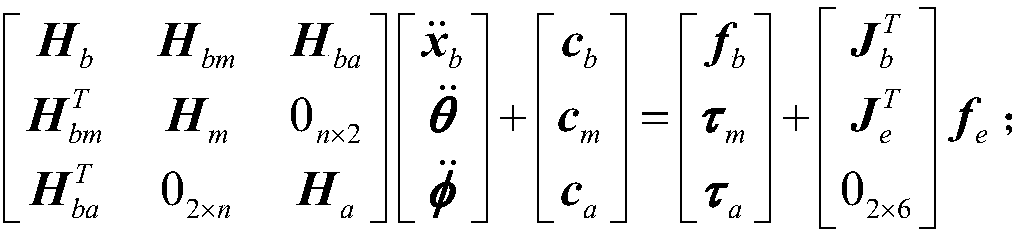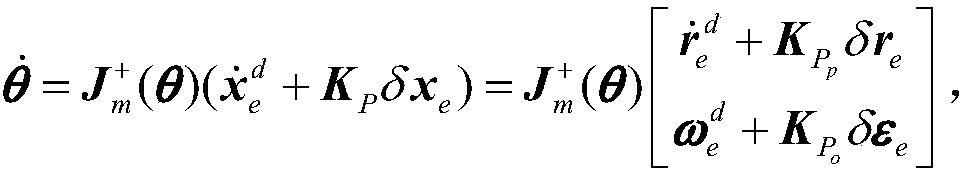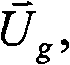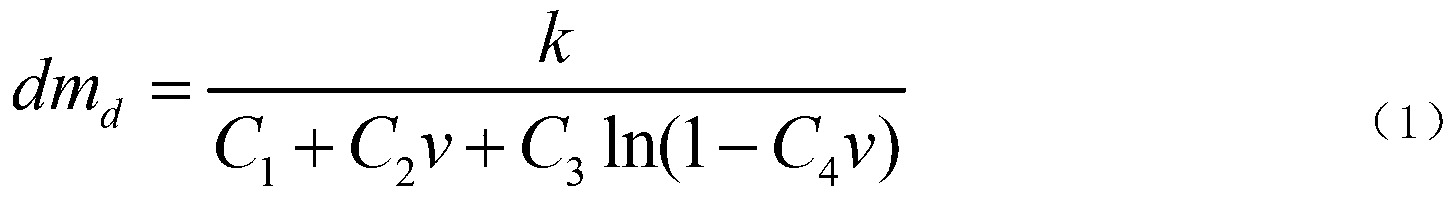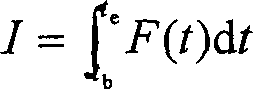Patents
Literature
139 results about "Momentum conservation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
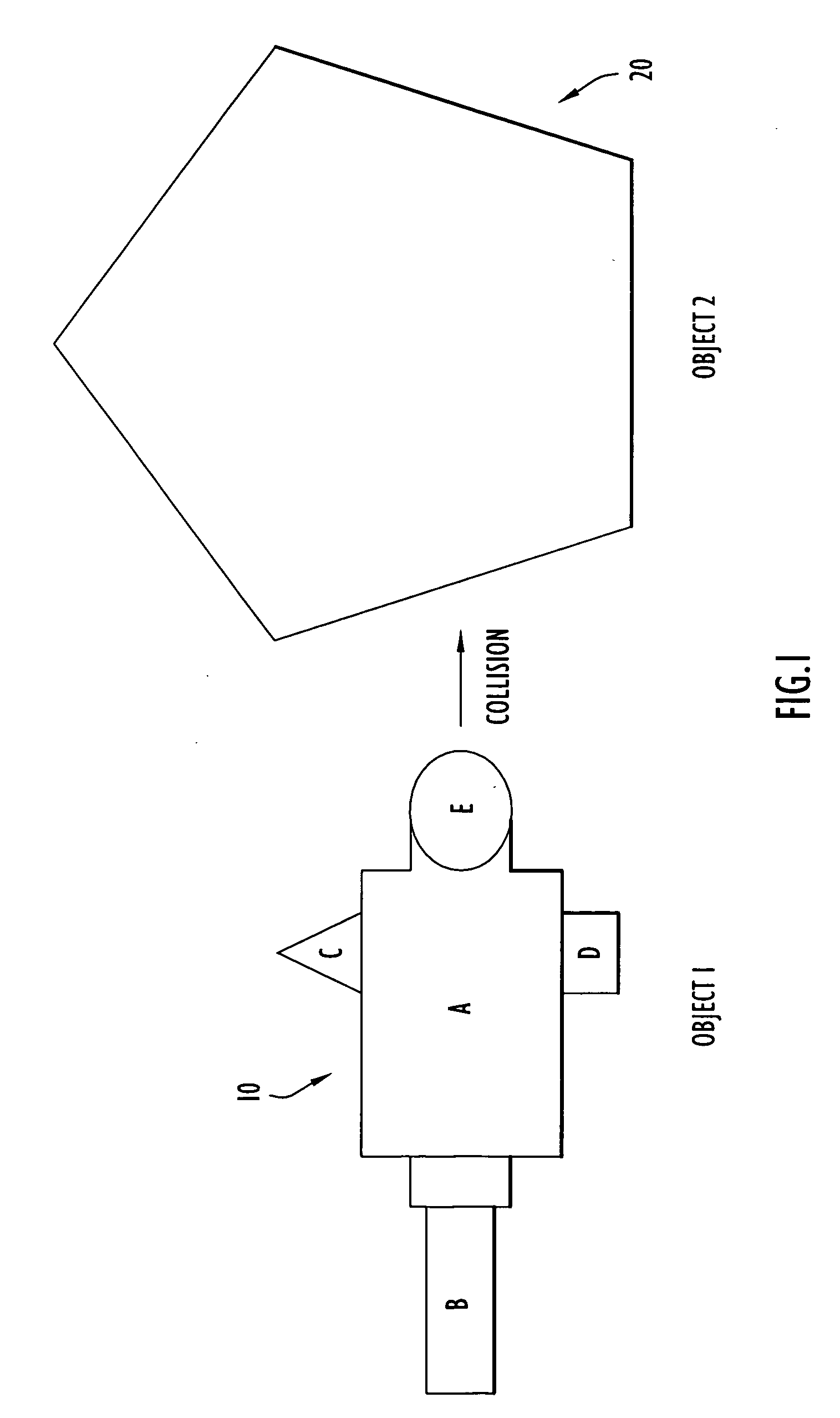
The law of momentum conservation can be stated as follows. For a collision occurring between object 1 and object 2 in an isolated system, the total momentum of the two objects before the collision is equal to the total momentum of the two objects after the collision.
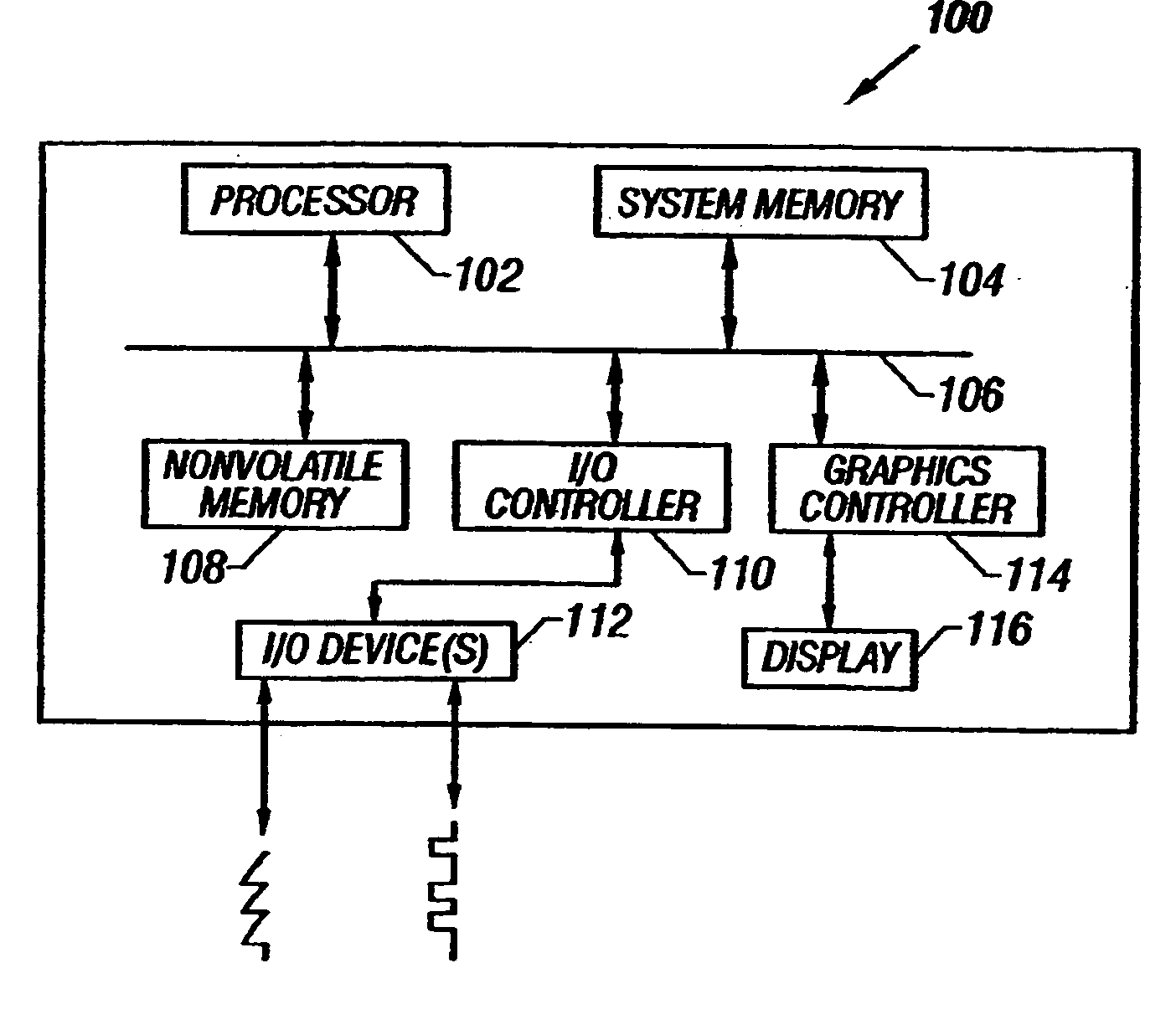
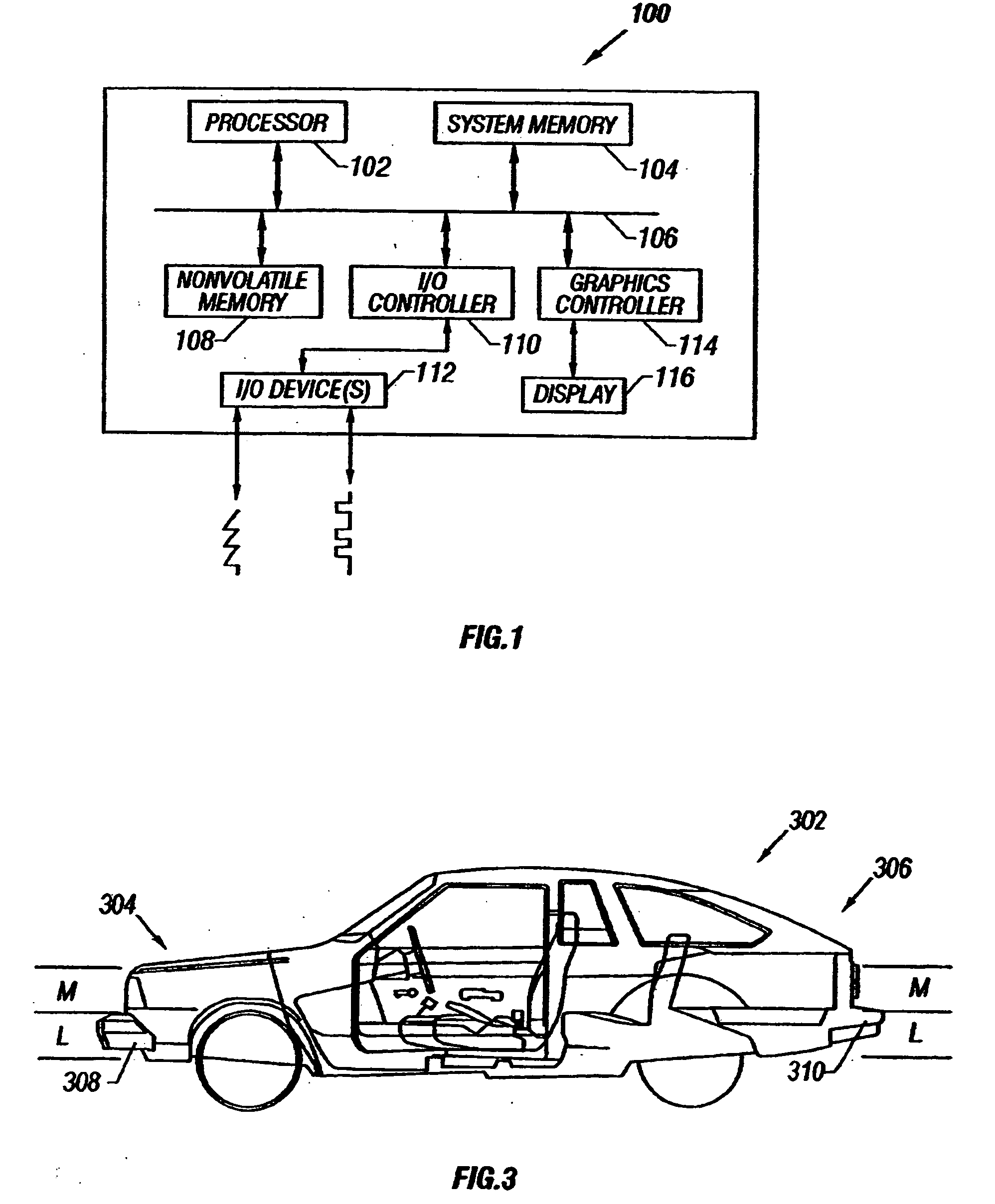
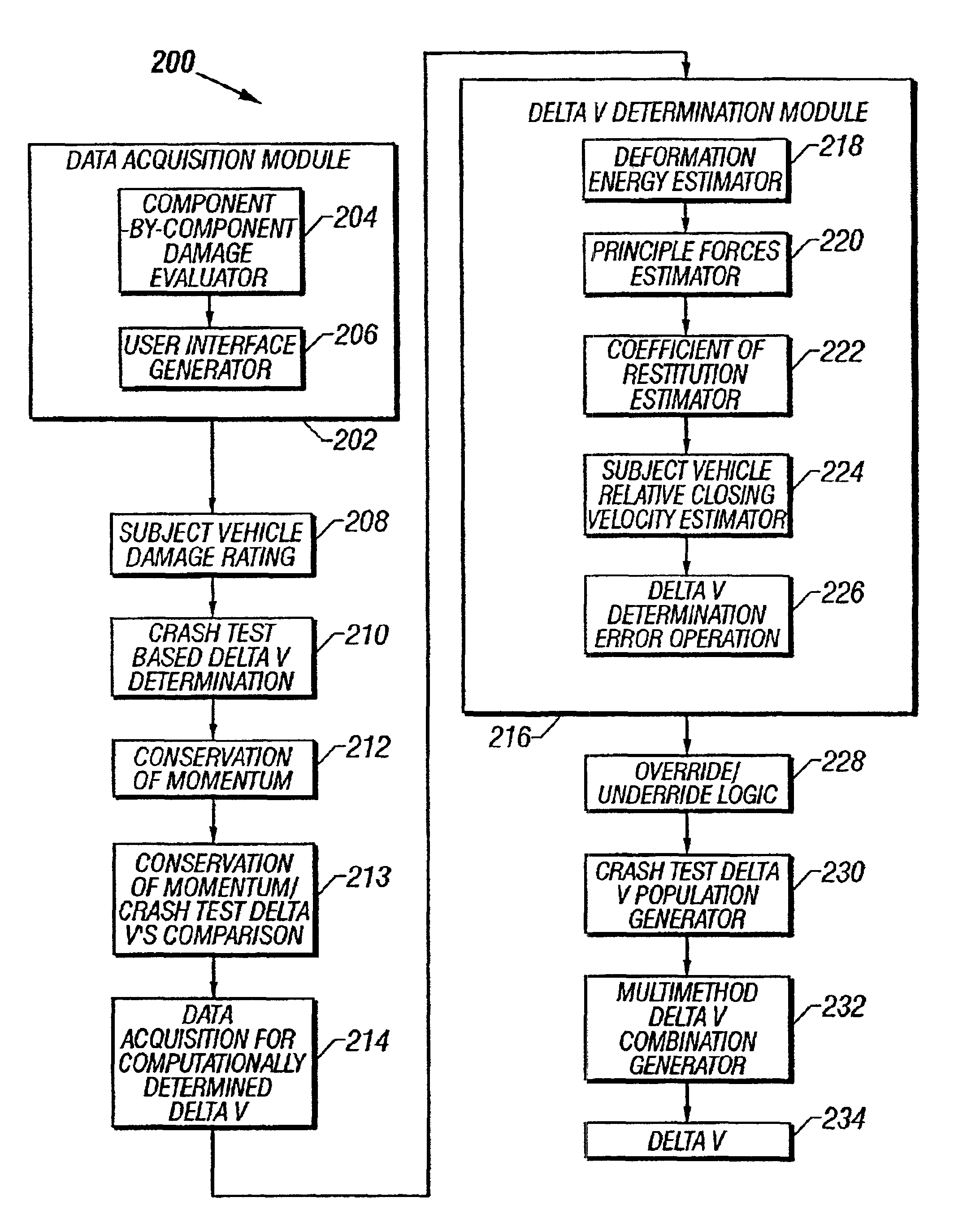
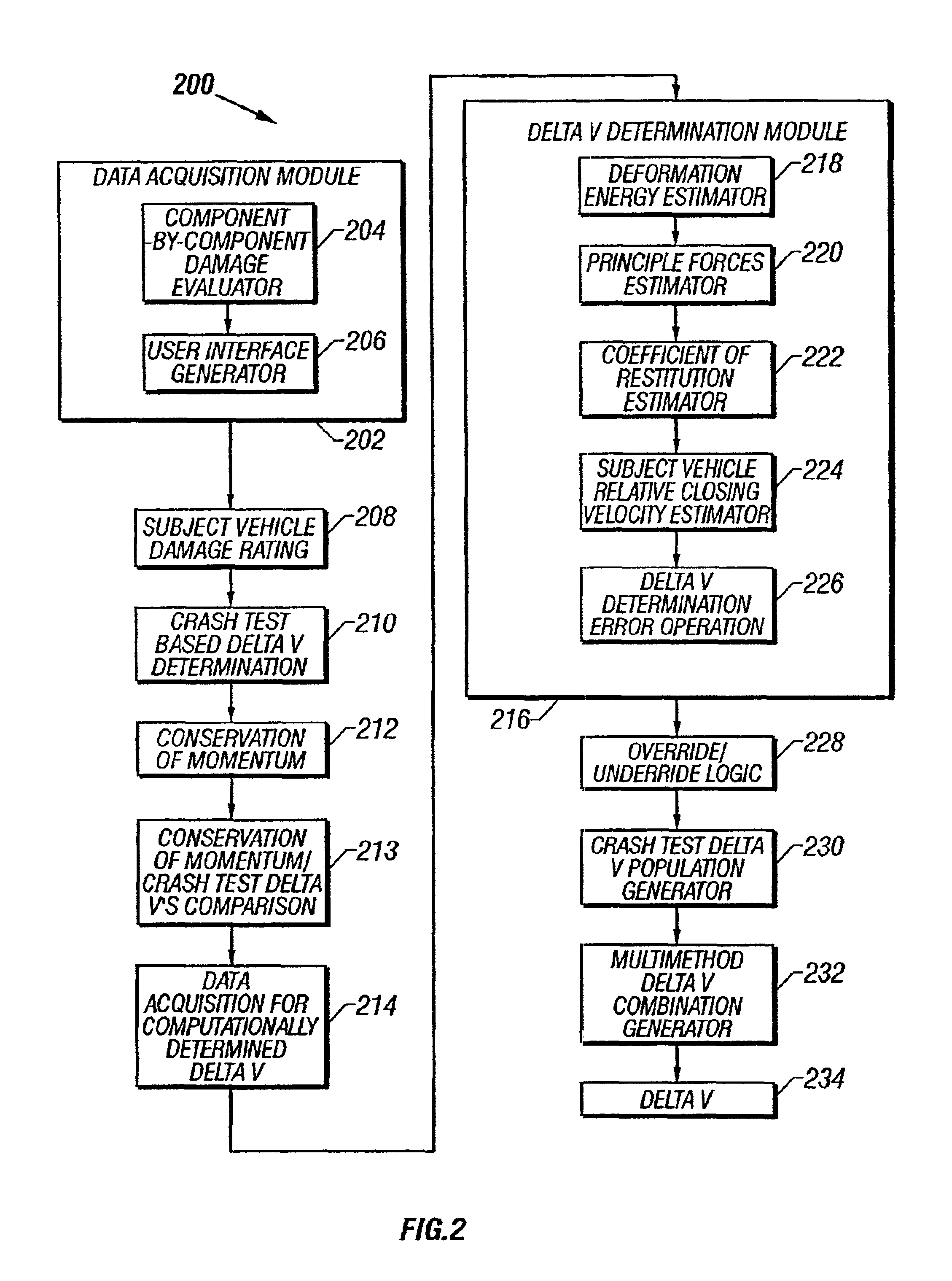
System and method for determining post-collision vehicular velocity changes
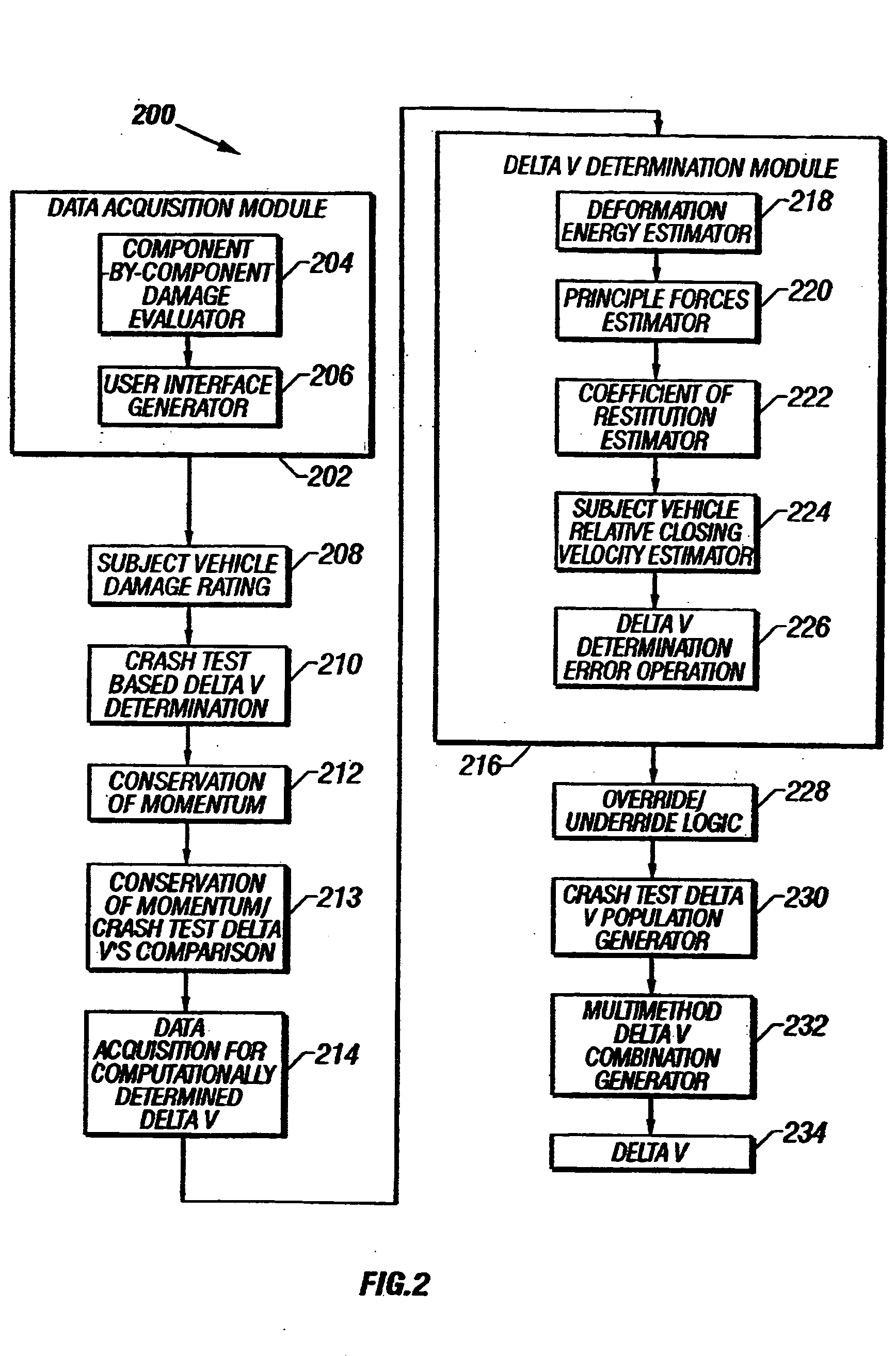
A system and method that utilizes information relating to vehicle damage information including damaged vehicle area information, crush depth of the damaged areas information, and vehicle component-by-component damage information to determine the relative velocities of vehicles involved in a collision. The change in velocity is estimated using a plurality of methods, and a determination is made as to which method provided a result that is likely to be more accurate, based on the damage information, and the types of vehicles involved. The results from each method may also be weighted and combined to provide a multi-method estimate of the closing velocity. The methods include using crash test data from one or more sources, estimating closing velocity based on the principals of conservation of momentum, and estimating closing velocity based on deformation energy resulting from the collision.
Owner:CCC INFORMATION SERVICES
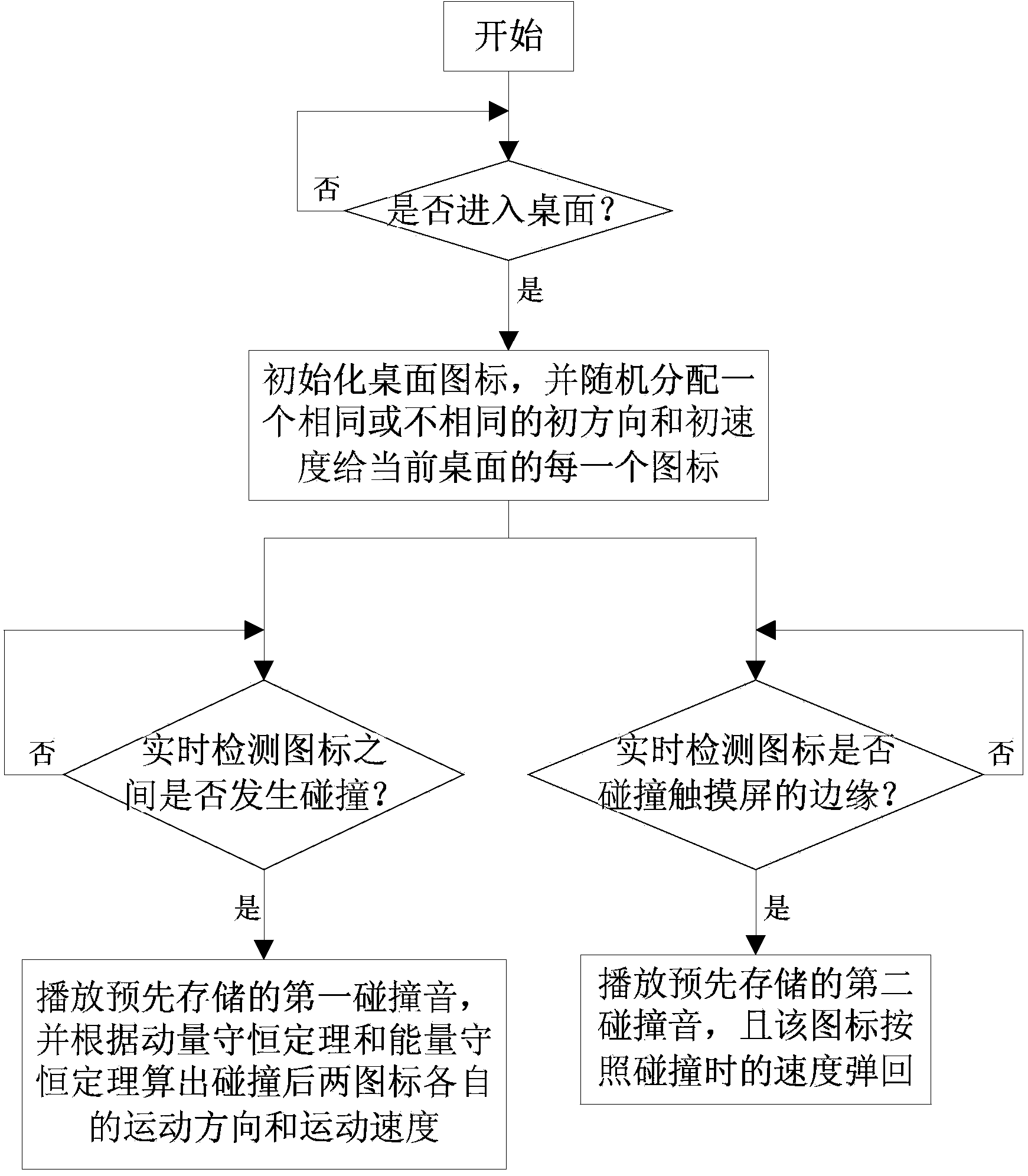
Vivid and interesting desktop icon displaying method and device
ActiveCN103838465AUnique displayImprove freshnessInput/output processes for data processingRandom assignmentTouchscreen
The invention discloses a vivid and interesting desktop icon displaying method and device. The method includes the following steps: when entering a desktop, initializing desktop icons, and randomly distributing same or different initial directions and initial speeds to all the desktop icons of the current desktop; detecting whether collision occurs among the icons or not in real time; if yes, playing a pre-stored first collision sound, and calculating respective motion directions and motion speeds of two collided icons according to the momentum conservation law and the energy conservation law; detecting whether the icons collide with the edge of a touch screen or not in real time; if yes, playing a pre-stored second collision sound, wherein the icons rebound in a collision speed. After the vivid and interesting desktop icon displaying method and device is applied, the terminal desktop displays showy dynamic effect and makes the icon collision sounds, and users can interact with the desktop and optionally change motion state of the icons, so that much interestingness is realized, and the users have a lot of fun and good use and operation experiences.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
System and method for estimating post-collision vehicular velocity changes
A system and method that utilizes information relating to vehicle damage information including damaged vehicle area information, crush depth of the damaged areas information, and vehicle component-by-component damage information to estimate the relative velocities of vehicles involved in a collision. The change in velocity is estimated using a plurality of methods, and a determination is made as to which method provided a result that is likely to be more accurate, based on the damage information, and the types of vehicles involved. The results from each method may also be weighted and combined to provide a multi-method estimate of the closing velocity. The methods include using crash test data from one or more sources, estimating closing velocity based on the principals of conservation of momentum, and estimating closing velocity based on deformation energy resulting from the collision.
Owner:CCC INFORMATION SERVICES
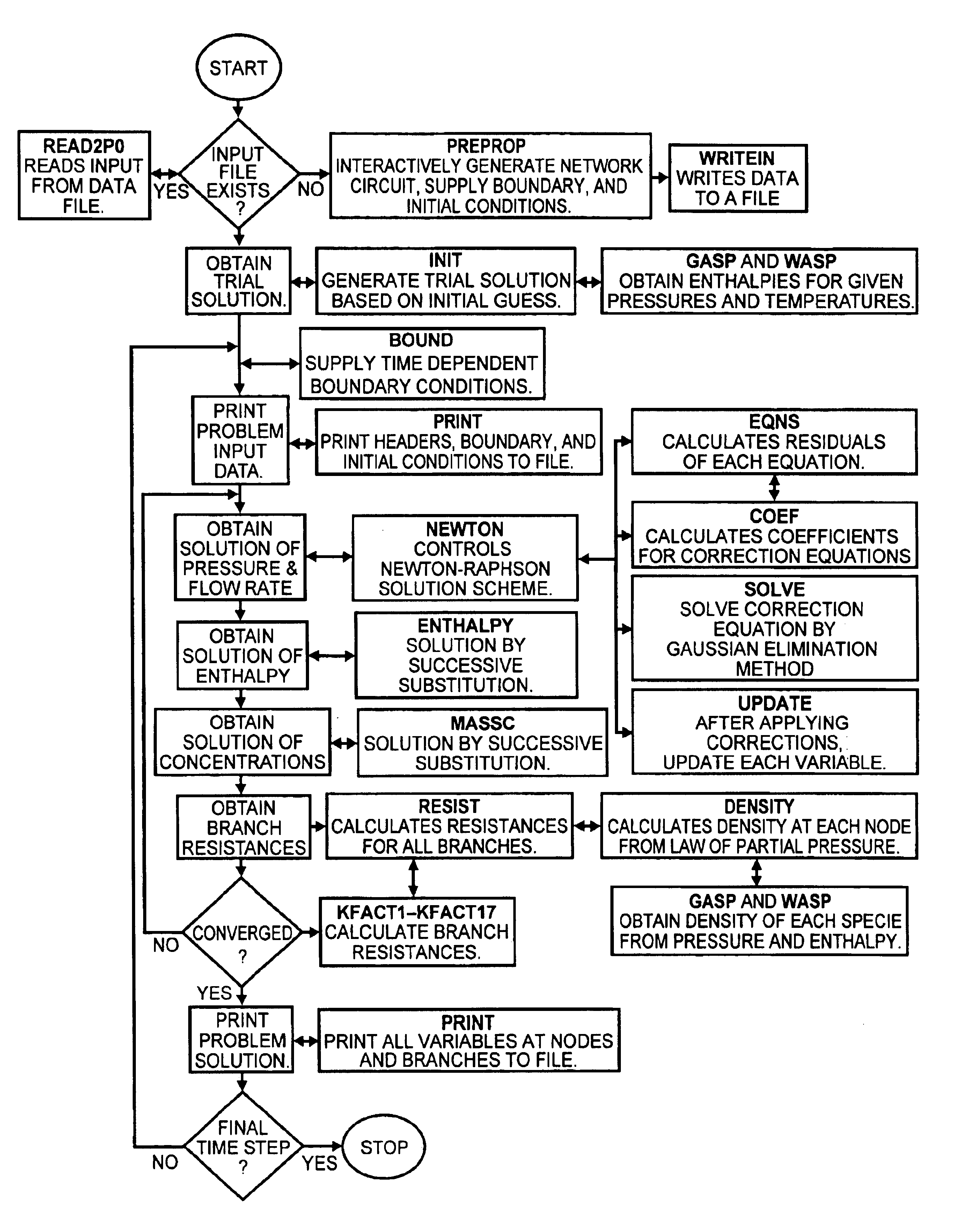
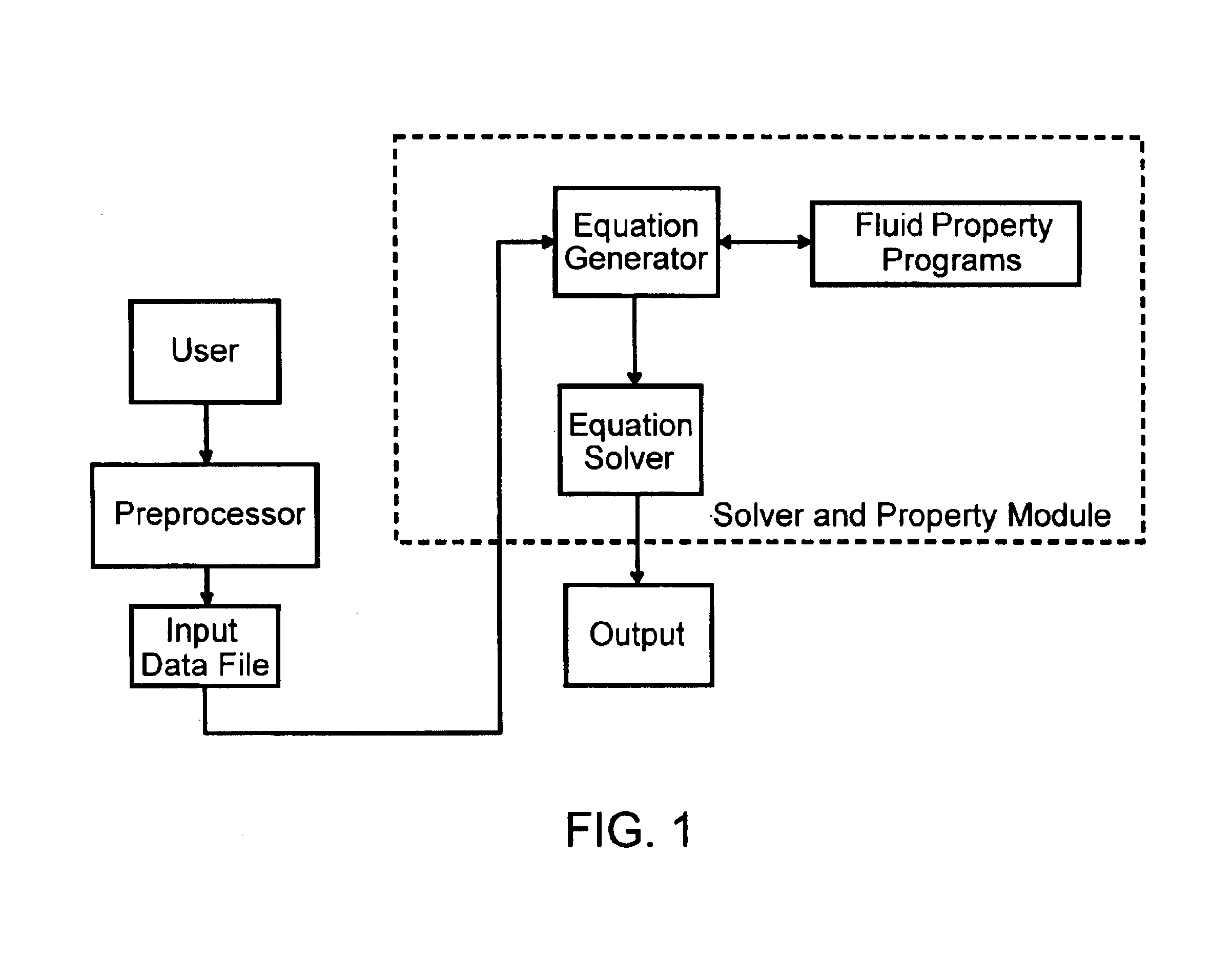
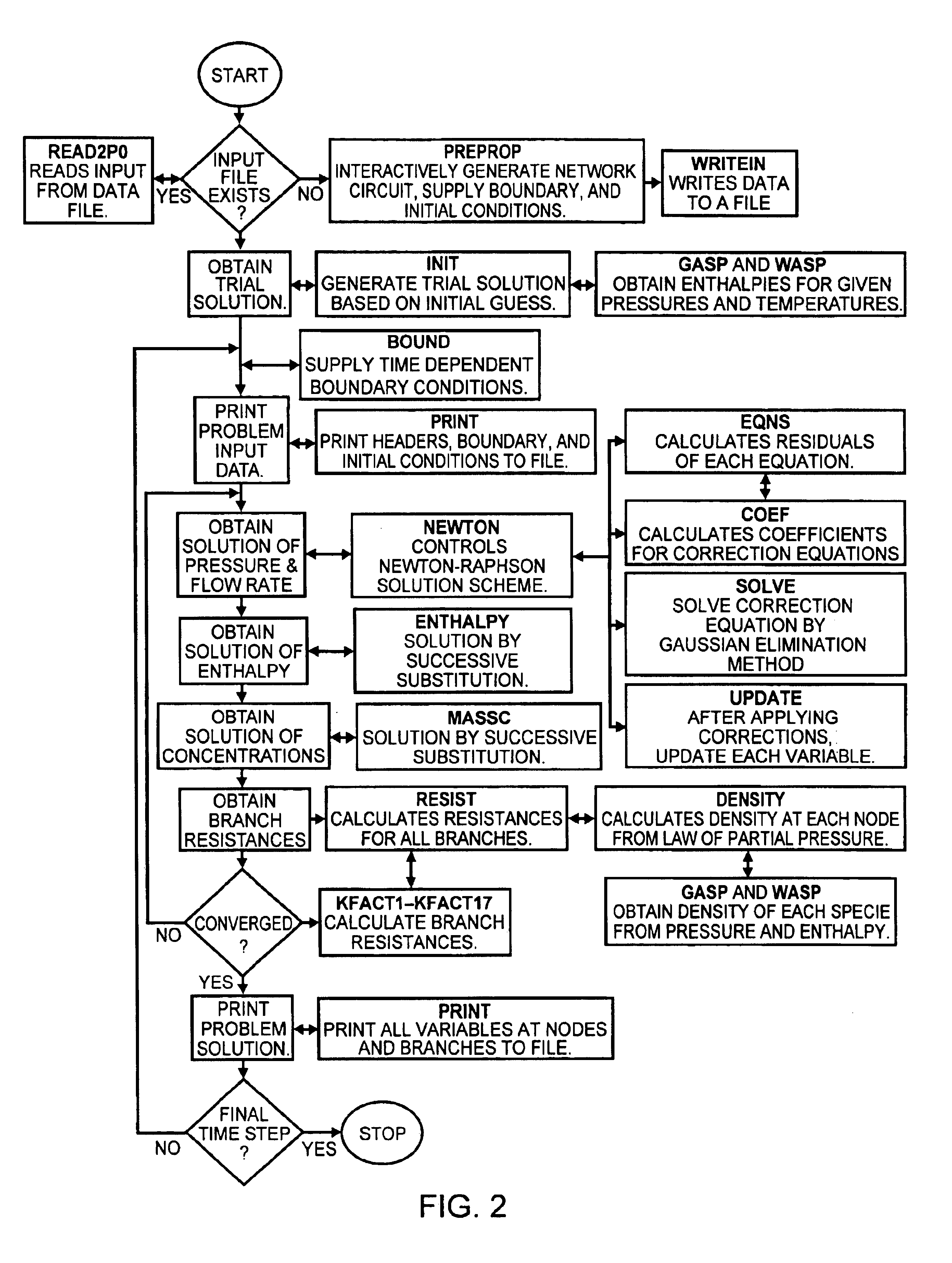
Generalized fluid system simulation program
InactiveUS6748349B1Simulator controlComputation using non-denominational number representationCompressibilitySubstitution method
A general purpose program implemented on a computer analyzes steady state and transient flow in a complex fluid network, modeling phase changes, compressibility, mixture thermodynamics and external body forces such as gravity and centrifugal force. A preprocessor provides for the interactive development of a fluid network simulation having nodes and branches. Mass, energy, and specie conservation equations are solved at the nodes, and momentum conservation equations are solved in the branches. Contained herein are subroutines for computing "real fluid" thermodynamic and thermophysical properties for 12 fluids, and a number of different source options are provided for modeling momentum sources or sinks in the branches. The system of equations describing the fluid network is solved by a hybrid numerical method that is a combination of the Newton-Raphson and successive substitution methods. Application and verification of this invention are provided through an example problem, which demonstrates that the predictions of the present invention compare most reasonably with test data.
Owner:NASA
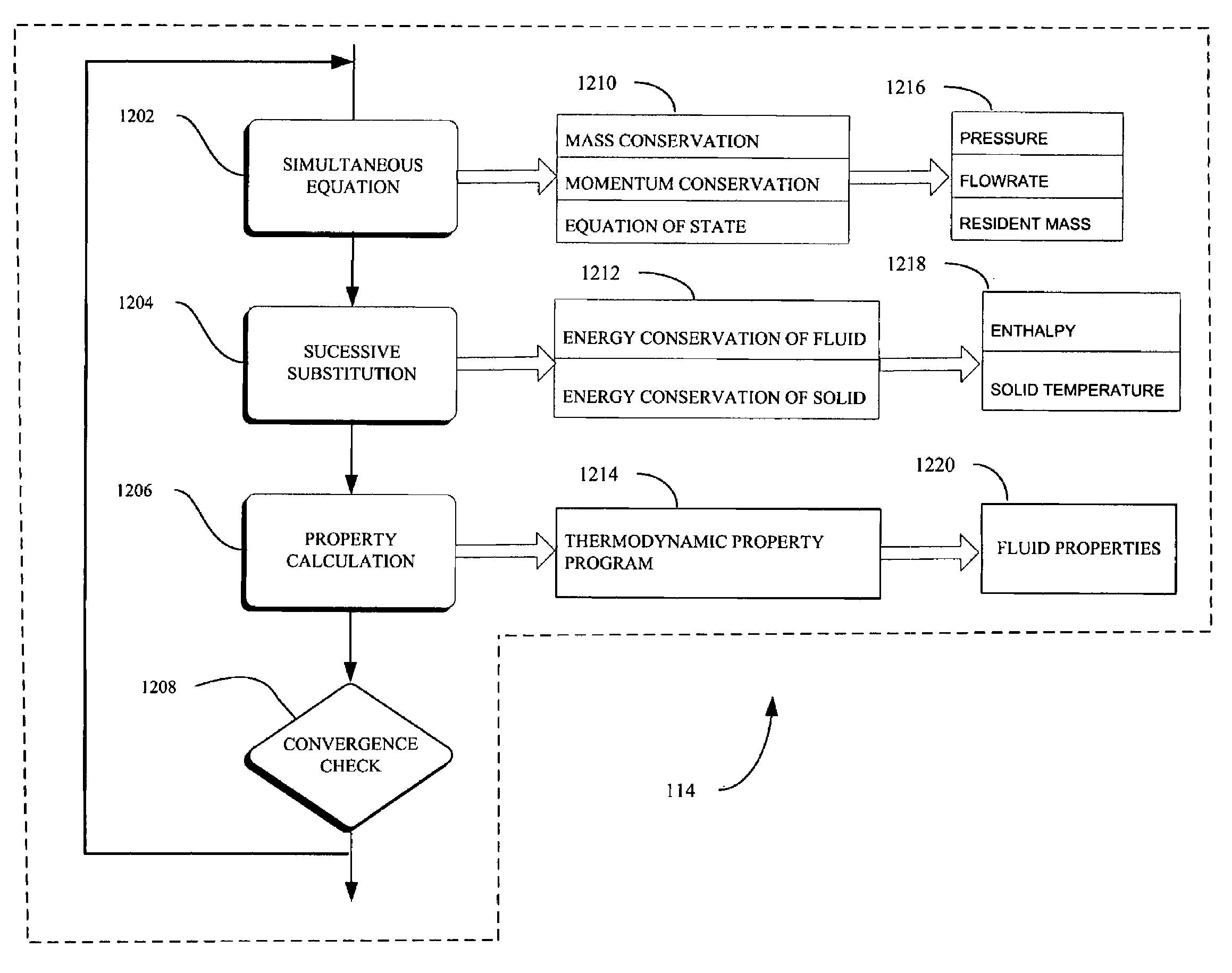
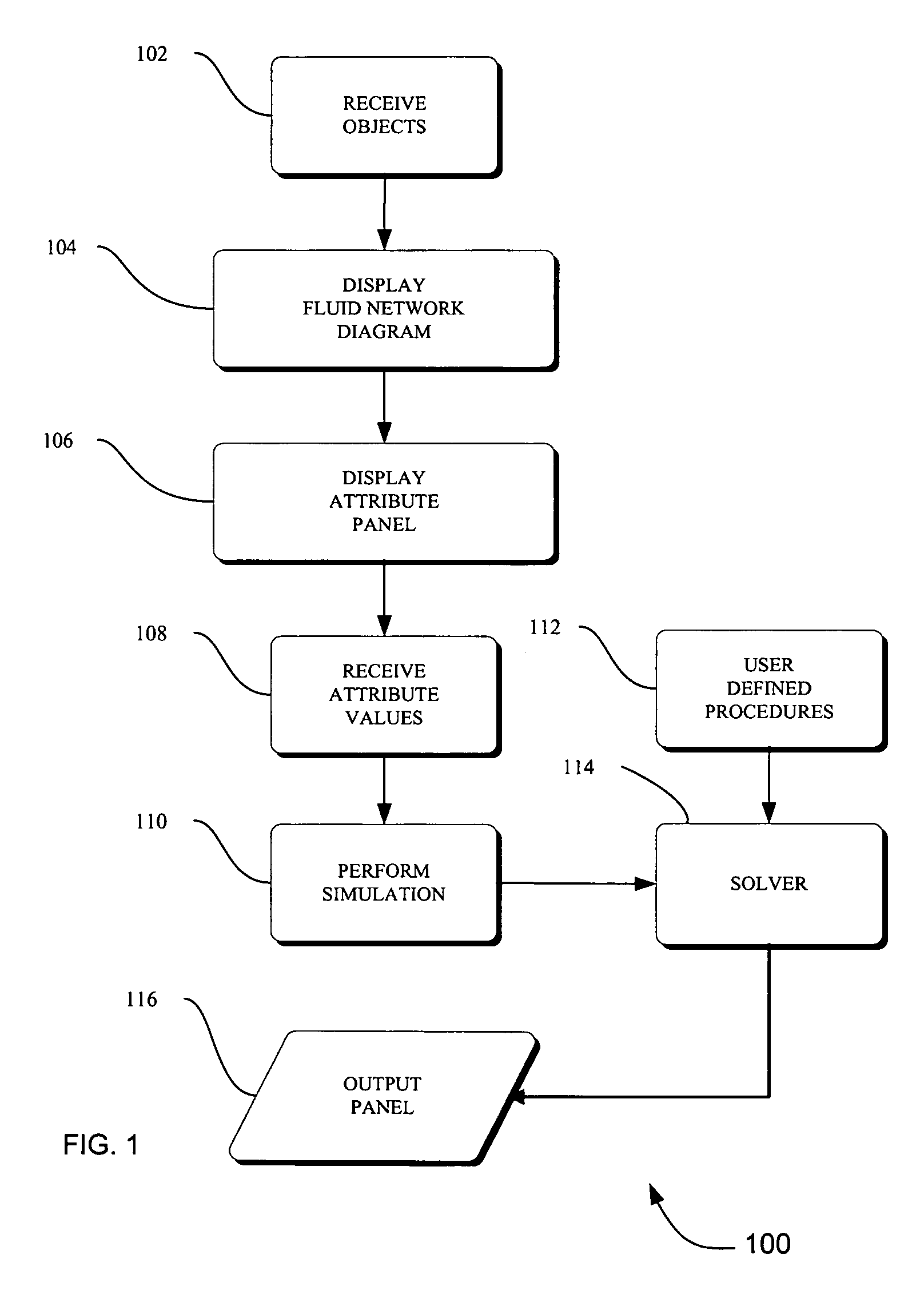
Method and apparatus for predicting unsteady pressure and flow rate distribution in a fluid network
InactiveUS7542885B1Computer controlComputation using non-denominational number representationCompressibilitySubstitution method
A method and apparatus for analyzing steady state and transient flow in a complex fluid network, modeling phase changes, compressibility, mixture thermodynamics, external body forces such as gravity and centrifugal force and conjugate heat transfer. In some embodiments, a graphical user interface provides for the interactive development of a fluid network simulation having nodes and branches. In some embodiments, mass, energy, and specific conservation equations are solved at the nodes, and momentum conservation equations are solved in the branches. In some embodiments, contained herein are data objects for computing thermodynamic and thermophysical properties for fluids. In some embodiments, the systems of equations describing the fluid network are solved by a hybrid numerical method that is a combination of the Newton-Raphson and successive substitution methods.
Owner:NASA
Aero-engine nonlinear model modeling method
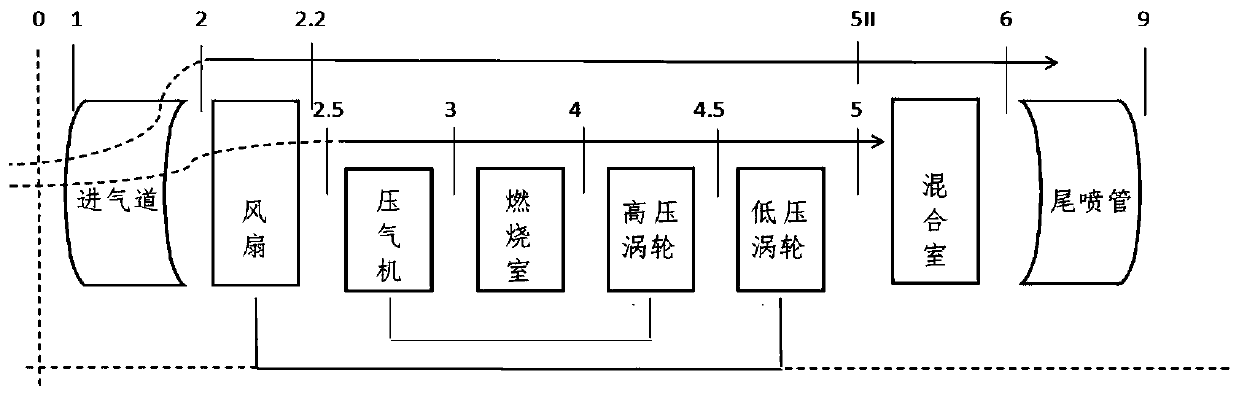
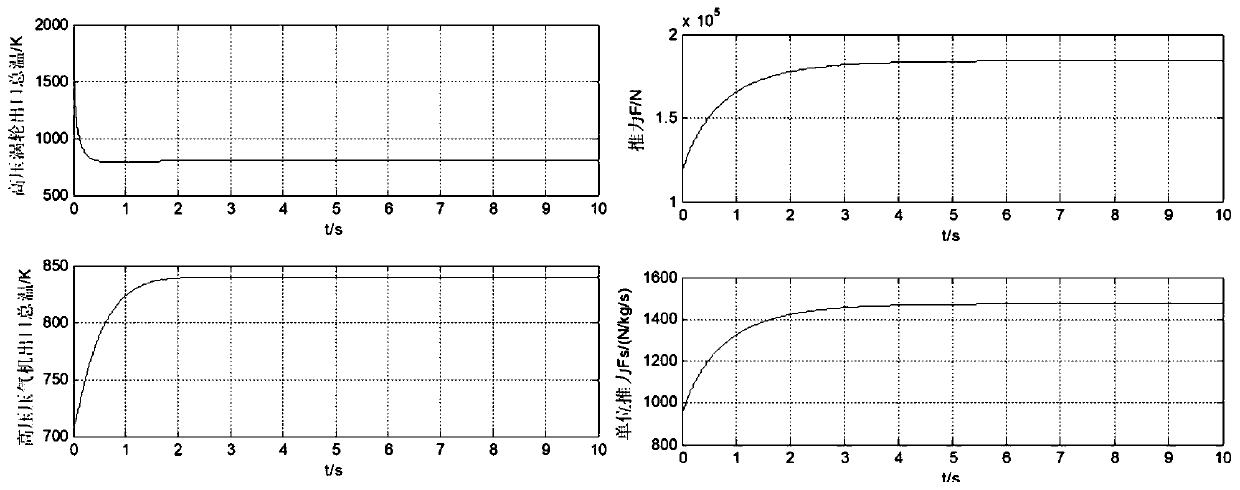
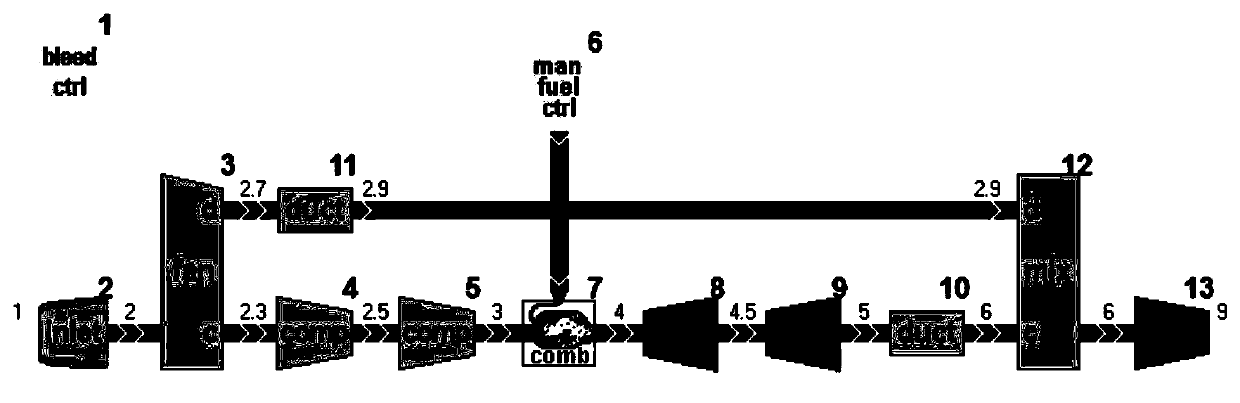
The invention belongs to the technical field of aero-engines, and particularly relates to an aero-engine nonlinear model modeling method. The method comprises the following steps: calculating an engine design point nonlinear model, and calculating a transmitter transition state nonlinear model; the method comprises the steps that an engine subsection model is established, and the model is mainly divided into an air inlet channel, a fan, a gas compressor, a combustion chamber, a turbine and an exhaust port according to the structure and function of an aero-engine; describing the aerothermodynamic law obeyed by each component during working by using a nonlinear equation in sequence, and establishing a component-level model of an aeroengine design point; the latter assumes that the characteristics of the parts in the transition state are the same as those in the steady state, and the volume effect of the parts is considered in numerical simulation in the transition state; only the volumetric effect of parts with large volumes is considered in calculation, and meanwhile momentum conservation is simplified to be replaced by the total pressure recovery coefficient of the channel, so thatenough engineering precision can be ensured, and calculation is greatly simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
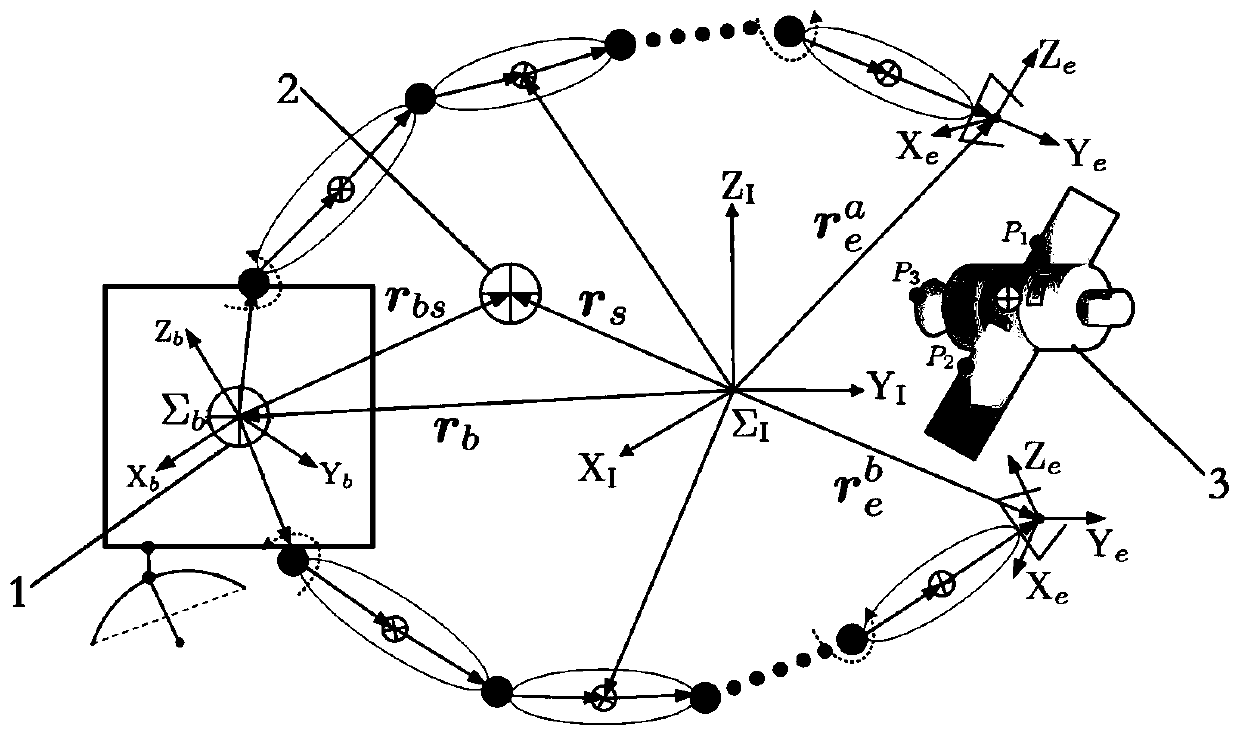
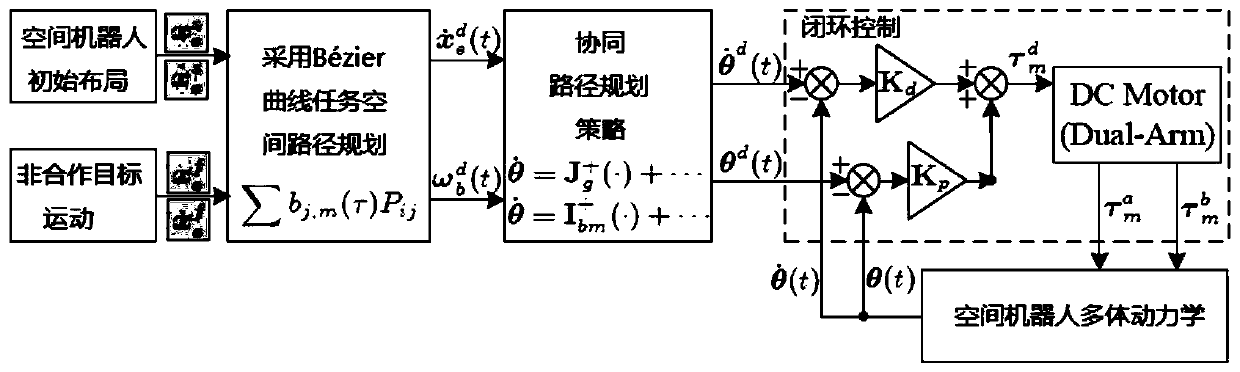
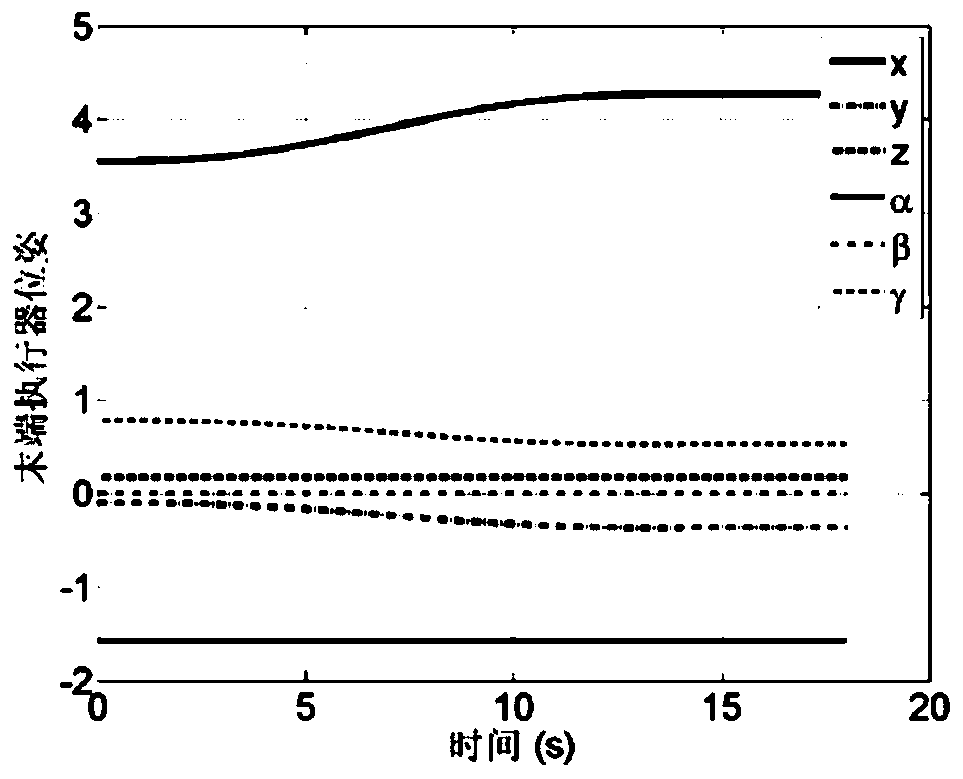
Collaborative path planning method for kinematic redundant two-arm space robot
ActiveCN110104216AImplementing a collaborative path planning methodSmall attitude disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic vehiclesKinematics equationsDynamic balance
The invention discloses a collaborative path planning method for a kinematic redundant two-arm space robot. The collaborative path planning method for the kinematic redundant two-arm space robot comprises the following steps that a dynamic equation and a kinematic equation of a space robot system are established; a redundant solution of an inverse kinematics equation of an end-effector is solved,and a system non-holonomic constraint equation is obtained through a momentum conservation equation; a task space constraint equation of the relationship between the end-effector motion and the attitude of a base is obtained through the system non-holonomic constraint equation; the path planning of the end-effector in a task space is obtained by using a quintic bezier curve, and path execution time is determined by the velocity and acceleration boundary of the end-effector; and the joint motion trajectory planning corresponding to different task priorities is obtained through the end-effectormotion equation and the task space constraint equation. The collaborative path planning method of the space two-arm robot is implemented, various tasks can be performed according to the priorities ofthe tasks such as a multi-arm collaborative task and a dynamic balancing task, and the operation ability of a space manipulator is greatly expanded.
Owner:RES & DEV INST OF NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV IN SHENZHEN +1
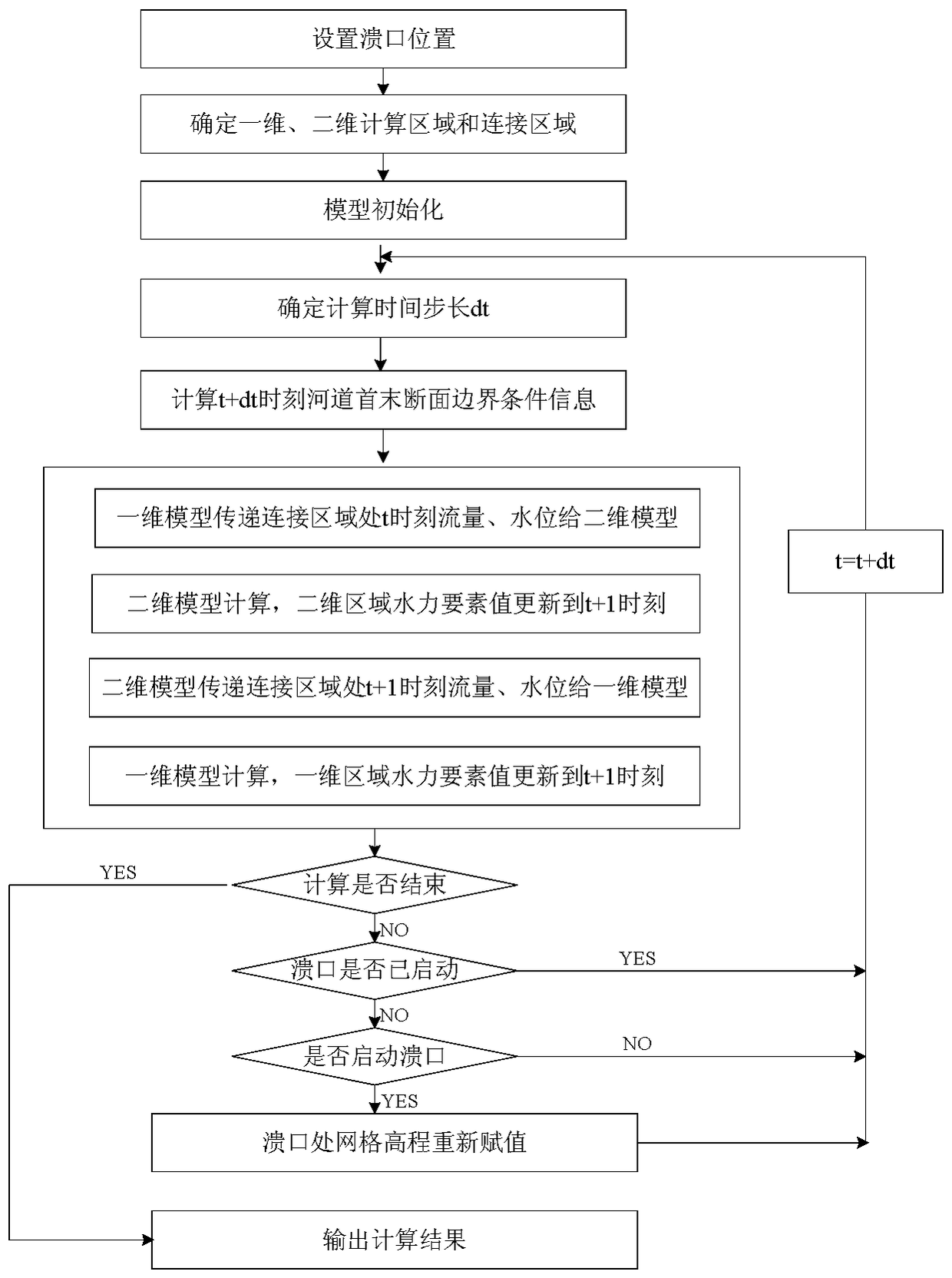
Coupling analysis method for one-dimensional mathematical model and two-dimensional mathematical model of river way outburst flood
ActiveCN108256193AImprove calculation accuracyQuality assuranceClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationShock waveResponse process
The invention provides a coupling analysis method for a one-dimensional mathematical model and two-dimensional mathematical model of river way outburst flood. After corresponding data is collected, adyke breach outflux inundated area and a river way section obviously influenced by dyke breach outflux are first dispersed by using a quadrilateral or triangular unstructured grid, and other river sections adopt one-dimensional cross-section data generalization. The one-dimensional model is solved by adopting a classical Presimann implicit format, the two-dimensional model is solved by adopting aGodunov format with a shock capturing ability. In order to avoid numerical oscillation, mass conservation and momentum conservation of the connection portion between the one-dimensional mathematical model and the two-dimensional mathematical model are ensured; according to the coupling analysis method for the one-dimensional mathematical model and two-dimensional mathematical model of river way outburst flood, provided connection portion is a transition region, one-dimensional model calculation and two-dimensional model calculation are both conducted in the transition region. After the dyke breach is started, the dyke breach outflux inundated area and a river way two-dimensional computing area automatically become an integrated two-dimensional computing area, and the calculation of dyke breach outflux process is completed by the two-dimensional model. The processing method can fully consider the hydrodynamic response process inside and outside the river way on the dyke breach, the numerical simulation precision of the dyke breach outflux process is improved, and the shortcoming in a traditional method is overcome that only a weir formula is adopted to calculate the dyke breach outflux process, so that the momentum exchange inside and outside the river way can not be considered.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Gaussian distribution-based wind turbine generator set wake flow analyzing and modeling method
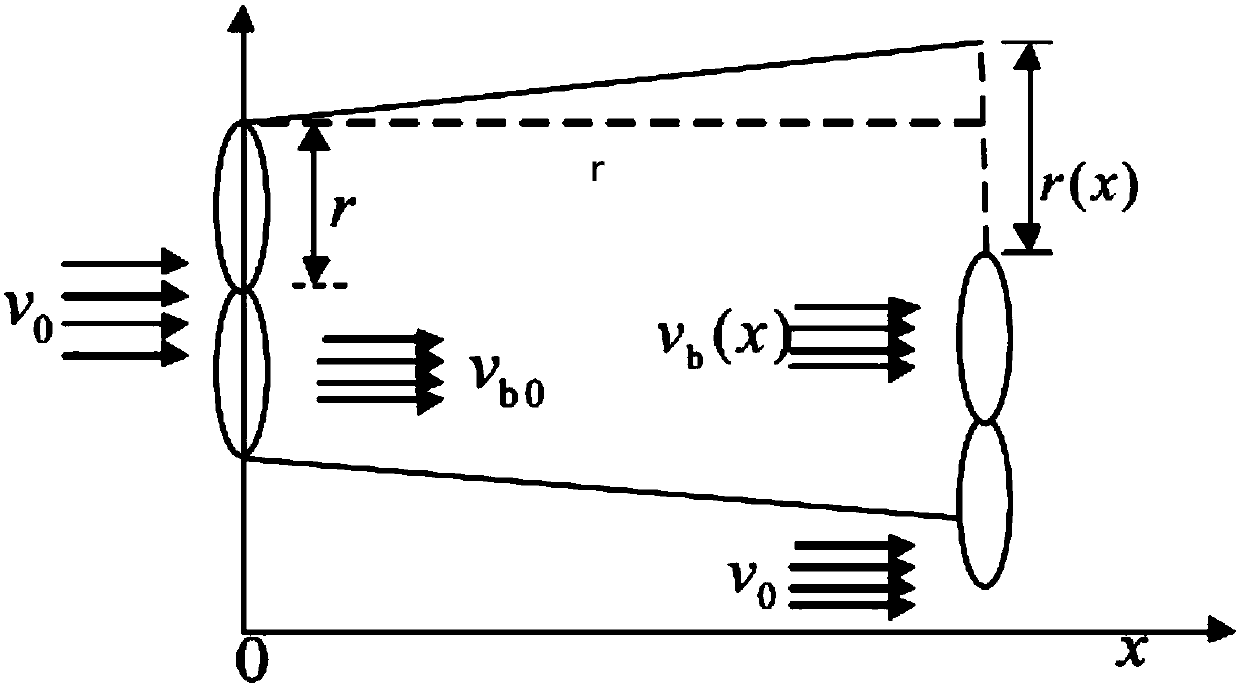
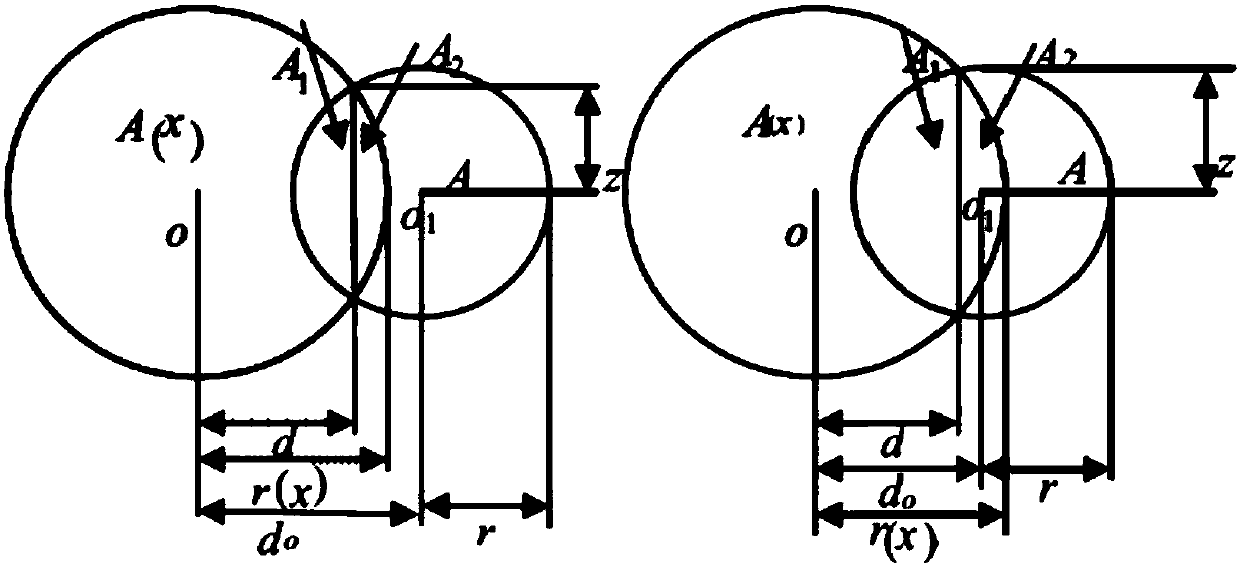
ActiveCN108108562AThe result is accurateUnity of formDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityModel method
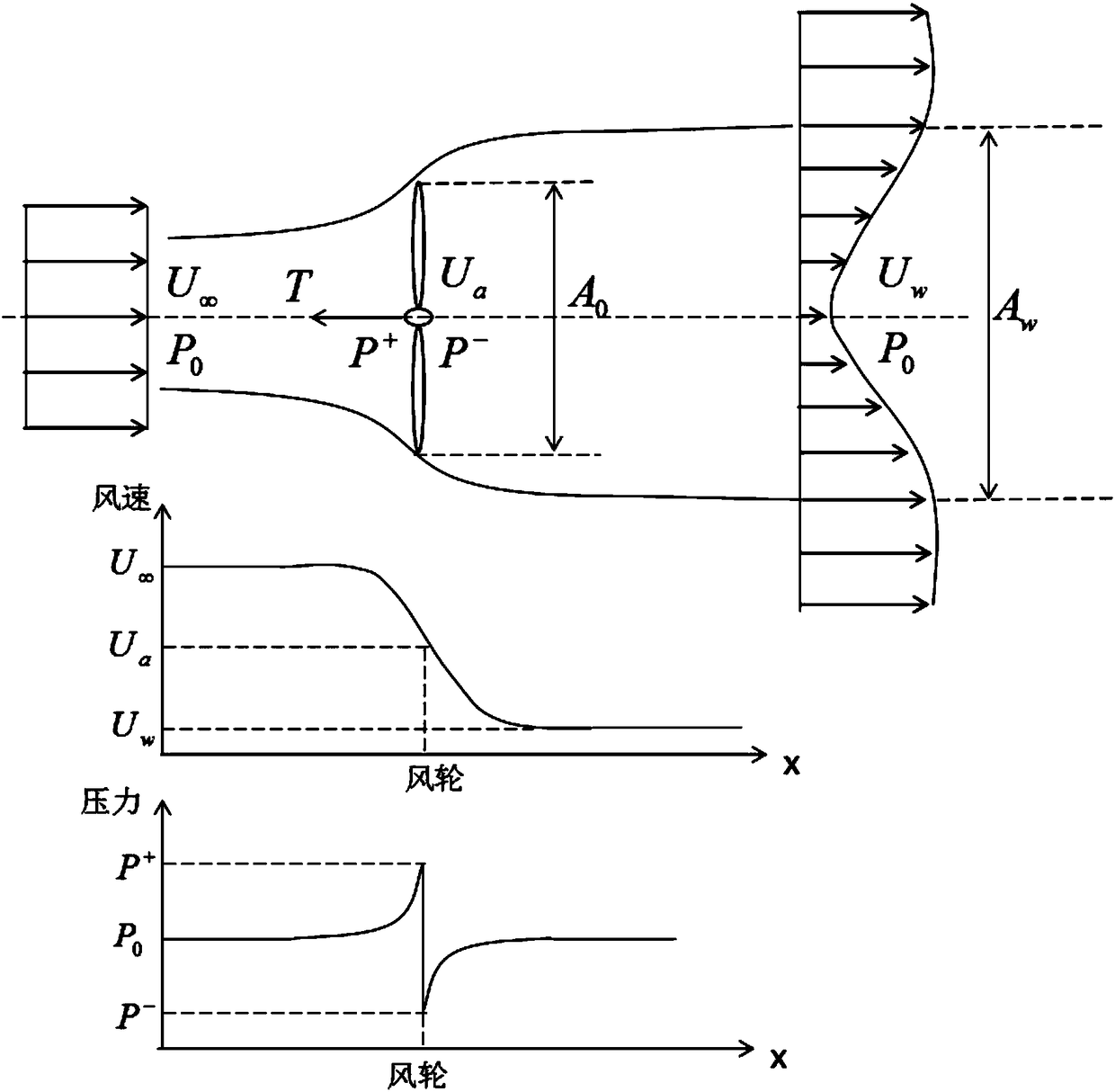
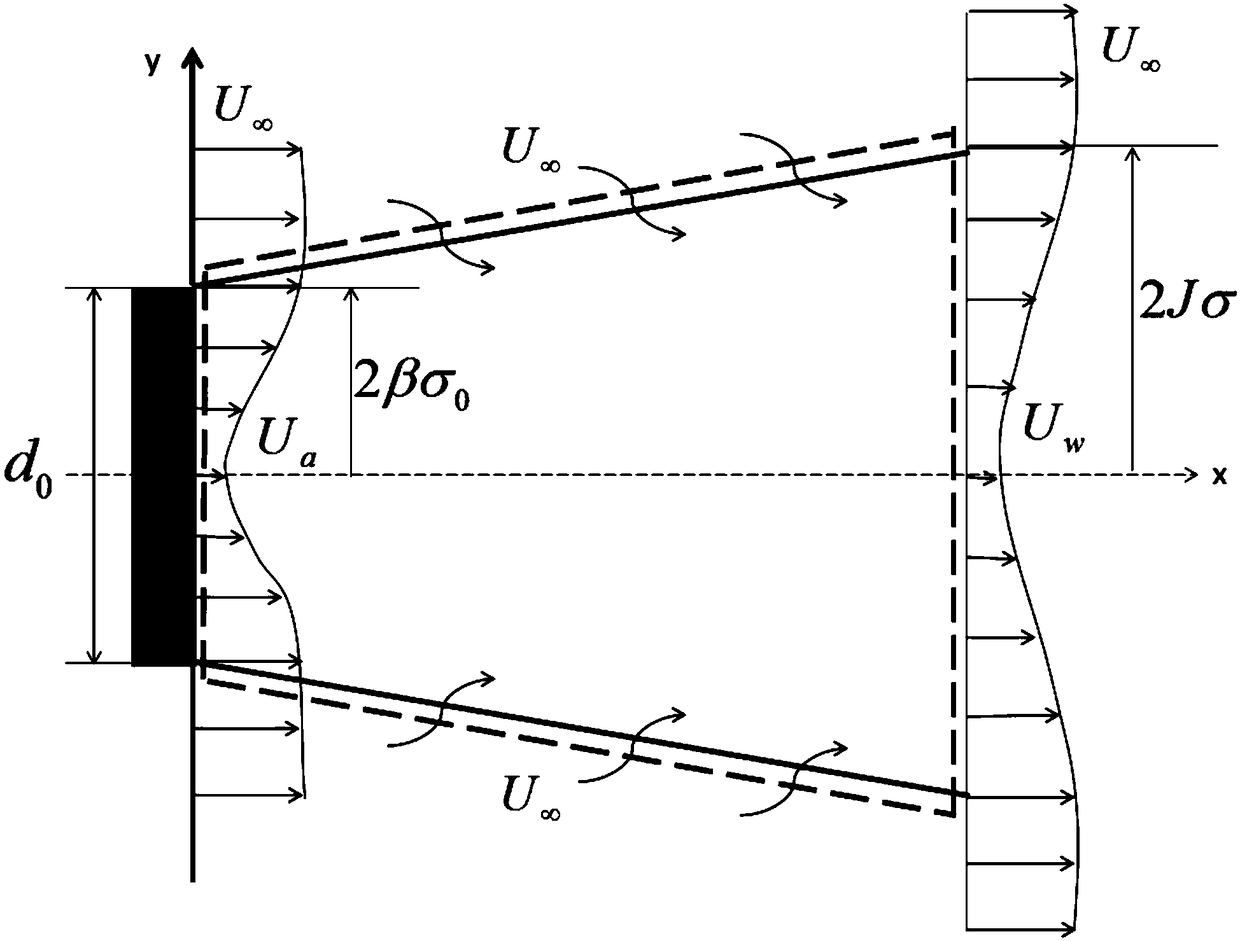
The invention belongs to the technical field of wind power generation micro-sitting selection and particularly relates to a Gaussian distribution-based wind turbine generator set wake flow analyzing and modeling method. The Gaussian distribution-based wind turbine generator set wake flow analyzing and modeling method, under the premise of appropriate assumptions, by combining the law of conservation of mass and the law of one-dimensional momentum conservation and according to the laws that wind speed loss radially follows Gaussian distribution and wake flow radius presents linear expansion, deducing a calculation model of wind turbine generator set wake zone wind speed distribution; according to analysis on wake flow speeds of different downstream positions, determining the value range ofdownstream wake boundary coefficients; by combining with the expansion law of wind turbine wake flow, determining the value range of wind turbine wake flow boundary coefficients. A simplified wake flow model acquired through the Gaussian distribution-based wind turbine generator set wake flow analyzing and modeling method can help rapidly, easily, conveniently and accurately calculate out wind speed distribution of wind turbine generator set wake zones and provide reference for taking into consideration wake flow effects during wind power generation micro-sitting selection.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method of evaluation wind flow based on conservation of momentum and variation in terrain
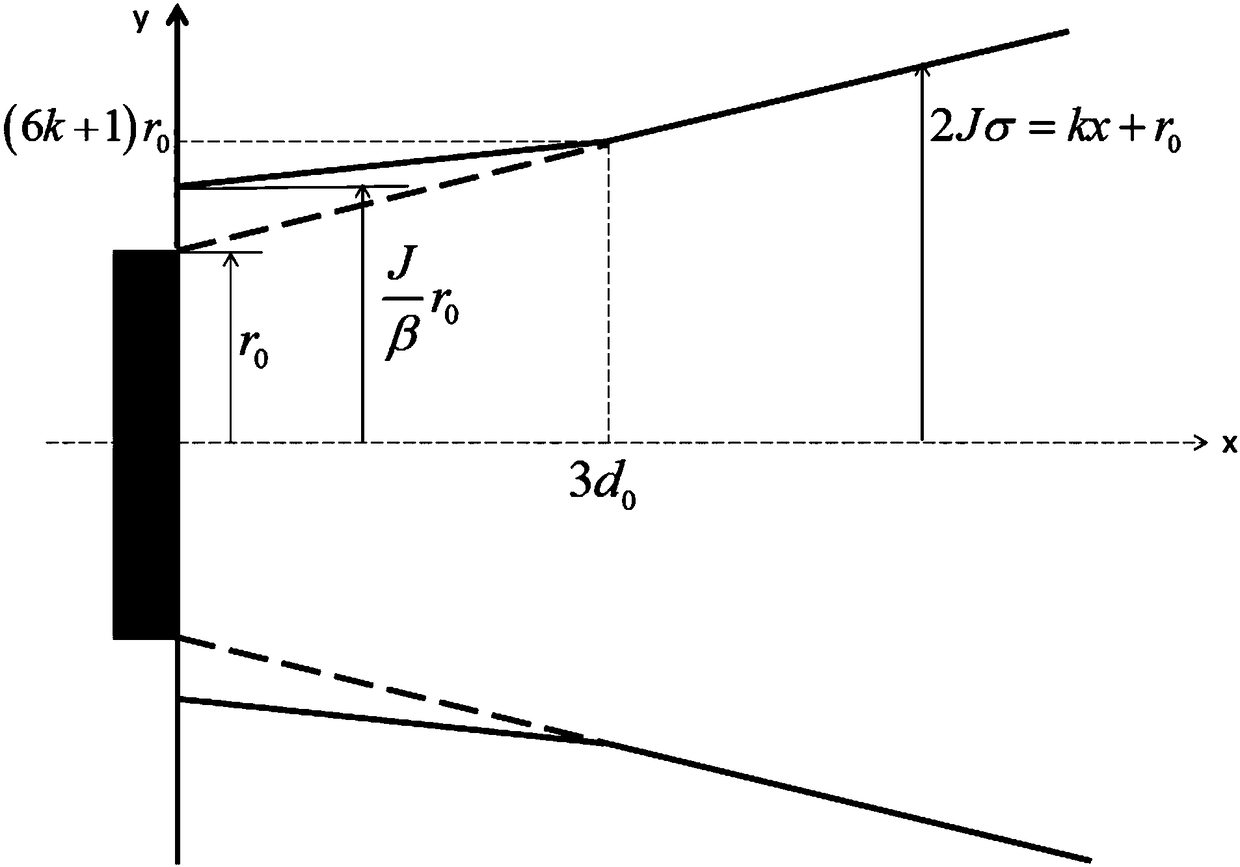
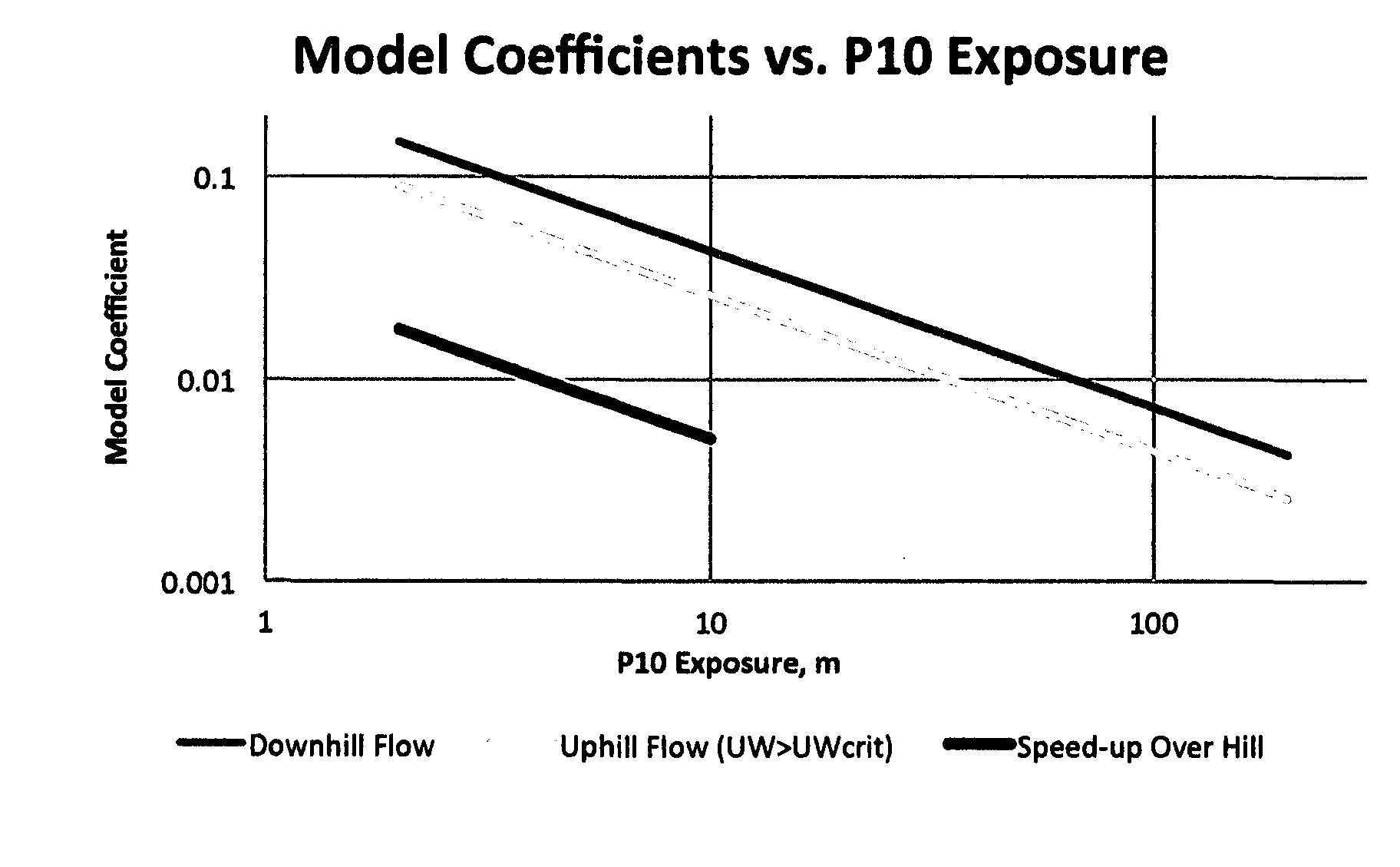
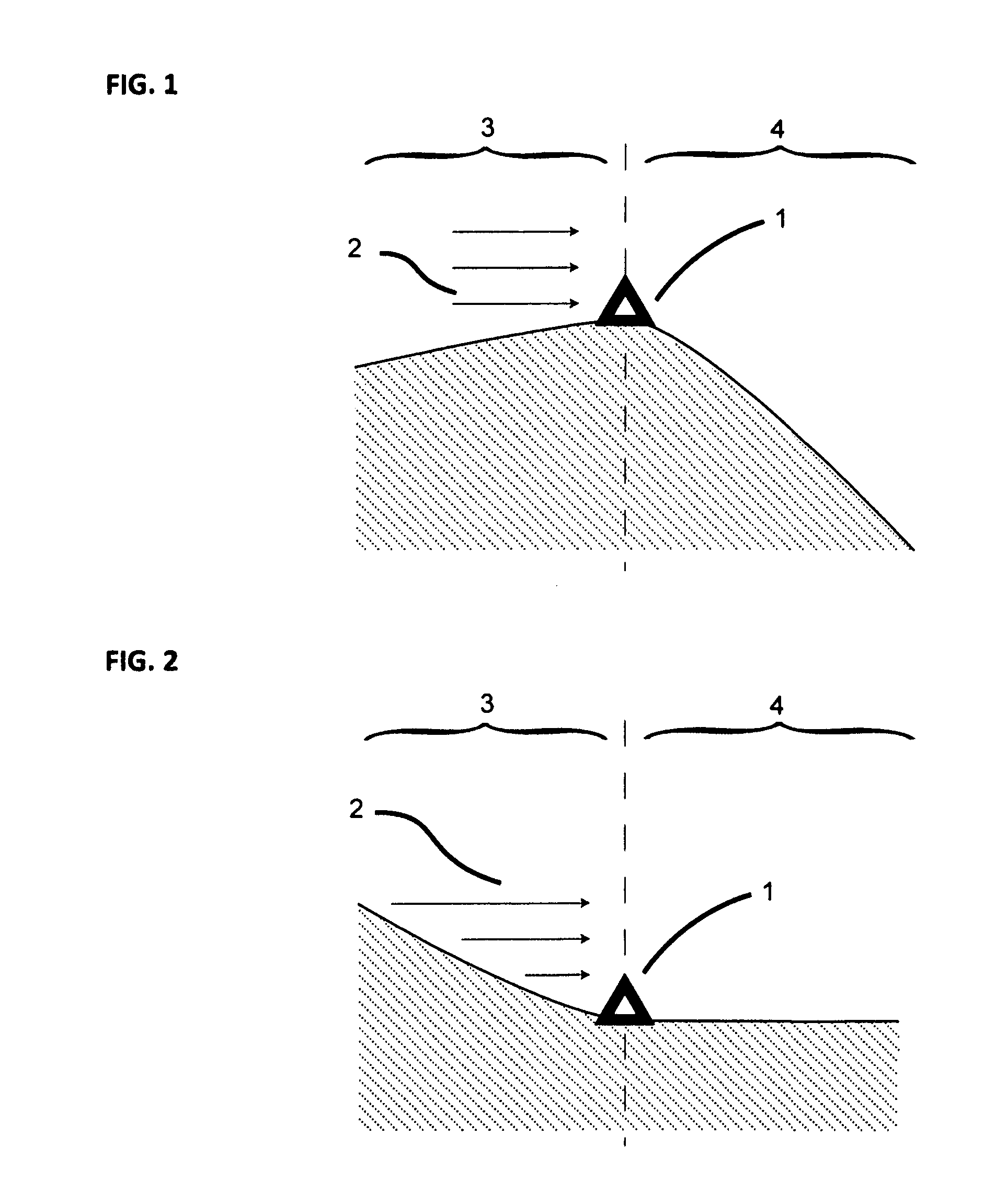
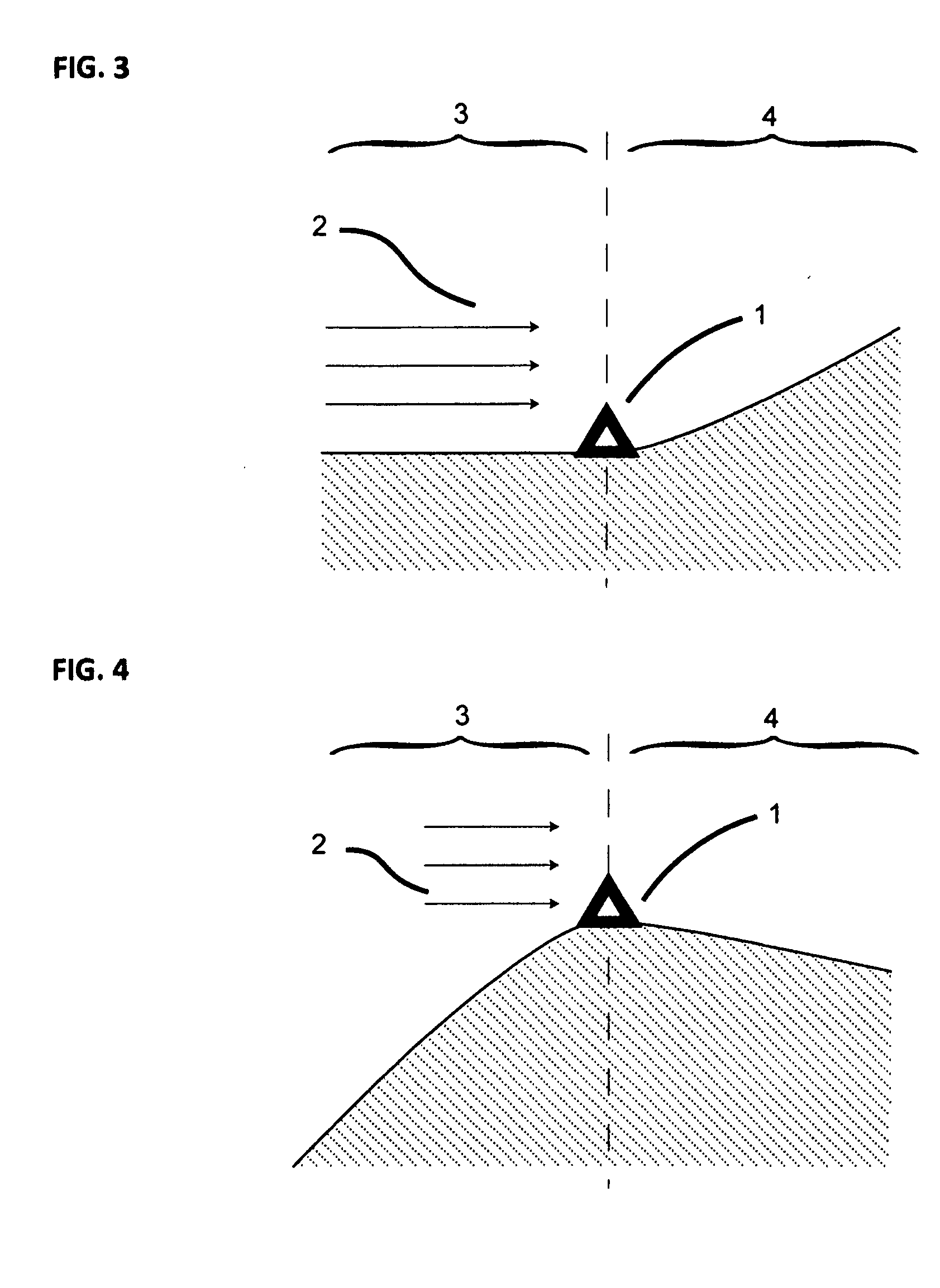
A method of modeling the spatial variation in wind resource at a prospective wind farm site. The method involves a simplified analysis of the Navier-Stokes equation and utilizes data from all of the met sites simultaneously to develop site-calibrated models. The model coefficients, mUW and mDW, describe the sensitivity of the wind speed to changes in the upwind and downwind terrain exposure and are defined for downhill and uphill flow. The coefficients are a function of terrain complexity and, since terrain complexity can change across an area, the estimates are performed in a stepwise fashion where a path of nodes with a gradual change in complexity is found between each pair of sites. Also, coefficients are defined for each wind direction sector and estimates are performed on a sectorwise basis. The site-calibrated models are created by cross-predicting between each pair of met sites and, through a self-learning technique, the model coefficients that yield the minimum met cross-prediction error are found.
Owner:ONE ENERGY ENTERPRISES INC
Automatic balancing device and method of motorcycle-type robot
ActiveCN107728635AAchieve upright self-balancingImplement searchAttitude controlMotor driveDevice form
The invention discloses an automatic balancing device and method of a motorcycle-type robot. The automatic balancing device is applied to the motorcycle-type robot, the motorcycle-type robot and the automatic balancing device form a single-dimensional inverted pendulum structure supported by two points, upright automatic balance of the motorcycle-type robot is achieved through the adoption of themomentum exchange principle in the inverted pendulum principles and according to the momentum conservation law; the automatic balancing device comprises a gesture collector for detecting gesture dataof a motorcycle body tilting leftwards and rightwards, a momentum wheel, a motor driving the momentum wheel to rotate and a motorcycle body controller connected with the gesture collector and the motor separately, the motorcycle body controller obtains the rotation data of the momentum wheel and the gesture data and utilizes a control algorithm to control the motor to output motor rotation data corresponding to the gesture data and the rotation data, and therefore the momentum wheel is controlled to rotate to achieve the upright automatic balance of the motorcycle-type robot.
Owner:北京赛曙科技有限公司
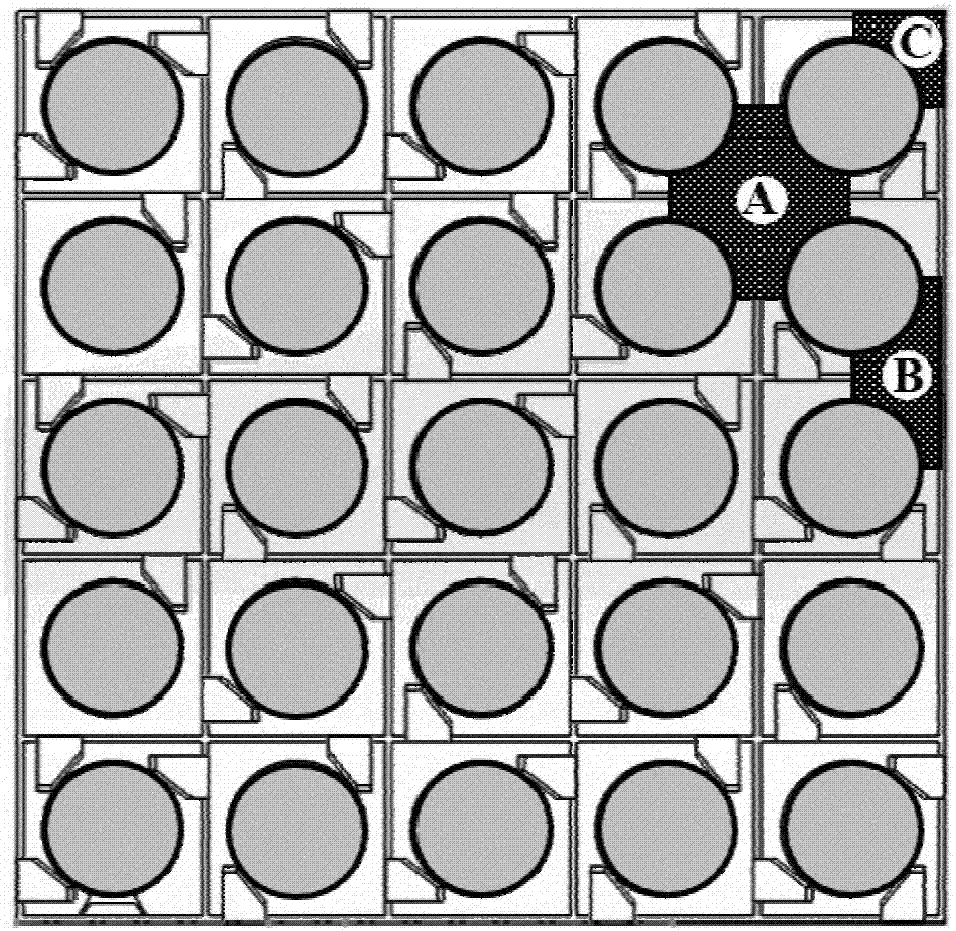
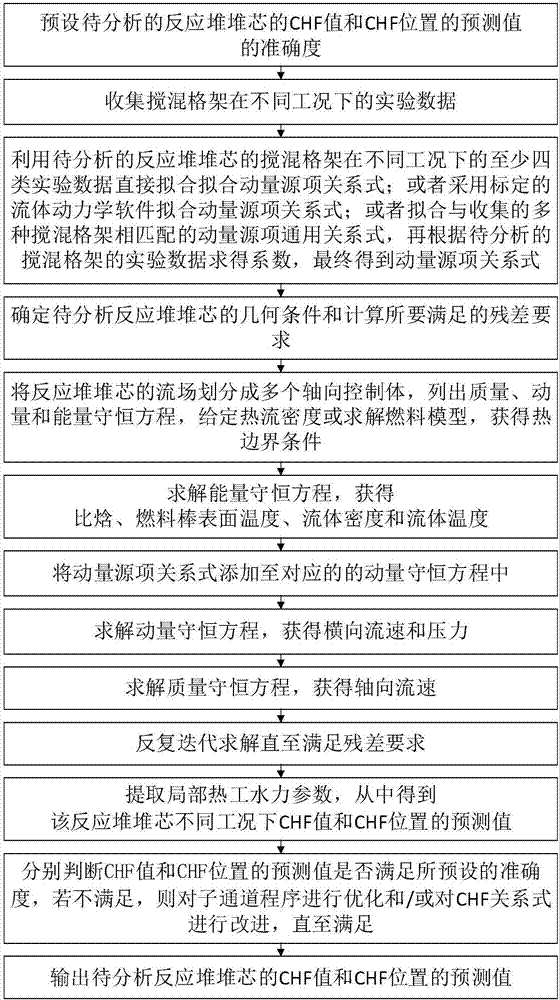
Resistance distribution-based method for analyzing sub-channel with grid mixing effect
ActiveCN106897478AAccurately reflectImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAnalysis methodMixing effect
The invention discloses a resistance distribution-based method for analyzing a sub-channel with a grid mixing effect. The method comprises the steps of collecting experimental data of multiple mixing grids including a mixing grid of a to-be-analyzed reactor core in different working conditions, fitting a momentum source term relational expression capable of reflecting mixing performance of key parts of the mixing grids, and adding the momentum source term relational expression to a corresponding momentum conservation equation; and by solving a mass conservation equation, the momentum conservation equation and an energy conservation equation, obtaining more accurate local thermo-hydraulic parameters in the reactor core, thereby enabling prediction of a critical heat flux (CHF) value and a CHF position to be more accurate. The method is not limited by a structure and a solving method of a sub-channel program, and can be widely applied to the calculation of various types of sub-channel programs including a sub-channel program of a uniform flow model, a drift flow model or a two-fluid model.
Owner:青岛德能创新科技有限公司
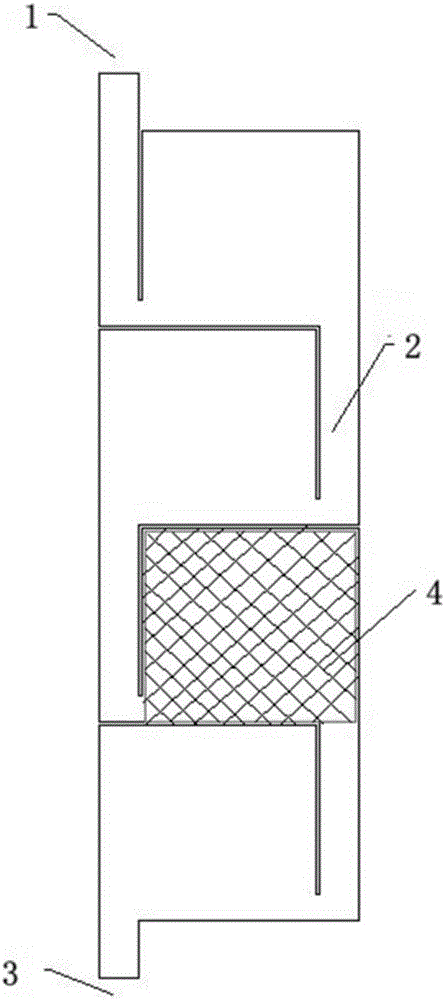
Photoetching machine workpiece stage magnetic preloading balance positioning system
InactiveCN102393611AHigh motion positioning accuracyGood real-time compensationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringPositioning system
A photoetching machine workpiece stage magnetic preloading balance positioning system belongs to the field of semiconductor photoetching technology; the system mainly comprises a base stage, a balance mass system, a magnetic preloading system, a motion unit, a silicon wafer stage, and a balance mass drift-resistant system; the balance mass system comprises two frames which nest each other, and has freedom degrees in the X and Y directions; the motion unit is disposed at the upper part; the impact force caused by the motion part to the base stage is weakened by momentum conservation principle;the balance mass drift-resistant system is used to compensate the position displacement of the balance mass system caused by external resistance during working; the magnetic preloading system is usedfor real-time compensation of the torsion of the workpiece stage along a Z axis; the invention can effectively reduce internal vibration, compensate the torsion of the workpiece stage along the Z axis, and thus greatly improve the motion positioning precision of the silicon wafer stage.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
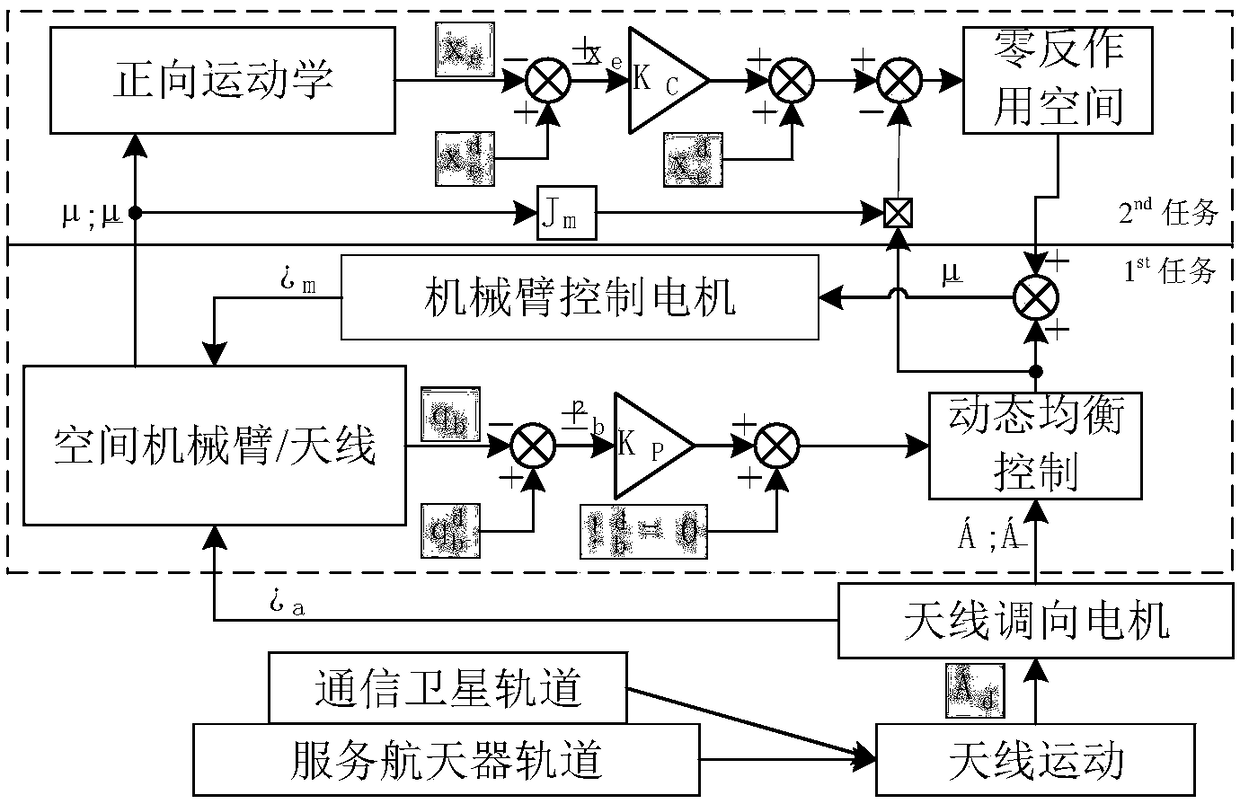
Method using mechanical arm to inhibit attitude interference of spacecraft pedestal
ActiveCN108132601AAttitude Interference SuppressionSuppress interferenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic vehiclesDynamic balanceDynamic models
The invention discloses a method using a mechanical arm to inhibit the attitude interference of a spacecraft pedestal. The method comprises the following steps that a many-body dynamic model is established according to configuration of a space robot, and a momentum conservation problem of the mechanical arm, an antenna and the pedestal is analyzed on the basis of the model; a track of the spatialmechanical arm is designed by considering the task priority on the basis of a dynamic balance control and zero-reaction space theory, so as to coordinate a tail-end executor task of the spatial mechanical arm and inhibit an attitude interference task of the satellite pedestal; and on the basis of the analysis, closed-loop inverse kinetic control of the spatial mechanical arm is designed, and the problem that error accumulation is increased gradually in pedestal attitude inhibition is solved. Concepts of dynamic balance control and zero reaction space are combined, and the track of the kineticredundancy mechanical arm is constructed to inhibit aircraft pedestal attitude interference caused by other rotation mechanisms.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
Method for testing actuating pressure of explosion contact surface of explosive and test device
The invention relates to a method for testing actuating pressure of an explosion contact surface of an explosive and a test device. According to the method, the purpose of test on the explosion pressure of the explosive under high temperature and high pressure (dozens of GPa) is achieved. The pressure on the explosion contact surface comprises change of pressure on the contact surface, which is caused by the pressure in an explosive detonation strengthening and attenuating process. Theoretical derivation for measuring the explosion pressure is realized by a higher mathematics calculus relation and value analysis method according to momentum conservation in order to realize measurement of the pressure on the explosion contact surface of the explosive. The test device is designed to comprise an explosion container, a throwing columnar rigid body, a high-speed camera, a data analysis system, a vacuum pump, a safety valve, a container for the throwing columnar rigid body, a detonation device and a scaleplate.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
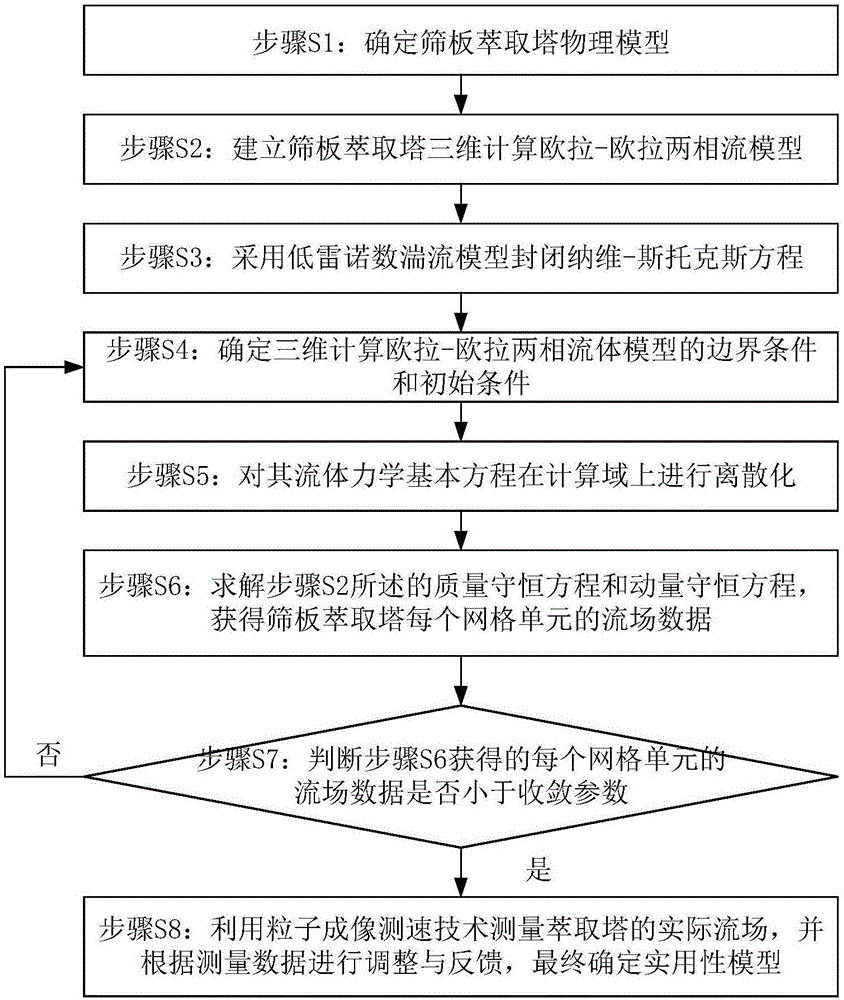
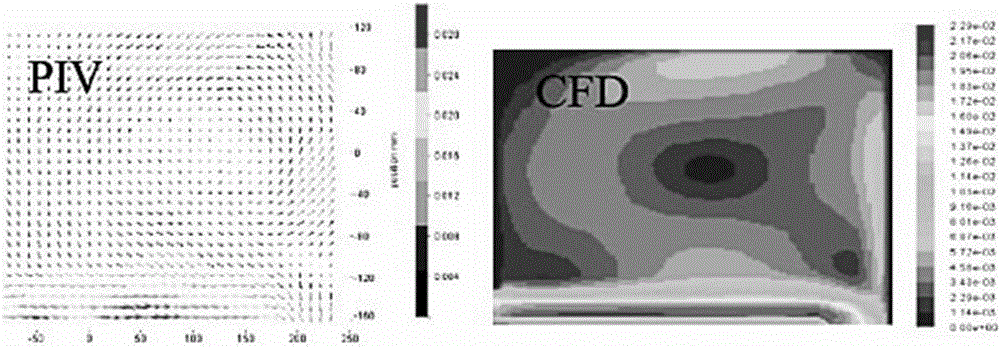
Method for calculating sieve plate extraction tower liquid flow field by using low Reynolds number turbulence model
InactiveCN106682348AAccurate calculation of hydrodynamic informationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPhysical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a method for calculating a sieve plate extraction tower liquid flow field by using a low Reynolds number turbulence model. The method includes the following steps: (1) determining a sieve plate extraction tower physical model; (2) establishing a sieve plate extraction tower three-dimensional calculation Euler-Euler two-phase flow model; (3) using the low Reynolds number turbulence model to seal a Navier-Stokes equation (N-S equation); (4) determining a boundary condition and an initial condition for solving the three-dimensional calculation Euler-Euler two-phase flow model; (5) performing discretization on a fluid mechanics basic equation in a computational domain; and (6) solving a mass conservation equation and a momentum conservation equation, and acquiring flow field data of each grid unit in the sieve plate extraction tower; and (7) measuring an actual flow field of the extraction tower by using a particle imaging velocity measurement technique, performing adjustment and feedback according to the measured data, and finally determining a practical model. The model method for precisely calculating the sieve plate extraction tower liquid flow field is implemented, and reliable fluid mechanics information for an actual design of the sieve plate extraction tower.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
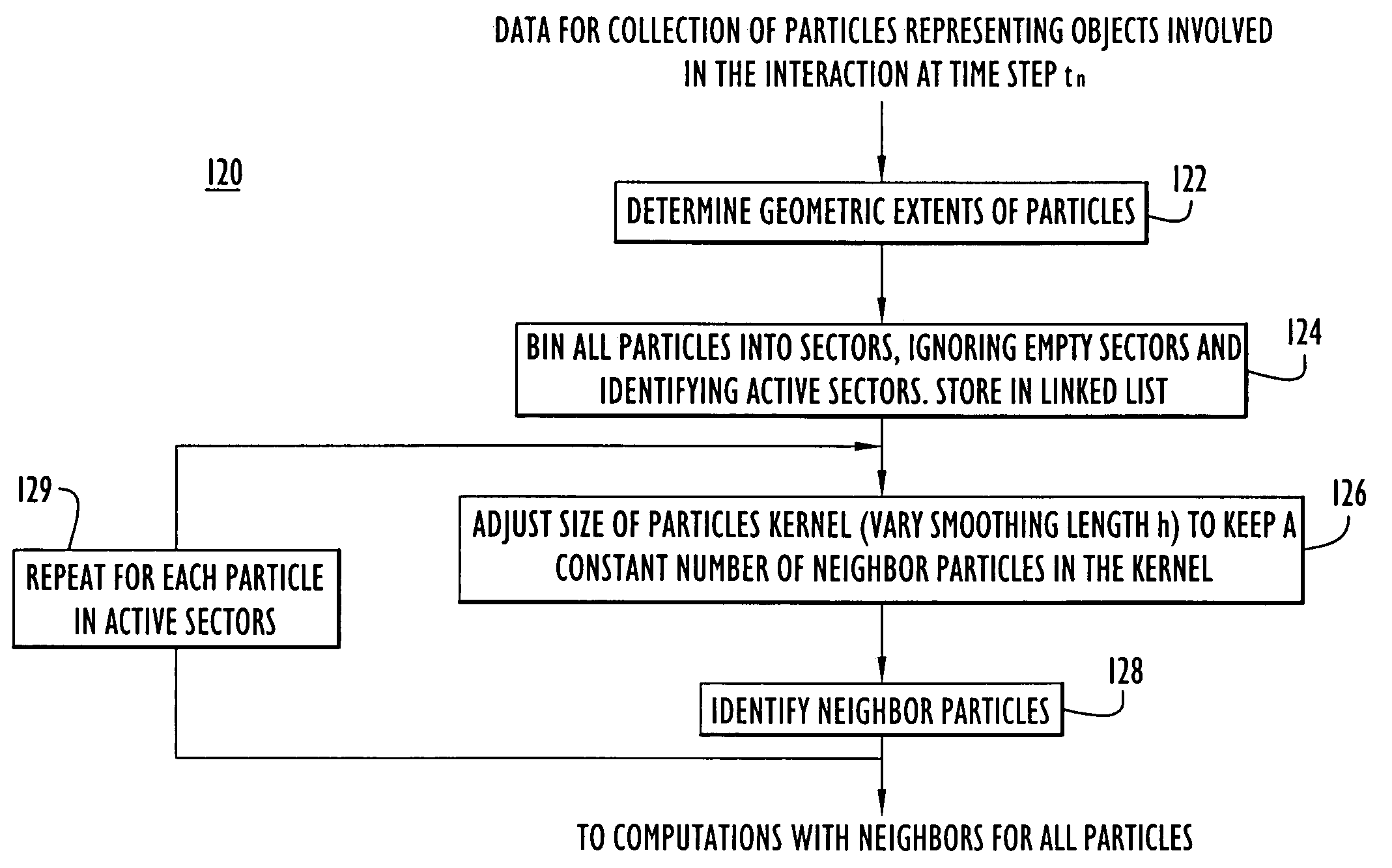
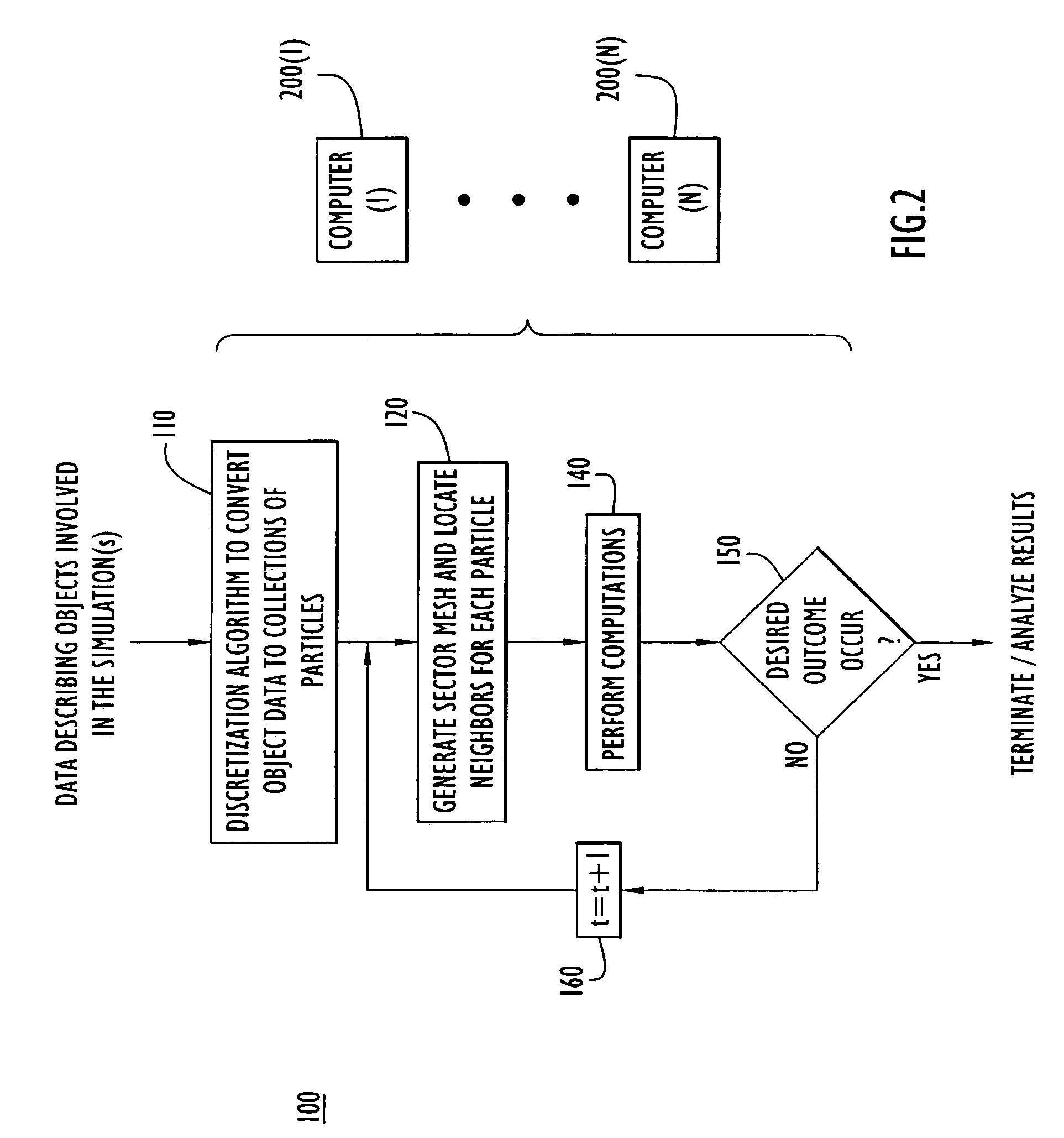
Sector meshing and neighbor searching for object interaction simulation
ActiveUS20090254316A1Reduce in quantityReduce running timeAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsData descriptionComputer science
Methods for computer-implemented simulation for the interaction of two or more objects are provided. Data describing particles that represent each of the objects is generated from geometric data for objects. The data for each particle describes a mass density, velocity and energy at a position of the corresponding object. The particles are grouped into sectors to define a computational mesh comprising a plurality of sectors, wherein each sector is a volume region at a position in space in which particles associated with the objects may reside. For each of a plurality of select particles, so called neighboring particles are determined that are within a region of influence with respect to a select particle. Computations are performed based on laws of conservation of mass, energy and momentum to produce updated values for mass, velocity, energy, pressure, stress and position for the particles at each of a plurality of time steps. According to one aspect, when determining neighboring particles for a given select particle, a search is made through a limited or bounded volume region with respect to the select particle that consists of the region of influence for the select particle at the previous time step and within those sectors in contact with or bordering the region of influence at the previous time step. According to another aspect, the plurality of select particles are identified as those particles that reside in an active sector, wherein an active sector is a sector that contains, or is adjacent to a sector that contains, particles that is actively involved in the engagement between the two objects. For example, an active sector is a sector that contains, or is adjacent to a sector that contains, at least one particle that has a velocity, pressure or stress greater than a corresponding predetermined amount.
Owner:PERATON INC
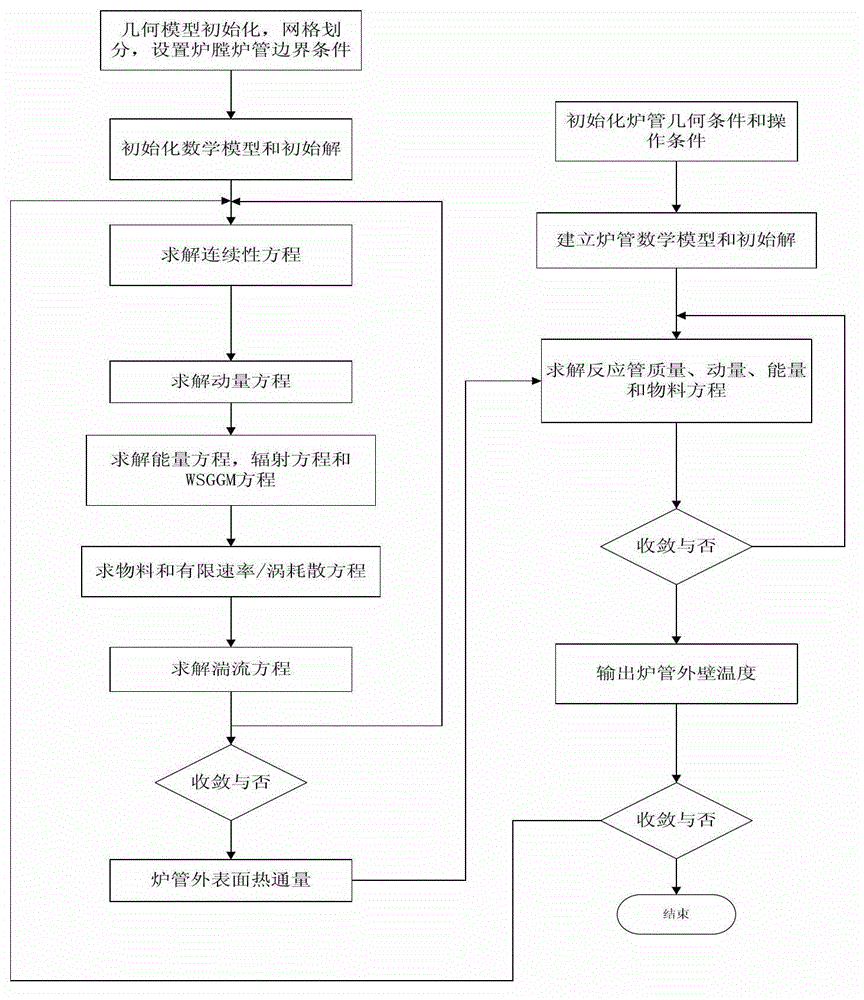
Modeling method for coupling numerical value of cracking reaction in furnace tube and combustion of industrial dichloroethane cracking furnace chamber
The invention provides a modeling method for a coupling numerical value of cracking reaction in a furnace tube and combustion of an industrial dichloroethane cracking furnace chamber. According to the method, the dichloroethane cracking furnace is divided into a furnace chamber model and a furnace tube model during modeling, and grids are divided on the furnace chamber and the furnace tube. The furnace chamber takes an outer tube wall temperature given by the furnace tube model as a boundary condition, important furnace chamber parameter distribution of the furnace chamber flue gas temperature, the speed, the component concentration and the like is calculated by a combustion model, a flowing model and a heat transmission model; the furnace tube takes a furnace tube heat flux calculated by the furnace chamber as a boundary condition, and process temperature, pressure and concentration distribution in a tube length direction is calculated through a cracking reaction model in the tube and taking mass conservation, momentum conservation, energy conservation relations in the tube, so that analyses of important economic targets of the dichloroethane cracking conversion rate, the selectivity, the unit consumption and the like under current operation conditions are facilitated, and guidance of filed process optimization is facilitated. The modeling method is applicable to various high-temperature cracking furnaces and has a wide adaptability.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring granule fluid two-phase stream reactor fluid phase component concentration distribution
InactiveCN101285753AAccurately measure component concentration profilesAccurate measurementSpecial data processing applicationsMaterial analysisFluid phaseMomentum conservation
The invention relates to a method for measuring the concentration distribution of compositions in a particle-fluid two-phase flow reactor. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, calculation of the mass conservation equation and the momentum conservation equation of each micro unit in a measuring area of the particle-fluid two-phase flow reactor and acquisition of the fluid-solid speed and the particle concentration distribution of each micro unit; S2, acquisition of matrixes which are formed by spacial discrete distribution of dilute and dense phase structural parameters; S3, acquisition of the composition concentration of dilute phase and dense phase; S4, calculation of the mean fluid density of the micro unit according to the composition concentration of the dilute phase and the dense phase, in which, if the mean fluid density meets the precision requirement, the fluid-solid speed, the particle concentration and the composition concentration are outputted and the operation is ended; if the mean fluid density fails to meet the precision requirement, the calculated mean fluid density of the dilute phase and the dense phase is substituted in the step S1, and the next iteration begins. The method introduces a multi-scale flow structure into the particle-fluid mass transfer measuring process, takes malconformation of local mass transfer into account, and more accurately measures the composition concentration distribution in the particle-fluid two-phase flow reactor.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
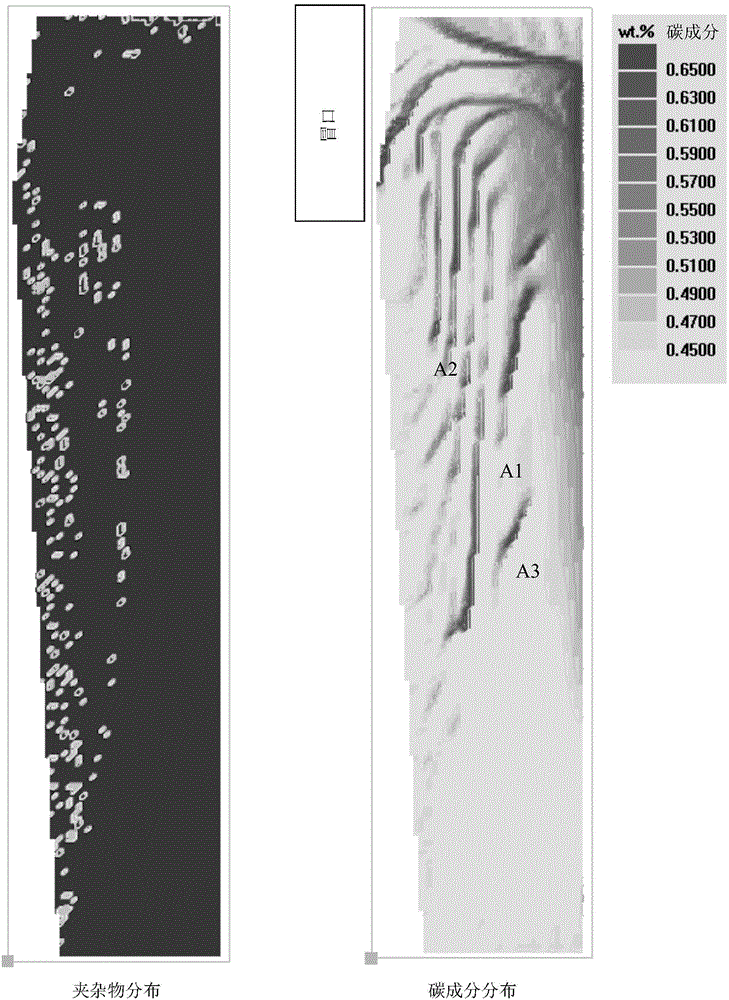
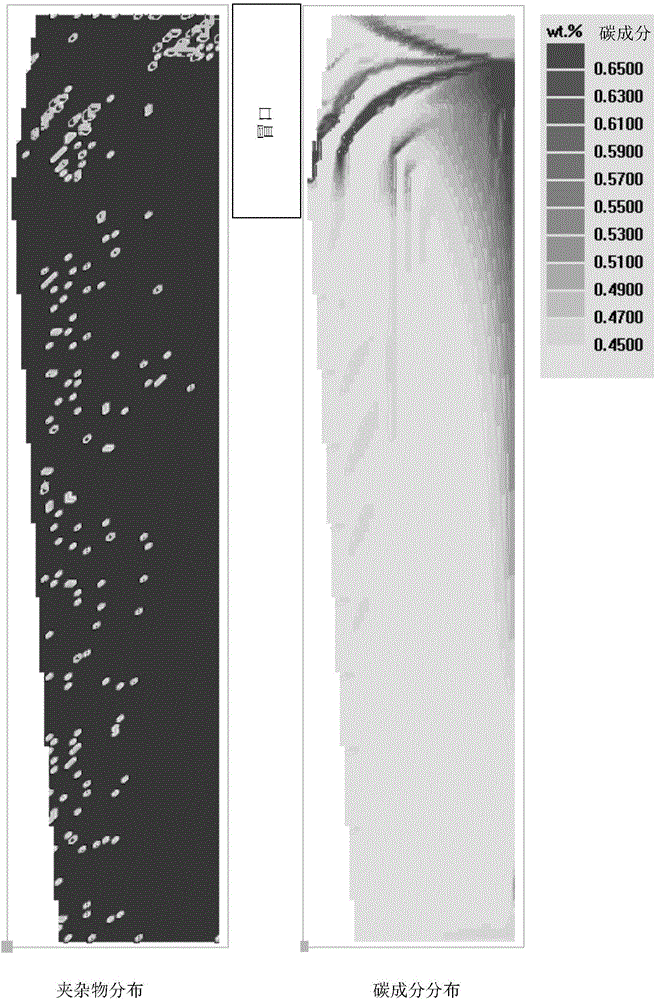
Ingot casting macrosegregation numerical simulation method
InactiveCN104881588AImprove qualityComprehensive forecastSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleIngot casting
The invention discloses an ingot casting macrosegregation numerical simulation method and belongs to the field of macrosegregation prediction. The problem that macrosegregation formed under the combined action of different physical mechanisms cannot be accurately predicted by existing macrosegregation calculation is solved. The ingot casting macrosegregation numerical simulation method comprises the steps that macroscale mesh generation is carried out on an ingot casting system to form a series of computing grids, and the positions of impurities in the ingot casting system in ingot casting grids are set; for the ingot casting grids, the impurity speed distribution, the cast ingot inner temperature distribution and cast ingot inner average composition distribution are obtained through the energy conservation equation, the composition conservation equation, the momentum conservation equation and the mass conservation equation; for all the computing grids except for the ingot casting grids, the casting grid energy conservation equation is calculated, and the cast grid inner temperature distribution is obtained; after solidification is finished, and the cast ingot inner average composition distribution is output. The ingot casting macrosegregation numerical simulation method accurately predicts macrosegregation formation, and is applicable to prediction of macrosegregation of sand molds and metal molds of various sizes.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
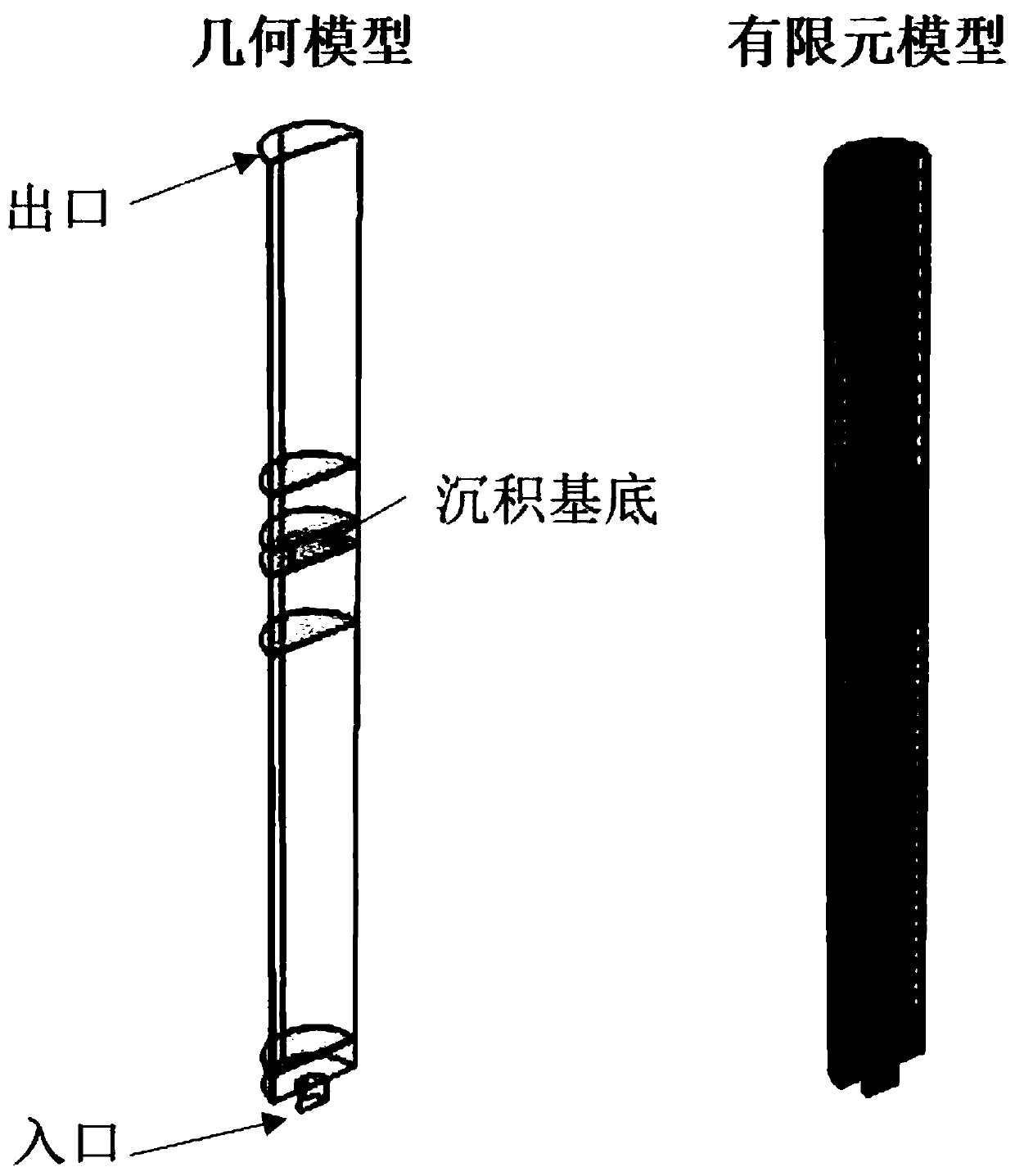
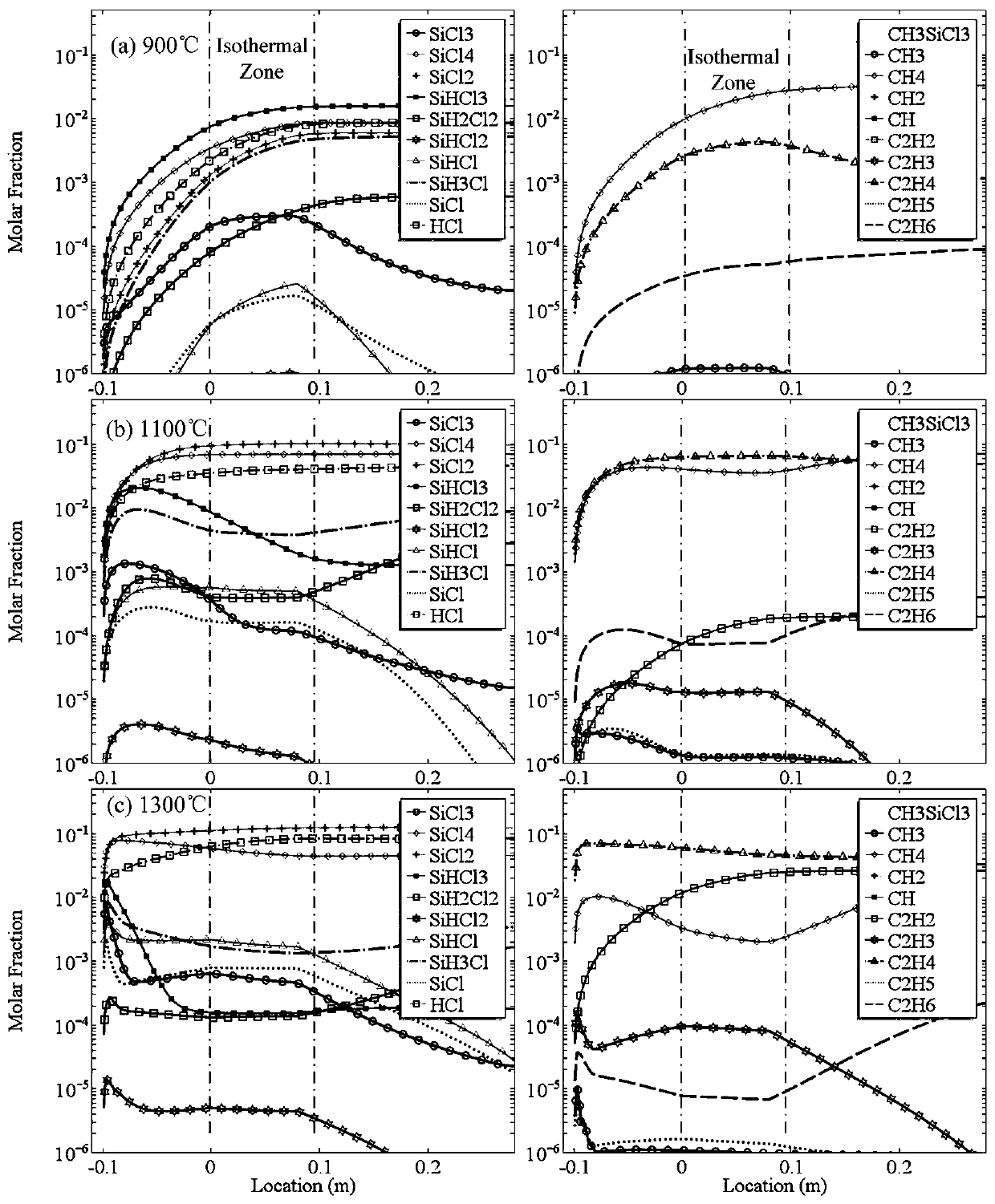
Chemical vapor deposition rate prediction method
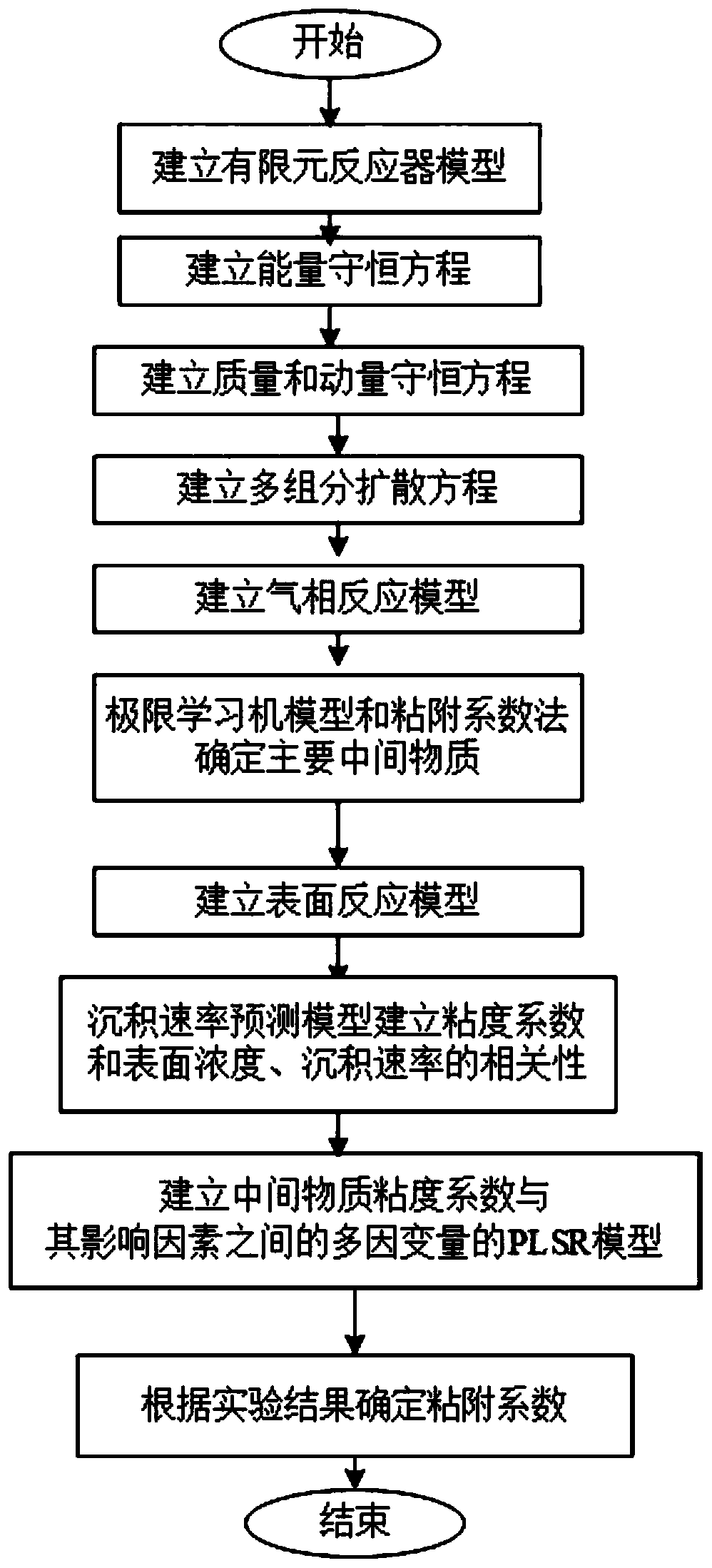
ActiveCN110598255AAccurate calculation of viscosity coefficientUniversalChemical property predictionChemical machine learningLearning machineGas phase
The invention discloses a chemical vapor deposition rate prediction method, and particularly relates to the field of chemical process research. The chemical vapor deposition rate prediction method comprises the following steps: building a finite element reactor model; establishing an energy conservation equation; establishing a mass conservation equation and a momentum conservation equation; establishing a multi-component diffusion equation; establishing a gas phase reaction model; determining main intermediate substances by an extreme learning machine model and an adhesion coefficient method;establishing a surface reaction model; establishing correlation between the viscosity coefficient and the surface concentration as well as the deposition rate by the deposition rate prediction model;establishing a multi-dependent-variable PLSR model between the viscosity coefficient of the intermediate substance and the influence factor of the intermediate substance; and determining an adhesioncoefficient according to an experimental result. According to the chemical vapor deposition rate prediction method, the simulation technology of machine learning and computational fluid mechanics is combined, and the dependence of model parameters on human experience is greatly reduced, and the important mesophase and the viscosity coefficient can be accurately determined through a small number ofexperiments, and the technical effects of high prediction result accuracy and high reliability are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
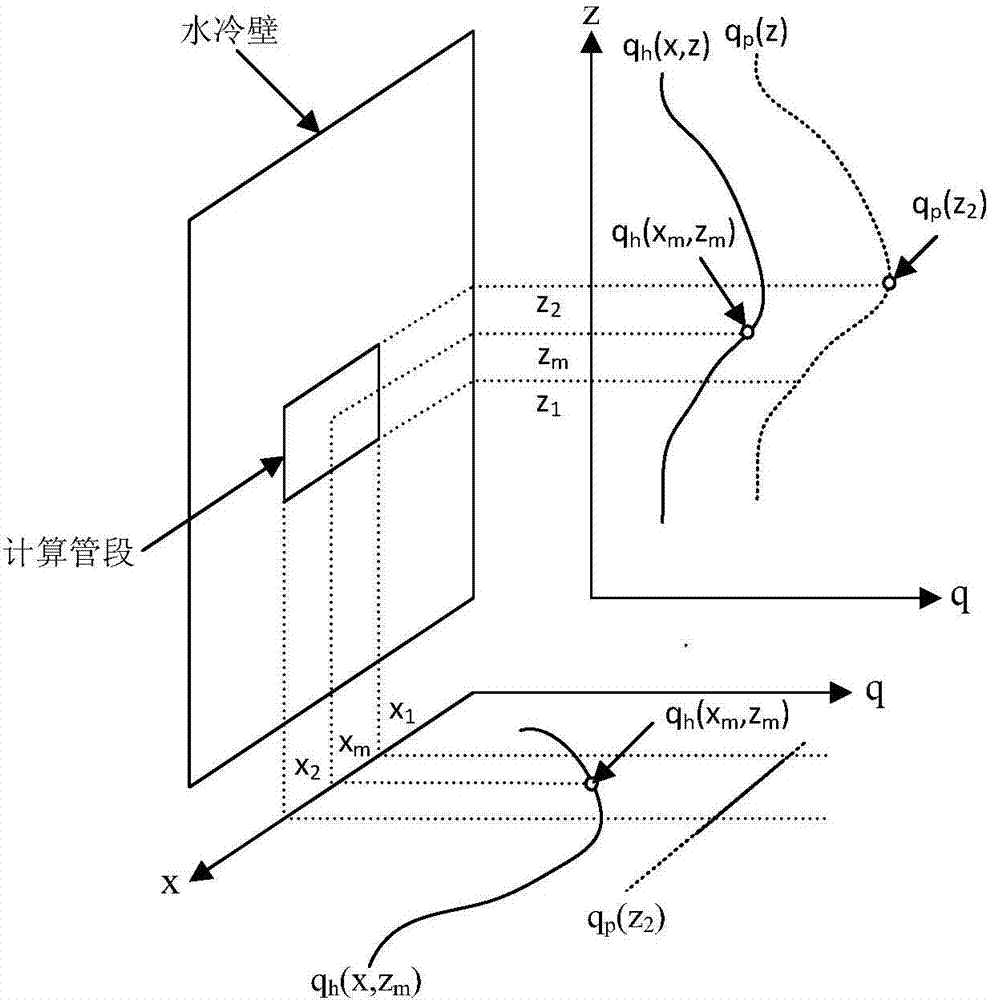
General hydrodynamic calculation method for ultra-supercritical boiler
ActiveCN106897547AFit closelyInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsSupercritical steam generatorCombustion
The invention discloses a general hydrodynamic calculation method for an ultra-supercritical boiler, and provides a flow network system method consisting of a nonlinear model applied to a computer. The calculation method is suitable for hydrodynamic calculation and wall temperature safety analysis of the ultra-supercritical once-through boiler under various boiler overall arrangement forms, various pipe coil forms, various combustion technologies and various mass velocity combinations. The method comprises the steps of simplifying a water wall into a flow network system consisting of elements such as a connecting pipe loop, a heated loop, a pressure node and the like according to structure characteristics of the water wall and heat load distribution of a furnace chamber; and building the nonlinear calculation model of flow distribution according to a mass conservation equation, a momentum conservation equation and an energy conservation equation. Through direct solving of a nonlinear equation set, flow distribution and node pressure distribution in the heated loop and a connecting pipe are determined, and based on this, boiler water wall flow and metal wall temperature are subjected to safety check, so that guidance calculation can be performed for design and safety check of the boiler.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +2
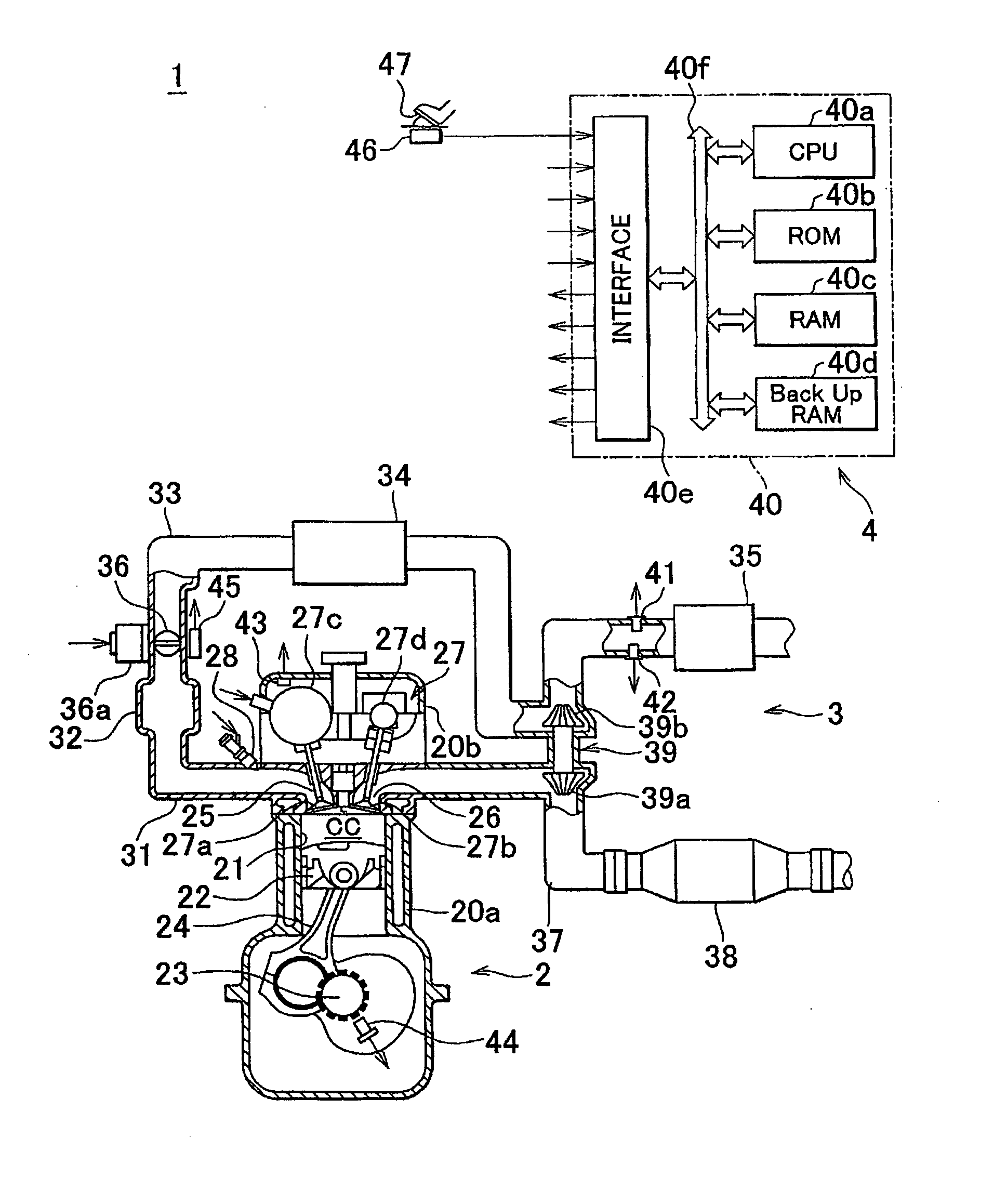
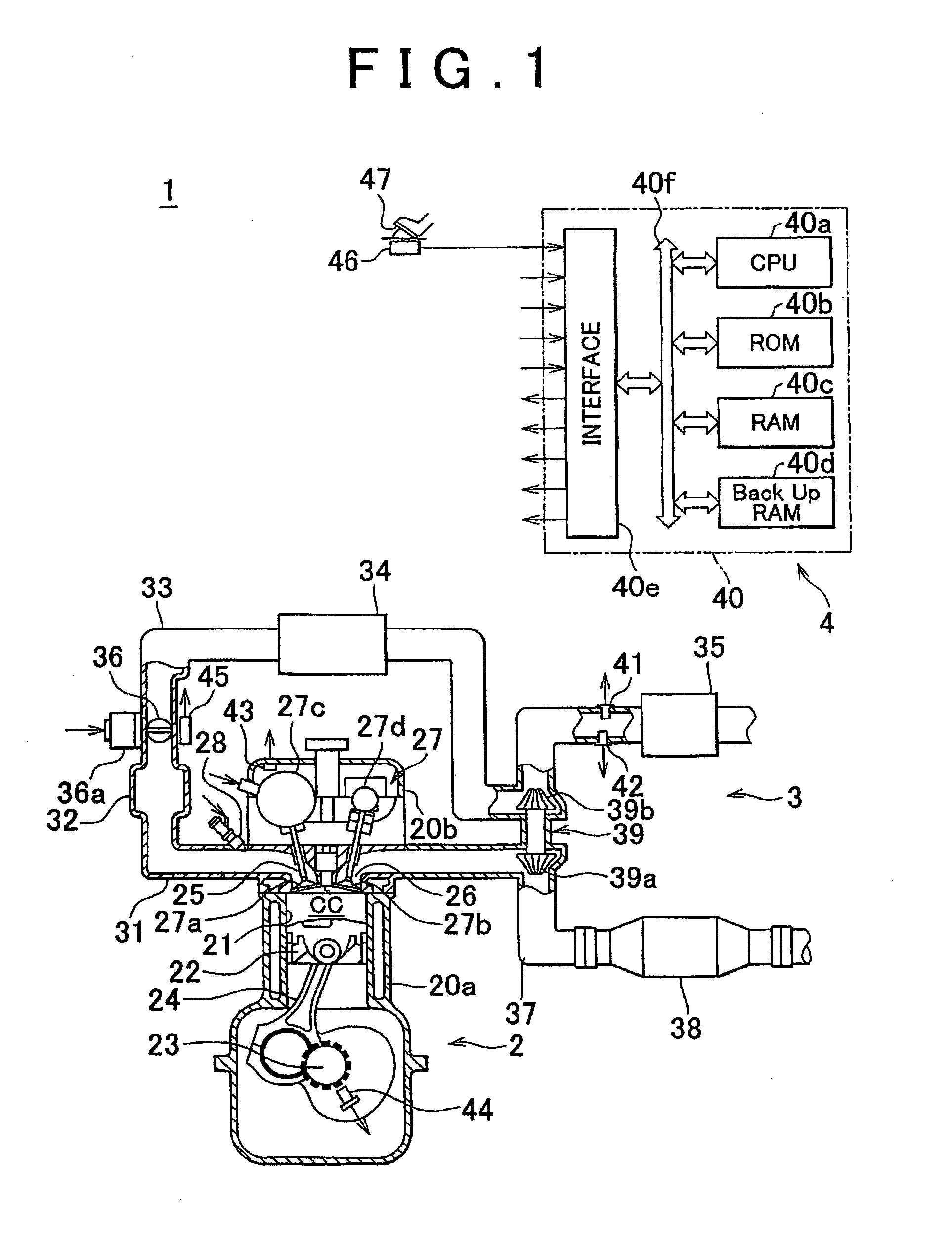
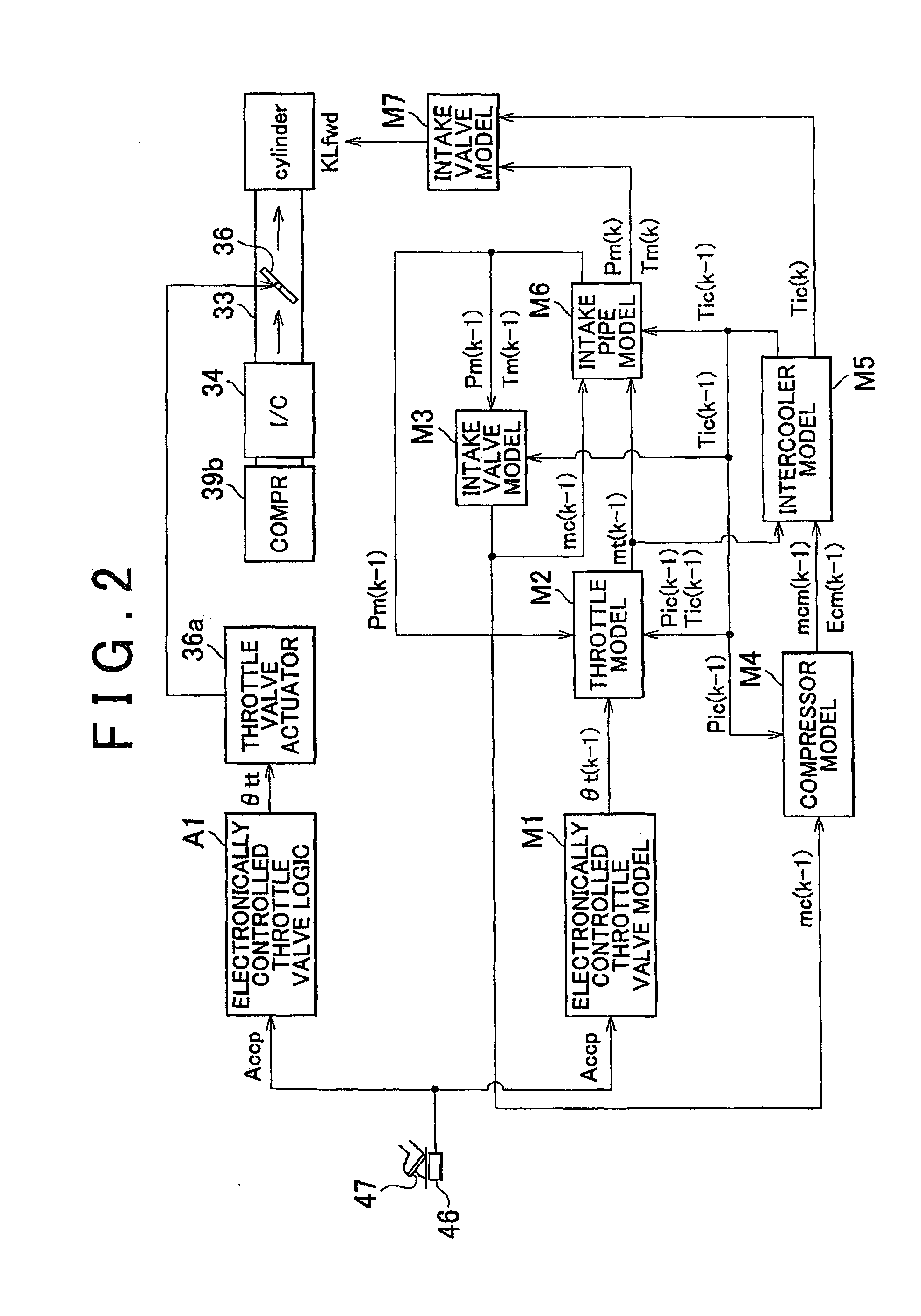
Internal combustion engine system control device
InactiveUS20110172898A1Easy to controlAccurate estimateElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineEngineering
A device with models constructed based on thermodynamics laws and fluid dynamics laws including the energy conservation law, momentum conservation law and mass conservation law. Compressor outflow flow rate calculation section calculates the flow rate of air that flows out of a compressor based on a relationship between an in-cylinder intake air flow rate during steady-state operation in an internal combustion engine system and supercharging pressure, which is pressure of air compressed by the compressor, and a value of the in-cylinder intake air flow rate calculated by in-cylinder intake air flow rate calculation section.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
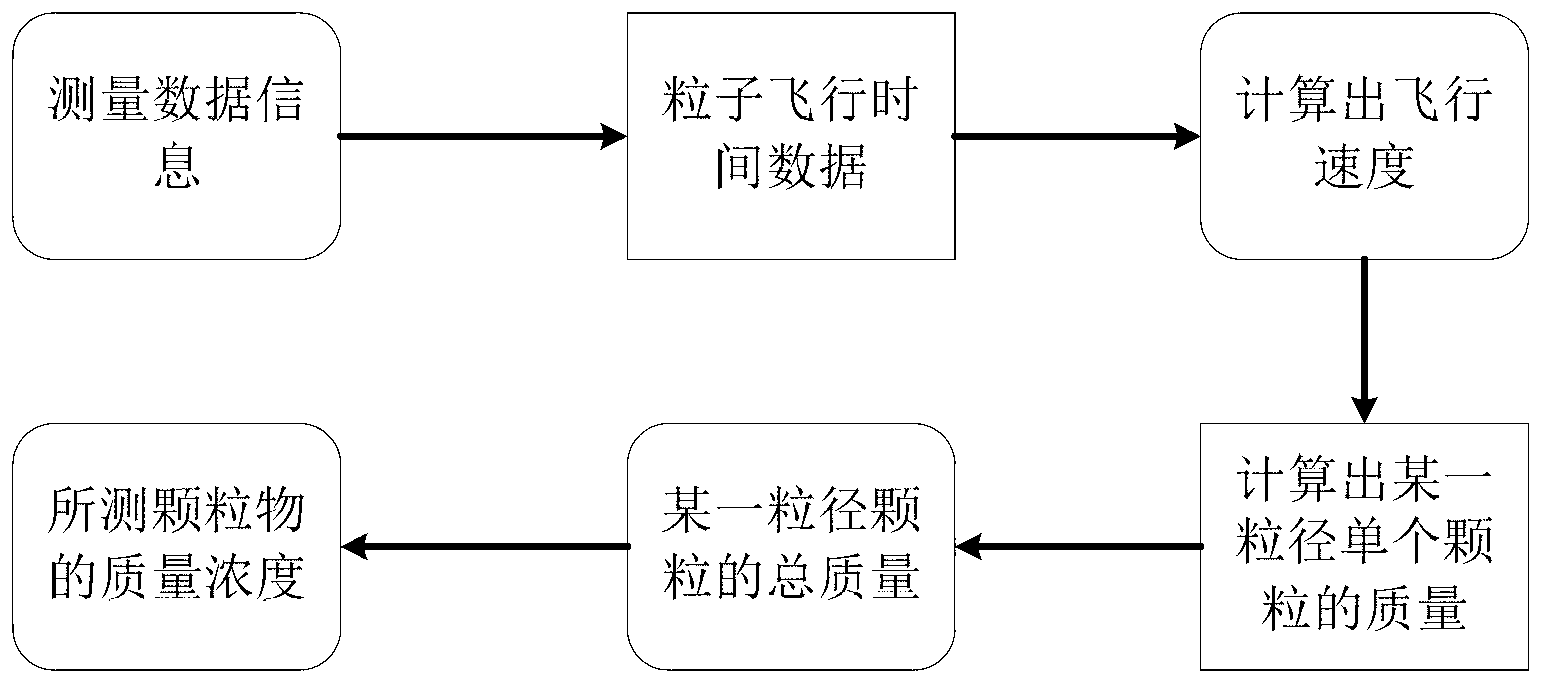
Method for inverting mass concentration of atmospheric particulates based on flight time of particulates
ActiveCN103234882AImprove inversion accuracyAvoid errorsParticle size analysisParticle suspension analysisParticulatesEngineering
The invention relates to a method for inverting the mass concentration of atmospheric particulates based on the flight time of the particulates. The mass concentration of the particulates can be inverted according to the flight speed and the sampling flow on the basis of an aerodynamic particulate spectrometer. According to the work principle of the aerodynamic particulate spectrometer, the particulates with different particle sizes have only speed up at any one point on an airflow track after the particulates pass through an accelerating nozzle, so the flight speed of particles can be obtained through the flight time. The relationship between the flight speed and the mass of the particles can be obtained according to a momentum conservation theorem and aerodynamic and hydromechanical principles, so the mass concentration of the particulates can be inverted through the flight speed and the sampling flow. The method provided by the invention can be used for inverting the mass concentration of the atmospheric particulates according to the dynamic feature of the particulates and provides an inversion algorithm capable of measuring the mass concentration of the atmospheric particulates accurately, in real time and on line.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
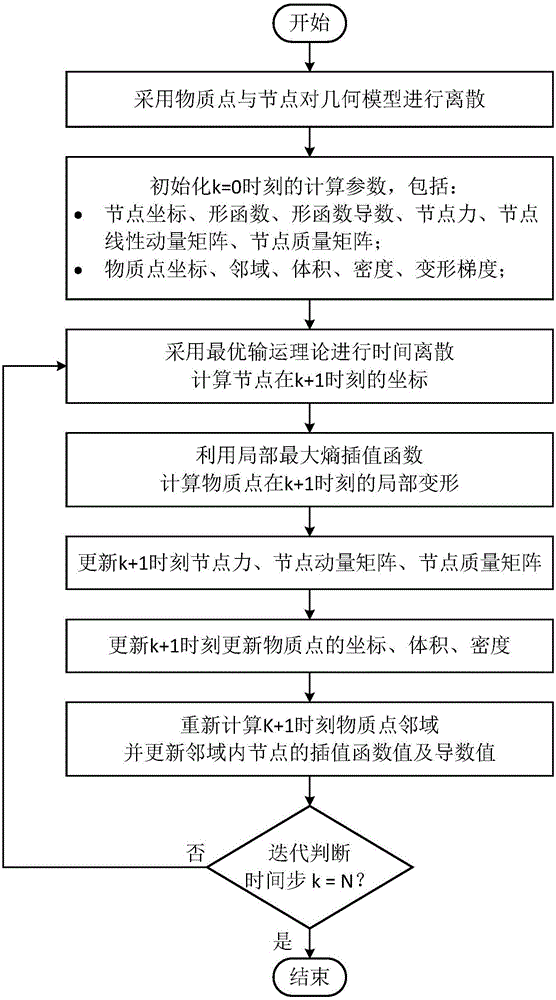
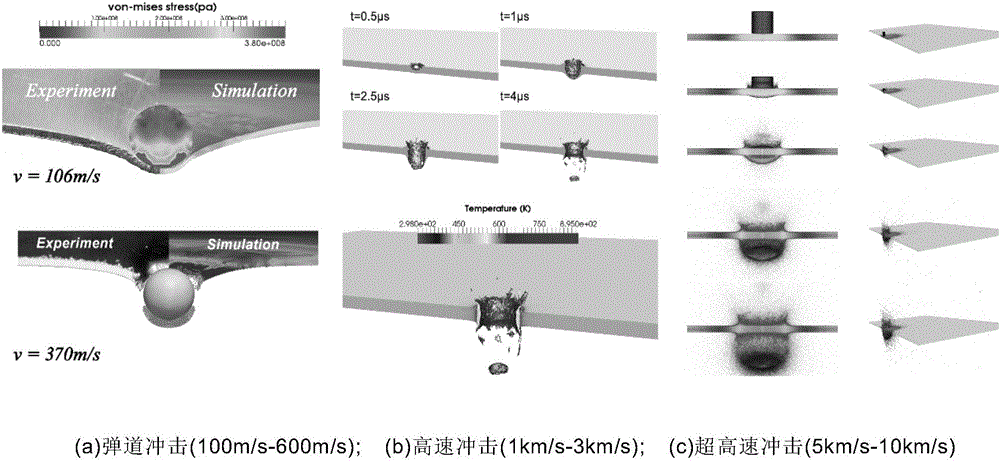
Optimal transportation meshless method for solving large deformation of material
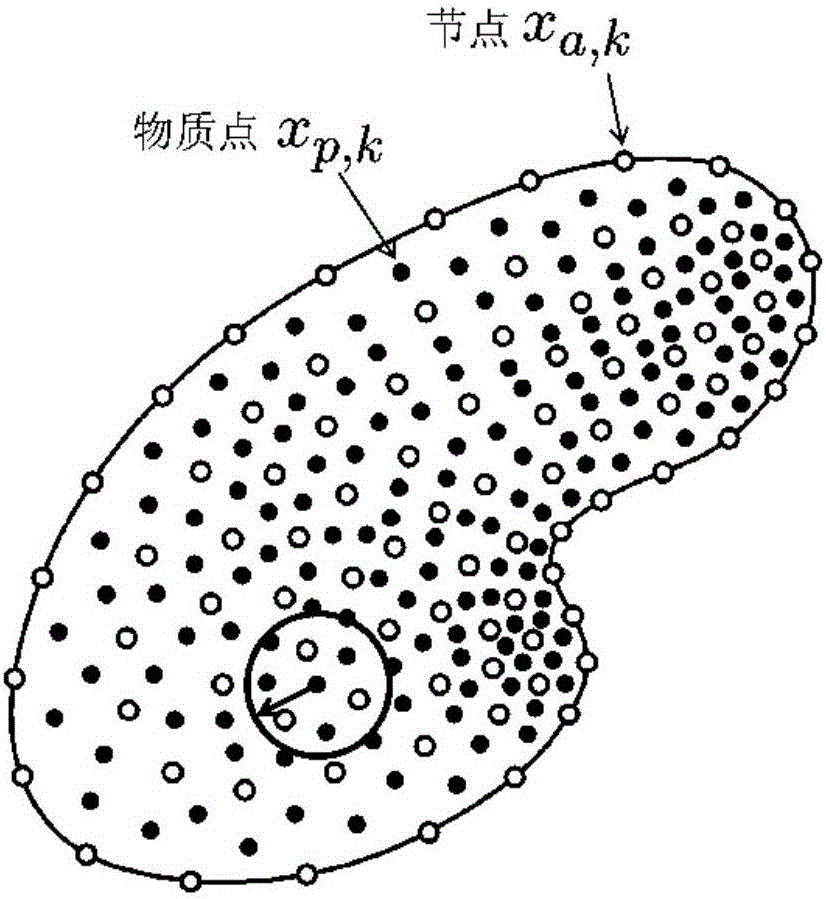
ActiveCN106446432AResolving Tensile Stress InstabilityAvoid high computationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsProblem domainMetallic materials
The invention relates to an optimal transportation meshless (OTM) method for solving large deformation of a material and aims at solving the problems of effective and stable solving of maximum deformation, high-speed impact and geometric distortion, metal material molding, multiphase coupling and the like. The OTM method adopts a material point and node pair original problem domain to perform discretion and adopts a local maximum entropy interpolation function to construct a continuous movement function, and the problem that mesh distortion caused in maximum deformation processed by adopting a finite element method, the problem that a Dirichlet boundary condition cannot be directly added for a meshless method, calculating misconvergence and the like are avoided. In addition, due to the fact that interpolation and integration are performed at different discrete points, an effective meshless numerical integration mode is provided, and the problem of tensile stress instability is solved. The OTM method serves as an incremental updating Lagrangian method to make mass conservation automatically achieved without solving. Time discretion is performed by adopting an optimal transportation theory, the momentum conservation and symplectic conservation of a discrete system are ensured, and the operation efficiency and precision are greatly improved.
Owner:云翼超算(北京)软件科技有限公司
Wind power prediction method and system in wind power plant
InactiveCN109783828AGood forecastEasy to set upSpecial data processing applicationsWind drivenPeaking power plant
The invention discloses a wind power prediction method and system in a wind power plant, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the wake flow speed of natural wind speed passing through blades of a wind driven generator through a pre-built wind speed model according to the law of conservation of mass; calculating the input wind speed of any wind driven generator in the wind power plant based on the law of conservation of momentum according to the wake flow speed; performing wake flow correction on the input wind speed according to the input wind speed to obtain a corrected input windspeed; obtaining a predicted wind speed through a wind speed prediction model according to the corrected input wind speed; and according to the predicted wind speed, performing wind power prediction through a dynamic time sequence neural network prediction model to obtain predicted wind power. By considering the wind speed model under the wake flow effect, wake flow correction is performed on theinput wind speed of the wind turbine generator of the whole wind power plant, and the corrected wind speed is used as the input of the wind speed prediction model, so that the obtained wind speed prediction precision is improved, and the wind power prediction precision is further improved.
Owner:BEIJING PUHUA YINENG WIND POWER TECH
Method for casting grain structure numerical value prediction
InactiveCN105665684AEffective predictionReduce computing timeComplex mathematical operationsGrain structureCrystal growth
The invention provides a method for casting grain structure numerical prediction, and relates to a prediction method of a casting grain structure. The method aims at solving the problems that in existing grain structure numerical prediction, the calculation time is long and the calculation amount is large. The method includes the steps of calculating a dendritic crystal growth kinetics KGT model first, obtaining the dendritic crystal tip radius-dendritic crystal tip growth speed change curve, conducting macro-scale mesh generation on a casting system, only calculating an energy conservation equation for a computational grid (i,j)chan= / 0 to obtain temperature field distribution, calculating a momentum conservation equation for a computational grid (i,j)chan=0 to obtain the metal liquid flowing speed in the computational grid, judging whether the computational grid (i,j)chan=0 is located on the solidification front or not, calculating the solidification front temperature gradient and the solidification front movement speed corresponding to the grid if yes, and outputting distribution of a grain growth morphology identification grain in a casting till solidification ends. The method is suitable for casting grain structure numerical prediction.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A magnetic levitation guide rail used for verifying momentum conservation law in high school physics
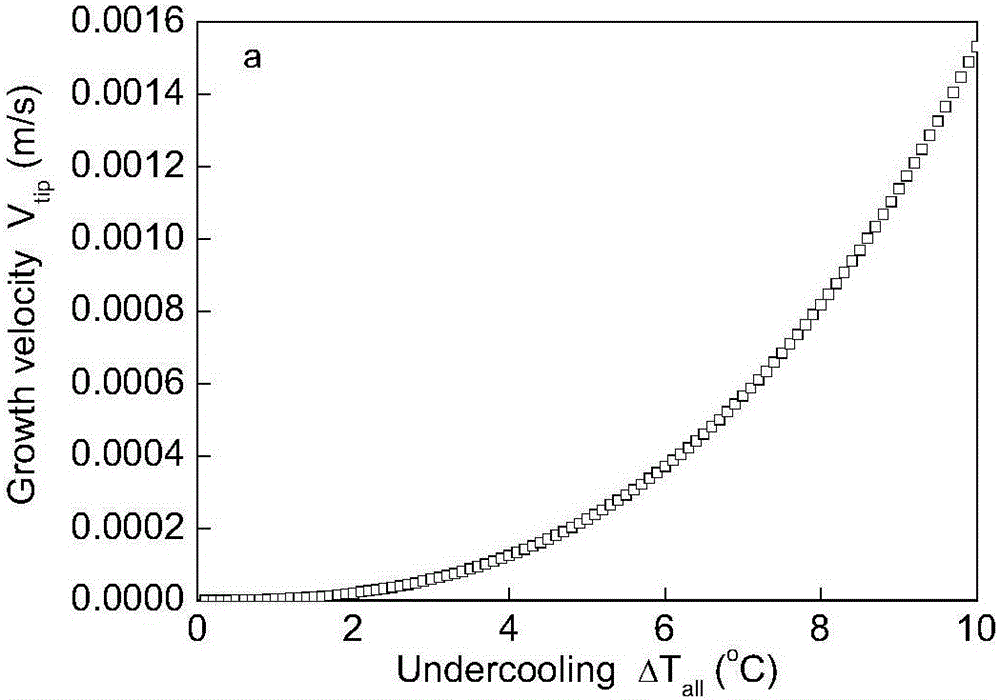
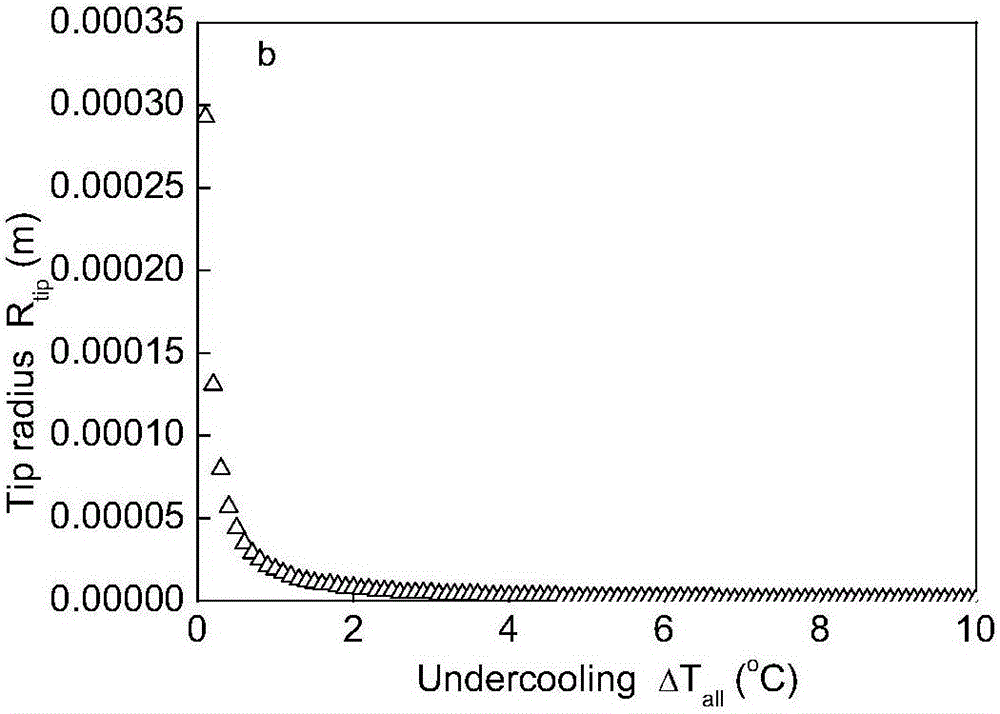
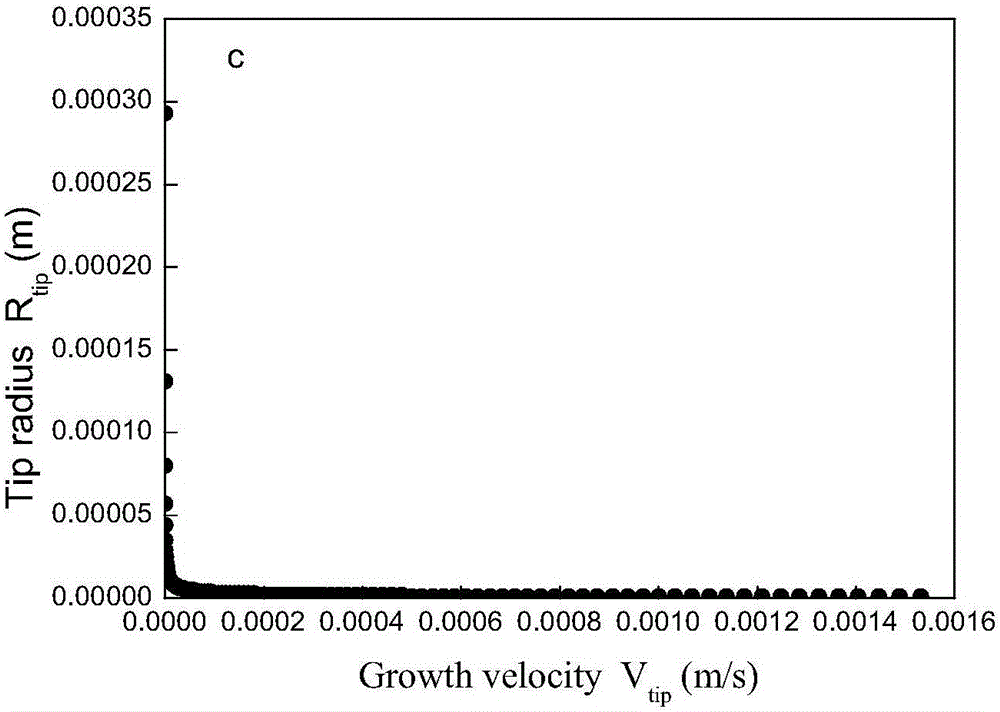
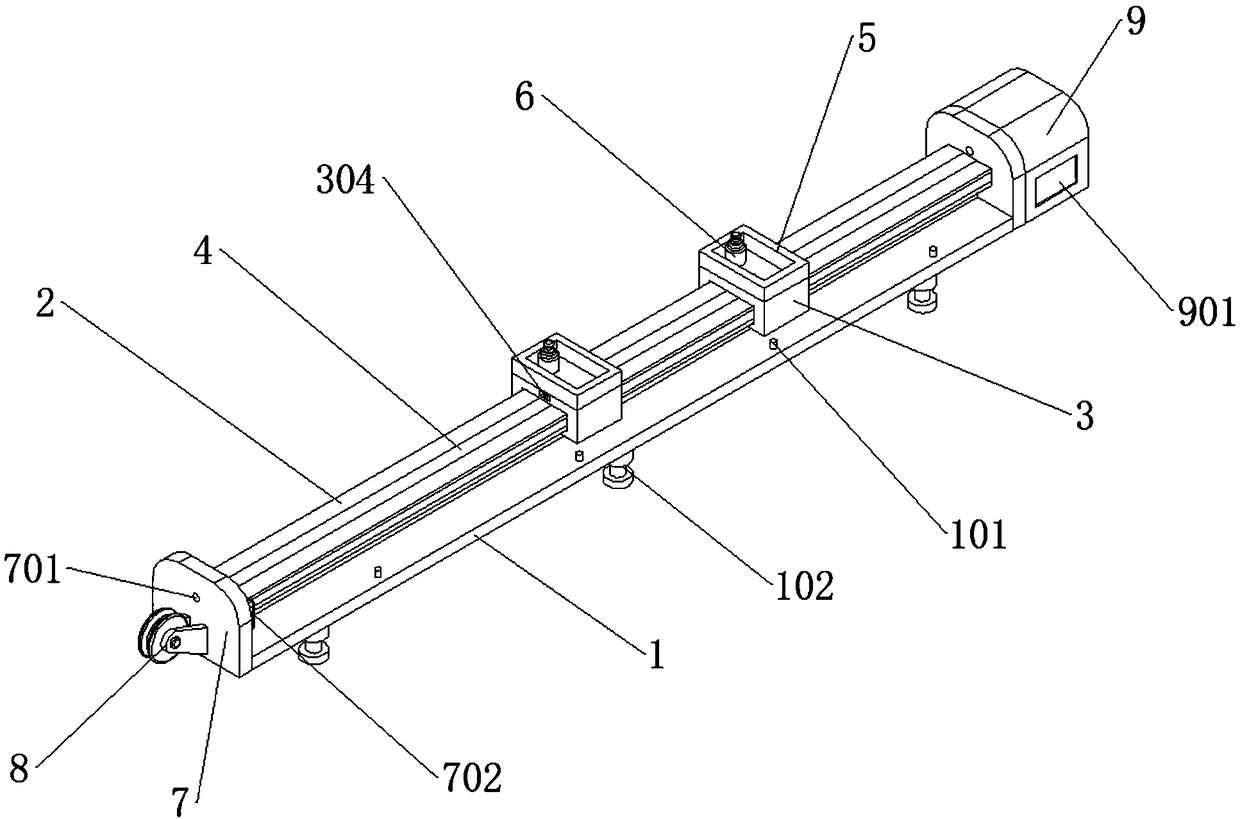
InactiveCN109192022AImprove teaching efficiencyEasy to operateEducational modelsEngineeringBlock match
The invention discloses a magnetic levitation guide rail used for verifying momentum conservation law in high school physics, belonging to the technical field of high school physics experiment equipment. The magnetic levitation guide rail includes a base, the upper end of the base is fixedly connected with a fixed guide rail, the fixed guide rail is sleeved with a pair of sliding blocks matched with the fixed guide rail, the two sliders have the same mass, There is a gap between the stationary guide and the slider, the lower end of the fixed guide rail is fixedly connected with a pair of firstsuspension magnets, the slider is fixedly connected with a second suspension magnet matched with the first suspension magnet, the principle of magnetic levitation can be realized, The invention replaces the air cushion guide rail of the external air pump in the high school experiment, is simple in operation and convenient in handling, solves various complicated assembly steps of the air pump usedin the prior art to a great extent, eliminates various potential safety hazards, greatly improves the teaching efficiency of teachers, and facilitates students to learn knowledge through the experiment quickly and accurately.
Owner:邰奕雯
Method and device for measuring resiliometer impact kinetic energy
InactiveCN1945272ARealize the source of magnitude problemReduce cost of measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementInvestigating material hardnessEngineeringMomentum conservation
The present invention is method and device for measuring impact kinetic energy of resiliometer and belongs to the field of resiliometer metering and calibrating technology. Through measuring the hammer impulse the attack rod transmits during attacking and calculating the striking speed of the hammer to the attack rod by means of the impulse-momentum conservation law, the impact kinetic energy of the resiliometer is obtained and used in metering and calibrating the resiliometer. The present invention may be used in different types of resiliometer, and has low measuring cost and fast and convenient resiliometer metering and calibrating.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF BUILDING RES
Component nonuniformity numerical prediction method for magnesium alloy casting parts
ActiveCN110245449AAccurate calculationPredicting Macrosegregation FormationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCellular automationEnergy conservation
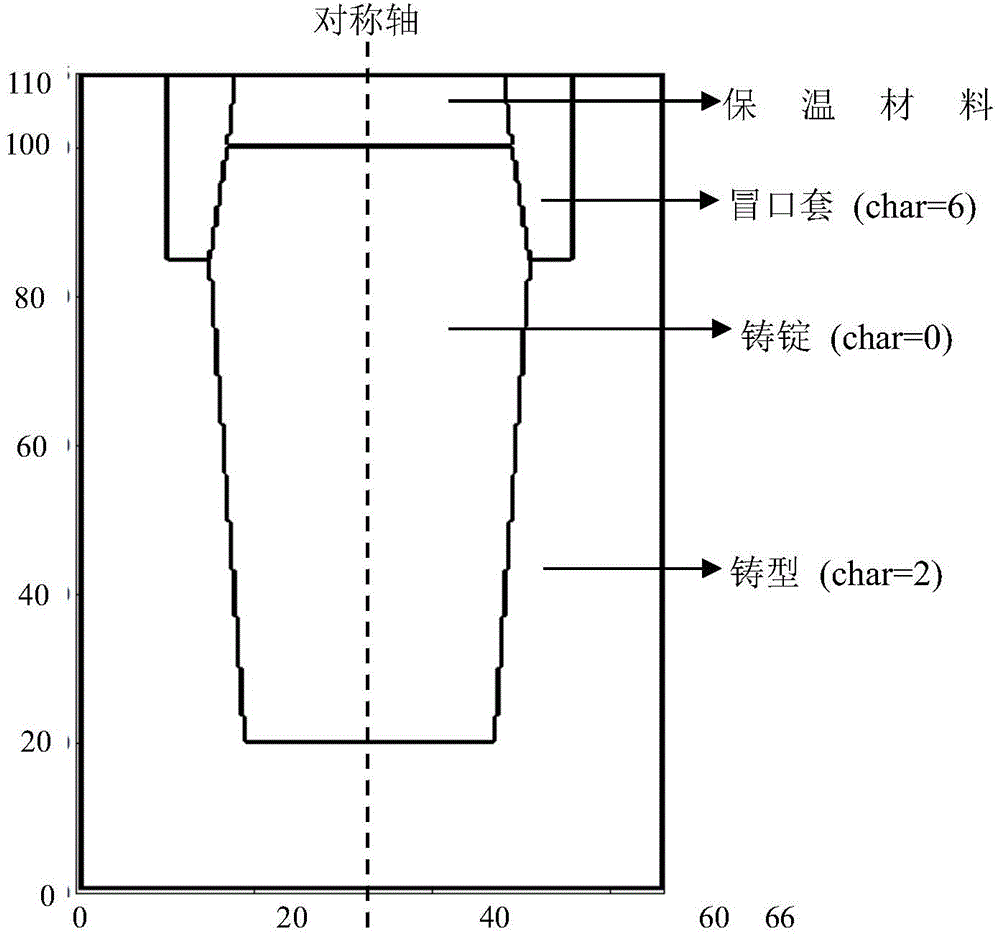
The invention discloses a component nonuniformity numerical prediction method for magnesium alloy casting parts, and relates to a component nonuniformity numerical prediction method for magnesium alloy casting parts. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem that macrosegregation formation of the magnesium alloy casting parts cannot be accurately predicted by an existing method. The component nonuniformity numerical prediction method comprises the following steps: 1, simulating the growth of alpha-Mg dendrites with different growth orientations by adopting a cellular automaton method to obtain a curve that the specific surface area of the dendrites changes along with the solid phase fraction; 2, performing mesh generation on the casting system; 3, calculating an energy, component and momentum conservation equation for all grids with subscript char = 0, and obtaining distribution of temperature, average component and speed in the casting parts; 4, calculating an energy conservation equation for all grids of which the subscript chars are not 0 to obtain temperature distribution; and 5, repeating the step 2, the step 3 and the step 4 until solidification is finished, and outputting an average component field in the casting parts. The component nonuniformity numerical prediction method is applied to the field of magnesium alloy casting part component prediction.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com