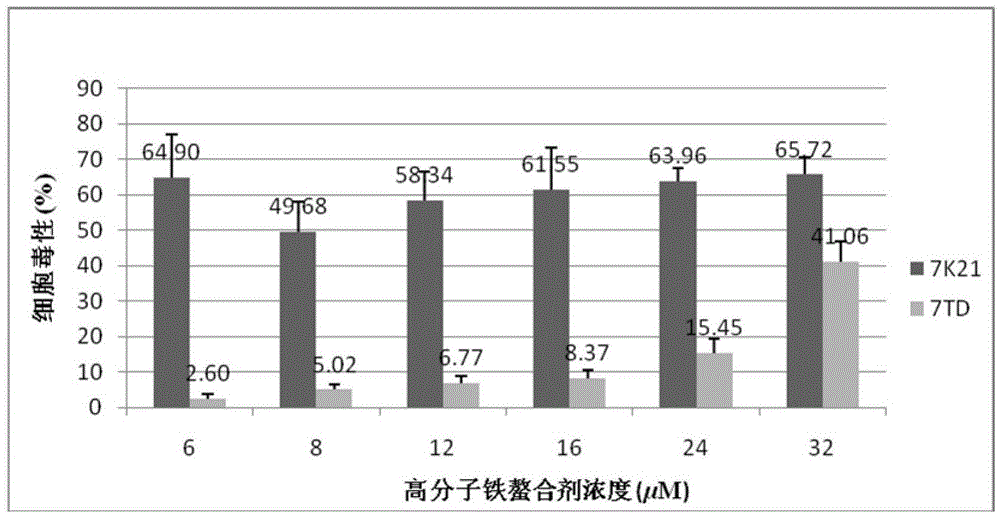
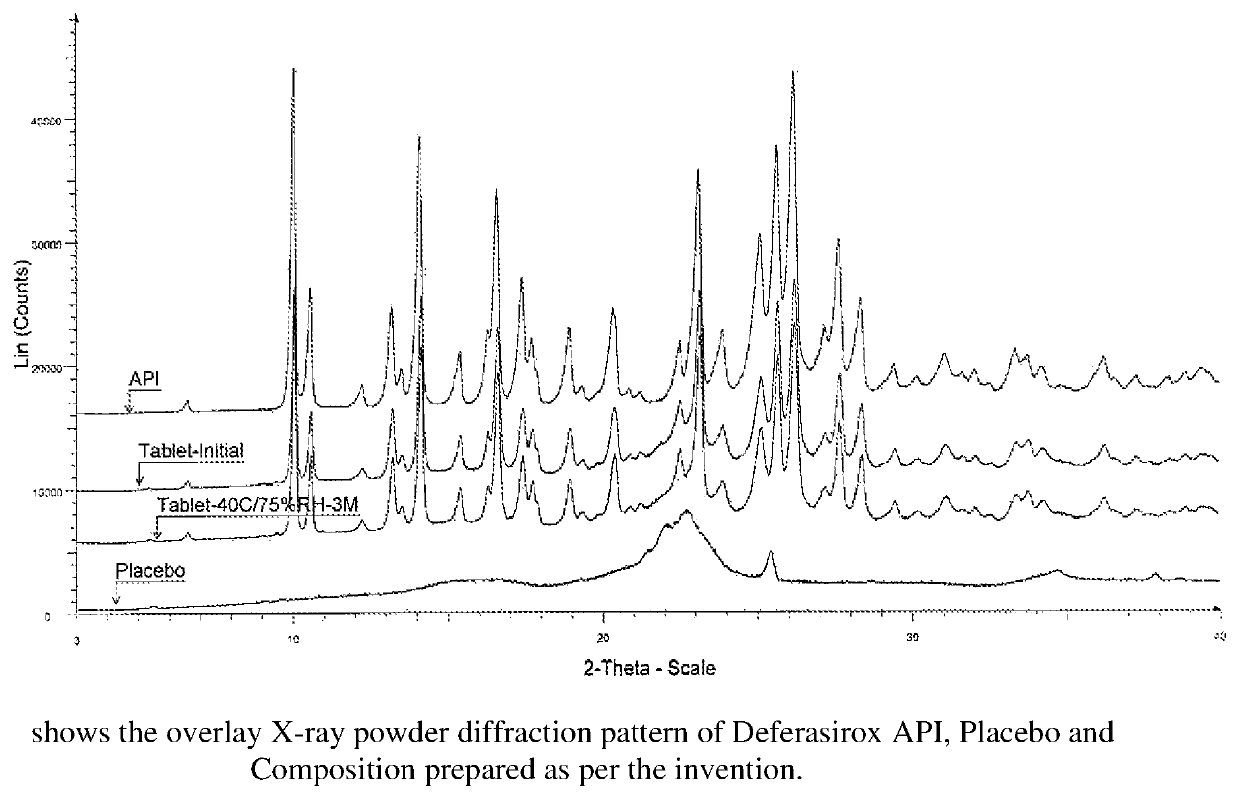
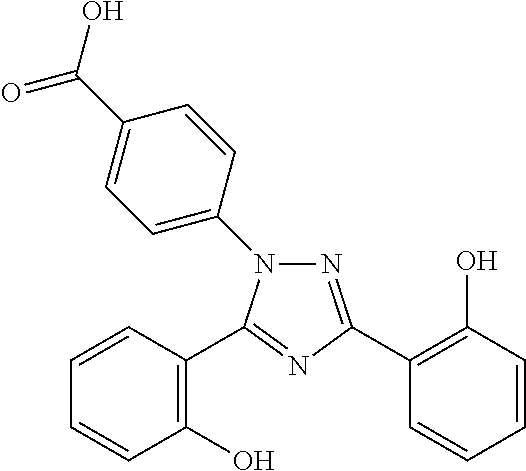
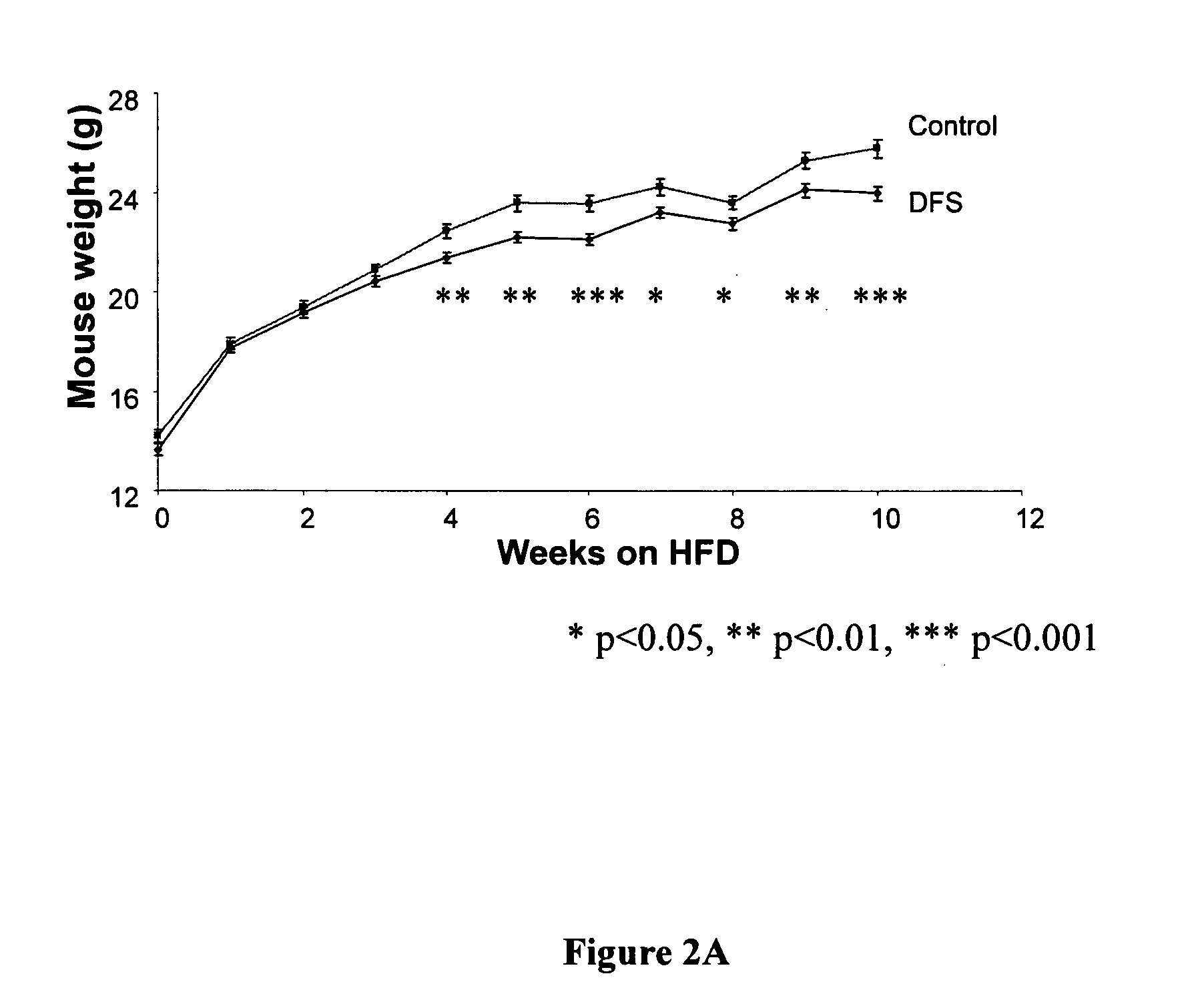
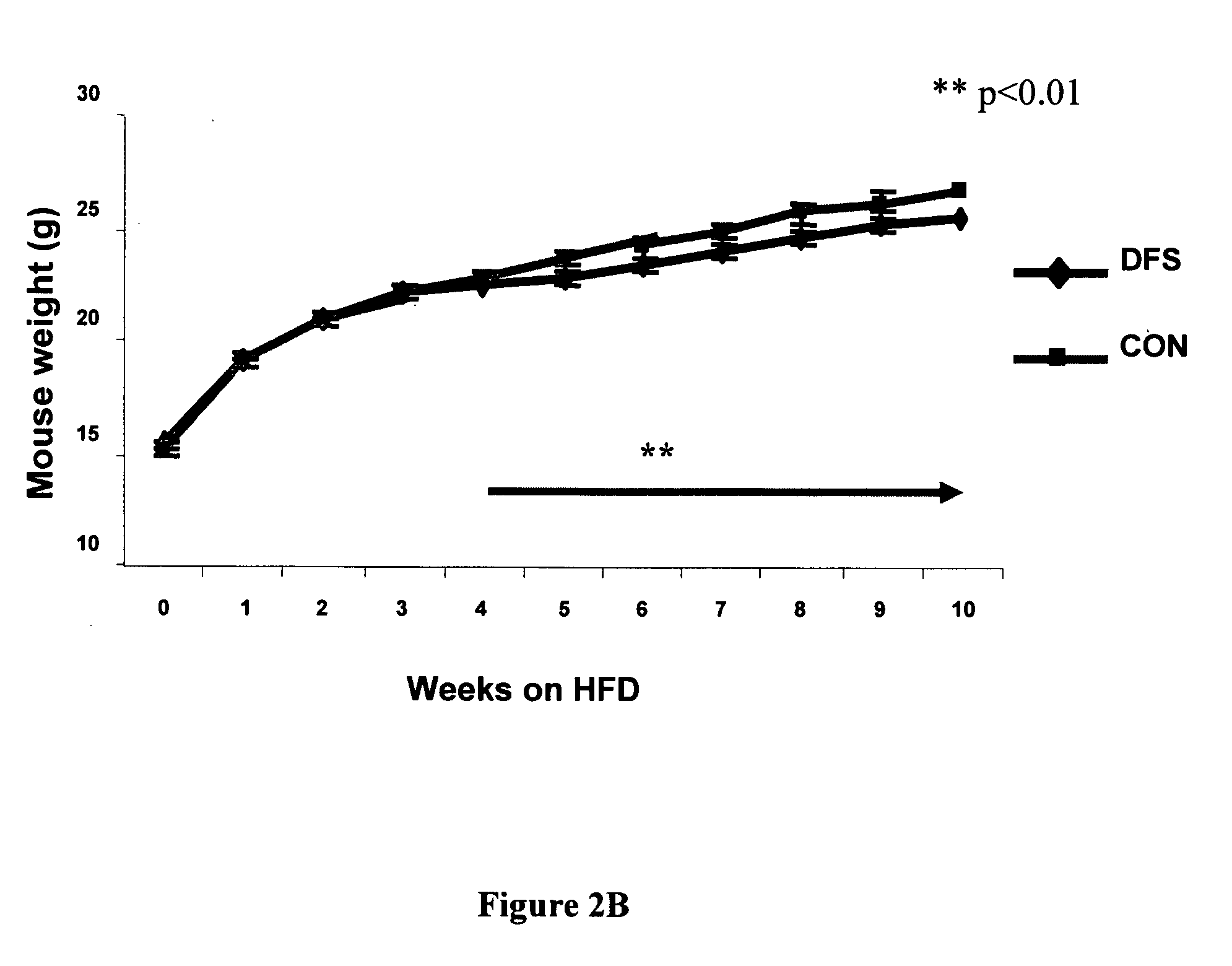
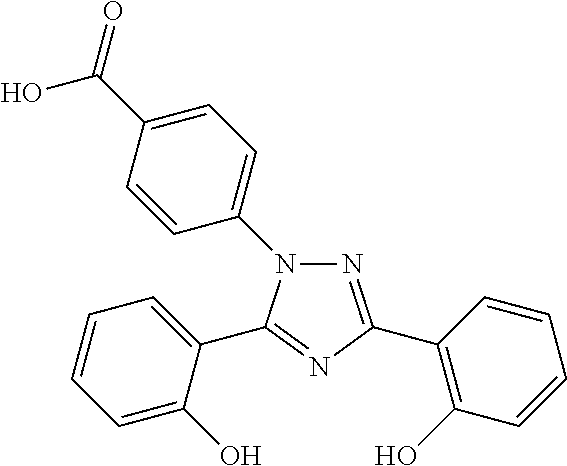
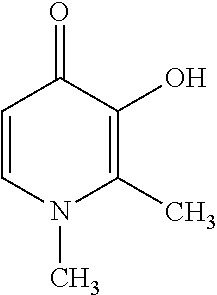
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Iron Chelating Agents" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Organic chemicals that form two or more coordination links with an iron ion. Once coordination has occurred, the complex formed is called a chelate. The iron-binding porphyrin group of hemoglobin is an example of a metal chelate found in biological systems.
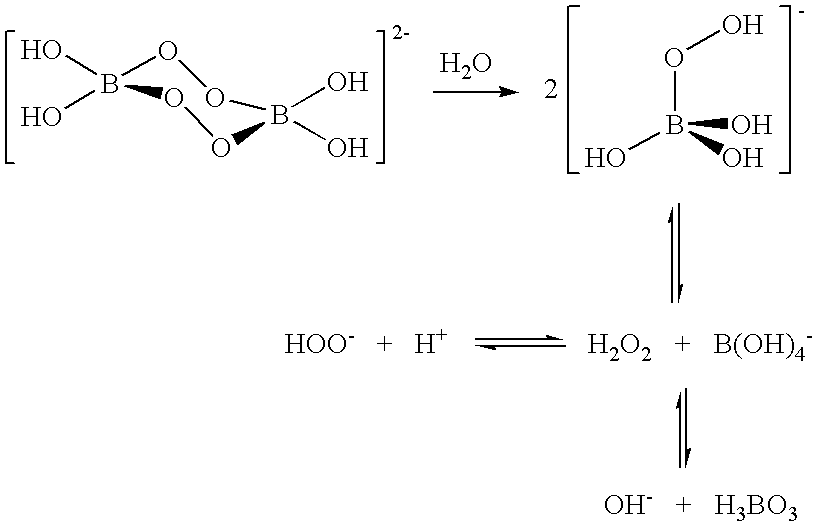
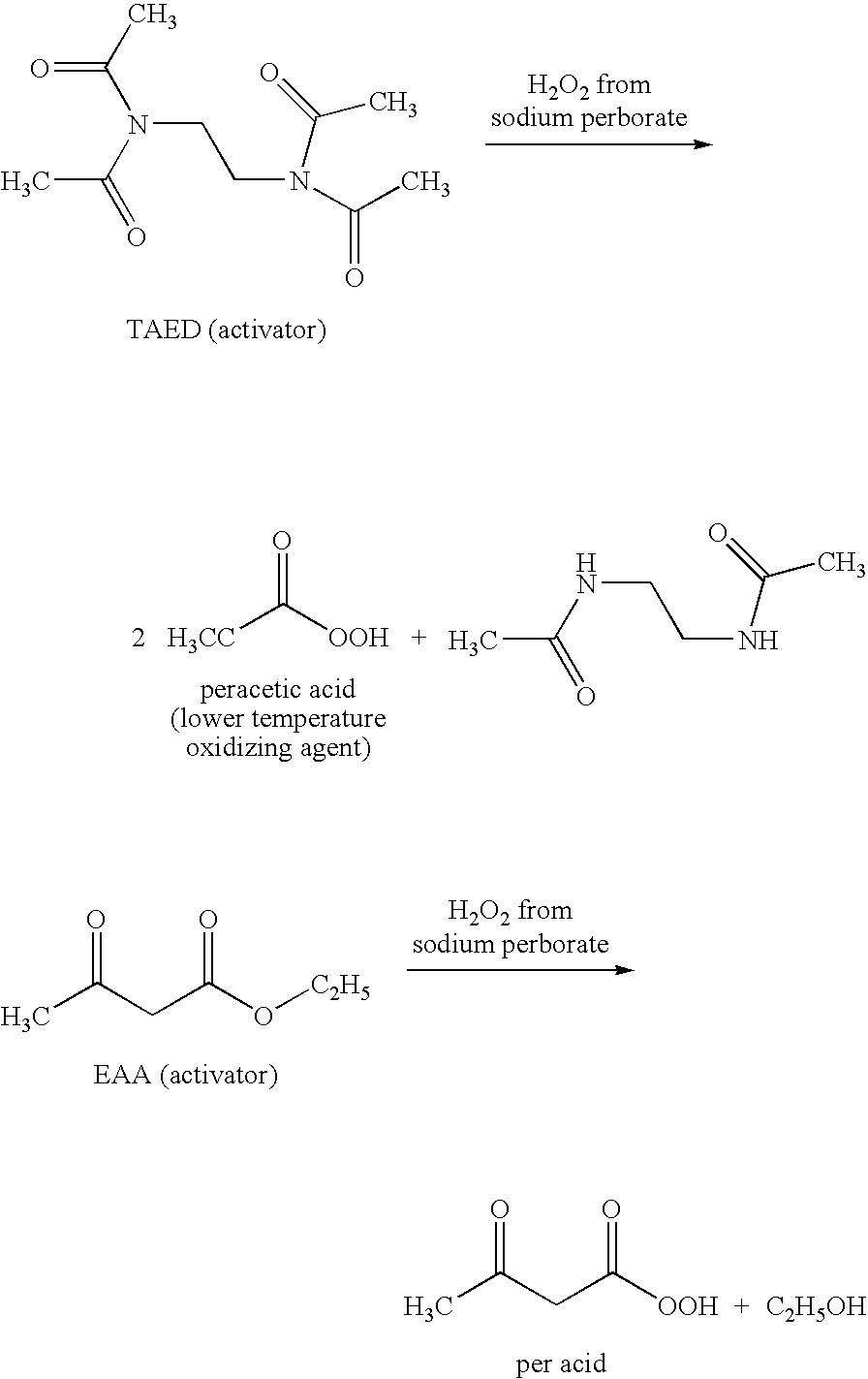
Compositions and methods for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer at very low temperature used in downhole well applications
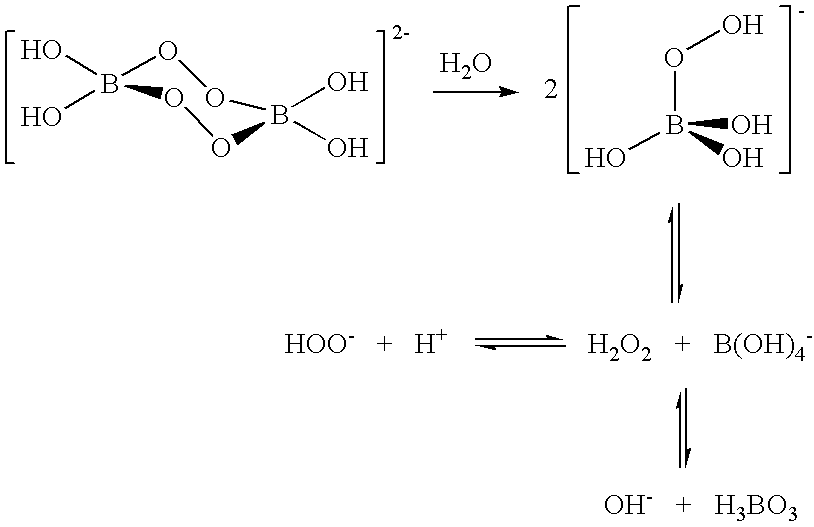
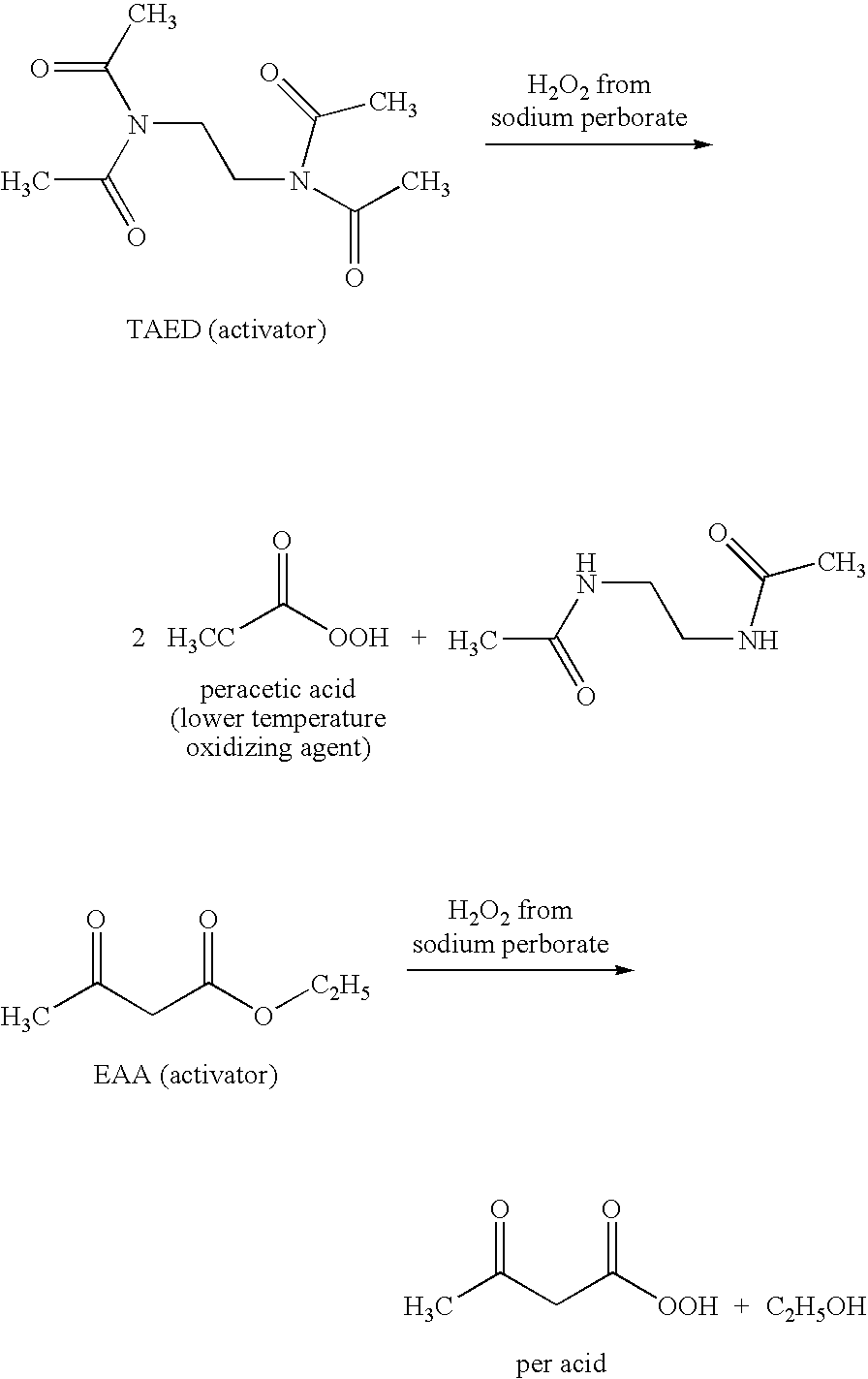
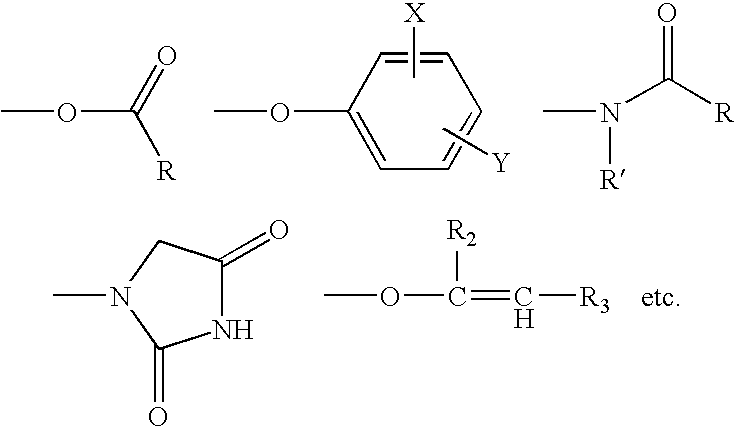
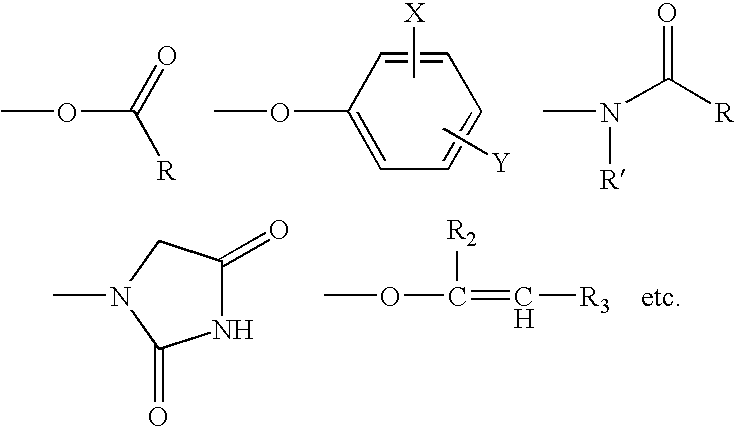
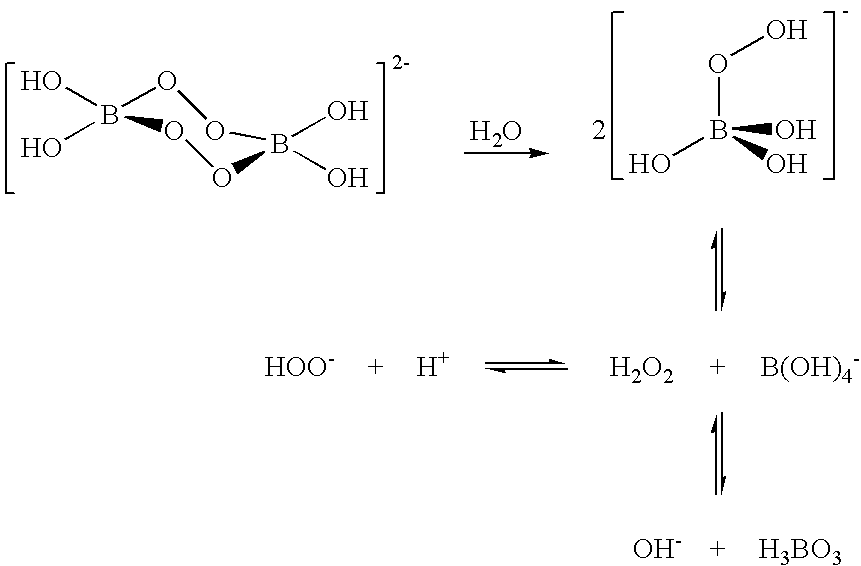
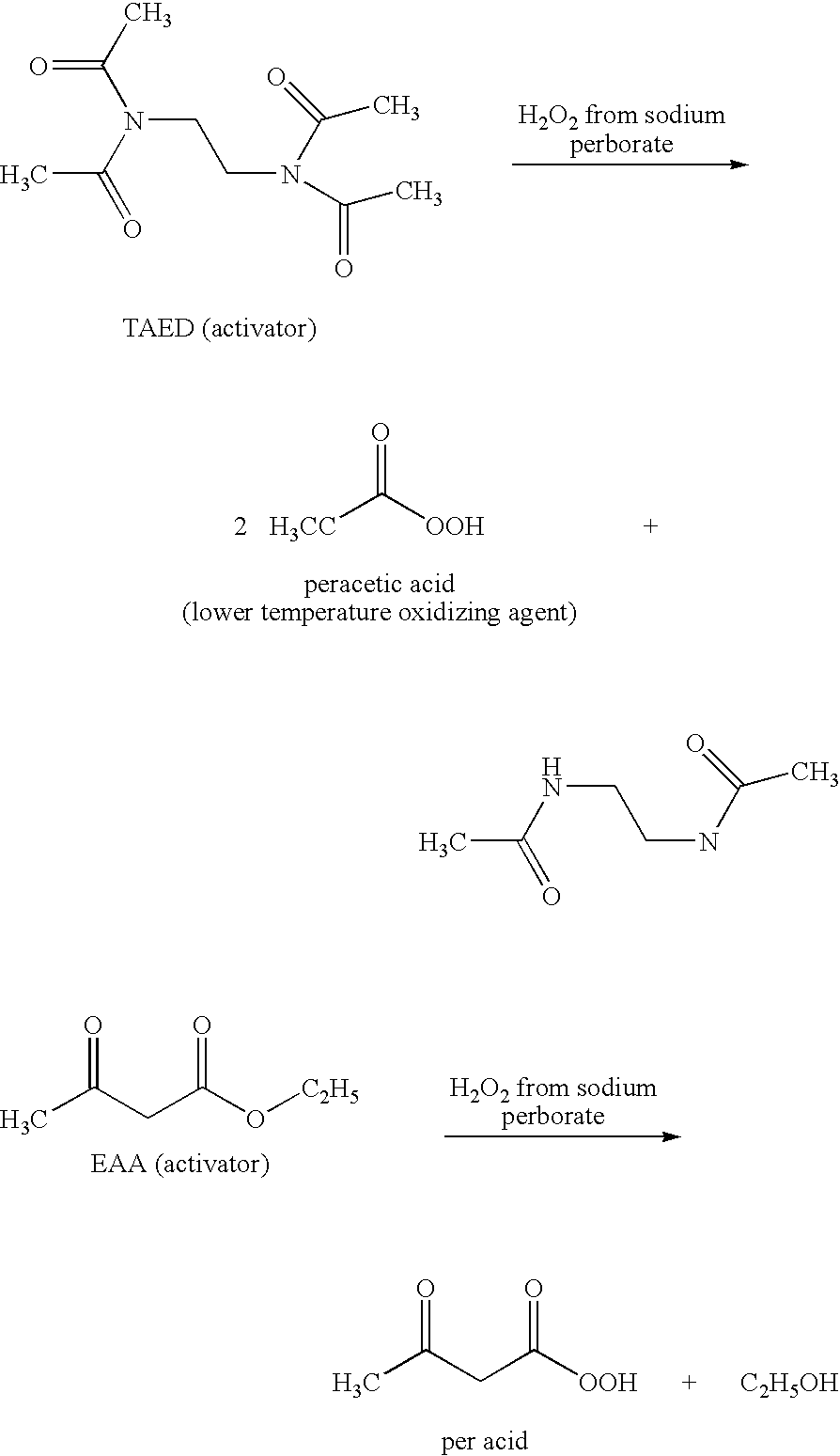
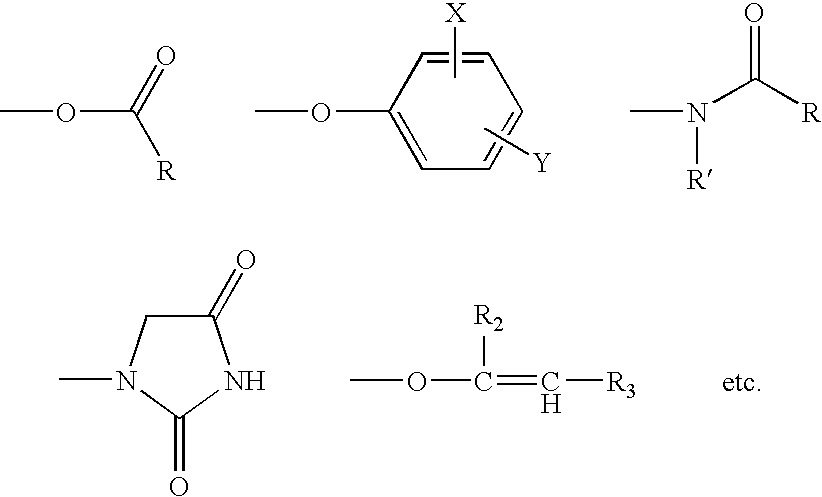
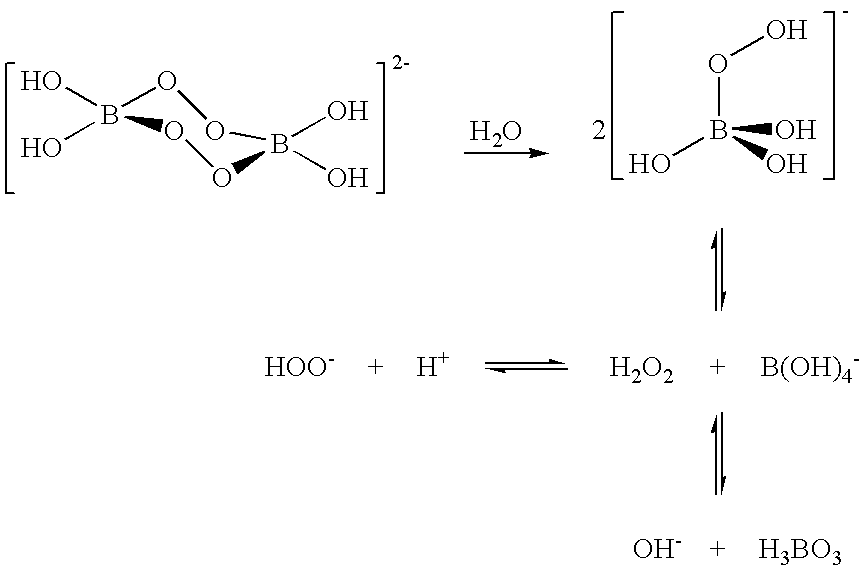
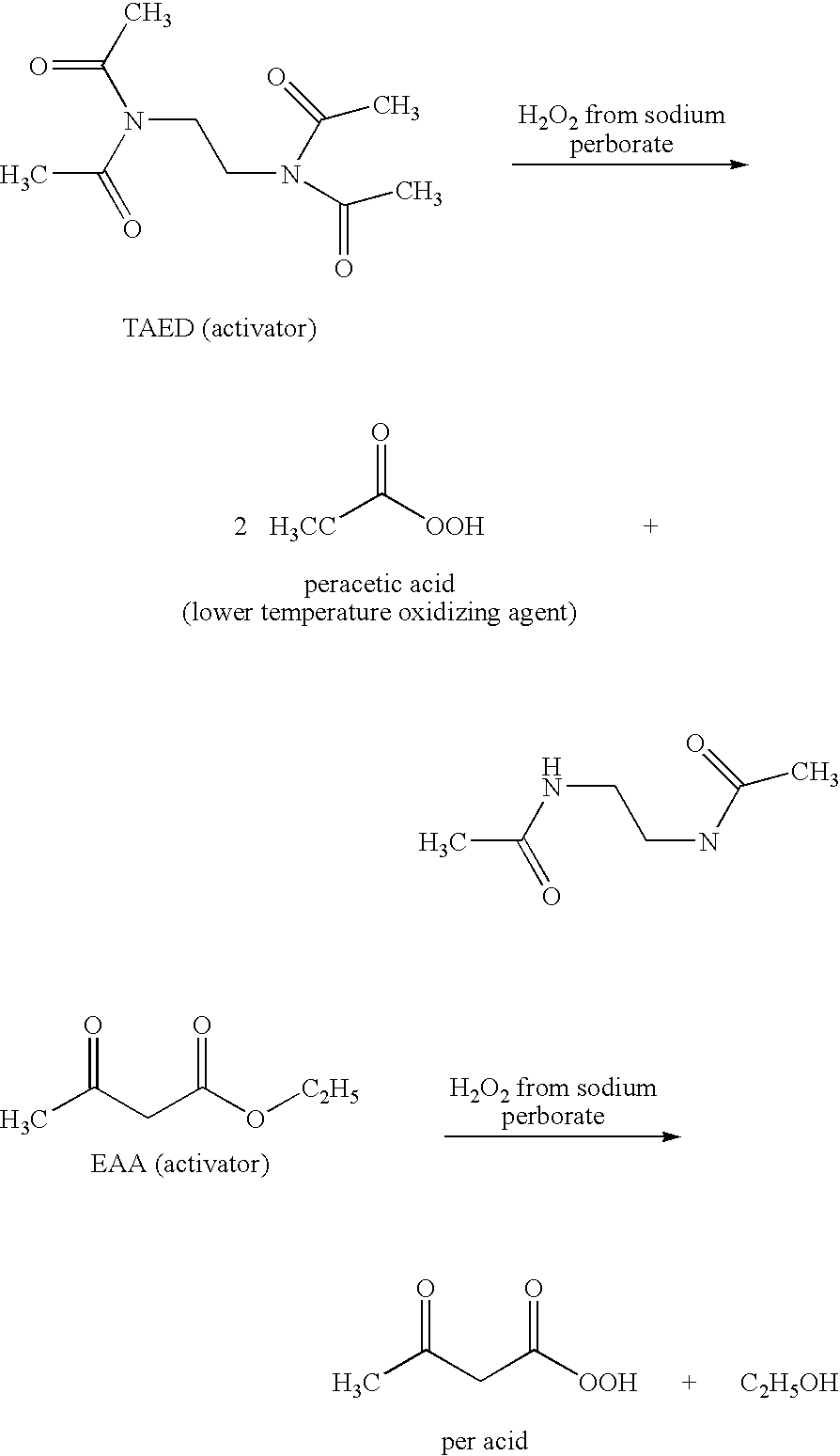
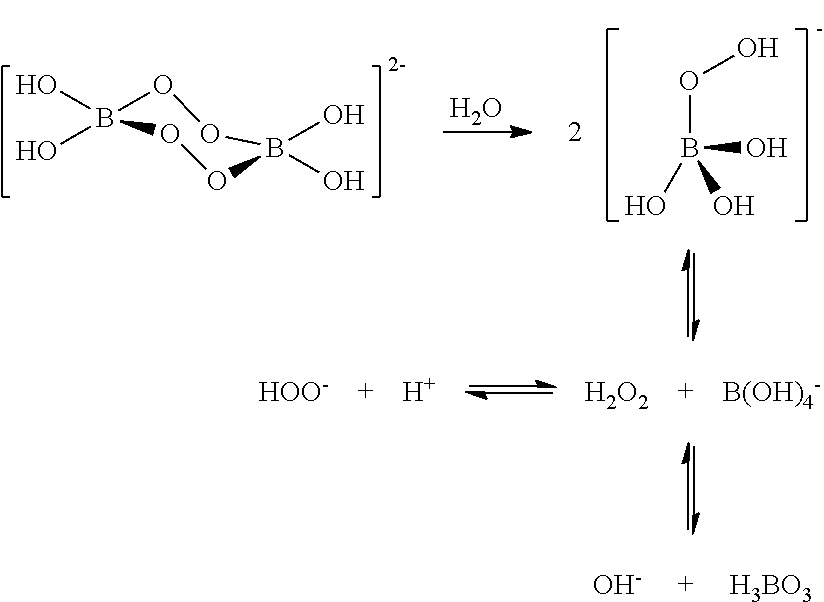
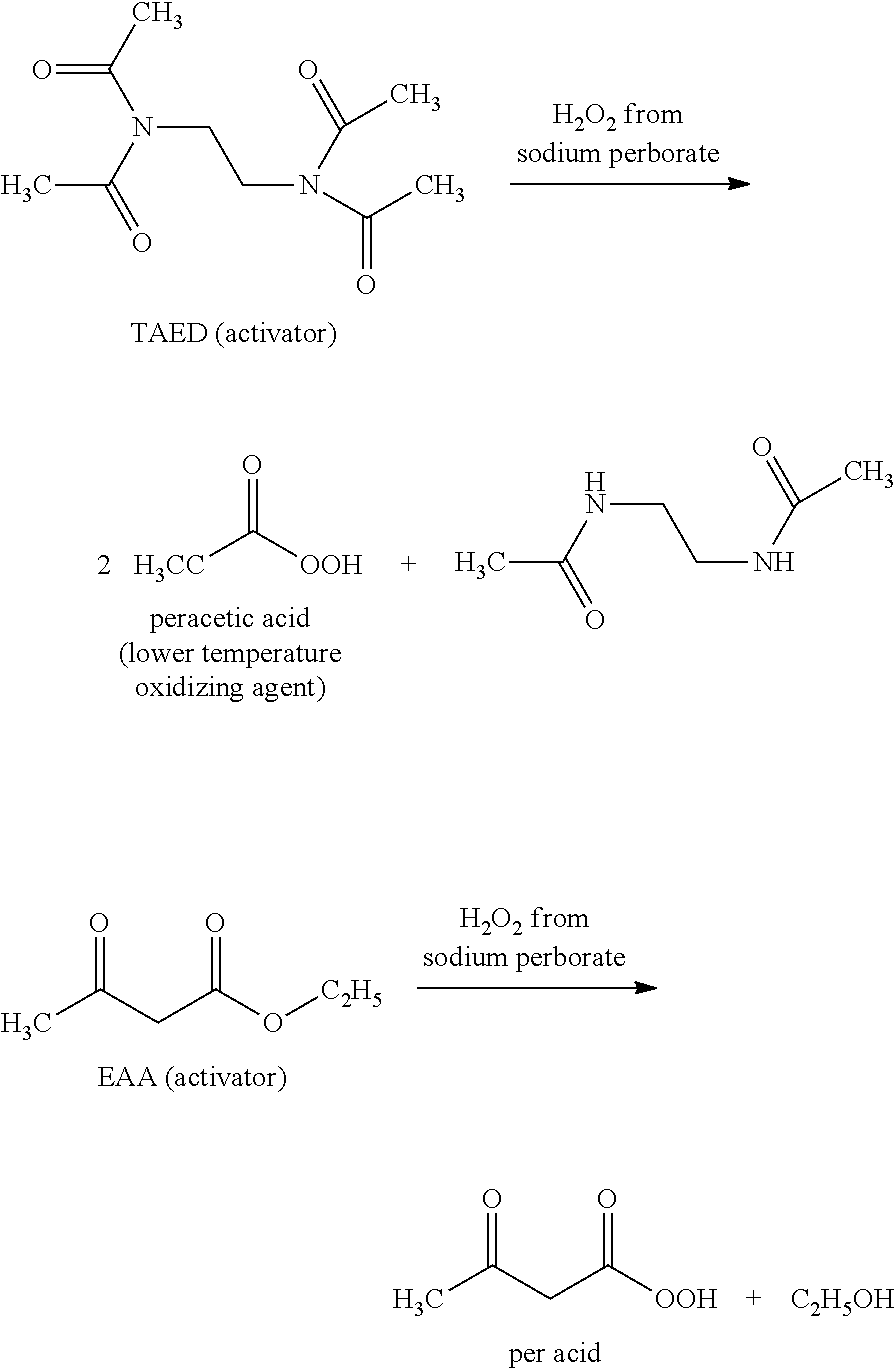
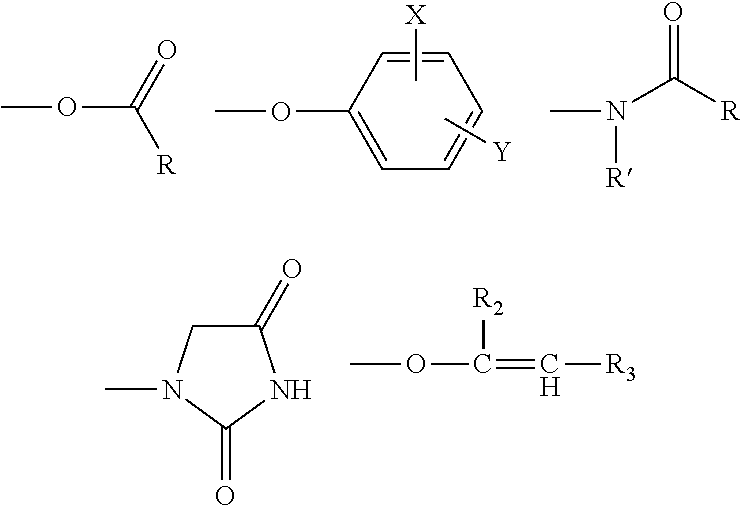
A composition for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation is provided, the composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted to be within an appropriate range for the type of activator. A method for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation, the method comprising the steps of: forming or providing a composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted within an appropriate range for the type of activator; and introducing the composition through a wellbore to treat a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation. The activator can be a water-soluble alkanoyl-donor compound or a chelated transition metal. Preferably, the composition further comprises an iron chelating agent. The composition and method are adapted for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer, such as xanthan. The method has particular applications where the static temperature of the portion of the wellbore or the portion of the subterranean formation to be treated is less than 100° F. (38° C.).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
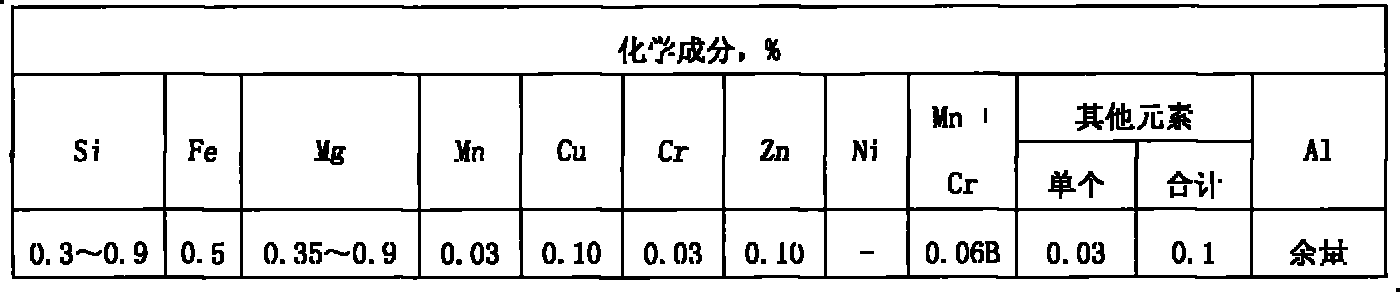
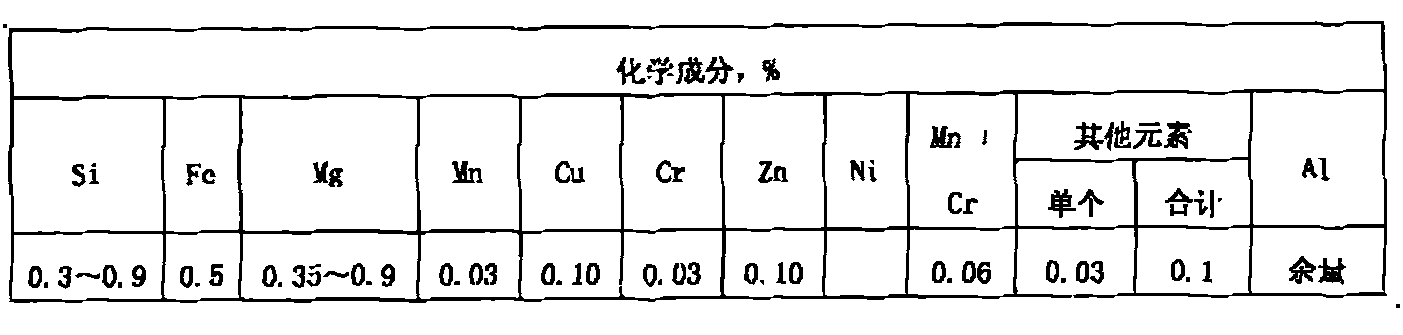
High strength alloy round aluminium rod and production method thereof
ActiveCN101956103AChange the way of beingChange speedMetal rolling arrangementsNitrogenHigh intensity
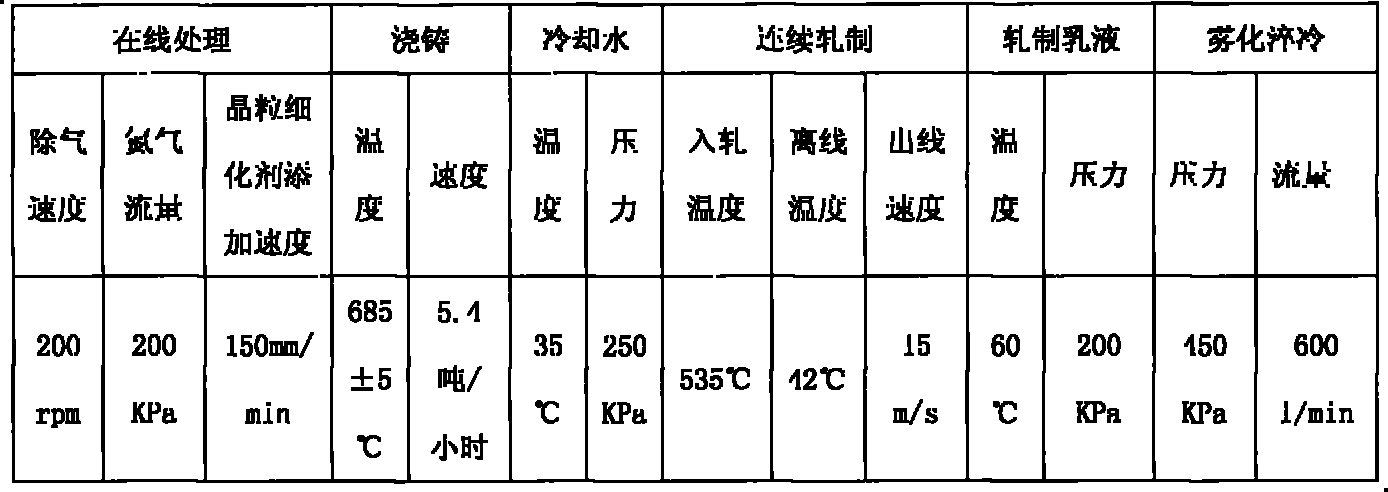
The invention provides a high strength alloy round aluminium rod and a production method thereof. Liquid aluminium with the content of more than 99.5% is added into a smelting furnace, the temperature is controlled to be 760-800 DEG C; silicon and magnesium and iron chelating agent are added, wherein the content of Si is controlled to be less than or equal to 0.6%, the content of Mg is controlled to be 0.3-0.9%, and the content of Fe is controlled to be less than or equal to 0.3%; aluminium melt is prepared, nitrogen is utilized to blow powder refining agent into the solution for refining, the usage amount of refining agent is 1.2kg / ton, and the pressure of nitrogen which is led in is 0.05-0.4MPa, thus obtaining aluminium melt with higher purity; and continuous casting and tandem rolling are carried out on aluminium melt subject to standing, before casting, Al-Ti-B rod is added in a chute at the speed of 150mm / min, so as to carry out online grain refinement treatment on the aluminium melt; and the rolled wire is subject to solid solution strengthening by virtue of an atomization quenching channel. Compared with common pure aluminium electrician round aluminium rod, the Al-Si-Mg alloy round aluminium rod of the invention has the advantages that: tensile strength is improved by 56.5%, the maximum can reach 64.6%; corresponding elongation is increased by 200%, the maximum can reach 228%; and resistivity is increased by only 28%.
Owner:YUNNAN ALUMINUM
Compositions and methods for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer at very low temperature used in downhole well applications
A composition for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation is provided, the composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted to be within an appropriate range for the type of activator. A method for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation, the method comprising the steps of: forming or providing a composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted within an appropriate range for the type of activator; and introducing the composition through a wellbore to treat a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation. The activator can be a water-soluble alkanoyl-donor compound or a chelated transition metal. Preferably, the composition further comprises an iron chelating agent. The composition and method are adapted for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer, such as xanthan. The method has particular applications where the static temperature of the portion of the wellbore or the portion of the subterranean formation to be treated is less than 100° F. (38° C.).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Compositions and methods for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer at very low temperature used in downhole well applications
ActiveUS20080173452A1Reduce the temperatureBreak viscosity increasingFluid removalFlushingWater solubleViscosity
A composition for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation is provided, the composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted to be within an appropriate range for the type of activator. A method for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation, the method comprising the steps of: forming or providing a composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted within an appropriate range for the type of activator; and introducing the composition through a wellbore to treat a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation. The activator can be a water-soluble alkanoyl-donor compound or a chelated transition metal. Preferably, the composition further comprises an iron chelating agent. The composition and method are adapted for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer, such as xanthan. The method has particular applications where the static temperature of the portion of the wellbore or the portion of the subterranean formation to be treated is less than 100° F. (38° C.).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Compositions and methods for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer at very low temperature used in downhole well applications
ActiveUS7923417B2Break viscosity increasingReduce probabilityFluid removalFlushingWater solubleViscosity
A composition for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation is provided, the composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted to be within an appropriate range for the type of activator. A method for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation, the method comprising the steps of: forming or providing a composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted within an appropriate range for the type of activator; and introducing the composition through a wellbore to treat a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation. The activator can be a water-soluble alkanoyl-donor compound or a chelated transition metal. Preferably, the composition further comprises an iron chelating agent. The composition and method are adapted for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer, such as xanthan. The method has particular applications where the static temperature of the portion of the wellbore or the portion of the subterranean formation to be treated is less than 100° F. (38° C.).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method and device for degrading nitrobenzene waste water in high gravity field through catalytic ozonation
ActiveCN104710000AAvoid it happening againImprove performanceWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsTreatment costsHydroxy compound
The invention provides a method and device for degrading nitrobenzene waste water in a high gravity field through catalytic ozonation, belongs to the technical field of nitrobenzene waste water ozonation degradation, and solves the problem that sedimentation of ferrous ions is caused when the initial pH value of the waste water is 7 to 10 in the conventional catalytic ozonation treatment method of nitrobenzene waste water. The method comprises the following steps: a ferrous iron chelating agent is mixed with nitrobenzene waste water of which the initial PH value is 7-10, the mixed solution is introduced into a high gravity reactor to react with ozone gas, and ozone dissolved in catalytic water generates hydroxyl free radicals, so that nitrobenzene compounds are degraded through ozonation. When the method provided by the invention is compared with the conventional bubbling reaction, the mass transfer rate of ozone is improved by two times; and besides, the ferrous iron chelating agent is combined with an ozonation process, therefore, ozone in the waste water is quickly decomposed, a lot of hydroxyl free radicals are generated, organic pollutants are quickly decomposed, and the oxidation efficiency is doubled; the process is simple, the treatment cost is reduced to the largest extent, the removal rate of nitrobenzene compounds reaches 95% or above, the mineralization rate reaches 80%, and the utilization ratio of ozone is improved by 1 to 2 times.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Compositions and methods for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer at very low temperature used in downhole well applications
A composition for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation is provided, the composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted to be within an appropriate range for the type of activator. A method for treating a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation, the method comprising the steps of: forming or providing a composition comprising: (a) water; (b) a source of hydrogen peroxide, and (c) an activator for the source of hydrogen peroxide; wherein the pH of the composition is adjusted within an appropriate range for the type of activator; and introducing the composition through a wellbore to treat a portion of a wellbore or a portion of a subterranean formation. The activator can be a water-soluble alkanoyl-donor compound or a chelated transition metal. Preferably, the composition further comprises an iron chelating agent. The composition and method are adapted for breaking a viscosity increasing polymer, such as xanthan. The method has particular applications where the static temperature of the portion of the wellbore or the portion of the subterranean formation to be treated is less than 100° F. (38° C.).
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Astaxanthin-containing aqueous composition, cosmetic preparation, and method for suppressing degradation of astaxanthin
ActiveCN103025306AExcellent stability over timeOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsBetaxanthinsAstaxanthin
Disclosed are: an aqueous cosmetic preparation which contains at least (A) astaxanthin, (B) 20 [mu]g / L or more of iron and (C) an iron chelating agent; and a method for suppressing degradation of astaxanthin, wherein an aqueous composition containing at least (A) astaxanthin and (B) 20 [mu]g / L or more of iron is made to contain (C) an iron chelating agent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Conjugate of 5-aminolevulinic acid and 3-pyridone-4-ketone and preparation method as well as use thereof
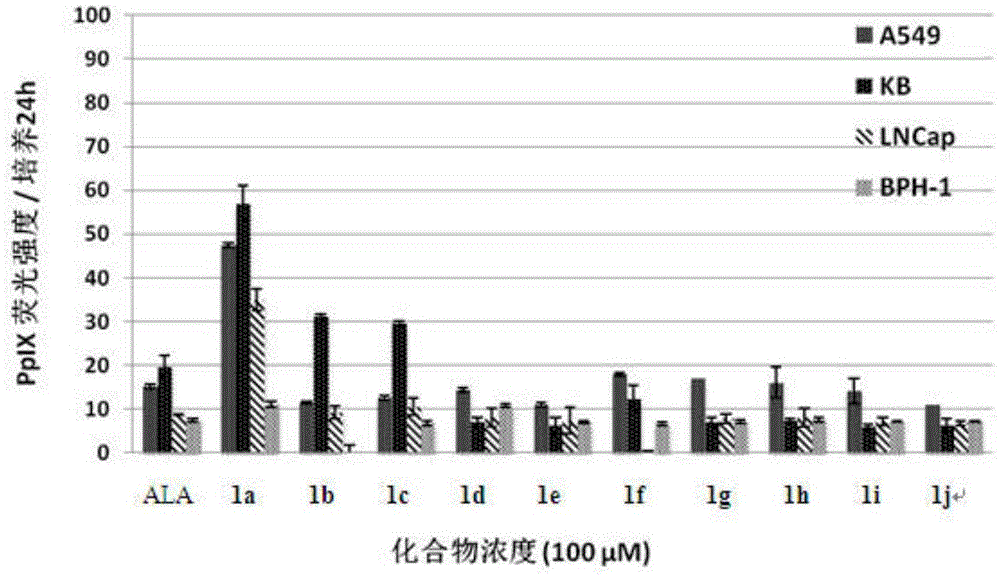
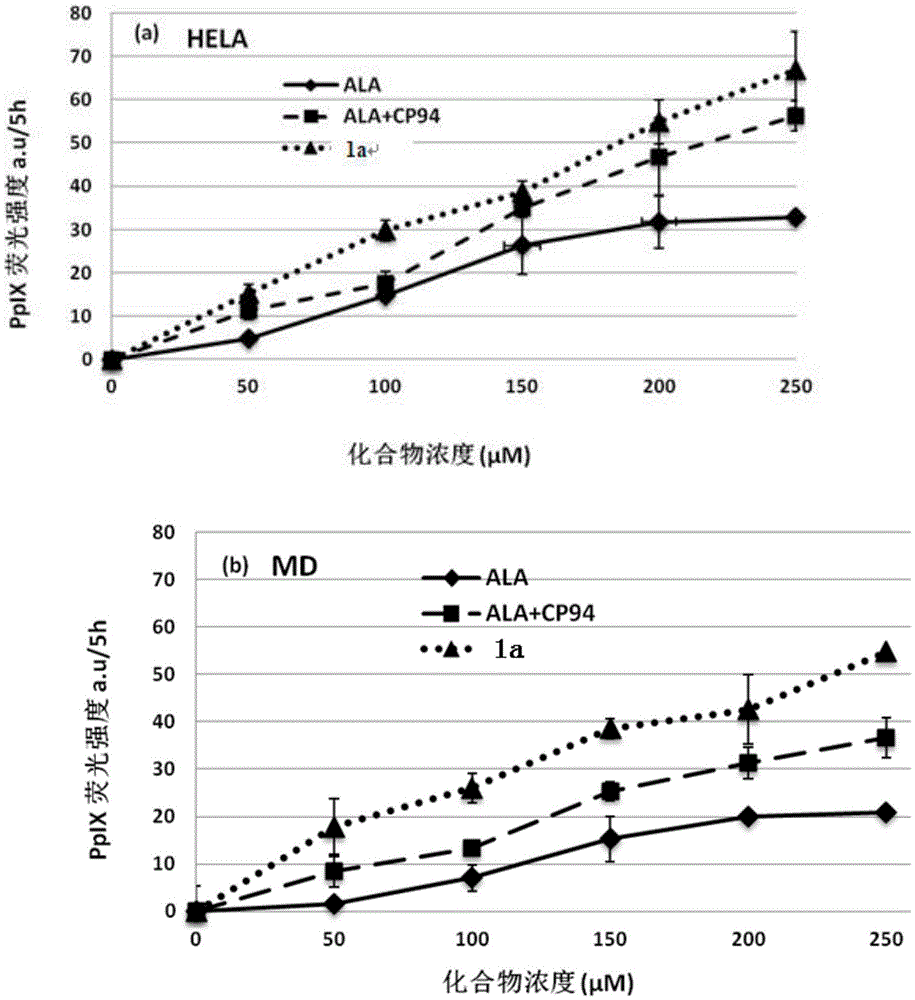
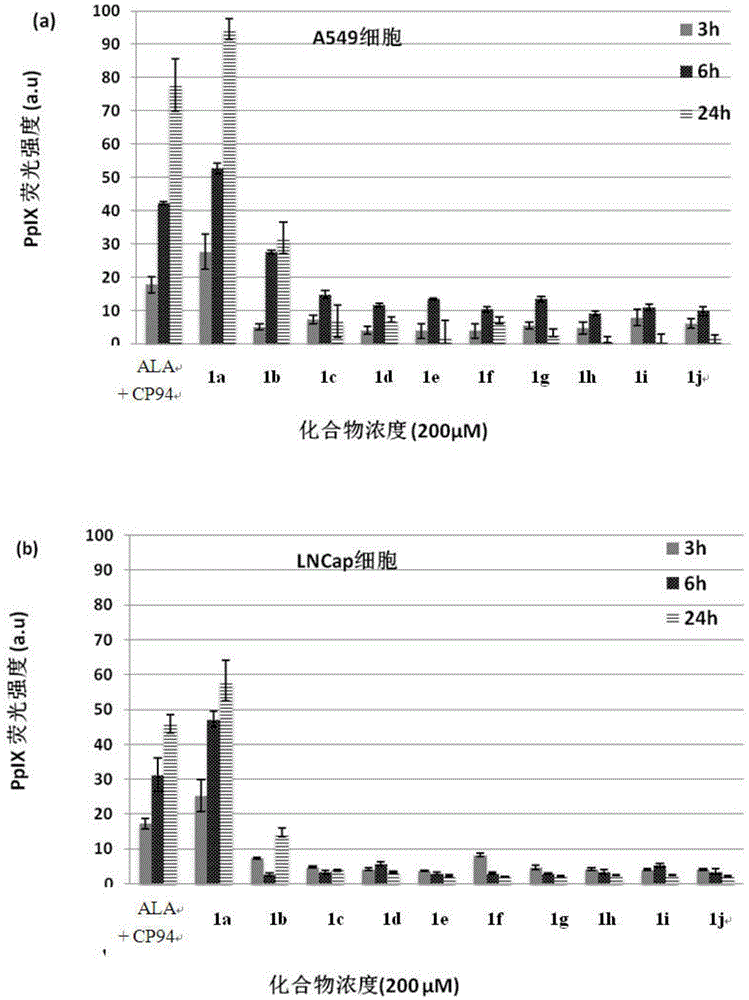
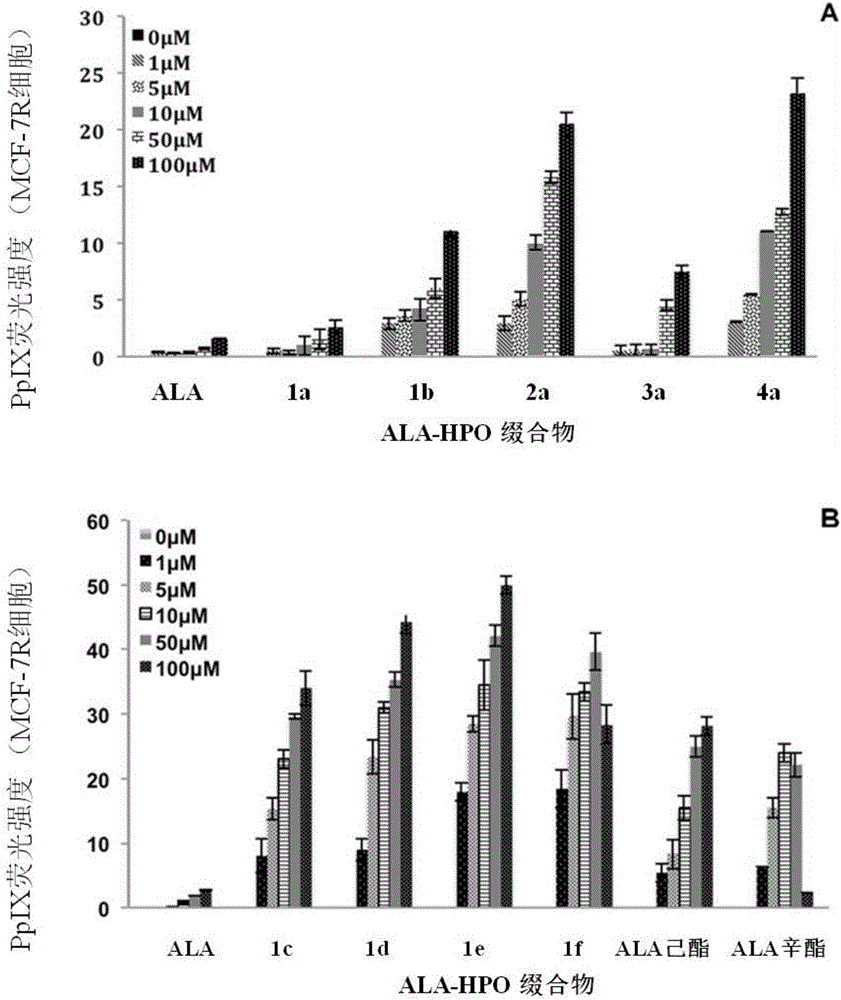
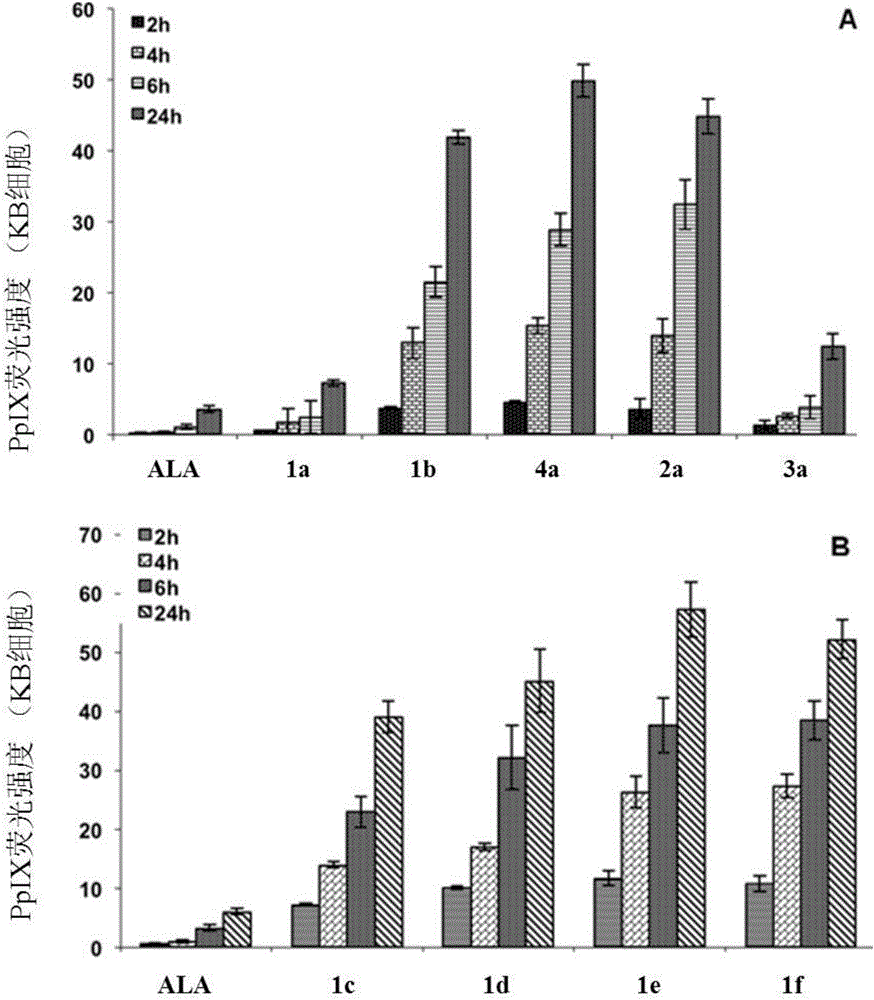
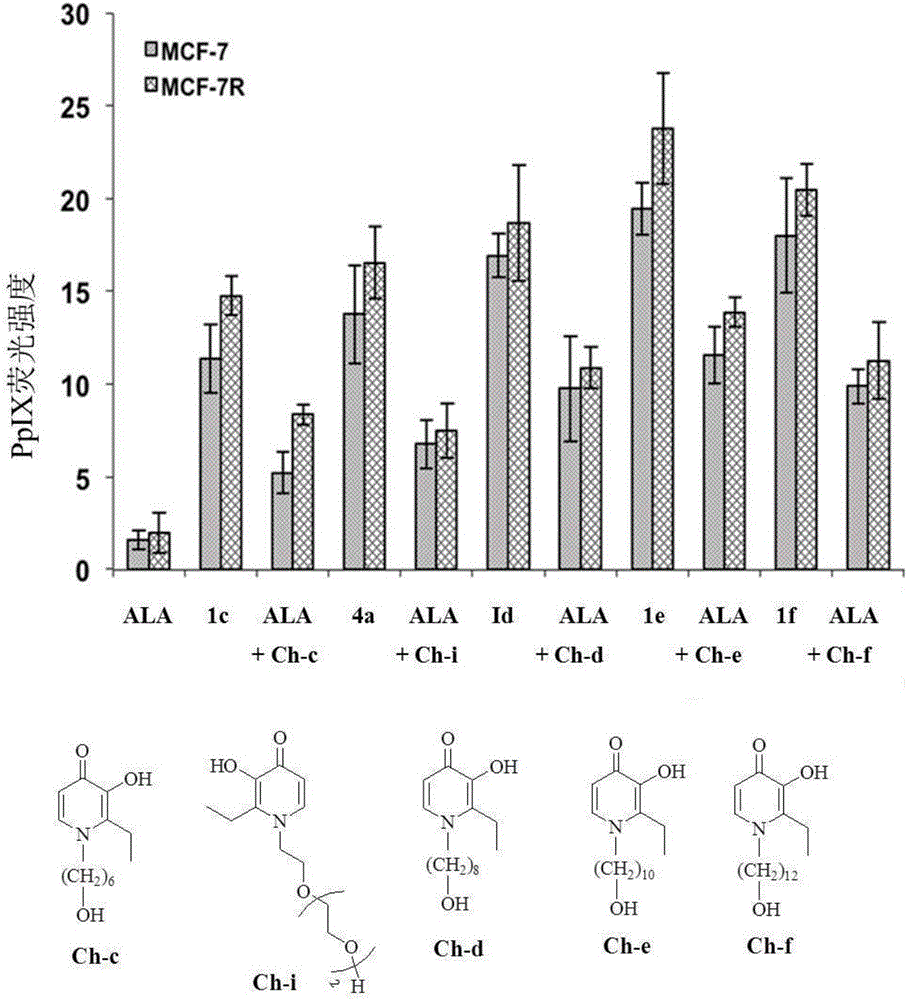
ActiveCN105481946AIncreased PpIX concentrationPhototoxicDipeptide ingredientsAntiviralsAmino-Levulinic AcidAminolevulinic Acid Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a conjugate of 5-aminolevulinic acid and 3-pyridone-4-ketone. The conjugate is a conjugate of the 5-aminolevulinic acid and the 3-pyridone-4-ketone as an iron chelating agent, and is an ALA-HPO conjugate; the structural formula of the ALA-HPO conjugate is shown in the description, wherein R is alkyl or substituent alkyl; R(minute) is from natural amino acids. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the ALA-HPO conjugate. The invention also discloses the use of the ALA-HPO conjugate, i.e., the ALA-HPO conjugate is used for preparing drugs for photodynamics therapy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
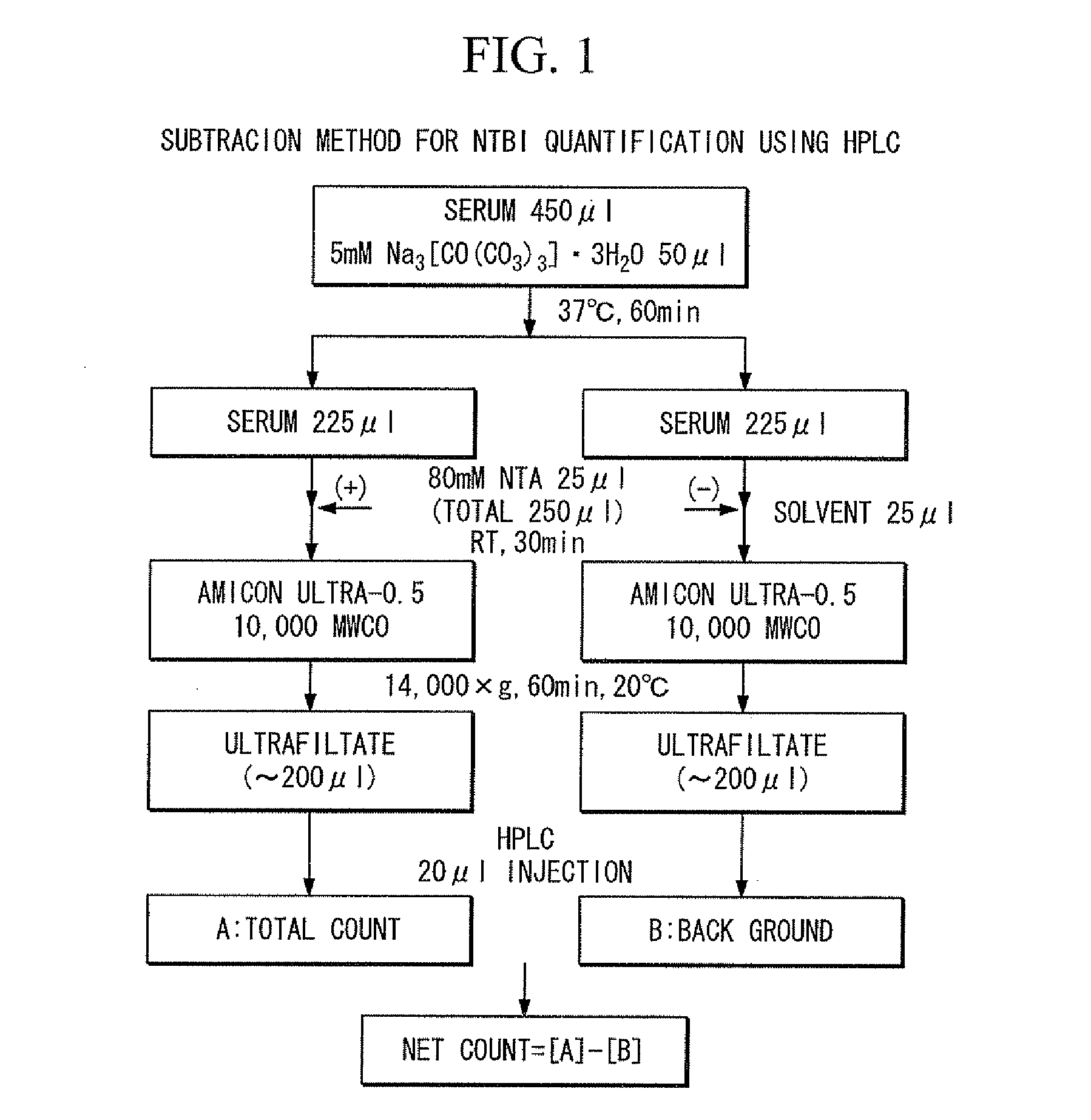
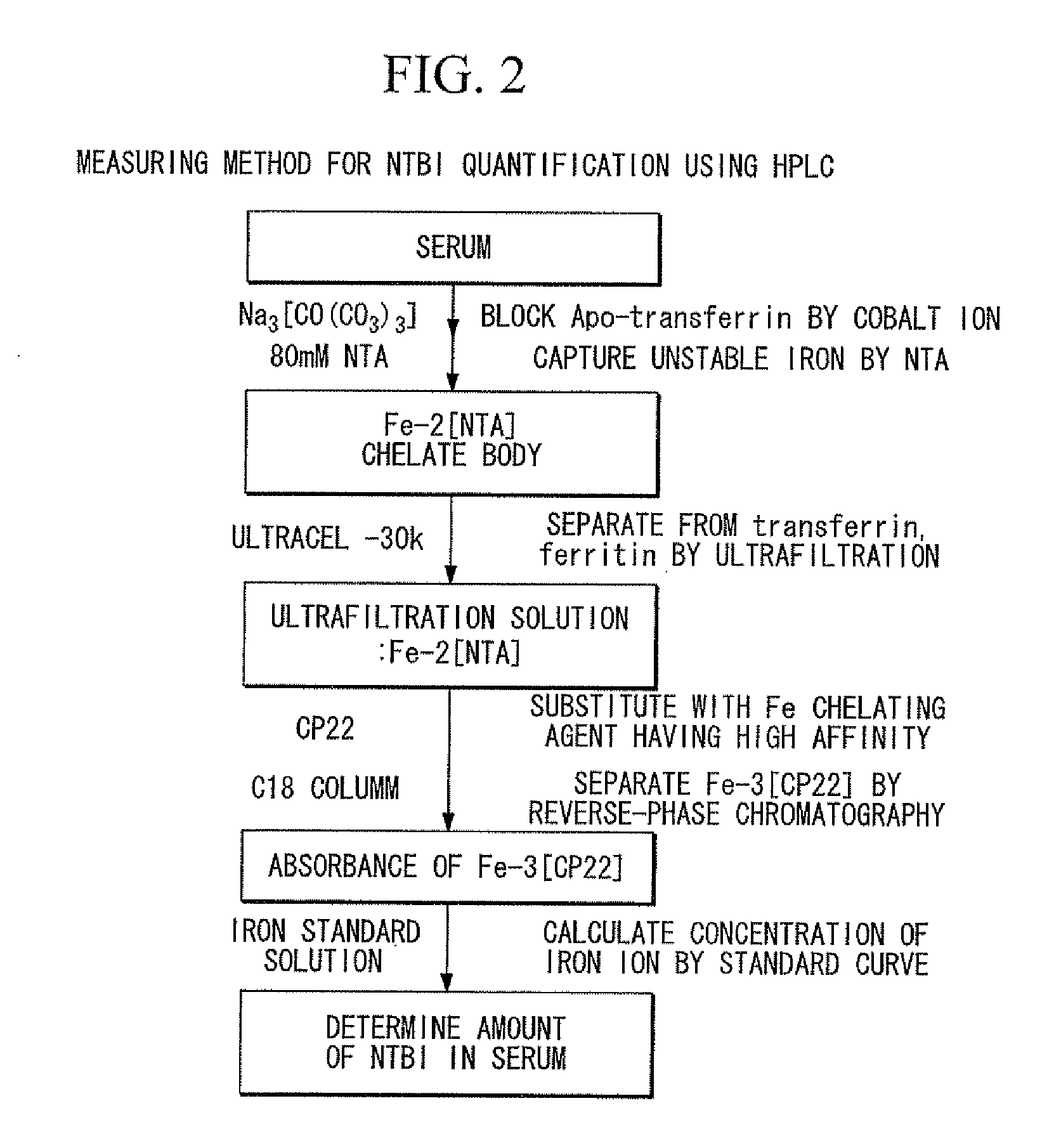
Iron chelating agent, method for producing same, method for determining amount of iron ions and method for trapping iron ions
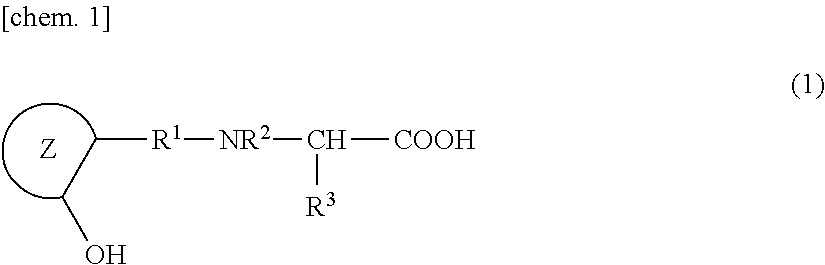
The present invention provides an iron chelating agent which can selectively chelate iron ions. The iron chelating agent of the present invention includes a compound represented by the following formula (1) or a salt thereof (wherein, ring Z represents an aromatic hydrocarbon ring or an aromatic heterocyclic ring; R1 represents an alkylene group; R2 and R3 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a hydrocarbon group or a group having chelating ability; and the total coordination number of the groups represented by R2 and R3 is 1 or 2.)
Owner:NAT UNIV ASAHIKAWA MEDICAL UNIV +1
Astaxanthin-containing aqueous composition, cosmetic preparation, and method for suppressing decomposition of astaxanthin
InactiveUS20130131184A1Improve stabilityAvoid decompositionCosmetic preparationsBiocideDecompositionAstaxanthin
Disclosed are an aqueous cosmetic preparation including at least astaxanthin, 20 μg / L or more of iron ions, and an iron chelating agent, and a method for suppressing the decomposition of astaxanthin in which an iron chelating agent is included in an aqueous composition including at least astaxanthin and 20 μg / L or more of iron ions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Compositions and Method for Treating Out Hydrogen Sulfide and Preventing Settling of Precipitate in an Environmentally Responsible Drilling and Packer Fluid
ActiveUS20130324442A1Easy to controlReduce differential pressureDrilling compositionIron ChelatingFerrous Gluconate
An environmentally responsible iron chelating additive and method for removing hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ions from drilling and packer fluids and preventing settling of precipitates. Iron chelating agents selected from the group consisting of ferrous lactate, ferrous gluconate, ferrous bis glycinate, ferrous citrate, ferrous acetate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous succinate, ferrous sacchrate, ferrous tartarate, ferrous glycine sulfate, ferrous glutamate, ferrous ascorbate, ferrous polymaltose, or a combination thereof, may be used. When the fluids are oil based, the iron chelating agents are added to the water phase of an emulsion, and the emulsion is added to the fluid. Viscosifiers may also be added to the drilling fluid with the emulsion.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Compositions and method for treating out hydrogen sulfide and preventing settling of precipitate in an environmentally responsible drilling and packer fluid
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
5-aminolevulinic acid/3-hydroxyl pyridone conjugate, preparation method therefor and use of 5-aminolevulinic acid/3-hydroxyl pyridone conjugate
ActiveCN106478493AImprove biological activityStrong phototoxicityOrganic chemistryPhotodynamic therapyAmino-Levulinic AcidAminolevulinic Acid Hydrochloride
The invention discloses conjugates of 5-aminolevulinic acid and 3-hydroxyl pyrid-4-one. The conjugates are conjugates of 5-aminolevulinic acid and an iron chelating agent, i.e., 3-hydroxyl pyrid-4-one and are ALA-HPO conjugates 1 to 4 separately. The invention further simultaneously discloses a preparation method for the conjugates of 5-aminolevulinic acid and 3-hydroxyl pyrid-4-one and use of the conjugates of 5-aminolevulinic acid and 3-hydroxyl pyrid-4-one. The conjugates can be used for preparing photodynamic therapy drugs and can also be used for preparing drugs for treating skin cancer, lung cancer or verruca acuminata.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Formamide pyridone iron chelating agent derivative with potential multi-target anti-AD activity as well as preparation method and application thereof
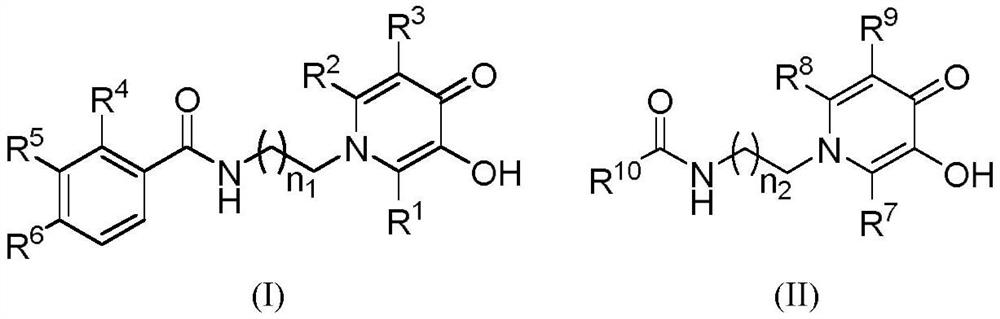
ActiveCN111995567AHas iron ion chelating propertiesHas MAO-B inhibitory activityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryOxidative enzymePharmaceutical medicine
The invention provides a formamide pyridone iron chelating agent derivative shown as a formula (I) or a formula (II) which is described in the specification and a preparation method and application thereof. The formamide pyridone iron chelating agent derivative shown in the formula (I) or the formula (II) and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof have the effects of inhibiting monoamine oxidase, chelating metal iron ions, resisting A beta and resisting oxidation activity. The derivative can be used for preparing medicines for resisting Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease or other diseases treated by inhibiting monoamine oxidase, chelating metal iron ions, resisting A beta and resisting oxidation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Application of artemisinin and/or iron chelating agent serving as parasite killing medicaments
InactiveCN106074502ATo achieve the purpose of killing insectsOrganic active ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsBiological bodyMedicine
The invention relates to application of artemisinin and / or an iron chelating agent serving as parasite killing medicaments. According to the specific scheme, artemisinin is used as a killing medicament for ordinary parasites or iron chelating agent resistant parasites, or the iron chelating agent is used as a killing medicament for the ordinary parasites or artemisinin resistant parasites, or a combined medicament of artemisinin and the iron chelating agent serves as a killing medicament for the artemisinin resistant parasites or the iron chelating agent resistant parasites. Compared with the prior art, on the basis of the principle that artemisinin or derivatives thereof block iron utilization of organisms and the principle that the iron chelating agent blocks iron utilization of the organisms, artemisinin or derivatives thereof and the iron chelating agent are combined and selected for use, and the killing effect on artemisinin resistant strains or iron chelating agent resistant strains can be improved.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Water-soluble fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107935664AScientific Mixing RatioTo offer comfortAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersSolubilityPhosphate
The invention relates to water-soluble fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The water-soluble fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40 to 55 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 10 to 15 parts of ammonium sulfate, 5 to 10 parts of potassium sulphate, 20 to 25 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 0.35 to 1 part of a copper chelating agent, 0.35 to 1 part of a zinc chelating agent, 0.4 to 1.1 parts of an iron chelating agent, and 0.35 to 0.9 part of borax. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting a nitrogen source, a phosphorus source and a potassium source into a dissolving tank, adding water to prepare paste, then putting the paste into another dissolving tank, adding microelements to prepare paste again, putting the produced paste intogranulation equipment to prepare semi-finished product fertilizer granules, performing drying, screening and cooling processes on the semi-finished product fertilizer granules, so as to obtain the finished product, namely the water-soluble fertilizer granules. The water-soluble fertilizer is low in production cost, high in water solubility, and complete in nutrient element coverage, realizes comprehensive utilization of waste, and eliminates environmental pollution.
Owner:襄阳华虹高科新材料有限公司
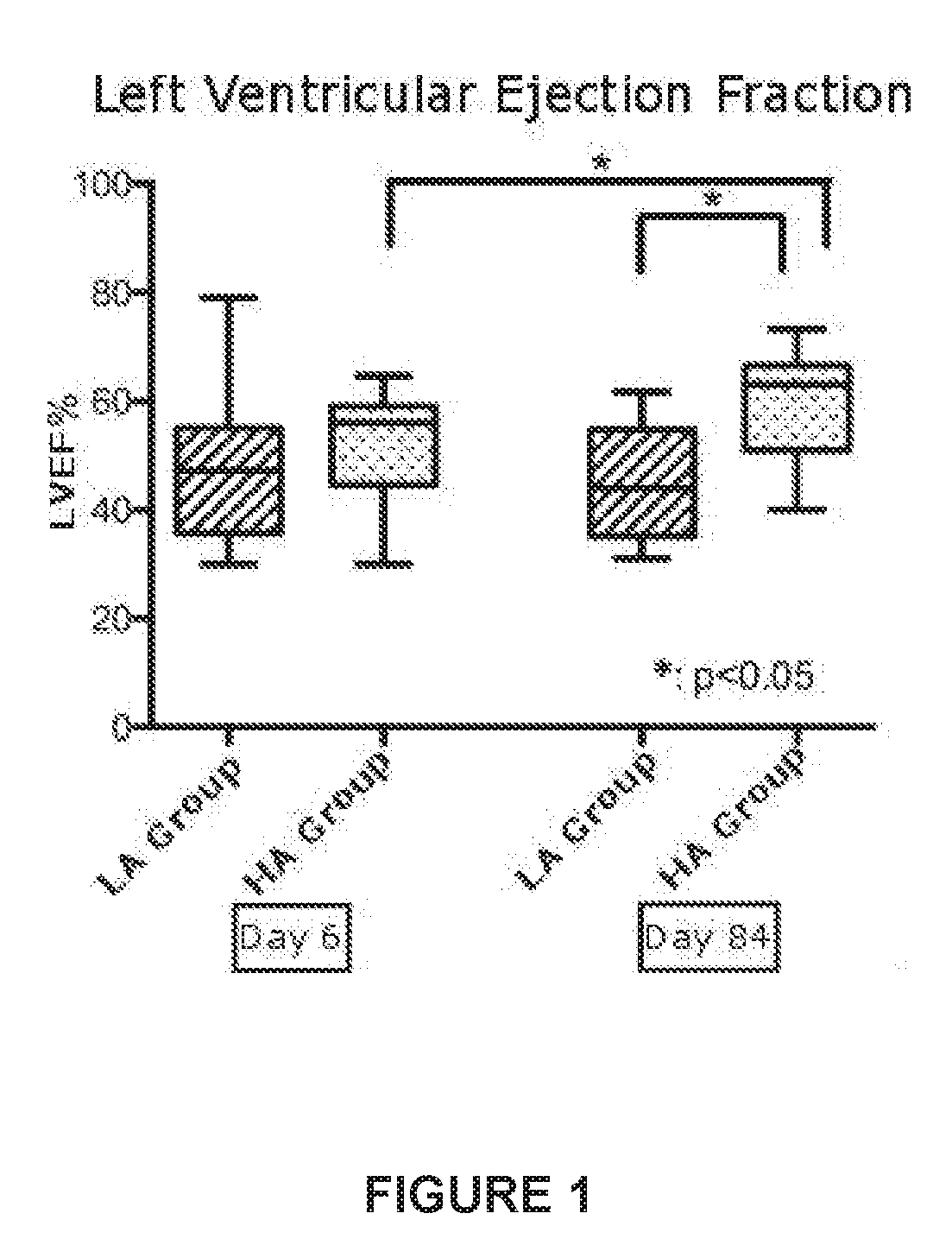
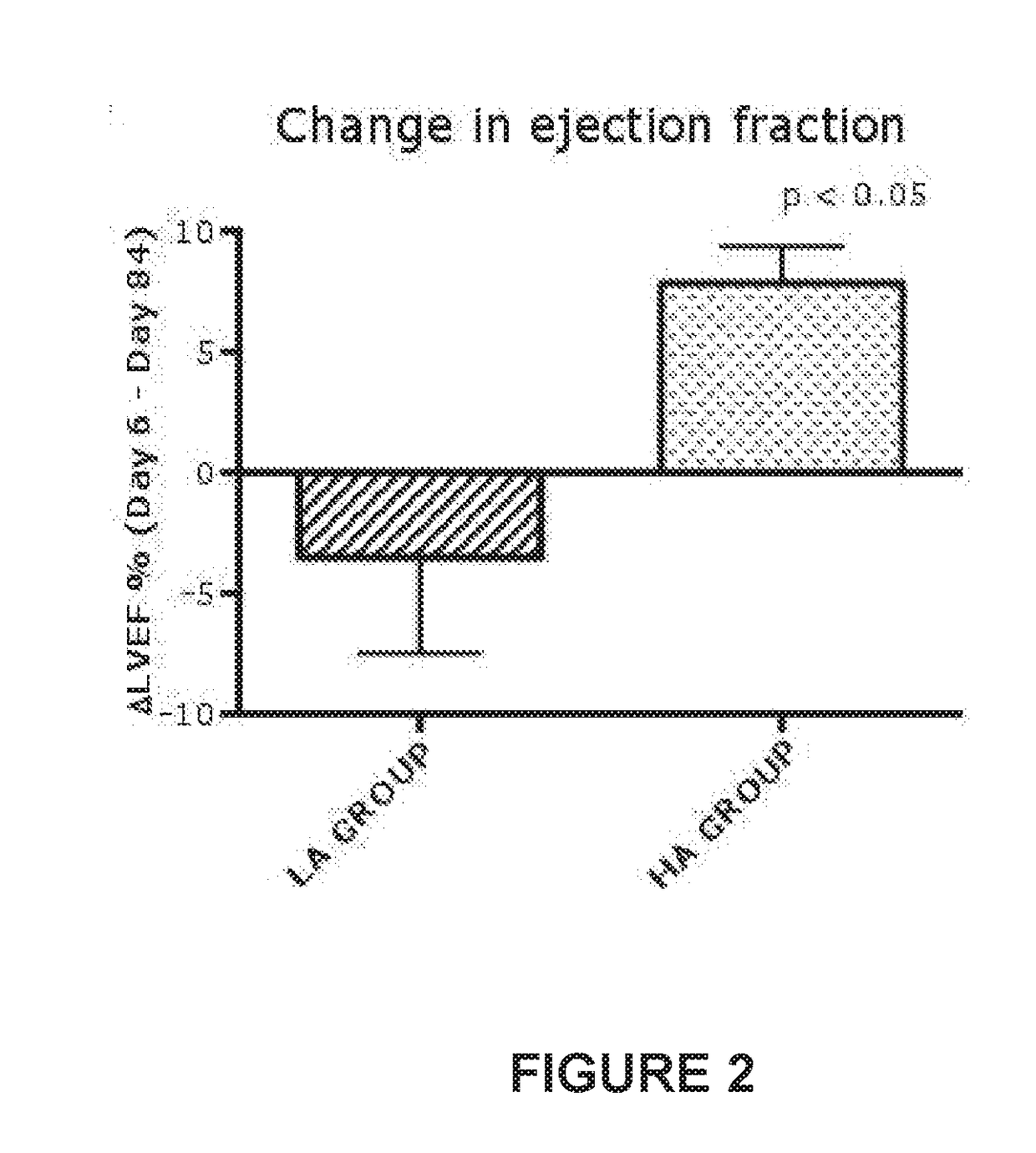
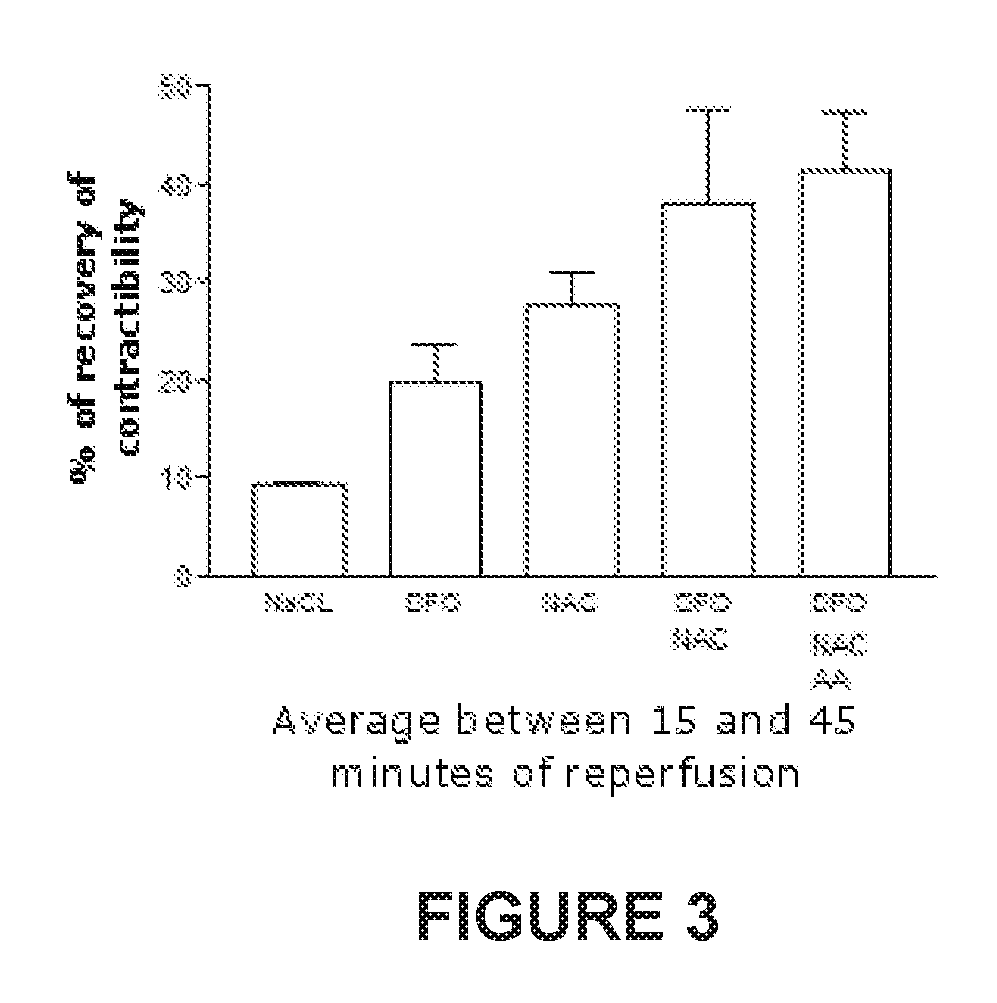
Injectable antioxidant formulation for intravenous use of sodium ascorbate in high dosage, n-acetyl cysteine, and deferoxamine; method of administration and use for preventing injury due to reperfusion; and kit
InactiveUS20170333393A1Avoid injuryPromote resultsPharmaceutical containersPharmaceutical delivery mechanismReperfusion injurySodium ascorbate
The invention refers to an injectable antioxidant formulation for intravenous use comprising sodium ascorbate in high dosage as a first antioxidant agent, N-acetyl cysteine as a second oxidant agent and deferoxamine as an iron chelating agent, plus pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. And an administration method of said formulation that results in a synergic and improved effect to prevent injury due to reperfusion in an organ. In particular, to prevent injury due to early and late reperfusion in patients diagnosed with acute myocardium infarction and indication of primary coronary angioplasty. The invention further refers to the use of the formulation to prevent injury due to reperfusion in patients with acute myocardium infarction, subjected to primary coronary angioplasty.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
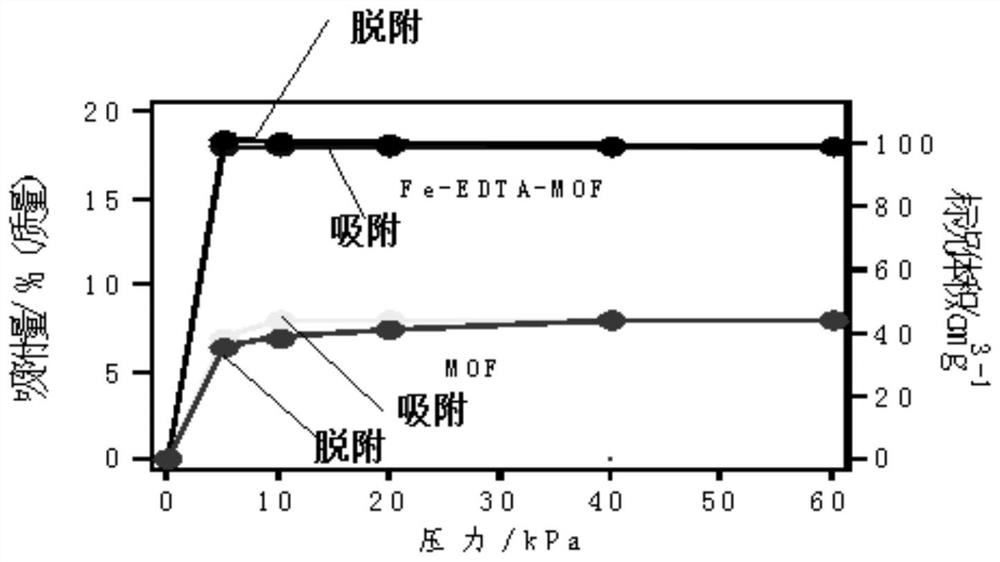
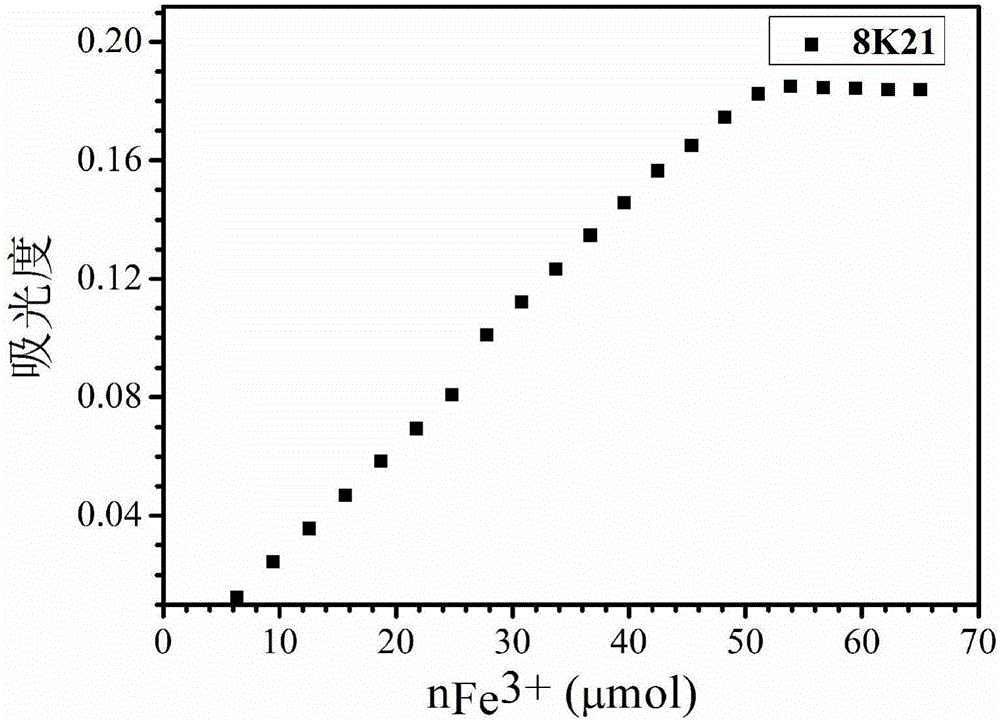
Iron-containing chelating agent embedded MOF material as well as synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN112387251AAchieve adsorptionImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationPhysical chemistryThermal desorption
The invention discloses an iron-containing chelating agent embedded MOF material, a synthesis method and application, the synthesis method comprises the steps of synthesizing the MOF material and synthesizing the iron-containing chelating agent embedded MOF material by taking the MOF material and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid chelated iron as raw materials, encapsulating the ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid chelated iron in internal gaps of the MOF material to obtain the iron-containing chelating agent embedded MOF material. The adsorption performance of the MOF material is greatly improvedby utilizing a large number of chemical bonds easy for oxygen binding in ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid and the affinity of Fe element to oxygen, and the adsorbed material can be subjected to thermal desorption, so that the reutilization of the material is realized.
Owner:TIBET UNIV
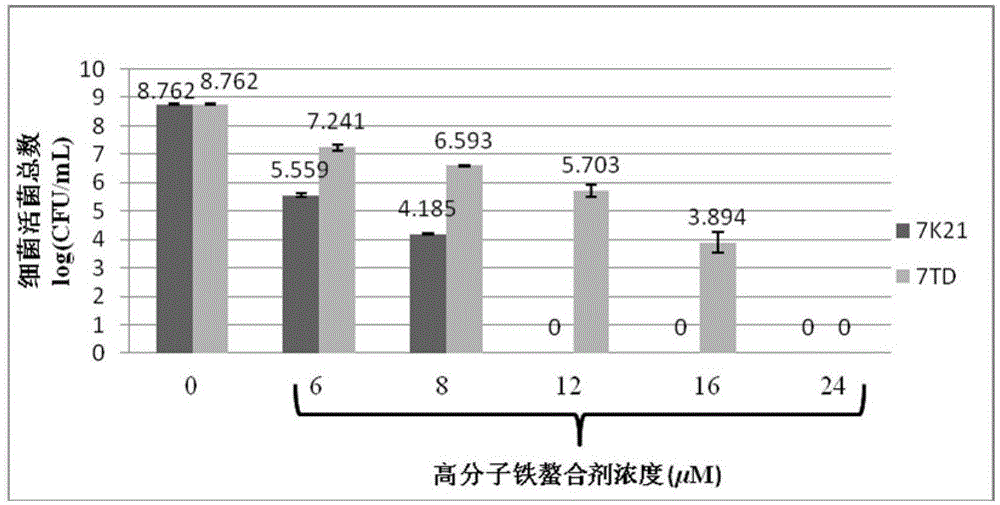
Use of 3-hydroxy-4-pyridone high-molecular iron chelating agent
ActiveCN105030819AHas antibacterial propertiesGood antibacterial effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectIron Chelating
The invention discloses a use of a 3-hydroxy-4-pyridone high-molecular iron chelating agent. The 3-hydroxy-4-pyridone high-molecular iron chelating agent has antibacterial effects and can be used as an antibacterial material. The 3-hydroxy-4-pyridone high-molecular iron chelating agent has excellent effects of resisting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. According to a mechanism of cation simulative antibacterial peptide formation from tertiary amine or secondary amine positive ion structures in a high-molecular iron chelating agent, interaction between a positive charge area and a negative charge area on a cell membrane, and iron chelating effects of an iron chelating agent, the normal growth environment around bacteria is destroyed and bacterium growth is inhibited so that bacteria cannot normally grow. The 3-hydroxy-4-pyridone high-molecular iron chelating agent cannot be absorbed by skin because of macro-molecule characteristics, does not produce toxic or side effects and can be used as an antibacterial material with dual antibiosis effects.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Immediate release pharmaceutical composition of iron chelating agents
ActiveUS10888519B2High drug loadingImprovement ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderPharmaceutical drugDeferasirox
The present invention relates to a stable, immediate release solid oral pharmaceutical compositions comprising iron chelating agents like Deferasirox and at least one pharmaceutical acceptable excipient wherein the composition is free of glidant. Prior art discloses various technical challenges and suggest restrictive and complex solutions for the development of immediate release dosage forms of Deferasirox such as utilizing a large number of excipients or non-conventional formulation techniques. The glidant free immediate release solid oral pharmaceutical composition of Deferasirox, prepared as per present invention exhibited desirable technical attributes like pharmaceutical stability, flow properties and comparable dissolution, bioequivalence against reference listed drug.
Owner:JUBILANT GENERICS
Method of increasing metabolism
InactiveUS20110003013A1Lower levelImprove liver functionHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideEnergy expenditureObesity
The present invention provides a method for increasing metabolism and / or energy expenditure in a subject, e.g., to treat or prevent obesity and / or a related condition and / or to reduce adiposity, the method comprising increasing the level and / or activity of Hypoxia Induced Factor 1α (HIF-1α) in a cell, tissue or organ of the subject, thereby increasing metabolism in the subject. The present invention also provides a method for increasing metabolism in a subject, the method comprising administering an iron chelating agent to the subject, thereby increasing metabolism in the subject.
Owner:GAVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES ST VINCENTS HOSPITAL
Use of siderophores to increase the current efficiency of iron plating solutions
InactiveUS7122105B1Photography auxillary processesFrom normal temperature solutionsFluvibactinVibriobactin
A method of electroplating iron or an iron alloy with a solution containing an iron-chelating agent to catalytically cycle the undesirable Fe(III) species back to Fe(II) for electroplating. The iron-chelating agents may be siderophores, specifically, for example, desferrioxamine E, desferrioxamine B, alcaligin, bisucaberin, putrebactin, rhodotorulic acid, enterobactin, vibriobactin, azotochelin, myxochelin, fluvibactin, and serratiochelin.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Fixed dose pharmaceutical composition comprising deferasirox and deferiprone
InactiveUS20150246027A1Increase the areaImprove solubilityBiocidePowder deliveryDeferasiroxDeferiprone
The present invention relates to a fixed dose pharmaceutical composition comprising iron chelating agents.
Owner:CIPLA LTD
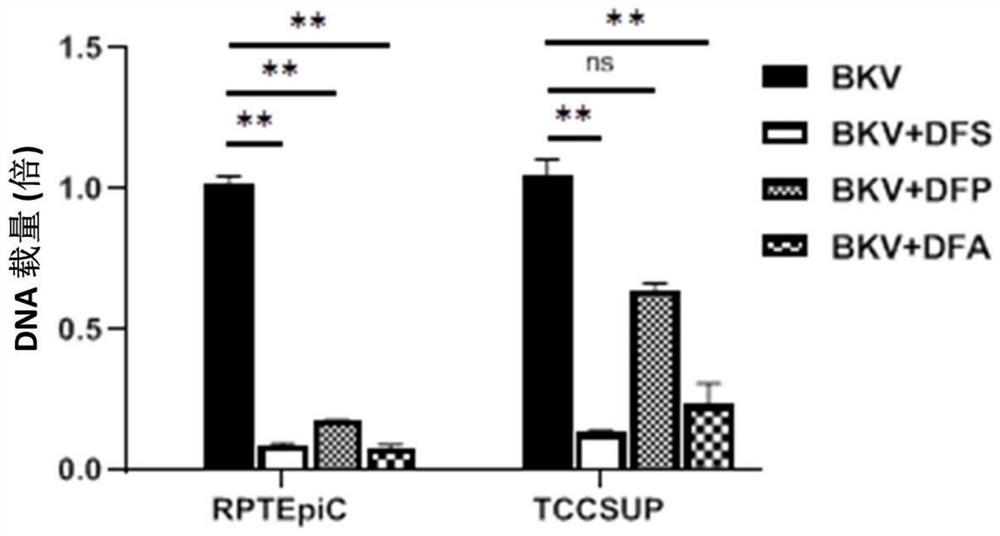
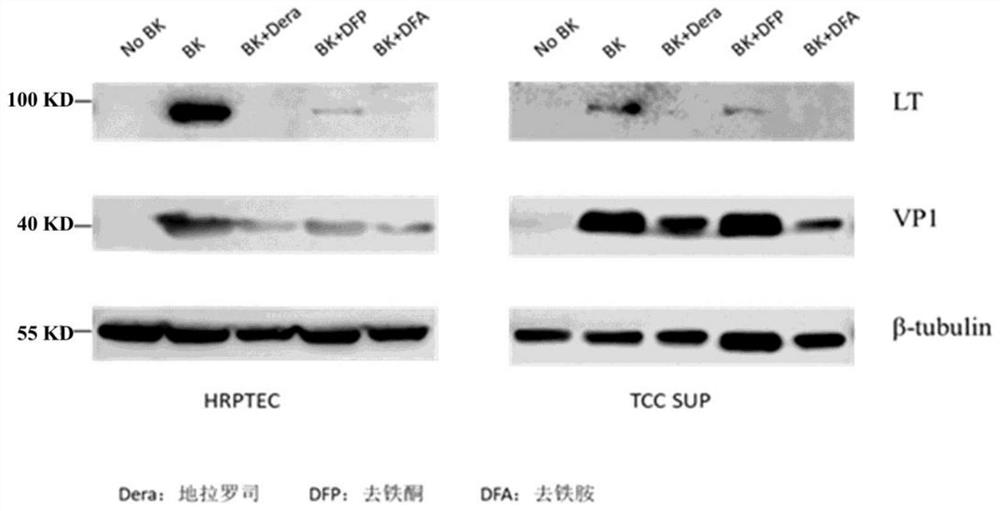
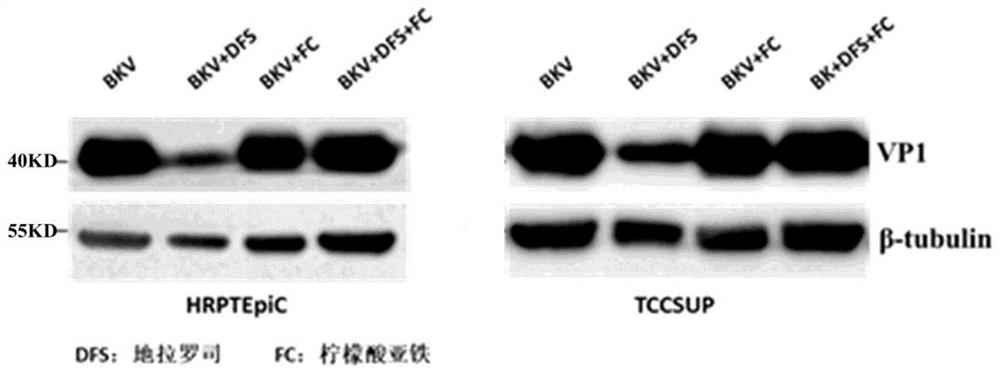
Application of iron chelating agent in preparation of medicine for treating or preventing polyomavirus infection
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, in particular to an application of an iron chelating agent in preparation of a medicine for treating or preventing polyoma virus infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
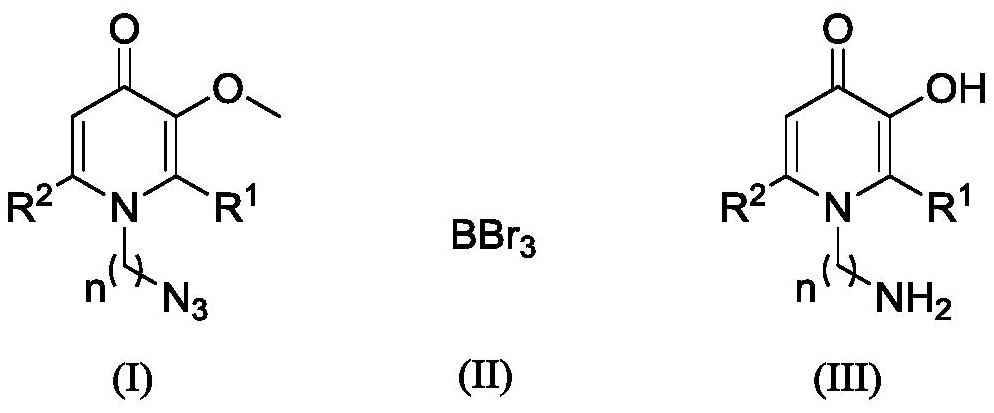
A kind of synthetic method of amino-containing hydroxypyridone compound
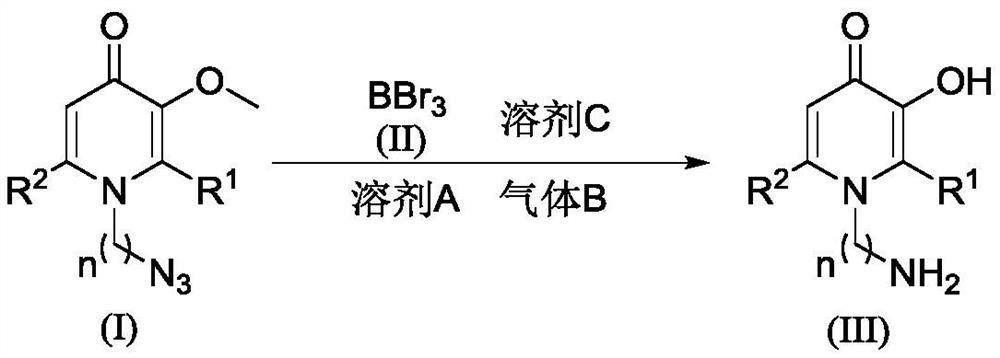
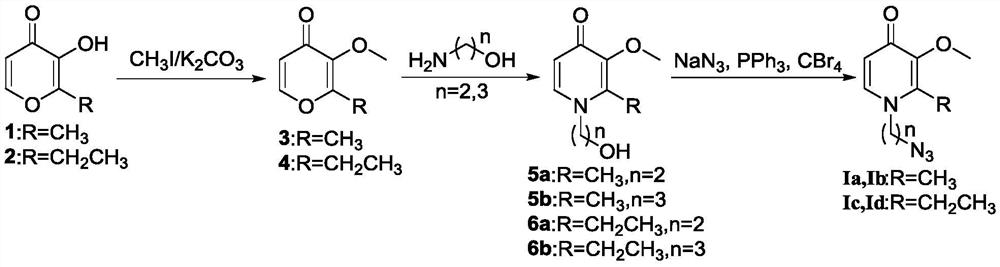
The invention discloses a synthetic method for an amino-containing 3-hydroxypyridine-4-ketone iron chelating agent as shown in a formula (III) which is described in the specification. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: with methyl-protected azido hydroxypyridone as shown in a formula (I) which is described in the specification as a raw material, allowing the methyl-protected azido-hydroxypyridine to generate reduction and demethylation reactions under the protection of boron tribromide as shown in a formula (II) which is described in the specification, a solvent A and gas B, after completion of the reactions, carrying out quenching with a solvent C, and carrying out post-treatment so as to obtain the amino-containing 3-hydroxypyridine-4-ketone compound as shown in the formula (III). Compared with a conventional method, the synthetic method provided by the invention adopts a boron tribromide reagent with mild reaction conditions, avoids the use of a metal catalyst, andhas simple and convenient operation and high reaction yield.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Application of deferiprone in inhibition of ototoxicity of aminoglycoside drugs
PendingCN113230410AElucidate the mechanism of injuryAvoid damageOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderOtotoxicityAminoglycoside Drugs
The invention discloses application of deferiprone in inhibition of ototoxicity of aminoglycoside drugs, and belongs to the field of drug-induced deafness. The invention discloses an application of deferiprone (DFP) in protection of hearing loss caused by aminoglycoside drugs. The DFP is the only oral active iron chelating agent and is clinically used for treating blood transfusion iron overload in thalassemia. According to the application, aminoglycoside drug damage, hair-like cells HEI-OC1 and mitochondrial autophagy occurrence levels in in-vitro cultured cochlea tissues are firstly researched, the protective effect of the DFP on the hair cells by regulating mitochondrial autophagy on the in-vitro cultured cochlea tissues is researched, and finally, the protective effect of the DFP on mouse hearing loss caused by aminoglycoside drugs is researched. A new thought is provided for treating drug-induced deafness, and a new target is provided for clinically helping a patient to recover and reconstruct an auditory function.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
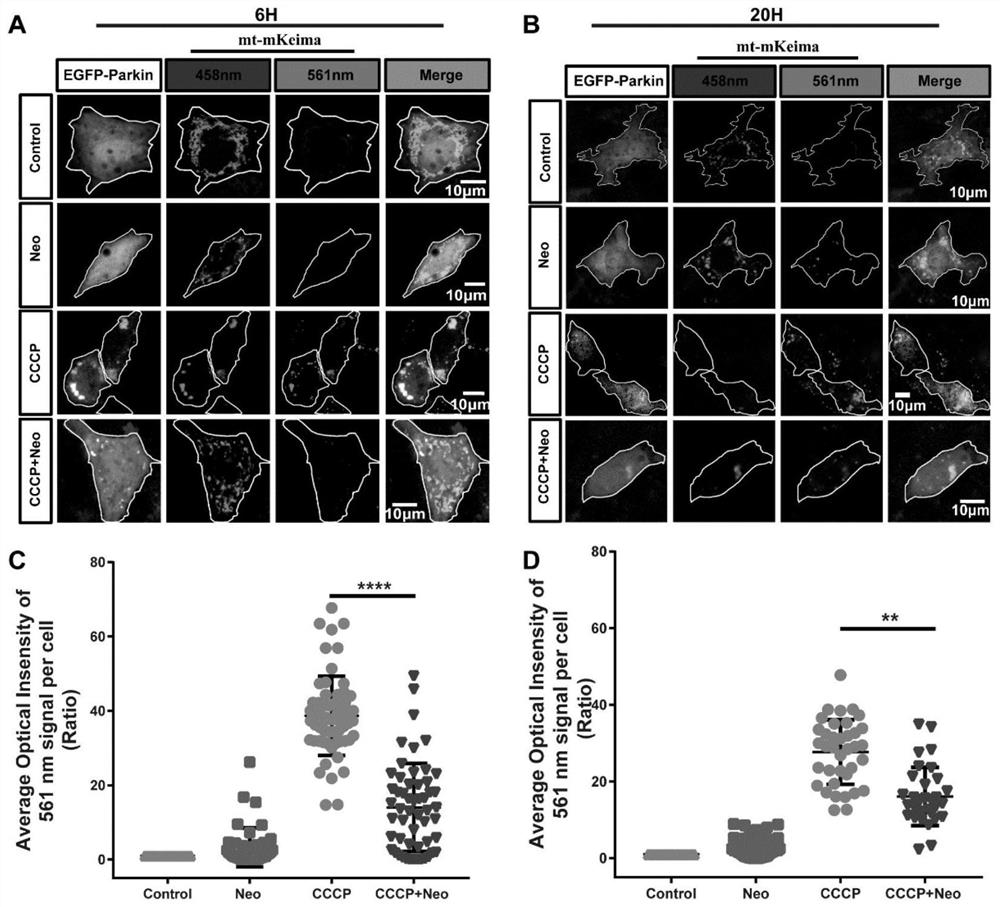
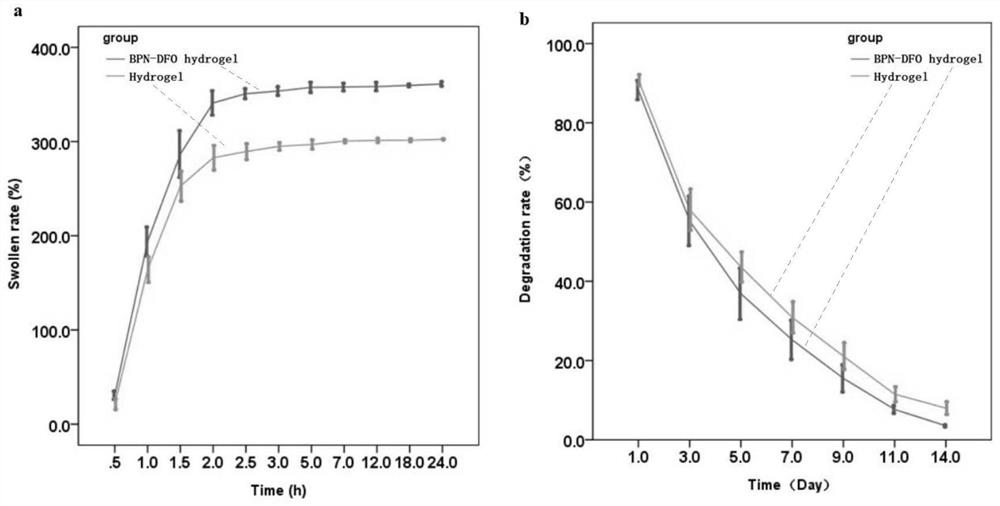
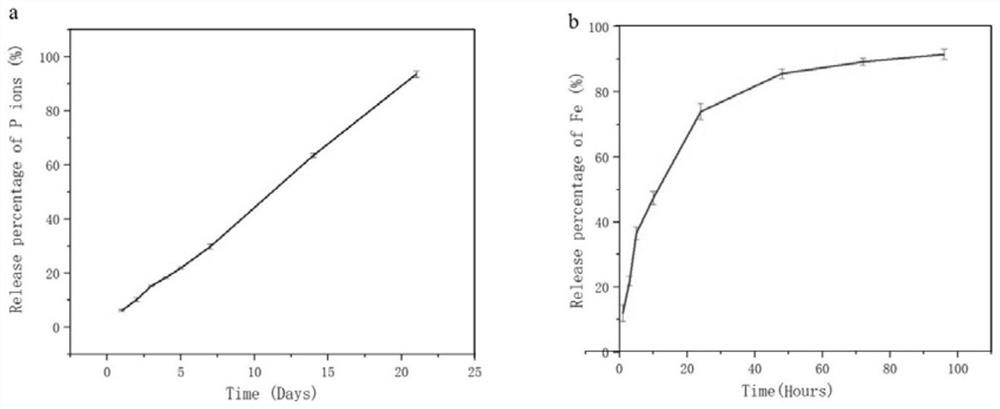
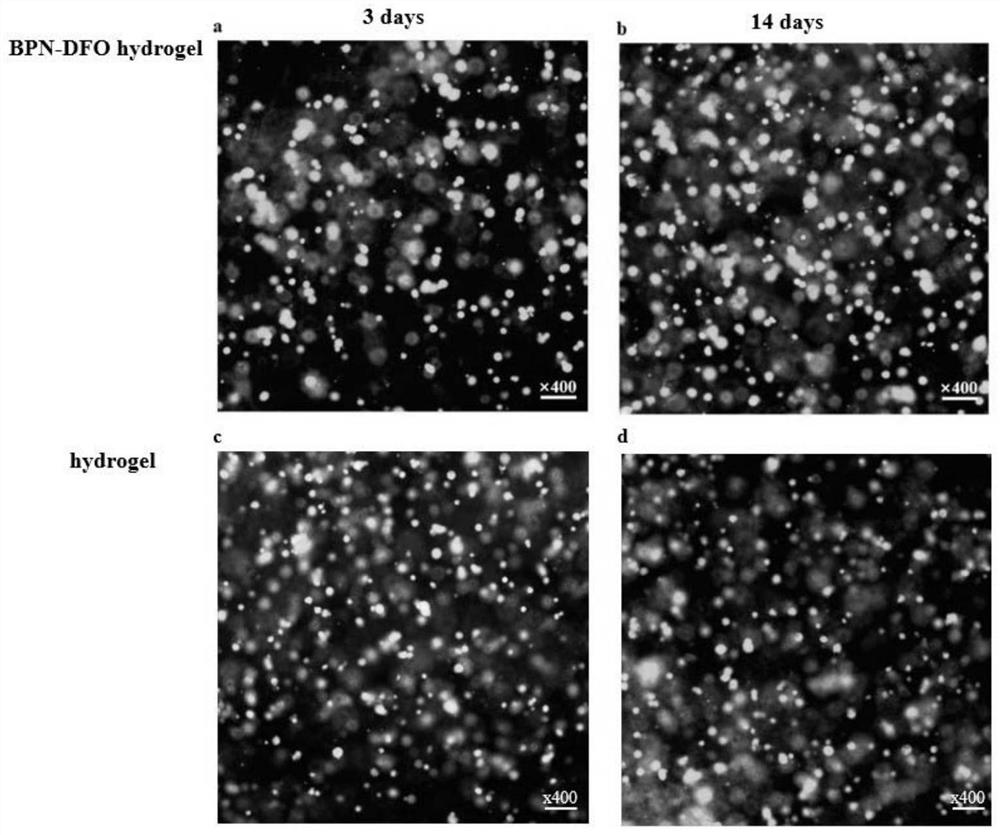
Preparation method and application of BPN-DFO gel scaffold
InactiveCN114569789APromote generationPromote swellingTissue regenerationProsthesisBiocompatibilityBlood vessel
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical materials, in particular to a preparation method and application of a BPN-DFO gel scaffold. Black phosphorus nanosheets (BPN) and deferoxamine (DFO) serve as bioactive components for promoting blood vessel and bone regeneration and are used for repairing ischemic bone defects, BPN can release controllable phosphorus, DFO serves as an iron chelating agent, angiogenesis can be promoted by activating vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and other key angiogenesis promoting genes, and the effect of repairing ischemic bone defects is achieved. The gel scaffold prepared by the invention has good swelling, degradation and release rates, and has good biocompatibility. The BPN-DFO (black phosphorus nanosheet and deferoxamine) gel scaffold shows that the expression of mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) related to bone regeneration and cell proliferation is obviously up-regulated. In vivo, the BPN-DFO gel stent can significantly improve osteogenesis and neovascularization at the ischemic bone defect part.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL CENT LIHUILI HOSPITACL
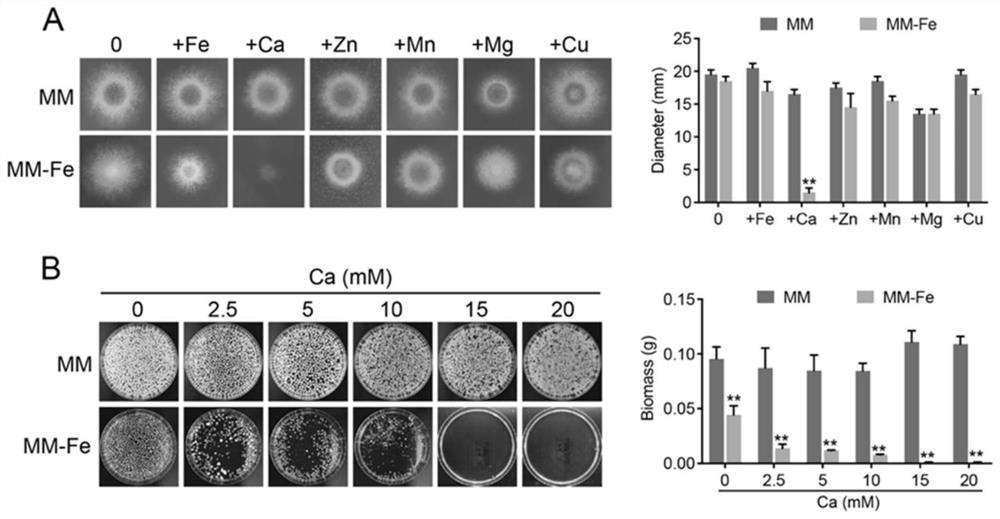
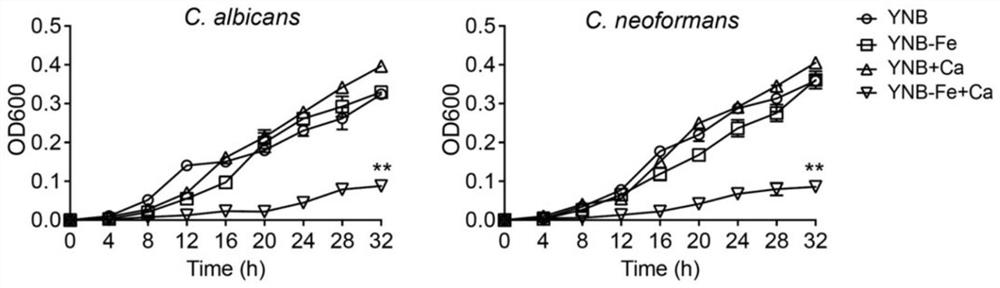
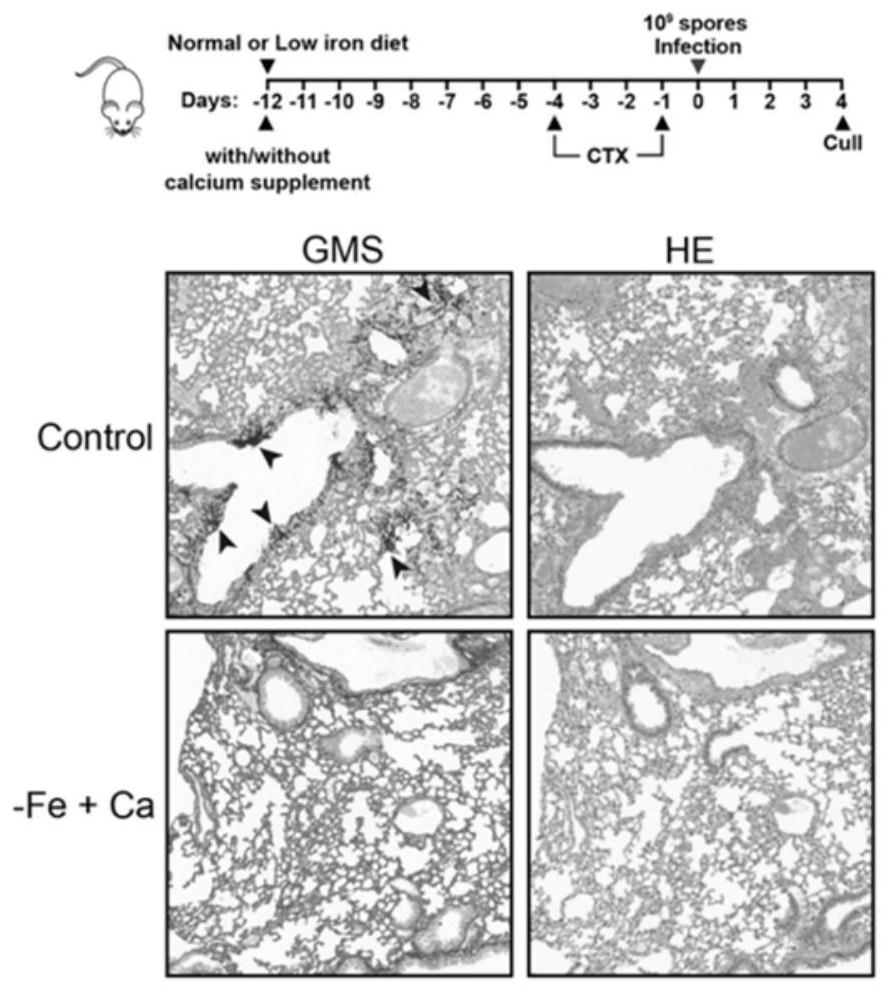
Method for inhibiting fungal growth by adjusting calcium and iron content and application thereof
PendingCN114456950AHost side effects are smallImprove securityBiocideFungiBiotechnologyAntifungal drug
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting fungal growth by adjusting calcium and iron contents and application thereof. The growth inhibition phenomenon of pathogenic fungi is caused by adding exogenous calcium in a low-iron environment, and it is proved that high calcium can inhibit absorption of fungi to iron, so that deletion of iron necessary for fungus growth is aggravated. According to the invention, the iron chelating agent is adopted to reduce the supply of iron nutrition, and calcium nutrition with a certain concentration is combined, so that the growth of aspergillus fumigatus can be obviously inhibited, and the inhibition effect is proved in an in-vitro culture medium and in a mouse body. The invention further finds that high-calcium and low-iron combined regulation can also inhibit pathogenic fungi-candida albicans and cryptococcus neoformans. The low-iron and high-calcium combined nutrition treatment technology disclosed by the invention can be popularized to control the growth of other types of pathogenic fungi such as plants, animals and the like, and is also effective to antifungal drug resistant strains.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
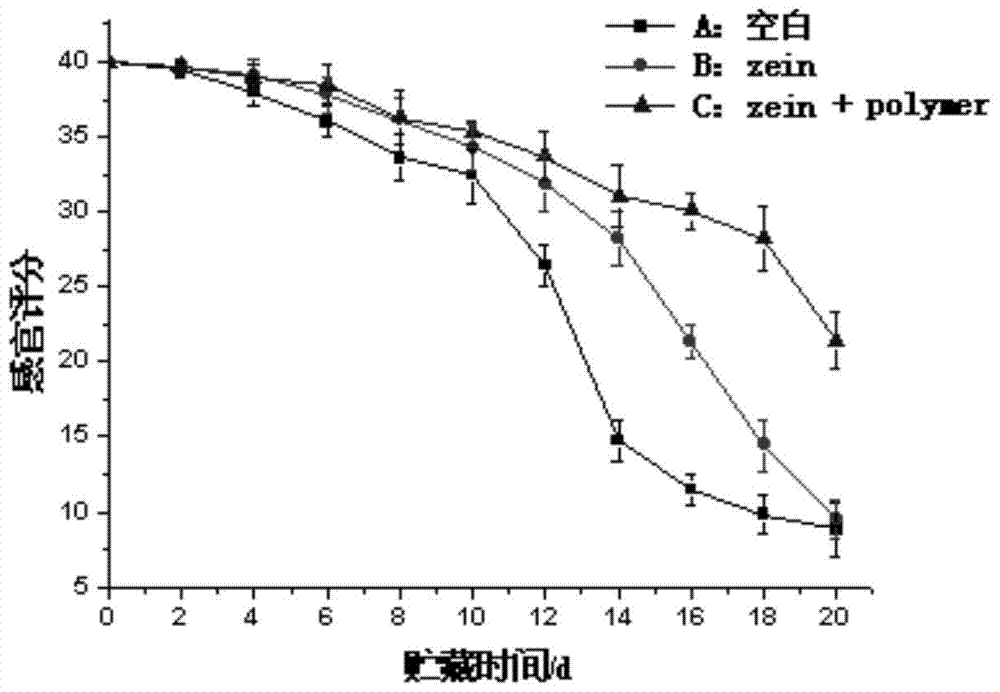
Preparation method and application of edible antibacterial film solution containing polymer iron chelating agent
ActiveCN105001431BStrong iron chelating abilityImprove barrier propertiesMeat/fish preservation by coatingVolume concentrationFood Preservers
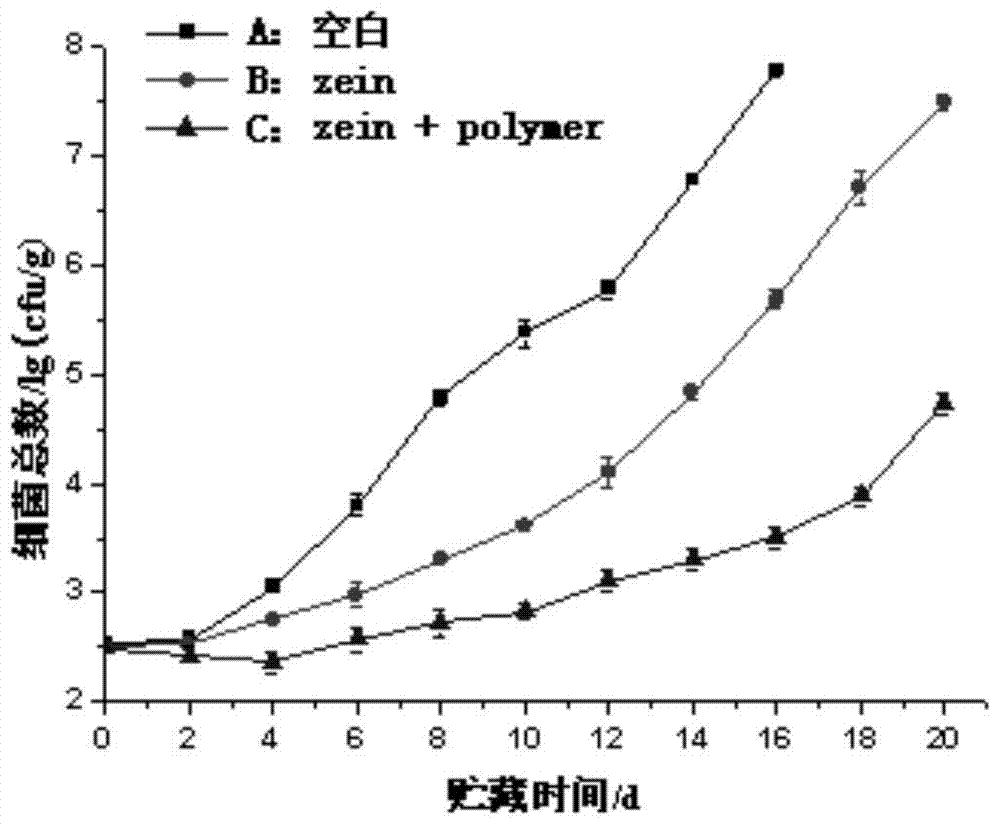
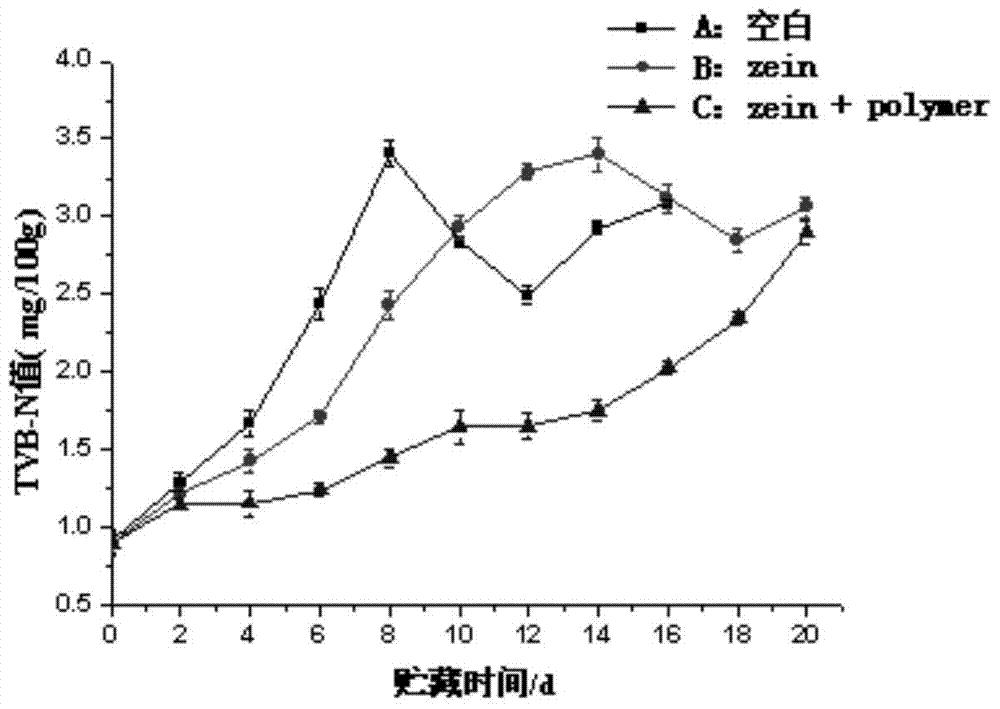
The invention discloses a preparation method of an edible antimicrobial membrane solution containing a polymer ferric chelating agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking a polymer ferric chelating agent and dissolving it with ultrapure water to prepare a polymer ferric chelating agent solution with its concentration being 20mg / mL; preparing a zein solution from 5g of zein, 40mL of ethanol with its volume concentration being 95% and 2mL of glycerin; adding the polymer ferric chelating agent solution into the zein solution until content of the polymer ferric chelating agent in a membrane solution obtained is 0.1-4mg / mL. Thus, the edible antimicrobial membrane solution containing the polymer ferric chelating agent is obtained. The edible antimicrobial membrane solution can be used in food preservation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com