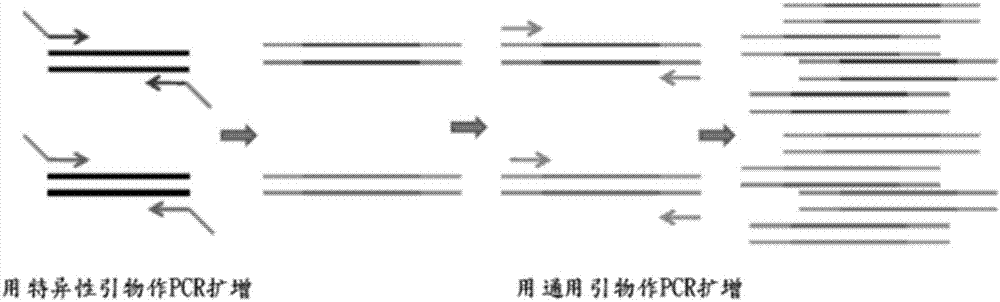
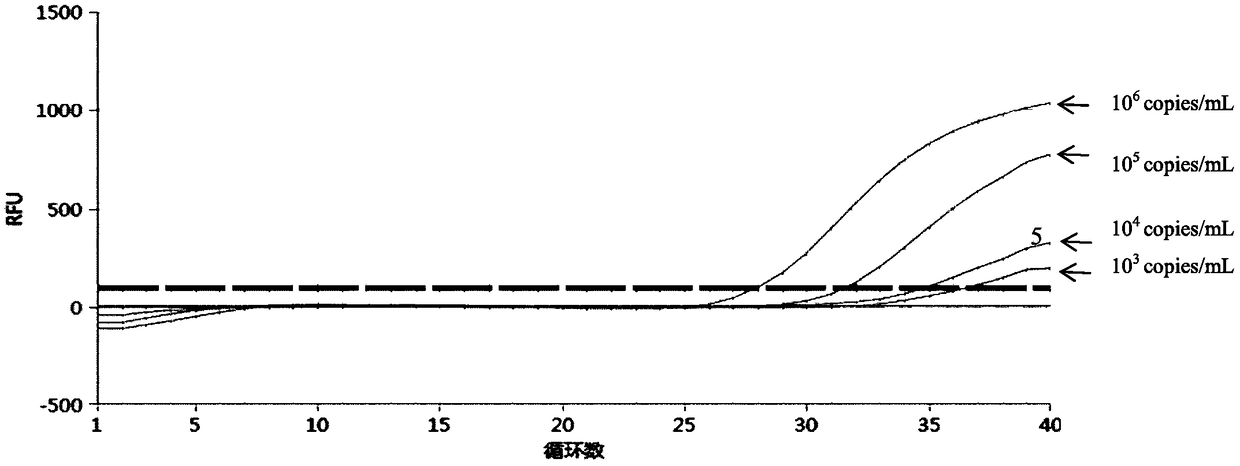
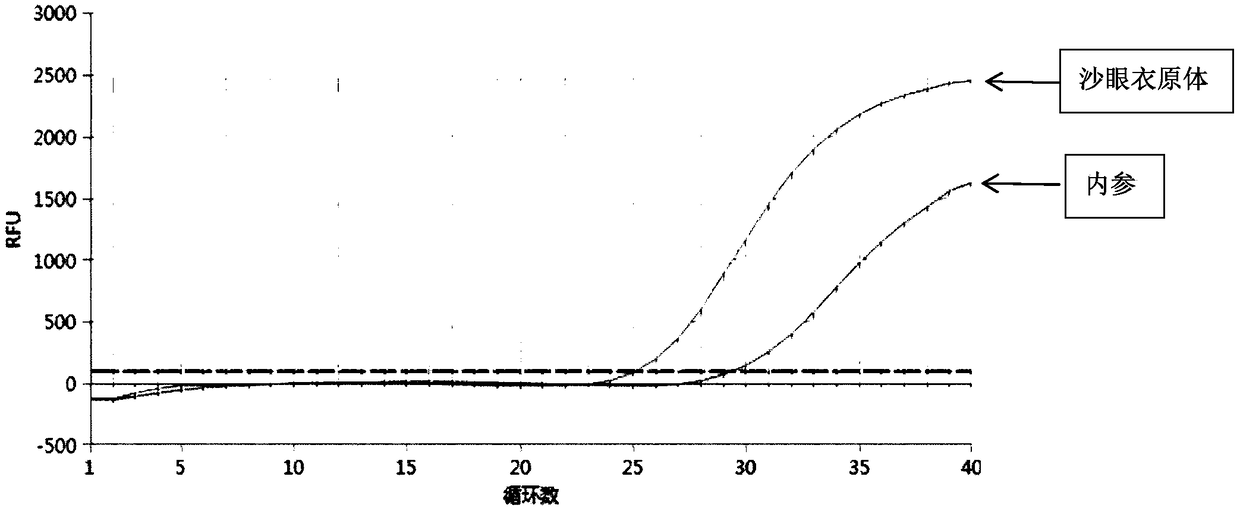
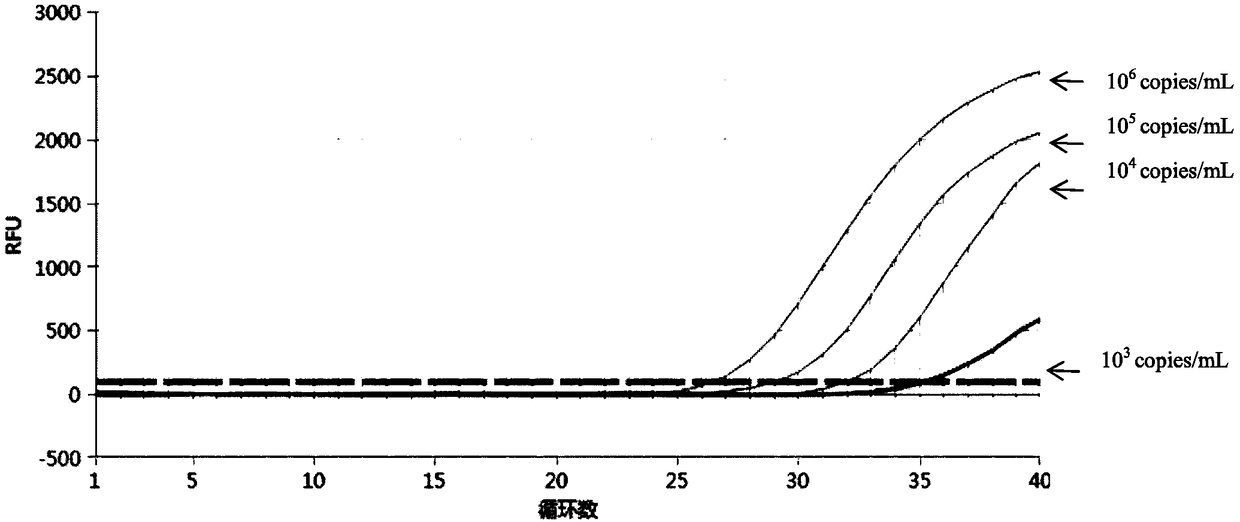
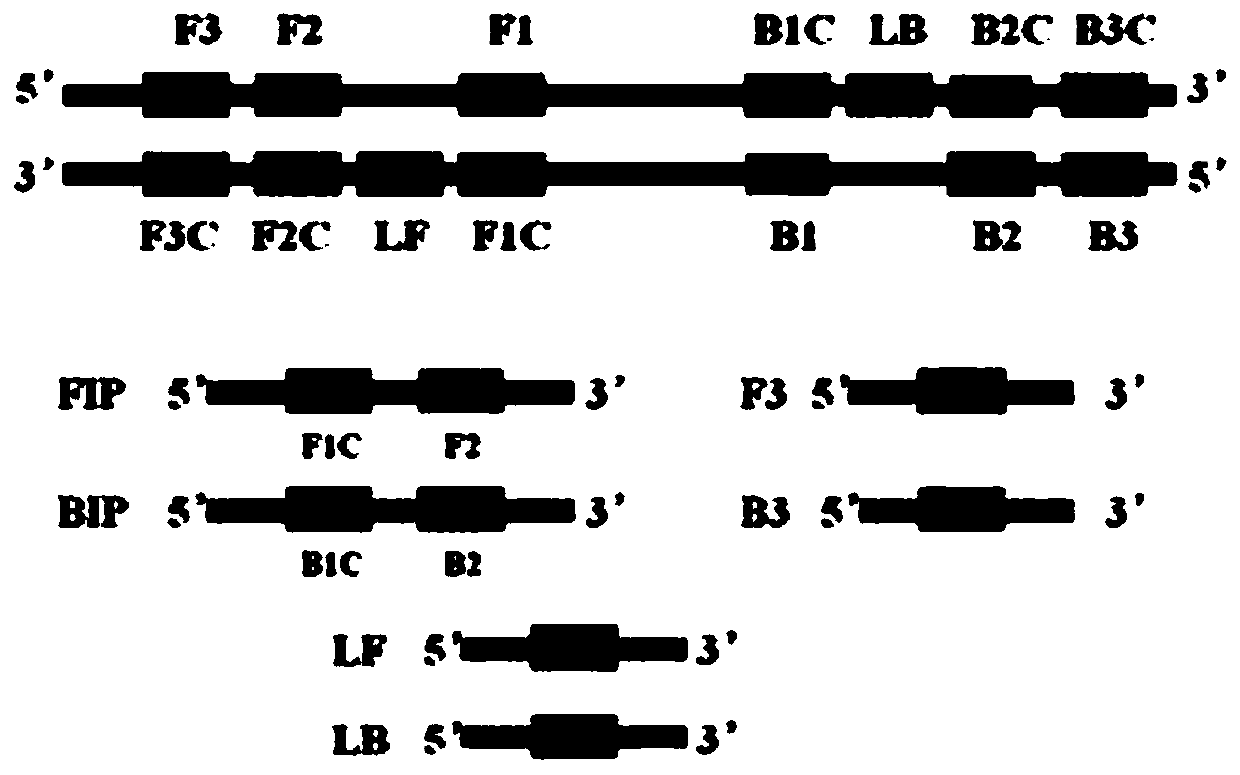
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Mycoplasma hominis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mycoplasma hominis is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycoplasma. M. hominis has the ability to penetrate the interior of human cells. Along with ureaplasmas, mycoplasmas are the smallest free-living organisms known.
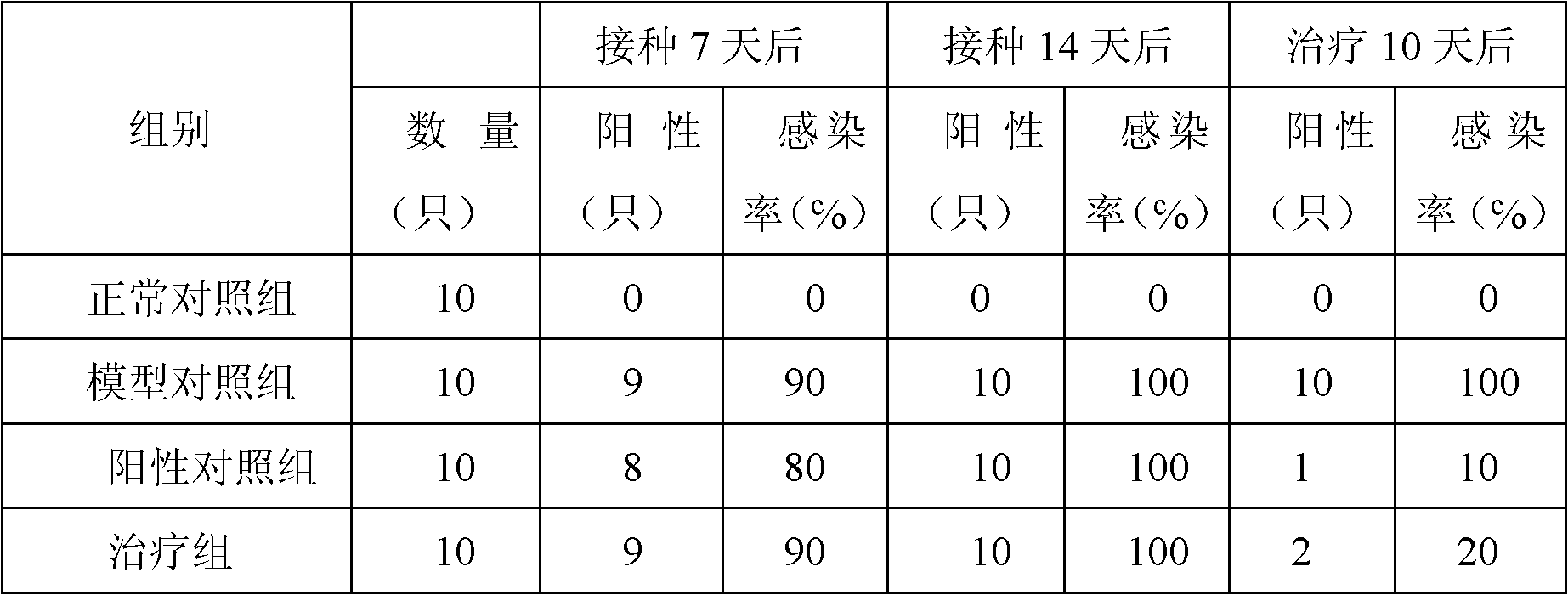
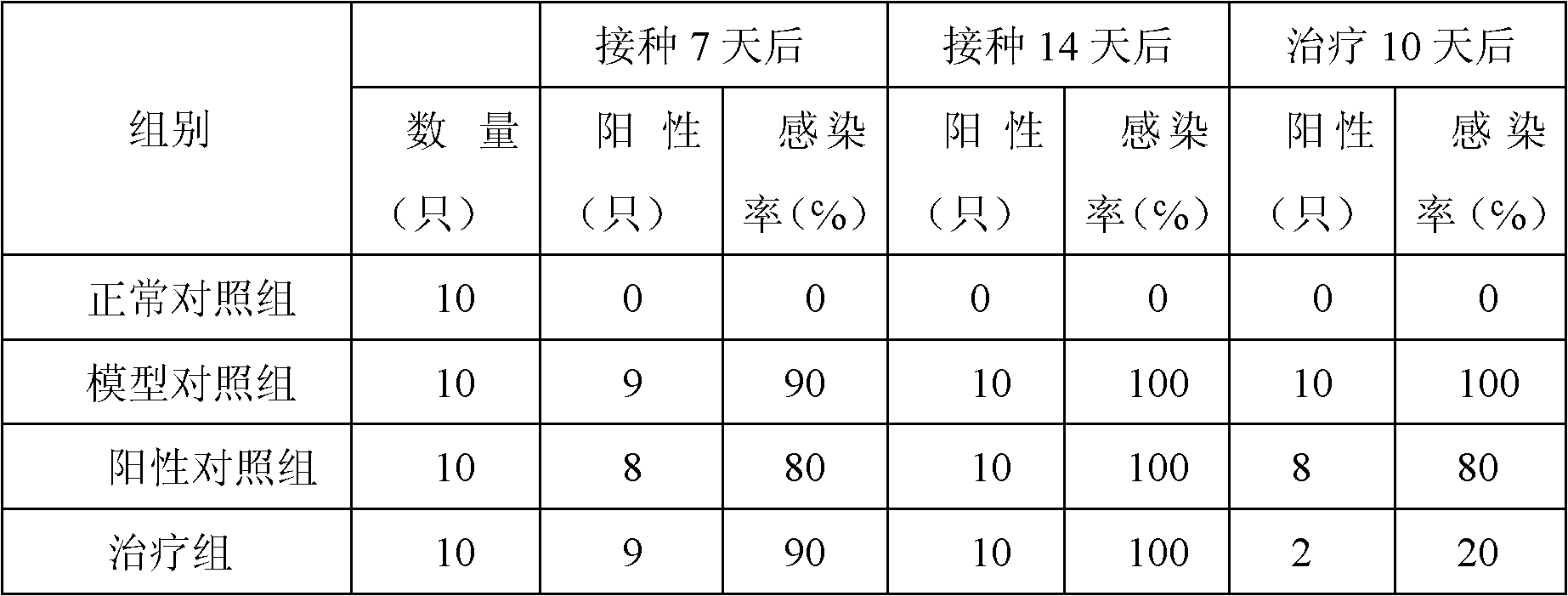
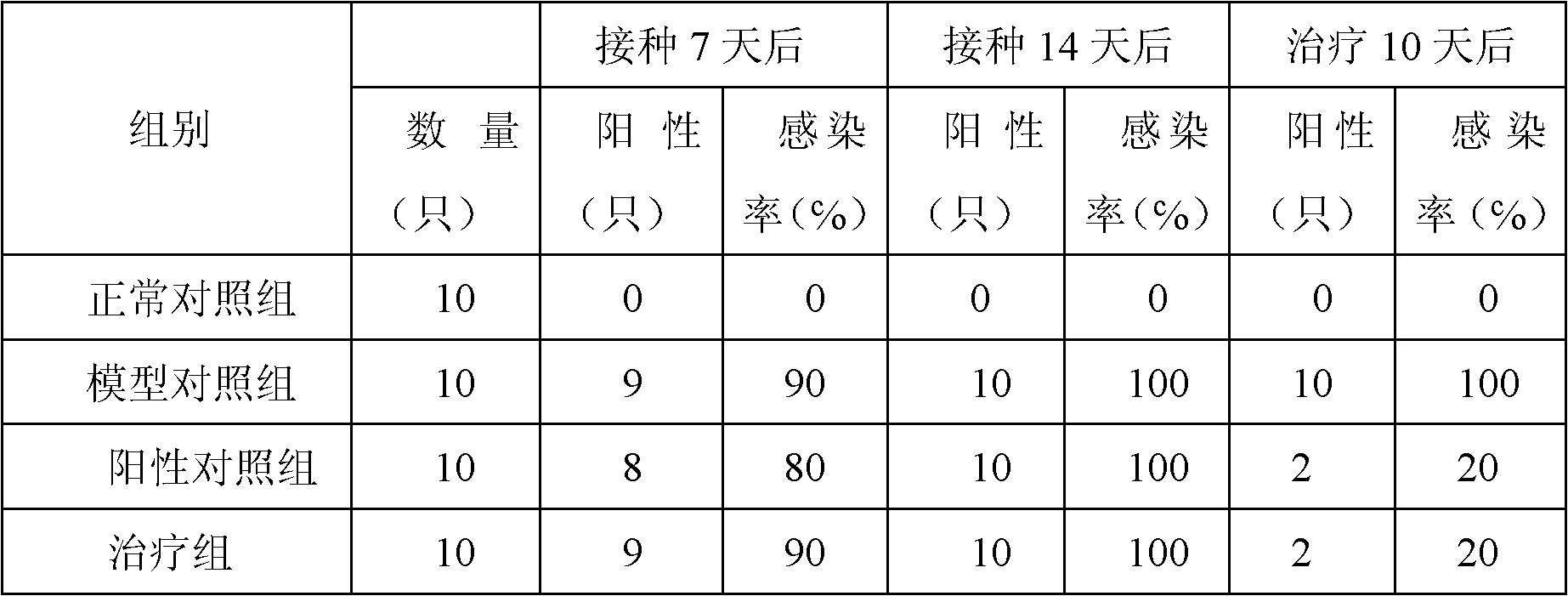
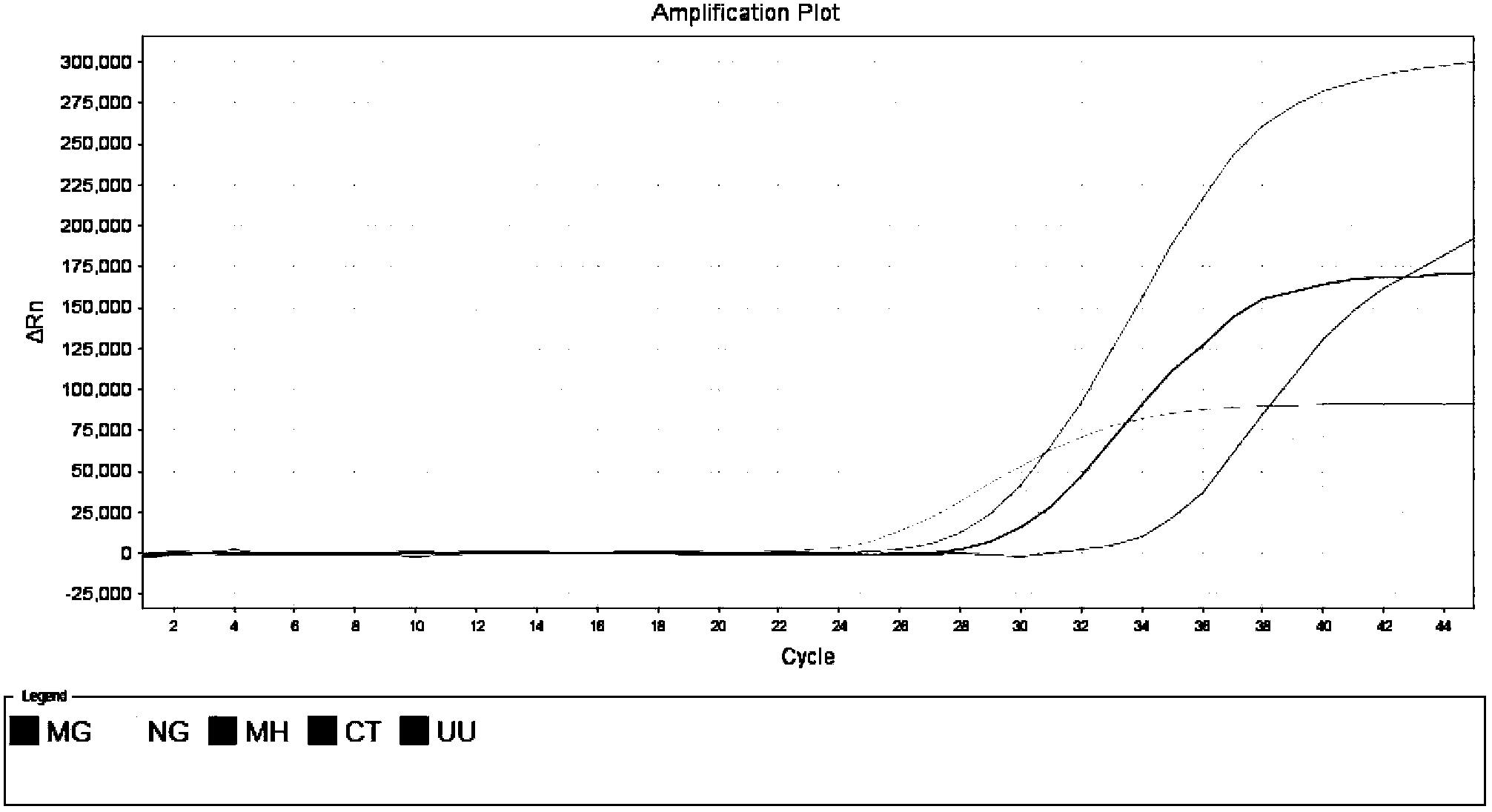
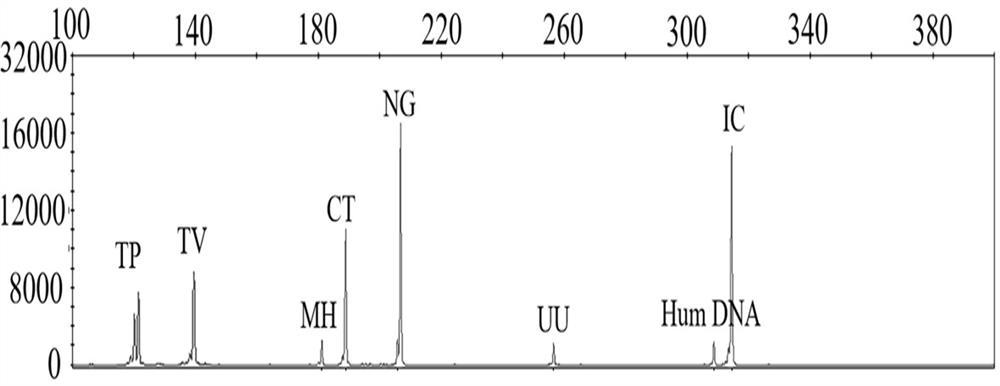
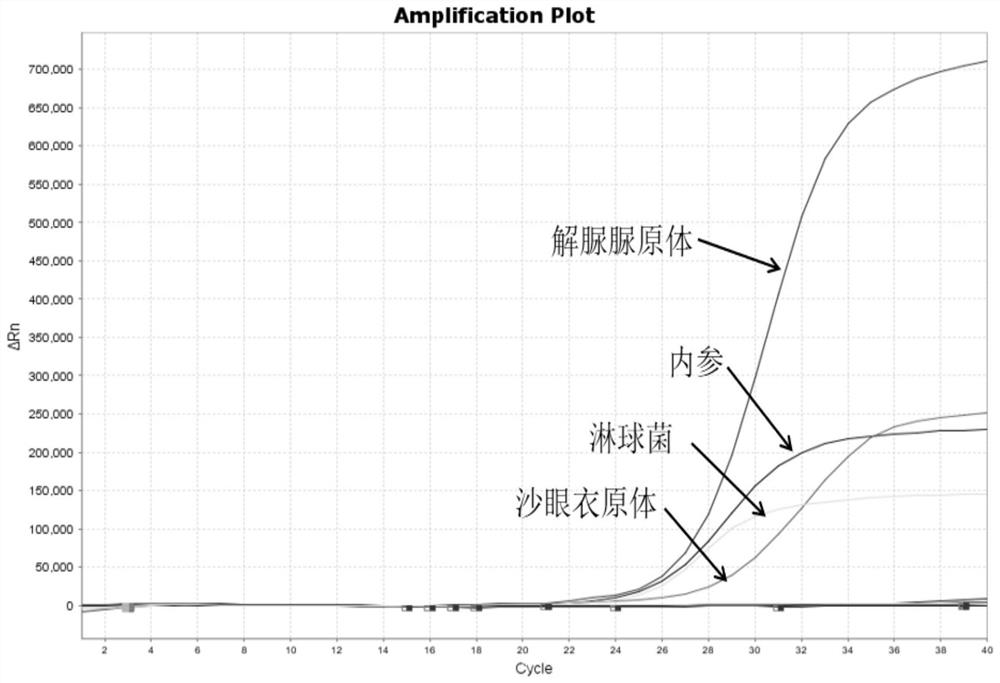
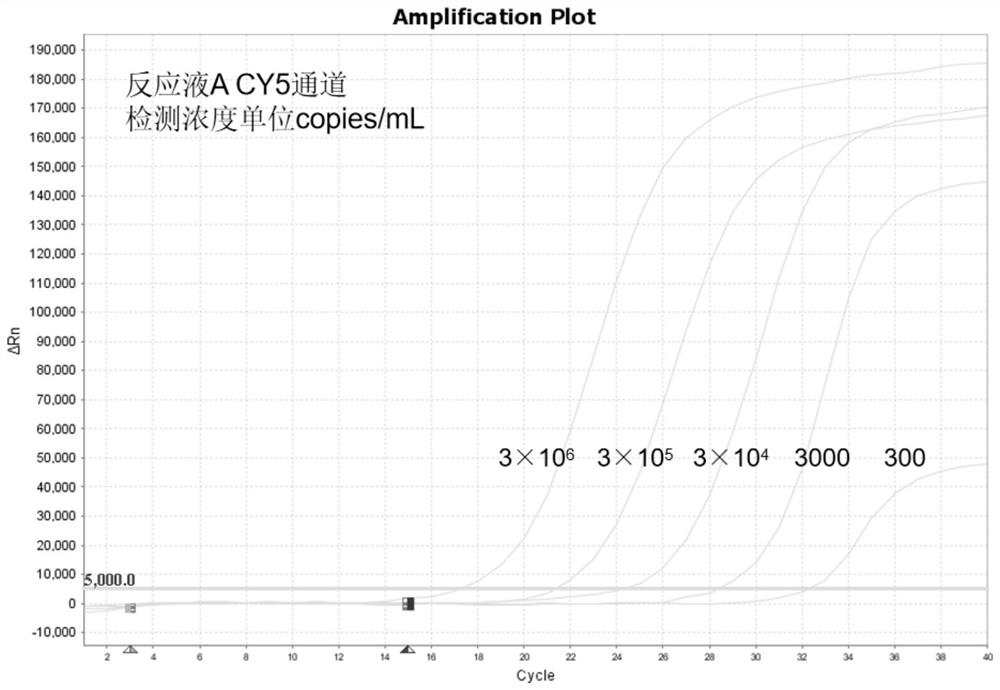
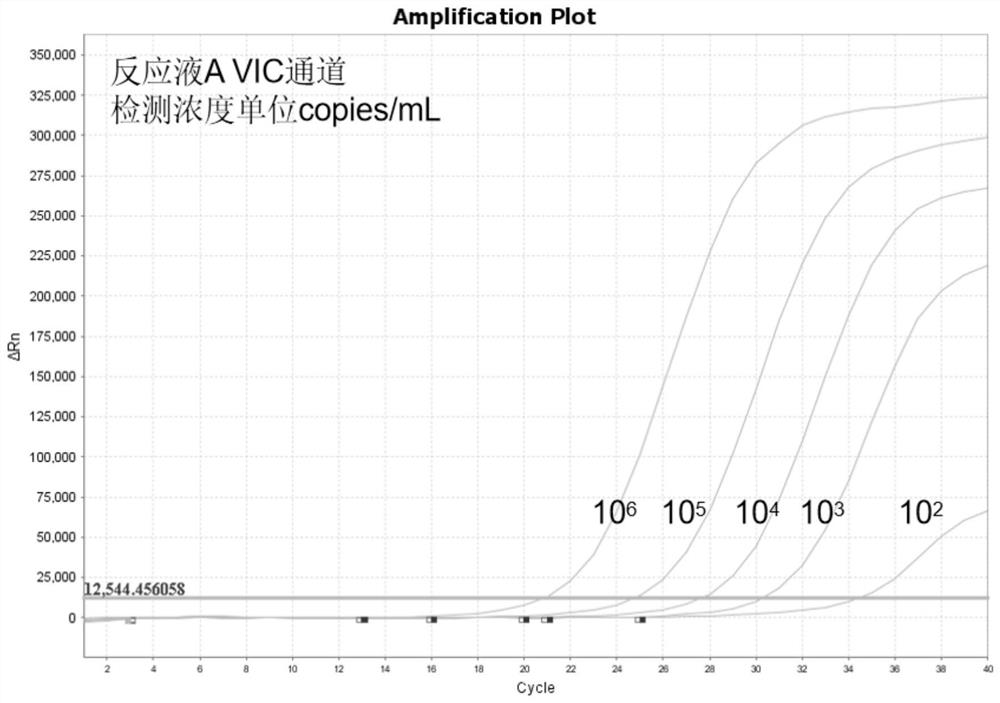
Quintuple fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) quick and hypersensitive detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN102888464AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMycoplasma hominisPcr method
The invention relates to a real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for quintuply detecting target nucleic acid in a nucleic acid extracting solution in a single PCR reaction vessel, which is used for detecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis and Mycoplasma genitalium in a sample.
Owner:苏州华益美生物科技有限公司
Kit for detecting mycoplasma hominis nucleic acid through PCR-fluorescence probe method and detecting method of kit
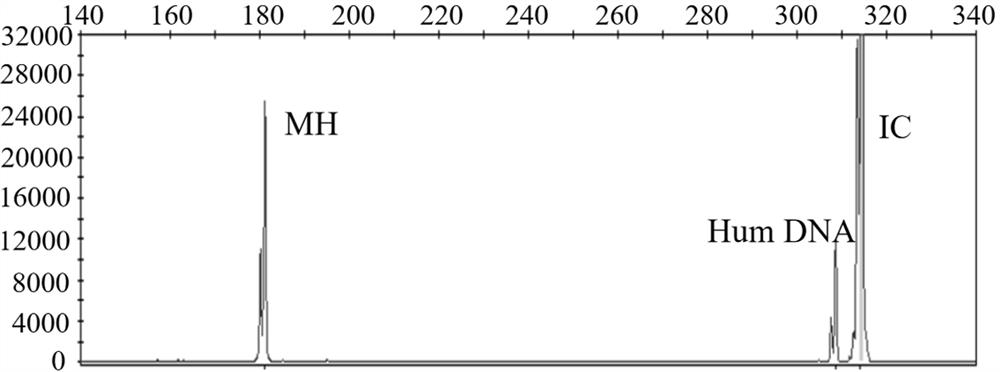
InactiveCN104988242AShort detection timeShort windowMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingPositive control
The invention relates to a kit for detecting mycoplasma hominis nucleic acid through a PCR-fluorescence probe method and a detecting method of the kit. The kit comprises a nucleic acid extracting set and a nucleic acid amplification detecting set. The nucleic acid amplification detecting set comprises PCR reaction liquid, negative control and positive control. The PCR reaction liquid comprises DNA polymerase, UNG enzymes, reaction buffer liquid, a primer, a probe and Mg2+. The positive control comprises positive plasmids and human genomes. The negative control comprises human genomes. The probe is a Taqman fluorescence probe. The special primer probe is designed according to an MH polymerase conservative target sequence by means of the kit and the method, the MH is rapidly detected through the PCR-fluorescence probe method, and the result is more reliable and accurate. Compared with an existing culture method, operation is easy and convenient and the speed is fast when mycoplasma hominis is identified; the whole process is completed within 3 hours; specificity and flexibility are high, and the result is visual.
Owner:SHANGHAI REPODX BIOTECH CO LTD
Solid culture medium for quick detection of mycoplasma, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102409076AImprove accuracyQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesColony countingMycoplasma hominis
The invention discloses a solid culture medium for quick detection of mycoplasma, and a preparation method thereof. By using the solid culture medium disclosed by the invention, the existence of ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis can be accurately detected, and the content of mycoplasmas can be quantitatively concluded by colony counting, thus greatly improving the accuracy and reliability. Simultaneously, by using the culture medium disclosed by the invention for detecting mycoplasmas, the result can be read after only 18 hours, thereby realizing quick detection of mycoplasmas, and finally confirming diagnosis of urogenital tract infection caused by ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis.
Owner:JIANGMEN KAILIN TRADE
PCR method of multiple sex propagate pathogene synchronous detection and kit
InactiveCN101935686AThe detection process is fastSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseMycoplasma hominis
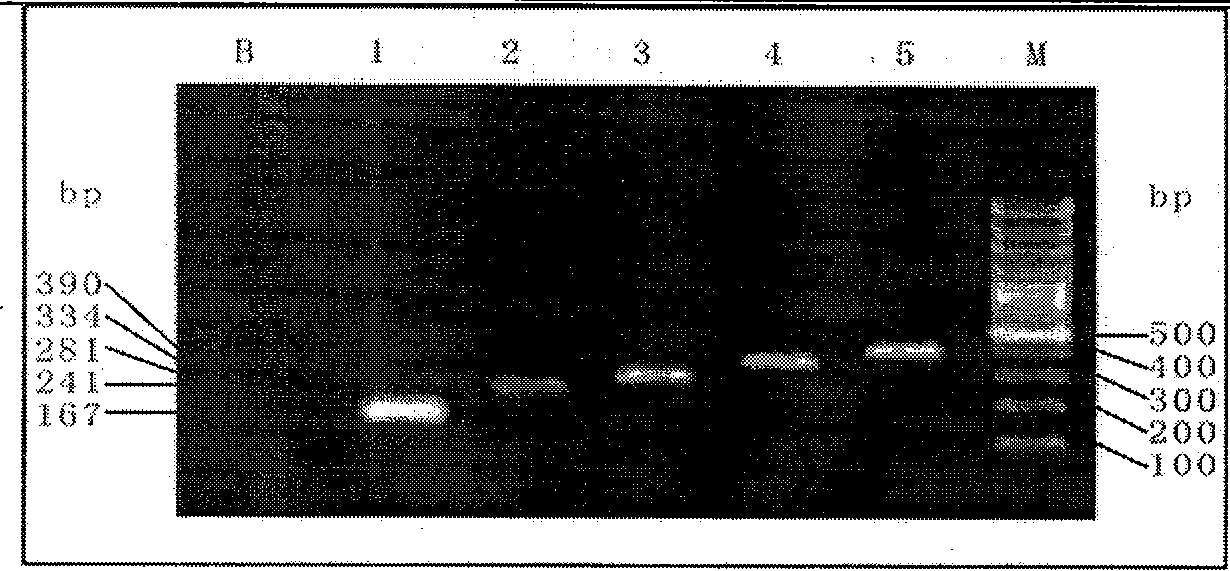
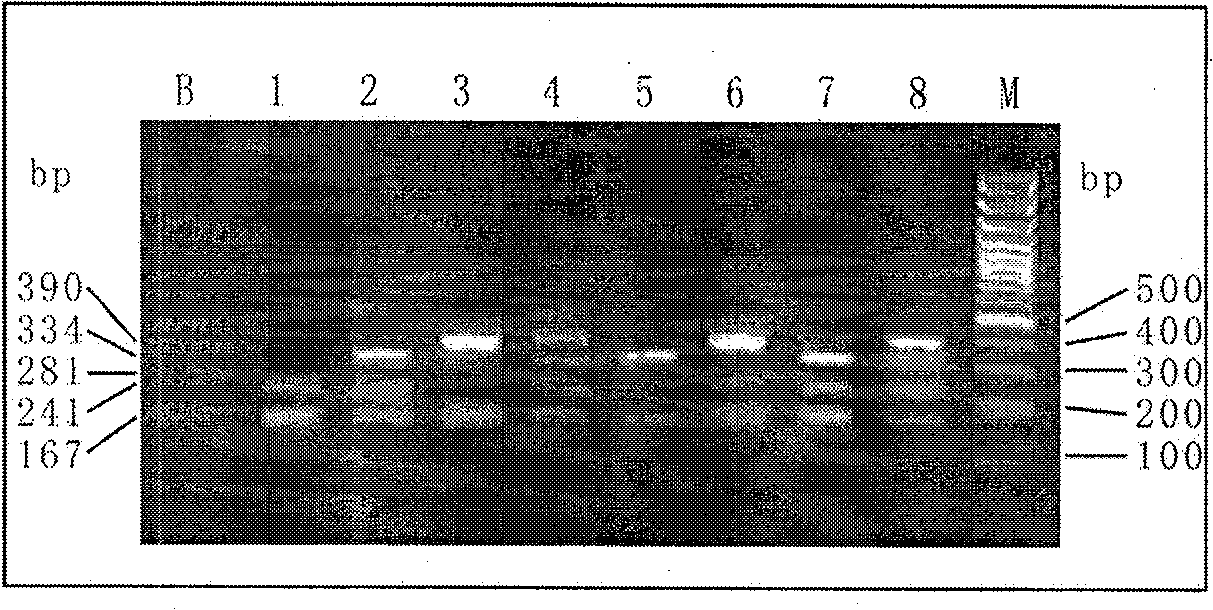
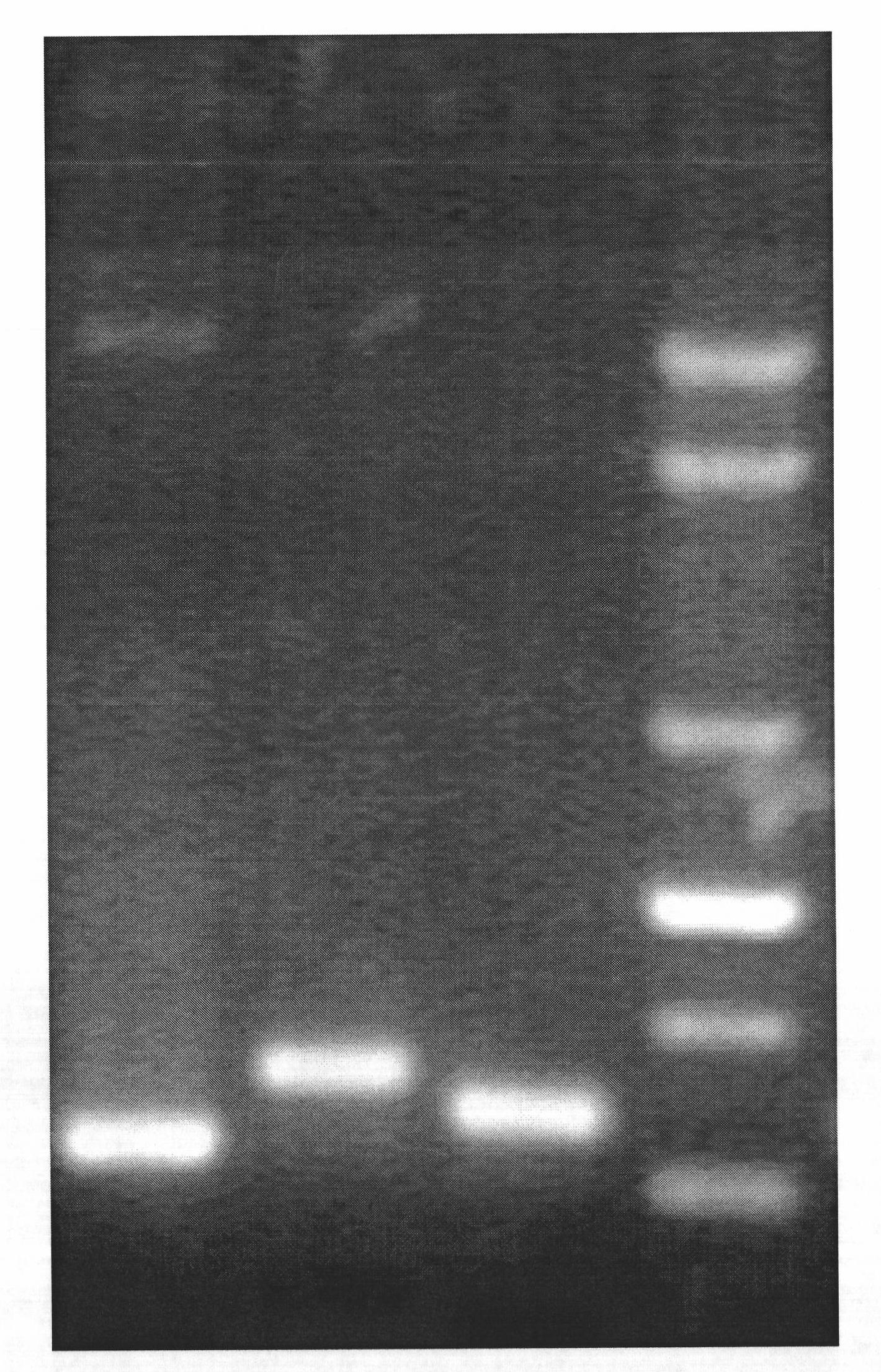
The invention discloses a single-tube multiple PCR method for synchronous rapid detection of five sex propagate pathogenes (neisseria gonorrhoeae (NG), mycoplasma hominis (MH), mycoplasma genitalium (MG), chlamydia trachomatis (CT) and ureaplasma urealyticum (UU)) and a kit. The method is characterized by amplifying the five pathogenes and performing gel electrophoresis separation and detection by reasonably designing a primer and optimizing the primer concentration combination and PCR condition in the same reaction tube and under the same heat cycle condition. The invention has the characteristics of sensitivity, rapidness, convenience, and the like of the classic PCR, mainly realizes synchronous detection of the five pathogenes, has lower cost, can be used for developing relative kits and is used for clinical diagnosis and epidemiological survey and control.
Owner:唐文志
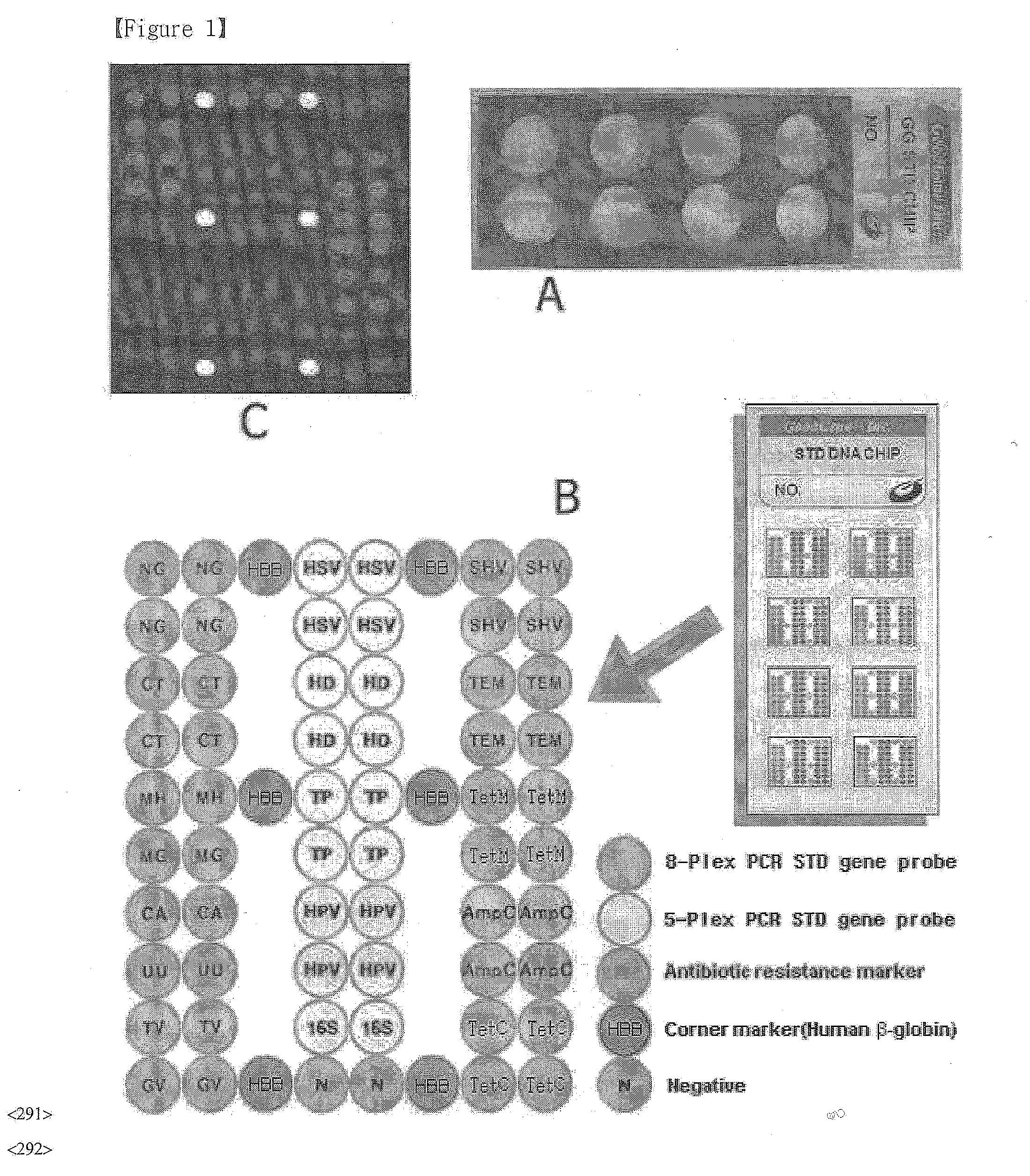
DNA chip, kit for detecting or genotyping bacteria causing sexually transmitted diseases, genotyping antibacterial drug resistance and detecting or genotyping method using the same
InactiveUS20120004113A1Quickly and accurately detectEasy to explainNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEscherichia coli
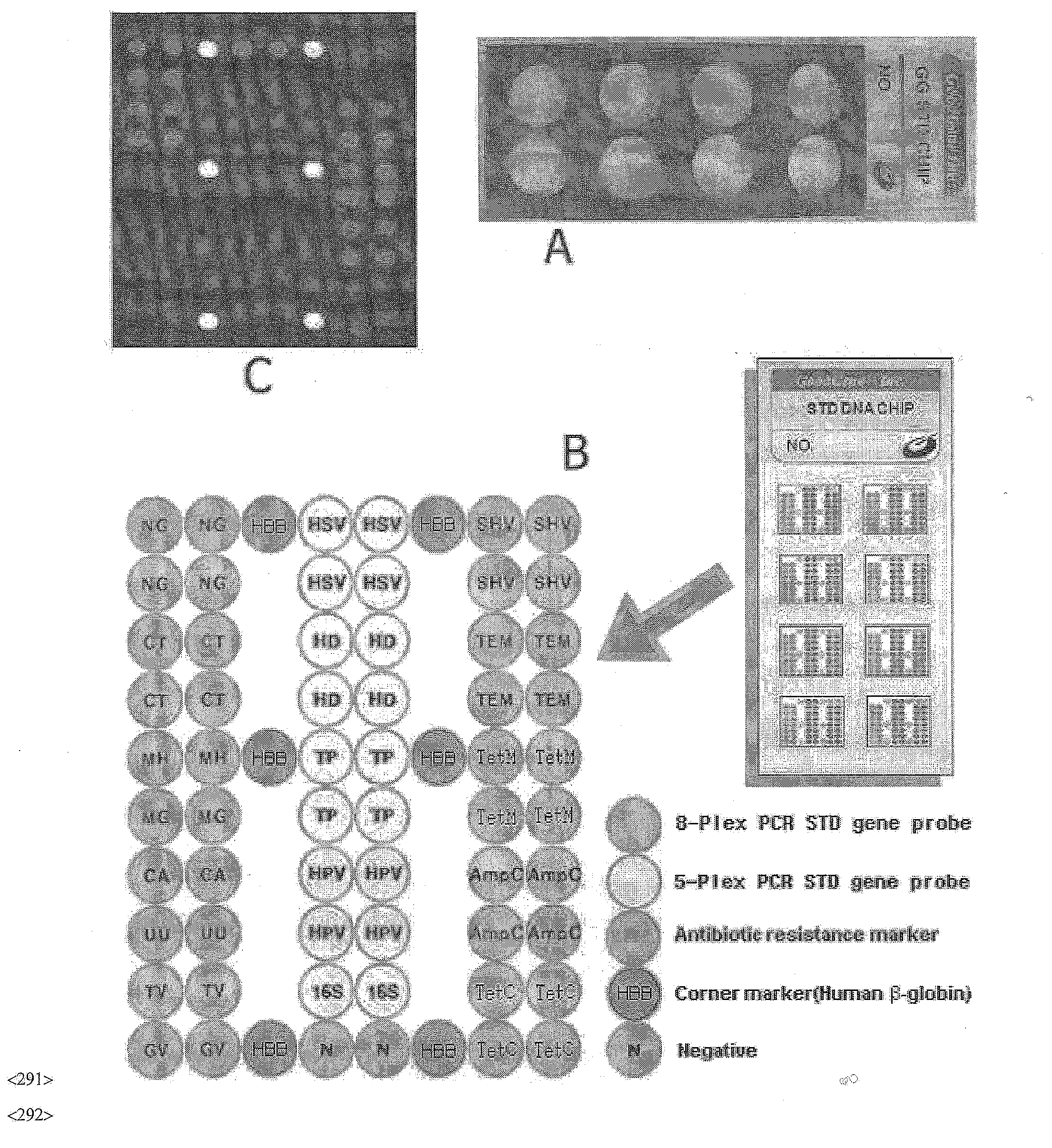
Disclosed are a DNA chip and a kit capable of quickly and accurately detecting or genotyping the highly prevalent and important eleven microbes causing sexually transmitted diseases (STD) Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis, syphilis-causing treponema, pallidum, chancroid-causing Haemophilus ducreyi, genital herpes-causing herpes simplex virus 1 and 2, human papillomavirus (HPV) and Trichomonas vaginalis and three related organisms Candida albicans, Gardnerella vaginalis and coliform bacteria and analyzing antibiotic resistance against tetracycline and lactam antibiotics, and a method for detecting or genotyping using the same. According to the present invention, the presence, genotype and antibiotic resistance of the fourteen organisms can be analyzed quickly and accurately from a DNA sample. With excellent sensitivity, specificity, reproducibility and accuracy of the 14 STD-causing and related microorganisms may be automatically identified quickly and accurately from multiple samples, and selection of antibiotics may be aided.
Owner:GOODGENE
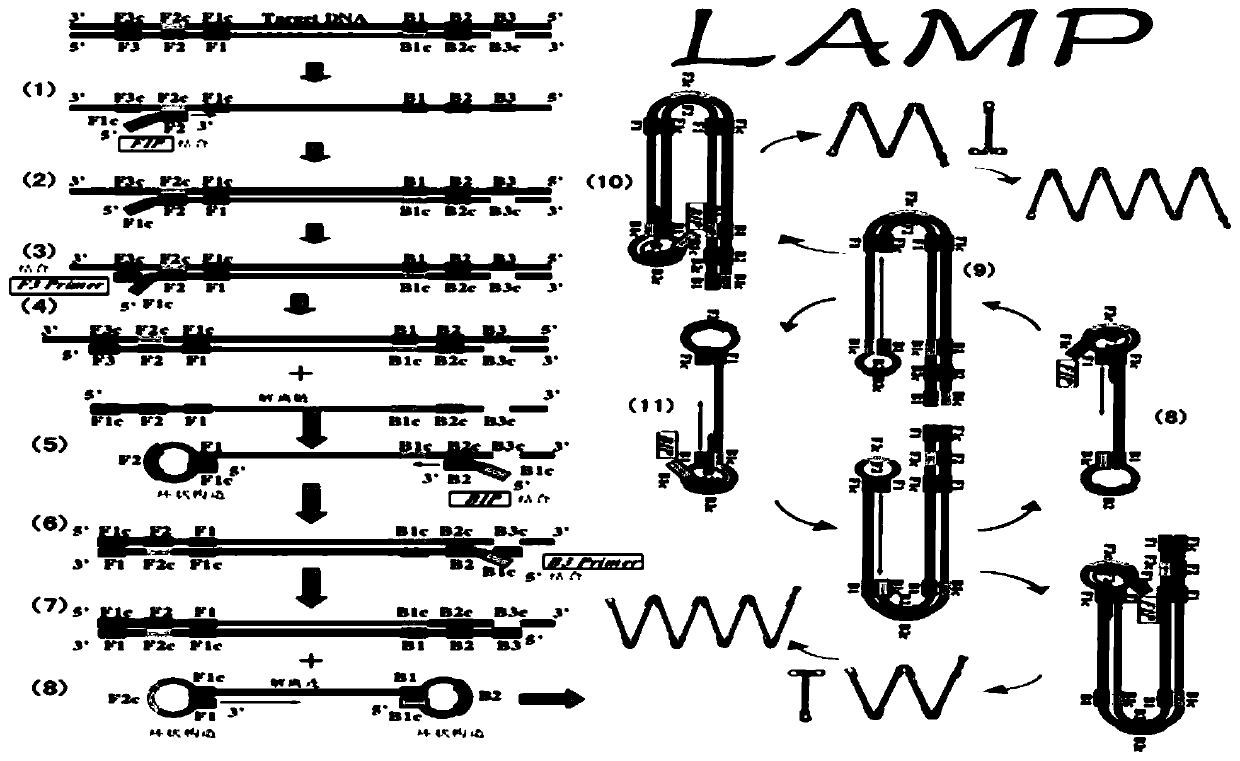
Method for detecting three kinds of urogenital canal mycoplasma by loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology
InactiveCN107686863AStrong specificityEfficient amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesConserved sequenceFluorescence
The invention discloses an LAMP detection method for three kinds of urogenital canal infection mycoplasma which are common for human and a dedicated primer and a kit thereof. The method is applied toperforming isothermal amplification on ureaplasma urealyticum (UU), mycoplasma genitalium (MG) and mycoplasma hominis (MH). The LAMP primer is designed according to specific conserved sequences of theUU, the MG and the MH, and each group of the primer includes four piece of oligonucleotide (shown in a table 1, a table 2 and a table 3 in the description). When being applied to the urogenital canalmycoplasma, the LAMP primer present white precipitate when being observed by the naked eyes; in positive reaction, after SYBR GREEN is added, fluorescent green is remarkably enhanced when being observed under an ultraviolet lamp. Detection results of a real-time turbidity meter show that product turbidity can be increased along with prolonging reaction time; after being detected by gel electrophoresis, the LAMP primer is in a trapezoid stripe. The LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention provides a novel technological platform for mycoplasma detection; a sample to be measured can be applied to DNA extracted by commercialized kits or purified DNA and is also suitable for coarse extracted DNA with a boiling method as a representative; the LAMP detection method is suitable for beingpopularized and applied in grassroots units, field monitoring and bedside detection.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method for multiple mycoplasma monoclonal antibodies and multi-linked immunoassay reagent
InactiveCN102199207AAvoid painSimple and fast operationImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMaterial analysisMycoplasma hominisImmuno detection
The invention relates to a preparation method for multiple mycoplasma monoclonal antibodies and a multi-linked immunoassay reagent. The preparation method is characterized by separately immunizing mice with mycoplasma pneumoniae, mycoplasma hominis and ureaplasma urealyticum for cell fusion and cloning to obtain three monoclonal antibodies with high specificity and high potency. A mycoplasma multi-linked immunoassay reagent is prepared by mixing the three monoclonal antibodies according to a certain ratio, is used for detecting the diseases infected by the three mycoplasmas, and can quickly and accurately detect mycoplasma diseases; and sampling without phlebotomizing does not bring pain to patients, thus providing patients with timely and effective treatment. The multi-linked immunoassay reagent does not generate harmful waste gas or waste water during preparation and use processes, and also does not bring any injury to patients and operators, thereby being an environment-friendly, safe, accurate and sensitive biological preparation.
Owner:黄威权
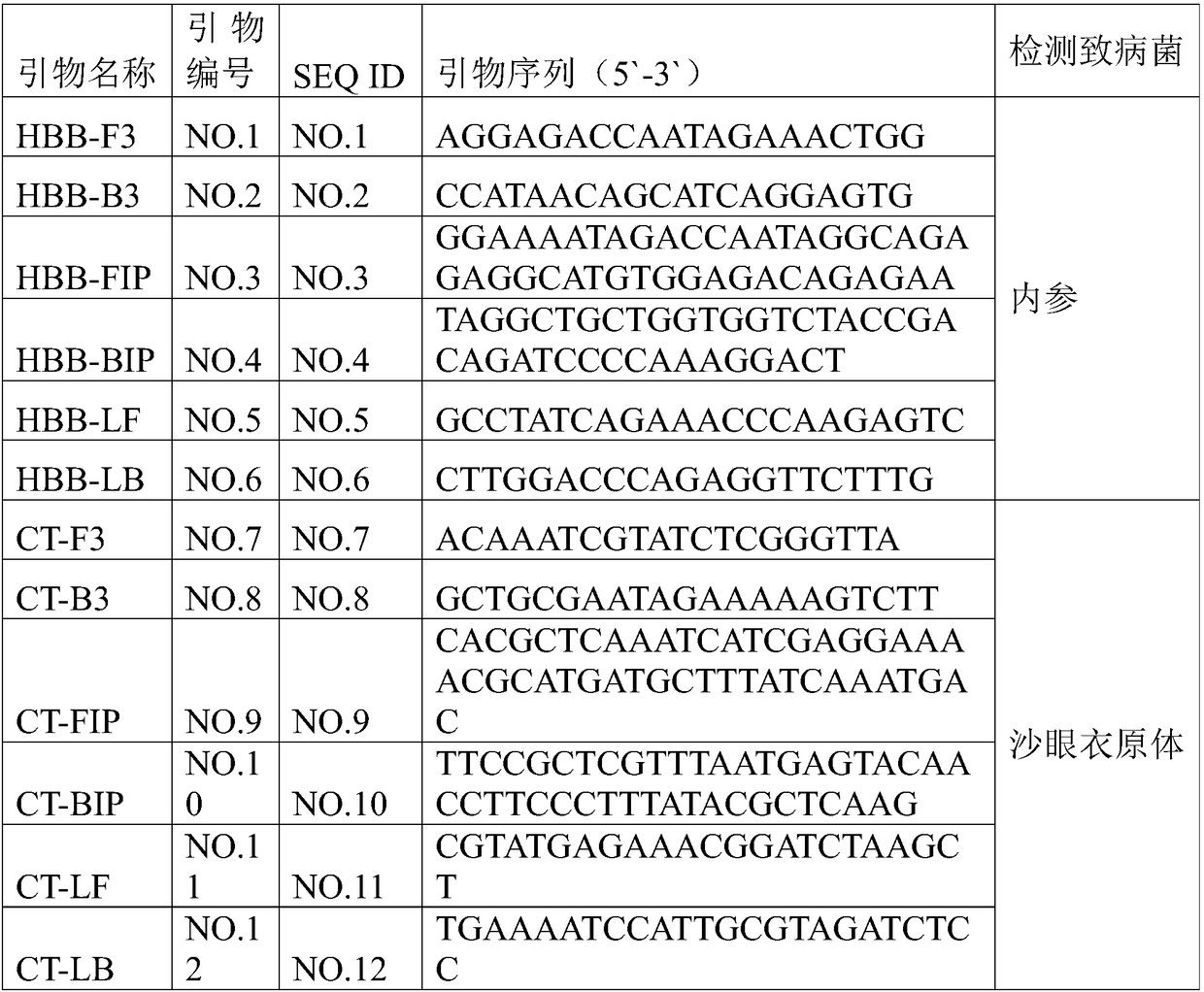
Composition and kit for simultaneously detecting mycoplasma urealytium, mycoplasma hominis and mycoplasma genitalium
ActiveCN101824471AImprove early detection rateSave operating timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseNucleotide
The invention discloses a composition and a kit for simultaneously detecting mycoplasma urealytium, mycoplasma hominis and mycoplasma genitalium, which comprise sequences shown by relevant SEQ ID No:1-6 or at least 15 nucleotide continuous fragments thereof, or the specific primers of sequences which have at most 5 nucleotide differences with the sequences shown by relevant SEQ ID No:1-6 or continuous fragments and sequences shown by SEQ ID No:7-9 or complementary sequences thereof or at least 15 nucleotide continuous fragments thereof or the specific probes of sequences which have at most 5 nucleotide differences with the. sequences shown by SEQ ID No:7-9 or the complementary sequences thereof or the 15 nucleotide continuous fragments The composition and the kit for simultaneously detecting the mycoplasma urealytium, the mycoplasma hominis and the mycoplasma genitalium can simultaneously detect three different mycoplasmas in one reaction system, and thereby, the early detection rate of the infectious diseases of urogenital systems is increased, the operation time of operation staffs is reduced, the detection cost is reduced and the financial burdens are relieved for patients.
Owner:北京鑫诺美迪基因检测技术有限公司
Gene chips for detecting of pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases and reagent kit for detecting
ActiveCN101407836ATimely diagnosisImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMycoplasma hominis
The invention provides a gene chip used for detecting the common pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases and a kit used for detection, wherein, the gene chip includes a solid phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase vector; the oligonucleotide probe mainly comprises a DNA segment or a complementary DNA segment thereof which is selected from Diplococcus gonorrhoeae, Ureaplasma urealyticum and the 16S rRNA gene of M.hominis, the outer membrane protein gene (ompA gene) of a Chlamydia trachomatis, the glycosidoprotein B gene (gB gene) of a herpes simplex virus (HSV) and the L1 gene of a papilloma virus (HPV). The gene chip and the kit can be utilized for achieving the goal of detecting the common pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases; the gene chip and the kit for detection are simple and convenient to be operated, have high flux, accuracy and repetitiveness; and the gene chip and the kit for detection can be applied to the clinic detection and epidemiology analyzing of medical and health organizations.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Pathogen nucleic acid-drug resistant gene detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN104513854AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMycoplasma hominisChlamydiae
The invention relates to the technical field of medical biology, and especially relates to a pathogen nucleic acid-drug resistant gene detection kit and an application technology thereof. The kit designed by the invention includes the following two kinds of compositions: a PCR reaction buffer solution, an enzyme mixed solution, and a chlamydia trachomatis / mycoplasma urealytium / mycoplasma hominis / drug resistant gene multiple reaction solution; or a PCR reaction buffer solution, an enzyme mixed solution, a chlamydia trachomatis / mycoplasma urealytium / mycoplasma hominis multiple reaction solution, and a drug resistant gene reaction liquid. The kit adopts a multi-fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, can simultaneously detect multiple target genes in a same PCR reaction tube, and provides a powerful technical support for simultaneous detection of pathogens and drug resistant genes. A method has the characteristics of less required amount on samples, low cost, simple and convenient operation, high sensitivity and good specificity, and has extremely great social and economic significances.
Owner:常州百代生物科技股份有限公司
Pepper extract with function of resisting infection of ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis
InactiveCN102058709AAnti-Ureaplasma urealyticumHas the effect of Mycoplasma hominis infectionAntibacterial agentsPlant ingredientsTreatment effectMycoplasma hominis
The invention provides a pepper extract with a function of resisting infection of ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis, relating to a pepper extract and aiming at solving the problems that the drug resistance of the ureaplasma urealyticum and the mycoplasma hominis to antibiotic is increased to cause poor treatment effect. The pepper extract is obtained by extraction through the following method: pepper is ground into powder, the powder is put into a supercritical CO2 extraction kettle, the extraction temperature is 30-55 DEG C, the separating temperature is 25-45 DEG C, the extraction pressure is 15-35MPa, the separation pressure is 4-6MPa, the flow of CO2 is 4-12, and the extraction time is 1-2 hours, and then the pepper extract is obtained. The pepper extract is non-toxic, has the functions of resisting the infection of ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis and resisting the infection of drug-resistant ureaplasma urealyticum and drug-resistant mycoplasma hominis, and is applied in the field of resisting the infection of mycoplasma.
Owner:黑龙江省中医研究院
Urogenital tract infection pathogen multi-detection primer group and detection device comprising same
ActiveCN108531623ASimplify the experimental operation processHigh detection throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle sampleMycoplasma hominis
Owner:无锡科智达科技有限公司
Rapid genotyping analysis and kits thereof
ActiveCN106906306AMicrobiological testing/measurementOrgan movement/changes detectionDiseaseMycobacterium tuberculosis
The present invention provides methods, primers, probes, and kits for identifying gene mutation or material genotyping. In one embodiment, the materials are disease-causing agents. In another embodiment, the present invention is applied to detecting multidrug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis, hepatitis B virus, beta-globulin mutation, thrombosis-related mutations; or multiple sexually transmitted diseases causing agents, including but not limited to, trichomonas vaginalis, chlamydia, neisseria gonorrhoeae, mycoplasma, mycoplasma hominis, ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycelia, Treponema pallidum, Herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 and human papilloma virus type 6 and type 11.
Owner:DIAGCOR LIFE SCI LTD
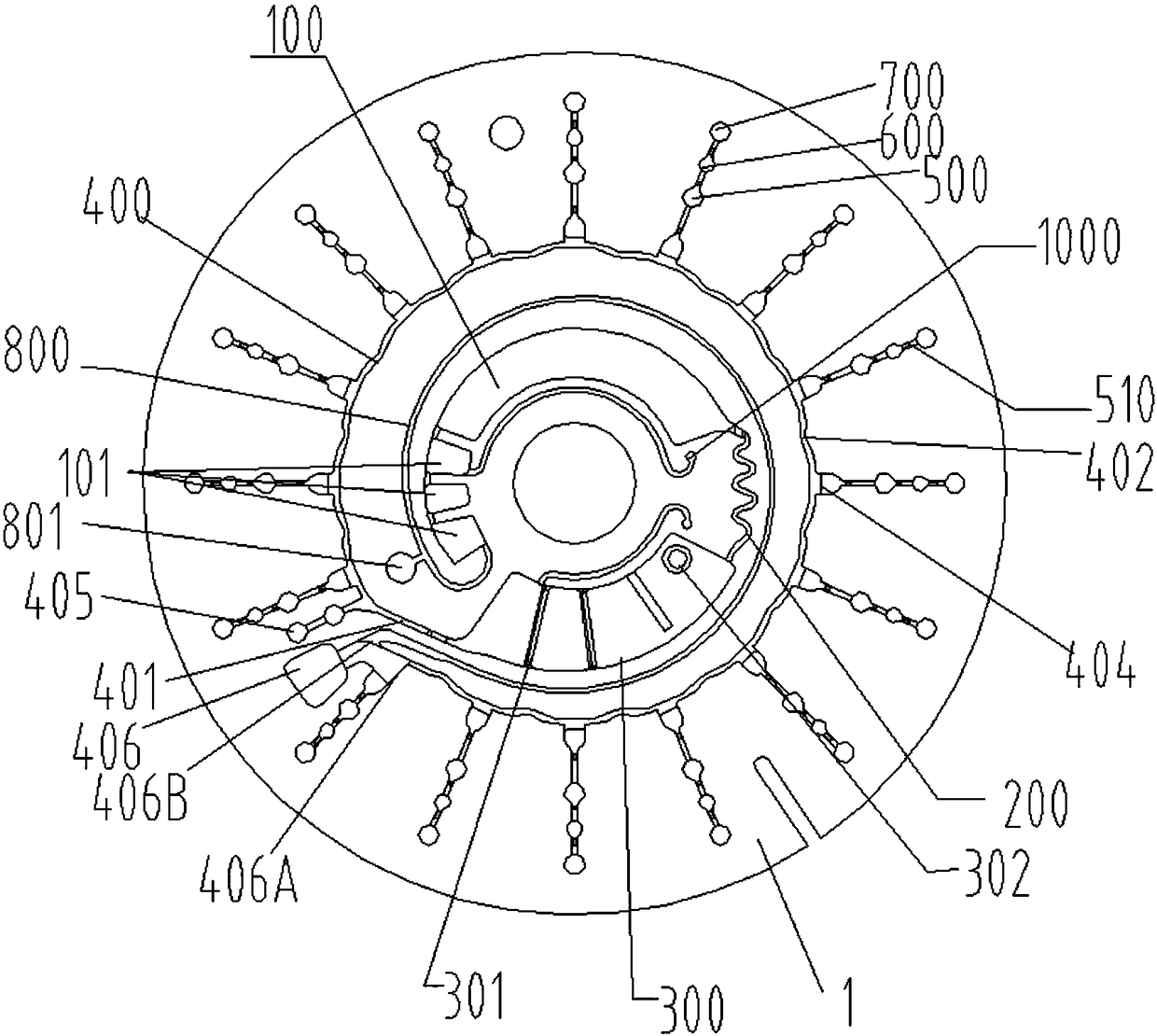
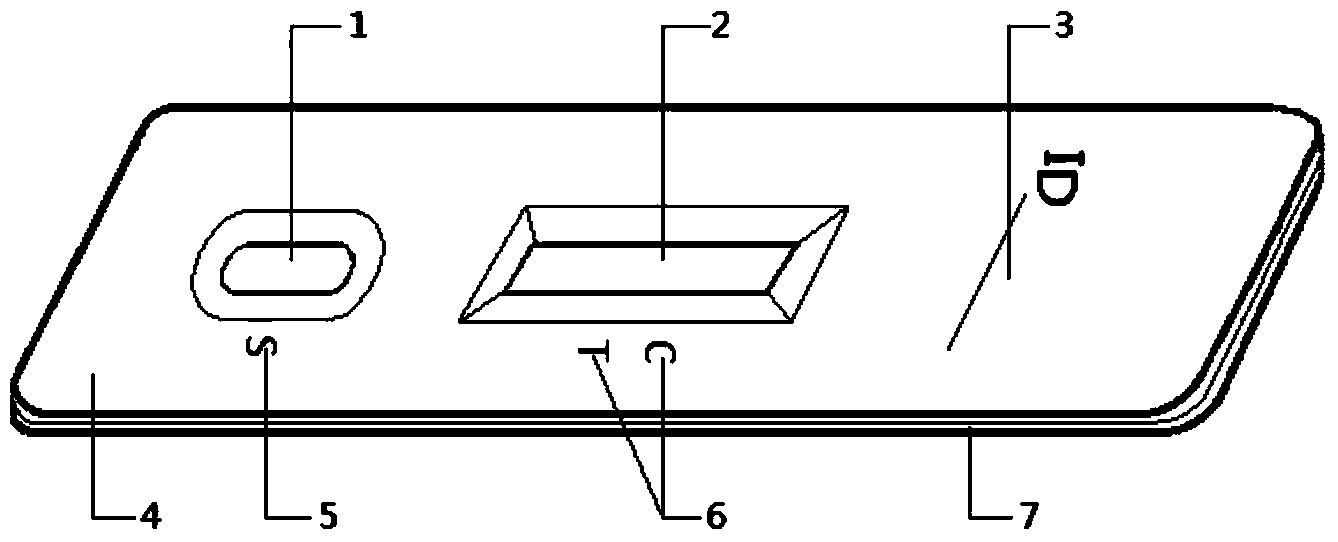
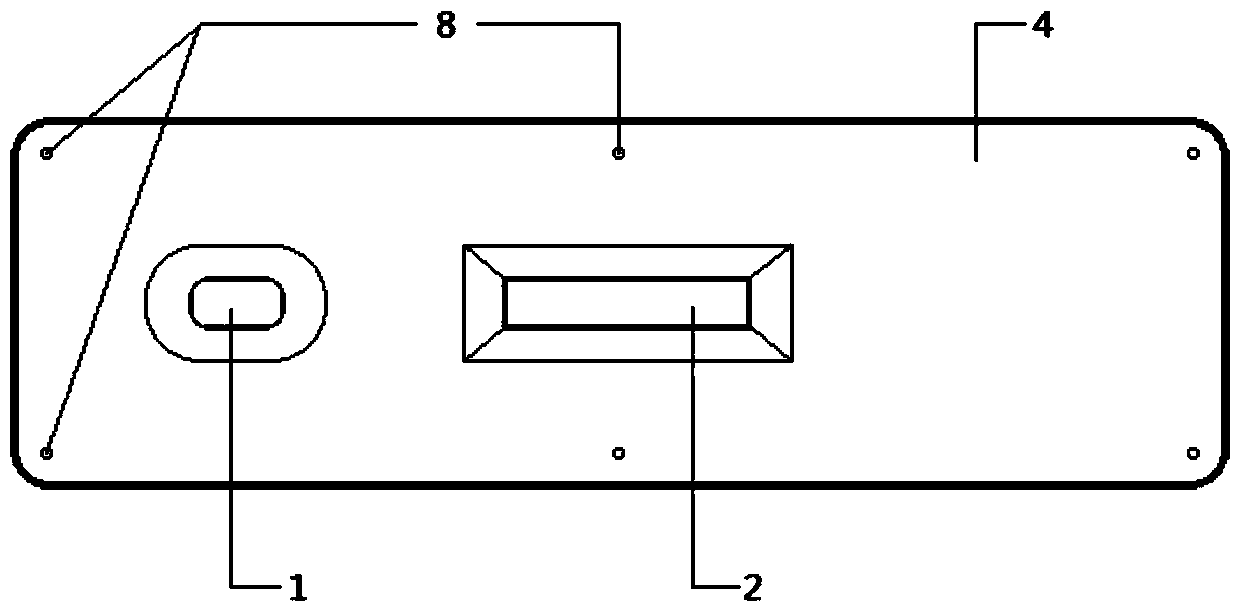
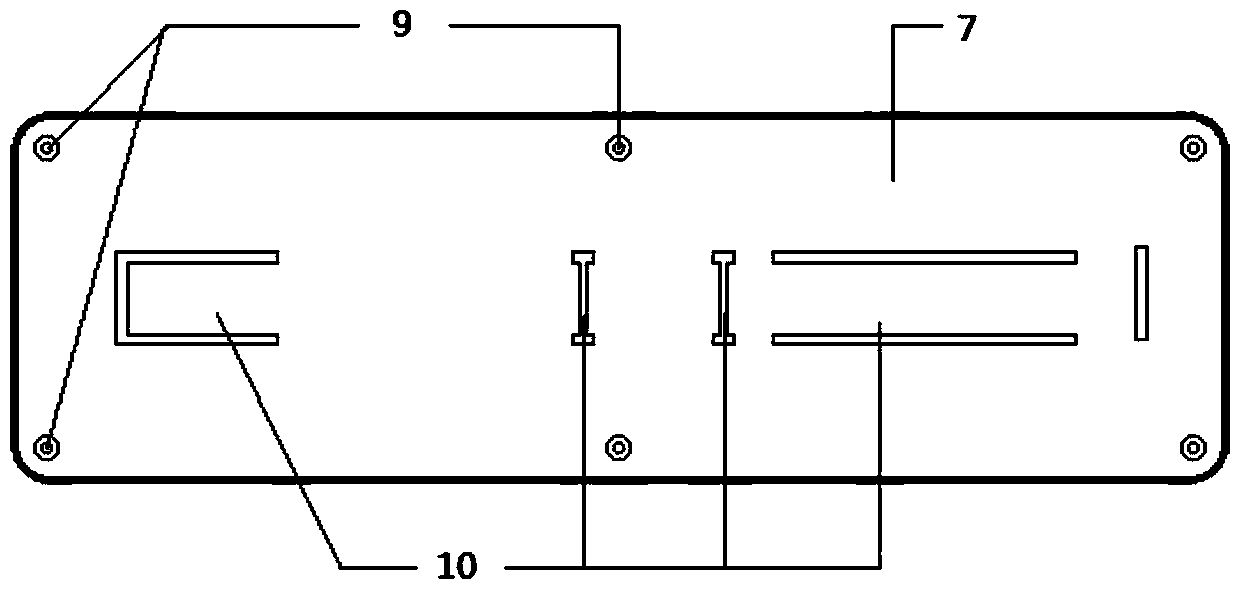
Mycoplasma hominis gold mark quick detection kit
The invention discloses a mycoplasma hominis gold mark quick detection kit and belongs to the field of clinical medicine detection. The kit consists of a clamping box and a test strip, wherein the clamping box comprises a box cover (4) and a box bottom (7); the detection test strip is arranged in the clamping box; a sample feeding hole (1) and an inspection window (2) are formed in the front side of the clamping box; a sample feeding hole tag (5), a result distinguishing illustration(6) and an information recording column (3) are printed on the front side of the box cover. According to the invention, the gold immunochromatographic assay technology is adopted, the engineering expression mycoplasma hominis Lmp1 protein is taken as an antigen to prepare a monoclonal antibody, the pair of high-performance mycoplasma hominis Lmp1 monoclonal antibodies with favorable pairing property are screened to respectively serve as a capture antibody and a detection antibody, and the mycoplasma hominis in secretion of the human body urogenital tract can be detected. The mycoplasma hominis gold mark quick detection kit has the advantages that the detection method is simple, the result display is accurate and quick, and special instrument equipment are not required.
Owner:李克生
Method for shortening mycoplasma clinical detection time under A-PEG-B array
InactiveCN101851661AExtension of timeMicrobiological testing/measurementControl releasePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for shortening mycoplasma clinical detection time under an A-PEG-B array, which belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving polyethylene glycol (PEG) having a repeated structure of --(OH2CH2O)n-- into an in-vitro diagnostic kit for culturing, identifying, quantifying and medicinally sensitizing ureaplasmaurealyticum (Uu) and mycoplasma hominis (Mh) to promote clinical recombination with the A-PEG-B array. In the method, in recombination reaction at the right end of the A-PEG-B array, the functions of the PEG in the complementation and controlled-release of all active substances are highlighted; in the recombination reaction at the left end of the A-PEG-B array, the osmotic pressure function of the PEG is highlighted; at the right end of the A-PEG-B array, the antibiotic capacity and biological activity of a culture medium are simultaneously improved; and at the left end of the A-PEG-B array, the detected Uu and Mh are repaired to different extents and the activity of the detected Uu and Mh on the culture medium is improved. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of obtaining detection results 12 to 24 earlier and remarkably shortening time for curing sicknesses to save patients.
Owner:其昌达生物高科技(上海)有限公司
Kit for detecting mycoplasma urealytium and human mycoplasma
ActiveCN106319028AAvoid the inconvenience of re-admission to see the resultsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMycoplasma hominisAniline
The invention discloses a kit for detecting mycoplasma urealytium and human mycoplasma. The kit comprises four detection reagents: a compound of L-proline and enzyme substrate as chromogen for detecting activity of proline aminopeptidase, a compound of L-leucine and enzyme substrate as chromogen for detecting activity of leucine aminopeptidase, a compound of alpha-D-glucoside and enzyme substrate as chromogen for detecting activity of alpha-glucosidase and a compound of neuraminic acid and enzyme substrate as chromogen for detecting activity of neuraminidase, wherein the chromogen is aniline, naphthaline, naphthol, indoxyl and derivative thereof. According to the invention, a dry chemical enzyme method is adopted for detecting the enzyme compounded in the growth process or the enzyme generated by stimulating host cells, so that the purpose of detecting and identifying mycoplasma urealytium and human mycoplasma can be achieved; and the kit has the advantages of high speed, convenience, accuracy, and the like.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Ureaplasma urealyticum/mycoplasma hominis combined rapid culture and drug sensitivity detection kit
InactiveCN104988206AResolve detectionResolve accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPenicillinArginine
Owner:姜洪波 +1
Yolk bioprotein foam filler and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105749277AAvoid infectionMaintain a healthy physiological environmentAntibacterial agentsEgg immunoglobulinsEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses a yolk bioprotein foam filler which is mainly composed of 8-10% of multi-link yolk protein, 0.1-0.3% of preservative, 40-50% of matrix and the balance of a foamer.The multi-link yolk protein is yolk bioprotein capable of being combined with various pathogens, and the pathogens include, but not limited to ureaplasma urealyticum, mycoplasma hominis, staphylococcus, streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Gardnerella vaginalis, gonococcus and Tritirachium album.The yolk bioprotein foam filler is mainly composed of yolk bioprotein aiming at inhibiting pathogenic bacteria, can be combined with corresponding pathogens, can effectively inhibit and remove pathogens, is effective on most bacteria, mycete and mycoplasma, does not have impact on probiotics, can maintain health and physiological environment of a reproductive system, does not enter blood, is higher in safety during local use, is free of irritation and side effect on human body, dependency, drug resistance and hypersensitivity and can be used for various clinical therapeutic products for vaginitis.
Owner:西安昱子生物科技有限公司
Mycoplasma quick detection reagent for non-gonococcal urethritis
InactiveCN101566621AFull of nutritionEasy to prepareMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFiltrationNutrition
The invention relates to a mycoplasma quick detection reagent for non-gonococcal urethritis, in particular to a quick detection test paper for macoplasma hominics and mycoplasma hominis and a preparation method thereof. The quick detection reagent can detect out the positive result of the mycoplasma in a genital tract, thereby having the function of the clinical diagnosis guidance and the clinical treatment and the significant meaning of preventing the abuse of antibacterial drugs. The mycoplasma quick detection reagent for the non-gonococcal urethritis is rich in nutrition and easy to prepare, achieves satisfied clinical application effect, solves the difficulty of bedside inoculation, is less polluted, has simple detection method, short time, strong selectivity, sensitive color change, high detection rate and good stability and can obtain a liquid for filtration enrichment and achieve the effects of permanently observing the growth condition of a colony after a sample is inoculated for 24 hours.
Owner:曲奕
Quintuple fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) quick and hypersensitive detection kit and application thereof
ActiveCN102888464BGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMycoplasma hominisFluorescent pcr
The invention relates to a real-time PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method for quintuply detecting target nucleic acid in a nucleic acid extracting solution in a single PCR reaction vessel, which is used for detecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis and Mycoplasma genitalium in a sample.
Owner:苏州华益美生物科技有限公司
Reagent kit for culturing and differentiating pathogenic mycoplasma and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101109746AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMycoplasma hominisMycoplasmal pneumonia
The invention pertains to the field of medical inspection, and relates to a reagent box and preparing method for the reagent box for culturing and distinguishing pathogenic mycoplasma, in particular to a method for culturing and distinguishing Ureaplasma urealyticum, mycoplasma hominis, and mycoplasmal pneumonia. The invention prepares basic culture medium based on the common features of clinically common pathogenic mycoplasma, which is applicable for direct culturing of mycoplasma hominis; prepares distinguishing reagent for mycoplasma hominis and mycoplasmal pneumonia based on the different culturing features of mycoplasma hominis and mycoplasmal pneumonia. After adding the distinguishing reagent for mycoplasma hominis or mycoplasmal pneumonia in the basic culture reagent, the culture medium is only applicable for the growth of mycoplasma hominis or mycoplasmal pneumonia, and culture and distinguish various pathogenic mycoplasma for human being. The invention further prepares the reagent box, which obviously makes convenience for the clinic detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI EASTDIAGNO MEDICAL TECH
Human mycoplasma detection system based on RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a and application thereof
PendingCN114395636ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleic acid detectionMicrobacterium
The invention discloses a mycoplasma hominis detection system based on RPA-CRISPR / Cas12a and application of the mycoplasma hominis detection system, and relates to the field of microbiological detection. The detection system comprises an RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) primer pair, a probe, crRNA (complementary Ribonucleic Acid) and AsCas12a protein, the sequences of the RPA amplification primer pair are as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4; the sequence of the probe is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 16; the crRNA is a sequence as shown in any one of SEQ ID NO: 10 to SEQ ID NO: 12. According to the three rapid nucleic acid detection methods for the mycoplasma hominis, which are constructed on the basis of the RPA-CRISPR / Cas12a detection system, the detection sensitivity is increased, and the method disclosed by the invention shows extremely high specificity, so that a new technical platform is provided for the detection of the mycoplasma hominis.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Genital tract pathogen nucleic acid detection kit
InactiveCN109457037AImprove stabilityReduce inconvenienceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingMycoplasma hominis
The invention discloses a genital tract pathogen nucleic acid detection kit which comprises a first detection component, a second detection component and a third detection component which are freeze-dried and simultaneously perform fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection after detection samples are added. The first detection component is used for detecting Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the second detection component is used for detecting mycoplasma urealytium and mycoplasma hominis, and the third detection component is used for detecting mycoplasmagenitalium. The kit can simultaneously detect five nucleic acids such as the Chlamydia trachomatis, the Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the mycoplasma urealytium, the mycoplasma hominis and the mycoplasma genitalium in a genital tract, detection of five pathogenic microorganisms is integrated into a consumable, reagent stability is improved by the aid of a freeze-drying process, the kit is disposable whenbeing used by each user, only single sampling and one-step operation are needed, laboratory operators are greatly free, detection cost is reduced, inconvenience of a patient is decreased, and the financial burden of the patient is relieved.
Owner:MERLIN BIOMEDICAL (XIAMEN) CO LTD
Gene chips for detecting of pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases and reagent kit for detecting
ActiveCN101407836BTimely diagnosisImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementNeisseria gonorrhoeaeEpidemiology
The invention provides a gene chip used for detecting the common pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases and a kit used for detection, wherein, the gene chip includes a solid phase vector and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid phase vector; the oligonucleotide probe mainly comprises a DNA segment or a complementary DNA segment thereof which is selected from Diplococcus gonorrhoeae, Ureaplasma urealyticum and the 16S rRNA gene of M.hominis, the outer membrane protein gene (ompA gene) of a Chlamydia trachomatis, the glycosidoprotein B gene (gB gene) of a herpes simplex virus (HSV) and the L1 gene of a papilloma virus (HPV). The gene chip and the kit can be utilized for achieving the goal of detecting the common pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases; the gene chip and the kit for detection are simple and convenient to be operated, have high flux, accuracy and repetitiveness; and the gene chip and the kit for detection can be applied to the clinic detection and epidemiology analyzing of medical and health organizations.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
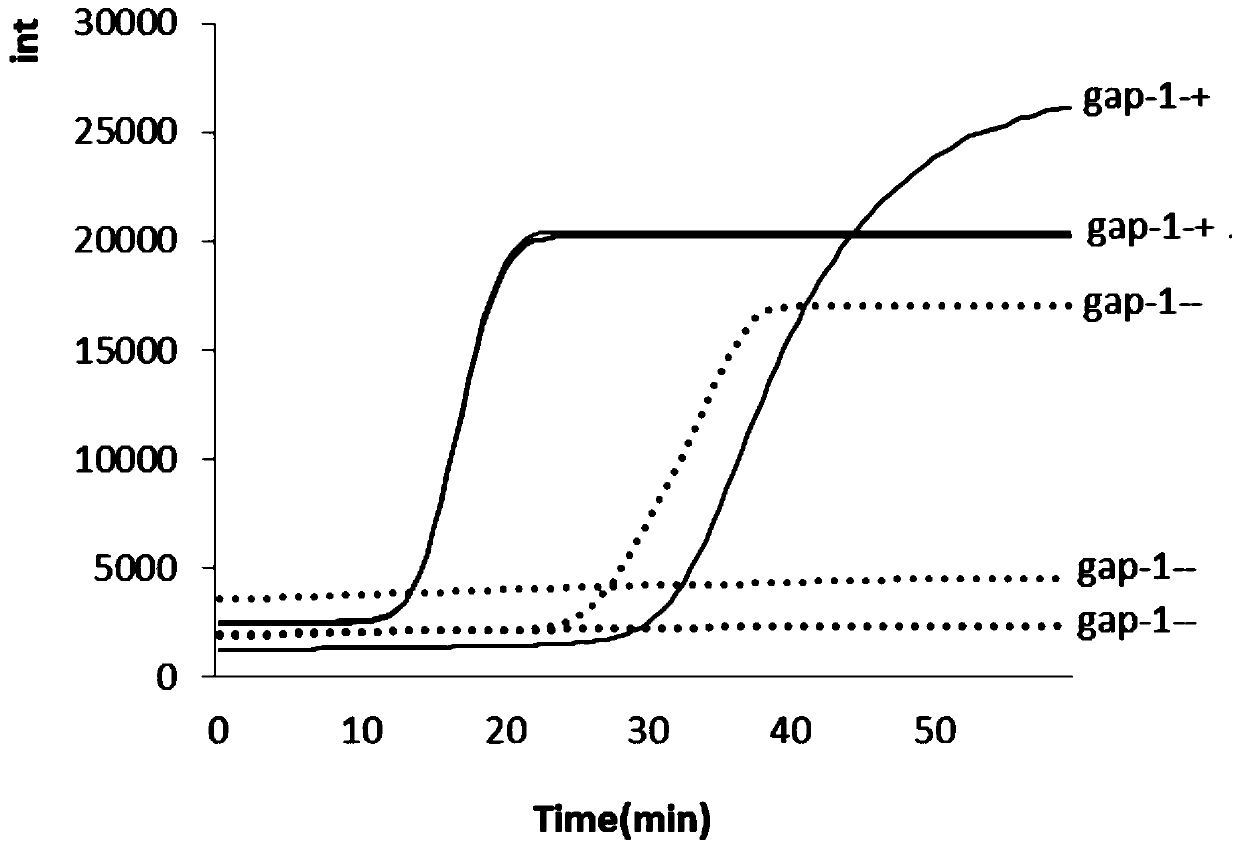
LAMP detection method and kit for mycoplasma hominis
PendingCN109943653AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMycoplasma hominisRepeatability
The invention provides a LAMP detection method and a kit for mycoplasma hominis. 4 or 6 specific primers are designed for 6 or 8 regions of a gap genes sequence gene of the mycoplasma hominis, a LAMPdetection primer group is obtained through creative labor design of an inventor, is used for detecting the mycoplasma hominis in a sample and has the characteristics of rapidness, accuracy, simplicity, cheapness, repeatability, good specificity and high sensitivity. The detection line reached 42 pg per microliter.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Detection system capable of curing sexually transmitted infection pathogens and a kit and application thereof
PendingCN112831581AReduce usageReduce medical costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMycoplasma hominisGenital secretion
The invention relates to a detection system capable of curing sexually transmitted infection pathogens and a kit and application thereof. The detection system comprises six pairs of primers for detecting treponema pallidum, trichomonad vaginalis, chlamydia trachomatis, neisseria gonorrhoeae, ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis, one pair of human DNA internal reference primers and one pair of system quality control internal reference primers. According to the detection system capable of curing the sexually transmitted infection pathogens and the kit thereof, the steps of conventional culture and the like are not needed, synchronous identification and semi-quantitative analysis of six pathogens difficult to culture can be directly carried out on a genital tract secretion sample in the same reaction system, and the detection system and the kit have the advantages of high specificity, high sensitivity, good repeatability, rapidness and accuracy; a comprehensive, accurate and low-cost etiological diagnosis basis can be provided for clinic and patients in the first time, and an important reference is provided for individualized medication and accurate medical treatment.
Owner:HUADONG HOSPITAL +1
Non-diagnostic method for accelerating time to detection of Mycoplasma under a-peg-b array
InactiveCN101851661BClinical test resultsExtension of timeMicrobiological testing/measurementControlled releasePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a method for shortening mycoplasma clinical detection time under an A-PEG-B array, which belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving polyethylene glycol (PEG) having a repeated structure of --(OH2CH2O)n-- into an in-vitro diagnostic kit for culturing, identifying, quantifying and medicinally sensitizing ureaplasmaurealyticum (Uu) and mycoplasma hominis (Mh) to promote clinical recombination with the A-PEG-B array. In the method, in recombination reaction at the right end of the A-PEG-B array, the functions of the PEG in the complementation and controlled-release of all active substances are highlighted; in the recombination reaction at the left end of the A-PEG-B array, the osmotic pressure function of the PEG is highlighted; at the right end of the A-PEG-B array, the antibiotic capacity and biological activity of a culture medium are simultaneously improved; and at the left end of the A-PEG-B array, the detected Uu and Mh are repaired to different extents and the activity of the detected Uu and Mh on the culture medium is improved. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of obtaining detection results 12 to 24 earlier and remarkably shortening time for curing sicknesses to save patients.
Owner:其昌达生物高科技(上海)有限公司
Kit and method for synchronously detecting multiple genital tract pathogens
PendingCN113444821AStrong specificityImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerNucleotide
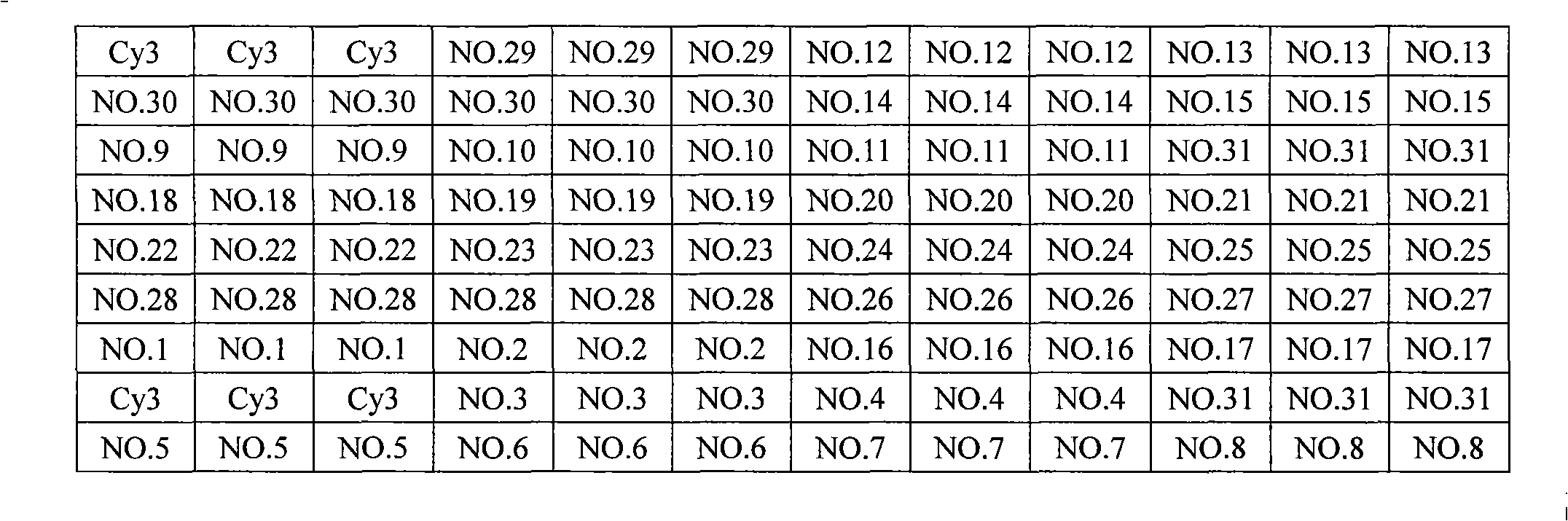
The invention discloses a kit and method for synchronously detecting multiple genital tract pathogens. The kit comprises a nucleic acid reaction solution; the nucleic acid reaction solution comprises a primer and a probe of gonococcus, a primer and a probe of ureaplasma urealyticum, a primer and a probe of chlamydia trachomatis, a primer and a probe of mycoplasma hominis, a primer and a probe of mycoplasma genitalium and a primer and a probe of herpes simplex virus type 2. Forward primers of the pathogens respectively comprise nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.7, SEQ ID NO.10, SEQ ID NO.13 and SEQ ID NO.16, reverse primers of the pathogens respectively comprise nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.5, SEQ ID NO.8, SEQ ID NO.11, SEQ ID NO.14 and SEQ ID NO.17, and the probes of the pathogens respectively comprise nucleotide sequences shown as SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.6, SEQ ID NO.9, SEQ ID NO.12, SEQ ID NO.15 and SEQ ID NO.18. The kit can be used for rapidly, accurately and synchronously detecting gonococcus, ureaplasma urealyticum, chlamydia trachomatis, mycoplasma hominis, mycoplasma genitalium and herpes simplex virus type 2, and is relatively strong in specificity and relatively high in sensitivity.
Owner:HEMOSMART MEDICAL TECH LTD
Camera-based automatic identification system for pathogen culture test result
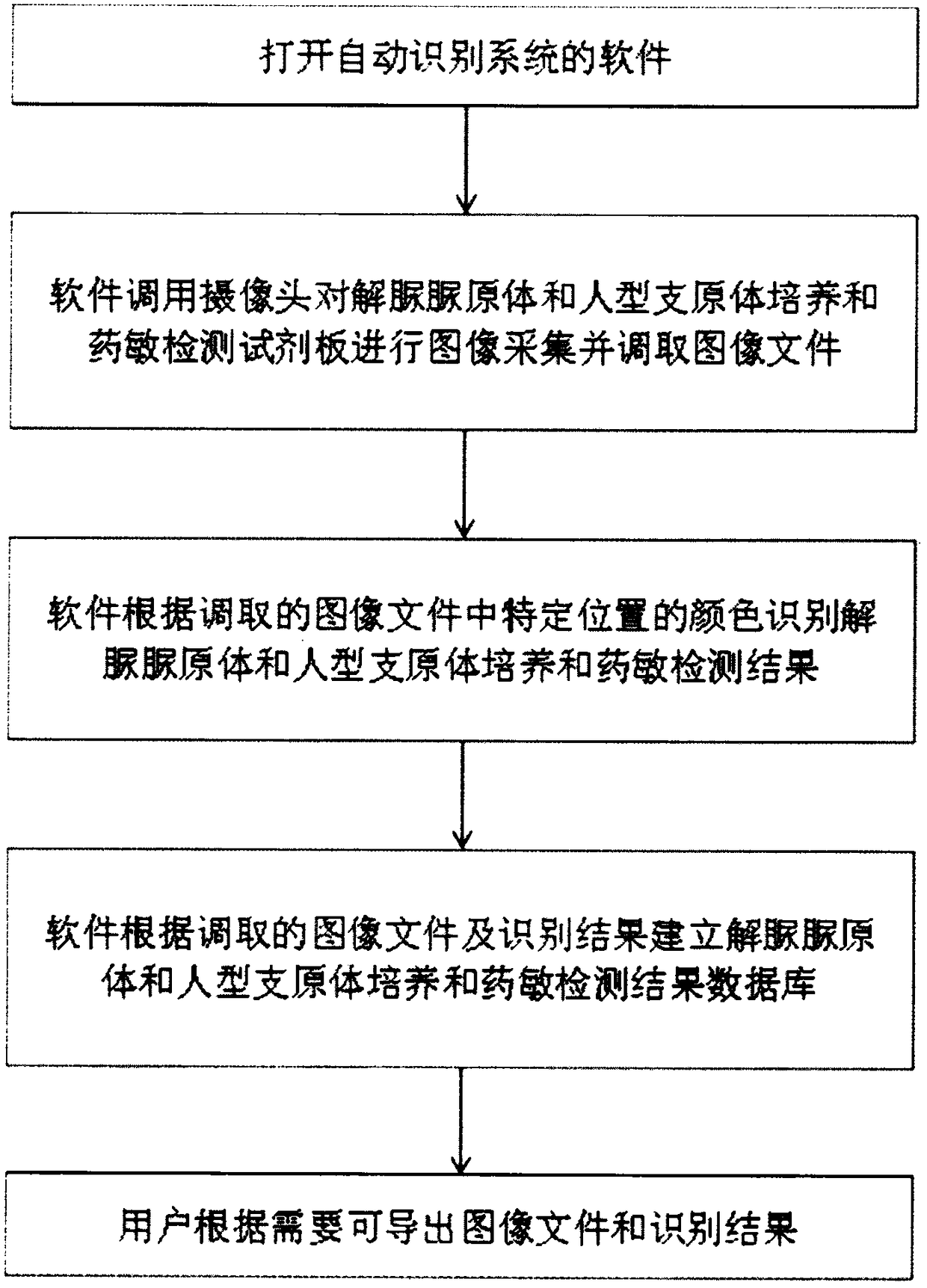
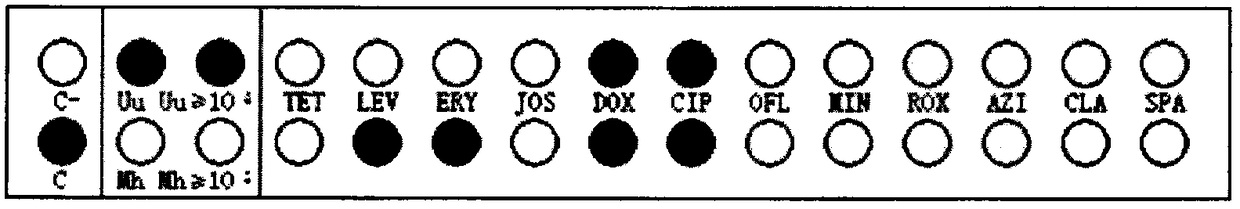
InactiveCN108537768AGuaranteed traceabilityIdentification specificationImage enhancementImage analysisMycoplasma hominis cultureColor recognition
The invention discloses a camera-based automatic identification system for the pathogen culture test result. Steps are as follows, firstly, the software of the automatic identification system is opened; ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis culture and drug sensitivity detection reagent plates under the culture for 24 hours and for 48 hours can be placed by a user below a camera as needed,the camera is called by the software to collect images of the reagent plates; the ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis culture and drug susceptibility result is identified by the software according to the color of the specific position in the called image file; the result under the culture for 24 hours and for 48 hours is comprehensively analyzed by the software; a ureaplasma urealyticumand mycoplasma hominis culture and drug susceptibility result database is established by the software according to the called image file and the identification result, image acquisition and automaticresult identification of any ureaplasma urealyticum and mycoplasma hominis culture and drug sensitivity test reagent plate result can be carried out by the user, and image files and the identification result of reagent plates collected in the past can be checked at any time.
Owner:林雪峰
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com