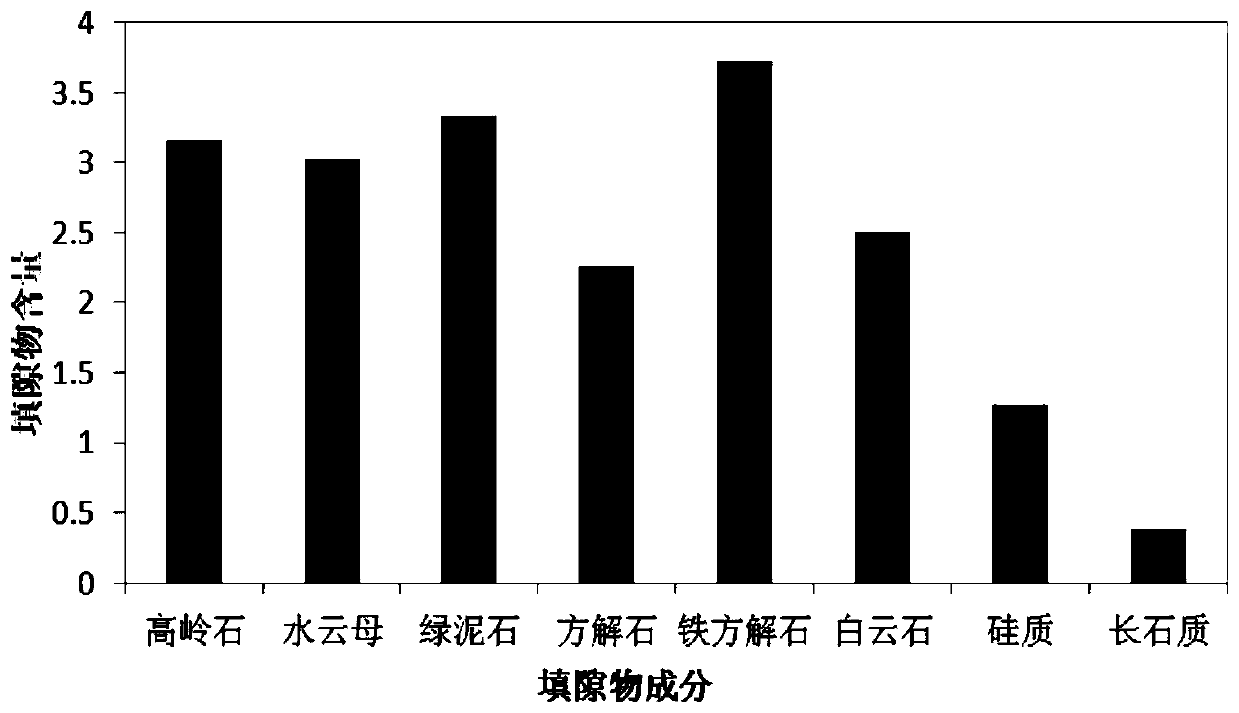
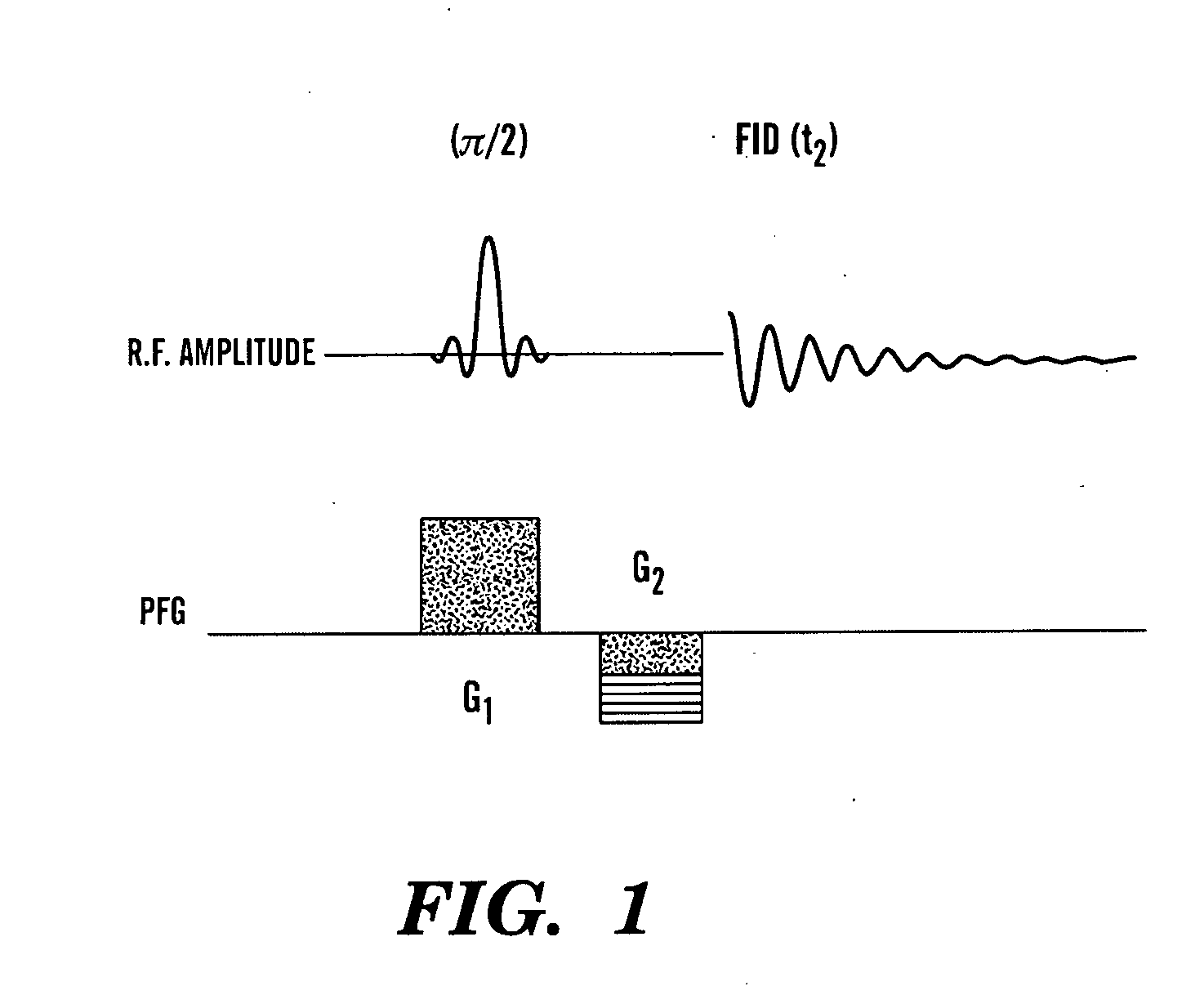
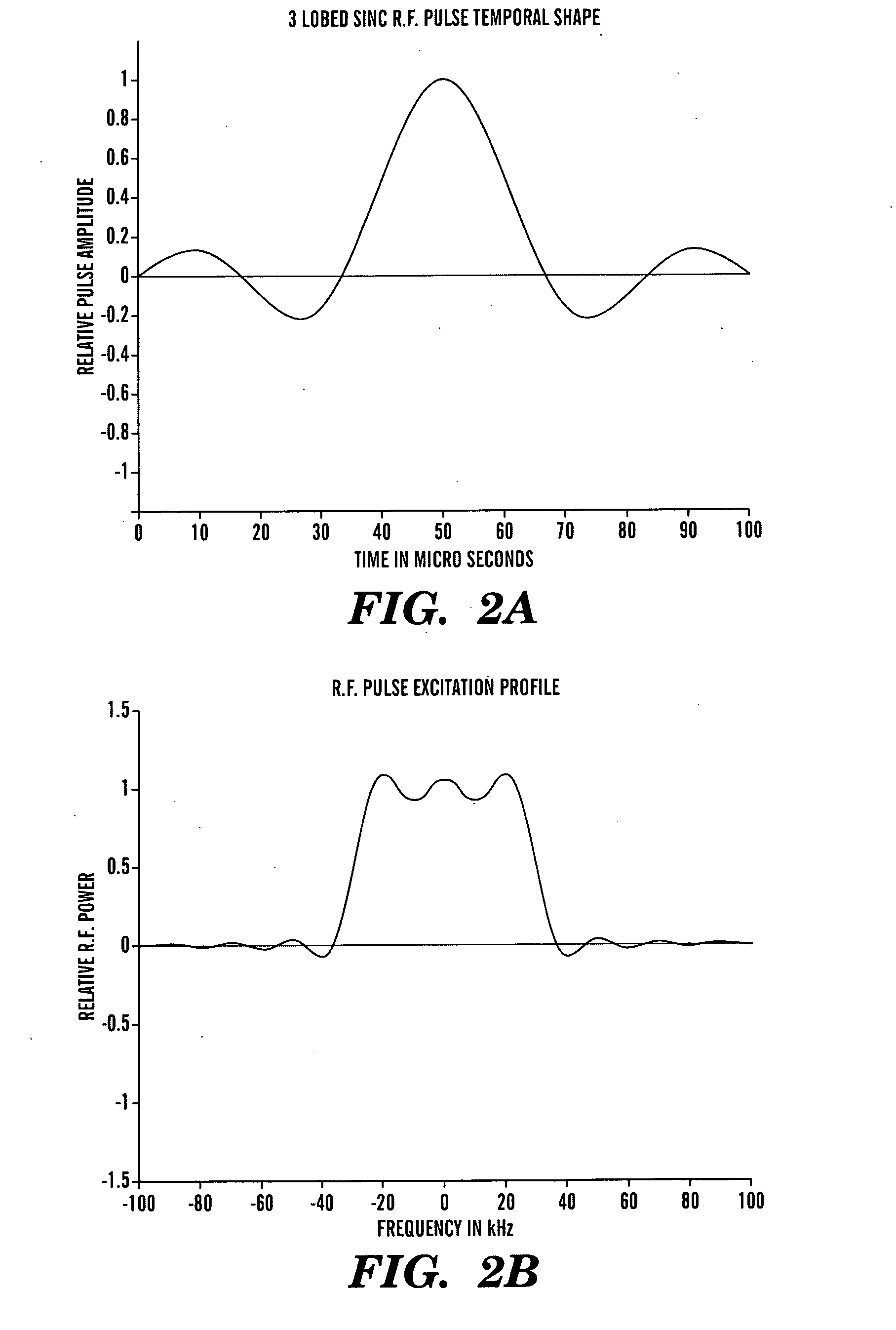
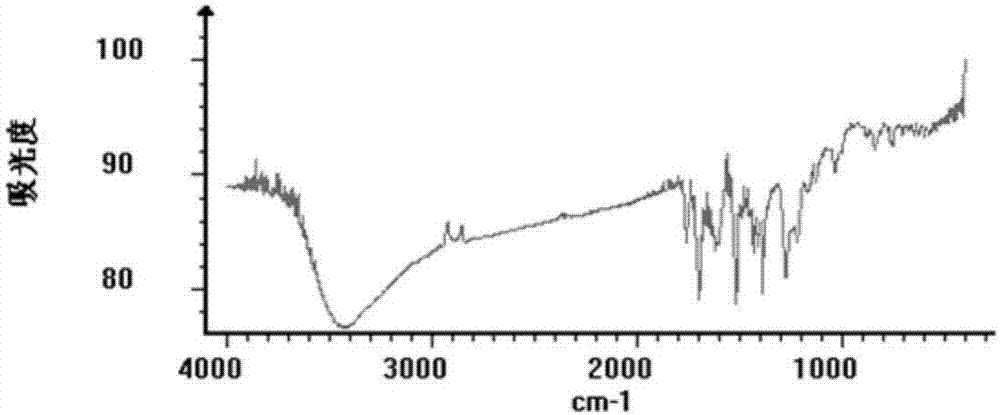
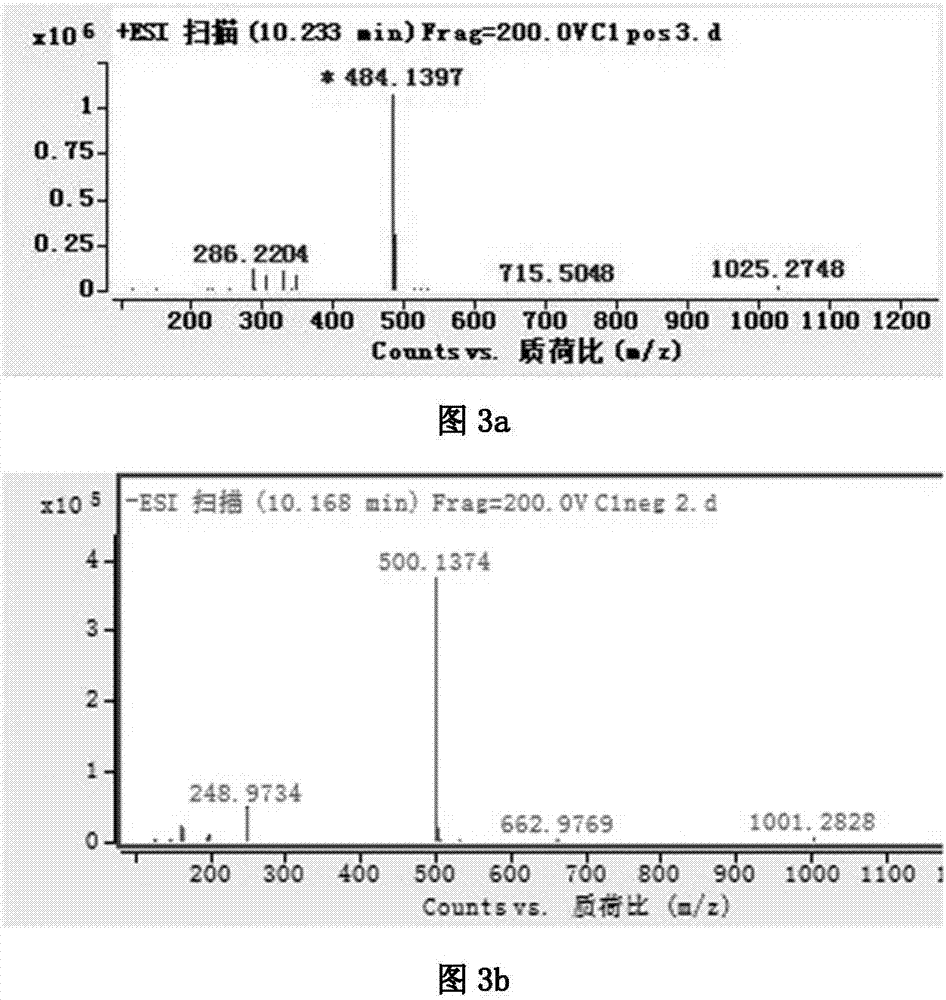
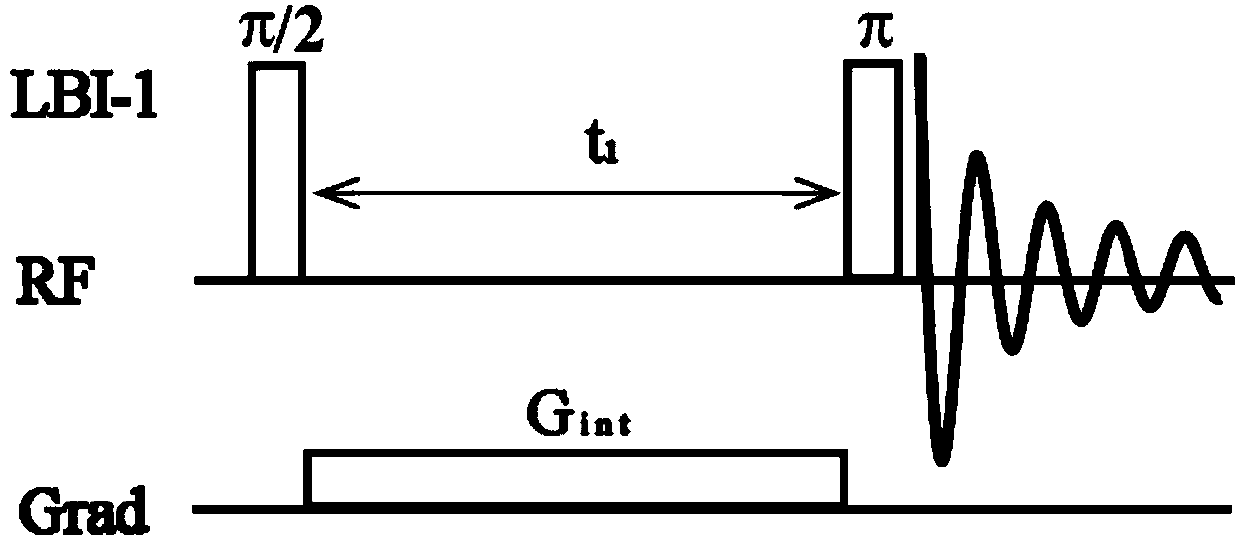
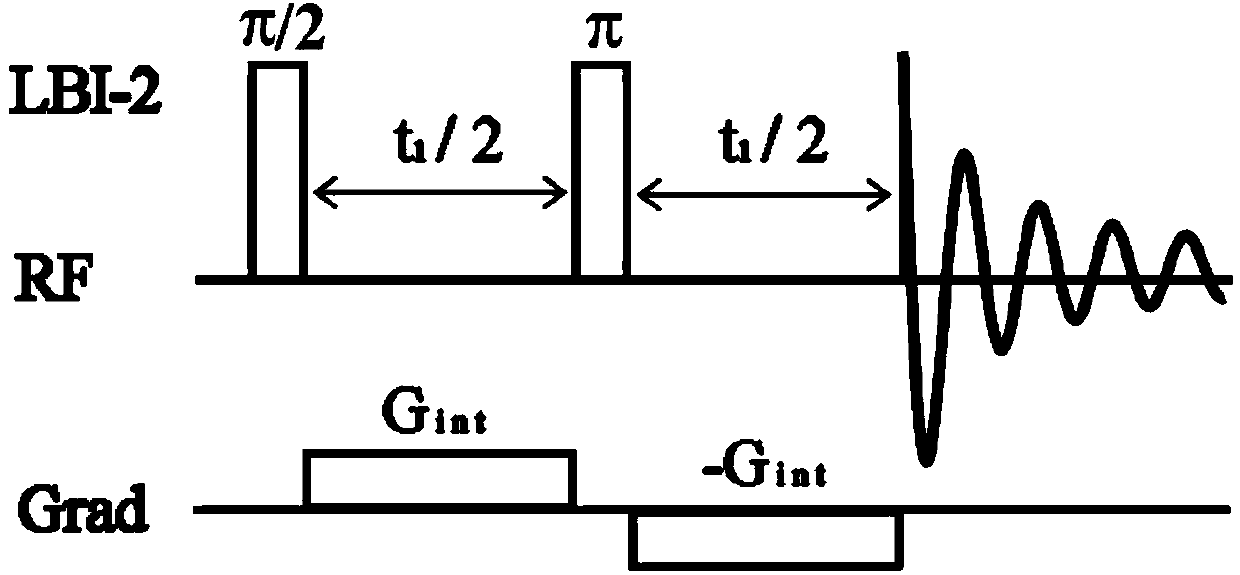
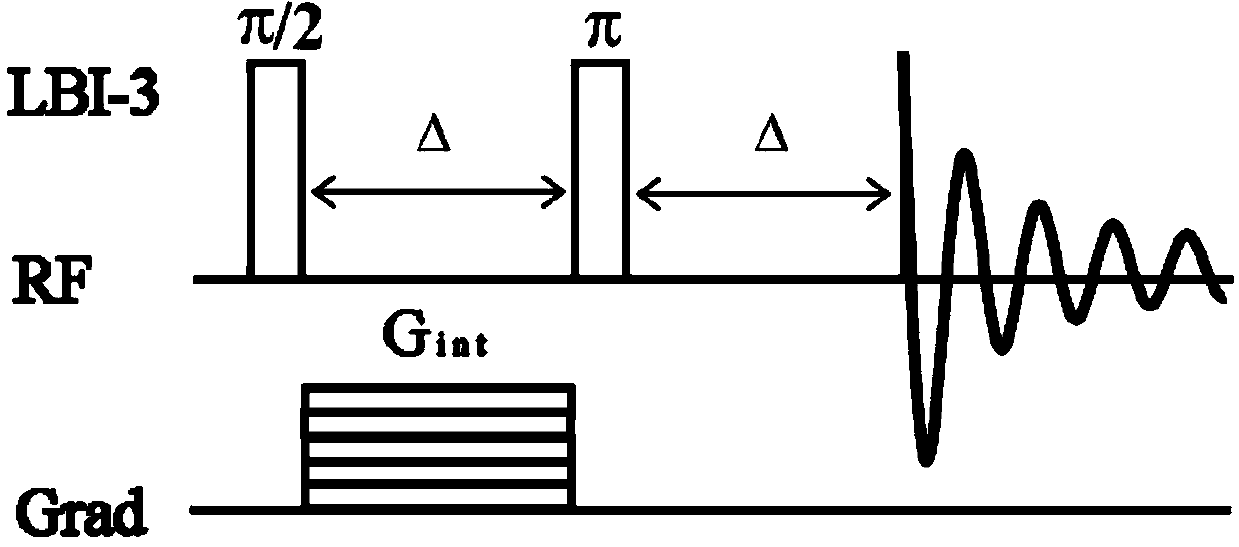
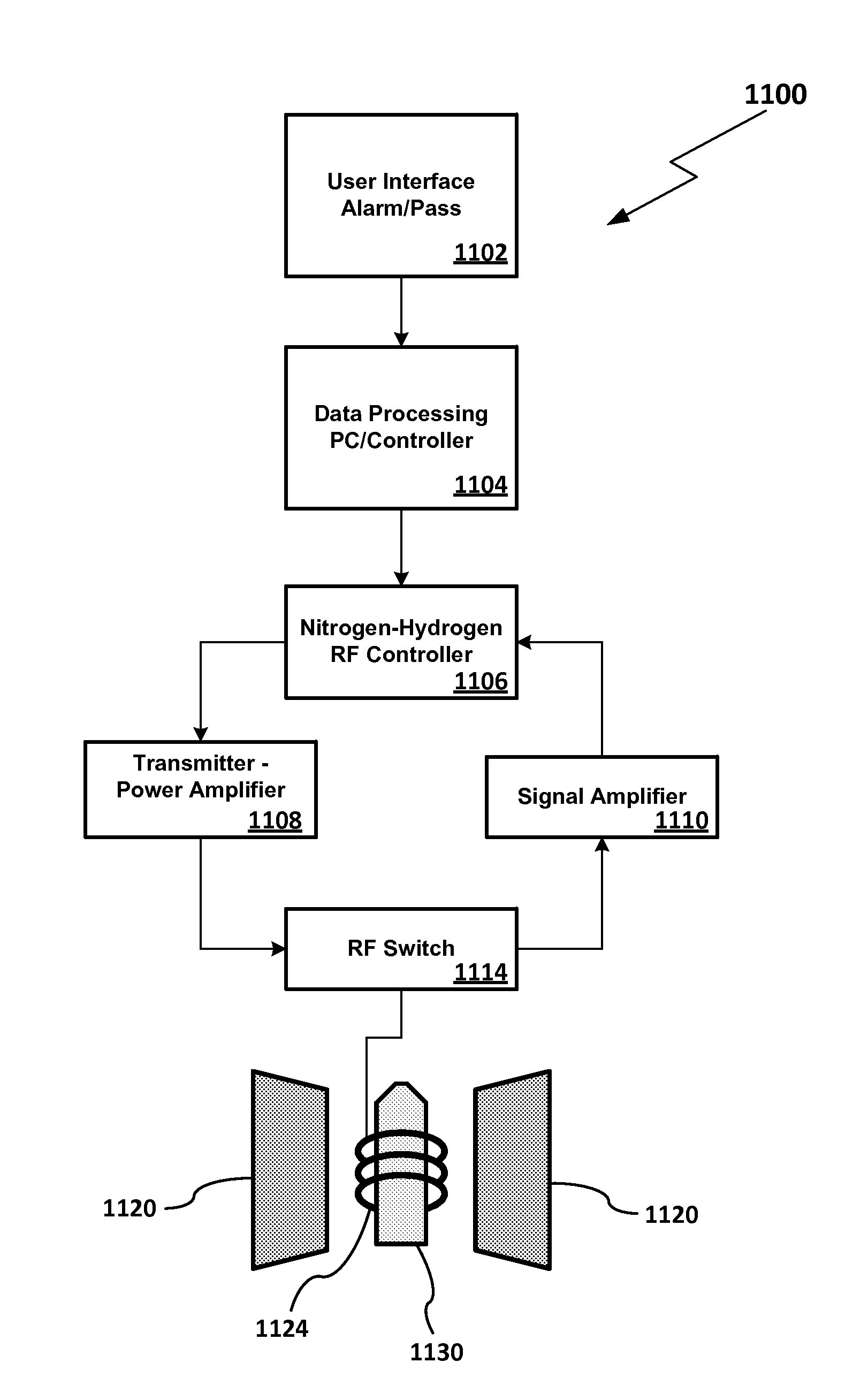
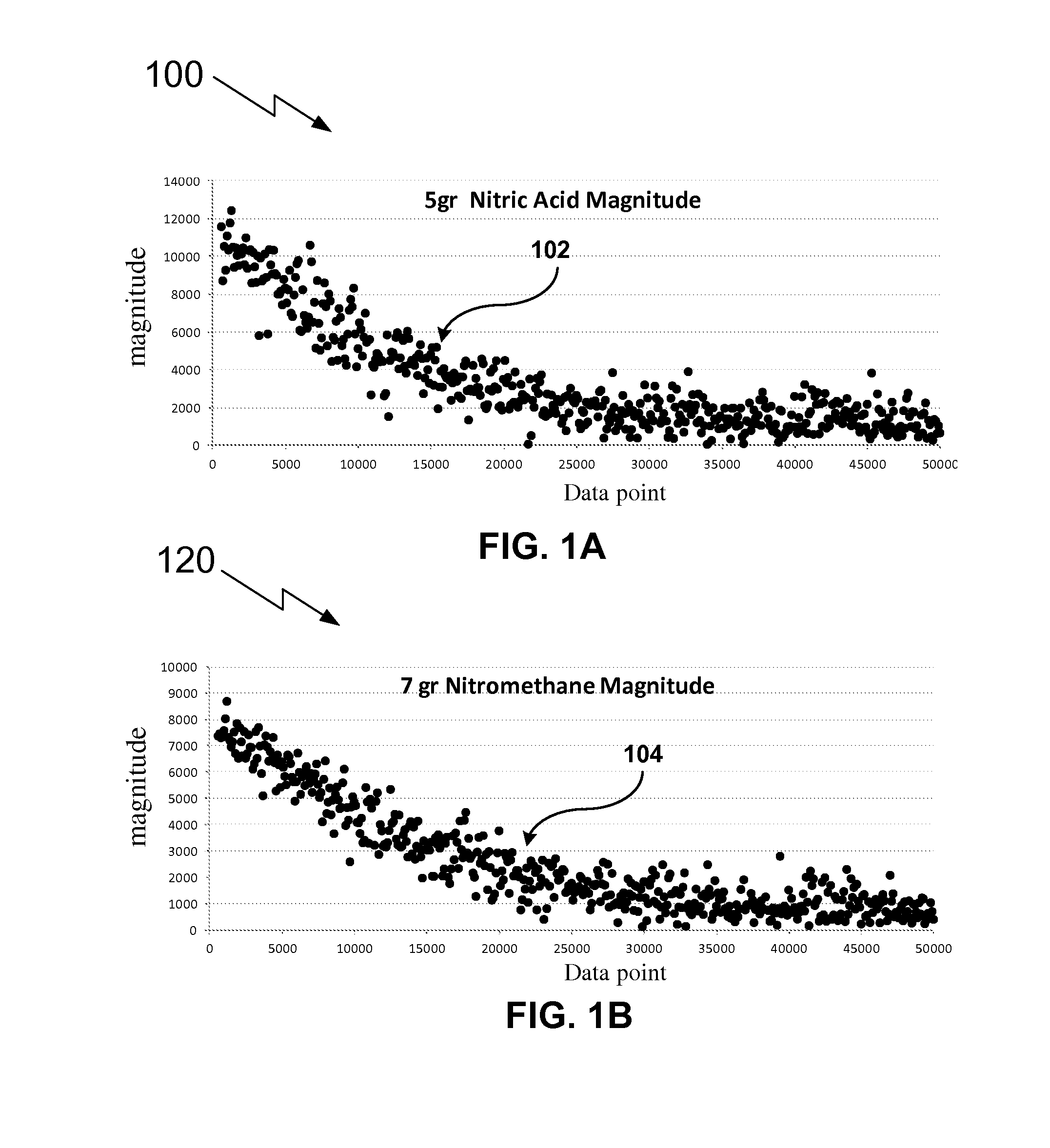
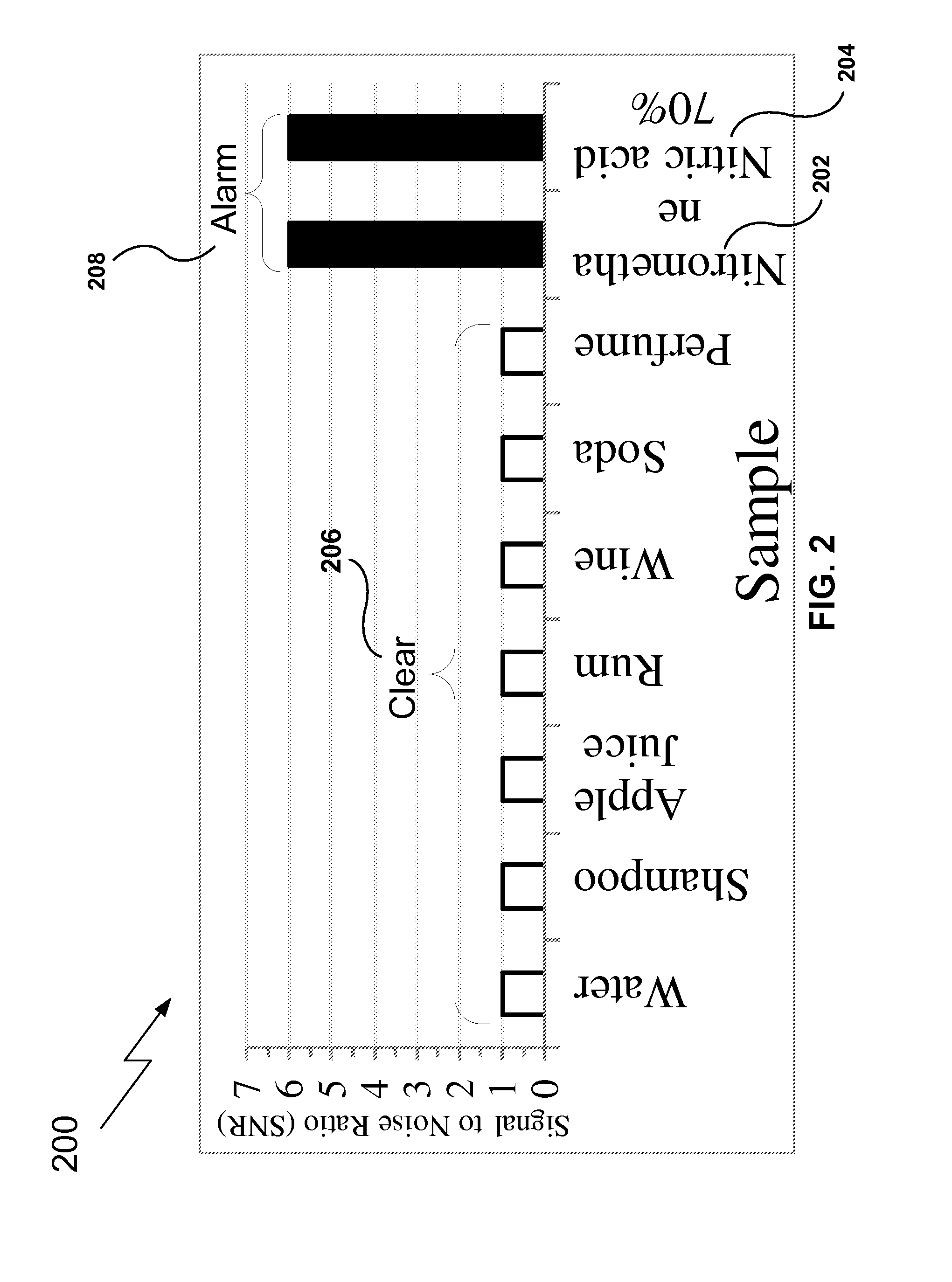
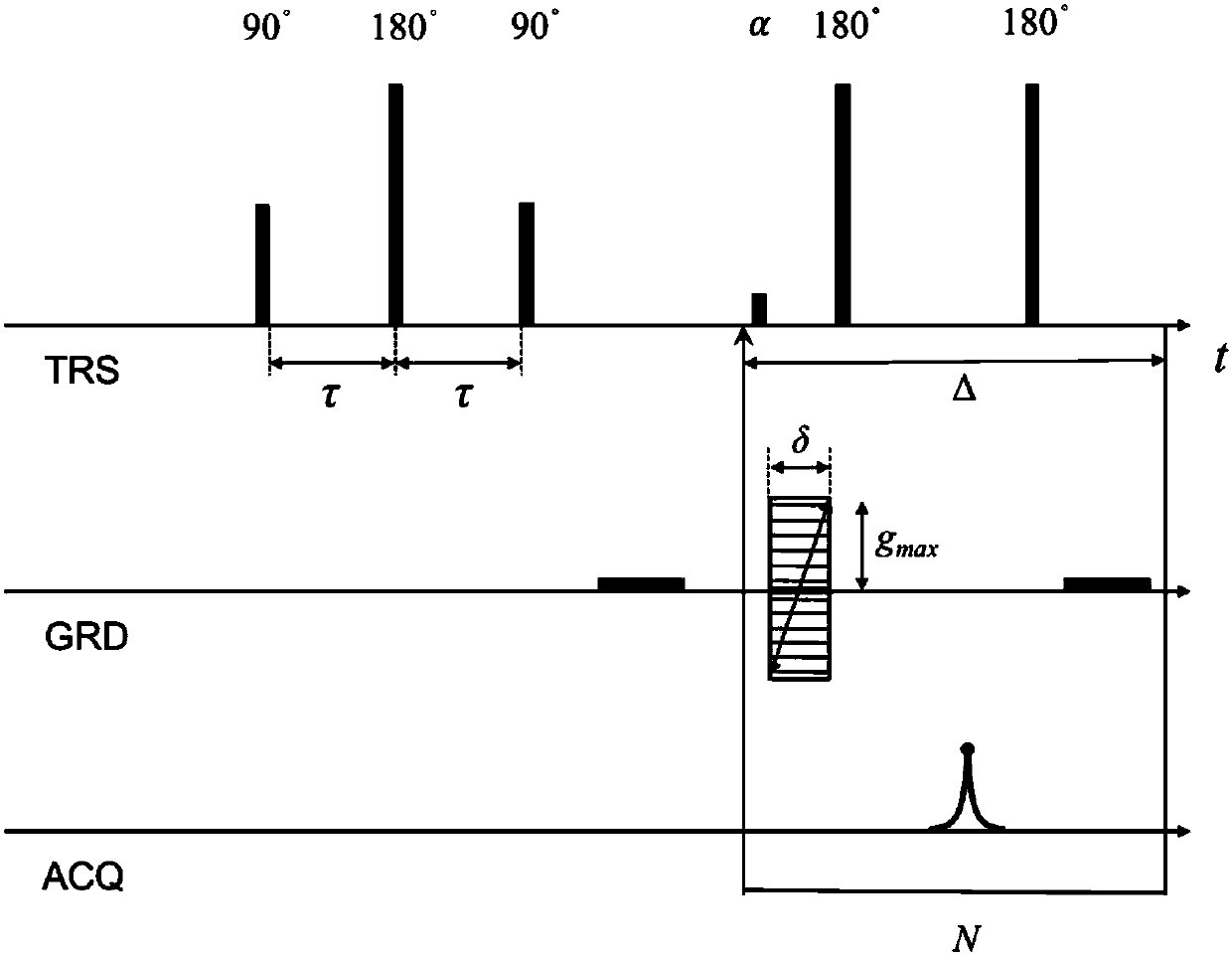
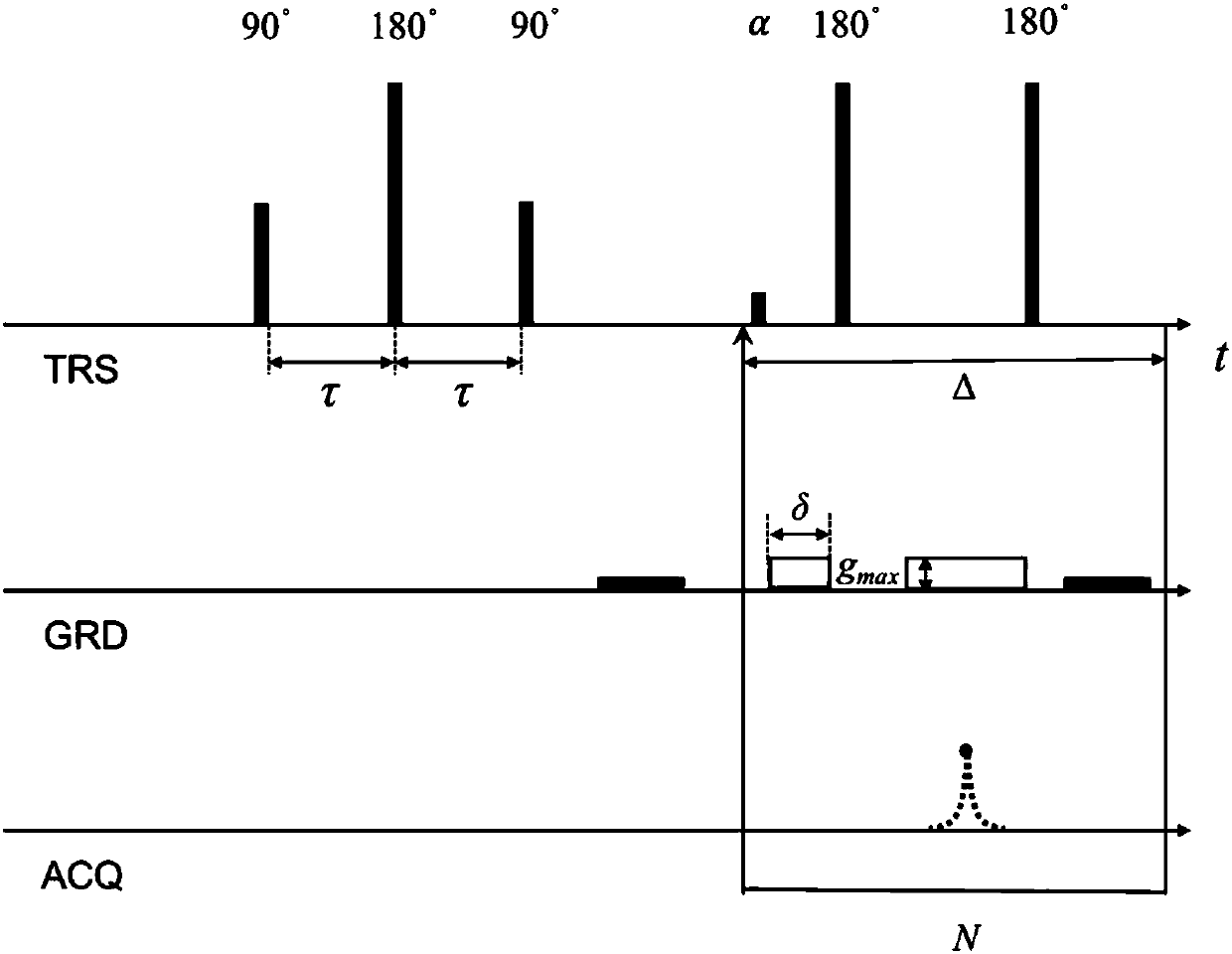
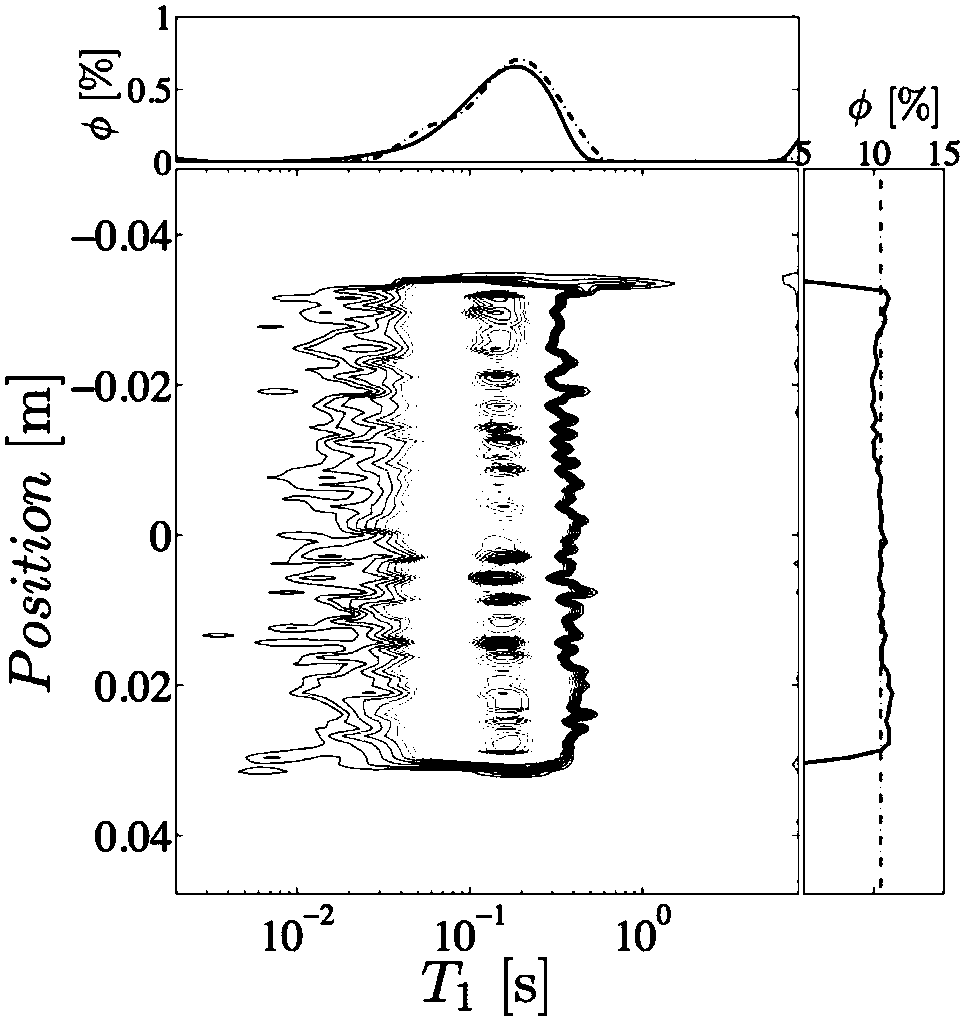
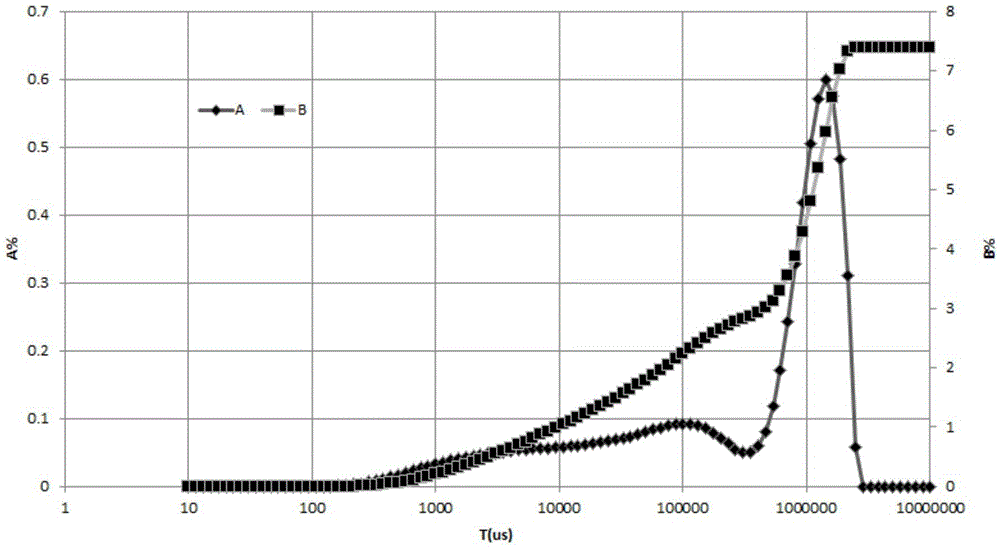
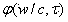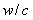Patents
Literature
100 results about "Carbon-13 NMR" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Carbon-13 (C13) nuclear magnetic resonance (most commonly known as carbon-13 NMR or ¹³C NMR or sometimes simply referred to as carbon NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to carbon. It is analogous to proton NMR (¹H NMR) and allows the identification of carbon atoms in an organic molecule just as proton NMR identifies hydrogen atoms. As such ¹³C NMR is an important tool in chemical structure elucidation in organic chemistry. C NMR detects only the ¹³C isotope of carbon, whose natural abundance is only 1.1%, because the main carbon isotope, ¹²C, is not detectable by NMR since its nucleus has zero spin.
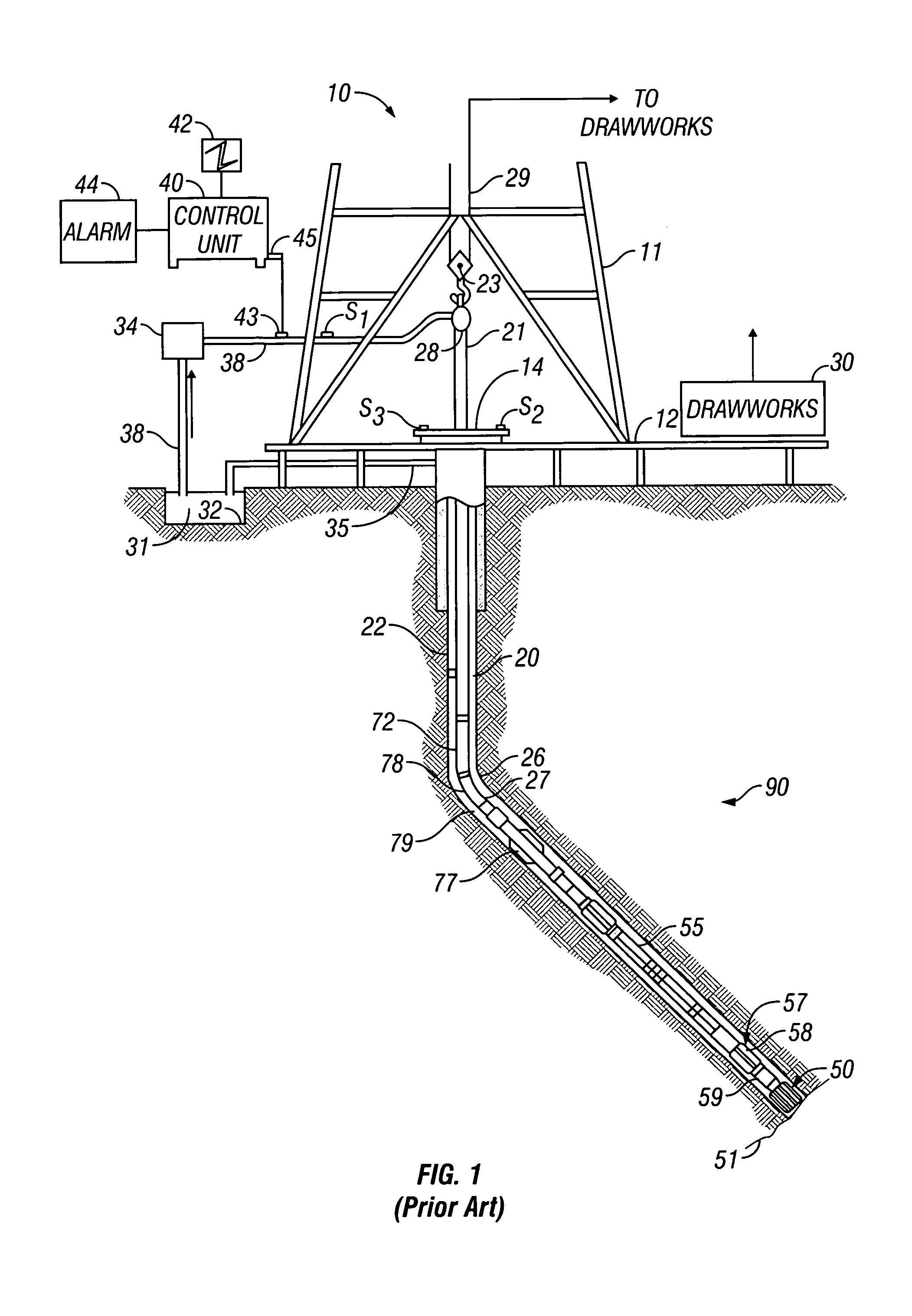
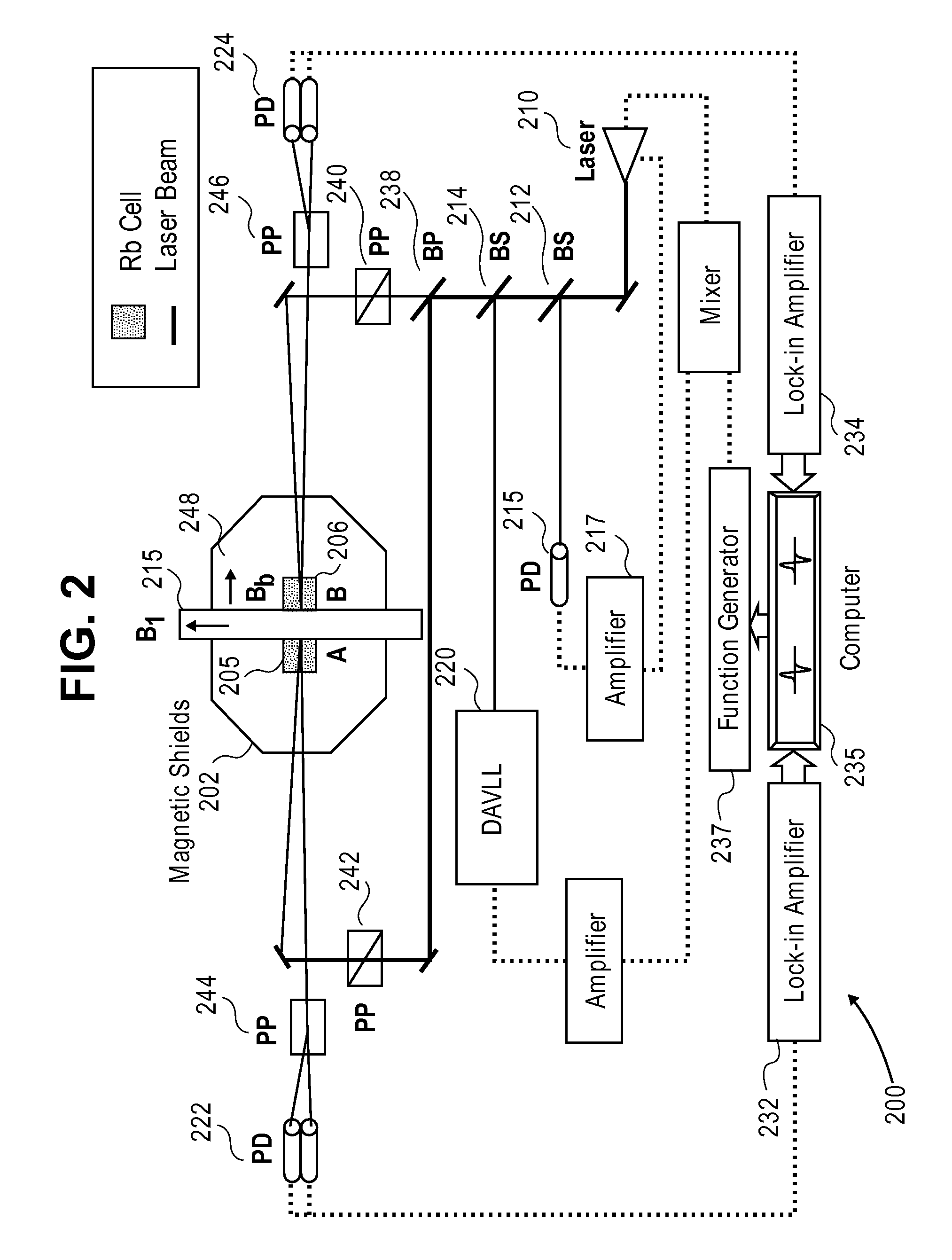
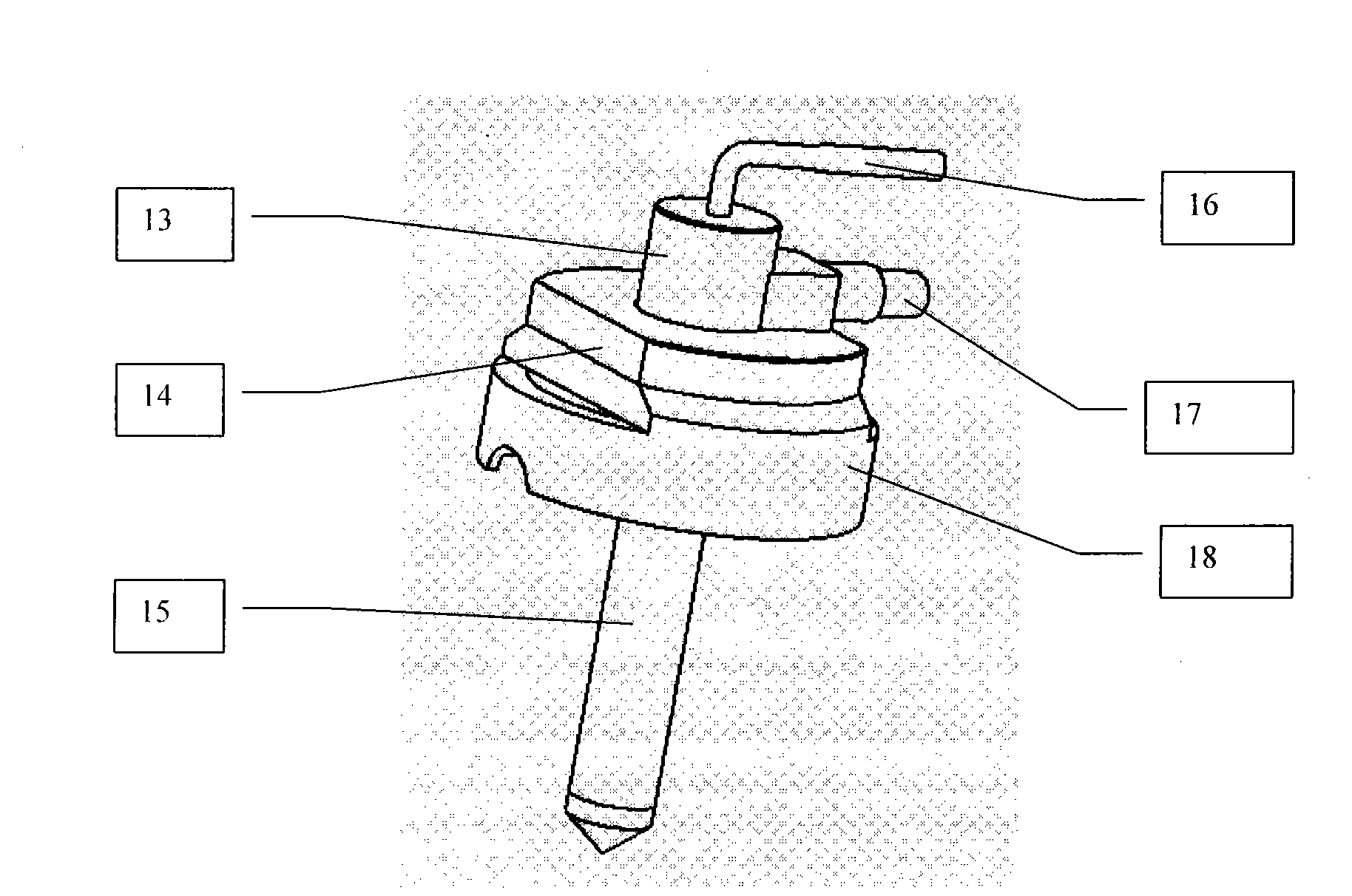
Downhole high resolution NMR spectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS7126332B2Increase amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onProton NMR
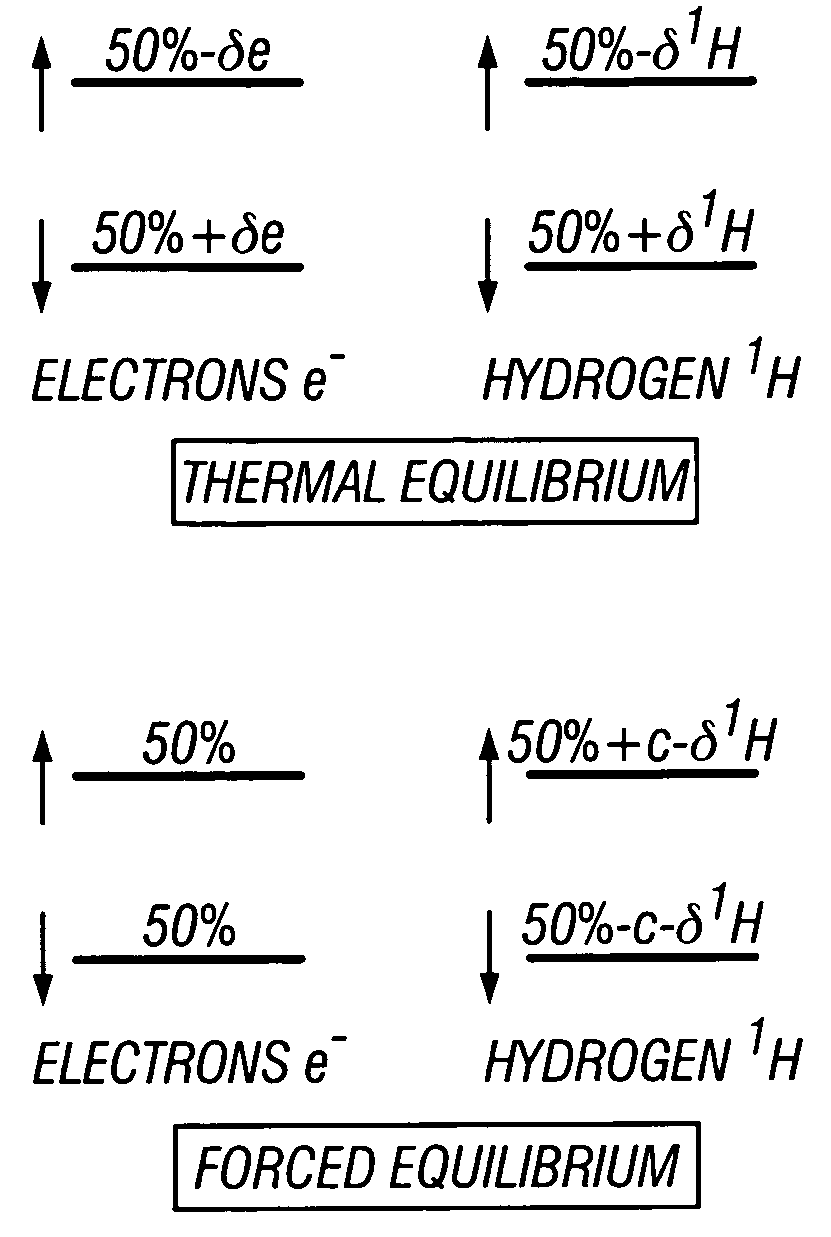
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Multiple catalyst system for olefin polymerization and polymers produced therefrom
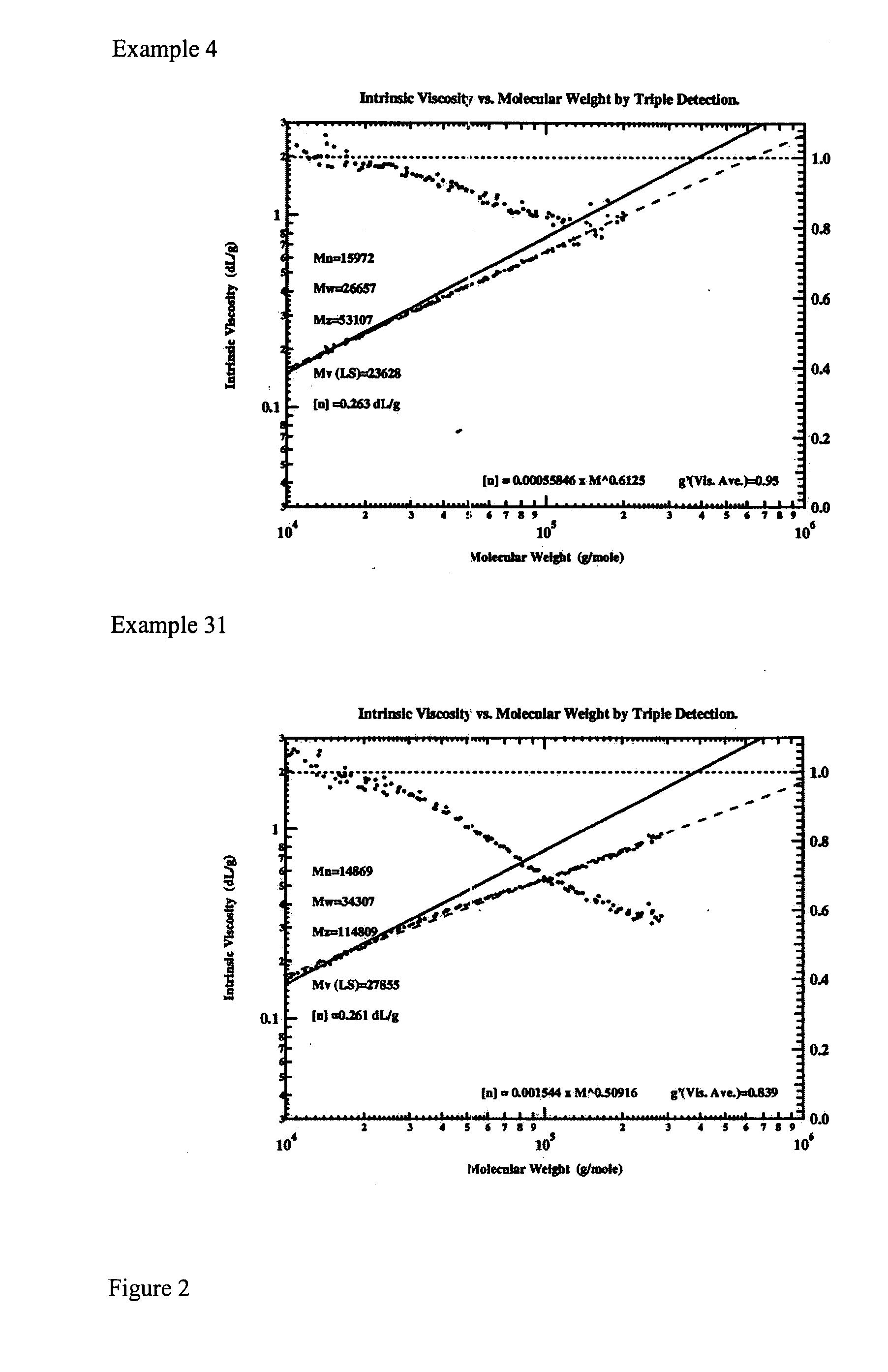
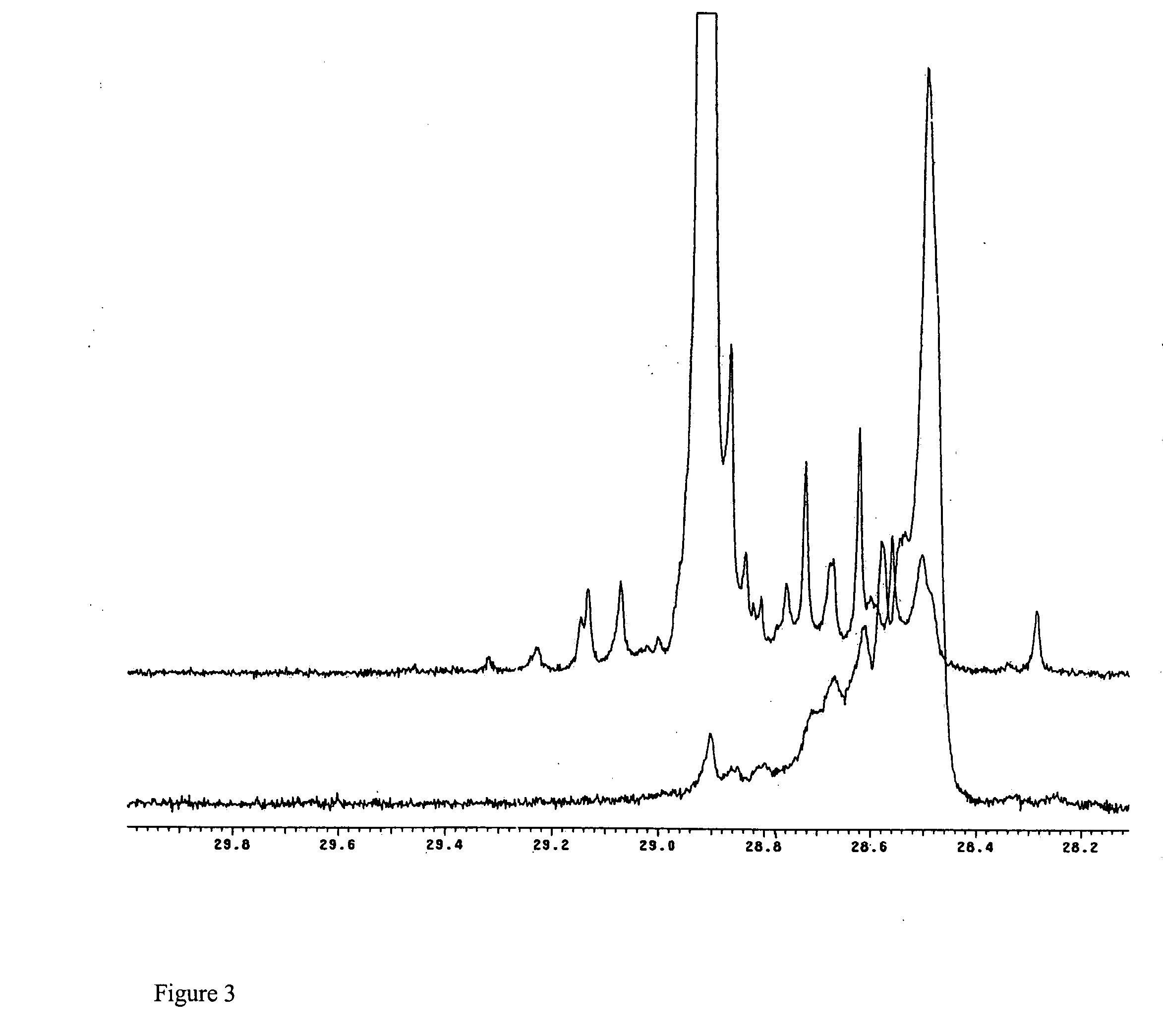
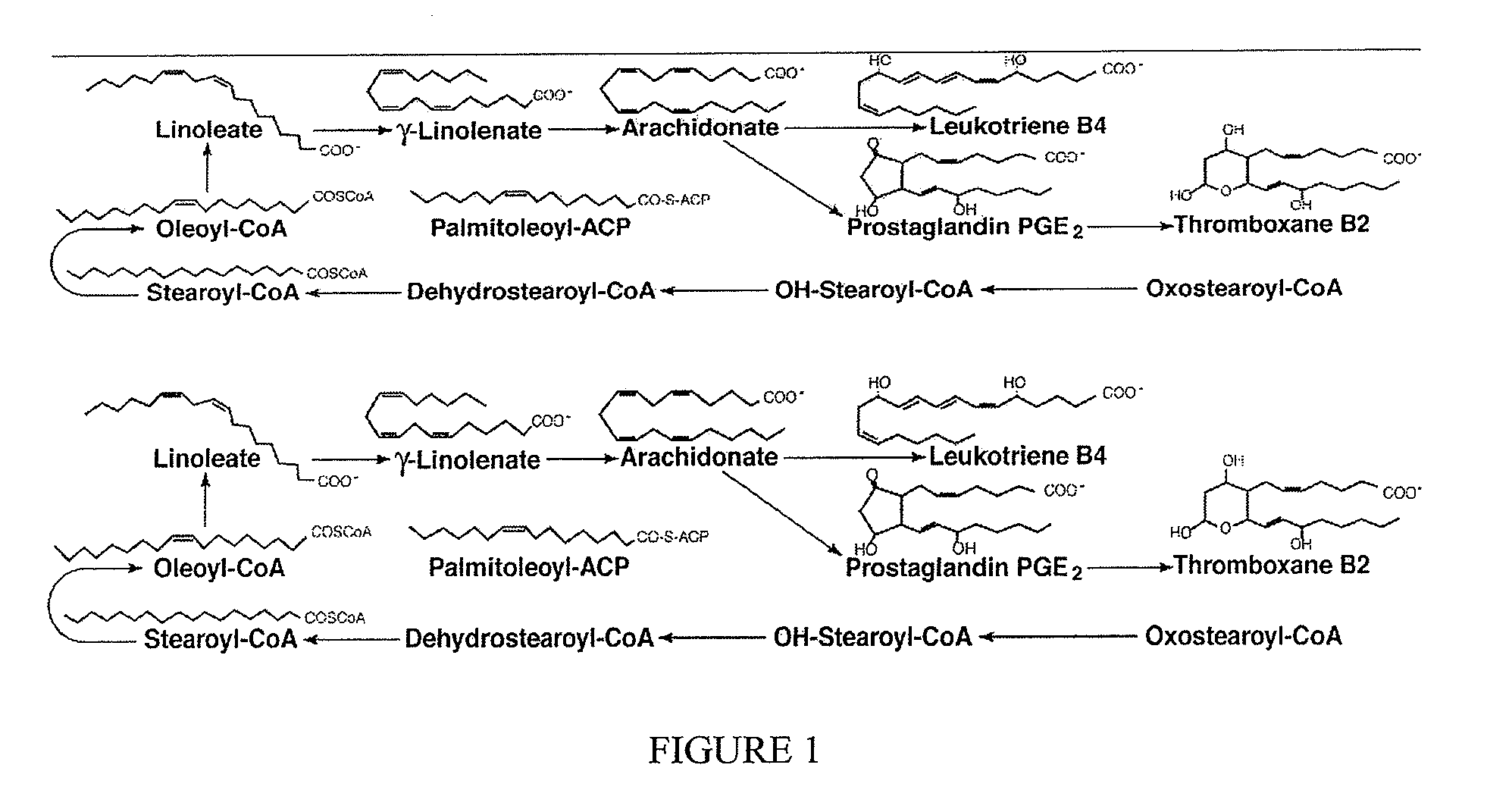
This invention relates to a polymer comprising one or more C3 to C40 olefins, optionally one or more diolefins, and less than 15 mole % of ethylene, where the polymer has: a) a Dot T-Peel of 1 Newton or more; and b) a branching index (g′) of 0.95 or less measured at the Mz of the polymer; c) an Mw of 100,000 or less. This invention also relates a polymer comprising one or more C3 to C40 olefins where the polymer has: a) a Dot T-Peel of 1 Newton or more on Kraft paper; b) a branching index (g′) of 0.95 or less measured at the Mz of the polymer; c) a Mw of 10,000 to 100,000; and d) a heat of fusion of 1 to 70 J / g. This invention also relates a polymer comprising one or more C3 to C40 olefins where the polymer has: a) a Dot T-Peel of 1 Newton or more on Kraft paper; b) a branching index (g′) of 0.98 or less measured at the Mz of the polymer; c) a Mw of 10,000 to 60,000; d) a heat of fusion of 1 to 50 J / g. This invention also relates to a homopolypropylene or a copolymer of propylene and up to 5 mole % ethylene having: a) an isotactic run length of 1 to 30 (isotactic run length “IRL” is defined to be the percent of mmmm pentad divided by 0.5× percent of mmmr pentad) as determined by Carbon 13 NMR, preferably 3 to 25, more preferably 4 to 20, b) a percent of r dyad of greater than 20%, preferably from 20 to 70% as determined by Carbon 13 NMR, and c) a heat of fusion of 70 J / g or less, preferably 60 J / g or less, more preferably between 1 and 55 J / g, more preferably between 4 and 50 J / g. This invention further relates to a process to produce an olefin polymer comprising: 1) selecting a first catalyst component capable of producing a polymer having an Mw of 100,000 or less and a crystallinity of 5% or less at selected polymerization conditions; 2) selecting a second catalyst component capable of producing polymer having an Mw of 100,000 or less and a crystallinity of 20% or more at the selected polymerization conditions; 3) contacting the catalyst components in the presence of one or more activators with one or more C3 to C40 olefins, at the selected polymerization conditions in a reaction zone; 4) obtaining the polymer. This invention further relates to a continuous process to produce a branched olefin polymer comprising: 1) selecting a first catalyst component capable of producing a polymer having an Mw of 100,000 or less and a crystallinity of 5% or less under selected polymerization conditions; 2) selecting a second catalyst component capable of producing polymer having an Mw of 100,000 or less and a crystallinity of 20% or more at the selected polymerization conditions; 3) contacting the catalyst components in the presence of one or more activators with one or more C3 to C40 olefins, and, optionally one or more diolefins; 4) at a temperature of greater than 100° C.; 5) at a residence time of 120 minutes or less; 6) wherein the ratio of the first catalyst to the second catalyst is from 1:1 to 50:1; 7) wherein the activity of the catalyst components is at least 100 kilograms of polymer per gram of the catalyst components; and wherein at least 20% of the olefins are converted to polymer.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS7573264B2Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceProton NMRSingle polarization
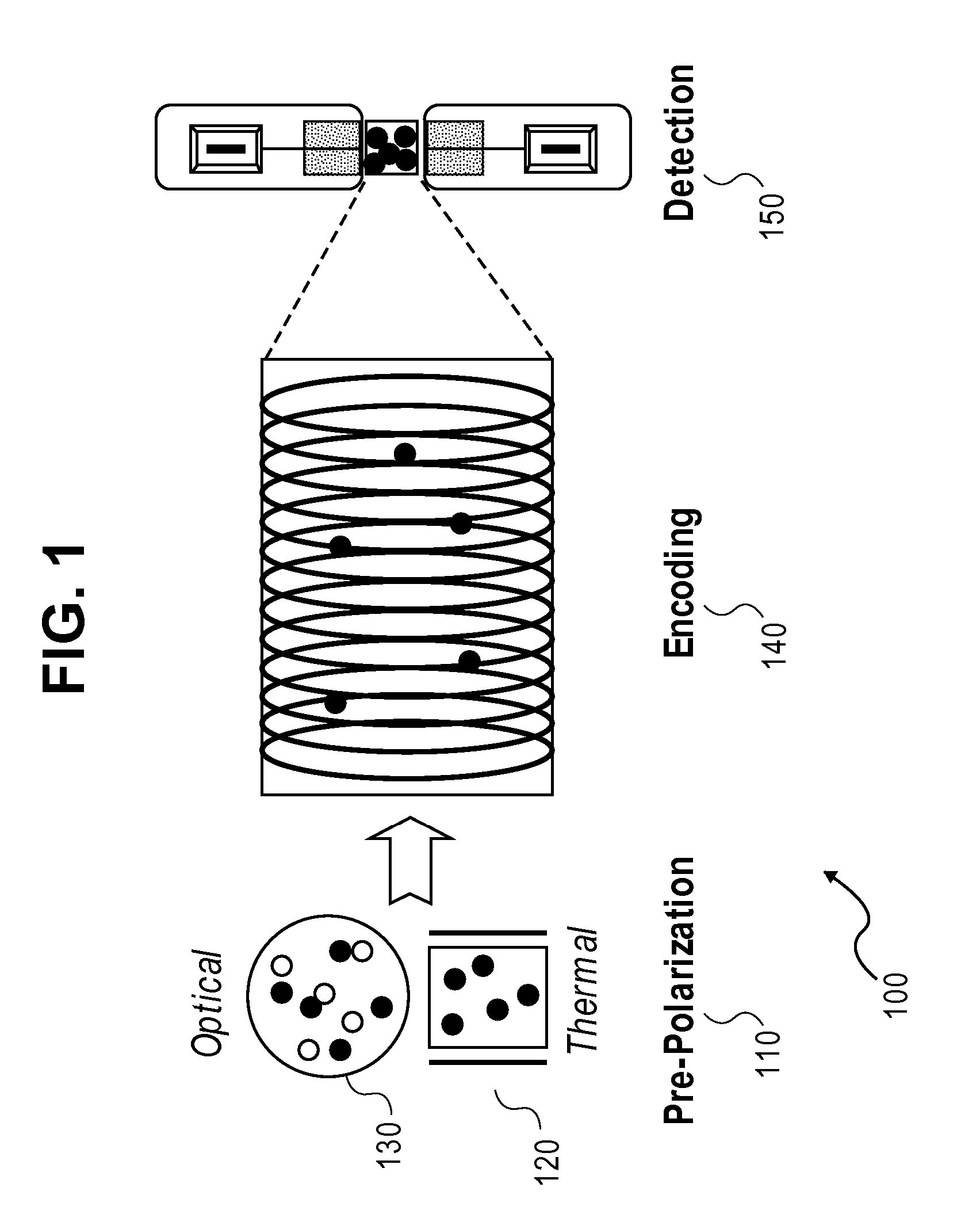
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
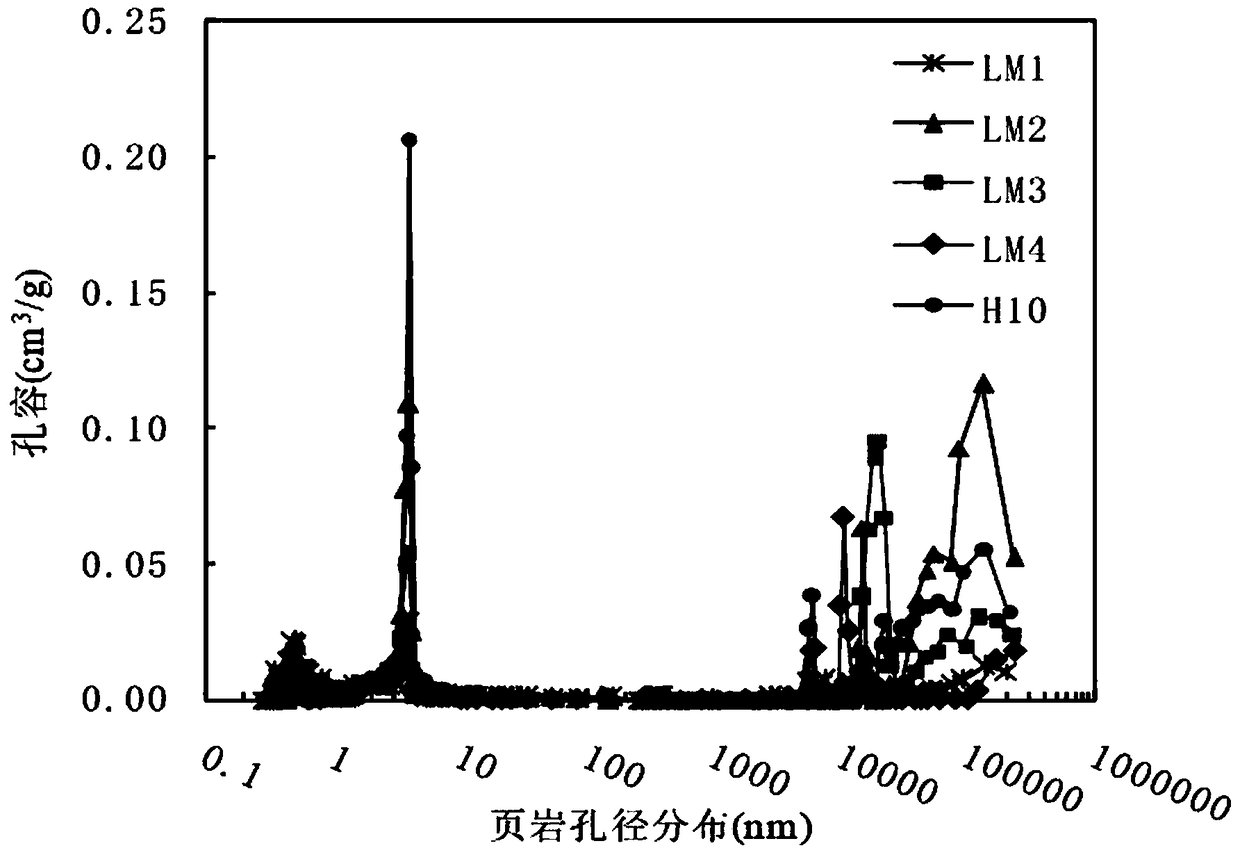
Shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN108169099AThe calculation result is accuratePracticalAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPore distributionHigh pressure
The invention discloses a shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The shale gas reservoir pore structure quantitative calculation methodcomprises the following steps: collecting cores; drilling parallel samples, carrying out oil and water self-adsorption nuclear magnetic resonance experiment measurement; contrastively analyzing the difference of a parallel sample oil and water nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum, and determining the distribution of different wetting pore types on the nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum; obtaining a shale gas reservoir full-pore distribution curve according to high-pressure pressurized mercury, nitrogen adsorption and carbon dioxide adsorption; furthermore, obtaining an intersection plate of pore diameters and corresponding T2 time; and according to the intersection plate of different pore types of pore diameters and corresponding T2 time, establishing a quantitative calculation model of the pore diameters according to the pore types. The method has the advantages that a shale gas reservoir pore full-pore distribution curve can be quantitatively calculated through the technology;simultaneously, the nuclear magnetism measurement is quick, simple and loss-free, and is higher in practicability by compared with high-pressure pressurized mercury, nitrogen adsorption and carbon dioxide adsorption; and compared with a conventional method, the calculation result is more accurate.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Metabolite detection using magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20080081375A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationMagnetic measurementsMetaboliteDisease cause
Methods using magnetic resonance, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), are provided for detecting metabolites in a sample. The methods are useful for the diagnosis or prognosis of a disease such as cancer and can also be used to determine or monitor a treatment protocol. The methods are useful in characterizing speciation in biological samples where mixtures are often encountered and chemical shifts of the same structural group of similar molecules can produce complicated overlapping resonances.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
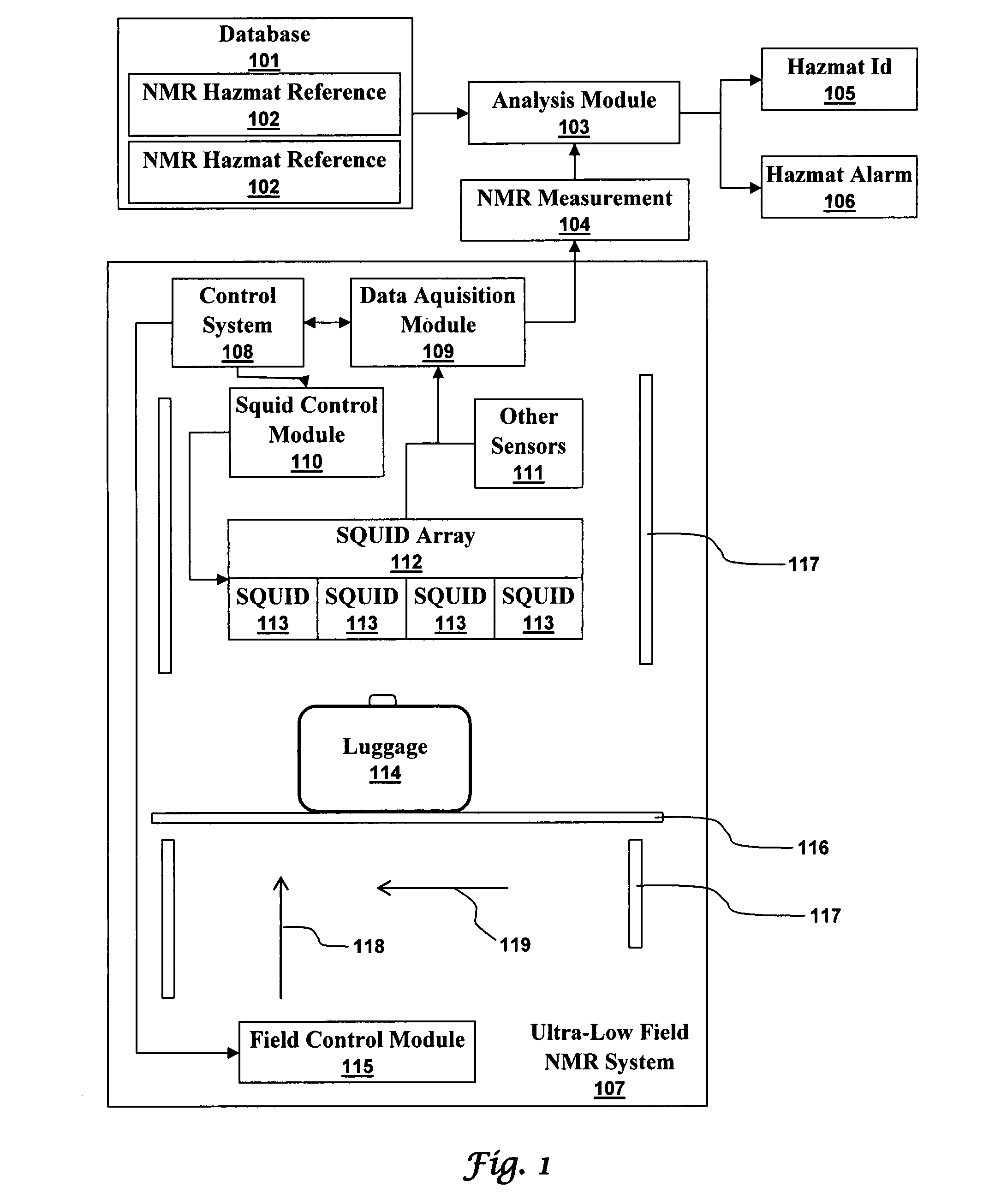
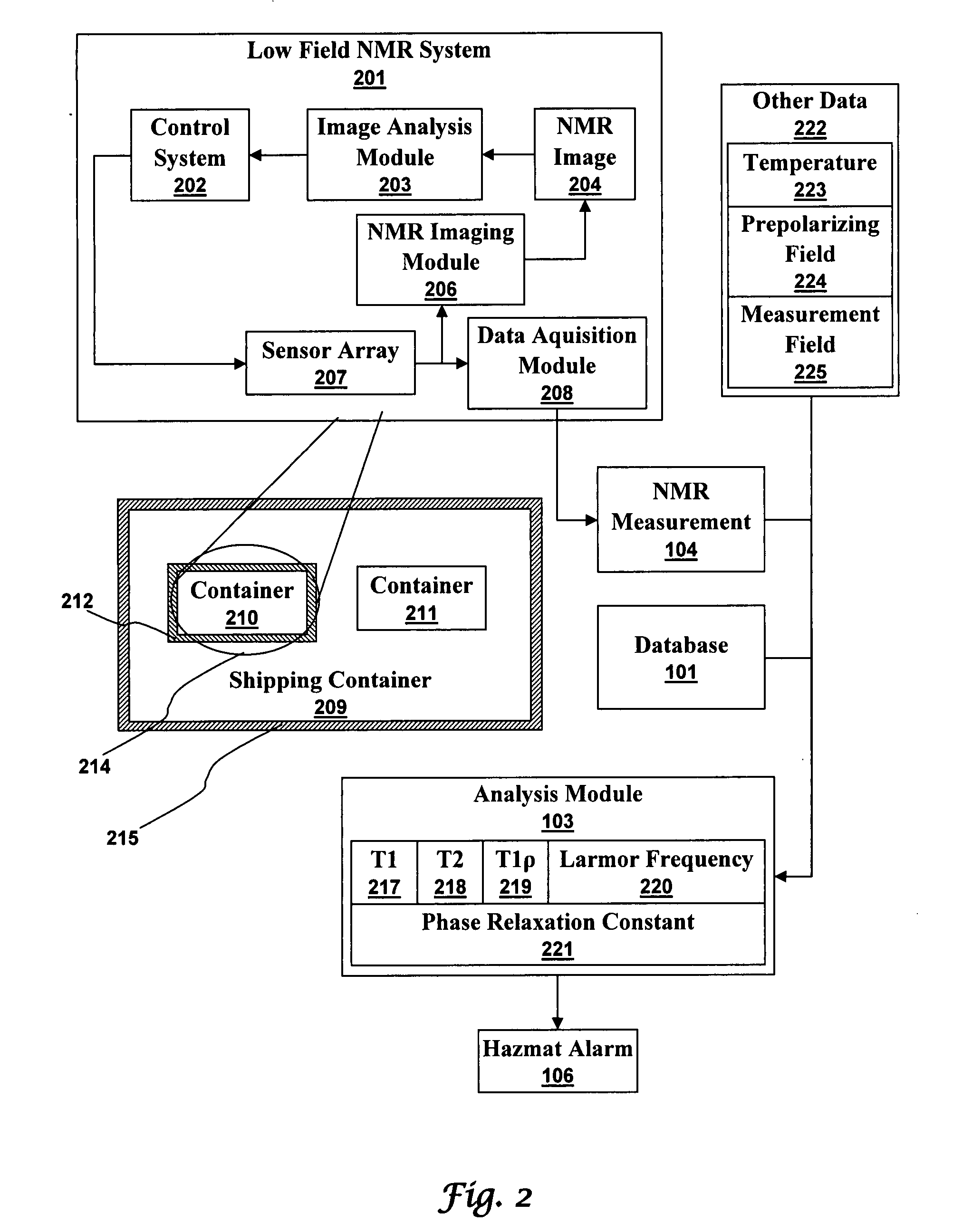
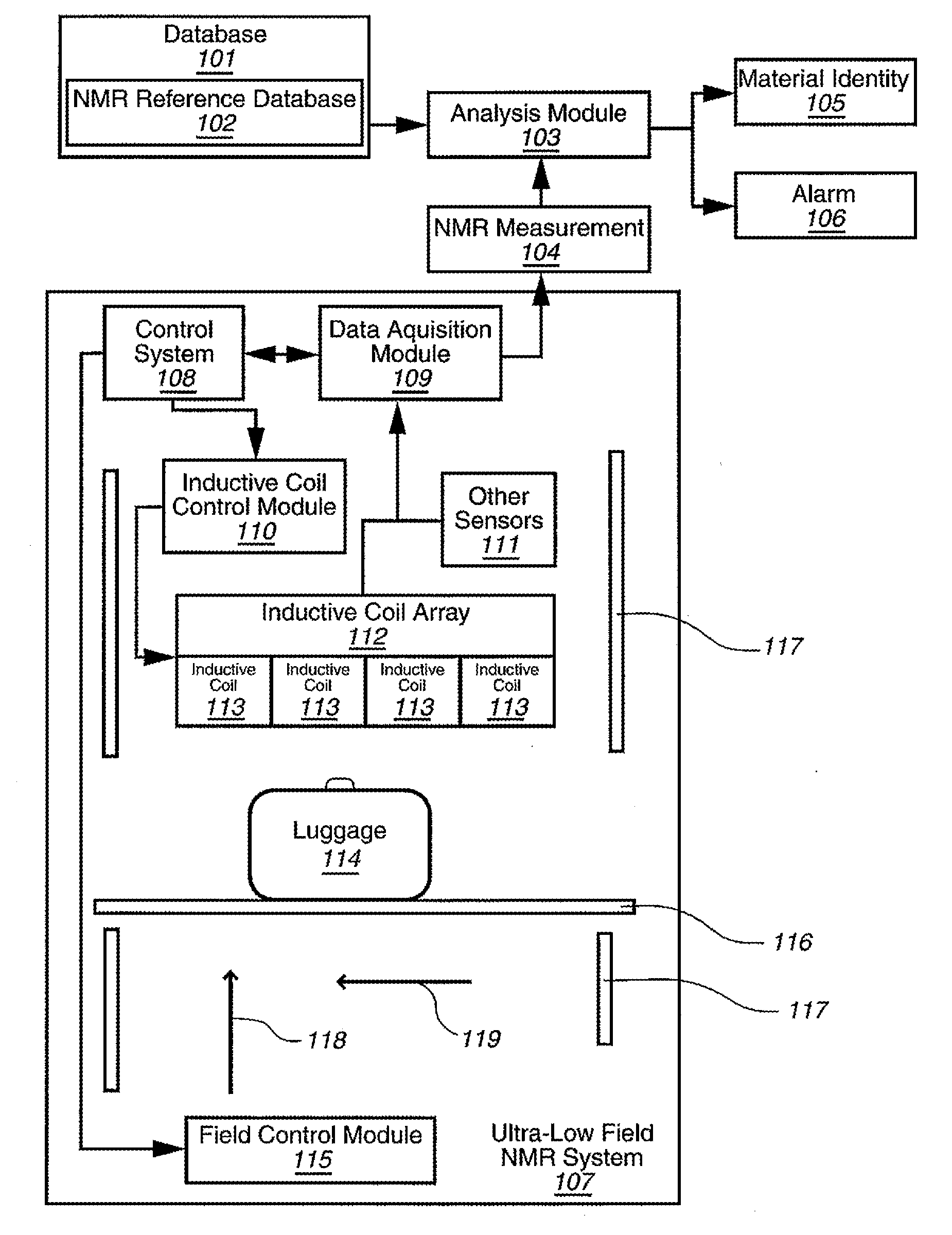
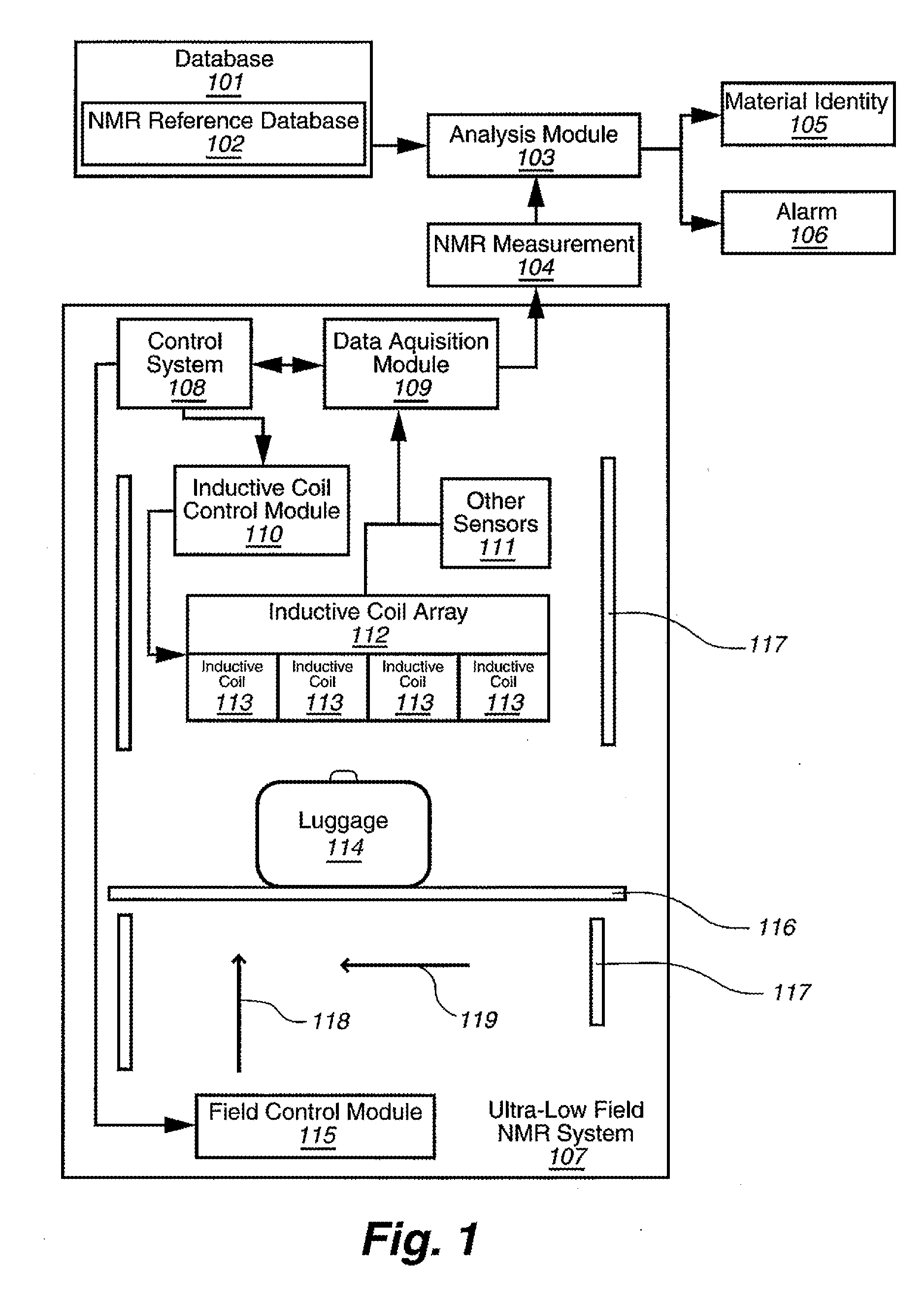
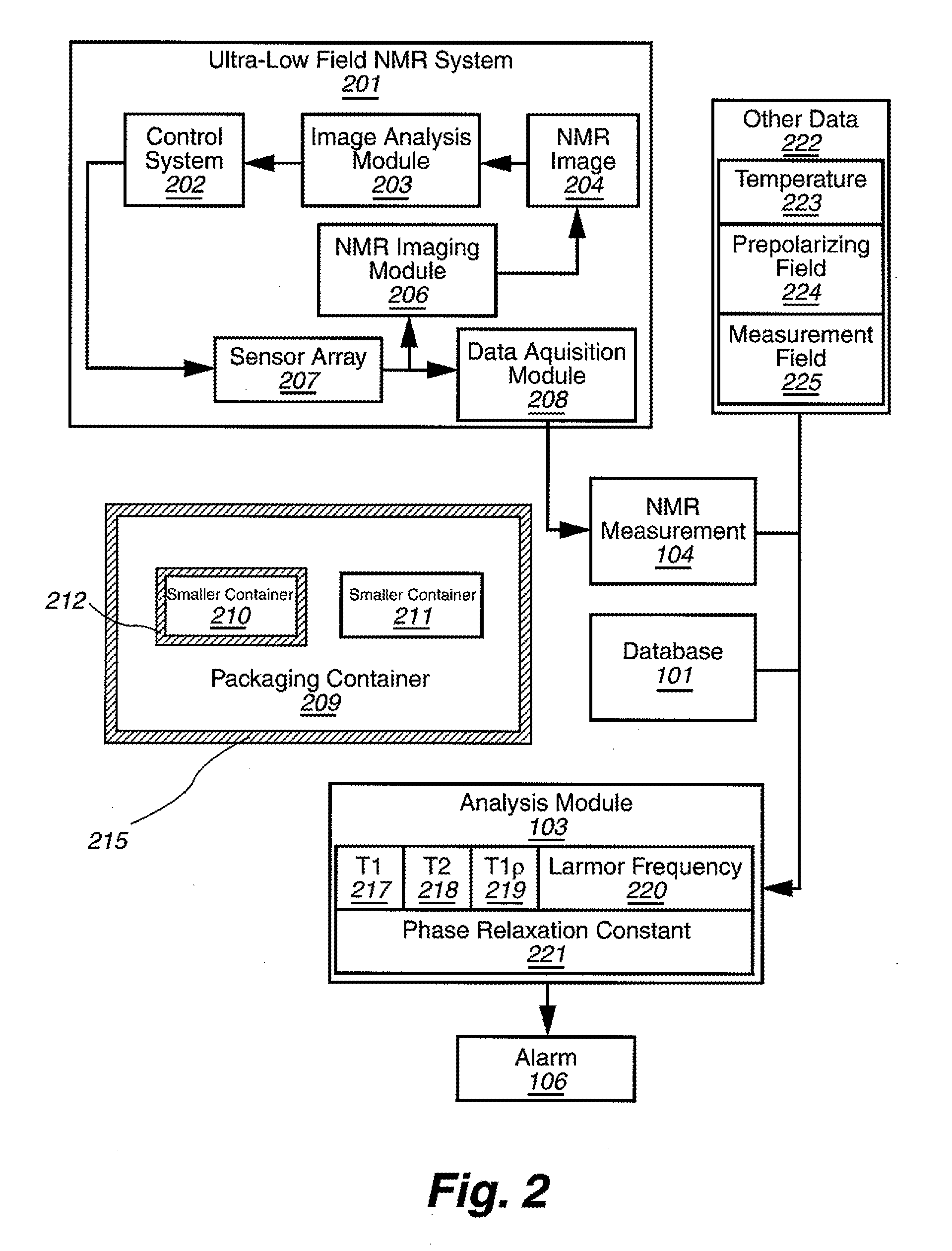
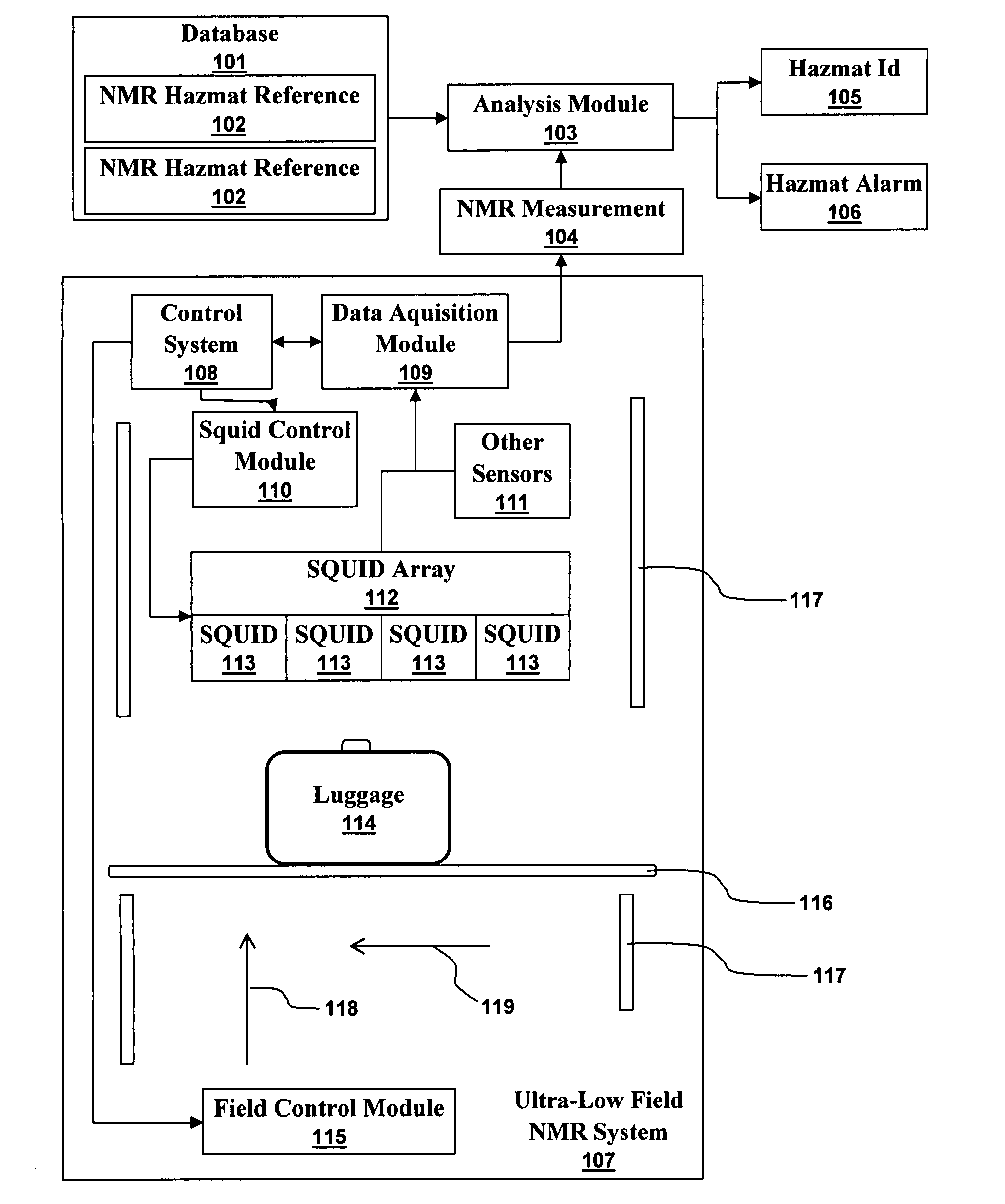
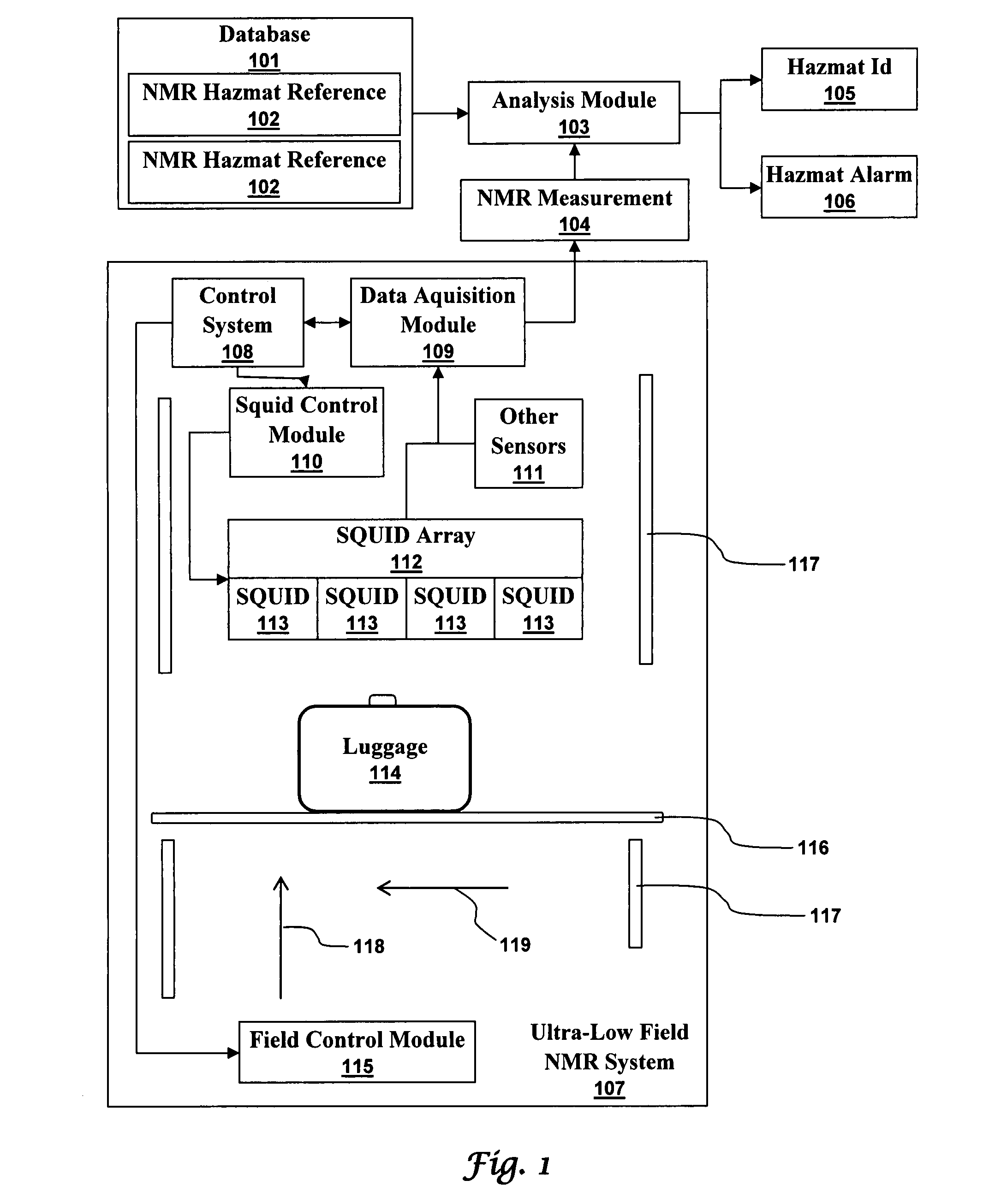
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20080284433A1Increased signal noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
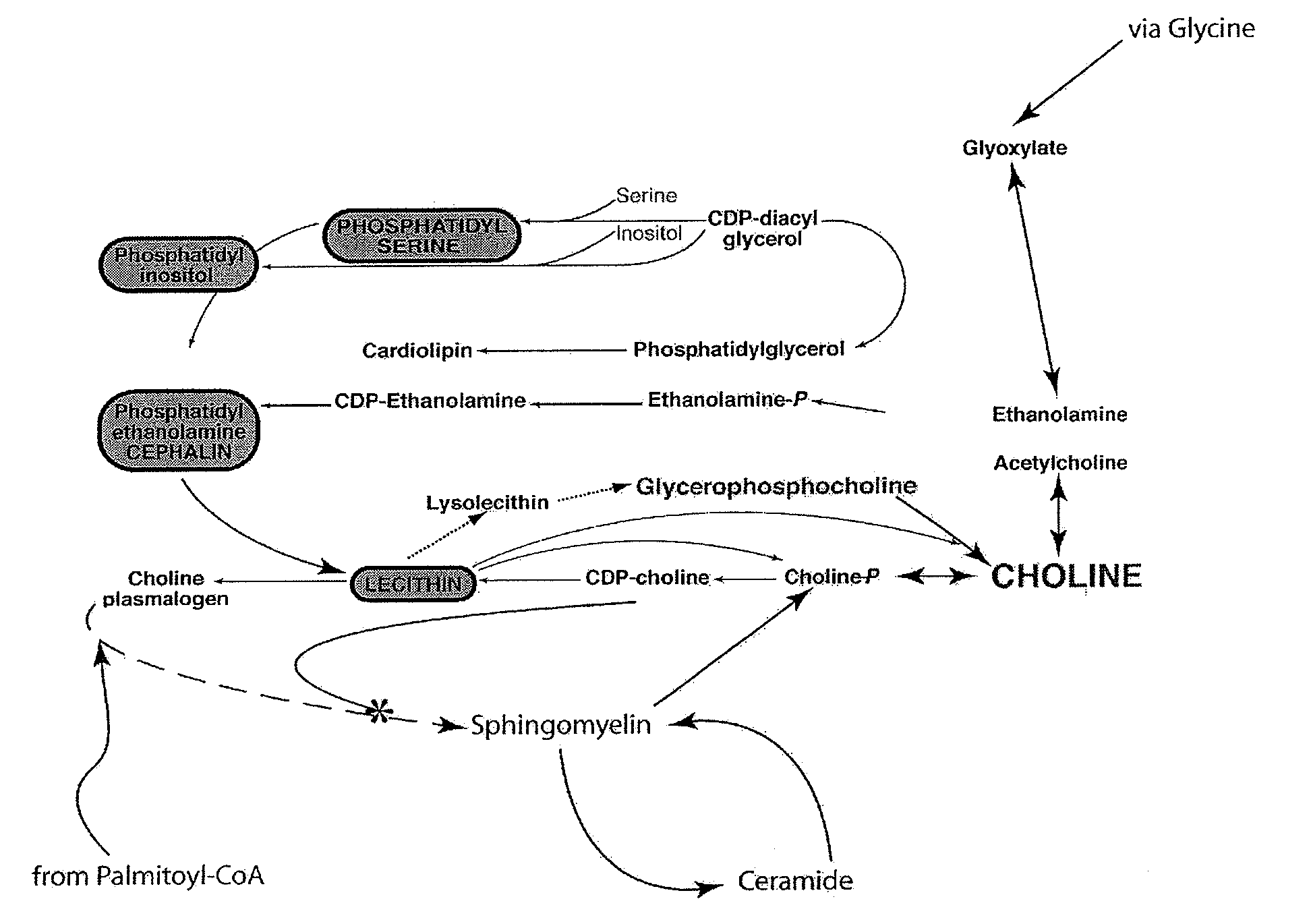
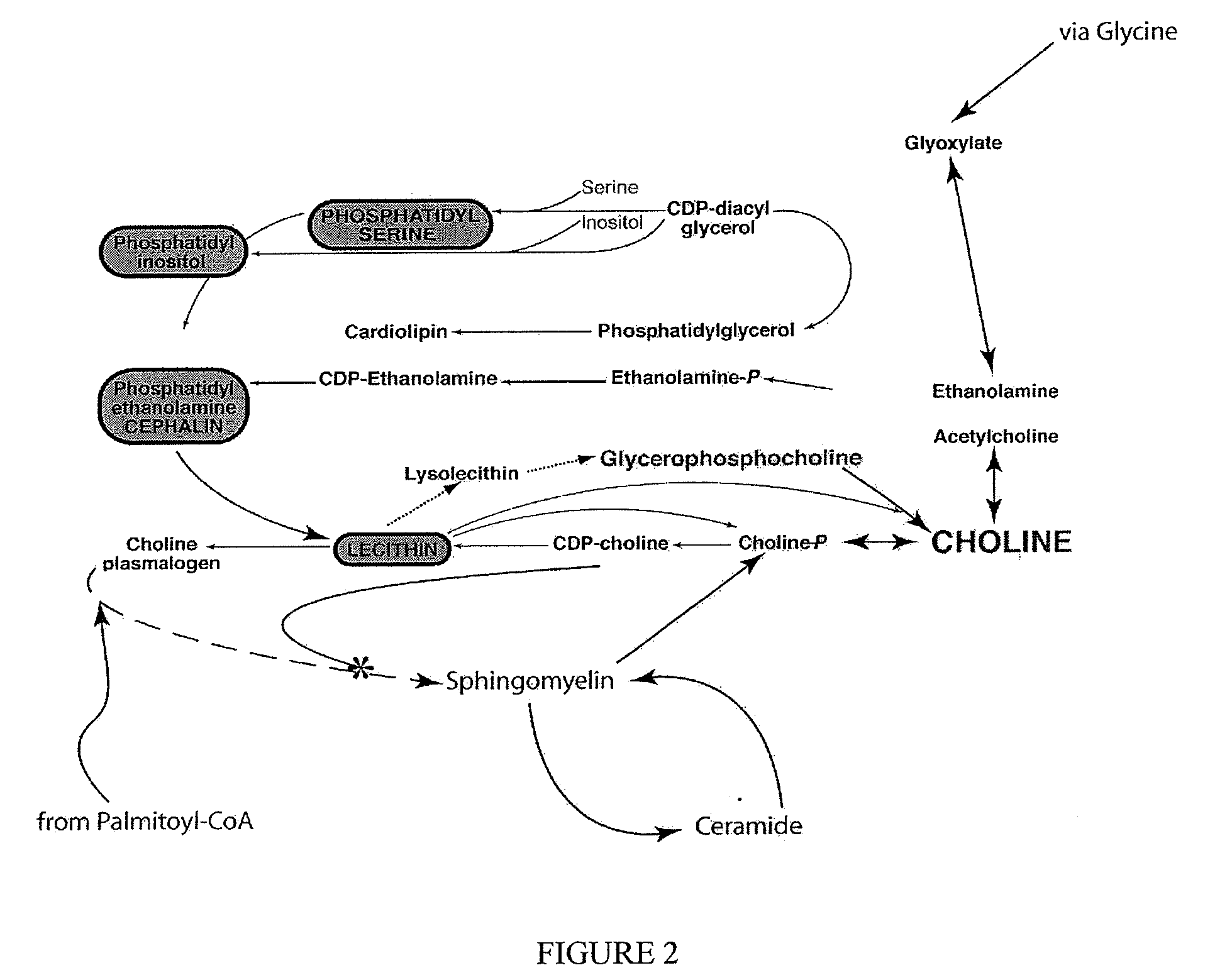
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy in non-uniform magnetic field
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
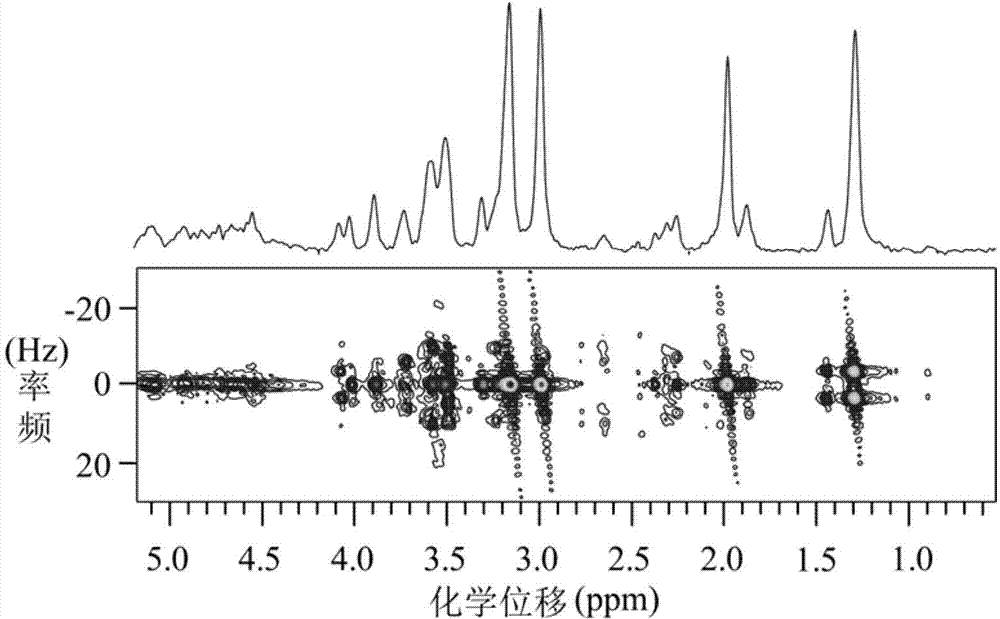
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy using light with orbital angular momemtum
InactiveUS20100327866A1Less noisyHigh resolutionLaser detailsAnalysis using optical pumpingTwo-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopySpectroscopy
The present invention relates to a device capable of producing a high resolution chemical analysis of a sample, such as fluid, based upon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where the nuclear magnetic polarizations of the sample are generated by sequentially illuminating the sample with a focused beam of light carrying angular orbital angular momentum (OAM) and possibly momentum (spin). Unlike in usual NMR used for magnetic nuclear resonance imaging (MRI) or spectroscopy, the invention does not make use of a strong magnet.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device and measurement method based on laser atomic magnetometer
ActiveCN102830381AHigh detection sensitivityLow running costMeasurements using NMRHelmholtz coilProton NMR
The invention discloses a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) device based on a laser atomic magnetometer, and the NMR device comprises a cesium atom vapor bubble, a magnetic shielding bushing which is sleeved on the cesium atom vapor bubble, three groups of Helmholtz coils which are arranged inside the magnetic shielding bushing, a polarization device which is used for polarizing cesium atoms inside the cesium atom vapor bubble, a laser transmitting device which is used for transmitting detection laser to the cesium atom vapor bubble, a detection device which is used for detecting an NMR signal of the detection laser penetrating the cesium atom vapor bubble and a pneumatic sample feeding device which is used for pre-polarizing a sample to be detected and can place the pre-polarized sample on the cesium atom vapor bubble. The invention also discloses a measurement method of an NMR based on the laser atomic magnetometer. The device and the method are high in detection sensitivity, free from needing low-temperature refrigeration, low in running cost and lower in working temperature.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance)
InactiveCN104807847AFast testThe test result is accurateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceCorrection algorithmSludge
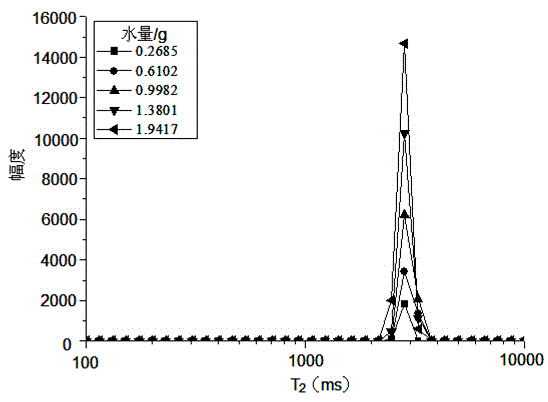
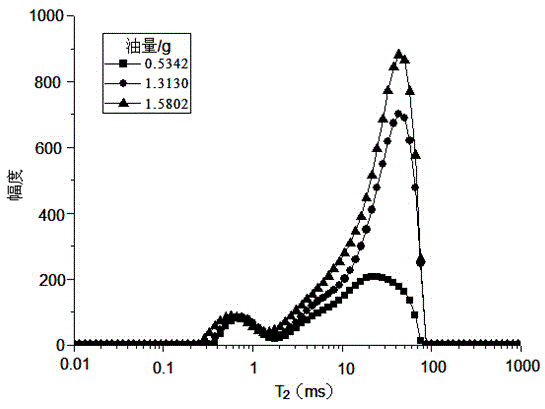
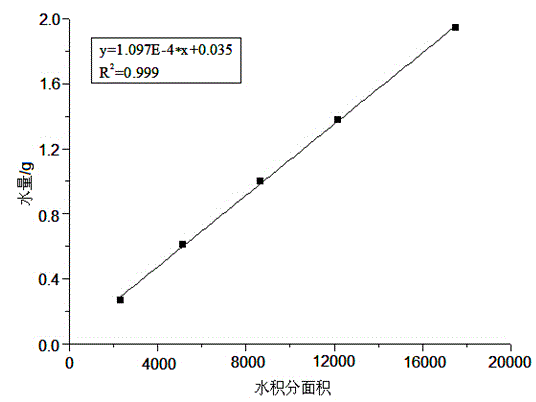
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously quantitatively analyzing water and oil in oily sludge through low-field NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance). The method comprises steps as follows: deionized water and crude oil are taken as standard samples to perform low-field NMR measurement, and calibration curves of water and oil are established; a to-be-measured sample which is uniformly stirred is divided into two parts and put in containers respectively, a reagent capable of realizing signal partition of oil and water is added to one part, and the mixture is uniformly stirred to form a sample a; the other part keeps unchanged and is taken as a sample b; the two samples are subjected to low-field NMR measurement to obtain an echo attenuation curve, and transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are obtained through inversion with a joint iterative correction algorithm; the transverse relaxation time T2 curves of the two samples are subjected to area integration and calculation to obtain integral areas of a water peak and an oil peak, and the calibration curves of water and oil are substituted to calculate water content and oil content of the to-be-measured sample b. The method can be suitable for measurement of content of water and oil in various kinds of oily sludge, and the measurement result is high in accuracy and good in repeatability and consumes short time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
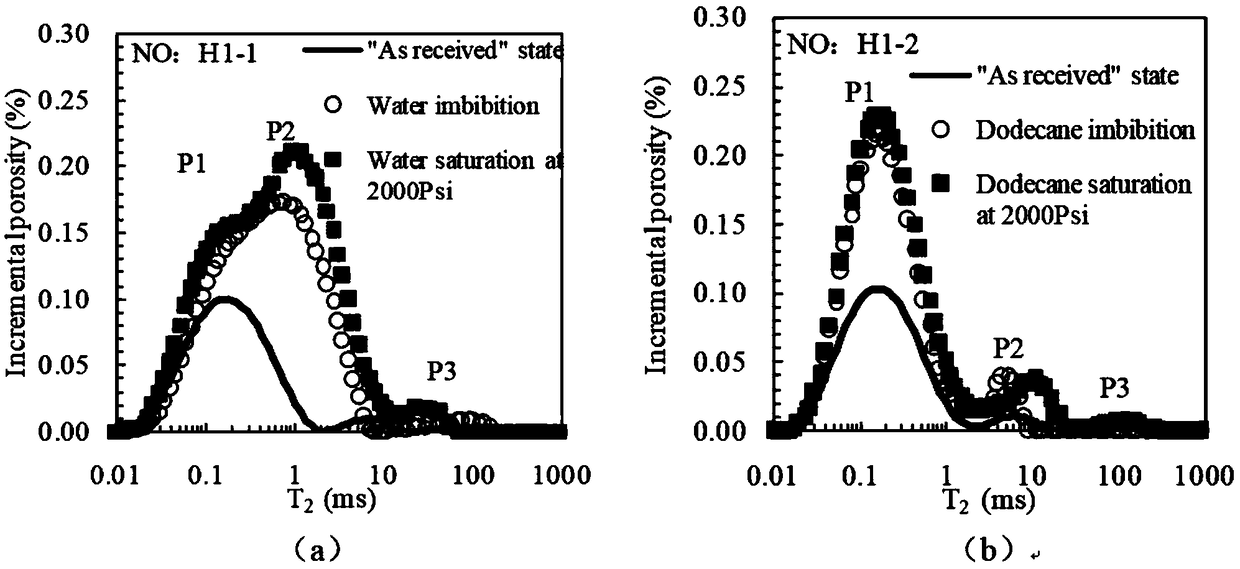
Shale pore structure detection method based on nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN106249306AClearly understand the changes in the size of poresAchieving Crack PredictionWater resource assessmentDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonancePore distributionWater state
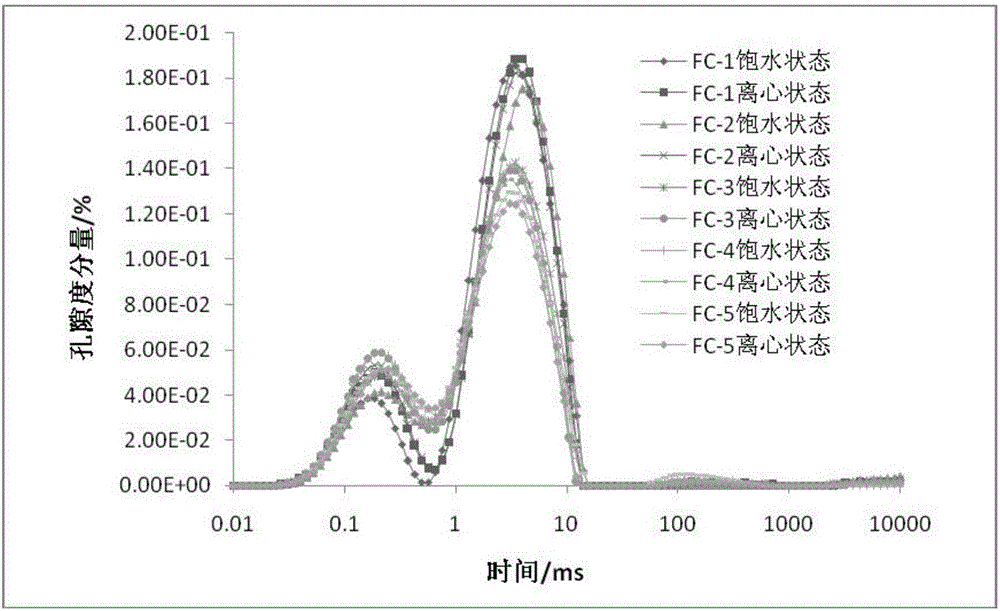
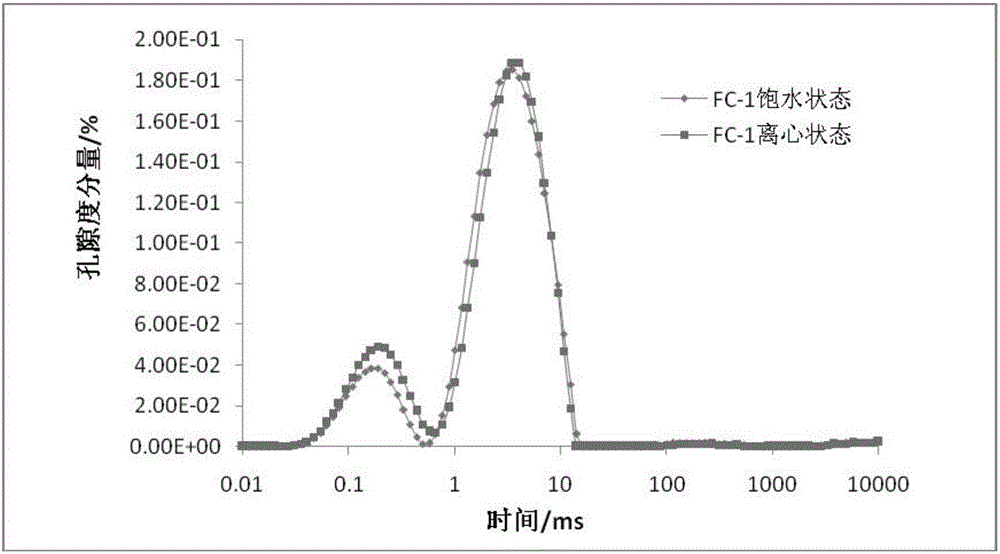
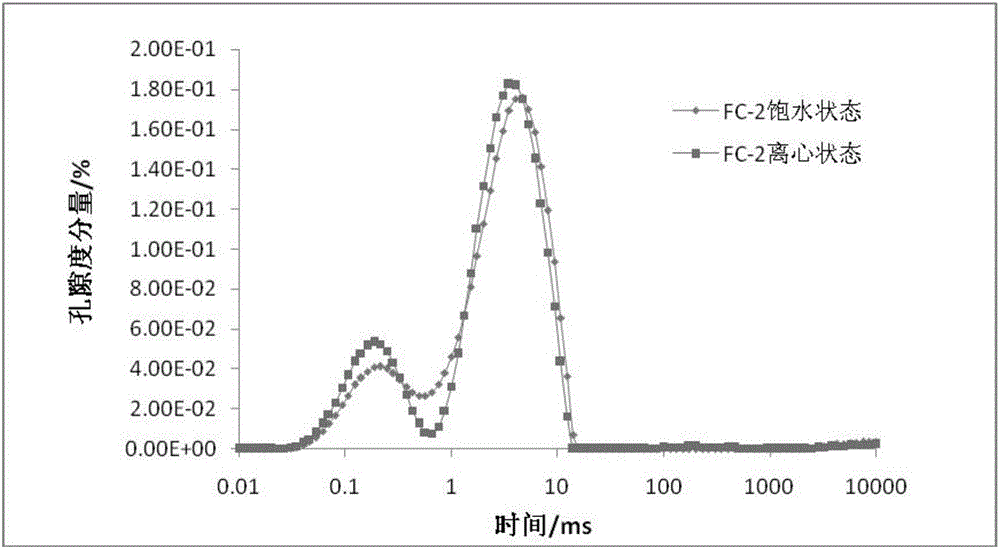
The invention provides a shale pore structure detection method based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the steps that a sample is processed into a cylinder; the sample is saturated with water at normal pressure for 12h, and then is taken out; CPMG pulse sequence test is carried out on the sample to acquire a spin-echo-series attenuation signal; the spin-echo-series signal is inversed to acquire a T2 spectrum distribution diagram and the details of each peak; and the T2 spectrum of acquired same sample under water saturation and centrifugation is analyzed in a coordinate system to acquire the change of the volume and quantity of pores of the sample. The shale pore structure is mainly studied in a saturated water state in the prior art of nuclear magnetic resonance, and the problems that the study angle is single and limited; only pore distribution can be studied; and fracture prediction cannot be carried out are solved. The method provided by the invention belongs to the technical field of petroleum exploration and development.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Method for nuclear magnetic resonance on-line detection of shale gas
ActiveCN105181728AEvaluate the statusAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
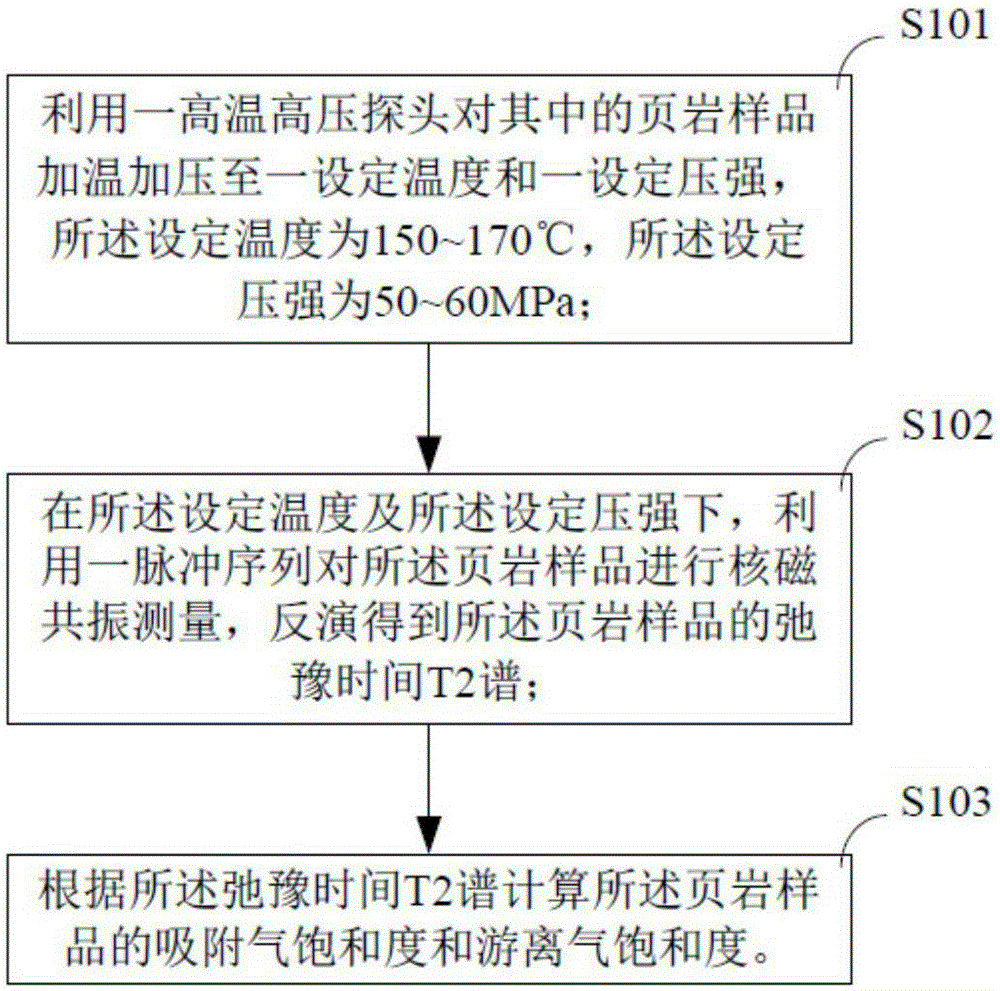
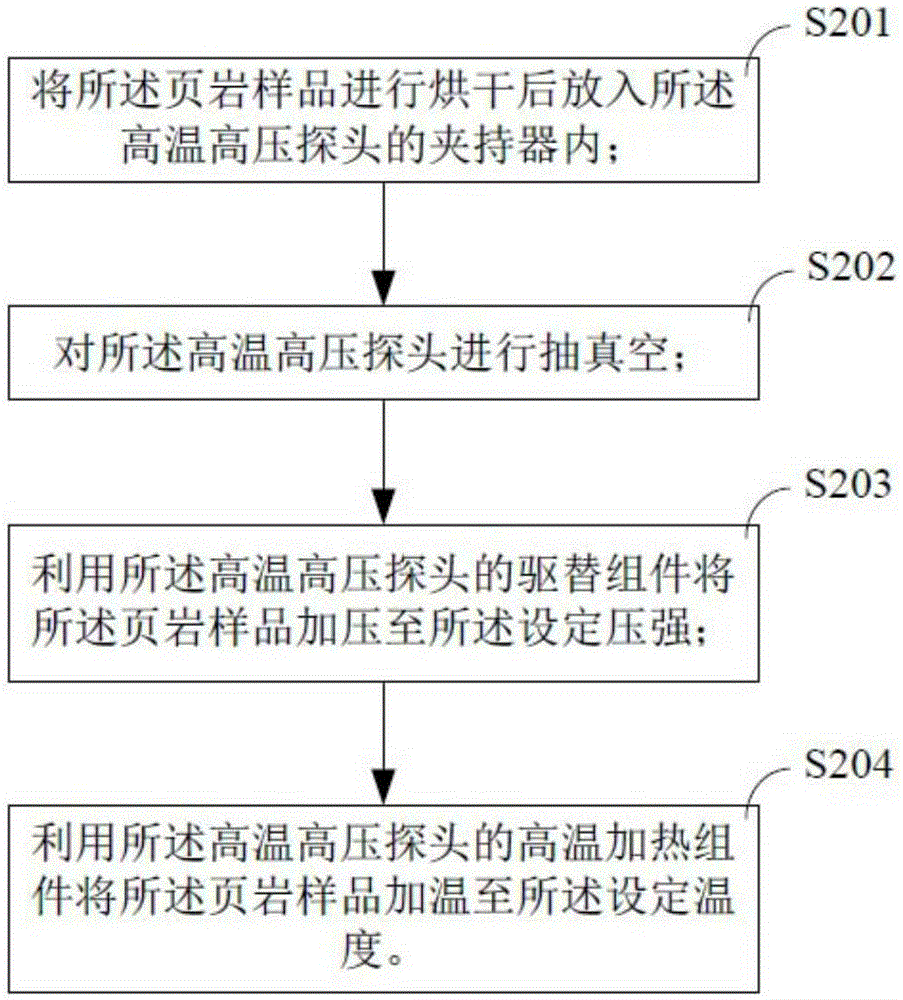
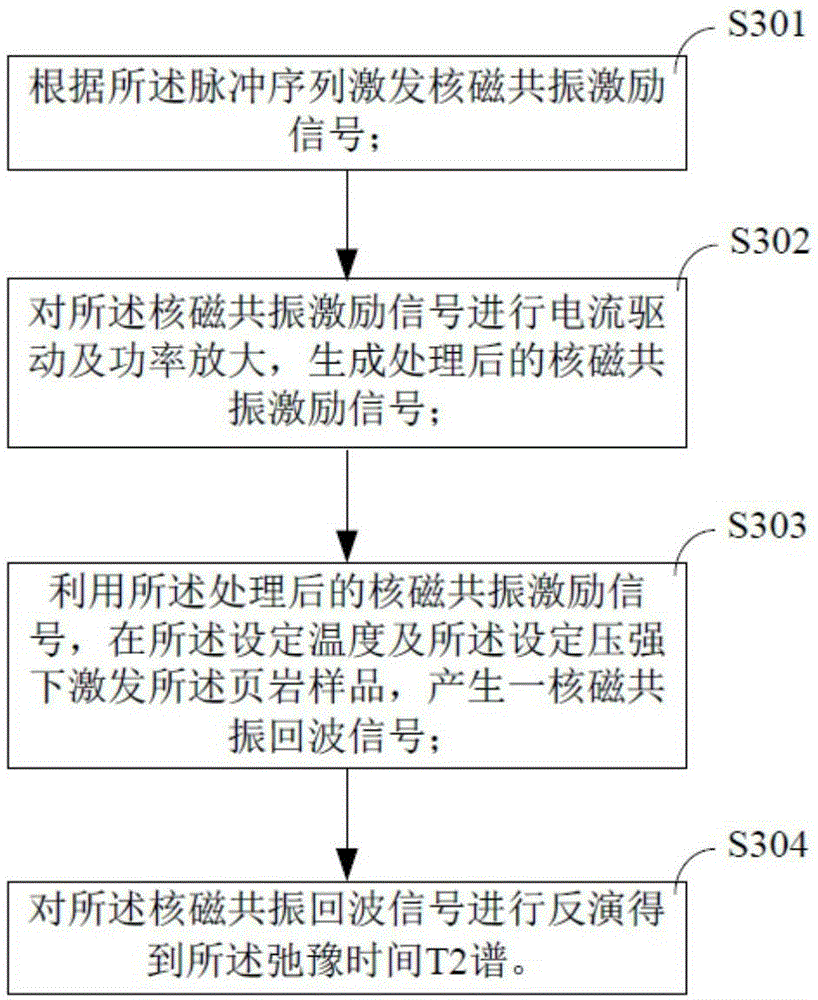
The invention provides a method for nuclear magnetic resonance on-line detection of shale gas. The method comprises steps: a shale sample is heated to a set temperature and pressurized to a set pressure by utilization of a high-temperature and high-pressure probe, the set temperature is 150-170 DEG C, and the set pressure is 50-60MPa; at the set temperature and the set pressure, the shale sample is subjected to nuclear magnetic resonance measurement by utilization of a pulse sequence, and the relaxation time T2 spectrum of the shale sample is obtained through inversion; the adsorbed gas saturability and the free gas saturability of the shale sample are calculated according to the relaxation time T2 spectrum. The detection method can evaluate occurrence of methane well and obtains the adsorbed gas saturability and the free gas saturability rapidly.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Hydration degree measurement method for cement-based materials based on nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN103399027AReduce mistakesEasy to operateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMuffle furnaceWater content
The invention discloses a hydration degree measurement method for cement-based materials based on nuclear magnetic resonance, which belongs to the technical field of cement material measurement. The hydration degree measurement method disclosed by the invention adopts a nuclear magnetic resonance technique to test nuclear magnetic signals of the cement-based materials at different ages; a relation between transverse relaxation time and the nuclear magnetic signals is obtained by inverse analysis; furthermore, a ratio of nuclear magnetic semaphores of left and right peaks is taken as a nuclear magnetic signal ratio of gel pore water and capillary pore water, and then the hydration degree of the cement-based materials to be detected at the age is solved according to a Powers model. Compared with traditional methods including a muffle furnace method and the like, the hydration degree measurement method disclosed by the invention is a nondestructive testing method, can reduce operation steps of a test greatly and shorten a testing period greatly, and can be used for monitoring samples continuously so as to ensure that the errors of test results are small; meanwhile, the method disclosed by the invention does not need to calibrate nuclear magnetic resonance semaphores and sample water content and directly adopts the ratio of the nuclear magnetic semaphores of the left and right peaks, namely a microstructure factor, as a parameter to represent the hydration degree, and therefore, measurement procedures and errors are reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
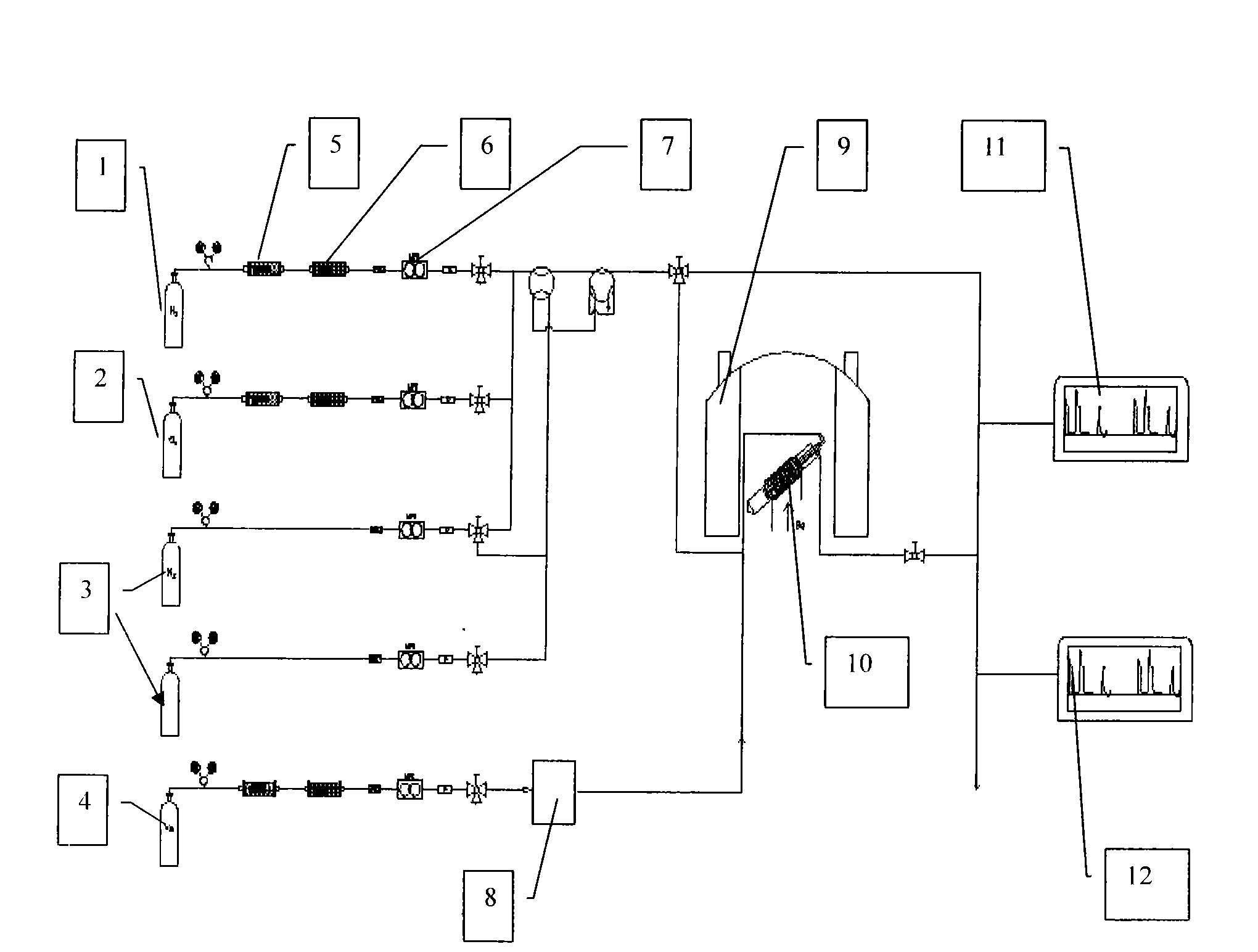
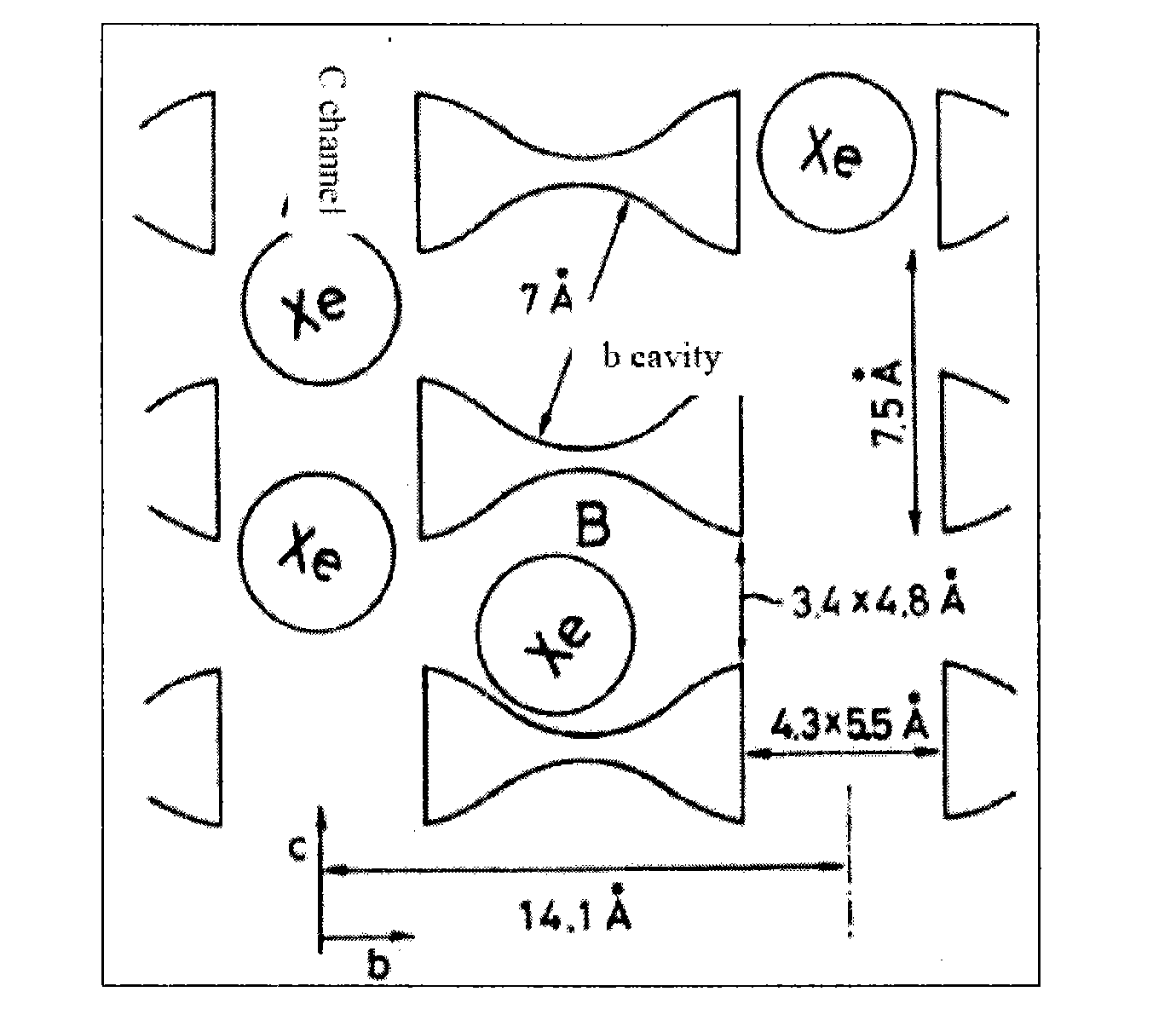
Multiphase catalytic reaction device for testing in situ solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN101634651AChemical analysis using catalysisComponent separationMagic angle spinningGas phase
The invention relates to a multiphase catalytic reaction device for testing in situ solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance, which is a magic angle spinning multiphase catalytic reactor in which an online solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance system, a quadrupole mass-spectrometer, a gas chromatograph and a laser-induced hyperpolarized 129Xe isotope probe are linked for use. The reactor can apply various solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance techniques to track and detect a catalyst structure, reaction intermediates and species with catalyst activity in the catalytic reaction process; reaction products are qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by the quadrupole mass-spectrometer and the gas chromatograph, so that the performance of the catalyst is evaluated; simultaneously, laser-induced hyperpolarized 129Xe isotope is used as a probe molecule to study the change of the catalyst structure, adsorption positions and diffusion behaviors of various species in the reaction process and the like. In-situ tracking in the catalytic reaction process and the mechanism of the catalytic reaction can be systematically studied through the various techniques.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
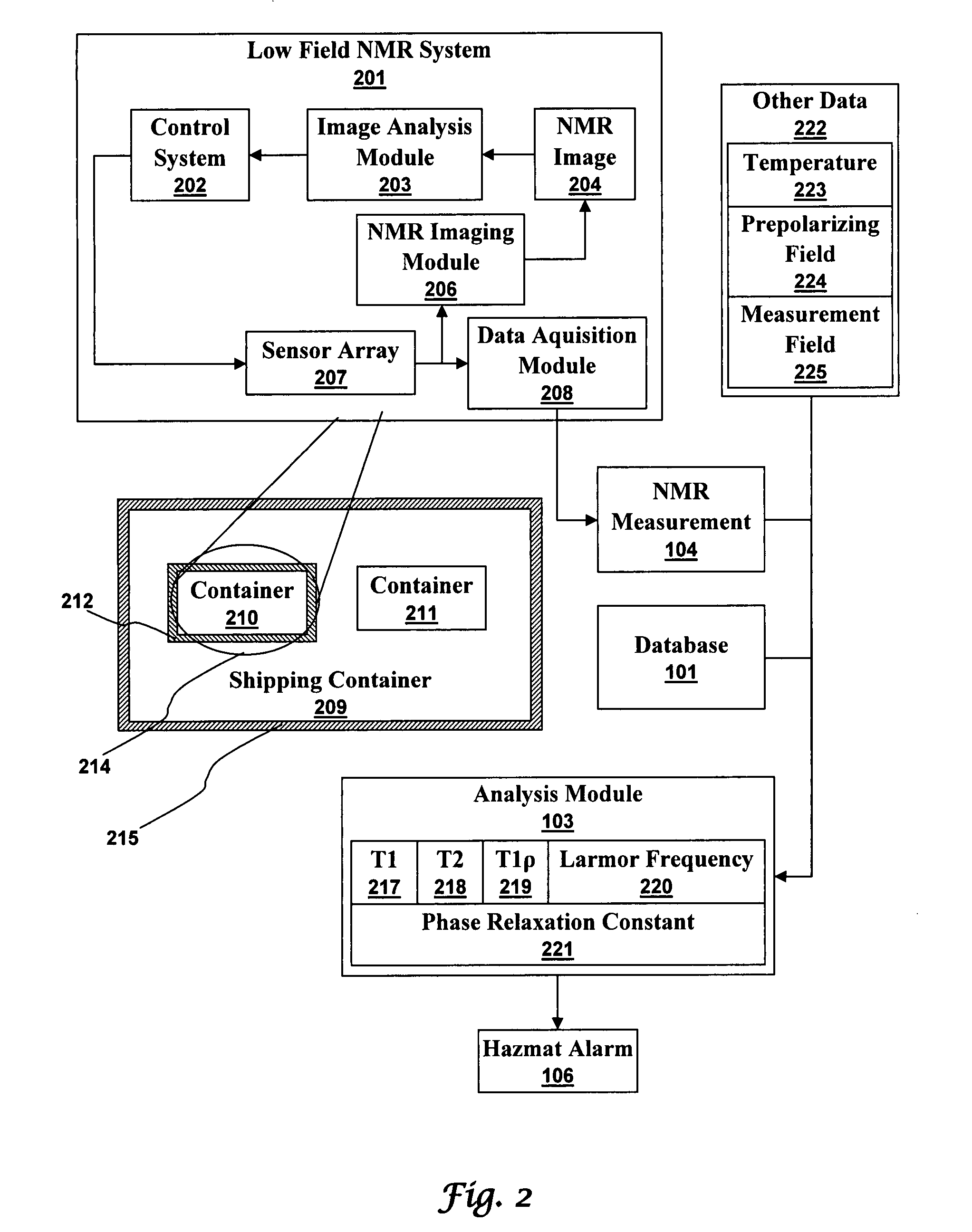
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20100219827A1Material analysis by using resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
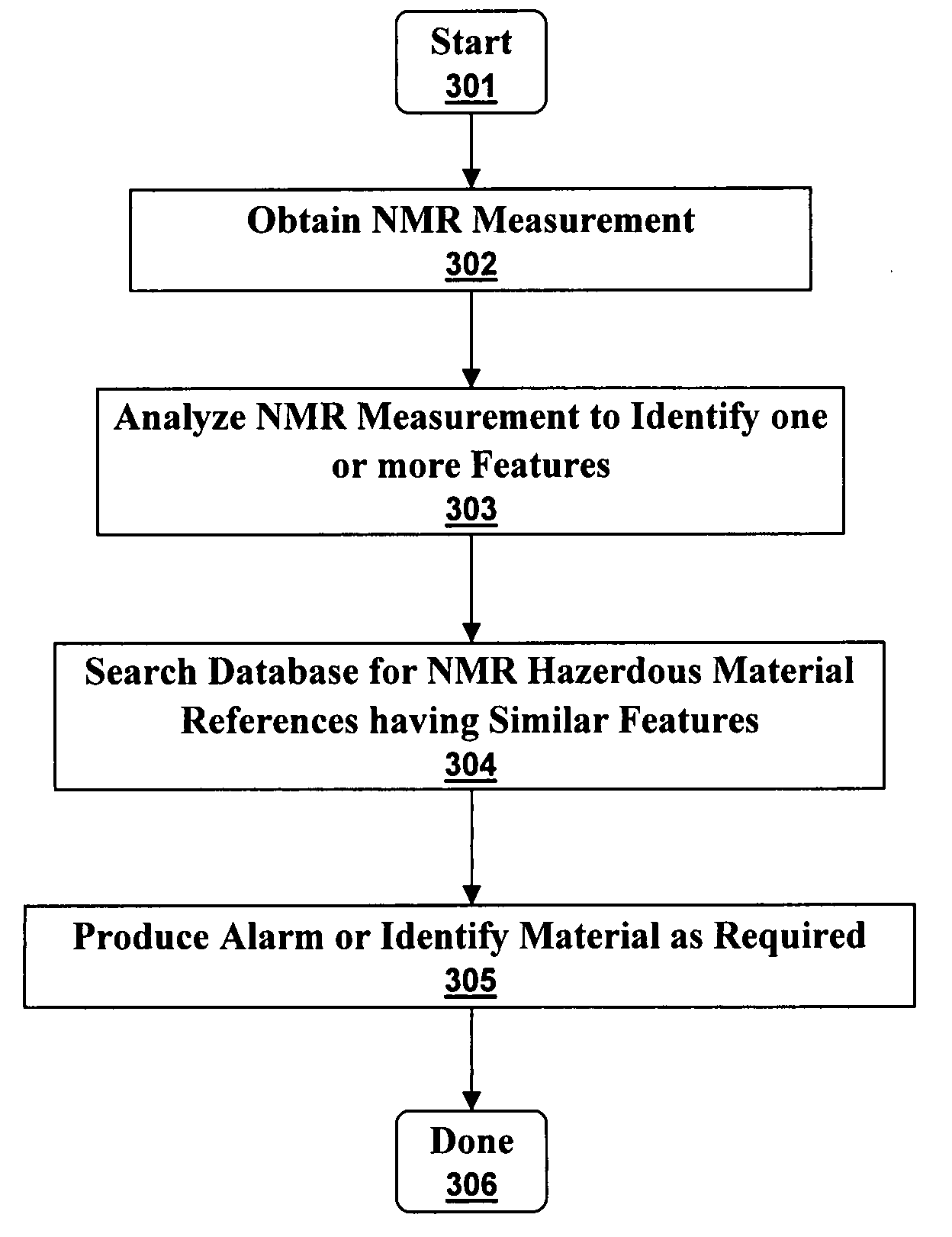
Method comprising obtaining an NMR measurement from a sample wherein an ultra-low field NMR system probes the sample and produces the NMR measurement and wherein a sampling temperature, prepolarizing field, and measurement field are known; detecting the NMR measurement by means of inductive coils; analyzing the NMR measurement to obtain at least one measurement feature wherein the measurement feature comprises T1, T2, T1ρ, or the frequency dependence thereof; and, searching for the at least one measurement feature within a database comprising NMR reference data for at least one material to determine if the sample comprises a material of interest.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS7688069B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsMaterial analysis by using resonanceHazardous substanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
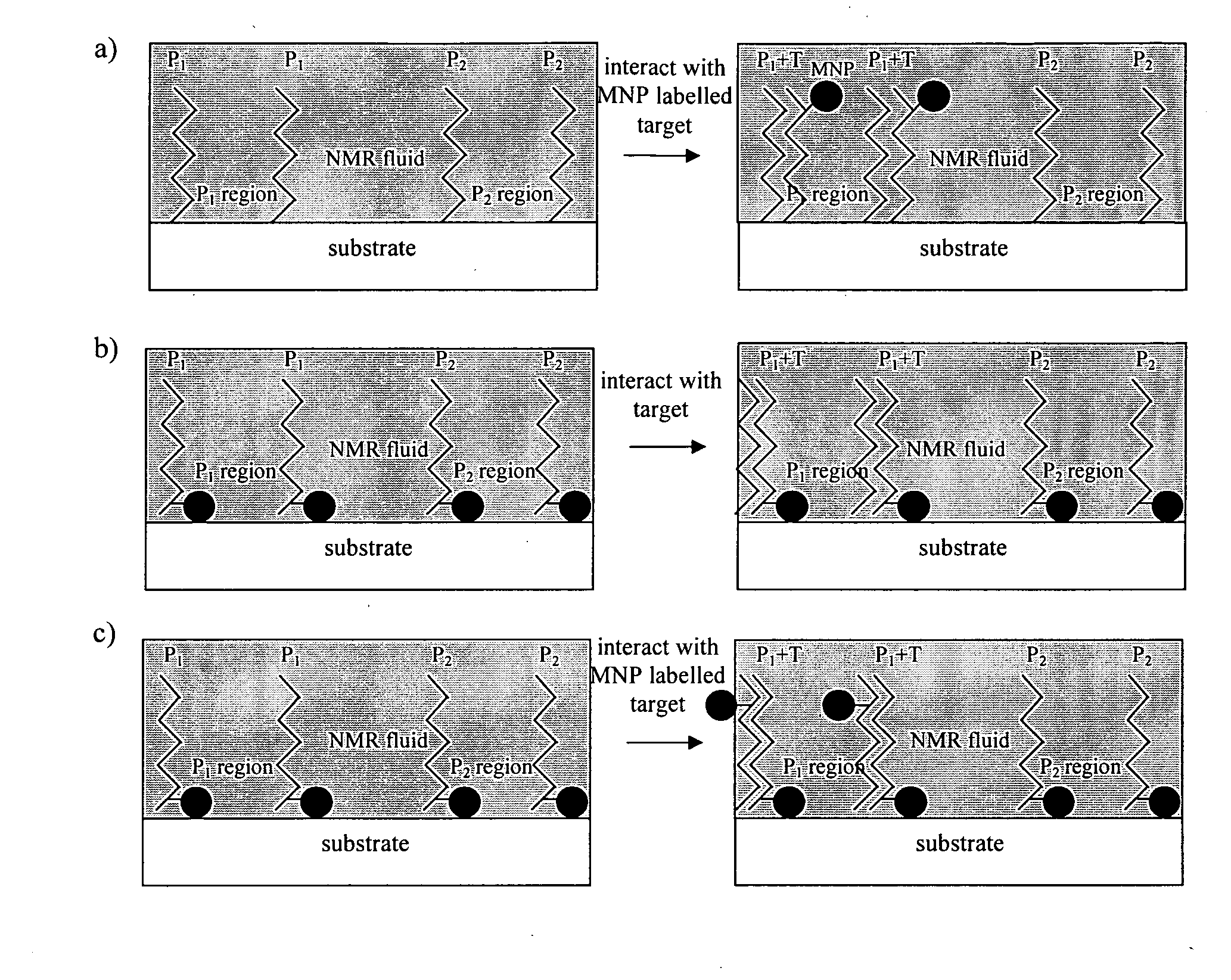
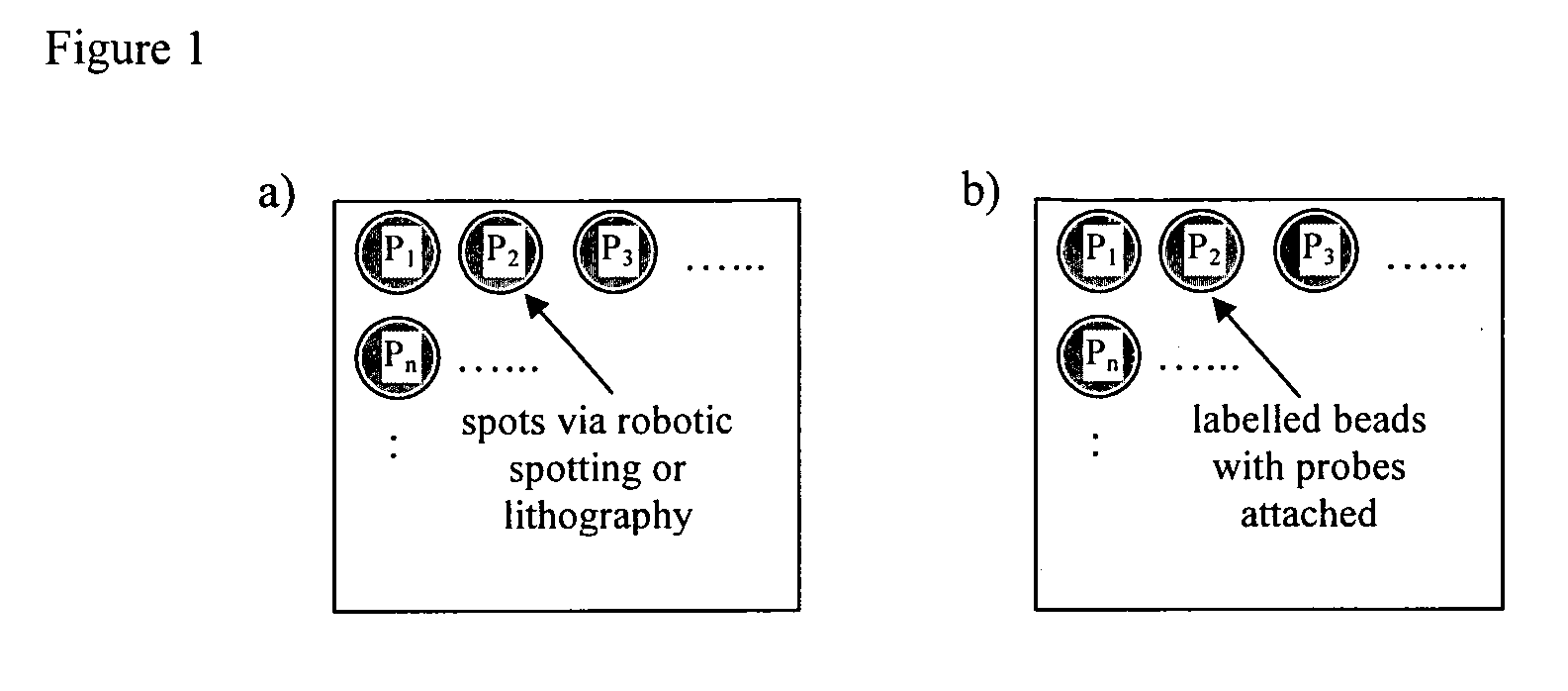
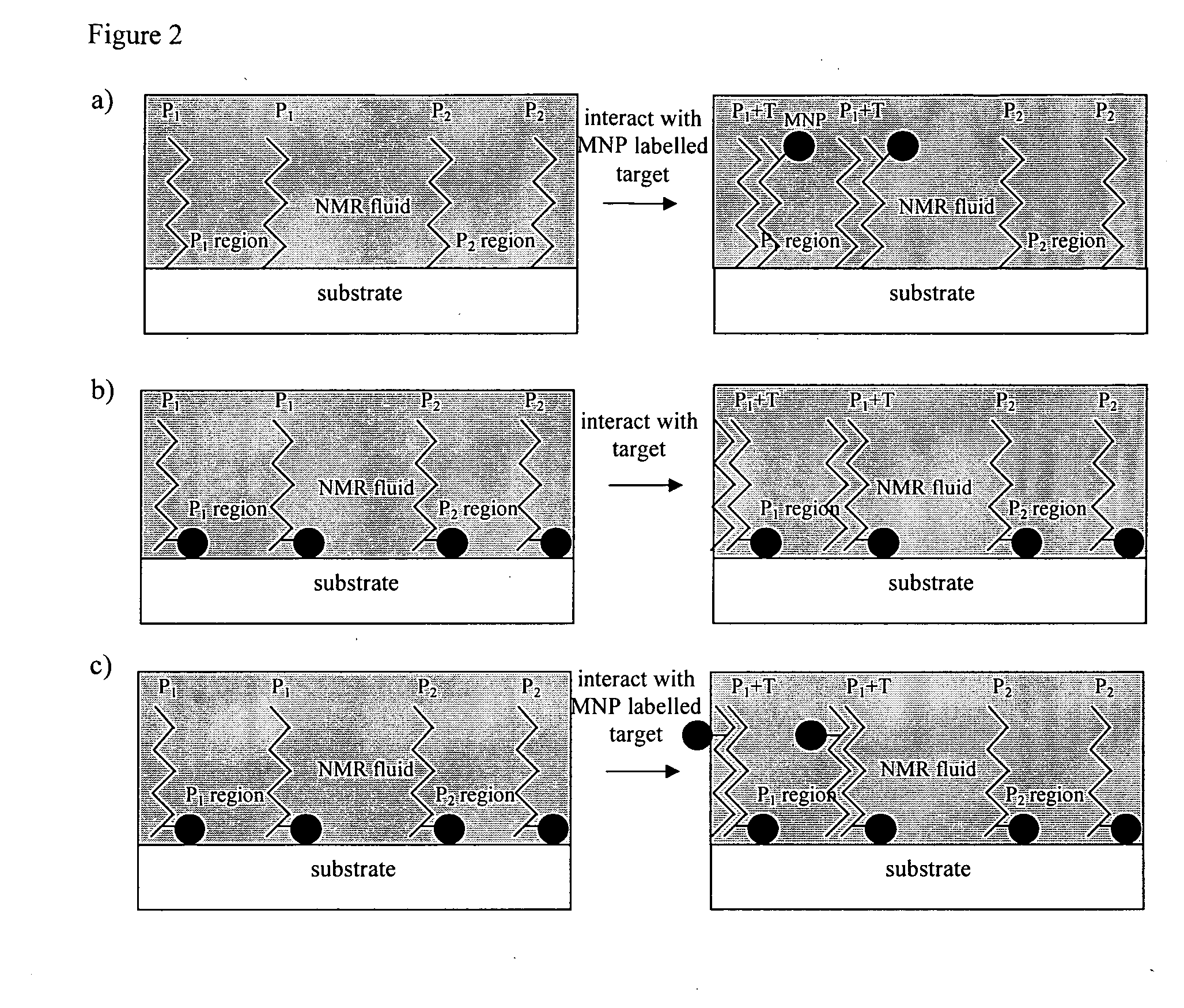
Method of detecting interactions on a microarray using nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20100160173A1Reduce signalingIncrease changeMagnetic measurementsLibrary screeningNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSpins
Methods of using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to detect the interaction of target substances with probes present at locations of a microarray are disclosed, and in particular methods of detecting the interaction of target substances present in fluids with an array comprising one or more probes present or locatable, e.g. in the case of a bead array, on a substrate at one or more locations. The methods are based on detecting the changes in the NMR signal arising from spin-carrying molecules present in a fluid in the vicinity of the probes that occur when target substances interact with probes in the array.
Owner:MCHALE GLEN +3
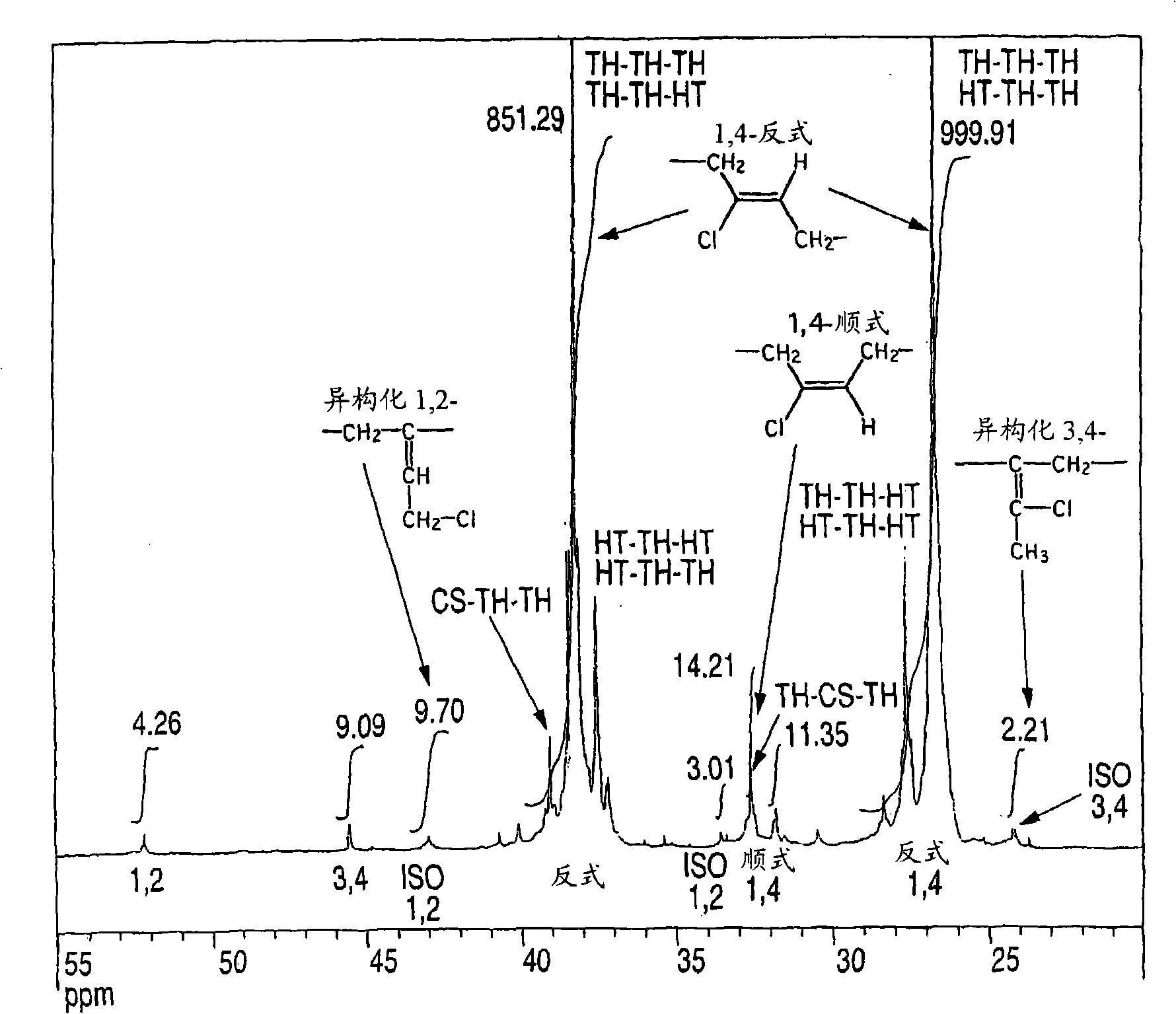
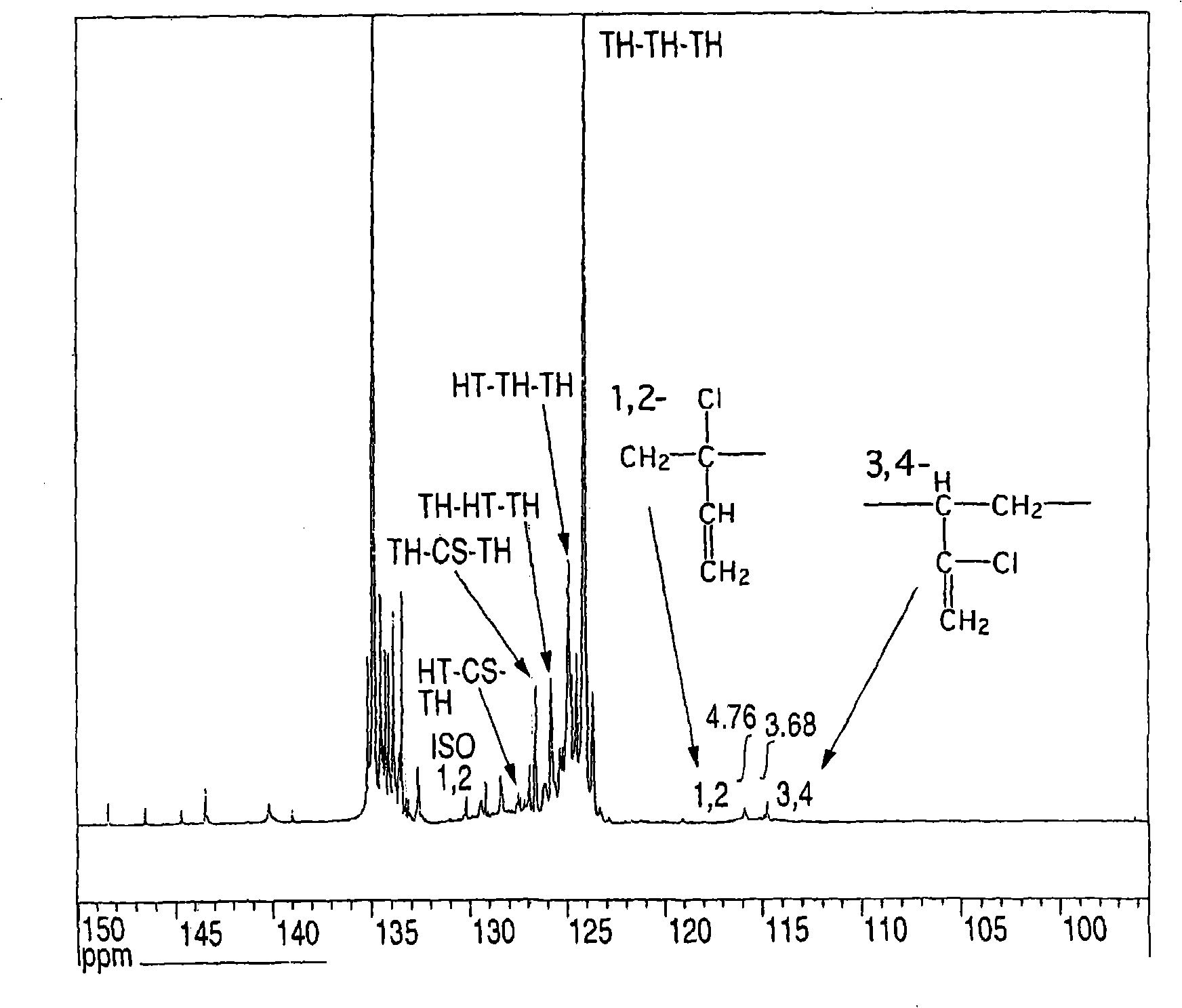
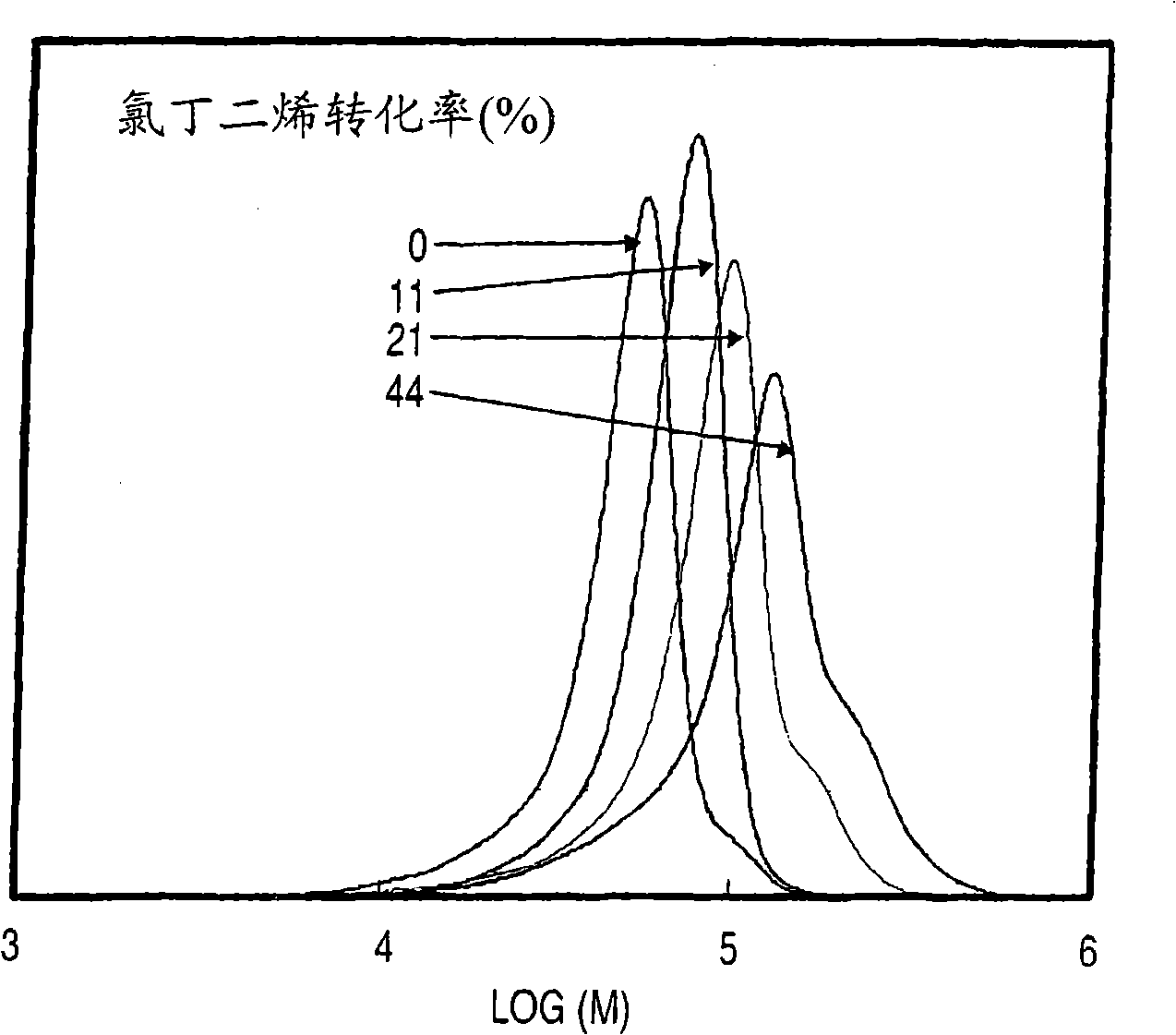
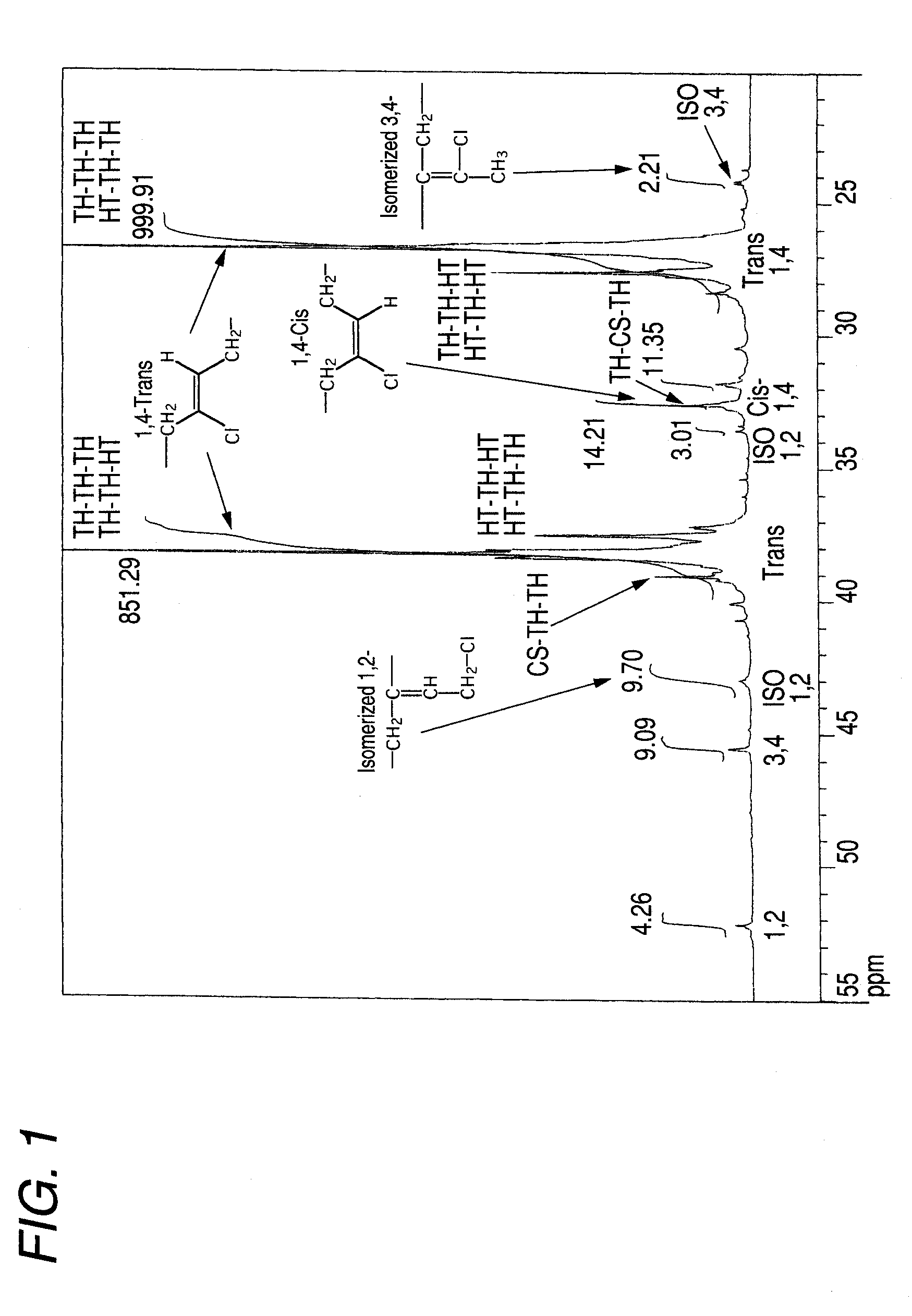
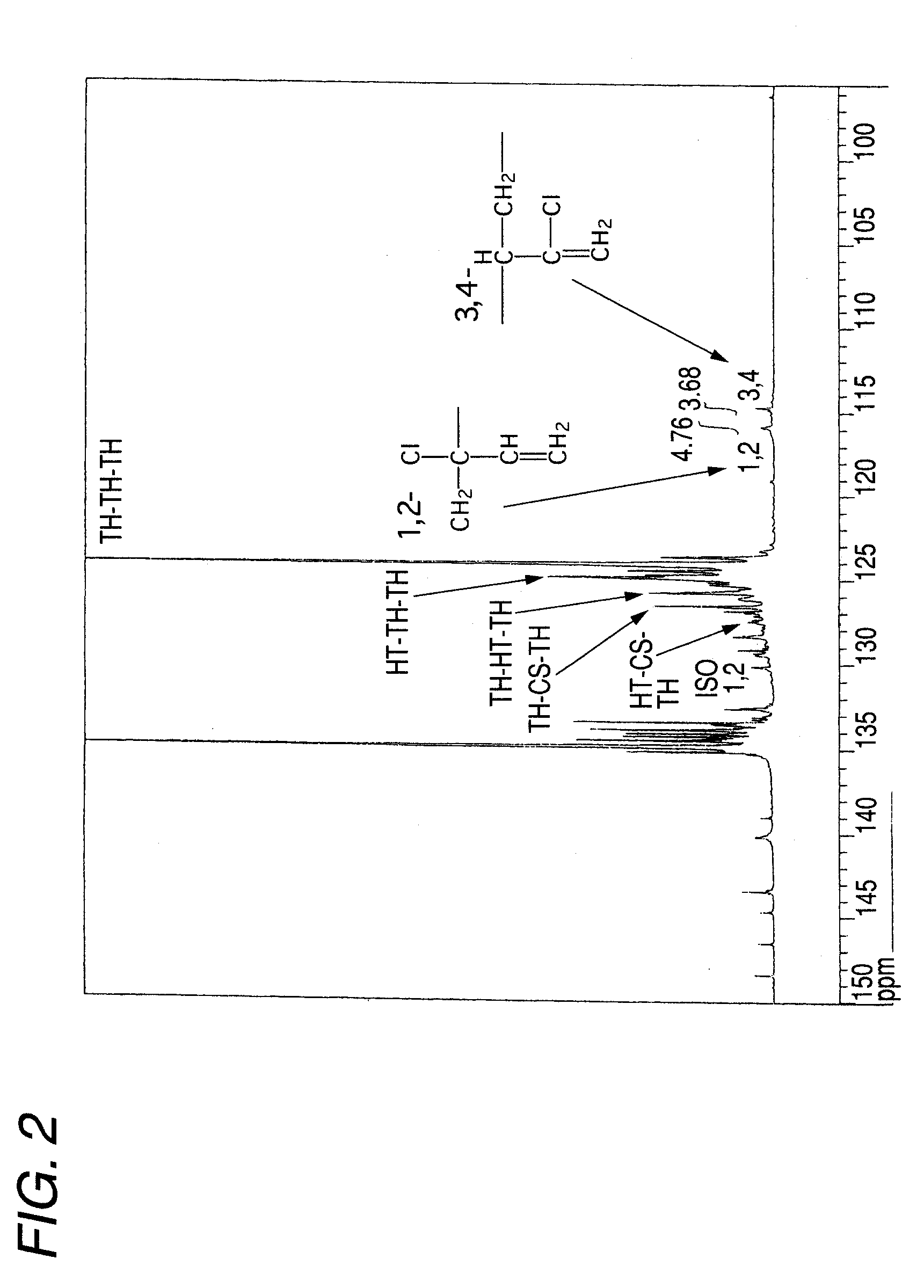
Chloroprene block copolymer and soapless polychloroprene latex, and processes for production of copolymer and latex
Disclosed are a novel polychloroprene copolymer, a soapless polychloroprene latex, and a process for producing the copolymer or latex in a simple manner, which are intended to be used for the improvement in adhesion property and water resistance of a conventional polychloroprene adhesive or the improvement in oil resistance and adhesion property of a conventional styrene-butadiene block copolymer. A chloroprene block copolymer comprising a polymer (A) having the composition represented by the general formula (1) in the description and a chloroprene polymer (B), the polymer (A) being linked to one terminal or both termini of the chloroprene polymer (B), and the total amount of the 1,2-bond and the isomerized 1,2-bond in the chloroprene polymer (B) as measured by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry being 2.0 mol% or less; a soapless polychloroprene latex comprising an amphiphilic chloroprene copolymer having a hydrophobic chloroprene polymer and a hydrophilic oligomer or polymer having an acidic functional group attached to the hydrophobic chloroprene polymer and 2 wt% or less of an emulsifying agent; and a process for producing the chloroprene block copolymer or soapless polychloroprene latex.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
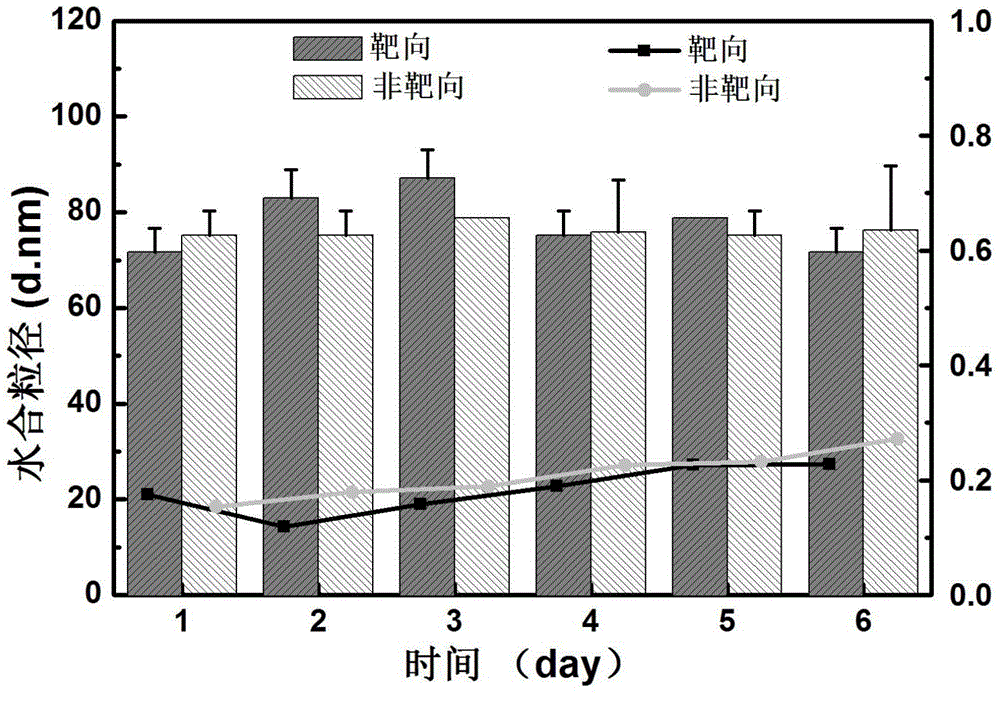
Tumor-targeted nuclear magnetic resonance/fluorescence dual-mode imaging contrast agent, preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN106390143AUniform particle size distributionImprove stabilityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetTumor targeting
The present invention provides a tumor-targeted nuclear magnetic resonance / fluorescence dual-mode imaging contrast agent, preparation and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the contrast agent is nanometer micro-particles formed by self-assembling a nuclear magnetic resonance amphiphilic molecule, a near-infrared fluorescent dye amphiphilic molecule and a tumor targeting amphiphilic molecule in a solution, can stably exists under a physiological pH value condition, can be specifically accumulated at a tumor site in a targeting manner, can significantly enhance the intensity of the MRI signal and the near-infrared fluorescence signal at a tumor lesion site, can improve the specificity and the sensitivity of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and near infrared fluorescence imaging scanning, and is expected to be adopted as the contrast agent for fluorescence guidance during tumor resection surgeries and postoperative nuclear magnetic resonance monitoring.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method of rapidly detecting metal ions and small-molecule compounds through nuclear magnetic resonance
ActiveCN106033066ASmall amount of sampleEasy to operateAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceWater qualityProton NMR
The invention relates to a method of quantitatively detecting metal ions and / or small-molecule compounds through nuclear magnetic resonance. The method includes steps of 1) providing a liquid to be detected and a detection primary liquid, and 2) adding the liquid to be detected into the detection primary liquid, measuring the nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time of the liquid mixture, and acquiring the content of the metal ions and / or small-molecule compounds in the liquid to be detected according to the measured nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation time. The method has advantages of simple operation, rapidness, a low cost, good selectivity, high sensitivity and capability of on-site real-time operation. The method is suitable for lake and river water quality survey, sewage discharging port water quality detection, and detection of melt mineral compounds, household water and various water samples or ethanol samples after treatment, and can be widely applied for the fields of food science, biomedicine, environmental science, analysis science, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chloroprene-based block copolymer, soapless polychloroprene-based latex, and processes for producing the same
InactiveUS20090036608A1Improve adhesionGood adhesivenessCarboxyl rubber adhesivesGraft polymer adhesivesPolymer scienceAdhesive
An object of the present invention is to provide a novel polychloroprene-based copolymer, a soapless polychloroprene-based latex, and a process for producing the same in a simple and convenient manner, which are intended to be used for the improvement in adhesiveness and water resistance of a conventional polychloroprene adhesive or the improvement in oil resistance and adhesiveness of a styrene-butadiene block copolymer.The invention relates to a chloroprene-based block copolymer comprising a polymer (A) having a composition represented by the following formula (1) and a chloroprene-based polymer (B), the polymer (A) being linked to one terminal or both terminals of the chloroprene-based polymer (B), and the total amount of the 1,2-bond and the isomerized 1,2-bond in the chloroprene-based polymer (B) as determined by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry being 2.0 mol % or less; a soapless polychloroprene-based latex comprising an amphipathic chloroprene copolymer having a hydrophobic chloroprene-based polymer and a hydrophilic oligomer or polymer having an acidic functional group linked to the hydrophobic chloroprene-based polymer and 2 wt % or less of an emulsifying agent; and a process for producing the same:wherein U represents hydrogen, a methyl group, a cyano group, or a substituted alkyl group; V represents a phenyl group, a substituted phenyl group, a carboxyl group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, a substituted alkoxycarbonyl group, an allyloxycarbonyl group, a substituted allyloxycarbonyl group, an acyloxy group, a substituted acyloxy group, an amido group, or a substituted amido group; X represents hydrogen, a methyl group, chlorine, or a cyano group; Y represents hydrogen, chlorine, or a methyl group; Q represents a polymerization residue of maleic anhydride, citraconic acid, maleic acid, fumalic acid, a maleate ester, or a fumalate ester; and k, n, and m each represents an integer of 0 or more.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
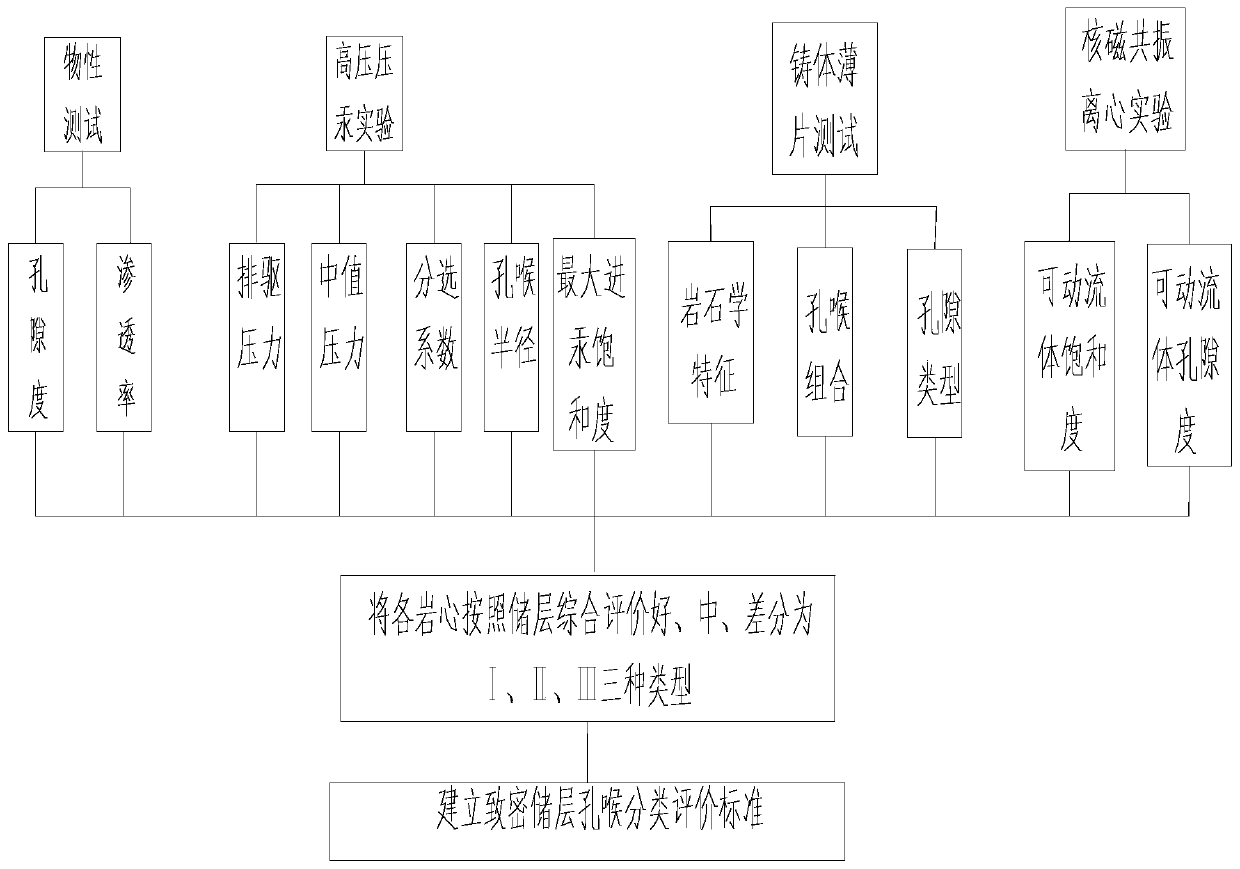
Method for assessing classification standard of tight reservoir pore structure based on nuclear magnetic resonance
PendingCN110160934AHigh precisionReduce storage performancePermeability/surface area analysisReservoir typeThroat
The invention discloses a method for assessing a classification standard of a tight reservoir pore structure based on nuclear magnetic resonance. The method comprises the following steps of 1, measuring the porosity and permeability of each rock center; 2, measuring the displacement pressure, mid-value pressure, sorting coefficient, pore throat radius and maximum mercury saturability of each rockcenter; 3, analyzing the petrologic feature of each rock center, and the pore throat combination and pore type of the rock center; 4, testing the movable fluid saturation and the movable fluid porosity parameter of each rock center; and 5, based on the abovementioned parameters, dividing the rock centers into I, II and III three types according to the good, middle and bad comprehensive assessmentof reservoirs, and building a classification assessment standard of the three kinds of reservoirs. The invention firstly provides the method for assessing the classification standard of the tight reservoir pore structure based on nuclear magnetic resonance; the reservoir types divided by the method are more accurate and scientific, and the basis is provided for subsequent exploration and development of the tight reservoirs.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Simultaneously cycled nmr spectroscopy
InactiveUS20090033326A1Compromised resolutionCompromised spectral widthDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The present invention relates to a method for simultaneously conducting multiple steps of a cycle of a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiment without the use of pulsed magnetic field gradients during signal detection in which one or more spatially selective radiofrequency pulses are applied to a sample under conditions effective to simultaneously spatially distribute the radiofrequency power associated with each of the cycle steps to a plurality of spatially discrete sections within the sample such that each section executes an individual step of the cycle and the resultant NMR signals from each of the cycle steps are produced simultaneously.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
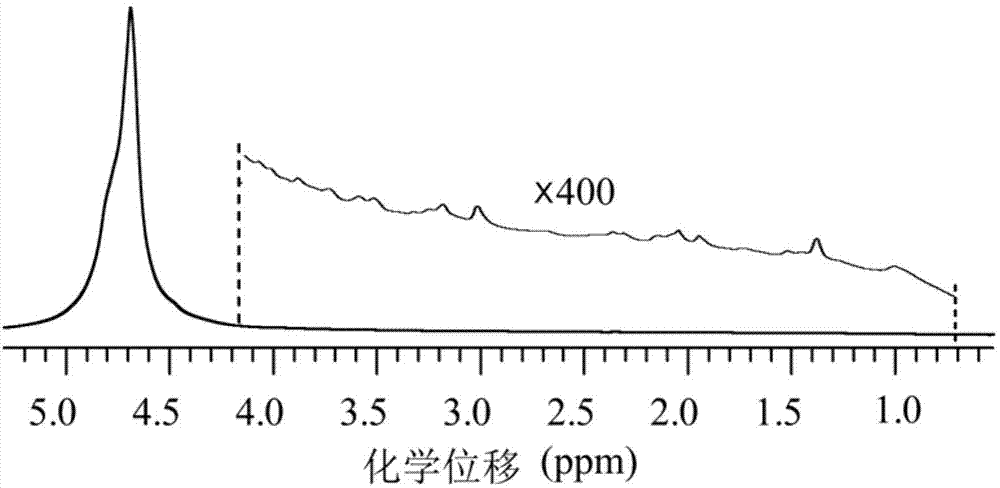
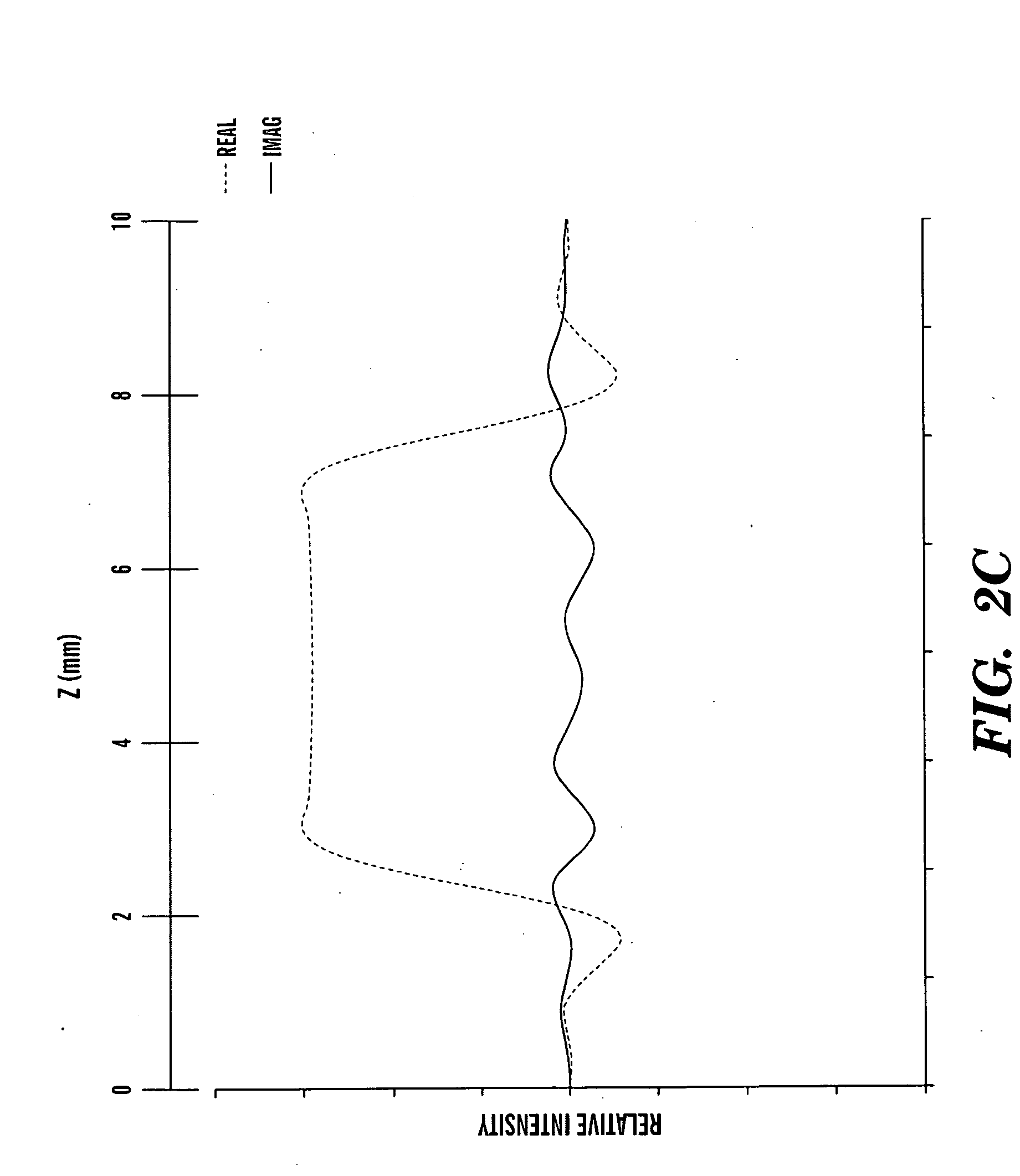
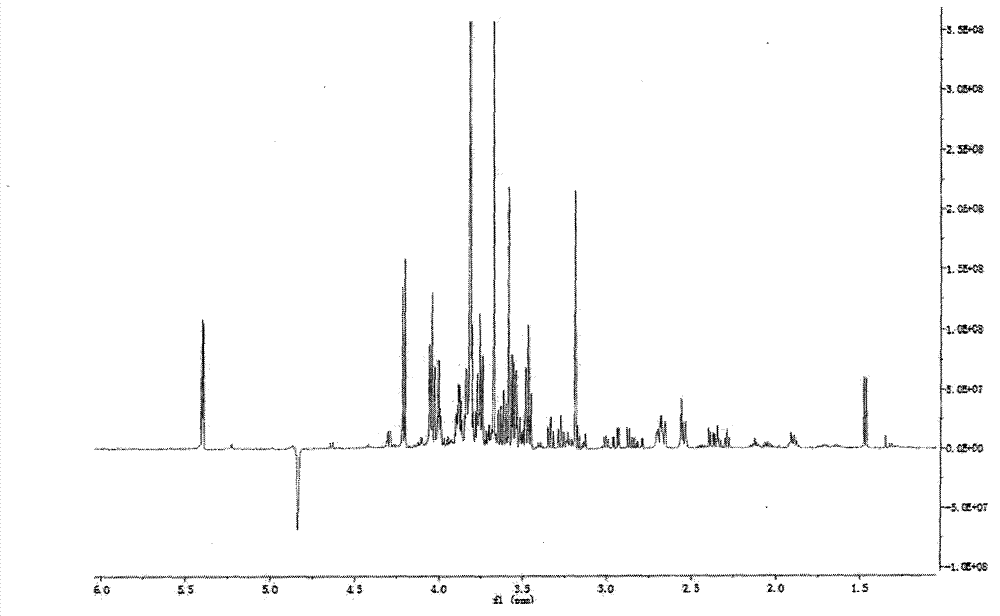
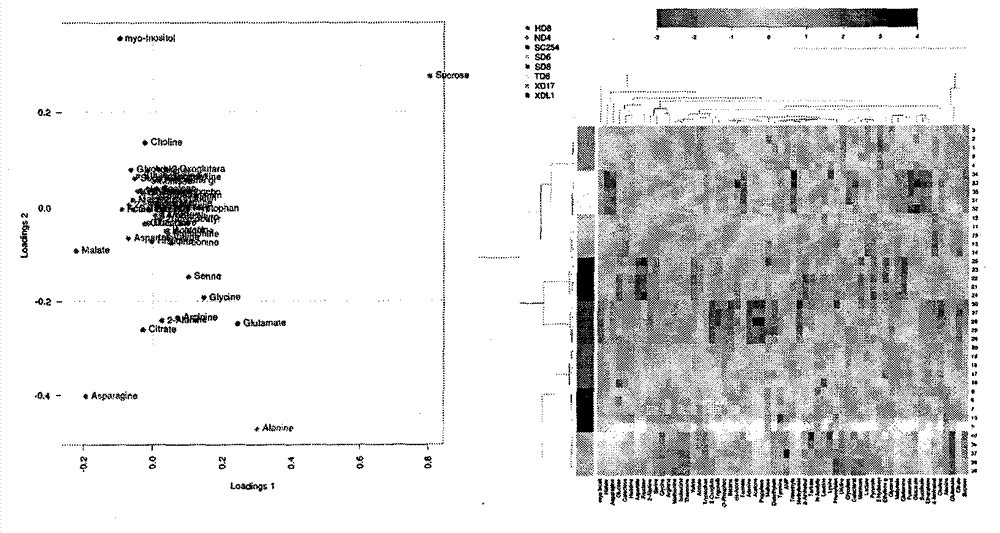
1H NMR (1H-nuclear magnetic resonance) evaluation method of vegetable soybean fresh seed quality
ActiveCN103245685AHighly subjectiveHigh randomnessAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMRMultivariate analysis
The invention relates to a 1H NMR (1H-nuclear magnetic resonance) evaluation method of vegetable soybean fresh seed quality, belonging to the field of fruit and vegetable quality analysis. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out low-temperature liquid nitrogen crushing and 50% methanol ultrasound quick extraction on different varieties of vegetable soybean samples with different qualities; then carrying out nuclear magnetic resonance signal collection on the samples under the same parameter condition, carrying out reversal convolution on collected spectrum, and carrying out Chenomx database matching and DSS internal label quantification to determine the compositions and contents of series metabolins such as soluble sugar, free amino acid and organic acid, thereby defining the characteristics of different vegetable soybean samples; and carrying out pattern recognition multivariate analysis according to a corresponding nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum fingerprint database to obtain an effective quality distinguishing and evaluation result. The method disclosed by the invention is comprehensive, correct, reliable, efficient, etc.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
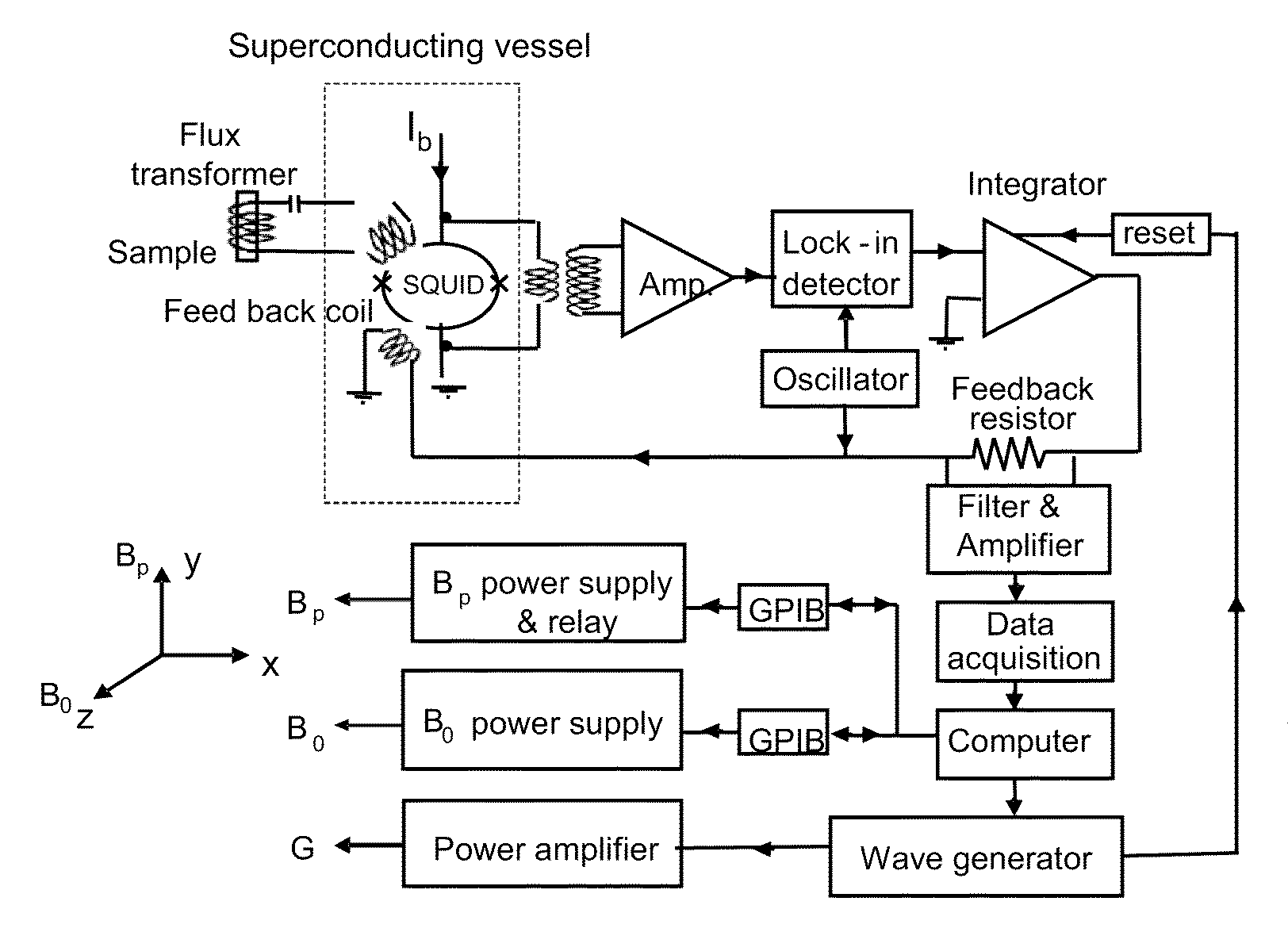
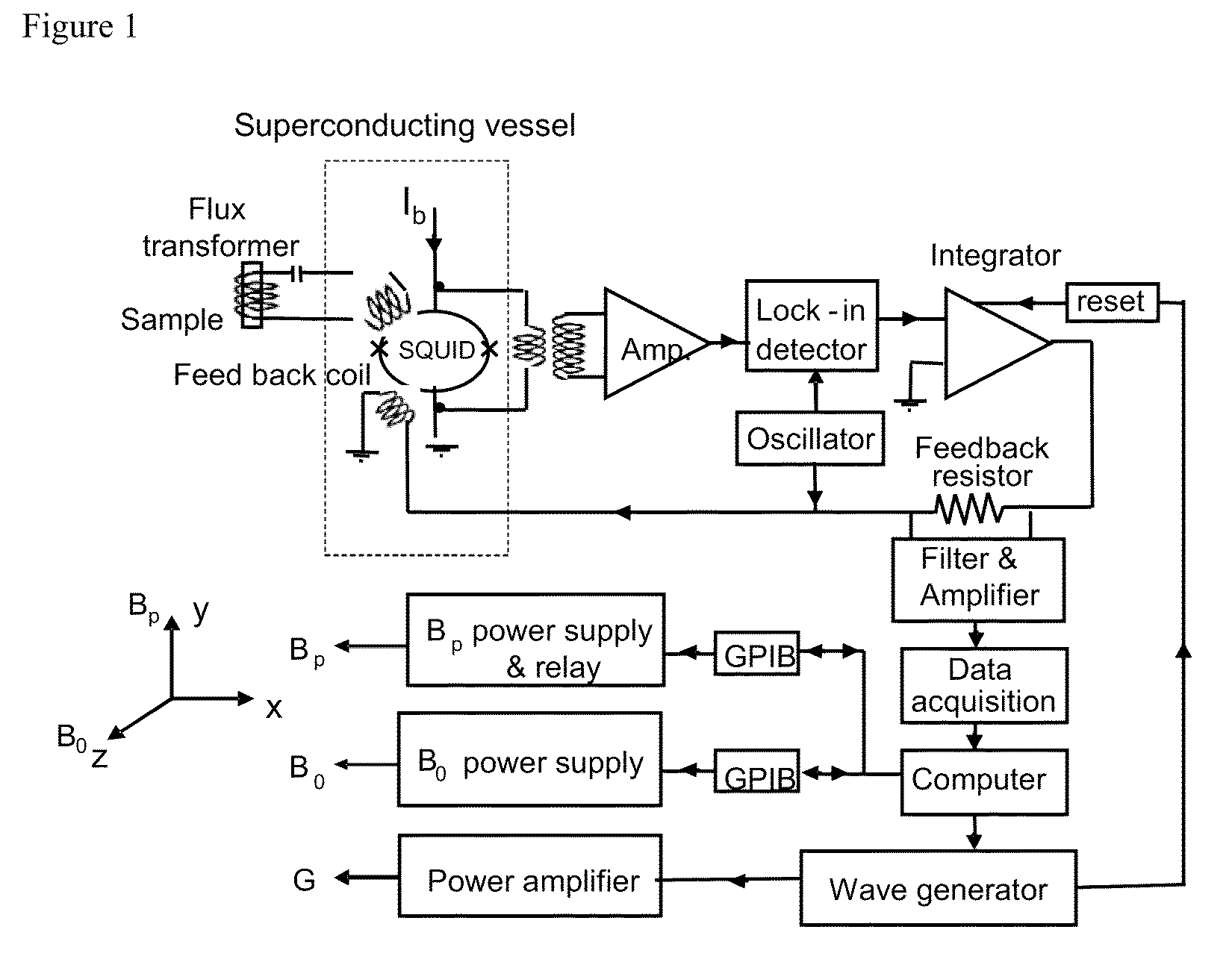
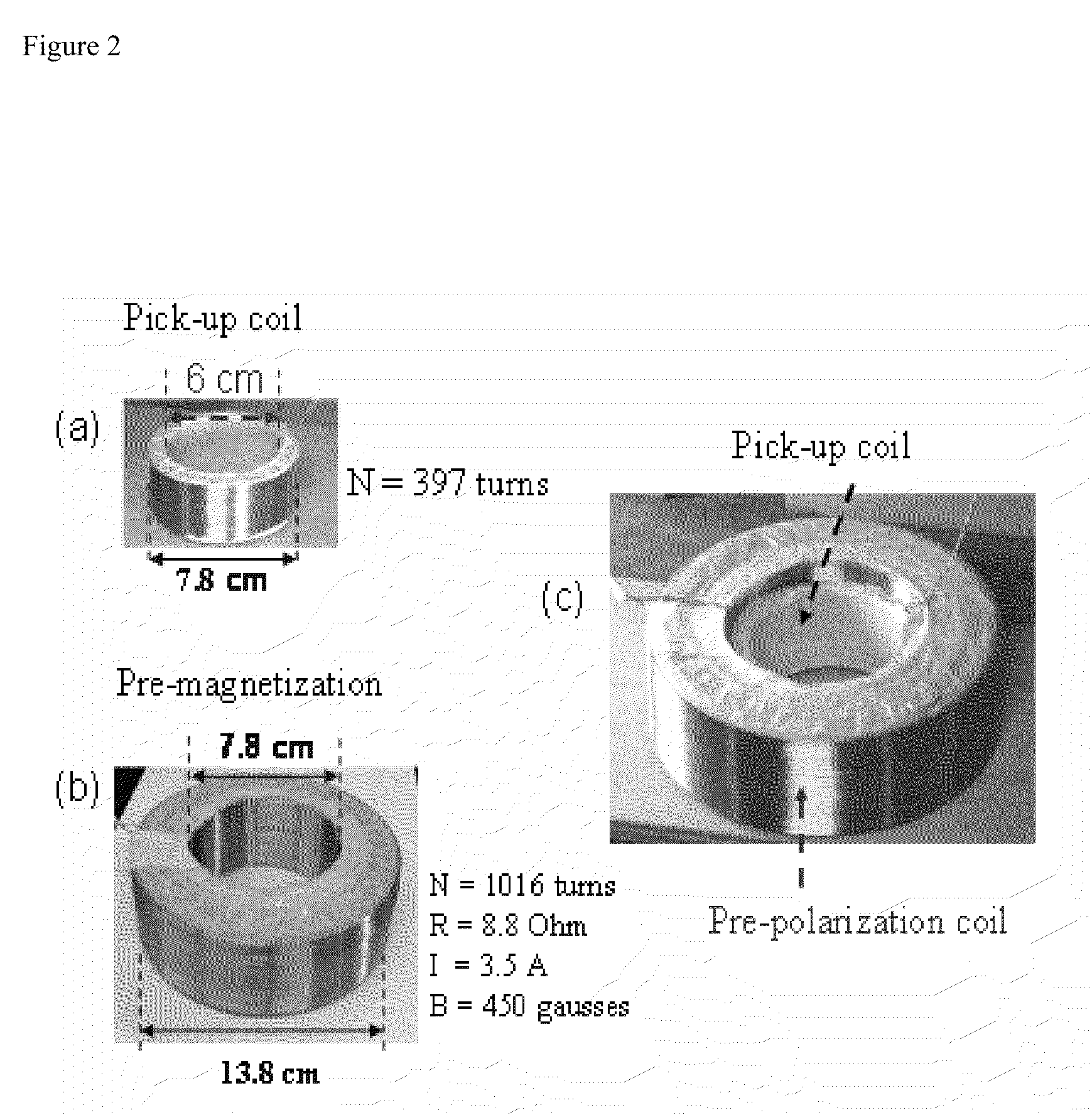
Squid detected nuclear magnetic resonance and imaging at ultra-weak fields
ActiveUS20100264921A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceEnvironmental noiseHigh critical temperature
The invention provides a high resolution proton nuclear magnetic reonance and imaging (NMR / MRI) in microtesla magnetic fields by using high critical temperature (high-Tc) superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer via a flux transformer. Both the SQUID and the input coupling coil are installed inside a superconducting vessel which shields environmental noise and set the SQUID in a stable operation condition. The present invention also offers the advantages of preserving the NMR signal even if the sample is far away from the SQUID detector.
Owner:HORNG HERNG ER +2
Isoindole alkaloid compound in purslane, and extraction and separation method of isoindole alkaloid compound
ActiveCN107459477AHigh purityAnti-inflammatoryOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryInfraredUltraviolet
The invention relates to the field of extraction and separation of traditional Chinese medicines, in particular to an isoindole alkaloid compound which is extracted, separated and identified from purslane, and an extraction and separation method of the isoindole alkaloid compound. The new alkaloid compound has a molecular formula of C28H23NO8 and is named as Oleraisoindole. The invention also provides the extraction and separation method of the isoindole alkaloid compound; the method comprises the steps of sequentially extracting by means of water boiling, extracting by using ethyl acetate, carrying out silica gel column chromatography, purifying by using an octadecylsilyl medium-pressure column and Sephadex LH-20, and carrying out liquid phase separation. The isoindole alkaloid compound is identified by using ultraviolet (UV), infrared ray (IR), HR-ESI-TOF-MS, hydrogen-1 nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR), carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (13C-NMR) and a two-dimensional nuclear magnetic spectrum analysis method. The compound has potential anti-inflammatory activity, anti-tumor activity, and the like; the invention also provides the preparation method of the compound, thus providing a lead compound and a theoretical basis for development of new medicines and new components.
Owner:LIAONING UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
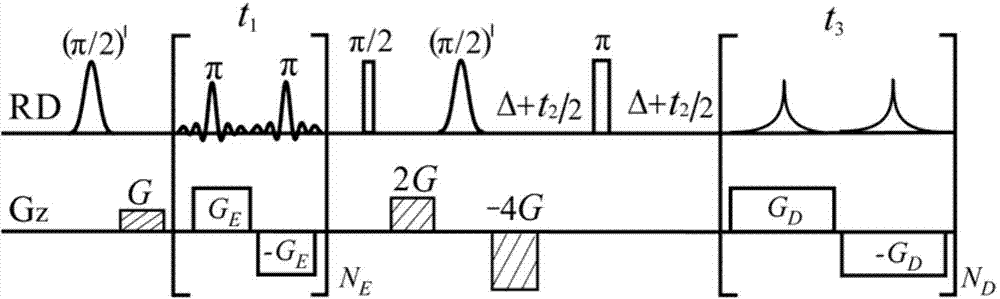
Method for obtaining high-resolution NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) spectra in inhomogeneous magnetic field
ActiveCN104198970ALower requirementQuantifiableMagnetic measurementsMagnetizationLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for obtaining high-resolution NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) spectra in an inhomogeneous magnetic field relates to a NMR spectrum. The method includes the steps: applying a radio frequency pulse to rotate a magnetization vector from an axis X to a plane XY; evolving while applying coherent gradient in a certain direction; applying a reunion pulse after the evolving is over to acquiring magnetic resonance signals; determining applying manner, intensity and direction of the coherent gradient, the method of which is that a half width LW is used to measure the degree of magnetic field inhomogeneity, Nu is taken as the gyromagnetic ratio of a magnetic core, effective test length of a sample is L, and the applying intensity on the gradient is set to be LW / (NuL); increasing and decreasing the intensity of the gradient to obtain corrected magnetic resonance signals; conducting fourier transforming to obtain coherence spectra of the NMR gradient and the inhomogeneous magnetic field; identifying coherent spectrum via the use of pattern recognition algorithms and recording spectral peak distribution map information; correcting the coherent spectrum; cumulatively projecting the corrected spectrum; finally obtaining one-dimensional high-resolution NMR spectra.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Detecting hazardous materials in containers utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance based measurements
InactiveUS20140225614A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceHazardous substanceElectromagnetic pulse
A method of detecting hazardous materials in containers utilizing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology. The presence of precursors (e.g., H202) and / or nitrogen in the liquid in the container is determined by placing the container in a static magnetic field, exciting the container with electromagnetic pulses having a frequency corresponding to proton NMR and 14N NMR, and receiving radio frequency (RF) signals through a probe. The excitation pulses are configured to enable detection of the presence of precursors and nitrogen in the container, and may comprise a sequence of short RF pulses. The presence of nitrogen and / or explosive precursors is determined by detecting and evaluating NMR measurement signal amplitudes and relaxation times from the received RF signals. An apparatus comprising a magnet that generates a magnetic field and a probe that generates RF pulses and receives NMR measurement signals from the sampled container in accordance with the aforementioned method.
Owner:PRADO PABLO J
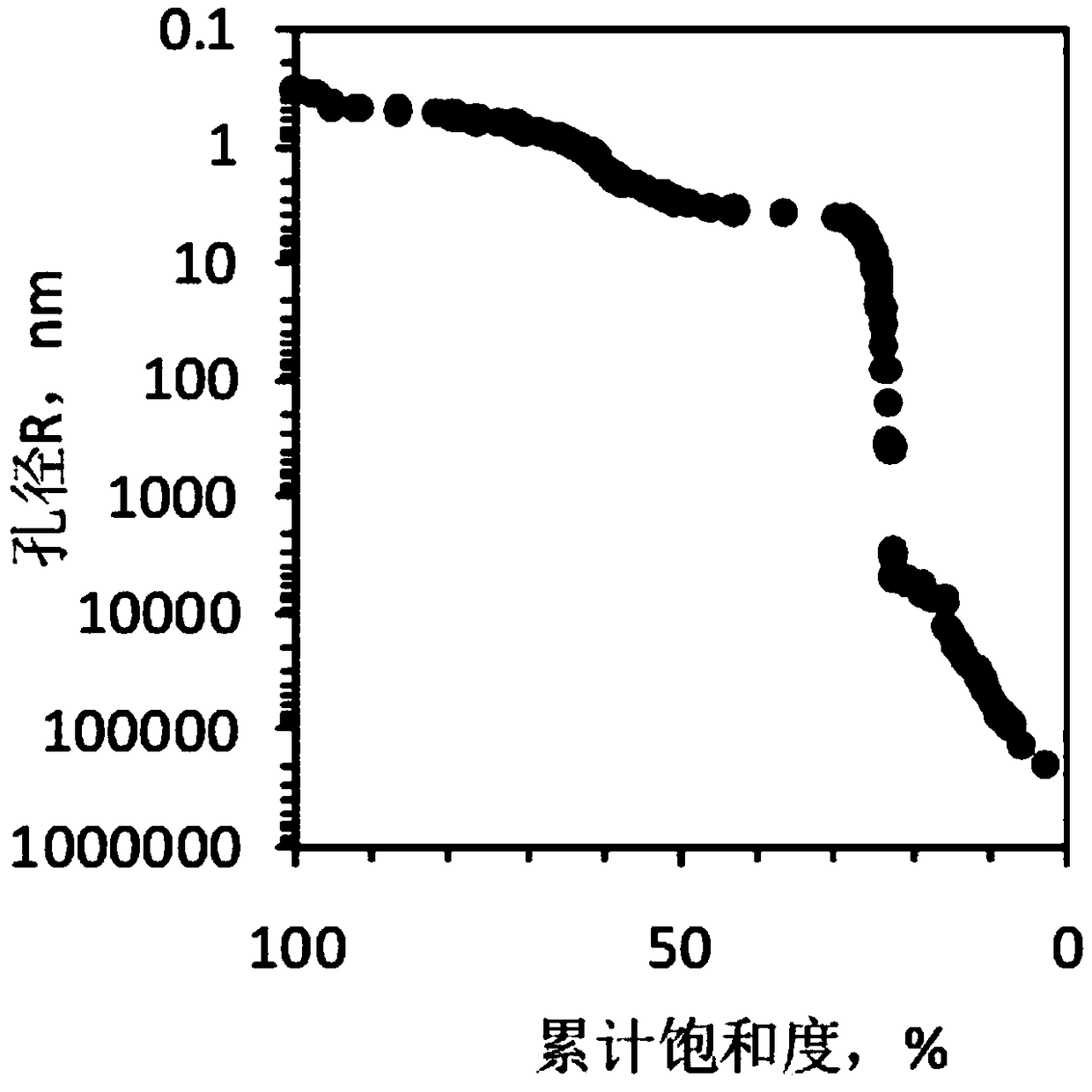
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for obtaining rock permeability profile
ActiveCN107561112AAccurate measurementSimple methodAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPorosityLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance method for obtaining a rock permeability profile. The method relies on a nuclear magnetic resonance weighted imaging method to obtain in situ porosity and pore size information of rock. A local connectivity factor is defined by a coupling relation of pore size distribution at adjacent layers, and the pore connectivity at adjacent locations is further considered, so that the evaluation effect of the permeability is improved, and a continuous permeability profile of the core in a certain axial direction is provided, thus the obtained permeation information is more detailed. The nuclear magnetic resonance method has important application space in the aspect of petroleum geological exploration and recovery efficiency improvement.
Owner:北京青檬艾柯科技有限公司
Method using nuclear magnetic resonance to measure rock porosity
InactiveCN105651805AConvenient researchAvoid churnAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePermeability/surface area analysisPorosityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method using nuclear magnetic resonance to measure rock porosity includes: machining rock with dissolution pores into a core column, and removing organic substances attaching to the core column; filling the dissolution pores of the core column with flexible water-absorption substances; submerging the core column into water under the pressure of 2-5MPa for 24-72 hours; taking out the core column, removing the water on the surface of the core column, and using a film to wrap the core column; performing a nuclear magnetic resonance experiment on the core column to obtain the porosity. The method has the advantages that the water-absorption substances are used to fill the dissolution pores of the rock so as to constrain the water in the dissolution pores, the water in the dissolution pores does not flow out of the dissolution pores during the nuclear magnetic resonance experiment, and the measured rock porosity is accurate.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com