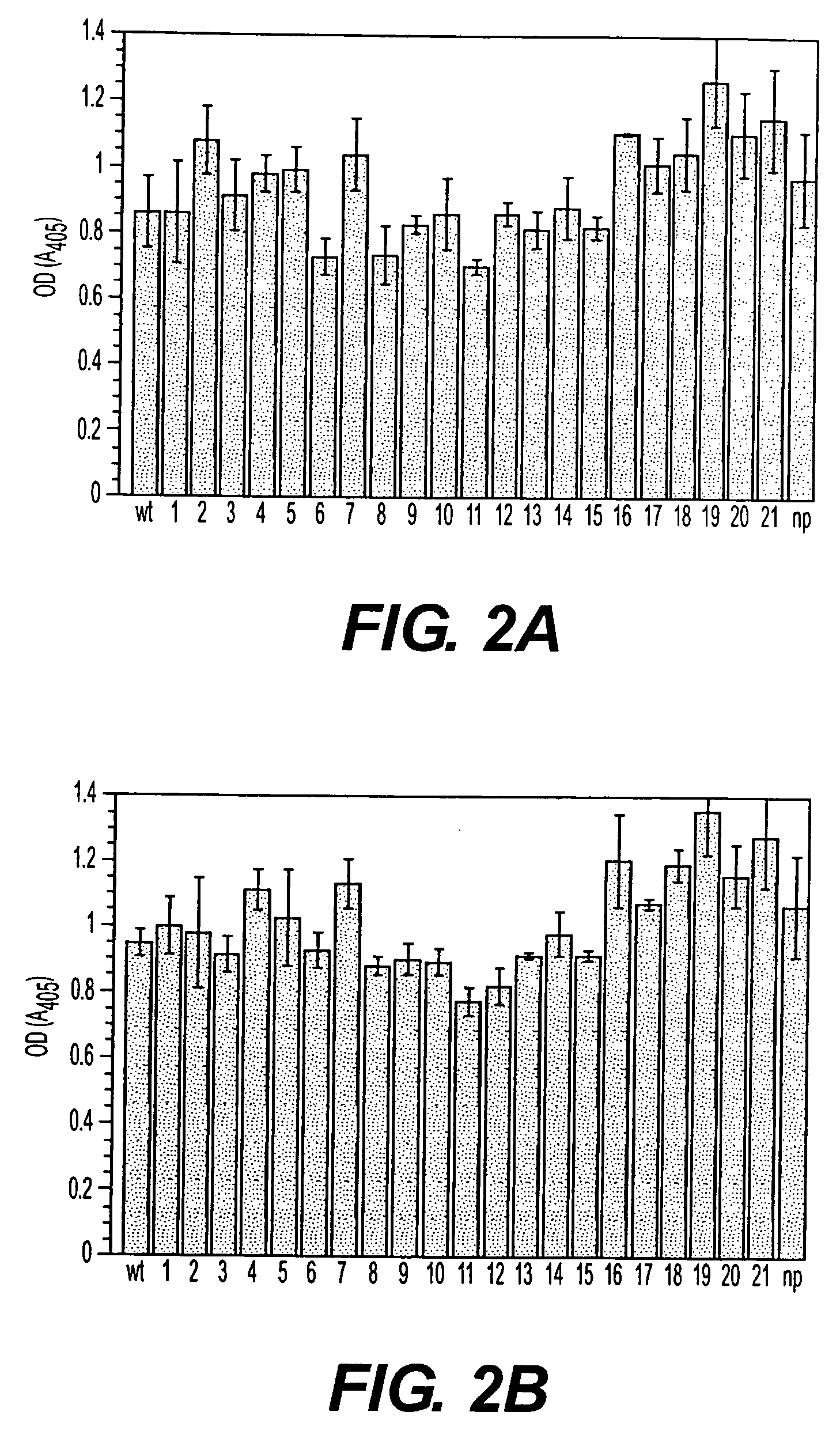
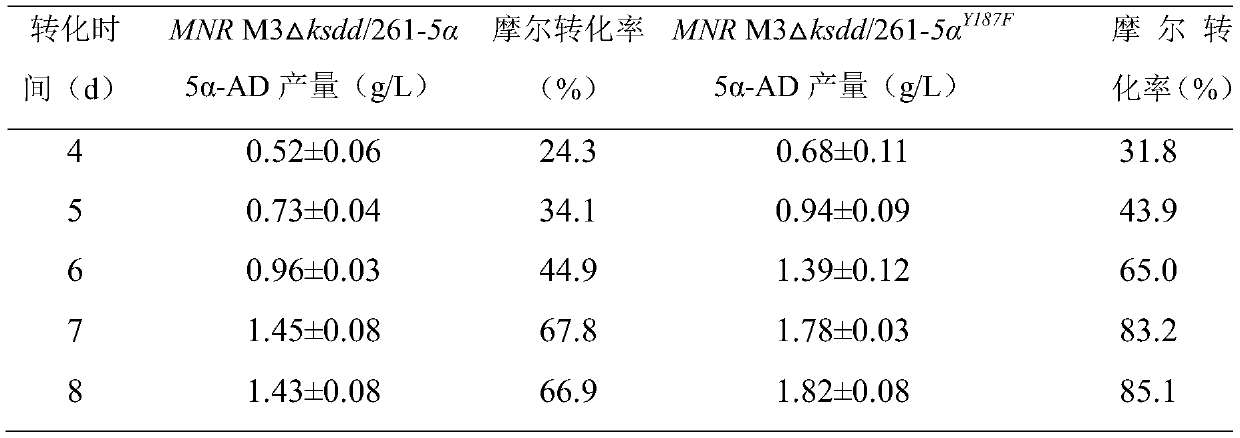
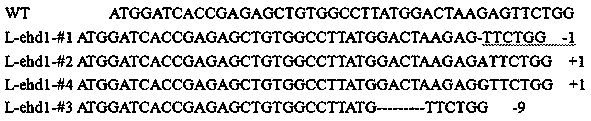Patents
Literature
42 results about "Site specific mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Site-specific mutation. site-spe·cif·ic mu·ta·tion. an alteration of the structure of a gene at a specific sequence, usually referring to experimentally produced changes in gene sequence.
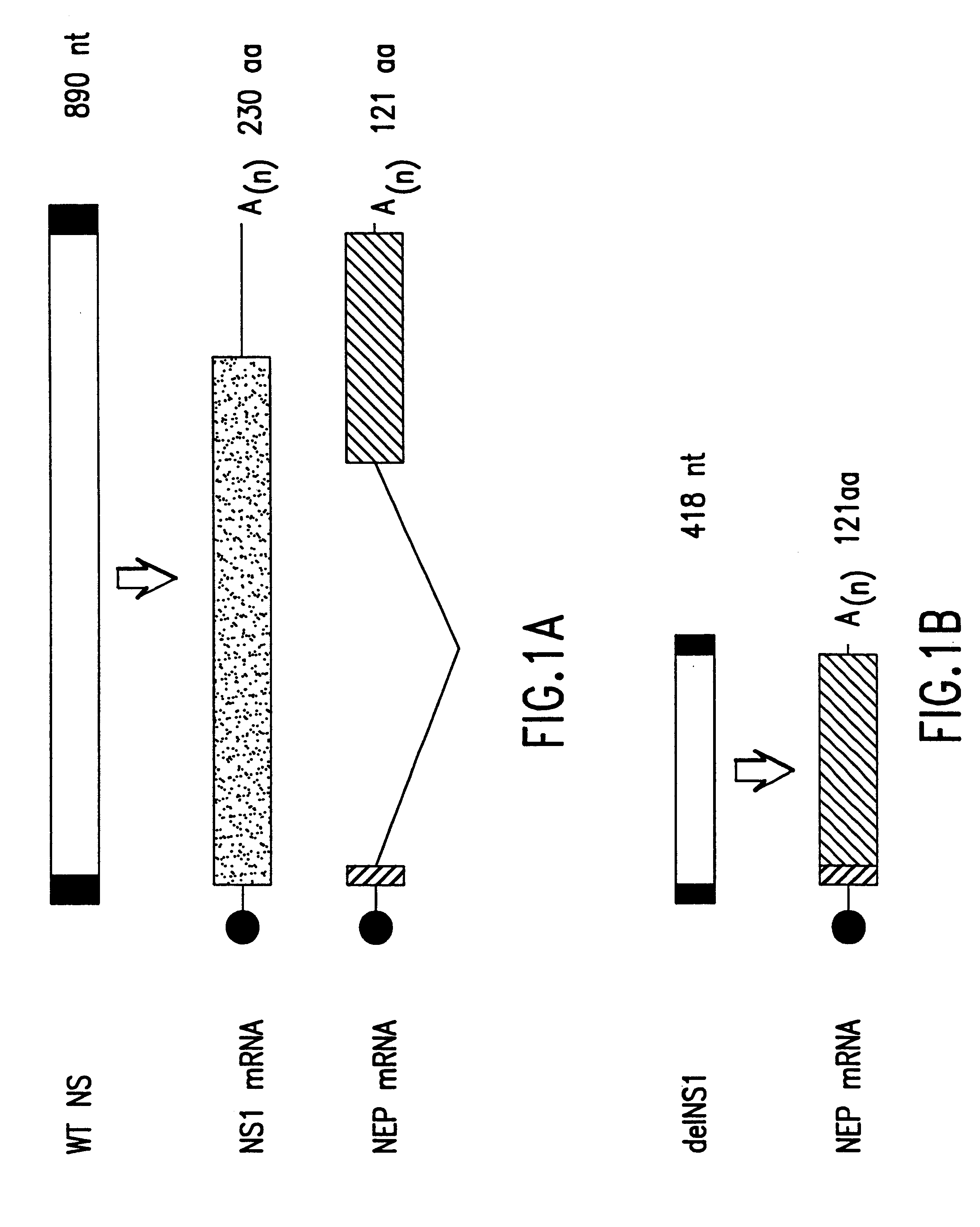
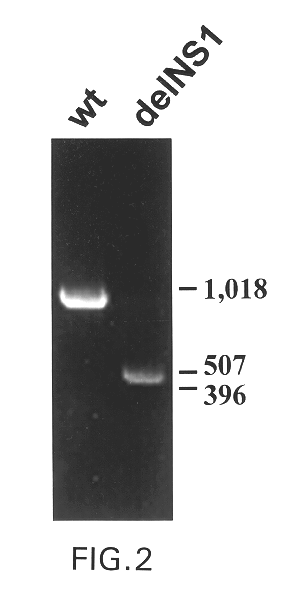
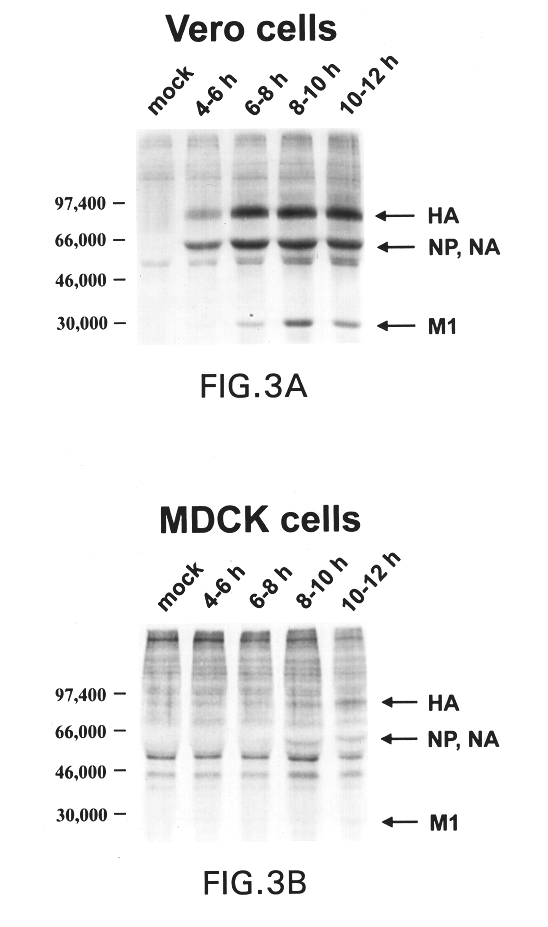
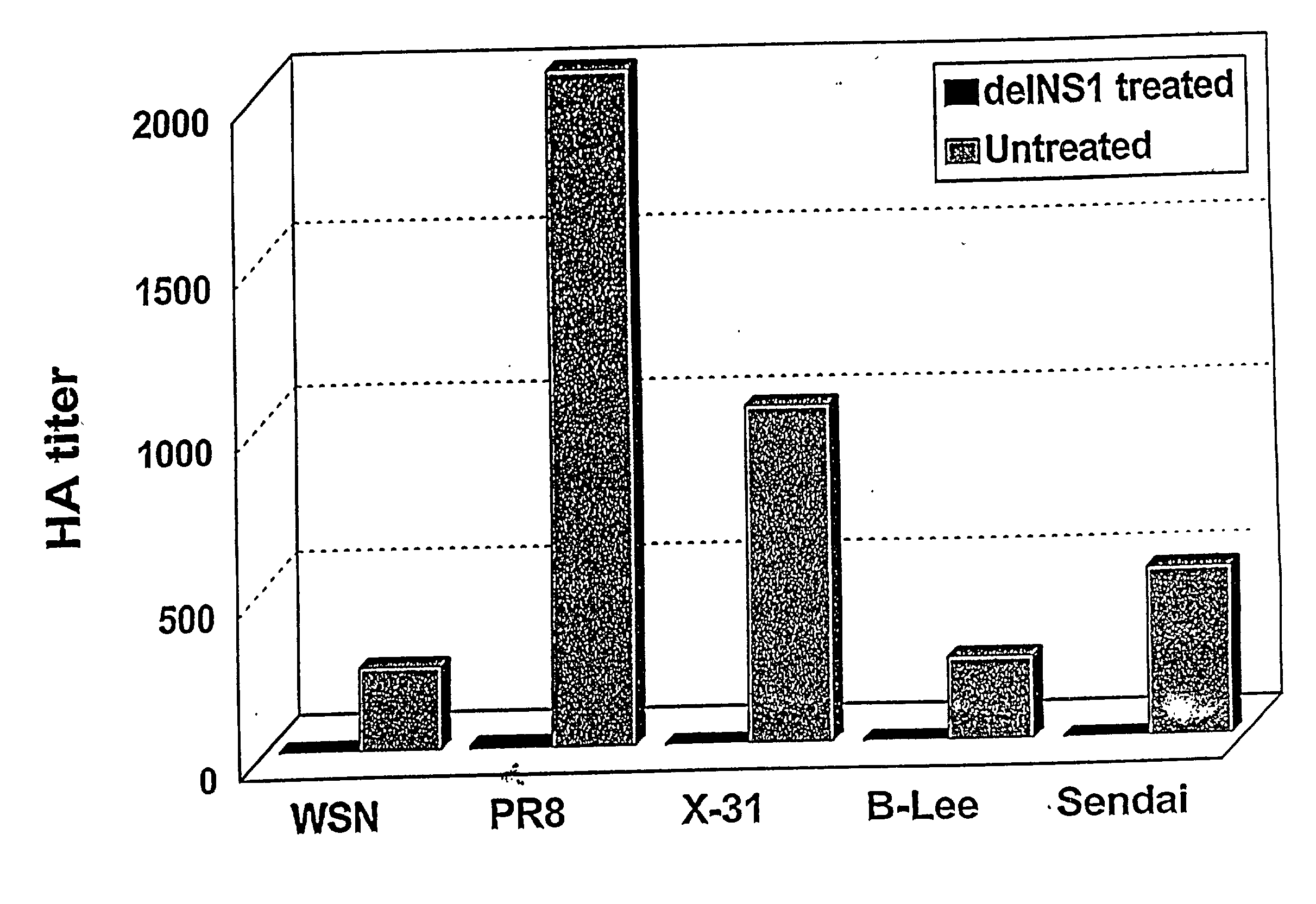
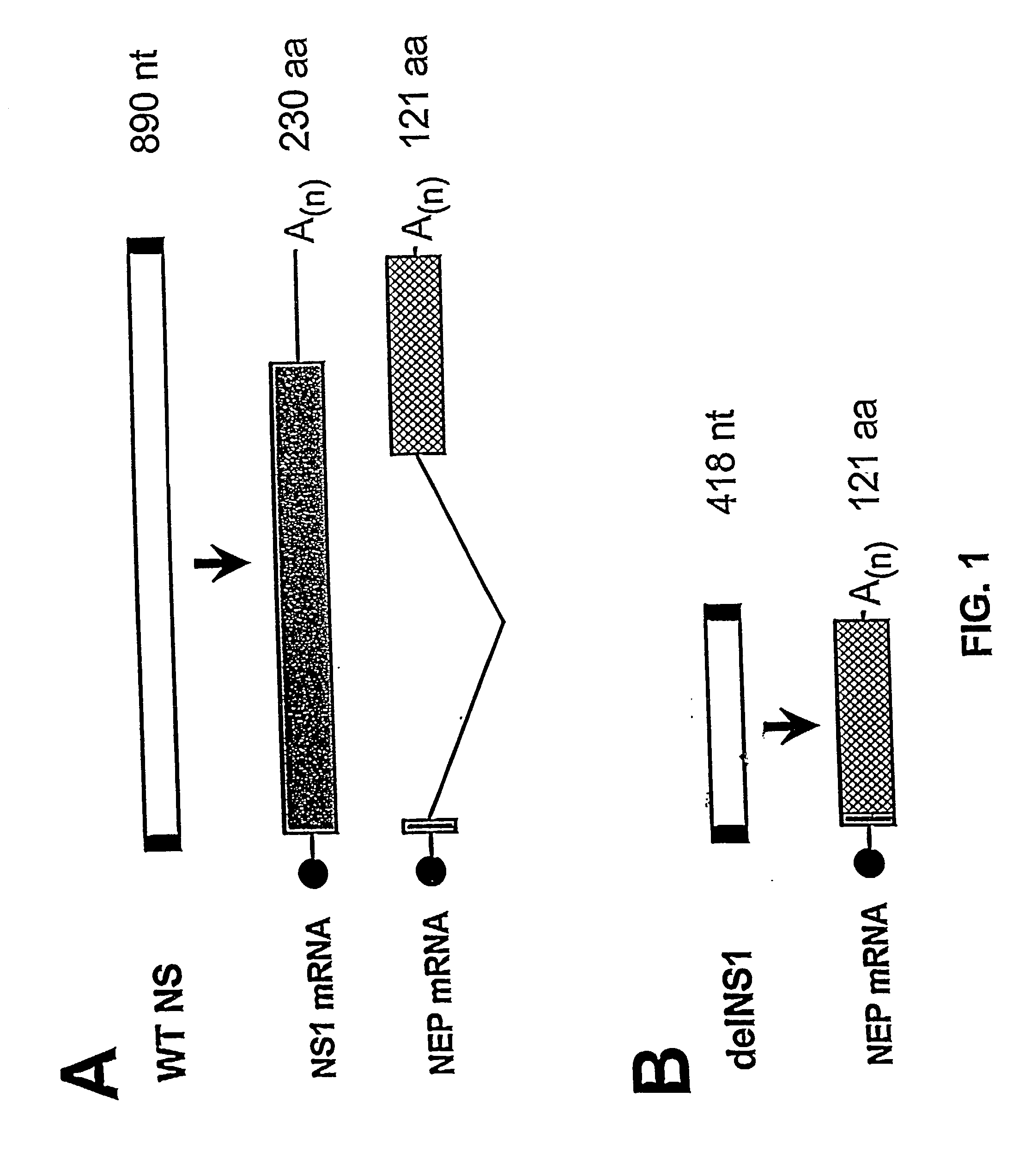
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
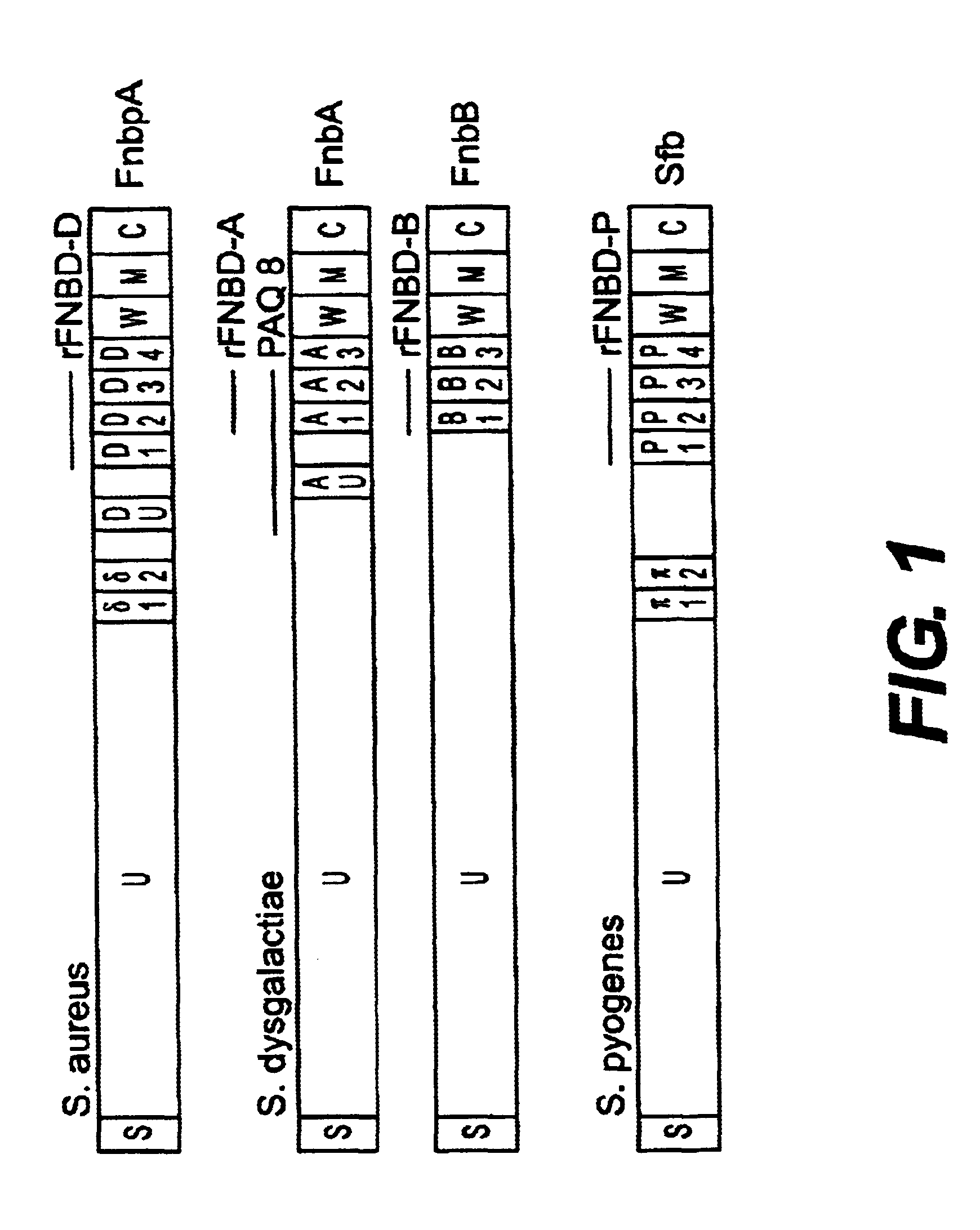
Fibronectin binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6685943B1Avoid problemsOvercomes drawbackPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPassive ImmunizationsStreptococcus pyogenes
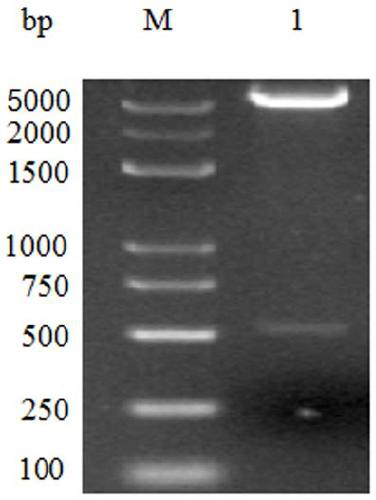
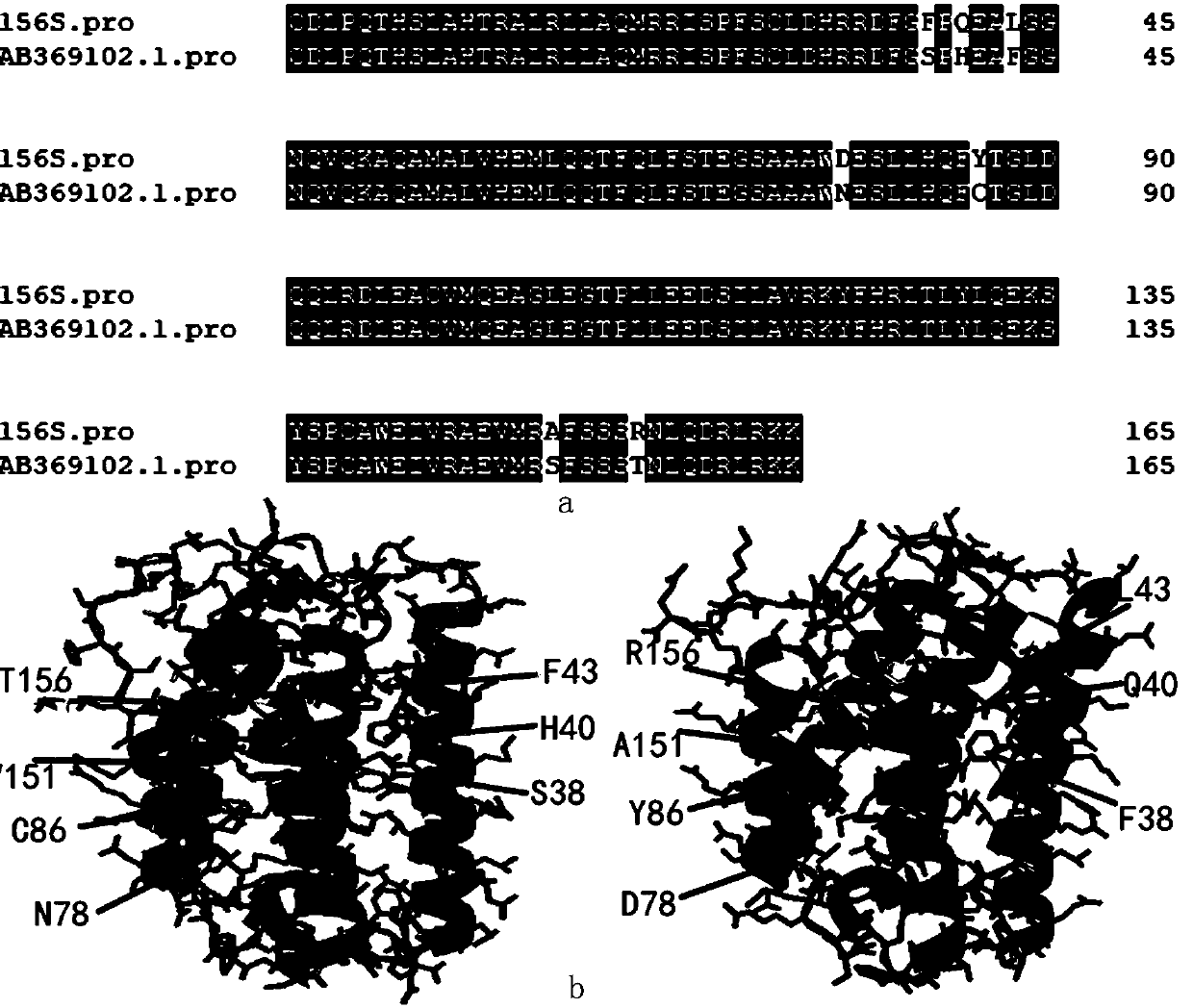
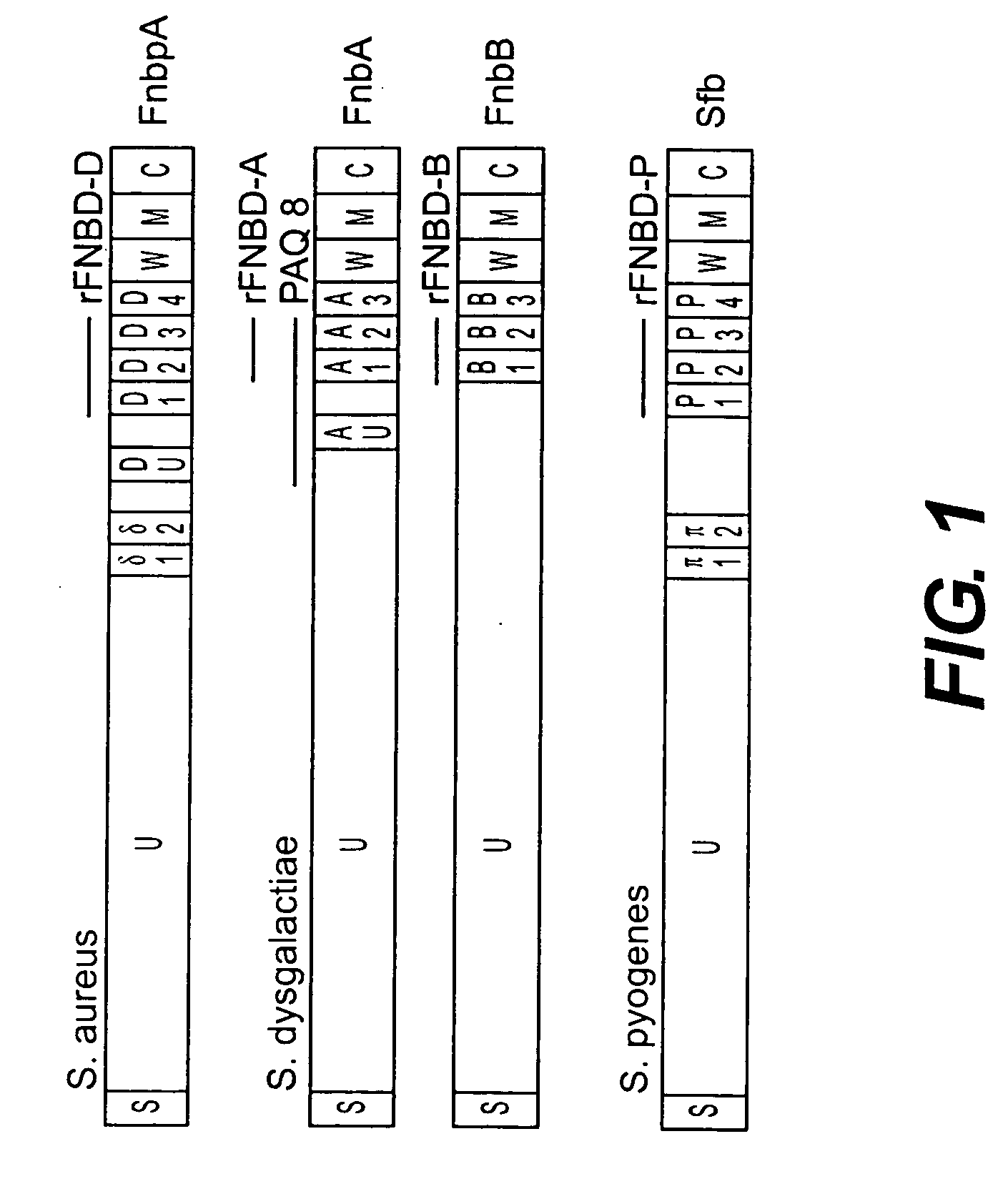
Disclosed are antibodies that block the binding of fibronectin protein to fibronectin. Also disclosed are site specifically-mutated and truncated peptide epitopes derived from the fnbA and fnbB genes of Staphylococcus aureus, the fnba and fnbB genes of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, and the sfb gene of Streptococcus pyogenes, and nucleic acid segments encoding these peptides and epitopes. The anti-(fibronectin binding site) antibodies, peptides and epitopes that give rise to antibodies that block the binding of fibronectin binding proteins to fibronectin, and DNA segments encoding these proteins and are of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of streptococcal and staphylococcal colonization in animals or humans. These. DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are proposed to be of use directly in the preparation of vaccines and also for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA +2
sc(Fv)2 SITE-DIRECTED MUTANT
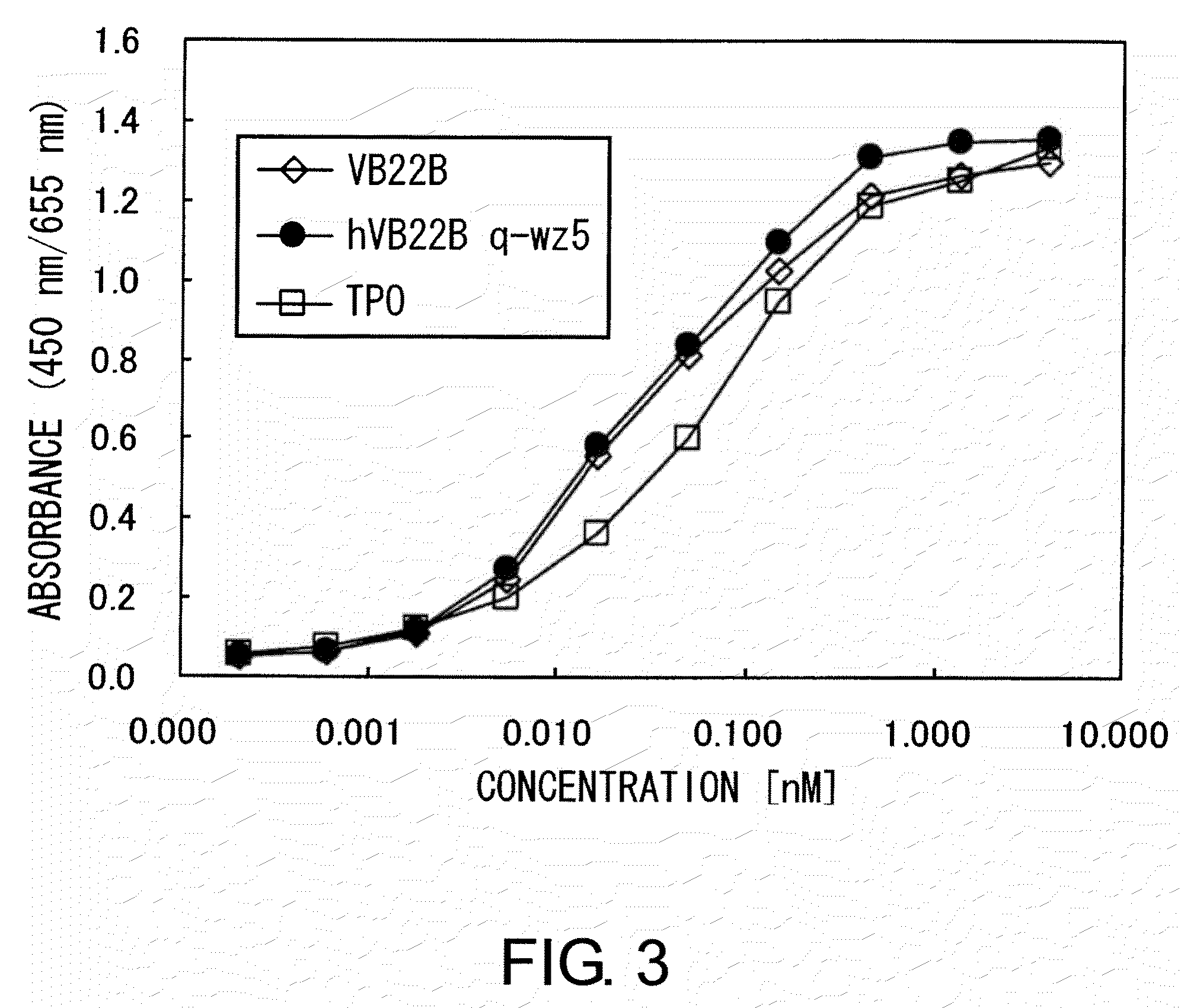
InactiveUS20090028854A1Increasing TmImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAmino acid substitutionBiology
To solve the above-mentioned problems, the present inventors introduced site-specific mutations into sc(Fv)2 and examined the stabilizing effects on sc(Fv)2. As a result, they succeeded for the first time in significantly increasing the Tm value of sc(Fv)2 by amino acid substitutions. Furthermore, they discovered that sc(Fv)2 is stabilized by introducing site-specific mutations into sc(Fv)2.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
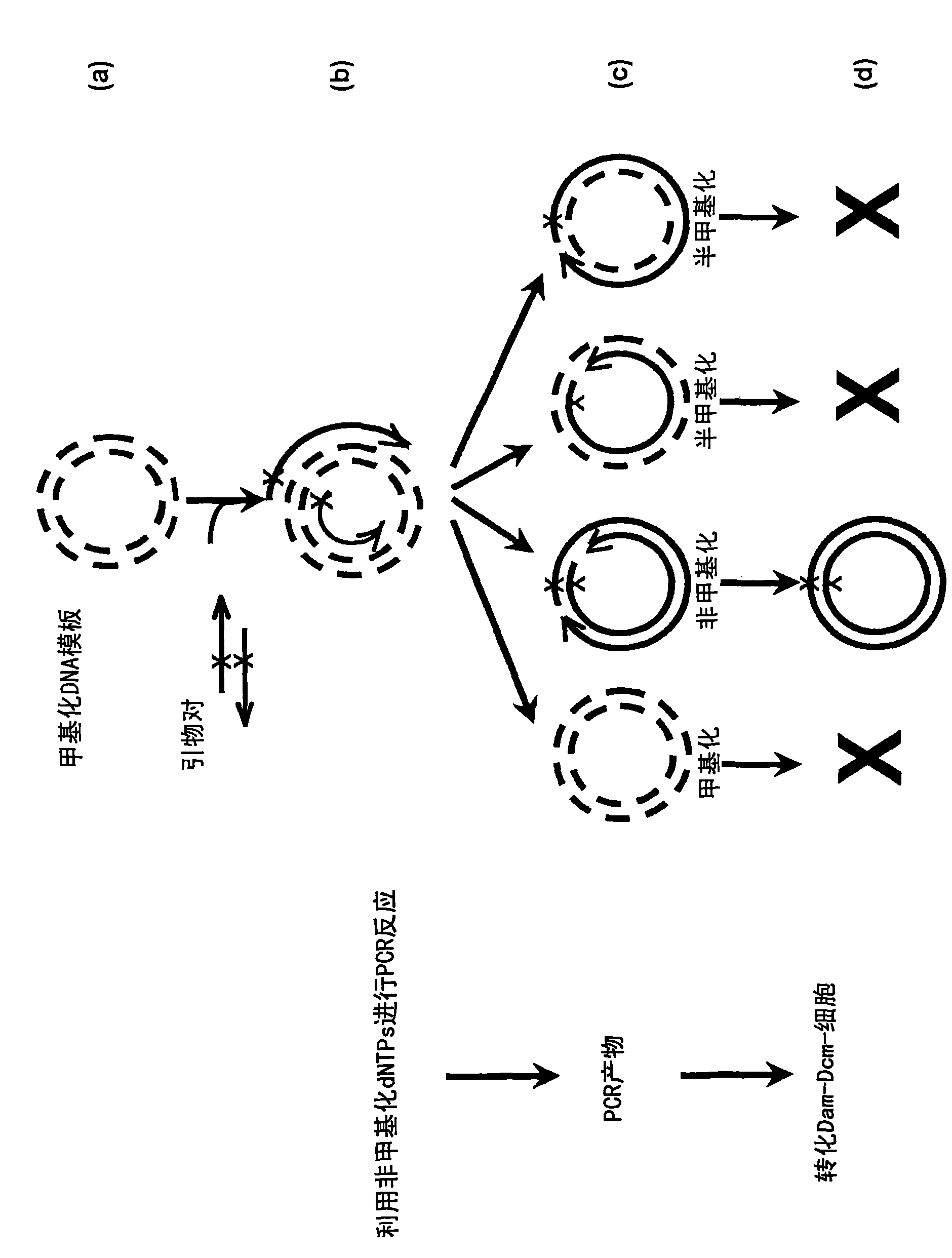
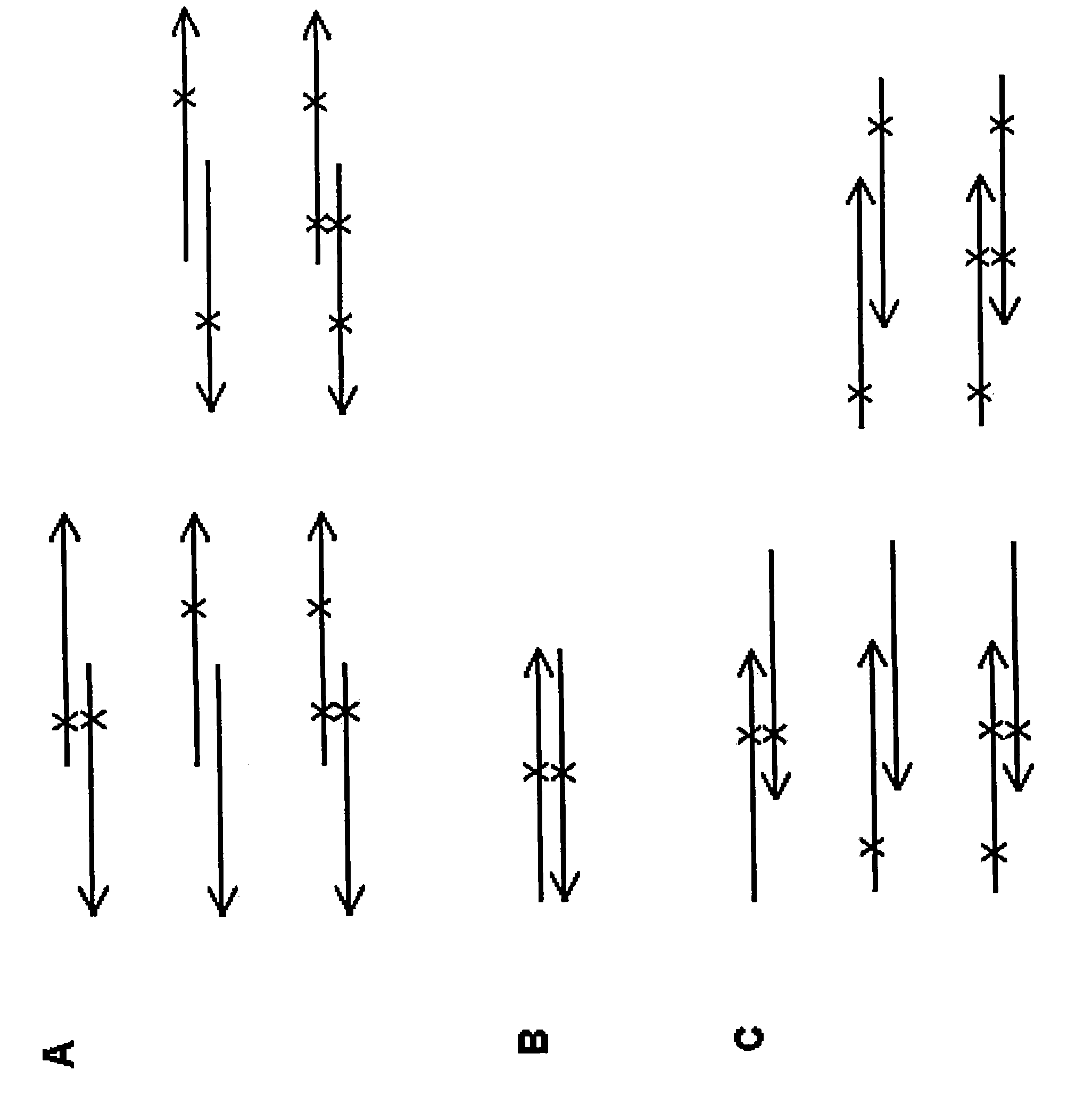
Site-directed mutagenesis in circular methylated DNA
InactiveUS20100267147A1Wide compatibilityEliminate effectiveBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliSite-directed mutagenesis
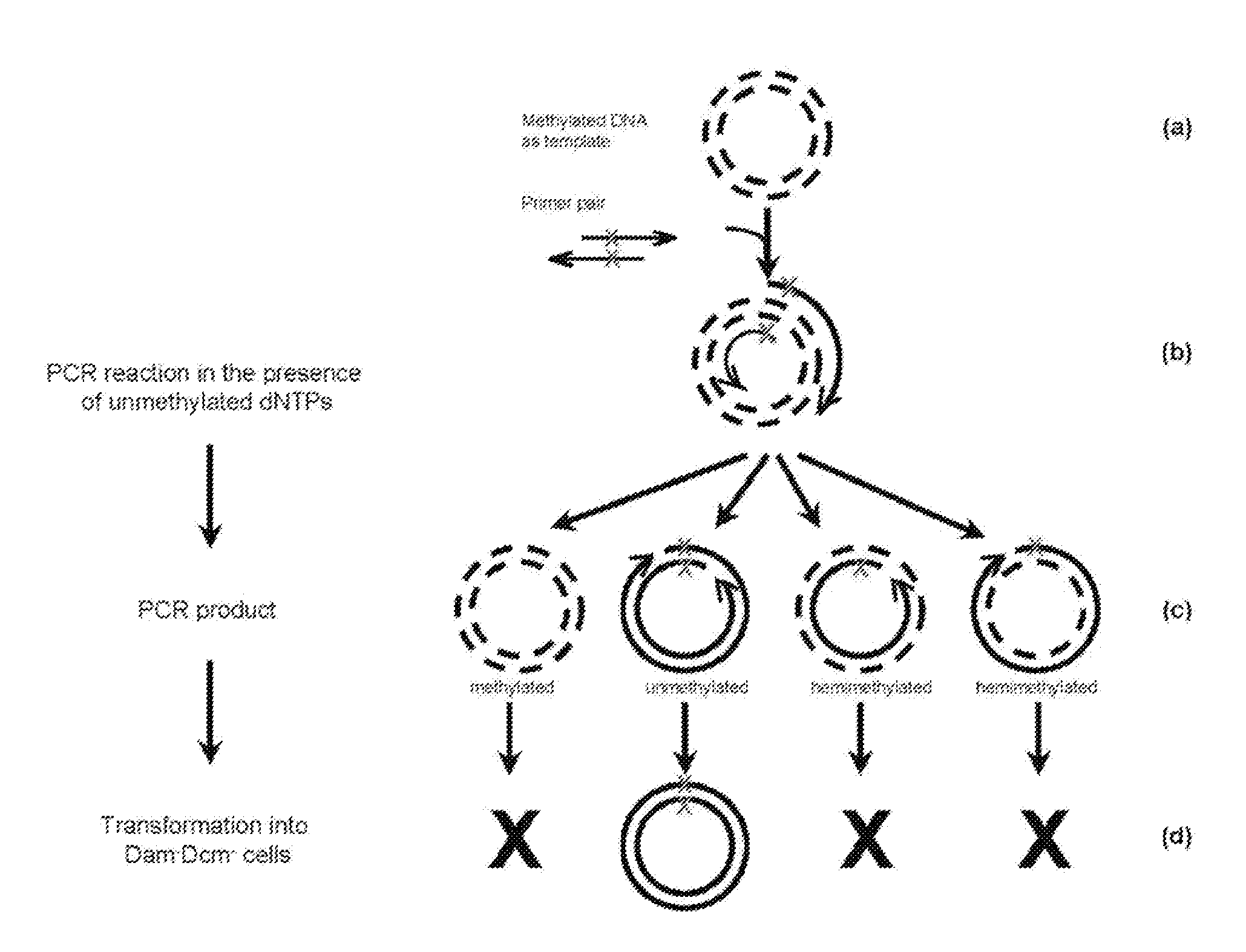
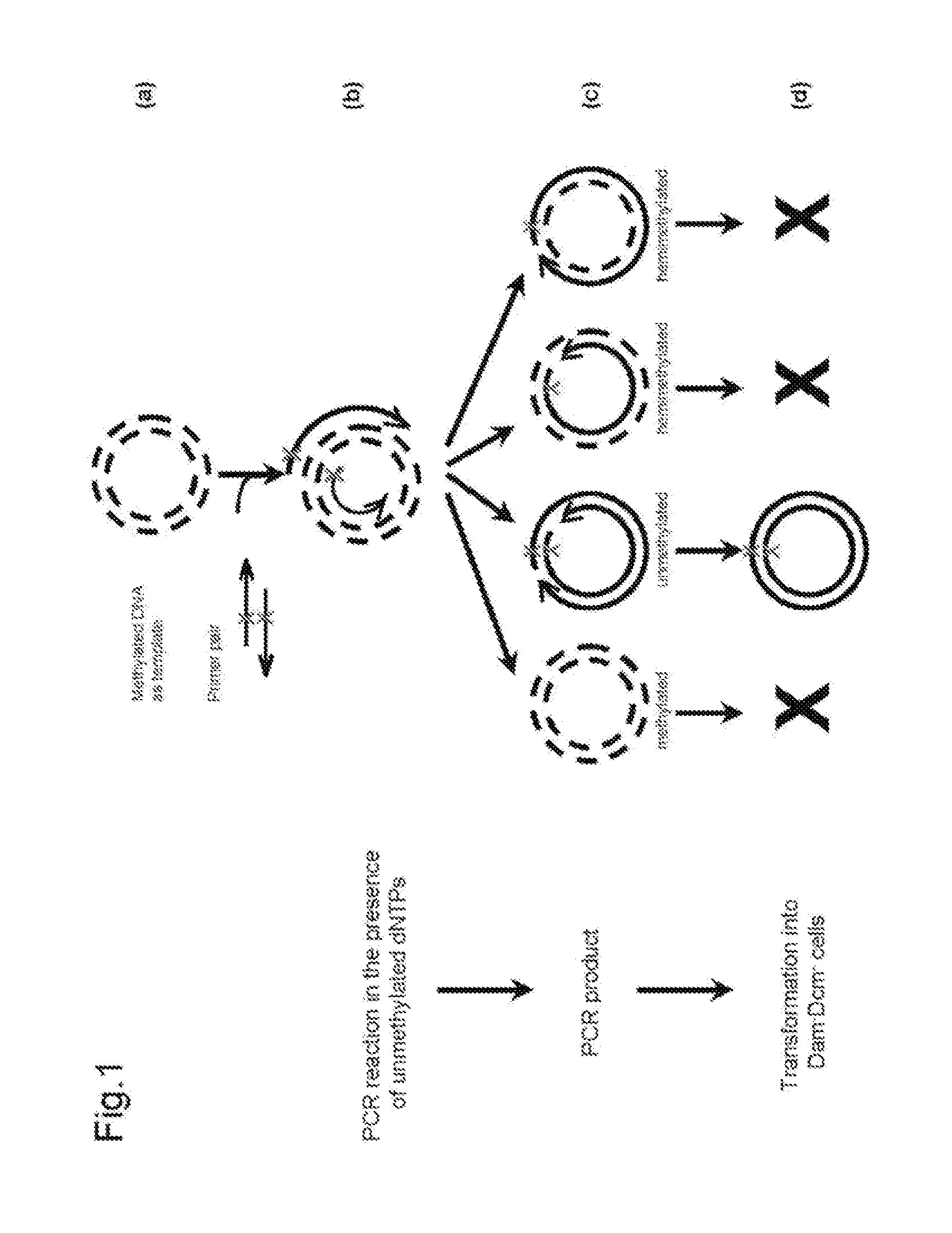
Site-specific mutation in methylated circular stranded DNA molecules is conferred by mutagenic primer pairs and methylase deficient Escherichia coli. The mutagenic primer pairs are complementary at 5′ end or 3′ end, or completely complementary to each other. Firstly, mutagenic primer pair is annealed to opposite strands of the methylated circular double-stranded parent DNA molecules. Then, polymerase chain reaction is performed by using unmethylated dNTPs to create unmethylated mutagenized double-stranded daughter DNA molecules. Finally, the reaction mixture of the methylated parent DNA molecules and unmethylated mutagenized daughter DNA molecules is transformed into a methylase deficient E. coli. The replication of methylated parent DNA is inhibited in methylase deficient host cell. In contrast, the unmethylated daughter DNA, which contains the desired mutation, are efficiently replicated in methylase deficient host cell and recovered thereafter. The invention also provides a kit for introducing site-specific mutations in accordance with the described method.
Owner:GM BIOSCI
Compositions and methods of enhancing immune responses
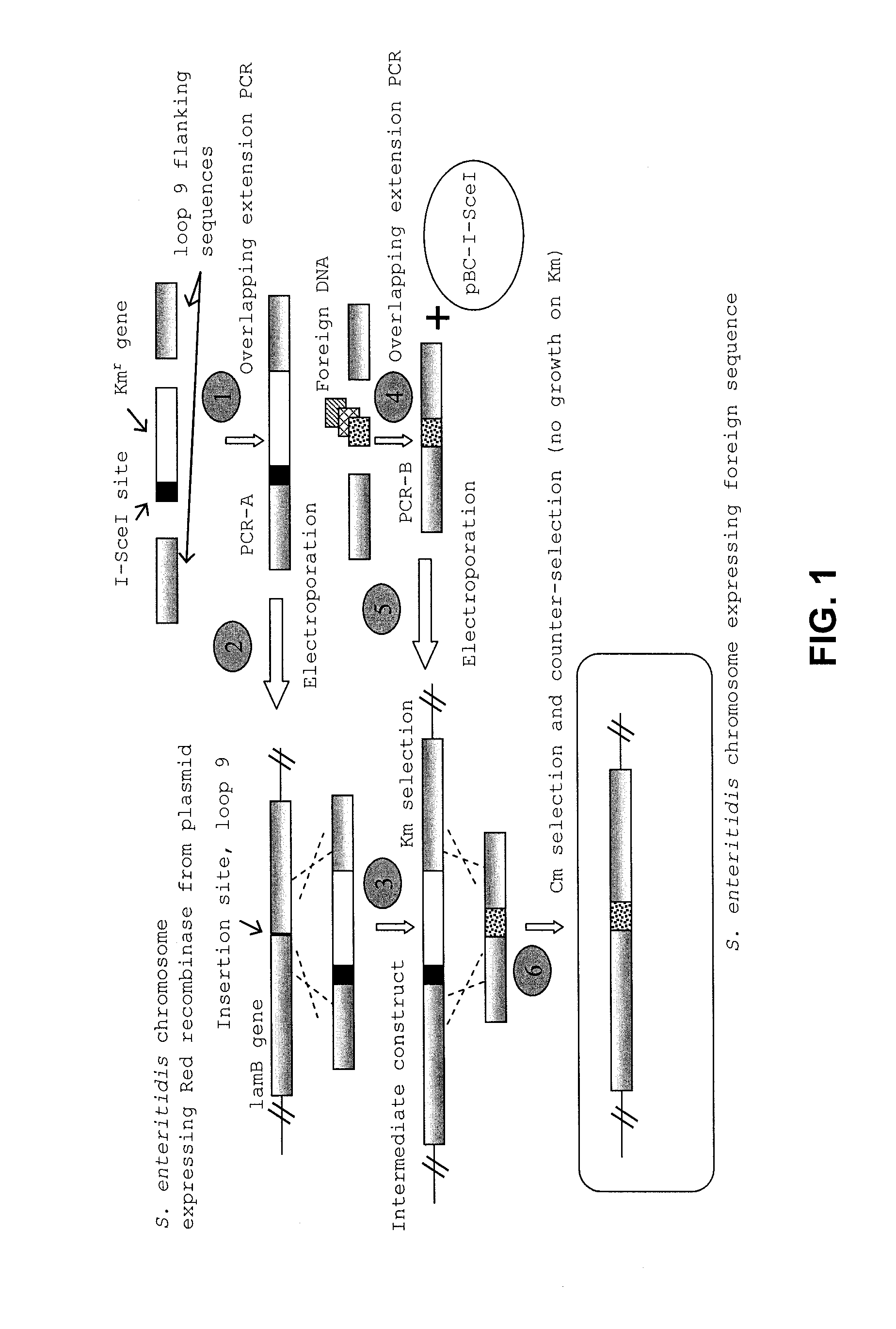
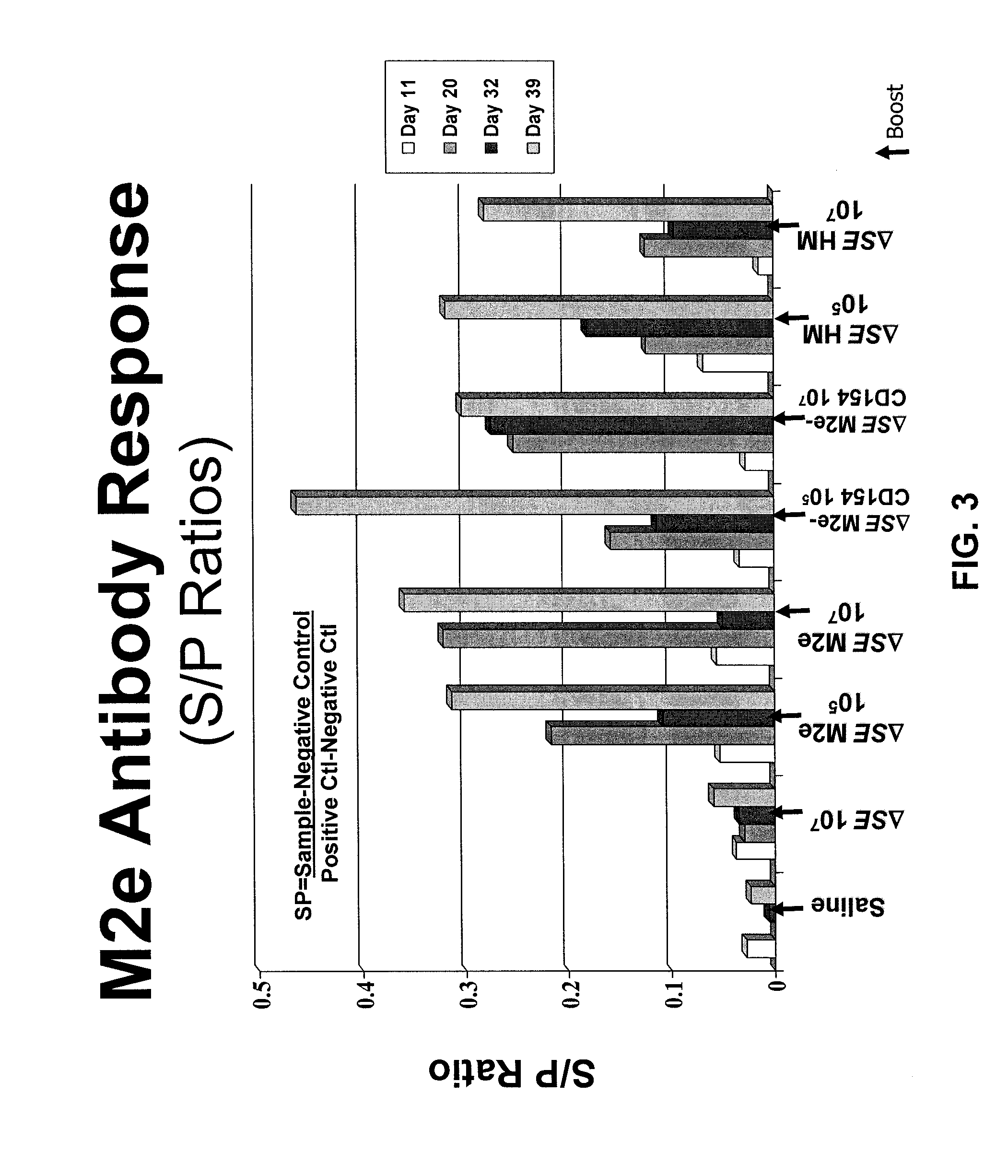
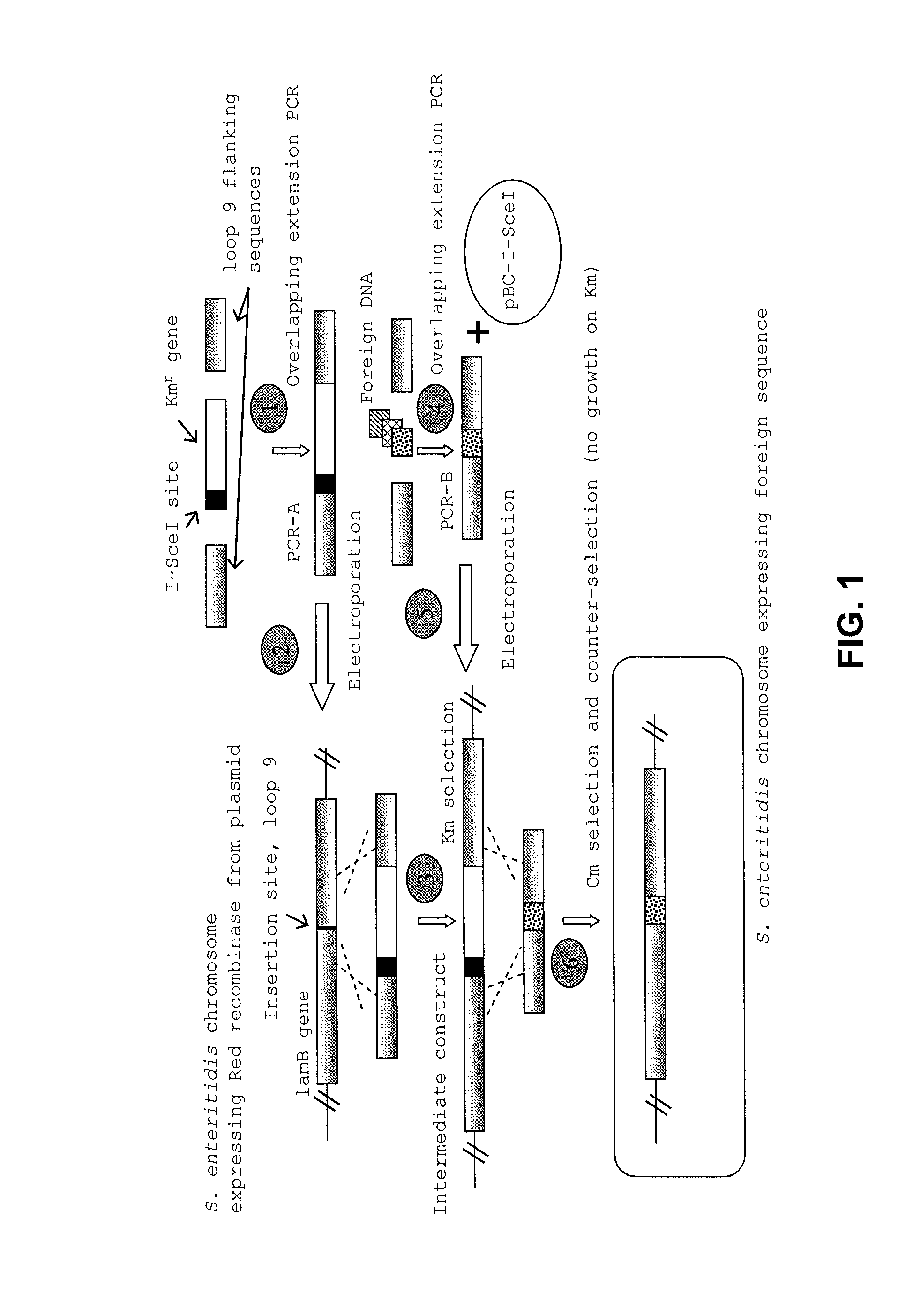
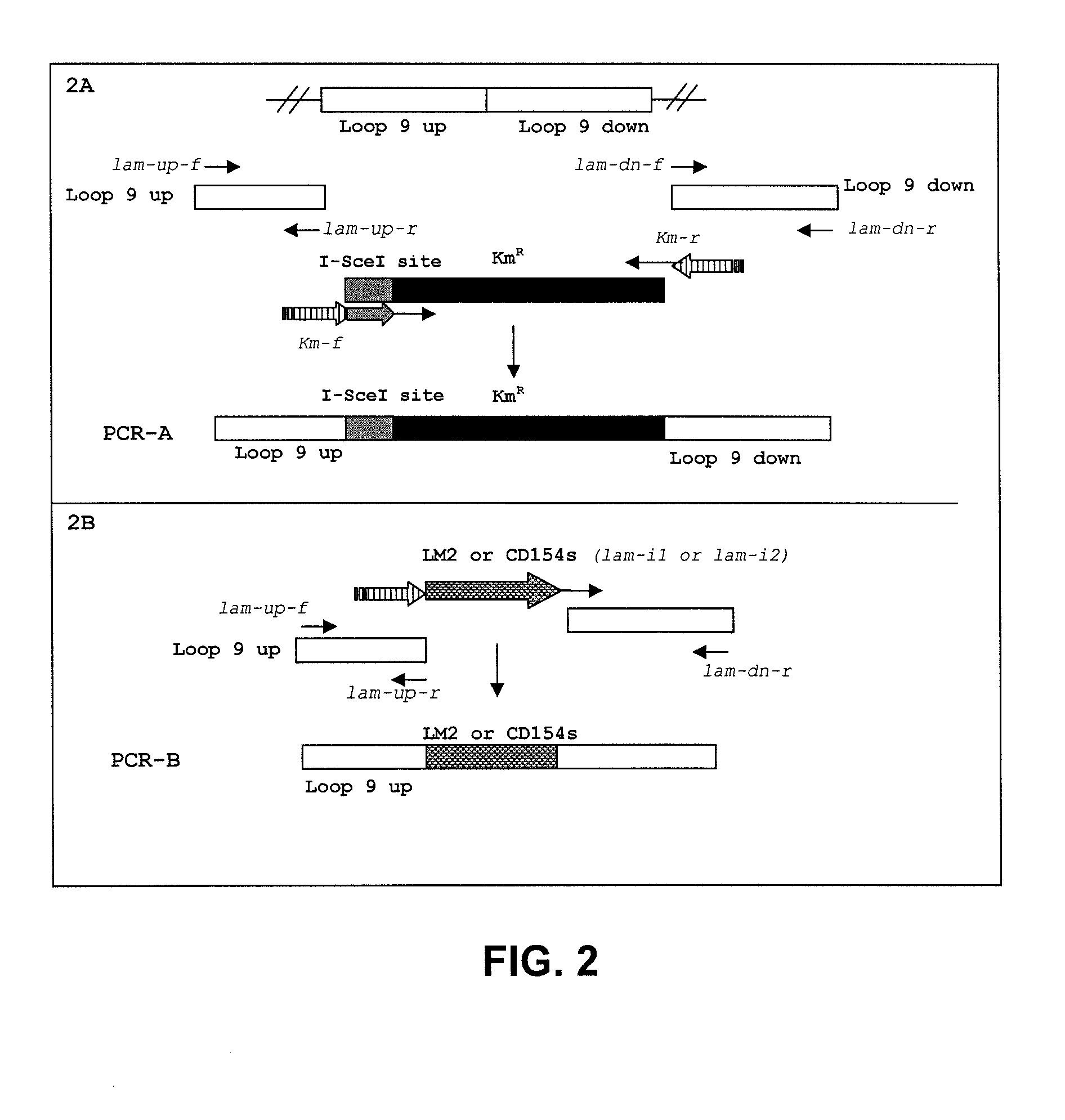
ActiveUS8604178B2Enhance immune responseReduce morbiditySsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaSalmonella enteritidisBacilli
Provided herein are Salmonella enteritidis 13A strains and compositions comprising these strains. Also provided are methods of enhancing an immune response against Influenza A and methods of reducing morbidity associated with an Influenza A infection. Methods of enhancing an immune response to a vaccine vector by expressing a polypeptide of CD 154 capable of binding CD40 are also disclosed. Methods of developing a bacterial vaccine vector are disclosed. Methods of generating scarless site-specific mutations in a bacterium are also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
Methods and compositions for DNA manipulation
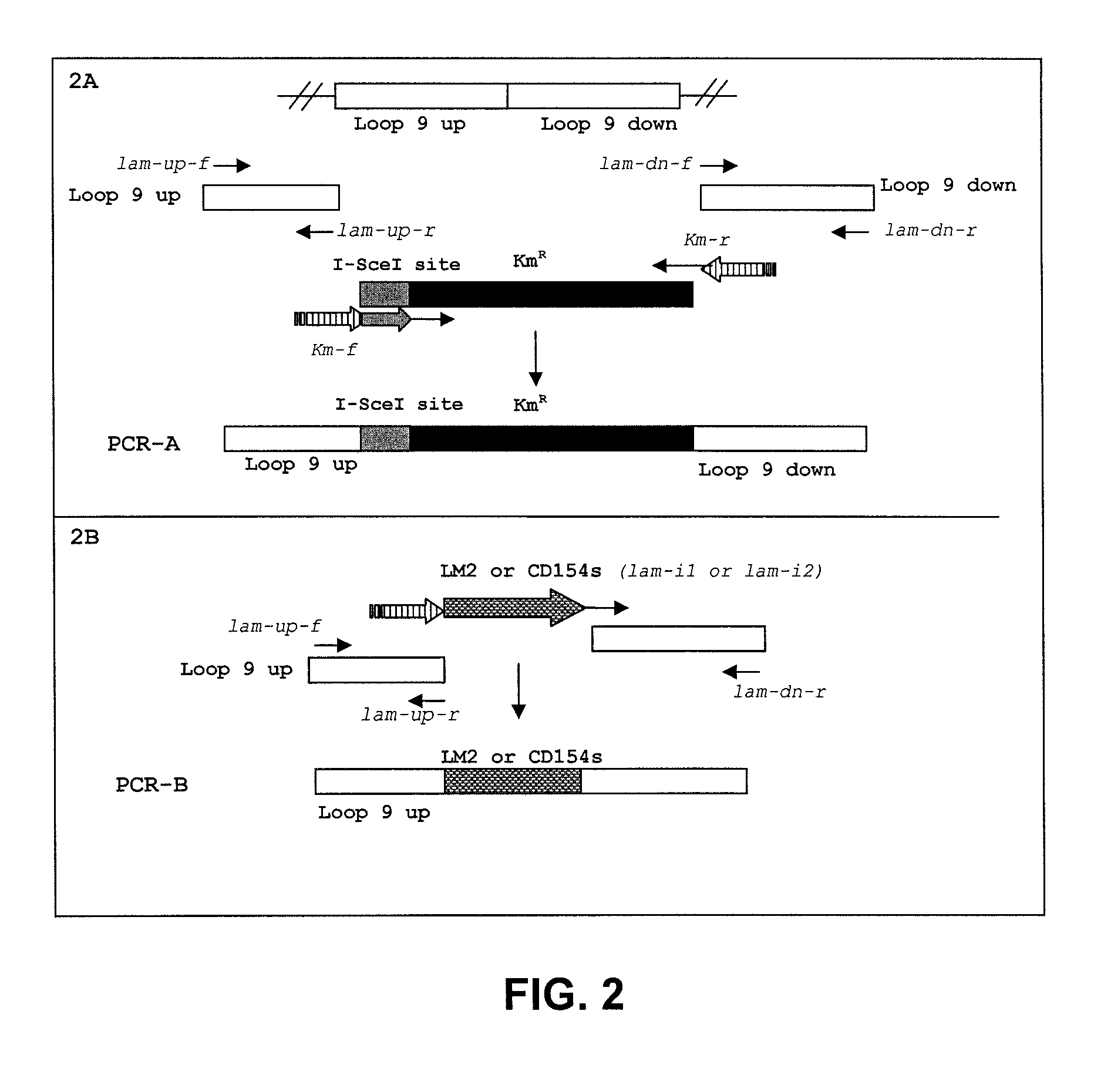
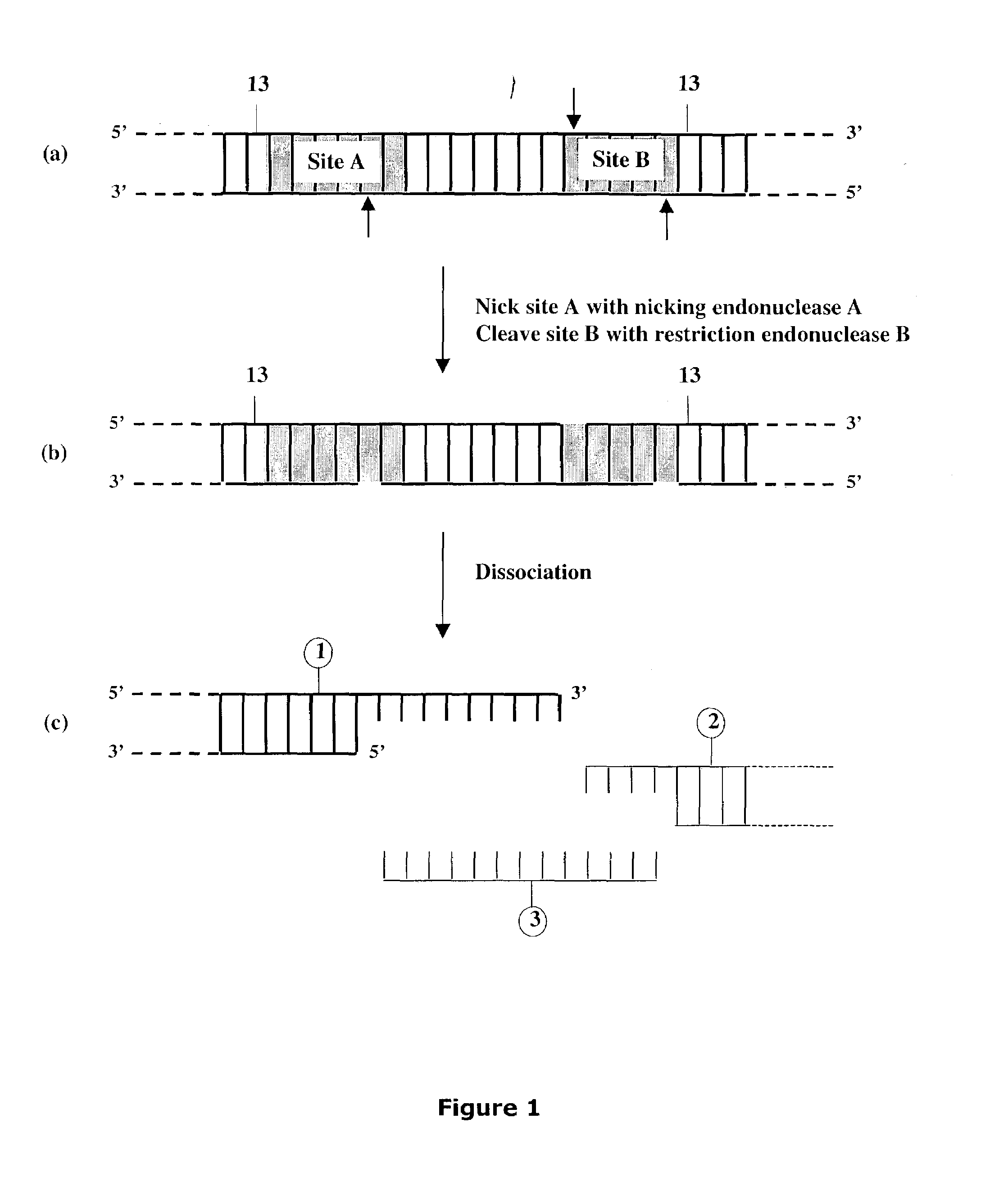
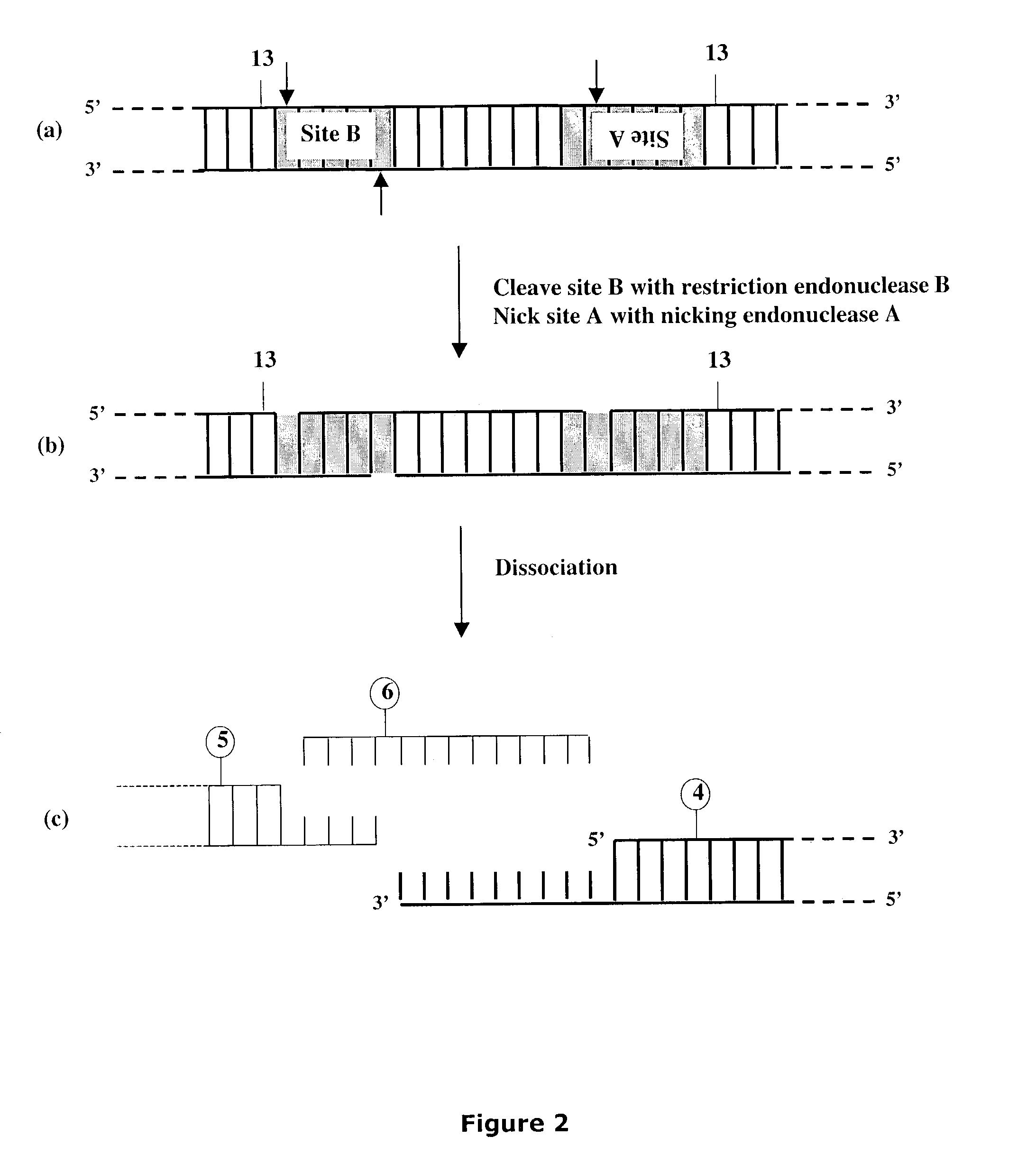
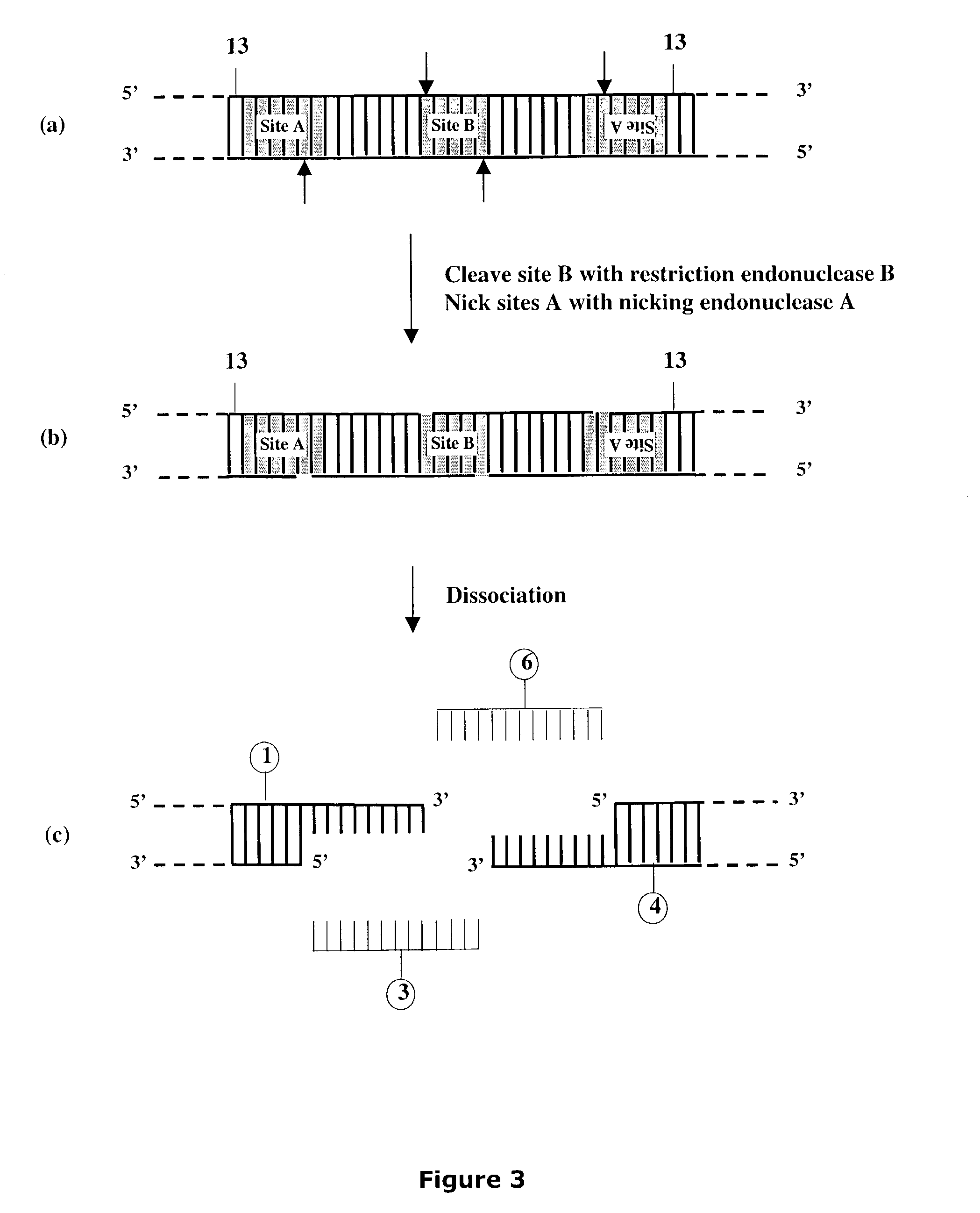
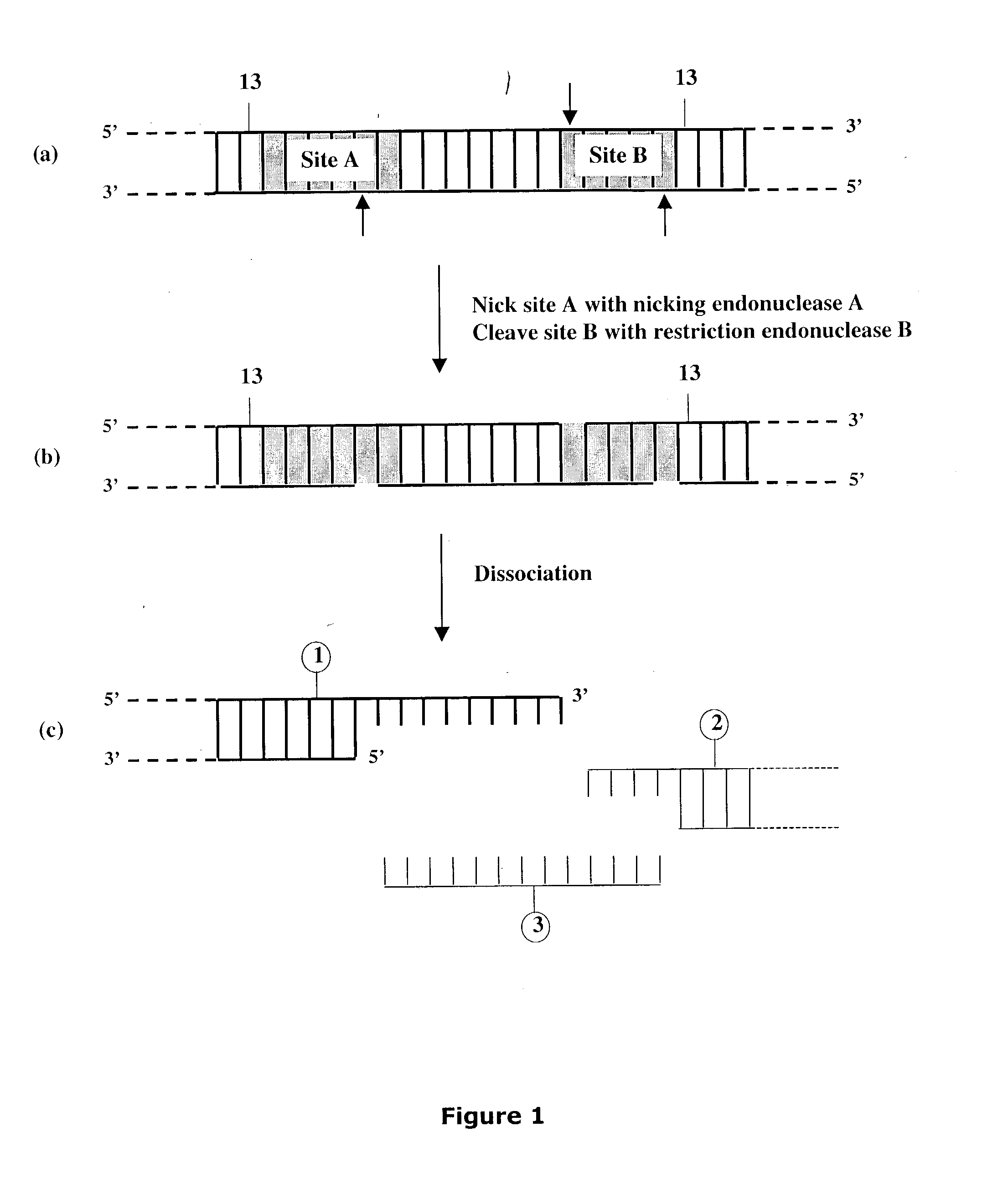
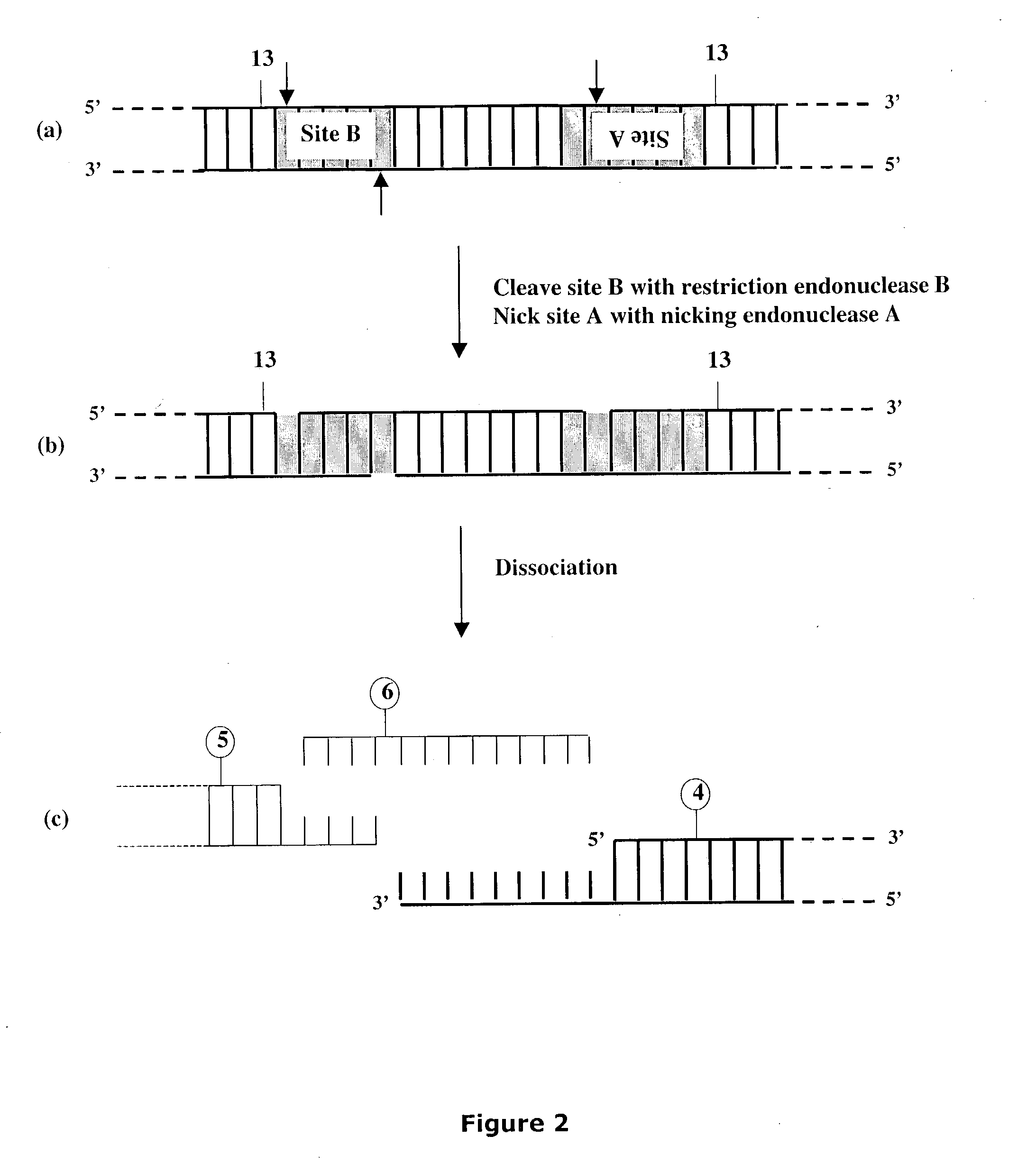
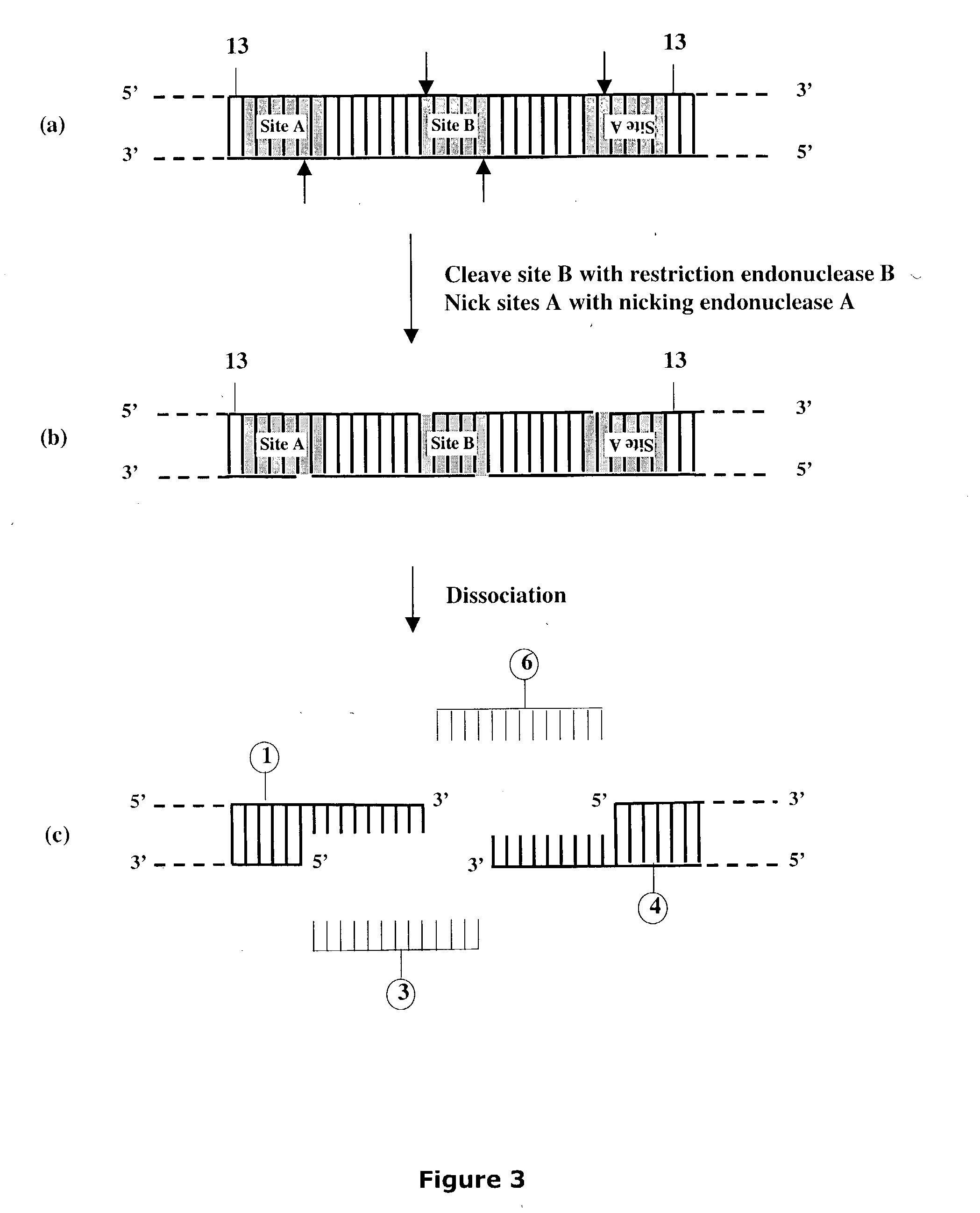
Methods and compositions are provided for generating a single-stranded extension on a polynucleotide molecule, the single-stranded extension having a desired length and sequence composition. Methods for forming single-stranded extensions include: the use of a cassette containing at least one nicking site and at least one restriction site at a predetermined distance from each other and in a predetermined orientation; or primer-dependent amplification which introduces into a polynucleotide molecule, a modified nucleotide which is excised to create a nick using a nicking agent. The methods and compositions provided can be used to manipulate a DNA sequence including introducing site specific mutations into a polynucleotide molecule and for cloning any polynucleotide molecule or set of joined polynucleotide molecules in a recipient molecule such as a vector of choice.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
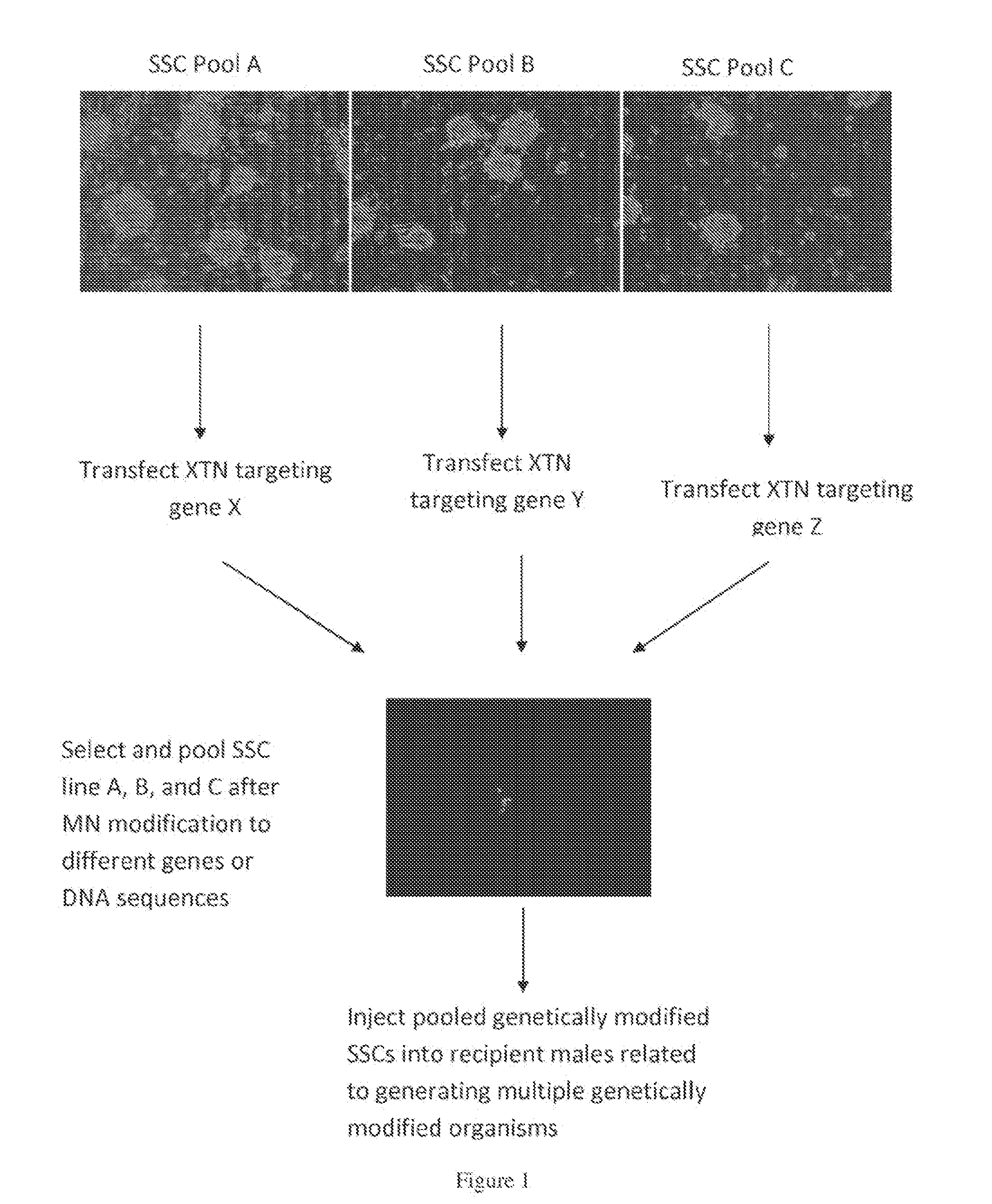
Methods for site-specific genetic modification in stem cells using xanthomonas tal nucleases (XTN) for the creation of model organisms
InactiveUS20140201858A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousXanthomonas campestris
The invention relates to organisms and compositions comprising one or more stem cells or one or more embryos, wherein the one or more stem cells or one or more embryos comprise one or more of the following mutations: (i) a deletion mutation; (ii) a knockout mutation; and / or (iii) an addition of a heterologous nucleic acid sequence; wherein the one or more mutations of (i), (ii), and / or (iii) are site-specific mutations caused by a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease (XTN). The invention also relates to method of mutating an embryo, iPS cell, stem cell, or more particularly a spermatogonial stem cell by exposing the nucleic acid sequence contained within such embryos or cell with a Xanthomonas TAL nuclease.
Owner:TRANSPOSAGEN BIOPHARM +1
Compositions and methods of enhancing immune responses
ActiveUS20110027309A1Reduce morbidityEnhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaSalmonella enteritidisBacilli
Provided herein are Salmonella enteritidis 13A strains and compositions comprising these strains. Also provided are methods of enhancing an immune response against Influenza A and methods of reducing morbidity associated with an Influenza A infection. Methods of enhancing an immune response to a vaccine vector by expressing a polypeptide of CD 154 capable of binding CD40 are also disclosed. Methods of developing a bacterial vaccine vector are disclosed. Methods of generating scarless site-specific mutations in a bacterium are also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS +1
Beta-glucosidase D mutant as well as expression plasmid and recombinant bacteria thereof
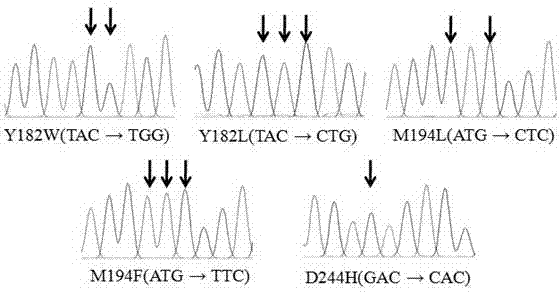
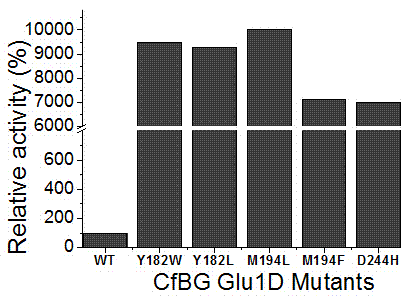
The invention relates to a beta-glucosidase D mutant as well as an expression plasmid and recombinant bacteria thereof and in particular relates to a beta-glucosidase D mutant with obviously improved enzymatic activities as well as an expression plasmid and recombinant bacteria thereof, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. Site-specific mutation is carried out on beta-glucosidase derived from Formosan termites to change tyrosine Y in the 182 bit to tryptophan W and leucine L respectively, change methionine M in the 194 bit to leucine L and phenylalanine F respectively and change aspartic acid D in the 244 bit to histidine H, wherein tryptophan W, leucine L, leucine L, phenylalanine F and histidine H are respectively expressed as Glu1D-Y182W, Glu1D-Y182L, Glu1D-M194L, Glu1D-M194F and Glu1D-D244H. The enzymatic activities of the mutant are respectively improved by 94.6 times, 92.9 times, 100.3 times, 71.4 times and 69.9 times compared with the enzymatic activities before mutation. The obtained beta-glucosidase mutant has substantially improved enzymatic activities, provides a favourable foundation for industrial application, can further meet the requirements of social production and has extensive application prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Enterpeptidase light chain variant with high activity and high stability
The present invention is characterized by that making the cysteine of 112th site of enterokinase light chain gene produce site-specific mutation, using colibacillus and microzyme to express enterokinase light chain variant, and utilizing Zn-Sepharose and STI-Sepharose affinity chromatography so as to obtain high-purity enterokinase light chain variant protein. As compared with wild enterokinase light chain said varient has higher stability and enzyme activity.
Owner:SUZHOU LANDING BIOPHARM CO LTD
Methods and compositions for DNA manipulation
Methods and compositions are provided for generating a single-stranded extension on a polynucleotide molecule, the single-stranded extension having a desired length and sequence composition. Methods for forming single-stranded extensions include: the use of a cassette containing at least one nicking site and at least one restriction site at a predetermined distance from each other and in a predetermined orientation; or primer-dependent amplification which introduces into a polynucleotide molecule, a modified nucleotide which is excised to create a nick using a nicking agent. The methods and compositions provided can be used to manipulate a DNA sequence including introducing site specific mutations into a polynucleotide molecule and for cloning any polynucleotide molecule or set of joined polynucleotide molecules in a recipient molecule such as a vector of choice.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
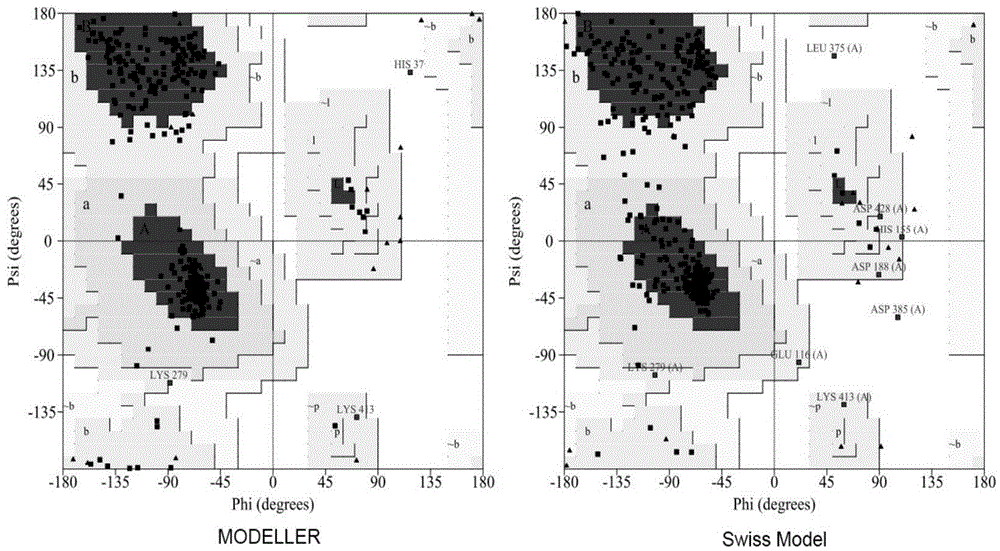
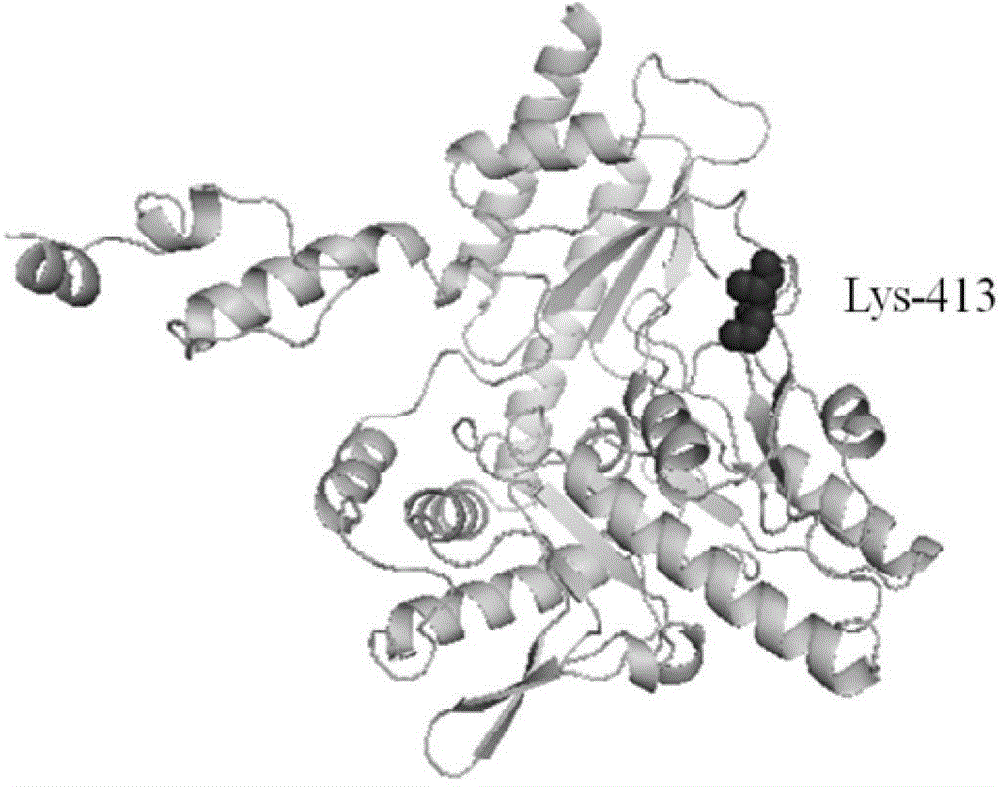
Method for preparing glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and mutant thereof
InactiveCN104694524AIncrease reaction rateEase of industrial productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for preparing a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant by utilizing ramachandran map information and a mutant thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a three-dimensional structural model of glutamic acid decarboxylase, carrying out dihedral angle reasonable evaluation to generate a ramachandran map, and determining an amino acid residue site in an unreasonable conformation area from the ramachandran map; designing a site-specific mutation primer aiming at the site, and carrying out site-specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by taking a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene as a template so as to obtain a site-specific mutation library; and screening the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant from the site-specific mutation library. Enzyme is rationally designed through structural information provided by the ramachandran map; in combination with a site-specific mutation technology, the mutation probability is effectively increased; the time is saved; the experimental efficiency is increased; mutant enzyme the catalytic activity of which is superior to wild type enzyme can be obtained by screening; the mutant enzyme is capable of increasing the reaction rate for generating gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof; and thus, industrial production of GABA is easily carried out.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Site-directed mutagenesis in circular methylated DNA
InactiveCN101600797AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEscherichia coliSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention provides a new method for conducting site-specific mutation in methylated circular stranded DNA molecules conferred by means of mutagenic primer pairs and methylase deficient Escherichia coli. The mutagenic primer pairs are complementary at 5' end or 3' end, or completely complementary to each other. Firstly, mutagenic primer pair is annealed to opposite strands of the methylated circular double-stranded parent DNA molecules. Then, polymerase chain reaction with DNA polymerase is performed by using unmethylated dNTPs to create unmethylated mutagenized double-stranded daughter DNA molecules. Finally, the reaction mixture of the methylated parent DNA molecules and unmethylated mutagenized daughter DNA molecules is transformed into a methylase deficient competent E.coli. The replication of methylated parent DNA is inhibited in methylase deficient host cell. In contrast, the unmethylated daughter DNA, which contains the desired mutation, are efficiently replicated in methylase deficient host cell and recovered thereafter. The invention also provides a kit for introducing site-specific mutagenesis in accordance with the method of the present invention.
Owner:乔苗
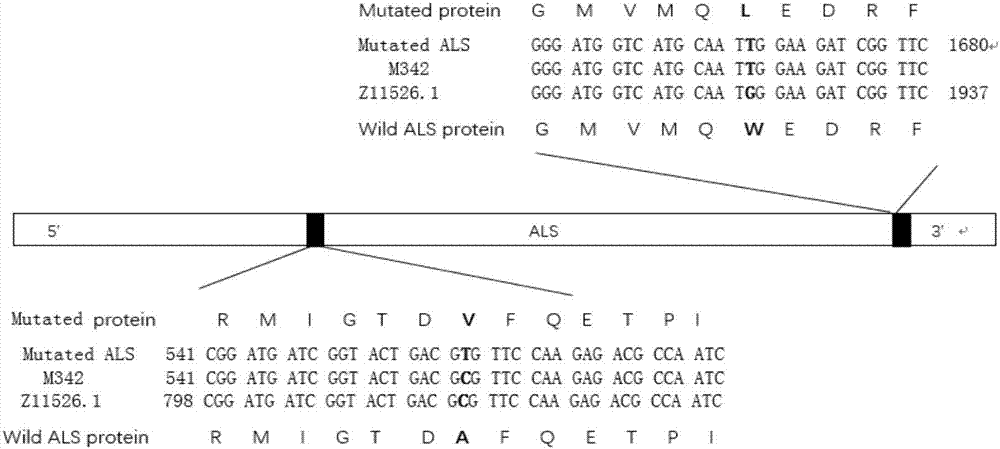
Rape multiple ALS (acetolactate synthase) inhibitor type herbicide-resistant gene based on in-vitro site-specific mutagenesis and application
InactiveCN107058350AEasy accessStrong resistanceTransferasesFermentationDouble mutationAcetolactate synthase
The invention relates to a rape multiple ALS (acetolactate synthase) inhibitor type herbicide-resistant gene based on in-vitro site-specific mutagenesis and application, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The gene mALS3 is obtained by introducing a new mutant site into the ALS3 gene sequence of the herbicide-resistant rape M342, and the site is positioned at the 560th site of the ALS3 gene; the original gene is alanine with a C alkaline group at the 187th site, the C alkaline group is mutated into a T alkaline group, and valine is formed at the 187th site. The rape mALS3 gene with double mutation sites A187V and W556L is obtained through an in-vitro site-specific mutation technique. The double mutation sites are not reported in the literatures of the rape genome. After preliminary functional verification of transgenic arabidopsis, the rape mALS3 gene with double mutation sites has the advantages that the obvious resistance on multiple ALS inhibitor herbicides, such as imidazolamide, tribenuron-methyl, difluorosulfonamide and bispyribac-sodium, is realized; the resistance gene can be used for the culturing of herbicide-resistant crops.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
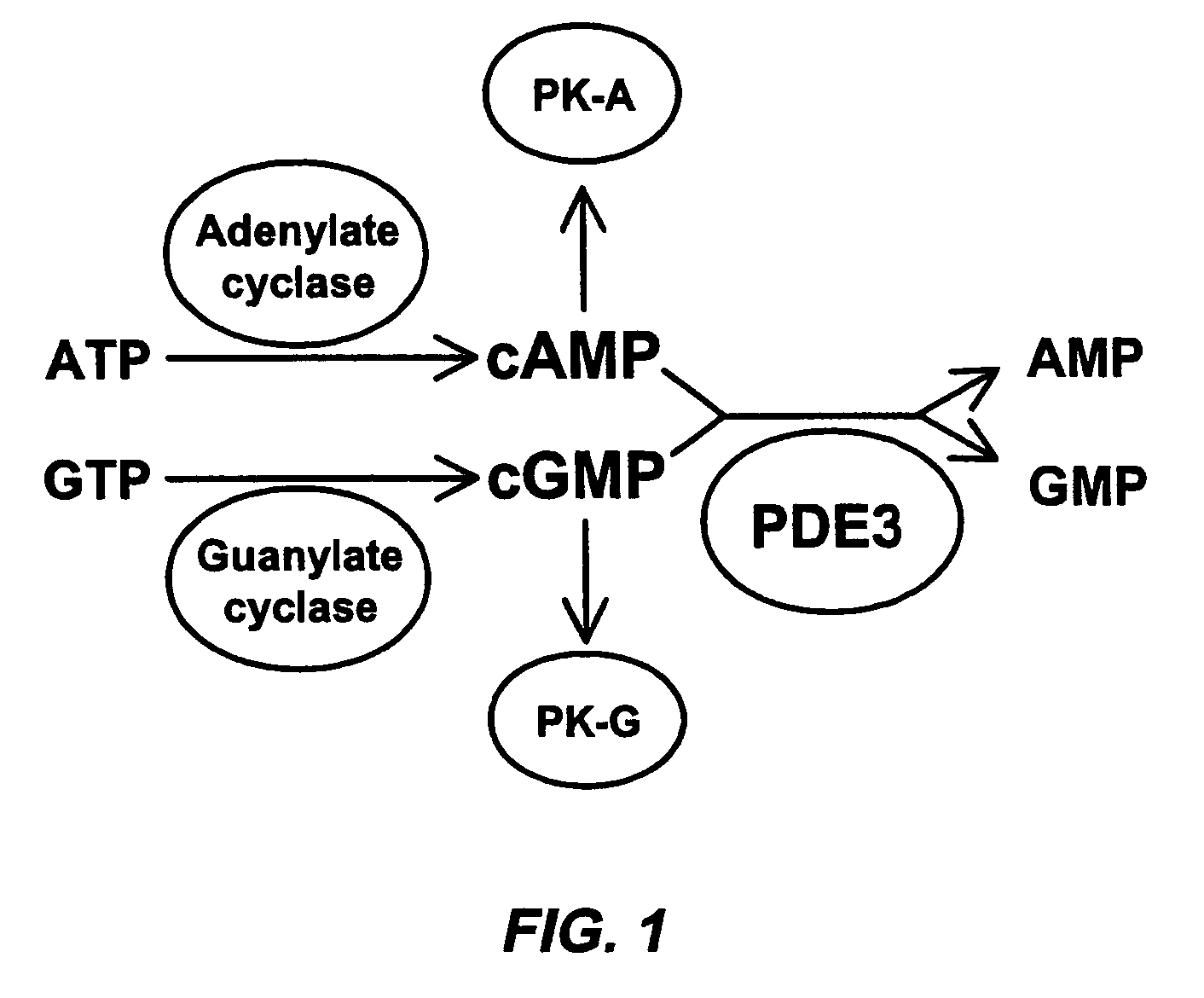
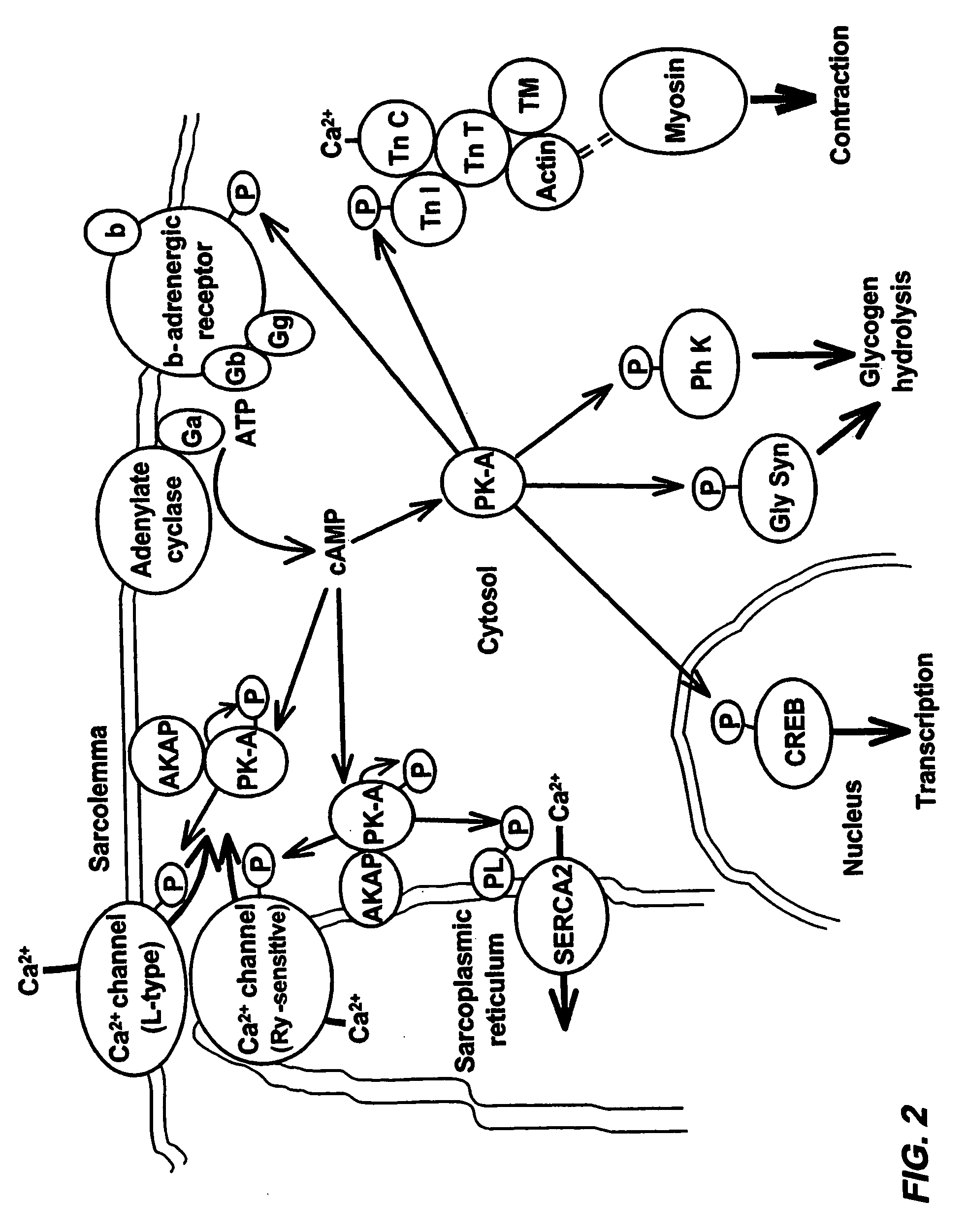
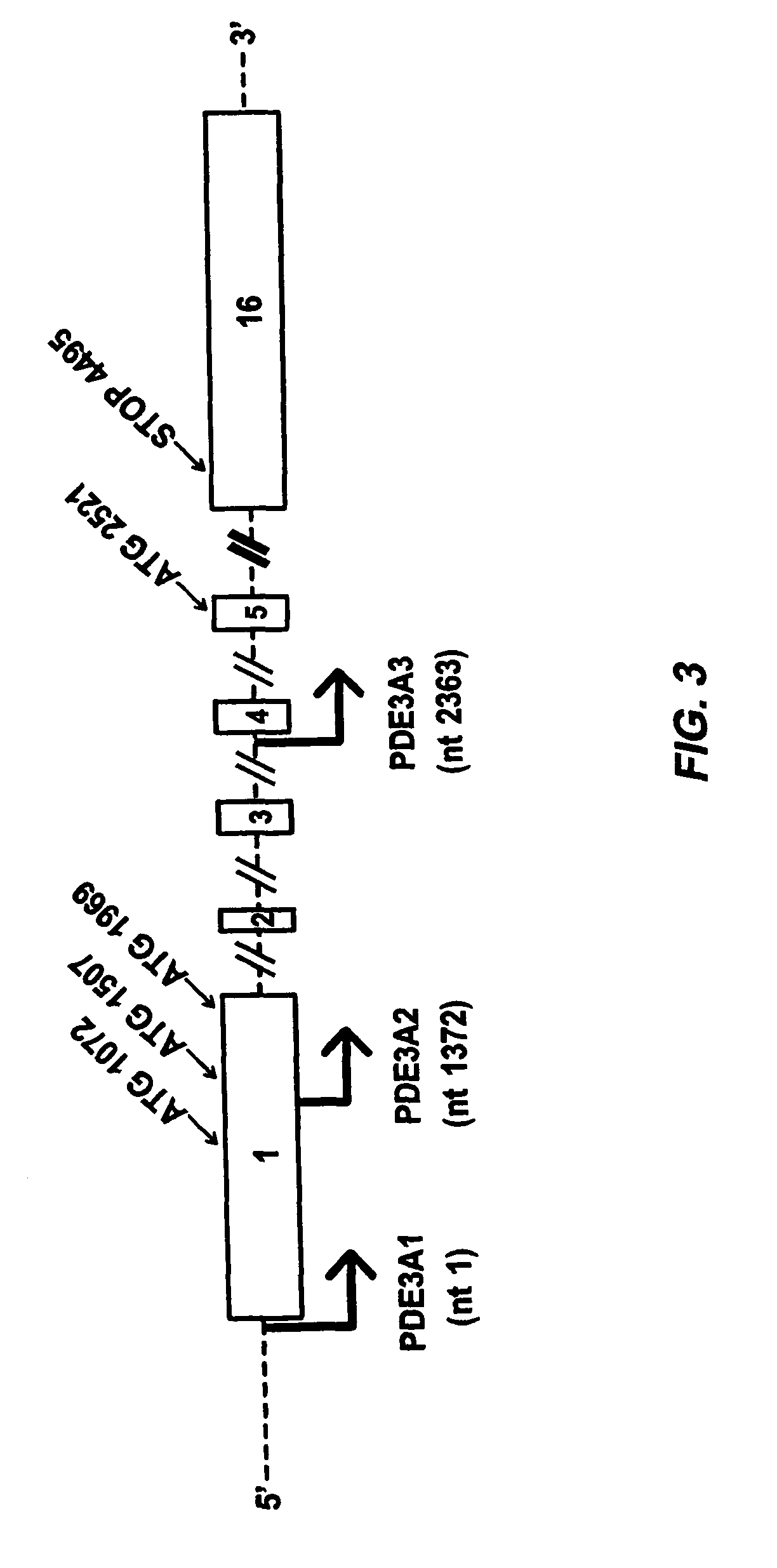
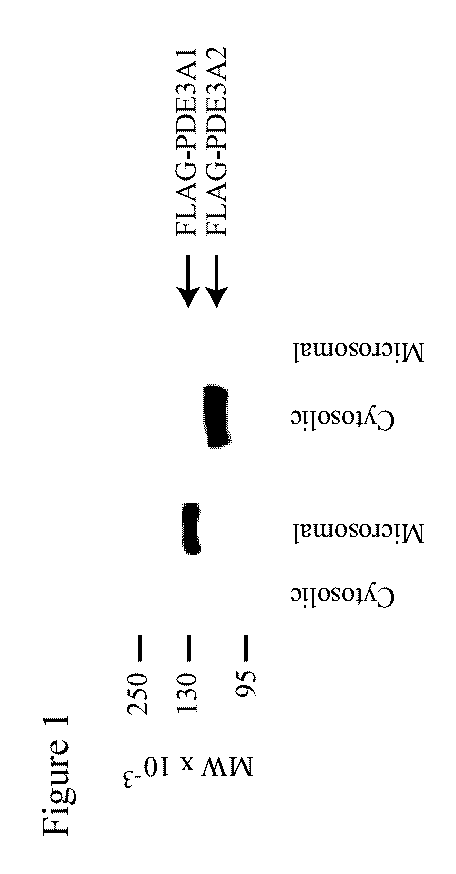
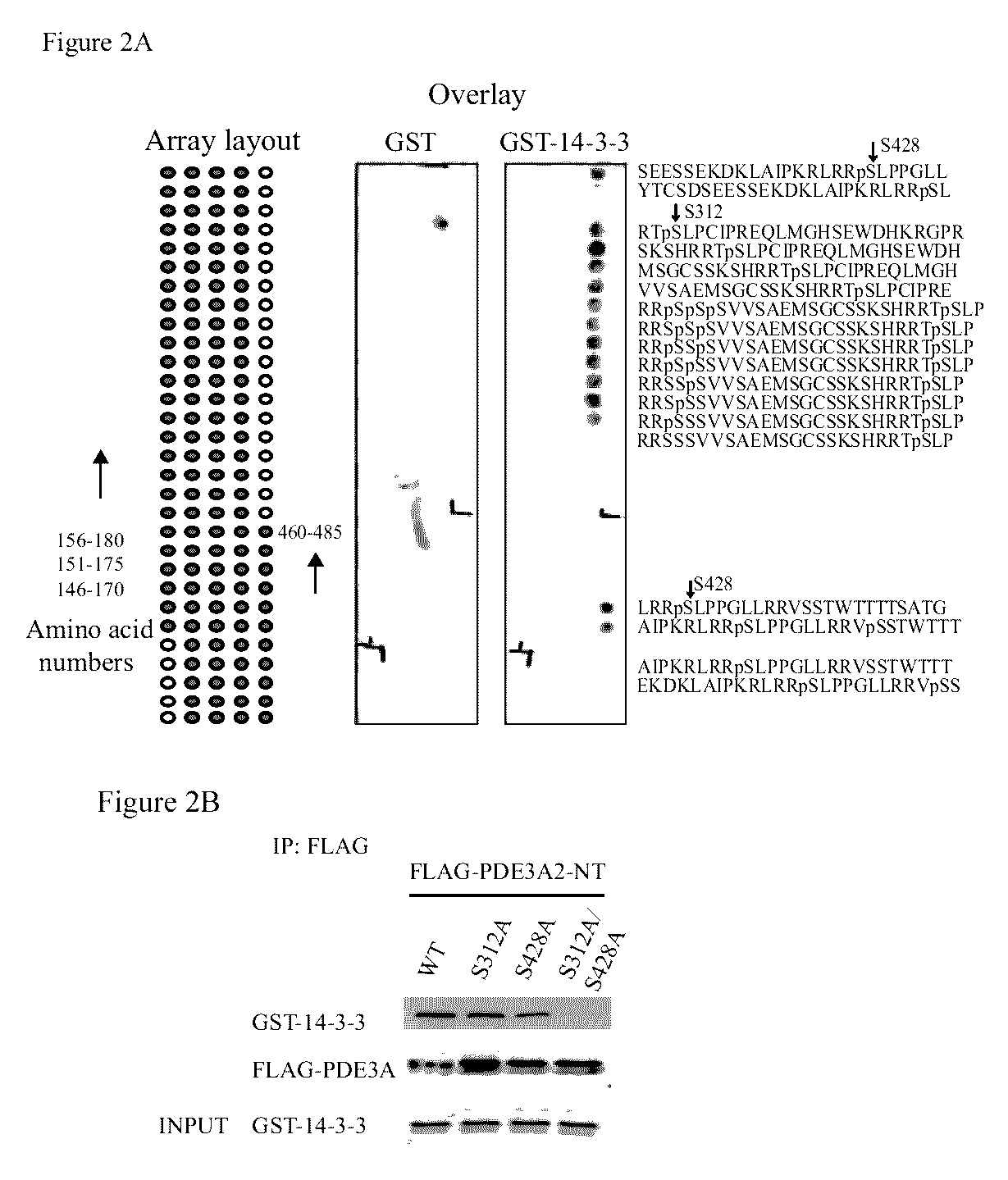
Isoform-selective inhibitors and activators of PDE3 cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases
InactiveUS8722866B2Reduce impactMortalityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsCyclic nucleotide phosphodiesteraseMutant
The present invention concerns methods and compositions related to type 3 phosphodiesterases (PDE3). Certain embodiments concern isolated peptides corresponding to various PDE3A isoforms and / or site-specific mutants of PDE3A isoforms, along with expression vectors encoding such isoforms or mutants. In specific embodiments, methods for identifying isoform-selective inhibitors or activators of PDE3 are provided, along with methods of use of such inhibitors or activators in the treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy, pulmonary hypertension and / or other medical conditions related to PDE3 effects on cAMP levels in different intracellular compartments.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
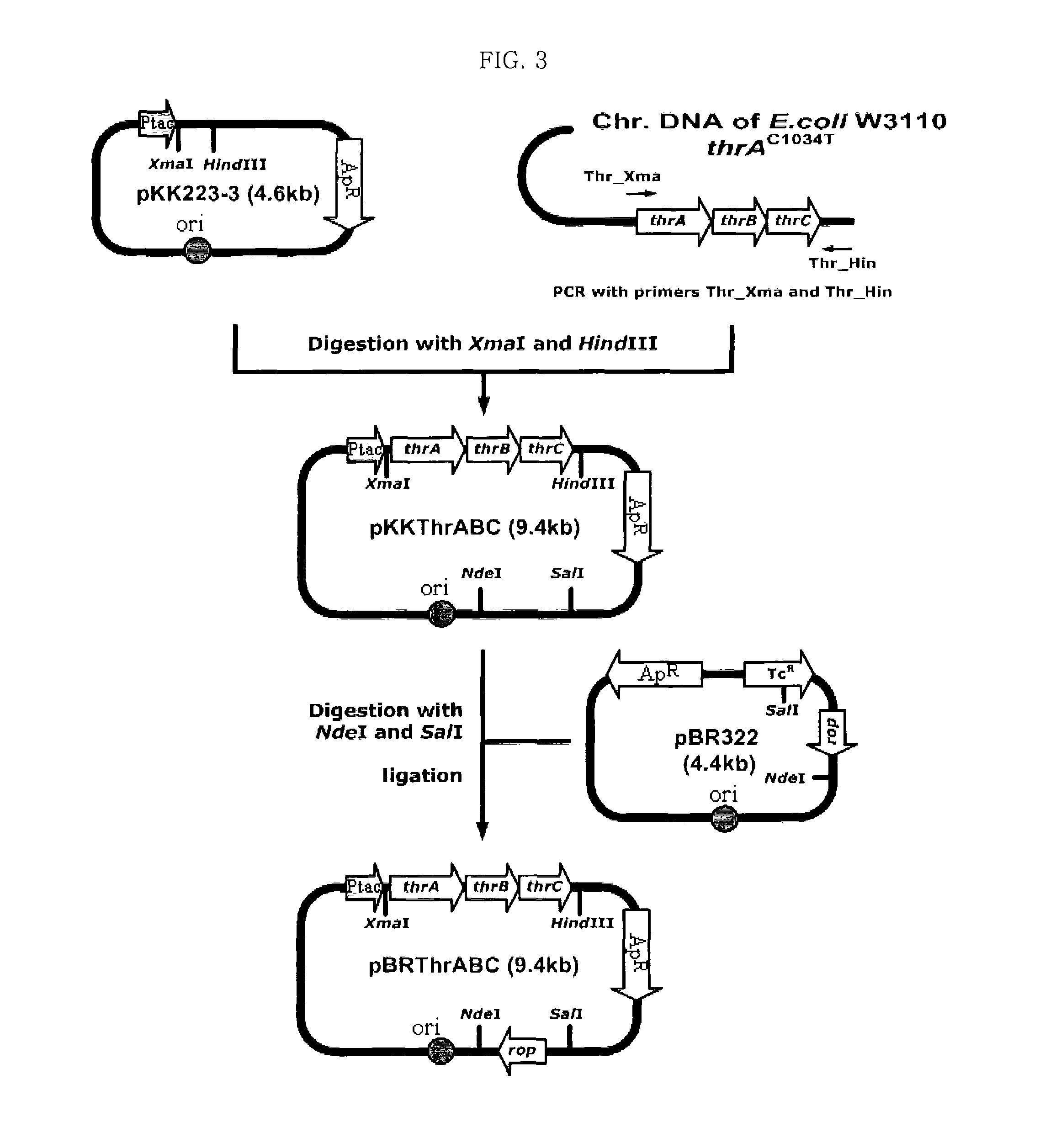
L-threonine overproducing microorganism and method for preparing L-threonine using the same
ActiveUS8852898B2Increase concentrationHigh yieldBiological testingFermentationRandom mutationL-threonine
The present invention relates to a mutant microorganism producing a high concentration of L-threonine in high yield, prepared using site-specific mutation, not random mutation, such as treatment with a mutation inducer, a method for preparing the same, and a method for preparing L-threonine using the mutant microorganism producing L-threonine. By using the mutant microorganism according to the present invention, L-threonine can be prepared at high yield, additional strain development becomes possible and their physiological phenomena can be easily understood since genetic information of L-threonine producing microorganism can be identified.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS20030157131A1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetically engineeredGenetic engineering
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:EGOROV ANDREI Y +1
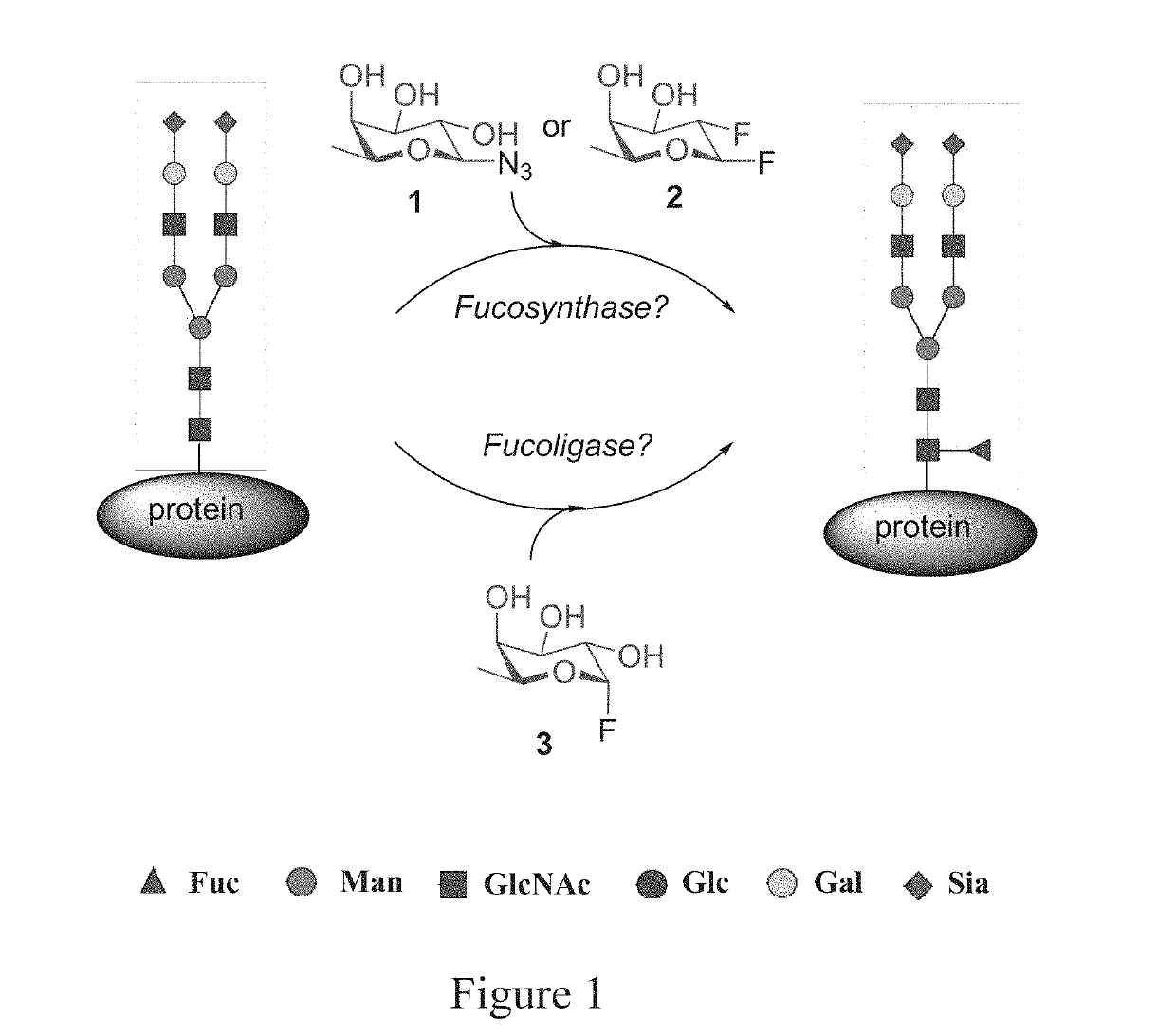
DESIGNER alpha 6-FUCOSIDASE MUTANTS ENABLE DIRECT CORE FUCOSYLATION OF INTACT N-GLYCOPEPTIDES AND N-GLYCOPROTEINS
ActiveUS20190185898A1Improve efficiencyReduced activityFusion with protease siteFermentationFucosylationCore glycosylation
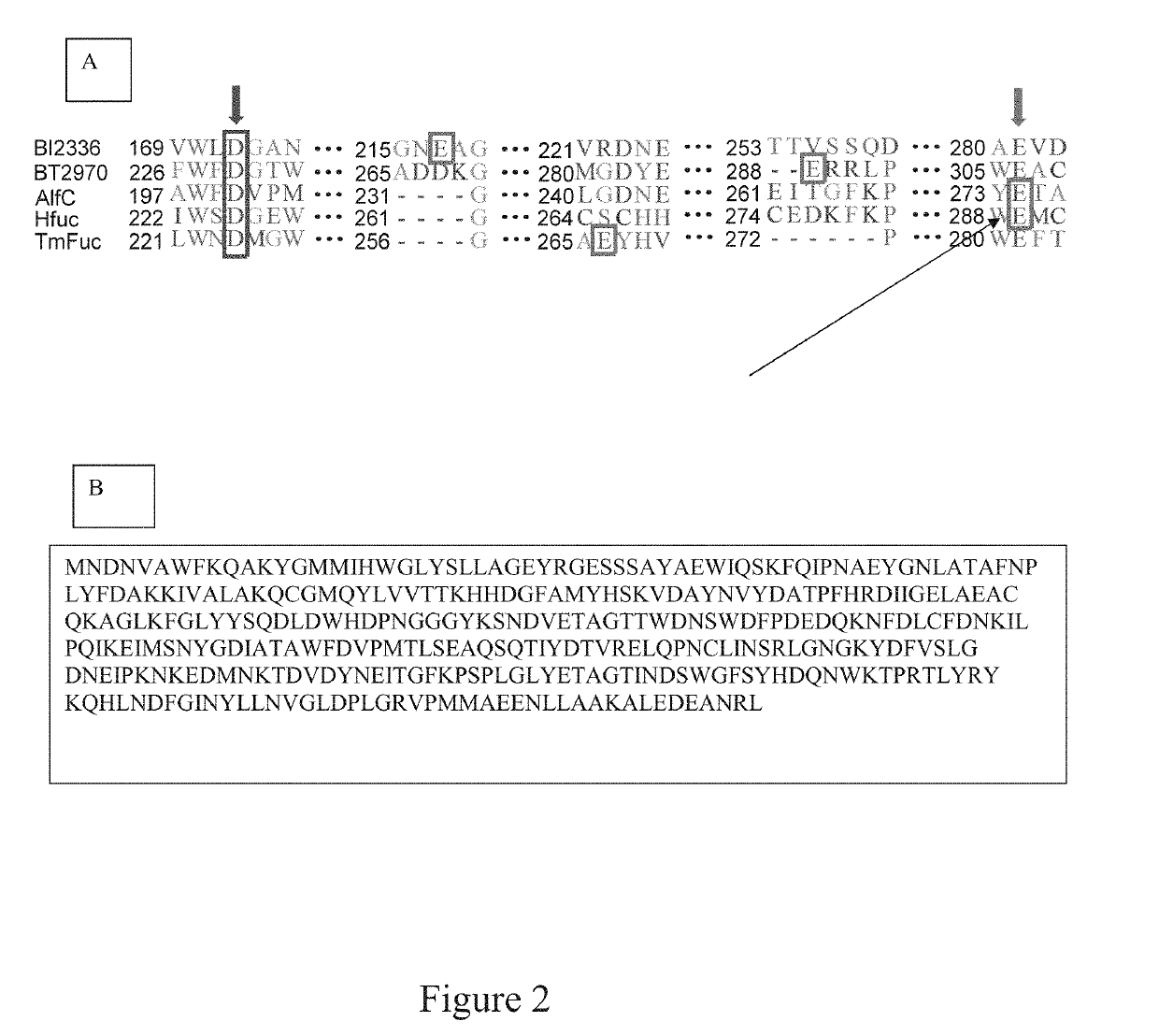
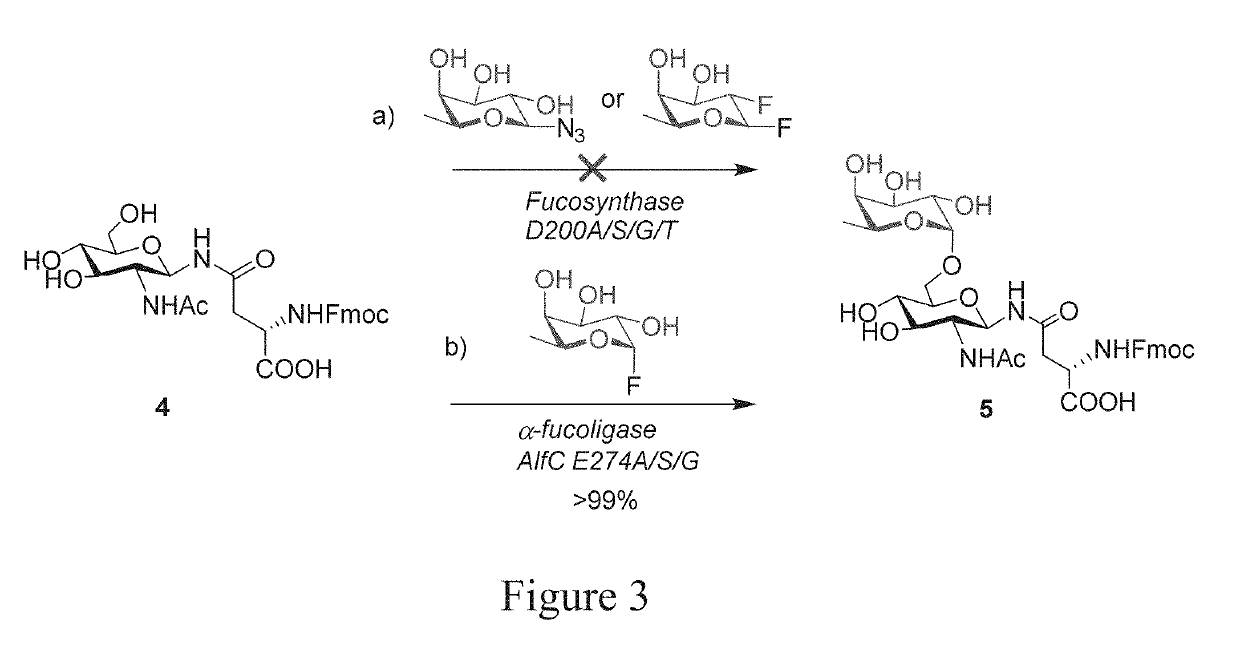
The present invention provides for novel fucosidase mutants that server as fuco-ligases for core fucosylation of a range of biological glycopeptides and glycoproteins including intact therapeutic antibodies. Several mutants with mutation at the general acid / base residue E274 of the Lactobacillus casei α1,6-fucosidase, including E274A, E274S, and E274G, were able to efficiently fucosylate a wide variety of complex N-glycopeptides and intact glycoproteins. The site specific mutants enable the transfer of fucose to a core GlcNAc-Asn residue and useful for drug delivery and vaccine development.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for high-specificity production of alpha-cyclodextrin
ActiveCN103484439ARaise the ratioSimplify the subsequent purification processFungiBacteriaWild typeGlucosyltransferases
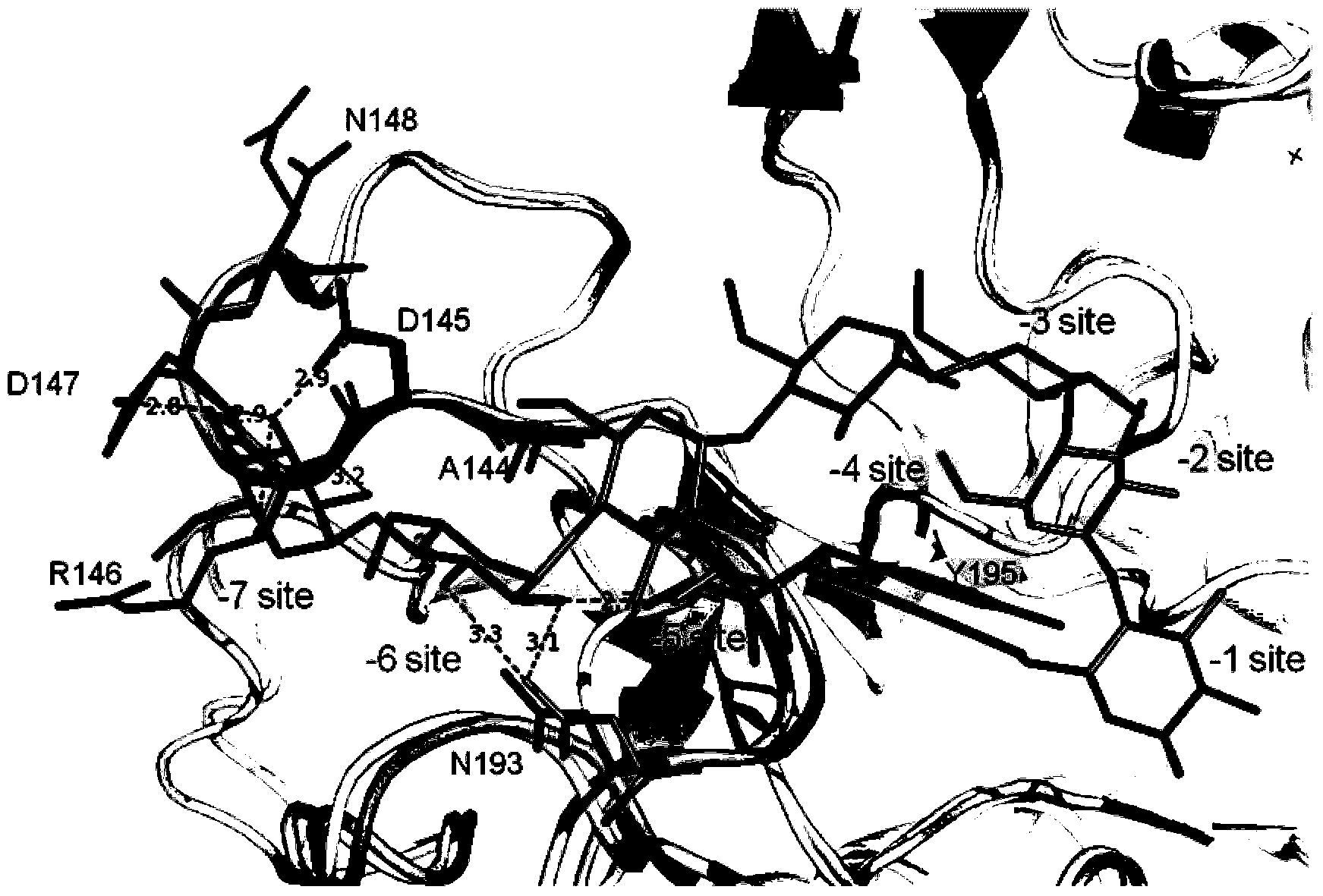
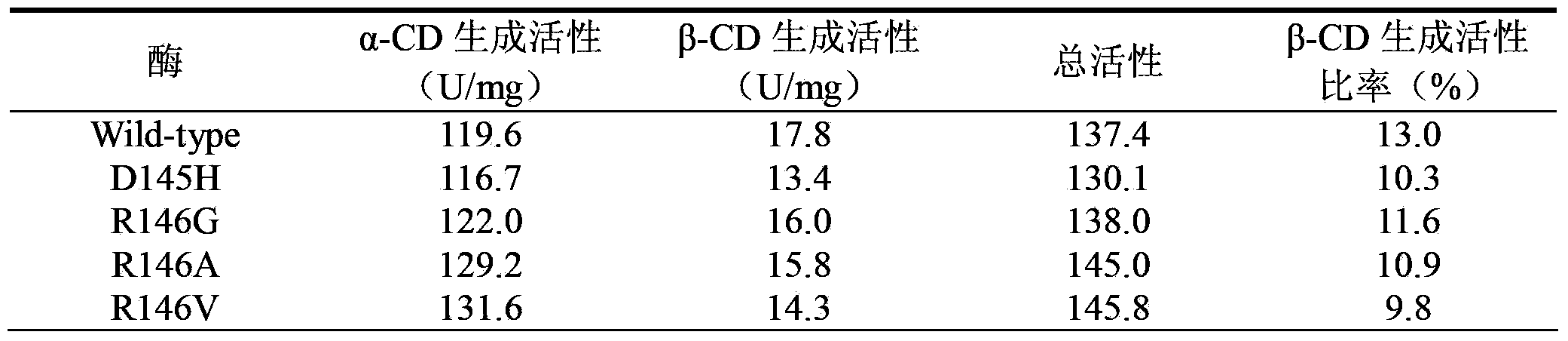
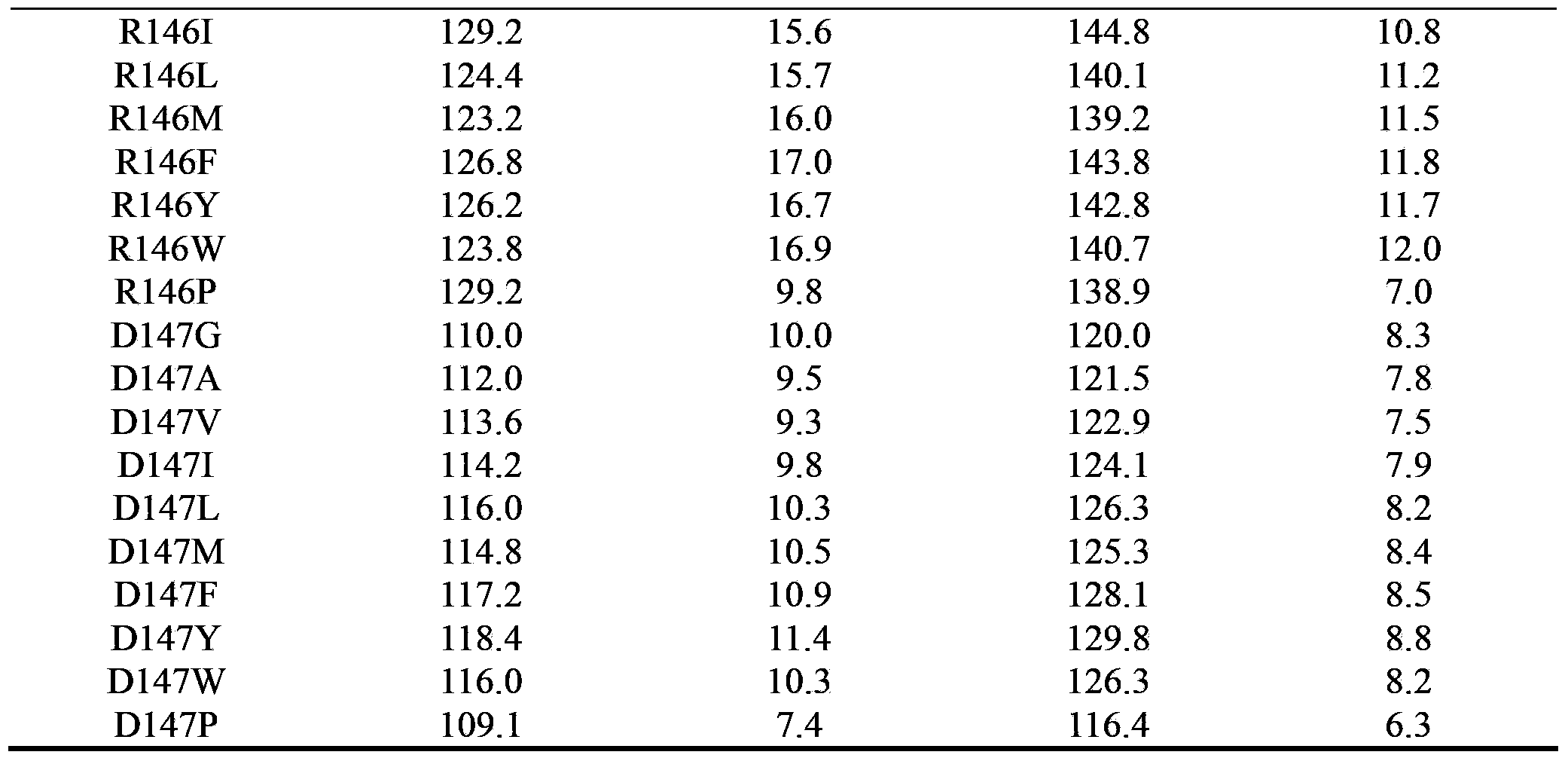
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for high-specificity production of alpha-cyclodextrin, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. The cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant is prepared by transforming CGTase derived from Paenibacillus macerans JFB 05-01 and carrying out site-specific mutation on 145-site Asp,146-site Arg and 147-Asp of CGTase. The production capacity of beta-cyclodextrin of the prepared single mutant enzyme is lowered than that of wild-type CGTase, the production capacity of alpha-cyclodextrin is slightly increased, and the specificity of a principal product alpha-cyclodextrin is improved; double mutants and three mutants are obtained through combined mutation at the mutation sites of the CGTase; compared with the wild-type CGTase, the production capacity of the beta-cyclodextrin of the mutants is remarkably lowered, the production capacity of the alpha-cyclodextrin is slightly improved, the specificity of the principal product alpha-cyclodextrin is improved, and therefore, the industrial production of the alpha-cyclodextrin is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Intact hepatitis c virus and the method for culturing it in a vitro cell culture
InactiveUS20040166488A1Easy to transcribeImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCell
The present invention relates to the establishment of an in vitro cell culture system for culturing the whole HCV proliferating virus by using molecular biology and gene recombinant technology. Said method comprises the step of amplifying from the serum of HCV patients the full-length HCV genome comprising the 98 nucleotides at the 3' end of the genome; site-specific mutating the NS5A and NS5B of HCV genome; inserting a marker gene IRES-GFP expression cassette into the NS5B 3' end in the mutated HCV genome; and transfecting the sensitive cells and culturing, to obtain the infectious HCV offspring virus.
Owner:YANGLING DAIYING BIOLOGICAL ENG
High-activity porcine interferon alpha mutant with 7 mutation loci and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN110343164AHigh activityImprove bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsInclusion bodiesMutated protein
The invention belongs to the field of interferons, and particularly relates to a high-activity porcine interferon alpha mutant with 7 mutation loci and a preparing method and application thereof. According to the high-activity porcine interferon alpha mutant with the 7 mutation loci and the preparing method and application thereof, a porcine interferon alpha gene is modified to obtain a new gene sequence, and through modification, the biological activity of the interferon is improved. An overlapped PCR method is applied to conducting site-specific mutation on the natural porcine interferon alpha gene, the modified gene is cloned to a pET-32a carrier to construct a recombinant plasmid, then the recombinant plasmid which is accurately identified is cloned into Rosetta expression bacteria forinduction expression and identification, recombinant protein is expressed in the form of an inclusion body, the molecular mass of the protein is about 32 KDa, after purification and dialysis treatment, the porcine interferon alpha mutant with high purity is obtained, and the antiviral activity is determined through cytopathic effect inhibition. As is shown through results, the antiviral activityof the mutant protein obtained through experiments is 8.15*10<8> U / mg, and increased by about 200 times compared with that of wild-type interferons expressed in vitro.
Owner:ANYANG INST OF TECH
Fibronectin binding protein compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS20050123552A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsStreptococcus pyogenesPassive Immunizations
Disclosed are antibodies that block the binding of fibronectin protein to fibronectin. Also disclosed are site specifically-mutated and truncated peptide epitopes derived from the fnbA and fnbB genes of Staphylococcus aureus, the fnbA and fnbB genes of Streptococcus dysgalactiae, and the sfb gene of Streptococcus pyogenes, and nucleic acid segments encoding these peptides and epitopes. The anti-(fibronectin binding site) antibodies, peptides and epitopes that give rise to antibodies that block the binding of fibronectin binding proteins to fibronectin, and DNA segments encoding these proteins and are of use in various screening, diagnostic and therapeutic applications including active and passive immunization and methods for the prevention of streptococcal and staphylococcal colonization in animals or humans. These DNA segments and the peptides derived therefrom are proposed to be of use directly in the preparation of vaccines and also for use as carrier proteins in vaccine formulations.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +2
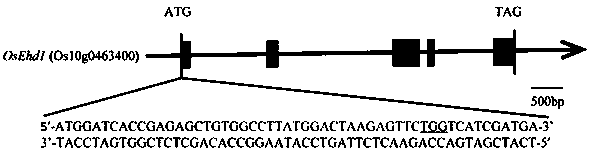
5 alpha-reductase mutant, genetic engineering bacterium and application of genetic engineering bacterium to realizing high-efficiency catalysis of 5 alpha-AD production
ActiveCN110628735AIncrease productionIncrease yield, its catalytic efficiencyBacteriaTransferasesHeterologousTyrosine
The invention provides a 5 alpha-reductase mutant. The 5 alpha-reductase mutant is obtained through site-specific mutation and reconstruction of 5 alpha-reductase, a genetic engineering bacterium of the 5 alpha-reductase mutant is constructed and applied to high-efficiency catalysis of 5 alpha-AD production, in the 5 alpha-reductase subjected to site-specific mutation and reconstruction, 187th tyrosine is mutated into phenylalanine, 5 alpha-reductase mutant recombinant plasmids are electrically transferred into mycobacterium neoaurum to be subjected to heterologous expression, then enzymatic activity and production efficiency are determined, the inventor finds that the enzyme activity of a mycobacterium neoaurum genetic engineering bacterium of the 5 alpha-reductase mutant is increased by2.3 times, the catalysis efficiency is improved by 22.8%, and the 5 alpha-AD production is increased to 1.78g / L from the original 1.45g / L; and when the 5 alpha-reductase mutant is used as a key enzymefor production of an important sterides medicine intermediate, the bioconversion efficiency and the yield of products can be obviously improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for breeding long-growth period japonica rice varieties by editing rice Ehd1 gene
InactiveCN108841855AProlong reproductive periodImprove ecological adaptabilityVectorsPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceLow latitude
The invention provides a method for breeding rice varieties by transferring japonica rice in the north to the south. The method comprises the following steps: designing a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing sitein a starting region of a rice Ehd1 gene receiving structural domain, constructing a gene editing vector, and transforming rice to achieve site-specific mutation of the Ehd1 gene so as to obtain a frameshift mutant of the Ehd1 gene and an in-frame deletion mutation strain with 3 amino acids deleted in the starting region of the receiving structural domain. Experiments prove that compared with thewild type, the growth period of the in-frame deletion mutation strain is moderately prolonged by about two weeks and the growth period of the frameshift mutant is delayed by nearly one month. By themethod provided by the invention, japonica rice materials with different prolonged growth periods can be quickly obtained, and the ecological adaptability of the existing excellent varieties is expanded; a high-efficiency gene knockout method and a high-efficiency breeding method can be provided for breeding the japonica rice varieties adapted to different ecological conditions in low-latitude regions.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
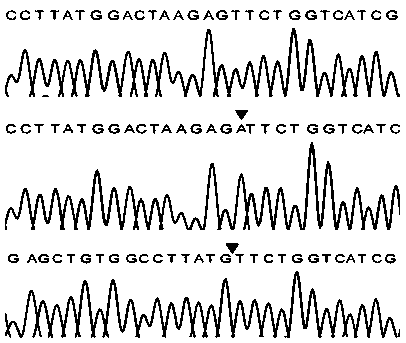
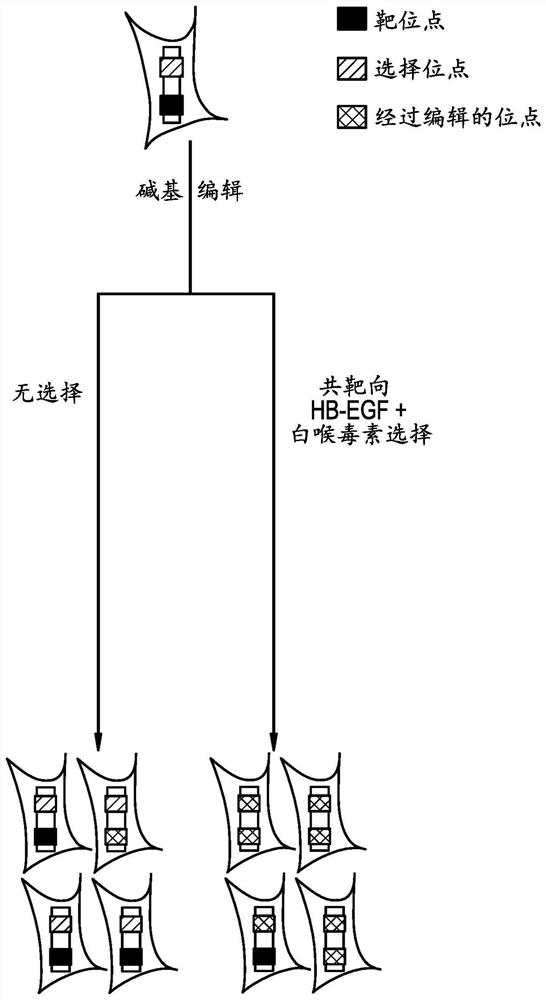
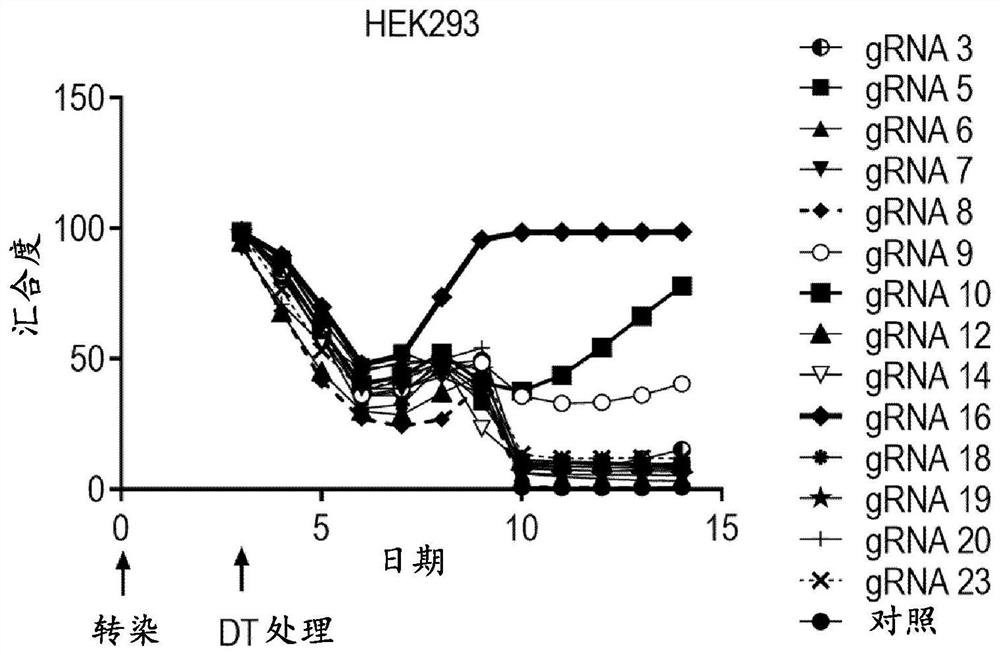
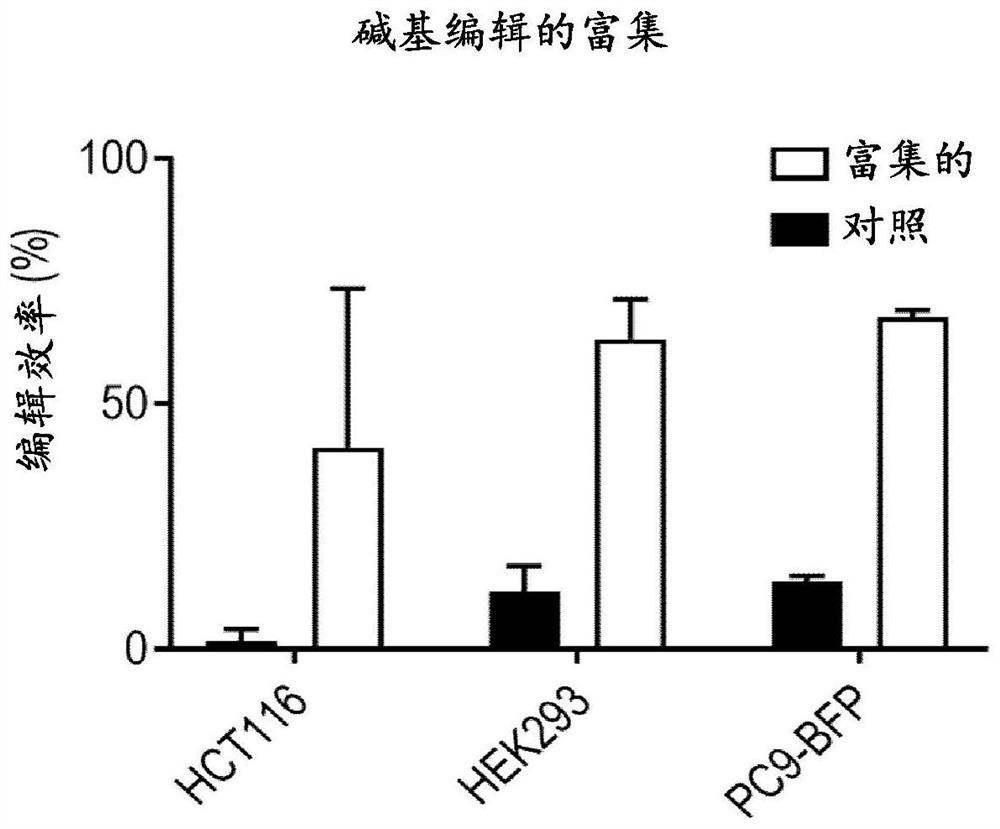
Compositions and methods for improved gene editing
The present disclosure provides methods of introducing site-specific mutations in a target cell and methods of determining efficacy of enzymes capable of introducing site-specific mutations. The present disclosure also provides methods of providing a bi-allelic sequence integration, methods of integrating of a sequence of interest into a locus in a genome of a cell, and methods of introducing a stable episomal vector in a cell. The present disclosure further provides methods of generating a human cell that is resistant to diphtheria toxin.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Marek's disease virus vaccine CV1988 strain VP22 gene
InactiveCN1513996AMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesProtective antigenAntigen
The UL49h gene fragment in the fibroblast genome of the duck embryo or chicken embryo infected by weak-toxic vaccine strain CV1988 / Rispens is amplified by DNA PCR method to obtain the PCR product, chich is then cloned and coded. After compared with the classical MDV strong-toxic GA strain, it is determined that said UL49h of weak-toxic CV1988 has 3 site-specific mutations and a deficient mutation. Said CV1988 VP22 gene or part of its gene sequence can be used to develop the protective antigen and medicine, and increase the immune protection effect of protein and the curative effect of medicine.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
6-methy salicylic acid synthetase transformed by genetic engineering and combinatorial biosynthesis of spirocyclic acetoacetic acid lactone antiboitic
ActiveCN101812103AHigh activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSalicylic acidStreptomyces antibioticus
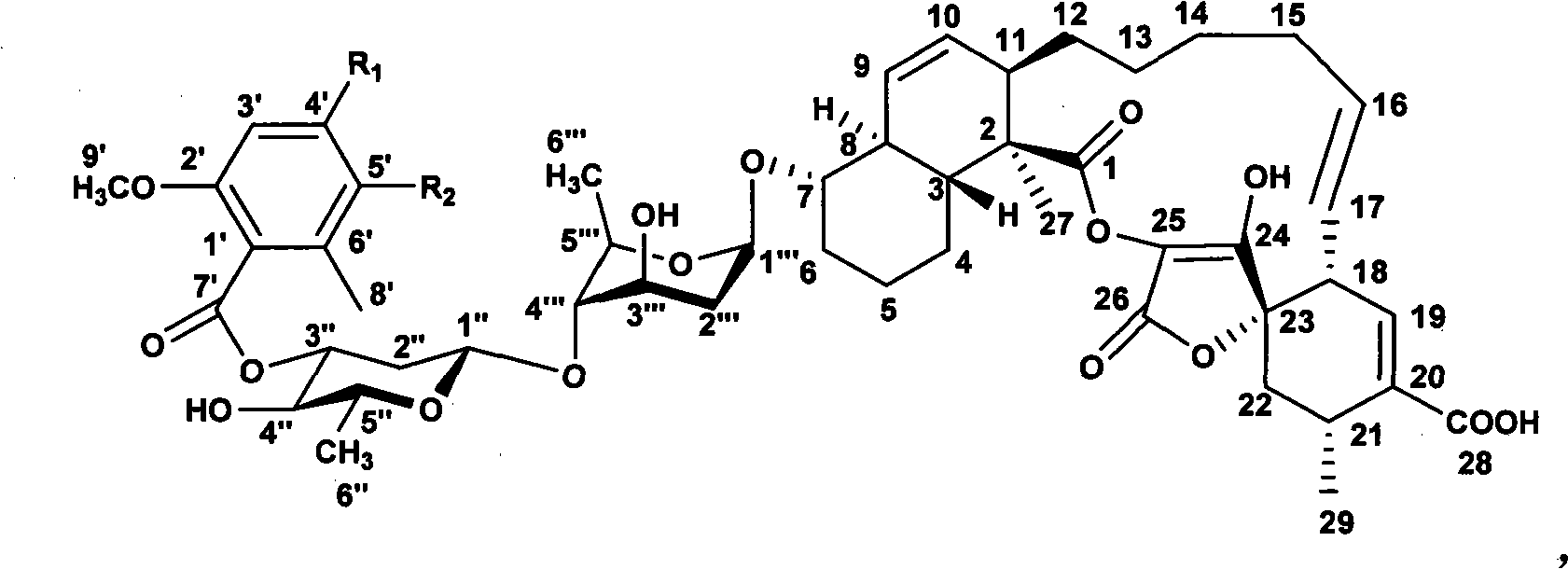
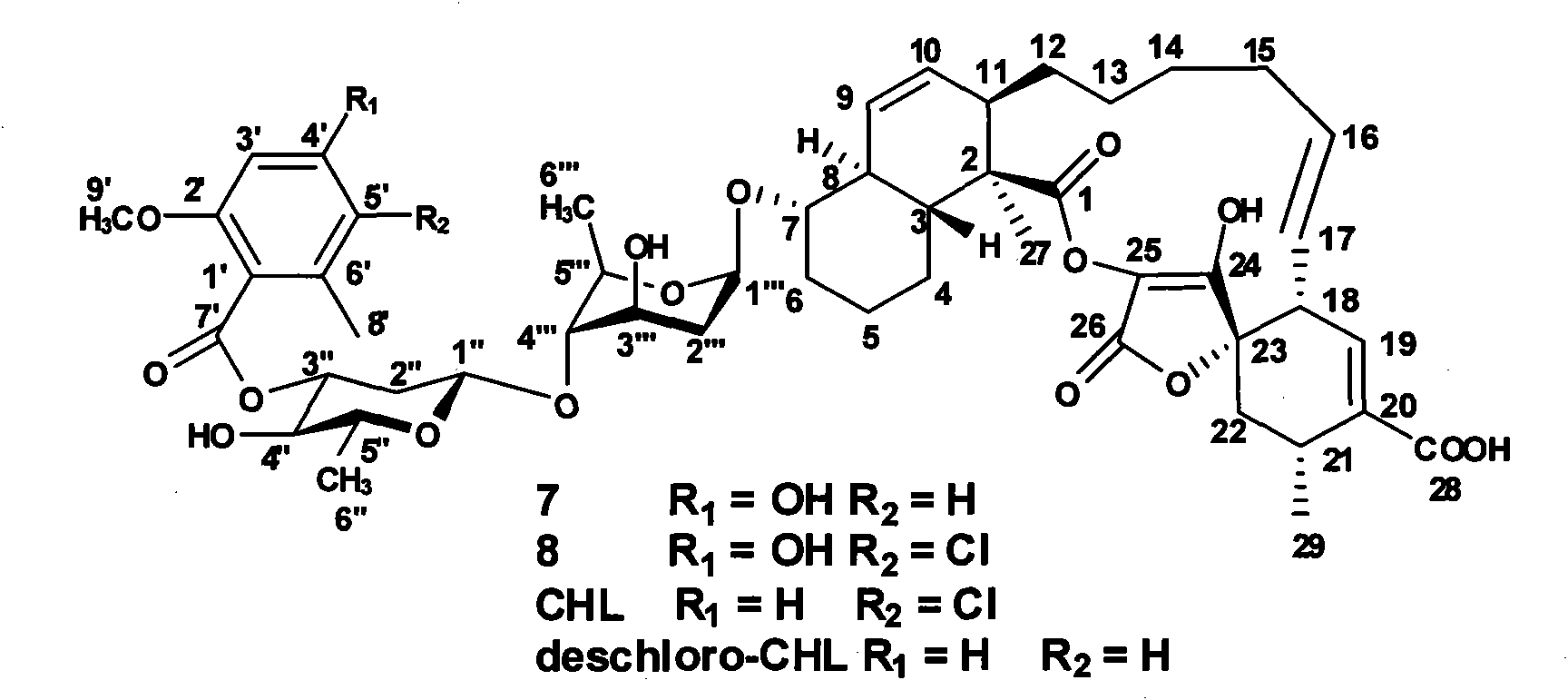
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing spirocyclic acetoacetic acid lactone antibiotic with higher activity by using combinatorial biosynthesis based on a genetic engineering method. The method is characterized by carrying out specific locus mutation on the keto-reduction (KR) conservation activity locus of a 6-methy salicylic acid (6-MSA) synthetase and genetically transforming the producing strain Streptomyces antibioticus DSM40725 of chlorothrichin (CHL) and fermenting to generate new chlorothrichin analogues 7 and 8 with improved biological activity. The favorable biological activity of the new chlorothrichin analogues 7 and 8 has values to be developed into medicaments.
Owner:国科新研国际技术转移有限公司
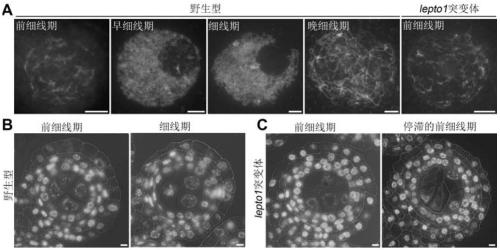
Application of LEPTO1 and encoded protein thereof in rice fertility control
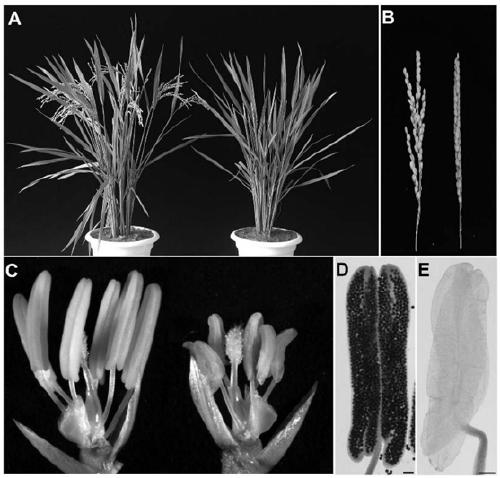
The invention discloses an application of LEPTO1 protein and the encoded gene thereof in regulating and controlling male fertility of plants. The present invention provides the use of a substance which inhibits the activity and / or level of LEPTO1 protein in the cultivation of male sterile plants, or a substance for inhibiting or reducing the expression of the LEPTO1 protein coding gene in the cultivation of male sterile plants. The inventors of the present invention apply a genetic editing technology to knock out the CRISPR-Cas9 gene in wild-type rice, which causes the development of pollen mother cells to stagnate in the pre-filament line stage and lead to chromosome degradation and final pollen abortion. The site-specific mutation LEPTO1 protein coding gene can be used for rice fertilitycontrol and hybrid seed production in combination with a tissue-specific gene knock-out technology, so that the method has important significance in rice breeding and can provide important biologicalresources for increasing rice yield and improving rice quality.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single domain heavy chain antibody capable of specifically combining c-Myc tag
ActiveCN106946993AHigh affinityImprove featuresOther chemical processesBiological material analysisAntigenMutant
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and particularly provides a single domain heavy chain antibody which is direct at a c-Myc tag. The antibody has an amino acid sequence represented as the SEQ ID No.1 and is used in the fields of immunodetection, antigen enrichment and purification, etc. The amino acid sequence can be used as a precursor and modified through random or site-specific mutation technology, thereby producing a mutant, which has better properties (e.g., affinity, specificity, stability, etc.) for further development of proteins or polypeptides applied in the fields of medicines, industry and agriculture.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Isoform-selective inhibitors and activators of PDE3 cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases
The present invention concerns methods and compositions related to type 3 phosphodiesterases (PDE3). Certain embodiments concern isolated peptides corresponding to various PDE3A isoforms and / or site-specific mutants of PDE3A isoforms, along with expression vectors encoding such isoforms or mutants. In specific embodiments, methods for identifying isoform-selective inhibitors or activators of PDE3 are provided, along with methods of use of such inhibitors or activators in the treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy, pulmonary hypertension and / or other medical conditions related to PDE3 effects on cAMP levels in different intracellular compartments. In particular, techniques are disclosed herein relating to the identification of a test compound that binds to an isolated polypeptide such as PDE3A2 and assaying the test compound for its ability to exhibit superior ability to interfere with binding of the isolated polypeptide when compared with at least a second isolated polypeptide such as of PDE3A1 and methods of treatment of cardiomyopathy, pulmonary hypertension involving the resulting test compound.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com