Patents
Literature
51results about How to "No bitter taste" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Novel technology for dark green tea fermentation
InactiveCN103564074AControlling the fermentation temperatureReduce humidityPre-extraction tea treatmentFiberAutomatic control
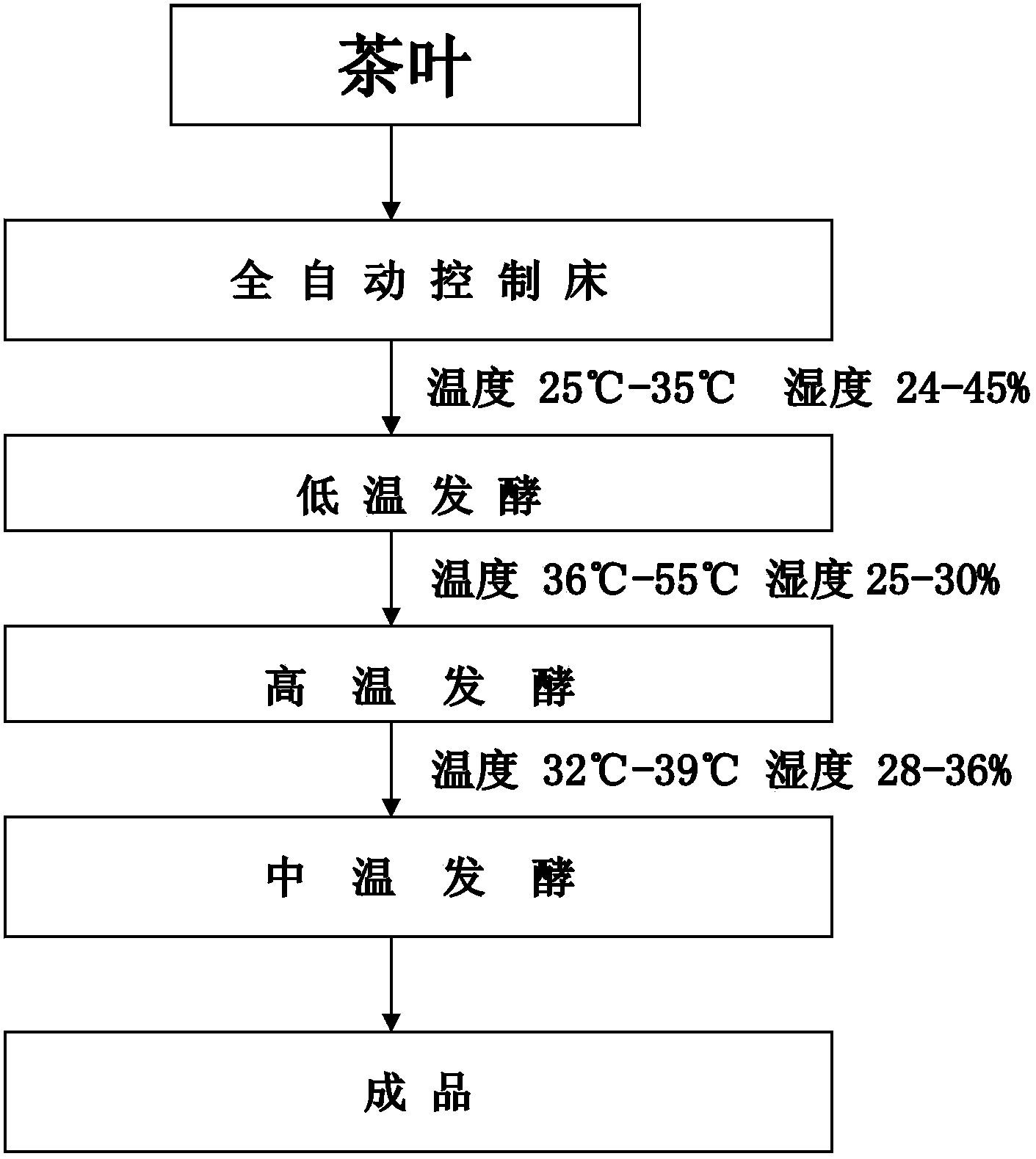
The invention discloses a novel technology for the dark green tea fermentation, and relates to a dark green tea fermentation method. The fermentation method comprises the following steps: subjecting fresh tea leaves to processes of tedding, enzyme inactivating, and rolling, and then placing the processed tea leaves on an auto-control machine to carry out pile fermentation; and is characterized in that the pile fermentation is divided into three phases: a. low-temperature fermentation: controlling the temperature in a range of 25 to 35 DEG C and the humidity in a range of 24 to 45%, carrying out the pile fermentation reactions for about 24 hours, wherein in this phase microzyme is cultured, and carbon dioxide is generated by the microzyme to decompose the caffeine in tea leaves; b. high-temperature fermentation: controlling the temperature in a range of 36 to 55 DEG C and the humidity in a range of 25 to 30%, carrying out the pile fermentation reactions for about 12 hours, wherein in this phase, fibers, pectin, and protein are fully decomposed into tea polysaccharide and glucose by various bio-enzymes, and catechin of tea polyphenol which is the main component of tea leaves is converted into theaflavin and thearubigins through the enzymatic action, and tea melanin is forbidden to be generated in this process; c. mid-temperature fermentation: controlling the temperature in a range of 32 to 39 DEG C and the humidity in a range of 28 to 36%, carrying out the pile fermentation reactions for about 6 hours, wherein in this phase lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacterium are generated, and then the lactic acid bacteria convert glucose into vitamin C, vitamin P, and a plurality of amino acids.
Owner:罗强
Maotai-flavor baijiu type agilawood wine and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105420050AImprove human immunityFragrant and mellowAlcoholic beverage preparationChemistryFlavor
The invention provides maotai-flavor baijiu type agilawood wine and a preparing method thereof. The wine is prepared from, by weight, 90-93 parts of maotai-flavor baijiu and 7-10 parts of agilawood wine mother liquor. The agilawood wine mother liquor is formed by soaking agilawood into maotai-flavor baijiu with the amount being 90-110 times that of the agilawood. According to the maotai-flavor baijiu type agilawood wine, fragrance and pharmacology ingredients in the agilawood can be soaked into the wine effectively, and the agilawood wine has the effects of anesthetizing, pain relieving, calming, cough stopping and blood reducing, can improve immunity of the human body, and is healthcare wine; the agilawood wine is outstanding in maotai-flavor, elegant in agilawood, pure, mild, full, long in aftertaste and free of bitter mouthfeel of medicinal liquor. According to the preparing method for the maotai-flavor baijiu type agilawood wine, at first, the method of soaking the agilawood into a part of baijiu to prepare the agilawood wine mother liquor and then carrying out blending is adopted, is beneficial for preserving wine flavor and traditional Chinese medicine fragrance, and has the advantages of being simple in technology, easy to realize and reasonable in ratio.
Owner:贵州习酒股份有限公司 +1
Cool refreshing areca nut and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107125755AFresh breathHas the effect of refreshing and anti-fatigueNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsSugarXylitol
The invention discloses cool refreshing areca nut which comprises, by weight, 20-70 parts of dried areca nut, 1-10 parts of white granulated sugar, 10-15 parts of malt syrup, 4-8 parts of xylitol, 0.2-0.8 part of pineapple oil essence, 0.2-0.8 part of sweet orange oil essence, 2-10 parts of lemon powder and a proper amount of edible salt. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the cool refreshing areca nut. The cool refreshing arecta nut avoids the problem that long-time chewing of arecta nut has impact on taste and is bad for tooth health, has good refreshing effect and is conducive to tooth health.
Owner:湖南品来品趣科技发展有限公司
Gold tea preparation method
InactiveCN103431104AHeat-clearing and detoxifyingHeatstroke preventionTea substituesChimonanthus salicifoliusTheanine
The present invention discloses a gold tea preparation method, which comprises: 1) collecting tender stem and leaf of Chimonanthus salicifolius, cleaning, and soaking the tender stem and leaf of the Chimonanthus salicifolius in an improvement solution for 1-2 h; 2) carrying out spreading-drying on the soaked tender stem and leaf of the Chimonanthus salicifolius for 3-5 h at a temperature of 10-15 DEG C; 3) drying the obtained tender stem and leaf of the Chimonanthus salicifolius in an oven until water content in the tender stem and leaf of the Chimonanthus salicifolius is 2-3%; 4) placing the dried tender stem and leaf of the Chimonanthus salicifolius in a rolling machine to roll 2-4 times; and 5) drying the rolled tender stem and leaf of the Chimonanthus salicifolius for 30-50 min at a temperature of 70-80 DEG C, cooling to a temperature of 20-30 DEG C, and drying for 20-30 min to prepare the gold tea. The gold tea produced by the preparation method has functions of heat clearing, detoxification, heatstroke prevention and summer-heat removing, and has characteristics of high tea polyphenol content and high theanine content. In addition, the infused tea has characteristics of good taste, no bitter taste, and sweet and refreshing taste.
Owner:句容市同心家庭农场有限公司
Chinese medicinal composition for treating enteritis
InactiveCN101259258AGood curative effectLow costAnthropod material medical ingredientsDigestive systemOnion bulbSide effect
The present invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine combination for remedying the enteritis, which is characterized by being made from the raw materials with the following parts by weight of 16 to 20 portions of figs, 0.9 to 1 portion of earthworm, 8 to 12 portions of dried gingers, 16 to 30 portions of onion bulbs, 40 to 50 portions of raw hawkthorn, 40 to 50 portions of Chinese dates, 10 to 20 portions of red beans, 25 to 30 portions of dragon blood and 30 to 50 portions of brown sugar. The traditional Chinese medicine combination for remedying the enteritis has the beneficial effects of good curative effect, low cost, moderate taste, no bitter taste, being mild for taking easily, no toxic and side effect, easy manufacturing method and simple and easily-found raw materials.
Owner:张桂松
Betel nut product for refreshing mind and keeping fit and beautifying body curve and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveCN108740878ANo bitter tasteFresh breathFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentFecesBetel
The invention discloses a betel nut product for refreshing spirit and keeping fit and beautifying body curve and a manufacturing process thereof. The betel nut product is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-70 parts of dried betel nuts, 15-20 parts of milkvetch roots, 3-5 parts of radix codonopsis, 2-4 parts of pseudo-ginseng, 3-5 parts of liquorice roots, 10-20 partsof Chinese wolfberry fruits, 1-3 parts of safflowers, 4-6 parts of largehead atractylodes rhizomes, 2-4 parts of peppermints, 3-5 parts of chongcha tea (aglossa dimidiata larva feces-brewed tea), 1-3parts of rosemary herbs and 20-30 parts of honey. Through the reasonable collocation of the peppermints, the chongcha tea, the rosemary herbs and other auxiliary materials, the betel nut product fullyexerts the cooling and tooth decay-preventing effects of the peppermints, so that long-time chewing of the betel nut product does not produce bitter or astringent mouthfeel, and has effects of refreshing breath and refreshing mind and arousing the brain; furthermore, the reasonable combination of the milkvetch roots, the radix codonopsis, the pseudo-ginseng, the liquorice roots, the Chinese wolfberry fruits, the safflowers and the largehead atractylodes rhizomes makes the betel nut product have effects of refreshing mind, resisting fatigue, keeping fit and beautifying body curve and slimmingbody, thus improving the medicinal value of the betel nuts.
Owner:陈辉
Industrialized method for producing high-quality and low-cost stuffing
The invention discloses an industrialized method for producing a high-quality and low-cost stuffing. The method comprises the following steps of: performing pretreatment processes such as cleaning, soaking, cooking and peeling on plant fruits or seeds so as to obtain a raw material stuffing; homogenizing the raw material stuffing once or twice under high pressure; adding oil, white granulated sugar, a sweet inhibitor, a thickening agent and an emulsifier into the homogenized raw material stuffing in turn and uniformly stirring the mixture in a wet and hot state; and cooling the stuffing, packaging and sterilizing so as to obtain the high-quality and low-cost stuffing, wherein the high-quality and low-cost stuffing comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 25 to 35 percent of plant fruits or seeds, 45 to 55 percent of white granulated sugar, 10 to 18 percent of edible oil, 0.015 to 0.03 percent of sweet inhibitor, 0.5 to 2 percent of thickening agent and 1 to 3 percent of emulsifier. The stuffing of the invention has the characteristics of low cost, low sweetness and long shelf life and is suitable for common people to eat.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bamboo salted egg and process method thereof
InactiveCN101385550APromote blood circulationReach blood viscosityFood preparationAnimal scienceSlurry
The invention discloses a processing method of bamboo salt eggs. Bamboo salt or bamboo salt solution and fresh eggs are soaked in slurry or water or sealed through a sealing method and put in a shady and dry place to obtain the bamboo salt egg products after 20-60 days. Overcoming the bitterness of eggs which are salted with common salt, the bamboo salt eggs have the advantages of natural, fresh and delicious taste, high mineral content, abundant nutritional value, easy digestion and absorption and long reservation time and the effects of strengthening body and preventing diseases.
Owner:简丽恒
Compound tilmicosin solid dispersing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106620668AAvoid damageGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEudragit LIrritation
The invention discloses a compound tilmicosin solid dispersing agent and a preparation method thereof. The compound tilmicosin solid dispersing agent comprises, by weight percentage, 1.0-2.0% of Eudragit L-100, 0.2-0.5% of sodium bisulfite, 10-30% of tilmicosin, 0.5-1% of lysozyme, 0.5-1% of aesculetin, 2-5% of polyvidone and the balance anhydrous dextrose. The solid dispersing agent prepared by the method has the advantages that the medicine effect of the tilmicosin is kept, bioavailability is increased evidently, good palatability is achieved, gastrointestinal tract irritation is avoided, cure rate can be increased greatly, controlled-release absorption is formed in the intestinal tract, plasma concentration is kept at the therapeutic dose for a long time, and the highest medicine utilization rate is achieved; in addition, the dispersing agent has an immunoregulation function and can recover macrophage immune activity.
Owner:WUHAN XINLIANDA BIOLOGY
Processing method of grape juice
InactiveCN109363017ATake advantage ofWon't happenFood shapingFood ingredient functionsVitis viniferaGrape juices
The invention provides a processing method of grape juice for solving the defects in the prior art. The processing method comprises the following steps: S1, picking grape raw materials and performingcleaning operation; S2, performing primary juicing operation on the cleaned grapes, and performing solid-liquid separation on the juiced product to obtain a liquid phase component A and a solid phasecomponent A; S3, performing liquid phase posttreatment operation on the liquid phase component A to obtain grape raw juice, and performing solid phase posttreatment operation on the solid phase component A to obtain grape raw powder and grape pectin particles; and S4, mixing the grape raw juice, the grape raw powder, the grape pectin particles and an additive according to predetermined proportionsto obtain the grape juice. The processing method of the grape juice provided by the invention fully utilizes the peel, pulp and stone components of the grapes, and the grape juice contains abundant nutrients without bitter and astringent taste. Meanwhile, grape waste cannot be generated, various natural effective components in the grapes are fully utilized, and the production cost, environmentalgovernance cost and the like are reduced.
Owner:BINCHUAN HUAQIAOZHUANGYUAN AGRI TECH DEV CO LTD
Biluochun tea noodles and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses Biluochun tea noodles and a preparing method of the Biluochun tea noodles; and the Biluochun tea noodles are prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 70-77 parts of wheat flour, 4-10 parts of Biluochun tea, 2-5 parts of fruits of Chinese wolfberry, 10-20 parts of corn flour, 5-15 parts of red dates, 1-2 parts of table salt, 1-2 parts of peanut oil and 12-18 parts of drinking water, wherein the water content of the red dates and the fruits of Chinese wolfberry does not exceed 5%. The Biluochun tea noodles prepared by using the method have smooth surfaces, are fresh and cool in mouth feel, free from bitter taste, good in toughness and rich in nutrition, have a long quality guarantee period under the condition that a preservative is not added into the noodles, and can meet the requirement of daily energy intake of people; and furthermore, the preparing method of the noodles is simple, controllable in conditions and easy in realization of industrialization.
Owner:何莉 +1
Preparation method of canned konjac
InactiveCN110477317ASmooth appearanceUniform textureFruit and vegetables preservationFood ingredient for microbe protectionFlavorPreservative
The invention relates to a preparation method of canned konjac. The preparation method of the canned konjac comprises the following steps: carrying out swelling treatment; carrying out refining treatment; carrying out cooling; carrying out sterilizing and preserving treatment; carrying out soaking treatment; and carrying out blending with soup so as to obtain a finished product. The canned konjacdisclosed by the invention is prepared from purely natural konjac powder as a raw material by adopting modern technology and equipment; and moreover, high-temperature sterilization is performed, so that the prepared canned konjac is an acidic konjac-series product which is carefully processed without addition of any preservatives. The acidic konjac-series product prepared by the preparation methodgets rid of the disadvantages of heavy alkaline flavor and astringent taste; and moreover, konjac prepared from the acidic konjac-series product is strong in elasticity, high in tenacity, fine and smooth in texture as well as pure in flavor. Being added into soup, the konjac does not make the soup turbid; and moreover, the konjac does not break after long-time cooking, and is very chewy, soft, tender, crispy, refreshing, high in palatability and good in taste.
Owner:陕西镇安华兴特色农产品开发有限公司
Processing technology for textured fish protein of tuna
InactiveCN107156693AHigh in proteinLow in fatFood thermal treatmentAlcoholic food ingredientsFiberWheat starch
The invention discloses a processing technology for textured fish protein of tuna. The processing technology is characterized in that tuna meat, isolated soybean protein, wheat starch and vital gluten are uniformly mixed, and the mixture is extruded by a twin-screw extruder for molding. Compared with the prior art, the processing technology has the following advantages: the obtained textured fish protein of tuna is high in protein contant, low in fat content and high in nutritional value, has the texture similar to that of natural animal muscle fibers and adopts a porous bulk textured structure; the textured fish protein is good in water solubility, free of bitter and fishy smells, good in chewing feeling, high in edible value and wide in application range, the added value of tuna products is improved, and a wide market prospect is achieved; and the raw material cost is low, the processing technology is simple, the production efficiency is high, and the processing technology is convenient to popularize.
Owner:舟山富晟食品科技有限公司
Method for preparing camellia fraterna scented tea
The invention discloses a method for preparing camellia fraterna scented tea, comprising the following steps: dipping and cleaning the camellia fraternal flowers; putting on an absorbent paper; drying in a dark ventilated environment at 8-15 degrees centigrade for 40-72 hours; warping the flowers with the absorbent paper after being dried until that the overlapping degree of the flower is a camellia fraternal flower of which the number of the layer is not great than 3, wherein the reuse powder is 500-700, and the time for inactivating through micro waves is 40s-80s, or the temperature is 120-140 degrees centigrade and the electric thermal inactivation time is 3-6.5 min; cooling the camellia fraternal flowers after being inactivated in 2 min, wherein the cooling temperature is not higher than 16 degrees centigrade, and the cooling time is 20-40 min; and drying at 40-45 degrees centigrade to obtain the camellia fraterna scented tea. The method has low manufacturing cost and does not have any additive during the process. The obtained camellia fraterna scented tea keeps the own color, has no light brown color, and has little loss of nutrition, such as camellia sinensis. The scented tea has unique taste and has no bitter taste of the tea leaves.
Owner:倪穗 +1
Processing method of orange juice
InactiveCN109363021AReduce manufacturing costMeet a wide range of sales requirementsFatty-oils/fats productionFood ingredient functionsOrange juiceChemistry
The invention provides a processing method of orange juice for solving the defects in the prior art. The processing method comprises the following steps: S1, picking orange raw materials and performing cleaning and separation operations to obtain pulp and peel; S2, performing juicing operation on the pulp, performing oil squeezing operation on the peel, and separately performing juicing posttreatment operation and oil squeezing posttreatment operation on all or partial products of a juicing product and an oil-squeezing product; and S3, proportionally mixing target materials obtained after performing juicing posttreatment operation and oil squeezing posttreatment operation oil squeezing to obtain the orange juice. The processing method of the orange juice provided by the invention fully utilizes the peel and pulp components of oranges, cannot generate orange waste, fully utilizes various natural effective components of the oranges, and reduces production cost, environmental governance cost, and the like. In addition, the orange juice simultaneously contains water-soluble substances and oily substances in the oranges, has a shelf life of 12 months or above, and meets the requirementsfor marketing in a large dimension.
Owner:BINCHUAN HUAQIAOZHUANGYUAN AGRI TECH DEV CO LTD
Desensitization oral composition and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111481453AThe desensitization effect is achievedLong-lasting and effective desensitizationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsDental canaliculiBiology
The invention belongs to the technical field of oral cavity articles, and provides a desensitization oral composition and a preparation method and application thereof. The desensitization oral composition disclosed by the invention comprises micron-sized hydroxyapatite coated calcium carbonate and micron-sized precipitated silicon dioxide. The mass fraction of the micron-sized hydroxyapatite coated calcium carbonate in the oral composition is 0.1%-30%, and the mass fraction of the micron-sized precipitated silicon dioxide in the oral composition is 0.1%-30%. The invention provides a desensitization oral composition free of sylvite and strontium salt. The desensitization effect is achieved by adding an oral composition of micron-sized hydroxyapatite coated calcium carbonate and micron-sizedprecipitated silicon dioxide; as the sizes of the two materials are smaller than the pore diameter (generally 3-5 microns) of the dental canaliculus, the dental canaliculus can be filled up during tooth brushing, and a channel between dental pulp nerves and the outside is blocked, so that the dental nerves cannot be stimulated by cold, hot, sour and sweet of the outside, and the effect of desensitizing teeth can be achieved when the desensitization oral composition is used every day.
Owner:YANGZHOU PERFECT DAILY CHEM
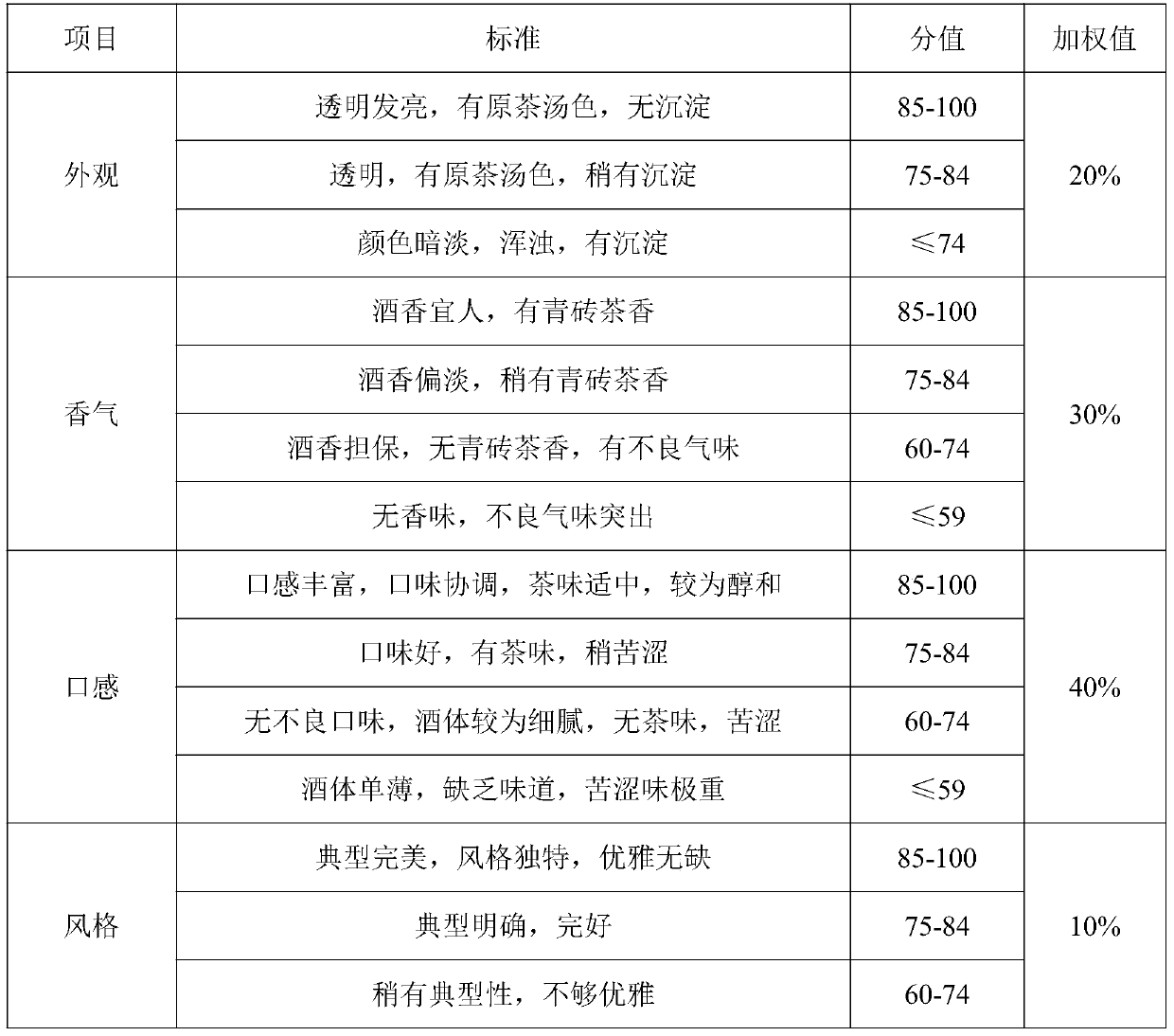
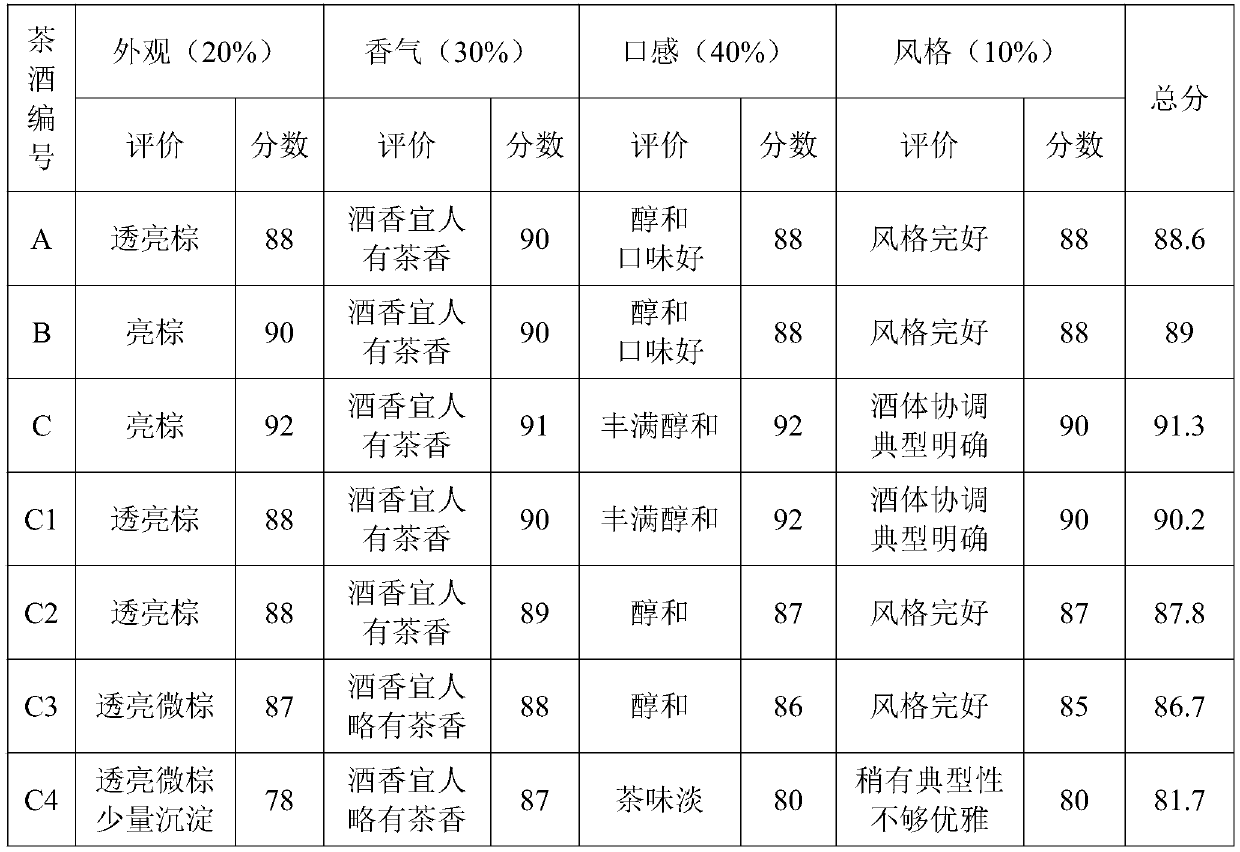
Green brick tea wine and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111196969AObvious health care functionPure Tea FragranceAlcoholic beverage preparationChemistryRice grain
The invention relates to a green brick tea wine and a preparation method thereof. The green brick tea wine takes rice, sorghum, wheat, a green brick tea liquid and flavoring fermented grains as main raw materials, and the green brick tea wine is obtained through four following steps: raw material pretreatment, fermentation, tea making and distillation. The green brick tea wine is obvious in healthcare function, pure in fragrance, excellent and pure in tea fragrance, soft and harmonious in wine body, soft, sweet, refreshing and long in aftertaste, has the fragrance and taste of green brick tea, is moderate in alcohol content, is high in contents of polyphenol, vitamins, amino acids, phospholipid, catechin and selenium in the green brick tea, and has high health care effects; the green brick tea wine prepared by the method is transparent in color and luster, gives people a fresh and pleasant feeling, achieves the tea flavor and the wine aroma, has attractive unique aroma, and is mellowand harmonious in taste, free of the bitter taste of the tea liquid, typical and elegant in style, and good in various sensory evaluation scores.
Owner:王凯华
Preparation method of tea wine
InactiveCN107746784ARich in nutrientsComprehensive health functionAlcoholic beverage preparationFermentationNutrientZiziphus jujuba
The invention discloses a method for preparing tea wine. The raw material composition comprises 15-18% millet, 3-5% tea and 10-17% Chinese herbal medicine. The Chinese herbal medicine comprises 2-4% wolfberry, 2-3% cassia seed, 3-5% jujube and 2-3% cinnamon by weight. The tea wine preparation method of the present invention has rich nutrients and health care functions of tea, the natural aroma of tea leaves, and the grain aroma of millet, richer nutrition, no bitter taste, mellow taste, and layered taste and smell. Adding enzymes for fermentation can make full use of the protein in tea and millet, and decompose the protein into amino acids that can be assimilated by yeast. The preparation method of the obtained tea wine has a unique taste and a long aftertaste.
Owner:FOSHAN GAOMING DISTRICT MINGCHENG TOWN NEW ENERGYNEW MATERIAL IND TECH INNOVATION CENT
A kind of viscous soy sauce and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses viscous soybean sauce and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: heating dark soy sauce to the temperature of 50-70 DEG C, adding bean flour or flour according to a weight ratio of the dark soy sauce to the bean flour or flour of 10:(4-6), or adding a mixture of the bean flour and flour according to a weight ratio of the dark soy sauce to the bean flour to flour of 10:(2-3):(2-3), stirring at the temperature of 50-70 DEG C for 30-60 minutes, cooling, performing secondary heating, adding condiments such as white sugar, caramel and salt, stirring at the temperature of 70-90 DEG C for 30-60 minutes, preserving the temperature at the temperature of 70-90 DEG C for 1-2 hours, standing, and cooling, thereby obtaining the finished viscous soybean sauce. The viscous soybean sauce disclosed by the invention is high in viscosity and delicious in taste, has strong sauce flavor, does not have any precipitate or impurities and is simple in preparation process, low in production cost and good in economic effects.
Owner:陈敏
Chinese medicinal composition for treating enteritis
InactiveCN101259258BGood curative effectLow costAnthropod material medical ingredientsDigestive systemOnion bulbCrab Apples
The present invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine combination for remedying the enteritis, which is characterized by being made from the raw materials with the following parts by weight of 16 to 20 portions of figs, 0.9 to 1 portion of earthworm, 8 to 12 portions of dried gingers, 16 to 30 portions of onion bulbs, 40 to 50 portions of raw hawkthorn, 40 to 50 portions of Chinese dates,10 to 20 portions of red beans, 25 to 30 portions of dragon blood and 30 to 50 portions of brown sugar. The traditional Chinese medicine combination for remedying the enteritis has the beneficial effects of good curative effect, low cost, moderate taste, no bitter taste, being mild for taking easily, no toxic and side effect, easy manufacturing method and simple and easily-found raw materials.
Owner:张桂松
Compound based on active polypeptides of sea bass fins
InactiveCN107223988AImprove resource utilizationImprove qualityFood ingredient functionsFood ultrasonic treatmentSide effectDecomposition
The present invention discloses a compound based on active polypeptides of sea bass fins. The compound comprises the following ingredients in parts by weight: 3-6 parts of active polypeptides of sea bass fins, 18-24 parts of collagen, 5-11 parts of polysaccharides of cistanche deserticola, 1-4 parts of lycium barbarum polysaccharides, 5-11 parts of hydroxymethyl cellulose, 0.1-0.3 part of trace element, 0.8-1.4 parts of vitamin E, 4-8 parts of fruit powder and 38-45 parts of water. Beneficial effects are as follows: the compound is rich and comprehensive in nutrition, easy for absorption, free of smelly and bitter tastes, refreshing and smooth in mouthfeel, and free of chemical preservatives and toxic and side effects, can be drunk by any consumers, can remove free radicals in body, reduces attacks of the free radicals on the body, can activate activities of superoxide dismutase, strengthens too much decomposition of peroxide, and thus plays functions of protecting and preventing aging of the body.
Owner:乐清益昌食品技术有限公司
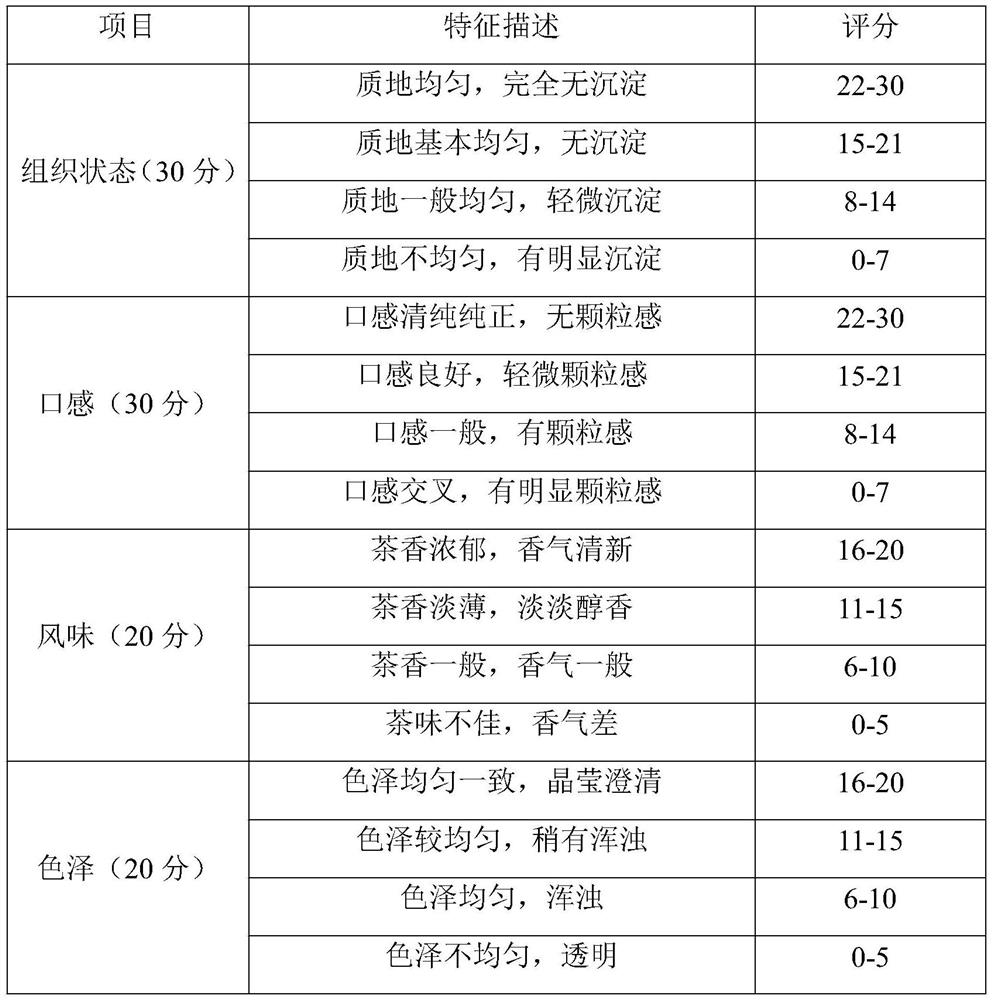
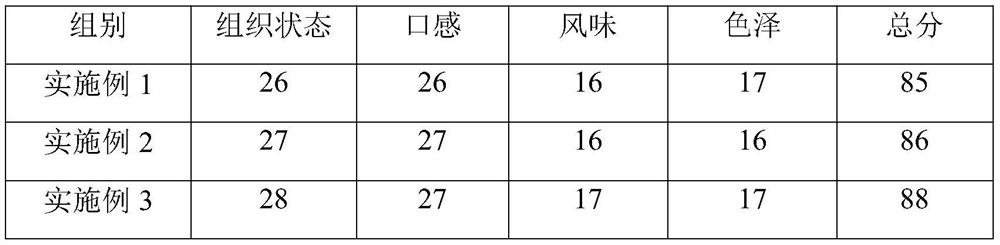
Perpetration method of konjaku can and konjaku can prepared by using same
The invention relates to a perpetration method of a konjaku can and a konjaku can prepared by using the same. The preparation method comprises the steps of: swelling, refining, cooling, retaining freshness in a sterilizing way, soaking and preparing a soup. The konjaku can is refined konjaku acid product which takes the pure natural konjaku powder as a raw material, is sterilized by a modern technology and equipment through a high temperature, and is free of any preservative. The acid konjaku can eliminate the defects that the konjaku is heavy in alkalinity and bitter in mouthfeel; and the prepared konjaku is high in elasticity, good in toughness, exquisite in tissues, pure in special flavor, pure when the konjaku is added into a soup, hard to rot after the konjaku is boiled for a long time, high in chewing feel, delicate, crisp, salubrious, good in palatability, and good in mouthfeel.
Owner:健盛食品股份有限公司
Squid textured fish protein and processing method
InactiveCN107136290AHigh in proteinGood water solubilityProtein composition from fishVegetable proteins working-upSolubilityNutritive values
The invention discloses squid textured fish protein and a processing method thereof. The squid textured fish protein comprises the following components in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of squids, 20-30 parts of soy protein concentrate, 10-20 parts of starch, 5-10 parts of wheat flour, 0.1-0.4 part of ethylhexylglycerin and 0.02-0.06 part of dipotassium glycyrrhizinate. The squid textured fish protein has the beneficial effect of being high in protein content, good in water solubility, free from fishy taste and bitter taste and high in nutrient value, has biting sense after being soaked with boiling water for 3 min, and conforms to the taste of common people; the squid textured fish protein is milky white in color, rich in fragrance, free from peculiar smell, convenient to color and rich in flavor, can be widely used for meat products, filling products, instant foods, leisure foods and the like, has broad market prospects; and the cost of raw materials is low, the processing method is simple and easy to operate, the production efficiency is high and the productivity is high, and the processing method is used for industrial production.
Owner:兰溪百晟食品科技有限公司
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating acute enteritis
InactiveCN102652824BGood curative effectLow costDigestive systemPlant ingredientsSide effectOfficinalis
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating acute enteritis. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 6-10 parts of mangnolia officinalis, 6-8 parts of common andrographis herb, 8-12 parts of ginger, 6-8 parts of polygonum cynanchoides hemsl, 40-50 parts of fresh hawthorn, 14-16 parts of cucurbitae semina, 4-6 parts of centaury, 10-20 parts of red phaseolus bean, 25-30 parts of radish, 4-6 parts of palmate neocinnamo, 10-12 parts of leaf loosestrife herb, 3-5 parts of linum stelleroides and 30-50 parts of brown sugar. The traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention has the beneficial effects of good treatment effect, low cost, moderate taste, no bitterness, temperate and easy taking, no toxic or side effects, simple preparation method, and simple and available raw materials.
Owner:顾湘
Chinese medicinal composition for treating enteritis
InactiveCN102319415BGood curative effectLow costOrganic active ingredientsAnthropod material medical ingredientsSide effectCurative effect
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal composition for treating enteritis. The Chinese medicinal composition is characterized by being prepared from the following bulk pharmaceuticals in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of wallich pepper stem and leaf, 4-6 parts of Tibet lyonia leaf, 6-8 parts of willow leaf, 3-5 parts of java bishopwood rootbark branchlet and leaf, 4-6 parts of flatstem rockvine stem and root, 8-12 parts of dried ginger, 10-14 parts of medicinal evodia fruit, 10-14 parts of Chinese magnoliavine fruit, 20-24 parts of red date, 10-20 parts of small red beans, 25-30 parts of dragon's blood, 30-50 parts of brown sugar, 2-4 parts of earthworm, 7-9 parts of malaytea scurfpea fruit and 8-10 parts of divaricate saposhnikovia root. The Chinese medicinal composition has the advantages of good curative effect, low cost, moderate taste, no bitter taste, mildness, easiness for taking, no toxic or side effect, simple preparation method and readily-available raw materials.
Owner:JINAN ASIA PHARMA TECH
Chinese medicine wine and preparing method
InactiveCN1299730CBalance yin and yangSufficient kidney qiDigestive systemAlcoholic beverage preparationEpimediumWolfiporia extensa
The Chinese medicine wine is prepared with eight kinds of Chinese medicinal materials, including ginseng, pilose antler, epimedium, desert cistanche, malaytea scurfpea fruit, schisandra, tuckahoe and saffron in certain proportion as well as white spirit. The preparation process includes pre-treating eight kinds of Chinese medicinal materials, mixing, heating to 100 deg.c to sterilize, soaking in white spirit and sealing for 28 days, filtering and packing. The present invention has comprehensive regulation on the higher nerve system, immunological system and endocrine system of human body, so that it has the health functions of raising thinking ability and raising body's adaptability.
Owner:杨玉忠
Tea leaf and kudzuvine root tea and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112586577AWith blood pressure loweringWith hypolipidemicTea extractionBiotechnologyTea leaf extract
The invention relates to the technical field of food processing, and tea leaf and kudzuvine root tea is prepared from a tea extract, a kudzuvine root extract and dextrin. The preparation method of thetea leaf and kudzuvine root tea comprises three steps of pretreatment, extraction and spray drying. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the following beneficial effects that the natural tea extract and the kudzuvine root extract are used as raw materials and are prepared into na instant drink in a special raw material ratio by a special preparation method; the tea leaf and kudzuvine root tea has both the unique fragrance of kudzuvine roots and the unique fragrance of tea leaves, has no sticky taste of the kudzuvine roots or the bitter taste of the tea leaves, and meanwhile, has theeffects of reducing blood pressure and blood fat, preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and the like. Through sensory evaluation, it can be seen that the formula combination of the tea leaf and kudzuvine root tea has a relatively good taste, texture state and flavor, and is suitable for industrial production and sales.
Owner:杭州高莼茶色素有限公司
Tea for treating acute enteritis
InactiveCN104474352AGood curative effectLow costPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryAdiantum capillus-venerisGinseng
The invention provides tea for treating acute enteritis. The tea is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 6-8 grams of ramulus cinnamomi, 5-7 grams of wrinkled gianthyssop herbs, 1-3 grams of hairyvein agrimonia, 2-4 grams of radix rehmanniae, 3-5 grams of poria cocos, 6-8 grams of pseudostellaria heterophylla, 4-6 grams of ginseng, 6-8 grams of astragalus, 4-6 grams of ophiopogon japonicas, 3-5 grams of rehmannia glutinosa, 2-4 grams of radix trichosanthis, 6-8 grams of kudzuvine roots, 5-7 grams of rhizomes of common yam, 8-10 parts of salvia miltiorrhiza, 8-10 parts of fructuslycii, 3-5 grams of viola verecunda, 1-3 grams of adiantum capillus-veneris, 2-4 grams of paper mulberry barks, 6-8 grams of polished round-grained rice and 3-5 grams of suaeda glauca. The tea has the beneficial effects that the curative effect is good, the cost is low, the tea is mild, does not taste bitter, is easy to take and has no toxic or side effect, the preparation method is simple, and the raw materials are easy to obtain.
Owner:JINAN WEICHUAN INFORMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com