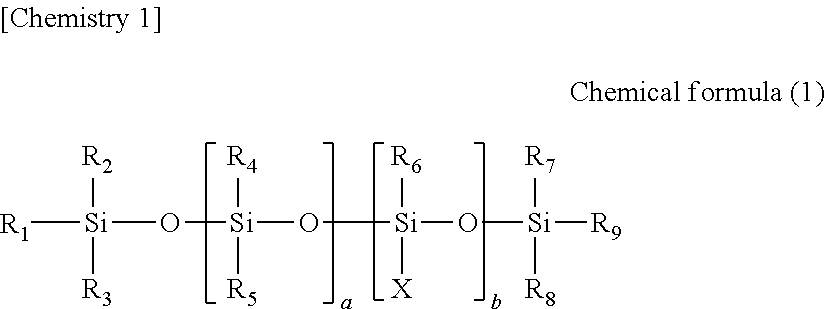
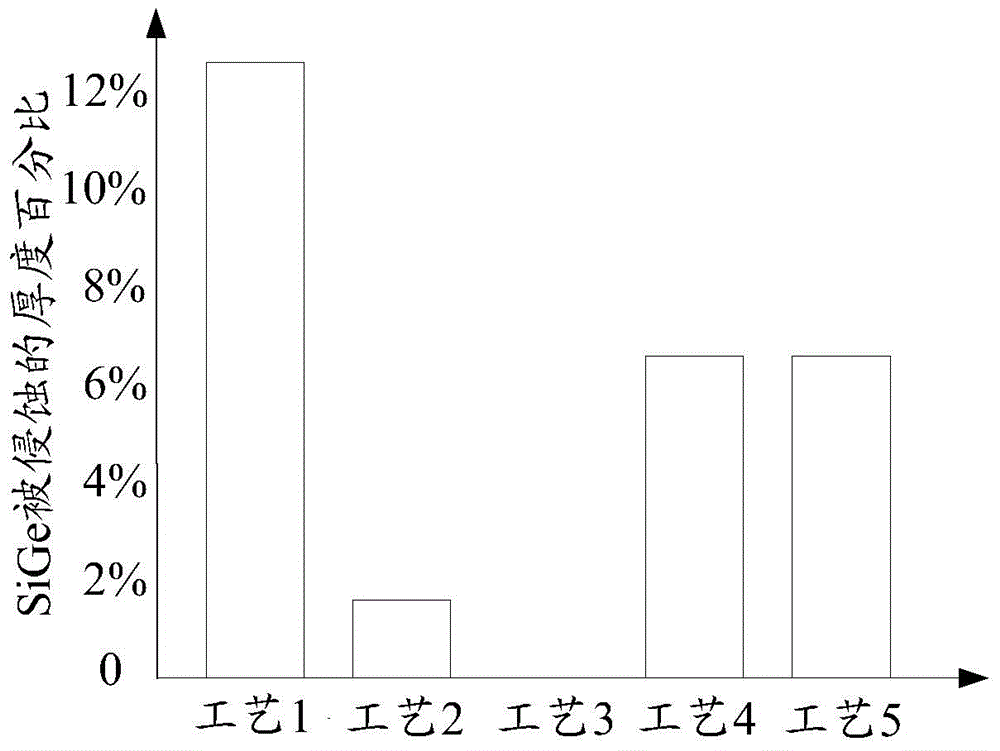
Patents
Literature
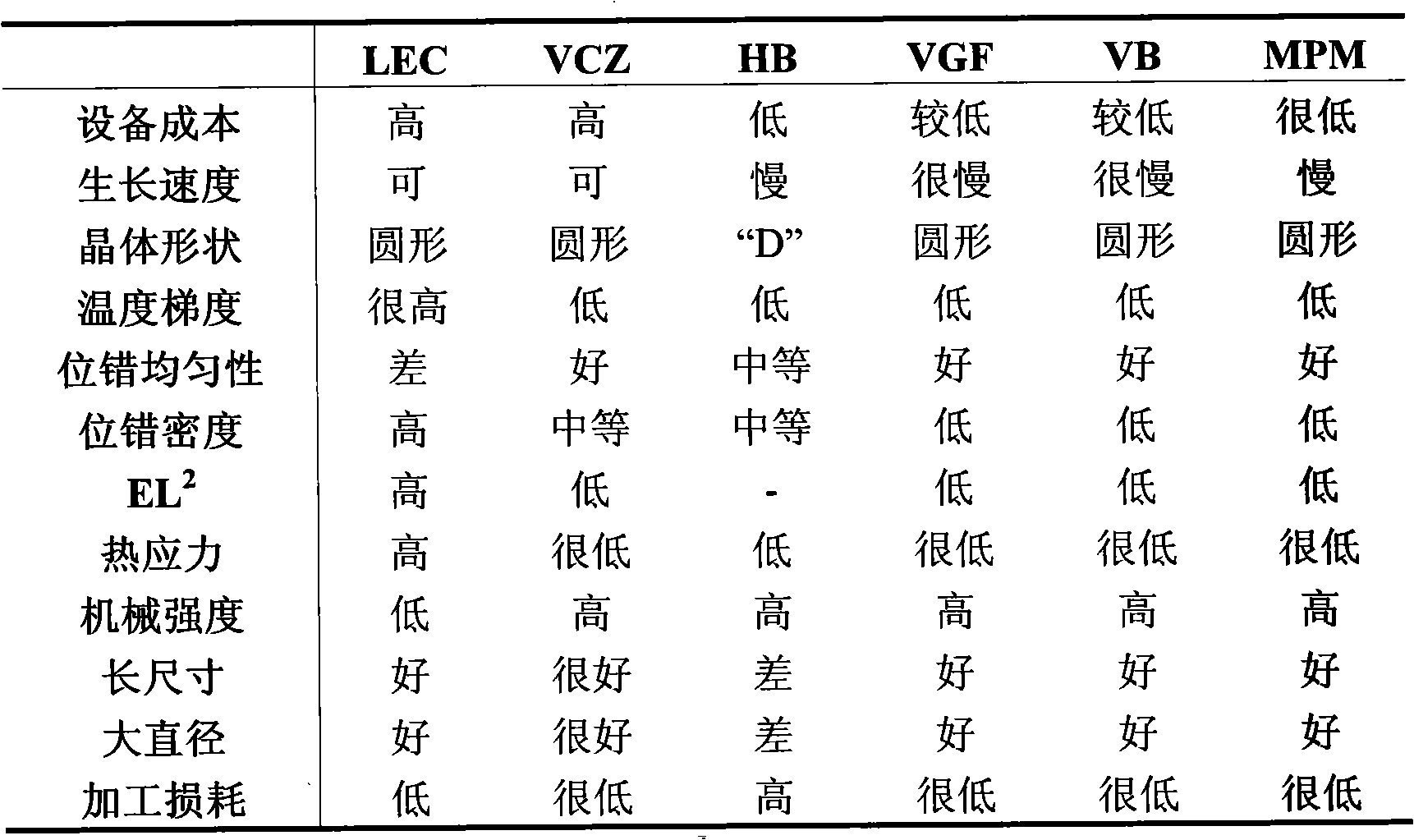
95results about How to "Reduce dislocation defects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
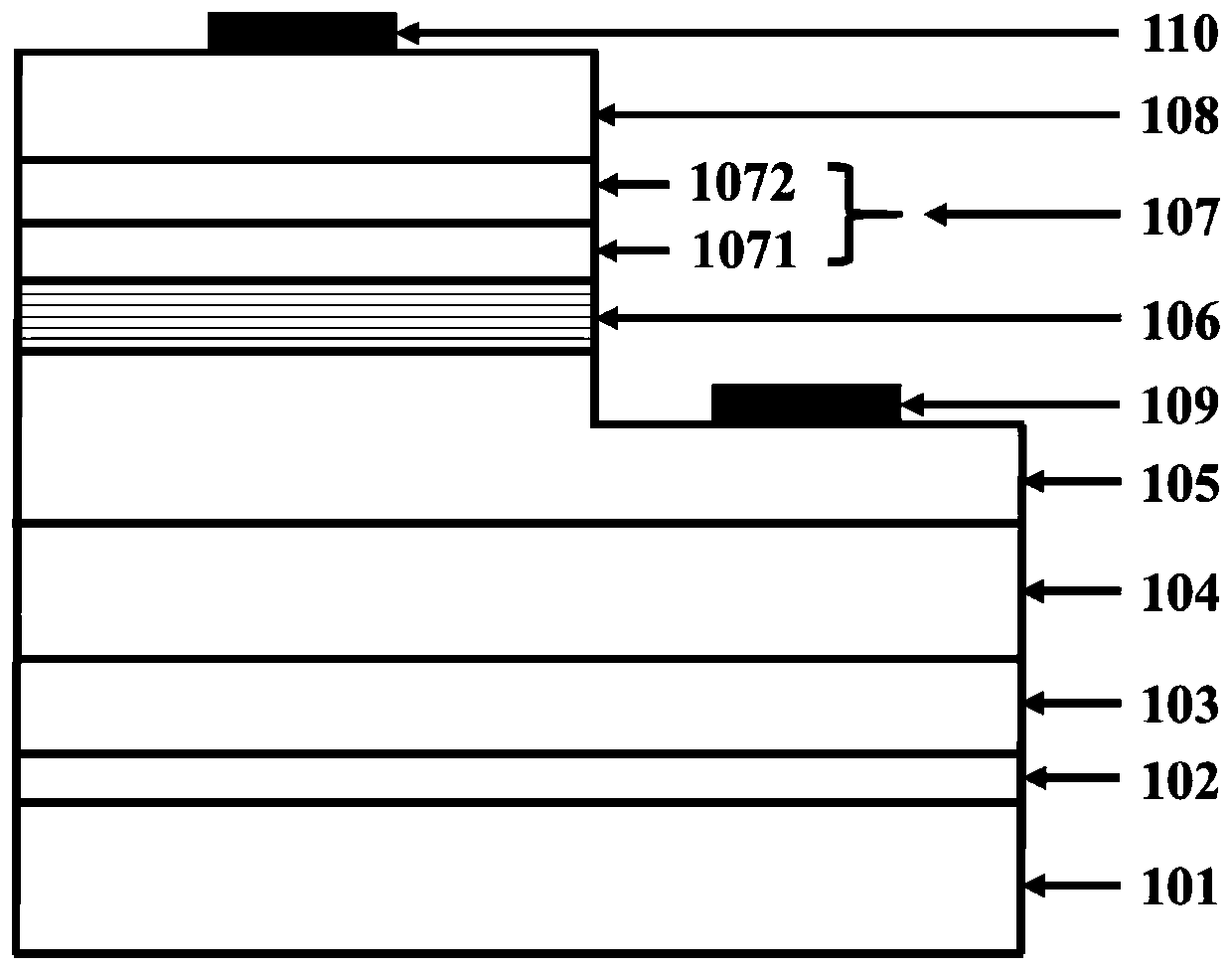
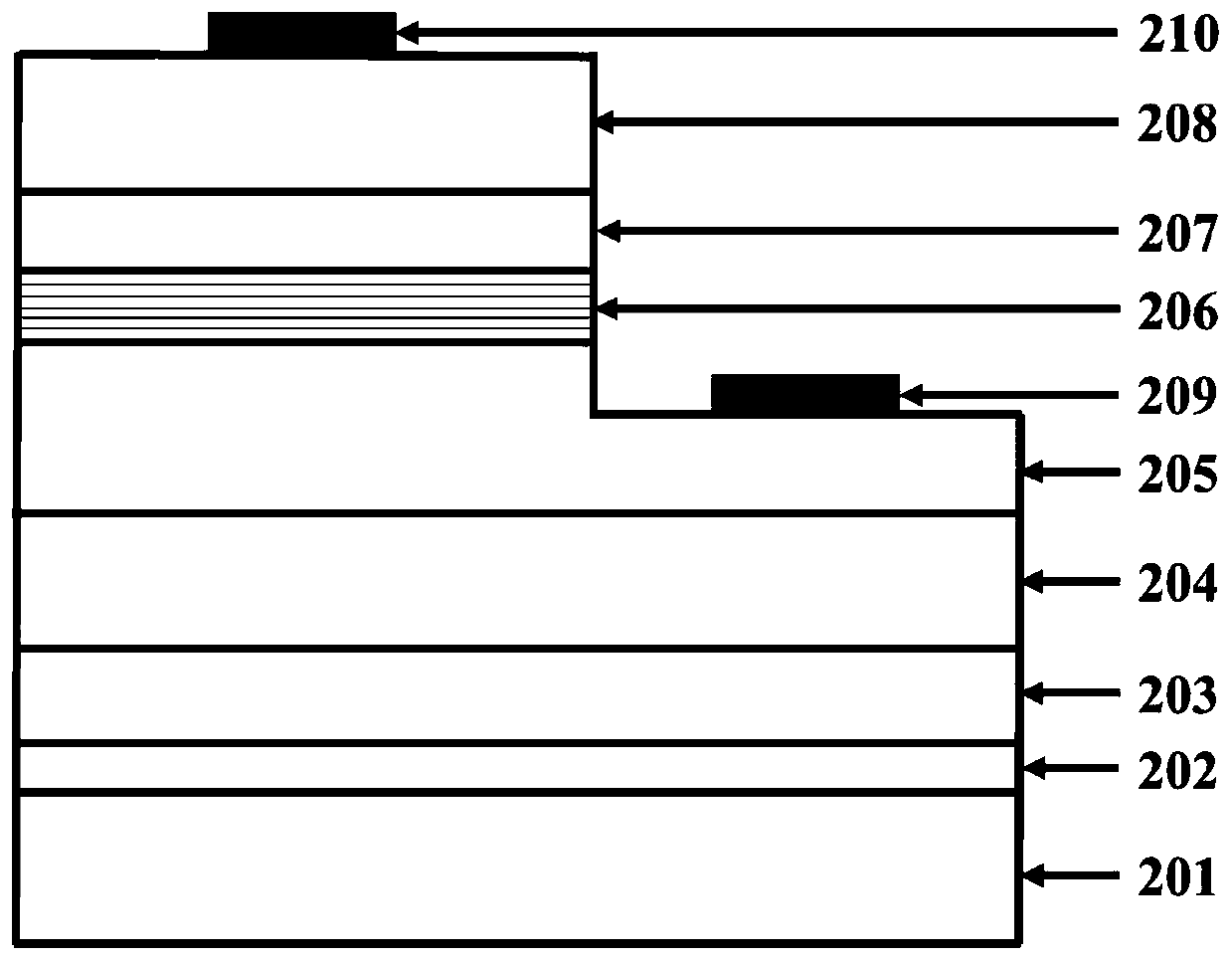
Inverted mounting LED chip based on double-faced shrinkage pool substrate and component gradual change buffer layer
InactiveCN102157654AImprove radiative recombination luminous efficiencyReduce defect densitySemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyQuantum well
The invention discloses an inverted mounting LED chip based on double-faced shrinkage pool substrate and component gradual change buffer layer, wherein the chip comprises a sapphire substrate distributed with 102-104 shrinkage pools at upper and lower surfaces, an AlxGa1-xN component gradual change buffer layer composed of an unit layer formed by k non-doping AlxGa1-xN epitaxial materials, a n-type GaN epitaxial layer, an InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well, a p-type GaN layer, a transparent ITO (indium tin oxide) conductive film, an inverted mounting welding electrode and a silicon substrate from upper to lower. The LED chip disclosed by the invention uses the shrinkage pool structure for improving the emergent probability of LED emergent lights, and increasing the heat radiation area and growth stress acting range of the substrate, so that the GaB epitaxial quality and the radiation composite luminous efficiency are improved; the buffer layer of the n-type GaN epitaxial layer is manufactured by the AlxGa1-xN with gradually reduced Al component, so that the light-emitting efficiency and the internal quantum efficiency of the LED are improved, and a relatively high light output power is obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for growing a silicon single crystal
InactiveUS6086671AReduce amountReduce the amount requiredPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDislocationSeed crystal
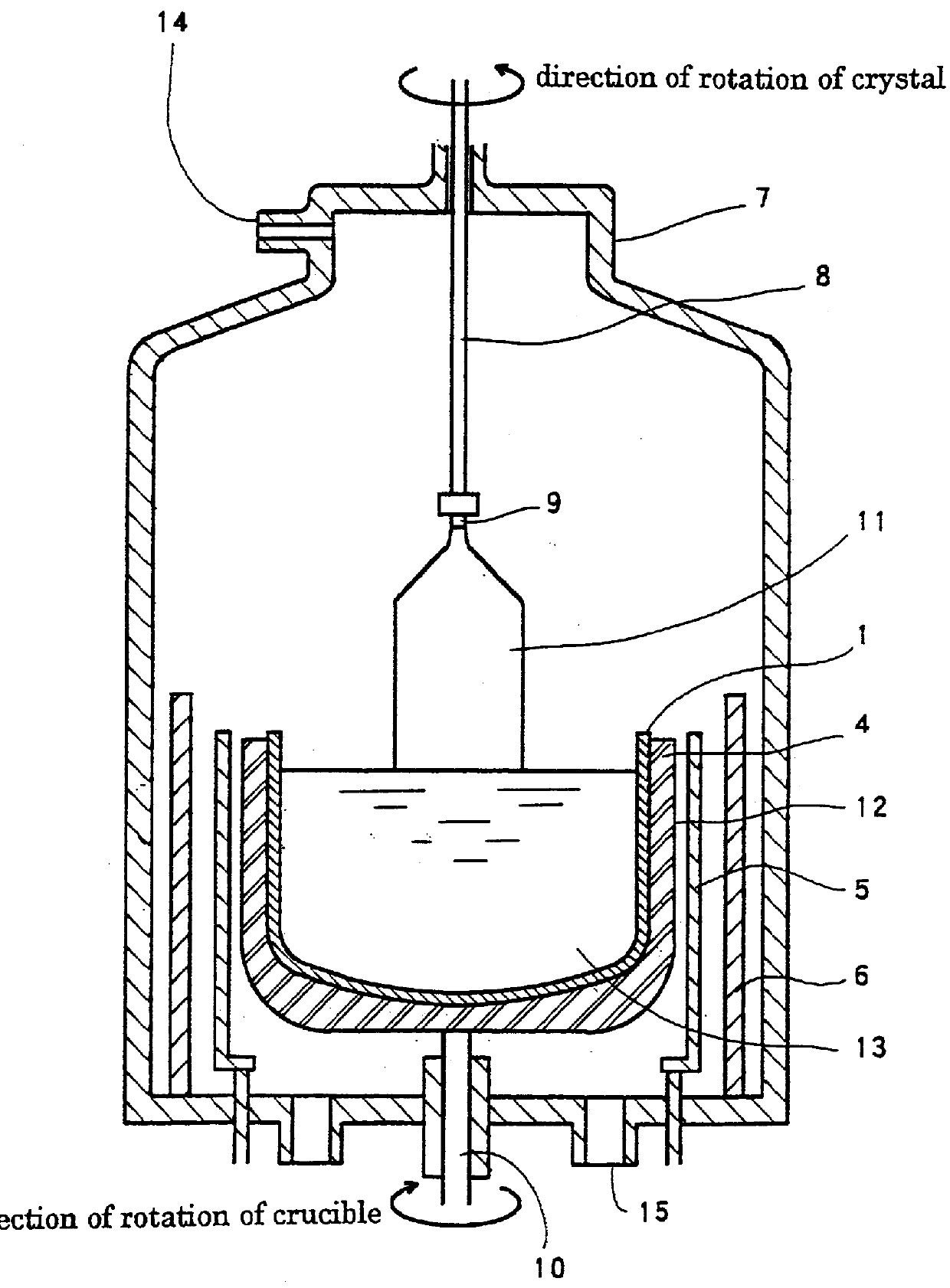
A method for melting a silicon starting material can suppress silica (SiO2) from melting out from a quartz crucible wherein the silicon starting material is melted and can provide a high-quality silicon single crystal in a high yield. The growth method comprises melting the silicon starting material charged in the crucible while applying thereto a static magnetic field, contacting a seed crystal to a surface of the silicon melt, and pulling the seed crystal upwardly to solidify the contacted melt. The silicon starting material charged in the crucible, which is under melting, is applied with a static magnetic field such as a Cusp magnetic field, a horizontal magnetic field and / or a vertical magnetic field. The application can control heat convection occurring in the crucible during the course of the melting of the starting material, thereby obtaining a silicon single crystal having a reduced number of dislocation defects.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
Epitaxial substrate, preparation method of epitaxial substrate and application of epitaxial substrate as growing epitaxial layer
ActiveCN102263171AReduce dislocation defectsQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin material handlingCarbon nanotubeOptoelectronics
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Preparation method of polycrystalline silicon
ActiveCN103469293AEasy to operateGuaranteed not to be completely meltedPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsThermal insulationPhysical chemistry
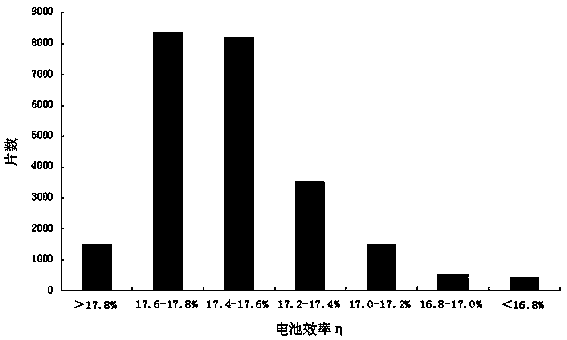
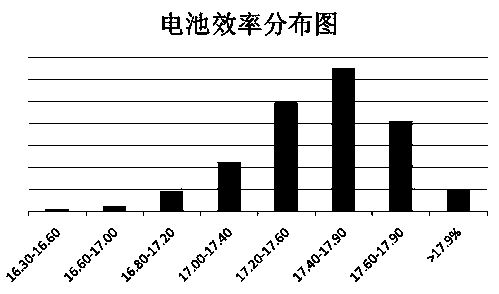
The invention discloses a preparation method of polycrystalline silicon. The preparation method of the polycrystalline silicon comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out pre-treatment on a quartz crucible, then paving a crystalline silicon chip material layer at the bottom of the quartz crucible, then placing silicon and mother alloy into the quartz crucible, charging, vacuumizing, and heating to melt silicon; after melting is finished, controlling the temperature of a heater to be 1540-1570 DEG C, lifting a thermal insulation cage until aperture a is 5-20mm, and controlling temperature TC2 to be no more than 1425 DEG C until broken polycrystals at the bottom are just molten, performing a temperature-fall period, and slowly opening the thermal insulation cage while slowly cooling in gradient; finally growing crystals, so that the polycrystalline silicon containing massive twin crystals is formed. A polycrystalline silicon slice prepared by adopting the preparation method is uniform in grain size, the battery efficiency is 0.2-0.3% higher than that of common polycrystalline silicon, the average battery efficiency of the whole silicon slice is more than 17.5%, and ratio of the silicon slice with the efficiency more than 17.4% is more than 65.0%.
Owner:HUNAN RED SUN PHOTOELECTRICITY SCI & TECH
GaN-based LED chip extending and growing method for reducing dislocation defects
InactiveCN101702418AReduce dislocation defectsLight in massSemiconductor devicesTime controlDislocation
The invention provides a GaN-based LED chip extending and growing method for reducing dislocation defects, comprising the following steps of: (1) firstly, growing a low-temperature GaN buffer layer or AlxGal-xN buffer layer on a substrate, and then growing a high-temperature undoped GaN layer on the buffer layer; (2) regulating the growing temperature in a reaction chamber to 600DEG C to 1100 DEG C ,and then independently introducing CP2Mg and NH3 into the reaction chamber, reacting the CP2Mg with the NH3 to form MgN on the high-temperature undoped GaN layer made in step (1), wherein the sizes and density of the holes are controlled through the time for introducing the CP2Mg; (3) continuously growing other extending materials of a GaN-based LED chip according to the normal method. The invention adopts the MgN to make a nano masking figure in situ to reduce the dislocation defects in a GaN-based material. Compared with SiN masking, the invention has no corrosion on the GaN material when making the MgN masking, and therefore, the GaN having no a masking position can not introduce more defects, and the GaN material with higher quality can be acquired.
Owner:Shandong Huaguang Optoelectronics Co. Ltd.
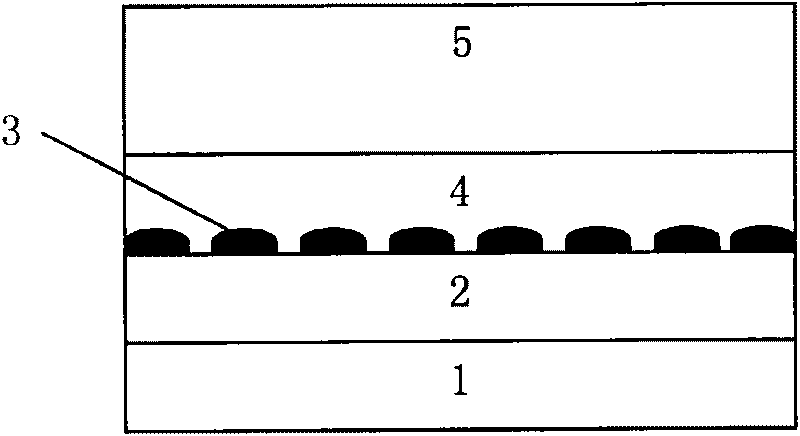
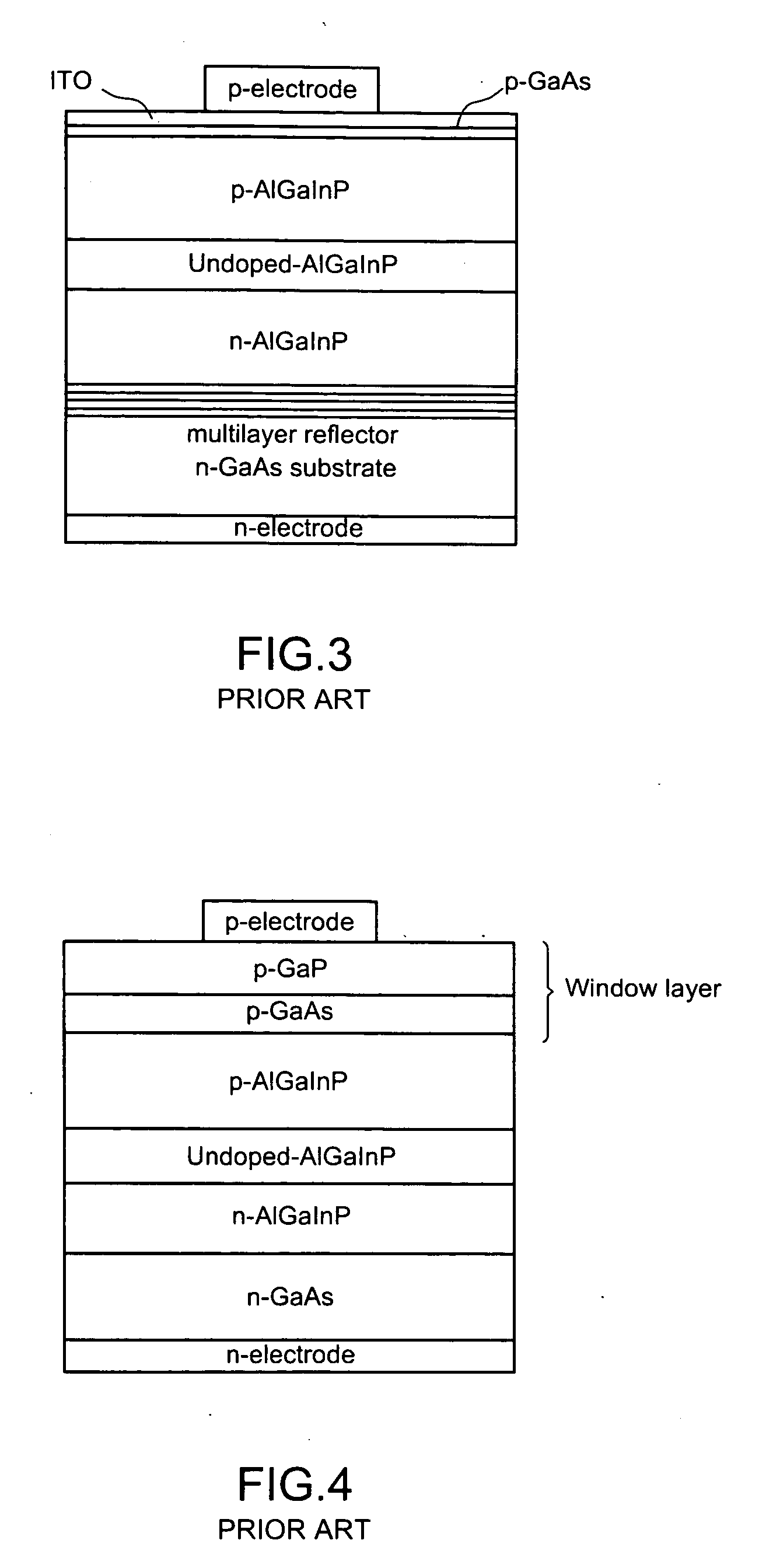
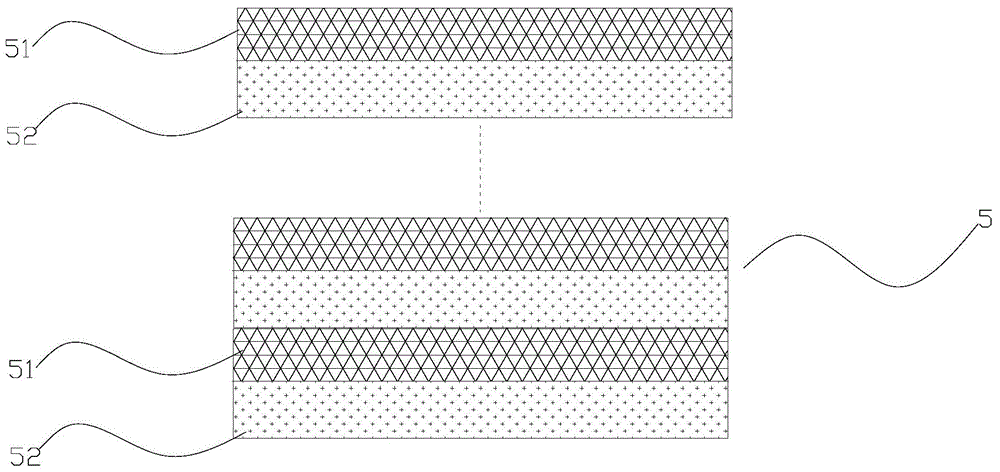
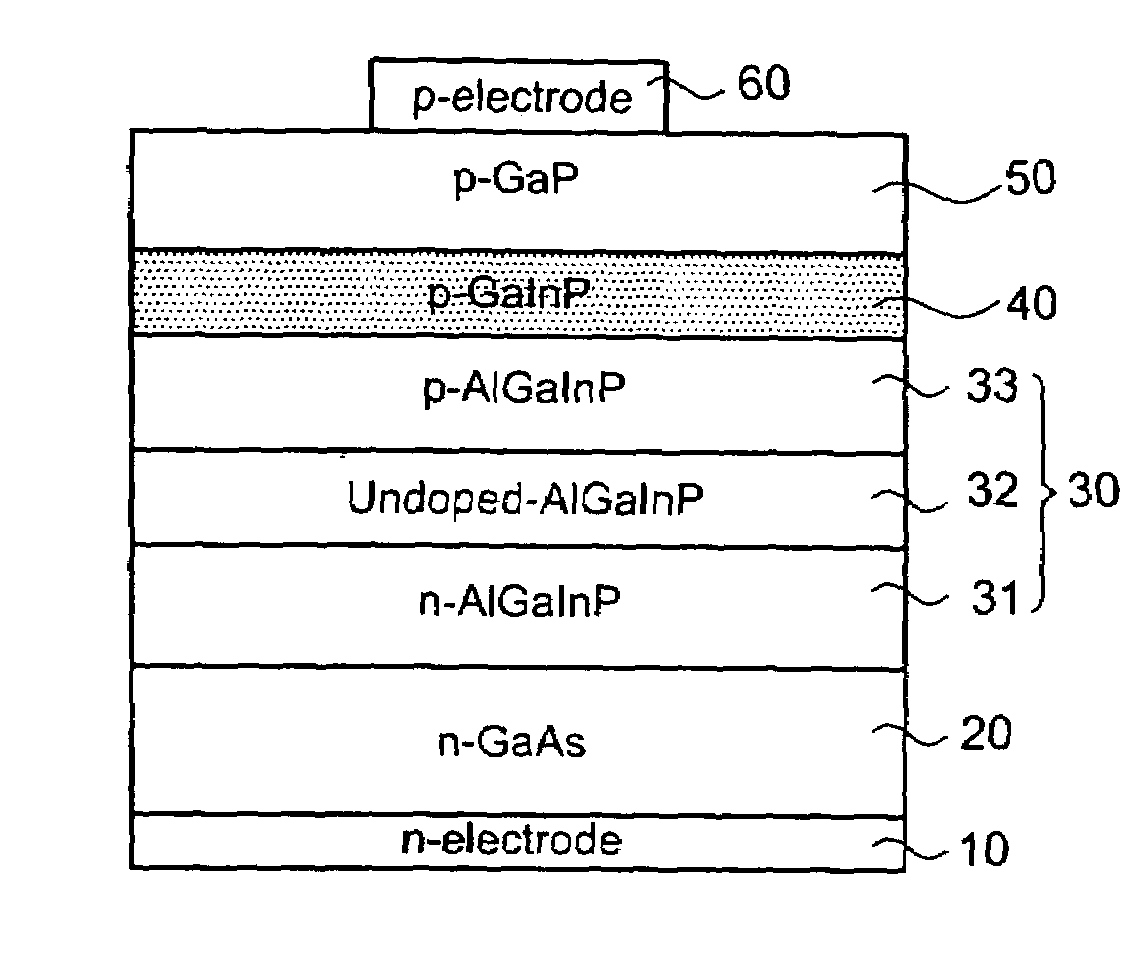
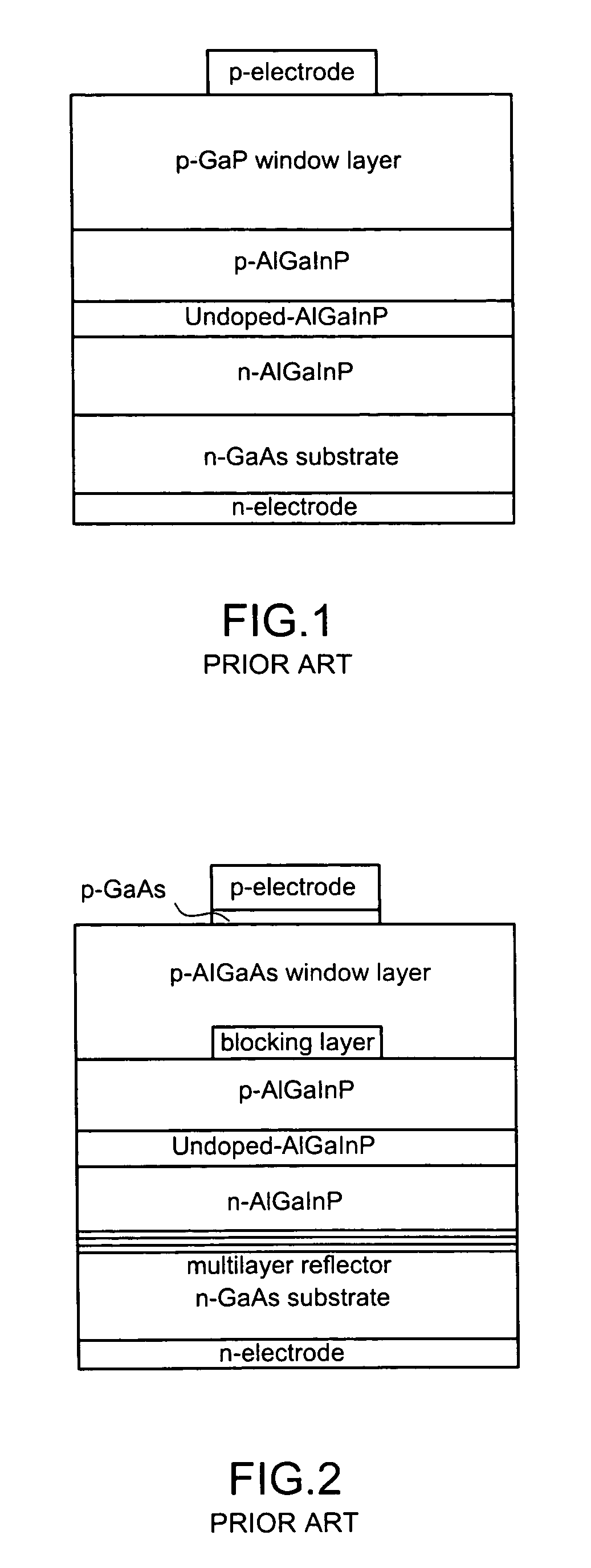
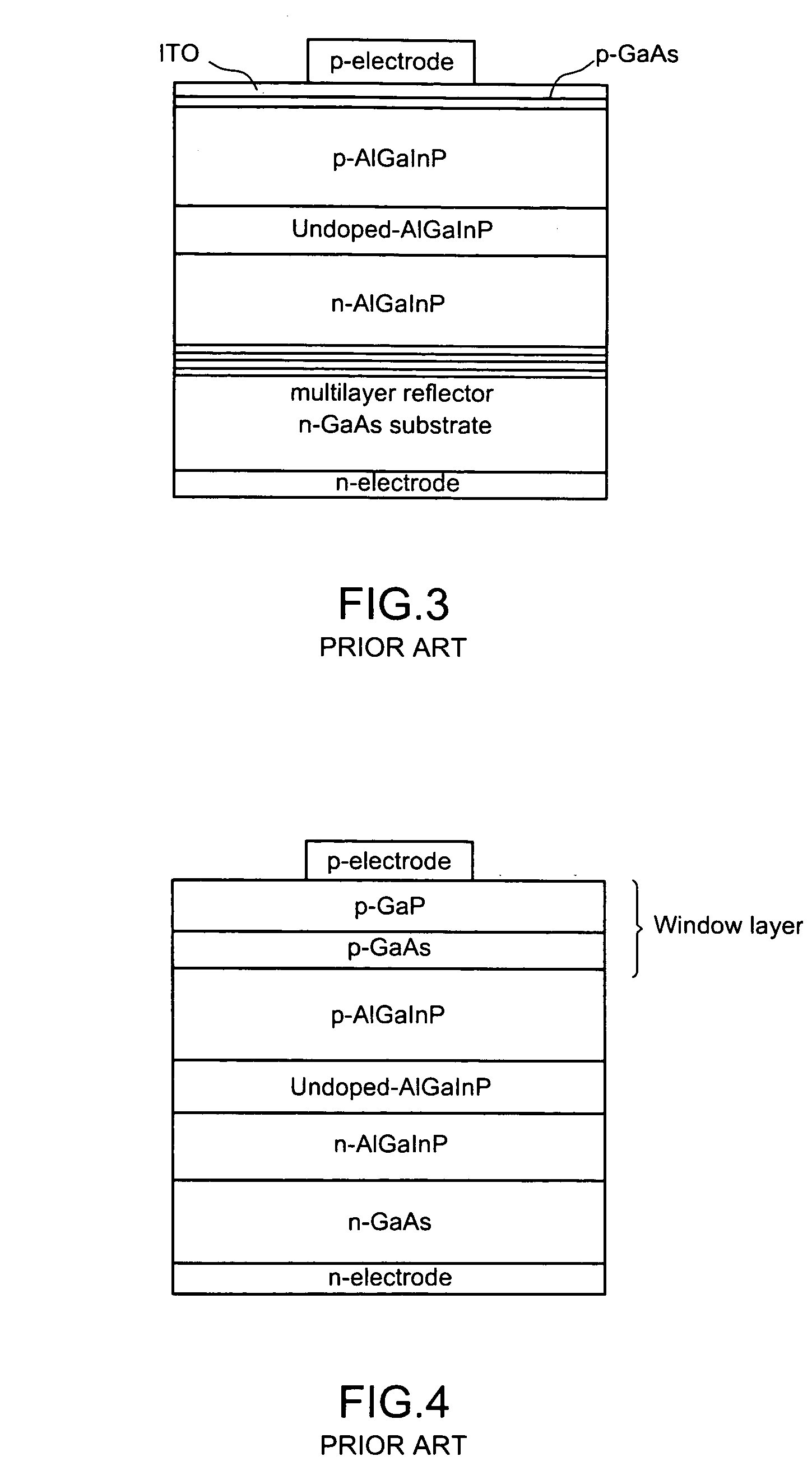
Window interface layer of a light-emitting diode
InactiveUS20070045608A1Reduce dislocation defectImprove quality of filmActive medium materialSemiconductor devicesElectric propertiesBand gap
This invention is about a window interface layer in a light-emitting diode which comprises an n-type GaAs substrate with an n-type ohmic electrode at the bottom side thereof; an n-type AlGaInP cladding layer formed atop the substrate; an undoped AlGaInP active layer formed atop the n-type cladding layer; a p-AlGaInP cladding layer formed atop the active layer; a p-type window layer made of GaP; a p-type ohmic electrode formed atop the p-type window layer; and a highly doped p-type interface layer made of GaxIn1-xP (0.6≦x≦0.9) and interposed between the p-type cladding layer and p-type window layer wherein the highly doped p-GaInP interface layer possesses a band gap which is higher than that of the active layer and, however, smaller than that of the p-type cladding layer, and wherein the lattice constant lies between GaAs and GaP. In this way, the p-GaInP interface layer is interposed between a p-GaP window layer and a p-AlGaInP cladding layer for enhancing the film quality and the luminous efficiency as well as improving the electric property.
Owner:ARIMA OPTOELECTRONICS
Improved Bridgman-Stockbarger method for compound semiconductor GaAs single crystal
InactiveCN101348940AHigh yieldSimple structurePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsDislocationSeed crystal
The invention relates to an improved falling crucible method growth method for compound semiconductor arsenide gallium monocrystal. The growth method comprises the following steps: a multi-position falling crucible furnace is used for the growth of compound semiconductor GaAs monocrystal; the furnace is designed with a plurality of positions, and can be used for the growth of a plurality of crystals; a raw material for high-purity arsenic-enriched multicrystal GaAs is synthesized first, and generally, the arsenic-enriched quantity is not more than 1mol percent; the raw material is fed into a PBN crucible with the bottom provided with crystal seed and seed crystal, and the PBN crucible is placed inside the static stable falling crucible furnace; the falling crucible furnace is designed with three temperature zones, namely a high-temperature zone T1, a gradient zone T2 and a low-temperature zone T3 which respectively plays a role in material smelting, growth and heat preservation; moreover, the furnace temperature is controlled to between 1,250 and 1,290 DEG C, and the position of the crucible is adjusted so as to ensure that the top of the seed crystal is molten; then the temperature is reduced at the speed between 0.2 and 3 millimeters / hour so as to start crystal growth; and when crystal growth is finished, in situ annealing of the crystal is carried out through adjusting the position of the crucible and controlling the furnace temperature. The improved falling crucible growth method has the advantages that the growth method combines the advantages of the prior VB method and VGF method, and adopts a plurality of crucibles so as to increase crystal yield; moreover, an in situ annealing method is adopted to overcome the disadvantage of dislocation caused by thermal stress.
Owner:徐家跃
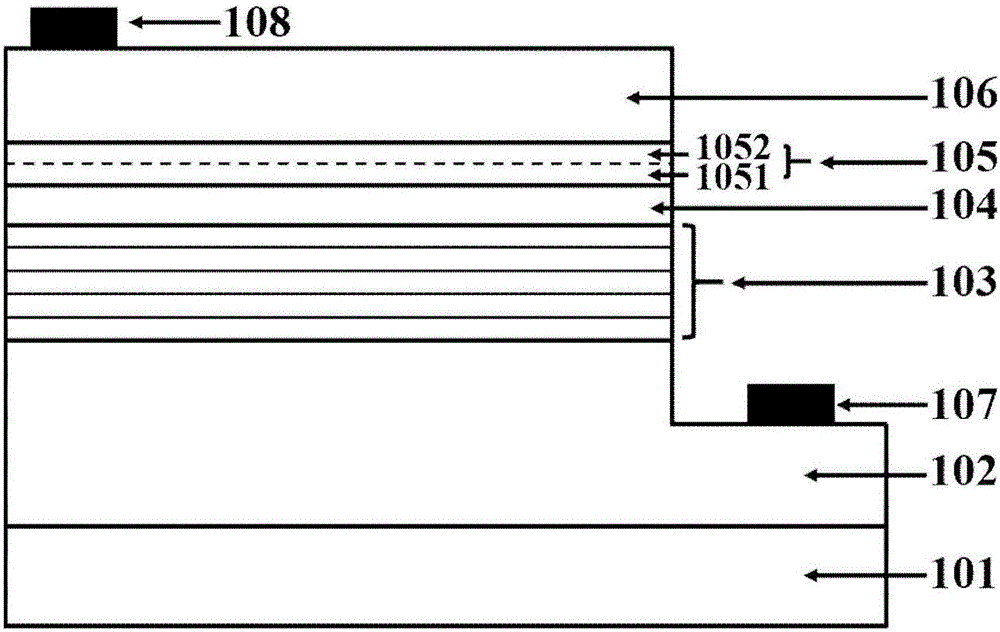
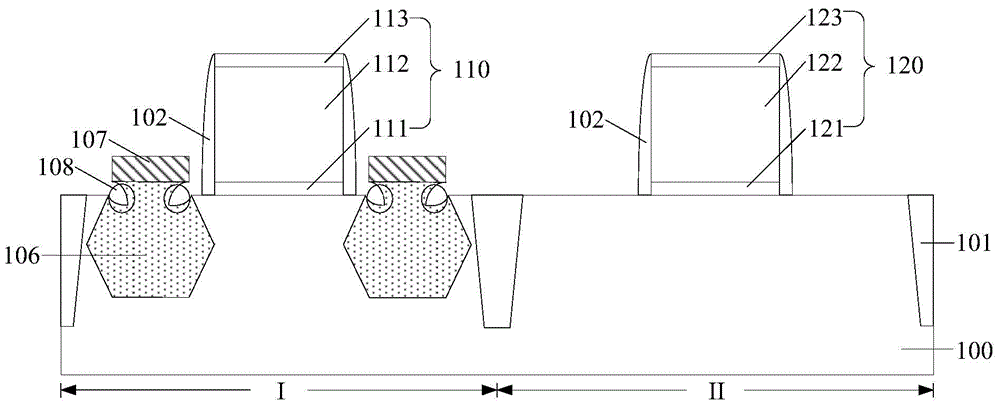
Light-emitting diode with composite polar face electron blocking layer
ActiveCN105870283AReduce leakage currentIncrease chanceSemiconductor devicesMultiple quantumElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses a light-emitting diode with a composite polar face electron blocking layer. The light-emitting diode comprises a substrate (101), a metal polar face n-type nitride layer (102), a metal polar face multiple quantum well layer (103), a metal polar face p-type nitride layer (104), a composite polar face p-type electron blocking layer (105) composed of a metal polar face p-type electron blocking layer (1051) and a nitrogen polar face p-type electron blocking layer (1052), a nitrogen polar face p-type nitride layer (106), an n electrode (7) arranged on the metal polar face n-type nitride layer and a p electrode (8) arranged on the nitrogen polar face p-type nitride layer, and the layers and the electrodes are arranged sequentially from bottom to top. A high electronic barrier is formed on a conduction band by the composite polar face electron blocking layer and blocks electrons from crossing a multiple quantum well active region to enter a p-type region, leakage currents can be reduced, and the probability of radiative recombination of the electrons and holes is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
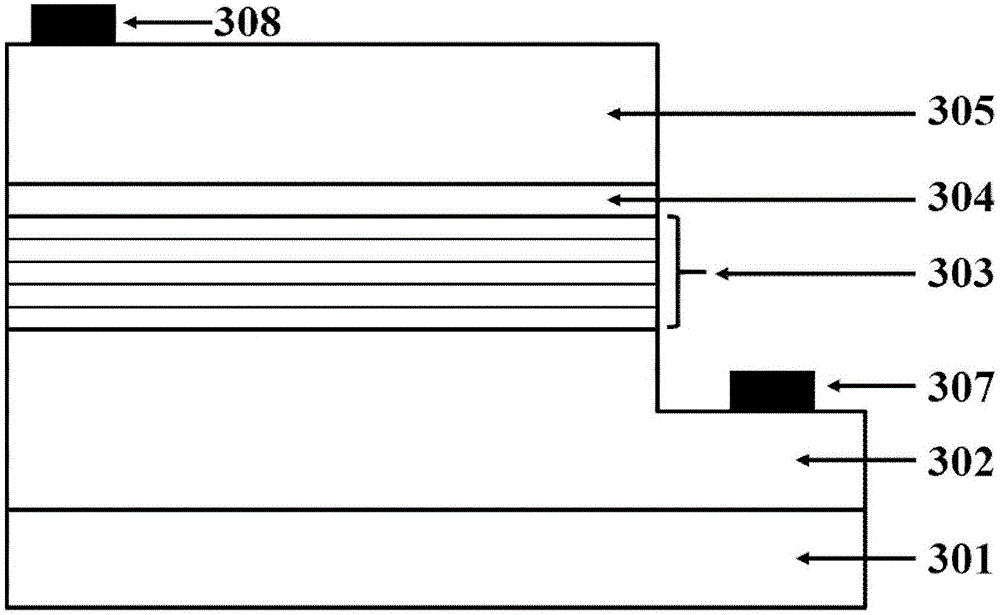
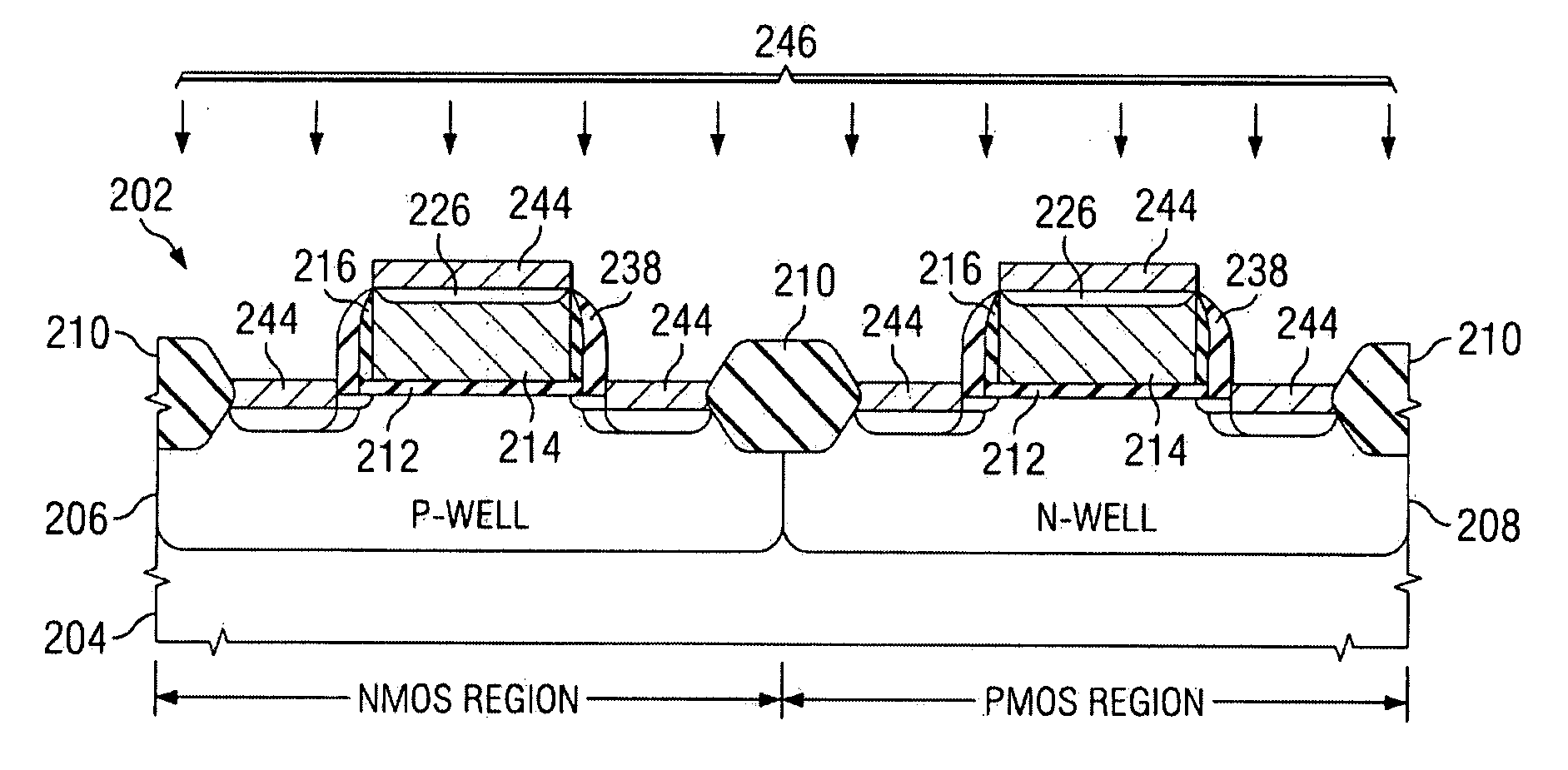
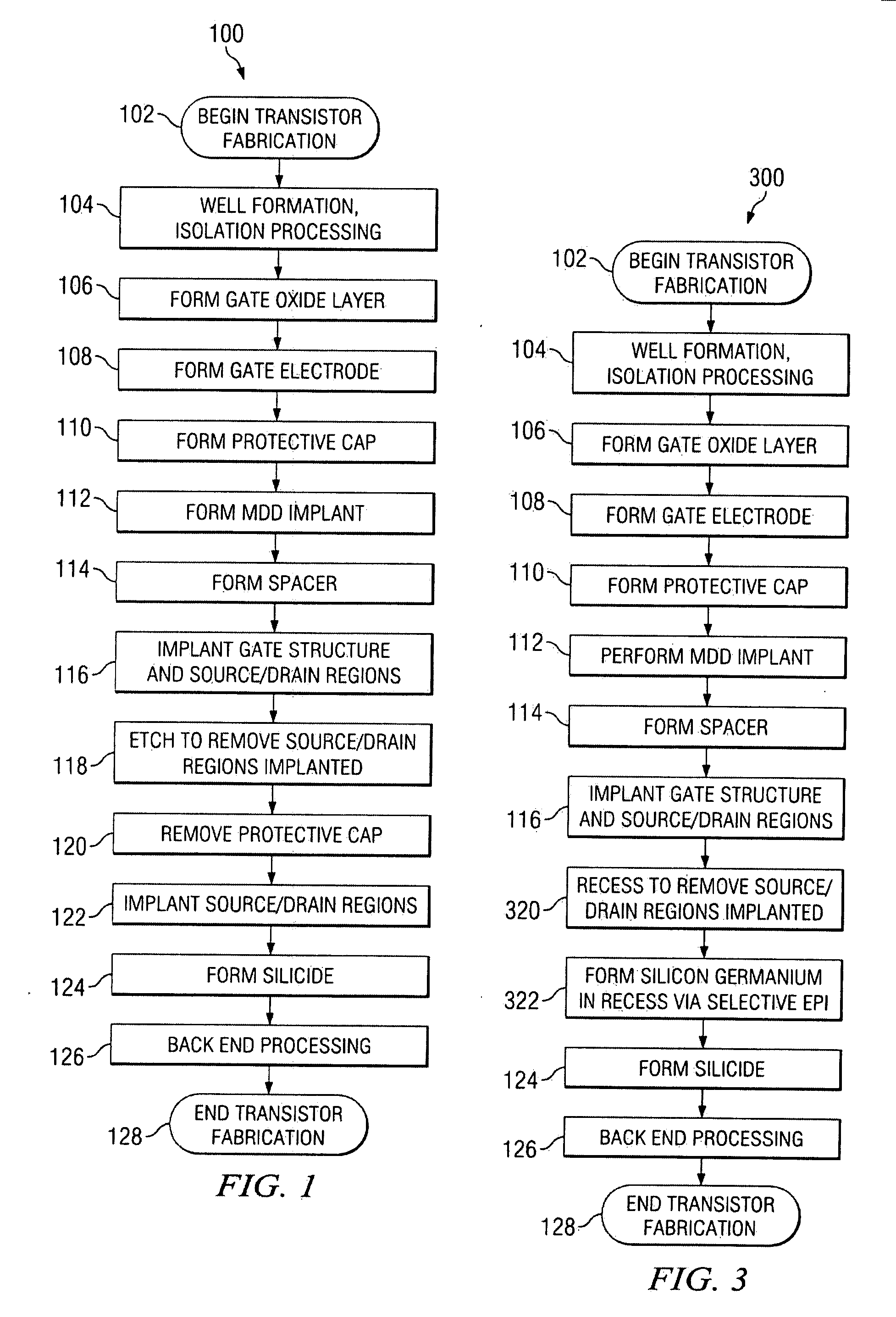
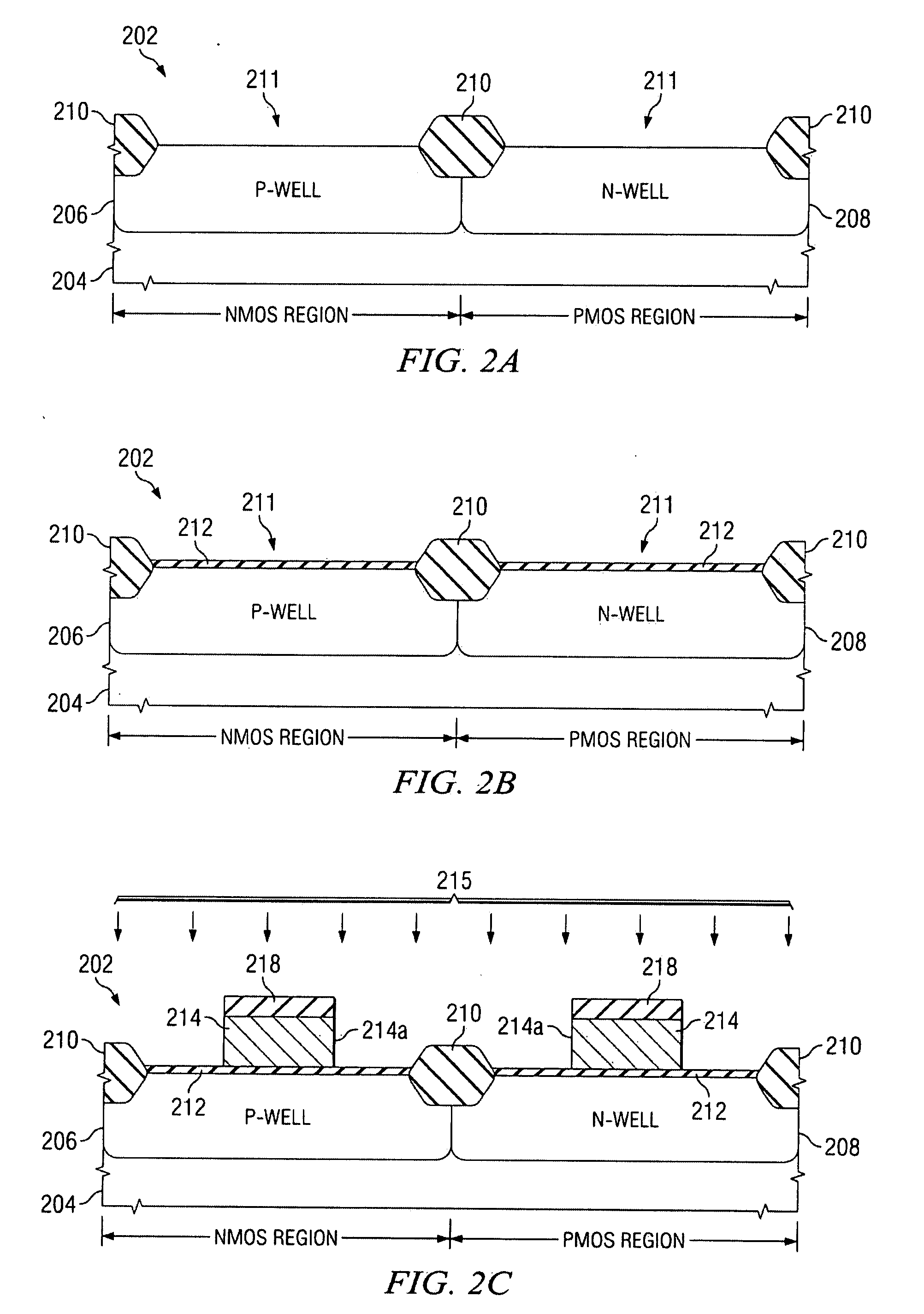
Method to improve transistor tox using si recessing with no additional masking steps
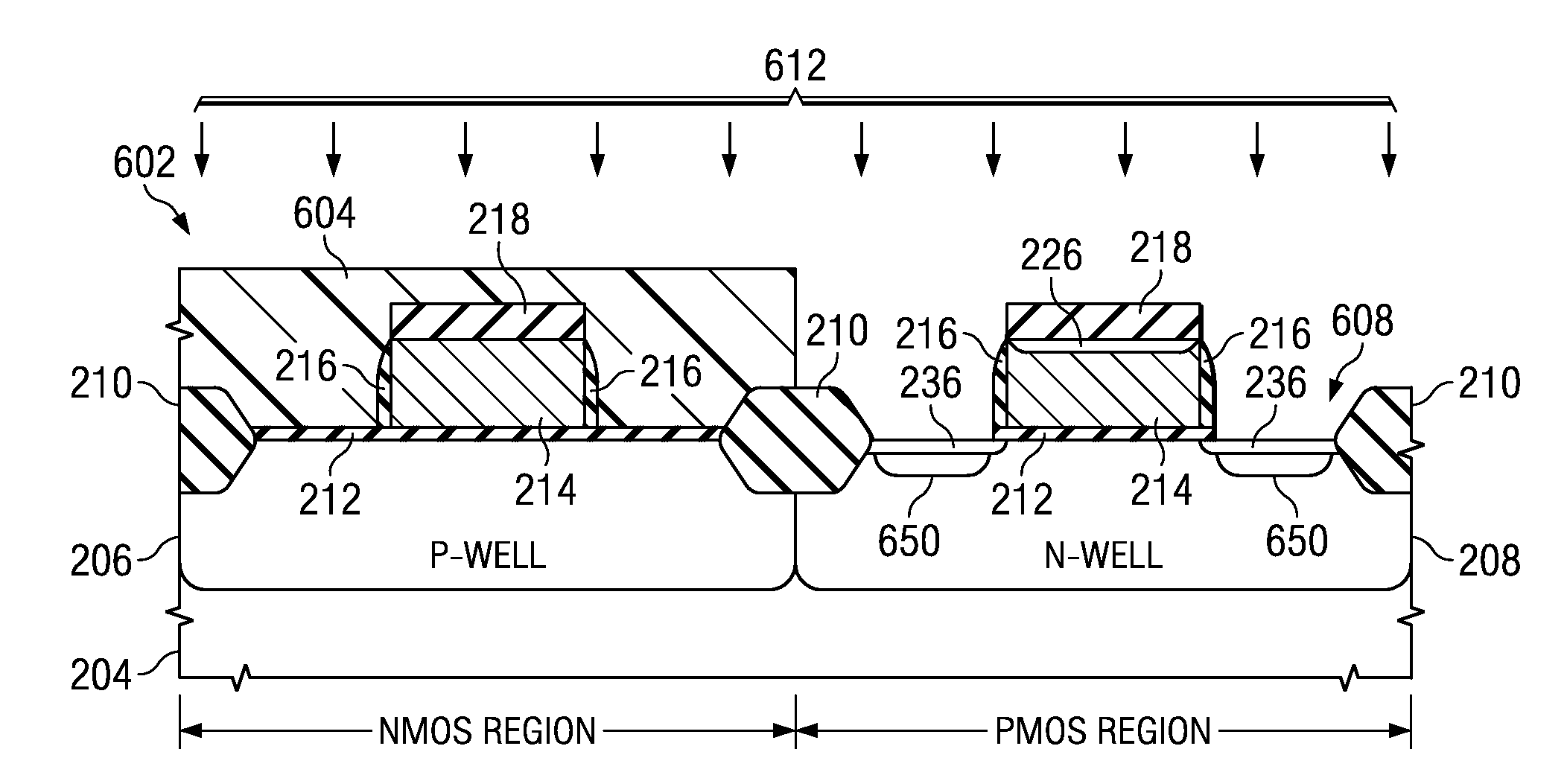
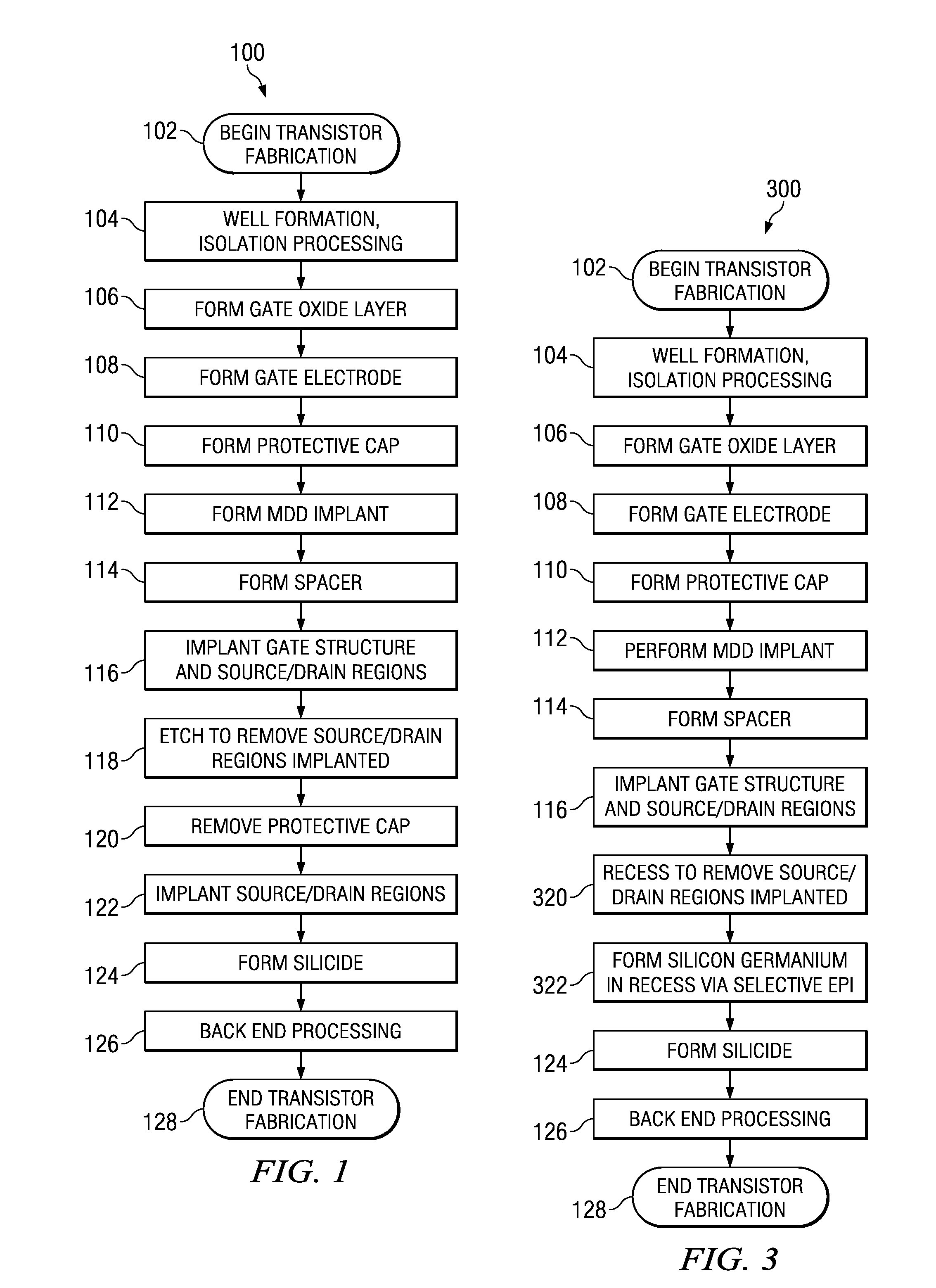
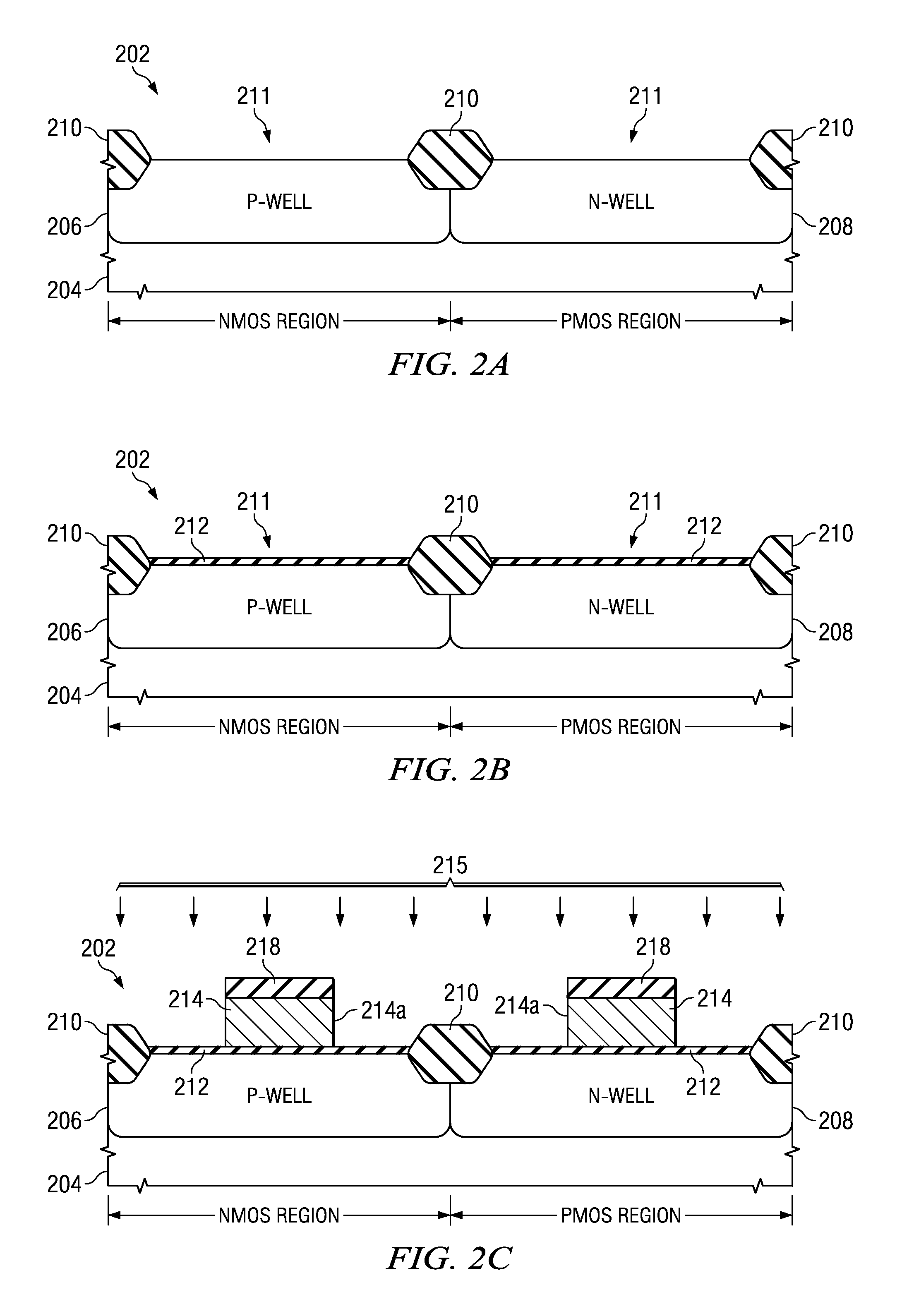
ActiveUS20090093095A1Reducing threading dislocation defectReduce dislocation defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorTransistor
A method of forming a transistor device is provided wherein a gate structure is formed over a semiconductor body of a first conductivity type. The gate structure is formed comprising a protective cap thereover and defining source / drain regions laterally adjacent thereto. A first implant is performed of a second conductivity type into both the gate structure and the source / drain regions. The semiconductor body is etched to form recesses substantially aligned to the gate structure wherein the first implant is removed from the source / drain regions. Source / drain regions are implanted or grown by a selective epitaxial growth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
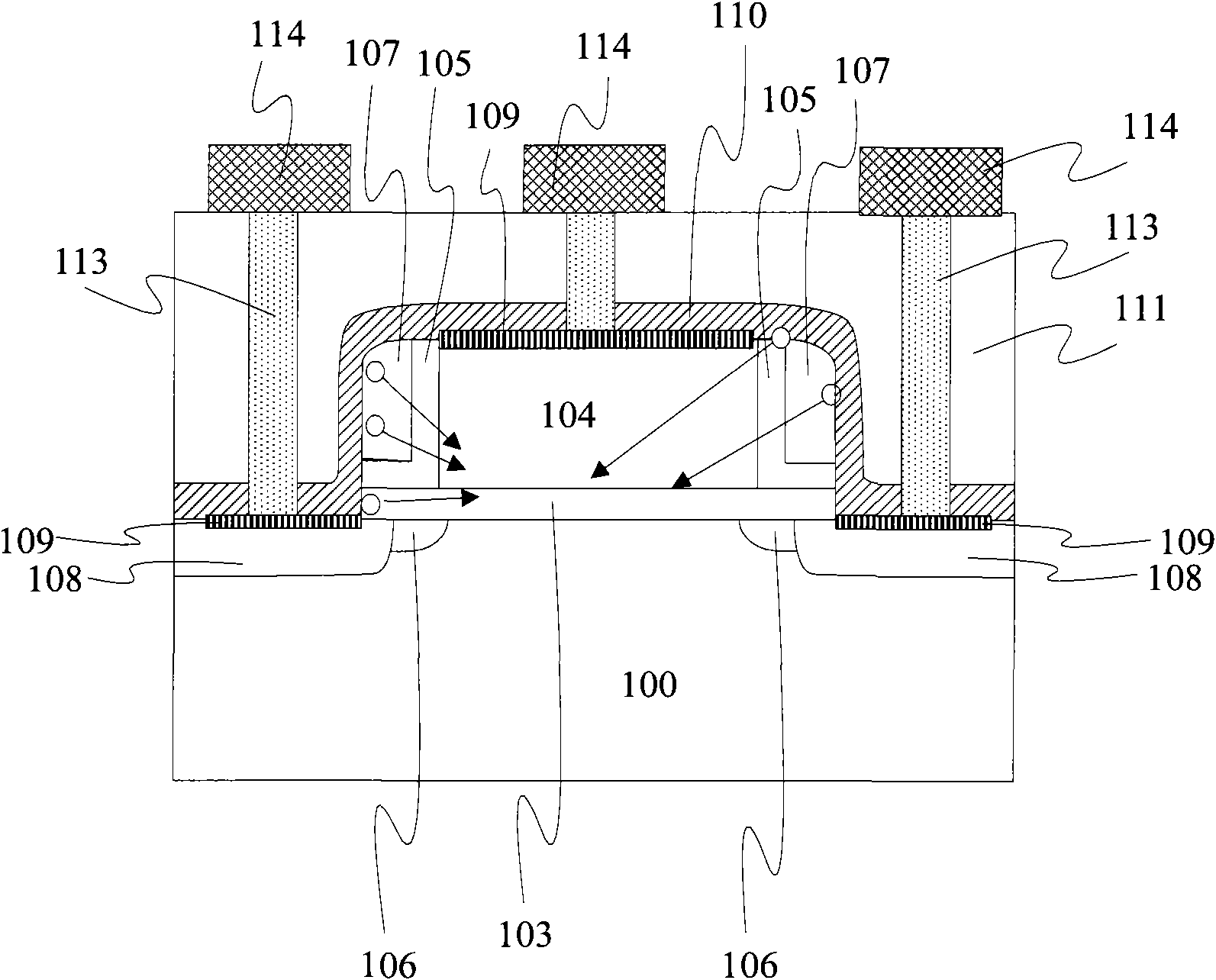
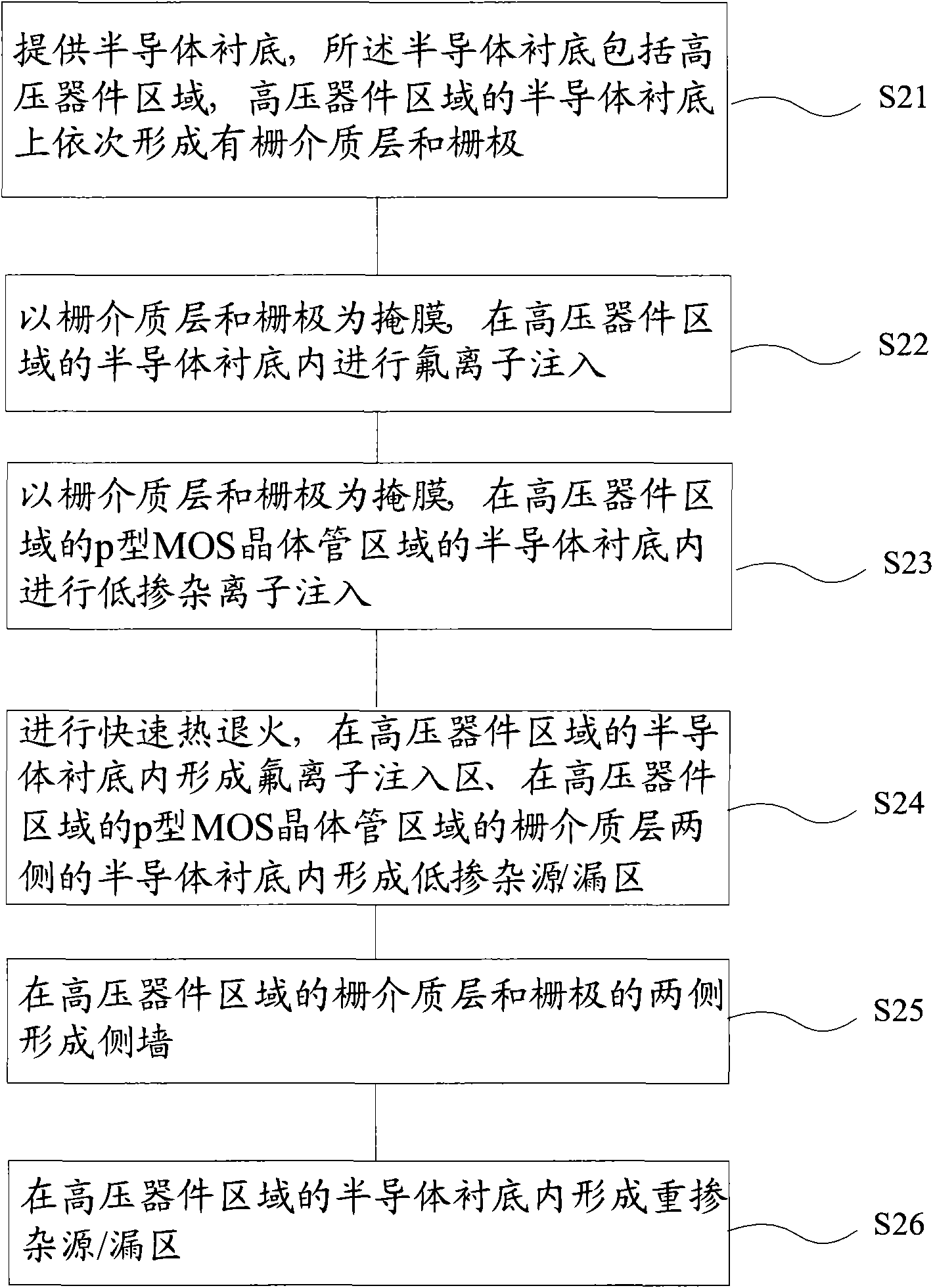
Semiconductor device, p-type MOS transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101572250AAvoid formingReduce dislocation defectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh pressureMedia layer
The invention relates to a semiconductor device, a p-type MOS transistor and a manufacturing method thereof. The method for manufacturing the semiconductor device comprises the following steps: providing a semiconductor substrate; taking a grid medium layer and a grid electrode as masks, and implanting fluorine ions into a semiconductor substrate in a high-voltage device region; taking the grid medium layer and the grid electrode as the masks, and implanting low doped ions into a semiconductor substrate in the p-type MOS transistor region of the high-voltage device region; performing quick thermal annealing; forming side walls on both sides of the grid medium layer and the grid electrode in the high-voltage device region; and forming a heavy doping source / drain region in the semiconductor substrate of the high-voltage device region. The invention also provides the semiconductor device, the p-type MOS transistor and the manufacturing method thereof. The invention is favorable for restricting the influence of the NBTI effect on the MOS transistor by forming a fluorine ion implantation region on a low doping source / drain region in the p-type MOS transistor region of the high-voltage device region, and simultaneously can reduce the hot carrier injection effect.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
Rectangular patterned Si substrate AlN template for GaN semiconductor material epitaxy and preparation method of rectangular patterned Si substrate AlN template
ActiveCN104018214AAvoid destructionPrevent edge topography from deterioratingPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCrystal orientation
The invention relates to a rectangular patterned Si substrate AlN template for a GaN semiconductor material epitaxy. The rectangular patterned Si substrate AlN template comprises a Si substrate and an AlN template layer epitaxially growing on the Si substrate with a crystal plane (111) as a crystal orientation, a plurality of mutually perpendicular strip-shaped grooves are etched on the AlN template layer to form a plurality of rectangular platforms which are independent with each other. The invention also relates to a method for preparing the patterned Si substrate AlN template. The method comprises the following steps of cleaning the substrate, growing the AlN layer and etching the rectangular platform. According to the rectangular patterned Si substrate AlN template for the GaN semiconductor material epitaxy, the yield is high and the cost is low, the prepared products have good uniformity and high quality.
Owner:广州市艾佛光通科技有限公司
Preparation method of polycrystalline silicon ingot
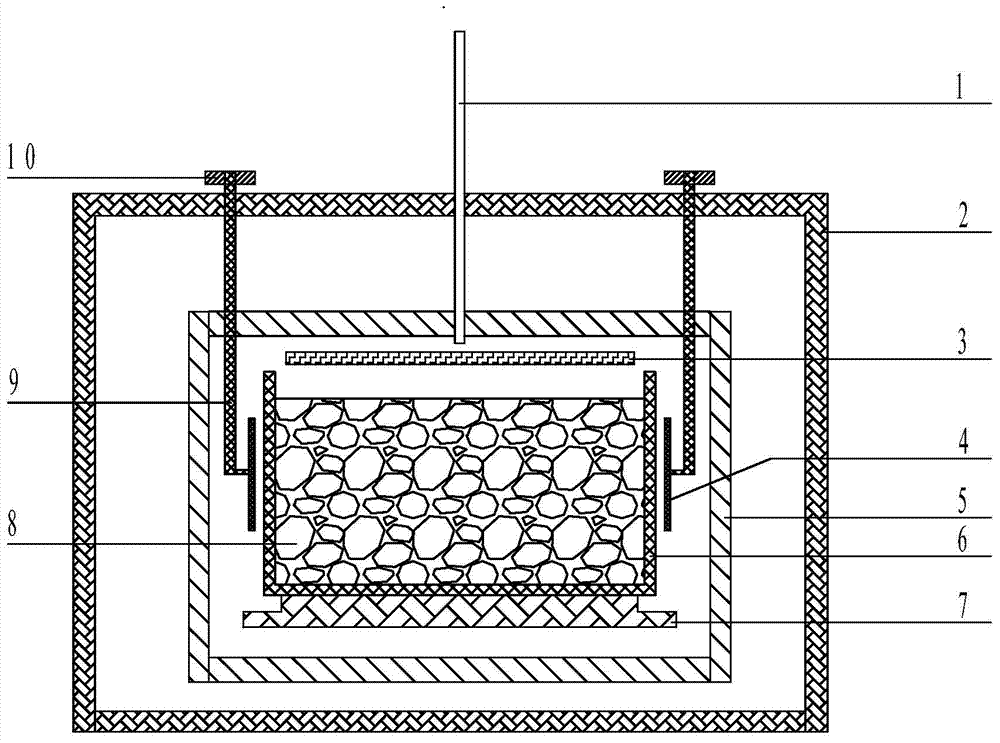
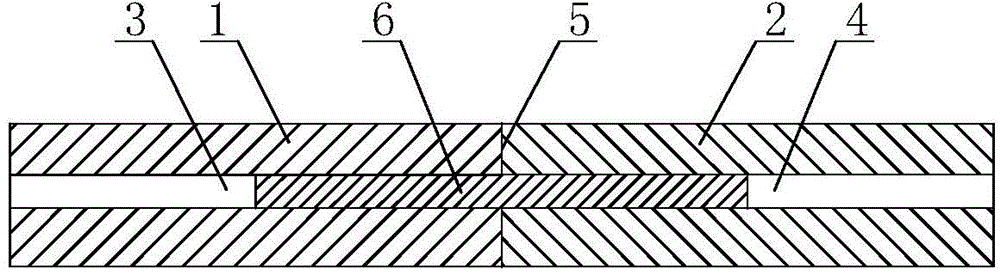
InactiveCN104711673AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyIngot casting process requirements are lowPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsVacuum pumpingSpray coating
The invention relates to a preparation method of a polycrystalline silicon ingot. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a binding agent, a dispersing agent, and silicon particles of which the purity is above 99.9 percent and the diameter is between 1 [mu]m and 5,000 [mu]m, are added into deionized water, a pulp is obtained after uniform mixing, and the mass percentage of the silicon particles in the pulp is not less than 50 percent; (2) in a quartz crucible with a silicon nitride coating on the inner surface, the pulp is applied on the surface of the silicon nitride coating through spray coating, roller coating or brush coating, so as to form a pulp layer with a thickness between 1 mm and 10 mm; the crucible with a silicon coating is obtained after drying; (3) the crucible with the silicon coating is sent into a polycrystalline silicon ingot furnace after being loaded with silicon materials, the silicon materials are heated after vacuum pumping, a silicon material melt is cooled for polycrystalline silicon growth after the silicon materials are completely molten, and the polycrystalline silicon ingot is obtained through annealing cooling after the polycrystalline silicon growth is completed. The polycrystalline silicon ingot obtained through the method can be used for the manufacturing of a solar battery, so that the average battery efficiency of a silicon wafer exceeds 18 percent.
Owner:HUNAN RED SUN PHOTOELECTRICITY SCI & TECH
Seed crystal splicing structure for ingot casting
InactiveCN104831343AImprove fitIncrease the area ratioPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsMortise and tenonIngot casting
The invention relates to a seed crystal splicing structure for ingot casting. The structure comprises mutually spliced seed crystal blocks, a splicing surface between adjacent seed crystal blocks is a plane vertical to the bottom of a crucible, the seed crystal blocks at one side of the splicing surface are provided with an elongated rectangular slot, the seed crystal blocks at the other side of the splicing surface are provided with an elongated rectangular projection suitable for being insert to the rectangular slot, and after the adjacent seed crystal blocks are spliced, the rectangular projection is insert to the rectangular slot, and a gap between splicing surfaces is lower than 0.5mm. The splicing surface of the seed crystal blocks are provided with the rectangular projection and the rectangular slot cooperating with each other to form a mortise and tenon joint structure to improve the lamination degree of the seed crystal splicing surface, and seed crystals at edges are expanded in the heating process, so the mortise and tenon joint structure is compact, the gap is small, the lamination of the adjacent seed crystal blocks is close, and the enlargement of the gap induced by cocking of edges of the seed crystal blocks is prevented, thereby the crystal dislocation defect is maximally reduced, and the monocrystalline area proportion is improved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor light-emitting device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140231841A1Less stressLess heatSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLight beamActive layer
A light-emitting device is disclosed including a light emitting structure comprising a lower layer of the first conductivity type, an active layer, an upper layer of the second conductivity type; a first electrode connected to the lower layer of the first conductivity type; a second electrode connected to the upper layer of the second conductivity type. The light emitting structure is formed using a shell member, which comprises a planar portion and a shell portion. The extent of growth defects such as misfit dislocations is reduced and the extraction of light and heat is improved in the present device. The beam profile of the device may be altered by patterning the light emitting structure instead of shaping the entire chip. The device may be manufactured in a way more compatible with the established, cost-effective processing and packaging methods for large size wafers from the IC industry.
Owner:WANG TIEN YANG
Seed crystal splicing method for monocrystalline-like silicon cast ingot
InactiveCN104775148AImprove fitIncrease the area ratioPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsMortise and tenonCrucible
The invention relates to a seed crystal splicing method for a monocrystalline-like silicon cast ingot. The monocrystalline-like silicon cast ingot comprises seed crystal blocks which are mutually spliced, wherein a splicing surface between adjacent seed crystal blocks is a plane perpendicular to the bottom of a crucible, two long-strip-shaped rectangular grooves are formed in each seed crystal block on one side of the splicing surface from top to bottom, two long-strip-shaped rectangular bumps which are suitable for being inserted into the rectangular grooves are arranged on each seed crystal block on the other side of the splicing surface, and after the adjacent seed crystal blocks are spliced, the rectangular bumps are inserted into corresponding rectangular grooves, and gaps among the splicing surfaces are less than 0.5mm. According to the monocrystalline-like silicon cast ingot disclosed by the invention, the rectangular bumps and the rectangular grooves which are matched mutually are arranged on the splicing surfaces of the seed crystal blocks to form mortise and tenon structures so as to ensure that the adhering degree of the seed crystal splicing surfaces can be improved; in a heating process, seed crystals on edges are heated to be expanded, the mortise and tenon structures are closer, the gaps become smaller, and the adjacent seed crystal blocks can be adhered more closely so as to prevent gap expansion caused by edge up-warping of the seed crystal blocks, so that crystal dislocation defects can be reduced to a highest extent, and the single crystal area proportion can be increased.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Polycrystalline silicon and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103422165AImprove material yieldLow costPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsSilicon chipCrystal growth
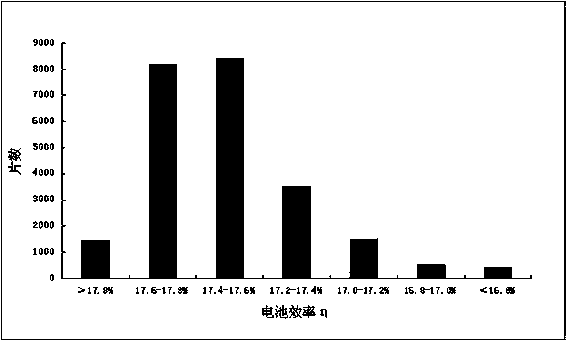
The invention discloses a preparation method of polycrystalline silicon. According to the method, the twin crystal growth control technology is adopted, the ordinary polycrystalline process is optimized, a heat insulation cage is quickly opened, and the opening of the heat insulation cage is adjusted to be 6-8cm; at the initial stage of growth of the crystal, the temperature of a heater is adjusted to be 1425-1440 DEG C, the heat insulation cage is slowly lifted, a layer of uniform dendritic crystal grows vertically on a nucleation source layer along the bottom of a crucible, then dendritic crystal is taken as the seed crystal, and vertically upward directionally grows to form the polycrystalline silicon. The polycrystalline silicon prepared by the invention contains a great quantity of twin crystals, as the twin crystals have the advantages that the interfacial energy of the twin crystals is low, the twin crystals are relatively more stable, and the like, and the polycrystalline silicon prepared by the method has the advantage of few dislocation defects, the battery efficiency of the polycrystalline silicon is higher than that of the ordinary polycrystalline silicon for 0.2-0.4%, the average battery efficiency of a whole silicon wafer reaches 17.5%, and the highest efficiency reaches 18.0%.
Owner:HUNAN RED SUN PHOTOELECTRICITY SCI & TECH
Seed crystal splicing structure suitable for directional solidification ingot casting
InactiveCN104775156AImprove stabilityImprove fitPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsIngot castingCrucible
The invention relates to a seed crystal splicing structure suitable for directional solidification ingot casting. The seed crystal splicing structure comprises seed crystal blocks which are spliced mutually, wherein L-shaped and inverted L-shaped structures are respectively arranged at splicing parts of the adjacent seed crystal blocks so that splicing surfaces are in the shape of mutually fastening steps, the adjacent seed crystal blocks are provided with two pairs of matched cylindrical holes at fastening parts, the cylindrical holes are perpendicular to the bottom of a crucible, after the seed crystal blocks are spliced, the paired cylindrical holes are spliced face to face to form cylindrical cavities, cylindrical silicon rods are inserted into the cylindrical cavities, and gaps between the cylindrical silicon rods and the cylindrical holes are less than 0.5mm. By inserting the silicon rods into the cylindrical holes, the stability of seed crystal block splicing can be improved, and the fitting degree of the seed crystal splicing surfaces can also be increased; and seed crystals on the edges expand by heat in a heating process, therefore, tenon and mortise structures are relatively tight, the gaps become small, and the adjacent seed crystal blocks are more tightly fitted to prevent the enlargement of the gaps caused by upwarp of the edges of the seed crystal blocks, thus reducing the defect of crystal dislocation to the greatest extent and improving the performance of photovoltaic devices.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Polysilicon ingot and manufacturing method of same
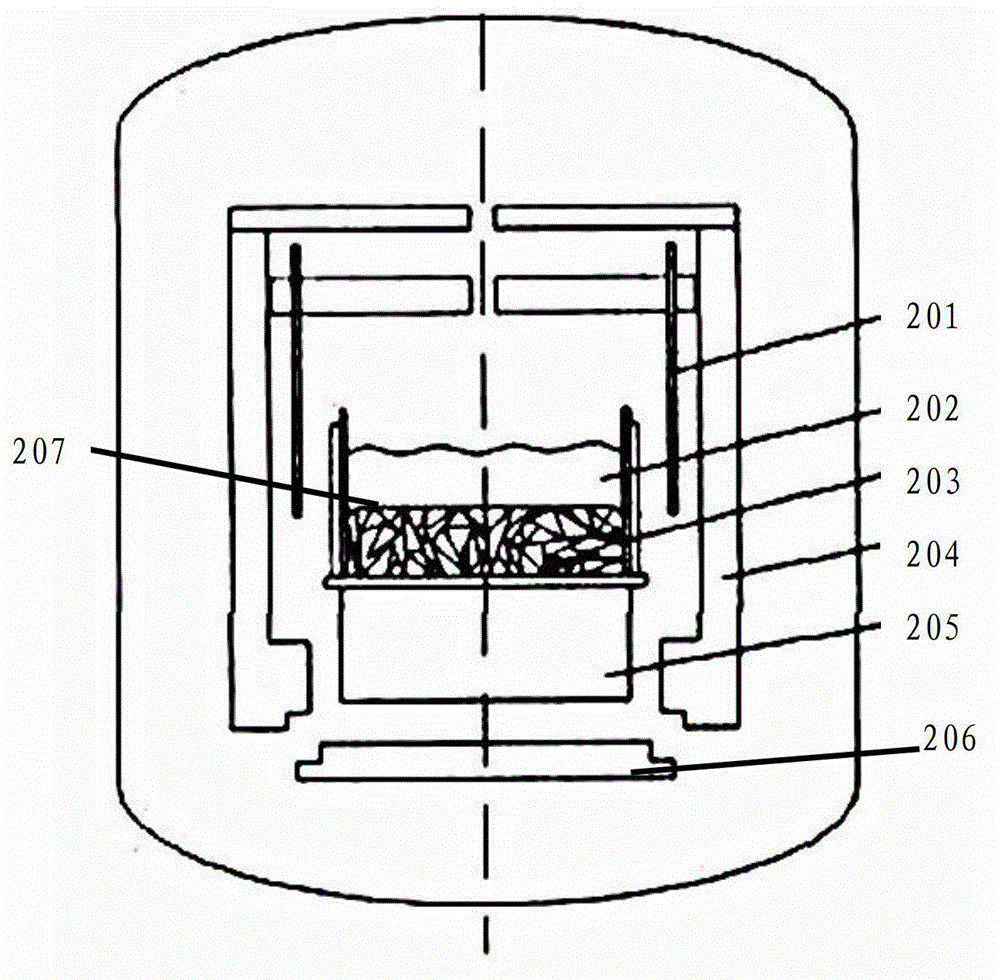
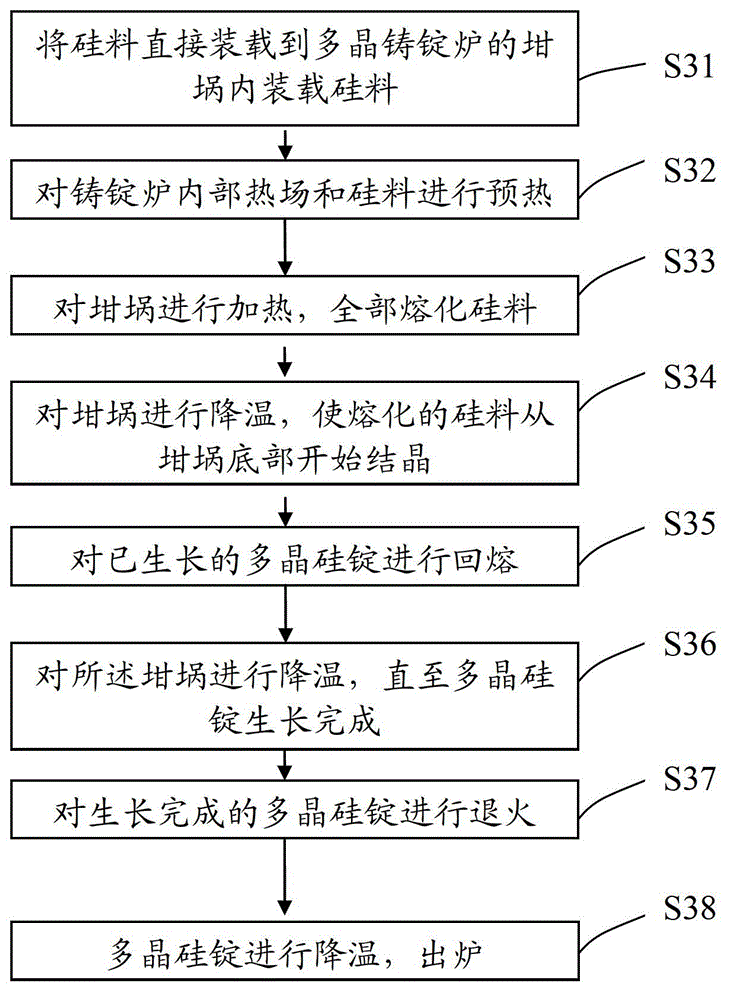
InactiveCN102943304AReduce dislocation defectsHigh-quality and efficient growth processPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsIngotDislocation
The invention discloses a polysilicon ingot and a manufacturing method of the polysilicon ingot. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of directly placing a silicon material into a crucible of a polycrystal ingot furnace; heating the crucible, thus completely melting the silicon material; cooling the crucible, thus allowing the molten silicon material to begin crystallizing at the bottom of the crucible; when the growing height of the polysilicon ingot is 20mm-60mm including the end point values, controlling the thermal field in the polycrystal ingot furnace, melting back the grown polysilicon ingot, and maintaining the solid state of the polysilicon ingot at the bottom of the crucible during the melting-back process; and cooling the crucible until the growth of the polysilicon ingot is finished. According to the embodiment of the invention, the polysilicon ingot of the early growth stage is melted back, therefore the dislocation defect of the polysilicon ingot is reduced, the impurity dephlegmation during the growth process is enhanced, the quality of the polysilicon ingot product is improved and the dislocation density magnitude order of the polysilicon ingot manufactured by the method is below 10<5>.
Owner:YINGLI ENERGY CHINA
Ingot furnace with movable side heater and ingot production process
InactiveCN103572365AShorten the timeReduce manufacturing costPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsHeat conductingReciprocating motion
The invention belongs to the field of polycrystalline silicon ingots, and particularly relates to an ingot furnace with a movable side heater and an ingot production process. The ingot furnace comprises a furnace body, wherein a quartz crucible is arranged in the furnace body, the side heater and a heat-preserving carbon felt are sequentially wound the outer wall of the quartz crucible from inside to outside, a top heater is fixedly arranged above the quartz crucible, a heat exchange block is arranged below the quartz crucible, heat conducting bars are equidistantly arranged on the side heater along the winding direction, and the other ends of the heat conducting bars are fixedly connected with an electrode rod at the top of the outside of the furnace body. The process comprises the steps of feeding materials and vacuumizing, feeding argon gas so as to increase pressure, heating for melting silicon materials, growing crystals, annealing and preserving heat, and cooling, wherein in the steps of heating and silicon material melting, the side heater carries out a reciprocating motion in the vertical direction of the quartz crucible; in the step of crystal growth, the side heater is kept in the middle of the quartz crucible; in the step of annealing and heat preservation, the side heater is kept at the lower part of the quartz crucible. According to the invention, the ingot production cost can be reduced by 5%.
Owner:QINGDAO XINSHIJI SOLAR ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Seed crystal jointing structure for oriented solidification of cast ingots
InactiveCN104818520AReduce gapIncrease the gapPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsMortise and tenonCrucible
The invention relates to a seed crystal jointing structure for oriented solidification of cast ingots. The seed crystal jointing structure comprises jointed seed crystal blocks, wherein jointing surface betweens two seed crystal blocks are planes which are vertical to the bottom of a crucible; a transverse columnar hole vertical to the jointing planes is formed in each seed crystal block; after adjacent seed crystal blocks are jointed, the transverse columnar holes are jointed to form a bar-shaped columnar cavity; a silicon rod inserts the columnar cavity. The transverse columnar holes are formed in the seed crystal blocks; two ends of the silicon rod insert the columnar holes of adjacent seed crystal blocks, thus jointing of the seed crystal blocks is realized; the jointing manner has a mortise-and-tenon jointing structure, thus lamination of the seed crystal jointing surfaces is improved. During heating, seed crystal at the edges is expanded by heating and the mortise-and-tenon jointing structure becomes relatively tight, thus expanding of seams caused by wrapped edges of the seed crystal blocks is prevented. The silicon rod and the columnar holes can be processed at one time through a drilling machine and are easily realized in industries; the jointing (inserting) method is simple, is easy to be mastered by operators and has relatively high practical value.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Method to improve transistor tox using si recessing with no additional masking steps
InactiveUS20110027954A1Reduce dislocation defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorTransistor
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Ultraviolet LED with polarized doped composite polar surface electron blocking layer
ActiveCN111599903AAvoid crystal quality degradationImprove luminous efficiencySemiconductor devicesMultiple quantumElectron blocking layer
The invention discloses an ultraviolet LED with a polarized doped composite polar surface electron blocking layer. The device comprises a substrate arranged in sequence from bottom to top, the devicecomprises a low-temperature AIN nucleating layer, a high-temperature AlN intermediate layer, a non-doped AlGaN buffer layer, an n-type AlGaN layer, an Alx1Ga (1-x) 1N / Alx2Ga (1-x) 2N multi-quantum well active region, a polarization doped composite polar surface electron blocking layer and a p-type Alx5Ga (1-x) 5N layer, an n-type ohmic electrode is arranged on the n-type AlGaN layer; wherein a p-type ohmic electrode is arranged on the p-type Alx5Ga1-x5N layer, and the polarization doped composite polar surface electron barrier layer comprises a nitrogen polar surface p-type Alx3Ga1-x3N electron barrier layer and a metal polar surface p-type Alx4Ga1-x4N electron barrier layer which are arranged from bottom to top. The polarized doped composite polar surface electron barrier layer has higherelectron barrier layer hole concentration, and hole injection of the p-type Alx5Ga1-x5N layer is facilitated; lattice mismatch between the active region and the electron blocking layer is reduced, and the crystal quality of the epitaxial layer is improved; the radiation recombination efficiency of electron holes in an active region is improved, and the light-emitting efficiency of the ultravioletlight-emitting diode is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
GaN-based light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxy structure containing ternary superlattice and preparation method of GaN-based LED epitaxy structure
InactiveCN105098008AReduce dislocation defectsImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLuminescenceLight-emitting diode
The invention relates to the technical field of luminescence of semiconductors, in particular to a GaN-based light-emitting diode (LED) epitaxy structure containing a ternary superlattice and a preparation method of the GaN-based LED epitaxy structure. According to the technical scheme, the GaN-based LED epitaxy structure comprises a patterned substrate, a buffer layer, a non-doped intrinsic GaN layer, an N-type GaN layer, a multi-InGaN / GaN quantum well active layer, a ternary superlattice layer and a P-type GaN layer, which are sequentially stacked; and the ternary superlattice layer is formed by growing the ternary superlattice which formed by an InGaN layer, an AlGaN layer and an MgGaN layer after growing a multi-quantum well layer. The GaN-based LED epitaxy structure has the beneficial effects that the dislocation defect of the quantum well layer and subsequent p-type GaN can be effectively reduced; the crystal quality of a GaN epitaxy film is improved; the carrier concentration can be effectively increased; and relatively good electronic blocking and diffusion are provided, so that the internal resistance is reduced, and the internal quantum efficiency is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI SHENGHE ELECTRONICS TECH
Window interface layer of a light-emitting diode
InactiveUS7199390B2Improve film qualityExcellent forward voltageActive medium materialSemiconductor devicesInterface layerActive layer
This invention is about a window interface layer in a light-emitting diode which comprises an n-type GaAs substrate with an n-type ohmic electrode at the bottom side thereof; an n-type AlGaInP cladding layer formed atop the substrate; an undoped AlGaInP active layer formed atop the n-type cladding layer; a p-AlGaInP cladding layer formed atop the active layer; a p-type window layer made of GaP; a p-type ohmic electrode formed atop the p-type window layer; and a highly doped p-type interface layer made of GaxIn1-xP (0.6≦x≦0.9) and interposed between the p-type cladding layer and p-type window layer wherein the highly doped p-GaInP interface layer possesses a band gap which is higher than that of the active layer and, however, smaller than that of the p-type cladding layer, and wherein the lattice constant lies between GaAs and GaP. In this way, the p-GaInP interface layer is interposed between a p-GaP window layer and a p-AlGaInP cladding layer for enhancing the film quality and the luminous efficiency as well as improving the electric property.
Owner:ARIMA OPTOELECTRONICS
Seed crystal splicing structure for like single crystal silicon cast ingot
InactiveCN104818521AImprove fitImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsMortise and tenonCrucible
The invention relates to a seed crystal splicing structure for a like single crystal silicon cast ingot. The seed crystal splicing structure comprises mutually spliced seed crystal blocks, a splicing surface between adjacent seed crystal blocks is a plane, an included angle alpha is formed between the plane and the bottom of a crucible and ranges from 30 degrees to 60 degrees, a rectangular slot is formed in the seed crystal block on one side of each splicing surface, and a rectangular bump suitable for inserting into the slot is arranged on the seed crystal block on the other side of the splicing surface. After the adjacent seed crystal blocks are spliced, the bumps are inserted into the slots, and the gaps between the splicing surfaces are smaller than 0.5mm. The splicing surfaces of the seed crystal blocks are provided with bumps and the slots which are mutually matched to form mortise and tenon joint structures, and the fitting degree of the splicing surfaces of the seed crystal blocks is improved. In the heating process, seed crystals at the edge are heated to expand, so that the mortise and tenon joint structures are closer, welding seams are changed smaller, the adjacent seed crystal blocks are closely fitted, largeness of the gaps caused by projecting of the edges of the seed crystal blocks are prevented, so that dislocation of the crystals is furthest decreased, and single crystal area ratio is increased.
Owner:NANTONG ZONGYI NEW MATERIAL
Light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112366261AImprove luminous efficiencyReduce mismatchSemiconductor devicesMolecular physicsMaterials science
The invention discloses a light emitting diode epitaxial wafer and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of light emitting diode manufacturing. The AlGaN sub-layers and the first GaNsub-layers which are alternately stacked can release certain stress in the growth process, and dislocation defects accumulated in the first composite layer are few. The buffer layer further comprisesa second composite layer stacked on the first composite layer, and the structure of the second composite layer can be a second GaN sub-layer and a MgN sub-layer which are alternately stacked, and a second GaN sub-layer and a BN sub-layer which are alternately stacked. The Mg atoms and B atoms in the BN sub-layer are small in particle size, vacancies generated by defects and dislocations in crystals can be filled in the growth process, so that the formation of the dislocations and the defects is reduced, the crystal quality of the buffer layer is improved, and the luminous efficiency of the finally obtained light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer is also improved.
Owner:HC SEMITEK ZHEJIANG CO LTD
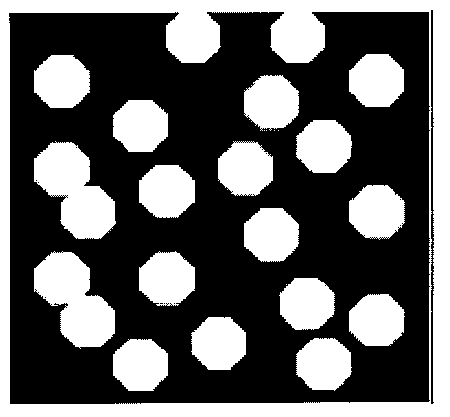
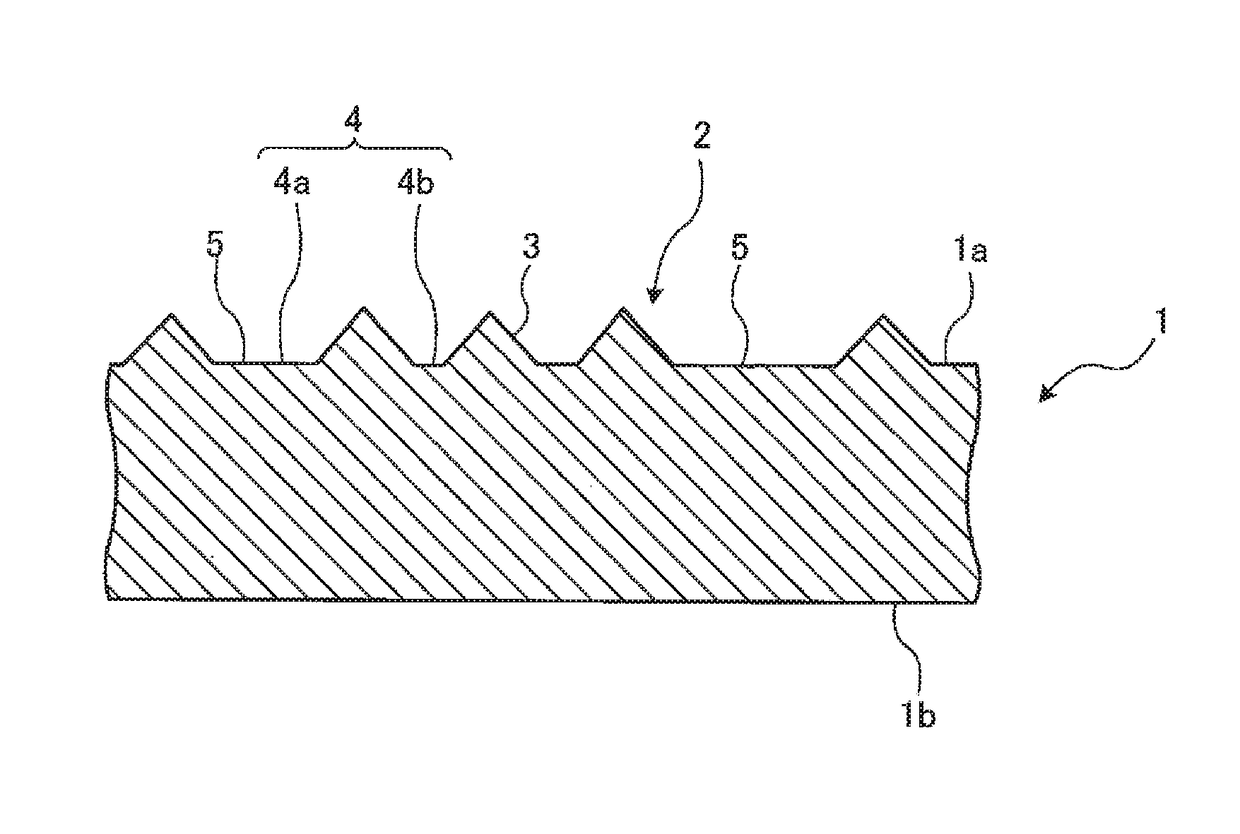
Optical substrate, substrate for semiconductor light emitting device and semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS20180254380A1Improve luminous efficiencyHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesConvex structureLight emitting device
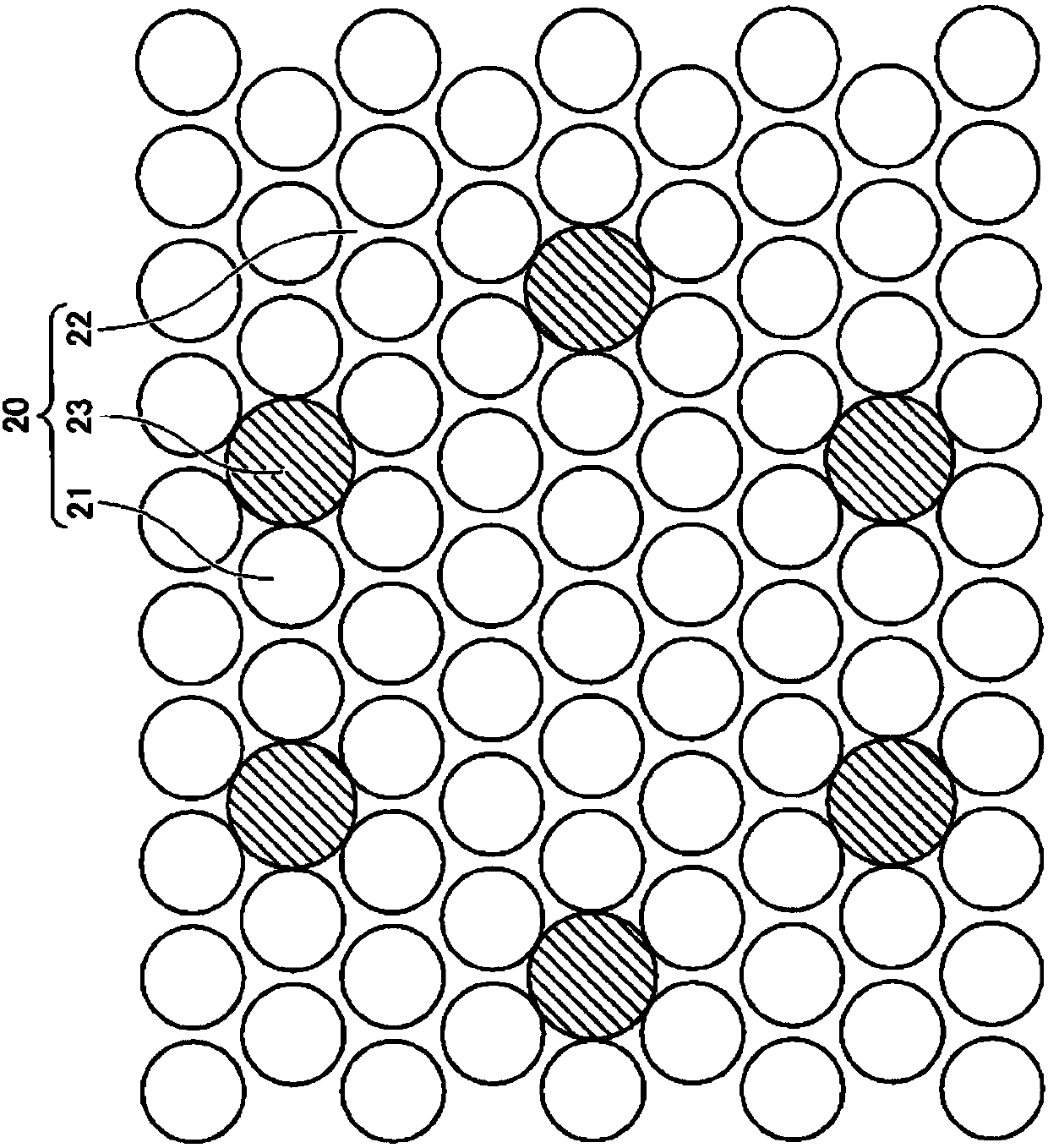
To provide semiconductor films for enabling semiconductor light emitting devices particularly having excellent luminous efficiency as compared with conventional devices to be manufactured with high yields, and semiconductor light emitting devices using the films, the present invention provides an optical substrate with a concavo-convex structure (20) formed on a part or the whole of a main surface, where the concavo-convex structure has regular toothless portions. The concavo-convex structure is comprised of convex portions (21), inter-convex portion bottom portions (flat portions) (22), and a concave portion (23) (toothless portion) having a flat plane in a position lower than a main surface formed of the inter-convex bottom portions. Further, it is preferable that the convex portions are arranged with an average pitch P0, the toothless portions are disposed on vertexes of a regular polygon, or disposed on a side of the regular polygon connecting between the vertexes, and that a length of the side of the regular polygon is longer than the average pitch P0.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Forming method of transistor
ActiveCN104425267AReduce dislocation defectsHigh densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilitySurface level
A method is provided for fabricating a transistor. The method includes providing a semiconductor substrate having a first region; and forming a first gate structure on a surface of the semiconductor substrate in the first region. The method also includes forming trenches in the semiconductor substrate at both sides of the first gate structure; and forming a first stress layer with one surface lower than the surface of the semiconductor substrate in the trenches. Further, the method includes forming a second stress layer containing carbon atoms with a surface leveling with or higher than the surface of the semiconductor substrate on the first stress layer; and forming a source region and a drain region in the semiconductor substrate at both sides of the first gate structure.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP +1
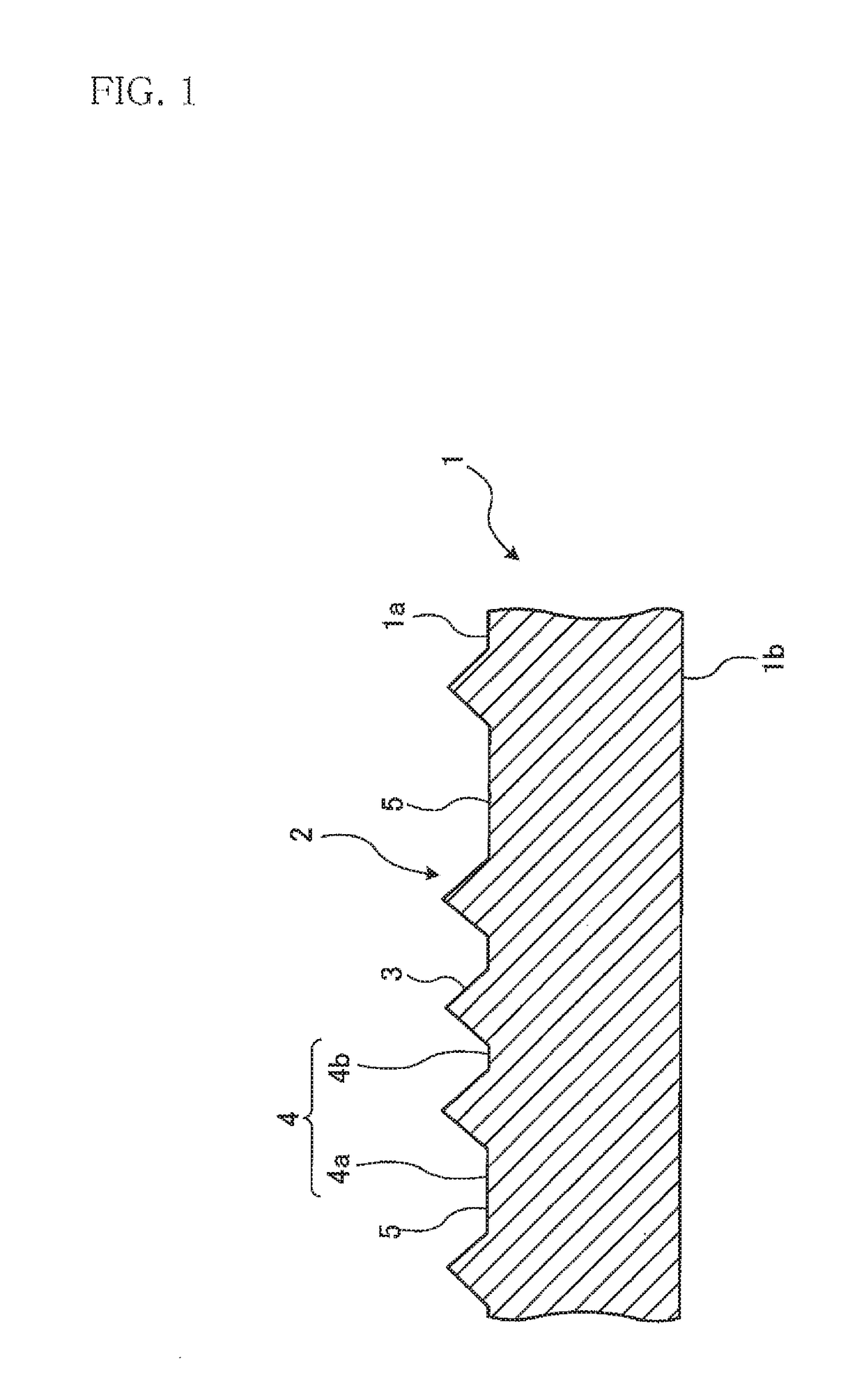
Optical substrate, substrate for semiconductor light emitting element, and semiconductor light emitting element
InactiveCN108028299AImprove luminous efficiencyReduce dislocation defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor film with which a semiconductor light emitting element having superior light emitting efficiency, especially compared to the prior art, can be manufactured with high yield, as well as a semiconductor light emitting element using the semiconductor film. The present invention is an optical substrate in which an uneven structure (20)is formed over part or an entirety of the principal surface, the uneven structure regularly including toothless sections. The uneven structure is constituted by projecting sections (21), inter-projecting sections bottom-sections (flat sections) (22), and recessed sections (23) (toothless sections) which have a flat surface positioned lower than the principal surface formed by the inter-projectingsections bottom-sections. The projecting sections are disposed at an average pitch P0, and the toothless sections are disposed at vertices of a regular polygon or on a side of the regular polygon thatconnects the vertices. The length of the side of the regular polygon is preferably longer than the average pitch P0.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Nitride semiconductor material and method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor crystal
InactiveCN101138073AReduce dislocation defectsHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric substrateX-ray
A nitride semiconductor material wherein a first nitride semiconductor layer group is provided on a semiconductor substrate or a dielectric substrate is characterized in that a surface of the first nitride semiconductor group has an RMS of 5nm or less, an X-ray half width fluctuation within +-30%, a surface light reflectivity of 15% or more and its fluctuation at +-10% or less, and a thickness of the first nitride semiconductor group is 25[mu]m or more. The nitride semiconductor material has excellent uniformity and stability, is manufactured at a low manufacturing cost and is useful as a substrate for nitride semiconductor devices.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com