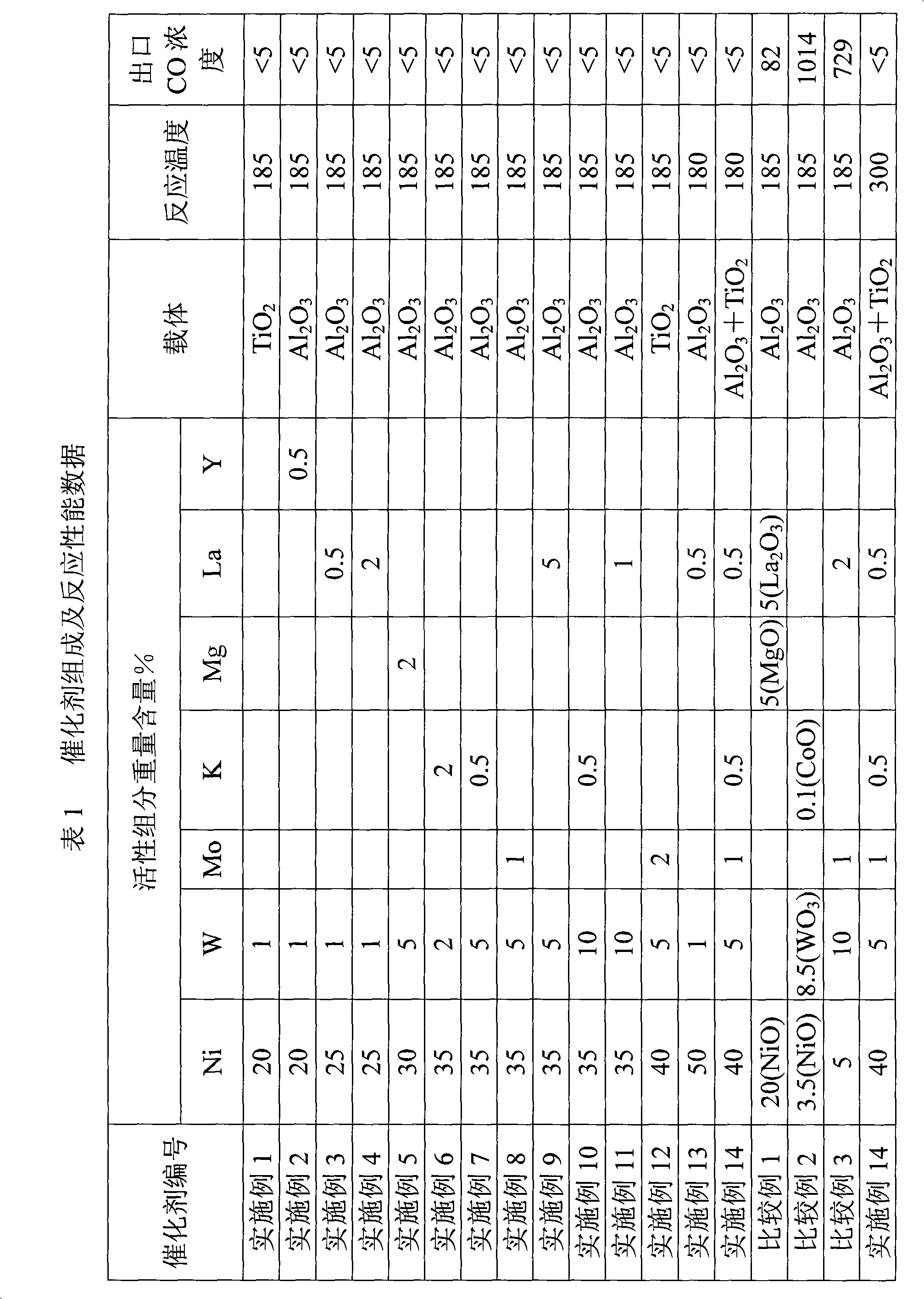
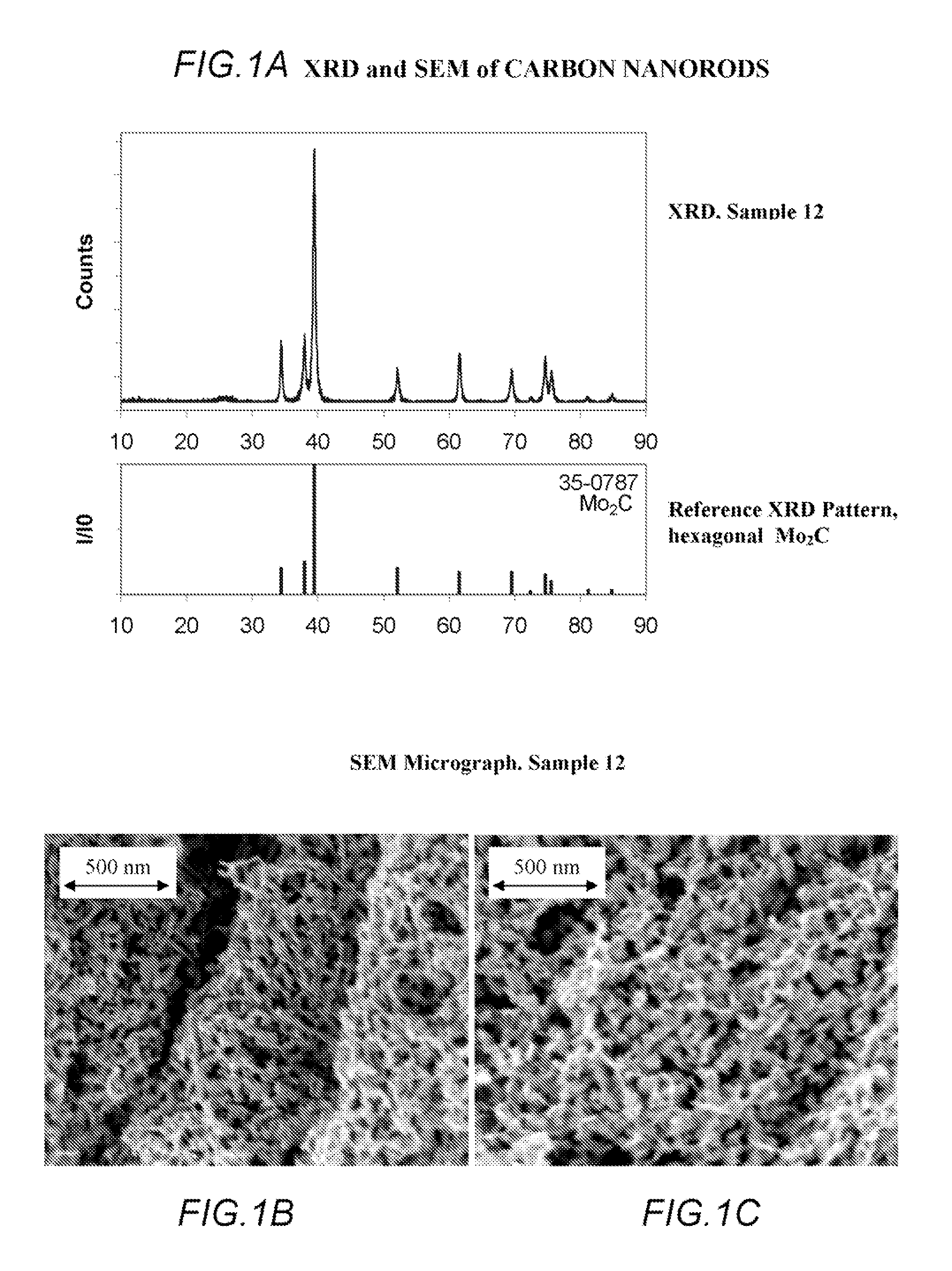
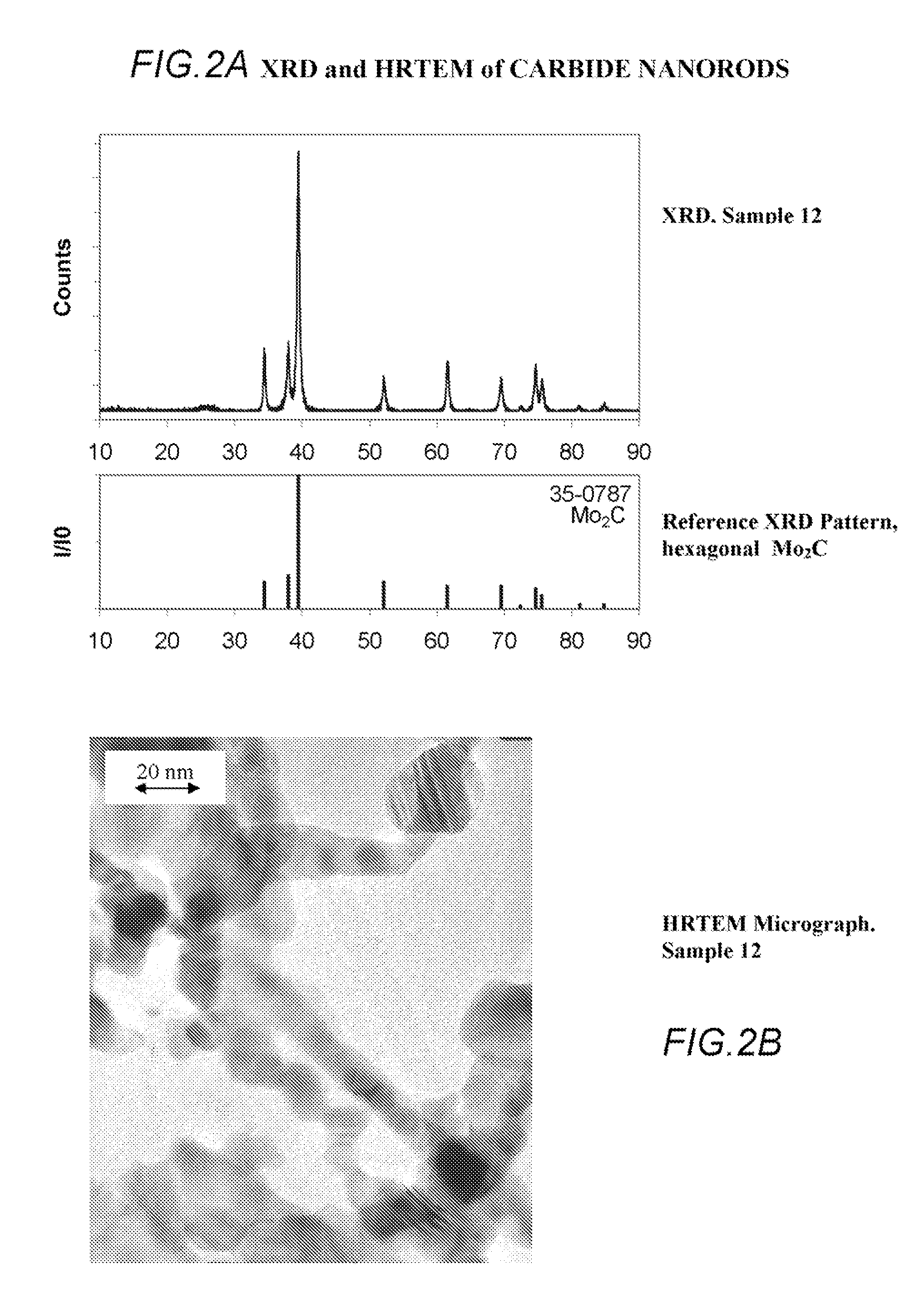
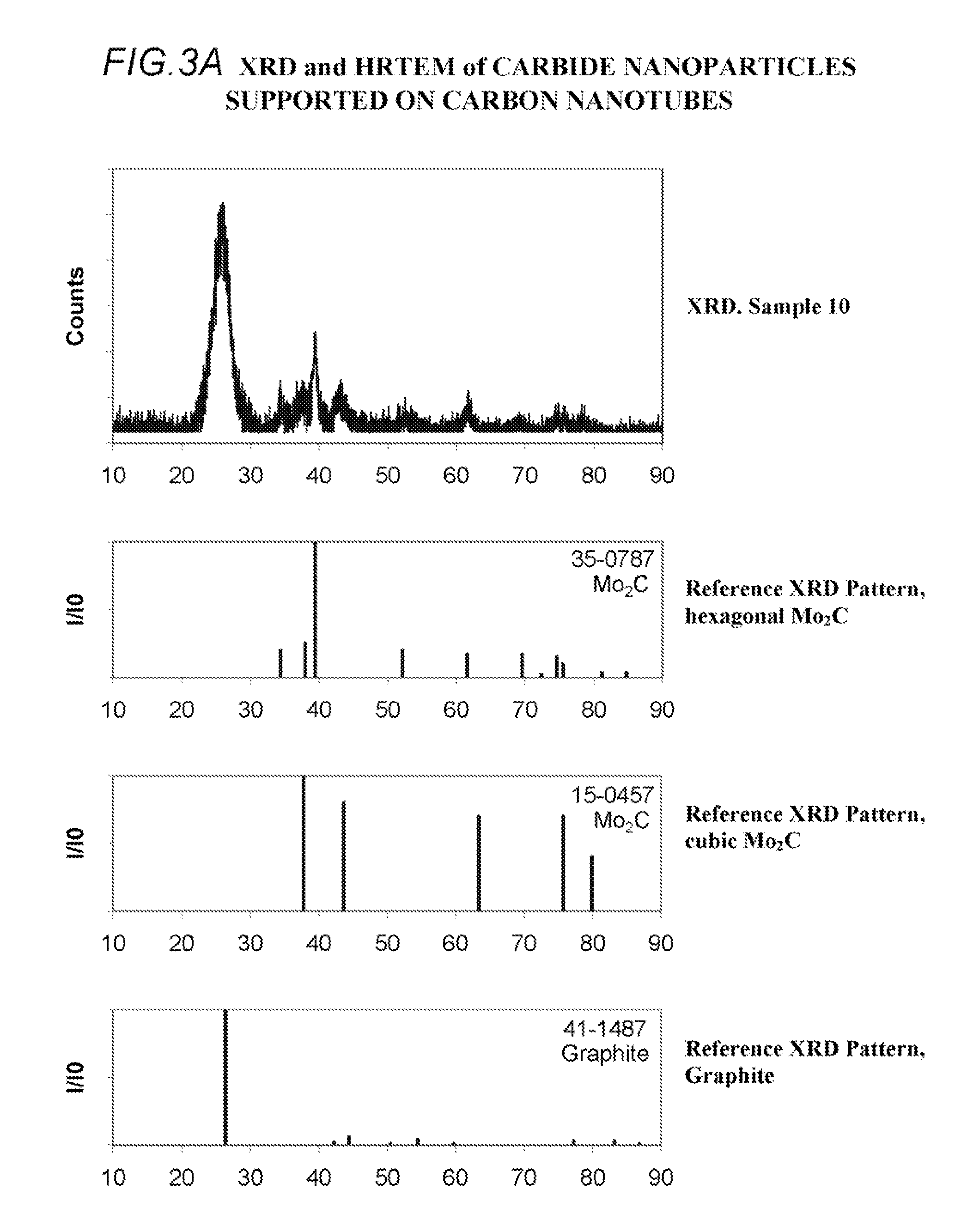
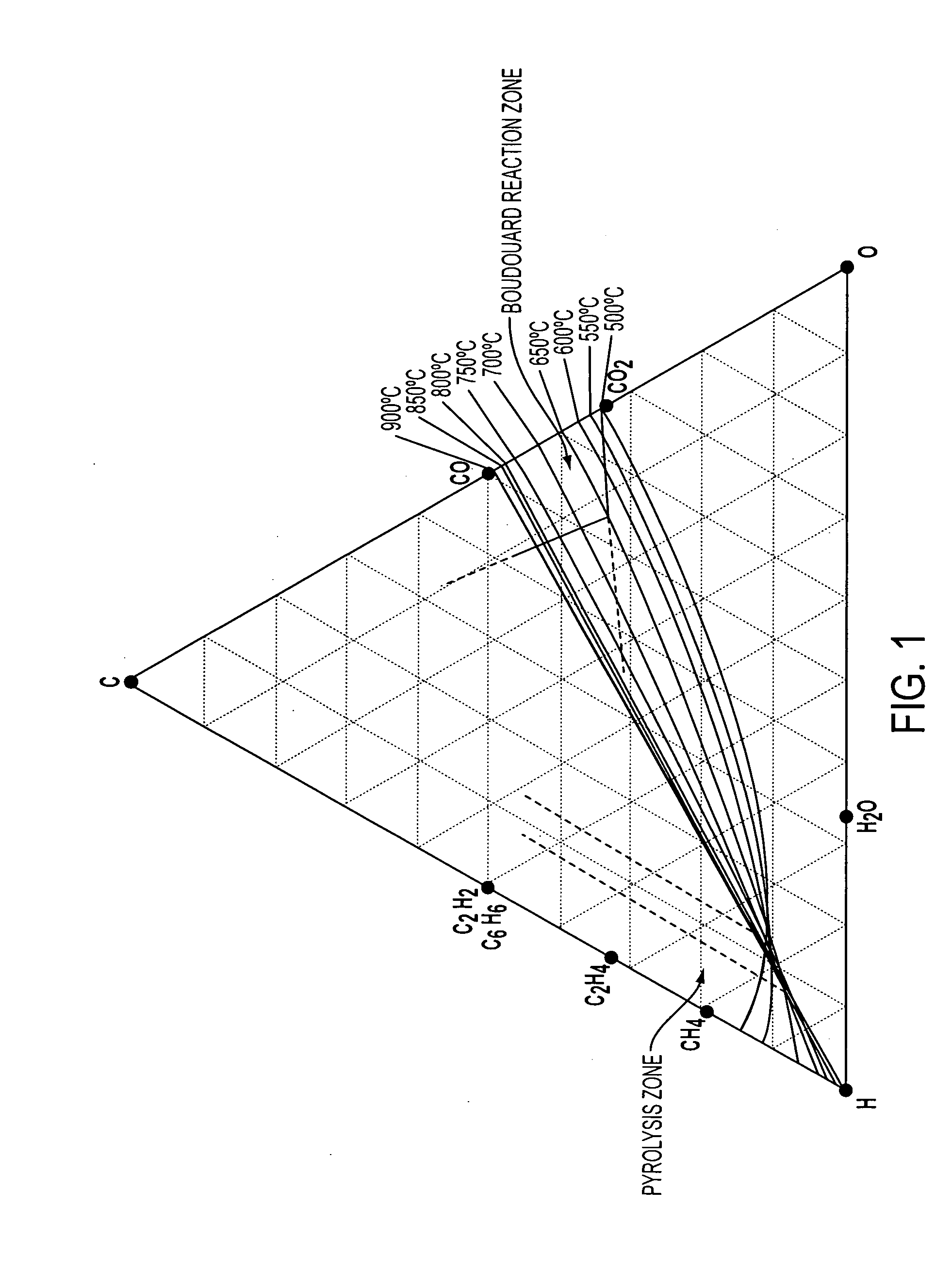
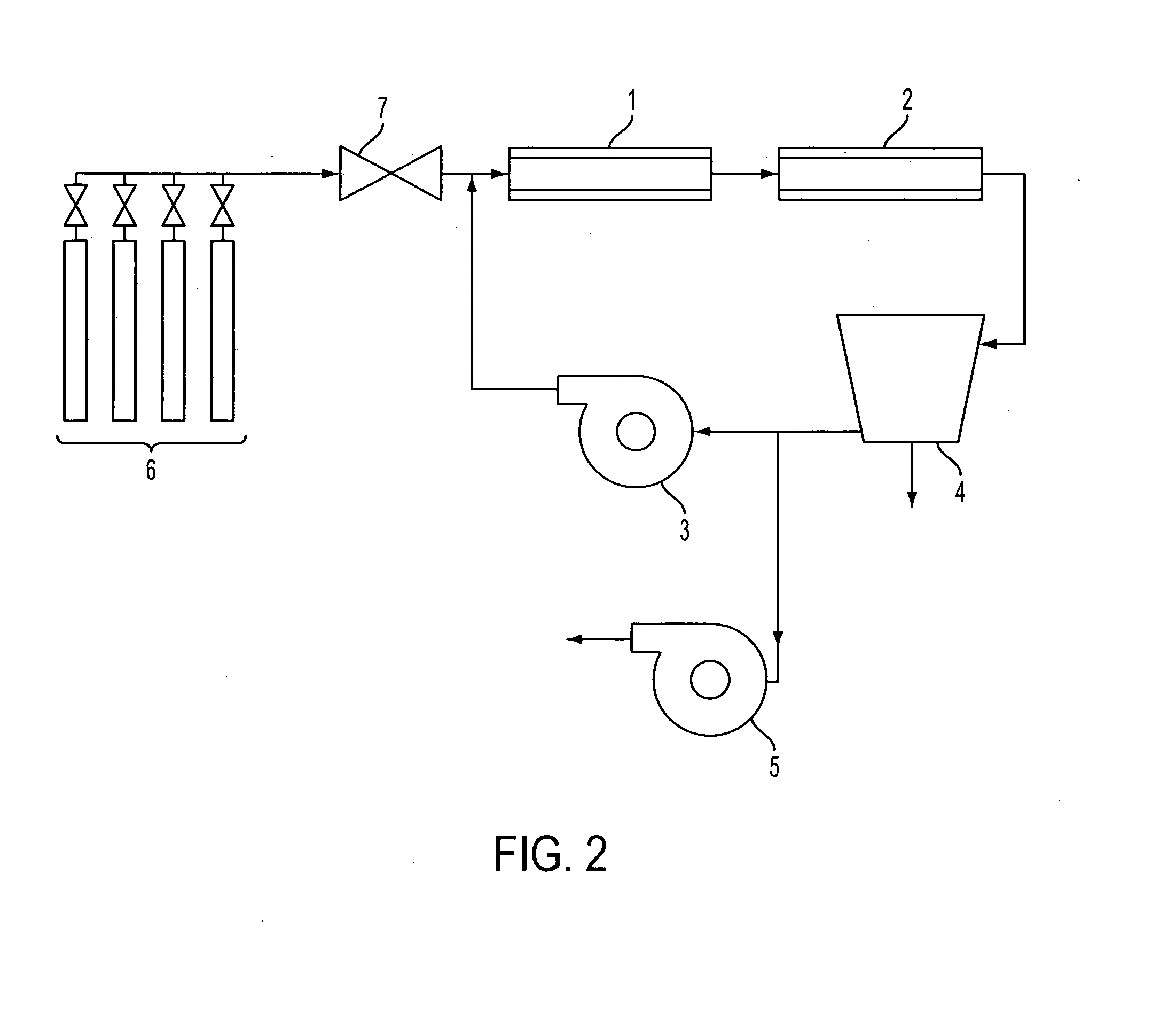
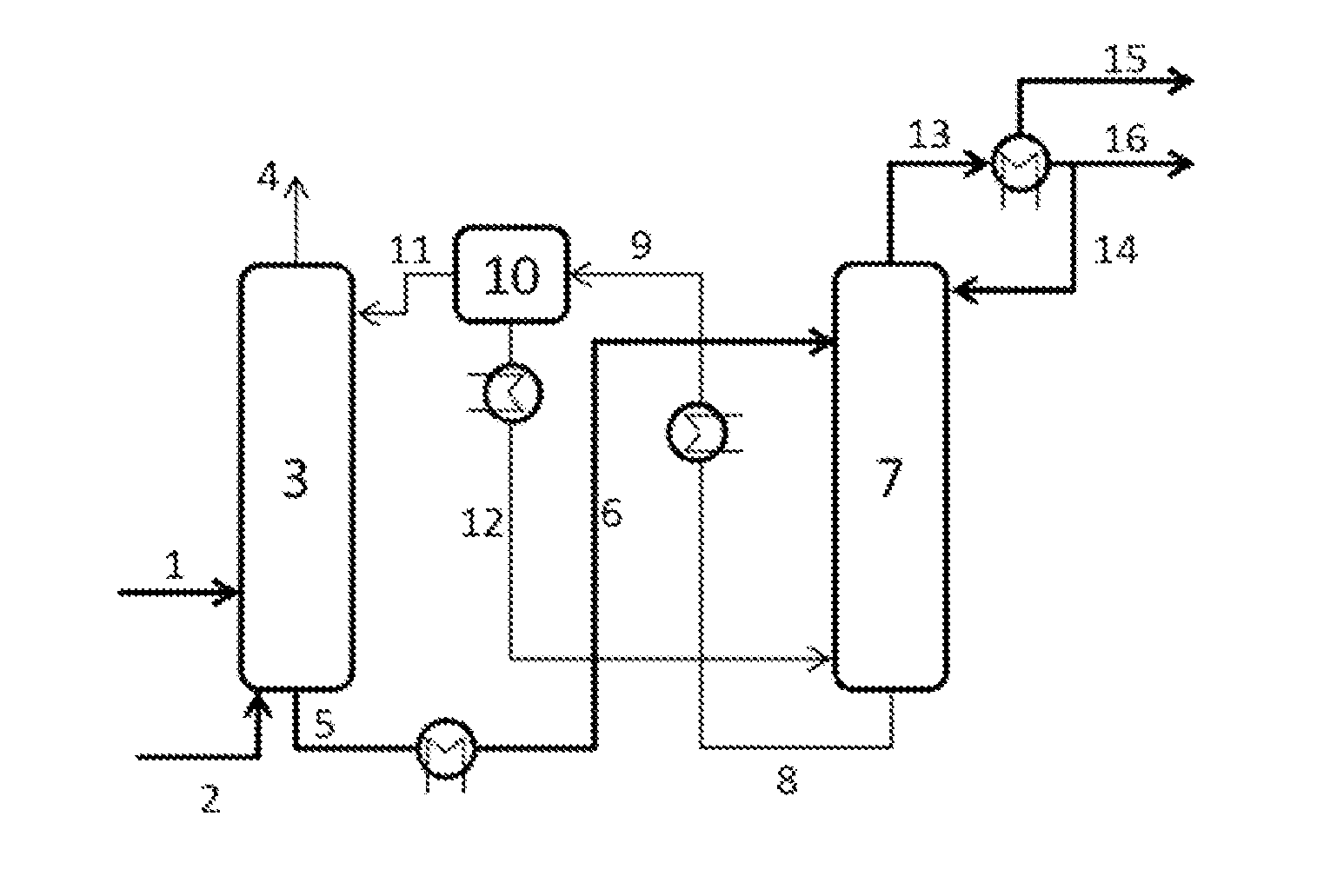
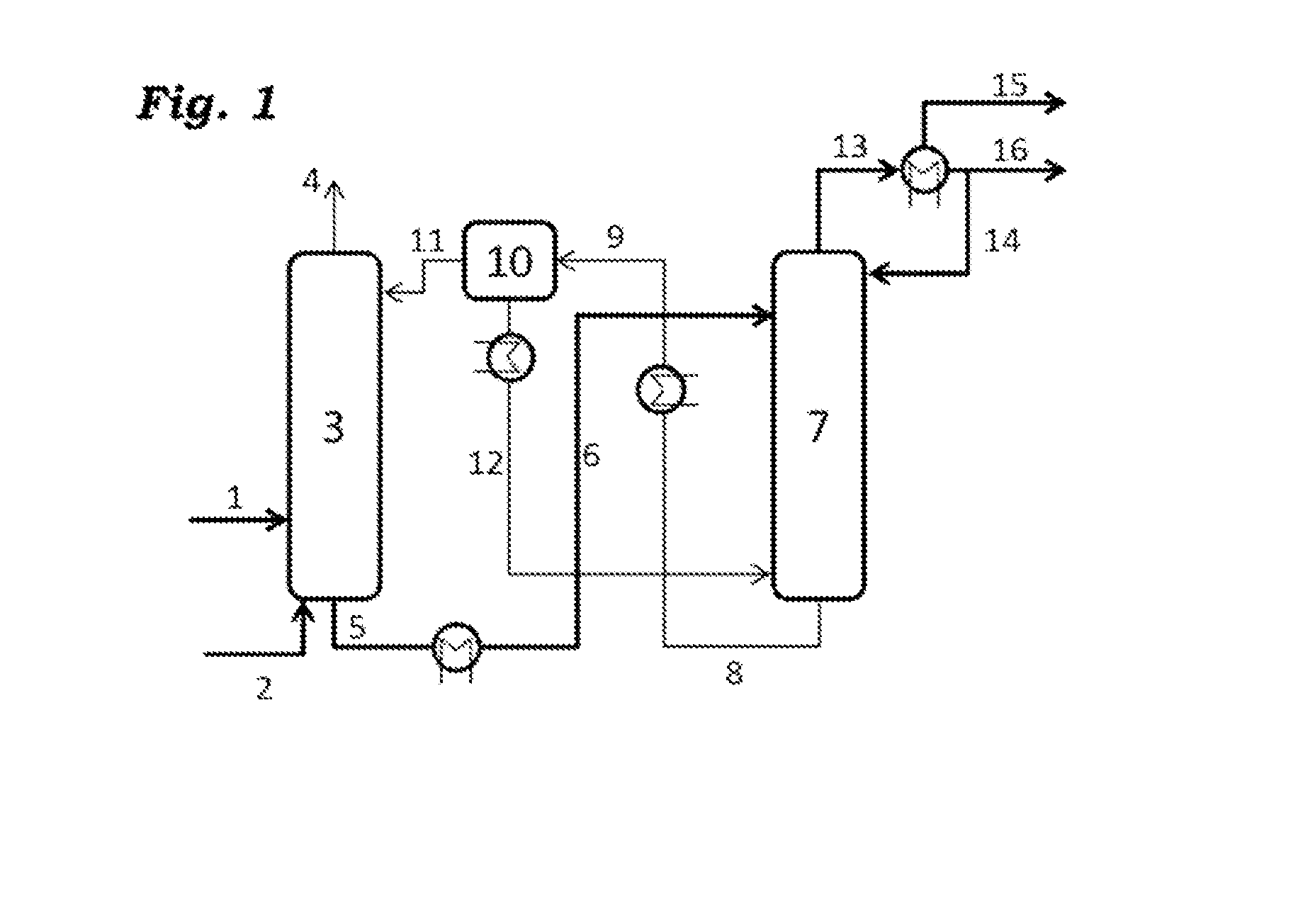
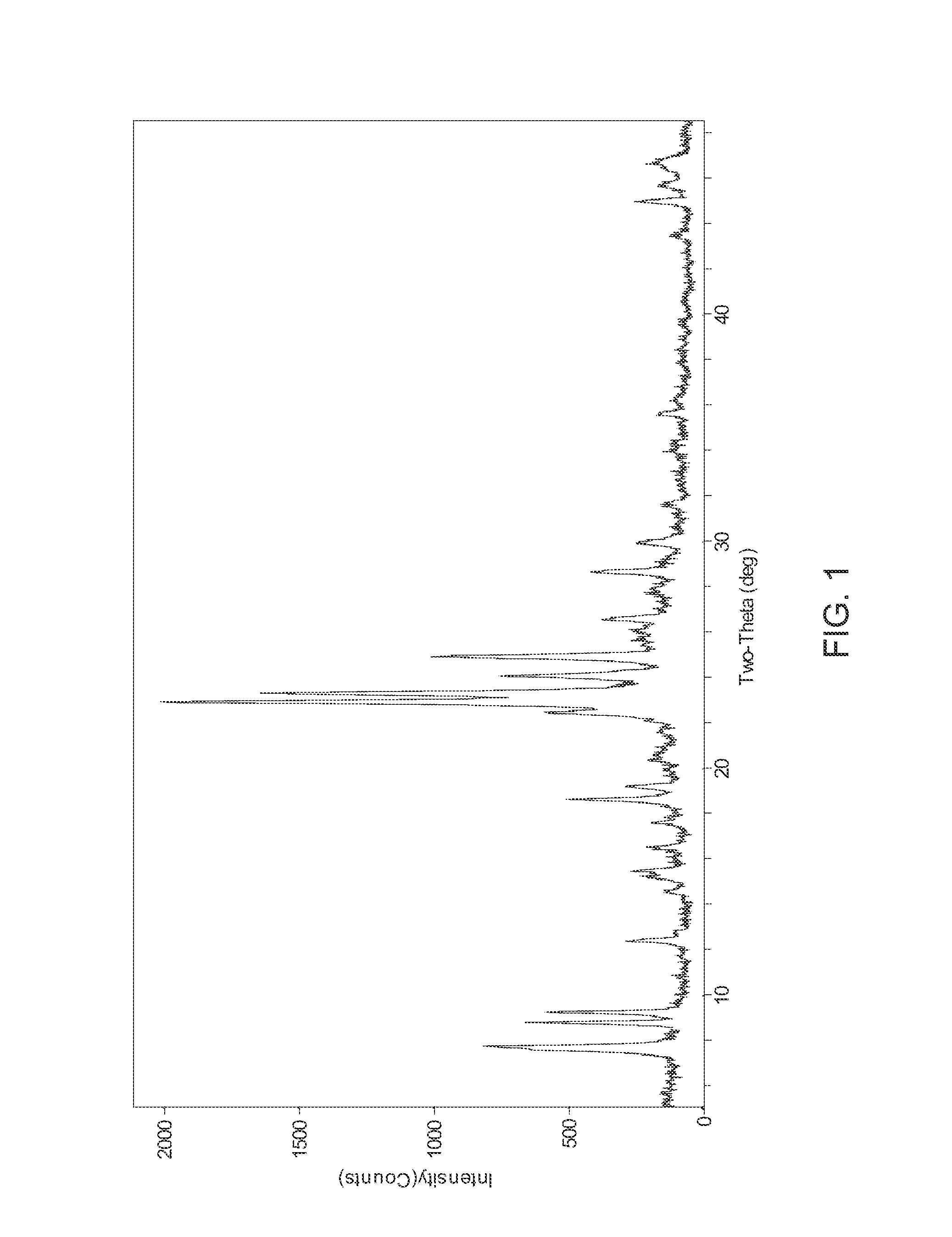
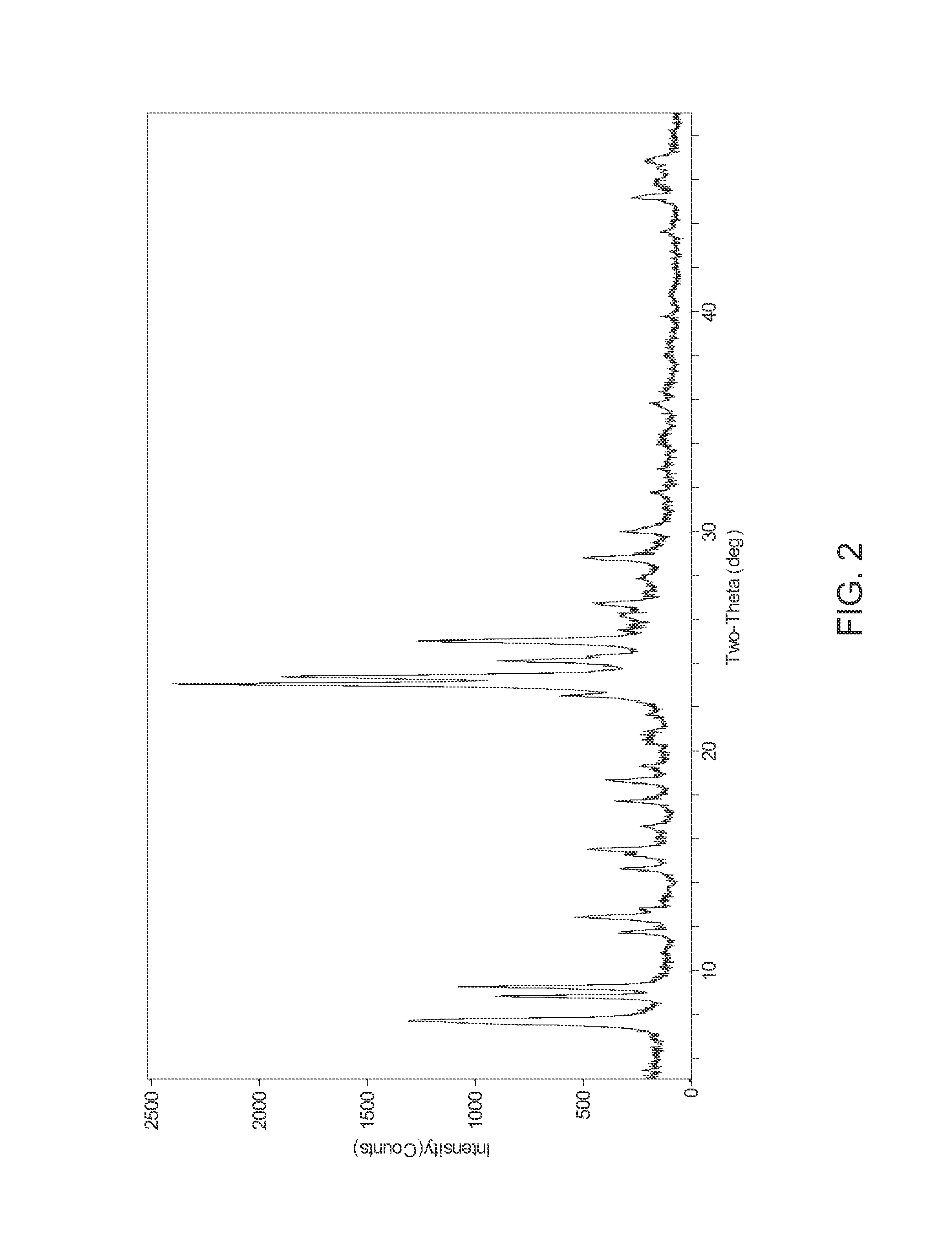
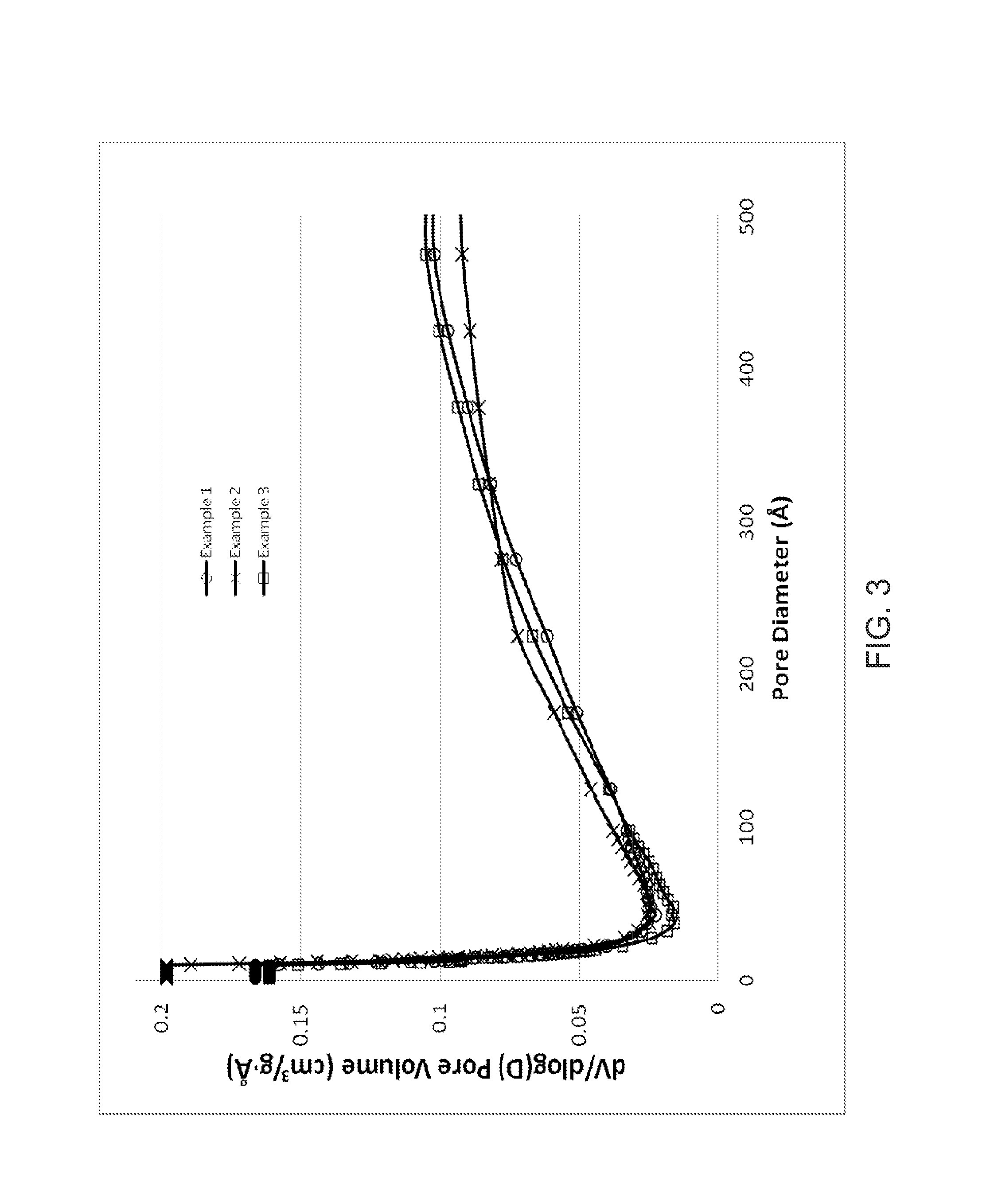
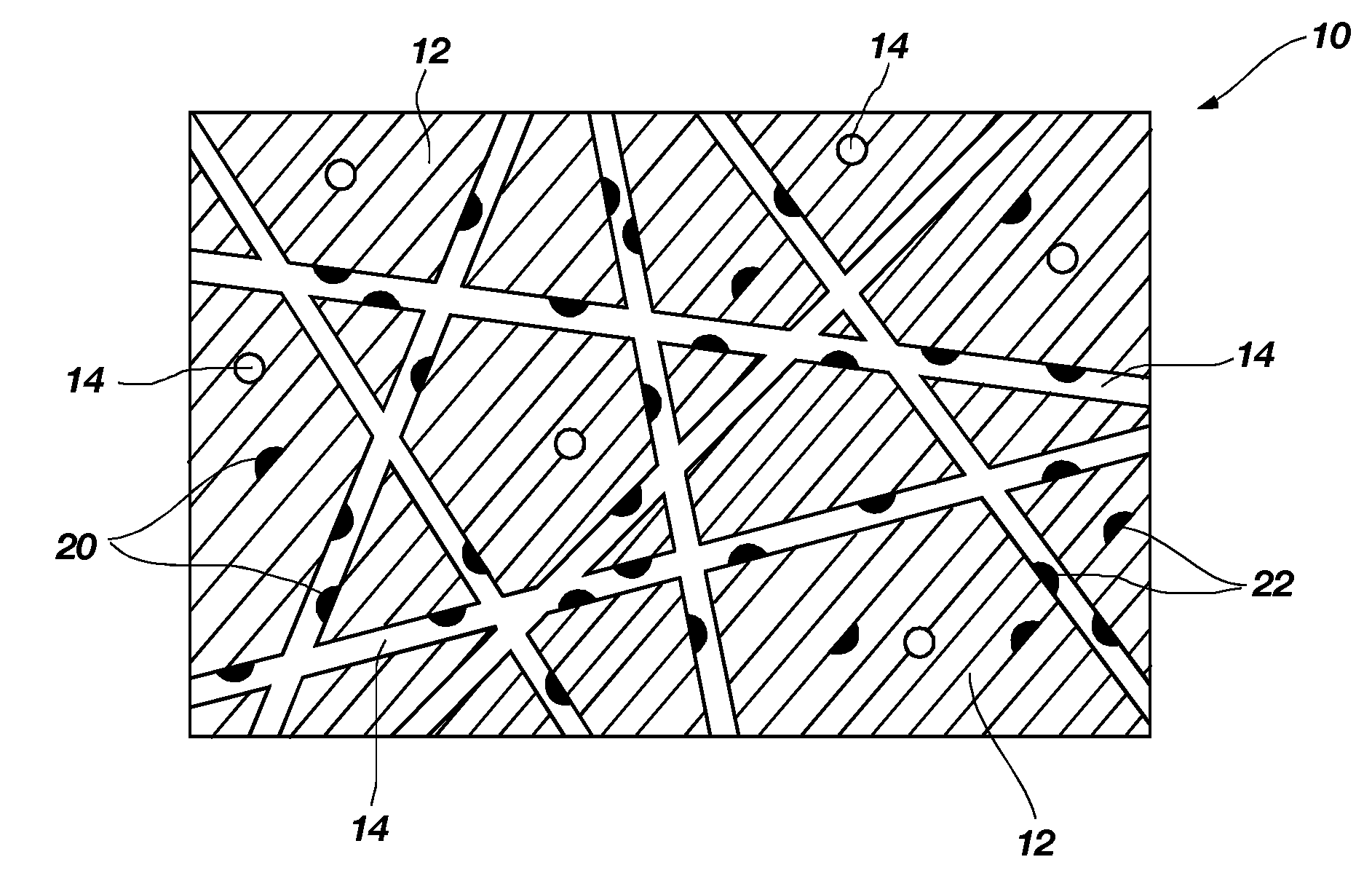
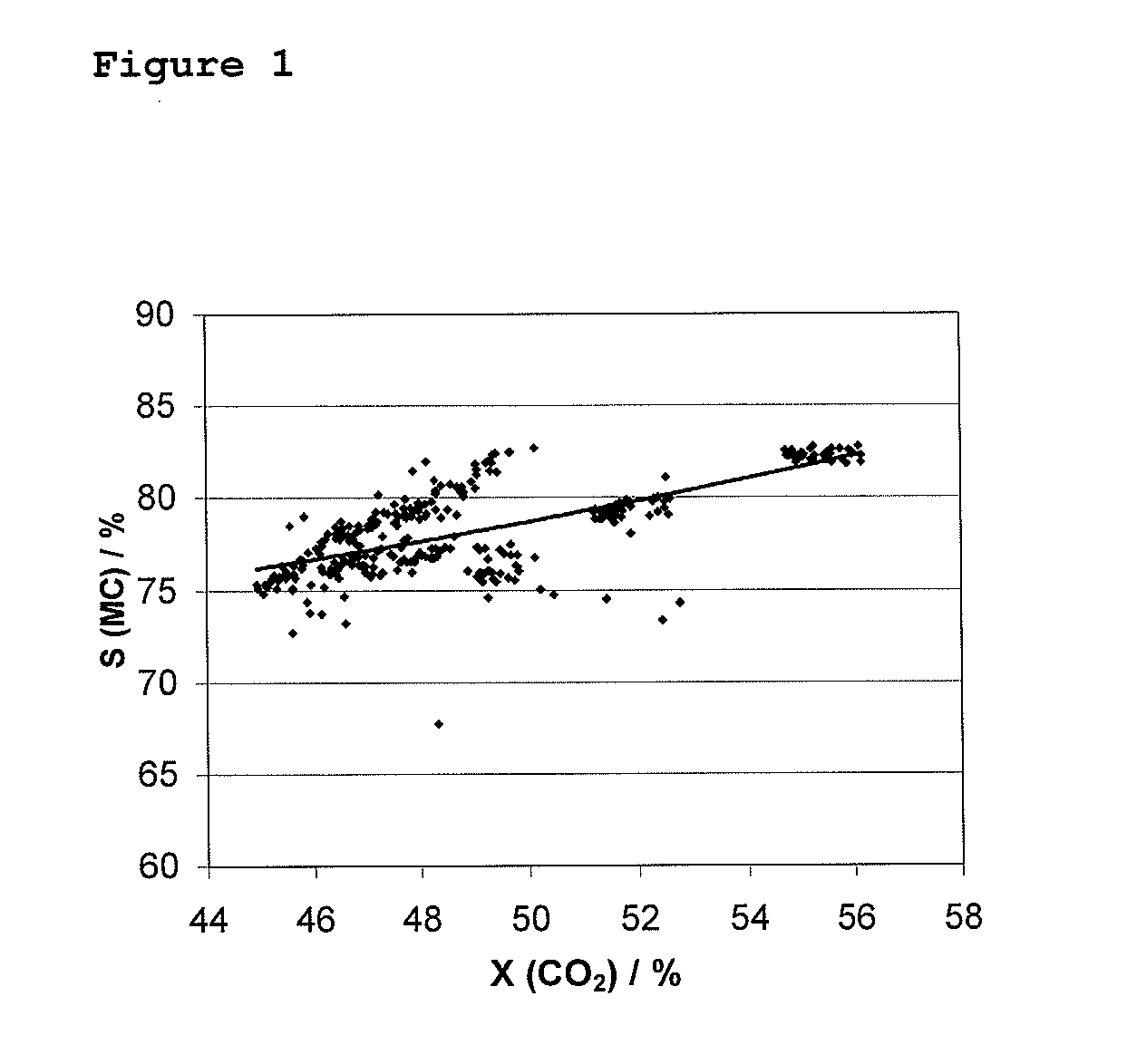
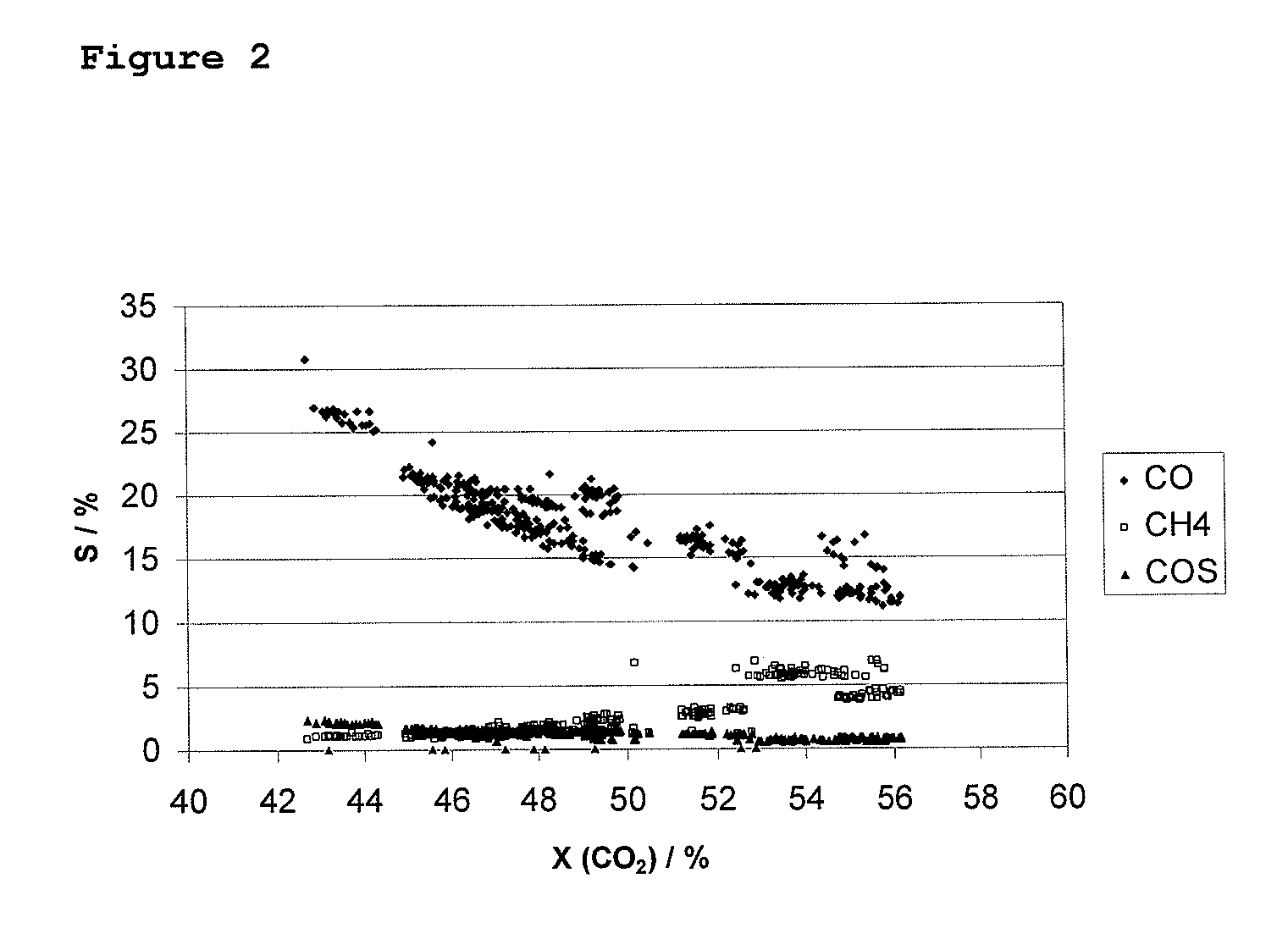
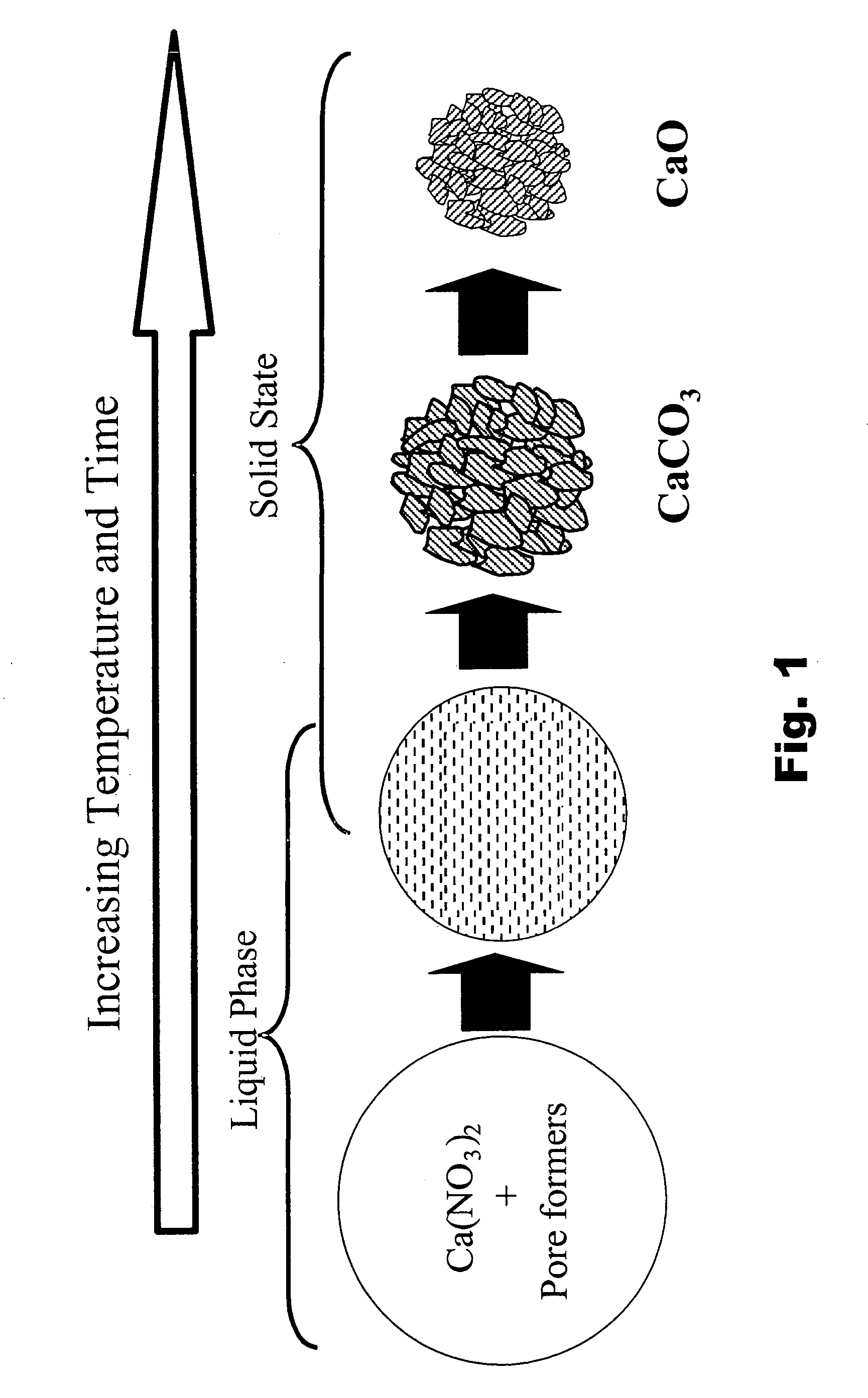
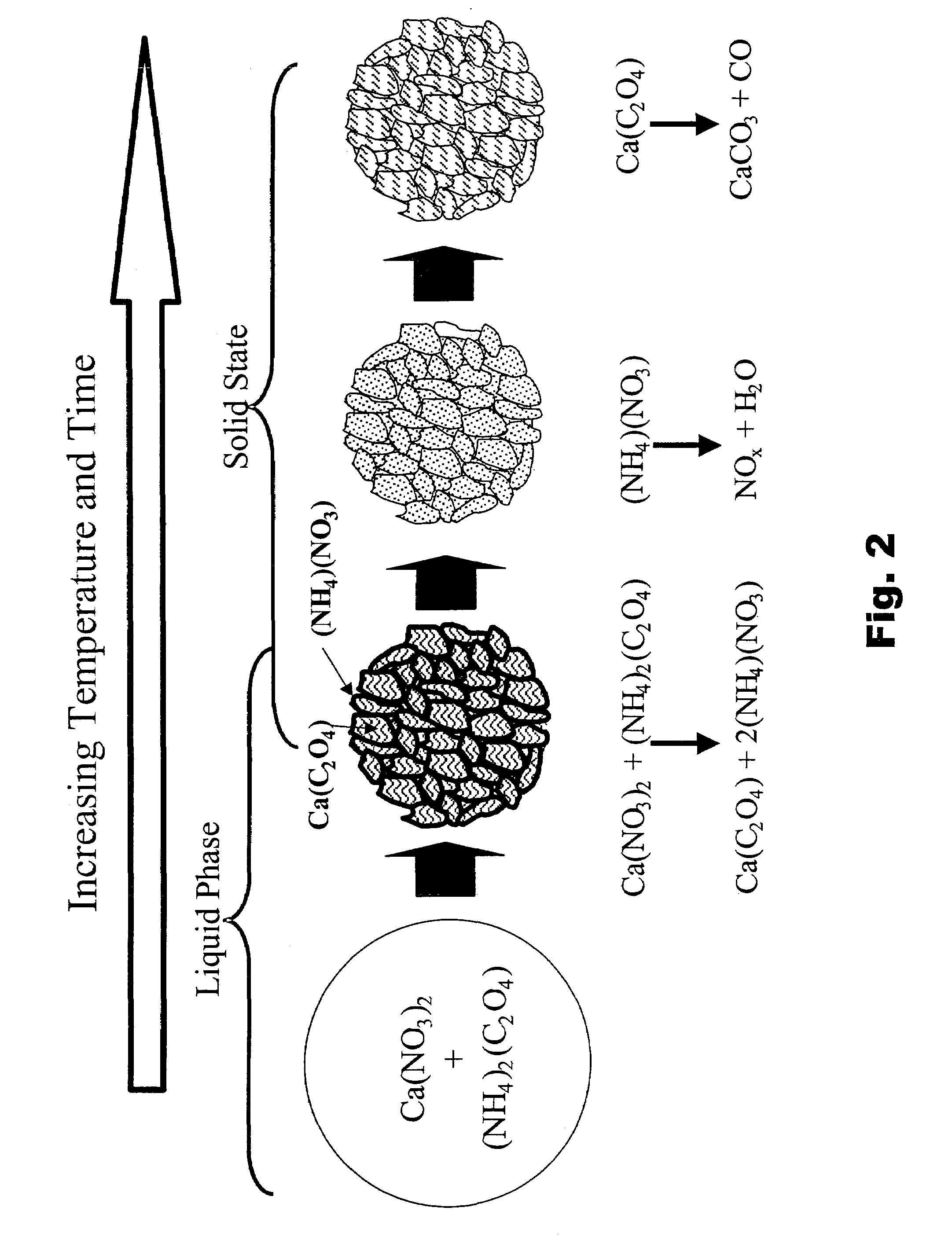
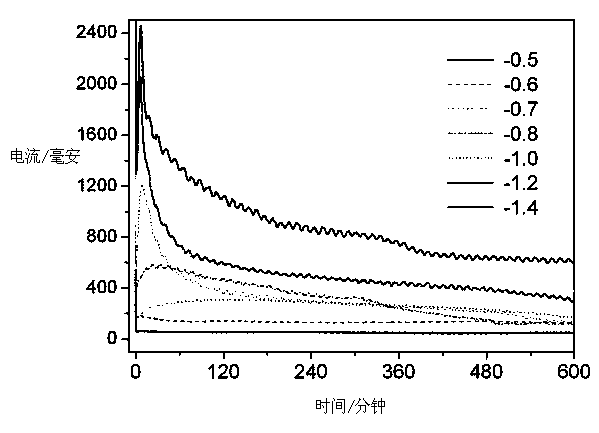
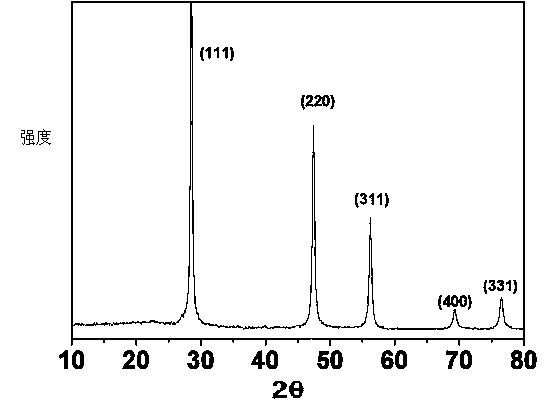
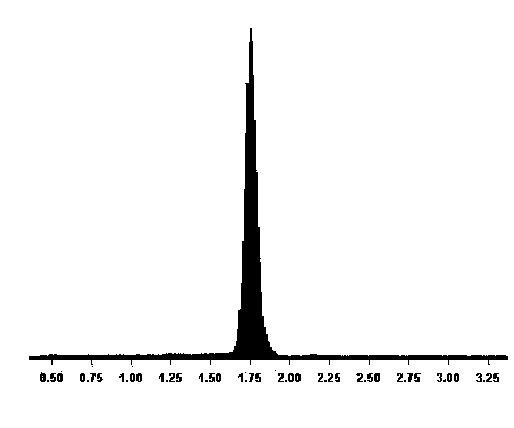
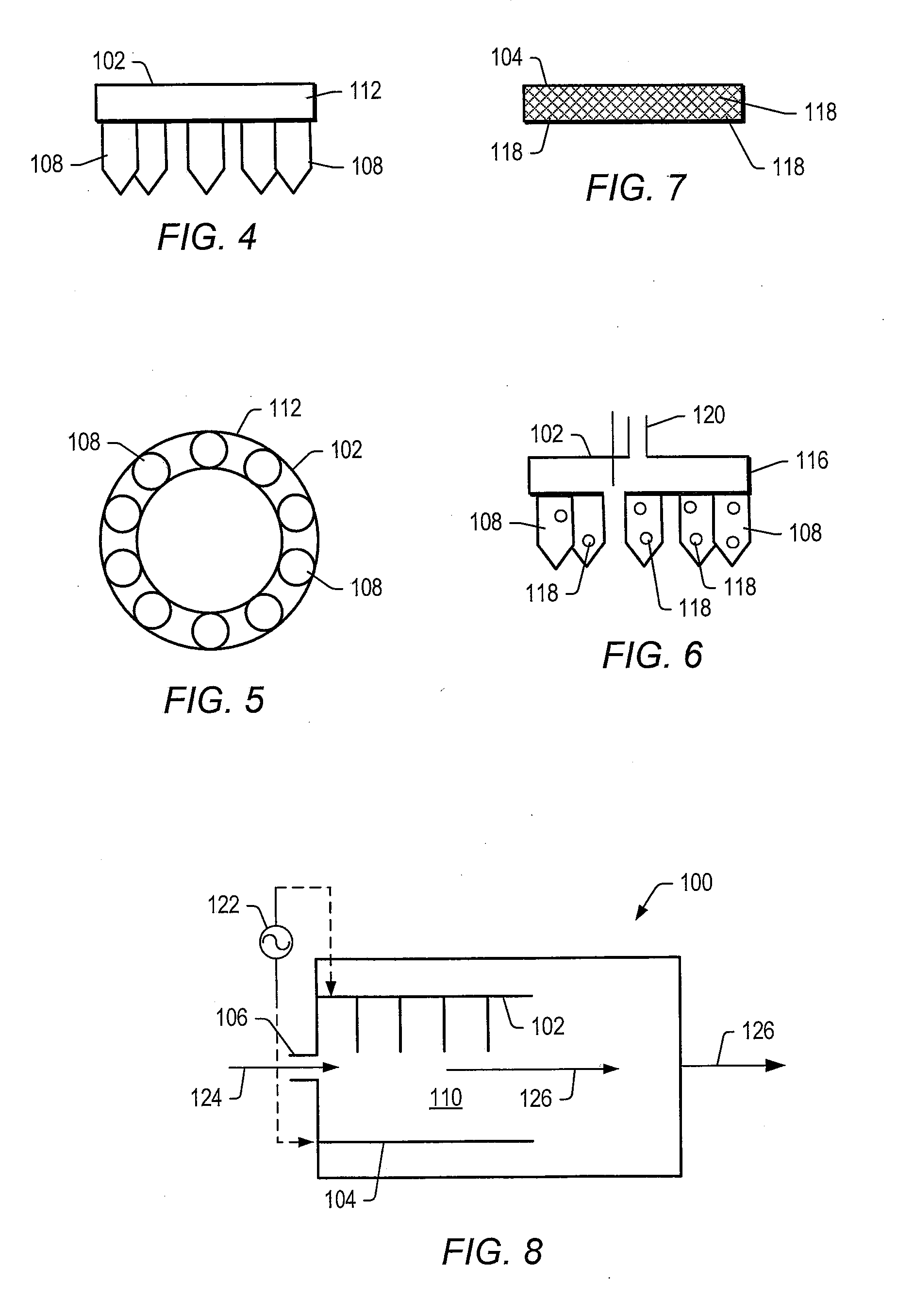
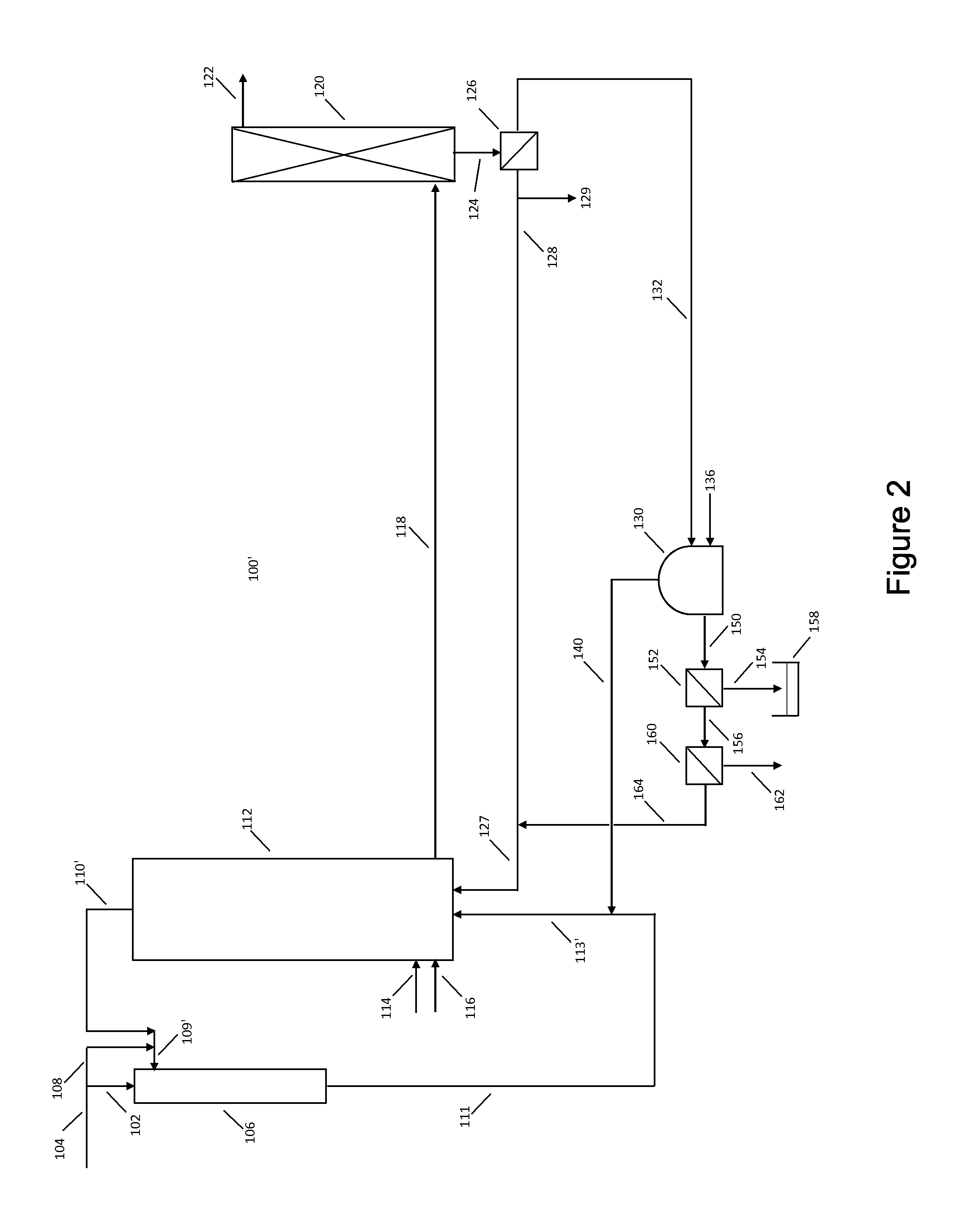
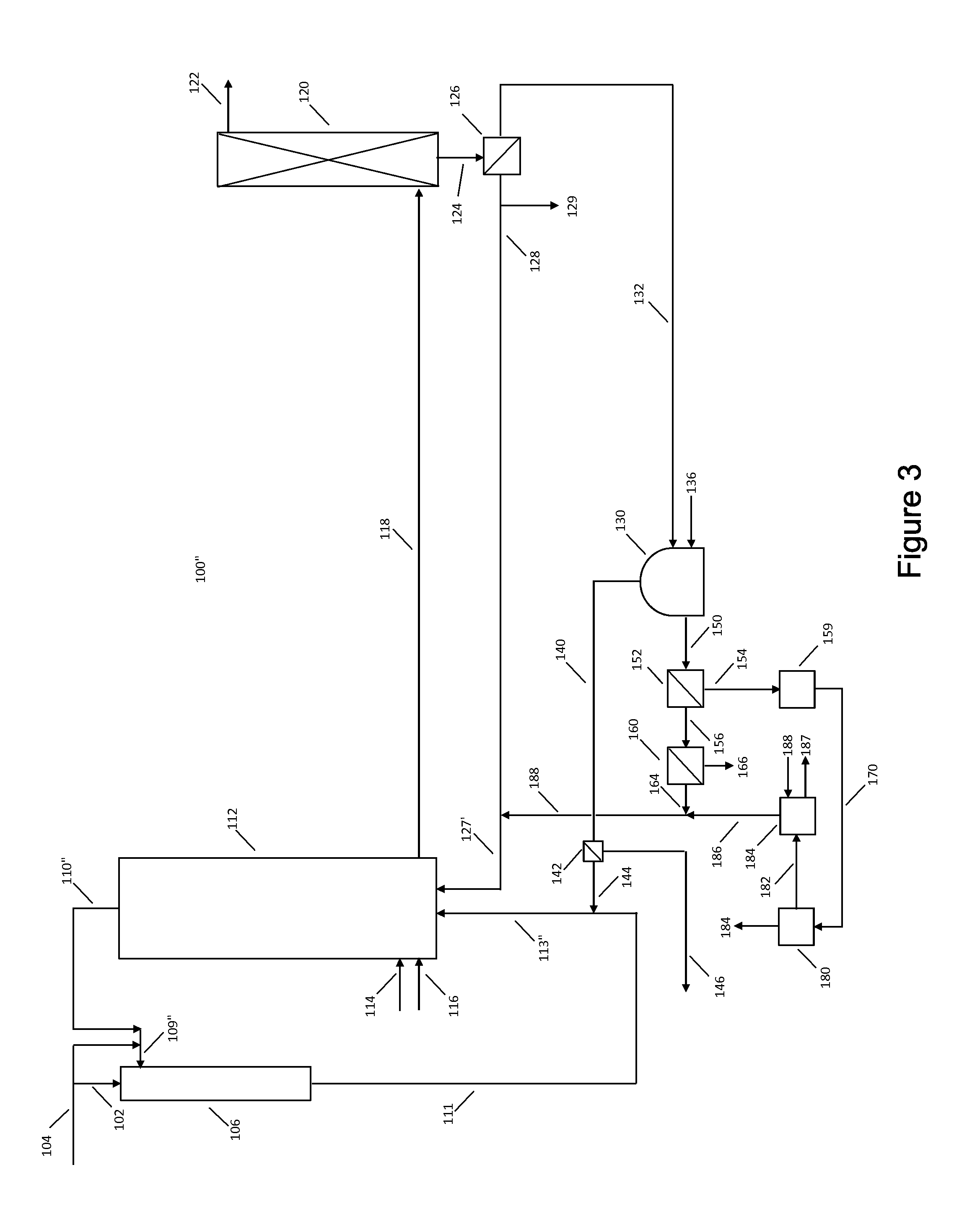
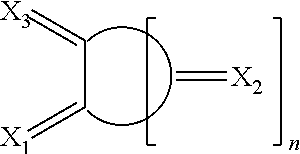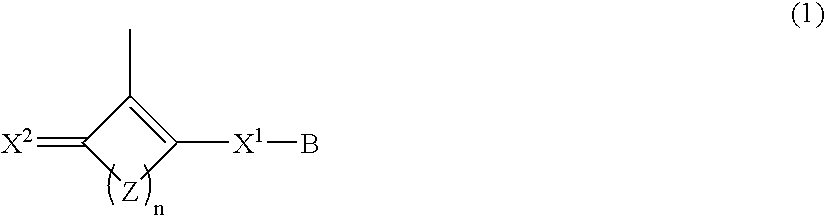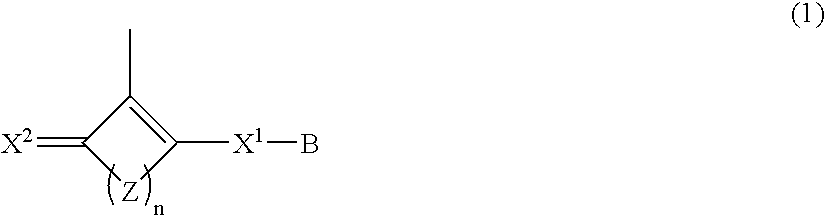Patents
Literature
123 results about "Oxocarbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An oxocarbon or oxide of carbon is a chemical compound consisting only of carbon and oxygen. The simplest and most common oxocarbons are carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) with IUPAC names carbon(II) oxide and carbon(IV) oxide respectively. Many other stable (practically if not thermodynamically) or metastable oxides of carbon are known, but they are rarely encountered, such as carbon suboxide (C₃O₂ or O=C=C=C=O) and mellitic anhydride (C₁₂O₉).
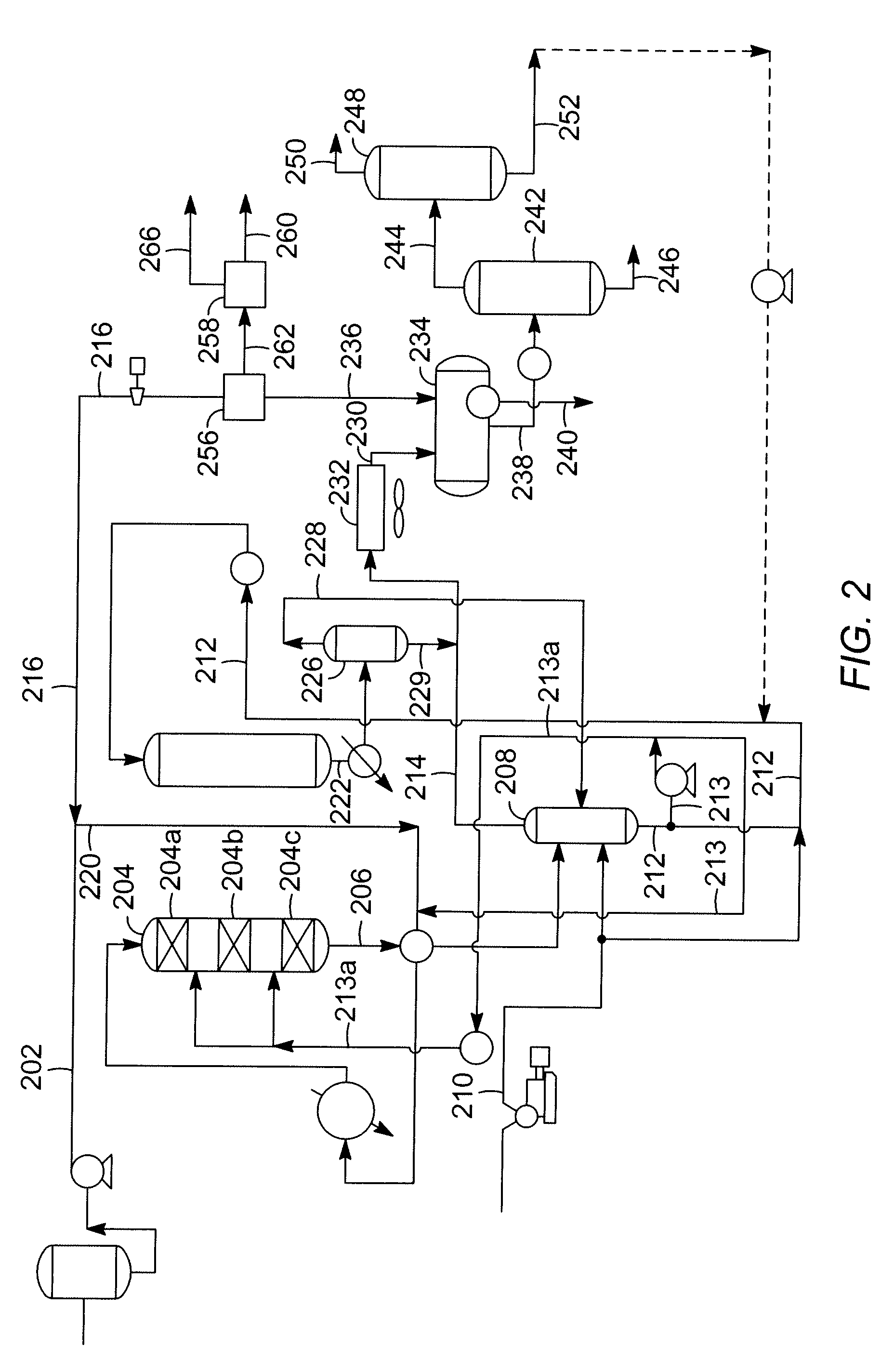
Thermocatalytic process for CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon from hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20020007594A1Pigmenting treatmentPressurized chemical processDecompositionBiological activation
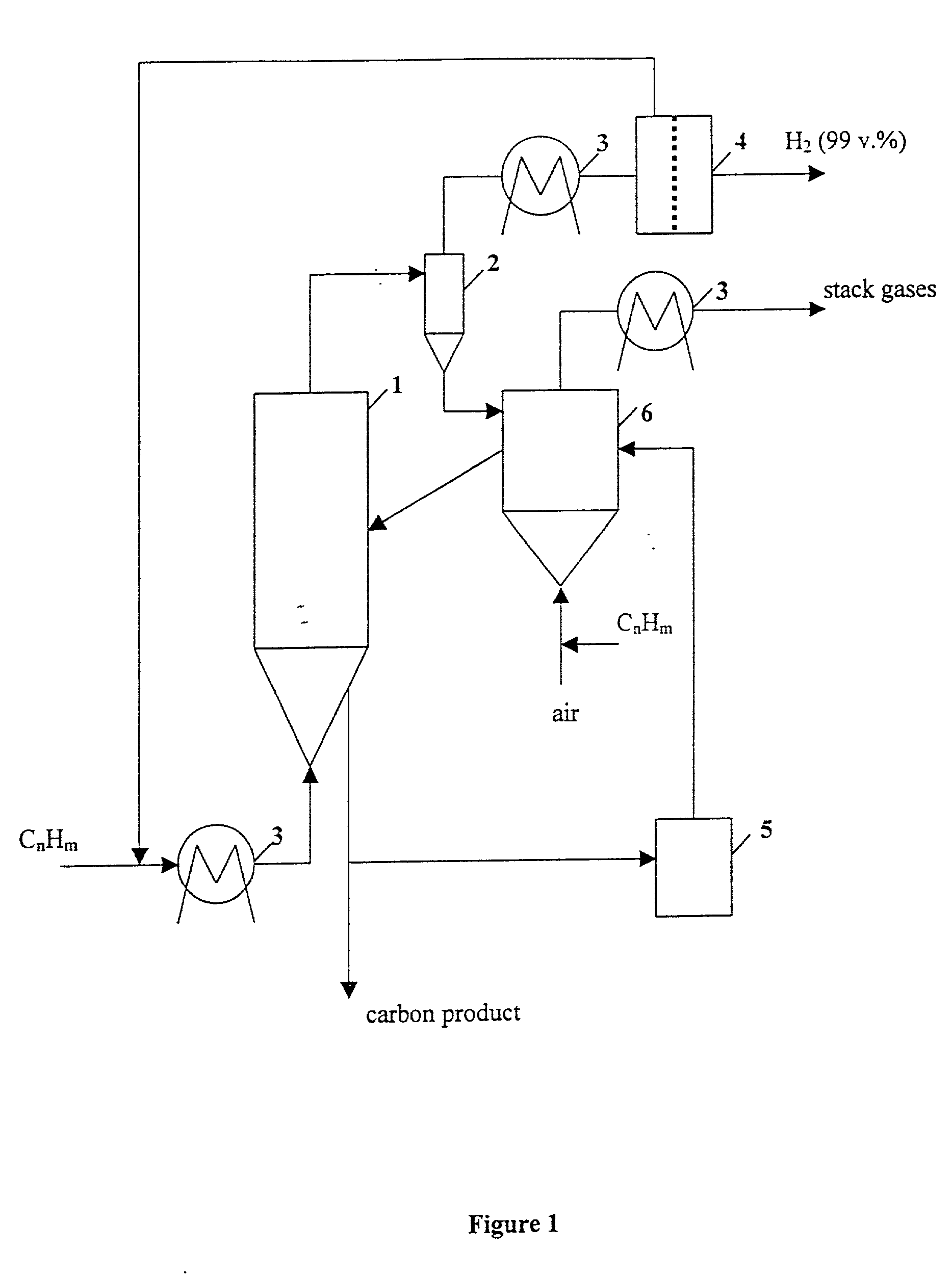
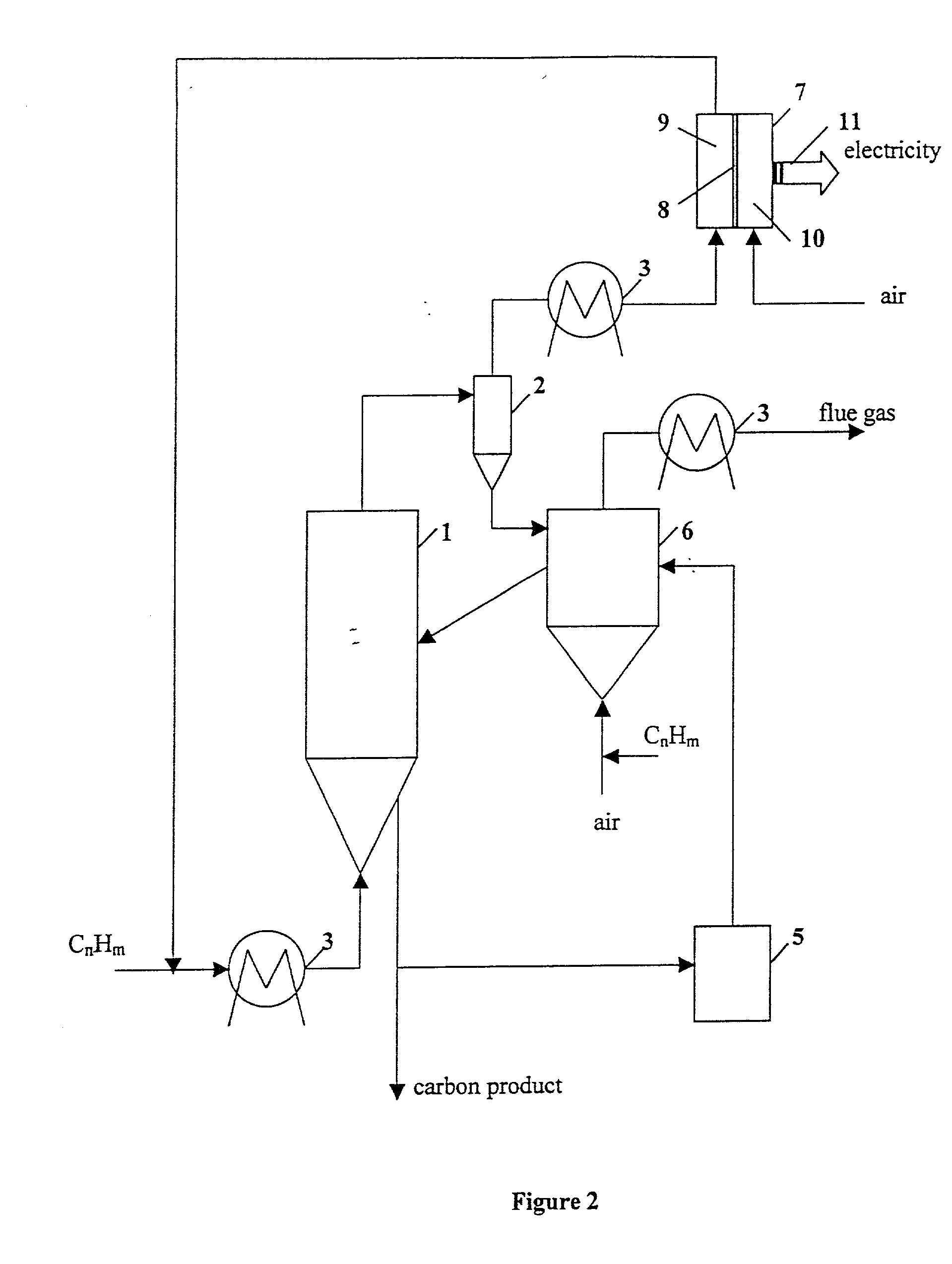
This invention relates to a novel process for sustainable CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon by thermocatalytic decomposition (or dissociation, pyrolysis, cracking) of hydrocarbon fuels over carbon-based catalysts in the absence of air and / or water. The process is applicable to any hydrocarbon fuel, including sulfurous fuels. Combination of a catalytic reactor with a gas separation unit allows to produce high purity hydrogen (at least, 99.0 v %) completely free of carbon oxides. In a preferred embodiment, sustainable continuous production of hydrogen and carbon is achieved by both internal and external activation of carbon catalysts. Internal activation of carbon catalyst is accomplished by recycling of hydrogen-depleted gas containing unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons back to the reactor. External activation can be achieved via surface gasification of carbon catalysts by hot combustion gases during catalyst heating. The process can conveniently be integrated with any type of fuel cell.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Production of Diesel Fuel from Biorenewable Feedstocks with Selective Separation of Converted Oxygen
A process has been developed for producing diesel boiling range fuel from renewable feedstocks such as plant and animal fats and oils, the process providing for sulfur management. The process involves catalytically treating a renewable feedstock by hydrogenating and deoxygenating to provide a hydrocarbon fraction useful as a diesel boiling range fuel. The hydrocarbon fraction is isomerized to improve cold flow properties. A selective separation such as a hot high pressure hydrogen stripper is used to remove at least the carbon oxides from the first zone effluent before entering the isomerization zone, and to provide liquid recycle to the treating zone at pressure and temperature. A vapor stream is separated from the isomerization effluent and at least carbon dioxide is removed using at least one selective or flexible amine solution absorber. The resulting hydrogen-rich stream is recycled to the deoxygenation reaction zone
Owner:UOP LLC
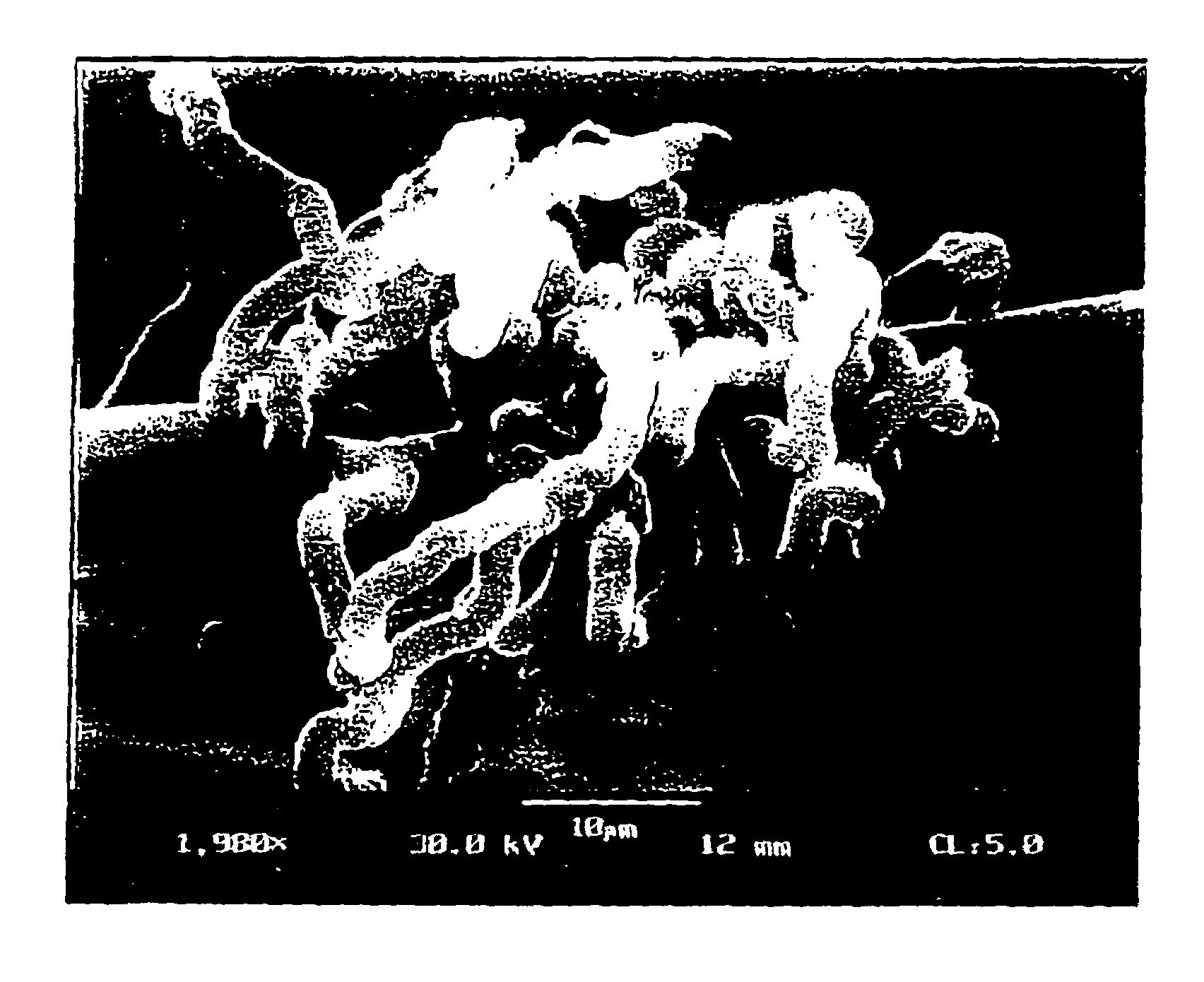
Filamentous carbon particles for cleaning oil spills and method of production
InactiveUS7473466B1Increase specific energy and overall energy efficiencyHydrogen/synthetic gas productionGlass/slag layered productsFiberCarbon nanotube
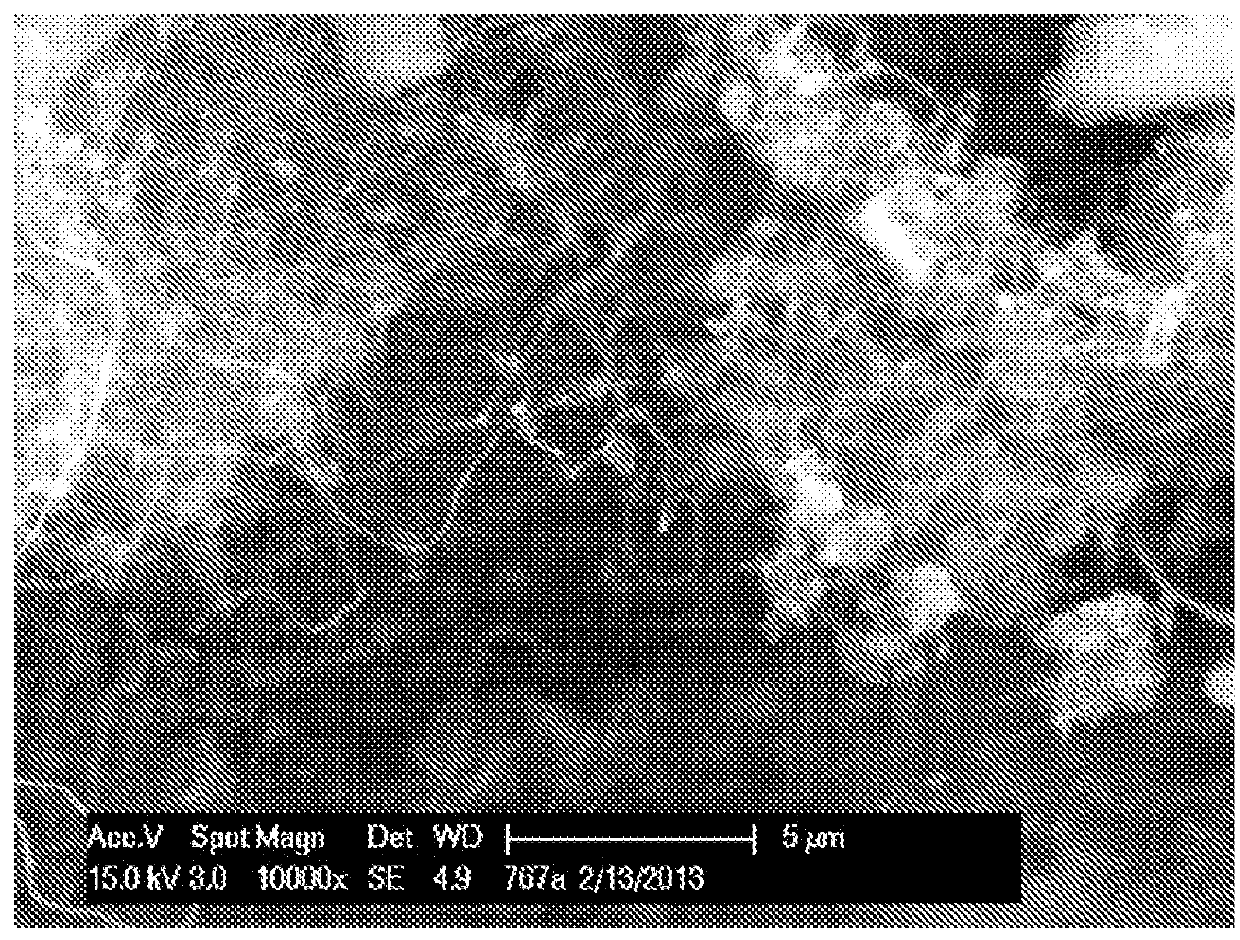
A compact hydrogen generator is coupled to or integrated with a fuel cell for portable power applications. In the process of producing hydrogen for the generator via thermocatalytic decomposition (cracking, pyrolysis) of hydrocarbon fuels in an oxidant-free environment, novel carbon products are produced with filamentary surfaces, “octopus”-like carbon filaments, single carbon nanotube fibers and the like. Two novel processes are disclosed for the production of carbon filaments and a novel filamentous carbon product useful in the clean-up of oil spills on the surface of water. The apparatus can utilize a variety of hydrocarbon fuels, including natural gas, propane, gasoline, and sulfurous fuels. The hydrogen-rich gas produced is free of carbon oxides or other reactive impurities, so it can be directly fed to any type of a fuel cell. The hydrogen generator can be conveniently integrated with high temperature fuel cells to produce an efficient and self-contained source of electrical power.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method for conversion of atmospheric carbon dioxide into useful materials
A method for converting carbon dioxide in a gaseous environment, including air into useful materials by use of renewable energy sources which comprises:(1) extracting carbon dioxide from a gaseous source using a sorbent such as sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, or potassium hydroxide;(2) utilizing wind power, solar power, or other renewable energy sources to regenerate said sorbent by membrane cell electrolysis or other similar method, simultaneously producing hydrogen (H2) gas;(3) releasing carbon dioxide from said sorbent; and(4) utilizing the Fischer Tropsch process, Mobil process, ICI process, or related or similar processes to convert carbon oxides to a hydrocarbon concomittantly with or after effecting the reverse water-gas shift reaction to convert said CO2 and H2 gas into carbon monoxide for reaction in said Fischer Tropsch process, Mobil process or ICI process.
Owner:KAPLAN THOMAS PROGER
Methanation catalyst for removing trace amounts of oxycarbide
ActiveCN101347735AImprove anti-toxic performanceImprove thermal stabilityHydrogen separation using solid contactMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMethanationAlkali metal oxide
The invention discloses a methanation catalyst of carbon oxides containing nickel, the methanation catalyst contains active components of a) nickel oxide, b) tungsten oxide and / or molybdenum oxide, and c) at least one active component which is selected from alkali metal oxides, alkaline earth metal oxides and rare earth metal oxides which are loaded on a carrier of the oxides, and the carrier of the oxides is aluminium oxide, silicon oxide, titanium oxide, zirconium oxide or the mixture thereof. The catalyst of the invention has very high activity at low temperature, high anti-poisoning capacity and thermal stability and broad application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
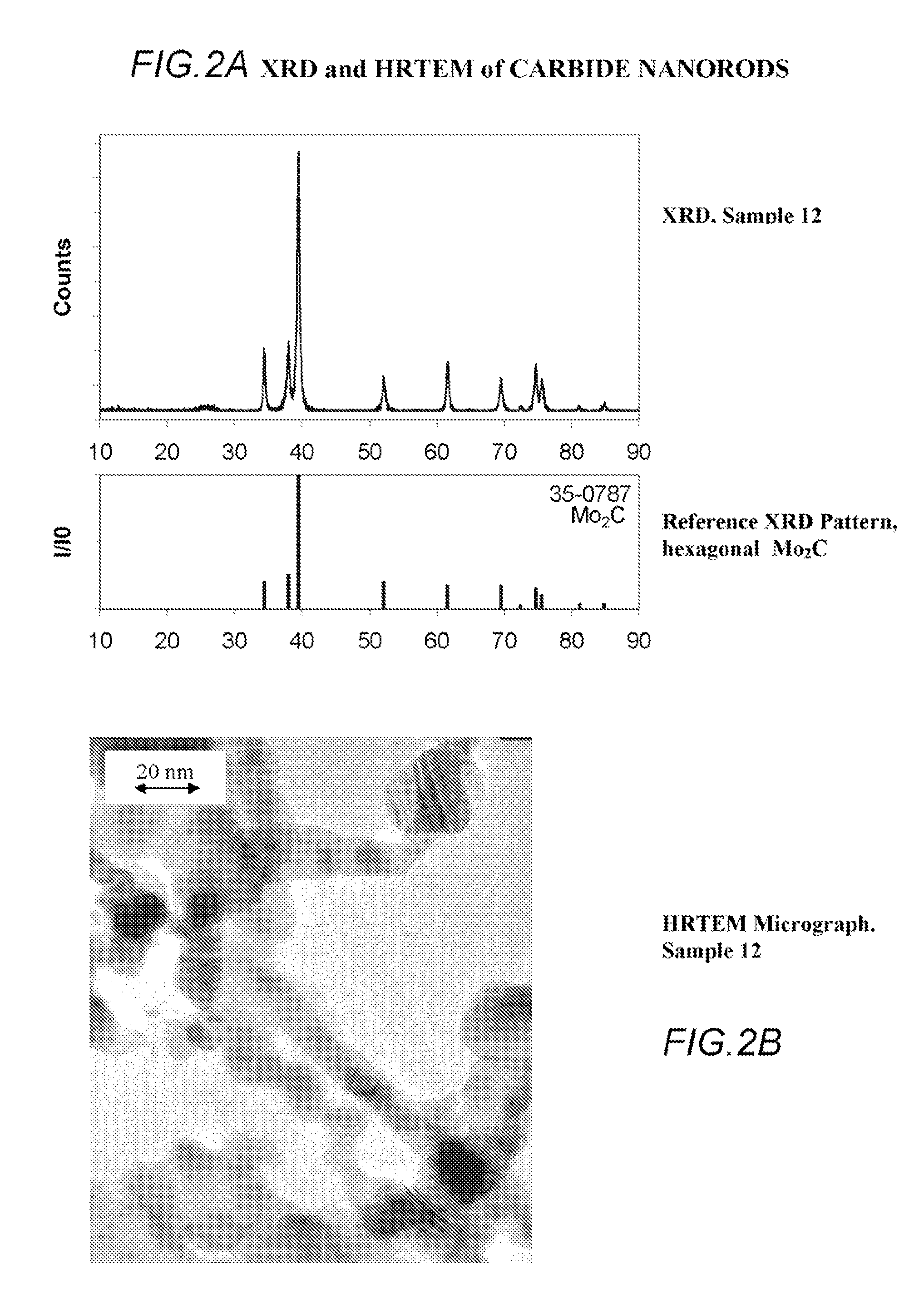
Methods of Making Carbide And Oxycarbide Containing Catalysts
InactiveUS20070179050A1High selectivityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsChemical reactionManufacturing technology
Methods for forming compositions including carbide-containing nanorods and / or oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides. Rigid porous structures including oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbide containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing modified carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are also provided. The compositions and rigid porous structures of the invention can be used either as catalyst and / or catalyst supports in fluid phase catalytic chemical reactions. Processes for making supported catalyst for selected fluid phase catalytic reactions are also provided.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
System and method for producing substittue natural gas from coal
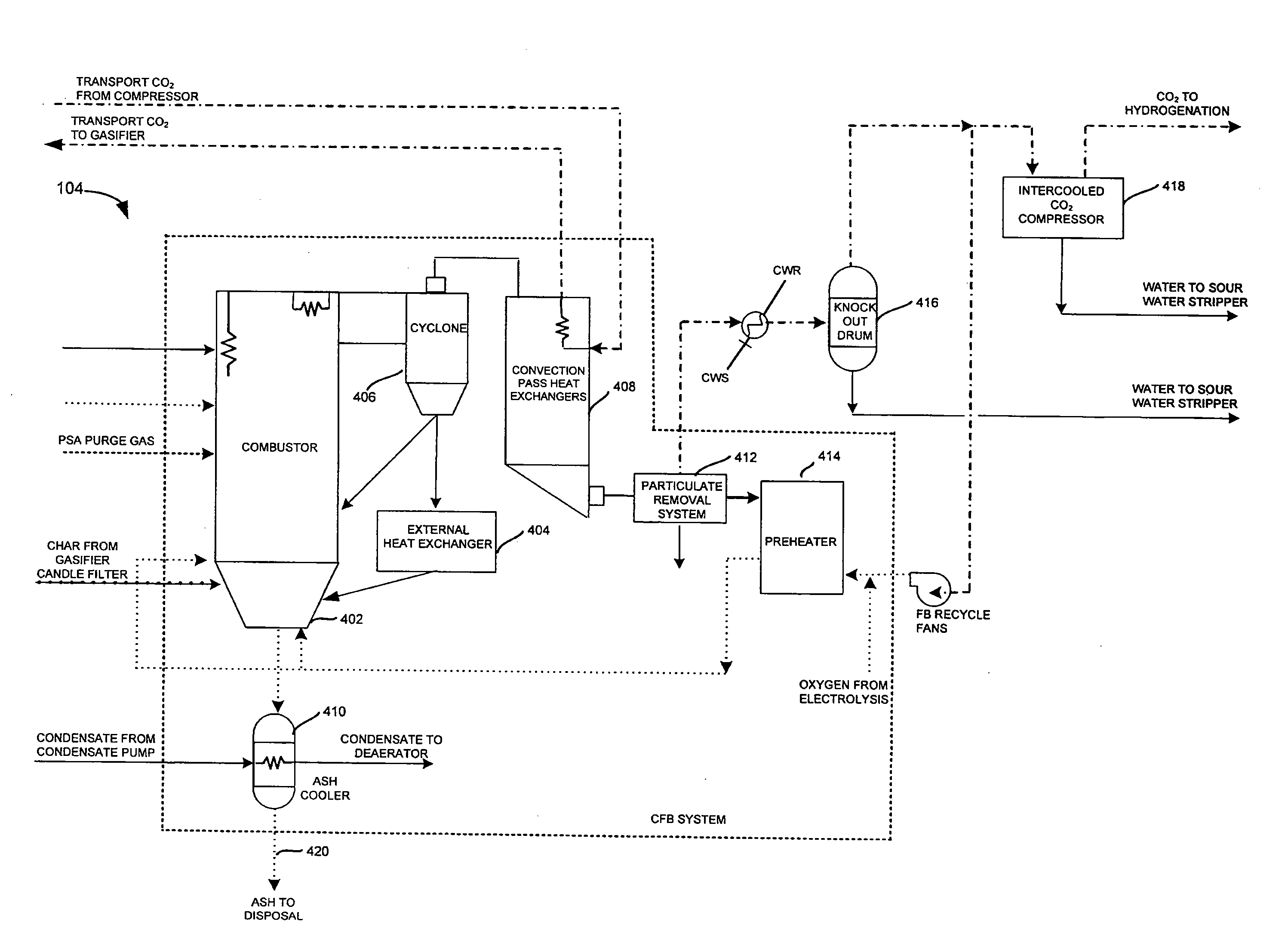
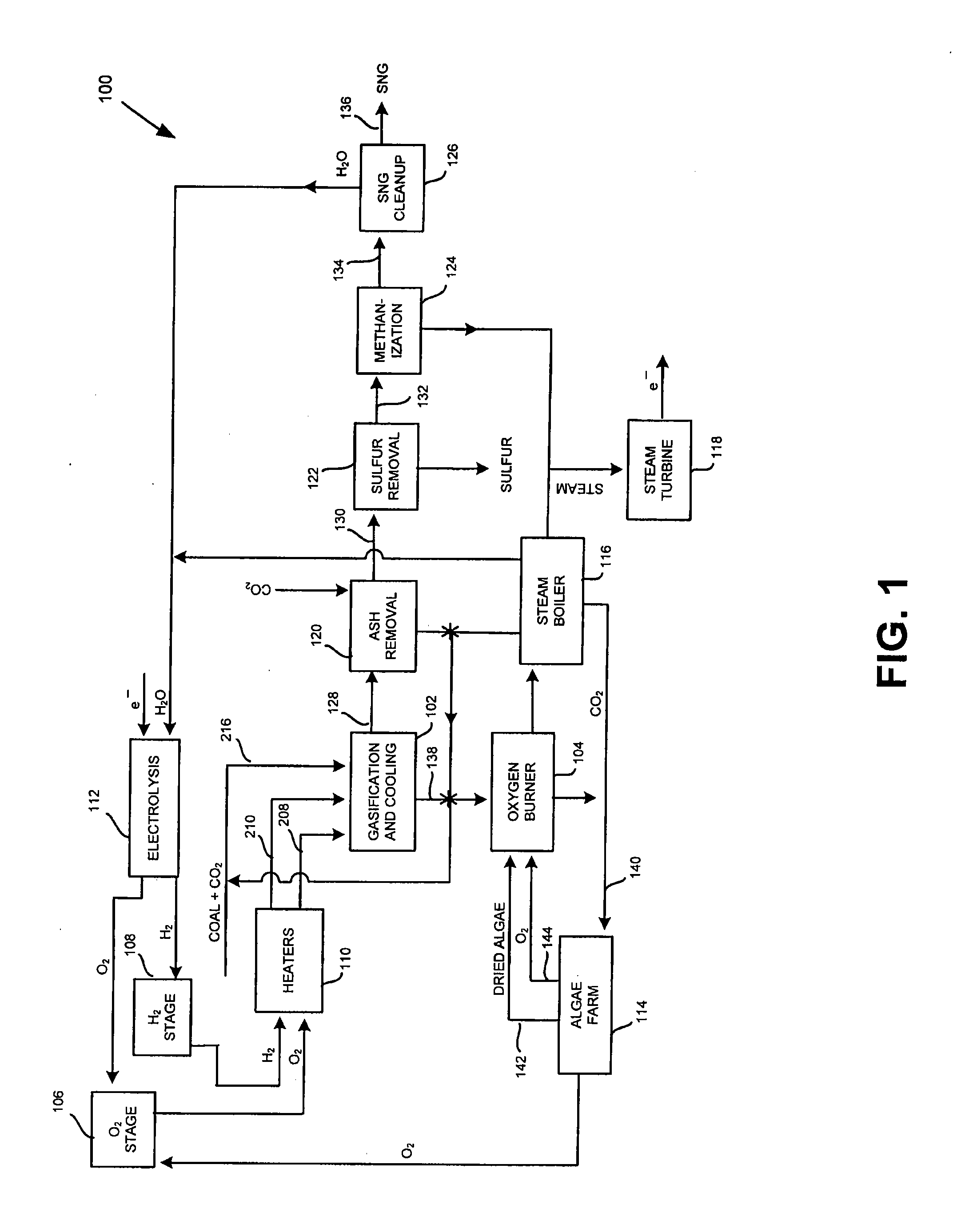
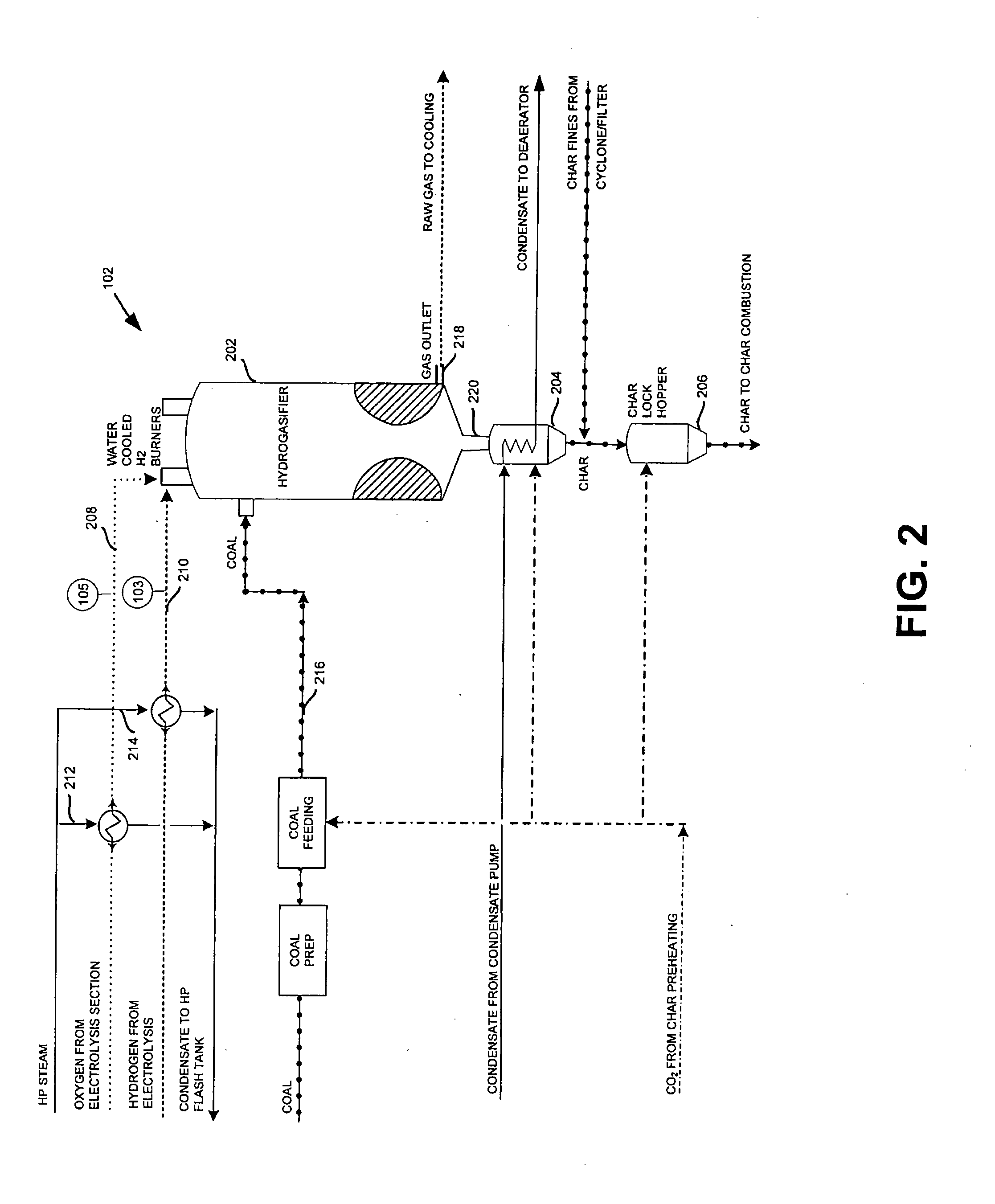
InactiveUS20080190024A1Produce electricityReduce productionBiofuelsGas modification by gas mixingElectricityCombustor
The present invention provides a system and method for producing substitute natural gas and electricity, while mitigating production of any greenhouse gasses. The system includes a hydrogasification reactor, to form a gas stream including natural gas and a char stream, and an oxygen burner to combust the char material to form carbon oxides. The system also includes an algae farm to convert the carbon oxides to hydrocarbon material and oxygen.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
Method of removing nitrogen oxides using an ilmenite material
InactiveUS6616904B1Easy to manageLess poisoningExhaust apparatusIsotope separationGas compositionInternal combustion engine
The invention relates to materials for removing the nitrogen oxides NO and NO2 present in exhaust gases, particularly from internal combustion engines of automotive vehicles running in a medium containing a superstoichiometric proportion of oxidizing agents, said materials being capable of absorbing the nitrogen oxides and of desorbing the nitrogen oxides when the temperature is raised, relative to the absorption temperature, or when the gas composition is changed to a rich mixture, said materials being mixed oxides in which the metals A and B are all octahedrally coordinated and are arranged to form the ilmenite structure ABO3. These materials absorb the nitrogen oxides and do not become poisoned in contact with the sulfur oxides and carbon oxides containing in the gases. In the presence of a group VIII metal, the material is capable of eliminating the adsorbed nitrogen oxides by reduction when the gas composition is changed to a rich mixture.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Fuel reformer catalyst and absorbent materials
InactiveUS20050232858A1Improve conversion efficiencyOther chemical processesHydrogen separation using solid contactProduct gasCarbon oxide
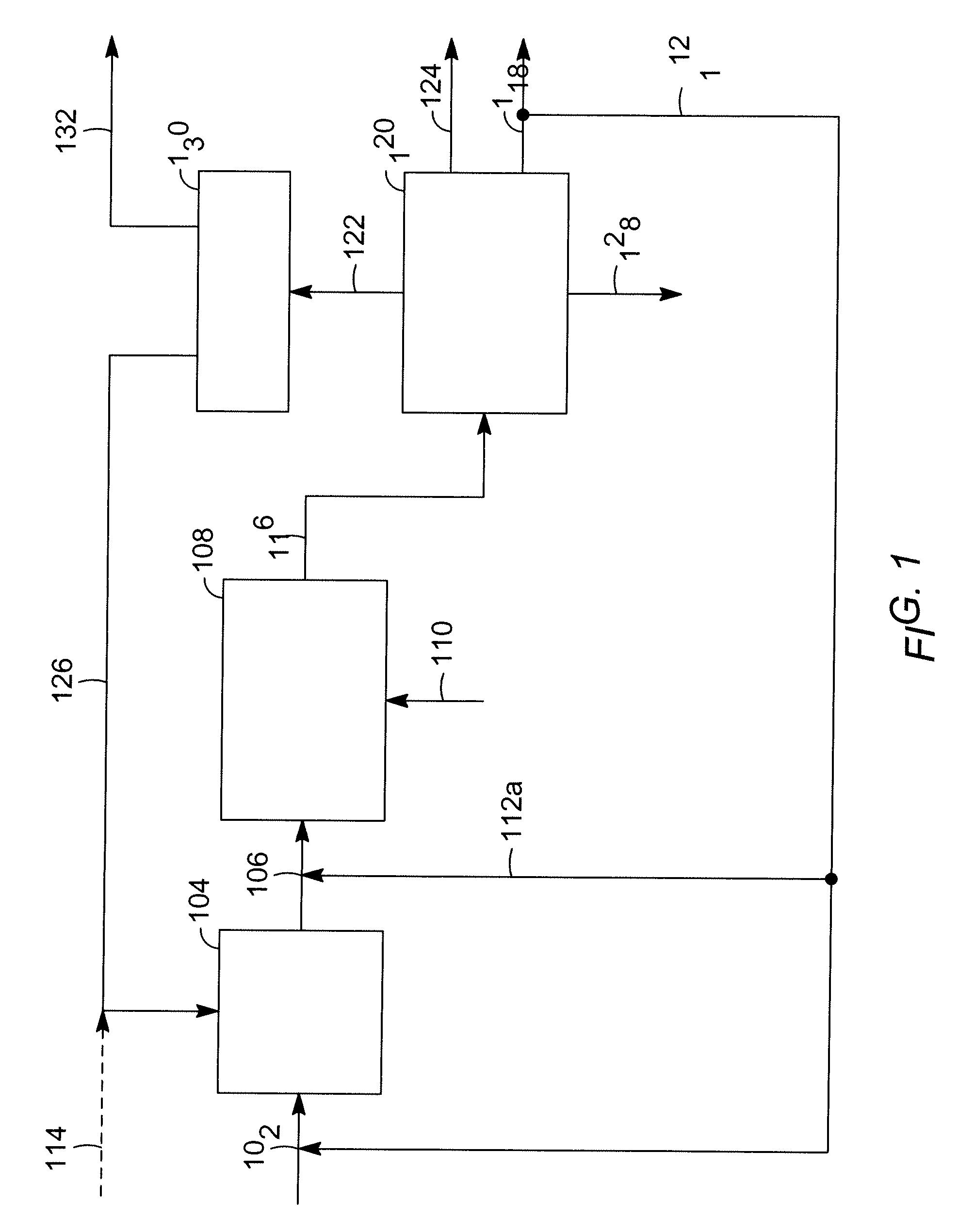
Materials that are useful for absorption enhanced reforming (AER) of a fuel, including absorbent materials and catalyst materials and methods for using the materials. The materials can be fabricated by spray processing. The use of the materials in AER can produce a H2 product gas having a high H2 content and a low level of carbon oxides.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Process for Preparing 1,3-Butadiene from N-Butenes by Oxidative Dehydrogenation
InactiveUS20140200380A1Hydrocarbon by hydrogenationDistillation purification/separationHydrocotyle bowlesioidesExtractive distillation
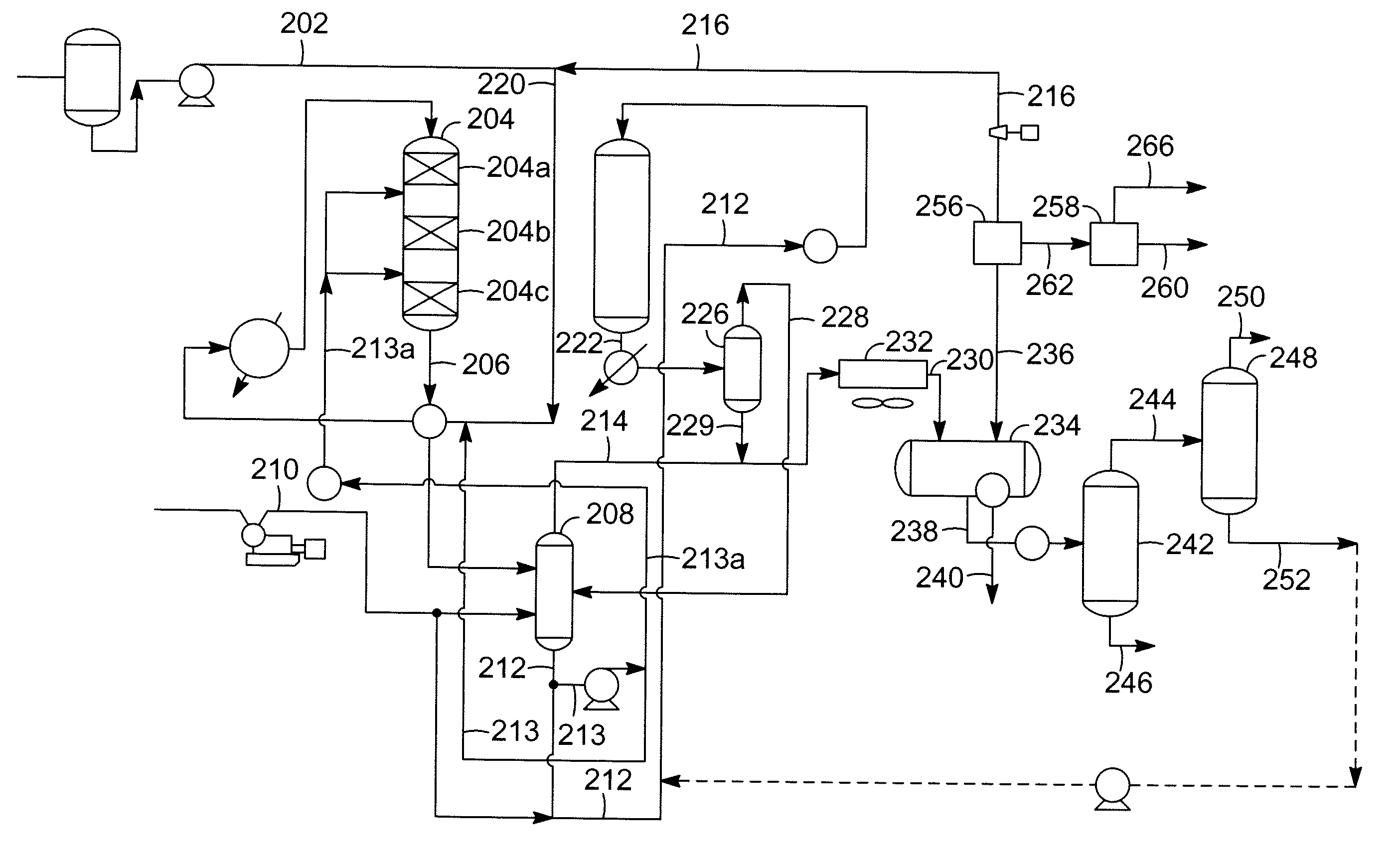
The invention relates to a process for preparing butadiene from n-butenes, which comprises the steps:A) provision of a feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes;B) introduction of the feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes and an oxygen-comprising gas into at least one oxidative dehydrogenation zone and oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butenes to butadiene, giving a product gas stream b comprising butadiene, unreacted n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, high-boiling secondary components, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;Ca) cooling of the product gas stream b by contacting with an organic solvent as coolant,Cb) compression of the product gas stream b in at least one compression stage, giving at least one aqueous condensate stream c1 and a gas stream c2 comprising butadiene, n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;D) separation of incondensable and low-boiling gas constituents comprising oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases as gas stream d2 from the gas stream c2 by absorption of the C4-hydrocarbons comprising butadiene and n-butenes in an absorption medium, giving an absorption medium stream loaded with C4 -hydrocarbons and the gas stream d2, and subsequent desorption of the C4-hydrocarbons from the loaded absorption medium stream to give a C4-product gas stream d1,E) separation of the C4 product stream d1 by extractive distillation using a solvent selective for butadiene into a stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent and a stream e2 comprising n-butenes;F) distillation of the stream f2 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent to give a stream g1 consisting essentially of the selective solvent and a stream g2 comprising butadiene.
Owner:BASF AG
Methods and structures for reducing carbon oxides with non ferrous catalysts
A method of reducing a gaseous carbon oxide includes reacting a carbon oxide with a gaseous reducing agent in the presence of a non-ferrous catalyst. The reaction proceeds under conditions adapted to produce solid carbon of various allotropes and morphologies, the selective formation of which can be controlled by means of controlling reaction gas composition and reaction conditions including temperature and pressure. A method for utilizing a non-ferrous catalyst in a reactor includes placing the catalyst in a suitable reactor and flowing reaction gases comprising a carbon oxide with at least one gaseous reducing agent through the reactor where, in the presence of the catalyst, at least a portion of the carbon in the carbon oxide is converted to solid carbon and a tail gas mixture containing water vapor.
Owner:SEERSTONE
Hydrocarbon synthesis process using an alkali promoted iron catalyst
InactiveUS20050203194A1Hydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMolecular sieve catalystsCompound (substance)Oxide
This invention relates to a high temperature Fischer-Tropsch (HTFT) hydrocarbon synthesis process comprising the conversion of a feed of H2 and at least one carbon oxide to hydrocarbons containing at least 30% on a mass basis hydrocarbons with five or more carbon atoms (hereinafter referred to as C5+ compounds). The conversion is carried out in the presence of an alkali-promoted iron hydrocarbon synthesis catalyst, and the process is characterised therein that the reaction mixture formed during the conversion contains less than 0.02 mol alkali per 100 g iron, and that the H2:carbon oxide molar ratio in the feed of H2 and carbon oxide is at least 2.
Owner:SASOL TEKHNOLODZHI PROPRIEHJTEHRI LTD
Process for the Oxidative Dehydrogenation of N-Butenes to Butadiene
InactiveUS20140200379A1Distillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsDesorptionExtractive distillation
The invention relates to a process for preparing butadiene from n-butenes, which comprises the following steps:A) provision of a feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes;B) introduction of the feed gas stream a comprising n-butenes and an oxygen-comprising gas into at least one dehydrogenation zone and oxidative dehydrogenation of n-butenes to butadiene, giving a product gas stream b comprising butadiene, unreacted n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;C) cooling and compression of the product gas stream b in at least one compression stage, giving at least one condensate stream c1 comprising water and a gas stream c2 comprising butadiene, n-butenes, water vapor, oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases;D) separation of incondensable and low-boiling gas constituents comprising oxygen, low-boiling hydrocarbons, possibly carbon oxides and possibly inert gases as gas stream d2 from the gas stream c2 byDa) absorption of the C4-hydrocarbons comprising butadiene and n-butenes in a high-boiling absorption medium, giving an absorption medium stream loaded with C4-hydrocarbons and the gas stream d2,Db) removal of oxygen from the absorption medium stream loaded with C4-hydrocarbons by stripping with an inert gas andDc) desorption of the C4-hydrocarbons from the loaded absorption medium stream to give a C4 product gas stream d1 which consists essentially of C4-hydrocarbons and comprises less than 100 ppm of oxygen;E) separation of the C4 product stream d1 by extractive distillation with a solvent which is selective for butadiene into a stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent and a stream e2 comprising n-butenes;F) distillation of the stream e1 comprising butadiene and the selective solvent to give a stream f1 consisting essentially of the selective solvent and a butadiene-comprising stream f2.
Owner:BASF AG
Catalytic pyrolysis using UZM-44 aluminosilicate zeolite
ActiveUS8609911B1Hydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCatalytic pyrolysisOrganic structure
A new family of aluminosilicate zeolites designated UZM-44 has been synthesized. These zeolites are represented by the empirical formula.NanMmk+TtAl1-xExSiyOz where “n” is the mole ratio of Na to (Al+E), M represents a metal or metals from zinc, Group 1, Group 2, Group 3 and or the lanthanide series of the periodic table, “m” is the mole ratio of M to (Al+E), “k” is the average charge of the metal or metals M, T is the organic structure directing agent or agents, and E is a framework element such as gallium. The process involves contacting a carbonaceous biomass feedstock with UZM-44 at pyrolysis conditions to produce pyrolysis gases comprising hydrocarbons. The catalyst catalyzes a deoxygenation reaction converting oxygenated hydrocarbons into hydrocarbons and removing the oxygen as carbon oxides and water. A portion of the pyrolysis gases is condensed to produce low oxygen biomass-derived pyrolysis oil.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method of fabricating a catalytic structure
A precursor to a catalytic structure comprising zinc oxide and copper oxide. The zinc oxide has a sheet-like morphology or a spherical morphology and the copper oxide comprises particles of copper oxide. The copper oxide is reduced to copper, producing the catalytic structure. The catalytic structure is fabricated by a hydrothermal process. A reaction mixture comprising a zinc salt, a copper salt, a hydroxyl ion source, and a structure-directing agent is formed. The reaction mixture is heated under confined volume conditions to produce the precursor. The copper oxide in the precursor is reduced to copper. A method of hydrogenating a carbon oxide using the catalytic structure is also disclosed, as is a system that includes the catalytic structure.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Methods of making carbide and oxycarbide containing catalysts
InactiveUS7576027B2High selectivityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsChemical reactionFluid phase
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Carbon oxide reduction with intermetallic and carbide catalysts
InactiveUS20160031710A1Easy to set upLow costMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationSolid carbonWater vapor
A method of reducing a gaseous carbon oxide includes reacting a carbon oxide with a gaseous reducing agent in the presence of an intermetallic or carbide catalyst. The reaction proceeds under conditions adapted to produce solid carbon of various allotropes and morphologies, the selective formation of which can be controlled by means of controlling reaction gas composition and reaction conditions including temperature and pressure. A method for utilizing an intermetallic or carbide catalyst in a reactor includes placing the catalyst in a suitable reactor and flowing reaction gases comprising a carbon oxide with at least one gaseous reducing agent through the reactor where, in the presence of the catalyst, at least a portion of the carbon in the carbon oxide is converted to solid carbon and a tail gas mixture containing water vapor.
Owner:SEERSTONE
Method of preparing graphene and anode mixture for lithium secondary battery including graphene prepared thereby
ActiveUS20150132654A1Increased ion mobilityNon-metal conductorsConductive materialPorous grapheneOxocarbon
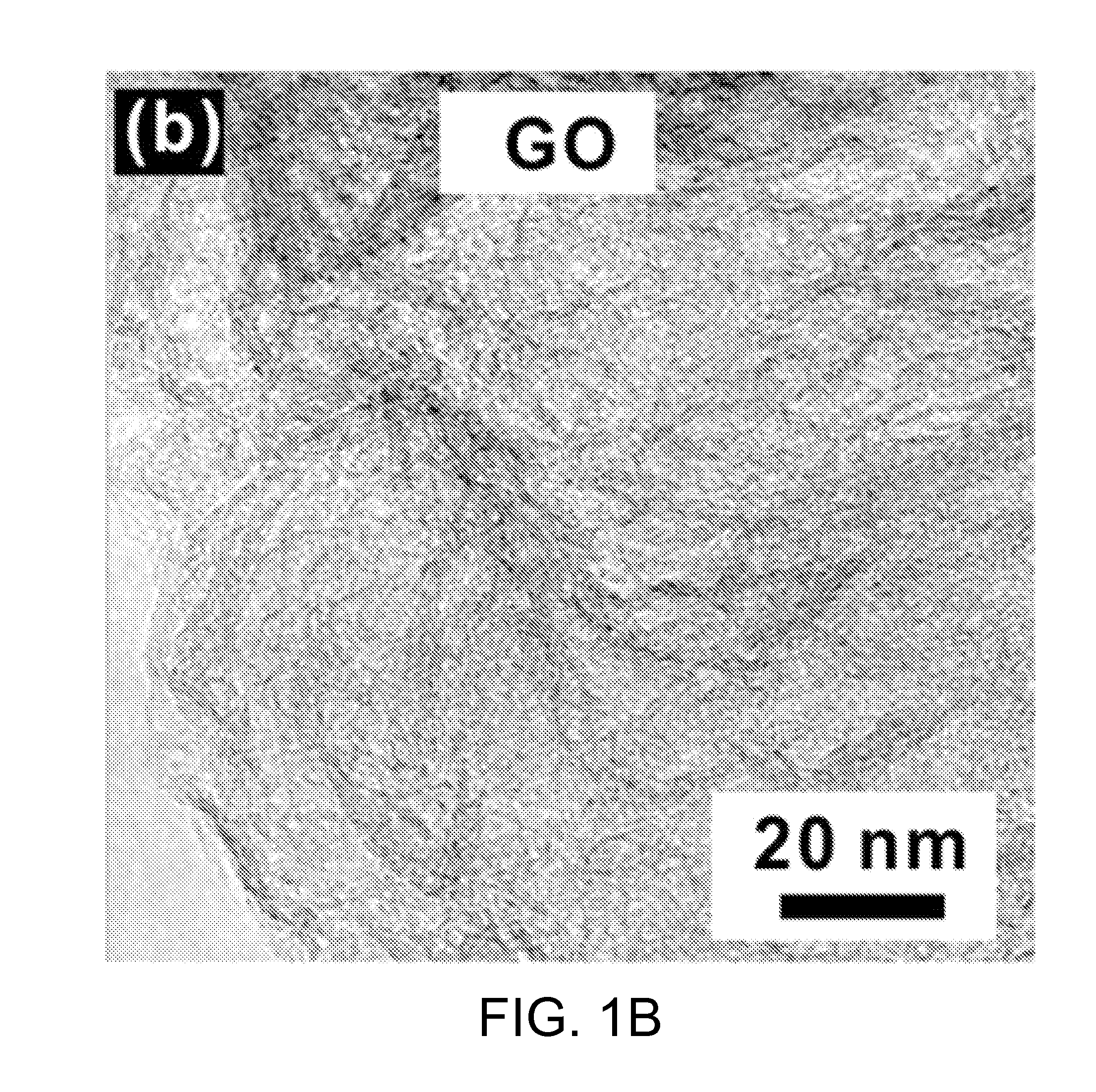
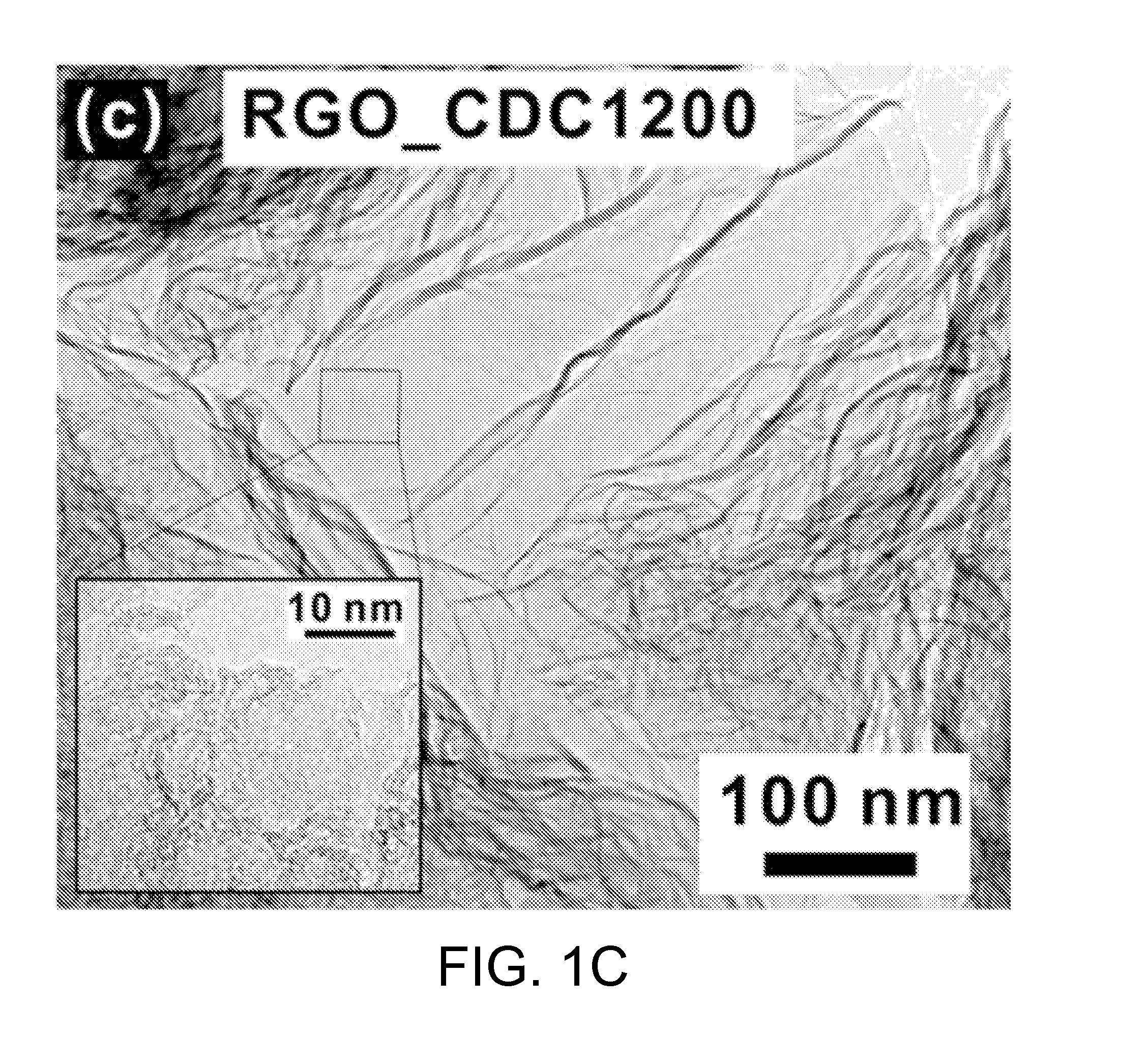
Disclosed herein is a method of preparing porous graphene from porous graphite, including 1) thermochemically reacting a highly crystalline carbide compound with a halogen element-containing gas to give a porous carbide-derived carbon; 2) treating the carbide-derived carbon with an acid, thus preparing a carbide-derived carbon oxide; and 3) reducing the carbide-derived carbon oxide. An anode mixture for a secondary battery including the graphene and an anode for a secondary battery including the anode mixture are also provided.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Production of lower molecular weight hydrocarbons
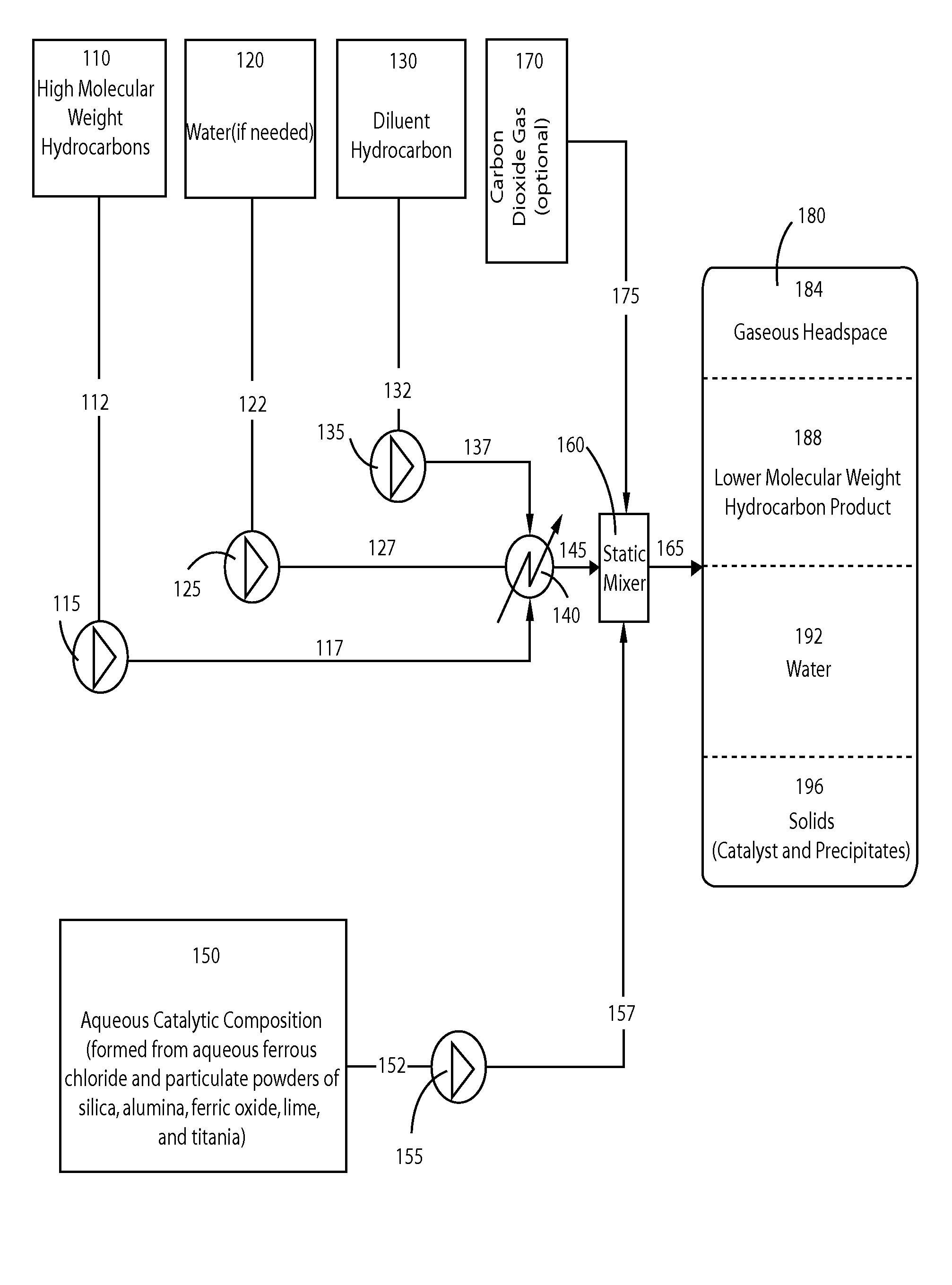
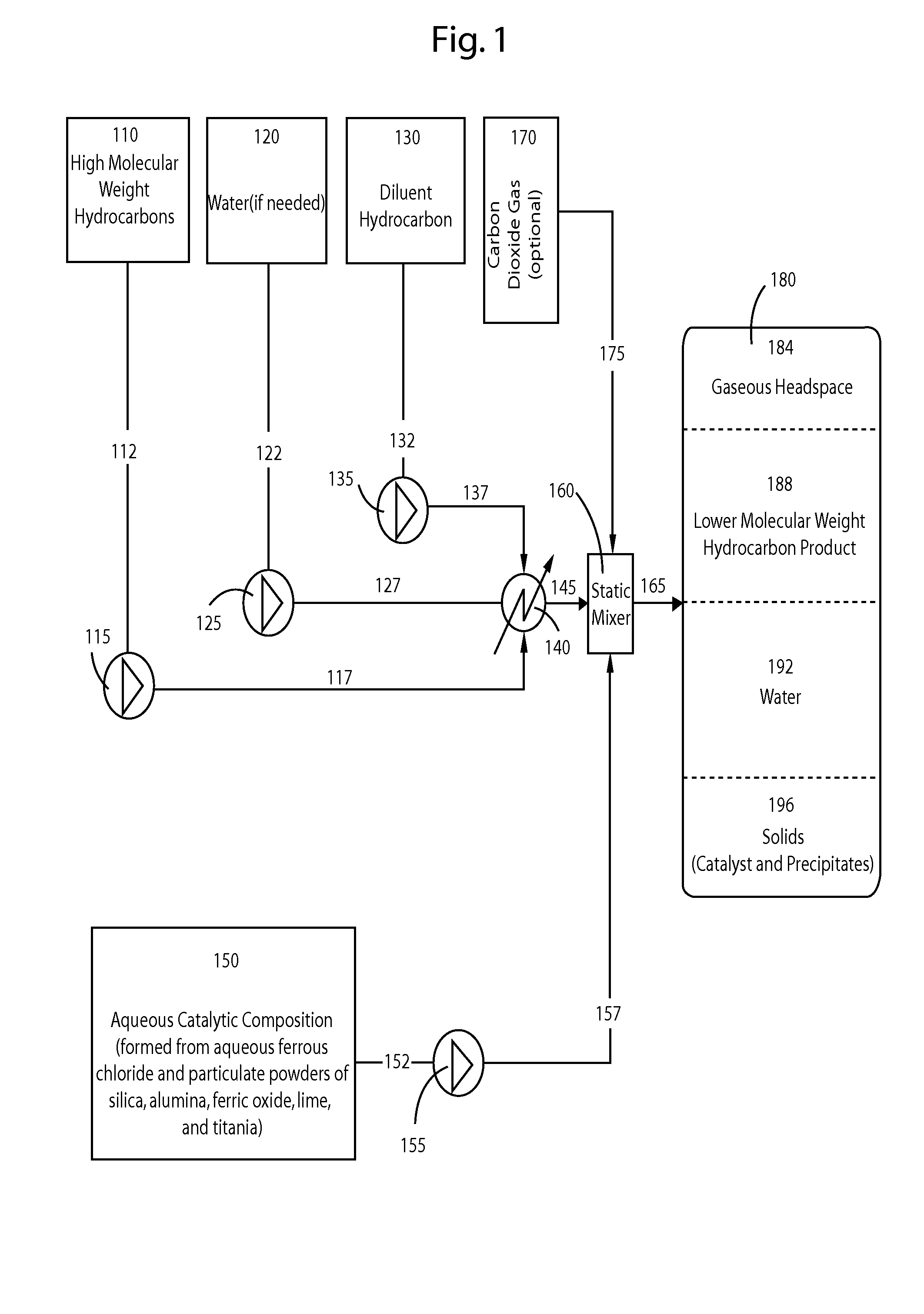
InactiveUS20080116111A1High densityHigh viscosityHydrocarbon oil crackingHigh molecular massCarbon oxide
The present invention relates generally to processes for upgrading (cracking and hydrogenation) of high molecular weight hydrocarbons using a catalytic composition at moderate temperatures, methods for stabilizing the upgraded product, and methods for reducing carbon oxides using a catalytic composition.
Owner:NEWTON JEFFREY P
Cerium-zirconium composite oxide with high specific surface area, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110252275AUniform distribution of dopingLarge specific surface areaGas treatmentHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsRare earthCerium
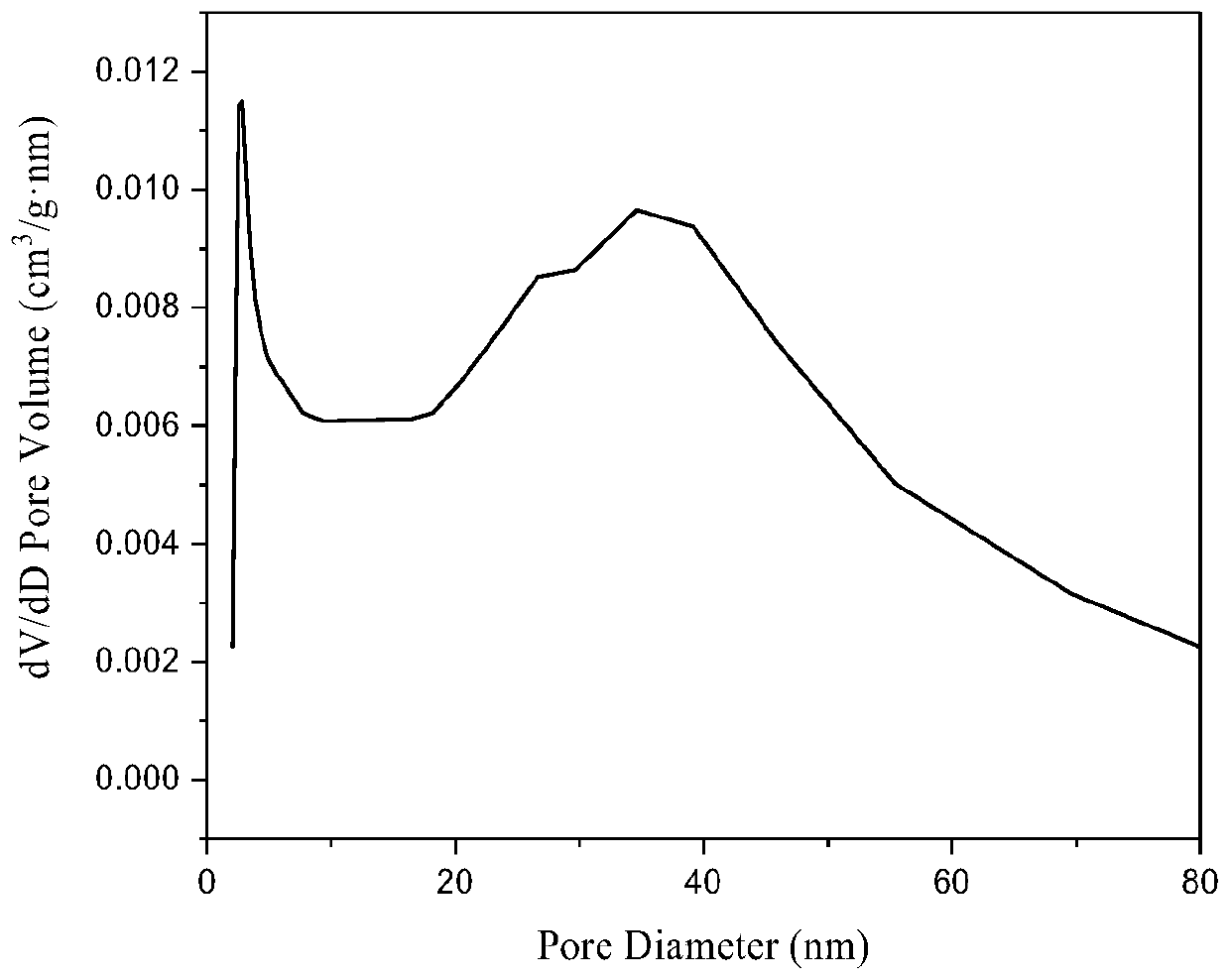
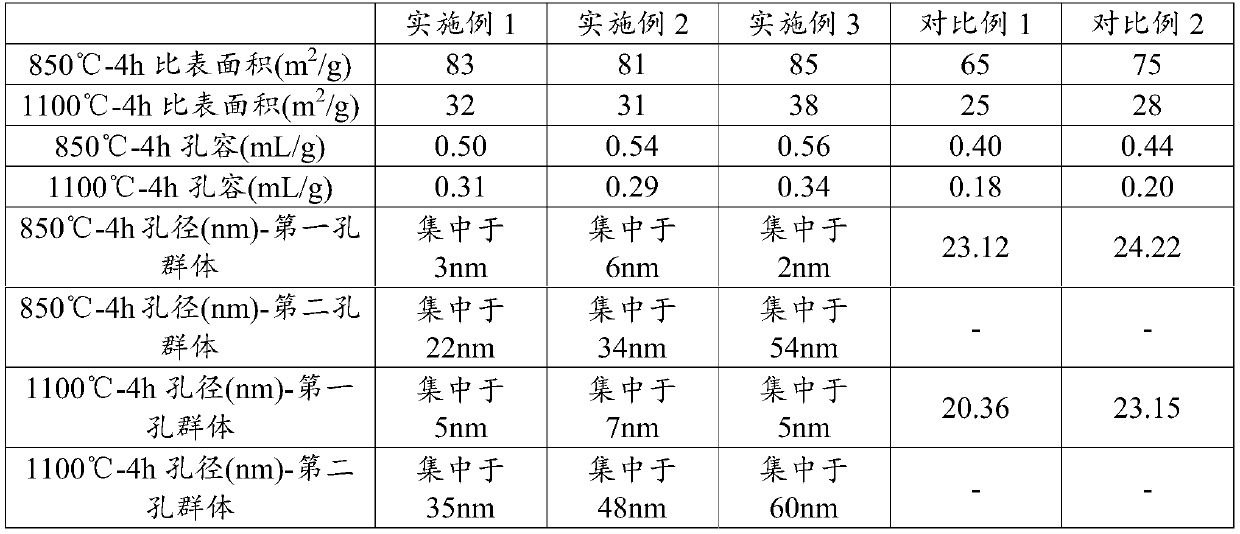
The present invention provides a cerium-zirconium composite oxide with a high specific surface area. The cerium-zirconium composite oxide comprises cerium oxide, zirconium oxide and at least one oxide of a rare earth metal element other than cerium, and the composite oxide has a specific surface area of 80 m<2> / g or above, a pore volume of 0.50-0.60 mL / g, an oxygen storage amount of 500-1200 [mu]mol O2 / g and two-hole group distributed apertures after subjected to heat treatment at 850 DEG for 4-8 h, wherein the diameter of the first pore group is concentrated at 1-8 nm, and the diameter of the second pore group is concentrated at 20-60 nm. The cerium-zirconium composite oxide provided by the invention has a higher specific surface area and a better pore volume distribution than composite oxides prepared by existing methods, has good low-temperature catalytic activity, and can be used for catalyzing hydrocarbons, carbon oxides and / or nitrogen oxides in mobile source exhaust gas. The invention also provides a preparation method of the cerium-zirconium composite oxide. The composite oxide which has uniform element crystal lattice doping distribution and does not produce phase separation can be prepared, and is of great significance to study mobile source exhaust gas treatment purifying agents containing the cerium-zirconium composite oxide.
Owner:SHANDONG SINOCERA FUNCTIONAL MATERIAL CO LTD
Method for preparing low dielectric films
InactiveCN1522462ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUnsaturated hydrocarbonGas phase
A low dielectric constant hydrogenated silicon-oxycarbide (SiCO:H) film is prepared by conducting chemical vapor deposition using, together with an O2-containing gas plasma, an organosilicon or organosilicate compound having at least one vinyl or ethinyl group, or a mixture of a saturated organosilicon or organosilicate compound and an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Catalyst for the preparation of methyl mercaptan
InactiveUS20080262270A1High selectivityManganese oxides/hydroxidesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesSide productCarbon dioxide
The present invention refers to a catalyst for the manufacture of methyl mercaptan from carbon oxides comprising Mo and K compounds and oxides or sulfides of metals chosen from the manganese group. The improvement of the present process consists of the fact that carbon dioxide can be converted with higher conversions and selectivities to methyl mercaptan as compared to state-of-the-art technologies, with only minor amounts of carbon monoxide being formed as side product. Simultaneously, carbon monoxide can be easily converted into carbon dioxide and hydrogen by reaction with water using established water-gas-shift-technologies thus increasing the overall selectivity to methyl mercaptan.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Fuel reformer catalyst and absorbent materials
InactiveUS7267811B2Enhanced reformingOther chemical processesHydrogen separation using solid contactPtru catalystOxocarbon
Materials that are useful for absorption enhanced reforming (AER) of a fuel, including absorbent materials and catalyst materials, and methods for using such materials for the conversion of carbon-based fuels to a H2-rich product gas. The materials can be fabricated by spray processing. The use of the materials in AER can produce a H2 product gas having a high H2 content and a low level of carbon oxides. The method for converting carbon-based fuels to a H2-rich product gas includes forming an intermediate gas product from the carbon-based fuel using a catalyst and contacting the intermediate gas product with an absorbent to absorb CO2. The absorbent can be regenerated while retaining a high absorption capacity.
Owner:CABOT CORP
Systems for producing solid carbon by reducing carbon oxides
InactiveUS20160023902A1Carbon preparation/purificationChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsSolid carbonCarbon oxide
An apparatus for producing solid carbon and water by reducing carbon oxides with a reducing agent in the presence of a catalyst includes a reactor configured to receive reaction gas comprising at least one carbon oxide, at least one reducing agent, and water. The apparatus includes at least one mixing means configured to mix the reagents to form a combined feed, a first heat exchanger configured to heat the combined feed, at least one heater configured to further heat the combined feed, and a reaction vessel configured to receive the combined feed. The reaction vessel is configured to contain a catalyst, to maintain predetermined reaction conditions of temperature and pressure, and has an output configured to deliver a tail gas to the first heat exchanger. The system also includes a product separator, a water separation unit, and a product packaging unit.
Owner:SEERSTONE
Preparation method and application of high-purity nanometer silicon
InactiveCN103882465AHigh purityImprove electrolysis efficiencyElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic agentEngineering
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity nanometer silicon. According to the method, calcium chloride or a calcium chloride-containing mixed fused salt is used as electrolyte, silicon dioxide or quartz is put in a metal current collector to serve as a cathode, graphite or an inert electrode is used as an anode, constant potential electrolysis is carried out under the condition that the electrolytic potential is controlled by adopting a reference electrode at a certain electrolysis temperature under the inert gas protection, thus obtaining the needed product, namely the high-purity nanometer silicon. The invention also discloses application of the high-purity nanometer silicon. The preparation method is high in electrolytic efficiency, the electrolytic efficiency is more than 70 percent, and the energy consumption is far lower than the energy consumption during silicon preparation through an industrial carbon heat method. In addition, lots of carbonic oxides are emitted in the process of preparing monatomic silicon through the industrial carbon heat method, and lots of charcoal is consumed. Moreover, the charcoal is not needed to serve as a reducing agent, an inert anode is adopted, and oxygen is discharged from the anode, so that zero emission is realized. Finally, the product obtained by the method is high in purity.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAFU STORAGE NEW TECH DEV +1
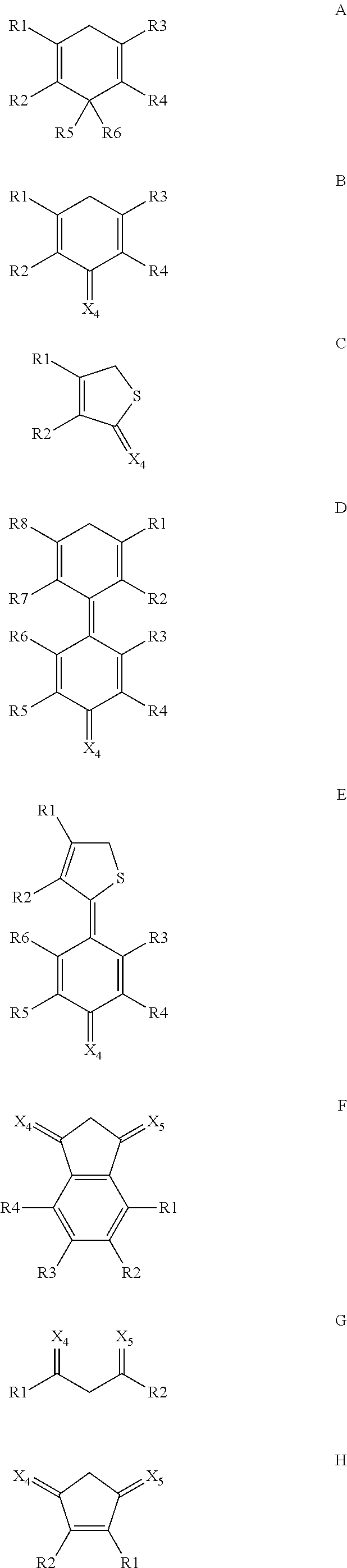
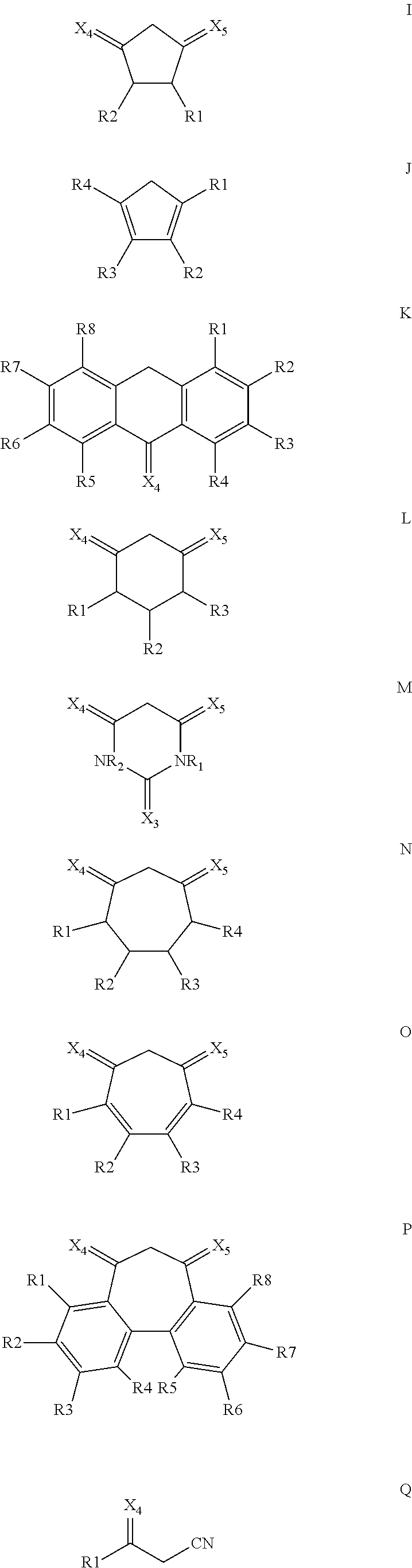
Oxocarbon-, pseudooxocarbon- and radialene compounds and their use
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
Methods and systems of producing fuel for an internal combustion engine using a plasma system at various pressures
InactiveUS20080128267A1Non-fuel substance addition to fuelDispersed particle separationPressure systemHydrogen
Systems and methods for production of fuel for an internal combustion engine are described herein. Systems may include a plasma reformer and an internal combustion engine. The plasma reformer may produce a plasma at pressures between about 0.3 atmospheres and about 5 atmospheres. The plasma reformer may produce a gas stream from the liquid feed. The gas stream may include molecular hydrogen and carbon oxides. At least a portion of the gas stream may be provided to an internal combustion engine.
Owner:TETROS INNOVATIONS LLC
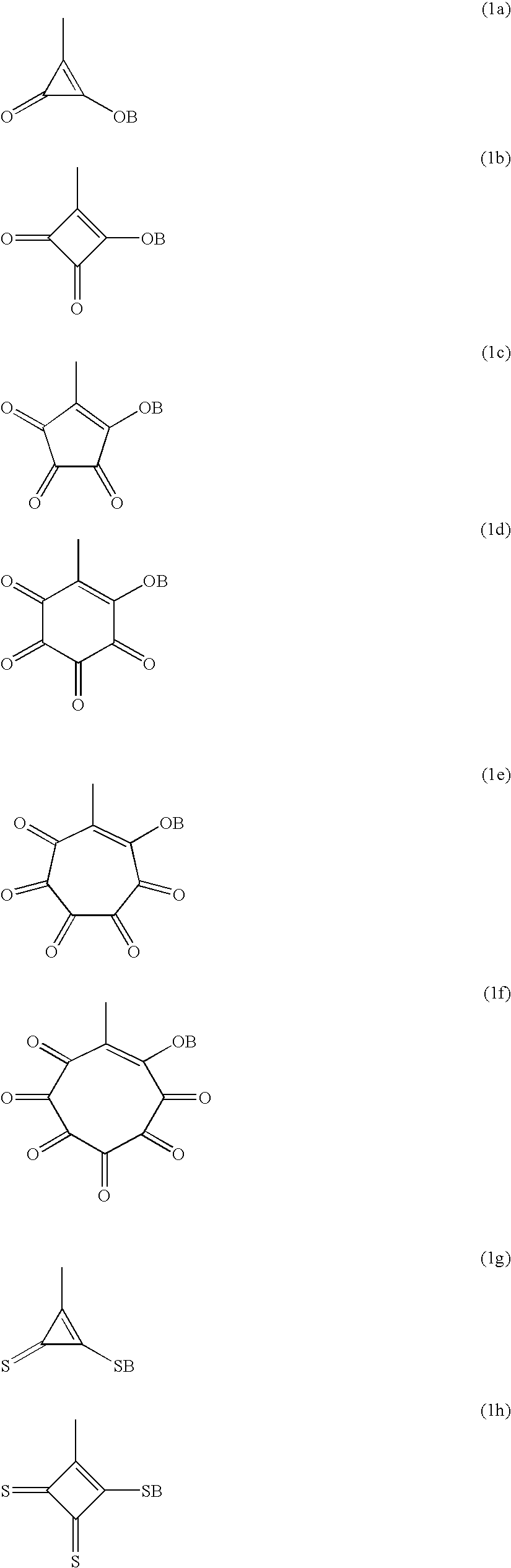
Polymer having oxocarbon group, and use thereof
InactiveUS20070218335A1Improve proton conductivityIon-exchanger regenerationConductive materialPolymer electrolytesPolymer science
Disclosed is a polymer having an oxocarbon group represented by the general formula (1). This polymer having an oxocarbon group is useful as a polymer electrolyte as the material for proton conductive membranes in solid polymer fuel cells which use a gas fuel such as a hydrogen gas or a liquid fuel such as methanol or dimethyl ether.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Method and installation for the production of synthesis gas
InactiveCN101448731ALow investment costReliable conversionHydrogenHydrogen/synthetic gas productionSteam reformingCatalytic transformation
According to the invention, synthesis gas is produced from a starting material, particularly natural gas, which contains hydrocarbons, by dividing a feed flow of the starting material into a first partial flow and a second partial flow. The first partial flow is fed to a steam reformer (4) in which said partial flow, along with steam, is catalytically converted into a gas flow containing carbon oxides. The first partial flow is then recombined with the second partial flow, and the combined gas flow is fed to an autothermal reformer (7) in which the gas flow is autothermally reformed to a synthesis gas along with oxygen-rich gas in the presence of a cracking catalyst. In order to be able to process a starting material that has a high concentration of higher hydrocarbons, the entire starting material is fed to a pre-reformer (2) upstream of the steam reformer (4) and upstream of the autothermal reformer (7), higher hydrocarbons being largely eliminated from the starting material in said pre-reformer (2).
Owner:卢吉股份有限公司
Integrated processes for anaerobically bioconverting hydrogen and carbon oxides to oxygenated organic compounds
InactiveUS20150132810A1Conveniently passedImprove digestibilityChemical industryBiofuelsSimple Organic CompoundsOxocarbon
Integrated processes are provided for the bioconversion of syngas to oxygenated organic compound with the ability to recover essential compounds for the fermentation and recycle the compounds to the fermentation.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com