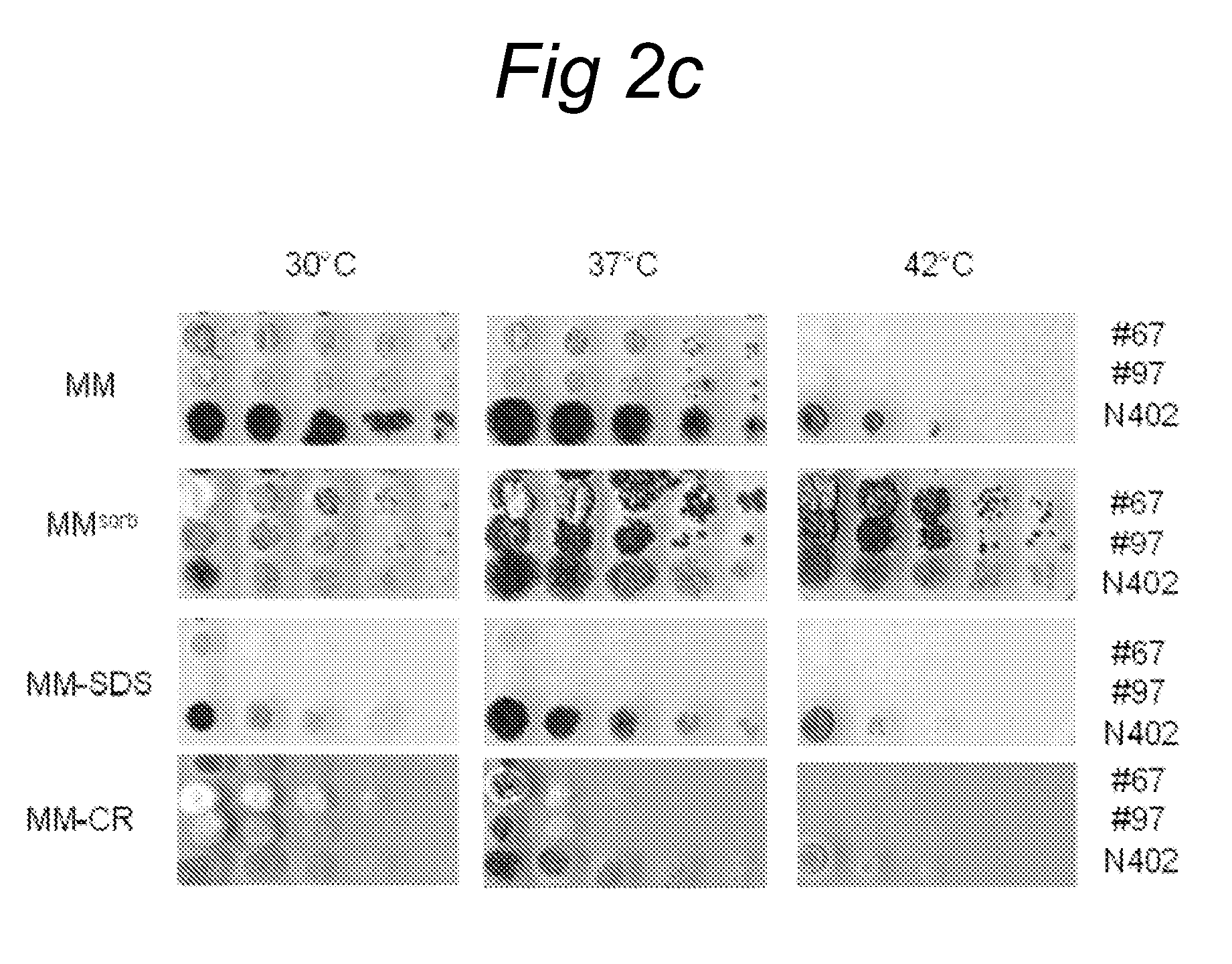
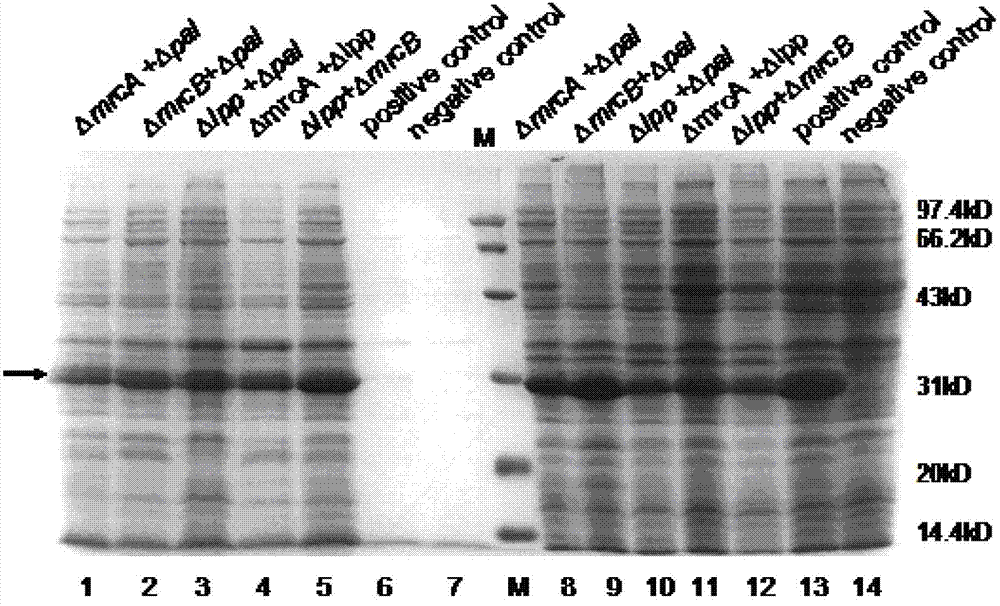
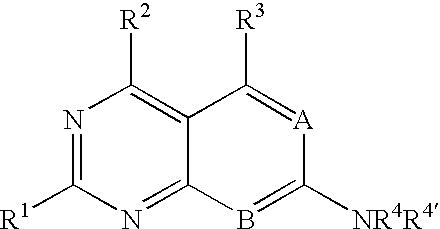
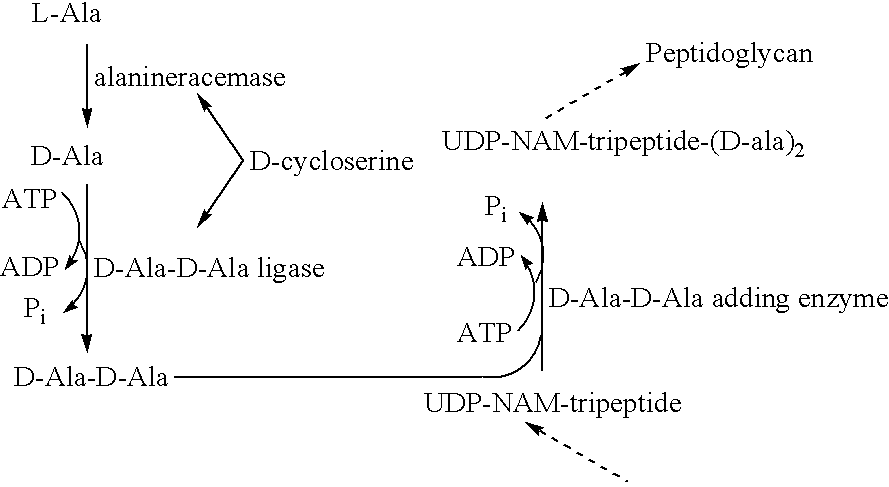
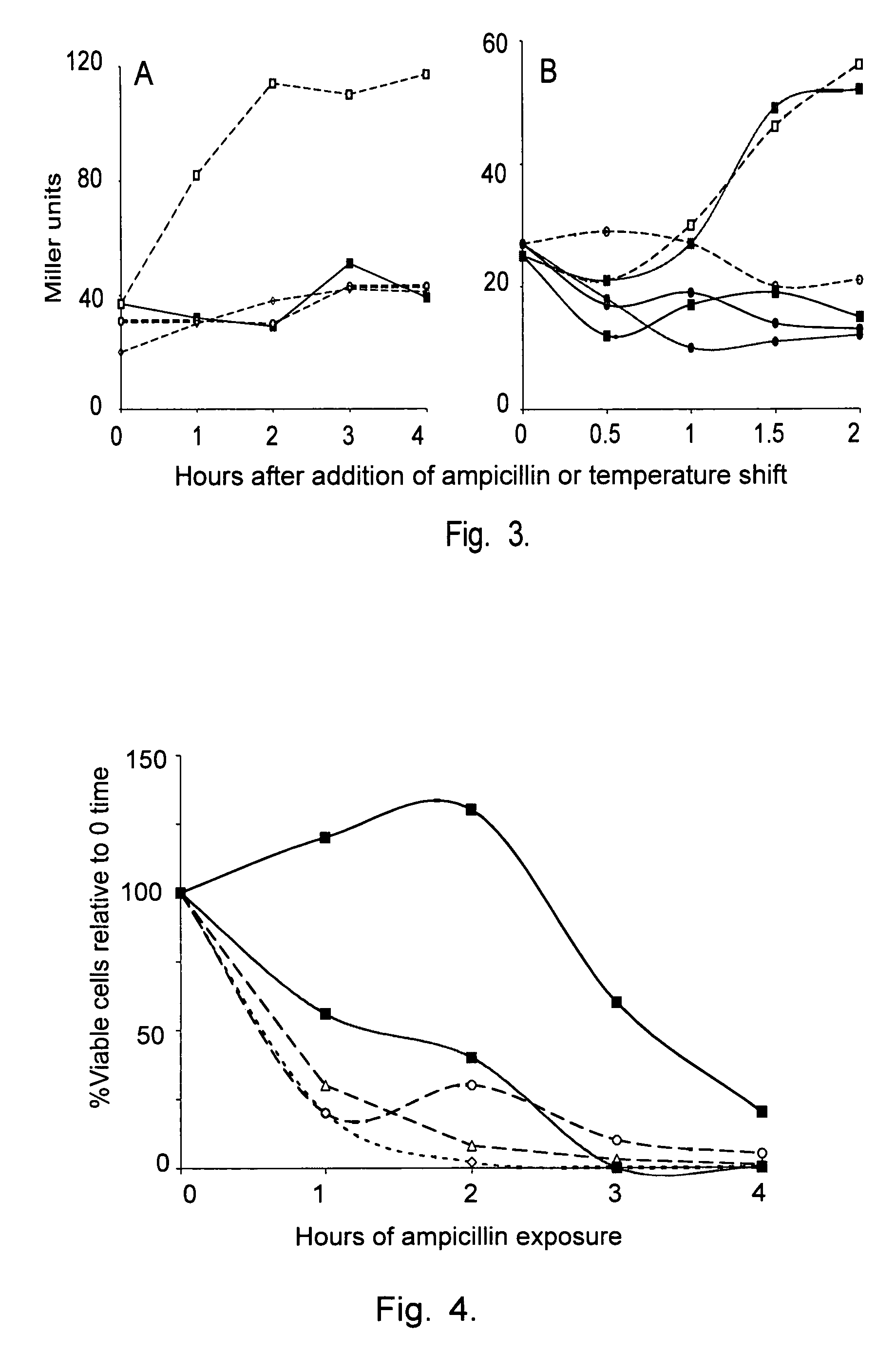
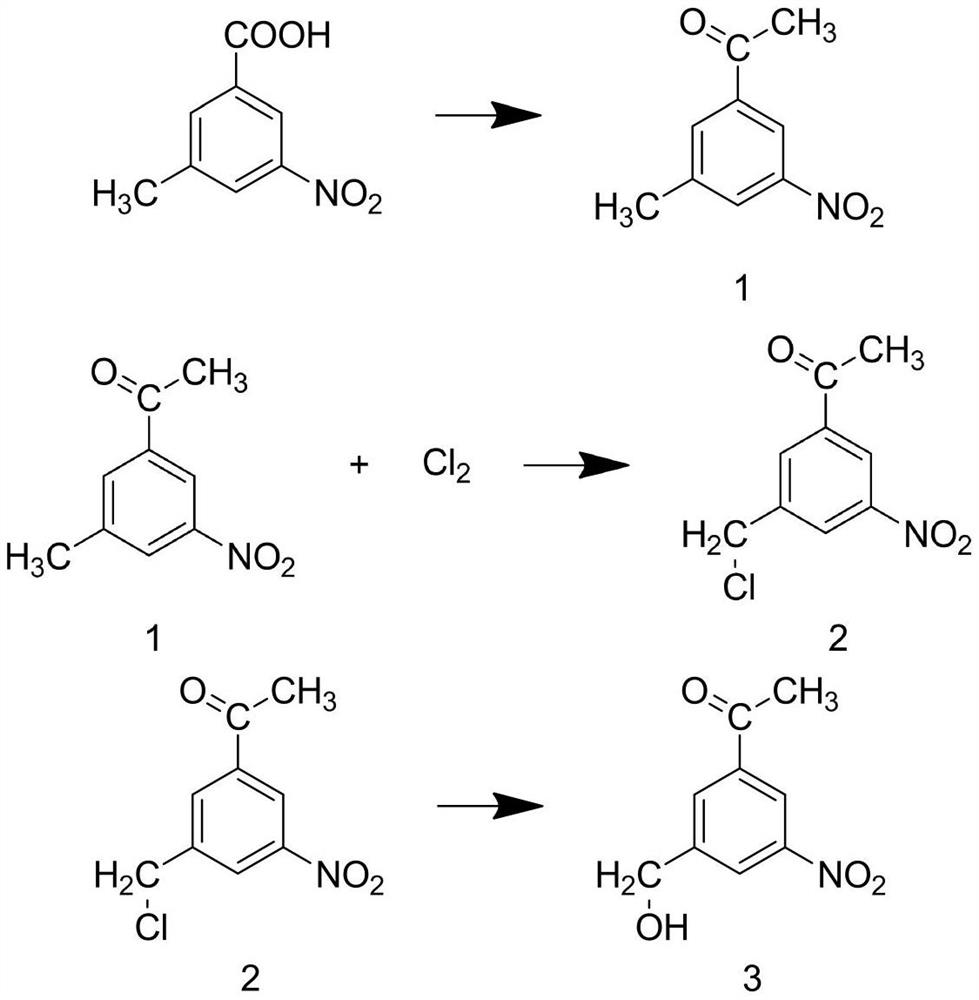
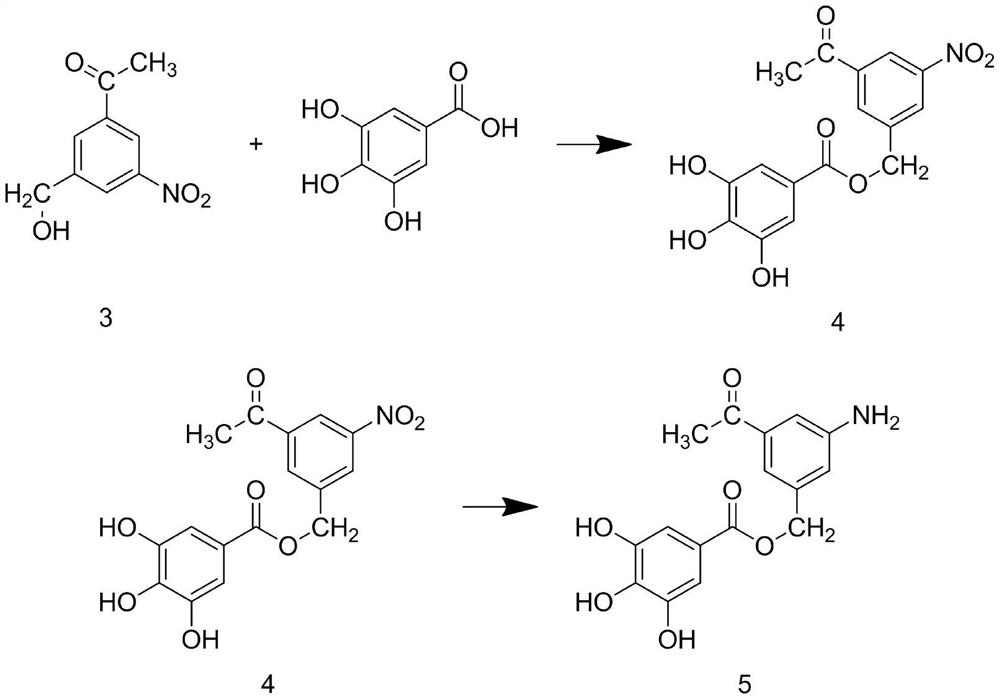
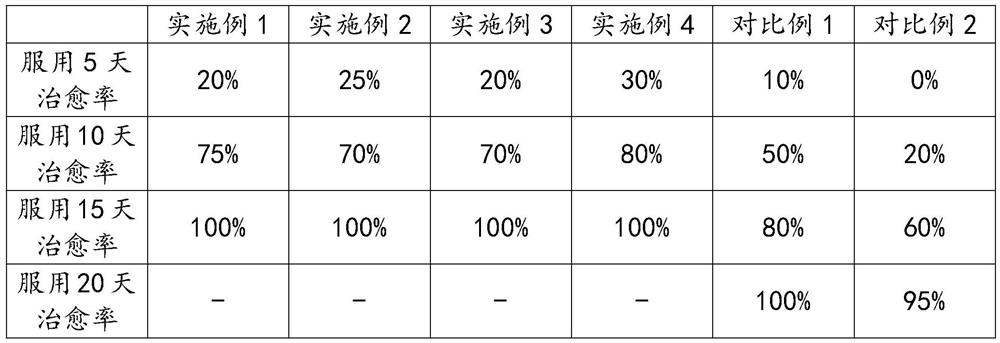
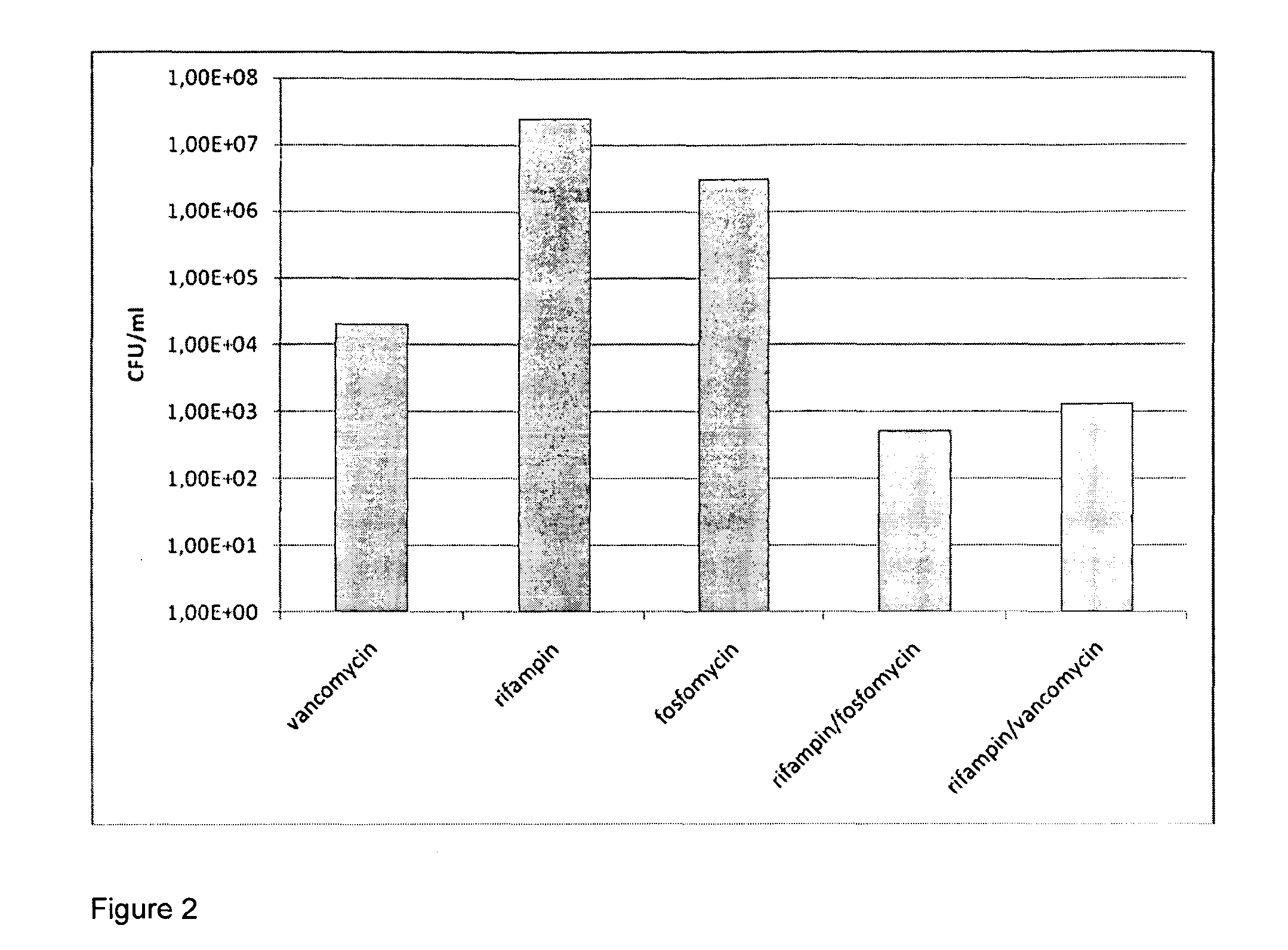
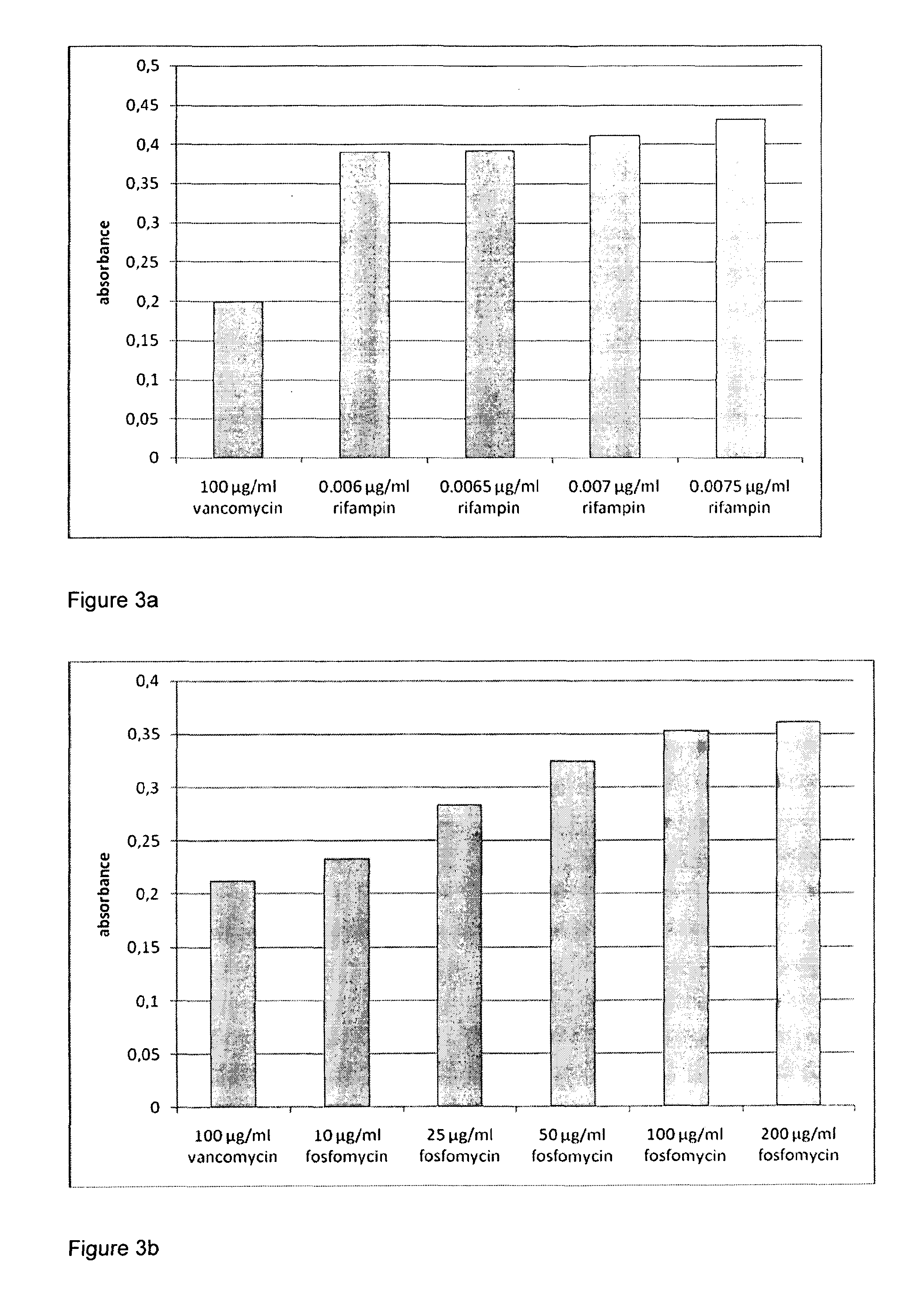
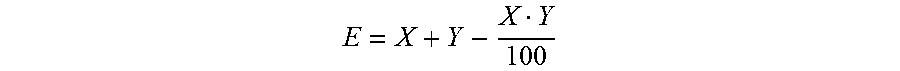Patents
Literature
43 results about "Cell wall synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The second class of antimicrobial drugs that interfere with cell wall synthesis are the glycopeptide antibiotics, which are composed of glycosylated cyclic or polycyclic nonribosomal peptides.
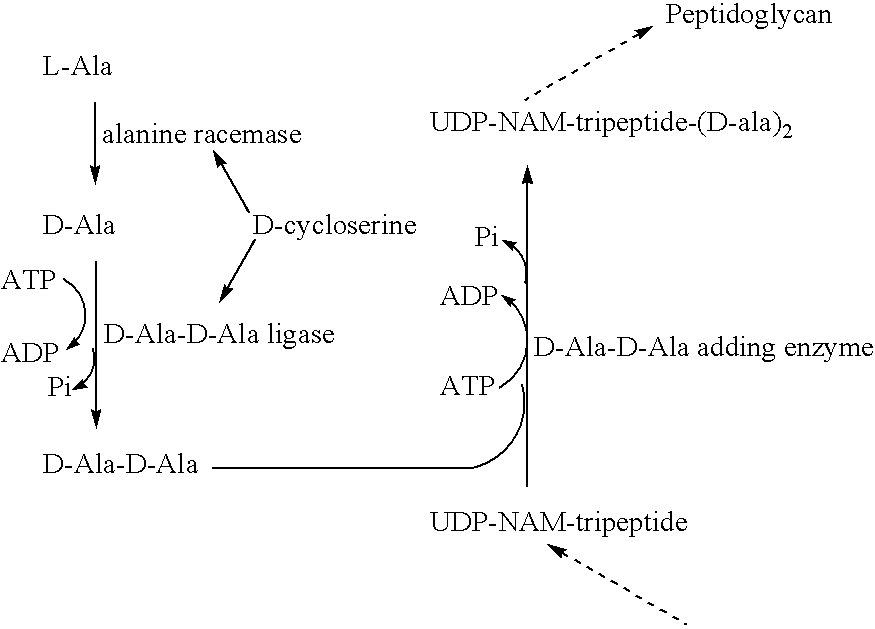
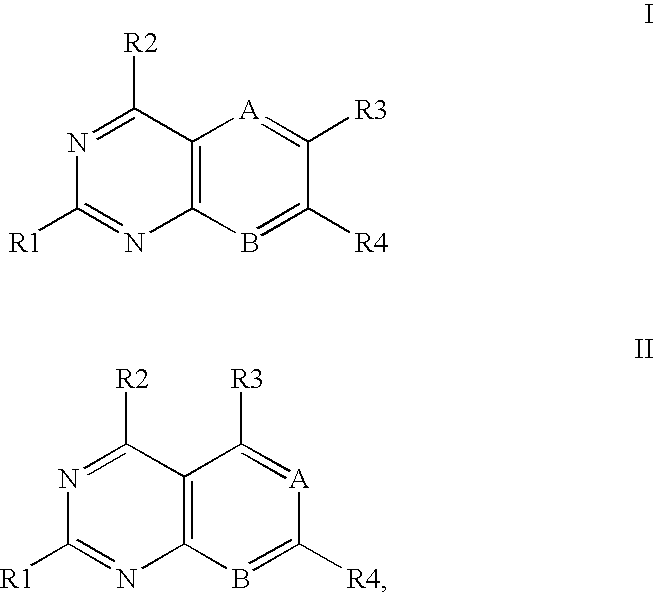
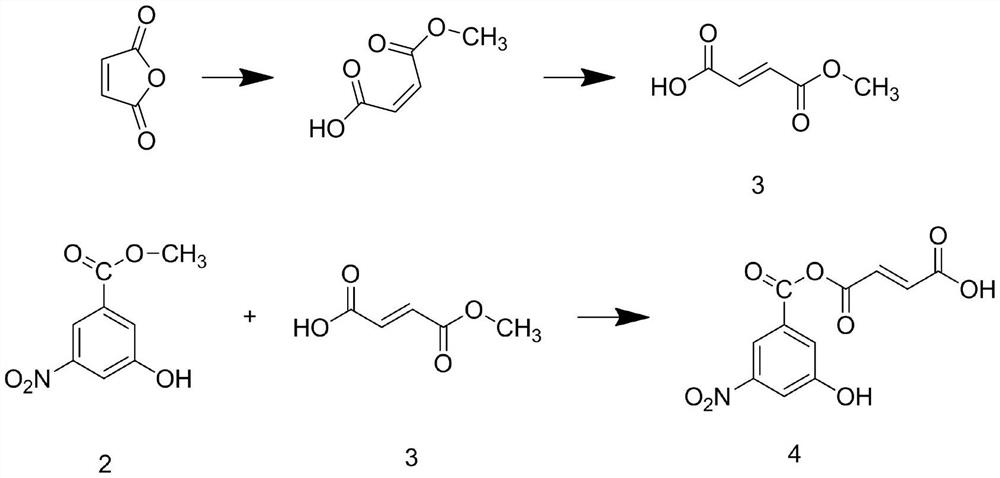
Heterocyclic compounds and uses thereof as d-alanyl-d-alanine ligase inhibitors
InactiveUS20080090847A1Enhanced selectivity and potencyStrong specificityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell membraneD-Ala-D-Ala ligase
The invention is based on the discovery of a new class of heterocyclic compounds having, for example, antibacterial properties. The D-Ala-D-Ala ligase enzyme is a critical pathway enzyme in the bacterial cell-wall synthesis. The compounds can bind to and inhibit the enzyme D-Ala-D-Ala ligase. The new compounds' activity combined with their ability to cross bacterial cell membranes makes them suitable for use as antibacterial drugs or other antibacterial applications.
Owner:PLIVA D D
Gene promoter originated from cotton and its application
InactiveCN1869233AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumAgricultural science
The invention discloses a plant gene promoter and the application. It is has one nucleotide sequence from: the DNA sequence in SEQ ID No: 1; nucleotide sequence of DNA sequence intercross limited in SEQ ID No: 1; the nucleotide sequence has transcription initiation function and has 90% homology of the nucleotide sequence limited by SEQ ID No: 1. The tobacco transgene examination proves theat pGhGlcat1 could endue report gene having high level expression in epidermal hair, top meristem region and androecium and gynoecia of plant flower apparatus. It could be used to improve the plant quality and the gene engineer of fastness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
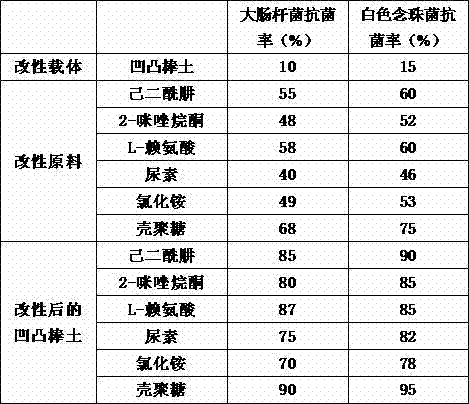
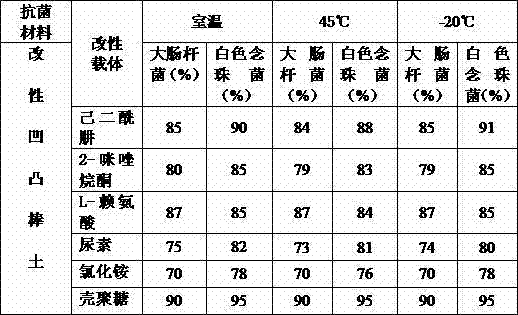
Attapulgite material with anti-bacterial function and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an attapulgite material with an anti-bacterial function and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the attapulgite material comprises the following main steps of: packaging certain materials containing amine groups onto the surface of the attapulgite by virtue of a functional water agent preparation process, a pelletizing process, a drying process and the like; enabling the attapulgite to have the special performances of the modified material while not damaging the structure of the attapulgite. The modified material can be used for absorbing bacteria with negative charges, so that negative charges on bacterial cell walls and cell membranes are not uniformly distributed, the synthesis of the cell walls is interfered, the cell wall synthesis and solubility equilibrium under the natural condition is broken through, and the bacteria are dissolved and died, and therefore, the anti-bacterial and bacteriostatic performances are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAIBAO MEDICAL SCI TECH
Anti-fungal screening method
The present invention relates to a method for identification of anti-fungal agents and their mode of actions. In particular, it relates to cell wall disturbing anti-fungal agents and to an assay to identify them. More particularly, it relates to a screening method for the identification of an anti-fungal compound, which method comprises (i) contacting a potential anti-fungal compound with a polypeptide which is involved in cell wall synthesis; and then (ii) identifying the effect which the potential anti-fungal compound has on the activity of the polypeptide, whereby reduced polypeptide activity is indicative for anti-fungal activity of the potential anti-fungal compound. It also relates to an overexpressing host cell and to a kit for performing the assay.
Owner:LEIDEN UNIVERSITY
Construction method for double-gene mutation escherichia coli used for secretory expression of recombinant protein
InactiveCN102827860AImprove leakage ratioIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenes mutationInclusion bodies
The invention discloses a construction method for double-gene mutation escherichia coli used for secretory expression of recombinant protein. According to the invention, pre-designed primers for the double-knockout-genes of cell membrane protein and cell wall synthetase gene are used for a PCR reaction so as to obtain gene targeting fragments of the double-knockout-gene, wherein two ends of each gene targeting fragment are 10 to 250 bp homologous sequences of a specific target gene and the middle part of each gene targeting fragment is a resistance labeled sequence; the fragments are respectively integrated into chromosomes of the host escherichia coli through electrotransformation so as to obtain a secretory double-gene mutation escherichia coli strain. The method provided by the invention increases the expression of recombinant exogenous proteins, reduces intracellular degradation of target proteins, decreases intracellular accumulation of the recombinant exogenous proteins and eradicates formation of inclusion bodies; the method discards a breaking process for cell walls, reduces pyrogen and simplifies separation and purification; thus, the purposes of reducing production cost and improving protein expression and product quality are achieved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
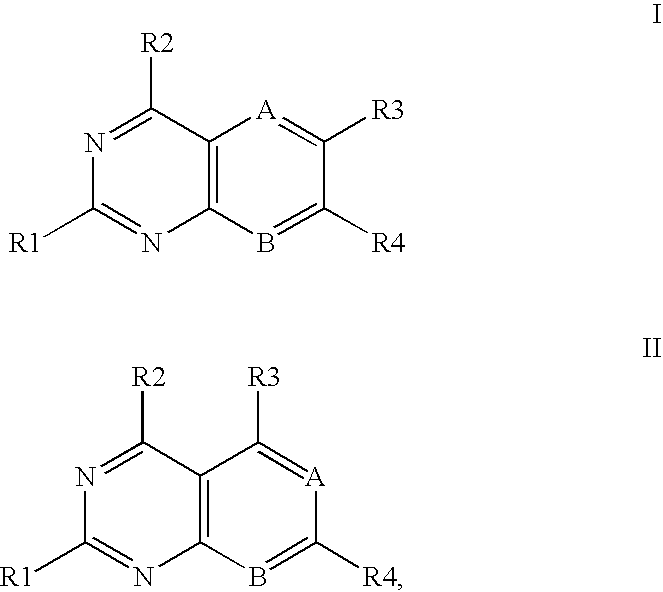
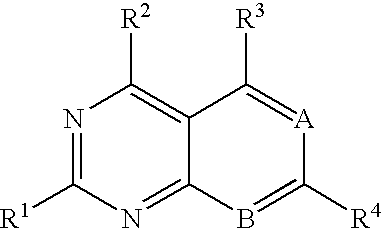
Heterocyclic compounds and uses thereof as D-alanyl-D-alanine ligase inhibitors
InactiveUS7345048B2Eliminate side effectsDifferent profileAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsThio-Acyl group
The invention relates to D-Ala-D-Ala ligase inhibitors having the formula:wherein R1 is NH2; R2 is NH2; R3 is selected from hydrogen, alkyl, amino, hydroxy, alkoxy, and alkylamino; and R4 and R4′ are each independently hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted, linear, branched, or cyclic, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, acyl, aralkyl, or alkaryl group wherein one or more carbon or hydrogen atoms may be substituted by a substituent selected from amino, alkylamino, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, thio, halogen, nitro, and carbonyl; wherein NR4R4′ incorporates a substituted or unsubstituted naphthyl group, wherein the substituents are selected from alkoxy, halogen, alkyl, and alkylene, and wherein said naphthyl group in NR4R4′ is bonded to N through a substituted or unsubstituted alkylene moiety. These compounds have antibacterial properties based on their ability to bind and inhibit D-Ala-D-Ala ligase, a critical pathway enzyme in bacterial cell-wall synthesis, and are suitable for various antibacterial uses.
Owner:PLIVA D D
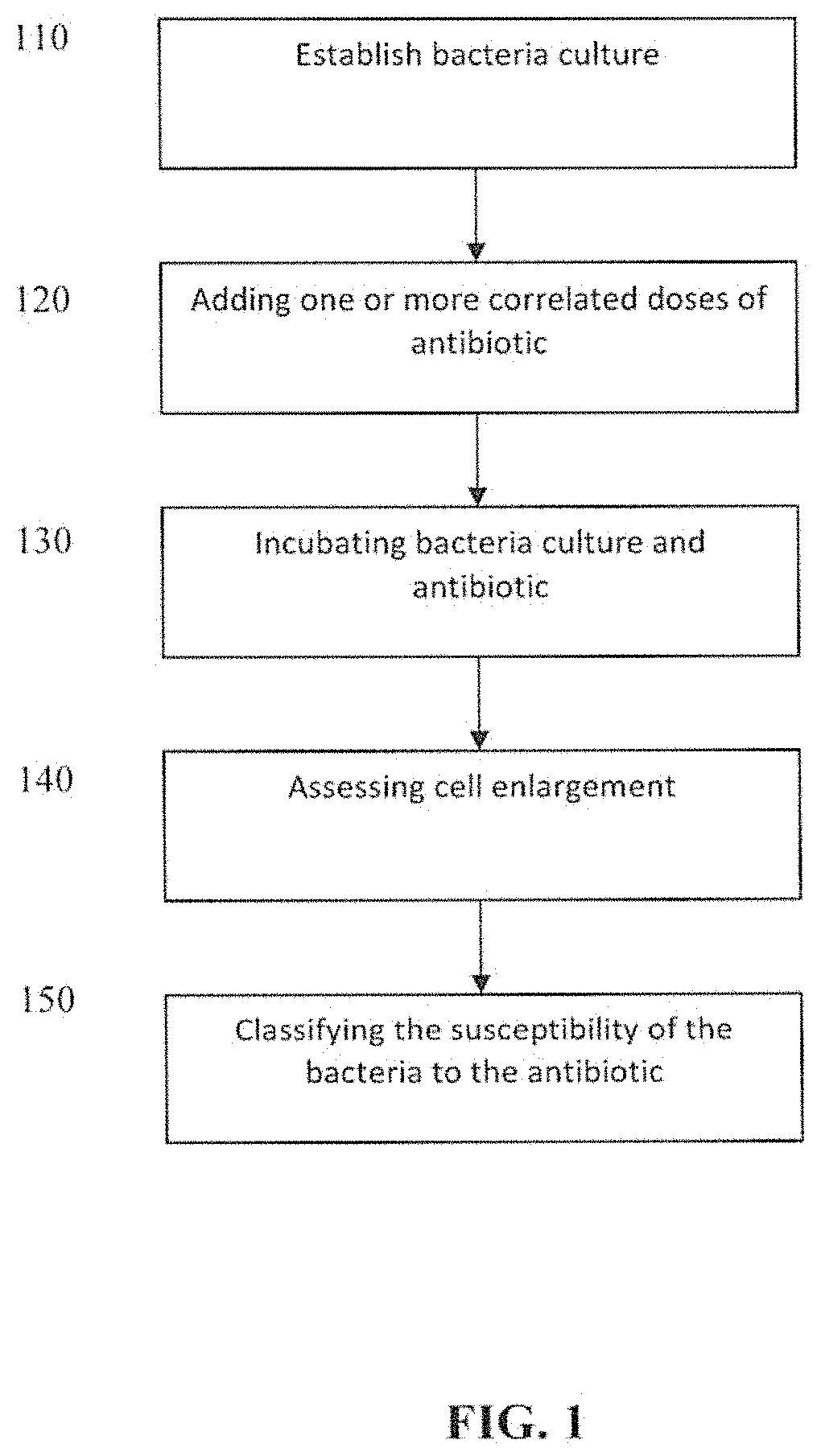
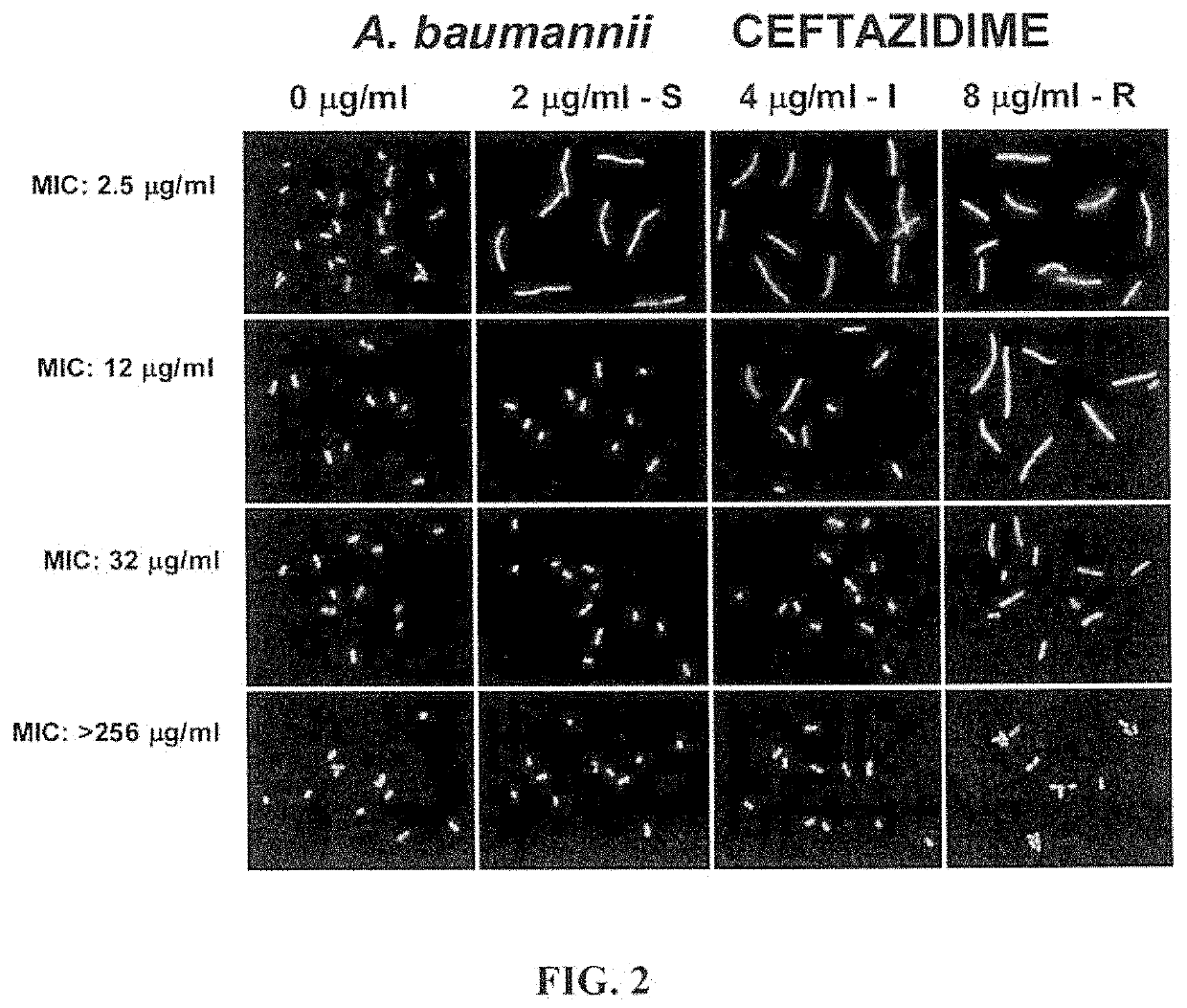
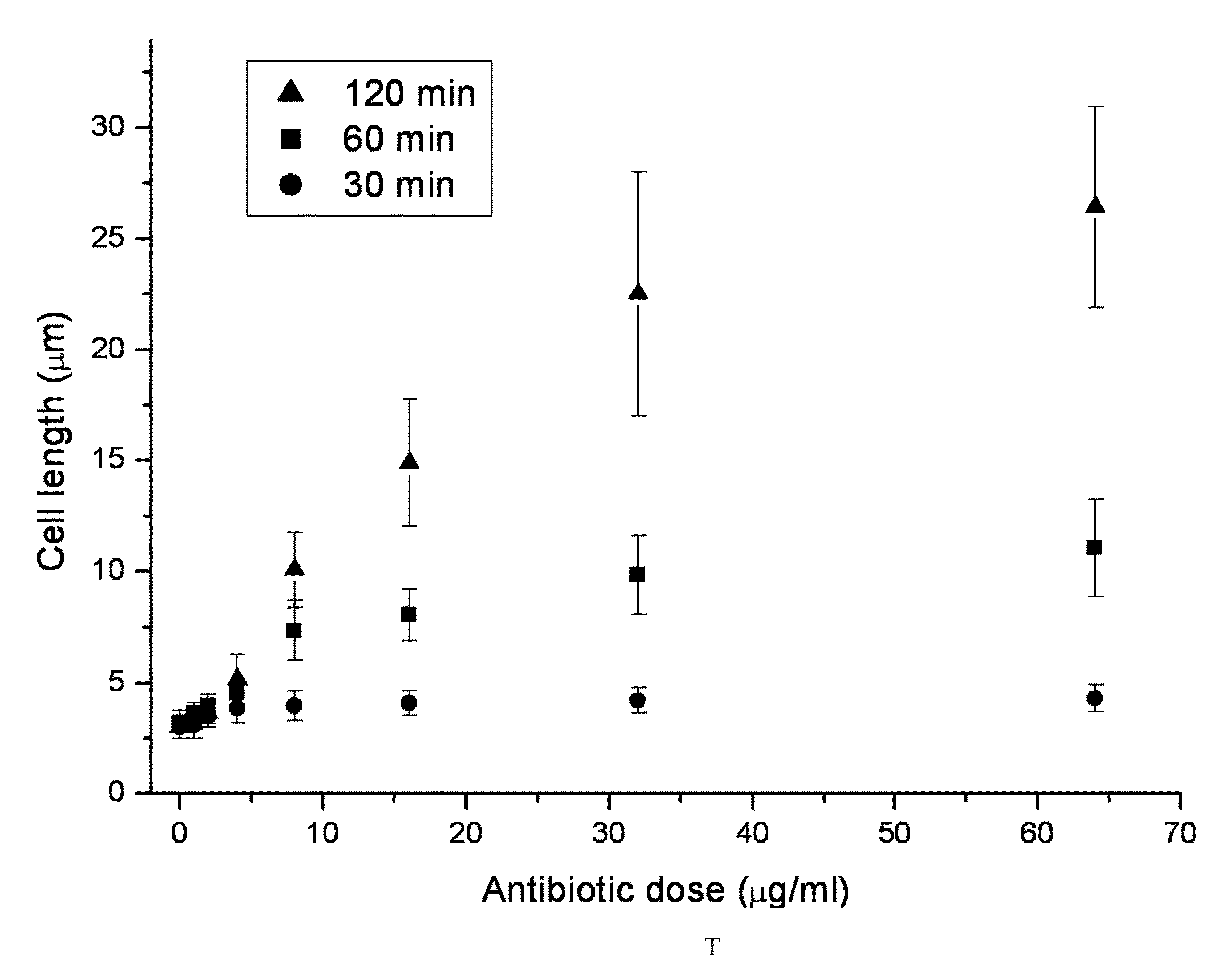
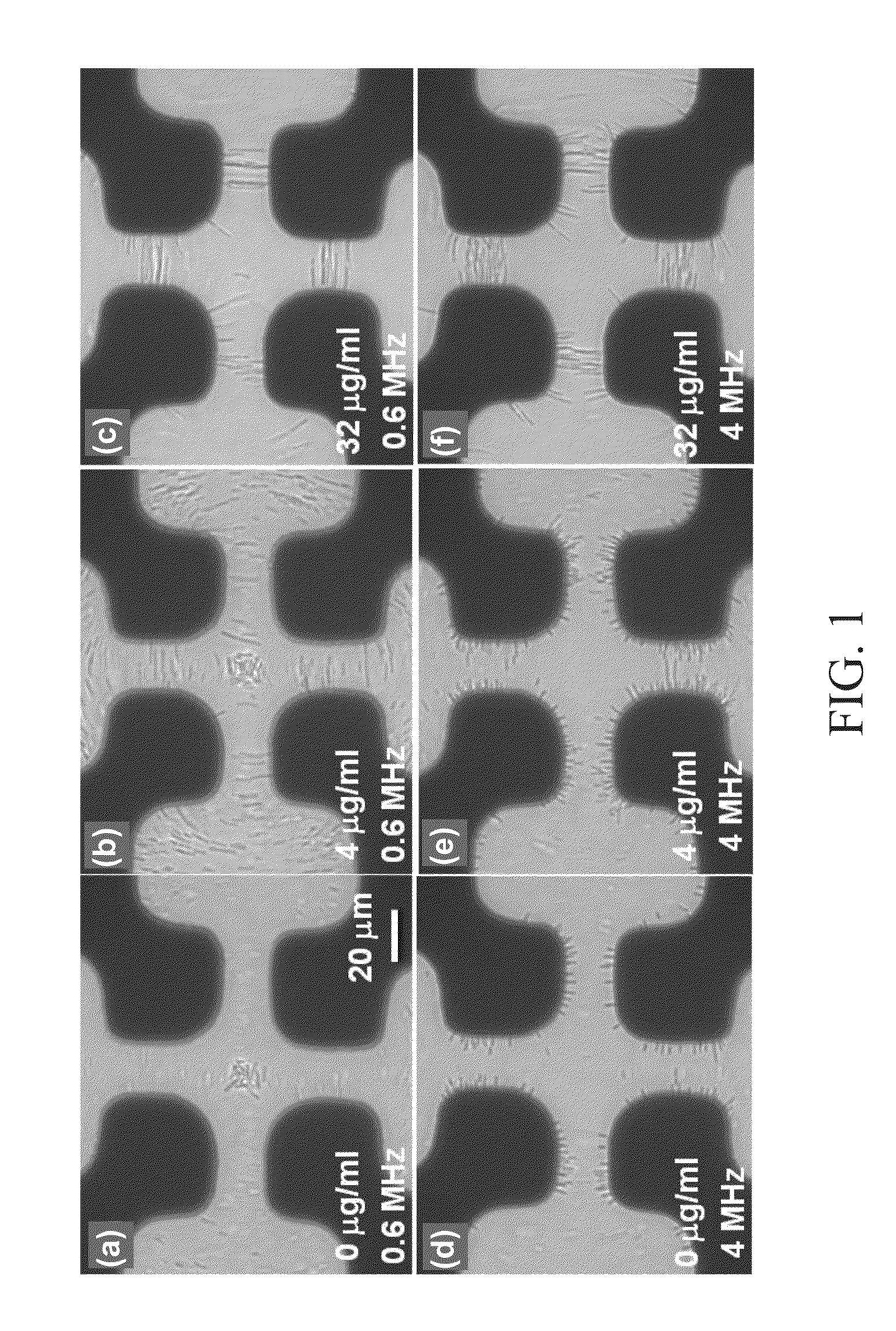
Method for antibiotic susceptibility testing and determining minimum inhibitory concentration of the antibiotic
InactiveUS20130008793A1Shorten the construction periodTesting duration has been reducedDielectrophoresisElectrostatic separatorsMinimum inhibitory concentrationMicrobiology
A method of antibiotic susceptibility testing is disclosed, and includes the following steps: (A) providing a sample to be tested wherein the sample contains a microbe; (B) adding an antibiotic into the sample, wherein the antibiotic serves to inhibit cell wall synthesis; (C) checking the sample by dielectrophoresis and observing a shape change of the microbe; and (D) determining whether the microbe is susceptible to the antibiotic according to the shape change thereof. The present invention also discloses a method for determining a minimum inhibitory concentration of the antibiotic.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Method for electrotransformation of Clostridium thermocellum
InactiveCN102653770AQuick importHigh yield ethanolMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionCellulosePenicillin
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism gene engineering, and particularly relates to a method for electrotransformation of a thermophilic anaerobic cellulose-degrading bacterium of Clostridium thermocellum. The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: pretreating Clostridium thermocellum cells with an antibiotic for inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis (such as penicillin, ampicillin, etc.), and then transforming the Clostridium thermocellum cells by a common commercial electrotransformation machine so as to reach the purpose of introducing exogenous DNA into the Clostridium thermocellum. The method has the advantages that exogenous DNA is rapidly introduced into Clostridium thermocellum cells through a common commercial electrotransformation machine, which lays a foundation for the realization of bacterial gene engineering operations (such as gene overexpression, gene knockout, etc.), and the construction of gene engineering bacterial strains suitable for ethanol industrial production.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for improving apparent catalytic activity of glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacteria
InactiveCN103773731AImprove apparent GAD catalytic activityImprove permeabilityMicroorganism based processesChemical cell growth stimulationGlutamate decarboxylaseCell membrane
The invention discloses a method for improving apparent catalytic activity of glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacteria. The method comprises the steps of inoculating the glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacteria into a culture medium for shake cultivation so as to obtain a seed solution; inoculating the seed solution into the culture medium for shake cultivation, adding an inducer for induction cultivation when OD600 is 0.6-0.8 hour, and simultaneously adding a cell wall synthesis inhibitor or surfactant into the culture medium so as to interfere in synthesis of recombinant bacteria cell walls or (and) cell membranes to achieve the purposes of enhancing the permeability of the bacteria and improving the apparent catalytic activity of the bacteria; and after induction cultivation, collecting the bacteria so as to obtain the glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacteria with the apparent catalytic activity improved. The method for improving apparent catalytic activity of glutamic acid decarboxylase recombinant engineering bacteria is free from multiple processing steps for permeability treatment after cultivation of conventional bacteria and is simple, convenient and efficient, and low in cost.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Modulating SOS response induction by antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS20070031874A1Efficient killingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSOS responseAntibiotic Y
Compositions and methods are provided for the use of SOS pathway targeted agents in antimicrobial formulations. The innate sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics is increased by disrupting a mechanism that normally activates the bacterial SOS response or by inhibiting steps in the SOS response pathway itself. SOS response induction can result from exposure of bacteria to certain antibiotics, including β-lactam antibiotics and other agents that affect cell wall synthesis. By transiently delaying bacterial cell division, SOS response induction interferes with bacterial killing by ordinarily lethal concentrations of these drugs A pharmaceutical composition comprising an SOS targeted agent is administered to a patient suffering from a microbial infection, in combination with an antibiotic that induces an SOS response. The identification of the SOS pathway as a target for modulating antibiotic action provides a basis for further therapeutic development, through screening assays designed to detect molecules or genes that act on these pathways.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Plastic used in drinking water bacteriostasis and sterilization
InactiveCN105623182AAvoid breedingInhibition eradicationBiocideAnimal repellantsMasterbatchCell membrane
The invention relates to plastic used in drinking water bacteriostasis and sterilization. According to the invention, an antibacterial component containing Ag element is added during an injection molding process of a masterbatch. The plastic comprises Ag element. The Ag element can influence microbe growth and reproduction, leading to the death of the microbes. With the Ag element, cell wall synthesis can be interfered, cell membrane can be damaged, protein synthesis can be inhibited, nucleotide synthesis can be interfered, and genetic information replication can be hindered, such that good bacteriostasis and sterilization functions are provided. The plastic of the masterbatch can prevent the excess of silver element in water. The plastic provided by the invention can be widely applied in surfaces directly contacting drinking water, such as drinking fountains, water purification machines, water delivery pipes, and the like.
Owner:TAOEE QINGDAO WATER PURIFICATION EQUIP MFG
Spiced beef preservation method
InactiveCN104247750AInhibition of respirationGrowth inhibitionMeat/fish preservation by coatingSpoilage bacteriaEnzyme system
The invention relates to a spiced beef preservation method. The spiced beef preservation method comprises the following steps of 1, taking edible gelatin, food-grade lactic acid, chitosan, potassium sorbate, nisin and water, mixing the above materials, and carrying out stirring to obtain a uniform fresh-keeping solution, and 2, directly spraying the fresh-keeping solution obtained by the step 1 to the surface of a spiced beef finished product and carrying out air drying so that a natural preservative film is formed on the surface of the air-dried spiced beef, or 3, leaching the spiced beef finished product in the fresh-keeping solution obtained by the step 1, and draining off the spiced beef finished product so that the natural preservative film is formed on the surface of the spiced beef. After use, the fresh-keeping solution forms a protective film so that preservative effects better than that of a single antiseptic can be obtained. The composite antiseptic can damage many important enzyme systems of microbes, inhibit microbial breathing effects, kill bacteria by influencing cell membrane permeability and inhibiting cell wall synthesis, produce synergism of all the antiseptics and inhibit growth and breeding of spoilage bacteria in spiced beef.
Owner:TIANJIN HEIZI FOOD
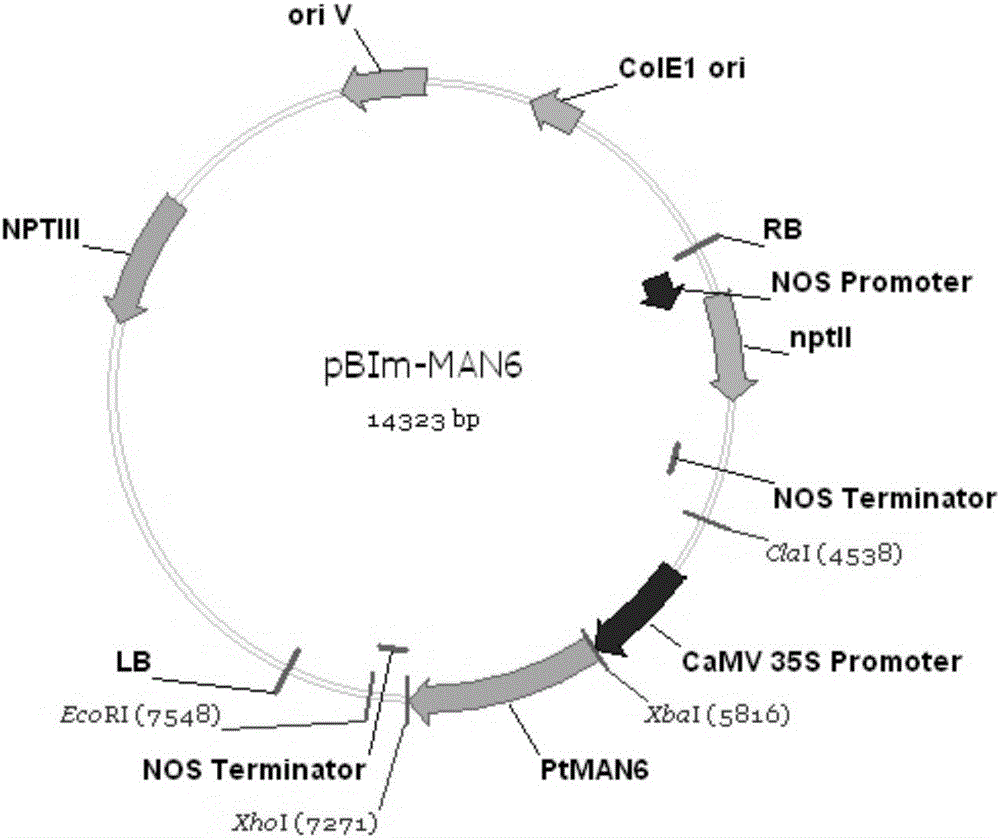
Related gene for regulating and controlling wood development and application thereof
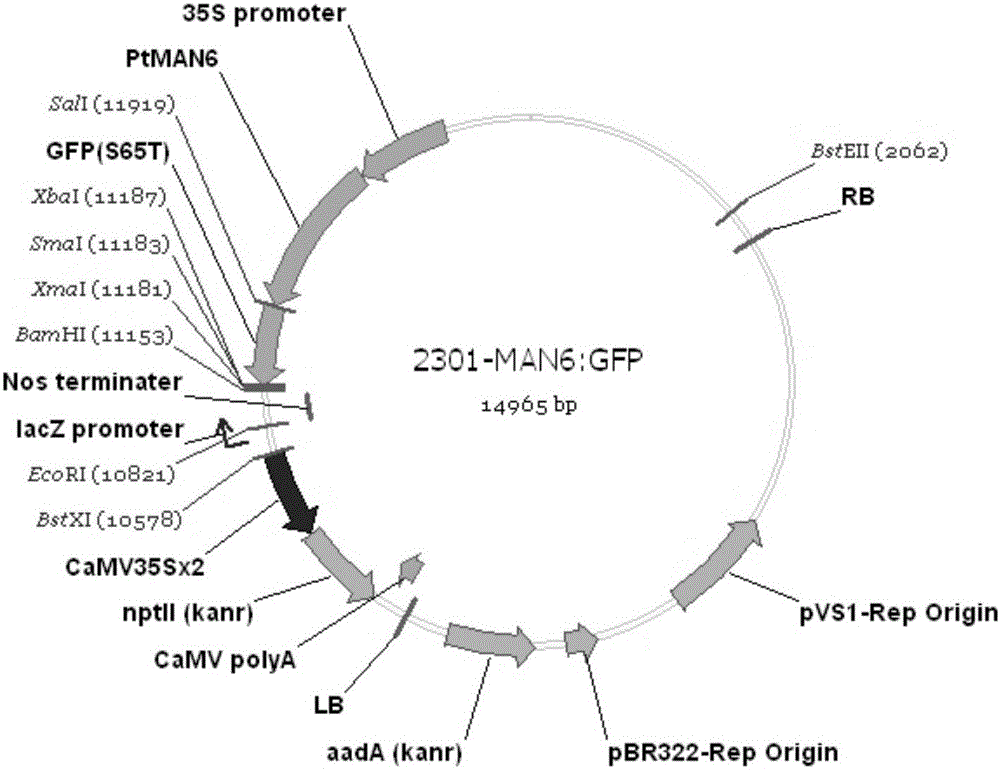
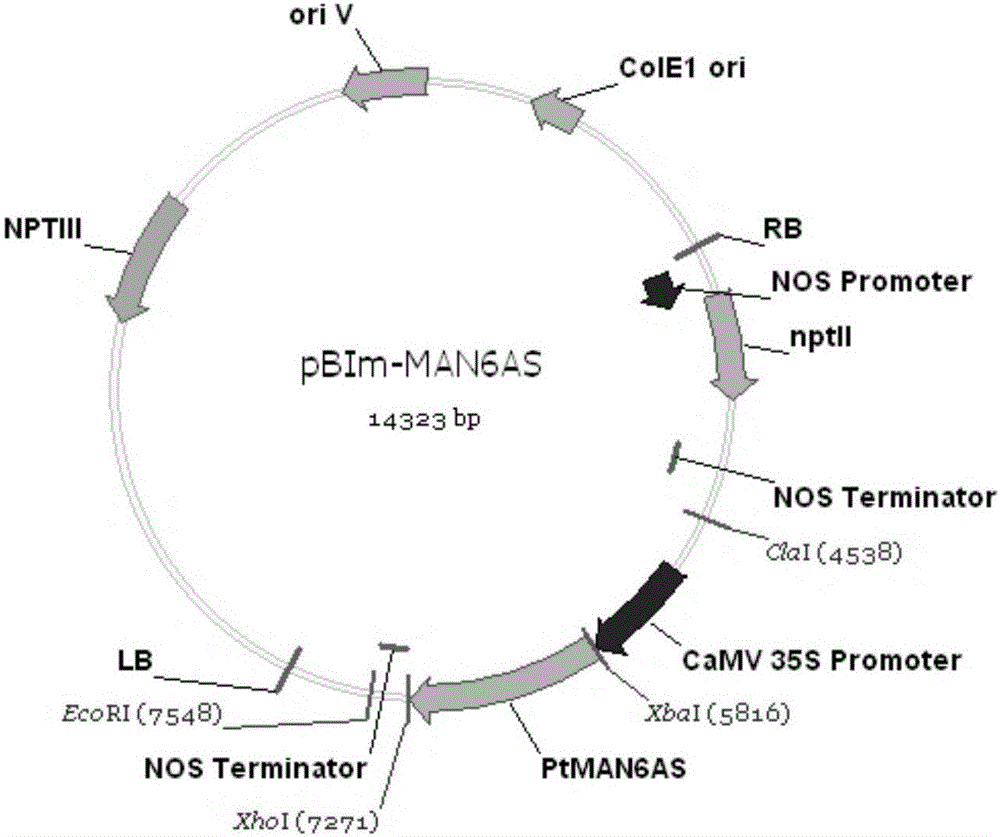
The invention relates to a related gene for regulating and controlling wood development and application thereof, and particularly provides a novel PtMAN6 polypeptide or a coding sequence thereof. An amino acid sequence of the PtMAN6 polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID NO.:2, and the coding sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.:1.The invention further provides a PtMAN6 gene and application of protein coded by the PtMAN6 gene. The PtMAN6 gene can reduce synthesis of xylem secondary cell walls and / or reduce accumulation of crystalline fiber biomass; mannan hydrolase of mannan hemicellulose can be enriched and degraded in plants by excessively expressing the PtMAN6; meanwhile, due to the regulating and controlling effect of the PtMAN6, the lignin content in transgenic plants is decreased, crystalline cellulose is decreased, and therefore the cost in lignocelluloses ethanol producing and paper making industry is greatly reduced; a promoter of the PtMAN6 gene has the specific duct cell positioning function and can precisely regulate and control expression of the gene in xylem duct cells.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Modulating SOS response induction by antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS7592154B2Efficient killingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSOS responseAntibiotic Y
Compositions and methods are provided for the use of SOS pathway targeted agents in antimicrobial formulations. The innate sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics is increased by disrupting a mechanism that normally activates the bacterial SOS response or by inhibiting steps in the SOS response pathway itself. SOS response induction can result from exposure of bacteria to certain antibiotics, including β-lactam antibiotics and other agents that affect cell wall synthesis. By transiently delaying bacterial cell division, SOS response induction interferes with bacterial killing by ordinarily lethal concentrations of these drugs A pharmaceutical composition comprising an SOS targeted agent is administered to a patient suffering from a microbial infection, in combination with an antibiotic that induces an SOS response. The identification of the SOS pathway as a target for modulating antibiotic action provides a basis for further therapeutic development, through screening assays designed to detect molecules or genes that act on these pathways.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine formula for treating leg cramp
InactiveCN112618662AChange permeabilityLong storage timeMuscular disorderNeuromuscular disorderVitamin CMycoprotein
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine formula for treating leg cramp. The traditional Chinese medicine formula comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of radix paeoniae alba, 3-5 parts of radix glycyrrhizae, 1-3 parts of caulis trachelospermi, 1-3 parts of caulis spatholobi, 3-5 parts of tripterygium wilfordii, 6-8 parts of herba lycopodii, 6-8 parts of ligusticum wallichii, 10-15 parts of angelica sinensis, 8-10 parts of cassia twig, 8-10 parts of radix angelicae pubescentis, 10-15 parts of astragalus membranaceus and 8-10 parts of rhizoma gastrodiae. Capsule liquid is prepared in the process of preparing a traditional Chinese medicine capsule, the capsule liquid has a good antibacterial effect, when mould makes contact with the surface of the capsule, synthesis of mould nucleic acid is inhibited, mould protein cannot be synthesized normally, meanwhile, the permeability of cell membranes is changed, cell wall synthesis is disturbed, and then the preservation time of traditional Chinese medicine granules is prolonged; and meanwhile, after the surface of the capsule is dissolved, cells absorb vitamin C and chitosan, so that a human body can well absorb medicinal components in the traditional Chinese medicine granules, and the treatment effect of the traditional Chinese medicine formula is quick and obvious.
Owner:栾如震
Composition comprising a biological control agent and a fungicide selected from inhibitors of amino acid or protein biosynthesis, inhibitors of ATP production and inhibitors of the cell wall synthesis
ActiveUS9380787B2Reduce application rateExpand the scope of activitiesBiocideAnimal repellantsFungicideAtp production
The present invention relates to a composition comprising at least one biological control agent. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of this composition as well as a method for reducing overall damage of plants and plant parts.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Method used for increasing 2,3-butylene glycol yield
ActiveCN103911398AIncrease profitIncrease concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationPenicillin2,3-Butanediol
The invention relates to a method used for increasing 2,3-butylene glycol yield. The method is mainly used for solving a problem of existing technology that yield of 2,3-butylene glycol is relatively low. According to the method, bacteria are subjected to high sugar resistance domestication firstly; the domesticated bacteria are used for fermentation culturing, and an antibiotic is added in fermentation culturing processes, wherein the antibiotic is at least one selected from penicillin, cephalosporin, bacillus, D-cycloserine, and the like which are capable of inhibiting cell wall synthesis, and polymyxin B, nystatin, amphotericin, or valinomycin which are capable of influencing cytomembrane functions, and adding concentration of the antibiotic ranges from 0.0001 to 5g / L. The method is capable of increasing 2,3-butylene glycol yield, and can be used for production of 2,3-butylene glycol.
Owner:SINOPEC SHANGHAI ENG +1
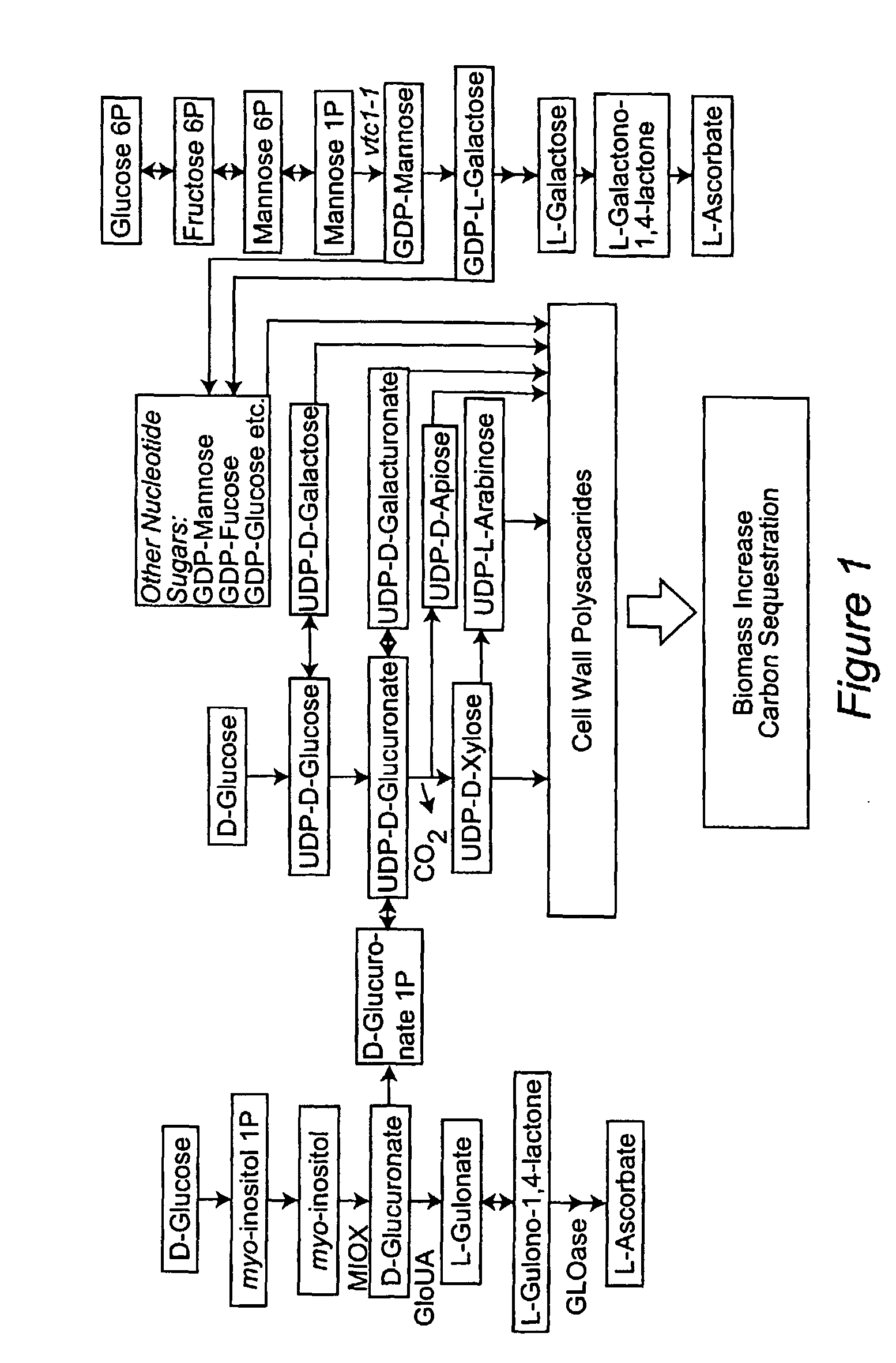
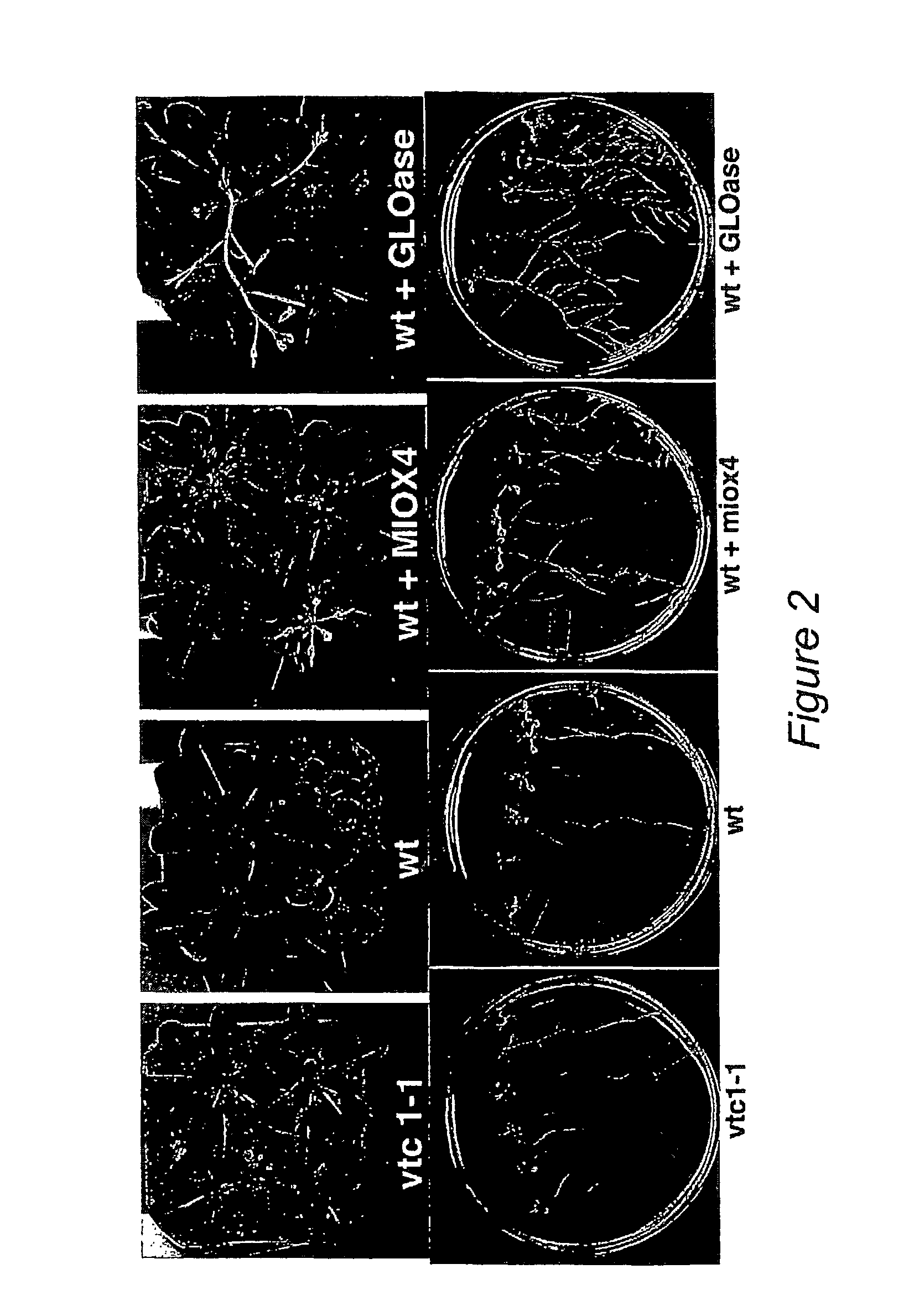
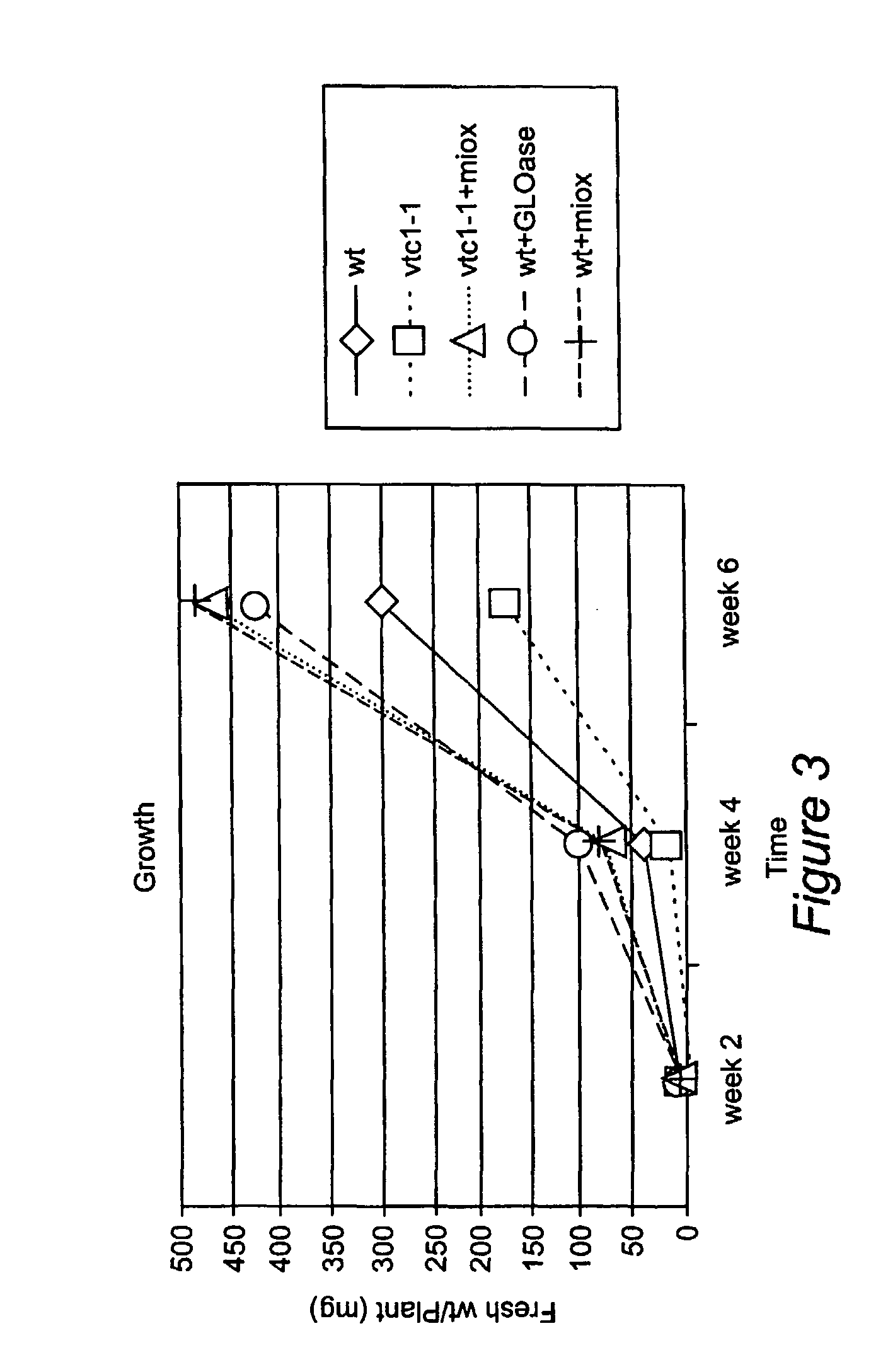
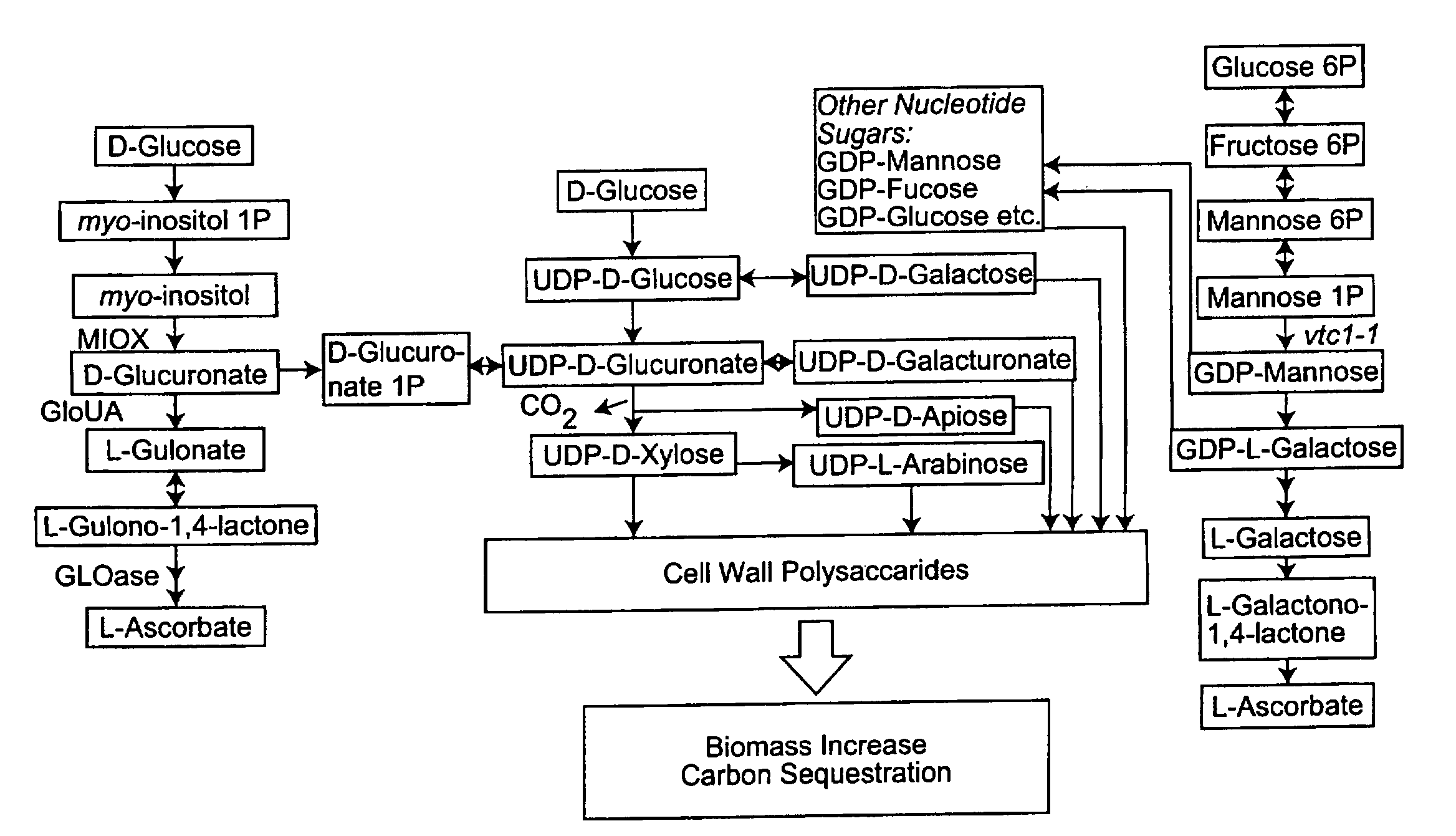
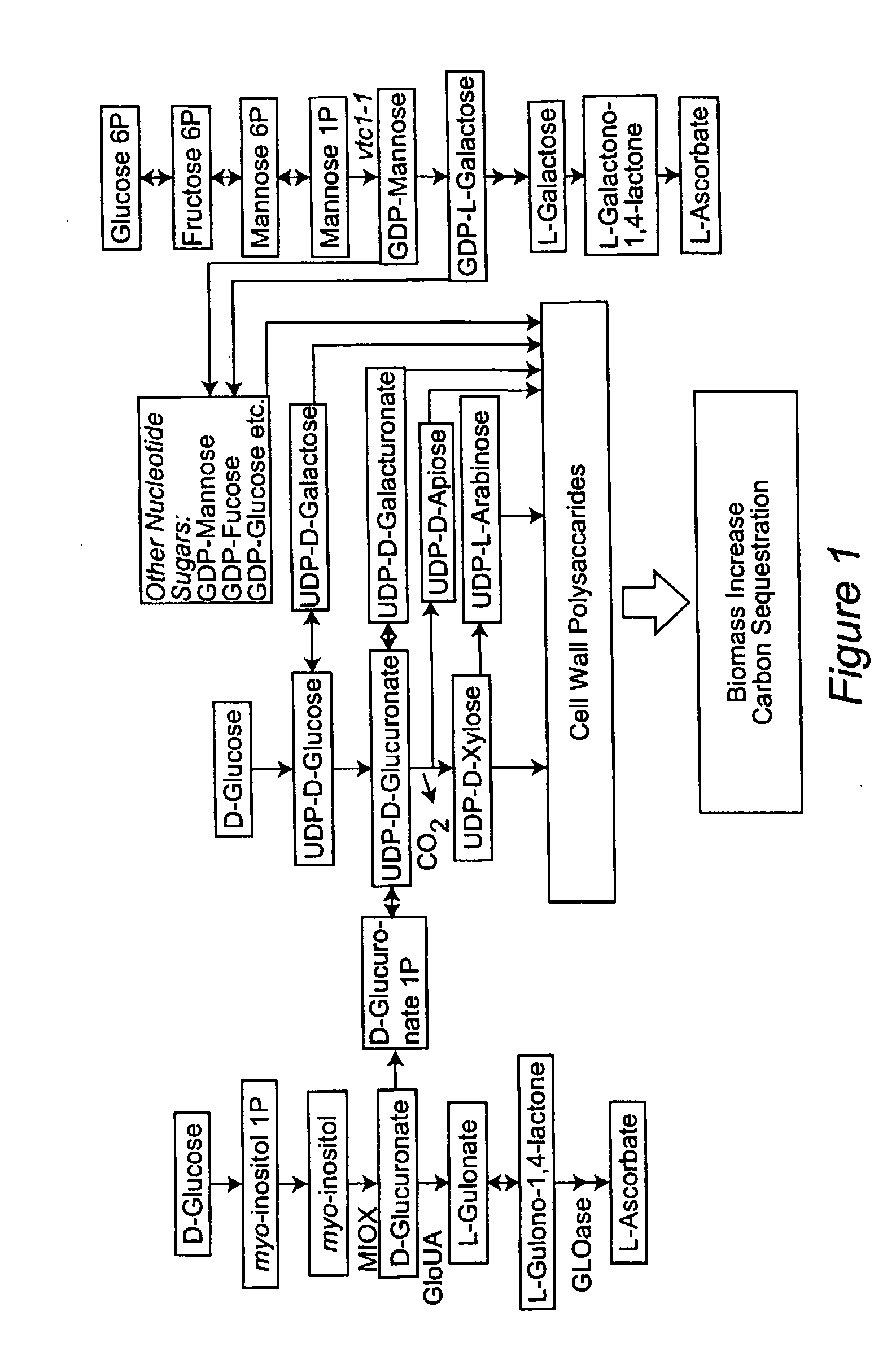
Stress tolerant transgenic plants over-expressing ascorbic acid and cell wall synthesis genes
ActiveUS9000267B2Reduce decreaseIncrease ratingsSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationGrowth plantOrganism
Methods are provided for increasing plant growth rate, biomass and tolerance to stress by genetically engineering plants to contain and express a gene of the ascorbic acid synthesis-cell wall synthesis network (e.g. GlcUA reductase, GLOase or MIOX). Transgenic plants that are genetically engineered in such a manner are also provided.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Pharmaceutical composition, substrate comprising a pharmaceutical composition, and use of a pharmaceutical composition
The invention relates to the use of a pharmaceutical composition for the local treatment or prevention of a tissue infection at an infection site, the pharmaceutical composition comprising at least two different antibiotics of group A or pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof, or an antibiotic of group A and at least one antibiotic of group B or pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives thereof. Group A comprises primarily intracellular active antibiotics working as inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase; as inhibitor of gyrase; or as inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis. Group B comprises primarily extracellular active antibiotics working as inhibitor of bacterial cell wall synthesis; or inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis; or by direct destabilization or rupture of the bacterial cell wall.The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of extracellular and / or intracellular microbial infected cells and / or for the prevention of microbial cell infections comprising at least one antibiotic acting as an inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase and / or at least one antibiotic affecting the bacterial cell wall or its synthesis, and a substrate carrying a pharmaceutical composition.The invention also relates to the use of a combination of at least one antibiotic acting as an inhibitor of bacterial RNA polymerase and at least one antibiotic affecting the bacterial cell wall or its synthesis as anti-adhesive against microorganisms on surfaces.
Owner:BIOMET DEUTLAND
DNA sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN106834309AIncreased levels of gene transcriptionGlycan content decreasedUnicellular algaeBiofuelsA-DNAOil production
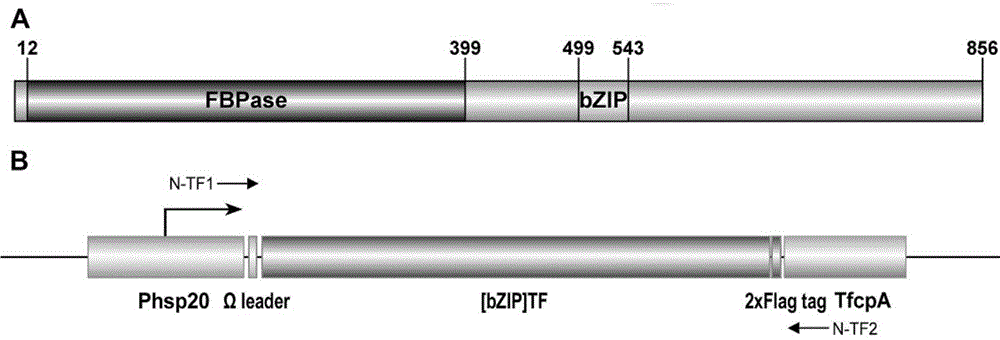
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and in particular relates to a DNA sequence and application thereof. The DNA sequence encodes a BZIP transcription factor, the BZIP transcription factor comprises a FBPcase structure domain and a BZIP structure domain, and the BZIP transcription factor can be used for up-regulation of a plurality of key genes in a TAG (triacylglycerol) and fatty acid synthesis pathway and down-regulation of cell wall synthesis related genes, so that the DNA sequence can be used in the field of microalgae-type bio-oil production, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Stress Tolerant Transgenic Plants Over-Expressing Genes of Ascorbic Acid Synthesis-Cell Wall
ActiveUS20080250526A1Increasing sequestrationReduce decreaseSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationGrowth plantTransgene
Methods are provided for increasing plant growth rate, biomass and tolerance to stress by genetically engineering plants to contain and express a gene of the ascorbic acid synthesis-cell wall synthesis network (e.g. GlcUA reductase, GLOase or MIOX). Transgenic plants that are genetically engineered in such a manner are also provided.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Construction method for double-gene mutation escherichia coli used for secretory expression of recombinant protein
InactiveCN102827860BIncrease productionReduce intracellular degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenes mutationInclusion bodies
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for culturing phyllostachys edulis protoplast and inducing cell wall regeneration and application of method
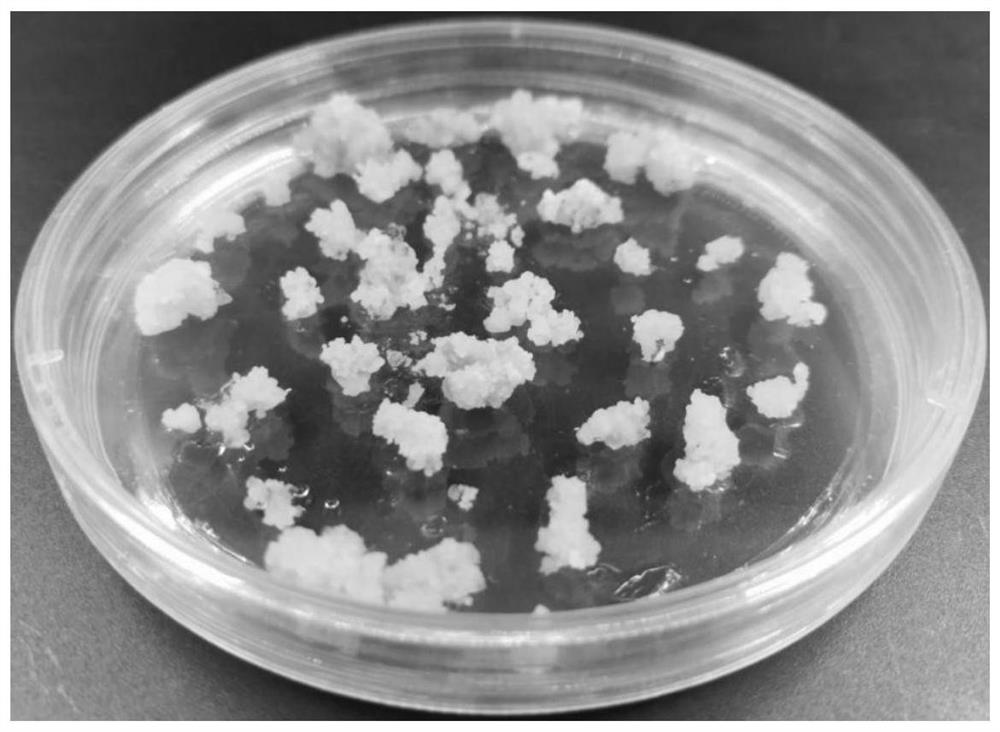
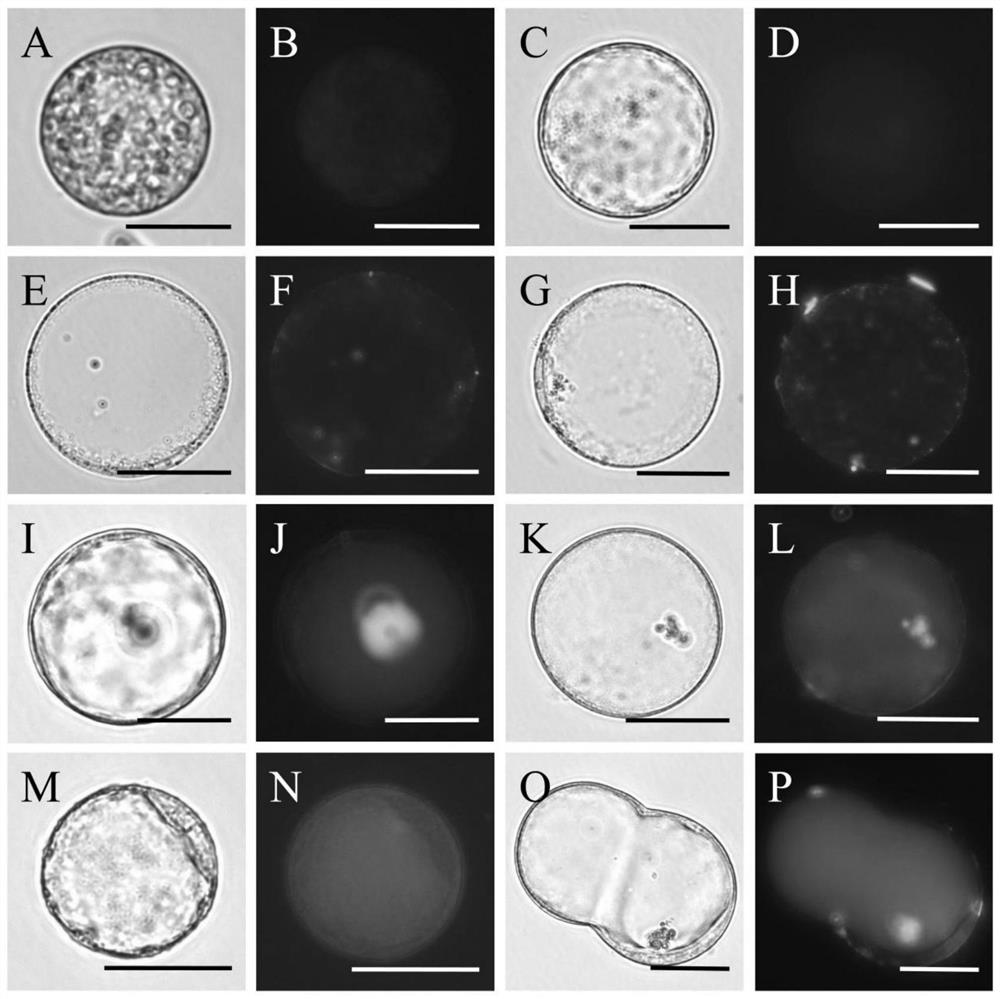
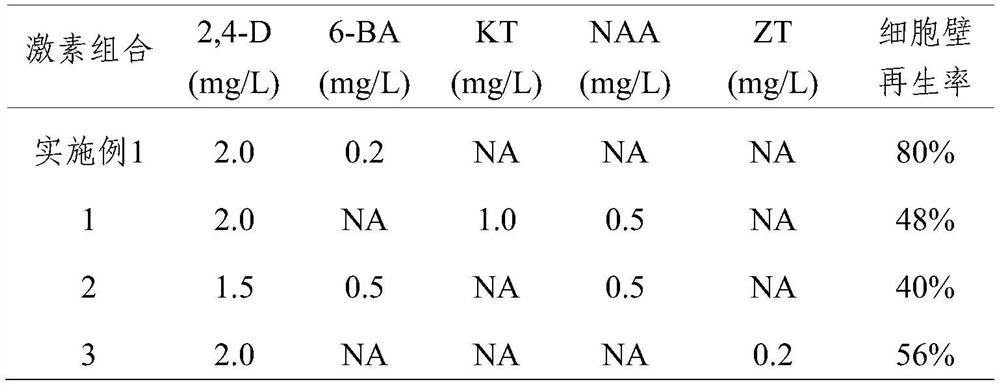
The invention relates to the technical field of plant tissue culture, in particular to a method for culturing phyllostachys edulis protoplast and inducing cell wall regeneration and application of the method. The protoplast derived from the phyllostachys edulis embryogenic callus is cultured and induced to regenerate the complete cell wall, the regeneration effect is excellent, the success rate is high, and meanwhile, the regeneration result has high repeatability. In addition, the protoplast and cell wall regeneration process can be monitored by the method; a feasible model is provided for researching cell wall synthesis and regulation control mechanisms of phyllostachys edulis and other species, material improvement, biomass energy and other fields; theoretical guidance is provided for improving the quality and yield of bamboo cell walls; and the method has profound influence and long-term significance on the construction and development of the bamboo industry.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Composition comprising a biological control agent and a fungicide selected from inhibitors of amino acid or protein biosynthesis, inhibitors of ATP production and inhibitors of the cell wall synthesis
ActiveUS9706777B2Reduce harmExpand the scope of activitiesBiocideAnimal repellantsFungicideAtp production
The present invention relates to a composition comprising at least one biological control agent. Furthermore, the present invention relates to the use of this composition as well as a method for reducing overall damage of plants and plant parts.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Method for the rapid determination of susceptibility or resistance of bacteria to antibiotics
PendingUS20220243248A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAntibiotic AgentsMicrobiology
Owner:ABM TECH
Probiotic filled chocolate candy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112602810AInhibit synthesisSynthetic interferenceClimate change adaptationFood preservationBiotechnologyCell membrane
The invention discloses a probiotic filled chocolate candy and a preparation method thereof. The probiotic filled chocolate candy is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-80 parts of cocoa powder, 3-5 parts of freeze-dried probiotic powder, 20-30 parts of high fructose corn syrup, 5-8 parts of butter, 3-5 parts of whole milk powder, 8-10 parts of fresh milk, 0.2-0.5 part of lactic acid and 0.5-1 part of a preservative. According to the preservative, an intermediate 3 reacts with an intermediate 2 to prepare an intermediate 4; the intermediate 4 is reduced, so that nitryl on molecules can be converted into amino, and therefore, an intermediate 5 can be prepared, and then the intermediate 5 is condensed with carboxyl on carboxymethyl chitosan; and the preservative can be to prepared, and the preservative can inhibit synthesis of mycotic nucleic acid and synthesis of mycotic protein, meanwhile, the permeability of cell membranes is changed, cell wall synthesis is disturbed, and damage to a human body after the preservative is eaten is avoided.
Owner:JIESHOU ZHAOLONG FOOD
Gene promoter originated from cotton and its application
The invention discloses a plant gene promoter and its application. The base sequence of the promoter is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Tobacco transgenic experiments proved that pGhGlcat1 can endow high-level expression of GUS reporter gene in epidermal trichomes, apical meristem region, and stamens and pistils of plant floral organs, indicating that GhGlcat1 plays a role in cotton fiber primary cell wall synthesis, cell elongation, floral organ development and stress The functional study of pGhGlcat1 provides clues for revealing the expression regulation mechanism of GhGlcat1. In addition, pGhGlcat1 can also be used in the genetic engineering improvement of plant quality and resistance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
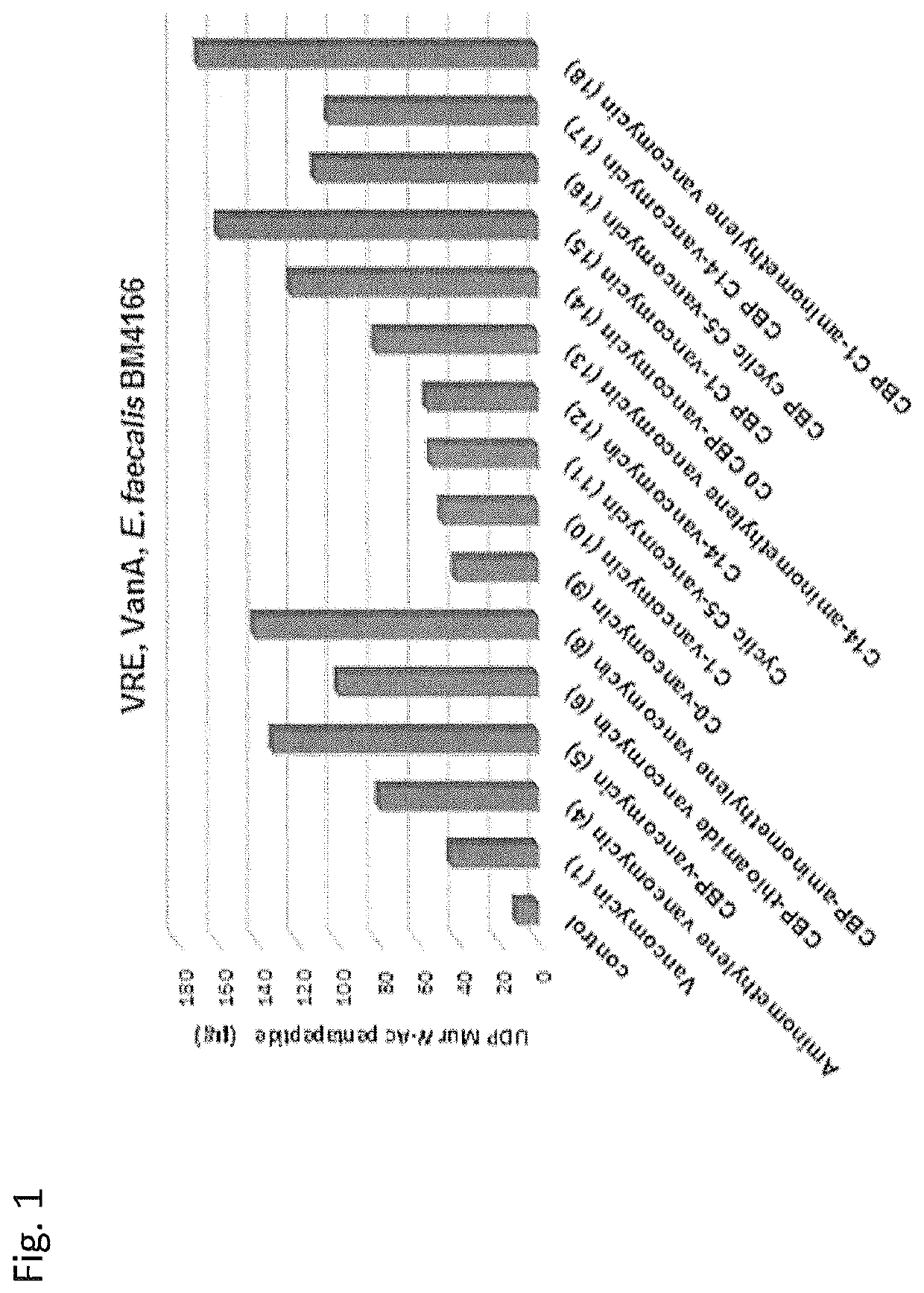
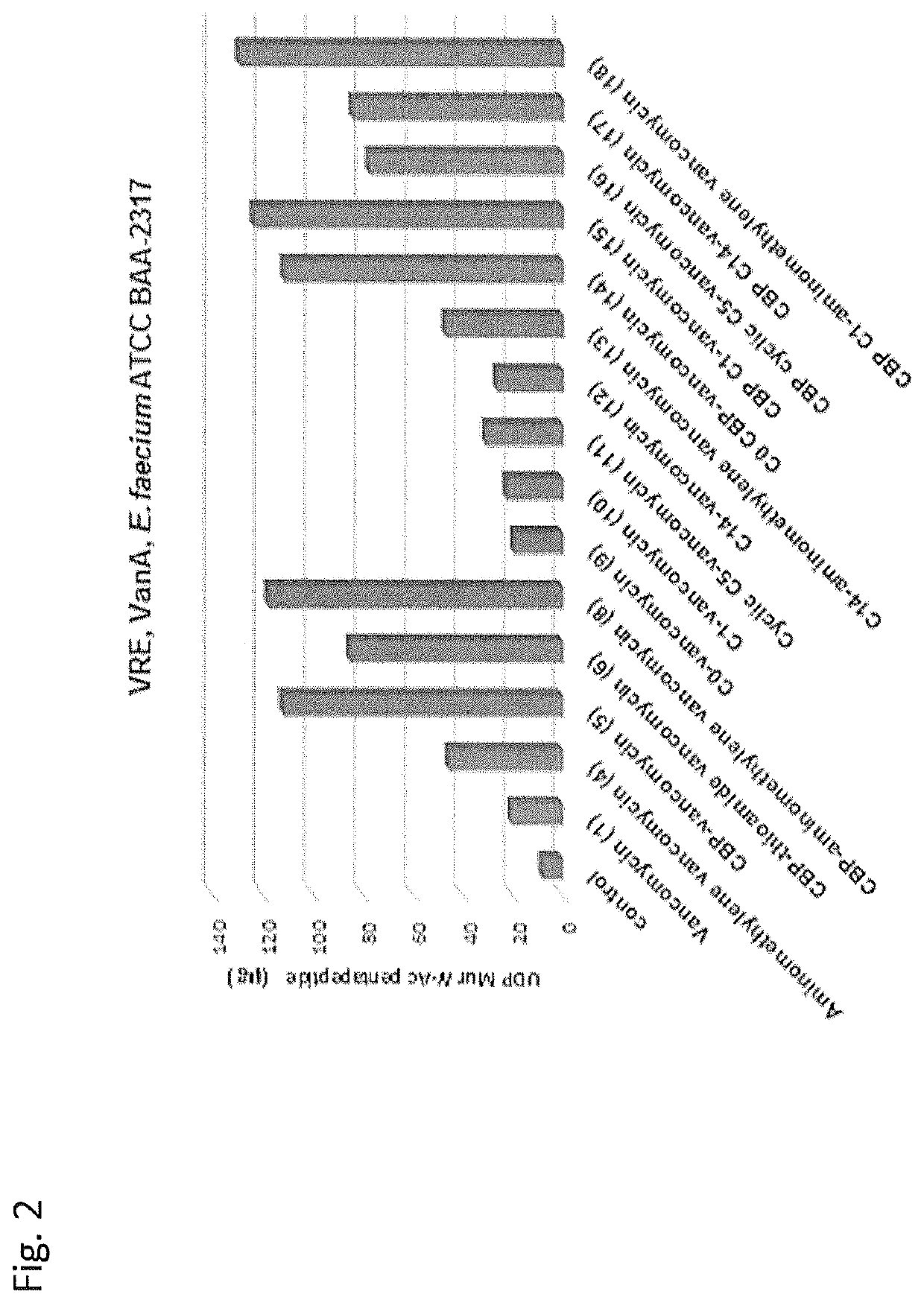
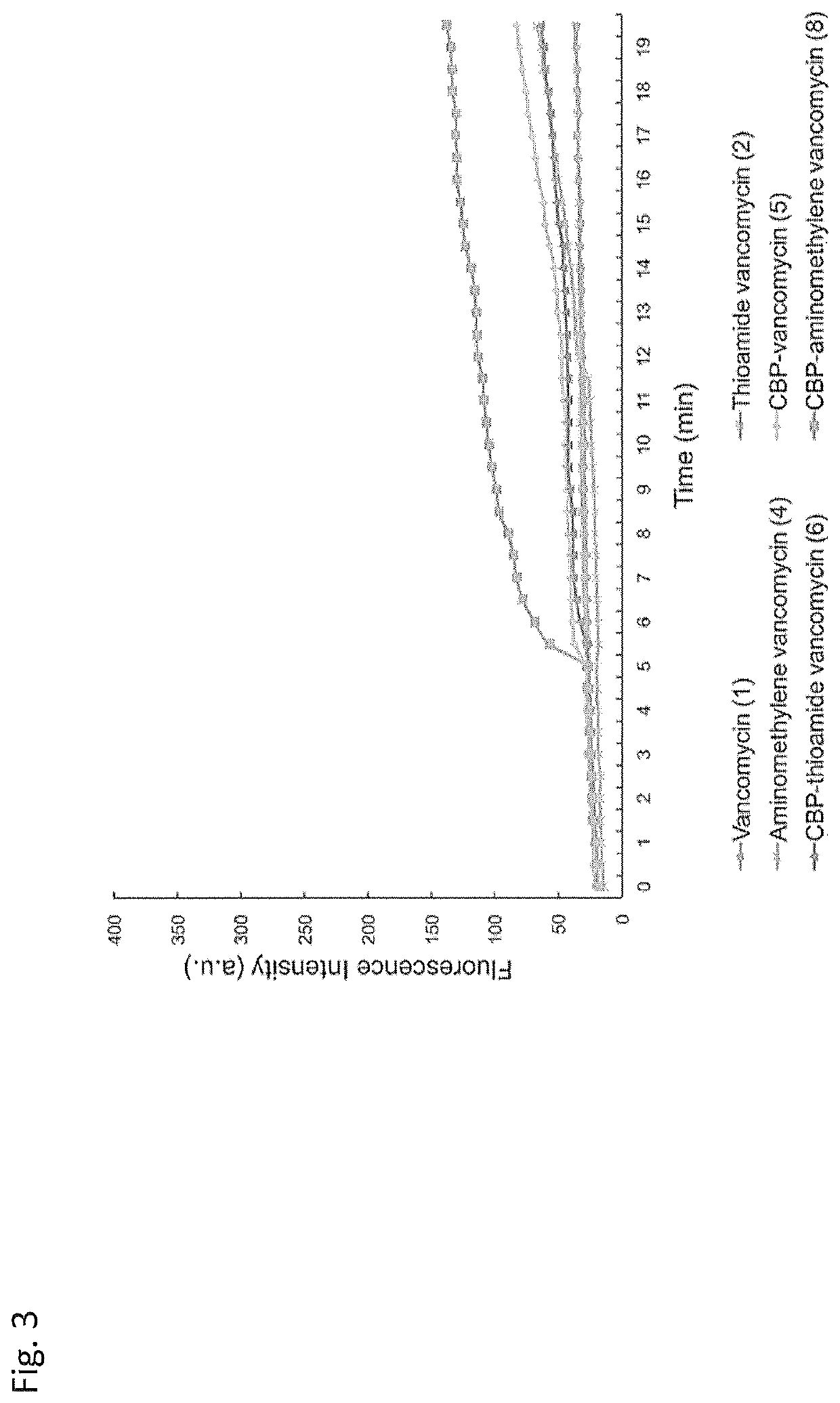
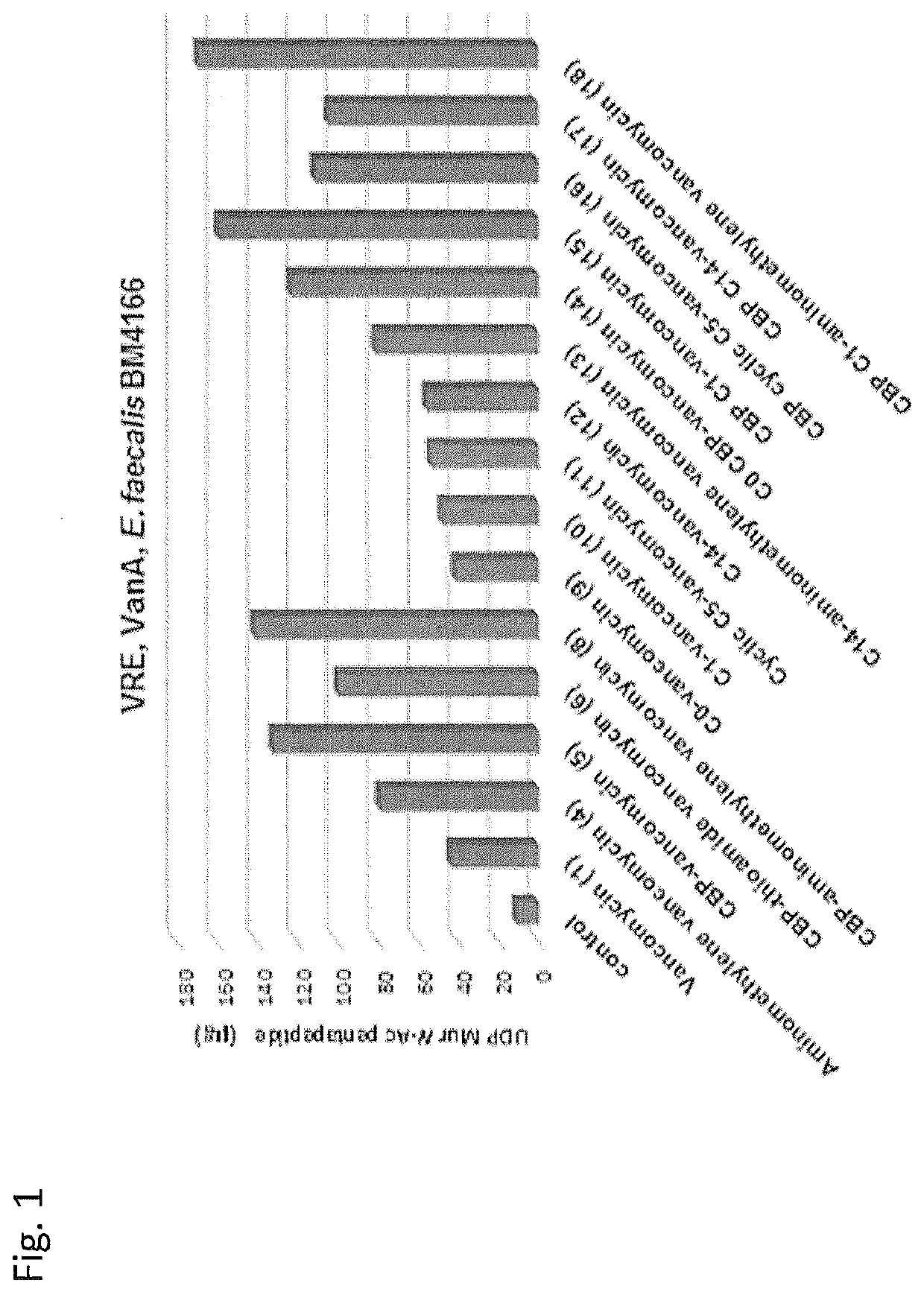
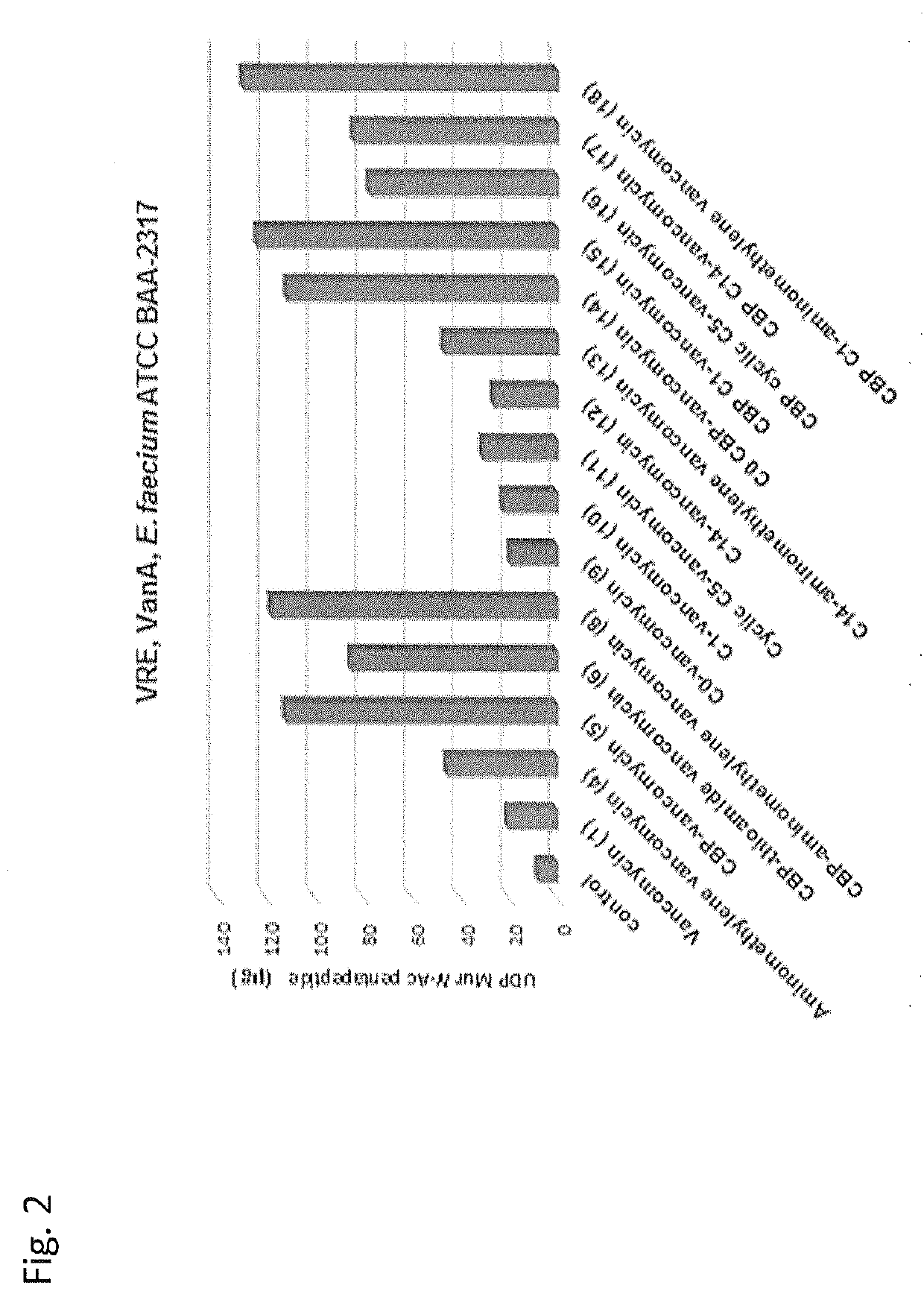
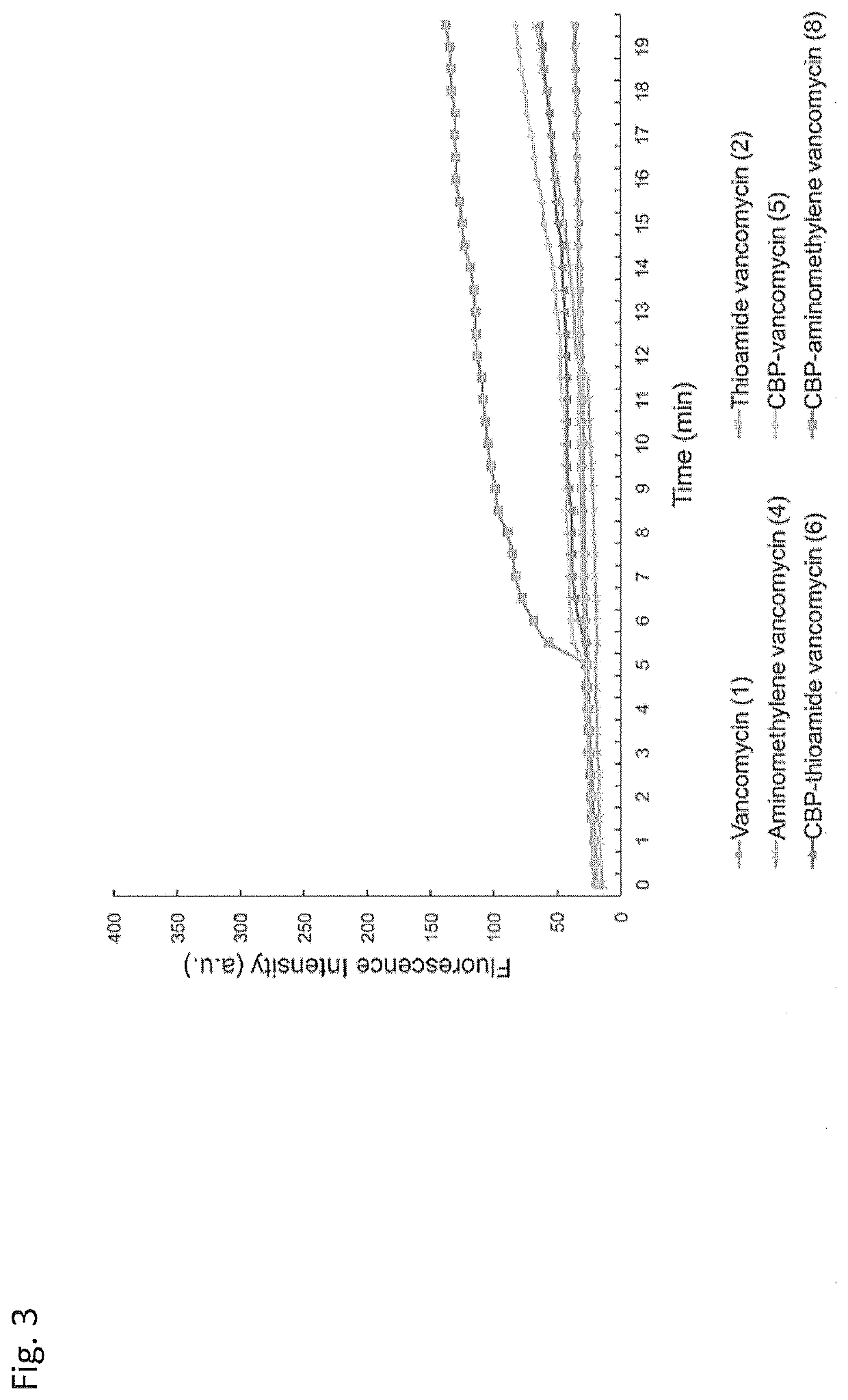
Peripheral modifications on pocket-redesigned vancomycin analogs synergistically improve antimicrobial potency and durability
ActiveUS10934326B2Little propensityLittle resistanceAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcquired resistanceGlycopeptide
A C-terminus modification to a binding pocket-modified vancomycin introduces a quaternary ammonium salt that provides a binding pocket-modified vancomycin analog with a second mechanism of action that is independent of D-Ala-D-Ala / D-Ala-D-Lac binding. The modification disrupts cell wall integrity and induces cell wall permeability complementary to the glycopeptide inhibition of cell wall synthesis, and provides synergistic improvements in antimicrobial potency (200-fold) against vancomycin-resistant bacteria. Combining the C-terminus and binding pocket modifications with an orthogonal (4-chlorobiphenyl) methyl addition to the vancomycin disaccharide provides even more potent antimicrobial agents whose activity can be attributed to three independent and synergistic mechanisms of action, only one of which requires D-Ala-D-Ala / D-Ala-D-Lac binding. The resulting modified vancomycins display little propensity for acquired resistance through serial exposure of vancomycin-resistant Enterococci and their durability against such challenges as well as their antimicrobial potency follow predicable trends. Methods of treatment with and compositions containing the modified vancomycins are disclosed.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for antibiotic susceptibility testing and determining minimum inhibitory concentration of the antibiotic
InactiveUS8911605B2MiniaturizationShorten the construction periodDielectrophoresisElectrolysis componentsShape changeMinimum inhibitory concentration
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Peripheral modifications on pocket-redesigned vancomycin analogs synergistically improve antimicrobial potency and durability
ActiveUS20200071359A1Little propensityPersistent antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcquired resistanceGlycopeptide
A C-terminus modification to a binding pocket-modified vancomycin introduces a quaternary ammonium salt that provides a binding pocket-modified vancomycin analog with a second mechanism of action that is independent of D-Ala-D-Ala / D-Ala-D-Lac binding. The modification disrupts cell wall integrity and induces cell wall permeability complementary to the glycopeptide inhibition of cell wall synthesis, and provides synergistic improvements in antimicrobial potency (200-fold) against vancomycin-resistant bacteria. Combining the C-terminus and binding pocket modifications with an orthogonal (4-chlorobiphenyl) methyl addition to the vancomycin disaccharide provides even more potent antimicrobial agents whose activity can be attributed to three independent and synergistic mechanisms of action, only one of which requires D-Ala-D-Ala / D-Ala-D-Lac binding. The resulting modified vancomycins display little propensity for acquired resistance through serial exposure of vancomycin-resistant Enterococci and their durability against such challenges as well as their antimicrobial potency follow predicable trends. Methods of treatment with and compositions containing the modified vancomycins are disclosed.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com