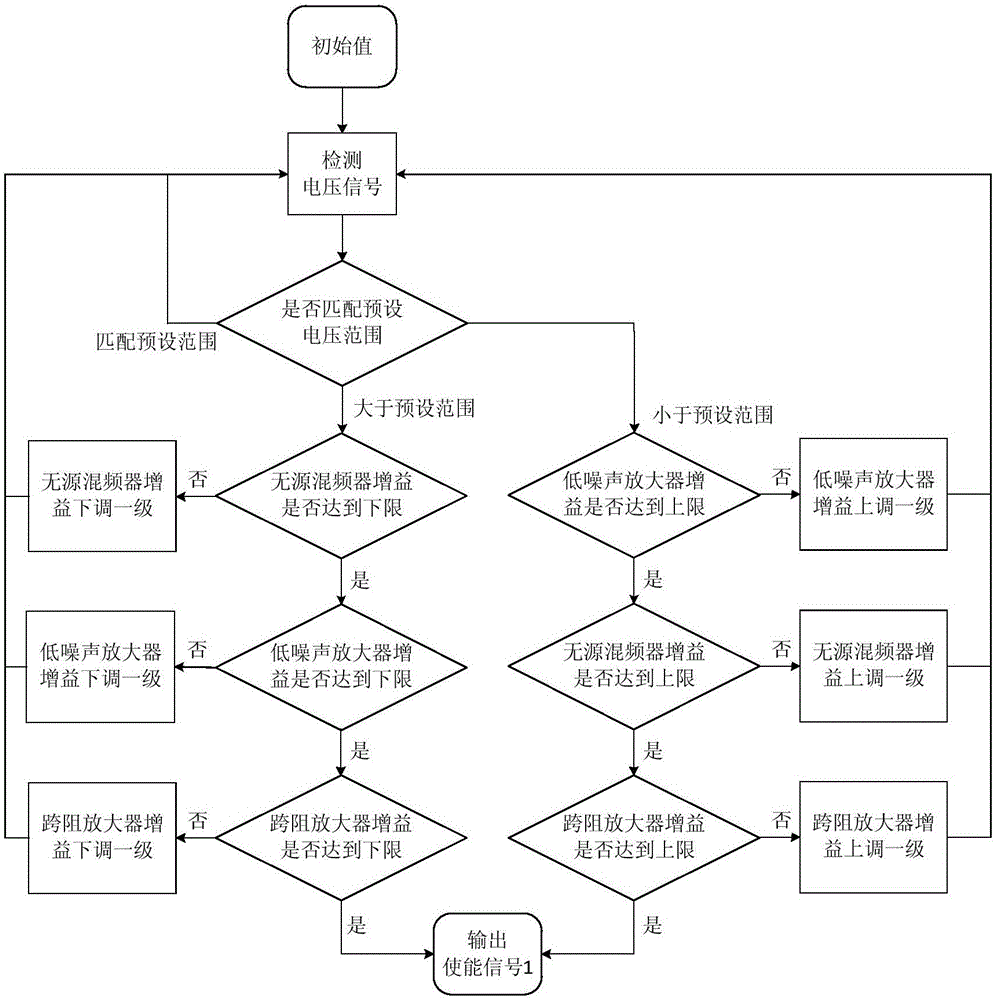
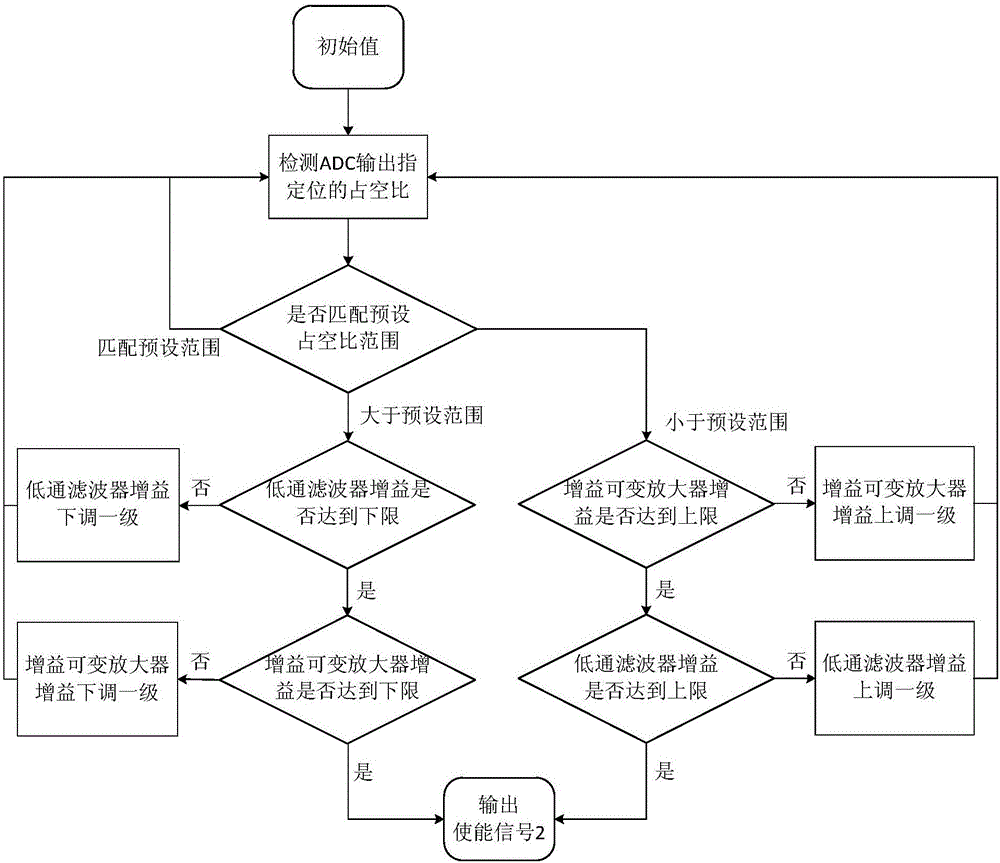
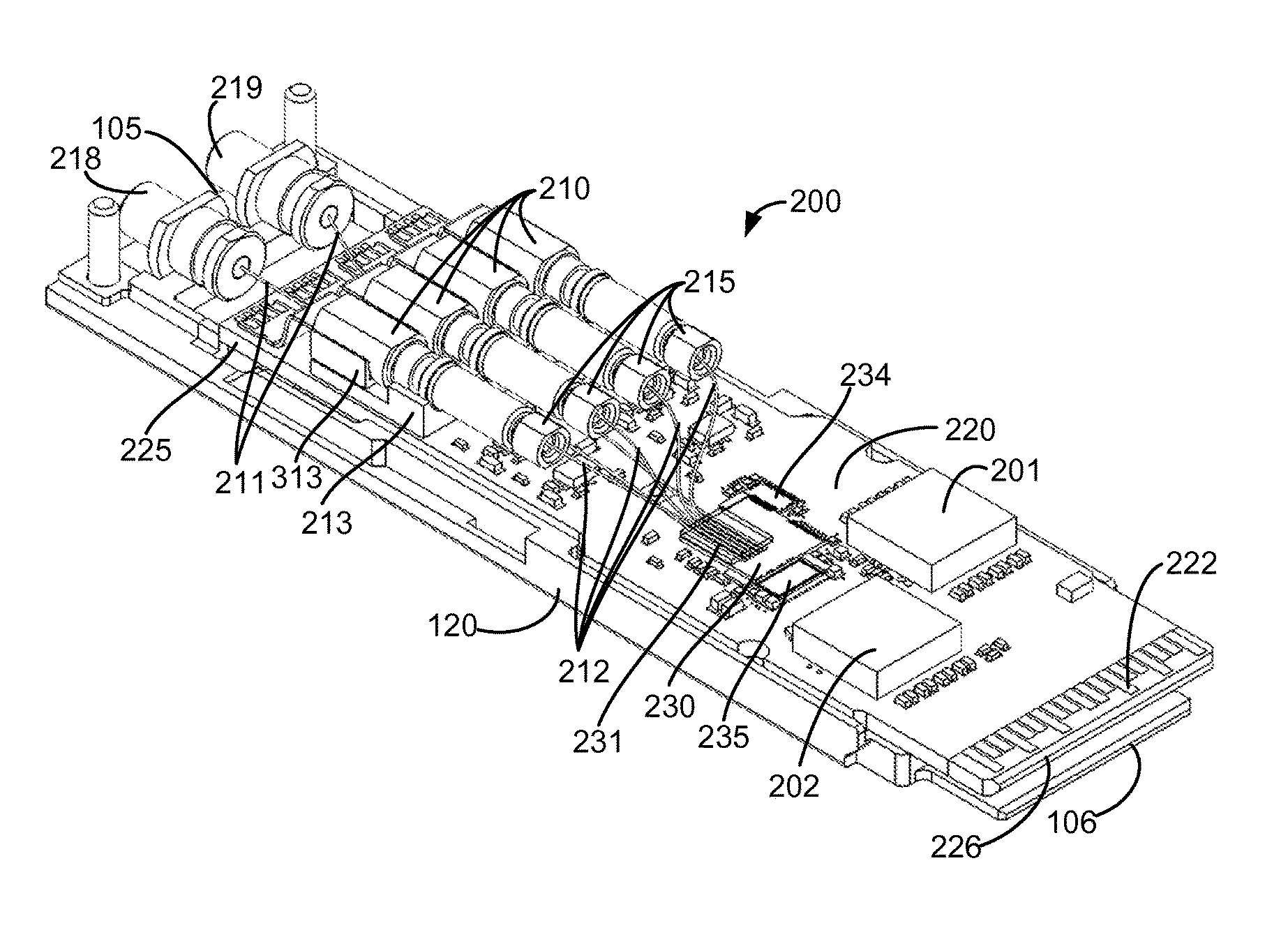
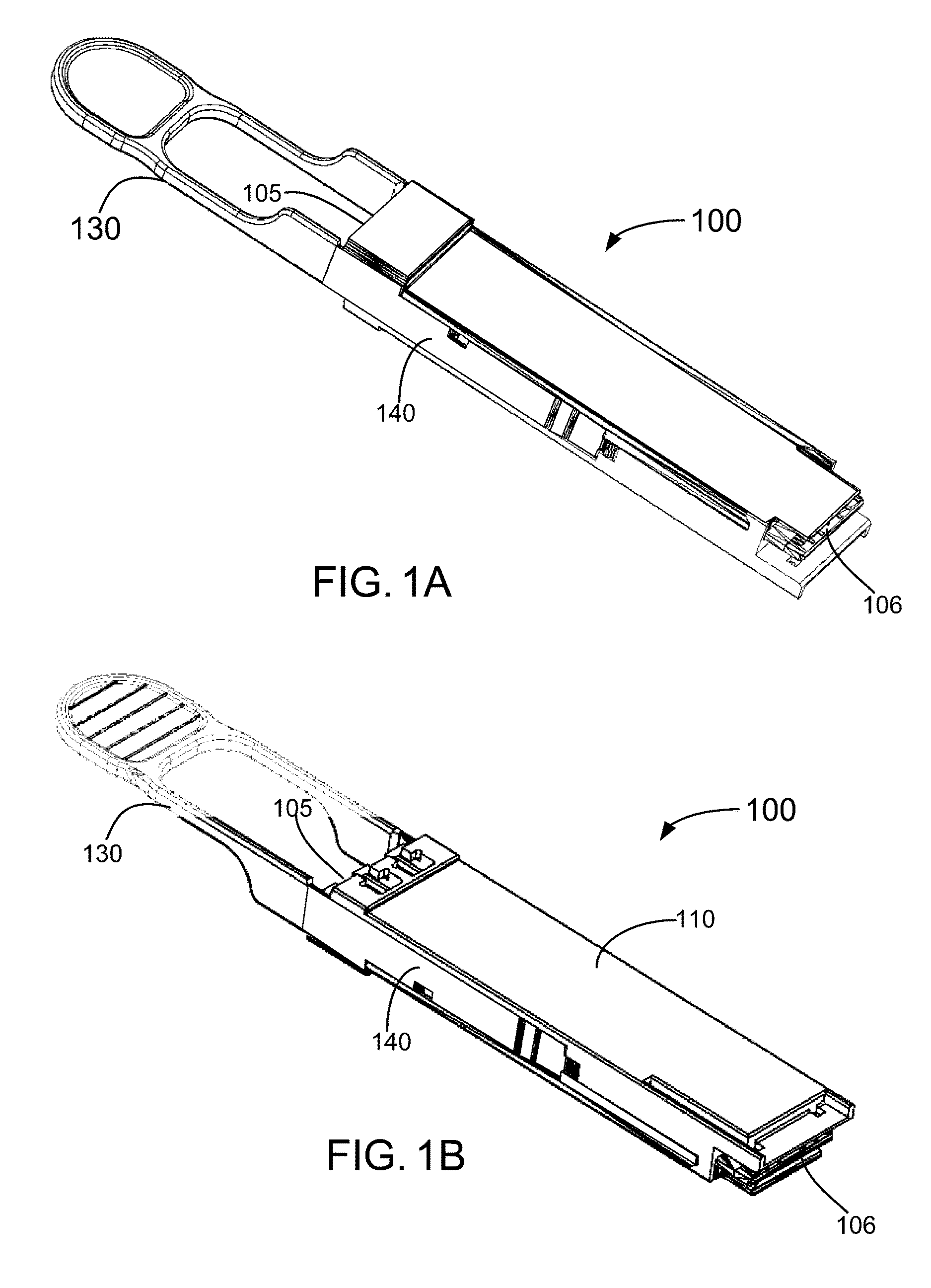
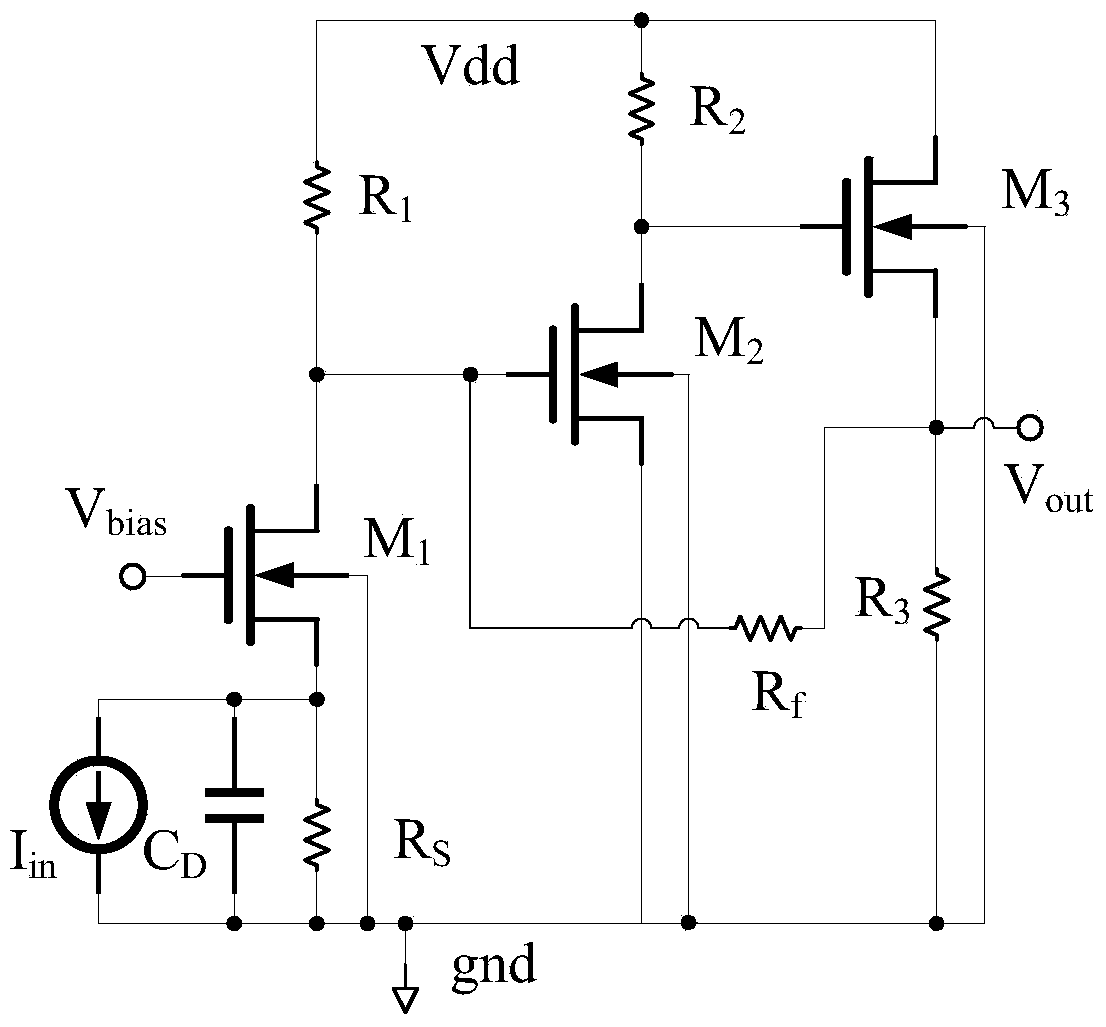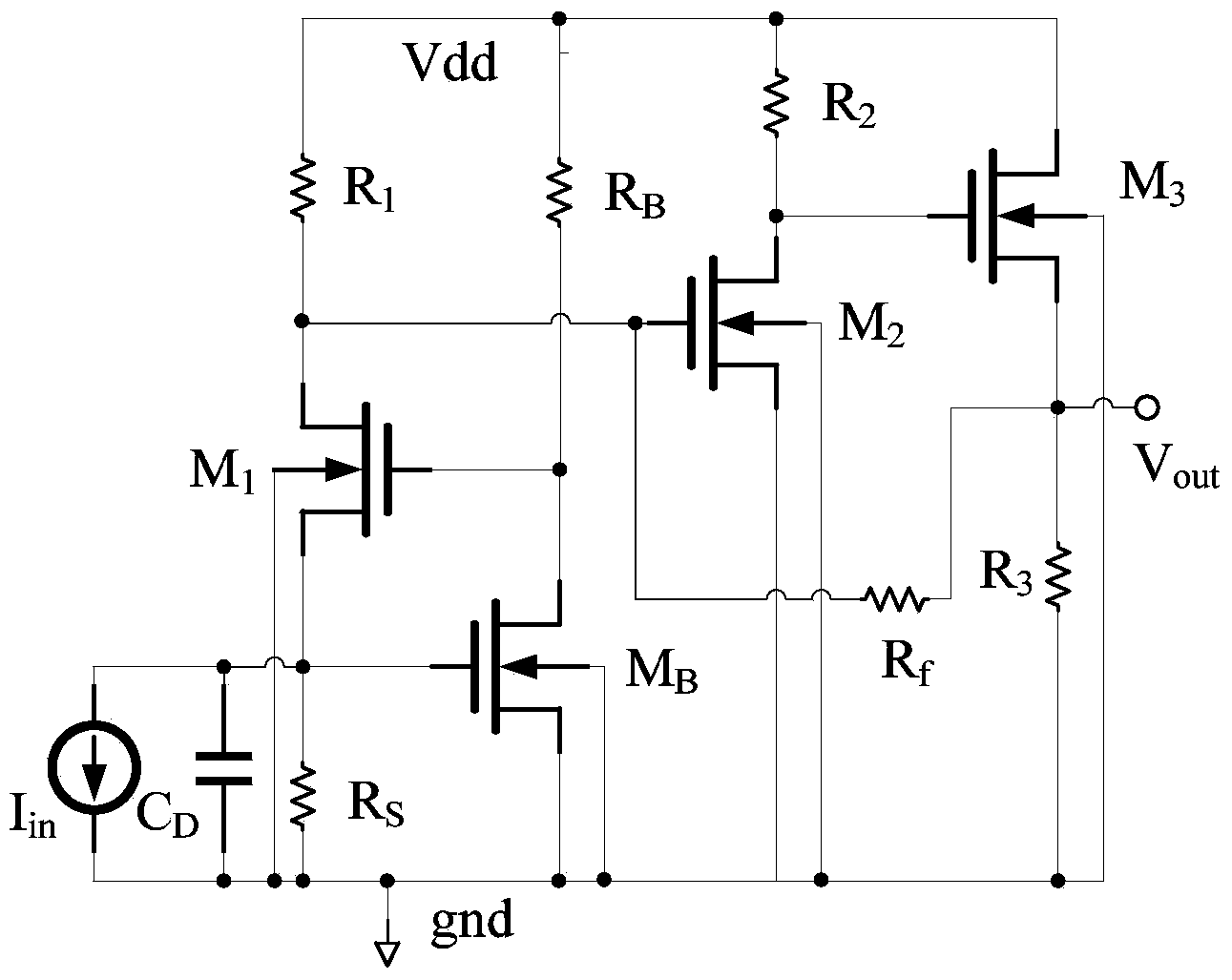Patents
Literature
517 results about "Trans impedance amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
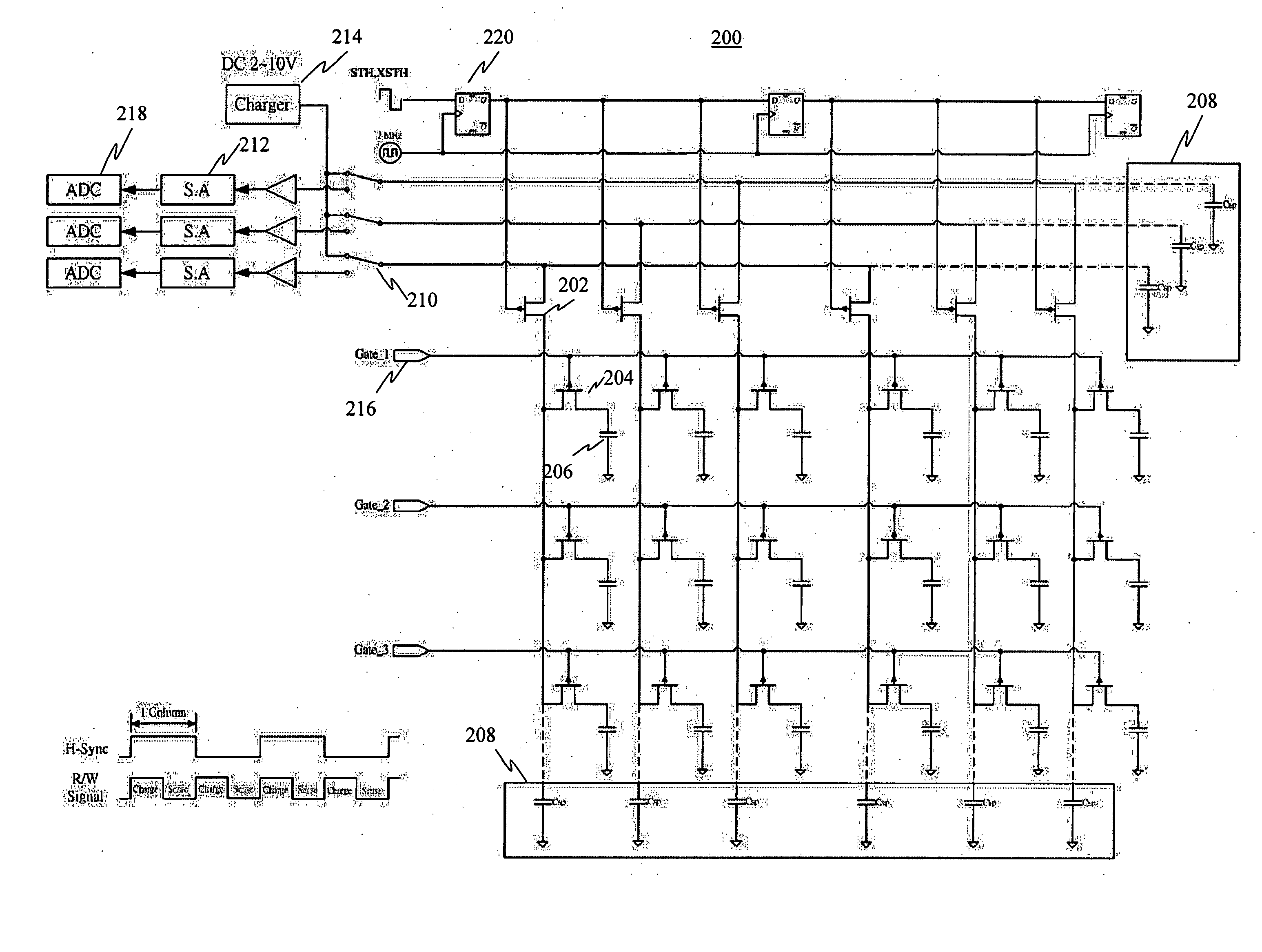
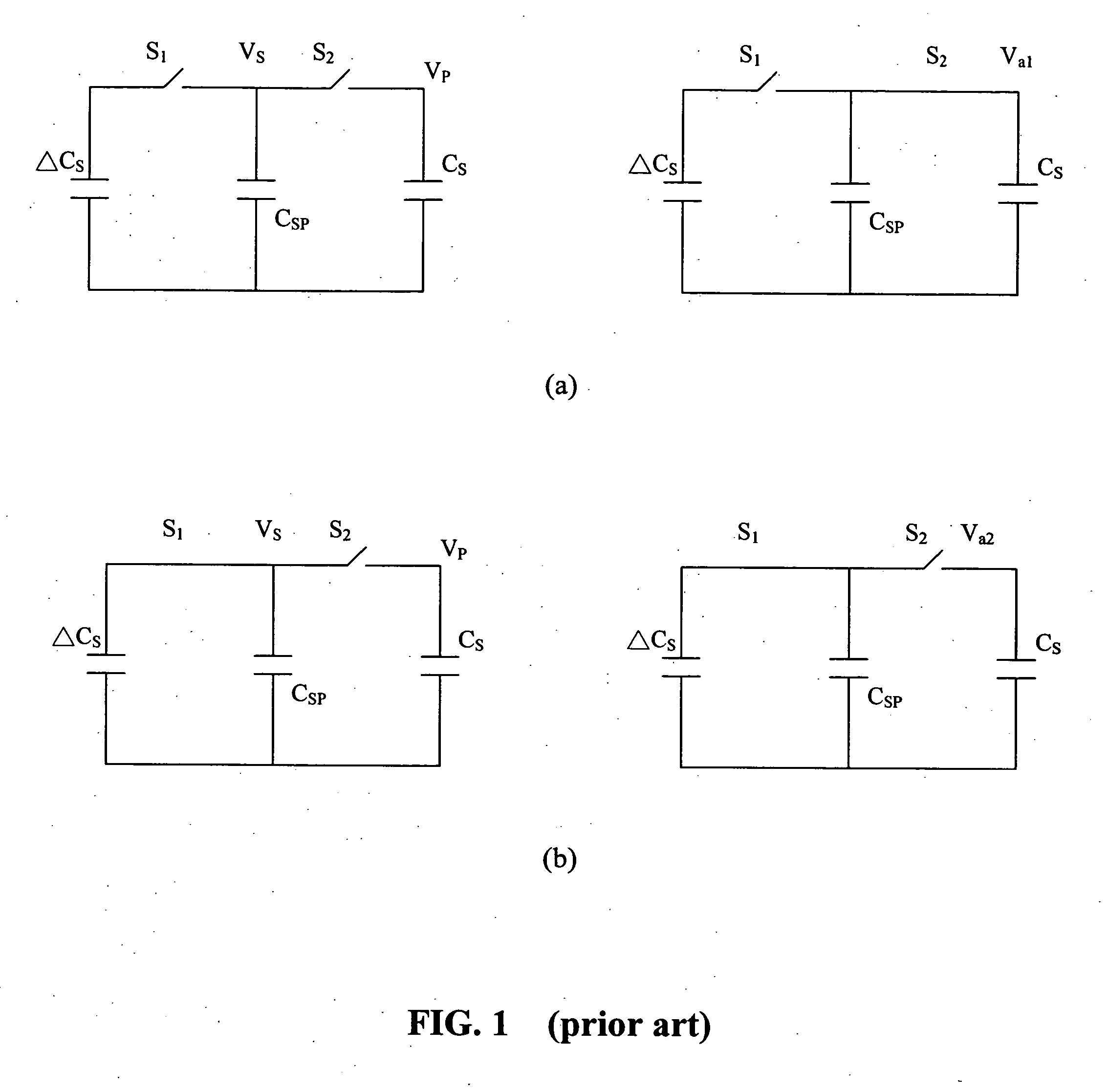
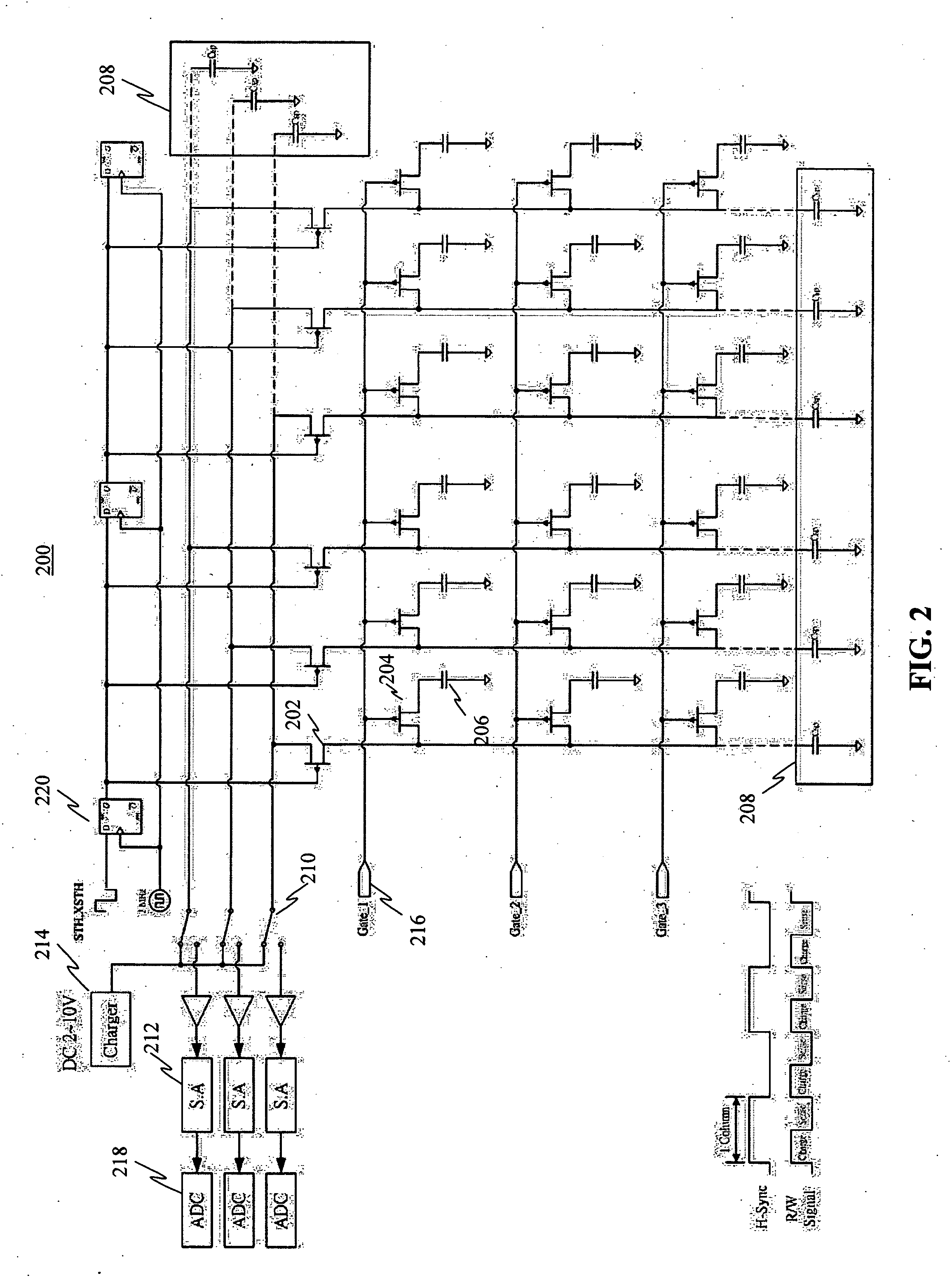
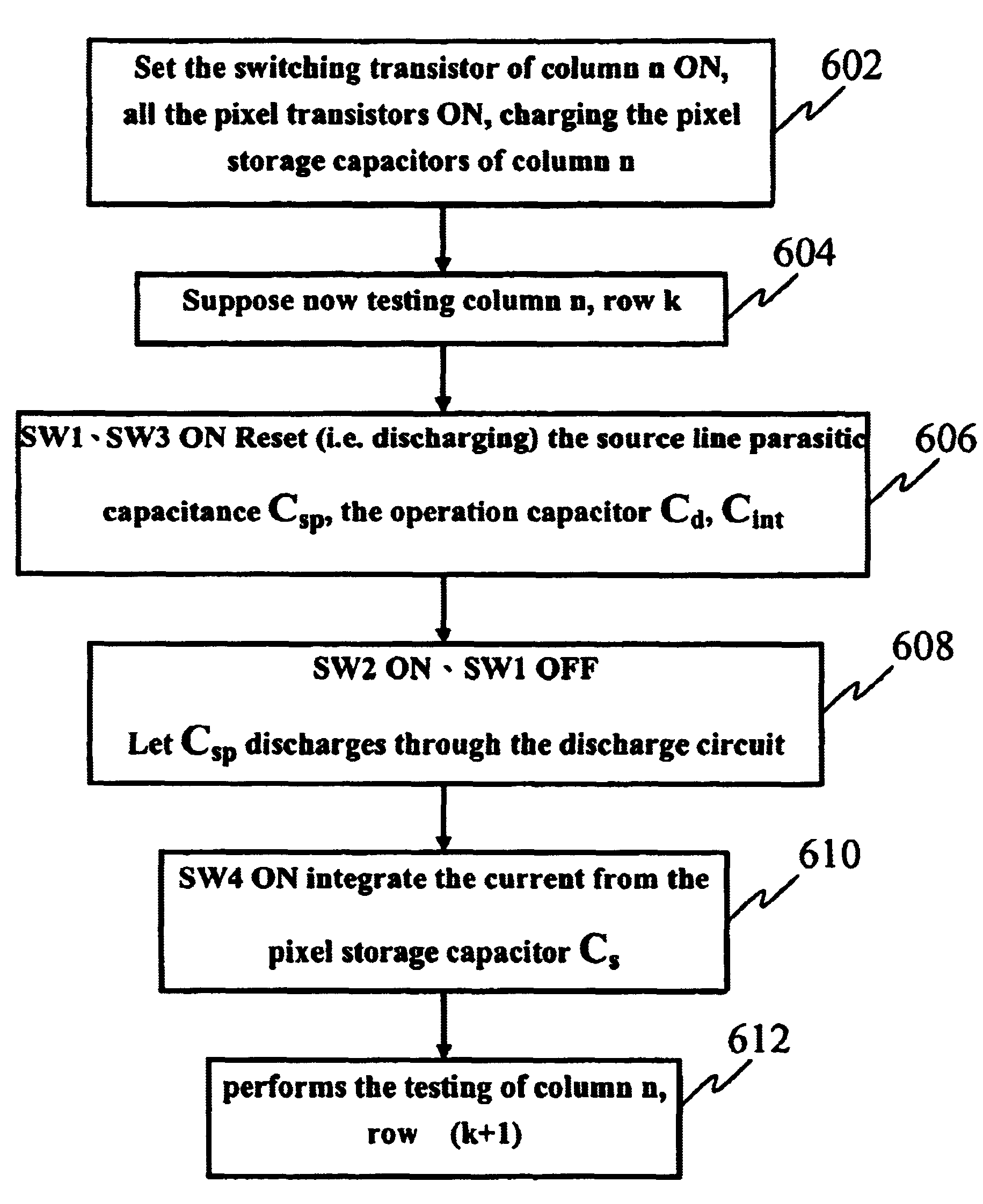
Testing apparatus and method for thin film transistor display array
InactiveUS20050024081A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceTransistor arrayHemt circuits
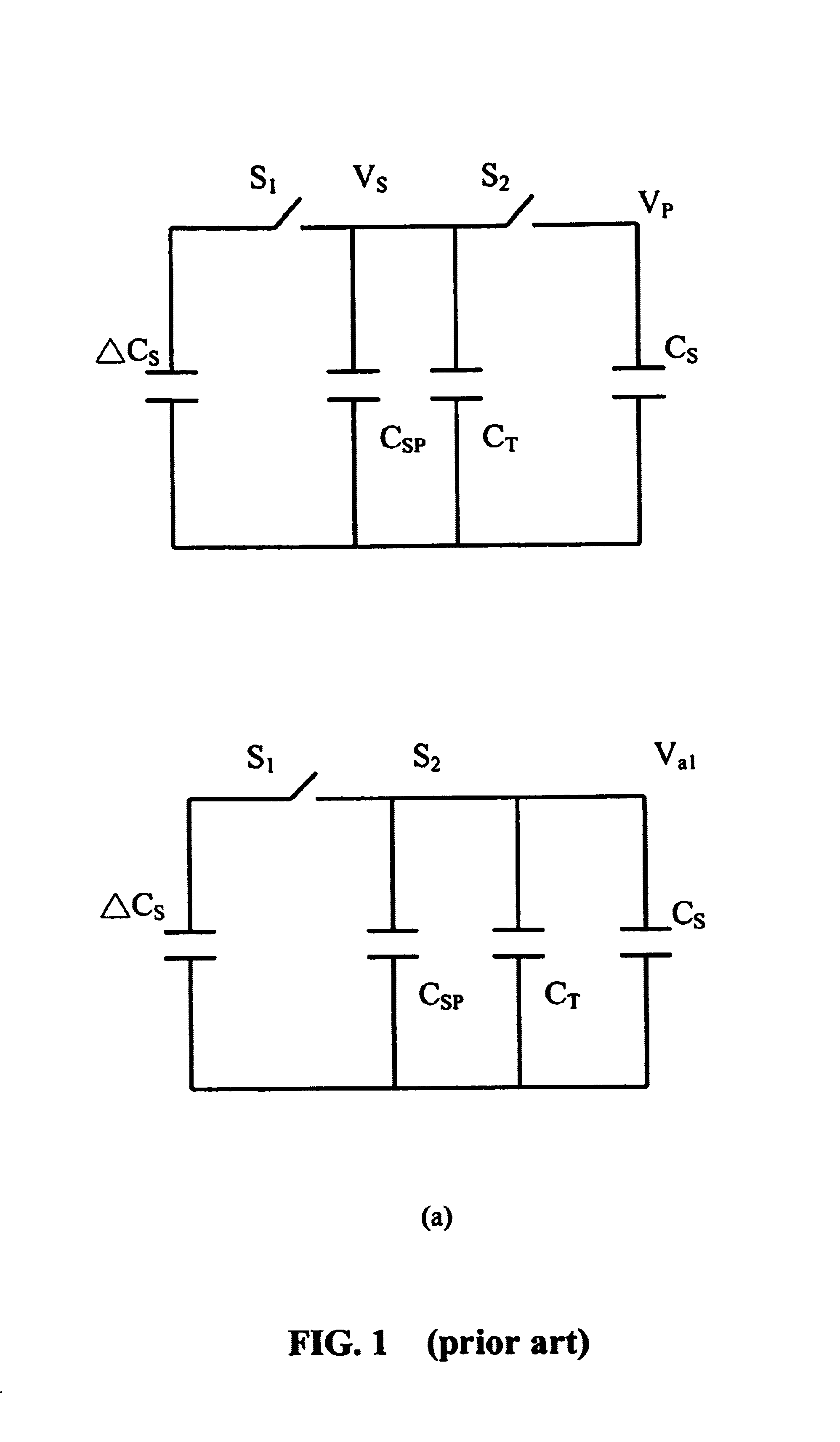
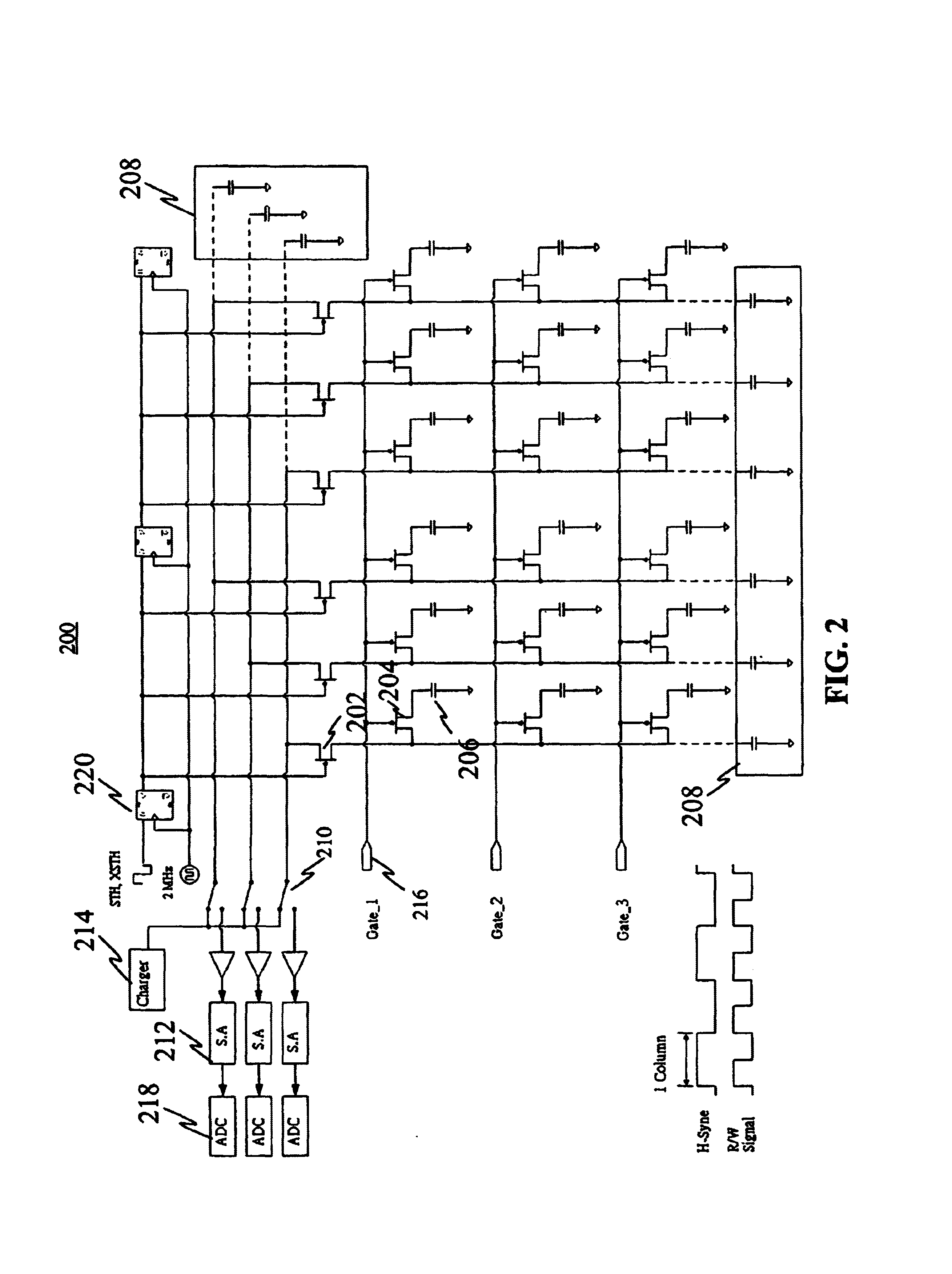
The present invention discloses a testing circuit and method for thin film transistor display array, for testing the yield of thin film transistor array. The testing circuit comprising: An array tester, a test panel (DUT), a sense amplifier array. The sense amplifier is composed by a plurality of trans- impedance amplifier unit and a plurality of parasitic capacitance discharge circuit unit. Every sense amplifier includes: a trans-impedance amplifier, which is implemented by an operational amplifier, two switches and an operation capacitance, the trans-impedance amplifier is used to form an integrated circuit, the output is transmitted to a sampling / hold circuit via a switch; a parasitic capacitance discharge circuit is used to form a discharge rout for the charge of the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:PRIMETECH INT CORP
Testing apparatus and method for thin film transistor display array
InactiveUS7102378B2Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceTransistor arrayAudio power amplifier
A testing circuit and method for thin film transistor display array, for testing the yield of a thin film transistor array is provided. The testing circuit includes an array tester, a test panel (DUT) and a sense amplifier array. The sense amplifier is composed of a plurality of trans-impedance amplifier units and a plurality of parasitic capacitance discharge circuit units. Every sense amplifier includes a trans-impedance amplifier, which is implemented by an operational amplifier, two switches and an operation capacitance. The trans-impedance amplifier is used to form an integrated circuit and the output is transmitted to a sampling / hold circuit via a switch. Also included is a parasitic capacitance discharge circuit that is used to form a discharge route for the charge of the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:PRIMETECH INT CORP
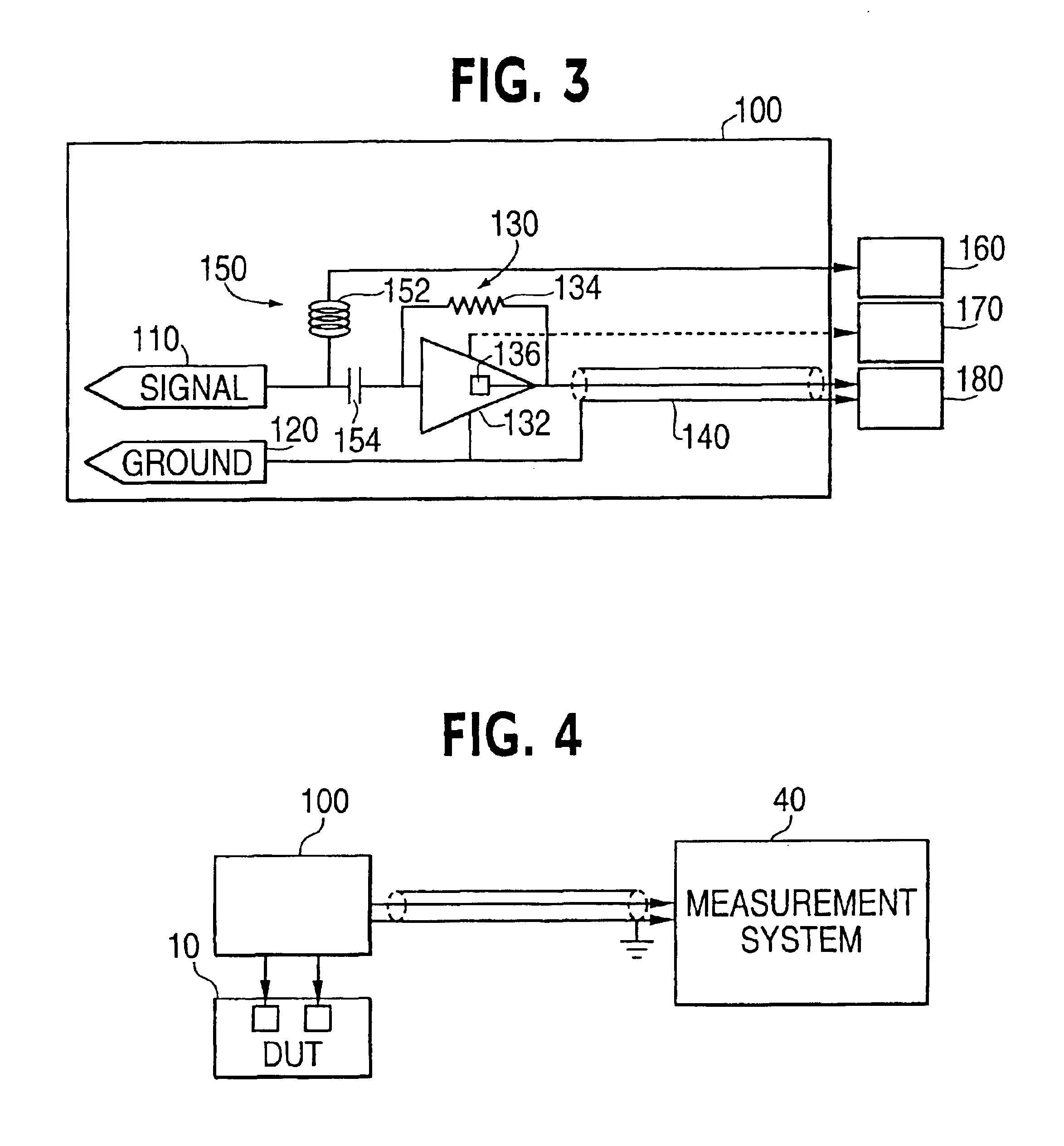
Current probe device having an integrated amplifier
InactiveUS6856129B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsAudio power amplifierIntegrated amplifier
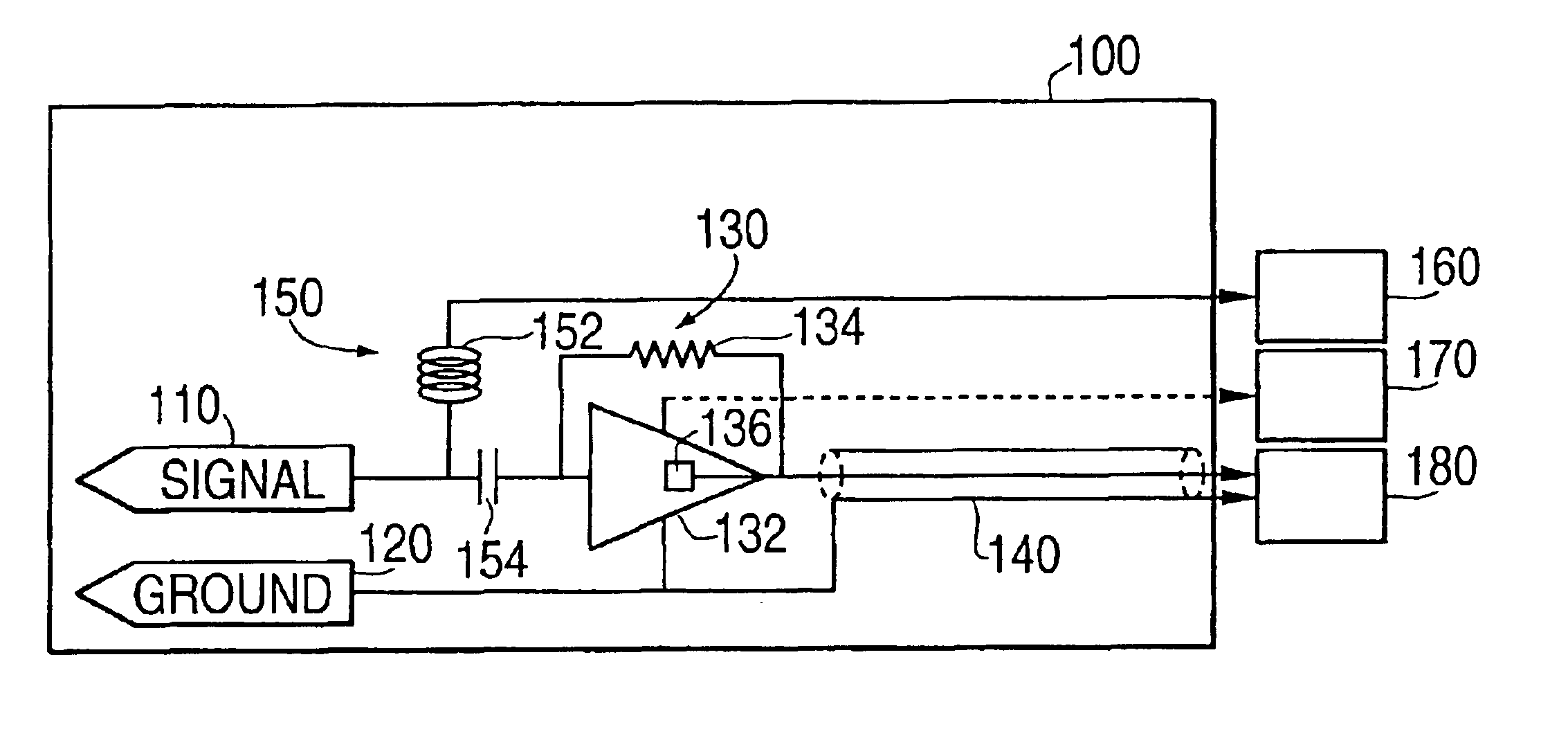
A measurement system is provided that includes a probe device having an integrated amplifier. The integrated amplifier may be a transimpedence amplifier that amplifies input current to an output voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Transconductance-enhancing passive frequency mixer
InactiveCN102412786AImprove linearityReduce power consumptionActive element networkMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceFrequency mixerHemt circuits
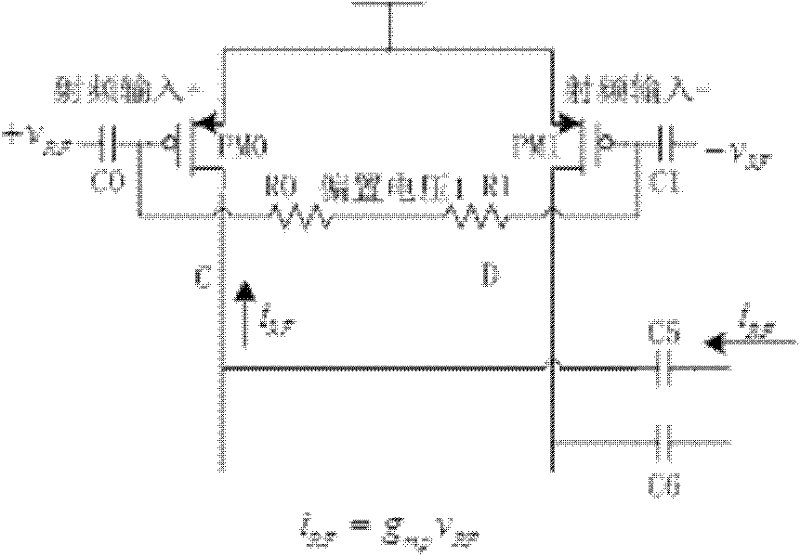
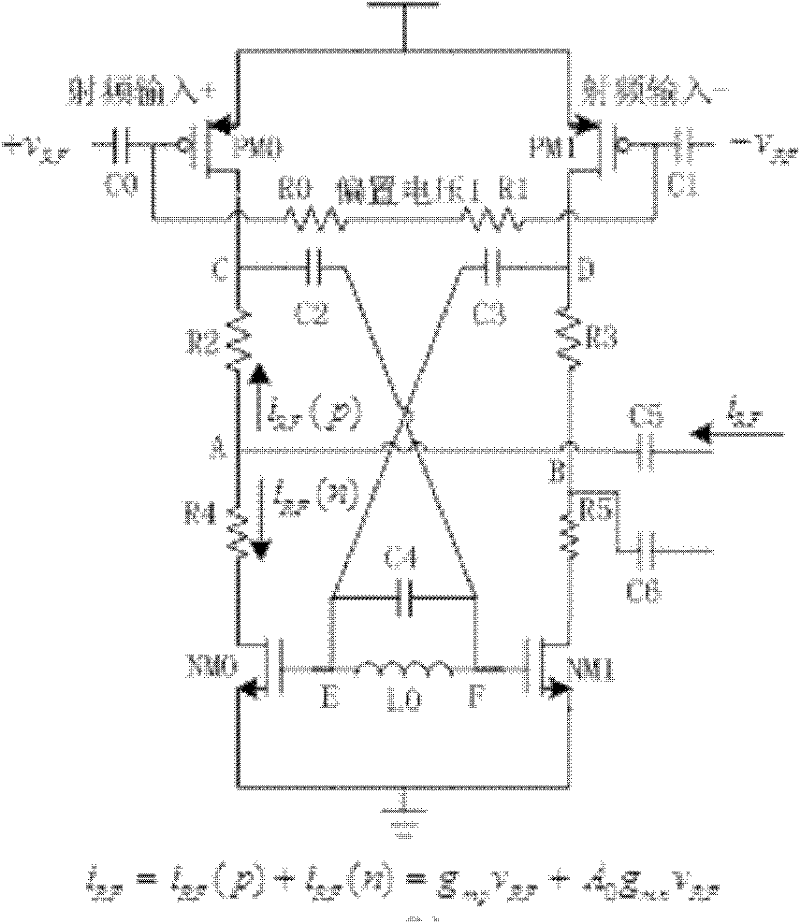
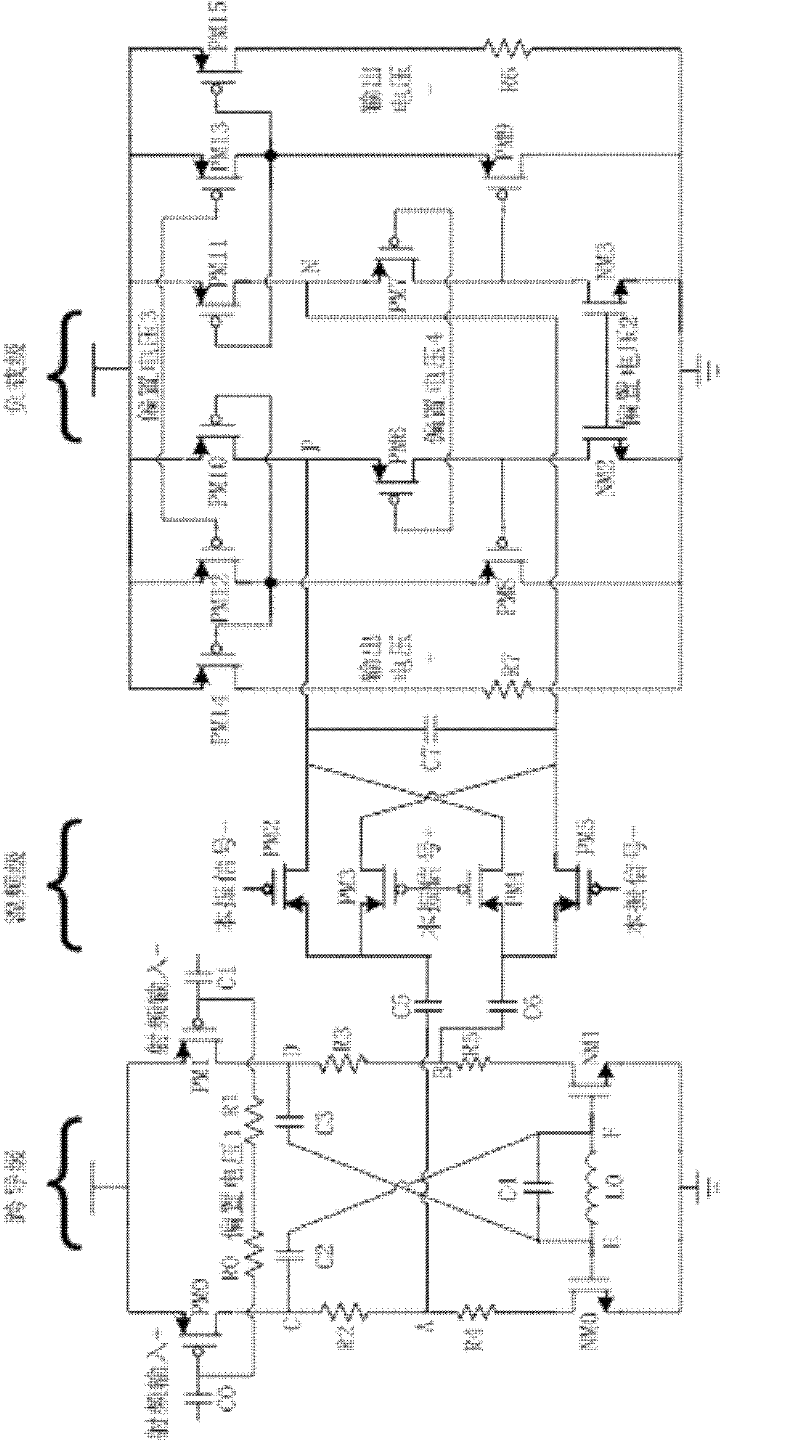
The invention discloses a transconductance-enhancing passive frequency mixer, which comprises a mixing stage and a biasing circuit, and further comprises a transconductance stage with a transconductance-enhancing function, a passive mixing switch pair and an enhanced load output stage, wherein the transconductance stage with a transconductance-enhancing function transforms an input radio-frequency voltage into a radio-frequency current; and frequency mixing of the radio-frequency current is achieved through the double-balance mixing switch pair, and the current after frequency mixing is transformed into a mid-frequency voltage for output through the transconductance-enhanced load output stage. As the transconductance stage uses a pre-amplifying transconductance-enhancing structure, transconductance is greatly enhanced, thus the same transconductance value can be achieved at a lower bias current, and an output mid-frequency current signal is generated after the radio-frequency current is modulated through the mixing stage. Voltage output is generated through a transresistance amplifier, and finally the mid-frequency voltage signal is obtained. As the transresistance amplifier uses a transconductance-enhancing structure, input impedance is reduced, and current utilization efficiency and port isolation are improved. The transconductance-enhancing passive frequency mixer provided by the invention has the characteristics of low power consumption, high conversion gain, good port isolation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV WUXI CAMPUS
Circuit for measuring outburst mode optical signal power
InactiveCN101510802AReduce speed requirementsImprove anti-interference abilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionAudio power amplifierPhotovoltaic detectors
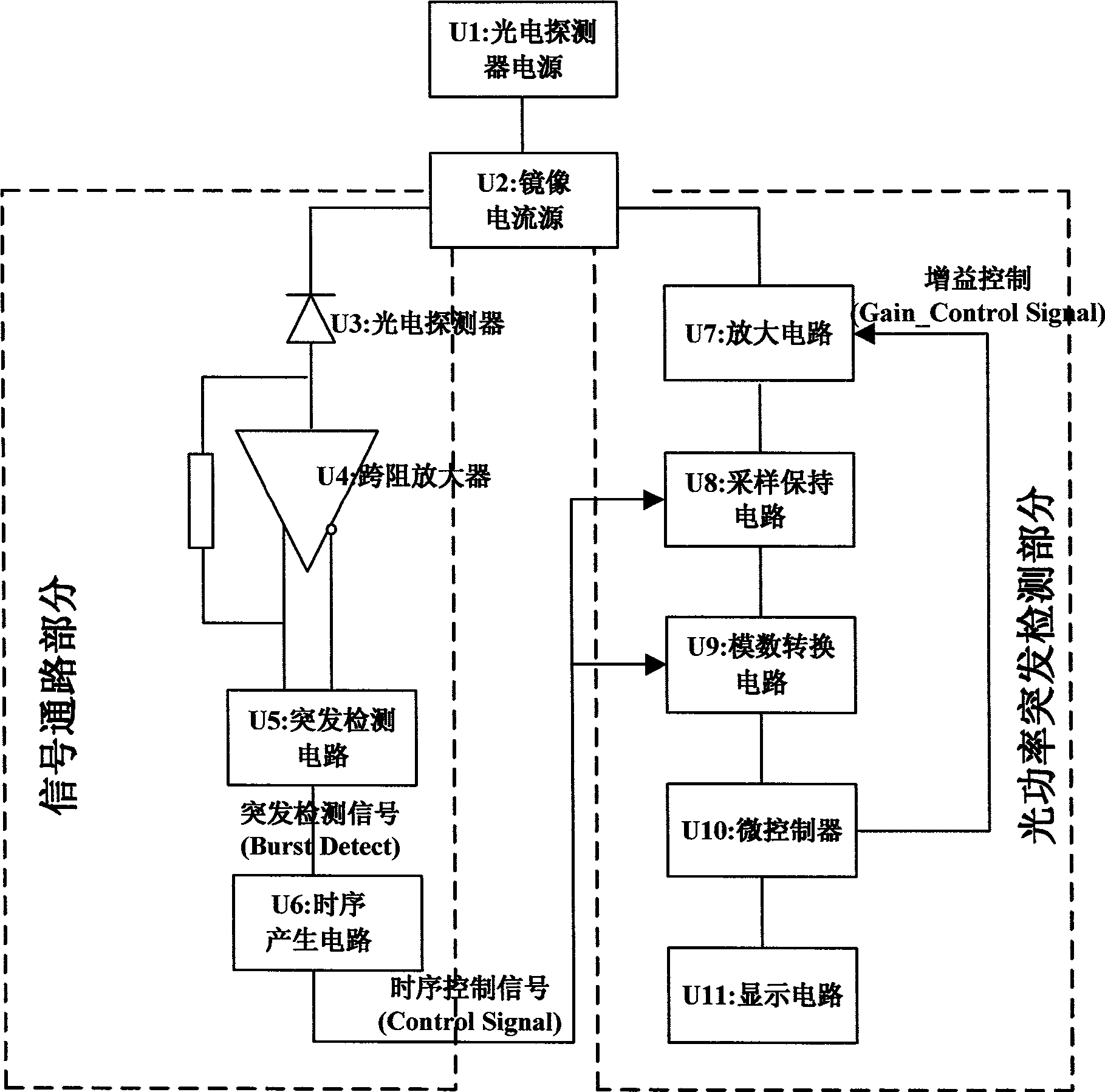
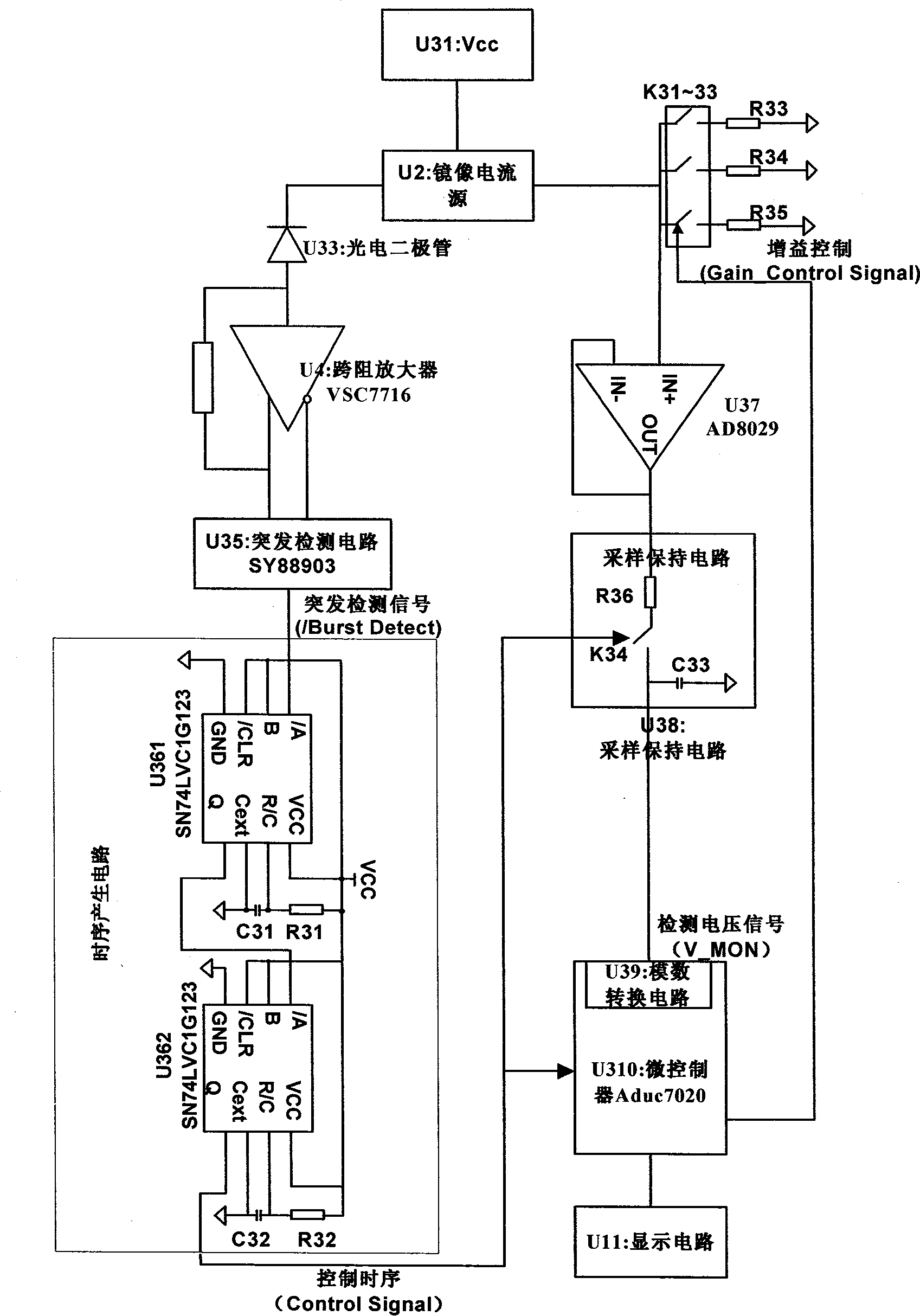
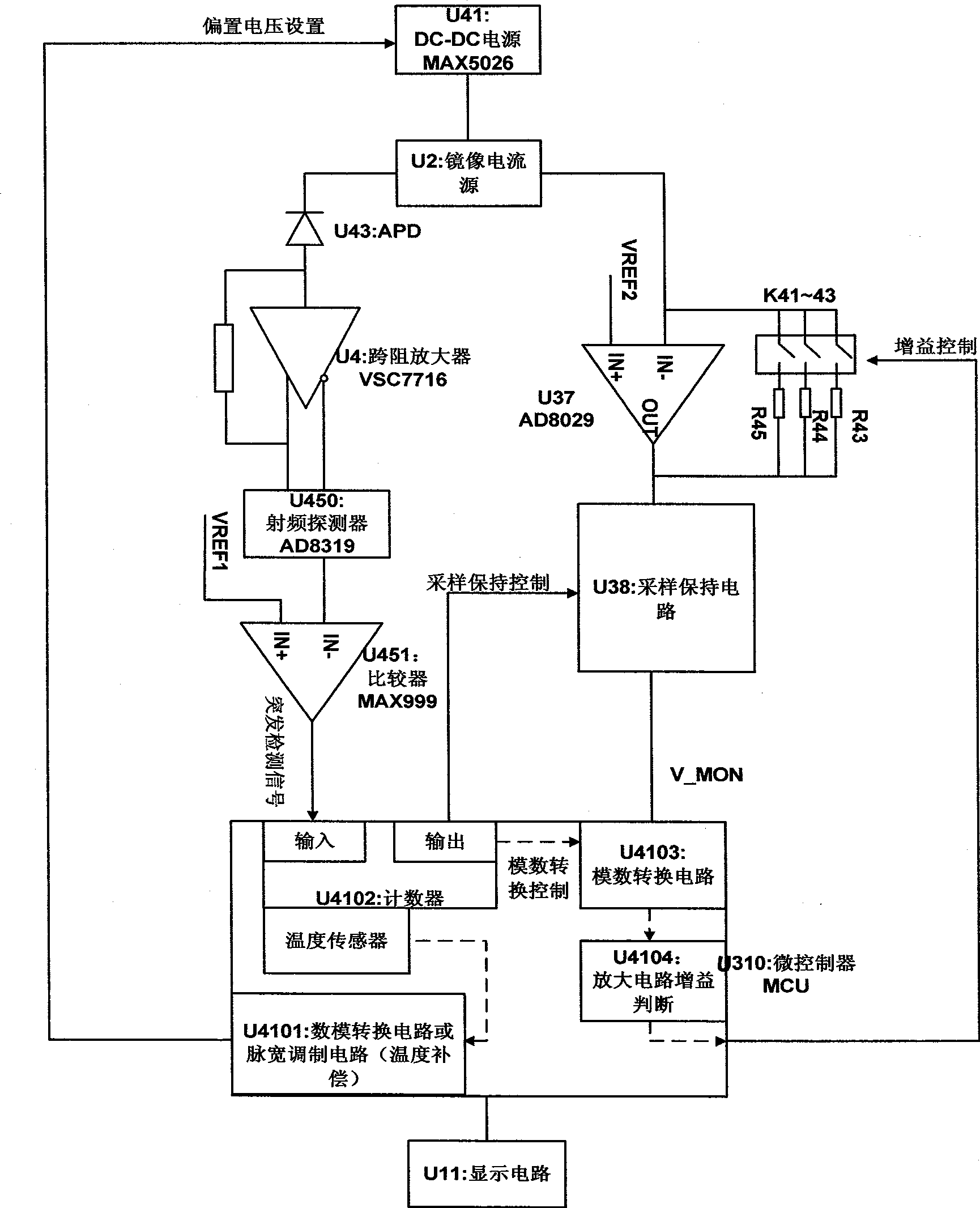
The invention discloses a burst mode optical signal power measuring circuit which comprises a photoelectric detector power supply, a mirror image current source and a subsequent circuit. The subsequent circuit is divided into a signal passage part and an optical power burst detecting part by the mirror image current source, wherein, in the signal passage part, optical current generates a burst detection signal by the photoelectric detector via a trans-impedence amplifier and a burst detection circuit, and the burst detection signal is used for triggering a time sequence generation circuit to generate a control time sequence for maintaining sampling and carrying out digital-to-analog conversion; in the optical power burst detection part, an amplifying circuit converts the mirror image current into a voltage signal; therefore, a sampling maintaining circuit and a digital-to-analog conversion circuit which are connected with the time sequence generation circuit can finish the burst detection of optical power under the control of the control time sequence. The burst mode optical signal power measuring circuit generates the mirror image current forming a proportion with the average optical current of the photoelectric detector by the mirror image current source, realizes the detection to the burst mode optical power under the control of the control time sequence, and can measure burst optical signal power with the length of hundreds of nanoseconds.
Owner:SUPERXON (CHENGDU) TECH LTD
Broadband radio frequency receiver
ActiveCN106788511AReduce complexityLarge dynamic rangeTransmissionTuned radio frequency receiverFinite impulse response
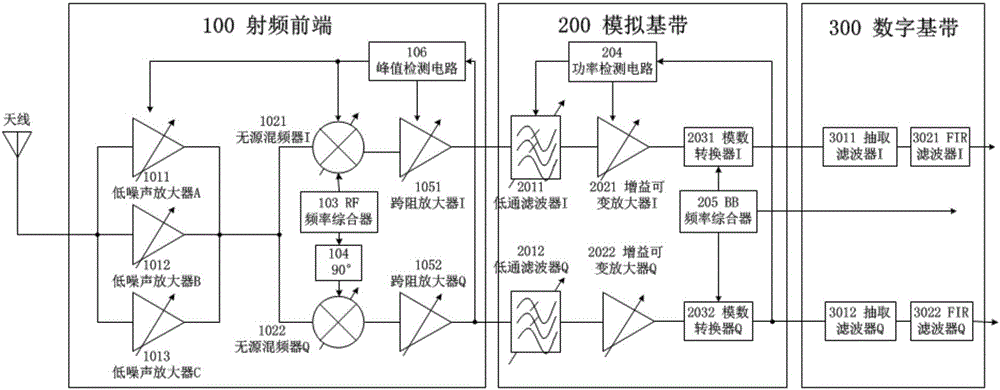
The invention relates to a broadband radio frequency receiver and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication electronics. The broadband radio frequency receiver comprises a radio frequency front end module, an analog base band module and a digital baseband module; a zero-intermediate frequency receiver structure with orthogonal down conversion frequency is adopted; a radio frequency input signal sequentially passes through a low noise amplifier, a passive mixer, a trans-impedance amplifier, a low pass filter, a gain variable amplifier, an analog-digital converter, a decimation filter and a finite impulse response (FIR) filter; multiple radio frequency input signals within 50MHz to 6.3GHz can be processed by switching a low noise amplifier group and configuring local oscillation frequency, a sampling clock, filter bandwidth and the like; an external band-pass filter is not needed, so that the complexity of the system is reduced and the integration level is improved; a working frequency band is widened, and the flexibility and the reliability of the system are improved; in addition, the dynamic range is widened by double loop automatic grain control of a peak detection circuit and a power detection circuit. The broadband radio frequency receiver can be designed into an IP (Internet Protocol) core monolithic integration or can be in an external cascade.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Package structure for photonic transceiving device
A photonic transceiver apparatus in Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) package. The apparatus includes a case having a base member, two partial side members, and a lid member to provide a spatial volume with an opening at a back end of the base member. Additionally, the apparatus includes a printed circuit board (PCB), installed inside the spatial volume over the base member having a pluggable electrical connector at the back end. Further, the apparatus includes multiple optical transmitting devices in mini-transmit-optical-sub-assembly package, each being mounted on a common support structure and having a laser output port in reversed orientation toward the back end. Furthermore, the apparatus includes a silicon photonics chip, including a fiber-to-silicon attachment module, mounted on the PCB and coupled to a modulation driver module and a trans-impedance amplifier module. Moreover, the apparatus includes a pair of optical input / output ports being back connected to the fiber-to-silicon attachment module.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
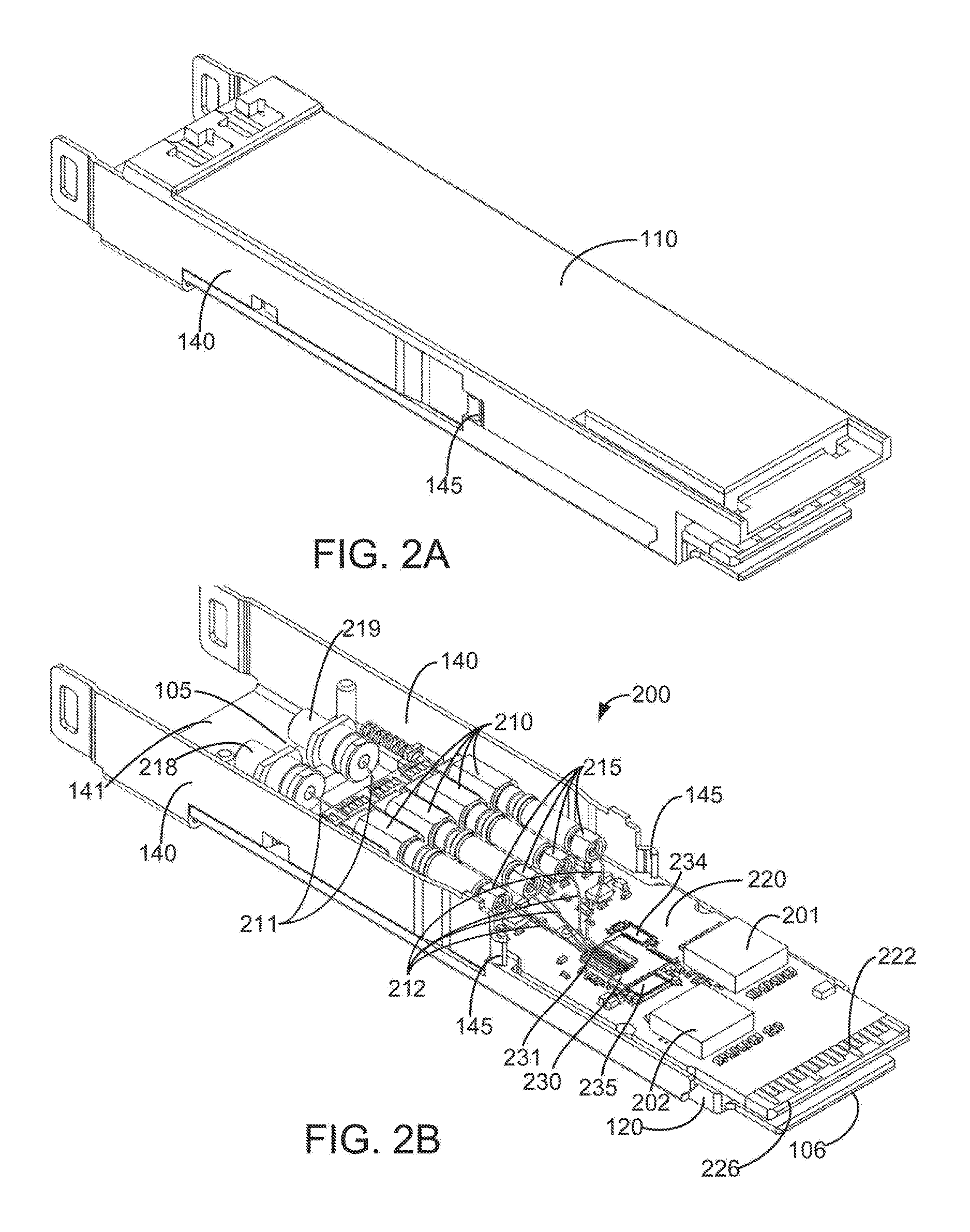
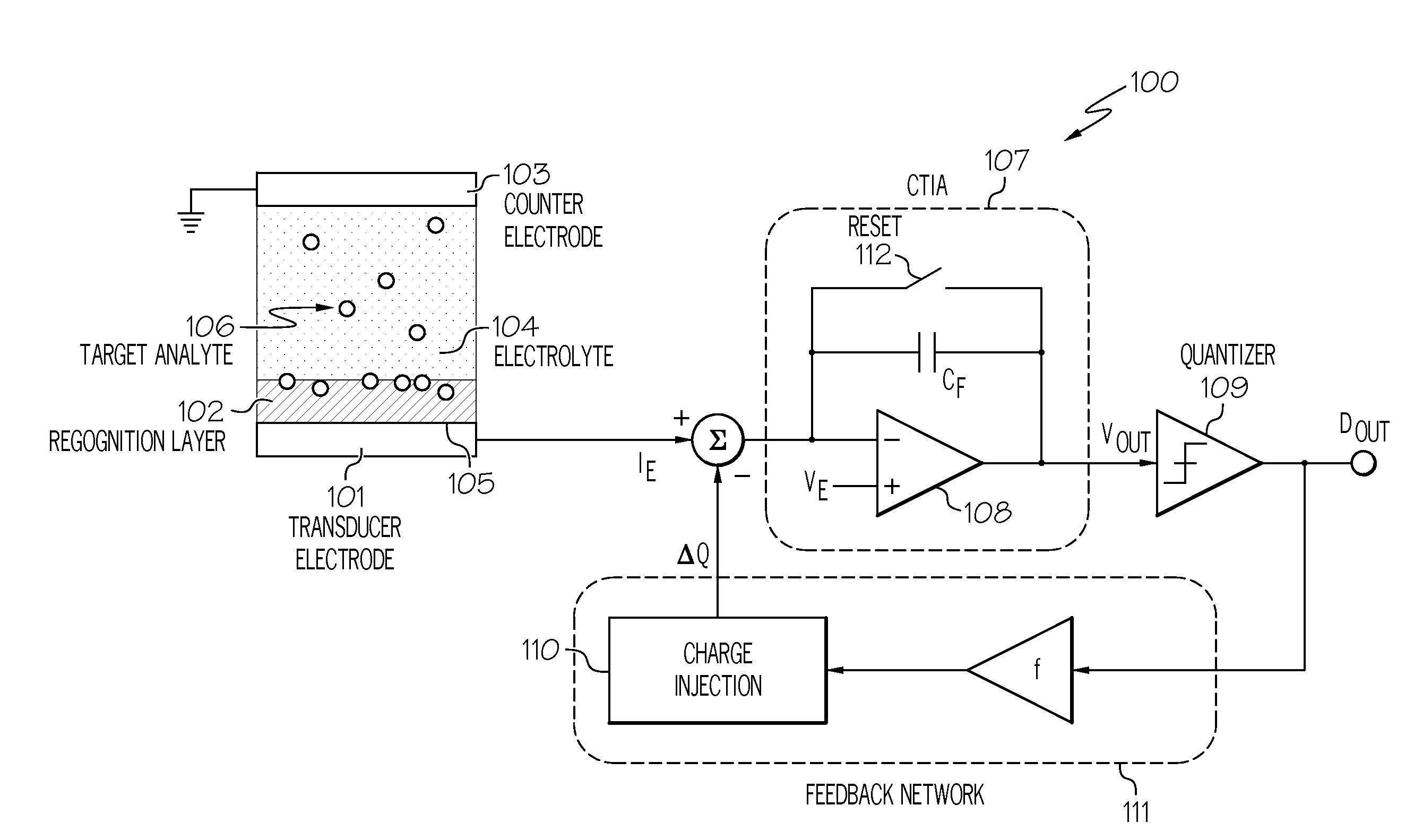
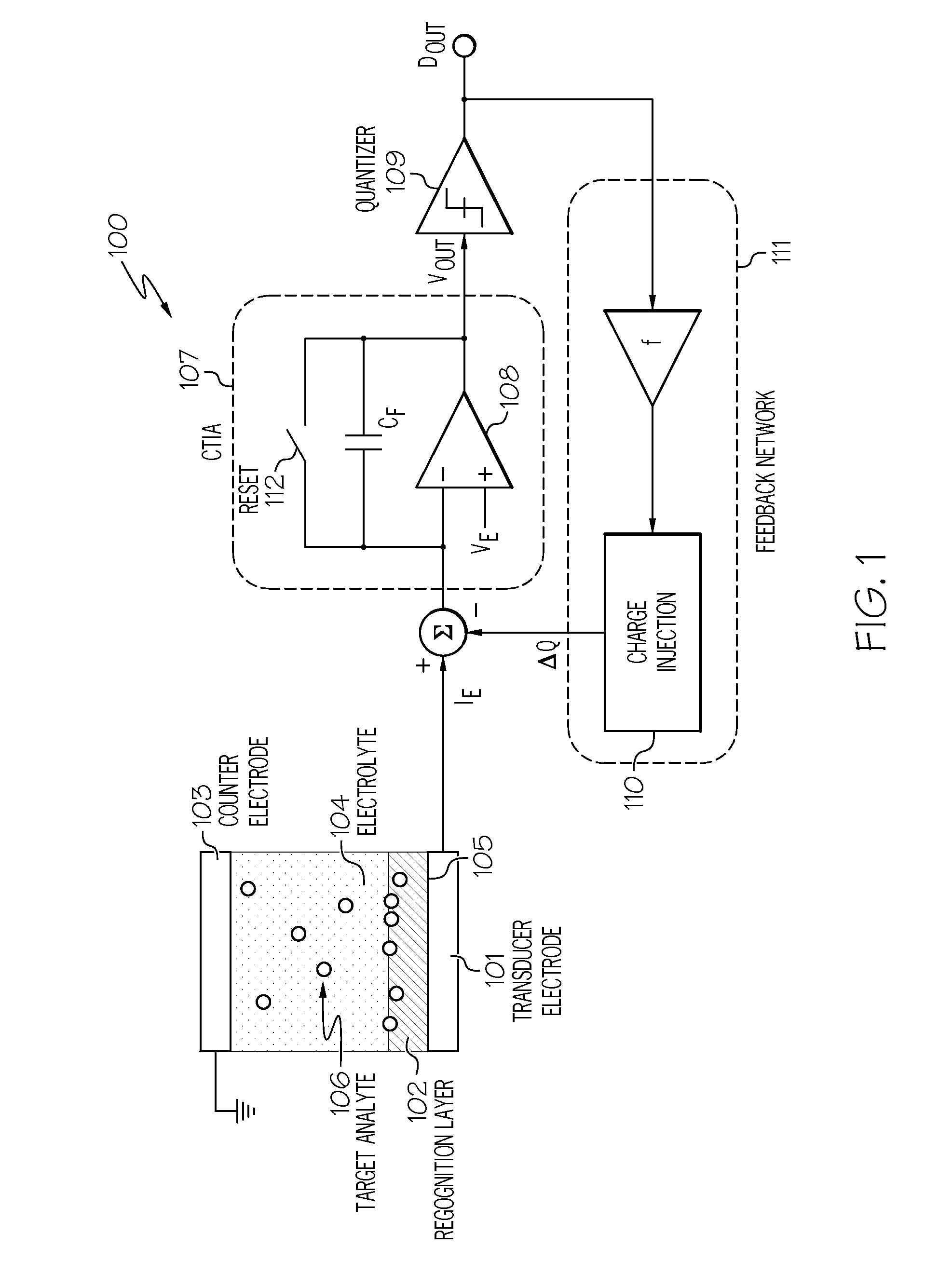
Integrated electro-analytical biosensor array
A biosensor pixel for measuring current that flows through the electrode surface in response to electrochemical interactions and a biosensor array architecture that includes such biosensor pixels. The biosensor pixel includes an electrode transducer configured to measure a current generated by electrochemical interactions occurring at a recognition layer placed directly on top of it in response to an electrical voltage placed across an electrode transducer-electrolyte interface. The biosensor pixel further includes a trans-impedance amplifier connected to the electrode transducer, where the trans-impedance amplifier is configured to convert the current into a voltage signal as the electrochemical interactions occur. Additionally, the biosensor pixel includes a 1-bit comparator coupled to the trans-impedance amplifier and a 1-bit digital-to-analog converter coupled to the 1-bit comparator, where the 1-bit digital-to-analog converter injects different levels of charge into an input of the trans-impedance amplifier at each cycle based on an output of the 1-bit comparator.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Photonic transceiving device package structure
ActiveUS9496959B1Improve cooling efficiencyEasy accessWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesFiberSilicon photonics
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Integrated Coherent Receiver Having a Geometric Arrangement for Improved Device Efficiency
ActiveUS20160285561A1Efficient and reliable assembly processIssue to overcomeFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesPhase shiftedComputer module
Disclosed herein is a monolithically integrated coherent receiver chip which has a geometric arrangement of the on-chip components that significantly improves the performance and the manufacturability of a coherent receiver module for Dual Polarization Quadrature Phase Shift Keyed (DP-QPSK) applications and other optical coherent detection systems. The coherent receiver chip comprises two optical hybrids, three optical inputs and eight electrical outputs with the two optical hybrids oriented perpendicular to the optical inputs and the electrical outputs which are widely spaced and arranged in a co-linear fashion that simplifies module design and assembly. The proposed geometric arrangement also replaces any optical waveguide crossings with vertical electrical-optical crossings and includes electrical transmissions which are used to minimize channel skew. The proposed configuration also has the additional benefit of improved thermal management by separating the module's trans-impedance amplifiers.
Owner:O NET COMM (SHENZHEN) LTD
Micro-mechanical resonant electrometer with ultra-high sensitivity
ActiveCN106645999AHigh sensitivityReduce the amplitudeElectrical measurementsBand-pass filterClosed loop
The invention, which belongs to the MEMS field, discloses a micro-mechanical resonant electrometer with ultra-high sensitivity. The method comprises a mechanical structure design method of an electrometer header and a testing circuit design method. Compared with the prior art using a movable resonator charge input polar plate, the mechanical structure design enables the conversion efficiency between the electrostatic force and the axial stress to be improved; and with a micro-mechanical lever, the electrostatic force increases to improve mechanical sensitivity. When an external charge is inputted, rigidity disturbance on a resonator I increases and thus the localization phenomenon of the mode becomes dramatic. Meanwhile, the two provided resonators with different structures employ differential detection structures; the differential amplification circuit is used for detecting the amplitudes of the resonators and eliminating feed-through signals, so that the signal to noise ratio of the detection signal can be improved. In terms of the testing circuit design, a closed-loop testing plane is employed. To be specific, a signal at a detection electrode passes through a trans-impedance amplifier, a subtracter, a band-pass filter and a comparator and then is loaded at an alternating-current drive electrode to form a closed loop; rectification and filtering are carried out on two paths of outputs of the subtracter and dividing is carried out to obtain a direct-current voltage signal reflecting an amplitude ratio of two resonators. With a closed-loop drive detection circuit, the amplitude and frequency noise of the resonator can be reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
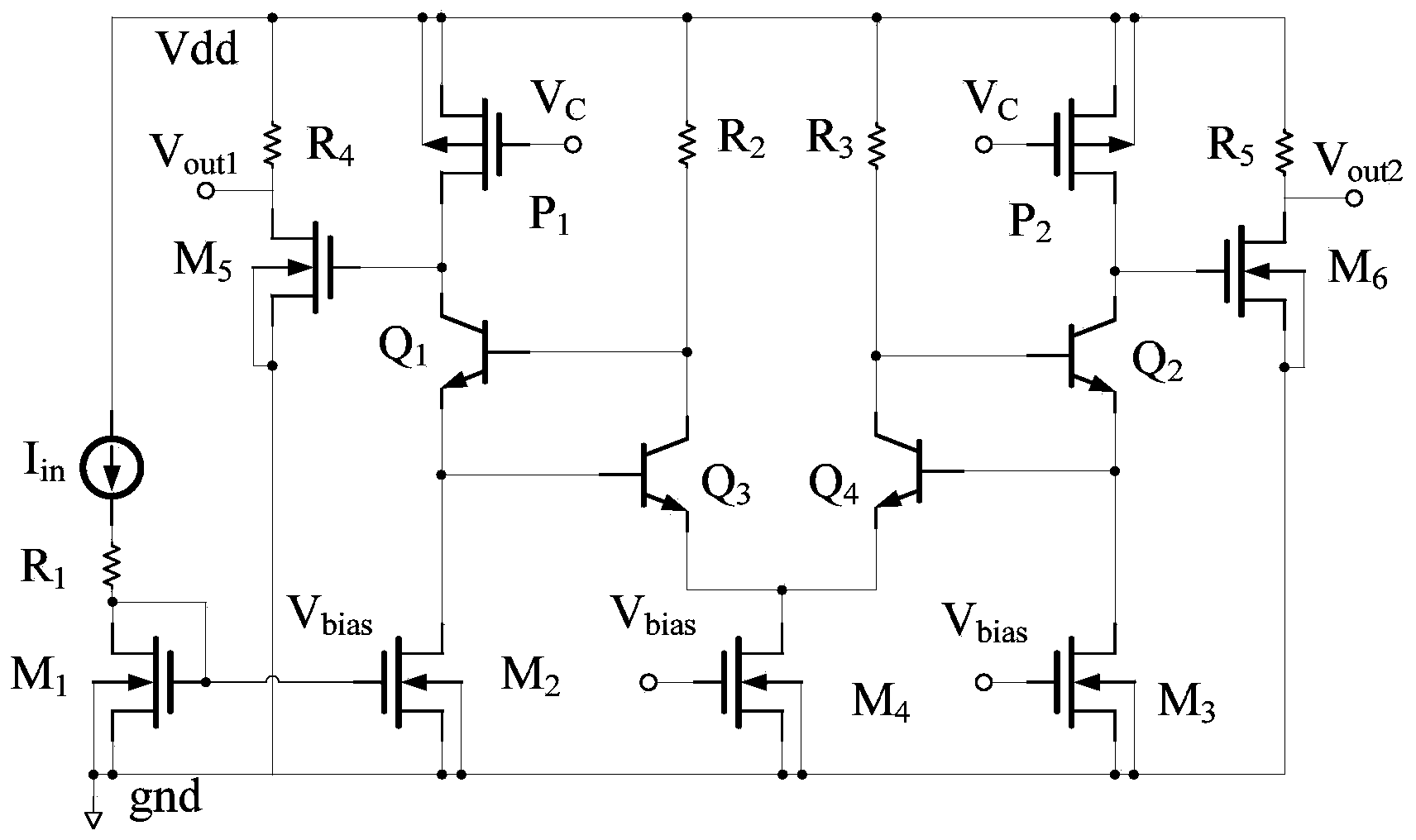
Trans-impedance amplifier with low noise and high gain-bandwidth product
ActiveCN101505140AWide signal bandwidthIncrease signal gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifiers controlled by lightCapacitanceLow noise
The invention provides an optical-receiver preamplifier for receiving analog or digital optical signals. The preamplifier comprises a high-gain amplifier A1, an input circuit, a negative-feedback impedor Zf, a low-gain amplifier A2 adjustable in gain and a feedback capacitor Cff, wherein the input circuit takes a photoelectric converter as a main component; the negative-feedback impedor Zf is connected with the reverse input end and the output end of the A1; the feedback capacitor Cff connects the output end of the A2 with the reverse input end of the A1; and the output end of the A1 can be directly connected with the input end of the A2 or can be connected with the input end of the A2 through a buffer. Output signals of the preamplifier are taken out from the output end of the A1 or the output end of the buffer, and can be directly subjected to subsequent signal processing or be further amplified and then subjected to subsequent signal processing.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
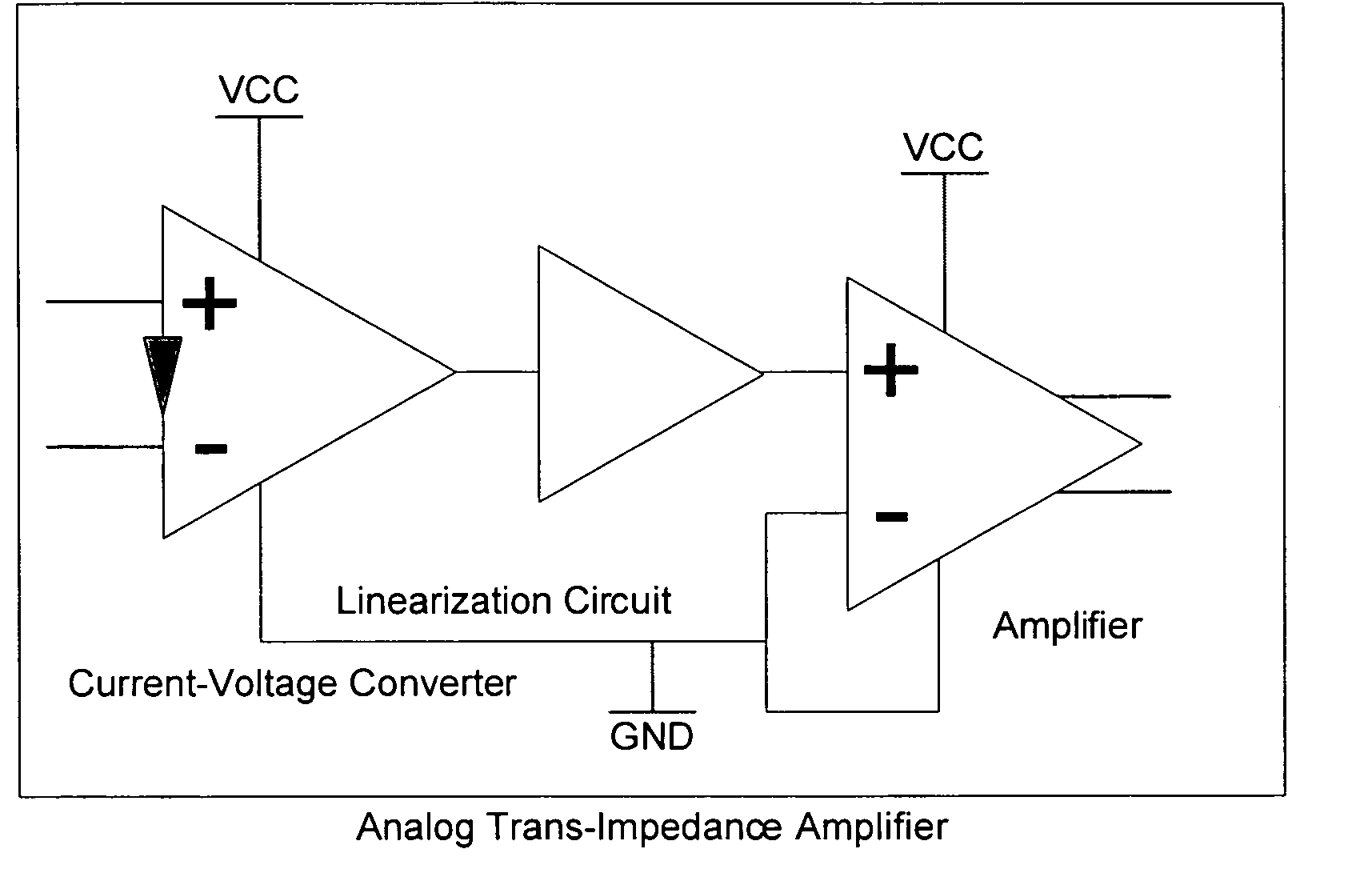
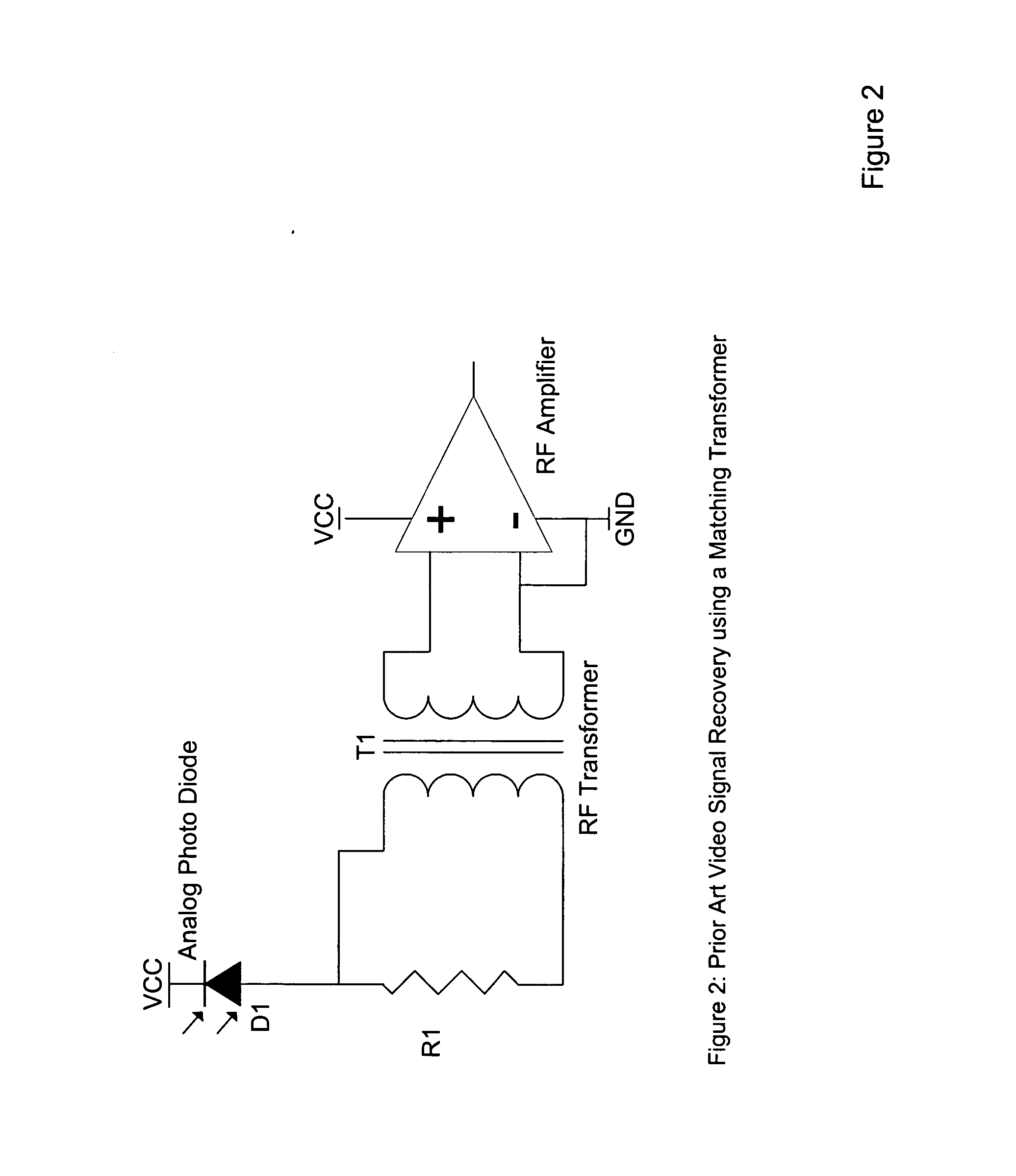
Linearized trans-impedance amplifier
InactiveUS20050195038A1Fast overload recoveryImprove accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceSmall amplitudeFiber
The disclosed systems and methods utilize an advanced linearized trans-impedance amplifier (ATIA) that allows for the recovery and amplification of low amplitude analog and digital signals. This disclosure further describes unique approaches of addressing issues inherent in the transmission and reception of small amplitude multi-carrier signals used for distribution of voice, video, and data communications over both fiber optic cables and free space transmitters
Owner:PARSEC TECH
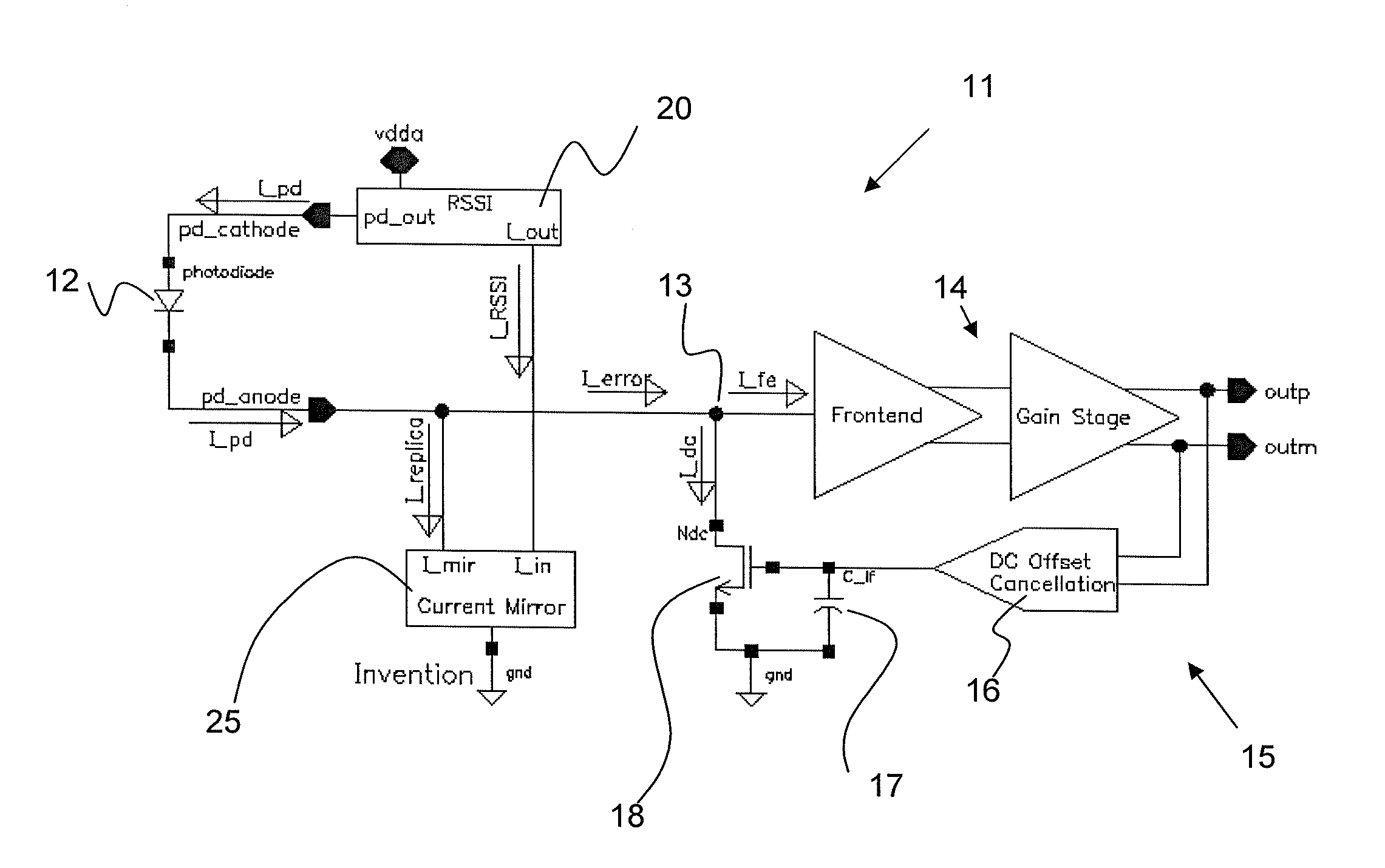
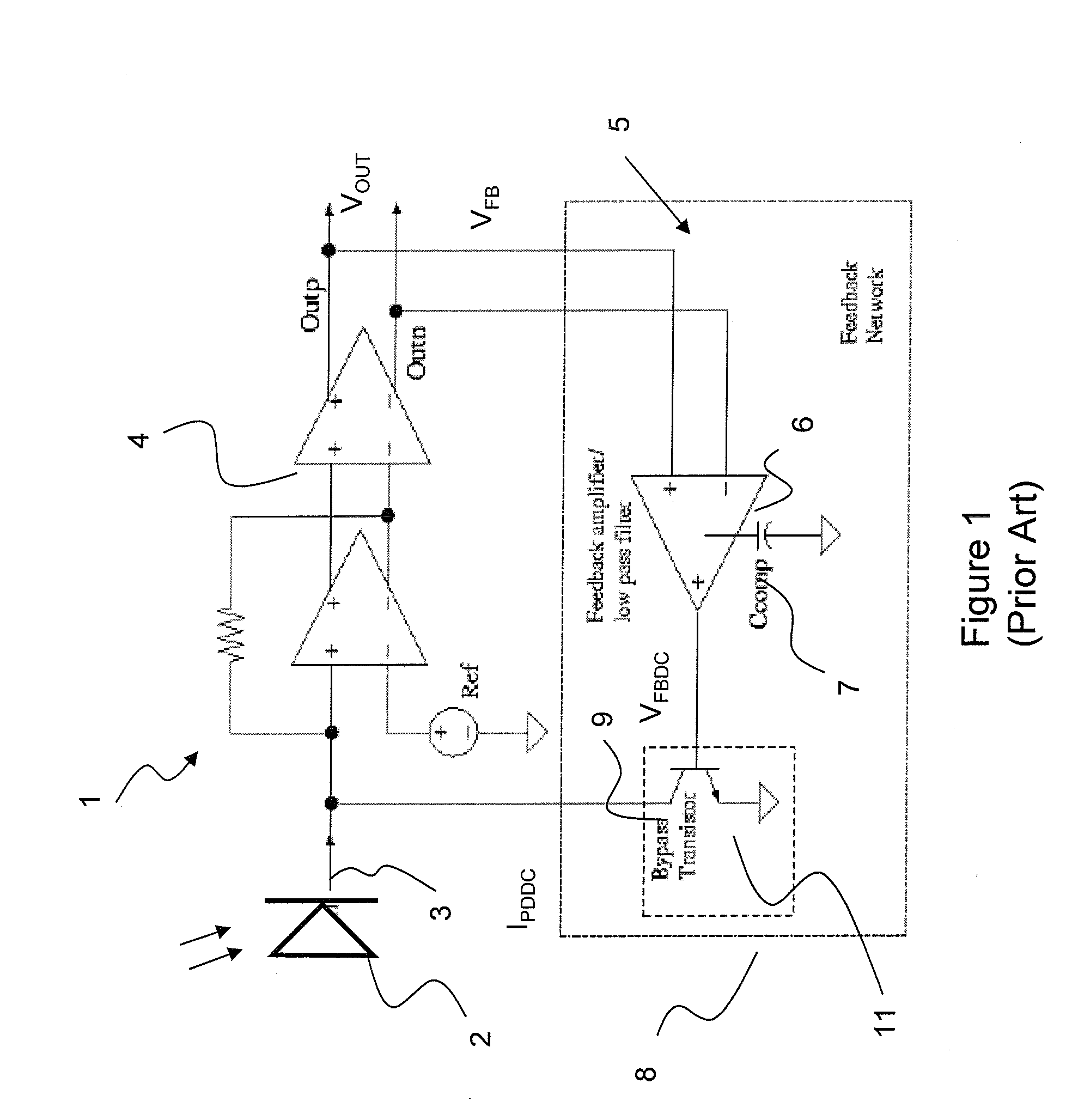
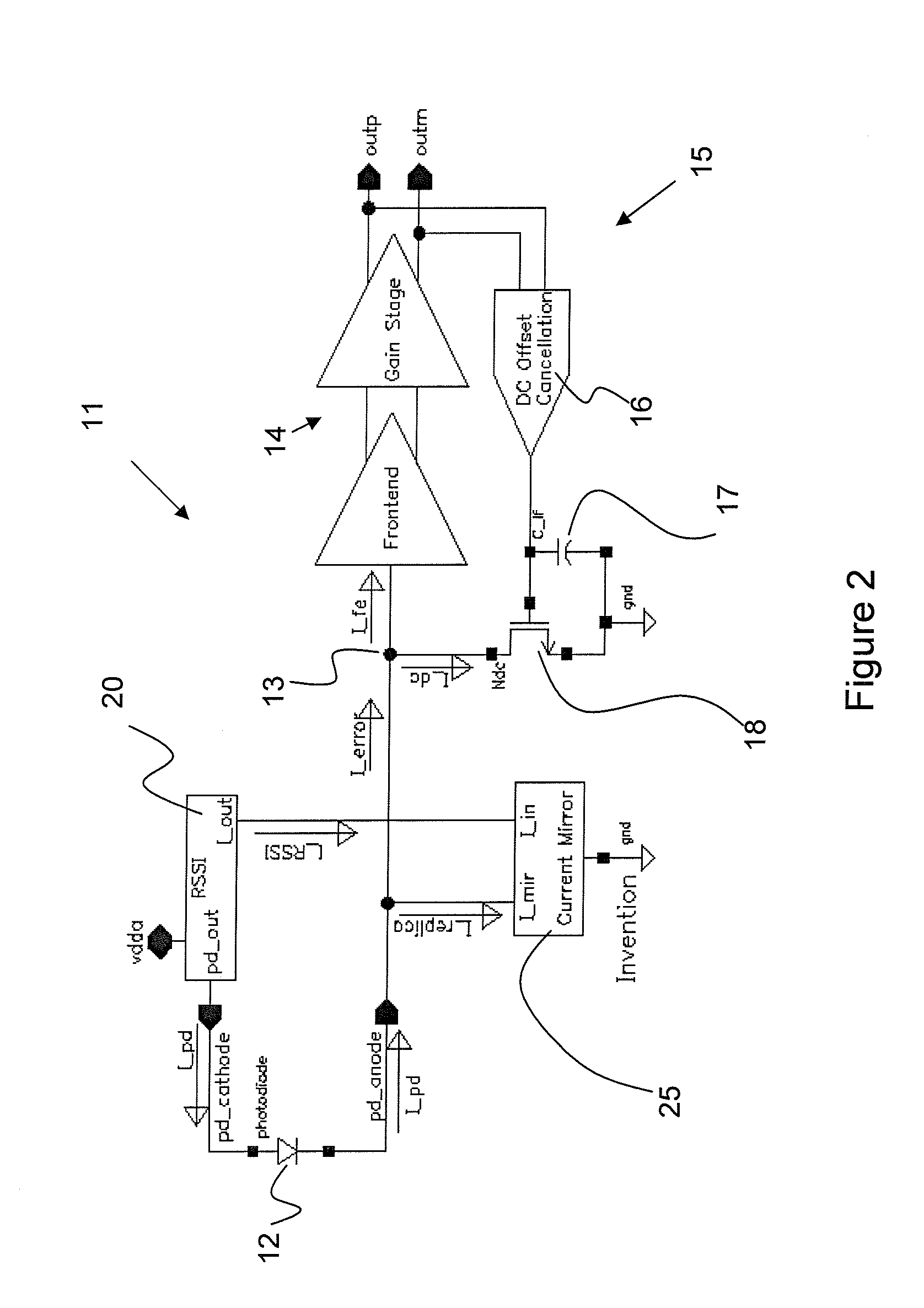
DC Offset Cancellation For A Trans-Impedance Amplifier
ActiveUS20080007344A1Gain controlAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierOffset cancellation
The invention relates to a DC offset cancellation circuit for a trans-impedance amplifier, which is typically used for converting an input current from a photodiode into an output voltage. The DC offset cancellation circuit utilizes the monitor current from a photodiode monitoring device to cancel the DC offset from the photodiode input current, enabling the conventional feedback circuit in the trans-impedance amplifier to be fully integrated.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
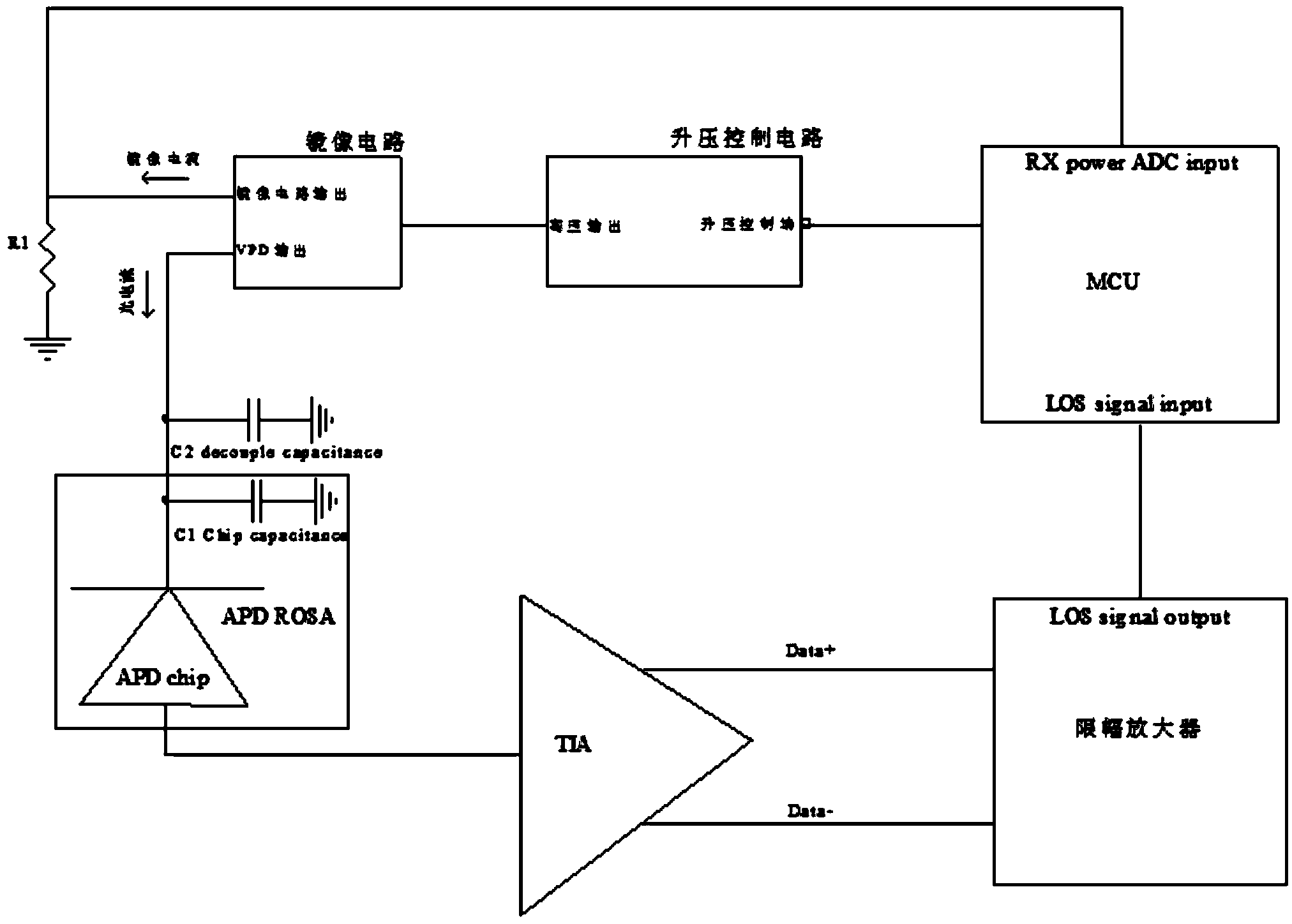
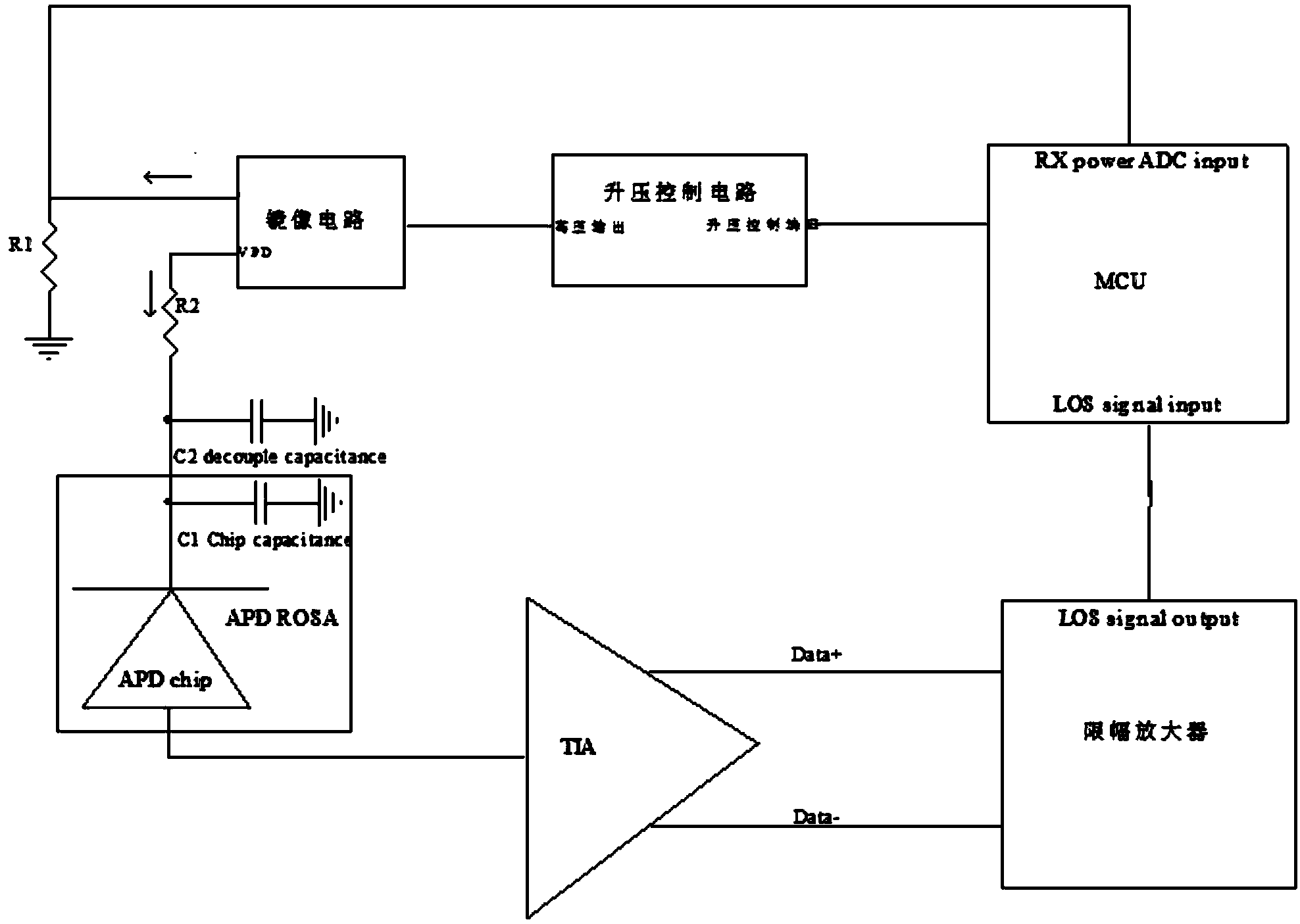
Circuit, optical module and method for protecting APD receiver
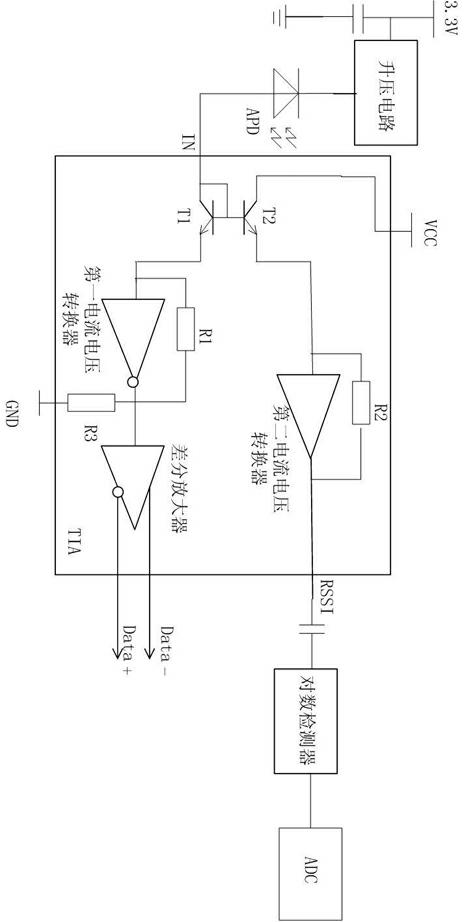
ActiveCN104320200AReduce bias voltageReduce the multiplication factorElectromagnetic receiversCapacitanceHemt circuits
The invention discloses a circuit for protecting an APD receiver. The circuit comprises the APD receiver, wherein the bias input end of the APD receiver is grounded through a first decoupling capacitor and a second decoupling capacitor, the bias input end of the APD receiver is connected with a first output end of a mirror image circuit, the input end of the mirror image circuit is connected with the output end of a boost control circuit, and the input end of the boost control circuit is connected with a microprocessor; the second output end of the mirror image circuit is grounded through a first resistor and meanwhile connected to the microprocessor; the microprocessor is connected with a signal losing LOS end of a limiting amplifier which is connected with a trans-impedance amplifier (TIA), the TIA is connected with the output end of the APD receiver, a second resistor is connected between the bias input end of the APD receiver and the first output end of the mirror image circuit, and the resistance value of the second resistor ranges from 10 K ohm to 100 K ohm. Through the circuit, an APD can be effectively protected against damage, the risk that a module loses efficacy is reduced, and the service life of the optical module is prolonged.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS CHENGDU
Low noise trans-impedance amplifiers based on complementary current field-effect transistor devices
ActiveUS20180219519A1High precisionIncrease speedLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceLow noiseAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a novel and inventive compound device structure for a low noise current amplifier or trans-impedance amplifier. The trans-impedance amplifier includes an amplifier portion, which converts current input into voltage using a complimentary pair of novel n-type and p-type current field-effect transistors (NiFET and PiFET) and a bias generation portion using another complimentary pair of NiFET and PiFET. Trans-impedance of NiFET and PiFET and its gain may be configured and programmed by a ratio of width (W) over length (L) of source channel over the width (W) over length (L) of drain channel (W / L of source channel / W / L of drain channel).
Owner:CIRCUIT SEED LLC
400 Gbps hot-plug high-speed optical transceiver module
ActiveCN104601244ARealize transmissionReduced assembly stepsElectromagnetic transceiversShortest distanceEngineering
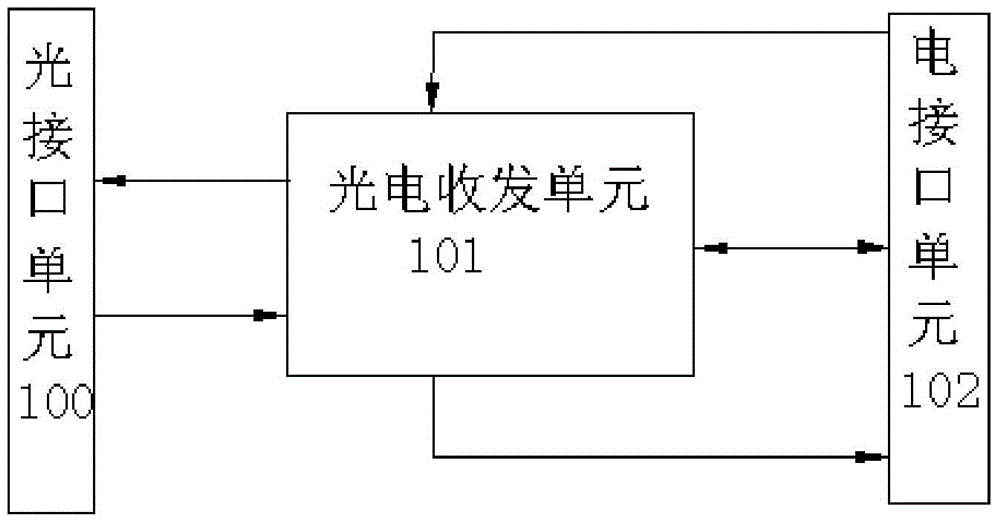
The invention provides a 400 Gbps hot-plug high-speed optical transceiver module which is suitable for the optical communication technical field. The 400 Gbps hot-plug high-speed optical transceiver module comprises an optical interface unit, a photoelectric transceiver unit and an electrical interface unit; the photoelectric transceiver unit is used for achieving the functions of photoelectric conversion and high-speed electrical signal processing through a photoelectric transceiver chip; the internal working process of the photoelectric transceiver chip comprises receiving an electrical signal input through the electrical interface unit by a transmitting terminal data clock recovery circuit, loading the electrical signal to a laser after the pretreatment through a driving circuit, converting the high-speed electrical signal into a high-speed optical signal through the laser, reusing the high-speed optical signal through a wavelength division multiplexer to be output, reusing the received optical signal into a 16-channel optical signal through a wavelength division demultiplexer to be transmitted to an optical detector and transmitting the 16-channel optical signal to a trans-impedance amplifier and a receiving terminal data clock recovery circuit after photoelectric conversion to be processed. According to the 400 Gbps hot-plug high-speed optical transceiver module, the factors such as the cost, the transmission loss, the chromatic dispersion and the size are considered to select different optical transceiver modules and accordingly the long-distance single-mode optical fiber transmission or the short-distance multimode transmission is implemented.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
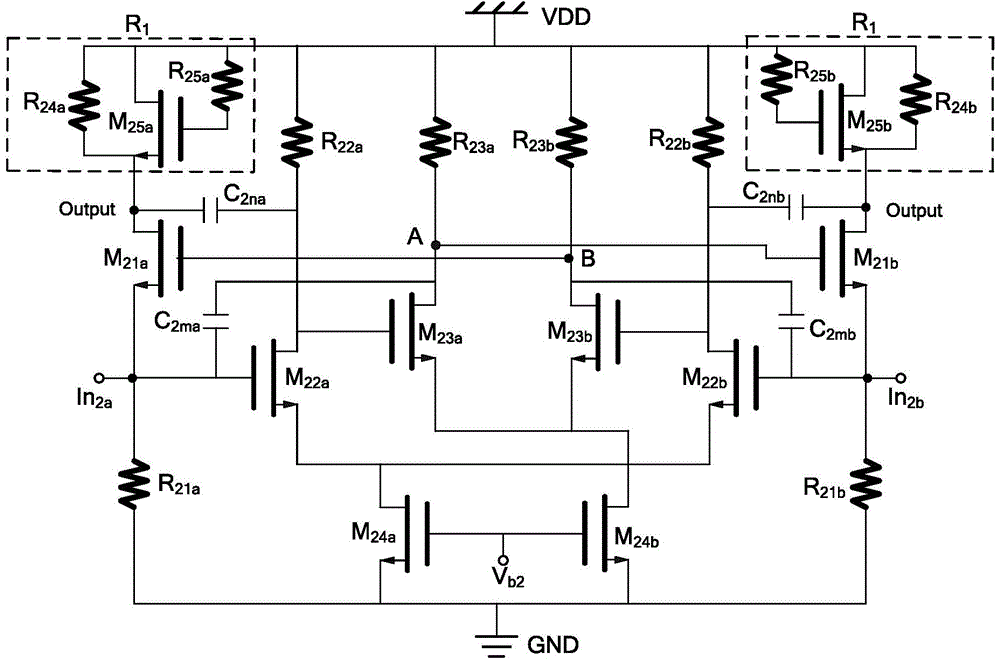
High-gain and low-noise differential trans-impedance amplifier
ActiveCN104113293ASimple structureFew tubesDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesLow noiseNegative feedback
The invention provides a high-gain and low-noise differential trans-impedance amplifier. The high-gain and low-noise differential trans-impedance amplifier comprises a current mirror, an adjusting type common-emitter and common-base trans-impedance amplifier and an output common-source amplifier, wherein the adjusting type common-emitter and common-base tarns-impedance amplifier comprises a common-base amplifying unit and a negative feedback common-emitter amplifying unit; the negative feedback common-emitter amplifying unit is arranged between an emitter and a base of the common-base amplifying unit and serves as a negative feedback channel; input current is copied by the current mirror in an equal proportion manner; the current mirror provides bias voltage for the common-base amplifying unit and the negative feedback common-emitter amplifying unit; the output common-source amplifier is connected between an output end of the adjusting type common-emitter and common-base trans-impedance amplifier and an output end of the high-gain and low-noise differential trans-impedance amplifier; and trans-impedance gain is increased. By the high-gain and low-noise differential tarns-impedance amplifier, received weak signals are amplified in a high-gain and low-noise manner, bandwidth is large, and a dynamic range of inputted current signals are reasonably set; and the high-gain and low-noise differential tarns-impedance amplifier has the advantages of easiness in design and monolithic integration.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
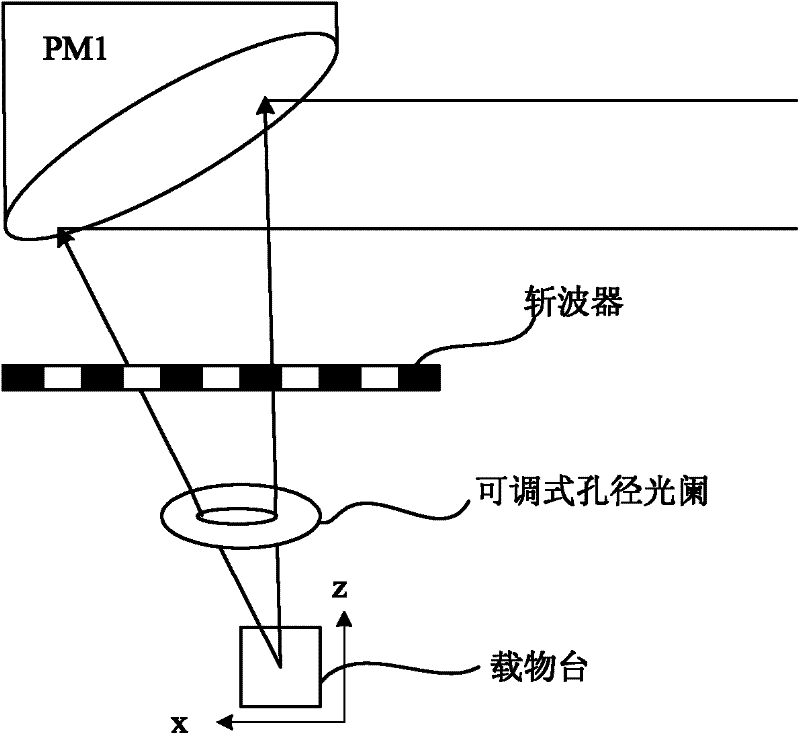
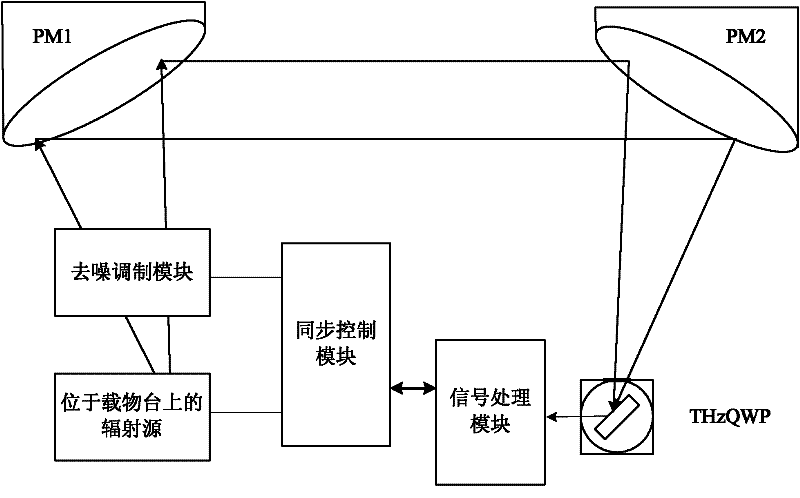
Passive thermal imaging detection system and method based on terahertz quantum well detector
ActiveCN102288299ARealize comprehensive applicationPyrometry using electric radation detectorsQuantum wellPhotodetector
The invention discloses a terahertz quantum well photodetector (THzQWP)-based passive thermal imaging detection system and a method thereof. A photoconduction THzQWP is taken as a photodetector, a self-designed radiation signal denoising modulation method, a synchronous control module and a signal transmission-convergence light path are adopted, and THzQWP-based passive thermal imaging detection is finished; a thermal radiation signal is modulated by an adjustable aperture diaphragm and a wave chopper at an acquisition end of the thermal radiation signal, and the modulation frequency is set by the wave chopper; a photoconduction mode is adopted at a signal detection circuit end of the THzQWP, the THzQWP receives the radiation signal through an off-axis parabolic mirror group convergence light path and extracts a THz signal, stable bias voltage is applied, THzQWP photocurrent is converted into voltage by a transimpedance amplifier, the voltage is amplified by a low noise amplifier, anddata is read by a phase-locked amplifier; and the read signal is recorded and processed by the synchronous control module, and thermal image information is acquired finally.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
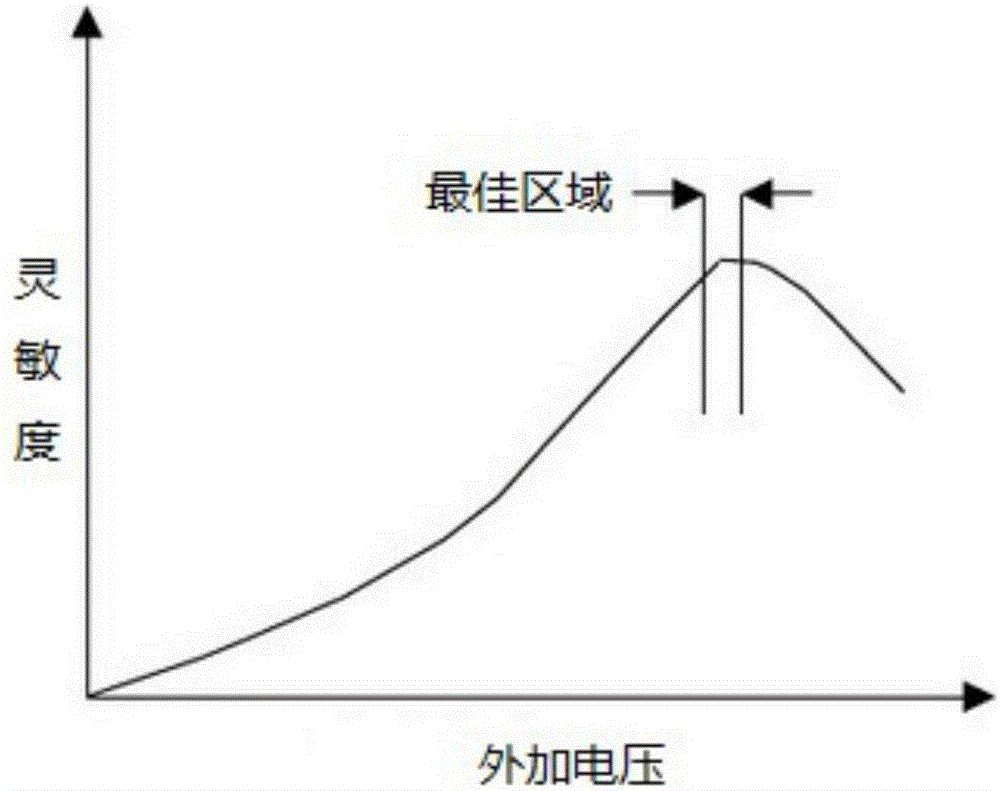
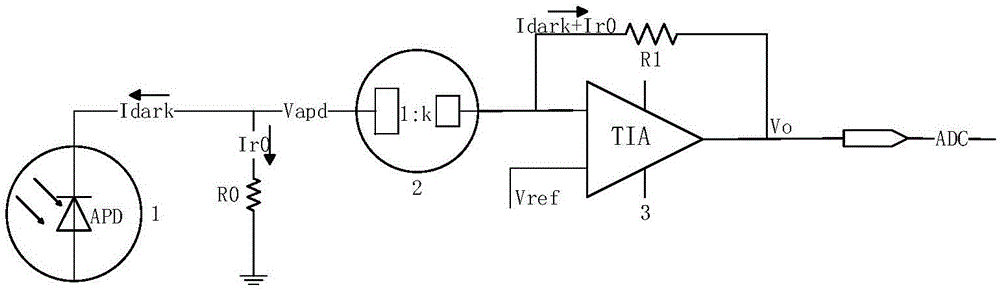
Method for calculating APD breakdown voltage and circuit thereof
ActiveCN106841970AImprove production yieldShorten the timeDiode testingAudio power amplifierOptical Module
The present invention provides a method for calculating APD breakdown voltage and a circuit thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding reserve voltage Vapd on an APD in a condition without light; 2, dark current (Idark) generated by the APD flows into a trans-resistance amplifier (3) after passing through a current mirror (2); 3, reversely calculating the dark current (Idark) through output voltage (Vo) of the trans-resistance amplifier (3); and 4, determining whether the dark current (Idark) of the APD is equal to 10 [Mu]A or not, if the dark current (Idark) of the APD is equal to 10 [Mu]A, allowing the APD at present to be the breakdown voltage of the APD, or else, repeatedly setting the Vapd, and returning back to the step 3. The method for calculating APD breakdown voltage and the circuit thereof can accurately find the Vbr of the APD so as to find reasonable reverse direction work voltage Vapd, are good in precision, efficiency and consistence, improve the yield rate of an optical module, improve production efficiency and reduce production cost.
Owner:CHENGDU SUPERXON COMM TECH CO LTD
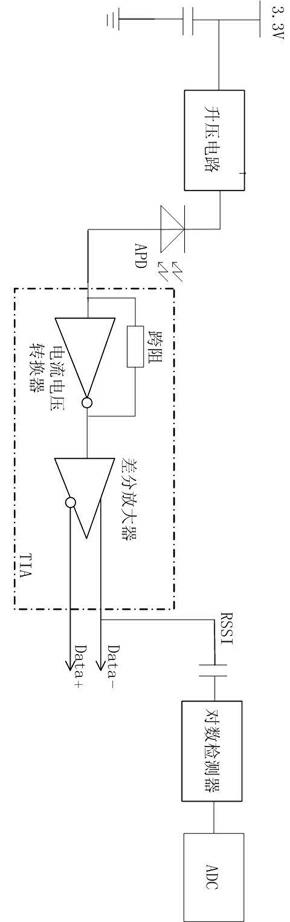
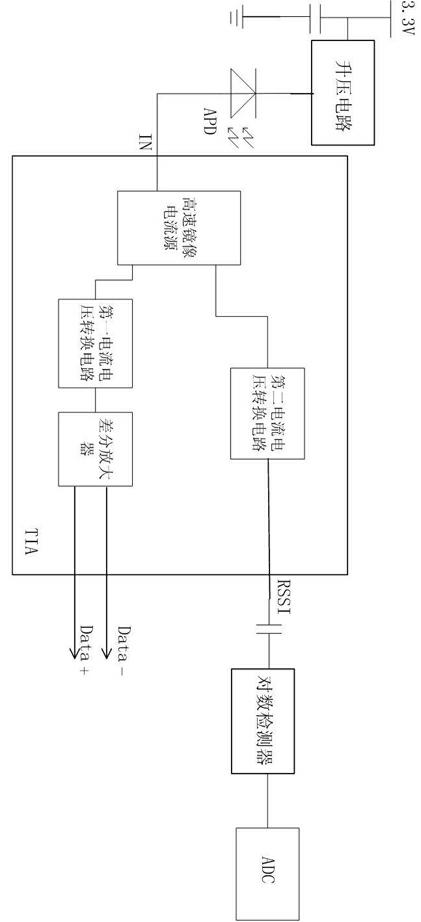
Transresistance amplifier with received signal strength indication (RSSI) function
InactiveCN102324899AImprove signal-to-noise ratioFacilitates optical power detectionAmplifiers controlled by lightElectric variable regulationEngineeringSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a transresistance amplifier with a received signal strength indication (RSSI) function. The transresistance amplifier is characterized in that an image current source and a second current voltage switching circuit are additionally arranged in an existing transresistance amplifier, so that an image current signal is generated and then converted into an image voltage signal used as an RSSI signal for output, thus the power loss brought by a differential amplifier device is eliminated; simultaneously the transresistance value of the second current voltage switching circuit ranges from 200ohm to 600ohm, thus the condition that the accuracy requirement of optical power detection cannot be met due to RSSI signal saturation caused by overlarge optical power can be prevented; and a BJT (bipolar junction transistor) image current source of a high-speed bandwidth small-signal triode is also used, so that the industrial cost is low while the speed requirement of signal high-speed transmission can be met; and finally the transresistance of a first current voltage switching circuit with a resistance value ranging from 800ohm to 2000ohm ensures that the signal-to-noise ratio of the differential amplifier is higher.
Owner:SUPERXON (CHENGDU) TECH LTD
Burst-mode optical receiver of differential output structure
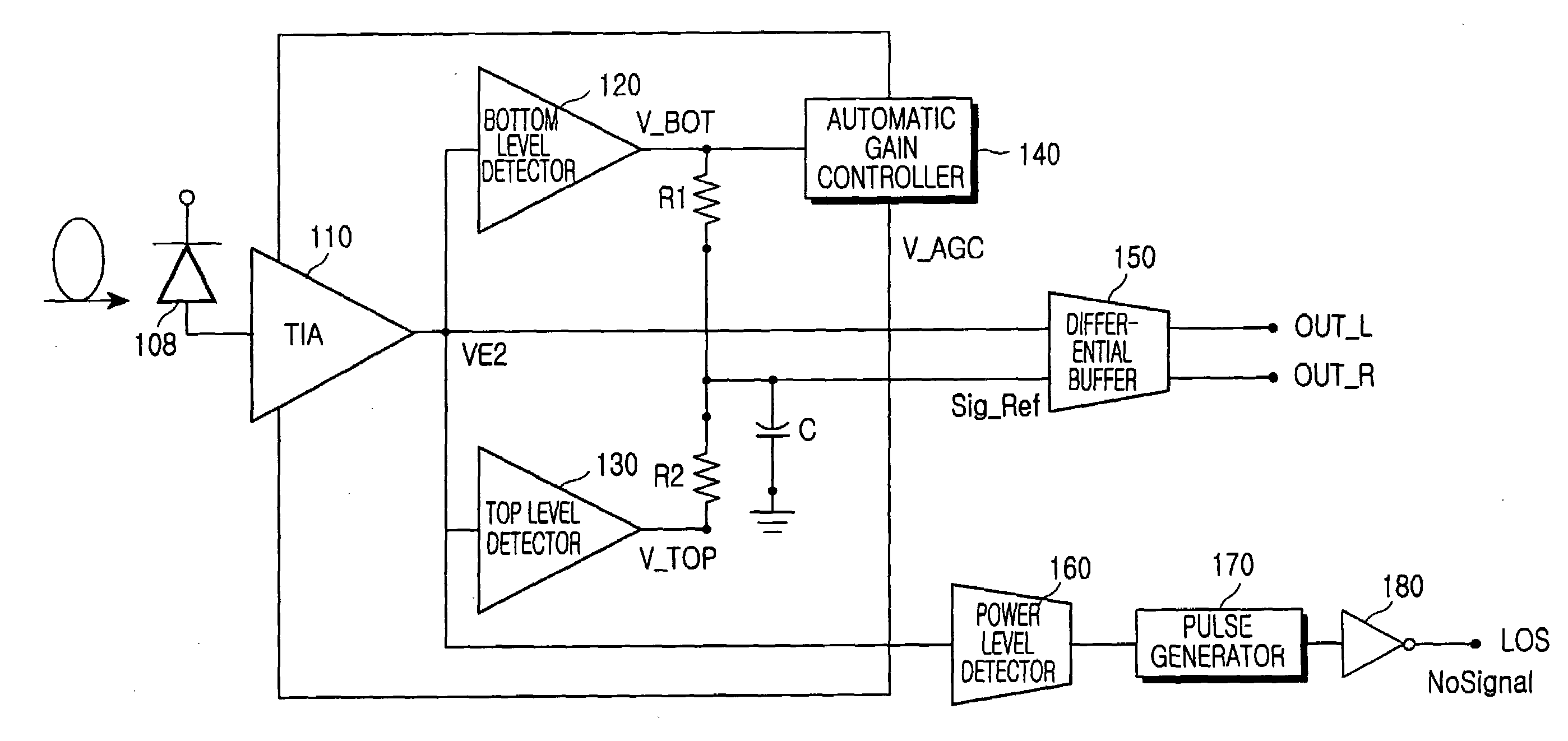
InactiveUS7218865B2Reduce distortionImprove receiver sensitivityGain controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAudio power amplifierEngineering
A burst-mode optical receiver of a differential-output structure is disclosed. The burst-mode optical receiver includes a trans-impedance amplifier for converting currents indicating the burst-mode signals into voltage signals, a bottom-level detector for detecting the bottom level of signals outputted from the trans-impedance amplifier, an automatic gain controller for automatically adjusting a gain to prevent the output waveforms of the tran-simpedance amplifier from being distorted after receiving the bottom-level signals detected by the bottom-level detector, a top-level detector for detecting the top level of signals outputted from the trans-impedance amplifier, a pair of resistors for generating a signal-reference voltage from the bottom- and top-level voltages, one side of each resistor being connected to the bottom- and top-level detectors, respectively, and the other sides of each resistor being connected to each other, and a differential buffer for receiving outputs from the trans-impedance amplifier and the signal-reference voltage from the pair of resistors and for eliminating the offsets generated from the bottom- and top-level detectors in order to supply two differential outputs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Signal intensity detection circuit of trans-impedance amplifier
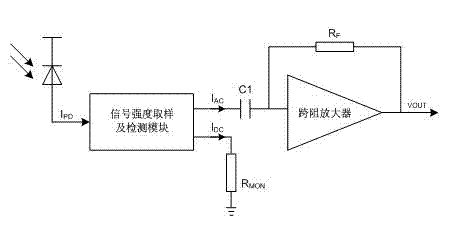
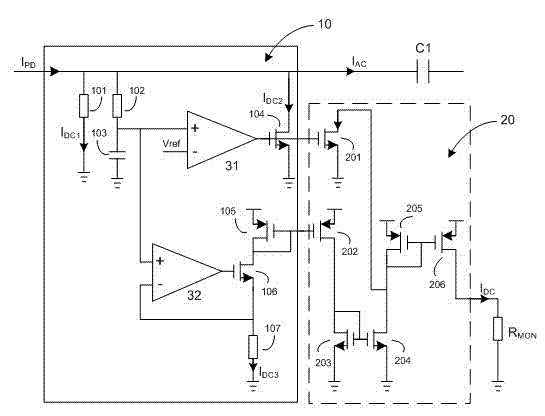
InactiveCN102890177AEliminate the effects ofAccurate detectionCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitancePhotocurrent
The invention provides a signal intensity detection circuit of a trans-impedance amplifier. The signal intensity detection circuit obtains a sampled signal from the output photocurrent IPD (Insertion Phase Delay) of a photoelectric diode (PD), and simultaneously separates the high-frequency component and the low-frequency component of the sampled signal from each other; the high-frequency component IAC enters a main trans-impedance amplifier module through a coupling capacitor C1, while the low-frequency component IDC is the signal intensity indication of the trans-impedance amplifier; and the main trans-impedance amplifier module achieves the trans-impedance amplification function of amplifying a tiny photocurrent to a voltage signal. The signal intensity detection circuit provided by the invention directly samples the input photocurrent signal and the detection result obtained in this way is quite correct; an adaptive nonlinear sampling circuit is adopted so that the detection accuracy is improved; simultaneously, the dynamic range of the input photocurrent is very wide; and the high-frequency component is separated from the photocurrent signal and fed into the main trans-impedance amplifier module; and therefore, the influence of the low-frequency component on the direct-current working point of the main trans-impedance amplifier module in the traditional structure is avoided.
Owner:武汉昊昱微电子股份有限公司
High-speed CMOS monolithic integration light receiver front end of cross coupling structure
InactiveCN104539373AHigh bandwidthImprove response isolationElectromagnetic receiversEngineeringVIT signals
The invention discloses a high-speed CMOS monolithic integration light receiver front end of a cross coupling structure. The high-speed CMOS monolithic integration light receiver front end comprises a photoelectric detector of a completely-symmetric structure, a trans-impedance amplifier of a difference structure, a direct current excursion eliminating unit, a three-stage sequence cascaded difference limiting amplifier and an output buffer stage; the trans-impedance amplifier of the difference structure is used for converting current signals output by the photoelectric detector into voltage signals and conducting preliminary amplification; the direct current excursion eliminating unit is used for eliminating direct current excursion led in by non-balanced signals at the input end of the trans-impedance amplifier and enables common mode levels at the output end of the trans-impedance amplifier to be coincident; the three-stage sequence cascaded difference limiting amplifier is used for amplifying the voltage signals output by the trans-impedance amplifier to be at the voltage level needed by a digital processing unit. Through the adoption of the cross coupling structure, the noise in-phase counteraction technology and the parallel type active inductor design, a high-speed and high-sensitivity standard CMOS monolithic integration light receiver can be achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pre-amplifier for an optical communication
ActiveUS20050140454A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention provides an optical receiver operable for optical signals each having different transmission speed. The optical receiver includes a light-receiving device, a pre-amplifier, a main amplifier, and a control circuit. The pre-amplifier, may be a trans-impedance amplifier, includes a parallel connection of a switching device and a resistor in a trans-impedance or a load element. By switching ON / OFF the switching device, the gain and the bandwidth of the pre-amplifier may be changed. By providing a filter circuit, whose cut-off frequency may be switched, in the main amplifier, the bandwidth of the optical receiver may be varied.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
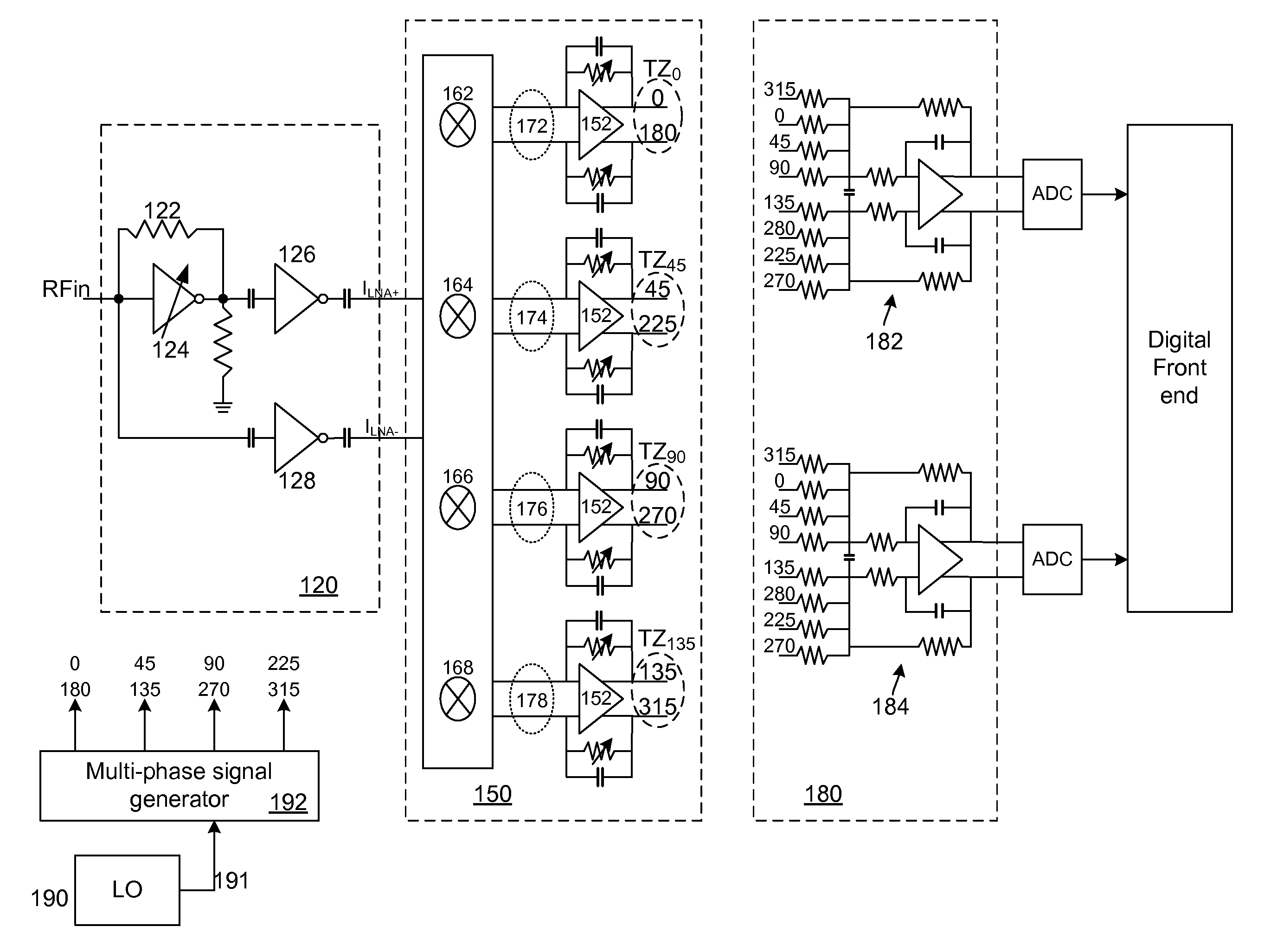
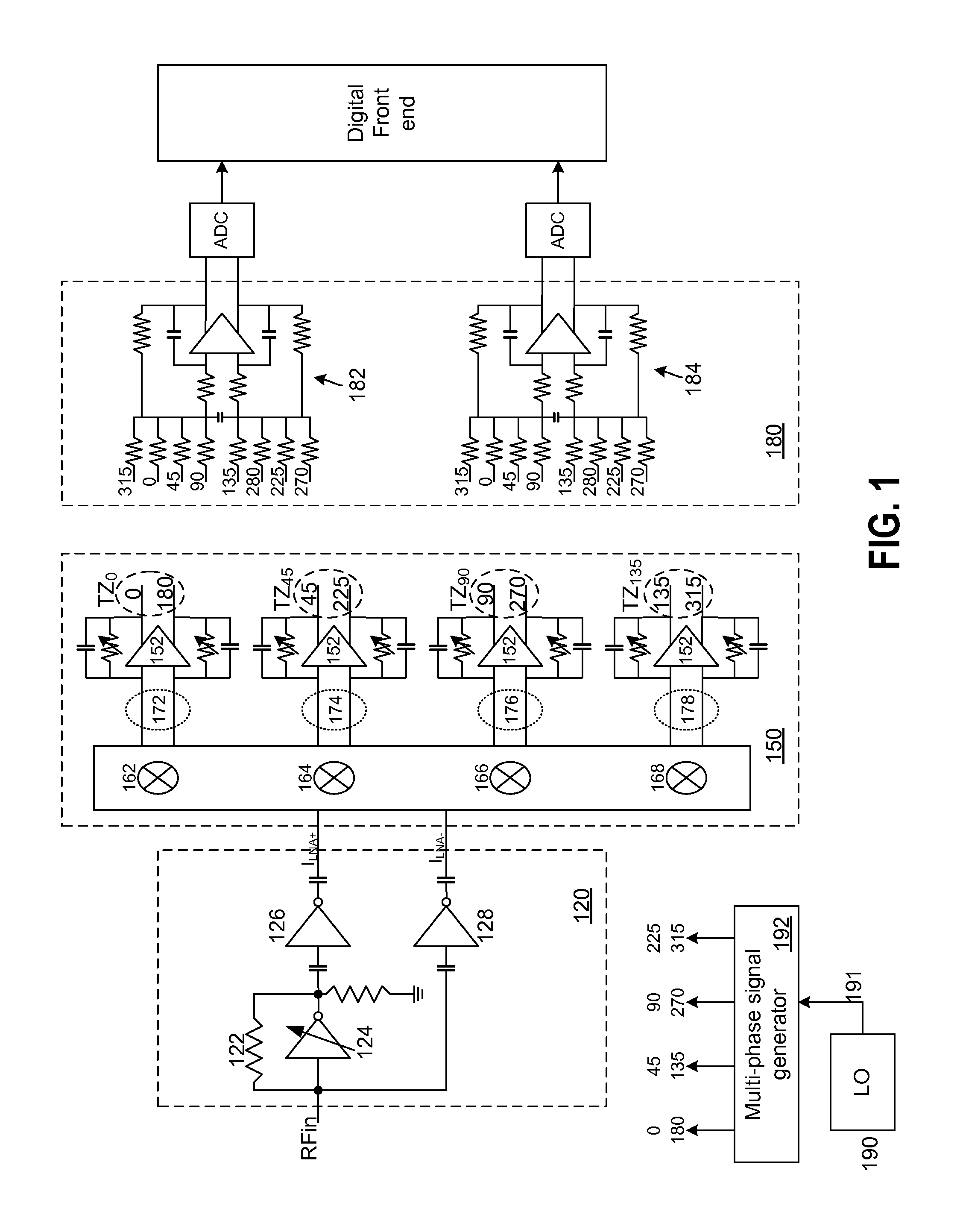
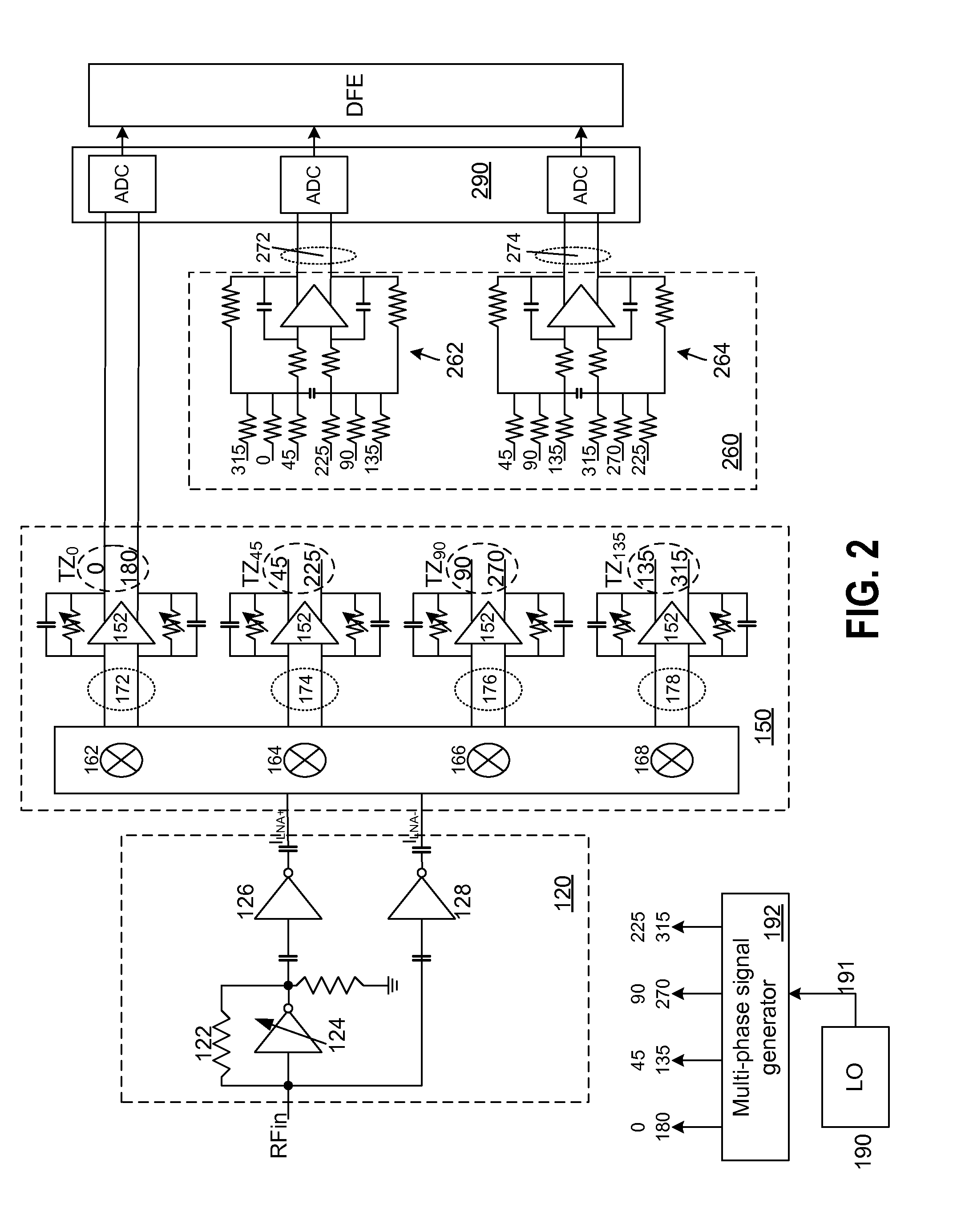
High dynamic range radio architecture with enhanced image rejection
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Differential Optical Receiver for Avalanche Photodiode and SiPM
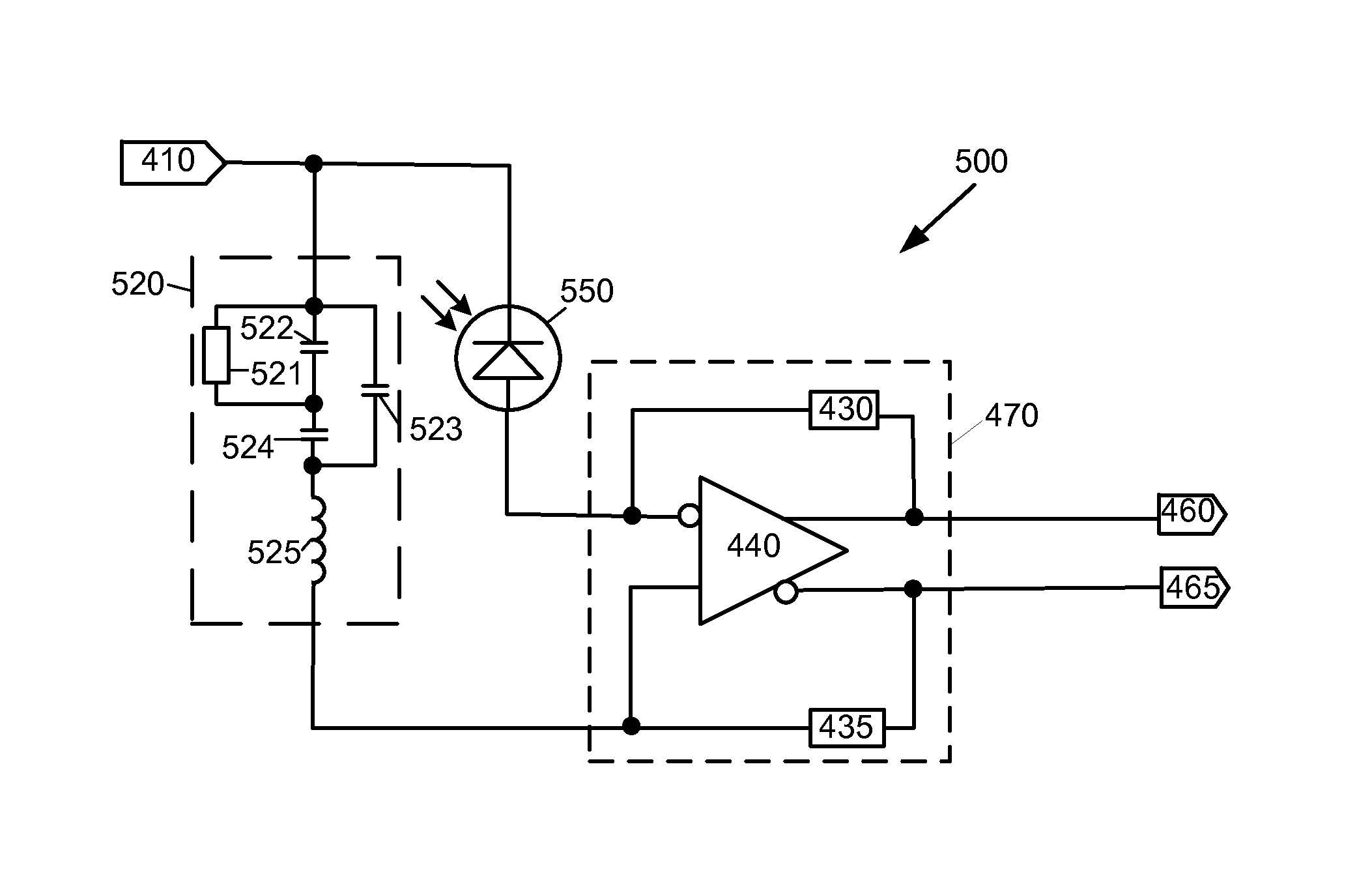
ActiveUS20140291487A1Voltage variesMaterial analysis by optical meansAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A device and method to immune an APD or SiPM optical receiver against photodetector voltage supply variation is presented. A differential trans-impedance amplifier includes one input connected to the photodetector and the other input connected to a high voltage supply variation sensing device. The sensing element includes a circuit replicating the impedance of the photodetector.
Owner:EXCELITAS CANADA
Gain-variable trans-impedance amplifier integrated circuit for pulse laser range finder echo receiver
ActiveCN101852851AReduce power consumptionReduce volumeElectromagnetic wave reradiationDigital controlIntegrated circuit design
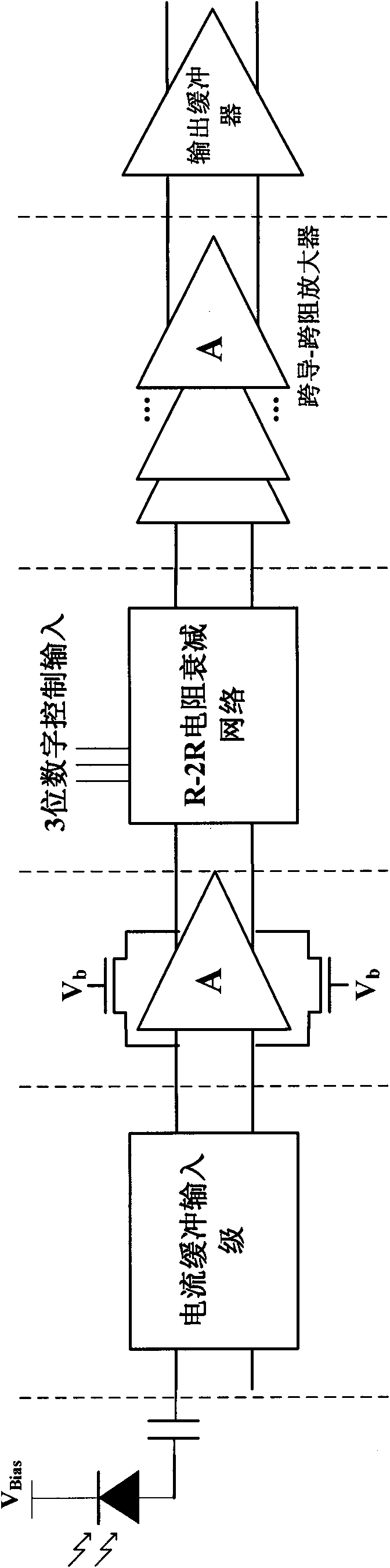
The invention discloses a gain-variable trans-impedance amplifier integrated circuit for a pulse laser range finder echo receiver, belonging to the technical field of integrated circuit design. The integrated circuit is based on the CMOS integration technology, a narrow pulse photo signal generated by a photoelectric detector is converted into a voltage signal via a current buffer and a difference trans-impedance amplifier, the voltage signal is attenuated by an R-2R resistance attenuating network according to a given attenuation times input by digital control, is amplified to a certain amplitude by a broadband voltage amplifier and is in buffer output by an output buffer. The invention has the advantages of realizing single chip integration for a multi-functional module circuit in the existing pulse laser range finder, improving the integrated level of a receiving circuit, lowering batch production cost for the system and being favor of realizing the multi-element laser echo detection at a high integration level.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High dynamic range radio architecture with enhanced image rejection
ActiveUS20110222633A1Modulation transferenceDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionPower flowAudio power amplifier
A circuit for down-converting an RF signal to a baseband signal includes a trans-admittance amplifier adapted to receive the RF signal and generate in response a pair of differential current signals. The circuit further includes a trans-impedance amplifier having at least four mixers and at least four linear amplifiers. The four mixers frequency down-convert the pair of differential current signals to generate four pairs of differential baseband current signals, wherein each pair of the differential baseband current signals has a different phase and is associated with each of the linear amplifiers. Additionally, the circuit includes a summing block that generates an in-phase signal using a first weighted sum of the four different baseband current signals and a quadrature signal using a second weighted sum of the four different baseband current signals. The circuit further includes an analog-to-digital converter for converting the in-phase and quadrature signals to respective digital representations.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
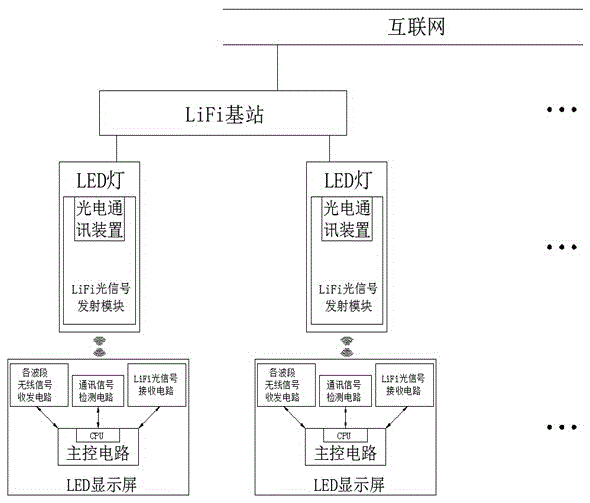
LED display screen indoor wireless communication system based on LiFi technology
ActiveCN105472779AThe way of use remains unchangedReliable high-speed and convenient wireless Internet accessNetwork topologiesClose-range type systemsThe InternetCommunication device
The invention discloses an LED display screen indoor wireless communication system based on LiFi technology The LED display screen indoor wireless communication system comprises indoor LED lamps and LED display screens disposed in the illumination range of the LED lamps. A LiFi optical signal transmitting module is disposed in each of the LED lamps, and a main control circuit, a communication signal detection circuit, a circuit for transceiving wireless signals in various wavebands, and a LiFi optical signal receiving circuit are disposed in each of the LED display screen. Each of the main control circuits is connected with the corresponding communication signal detection circuit, the corresponding circuit for transceiving the wireless signals in various wavebands, and the corresponding LiFi optical signal receiving circuit. Each of the LiFi optical signal transmitting modules is connected with a LiFi wireless communication Internet signal source. Each of the LiFi optical signal transmitting modules of the LED lamps comprises a photoelectric communication device, which comprises an LED driver, an LED lamp bead, a PIN photoelectric diode, and a trans-impedance amplifier. A LiFi base station comprises an optical link, and is used to establish connection between an access end and an Internet end, and can be used for processing the electric signals, receiving and / or transmitting the electric signals.
Owner:福建晶彩光电科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com