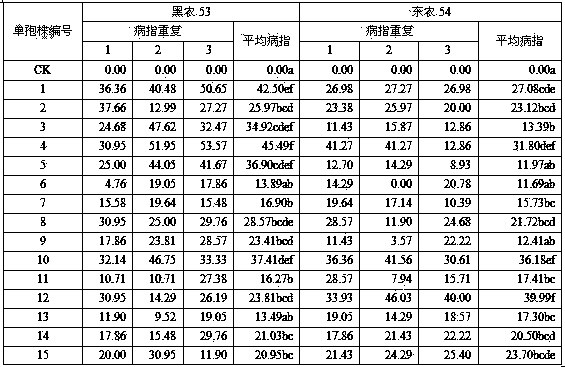
Patents
Literature
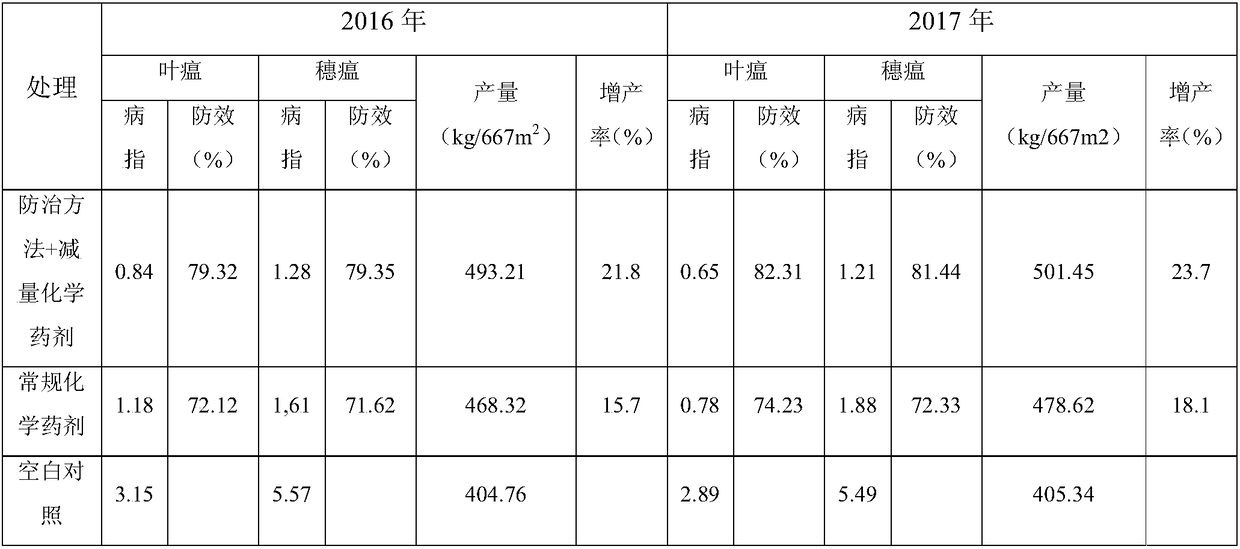
34 results about "Conidiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Conidiation is a biological process in which filamentous fungi reproduce asexually from spores. Rhythmic conidiation is the most obvious output of fungal circadian rhythms. Neurospora species are most often used to study this rhythmic conidiation. Physical stimuli, such as light exposure and mechanical injury to the mycelium trigger conidiation; however, conidiogenesis itself is a holistic response determined by the cell's metabolic state, as influenced by the environment and endogenous biological rhythms.
Production method for morchella importuna cultivars
The invention discloses a production method for morchella importuna cultivars. The production method comprises the following steps of: routinely inoculating morchella importuna stock seeds which are cultured at 18 to 20 DEG C for 3 to 5 days to a glass bottle containing a culture material which comprises 70 to 90 percent of wheat, 8 to 28 percent of soil, 1 to 1.5 percent of lime and 0.5 to 1 percent of calcium superphosphate, and culturing the morchella importuna stock seeds at 18 to 23 DEG C for 15 to 20 days under a dark condition to obtain the morchella importuna cultivars. According to the method, the activity of morchella importuna hyphae can be kept, and sclerotia can be quickly produced; and a production process is simple, and conidia are high in yield and easy to seed.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Actinomyces Israeli production technology, Actinomyces Israeli preparation and Actinomyces Israeli production apparatus
InactiveCN103667079AGuaranteed oxygenMaintain humidityBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsConidiationOxygen
The invention discloses an Actinomyces Israeli production technology, an Actinomyces Israeli preparation and an Actinomyces Israeli production apparatus. The production technology adopts a liquid-solid biphasic cultivation method to realize the mass production of Actinomyces Israeli, liquid fermentation is carried out to obtain a large amount of mycelia and blastospores and a small amount of conidiospores, and the above obtained substances are transferred to a solid cultivation medium to generate a large amount of aerial conidiospores. An Actinomyces Israeli pill or pulvis prepared through the technology is convenient to store, and can be dissolved in a 0.1M sodium citrate solution or is diluted by adding water when the pill or pulvis is used. The production apparatus comprises a disc body, the base plate of the disc body is punched with a plurality of holes, and at least one metal screen covering all the holes is fixed on the base plate. The apparatus guarantees the oxygen and humidity required by the solid cultivation of the Actinomyces Israeli, effectively prevents the living contaminants, and substantially improves the sporulation quantity of the Actinomyces Israeli.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
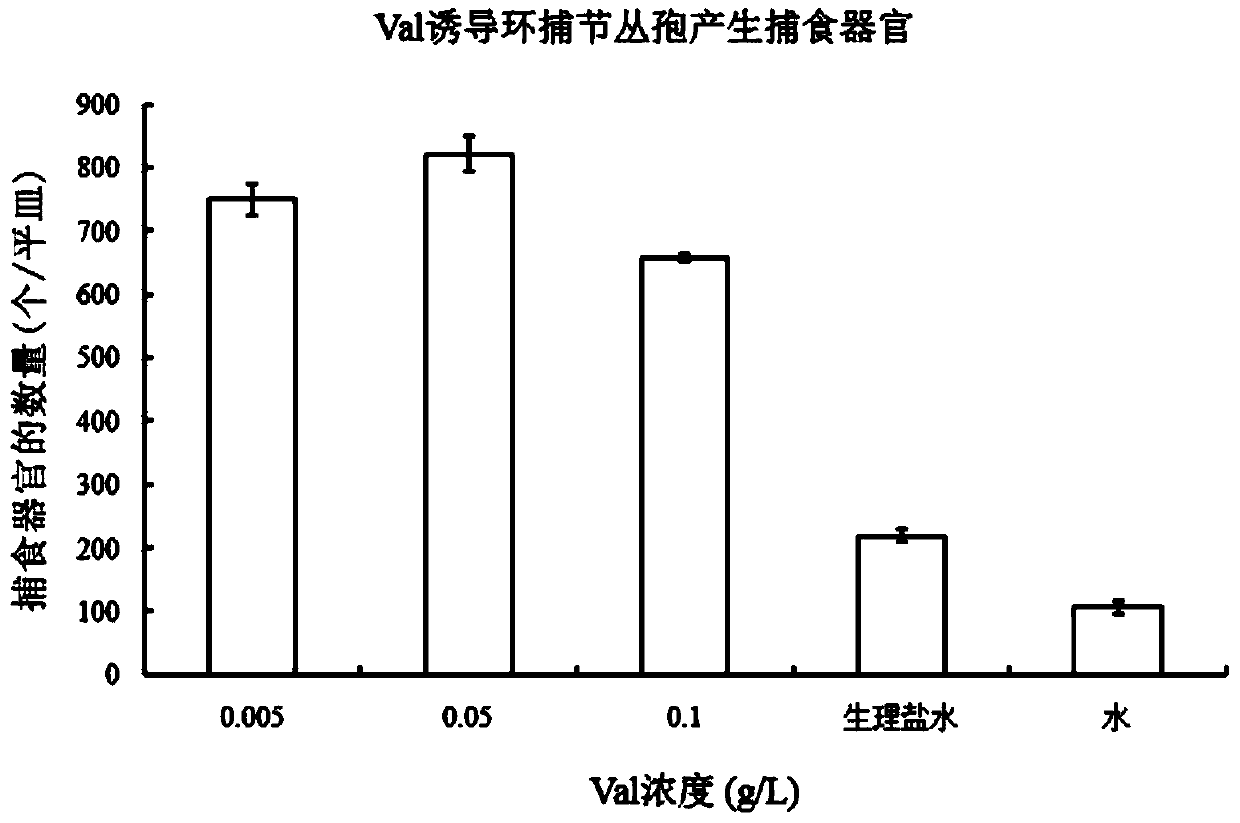
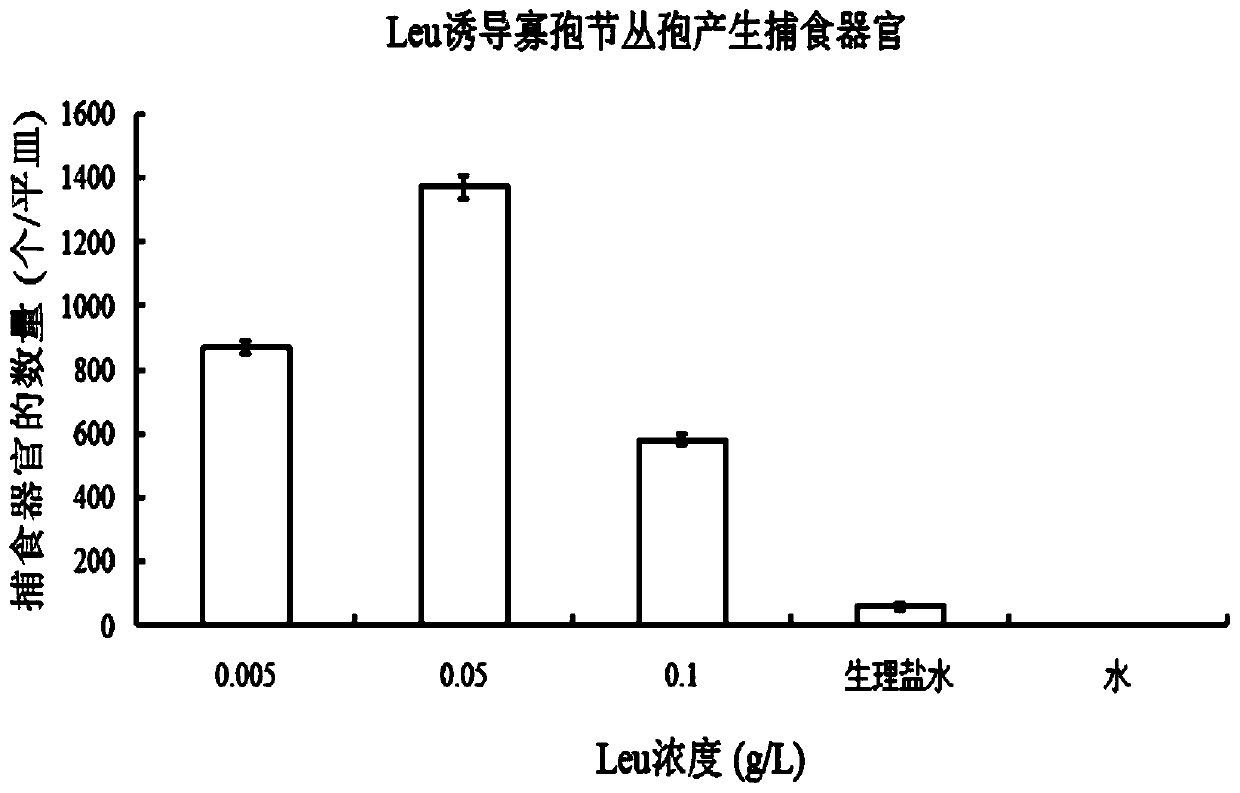
Method for inducing nematode-trapping fungi to produce capturing devices through amino acid
InactiveCN104004668ASimple methodGood repeatabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesConidiationNematode
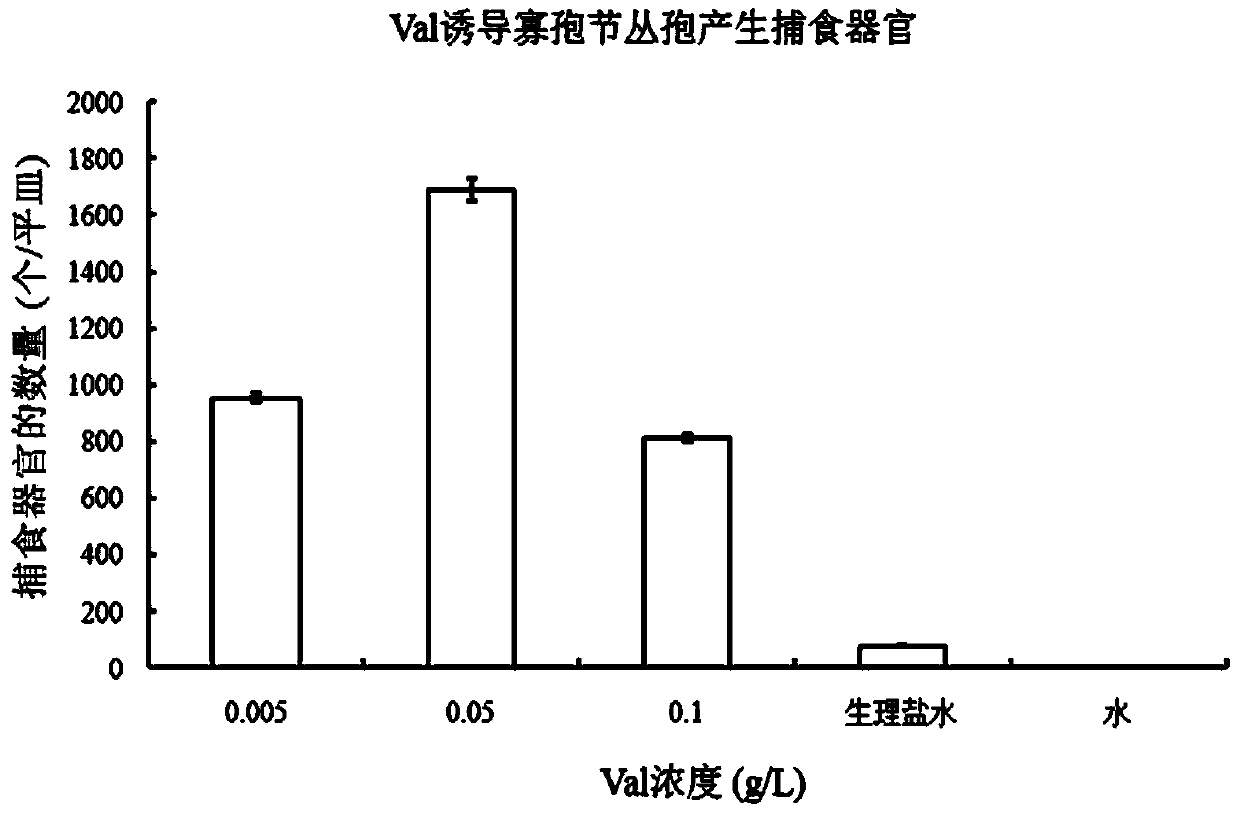
The invention relates to a method for inducing nematode-trapping fungi to produce capturing devices through amino acid, and belongs to the field of microbiology application. The method comprises the steps of preparing an amino acid solution, cultivating the nematode-trapping fungi, collecting spores, soaking the spores in the amino acid solution and inducing the capturing devices. The method includes the specific steps that a, the amino acid used in amino acid solution preparation is valine or leucine or glutamic acid; b, conidia of the nematode-trapping fungi are adopted in the inducing step of the capturing devices, and the capturing devices are induced in a soaking mode through the amino acid solution. The method for inducing the nematode-trapping fungi to produce the capturing devices through the amino acid has the advantages that the spores of the nematode-trapping fungi are cultivated and collected, the valine or the leucine or the glutamic acid is used for soaking the spores, and the nematode-trapping fungi can be induced to produce a large number of capturing devices. The method is easy to operate and good in repeatability, a large number of capturing devices can be obtained, and a good experimental material is provided for further studying molecular mechanisms formed by the capturing devices of the nematode-trapping fungi.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Fusarium oxysporum single spore isolation method for soybean root rot
InactiveCN104357333AAvoid easy separationIncrease in sizeFungiMicroorganism based processesIsolation effectSpore
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum single spore isolation method for the soybean root rot. The fusarium oxysporum single spore isolation method is provided for solving the problems that a soybean fusarium oxysporum single spore is small, is in light color and is not easy to isolate. The fusarium oxysporum single spore is enlarged in size after germinating, then dilution is carried out until a spore suspension with only 1-2 spores in average every 10 <Mu>L is obtained, and isolated conidium is further confirmed in a round hole grid in a 96-mesh cell culture plate cover through an inverted microscope to be a single spore. Compared with other single spore isolation methods, the method is good in operability, high in accuracy, high in speed, excellent in isolation effect, and simple in equipment. The method is accurate, simple and feasible, and a large batch of fusarium oxysporum single spores can be isolated within a short period of time in a lab. Therefore, the method is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Magnaporthe grisea MoLON1 gene function and application thereof
The Magnaporthe grisea MoLON1 gene function and application thereof belong to the field of bioengineering technology, and the invention relates to the function in the pathogenic processes of Magnaporthe grisea MoLON1 gene and purification and purpose of coding proteins thereof. The gene and the ATP-dependent protease Lon1 in yeast, Escherichia coli and other organisms have high homology, and the gene codes 1119 amino acids and contains one intron and two exons. The knockout of MoLON1 gene leads to minimizing of Magnaporthe grisea aerial hyphae quantity, reduction of conidiospore output, basic deprivation of expansion capability of infective hyphae in the paddy rice leaf cells, and improvement of sensitivity to a plurality of adverse conditions; the invention also relates to expression and purification of proteins coded by the MoLON1 gene, and gene can be used as a candidate target for designing and screening anti-Magnaporthe grisea novel medicament.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Artificial inoculation method of alternaria alternata
The invention discloses an artificial inoculation method of alternaria alternata, in which an alternaria alternata spore suspension liquid is injected through wounds on in-vitro leaves to performing inoculation to manure leaves, wherein conidium of the alternaria alternate can directly enter the leaves so that the conidium can be germinated and reproduced with moisture and host mesophyll tissue nutrition and then is extended intercellularly, so that disease spots formed by local tissue death is enlarged in a large area, thereby achieving effects of high inoculation rate and moderate disease degree. The invention provides the simple, convenient, quick and accurate artificial inoculation method for identification of pathogenicity and interspecific difference of different alternaria alternata in main production area of tobacco in our country and screening of resistant variety of the alternaria alternata. The artificial inoculation method has an excellent application value.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Process for clone gene of virus host factor
A method for cloning the virus host factor gene by use of dual-chain RNA low-poison virus (chesnut blight bacterium system) includes such steps as light irradiating to induce the generation of conidia of chestnut phytophthora disease bacteria, inducing to obtain mutant, purifying, discriminating the virus carried by said mutant, testing the activity of its mRNA precursor, transforming and complementing of said mutant, discriminating, sequentially the exogenous DN'A fragment of the transformed plasmid with complem entary power, and configuring gene map.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for preparing conidia of lasiodiplodia theobromae
ActiveCN104974975AIncrease the number ofStrong pathogenicitySpore processesLasiodiplodia theobromaeConidiation
The invention discloses a method for preparing conidia of lasiodiplodia theobromae. The method comprises the following steps: 1) inoculating lasiodiplodia theobromae onto a PDA (potato dextrose agar) culture medium to be cultured until a colony grows vigorously; 2) selecting a grape variety sensitive to lasiodiplodia theobromae, cutting healthy green grape branches into 30cm sections and sterilizing the surfaces of the sections; 3) punching holes in the green branches and removing the phloem; preparing hypha blocks from the colony with a sterilized puncher, inoculating the prepared hypha blocks in the holes, wrapping the hypha blocks with films to preserve moisture and inserting the inoculated branches in tissue culture containers filled with sterile water to be cultured at 28 DEG C; culturing for 48 hours under the condition that the relative humidity is more than 90%, and then maintaining the humidity at 70% and culturing for 5-10 days. The method has the beneficial effects that the preparation time of conidia can be shortened; prepared spore suspension has small spore difference, stable quality and strong pathogenicity and provides guarantees for pathogenicity identification, population genetic differentiation, pathogenesis analysis, and the like of lasiodiplodia theobromae.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Specific amplification primer for detecting marssonina coronaria and detection method
InactiveCN101892308AAchieving the purpose of amplificationAvoid separationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationConidiationPaper sheet
The invention discloses a specific amplification primer for detecting marssonina coronaria. A method for quickly obtaining gene segments of the marssonina coronaria by using the specific primer aims to prevent obstruction brought to actual researches by the difficult separation of pathogenic bacteria. The invention also discloses a rapid molecular detection method for the marssonina coronaria by using the specific amplification primer, which comprises the following steps of: first collecting field diseased leaves and picking and placing the acervulus of the marssonina coronaria on a white paper sheet with a sterilized insect needle; then preparing a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system; next transferring the acervulus into a small PCR amplification tube in which the PCR system is arranged and performing centrifugation to completely immerse the acervulus in the prepared PCR system; and finally performing PCR amplification and detecting the amplification product. By changing the PCR amplification reaction system and the amplification procedure, the target segment of the pathogenic bacteria can be directly amplified. The primer and the method prevent the separation of the pathogenic bacteria and additional DNA extraction, shorten a test flow and improve the detection efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Ophiocordyceps sinensis strain with high spore yield
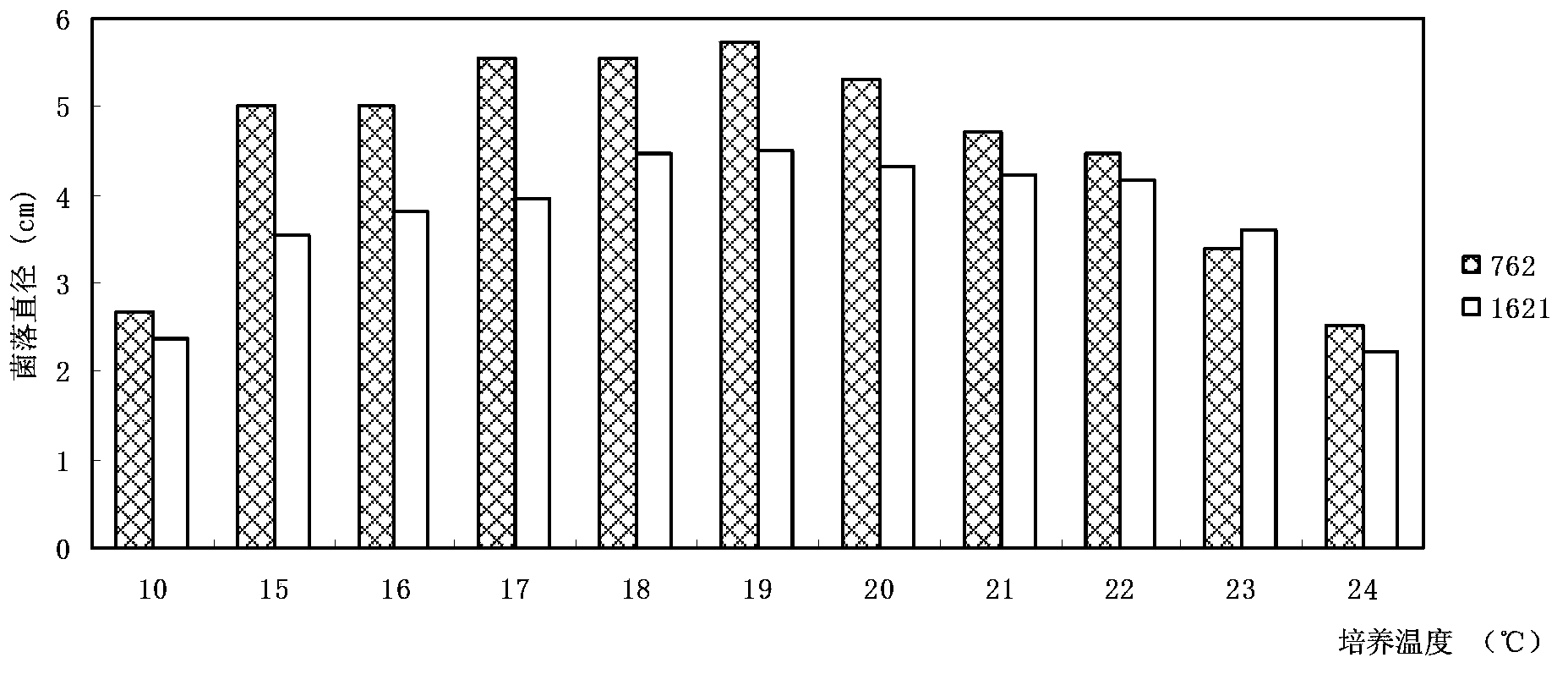
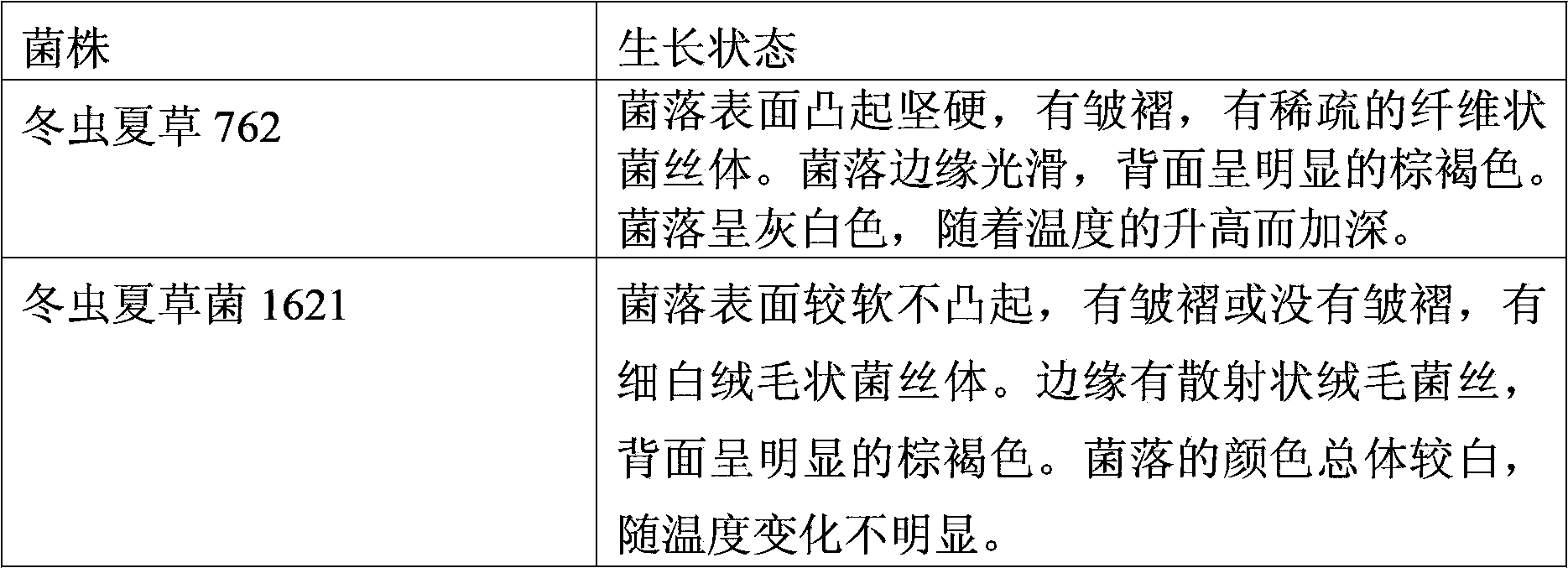
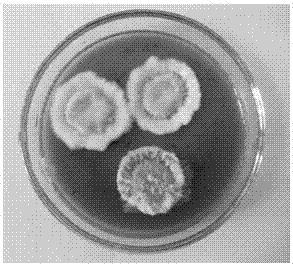
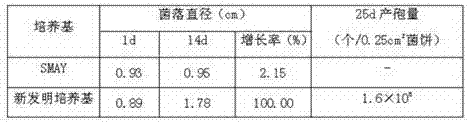
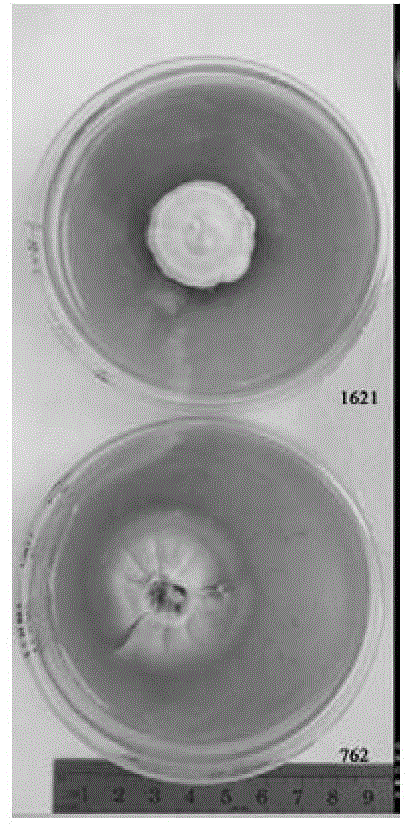
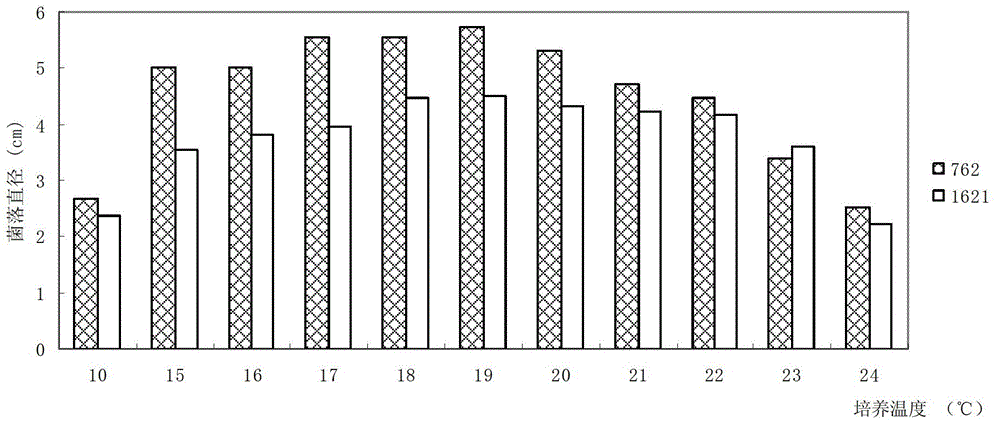
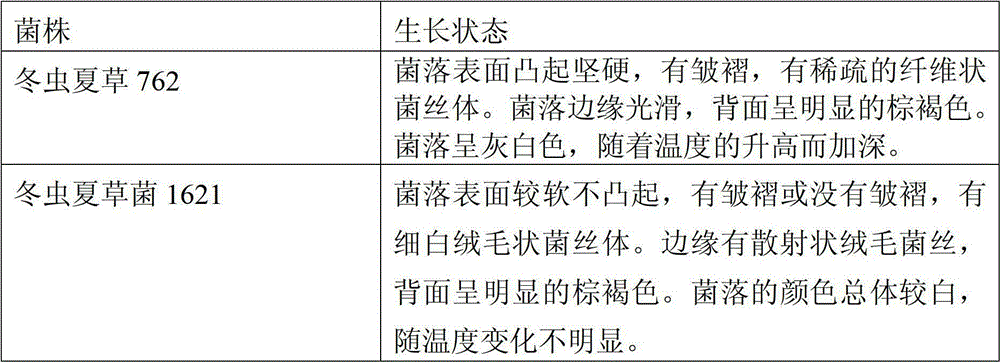
The invention discloses an Ophiocordyceps sinensis strain with high spore yield. The Ophiocordyceps sinensis strain with high spore yield provided by the invention is Ophiocordyceps sinensis 1621, the registered number of which in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.6445. The Ophiocordyceps sinensis 1621 has a fast mycelium growth speed, short conidiospore generation time and high spore yield.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Regular morphology of fusarium oxysporum laboratory material and preparation and application method thereof
InactiveCN106701654AConvenience to workHigh quality stock formMicroorganism based processesSpore processesSporeFusarium oxysporum
The invention discloses a regular morphology of a fusarium oxysporum laboratory material and a preparation and application method thereof. Fusarium oxysporum pure and pollution-free conidiospore is used as a regular morphology of the laboratory material. The conidiospore serving as the regular morphology is stored in sterile water. The preparation and application method comprises the following steps that 1, a triangular flask serves as a culture container to prepare the fusarium oxysporum conidiospore; 2, the regular morphology of the fusarium oxysporum material is prepared; 3, the conidiospore content of the regular morphology of the fusarium oxysporum material is calibrated; 4, the regular morphology of the fusarium oxysporum material is daily stored; 5, the regular morphology of the fusarium oxysporum material is applied. The regular morphology has the characteristics and advantages that the conidiospore serving as the regular morphology can suspend to grow in pure water and can be instantly restored to normal growth when being transferred to a culture medium; the regular morphology can be applied in relevant work at any time, a thallus material can be directly provided for a test link needing the conidiospore, the working process needing to repeatedly prepare and culture the conidiospore when a mycelium is used as a commonly prepared material can be omitted, and work is convenient and quick; 3, the triangular flask serves as the culture container, and pure and pollution-free conidiospore liquid is easy to prepare; the conidiospore content of the commonly prepared conidiospore liquid can be calibrated and can be accurately quantified and taken in application, and standardization of a technical method is promoted.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for biological prevention and control of rice field diseases
ActiveCN109168802AStrong disease resistanceInhibition of germinationFabaceae cultivationCultivating equipmentsDiseaseConidiation
The invention provides a method for the biological prevention and control of rice field diseases. The method comprises the steps of (1) performing straw returning and plowing with a furrow plow on a rice field and placing earthworms, and (2) sowing grass on the rice field, then ploughing the grass into the field, and planting rice in the season. The invention provides the method for the biologicalprevention and control of rice field diseases, while the earthworms are placed in a disease rick field, the matched agronomic technique is employed, certain specific crops are planted, the mycelium and sclerotia of fungal diseases such as rice blast and banded sclerotial blight can be eliminated or reduced at the source of soil, the conidial germination is inhibited, and therefore, the purposes of controlling the rice field diseases and reducing the amount of chemical pesticides are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection primers for fusarium verticillioide, kit containing primers and application
InactiveCN105803073AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPlant tissueConidiation
The invention provides specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection primers for fusarium verticillioide. The primers comprise Pr40 and Pf40 (represented as Seq ID No.1 and 2). On the basis of differences between the fusarium verticillioide and other fusarium strains on a TEF-1alpha gene sequence, a series of primers for detecting the fusarium verticillioide are designed, the primers Pr40 / Pf40 with the highest specificity and the highest sensitivity are screened out, a PCR detection system is built on that basis, and the fusarium verticillioide can be detected rapidly and accurately from pathogenic plant tissue. A detection kit prepared with the method is simple and convenient to operate, good in specificity and high in sensitivity, can be used for detecting various forms of propagules such as mycelia, conidia and the like of the fusarium verticillioide and has great significance in the aspects of early warning of the fusarium verticillioide epidemic situation, pathogen surveillance in an epidemic area and the like.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
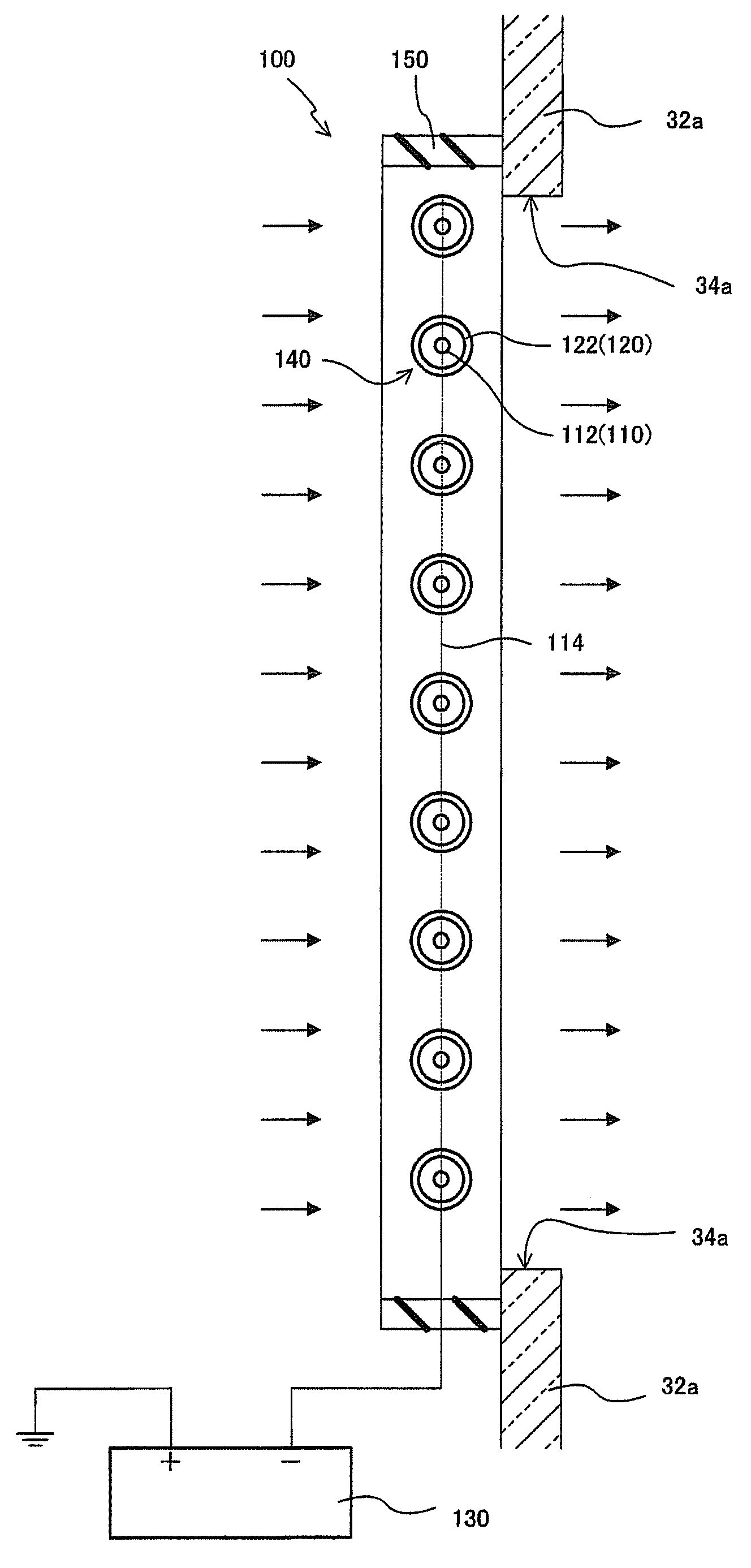
Fungi preventing method, flying organism removing apparatus and plant protecting apparatus by adsorption of conidia using dielectric polarization
InactiveUS8105418B2Avoid it happening againEfficient removalCombination devicesIsotope separationBiological bodySpore
A method is provided which can efficiently remove conidia and microbe or the like of a phytopathogen from air and does not cause generation of ozone originated from discharge or so, thereby preventing occurrence of a plant disease without damaging a plant. There are also provided a flying organism removing apparatus and a plant protecting apparatus which can adequately capture flyable organisms, such as spores of a phytopathogen and / or small vermin, by applying an electrostatic field to the flyable organisms. An electrostatic field generated by dielectric polarization is applied to flyable organisms.
Owner:LOCAL INC ADMINISTATIVE AGENCY RES INST OF ENVIRONMENT AGRI & FISHERIES OSAKA PREFECTURE +2
Method for extracting wheat powdery mildew DNA from catching band of spore catcher
InactiveCN103255129AThe result is accurateThe result is objectiveMicroorganism based processesDNA preparationDisease monitoringSpore
The invention relates to a method for extracting wheat powdery mildew DNA from the catching band of a spore catcher, and belongs to the plant disease prevalence monitoring field, wherein the method is used for extracting the DNA of powdery mildew conidiospore collected by the spore catcher. The method comprises the following steps: eluting and wall-breaking wheat powdery mildew conidiospores collected on the catching band of the spore catcher, and extracting and purifying DNA of the wall-broken conidiospores to develop the disease outbreak and prevalence monitoring service through utilizing a molecular biological quantitative research technology. The DNA extracted in the invention can be used for accurately and quantitatively detecting the wheat powdery mildew conidiospores collected with the spore catcher, and can also be directly used for the drug resistance monitoring. The method can be popularized in various regions as a disease monitoring technology.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for evaluating strawberry stamen gray mold resistance
The invention discloses a method for evaluating strawberry stamen gray mold resistance. The method comprises the steps: A, picking off flowers with stalks from a plant when the strawberry flowers areat the beginning of squaring stage; B, inserting the flowers in solidified water agar, culturing in vitro under an illumination condition; C, picking off petals from the flowers by a tweezer; D, dipping botrytis cinerea conidiospore suspension by a brush pen, coating stamen anther with conidiospore for inoculating; inoculating botrytis cinerea sclertium onto a PDA culture medium; E, re-inserting the flower into the solidified water agar, placing under a constant temperature and illumination condition for culturing in vitro; F, removing young strawberry fruit from sepals, G, measuring the length of the disease spot on filaments, respectively classifying a disease index of each stamen; H, respectively calculating the disease index of each variety; I, classifying the gray mold resistance of each variety according to the disease index of each variety. The method provided by the invention is simple and easy to operate. The method can be used for quickly identifying the gray mold resistanceresistance of sepals of strawberry varieties.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for artificially cultivating batryticated silkworms based on Beauveria bassiana
ActiveCN110352920AIncrease profitGood moisturizing effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyConidiation
The invention provides a method for artificially cultivating batryticated silkworms based on Beauveria bassiana. The method is characterized in that batryticated silkworms artificially cultivated arecylindrical in shape and wrinkled and flexural, each batryticated silkworm is 4.30+ / -0.35 cm in length and 0.5+ / -0.1 cm in diameter, ten thousands of batryticated silkworms weigh 7-8 kg, milky white powdery mycelia and conidia are present on the surface of the batryticated silkworms, the batryticated silkworm are stiff and brittle, their ends are flat and smooth, the batryticated silkworms are inbright amber color, silk gland rings are visualized, and the content of ammonium oxalate tested through high-performance liquid chromatography is 6.00-6.20%; the batryticated silkworms are made by means of preparing a spore suspension inoculum, cultivating Beauveria bassiana, preparing an infected spore liquid, and preparing Beauveria bassiana spores for artificial production of batryticated silkworms. The method herein has the advantages that the method is simple and has low requirement on the production environment and production equipment, production cost is reduced greatly, pollution by sundry bacteria from the production is relieved, separating spores and a culture substrate after drying is not required, subpackaging directly to obtain products is available, nearly all spores are recyclable, the method is very suitable for rapid production of Beauveria bassiana in small-sized enterprises and production institutes and can provide improved economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV
Process for screening madicine of antivirus
A method for screening antivirus medicine is based on a test system composed of dual-chain RNA virus and its natural host (chestnut blight bacterium). The chestnut blight bacterium EP-721(-) without virus shows orange color and the chestnut blight bacterium carrying virus CHV1-EP721 shows white color. After the latter is treated by an antivirus medicine, the effect of said medicine can be determined according to the color variation.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Specific PCR amplification primers and specific PCR detection system of fusarium graminearum and applications
PendingCN106868176AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseased plantPropagule
The invention provides specific PCR amplification primers and a specific PCR detection system of fusarium graminearum. The primers comprise Fg18TF and Fg18TR (Seq ID NO:1 and 2) and a pair of nested outer primers HW18TF / HW18TR (Seq ID No:3 and 4). Based on the differences of fusarium graminearum and other fusaria on the aspect of beta-tubulin gene sequences, a series of primers for detecting fusarium graminearum are designed, the primers Fg18TF and Fg18TR with the strongest specificity are selected, meanwhile, the detection sensitivity is improved by designing the pair of nested outer primers HW18TF / HW18TR, on the basis, the PCR detection system is established, and fusarium graminearum can be rapidly and accurately detected from the tissue of diseased plants and the complicated pathogenic bacteria environment in the soil. A detection kit constructed according to the method is easy and convenient to operate, good in specificity, and high in sensitivity, can detect propagules in various forms of fusarium graminearum, such as hyphae and conidia, and has the great significance in the aspects of early warning for fusarium graminearum epidemic situation and pathogen surveillance of epidemic areas.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Culture medium and preparation method for promoting spore production of Nomura rayii
InactiveCN104673740BShorten sporulation timeHigh sporulationMicroorganism based processesSpore processesSporeBiotechnology
The invention aims to provide a culture medium for promoting spore production of nomuraea rileyi and a preparation method. According to the culture medium for promoting spore production of nomuraea rileyi and the preparation method, conidiospore of nomuraea rileyi can be obtained more rapidly and more effectively. According to the scheme, appropriate insect tissue components are added, the nutrition-allocated proportion is changed, stimulating factors for nomuraea rileyi growth are increased, and accordingly, the culture efficiency is improved.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
A strain of Cordyceps sinensis with high sporulation
The invention discloses an Ophiocordyceps sinensis strain with high spore yield. The Ophiocordyceps sinensis strain with high spore yield provided by the invention is Ophiocordyceps sinensis 1621, the registered number of which in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No.6445. The Ophiocordyceps sinensis 1621 has a fast mycelium growth speed, short conidiospore generation time and high spore yield.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for screening madicine of antivirus
InactiveCN1324144CStrong conidia capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementUse medicationAntiviral drug
A method for screening antivirus medicine is based on a test system composed of dual-chain RNA virus and its natural host (chestnut blight bacterium). The chestnut blight bacterium EP-721(-) without virus shows orange color and the chestnut blight bacterium carrying virus CHV1-EP721 shows white color. After the latter is treated by an antivirus medicine, the effect of said medicine can be determined according to the color variation.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Separation method of tobacco root black rot bacteria
InactiveCN108384725ASolve the problem that is easily covered by other fungiGrowth inhibitionFungiMicroorganism based processesPenicillinNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a separation method of tobacco root black rot bacteria. The method includes the steps: acquiring rhizosphere soil of tobacco plants with tobacco root black rot symptoms; dryingand grinding the acquired rhizosphere soil; adhering the grinded rhizosphere soil onto carrot slices; placing the carrot slices adhered to the soil into a culture vessel to culture the carrot slicesfor 2-4 days; flushing the carrot slices by the aid of sterile water with 50 micro-liters / milliliters of penicillin and 50 micro-liters / milliliters streptomycin sulfate; continuing to culture the flushed carrot slices for 2-4 days; selecting mildew layers with tobacco root black rot typical symptoms on the carrot slices; purifying, culturing and storing the mildew layers. Growth of the tobacco root black rot bacteria is induced to restrain other bacteria from growing by the aid of different effects of components of carrot slices on the tobacco root black rot bacteria and the other fungi, and the separation method solves the problem that the other fungi easily covers the tobacco root black rot bacteria. The surfaces of treated carrot slices can rapidly grow hyphae, typical conidiophore stalks, conidiophores and chlamydospores, and the success rate reaches 96% or more.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
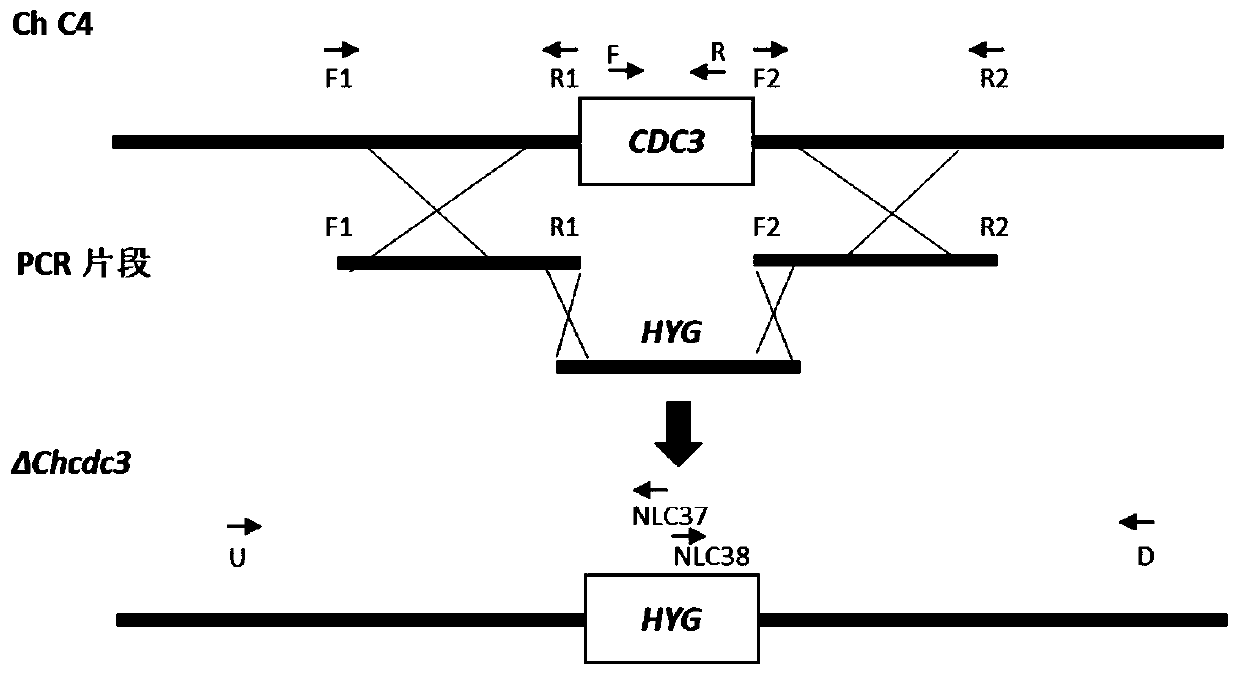
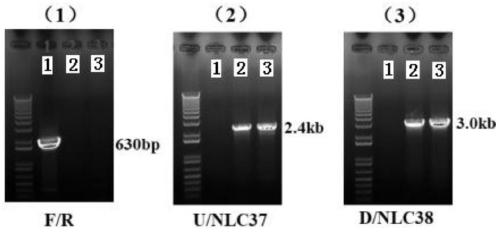
Cochliobolus heterostrophus ChCDC3 gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a cochliobolus heterostrophus ChCDC3 gene and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism genetic engineering. The DNA sequence of the ChCDC3 gene which is from cochliobolus heterostrophus and used for controlling the growth speed of colonies, conidium formation and ascospore formation provided by the invention is as shown in SEQID No:1, andthe amino acid sequence of protein coded by the provided ChCDC3 gene is as shown in SEQID No:2. The ChCDC3 gene can be applied to the genetic engineering field of plants for resisting corn southern leaf blight. The protein ChCDC3 for controlling the growth speed of colonies of the cochliobolus heterostrophus, conidium formation and ascospore formation is subjected to deletion, mutation or modification, the growth of the cochliobolus heterostrophus is slow, the conidium formation and the ascospore formation are limited, lifecycle of the cochliobolus heterostrophus is obstructed, the ChCDC3 gene can be used as a target to be applied to designing and screening corn southern leaf blight resisting medicaments, especially the protein does not exist in plants, and the ChCDC3 gene is safe to theplants.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for determining germination rate of spores of sphaeropsis sapinea of pinus tabuliformis
The invention provides a method for determining the germination rate of spores of sphaeropsis sapinea of pinus tabuliformis. The method comprises the following steps of sterilizing the surfaces of plant tissues of the pinus tabuliformis with a sphaeropsis sapinea pycnidium, culturing, observing a germination situation of the pycnidium through using an optical microscope during a culturing process, and calculating a germination rate of the pycnidium; acquiring the germination rate of the spores through calculating according to the following formula: the germination rate of the spores is equal to 0.195 + 0.864* the germination rate of the pycnidium. According to the method provided by the invention, a linear relation exists between the germination rate of the pycnidium of the sphaeropsis sapinea of the pinus tabuliformis and the germination rate of the spores, and can be expressed through a one-unknown-quantity regression equation approximatively, the germination rate of the spores of the sphaeropsis sapinea of the pinus tabuliformis is measured by utilizing the regression equation, and a test is carried out on a predicted value and an actual value of the germination rate of the spores so as to discover that no significant difference exists between the predicted value and the actual value, so that the method of measuring and calculating the germination rate of the spores by utilizing the germination rate of the pycnidium has a scientific basis, is simple and convenient, and can be used as a substituting method for determining the germination rate of the spores.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Gene affecting pathogenicity and generation of conidium and originated from cabbage fusarium wilt bacteria and application of same
ActiveCN103319578BWeaken the ability to infectFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a gene affecting pathogenicity and generation of conidium and originated from cabbage wither disease bacteria and the application of the same. The protein is an amino acid residue sequence with SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. Trans-gene tests have shown that the gene has the function of affecting pathogenicity of cabbage wither fusarium wilt bacteria and generation of conidium, and the gene can largely reduce the pathogenicity and conidium generation ability after the cabbage wither disease bacteria is inactivated.
Owner:京科智宝(北京)农业科技有限公司
Method for cultivating aspergillus versicolor HY12 strains
ActiveCN109504647AFast growth and reproductionHigh fatality rateFungiMicroorganism based processesConidiationHabit
The invention provides a method for cultivating aspergillus versicolor HY12 strains. The method comprises steps of preparation of aspergillus versicolor HY12 strain conidium suspension and fermentation cultivation. According to the method for cultivating aspergillus versicolor HY12 strains provided by the invention, by researching growth and propagation habits of the aspergillus versicolor HY12 strains, the aspergillus versicolor HY12 can achieve an extremely high growth and propagation rate within a short time by utilizing the cultivation method in the invention, and lots of conidiums can beproduced. The method has a high teratogenesis rate and fatality rate on prodenia litura, lays an experimental foundation for later control of the prodenia litura, and provides favorable reference forcontrol of other injurious insects in the field.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for prolonging in vitro preservation duration of blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici
ActiveCN108641962AChanging the Resurrection Inoculation MethodLight in massMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationSporeConidiation
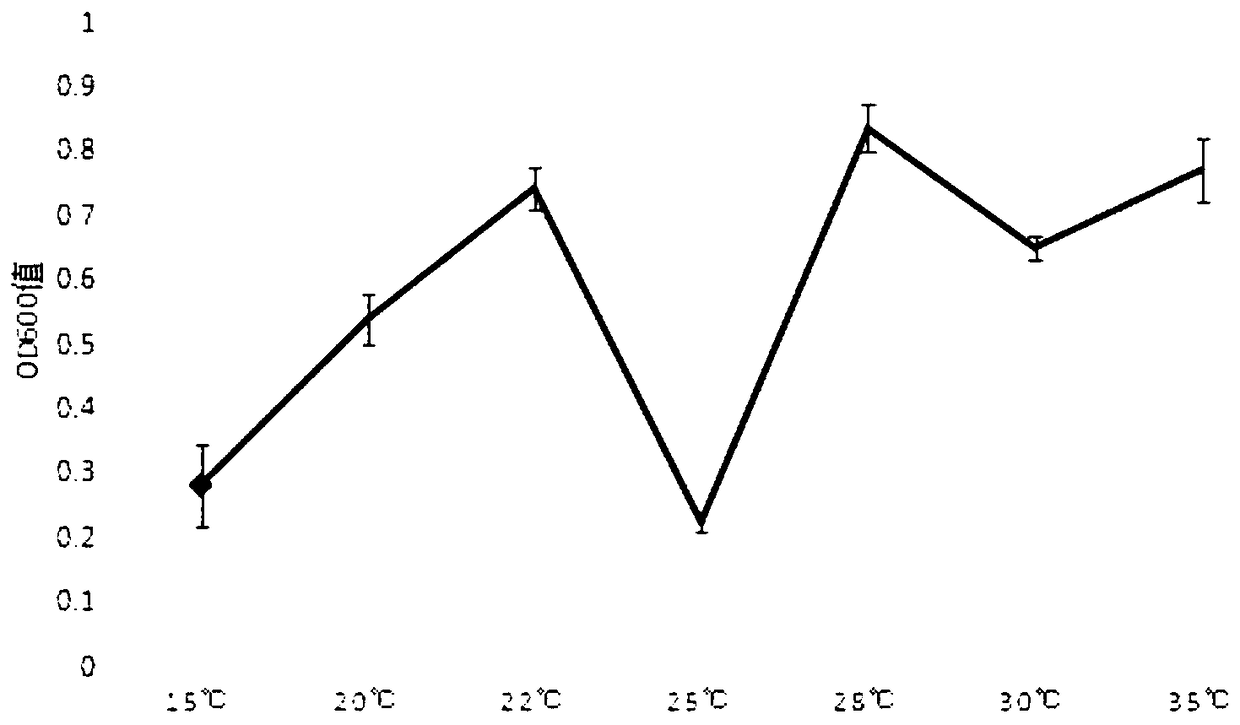
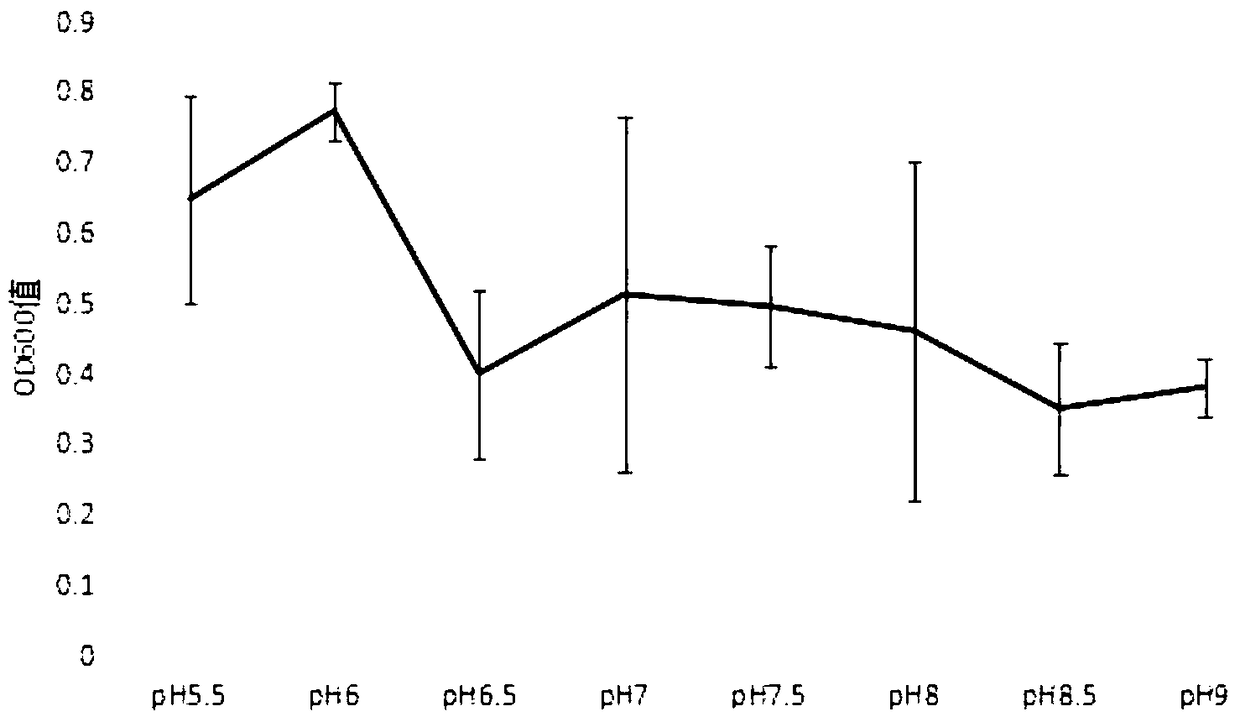
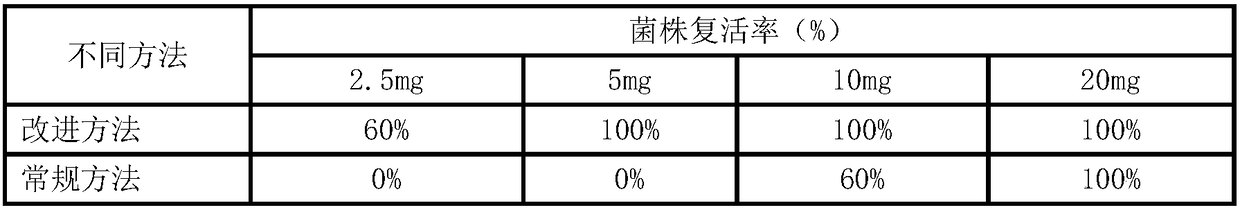
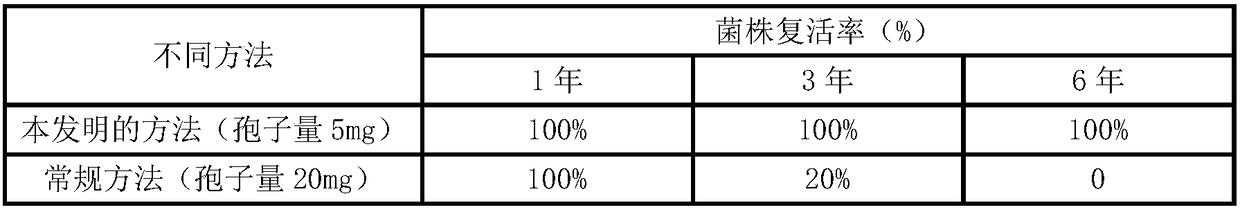
The invention discloses a method for prolonging in vitro preservation duration of blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici, and belongs to the technical field of application of preservation methods of plant pathogen obligate parasites. The blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici, which belongs to plant pathogen obligate parasites, can survive with the existing of wheat leaf hosts. A method, discovered by the inventor, can achieve in vitro preservation of the blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici without the assistance of hosts, however, the method has the shortcomings that the method is short in preservation duration,the method needs to collect a great amount of conidia and the like; on the basis, a strain resurrection inoculation mode is adopted, and blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici spores undergo in vitro preservation through suspension of a perfluoroalkane solution, so that in vitro preservation duration of the blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici spores is improved by six times in comparison with that of an original method, namely the in vitro preservation duration is prolonged to six years from original one year, and the mass of the required spores is reduced by four times. With the application of the methodprovided by the invention, shortcomings of existing methods can be overcome; and smooth implementation of related researches on blumeriagraminisf .sp .tritici pathogenic bacteria can be fully guaranteed.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION & SOIL FERTILIZER HUBEI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for reproducing verticillum lecanii and recovering vigor of verticillum lecanii by using larvas of argyrogramma agnata
InactiveCN104838892AKeep aliveRestore activityCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationSporeConidiation
The invention provides a method for reproducing verticillum lecanii and recovering vigor of the verticillum lecanii by using larvas of argyrogramma agnata, and belongs to the biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps of feeding the argyrogramma agnata; culturing the verticillum lecanii; preparing conidium liquid of the verticillum lecanii; preparing the prepared conidium liquid into suspension liquid; uniformly spraying the suspension liquid to the larvas of the argyrogramma agnata until surfaces of the larvas are wet; placing the larvas in a sterile artificial climate room and culturing the larvas until hyphae grow on the larvas fully; collecting the larvas; dewatering and drying the larvas; and storing the larvas in a refrigerator of which the temperature is minus 95 DEG C to minus 78 DEG C. In a reproduction process of the verticillum lecanii reproduced by the method, the vigor and the infection ability of strain spores can be kept for a long time. Moreover, by the method, the vigor and the infection ability of strains of which the infection ability and the vigor are reduced severely can be recovered.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Using method of anti-disease composition of corn ear conidia
The invention discloses a using method of an anti-disease composition of corn ear conidia. The using method comprises the following steps: A, preparing an original liquid which comprises 12% triadimefon wettable powder, 10% polyethylene glycol, monopotassium phosphate, artemisinin, indirubin, carboxymethyl cellulose sodium, oxalic acid and 5% aluminum sulfate; B, cultivating corn: selecting disease-free corn seeds, soaking the corn seeds by the original liquid in a 400 times in volume ratio for 1.5-2 hours, and taking out the corn seeds, washing the corn seeds by clean water, and drying the corn seeds in the sun, accelerating germination and seeding; C, during disease, adding water into the original liquid to be diluted to 600 time liquid for spraying work; and C, while spraying, adding water into the original liquid to be diluted to 500 time liquid for root irrigating operation. The using method disclosed by the invention is simple, and the used product is simple in using method, simple in proportion, convenient to use and good in northern leaf spot treatment effect. Tests show that 400-600 time liquid of the mixture has an obvious inactivating effect on conidiophore and conidia of pathogenic bacteria, and is good in sterilizing effect.
Owner:江显晖
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com