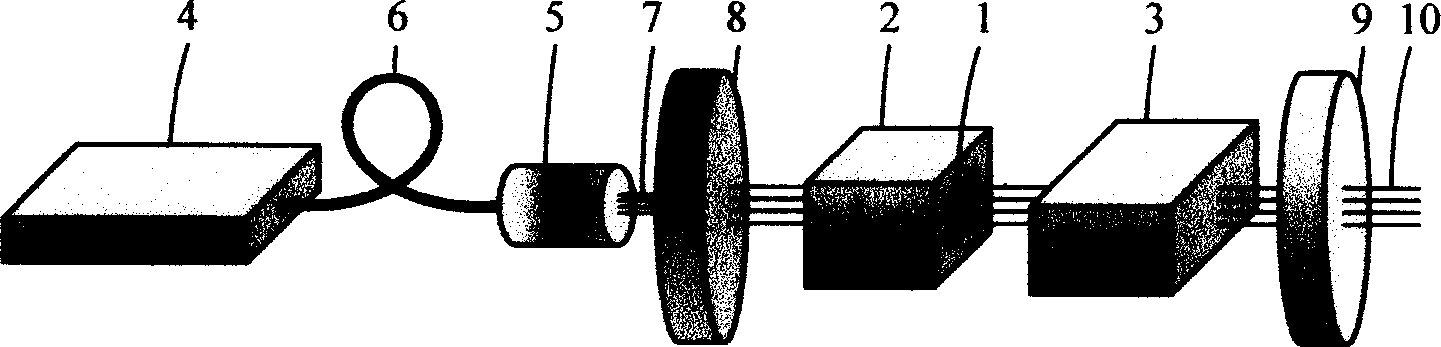
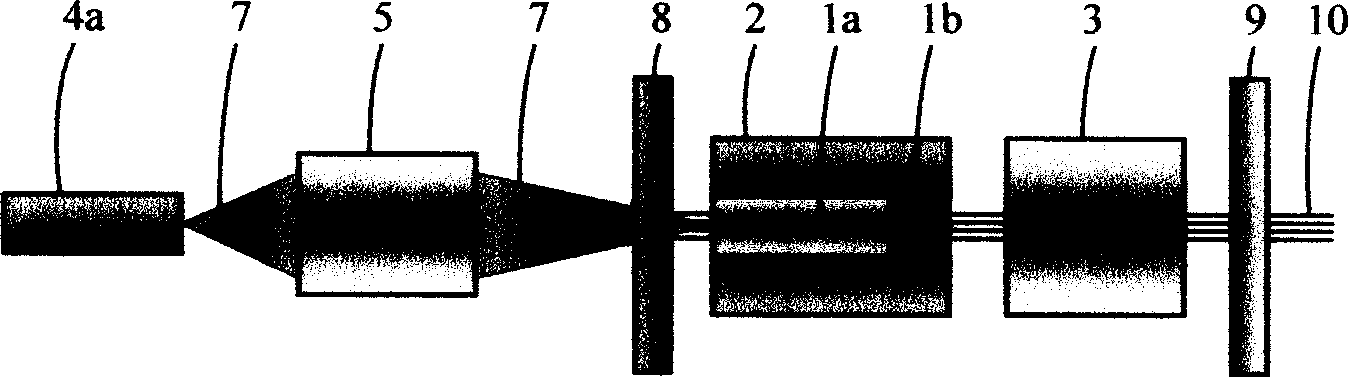
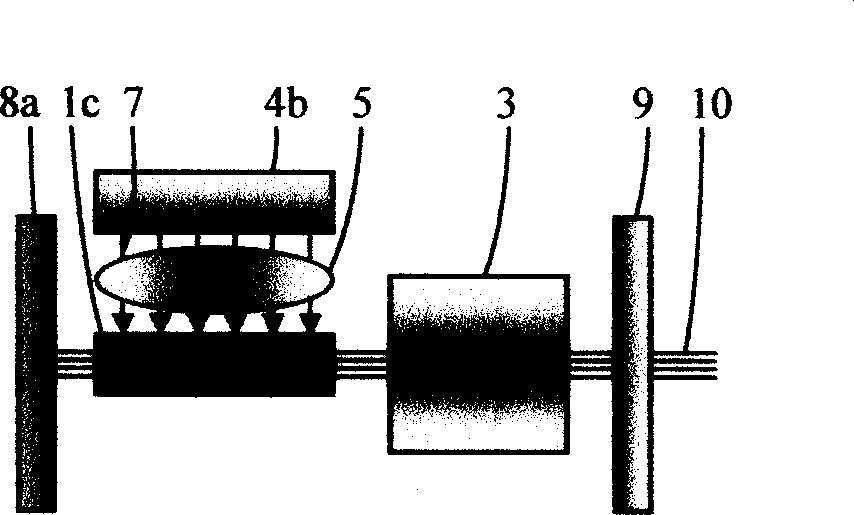
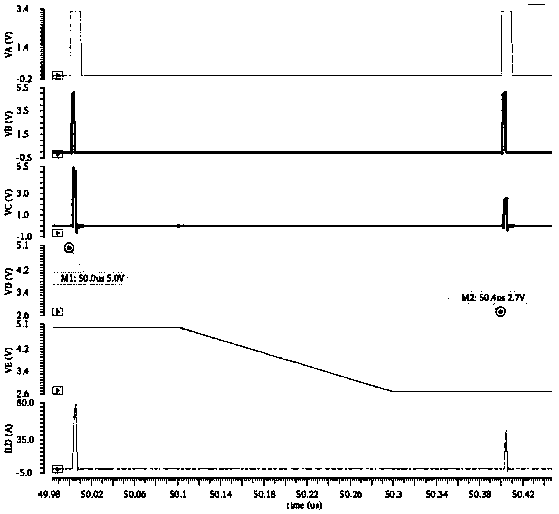
Patents
Literature
124results about How to "Narrow pulse width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
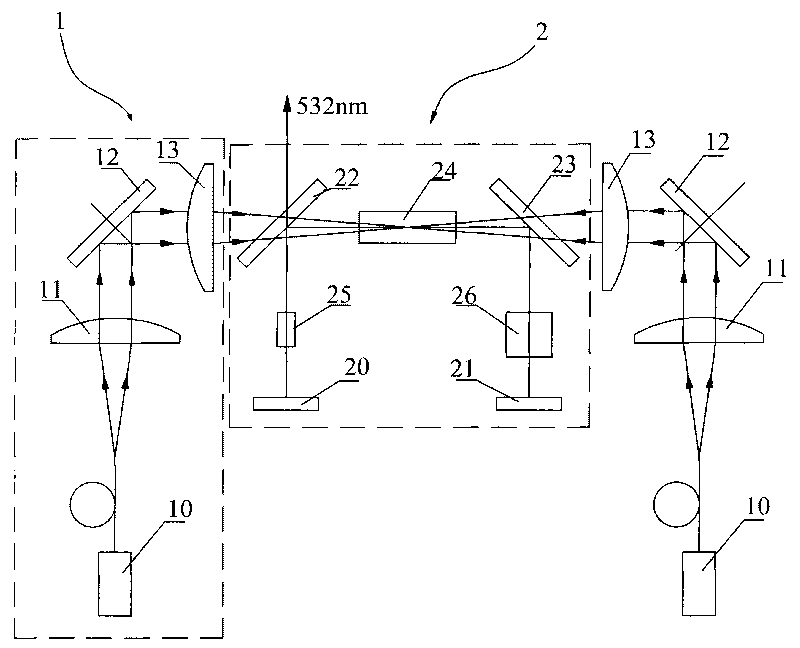
Active and passive Q-adjusted single longitudinal mode laser
InactiveCN1645691AShort pulse widthHigh degree of polarizationOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialResonant cavityLongitudinal mode
The invention consists of pumping source, cavity, and a group of coupling device set between the pumping source and cavity, and connected with pumping source through optical fiber. The cavity consists of front cavity mirror and back cavity mirror coated with film. The double-doped crystals and active Q-switch are set between the front and back mirrors. A cooling device is set on the double-doped crystals. The invention features using active Q-switch to control the passive Q-switch for getting prelase pulse, and using saturable absorption crystals as longitudinal mode selector for making the solid single longitudinal mode laser work under higher pumping power.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
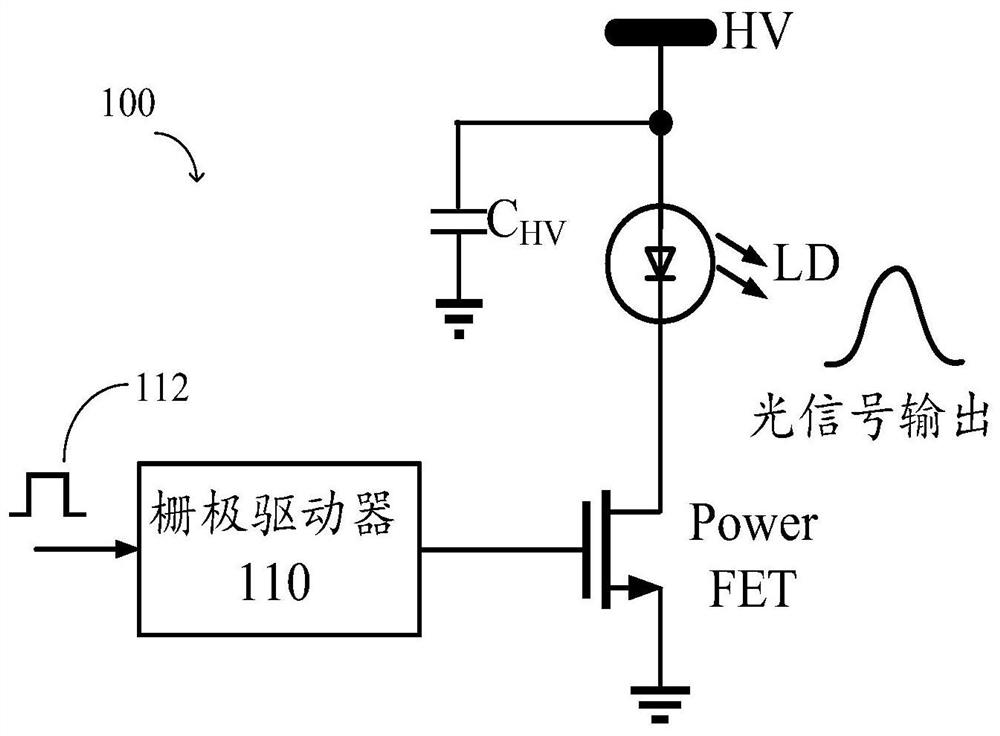
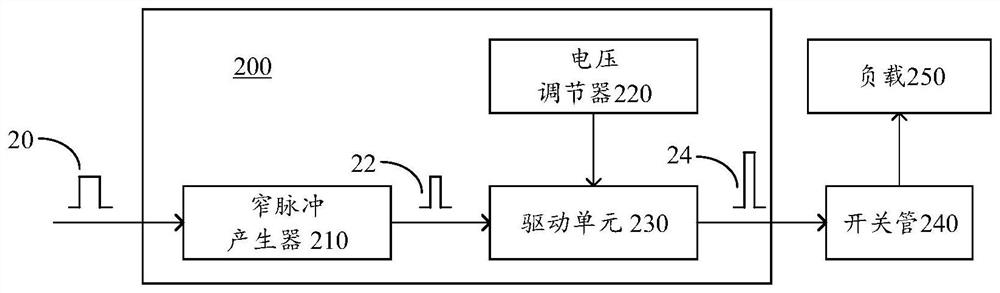
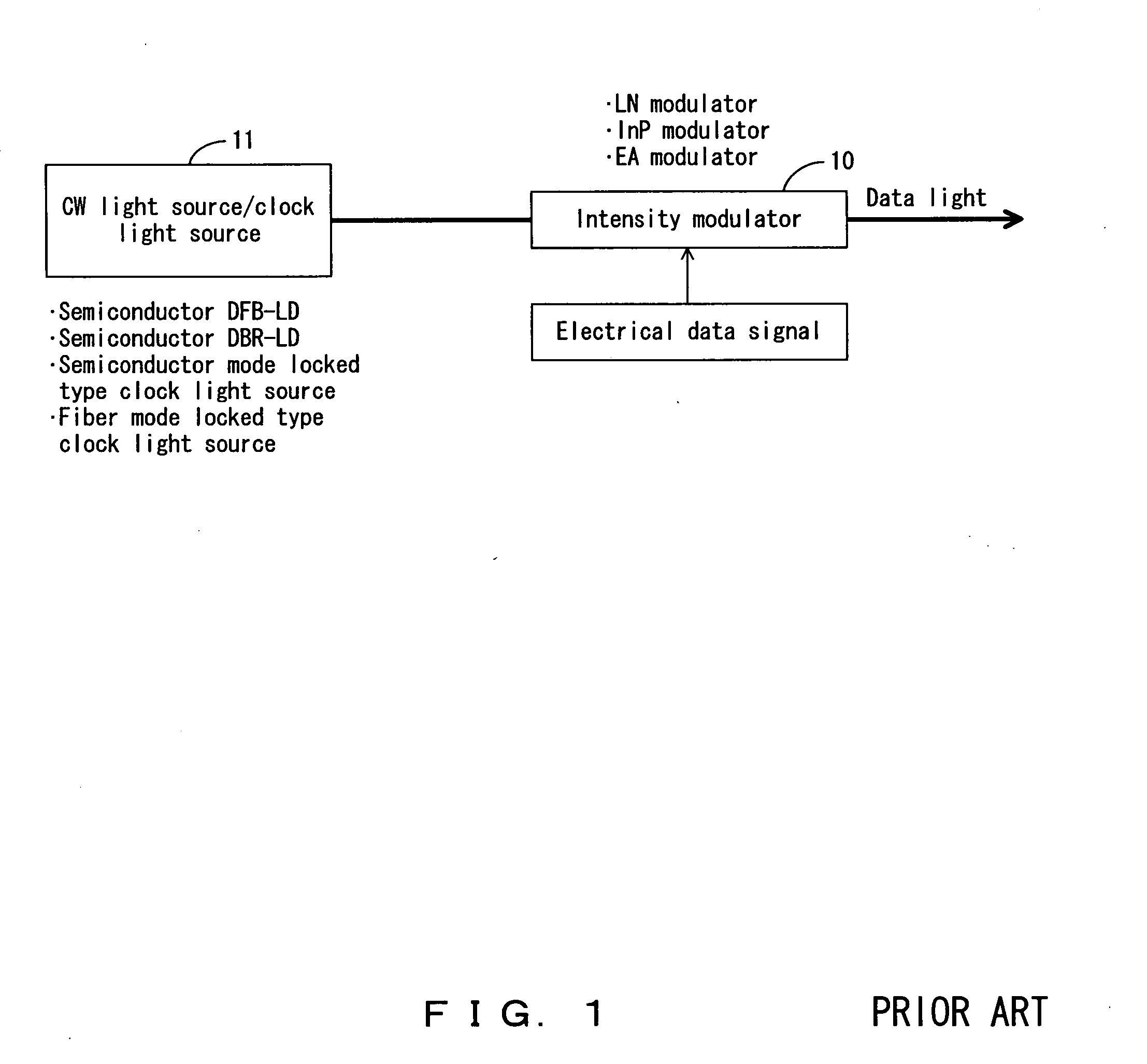
Driving circuit, driving method and laser system
ActiveCN110492349AEasy to adjustNarrow pulse widthLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersVoltage regulationEngineering
The invention relates to a driving circuit, a driving method and a laser system. The driving circuit comprises a narrow pulse generator configured to generate a first narrow pulse based on an input pulse, the pulse width of the first narrow pulse being smaller than the pulse width of the input pulse; a voltage regulator configured to generate an adjustable output voltage; and a drive unit, which is coupled with the narrow pulse generator and the voltage regulator and is configured to form the second narrow pulse based on the first narrow pulse and the output voltage; wherein the second narrowpulse is suitable for driving the switching tube, the pulse width is approximately equal to the pulse width of the first narrow pulse, and the amplitude of the second narrow pulse depends on the magnitude of the output voltage of the voltage regulator. Thus, an output pulse whose pulse width and amplitude are independently adjustable can be formed. When the output pulse is used for driving the laser, the light emitting energy of the laser can be quickly adjusted in a large dynamic range.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
High-speed narrow pulse modulation driving power supply for semiconductor laser
ActiveCN101895058AHigh frequencyCutting edge fastLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlCapacitanceMOSFET
The invention discloses a high-speed narrow pulse modulation driving power supply for a semiconductor laser. The high-speed narrow pulse modulation driving power supply comprises a semiconductor laser driving circuit and a high-precision temperature control circuit, wherein the semiconductor laser driving circuit adopts a high-speed MOSFET as a switch. The driven semiconductor laser can output the required laser pulse with high frequency, quick advancing front, narrow pulse width, controllable pulse peak and smooth waveform according to the parameters of the semiconductor laser by changing the power supply voltage, resistance and capacitance in the driving power supply circuit.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
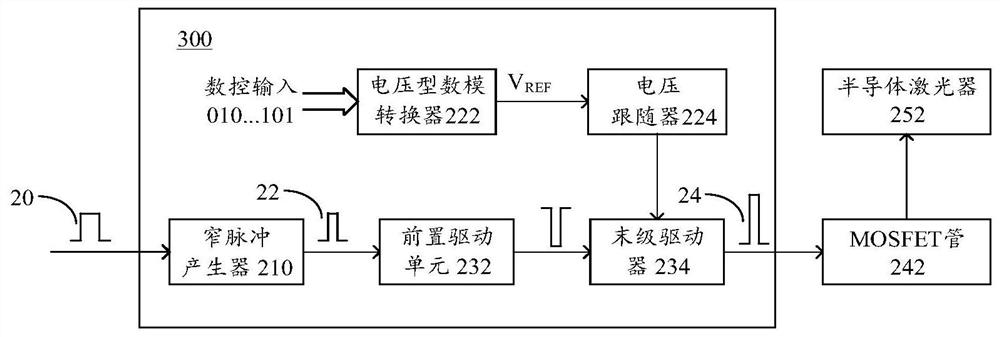
Driving circuit, driving method and laser system
ActiveCN110492349BEasy to adjustNarrow pulse widthLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersHemt circuitsVoltage regulation
The present disclosure relates to driving circuits, driving methods and laser systems. The drive circuit includes: a narrow pulse generator configured to generate a first narrow pulse based on an input pulse, the pulse width of the first narrow pulse being smaller than the pulse width of the input pulse; a voltage regulator configured to generate a regulated output voltage; and a drive unit coupled to the pulse generator and the voltage regulator and configured to form a second pulse based on the first pulse and the output voltage, wherein The second narrow pulse is suitable for driving the switch tube, the pulse width is approximately equal to the pulse width of the first narrow pulse, and the amplitude of the second narrow pulse depends on the output voltage of the voltage regulator. Thus, output pulses with independently adjustable pulse width and amplitude can be formed. When such an output pulse is used to drive the laser, the luminous energy of the laser can be quickly adjusted within a large dynamic range.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
Device and method for improving surface quality of selective laser melting (SLM) forming piece through integrated double-type laser light
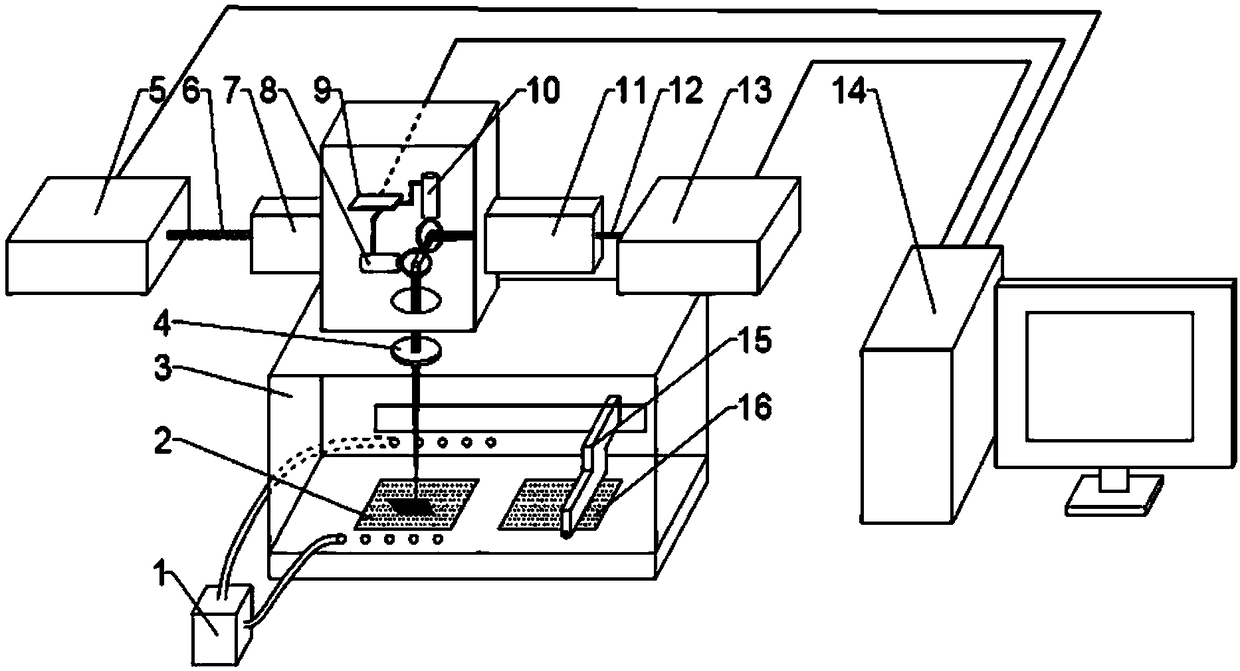
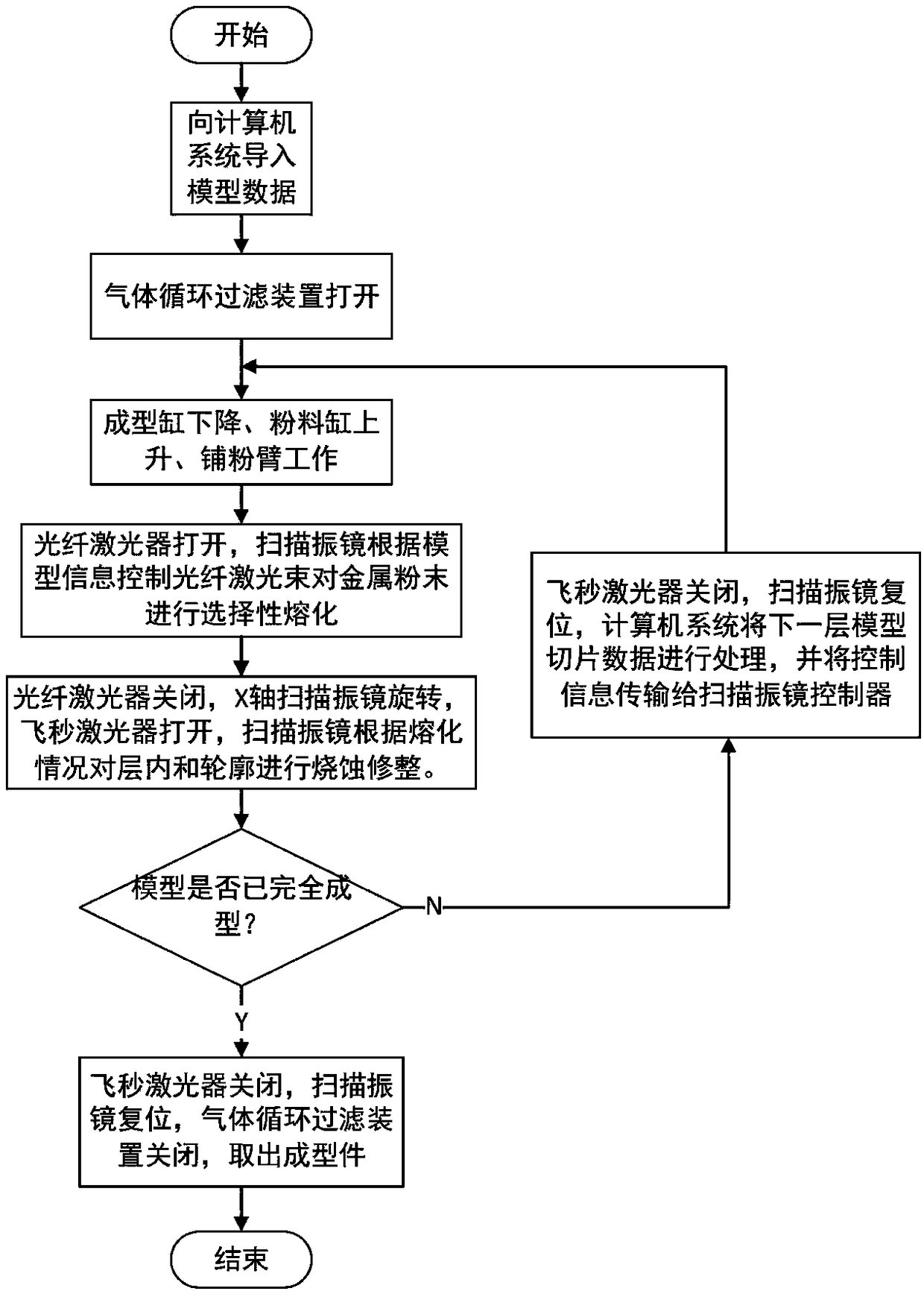
PendingCN108311697AImprove yieldImprove performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingSelective laser sintering
The invention discloses a device and a method for improving the surface quality of a selective laser melting (SLM) forming piece through an integrated double-type laser light. The device comprises anoptical fiber laser, an optical fiber laser beam expanding collimator, a femtosecond laser, a femtosecond laser beam expanding collimator, a scanning galvanometer, a lens and the like. During an SLM layered manufacturing process, a femtosecond laser technology is used for ablating and reconditioning spheroidization, bulges, powder adhesion and other defects probably occurred in each forming layerand a profile, so that the surface quality of each SLM forming layer is improved without producing an extra heat influence, the roughness of an upper surface and side surfaces of an SLM forming pieceare improved during an accumulation process, performance indexes such as the compactness and the size precision of the parts are improved, and the rejection rate of SLM processing is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Optical device
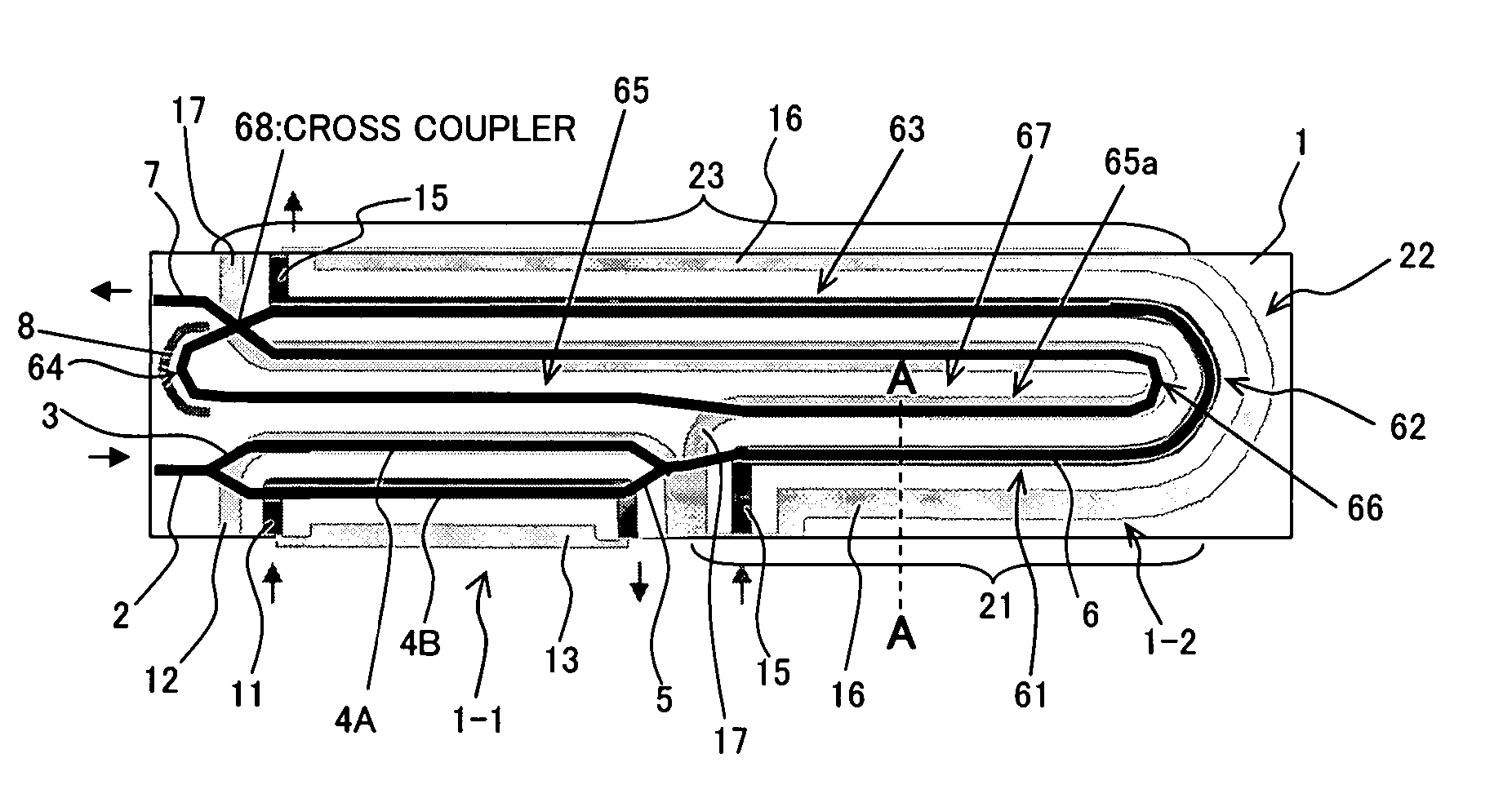
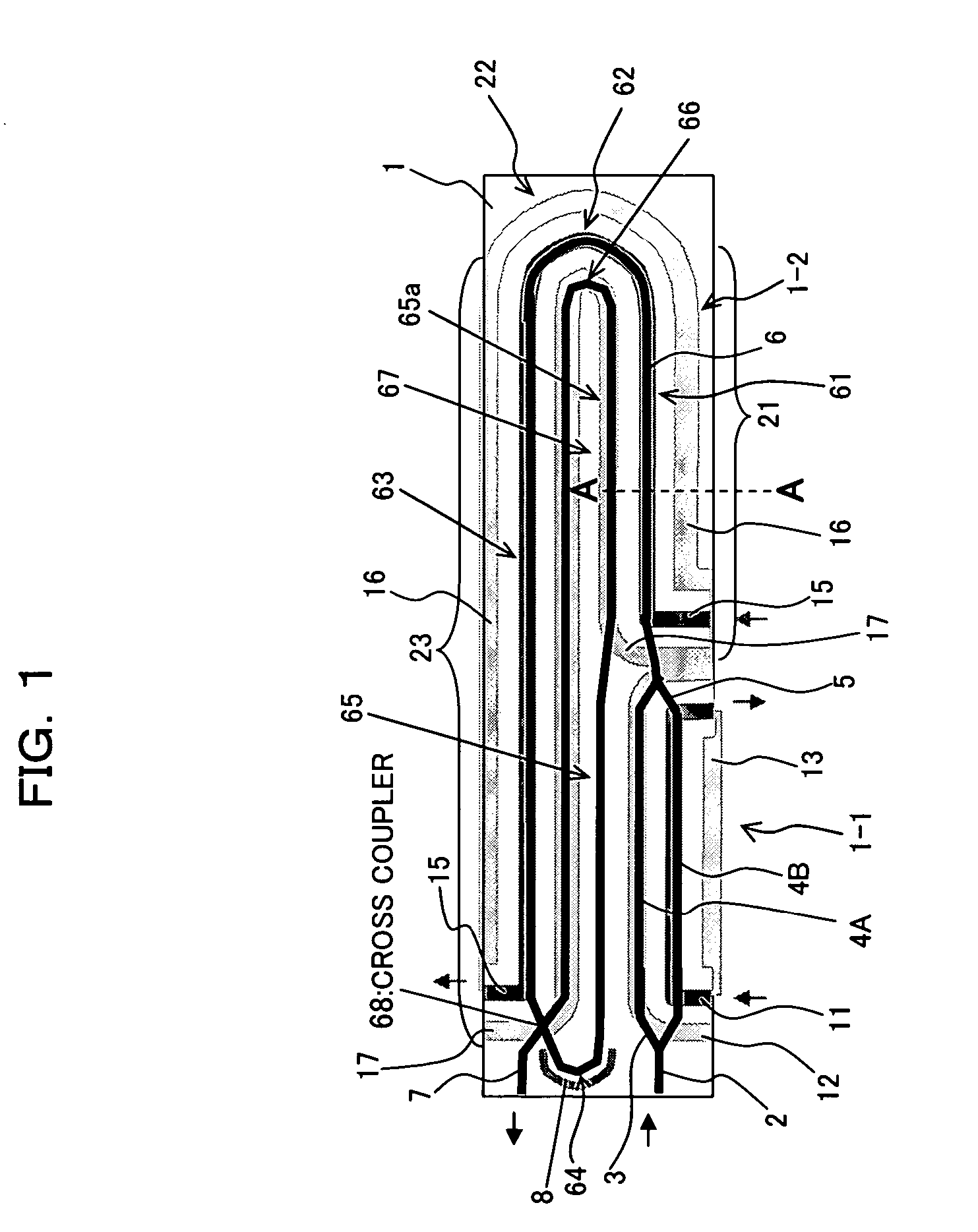
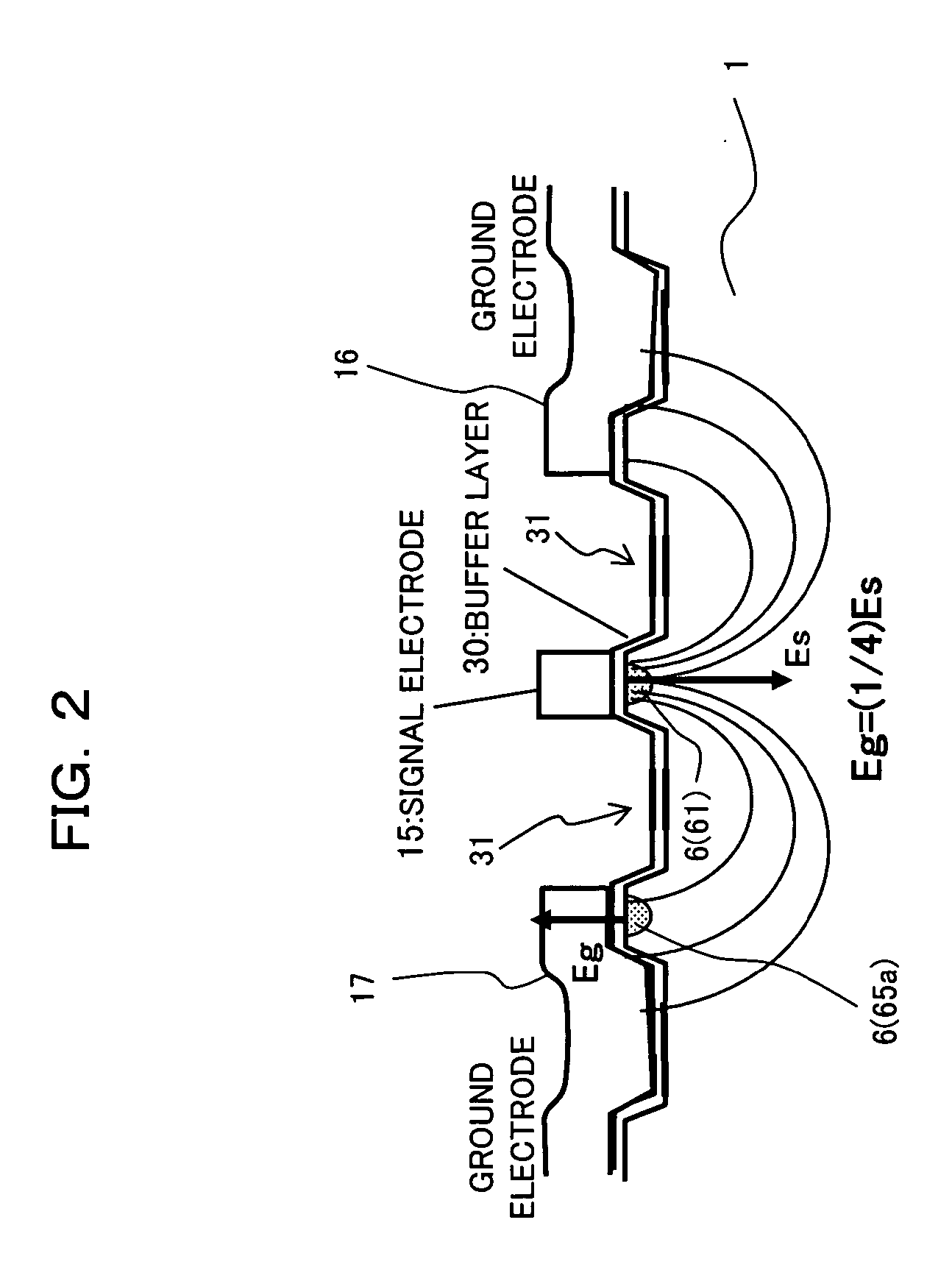
InactiveUS20060210212A1High outputNarrow pulse widthCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsWaveguideModulation index
An optical device having a substrate having an electro-optical effect, an optical waveguide formed in the substrate, and an electric field emission electrode, and an electric field convergence electrode to which an electric field emitted from the electric field emission electrode converges. The optical waveguide is formed such that light propagating through the optical waveguide passes through an area under the electric field emission electrode or an area under the electric field convergence electrode and then passes through a remaining electrode. As a result, even when an interaction length is increased, the optical device acquires (increases) a modulation index appropriate to the increase in interaction length, thereby diminishing a drive voltage.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Ultrashort stable mode locked fiber laser at one micron by using polarization maintaining (PM) fiber and photonic bandgap fiber (PBF)
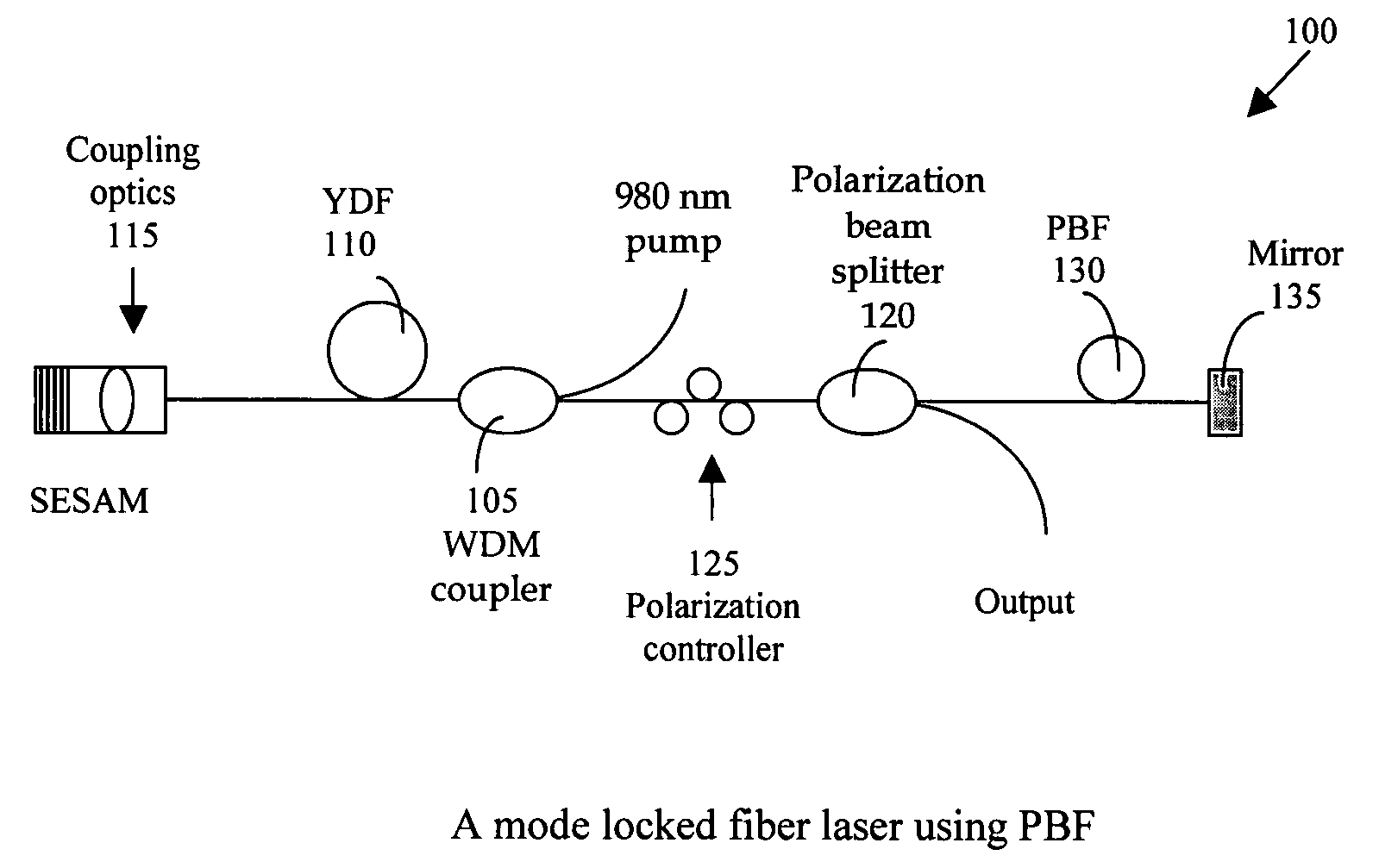
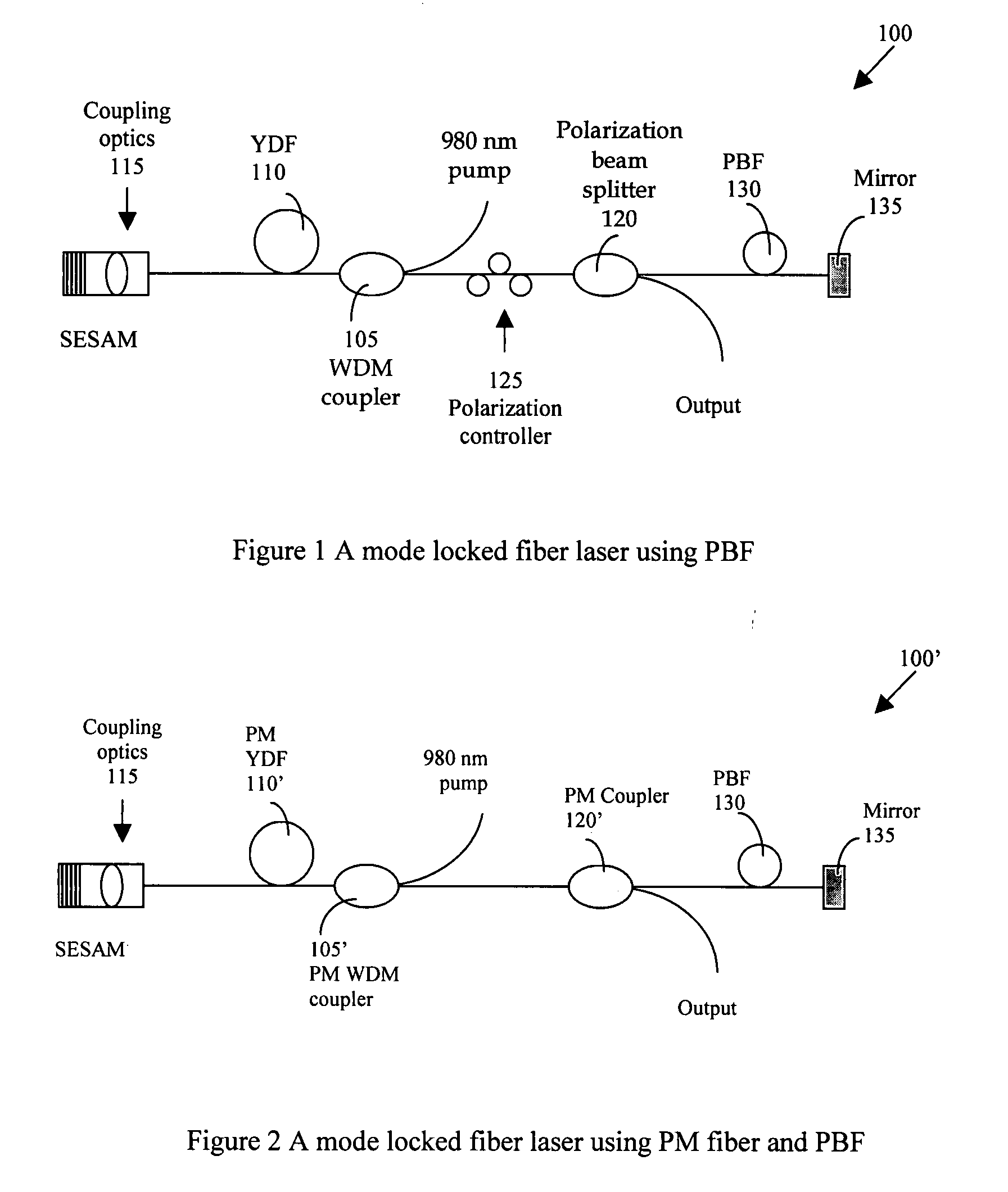
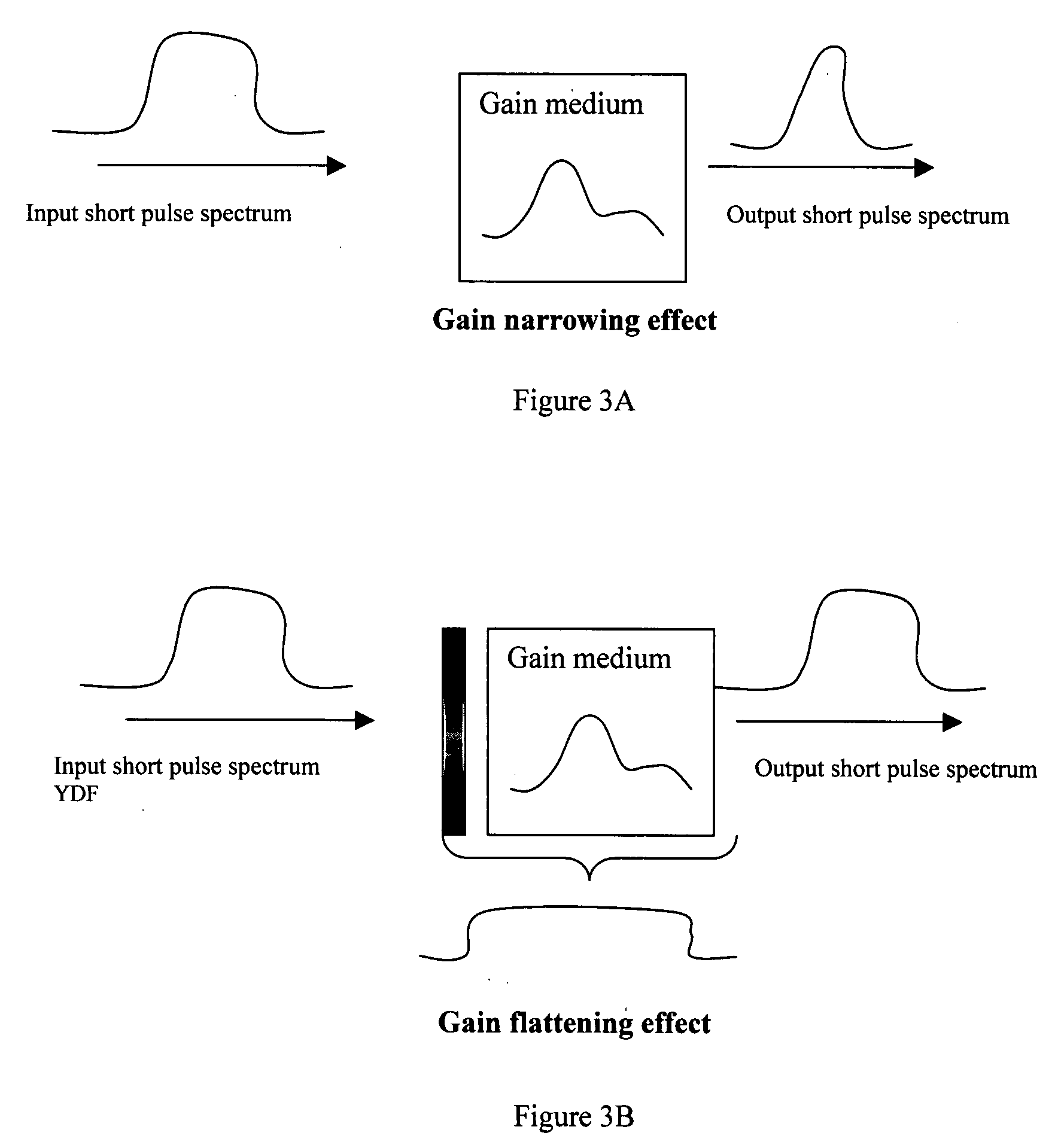
InactiveUS20080151945A1Improves pulse shapeNarrow bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsMode locked fiber laserPhotonic bandgap
A fiber laser cavity that includes a laser gain medium for receiving an optical input projection from a laser pump. The mode-locked fiber laser further includes an all fiber based laser cavity including a dispersion management fiber segment for generating a negative (anomalous) to match a positive normal dispersion. The dispersion management fiber segment further coordinates with a polarization-controlling device for generating a polarization maintenance (PM) output laser pulse with a narrow pulse width.
Owner:POLARONYX
All-fiber Q-switched laser
ActiveUS7130319B1Narrow pulse widthFast repetition rateLaser using scattering effectsQ factorBroadband
An all-fiber Q-switched laser includes a gain fiber spliced between narrowband and broadband fiber gratings that define a polarization-dependent resonant cavity. The narrowband grating is, for example, formed in a PM fiber to create a polarization-dependent reflection band. A modulator applies stress to the fiber chain to induce birefringence and switch the cavity Q-factor to alternately store energy in the gain fiber and then release the energy in a laser pulse.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
High repetition frequency harmonic wave mode locking fiber laser based on external continuous light injection
ActiveCN106129791AHigh repetition rateNarrow pulse widthActive medium shape and constructionContinuous lightMode locked fiber laser
The invention relates to a high repetition frequency harmonic wave mode locking fiber laser based on external continuous light injection, comprising a laser pumping source, a wavelength division multiplexing device, an optical isolator, a continuous light source, an optical coupler, a saturable absorber and a gain fiber, wherein the laser pumping source is connected to the pumping input terminal of the wavelength division multiplexing device, and the wavelength division multiplexing device is in connection with the optical isolator, and is then connected to the optical coupler together with the continuous light source; the optical coupler comprises a laser signal output terminal and a signal connection output terminal, wherein the signal connection output terminal is successively in connection with the saturable absorber and the gain fiber; the gain fiber is then in connection with the wavelength division multiplexing device; glowing ions are doped in the fiber core of the gain fiber. The high repetition frequency harmonic wave mode locking fiber laser has the characteristics of simple structure and low cost; through the combination between the continuous light source and a passive mode locking fiber laser, high repetition frequency harmonic wave mode locking is realized; in addition, outputted optical pulses possess the advantages of high repetition rate and narrow pulse width.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Seismic geophysical surveying
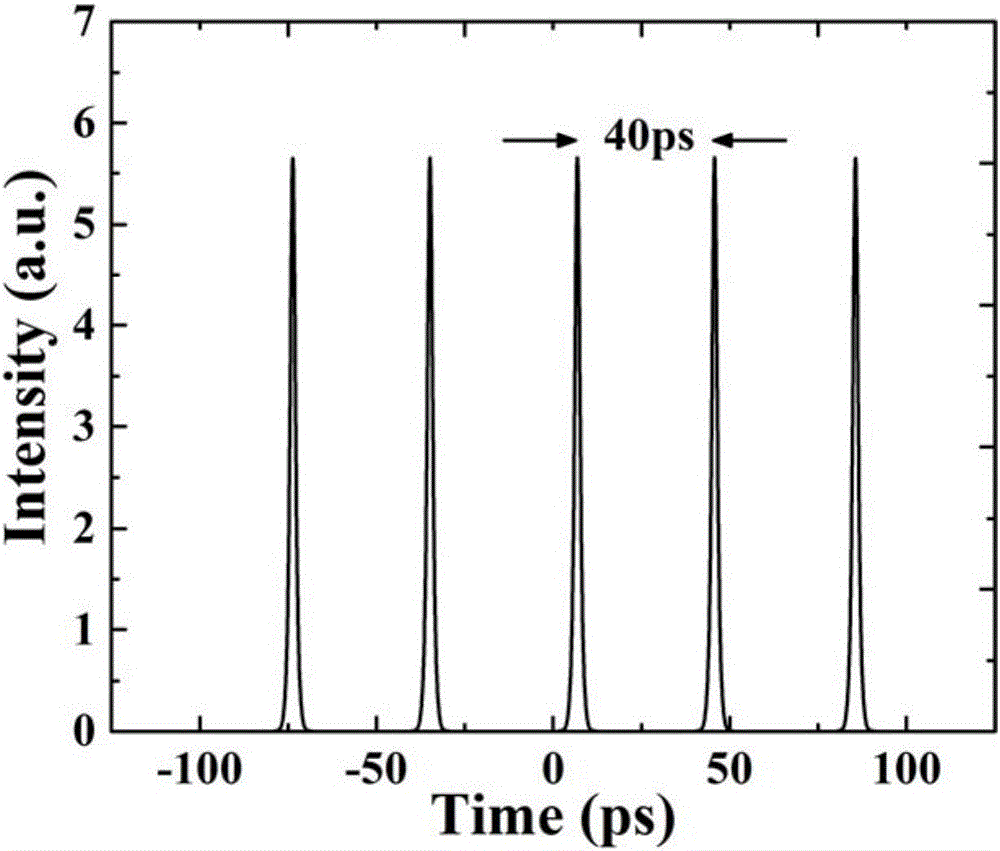
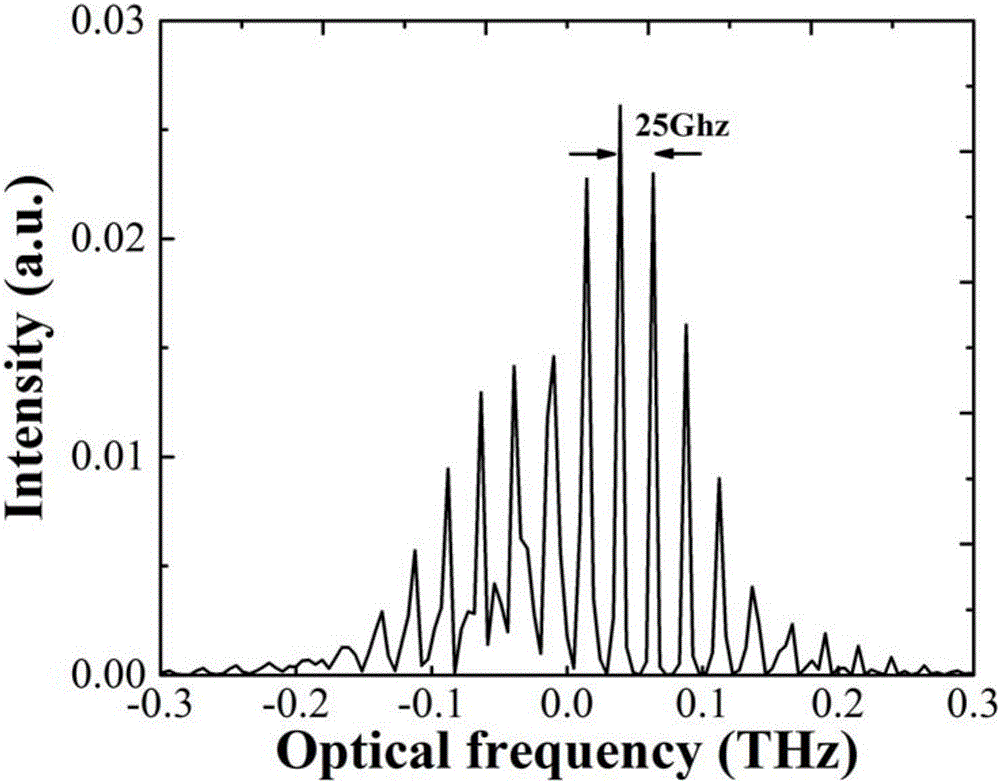
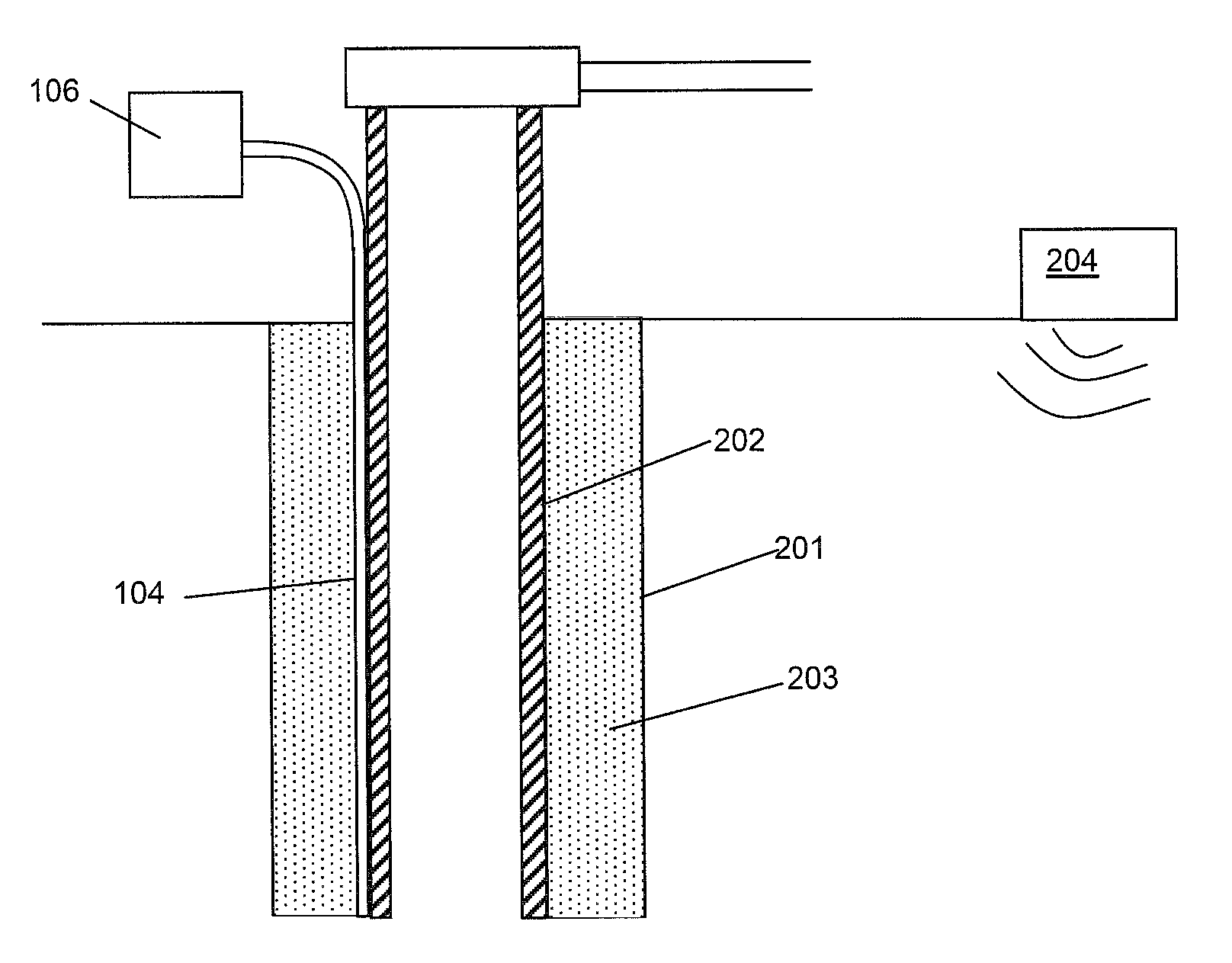
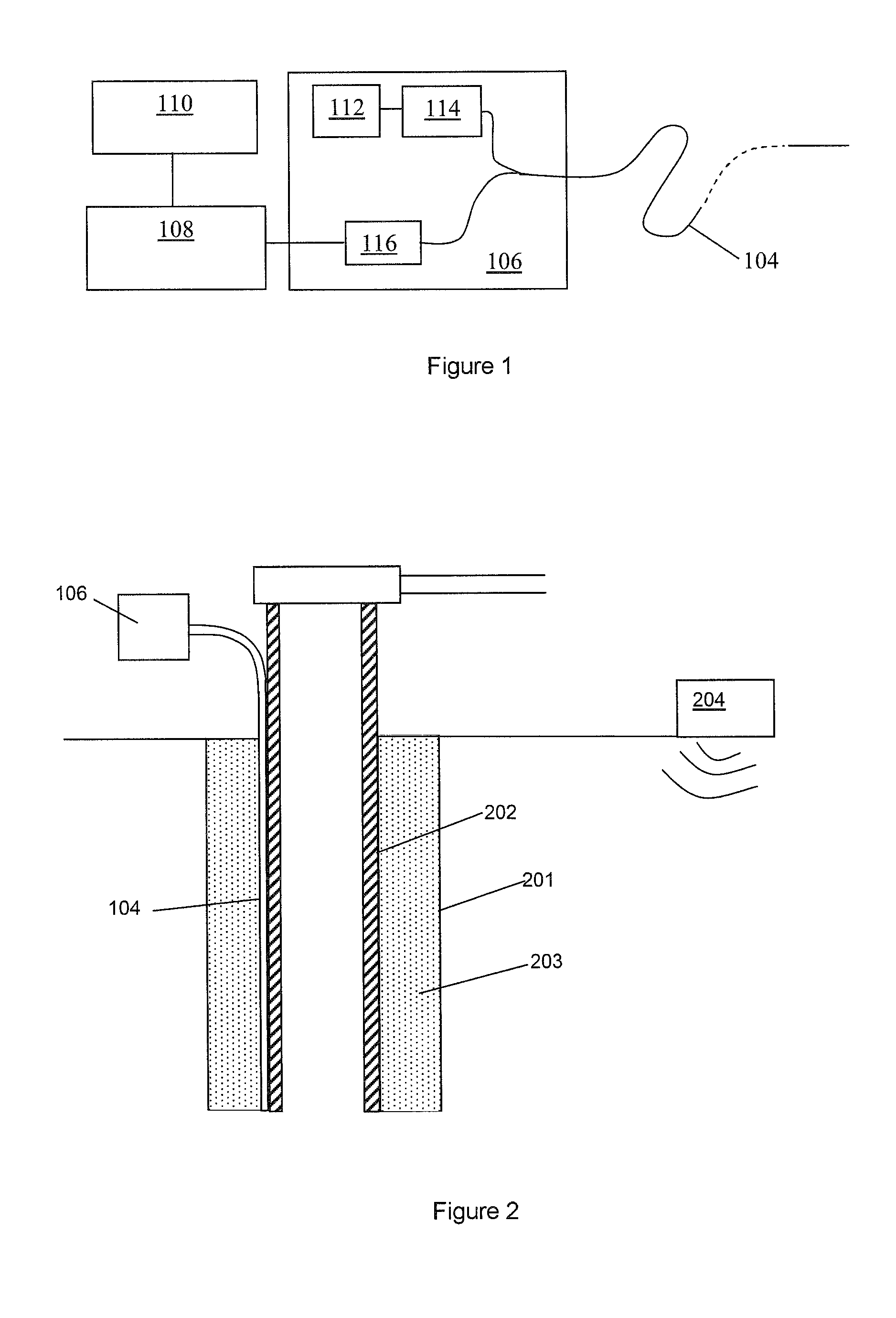
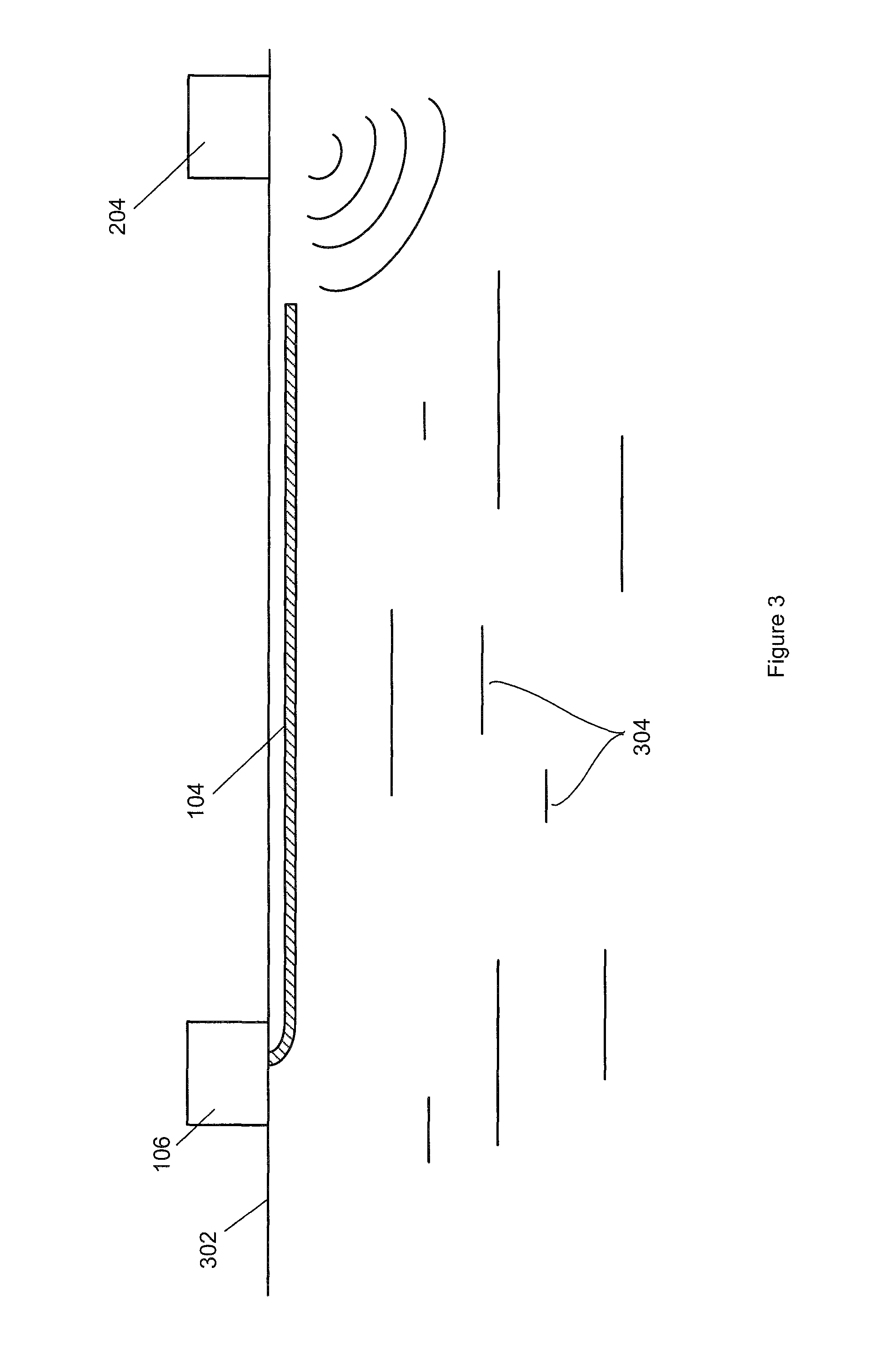
ActiveUS9465126B2Narrow pulse widthImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic energy generationSeismic signal transmissionSensor arrayFiber
The present invention relates to an apparatus for use in geophysical surveying. Geophysical surveying typically involves stimulating an area of interest with a seismic source (204) and detecting the response in a sensor array. The application describes a fiber optic distributed sensing apparatus having a source (112) of electromagnetic radiation for repeatedly launching interrogating electromagnetic radiation into an optic fiber (104) deployed in said of area interest, a sampling detector (116) for sampling radiation back-scattered from the fiber; and a processor (108) arranged to process the back-scattered radiation to provide, for each of a plurality of longitudinal sensing portions of optic fiber, an indication of any incident acoustic signals affecting that sensing portion. The sampling detector is arranged to acquire a plurality of diversity samples for each said longitudinal sensing portion. The processor is configured process the diversity samples in diversity channels to determine a measurement signal indicative of any acoustic disturbance; correlate the measurement signal from each channel with a signal indicative of the seismic stimulus applied; and combine the correlated measurement signals to provide an overall measurement signal for the longitudinal sensing portion. The processor may apply a quality metric to the correlated data before performing the combination based on the quality metric. By correlating the individual diversity channels with the stimulus signal prior to performing the analysis of the measurement signal for a particular longitudinal section of optic fiber, the signal to noise ratio can be improved.
Owner:OPTASENSE HLDG LTD
Circuit structure of narrow-pulse-width high-repetition-frequency pulse current source
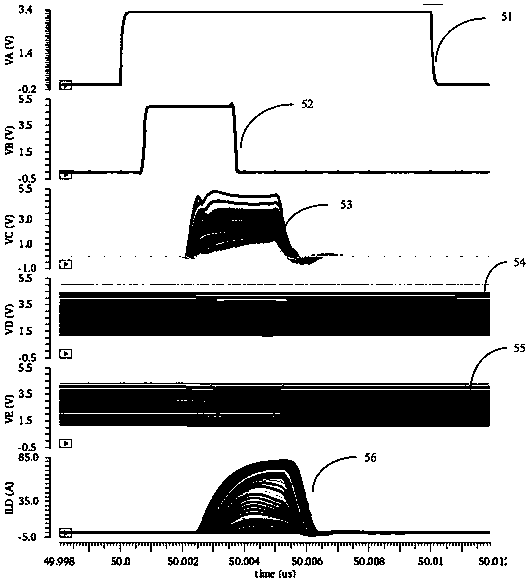
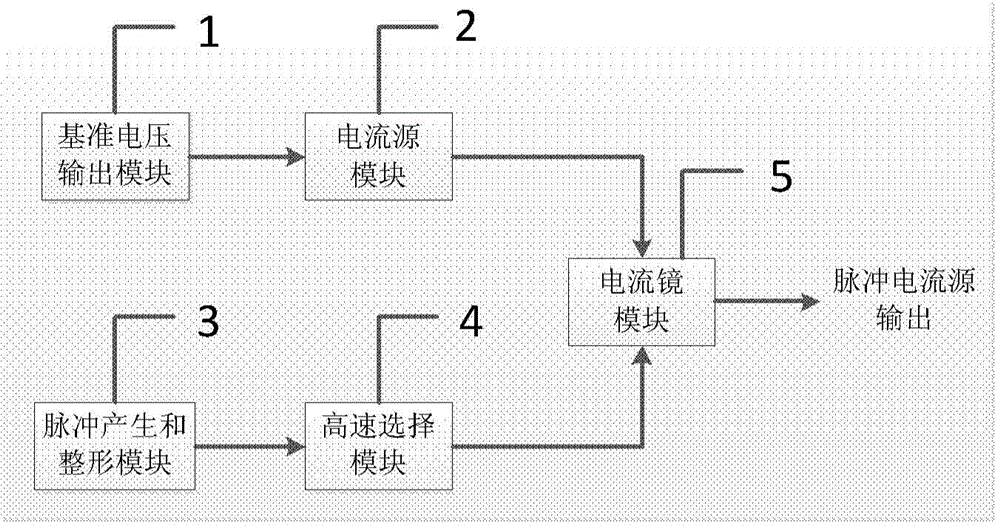
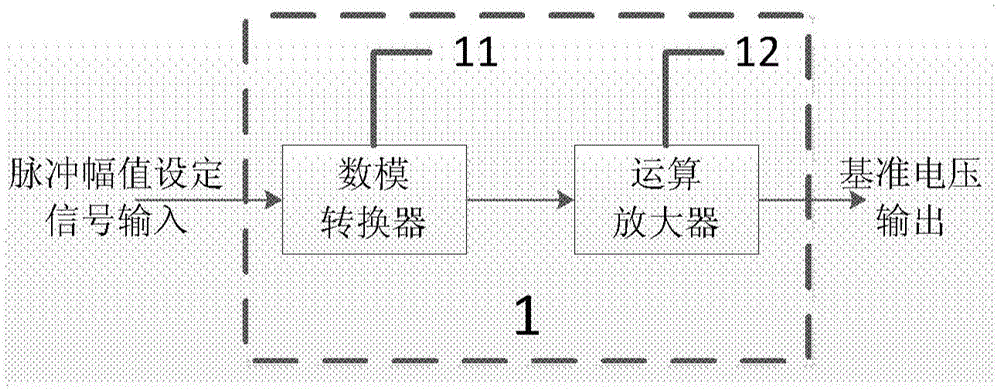
ActiveCN104135253ARealize digital controlRealize regulationPulse duration/width modulationLeading edgeElectricity
The invention discloses a circuit structure of a narrow-pulse-width high-repetition-frequency pulse current source. The circuit structure is characterized by comprising an adjustable reference voltage input module (1), a current source module (2), an adjustable narrow pulse generating and shaping module (3), a high-speed selection module (4) and a current mirror module (5), wherein the adjustable reference voltage input module (1), the current source module (2) and the current mirror module (5) are electrically connected in sequence; and the adjustable pulse generating and shaping module (3), the high-speed selection module (4) and the current mirror module (5) are electrically connected in sequence. By adopting the circuit structure, the pulse width, the current magnitude and the pulse frequency can be adjusted. Moreover, the circuit structure has the advantages of narrow pulse width, high repetition frequency, high current, small overshoot and steep leading edge.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
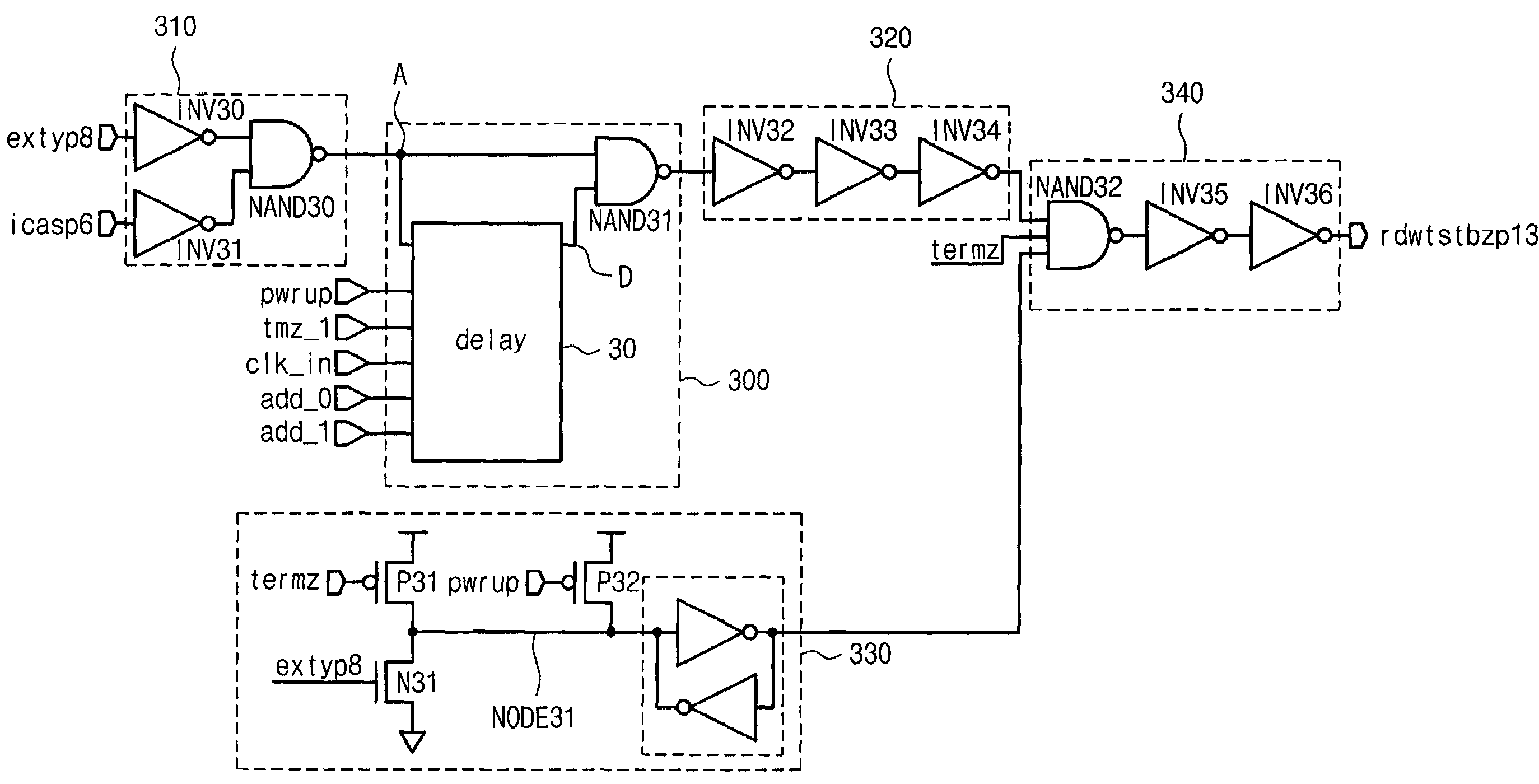
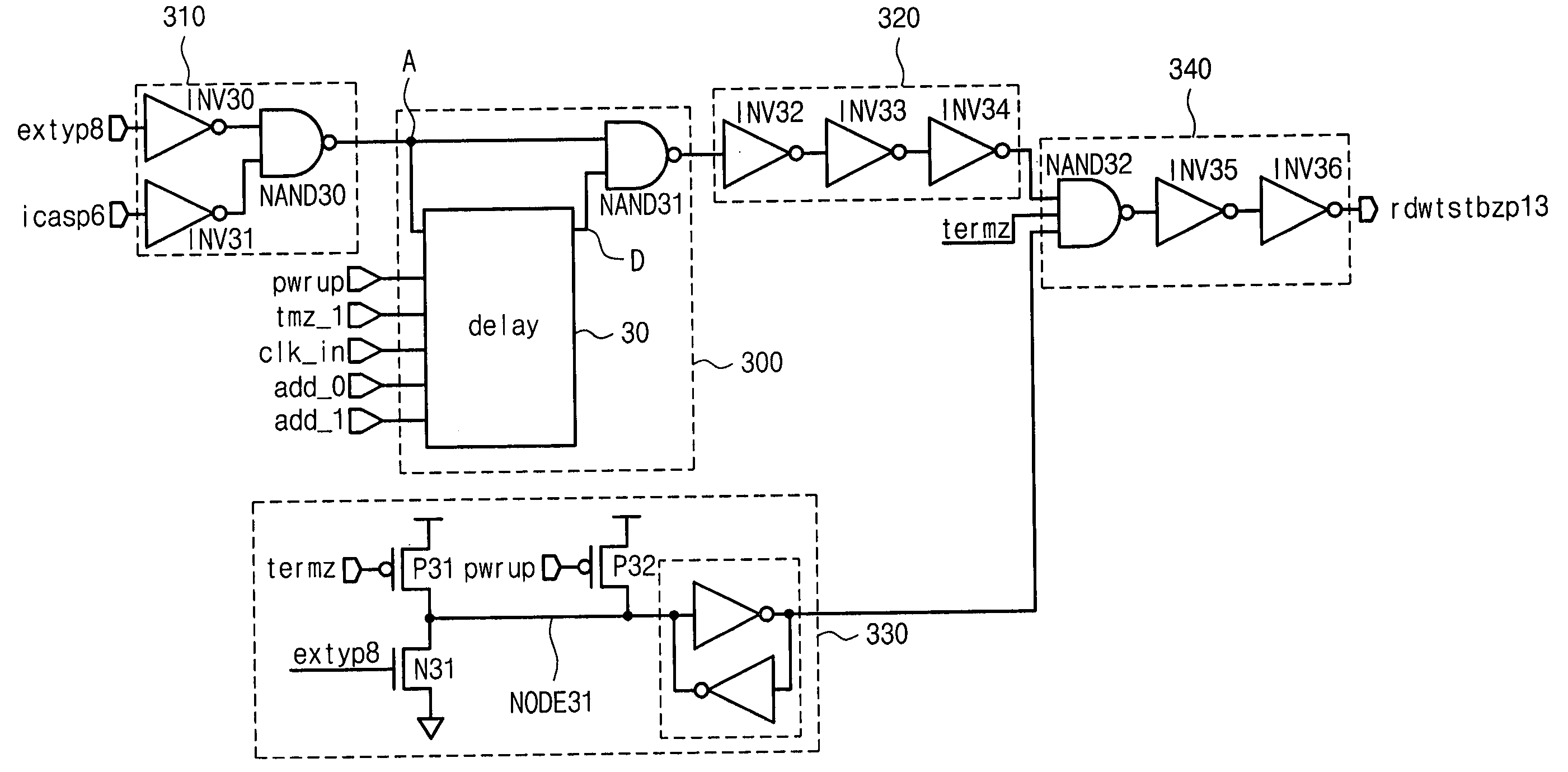
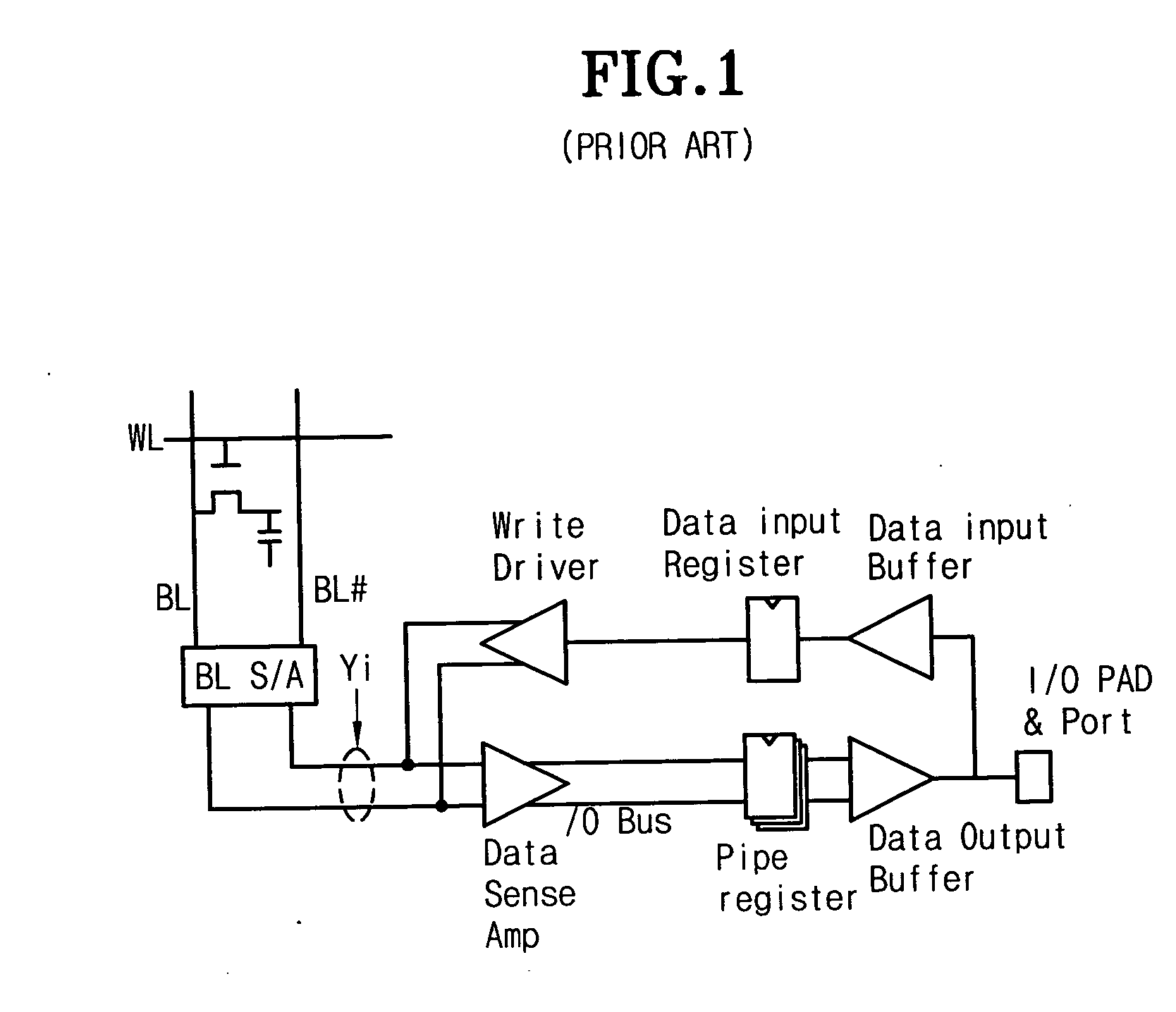
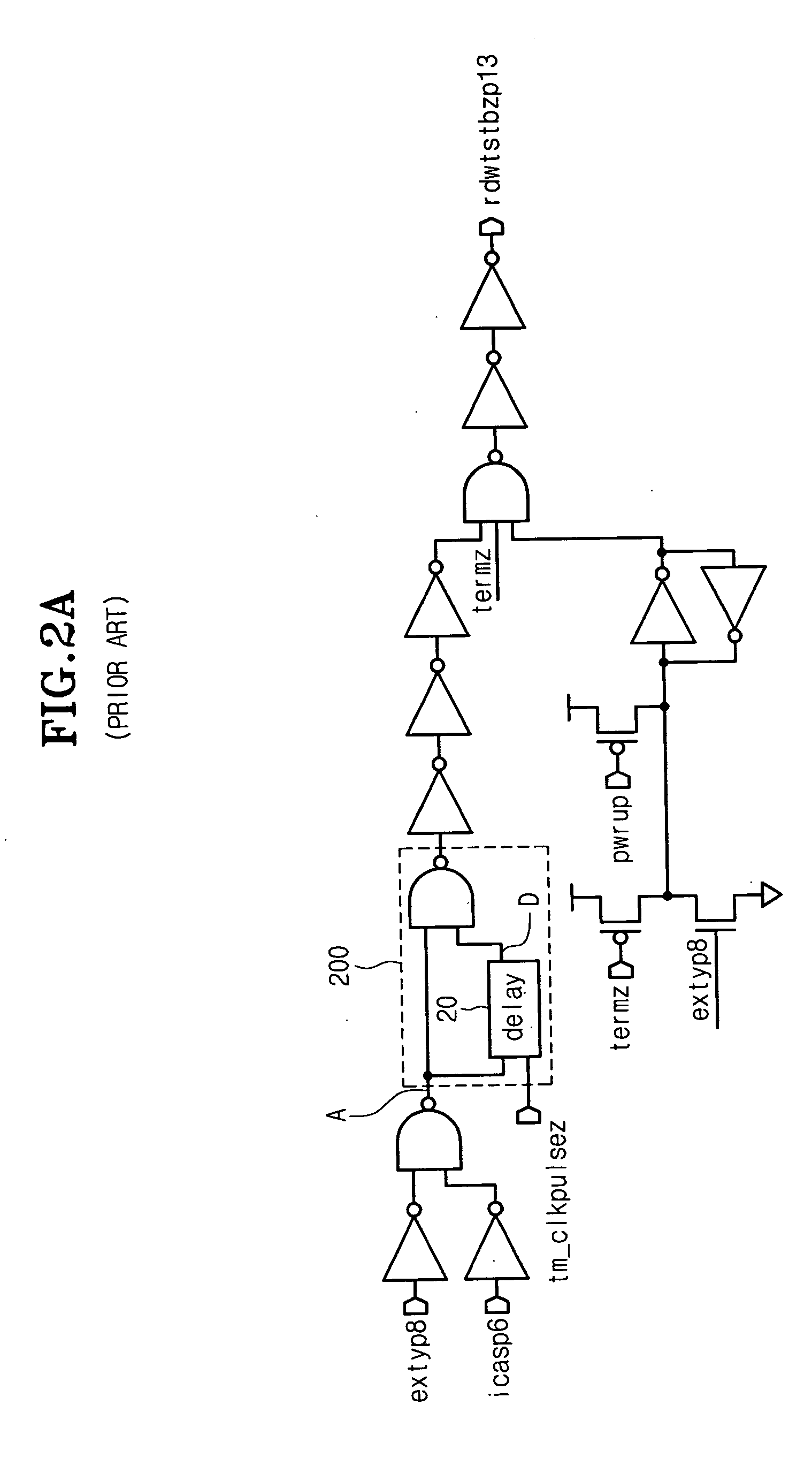
Circuit for controlling an enabling time of an internal control signal according to an operating frequency of a memory device and the method thereof
ActiveUS7142469B2Short maintenance periodNarrow pulse widthDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
Provided is a circuit for controlling a data bus connecting a bitline sense amplifier to a data sense amplifier in accordance with a variation of an operating frequency of a memory device, being comprised of a pulse width adjusting circuit for varying a pulse width of an input signal in accordance with the operating frequency of the memory device after receiving the input signal, a signal transmission circuit for buffing a signal outputted from the pulse width adjusting circuit, and an output circuit for outputting a first signal to control the data bus in response to a signal outputted from the signal transmission circuit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Ultrashort pulse fiber laser based on WS2/graphene heterojunction
InactiveCN106129797AEvenly distributedQuality improvementActive medium shape and constructionHeterojunctionMode locked fiber laser
The invention provides a WS 2 A method for preparing a graphene heterojunction thin film, and a method for building a passively mode-locked fiber laser based on the heterojunction thin film. The method includes: First, a large area of uniform WS 2 The films were prepared by magnetron sputtering, and then the graphene was transferred to |WS 2 thin film, forming WS 2 / graphene heterojunction, and then etched by strong alkali solution to obtain independent WS 2 / Graphene heterojunction thin film, which can be used as a saturable absorber to generate ultrashort pulse laser when placed in the optical fiber optical system. The present invention innovatively adopts WS 2 / graphene heterojunction films while overcoming WS 2 The passive mode-locked pulse width is not narrow enough and the graphene modulation depth is small, so that an ultrashort pulse fiber laser with a large modulation depth can be obtained.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Optical device
InactiveUS7603002B2High outputNarrow pulse widthCoupling light guidesNon-linear opticsWaveguideModulation index
An optical device having a substrate having an electro-optical effect, an optical waveguide formed in the substrate, and an electric field emission electrode, and an electric field convergence electrode to which an electric field emitted from the electric field emission electrode converges. The optical waveguide is formed such that light propagating through the optical waveguide passes through an area under the electric field emission electrode or an area under the electric field convergence electrode and then passes through a remaining electrode. As a result, even when an interaction length is increased, the optical device acquires (increases) a modulation index appropriate to the increase in interaction length, thereby diminishing a drive voltage.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
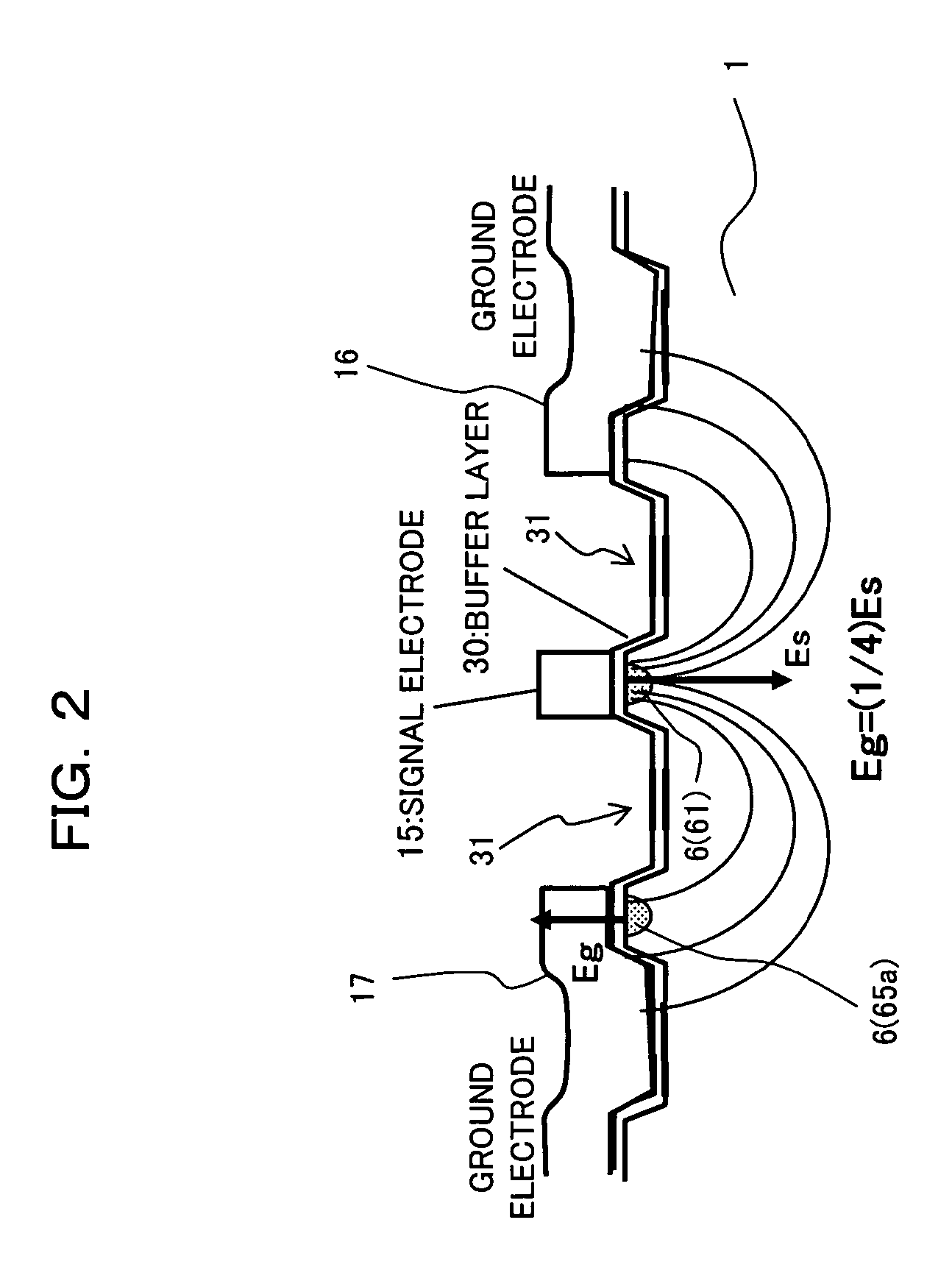
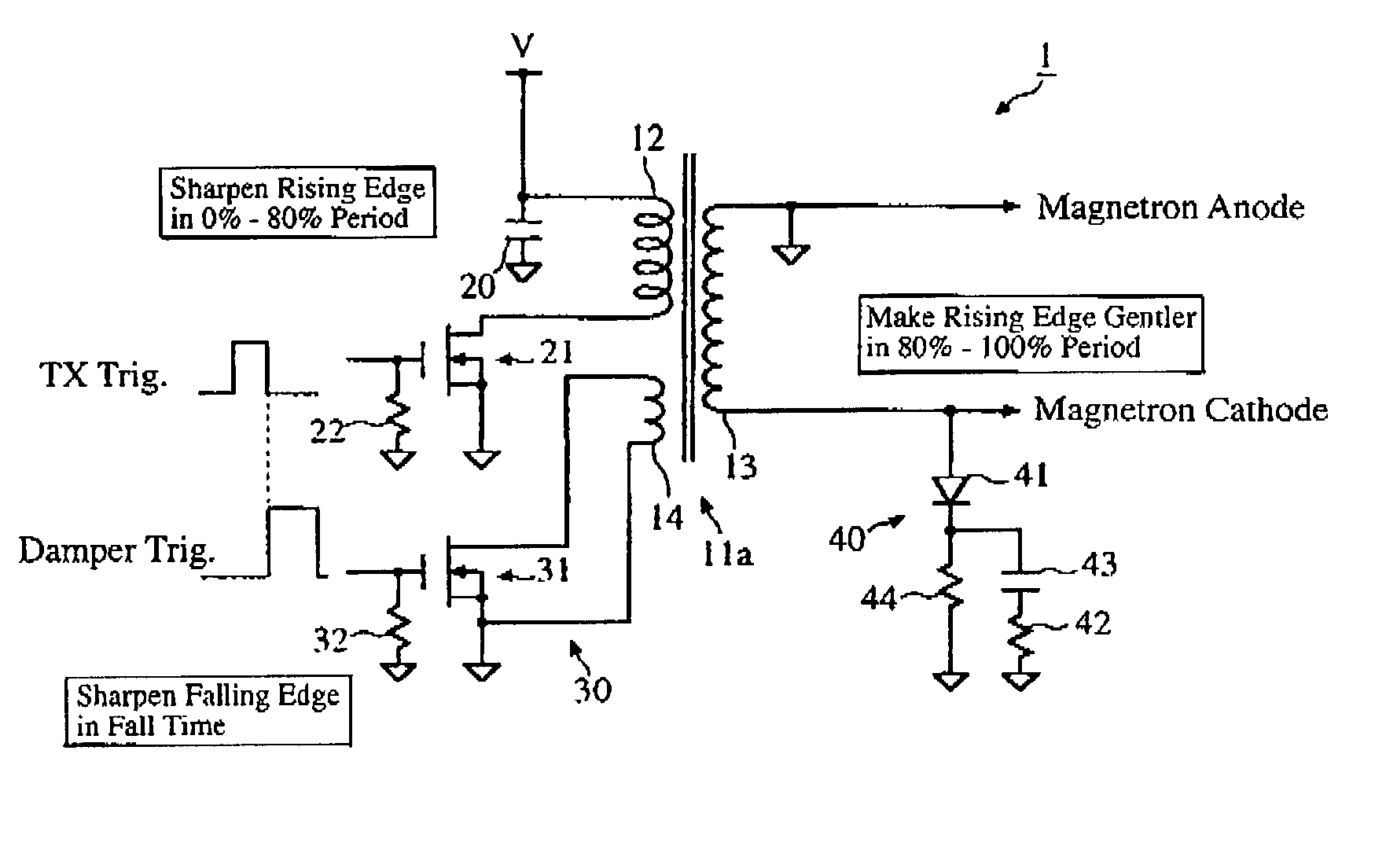
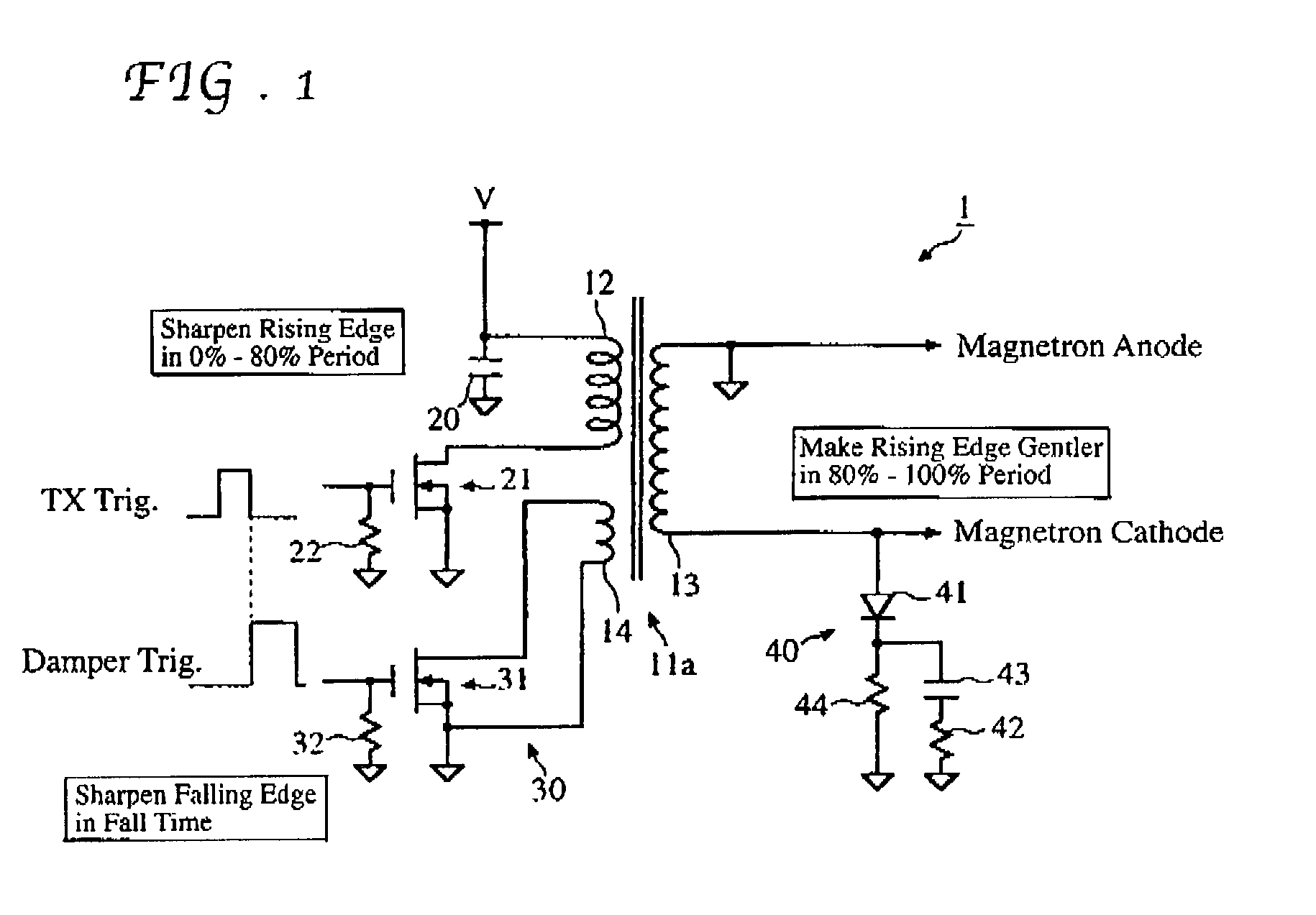
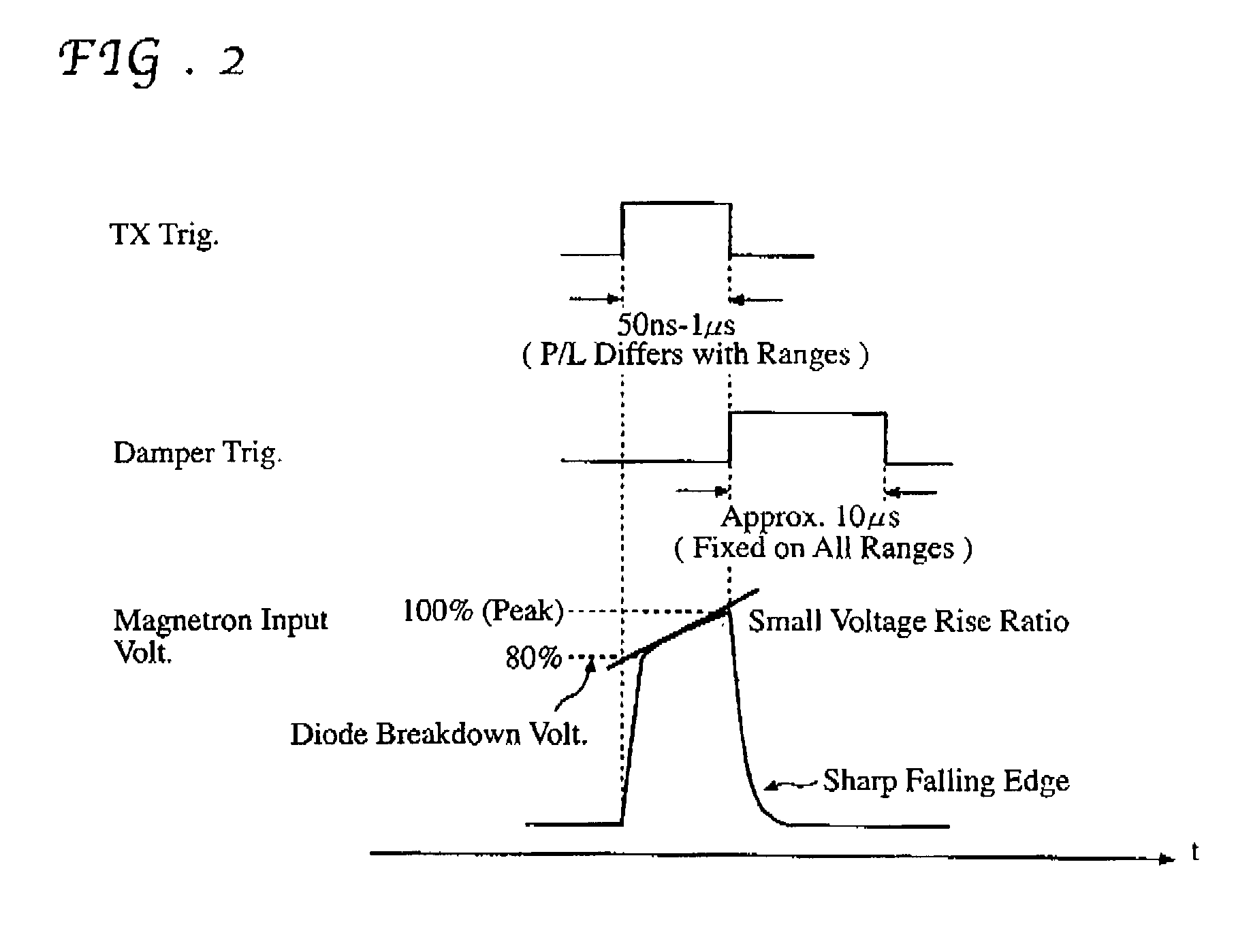
Magnetron drive circuit
InactiveUS20030058160A1Eliminate needLower the resistance valueMagnetronsPulse generation by energy-accumulating elementLoad circuitPeak value
The invention provides a magnetron drive circuit which drives a magnetron to produce a generally rectangular-shaped narrow transmission pulse having sharply shaped rising and falling edges. The magnetron drive circuit includes a nonlinear load circuit and an active damper circuit. The nonlinear load circuit becomes on at around 80% of a peak output voltage of a pulse transformer (at which the magnetron begins to oscillate) is connected to a secondary winding of the pulse transformer in parallel with the magnetron. The active damper circuit absorbs residual energy left in the pulse transformer without any need for an absorption resistor conventionally connected between both ends of a primary winding of the pulse transformer.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
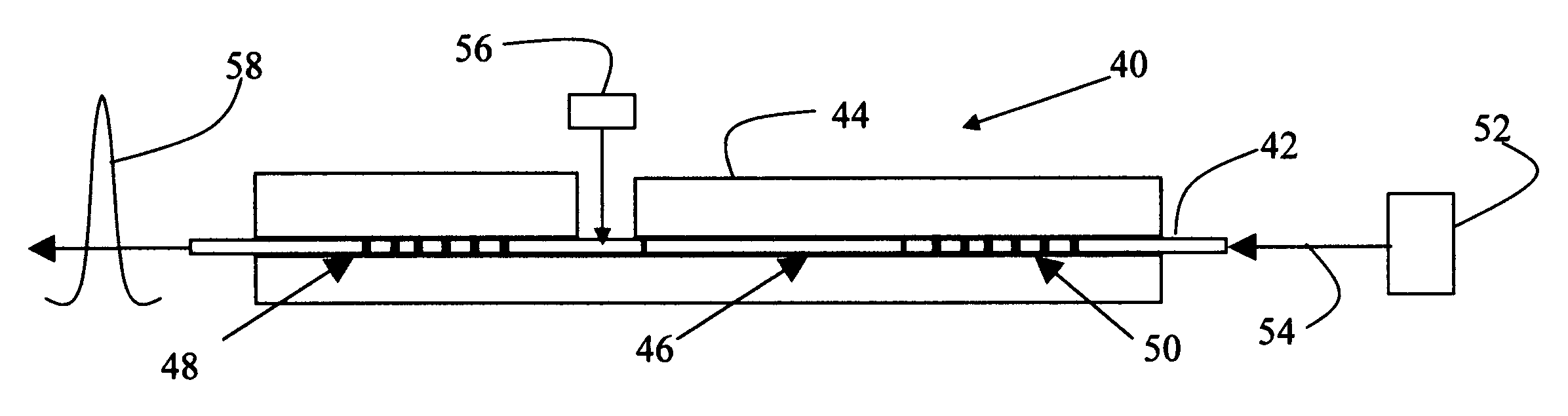
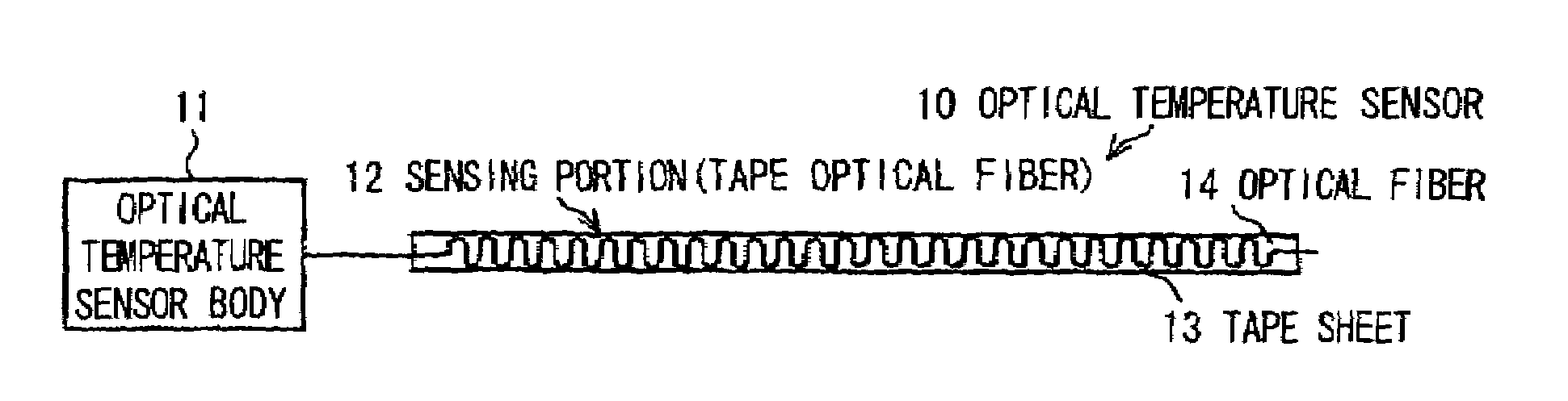
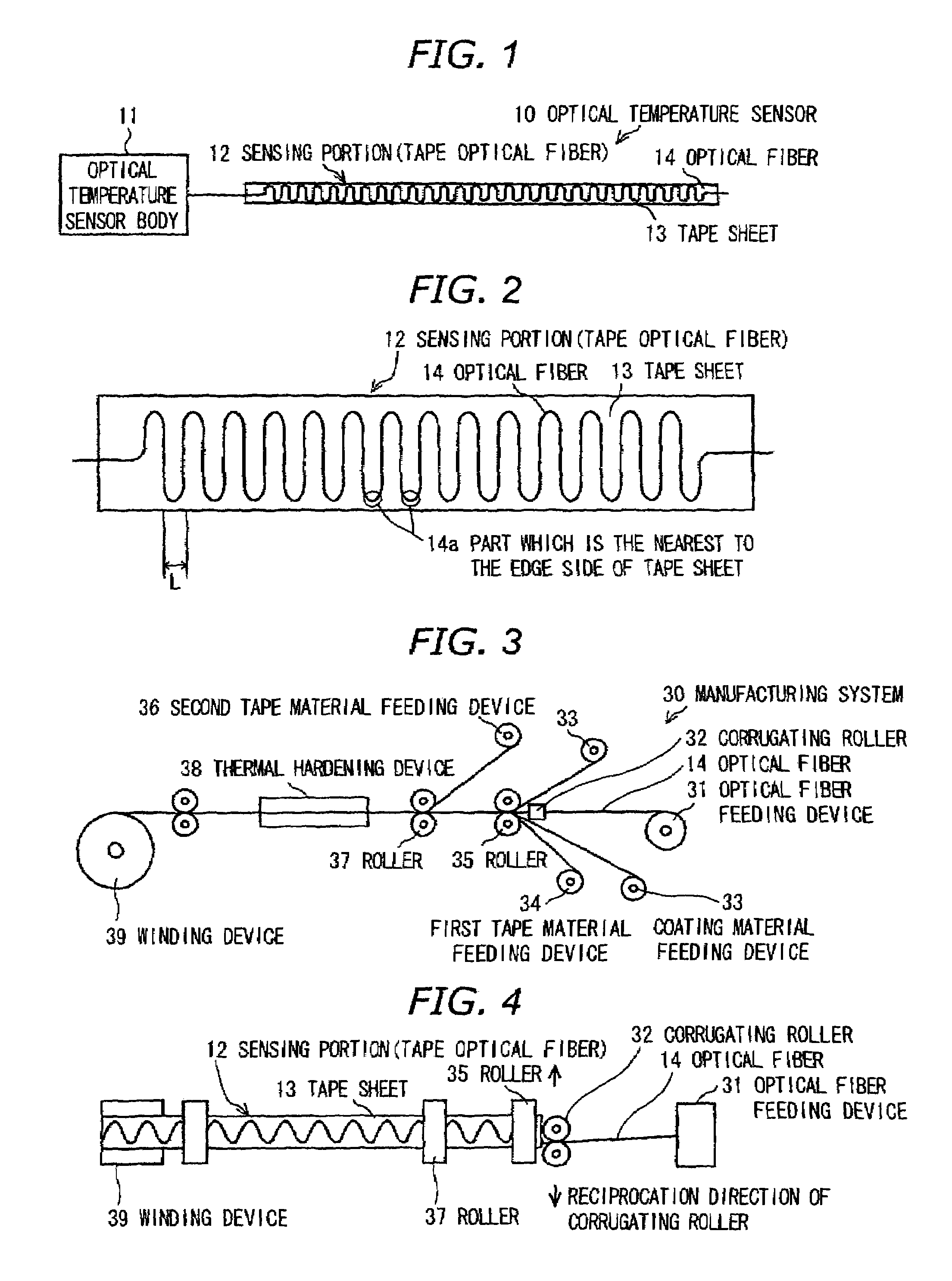
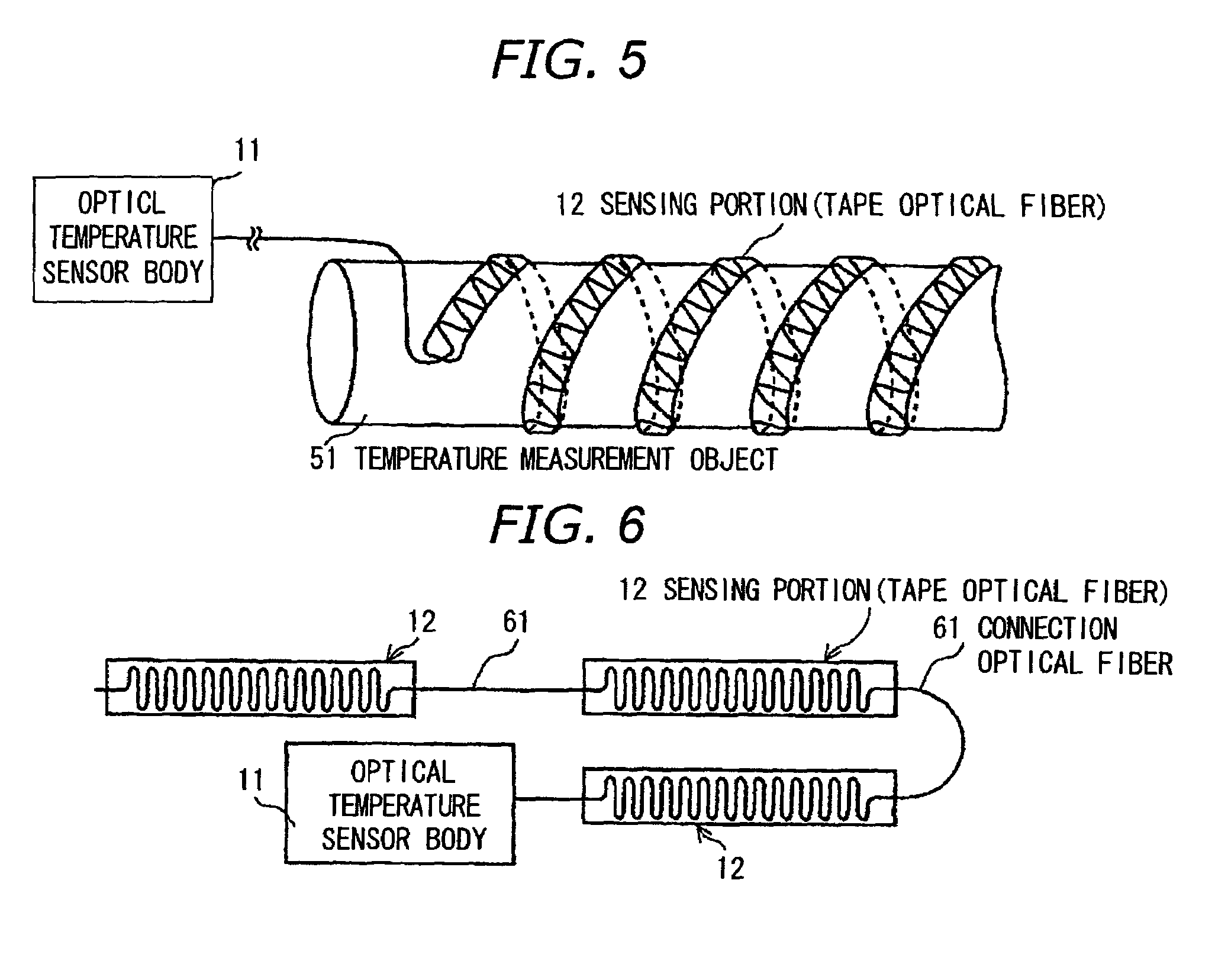
Optical sensor, optical temperature-measuring device and measuring method using the optical sensor
InactiveUS7495207B2Improved Axial ResolutionHigh sampling frequencyLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryMeasurement pointPhotodetector
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
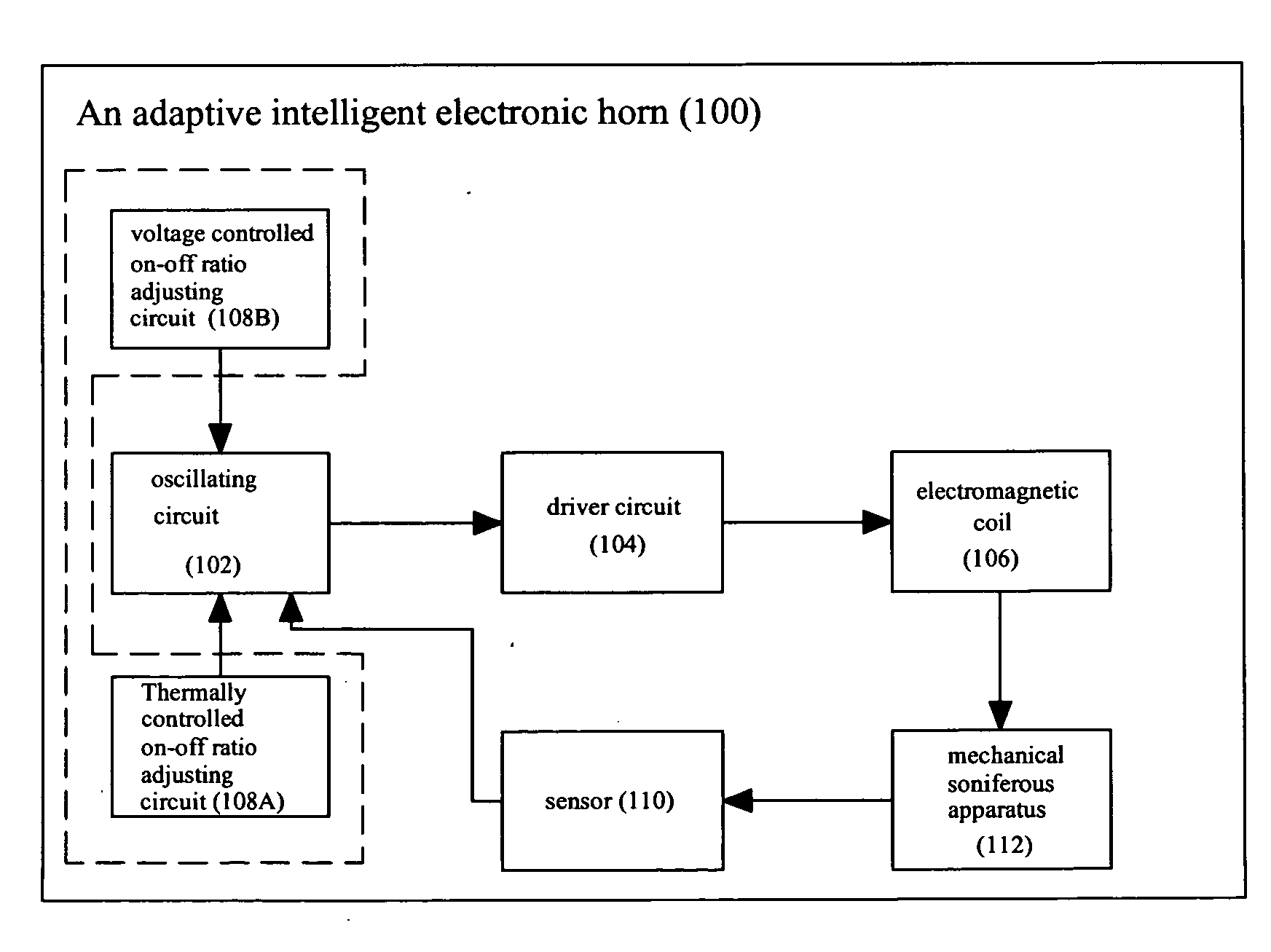
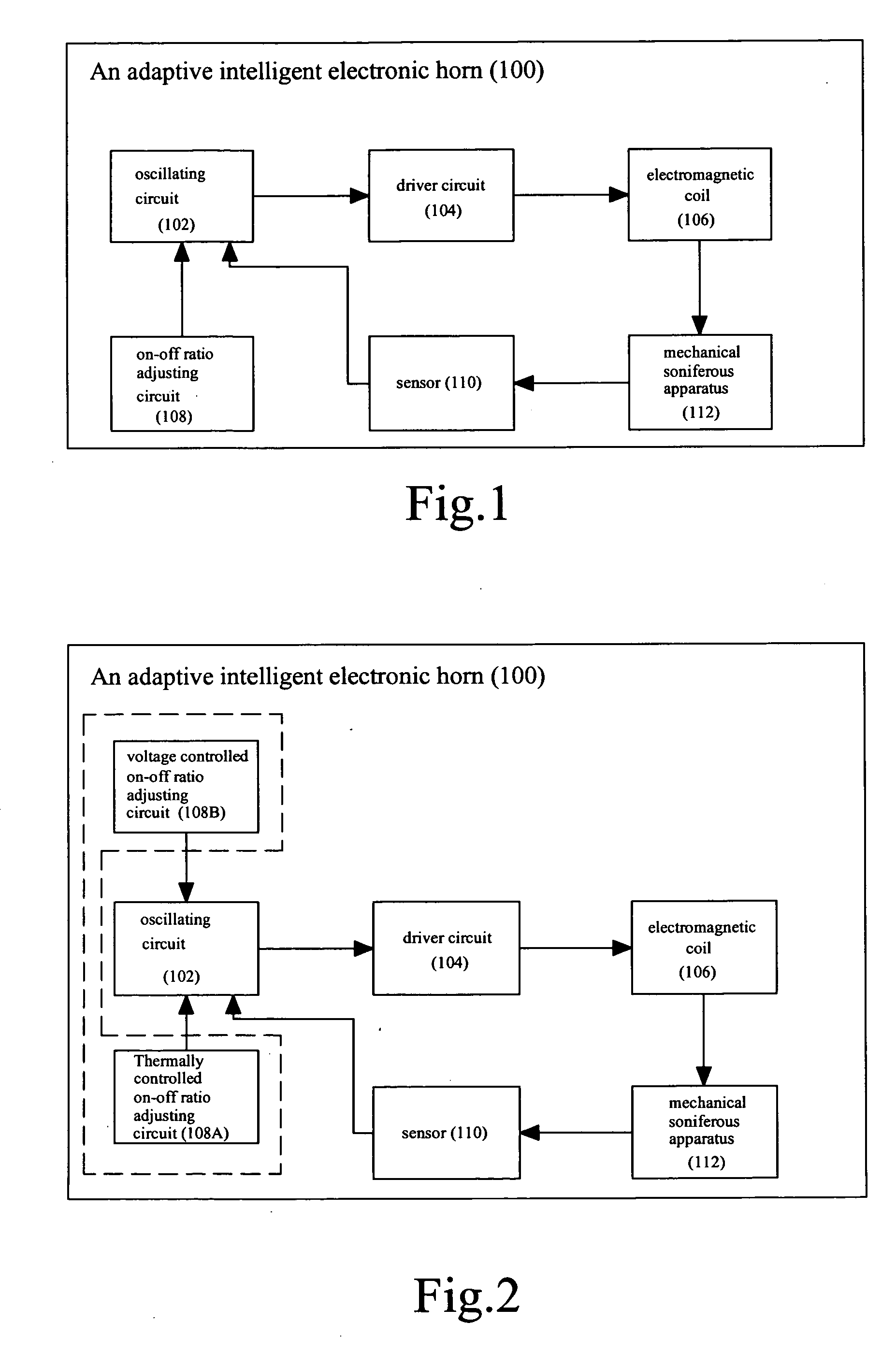
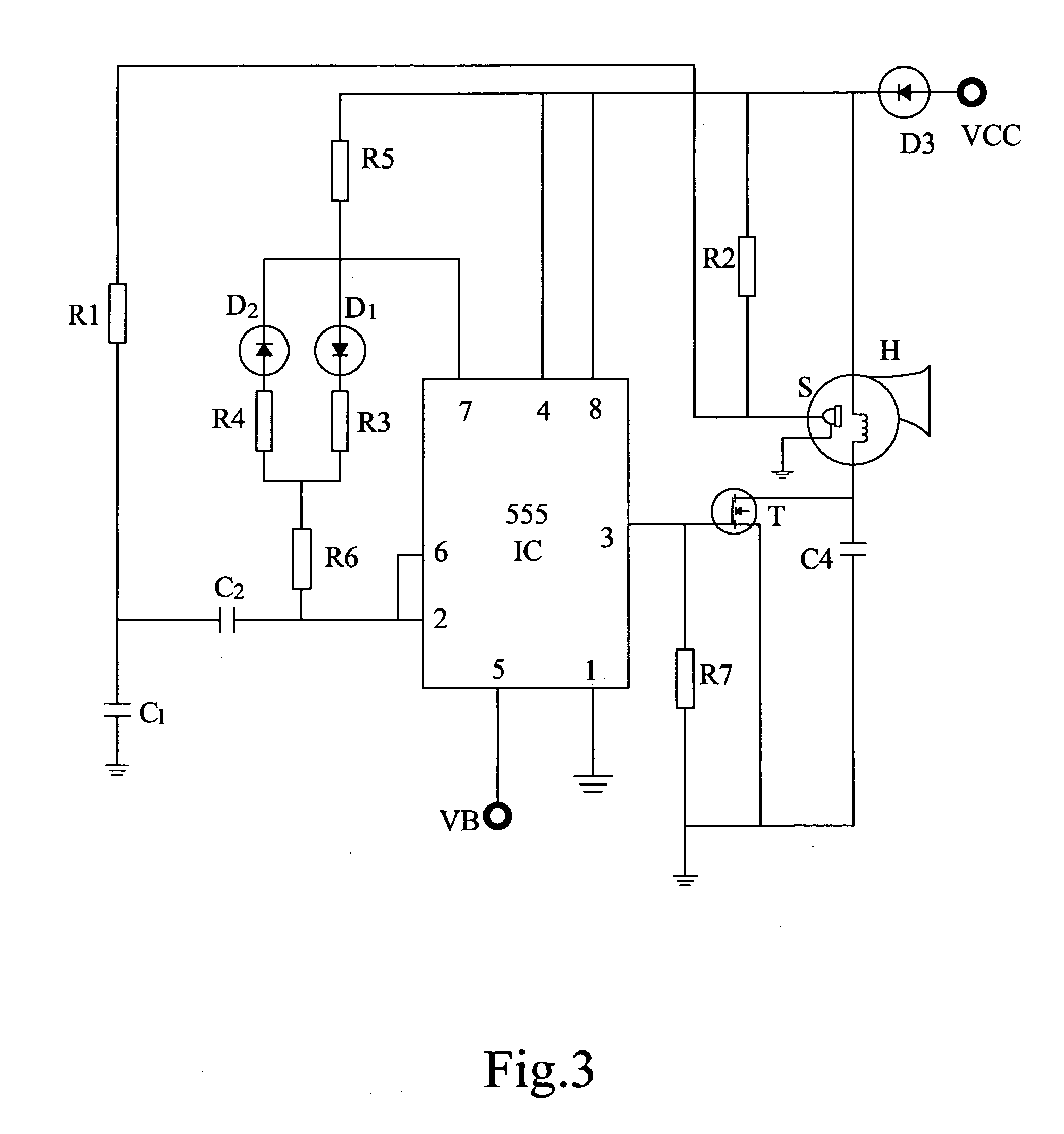
Adaptive intelligent electronic horn
InactiveUS20080309466A1Wide range pulse widthNarrow pulse widthFluid removalMechanical vibrations separationDriver circuitControl signal
An adaptive intelligent electronic horn (100) comprises a mechanical soniferous apparatus (112), an electromagnetic coil (106), a driver circuit (104) and an oscillating circuit (102). A sensor (110) is provided between the mechanical soniferous apparatus (112) and the oscillating circuit (102). An on-off ratio adjusting circuit (108) is provided at the input end of the oscillating circuit (102). The sensor (110) measures the oscillation frequency of the mechanical soniferous apparatus (112) and feedbacks the measured oscillation frequency signal to the oscillating circuit (102). The on-off ratio adjusting circuit (108) controls a pulse width of an oscillation signal from the oscillating circuit (102) based on a voltage of power supply and / or an ambient temperature. The oscillating circuit (102) outputs corresponding oscillation signal to the driver circuit (104) based on the oscillation frequency signal received from the sensor (110) and / or the control signal from the on-off ratio adjusting circuit (108).
Owner:ZHAO HONGWEI
Optical device for optical communication
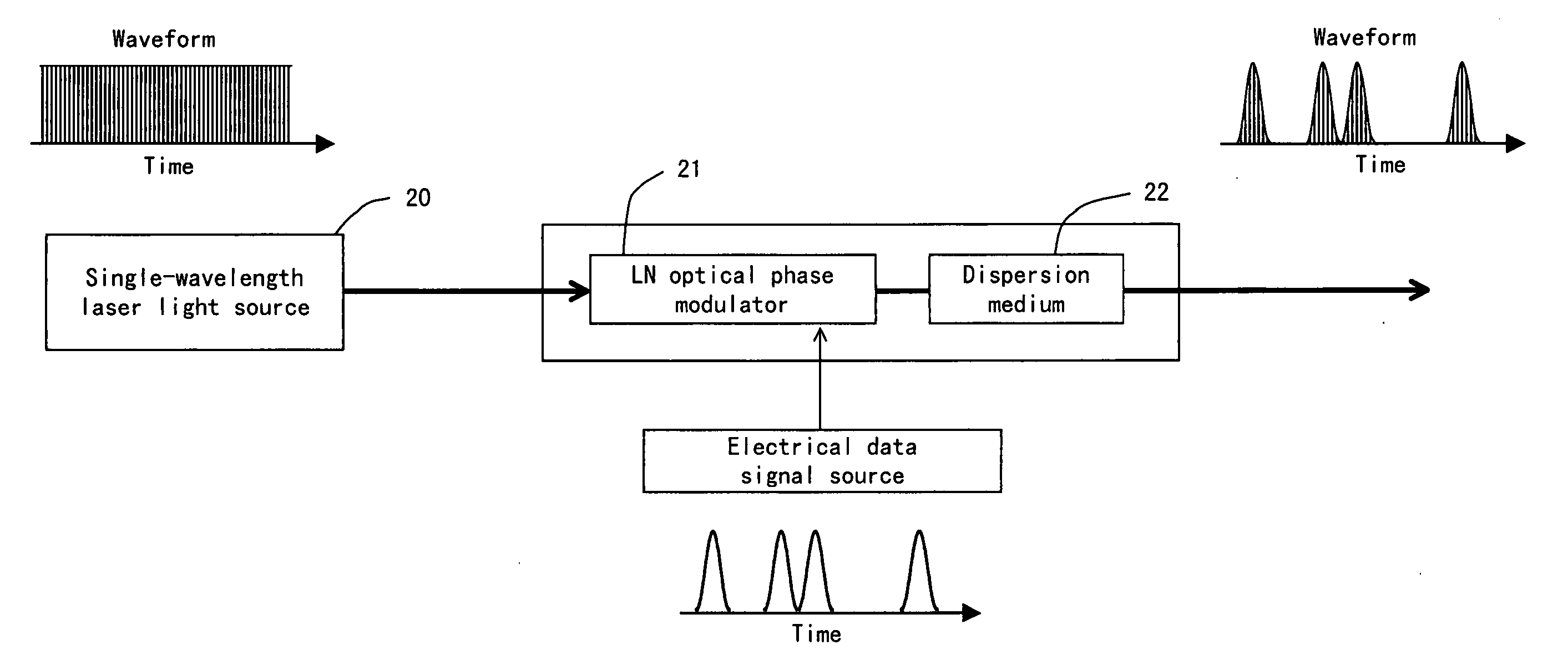
ActiveUS20050190432A1Data stabilityImprove OSNRTime-division optical multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationLaser lightOptical communication
An optical phase modulator made of lithium niobate or the like phase-modulates the output light of a single-wavelength laser light source 20 that emits CW light, and the phase-modulated light is inputted to a dispersion medium 22. The positive chirp and negative chirp of light to which frequency chirp is applied by phase modulation draw near in the dispersion medium and an optical pulse is generated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
All-solid-state femtosecond laser of passive mode locking Nd,Y:CaF2 of diode pumping
InactiveCN104051943ANarrow pulse widthReduce manufacturing costActive medium materialAll solid stateResonant cavity
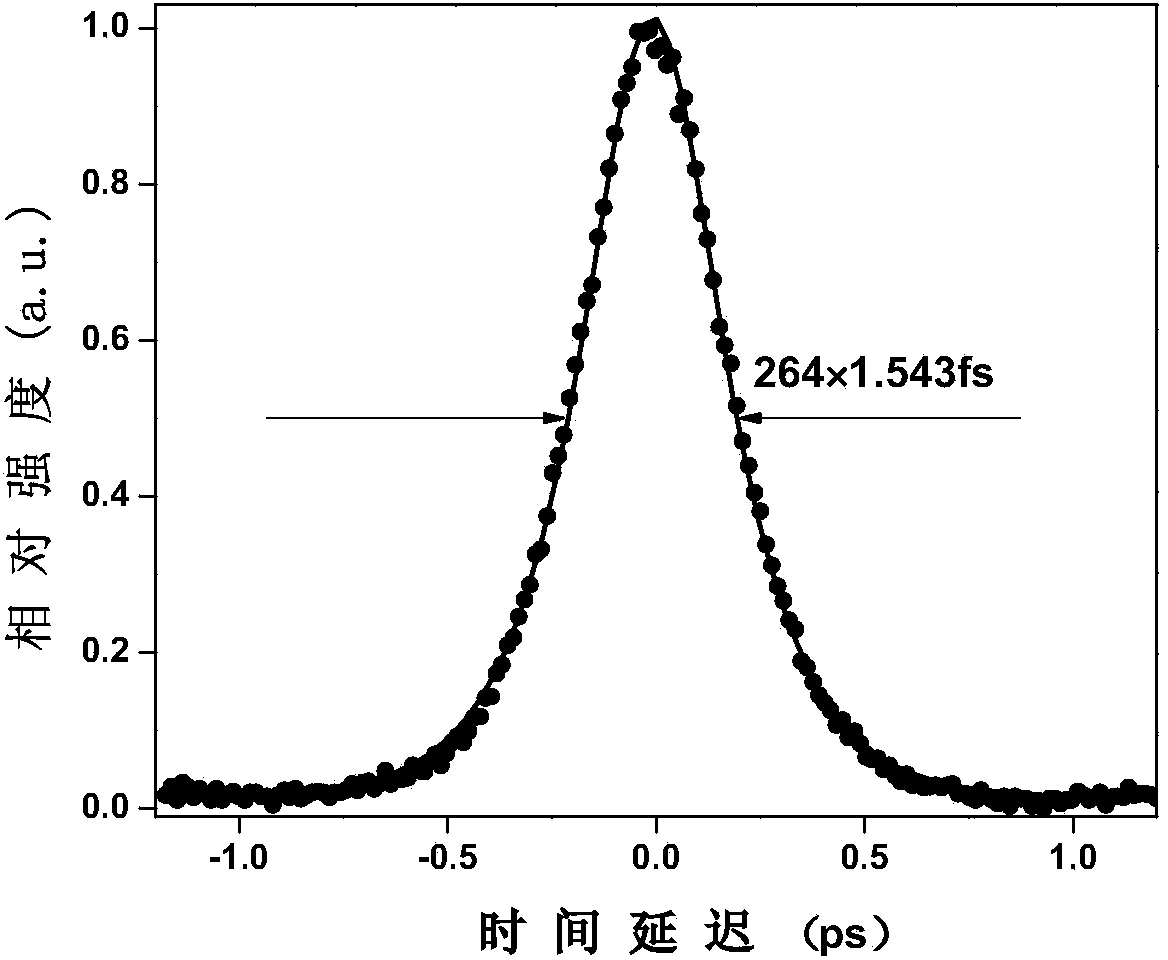
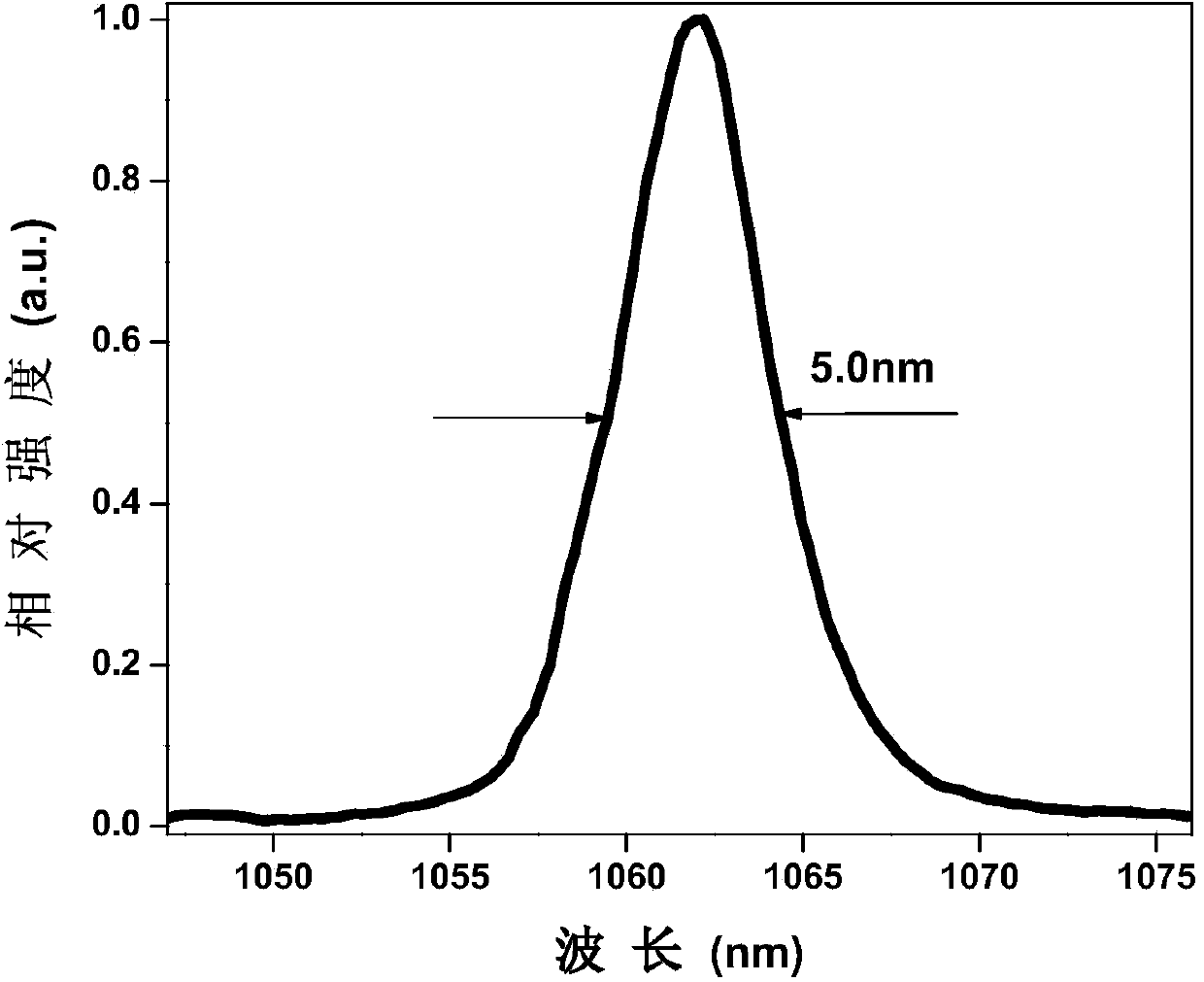
The invention discloses an all-solid-state femtosecond laser of passive mode locking Nd,Y:CaF2 of diode pumping. An Nd,Y:CaF2 laser crystal of the laser receives pumping laser penetrating through an optical coupling focusing system and a dichroic mirror; a first concave mirror, a second concave mirror and the dichroic mirror form a compact type confocal folded cavity; a third concave mirror focuses gain laser in a resonant cavity to a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror; the semiconductor saturable absorber mirror is used for starting and maintaining stable mode locking; a first GTI mirror and a second GTI mirror are used for compensating for positive chromatic dispersion in the resonant cavity; a coupling output mirror is used for outputting a stable passive mode locking pulse sequence. The all-solid-state femtosecond laser formed in the mode that a pumping source based on a laser diode is obtained, CaF2 with Nd3+ and Y3+ co-doped serves as a gain medium, the GTI mirrors are used for compensating for chromatic dispersion and the semiconductor saturable absorber mirror is used for starting mode locking, and the stable mode locking pulse sequence with the pulse width of 264 fs is output inside the resonant cavity. A laser diode pumping technology is adopted, so that the all-solid-state femtosecond laser has broader application prospects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Femtosecond mode-locked pulsed optical fiber laser based on single-walled nanotube
InactiveCN108011288ACompact structureLow costActive medium shape and constructionGratingCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a dispersion management type femtosecond mode-locked pulsed optical fiber laser based on a single-walled nanotube. The dispersion management type femtosecond mode-locked pulsedoptical fiber laser comprises a pumping source and a laser annular chamber formed by a wavelength division multiplexer, an ytterbium-doped single-mode gain optical fiber, two optical fiber couplers,three optical fiber collimators, four high-reflection mirrors, four transmission gratings, a polarization-independent optical isolator, a polarization controller, a saturable absorbing device, a single-mode optical fiber, and a spatial optical path, and the overall optical path is divided into two portions including a laser resonant cavity and an outside-cavity compressor. According to the laser,mode-locked femtosecond pulsed laser of mode-locked laser output, direct output of 450 fs, and outside-cavity compression output of 198 fs can be realized on the single-mode ytterbium-doped gain optical fiber, a feasible scheme is provided for acquisition of narrow-pulse-width laser of a saturable absorber based on a novel material, the structure is simple and small, the cost is low, the pulse output with high repetition rate and direct femtosecond level is achieved, the laser can be widely applied to the fields of scientific research and industries etc., and the application prospect and the business value are good.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
High repetition frequency narrow pulse width semiconductor pumping green laser
ActiveCN101719625AIncrease powerImprove conversion efficiencyActive medium materialResonant cavityLight beam
The invention discloses a high repetition frequency narrow pulse width semiconductor pumping green laser which comprises two groups of pumping coupled focus systems and a cavity resonator, wherein the two groups of pumping coupled focus systems are respectively positioned at both ends of the cavity resonator; and pumping light emitted by the pumping coupled focus systems enters into a laser work crystal in a two-face pumping cavity resonator in the cavity resonator. By adopting the high repetition frequency narrow pulse width semiconductor pumping green laser of the invention, the produced green laser beam has good quality, and the transfer efficiency is high.
Owner:深圳华工新能源装备有限公司
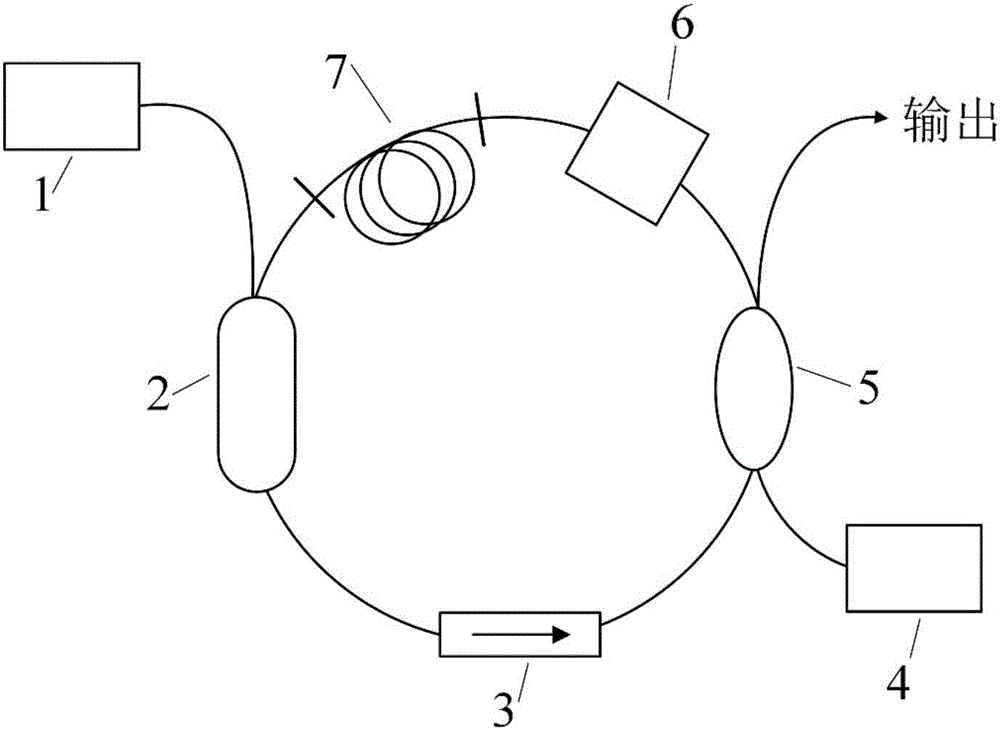
High-repetition-frequency passive-mode-locking ultrashort-pulse all-fiber laser
InactiveCN102368585AHigh repetition rateNarrow pulse widthOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionNonlinear opticsLaser technology
A high-repetition-frequency passive-mode-locking ultrashort-pulse all-fiber laser belongs to a laser technology and the nonlinear optics field. The laser mainly comprises: a laser pumping source, a wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber bragg grating, a doped fiber, a saturable absorber and the like. A short linear cavity is used to realize the high repetition frequency of the passive mode locking and ultrashort laser pulse output. The high-repetition-frequency ultrashort-pulse fiber laser uses a design of an all-fiber structure. Through multistage fiber power amplifiers, average output power can reach hundred watts. Therefore, by using the high-repetition-frequency ultrashort-pulse all-fiber laser, industrialization application is easy to be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Circuit for controlling an enabling time of an internal control signal according to an operating frequency of a memory device and the method thereof
ActiveUS20050213400A1Narrow pulse widthReduce pulse widthDigital storageSense amplifierAudio power amplifier
Provided is a circuit for controlling a data bus connecting a bitline sense amplifier to a data sense amplifier in accordance with a variation of an operating frequency of a memory device, being comprised of a pulse width adjusting circuit for varying a pulse width of an input signal in accordance with the operating frequency of the memory device after receiving the input signal, a signal transmission circuit for buffing a signal outputted from the pulse width adjusting circuit, and an output circuit for outputting a first signal to control the data bus in response to a signal outputted from the signal transmission circuit.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
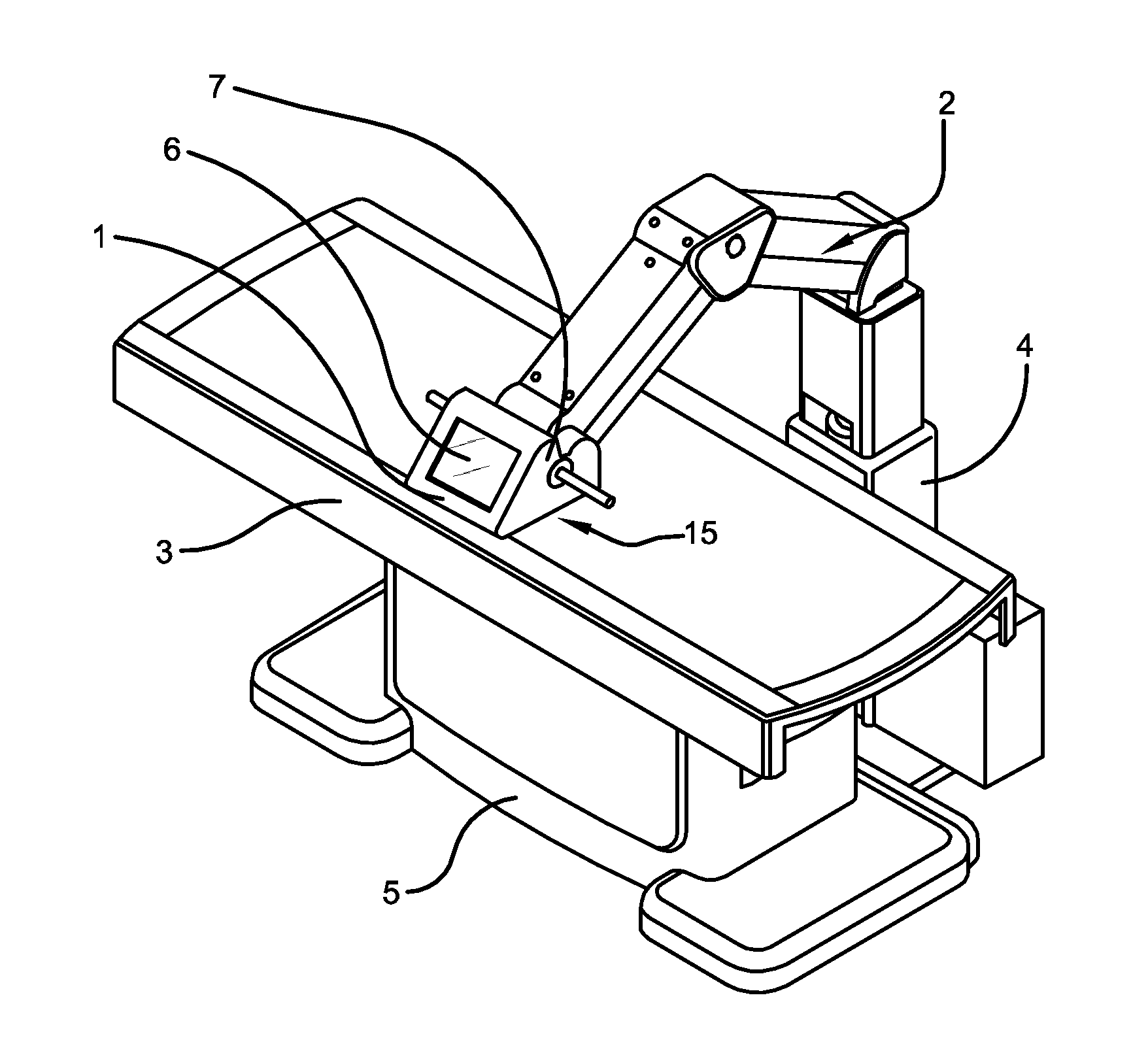
Ultrasonic fat reduction and body shaping machine
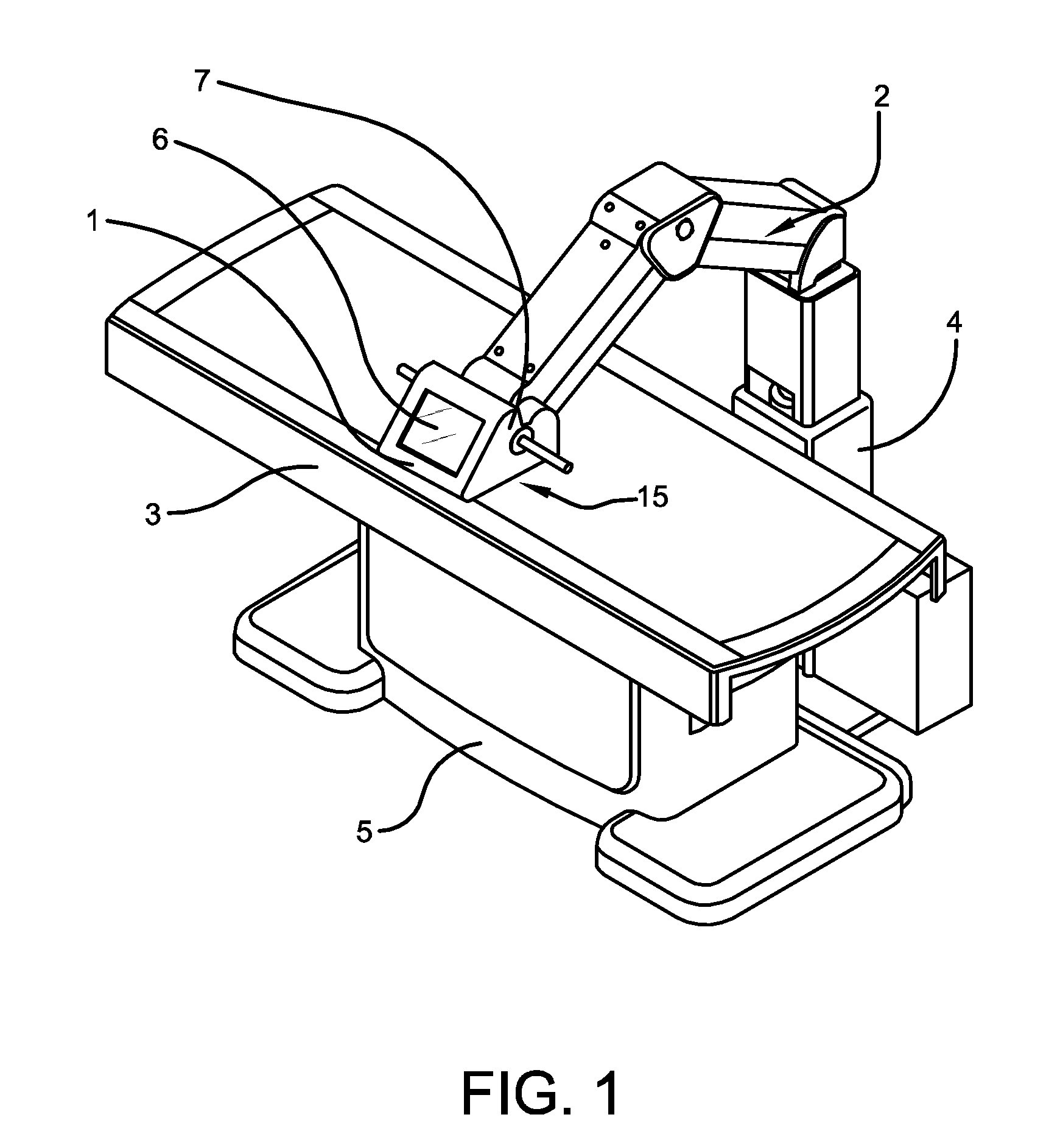
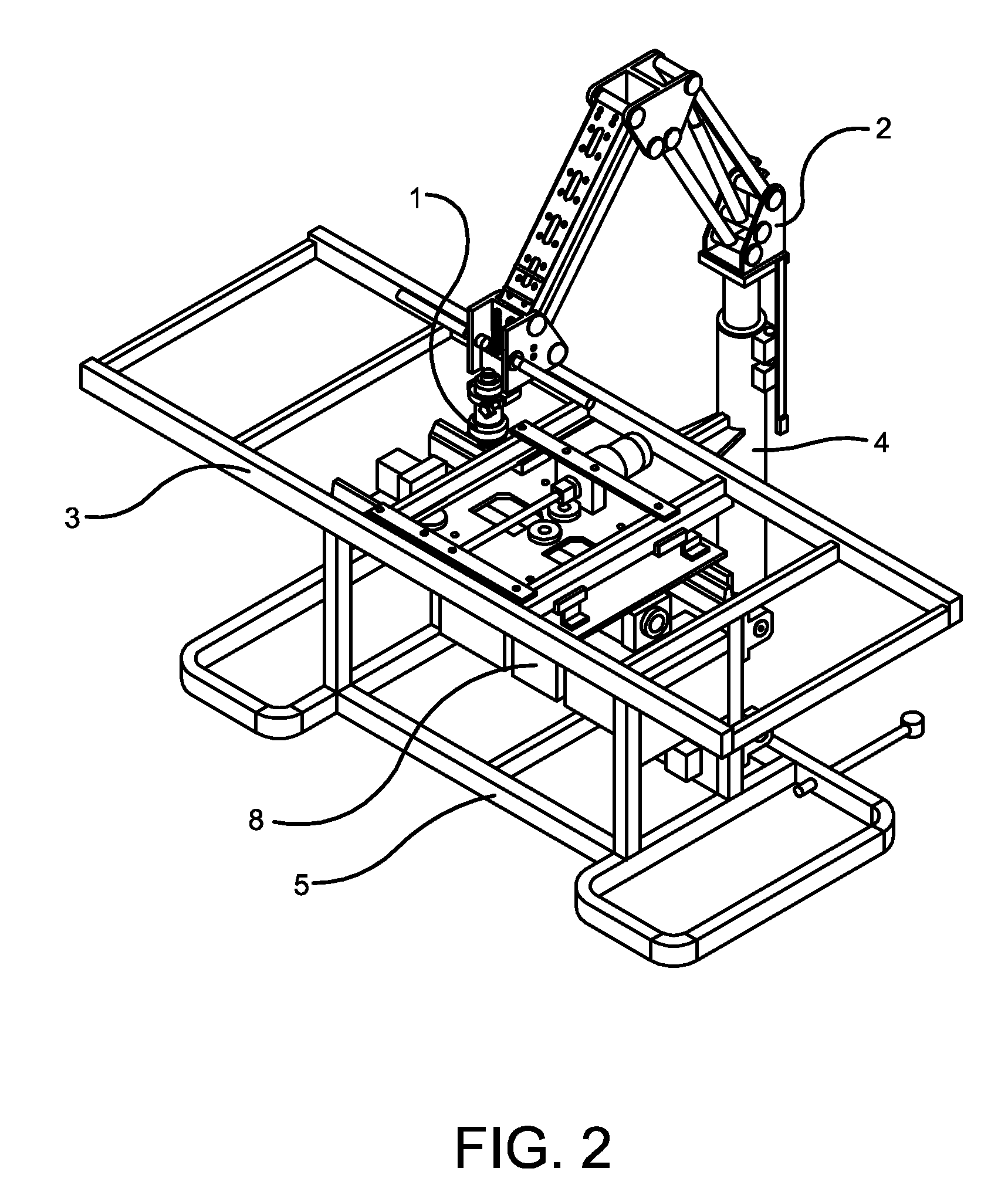
InactiveUS20120010542A1Easy to disassembleEasy to operateUltrasound therapyOperating tablesMedicineHigh intensity
The invention discloses an ultrasonic fat reduction and body shaping machine that includes a treatment head (1), a wave source carrying apparatus (15), a mechanical arm (2), a treatment bed, a lift cylinder body, a touch screen (6) and control circuits (8). A menu for user selection operation is provided on the touch screen (6). The treatment head (1) is clamped in the wave source carrying apparatus (15 s as to be fixedly connected to the mechanical arm (2) as a whole. The mechanical arm (2) is fixedly connected to the lift cylinder body that is fastened on the treatment bed-base (5). The invention is to provide an ultrasonic fat reduction and body shaping machine that facilitates assembling and disassembling of a treatment head, elevates and descends a mechanical arm freely. The ultrasonic fat reduction and body shaping machine has an ultrasonic frequency of 1 MHz to 3 MHz using an ultrasonic emission mode with high intensity, narrow pulse width and low duty cycle.
Owner:BEIJING HUIFUKANG MEDICAL TECH
2.79 mu m Q-switched erbium laser dental instrument
InactiveCN103300934AHas removedShort pulse widthSurgical instrument detailsDental toolsEngineeringPolarizer
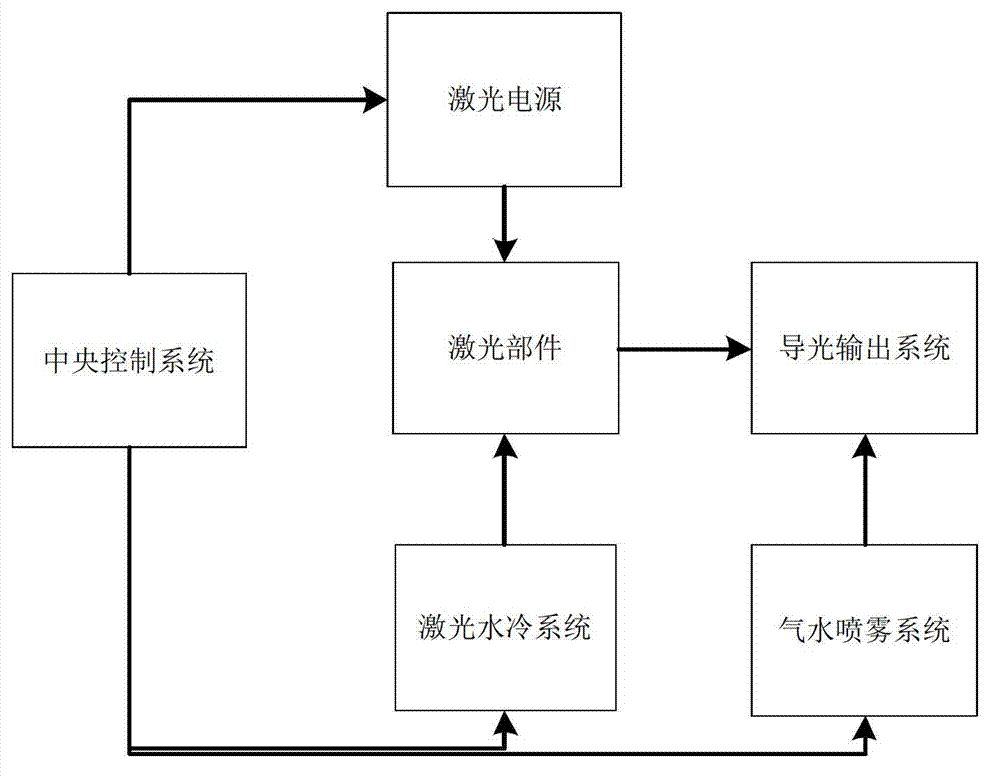
The invention discloses a 2.79 mu m Q-switched erbium laser dental instrument. The 2.79 mu m Q-switched erbium laser dental instrument comprises a laser power supply, a laser component, a laser water cooling system, a light guide output system, a gas and water spraying system and a central control system; the laser power supply is used for providing energy to the laser component; the laser component consists of a total-reflection chamber piece, a polarizer, a Q-switched crystal, a xenon lamp, a laser rod, a light condensing chamber, a wave plate and an output chamber piece; the laser water cooling system is used for cooling the laser rod and the xenon lamp in the laser component; the light guide output system is used for conducting laser, and is convenient to operate and use; the gas and water spraying system is used for spraying a mixture of gas and water to a laser acted tooth tissue, and has the effects of reducing the temperature of the tissue and participating laser treatment; the central control system is used for controlling the parameters of the laser power supply, the laser water cooling system and the gas and water spraying system to ensure the coordination work among the subsystems. The 2.79 mu m Q-switched erbium laser dental instrument has pulse Q-switched laser which has short pulse width and high peak power and acts the tooth tissue to improve ablation precision; meanwhile, the thermal damage to peripheral tissues also can be effectively reduced; the pain of a patient can be reduced effectively.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
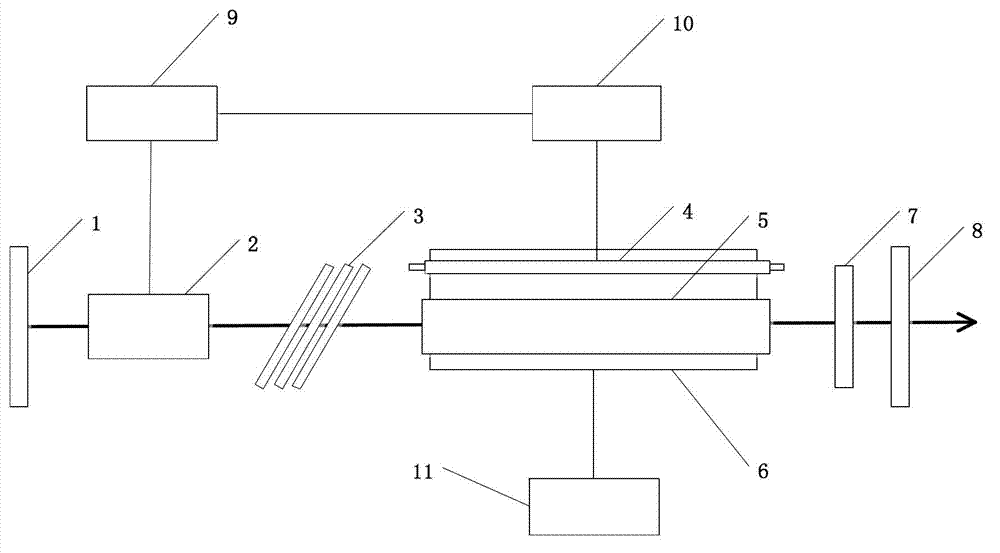
Medical 2.79-micrometer electro-optical Q-switched Cr, Er: YSGG laser device
The invention discloses a medical 2.79-micrometer electro-optical Q-switched Cr, Er: YSGG (Erbium, Chromium: Yttrium-Scandium-Gallium-Garnet) laser device which comprises a total reflection cavity sheet, a Q-switched crystal, a polarizer, a xenon lamp, a laser rod, a condensation cavity, a wave sheet, an output cavity sheet, a laser power supply and a laser water cooling system, wherein the laser rod and the xenon lamp are mounted in parallel in the condensation cavity, and connected with the water cooling system; the water cooling system cools the condensation cavity, and the laser rod and the xenon lamp in the condensation cavity; the laser power supply provides electric energy for the xenon lamp, and has a function of coordination, such as controlling the xenon lamp, an electro-optical Q switch, and the water cooling system; a Q-switched power supply in the power supply controls the opening time of the electro-optical Q switch, provides Q-switched high voltage, and is connected with two electrodes of the Q-switched crystal; the two electrodes are positioned on the two sides of the Q-switched crystal, and clung to the surface of a Y-Z plane of the Q-switched crystal, and are parallel to a laser oscillation path; the electro-optical Q switch consists of the polarizer and the electro-optical Q-switched crystal; the Q-switched crystal is a lanthanum gallium silicate (LGS) crystal; the laser rod is a Cr, Er: YSGG laser crystal; and the wave sheet is a 1 / 4 wave sheet. The laser device has the characteristics of stable output power, and uniform light spot intensity distribution.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pulsed light generation method
InactiveUS20120307850A1High effective pulse energyNarrow pulse widthLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersBandpass filteringOptical fiber amplifiers
The present invention relates to a method of enabling generation of pulsed lights each having a narrow pulse width and high effective pulse energys. A pulse light source has a MOPA structure, and comprises a single semiconductor laser, a bandpass filter and an optical fiber amplifier. The single semiconductor laser outputs two or more pulsed lights separated by a predetermined interval, for each period given according to a predetermined repetition frequency. The bandpass filter attenuates one of the shorter wavelength side and the longer wavelength side, in the wavelength band of input pulsed lights.
Owner:MEGAOPTO
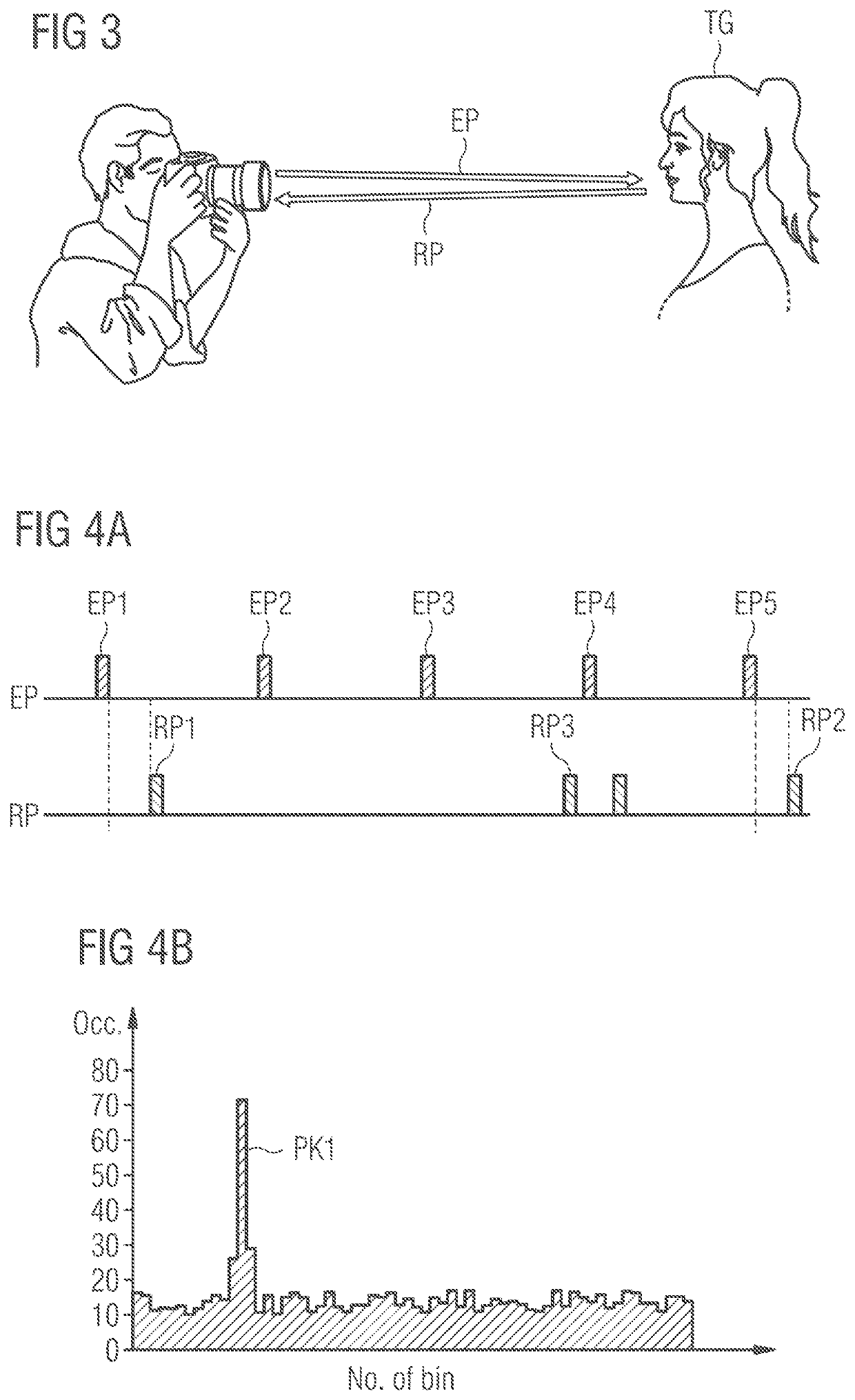
Method for calibrating a time-of-flight system and time-of-flight system
PendingUS20200271765A1Reduce the impactAccurate measurementWave based measurement systemsTime of flight sensorControl signal
A method is presented for calibrating a time-of-flight system having a time-of-flight sensor located behind a cover plate. The method involves emitting a plurality of sending pulses of light in response to respective trigger pulses of a control signal and detecting received pulses of light. Respective difference values are determined which are representative of a time period between one of the sending pulses and one of the received pulses. The difference values are accumulated into a number of bins of at least one histogram. The method further involves recording at least one crosstalk response in the histogram within a predetermined range of bins, and calibrating the histogram using the recorded crosstalk response. Finally, an output signal is generated which is indicative of a time-of-flight based on an evaluation of the calibrated histogram.
Owner:AMS AG
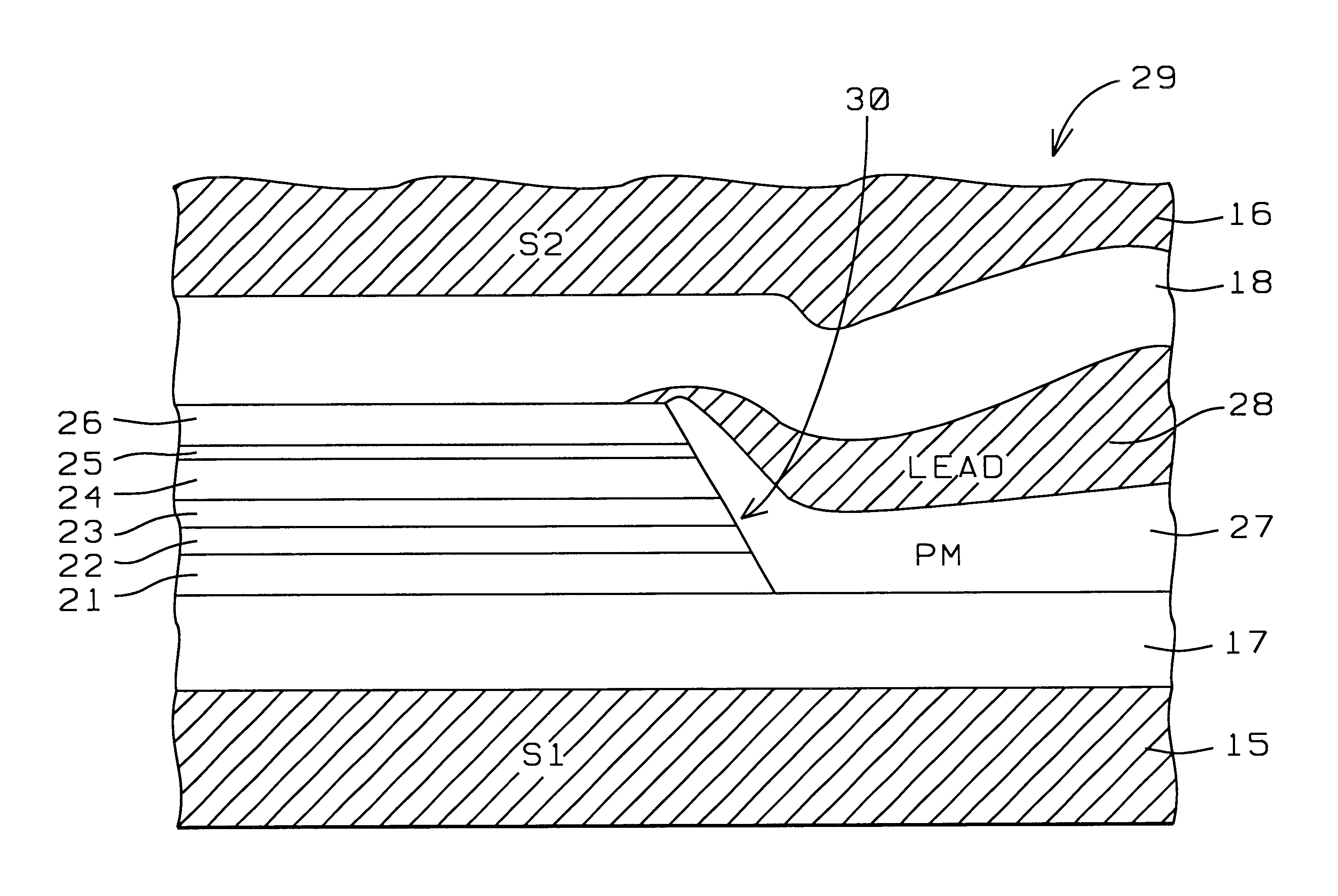
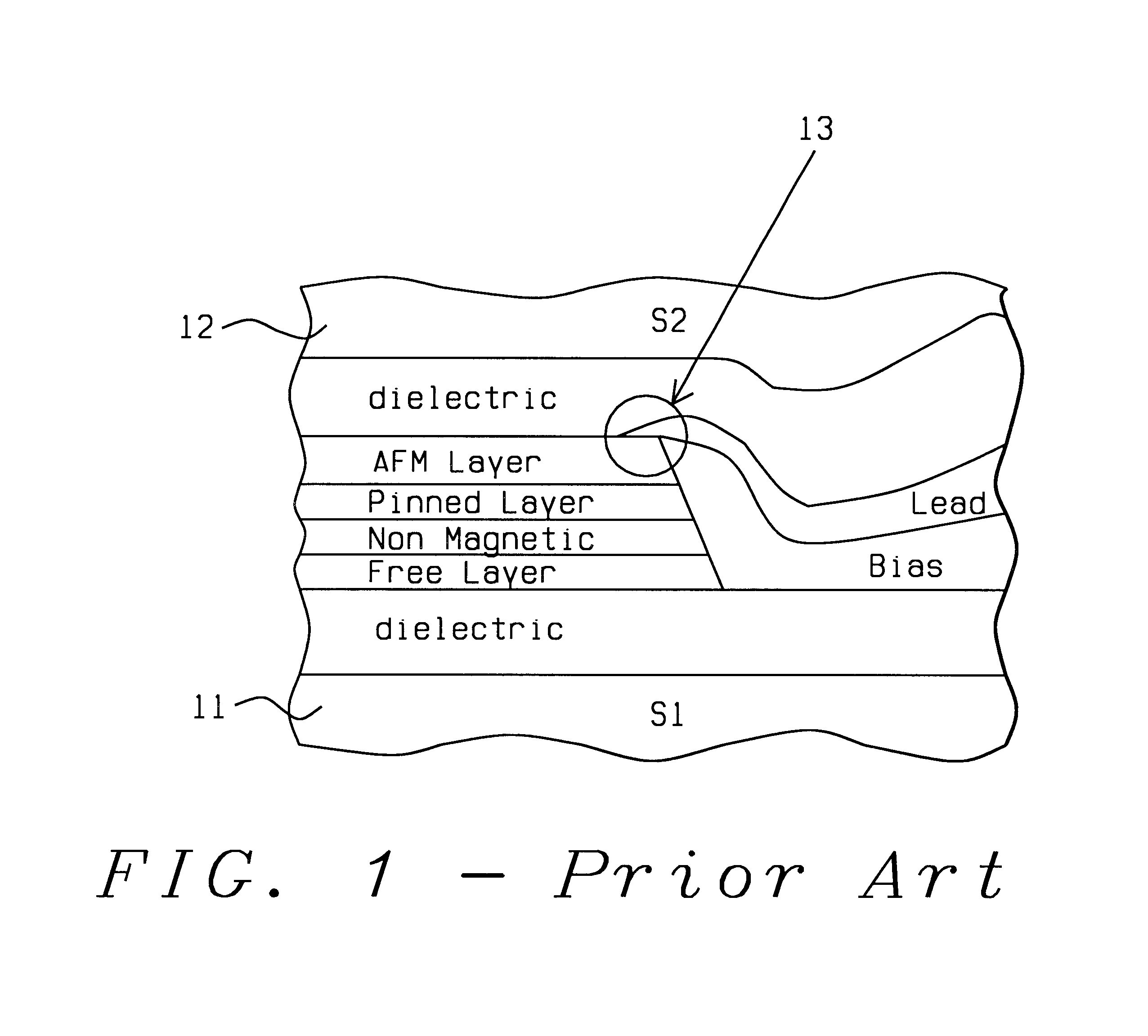
Process to manufacture a top spin valve
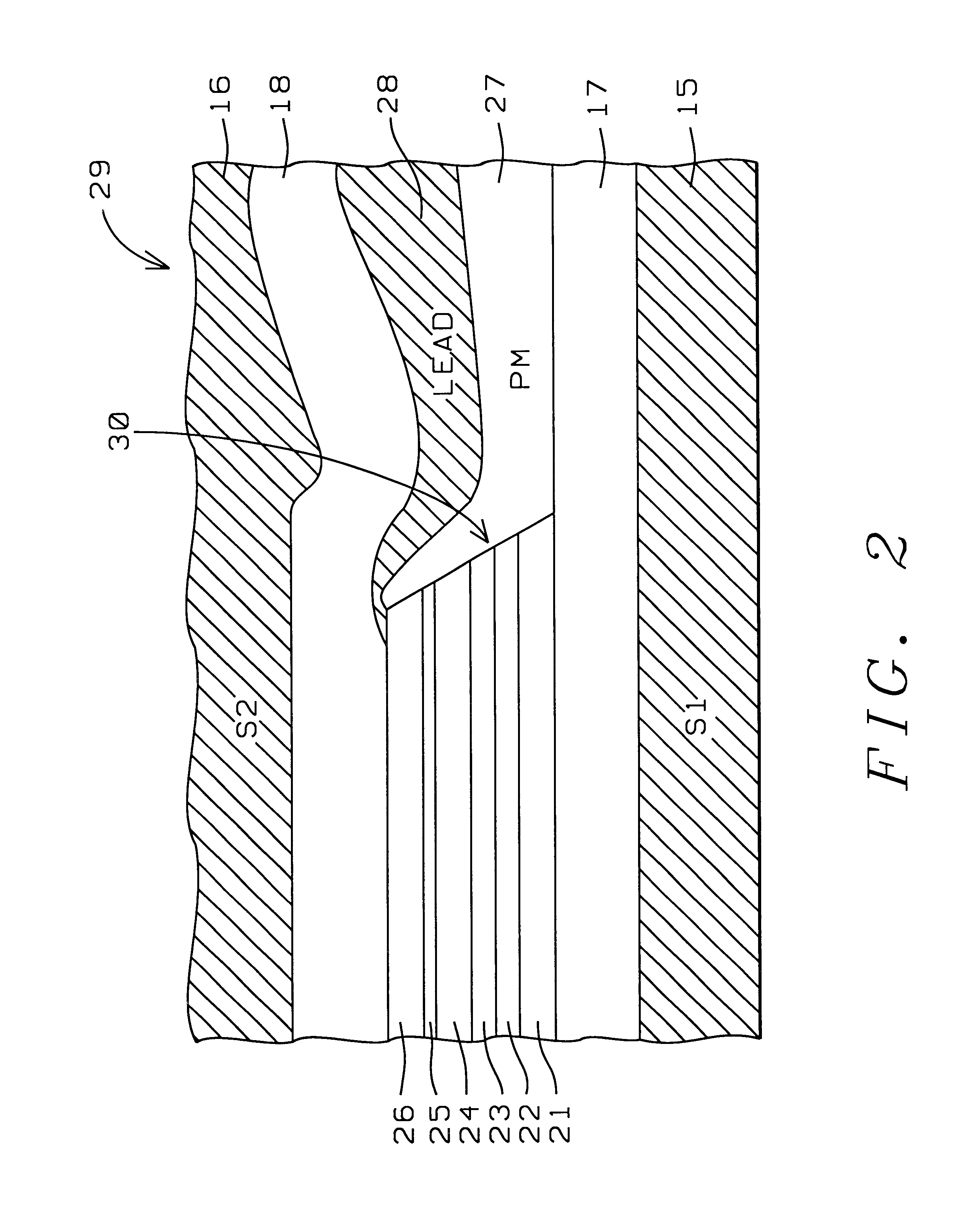
InactiveUS6885527B1Large shield-to-shield spacingNarrow feedback pulse widthLiquid surface applicatorsSolid-state devicesRotary valveEngineering
Currently, the shield-to-shield separation of a spin valve head cannot be below about 800 Å, mainly due to sensor-to-lead shorting problems. This problem has now been overcome by inserting a high permeability, high resistivity, thin film shield on the top or bottom (or both) sides of the spin valve sensor. A permeability greater than about 500 is required together with a resistivity about 5 times greater than that of the free layer and an MrT value for the thin film shield that is 4 times greater than that of the free layer. Five embodiments of the invention are described.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Ultra-wide band imaging method and device with enhanced focusing
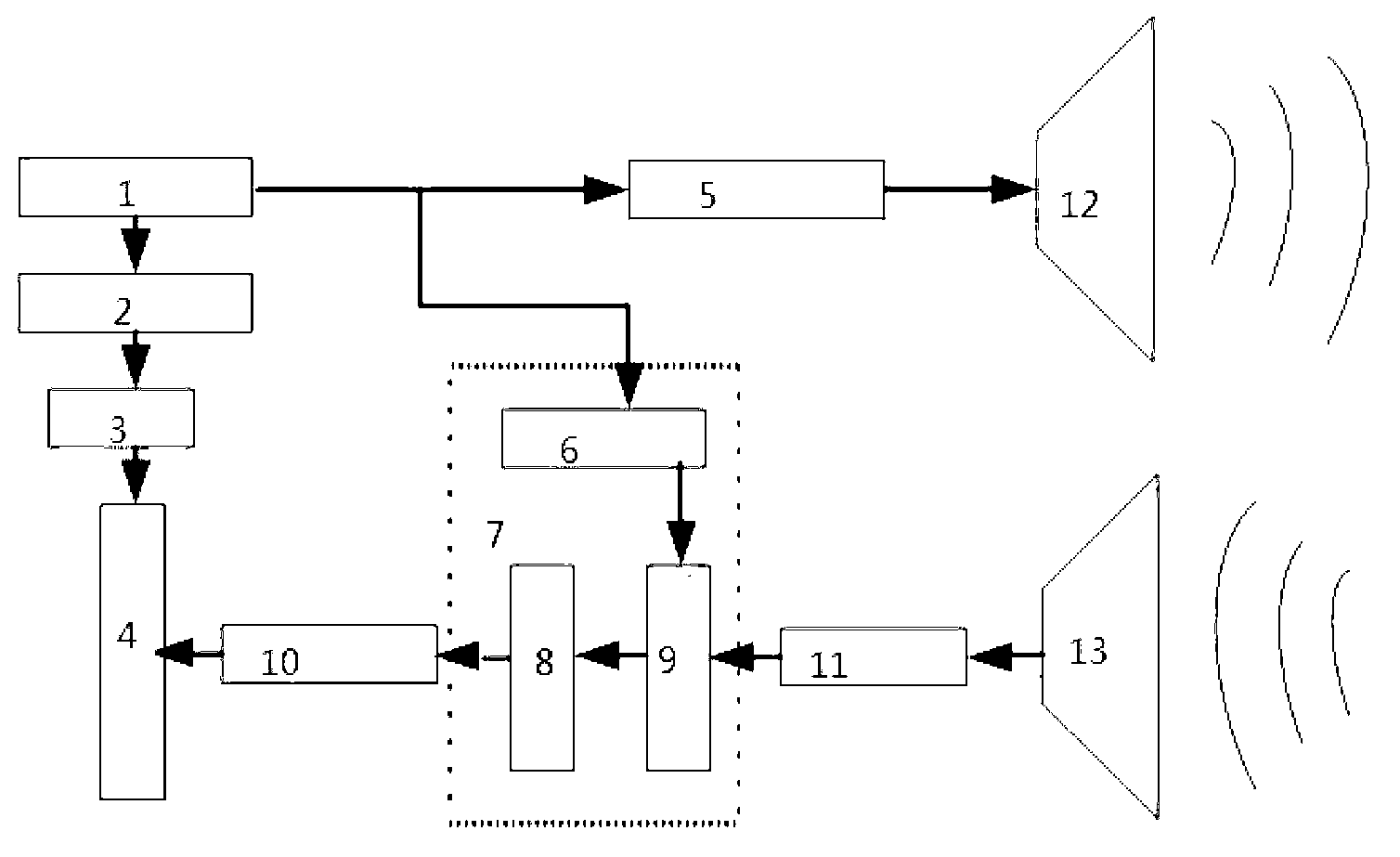
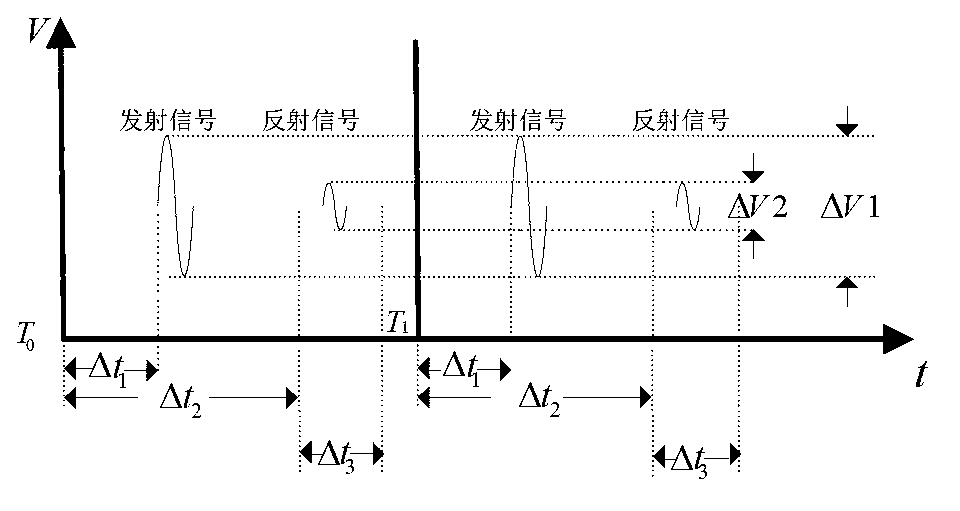
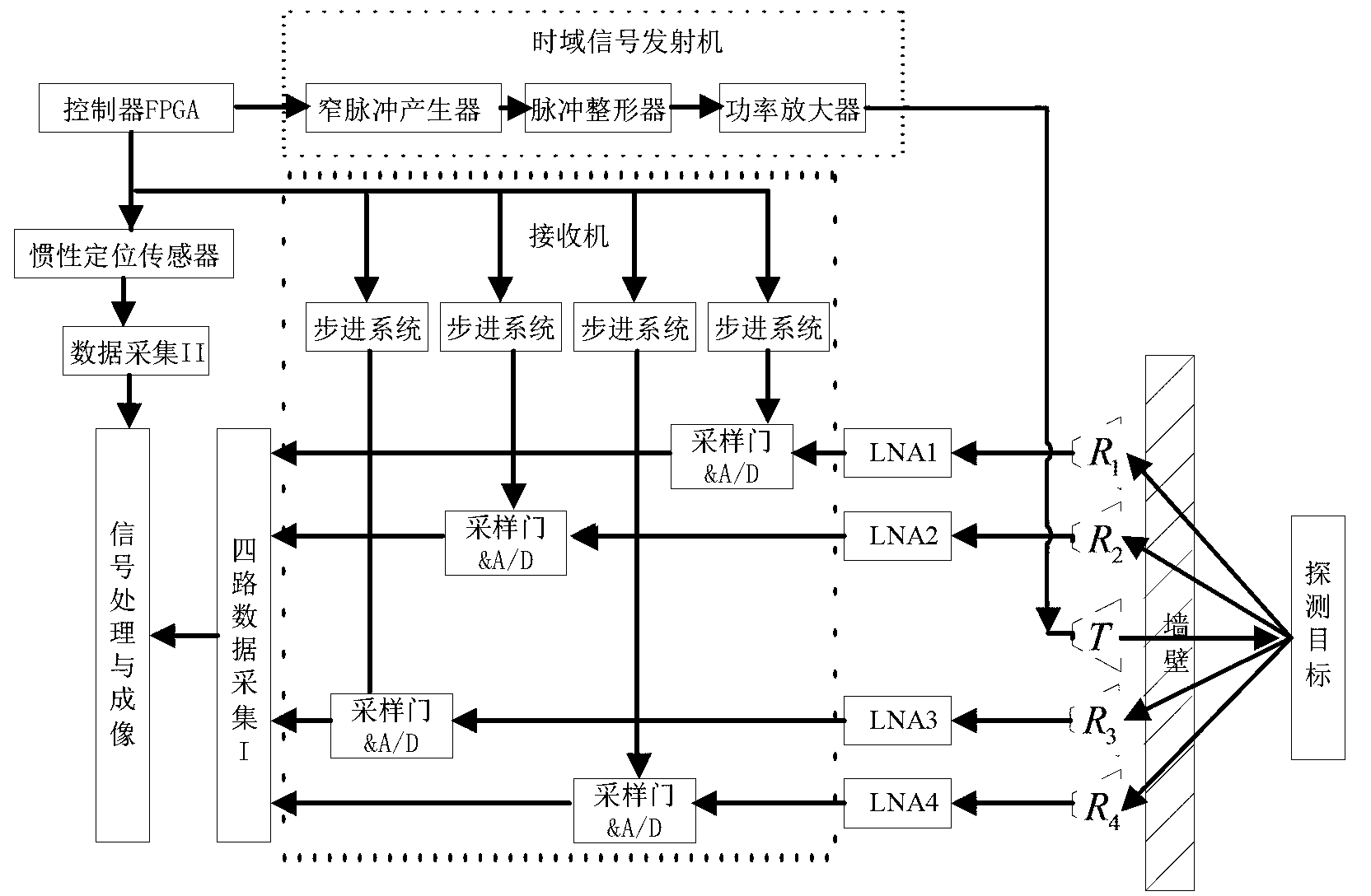
ActiveCN103176182ANarrow pulse widthHigh positioning accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumData acquisition
The invention discloses an ultra-wide band imaging method and device with enhanced focusing. A controller FPGA (filed programmable gate array) 1 controls a time domain transmitter to transmits a narrow pulse signal with nanosecond width and high band-width frequency spectrum. The narrow pulse signal is radiated by a transmitting antenna array 12 to probe a target. A receiving antenna array transmits a received weak reflection signal to a noise amplifier 11, the amplified signal enters a receiver 7, the receiver 7 analyzes the received high-speed weak signal into a digital signal, and the digital signal is transmitted to a signal processing and imaging module 4 through a multi-channel data acquisition unit 10. In the mean time, the controller FPGA 1 controls an inertial positioning sensor 2 to measure acceleration of equipment in real time, a data acquisition unit 3 transmits the measuring result to the signal processing and imaging module 4, and the position of the target is analyzed through an imaging algorithm program.
Owner:山东山科感测智慧科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com