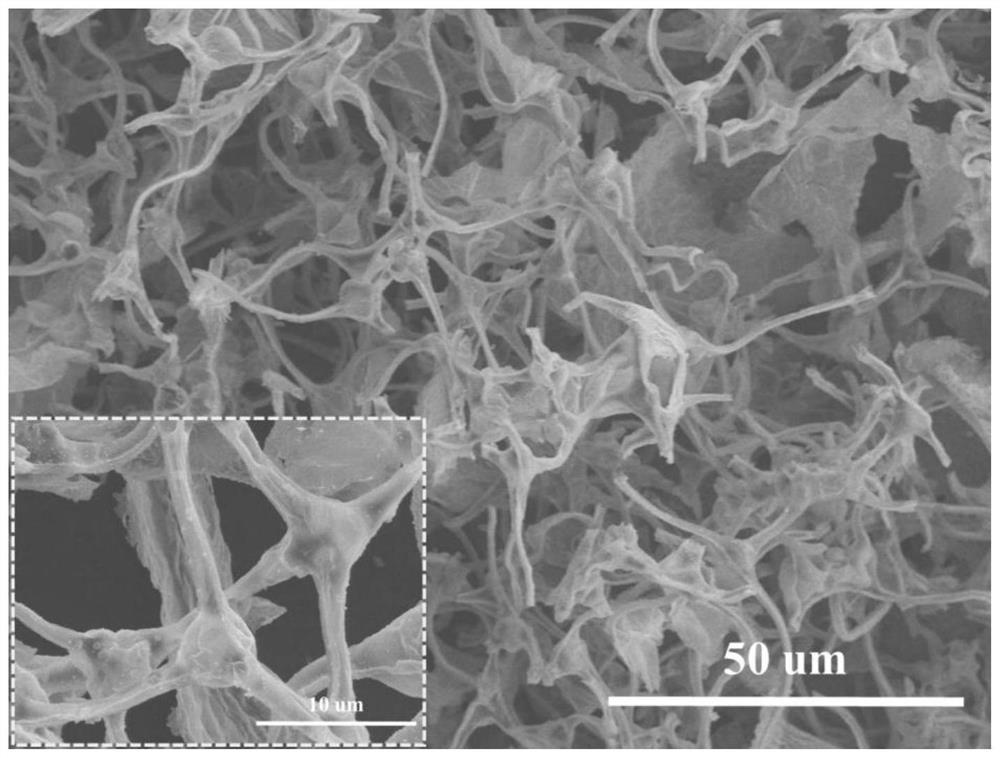
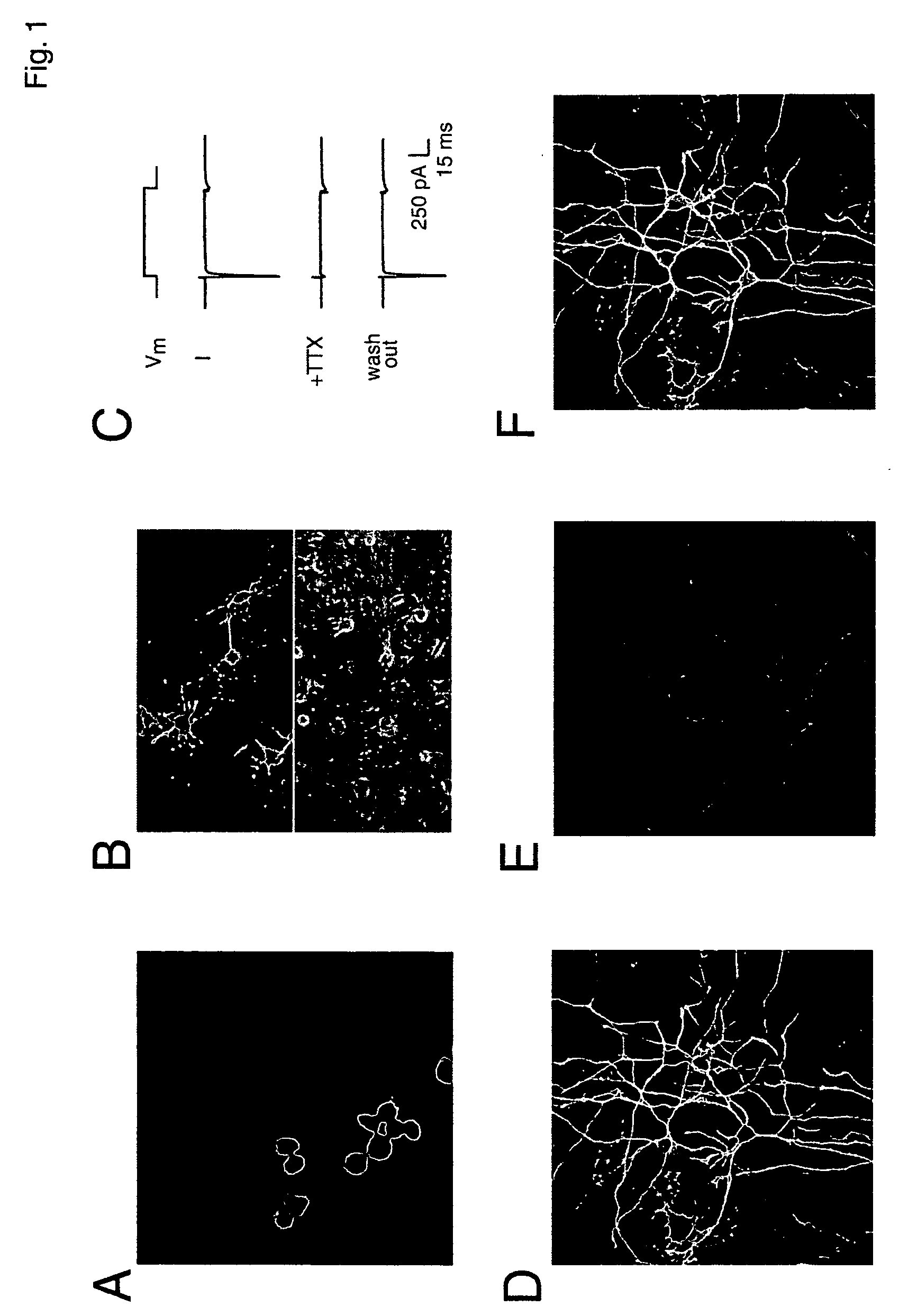
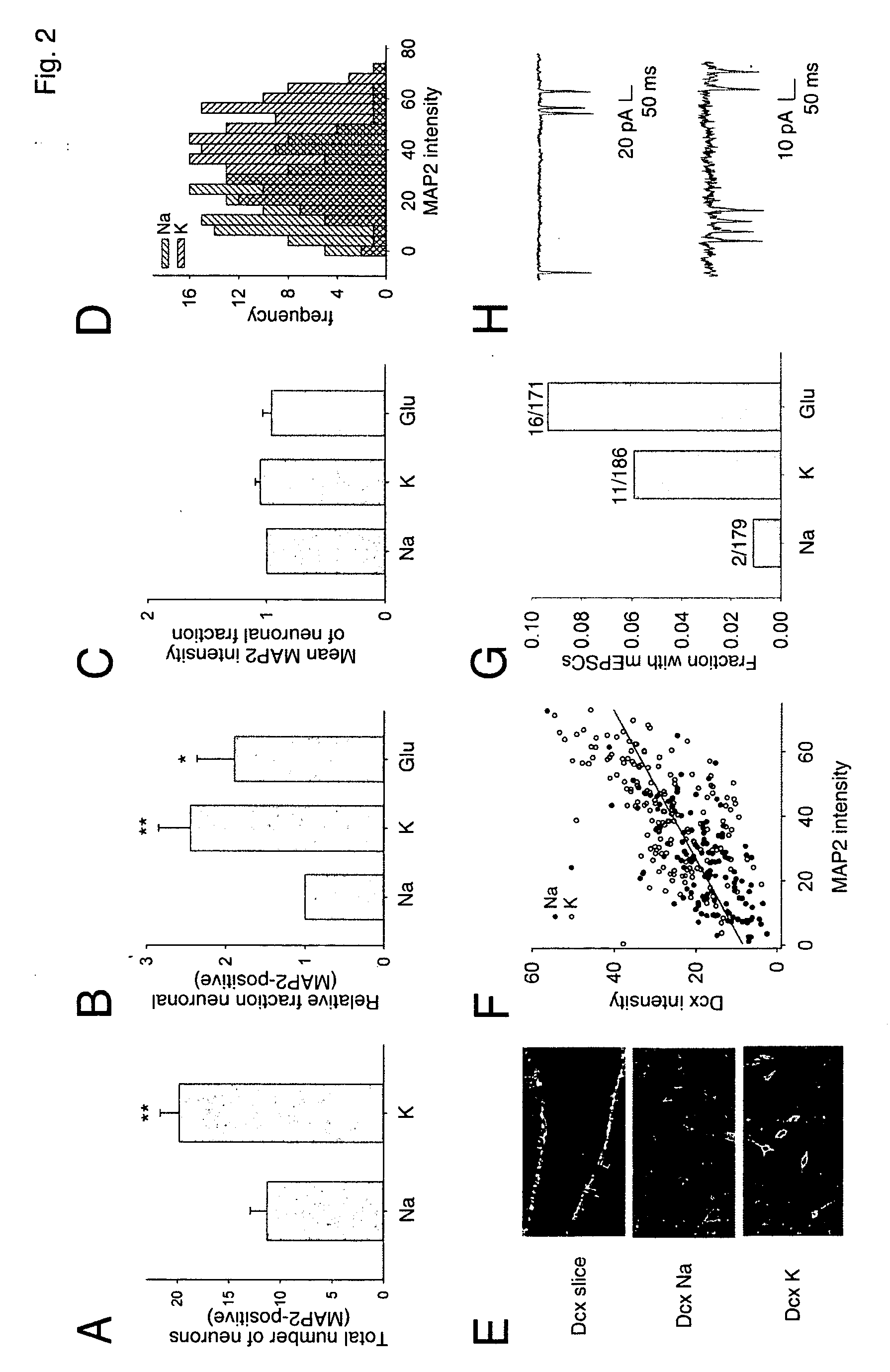
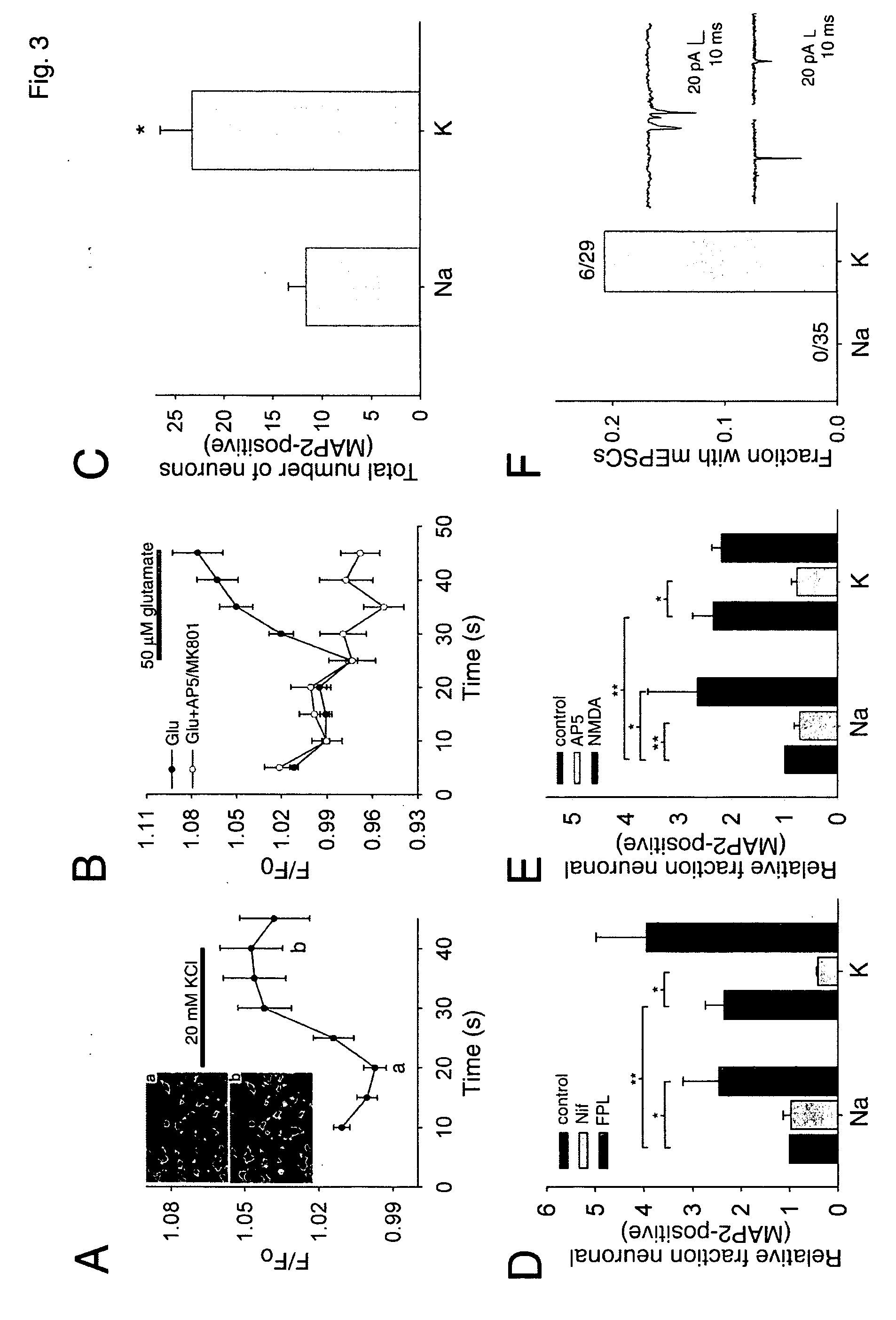
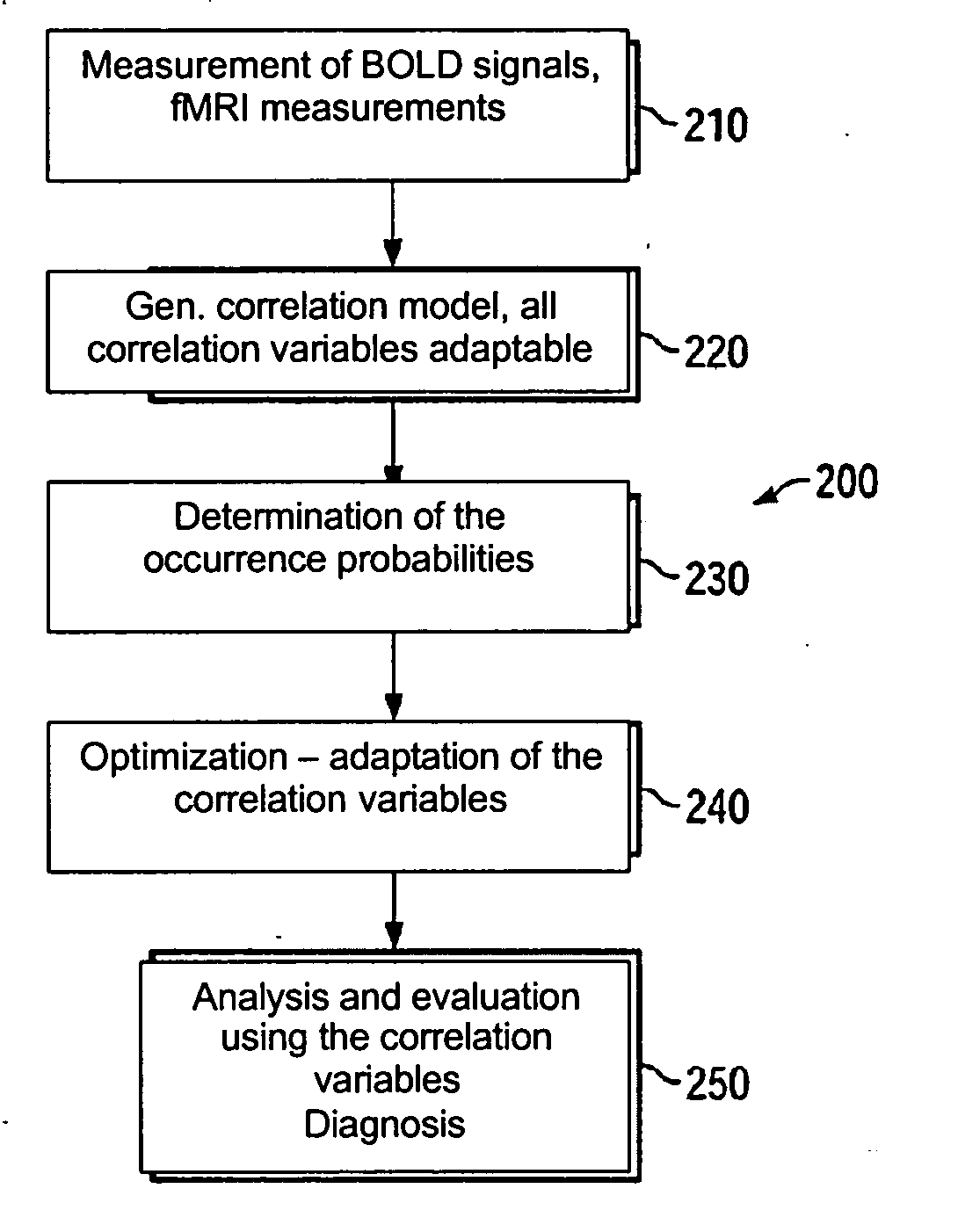
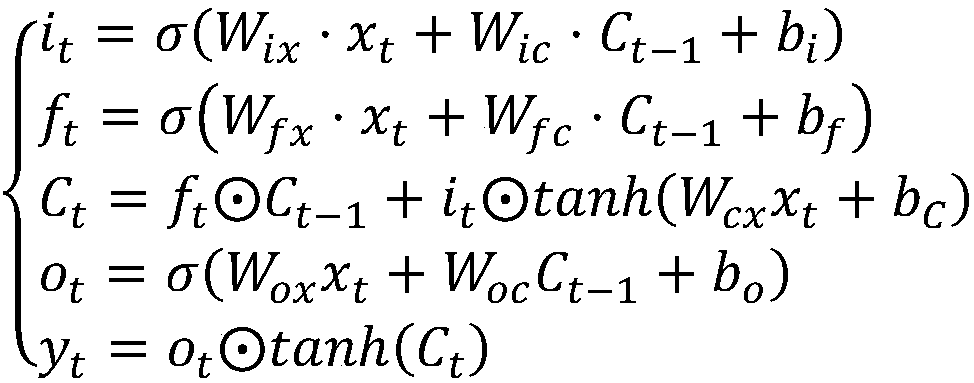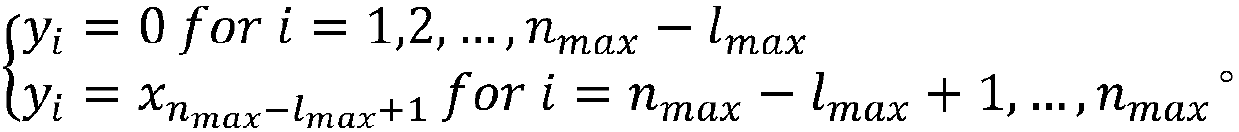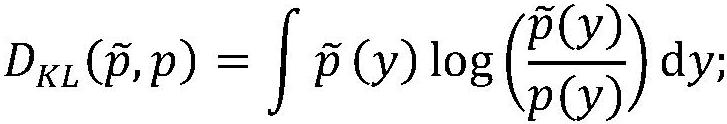Patents
Literature
43 results about "Neuron structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
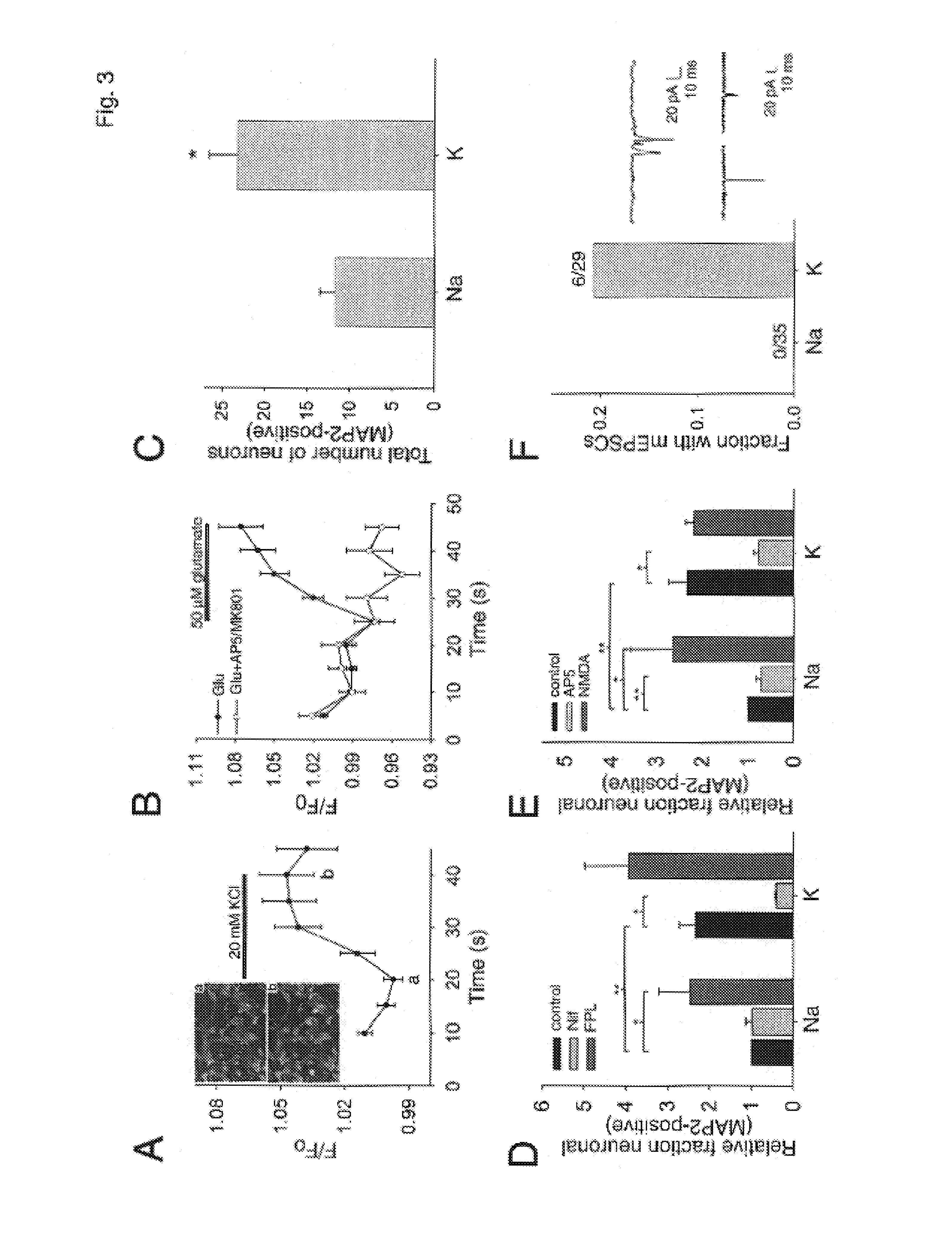
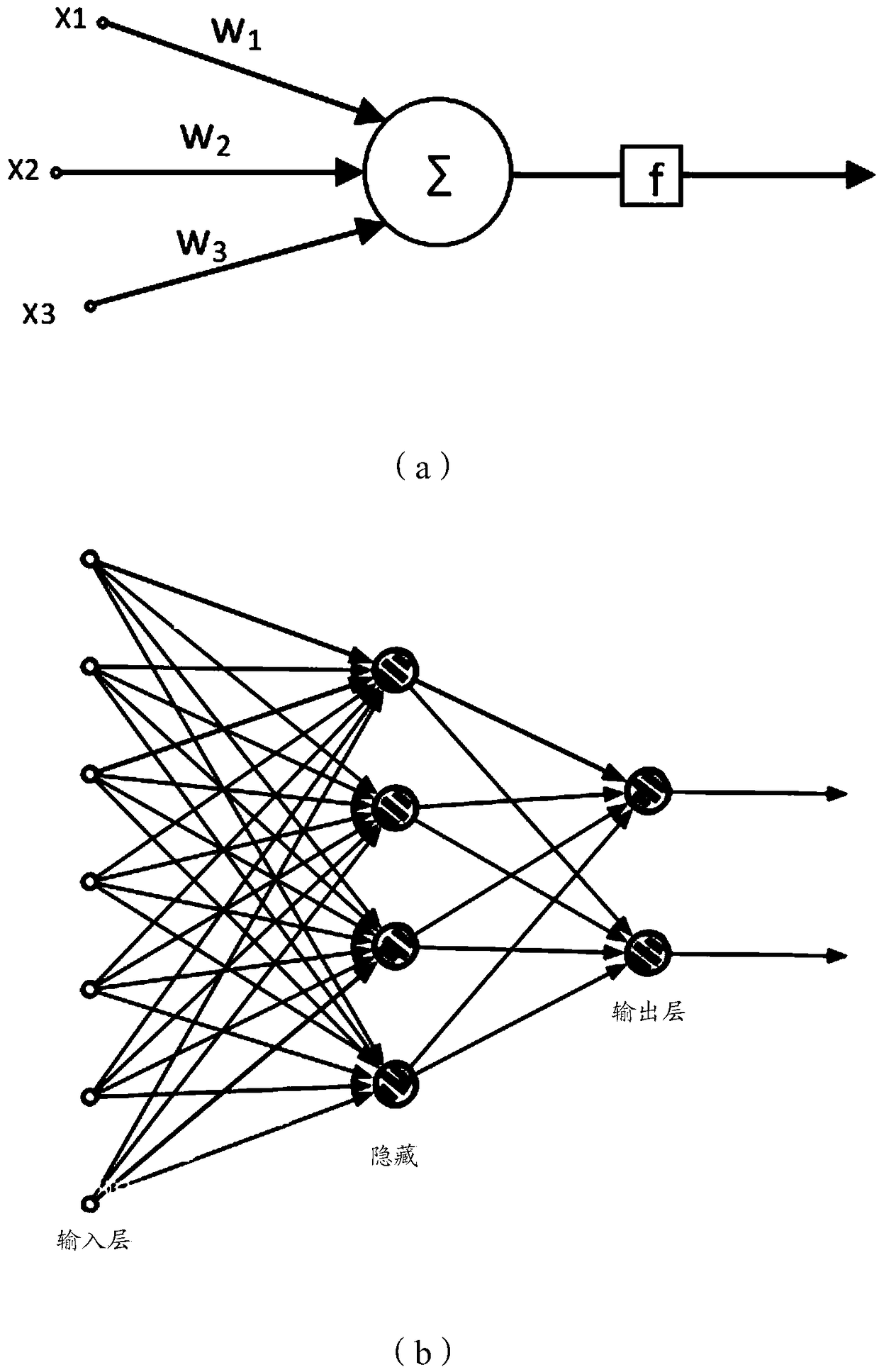
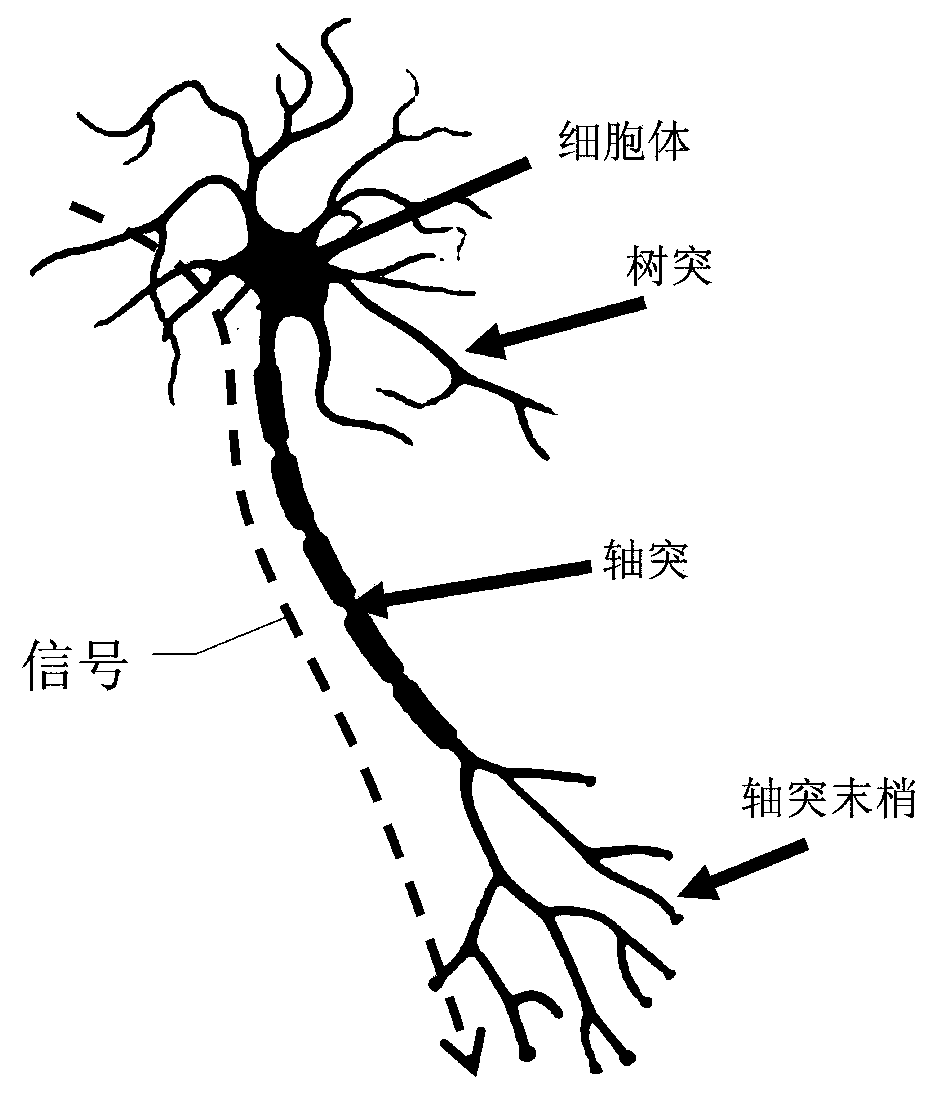
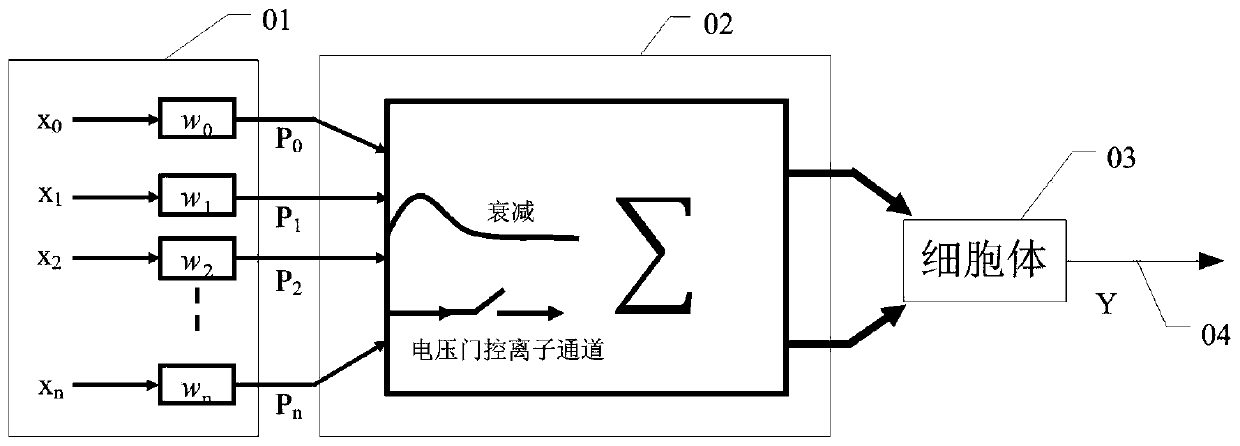
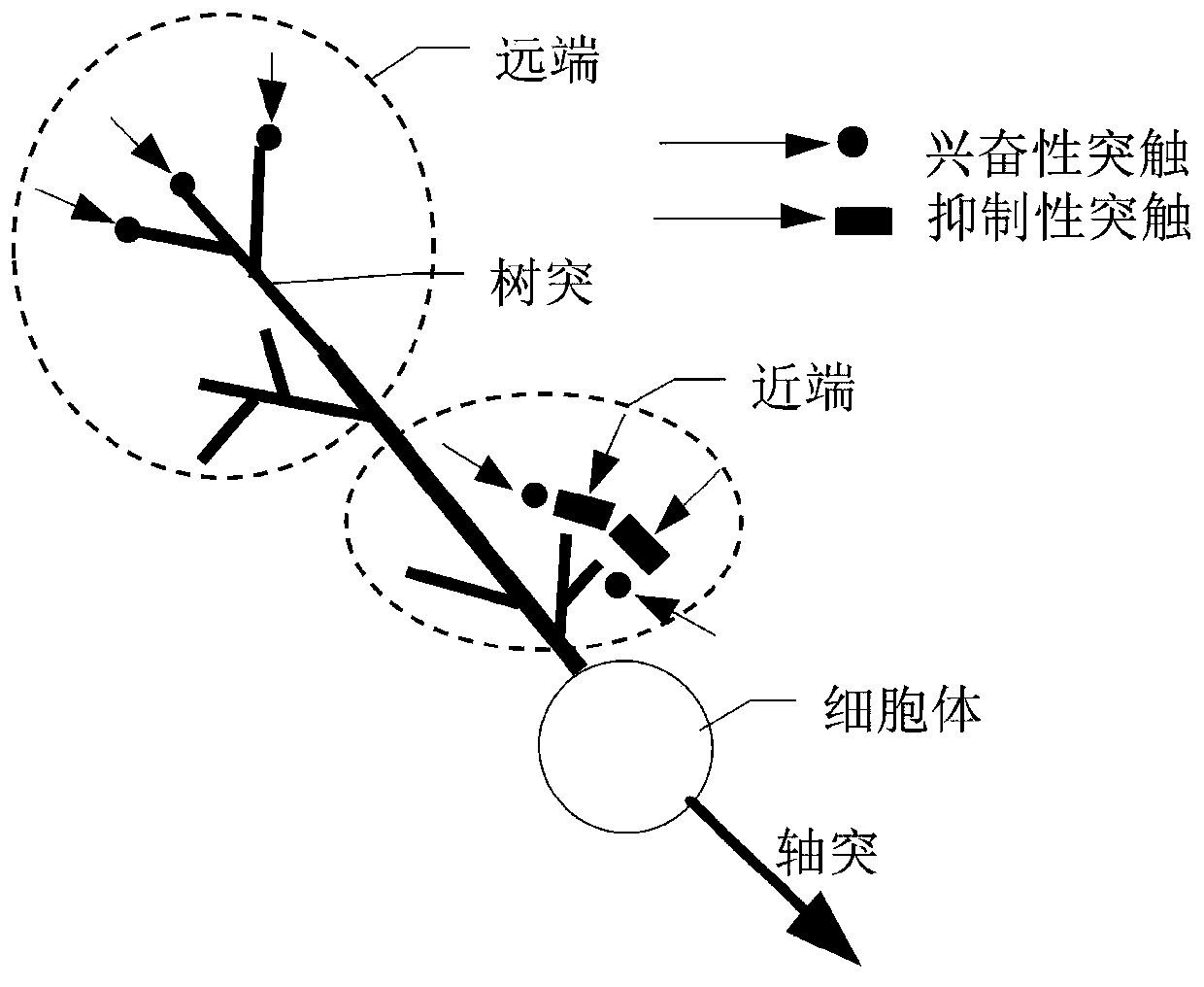
Having surveyed the general features of neuron structure, interactions, and simple circuits, let us turn to the mechanism by which a neuron generates and conducts electric impulses. SUMMARY The cell body of a neuron contains the nucleus and lysosomes and is the site of synthesis and degradation of virtually all neuronal proteins and membranes.
Coupling of excitation and neurogenesis in neural stem/progenitor cells
ActiveUS20050267011A1Increase neuronal cellPromoting neurogenesisElectrotherapyNervous disorderProgenitorNR1 NMDA receptor
Coupling of excitation to neurogenesis in proliferating post-natal NPCs is demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Neurogenesis is potently enhanced by excitatory stimuli, and involves Cav1.2 / 1.3 channels and NMDA receptors. These Ca2+ influx pathways are located on the proliferating NPCs, allowing them to directly sense and process excitatory stimuli. Excitation increases the fraction of NPC progeny that are neurons, and increases total neuron number. Signaling in this pathway leads to rapid induction of a proneural gene expression pattern involving the bHLH genes HES1, Id2, and NeuroD, and the resulting cells become fully functional neurons defined by neuronal morphology, expression of neuronal structural proteins, expression of neuronal TTX-sensitive voltage gated Na+ channels, and synaptic incorporation into active neural circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
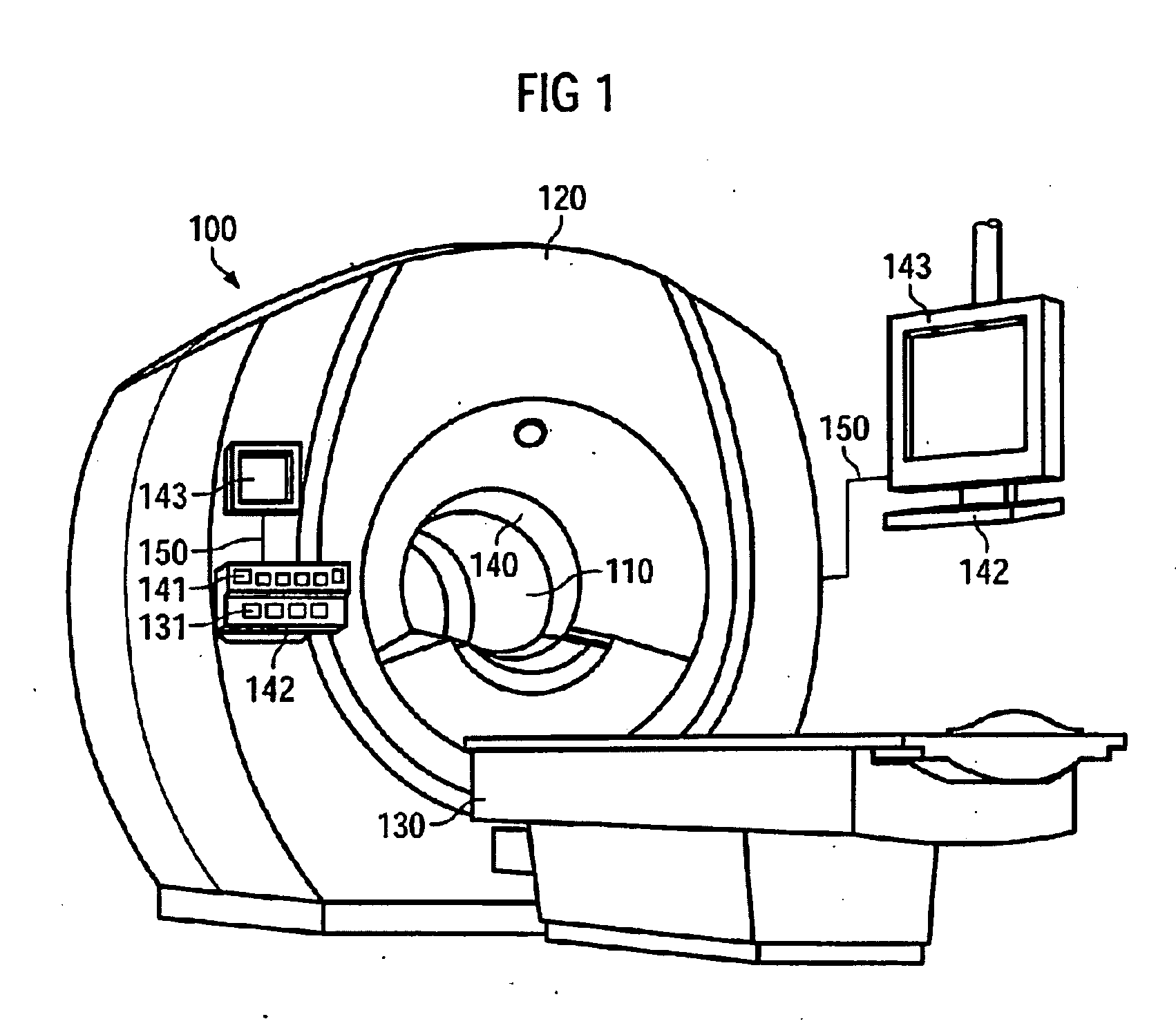
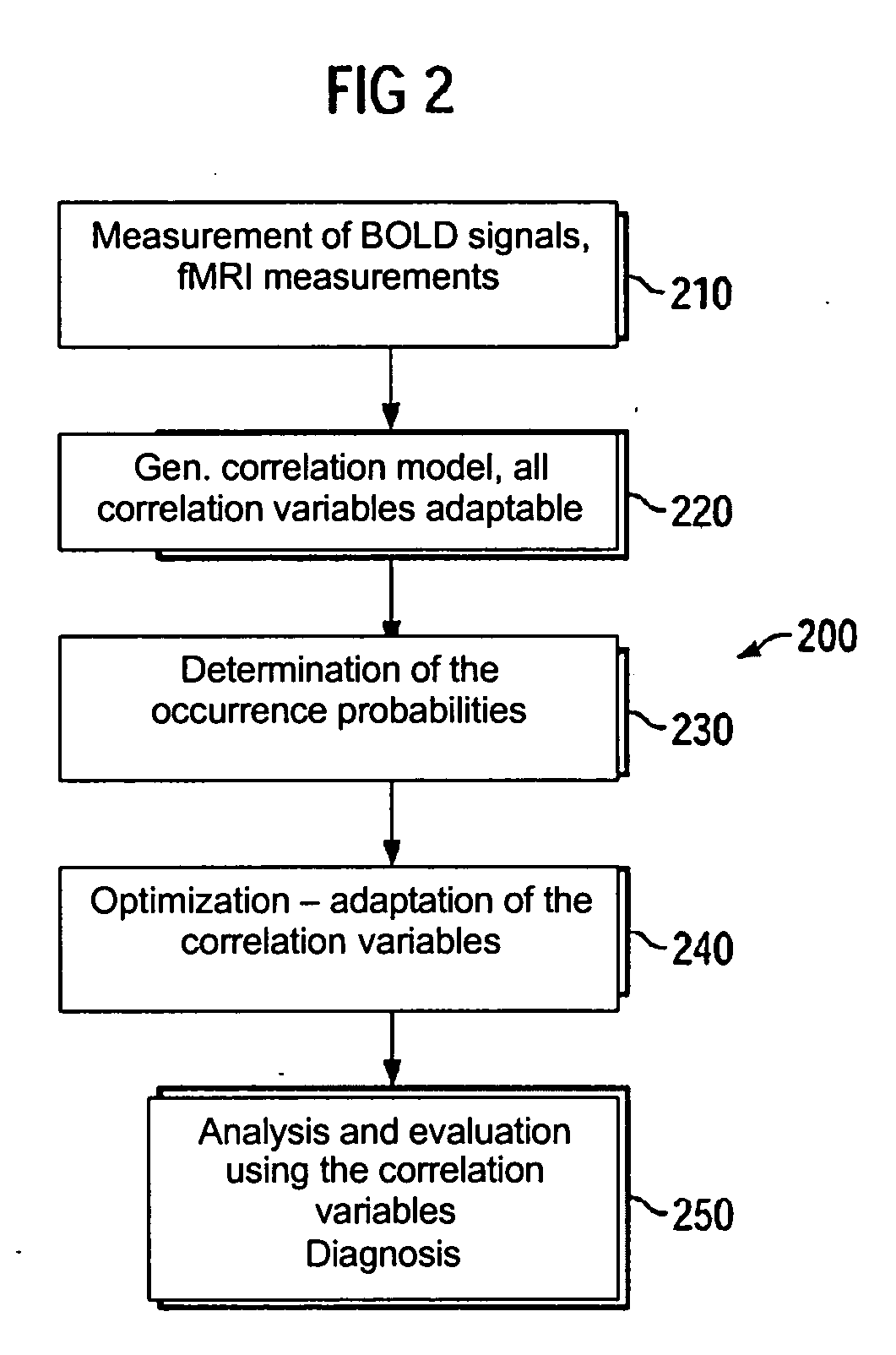
Method for analyzing effectiveness of pharmaceutical preparation
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Coupling of excitation and neurogenesis in neural stem/progenitor cells
ActiveUS7670838B2Increase neuronal cellPromoting neurogenesisElectrotherapyNervous disorderNR1 NMDA receptorProgenitor
Coupling of excitation to neurogenesis in proliferating post-natal NPCs is demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Neurogenesis is potently enhanced by excitatory stimuli, and involves Cav1.2 / 1.3 channels and NMDA receptors. These Ca2+ influx pathways are located on the proliferating NPCs, allowing them to directly sense and process excitatory stimuli. Excitation increases the fraction of NPC progeny that are neurons, and increases total neuron number. Signaling in this pathway leads to rapid induction of a proneural gene expression pattern involving the bHLH genes HES1, Id2, and NeuroD, and the resulting cells become fully functional neurons defined by neuronal morphology, expression of neuronal structural proteins, expression of neuronal TTX-sensitive voltage gated Na+ channels, and synaptic incorporation into active neural circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
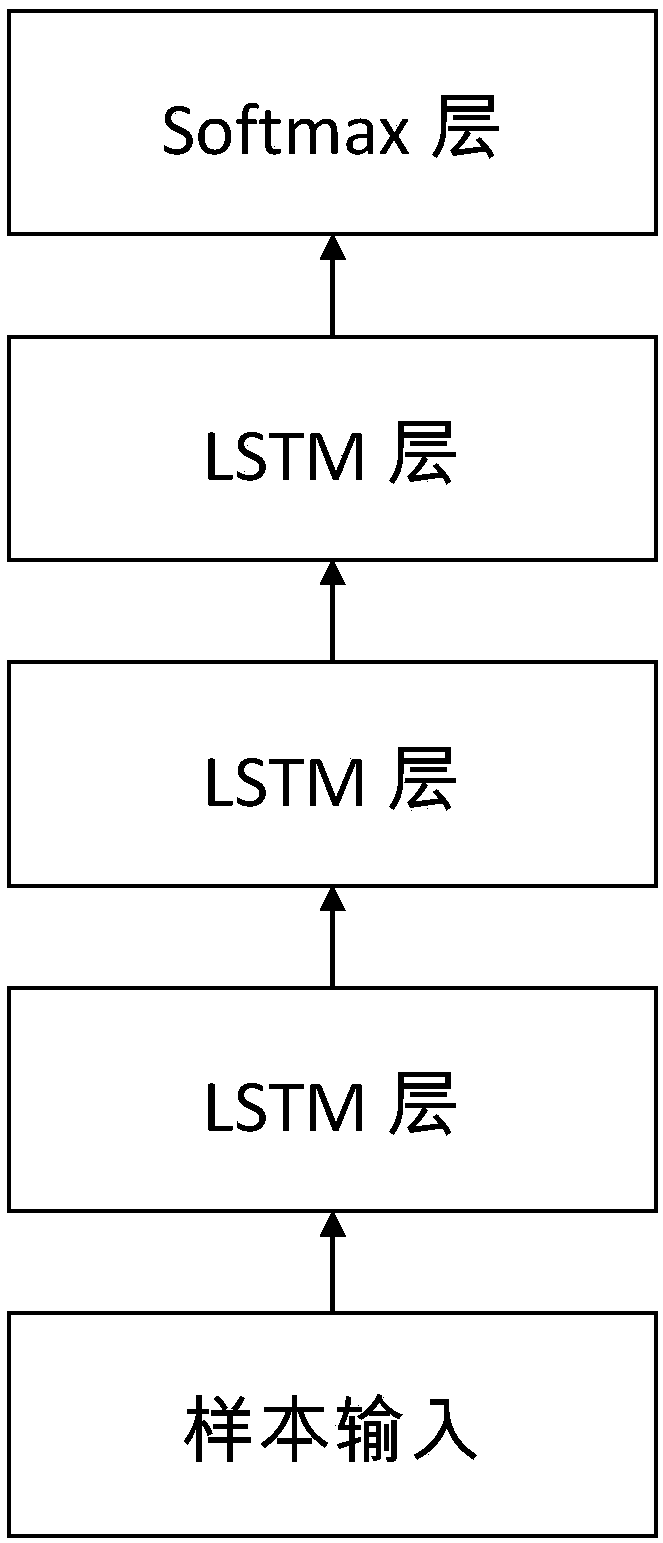
Method for classifying multi-variable time sequences based on deep long/short-term memory neural network
ActiveCN108182259AHigh precisionUniversalCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHidden layerData set
The invention discloses a method for classifying multi-variable time sequences based on a deep long / short-term memory neural network. The method includes the steps of by selecting long / short-term memory neuron structures as hidden layer neuron structures of a recurrent neural network, overlapping long / short-term memory neurons, and designing a deep layer recurrent neural network classification framework, thereby achieving the aim of improving the classification accuracy of multi-variable time sequence data. It is found through experimental comparison that accuracy is higher compared with an existing classification model and universality is achieved on time sequence data set classification tasks in multiple fields.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
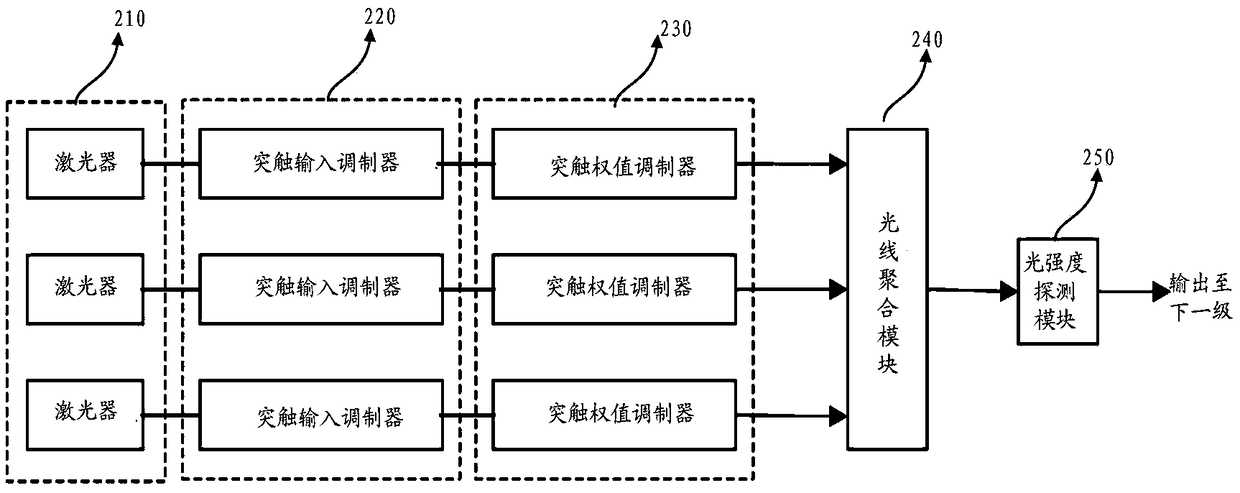
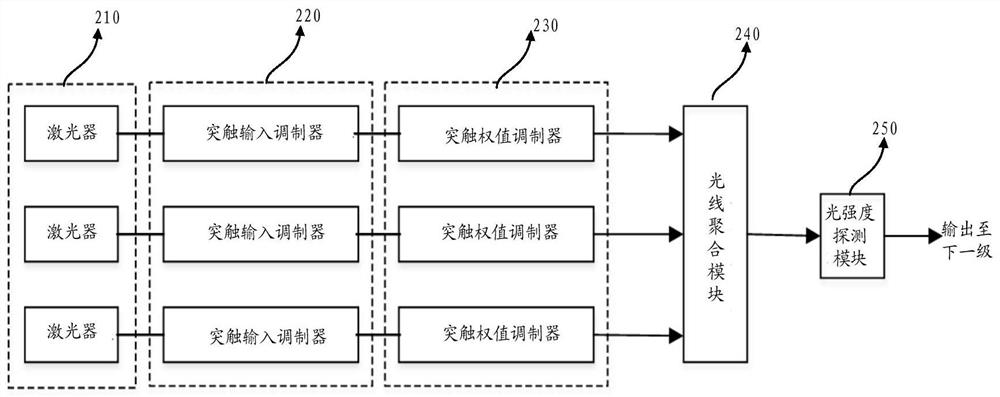
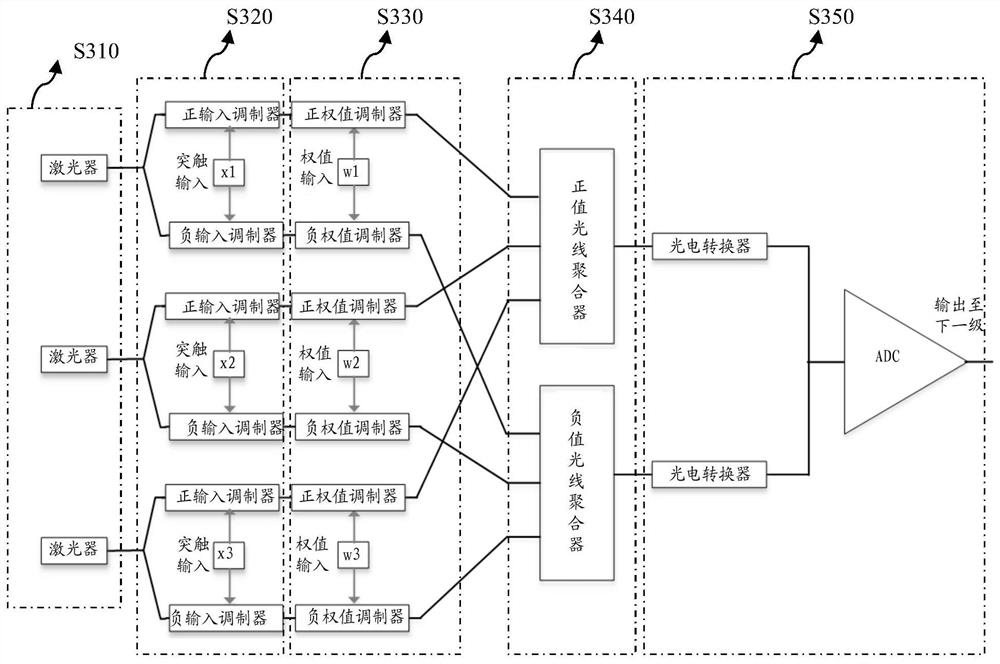
An optical neuron structure and a neural network processing system including the structure
ActiveCN109376855AHigh speedReduce energy consumptionPhysical realisationSynaptic weightNerve network
The present invention provides an optical neuron structure and a neural network processing system including the structure. The neuron structure comprises a synaptic input modulation module, a synapticweight modulation module, a light aggregation module and a light intensity detection module, wherein, the synaptic input modulation module is used for receiving an optical signal and performing optical path modulation under the control of an electrical signal associated with the input neuron; A synaptic weight modulation module for performing modulation of an optical signal of the bearer input neuron under control of an electrical signal associated with the weight; The light aggregation module is used for aggregating the output optical signals of a plurality of synaptic weight modulation modules; The light intensity detection module is configured to convert an output light signal from the light aggregation module into an electrical signal and perform an activation operation. The optical neuron structure of the invention and the neural network processing system including the structure can realize the fast calculation of the neural network.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
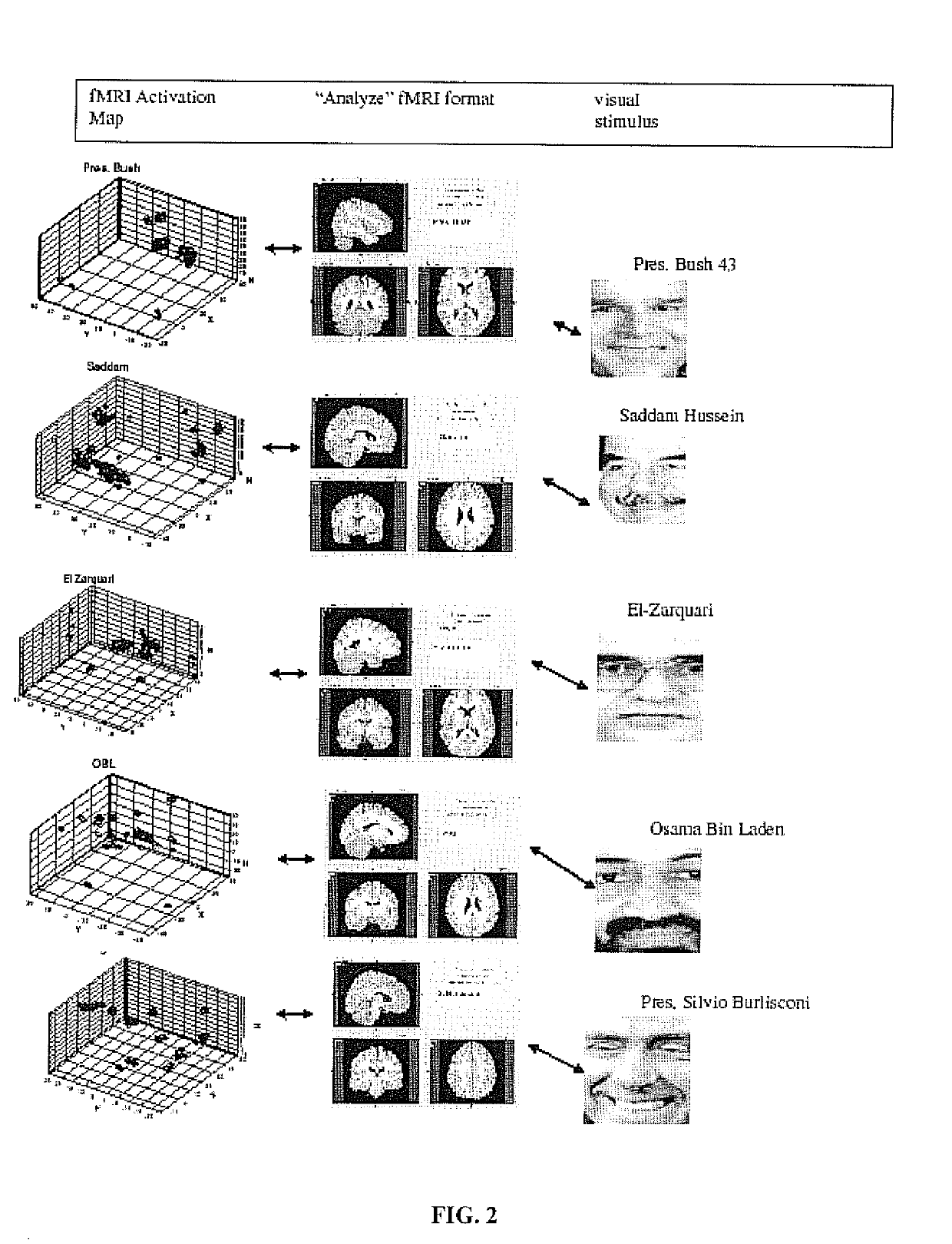
Brain function decoding process and system
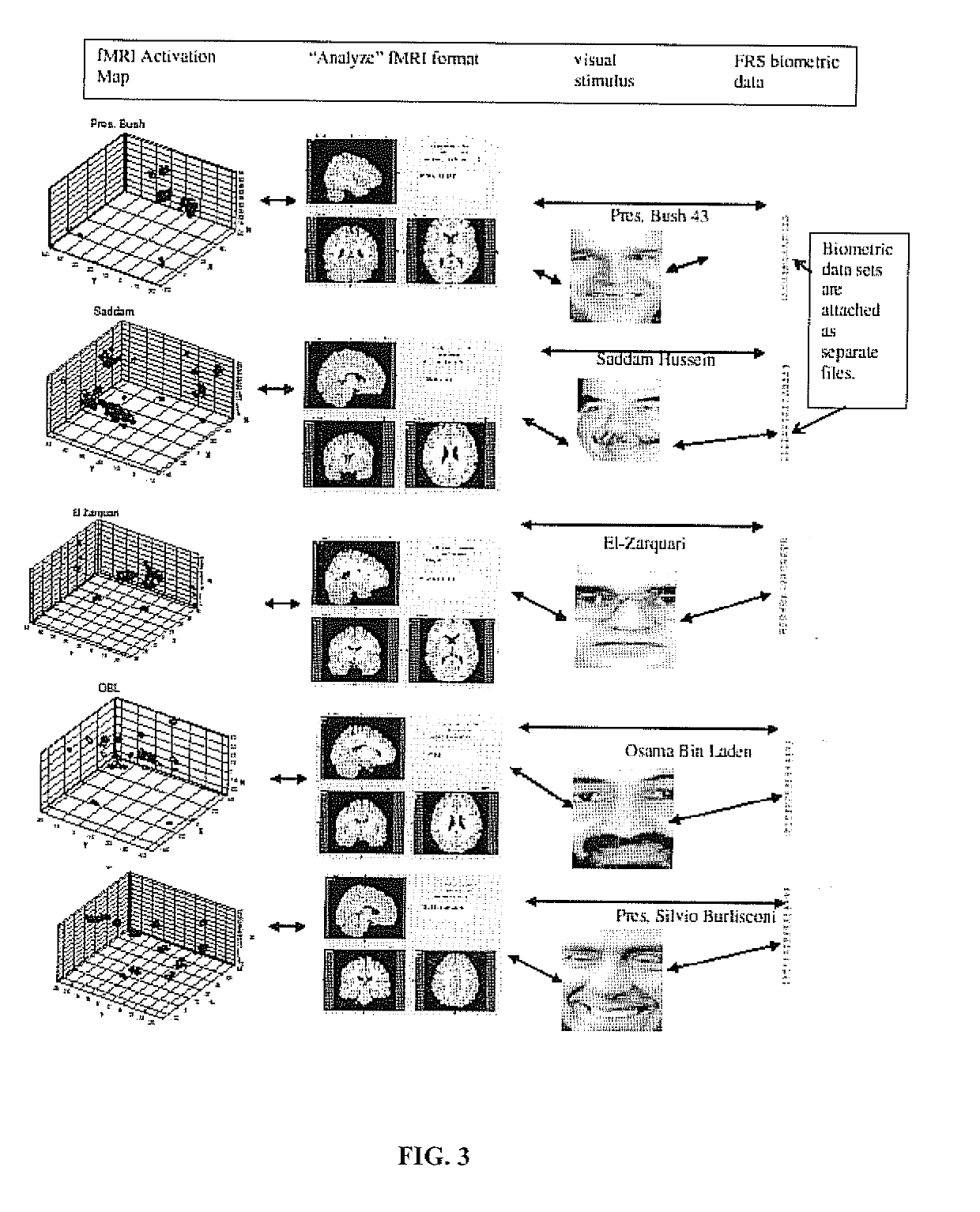
InactiveUS20190159712A1Improve responseMedical imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsBiometric data
A process of correlating cognitive response to a stimulus is provided by collecting biometric data with a camera having a microprocessor for modifying an image by localizing eyes within a face in the image, collecting neural activity data from a subject while exposed to a stimulus and mapping neural activation in response to the stimulus onto neuronal structure of a subject brain. A unique three-dimensional cognitive engram representative of the neural activity caused by the stimulus is then constructed. The cognitive engram is then compiled in a database containing a plurality of engrams, each of which is associated with a different stimulus for interpreting cognitive response. Then, each unique three-dimensional cognitive engram stored in the database is correlated with the biometric data representative of a stimulus.
Owner:MARKS DONALD H
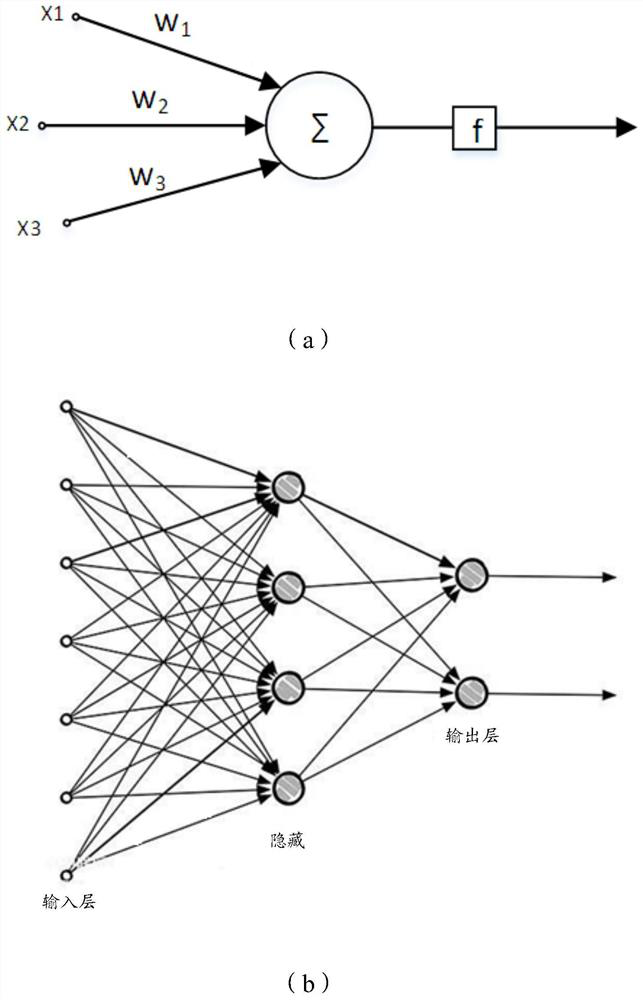
Multilayer perceptron artificial nerve network based on residual error network
InactiveCN106779062ASmall amount of calculationEasy to useNeural learning methodsHidden layerNerve network
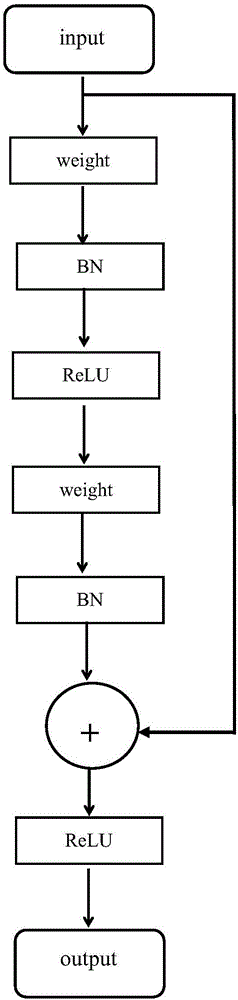
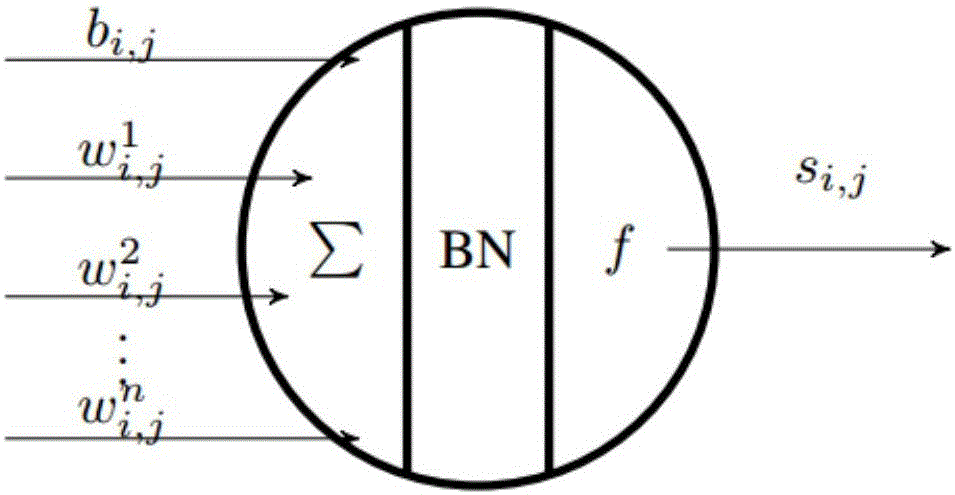
The invention discloses a multilayer perceptron artificial nerve network based on a residual error network; the multilayer perceptron artificial nerve network based on the residual error network comprises a plurality of network module structures; a full connection mode is employed to replace the convolution in the residual error nerve network; Neuron units in the network module structures can obtain the output of the complete residual error module through the output of each hidden layer, wherein the output of each hidden layer refers to si=ReLU[BN(neti)]; the complete residual error module output refers to oi=ReLU[BN(neti+1)+neti]. The multilayer perceptron artificial nerve network is based on the residual error network, small in computational complexity, high in accuracy, and can be applied to more fields besides the image field.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods for treating early stage or mild neurological disorders
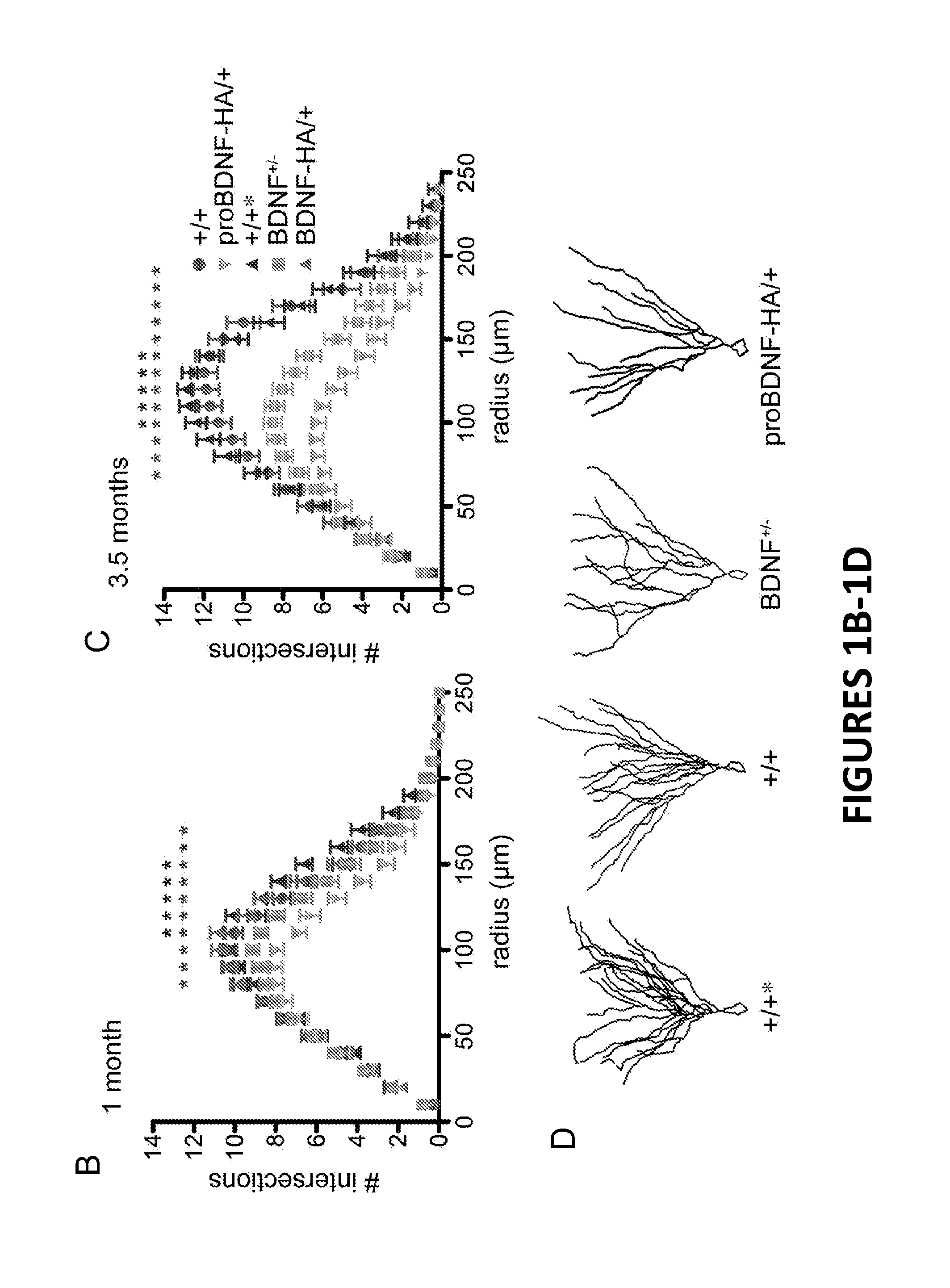
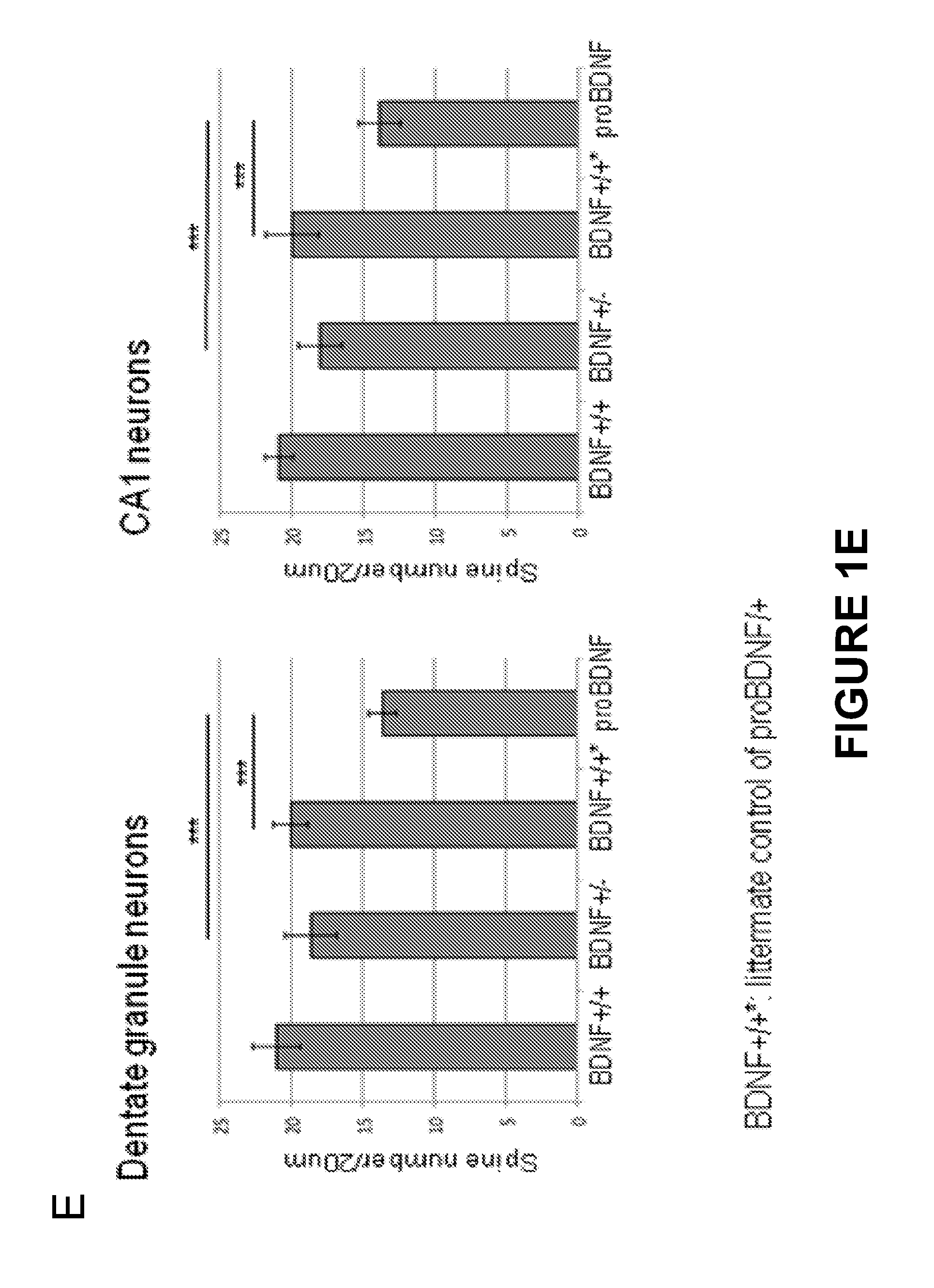
InactiveUS20130336988A1Reducing and/or preventing unwanted reduction in synaptic spinesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineNeuron
This disclosure relates to modulation of the interactions between proNTs and p75NTR / SorCS2 expressed on neuronal cells. Inhibition of such interactions is useful for reducing unwanted synaptic elimination, neurite pruning and / or other neuronal structural collapses, and for treating early stage and mild neurological disorders including mild cognitive impairment.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Rapid neuron staining method based on Golgi silver staining method
InactiveCN103471898AEffective detection meansOvercoming long-term operationsPreparing sample for investigationNervous systemMicroscopic observation
The invention discloses a rapid neuron staining method based on a Golgi silver staining method. The rapid neuron staining method based on the Golgi silver staining method is characterized in that according to mass volume ratio concentration, the aqueous solution with 5 % of potassium dichromate, the aqueous solution with 5 % of mercuric chloride and the aqueous solution with 5 % of potassium chromate are prepared into a Golgi silver staining solution in the volume ratio of 1:1:1, a brain tissue is soaked in the silver staining solution at 37 DEGCfor 36-48 hours, the soaked brain tissue is sliced on a vibrating slicer, tissue sections are arranged on a glass slide coated with gelatin, the tissue sections stay overnight, then conventional ammonia developing is conducted, gradient alcohol dehydration is conducted, the transparency process is conducted by xylene, finally, the tissue sections are sealed by netrual gum, and the tissue sections are observed through a microscope. According to the rapid neuron staining method based on the Golgi silver staining method, staining can be conducted on each encephalic region of the brain, the staining result is clear, details are obvious, and research staff can observe the neuron structure of the brain tissues conveniently, the convenient and fast means is provided for case analysis of nervous system lesions, and the rapid neuron staining method based on the Golgi silver staining method has significant meanings for the field of foundational research of neurology.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
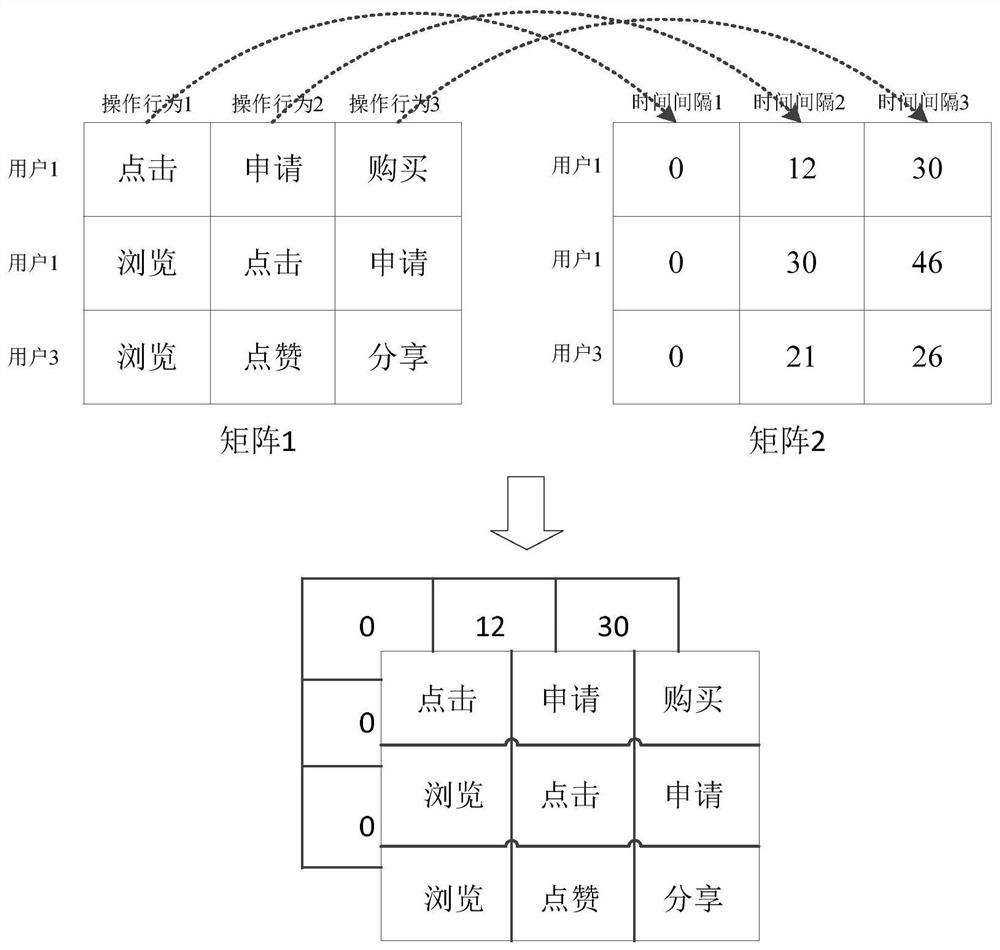
User behavior feature extraction method, device, equipment and system
ActiveCN111709754AAccurate extractionEfficient and accurate establishmentNeural architecturesProtocol authorisationFeature extractionSimulation
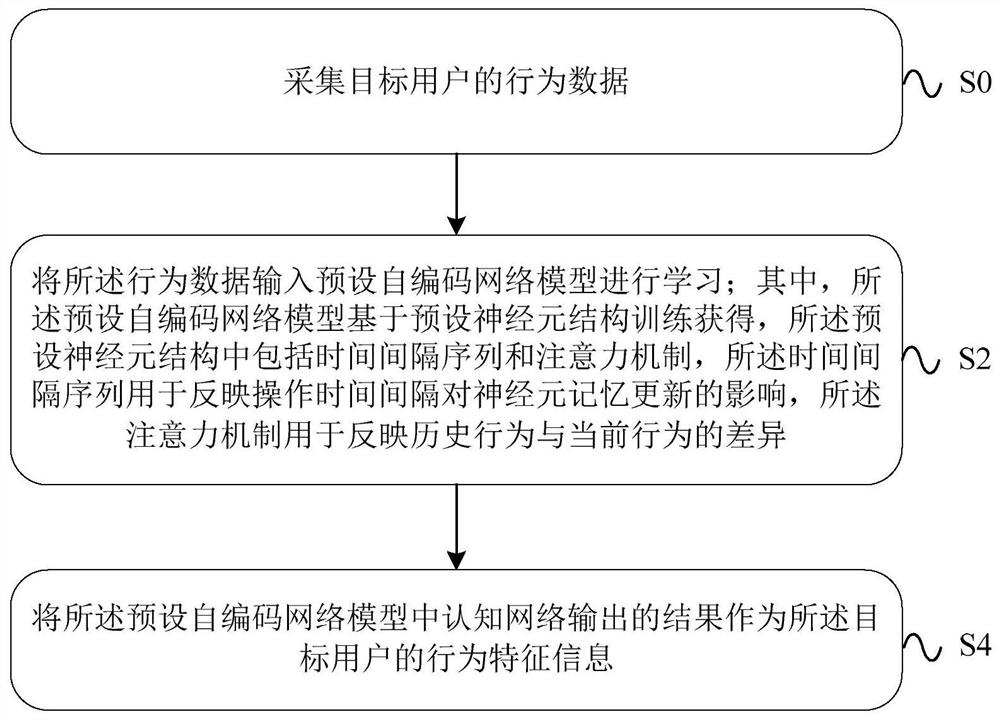
The invention provides a user behavior feature extraction method, device, equipment and system. The method comprises the steps of collecting behavior data of a target user; inputting the behavior datainto a preset self-encoding network model for learning, wherein the preset self-encoding network model is obtained by training based on a preset neuron structure,the preset neuron structure comprisesa time interval sequence and an attention mechanism, the time interval sequence is used for reflecting the influence of an operation time interval on neuron memory updating, and the attention mechanism is used for reflecting the difference between a historical behavior and a current behavior; and taking a result output by a cognitive network in the preset self-encoding network model as behavior characteristic information of the target user. By utilizing the embodiment of the invention, the user behavior characteristics can be extracted more accurately, and the anti-fraud detection difficultyis reduced.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
Self-organized solid-state synthetic neuronal structure
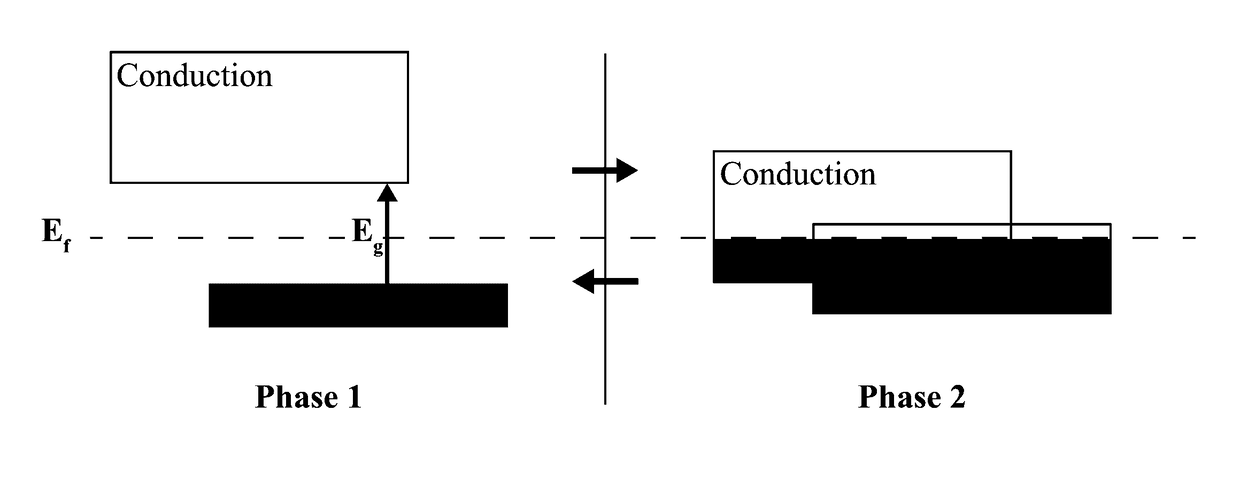
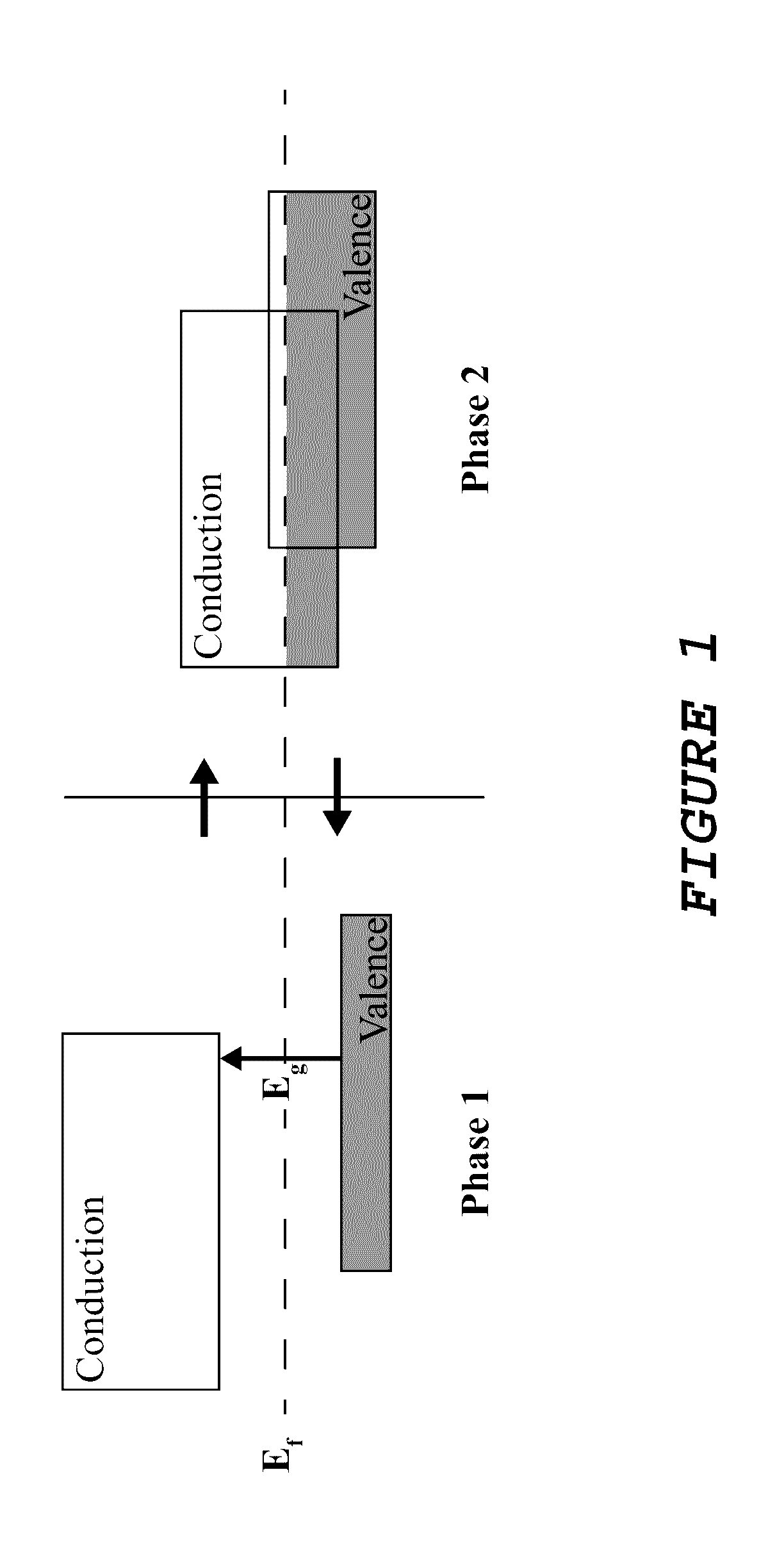
A synthetic neuronal structure makes use of a semiconductor-metal phase transition material having material regions separated by discontinuities. The discontinuities represent interfaces such that different phases in two adjacent regions result in a metal-semiconductor interface. The interface supports a charge accumulation and a discharge of accumulated charge when an activation energy provided, for example, by electrical current, localized heating or optical energy, reaches a threshold necessary for breakdown of a potential barrier presented by the interface, and thus mimics a leaky integrate-and-fire neuron. With many such interfaces distributed through the structure, the local inputs to a neuron become a weighted sum of energy from neighboring neurons. Thus, different combinations of signals at one or more inputs connected to the structure will favor different neural pathways through the structure, thereby resulting in a neural network.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
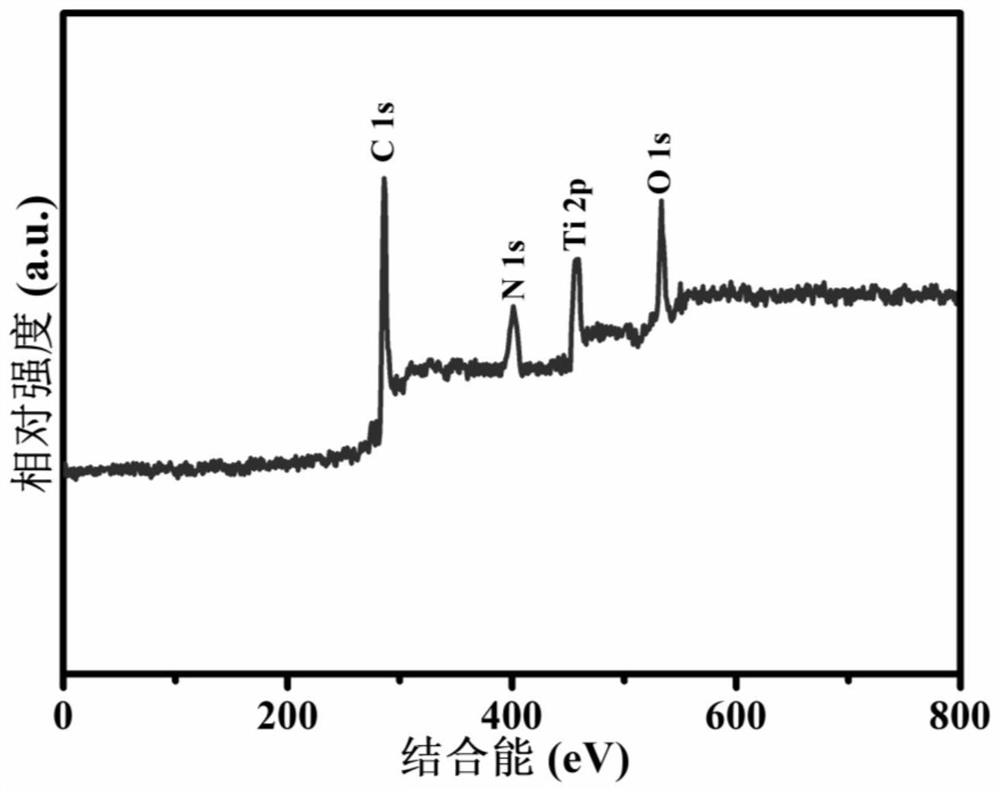
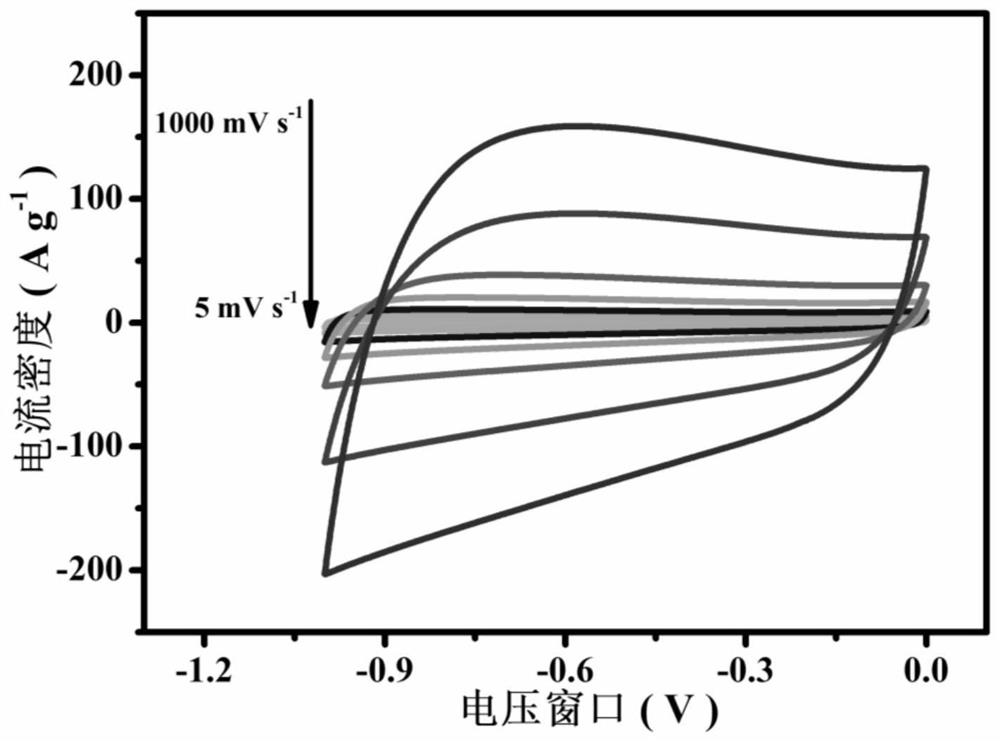
MXene/nitrogen-doped carbon foam composite material with 3D porous neuron-like structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111977656ARich ether bondStable mechanical propertiesHybrid capacitor electrodesTitanium carbideCapacitanceHigh capacitance
The invention relates to an MXene / nitrogen-doped carbon foam composite material with a 3D porous neuron-like structure and a preparation method thereof. The composite material takes porous nitrogen-doped carbon foam as a skeleton, pores of the porous nitrogen-doped carbon foam are of a neuron-like structure, and MXene nanosheets are uniformly deposited on the surface of the skeleton and dispersedamong the pores of the porous nitrogen-doped carbon foam. According to the MXene / nitrogen-doped carbon foam composite material provided by the invention, stacking and aggregation of the MXene nanosheets are effectively prevented, the composite material as an electrode material can provide more contact sites, the permeation of electrolyte is promoted, an effective channel is provided for the transmission of ions in electrodes, the ion transfer is accelerated, the capacitance and the rate performance can be significantly improved, and the assembled all-solid-state supercapacitor device has highcompressibility and excellent cycle stability, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Neuron model displacement or deformation monitoring method of electric transducer embedded with microcomputer
ActiveCN104101325AOvercome environmental problemsOvercome limitationsMeasurement devicesUltrasonic sensorDeformation monitoring
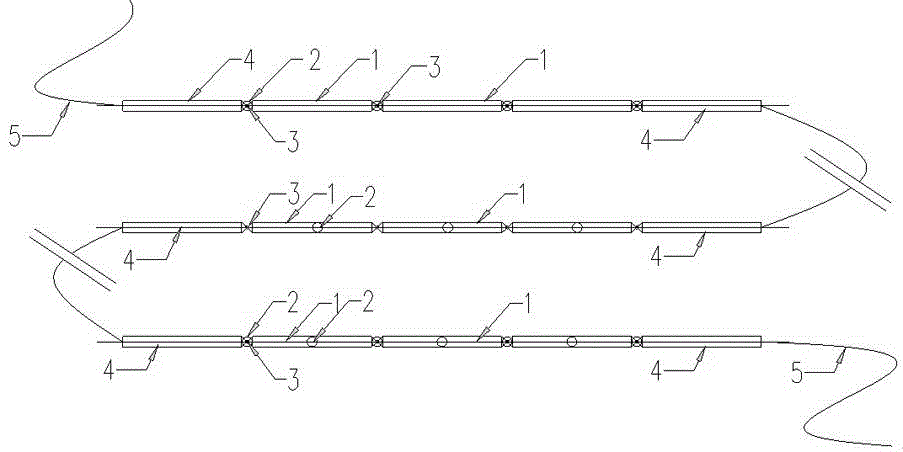
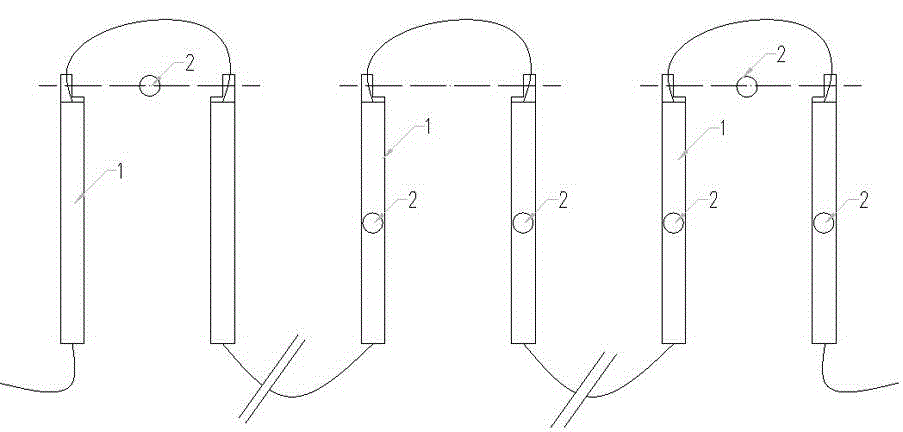
The invention relates to a displacement test method which is suitable for static and dynamic displacement measurement of a structure of scale in a long line range or a space range. The neuron model displacement or deformation monitoring method of an electric transducer embedded with a microcomputer is characterized in that a multi-point neuron structure model, the transducer as a neuron body and a supplement rigid rod as a neuron myelin are connected to form a neuron basic unit assembly; a number of neuron assemblies are connected in series to form a nerve chain; and a start node is used as a benchmark to acquire the relative displacement of each unit to determine the attached structure deformation. Compared with the prior art, the structure deformation and dynamic characteristic measuring method provided by the invention can overcome the limits of traditional mechanical temporary test and optical test method environment impacts and high cost price, and is especially suitable for large range or long scale and multi-point long-term monitoring, such as longitudinal and transverse deformation measurement and real-time monitoring of a building, a bridge, a tunnel, a dam, a slope and other structures.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
System and method of multiple-target control of intelligent power grid
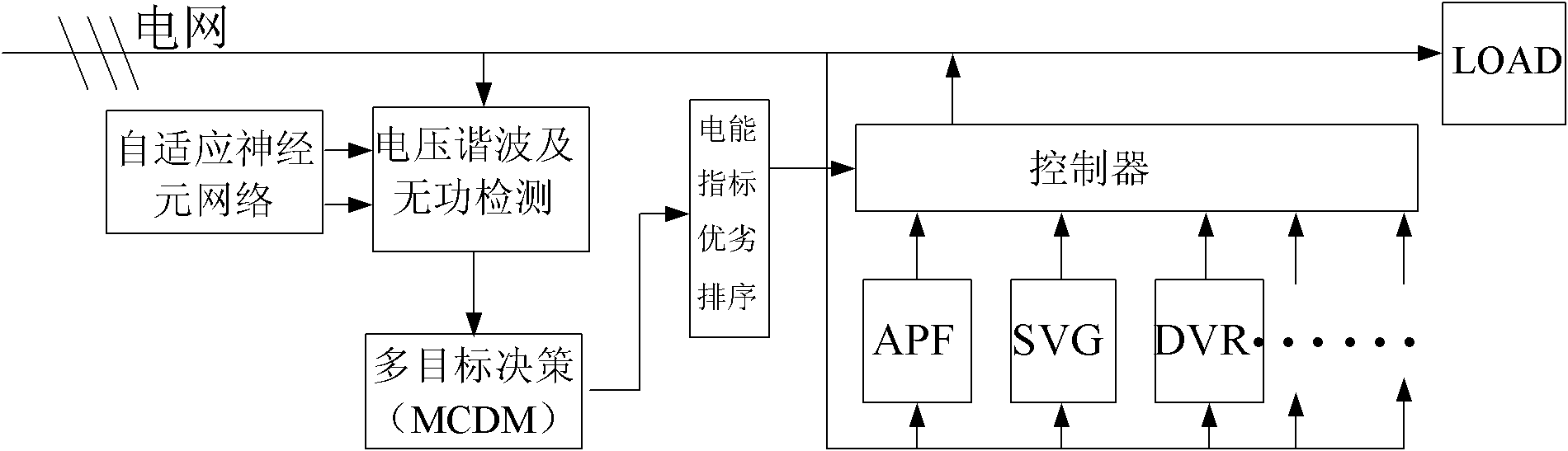
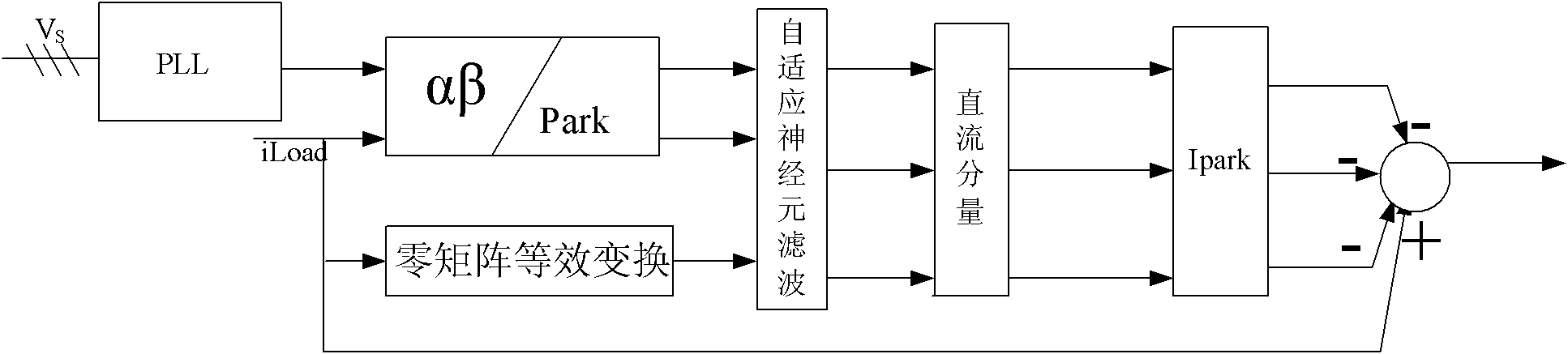
ActiveCN103219724ASafe electricity environmentReliable electricity environmentActive power filteringAc network voltage adjustmentPower qualitySmart grid
The invention discloses a system and a method of multiple-target control of an intelligent power grid. Load current harmonics and idle components are directly separated from the system, the fluctuation situations of voltage are monitored at the same time, a multi-objective decision theory is adopted, targets are regulated according to different power qualities, and the work modes of APF, SVG, DVR and other devices are coordinated, so that the aim of improving power grid quality to the maximum extent is reached. The system of the multiple-target control of the intelligent power grid is mainly formed by an idle detecting unit based on self-adaptive linear neuron structural harmonics and a controller, wherein the idle detecting unit based on the self-adaptive linear neuron structural harmonics is mainly formed by a sampling unit, a current control circuit and a control unit. The sampling unit is connected on a power grid power supply with load, and the sampling unit and the control unit are connected through the current control circuit.
Owner:NANJING APAITEK TECH
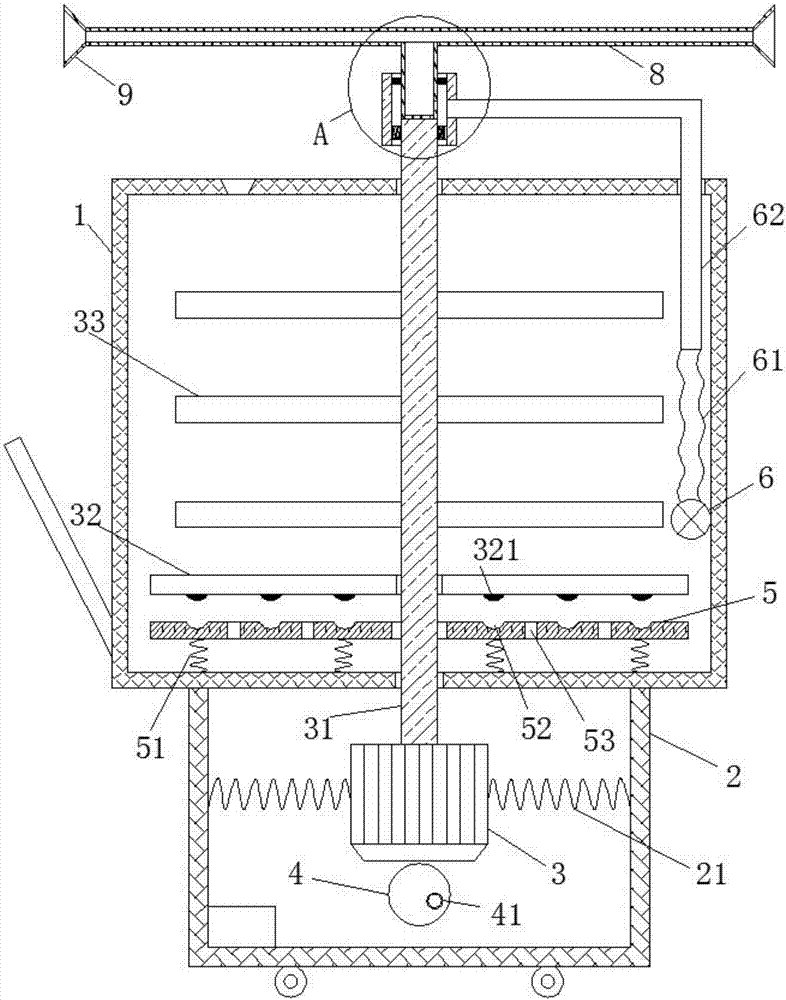
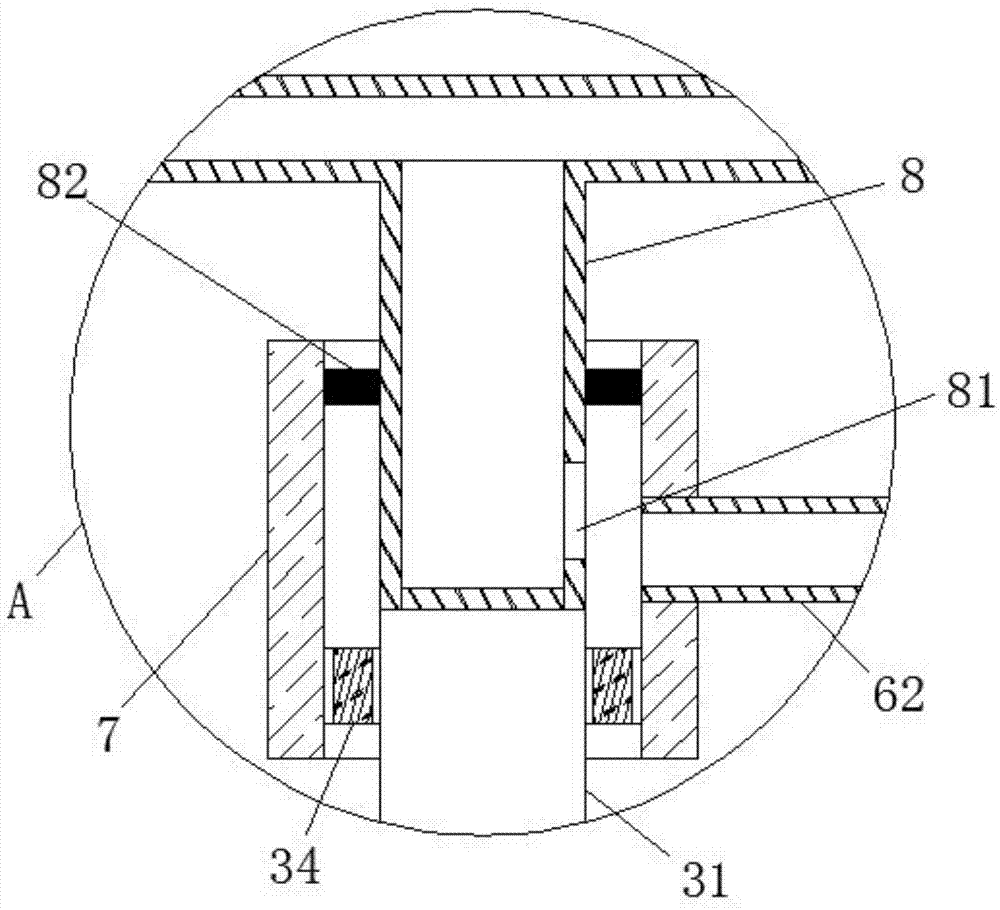
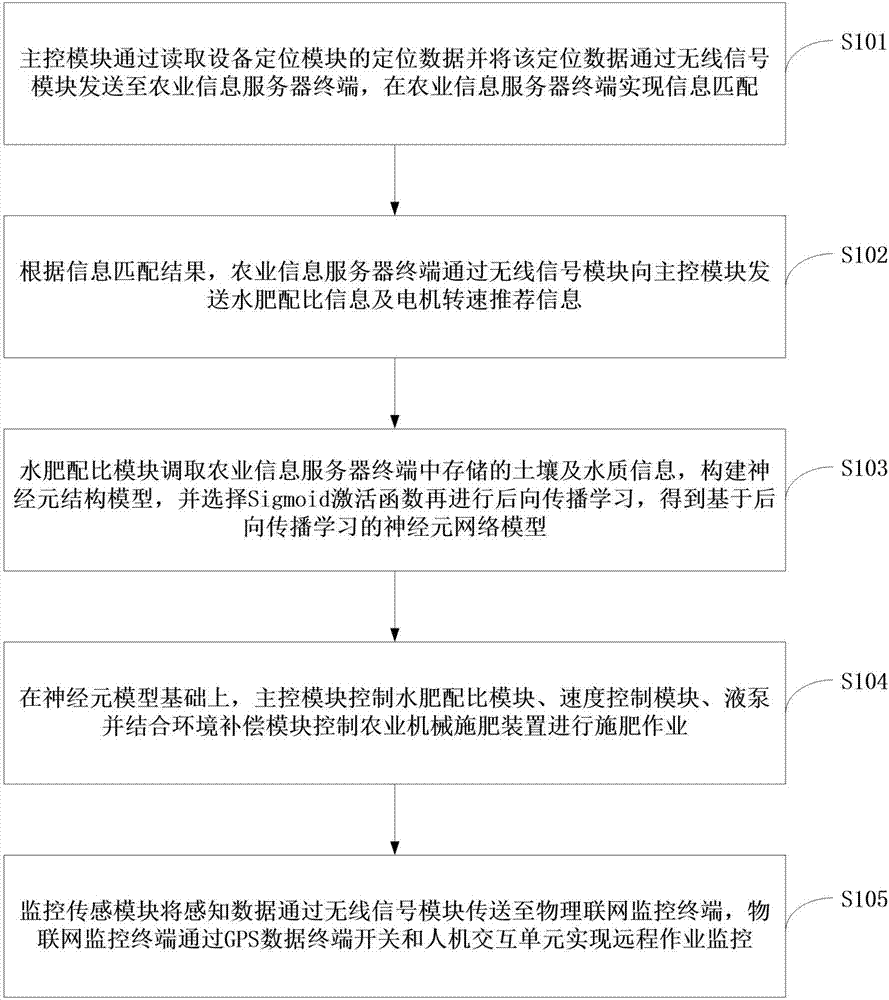
Intelligent agricultural machinery fertilization method and device based on Internet of things
The invention relates to the technical field of agricultural machinery, and specifically relates to an intelligent agricultural machinery fertilization method and device based on the Internet of things. According to the invention, an agricultural information server terminal sends water and fertilizer ratio information and motor speed recommendation information to a main control module through a wireless signal module according to a geographical location information matching result, a water and fertilizer ratio module builds a neuron structure model, the main control module controls the water and fertilizer ratio module, a speed control module and a liquid pump on the basis of the neuron model and controls an agricultural machinery fertilization device to perform a fertilization operation by combining an environment compensation module, an Internet of things monitoring terminal realizes remote operation monitoring through a GPS data terminal switch and a man-machine interaction unit, the water and fertilizer ratio module is controlled to realize different ratios, the motor is controlled to realize different rotating speeds and the liquid pump is controlled to realize different operating conditions according to the recommended operation information, uncertain systems can be learnt and adapted by using the neural network, a method basis is provided for variable rate fertilization, and the scientificity and the reliability of the operation are improved.
Owner:长沙善道新材料科技有限公司
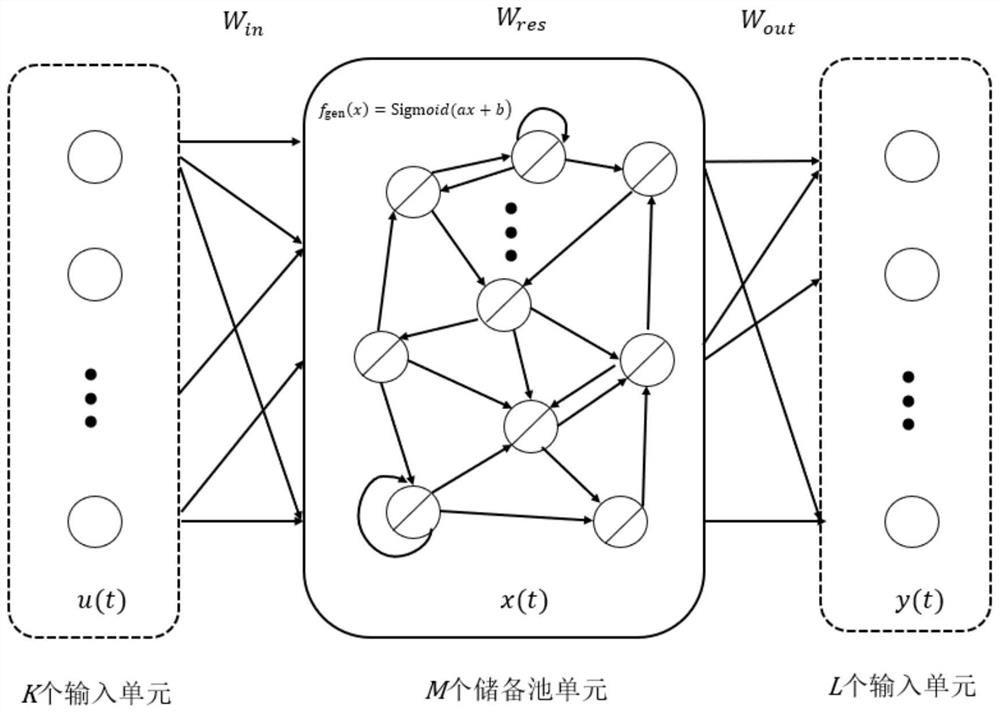
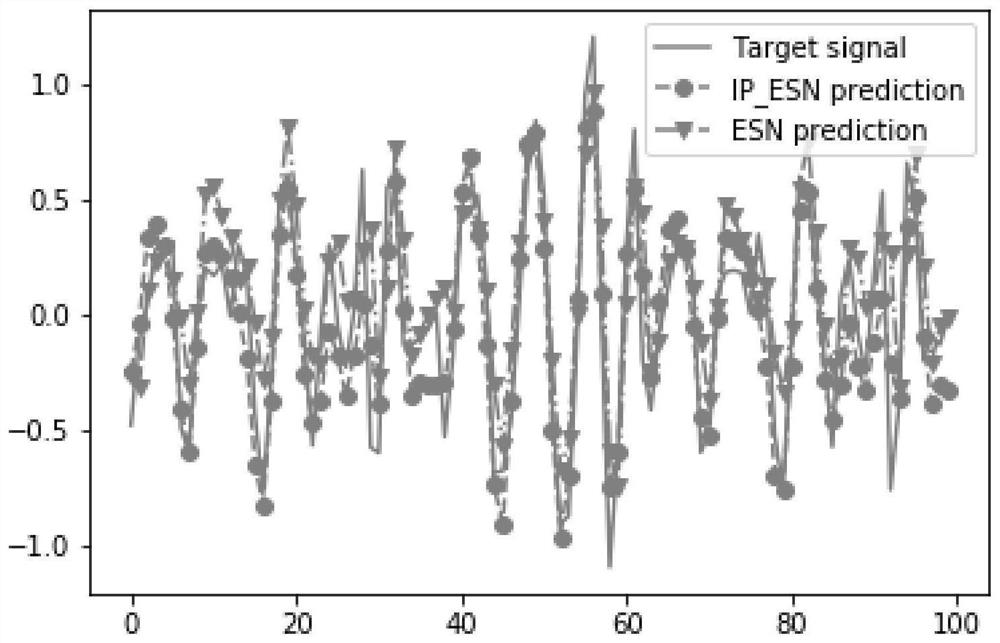
Ship motion forecasting method based on intrinsic plasticity echo state network
ActiveCN111709140AImprove forecast accuracyImprove securitySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationActivation functionAlgorithm
The invention provides a ship motion forecasting method based on an intrinsic plasticity echo state network, which comprises the following steps: acquiring historical data of swaying of a ship in a sailing process for modeling, inputting a target moment t, forecasting a motion attitude of the ship at the moment t based on an intrinsic plasticity echo state network model, and adopting correspondingmotion compensation according to a forecast value, wherein the internal plasticity echo state network is a plasticity neural network obtained by optimizing different neurons in the storage pool according to a plasticity rule; the invention is characterized by introducing IP (Intrinsic Plasticity) parameters a and b, constructing an activation function fgen (x) = tanh (ax + b) according to a plasticity rule established by KL divergence (kullback-leibler divergence, KL-divergence), so as to change a single neuron structure in a storage pool; the IP parameter optimization target is that the output of neurons in the reserve pool conforms to the maximum entropy distribution, and the purpose that the reserve pool can capture and carry more input information is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Artificial sensory neuron structure based on multi-side gate synaptic device and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112949843AImprove ionic conductivityReduce energy consumptionNeural architecturesPhysical realisationElectrical connectionSensory neuron
The invention discloses an artificial sensory neuron structure based on a multi-side grid synaptic device and a preparation method thereof. The artificial sensory neuron structure comprises at least two piezoelectric nano-generators used for external force induction and a synaptic device used for processing at least two voltage input signals, wherein the synaptic device is an electric double-layer transistor; the double-electrode-layer transistor takes an electrolyte material as a gate medium, takes an oxide semiconductor as a channel layer, and is provided with at least two plane side gates; and each piezoelectric nano generator is electrically connected to one side grid of the electric double-layer transistor. According to the artificial sensory neuron structure, the planar multi-side grid structure and the double-electric-layer coupling characteristic of the double-electric-layer transistor are fully exerted, and two or more sensors can be connected to different side grids of one transistor at the same time, so that induction and processing of various external signals are realized; the limitation that one synaptic device of a traditional artificial sensory neuron structure processes one sensing device signal is broken through.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
System, method, and computer-accessible medium for processing brain images and extracting neuronal structures
PendingUS20210049338A1Minimize impactMaximize the effectImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresRadiology
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for solving multi-target shortest path in time-varying environment based on neural network
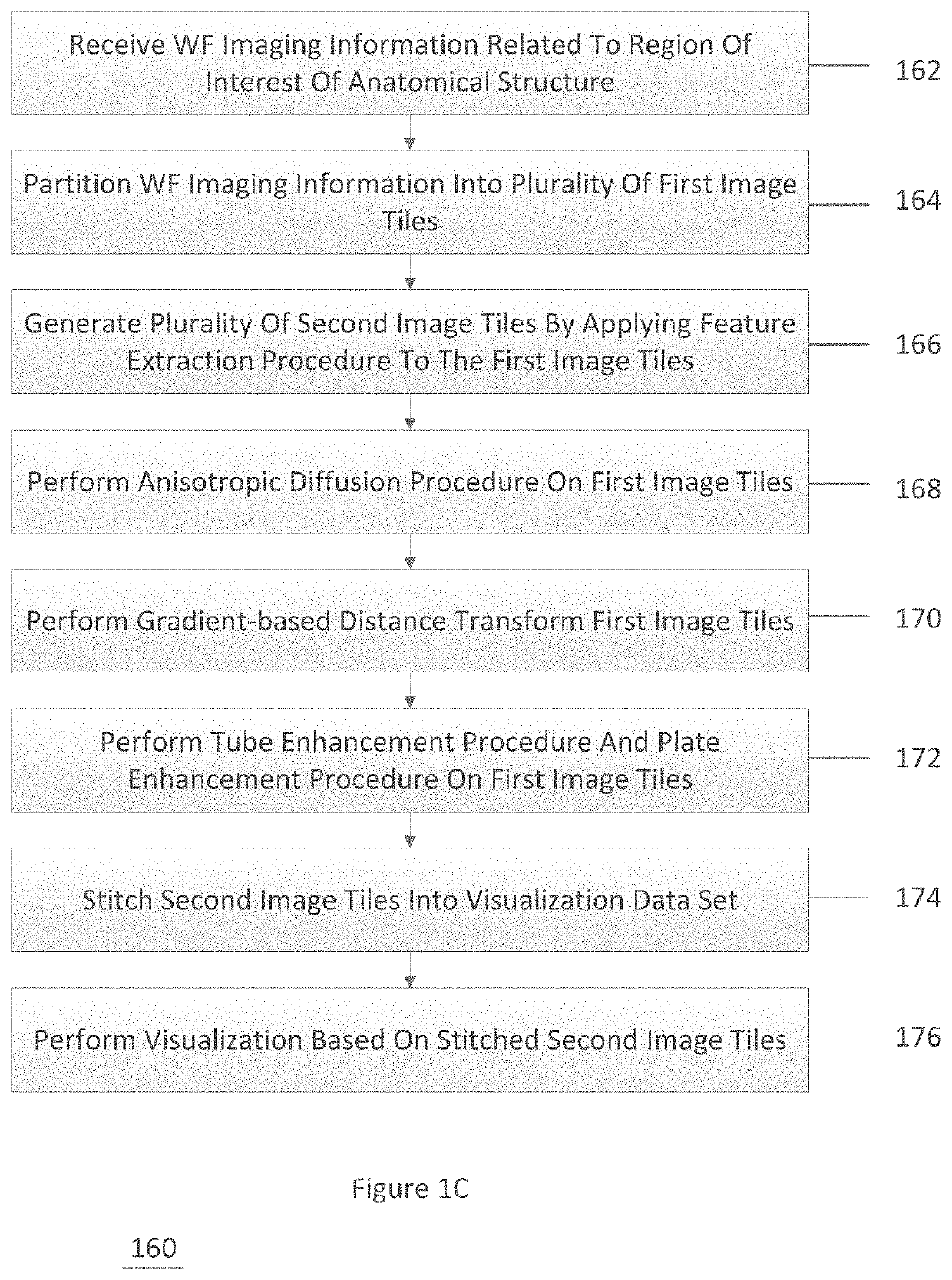
PendingCN112836845AImprove computing powerImprove computing efficiencyForecastingPhysical realisationTopology informationAlgorithm
A method for solving a multi-target shortest path in a time-varying environment based on a neural network comprises the following steps: monitoring and collecting data of an urban traffic network in real time by using map software, collecting a cost function of each edge in the network, and constructing a traffic network model; in combination with the topological structure of the network, designing a brand-new neuron structure and constructing a neural network model. Topological information of a traffic network is loaded into a neural network model, a neuron wave generator and a neuron filter are used for sending automatic waves to subsequent neuron, other neuron in the network is activated, and each neuron ignores response to part of waves through the filter. According to the method, non-optimal sub-paths are pruned by designing the neural network, so that the calculation complexity is greatly reduced, and the problem of accurately solving the multi-target shortest path in the network optimization field in a time-varying environment is solved. In addition, the problem solving speed is increased through parallel computing of the neural network.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Modeling device and method for preparing multiple cerebral infarction from soft autologous blood microembolus
The invention discloses a multiple cerebral infarction modeling device and method prepared from soft autologous blood microembolus, and relates to the field of animal modeling. The method comprises the following steps: injecting autologous blood soft microembolus coated with carrageenan into the brain of a rat through an external carotid artery, establishing a multiple cerebral infarction animal model, detecting cerebral infarction disease related experimental markers, observing pathological changes of brain tissues, neuronal structure changes and generation of spatial behavior dysmnesia, and establishing a multiple cerebral infarction animal model. Comprising the steps of red tetrazole staining, hematoxylin-eosin staining, immunohistochemistry, water maze and Bass maze. The rat model proves that the rat has spatial behavior memory disorder, neurons and brain tissues have pathological mechanism changes, and an animal model with similar pathogenesis processes is provided for researching clinical multiple cerebral infarction. The establishment of the animal model has an important value for deepening the treatment research of multiple cerebral infarction diseases.
Owner:CHENGDE MEDICAL UNIV
Artificial neuron structure and its preparation method, signal and time extraction method
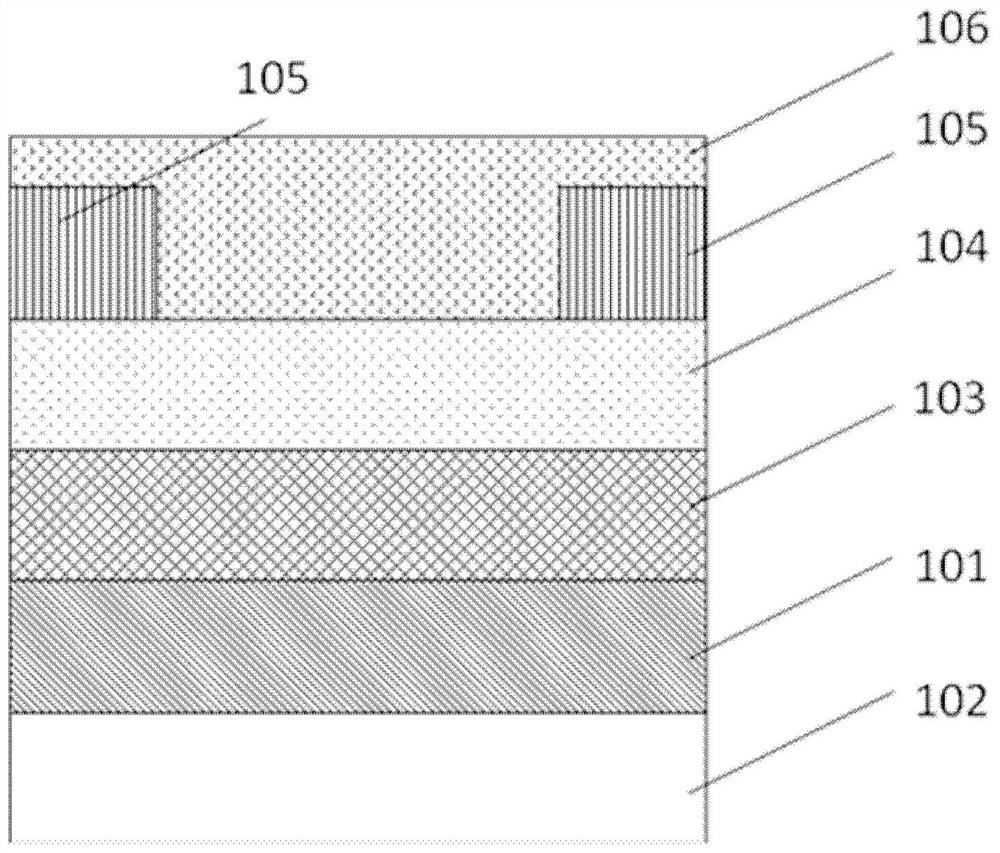
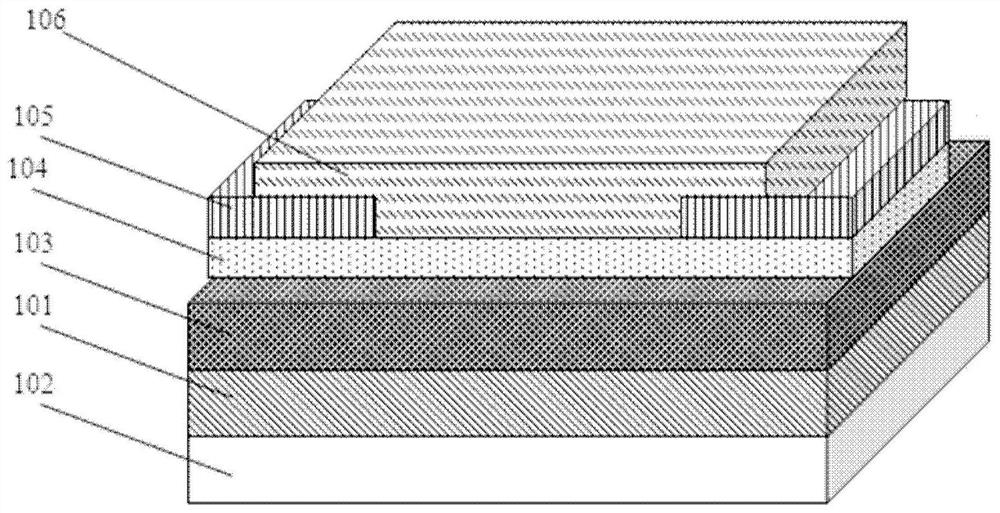
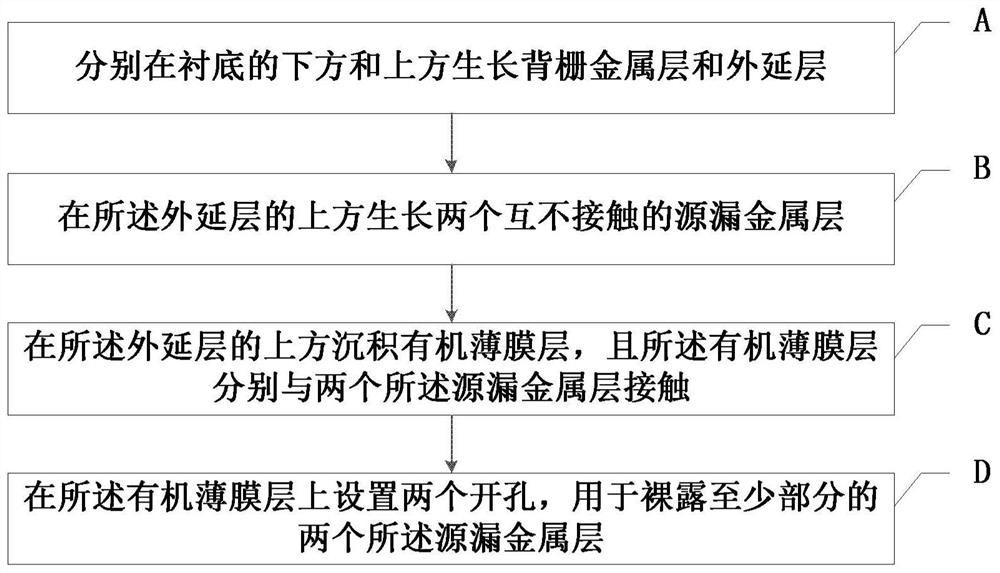
ActiveCN108336145BAchieve outputReduce static power consumptionTransistorPhysical realisationOrganic filmHemt circuits
The present invention provides an artificial neuron structure, a preparation method thereof, and a signal and time extraction method, wherein the artificial neuron structure includes: a substrate; a back gate metal layer located under the substrate; an epitaxial layer located under the substrate Above the substrate; two non-contact source and drain metal layers, located above the epitaxial layer; and an organic thin film layer, respectively in contact with the two source and drain metal layers, and stacked on the epitaxial layer wherein, the organic thin film layer is provided with two openings for exposing at least part of the two source and drain metal layers. By simulating the working principle of biological neurons, the artificial neuron structure uses the charge provided by the electrochemical reaction to regulate the carrier concentration distribution in the semiconductor channel, and realizes the corresponding output for various electrical stimuli; it has the characteristics of time-varying; it can The power-off operation reduces the static power consumption to zero, and is suitable for low-power circuit applications; it also has a very wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
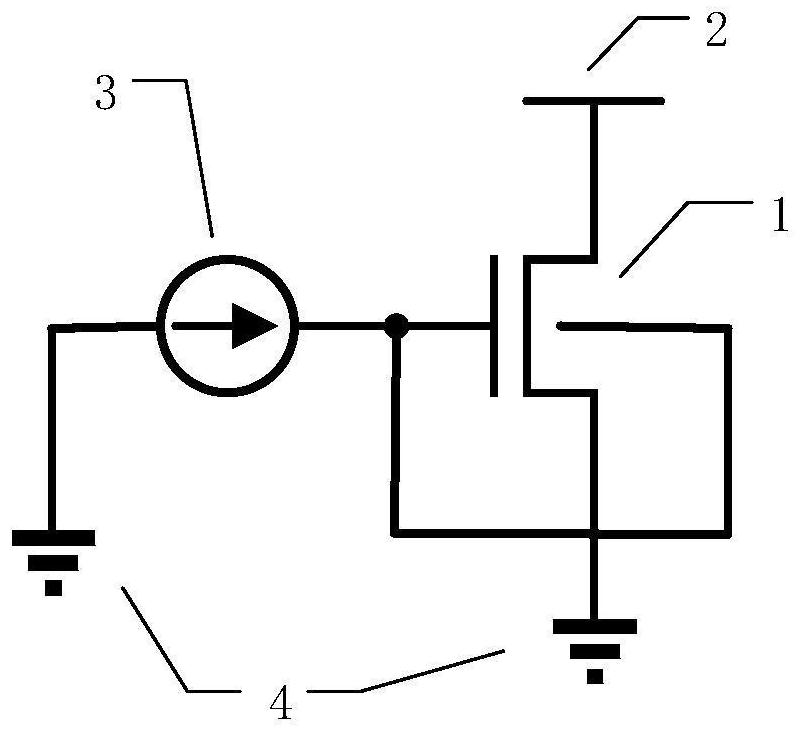
Neuron structure based on partial depletion type silicon-on-insulator and working method thereof
PendingCN114050165AEasy front-end integrationEasy to operateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceFloating body effect
The invention provides a neuron structure based on partial depletion type silicon-on-insulator and a working method thereof. The structure comprises a PD-SOI NMOS transistor, the drain electrode of the PD-SOI NMOS transistor receiving a constant voltage, and the grid electrode and the body electrode of the PD-SOI NMOS transistor receiving a constant current; and the source electrode is grounded. According to the invention, an LIF neuron model is used, a single NMOS PD-SOI transistor is adopted, the body potential of the PD-SOI device can be effectively controlled because the body and the substrate of the PD-SOI device are isolated by an oxide layer, and each neuron can be isolated by the oxide layer, so that a single neuron can be conveniently operated by using current; a single PD-SOI transistor is used for realizing the function of an LIF neuron, and an SOI floating body effect is used for accumulating and transmitting charges so as to replace a capacitor and a reset circuit; compared with a neuron based on a CMOS complex circuit structure, a large number of circuit structures such as transistors and capacitors are omitted, the occupied area of the unit structure is reduced, and the integration density can be improved if a neural network is constructed.
Owner:天津市滨海新区微电子研究院
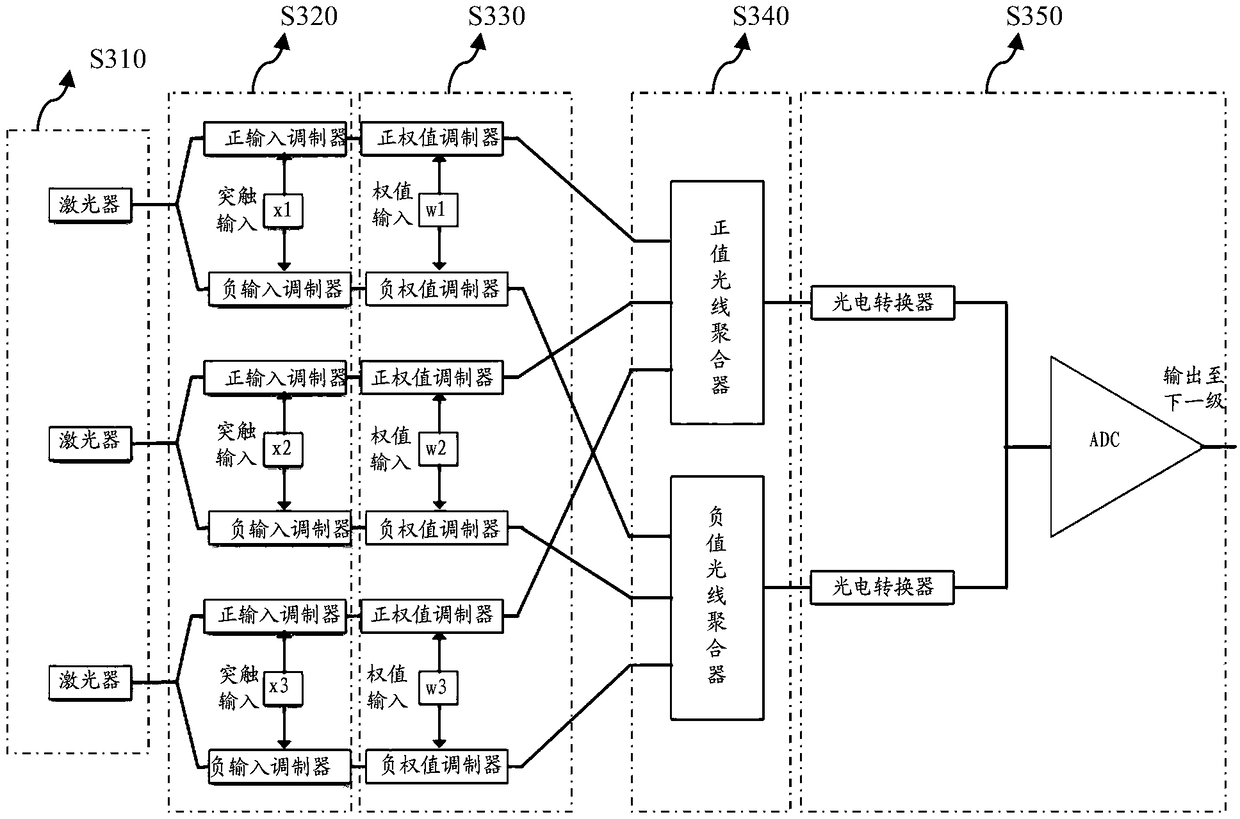
An optical neuron structure and a neural network processing system containing the structure
ActiveCN109376855BHigh speedReduce energy consumptionPhysical realisationSynaptic weightLight signal
The invention provides an optical neuron structure and a neural network processing system containing the structure. The neuron structure includes a synaptic input modulation module, a synaptic weight modulation module, a light aggregation module and a light intensity detection module, wherein the synaptic input modulation module is used for receiving optical signals and controlling electrical signals associated with input neurons Perform optical path modulation; the synaptic weight modulation module is used to perform modulation on the optical signal carrying the input neuron under the control of the electrical signal associated with the weight; the light aggregation module is used to modulate multiple synaptic weights The output optical signal of the module is aggregated; the light intensity detection module is used to convert the output optical signal from the optical aggregation module into an electrical signal and perform an activation operation. The optical neuron structure and the neural network processing system containing the structure of the present invention can realize the fast calculation of the neural network.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
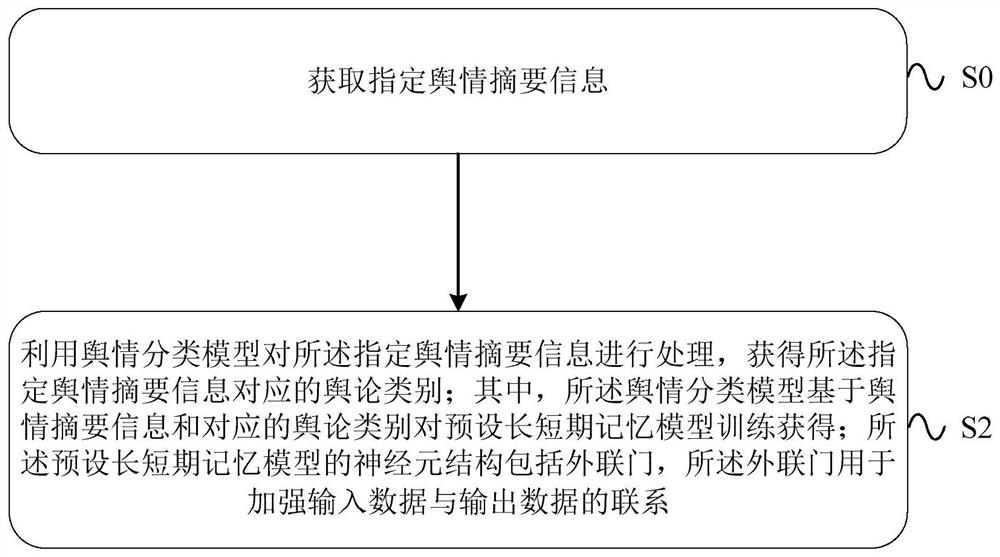
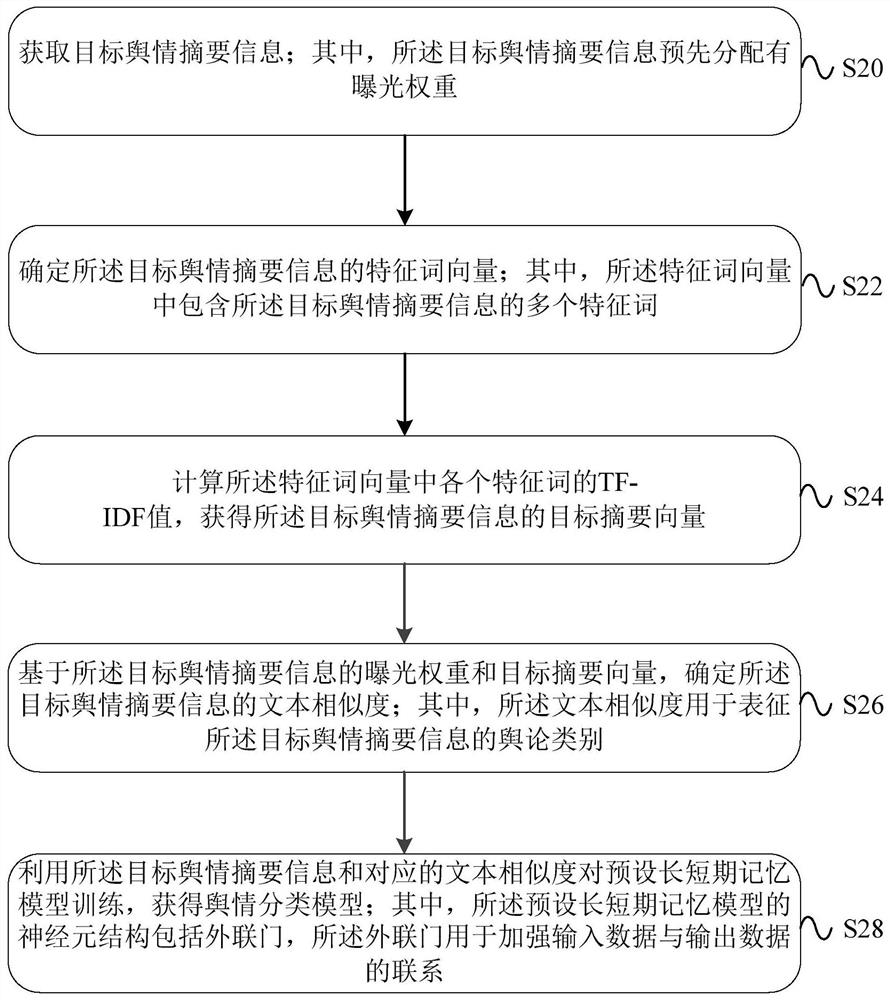
Method, device and equipment for determining public opinion categories
PendingCN113515626AEfficient and accurate determinationNeural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsShort-term memoryEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a method, a device and equipment for determining public opinion categories. The method, the device and the equipment for determining the public opinion categories can be applied to the technical field of big data. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring specified public opinion abstract information; and processing the specified public opinion summary information by utilizing a public opinion classification model to obtain a public opinion category corresponding to the specified public opinion summary information, wherein the public opinion classification model is obtained by training a preset long and short term memory model based on public opinion abstract information and a corresponding public opinion category, and the neuron structure of the preset long and short-term memory model comprises an external connection gate, and the external connection gate is used for enhancing the connection between input data and output data. The public opinion category can be efficiently and accurately determined by utilizing the embodiment of the specification.
Owner:INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL BANK OF CHINA
Self-organizing T-S fuzzy neural network control method of grid-connected inverter
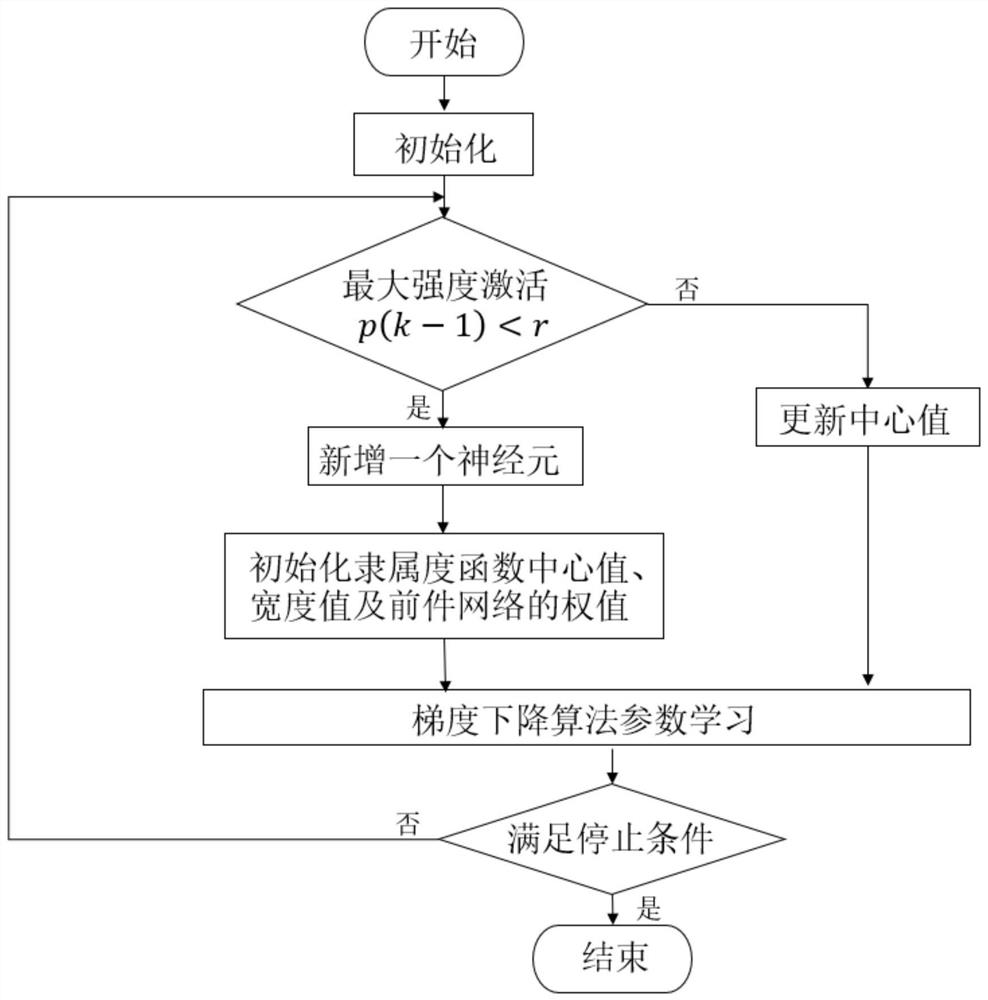
InactiveCN114660944ASimple structure calculationGood for mathematical analysisAdaptive controlFuzzy ruleArtificial intelligence
The invention discloses a self-organizing T-S fuzzy neural network PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) controller for controlling a grid-connected inverter. A concept of intensity activation is added to a controller algorithm on the basis of a T-S fuzzy neural network. The essence of the method is that a fuzzy rule layer activation intensity method is adopted, a neuron structure is adaptively adjusted according to an actual environment, a proper control structure is constructed, and the performance and scale of the whole network can be better determined and improved due to the online learning capability and the powerful fault-tolerant capability of the method, so that the control precision is improved. And meanwhile, a gradient descent method is adopted to adjust each parameter of the controller in real time, so that the control system has better anti-interference capability and dynamic performance.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Self-organized solid-state synthetic neuronal structure
A synthetic neuronal structure makes use of a semiconductor-metal phase transition material having material regions separated by discontinuities. The discontinuities represent interfaces such that different phases in two adjacent regions result in a metal-semiconductor interface. The interface supports a charge accumulation and a discharge of accumulated charge when an activation energy provided, for example, by electrical current, localized heating or optical energy, reaches a threshold necessary for breakdown of a potential barrier presented by the interface, and thus mimics a leaky integrate-and-fire neuron. With many such interfaces distributed through the structure, the local inputs to a neuron become a weighted sum of energy from neighboring neurons. Thus, different combinations of signals at one or more inputs connected to the structure will favor different neural pathways through the structure, thereby resulting in a neural network.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE
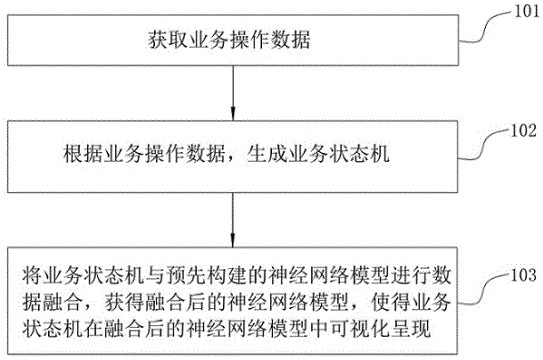
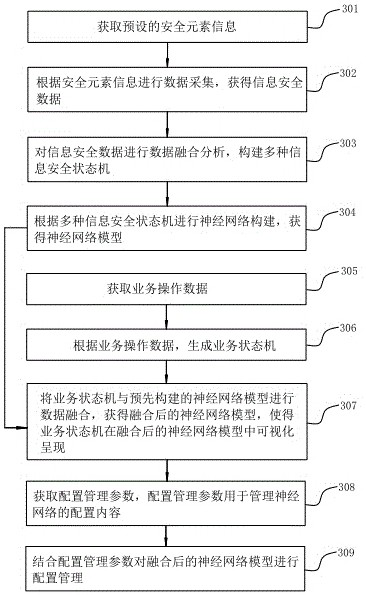
A data visualization method, device, and storage medium
ActiveCN113297314BImprove visualizationQuick responseVisual data miningStructured data browsingEngineeringNetwork model
The present application discloses a data visualization method, device, and storage medium. The method includes: acquiring business operation data, and generating a business state machine according to the business operation data. Data fusion of the business state machine and the pre-built neural network model is performed to obtain the fused neural network model, so that the business state machine can be visualized in the fused neural network model. Implementing the embodiments of the present application can simulate the neuron structure of the human brain, present the newly added business operation content and dynamic change process from multiple visual dimensions, so that the business state machine can be visualized in the fused neural network model, thus breaking the flat It can effectively improve the visualization effect of large data volume.
Owner:SHENZHEN Y& D ELECTRONICS CO LTD
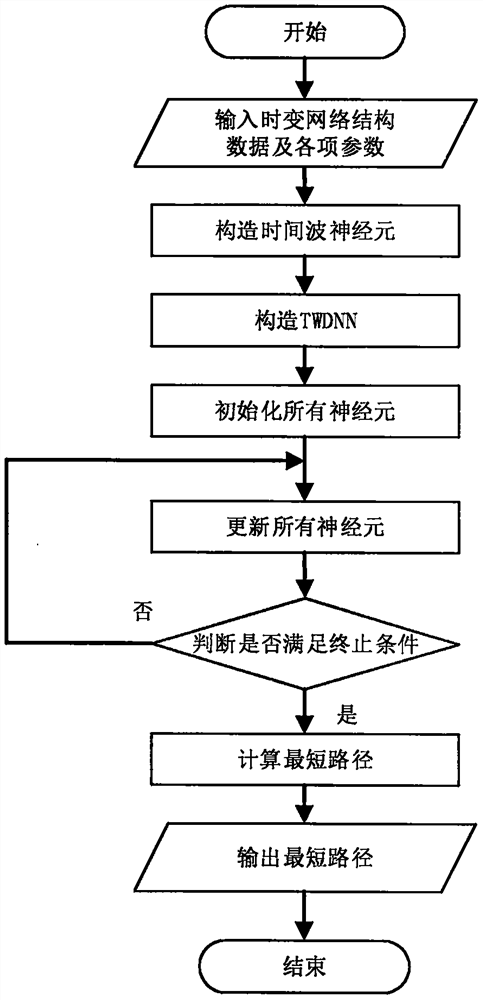
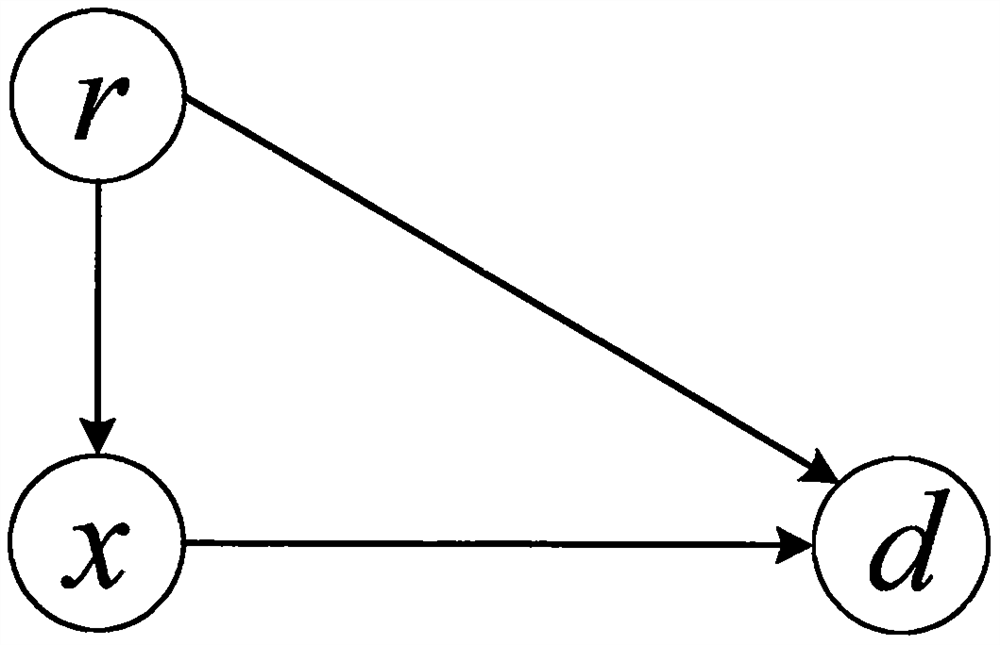
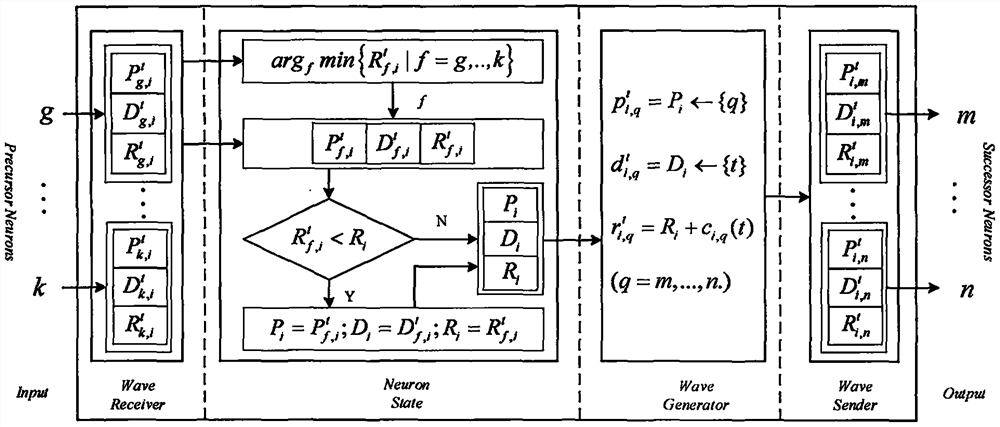
Constraint time-varying shortest path solving method based on time wave delay neural network
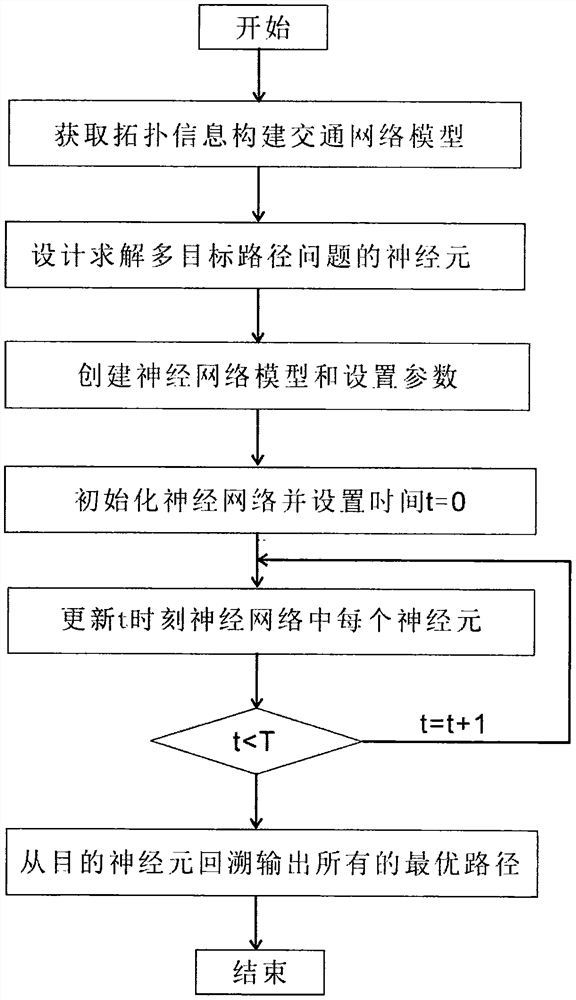
The invention discloses a constrained time-varying shortest path solving method based on a time wave delay neural network, and the method comprises the steps of solving a constrained time-varying shortest path problem(CTSPP for short) through the construction of a time wave delay neural network (TWDNN for short). The designed TWDNN is a novel neural network based on time wave delay neurons, the difference between the TWDNN and a traditional neural network is that the TWDNN does not need any training, and the design of the TWDNN comprises neuron structure design and neural network structure design. Each neuron on the time wave delay neural network is composed of an input part, a wave receiver part, a neuron state part, a wave generator part, a wave transmitter part and an output part. The wave is a medium for exchanging information among the neurons, the propagation delay of the wave among the neurons is equivalent to the transmission delay of a data packet on a network, and the output of the shortest path is based on the time wave received by the target neuron. Experimental results show that the method provided by the invention is superior to the existing method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Circuit structure and its driving method, neural network
A circuit structure, its driving method, and neural network. The circuit structure includes: at least one circuit unit, each circuit unit includes a first group of resistive switching devices and a second group of resistive switching devices, the first group of resistive switching devices includes resistance gradient devices, and the second group of resistive switching devices includes resistance switching devices The abrupt change device, the first group of resistive switching devices and the second group of resistive switching devices are connected in series, and the resistance value of the first group of resistive switching devices is greater than the resistance value of the second group of resistive switching devices when no voltage is applied. In the circuit structure, the resistance gradient device and the resistance mutation device are connected in series to form a neuron-like structure, so as to realize the function of simulating human brain neuron. The resistance value of the resistance gradient device changes slowly under the applied voltage, which can be used to simulate the behavior of the S-shaped growth curve of biological dendrites. The circuit structure has the advantages of simple structure, low power consumption, small area, complex functions and easy compatibility with standard CMOS technology.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
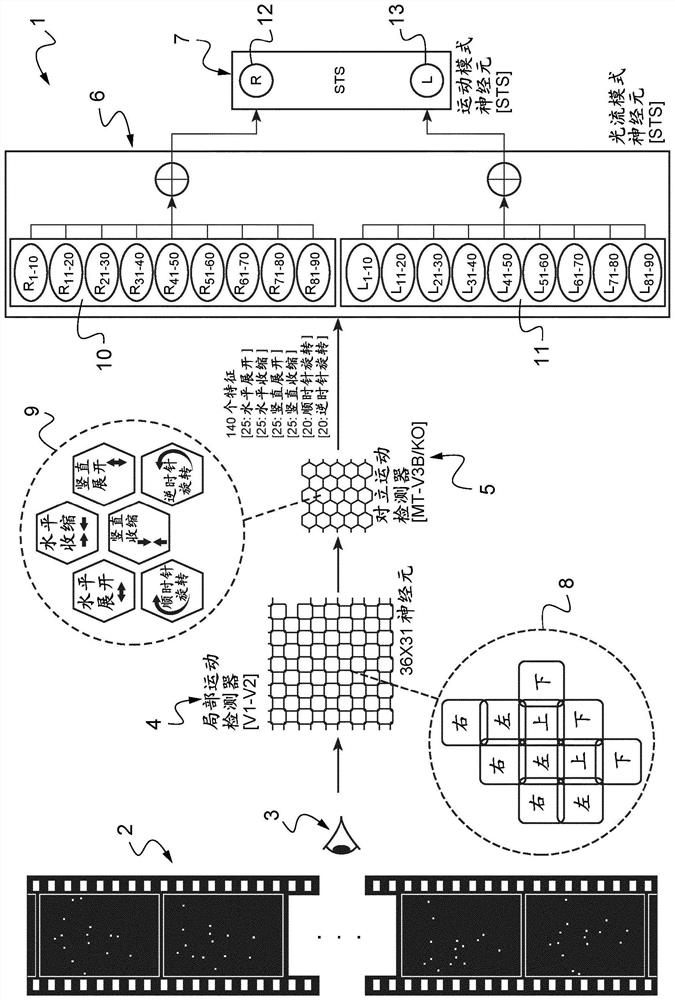
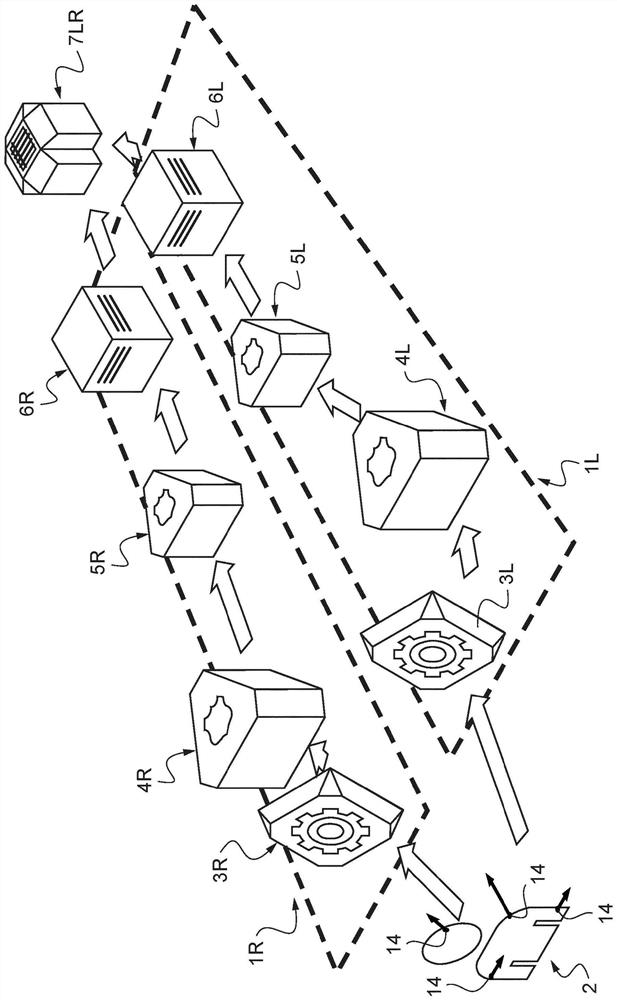
System for simulating decision-making process in brain of mammal with respect to visually observed movement of body
The invention is a system (1) that simulates a decision process in a mammalian brain with respect to a motion characteristic relating to a visually observed body posture of a body by means of a simulated visual path comprising an interface towards a simulated neuronal structure, the system includes an interface that converts at least luminescence information of the observed body into an optical flow data stream that delivers information relating to the visually observed body and that can be processed in the simulated neuron structure, the system being a feed-forward system that can be coupled to the simulated neuron structure. And from the visual observation that the decision comprises hierarchically: the simulated visual path and its interface (3, 3L, 3R); a simulated local motion direction detection neuron structure (4, 4L, 4R) for detecting the motion direction by means of a receptive field; a simulated opposition motion detection neuron structure (5, 5L, 5R) for detecting opposition motion at least relating to expansion and contraction; a simulated complex pattern detection neuron structure (6, 6L, 6R) for globally detecting an optical flow pattern over the entire visual observation and according to the evolution of the entire visual observation during the time, the detectable pattern being a prototype pattern; and a simulated motion pattern detection neuron structure (7, 7LR) for detecting a motion pattern and providing a decision regarding a motion characteristic. According to the invention, the neurons of the simulated motion pattern detection neuron structure (7, 7LR) comprise a forgetting ability that is a function of the delay and for each neuron an activity of the neuron.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com