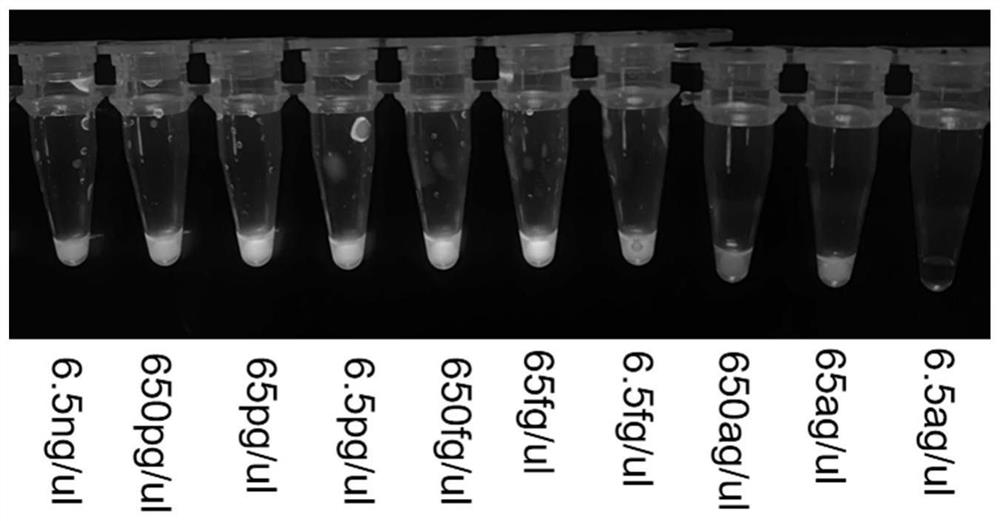
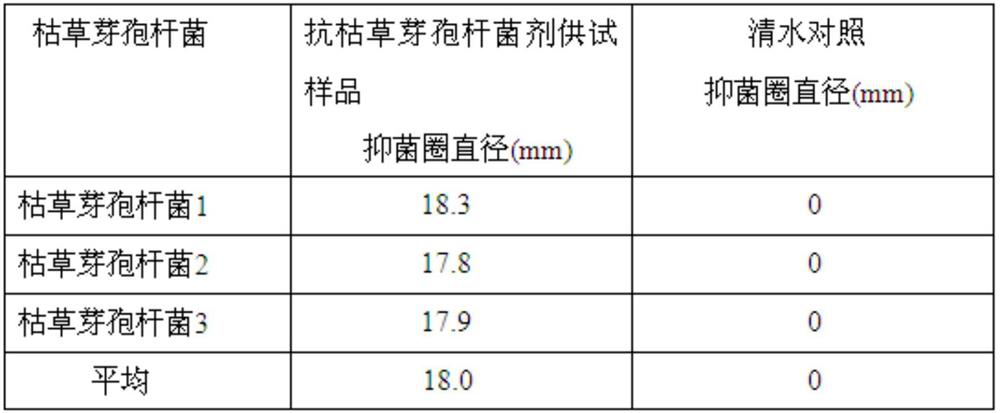
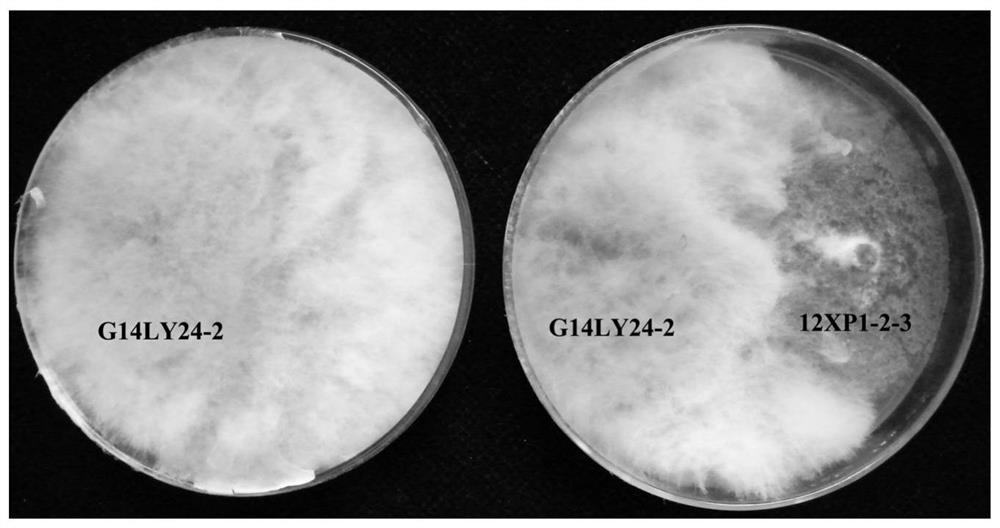
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Chaetomium sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Endophytic fungi chaetomium globosum strain, microbial agent and application thereof
InactiveCN102311925APromote growth and developmentImprove adaptabilityBiocidePlant growth regulatorsLaboratory culturePathogen
The invention discloses an endophytic fungi chaetomium globosum strain, a microbial agent and an application thereof. The strain is named as chaetomium globosum strain ND 35, the preservation organization is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date is 9th,10,2010, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 4136. The strain is a biological beneficial bacteria with a plurality of biological control effect mechanisms, and has the plant pathogen inhibition capability with broad-spectrum and high-efficiency, and also has capability for promoting a plurality of plants growth, and is suitable for industrial production, the shelf life is long which is suitable for preventing and treating the plant diseases, so that the strain is used for producing the biological bactericide products for preventing and treating a plurality of plant diseases and multifunctional biofertilizer products for promoting the growth of plants.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Chaetomium globosum and application thereof
ActiveCN104694397AField disease preventionHave a growth-promoting effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a chaetomium globosum FSR-74. The collection unit of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection date of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 is September 19, 2014 and the collection number of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 is CGMCC No. 9690. The strain is relatively slow in growth and has light brown colonies and an irregular wave-like edge when subjected to plate culture at 25 DEG C in a potato dextrose agar (PDA) culture medium. FSR-74 ascocarps are supergene and fixed on the surface of a matrix by rhizoids; top hair is wavy, brown and has intervals, and dense wart points are arranged on the surface; 8 ascospores are arranged in an ascus; the ascospores are shaped like lemons and have single apical bud holes. The chaetomium globosum FSR-74 has an efficient broad-spectrum bacteriostatic effect against main pathogenic bacteria causing ginseng rust rot, blight, sclerotinia rot, rust rot, blackspot, sheath blight and gray mold. The invention further provides a biological control mechanism and application of the chaetomium globosum FSR-74 in prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases, as well as application in preparation of a microbial agent for preventing and treating the plant fungal diseases.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
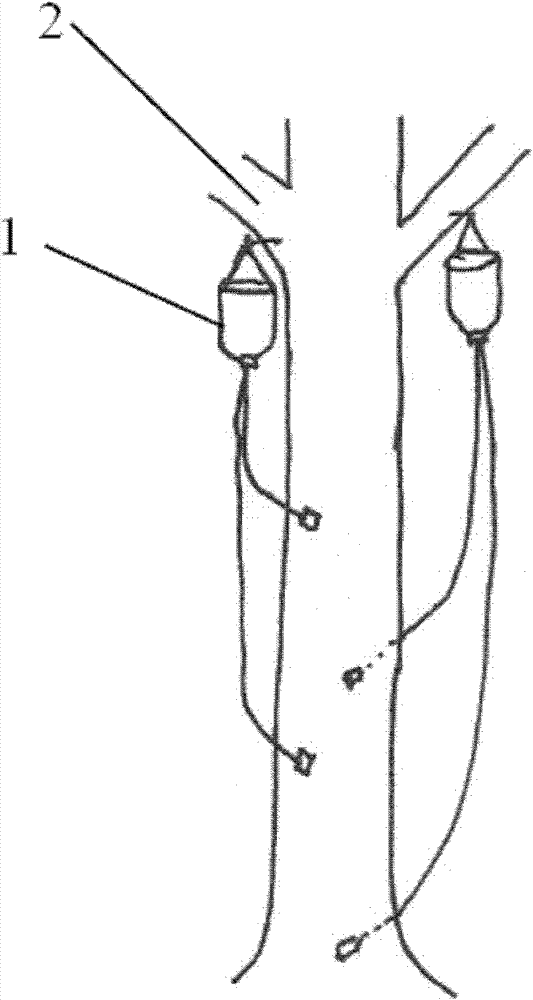
Method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood
ActiveCN102302041AShorten the cycle of producing agarwoodSimple and fast operationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFusariumAquilaria sinensis
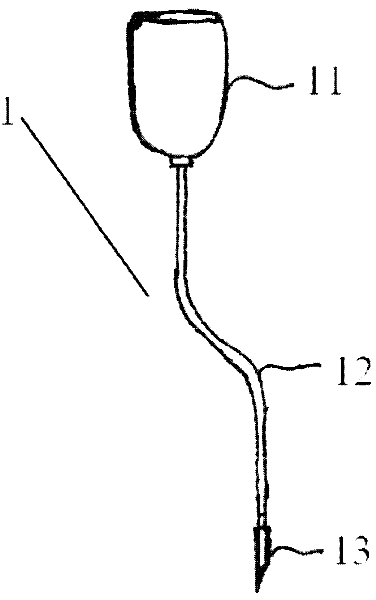
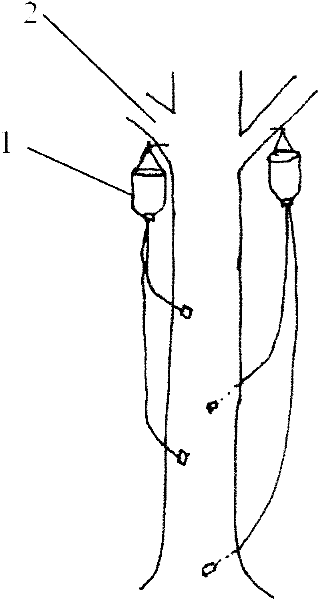
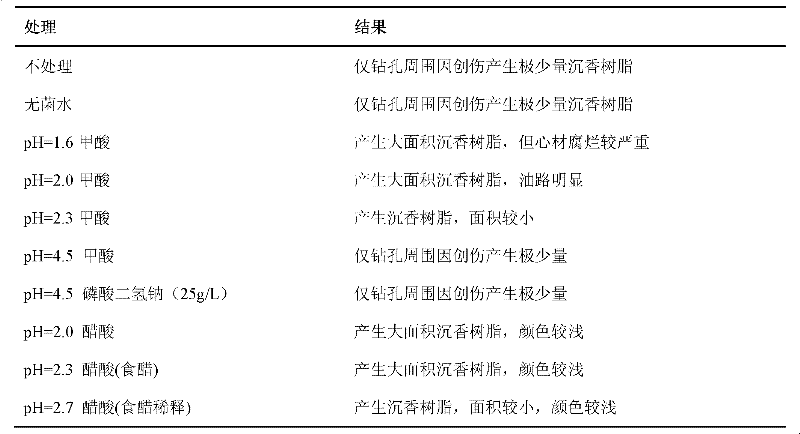
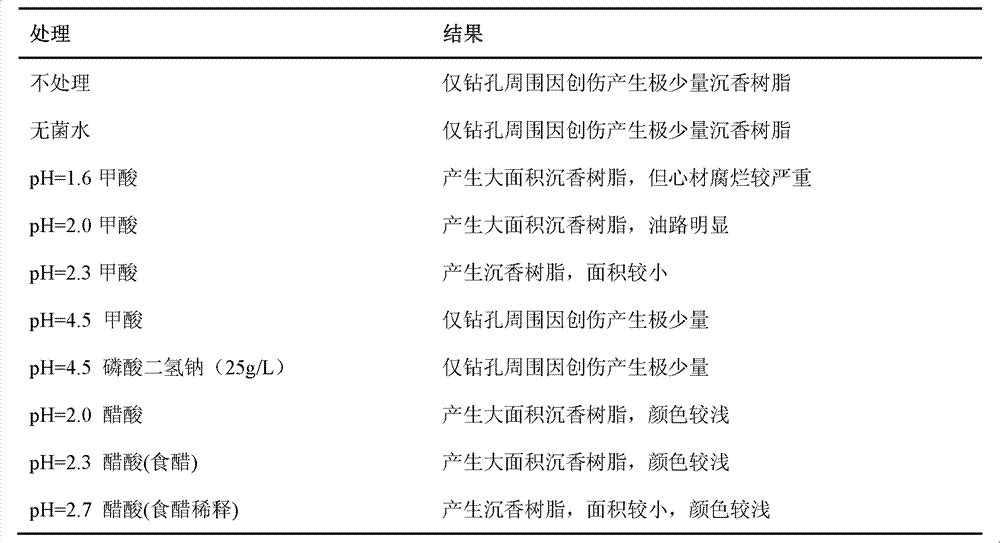
The invention discloses a method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood. The method comprises the following steps of: injecting a methanoic acid or acetic acid solution with pH value of 1.5-3 or a mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid into xylem of Aquilaria sinensis [Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg]; respectively injecting the solution together with fungi, suchas Botryosphaeria rhodina, Hypocrea jecorina, Fusarium sp., Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Ampelomyces sp, Khuskia sp, Fungal endophyte sp.A 16, Pestalotiopsis sp., Hypocrea lixii and Chaetomium sp.or injecting the solution and the fungi in a mixed way; and inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood. According to the invention, the methanoic acid or acetic acid solution or the mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid is injected into the xylem of the Aquilaria sinensis to induce the Aquilaria sinensis to generate defense reaction so as to generate the agilawood; and alarge amount of agilawood are generated by using the method. The method for manually inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost and suitability for manually making agilawood on a large scale by using Aquilaria sinensis trees; and a large amount of agilawood can be effectively generated by the Aquilaria sinensis. According to the invention, the agilawood producing period of the Aquilaria sinensis is largely reduced, the agilawood can be generally obtained after 6-24 months, the production cost is reduced, the market requirements are satisfied, and important economic, social and ecological benefits are obtained in aspects of protection and sustainable utilization of the Aquilaria sinensis, economic development of mountainous regions and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Chaetomium globosum and application theroef
The invention discloses chaetomium globosum with strong inhibition effect agaisnt anthracnose pathogens of apples. The chaetomium globosum is registered and booked with the number being CGMCC No. 10609 in general microorganism center of China committee for culture collection of microorganisms, and the collection date is march 11th, 2015. The chaetomium globosum HY1 disclosed by the invention is endophytic fungi of glehnia littoralis as a threatened plant, both fermentation liquor and mycelium extracting solution of the chaetomium globosum have strong inhibition effect against the anthracnose pathogens of the apples, and also have certain inhibition action against other plant pathogens, and the strain has wide application prospect in the aspects of preventing and treating the anthracnose pathogens of the apples and the like.
Owner:黑龙江瑟高生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of antibacterial fermentation liquid of Solidago canadesis endophytic fungi
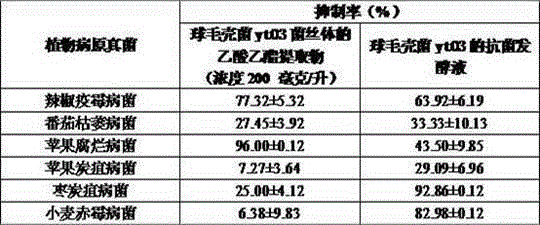
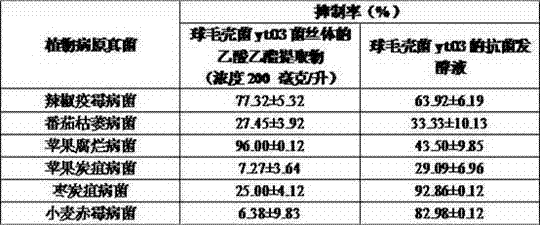
The invention relates to a preparation method of an antibacterial fermentation liquid of Solidago canadesis endophytic fungi, which comprises the following operation steps: 1. activating strain; 2. carrying out first-stage seed culture; 3. carrying out second-stage seed culture; and 4. carrying out fermentation culture to obtain brown Solidago canadesis endophytic fungus fermentation liquid, filtering the Solidago canadesis endophytic fungus fermentation liquid in aseptic condition to remove mycelia, and then passing a 0.22 mu m filter to obtain the antibacterial fermentation liquid of Solidago canadesis endophytic fungi. According to the invention, the preparation method of antibacterial fermentation liquid of Chaetomium globosum yt03 with broad spectrum antibacterial activity is determined; and antibacterial test finds that the Chaetomium globosum yt03 antibacterial fermentation liquid has relatively significant hypha growth inhibiting action on six tested plant pathogenic fungi.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Chaetomium globosum and application thereof in promoting growth and increasing yield of wheat
InactiveCN112080433AIncrease productionIncrease chlorophyll contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
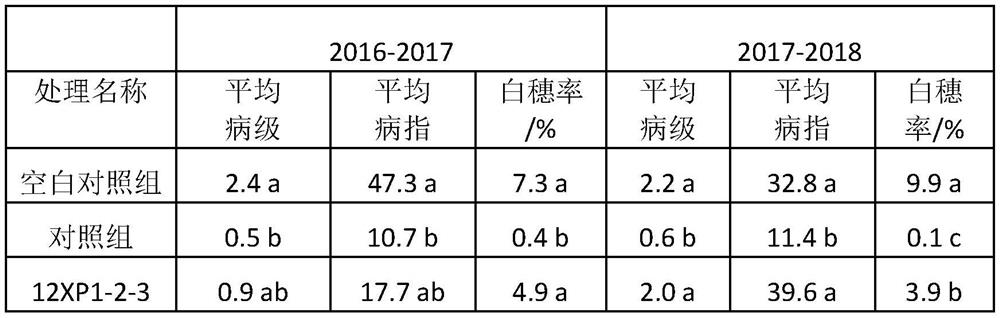
The invention provides chaetomium globosum (Chaetomium globosum), which has a preservation name of 12XP1-2-3 and a preservation number of CGMCC No.17183, wherein the preservation unit is the China general microbiological culture collection centre; and the preservation date is January 23th, 2019. The invention further provides application of chaetomium globosum in promoting growth and increasing yield of wheat. Field test results show that: when the chaetomium globosum 12XP1-2-3 provided by the invention is used for wheat seed coating treatment, the chlorophyll content of leaves can be increased by 1.9%-14.7% in the booting stage; and the wheat yield can be increased by 2.3%-10.9%.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Separation and purification method of endophytic fungi of solidago canadensis
InactiveCN102690759AObvious growth effectGrowth inhibitory effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a separation and purification method of endophytic fungi of solidago canadensis. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, collecting stems and leaves of the solidago canadensis; 2, carrying out solid culture and sterility test on the stems and the leaves; and 3, carrying out isolated culture on the endophytic fungi of tissues of the solidago canadensis to obtain the endophytic fungi of the solidago canadensis. A fungus colony has silk velvet texture and a villous surface, does not generate pigment and is light olivaceous and black brown at the back; and the gene complex of the endophytic fungi ITS of the solidago canadensis is composed of 602 basic groups (bp). The geomicrobiology status of a bacterial strain of chaetomiumglobosumyt03 with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity is determined, and the endophytic fungi is found to have relatively remarkable role in inhibiting mycelial growth of six provided plant pathogenic fungi through antibacterial test of the fermentation liquid of the chaetomiumglobosumyt03.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood
ActiveCN102302041BShorten the cycle of producing agarwoodSimple and fast operationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsFusariumAquilaria sinensis
The invention discloses a method for manually inducing Aquilaria sinensis to generate agilawood. The method comprises the following steps of: injecting a methanoic acid or acetic acid solution with pH value of 1.5-3 or a mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid into xylem of Aquilaria sinensis [Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg]; respectively injecting the solution together with fungi, suchas Botryosphaeria rhodina, Hypocrea jecorina, Fusarium sp., Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Ampelomyces sp, Khuskia sp, Fungal endophyte sp.A 16, Pestalotiopsis sp., Hypocrea lixii and Chaetomium sp.or injecting the solution and the fungi in a mixed way; and inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood. According to the invention, the methanoic acid or acetic acid solution or the mixed solution of methanoic acid and acetic acid is injected into the xylem of the Aquilaria sinensis to induce the Aquilaria sinensis to generate defense reaction so as to generate the agilawood; and alarge amount of agilawood are generated by using the method. The method for manually inducing the Aquilaria sinensis to generate the agilawood, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low cost and suitability for manually making agilawood on a large scale by using Aquilaria sinensis trees; and a large amount of agilawood can be effectively generated by the Aquilaria sinensis. According to the invention, the agilawood producing period of the Aquilaria sinensis is largely reduced, the agilawood can be generally obtained after 6-24 months, the production cost is reduced, the market requirements are satisfied, and important economic, social and ecological benefits are obtained in aspects of protection and sustainable utilization of the Aquilaria sinensis, economic development of mountainous regions and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
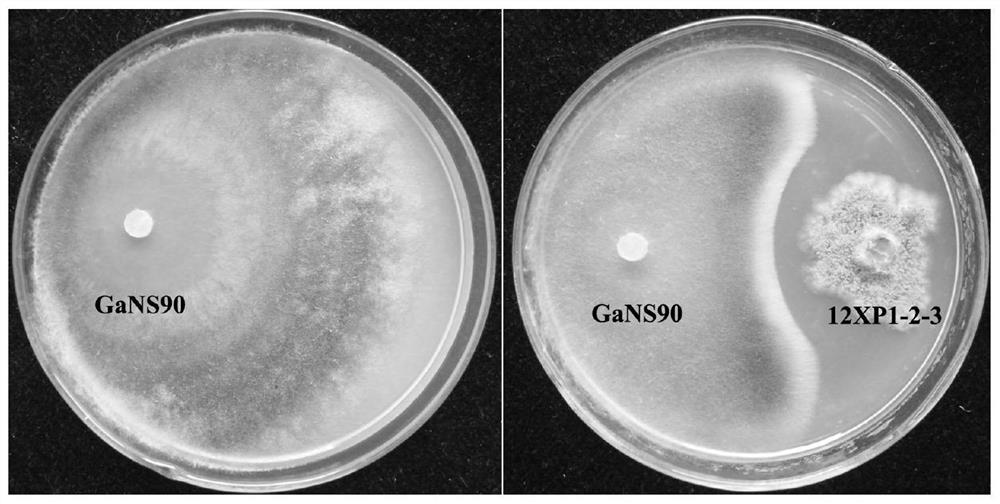
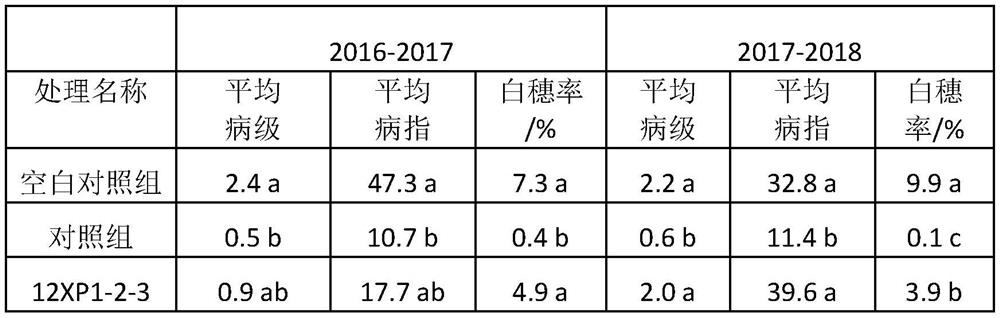
Application of chaetomium globosum in preventing and treating wheat take-all
ActiveCN111869682AReduce the disease indexIncrease plant heightBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicroorganism
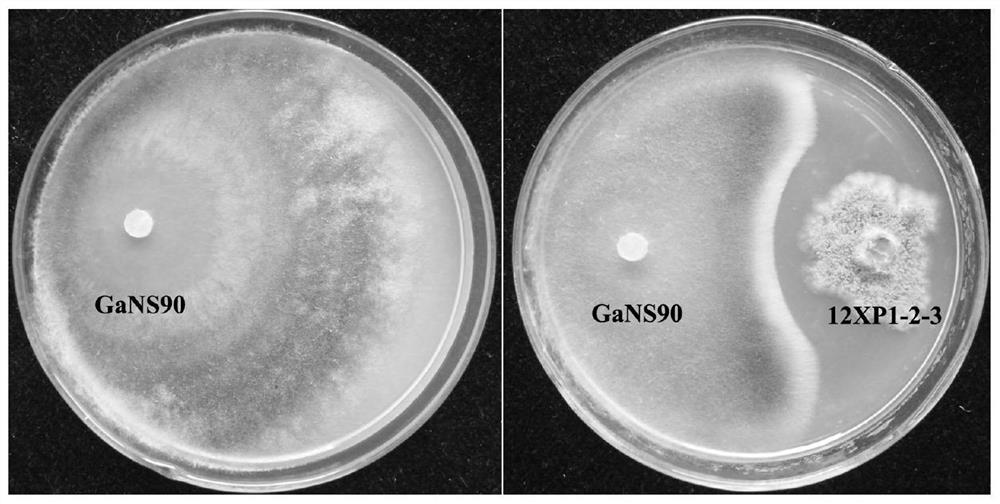
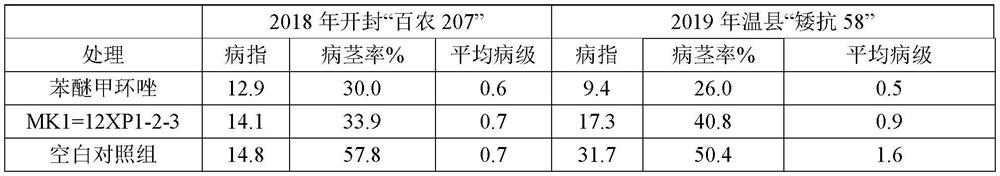
The invention provides an application of chaetomium globosum in prevention and treatment of wheat take-all, the preservation name of the chaetomium globosum is 12XP1-2-3, the preservation number is CGMCC No.17183, the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation date is January 23, 2019. The inhibition rate of the chaetomium globosum 12XP123 onwheat take-all pathogens GaNS90 on a flat plate is 45.4%, and field test results show that when the chaetomium globosum 12XP1-2-3 is used for wheat seed coating treatment, the white spike rate and the disease index of wheat can be obviously reduced.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chaetomium globosum, fungicide, seed soaking solution and application thereof
ActiveCN113234602AImprove drought resistanceImprove salt and alkali resistanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyFungicide
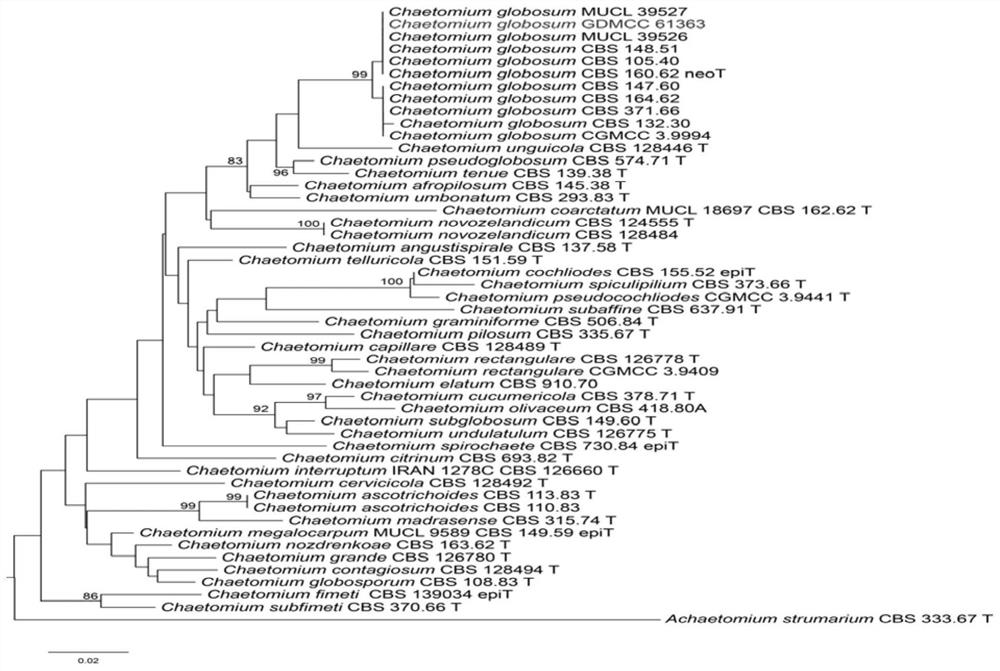
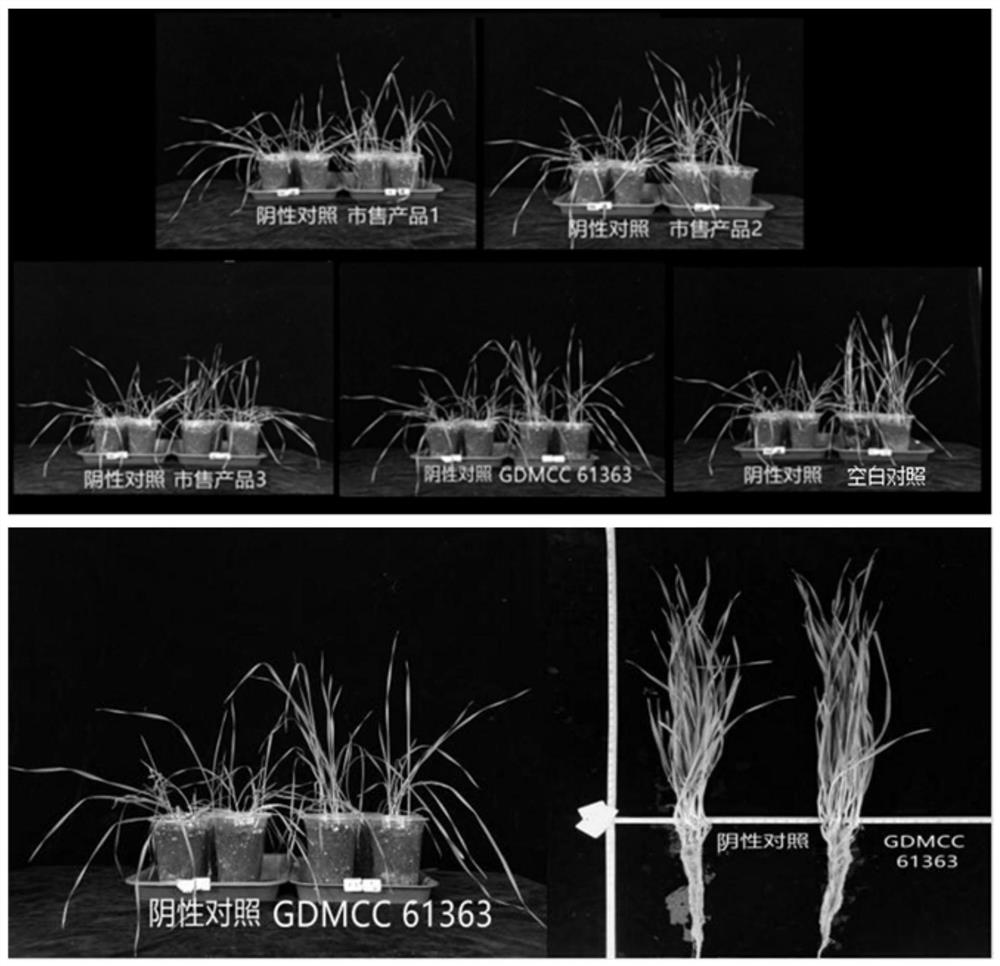
The invention discloses chaetomium globosum, a fungicide, a seed soaking solution and an application thereof, and relates to the technical field of agricultural biology. The strain is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center, the preservation number is GDMCC No: 61363, and the taxonomic name of the strain is Chaetomium globosum. Experiments prove that the strain has broad spectrum for improving the stress resistance of crops, and can obviously improve the drought resistance and saline-alkali resistance of the crops. Under the stress of a drought environment, the chaetomium globosum MN110495 can generate substances such as exopolysaccharides and antioxidants to resist the drought environment, so that the drought resistance of various plants such as fruits, vegetables and food crops is improved. The chaetomium globosum also has the effects of promoting seed germination and crop growth.
Owner:MOON (GUANGZHOU) BIOTECH CO LTD
Microbial compound inoculum for production of cellulosic ethanol and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a microbial compound inoculum for the production of cellulosic ethanol and a preparation method thereof, relating to a compound inoculum and a preparation method thereof, and solving the problems that the cost of fermentation production of cellulosic ethanol is high due to the adoption of a rinsing and detoxification method, and the ultimate yield of the ethanol is low because the rinsing and detoxification method loses the nutrition elements in the lignocellulose. The microbial compound inoculum is mainly prepared from a trichoderma koningii spore suspension, an aspergillus oryzae spore suspension and a chaetomium cupreum spore suspension. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing the trichoderma koningii spore suspension, the aspergillus oryzae spore suspension and the chaetomium cupreum spore suspension; and secondly, mixing and inoculating the mixed spore suspension in a culture medium for cultivation to obtain the microbial compound inoculum. The microbial compound bacterium has few dosage and reduces the cost of the fermentation production of cellulosic ethanol, and the ethanol prepared from the microbial compound inoculum has high ultimate yield.
Owner:江苏哈宜环保研究院有限公司
Application of a kind of Chaetomium globosa in the prevention and treatment of wheat stem rot
The invention provides an application of Chaetomium globosa in preventing and treating wheat stem base rot. The preservation name of the Chaetomium globosa is 12XP1-2-3, the preservation number is CGMCC No.17183, and the preservation unit is China Microbial Bacteria The General Microbiology Center of the Species Depository Management Committee, the deposit date is January 23, 2019. The field test results showed that using Chaetomium globulus 12XP1‑2‑3 to coat wheat seeds could reduce the diseased stem rate, disease grade and disease index by 19.0%‑41.3%, 43.7% and 4.7%‑45.4%, respectively.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
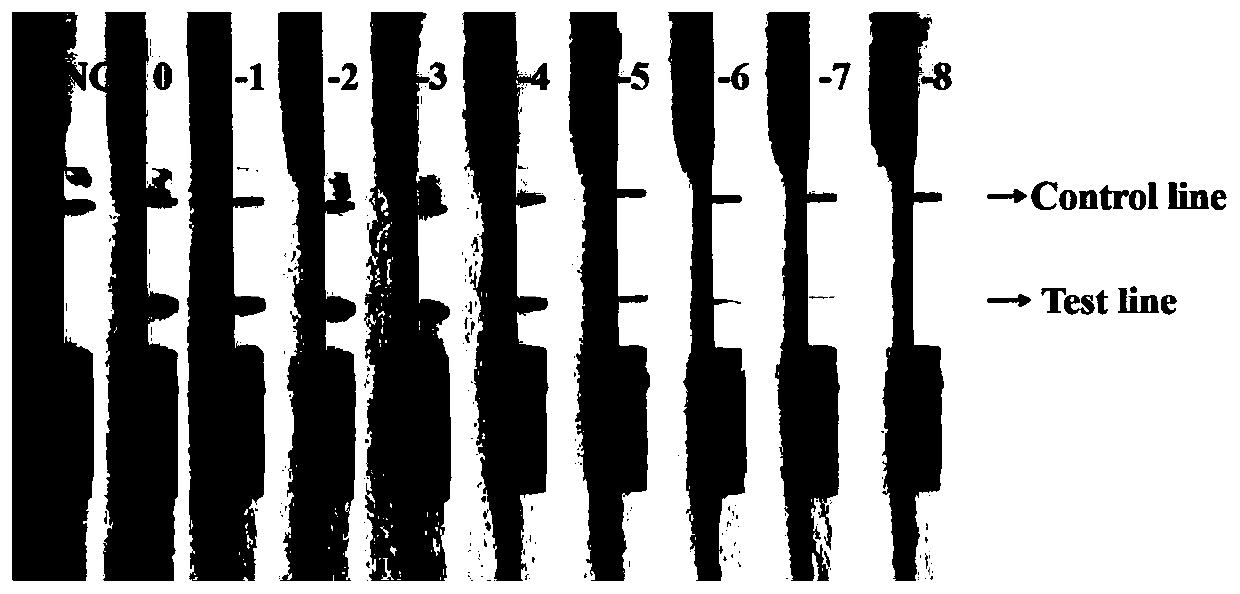
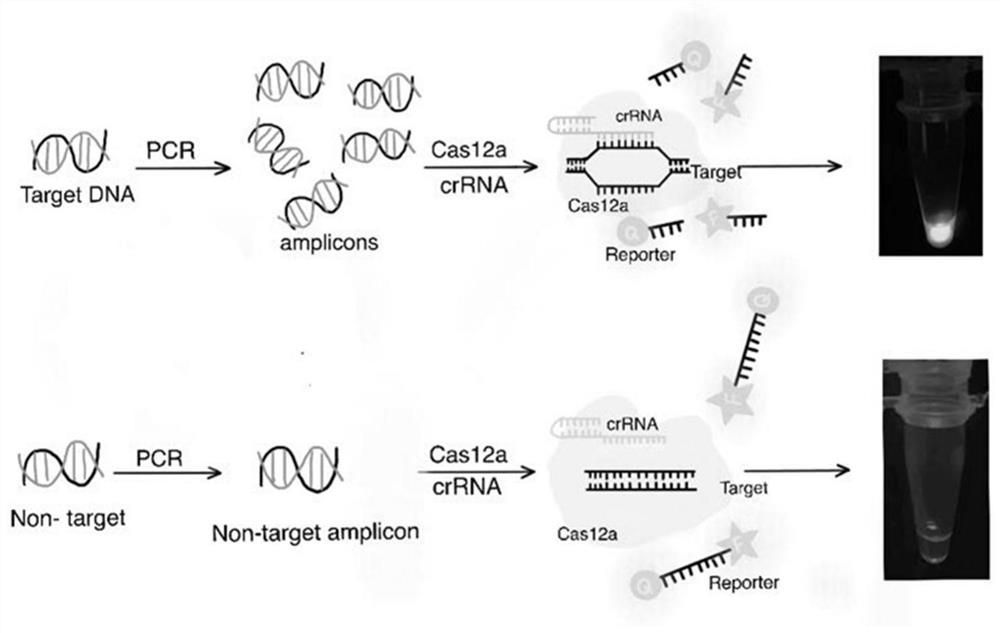
Method for visually detecting Hangzhou white chrysanthemum leaf blight chaetomium globosum by using CRISPR/Cas12a system
PendingCN114836570AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNuclease
The invention provides a method for visually detecting Hangzhou white chrysanthemum chaetomium globosum C.globosum by utilizing a CRISPR / Cas12a (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR associated 12a) system. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying a specific gene segment of Hangzhou white chrysanthemum chaetomium globosum C.globosum by virtue of a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology; under the mediation of crRNA, Cas12a specifically recognizes an amplification product and activates nuclease activity, so that any base sequence ssDNA (Reporter) of which the two ends are modified with FAM and BHQ1 is cut, and an FAM-ssDNA fragment and a BHQ1-ssDNA fragment are formed; the FAM-ssDNA and the BHQ1-ssDNA can show fluorescence under the irradiation of a blue light transmission instrument, so that the detection on the Hangzhou white chrysanthemum chaetomium globosum C.globosum is realized. The method is simple and portable to operate, does not depend on large-scale instruments and equipment, is low in cost, high in sensitivity and strong in specificity, and has a certain application prospect.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for producing chitinase through fermentation of chaetomium globosum and application of chitinase
ActiveCN111944789AIncrease vitalityHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention discloses a method for producing chitinase through fermentation of chaetomium globosum and application of the chitinase. According to the method, chaetomium globosum HY1 is adopted for strain activation, an activation culture medium comprises glucose, peptone, monopotassium phosphate and disodium hydrogen phosphate, then shake cultivation or fermentation tank cultivation are carriedout, a fermentation medium comprises soluble starch, glycerin, tryptone, yeast powder, corn steep liquor, NH4NO3, MnSO4, MgSO4, Na2HPO4, K2HPO4 and colloidal chitin, and chitinase produced through fermentation is used for preparing chitosan oligosaccharide. The culture method is simple, the nutritional requirement is not high, and the chitinase produced by liquid state fermentation is high in activity and has a relatively great industrial application value.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Chaetomium globosum HJF 13 strain and application thereof
The invention provides chaetomium globosum and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of applied microbiology. The chaetomium globosum (chaetomium cochliodes) HJF 13 strain disclosed by the invention is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 9, 2021, and the preservation number of the chaetomium globosum HJF 13 strain is CCTCC NO: M2021343. An anti-bacillus subtilis agent prepared from the strain through liquid fermentation culture has a relatively good inhibition effect on bacillus subtilis and can be used for preventing and treating the bacillus subtilis. The invention has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, low raw material cost and simple production process, and has potential and practical application value in the fields of daily chemical products, food, industrial products and the like.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of chaetomium globosum in prevention and treatment of wheat stem rot
The invention provides application of chaetomium globosum in prevention and treatment of wheat stem rot. The preservation name of the chaetomium globosum is 12XP1-2-3, the preservation number is CGMCCNo.17183, the preservation institution is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation date is January 23, 2019. Field trial results show that when the chaetomium globosum 12XP1-2-3 is used for wheat seed coating treatment, the disease stem rate, the disease grade and the disease index can be reduced by 19.0%-41.3%, 43.7% and 4.7%-45.4% respectively.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of preparation method and use of secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus chaetomium sp of Eucalyptus margina
ActiveCN109295122BStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologySecondary metabolite
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a secondary metabolite of the endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp., the method comprising: (1) activating and subculturing the endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp. on PDA solid medium, Then shake culture in PDB liquid medium; (2) ferment and cultivate the liquid seeds obtained in step (1) in rice medium to obtain solid fermented product; (3) solid fermented product is extracted by methanol cold immersion, filtered, The filtrate is concentrated to obtain a crude extract, and the crude extract is suspended in water and extracted with petroleum ether and ethyl acetate to obtain the crude extract of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate layer respectively; (4) by vacuum column chromatography, dextran Compound A‑F was obtained by gel column chromatography and semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatography. The method of the invention separates the secondary metabolites of the endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp., and the secondary metabolites have antibacterial and antitumor effects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
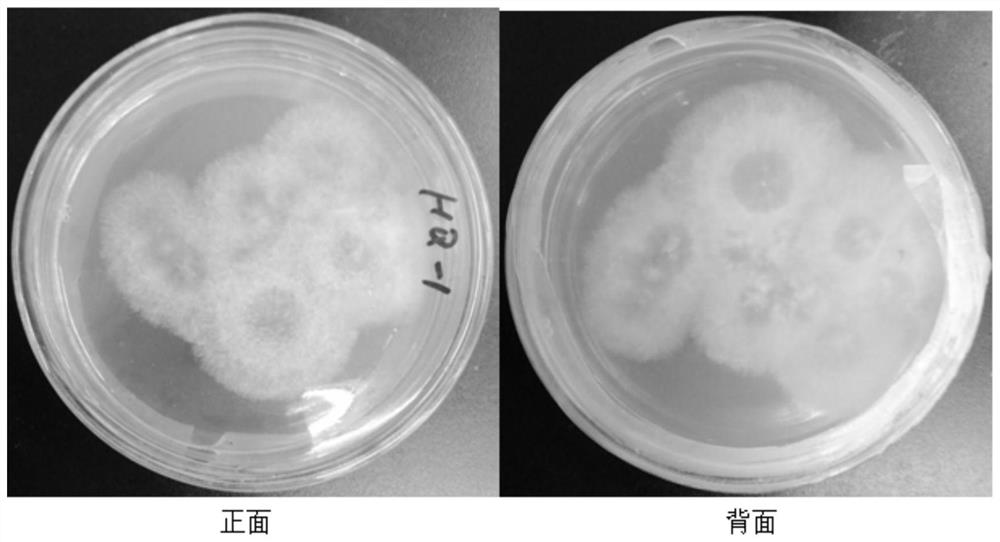
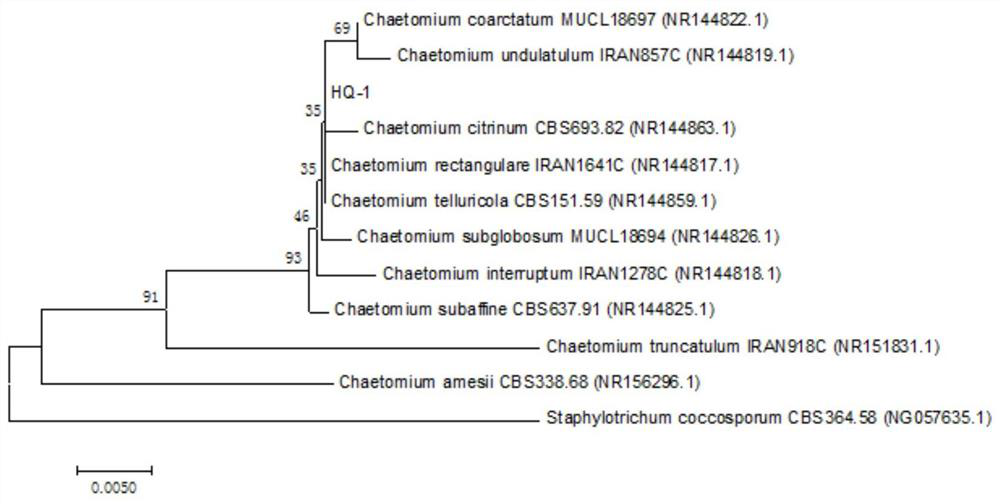
A Strain of Astragalus endophytic Chaetomium sp. HQ-1 and Its Application
ActiveCN109971655BHigh antibacterial activityEnhanced inhibitory effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAntibiosis
The invention discloses an endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp. HQ-1 with good antibacterial activity. The astragalus endophyte HQ‑1 active product differanisole A to G + Bacteria Staphylococcus aureus S.aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA, Listeria monocytogenes L.monocytogenes showed moderate inhibitory activity. It showed a strong inhibitory effect on the pathogenic fungus S. rolfsii, indicating that differanisole A has the potential as an agricultural antibiotic. The astragalus endophytic fungus Chaetomium sp.HQ‑1 provided by the invention can provide new resources and approaches for the production of antibacterial drugs, especially for the production of agricultural antibiotics against plant pathogenic fungi.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of chaetomium elatum in denitration of nitrocellulose
InactiveCN112870620AReduce nitrogen contentControl the degree of denitrificationBiotechnologyCellulose
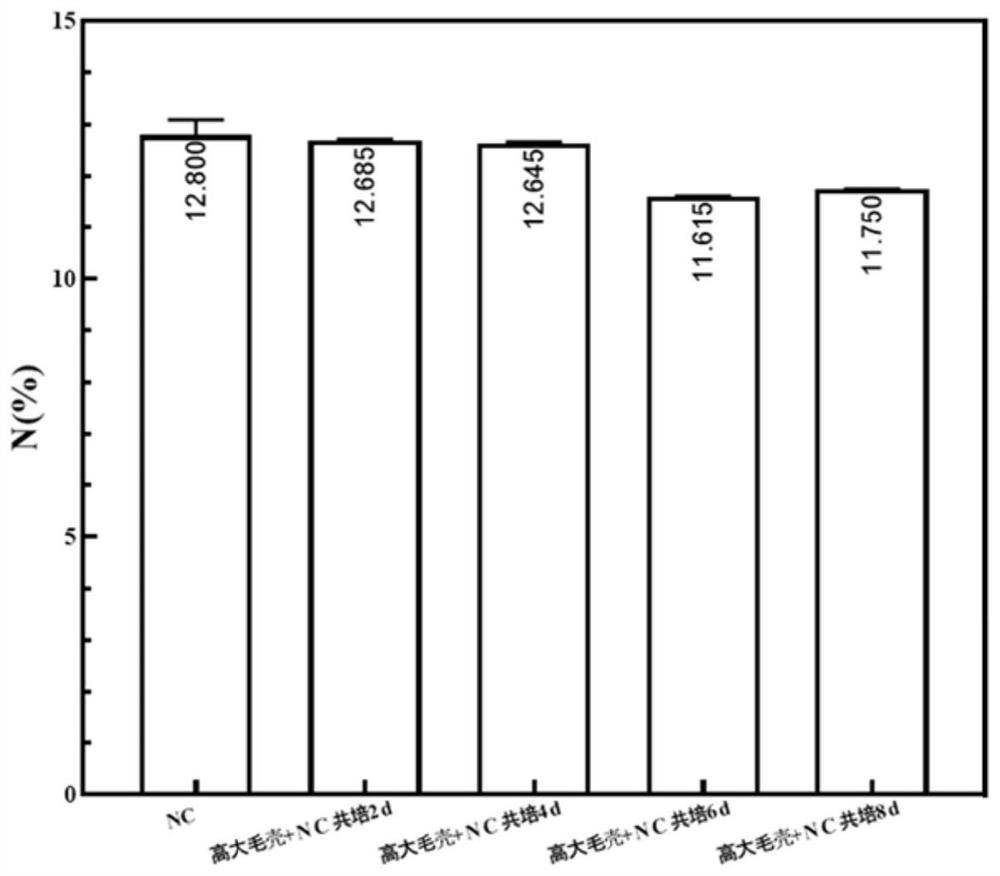
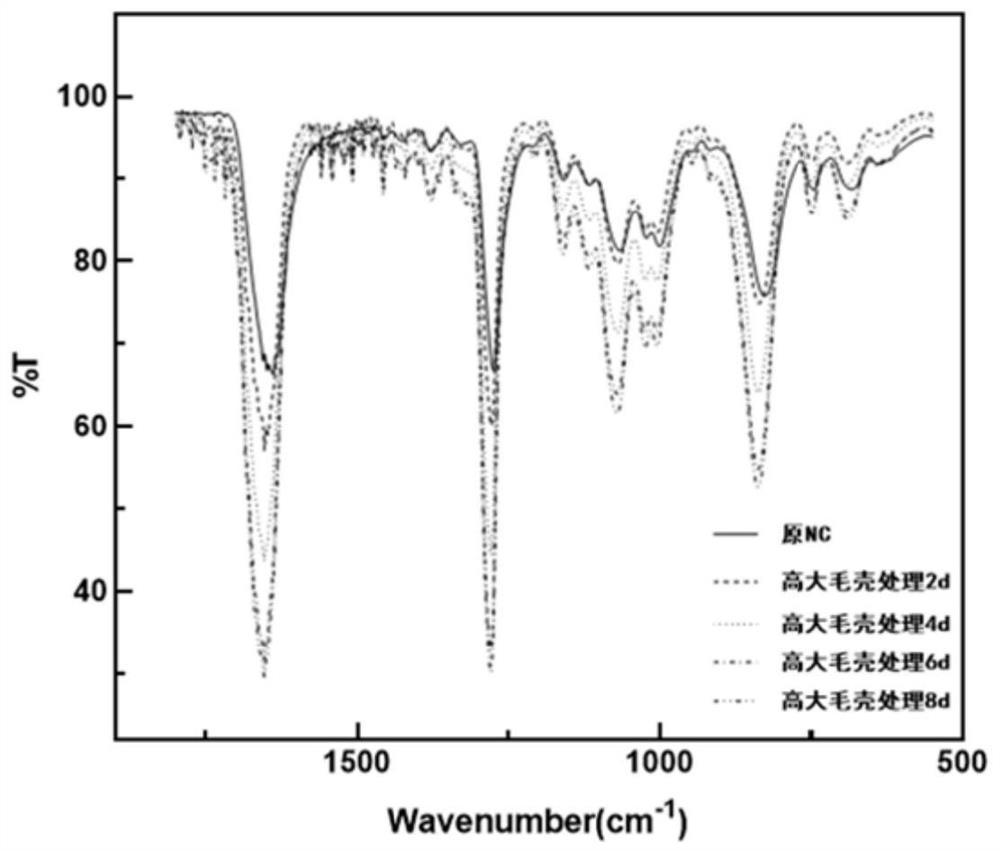
The invention discloses an application of chaetomium elatum in denitration of nitrocellulose. The application is characterized in that a chaetomium elatum strain converts nitrocellulose, denitration is completed in the conversion process, and nitrate and nitrite can be converted into own nutrient substances in the conversion process, so that better growth of the strain is achieved, and pollution is reduced; a culture medium is simple in components, readily available in raw materials and suitable for industrial production; and nitrocellulose is subjected to denitration treatment by using a single microbial strain, so that the denitrification degree of the nitrocellulose can be controlled more simply and conveniently, and a good foundation is laid for later research on the nitrogen reduction mechanism of the nitrocellulose. According to the invention, alkali hydrolysis pretreatment is not needed before denitration conversion, and a cellulose main chain cannot be damaged; no anaerobic environment is needed in the denitration process of the chaetomium elatum on the nitrocellulose, and the conversion environment is relatively simple; after the strain is co-cultured with nitrocellulose for 14 days, the nitrogen content of nitrocellulose with the original nitrogen content of 13.03% can be reduced to 10.43%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A kind of method of extracting oosporin from Chaetomium chaetomium fermented liquid
InactiveCN107652173BIncrease productionHigh purityQuinone separation/purificationMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyOrganic solvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for extracting oosporein from a chaetomium cupreumfermentation liquor. The method comprises the steps thatchaetomium cupreum is obtained through screening and separation and is fermented, filtered, concentrated, acidized, extracted, re-concentrated and crystallized, and the oosporein is finally obtained.The oosporein directly acts on plant diseases, the limitations of the chaetomium cupreum serving as a biocontrol bacterium for biological prevention and control are overcome, use of medication is accurate, plant damage is reduced, the dosage of an organic solvent for extracting the oosporein by using a direct extraction method is decreased, the energy consumption needed by oosporein extraction isreduced, the extracting efficiency is improved, the effect of conveniently and quickly obtaining high-purity oosporein at low energy consumption is achieved, and the method has a great popularizationand use value.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
A kind of method and application of Chaetomium globosa fermentative production of chitinase
ActiveCN111944789BIncrease vitalityHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention discloses a method for fermenting and producing chitinase by Chaetomium globosa and its application. The strain is activated by using Chaetomium globosa HY1, and the activation medium includes glucose, peptone, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, dihydrogen phosphate Sodium; then shaker culture or fermenter culture, the fermentation medium includes soluble starch, glycerol, tryptone, yeast powder, corn steep liquor, NH 4 NO 3 , MnSO 4 , MgSO 4 、Na 2 HPO 4 、K 2 HPO 4 , Colloidal chitin, the chitinase produced by fermentation is used for the preparation of chitooligosaccharides. The cultivation method of the invention is simple, the nutritional requirements are not high, the chitinase produced by liquid fermentation has high activity, and has great industrial application value.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
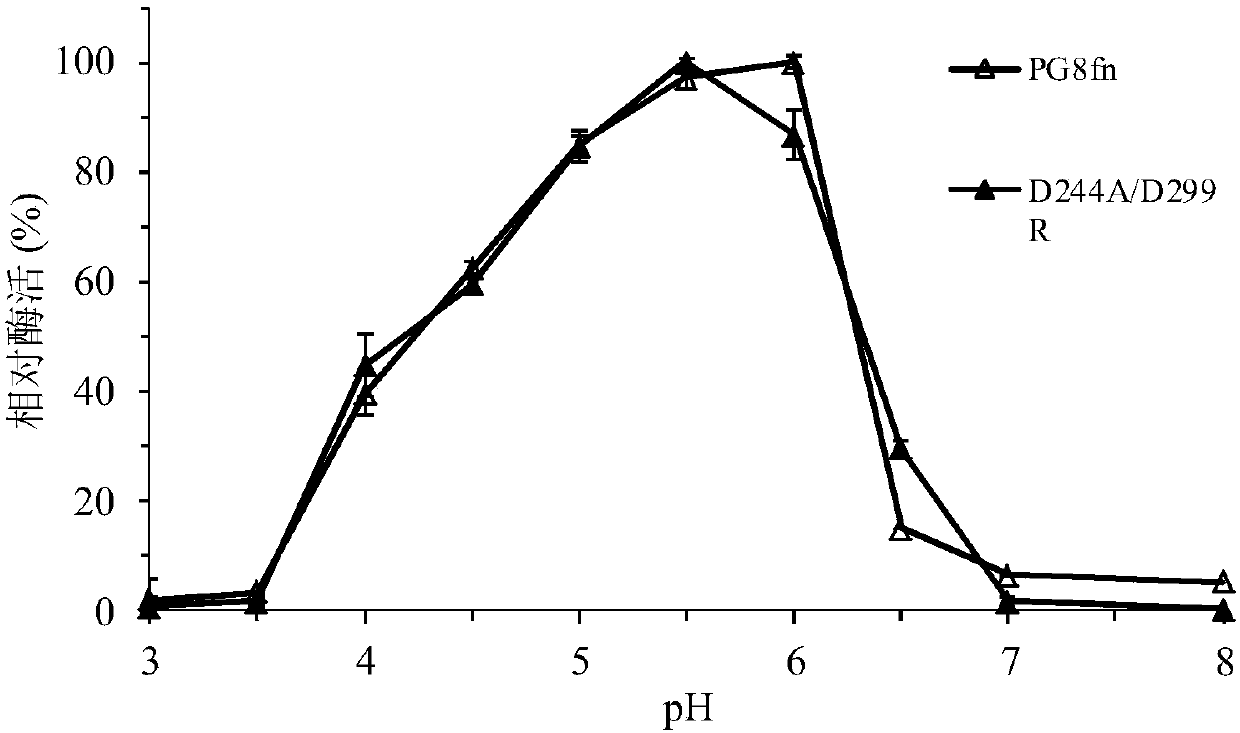
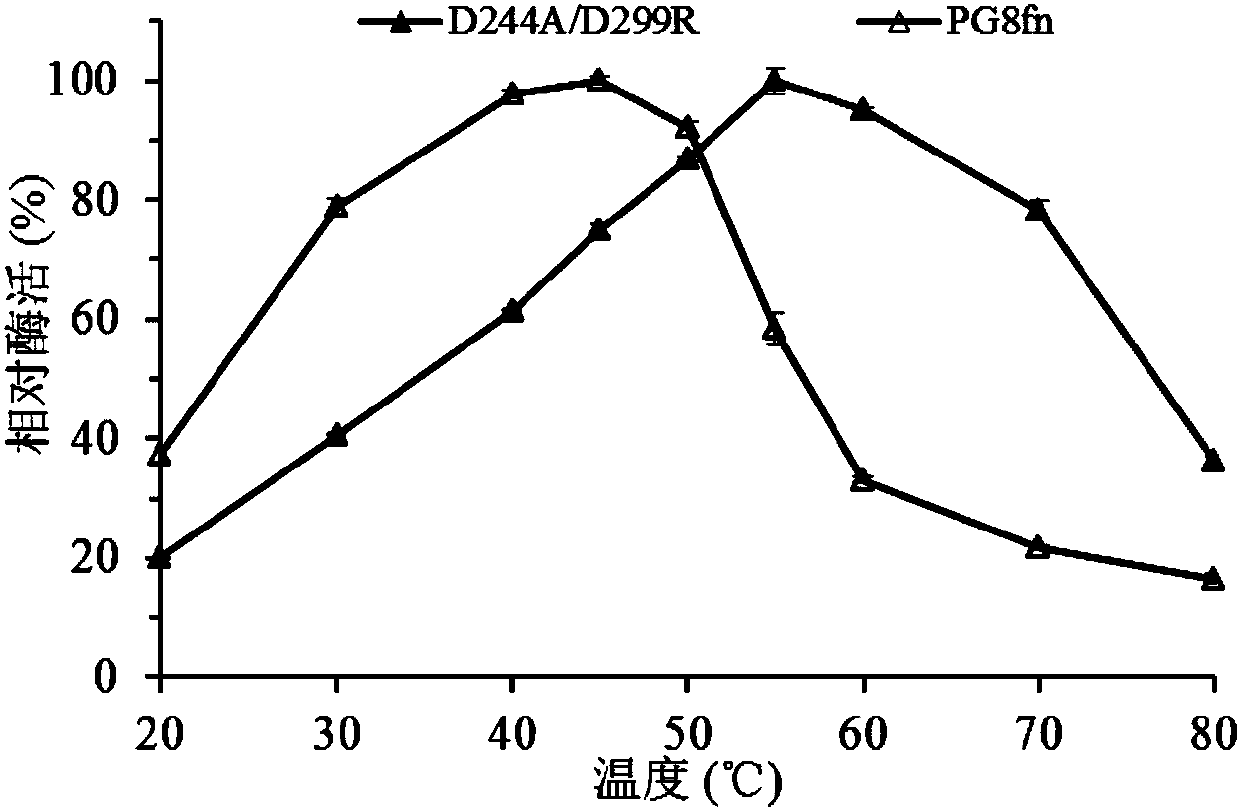
A kind of heat-resistant chaetomium polygalacturonase mutant and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN104818260BImprove thermal stabilityMeet the needs of plasmid (instantaneous high temperature) processingFungiMicroorganism based processesPentagalacturonic acidMutant
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a high temperature resistant chaetomium polygalacturonase mutant and an encoding gene and an application thereof. Polygalacturonase from achaetomium sp.xz8 is used as a female parent, and the polygalacturonase mutant with improved heat stability is obtained through rational design and molecular biological technique. Related amino acid mutation is combined mutation (ASA, Asp244Ala / Asp299Arg) of two points Asp244Ala and Asp299Arg in each mutant sequence. Optimum temperature, T50 and T1 / 2 of the mutant are improved in comparison with those of wild type enzyme. The optimum temperature is increased from 45 DEG C to 55 DEG C, T50 is increased from 56 DEG C to 73 DEG C, half-life period T1 / 2 at 50 DEG C is increased from 1.5h to 10h, half-life period T1 / 2 at 55 DEG C is increased from 33min to 78min, and Tm value is increased from 43.8 DEG C to 54.1 DEG C. Besides, the mutant keeps enzyme catalytic activity which is equal to that of the wild type enzyme. Application demands in fields of feedstuff, foodstuff and the like can be met.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of antibacterial fermentation liquid of Solidago canadesis endophytic fungi
The invention relates to a preparation method of an antibacterial fermentation liquid of Solidago canadesis endophytic fungi, which comprises the following operation steps: 1. activating strain; 2. carrying out first-stage seed culture; 3. carrying out second-stage seed culture; and 4. carrying out fermentation culture to obtain brown Solidago canadesis endophytic fungus fermentation liquid, filtering the Solidago canadesis endophytic fungus fermentation liquid in aseptic condition to remove mycelia, and then passing a 0.22 mu m filter to obtain the antibacterial fermentation liquid of Solidago canadesis endophytic fungi. According to the invention, the preparation method of antibacterial fermentation liquid of Chaetomium globosum yt03 with broad spectrum antibacterial activity is determined; and antibacterial test finds that the Chaetomium globosum yt03 antibacterial fermentation liquid has relatively significant hypha growth inhibiting action on six tested plant pathogenic fungi.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
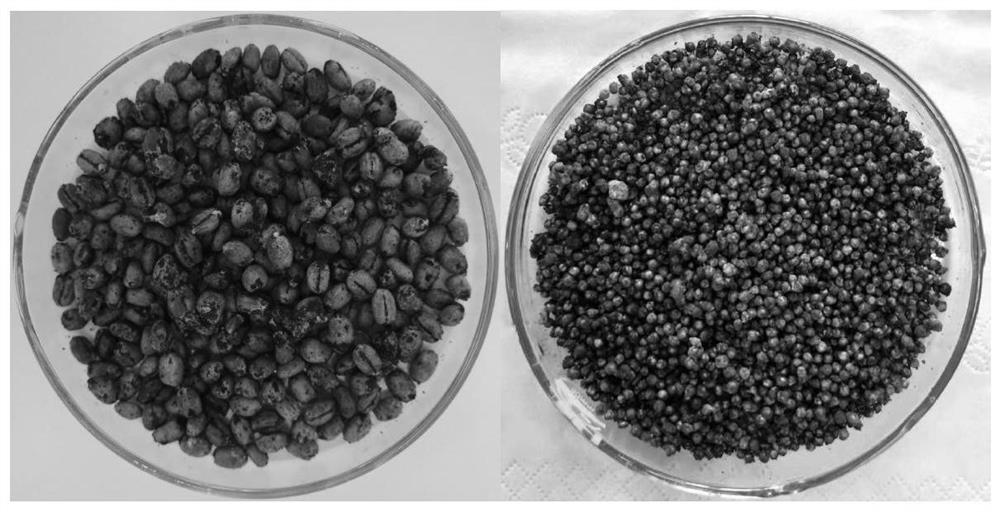
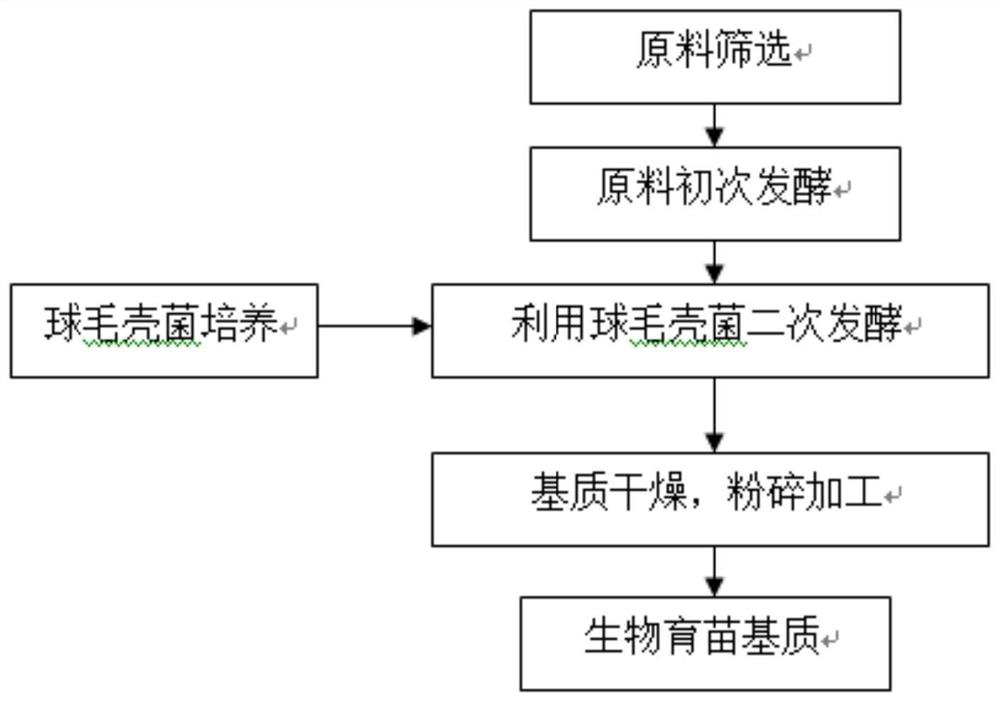
Preparation method and application of a kind of Chaetomium globosa biological seedling substrate
ActiveCN109315265BStrong stress resistanceExtended shelf lifeGrowth substratesCulture mediaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a biological seedling raising substrate of chaetomium globosum, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. The method comprises the steps that after preliminary fermentation is performed on agricultural waste, the agricultural waste is inoculated with chaetomium globosum ND35 sexual conidial powder to perform secondary fermentation, so that a functional flora taking chaetomium globosum as the main microorganisms in the substrate, and the biological seedling raising substrate of chaetomium globosum is obtained. The agricultural waste comprises, but is not limited to, bark, wood chips, straw and the like. The preparation method and application of the biological seedling raising substrate of chaetomium globosum have the advantages of being simple, being capable of being directly applied to the seedling raising stages of tomatoes, cucumbers and other plants, planting chaetomium globosum ND35 bacterial strains into the plants more directly and quickly, and being beneficial to the plants perpetually; the biological seedling raising substrate of chaetomium globosum is an excellent seedling raising substrate, can be applied to industrialized seedling raising of various plants, fills in the blank of domestic excellent substrates, replaces imported substrates, promotes the healthy development of industrialized seedling raising of vegetables, and has great economic and social benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Solid-state fermentation method of chaetomium globosum, prepared microbial inoculum and application of microbial inoculum
ActiveCN111944705ABroad spectrum antibacterialEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyRoot-knot nematode
The invention discloses a solid state fermentation method of chaetomium globosum, a prepared microbial inoculum and an application of the microbial inoculum. The chaetomium globosum HY1 is adopted toperform strain activation, then solid fermentation is performed, after the solid fermentation is ended, a solid culture is scattered and uniformly mixed, and the mixture is placed in a shady, cool andventilated place to be aired and crushed to obtain the agricultural composite biocontrol microbial inoculum, and the microbial inoculum is used for preventing and treating agricultural root-knot nematodes and soil-derived phytopathogens. The process is simple to operate, parameters are easy to control, the composite biocontrol microbial inoculum produced by solid-state fermentation has high capacity of killing root-knot nematodes and soil-derived phytopathogens, and has wide application prospect and remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Primer for detecting chaetomium globosum in jet fuel, application and detection method
ActiveCN111304354AQuality assuranceEnsure flight safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGeneticsEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and discloses a primer for detecting chaetomium globosum in jet fuel, application and a detection method. The primer for detectingthe chaetomium globosum comprises an outer primer F3, an outer primer B3, an inner primer FIP, an inner primer BIP and a loop primer LB; and the sequence of the outer primer F3 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, the sequence of the outer primer B3 is shown as SEQ ID NO.2, the sequence of the inner primer FIP is shown as SEQ ID NO.3, the sequence of the inner primer BIP is shown as SEQ ID NO.4, and the sequence of the loop primer LB is shown as SEQ ID NO. 5. The detection method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:LOGISTICAL ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Radix astragali endophytic Chaetomium sp. HQ-1 and application thereof
ActiveCN109971655AHigh antibacterial activityEnhanced inhibitory effectFungiMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic YBiology
The invention discloses radix astragali endophytic Chaetomium sp. HQ-1 with high antibacterial activity. An active product, differanisole A, of the radix astragali endophytic Chaetomium sp. HQ-1 has medium inhibitory activity on G+ staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and listeria monocytogenes. The strong inhibitory effect on pathogenic sclerotium rolfsii indicates that the differanisole A has a potential of serving as an agricultural antibiotic. The radix astragali endophytic Chaetomium sp. HQ-1 can be used for preparing antibacterial drugs, especially providing a new resource and a new approach for production of agricultural antibiotics for resisting plant pathogenic fungi.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of a kind of Chaetomium globosa in the control of wheat take-all
ActiveCN111869682BReduce the disease indexIncrease plant heightBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides an application of Chaetomium globosa in the prevention and treatment of wheat take-all. The preservation name of the Chaetomium globosa is 12XP1-2-3, the preservation number is CGMCC No.17183, and the preservation unit is China Microorganisms The General Microorganism Center of the Preservation Management Committee, the deposit date is January 23, 2019. The Chaetomium globosa 12XP1‑2‑3 has an inhibitory rate of 45.4% on the flat plate to the pathogen GaNS90 of wheat take-all. Reduce white ear rate and disease index of wheat.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chaetomium globosum and application of chaetomium globosum in preparation of medicament for preventing and treating wheat sharp eyespot
The invention discloses chaetomium globosum, which is a chaetomium globosum (Chaetomiumglobosum) 12CG5-11 strain, is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 4, 2020, has a preservation number of CGMCC No.19939, has a preservation address of No. 3, No.1 yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and is named as chaetomium globosum (Chaetomiumglobosum) in taxonomy. The chaetomium globosum spore liquid is produced through fermentation of a millet grain culture medium, the chaetomium globosum spore liquid is applied to preparation of a medicament for preventing and treating wheat sharp eyespot, and field test results show that after the chaetomium globosum 12CG5-11 spore liquid is sprayed in the sowing period of wheat, the prevention effects on the wheat sharp eyespot in the jointing period and the mature period reach 47.83% and 53.40% respectively.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com