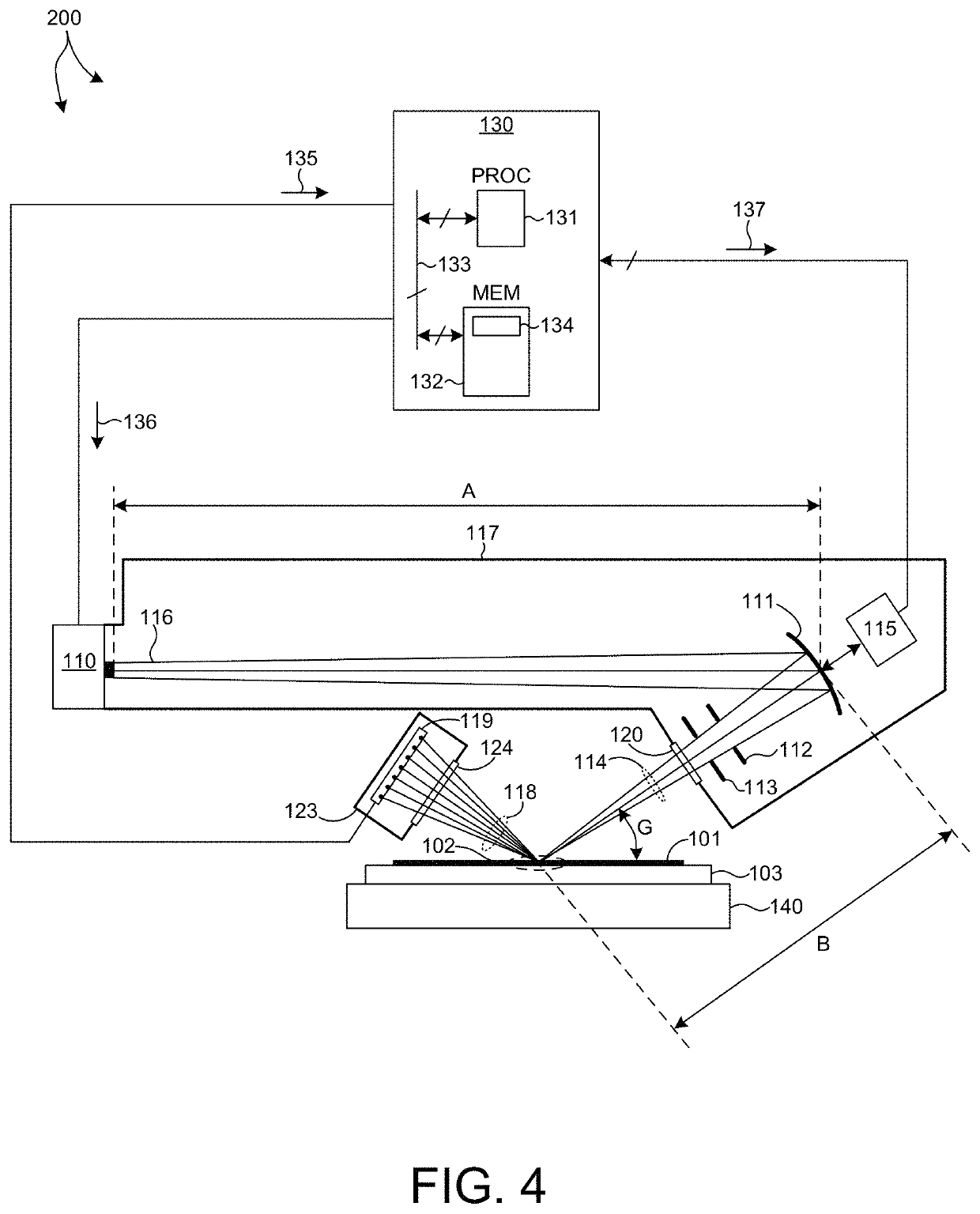
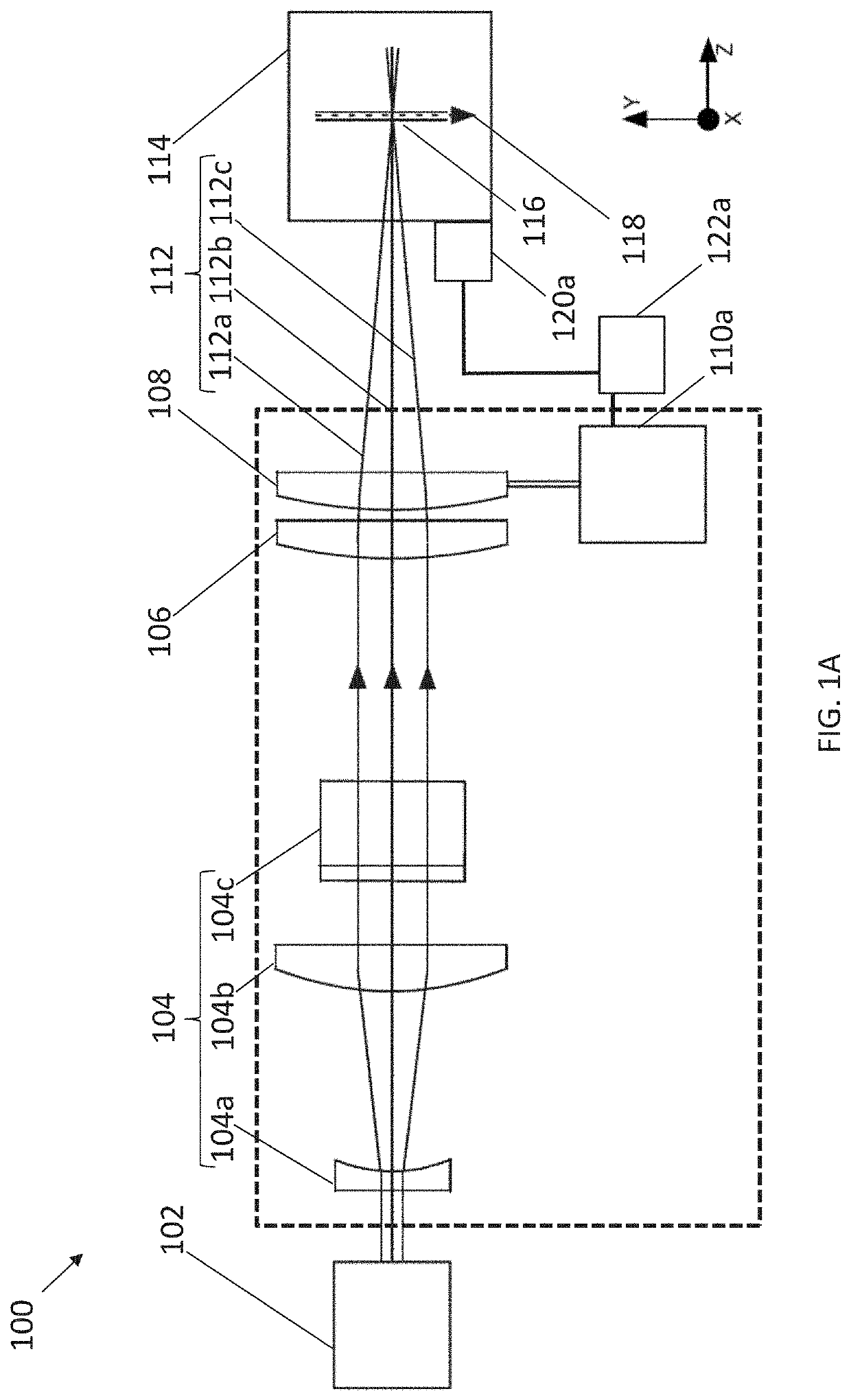
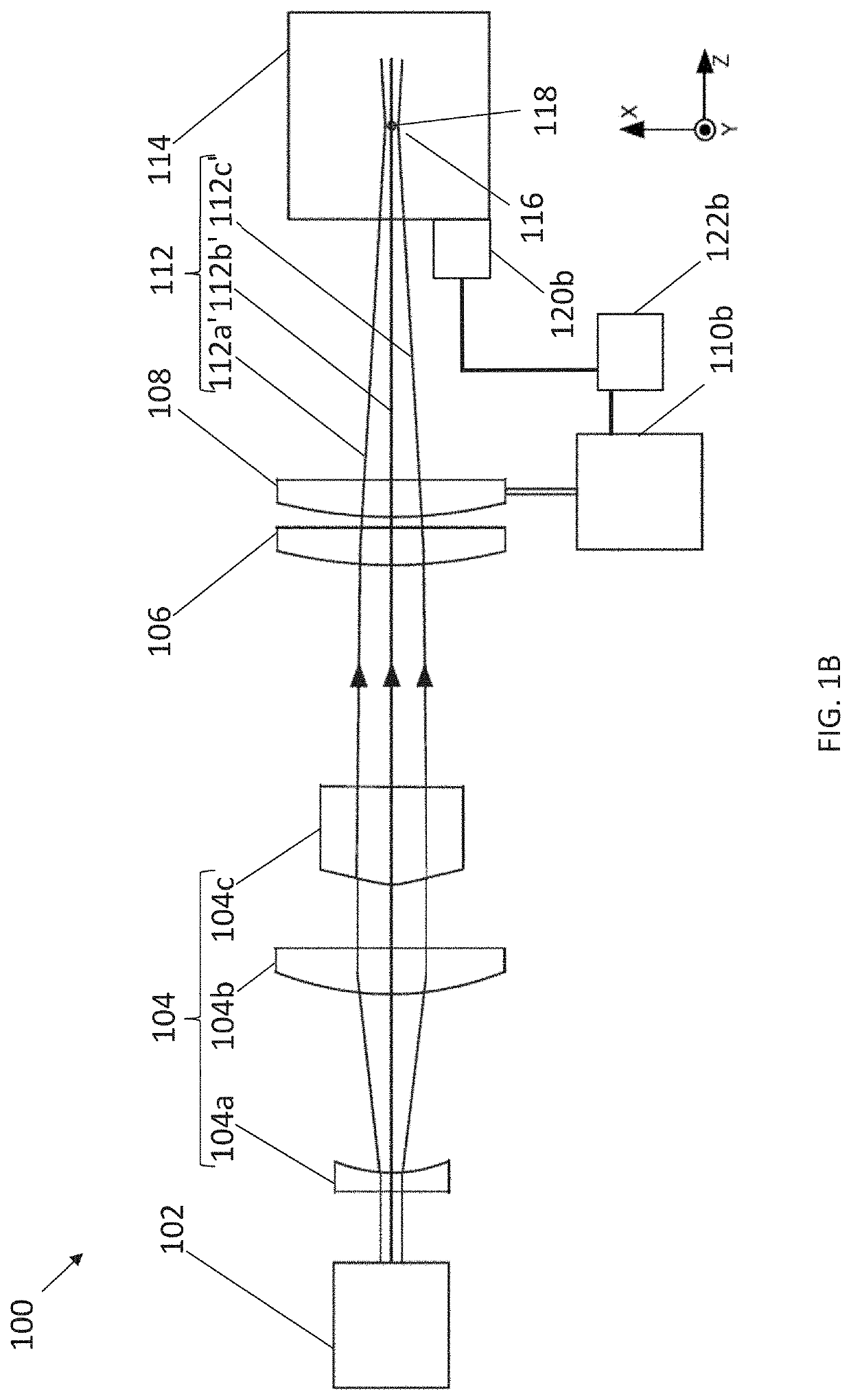
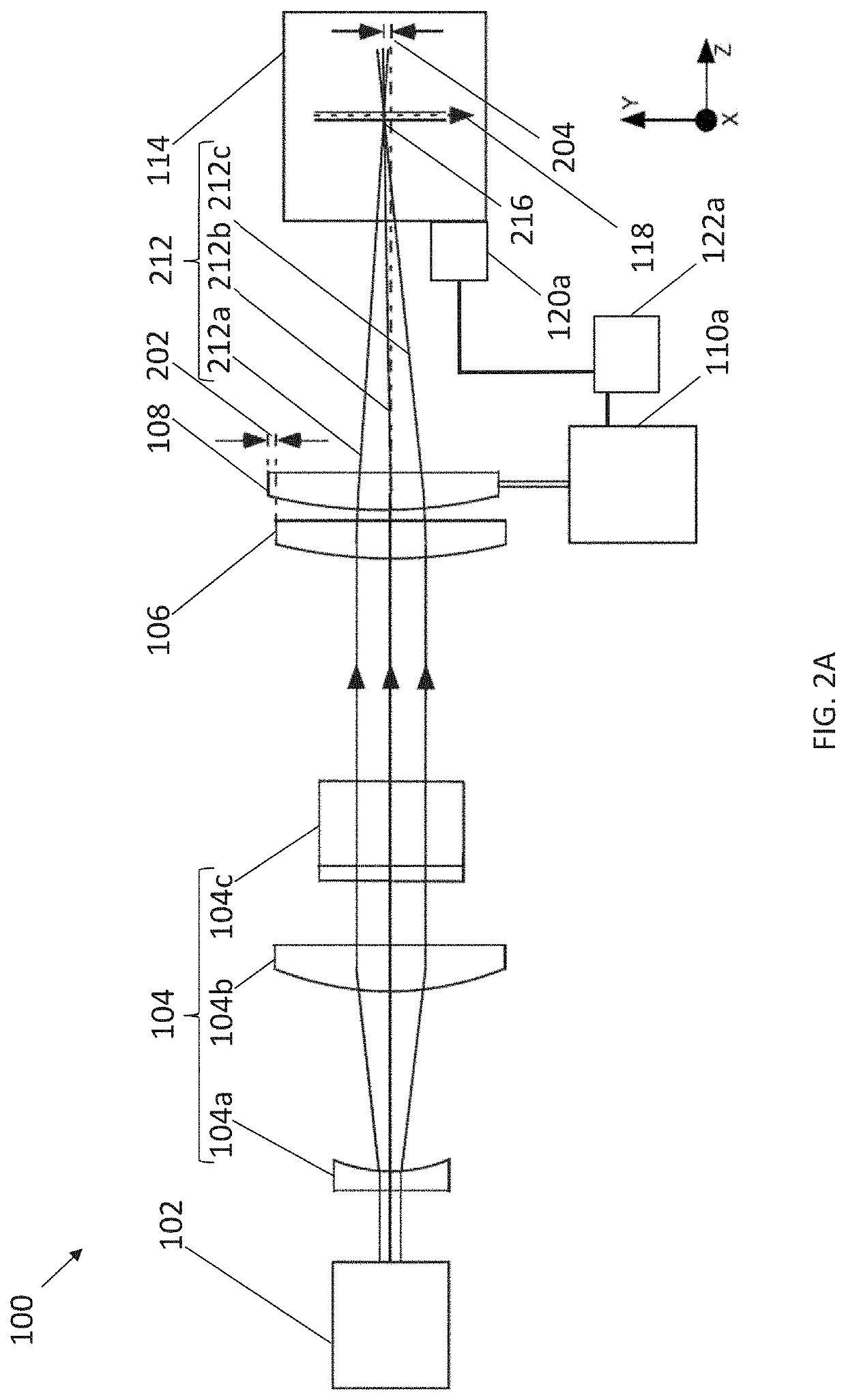
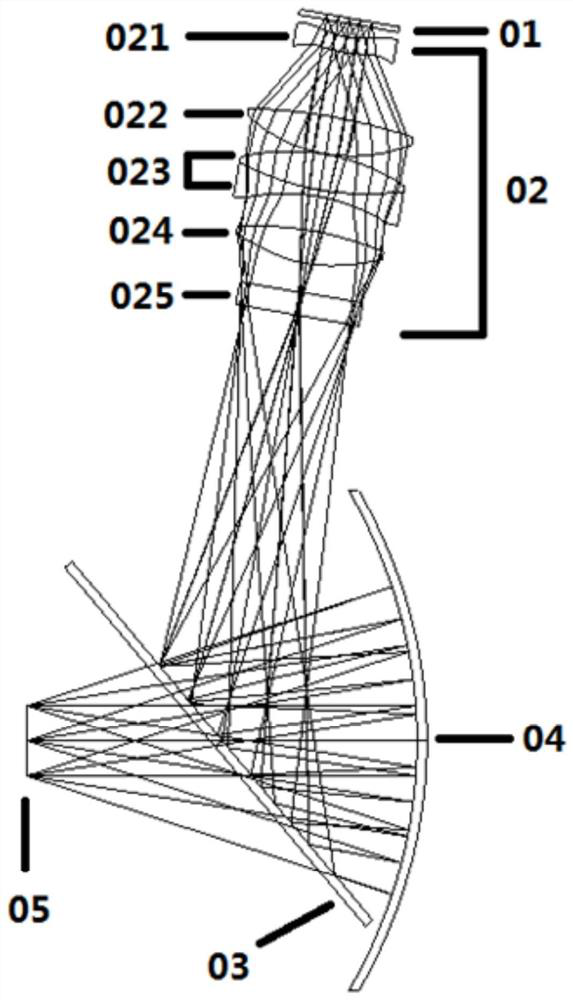
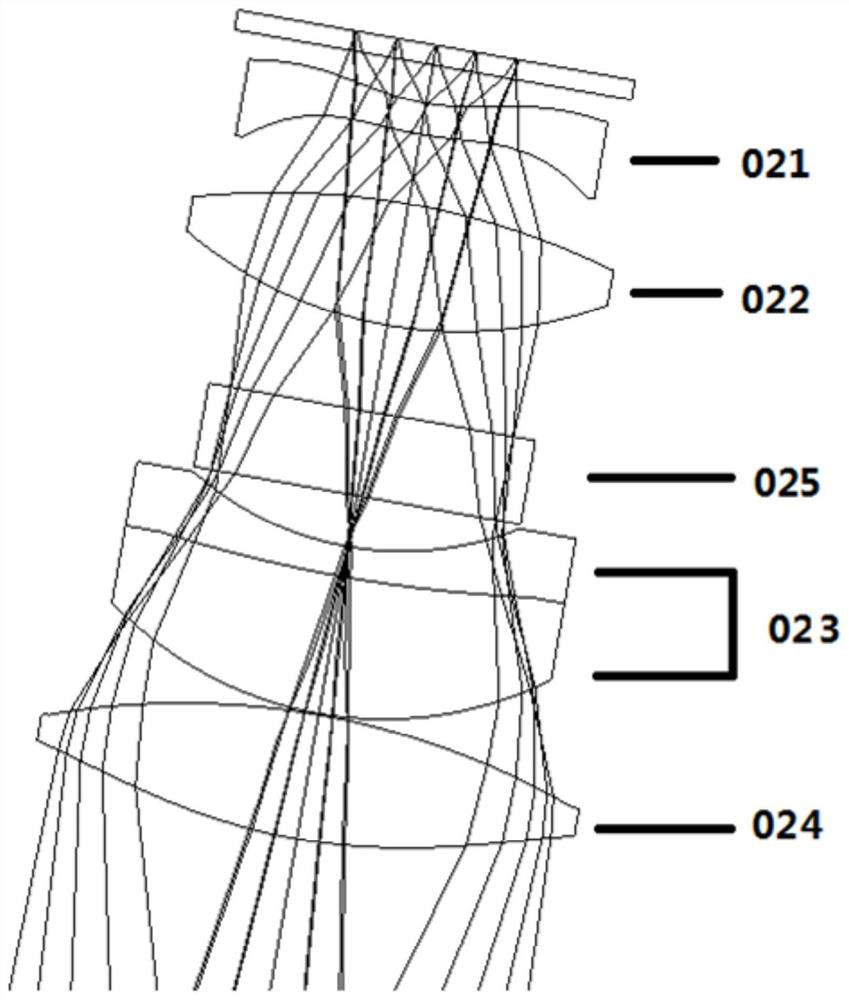
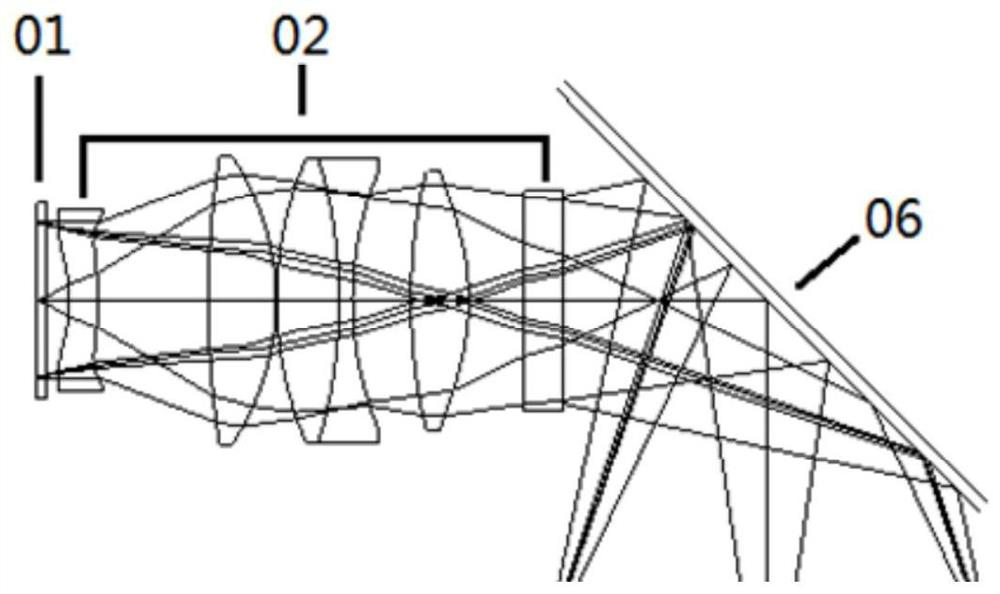
Patents
Literature
105 results about "Focus (optics)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by aberrations of the imaging optics. In the absence of significant aberrations, the smallest possible blur circle is the Airy disc, which is caused by diffraction from the optical system's aperture. Aberrations tend to get worse as the aperture diameter increases, while the Airy circle is smallest for large apertures.
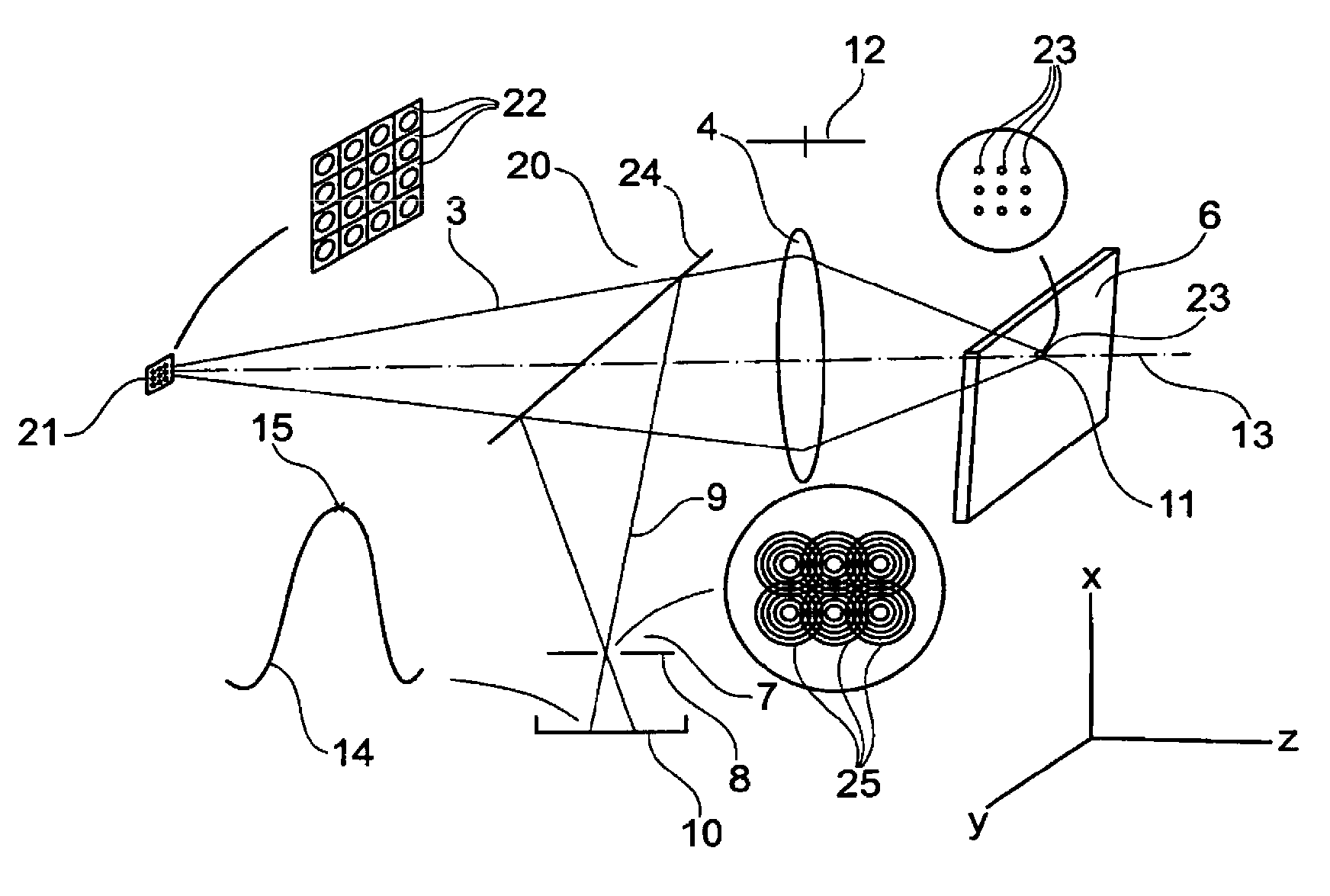
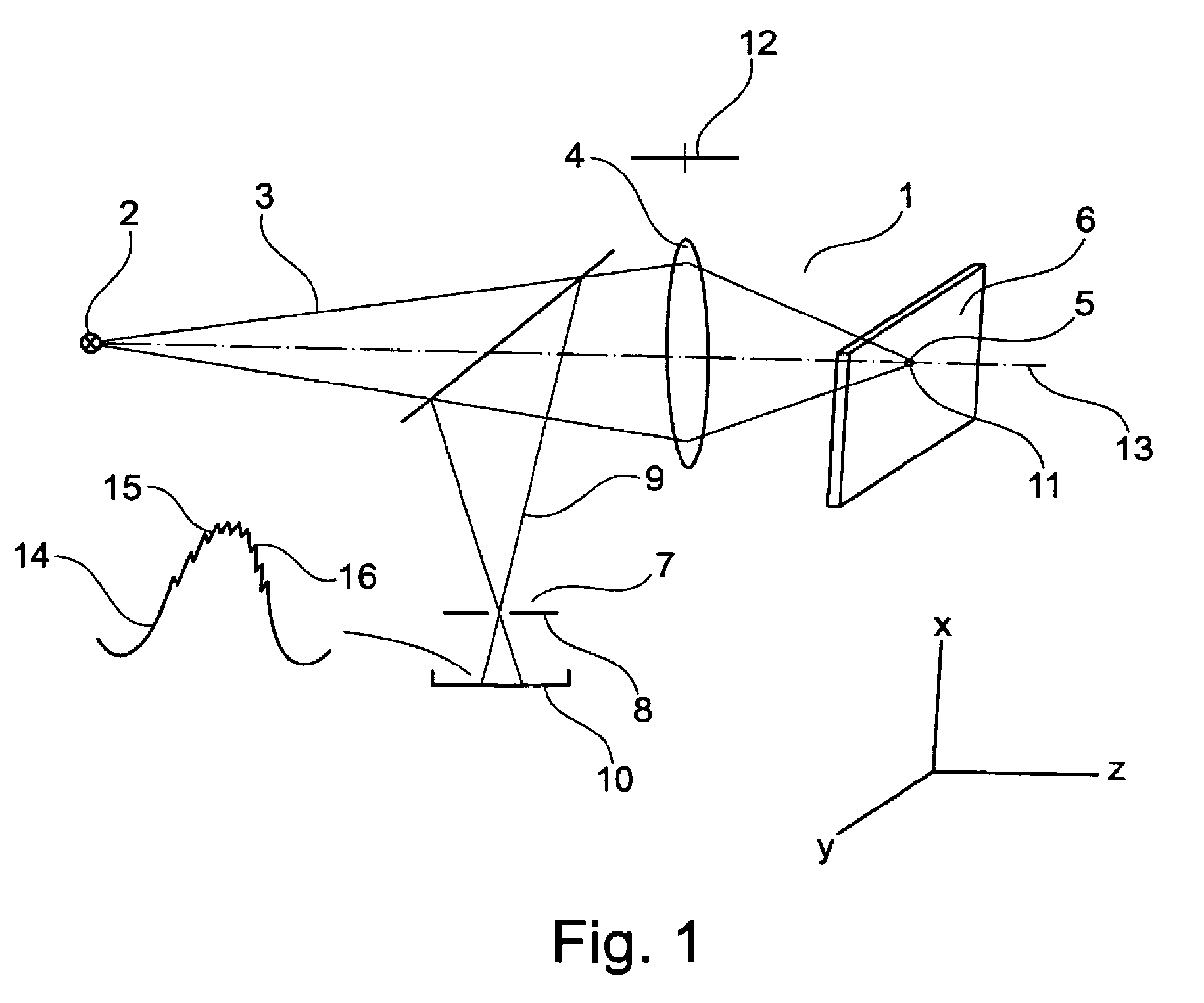
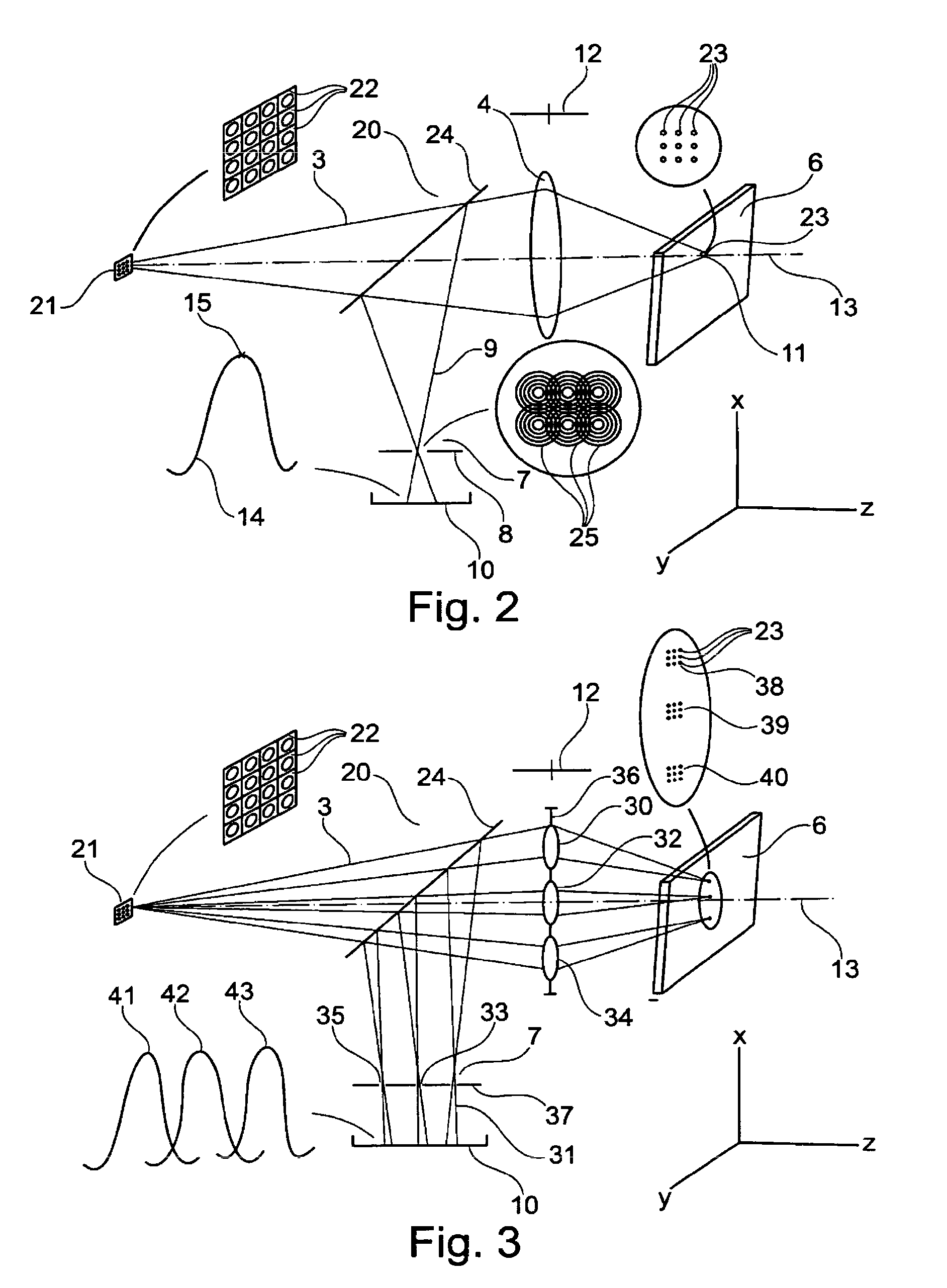
Ophthalmic instrument with adaptive optic subsystem that measures aberrations (including higher order aberrations) of a human eye and that provides a view of compensation of such aberrations to the human eye
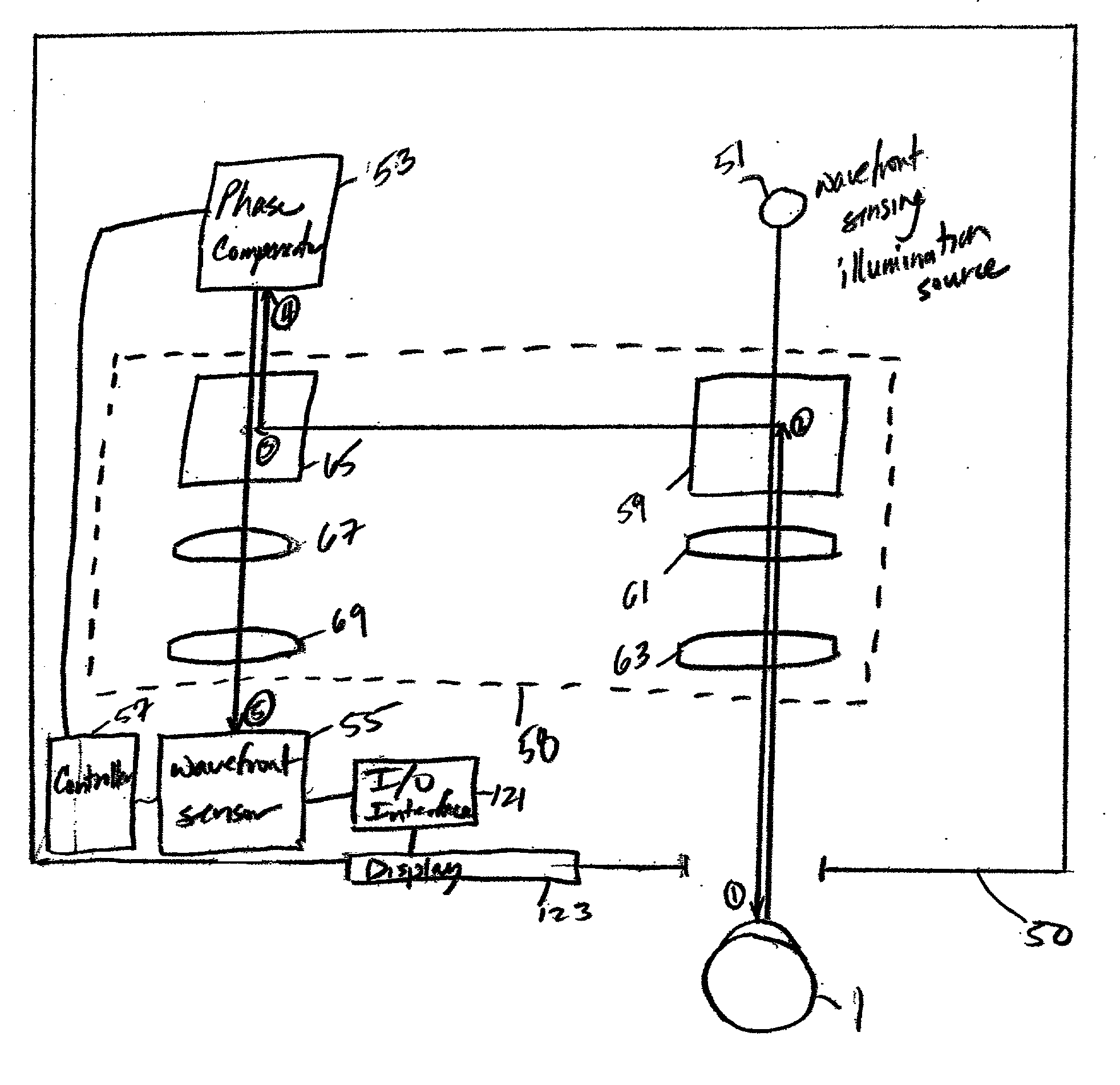
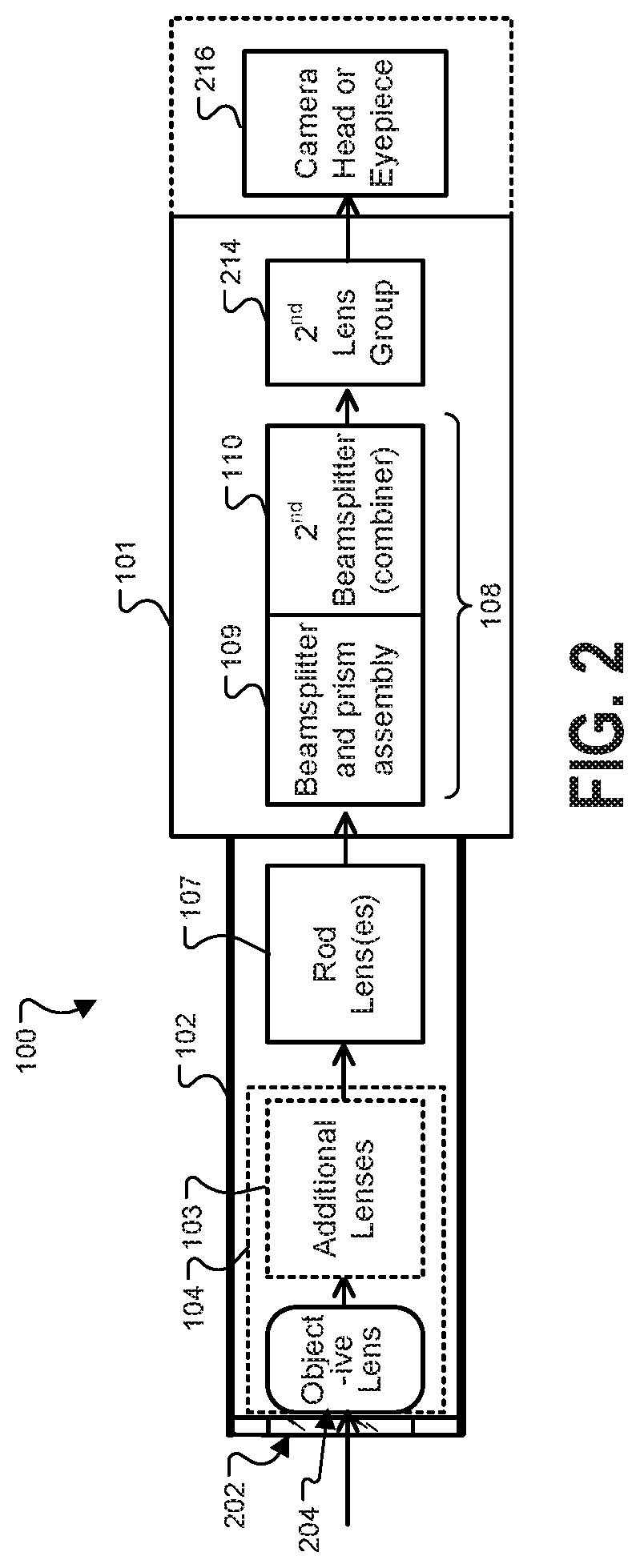
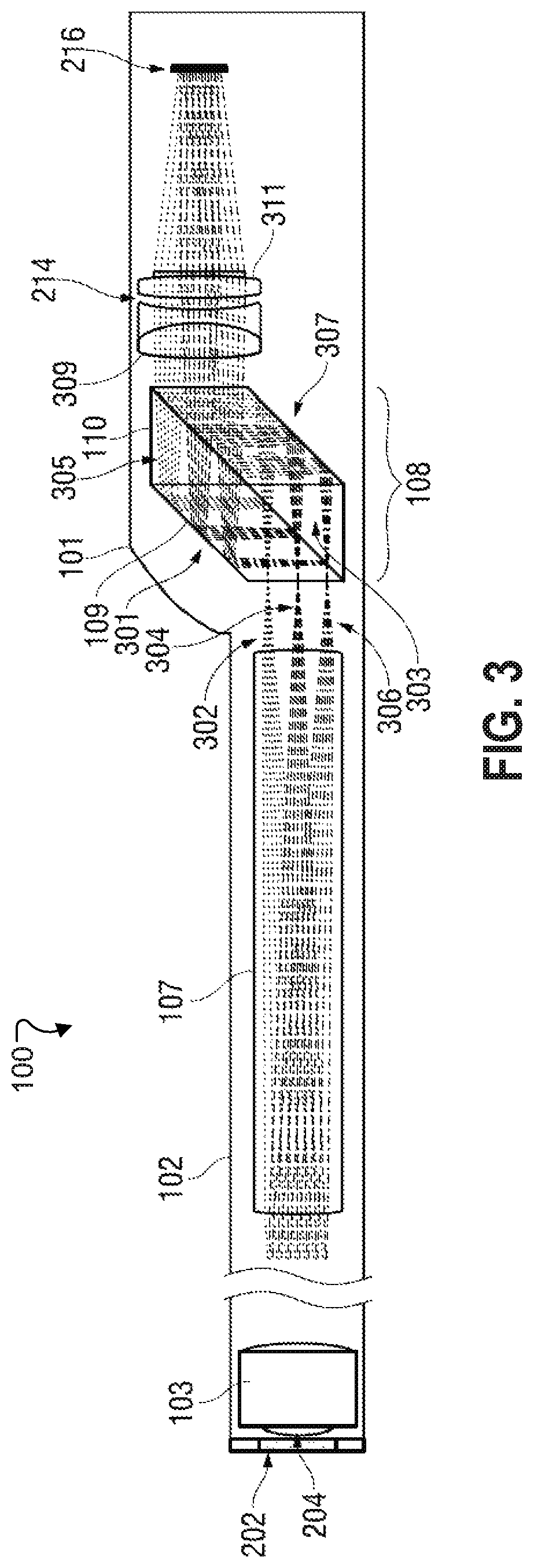
An improved ophthalmic instrument for in-vivo examination of a human eye including a wavefront sensor that estimates aberrations in reflections of the light formed as an image on the retina of the human eye and a phase compensator that spatially modulates the phase of incident light to compensate for the aberrations estimated by the wavefront sensor Optical elements create an image of a fixation target at the phase compensator, which produces a compensated image of the fixation target that compensates for aberrations estimated by the wavefront sensor. The compensated image of the fixation target produced by the phase compensator is recreated at the human eye to thereby provide the human eye with a view of compensation of the aberrations the human eye as estimated by the wavefront sensor. The phase compensator preferably comprises a variable focus lens that compensates for focusing errors and a deformable mirror that compensates for higher order aberrations. The optical elements preferably comprise a plurality of beam splitters and a plurality of lens groups each functioning as an afocal telescope. In addition, instruments and systems are provided that exploit these capabilities to enable efficient prescription and / or dispensing of corrective optics (e.g., contact lens and glasses).
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP +1
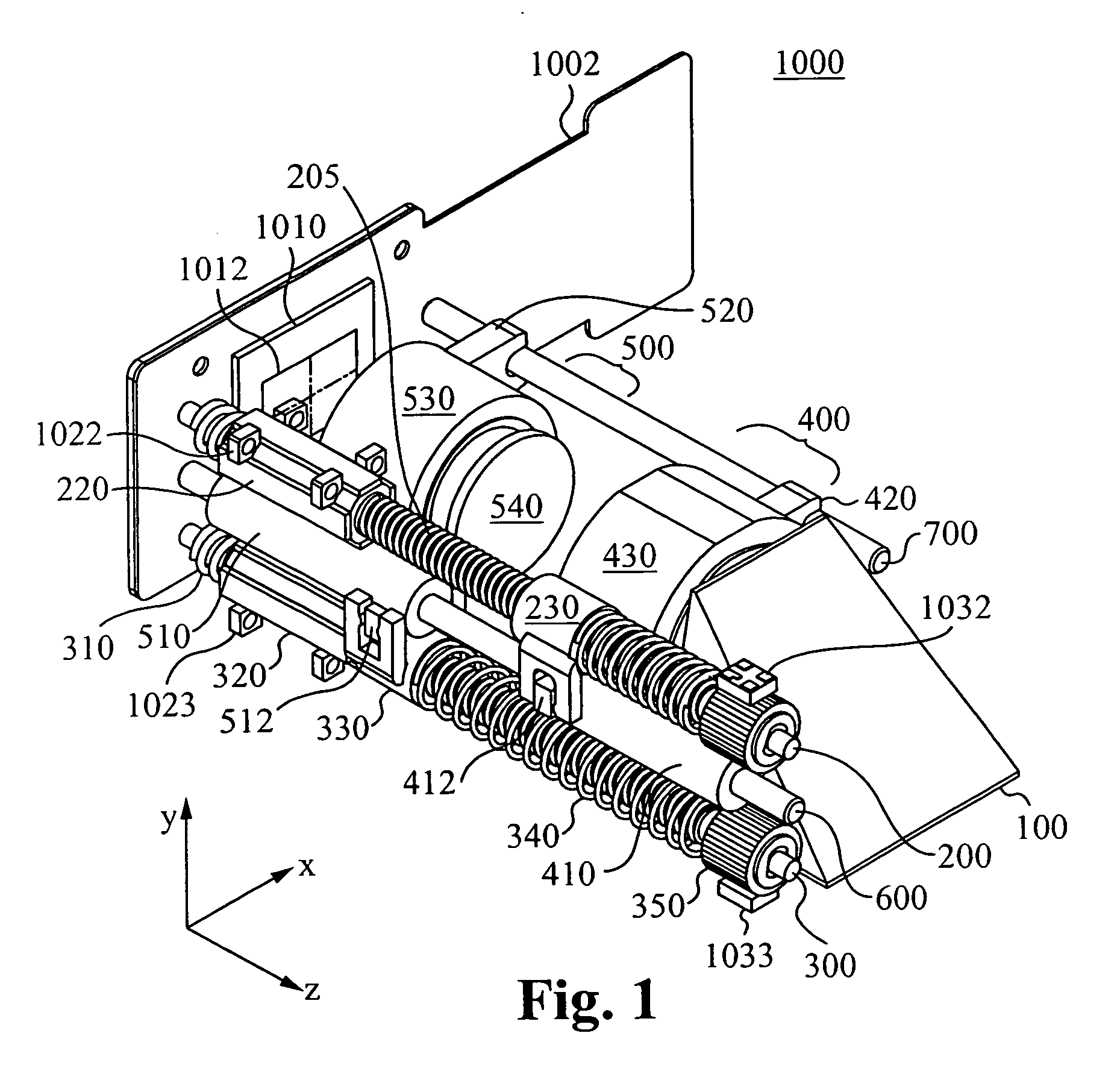
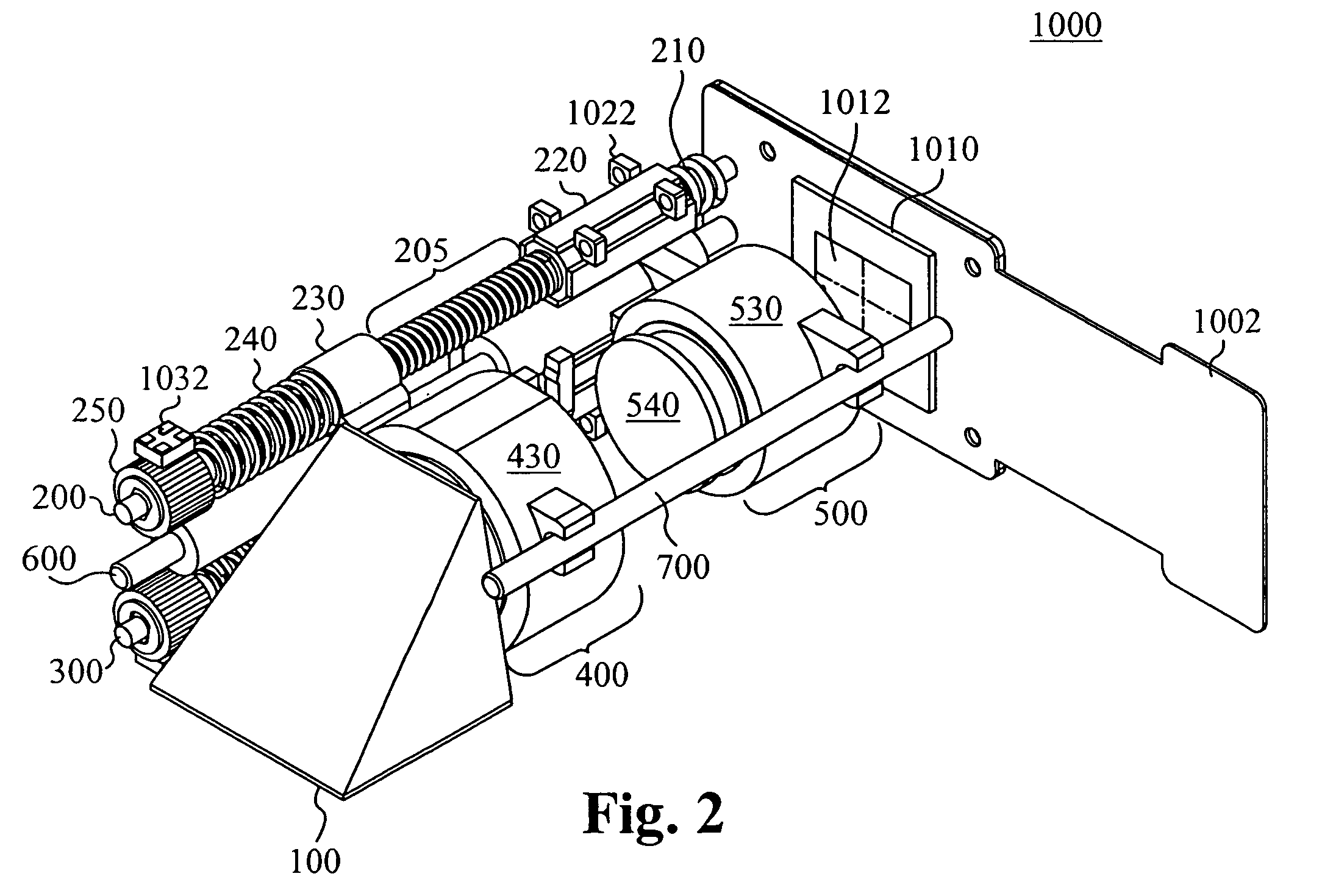
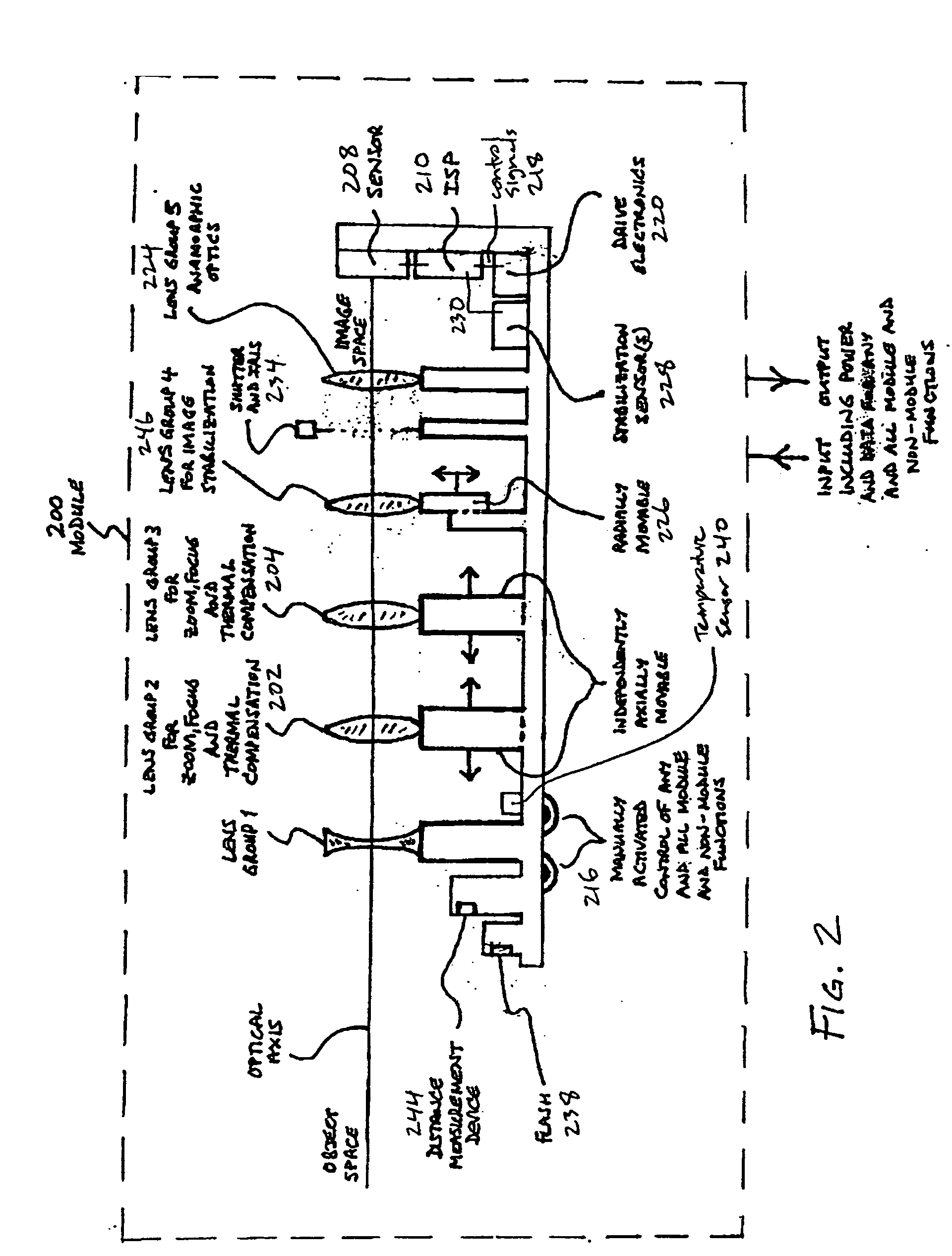
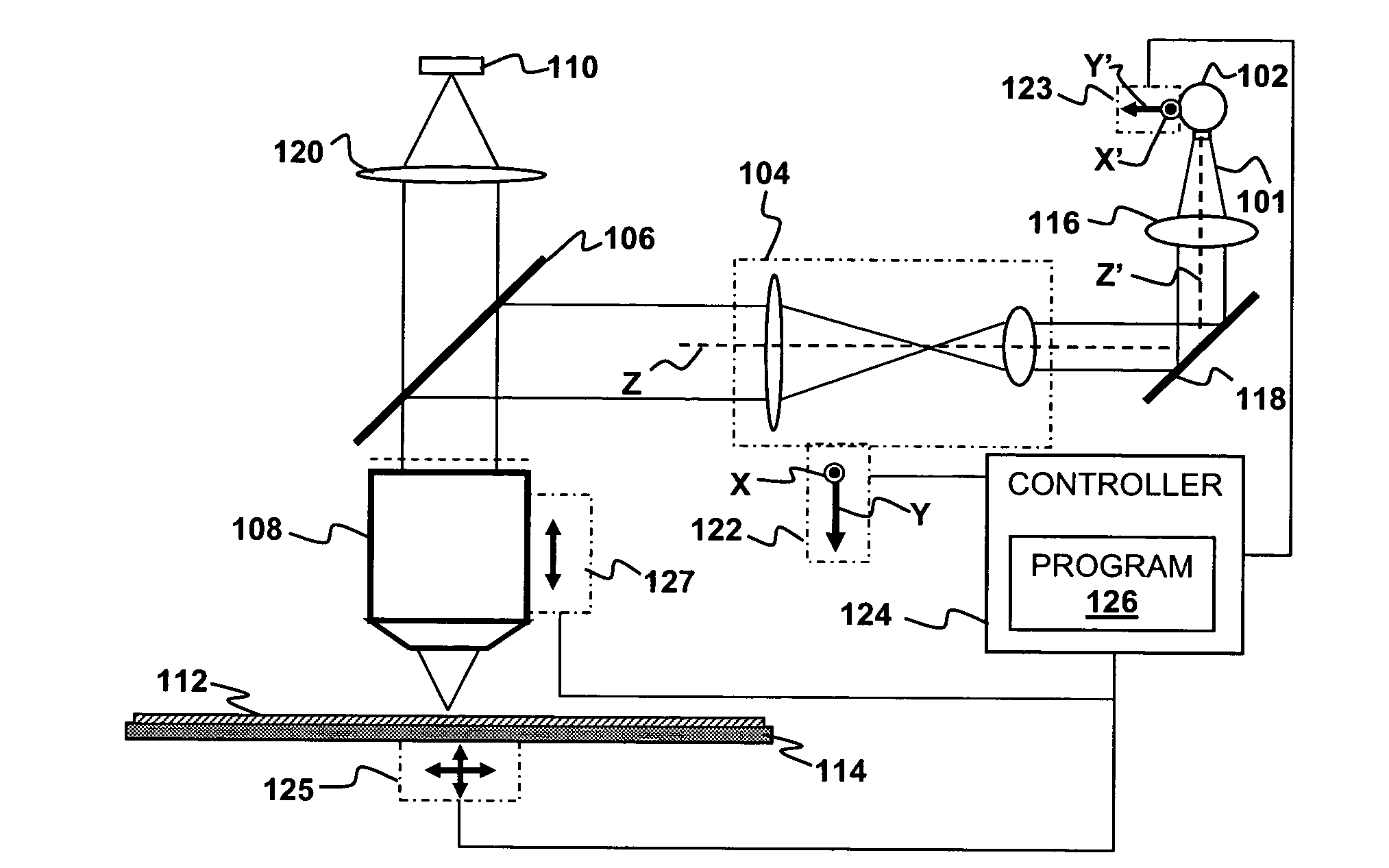
Auto-focus and zoom module
ActiveUS20070053672A1Prevent reboundTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusOptical ModuleMagnification
An optical module includes a first optics group, a second optics group, and an image sensor, wherein the first optics group and second optics group are configured to provide an image having a focus and a magnification to the image sensor. In some embodiments of the present invention, a first optics assembly includes a first optics group coupled to a threaded portion of a first lead screw so that rotation of the first lead screw results in translation of the first optics group along an axis of the first lead screw, a first actuator for rotating the first lead screw; and a first sensing target configured to permit detection of rotation of the first lead screw. In some embodiments of the present invention a second optics assembly includes a second optics group coupled to a threaded portion of a second lead screw so that rotation of the second lead screw results in translation of the second optics group along an axis of the second lead screw, a second actuator for rotating the second lead screw, and second means for sensing configured to detect rotation of the second lead screw.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
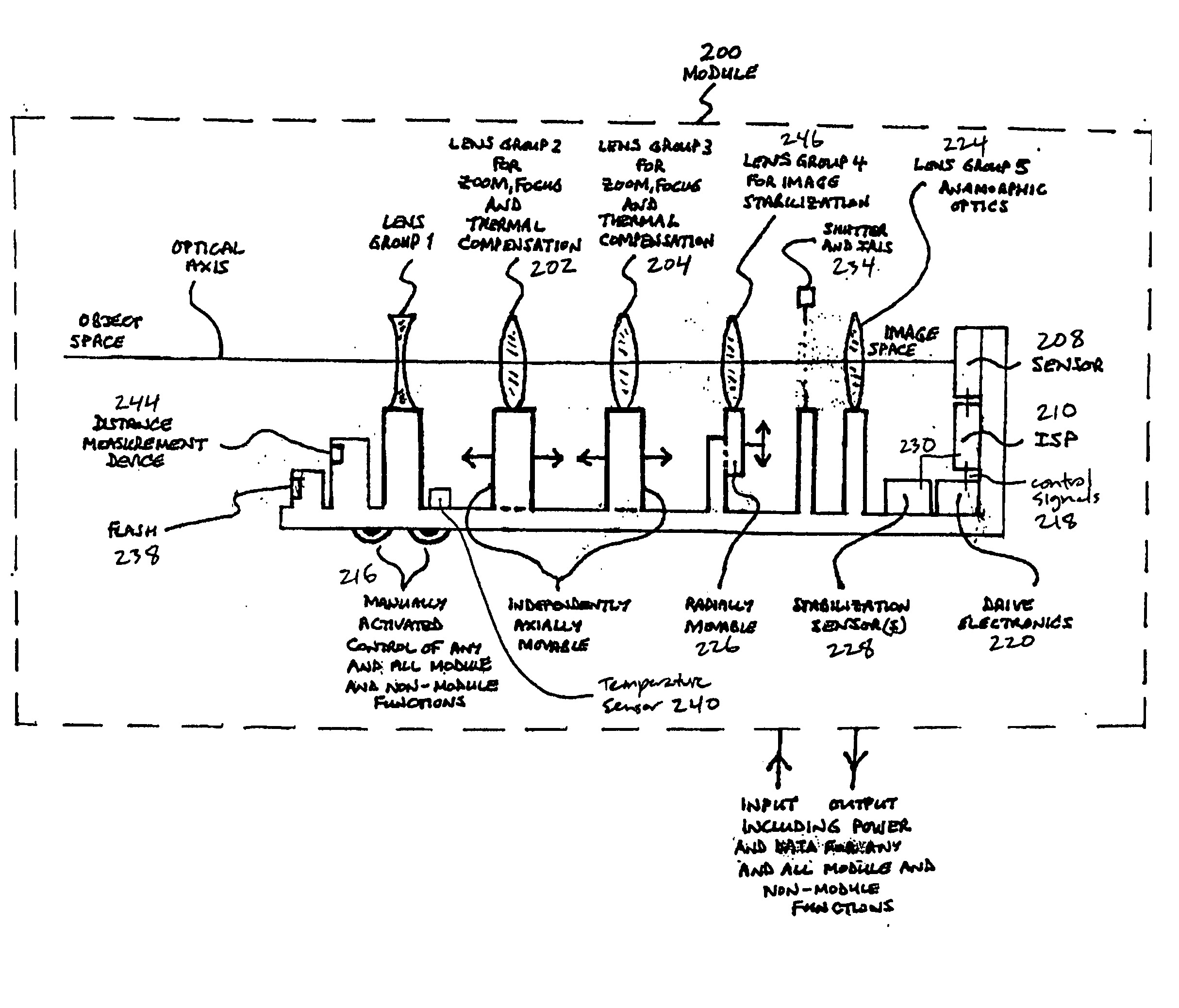
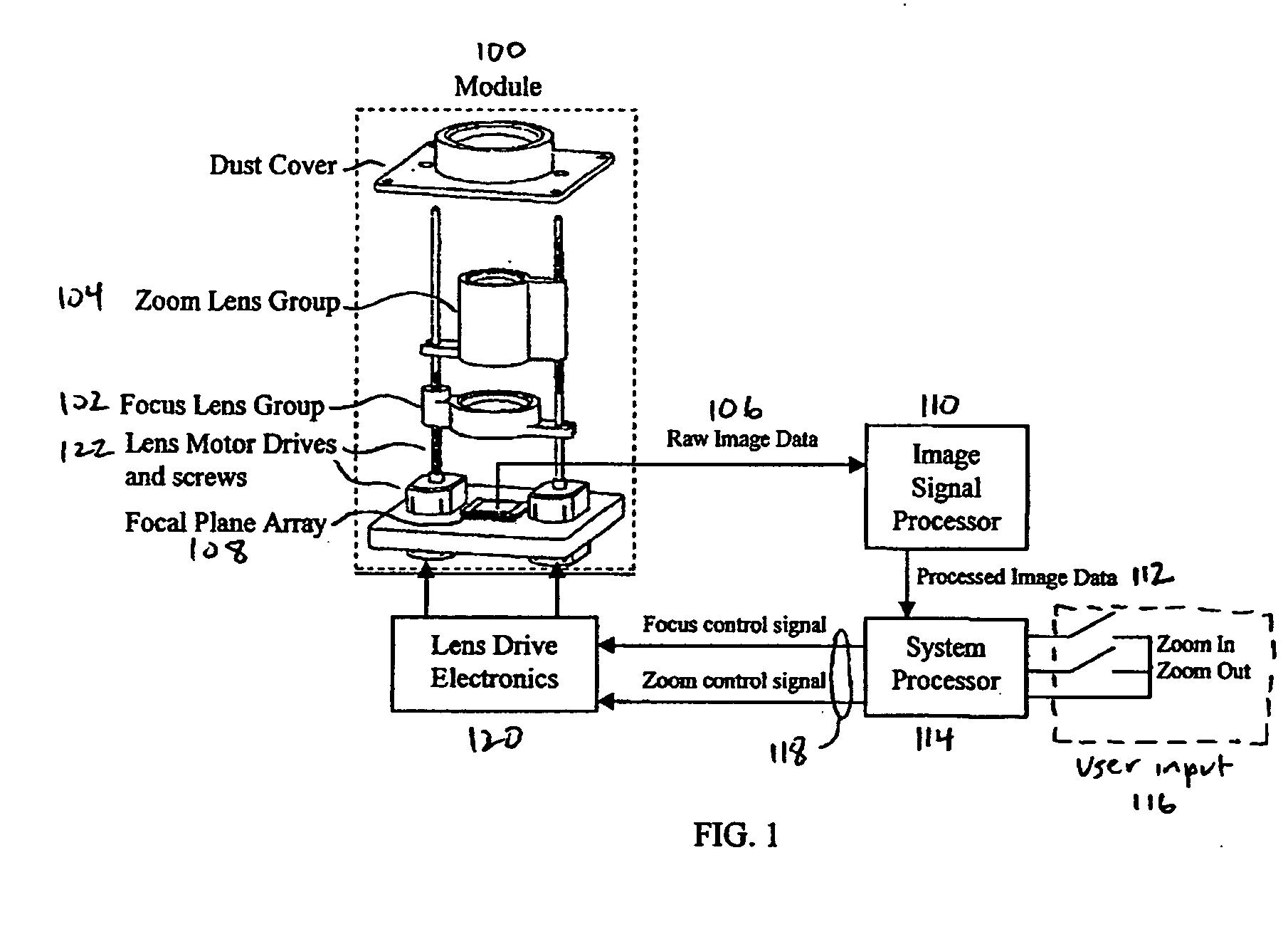
Method and apparatus for controlling a lens, and camera module incorporating same
InactiveUS20060045504A1Reduce the amount requiredShorten the timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFlash light
An efficient image capture system is disclosed that integrates functions to control a lens including one or more of focus or object distance, zoom, temperature compensation, and stabilization within an image signal processor (ISP) with appropriate algorithms. In particular, the integrated ISP circuitry may control the motion of the focus and zoom optics of an optical assembly, control stabilization, control the flash, provide enhanced functions and features for controlling the zoom and focus lenses to enable enhanced image capture sequences and / or tracking lens data, provide a set of algorithms within the ISP to alter the aspect ratio (both height and width of an image) of the image, for example to compensate for the addition of an anamorphic lens, and integrate an anamorphic lens into the module to alter an image's projected aspect ratio onto the focal plane array.
Owner:DYNAMAX IMAGING
Method for improving optical scanning holographic tomography effect
InactiveCN104159094ASmall viewing impactEvenly distributed noiseImage enhancementSteroscopic systemsOptical scanning holographyOptical tomography
The invention discloses a method for improving an optical scanning holographic tomography effect, and belongs to the field of optical tomography. The method can solve the defect in the conventional optical scanning technology that restored section images have louder out-of-focus noise, in real time. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a random phase in the optics encryption technique, changing a certain pupil function in a conventional optical scanning holographic system into a stochastic phase pupil function, and equaling restore of out-of-focus layer images into decryption under the condition of mistakenly decrypting a secret key, thereby enabling the out-of-focus layer images overlaid on the restored section images to be gaussian white noise with statistical independence and greatly reducing the influence of the out-of-focus noise on the focus layer images. Meanwhile the out-of-focus noise can also be filtered through design of a gaussian filter, so that the longitudinal resolution of the system can be improved; besides, through the adoption of the method, the bandwidth of the optical transfer function is wider, and the transverse resolution of the restored section images can be higher.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Scanning optical probe
InactiveUS20170143196A1Reducing health care costReduce laborSurgical needlesEndoscopesLight beamMedical imaging
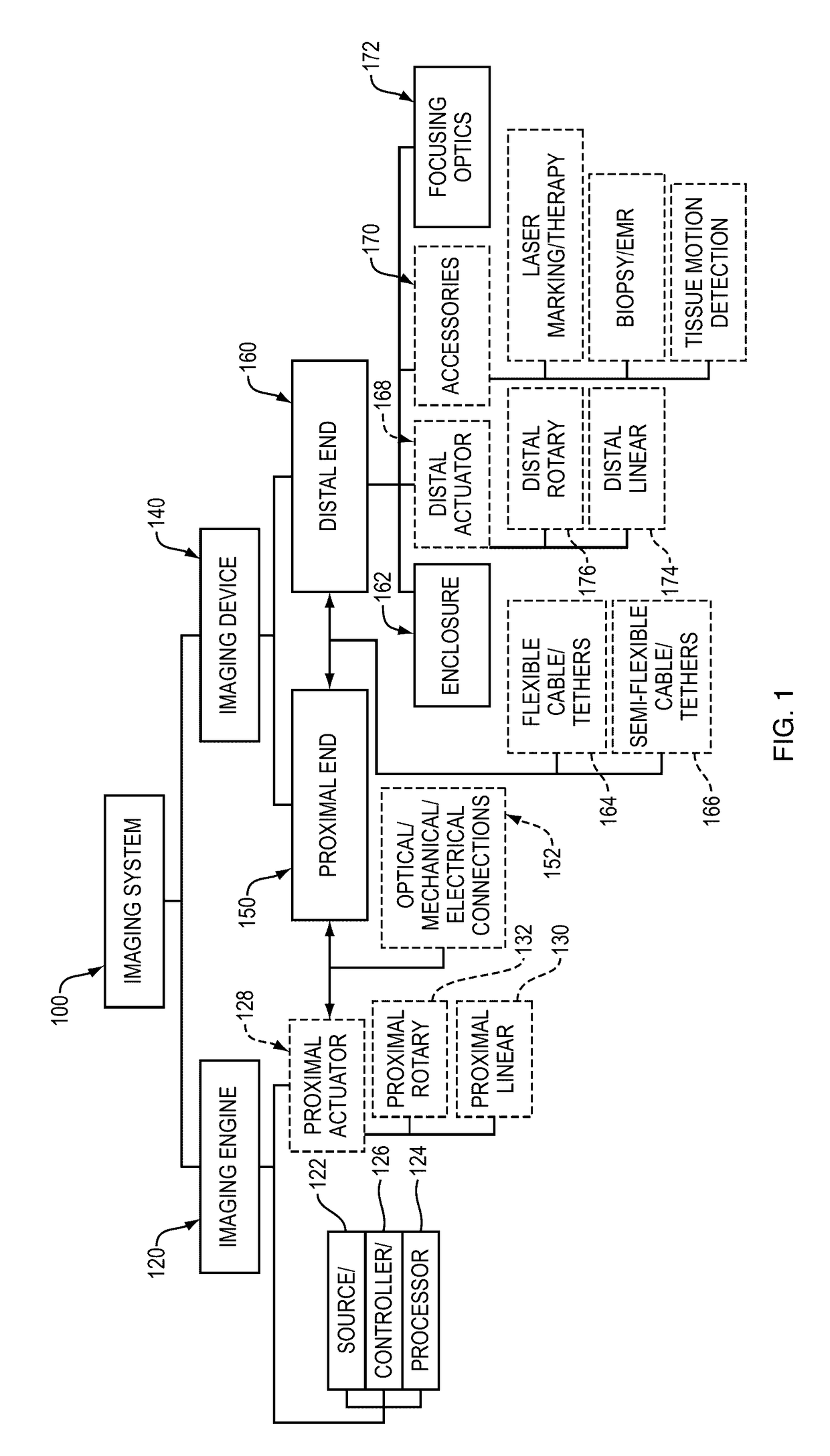
The invention pertains to an apparatus and methods of a medical imaging device for obtaining images from the walls of luminal organs or a surgical cavity. The invention is a rigid enclosure that is capable of passage through luminal organs or introduction into surgical cavities, and obtains images by rapidly scanning a focused light beam on the tissue to be imaged and receiving light from the tissue. The invention has at least one beam scanning mechanism and has multiple embodiments of scanning and focusing optics at different regimes of numerical aperture. The invention also describes methods for correcting inaccurate beam scanning. The device is capable of performing imaging, image guided therapy, tissue excision, or other interventional procedures.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Mirror image focus eclipsed direction changeable parallel light energy flux density multiplier and design method thereof
InactiveCN101034204AIncrease light collecting areaEasy commissioning and maintenanceSolar heating energySolar heat devicesPhysicsFocal position
This invention is the light energy stream density doubler and design method of mirror image focal point overlapping parallel energy, which style is changeable, it belongs to optics technology application domain, and especially the solar energy condenses the area of technology. This invention is combined of the combination paraboloid condenser, the column catopter and the paraboloid leading the glossy ware by the combination parabola circling the axis of symmetry revolving along the central shaftconnects in turn. Among them , combination paraboloid condenser is obtained like this: The parabola sharpening the edge of flat surface inner making progress translates along the horizontal direction to satisfy the specific condition the distance, after thetranslation parabola and the original parabola intercross, removes the parabola sections having point of inflection on both sides of intersection, obtains a conic combination parabola plane figure , circles its axis of symmetry to revolve then obtains a combination paraboloid. Then truncates its pinnacle part horizontally , and enables the section position to not be lower than the parabola focal point position, also the section width happens to half of focal distance between two parabolas .
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Use of a reference source with adaptive optics in biological microscopy
ActiveUS20100105105A1Raise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMicro imagingStrehl ratio
Methods of microscopic imaging of biological tissue using adaptive optics technology to improve the image focus and sharpness. Wavefront measurements are taken by using a novel method of seeding biological tissue by using a fluorescent microsphere as a “guide star” as a natural point-source reference. The current methods are capable of improving the Strehl ratio of modern biological microscopes as much as 15 times.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Imaging system having a fine focus
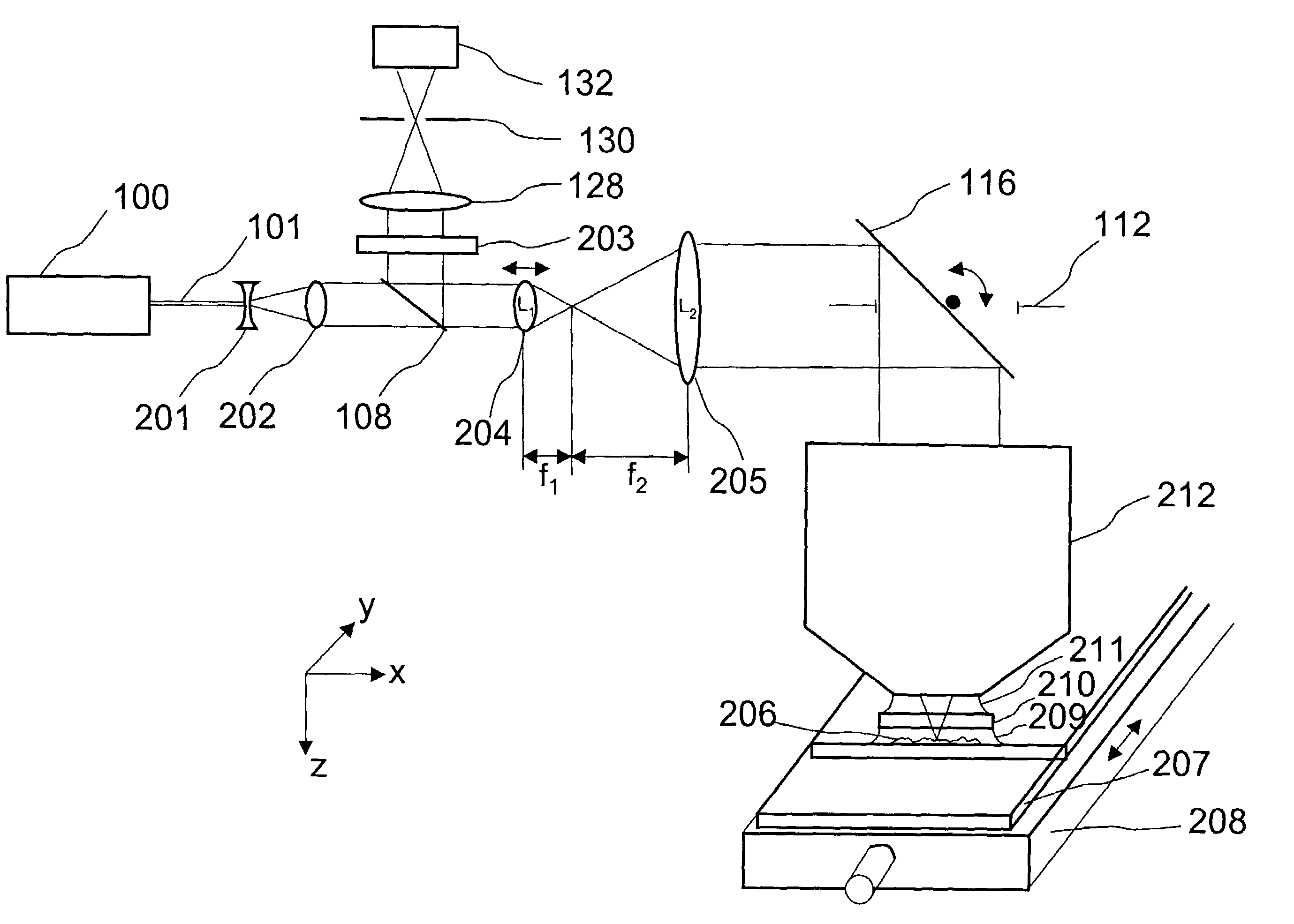
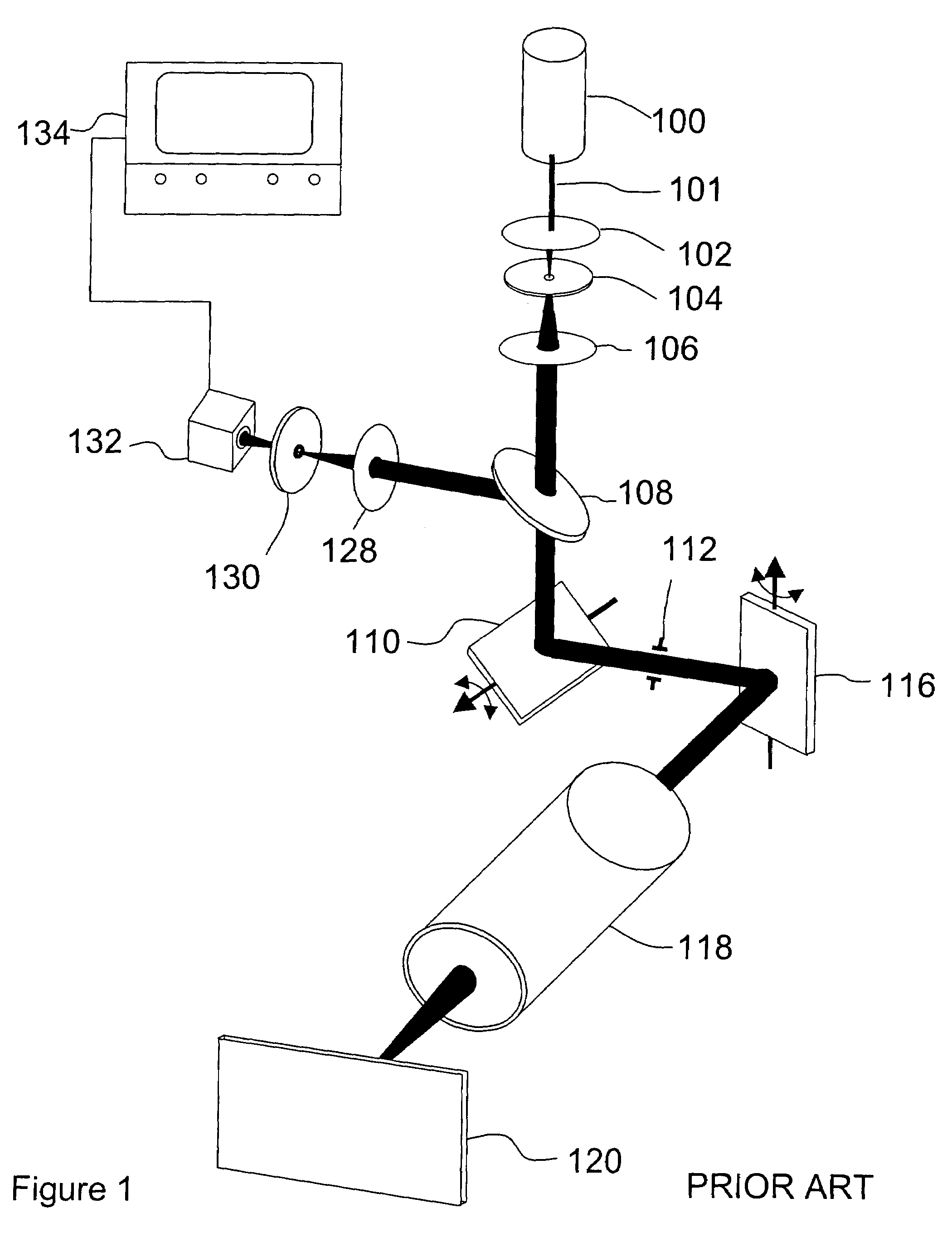
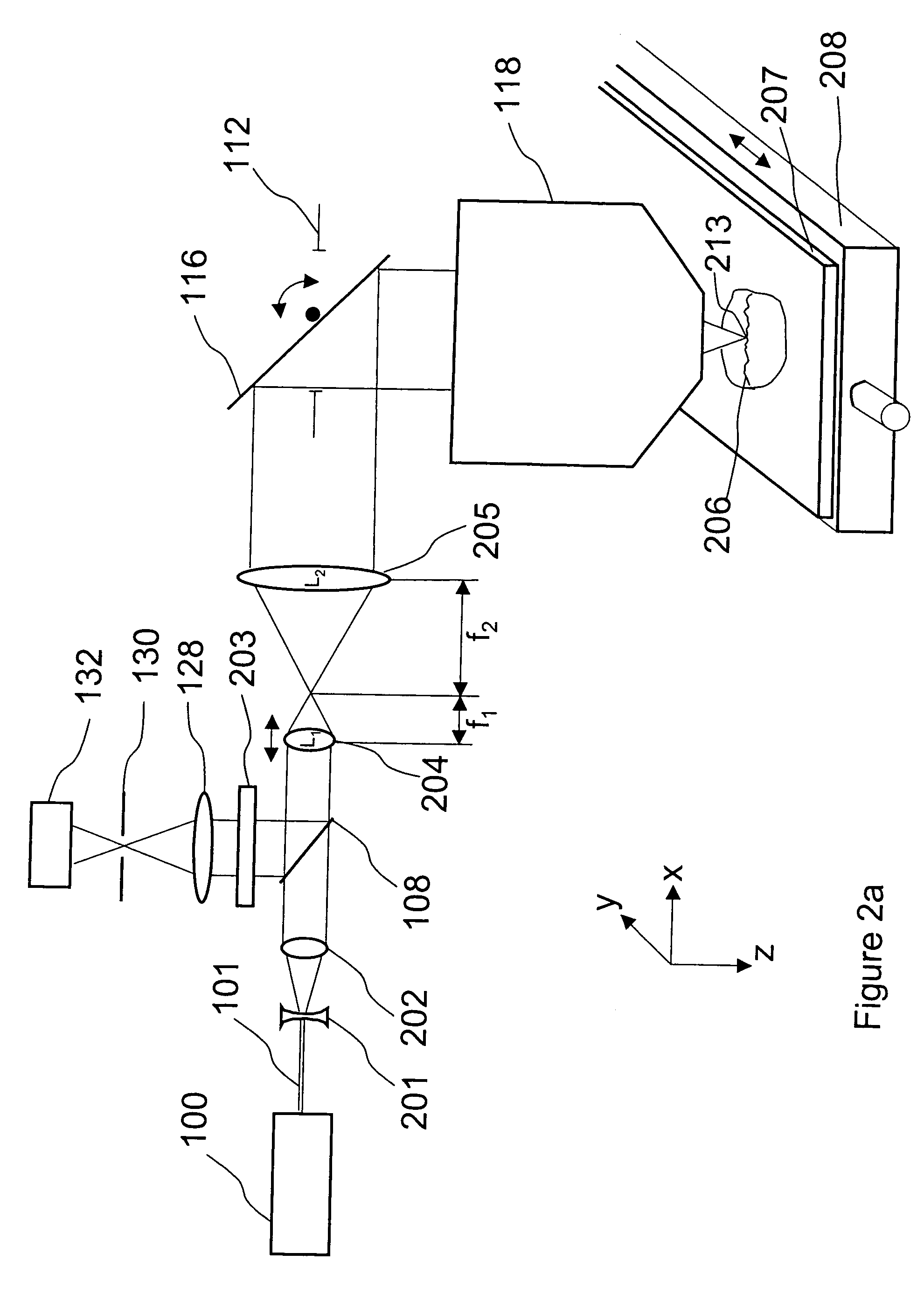
A new high resolution confocal and non-confocal scanning laser macroscope is disclosed which achieves fine focus and control of focus position by moving a lens in the intermediate optics. This arrangement is particularly useful for imaging specimens where it is difficult to focus by changing the distance between the scan lens and the specimen, for example for in-vivo imaging, photodynamic therapy, and image-guided surgery. It is also important to keep the lens-to-specimen distance constant when a liquid-immersion scan lens is used, in order to maintain a constant thickness of liquid between the lens and the specimen. In addition to being useful for confocal slicing, motion of the intermediate lens under computer control also enables dynamic focus and the ability to move the focal spot along a general path inside the specimen. Several applications of the imaging system are described. The macroscope images macroscopic specimens in reflected light, transmitted light, fluorescence, photoluminescence and multi-photon fluorescence.
Owner:HURON TECH INT
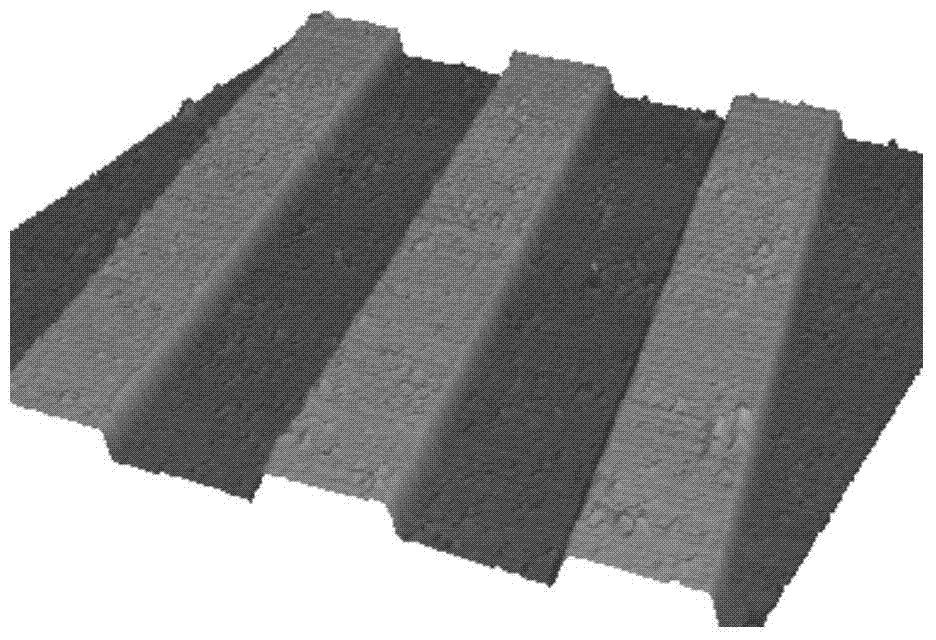
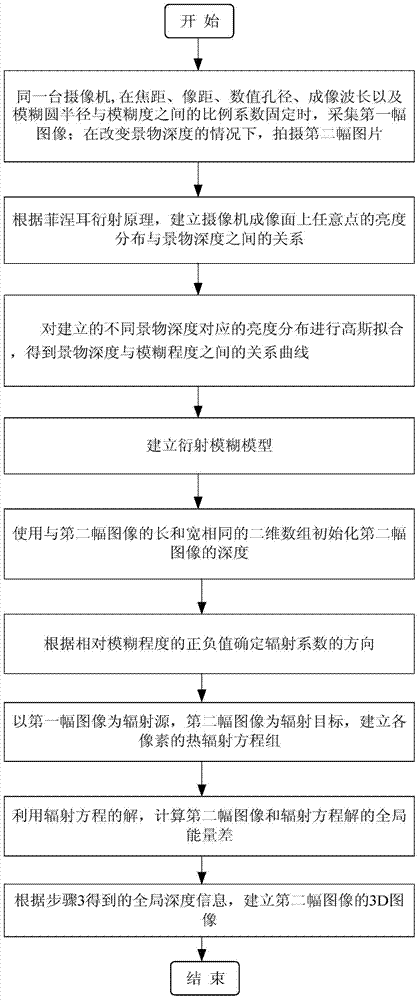
Single-vision overall depth information acquisition method based on diffraction blurring
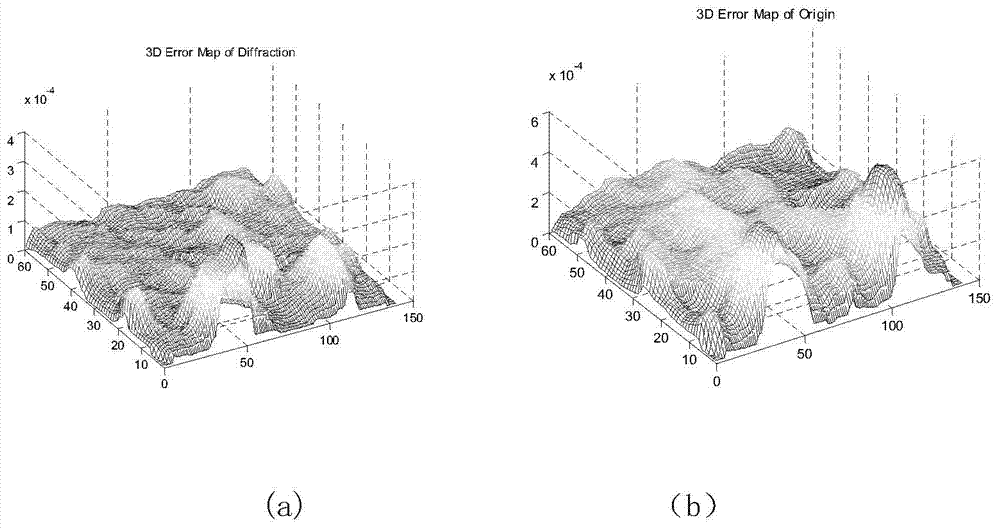
The invention discloses a single-vision overall depth information acquisition method based on diffraction blurring and belongs to the technical field of image processing. A first image is collected when the focal length, the image distance, the numerical aperture, the imaging wave length and the proportionality coefficient between the blur circle radius and the ambiguity of the same camera are fixed; under the condition that the aspects are not changed, the distance between the camera and an object is changed, and then a second image is collected, wherein the change magnitude of the distance is delta s; a diffraction blurring model is established and used for describing the relation between the depth of the object and the image blurring degree; the diffraction blurring model and the two blurred images are used for determining the overall depth information of the second image; a 3D image of the second image is formed according to the obtained overall depth information. According to the single-vision overall depth information acquisition method based on diffraction blurring, the diffraction mechanism is fused into traditional geometrical optical convex lens blurring imaging, a mathematical model of the relation between diffraction blurring and the 3D depth of the object is established, and the accuracy of an out-of-focus object depth acquisition method based on traditional geometrical optics is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
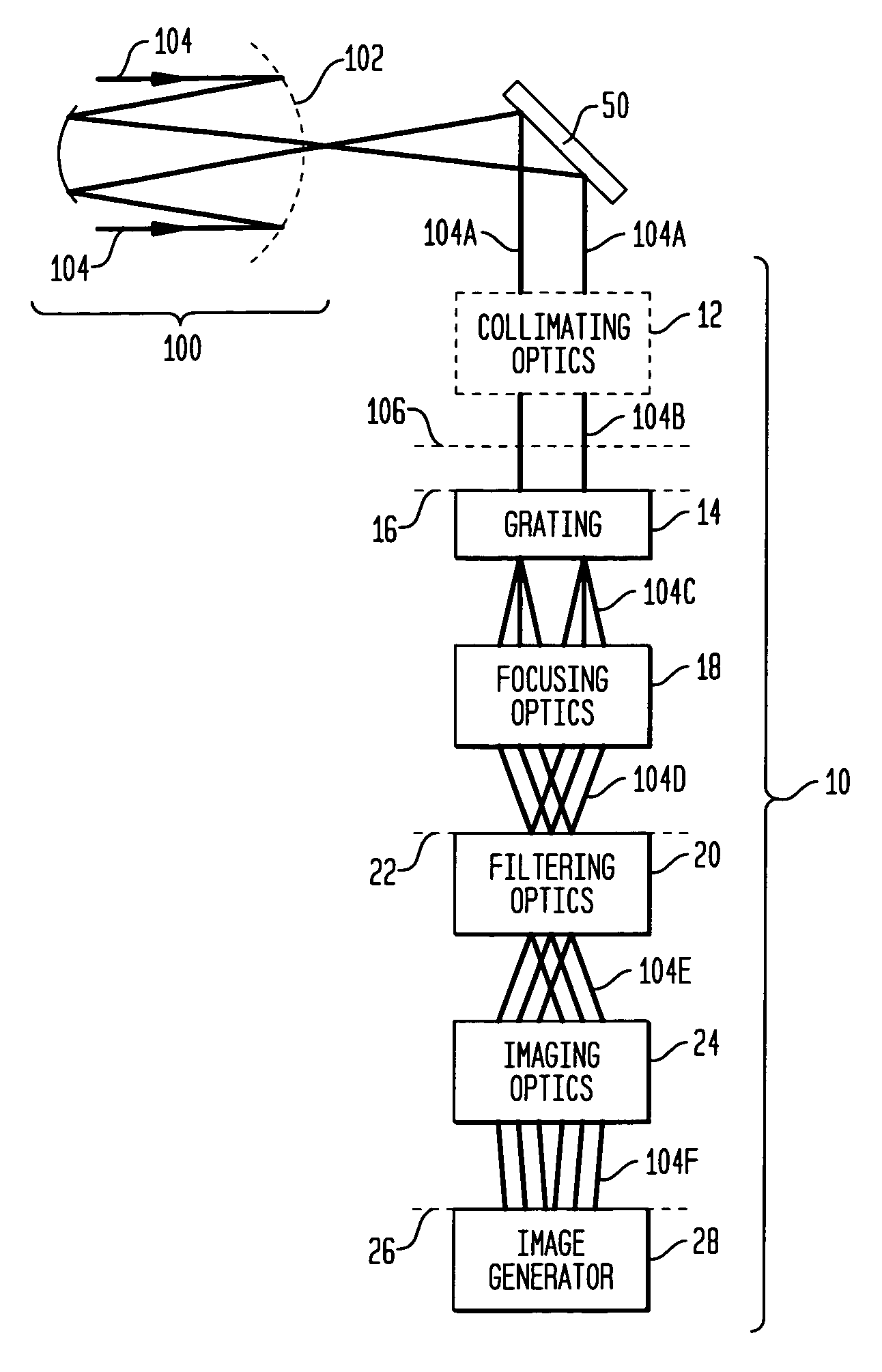
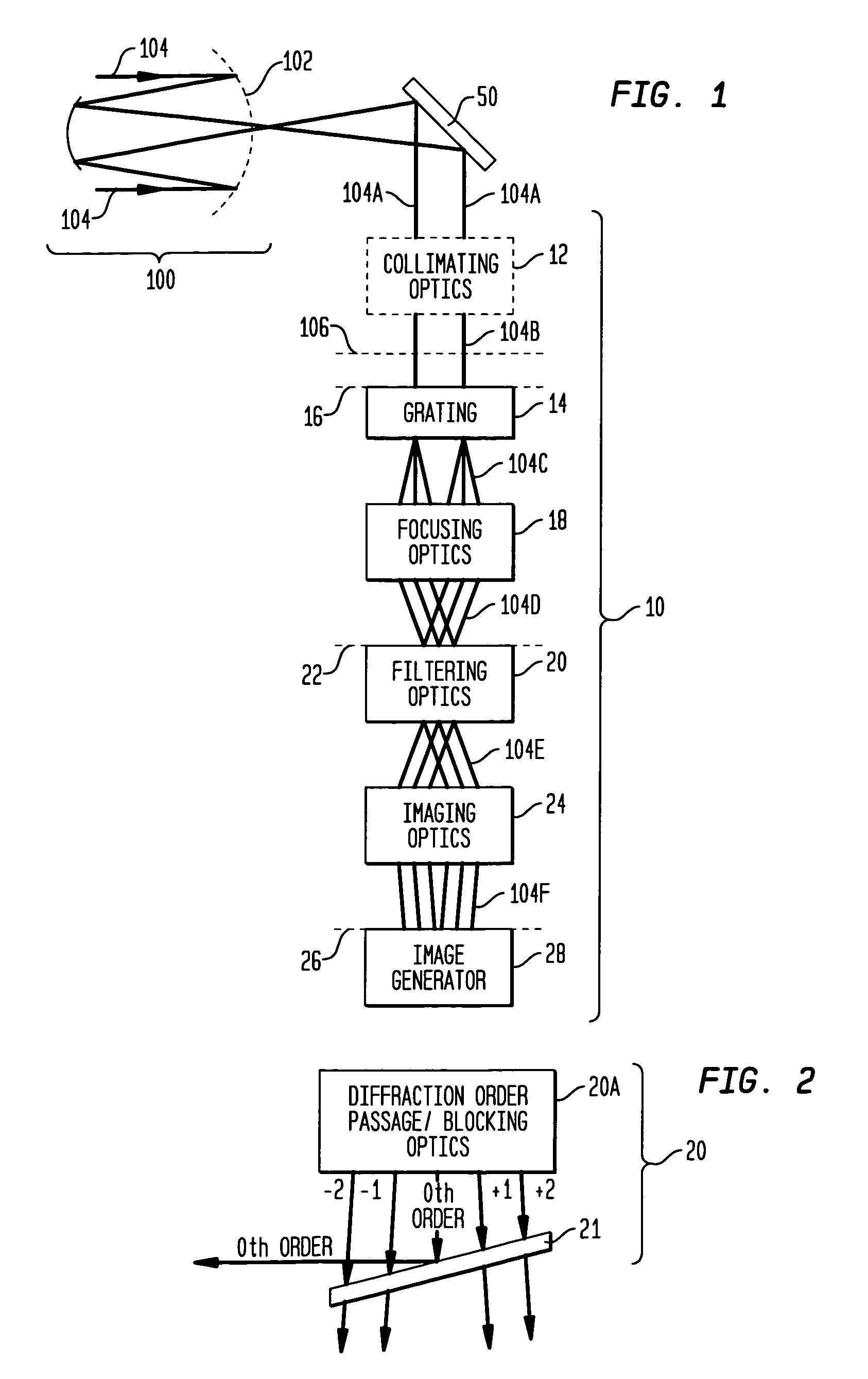
Achromatic shearing phase sensor for generating images indicative of measure(s) of alignment between segments of a segmented telescope's mirrors
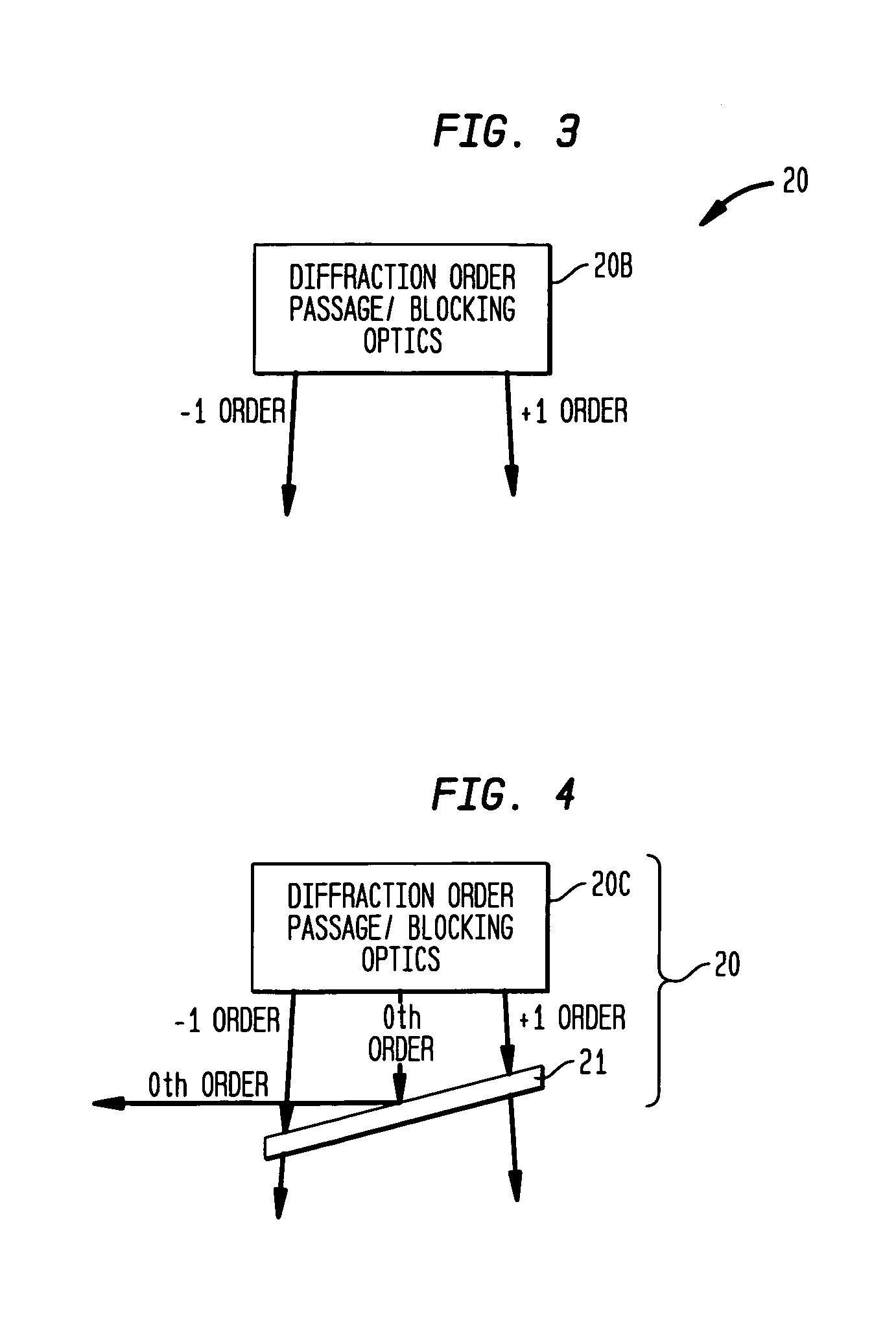
InactiveUS7106457B1Interfere with useInformation can be usedOptical measurementsUsing optical meansDiffraction orderGrating
An achromatic shearing phase sensor generates an image indicative of at least one measure of alignment between two segments of a segmented telescope's mirrors. An optical grating receives at least a portion of irradiance originating at the segmented telescope in the form of a collimated beam and the collimated beam into a plurality of diffraction orders. Focusing optics separate and focus the diffraction orders. Filtering optics then filter the diffraction orders to generate a resultant set of diffraction orders that are modified. Imaging optics combine portions of the resultant set of diffraction orders to generate an interference pattern that is ultimately imaged by an imager.
Owner:NASA +1
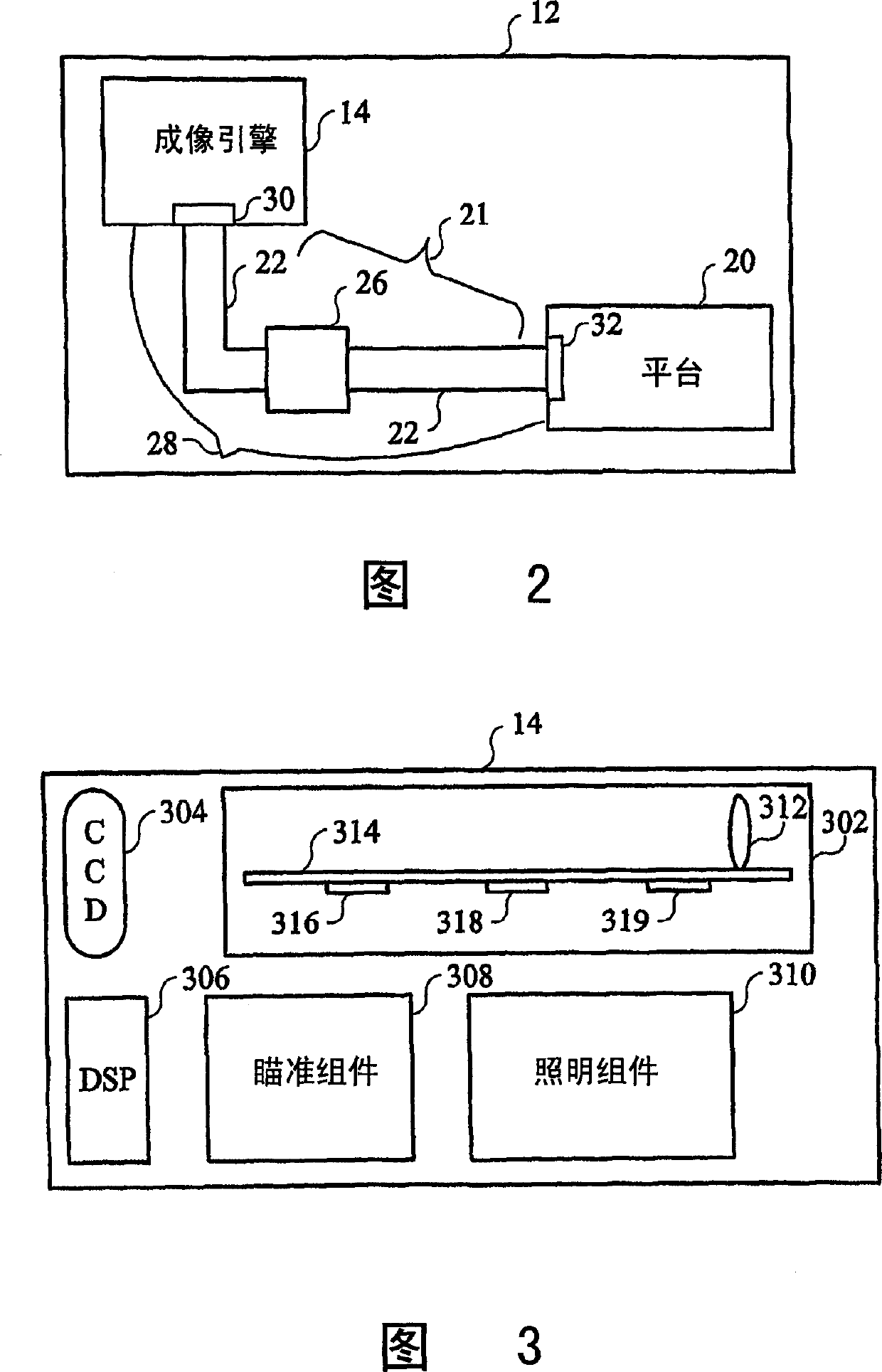
Optical code reader with autofocus and interface unit
An optical code reader (12) having structure for focusing an imaging optical assembly onto a target image. The optical code reader includes a chassis (910) and an imaging optics assembly (914) pivotally mounted on the chassis. The imaging optics are placed within the optomechanical barrel assembly. Pivoting of the optomechanical barrel assembly adjusts the focus of the imaging optics on the target image. The optical code reader also includes an illumination device (918) and an aiming device (920). An interface assembly (28) connects the imaging engine (14) of the imaging optics assembly to the circuit assembly of the optical code reader. The imaging engine (14) is removably positioned and / or sized and configured to fit a predetermined build factor.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
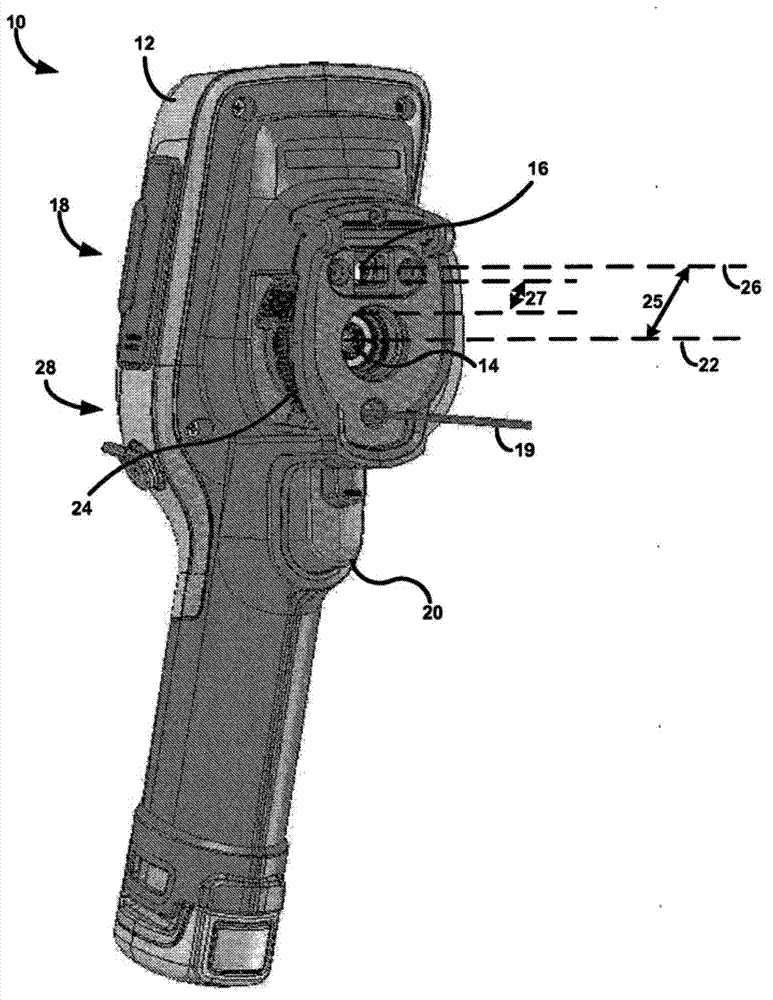
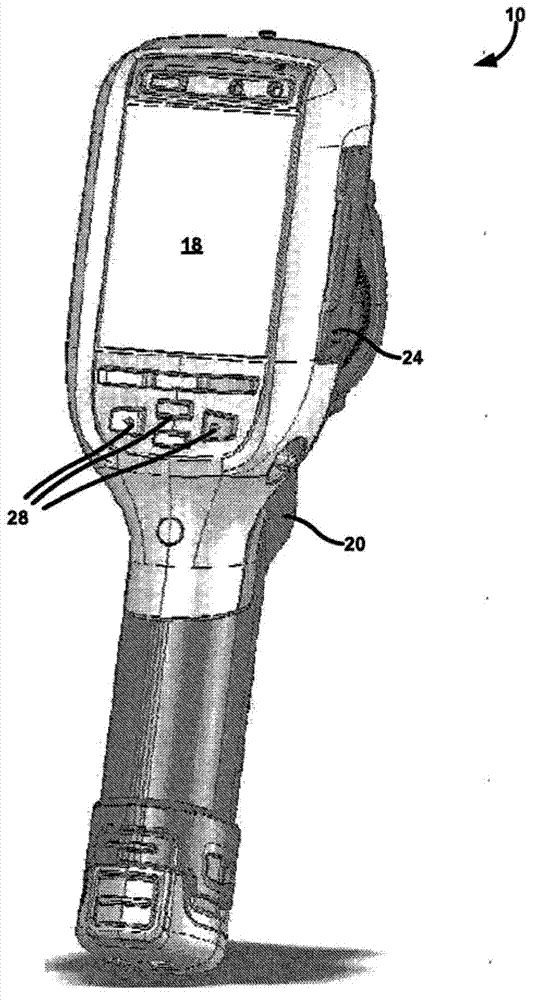
Thermal imaging camera with infrared lens focus adjustment
A thermal imaging camera may be used to capture a visible-light (VL) image and an infrared (IR) image. In some examples, the camera includes adjustable focus IR optics. For example, the camera may include a focus mechanism coupled to the IR optics and configured to move the IR optics to various focus positions so as to focus the IR optics. The various focus positions may include a hyperfocal position in which a scene is in focus between a set distance and infinity, and a plurality of focus positions in which the scene is in focus between the set distance and a minimum focus distance. Depending on the configuration of the camera, the IR optics of the camera may define an F-number greater than 1.0, and an axis of the IR optics may be offset from an axis of the VL optics by a distance less than 1.7 inches.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
Method for creating, trapping and manipulating a gas bubble in liquid
InactiveCN102066903AMaterial analysis by optical meansSurgical instrument detailsFocal zoneLight beam
A method for producing, trapping and manipulating a gas microbubble in liquid is disclosed. The method includes providing a pulsed laser source for generating a pulsed laser radiation and focusing optics; and focusing a pulsed laser radiation to a focal zone within the liquid, with energy exceeding the threshold of optical breakdown in the liquid at the focal zone. It is also suggested to use focusing optics to focus the laser beam to a focal point at a depth close to the compensation depth of the focusing optics for spherical aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMS GMBH
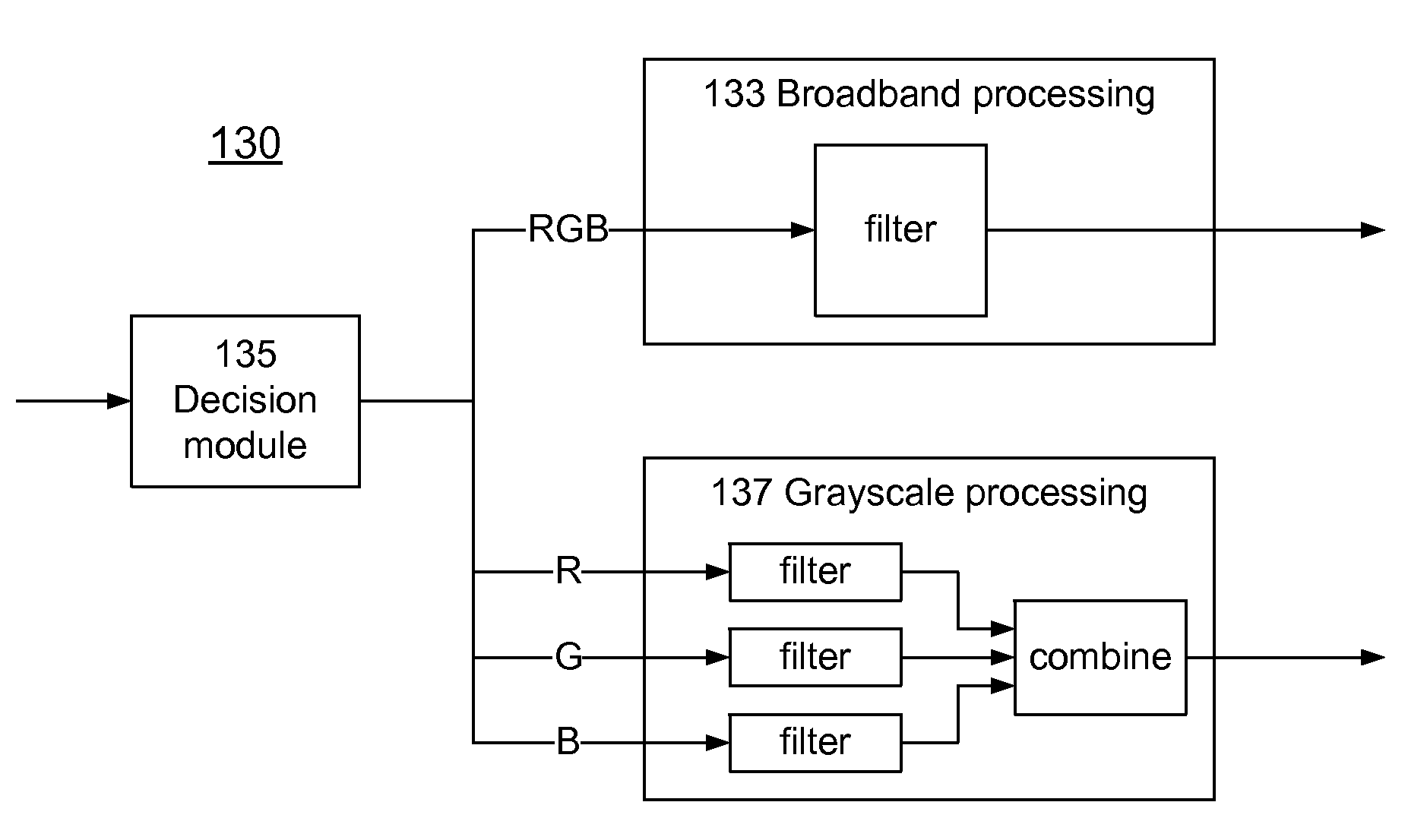
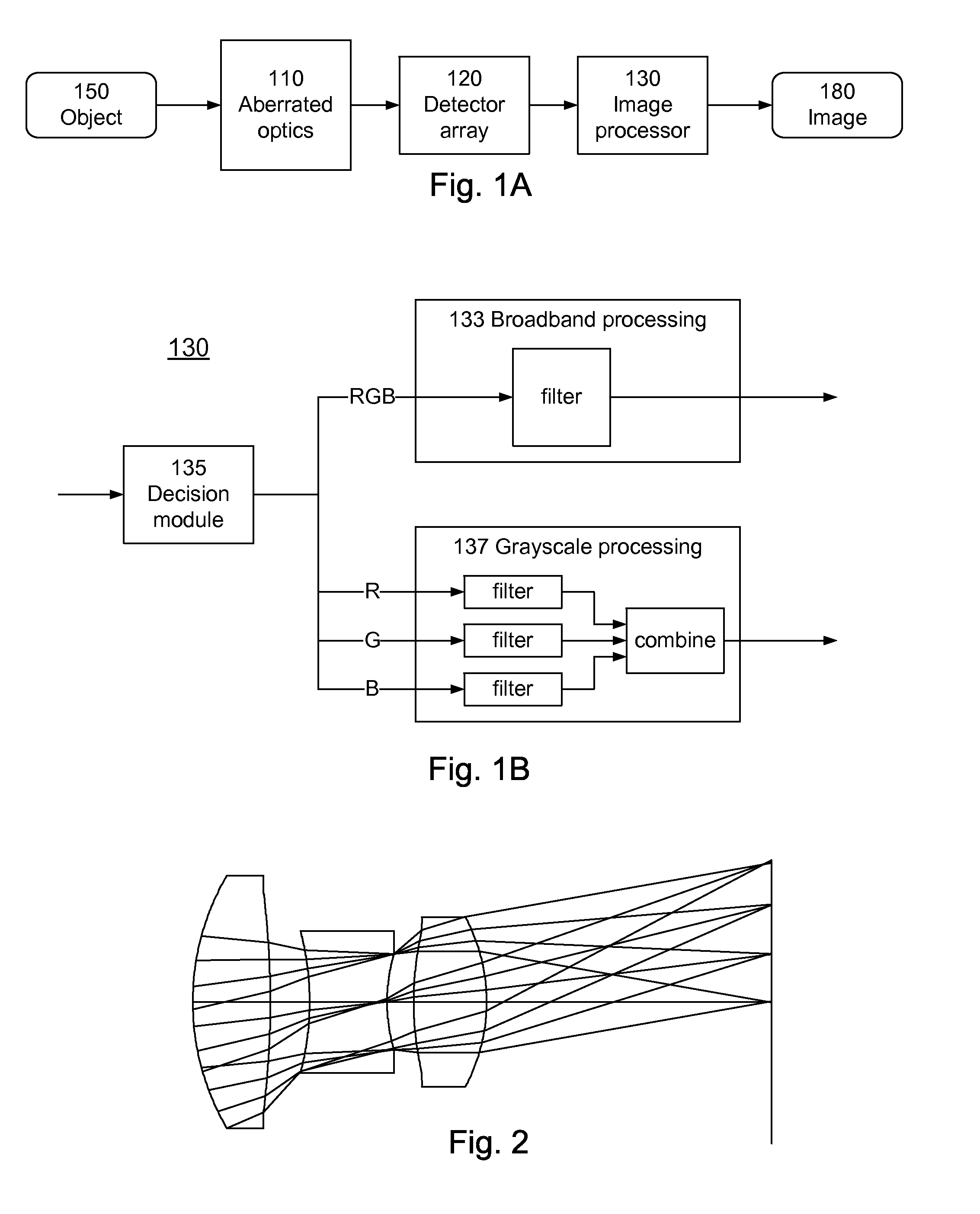
Dual-Mode Extended Depth-of-Field Imaging Systems
InactiveUS20110074988A1Increase heightIncrease rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageImaging processing
A digital-optical imaging system can be operated in two modes, which shall be referred to as broadband mode and grayscale mode. In broadband mode, different color images are captured and then image processed together. The optics are intentionally aberrated to increase the depth of field, with the image processing compensating for the aberrations. In grayscale mode, the different color images are captured and then image processed separately. The color images are assumed to be correlated so that it is not necessary to have clear images of all color channels. Accordingly, the optics are designed so that the different color images focus at different locations, thus increasing the overall depth of field where at least one color image is in focus.
Owner:RICOH KK
Manually adjustable ruggedized focus mechanism
InactiveUS8033670B2Reduce riskEasy to masterTelevision system detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsCMOS sensorEngineering
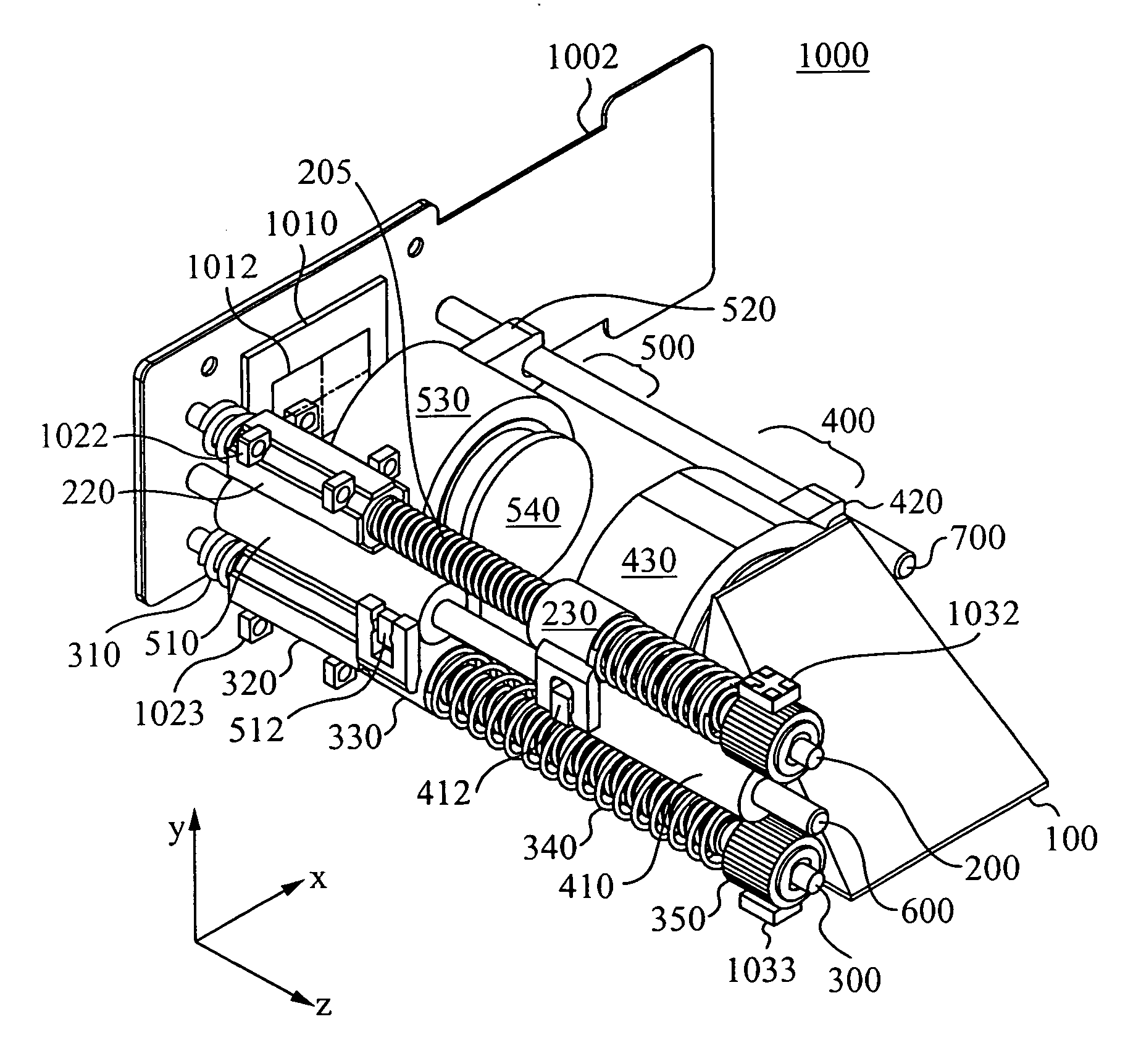
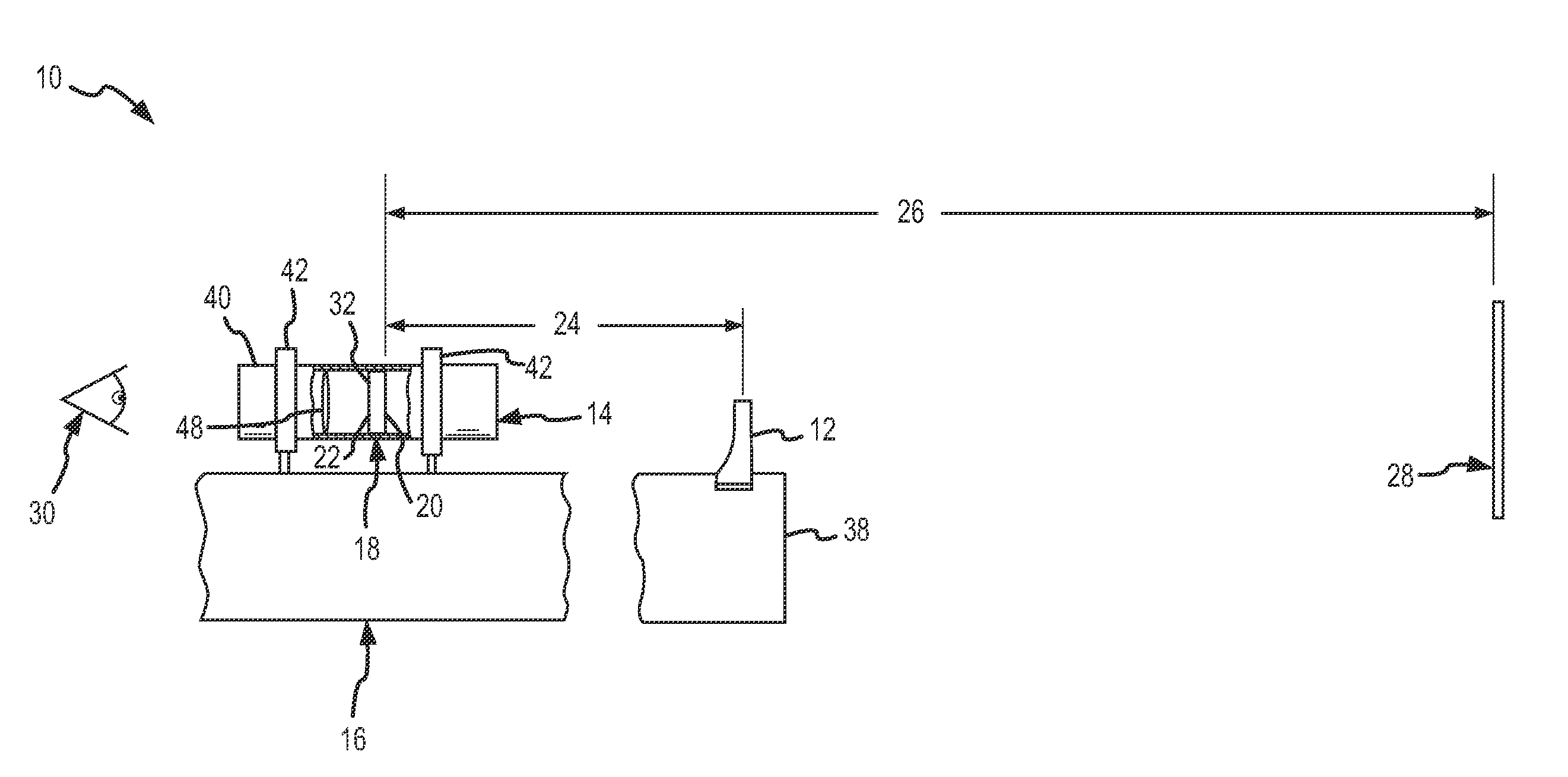
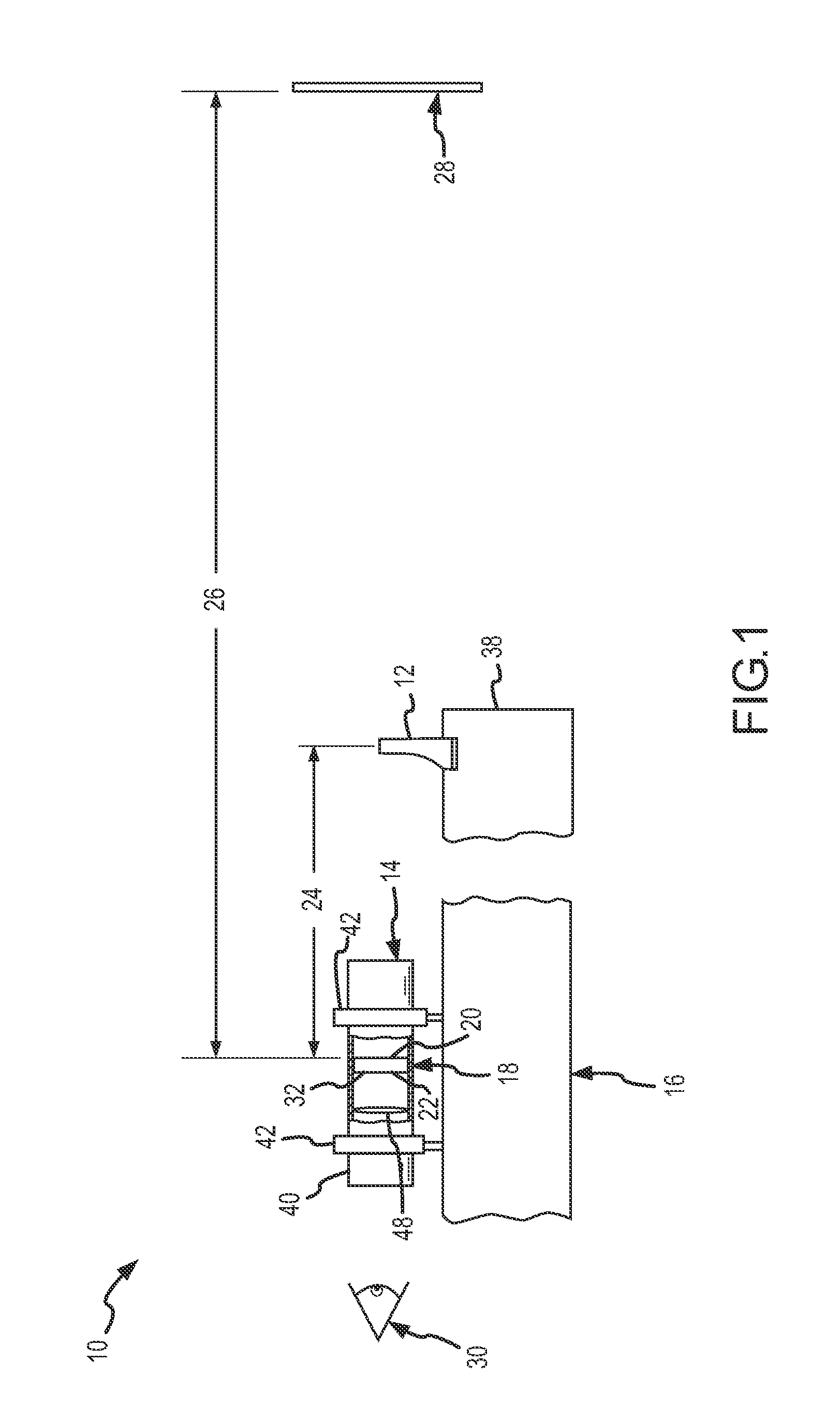
The invention provides, in some aspects, devices for image acquisition that use seals (e.g., O-rings) between concentrically disposed portions of an enclosure and an optics assembly (or sub-assemblies thereof) in order to protect image acquisition components from the surrounding environment (and vice versa) while, at the same time, providing adequate friction for both adjusting and locking focus. Such devices include, in one aspect of the invention, an image capture medium (e.g., a CMOS sensor, CCD array, etc.) that is disposed within an enclosure and an optics assembly that is also disposed within that enclosure, rotatably. The optics assembly, which includes at least a lens, can have a cylindrical outer diameter along at least a portion of its length that is received within the enclosure along a length that has a corresponding cylindrical inner diameter. A first seal (e.g., an “O-ring”) is disposed between, and in contact with, the optics assembly and the enclosure, e.g., along these corresponding lengths. That seal permits rotation of the optics assembly for purposes of focusing the lens, while preventing (or reducing a risk of) contamination from the environment (e.g., water, chemicals, dirt, dust, etc.) from entering into the enclosure and vice versa.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Projection lens and liquid crystal projector
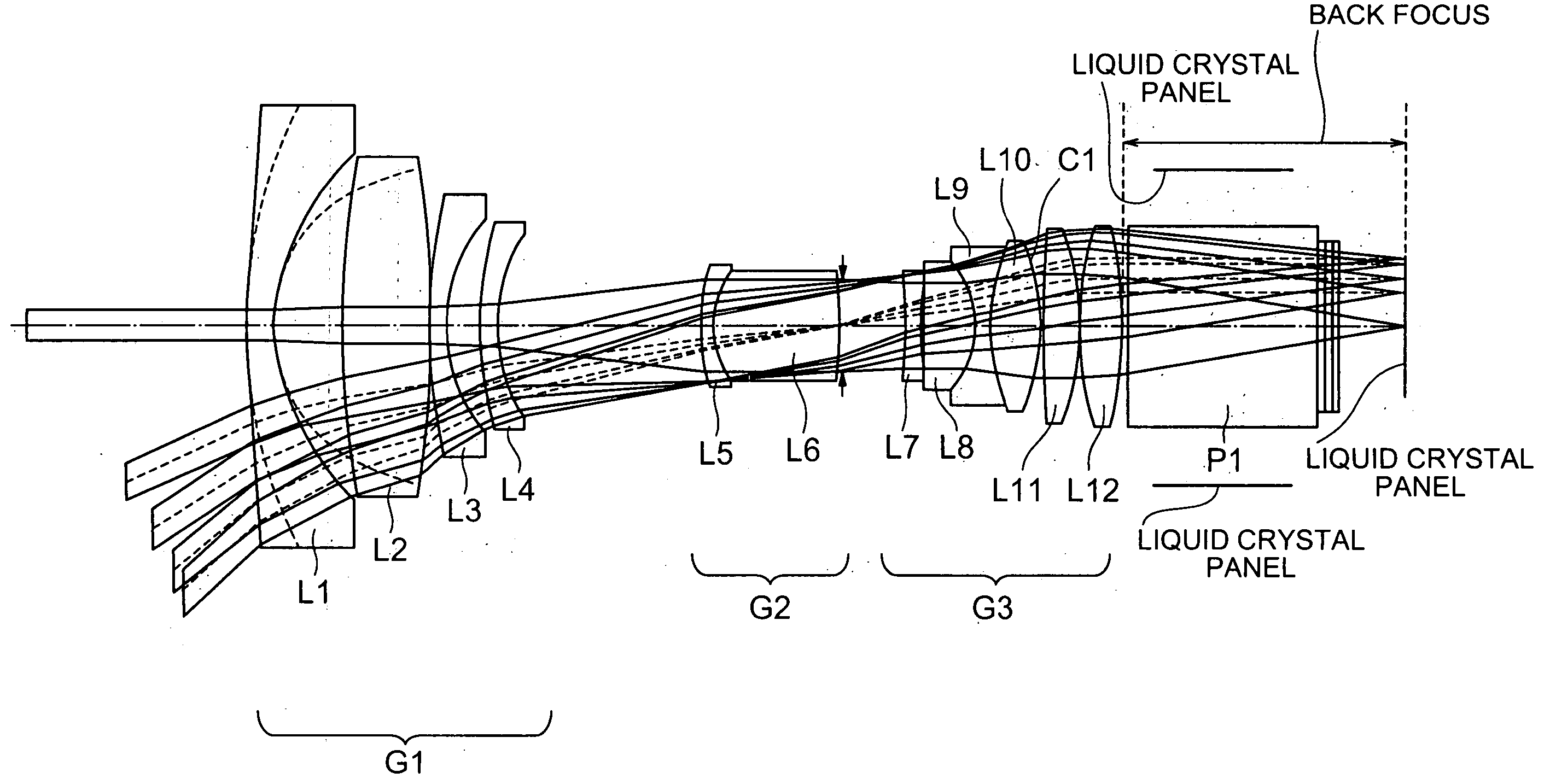
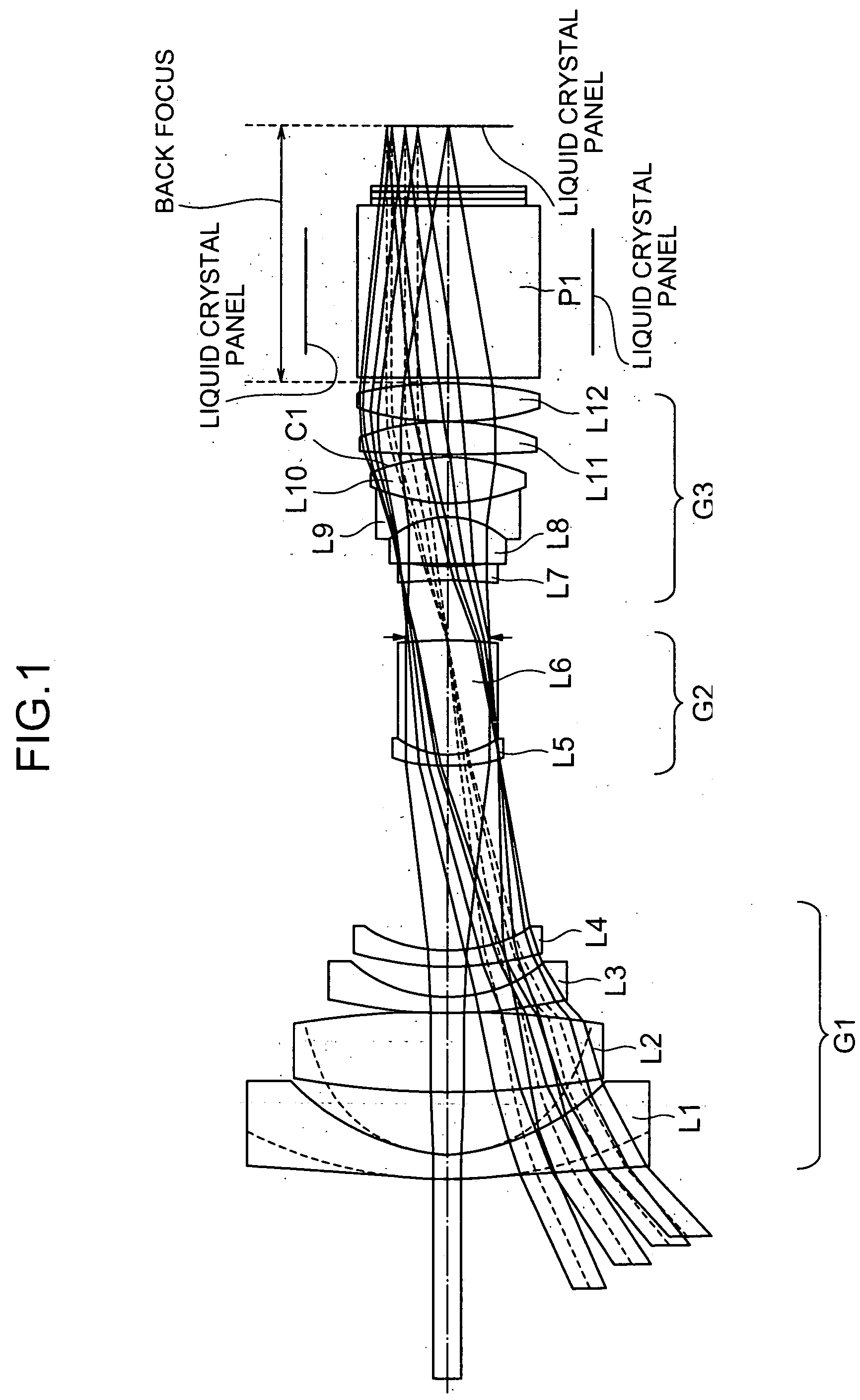
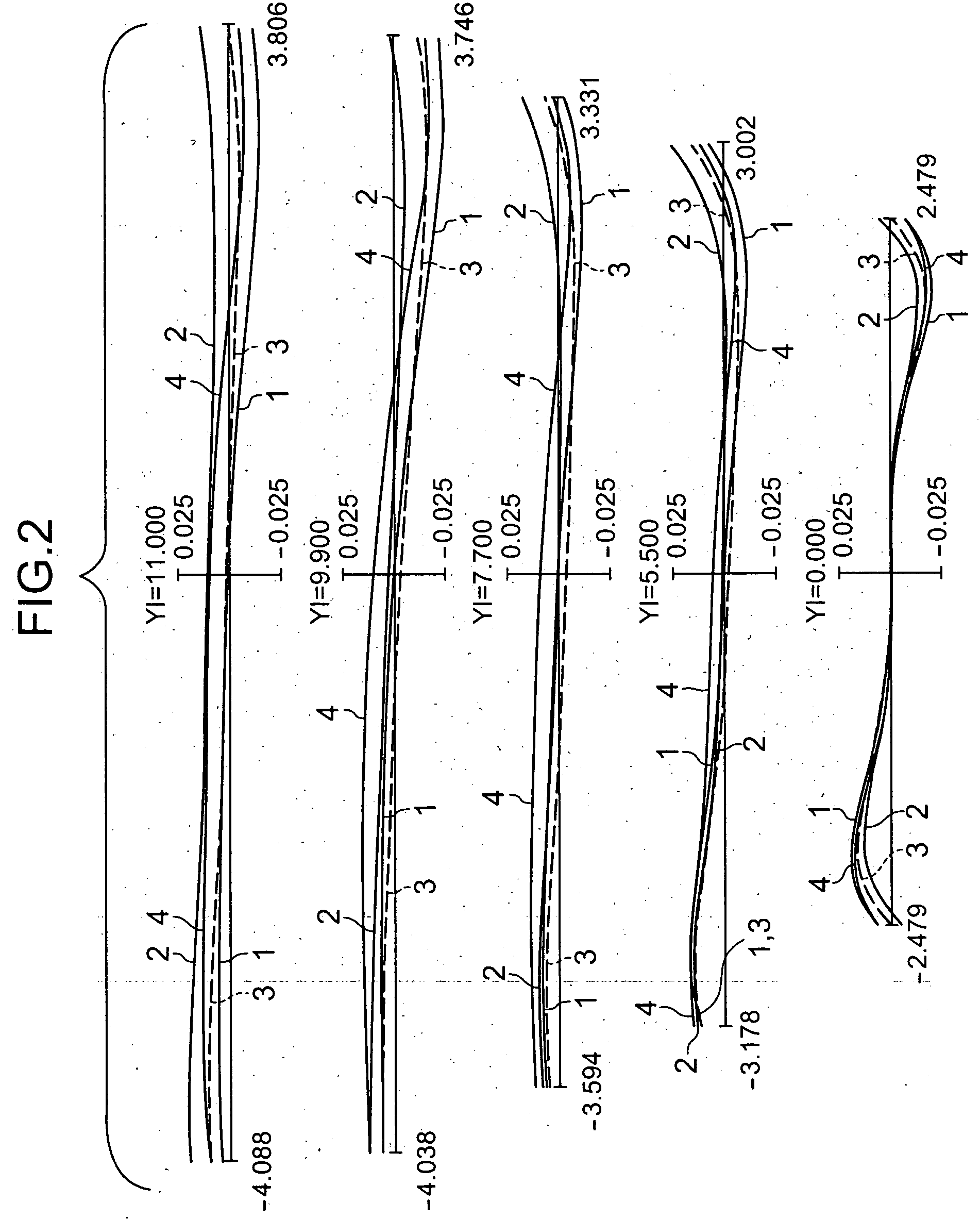
The present invention is directed to a projection lens that has a sufficiently long back focus to enable a wide-angle projection and has astigmatism, abaxial spherical aberration (coma), distortion, and other types of aberration satisfactorily corrected. The projection lens includes first to third groups of lenses G1, G2 and G3. The first group of lenses G1 consist of four pieces of lenses, and the first or foremost negative one of the lenses is an aspheric lens. The second group of lenses G2 consist of two pieces of lenses, and the first or foremost negative one and the second positive one of the lenses are joined together. The third group of lenses G3 consist of six pieces of lenses, and the second foremost positive one, the third negative one, and the fourth positive one of the lenses are joined together. The projection lens is characterized in that the following formulae are satisfied; bf / f>=2.8 (1) 1.1<=f2 / f3<=1.6 , and (2) 1.65<=|f1| / f<=2.05, (3) where f1, f2 and f3 are focal lengths unique to the first, the second and the third groups of lenses G1, G2 and G3, respectively, and f and bf are total focal length and back focus of the whole optics, respectively.
Owner:TAMRON
Test device for planar three-dimensional shape based on multiple-beam angle adaptive optics and processing method thereof
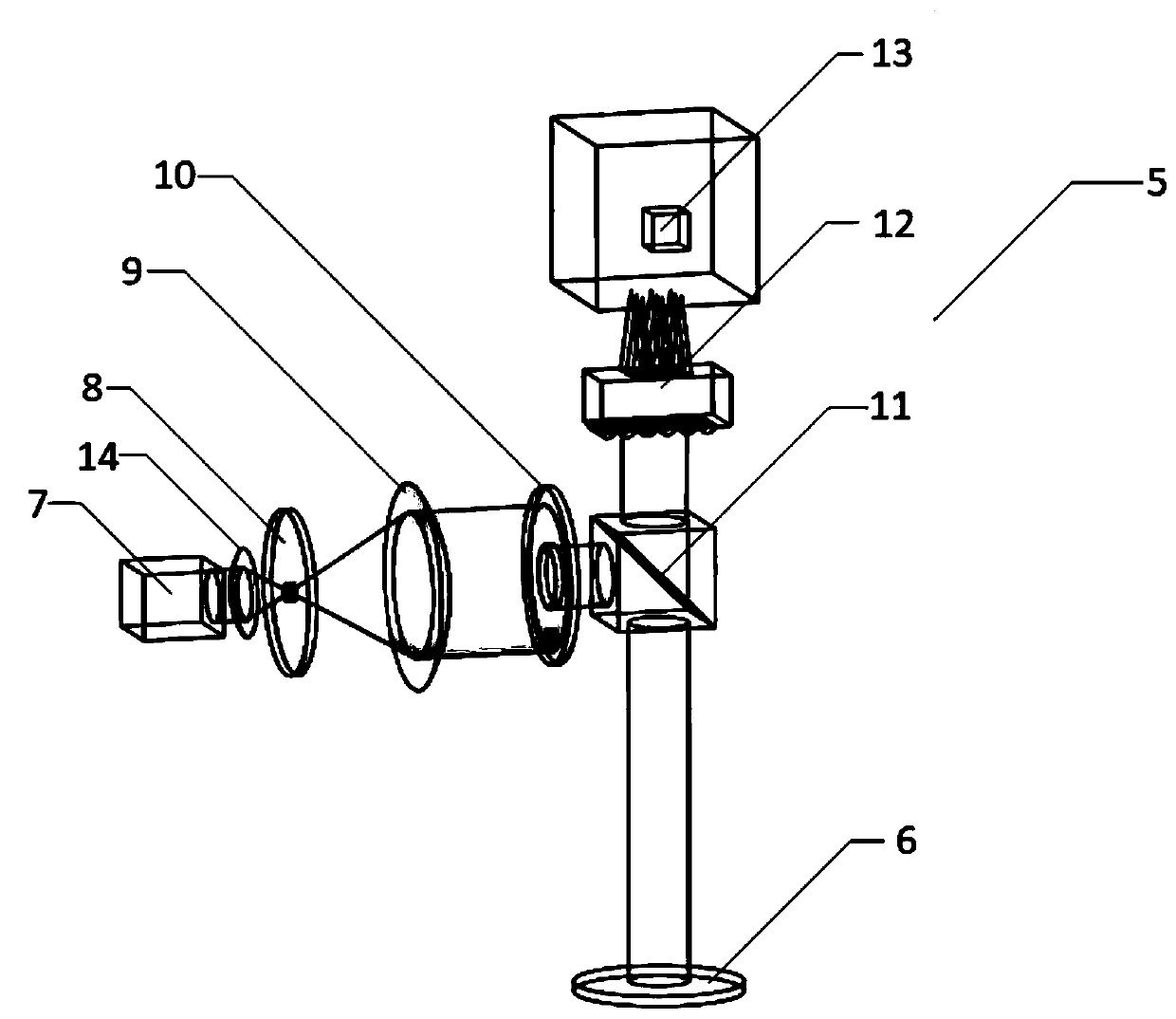
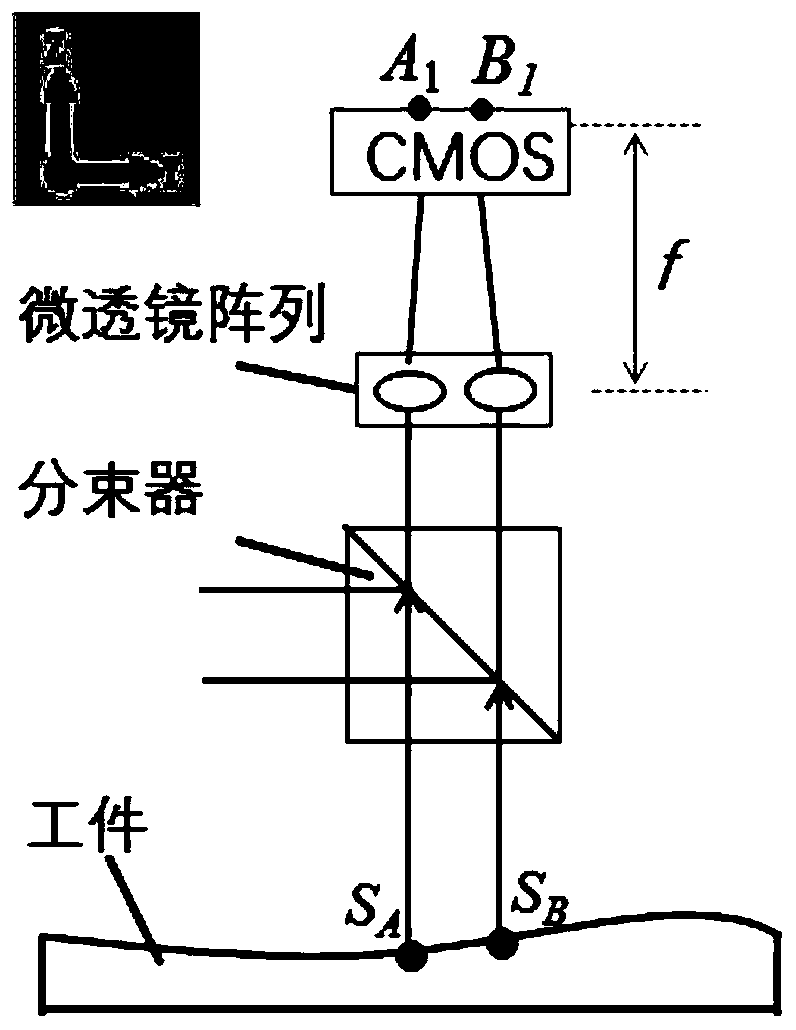
The invention discloses a test device for a planar three-dimensional shape based on multiple-beam angle adaptive optics and a processing method thereof. The test device mainly comprises a bearing platform, a bracket, a XY platform, a rotating platform, a tilting platform and a multi-beam angle sensor. Laser beams generated by a semiconductor laser in the technical solution of the invention pass through a pinhole of a first filter plate, and is aligned by a collimator lens, and then projected on surface of a workpiece under action of a beam splitter. Reflected beams from surface of the workpiece completely reach a microlens array through the beam splitter. Incident light is divided into a plurality of small samples by the microlens array and then focused on a detector array, thereby producing many separated optical focuses on a CMOS camera. The positions of the optical focuses are directly related to a slope of the workpiece. An algorithm is used to process an images detected from the CMOS camera, determine the positions of the focuses, finally calculate the slope by comparing with an original position, and reconstruct a contour from the slope.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Sighting optics
One embodiment of sighting optics according to the teachings provided herein may comprise a front sight and a rear sight positioned in spaced-apart relation. The rear sight includes optical element having a first focal length and a second focal length. The first focal length is selected so that it is about equal to a distance separating the optical element and said front sight and the second focal length is selected so that it is about equal to a target distance. The optical element thus brings into simultaneous focus for a user images of the front sight and the target.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
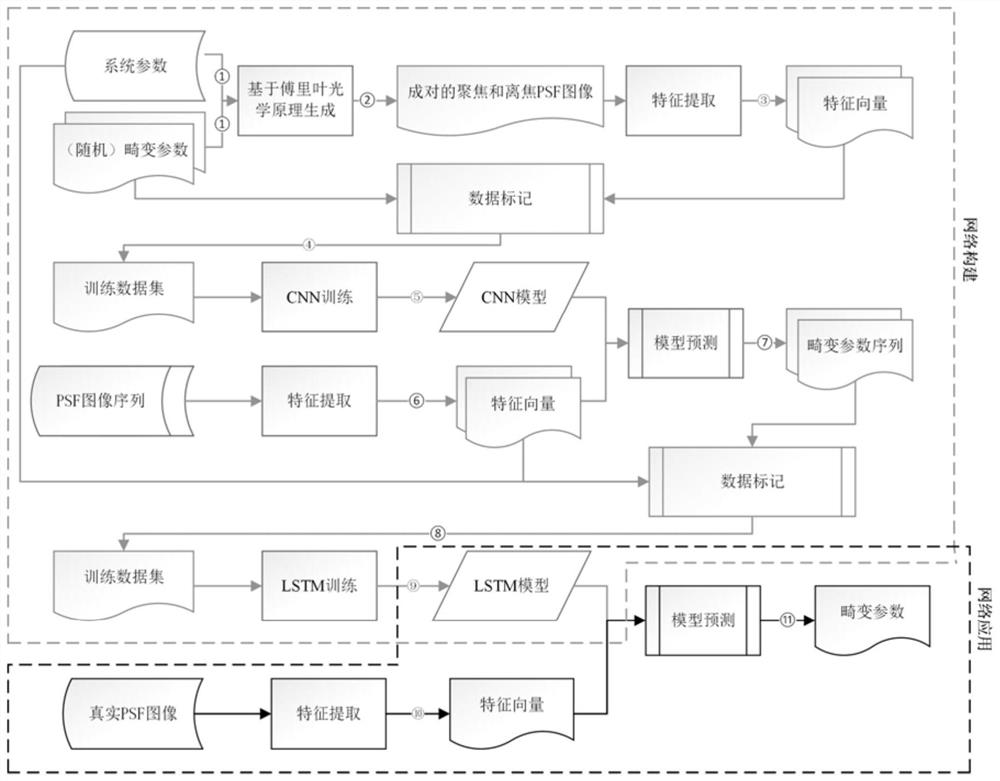
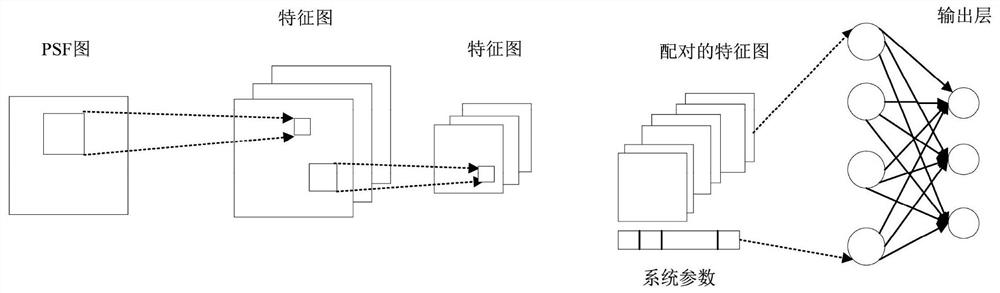
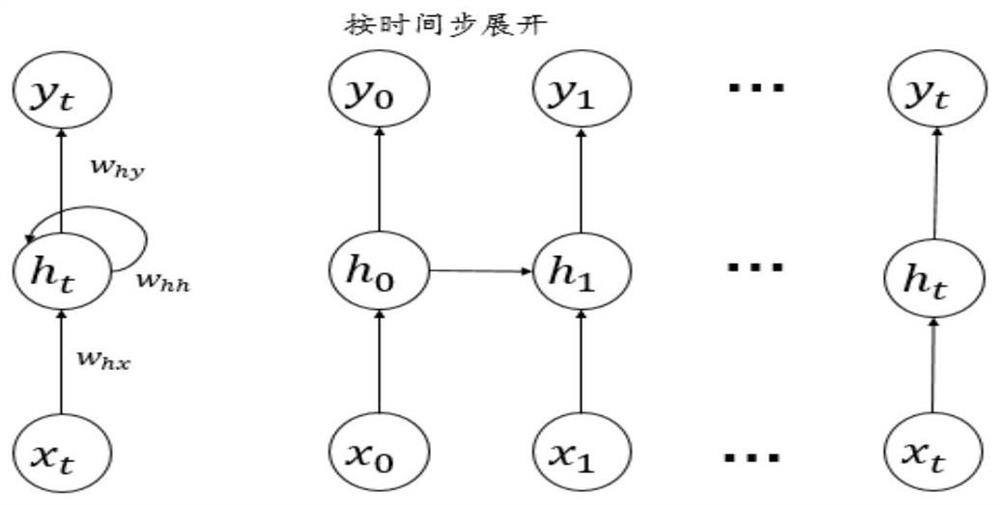
Wavefront phase difference detection method based on long short-term memory deep network
ActiveCN113158487AMeet the actual needs of wavefront distortion correctionRun fastDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesData setFourier optics
The invention discloses a wavefront phase difference detection method based on a long short-term memory deep network. The wavefront phase difference detection method comprises the steps of inputting characteristic parameters of a certain actual optical system and generating a training data set; generating a focus plane PSF image i1 (x, y) and an out-of-focus PSF image i2 (x, y) from the training data set according to the Fourier optics principle; extracting feature vectors of the focal plane PSF image i1 (x, y) and the out-of-focus PSF image i2 (x, y) as input data; extracting a feature vector of a PSF image sequence collected from an actual optical system; inputting the PSF image sequence into the trained convolutional neural network model according to a time sequence t to determine a wavefront distortion phase so as to obtain a series of distortion phase parameters for training; and generating input data and output data for LSTM deep network training, initializing network parameters, and repeatedly training the LSTM deep network until a loss function of the LSTM deep network is converged.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
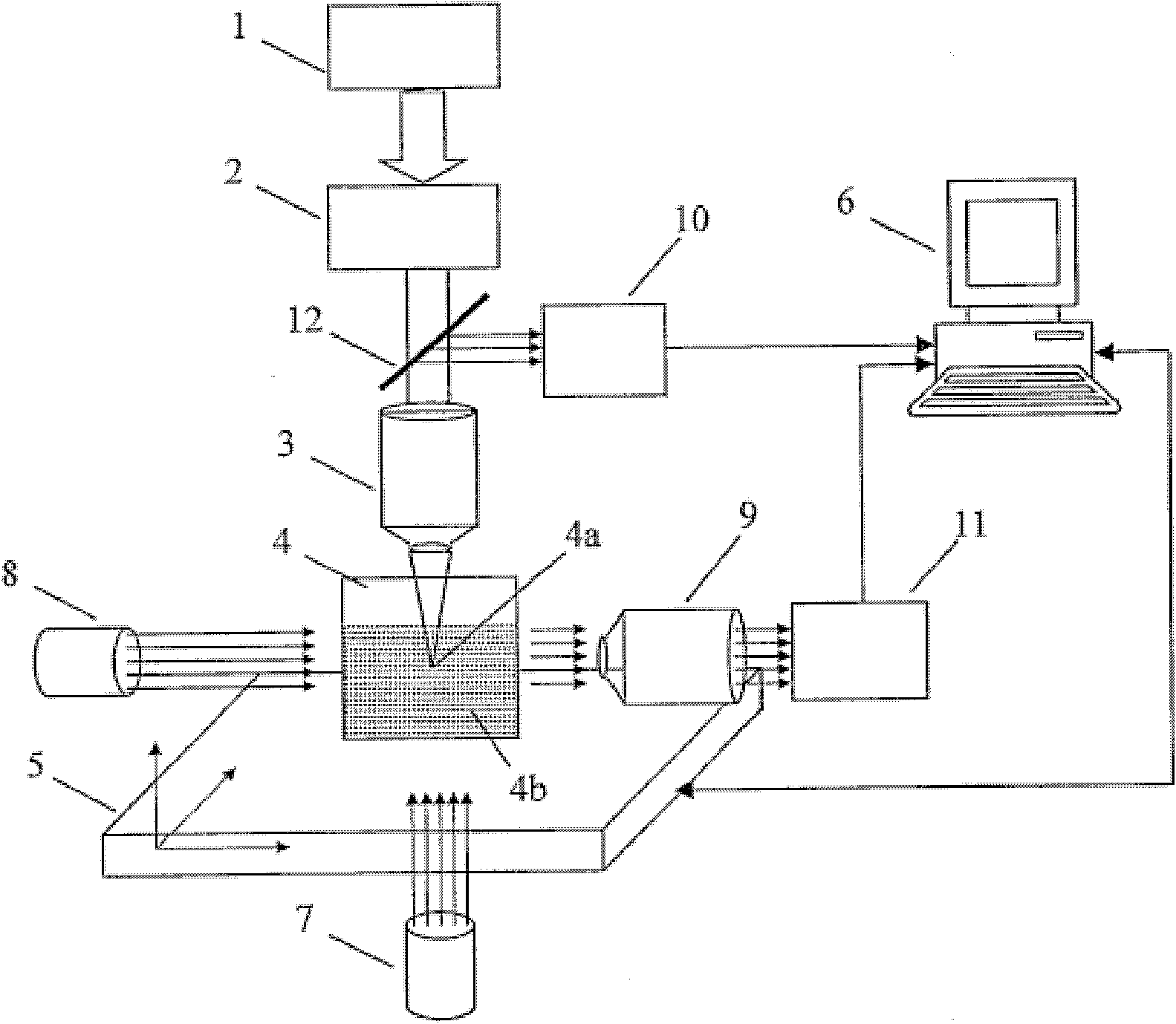
Method and device for three-dimensional confocal measurement
The invention relates to a method and a device for three-dimensional measurement of an object. The device includes a laser source for generating an illumination beam, a focusing optics for focusing the illumination beam on at least one measuring point on a surface of the object to be measured, a detector for detecting an observation beam reflected by the surface of the object, a confocal observation optics which allows only the observation beam that is focused on the surface of the object to pass through to the detector. The laser source includes multiple coherent laser elements, the laser elements simultaneously emitting illumination beams that are focused on multiple measuring points on the surface of the object, so that the laser elements are arranged to reduce the speckle effect in the 3D-image data generated by the measurement.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
Pattern recognition matching for bright field imaging of low contrast semiconductor devices
InactiveUS7538868B2Reduce failurePhotometry using reference valuePhotomechanical treatmentLight beamPeak value
Calibration of pattern recognition in bright field imaging systems is disclosed. A target pattern on a substrate on the stage is brought into focus of a bright field system. The image is scanned in a first direction while measuring an edge scattering pattern from a feature of the target pattern. The edge scattering pattern is characterized by first and second peaks. A position of the bright field system's illuminator or beam shaping and relay optics is adjusted perpendicular to an optical path until the first and second peaks are approximately equal in height.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Methods and systems for semiconductor metrology based on polychromatic soft X-Ray diffraction
ActiveUS11333621B2Maximizes contentSmall spot sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementWaferingAngle of incidence
Methods and systems for performing measurements of semiconductor structures based on high-brightness, polychromatic, reflective small angle x-ray scatterometry (RSAXS) metrology are presented herein. RSAXS measurements are performed over a range of wavelengths, angles of incidence, and azimuth angles with small illumination beam spot size, simultaneously or sequentially. In some embodiments, RSAXS measurements are performed with x-ray radiation in the soft x-ray (SXR) region at grazing angles of incidence in the range of 5-20 degrees. In some embodiments, the x-ray illumination source size is 10 micrometers or less, and focusing optics project the source area onto a wafer with a demagnification factor of 0.2 or less, enabling an incident x-ray illumination spot size of less than two micrometers. In another aspect, active focusing optics project programmed ranges of illumination wavelengths, angles of incidence, and azimuth angles, or any combination thereof, onto a metrology area, either simultaneously or sequentially.
Owner:KLA CORP
Beam forming with focus location adjustment
ActiveUS20200341286A1Reduce degradationLaser beam welding apparatusMaterial analysisBeam sourceLight beam
An apparatus includes a beam source, beam forming optics, a first focusing lens having a focal length, a second focusing lens having a focal length similar to the focal length of the first lens, and a lens translator configured to move the second lens transversely relative to the beam forming optics and to the first lens, and thereby move the elongated focus transversely. In some embodiments, the beam forming optics are positioned between the beam source and the first focusing lens, the first focusing lens is positioned between the beam forming optics and the second focusing lens, and the beam forming optics, the first focusing lens, and the second focusing lens are arranged to receive a beam of laser radiation from the beam source and to form the beam into an elongated focus.
Owner:COHERENT INC
All-solid-state focus-adjustable micro lens based on IPMC driving
The invention relates to the field of optics and the field of MEMS, and concretely relates to a focus-adjustable micro lens. The micro lens is structurally characterized in that a flexible polymer isplaced between a glass film and supporting glass, the glass film is small in hardness and prone to deformation, and the supporting glass is large in hardness and not prone to deformation. An intelligent material IPMC annular driver is placed on the topmost layer. A metal shell is arranged on the outermost side of the whole structure and plays a role in supporting and protecting. When voltage is applied to the annular IPMC, the outer side of the IPMC is fixed, downward displacement is generated on the inner side of the IPMC, the glass film and a flexible polymer deform, and a plano-convex lensstructure is formed. Through different applied voltages, driving forces generated by the IPMC are different, convex curvatures of the plano-convex lenses are different, and focal lengths are different. The micro lens is a typical MEMS integrated product and has the advantages of being small in size, low in power consumption, simple in structure, free of magnetic interference and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN NORMAL UNIV
Method of and device for capturing 3D data of one or more airborne particles
InactiveUS9164120B2Optimize power outputReduce loadPropellersPump componentsOptical propertyComputer science
Disclosed is a method of capturing 3D data of one or more airborne. At least one image of the one or more airborne particles is taken by a plenoptic camera of which the geometry and the optical properties of its optics are known, and the distance of a plane of focus with at least one selected particle of the one or more airborne particles from a defined reference location is determined by use of the captured image together with the known optical properties and the known geometry of the optics of the plenoptic camera.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and system of laser-driven intense x-ray photons imaging
ActiveUS20210219410A1Increase contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube with very high currentLasing wavelengthParticle physics
A X-ray source, comprising a laser, of a pulse duration of at most 40 fs, instantaneous power of at least about 80TW, a pulse repetition rate of at least 1 Hz; an optical compressor spectrally shaping the laser beam; focusing optics in the range between f#10 and f#15; and a gas target of electron density after ionization by the laser beam in a range between 1018 cm3 and 1019 cm−3; wherein the focusing optics focuses the laser beam in the gas target, and interaction of the focused laser beam with the gas target generates an X-ray beam, with a focused laser amplitude a0, given by a0=0.855 [IL (1018W / cm2)λL,2 (μm)]1 / 2, where IL is the on-target laser intensity and λL is the laser wavelength, of at least 2 and a P / Pc ratio value of at least 20, with P being the beam power and Pc a critical power given by Pc=17 (nc / n) GW where n is the electron density and nc is a critical electron density at which the plasma acts as a mirror reflecting the laser beam.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN +1
Rainbow particle imaging velocimetry for dense 3D fluid velocity imaging
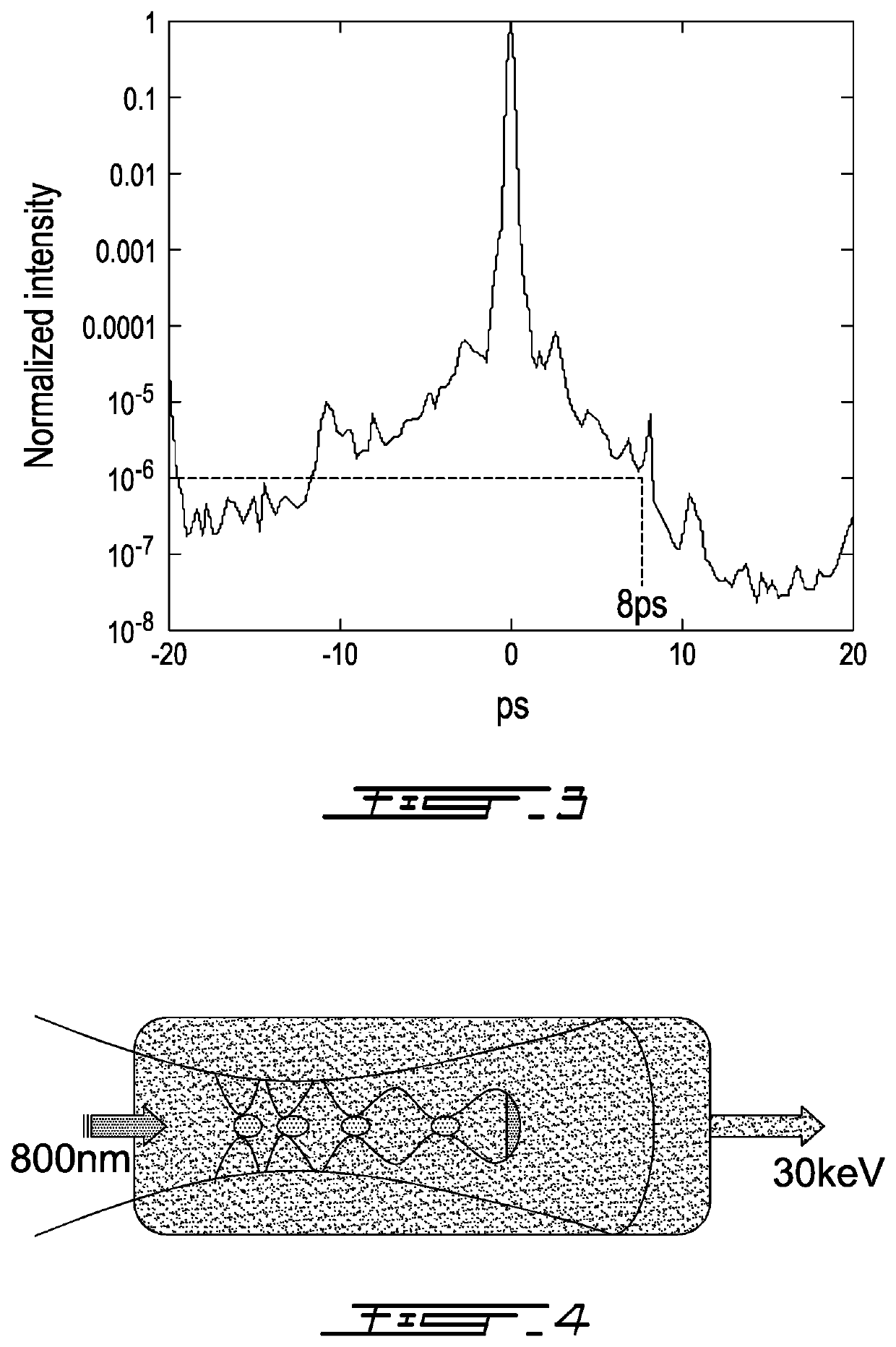
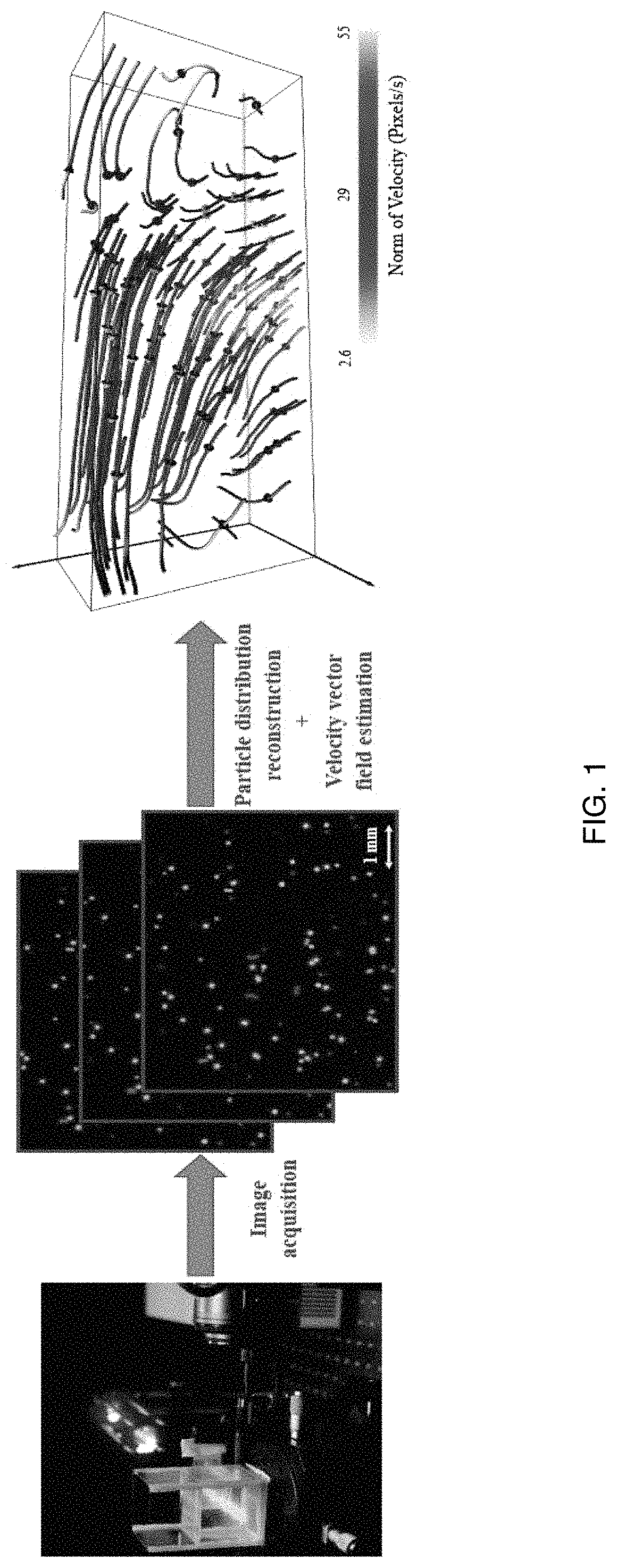
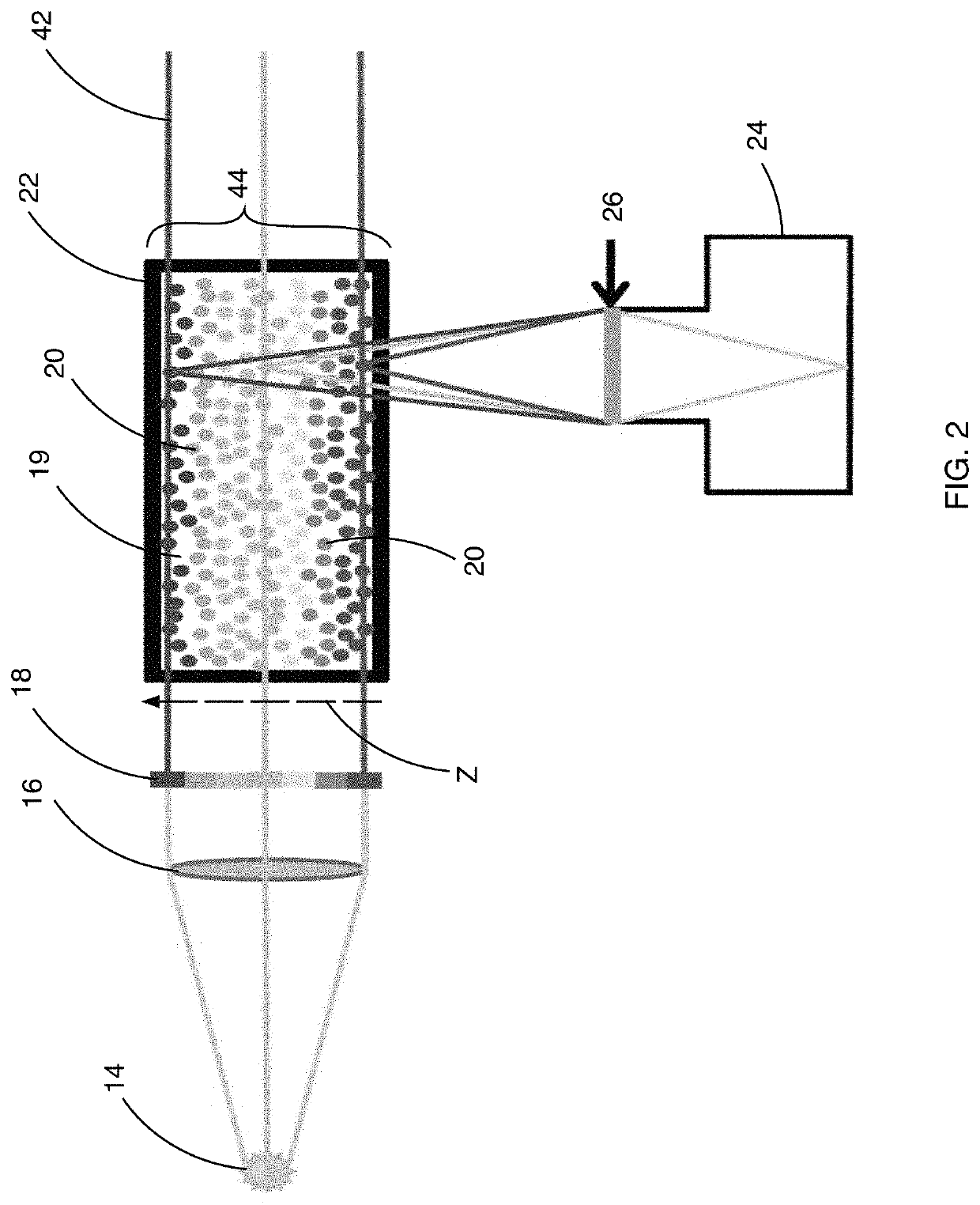
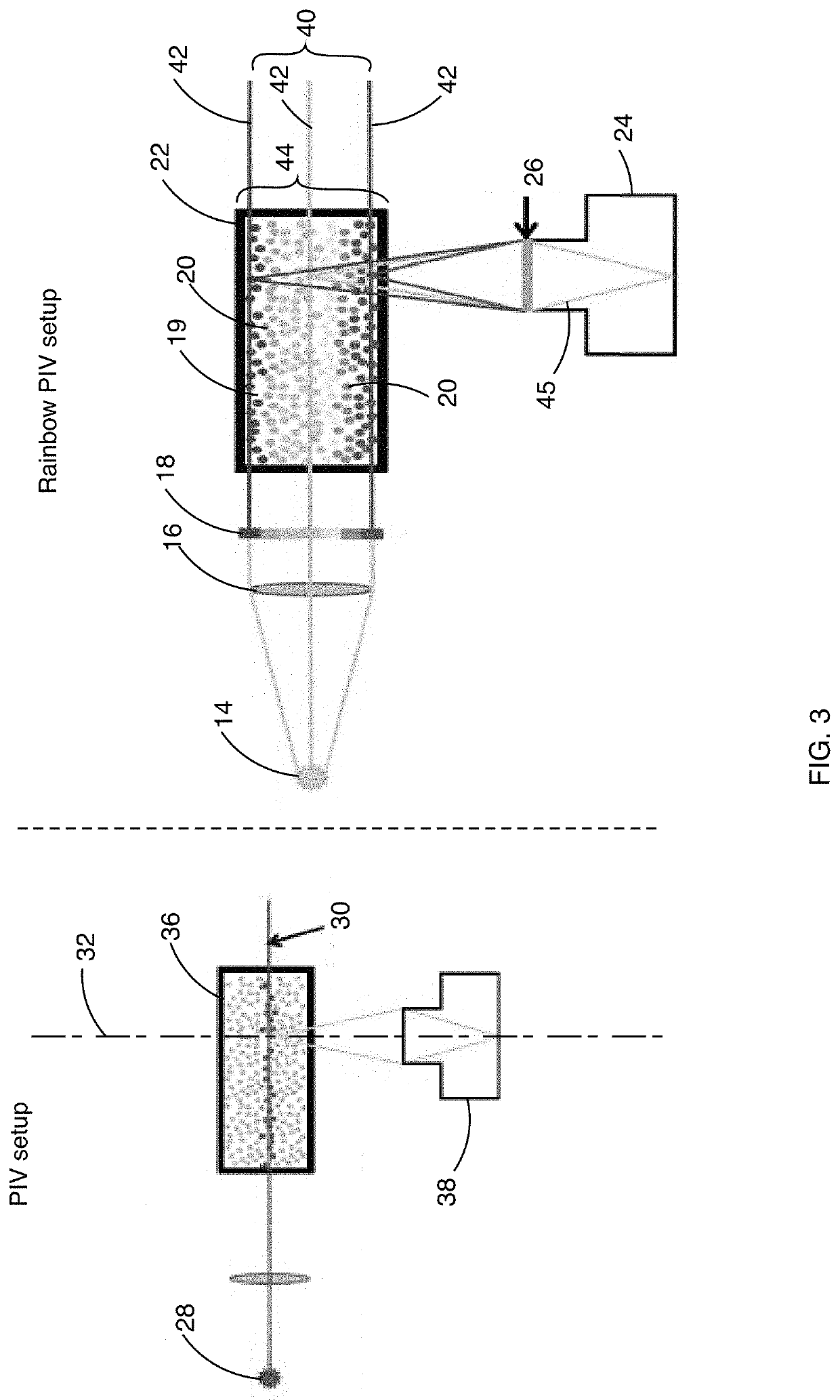
ActiveUS10782311B2Increase horizontal resolutionIncrease depth of field2D-image generationFull-field flow measurementParticle imagingRainbow
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lens group and near-to-eye display equipment
The invention provides a lens group and near-to-eye display equipment, and relates to the technical field of optics; and the lens group comprises a focusing convergent lens assembly, a first optical element and a second optical element which are sequentially arranged in a light outgoing direction. The first optical element is used for enabling an incident light beam to be partially transmitted andpartially reflected, a reflected light beam, reflected by the first optical element, of the convergent light beam emitted from the focus-adjustable convergent lens assembly is emitted towards a second optical element, and after being reflected by the second optical element, the reflected light beam is imaged in a target area through the first optical element. When a myopia or hyperopia user findsthat an image is not clear when watching a picture in a target area through the lens group, the focal length of the whole lens group can be adjusted by adjusting the focal length of the focus-adjustable converging lens assembly, so that the watching requirement of the myopia or hyperopia user when using the lens group is met, and the use experience of the user is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CRYSTAL OPTECH
Fluorescence imaging scope with reduced chromatic aberration
Improved fluoresced imaging (FI) endoscope devices and systems are provided to enhance use of endoscopes with FI and visible light capabilities. An endoscope device is provided for endoscopy imaging in a white light and a fluoresced light mode. A chromatic adjustment assembly, typically implemented with prisms, compensates for a chromatic focal difference between the white light image and the fluoresced light image caused by the dispersive properties of the optical materials or optical design employed in the construction of the optical channel. The assembly is placed optically between the most proximal rod lens of the endoscope and the focusing optics, typically at an internal telecentric image space, to improve the chromatic correction. The prism assembly directs incoming light with different spectral content along separate paths which compensate for chromatic aberration.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Method and device for optical surface measurement by means of a confocal sensor
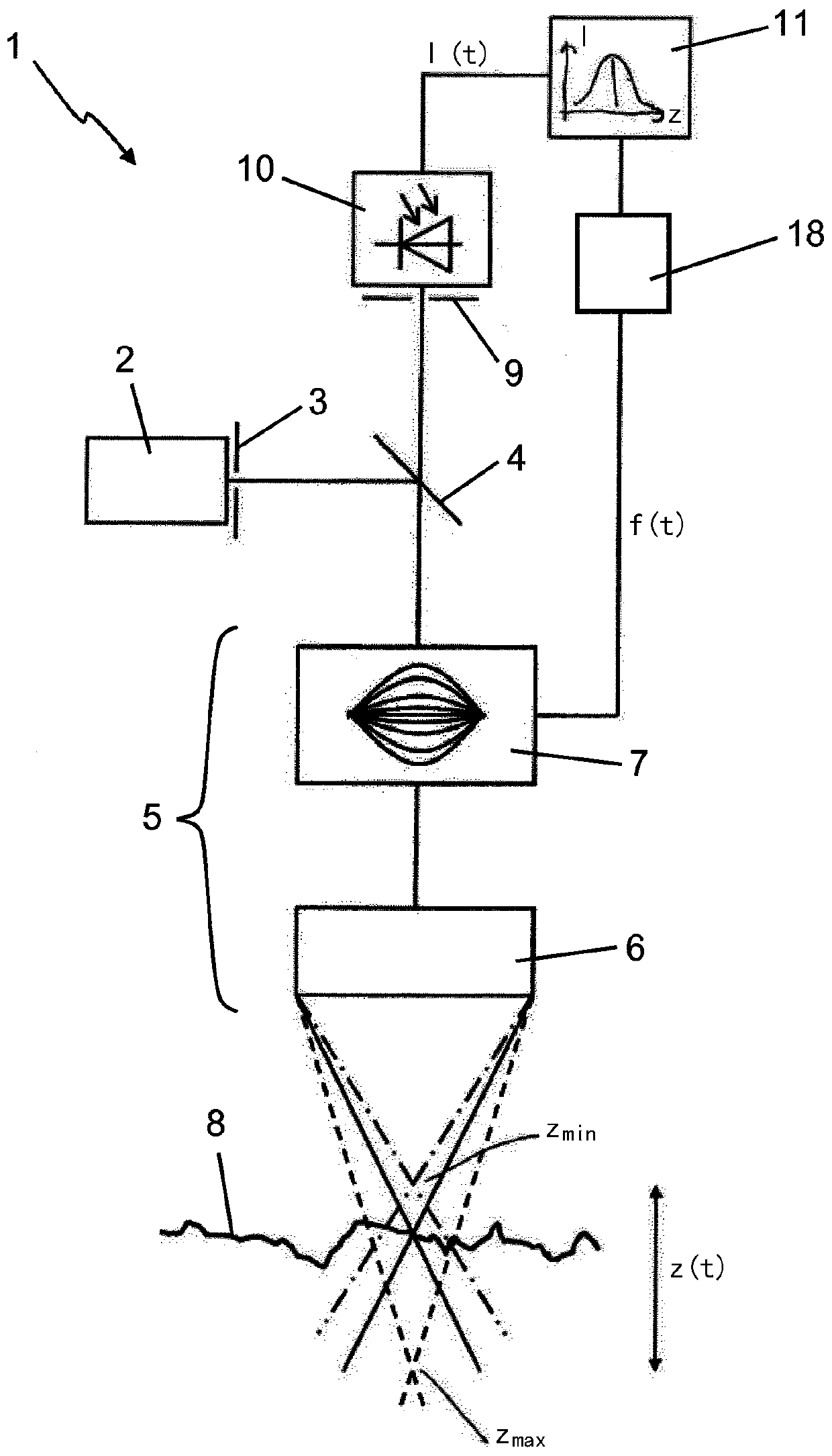
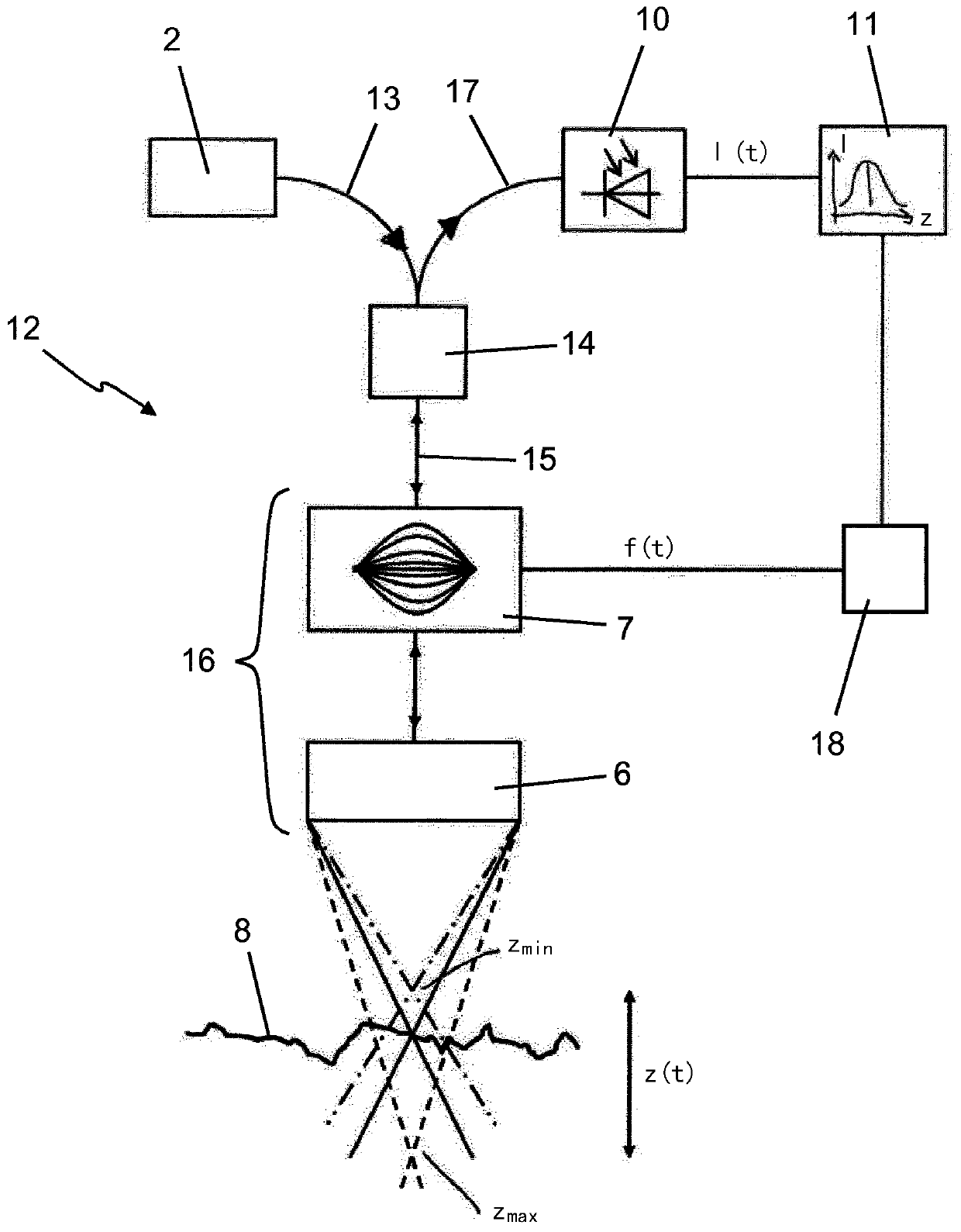
The invention relates to a method and a device for the optical measurement of technical surfaces by means of a confocal sensor, where light from a light source (2) is directed towards the surface (8)of a sample to be measured by means of an optical system (5, 16). According to the invention, the optical system (5, 16) comprises an electrically controlled adaptive optics (7), wherein the focus ofthe optical system (5, 16) is varied by an electric signal (f (t)) in the Z-direction. The light reflected back from the sample surface (8) is directed to at least one photosensor (10), where the sensor signal is measured over time by means of a detection device (11) and the time of a signal maximum is determined. The detection device (11) derives the height Z of the surface (8) from the electricsignal at the time of the signal maximum.
Owner:NANOFOCUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com