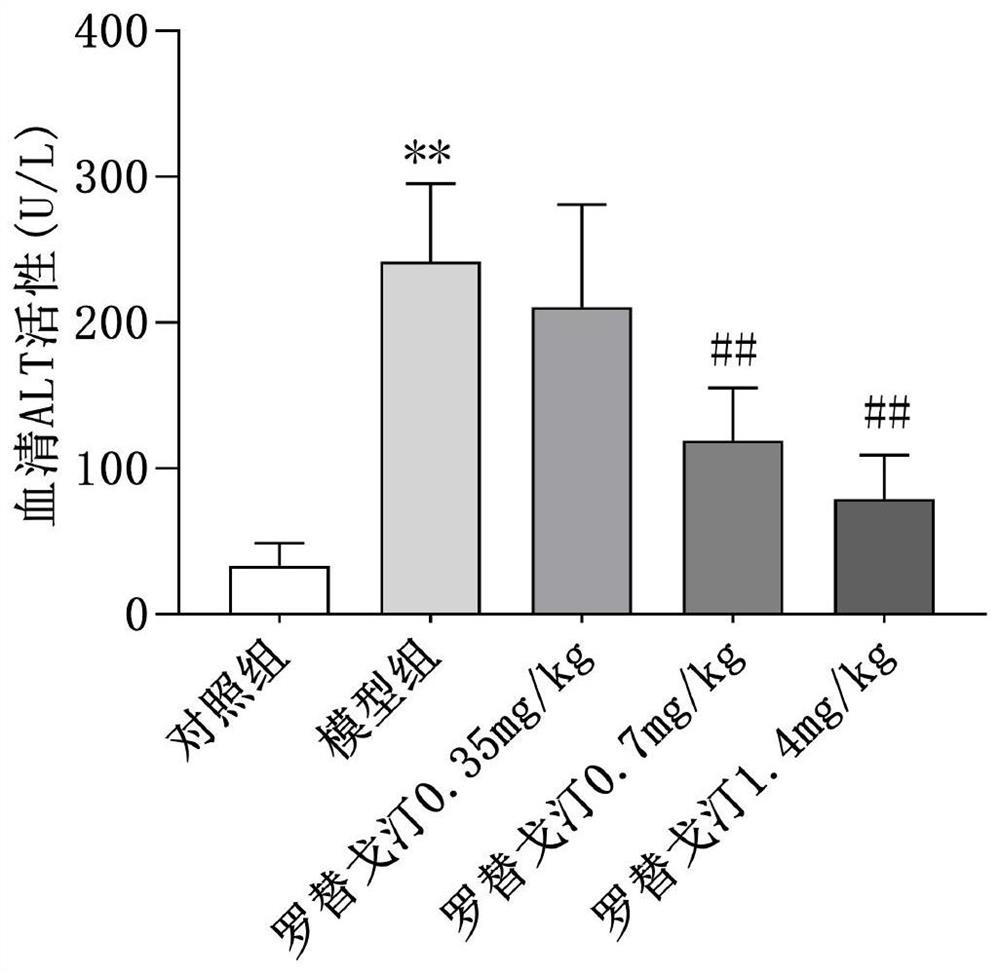
New application of rotigotine in preparation of acute liver injury resisting drug
InactiveCN112569226AReduce pathological damageReduce diffuse bleedingOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminasePharmaceutical medicine
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, discloses a new application of rotigotine in preparation of an acute liver injury resisting medicine, and particularly discloses an application of rotigotine in preparation of the acute liver injury resisting medicine. Rotigotine can reduce the levels of alanine transaminase (ALT) and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase (AST) in serum of mice with liverinjury induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) / D-Gal, reduce the concentration of TNF-alpha in serum of mice with acute liver injury, relieve pathological injury of liver tissues and reduce diffuse hemorrhage of the liver tissues. Pharmacological experiments prove that rotigotine has the effect of relieving acute liver injury, and a new prevention or treatment drug is provided for liver injury.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Drunkenness-delaying liver protecting tablets and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110693993AReduce absorptionReduce drunkennessOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseTectorial membrane
The invention discloses drunkenness-delaying liver protecting tablets and a preparation method thereof. The liver protecting tablets comprise 200-400 parts of Tulipa edulis bulb extract and 400-500 parts of a gastric mucosa protecting agent. The liver protecting tablets have the advantages that the Tulipa edulis bulb extract with colchicine removed and the gastric mucosa protecting agent are usedas main drugs, a protection film is formed in vivo by the drugs, activity of alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate amino transferase (AST), total antioxidant capacity (TEAC), activity of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), activity of glutathione peroxidase (GPx), activity of catalase (CAT), total SOD activity, content of reduced glutathione (GSH) and content of malonaldehyde (MDA) in vivo can be adjusted to slow down alcohol absorption while inhibiting excessive oxidative stress caused by alcohol, an endogenous antioxidation system is protected, and activity of ALDH is improved, so that efficacy of delaying drunkenness and improving alcoholic liver injury is realized.
Owner:安佰超
Application of Methane Injection in Preparation of Drugs for Treating Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
InactiveCN103690481BAvoid damageReduce deathHydrocarbon active ingredientsDigestive systemSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseRat liver
The invention discloses an application of methane injection in preparation of medicaments for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury, which comprises a preparation method of the methane injection. Animal experiments are performed on the methane injection, and the results prove that the methane injection can be used for obviously reducing the level of alanine transaminase, reducing liver injury and reducing hepatocyte apoptosis against a rat model with liver ischemia-reperfusion injury, so that the methane injection can be used for treating the liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Thus, the methane injection disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the medicaments for treating the ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for quantitative detection of alanine aminotransferase in solution based on copper nanocluster fluorescent probe
InactiveCN109596580BOptically stableSmall particle sizeFluorescence/phosphorescenceSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseFluoProbes
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively detecting alanine transaminase in a solution based on a copper nanocluster fluorescent probe, wherein a copper nanocluster with glutathione as a protective agent is used as a fluorescent probe, and the content of alanine transaminase in the solution is specifically detected through a fluorescence "off-on" mode. The label-free, highly sensitive and selective detection of alanine transaminase is achieved by adopting the fluorescence "off-on" mode. The method is simple and rapid, the specific detection of alanine transaminase can be realized, the detection linear range is wide, and the detection limit is low. The method in the invention has good detection sensitivity and selectivity and has good application prospects in disease detection, clinical application and other aspects.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Alpha-oxoglutarate content measurement kit and measurement method thereof
PendingCN110609003AThe test result is accurateReduce experiment costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminasePhosphate
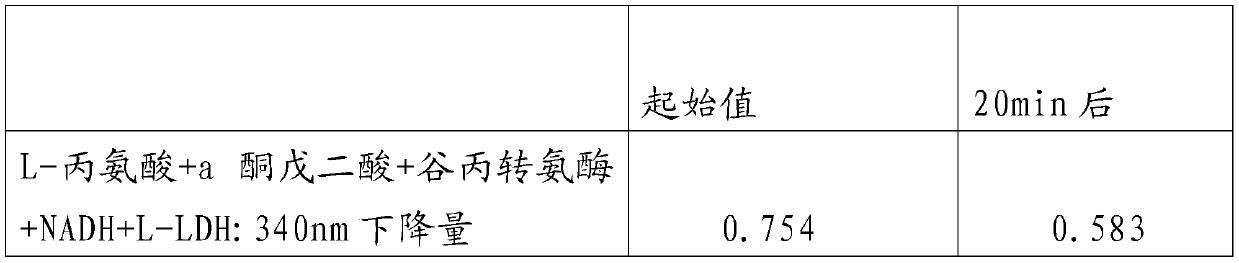
An Alpha-oxoglutarate content measurement kit comprises a box main body, a cover plate, a rotation shaft and a fixed seat. A detection method comprises the steps of sample preparation, in which a sample is taken, PH7.8 phosphate buffer liquid is added for grinding, centrifugation is performed for 10 minutes, a supernatant liquid is waited for measurement; detection step, in which the detection step comprises the steps of 1, pre-heating by a photometer, and performing zero setting with distilled water; 2, adding a standard point, alanine, NAD+, glutamate dehydrogenase, 2-(4-iodobenzene)-3-(4-nitrobenzene)-5-(thiobenzoate)-2H-tetrazolium salt, a phosphate buffer liquid and alanine aminotransferase into a standard measurement pipe, adding alanine, NAD+, glutamate dehydrogenase, 2-(4-iodobenzene)-3-(4-nitrobenzene)-5-(thiobenzoate)-2H-tetrazolium salt, a phosphate buffer liquid and alanine transaminase into a blank pipe, adding the to-be-measured supernatant liquid and then adding constituents in the blank pipe into a sample measurement pipe, and adding the to-be-measured supernatant liquid, NAD+, glutamate dehydrogenase, L2-(4-iodobenzene)-3-(4-nitrobenzene)-5-(thiobenzoate)-2H-tetrazolium salt and a phosphate buffer liquid into a contrast pipe; and 3, immediately and uniformly mixing, reacting for 30 min, transferring to a glass cell, reading a light absorption value A of each pipe, and calculating Alpha-oxoglutarate(Alpha-KG) content according to sample mass. The method is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:苏州格锐思生物科技有限公司
A kind of construction method of the mouse model of hepatitis B virus infection
ActiveCN104212835BDoes not induce an immune responseSimplify the build processIn-vivo testing preparationsVector-based foreign material introductionSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseImmunodeficiency
Owner:张欣欣 +6
Alanine transaminase enzymes and methods of use
InactiveUS7914985B2High activityMore diagnostic valueSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseAlanine transaminase
Novel alanine transaminase (ALT) polypeptides and the use thereof as a diagnostic marker to predict and monitor tissue damage and / or tissue malfunction. The ALT polypeptides are murine and / or rattus ALT polypeptides and said ALT polypeptides are used to detect, predict and / or determine hepatic processes of an animal, particularly mice and / or rats.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Construction method of escherichia coli with high yield of L-tryptophan and low yield of L-alanine
InactiveCN114591992AIncrease productionReduce outputBacteriaFood processingEscherichia coliSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminase
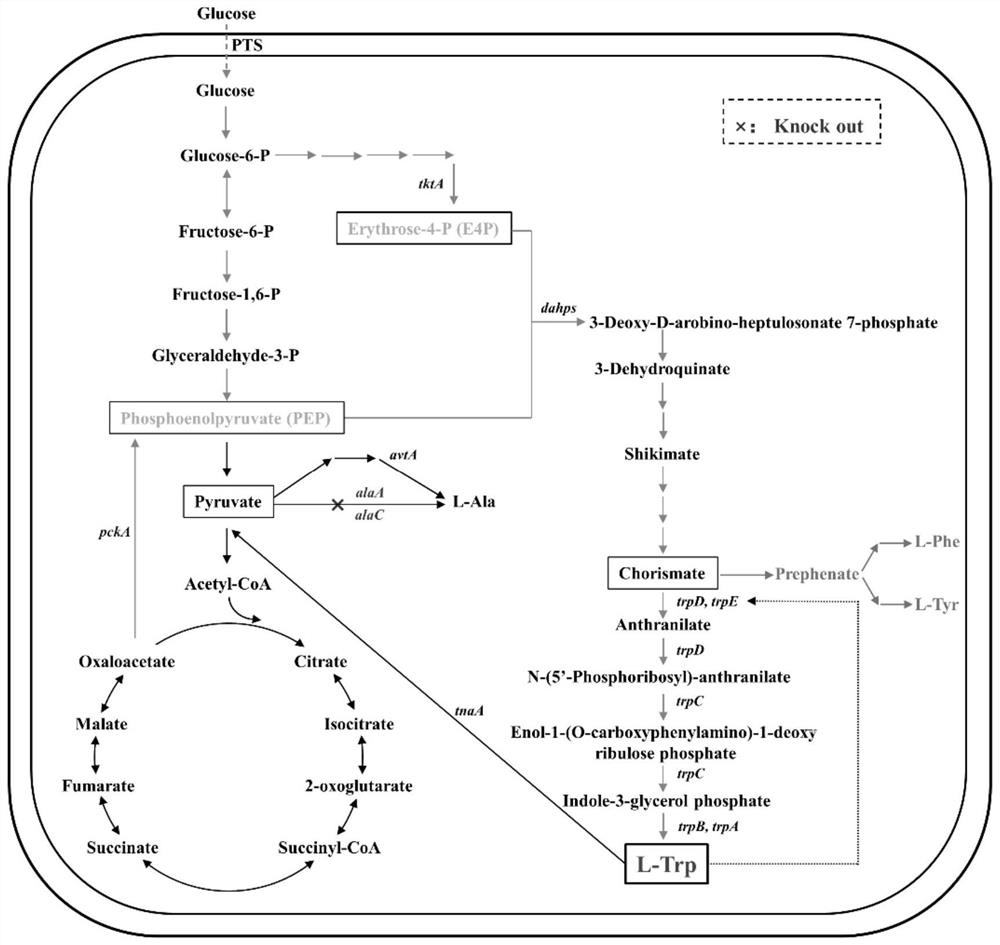
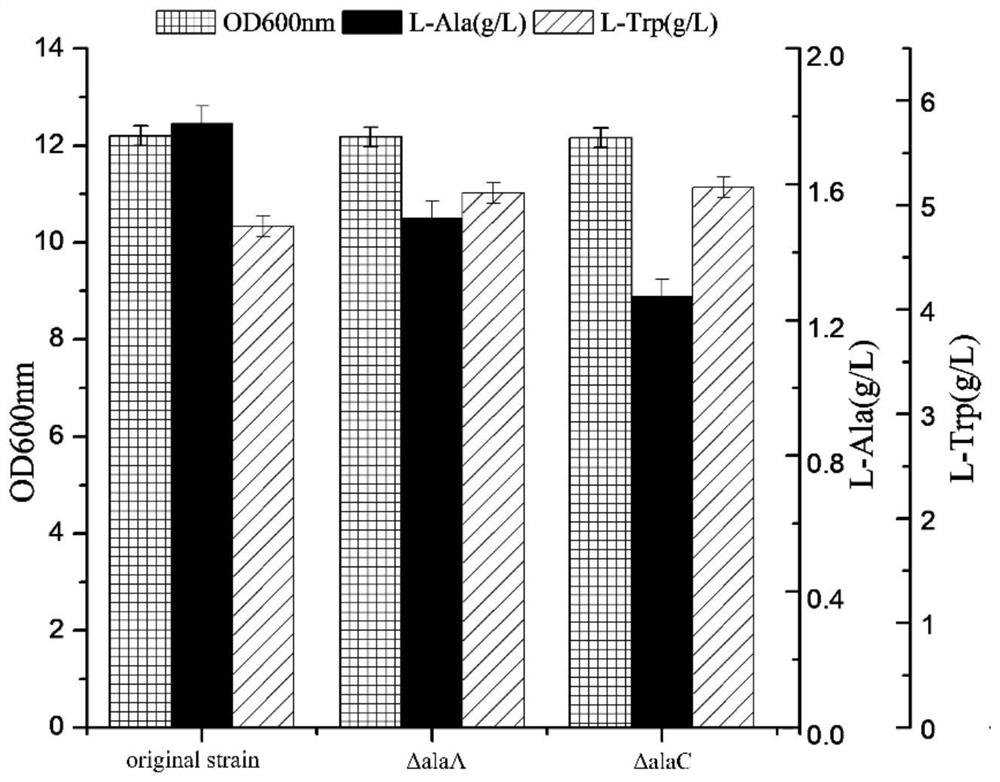
The invention discloses a construction method of Escherichia coli with high yield of L-tryptophan and low yield of L-alanine, which comprises the following steps: respectively designing knockout primer pairs with homologous arms according to sequence information of alaA and alaC in E.coli K-12 alanine transaminase genes of the E.coli K-12 alanine transaminase genes, and knockout amino transferase genes alaA and alaC to obtain L-tryptophan with high yield and low yield of L-alanine. The recombinant escherichia coli can more fully utilize the carbon metabolic flow to synthesize the L-tryptophan, so that the yield of the L-tryptophan is increased, the yield of an L-alanine by-product in a metabolic pathway of the escherichia coli is reduced, and the pressure of product purification is relieved.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Compound medicament for treating chronic liver disease and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103127273BDigestive systemPlant ingredientsSerum glutamate pyruvate transaminaseAcute toxicity testing
The invention relates to a compound medicament for treating a chronic liver disease and a preparation method thereof. The compound medicament is prepared from artemisia capillaries, artemisia rupestris, cichorium glandulosum boiss et huet, rose, rhubarb and licorice which are used as raw materials and medicinal accessories and prepared into an oral preparation, syrup granules, hard capsules and tablets by adopting a method of solvent extraction, impurity removal, concentration and drying. The active ingredients in the compound medicament are dissolved by adopting a reasonable extraction method according to the Uyghur medicinal theory, the characteristics of national medicine and the long-term folk clinical practice of the Uyghur nationality, so that the medicinal effects are enhanced, and the bioavailability is improved. Animal experiments prove that the compound medicament has a protective effect on liver injury. Pharmacodynamic experiments show that the extract obtained by the method can inordinately reduce the alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transferase (AST) levels in mouse serum of a liver injury model, the pathological symptoms in each medication administration team are relieved, and the liver injury is protected. Acute toxicity experiments show that the maximum dosage of the extract obtained by the method is equivalent to 337 folds of clinical human proposed dosage according to mouse intragastric single-time administration toxicity test, and the extract is nontoxic and safe.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of medicine composition in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating fatty liver
ActiveCN103301243AImprove lesionRelieve the severity of the diseaseDigestive systemLeech/worm material medical ingredientsHigh-density lipoproteinInflammatory cell
The invention relates to an application of a medicine composition in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating fatty liver. The medicine composition is mainly composed of the six traditional Chinese medicines including astragalus membranaceus, glossy privet fruit, leech, rheum officinale, radix pseudostellariae and barbary wolfberry fruit. The medicine composition has the functions of reducing the index values of serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TCH), TG (triglyceride) in liver tissues and the like in a fatty liver model, increasing the index values of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in serum and the like, and reducing the index values of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH) and the like in the liver tissues. Simultaneously, the medicine composition is further capable of reducing the degrees of the vacuolar degeneration, debonding degeneration, fatty degeneration, diffuse tissue necrosis and inflammatory cell diffuse infiltration of liver tissues in the fatty liver models of rats and mice. The results prove that the medicine composition has a definite curative effect on fatty liver.
Owner:SICHUAN JISHENGTANG PHARMLS
Application of medicine composition in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating fatty liver
ActiveCN103301243BImprove lesionRelieve the severity of the diseaseDigestive systemLeech/worm material medical ingredientsHigh-density lipoproteinInflammatory cell
The invention relates to an application of a medicine composition in preparation of medicines for preventing or treating fatty liver. The medicine composition is mainly composed of the six traditional Chinese medicines including astragalus membranaceus, glossy privet fruit, leech, rheum officinale, radix pseudostellariae and barbary wolfberry fruit. The medicine composition has the functions of reducing the index values of serum triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TCH), TG (triglyceride) in liver tissues and the like in a fatty liver model, increasing the index values of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in serum and the like, and reducing the index values of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH) and the like in the liver tissues. Simultaneously, the medicine composition is further capable of reducing the degrees of the vacuolar degeneration, debonding degeneration, fatty degeneration, diffuse tissue necrosis and inflammatory cell diffuse infiltration of liver tissues in the fatty liver models of rats and mice. The results prove that the medicine composition has a definite curative effect on fatty liver.
Owner:SICHUAN JISHENGTANG PHARMLS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com