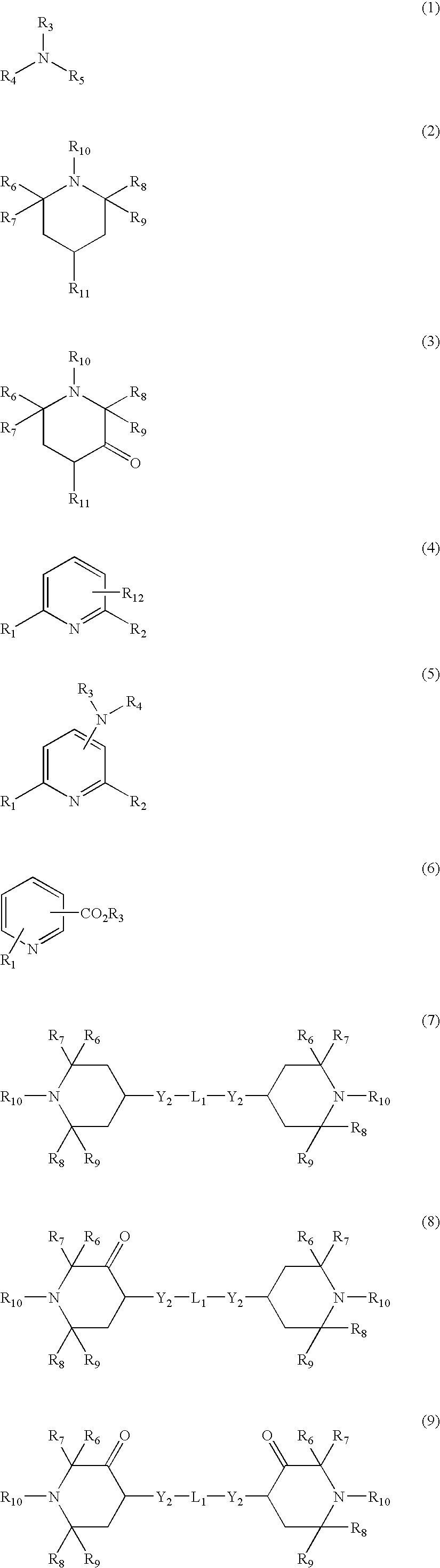
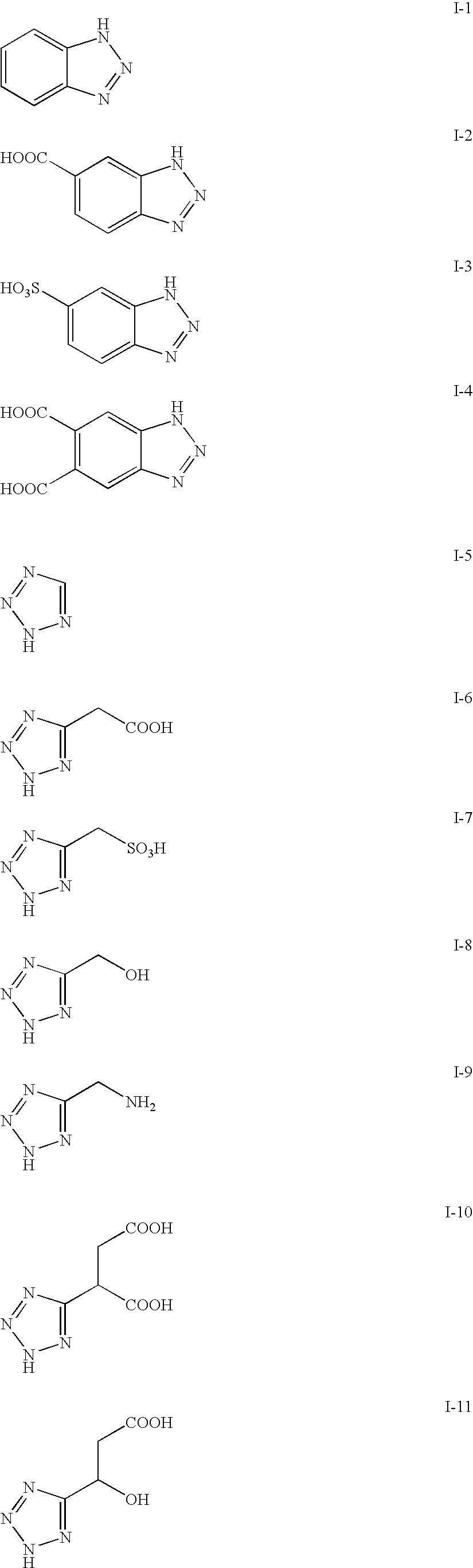
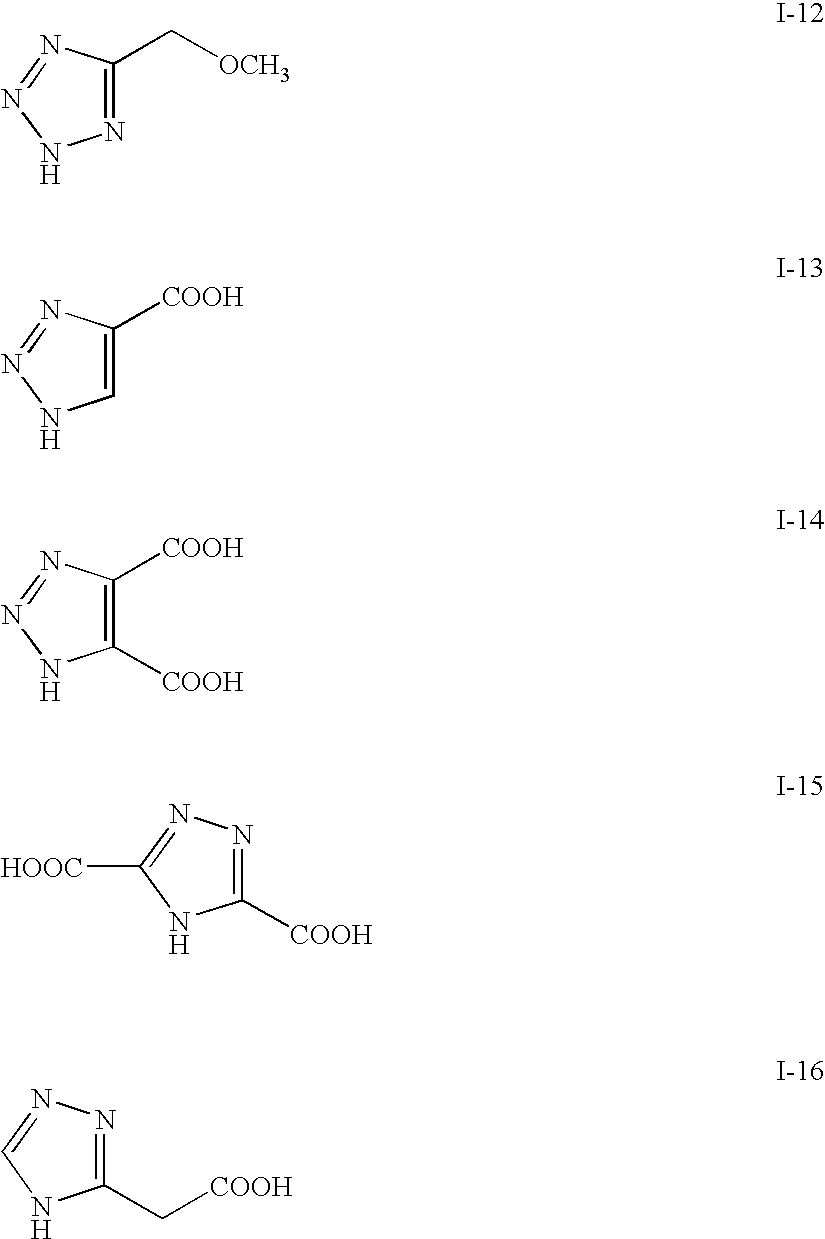
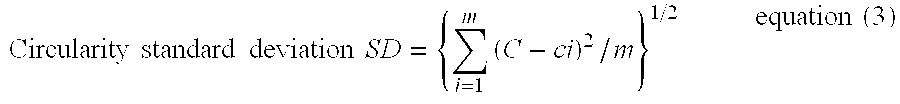Patents
Literature
112 results about "Aluminium atom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diagram of aluminum atom. Aluminum is one of the heavier atoms that forms inside a red giant star after a star begins to run out of fuel. An atom of aluminum has 13 protons, 14 neutrons, and 13 electrons, so it’s a kind of metal.
Ansa group 4 metal bis ( mu -substituted) aluminum complexes
InactiveUS6140521AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationBridging ligandAluminum metal
Ansa bis( mu -substituted) Group 4 metal and aluminum compounds comprising a single Group 4 metal atom and two aluminum metal atoms corresponding to the formula: wherein: L' is a pi -bonded group, M is a Group 4 metal, J is nitrogen or phosphorus; Z is a divalent bridging group causing the complex to have an ansa structure, R' is an inert monovalent ligand; r is one or two; X independently each occurrence is a Lewis basic ligand group able to form a mu -bridging ligand group, and optionally the two X groups may be joined together, and A' independently each occurrence is an aluminum containing Lewis acid compound that forms an adduct with the metal complex by means of the mu -bridging groups, and optionally two A' groups may be joined together thereby forming a single difunctional Lewis acid containing compound, and a method of preparation comprising contacting a charge-neutral Group IV metal coordination complex having at least two Lewis basic groups with at least two molar equivalents of charge-neutral aluminum coordination complexes having Lewis acidic aluminum atoms such that at least two of the aluminum atoms of the aluminum coordination complexes bond to at least two of the Lewis basic groups of the Group IV coordination complex.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
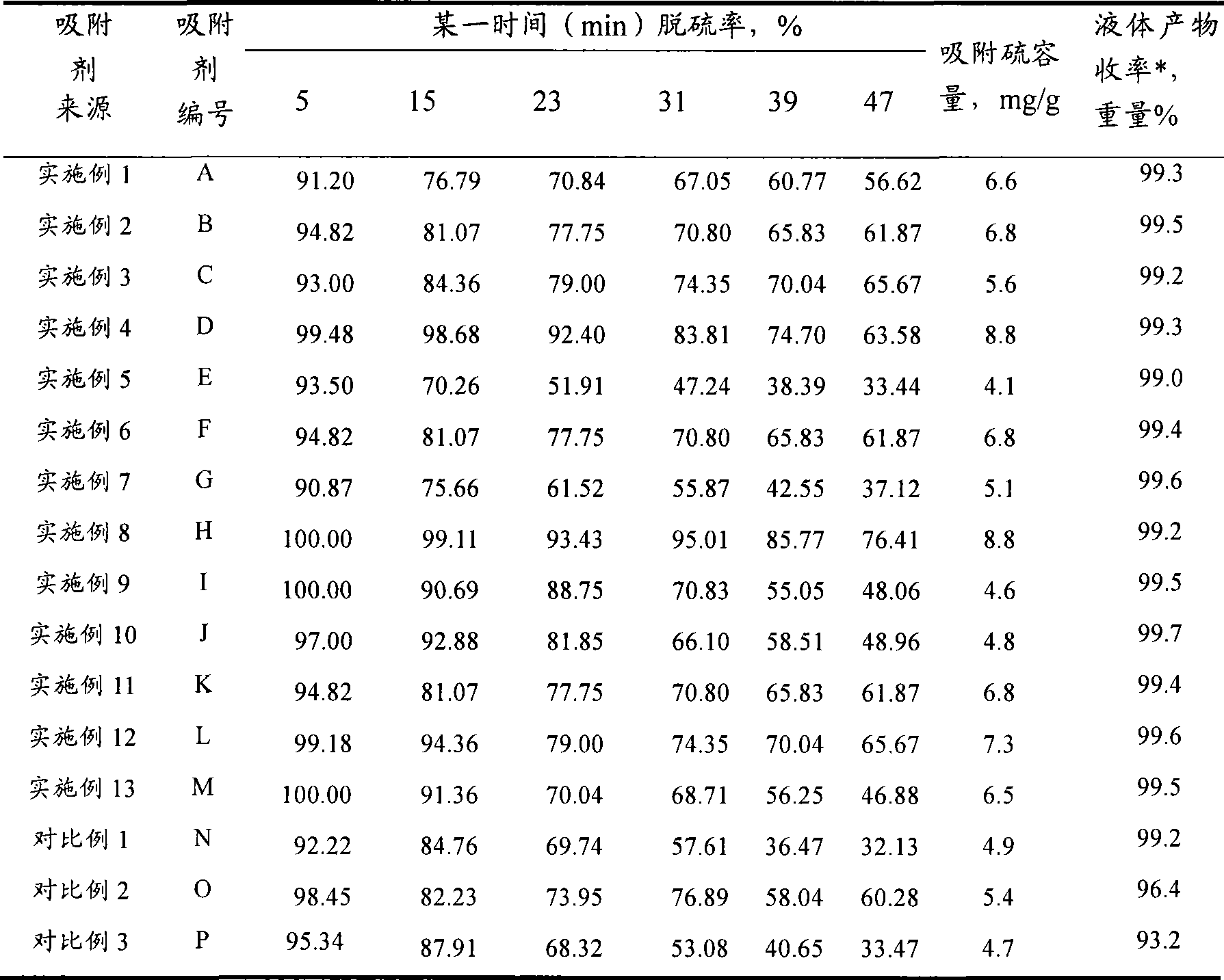
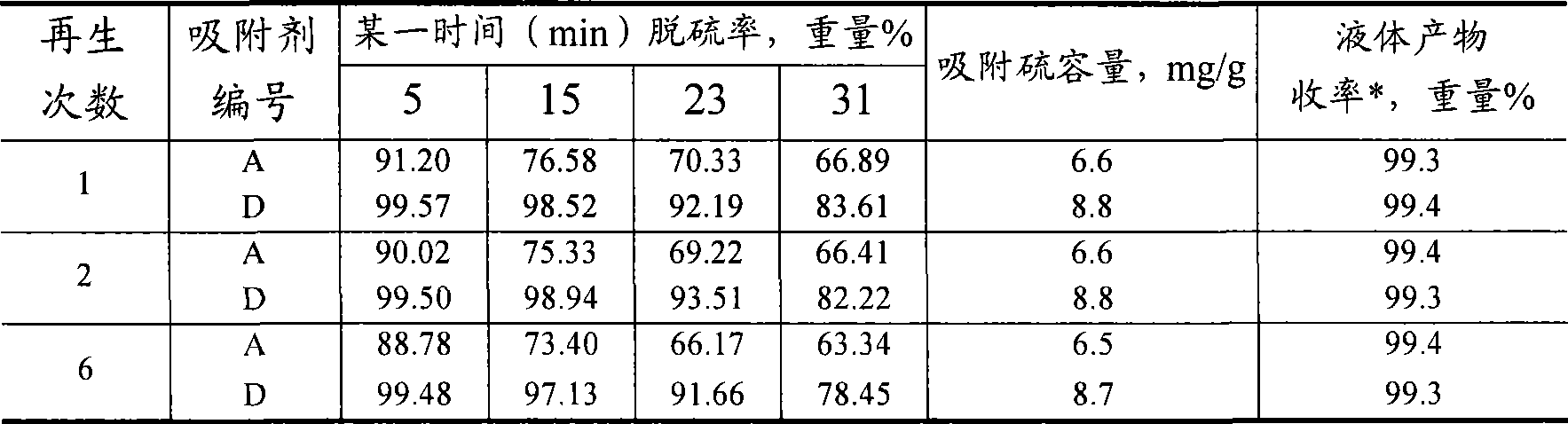
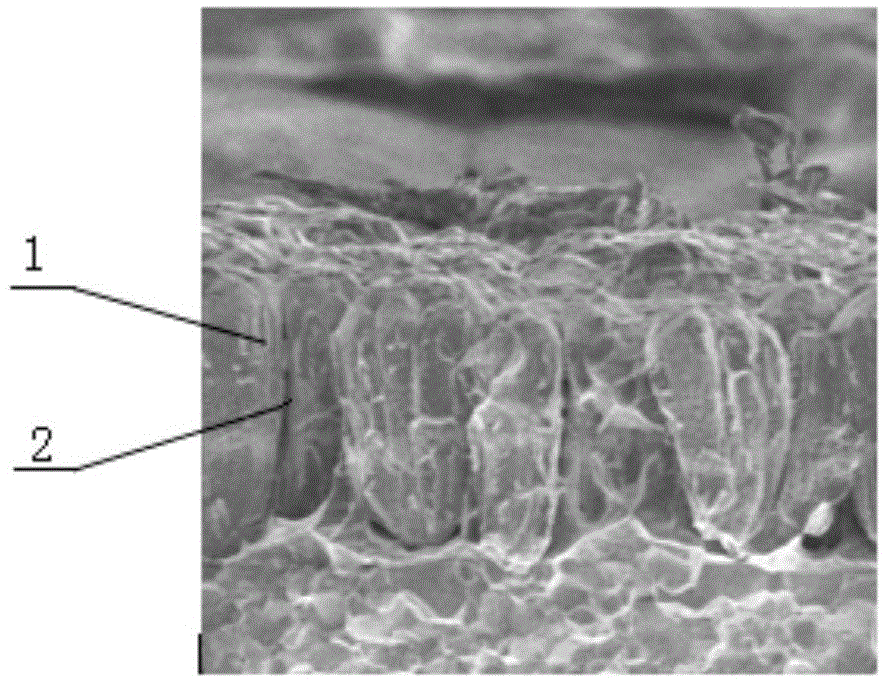
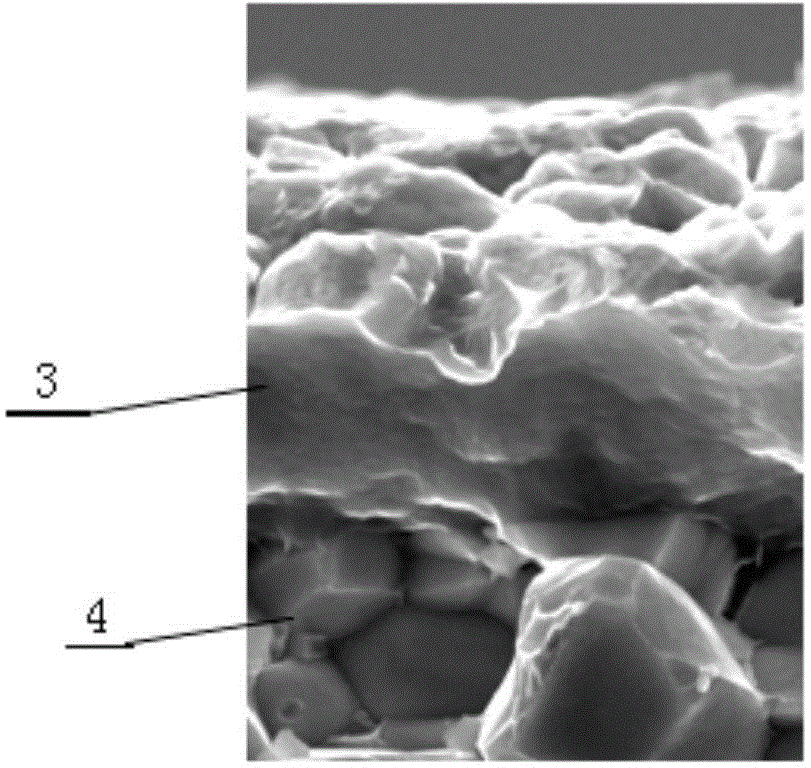
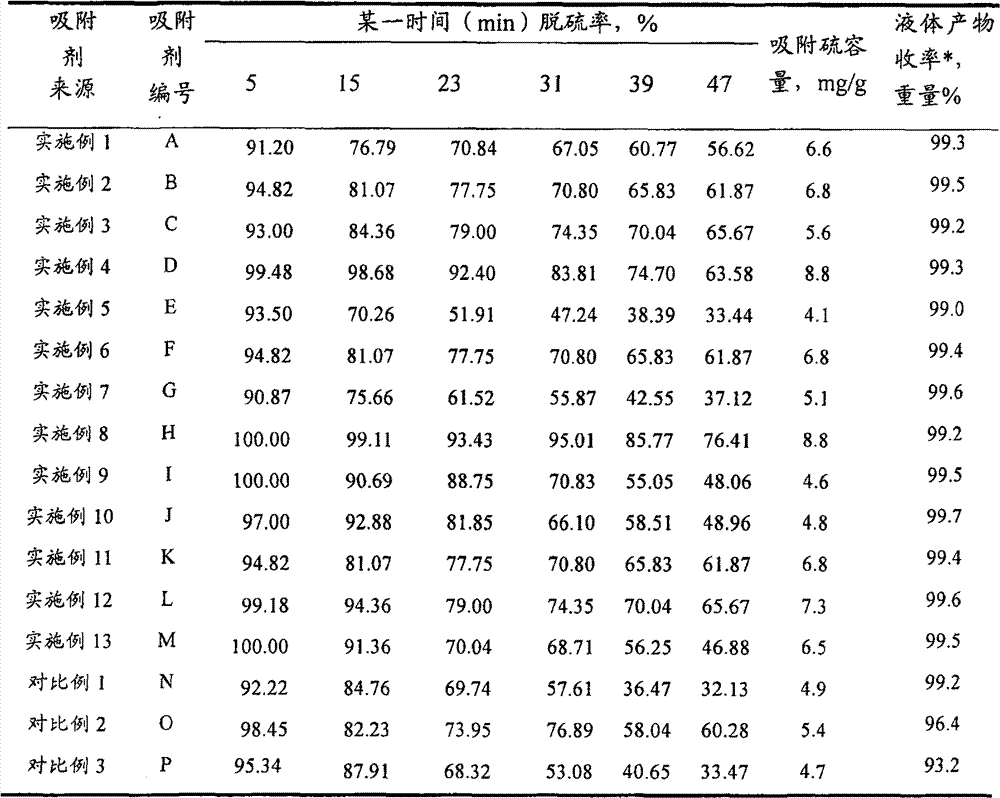
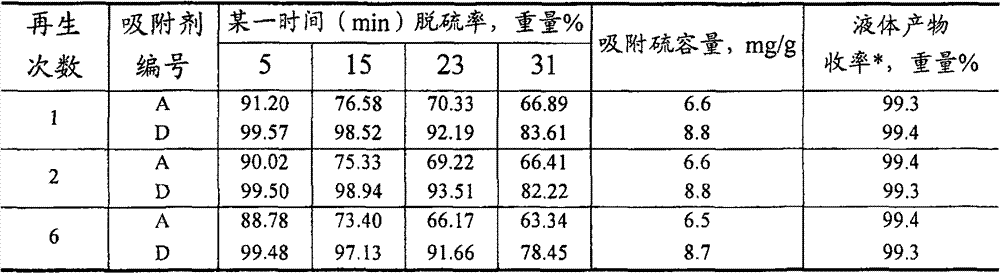
Hydrocarbon oil desulphurization adsorbing agent and use method thereof
ActiveCN101481627AUniform pore structureLarge adsorption and desulfurization capacityHydrocarbon oils refiningMolecular sieveSulfur
A spraytex desulfurization sorbent contains molecular sieve and metal oxide having the function of absorbing sulfur; wherein, the mol ratio between silicon atom and aluminium atom of the molecular sieve is 50-750, and the weight ratio between the molecular sieve and metal oxide having the function of absorbing sulfur is 45-98:2-55. The desulfurization sorbent has large capacity, and can be used for absorbing and decarbolizing spraytex, thus having high desulfurization efficiency and high yield of the spraytex.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Aluminum containing polyester polymers having low acetaldehyde generation rates
ActiveUS20070066791A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCeramic shaping apparatusPolyesterPolymer science
A polyester polymer composition containing polyester polymers such as polymers having repeating ethylene terephthalate units, aluminum atoms in an amount of at least 3 ppm based on the weight of the polymer, the polyester polymers having an It.V. of at least 0.72 dL / g obtained through a melt phase polymerization and a residual acetaldehyde level of 10 ppm or less. Also provided are polyester polymer compositions containing polyester polymers and: (i) aluminum atoms (ii) alkaline earth metal atoms or alkali metal atoms or alkali compound residues, and (iii) a catalyst deactivator such as a phosphorus compound. The phosphorus compound is added to the polyester melt either late in the polycondensation or upon remelting a solid polyester polymer. The polyester polymer exhibits good L* brightness, clarity, and low levels of acetaldehyde generated upon melting.
Owner:ALPEK POLYESTER SA DE CV
Metal-polishing composition and chemical-mechanical polishing method
InactiveUS20080057716A1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaSilicon dioxide
A metal-polishing composition includes colloidal silica particles, which has a ratio of minor axis / major axis of 0.2 to 0.8 and a surface at least partially covered with aluminum atoms, comprises in an amount of 50% or more with respect to total abrasives. The metal-polishing composition preferably includes an oxidizing agent, an organic acid or the like. The colloidal silica constituting the colloidal silica particles is preferably formed by hydrolysis of alkoxysilane. The major axis of the colloidal silica particles is preferably in a range of 20 nm to 100 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Toner
InactiveUS8497054B2Improve charging effectExcessive charging can be suppressedDevelopersSiliconAluminium atom
Provided is a toner in which faulty transfer under an extremely-low-temperature, low-humidity environment hardly occurs, including toner particles and a zeolite as an external additive, in which a ratio of the alminium atoms to a total of the silicon atoms and the aluminium atoms contained in the zeolite is 0.2 to 24.0%.
Owner:CANON KK
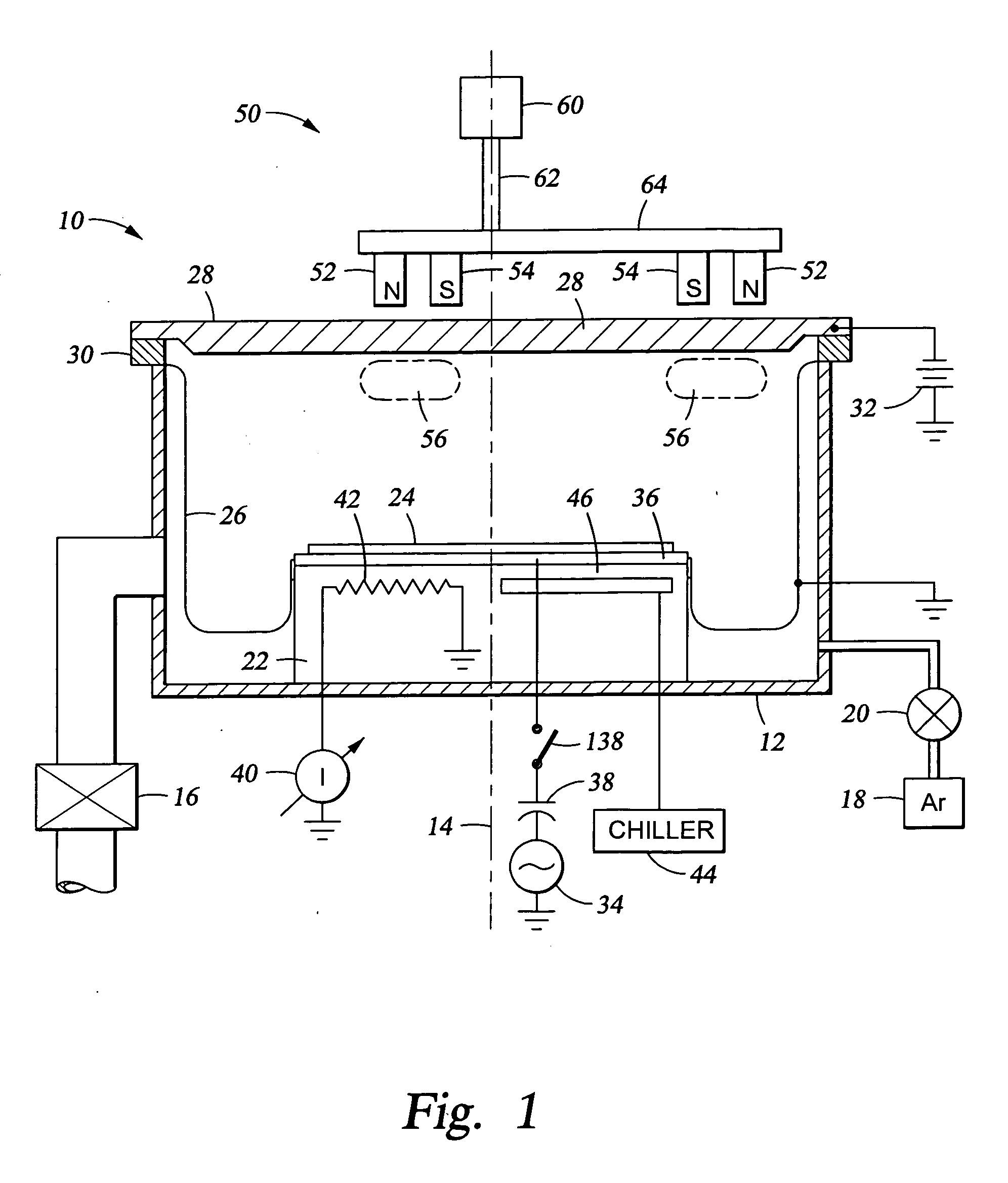
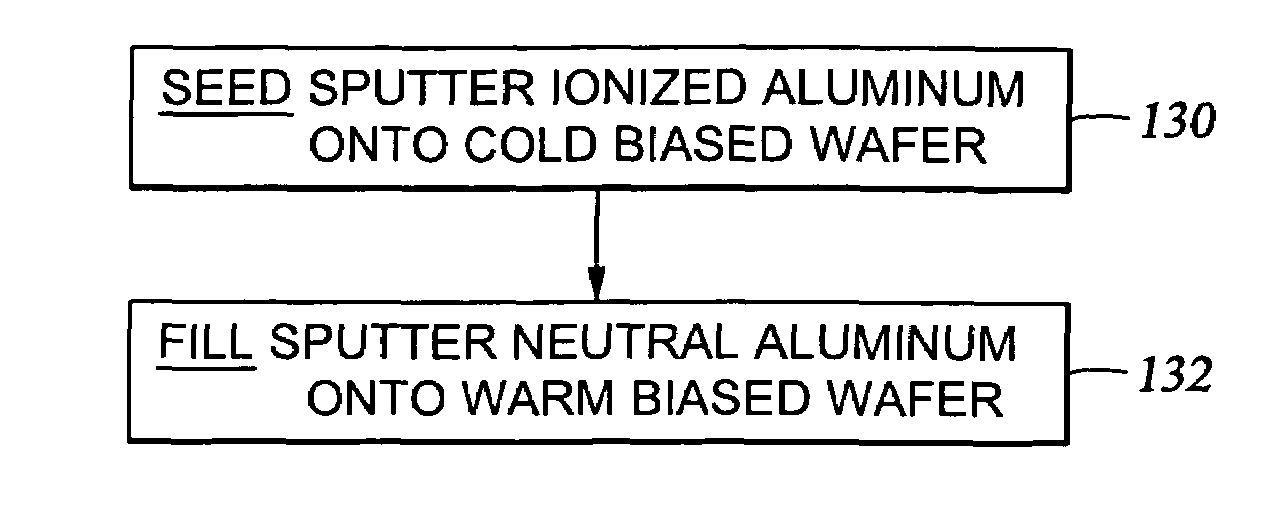
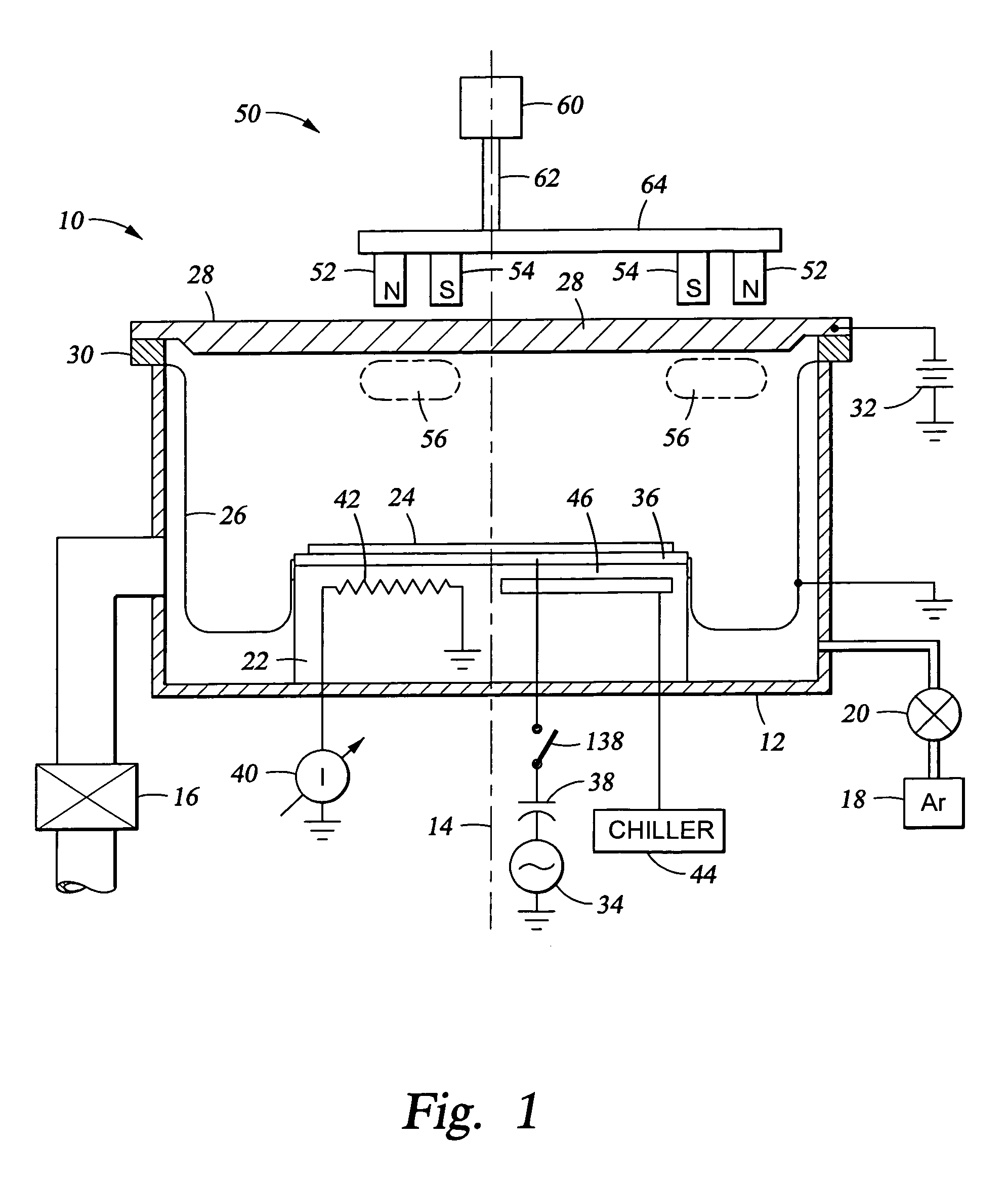
Aluminum sputtering while biasing wafer
An aluminum sputtering process including RF biasing the wafer and a two-step aluminum fill process and apparatus used therefor to fill aluminum into a narrow via hole by sputtering under two distinctly different conditions, preferably in two different plasma sputter reactors. The first step includes sputtering a high fraction of ionized aluminum atoms onto a relatively cold wafer, e.g., held at less than 150° C., and relatively highly biased to attract aluminum atoms into the narrow holes and etch overhangs. The second step includes more neutral sputtering onto a relatively warm wafer, e.g. held at greater than 250° C., and substantially unbiased to provide a more isotropic and uniform aluminum flux. The magnetron scanned about the back of the aluminum target may be relatively small and unbalanced in the first step and relatively large and balanced in the second.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Transition-metal-containing zeolite
InactiveUS20150218007A1Increased durabilityHigh catalytic activityAluminium compoundsGlass/slag layered productsHydrothermal synthesisSilicon
A transition-metal-containing silicoaluminophosphate zeolite having excellent high-temperature hydrothermal durability is easily and efficiently produced. A method for producing a transition-metal-containing zeolite that contains a silicon atom, a phosphorus atom, and an aluminum atom in at least its framework structure includes hydrothermal synthesis using an aqueous gel containing a silicon atom raw material, an aluminum atom raw material, a phosphorus atom raw material, a transition metal raw material, and a polyamine (other than diamines). A transition-metal-containing silicoaluminophosphate zeolite produced by hydrothermal synthesis using a zeolite raw material and the aqueous gel containing the transition metal raw material and the polyamine has excellent high-temperature hydrothermal durability and high catalytic activity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Preparation method for silicon-aluminium composite oxide with controllable pore structure
The invention discloses a preparation method for a silicon-aluminium composite oxide with a controllable pore structure. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: neutralizing an aluminium source compound and a silicon source compound to form gel under normal pressure; after the gel is formed, and transferring the gel into a high-pressure kettle; controlling certain conditions to perform hydrothermal aging, performing solid-liquid separation, washing and drying to obtain silicon-aluminium composite oxide powder with different pore sizes. Compared with the prior art, neutralizing-hydrothermal treatment is performed on the silicon-aluminium composite oxide in the method, so that reactants are fully and uniformly mixed; an effective mutual effect between silicon atoms and aluminium atoms is ensured; the syneresis depth of silicon-aluminium gel is regulated by controlling different hydrothermal conditions and hydrothermal times, so that the gels with different skeleton strengths are obtained; therefore, the pore structure of the silicon-aluminium gel can be regulated in a lager range; the proportion of the effective pore accounting for the prepared silicon-aluminium composite oxide is obviously improved; 80 percent of the pores are distributed within the range of + / -2nm in a concentrated manner.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Transition-metal-containing zeolite
ActiveUS20130266785A1Excellent hydrothermal durabilityHigh catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesHydrothermal synthesisSilicon
A transition-metal-containing silicoaluminophosphate zeolite having excellent high-temperature hydrothermal durability is easily and efficiently produced. A method for producing a transition-metal-containing zeolite that contains a silicon atom, a phosphorus atom, and an aluminum atom in at least its framework structure includes hydrothermal synthesis using an aqueous gel containing a silicon atom raw material, an aluminum atom raw material, a phosphorus atom raw material, a transition metal raw material, and a polyamine (other than diamines). A transition-metal-containing silicoaluminophosphate zeolite produced by hydrothermal synthesis using a zeolite raw material and the aqueous gel containing the transition metal raw material and the polyamine has excellent high-temperature hydrothermal durability and high catalytic activity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Hydrocracking process using a zeolite modified by basic treatment
ActiveUS20110108459A1Good choiceHigh degreeAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsActive phaseChemistry
The present invention describes a hydrocracking and / or hydrotreatment process using a catalyst comprising an active phase containing at least one hydrogenating / dehydrogenating component selected from the group VIB elements and the non-precious elements of group VIII of the periodic table, used alone or in a mixture, and a support comprising at least one dealuminated zeolite Y having an overall initial atomic ratio of silicon to aluminium between 2.5 and 20, an initial weight fraction of extra-lattice aluminium atoms greater than 10%, relative to the total weight of aluminium present in the zeolite, an initial mesopore volume measured by nitrogen porosimetry greater than 0.07 ml·g−1 and an initial crystal lattice parameter a0 between 24.38 Å and 24.30 Å, said zeolite being modified by a) a stage of basic treatment comprising mixing said dealuminated zeolite Y with a basic aqueous solution, and at least one stage c) of thermal treatment.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Heat-resistant wrought magnesium alloy containing calcium and neodymium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105671390AImprove high temperature performanceUniform microstructureRare-earth elementUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a heat-resistant wrought magnesium alloy containing calcium and neodymium and a preparation method thereof. The heat-resistant wrought magnesium alloy comprises, by mass percentage, 2.5-3.5 wt.% of Al, 0.30-0.60 wt.% of Ca, 0.5-2.0 wt.% of Nd and the balance Mg and unavoidable impurities, wherein the total number of the impurities is smaller than 0.06 wt.%. The preparation method is realized by adding the alkaline-earth element calcium and the rare-earth element neodymium in a compounding mode in combination with a hot extrusion process. The certain amount of calcium is added in the Mg-Al system magnesium alloy and can be combined with aluminum atoms to form a high-melting-point Al2Ca phase; the rare-earth neodymium is added, so that the grain can be effective refined; meanwhile, the neodymium and the aluminum in the alloy can form a high-temperature stable rare earth phase, and the strength of the material is improved. The alloy subjected to hot extrusion has a compact structure and a fine grain size, thereby having high strength at high temperature and meanwhile guaranteeing certain plasticity (higher than 39%).
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Alkene oligomerization process
ActiveCN102471702AMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionAqueous sodium hydroxideAlkene
Disclosed is a process for producing a hydrocarbon fraction rich in components boiling in the range typical for diesel fuel comprising contacting a feedstock comprising one or more C2 to C10 alkenes with a modified zeolite catalyst having a one-dimensional micropore structure consisting of channels made from rings containing between 8 and 12 silicon / aluminium atoms at a temperature in the range 100 to 5000C and pressure in the range 0.1 to 200 bar characterised in that the modified zeolite catalyst is one which has been prepared by treating a corresponding zeolite precursor with an alkaline solution. The alkaline solution used to treat the zeolite precursor can be for example aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. Relative to equivalent untreated zeolites the modified zeolite catalysts described show improved catalyst life and selectivity to hydrocarbons boiling in the range 250 to 3500C.
Owner:BP OIL INT LTD +1
Method for manufacturing paper board
ActiveCN102733262AImprove sizing effectWater-repelling agents additionPaper/cardboardAluminium sulfatePaperboard
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a paper board, wherein the paperboard is provided with an excellent sizing property and an excellent showing performance even if under a condition of using a paper pulp containing a lot of aluminium component or a condition of not adding calcium carbonate. The method for manufacturing a paper board comprises the steps of using a polymerized component at least containing (methyl) acrylamide (a1) and diallyl amine or salt thereof to obtain (methyl) acrylamide copolymer and ketene dipolymer sizing agent (B), and manufacturing papers with a base material paper pulp containing waste paper pulp and aluminium atoms converted for more than one wt.% from 16 aluminum sulfate hydrate relative to the drying weight of the base material paper pulp under a PH value of 6-8.
Owner:ARAKAWA CHEM IND LTD
Multilayer structure, device using the same, method for producing the multilayer structure, and method for producing the device
ActiveUS20150155409A1Highly reliable barrier propertyIncreased durabilitySynthetic resin layered productsSolid-state devicesIr absorptionAbsorbance spectra
Provided are a novel multilayer structure that can be used to protect a device and a device using the multilayer structure. The disclosed multilayer structure is a multilayer structure including a substrate and a barrier layer stacked on the substrate. The 3% strain tension of the substrate in at least one direction is at least 2000 N / m. The barrier layer contains a reaction product (R). The reaction product (R) is a reaction product formed by a reaction at least between a metal oxide (A) and a phosphorus compound (B). In an infrared absorption spectrum of the barrier layer in a range of 800 to 1400 cm−1, a wavenumber (n1) at which maximum infrared absorption occurs is in a range of 1080 to 1130 cm−1. A metal atom constituting the metal oxide (A) is essentially an aluminum atom.
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Catalyst for nitrogen oxide removal
InactiveUS20130281284A1Excellent nitrogen oxide removal performanceGood maintenance characteristicsGas treatmentMolecular sieve catalystsSlurryNitrogen oxide
[Object] To provide a catalyst for nitrogen oxide removal having no degradation problem caused by adsorbed water when a temperature is raised sharply and exhibiting excellent nitrogen oxide removal performance and retentive characteristic thereof.[Solution] A catalyst for nitrogen oxide removal, containing a metal-loading zeolite, wherein the zeolite contains a silicon atom, an aluminum atom, and a phosphorus atom in a framework structure, and the amount of water adsorption of the catalyst at 25° C. and a relative vapor pressure of 0.5 is 0.05 to 0.2 (kg-water / kg-catalyst) or less. A method for manufacturing this catalyst for nitrogen oxide removal, the method including the steps of drying a mixed slurry containing a metal source, the zeolite, and metal oxide particles having an average particle diameter of 0.1 to 10 μm and / or an inorganic binder and calcining the resulting dry powder.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PLASTICS INC
Recording sheets for ink jet printing
InactiveUS20050053735A1Good storage stabilityAvoid excessive changesPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyChemical compoundInorganic compound
A recording sheet for ink jet printing is described, which consists of a support having coated thereon at least one ink-receiving layer consisting of binders and at least one nanocrystalline, nanoporous inorganic compound, wherein the recording sheet contains polynuclear aluminium hydroxo complexes with at least 13 aluminium atoms. Aluminium hydroxo complexes containing polycations with 13 or 30 aluminium atoms are preferred.
Owner:ILFORD IMAGING SWITZERLAND GMBH
Hydrocracking process using a zeolite modified by basic treatment
ActiveUS20130090233A1Good choiceHigh degreeAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsActive phasePorosimetry
The present invention describes a hydrocracking and / or hydrotreatment process using a catalyst comprising an active phase containing at least one hydrogenating / dehydrogenating component selected from the group VIB elements and the non-precious elements of group VIII of the periodic table, used alone or in a mixture, and a support comprising at least one dealuminated zeolite Y having an overall initial atomic ratio of silicon to aluminium between 2.5 and 20, an initial weight fraction of extra-lattice aluminium atoms greater than 10%, relative to the total weight of aluminium present in the zeolite, an initial mesopore volume measured by nitrogen porosimetry greater than 0.07 ml·g−1 and an initial crystal lattice parameter a0 between 24.38 Å and 24.30 Å, said zeolite being modified by a) a stage of basic treatment comprising mixing said dealuminated zeolite Y with a basic aqueous solution, and at least one stage c) of thermal treatment.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Olefin Oligomerization Process
InactiveCN102295951AMolecular sieve catalystsLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionBoiling pointPotassium
Disclosed is a process for producing a hydrocarbon fraction rich in components boiling in the range typical for diesel fuel comprising contacting a feedstock comprising one or more C 2 to C 10 alkenes with a zeolite catalyst having partially neutralised acidity and a one-dimensional or two dimensional micropore structure consisting of channels made from rings containing between 10 and 12 silicon / aluminium atoms at a temperature in the range 373 to 773 K and pressure in the range 0.1 to 200 bar characterised in that the partially neutralized zeolite catalyst contains both protons and basic cations. The basic cations are preferably selected from the group comprising Group IA and IIA cations (preferably sodium, potassium, caesium or mixtures thereof). Relative to their equivalent fully protonic forms the partially neutralized zeolite catalysts described show improved catalyst life and selectivity to hydrocarbons
Owner:BP OIL INT LTD +1
Catalyst for polymerization of polyester, polyester and process for preparing polyester
The invention provides a polyester, preparation method thereof and polyester polymeric catalyst, wherein the polyester is prepared by polymeric catalysts using metal components expert for antimony and germanium as main metal components of the catalysts, capable of improving the block of filters during the formation, and selected from the group consisting of at least one of alkaline metals and compounds thereof and alkaline-earth metals and compounds thereof and the group consisting of at least one of aluminium and compounds thereof with the amounts making them meet with the followings formulas (1) and (2) that M is less than 0.05, and (2) M / Al is less than 20, where M represents the mol% in total of the alkaline metal atoms and alkaline-earth metal atoms in the polyester corresponding to the acid components, and Al represents the mol% of the aluminium atom in the polyester corresponding to the acid components. The polyester can be used for fibres, films, hollow moulds and the like.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
Aluminum sputtering while biasing wafer
An aluminum sputtering process including RF biasing the wafer and a two-step aluminum fill process and apparatus used therefor to fill aluminum into a narrow via hole by sputtering under two distinctly different conditions, preferably in two different plasma sputter reactors. The first step includes sputtering a high fraction of ionized aluminum atoms onto a relatively cold wafer, e.g., held at less than 150° C., and relatively highly biased to attract aluminum atoms into the narrow holes and etch overhangs. The second step includes more neutral sputtering onto a relatively warm wafer, e.g. held at greater than 250° C., and substantially unbiased to provide a more isotropic and uniform aluminum flux. The magnetron scanned about the back of the aluminum target may be relatively small and unbalanced in the first step and relatively large and balanced in the second.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
High-efficient and economical Cr-Al-Si co-cementation technology for steel
InactiveCN108286032AImprove conductivityLow costSolid state diffusion coatingAluminiumHigh concentration
The invention relates to a technology of carburizing Cr, Al and Si into the surface of steel simultaneously in a high-efficient and economical way so as to improve high-temperature-oxidation-resistance and abrasion-resistance of the steel. The cementation treatment temperature of the technology is between 750 DEG C to 900 DEG C; a cementation agent consists of high-carbon ferro-chrome powder, aluminum powder, iron powder, silicon carbonate, ammonia chloride powder, charcoal powder and the like; reaction of the high-carbon ferro-chrome, the silicon carbonate, the aluminum powder and the like with the ammonia chloride is promoted by utilizing an AC field; high-concentration active chromium atoms, silicon atoms and aluminum atoms are obtained at a condition which is lower than a traditional treatment temperature; the cementation speed of the chromium, aluminum and silicon at a low treatment temperature is effectively through the thermal effect of the AC field and an electromagnetic effect; and the cementation technique is stabilized and the cementation amount of the silicon in a cementation layer is adjusted by adjusting the adding amount of the iron powder. Compared with a traditional Cr-Al-Si co-cementation technology, the technology has the advantages that the treatment temperature is low; cost of raw materials is low; technological material costs can be greatly reduced; the cementation speed can be increased by as high as 6 times; and high-efficient and economical Cr-Al-Si co-cementation is realized.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing molecular sieve by using Hangjin 2# soil as raw material and prepared molecular sieve
ActiveCN102616802ALarge reservesExpand sourceCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesChemical industryPetrochemical
The invention relates to a method for preparing a molecular sieve by using Hangjin 2# soil as a raw material and a prepared molecular sieve. The method is used for preparing the molecular sieve by taking the Hangjin 2# soil as the raw material and taking sodium hydroxide as an activating agent through an alkali melting method. The method comprises the following specific steps of: (1), after mixing the Hangjin 2# soil with sodium hydroxide according to a certain proportion, roasting and activating; (2), after grinding a roasted product, mixing the roasted product with water or directly mixing the roasted product with water to prepare a mixed solution, and adjusting the mol ratio of silicon atoms to aluminium atoms of the mixed solution to 2.5-6.0 by adding or not adding aluminium sulphate; and (3), crystallizing the mixed solution prepared in the step (2), wherein the mol ratio of silicon atoms to aluminium atoms of the mixed solution meets with requirements. According to the invention, the method is simple and feasible; the material for preparing the molecular sieve comes from a variety of sources; the preparation cost of the molecular sieve is low; the purity of the molecular sieve (P type zeolite molecular sieve) disclosed by the invention is above 90%; and the method can be widely applied in the fields, such as environment protection, metallurgy, chemical industry, electronics, petrochemical engineering, natural gas and the like, in particular water treatment of denitrification and dephosphorization.
Owner:内蒙古天德科技发展股份有限公司
Catalyst for reducing nitrogen oxides and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20120028789A1Improve abilitiesLower capability requirementsMaterial nanotechnologyGas treatmentDesorptionWater vapor
The object is to provide an exhaust gas reduction catalyst that exhibit high nitrogen oxide reduction performance, and to provide a simple and efficient method for producing the catalyst, in which the amount of the waste liquid is reduced, further, an object of the invention is to provide a zeolite-containing catalyst for reducing nitrogen oxides, which does not use an expensive noble metal or the like and which has high nitrogen oxide reduction performance. The present invention relates to a catalyst for reducing nitrogen oxides, which comprises: zeolite at least containing an aluminium atom and a phosphorus atom in the framework thereof; and a metal supported on the zeolite, wherein a coefficient of variation of intensity of the metal is at least 20%, when performing an elemental mapping of the metal in the catalyst with an electron probe microanalyzer, and, a catalyst for reducing nitrogen oxides, which comprises the zeolite containing at least a silicon atom, a phosphorus atom and an aluminium atom, and having an adsorption retention rate of at least 80% in a water vapor cyclic adsorption / desorption test at 90° C.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Two-dimensional ultra-thin SAPO-34 molecular sieve sheeting material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108975345AContent adjustableHuge external areaMaterial nanotechnologyMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular sieveCrystal structure
The invention discloses a two-dimensional ultra-thin SAPO-34 molecular sieve sheeting material. The thickness is 1-25 nanometers, and a crystal structure is a SAPO-34 molecular sieve, wherein a silicon / aluminium atom ratio is 0.05-0.3. The two-dimensional ultra-thin SAPO-34 molecular sieve sheeting material is characterized in that cheap easy-to-get aluminium phosphate, a silicon source and organic amine are used as reactants, through a chemical method, a layered precursor is exfoliated, and then gaseous phase crystallization is conducted to prepare the two-dimensional ultra-thin SAPO-34 molecular sieve sheeting material. The two-dimensional ultra-thin SAPO-34 molecular sieve sheeting material has a an enormous surface area, the silicon content is adjustable in a certain range, and a method is pervasive; the material has multiple advantages and can be subjected to industrial large-scale production; the method is little in template usage, suitable for industrial large-scale production and low in cost, and basically, no environmental pollution is generated. The invention discloses the preparation method of the two-dimensional ultra-thin SAPO-34 molecular sieve sheeting material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Magnet surface treatment method
InactiveCN104419926AIncrease ionization rateImprove anti-corrosion performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHigh energyEvaporation
The invention provides a magnet surface treatment method which comprises: a step of vacuum ion plating, and a step of passivation treatment of the plated film in a passivating solution containing trivalent chromate. When compared with a pure evaporation plating method, the vacuum ion evaporation plating method adopted by the invention has an additional ion source, and thus provides a high ionization rate for aluminium atoms. Aluminium ions are accelerated by a negative bias electric field, and are deposited on a product surface with a higher energy; thus a continuous plated layer without crystal boundaries is formed; the bonding force between the plated layer and the substrate is good; and better anticorrosion effect of the plated layer is achieved. In addition, according to the invention, the product subjected to vacuum ion evaporation aluminization is passivated by trivalent chromate, which provides the plated layer with very good anticorrosion performance, and prevents environment pollution.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONG KE SAN HUAN HI TECH
Hydrocarbon oil desulphurization adsorbing agent and use method thereof
ActiveCN101481627BUniform pore structureLarge adsorption and desulfurization capacityHydrocarbon oils refiningMolecular sieveSorbent
A spraytex desulfurization sorbent contains molecular sieve and metal oxide having the function of absorbing sulfur; wherein, the mol ratio between silicon atom and aluminium atom of the molecular sieve is 50-750, and the weight ratio between the molecular sieve and metal oxide having the function of absorbing sulfur is 45-98:2-55. The desulfurization sorbent has large capacity, and can be used for absorbing and decarbolizing spraytex, thus having high desulfurization efficiency and high yield of the spraytex.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
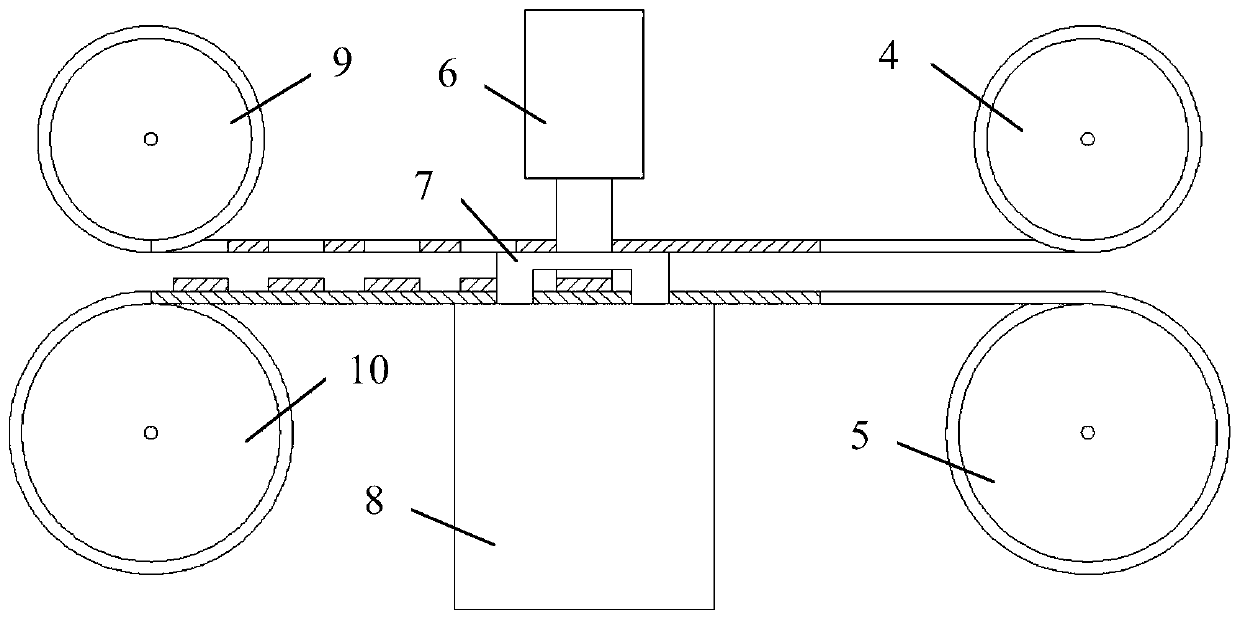
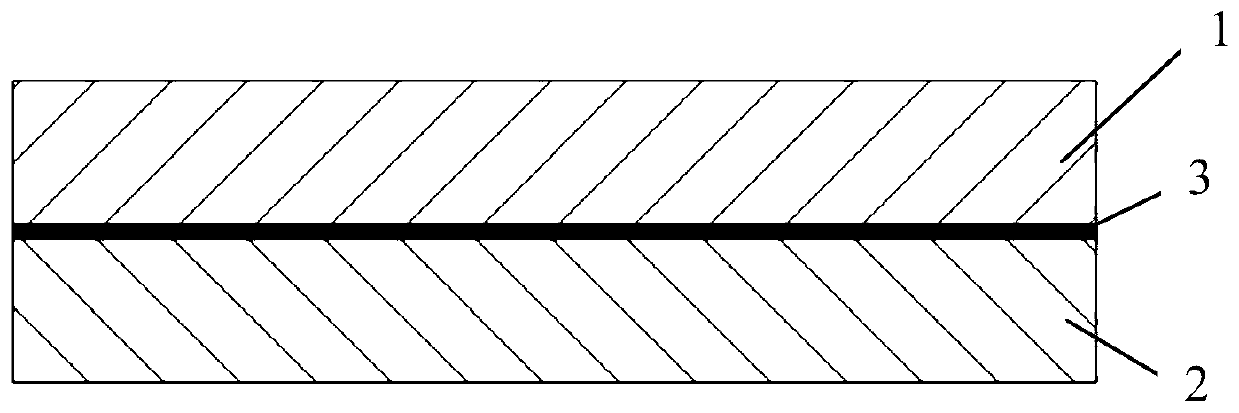
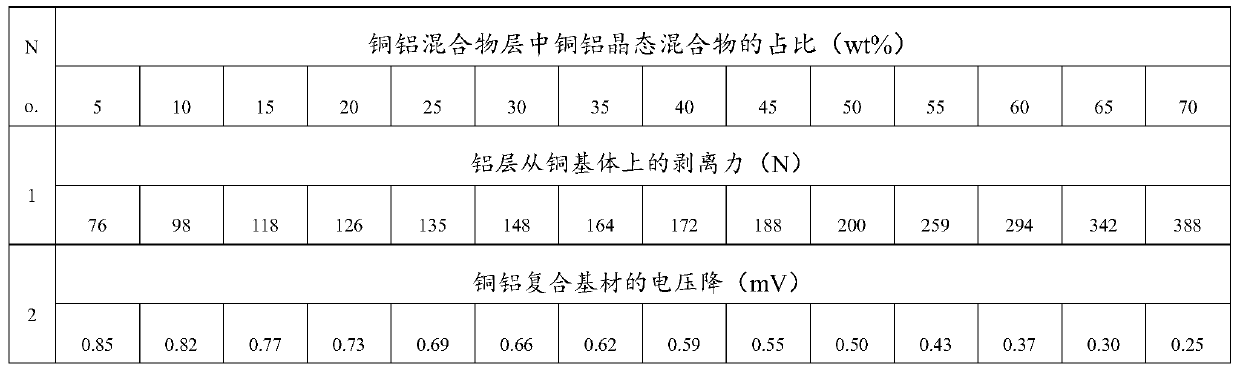
Copper-aluminum composite substrate and pressure diffusion welding method and application thereof
ActiveCN110216939AAvoid Galvanic CorrosionImprove electrical performanceConductive materialLaminationElectrochemistryAluminum composites
The invention discloses a copper-aluminum composite substrate comprising a copper matrix and an aluminum layer. The aluminum layer is disposed on at least one surface of the copper matrix, and a copper-aluminum mixture layer in which copper and aluminum atoms are interpenetrated or copper and aluminium atoms are bonded to each other is formed between the copper matrix and the aluminum layer, withthe copper-aluminum mixture layer containing at least 50 wt% of a copper-aluminum crystalline mixture. The invention also discloses a pressure diffusion welding method and application of the copper-aluminum composite substrate. A problem of electrochemical corrosion in copper-aluminum connection is solved, and a material which can replace a copper material to manufacture a copper-aluminum connecting electrical terminal is provided, allowing copper-aluminum connection to have long service lifetime, low processing cost and less energy consumption.
Owner:JILIN ZHONG YING HIGH TECH CO LTD
Process for Isomerizing an Aromatic C8 cut in the presence of a catalyst based on a Dealuminated Euo Zeolite
ActiveUS20080275281A1Improve catalytic performanceHigh selectivityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic acidStructure type
A process is described for isomerising an aromatic cut containing at least one aromatic compound containing eight carbon atoms per molecule, comprising bringing said cut into contact with a catalyst containing a zeolite with structure type EUO, said catalyst having been prepared using a process comprising at least the following steps:i) synthesizing at least one zeolite with structure type EUO having an overall Si / Al atomic ratio in the range 5 to 45;ii) dealuminating the zeolite obtained at the end of said step i) using at least one treatment with an aqueous solution of a mineral acid or an organic acid, such that at least 10% by weight of the aluminium atoms are extracted from said zeolite from said step i);iii) forming said dealuminated zeolite with a matrix;iv) depositing at least one metal from group VIII of the periodic table of the elements, the order of carrying out said steps iii) and iv) being inconsequential following on from said step ii).
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Toner
InactiveUS20110097660A1Improve charging effectExcessive charging can be suppressedDevelopersSiliconAluminium atom
Provided is a toner in which faulty transfer under an extremely-low-temperature, low-humidity environment hardly occurs, including toner particles and a zeolite as an external additive, in which a ratio of the alminium atoms to a total of the silicon atoms and the aluminium atoms contained in the zeolite is 0.2 to 24.0%.
Owner:CANON KK
Modified zeolite catalyst
InactiveCN102470353AImprove anti-passivation performanceGood choiceMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAqueous sodium hydroxideNitrogen gas
A modified zeolite catalyst derived from a zeolite of a structural type which consists of a one-dimensional micropore structure of channels made from rings containing between 8 and 12 silicon / aluminium atoms is disclosed. It consists substantially of a plurality of crystallites having additional mesoporosity whose volume is in the range 0.09 to 0.25 ml3g-1 as measured by nitrogen absorption at 77 K and calculated by the BJH method. The mesoporosity may be introduced into the crystallites by e.g. treatment with aqueous sodium hydroxide at a pH at 25 C in excess of 8 for an extended period at elevated temperature. The catalyst shows improved resistance to catalyst deactivation and greater selectivity to higher hydrocarbons when used to e.g. oligomerize light alkenes e.g. propene or the butenes.
Owner:BP OIL INT LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com