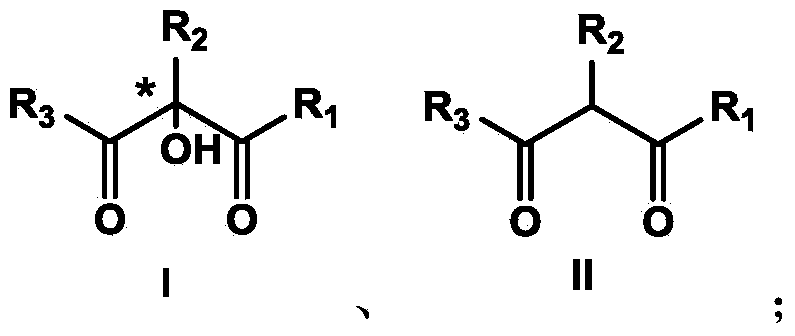
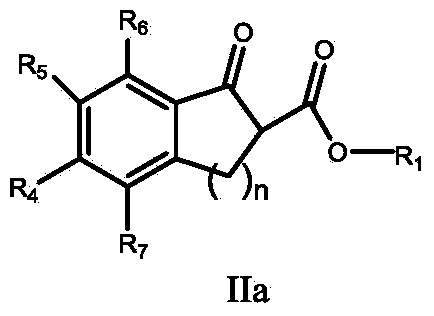
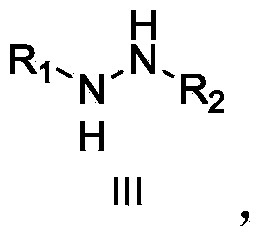
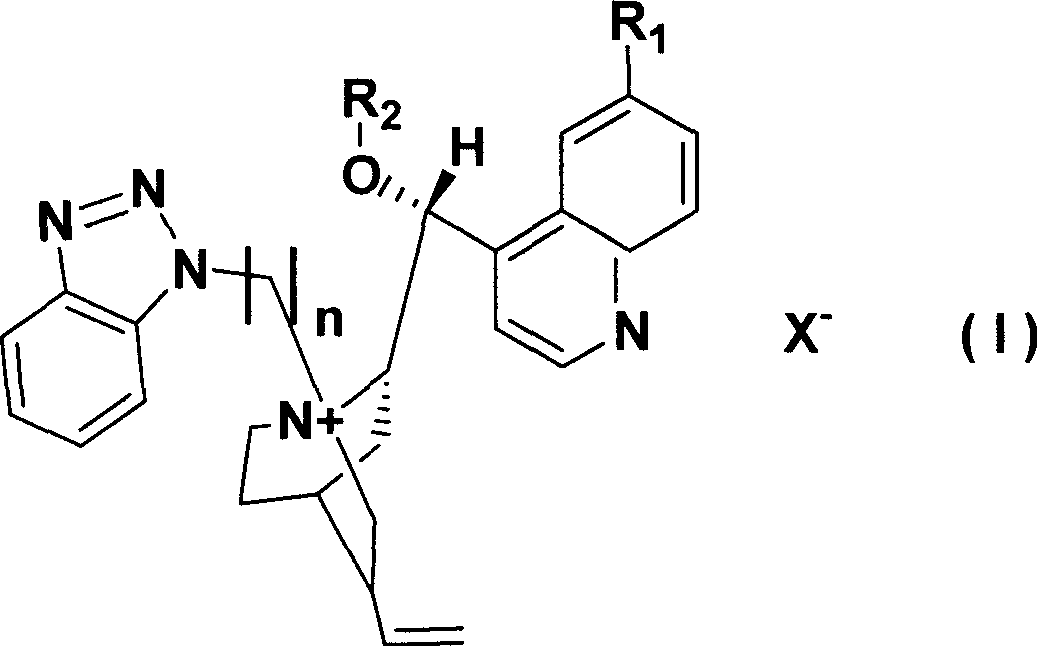
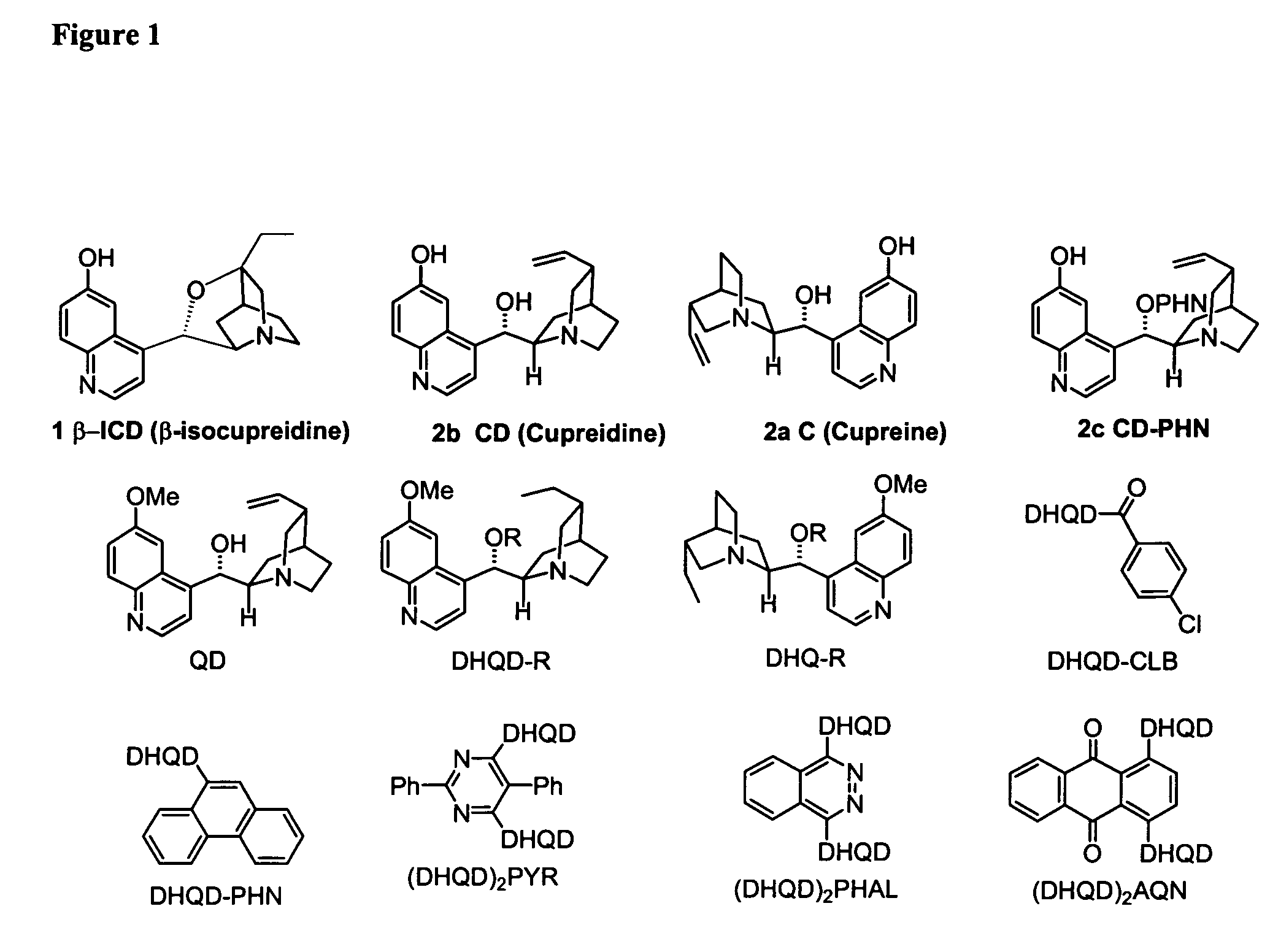
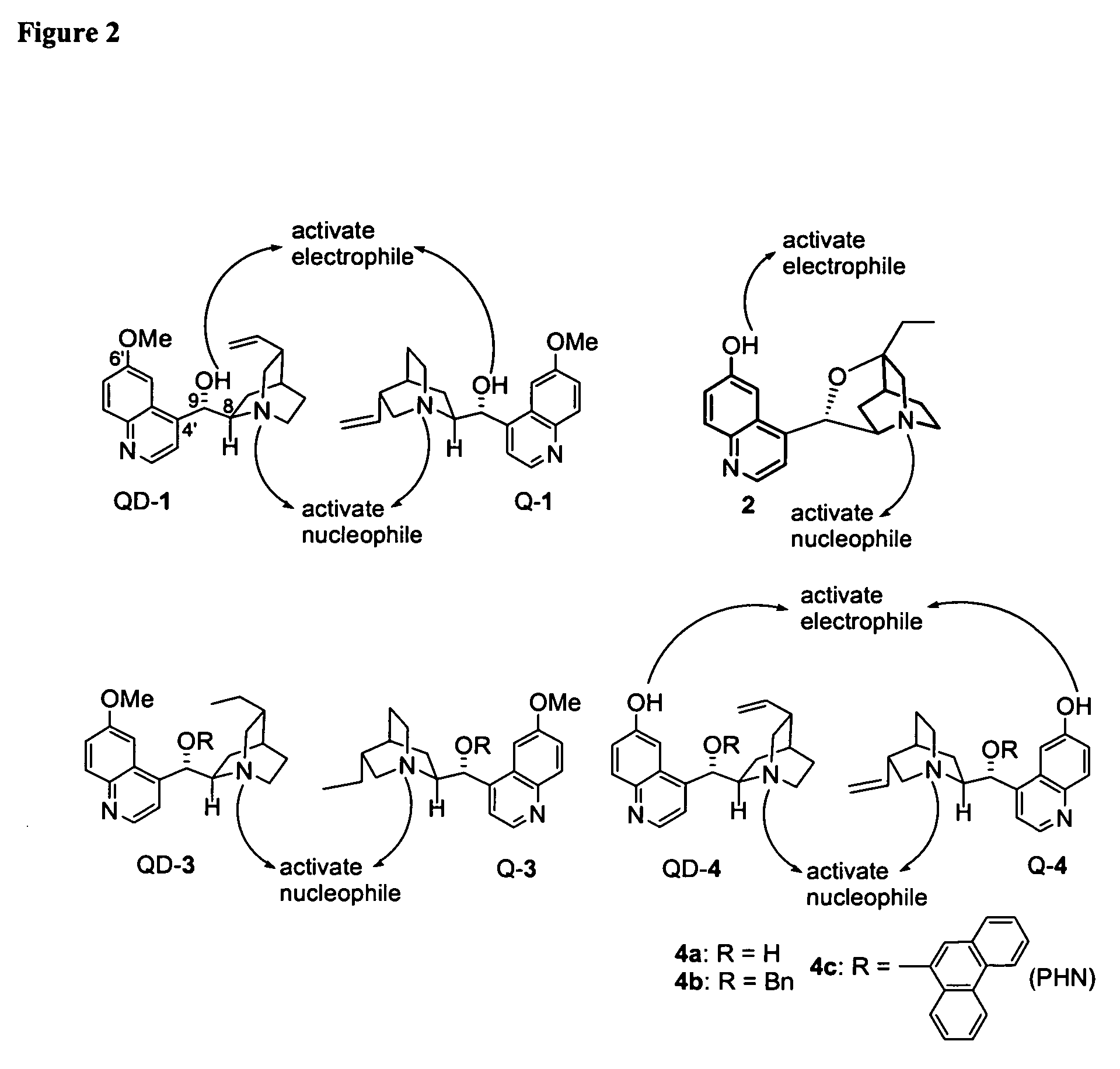
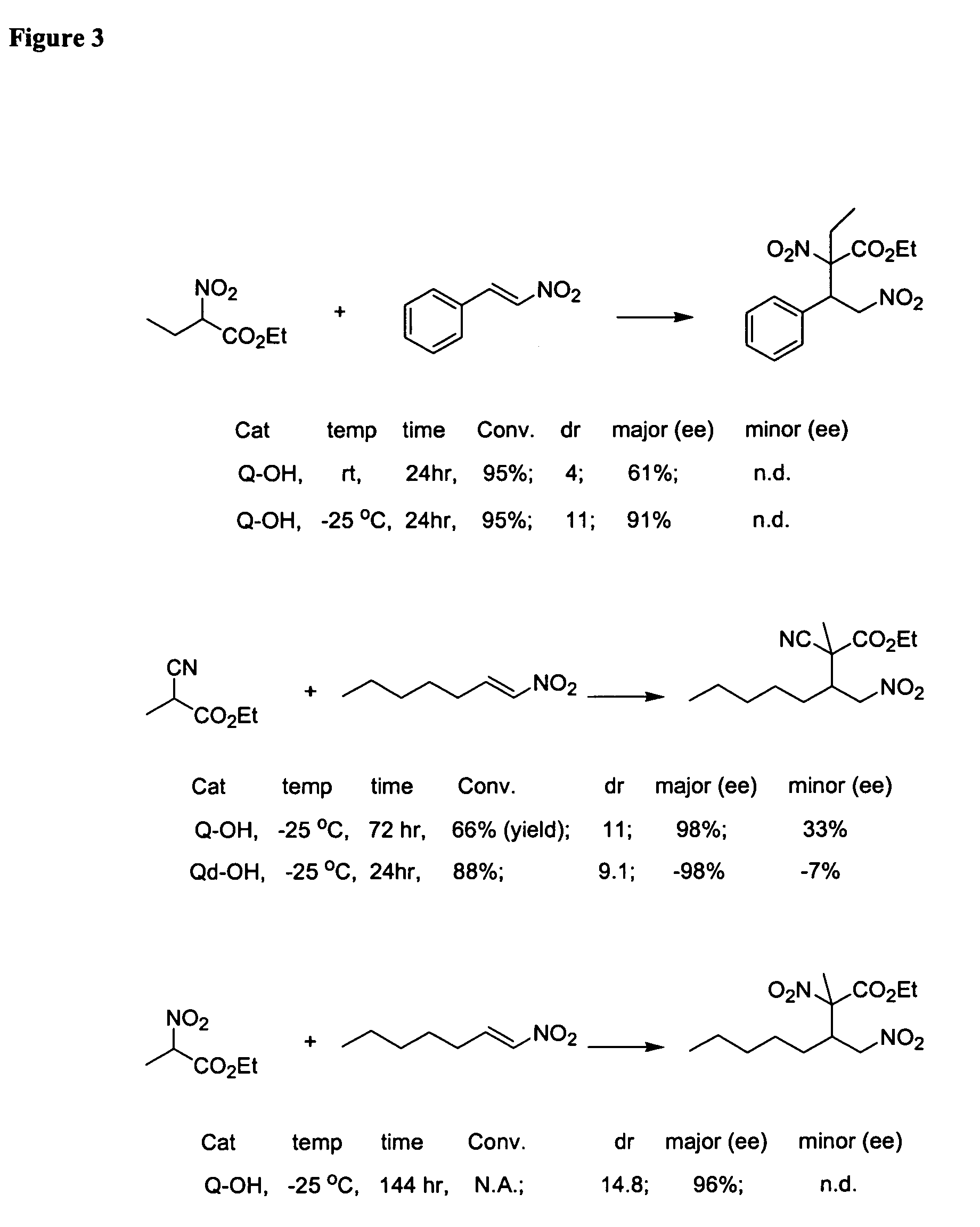
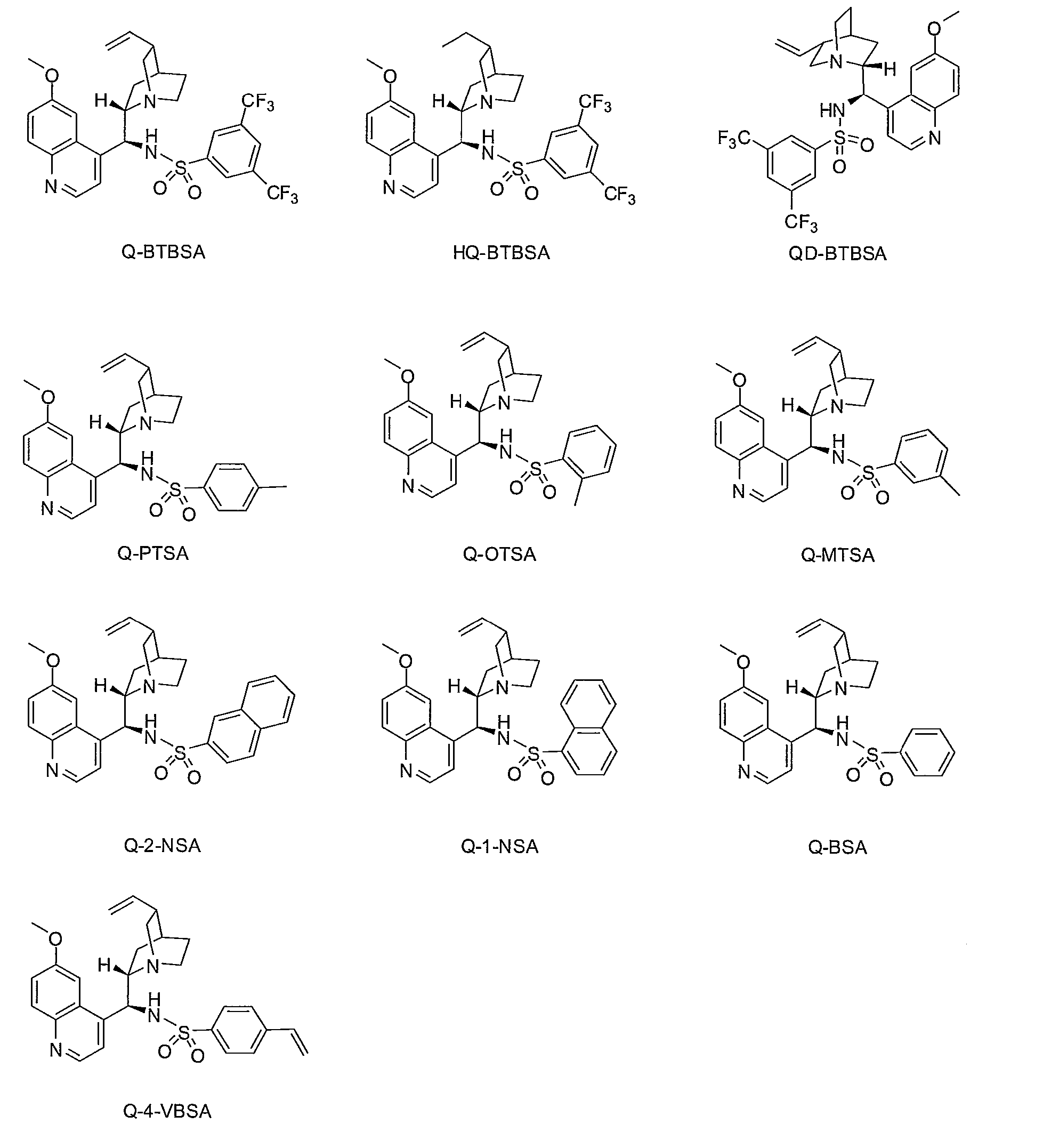
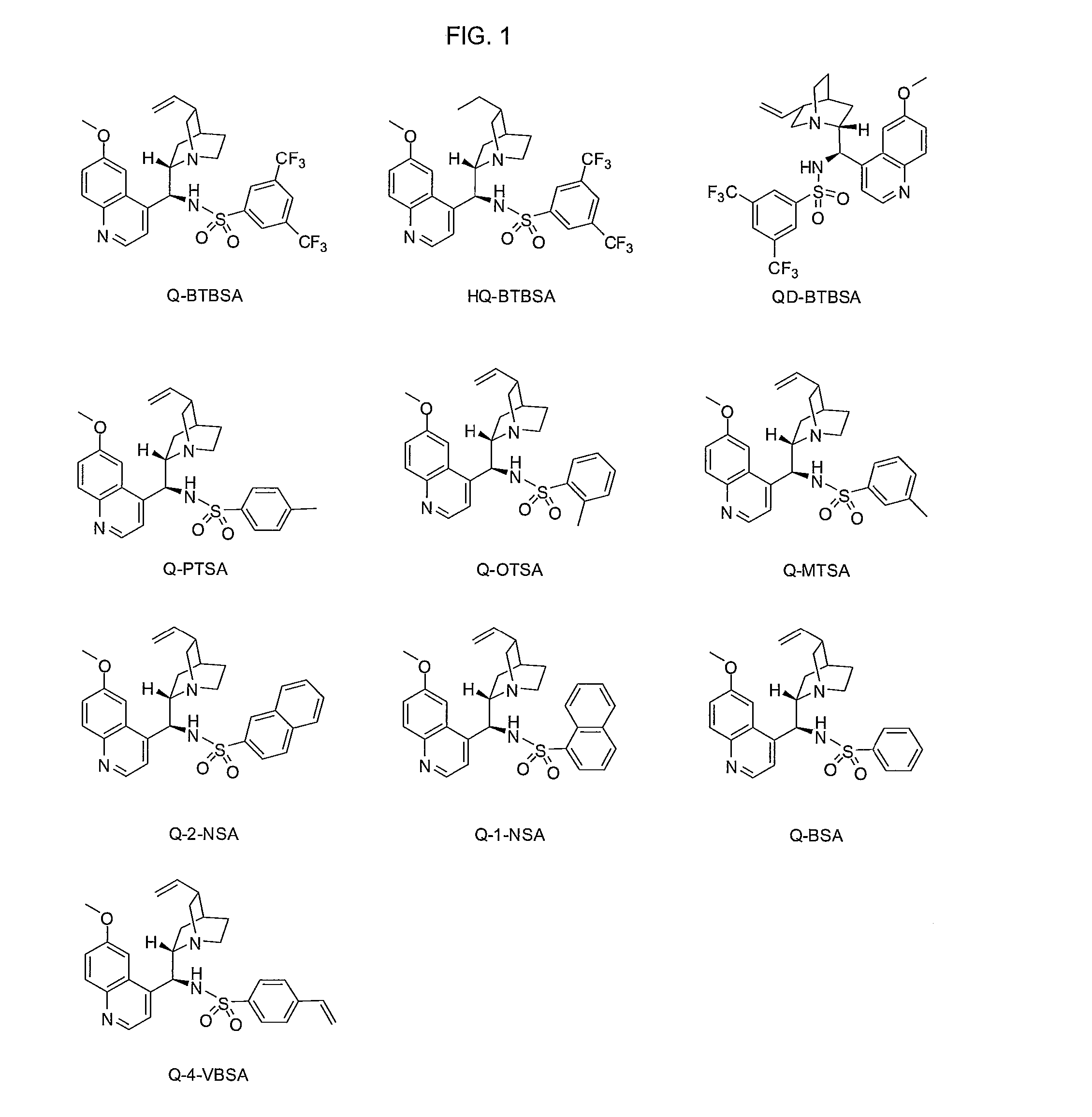
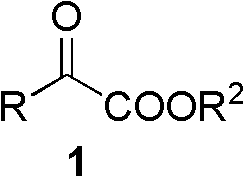
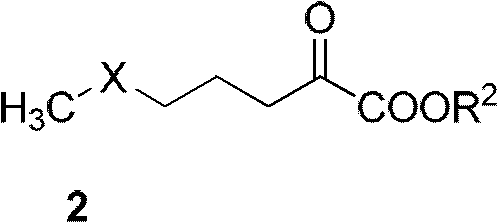
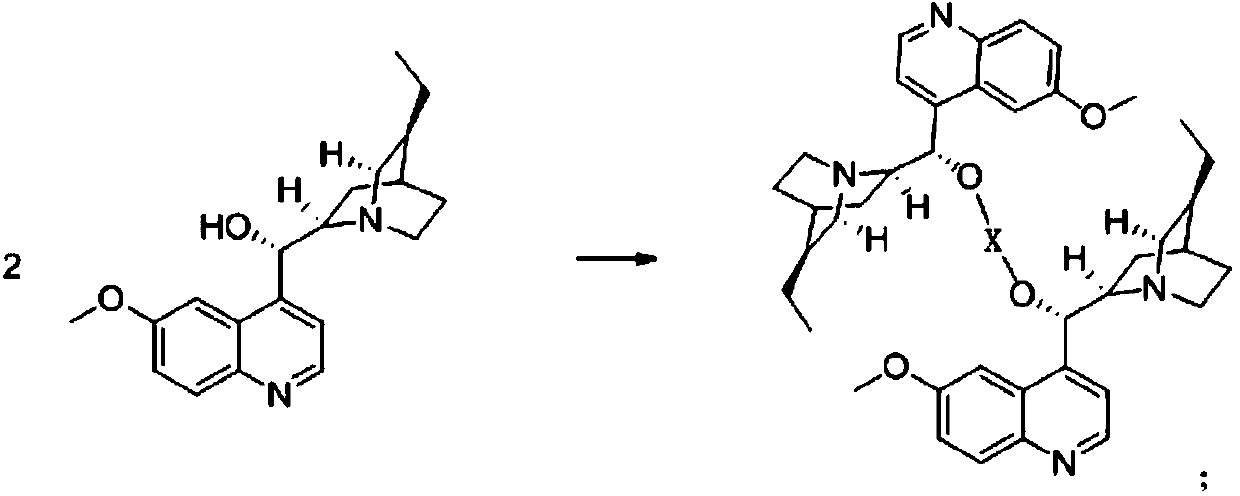
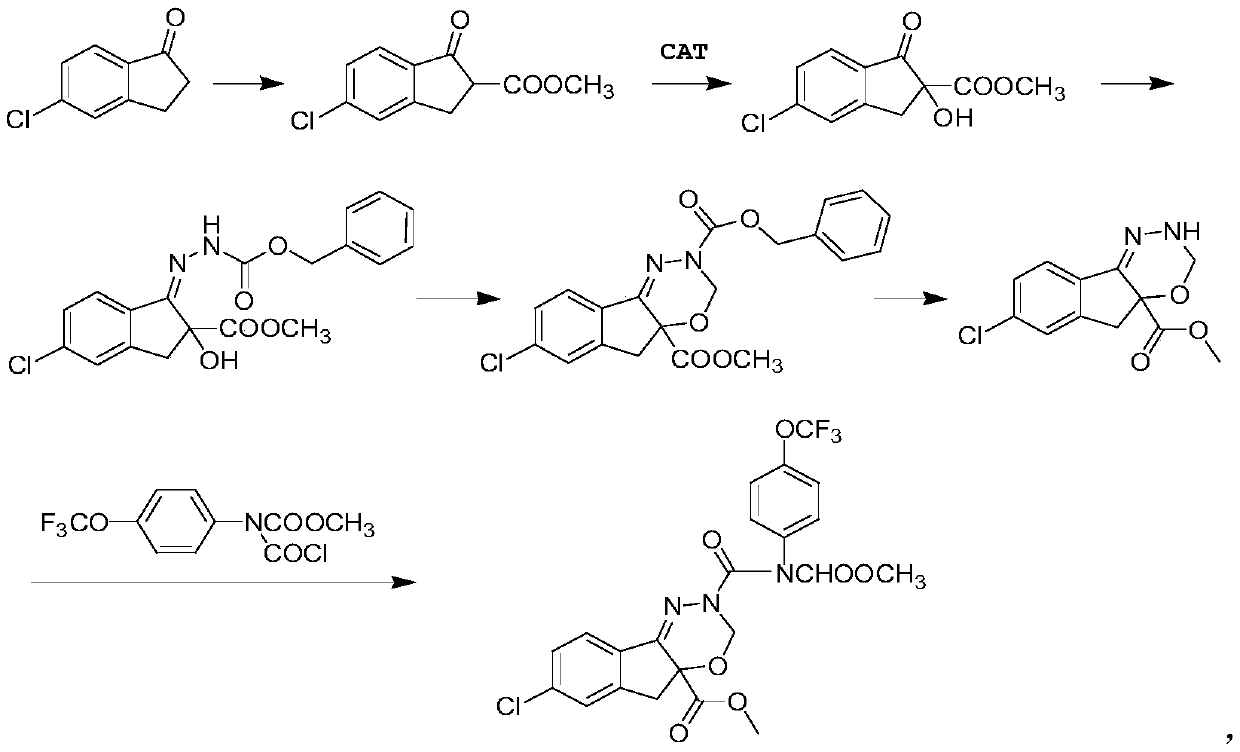
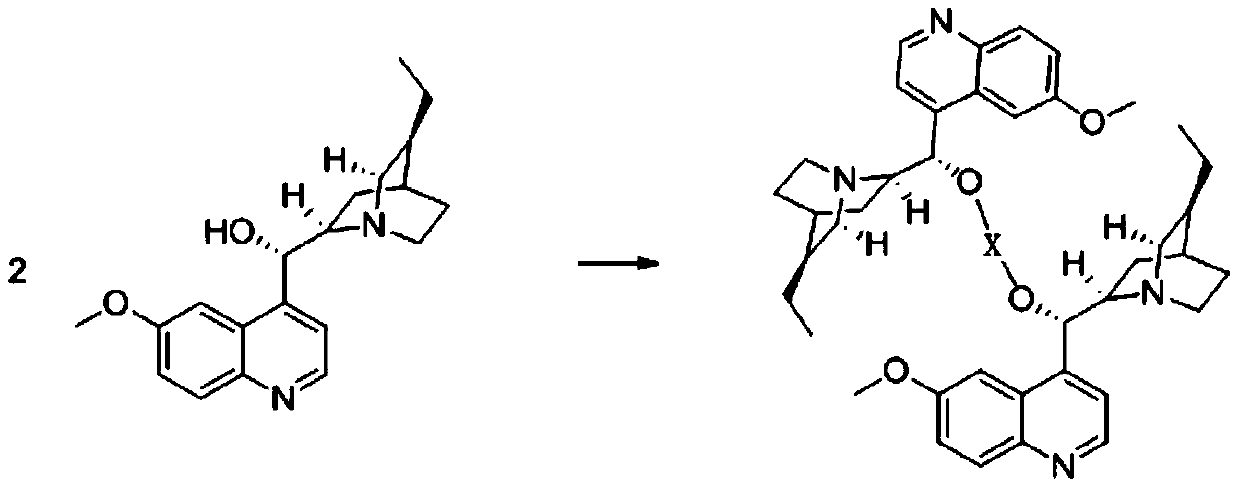
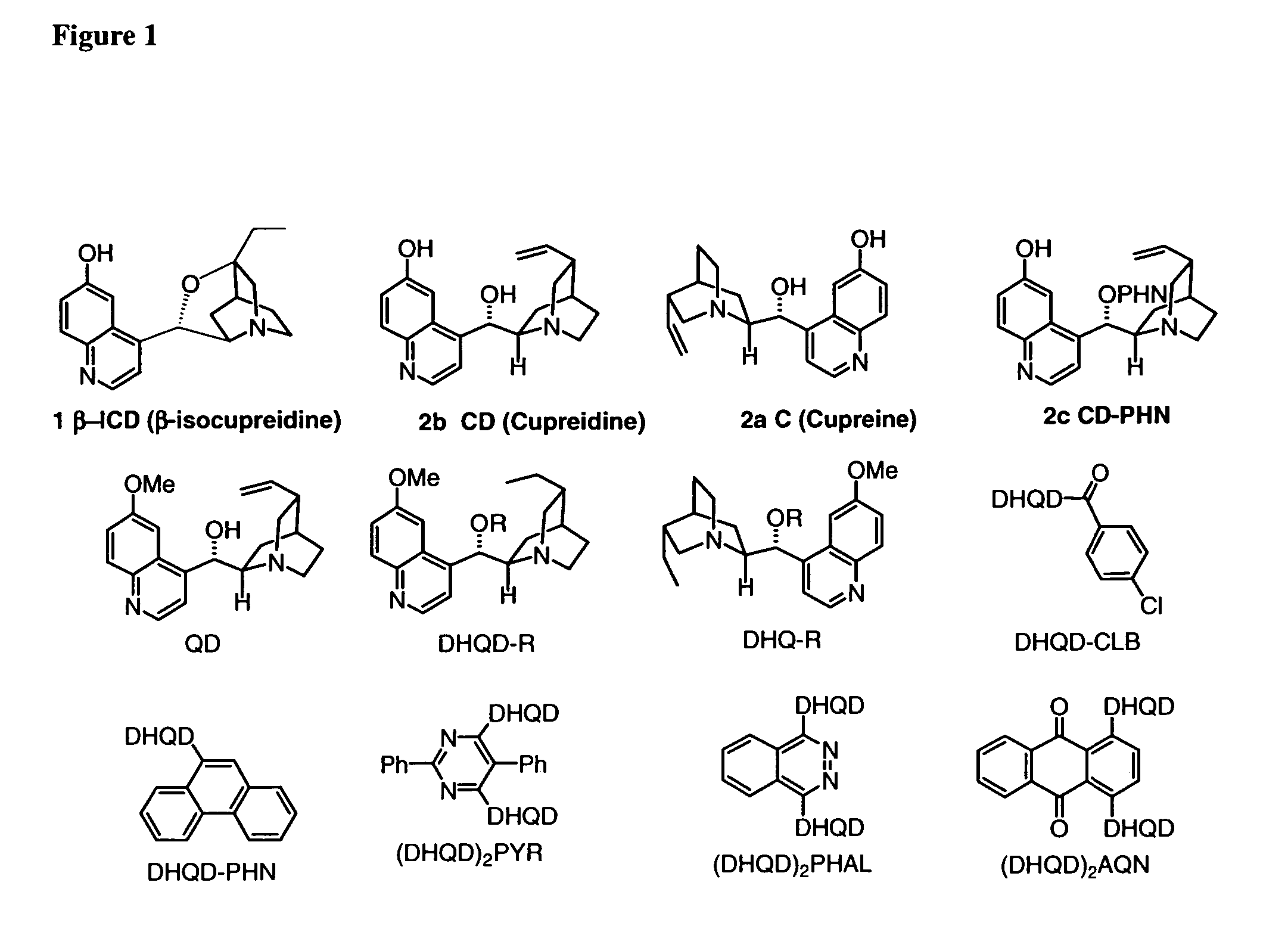
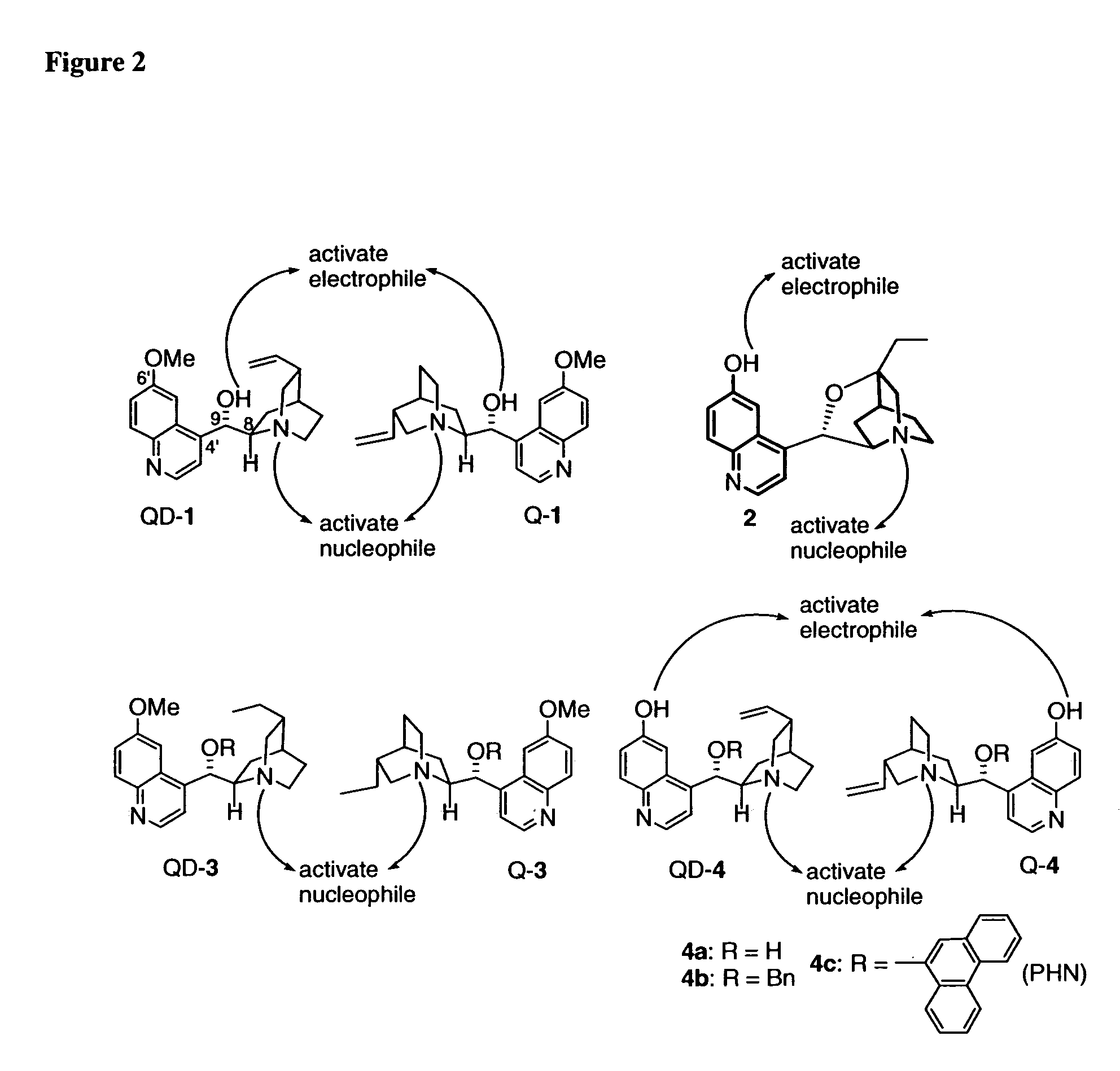
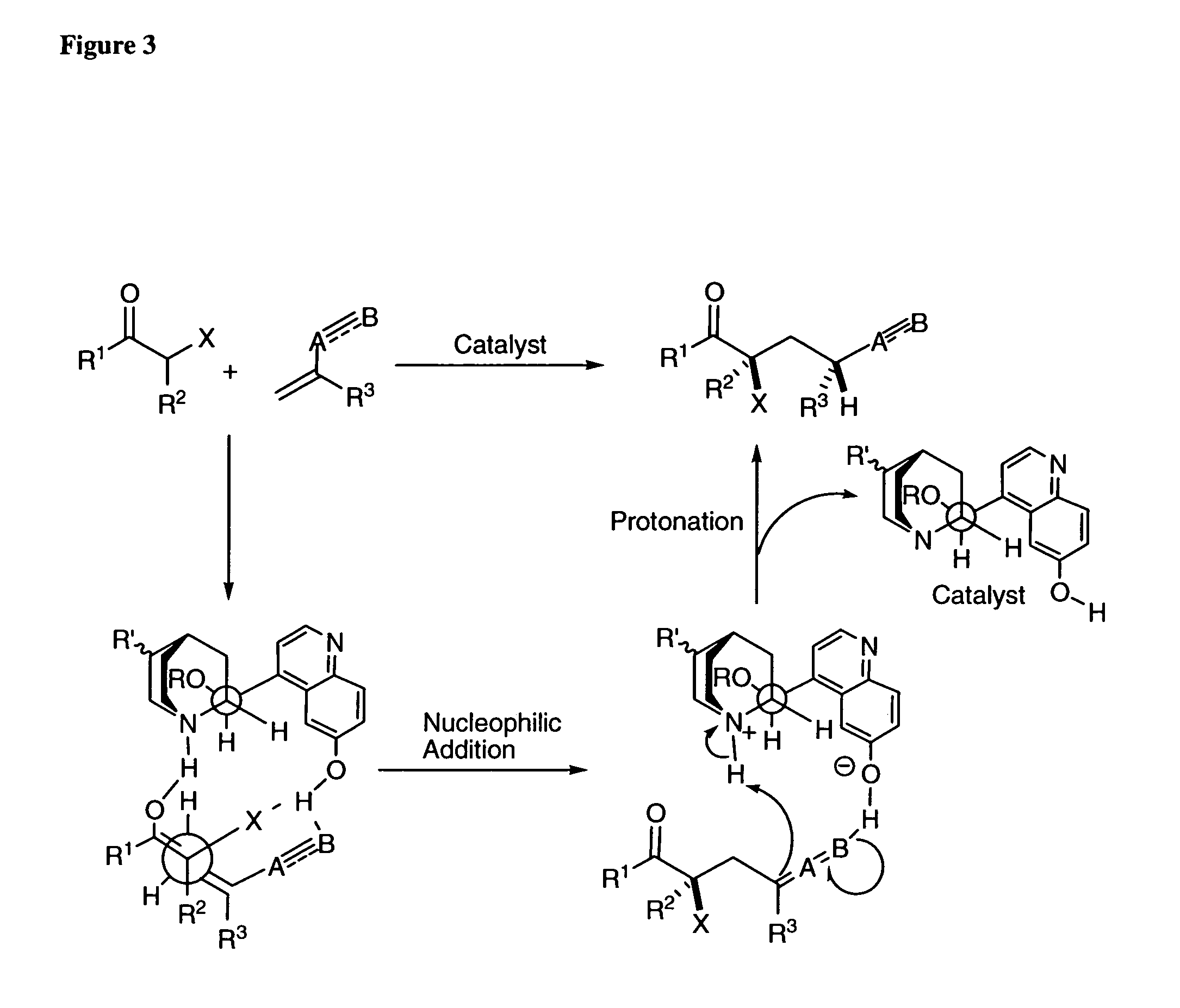
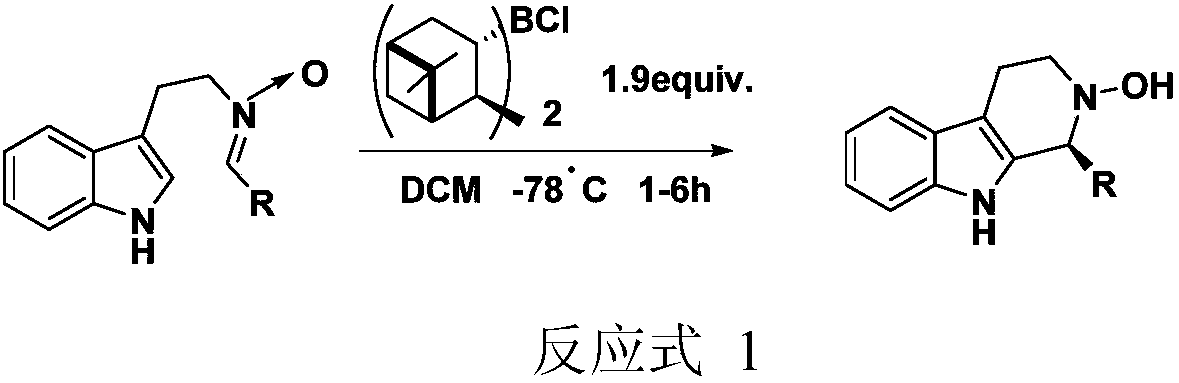
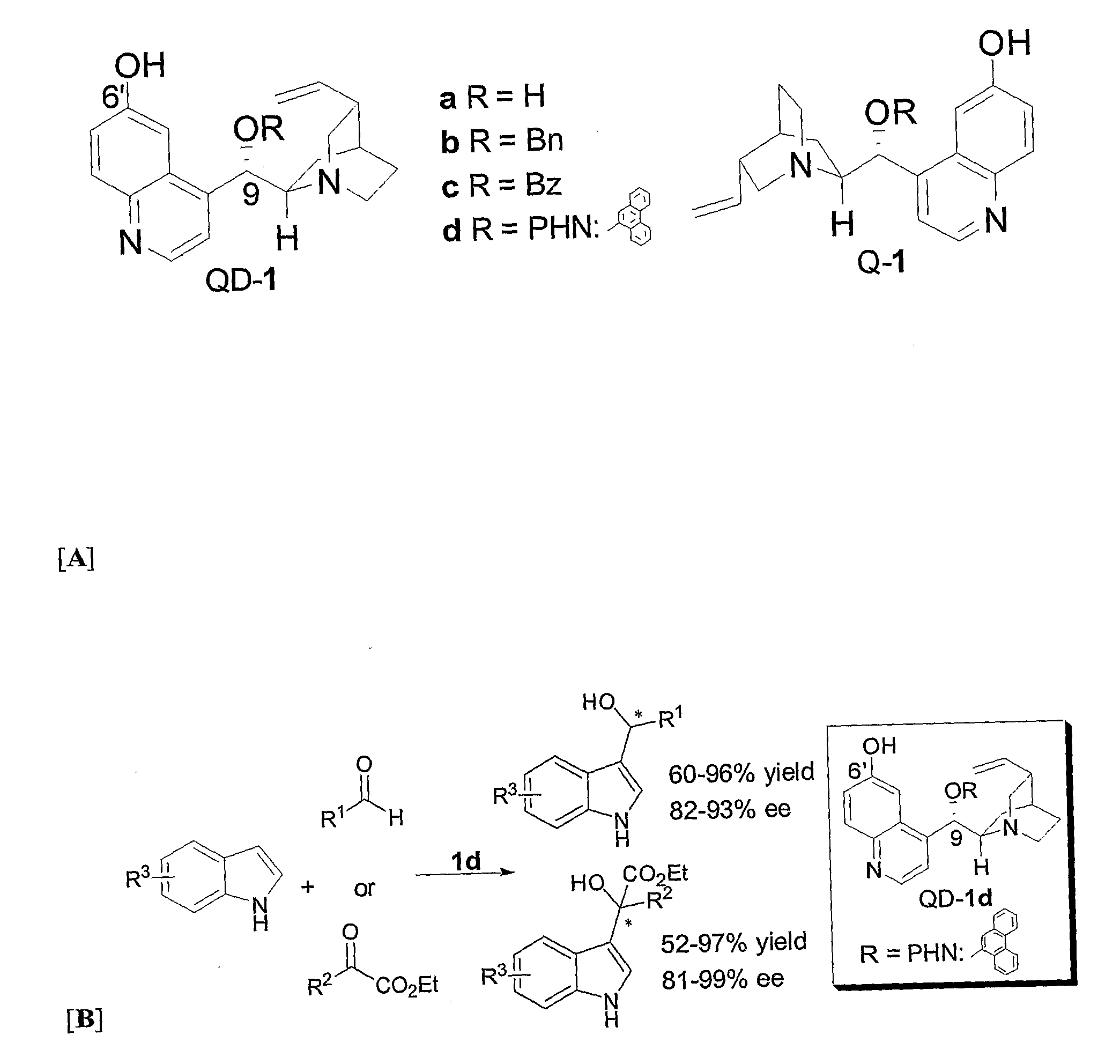
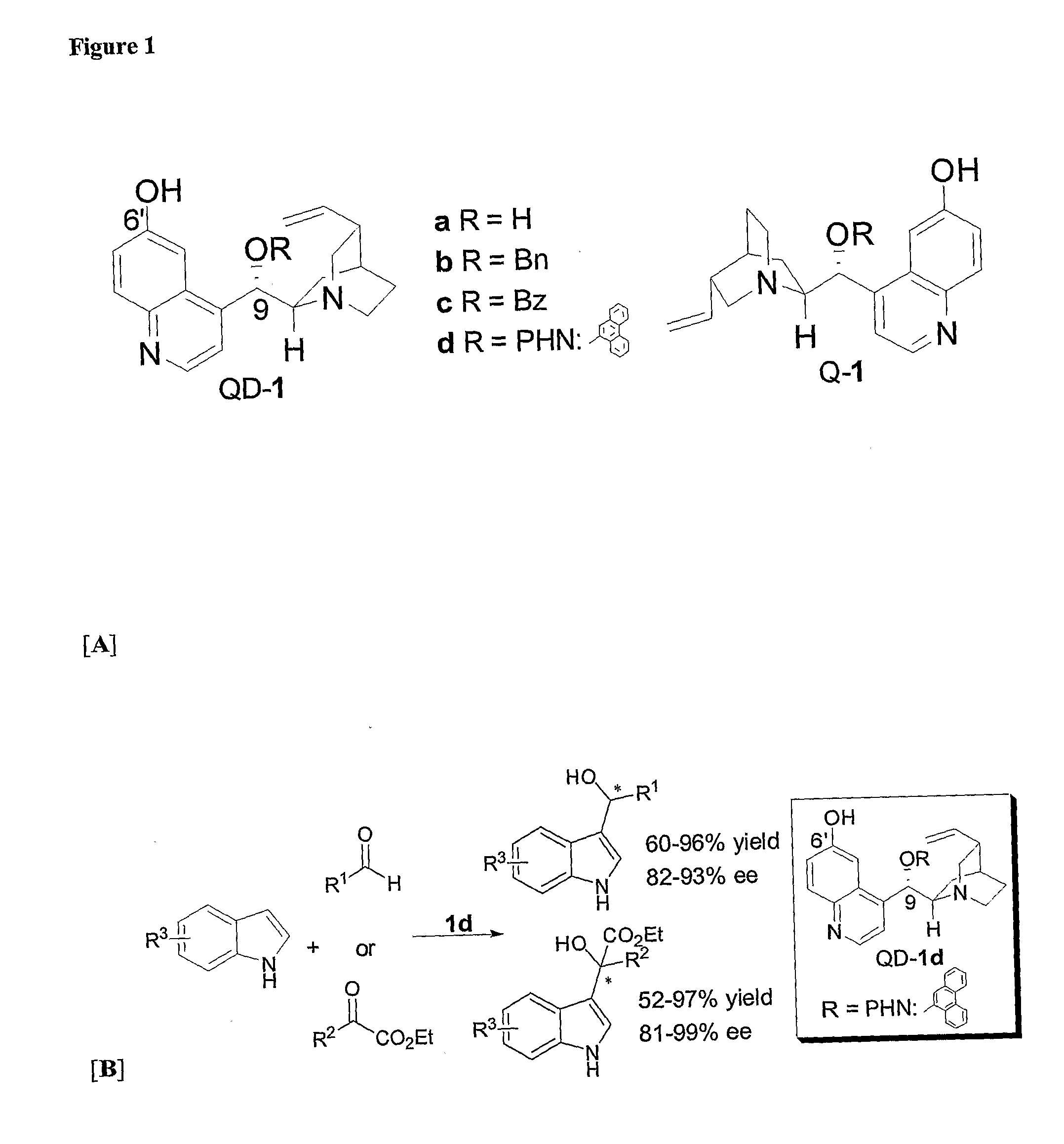
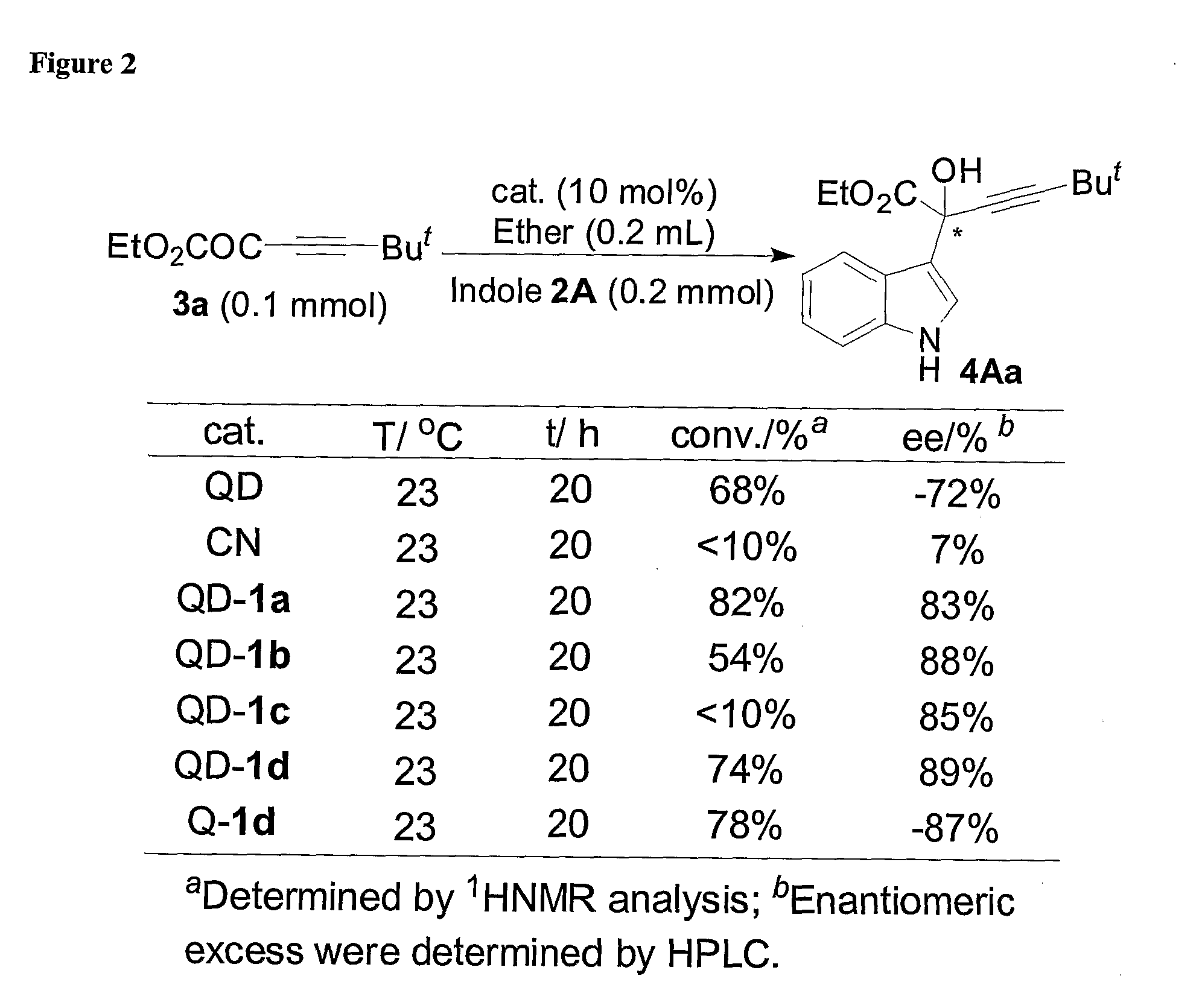
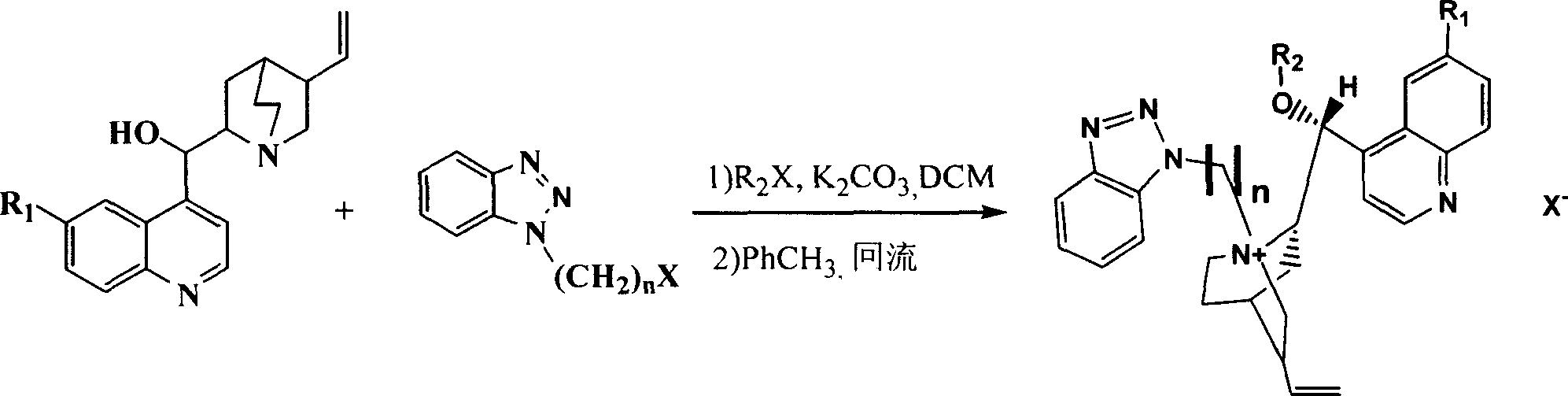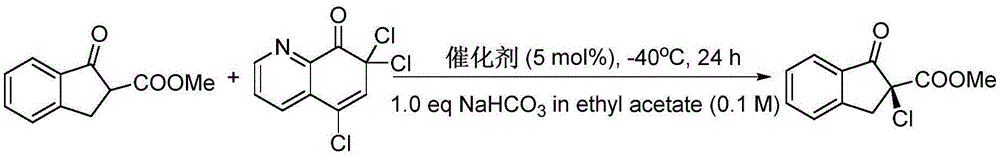Patents
Literature
100 results about "Cinchona Alkaloids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alkaloids extracted from various species of Cinchona.
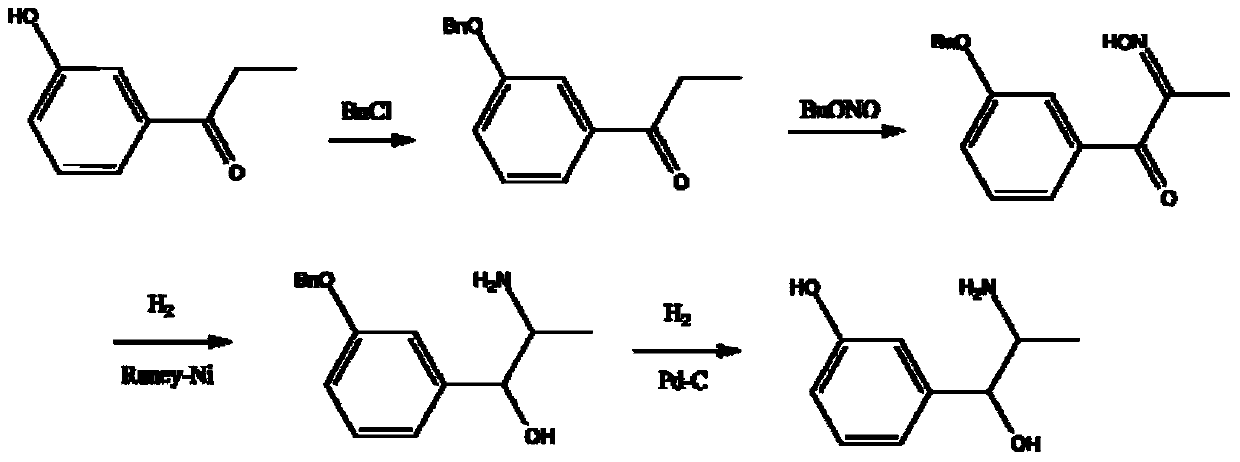
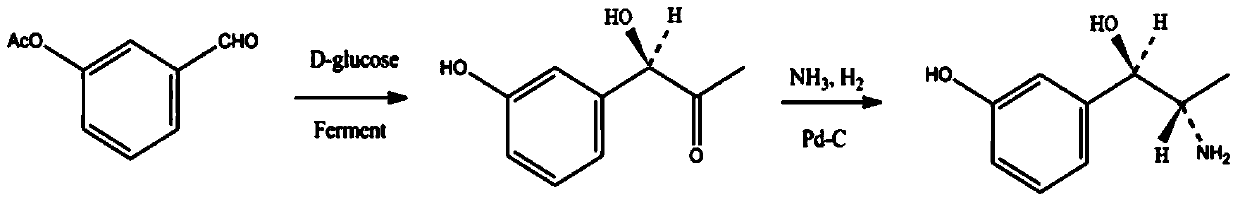
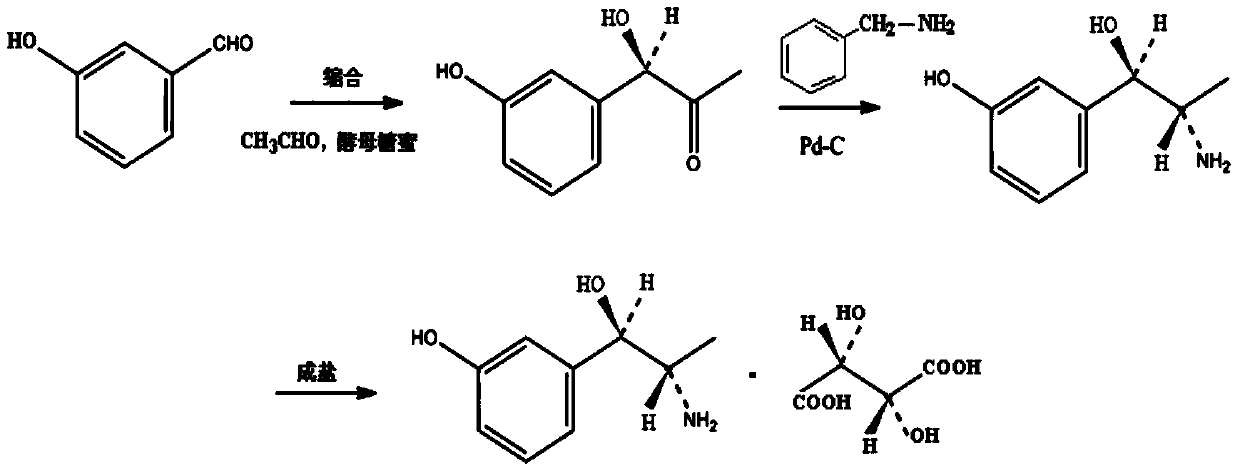
Synthesis method of metaraminol bitartrate
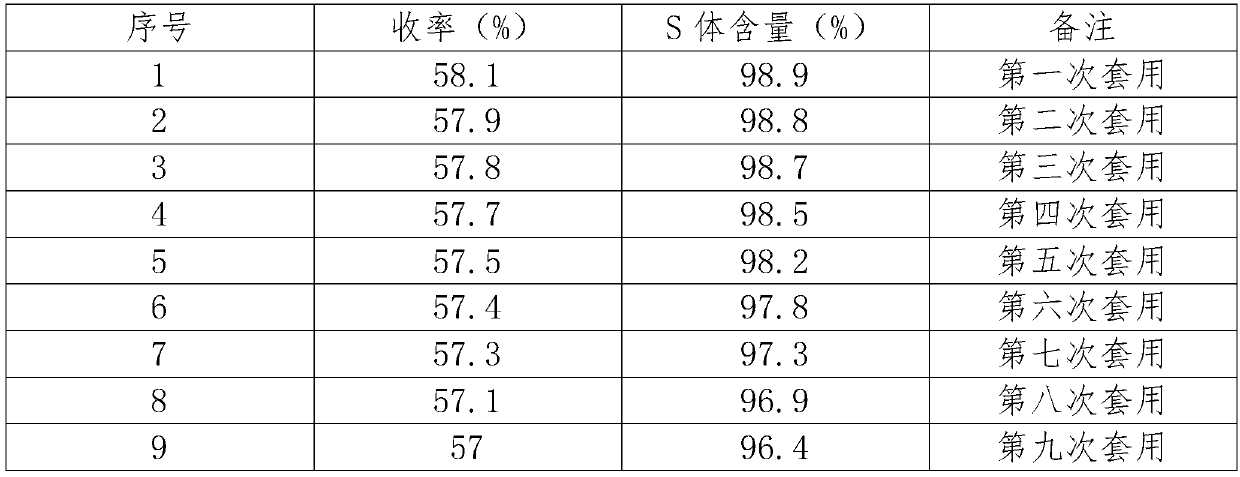
ActiveCN103739504AEasy to controlFew synthetic stepsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid salt preparationSynthesis methodsSpatial configuration
The invention discloses a synthesis method of metaraminol bitartrate, and in particular provides a method for synthesizing metaraminol bitartrate by using a chiral catalysis method. The synthesis method comprises the steps: catalyzing a chiral addition reaction of hydroxybenzaldehyde and nitroethane by using a chiral catalyst system consisting of cinchona alkaloid, copper acetate hydrate and less imidazole to obtain an addition product with a dominant required spatial configuration, and then reducing nitro by using hydrogen in the presence of Pd-C to obtain amine to obtain aramine, and salifying the aramine with L(+)-tartaric acid to obtain a final product metaraminol bitartrate. According to the synthesis method, an enzyme catalyst is prevented from being used, a raw material of the synthesis reaction is easily available, the chiral catalyst is easily purchased or prepared self, the synthesis steps are relatively less, the chiral control efficiency is higher, the enantioselectivity is high, the yield is good, the reaction operation is easily controlled, and is safe and reliable, and the foundation is laid for the later industrialized amplification production.
Owner:广州普星药业有限公司
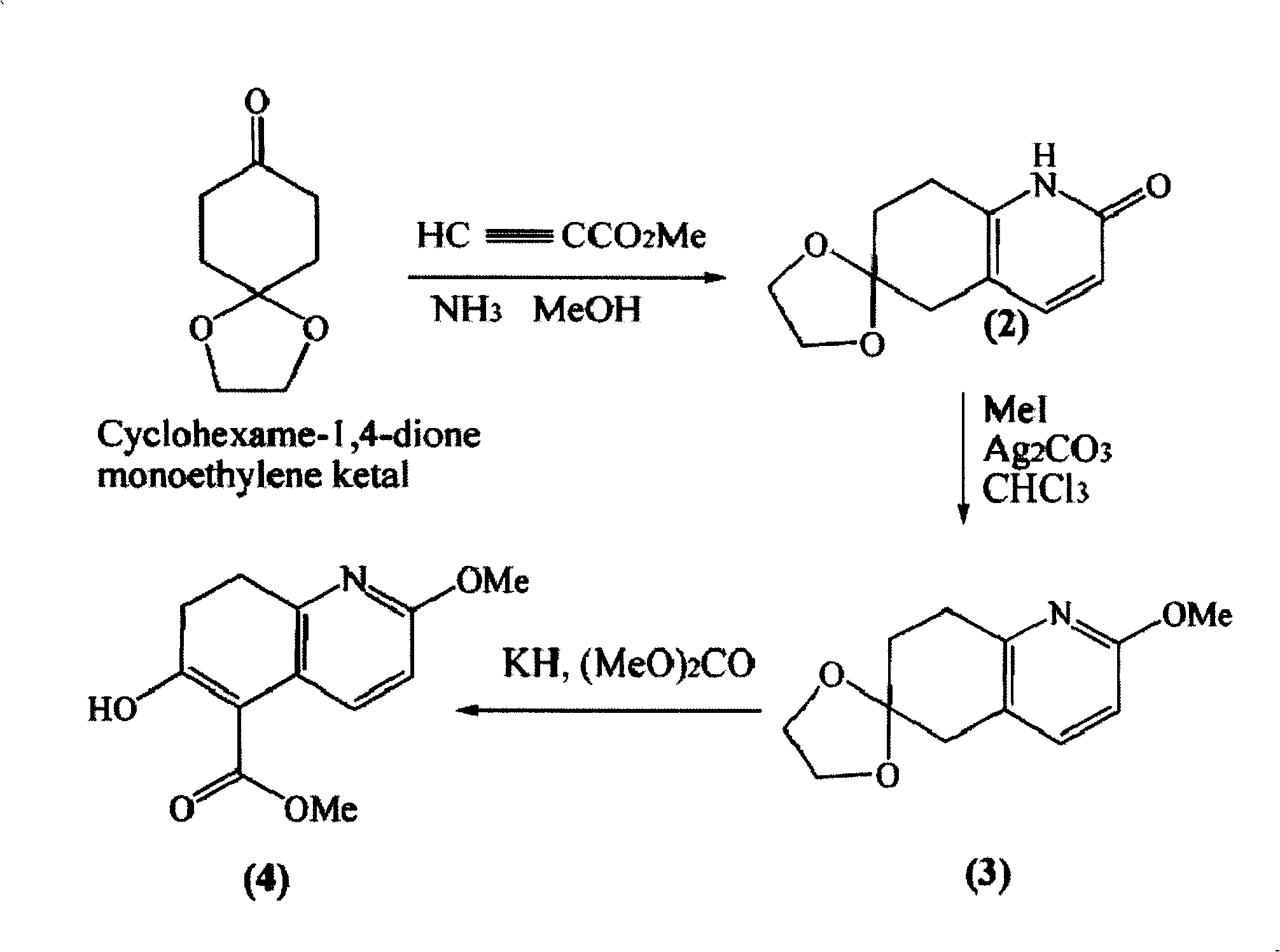
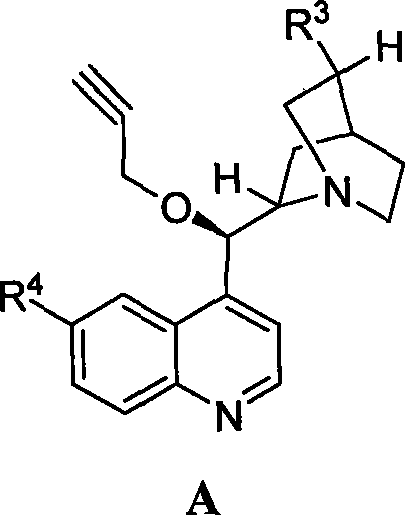
Asymmetric synthesis for chiral huperzine A
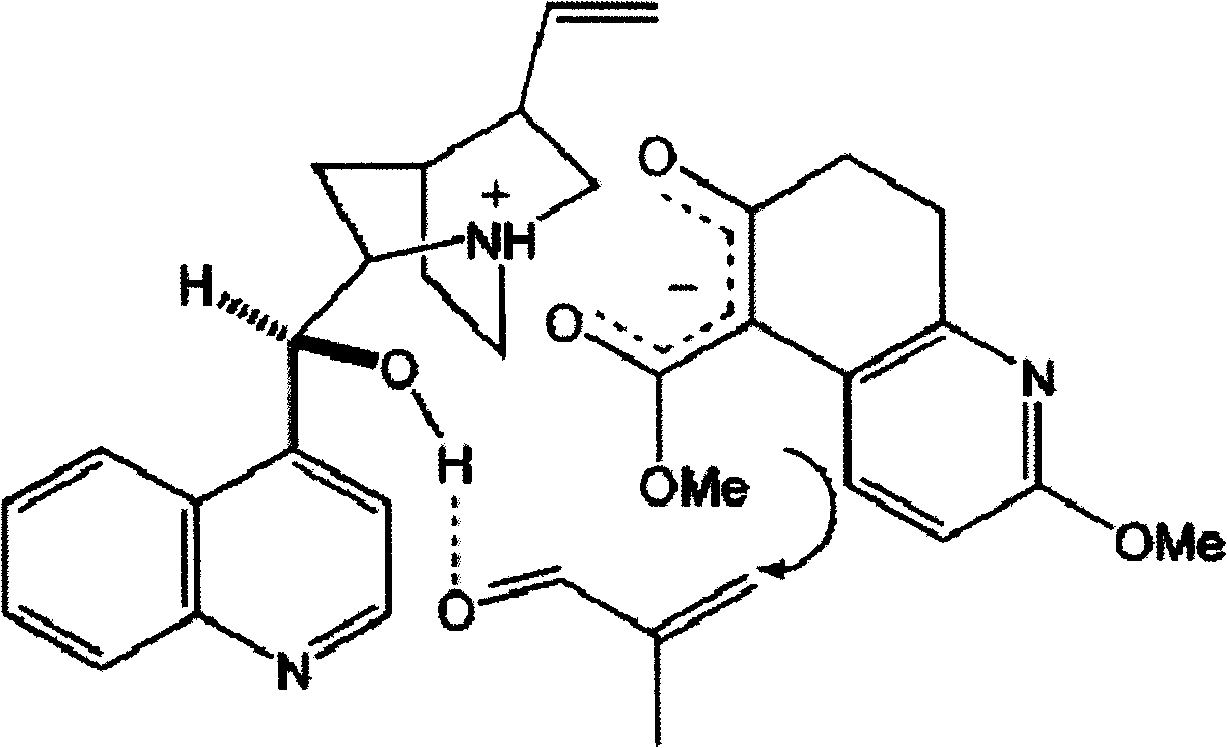
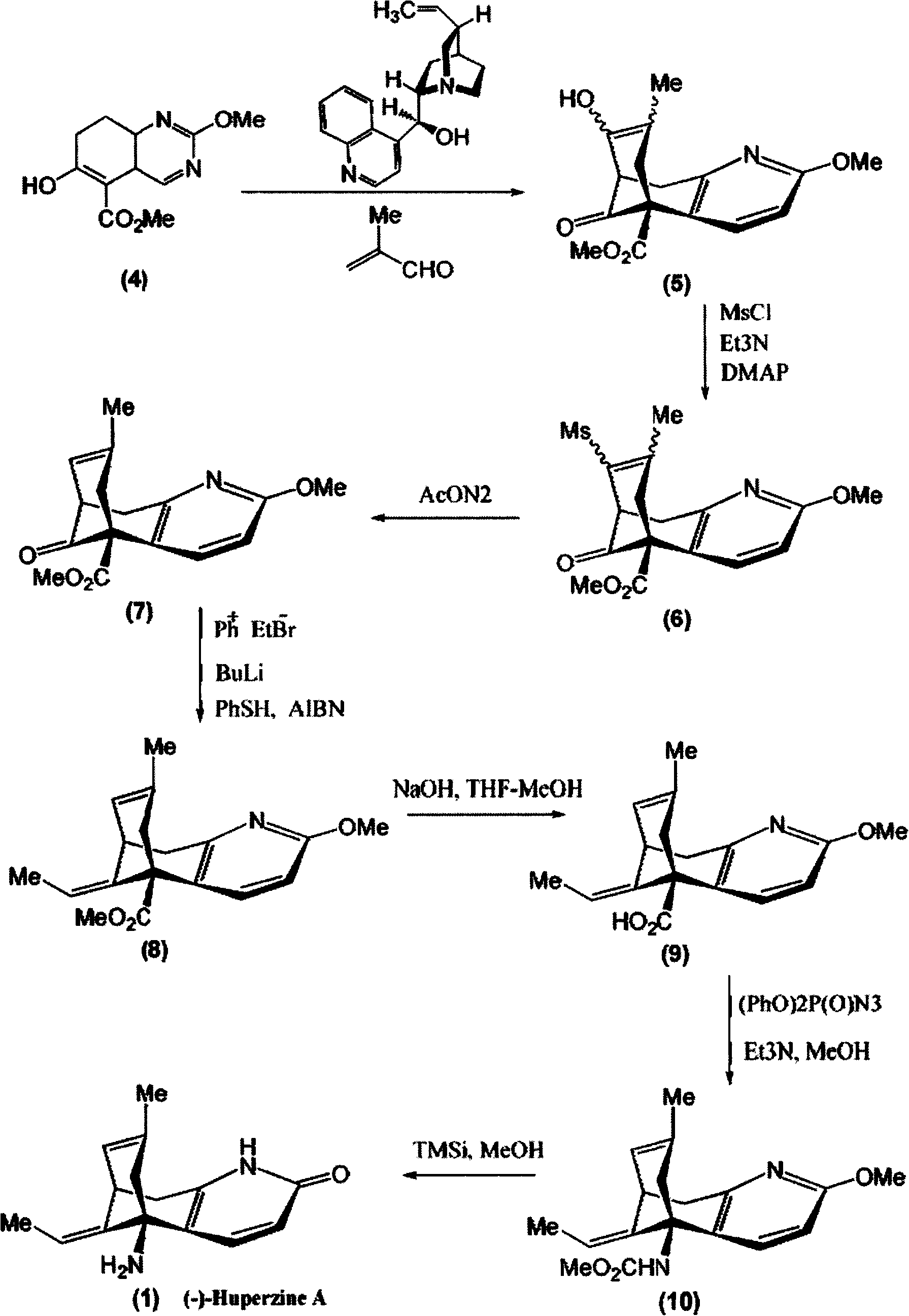
Disclosed is an asymmetric total-synthesis method for chiral huperzine a. The method takes 1,4-dihydro-spiro (4,5) -8 -decanone as starting material to get benzoate through hydroxymethylation and the treatment of benzoyl chloride and K2CO3; the benzoate is reacted with hydrogen sulfate O-methyl iso urea to get quinazoline; after the ketal is eliminated, Mander reagent is used for methyl esterification reaction so as to obtain beta-keto ester. Chiral ammonia, such as cinchona alkaloid, is used to promote the tandem asymmetric Michael addition / aldol condensation reaction of beta-keto esters and methyl acrolein. The compound carboxylate of diastereoisomer is reacted with MsCl, triethylamine and DMAP to get transformed. Through TMSI and MeOH processing, the protective group is removed so as to obtain optically pure-chiral huperzine a.
Owner:京山瑞生制药有限公司 +1
Method for synthesizing (4S,5R)- half-ester
InactiveCN101157655AHigh enantioselective catalytic effectHigh yieldOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAsymmetric synthesesAlcoholOrganic solvent
The invention pertains to the technical field of organic chemistry, in particular to a synthesis method of (4S, 5R)-semi-ester. The method carries out the enantioselective open-loop of cyclic acid anhydride and alcohol under the catalysis of cinchona alkaloid so as to prepare the (4S, 5R)-semi-ester. The reaction is carried out in the organic solvent in the states of normal pressure, compression or decompression, the reaction temperature is -80 DEG C to 25 DEG C, the reaction time is 10 to 80 hours, the total yield is more than 90 percent, and the ee is more than 98.5 percent. The raw materials of the method of the invention are easy to obtain, the catalyst can be reclaimed quantitatively, the reaction conditions are mild, and the yield and the stereoselectivity are high, so the invention is applicable to industrialization production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
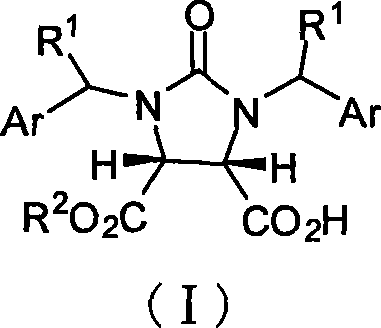
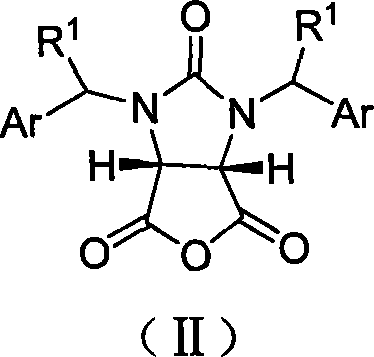
Beta-amino acid esters having optical activity and containing benzothiazole groups and synthetic method and application thereof
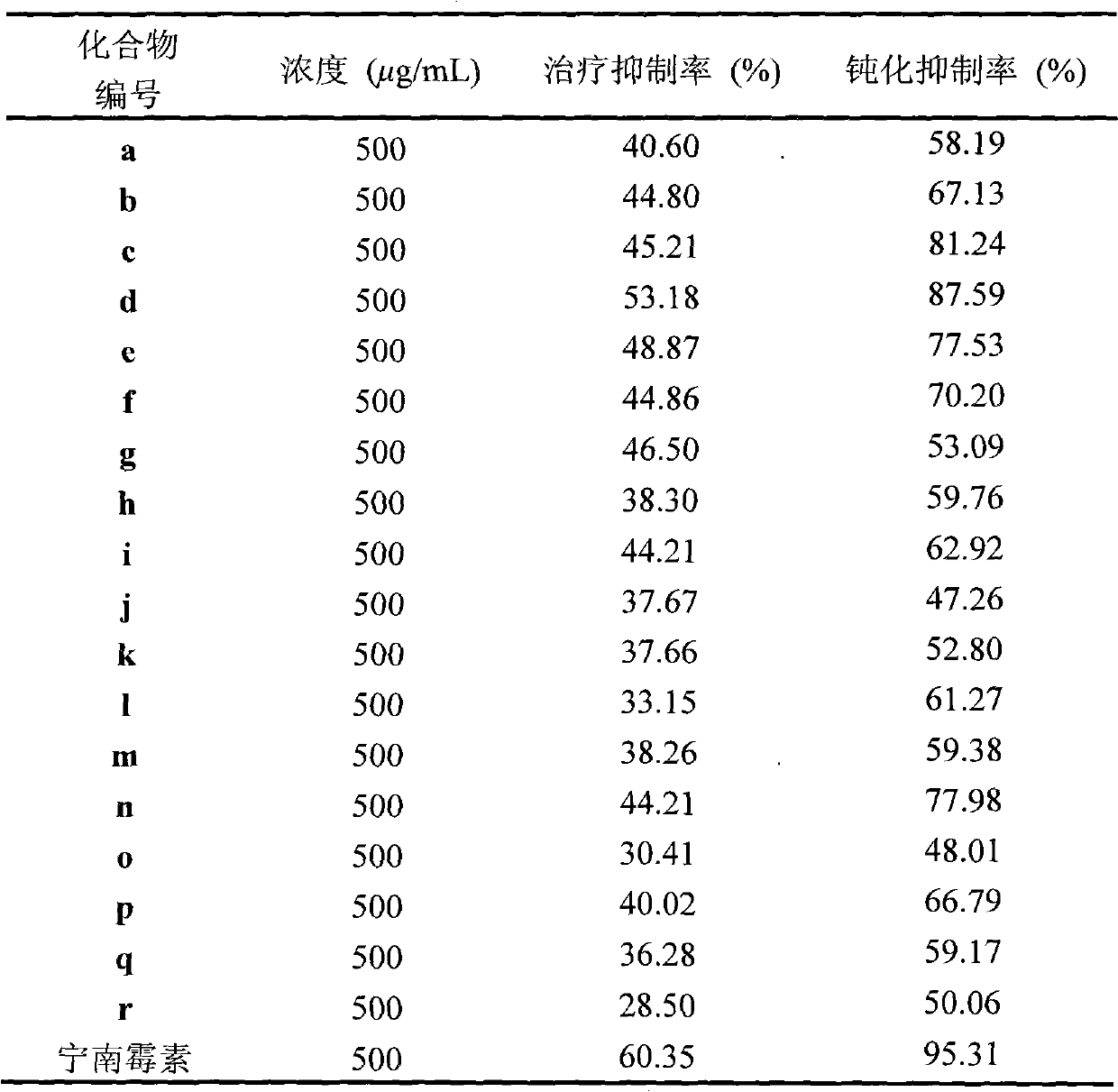
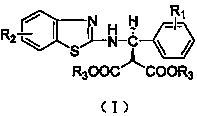
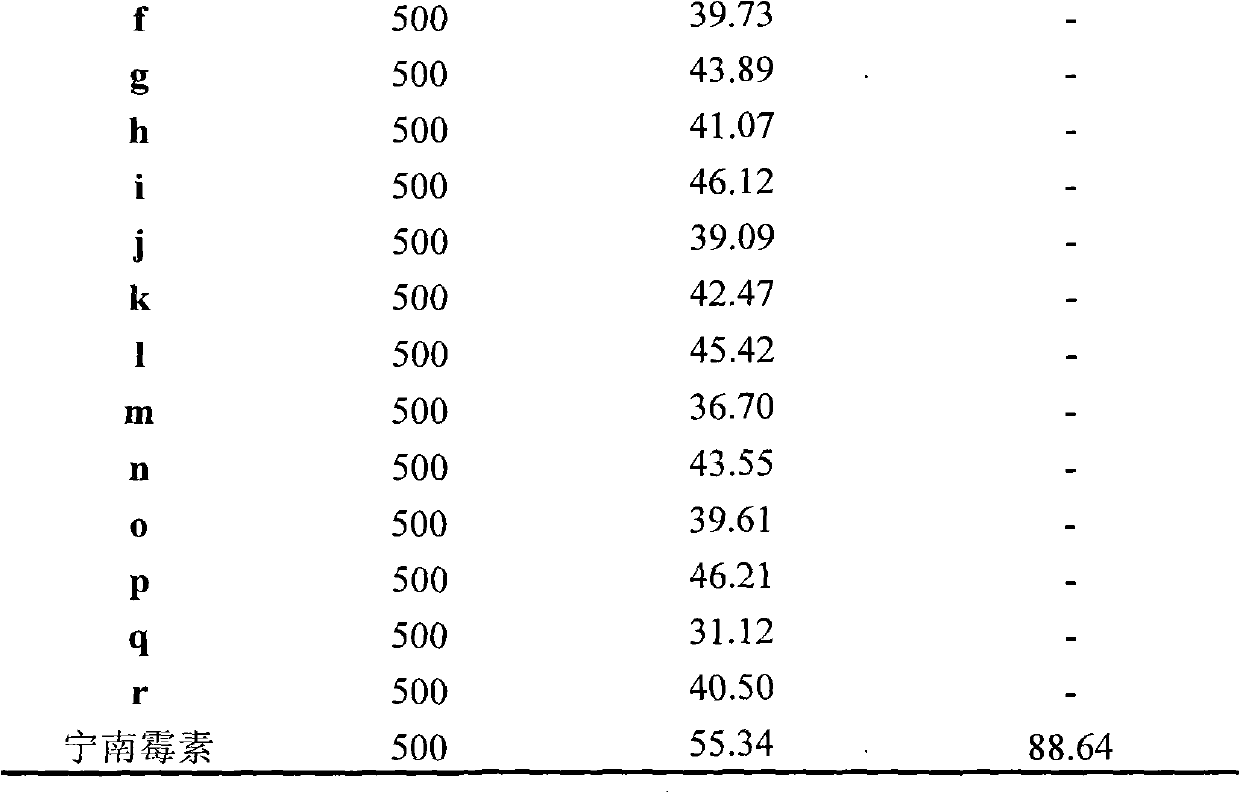
The invention discloses a synthetic method and bioactivity of beta-amino acid esters which have optical activity and contain benzothiazole groups. The beta-amino acid esters which have optical activity and contain the benzothiazole groups have the structure shown in the general formula (I), and in the formula, R1 is a group of hydrogen, p-chloro, o-chloro, p-fluoro, o-fluoro, p-methyl, o-methoxy and the like; R2 is a group of 4-methyl, 6-methoxy and the like; and R3 is a group of methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl and the like. The invention introduces Mannich reaction which uses organic catalyst of cinchona alkaloid thiourea to catalyze benzothiazole imine and malonate, the product is obtained by one-step synthesis, and the reaction yield and the selectivity to enantiomer are both high. Compounds c, d and e in the inveniton have high therapeutic and passivation inhibiting effects towards tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) and cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) and show good anti-plant virus activity.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Nanometer structure cinchona alkaloid thiourea multi-phase bionic catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101168134AOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsThioureaActive component
Provided is a nanostructured polyphase biomimetic catalyst of quinine and a process for preparing same, belonging to the catalytic field of preparing technology of biomimetic catalyst. The method for preparation of the novel catalyst is that mesoporous material with a nanometer-sized bore diameter is employed to be a vector, a functional group provided by the vector is employed to be a first platform and reacts with substance which has active primitives, and further a second reactive platform is provided and is assembled in situ inside a nanostructured space, thereby forming the objective catalyst. The catalyst has the characteristics that active components are assembled via high dispersion in a one-dimensional or three-dimensional straight-through nanometer-sized pore passage, forming a nanostructured chiral molecule reactor, and displaying the high asymmetric inductivity. The value of the catalyst is higher than the homogeneous phase catalytic level, and the catalyst has the high reutilization property and important adaptation value. Further, the invention is easy to be commercially developed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Supported osmates, process for preparation thereof, and a process for the preparation of chiral vicinal diols using supported osmate catalyst
The present invention provides a supported osmate useful as a reusable catalyst in the preparation of vicinal diols. The present invention also relates to a process for the preparation of supported osmates of the formula (S-NR3)2OsO4.nH2O wherein S is a support, R is an alkyl group, n is the number of water molecules and use thereof in the preparation of vicinal diols by asymmetric dihydroxylation (AD) of olefins in presence of cinchona alkaloid compounds.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Novel method for asymmetric alpha-hydroxylation of photo-oxygenation beta-dicarbonyl compound based on C-2' phase transfer catalyst
InactiveCN105732387AHigh catalytic activityGood substrate applicabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhotosensitizerOrganic synthesis
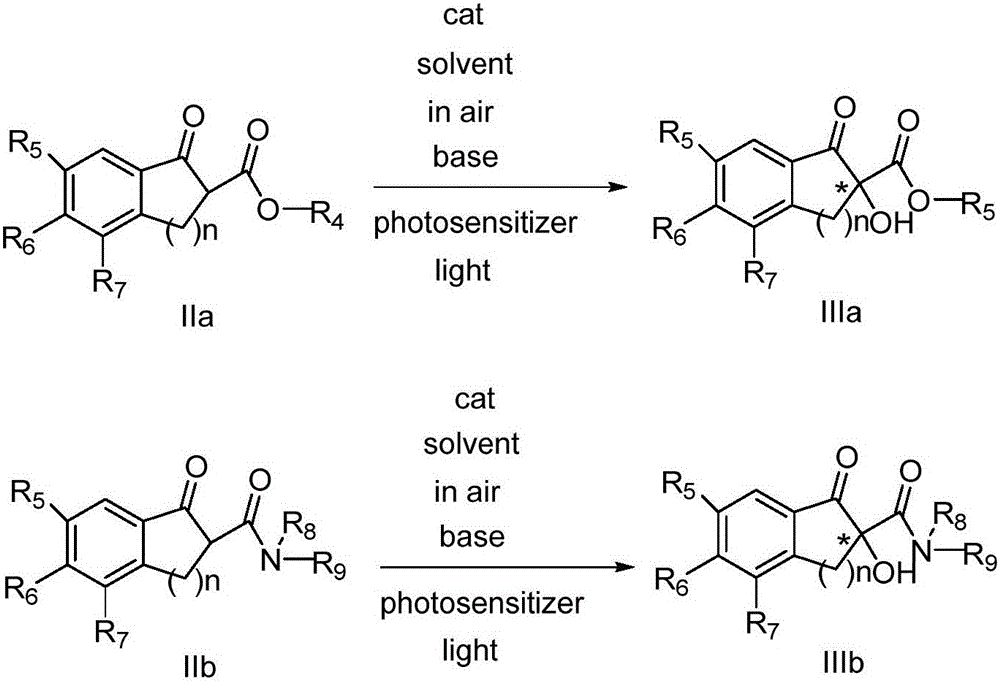
The invention belongs to the technical fields of organic synthesis and provides a novel method for asymmetric alpha-hydroxylation of a photo-oxygenation beta-dicarbonyl compound based on a C-2' phase transfer catalyst.The beta-dicarbonyl compound, the cinchona alkaloid C-2' phase transfer catalyst and an organic photosensitizer are stirred in a solvent, alkali is added, strong stirring reaction is performed in the air under the condition of visible light, the reaction temperature is 50-70 DEG C, the reaction time is 1-4 hours, and a chiral alpha-hydroxyl-beta-dicarbonyl compound with the yield no lower than 70% and the enantiomeric excess selectivity no lower than 60% ee is obtained; derivatization is conducted on a cheap cinchona alkaloid C-2' potential easy to obtain a series of chiral phase transfer catalysts having higher catalytic activity, molecules are successively oxidized into an oxidant, and the asymmetric alpha-hydroxylation of the photo-oxygenation beta-dicarbonyl compound is achieved.The method has good substrate applicability and environmental friendliness.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound using cinchona alkaloid derivative as catalyst
InactiveCN103333069AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationReaction temperatureQuinidine
The invention discloses a preparation method of an alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound using a cinchona alkaloid derivative as a catalyst. In the condition that the cinchona alkaloid derivative is used as the catalyst, a compound is caused to be in contact with oxidants including oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and alkyl hydroperoxide; the compound and the oxidant in contact are mixed and stirred in an inert solvent for reaction; after the reaction is ended, the alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound is obtained by separation, wherein the inert solvent comprises halogenated hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon, alkane and the like; the dosage molar ratio of the peroxide, which is used as the oxidant, to a beta-dicarbonyl compound is 1-30; the dosage of the catalyst III is 0.5-50mol%; the reaction temperature is minus 78 to 50 DEG C. According to the novel preparation method of the alpha-hydroxy-beta-dicarbonyl compound using the cinchona alkaloid derivative as the catalyst disclosed by the invention, cinchona alkaloid quinine and cinchona alkaloid quinindium, which are main alkaloids in the bark of cinchona and congener, are widely applied to organic unsymmetrical catalytic reaction.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation of imidazole type ionic liquid derived by cinchona alkaloid
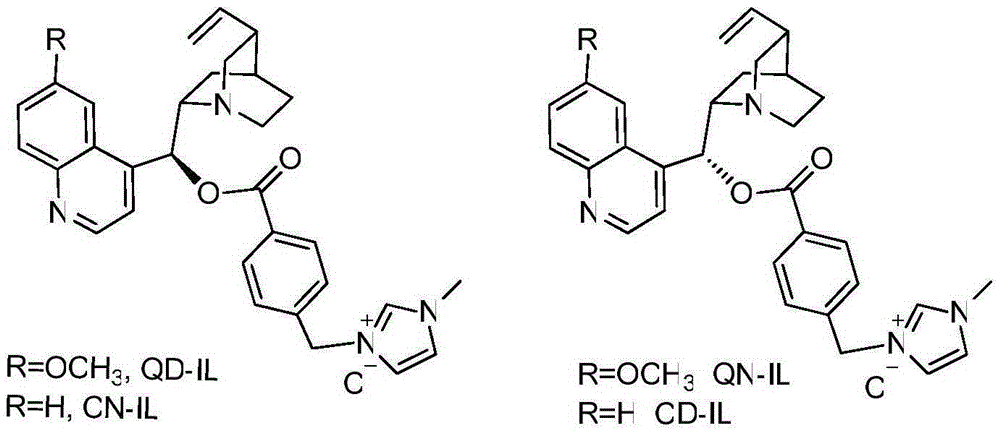
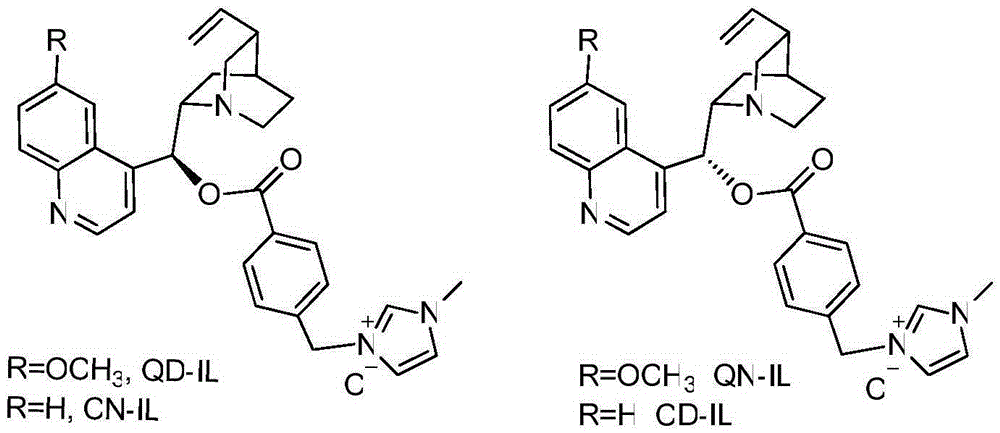
InactiveCN105330662AHigh catalytic activityIncrease profitOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIonic liquidEnantio selectivity
The invention discloses the preparation of imidazole type ionic liquid derived by cinchona alkaloid. The preparation is characterized by adopting quinine or cinchonine to modify 9-hydroxyl of the cinchona alkaloid; carrying out a replacement reaction on chloride salt of obtained imidazole type ionic liquid and inorganic metal salt; preparing imidazole type ionic liquid catalysts of different anions. Compared with the prior art, the preparation disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the catalytic activity is high, the catalysts are easily separated and recycled and can be reused again, the preparation is simple, post-processing is easy, the stability of the catalysts is greatly increased, the application range of the catalysts in a micromolecular organic asymmetric reaction is expanded, reaction conditions are optimized, reaction requirements are reduced, the catalytic activity and the enantioselectivity of a chiral imidazole type ionic liquid catalyst in an asymmetric reaction are further increased, and great significance is obtained for researching medicinal chemistry and medical intermediate compounds.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
In-situ synthesizing method of chirally-modified palladium nanometer material of different morphologies
InactiveCN108031834ATransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusBenzaldehydeReaction temperature
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic materials, and particularly discloses an in-situ synthesizing method of a chirally-modified palladium nanometer material of different morphologies. A traditional surface covering agent is replaced with a chirally modifying agent (such as chiral amino acid, chiral carboxylic acid and chiral cinchona alkaloid) with amido groups, carboxyl groups and other functional groups, the growth speed of different palladium crystal faces is controlled, ascorbic acid, benzaldehyde and the like serve as a reducing agent to reduce metal precursors of palladium, and the chirally-modified palladium nanometer material is synthesized in situ. By adjusting the type of the chirally modifying agent, the type of a reducing agent and the reaction temperature, the chirally-modified palladium nanometer material of different morphologies such as cuboid shape, flower shape, polyhedron, dendrite and cluster shape can be obtained. The synthesized chirally-modified palladium nanometer material serves as the chirally-modified metal catalyst and has wide application prospects in multi-phase asymmetrical catalysis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing alpha-hydroxyl-beta-dicarbonyl compound through activating oxygen in air by using hydrazine
InactiveCN104193620AHigh yieldMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAlkaneEnantiomer
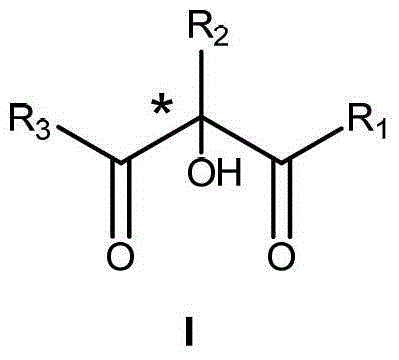
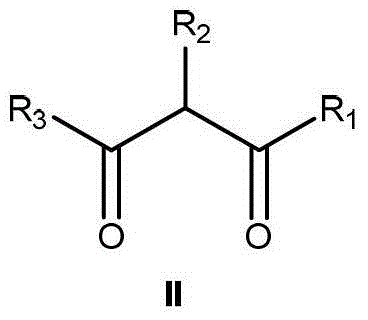
The invention relates to a method for preparing a compound I (the compound is achiral, racemized or enantiomer-enriched in the indicated hydroxylation center). The method comprises the steps of adding organic hydrazine and a compound II under the condition that alkali is used as a catalyst, and enabling the organic hydrazine and the compound II to be in contact with a gas containing oxygen molecules to obtain the compound I with the highest yield of 98%. The product obtained by carrying out mixed reaction in a solvent by taking chiral alkali such as cinchona alkaloid as a catalyst and the compound II as a substrate is used as the enantiomer-enriched compound I with the highest yield of 95% and the ee value of 85%. The solvent comprises halogenated hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon, alkane, ether solvents and the like. Molecular oxygen is activated by using organic hydrazine compounds to realize the alpha-hydroxylation reaction of a beta-dicarbonyl compound, so that the method is relatively high in atom economy and environment-friendly. The method is a novel method for preparing various chiral or achiral alpha-hydroxyl-beta-dicarbonyl compounds through activating molecular oxygen by using organic hydrazine compounds.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Application of ordered mesoporous carbon material-loaded platinum catalyst in alpha-keto ester asymmetrical catalytic hydrogenation reaction
InactiveCN102093218AImprove stabilityNot easy to loseOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSolventChrysolophus pictus
The invention provides application of an ordered mesoporous carbon material-loaded platinum catalyst in an alpha-keto ester asymmetrical catalytic hydrogenation reaction. The ordered mesoporous carbon material-loaded platinum catalyst is subjected to pretreatment at the atmosphere of hydrogen; and then the pre-treated ordered mesoporous carbon material-loaded platinum catalyst, golden pheasant alkaloid, solvent and alpha-keto ester are subjected to an asymmetrical catalytic hydrogenation reaction in a reaction kettle by a virtue of introducing hydrogen under the condition of electromagnetic stirring. In the invention, the ordered mesoporous carbon material-loaded platinum catalyst is subjected to chirality modification with cinchonidine or cinchonine, so as to represent an excellent catalytic property in the alpha-keto ester asymmetrical catalytic hydrogenation reaction.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Phosphoric acid amide bifunctional catalyst and synthetic method thereof
ActiveCN102309984AEasy to synthesizeSave raw materialsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsO-Phosphoric AcidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a phosphoric acid amide bifunctional catalyst derived from cinchona alkaloid and a synthetic method thereof. According to the invention, the chiral phosphoric acid amide bifunctional catalyst with high efficiency catalytic activity provided in the invention is prepared in one step by reacting corresponding primary amine produced by ammonification of cinchona alkaloid and derivatives thereof with phosphoric acid acyl chloride. The catalyst provided in the invention has the advantages of a novel structure, stable properties, high catalytic activity, etc., and the synthetic method for the catalyst is simple.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of macromolecule loaded quinine type compound
InactiveCN101417241AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic solventPolystyrene
The invention provides a preparation method used for preparing compounds such as cinchona alkaloid loaded by polymer, comprising the steps as follows: with the existence of organic solvent and inorganic alkali or organic alkali, the compounds such as the cinchona alkaloid reacts with chloromethylated porous polystyrene resin for 10-60 at the temperature ranging from 20 DEG C to a reflux temperature; subsequently, the resin is filtrated; and the molar ratio of chloromethyl and alkali in the porous polystyrene resin of the compounds such as the cinchona alkaloid is 0.6-2.5:1:1.0-3.0. The compounds such as the cinchona alkaloid loaded by polymer prepared by the method is used as the catalyst, has simple operation, can be circularly used, is friendly to the environment, and can be more widely applied to the preparation of chiral compounds.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Cinchona alkaloids compound and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a cinchona alkaloids compound with a new macrocyclic structure, and a preparation method thereof. The cinchona alkaloids compound is prepared with cinchona alkaloids quinidine as a substrate. According to the preparation method, quinidine is subjected to a halogen cyclization reaction, such that the new macrocyclic structure is obtained. Related derivatives can be obtained through the changes on the C11-locus. The cinchona alkaloids compound provided by the invention can be used as a novel chiral catalyst or a ligand. The preparation method is simple, and yield is high.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
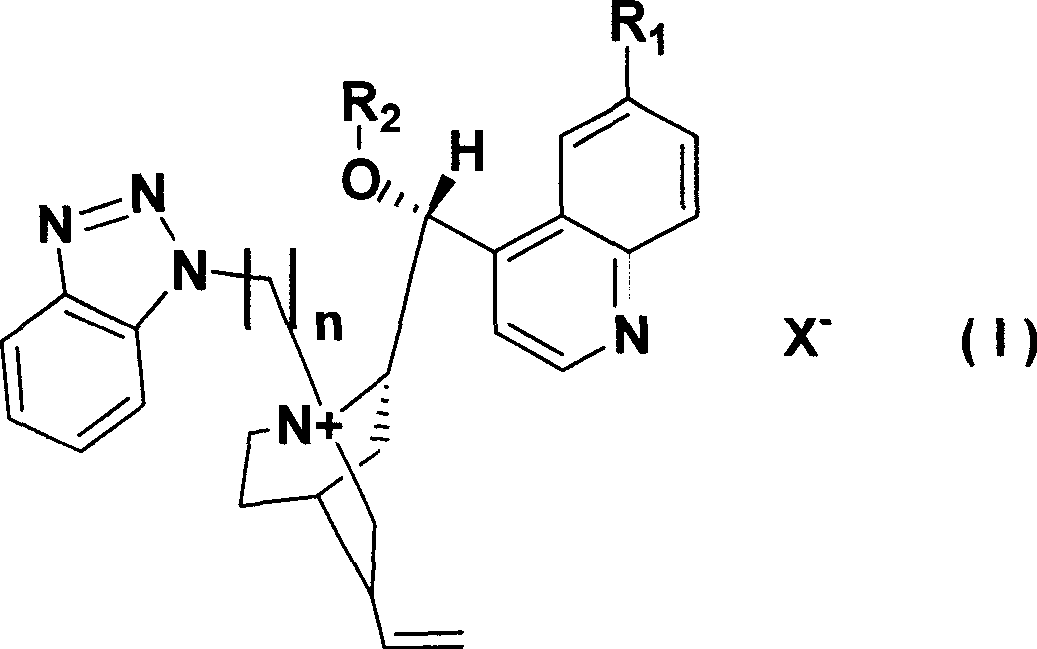
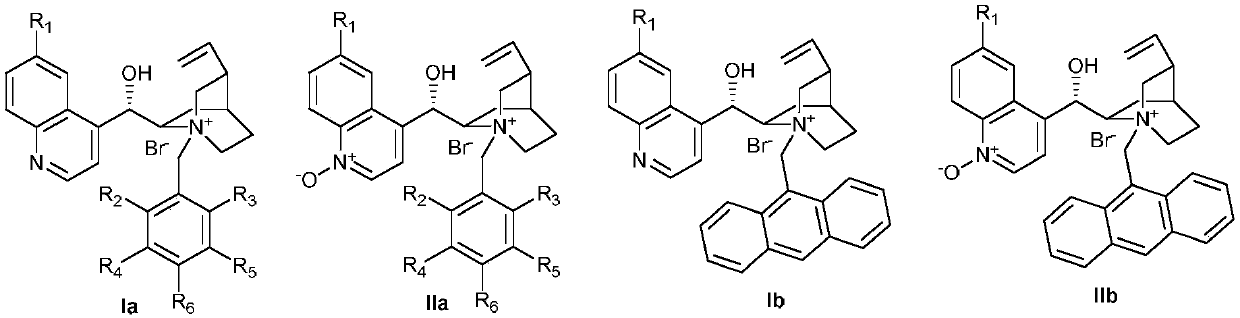
Cinchona alkaloid quaternary ammonium salt derivatives as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101531658AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSynthesis methodsHigh activity
The invention relates to cinchona alkaloid quaternary ammonium salt derivatives and a synthesis method thereof as well as application of the derivatives in synthetizing high optical purity natural amino acid and non-natural amino acid. A structural general formula (I) represents a chiral cinchona alkaloid quaternary ammonium salt, wherein R1 is methoxyl, hydroxyl, hydrosulfuryl or hydrogen; R2 is alkyl with 3 to 20 carbon atoms; X is halogen; and n is a positive integer from 1 to 4. The cinchona alkaloid quaternary ammonium salt catalyst has high activity in an alkylation reaction, good stereoselectivity, high catalysis efficiency, a wide substrate range and good asymmetric induction.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Asymmetric Michael and Aldol additions using bifunctional cinchona-alkaloid-based catalysts
InactiveUS20060014956A1Silicon organic compoundsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationLeaving groupKetone
One aspect of the present invention relates to quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method of preparing a derivatized quinine-based or quinidine-based catalyst comprising 1) reacting quinine or quinidine with base and a compound that has a suitable leaving group, and 2) converting the ring methoxy group to a hydroxy group. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a chiral, non-racemic compound from a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or azo compound or prochiral aldehyde or prochiral ketone, comprising the step of: reacting a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or azo compound or prochiral aldehyde or prochiral ketone with a nucleophile in the presence of a catalyst; thereby producing a chiral, non-racemic compound; wherein said catalyst is a derivatized quinine or quinidine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of kinetic resolution, comprising the step of: reacting racemic chiral alkene with a nucleophile in the presence of a derivatized quinine or quinidine.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Cinchona-based bifunctional organocatalysts and method for preparing chiral hemiesters using the same
ActiveUS20110213151A1Low toxicityHigh industrial usefulnessOrganic chemistryDesymmetrizationOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to cinchona-based bifunctional organocatalysts and methods for preparing chiral hemiesters using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods for preparing chiral hemiesters from prochiral or meso cyclic acid anhydrides via desymmetrization, using bifunctional cinchona alkaloid catalysts comprising sulfonamide functional groups.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Multifunctional catalyst useful in the synthesis of chiral vicinal diols and process for the preparation thereof, and process for the preparation of chiral vicinal diols using said multifunctional catalysts
InactiveUS20030176746A1Possible to realizeSimple processOrganic chemistry methodsPreparation by hydroxy group additionCouplingDiol
The present invention relates to a multifunctional reusable catalyst and to a process for the preparation thereof on a single matrix of the support to perform multicomponent reaction in a single pot. The multifunctional catalysts of the invention are useful for the synthesis of chiral vicinal diols by tandem and / or simultaneous reactions involving Heck coupling, N-oxidation and AD reaction of olefins in presence of cinchona alkaloid compounds both as an native one and immobilized one in the said matrix support. This invention also relates to a process for preparing vicinal diols by asymmetric dihydroxylation of olefins in presence of cinchona alkaloid compounds employing reusable multifunctional catalysts as heterogeneous catalysts in place of soluble osmium catalysts.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Synthetic method of alpha-amino acid with photolytic activity
InactiveCN102766058AMild reaction conditionsEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAmino estersBenzylamine
The invention belongs to an amino acid compound, especially to a synthetic method of alpha-amino acid with photolytic activity by asymmetric biomimetic transamination. The synthetic method comprises the following steps of: using alpha-keto ester and benzylamine as raw materials, using cinchona alkaloid derived chiral base A or chiral base B as a catalyst to catalyze alpha-keto ester with different structures by one kettle way to carry out asymmetric transamination, carrying out post-treatment such as hydrolysis, extraction, column chromatography and the like, synthesizing to prepare alpha-amino ester with photolytic activity, and finally carrying out hydrolysis to obtain (chiral)alpha-amino acid with photolytic activity. Enantiomeric excess value (ee value) can be as high as 92%.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for catalyzing synthesis of indoxacarb key intermediate and application of catalyst
ActiveCN110511217AReduce dosageThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsChemical synthesisDihydroquinidine
The invention relates to the field of chemical synthesis, and particularly discloses a catalyst for catalyzing the synthesis of an indoxacarb key intermediate and application of the catalyst. According to the catalyst, metal in metal compounds such as a manganese compound, a copper compound and a zirconium compound is used as a coordination center, cinchona alkaloid chiral compounds such as dihydroquinidine (DHQD) are used as ligands to form a chiral complex catalyst, the novel catalyst is applied to an asymmetric synthesis reaction of tert-butyl hydroperoxide and 5-chloro-2-methoxycarbonyl-1-indanone ester, the selectivity in the asymmetric synthesis process is greatly improved, and the content of an S-form is increased from 75% to 99% or above; and moreover, the use amount of the catalyst is low, a synthesis process is simple, it is conducive to industrialization, and a good foundation is laid for production of high-quality indoxacarb.
Owner:JINGBO AGROCHEM TECH CO LTD
Asymmetric carbon-carbon-bond-forming reactions catalyzed by bifunctional cinchona alkaloids
InactiveUS7582764B2Carbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationThioureaDiimide
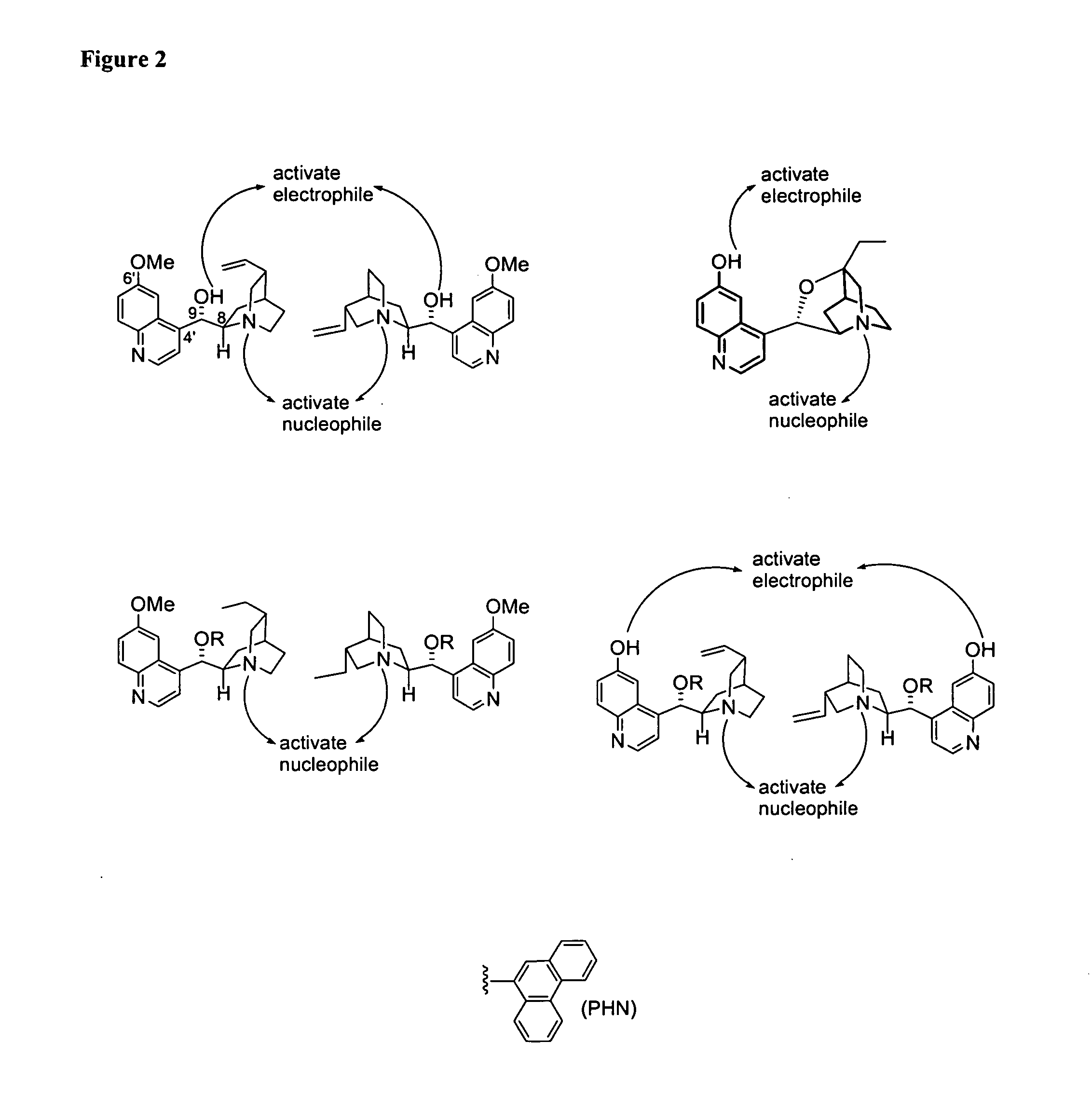
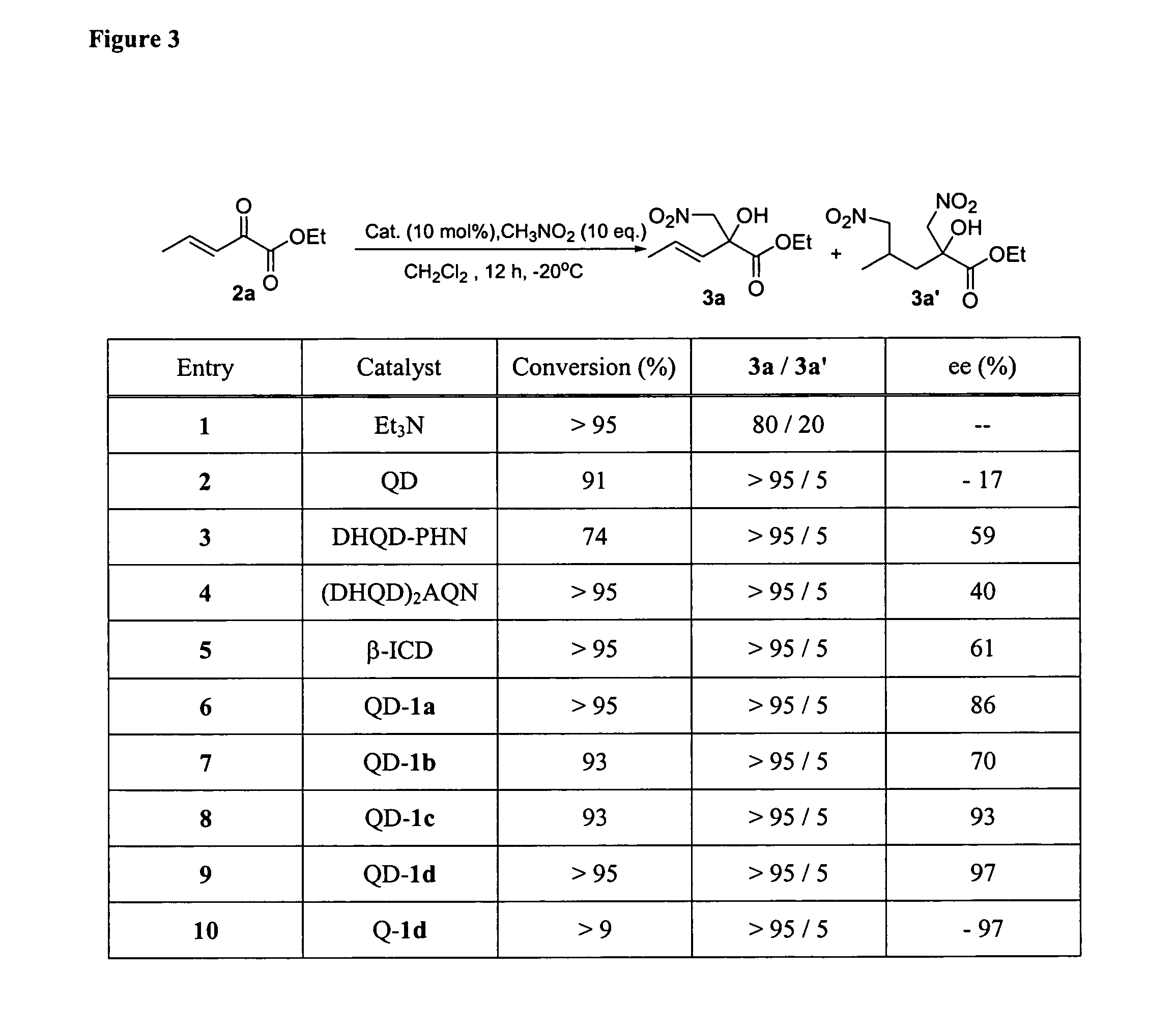
One aspect of the present invention relates to quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain a hydroxy group at the 6′ position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an O-aryl group or an O-aroyl group at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an optionally substituted O-diazene group or an optionally substituted O-benzoyl group at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain a thiourea at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an NH(═S)NH-aryl group at the C9 position. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a chiral, non-racemic compound from a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or prochiral imine, comprising the step of: reacting a prochiral alkene or imine with a nucleophile in the presence of a catalyst; thereby producing a chiral, non-racemic compound; wherein said catalyst is a derivatized quinine or quinidine. In certain embodiments, the nucleophile is a malonate or β-ketoester. In certain embodiments the nucleophile is an alkyl or aryl or aralkyl 2-cyano-2-alkylacetate. In certain embodiments the nucleophile is an alkyl or aryl or aralkyl 2-cyano-2-alkylacetate.Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of kinetic resolution, comprising the step of: reacting a racemic aldehyde or racemic ketone with a nucleophile in the presence of a derivatized quinine or quinidine, thereby producing a non-racemic, chiral compound. In certain embodiments, the kinetic resolution is dynamic.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Application and application method of cinchona alkaloid squaramide derivative as catalyst in asymmetric P-S reaction
ActiveCN107552089AEasy to manufactureHigh yieldOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPictet–Spengler reactionOrganic solvent
The invention particularly relates to an application and an application method of a cinchona alkaloid squaramide derivative as a catalyst in an asymmetric P-S reaction. The application method comprises the steps as follows: a tetrahydro-beta-carboline derivative shown in formula (IV) is prepared through a cyclization reaction in an anhydrous organic solvent A at 0-100 DEG C with a tryptamine derivative and an aldehyde compound as substrates and the cinchona alkaloid squaramide derivative as the catalyst, the yield is 60%-99%, and the ee value is 80%-99%. Compared with the prior art, the asymmetric Pictet-Spengler reaction is promoted by use of the organic alkali catalyst for the first time, the ee value of the tetrahydro-beta-carboline derivative is significantly increased, and the application method has the characteristics of being convenient to operate, lower in cost and the like and has higher application value and potential social and economic benefits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Asymmetric aldol additions using bifunctional cinchona-alkaloid-based catalysts
InactiveUS20070112199A1High enantioselectivityGood to excellent yieldOrganic chemistryKetoneEnantio selectivity
One aspect of the present invention relates to asymmetric catalytic nitroaldol (Henry) reactions with ketones as the electrophilic component. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to asymmetric nitroaldol reactions with α-keto esters catalyzed by a new C6′-OH cinchona alkaloid catalyst. In certain embodiments, this reaction is operationally simple and affords high enantioselectivity as well as good to excellent yield for an exceptionally broad range of α-keto esters.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Preparation method of s-isomer indoxacarb
ActiveCN109701655AThe synthesis process is simpleReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical synthesisSalicylaldehyde
The invention relates to the field of chemical synthesis, and particularly discloses a brand-new catalyst and a preparation method of s-isomer indoxacarb by using the catalyst, the catalyst is prepared from 3-tert-butyl-5-chloromethyl salicylaldehyde and cyclohexanediamine as raw materials, the catalyst is used for replacing original cinchonine and other cinchona alkaloid catalysts, and is appliedto asymmetric synthesis reaction of tert-butyl hydroperoxide and 5-chloro-2-methoxycarbonyl-1-indanone ester, the selectivity of the asymmetric synthesis process is greatly improved, and the contentof the s-isomer indoxacarb is increased from 75% to more than 98%, the recycling of the high-efficiency chiral catalyst is realized, the production cost is greatly reduced, the synthesis process of the catalyst is simple, the industrialization is facilitated, and a good foundation is laid for producing high-quality indoxacarb.
Owner:JINGBO AGROCHEM TECH CO LTD
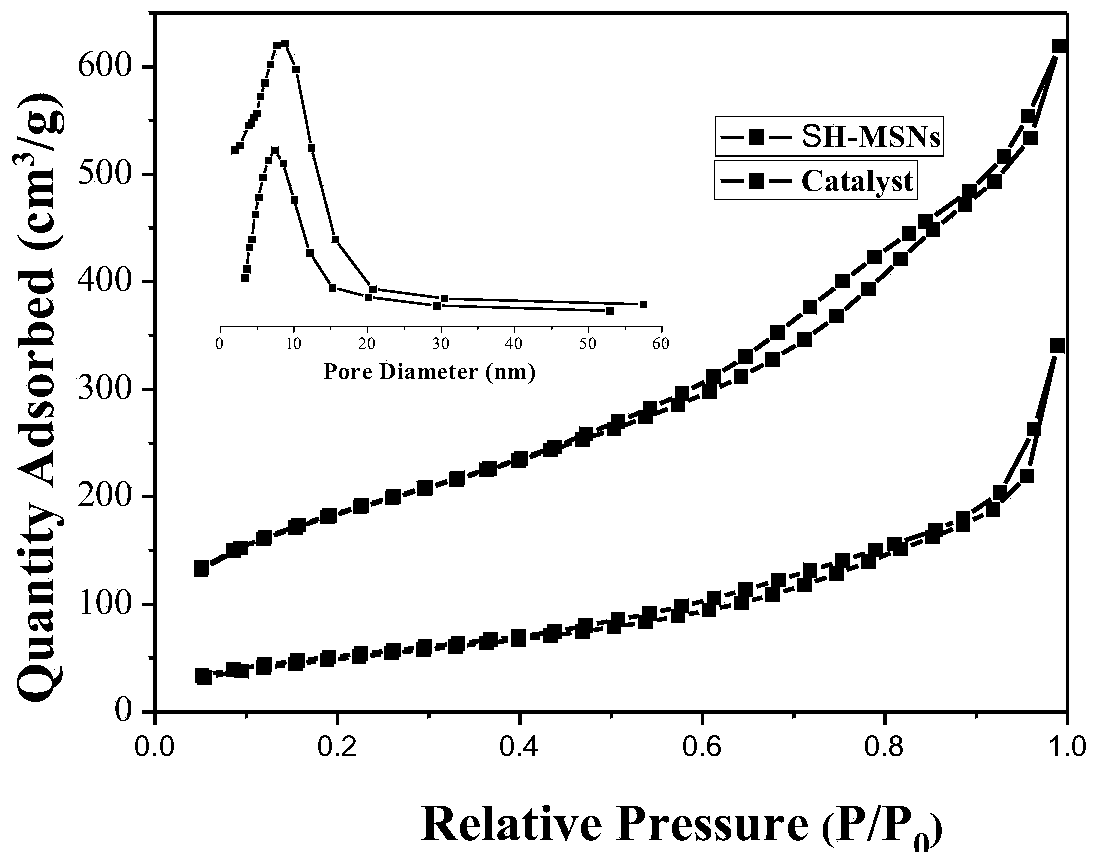
Chiral cinchona alkaloid-squaramide catalyst (CSF-MSNs) loaded on inorganic meso-porous silicon and preparation thereof
InactiveCN104353490AEasy to makeCheap manufacturingOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSynthesis methodsClick chemistry
The invention discloses a chiral cinchona alkaloid-squaramide catalyst (CSF-MSNs) loaded on an inorganic meso-porous silicon material and a synthesis method thereof. A chiral squaramide homogeneous catalyst of cinchona alkaloid and a sulfydryl functional carrier SH-MSNs are respectively synthesized, and then, a heterogeneous catalyst (CSF-MSNs) is made by a click chemistry method through the click bonding of sulfydryls on the material and double bonds in squaramide. The catalyst has the advantages that (1), the heterogeneous catalyst can be recycled and reused by a centrifuge method after finishing reaction and still has strong activity after being recycled for ten times; (2), the preparation of the sulfydryl functional material (SH-MSNs) is simpler and low in cost, and the sulfydryl functional material (SH-MSNs) can be further used for the immobilization of various chiral cinchona derivative catalysts; (3) the chiral cinchona alkaloid-squaramide catalyst has high thermodynamic stability, shows rich sulfydryls and can be further modified.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of cross-linking type polymerization catalyst
InactiveCN105348428AIncrease profitEasy to separateOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCross-linkBenzene
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a cross-linking type polymerization catalyst. The preparation method is characterized by including performing a synthesis reaction to form an intermediate compound of which molecule contains vinyl benzene by using cinchona alkaloid and derivative of vinyl benzene, and performing a polymerization reaction of the intermediate compound and the cross-linking agent divinyl benzene to form a polymer catalyst in the presence of an initiator. The catalyst is used for an asymmetric alpha-chlorination catalytic reaction of beta-ketonic ester and chlorinated reagent, has high catalytic activity, is easy to separate, and can be recycled. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method has simple preparation, easy operation, easy post-treatment, high raw material utilization ratio, optimized reaction condition and reduced reaction requirement, especially is used for the compound obtained by constructing a chiral center on the different carbon of beta-ketonic ester, and has an important practical significance of researching medicinal chemistry and medical intermediate compound.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Asymmetric Friedel-Crafts Alkylations Catalyzed By Bifunctional Cinchona Alkaloids
In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to methods for asymmetric Friedel-Crafts alkylation catalyzed by bifunctional cinchona alkaloids. In certain embodiments, the catalyst is a 6′-OH cinchona alkaloid. In certain embodiments, the electrophile is an α-ketoester or aldehyde. In certain embodiments, the nucleophile is an aromatic heterocycle. In certain embodiments, the nucleophile is an aromatic N-containing heterocycle. In certain embodiments, the nucleophile is an indole. In certain embodiments, the methods of the invention are relatively insensitive to concentration, temperature, air and moisture.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Synthetic method of tea geometrid tea geometrid
InactiveCN106967014AHigh stereoselectivitySimple and fast operationOrganic chemistry methodsBoron trifluorideDrugs synthesis
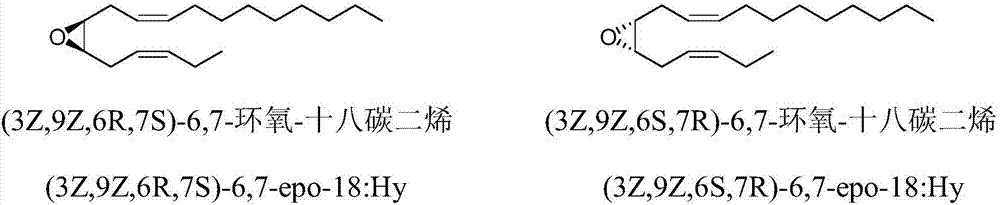
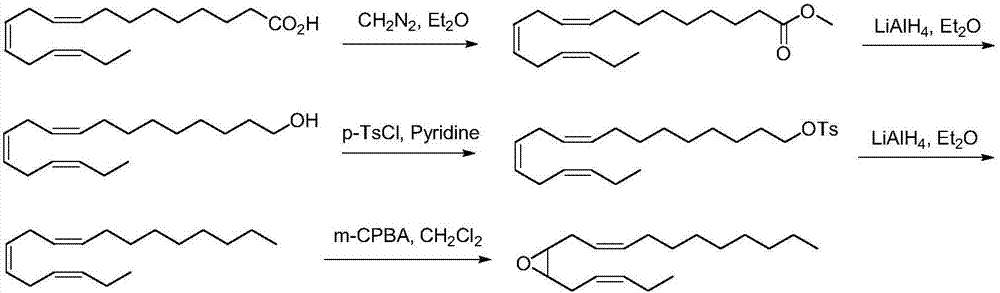
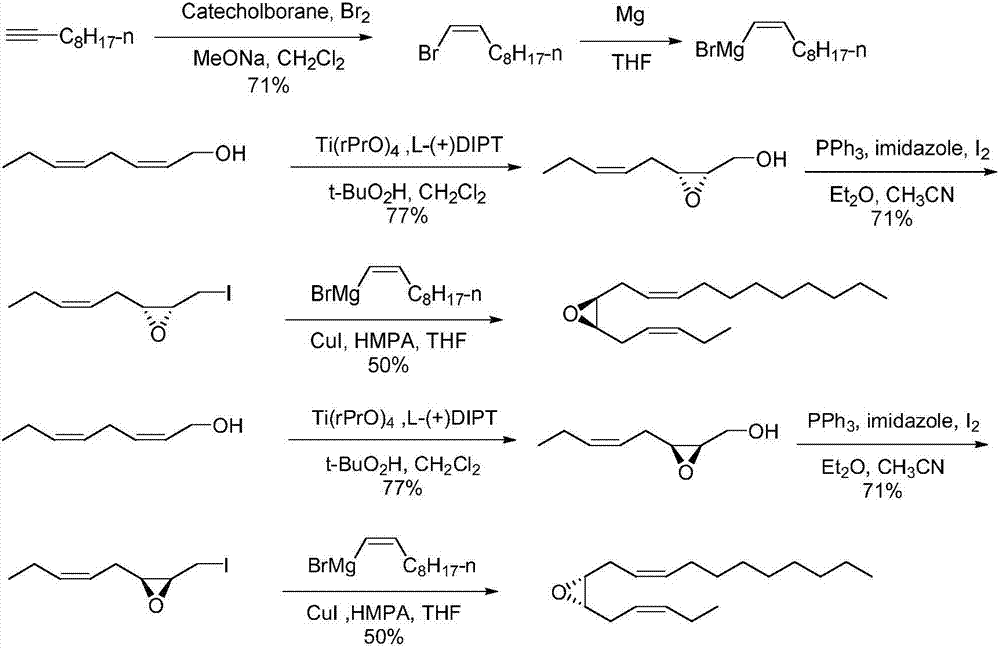
The invention discloses a synthetic method of tea geometrid tea geometrid, and belongs to the drug synthesis field. Particularly, (2E)-2- alkenyl-5-alkynyl-1-octanol is prepared to be chirality 5- alkynyl-1, 2, 3-trioctanol under the function of cinchona alkaloid catalyst. Under the alkali condition, the trioctanol and para-toluene formyl chloride are reacted to generate 1, 2-epoxy-3- tosylate-5- octyne; under the alkali condition, the 1, 2-epoxy-3- tosylate-5- octyne and 1-decyne, boron trifluoride are reacted to generate 3, 9-diyne-6-tosylate-7-octadecanol. Then the 3, 9-diyne-6-tosylate-7-octadecanol is reacted with potassium carbonate to generate 6, 7-epoxy-3, 9-diyne octodecane; at last, tea geometrid tea geometrid is acquired through catalytic hydrogenation. The synthetic method of tea geometrid tea geometrid is simple in operation, gentle in condition, and suitable for massive production.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
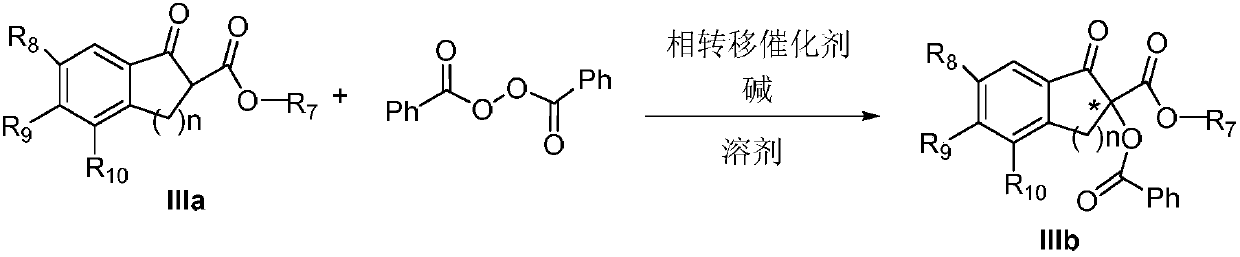
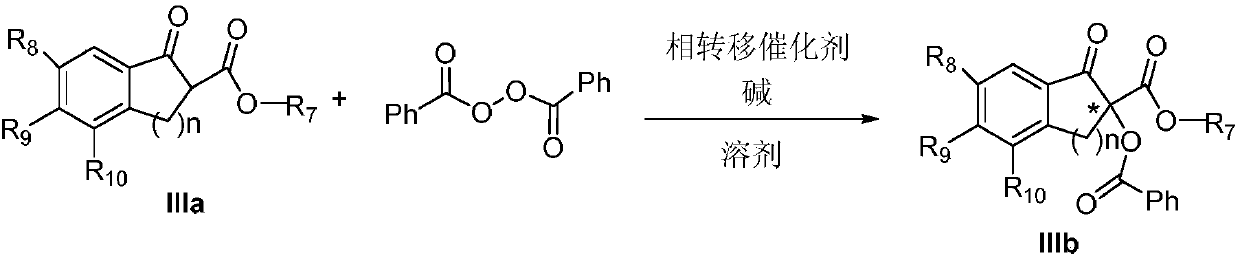
Method for achieving asymmetrical alpha-benzoylation through phase-transfer catalysis of beta-keto ester
ActiveCN107721858AEasy to separateNovel and effective wayOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsBenzoyl peroxideDibenzoyl Peroxide
The invention discloses a method for achieving asymmetrical alpha-benzoylation through phase-transfer catalysis of beta-keto ester and belongs to the technical field of synthesis of alpha-oxo-beta-keto ester compounds having optical activity. According to the technical scheme, the method is characterized in that a beta-keto ester compound, a phase transfer catalyst, benzoyl peroxide and an alkaline solution perform stirring reaction in a solvent at the temperature of -78 to 60 DEG C to prepare a chiral alpha-benzoyl-beta-keto ester compound, and a reaction equation in the preparation process is shown in the description. The effectiveness of the method is achieved by using cheap cinchona alkaloid quaternary ammonium salt easy to obtain, asymmetrical alpha-benzoylation of the beta-keto estercompound and the benzoyl peroxide is successfully achieved by adopting the method for the first time, and a novel and effective way is provided for synthesis of the alpha-oxo-beta-keto ester compounds having optical activity.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com