Patents
Literature
49results about How to "Increased tensile strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
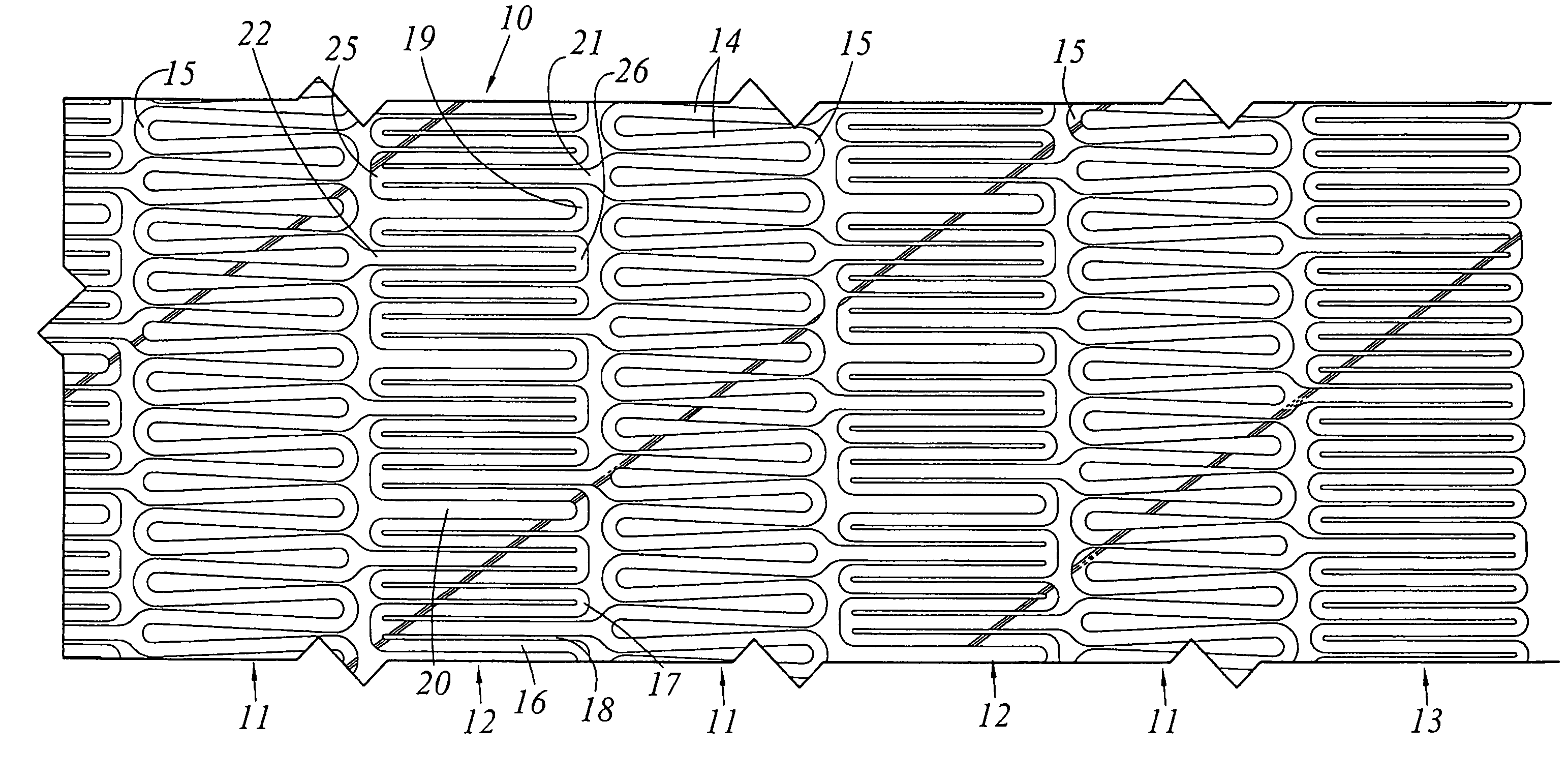
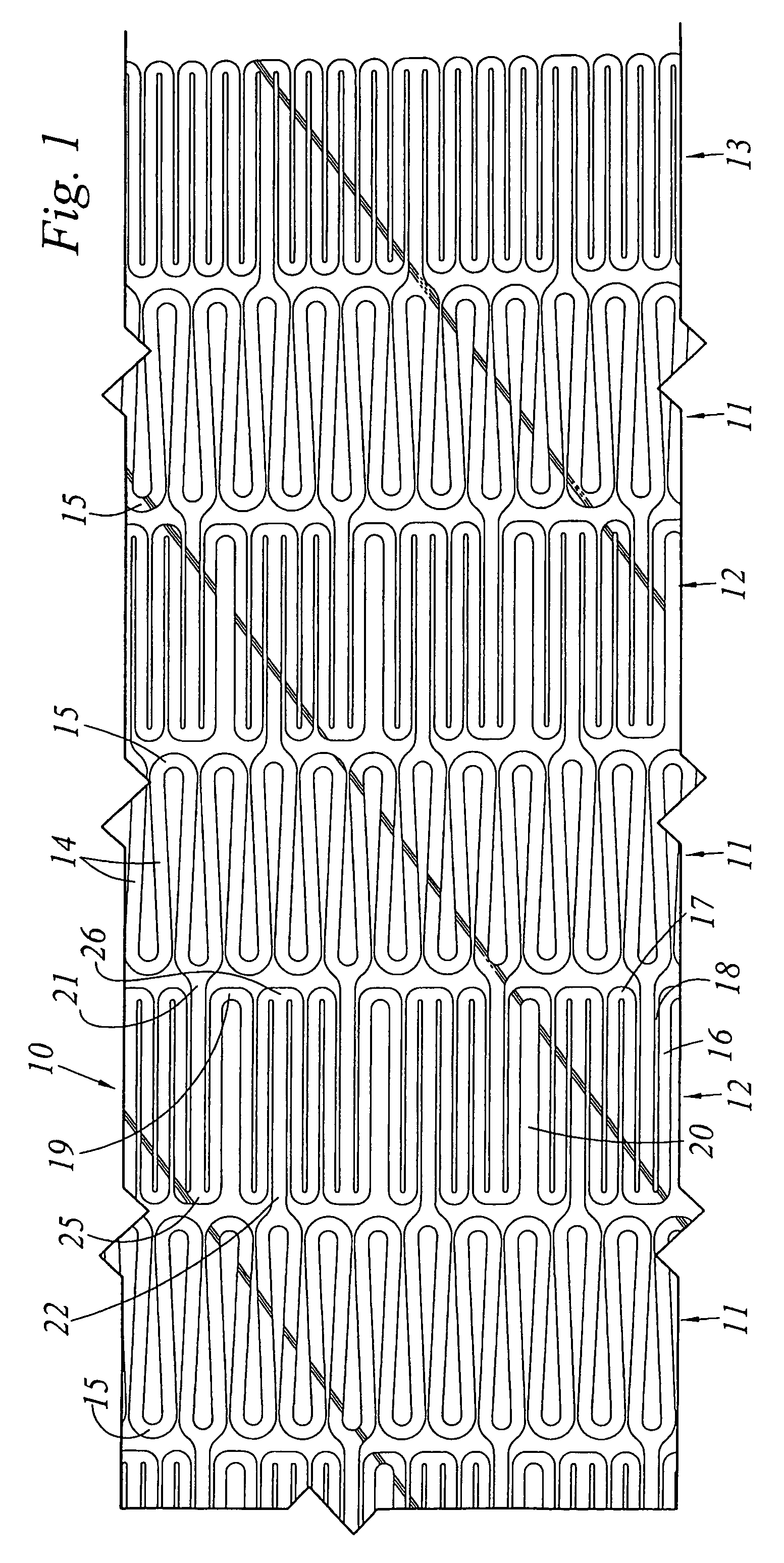
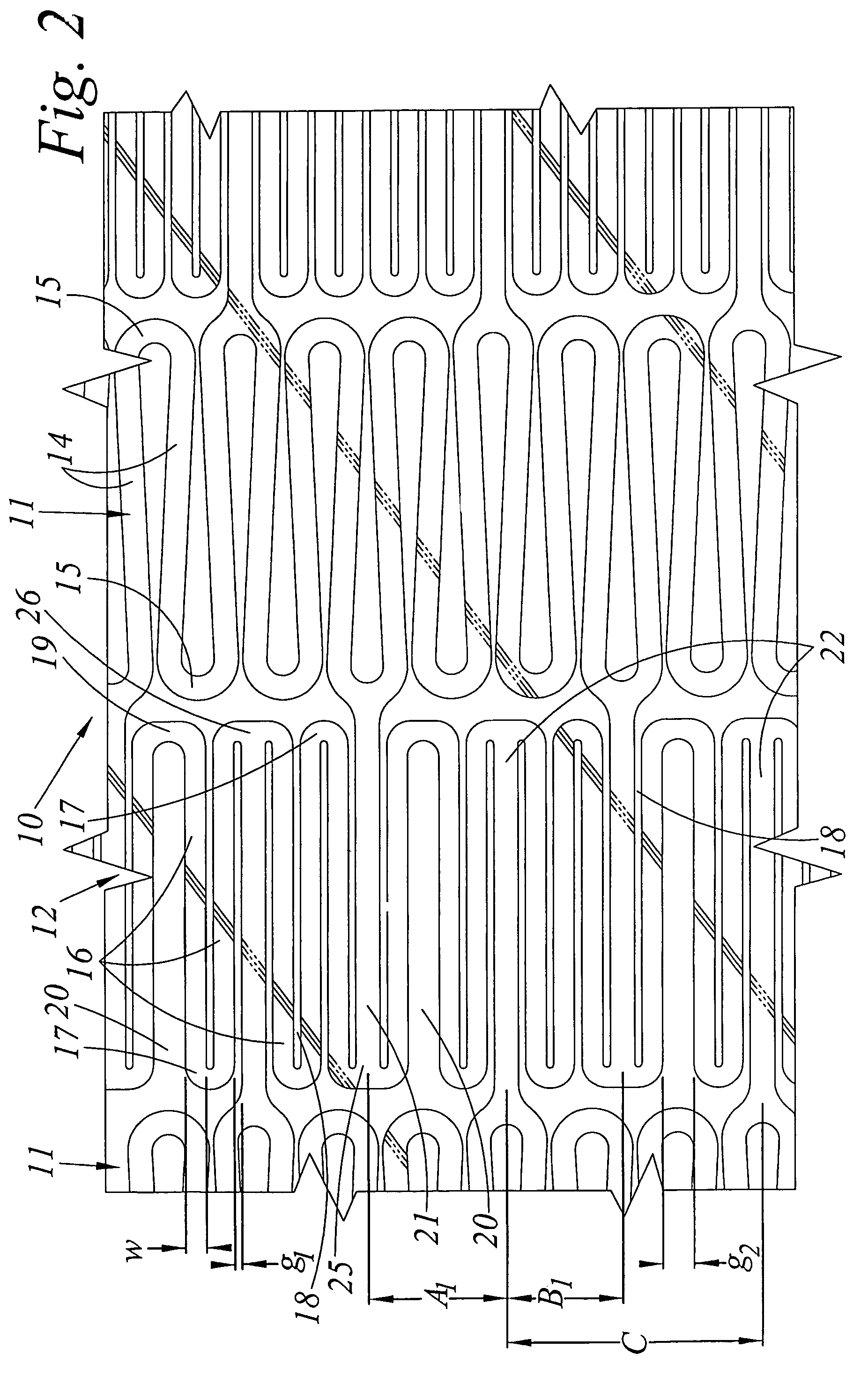
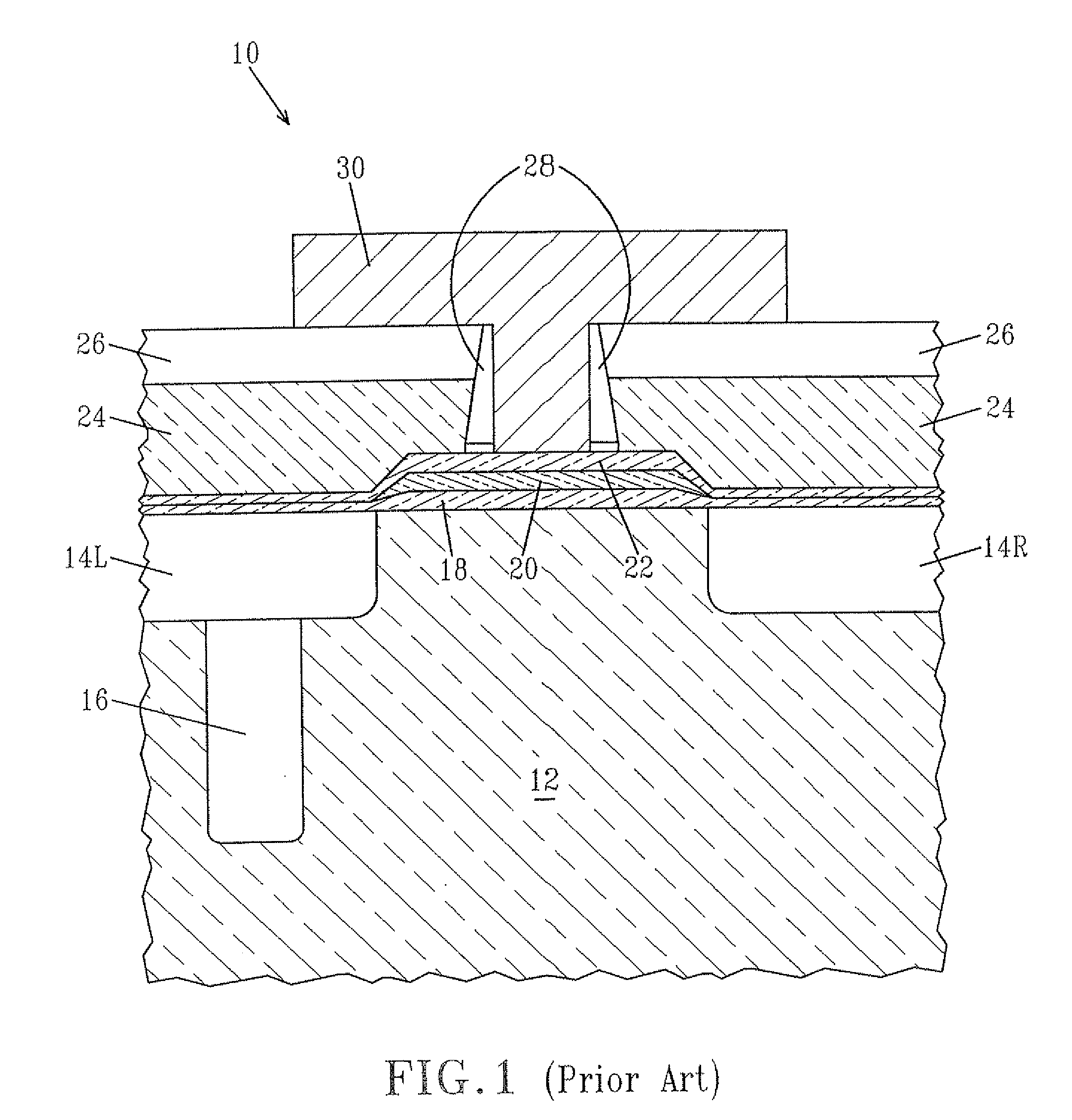
Cannula stent
ActiveUS7172623B2Optimize allocationIncreasing selected widthStentsBlood vesselsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A stent (30) formed from cannula and having flexible segments (31) and high hoop strength segments (32) alternating therealong. Longitudinal struts or tie bars (41) interconnect the segments. Minimal length reduction of the strut occurs upon expansion. In the high hoop strength segment (32), struts (37) in a zig-zag configuration (Gianturco Z-stent) are initially parallel in the unexpanded strut condition. In the flexible segment (31), struts (58) extend from a respective C-shaped bend (59) to converge at the opposite ends thereof when unexpanded. In one embodiment, certain adjacent struts (39–41) of the hoop segment are spaced apart by elongated openings or gaps (46, 48) interposed therebetween and interconnected at their respective ends (42, 44) to form a T-shaped strut interconnection (45). The selected width (50, 51) of the first and third struts (54, 57) increases toward the ends (47, 48) of the elongated openings (46, 48) adjacent the strut interconnection (45). This strut width increase about one end of the strut significantly reduces the tensile strain exhibited about the opening end when the stent is radially expanded during manufacture. The tip length (52, 55) of the struts about the interconnection (45) is also adjusted (increased) along with the other C-shaped strut interconnections (59, 71) to further distribute the tensile strain developed during radial expansion.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
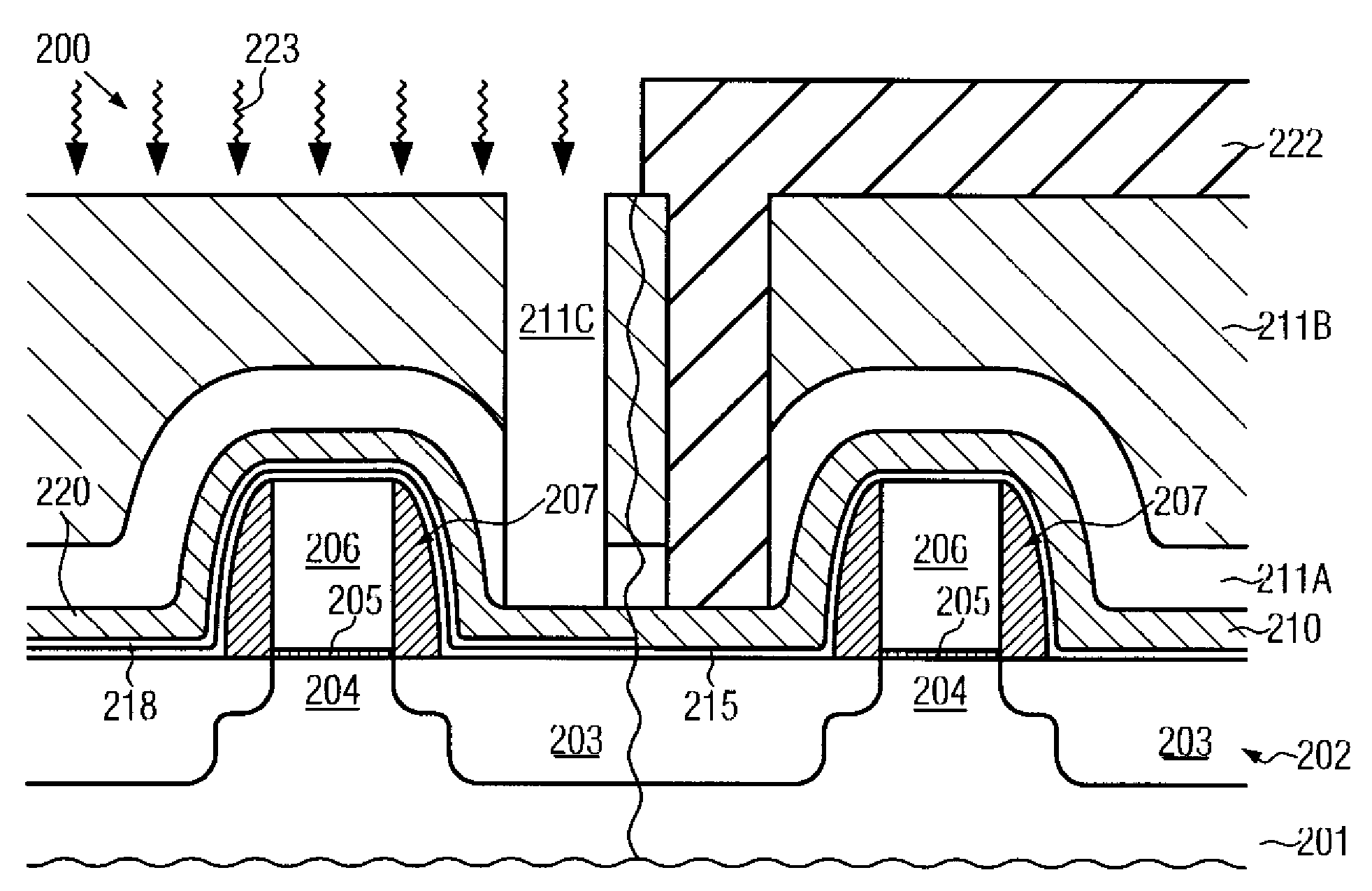
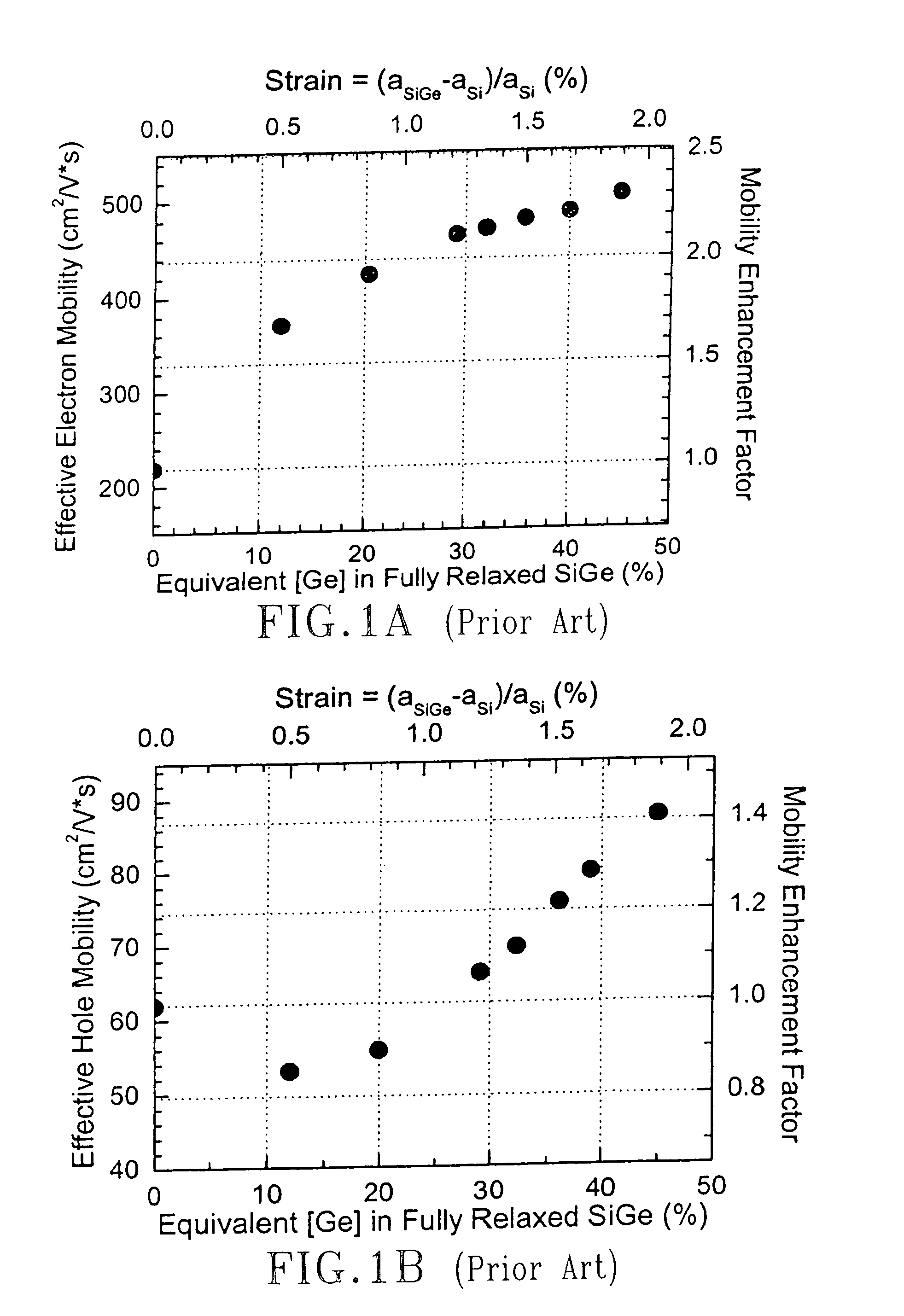
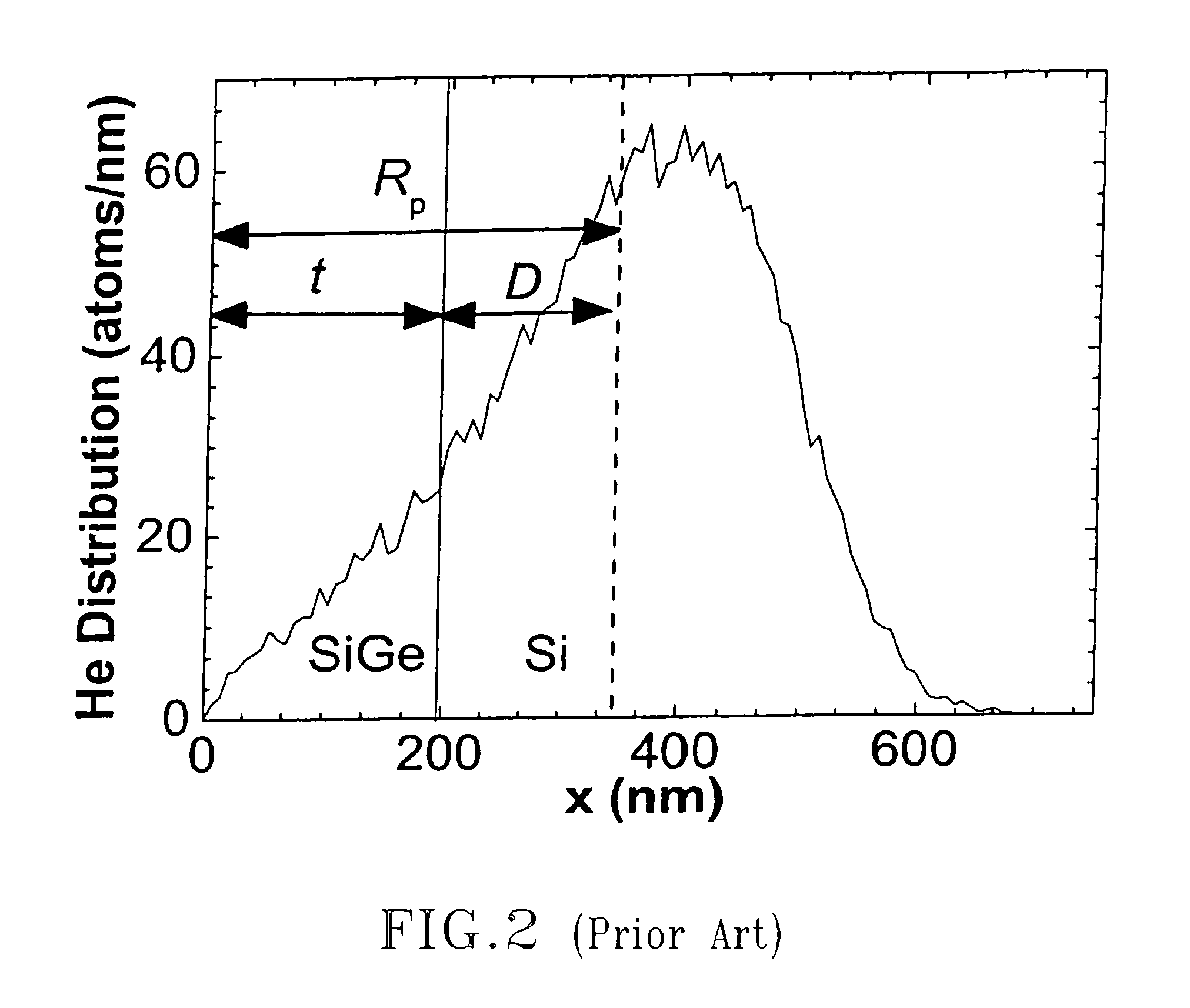
Hetero-integrated strained silicon n-and p-MOSFETs
InactiveUS20060091377A1Prevent implantationReduce processing stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETSemiconductor structure
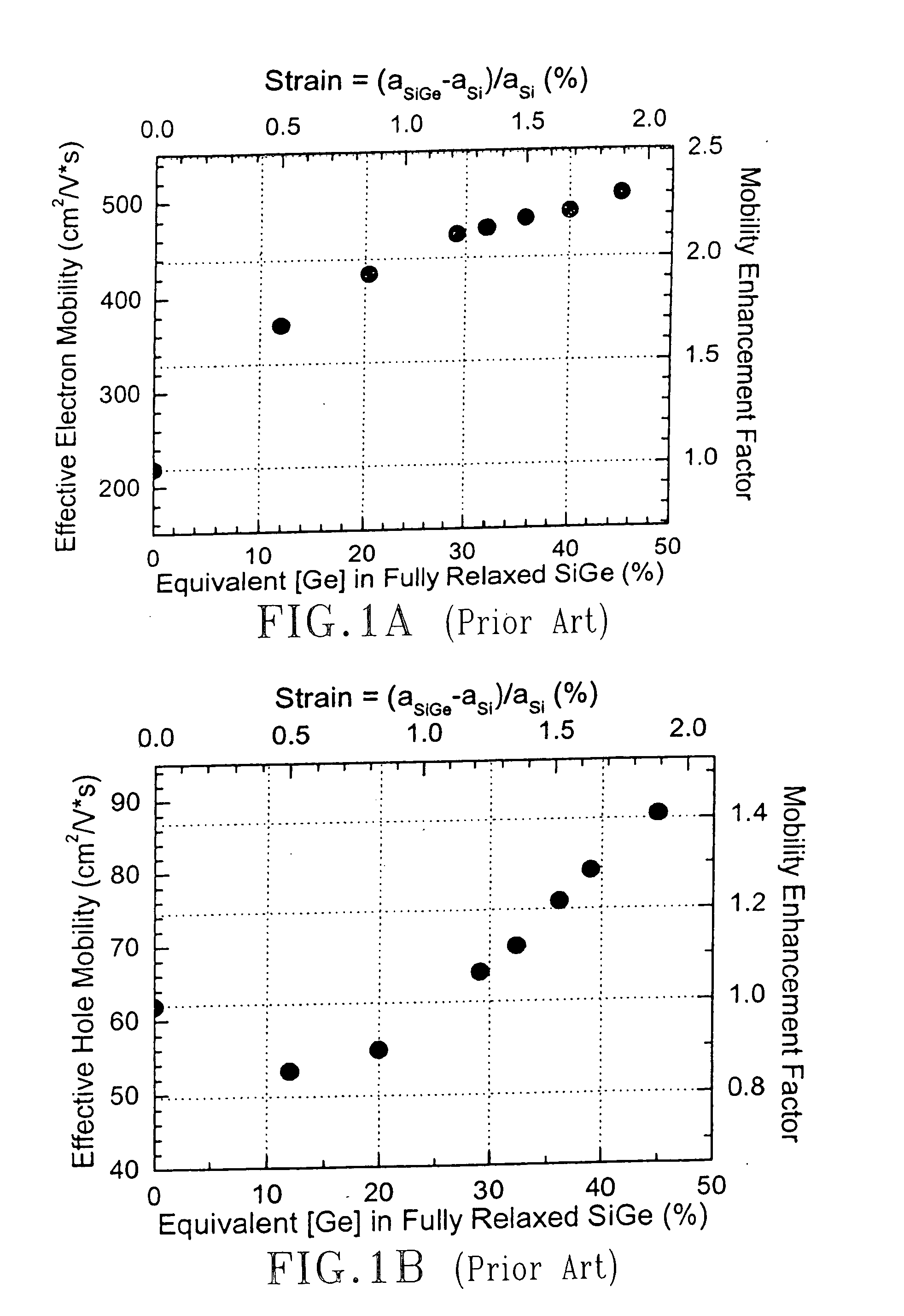
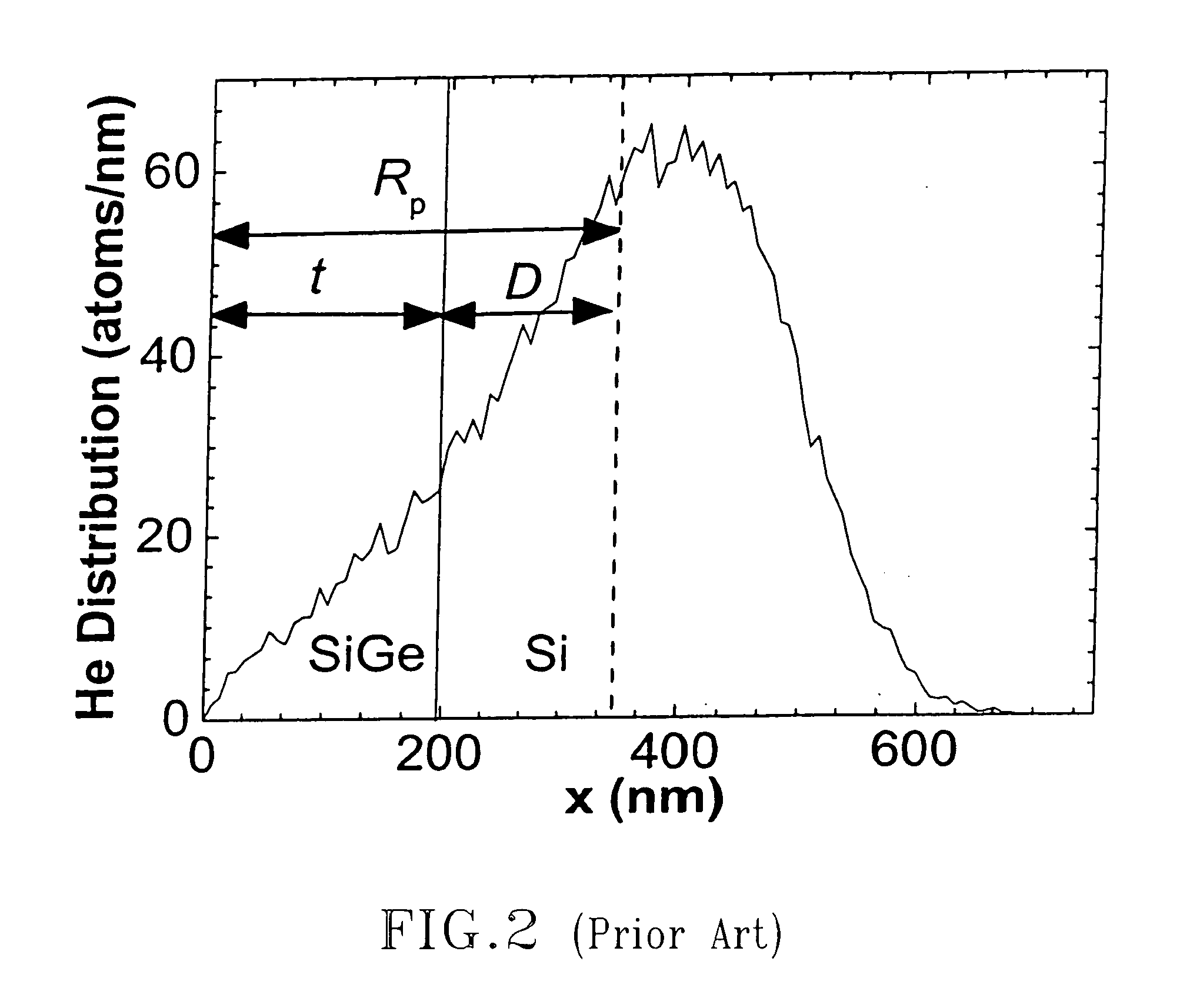
The present invention provides semiconductor structures and a method of fabricating such structures for application of MOSFET devices. The semiconductor structures are fabricated in such a way so that the layer structure in the regions of the wafer where n-MOSFETs are fabricated is different from the layer structure in regions of the wafers where p-MOSFETs are fabricated. The structures are fabricated by first forming a damaged region with a surface of a Si-containing substrate by ion implanting of a light atom such as He. A strained SiGe alloy is then formed on the Si-containing substrate containing the damaged region. An annealing step is then employed to cause substantial relaxation of the strained SiGe alloy via a defect initiated strain relaxation. Next, a strained semiconductor cap such as strained Si is formed on the relaxed SiGe alloy.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Functionally strained optical fibers
InactiveUS6898355B2Eliminating and greatly reducing impactImproved strain distributionCladded optical fibreOptical articlesTensile strainFiber
The present invention introduces a concept of “smart” ribbons, which use functionally tensioned optical fibers during the manufacture of fiber optic ribbons to create fiber ribbons with controlled geometrical configuration, optimized strain distribution and reduced attenuation. The ribbons may have flat or bowed cross section and be straight along the length or curved in its plane, or twisted unidirectionally, or periodically. These shapes and residual stress-strain state are induced and controlled by using tension functions instead of traditional constant-value tension per fiber during the ribbon manufacture. Further, the present invention reduces signal loss and / or attenuation in ribbon fibers caused by an increase in the strain variation from tensile strain to compressive strain along the length of the individual fibers when ribbons are manufactured, stacked, stranded around a strength member or twisted and bent during cable installation. In a first embodiment of the present invention, either a symmetric or non-symmetric load distribution is applied across the fibers being placed or drawn into a ribbon structure to eliminate or control residual twist in a completed fiber ribbon. Additionally, in the present invention, the load distribution on the fibers of a ribbon can be varied (e.g. periodically changed) along the length of the ribbon to provide a ribbon with the required design characteristics for any particular application. In a second embodiment of the invention, a fiber optic ribbon is made up of a plurality of sub-unit ribbons arranged in substantially the same plane. Each sub-unit ribbon includes a plurality of optical fibers coated by sub-unit matrices.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Complementary semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
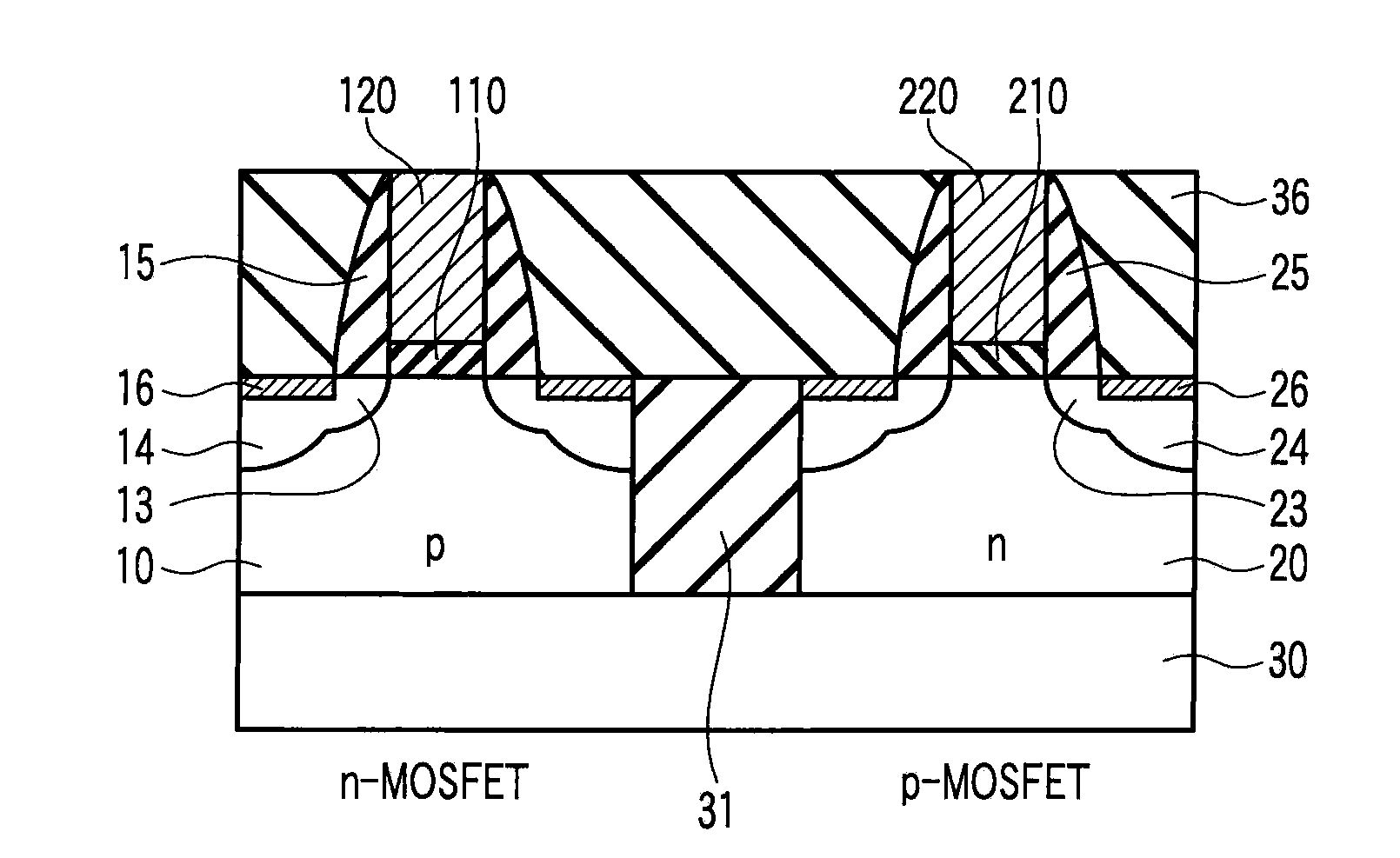
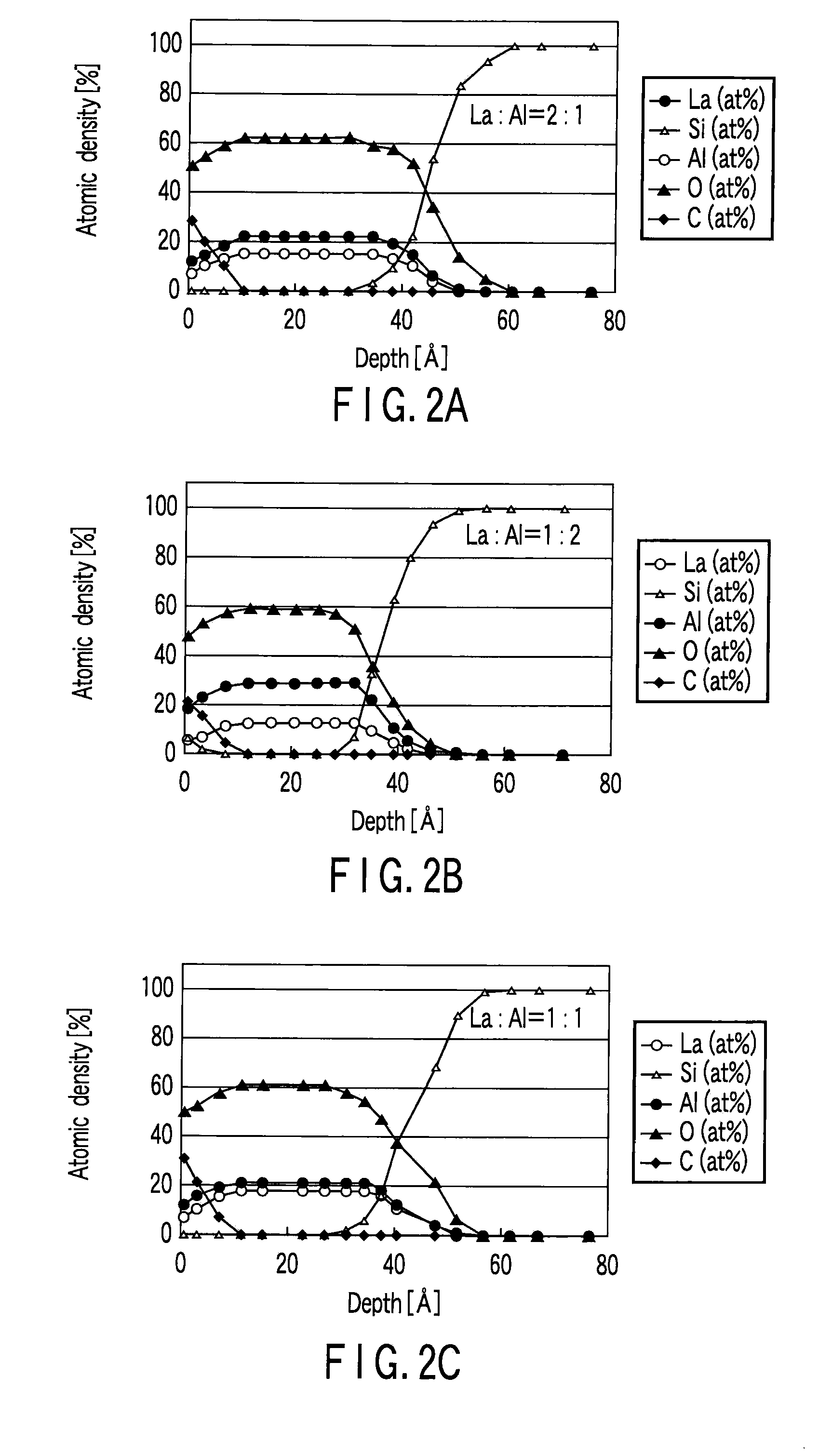
InactiveUS20090114995A1Increased tensile strainSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialAtomic density
A complementary semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first semiconductor region formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate, a second semiconductor region formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate apart from the first semiconductor region, an n-MIS transistor having a first gate insulating film including La and Al, formed on the first semiconductor region, and a first gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, and a p-MIS transistor having a second gate insulating film including La and Al, formed on the second semiconductor region, and a second gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film, an atomic density ratio Al / La in the second gate insulating film being larger than an atomic density ratio Al / La in the first gate insulating film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
N-channel field effect transistor having a contact etch stop layer in combination with an interlayer dielectric sub-layer having the same type of intrinsic stress
InactiveUS20080054415A1Increase the tensile stressEfficient mechanismSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesStress conditionsEngineering
By forming a tensile silicon dioxide layer on the basis of a sub-atmospheric deposition technique, the strain-inducing mechanism of a tensile contact etch stop layer for N-channel transistors may be significantly improved. Consequently, for otherwise identical stress conditions, the performance of a respective N-channel transistor may be significantly enhanced.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
High-flexibility and low-shrinkage fiber reinforced cement-based composite material
The invention belongs to the technical field of building materials, and in particular relates to a high-flexibility and low-shrinkage fiber reinforced cement-based composite material. The composite material is prepared by mixing cement, coal ash, silicon powder, gypsum, an expanding agent, a water reducing agent, a shrinkage reducing agent, a defoaming agent, a thickening agent, fine sand, fibers and water, wherein the total mass percentage of the cement, the coal ash, the silicon powder, the gypsum, the expanding agent, the water reducing agent, the shrinkage reducing agent, the defoaming agent, the thickening agent, the fine sand and the fibers is 77-85 percent, and the mass percentage of the water is 15-23 percent. The fiber reinforced cement-based composite material has the performance characteristics of low shrinkage, high flexibility, small crack width, quickness in condensation and early strength and is high in compressive strength and good in synergism with other materials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
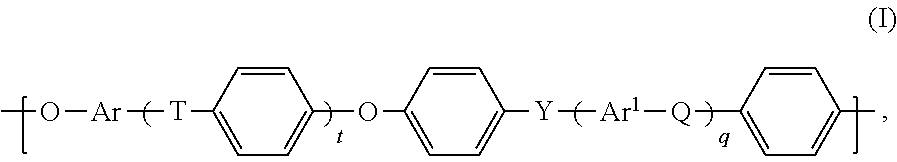
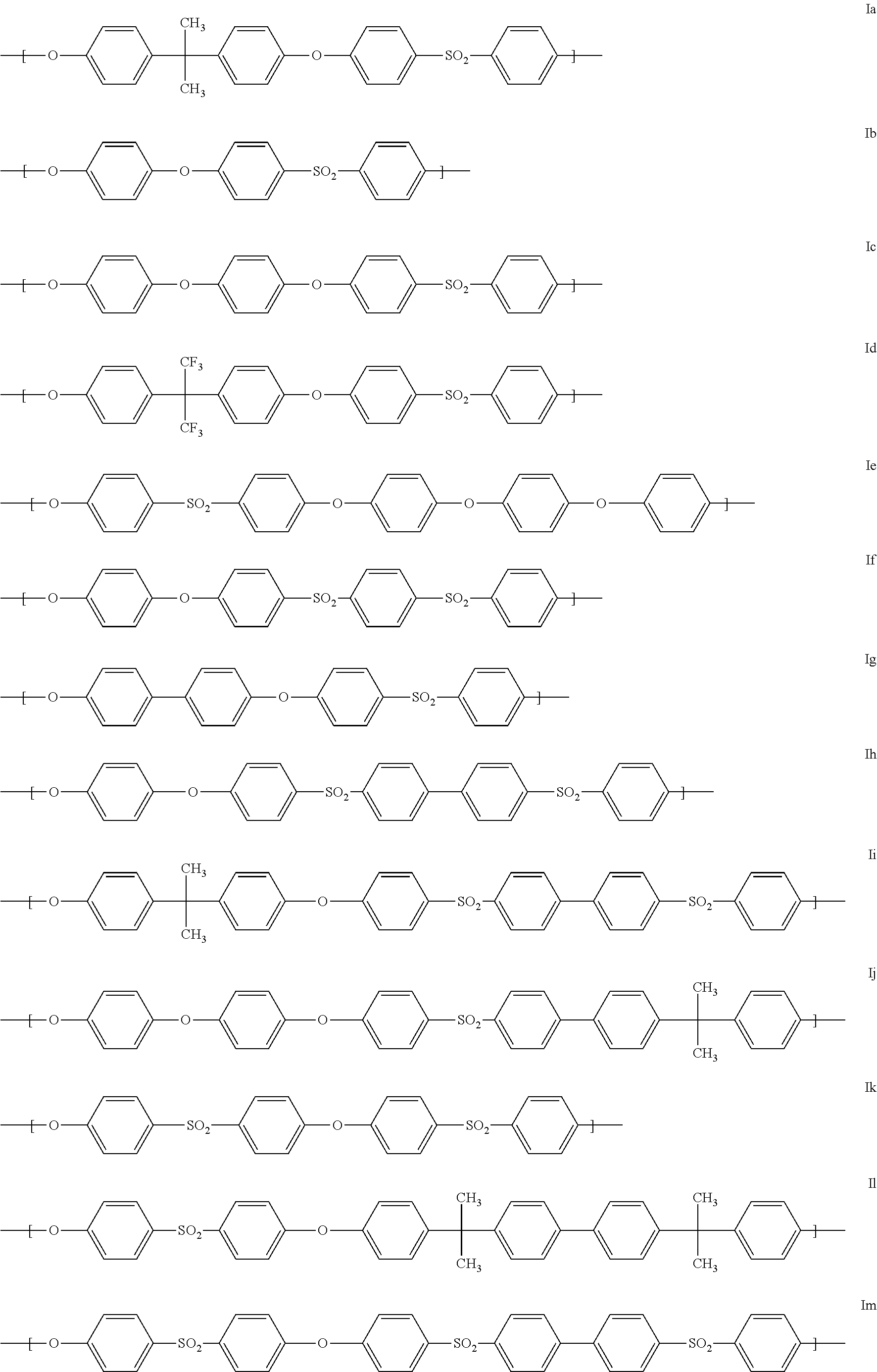
Blends of polyarylene ethers and polyarylene sulfides
The present invention relates to thermoplastic molding compositions comprising the following components:(A) at least one polyarylene ether (A1) having an average of at most 0.1 phenolic end group per polymer chain and at least one polyarylene ether (A2) having an average of at least 1.5 phenolic end groups per polymer chain,(B) at least one polyarylene sulfide,(C) at least one functionalized polyarylene ether comprising carboxy groups,(D) at least one fibrous or particulate filler, and(E) optionally further additives and / or processing aids.The present invention further relates to a process for producing the thermoplastic molding compositions of the invention, to the use of these for producing moldings, fibers, foams, or films, and to the resultant moldings, fibers, foams, and films.
Owner:BASF AG
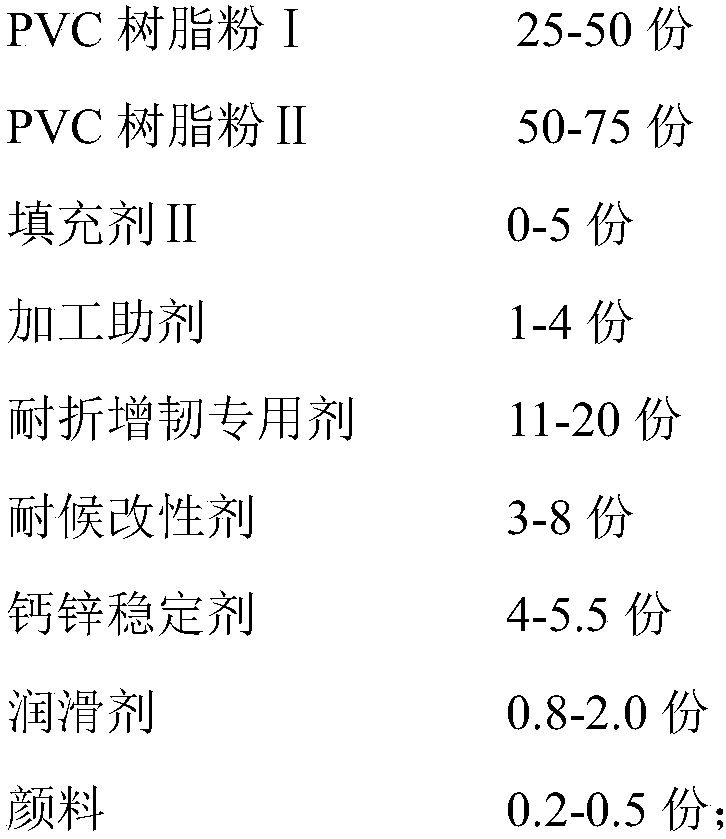
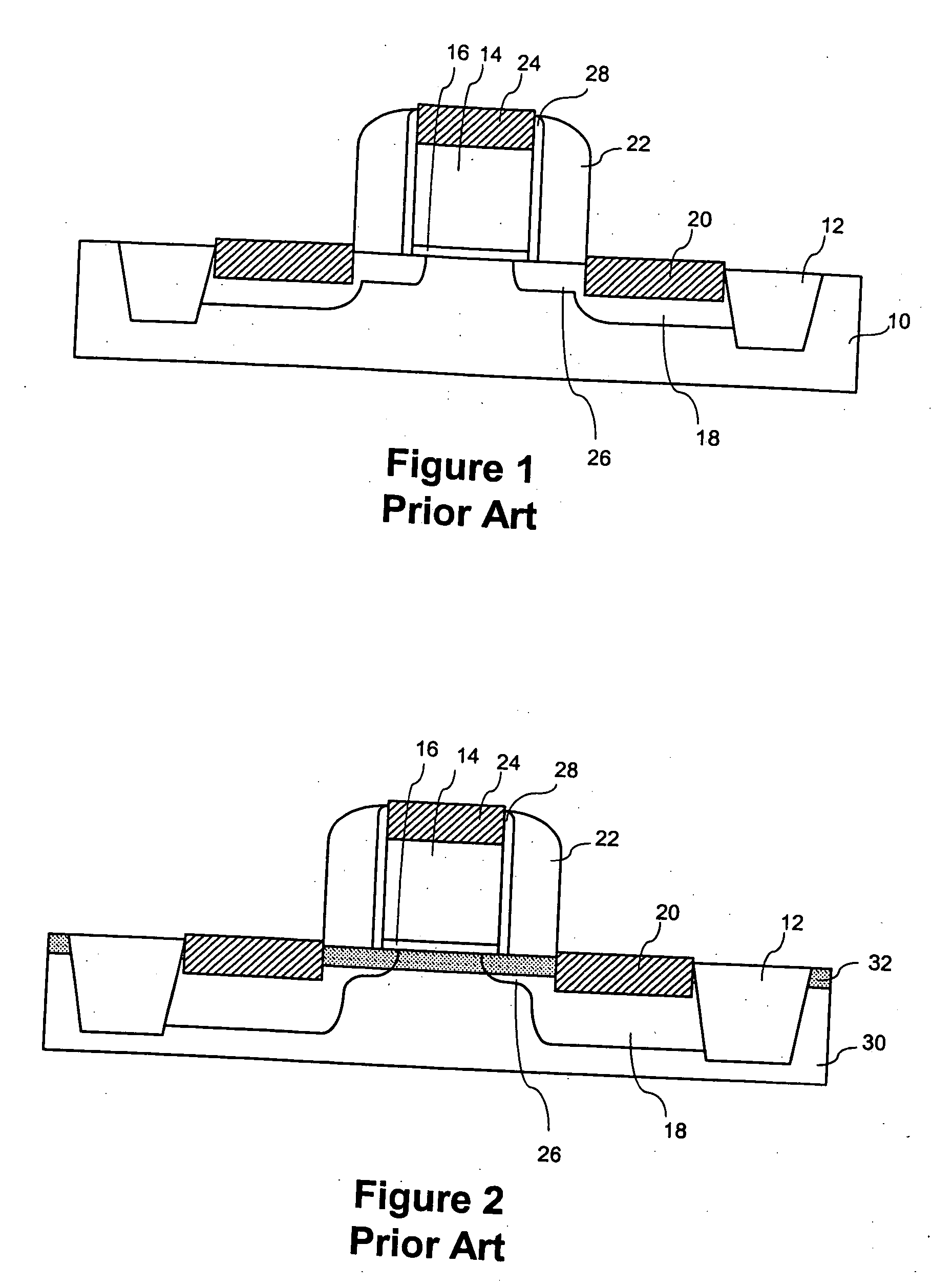
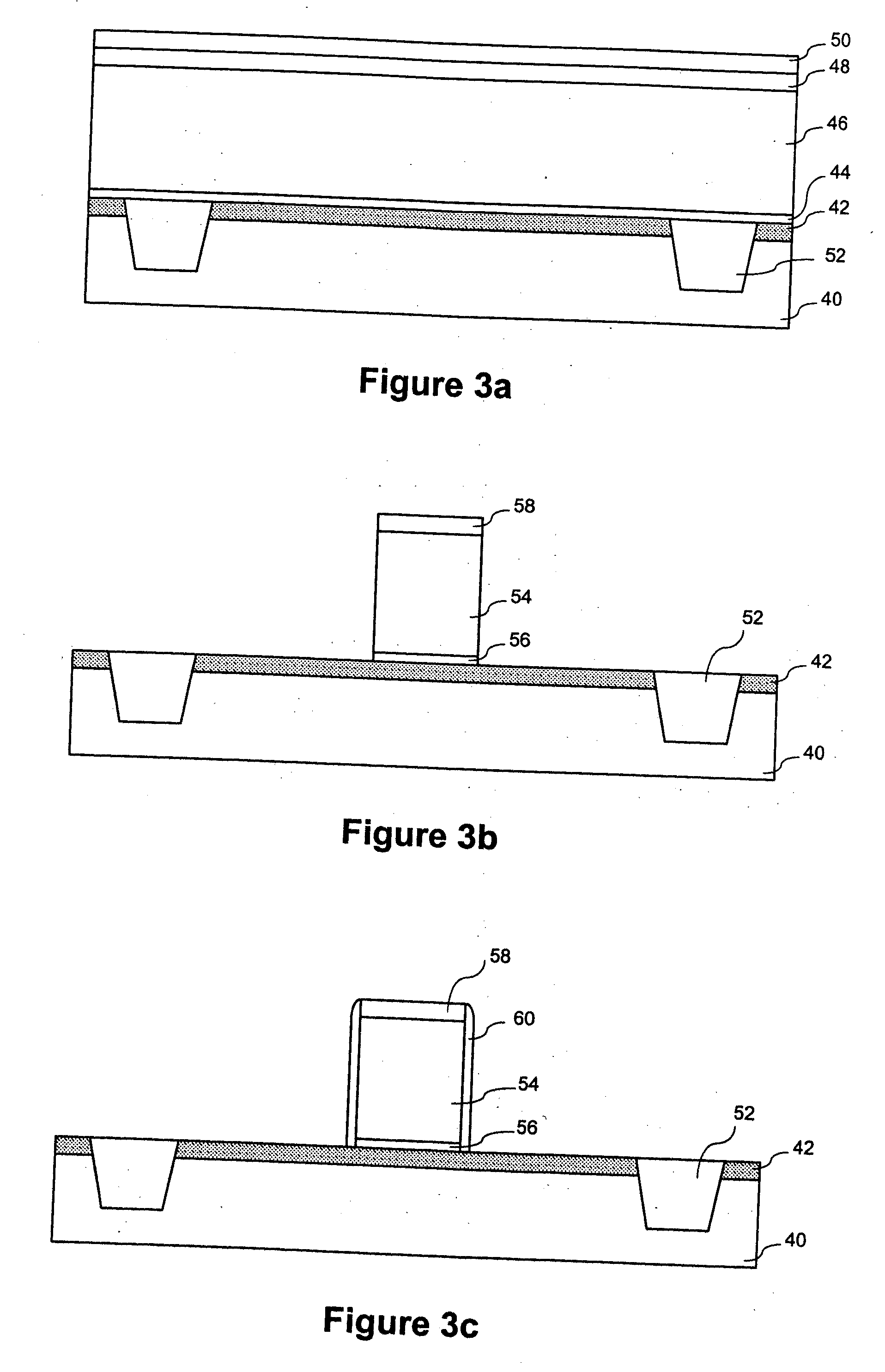
Semiconductor with tensile strained substrate and method of making the same
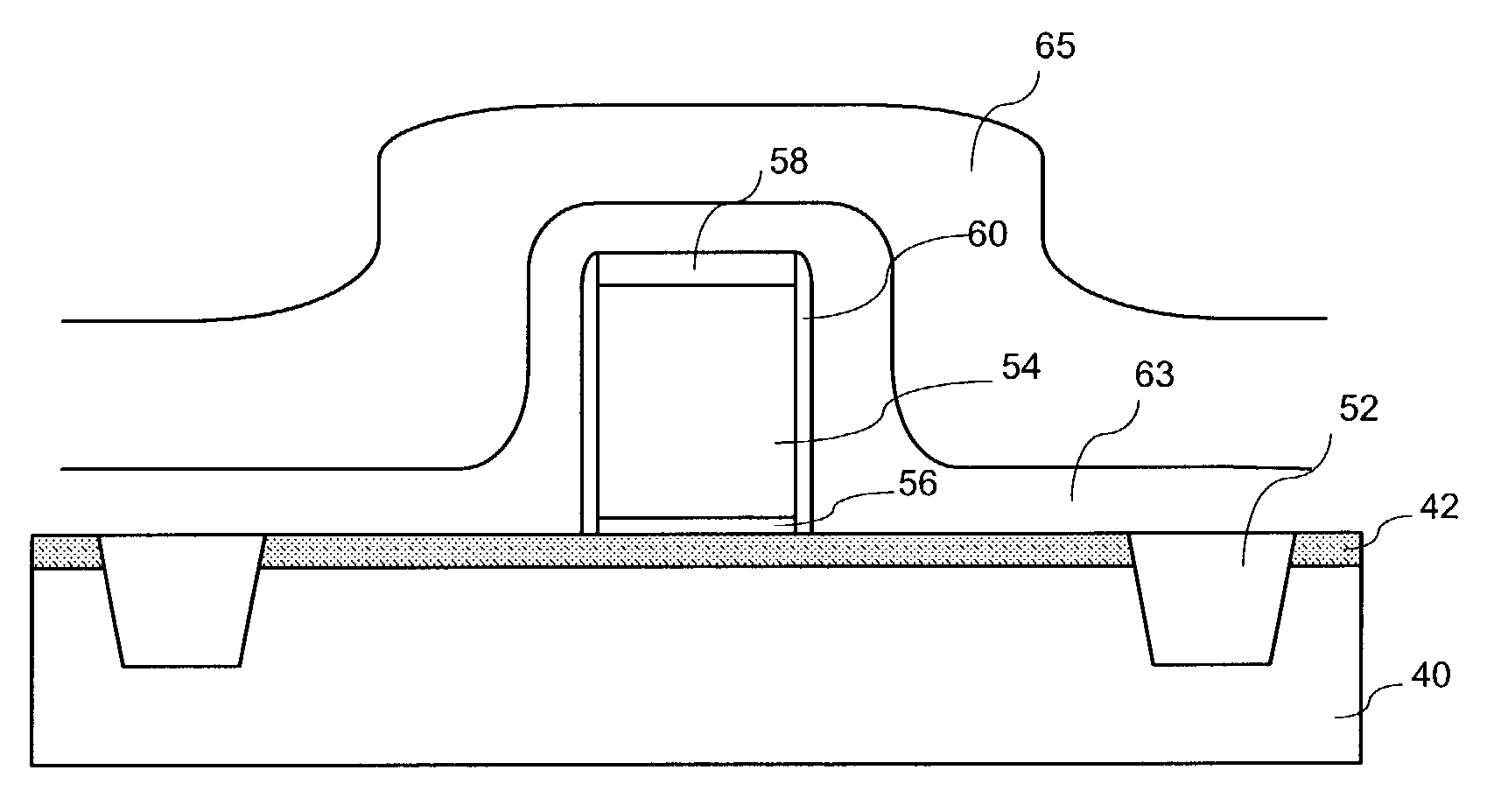
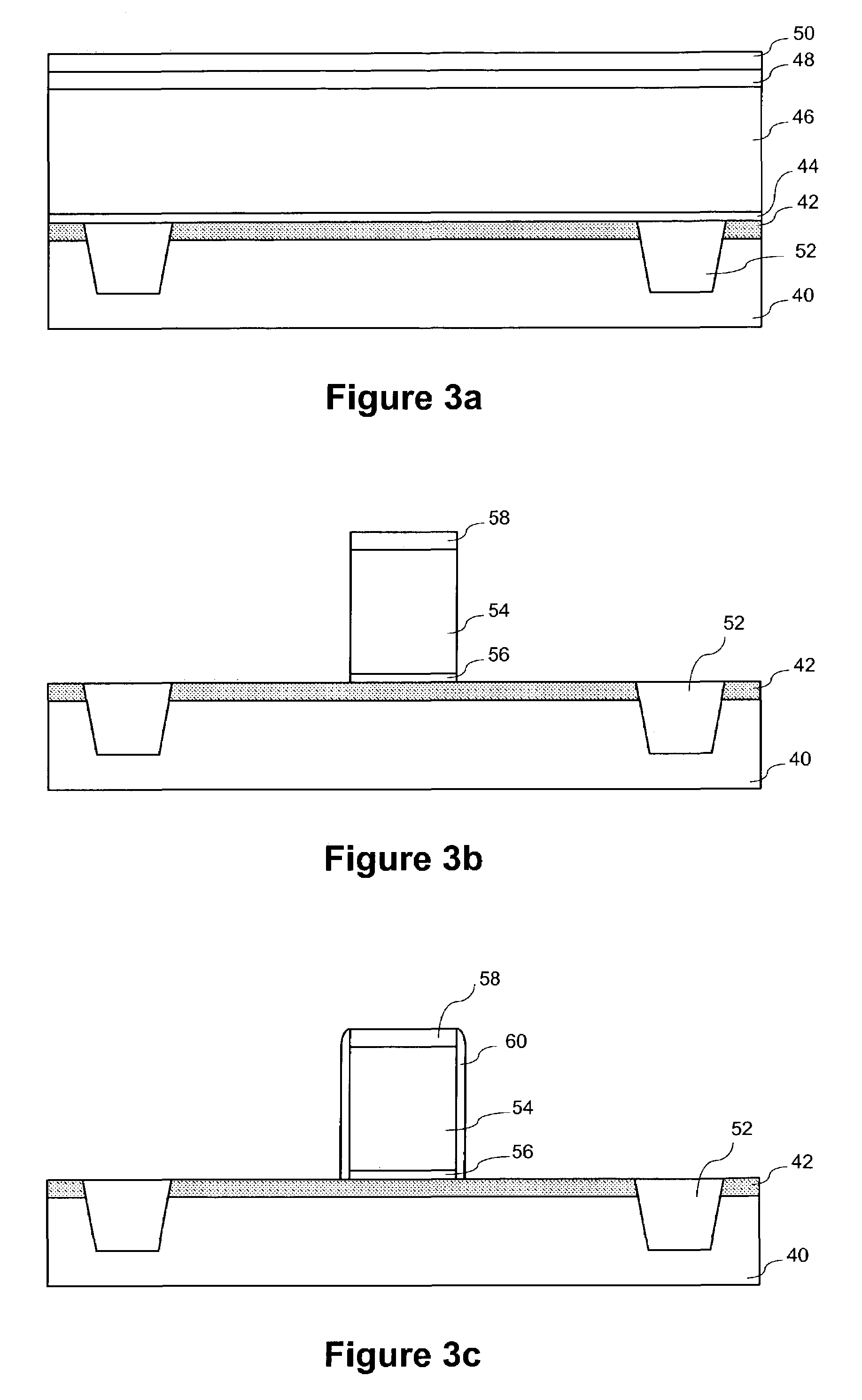
InactiveUS7001837B2Increase tensile strainIncreased tensile strainSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsOxide semiconductor
An exemplary embodiment relates to a method for forming a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET). The method includes providing a substrate having a gate formed above the substrate and performing at least one of the following depositing steps: depositing a spacer layer and forming a spacer around a gate and gate insulator located above a layer of silicon above the substrate; depositing an etch stop layer above the spacer, the gate, and the layer of silicon; and depositing a dielectric layer above the etch stop layer. At least one of the depositing a spacer layer, depositing an etch stop layer, and depositing a dielectric layer comprises high compression deposition which increases in tensile strain in the layer of silicon.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Transparent polyamide moulding compositions with high tensile strain at break
A polyamide moulding composition with particularly good tensile strain at break consisting of the following constituents: (A) 50 to 100% by weight of at least one transparent polyamide composed of: (a1) 55 to 77 mol % of acyclic, aliphatic diamine having 5-10 carbon atoms; (a2) 23 to 45 mol % of cycloaliphatic diamine having 6-36 C atoms, where the proportions of (a1) and (a2) are based on the entirety of the diamines used; (a3) 40 to 80 mol % of aromatic dicarboxylic acid or a mixture of such dicarboxylic acids; and (a4) 20 to 60 mol % of acyclic, aliphatic dicarboxylic acid having 8 to 16 carbon atoms, or a mixture of such dicarboxylic acids, where the proportions of (a3) and (a4) are based on the entirety of the dicarboxylic acids used; and (B) 0-50% by weight of additives,; where the entirety of components (A) and (B) gives 100% by weight.
Owner:EMS PATENT AG
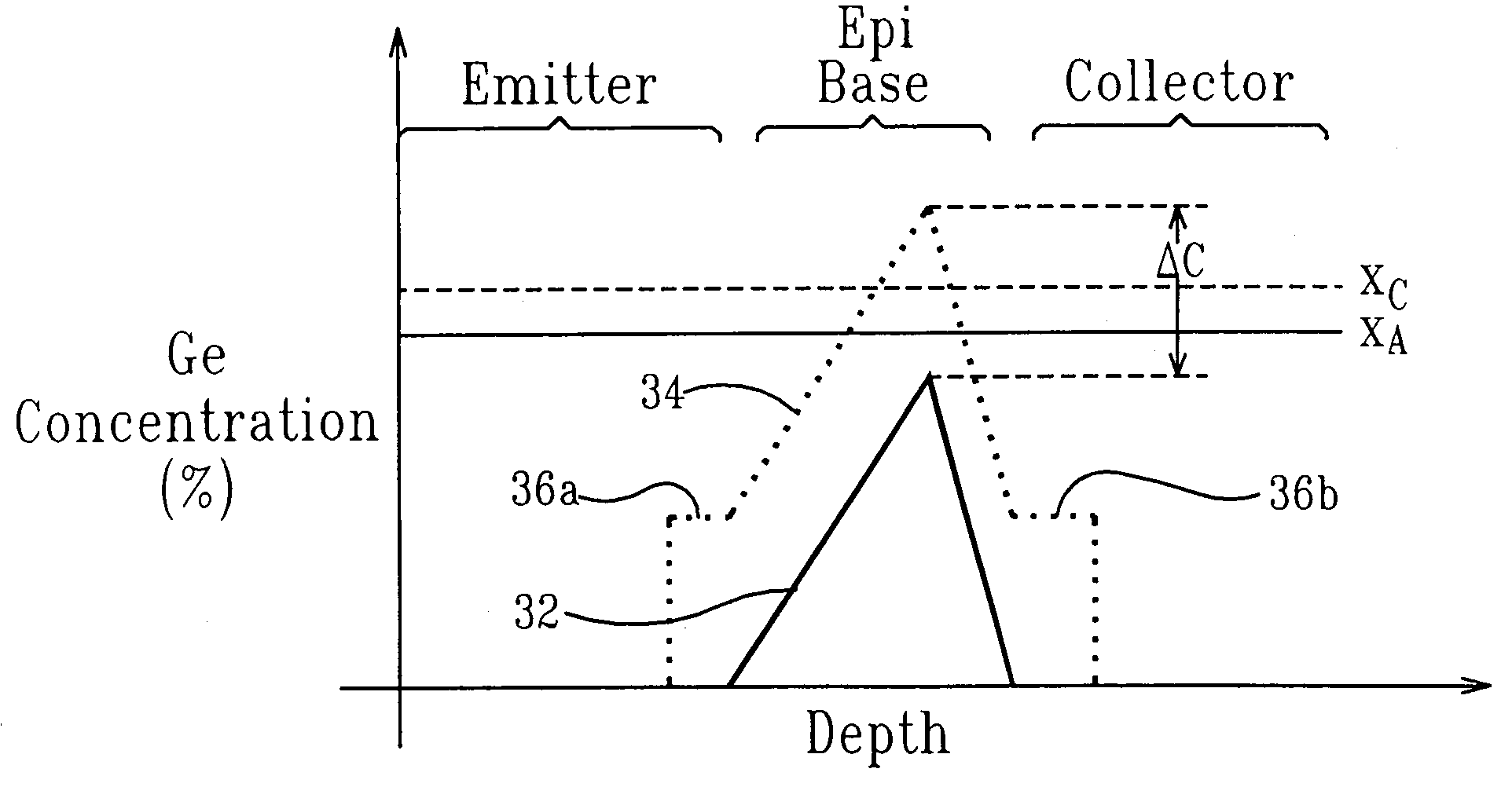
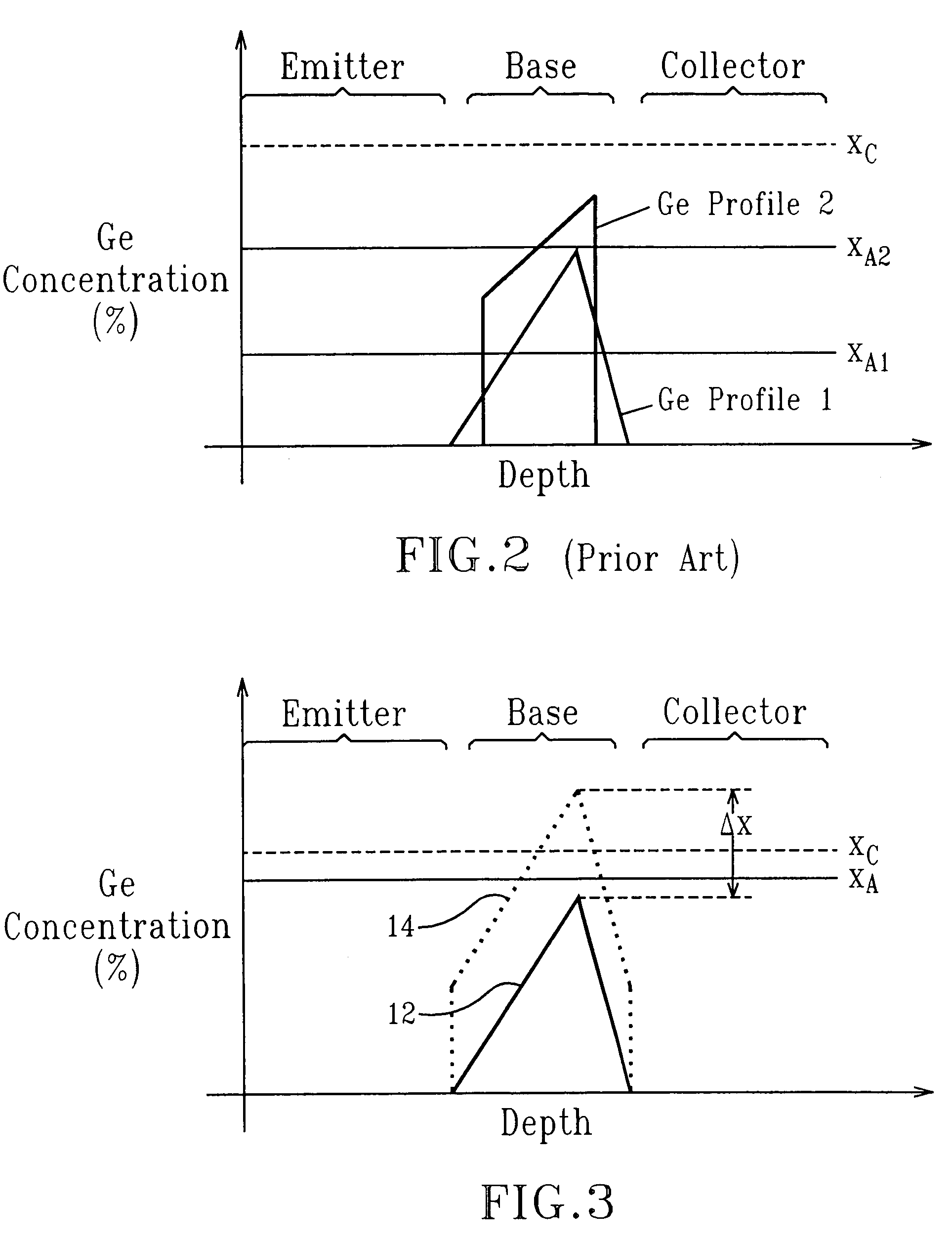
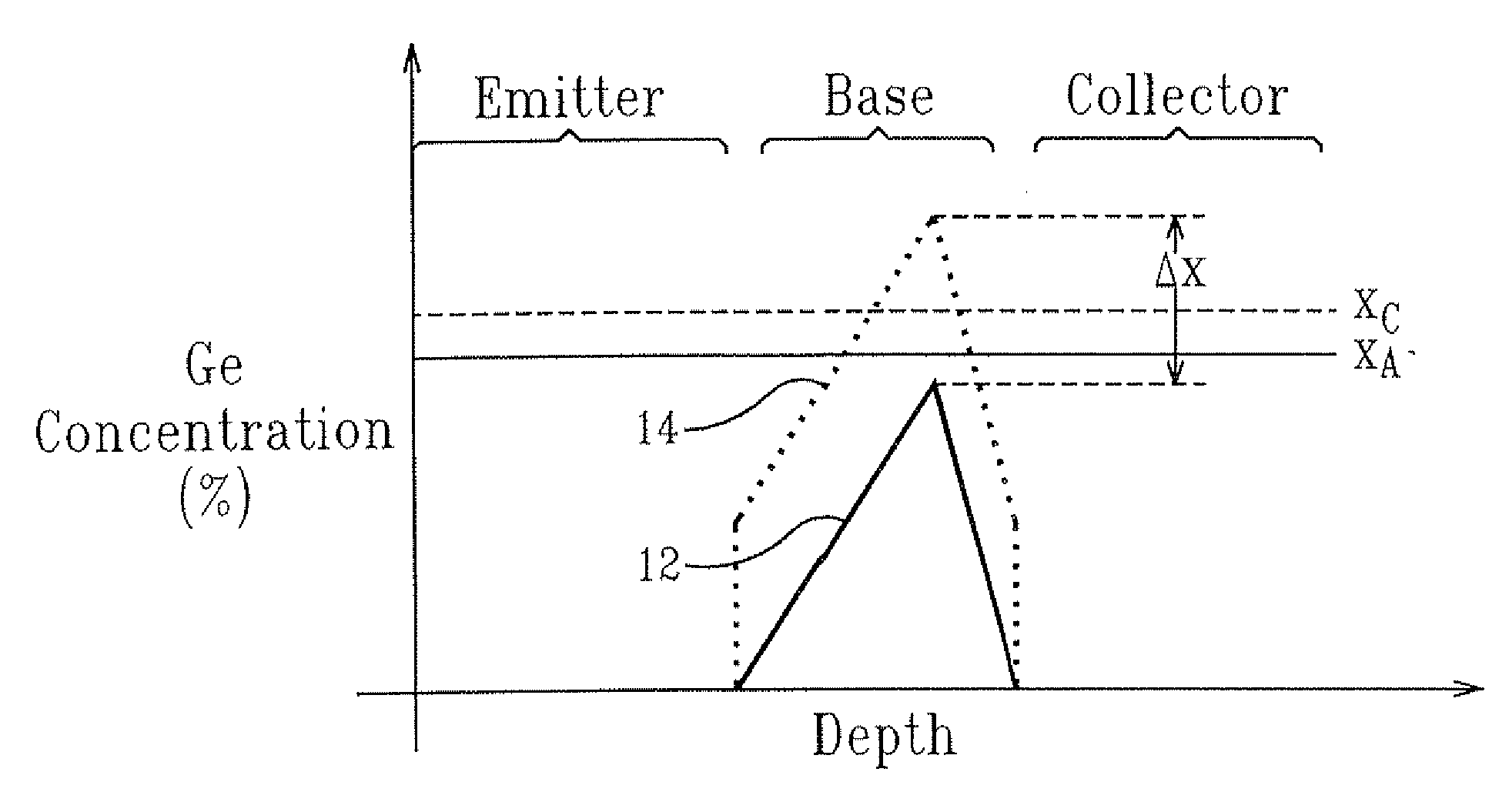
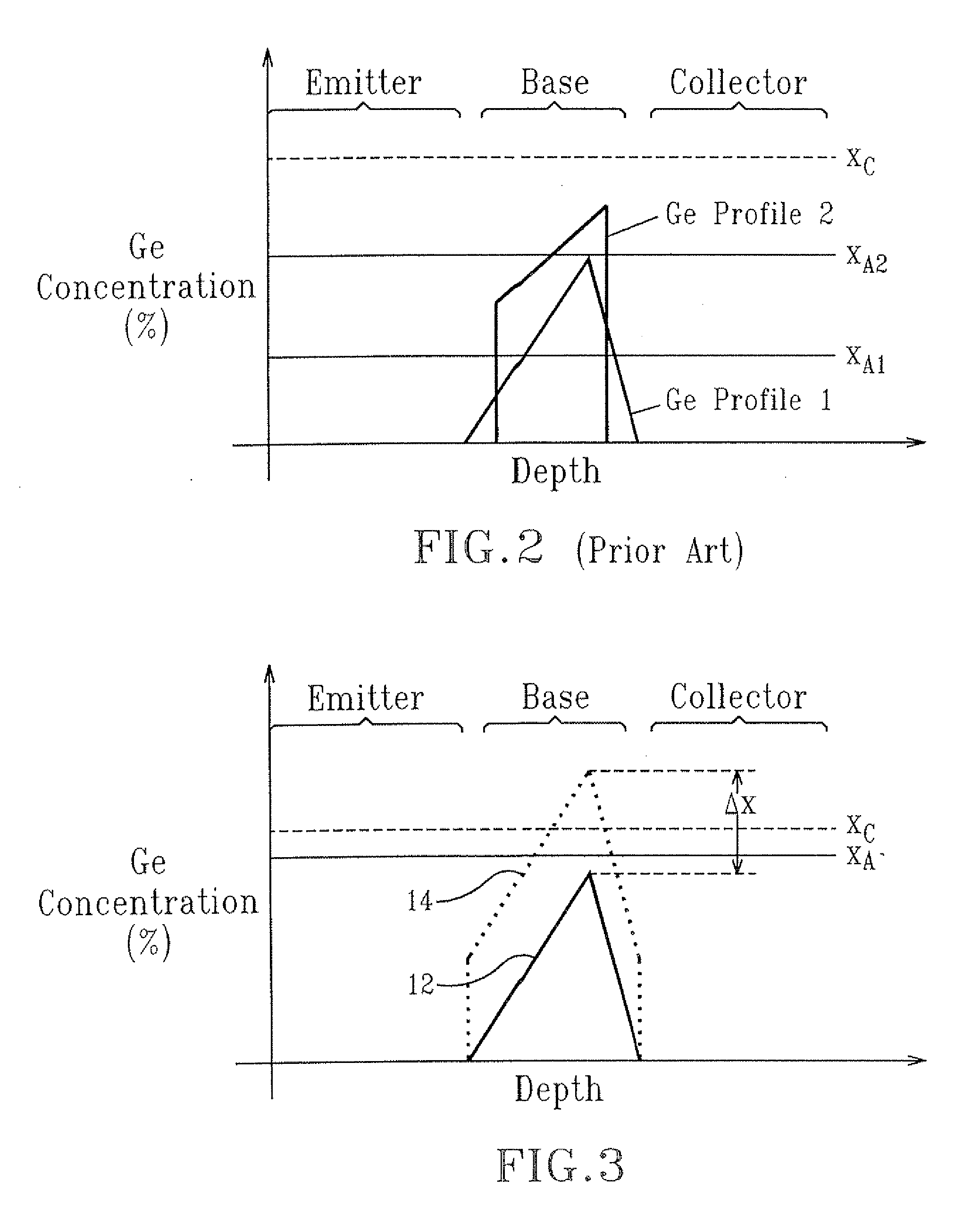
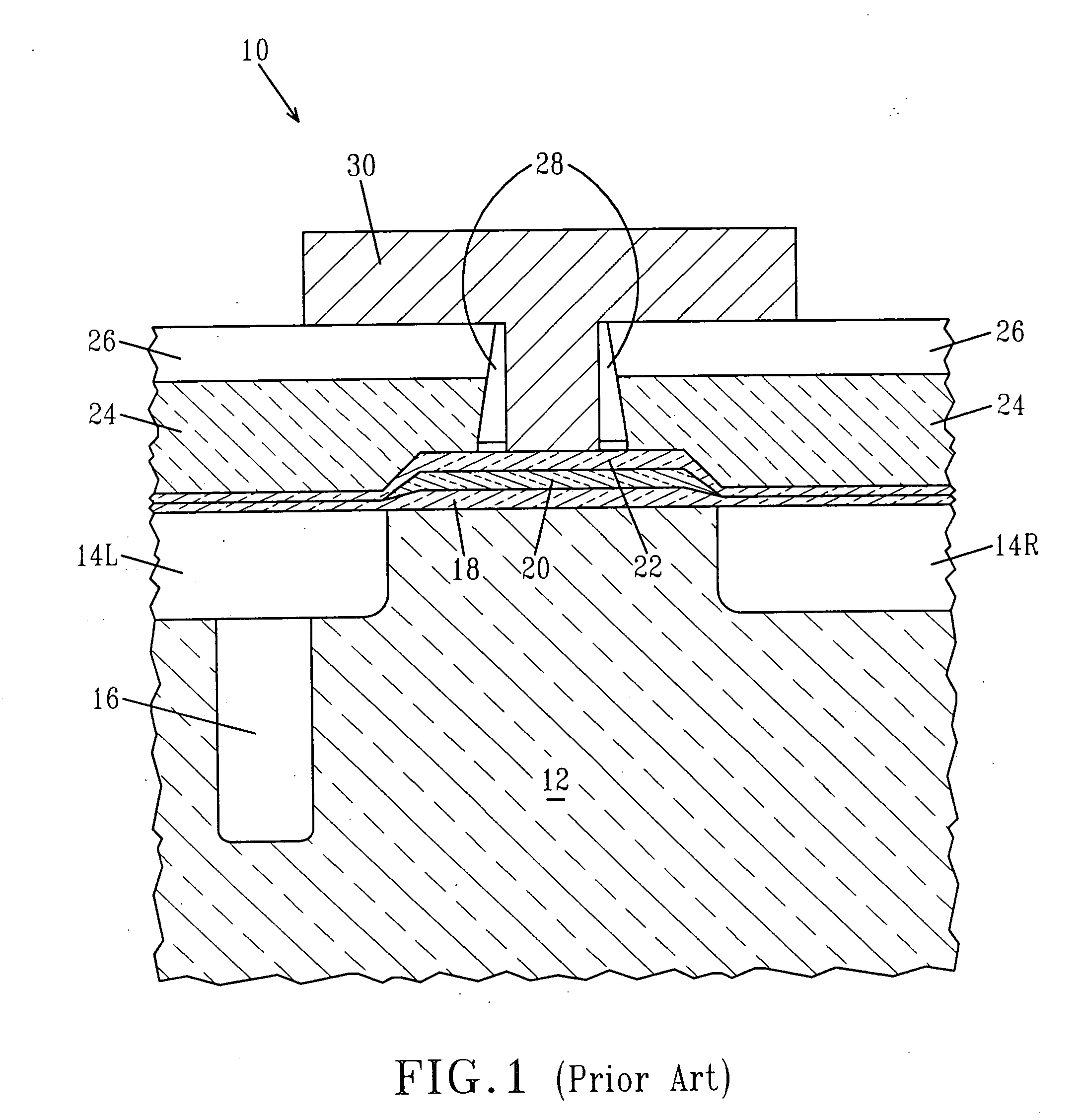
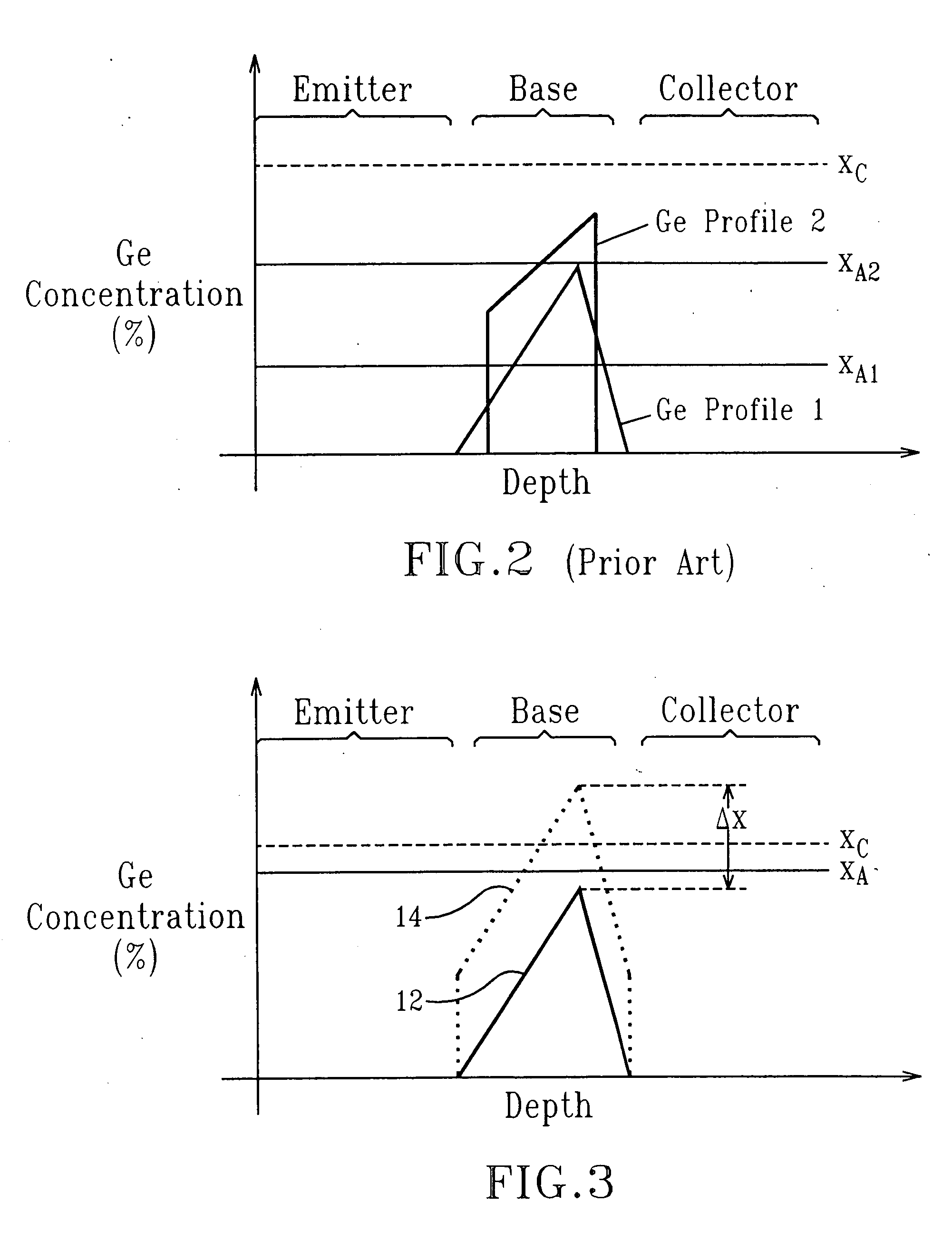
Mobility enhancement in SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistors
InactiveUS7544577B2Improve performanceIncreasing biaxial strainSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionCharge carrier mobility
The present invention relates to a high performance heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) having a base region with a SiGe-containing layer therein. The SiGe-containing layer is not more than about 100 nm thick and has a predetermined critical germanium content. The SiGe-containing layer further has an average germanium content of not less than about 80% of the predetermined critical germanium content. The present invention also relates to a method for enhancing carrier mobility in a HBT having a SiGe-containing base layer, by uniformly increasing germanium content in the base layer so that the average germanium content therein is not less than 80% of a critical germanium content, which is calculated based on the thickness of the base layer, provided that the base layer is not more than 100 nm thick.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
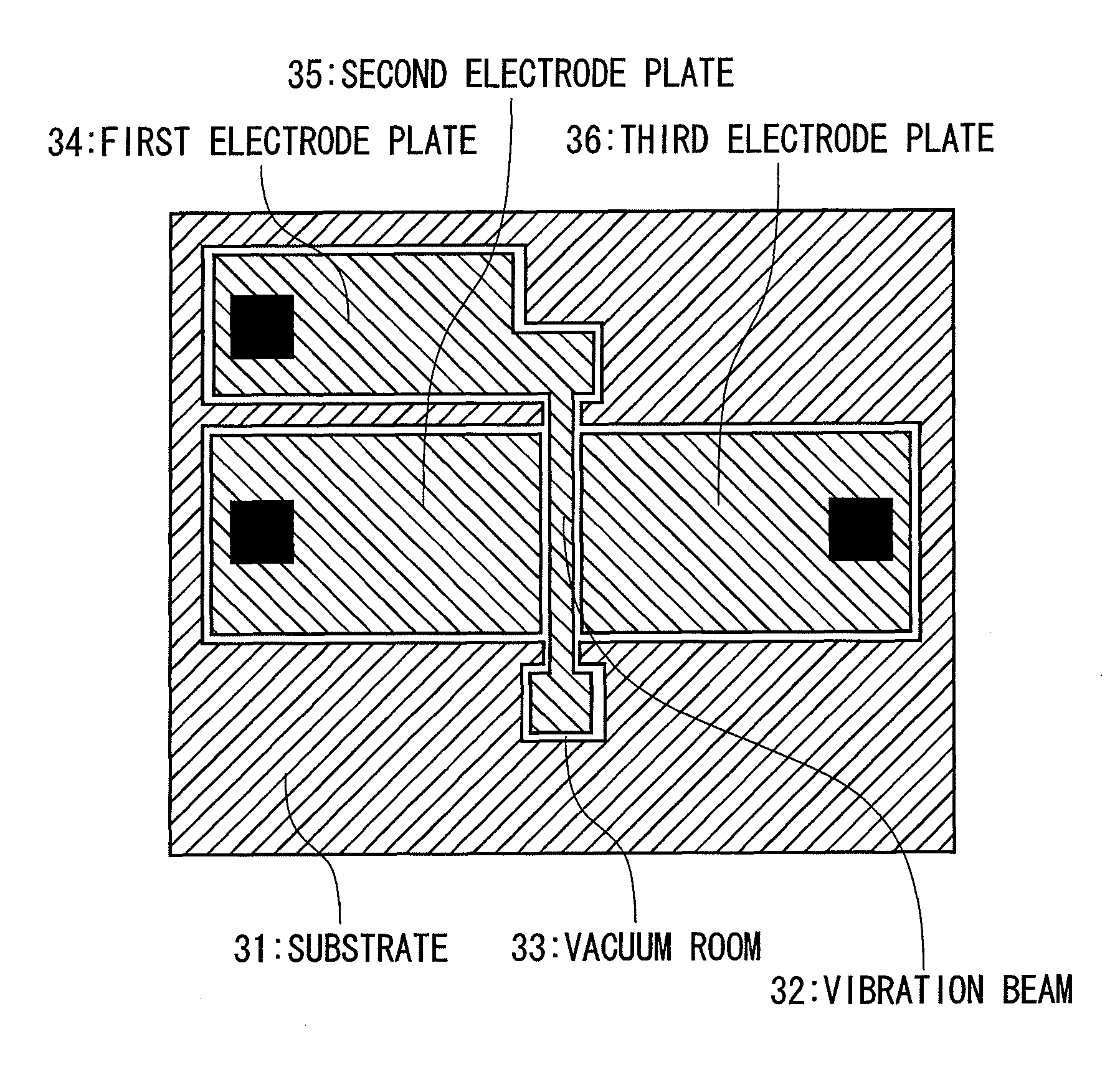
Method of manufacturing resonant transducer
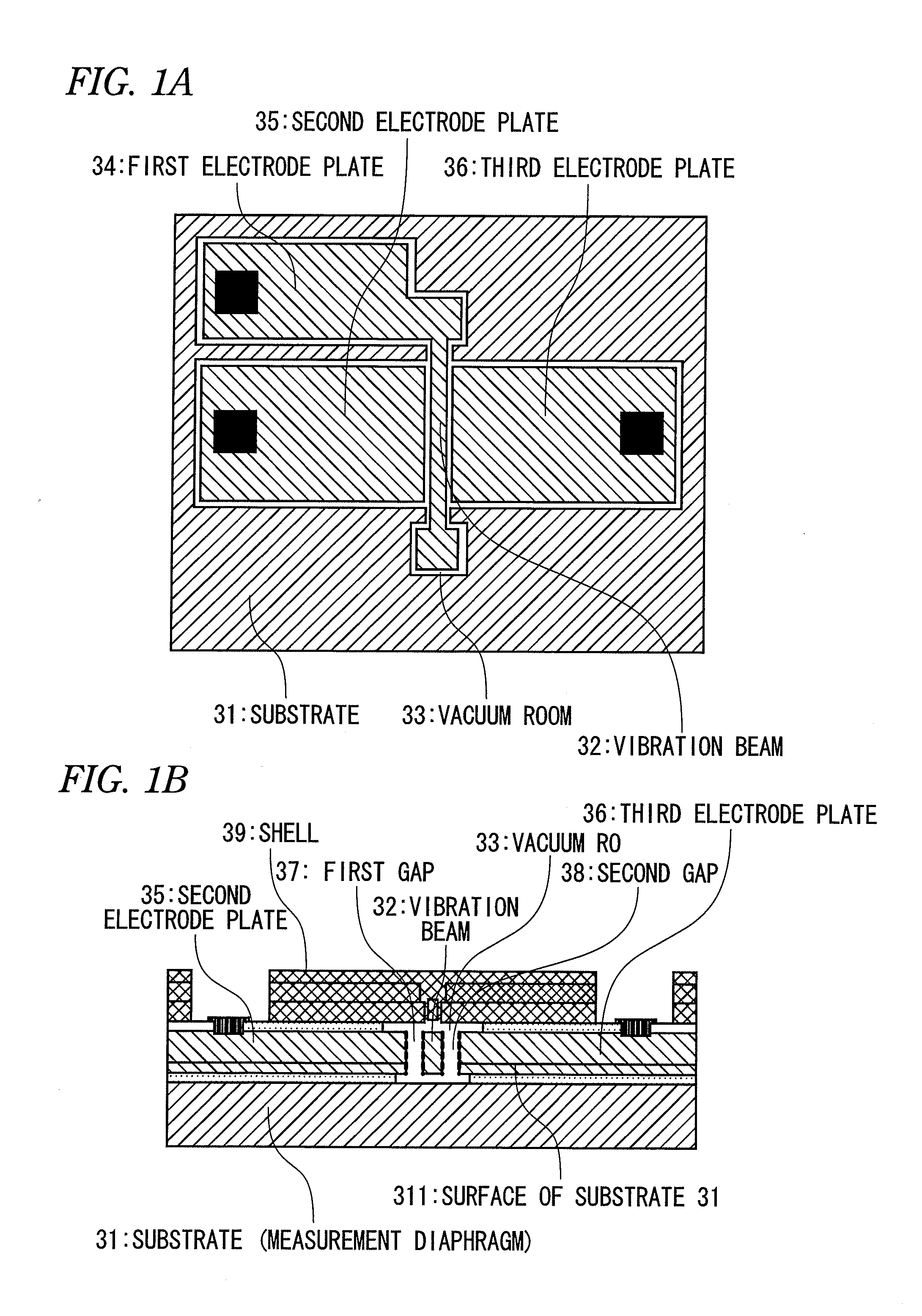
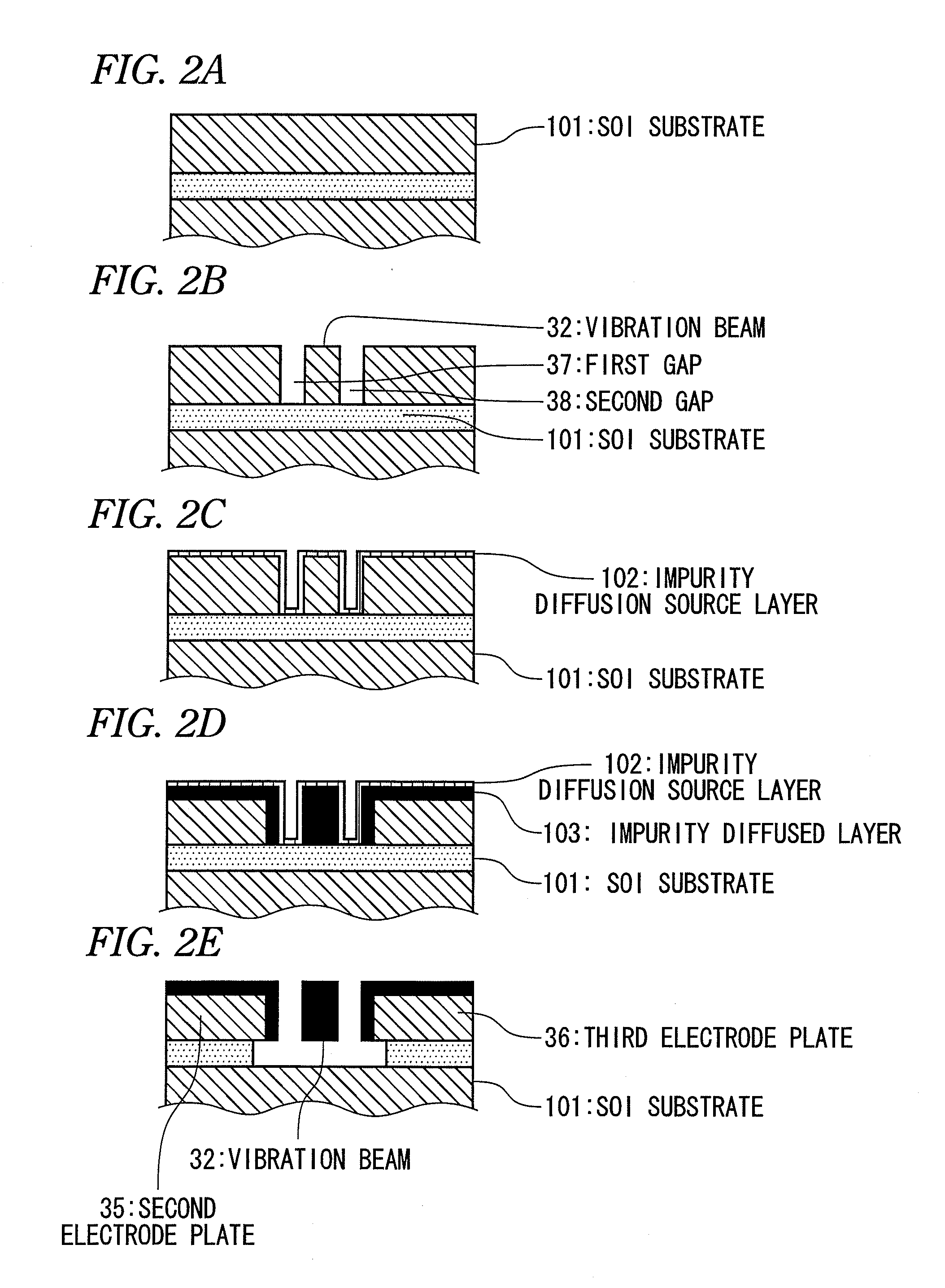
ActiveUS20130139377A1Improve accuracyIncreased tensile strainElectrical transducersImpedence networksImpurity diffusionTransducer
A method of manufacturing a resonant transducer having a vibration beam includes: (a) providing an SOI substrate including: a first silicon layer; a silicon oxide layer on the first silicon layer; and a second silicon layer on the silicon oxide layer; (b) forming a first gap and second gap through the second silicon layer by etching the second silicon layer using the silicon oxide layer as an etching stop layer; (c) forming an impurity diffusion source layer on the second silicon layer; (d) forming an impurity diffused layer in a surface portion of the second silicon layer; (e) removing the impurity diffusion source layer through etching; and (f) removing at least a portion of the silicon oxide layer through etching such that an air gap is formed between the first silicon layer and a region of the second silicon layer surrounded by the first and second gaps.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Special heat dissipation electrostatic spraying coating for LED lamp
InactiveCN106675329AImprove brittle defectsImprove bending strengthPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyModified carbon
The invention discloses a special heat dissipation electrostatic spraying coating for an LED lamp. The heat dissipation electrostatic spraying coating is prepared from the following raw materials: epoxy resin, polyurethane, unsaturated polyester resin, maleic anhydride, methyl tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, m-phthalic anhydride, 2,4,6-tri(dimethylamine methyl) phenol, trimethylolpropane, 2-butyl-2-ethyl-1,3-propylene glycol, magnesium nitride, modified carbon nano tube, graphene, nano calcium carbonate, cerium oxide, silica powder, hexamethyl-disilazane, phenyltrimethoxysilane, phenyl methyl dimethoxysilane, dibutyltin dilaurate, a leveling agent and benzoin, wherein the epoxy resin is a mixture of biscyclopentadiene dioxide epoxy resin and o-cresol formaldehyde epoxy resin. The heat dissipation electrostatic spraying coating is high in heat dissipation property and high in high temperature resistance, and the service life of the LED lamp can be prolonged.
Owner:TIANCHANG JINLING ELECTRONICS
Conductive large-strain carbon nanotube composite film as well as preparation method and test method thereof
ActiveCN109502570AImprove conductivityImprove flexibilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSingle-walled nanotubesTensile strainComposite film
The invention proposes a conductive large-strain carbon nanotube composite film as well as a preparation method and a test method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step (1) preparing single-walled carbon nanotube films by a chemical vapor deposition method; step (2) collecting the single-walled carbon nanotube films prepared in the step (1) by a rotating drum wheel, immersing the drum wheel in a composite solution while collecting the single-walled carbon nanotube films, superimposing the single-walled carbon nanotube films and the composite solution one by one toform a composite film on the single-walled carbon nanotube films, and preparing a single-walled carbon nanotube composite film along with the rotation of the drum wheel; and step (3) taking out the drum wheel with the single-walled carbon nanotube composite film in the step (2) from the composite solution, then rotating to make the composite film uniform, and then drying. According to the invention, problems of small tensile strain and poor toughness of the single-walled carbon nanotube composite film in the prior art are solved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Super-high toughness cement base composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107417199AIncrease viscosityImprove water retentionClimate change adaptationTensile strainToughness
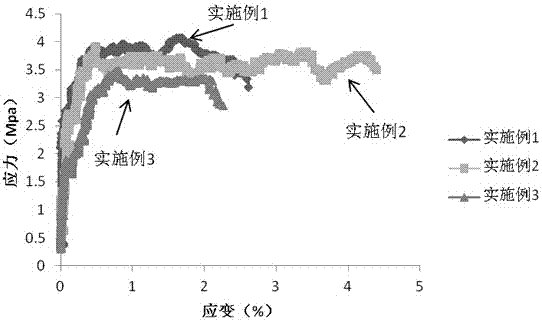
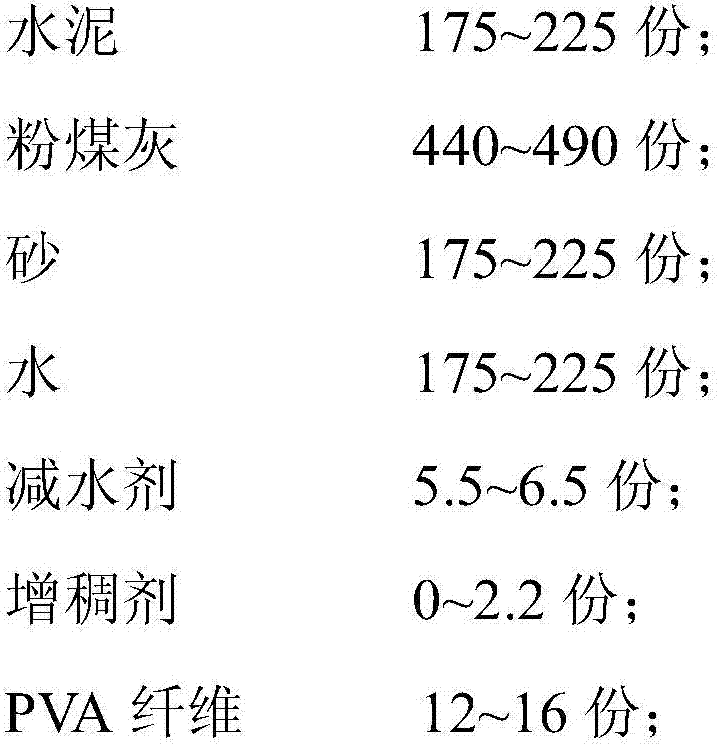
The invention discloses a super-high toughness cement base composite material. The super-high toughness cement base composite material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 175-225 parts of cement, 440-490 parts of coal ash, 175-225 parts of sand, 175-225 parts of water, 5.5-6.5 parts of water reducing agent, 0-2.2 parts of thickening agent, and 12-16 parts of PVA fiber. A preparation method of the super-high toughness cement base composite material comprises the steps of first, mixing cement, coal ash, sand and thickening agent uniformly; then adding water and water reducing agent, and mixing uniformly; and finally, adding PVA fiber, stirring till PVA is dispersed uniformly, so as to obtain the super-high toughness cement base composite material. The tensile strength of the super-high toughness cement base composite material reaches 3MPa-4.5MPa, and the tensile strain thereof reaches 2.5%-4.5%.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
PVC foamed fold-proof plate and preparation method thereof
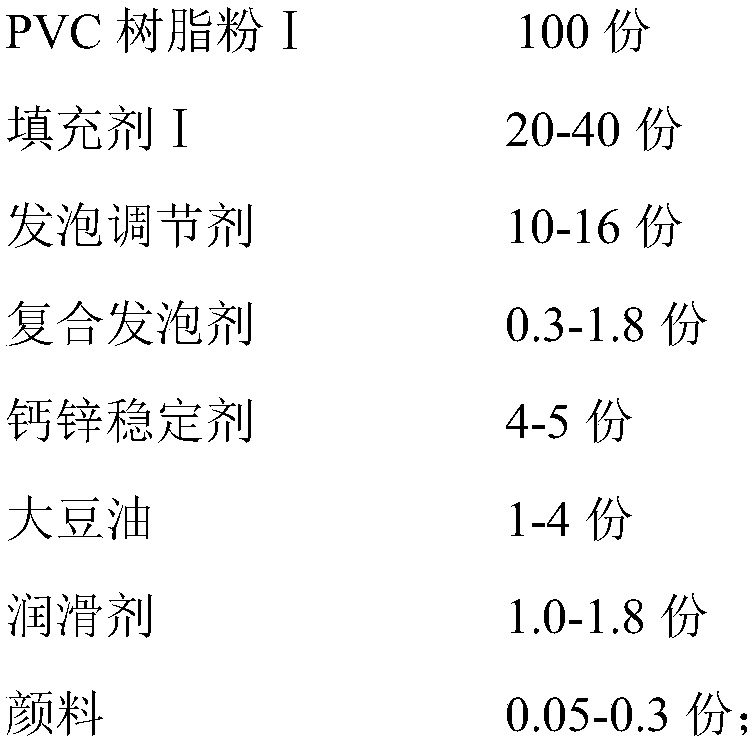
ActiveCN109591419AImprove liquidityFine foamSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer sciencePolyvinyl chloride
The invention belongs to the technical field of polyvinyl chloride plates, and particularly relates to a PVC foamed fold-proof plate and a preparation method thereof. The PVC foamed fold-proof plate comprises a core layer and surface layers, wherein the core layer is made from a foamed PVC material, and is prepared from PVC resin powder I, filler I, foaming regulator, compound foaming agent, calcium-zinc stabilizer, soybean oil, a lubricating agent and pigment; the upper surface layer and the lower surface layer are made of same raw materials; the surface layer is prepared from PVC resin powder I, PVC resin powder II, filler II, a processing aid, a fold-proof toughening specific agent, a weather-resistant modifying agent, calium-zinc stabilizer, a lubricating agent and pigment; and the fold-proof toughening specific agent is high-molecular-weight chlorinated polyethylene acrylate grafted polymer. The PVC foamed fold-proof plate has the advantages of high strength, pulling and folding resistance, surface cracking prevention, large-angle fold use availability and no mark, few combined joint and joint surface of the composition, environmental friendliness, sanitation, convenience in cleaning, high cost performance and wide application range.
Owner:SHANDONG BODO PLASTICS CO LTD
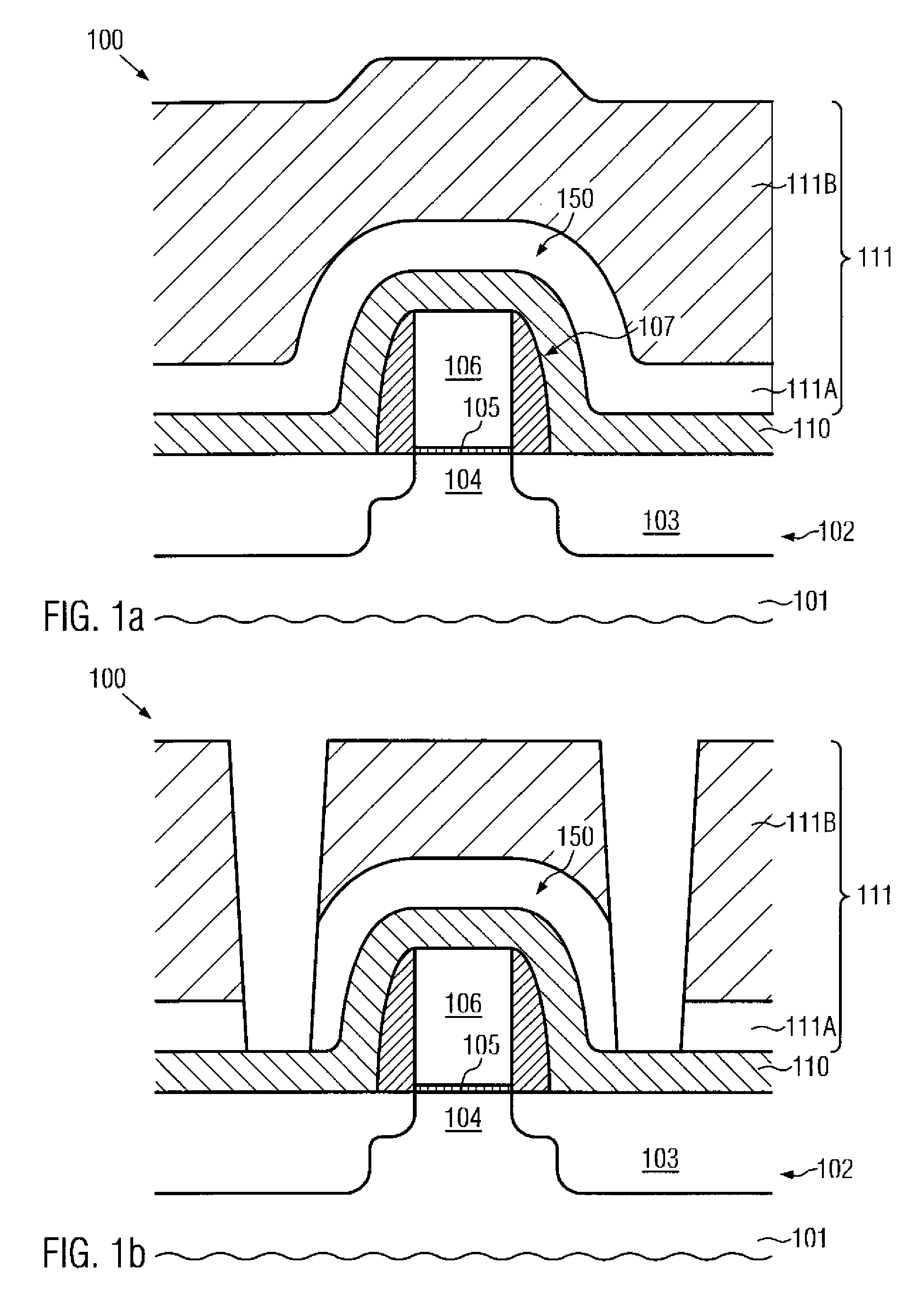
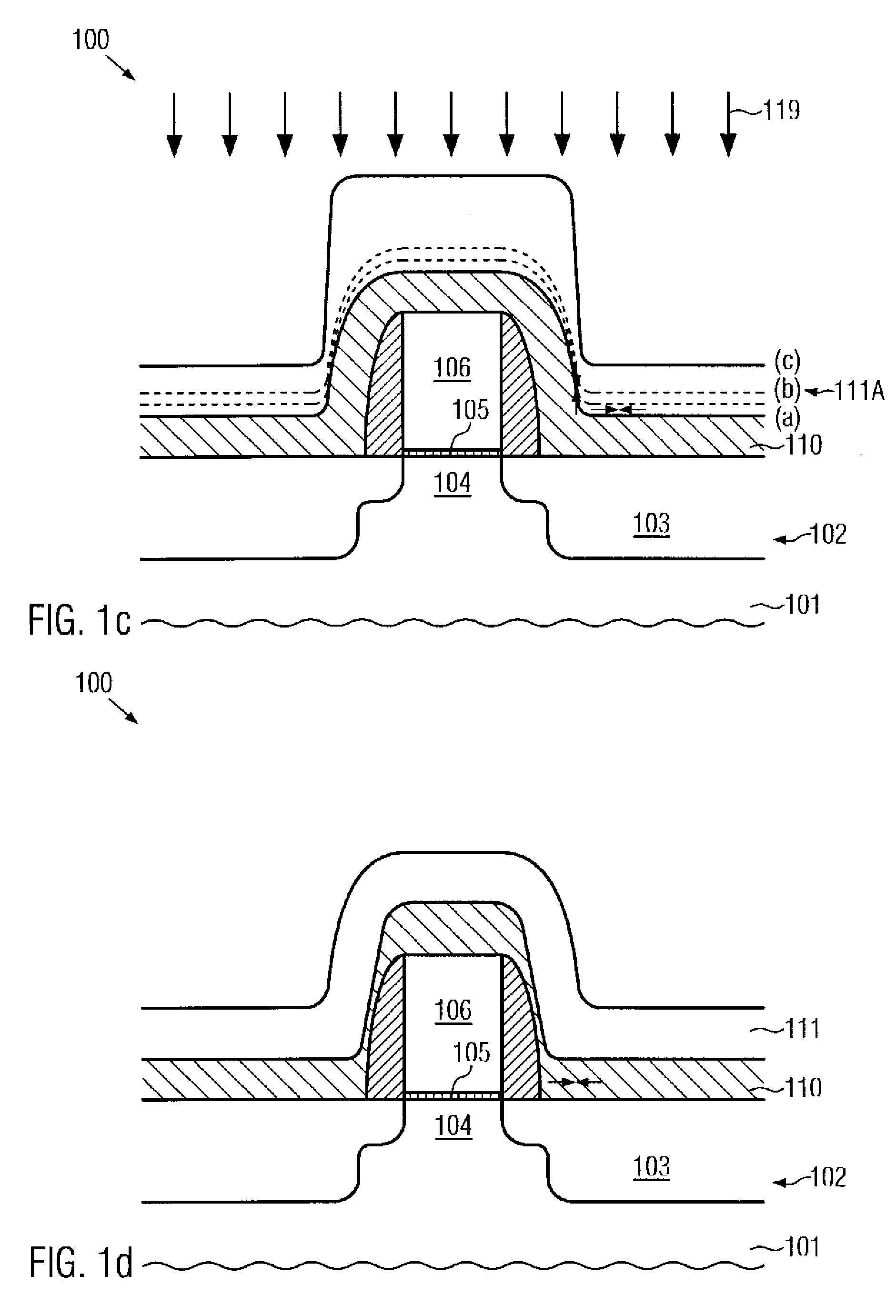
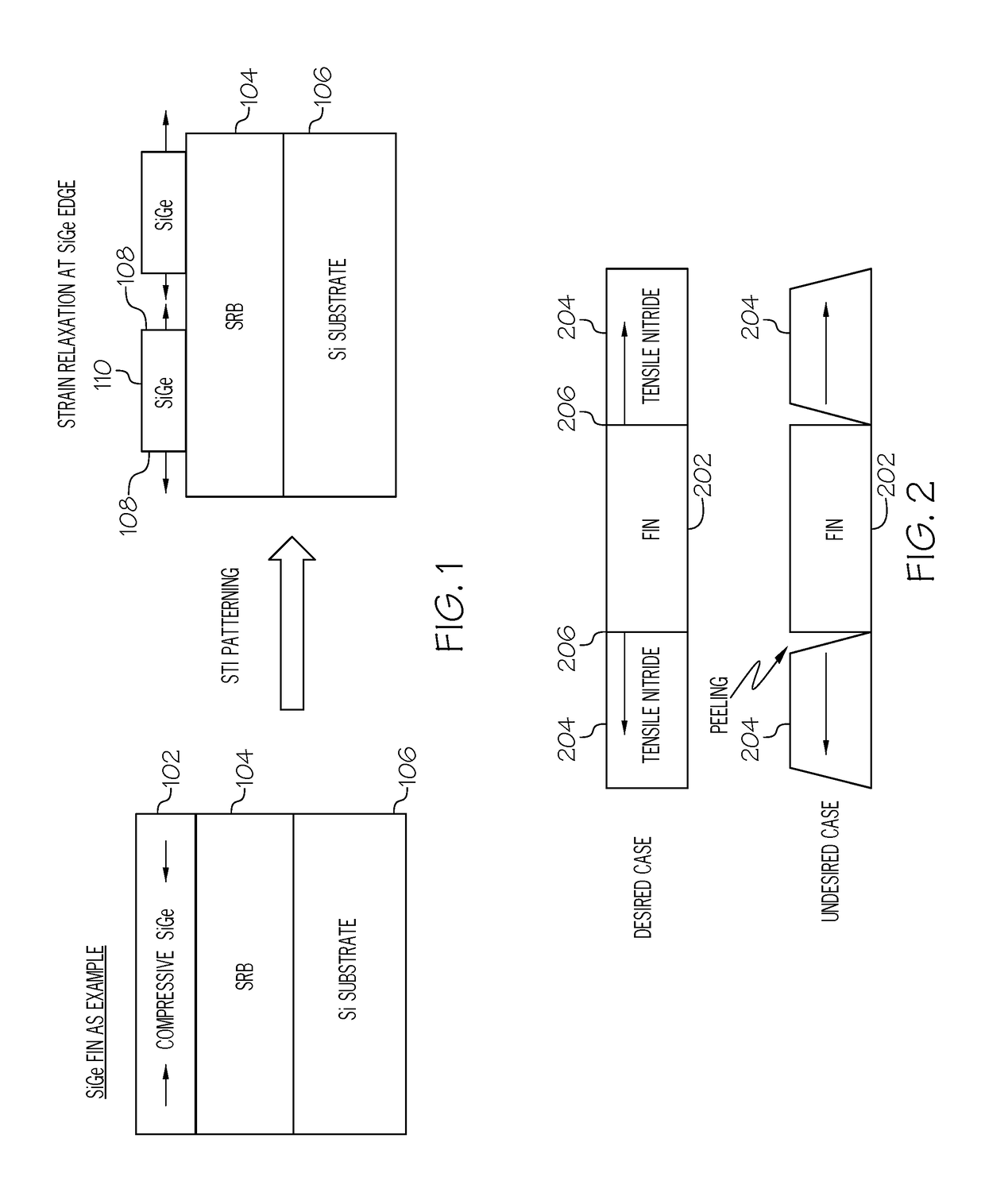
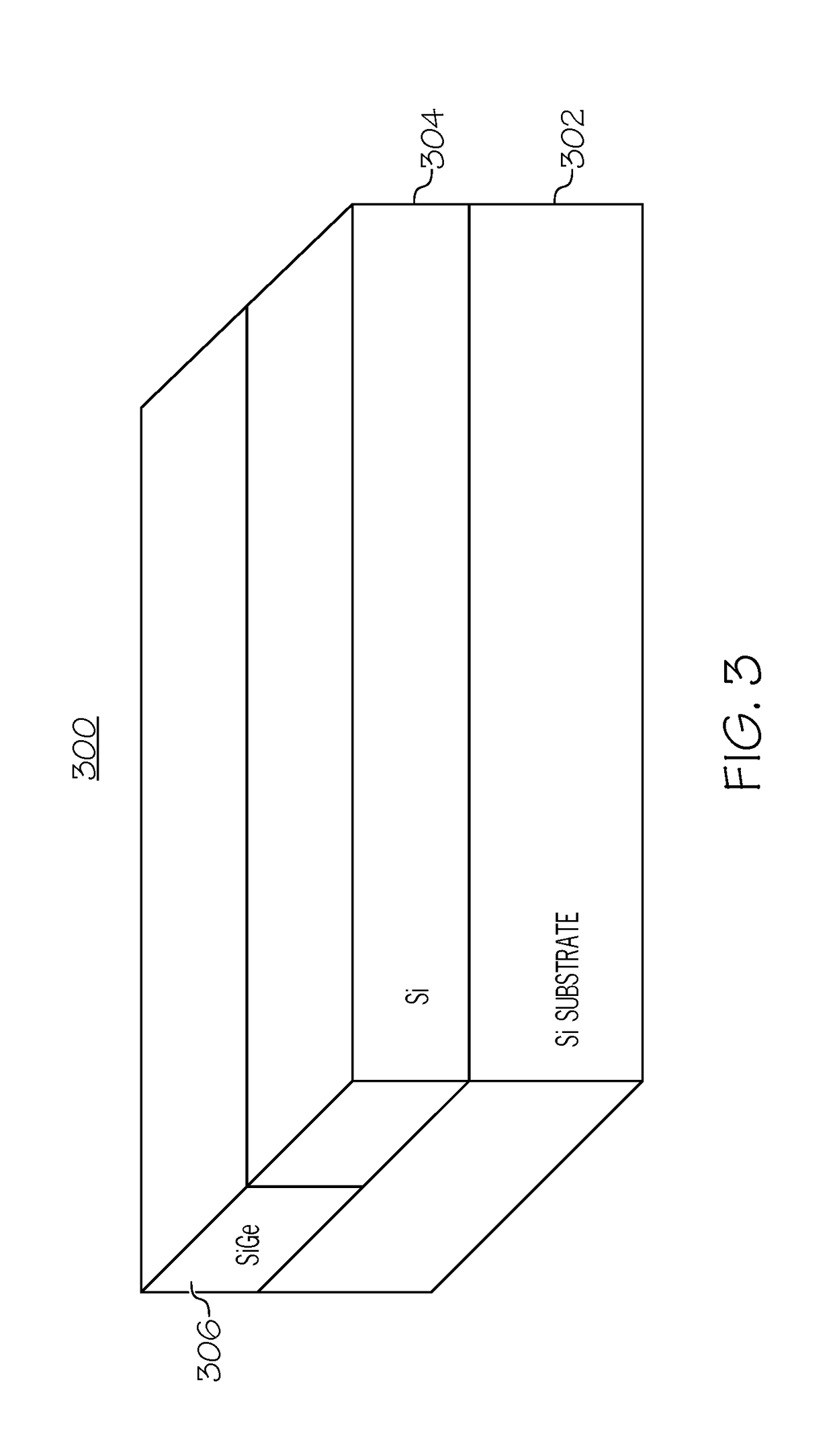
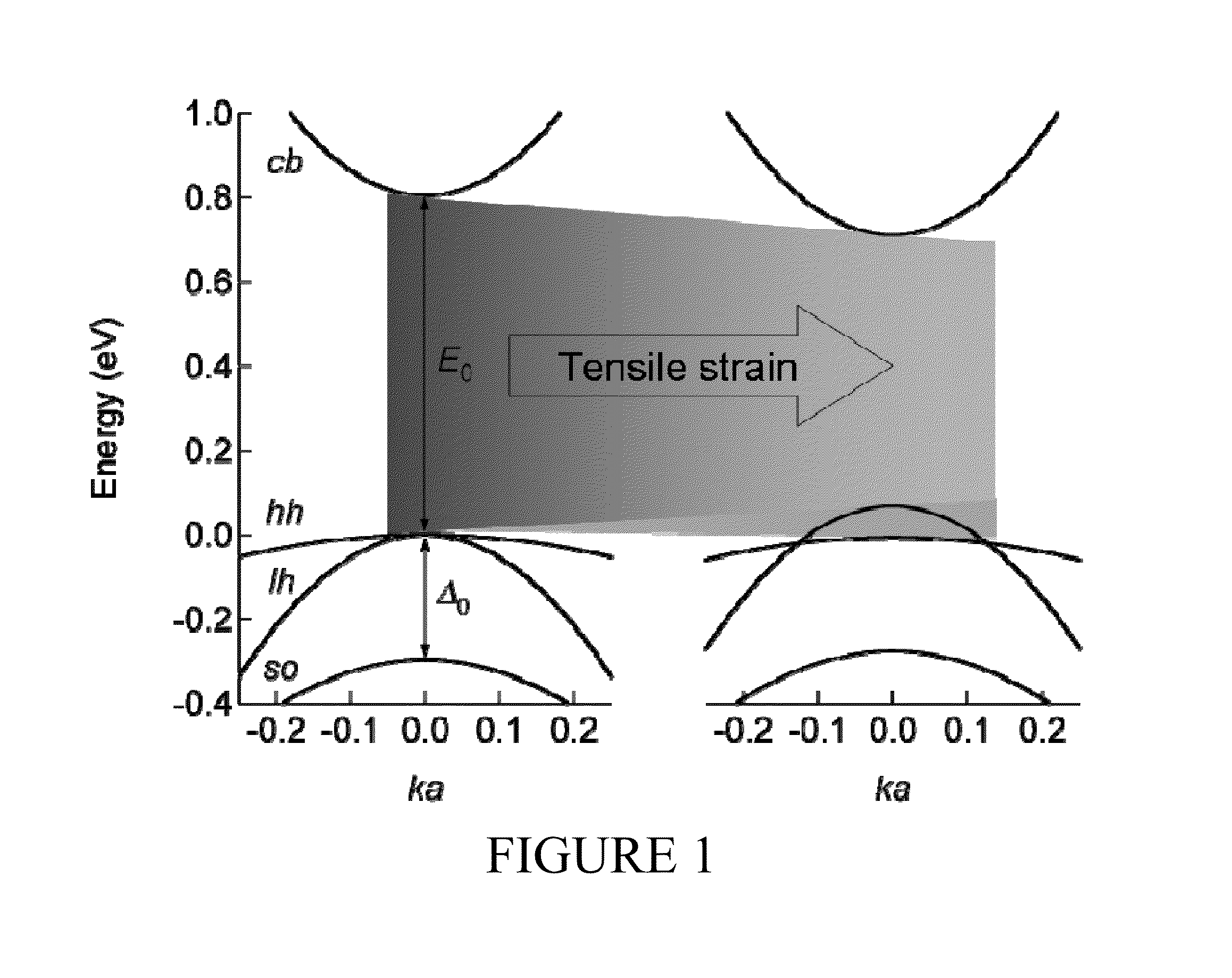
Tensile strained substrate
InactiveUS20060138479A1Increased tensile strainTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETTensile strain
An exemplary embodiment relates to a method for forming a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET). The method includes providing a substrate having a gate formed above the substrate and performing at least one of the following depositing steps: depositing a spacer layer and forming a spacer around a gate and gate insulator located above a layer of silicon above the substrate; depositing an etch stop layer above the spacer, the gate, and the layer of silicon; and depositing a dielectric layer above the etch stop layer. At least one of the depositing a spacer layer, depositing an etch stop layer, and depositing a dielectric layer comprises high compression deposition which increases in tensile strain in the layer of silicon.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
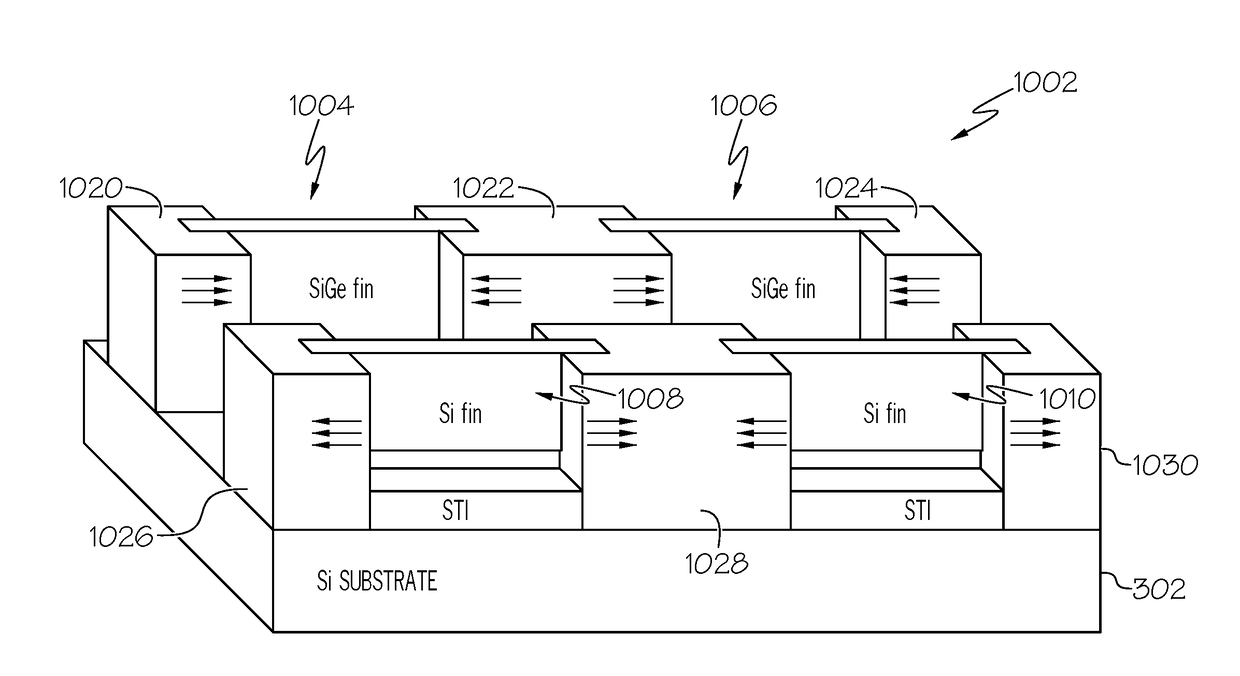
Structure and method for forming strained finfet by cladding stressors
ActiveUS20180047845A1Prevent stress relaxationPrevent/recover strain relaxationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringNitride
Various methods and structures for fabricating a strained semiconductor fin of a FinFET device. A strained semiconductor fin structure includes a substrate, a semiconductor fin disposed on the substrate, the semiconductor fin having two fin ends, and a stressor material cladding wrapped around a portion of each of the two fin ends forming a strained semiconductor fin that includes at least one strained channel fin having stressor cladding wrapped around at least one end of the strained channel fin thereby straining the at least one strained channel fin. The stressor cladding can be a compressive nitride stressor to compressively strain a compressively strained silicon germanium fin. The stressor cladding can be a tensile nitride stressor to tensily strain a tensily strained silicon fin.
Owner:IBM CORP
Concrete sensor with multi-intelligence characteristic and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112268933AEnhanced Perceptual CharacteristicsSensitive characteristics are stable and highly sensitiveMaterial resistanceMoisture capacityStructural engineering
A concrete sensor with a multi-intelligence characteristic comprises the following components in percentage by weight: cement to nano silicon dioxide to slag to sand to water reducing agent to defoaming agent to three-dimensional carbon nano material aqueous dispersion liquid =1:(0.05-0.12):(0.1-0.2):(0.8-1.2):(0.02-0.03):(0.001-0.004):(0.240-0.284), the volume content of steel fibers is 1.0-2.0%,and the volume content is 0.5-1.5%. The invention further provides a preparation method of the concrete sensor with the multi-intelligence characteristic. The problems that intelligent concrete onlyserves as a single performance sensor, and the sensing performance is reduced after the load exceeds the elastic range of the intelligent concrete or the intelligent concrete cracks are solved, and meanwhile the temperature, humidity and load state change of the structure can be stably monitored.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Multilayer coextruded shrink labels of oriented polystyrene film containing small rubber particles and low rubber particle gel content and block copolymers
InactiveUS20100215877A1Improve toughnessHigh secant modulusWrappers shrinkageShrinkage connectionsMultilayer membraneGeneral purpose
A multilayer film comprises at least 3 layers including a first outer layer, a second outer layer and between the first and second outer layers at least one core layer. The first and second outer layers each comprise at least about 75 weight percent of (a) at least one high impact polystyrene (HIPS) component. The at least one core layer comprises (b) at least one styrene block copolymer that is present at a concentration of at least about 2 weight percent of the polymers in the film; and-polymers (a), (b) and (c) at least one general purpose polystyrene having a weight-average molecular weight of more than 200,000 grams per mole and 350,000 grams per mole or less and that is present at a concentration of at least about 10 weight percent and up to at most about 50 weight percent of the polymers in the composition account for 100 percent by weight of the polymers in the polymer composition excluding polymeric additives.
Owner:TRANSILWRAP COMPNAY INC
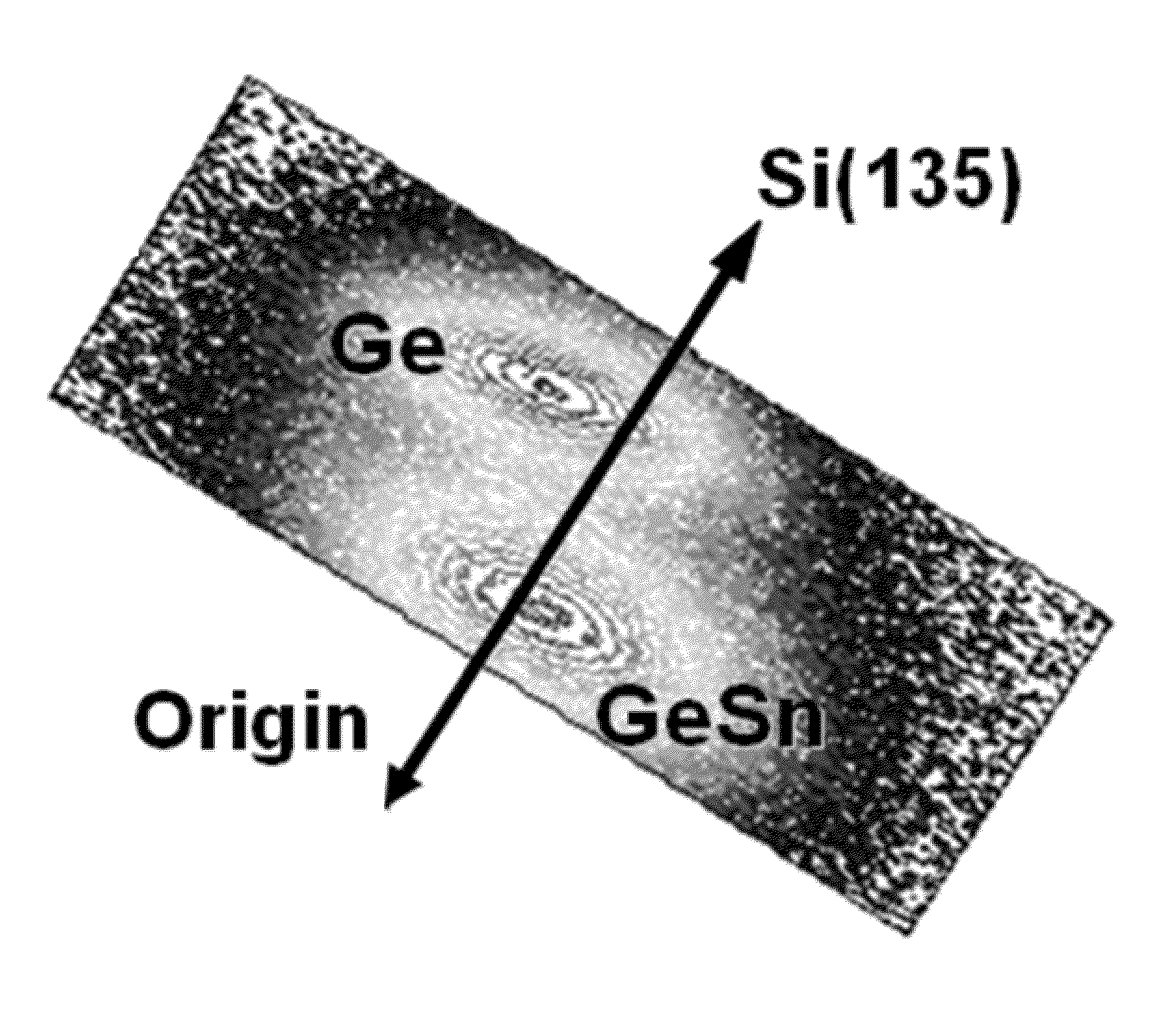
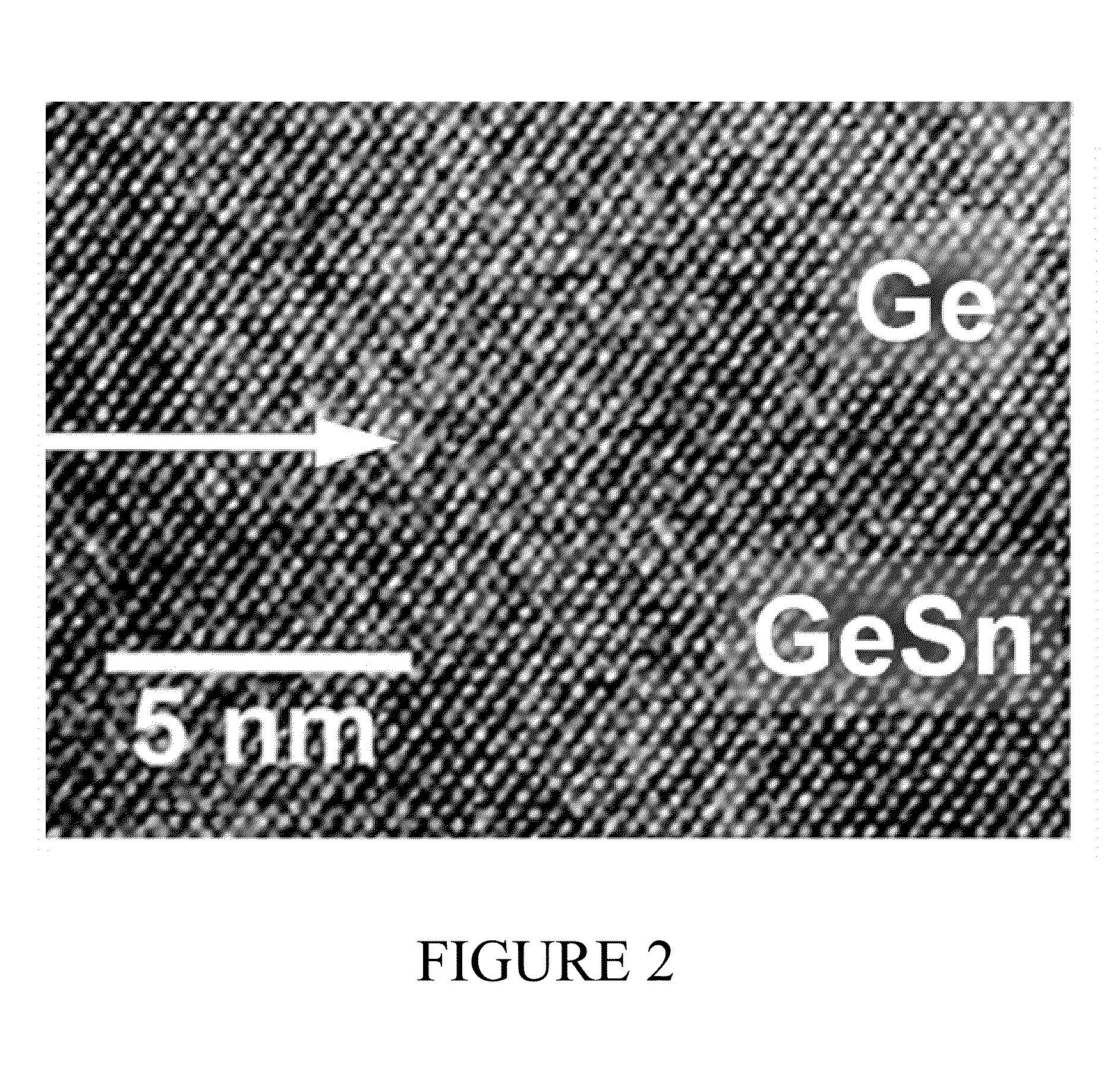
Methods and Compositions for Preparing Tensile Strained Ge on Ge1-ySNy Buffered Semiconductor Substrates
InactiveUS20110198729A1Improve responseEasy to assembleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainSemiconductor structure
The present disclosure describes methods for preparing semiconductor structures, comprising forming a Ge1-ySny buffer layer on a semiconductor substrate and forming a tensile strained Ge layer on the Ge1-ySny buffer layer using an admixture of (GeH3)2CH2 and Ge2H6 in a ratio of between 1:10 and 1:30. The disclosure further provides semiconductor structures having highly strained Ge epilayers (e.g., between about 0.15% and 0.45%) as well as compositions comprising an admixture of (GeH3)2CH2 and Ge2H6 in a ratio of between about 1:10 and 1:30. The methods herein provide, and the semiconductor structure provide, Ge epilayers having high strain levels which can be useful in semiconductor devices for example, in optical fiber communications devices.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Upgraded recycled relatively polyethylene rich polyolefin materials
PendingUS20210347970A1Improve mechanical propertiesIncrease strainPlastic recyclingPolypropyleneIndustrial waste
A polyethylene-polypropylene composition obtainable by blending a) 80 to 97 wt.-% of a blend (A) comprising A-1) polypropylene and A-2) polyethylene, wherein the ratio of polypropylene to polyethylene is from 3:7 to 13:7, and wherein blend (A) is a recycled material, which is recovered from a waste plastic material derived from post-consumer and / or post-industrial waste; and b) 3 to 20 wt.-% of a compatibilizer (B) being a heterophasic random copolymer comprising a random polypropylene copolymer matrix phase and an elastomer phase dispersed therein, whereby the heterophasic random copolymer has—a xylene insolubles content (XCI) of from 65 to 88 wt.-% (ISO 16152, led, 25° C.), and—a xylene soluble content XCS of 12 to 35 wt.-% (ISO 16152, led, 25° C.), the XCS fraction having an intrinsic viscosity (measured in decalin according to DIN ISO 1628 / 1 at 135° C.) of 1.2 dl / g to less than 3.0 dl / g, and—a flexural modulus of from 300 to 600 MPa (ISO 178, measured on injection moulded specimens, 23° C.); whereby the ratio of MFR2 (blend (A)) / MFR2 (compatibilizer (B)) (ISO1133, 2.16 kg load at 230° C.), is in the range of 0.5 to 1.5.
Owner:BOREALIS AG
Functionally strained optical fibers
InactiveUS20050185904A1Eliminating and greatly reducing impactMinimize changesOptical articlesFibre mechanical structuresFiberTensile strain
The present invention introduces a concept of “smart” ribbons, which use functionally tensioned optical fibers during the manufacture of fiber optic ribbons to create fiber ribbons with controlled geometrical configuration, optimized strain distribution and reduced attenuation. The ribbons may have flat or bowed cross section and be straight along the length or curved in its plane, or twisted unidirectionally, or periodically. These shapes and residual stress-strain state are induced and controlled by using tension functions instead of traditional constant-value tension per fiber during the ribbon manufacture. Further, the present invention reduces signal loss and / or attenuation in ribbon fibers caused by an increase in the strain variation from tensile strain to compressive strain along the length of the individual fibers when ribbons are manufactured, stacked, stranded around a strength member or twisted and bent during cable installation. In a first embodiment of the present invention, either a symmetric or non-symmetric load distribution is applied across the fibers being placed or drawn into a ribbon structure to eliminate or control residual twist in a completed fiber ribbon. Additionally, in the present invention, the load distribution on the fibers of a ribbon can be varied (e.g. periodically changed) along the length of the ribbon to provide a ribbon with the required design characteristics for any particular application. In a second embodiment of the invention, a fiber optic ribbon is made up of a plurality of sub-unit ribbons arranged in substantially the same plane. Each sub-unit ribbon includes a plurality of optical fibers coated by sub-unit matrices.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Flexible display
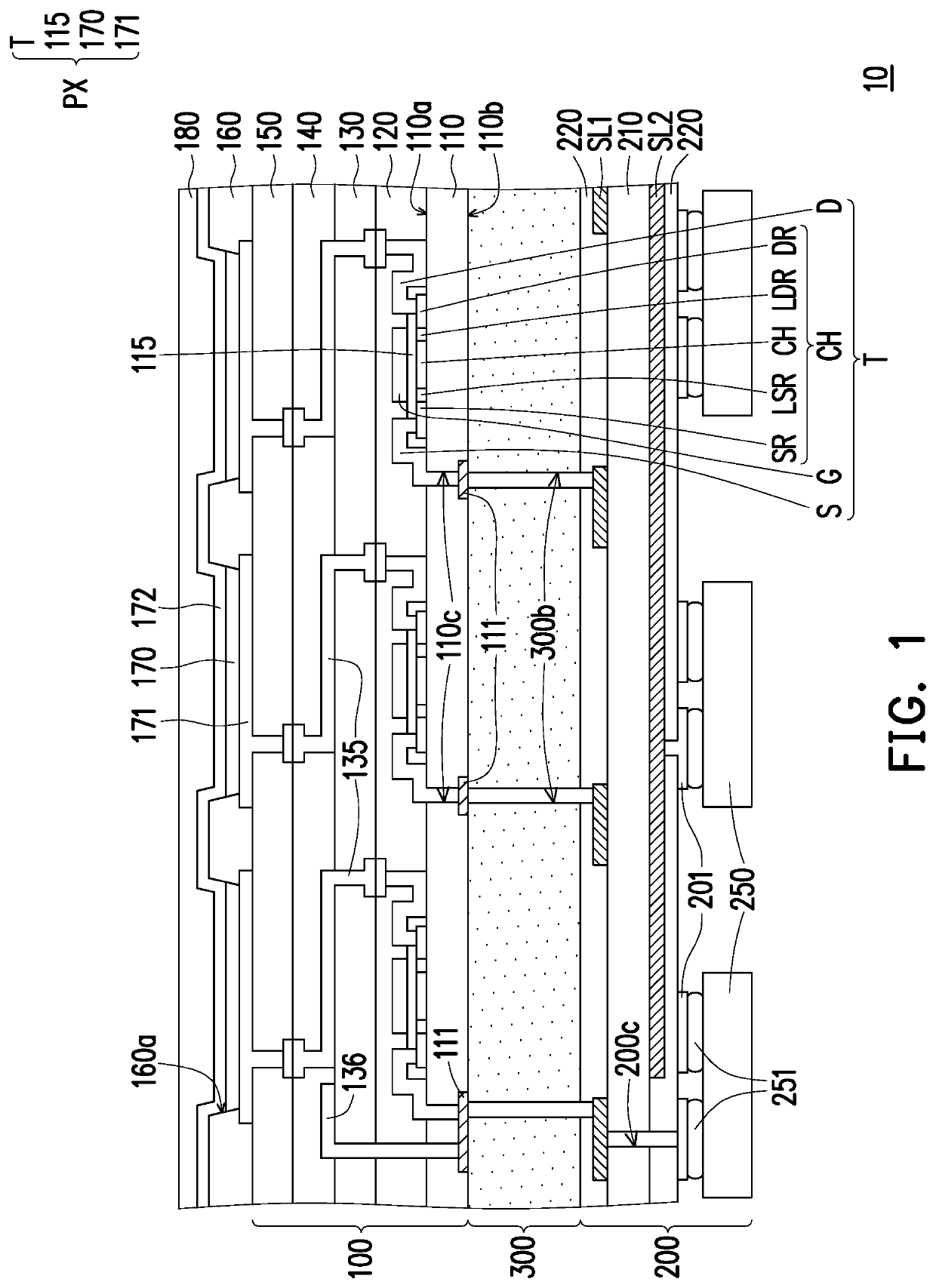
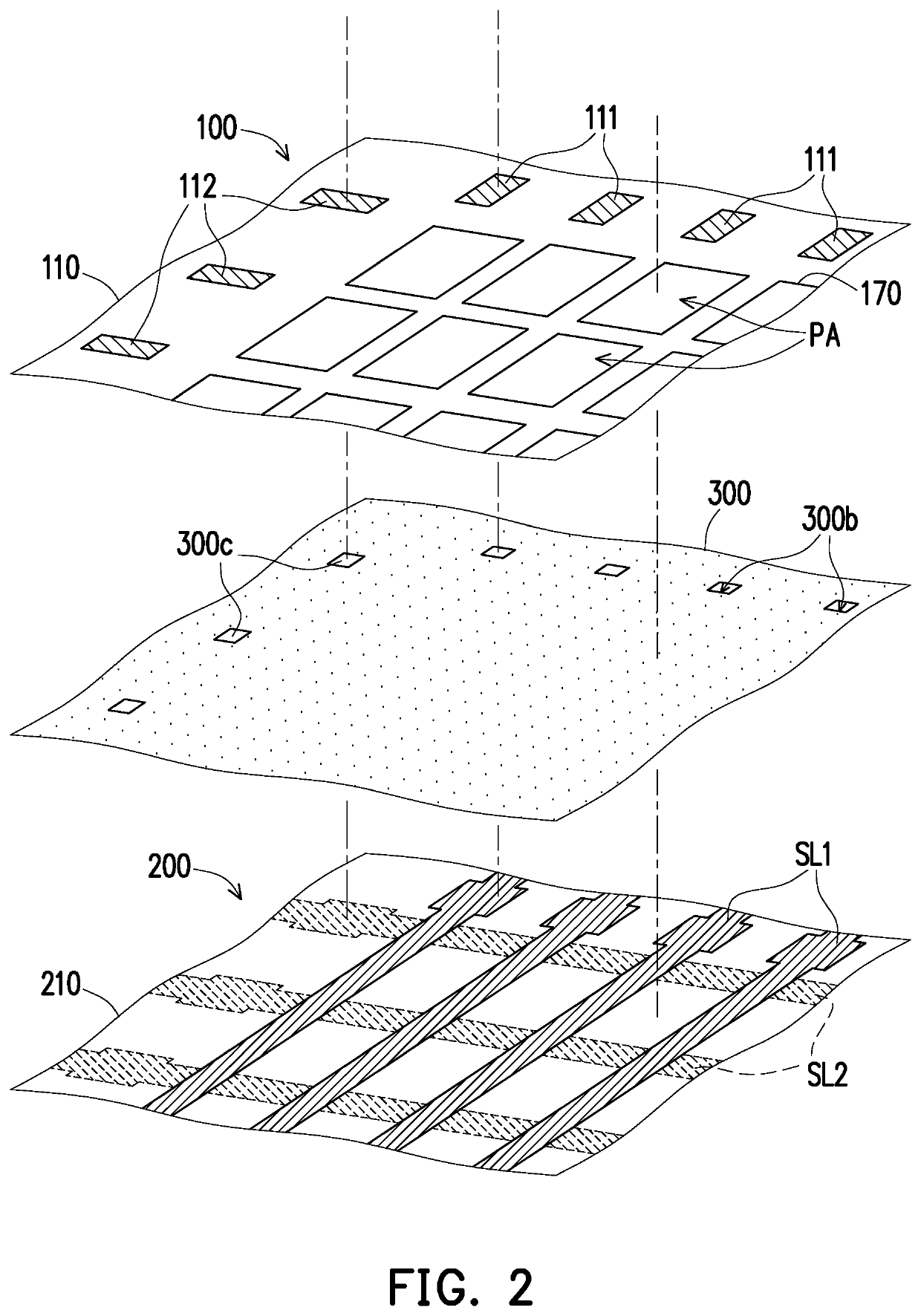
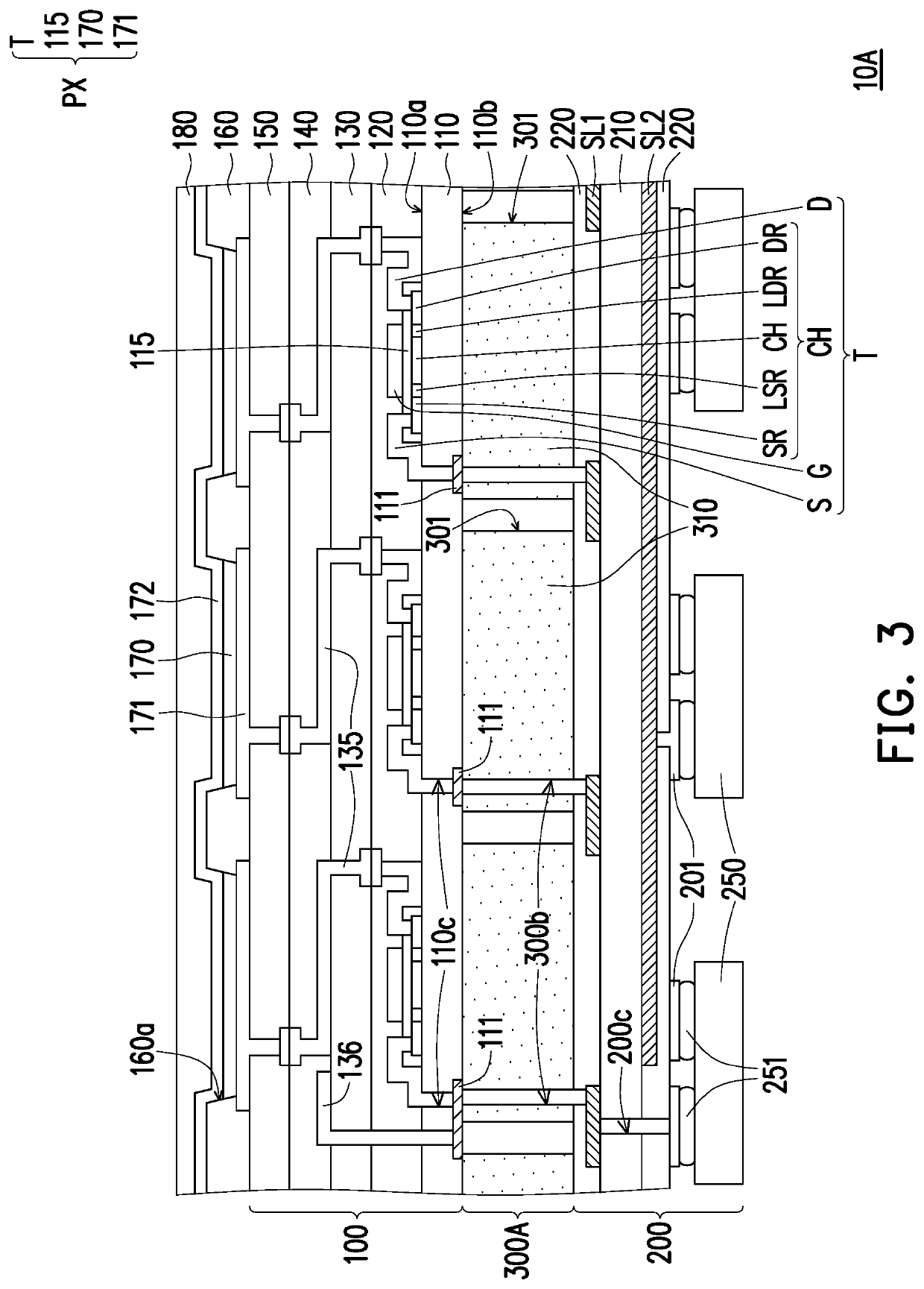
ActiveUS20200359499A1Good bending toleranceImproving bending tolerancePrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesFlexible circuitsDisplay device
A flexible display including a buffer layer, a plurality of pixel structures, a plurality of first pads, a plurality of first conductive through holes, a flexible circuit board and an adhesive layer is provided. The pixel structures are disposed on a first surface of the buffer layer. The first pads are disposed on a second surface of the buffer layer. The first conductive through holes are embedded in the buffer layer. The first pads are respectively electrically connected to the pixel structures through the first conductive through holes. The adhesive layer is disposed between the second surface of the buffer layer and the flexible circuit board. An orthogonal projection of the adhesive layer on the buffer layer overlaps an orthogonal projection of the pixel structures on the buffer layer. The first pads are electrically connected to first signal lines of the flexible circuit board.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Hetero-integrated strained silicon n- and p-MOSFETs
InactiveUS7273800B2Reduce processing stepsSubstrate surface is maintainedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETSemiconductor structure
The present invention provides semiconductor structures and a method of fabricating such structures for application of MOSFET devices. The semiconductor structures are fabricated in such a way so that the layer structure in the regions of the wafer where n-MOSFETs are fabricated is different from the layer structure in regions of the wafers where p-MOSFETs are fabricated. The structures are fabricated by first forming a damaged region with a surface of a Si-containing substrate by ion implanting of a light atom such as He. A strained SiGe alloy is then formed on the Si-containing substrate containing the damaged region. An annealing step is then employed to cause substantial relaxation of the strained SiGe alloy via a defect initiated strain relaxation. Next, a strained semiconductor cap such as strained Si is formed on the relaxed SiGe alloy.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
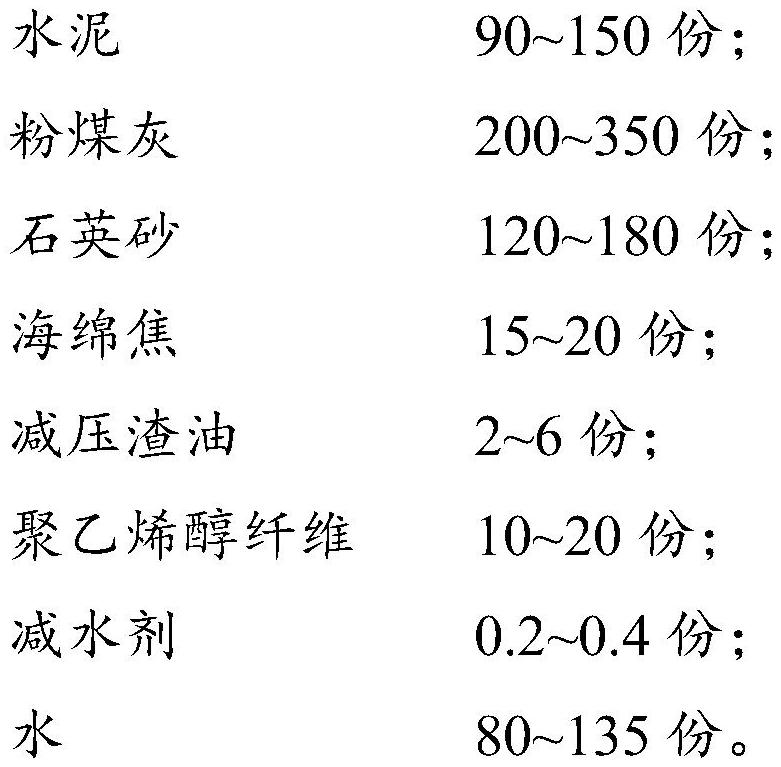
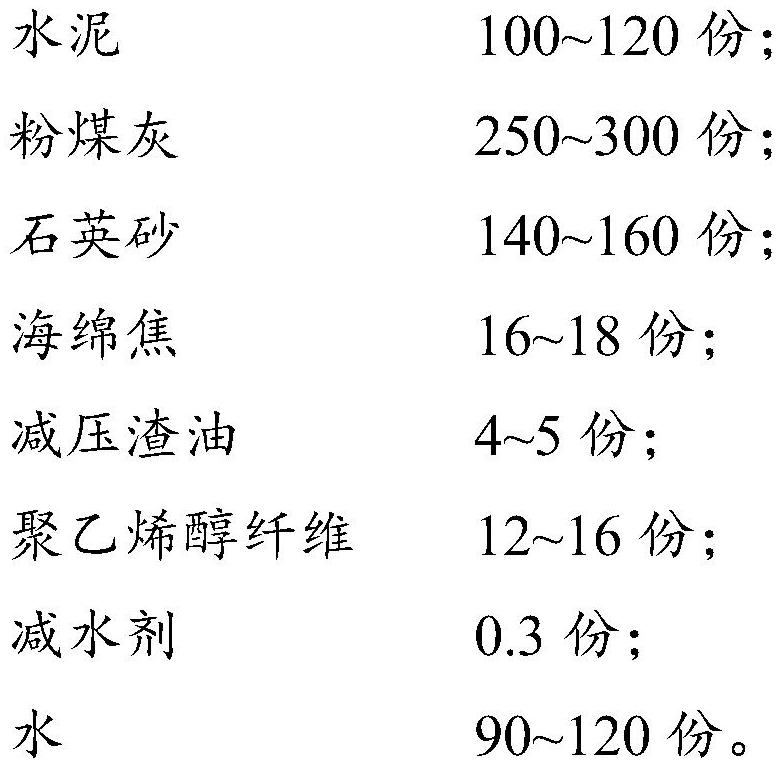
Sponge coke and vacuum residue modified high-ductility concrete and preparation method thereof
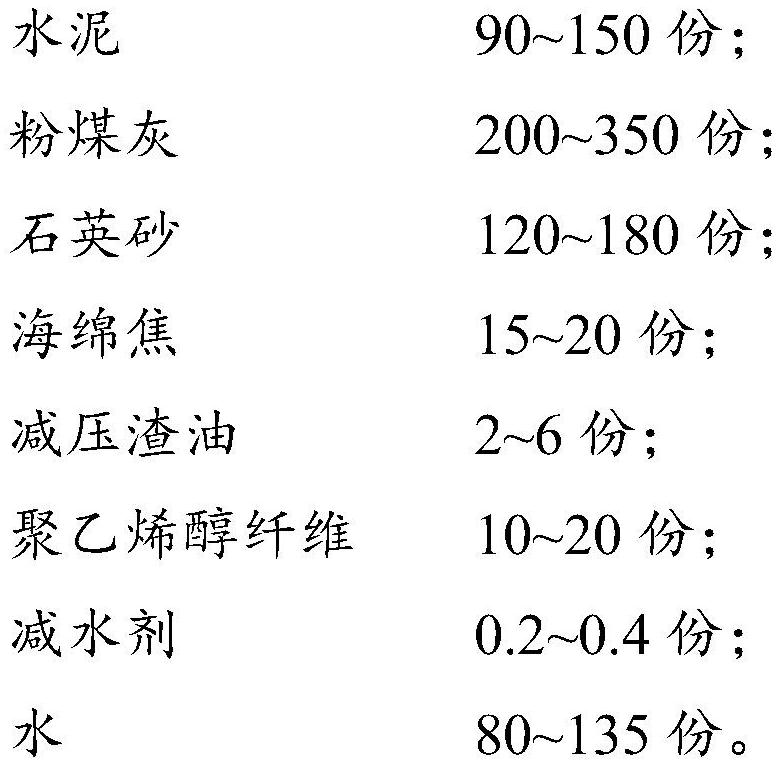
The invention provides sponge coke and vacuum residue modified high-ductility concrete and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of fiber concrete. The high-ductility concrete provided by the invention comprises the following components in parts by mass: 90-150 parts of cement, 200-350 parts of fly ash, 120-180 parts of quartz sand, 15-20 parts of sponge coke, 2-6 parts of vacuum residue, 10-20 parts of polyvinyl alcohol fiber, 0.2-0.4 part of a water reducing agent, and 80-135 parts of water. The sponge coke and the vacuum residue are used as concrete admixtures and have a synergistic effect, so that the chemical bonding energy between the polyvinyl alcohol fiber and a cement hydration product can be effectively reduced, and the probability that the polyvinyl alcohol fiber is broken by pulling is reduced, thereby improving the tensile deformation capacity of the high-ductility concrete material and improving the ultimate tensile strength and tensile strain of the high-ductility concrete.
Owner:CHINA ROAD & BRIDGE +1
MOBILITY ENHANCEMENT IN SiGe HETEROJUNCTION BIPOLAR TRANSISTORS
InactiveUS20090224286A1Improve performanceIncreasing biaxial strainSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionCharge carrier mobility
The present invention relates to a high performance heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) having a base region with a SiGe-containing layer therein. The SiGe-containing layer is not more than about 100 nm thick and has a predetermined critical germanium content. The SiGe-containing layer further has an average germanium content of not less than about 80% of the predetermined critical germanium content. The present invention also relates to a method for enhancing carrier mobility in a HBT having a SiGe-containing base layer, by uniformly increasing germanium content in the base layer so that the average germanium content therein is not less than 80% of a critical germanium content, which is calculated based on the thickness of the base layer, provided that the base layer is not more than 100 nm thick.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Hydrogel vascular embolism material and shape memory embolism treatment method
ActiveCN110559470ASimple preparation processReduce manufacturing costSurgical adhesivesHydrophilic monomerCross-link
The invention discloses a hydrogel vascular embolism material and a shape memory embolism treatment method. The hydrogel vascular embolization material is obtained by free radical copolymerization ofa hydrophobic monomer containing a benzene ring, a hydrophilic monomer capable of forming an intermolecular hydrogen bond and a cross-linking agent, the hydrogel vascular embolization material is formed by crosslinking physical crosslinking points formed by hydrophobic association and hydrogen bond interaction and covalent crosslinking points generated by chemical crosslinking. The vascular embolism material can achieve the purpose of vascular embolism, has excellent mechanical properties, and has the characteristics of relatively high breaking strain and breaking stress, excellent fatigue resistance, excellent resilience and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mobility enhancement in SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistors
InactiveUS20070045775A1Improve performanceIncreasing biaxial strainSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionCharge carrier mobility
The present invention relates to a high performance heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) having a base region with a SiGe-containing layer therein. The SiGe-containing layer is not more than about 100 nm thick and has a predetermined critical germanium content. The SiGe-containing layer further has an average germanium content of not less than about 80% of the predetermined critical germanium content. The present invention also relates to a method for enhancing carrier mobility in a HBT having a SiGe-containing base layer, by uniformly increasing germanium content in the base layer so that the average germanium content therein is not less than 80% of a critical germanium content, which is calculated based on the thickness of the base layer, provided that the base layer is not more than 100 nm thick.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of enhancing dopant incorporation in epitaxial film using halogen molecules as reactant in depostion
InactiveCN105047526AIncrease the tensile stressLow resistivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHalogenChemistry
The embodiment of the invention generally relates to a method for forming a silicon epitaxial layer on a semiconductor device. The method provided by the invention comprises heating a substrate disposed in a processing volume of a processing cavity, and exposing the substrate in a catalyst gas or one or more than one deposition gases to perform a deposition technology so as to form the silicon epitaxial layer on the substrate. The catalyst gas comprises halogen molecules, and the one or more than one deposition gases comprise a silicon source and the sources of a dopant. In one embodiment, the catalyst gas comprises chlorine.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Multilayer coextruded shrink labels of oriented polystyrene film containing small rubber particles and low rubber particle gel content and block copolymers
InactiveUS8431198B2Improve clarityLow hazeWrappers shrinkageSynthetic resin layered productsGeneral purposeEngineering
A multilayer film comprises at least 3 layers including a first outer layer, a second outer layer and between the first and second outer layers at least one core layer. The first and second outer layers each comprise at least 75 weight percent of (a) at least one high impact polystyrene component. The core layer(s) comprises(s) (b) at least one styrene block copolymer that is present at a concentration of at least about 2 weight percent of the polymers in the film; and polymers (a), (b) and (c) at least one general purpose polystyrene having a Mw of more than 200,000 and 350,000 or less and that is present at a concentration of at least about 10 wt. % and up to at most about 50 wt. % of the polymers in the composition account for 100 percent by weight of the polymers in the polymer composition excluding polymeric additives.
Owner:TRANSILWRAP COMPNAY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com