Patents
Literature
169results about "Heat treatment application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
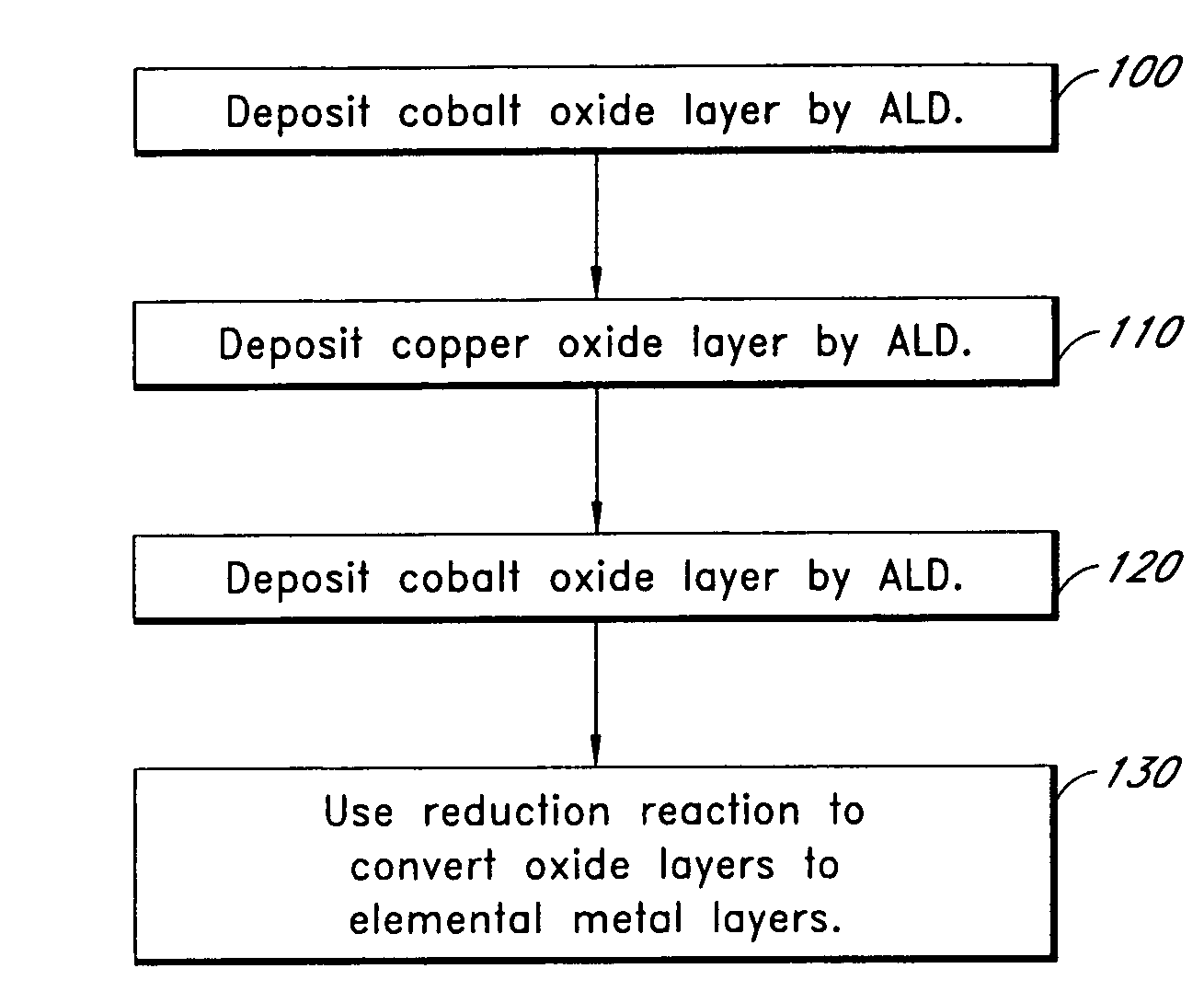
Thin films for magnetic device
InactiveUS7220669B2Inhibit migrationIncreasing the thicknessNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismDielectricThin layer
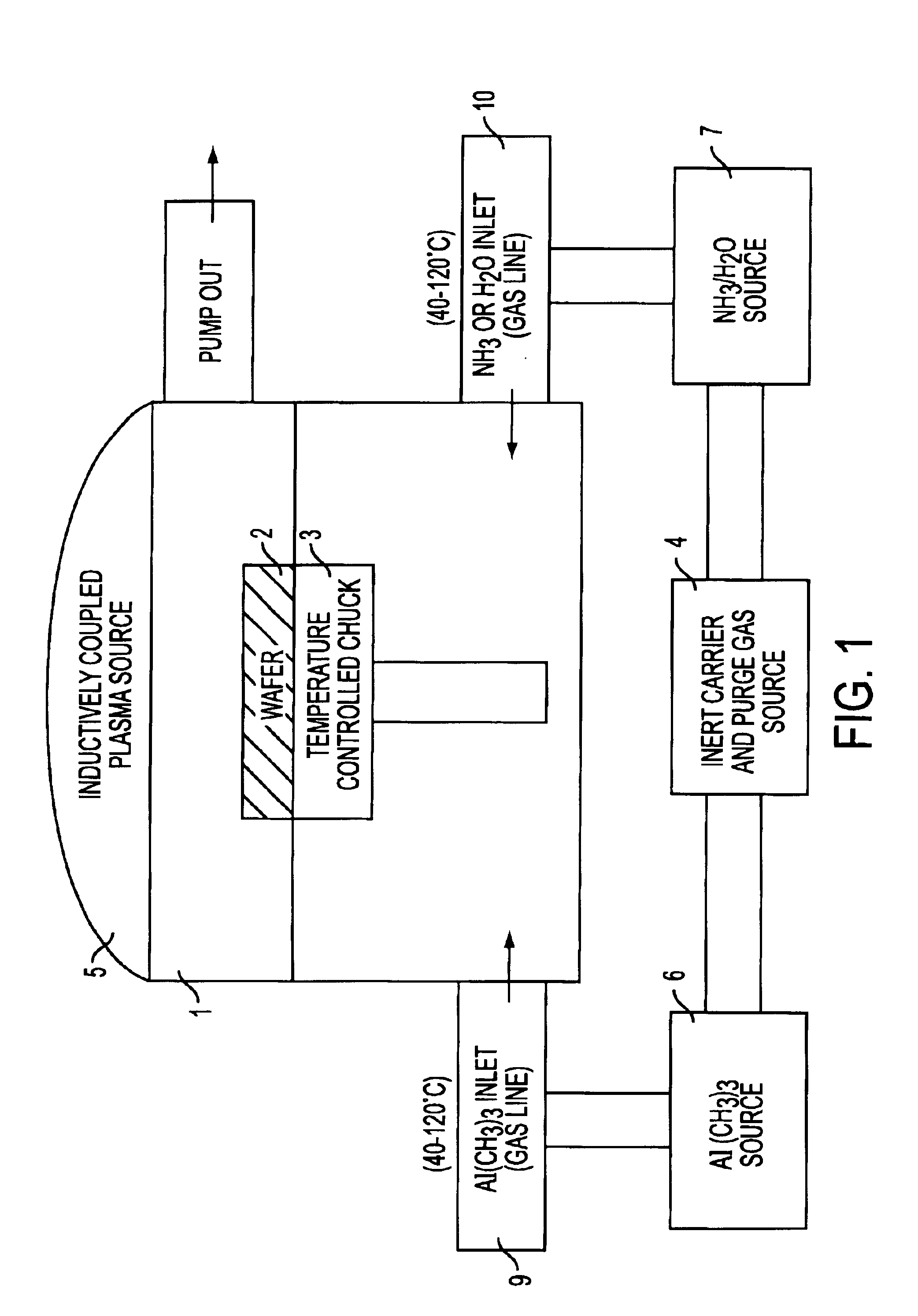
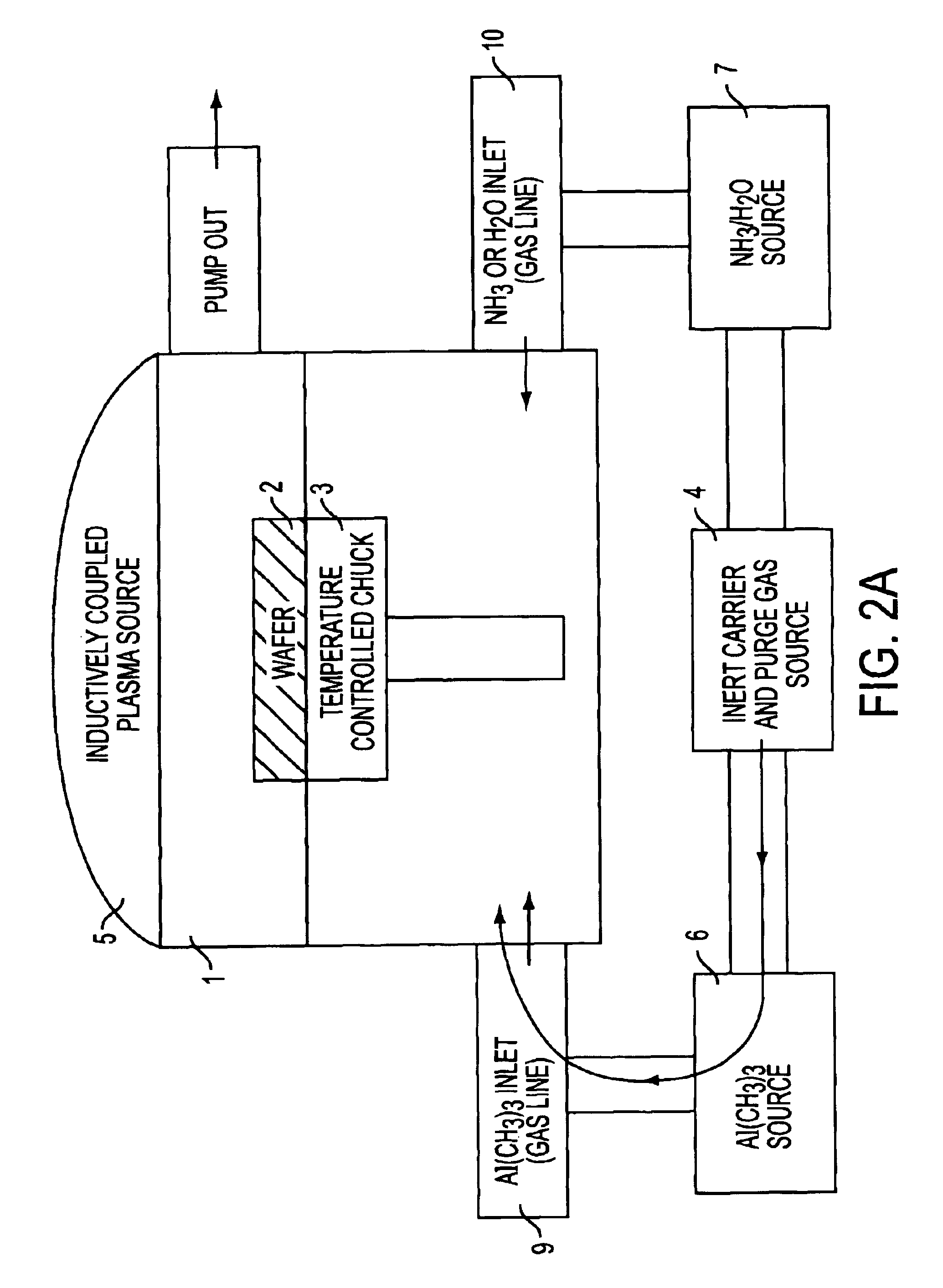
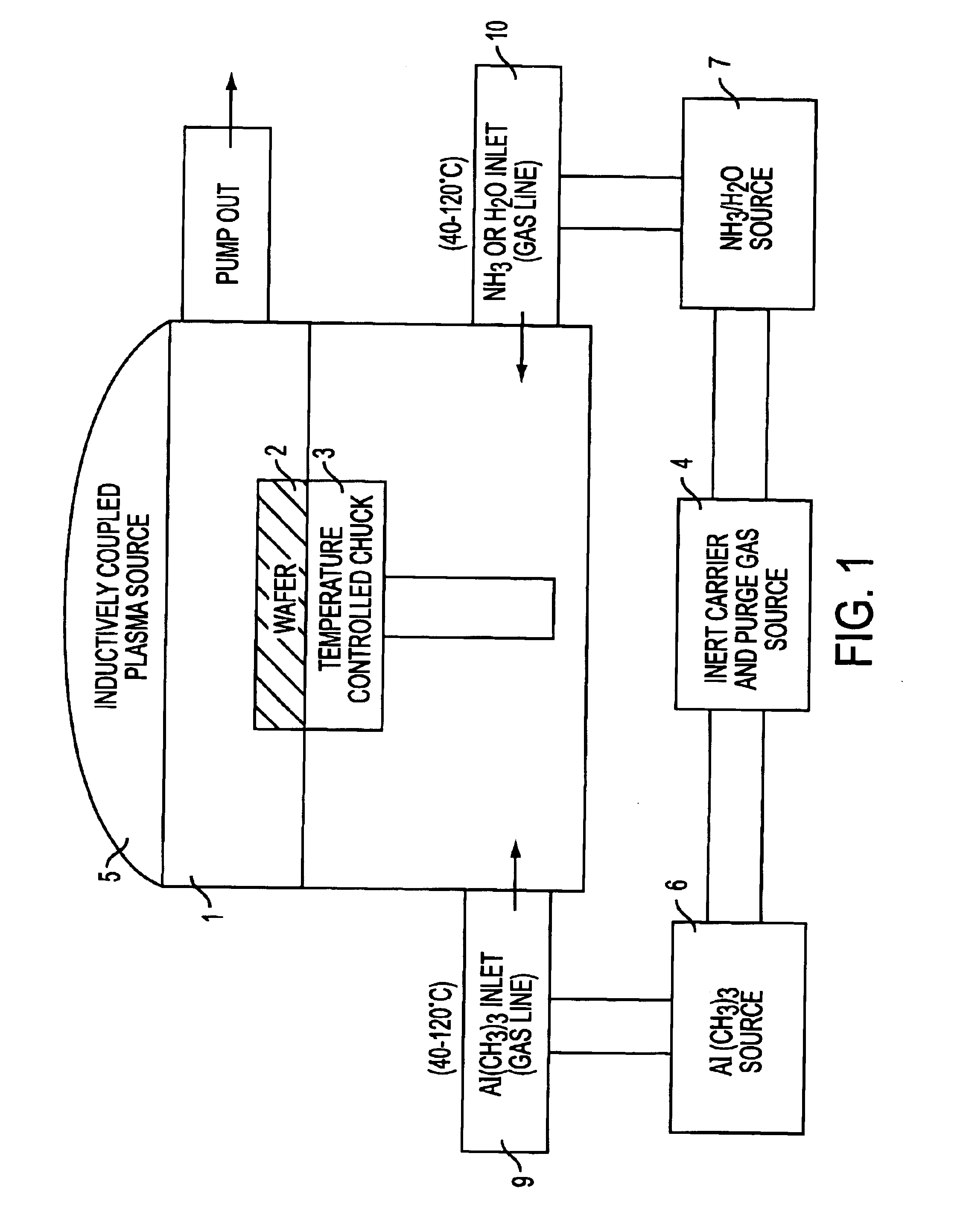
Methods are provided for forming uniformly thin layers in magnetic devices. Atomic layer deposition (ALD) can produce layers that are uniformly thick on an atomic scale. Magnetic tunnel junction dielectrics, for example, can be provided with perfect uniformity in thickness of 4 monolayers or less. Furthermore, conductive layers, including magnetic and non-magnetic layers, can be provided by ALD without spiking and other non-uniformity problems. The disclosed methods include forming metal oxide layers by multiple cycles of ALD and subsequently reducing the oxides to metal. The oxides tend to maintain more stable interfaces during formation.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
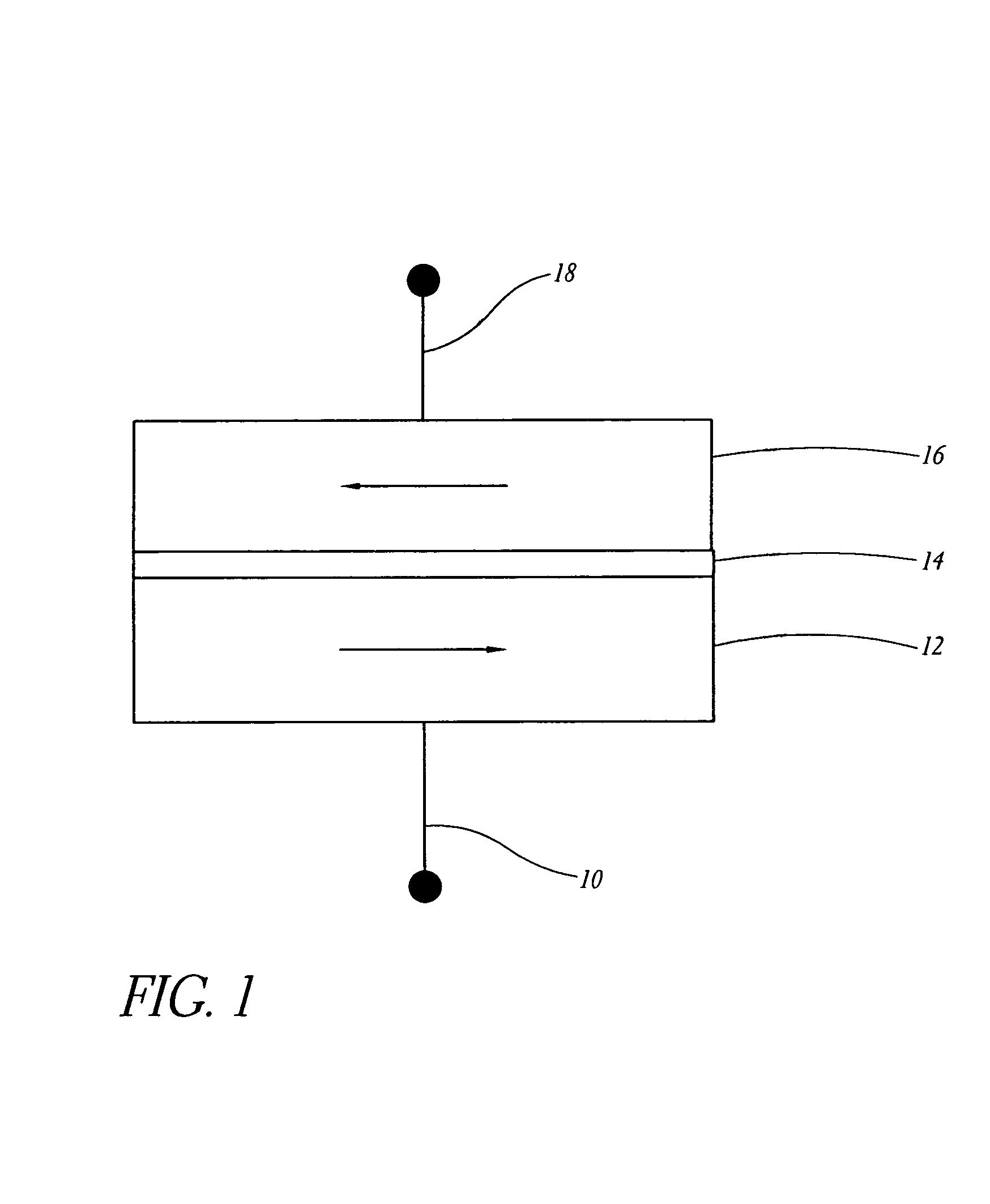
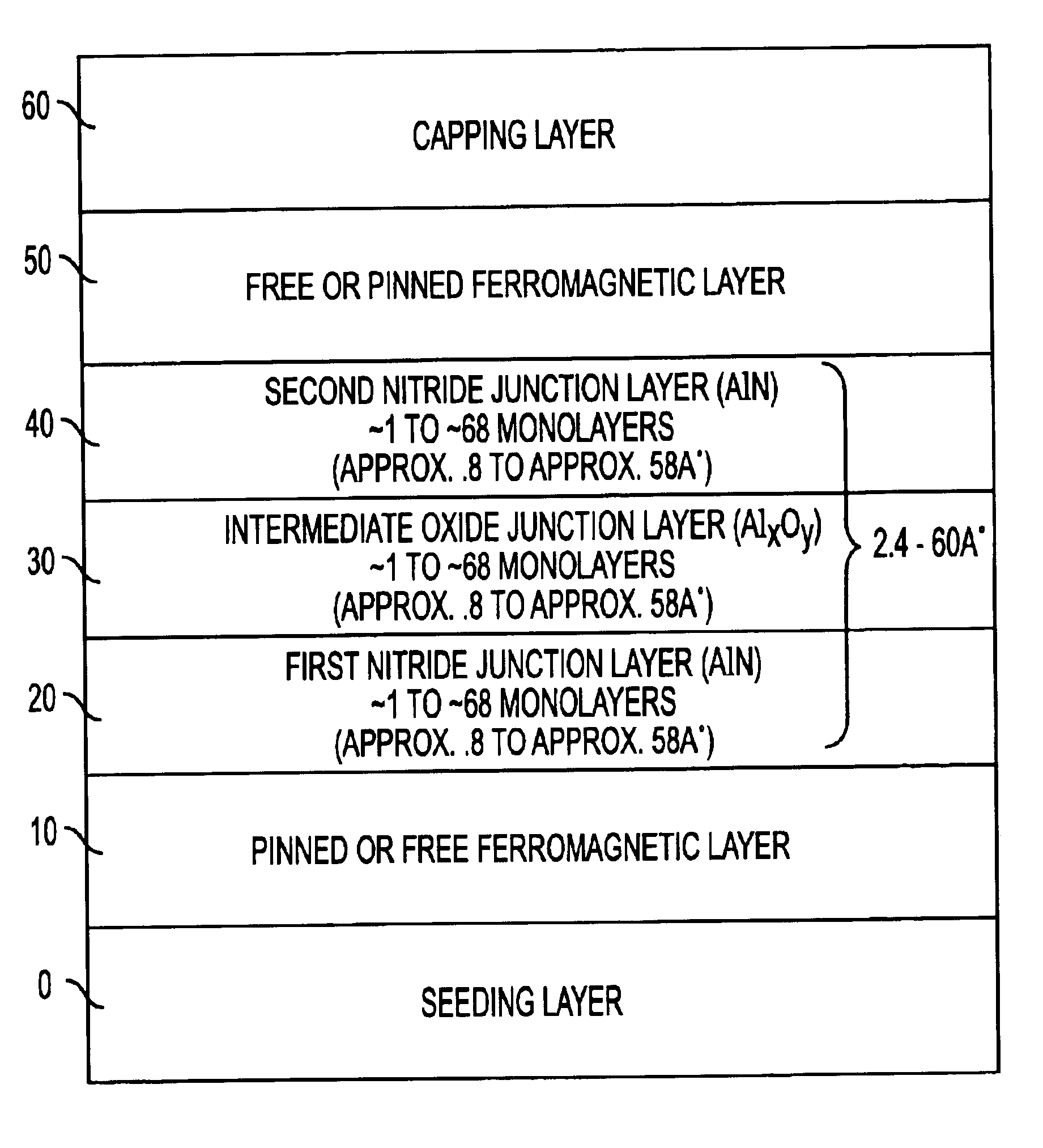
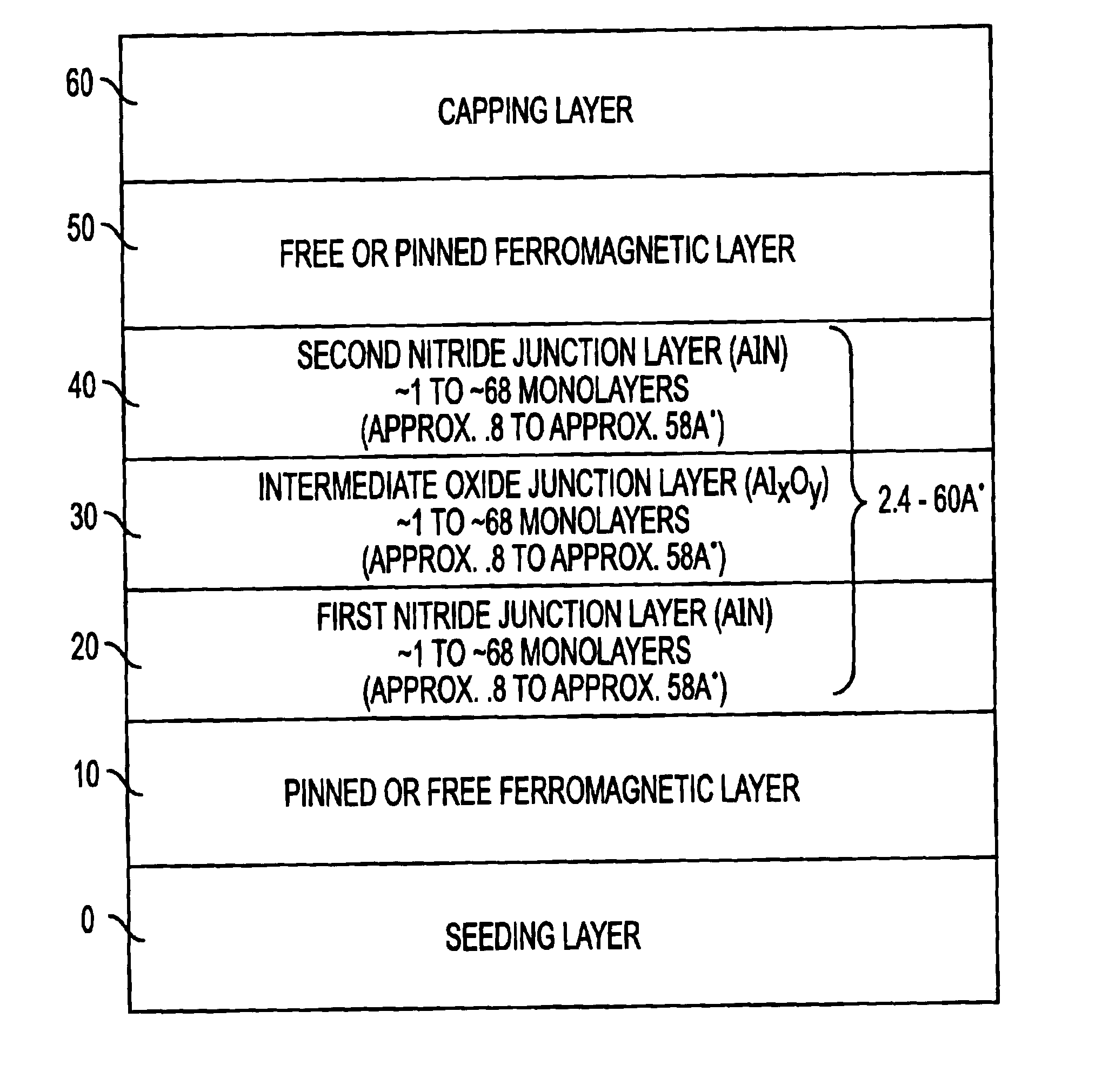
Method of fabricating a multilayer dielectric tunnel barrier structure
InactiveUS6849464B2Reduce resistanceGood shape retentionNanomagnetismChemical vapor deposition applicationMagnetic memoryNitride
A multilayer dielectric tunnel barrier structure and a method for its formation which may be used in non-volatile magnetic memory elements comprises an ALD deposited first nitride junction layer formed from one or more nitride monolayers i.e., AlN, an ALD deposited intermediate oxide junction layer formed from one or more oxide monolayers i.e., AlxOy, disposed on the first nitride junction layer, and an ALD deposited second nitride junction layer formed from one or more nitride monolayers i.e., AlN, disposed on top of the intermediate oxide junction layer. The multilayer tunnel barrier structure is formed by using atomic layer deposition techniques to provide improved tunneling characteristics while also providing anatomically smooth barrier interfaces.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
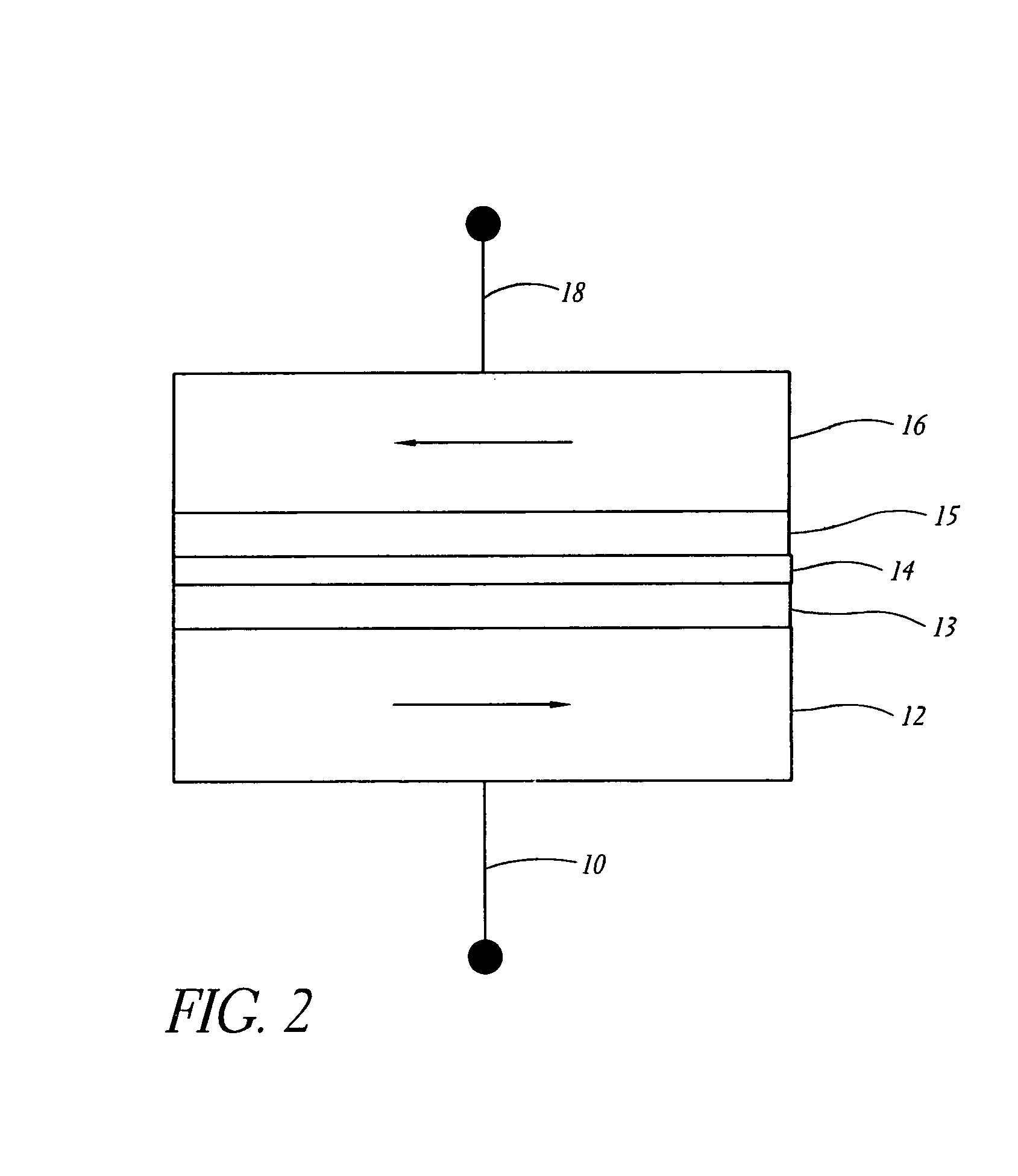
Multilayer dielectric tunnel barrier used in magnetic tunnel junction devices, and its method of fabrication
InactiveUS6900455B2Reduce resistanceGood shape retentionNanomagnetismChemical vapor deposition applicationDielectricMagnetic memory
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Spin-valve thin-film magnetic element and method for making the same
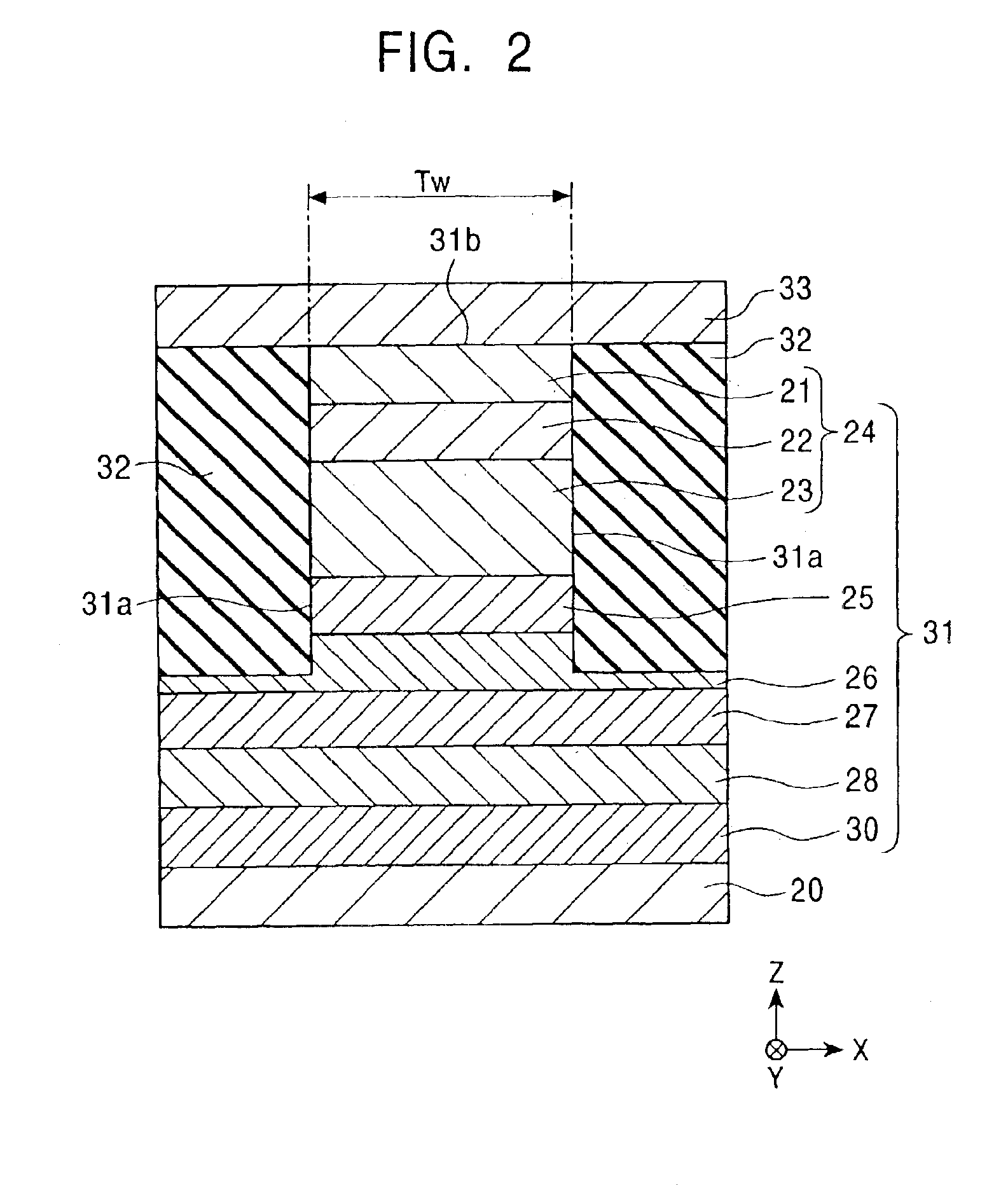
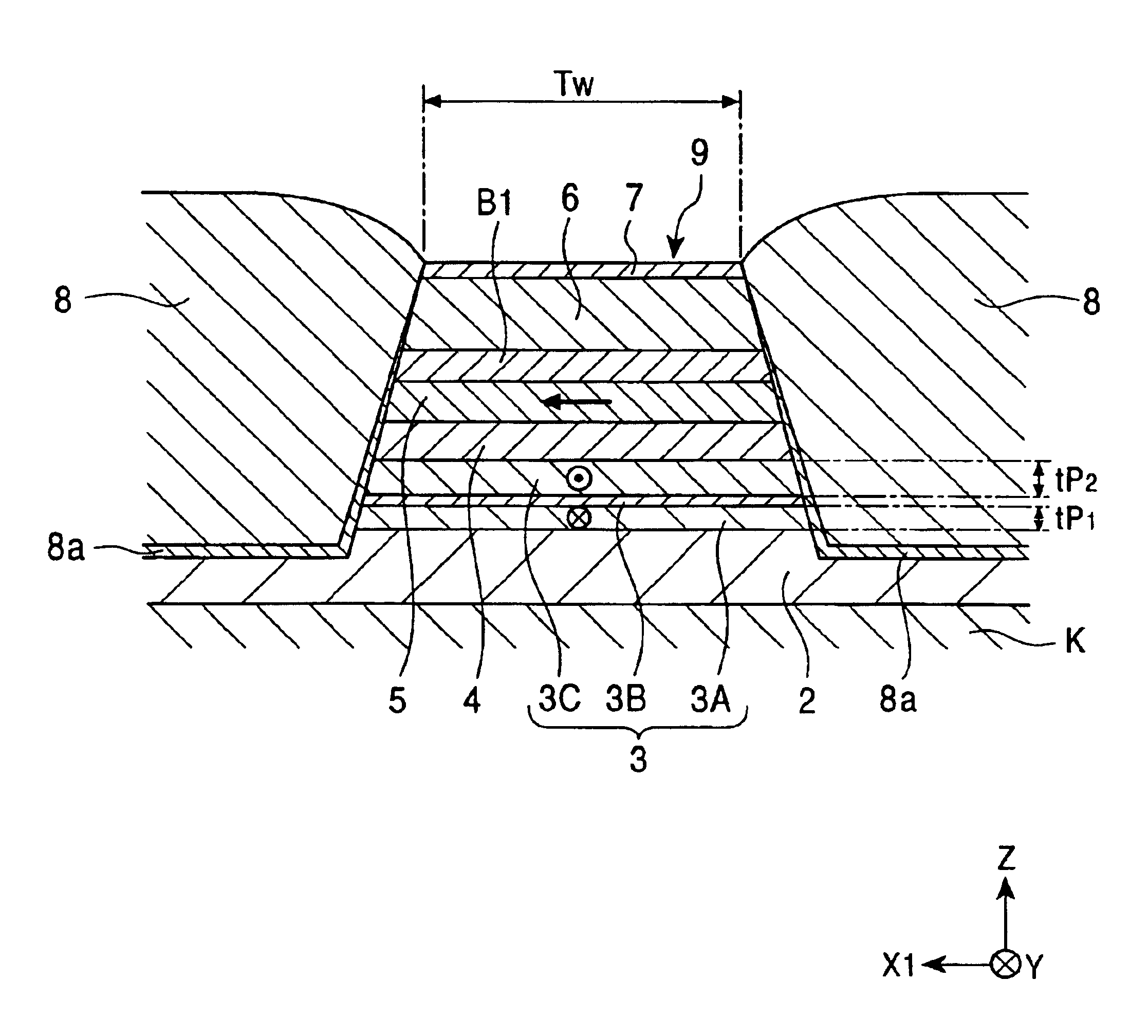
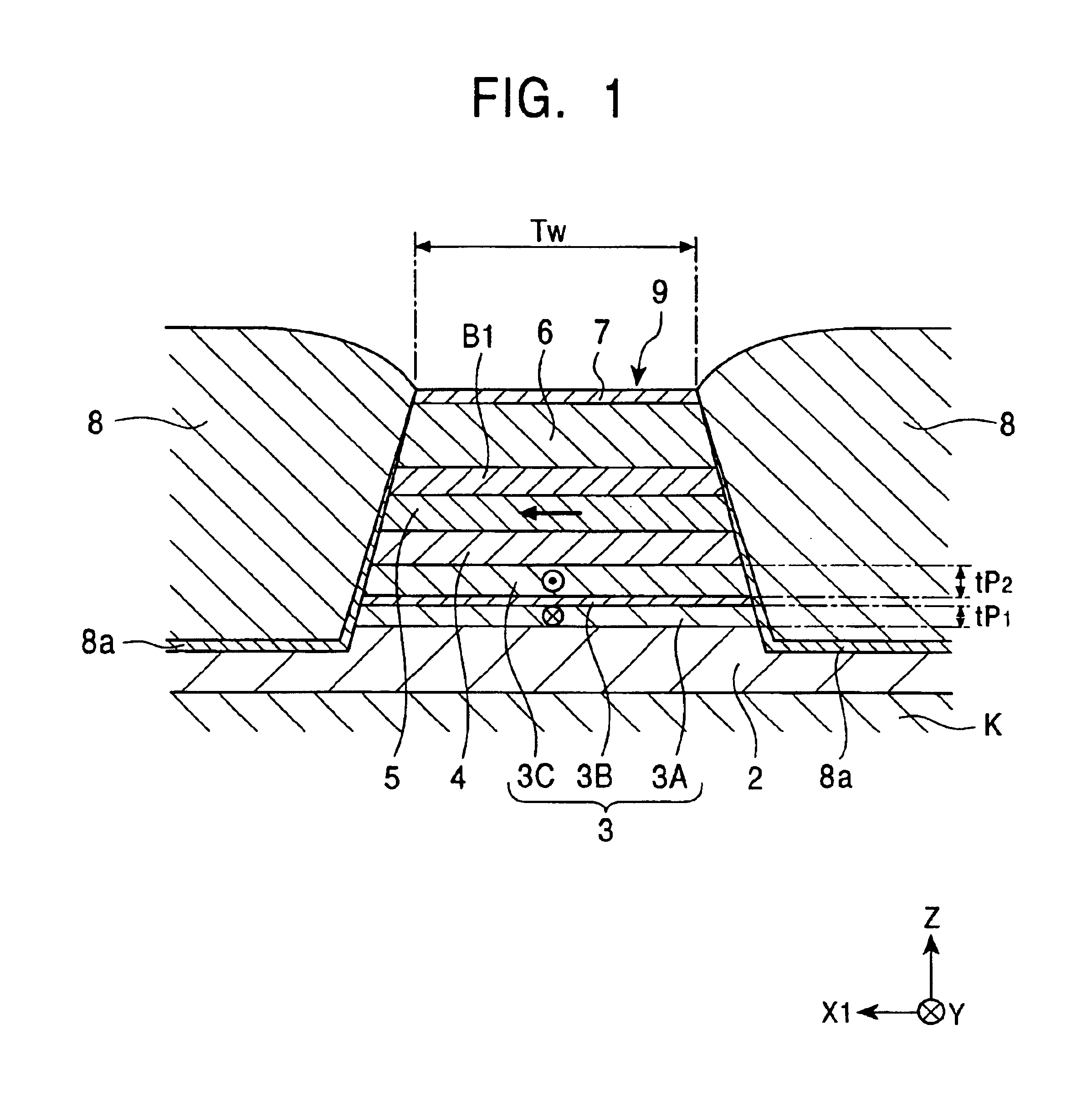
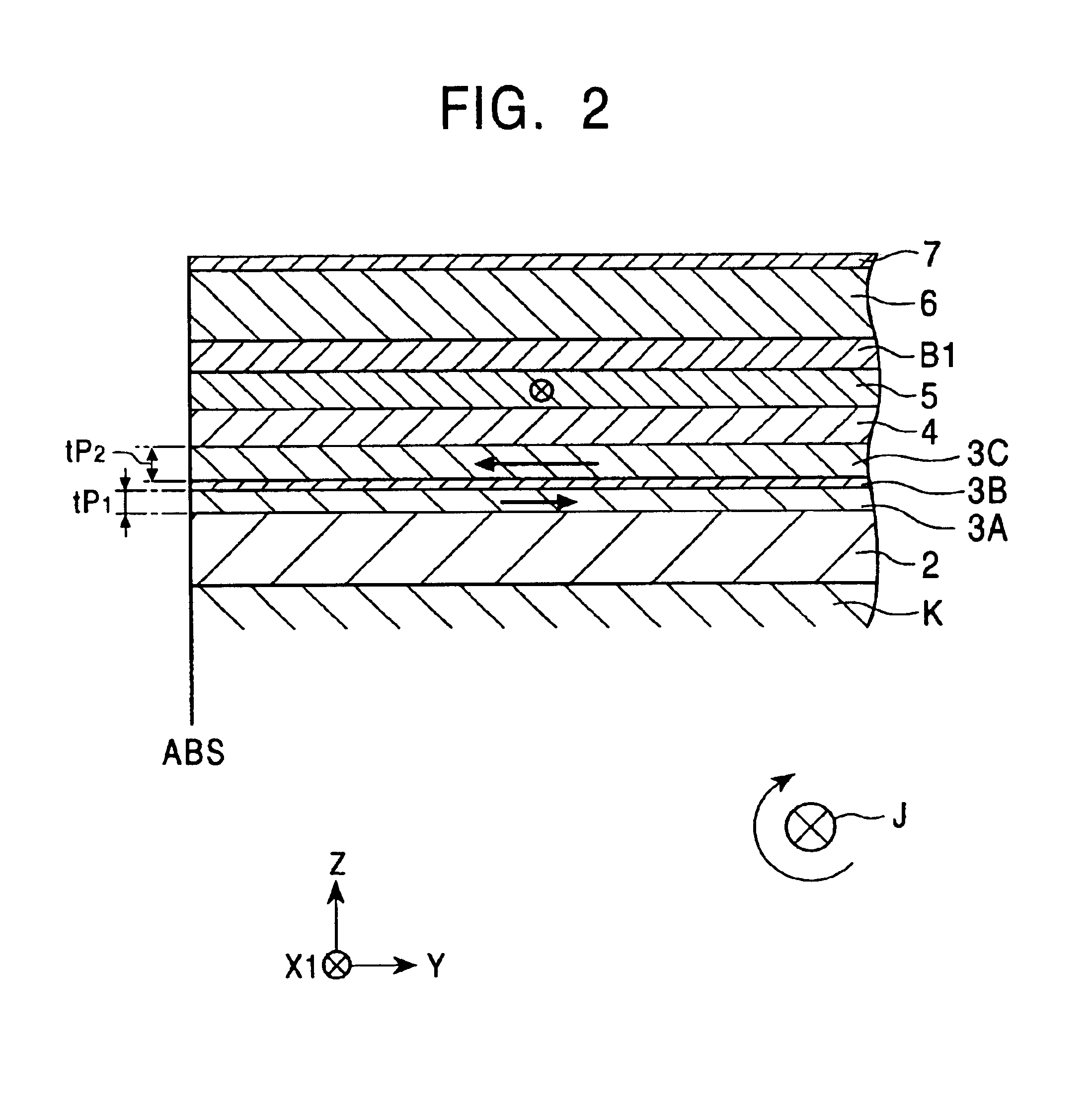
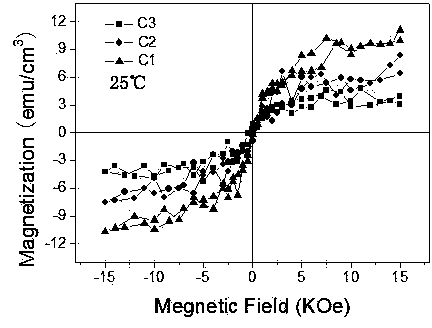
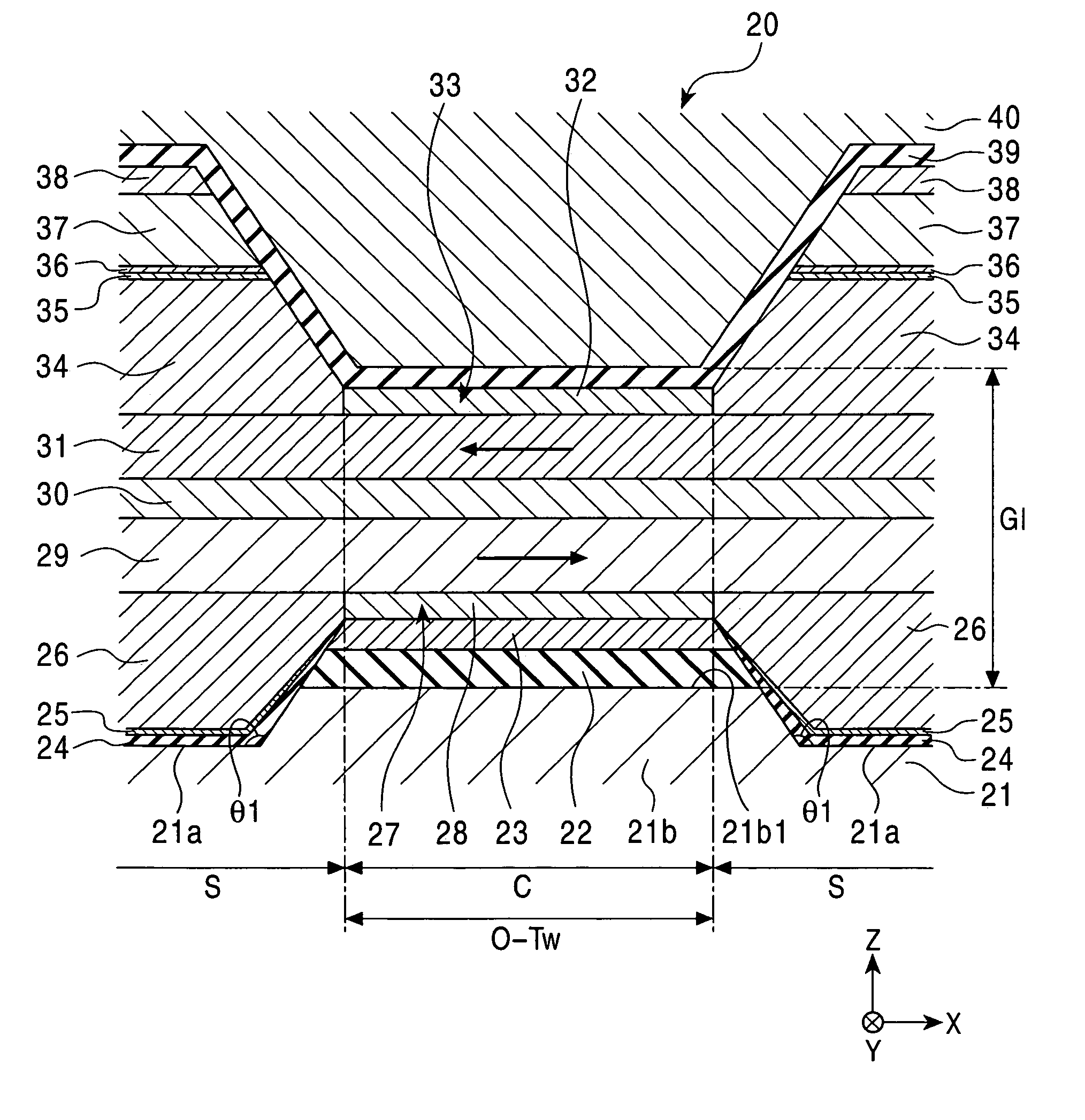
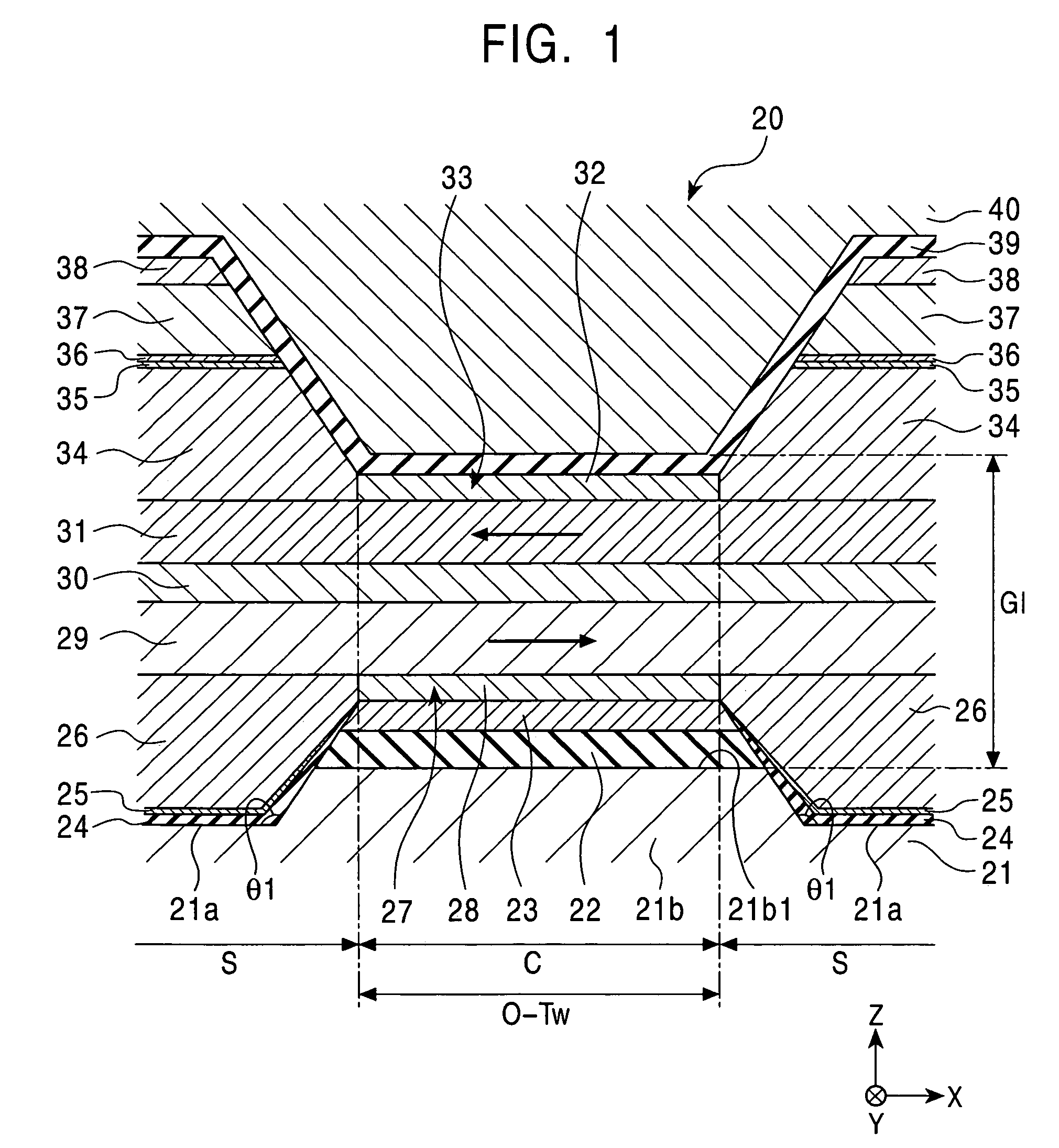
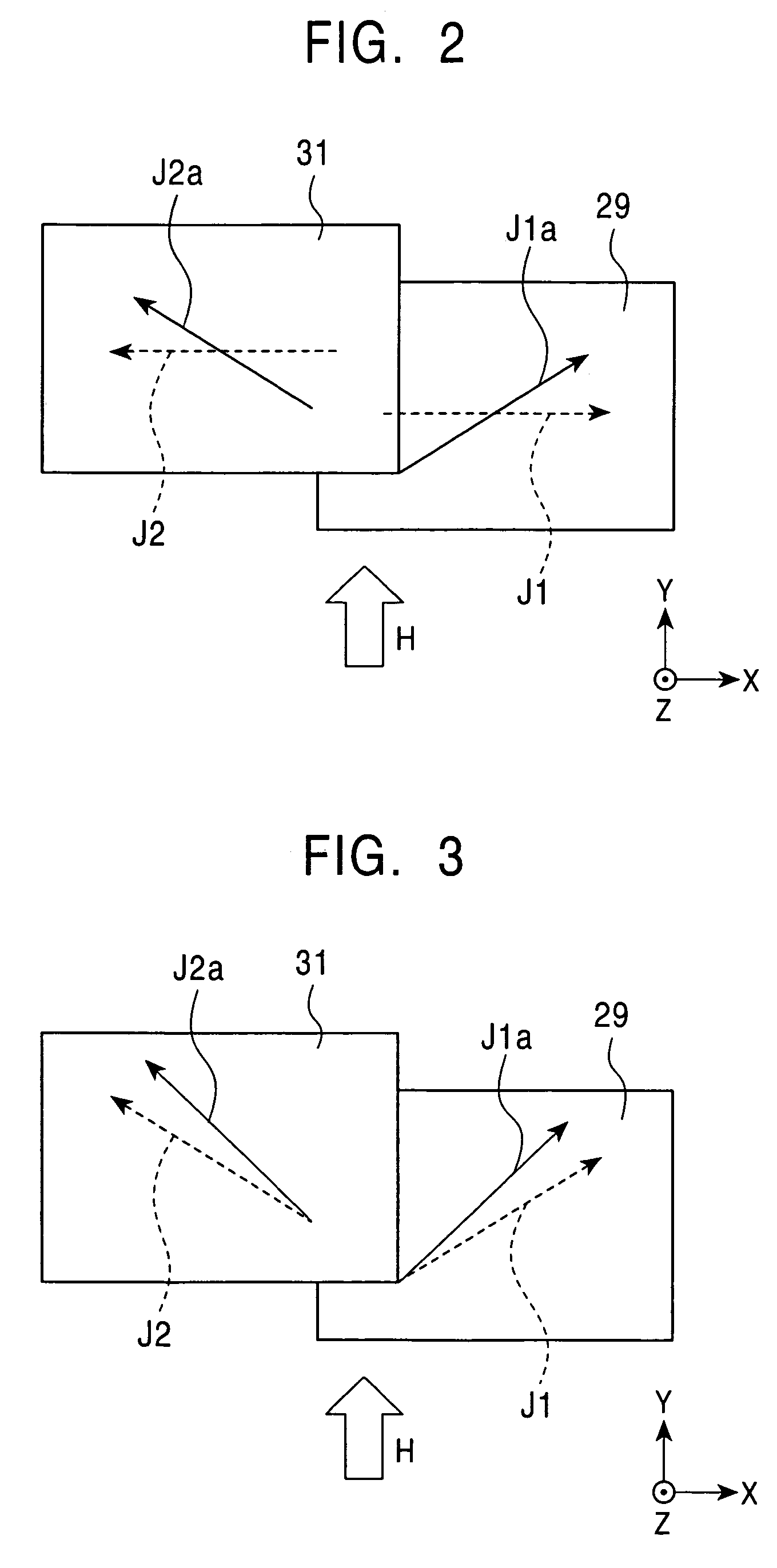
A spin-valve thin-film magnetic element includes a substrate, a composite formed thereon, and electrode layers formed on both sides of the composite. The composite includes an antiferromagnetic layer, a pinned magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic conductive layer, a free magnetic layer, a mean-free-path-extending layer, and an exchange bias layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer may be a back layer or a mirror reflective layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer extends the mean free path of spin-up conduction electrons in the spin-valve thin-film magnetic element. This spin-valve thin-film magnetic element meets trends toward a narrower track width.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Magnetic laminated structure and method of making
InactiveUS20060141139A1Chemical vapor deposition applicationVacuum evaporation coatingMicrometerMaterials science
An article comprising a multilayered structure comprising a series of magnetic layers is provided. The magnetic layers comprise a magnetic material, and an insulating layer is disposed between successive magnetic layers. Each magnetic layer has a thickness of at least about 2 micrometers and magnetic material has an average grain size less than 200 nm. Also provided is a method for making the article.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
CPP type magnetoresistive sensor including pinned magnetic layer provided with hard magnetic region
InactiveUS6893740B2High film thicknessEasily reliably bringNanomagnetismChemical vapor deposition applicationMagnetizationMagnetic layer
A magnetoresistive sensor and a method of manufacturing the magnetoresistive sensor are provided, which can effectively increase ΔRA, and which can more easily and reliably bring magnetization of a free magnetic layer and magnetization of a pinned magnetic layer into an orthogonal state than the related art. By forming the pinned magnetic layer of a multilayered structure comprising a first hard magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic layer, and a second hard magnetic layer, the magnetization of the free magnetic layer and the magnetization of the pinned magnetic layer can be more easily and reliably brought into an orthogonal state than in the related art. Also, the pinned magnetic layer can be formed in a larger film thickness than that in the related art. Accordingly, the product (ΔRA) of a resistance change amount (ΔR) and a sensor area (A) in a direction parallel to film surfaces can be increased.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Iron nitride thin film and methods for production thereof
InactiveUS20020117102A1High crystallinityMaintain good propertiesPolycrystalline material growthChemical vapor deposition applicationIron nitrideOptoelectronics
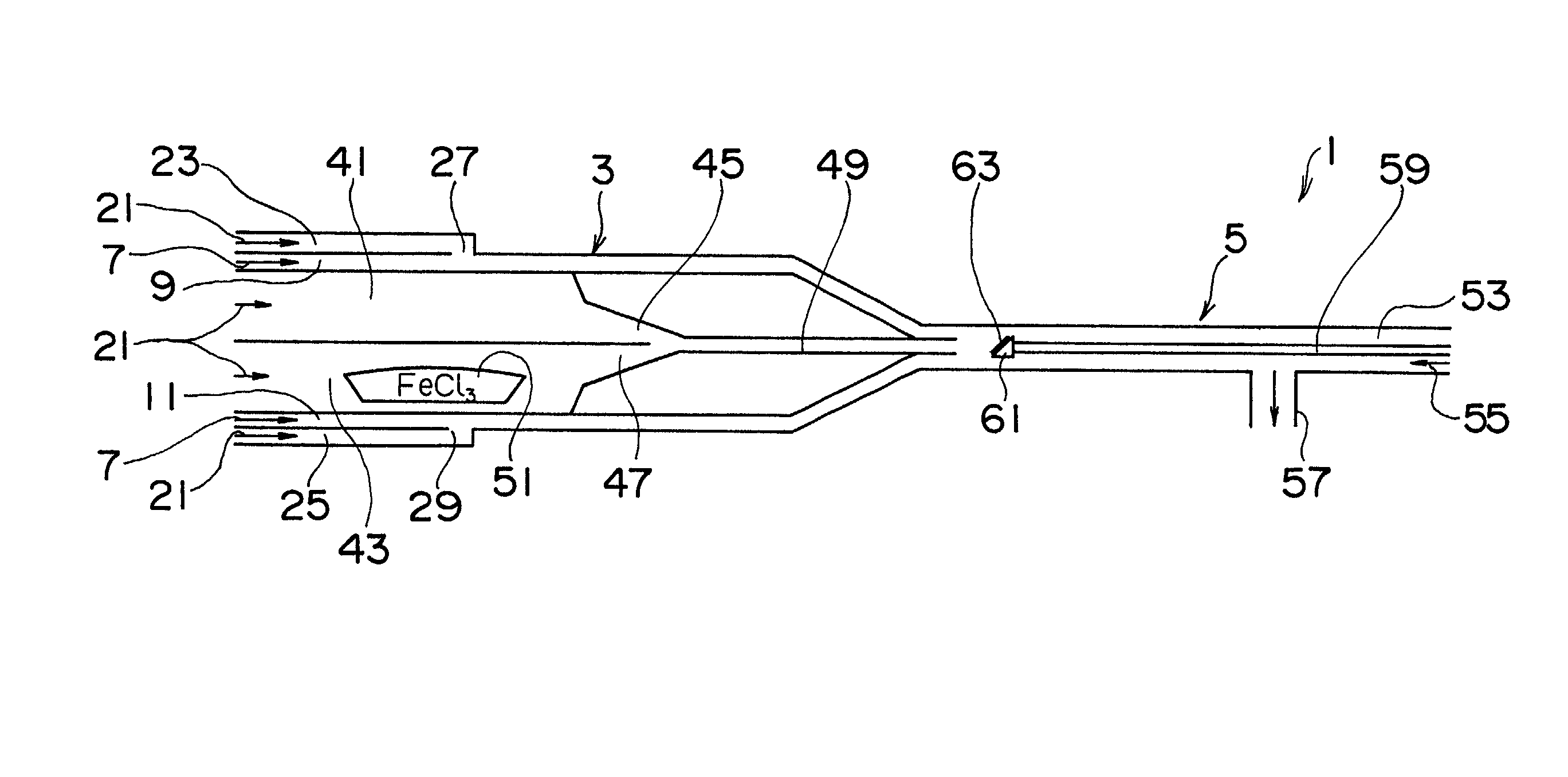
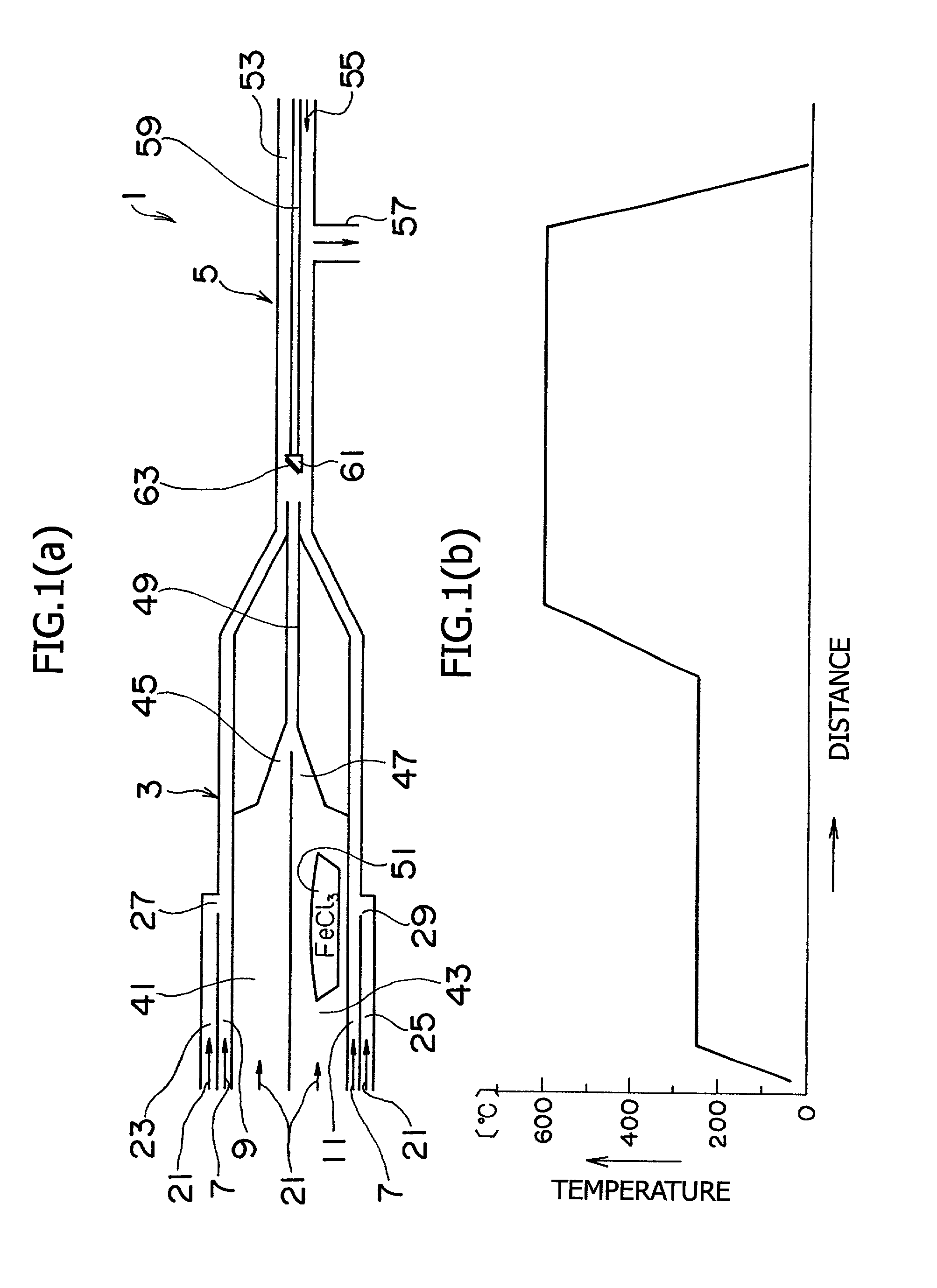
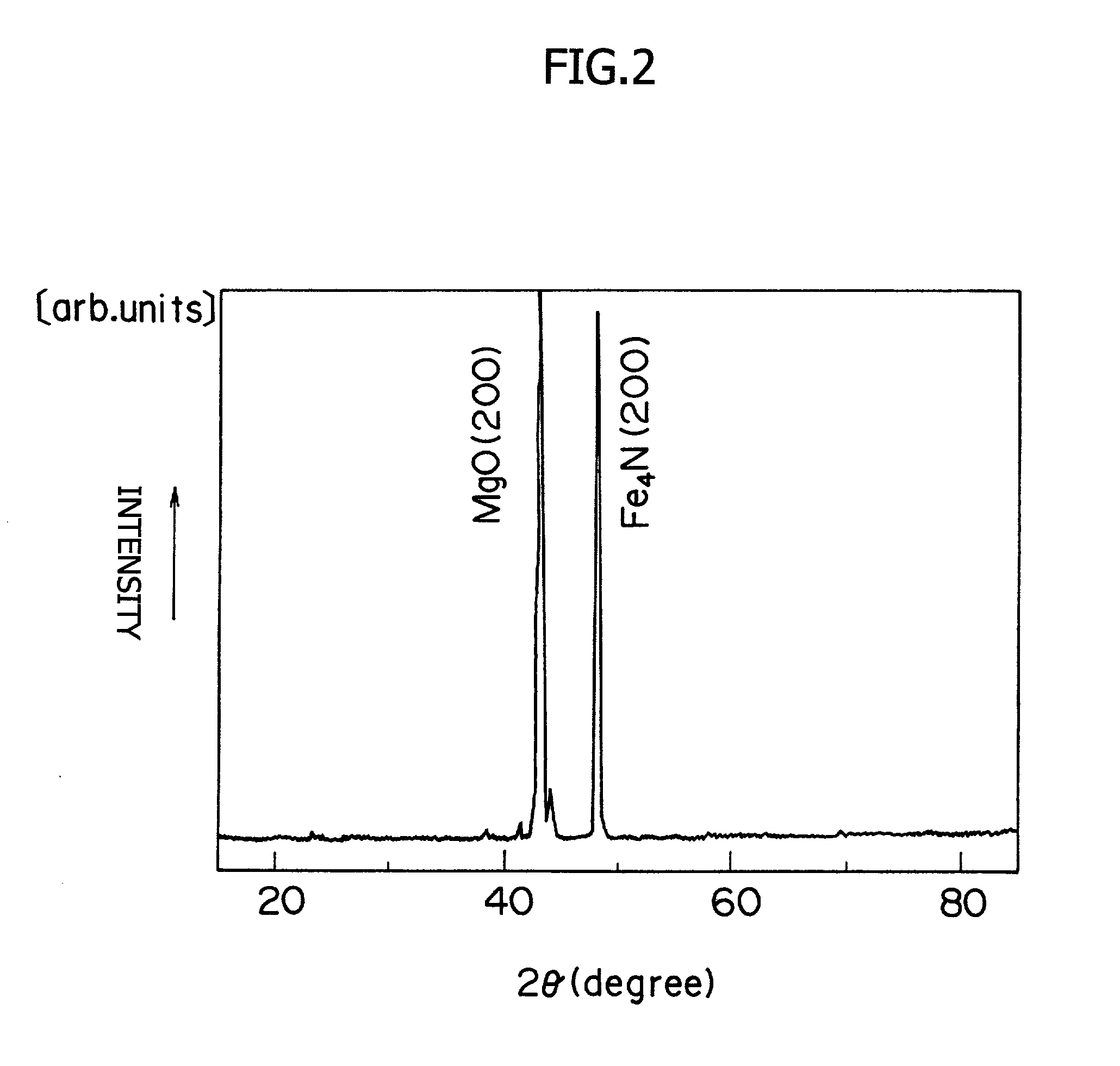
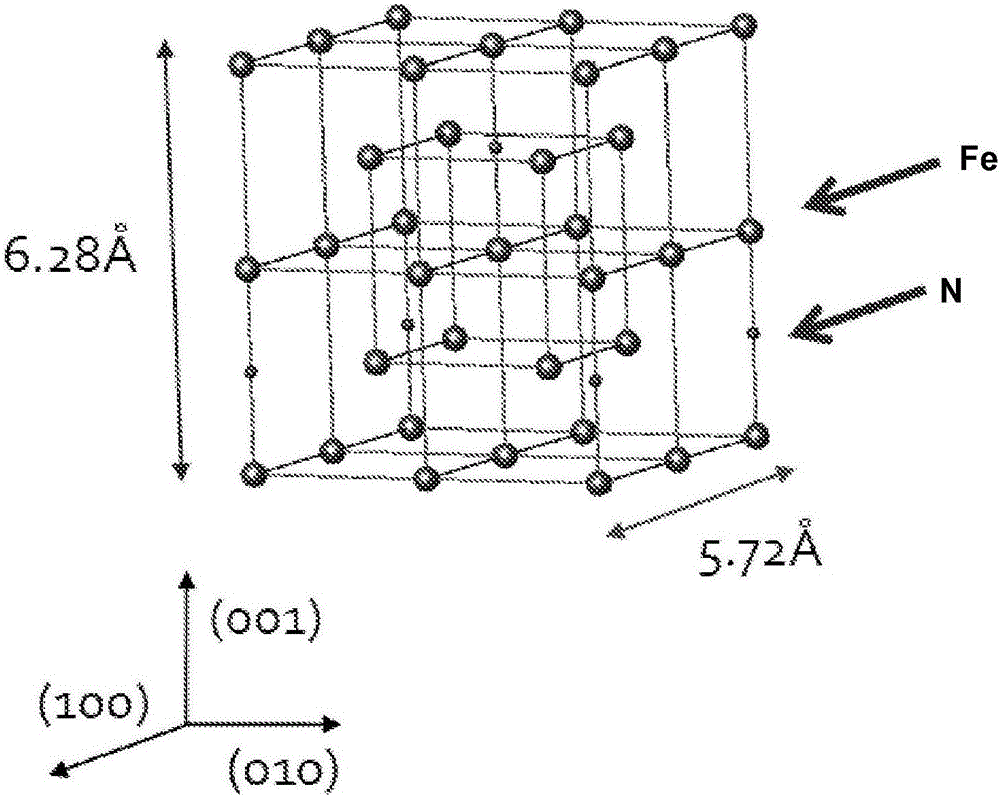
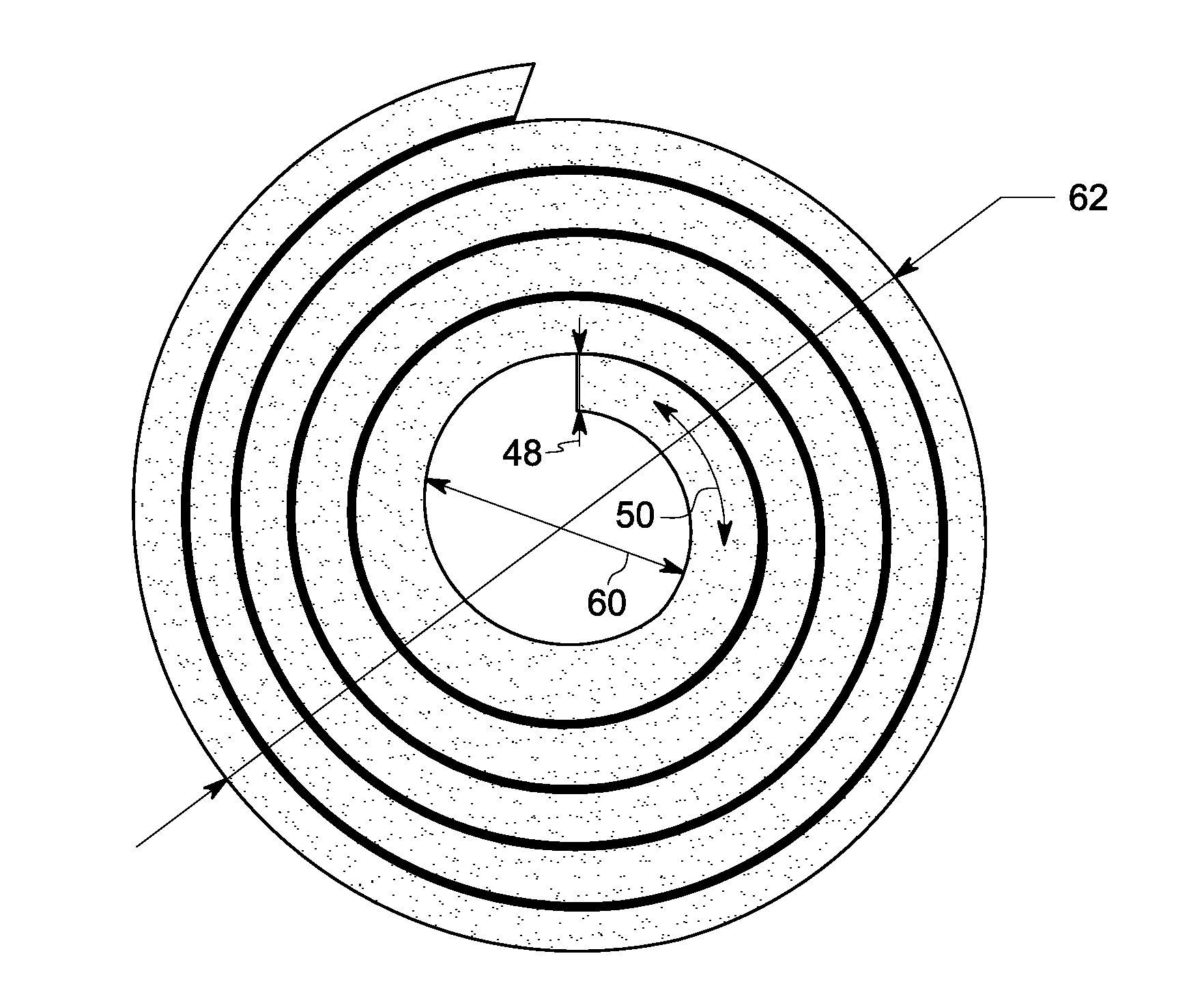
The present invention provides a method for the preparation of an iron nitride thin film by which an iron nitride thin film having a high growth rate can be epitaxially grown under atmospheric pressure without using any expensive vacuum system or raw materials, and an iron nitride thin film prepared by this method. This method for the preparation of an iron nitride thin film comprises the steps of vaporizing an iron halide used as a raw material 51 for the preparation of a thin film and reacting the resulting iron halide gas with a nitrogen source gas 7 containing nitrogen to produce an iron nitride gas; and preparing an epitaxial film of iron nitride 63 on a substrate 61 by allowing the iron halide gas to become adsorbed on the substrate 61 under atmospheric pressure and grow epitaxially thereon.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Method for preparing magnetic thin film
InactiveCN102103919ARich film forming methodsImprove controllabilityChemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationDiffusion methodsControllability
The invention provides a method for preparing a magnetic thin film. The method comprises the steps of preparing a magnetic filler, preparing a magnetic film forming matter matrix, forming a film and applying a magnetic field. In the method, the technology that magnetic nano or micron material fillers in such film forming matters as resins, rubbers, plastics, coatings and other high polymers are directionally and orderly arranged under the action of the external magnetic field is adopted, and the bearing media of the magnetic thin film or magnetic nano thin film are expanded under the premise of maintaining the anisotropy characteristic of the magnetic nanocrystals, thus expanding the application field of the bearing media. The method has the following advantages: the bearing media of the magnetic nanocrystals can be resins, rubbers, plastics, coatings, other high polymers and other flexible media rather than to be only limited to hard substrates; besides the precipitation method and the self-assembly method, the film forming methods also include a drawing method, a blowing method, a calendering method, a diffusion method and the like; and the stepwise synthesis process is adopted, thus improving the controllability of the synthesized product and being beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:SUNDIA MEDITECH COMPANY LTD
RFeB-based magnet
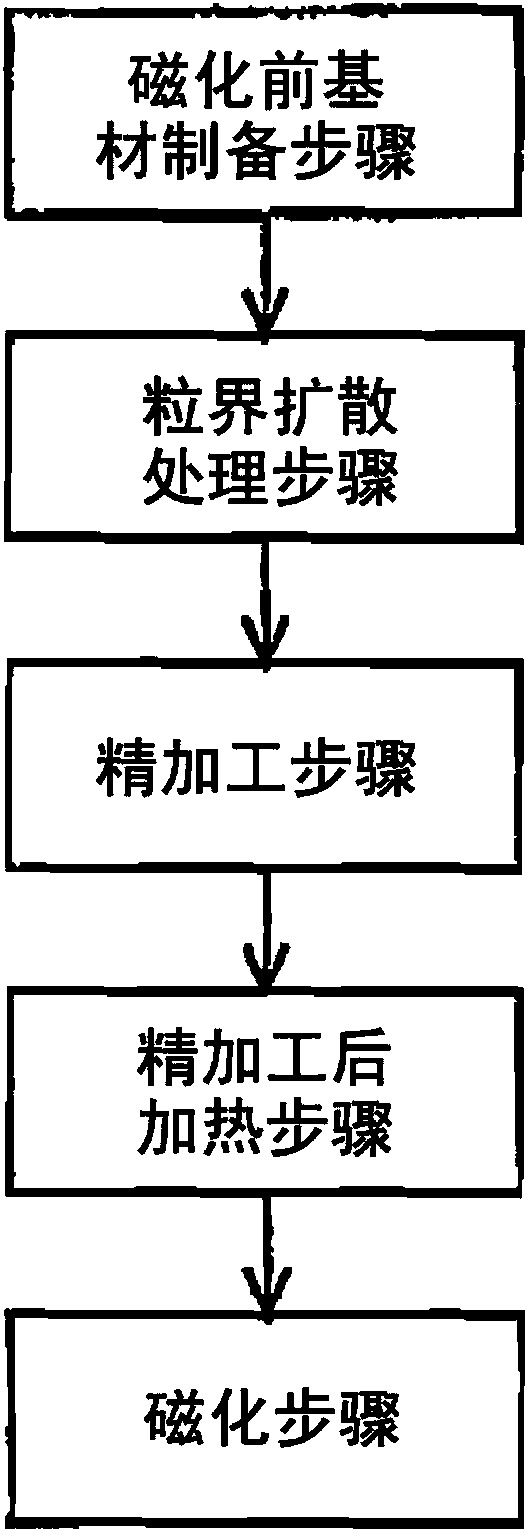
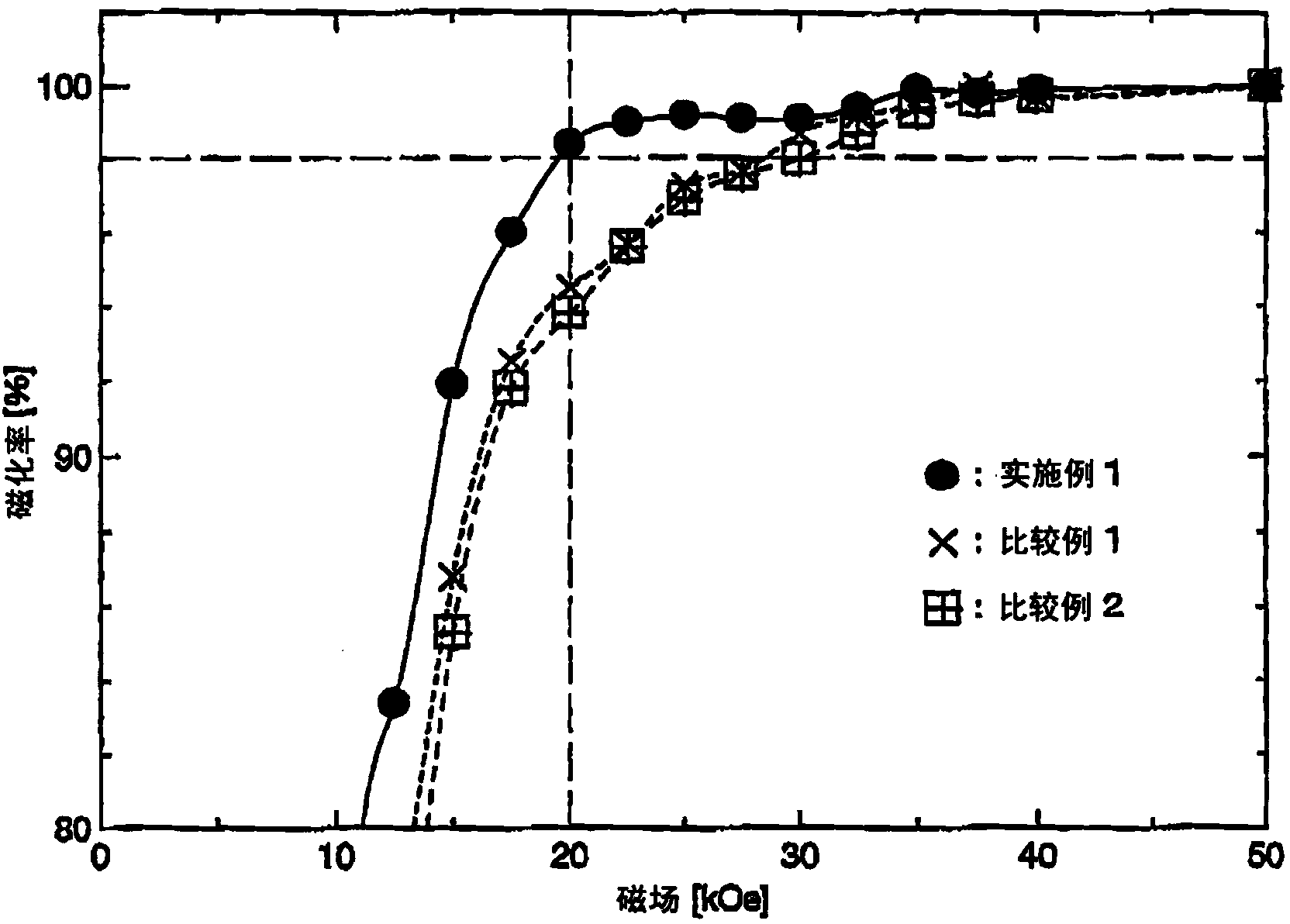
InactiveCN104078179AFully magnetizedChemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationRare-earth elementAlloy
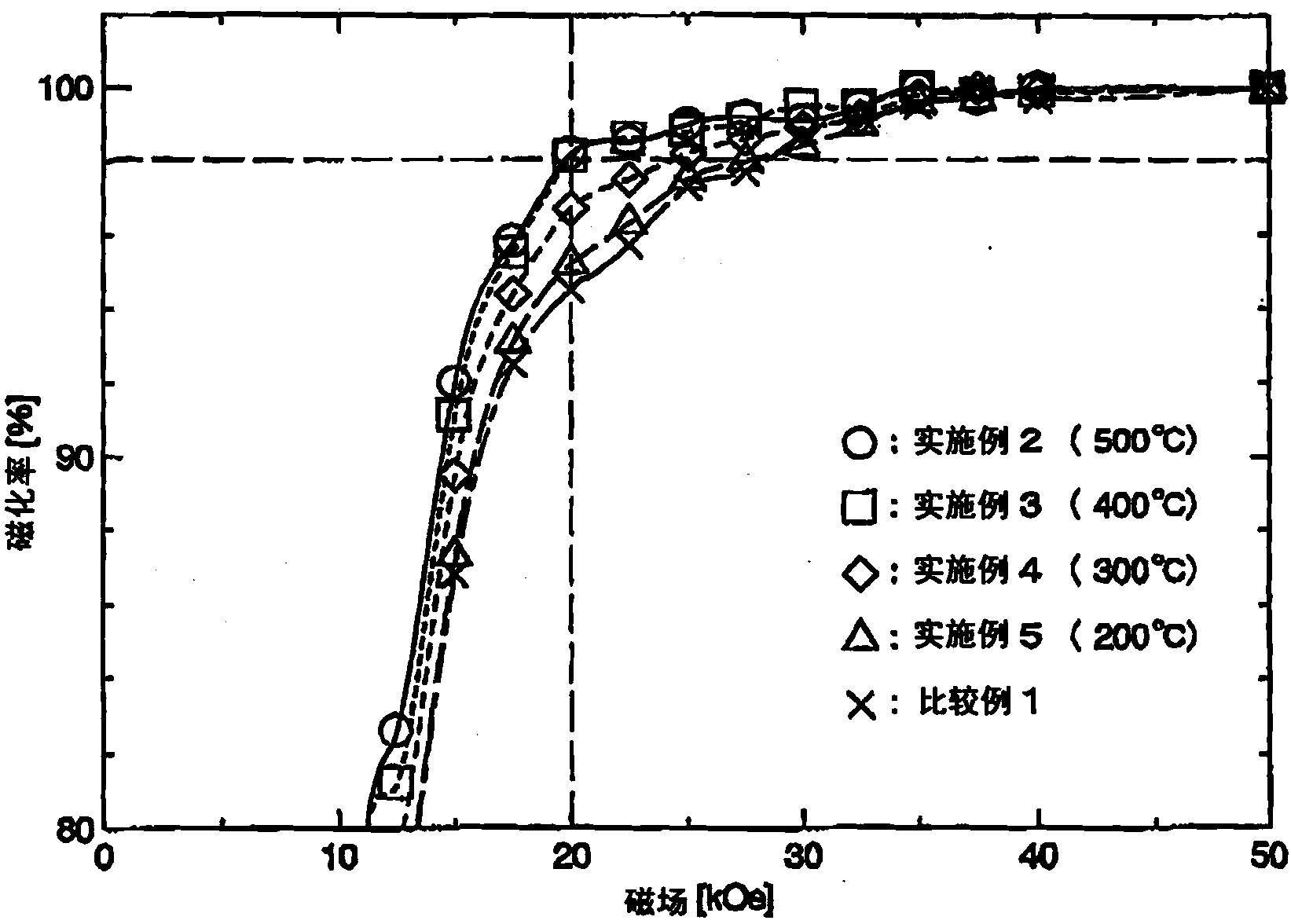
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a RFeB-based magnet, as a rare earth element R, a light rare-earth element RL, namely, Nd and / or Pr. The method comprises: a step of preparing a pre-magnetized substrate for a RFeB-based magnet from raw material alloy powder of a RFeB-based magnet, with an average particle diameter of less than 5[mu]m; a step of grain boundary diffusion treating by heating the pre-magnetized substrate to a predetermined temperature in a state in which a deposit with a heavy rare-earth element RH, which is Tb, Dy and / or Ho is applied to a surface of the pre-magnetized substrate; a step of machining precision of the pre-magnetized substrate after the grain boundary diffusion treatment to obtain the pre-magnetized substrate in the shape of the final product, thereby producing a precision-worked body; and a step of post-precision-machining heating of a precision-worked body at a temperature of 200 to 900 DEG C.
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
Heat treatment apparatus
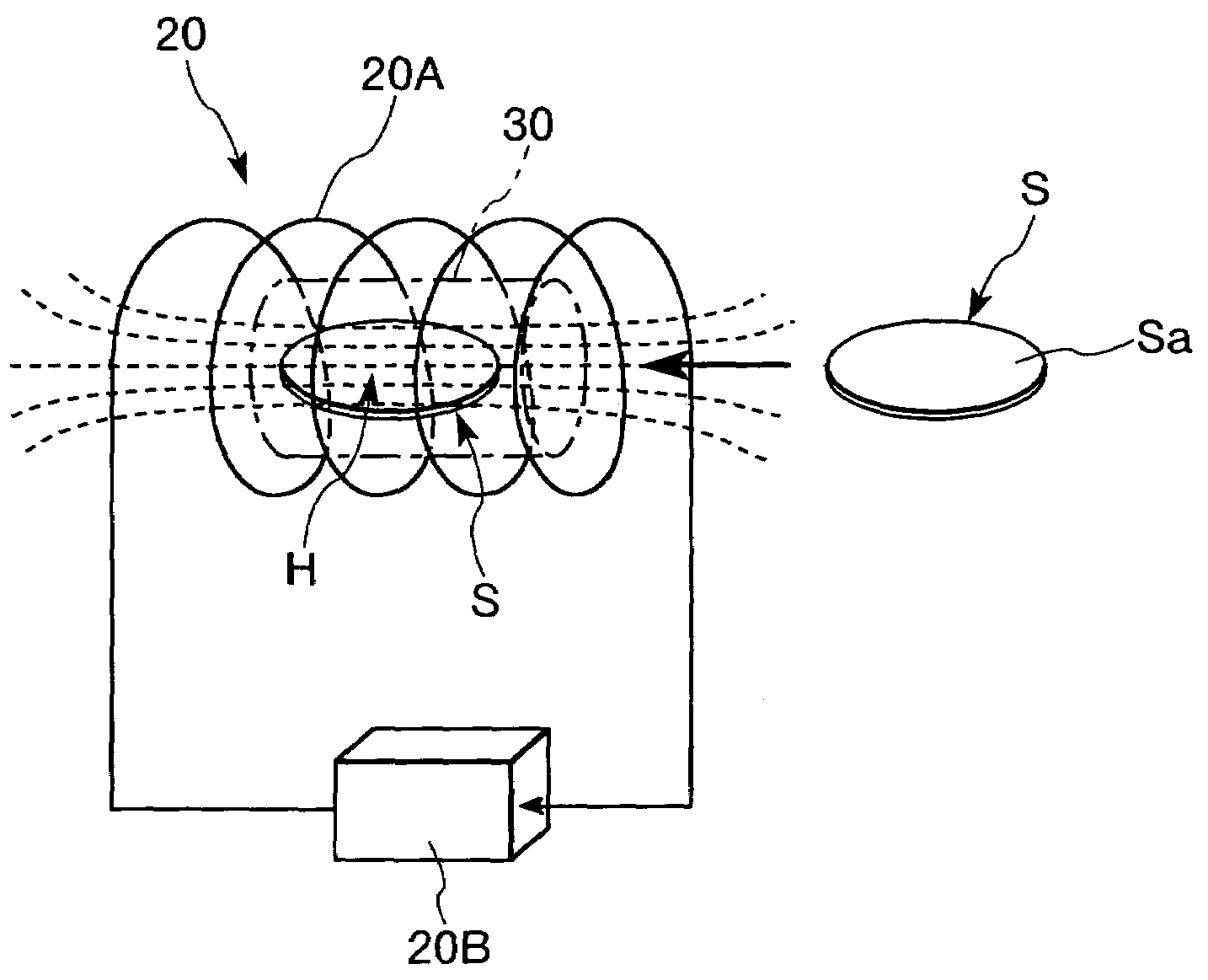
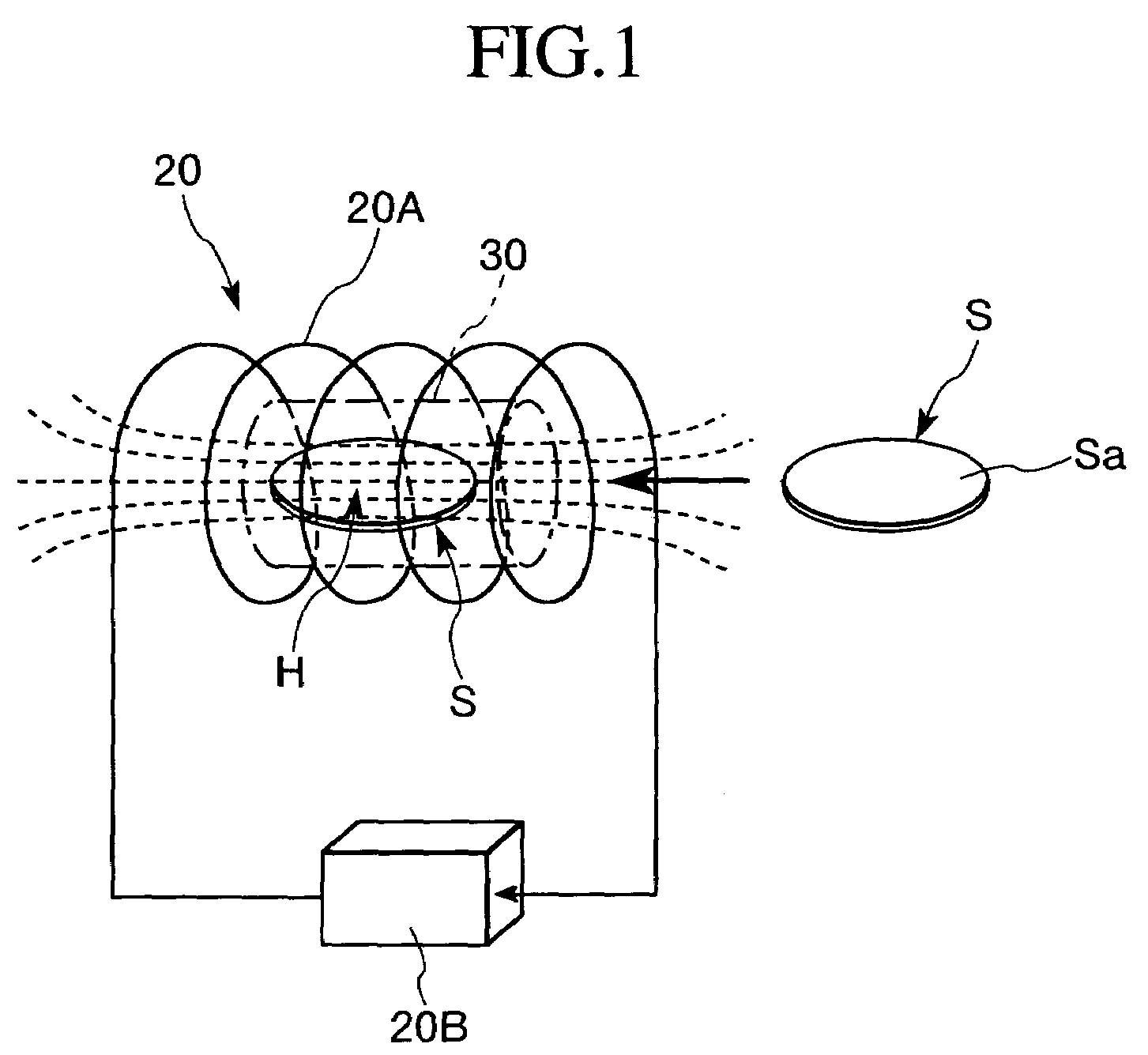
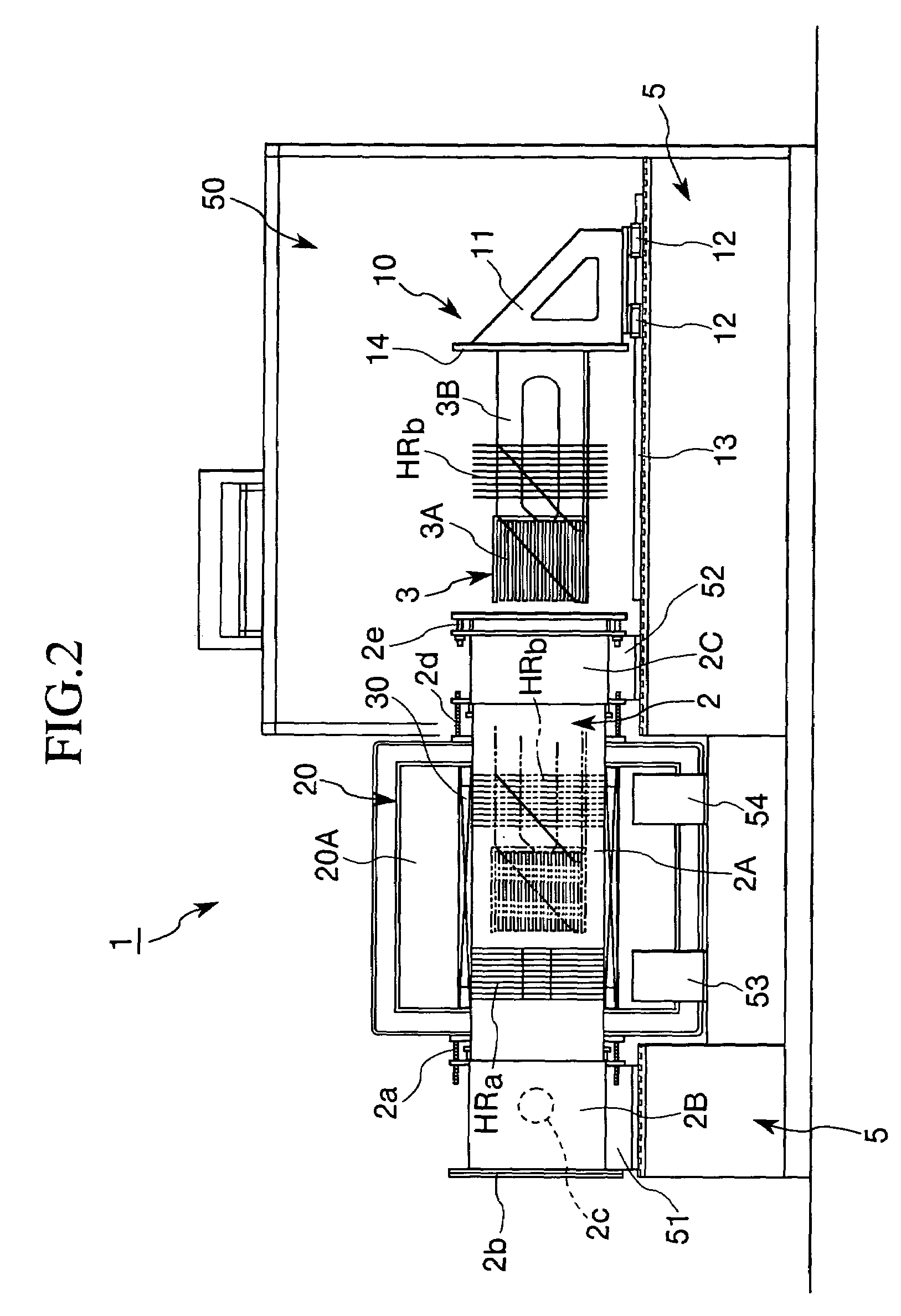
ActiveUS7179416B2Simple configurationSaving of weight and heightChemical vapor deposition applicationMuffle furnacesHeat treatedPhysics
In a heat treatment apparatus, the direction of the magnetic field generated by the magnetic field generating device in the region in which the object of treatment is heat-treated and the conveying direction of the conveying device in which the object of treatment is conveyed into the heat treatment vessel are in parallel with each other, and are in parallel with the horizontal direction of the entire heat treatment apparatus. The object of treatment is heat-treated with the main surface thereof arranged in parallel with the direction of the magnetic field generated by the magnetic field generating device in the heat treatment region.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for manufacturing magnetoresistive element
InactiveUS7785662B2High purityFavorable areal resistance RANanomagnetismChemical vapor deposition applicationNoble gasMagnetization
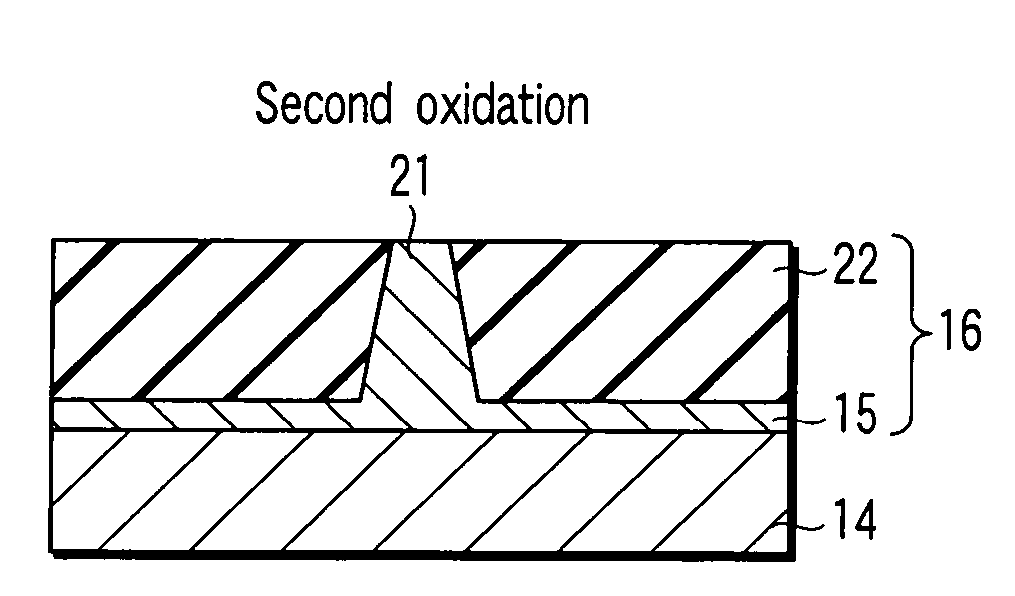
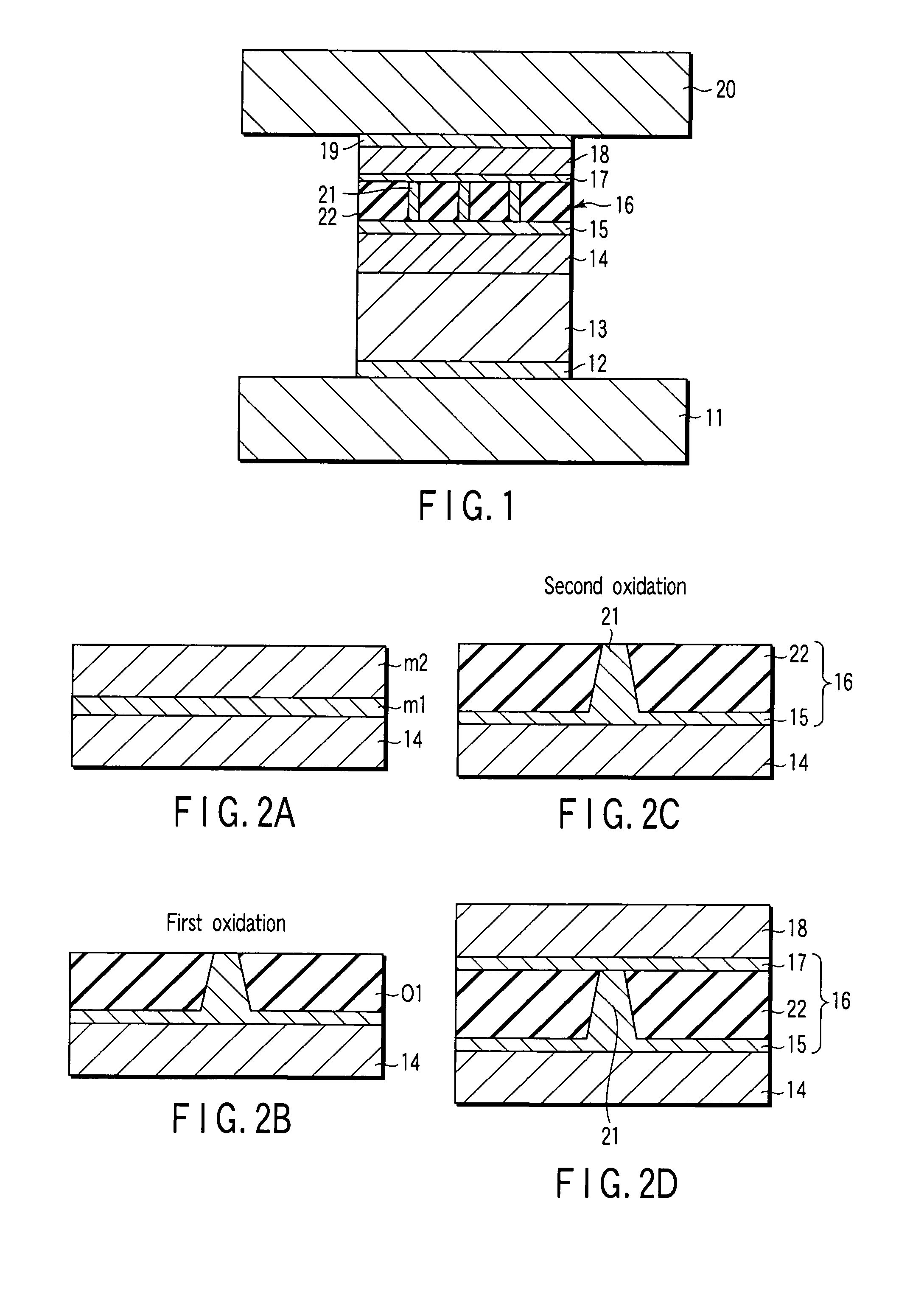
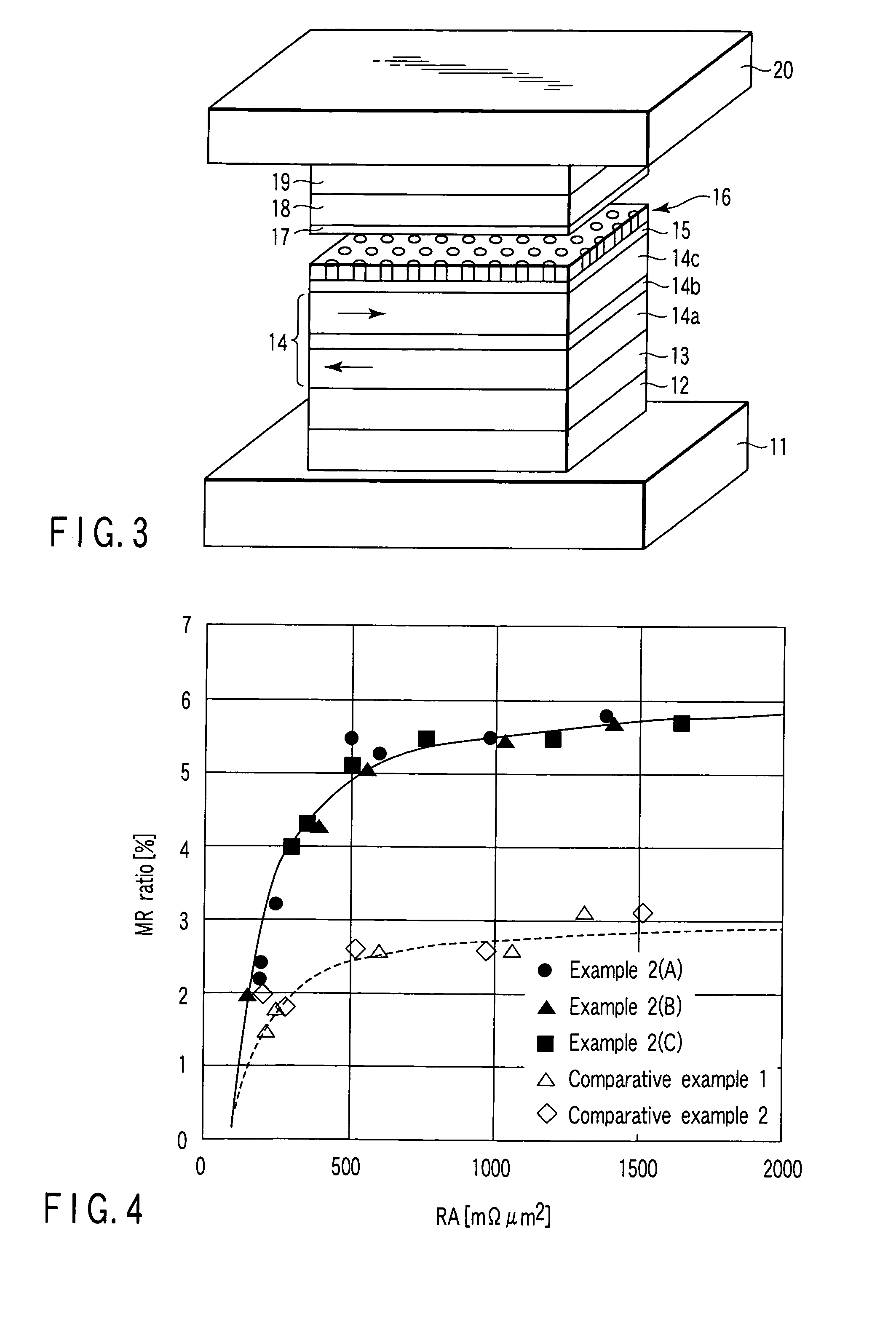
There is provided a method for manufacturing a magnetoresistive element having a magnetization pinned layer, a magnetization free layer, and a spacer layer including an insulating layer arranged between the magnetization pinned layer and the magnetization free layer and current paths passing through the insulating layer. The method includes, in producing the spacer layer, depositing a first non-magnetic metal layer forming the current paths, depositing a second metal layer to be converted into the insulating layer on the first non-magnetic metal layer, and performing two stages of oxidation treatments in which a partial pressure of an oxidizing gas in a first oxidation treatment is set to 1 / 10 or less of a partial pressure of an oxidizing gas in a second oxidation treatment, and the second metal layer being irradiated with an ion beam or a RF plasma of a rare gas in the first oxidation treatment.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
System having a TMR sensor with leads configured for providing joule heating
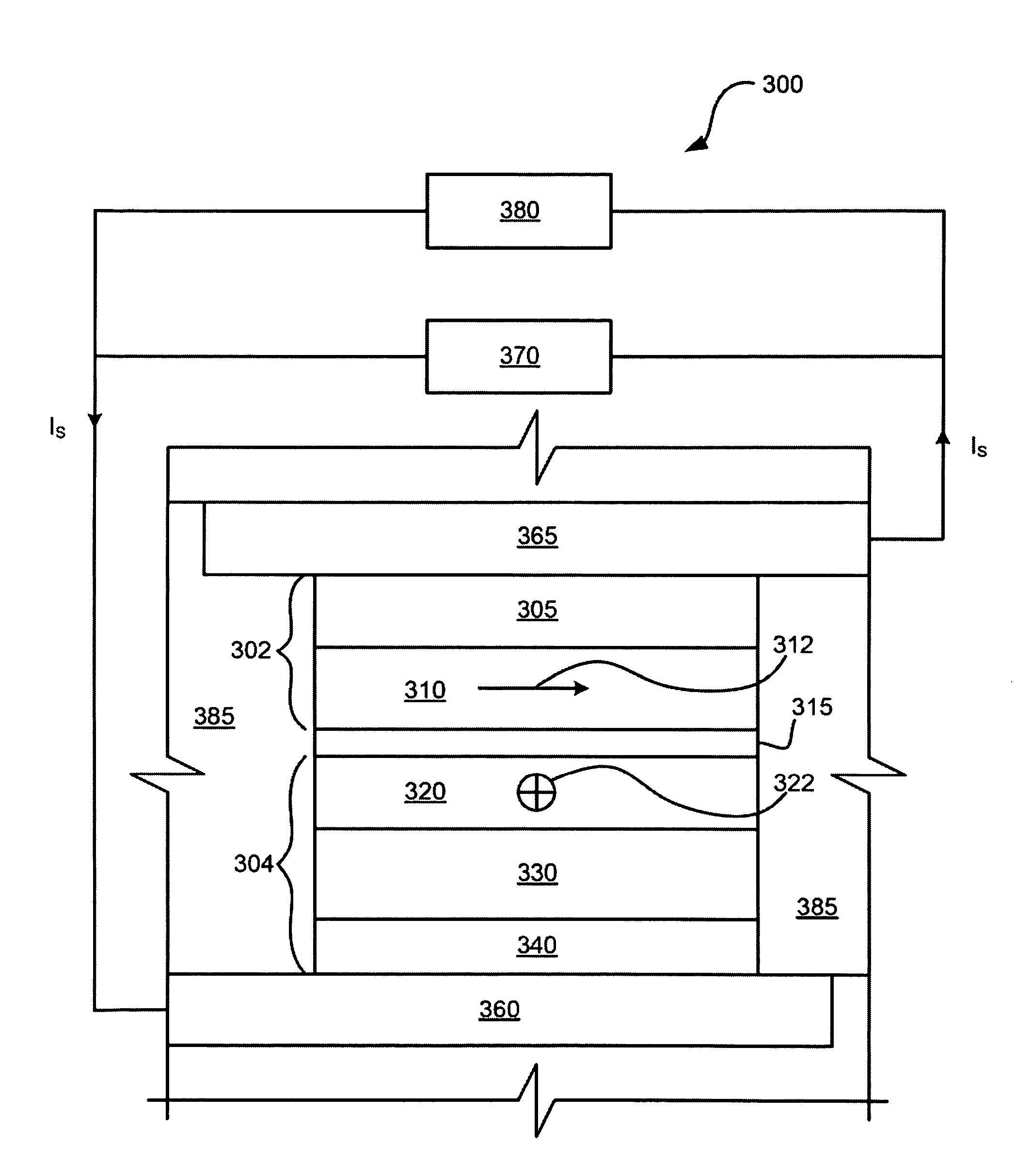
A method in one embodiment includes applying a current to a lead of a tunneling magnetoresistance sensor for inducing joule heating of the lead or a heating layer, the level of joule heating being sufficient to anneal a magnetic layer of the sensor; and maintaining the current at the level for an amount of time sufficient to anneal the tunneling magnetoresistive (TMR) sensor. A system in one embodiment comprises a first lead coupled to one end of a tunneling magnetoresistance sensor stack; a second lead coupled to another end of the sensor stack; and a third lead coupled to the first lead, the third lead being selectively coupleable to a ground, wherein a current applied to the first lead at a predetermined level when the third lead is coupled to the ground induces joule heating of the first lead or a heating layer coupled to the first and third leads, the joule heating applied for a predetermined amount of time being sufficient to anneal a magnetic layer of the sensor. Additional systems and methods are also presented.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor memory device utilizing tunnel magneto resistive effects and method for manufacturing the same
There is provided, according to one embodiment of this invention, a semiconductor memory device including first memory elements to store a first state or a second state according to a change in resistance value, each of the first memory elements including one terminal and the other terminal, the first memory elements arranged parallel with each other, a first wiring connected with the one terminal of each of the first memory elements, and a second wiring formed in parallel with the first wiring and connected with the other terminal of each of the first memory elements, wherein the first state or the second state stored in one of selected from the first memory elements is read out by delivering an electric current from one of the first and second wirings via the one of selected from the first memory elements to the other of the first and second wirings.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for improving magnet coercive force
ActiveCN105070498AImprove coercive forceReduce manufacturing costChemical vapor deposition applicationLiquid applicationRare-earth elementHeat treated
Owner:BAOTOU TIANHE MAGNETICS TECH CO LTD
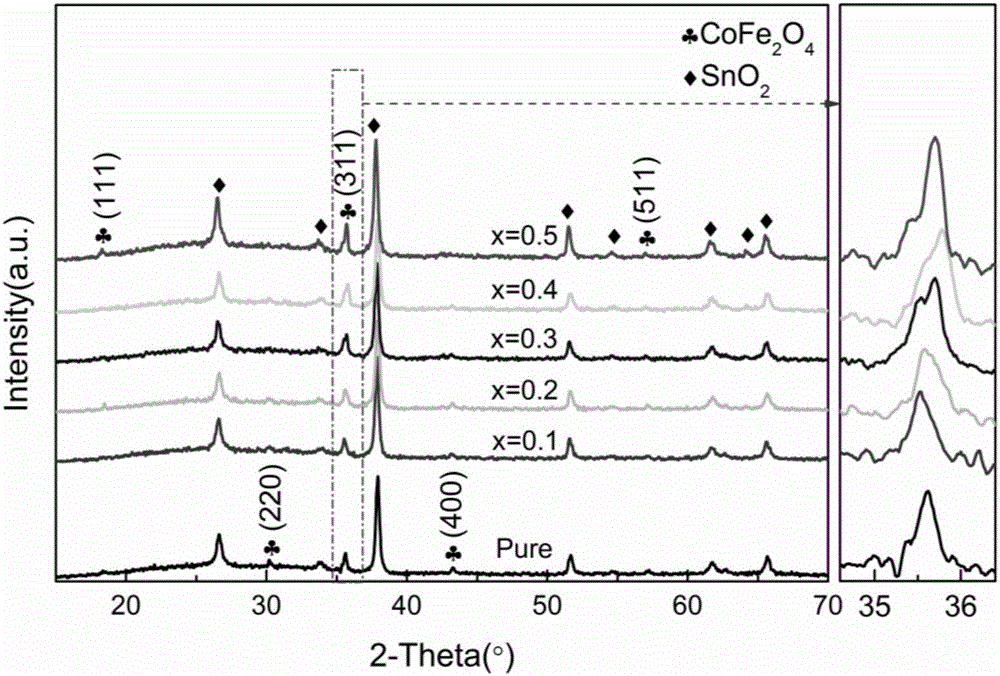
Spinel type Col-xMnxFe2O4 ferromagnetic film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105819848AHigh purityImprove uniformityChemical vapor deposition applicationLiquid applicationMANGANESE ACETATEAcetic anhydride
The invention provides a spinel type Col-xMnxFe2O4 ferromagnetic film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving cobalt nitrate, manganese acetate and ferric nitrate into ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetic anhydride according to the mole ratio of (1-x): x: 2, wherein x ranges from 0.1 to 0.5, and conducting stirring, so that a Co1-xMnxFe2O4 precursor solution is obtained; preparing the spinel type Col-xMnxFe2O4 ferromagnetic film which is high in compactness and uniform in grain size and grows in the preferred orientation of a (311) crystal face on a substrate through a spin-coating method and a layer-by-layer annealing process. According to the spinel type Col-xMnxFe2O4 ferromagnetic film and the preparation method thereof, a sol-gel process is adopted, the equipment requirement is simple, it is easy to meet the experiment conditions, the film is suitable for large-area film formation, chemical components are precise and controllable, and ferromagnetic performance of the Col-xMnxFe2O4 ferromagnetic film can be regulated and controlled through the doping amount of the Mn element.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
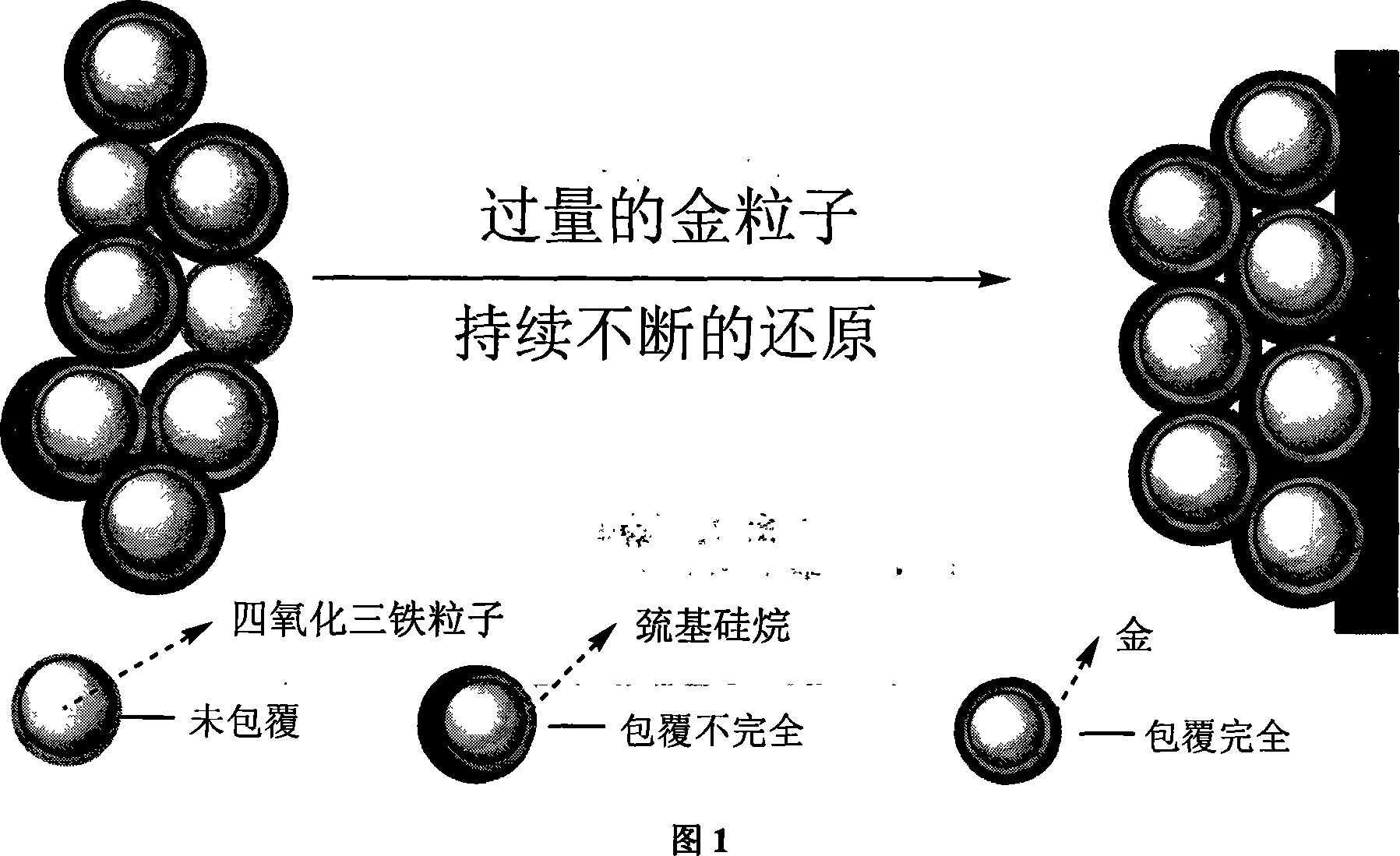
Fe3O4 Au magnetic deposition film preparation method
InactiveCN101145425AAchieve preparationLow costChemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationNanometreMetal
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing Fe3O4-Au magnetic deposited thin film. The method is characterized in that the sample is prepared by continuously reducing metal ions onto the amino- or sulfhydryl-functionalized magnetic nano-particles by using a wet chemistry method. The method can produce the Fe3O4-Au magnetic deposited thin film with rapidness and visualization, and is the novel method with easy operation, rapidness, high yield and good application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH +3
Magnetic thin film, magnetoresistance effect device and magnetic device using the same
InactiveUS20090015969A1Large capacityIncrease speedNanomagnetismChemical vapor deposition applicationGiant magnetoresistanceValence electron
Magnetic thin film having high spin polarizability and a magnetoresistance effect device and a magnetic device using the same, provided with a substrate (2) and Co2MGa1-xAlx thin film (3) formed on the substrate (2), the Co2MGa1-xAlx thin film (3) has a L21 or B2 single phase structure, M of the thin film is either one or two or more of Ti, V, Mo, W, Cr, Mn, and Fe, an average valence electron concentration Z in M is 5.5≦Z≦7.5, and 0≦x≦0.7, shows ferromagnetism at room temperature, and can attain high spin polarizability. A buffer layer (4) may be inserted between the substrate (2) and the Co2FexCr1-xAl thin film (3). The tunnel magnetoresistance effect device and the giant magnetoresistance effect device using this magnetic thin film can attain large TMR and GMR at room temperature under the low magnetic field.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
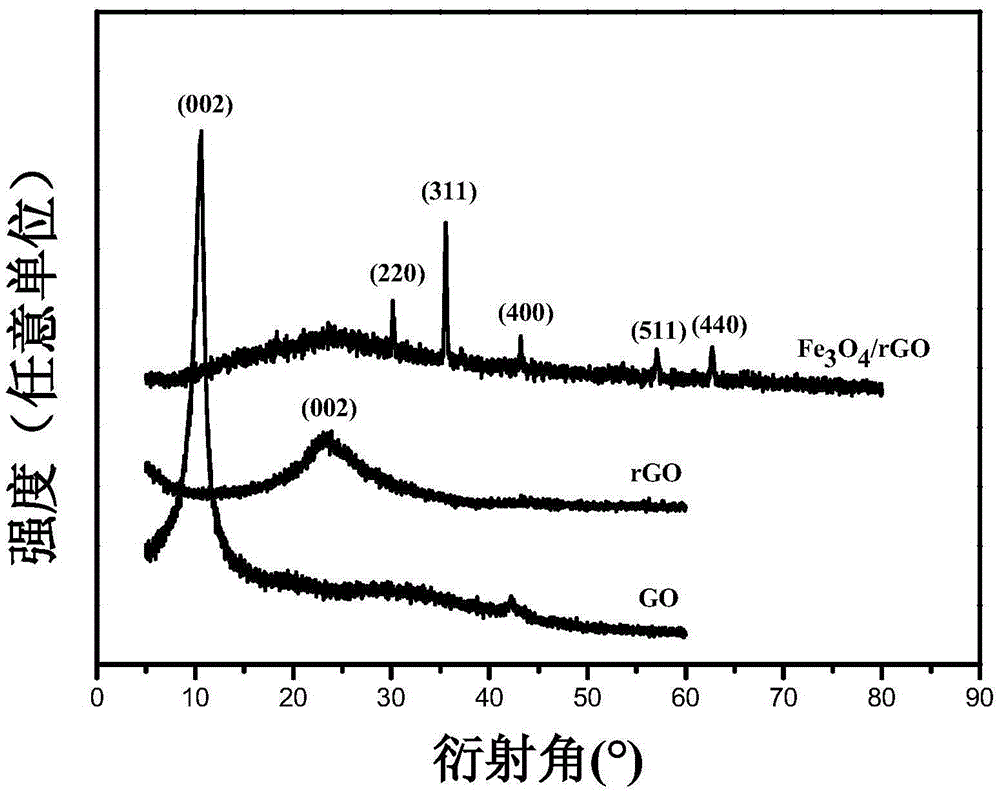
Preparation method of Fe<3>O<4>/graphene composite membrane
InactiveCN105609305ALow costUniformity controllableNanostructure applicationChemical vapor deposition applicationGrapheneElectron
The invention relates to a preparation method of an Fe<3>O<4> / graphene composite membrane. In summary, according to the method, by the process of mixing graphene oxide with Fe<3>O<4> nano-particles at a certain ratio to obtain a mixture solution, the Fe<3>O<4> / graphene composite membrane is prepared under drying and low-temperature stepped heating reduction conditions. The product prepared by the method is good in complex condition; the Fe<3>O<4> nano-particles are uniform to disperse; and the composite membrane has ferromagnetic property. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to control; industrial production is facilitated; and the prepared self-supported composite membrane has a broad application prospect in the fields of information, electrons, energy, biology, military industry and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for fabricating L10 phase alloy film
InactiveUS20060021871A1Chemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationRoom temperatureAlloy
A method for fabricating an L10 alloy film is provided. The method includes steps of (a) providing a substrate; (b) heating the substrate as a preheated substrate at a first temperature ranged from 100° C. to 600° C. for a time period ranged from 5 minutes to 120 minutes, and then cooling the substrate to room temperature in the sputtering chamber; (c) depositing an alloy film on the preheated substrate; and (d) annealing the alloy film at a second temperature ranged from 200° C. to 500° C. to form the alloy film.
Owner:CHANG CHING RAY
Method for increasing coercive force of magnets
ActiveUS20170062103A1Improve coercive forceImprove remanenceChemical vapor deposition applicationLiquid applicationRare-earth elementLutetium
The present invention provides a method for improving coercive force of magnets, this method comprises steps as follows: S2) coating step: coating a coating material on the surface of a magnet and drying it; and S3) infiltrating step: heat treating the magnet obtained from the coating step S2). The coating material comprises (1) metal calcium particles and (2) particles of a material containing a rare earth element; the rare earth element is at least one selected from Praseodymium, Neodymium, Gadolinium, Terbium, Dysprosium, Holmium, Erbium, Thulium, Ytterbium and Lutetium. The method of the present invention can significantly increase coercive force of a permanent magnet material, while remanence and magnetic energy product hardly decrease. In addition, the method of the present invention can significantly decrease the amount of a rare earth element, and accordingly, decrease the production cost.
Owner:BAOTOU TIANHE MAGNETICS TECH CO LTD
Magnetic sheet and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20140134401A1Improve productivityReduce manufacturing costChemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationPliabilityEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Easy axis oriented FePt, CoPt vertical magnetic recording thin film preparing method
InactiveCN1845242AGood orientationGuaranteed smoothnessChemical vapor deposition applicationMagnetic field orientationOptoelectronicsThermal treatment
The invention relates to a method for preparing the FePt, CoPt vertical magnetic record film, wherein said method comprises: (1) preparing FePt (M) or CoPt (M) film whose crystal is cubic, while M is one of C, P, B non-metal elements or one of Ag, Cu, Sn, Pb, Bi, Ga, and In whose fusion point is lower than Fe; (2) arranging FePt (M) or CoPt (M) film into magnetic film whose direction is vertical to the film; then processing laser thermal treatment on the film. The invention can make magnetic axle of iron magnetic crystal of film be arranged vertically to the film. And it ahs simple process and easy control, while it can confirm the film fineness.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multilayer iron nitride hard magnetic materials
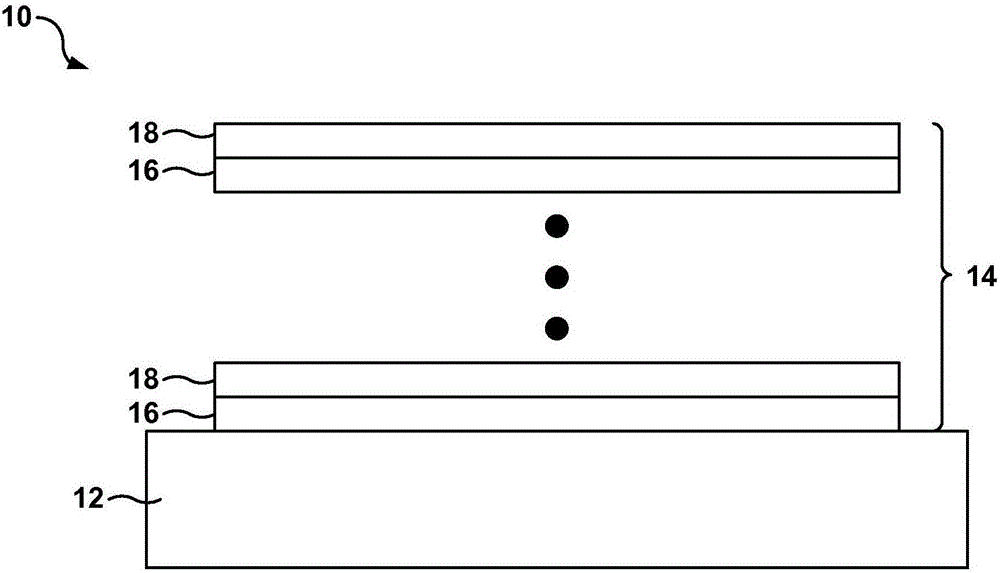
The disclosure describes multilayer hard magnetic materials including at least one layer including alpha"-Fe16N2 and at least one layer including alpha"-Fe16(NxZ1-x)2 or a mixture of alpha"-Fe16N2 and alpha"-Fe16Z2, where Z includes at least one of C, B, or O, and x is a number greater than zero and less than one. The disclosure also describes techniques for forming multilayer hard magnetic materials including at least one layer including alpha"-Fe16N2 and at least one layer including alpha"-Fe16(NxZ1-x)2 or a mixture of alpha"-Fe16N2 and alpha"-Fe16Z2 using chemical vapor deposition or liquid phase epitaxy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Layered structure, switching element, magnetic device, and method for manufacturing layered structure
InactiveCN106062901AStable magnetization orientationImprove recording densityChemical vapor deposition applicationSolid-state devicesIn planePerpendicular magnetization
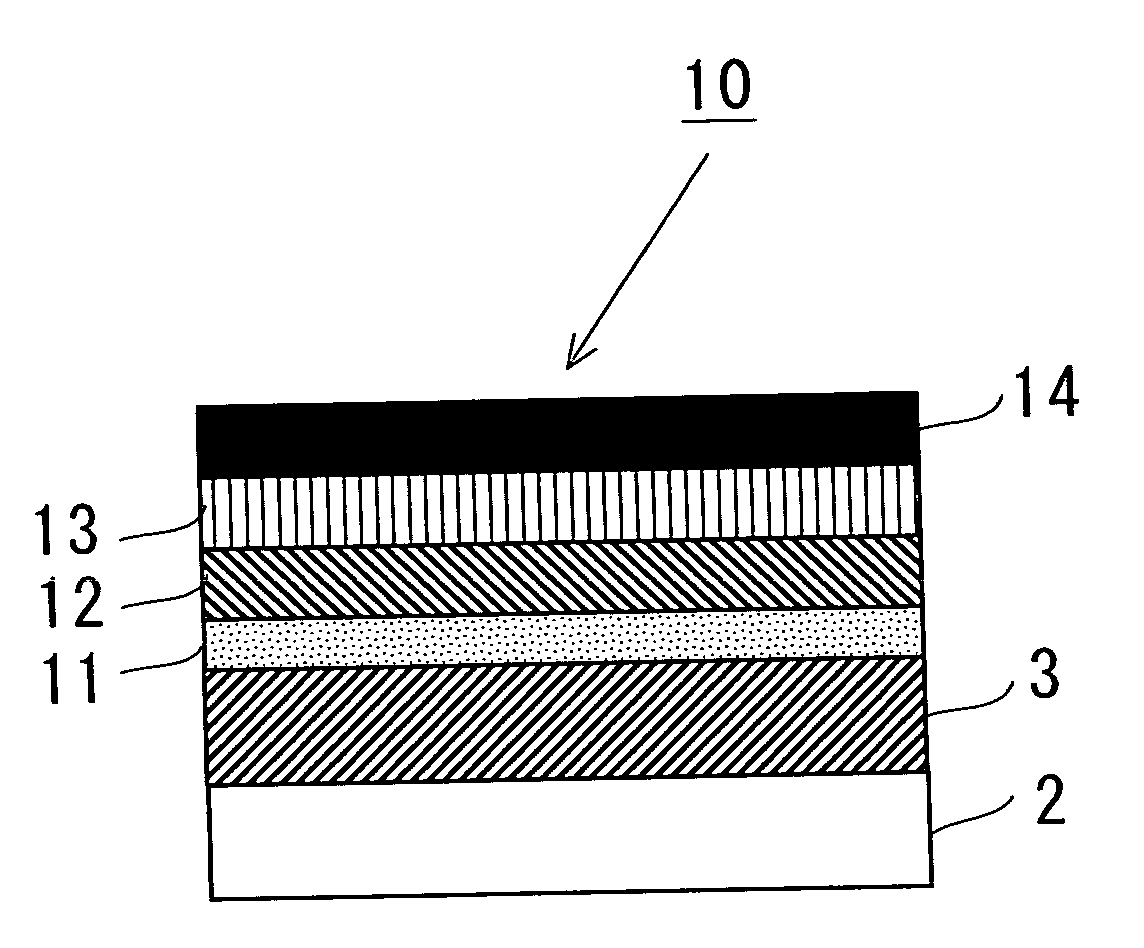
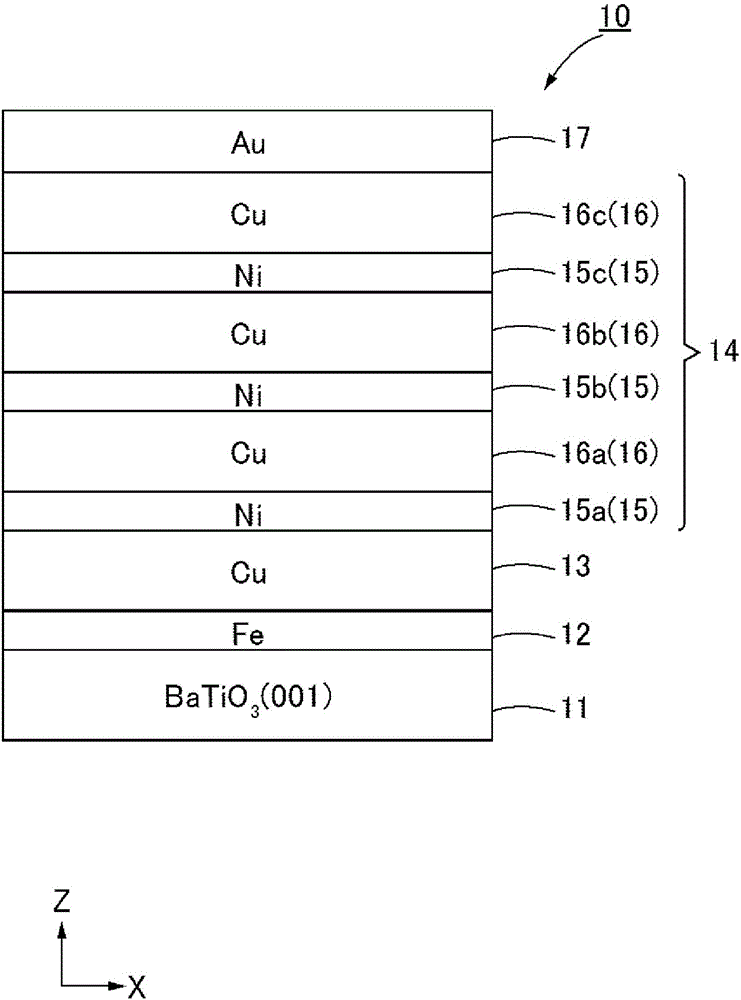
This invention produces more stable perpendicular magnetization and makes it possible to use a voltage to switch between perpendicular magnetization and in-plane magnetization. This multiferroic layered structure (10), which exhibits both ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism, is characterized by having the following: a ferroelectric layer (11) comprising a ferroelectric material that exhibits ferroelectricity; an underlayer (12) that is laminated to one surface of the ferroelectric layer and consists primarily of a metal that is lattice-matched to the aforementioned ferroelectric material; an intermediate layer (13) that is laminated to one surface of the underlayer and consists primarily of a non-magnetic material; and a ferromagnetic / non-magnetic multilayer-film layer (14) that is laminated to one surface of the intermediate layer and comprises three or more pairs of alternating ferromagnetic layers (15) each consisting primarily of a ferromagnetic material and non-magnetic layers (16) each consisting primarily of a non-magnetic material.
Owner:TOKYO INST OF TECH
Spinel-type tetragonal phase CuFe2O4 ferromagnetic film and preparation method thereof
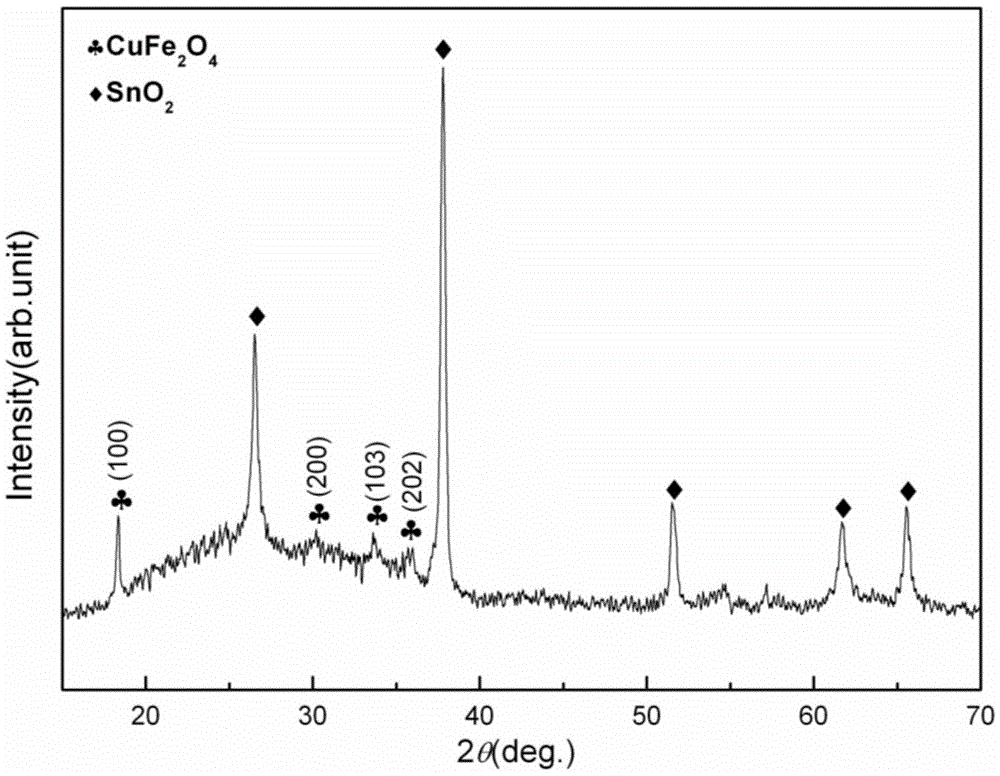
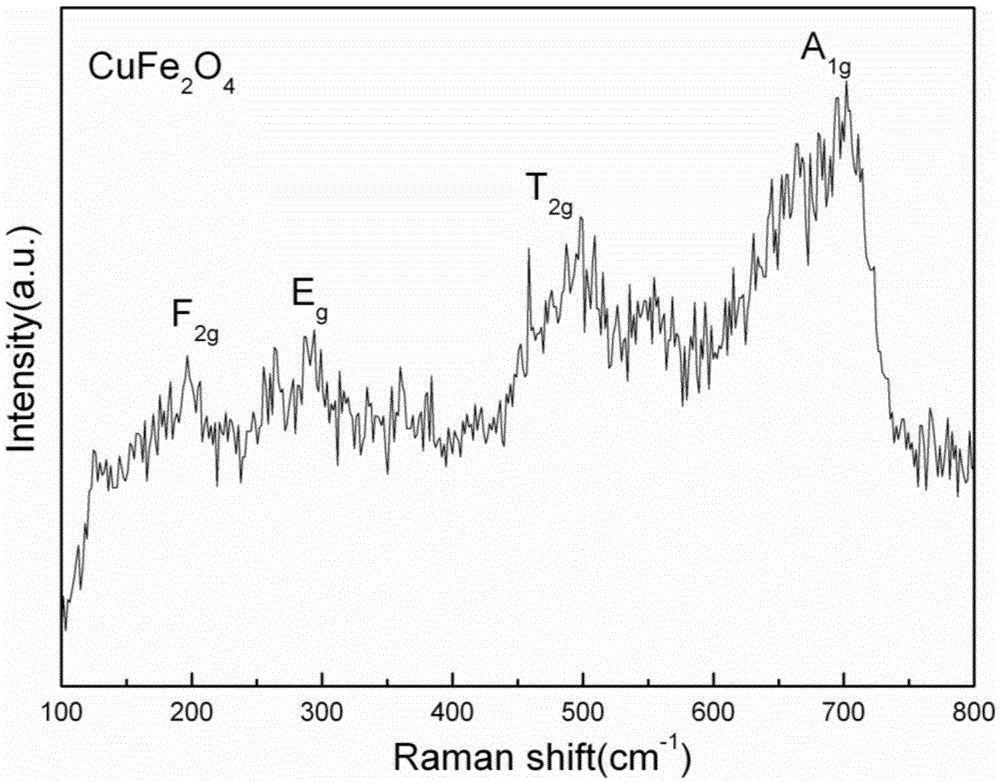
ActiveCN105632756AEasy to manufactureEasy to introduceChemical vapor deposition applicationLiquid applicationAcetic anhydrideCopper nitrate
The invention provides a spinel-type tetragonal phase CuFe2O4 ferromagnetic film and a preparation method thereof. Copper nitrate and ferric nitrate are dissolved in ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetic anhydride according to the mole ratio of 1:2, stirring is performed to obtain a uniform CuFe2O4 precursor solution, and the spinel-type tetragonal phase CuFe2O4 ferromagnetic film high in density and uniform in grain size is prepared on a substrate by adopting a spin-coating method and a step-by-step annealing process. A sol-gel process is adopted, the device requirements are simple, the film is suitable for making on large surfaces and irregular-shaped surfaces, and chemical components are precisely controllable. The saturation magnetization intensity Ms of the made spinel-type tetragonal phase CuFe2O4 ferromagnetic film is 110 emu / cm<3>, the remanent magnetization intensity Mr is 71 emu / cm<3>, and a coercive force Hc is 810 Oe.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ferromagnetic/antiferromagnetic multilayer membrane material with pinning and its preparing method
InactiveCN1845266AExchange Bias Field EnhancementMagnetically stableChemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationMultilayer membraneHeat stability
The invention relates to a preparation method for a pinning ferromagnetic / antiferromagnetic multilayer film material comprises: with the vacuum deposition coating method and reannealing technique, preparing a buffer layer, a ferromagnetic layer and an antiferromagnetic layer on the substrate in turn, or arranging an antiferromagnetic layer on the buffer layer then a ferromagnetic layer and a protective layer. Compared with prior art, in this pinning system, it introduces (Cr1-xMnx)0.5+delta Pt0.5-delta (0.3<=x<=0.6; |delta|<0.06) as pinning material with well thermal stability, large exchange offset field and super corrosion resistance. This invention is simple and fit to industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spin-valve thin-film magnetic element and method for making the same
InactiveUS7054115B2High detection sensitivityImprove heat resistanceNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMean free pathSpecular reflection
A spin-valve thin-film magnetic element includes a substrate, a composite formed thereon, and electrode layers formed on both sides of the composite. The composite includes an antiferromagnetic layer, a pinned magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic conductive layer, a free magnetic layer, a mean-free-path-extending layer, and an exchange bias layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer may be a back layer or a mirror reflective layer. The mean-free-path-extending layer extends the mean free path of spin-up conduction electrons in the spin-valve thin-film magnetic element. This spin-valve thin-film magnetic element meets trends toward a narrower track width.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Resonator structures and method of making
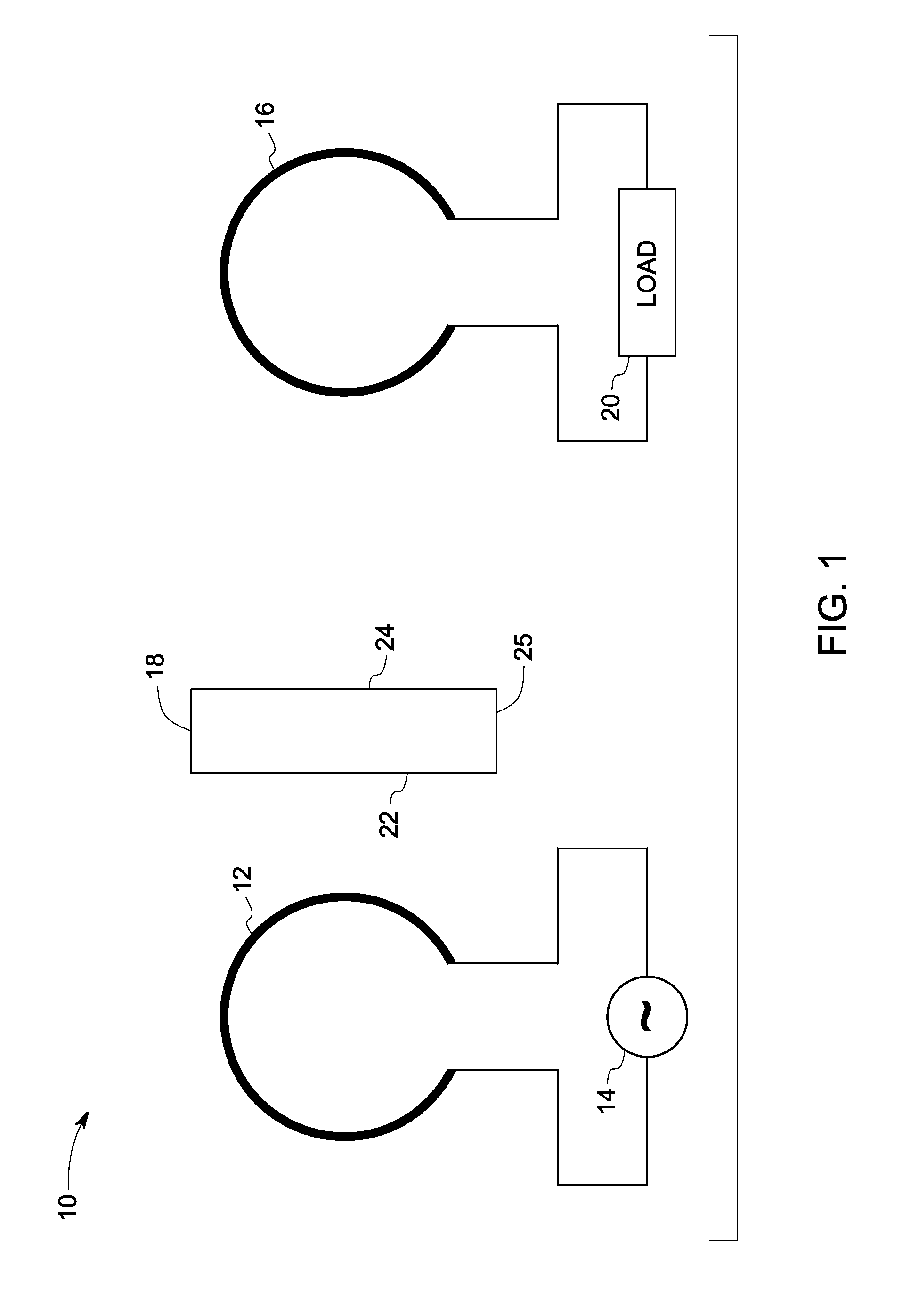
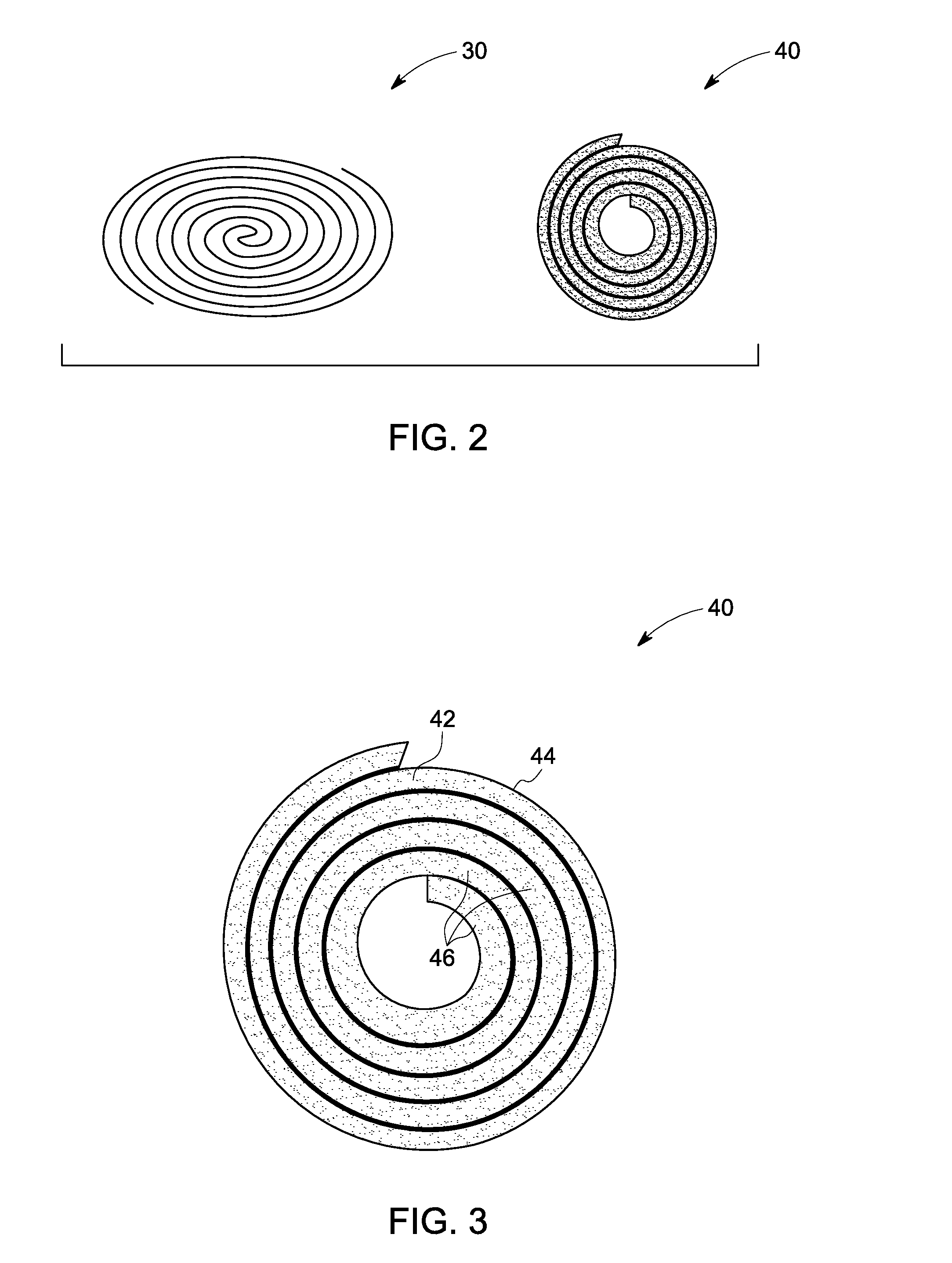
A resonator in the Swiss-roll structure, method of making the resonator structure and the system employing the resonator are disclosed. The resonator includes a plurality of layers, including a ceramic layer and a metallic layer. The ceramic and metallic layers are configured in a Swiss-roll form such that the neighboring ceramic layers are separated by the metallic layer. Further, the ceramic layer includes materials that have a dielectric constant of at least about 10 and dielectric loss tangent less than about 0.01 in the frequency range of about 1 KHz to about 100 MHz. The method of forming the resonator includes the steps of disposing a metallic layer, depositing a dielectric ceramic layer, and forming a Swiss-roll structure of the metallic and ceramic layers. Alternate method includes swaging the dielectric material filled metal tubes and forming into Swiss-rolls. Further steps include heat treating the resultant Swiss-roll structure in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or reducing atmosphere to form a monolithic Swiss-roll structure, such that the air gap between turns of the Swiss-roll structure is less than about 1 μm.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Praseodymium- iron- co-doped strontium titanate multiferroic film and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN103833353ASimple preparation processLow costChemical vapor deposition applicationHeat treatment applicationOxideTitanate
A praseodymium- iron- co-doped strontium titanate multiferroic film and a preparation process thereof are disclosed. The strontium titanate film comprises a material the formula of which is Sr[1-x]PrxTi[1-y]FeyO3, wherein 0.025<=x<=0.075, and 0.05<=y<=0.3. The preparation process includes: weighing strontium acetate, praseodymium oxide, butyl titanate and ferric nitrate according to the molar ratio in the formula, dissolving the strontium acetate and the butyl titanate with acetic acid and ethylene glycol monomethyl ether in two steps, dissolving the ferric nitrate with the ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, reacting concentrated nitric acid with the praseodymium oxide, mixing to form a solution C having a concentration of 0.2 mol / L, whirl-coating the solution C in a whirl coating machine, drying and performing thermal decomposition until the film thickness reaches 300 nm, and annealing to obtain the Sr[1-x]PrxTi[1-y]FeyO3 film. Ferroelectricity and magnetism of strontium titanate, which are induced by praseodymium- iron- co-doping, occur around the room temperature. Preparation of a novel single-phase multiferroic material is achieved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic sensing element including a pair of antiferromagnetic layers separated by spacer section in track width direction and method for fabricating same
InactiveUS7212383B2Easily and properly fabricatedSide reading can be preventedChemical vapor deposition applicationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsCrystal structureMolecular physics
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Popular searches
Thermal decomposition application Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Record information storage Digital storage Substrate/intermediate layers Spin-exchange-coupled multilayers Galvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatment Magnetic layers Semiconductor devices Conductive/insulating/magnetic material on magnetic film application
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com