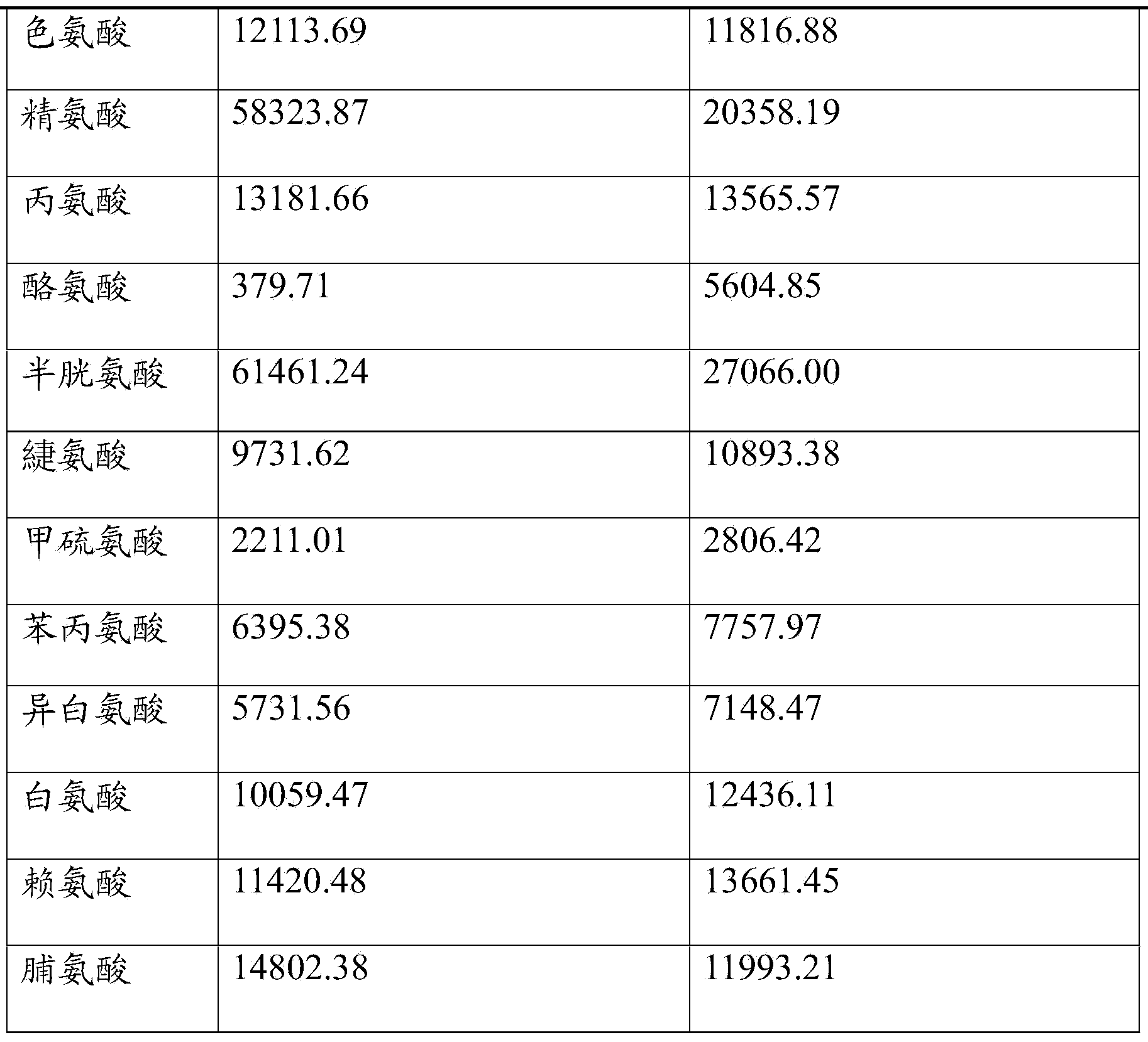
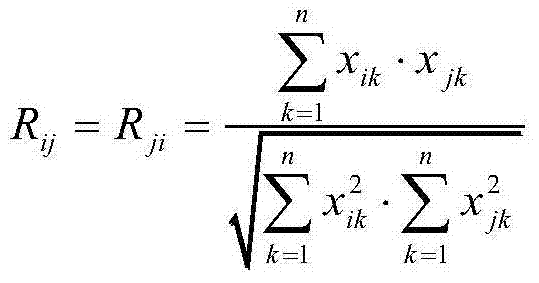Patents
Literature
57 results about "Cordyceps crinalis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
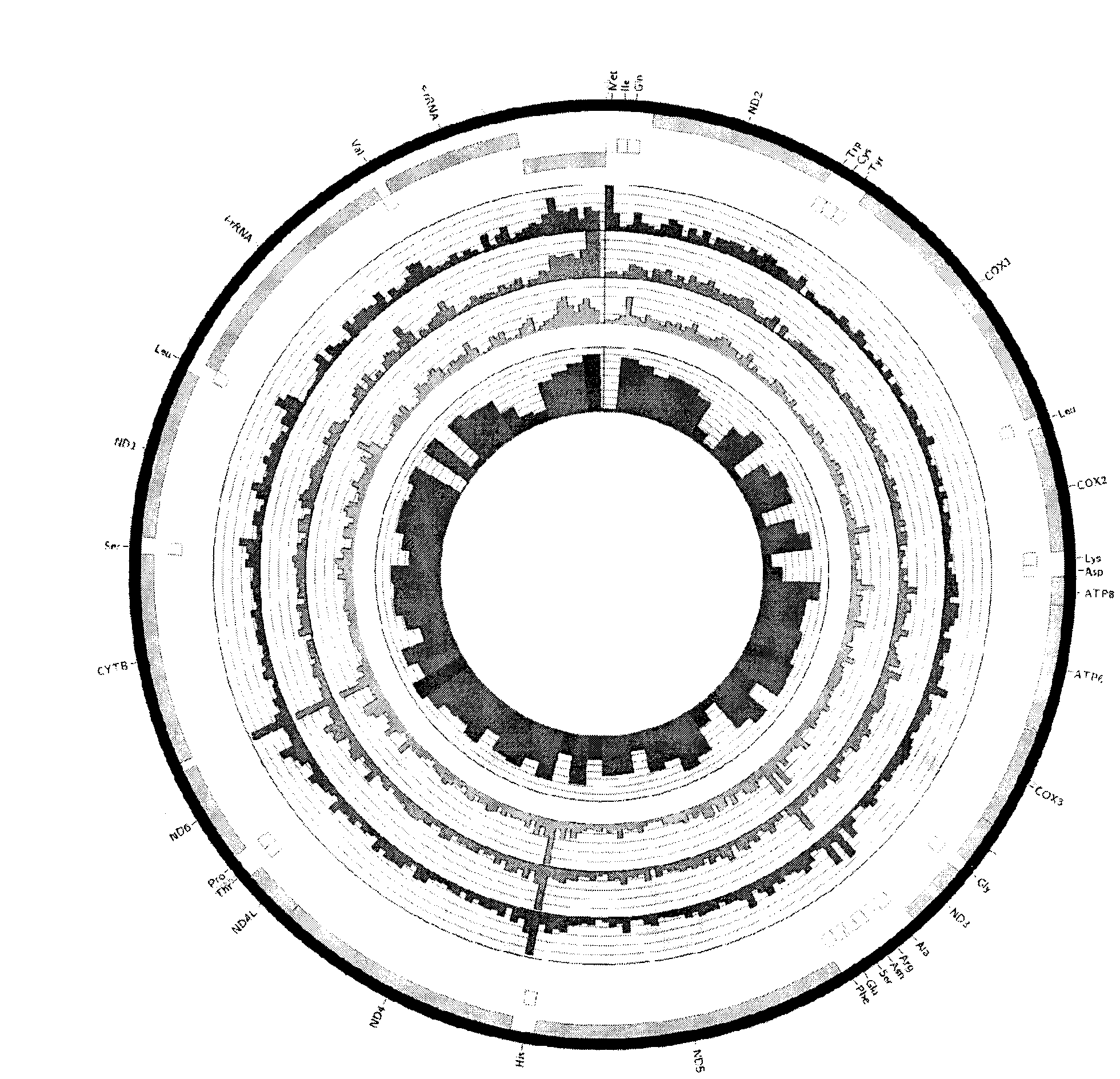
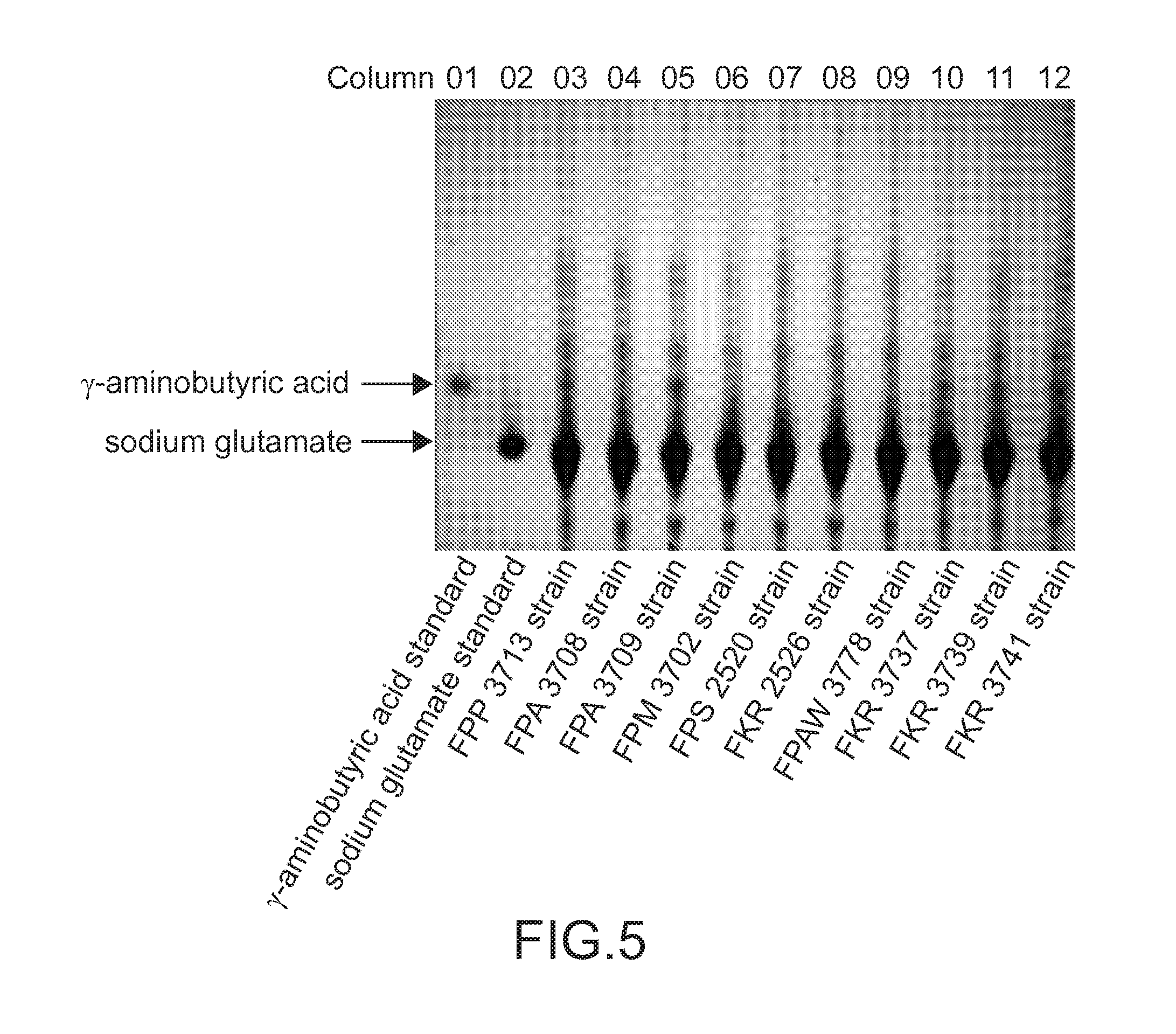
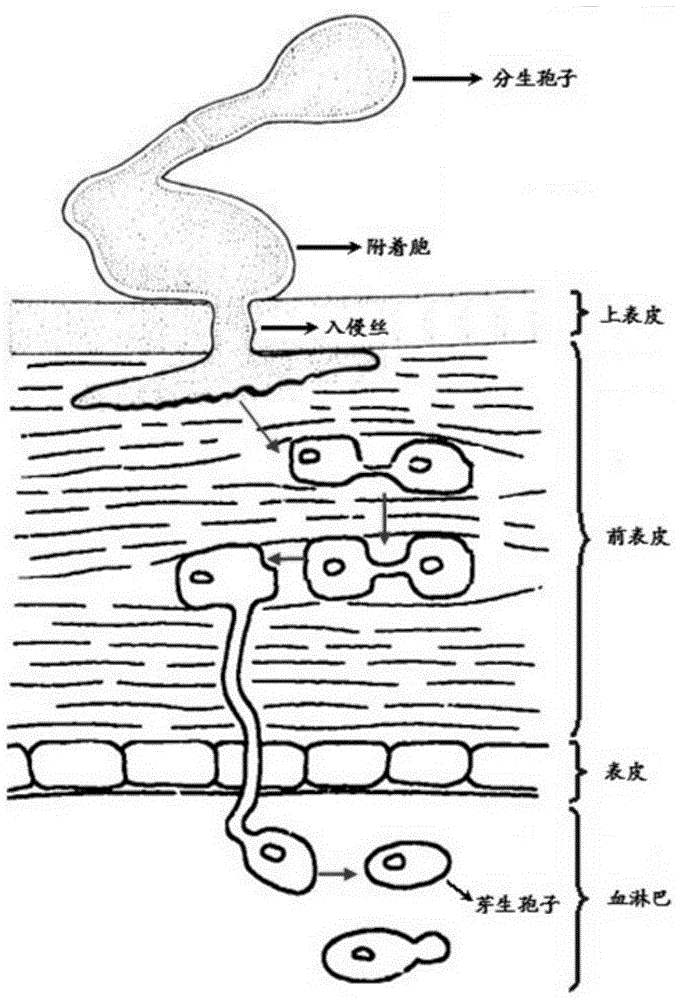
O. crinalis was first reported as Cordyceps crinalis by Ellis in 1920, and reported and described by Mains (1940; 1958), Kobayasi and Shimizu , and then revised by Sung et al. based on its morphology. This revision was strongly supported by our molecular phylogenetic evidence.
Culturing method of cordyceps militaris rich in effective component (schisandra chinensis)
InactiveCN102224790AIncrease contentIncrease nutritionHorticultureFertilizer mixturesCordycepsAdenosine
The invention discloses a culturing method of cordyceps militaris rich in effective component (schisandra chinensis) and relates a culturing method of cordyceps militaris, and the method can be used for simplifying traditional Chinese medicine for compatibility, and improving the utilization rate of the cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps: 1. activating a strain; 2. preparing a liquid strain; 3. smashing and diluting the liquid strain, and inoculating the smashed and diluted strain to a solid culturing medium of the cordyceps militaris rich in schisandra chinensis, and carrying out dark culture to obtain a mycelium; culturing the mycelium under illumination to obtain a mature sporocarp; continuously culturing until a stroma grows to 4-8cm and an orange power substance appears on the surface of the stroma; and harvesting. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: based on the mutual effect of the components in the schisandra chinensis and cordyceps sinensis growth metabolism, the contents of adenosine and cordycepin are improved, and simultaneously a cordyceps sinensis sporocarp with an effective component (schisandra chinensis) is generated, thereby playing roles in utilizing the cordyceps militaris and carrying out compatibility on the cordyceps militaris, simplifying the compatible method of the schisandra chinensis and the cordyceps militaris, and improving the nutrition and medical value of the schisandra chinensis.
Owner:王淑华
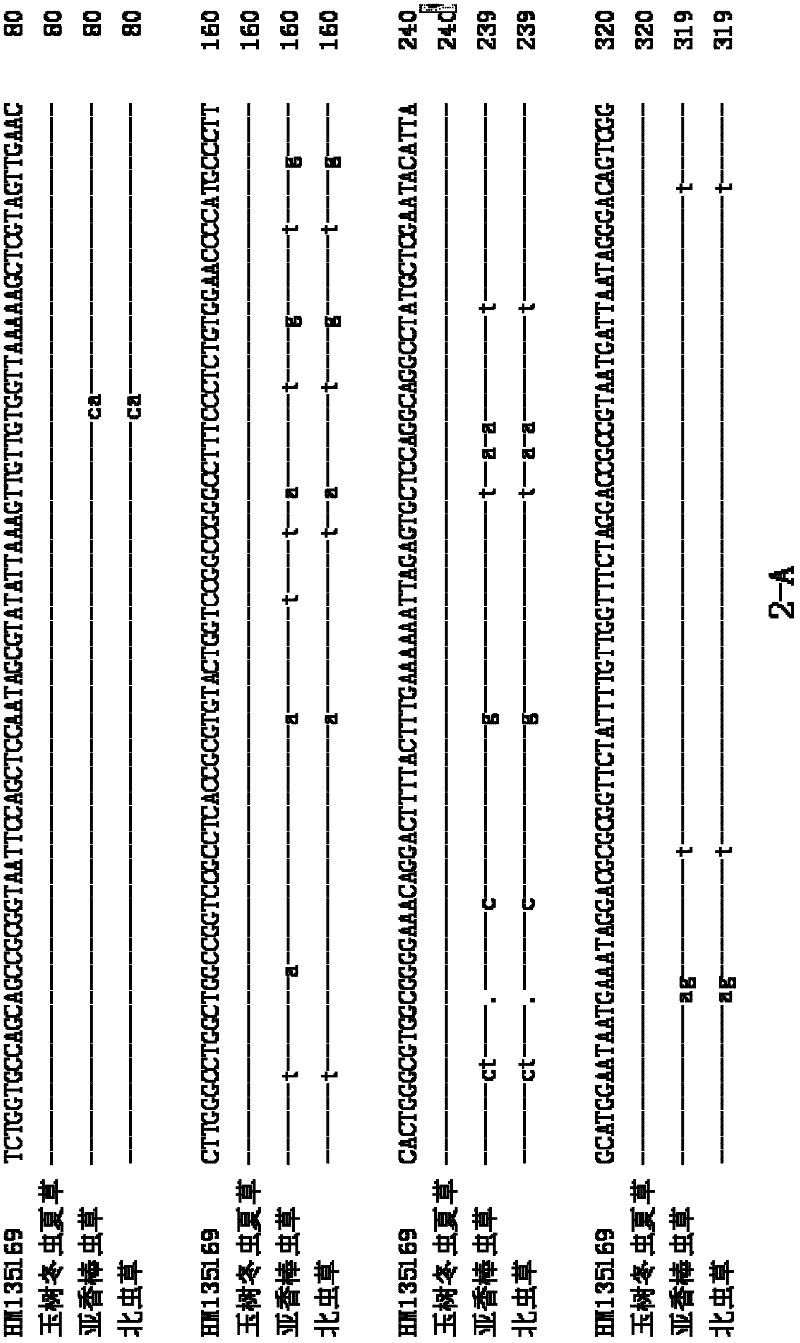
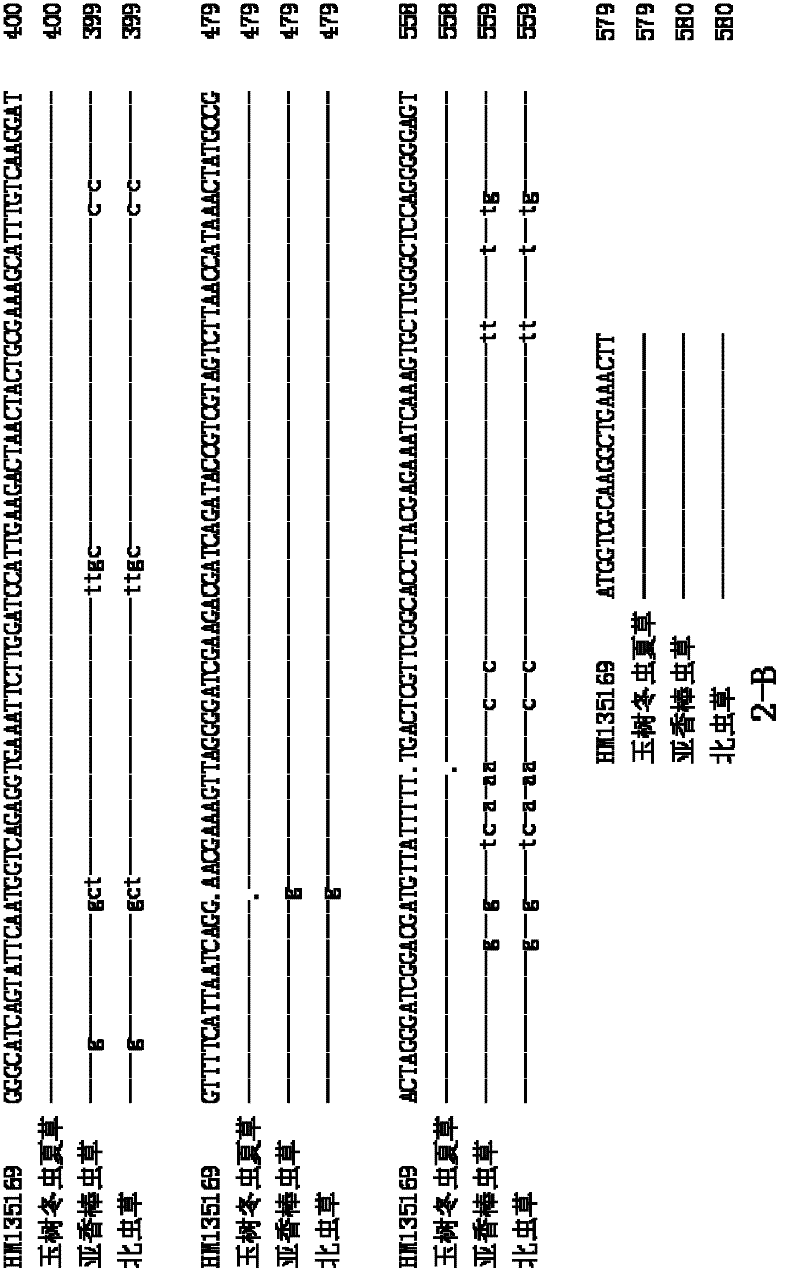
Mitochondrial gene sequence for identifying Cordyceps sinensis and method
InactiveCN103255200AReduce dosageReduce lossMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideCordyceps crinalis
The invention provides a mitochondrial gene sequence for identifying authenticity and quality of Cordyceps sinensis and an operation method thereof. According to the method, differences of mitochondrial genes between ghostmoth and other lepidopteran insects are compared and thus high-variability areas can be searched. Specific primers of the ghostmoth are designed to obtain sequences of corresponding sections of mitochondria of host insects; if a nucleotide difference rate is less than 1-1.5 %, the insects are determined to be a same species but different individuals, and if the nucleotide difference rate is more than 6 %, the insects are determined to be a same genus but different species, thereby not only identifying whether to-be-detected samples are the Cordyceps sinensis formed with Hepialus larvae as the host insects, but also determining producing areas of the to-be-detected samples, and thus determining the authenticity and grades of the to-be-detected samples The method is simple in steps, easy to operate, and few in sample amount, and can minimize sample loss. According three pairs of the specific primers provided by the invention, the authenticity and the grades of the samples can be rapidly and conveniently detected through detecting whether the samples have same or similar nucleotide sequences as well as similarity of the nucleotide sequences.
Owner:上海立得生物科技有限公司
Cultivation method of selenium-enriched Cordyceps militaris mother culture
InactiveCN102428834AIncrease selenium contentIncrease productionHorticultureBiotechnologyMother culture
A cultivation method of selenium-enriched Cordyceps militaris mother fungi belongs to the technical field of the cultivation of Cordyceps militaris. The cultivation method comprises the following steps: 1) cultivating selenium-enriched strains on a test tube slant; 2) cultivating selenium-enriched Cordyceps militaris liquid strains; and 3) cultivating the selenium-enriched Cordyceps militaris. The cultivation method uses organic selenium yeast which has the lowest inhibitory effect on the growth of Cordyceps militaris, thus the selenium content of the culture medium is up to 50mg / L, the selenium content of the cultivated Cordyceps militaris is up to 35-50mg / kg which is triple of the selenium content of Cordyceps militaris with additional inorganic selenium, and the yield is increased by 20%.
Owner:骆新春
Duplex PCR authentication method of cordyceps sinensis original powder
ActiveCN103233062AAmplification conditions are easyPrimer specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDuplex pcrHousekeeping gene
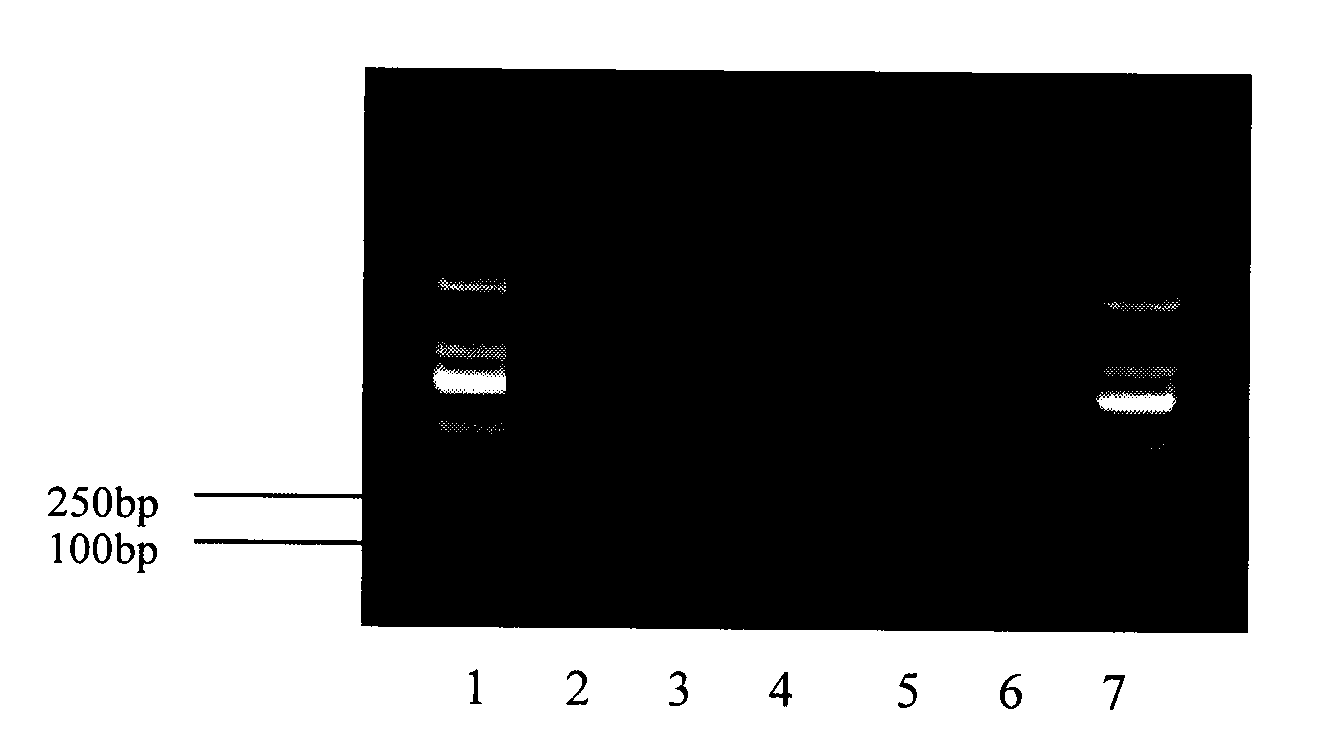
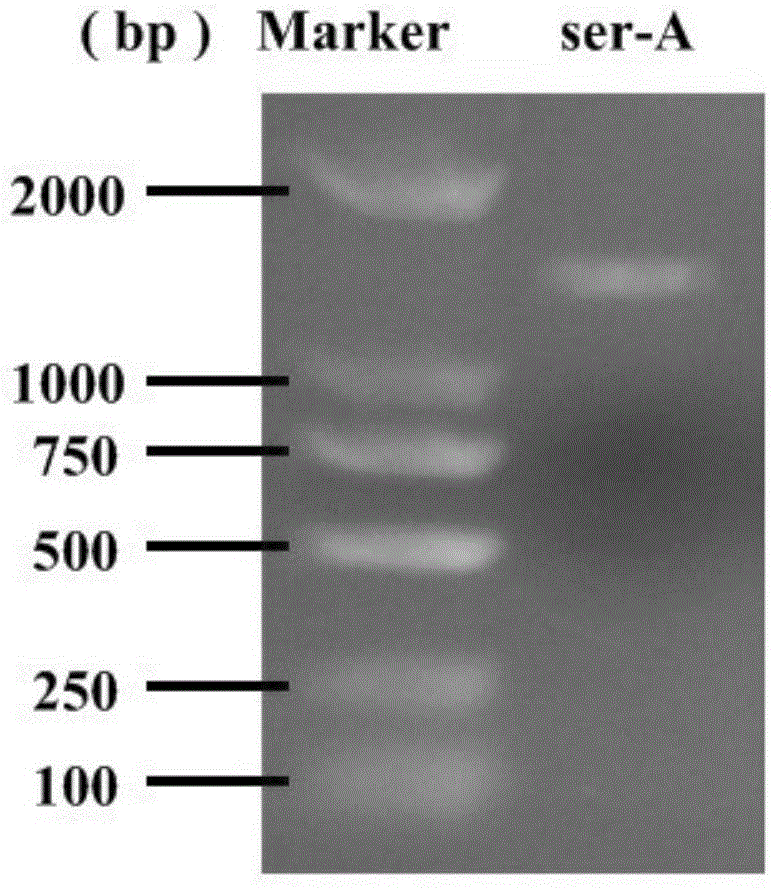
The invention discloses a duplex PCR authentication method of cordyceps sinensis original powder. The method adopts a technical scheme that cordyceps sinensis original powder genome DNA is adopted as a template; with PCR primers designed by the invention, a single-tube duplex PCR reaction is carried out, and characteristic housekeeping genes of a cordyceps sinensis strain and a host hepialus are simultaneously amplified, wherein actual amplified fragments are respectively 320bp and 136bp; and through agarose gel electrophoresis detection, product authenticity is determined. With the method provided by the invention, cordyceps sinensis original powder can be specifically identified, and sample authenticity detection can be completed simply with three steps of DNA extraction, PCR amplification, and electrophoresis detection. The operation is simple and is easy to command, and accuracy is high.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD +1
Preparation method of selenium-rich cordyceps sinensis mycelia
InactiveCN103070011AImprove biological activityMild reaction conditionsAnimal feeding stuffHorticultureBiotechnologySolvent
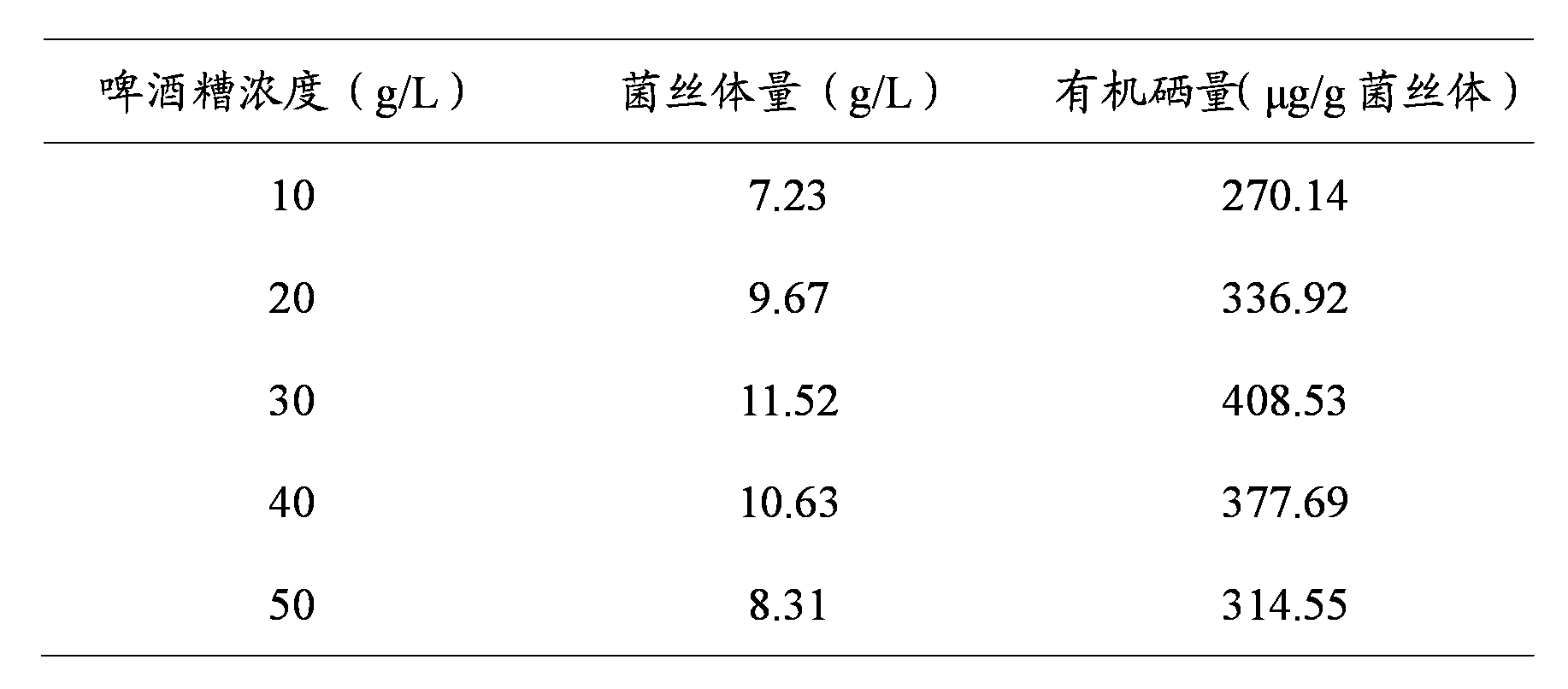
The invention provides a preparation method of selenium-rich cordyceps sinensis mycelia. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating cordyceps sinensis stains in a liquid fermentation culture medium with brewer's grains as a matrix; and culturing for 4-8 days under the conditions of 20-30 DEG C and 120-200 r / min to obtain the selenium-rich cordyceps sinensis mycelia in fermentation liquor, wherein the liquid fermentation culture medium is prepared from the following components: 10-50 g / L of brewer's grains, 10-30 mg / L of Na2SeO3 and water serving as a solvent with pH (Potential of Hydrogen) of 4-8. The obtained fermentation liquor can be further separated by the conventional method to obtain the selenium-rich cordyceps sinensis mycelia. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, low production cost, less equipment investment and easiness in realization of industrialization, and the obtained mycelia have stronger biological activity, so that a breakthrough is expected to be made in prevention and treatment of animal diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Molecular ID and identification method of cordyceps sinensis
InactiveCN104830970AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCordyceps crinalisMycelium
The invention relates to a molecular ID of cordyceps sinensis, wherein the molecular ID includes a nucleotide sequence represented as the SEQ ID No.1 and / or the SEQ ID No.2. By means of the molecular ID and an identification method, the cordyceps sinensis can be separated from fake products being similar with the cordyceps sinensis in appearance. The method is wider in applicability and can be used for detecting any samples of which DNA can be extracted, so that quick and accurate identification of raw material drugs and mycelium of the cordyceps sinensis can be achieved.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Hirsutella sinensis ZJB18002 and application thereof
ActiveCN109082382AExpand biological applicationsIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesCordyceps crinalisMicrobiology
The invention discloses Hirsutella sinensis ZJB18002 and application thereof in production of cordycepic acid, and provides a novel slant medium for isolating Hirsutella sinensis, a biological identification method of Hirsutella sinensis, and a method to acquire a strain with 2-3 times higher yield of cordycepic acid through mutagenesis. An effective means to widen the biological application rangeof Hirsutella sinensis is provided, and the methods and the medium above have a major application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
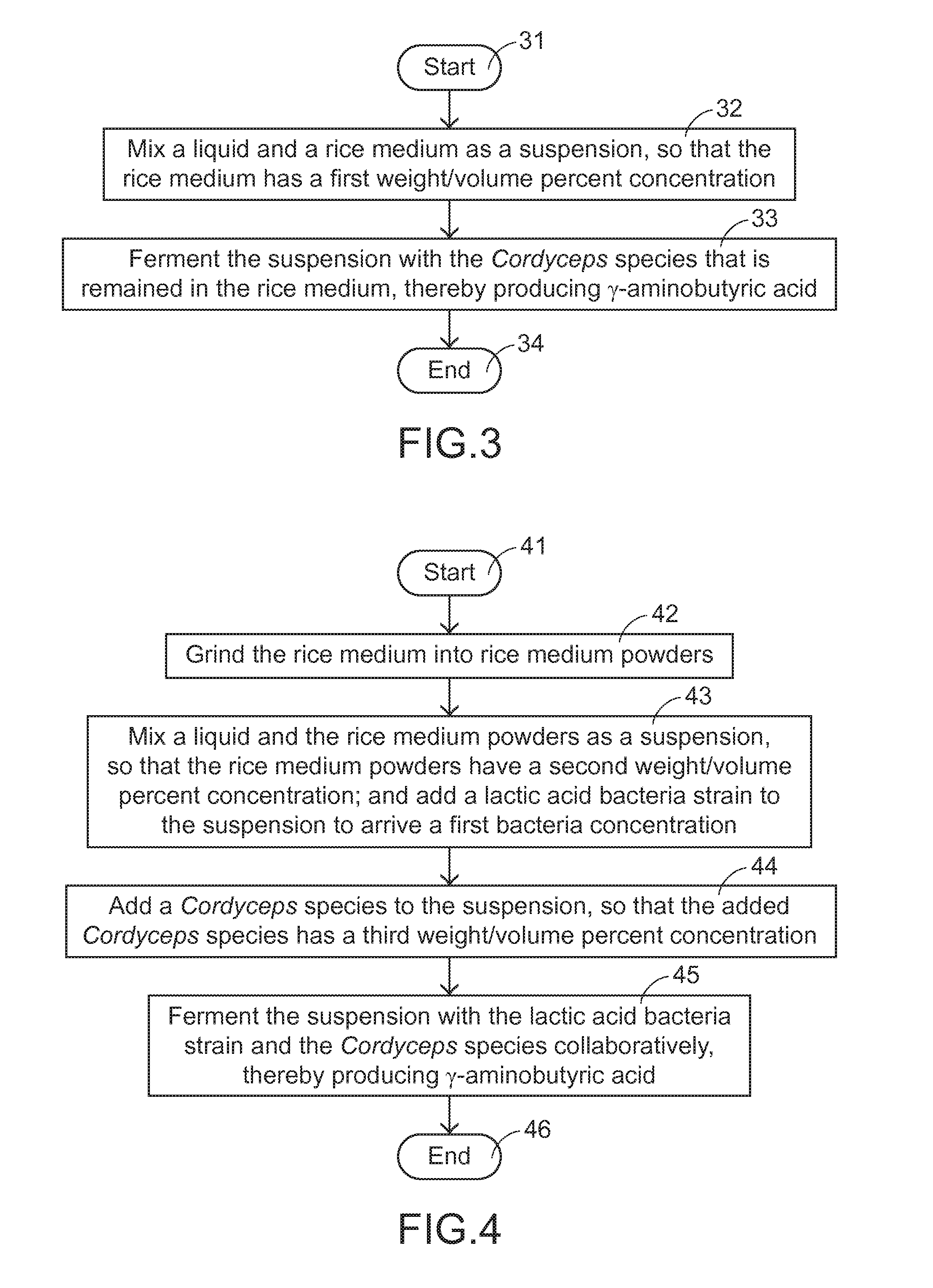
Method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by fermenting rice medium from preparation of cordyceps species and application thereof
InactiveUS20130316067A1Increase concentrationFermentationFood preparationLactobacillusCordyceps crinalis
The present invention provides a method for producing γ-aminobutyric acid by fermenting a rice medium from the preparation of a Cordyceps species and the application thereof. Firstly, water and an appropriate amount of rice medium are mixed together to form a fermentation broth. Secondly, add lactic acid bacteria to the fermentation broth. Then, the fermentation broth is fermented by both of the Cordyceps species retained in the rice medium and the lactic acid bacteria. Consequently, the γ-aminobutyric acid is produced. Moreover, the fermentation broth prepared by this method can be applied to a health food or drink.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Method for directly measuring content of cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide peptide in cordyceps sinensis product
InactiveCN104090038AAccurate measurementEasy to measureComponent separationCordyceps crinalisQuality control
The invention relates to a method for simply, quickly, directly and accurately measuring the connect of cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide peptide in a cordyceps sinensis product. The method comprises the following steps: performing simple pretreatment on a sample, and qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing through a high performance liquid chromatography photo-diode array (HPLC-PDA) detector. By utilizing the advantages of accurate quantification of high performance liquid chromatography, accurate spectral analysis qualification of the PDA detector and the like, the method can be used for simply, quickly, accurately and directly measuring the connect of cordyceps sinensis polysaccharide peptide in the ordyceps sinensis product, and a simple, reliable and easily-popularized method is supplied to authentication analysis, quality evaluation and quality control of health efficacy factors in the cordyceps sinensis product.
Owner:黄宏南
Chitinase A coming from cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis, encoding gene and application of two
ActiveCN104130992AEnhance expressive abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a chitinase A which comes from a corbrin-capsule-producing strain cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis and participates in hydrolysis of colloid chitin for generating N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, a gene encoding the enzyme, and application of the enzyme and the gene. The amino acid sequence of chitinase A is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. A cloned DNA of the provided nucleotide sequence can be transferred into an engineering bacterium through a transduction, transformation or conjugal transferring method. By adjusting chitin hydrolysis and expression of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthetic gene, a host is endowed with property of highly expressing chitinase A, an effective approach is provided for expanding biological application of chitinase A, and important application prospect is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
Cordyceps sinensis oral tablet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104605334ACan play a roleAids in absorbencyOrganic active ingredientsPill deliverySolid componentMedicine
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Solid fermentation method for cordyceps sinensis mycelia
InactiveCN105586265AShort fermentation cycleFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a solid fermentation method for cordyceps sinensis mycelia. The method comprises the steps of strain culture and solid fermentation culture, wherein Hirsutella sinensis is adopted as a strain, and a solid medium is inoculated with the strain for fermenting production. Effective ingredients of the product prepared according to the solid fermentation method are consistent with or approximate to those of wild cordyceps sinensis; besides, cost is low, process control is simple, pollution is avoided, and safety and effectiveness are achieved.
Owner:李光辉
Method for culturing cordyceps sinensis by performing endogenous pressurization and artificial infection of hirsutella sinensis on hepialus larvae
The invention relates to a method for culturing cordyceps sinensis by performing endogenous pressurization and artificial infection of hirsutella sinensis on hepialus larvae, belonging to the technical field of artificial culture of the cordyceps sinensis. The method comprises the steps of: mixing the following components in percentage by weight: 28-34% of bombyx mori pupae, 5-7% of potatoes, 0.008-0.01% of magnesium sulfate, 0.035-0.05% of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and the balance of water, boiling, filtering and sterilizing to prepare an aseptic infection stock solution; taking the hirsutella sinensis as an infection bacteria source, picking pure mycelia through inoculating needles, placing the pure mycelia into the aseptic infection stock solution according to the proportion that the hirsutella sinensis picked by 10-15 needles are placed into every 5ml of the aseptic infection stock solution, grinding and then preparing an infection source bacterial solution; and sucking the infection source bacterial solution through a syringe, inserting a needle head from the excretory opening of each hepialus larva to press 0.3-0.5ml of the infection source bacterial solution into the intestinal tract of the larva, then placing the larvae in the shade and culturing under the conditions that the temperature is 17-21 DEG C and the relative humidity is 78-85% for more than 15 days. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of infection rate of up to above 90 percent, short period, low cost and great application prospects for large-scale culture of the cordyceps sinensis.
Owner:许继宏
Method for improving cordycepin output in cordyceps militaris fermentation broth
ActiveCN103416223AIncrease productionShort fermentation timeSugar derivativesHorticultureOleic Acid TriglycerideMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a method for improving cordycepin output in cordyceps militaris fermentation broth. A cordyceps militaris strain (cordyceps militaris) preserved by the China general microbiological culture collection management committee is adopted, and the strain preservation number is CCGMC3.4655. The method includes the steps of inoculating a seed solution of the cordyceps militaris, performing submerged fermentation for 2 to 5 days in a rotary shake-flask cabinet at the temperature of 20 DEG C to 26 DEG C and at the rotating speed of 140 rounds per minute to 190 rounds per minute, refilling 1.0g / L to 3.0g / L of the mixture of oleic acid and adenine, wherein the mass ratio of the mixture to the fermentation broth is 1:3 to 3:1, and continuously fermenting for 4 to 7 days under the conditions that the temperature ranges from 20 DEG C to 26 DEG C and the rotating speed ranges from 140 rounds per minute to 190 rounds per minute. According to the method, the cordycepin output reaches up to 813.7mg / L.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Cordyceps sinensis fluid medium, and method used for culturing cordyceps sinensis with cordyceps sinensis fluid medium
ActiveCN107586725AGood adhesionImprove absorption rateFungiMicroorganism based processesPenicillinHydrolysate
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism technology, and discloses a cordyceps sinensis fluid medium. The cordyceps sinensis fluid medium is prepared from 50 to 60g of a fibrous material, 50 to 60g of a vinasse hydrolysate, 70 to 80g of potato extraction solution, 30 to 40g of glucose, 2g of magnesium sulfate, 1g of streptomycin, 1g of penicillin, and 0.01g of vitamin B1. A preparationmethod comprises following steps: the above ingredients are delivered into a container, an obtained mixture is diluted with water to 1L, the pH value is adjusted to 6.5 to 6.8, sterilization in an autoclave is carried out, wherein the pressure is maintained for 15min when the temperature is increased to 121 DEG C, an obtained product is taken out from the autoclave, and is cooled to room temperature. The invention also discloses a method used for culturing cordyceps sinensis with the cordyceps sinensis fluid medium. The cordyceps sinensis fluid medium is reasonable in composition, and low in cost; and the quality of cultured products is improved greatly.
Owner:邸超
Infrared spectroscopic analysis and authentication method for cordyceps sinensis stromata
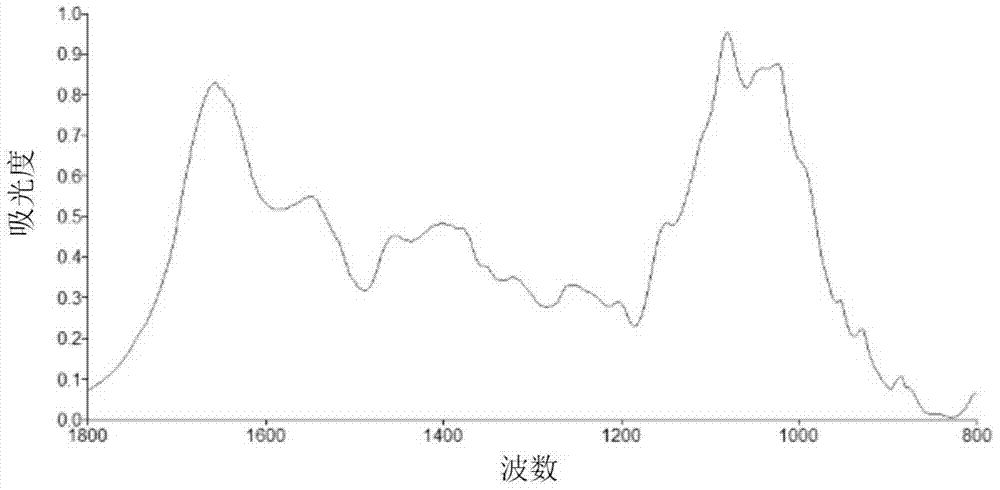
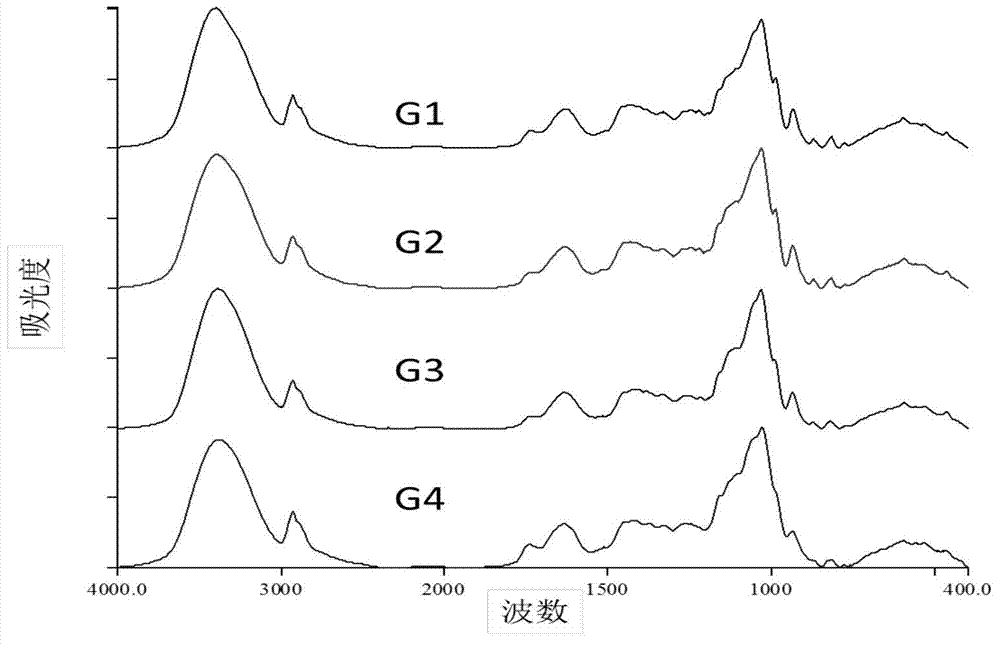
ActiveCN103698296AIdentify objectiveAccurate identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansInfraredCordyceps crinalis
The invention relates to the field of analytical chemistry, and in particular to an infrared spectroscopic analysis and authentication method for cordyceps sinensis stromata. The invention aims at solving the technical problem that cordyceps sinensis stromata are difficult to distinguish the true from the false at present. The technical scheme for solving the technical problem of the invention is to provide a method for rapidly and accurately authenticating cordyceps sinensis stromata. The method comprises the following steps: a, drawing a standard spectrum of the cordyceps sinensis stromata; b, acquiring the necessary characteristic peaks of the infrared spectrums of the cordyceps sinensis stromata and the common characteristic peaks of the infrared spectrums of the cordyceps sinensis stromata; c, authenticating the characteristic peaks of the infrared spectrums of the tested cordyceps sinensis stroma samples and the similarity of the infrared spectrums. The invention provides a new method for rapidly and accurately authenticating the cordyceps sinensis stromata.
Owner:QINGHAI SPRING MEDICINAL RESOURCES TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Culture method of cordyceps sinensis anamorphic hirsutella sinensis pure strain
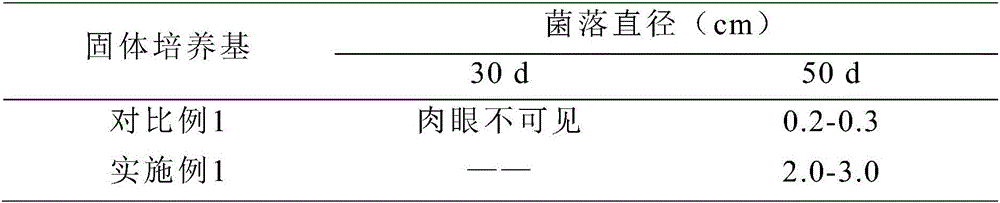
InactiveCN106010978ASeparate applicationConvenient and quick separabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCordyceps crinalis
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbe culture and relates to a culture method of a cordyceps sinensis anamorphic hirsutella sinensis pure strain. The culture method comprises the following steps: A sampling: acquiring a wild cordyceps sinensis stroma of which ascospore is not ejected out, and storing; B separating: taking a strain in the cordyceps sinensis stroma, and inoculating into a flat plate under a sterile condition; C culturing, performing constant-temperature culture of the flat plate containing the strain in a culture box to obtain a hirsutella sinensis bacterial colony; D purifying, transferring the bacterial colony in the step C to a new flat plate for culture to obtain the hirsutella sinensis pure strain. By adoption of the culture method, the hirsutella sinensis pure strain can be obtained more easily, and the culture method is suitable for separating the cordyceps sinensis strain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Enzyme for synthesizing and metabolizing adenine of Cordyceps sinensis(Berk.)Sacc. Hirsutella sinensis, and gene and application of enzyme
InactiveCN102690797AEnhance expressive abilityIncrease productionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to an adenine phosphoribosyltransferase for synthesizing and metabolizing an adenine from adenine nucleotide of Cordyceps sinensis(Berk.)Sacc. Hirsutella sinensis from 'Bailing' production strain, a gene coding the enzyme and application of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. The amino acid sequence of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase is shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the coding gene of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase corresponds to the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 2. According to the invention, the metabolizing way for synthesizing the adenine from the adenine nucleotide is researched in detail from the principle, and the cloned DNA containing the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred to an engineering strain by transduction, transformation and combined transfer; through regulating the gene expression of the adenine biological synthesis, the host adenine is endowed with high expressivity, an effective way is provided for increasing the yield of the adenine, and the invention has a great application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for identifying cordyceps sinensis through microscopic staining
ActiveCN102589956ALess susceptible to interferenceProtect interestsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansPlant tissueStaining
The invention belongs to the field of crude medicine identification, and particularly relates to a method for identifying cordyceps sinensis through microscopic staining. The invention aims to solve the technical problem that the authenticity of the cordyceps sinensis powder which is circulated and sold in the market is difficult to identify. The technical scheme for solving the problem is to provide the method for accurately identifying the cordyceps sinensis powder. The method comprises the following steps that: the cordyceps sinensis powder to be inspected is taken, stained and produced into a smear; and the produced smear is subjected to microscopic observation under a microscope, if the special structure of the cordyceps sinensis of each smear can be clearly observed, the obvious blue spots under the iodine staining are not existed, and the obvious plant tissues are not observed, the cordyceps sinensis powder can be identified to be pure, otherwise, the cordyceps sinensis powder is not pure. The method can clearly identify the fine medicinal slice powder and the matter which does not belong to the cordyceps sinensis, is low in cost, has high efficiency, is not easy to be disturbed by various addition ingredients, and has very high accuracy and a good application prospect in the field.
Owner:QINGHAI SPRING MEDICINAL RESOURCES TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Cordyceps sinensis fluid medium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106148198AGood technical effectFungiMicroorganism based processesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTBeef extract
The invention relates to a cordyceps sinensis fluid medium and a preparation method thereof. The cordyceps sinensis fluid medium comprises the following materials by weight percent: 10-30% of jerusalem artichoke, 1-5% of potato, 1-5% of beef extract, 1-6% of fish meal, 0.03-0.08% of vitamin B1, 0.02-0.06% of riboflavin, 0.01-0.05% of folic acid, 0.05-0.1% of magnesium sulfate, 0.06-0.1% of sodium chloride, and the balance of water. The jerusalem artichoke powder is firstly used for the cordyceps sinensis fluid fermentation medium, an excellent technological effect is acquired, the quality of the obtained cordyceps sinensis is high, and active ingredients of the obtained cordyceps sinensis are rich.
Owner:青海珠峰冬虫夏草工程技术研究有限公司
A method for increasing the biomass of pure Cordyceps sinensis fungus-Cychosporum mycelia
ActiveCN102283011ALow investment costSimple processHorticultureFertilizer mixturesMetabolitePh buffering
The invention discloses a method for improving biomass of pure cordyceps fungi-hirsutella hepiali chen et shen mycelia. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing cordyceps fungi strain-hirsutella hepiali chen et shen under a low-temperature environment by adopting bottle separated solid culture medium, and controlling the moisture content of the solid culture medium and adding a pH buffering agent to improve and eliminate black metabolite generated in the culture process, so that the physical volume of the propagated mycelia accounts for over 80 percent of the volume of the culture medium. The method has the advantages of simplicity in process, low equipment requirement and low investment cost; and the physical volume of the propagated mycelia accounts for over 80 percent of the volume of the culture medium.
Owner:QUANZHOU ZHIDE CORDYCEPS SINENSIS FUNGI DEV CO LTD
PCR primer pair, kit and method for identifying true cordyceps sinensis and false cordyceps sinensis
InactiveCN102226217AAmplify the target fragmentAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCordyceps crinalisHorticulture
The invention relates to the field of medicinal material identification, more specifically to indentify true cordyceps sinensis and false cordyceps sinensis. A specific and reliable method of the present invention for detecting and identifying cordyceps sinensis is provided to solve technical problems. The present invention provides a PCR primer pair, a kit and a method for identifying true cordyceps sinensis and false cordyceps sinensis so as to solve technical problems. The sequence of the primer pair are: an upstream primer denotes 5<,>CAATAAATACCGATACAGGGC 3<,>; a downstream primer denotes 5<,>TGTC TGGACCTGGTGAGTTT 3<,>. According to the invention, target fragments of cordyceps sinensis and the common counterfeits can be effectively amplified by the primer pair, and can be accurately identified, thereby, the invention has good application prospects.
Owner:张雪峰
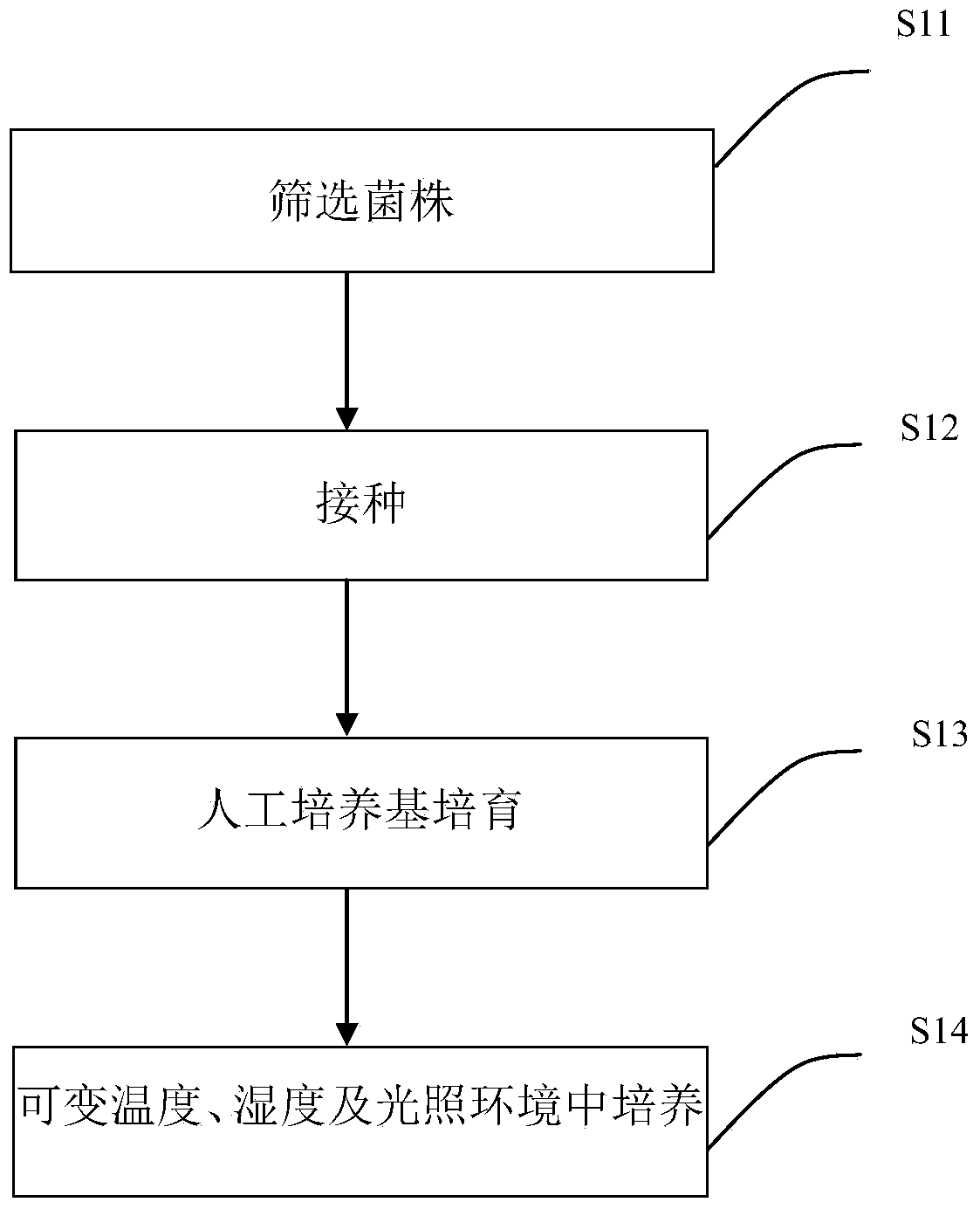
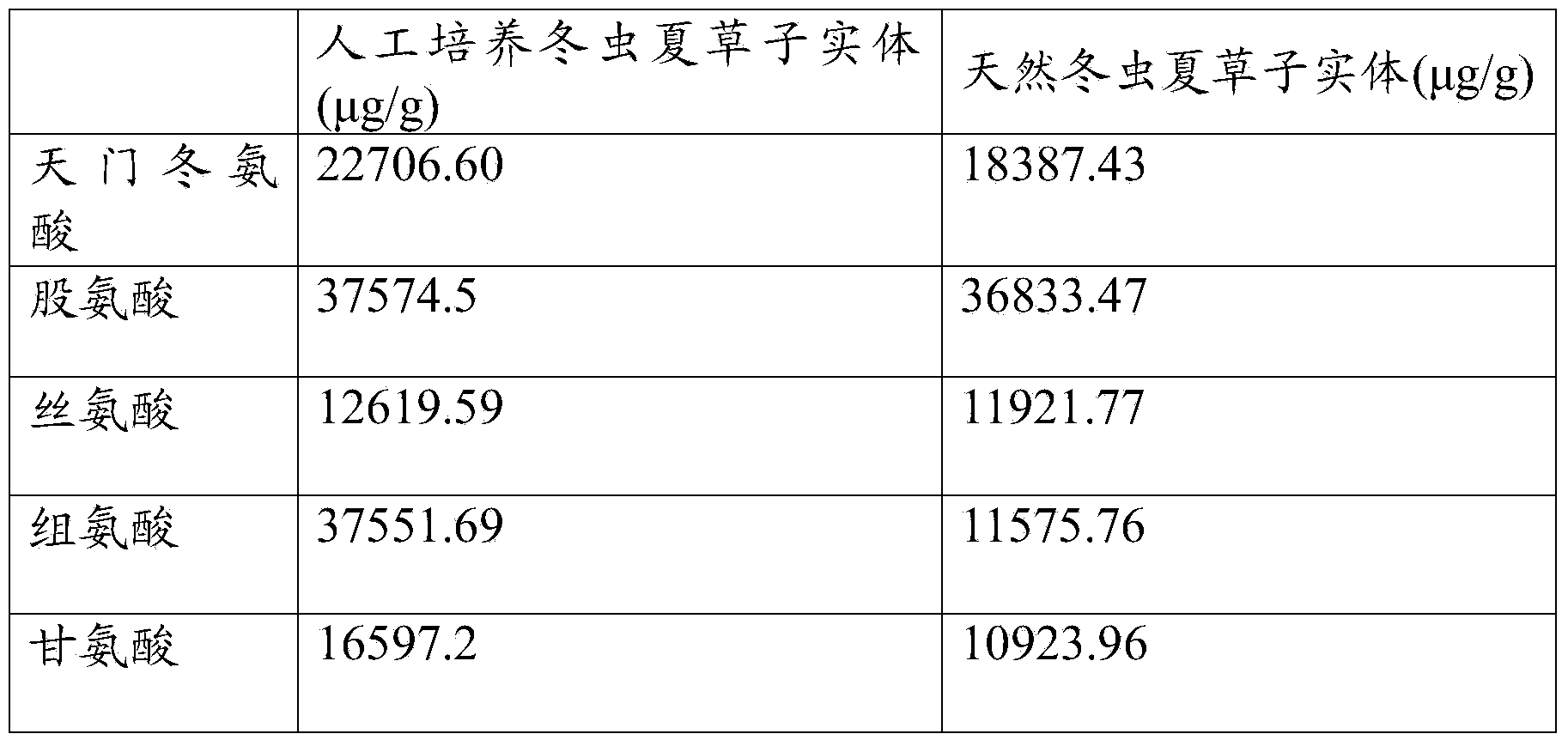
Cultivation method of cordyceps sinensis sporocarps and composition and application of cordyceps sinensis sporocarps
The invention discloses a method for cultivating cordyceps sinensis sporocarps, a cordyceps sinensis sporocarp composition and an application thereof. The method for cultivating the cordyceps sinensis sporocarps comprises the following steps: screening a dominant strain, wherein the dominant strain can be used for rapidly and stably producing the cordyceps sinensis sporocarps; inoculating the dominant strain into an artificial culture medium containing a silkworm chrysalis extracting solution, peptone, a yeast extract, glucose, superfine sand, food-grade carboxymethyl cellulose, trace elements and food-grade agar powder or agarose gel; and performing cultivation in an environment with a changeable temperature and LED (Light-Emitting Diode) illumination to fulfill the aims of industrial scale and mass production of the cordyceps sinensis sporocarps. As proved by detection, the cordyceps sinensis sporocarps cultivated by using the method are higher in indicating components such as polysaccharides, cordycepic acid and adenosine than natural cordyceps sinensis sporocarps.
Owner:SYNGEN BIOTECH
Cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis purine anabolism enzyme, gene thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102747057AEnhance expressive abilityIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to a purine nucleosidase participating in purine-nucleoside-initiated anabolism of purine such as adenine, guanine, hypoxanthine, xanthine, and the like. The purine nucleosidase is obtained from a Bailing production fungus which is cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis. The invention also relates to a purine nucleosidase coding gene, and an application of the purine nucleosidase. The amino acid sequence of the purine nucleosidase is represented as SEQ ID No.1. The nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is represented as SEQ ID No.2. From the respective of the principle, the invention makes detailed researches in the metabolic pathway in purine synthesis of purine nucleoside. The cloned DNA of the nucleotide sequence provided by the invention can be transferred into engineering fungus through methods of transduction, transformation, and conjugation transferring. Through the regulation upon the expression of biosynthesis gene of purine, high-expression is provided for host purine, such that an effective way for increasing purine yield is provided. Therefore, the invention has important application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Application of L-proline in increasing blastospore quantity and mycelial biomass of Cordyceps sinensis
ActiveCN110024623AShorten the time of artificial cultivationIncrease biomassCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationDry weightFermentation
The invention discloses application of L-proline in increasing blastospore quantity and mycelial biomass of Cordyceps sinensis. In order to solve the problem of how to increase mycelial biomass duringliquid fermentation of Cordyceps sinensis and the problem of how to acquire massive infection blastospores during artificial cultivation of entomogenous fungi with Cordyceps sinensis, L-proline is added to a Cordyceps sinensis medium to induce Cordyceps sinensis to efficiently produce blastospores; after Cordyceps sinensis spores are induced to the medium with the L-proline and cultured for 30 days, the quantity of blastospores is 1.49-5.26 times as high as that of a group with no addition; after 45 days of cultivation, the quantity of the blastospores is increased by 17-52.6 times; after 60days of cultivation, mycelial dry weight is increased by 15.67-66.44%. The blastospores for infecting Hepialus armoricanus so as to artificially cultivate entomogenous fungi with Cordyceps sinensis can be acquired more efficiently herein; the efficiency of acquiring mycelia by liquid fermentation of Cordyceps sinensis can be improved; artificial cultivation time of Cordyceps sinensis can be shortened; cultivation cost can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Medium for cultivating Cordyceps sinensis, artificial cultivation method of Cordyceps sinensis and products of Cordyceps sinensis
The invention provides a culture medium used for culturing cordyceps sinensis, which comprises 1000 parts by weight of water, 500 to 1500 parts by weight of starch material, 10 to 35 parts by weight of coconut water, 2 parts by weight of peptone, 10 to 30 parts by weight of chop soup, and 10 to 30 parts by weight of sucrose, and is used for an artificial culturing method of cordyceps sinensis andproviding a cordyceps sinensis product.
Owner:连启西
Serine proteinase coming from cordyceps sinensis, encoding gene and application of two
ActiveCN104130994AEnhance expressive abilityExpand biological applicationsBacteriaHydrolasesSerine proteinasesNucleotide
The invention provides a serine proteinase which comes from cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis and participates in hydrolysis of macro-molecule protein for generating micromolecule protein, an encoding gene and application of the two. The amino acid sequence of the serine proteinase is shown as SEQ ID No. 1, and the sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. Detailed research is performed on the serine proteinase at a principle level in the process of the serine proteinase infecting hepialidae larva, and the serine proteinase which comes from the corbrin-capsule-producing strain cordyceps sinensis hirsutella sinensis and participates in the infection mechanism, and the encoding gene thereof are provided. A cloned DNA of the provided nucleotide sequence can be transferred into an engineering bacterium through a transduction, transformation or conjugal transferring method. By adjusting expression of the proteolytic enzyme gene, a host is endowed with property of highly expressing serine proteinase, an effective approach is provided for expanding biological application of serine proteinase, and important application prospect is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +2
High performance liquid chromatography for rapidly identifying cordyceps sinensis and cordceps militaris
InactiveCN102327298ASimple and fast operationAccurate identificationComponent separationPlant ingredientsCordycepsCordyceps crinalis
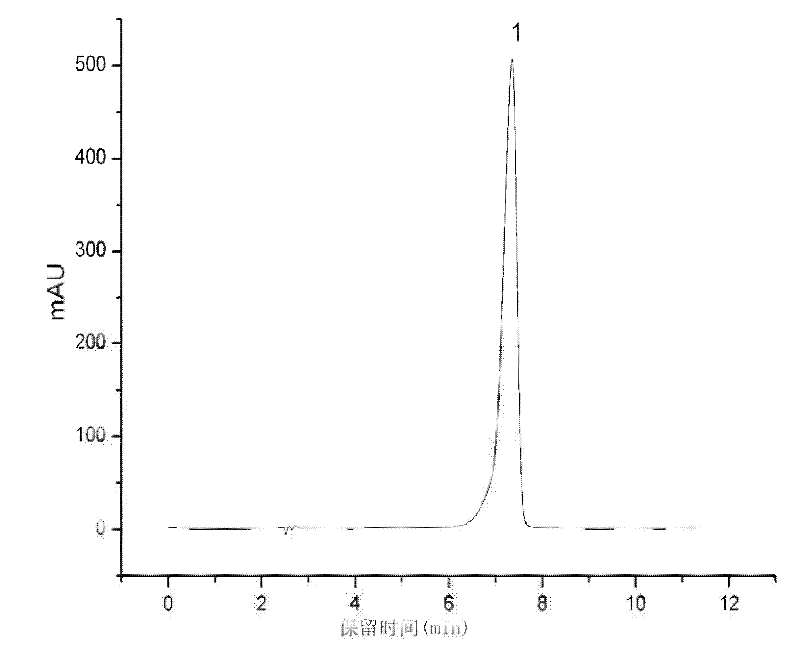
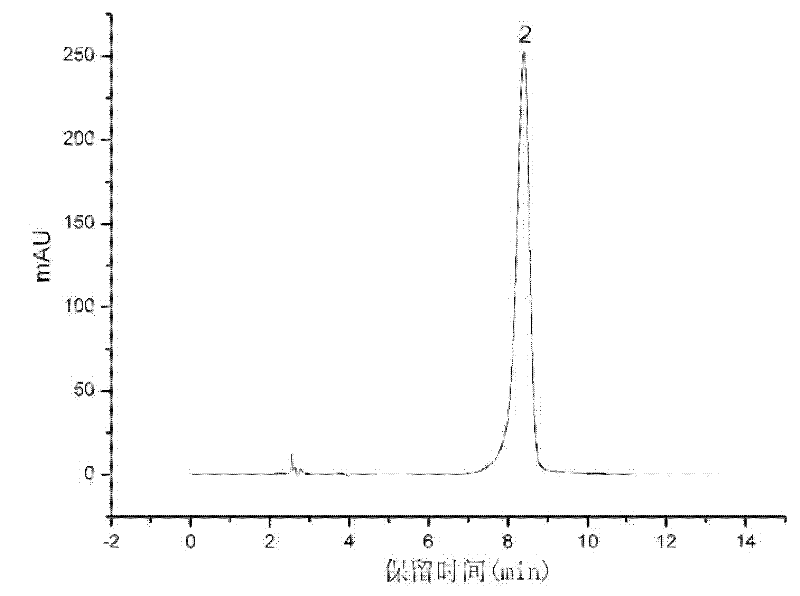
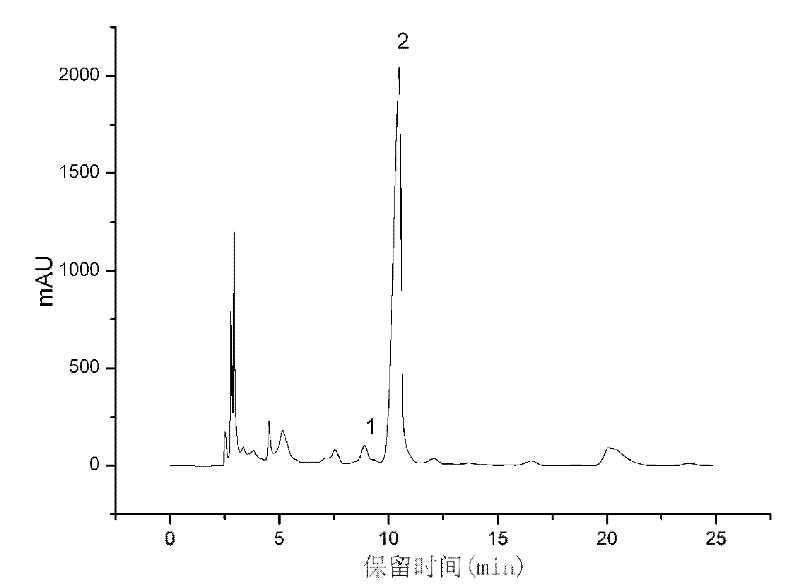
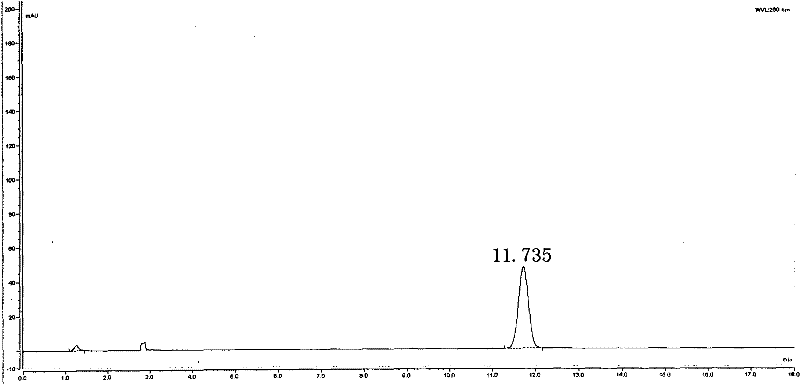
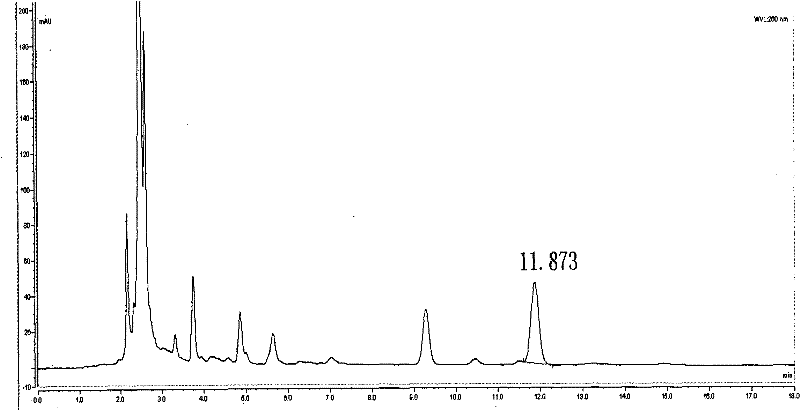
The invention relates to a method for rapidly identifying cordyceps sinensis and cordceps militaris by adopting high performance liquid chromatography. Cordycepins from different sources (cordyceps sinensis and cordceps militaris) can be separated under a certain chromatograph conditions, the cordyceps sinensis as quality goods is selected as a standard product used for identifying whether unknown samples are cordyceps sinensis or cordceps militaris, and the identification other types of worm grass is not related. The method comprises the steps of: taking 0.1ml of tested solution and 0.4ml of cordyceps sinensis extraction solution, uniformly stirring, feeding samples and detecting, wherein the chromatograph conditions include a C18 column, methanol-0.1 percent phosphoric acid water solution as a flowing phase (14.8:85.2), a flowing velocity of 1.0mL / min, a detection wavelength of 260nm and a column temperature of 30 DEG C. The separation degree of cordycepin peaks of two different kinds (cordyceps sinensis and cordceps militaris) reaches above 90 percent, and cordycepin peaks of a mixed sample of cordyceps sinensis from different geographical provenances are not separated, therefore, the cordyceps sinensis and the cordceps militaris can be rapidly and accurately identified.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE INST
Method for extracting cordyceps sinensis extract
The invention discloses a method for extracting a cordyceps sinensis extract. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing cordyceps sinensis micro-powder; 2, adding the cordyceps sinensis micro-powder into an acid solution, heating, performing ultrasonic treatment, adjusting the pH value of the system, and filtering, thereby obtaining an extraction liquid; and 3, performing depressurized concentration on the extraction liquid, thereby obtaining the cordyceps sinensis extract. The method for extracting the cordyceps sinensis extract is simple in process, gentle in condition and high in extract content.
Owner:XINING GONGJIN NEW MATERIAL TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Culture medium used for culturing cordyceps sinensis, artificial culturing method of cordyceps sinensis and cordyceps sinensis product
The invention provides a culture medium used for culturing cordyceps sinensis, which comprises 1000 parts by weight of water, 500 to 1500 parts by weight of starch material, 10 to 35 parts by weight of coconut water, 2 parts by weight of peptone, 10 to 30 parts by weight of chop soup, and 10 to 30 parts by weight of sucrose, and is used for an artificial culturing method of cordyceps sinensis andproviding a cordyceps sinensis product.
Owner:连启西
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com