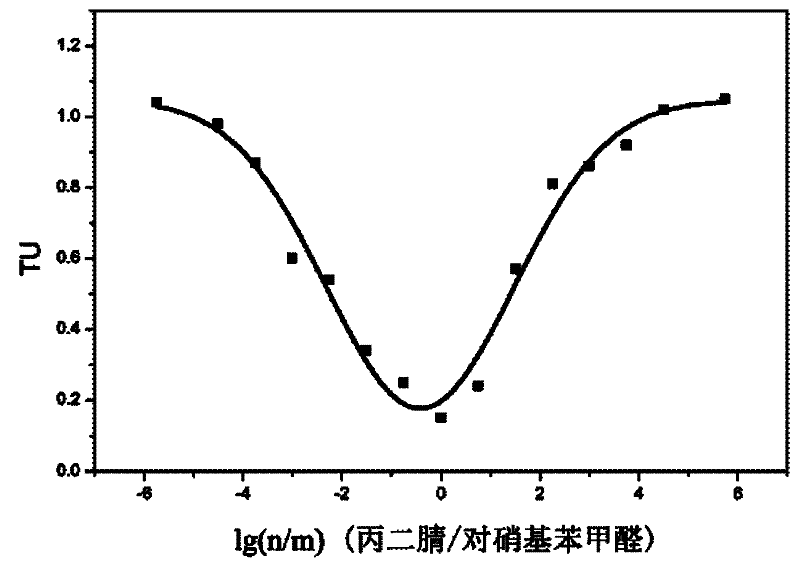
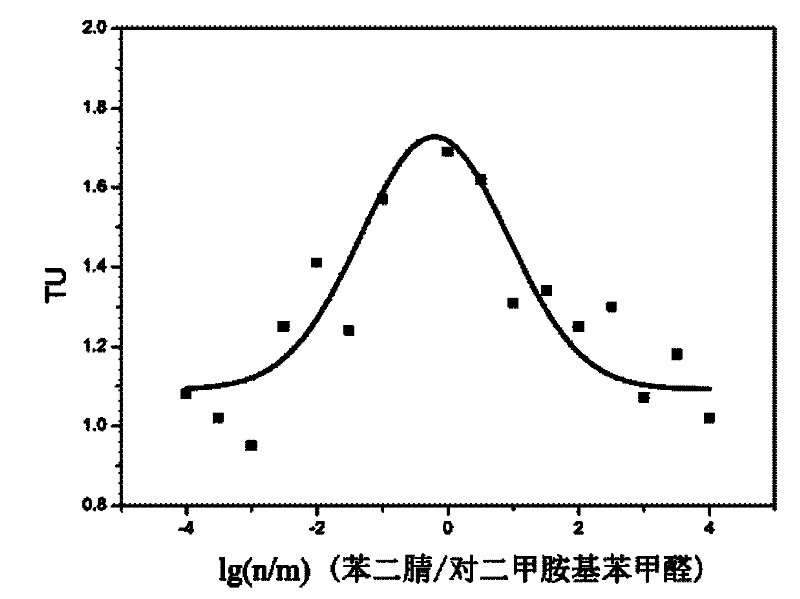
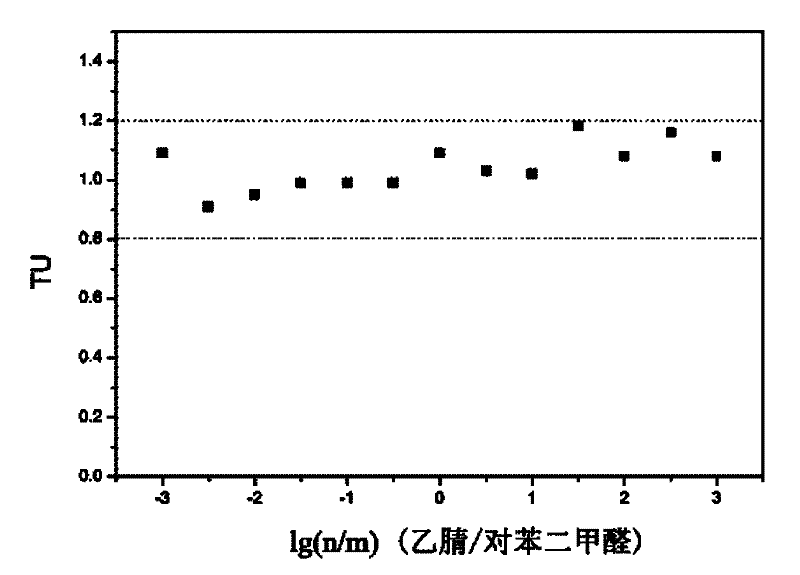
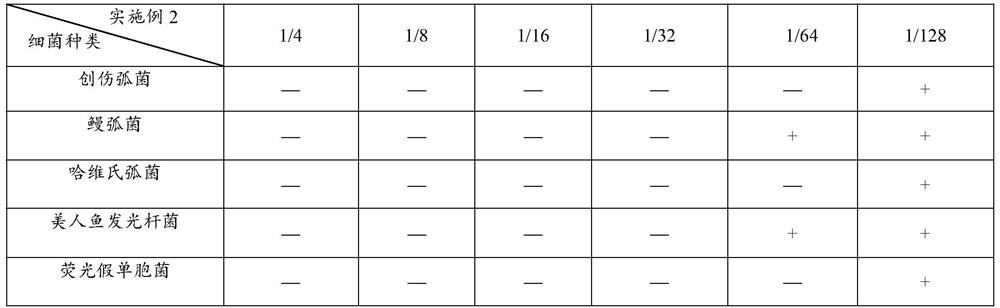
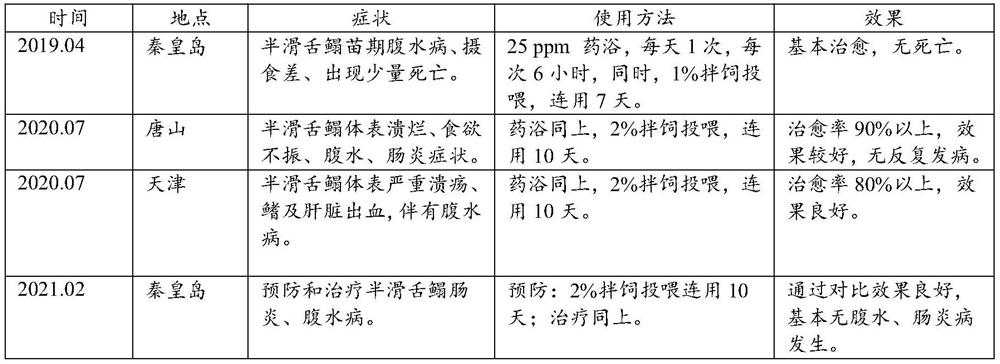
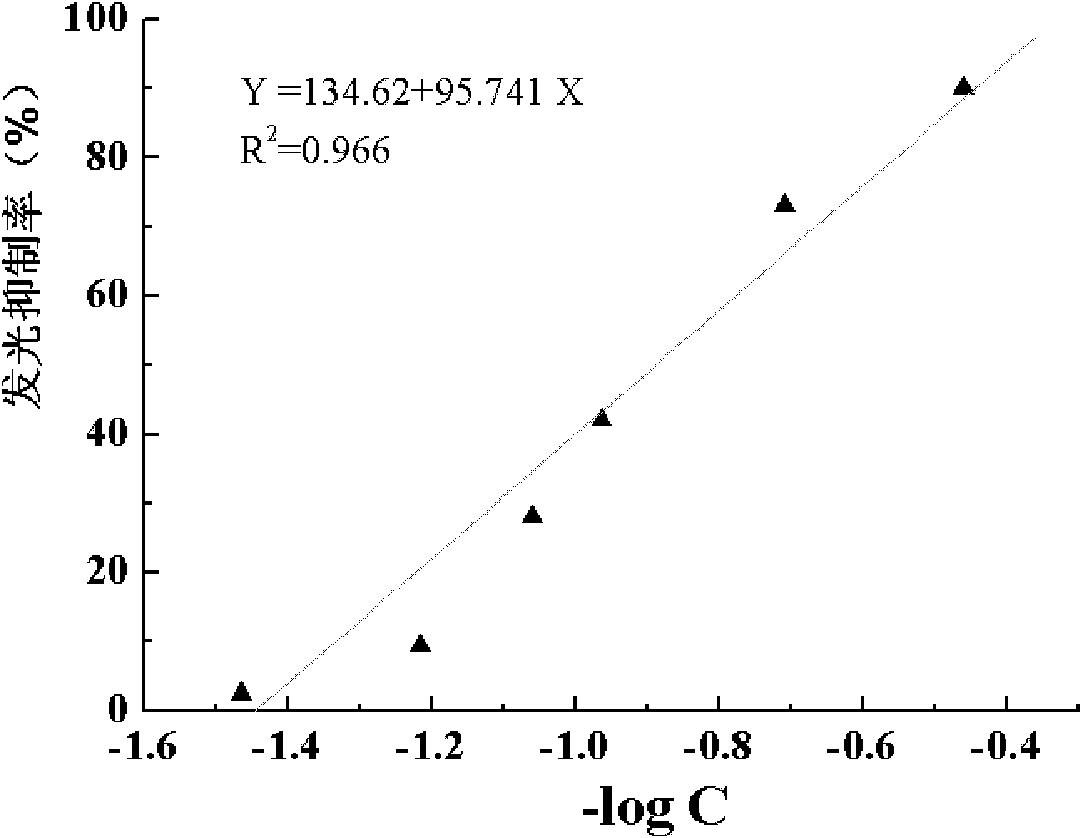Patents
Literature
43 results about "Photobacterium phosphoreum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
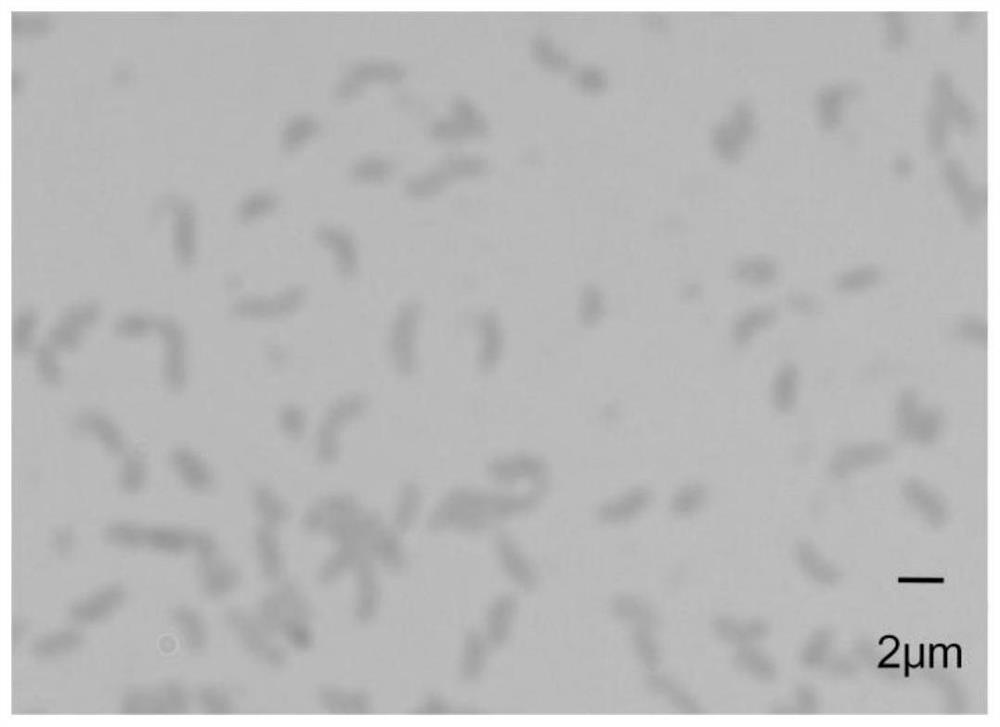
Photobacterium phosphoreum or Vibrio phosphoreum is a Gram-negative bioluminescent bacterium living in symbiosis with marine organisms. It can emit bluish-green light (490 nm) due to a chemical reaction between FMN, luciferin and molecular oxygen catalysed by an enzyme called luciferase.
Luminous bacteria and application thereof in detecting general biological toxicity in food or water sample
InactiveCN101560491AEffective assessmentAccurate assessmentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyBacteria
The invention discloses luminous bacillus CCTCC M 208027 and application thereof in detecting general biological toxicity in a food or water sample. The invention also discloses a kit that contains luminous bacillus CCTCC M 208027 and is capable of detecting general biological toxicity in the food or water sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photobacterium damsela rapid detection primer, kit and application
InactiveCN103981270AResolution cycleSolve the costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiochemistryPhotobacterium phosphoreum
The invention discloses a photobacterium damsela rapid detection primer, a kit and an application. The primer consists of an outer primer and an inner primer, wherein the outer primer consists of an outer primer upstream primer shown by SEQ ID NO.1 and an outer primer downstream primer shown by SEQ ID NO. 2; the inner primer consists of an inner primer upstream primer shown by SEQ ID NO.3 and an inner primer downstream primer shown by SEQ ID NO.4. The problems that the detection of photobacterium damsela is long in cycle and high in detection cost, can not be applied to on-site detection, and the like in the prior art can be solved by adopting the photobacterium damsela rapid detection primer; the primer disclosed by the invention is rapid and ordered in detection, realizes the routinization and standardization of the detection process, is standard in operation, and is hard to cause errors; an amplification primer has very good specificity and accuracy; by adopting a method of embedding dyes, a reaction pipe does not need to be opened after completing reaction, and results can be directly observed by naked eyes after taking out the reaction pipe, thus preventing amplified products from polluting follow-up samples to be detected, and improving the application reliability of the kit.
Owner:天津市水产技术推广站
Photobacterium damselae hemolysin Hlych protein having immunoprotection effect
ActiveCN108330142AImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiological material analysisWestern blotProkaryotic expression
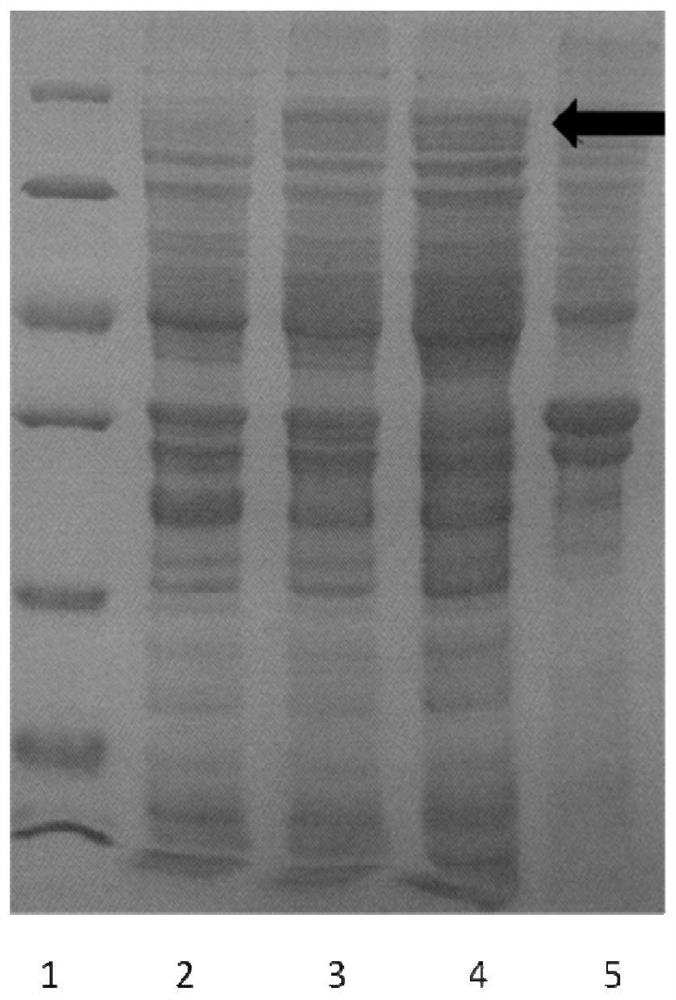
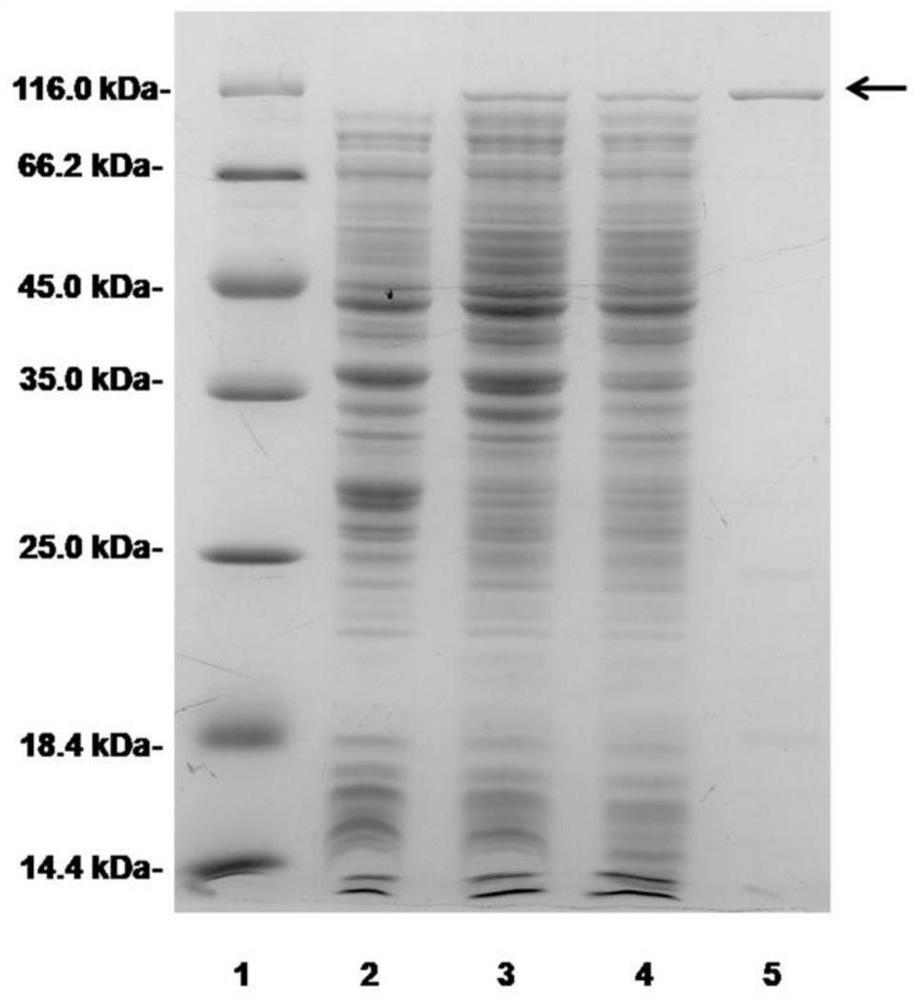
The invention discloses a photobacterium damselae hemolysin Hlych protein having immunoprotection effect. By constructing a recombinant vector pMD18T-hlych, a recombination expression vector pET32a-hlych and a prokaryotic expression hlych gene, the recombinant Hlych protein is prepared, SDS-PAGE analysis and Western blot are used for verifying the Hlych protein, and an animal protection experimentis used for evaluating the protection force. The Hlych protein of photobacterium damselae has good immunoprotection force, and establishes a base for a gene engineering subunit vaccine of photobacterium damselae.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Biological pesticide based on chitosan and entomopathogenic nematodes
Biological pesticide, based on chitosane and entomopathogen nematodes. The invention consists of a new pesticide formulation, bio-stimulating and with fungicide effects, combining the bio-stimulating action due to chitosane to the biological control of plagues in agricultural and forest crops, due to phytopathogen insects by entomopathogen nematodes of the Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae families. There is a synergic action between the bio-stimulating and the biological pesticide due to the action of symbiotic bacteria of the Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus genres, carrying the nematodes of these families. The aforementioned action is synergically enhanced by the bio-stimulating effect of chitosane over plants, on favouring the radicular development and degree of lignification and provoking the elicitation of phytoalexins producer genes, as a defensive mechanism.
Owner:IDEBIO
Luminous bacteria and methods for the isolation, identification and quantitation of toxicants
InactiveUS7713690B1Rapid and accurate methodComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementToxicantFish extract
Methods for the isolation and identification of a toxicant in a sample are disclosed. Luminescent biological agents (i.e., bacteria) having sensitivity to a toxicant or an isolatable component in a sample are used to provide visually discernable zones of luminescent inhibition in the presence of a toxicant (or) in the presence of an isolatable sample component as separated by paper or thin layer chromatography. Kits for use in conjunction with the identification of a toxicant in a sample are also described, which include a luminescent biological reagent as the visualizing agent. Particular examples of luminescent bacterial agents useful in the practice of the present invention include photobacterium leoganthi, photobacterium phosphoreum, Vibrio fischeri, Vibrio harveyi a luminescent fungi, a luminescent fish extract, a luminescent dinoflagellate and fluorescent microorganisms, such as Cypridina. Potential toxicants in a liquid sample, a solid sample, or in a gaseous sample may be identified and further chemically characterized using the described methods. The isolation of potential toxicants in a sample through the processing of a sample through a separation phase matrix such as chromatography paper or TLC plate, followed by exposure to luminescent biological agent, provides for a rapid and inexpensive method for identifying pesticides, herbicides and heavy metals in a known or unknown sample.
Owner:BECVAR JAMES E +1
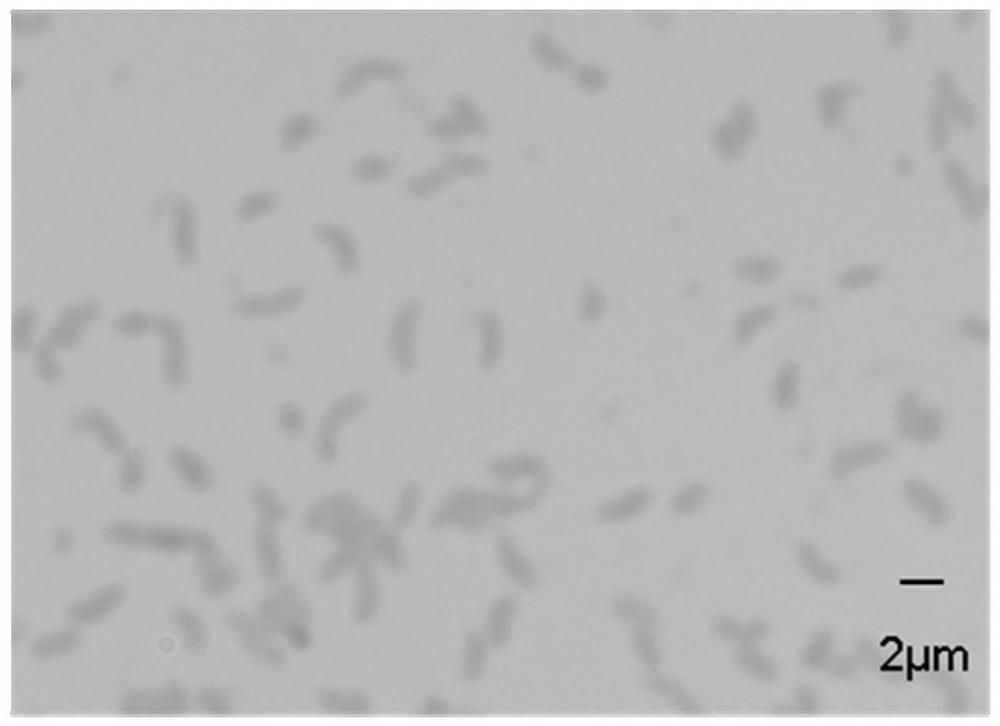
Photobacterium sp. QA16 as well as culture method and application thereof
The invention relates to a photobacterium sp. QA16 as well as a culture method and application thereof. The photobacterium sp. QA16 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture CollectionCenter (CGMCC) on August 26, 2020, the preservation address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No.3, Yard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.20556. The photobacterium sp. QA16 strain can be used for preparing a chondroitin sulfate lyase, and the chondroitin sulfate lyase can degrade chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate and is chondroitin sulfate ABC enzyme. The photobacterium sp. QA16 strain can be applied to structural research of the chondroitin sulfate, can also be applied to the fields of medicines, cosmetics and the like, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Pomfret photobacterium damsela strain and inactivated vaccine
ActiveCN109880766ASimple preparation processStable outputAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMicroorganismImmune effects
The invention provides pathogenic bacteria separated from pomfret intestinal tract affected with photobacterium damsela, wherein the pathogenic bacteria are photobacterium damselae. The photobacteriumdamsela was deposited on December 7, 2018 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center located at No. 1 Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing China. A process for preparing an inactivated vaccine against pomfret photobacterium damsela is simple, the yield is stable, and the cost is low, and a large number of inactivated vaccines having a high immune effect can be acquired. The inactivated vaccine prepared by the method has an immune protection rate of 70%. The vaccine is a pure biological preparation, has the advantages of safety and environmental protection and does notcause drug residue and environmental pollution, and the method can fundamentally prevent the occurrence and prevalence of the pomfret photobacterium damsela, and provides technical support for the large-scale preparation of the inactivated vaccine against the pomfret photobacterium damsela.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for quickly and quantitatively screening captan residue in fruit through high-performance thin-layer chromatography coupled with photobacterium phosphoreum biosensing
InactiveCN109884239AQuick screeningAchieving High-Throughput Screening RequirementsComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementChromatographic separationHazardous substance
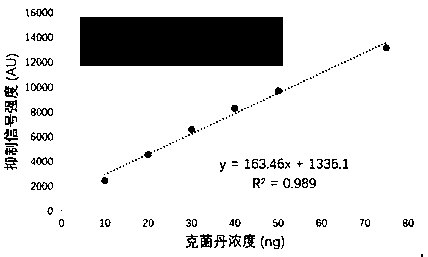
The invention discloses a method for quickly and quantitatively screening captan residue in fruit through high-performance thin-layer chromatography coupled with photobacterium phosphoreum biosensing,and belongs to the technical field of the food detection. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing sample preparation and sample cleaning on fruit homogenate through solid-liquidextraction, and then developing an extract through high-performance thin-layer chromatography, enabling the target captan to separate from a sample interference matrix substance in extraction liquid,and then coupling a chromatographic separation result with the photobacterium phosphoreum biosensing through a dipping manner; and quantitatively assessing the target captan residue concentration in the fruit by combining the bioluminescence autography with digital image analysis. The invention establishes a method for quickly and quantitatively screening captan residue in fruit through high-performance thin-layer chromatography coupled with photobacterium phosphoreum biosensing, the method has the advantages of being quick, accurate and economic; and meanwhile, the method example for quicklyand reliably screening harmful substance residue with invisible spectrum characteristic in the food is provided based on the establishment of the high-performance thin-layer chromatography and bioluminescence autography coupled detection method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compatibility method for acquiring optimal combined biological effect by testing binary mixture
InactiveCN102226806AOptimal biological effect pointSimple and easy to predictChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingIndicator organismPhotobacterium phosphoreum
The invention belongs to the field of environmental protection, and discloses a compatibility method for acquiring an optimal combined biological effect by testing a binary mixture. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the testing method is based on GB / T 15441-1995, and photobacterium phosphoreum is used as an indicator organism to test the single toxicity EC50-A and EC50-B of A and B compounds; (2) according to the EC50-A and the EC50-B, a mixed solution with an equivalent effect ratio is prepared by a testing method which is based on GB / T15441-1995, the biological effect concentration of the mixed solution is tested to obtain the concentration CA and CB of A and B in a mixed system when inhibition of the mixed system to the biological effect is 50 percent, and a combined biological effect index TU1:1 is calculated in the equivalent effect ratio; and (3) a combined biological effect regulation of the binary mixed system can be predicted according to the testing result TU1:1 of the combined biological effect, which is calculated in the equivalent effect ratio, and the optimal biological effect point can be acquired. The method can be applied in the aspects of environmental science, medication, pesticide and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Photobacterium phosphoreum and application thereof
InactiveCN103805541AEasy to get ingredientsSimple ingredientsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a microorganism bacterial strain and application thereof, and particularly relates to a photobacterium phosphoreum and application thereof, overcoming the defects that no report about photobacterium phosphoreum which is used in production of alginate lyase in the prior art is available, the alginate lyase produced by other bacterial strains has low output and is poor in storage stability, which greatly limits the use in industrial production. The photobacterium phosphoreum SRU-2 is preserved in China Center For Type Culture Collection on December 29, 2013 with a preservation number of CCTCC M2013723. The bacterial strain can be used for producing alginate lyase. The alginate lyase produced by the photobacterium phosphoreum has high output, and the alginate lyase liquor has good storage stability, so that the application range of the alginate lyase in industrial production is greatly enlarged.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHUREN UNIV
Multivalent inactivated vaccine against photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111388660ASignificant pathogenicitySignificant immunogenic variabilityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMarine aquacultureDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of prevention and control of mariculture diseases, and particularly relates to a multivalent inactivated vaccine against photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: screening two photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae strains with difference in pathogenicity and immunogen, respectively carrying out whole-bacterium inactivation on the two strains, adding Chinese wolfberry polysaccharide, and conducting mixing to obtain the multivalent inactivated vaccine. The vaccinehas an outstanding immune protection effect on marine fishes, and can effectively prevent and control infection of photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
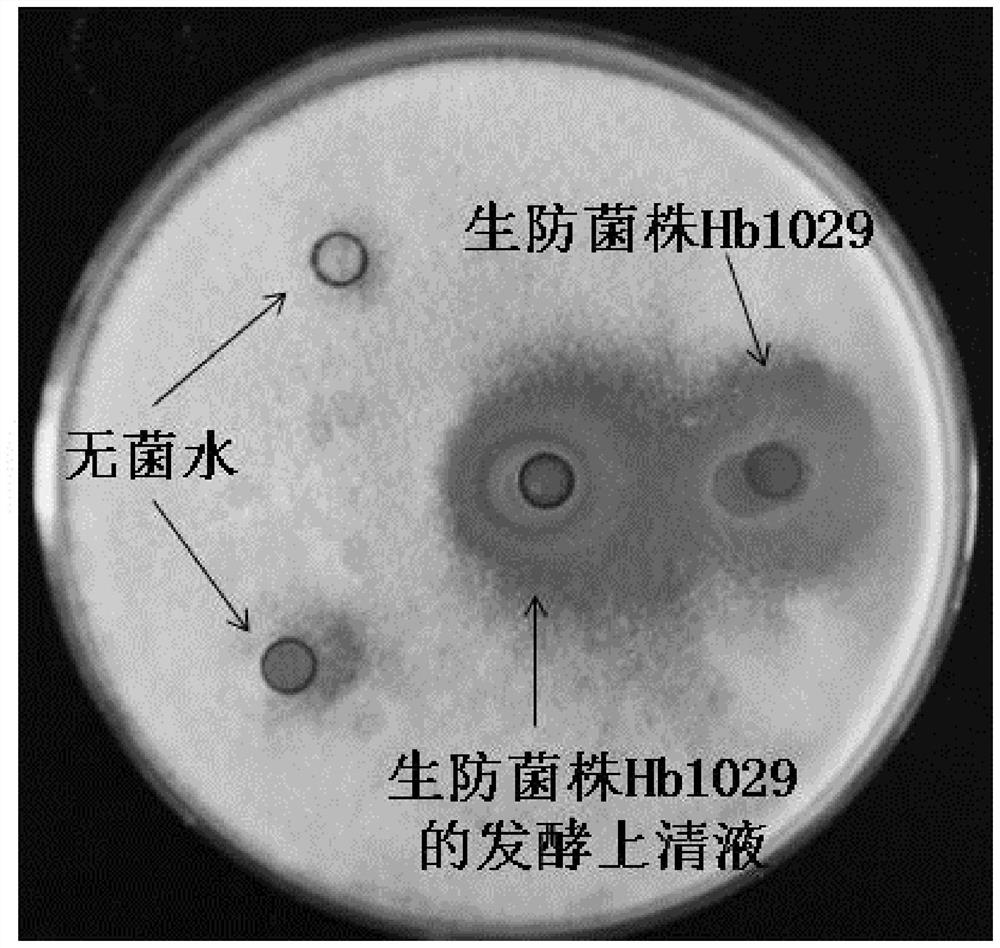
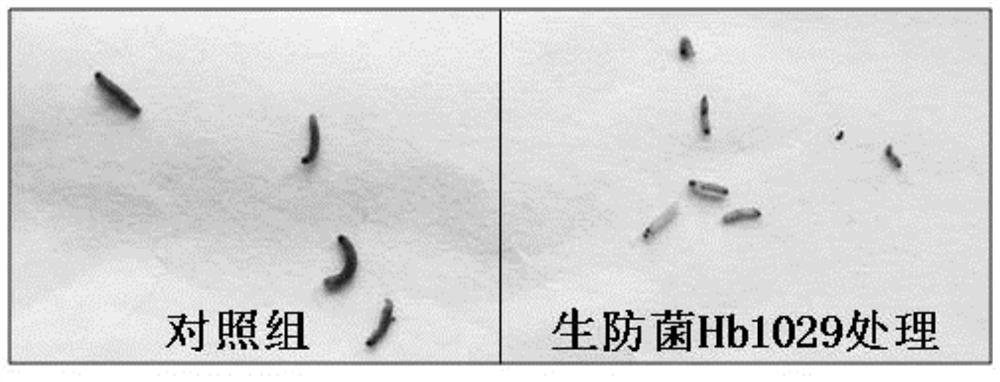
Photorhabdus luminescens Hb1029 and application thereof
ActiveCN107916237AHas insecticidal and antibacterial effectsBroad spectrum of prevention and treatmentBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationBiotechnologyBacteroides
The invention discloses photorhabdus luminescens Hb1029 and application thereof. Experiments prove that the photorhabdus luminescens Hb1029 shows a good inhibitory effect against various plant bacterial pathogens such as banana fusarium wilt, tomato fusarium wilt, guava shoot blight, pitaya fruit rot as well as multiple plant fungi and citrus canker; furthermore, the photorhabdus luminescens Hb1029 has an activity of inhibiting growth and development of or killing plant pests such as beet armyworm, citrus fruit fly, and citrus leaf miner. The biocontrol bacterium has insecticidal and bacteriostatic effects and a broader spectrum of prevention and control. After being subjected to subculture for a plurality of times, the strain has stable insecticidal and antibacterial effects. The photorhabdus luminescens Hb1029 has a good preservation effect when being used for fresh fruit preservation, and has very good safety at the same time, thus having an important economic significance.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
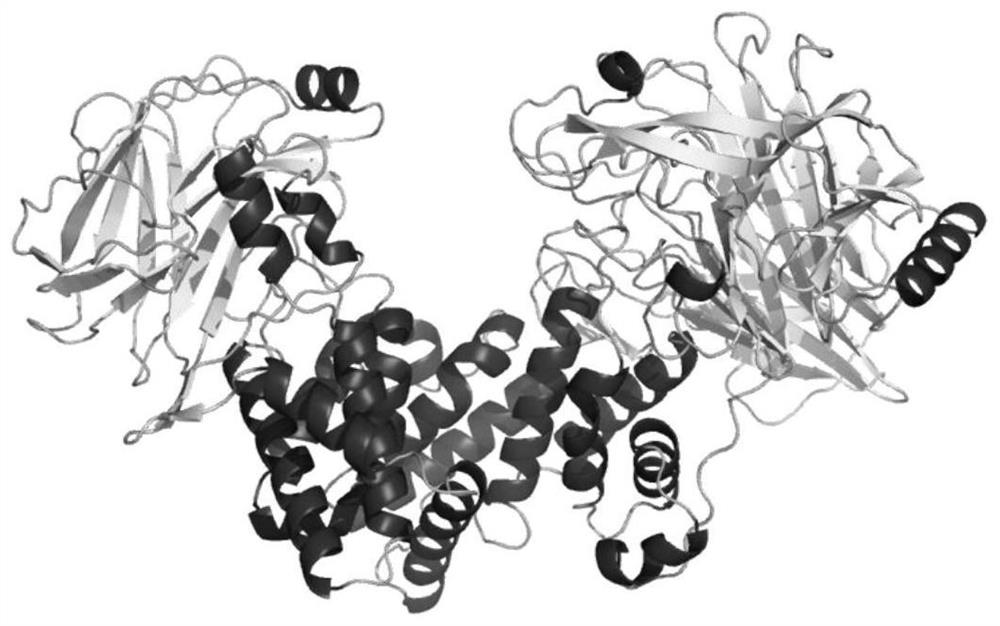
Photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, gene coding photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, and applications of photobacterium leiognathi luciferase
ActiveCN104845986AGood linear relationshipReduce testing costsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminescent bacteriaRecombinant escherichia coli
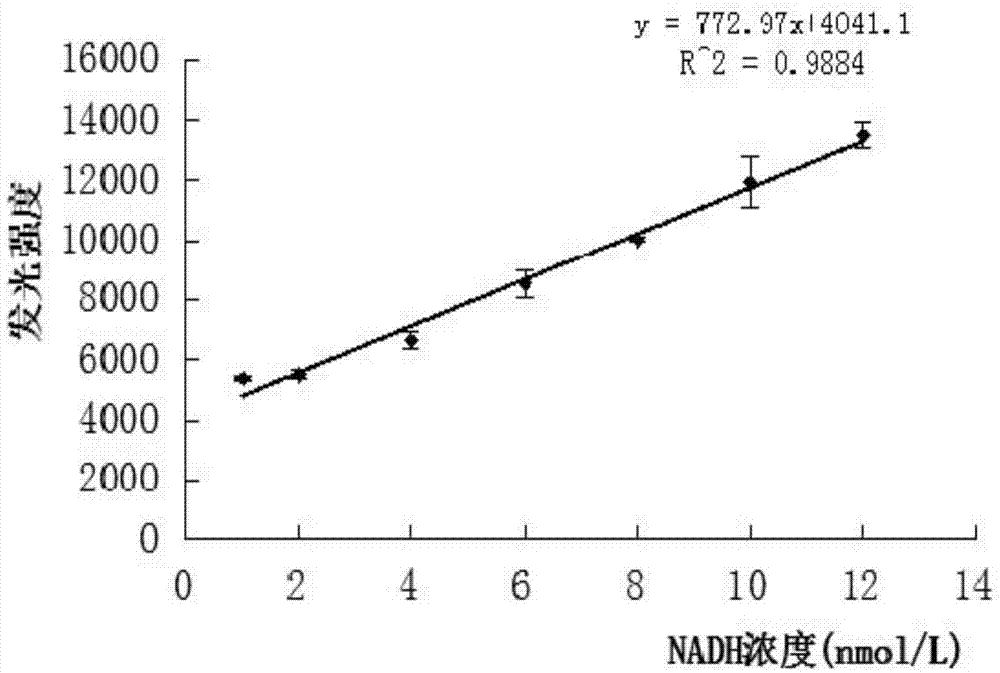
The present invention relates to a photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, a gene coding the photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, and applications of the photobacterium leiognathi luciferase, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The present invention provides a photobacterium leiognathi luciferase gene, which can achieve efficient expression in escherichia coli and can be used for quantitative NADH detection so as to provide possibility for replacement of the luminescent bacteria double enzyme system detection. According to the present invention, with the introduction of the photobacterium leiognathi luciferase gene LuxAB, the conditions are optimized to make the exogenous luciferase protein achieve the efficient expression in the escherichia coli, the escherichia coli RosettaDE3 contains high activity FMN-NADH oxidoreductase so as to achieve the in vitro luminescence of the recombinant escherichia coli double enzyme body, and the obtained product is used for NADH detection.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Photobacterium lyophilized powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107502567AImprove stabilityGood storage stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism preservationPhysical chemistryPhotobacterium phosphoreum
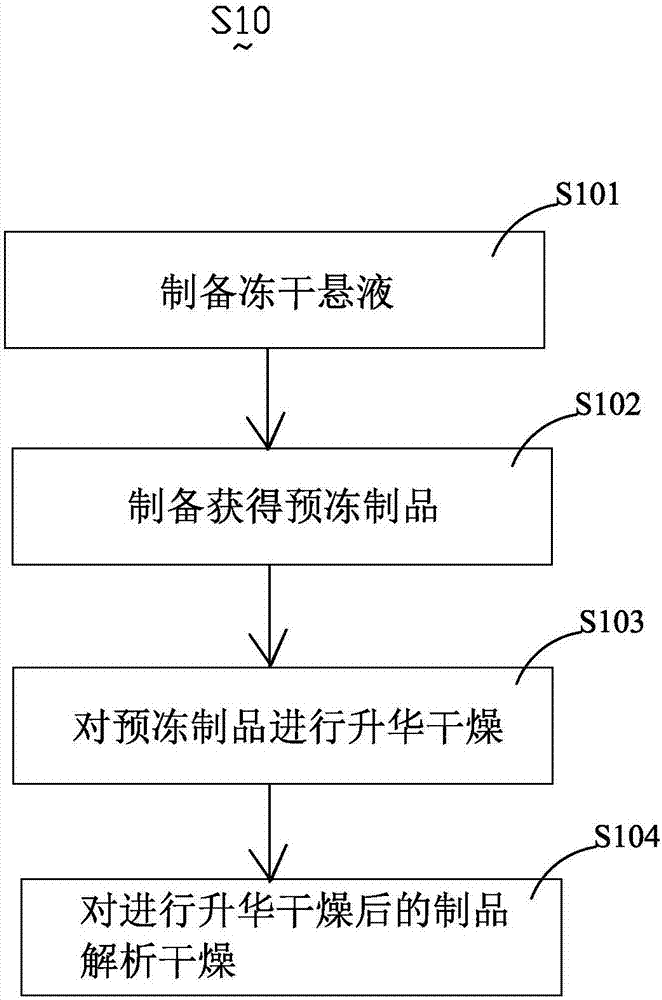
The present invention relates to photobacterium lyophilized powder and a preparation method thereof, desired photobacterium and a protective additive are mixed to form a lyophilized suspension; the lyophilized suspension is frozen to pre-freezing temperature to obtain a pre-frozen product, sublimation drying and desorption drying are in turn performed on the pre-frozen product, the sublimation drying includes at least two temperature-raising and temperature-maintaining processes, so that the pre-frozen product is gradually raised from the pre-freezing temperature to first temperature, and the first temperature is 48 DEG C-64 DEG C higher than the pre-freezing temperature. The present invention further provides the photobacterium lyophilized powder, and the photobacterium lyophilized powder is prepared by the preparation method of the photobacterium lyophilized powder. The method overcomes the problem of the poor stability of the existing photobacterium lyophilized powder, improves the storage stability of the photobacterium lyophilized powder and prolongs the shelf life of the photobacterium lyophilized powder.
Owner:深圳市朗石科学仪器有限公司
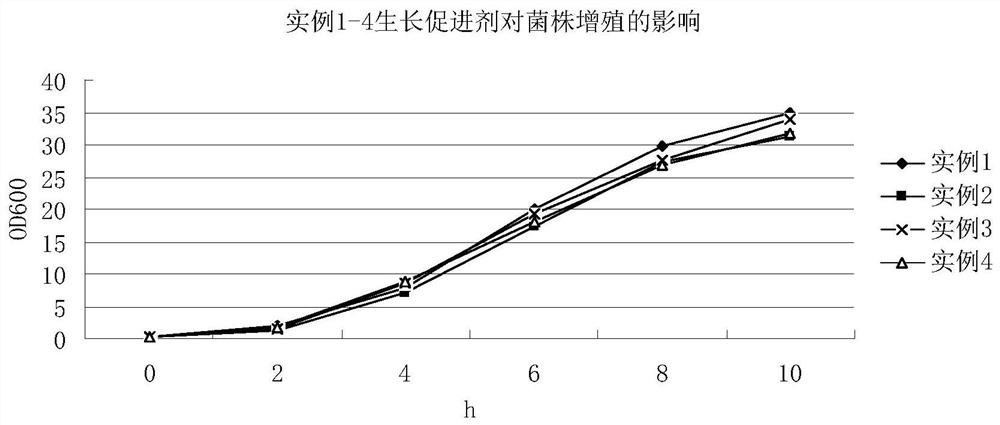
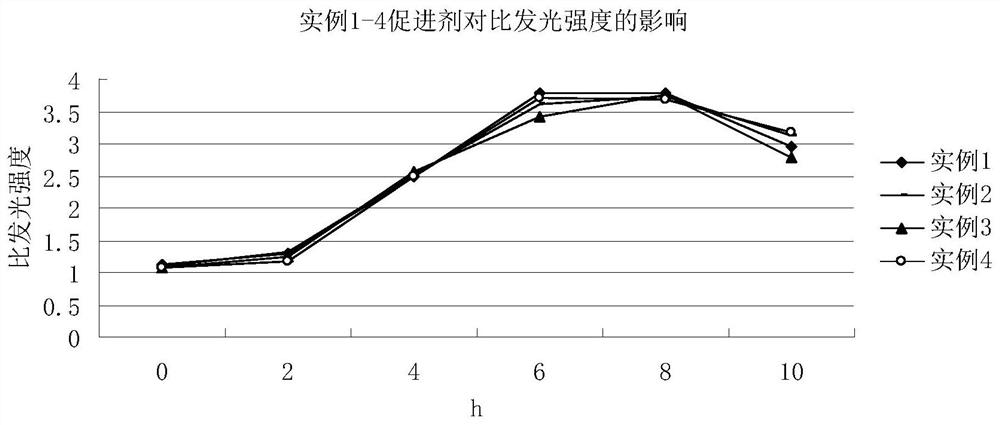
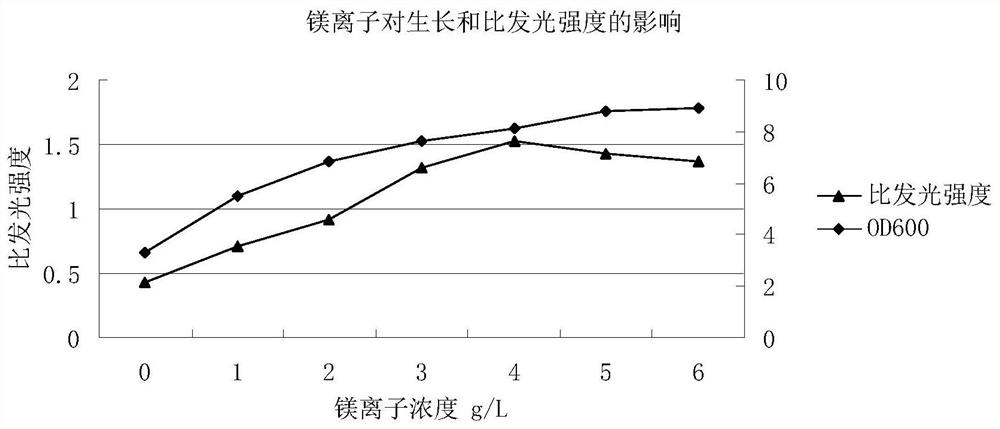
Photobacterium phosphoreum growth promoter used for monitoring water body pollutants and application of photobacterium phosphoreum growth promoter
ActiveCN111979140AProliferate fastRestore activityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacterosiraYeast cell extract
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and discloses a photobacterium phosphoreum growth promoter used for monitoring water body pollutants. The photobacterium phosphoreum growth promoter comprises components as follows: sodium chloride, urea, glucose, magnesium chloride, oxaloacetic acid, adenosine, yeast extract and formic acid. The photobacterium phosphoreum growth promoter used for monitoring the water body pollutants can rapidly recover and enlarge cultivation, thereby saving monitoring time and reducing burdens of enterprises.
Owner:山东瑞泽检测评价技术服务有限公司 +1
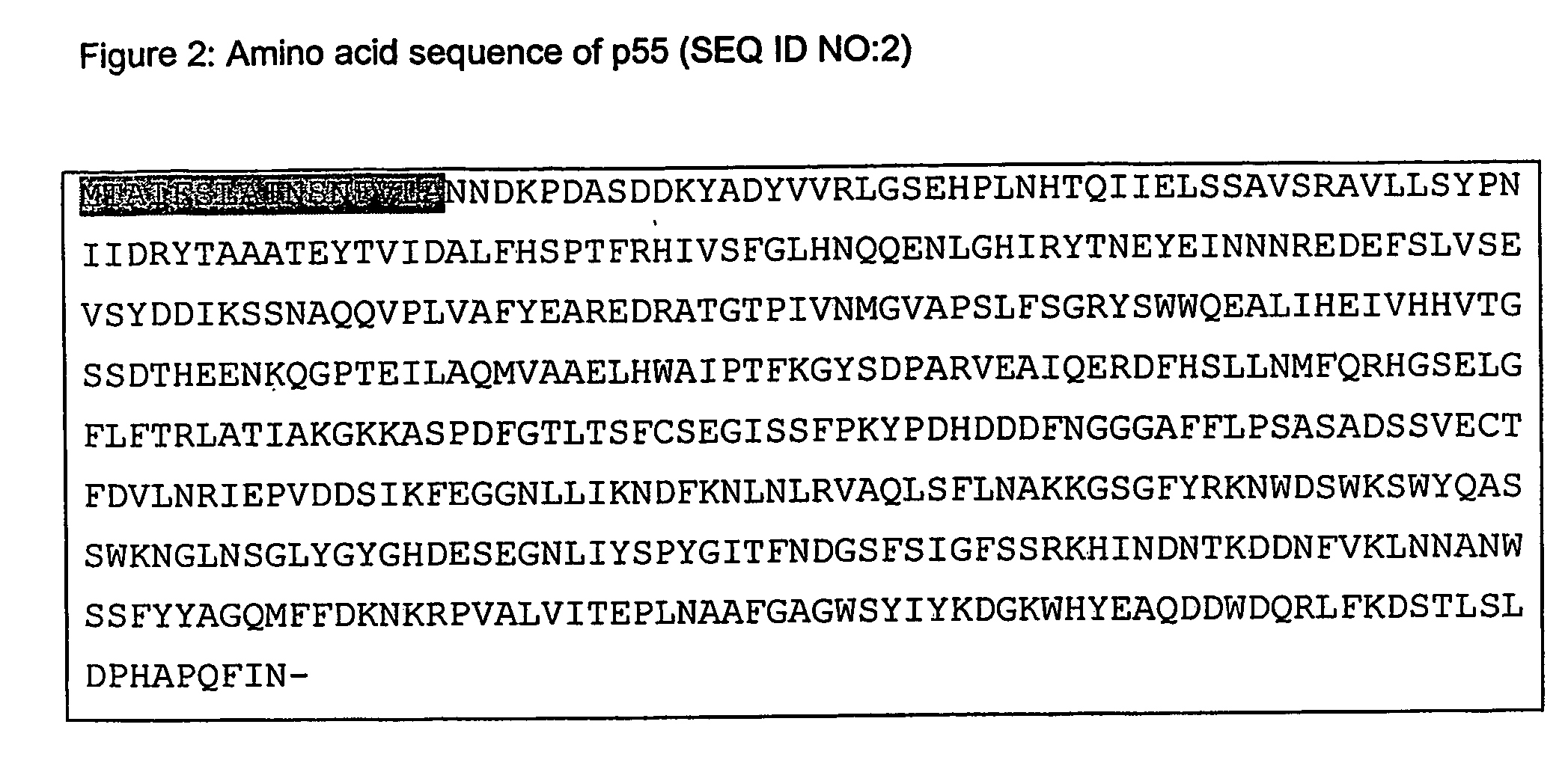
Protein from photobacterium damselae and use thereof
A derivative of a 55 kDa extracellular protein from Photobacterium damselae subsp. Piscicida is the basis for a vaccine against Photobacterium infection, and thereby protects fish from pasteurellosis.
Owner:ELANCO TIERGESUNDHEIT AG
Compound Chinese herbal medicine for preventing and treating bacterial diseases of cynoglossus semilaevis and preparation method of compound Chinese herbal medicine
InactiveCN113057988AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticAntibacterial agentsPlant ingredientsBiotechnologyVibrio anguillarum
The invention discloses a compound Chinese herbal medicine for preventing and treating bacterial diseases of cynoglossus semilaevis and a preparation method of the compound Chinese herbal medicine. The invention belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine. The compound Chinese herbal medicine is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-4 parts of radix scutellariae, 2-4 parts of fructus mume, 1-2 parts of fructus forsythiae, 2-4 parts of climbing groundsel herb and 1-3 parts of pomegranate rind. The compound Chinese herbal medicine can be effectively used for preventing and treating bacterial diseases caused by vibrio vulnificus, vibrio anguillarum, vibrio harveyi, photobacterium damnii, pseudomonas fluorescens and the like; the medicinal components belong to natural Chinese herbal medicines, meet the food safety requirements, enhance the palatability of fishes, have no toxic or side effect on fishes, can reduce and replace the use of antibiotics, are simple and convenient in use method, small in dosage and low in cost, can be used for current fish culture production, and can improve the culture survival rate and the product quality.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Luminous bacteria and methods for the isolation, identification and quantitation of toxicants
Methods for the isolation and identification of a toxicant in a sample are disclosed. Luminescent biological agents (i.e., bacteria) having sensitivity to a toxicant or an isolatable component in a sample are used to provide visually discernable zones of luminescent inhibition in the presence of a toxicant (or) in the presence of an isolatable sample component as separated by paper or thin layer chromatography. Kits for use in conjunction with the identification of a toxicant in a sample are also described, which include a luminescent biological reagent as the visualizing agent. Particular examples of luminescent bacterial agents useful in the practice of the present invention include Photobacterium leoganthi, Photobacterium phosphoreum, Vibrio fischeri, Vibrio harveyi a luminescent fungi, a luminescent fish extract, a luminescent dinoflagellate and fluorescent microorganisms, such as Cypridina. Potential toxicants in a liquid sample, a solid sample, or in a gaseous sample may be identified and further chemically characterized using the described methods. The isolation of potential toxicants in a sample through the processing of a sample through a separation phase matrix such as chromatography paper or TLC plate, followed by exposure to luminescent biological agent, provides for a rapid and inexpensive method for identifying pesticides, herbicides and heavy metals in a known or unknown sample.
Owner:BECVAR LAURA
A Strain of Photobacterium hb1029 and Its Application
ActiveCN107916237BHas insecticidal and antibacterial effectsBroad spectrum of prevention and treatmentBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationBiotechnologyCitrus volkameriana
The invention discloses a strain of photobacterium Hb1029 and its application. Experiments have proved that the photobacterium Hb1029 of the present invention is effective against various plant fungi such as banana wilt, tomato wilt, guava branch blight, pitaya fruit rot, and citrus. Canker and other plant bacterial pathogens have shown good inhibitory effect; meanwhile, Photobacterium Hb1029 has growth inhibitory or insecticidal activity against plant pests such as beet armyworm, Bactrocera dorsalis, and citrus leaf miner. The biocontrol bacterium has insecticidal and bacteriostatic effects, and has a wide control spectrum. Moreover, the insecticidal and antibacterial effects of the bacterial strain are stable after repeated subculture. It has a good fresh-keeping effect when used for fruit fresh-keeping, and has good safety at the same time, and has important economic significance.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Dna vaccine against pseudotuberculosis in marine fish
ActiveCN104736169AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsNucleotideA-DNA
Provided is a DNA vaccine for use in fish which induces protective immunity against pseudotuberculosis. As the active component, this DNA vaccine contains DNA containing a nucleotide sequence that encodes a polypeptide that is immunogenic against Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, or contains an expression vector containing said DNA.
Owner:TOKYO UNIV OF MANNE SCI & TECH
Multiplex PCR detection method of pathogenic bacteria of fish sarcoidosis
PendingCN110878365AImprove throughputFormulate prevention and control strategies in a timely mannerMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexGenomic DNA
The invention relates to a PCR detection method of pathogenic bacteria of fish sarcoidosis, comprising the following steps of: extracting genomic DNA of Aeromonas hydrophila, Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, Nocardia asteroids, Aeromonas schubertii, Nocardia seriolae and Nocardia salmonicida; carrying out primer design on the genomic DNA of pathogenic bacteria; and carrying out amplification and detection on the genomic DNA of Aeromonas hydrophila, Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida, Nocardia asteroids, Aeromonas schubertii, Nocardia seriolae and Nocardia salmonicida. Various pathogenic bacteria of sarcoidosis can be detected by the method, and the method has high specificity and sensitivity.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIV +1
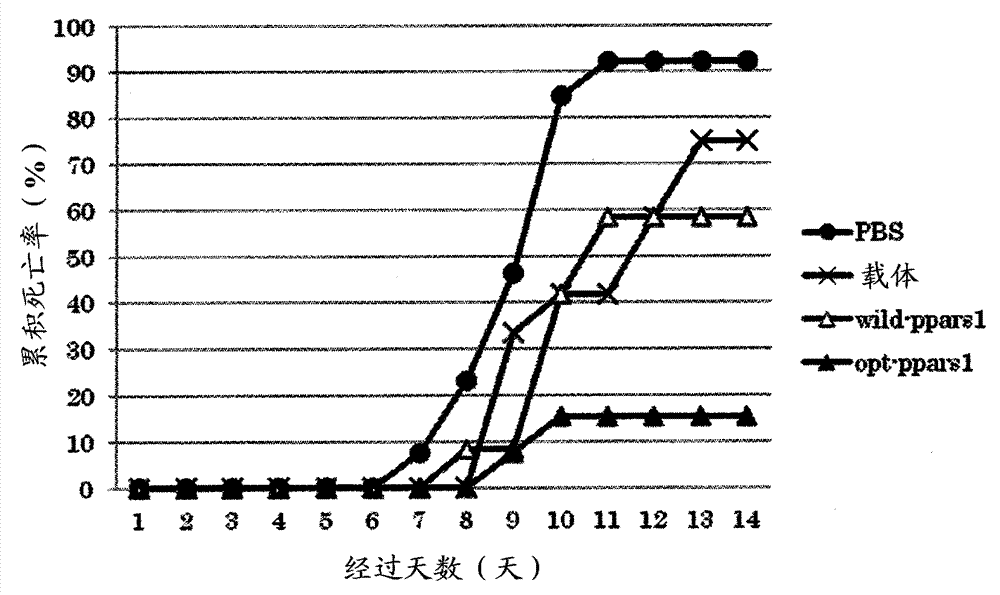
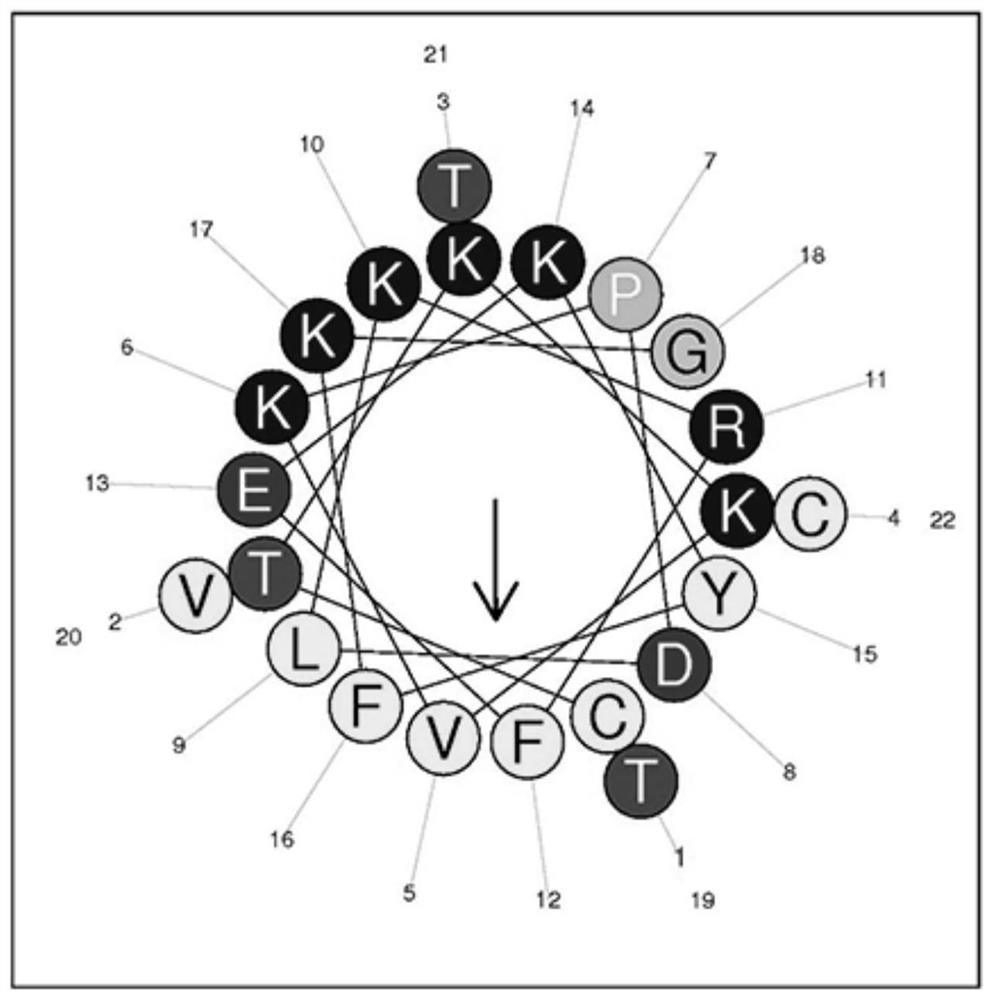
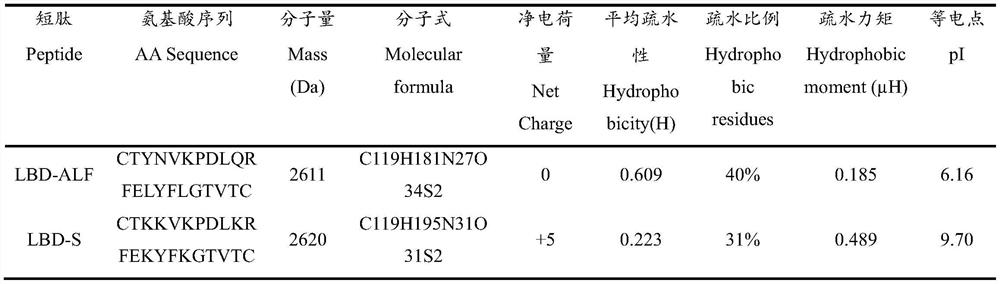
Antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S and application and medicine thereof
ActiveCN113563427AReduce hydrophobicityStrong hydrophilic and lipophilicAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibacterial activityOligopeptide
The invention provides an antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S as well as application and a medicine thereof, and relates to the field of biotechnology. The invention provides an antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S. The amino acid sequence of the antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S is CTKKVKPDLKRFEKYFKGTVTC. The inventor finds that the antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S has low hydrophobicity, high hydrophilicity and lipophilicity and high antibacterial activity, and the antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S can be applied to gram-negative bacteria and gram-positive bacteria, such as bacillus subtilis, corynebacterium glutamicum, micrococcus lyticus, micrococcus luteus, photobacterium damsonii and the like. Compared with the antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-ALF before modification, the antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-S provided by the invention has the advantages that the inhibition effect on the bacillus subtilis, the corynebacterium glutamicum and the micrococcus lyticus is obviously enhanced, and the antibacterial oligopeptide LBD-Scan be used for preparing antibacterial products.
Owner:北京师范大学珠海校区
An immunoprotective Photobacterium mermaid hemolysin hly ch protein
ActiveCN108330142BImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiological material analysisWestern blotProkaryotic expression
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation and application methods of photobacterium damsela vaccines of cynoglossus semilaevis
InactiveCN102139103BStrong immune responseImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsBiotechnologyCynoglossus semilaevis
The invention provides a preparation method of photobacterium damsela vaccines of cynoglossus semilaevis, which is characterized by comprising the steps of: inoculating ST1 strains of photobacterium damsela on an ordinary nutrient agar bouillon culture medium, cultivating for 24h at the temperature of 28 DEG C, and adding formaldehyde with the final concentration of 0.3% into the culture medium to inactivate the photobacterium damsela for 48h at the temperature of 28 DEG C so as to obtain inactivated bacteria; soaking milkvetch roots with distilled water, and then decocting, filtering and concentrating to obtain milkvetch lixivium; and mixing the inactivated bacteria and the obtained milkvetch lixivium to prepare the photobacterium damsela vaccines of the cynoglossus semilaevis. In the invention, the vaccines have the advantages of enabling the cynoglossus semilaevis to produce good immune response, enhancing the immunity of the cynoglossus semilaevis to the pathogen (photobacterium damsela), and increasing the survival rate of cultivated cynoglossus semilaevis, the output of the cultivated cynoglossus semilaevis, and the economic benefit of the cultivation and production of the cynoglossus semilaevis. The problem that the cynoglossus semilaevis is easy to catch diseases caused by the photobacterium damsela during the cultivation and production process at present is fundamentally solved. The invention also discloses an application method of the photobacterium damsela vaccines of the cynoglossus semilaevis.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
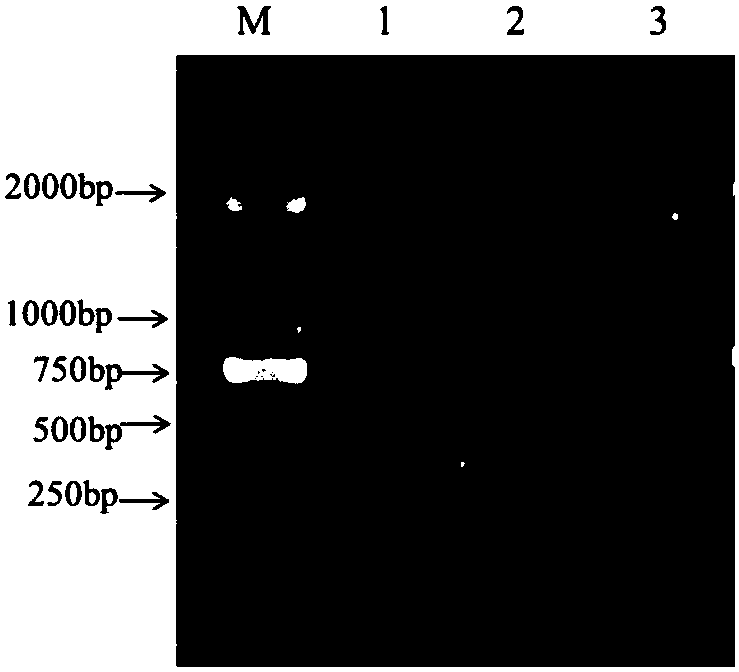
RPA reaction system suitable for rapid detection of Photobacterium mermaida mermaid subspecies
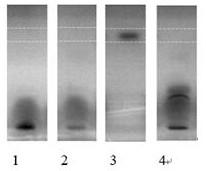
ActiveCN111621550BAccurate identificationHighly conservativeMicrobiological testing/measurementMarine aquacultureGel electrophoresis
The invention belongs to the technical field of mariculture disease prevention and control, and in particular relates to an RPA reaction system suitable for rapid detection of Photobacterium mermaid subspecies mermaid. Specific primers were designed to carry out the amplification reaction of recombinase polymerase, and after gel electrophoresis verification of the product, it was judged qualitatively whether the detection sample contained Photobacterium mermaida subsp. The invention provides a stable, specific and highly efficient Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) reaction system of Photobacterium mermaidi subsp. The research on RPA detection technology of Photobacterium mermaid subspecies has laid a technical foundation for the accurate and rapid detection of RPA of Photobacterium mermaid subspecies.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
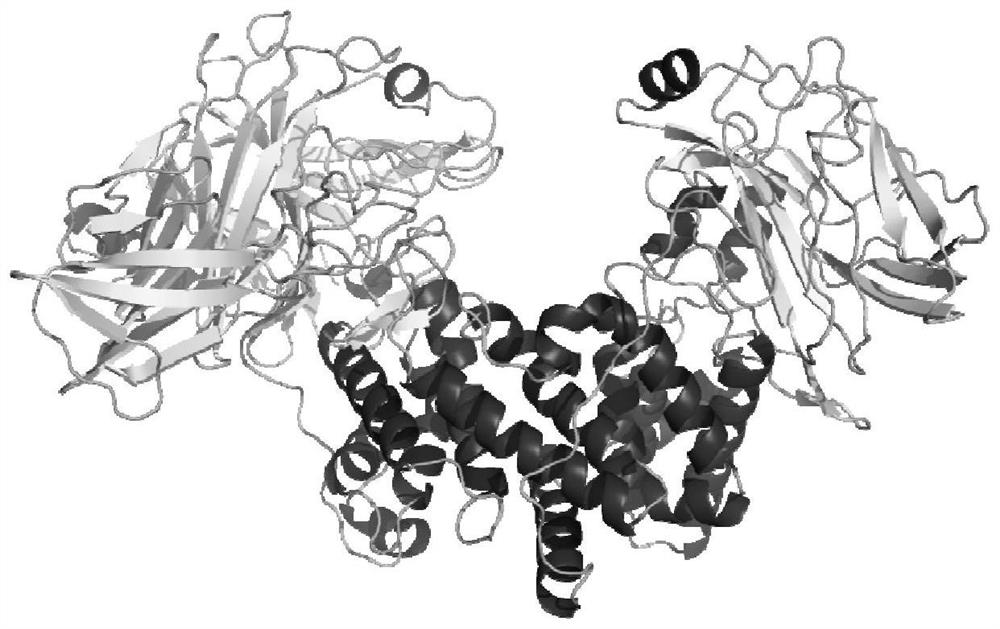
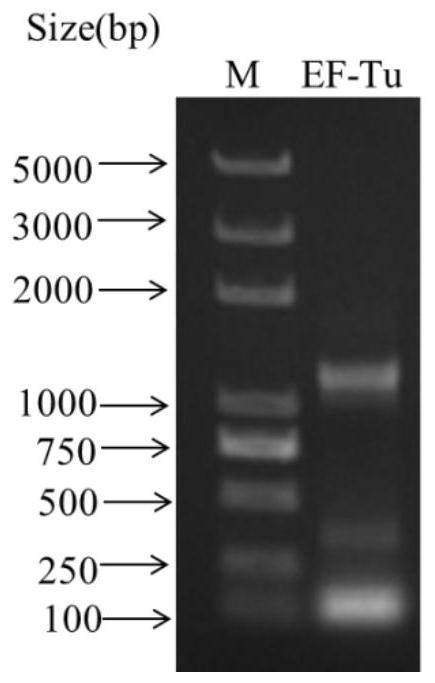
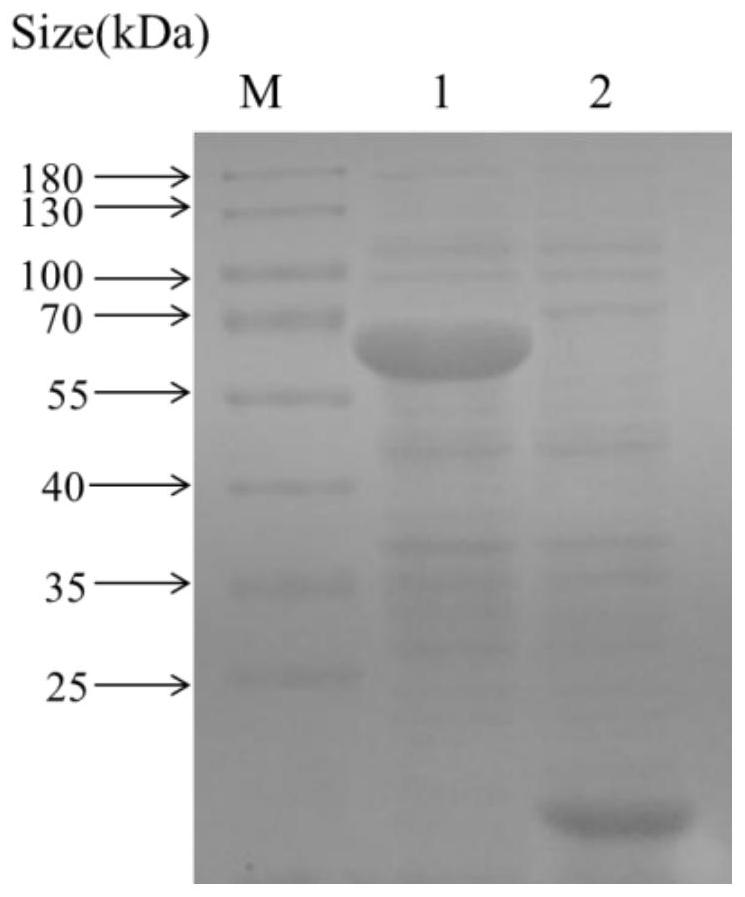
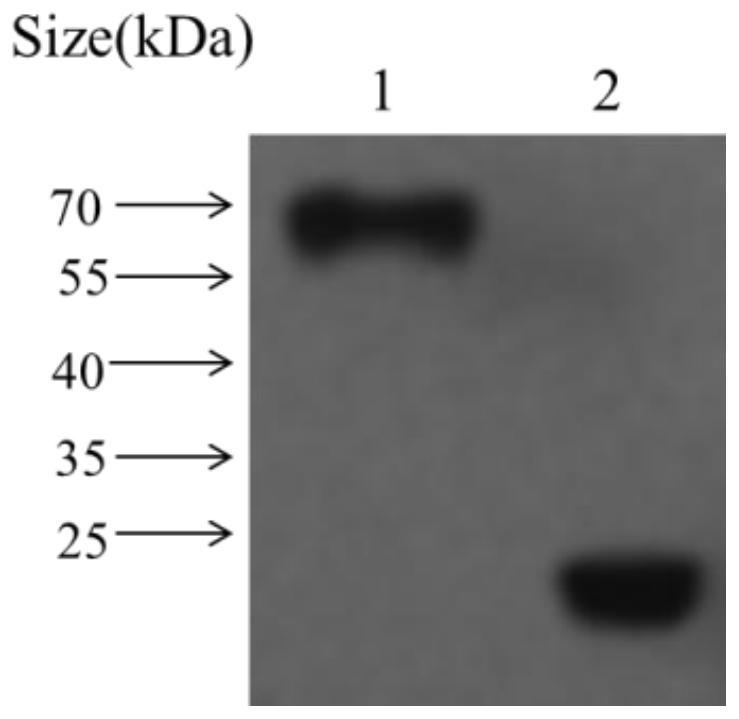
An Extracellular Protein ef-tu from Photobacterium mermaidus
ActiveCN109395071BGood immune protectionGood antigenicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsExtracellular proteinsProkaryotic expression
The invention discloses an application of an extracellular protein EF-Tu of Photobacterium mermaidi with immune protection function in the preparation of a subunit vaccine of Photobacterium mermaidi, wherein the preparation method of the extracellular protein EF-Tu of Photobacterium mermaidi comprises pMD18-T Construction of ‑EF‑Tu recombinant vector, construction of plasmid pET32a‑EF‑Tu, inducible expression of extracellular protein EF‑Tu of Photobacterium mermaida and verification of extracellular protein EF‑Tu of Photobacterium mermaidi. The present invention provides an extracellular protein EF-Tu of Photobacterium mermaidi with immune protection, which is expressed and purified by a prokaryotic expression system, and the immune protection of the extracellular protein EF-Tu of Photobacterium mermaidi is evaluated through animal experiments. It lays the foundation for the further development of photobacteria mermaid subunit vaccine and nucleic acid vaccine selection.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A kind of chondroitin sulfate lyase and its encoding gene and application
ActiveCN112251426BEasy to purifyStable physical and chemical propertiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideLyase
The present invention relates to a chondroitin sulfate lyase and its encoding gene and application. The chondroitin sulfate lyase enCSase in the present invention is isolated from Photobacterium sp. QA16, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The chondroitin sulfate lyase enCSase in the present invention is a new type of CSase ABC enzyme, which has high enzymatic activity on chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate and hyaluronic acid, and degrades chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate and hyaluronic acid. It is in endonuclease mode; it can be used in the preparation of chondroitin sulfate oligosaccharide, dermatan sulfate oligosaccharide and hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide, and has broad application prospects in the fields of medicine and food.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for detecting toxicity of luminescent bacteria
InactiveCN102213721BGood reproducibilityWide range of detection limitsMicrobiological testing/measurementLuminous intensityLuminescent bacteria
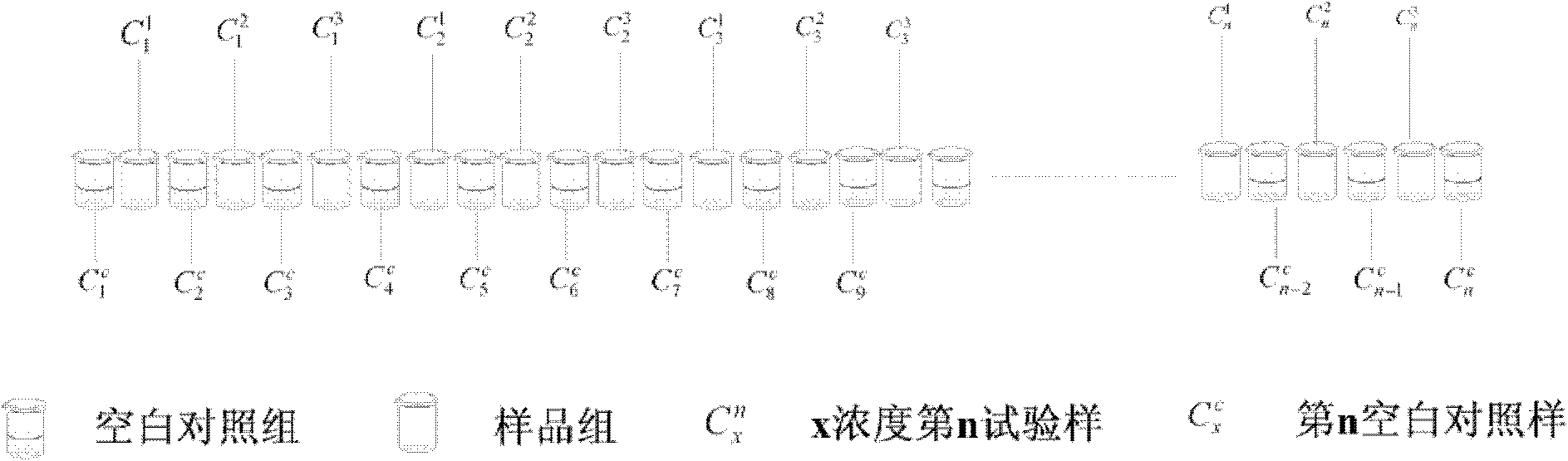
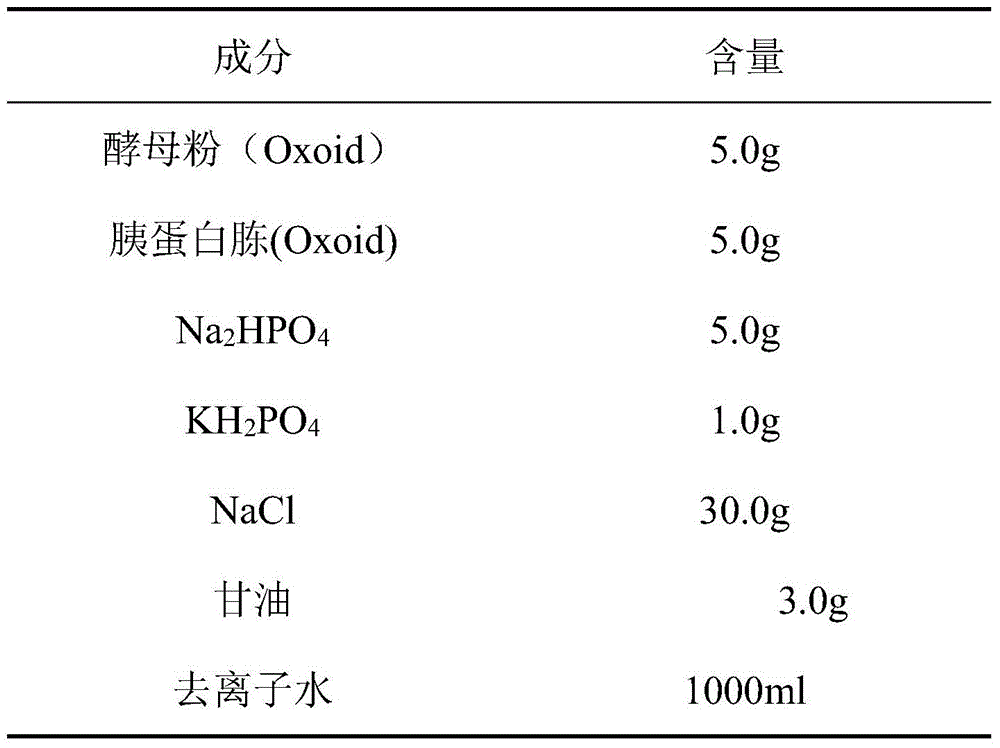
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of environmental pollution, and discloses a method for detecting the toxicity of luminescent bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, activating strains, namely dissolving freeze dried powder of photobacterium phosphoreum, inoculating on a slant and generating the strains for 3 times for later use; 2, culturing the strains, namely inoculating the generated strains to a liquid nutrient medium by using an inoculating loop and culturing for 12 hours at the temperature of 20 DEG C and at 180rpm; 3, balancing bacteria liquid, namely adding an appropriate amount of the bacteria liquid into 20 milliliters of NaC1 solution at the concentration of 3 percent, controlling light value measurement ranges to be between 0.5 and 5million, and agitating for 40 minutes at the temperature of 20 DEG C; 4, adding samples and detecting luminous intensity, namely adding the bacteria liquid which is agitated for 40 minutes into 200 to 800 microliters of NaC1 blank solution at the concentration of 3 percent and 800 microliters of NaC1 polluted solution at the concentration of 3 percent by using a continuous sample injector, immediately and uniformly mixing for 2 minutes on a vortex mixer, standing for 15 minutes at the temperature of 20 DEG C, and placing a sample in a fluorescence detector to detect the luminous intensity; and 5, calculating the suppression ratio of the sample to the luminous intensity by a double alternate comparison method. The method has the characteristics of convenience and high precision.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Lyophilized powder of Photobacter lumina and preparation method thereof
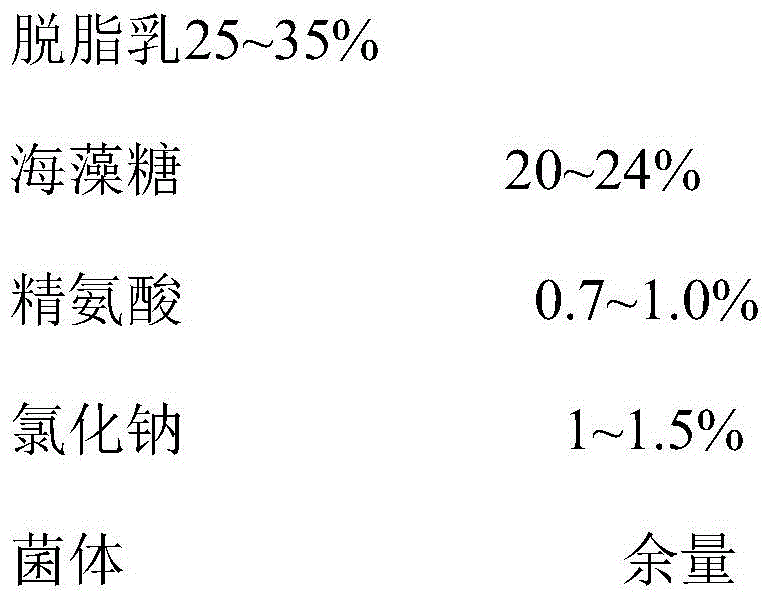
ActiveCN104762209BImprove frost resistanceImprove protectionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingArginine
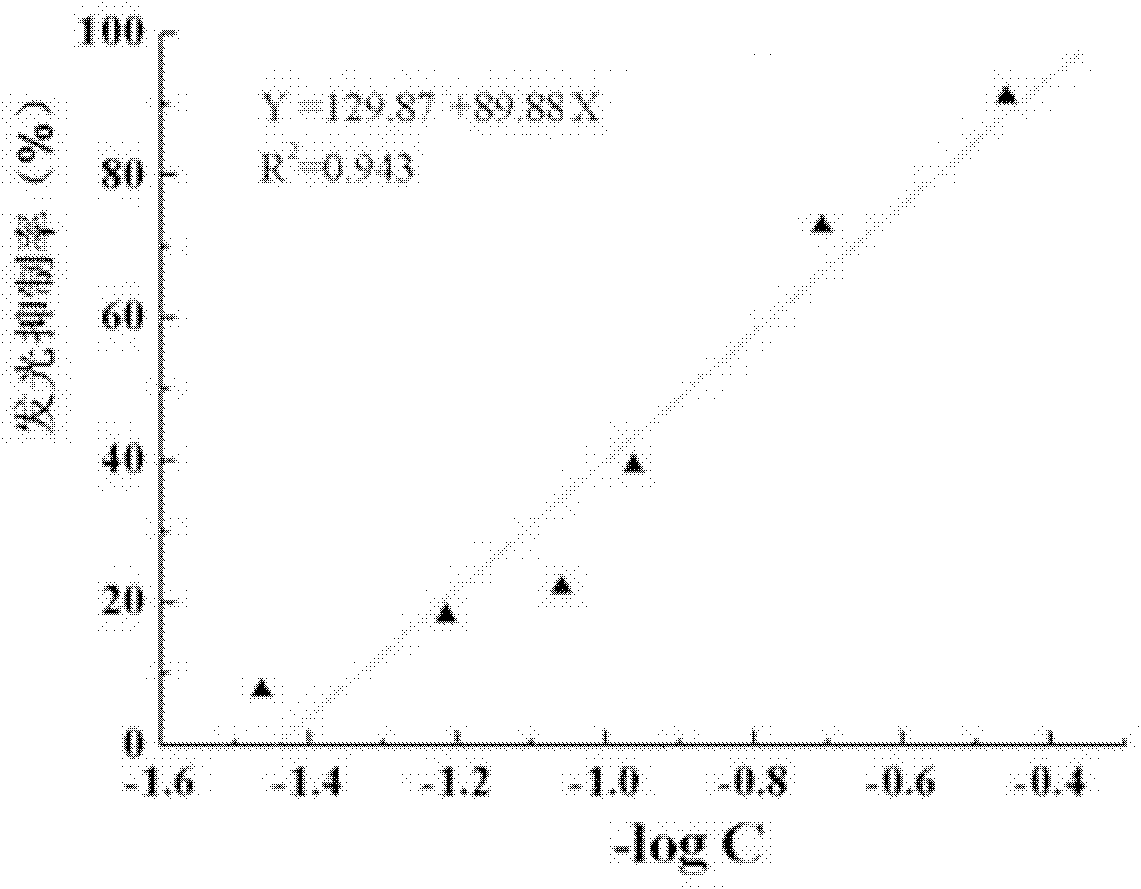
The invention discloses photobacterium phosphoreum freeze-dried powder and a preparation method thereof. The photobacterium phosphoreum freeze-dried powder comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 25-35 percent of skimmed milk, 20-24 percent of mycose, 0.7-1.0 percent of arginine, 1-1.5 percent of sodium chloride and the balance of thalli. The photobacterium phosphoreum freeze-dried powder adopts a compound cryoprotectant; and experiments prove that the compound cryoprotectant is greatly improved in freezing resistance, has a higher protective property than a simplex protective agent and has good stability. The average value of luminous intensity of the photobacterium phosphoreum freeze-dried powder provided by the invention is about 1,843mv and approximate to a model expected value 1,820. When the toxicity of ZnSO4.7H2O, K2Cr2O7 and C6H5OH is detected with photobacterium phosphoreum freeze-dried powder prepared in different batches, the results show that the EC50 value variation coefficients detected by the photobacterium phosphoreum freeze-dried powder prepared in different batches are less than 6%.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for improving enzymatic activity of glycosyltransferases
InactiveUS20090087894A1Improve enzymatic activityIncrease enzyme activitySugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismSialyltransferase
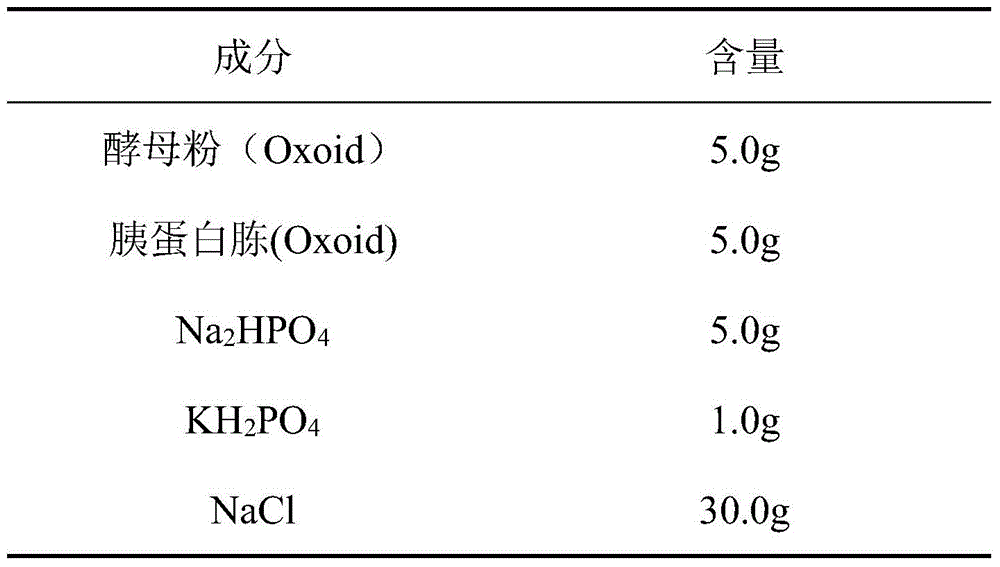
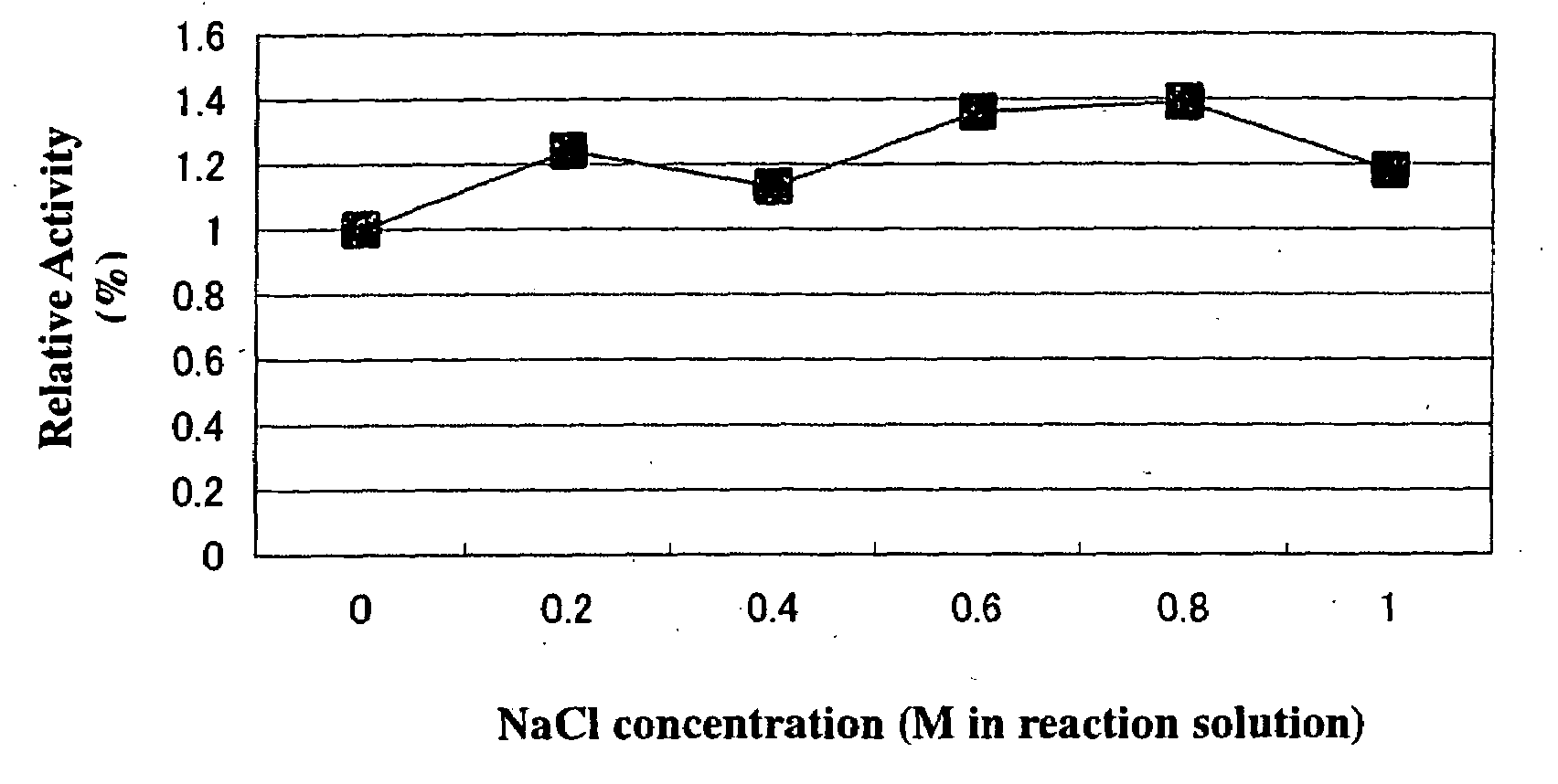
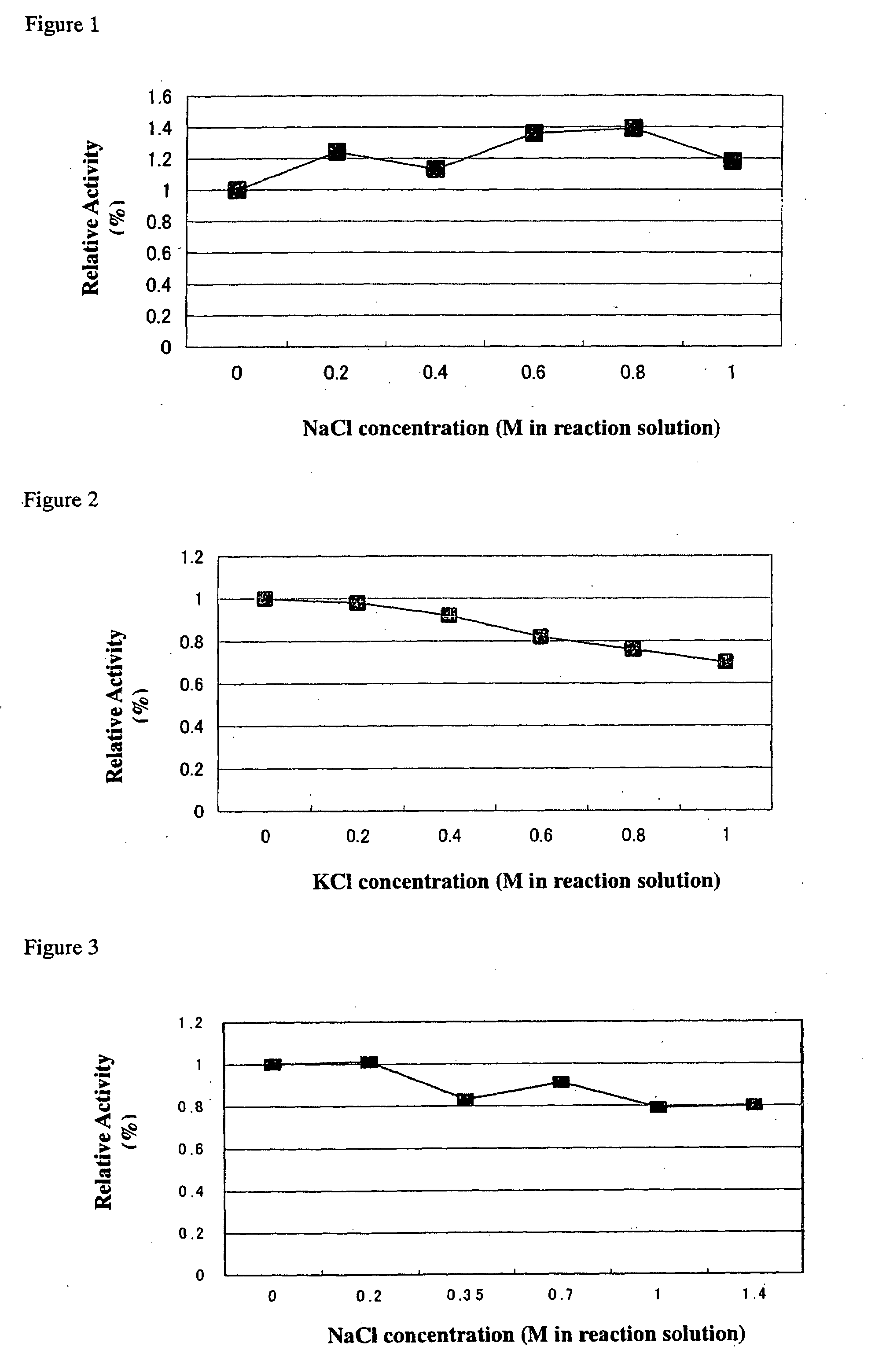
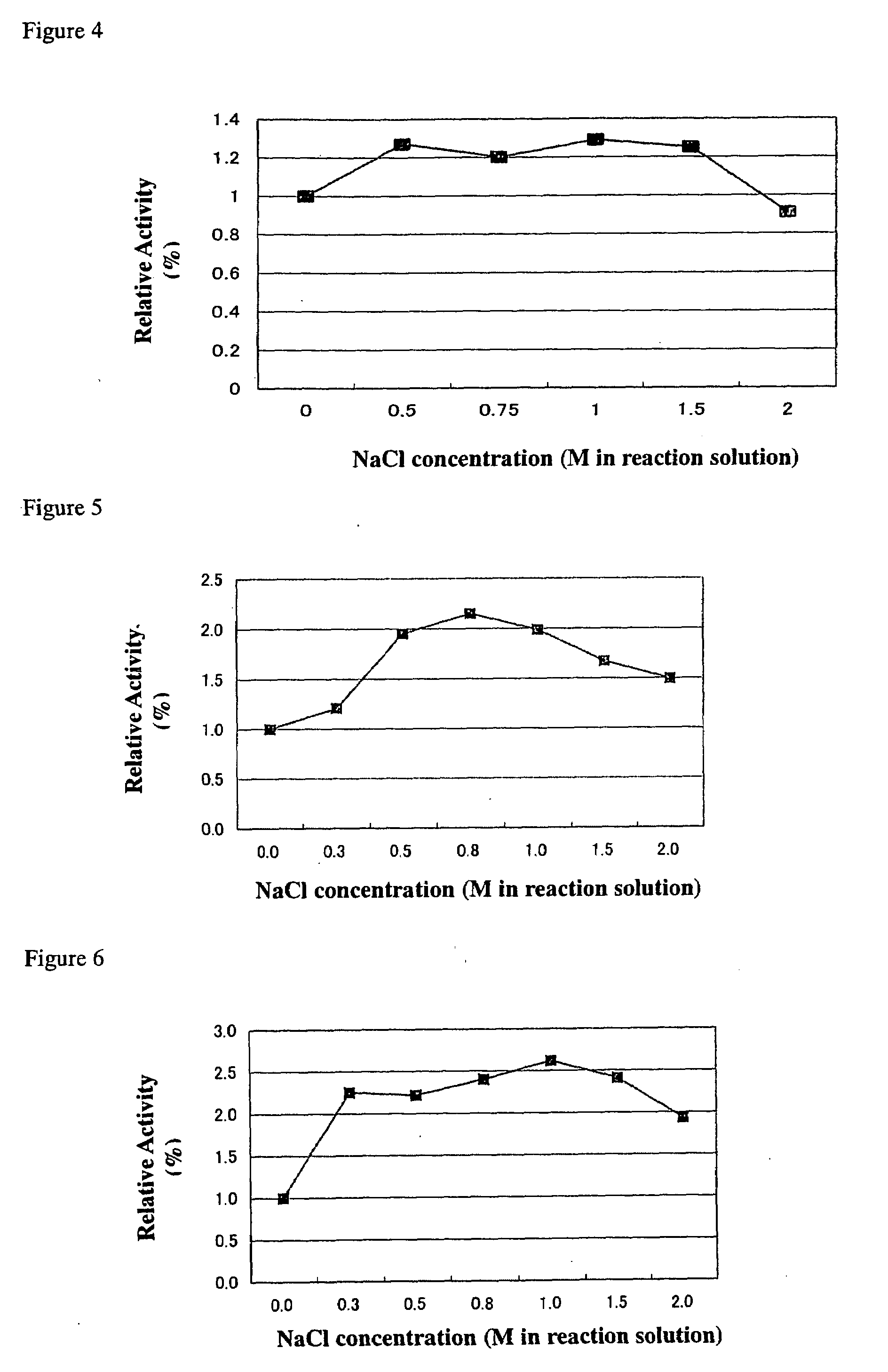
The present invention provides an inexpensive and simple method which allows efficient glycosylation with glycosyltransferases derived from microorganisms of the Vibrionaceae family when compared to conventional enzymatic reaction systems.According to the method of the present invention, glycosyltransferases derived from microorganisms of the Vibrionaceae, such as β-galactoside-α2,6-sialyltransferase derived from Photobacterium damselae, β-galactoside-α2,3-sialyltransferase derived from Photobacterium phosphoreum and β-galactoside-α2,3-sialyltransferase derived from Vibrio sp., enhance their enzymatic activity when an appropriate amount of NaCl is added to their enzyme reaction systems.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com