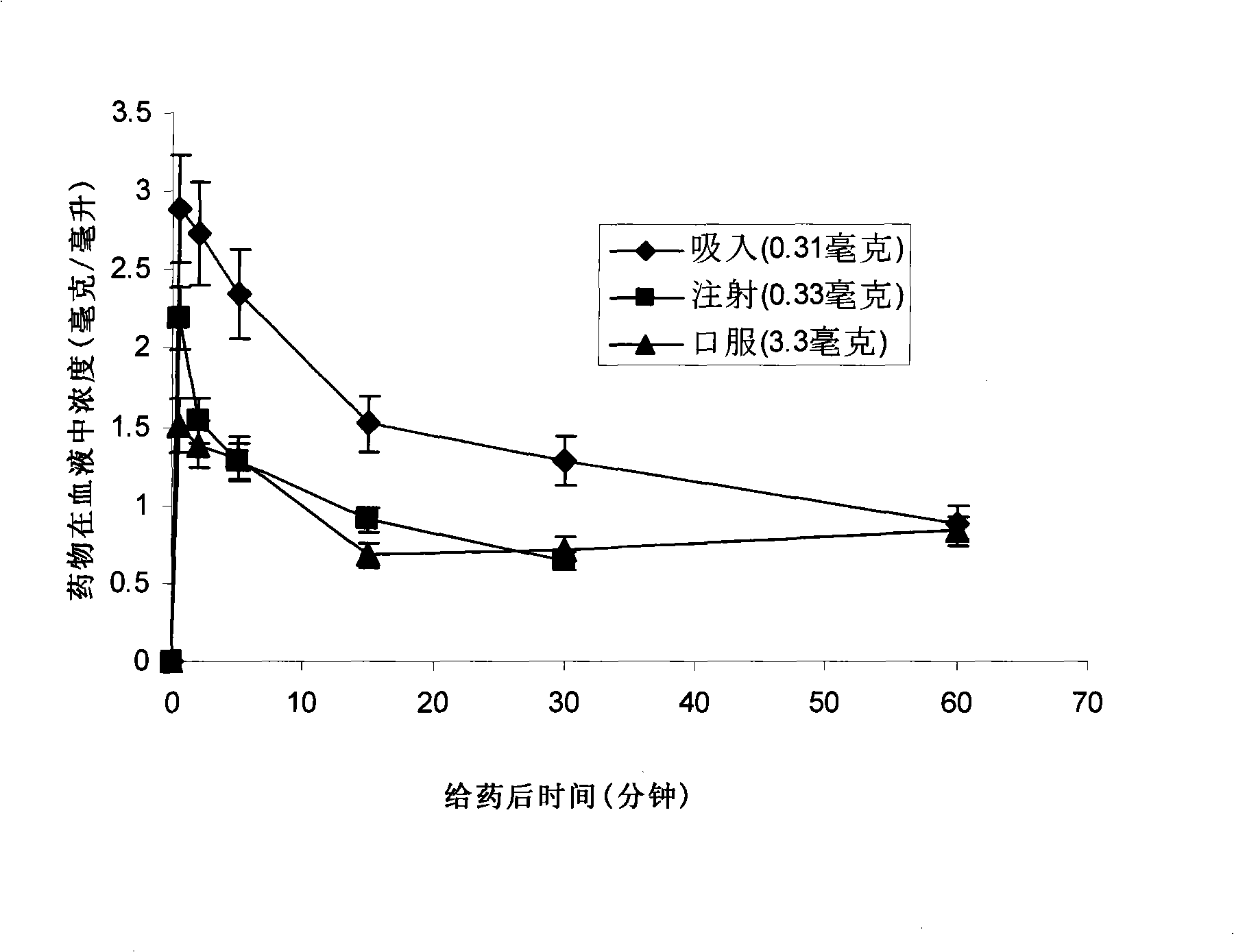
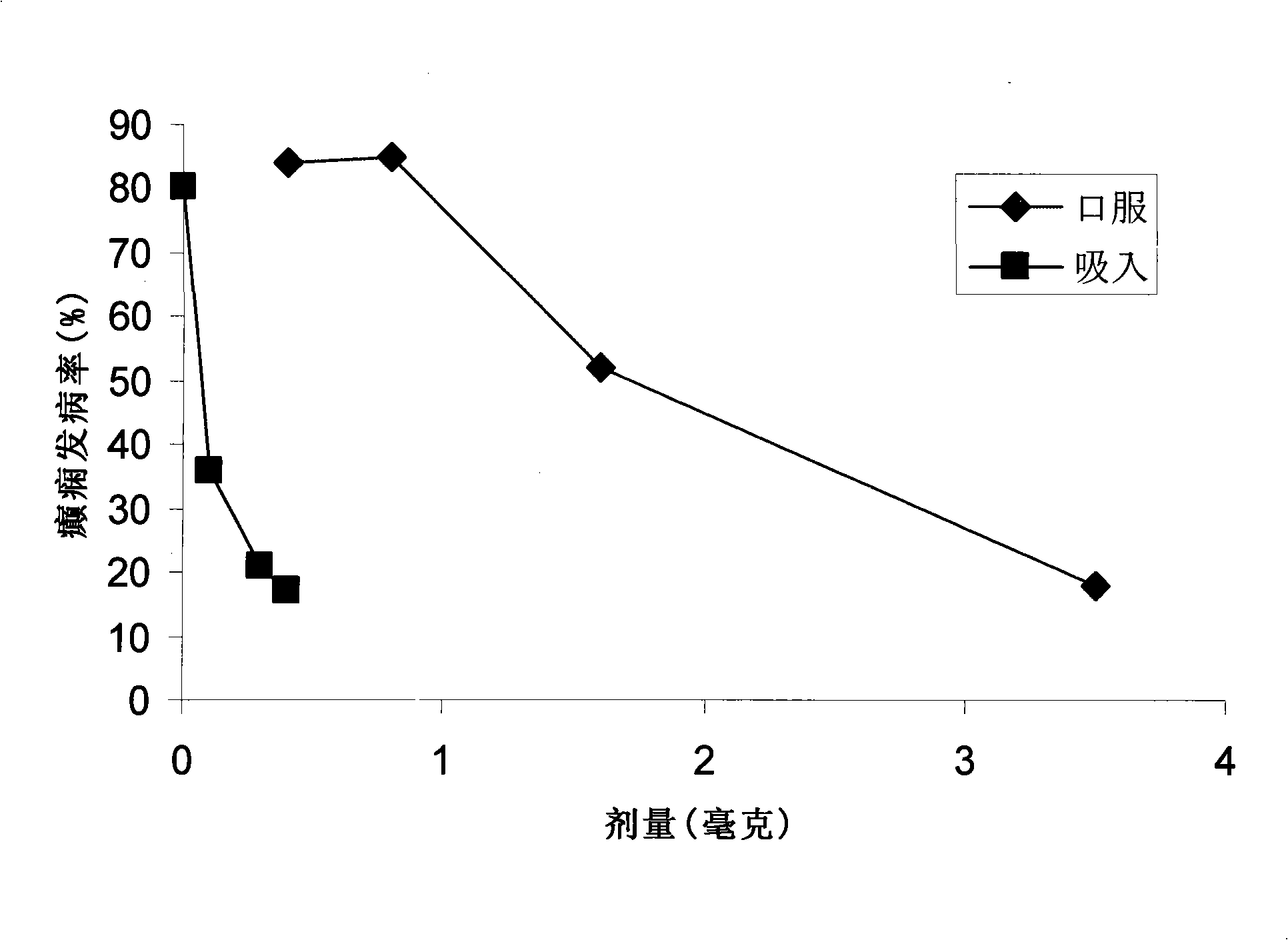
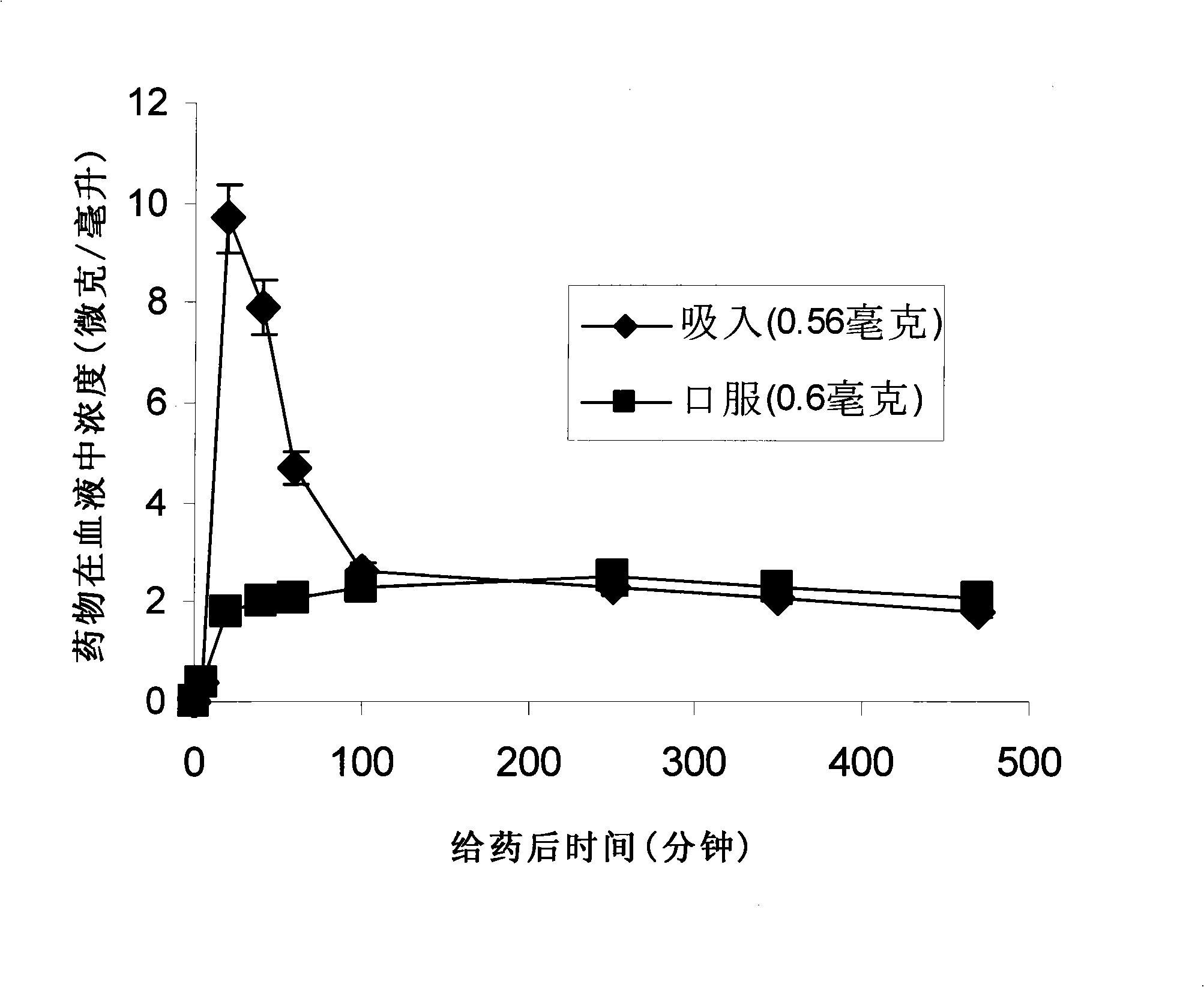
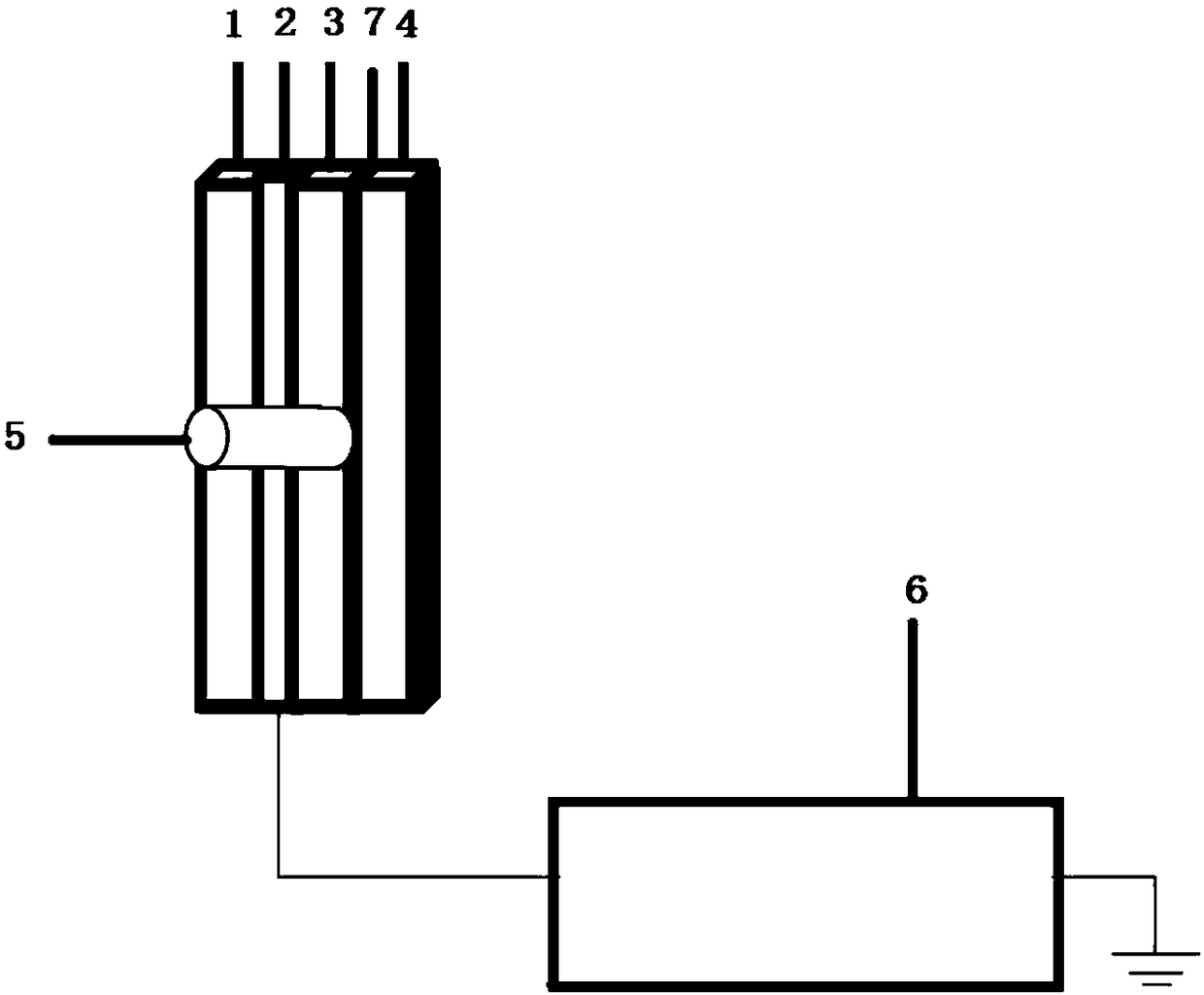
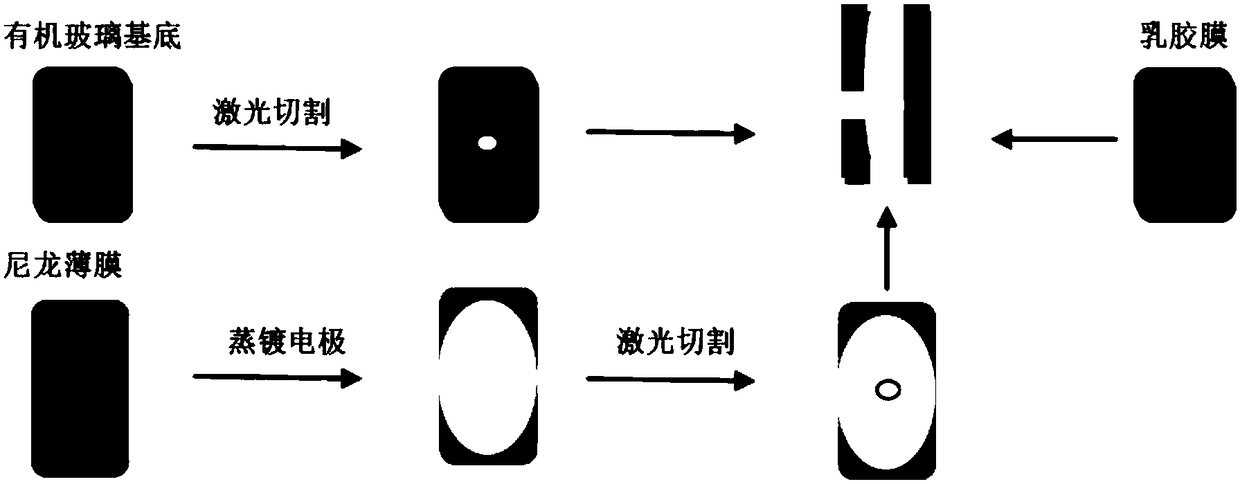
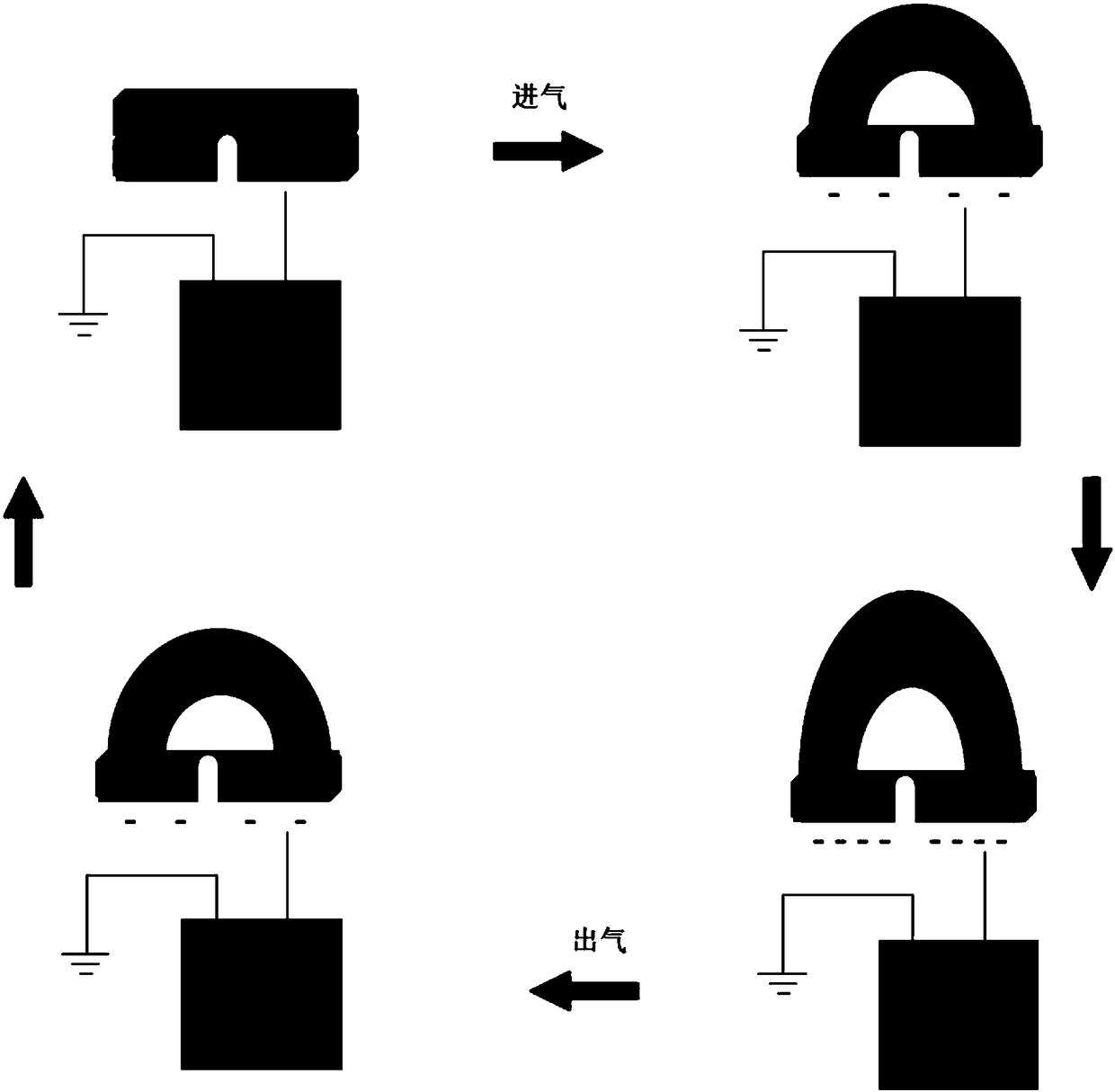
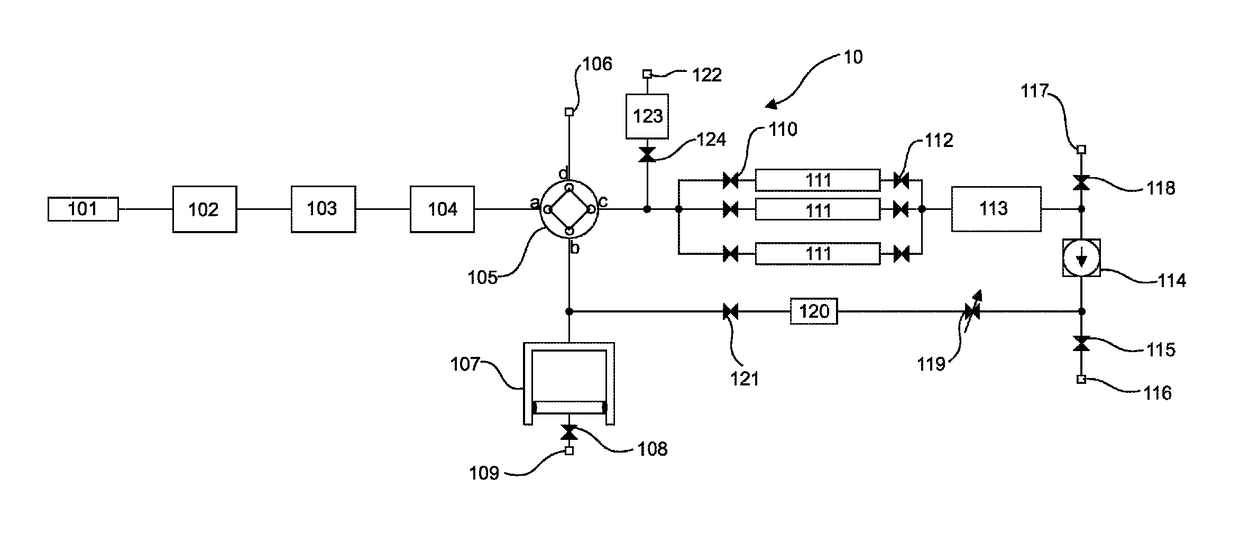
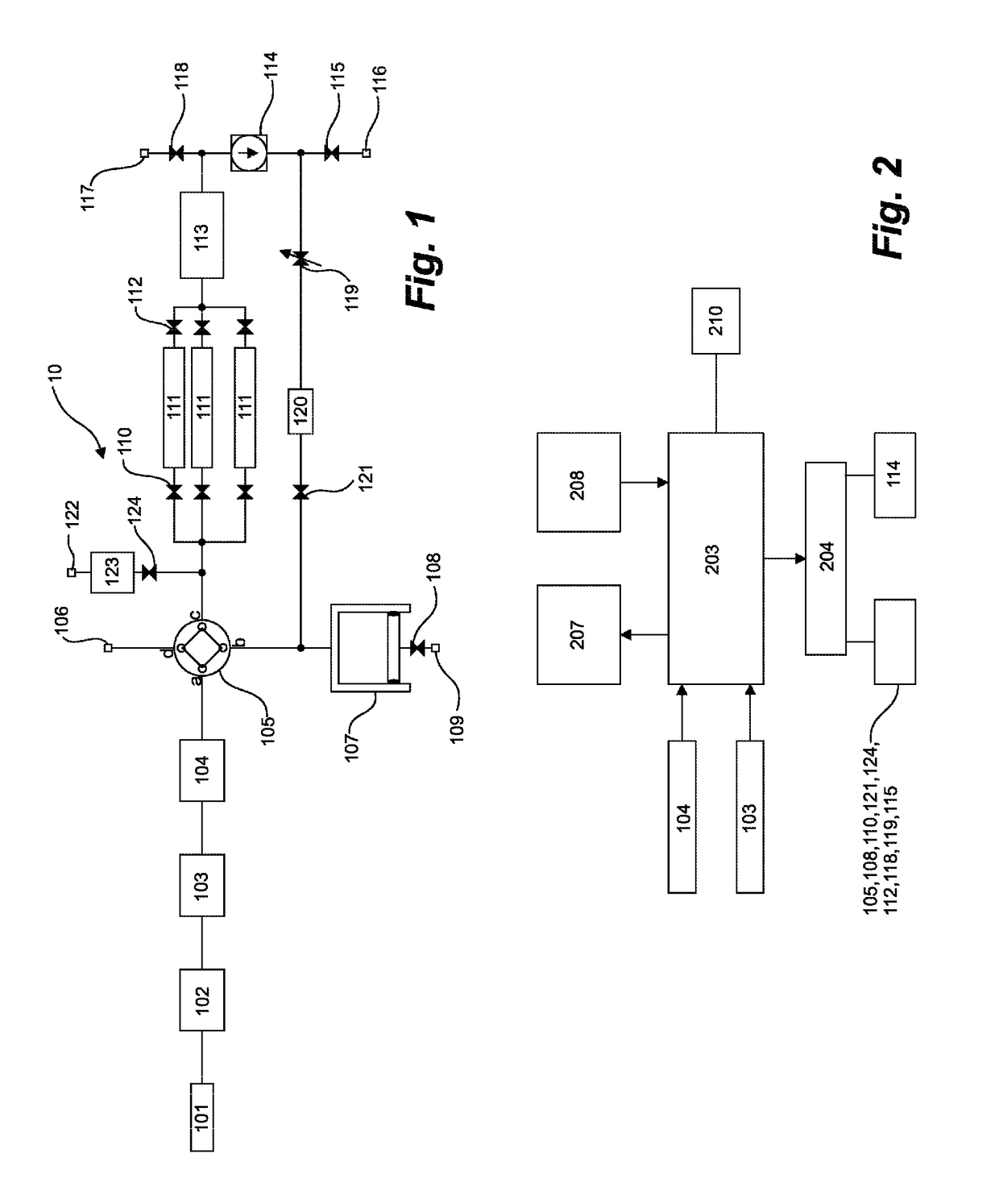
Patents
Literature
236 results about "Pulmonary alveolus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin alveolus, "little cavity") is a hollow cup-shaped cavity found in the lung parenchyma where gas exchange takes place. Lung alveoli are found in the acini at the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely on the respiratory bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out.
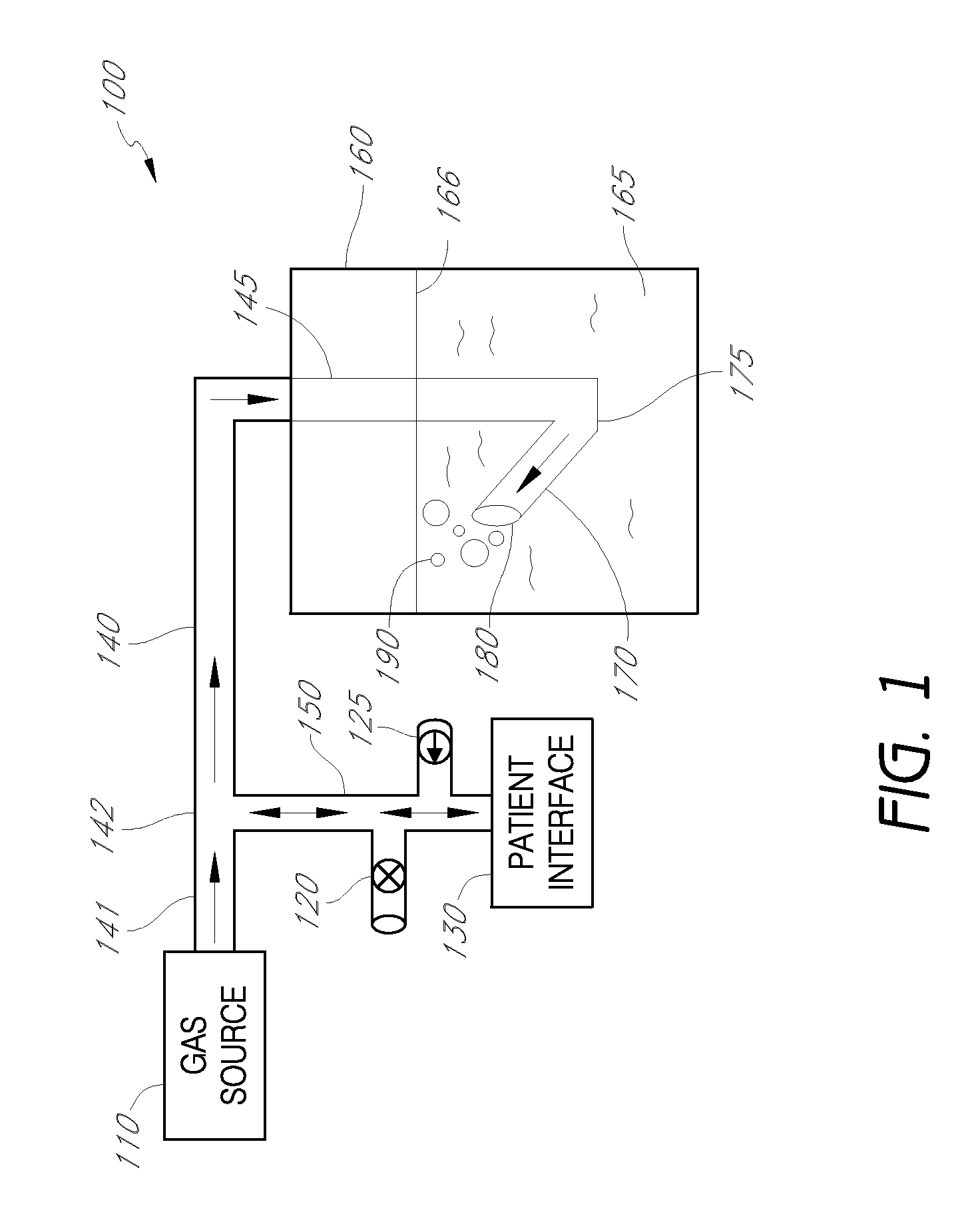
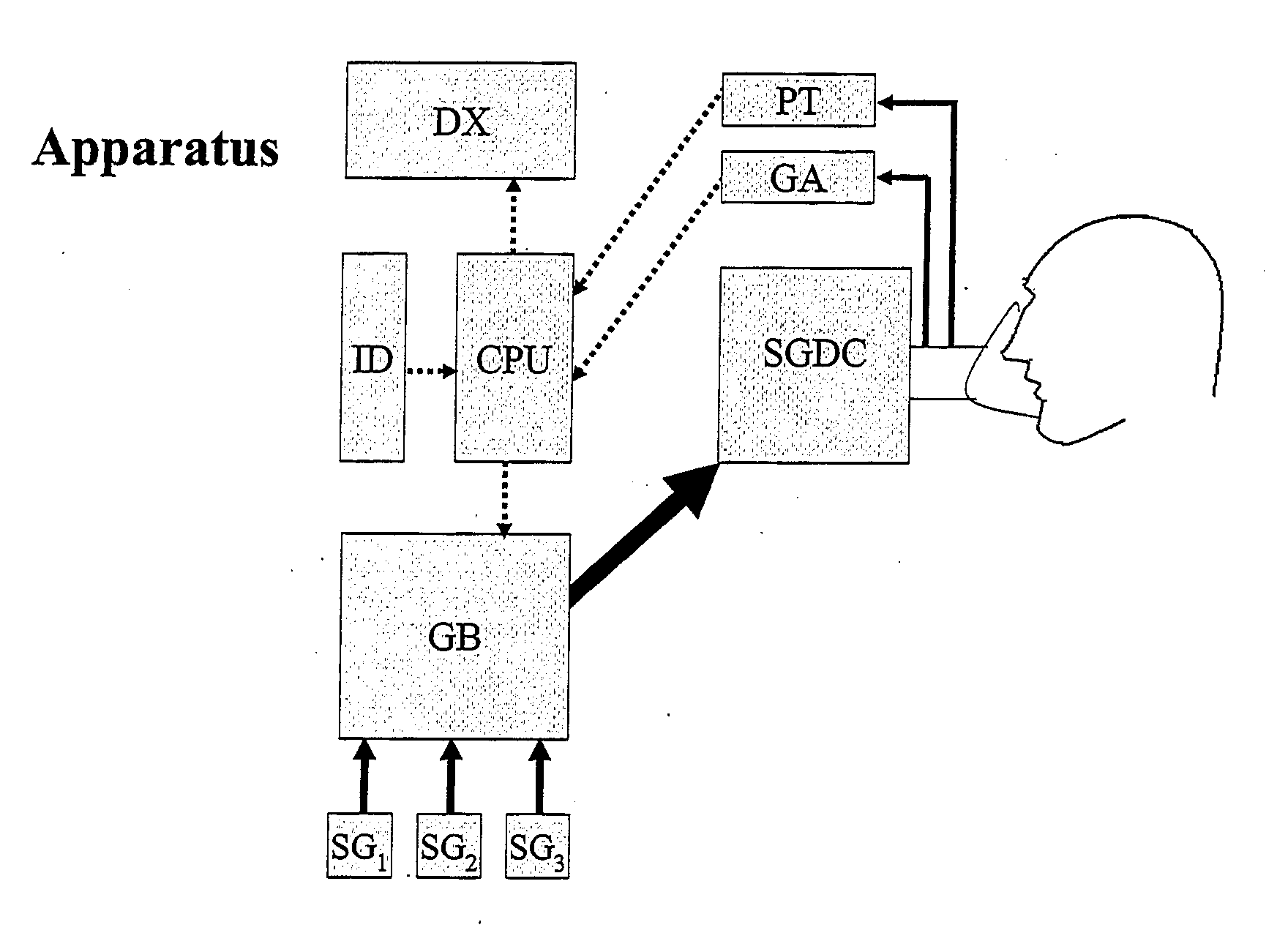
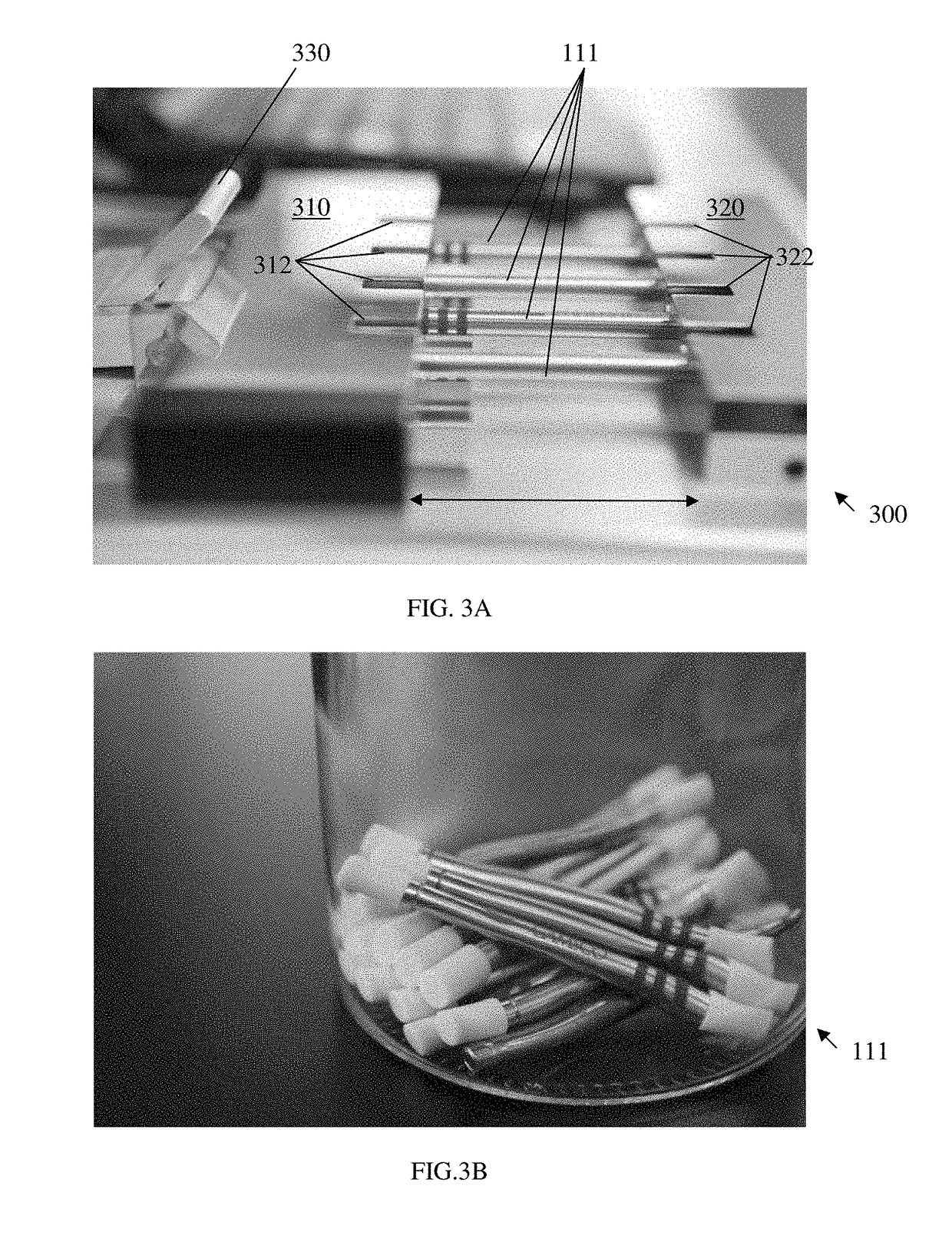
Apparatus and method for lung analysis
InactiveUS20060100666A1Reliable and reproducible transducer positioningEnhanced couplingOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart defibrillatorsAcoustic transmissionCOPD
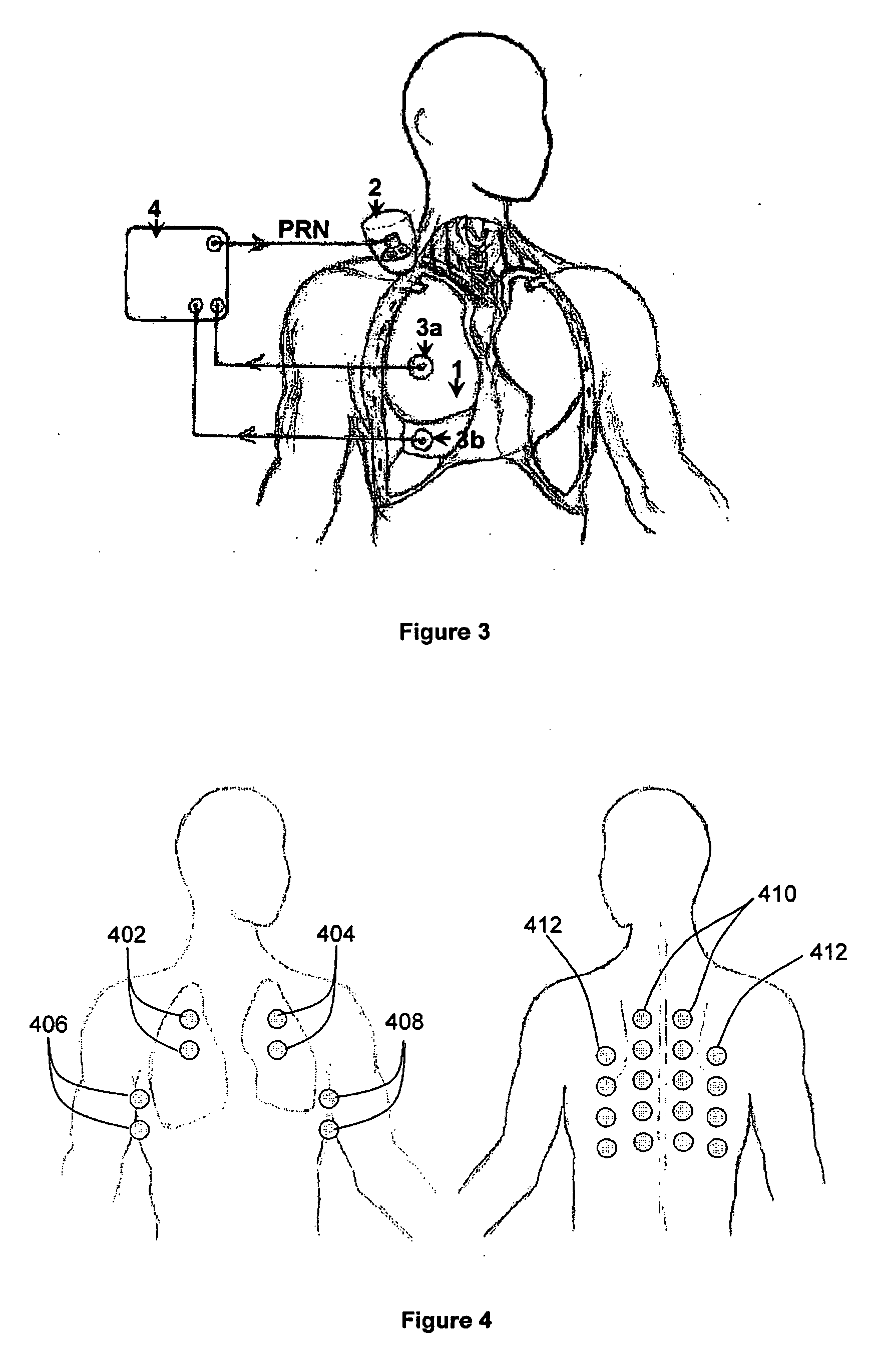
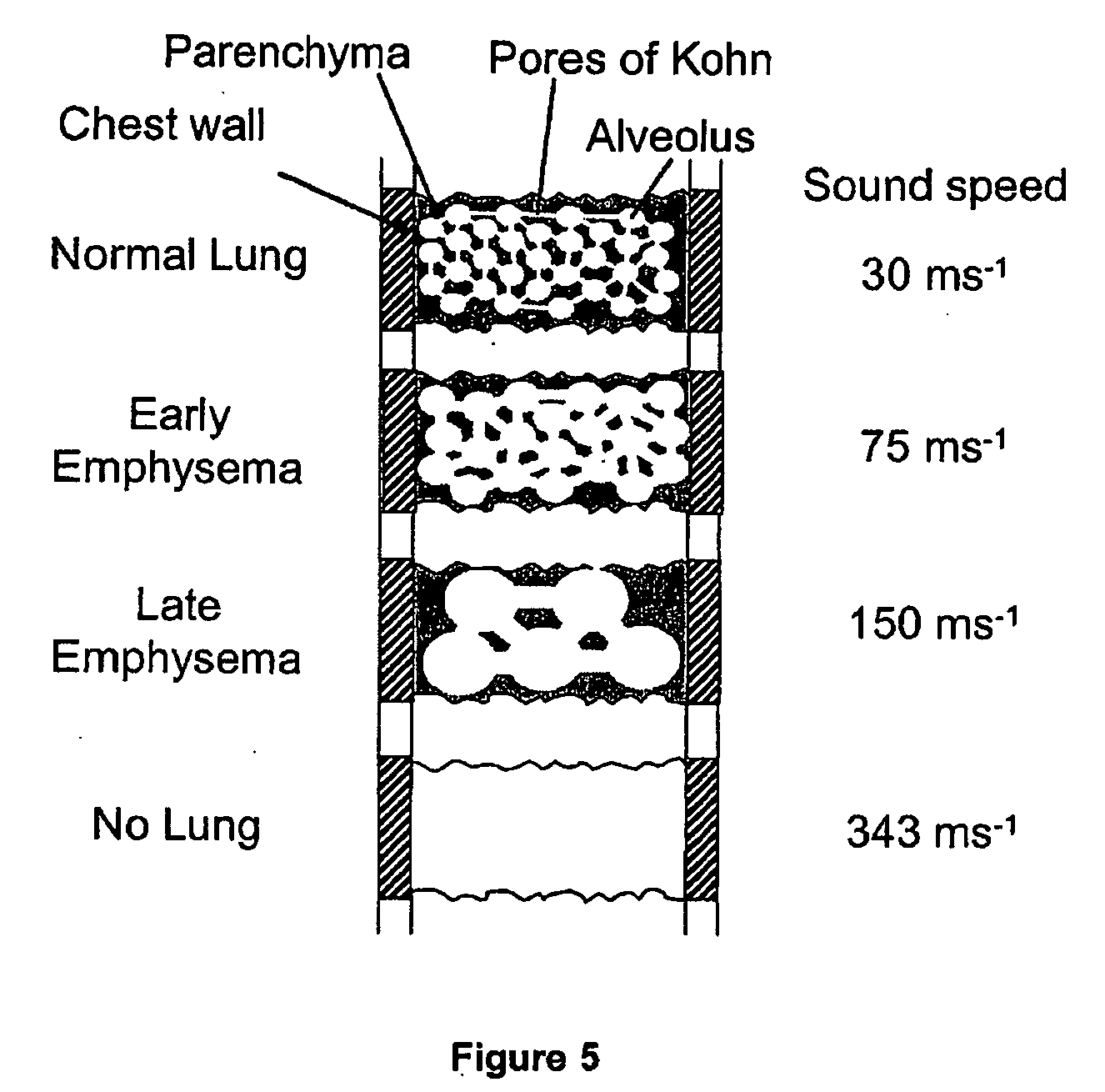
An apparatus and method of detecting COPD and in particular, emphysema utilizes a change in acoustic transmission characteristics of a lung due to e.g. the appearance of fenestrae (perforations) in the alveoli of the lung. The use of acoustic signals may provide good sensitivity to the existence of alveolar fenestrae, even for microscopic emphysema, and the appearance and increase in fenestrae may be determined by monitoring acoustic transmission characteristics such as, for example, an increase in acoustic signal velocity and velocity dispersion, and / or a change in attenuation. A transmitter may be located in e.g. the supra-clavicular space and receivers may be mounted on the chest. Measurements may be correlated between pairs of receivers to determine acoustic transmission profiles.
Owner:PULMOSONIX
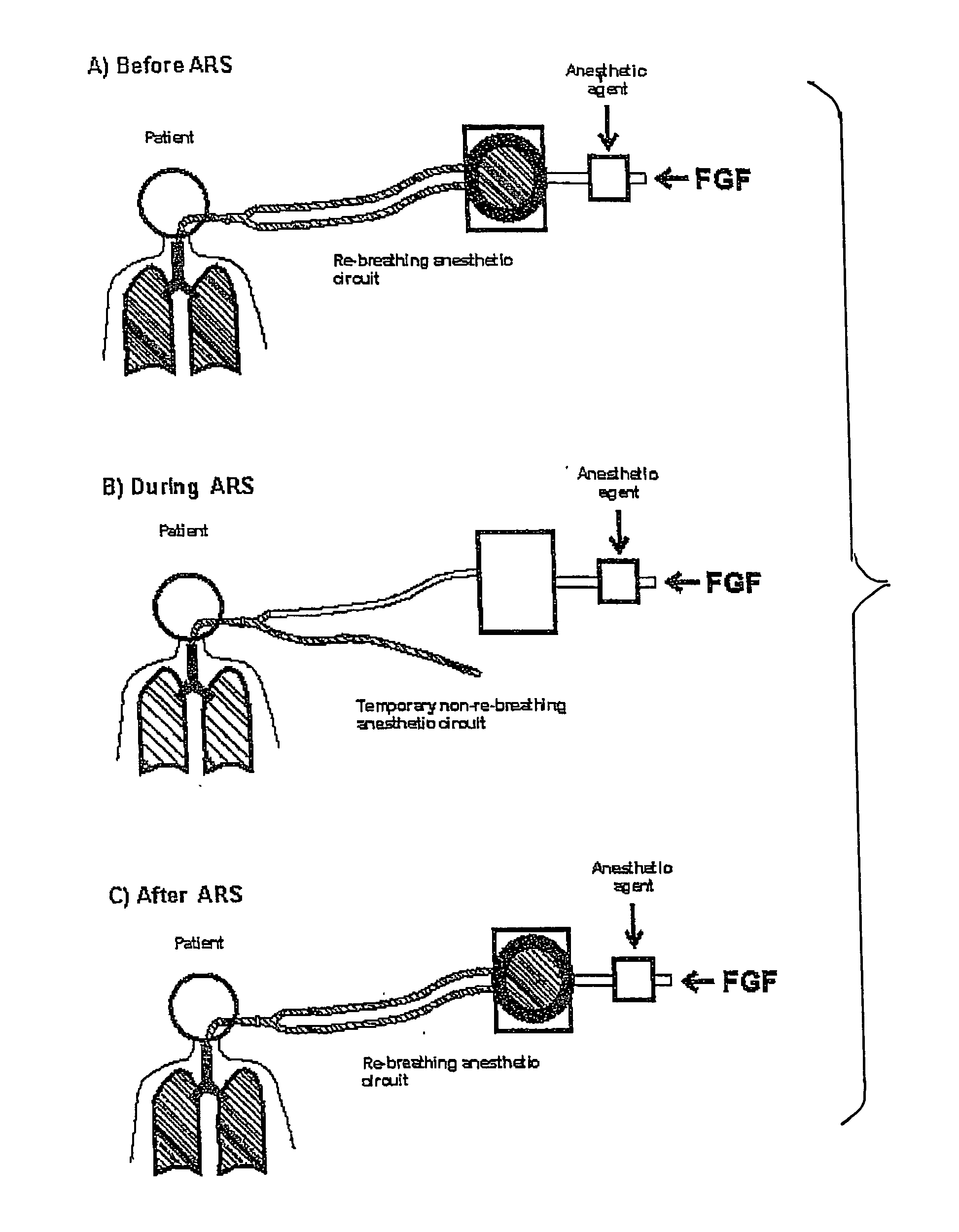
Method and apparatus for breathing during anesthesia
InactiveUS6123072AEliminate the problemMinimize movementRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingWhole body
A method and apparatus are provided for ventilation of patients during general anesthesia. Breathing gas is supplied to the patient during anesthesia at a controlled volume above the functional residual capacity of the patient's lungs. The patient is allowed to spontaneously respire when the volume of breathing gas is above the functional residual capacity. The pressure of the breathing gas is periodically reduced to facilitate expulsion of carbon dioxide-containing gas from the patient. The system promotes alveolar ventilation, carbon dioxide excretion, oxygenation and respiratory monitoring in patients who receive general anesthesia.
Owner:DOWNS JOHN B
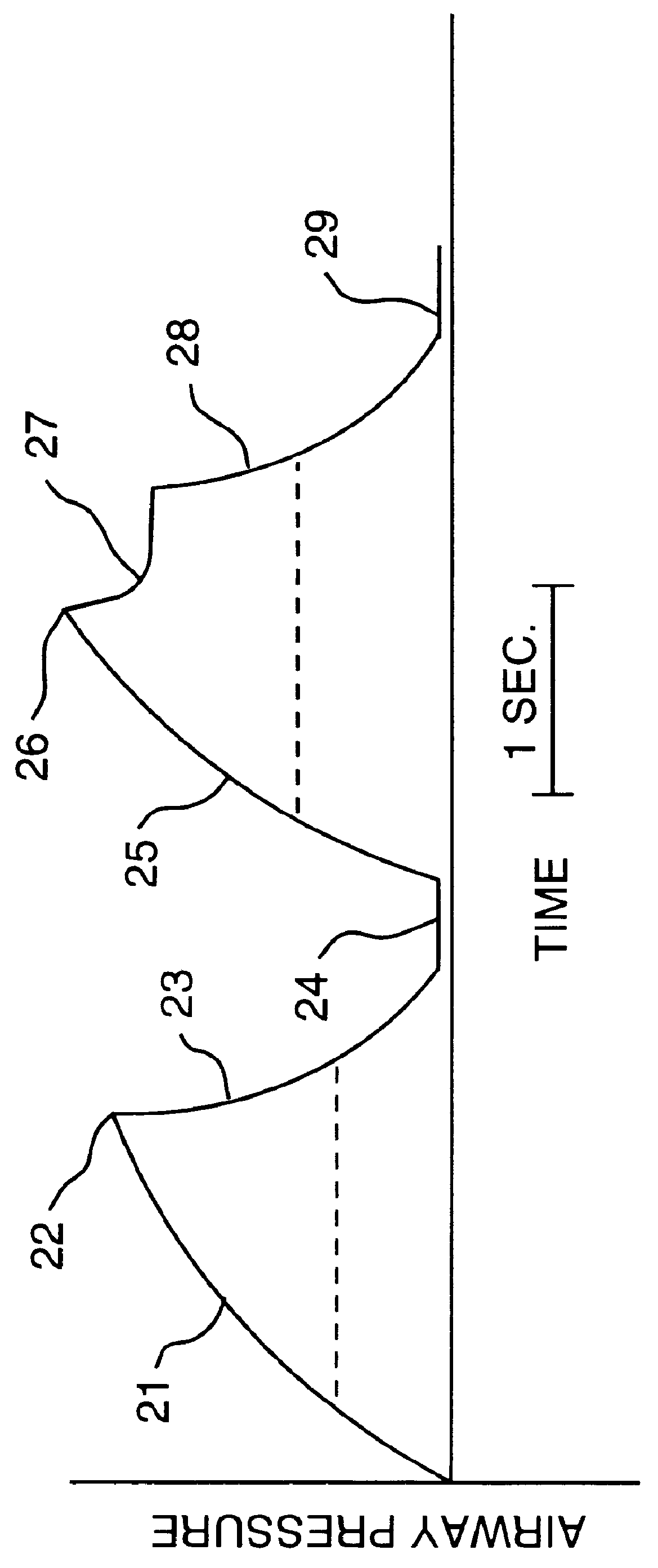
Broad-band, low frequency, high-amplitude, long time duration, oscillating airway pressure breathing apparatus and method utilizing bubbles
ActiveUS20110073112A1Stabilize lung volumeIncrease gas exchangeTracheal tubesRespiratory masksMeasurement deviceFrequency spectrum
It has been discovered that high amplitude, low frequency, broadband spectrum pressure oscillations of sufficient time duration can help stabilize lung volumes and improve gas exchange in a patient receiving ventilation assistance by helping to recruit and stabilize alveoli. A novel device is presented which can produce pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum and long time duration. Additionally, the device can maintain a patient's mean airway pressure at one or more controlled levels. The device can control the oscillatory amplitude, frequency range and composition, time duration, and mean airway pressure levels by adjusting certain device parameters, such as the angle and depth of the device in a fluid. A device and mechanical system for remotely adjusting and measuring the angle of the device in a fluid are also disclosed. Furthermore, a device and system are disclosed that can deliver pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum, long time duration, and multiple mean airway inspiratory and expiratory pressure levels. The device and system also provide means for controlling respiration timing in a patient, including: breaths per minute, inspiratory time, and the ratio of inspiratory to expiratory time.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
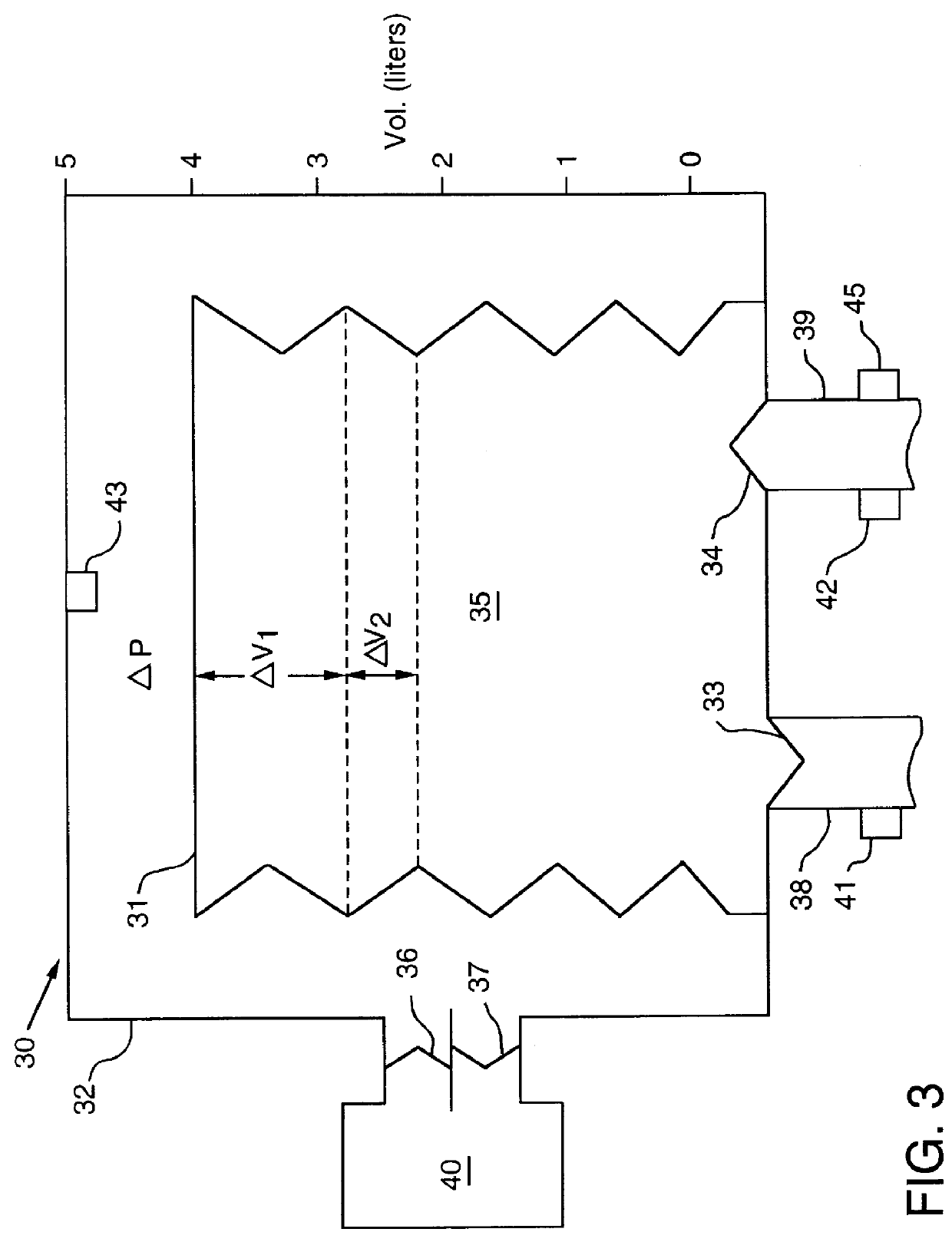
System and Method for Assessing Real Time Pulmonary Mechanics
ActiveUS20120330177A1Accurate calculationAccurate informationRespiratorsRespiratory organ evaluationRestrictive lung diseaseTreatment effect
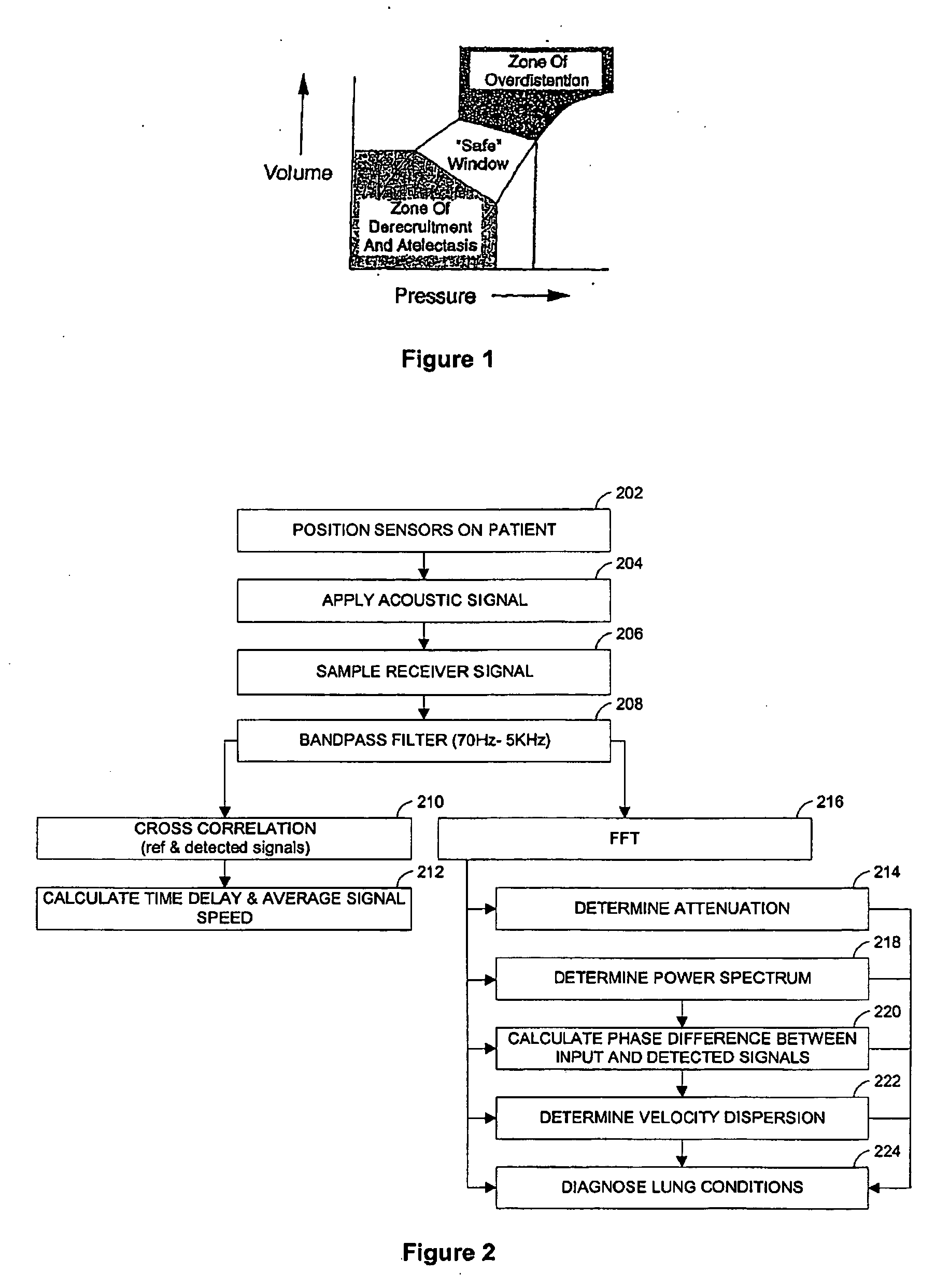
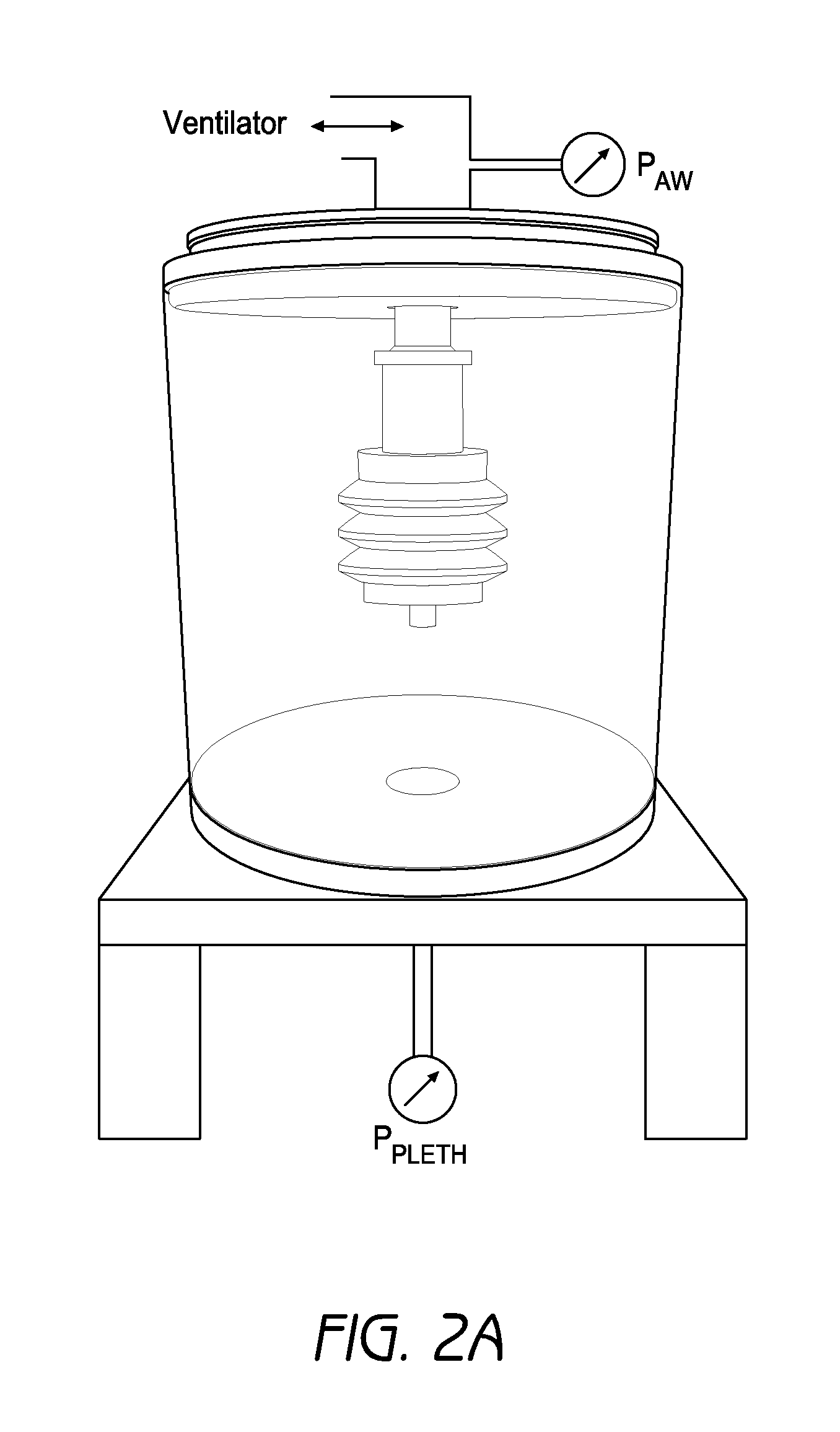
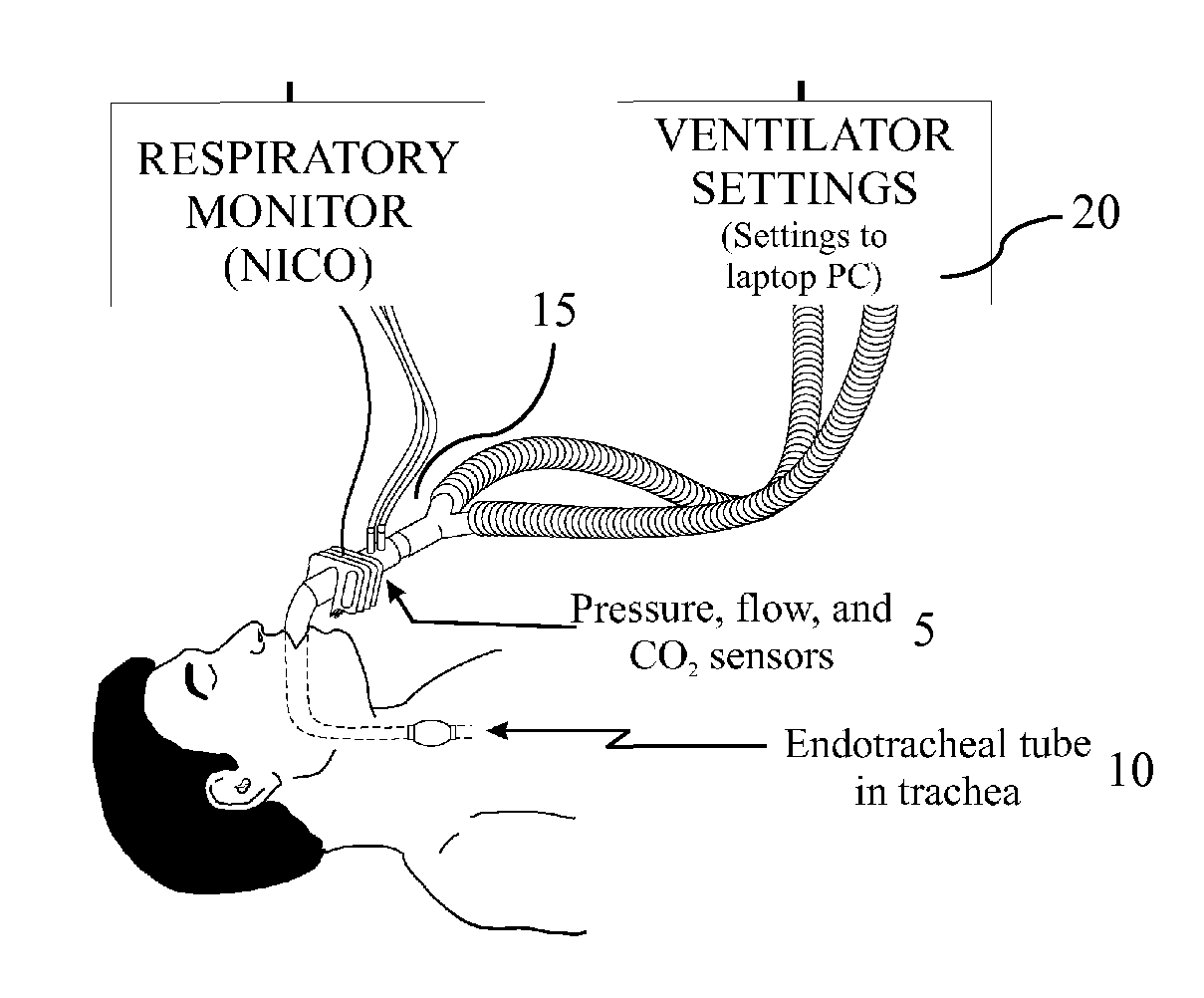
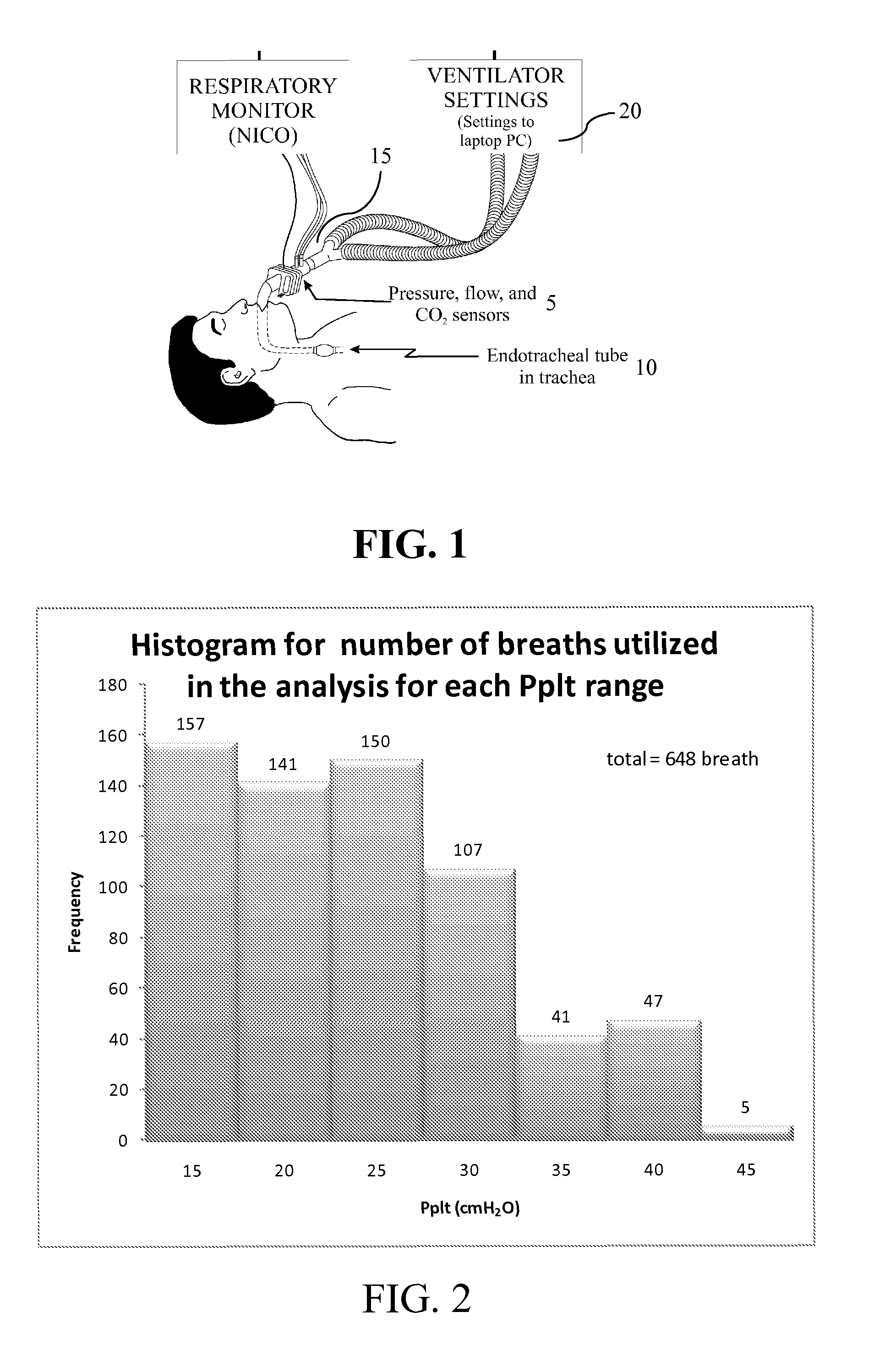
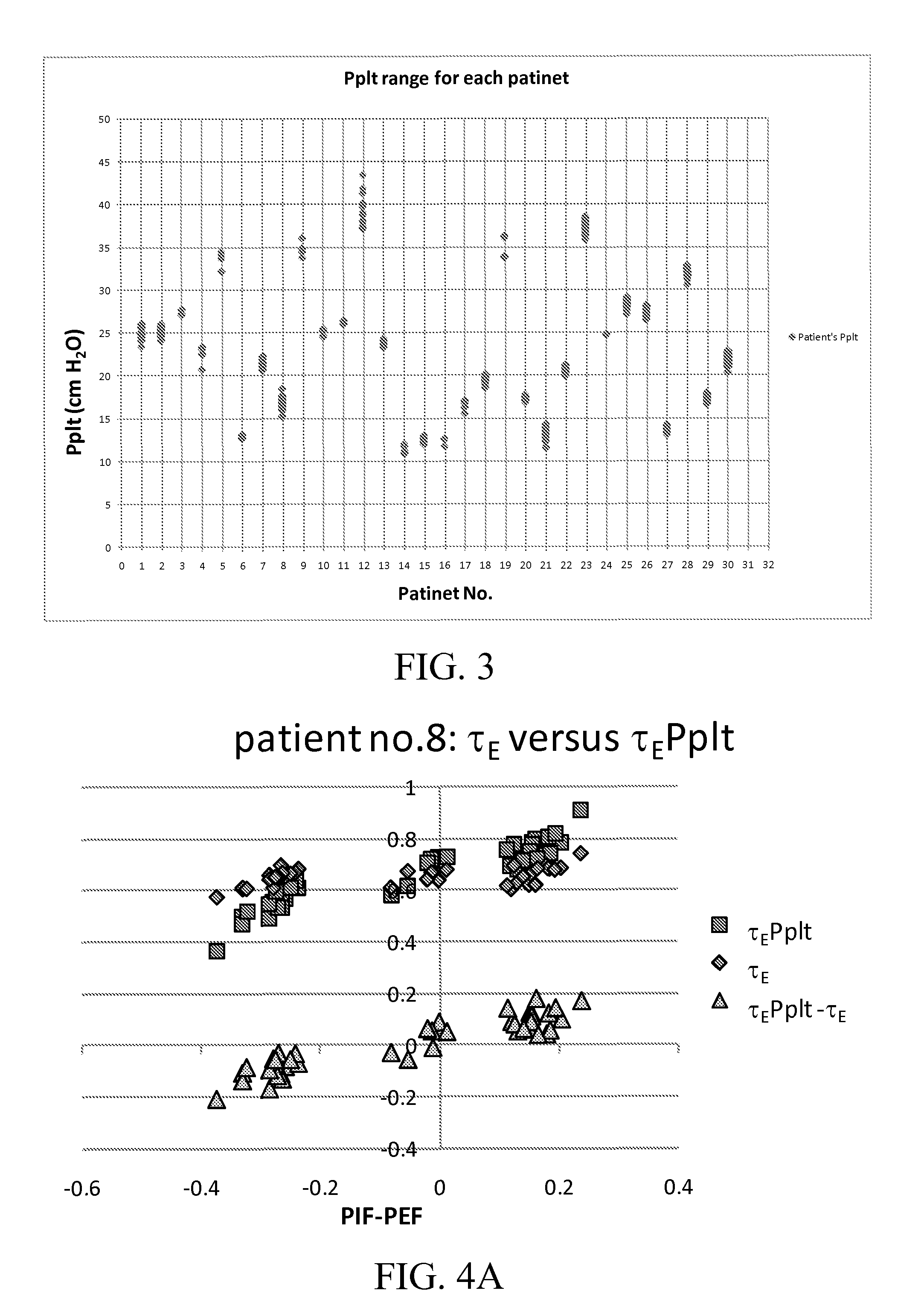
A system and method of calculating an accurate estimate of pulmonary mechanics of a patient, including but not limited to compliance, resistance, and plateau pressure without modification of ventilator flow pattern. The accurate estimation of pulmonary mechanics is derived from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using novel mathematical models. These estimated figures for pulmonary mechanics (respiratory system compliance and resistance) are important for monitoring patient treatment efficacy during mechanical ventilation and ensuring alveoli do not over distend to avoid baro- and / or volutrauma, especially in patients with restrictive lung diseases. The subject method of calculating these accurate estimated figures for pulmonary mechanics is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +1
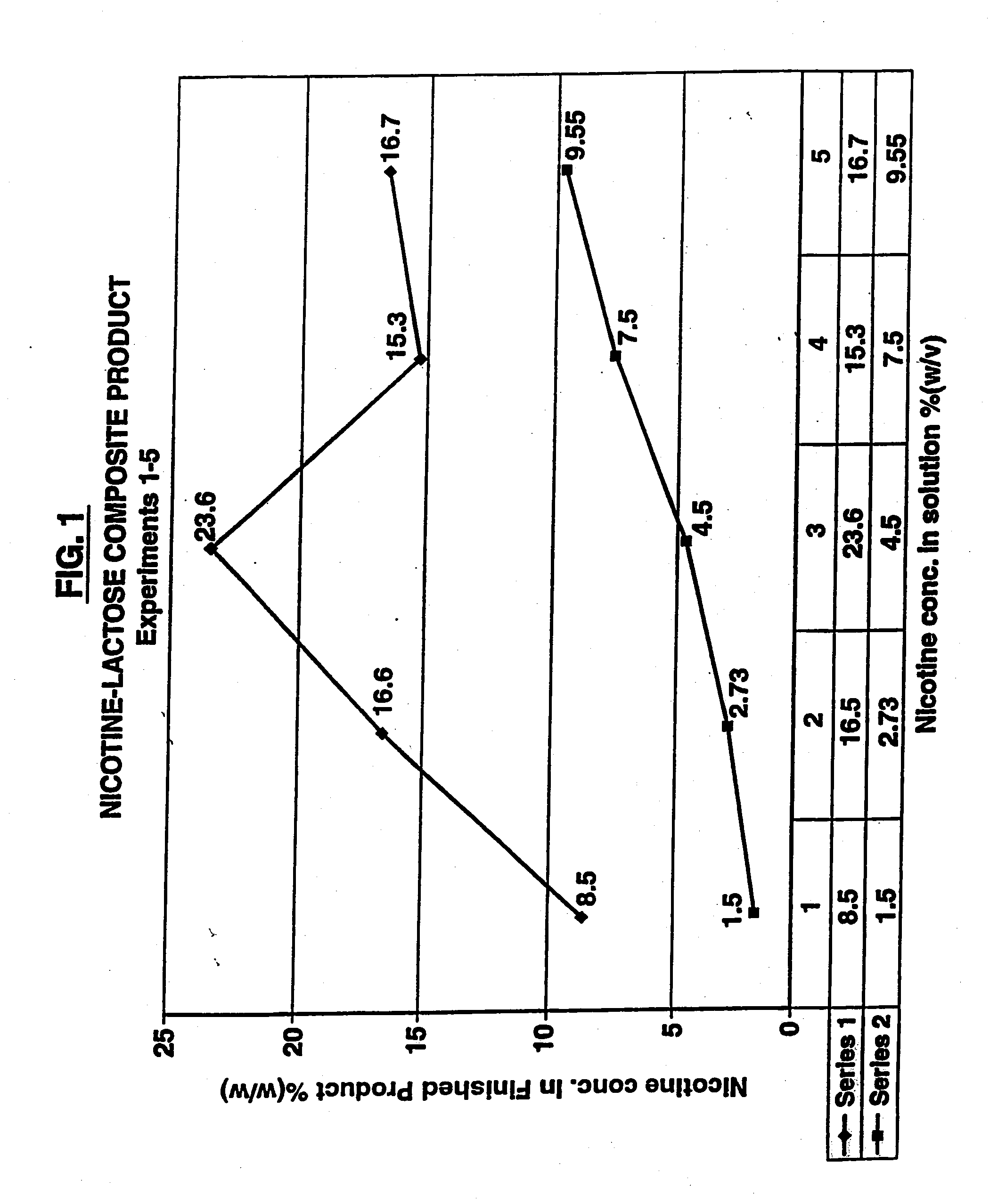
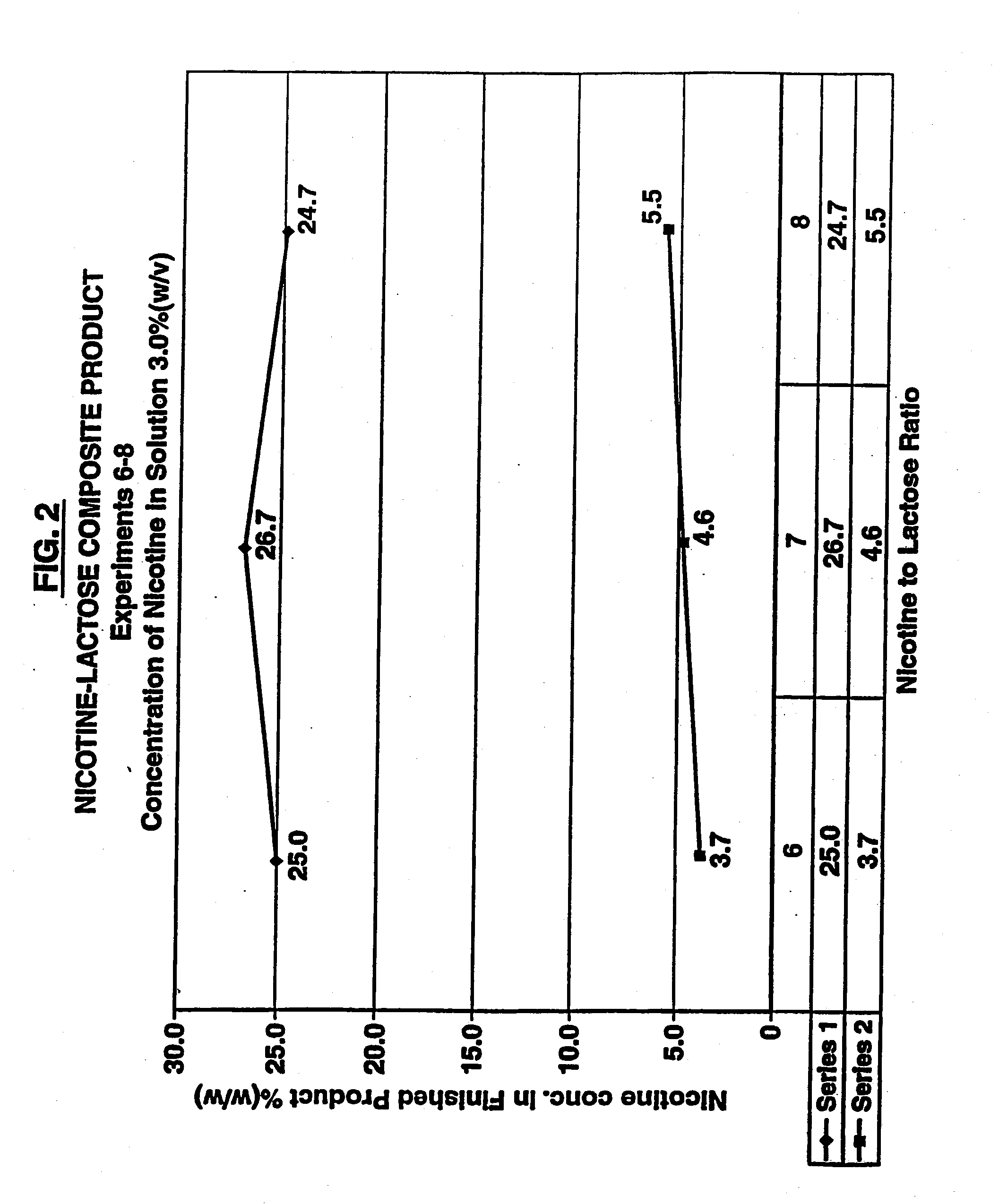
Method of producing a nicotine medicament and a medicament made by the method
InactiveUS20120042886A1Efficiently conveyedImprove efficiencyTobacco preparationPowder deliveryNicotineSpray drying
A method of producing a nicotine medicament for use in an inhaler comprises combining nicotine, a non-spheronized sugar and a liquid carrier including water to produce a flowable mixture and spray drying the flowable mixture at conditions to produce particles of the nicotine medicament suitable for delivery to the alveoli and lower airways of the person. Also disclosed is a nicotine medicament made by the method. The nicotine composition produced by this method is a composite particle suitable for tobacco replacement or withdrawal therapy.
Owner:SANSA BARBADOS
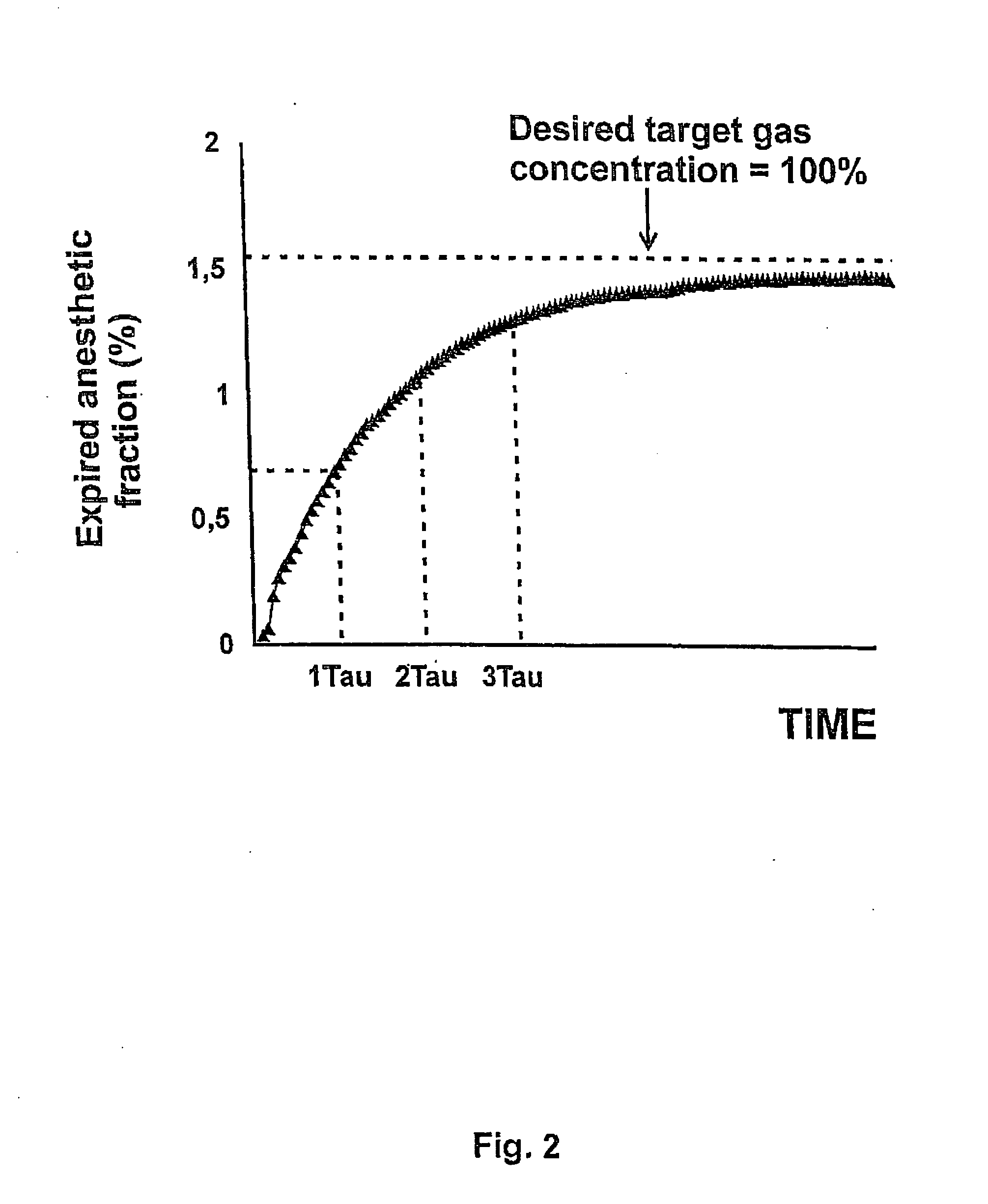
Method and apparatus for changing the concentration of a target gas at the blood compartment of a patient's lung during artificial ventilation
InactiveUS20070089741A1Reduce negative impactGas exchange during ventilationRespiratorsBreathing masksArtificial ventilationRespirator
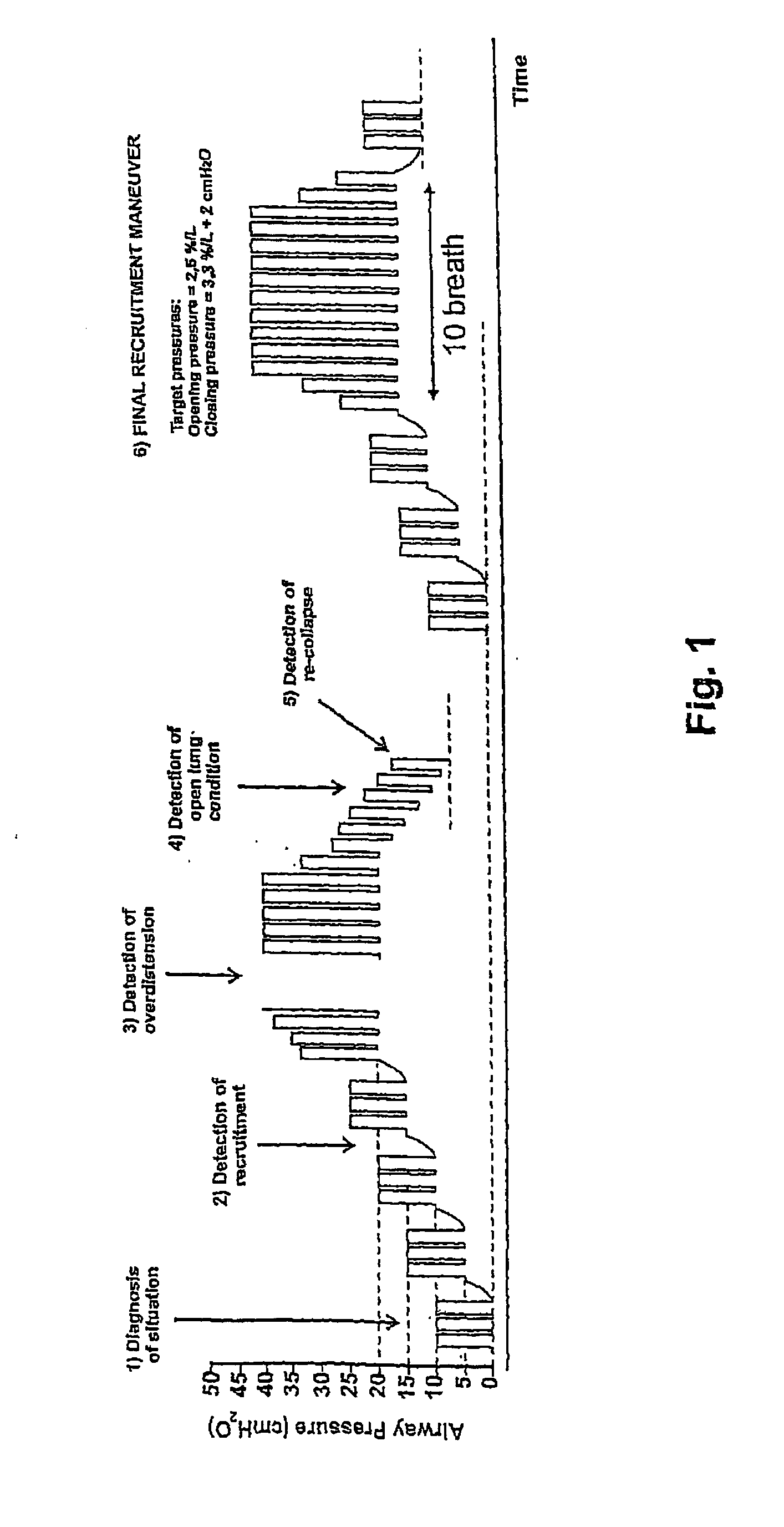
The invention refers to a method and apparatus for changing the concentration of a target gas at the blood compartment of a patient's lung from an actual target gas concentration to a desired target gas concentration during artificial ventilation with an inspiratory gas composition by a respirator being controlled via a set of ventilation parameters. In order to decrease the negative effects of general anaesthesia during artificial ventilation even further, the method according to the invention comprises the following steps: a) ventilating the lung in a first ventilation stage, and b) ventilating the lung in a second ventilation stage in which alveolar recruitment is promoted.
Owner:BOHM STEPHAN +2
System for estimating state of critically ill patient in obstetrical department
InactiveCN101554322AImprove the level of treatmentReduce mortalitySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringNervous systemCritically ill
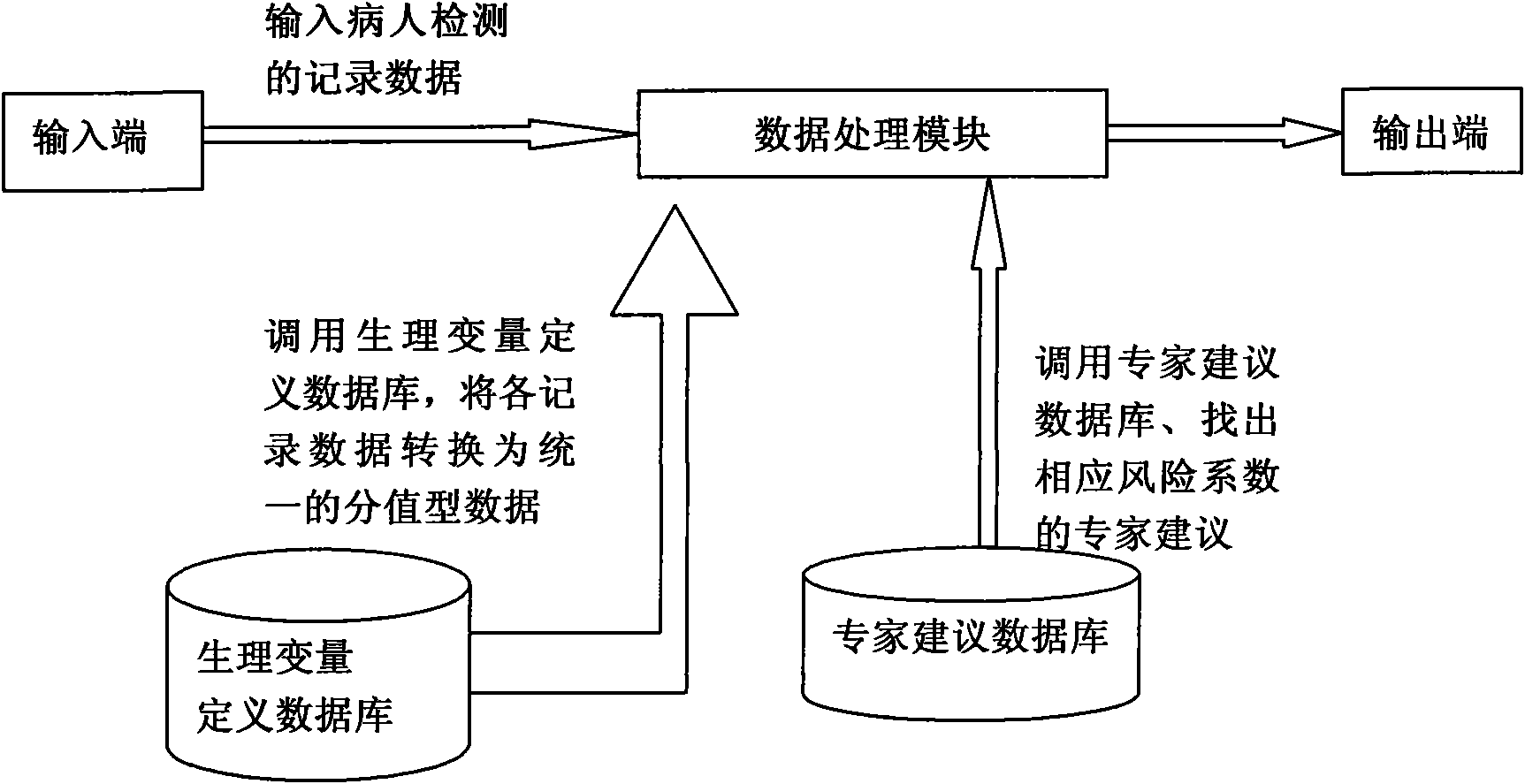
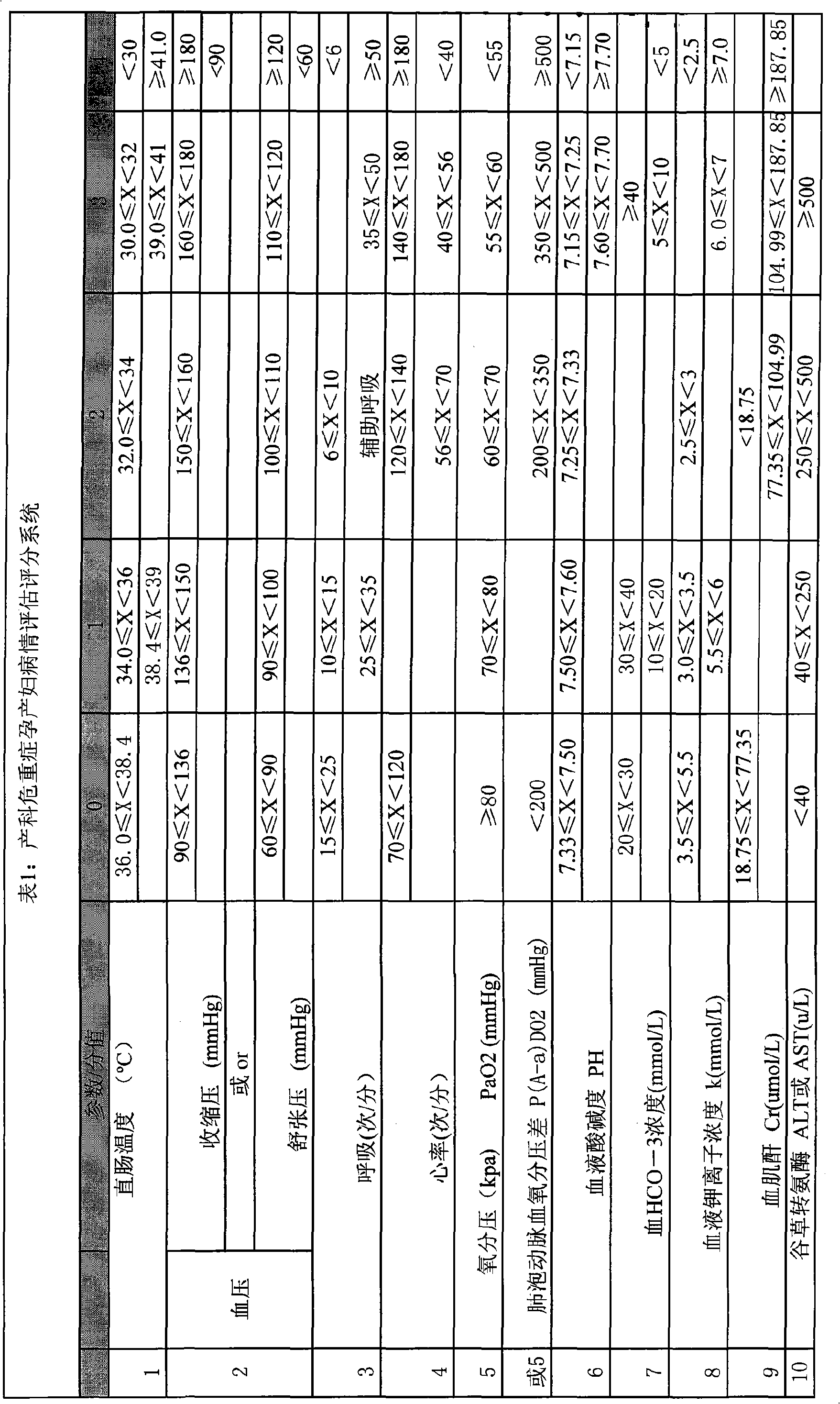
The invention discloses a system for estimating the state of a critically ill patient in an obstetrical department, which comprises an input end, an output end and a data processing module. Firstly, measured heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, breathing rate, pH, blood HCO-3 concentration, oxygen partial pressure, alveolar arterial blood oxygen tension difference, potassium ion concentration, hematokrit, white cell count, platelet count, fibrinogen, glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, albumin, bilirubin, creatinine, blood glucose concentration and nervous system grading data are input the system through the input end; the data processing module evaluates a death risk factor; and at last, the output end directly reflects the result of the patient and the expert suggestion. The invention can not only accurately evaluate the critical degree of the state of the patient and predict the death risk, but also can provide quantitative indexes for changing to a three-class hospital, and is beneficial to improve the treatment level of the critical state of the obstetrical department and lower the death rate of pregnant and lying-in women and perinatal infants.
Owner:陈敦金 +1
High Frequency Airway Oscillation For Internal Airway Vibration
InactiveUS20160121062A1Facilitated releaseRespiratorsChiropractic devicesHigh-frequency ventilationBiomedical engineering
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for determining alveolar opening and closing
InactiveUS7122010B2Prevent crashEfficient exchangeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceRadiology
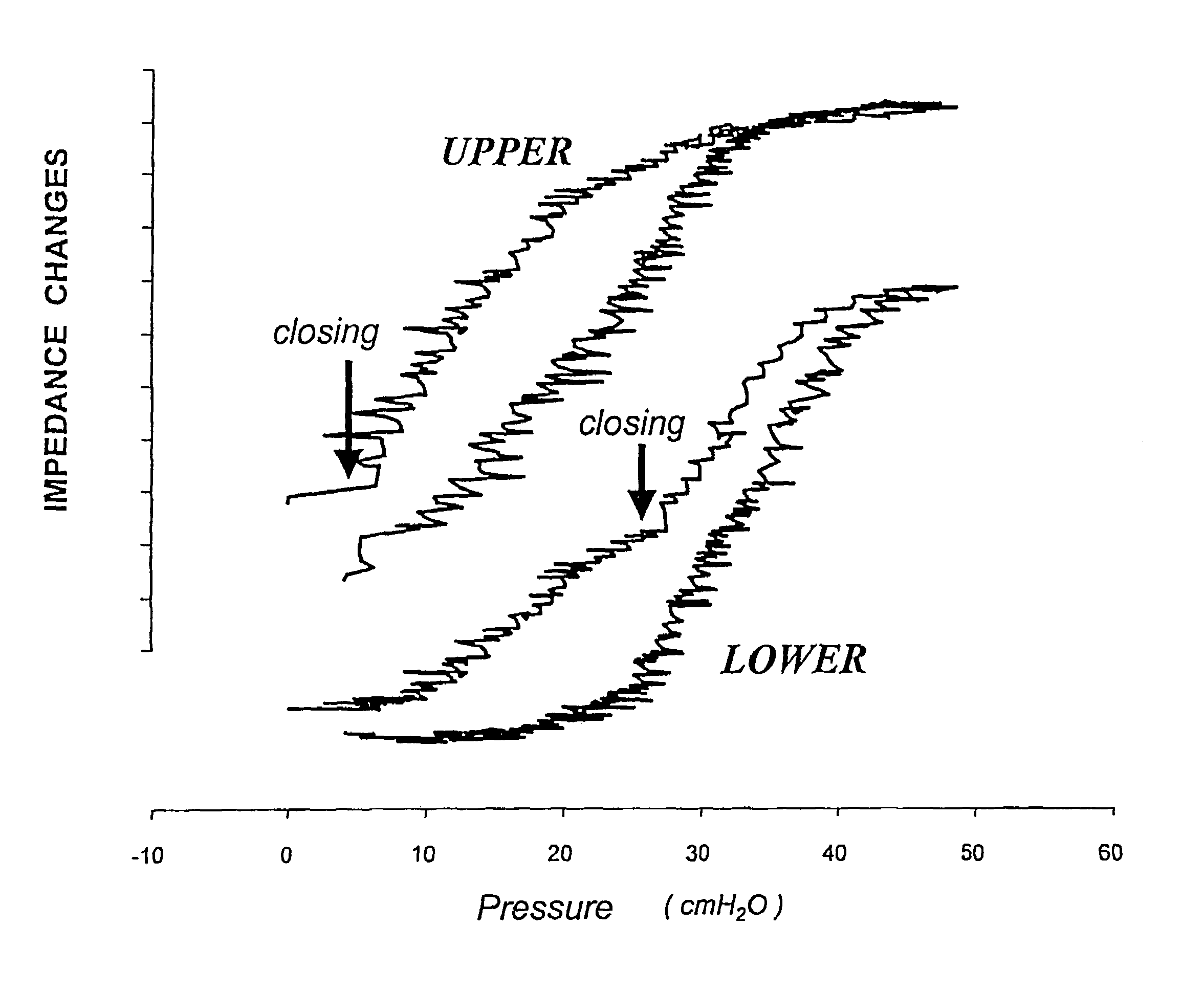
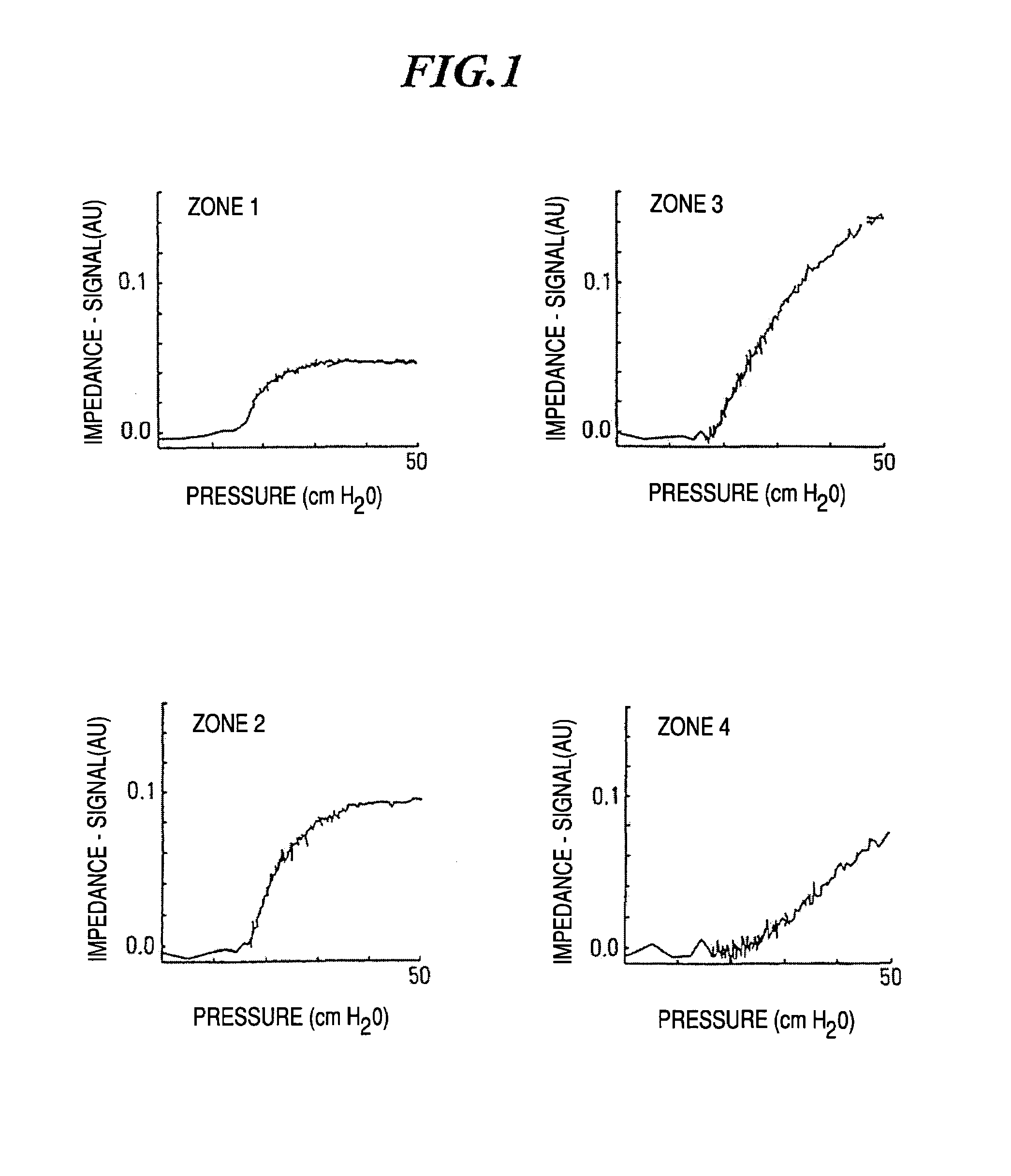
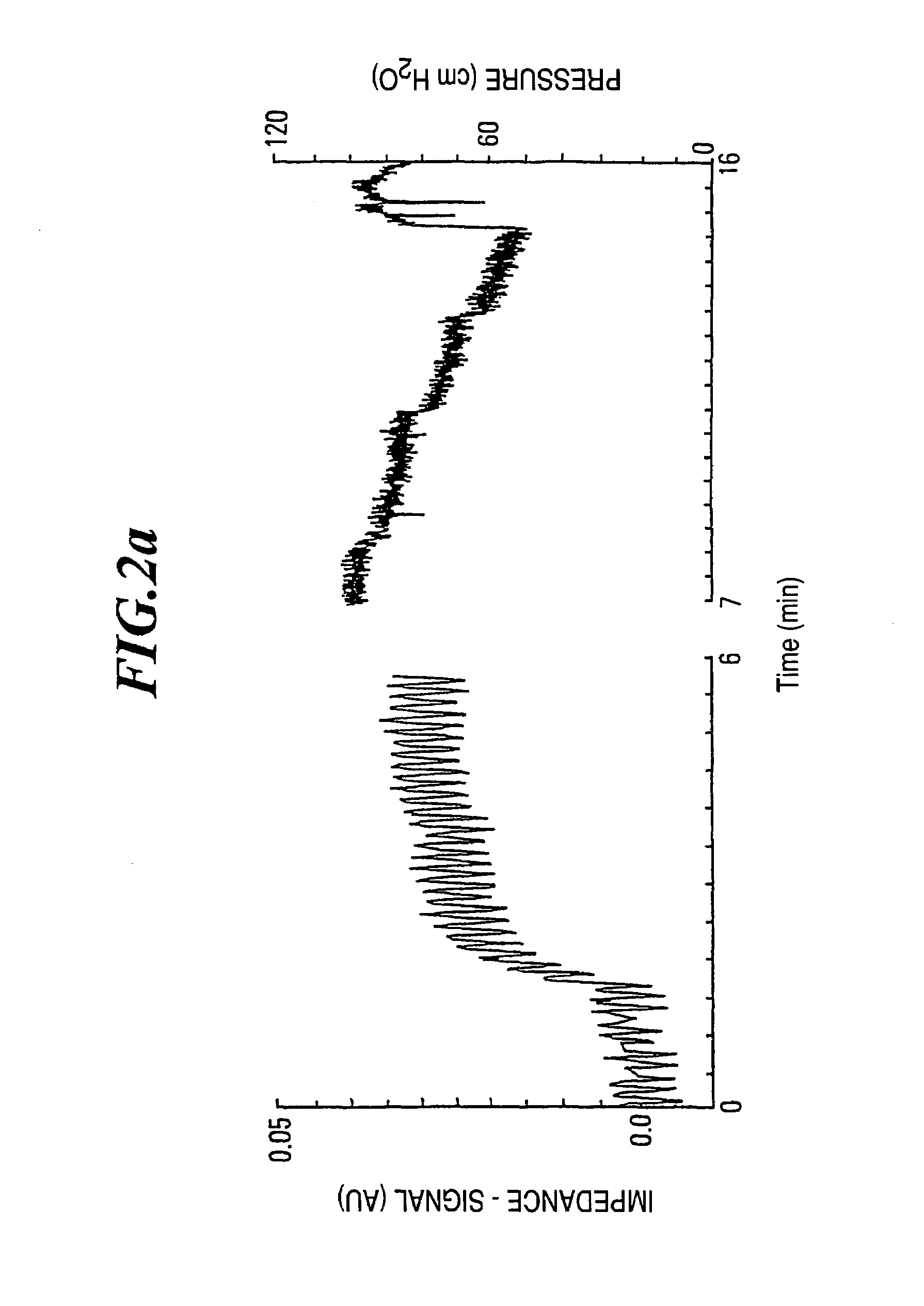
The invention refers to a method for the regional determination of the alveolar opening and alveolar closing of the lung depending on the respiration pressure, wherein according to the method of electrical impedance tomography, an impedance signal is measured in at least one lung zone depending on the respiration pressure. The alveolar opening or closing of a lung zone is determined, in particular to enable an improved artificial respiration.
Owner:TIMPEL MEDICAL BV
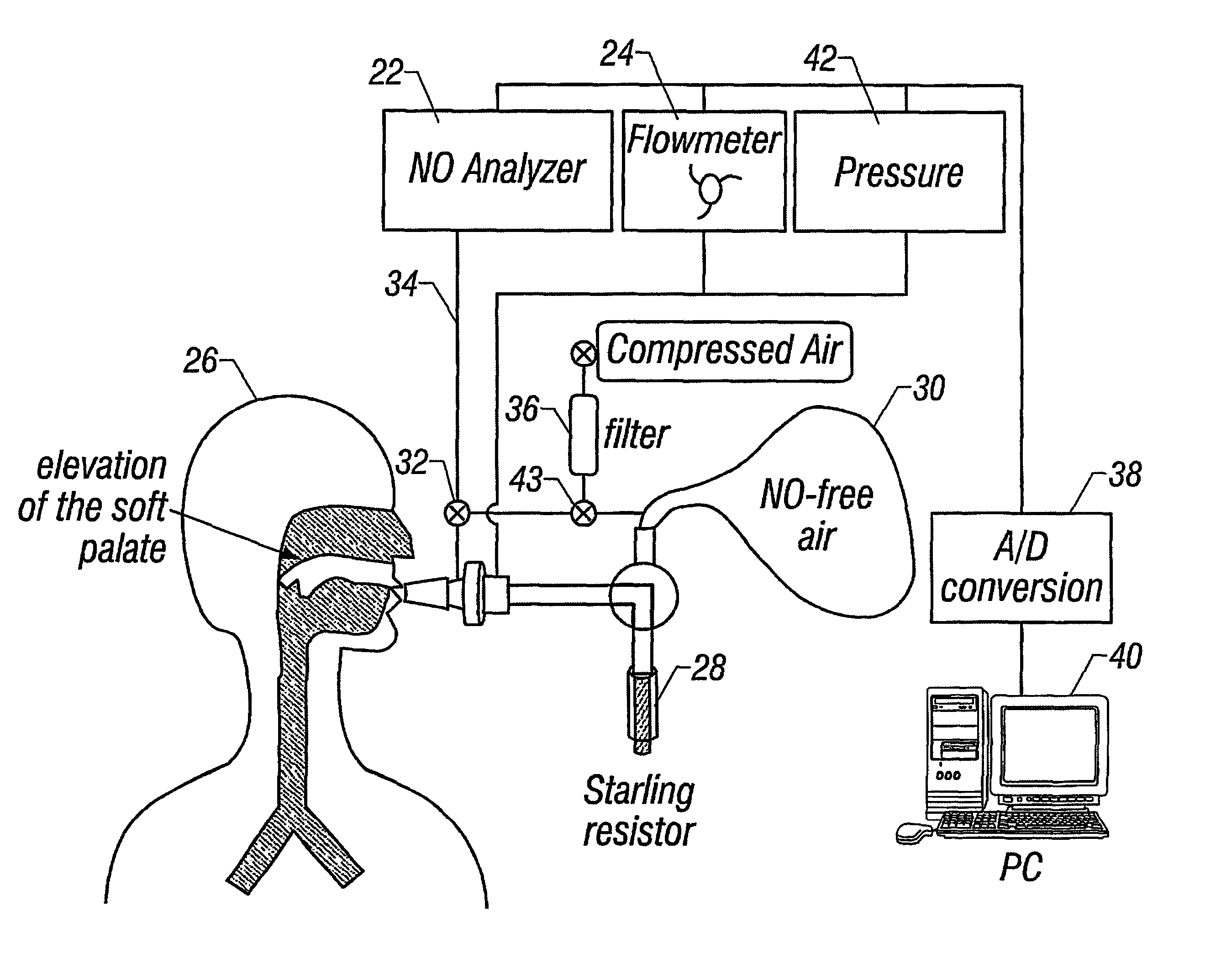
Apparatus and method for the estimation of flow -independent parameters which characterize the relevant features of nitric oxide production and exchange in the human lungs
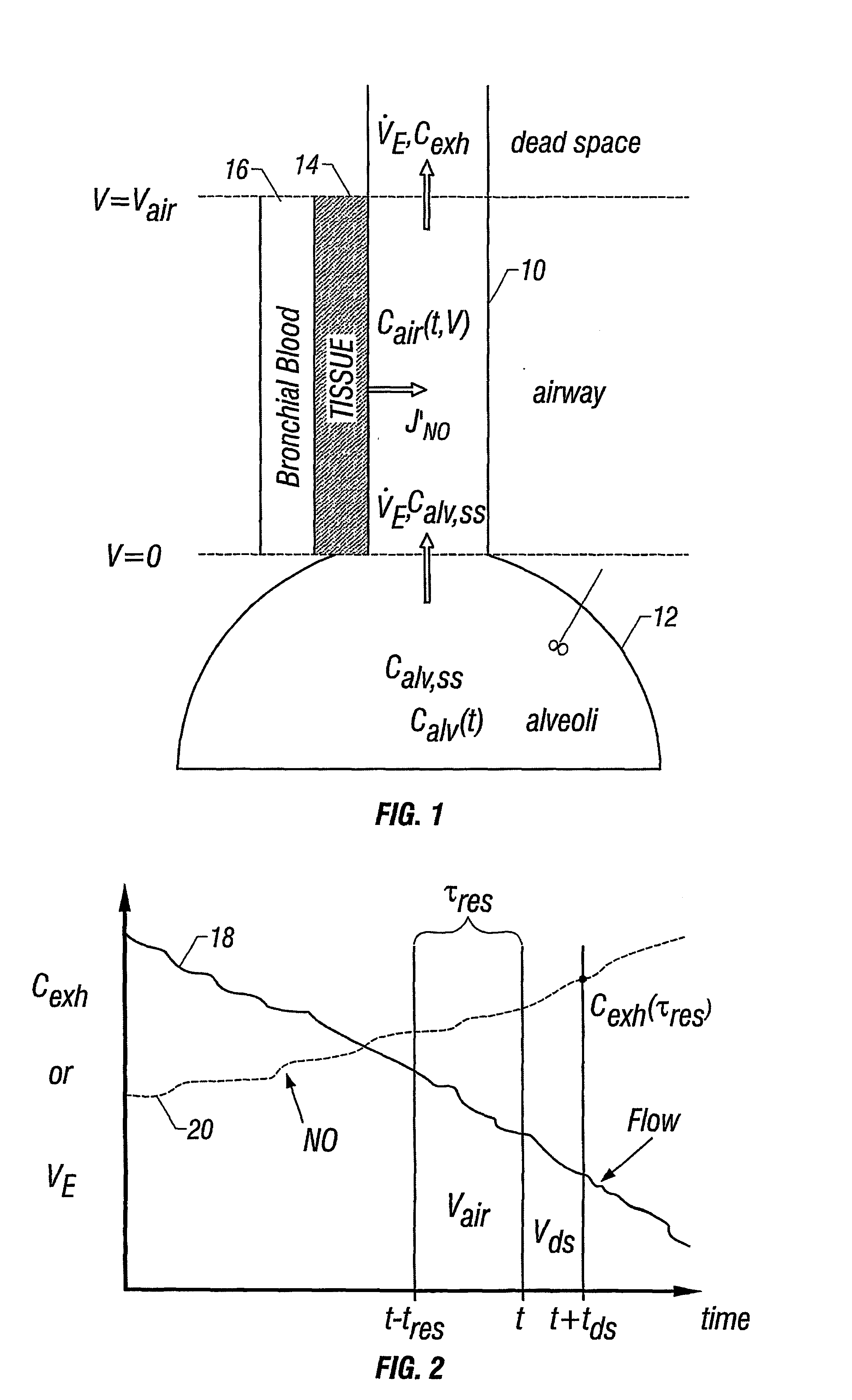
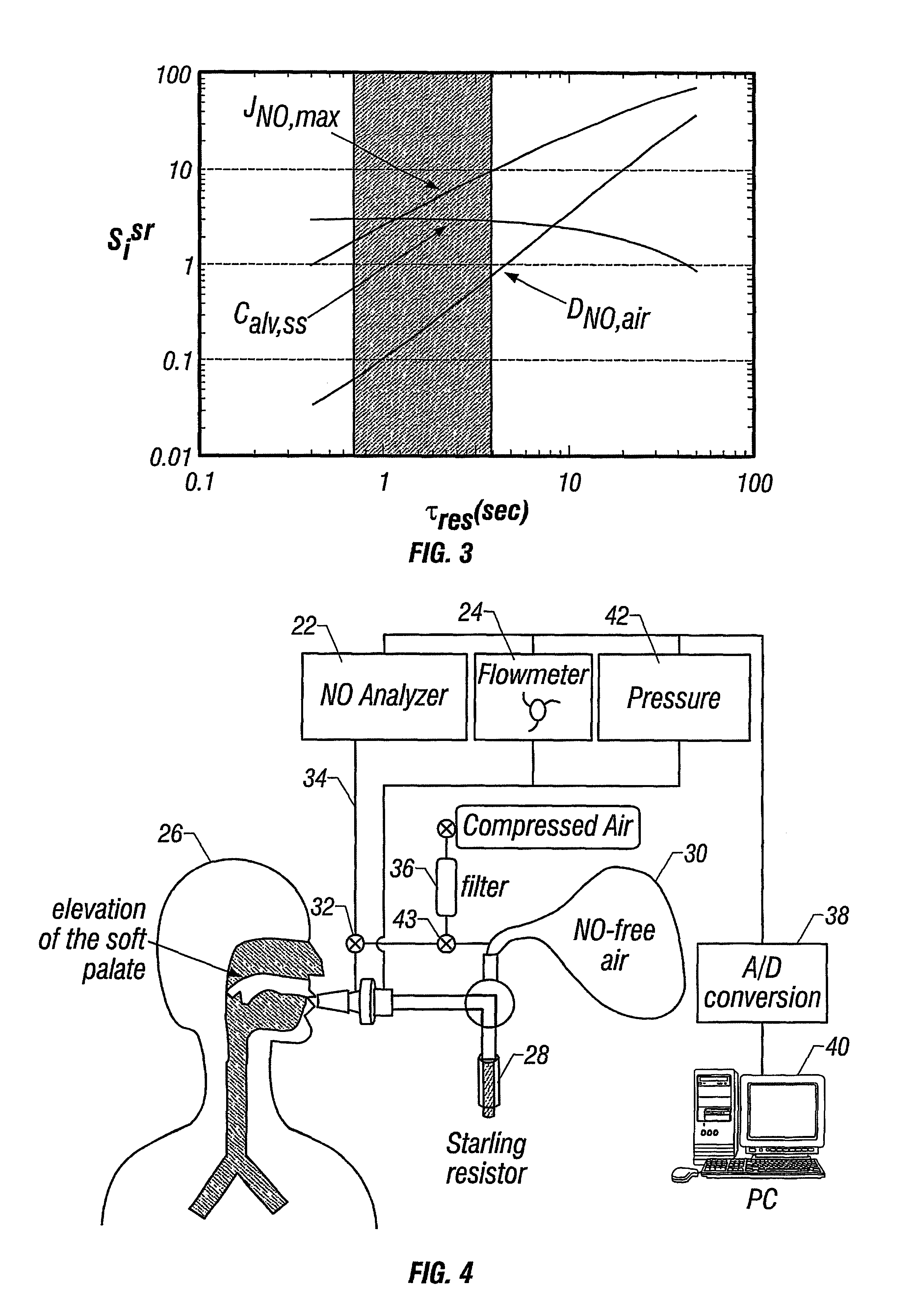
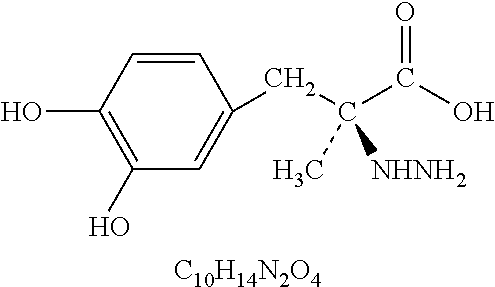
InactiveUS6866637B2Withdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationMaximum fluxConfidence interval
The invention provides an estimation of key flow-independent parameters characteristic of NO exchange in the lungs, namely: 1) the steady state alveolar concentration, Calv,ss; 2) the maximum flux of NO from the airways, JNO,max; and 3) the diffusing capacity of NO in the airways, DNO,air. The parameters were estimated from a single exhalation maneuver comprised of a pre-expiratory breathhold, followed by an exhalation in which the flow rate progressively decreased. The mean values for JNO,max, DNO,air, and Calv,ss do not depend on breathhold time for breathhold times greater than approximately 10 seconds. A priori estimates of the parameter confidence intervals demonstrates that a breathhold no longer than 20 seconds may be adequate, and that JNO,max be can estimated with the smallest uncertainty, and DNO,air the largest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pulmonary Delivery for Levodopa
In one aspect, the invention is related to a method of treating a patient with Parkinson's disease, the method including administering to the respiratory tract of the patient particles that include more than about 90 weight percent (wt %) of levodopa. The particles are delivered to the patient's pulmonary system, preferably to the alveoli or the deep lung.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
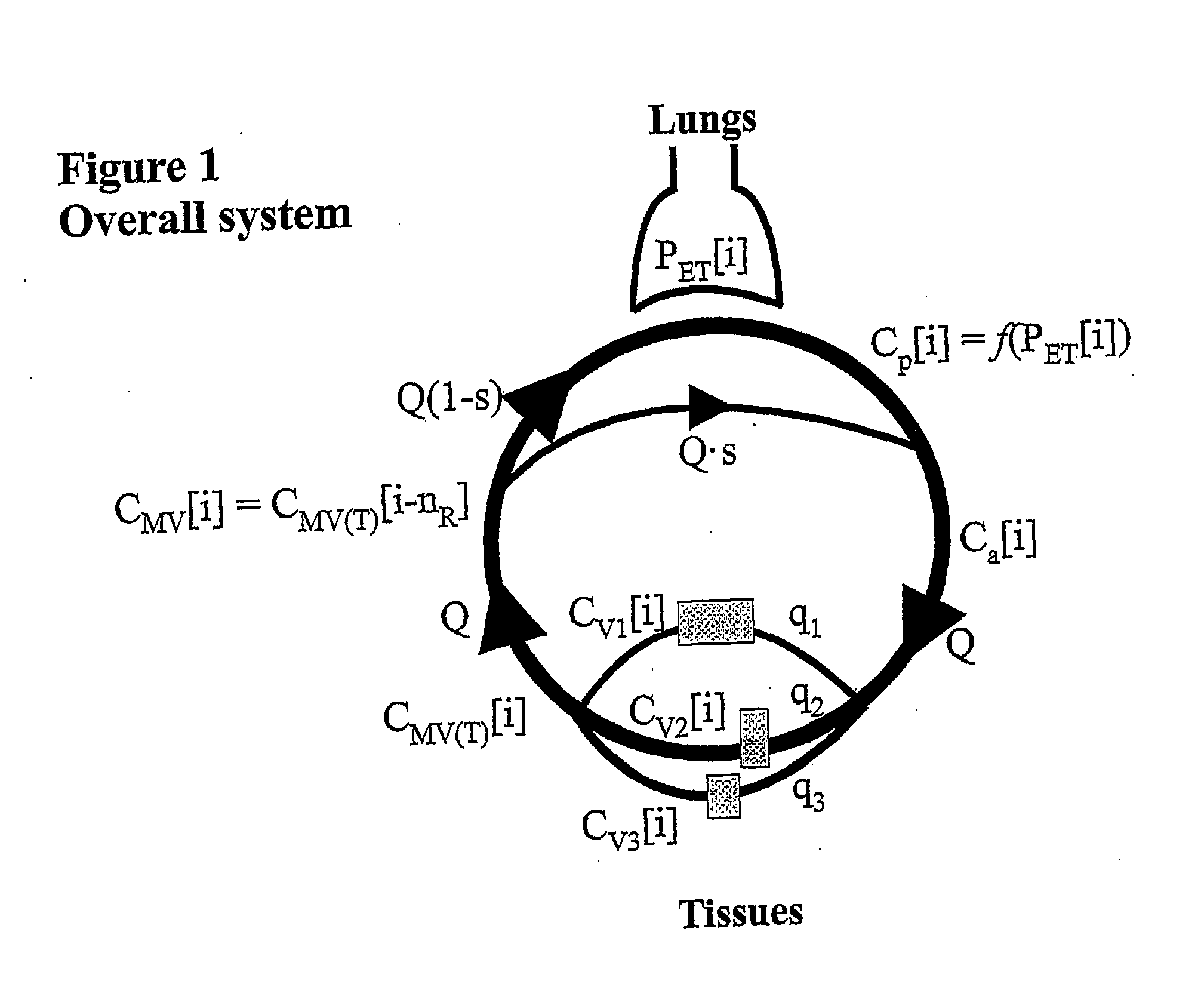
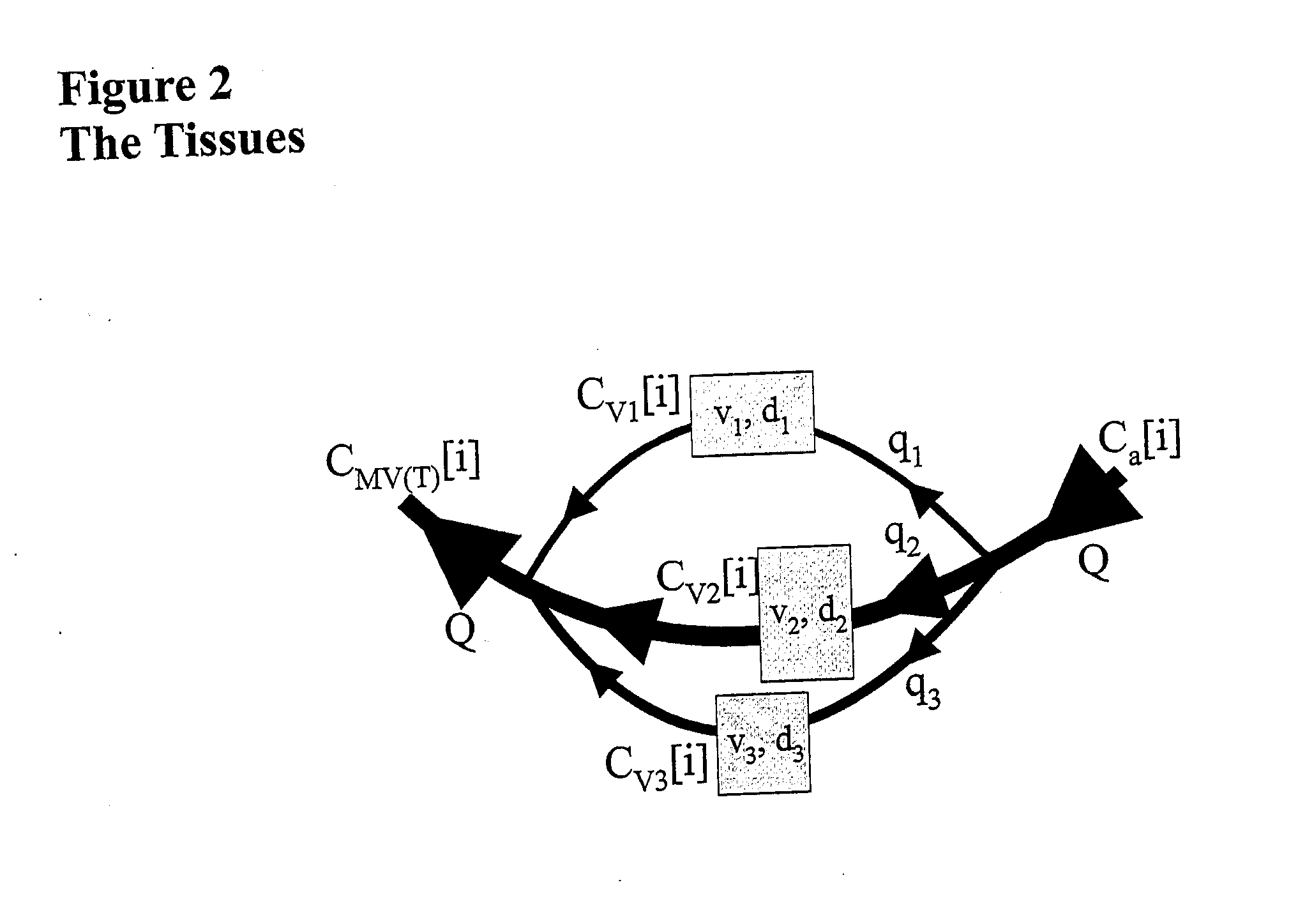
Apparatus to attain and maintain target end tidal partial pressure of a gas
InactiveUS20140311491A1Improve targetingAccurately implementedRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringProduct gas
A processor obtains input of a logistically attainable end tidal partial pressure of gas X (PetX[i]T) for one or more respective breaths [i] and input of a prospective computation of an amount of gas X required to be inspired by the subject in an inspired gas to target the PetX[i]T for a respective breath [i] using inputs required to utilize a mass balance relationship, wherein one or more values required to control the amount of gas X in a volume of gas delivered to the subject is output from an expression of the mass balance relationship. The mass balance relationship is expressed in a form which takes into account (prospectively), for a respective breath [i], the amount of gas X in the capillaries surrounding the alveoli and the amount of gas X in the alveoli, optionally based on a model of the lung which accounts for those sub-volumes of gas in the lung which substantially affect the alveolar gas X concentration affecting mass transfer.
Owner:KLEIN MICHAEL +5
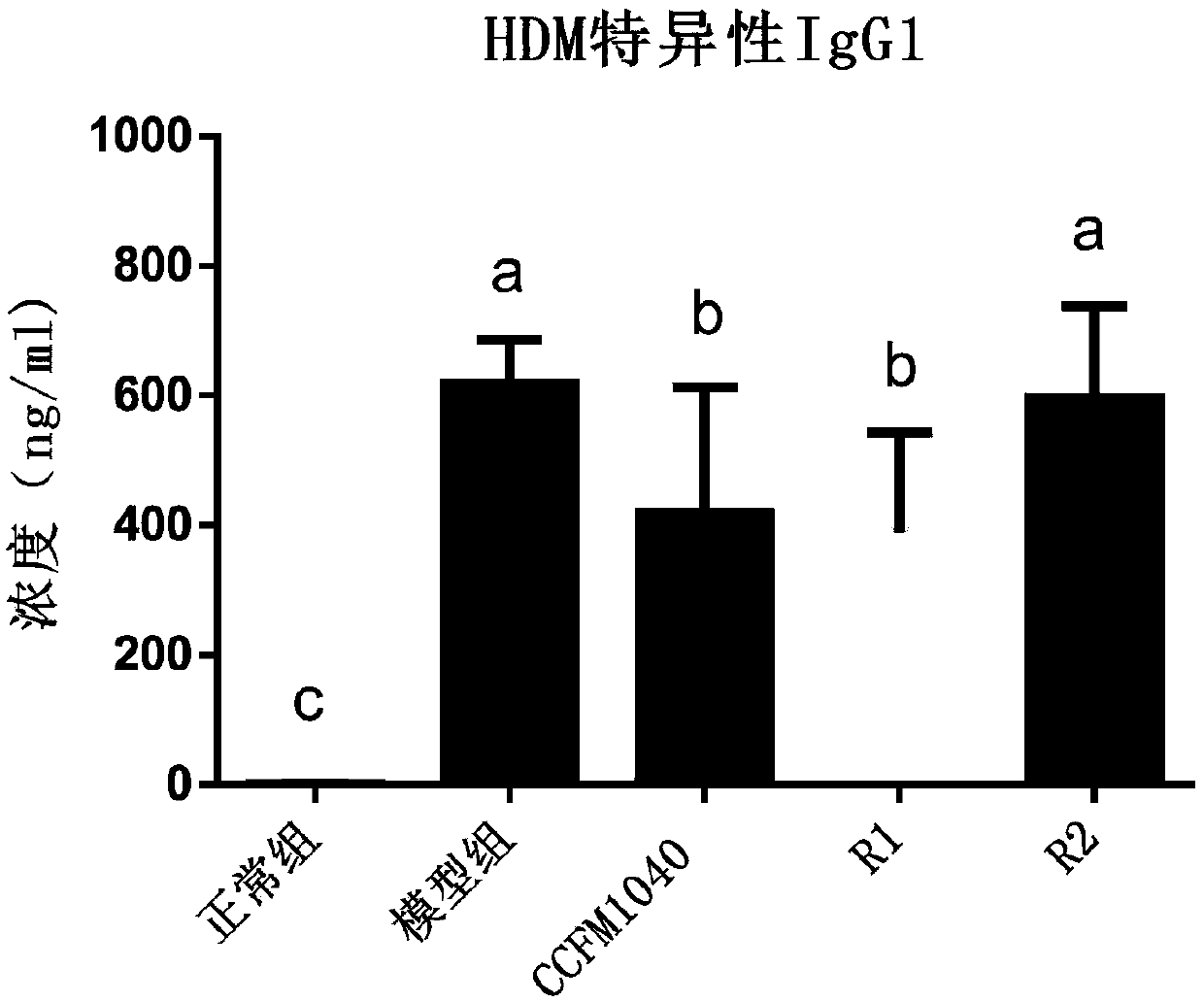
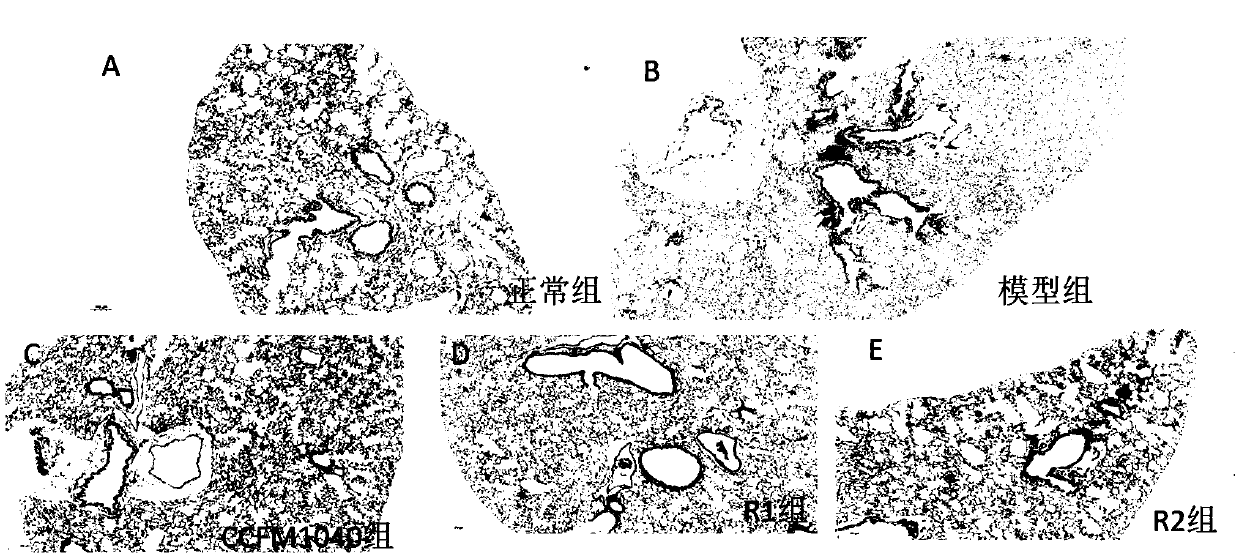
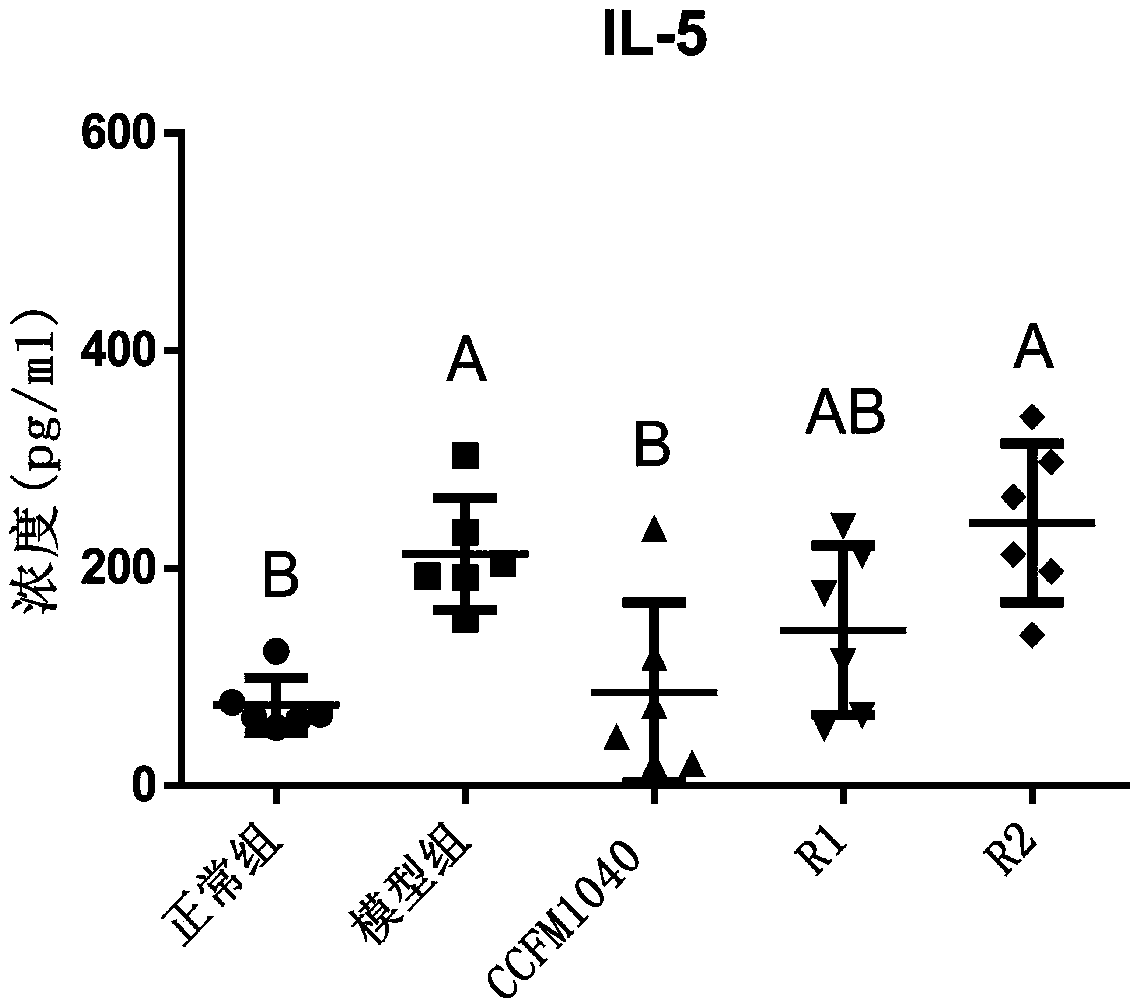
Lactobacillus reuteri capable of alleviating allergic asthma and application thereof
ActiveCN109628359AAlleviate allergic asthmaReduce inflammationBacteriaLactobacillusAlveolar lavage fluidMicroorganism
The invention discloses lactobacillus reuteri capable of alleviating allergic asthma and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The lactobacillus reuteri has an effect ofrelieving allergic asthma, which is embodied by: (1) significantly reducing lung inflammation in mice with allergic asthma; (2) significantly inhibiting the generation of dust mite specific immunoglobulin IgG1 in serum of allergic asthma mice; (3) significantly reduced the contents of IL-5 and IL-13 in alveolar lavage fluid of mice with allergic asthma; (4) significantly reducing the content of IL-17A in alveolar lavage fluid of mice with allergic asthma, and thus the lactobacillus reuteri has great application prospects in the preparation of products for preventing and / or treating allergic asthma.
Owner:无锡特殊食品与营养健康研究院有限公司
Artificial sputum suction model
InactiveCN101996511AIncrease interest in practiceImprove the quality of training and teachingEducational modelsMedicineThreaded pipe
The invention relates to a medical model, in particular to an artificial sputum suction model. The model comprises a simulation trachea and a simulation lung, wherein the simulation lung comprises two hollow air bags; the simulation trachea is an inversed 'Y'-shaped plastic threaded pipe; the two hollow air bags serving as the simulation lung are connected to the lower end of the inversed 'Y'-shaped plastic threaded pipe respectively; the plastic threaded pipe is communicated with inner cavities of the hollow air bags; end parts of the plastic threaded pipe communicated to the inner cavities of the hollow air bags are connected with polycystic rubber balls serving as pulmonary alveoli respectively; and the polycystic rubber balls are arranged in the two air bags respectively. The artificial sputum suction model has better simulation effect, higher practicability and novelty.
Owner:EASTERN LIAONING UNIV
Ultra-fine dry powder particle suitable for drug administration for lung, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101317821AGood aerosolization propertiesLow biological toxicityPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsAdditive ingredientVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses a superfine drymeal granule suitable for pulmonary administration and a preparation method thereof. The drymeal granule has good air-atomizing property. With smaller geometric dimension, the drymeal granule can deposit in the alveolus area to maximum extent, so the active molecule of the medicine has higher bioavailability. In addition, the drymeal granule can be used for DNA and RNA lung administration. The invention is also designed to introduce how to use volatility salt to prepare the superfine drymeal granule with good air-atomizing property. The invention solves the technique defects of the over size of the drymeal granule, the low density of the granule, inconvenient application and easy inactivation of active drug ingredients caused by the sharp decline of the air-atomizing property resulting from the water absorbability in the lung superfine drymeal granule prepared by the existing drymeal preparation technique. Meanwhile, the invention also solves the problem that the drymeal produced by the spray drying technology which is developed by Nektar Company, U.S.A, has relatively small deposition rate in the alveolus area and can not be used for transmitting protein, peptide or nucleic acid drugs containing DNA and RNA, and the like, caused by relatively small granule size and relatively high granule density.
Owner:杭州畅溪制药有限公司
Pulmonary alveolus bionic structure based flexible self-driving gas sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108241017AReduce measurement errorImprove output performanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringProcessing cost
The invention relates to a pulmonary alveolus bionic structure based flexible self-driving gas sensor belonging to the technical field of gas sensors. The gas sensor comprises insulating bases which are sequentially laminated from top to bottom, a first friction electrification layer with two sides respectively deposited with an electrode layer and a gas sensitive film layer and a second frictionelectrification layer adopting an elastic material, wherein the first and second friction electrification layers are fixed at the peripheral edge; a gas channel is formed in the center of the insulating bases, an electrode layer, the first friction electrification layer and the gas sensitive film layer; under the action of air flow, unfixed parts of the first and second friction electrification layers form contact-separation circulation to generate induced charge, so as to output an electric signal with gas concentration characteristics to the outside. Compared with conventional gas sensors, gas concentration can be detected spontaneously without an external power supply system, the output performance of the sensor is steady, the structure is light and easy to carry, and the gas sensor iseasy to mount and place, simple to make, low in processing cost, and favorable for realizing large scale production of self power supply respiration sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
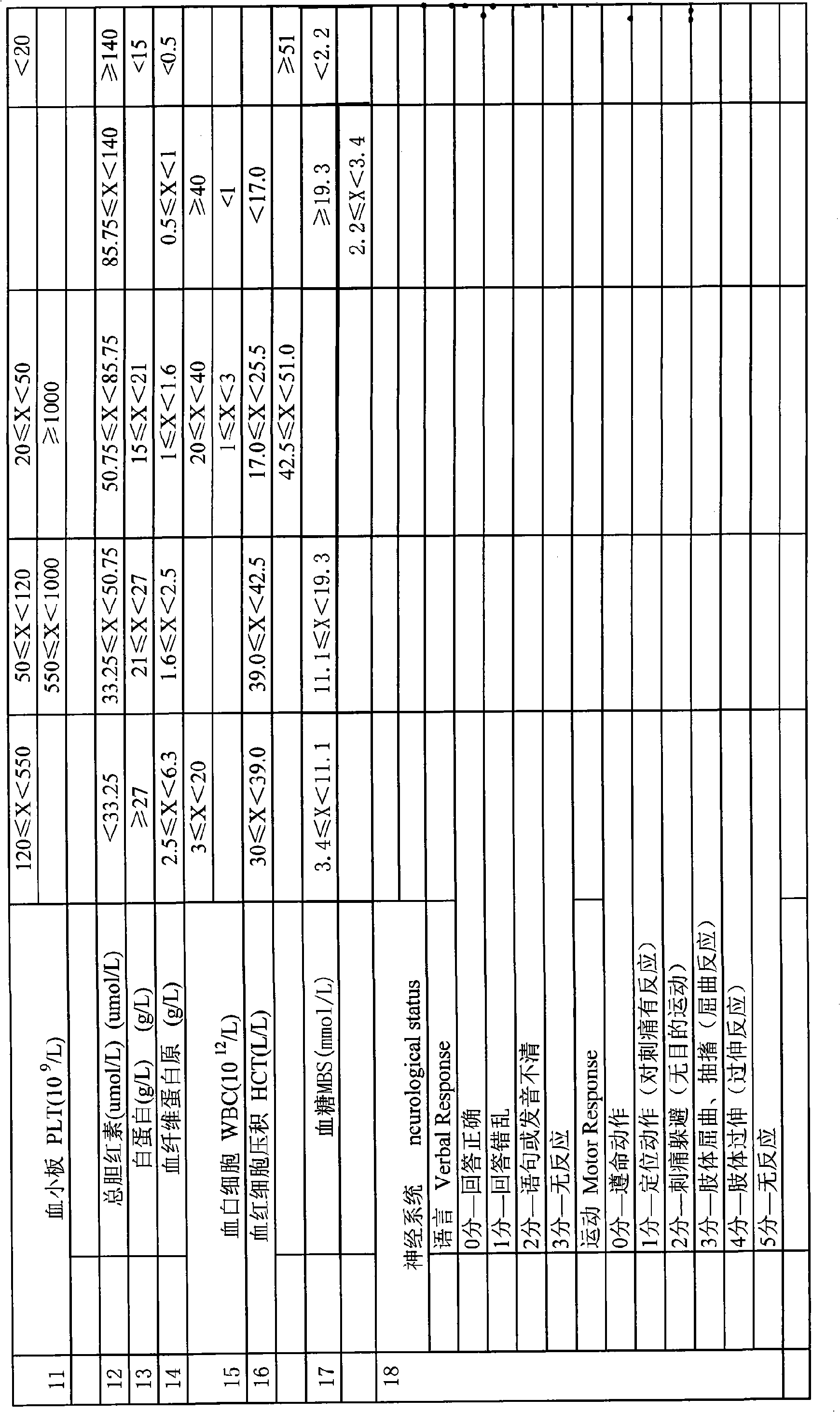
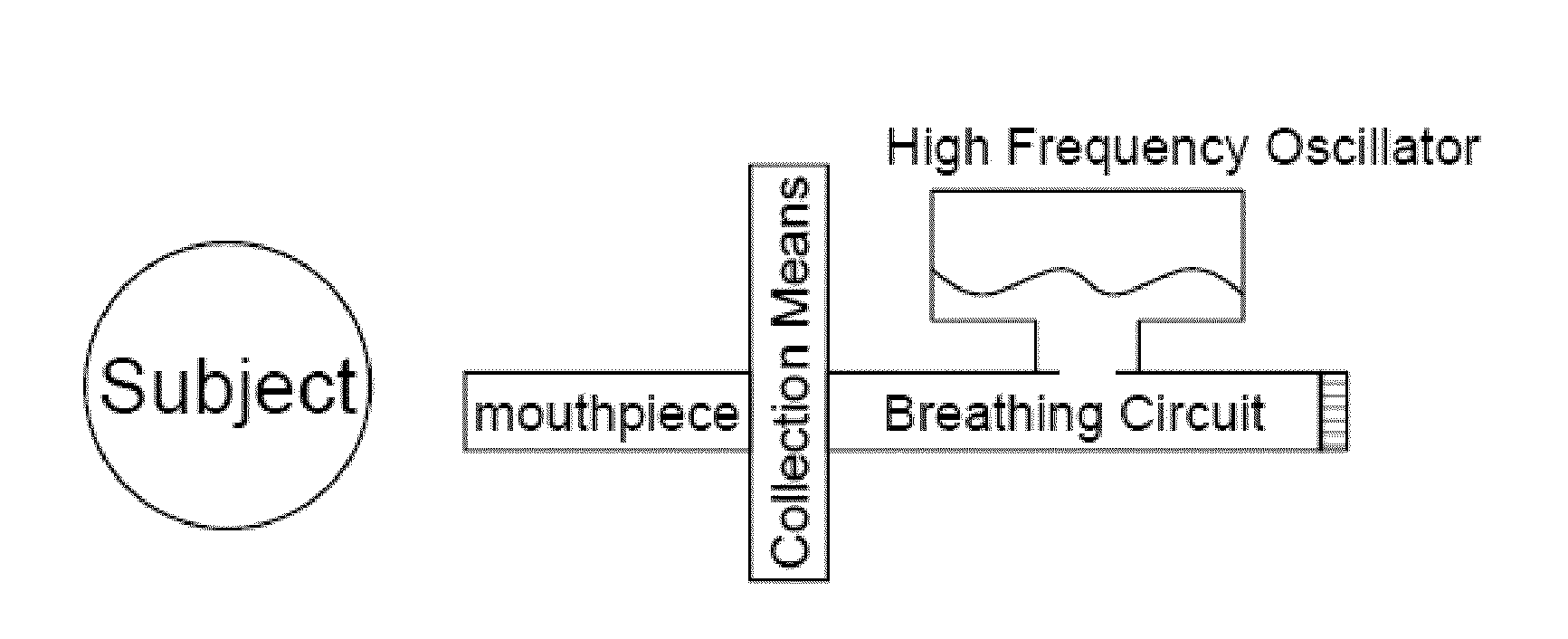
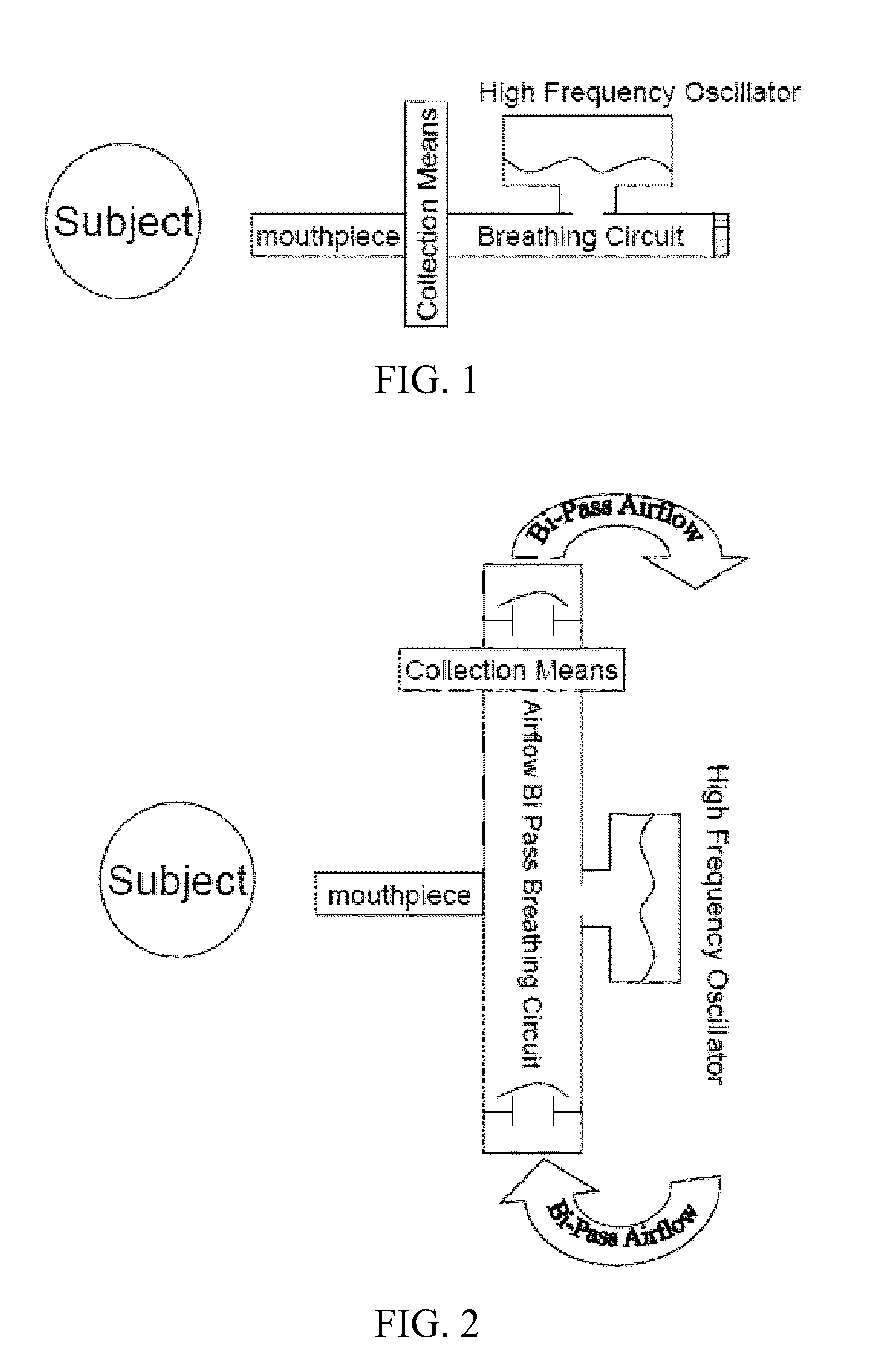
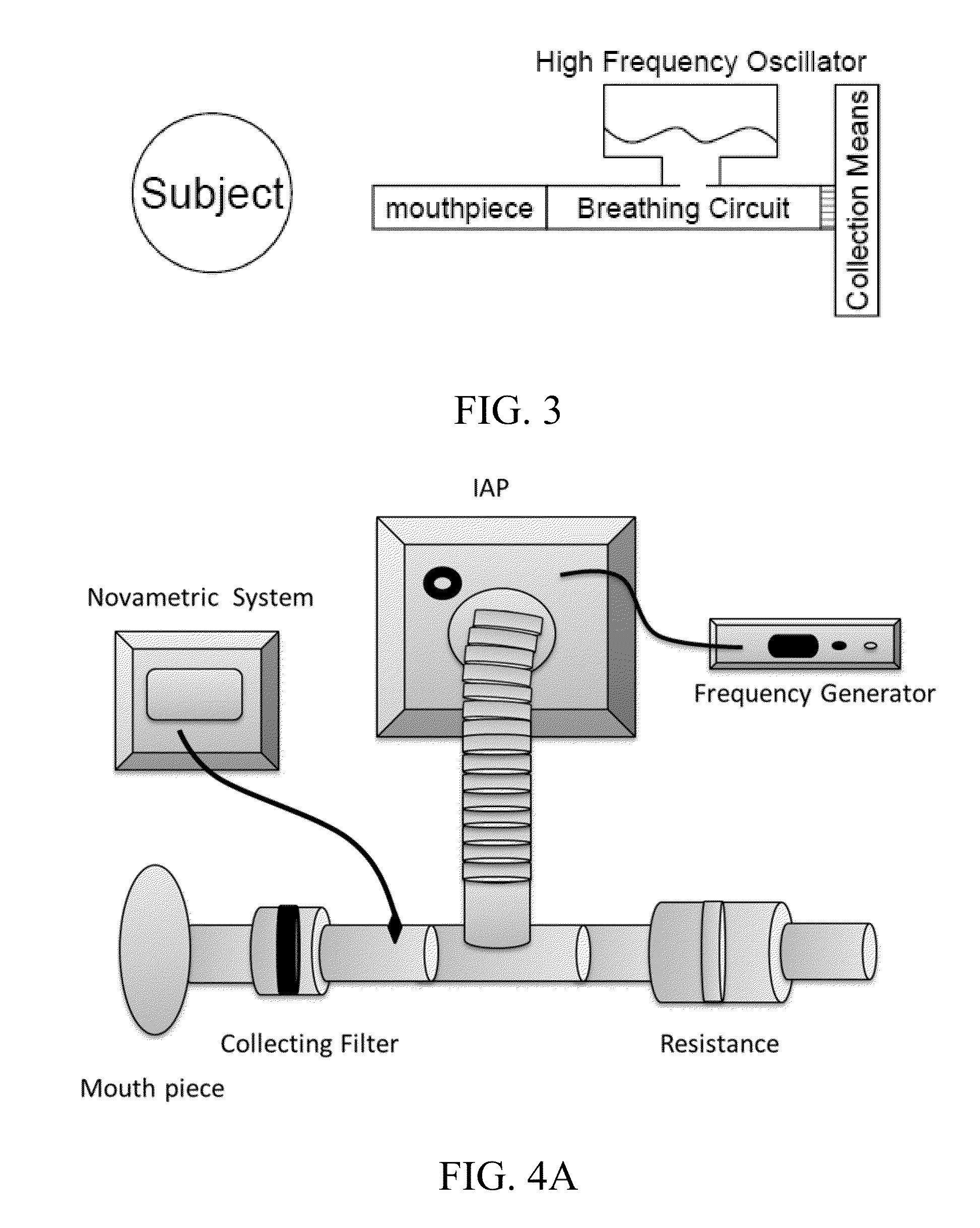
Alveolar breath collection apparatus
ActiveUS9918661B2Accurate samplingPrevent VOC cross-contaminationGas treatmentDispersed particle separationAir sampleSorbent tube
An apparatus for collecting volatile compounds in human breath. The apparatus includes a device for discriminating between alveolar and non-alveolar portions of exhaled breath, a device for measuring volume of exhaled breath, a chamber with a piston or similar compressible device with clean internal services designed to collect a precise volume of alveolar breath, a pump to draw the exhaled breath from the chamber through at least one sorbent tube, a subsystem for introducing a clean gas into the chamber to expand it and for purging the tubing of the system, and a subsystem for selectively collecting a room air sample. A manifold is provided in the apparatus for receiving sorbent tubes and comprises an input block and output block, and a locking lever for actuating the input and output blocks linearly towards and away from each other and selectively locking them in a fully closed position.
Owner:PICOMOLE INSTR INC
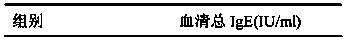
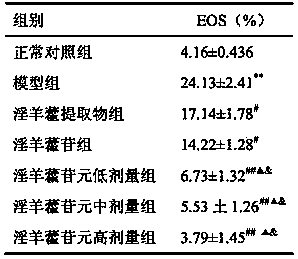
Application of anhydroicaritin in preparation of drugs used for treating asthma
InactiveCN103622947AHighlight the advantages of treatmentSmall toxicityOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDrugAsthma
The invention provides application of anhydroicaritin in preparation of drugs used for treating asthma, which belongs to the field of medicine. Anhydroicaritin is a Chinese herbal monomer extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine epimedium; when used for treating asthma, anhydroicaritin can substantially reduce total IgE content in the serum of a patient with asthma and the rates of IL-4, IFN-r and eosinophilic granulocytes in the pulmonary alveoli of the patient, and anhydroicaritin has a better treatment effect on the patient with asthma compared with those of an epimedium extract and icariin. Anhydroicaritin has the advantages of comprehensive effects, small side effects and wide clinical application prospects when used for treatment of asthma.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Measurement experiment system of human alveolar aerosol deposition
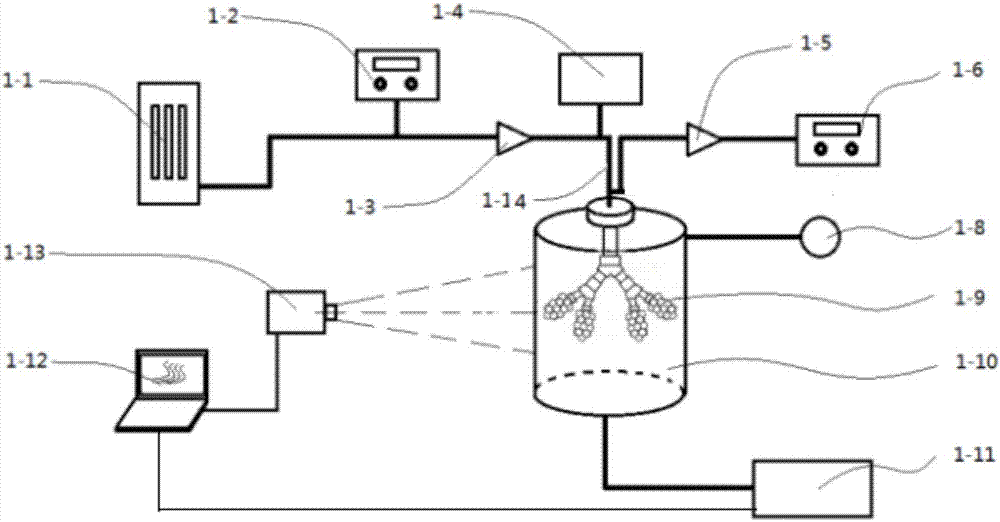
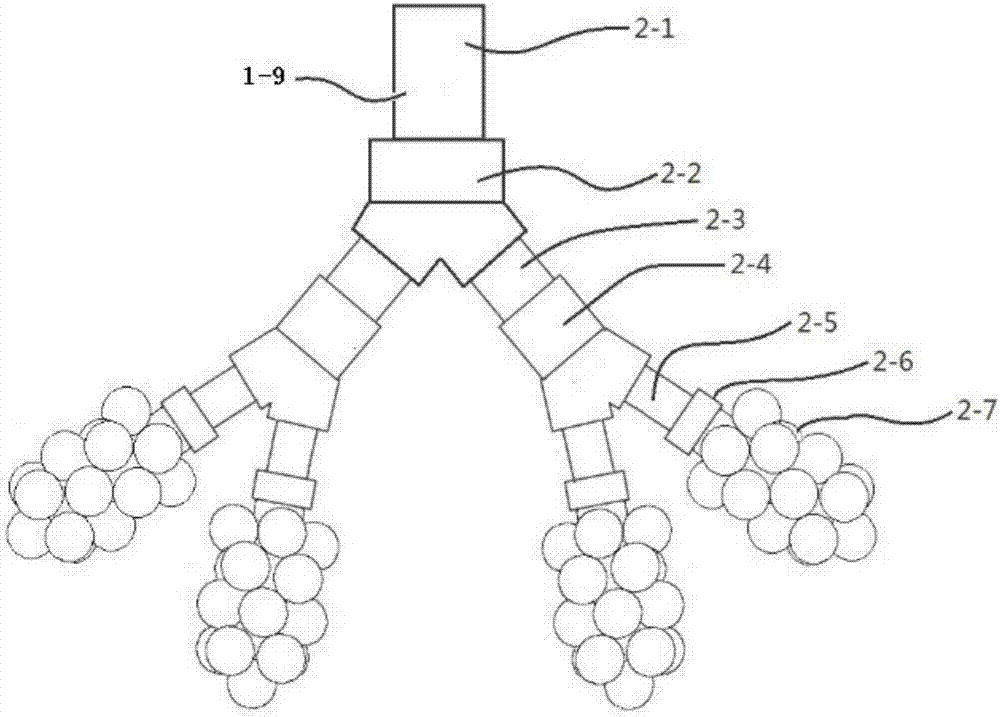
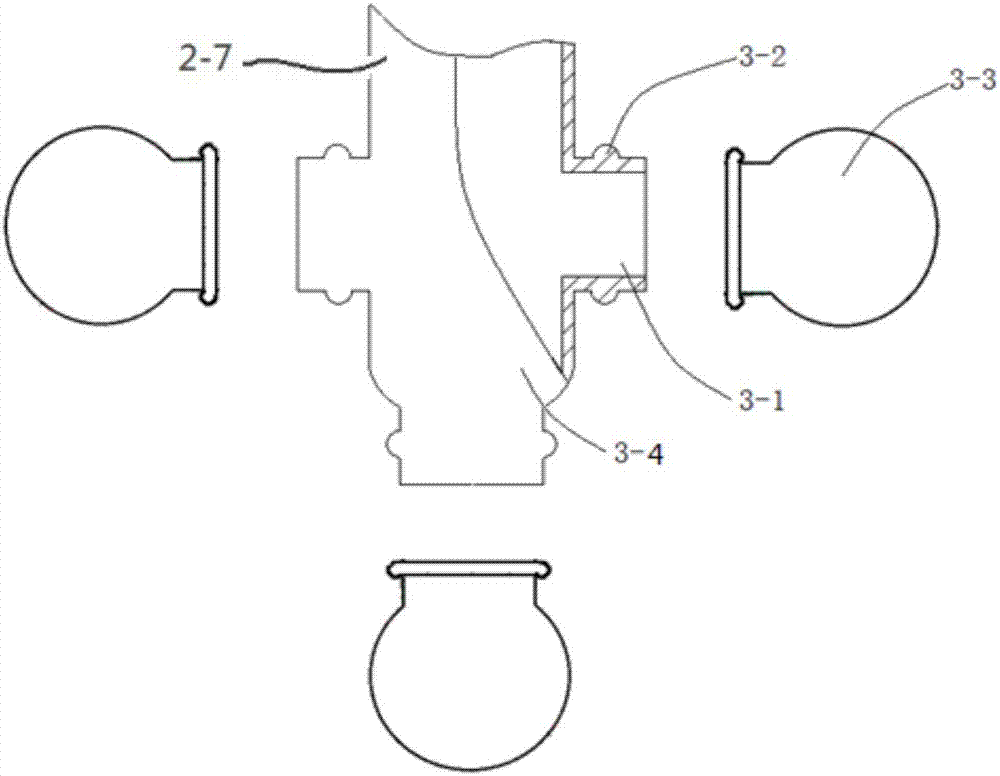
The invention discloses a measurement experiment system of human alveolar aerosol deposition. A standard particle generator and an expiratory aerosol particle counter are connected with a one-way inlet valve through a pipe respectively; a mains pipe after the one-way inlet valve joins a pipe connected with a humidifier through the pipe penetrates a cover of a transparent experiment container and is connected with a pulmonary acinus experiment model arranged in the transparent experiment container, and the bottom of the transparent experiment container is connected with a simulated respiratory pump through a pipe; a pressure gauge is arranged on the transparent experiment container; an expiratory aerosol particle counter is connected with a one-way exhaust valve and the mains pipe through a pipe sequentially; a computer equipped with a data analysis system is electrically connected with a PIV particle tracer and the simulated respiratory pump, and the PIV particle tracer is arranged on one side of the transparent experiment container. The system can provide external measurement of the deposition rate of inhalable particulate matter under conditions of different particulate sizes, respiratory modes as well as different environmental humidity and pathological conditions.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
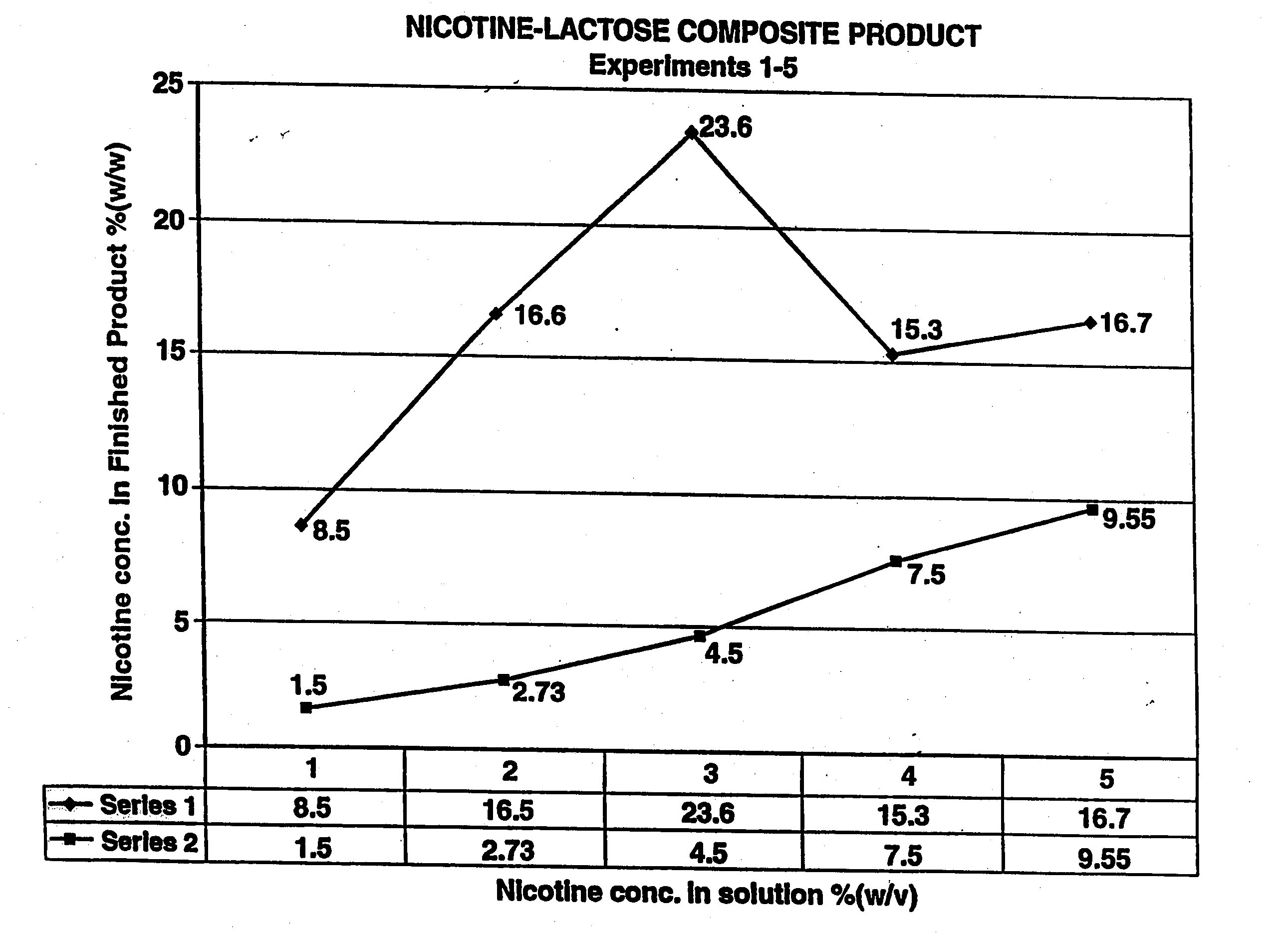
Method of producing a nicotine medicament and a medicament made by the method
A method of producing a nicotine medicament for use in an inhaler comprises combining a nicotine formulation, a sugar and a liquid carrier including water to produce a flowable mixture and drying the flowable mixture at conditions to produce particles of the nicotine medicament suitable for delivery to the alveoli and lower airways of the person. Also disclosed is a nicotine medicament made by the method. The nicotine composition produced by this method is a composite particle suitable for tobacco replacement or withdrawal therapy.
Owner:NICO PUFF
Three-dimensional tumor model decellularization porous scaffold, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107988158AImprove adhesionPromote growthCell culture supports/coating3D cultureCell-Extracellular MatrixCell adhesion
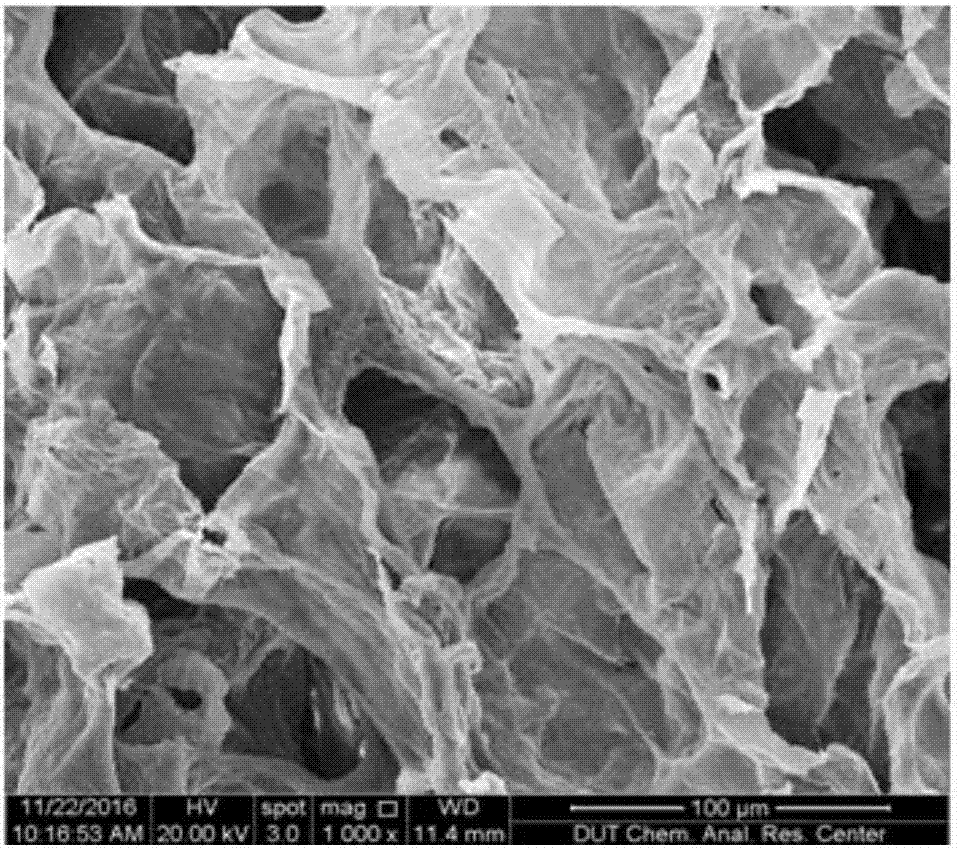
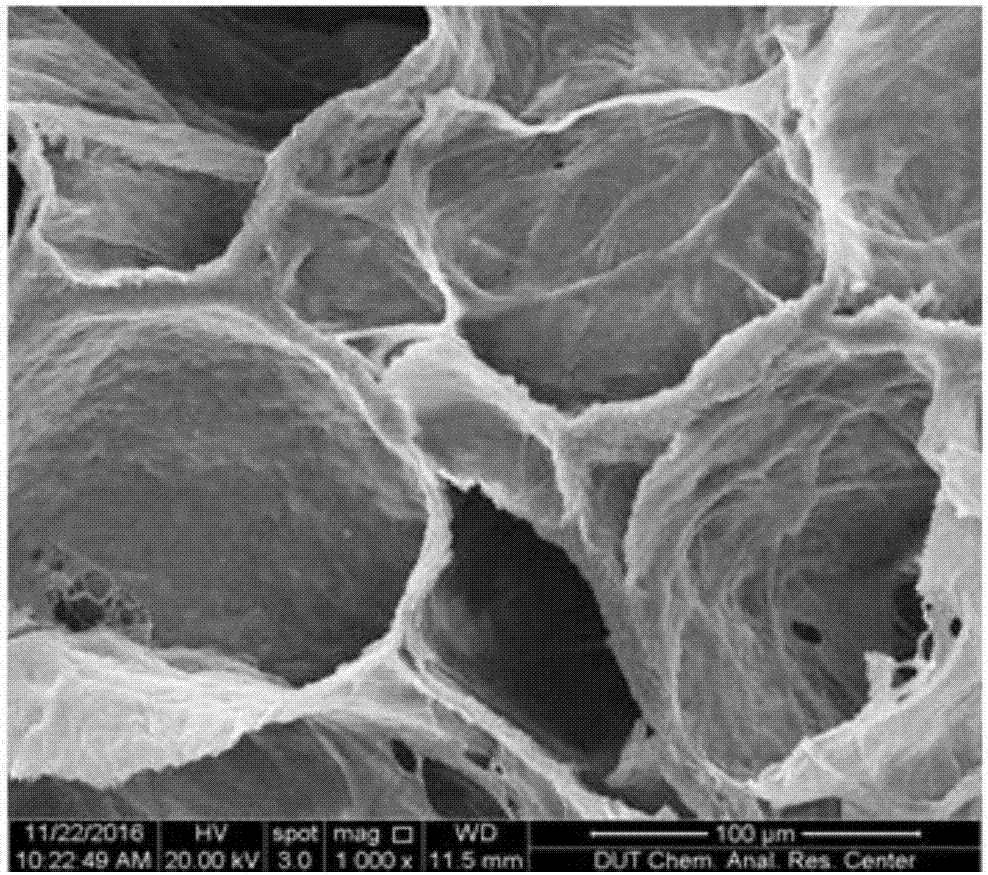
The invention belongs to the fields of cell biology and tumor tissue engineering materials and provides a three-dimensional tumor model decellularization porous scaffold, a construction method and application thereof. The whole pig lung scaffold is prefrozen, a uniform part without obvious bronchi is selected and sliced, purified water and PBS are added for cleaning until no blood streak is formed, removing cells with sodium dodecyl sulfate and TritonX-100, and freezing, drying and chemical crosslinking methods are adopted, so that a crosslinked decellularization pig lung three-dimensional tumor model scaffold is obtained. The three-dimensional tumor model decellularization porous scaffold provided by the invention has the advantages that decellularization matrix sourced from pig lung tissues is taken as a scaffold material for constructing a tumor model, on the basis of effectively removing cell components, a pulmonary alveolus-bronchus structural vein network is reserved as soon as possible, a natural extracellular matrix microenvironment can be simulated, and cell adhesion, growth and proliferation are facilitated. The in vitro constructed three-dimensional tumor model after cells are inoculated has a tissue structure closer to an in vivo tissue and is applicable to screening study of anticancer drugs.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Cryptotanshinone for preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis and application thereof
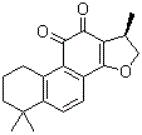
InactiveCN106798737AAntibacterialAnti-inflammatoryOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderDiseaseSalvia miltiorrhiza
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to cryptotanshinone for preventing and treating pulmonary fibrosis and an application thereof. The cryptotanshinone (I) is quinone diterpene extracted from the root part of salviae miltiorrhizae; the modern pharmacological research shows that the cryptotanshinone has a bacteriostatic effect, an anti-inflammatory effect and a hormone-like pharmacologic effect, and is clinically used for treating myocardial fibrosis, lung acute injury and arthritis, can be used for preventing and / or treating a pulmonary fibrosis disease, can also be used for preparing medicines for reducing body weight of a pulmonary fibrosis rat, a lung coefficient and the content of hydroxyproline in tissue and can be used for preparing the medicines for reducing the content of IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF-alpha in a bronchoalveolar lavage liquid and the medicines of effecting the pathogeny structure of pulmonary fibrosis tissue of the rat. The formula (I) is as shown in the specification.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Method for treatment of emphysema
Disclosed is a method for treatment of emphysema by which it is possible to reduce the volume of pulmonary alveoli or alveolar sacs abnormally enlarged with destruction by emphysema. The method for treatment of emphysema includes: (a) inserting a catheter having a balloon into a bronchus or bronchiole; (b) dilating the balloon to occlude the bronchus or bronchiole; (c) shrinking pulmonary alveoli or alveolar sacs on the downstream side of the bronchus or bronchiole occluded in the step (b); and (d) injecting a hardening agent through the catheter into the respiratory region and hardening the hardening agent.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Apparatus for testing breath alcohol with discrimination between alveolar and upper respiratory tract alcohol
InactiveUS7122154B1Reliably detectWithdrawing sample devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringChemistryCarbon dioxide
A method and infrared sensing device for determining the concentration of alveolar alcohol in a breath sample exhaled by a subject into an infrared sensing device. The presence of alcohol from the upper respiratory tract of the subject is detected by continuously monitoring alcohol and carbon dioxide, normalizing alcohol values with respect to carbon dioxide, calculating a difference between normalized alcohol concentration and carbon dioxide concentration over time, integrating (summing) the difference, and comparing the integrated difference with a threshold. This technique accurately and consistently detects the presence of mouth alcohol in the sample before the presence of carbon dioxide which originates in deep lung breath.
Owner:INTOXIMETERS
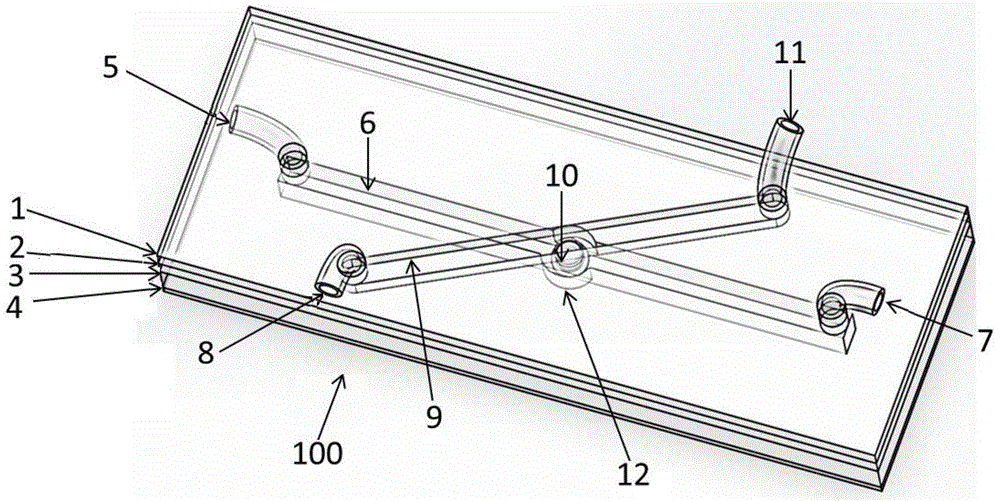
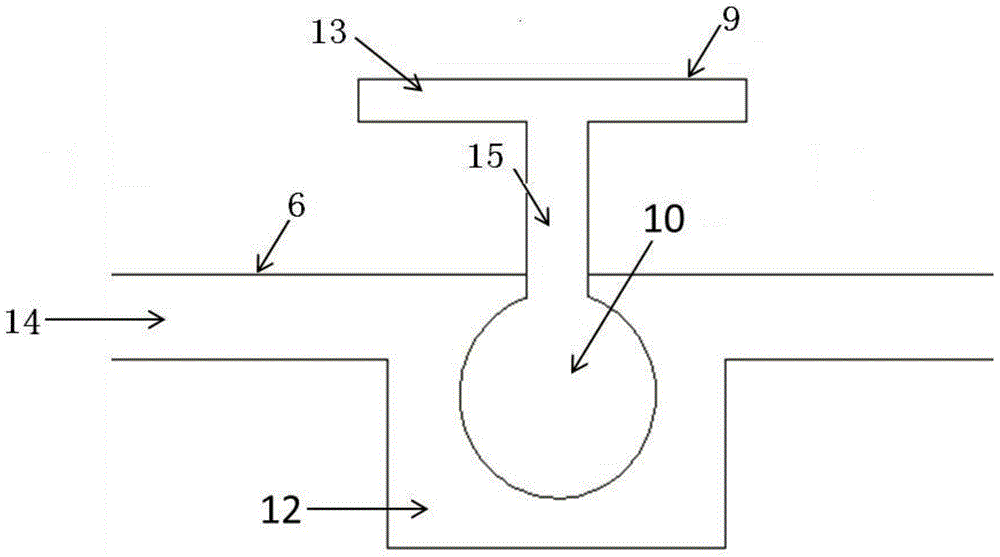
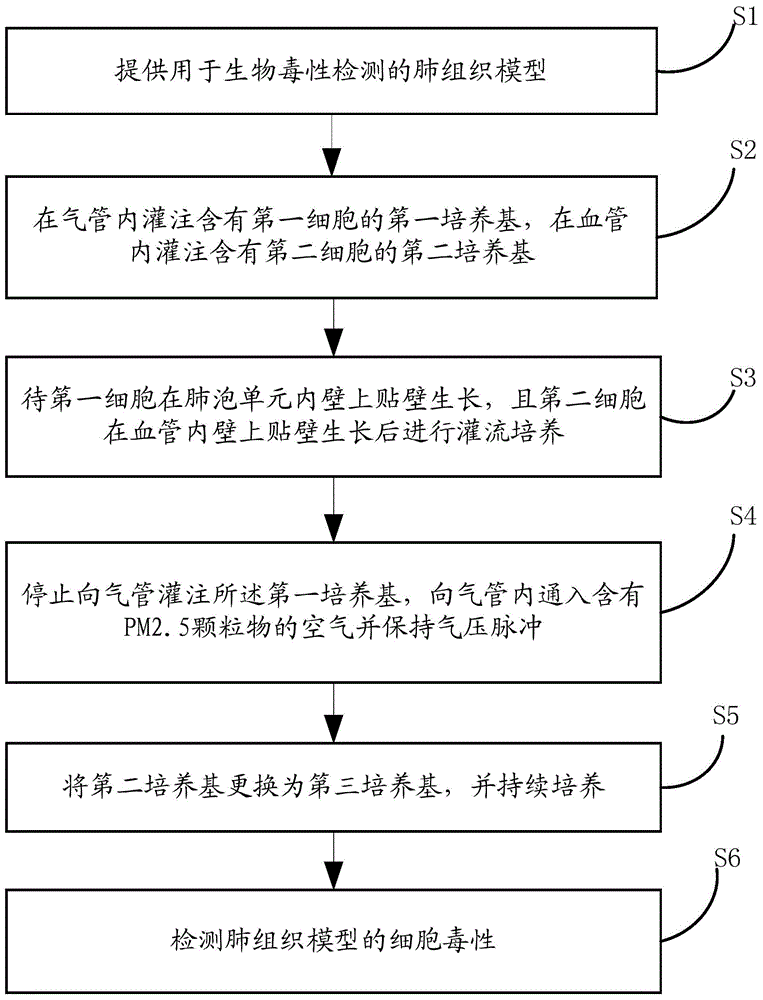
Lung tissue model for biotoxicity detection and biotoxicity detection method
The invention discloses a lung tissue model for biotoxicity detection and a biotoxicity detection method. The lung tissue model comprises a trachea, a blood vessel and an alveolus pulmonis unit, wherein an air passage is defined in the trachea, and an air inlet and an air outlet, which are communicated with the air passage respectively are formed at two ends of the trachea; a blood passage is defined inside the blood vessel, and a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet which are communicated with the blood passage respectively are formed at the two ends of the blood vessel, a cavity is defined in the alveolus pulmonis unit, an elastic ventilate membrane is formed on the wall of the alveolus pulmonis unit, the alveolus pulmonis unit is arranged in the blood passage, and the cavity is communicated with the air passage. By adopting the lung tissue model, an air exchanging function and a breathing strain effect of the lung blood in the body can be simulated; through planting cells in the alveolus pulmonis unit, the structure and function of the alveolus pulmonis unit in a body and inflammation reaction of immune cells can be simulated in the subsequent culture process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
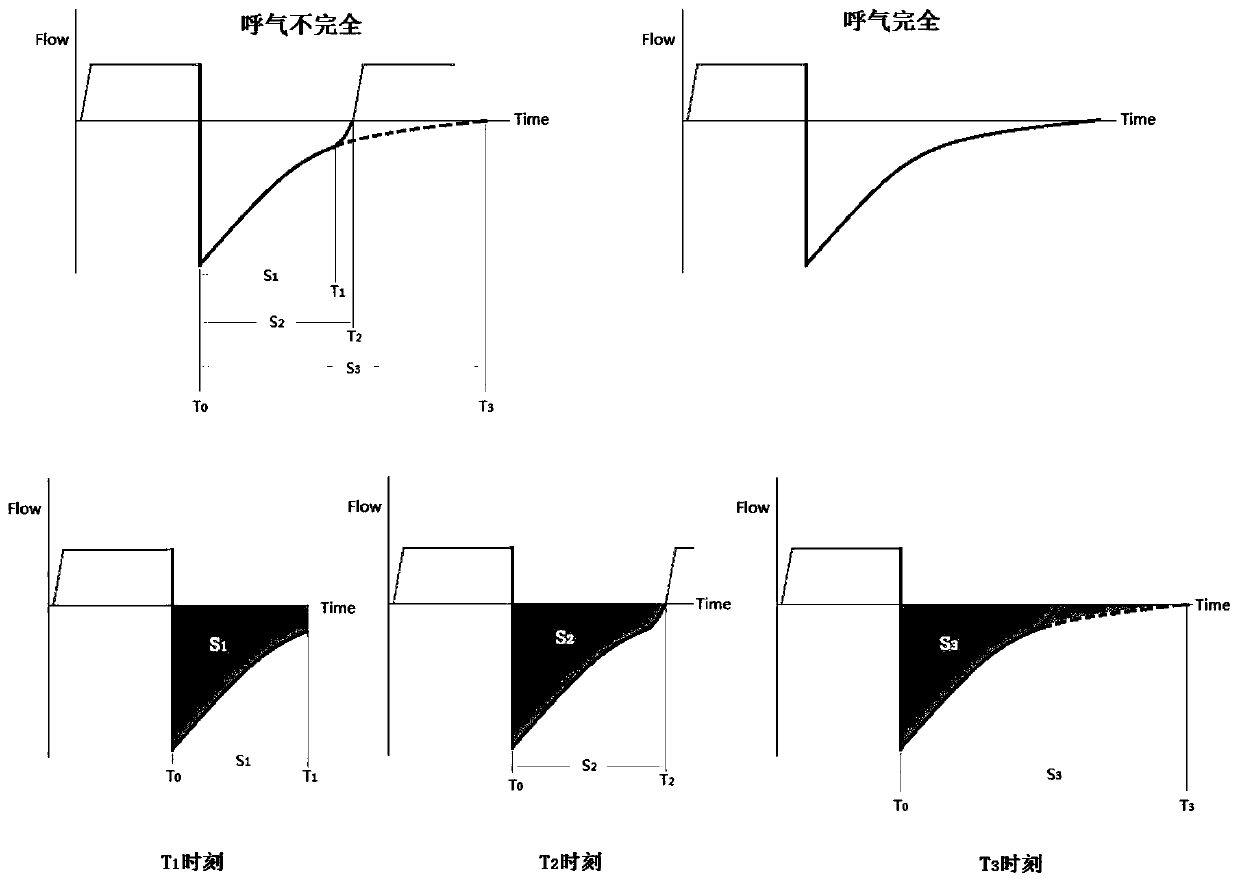
Method for estimating dynamic positive end-expiratory pressure in mechanical ventilation
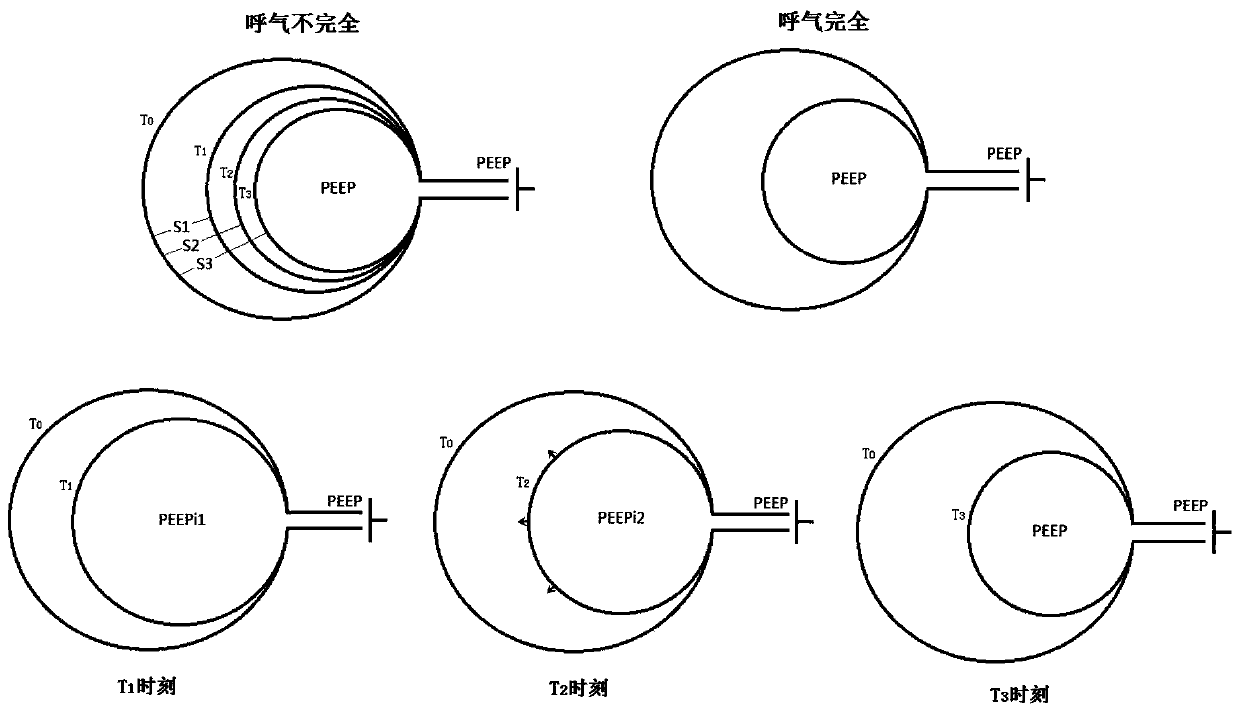
PendingCN111544719APromote respirationImprove survival rateRespiratorsPositive pressureInspiratory force
The invention provides a method for estimating dynamic positive end-expiratory pressure in mechanical ventilation, and mainly relates to the field of research on dynamic positive end-expiratory pressure in mechanical ventilation. According to the invention, an expiration curve is used as a research object, and the positive pressure (positive end-expiratory pressure 1, PEEPi1) in the pulmonary alveoli at the moment before the inflection point and the assumed positive pressure (positive end-expiratory pressure 2, PEEPi2) in the pulmonary alveoli when the actual expiratory flow is 0 and if the inspiration force does not exist according to the difference between the areas under an actual expiratory curve and an imaginary tracing curve and the compliance of a respiratory system. The method hasthe beneficial effect that when a patient uses a breathing machine, reference for setting parameters of the breathing machine can be provided for medical staff, so that the patient uses the breathingmachine to achieve the best breathing effect, and the survival probability of the patient is further improved.
Owner:武云珍
Phospholipid formulations and uses thereof in lung disease detection and treatment
InactiveUS20070010429A1Deter/inhibit damagePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAir sacsSURFACTANT BLEND
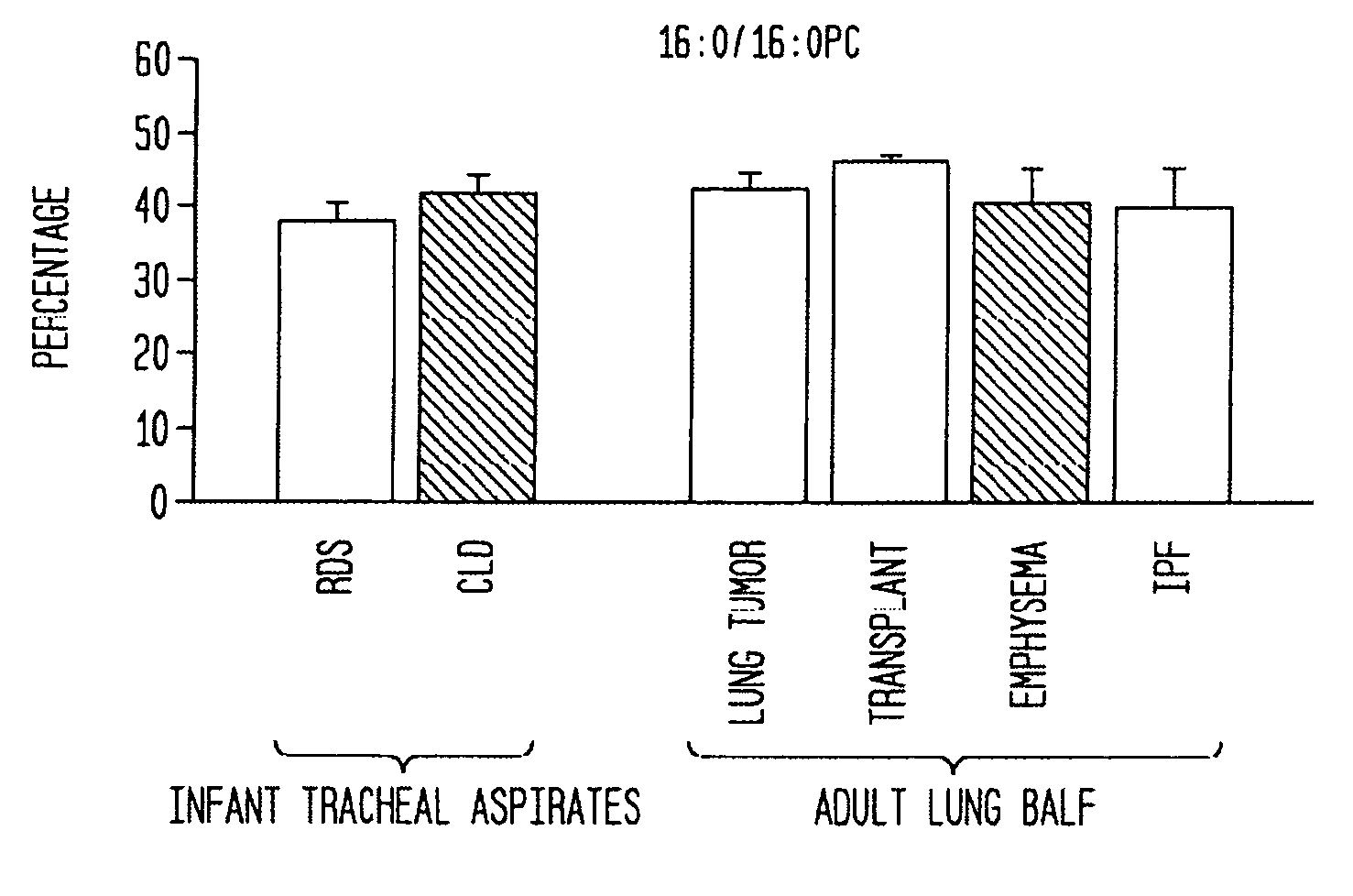
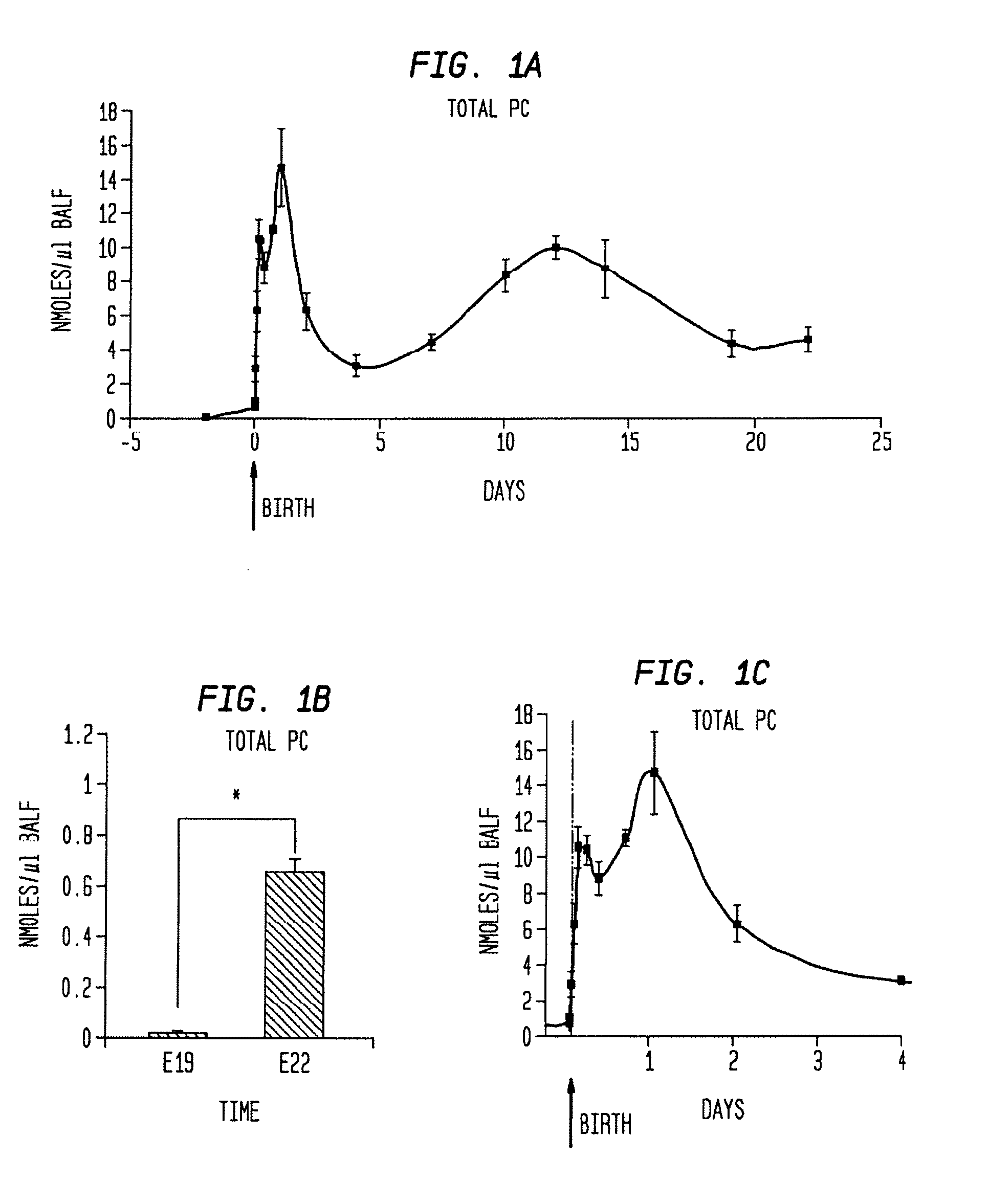
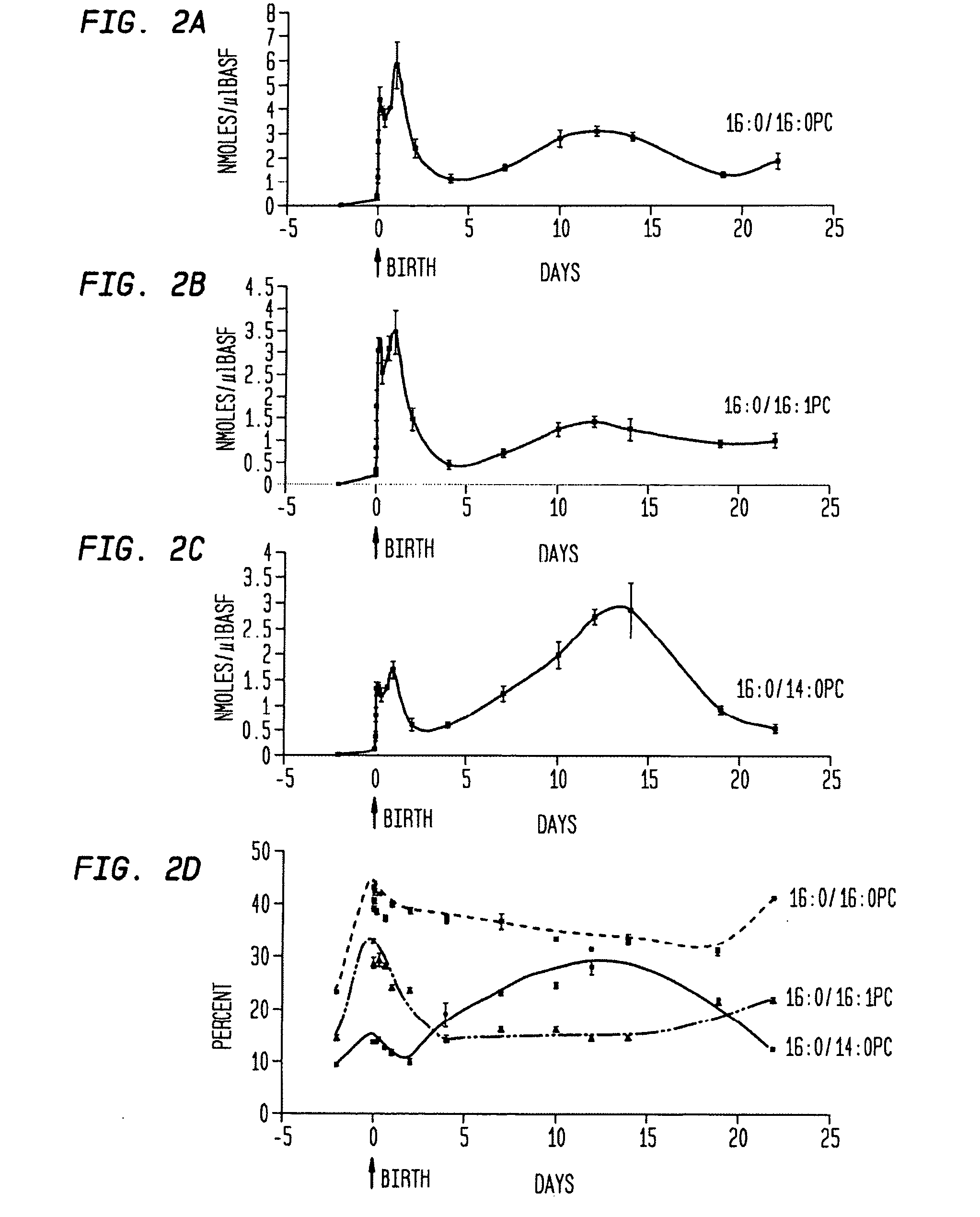
Disclosed are methods and compositions that are useful in the detection and therapy of diseases (e.g., emphysema) and damage that afflict the lungs. In some aspects, the compositions comprise a formulation enriched for a species of phosphatidylcholine, such as palmitoylmyristoyl phosphatidylcholine (16:0 / 14:0PC). The compositions may further be described as lung surfactant supplement preparations particularly useful in the treatment of pulmonary diseases and afflictions prevalent among premature infants, and in particular, Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS). A PC marker is also disclosed, 16:0 / 14:0PC, that may be used to detect pulmonary disease or reduced / compromised alveolar function in an animal. Phospholipid profiles of 16:0 / 14:0PC, 16:0 / 16:1PC and 16:0 / 16:0PC are also provided, and are correlated with particular pulmonary diseased states.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
Non-invasive device and method for the diagnosis of pulmonary vascular occlusions
InactiveUS7066892B2Accurate diagnosisLayered productsWithdrawing sample devicesTidal volumeNon invasive
The invention involves a device and method for ascertaining the functioning of the respiratory system and, in particular, for measuring the efficiency of alveolar ventilation of a patient. The device comprises an apparatus containing sensors for measuring the oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations as well as the volume of air inhaled and exhaled by a patient. The patient is provided a mouthpiece for breathing into and out of the device, which subsequently measures the oxygen and carbon dioxide partial pressures of inhaled and exhaled air. From these measurements, the efficiency of alveolar ventilation during each tidal volume breath may be calculated.
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Anion releasing painting and calligraphy pigment and manufacturing method thereof
An anion releasing painting and calligraphy pigment is a novel healthy and environmental-friendly culture article releasing anions. The anion releasing pigment can permanently release anions, and the number of the released anions is more than 1500 / cm. The anion releasing painting and calligraphy pigment has the efficiency of permanently and persistently releasing anions, removing harmful gas and abnormal taste, resisting and inhibiting bacteria, radiating far infrared and resisting electromagnetic radiation. The pigment is beneficial to human body health, can improve an alveolar secretion function and pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange functions, improve microcirculation, enhance the immunity of organisms and purify air, and has bacteriostatic function and good medical healthcare function.
Owner:张强
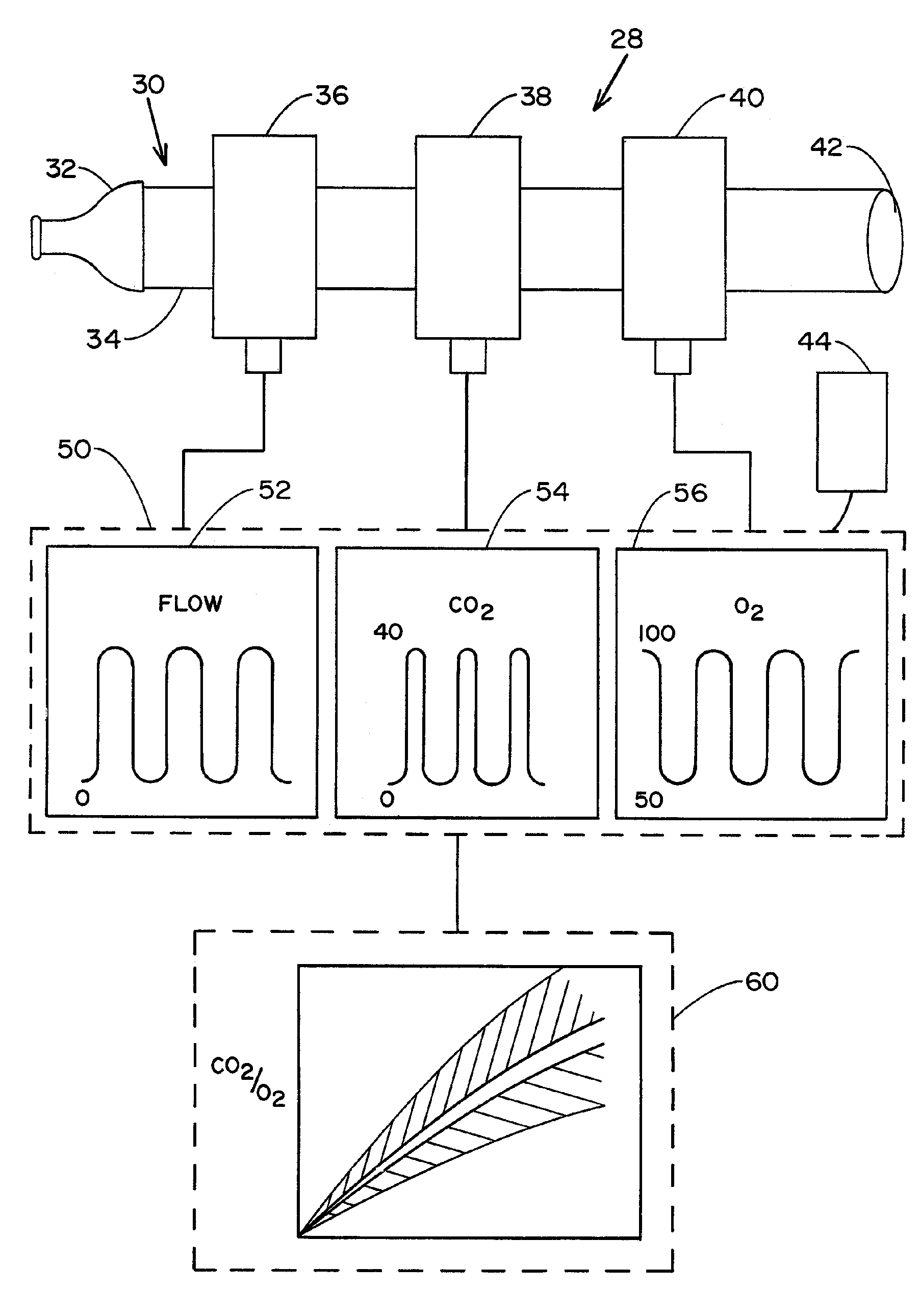
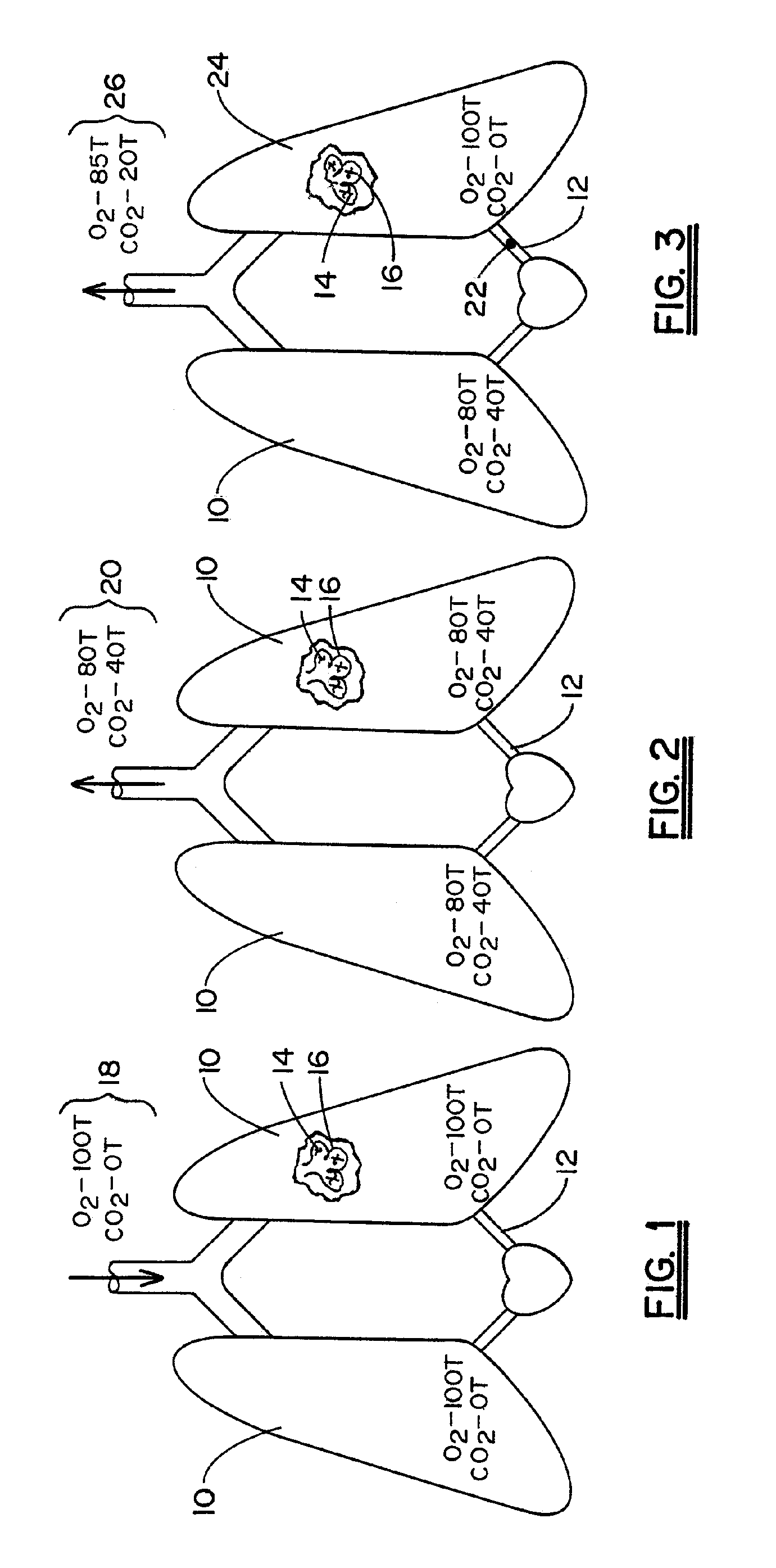
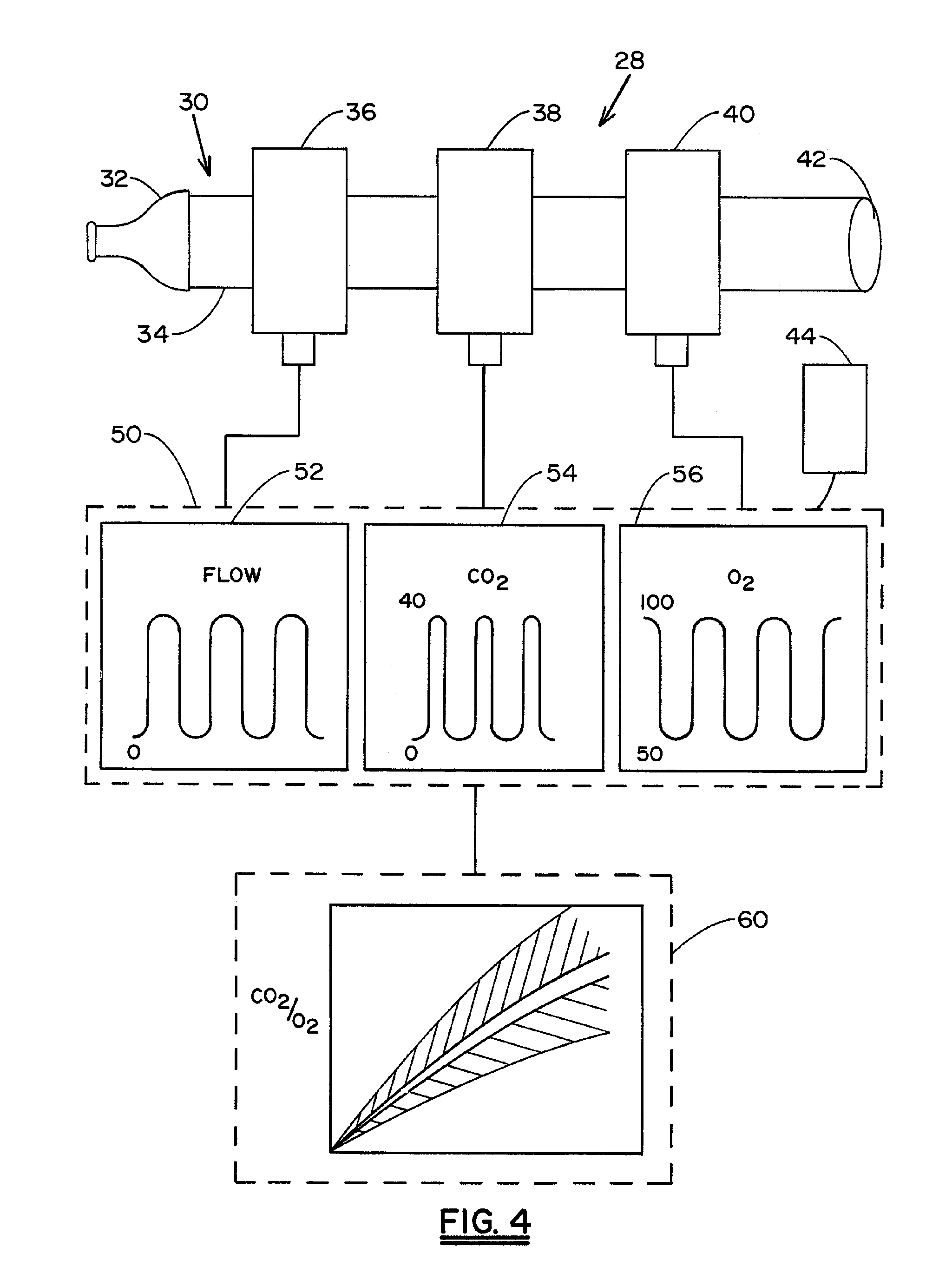
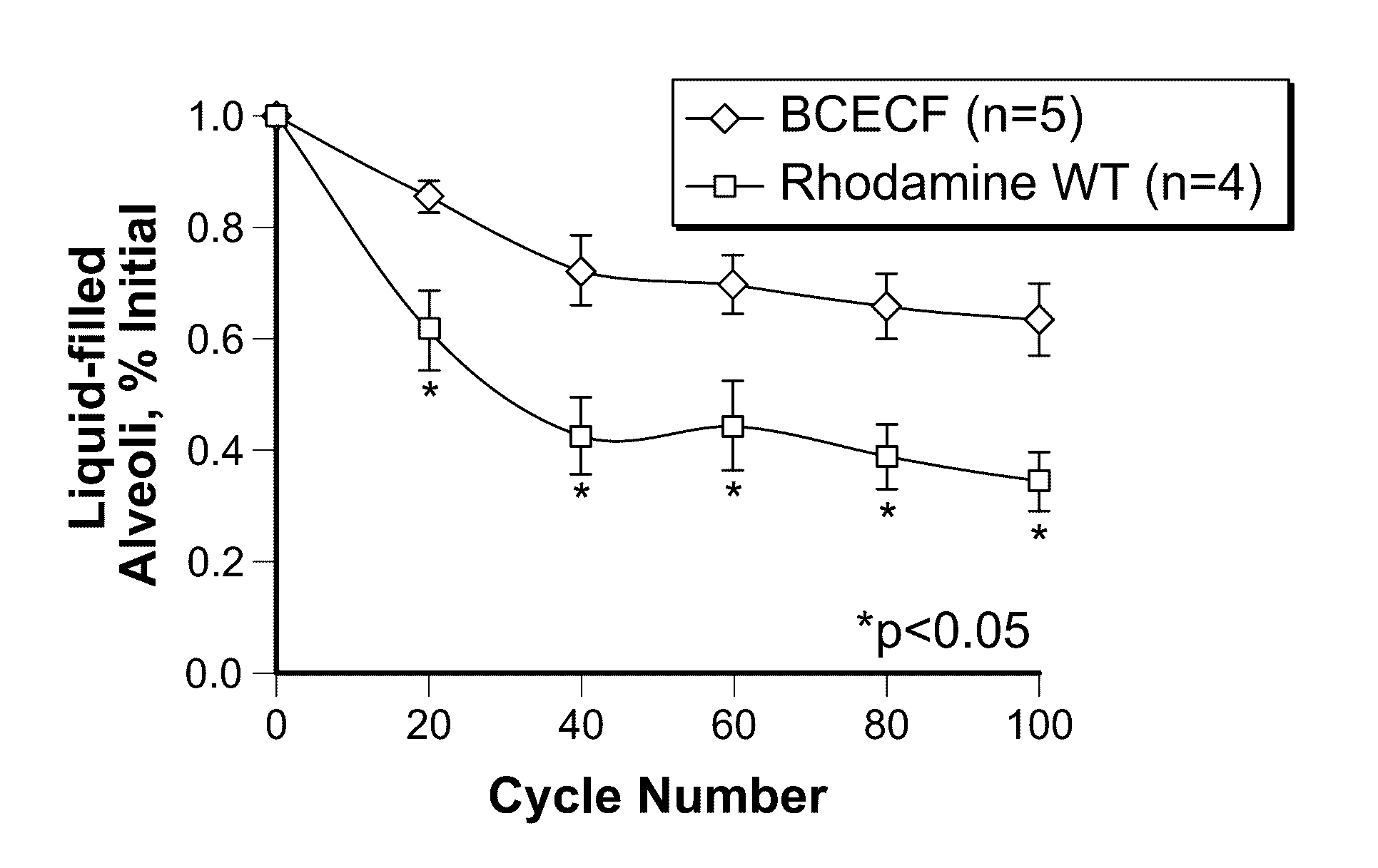
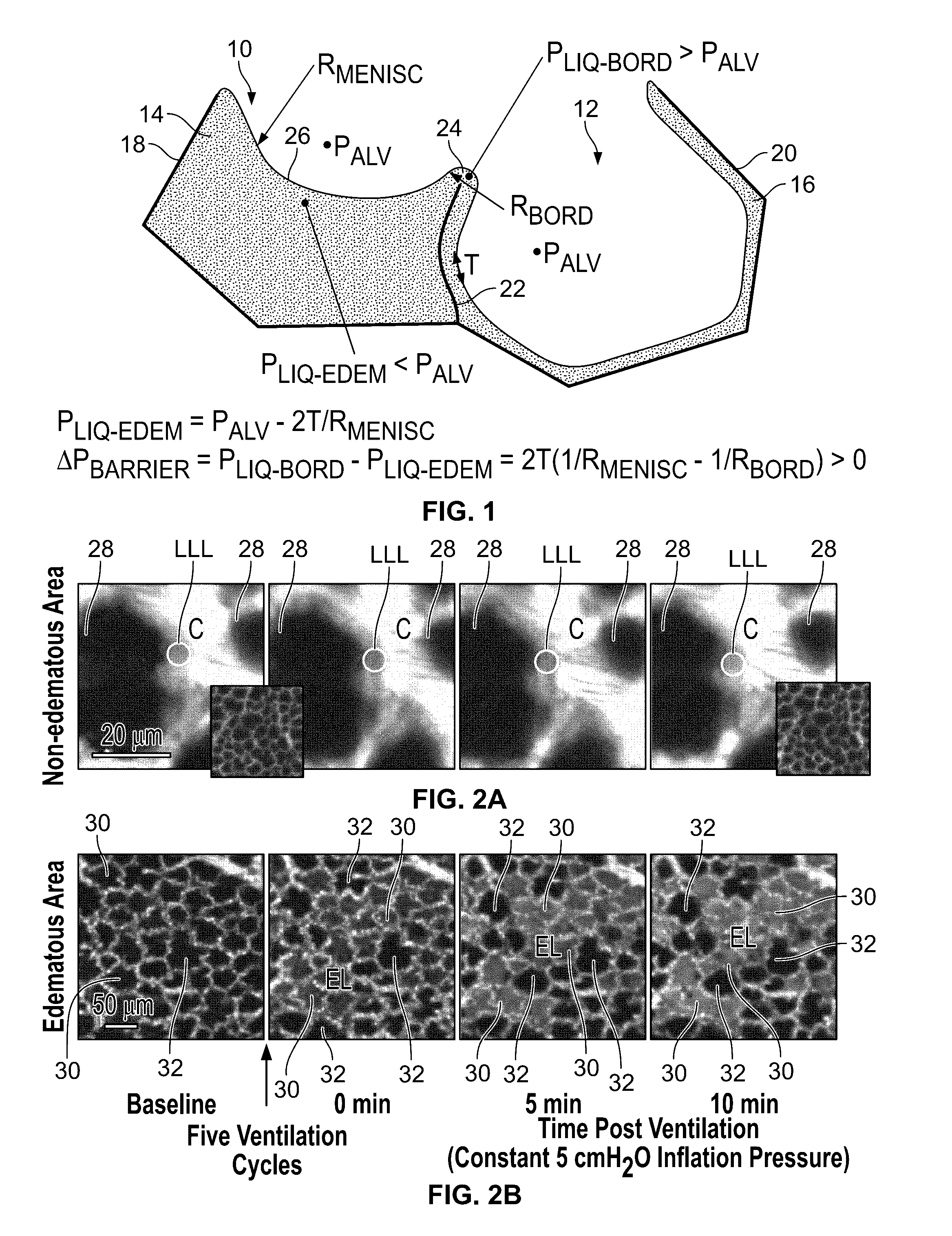
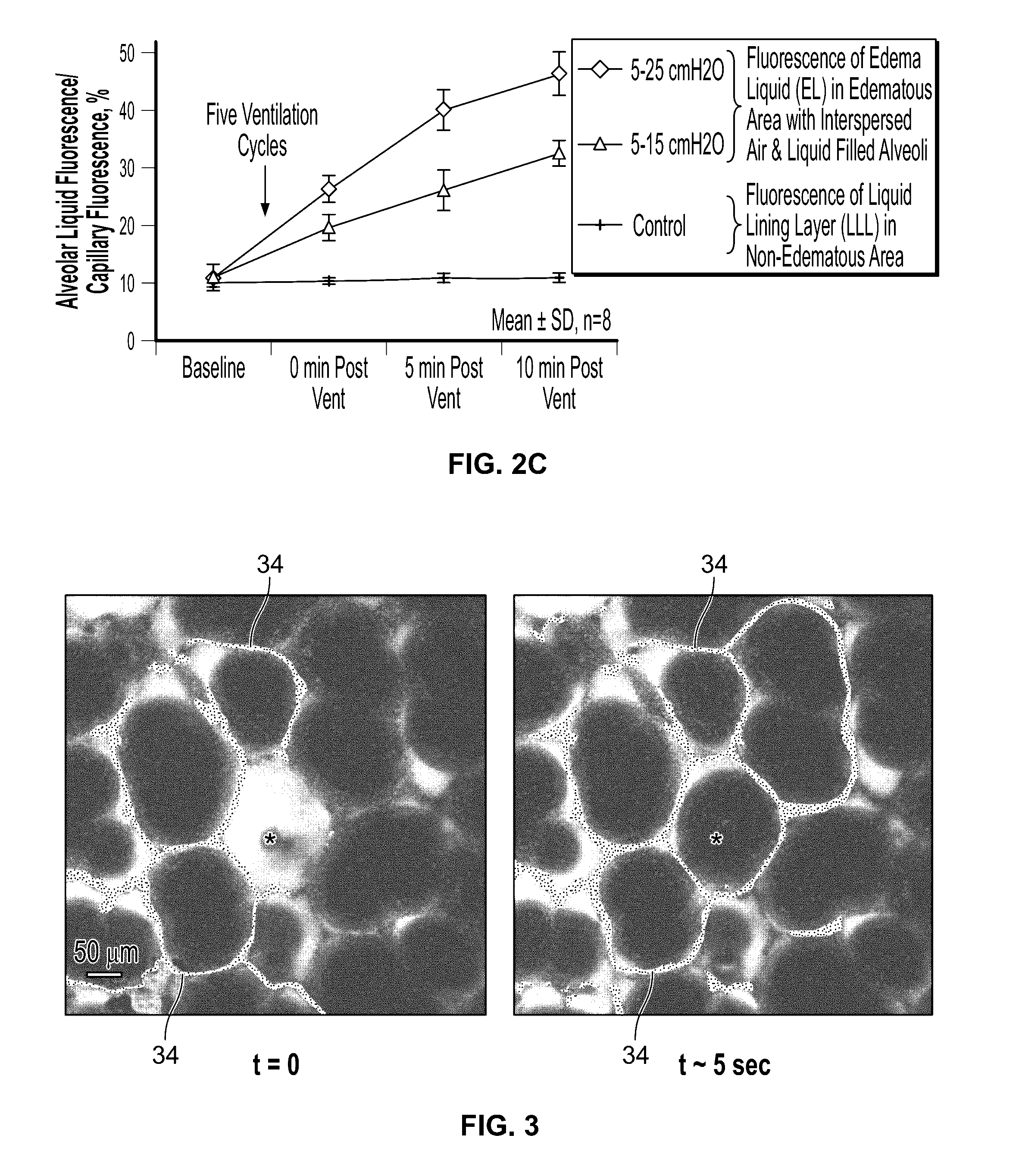
Reducing ventilator-induced lung injury
ActiveUS9504796B2Lessen over-distension injuryPromote equitable edema liquid redistributionRespiratorsMedical devicesAir liquid interfaceIntensive care medicine
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com