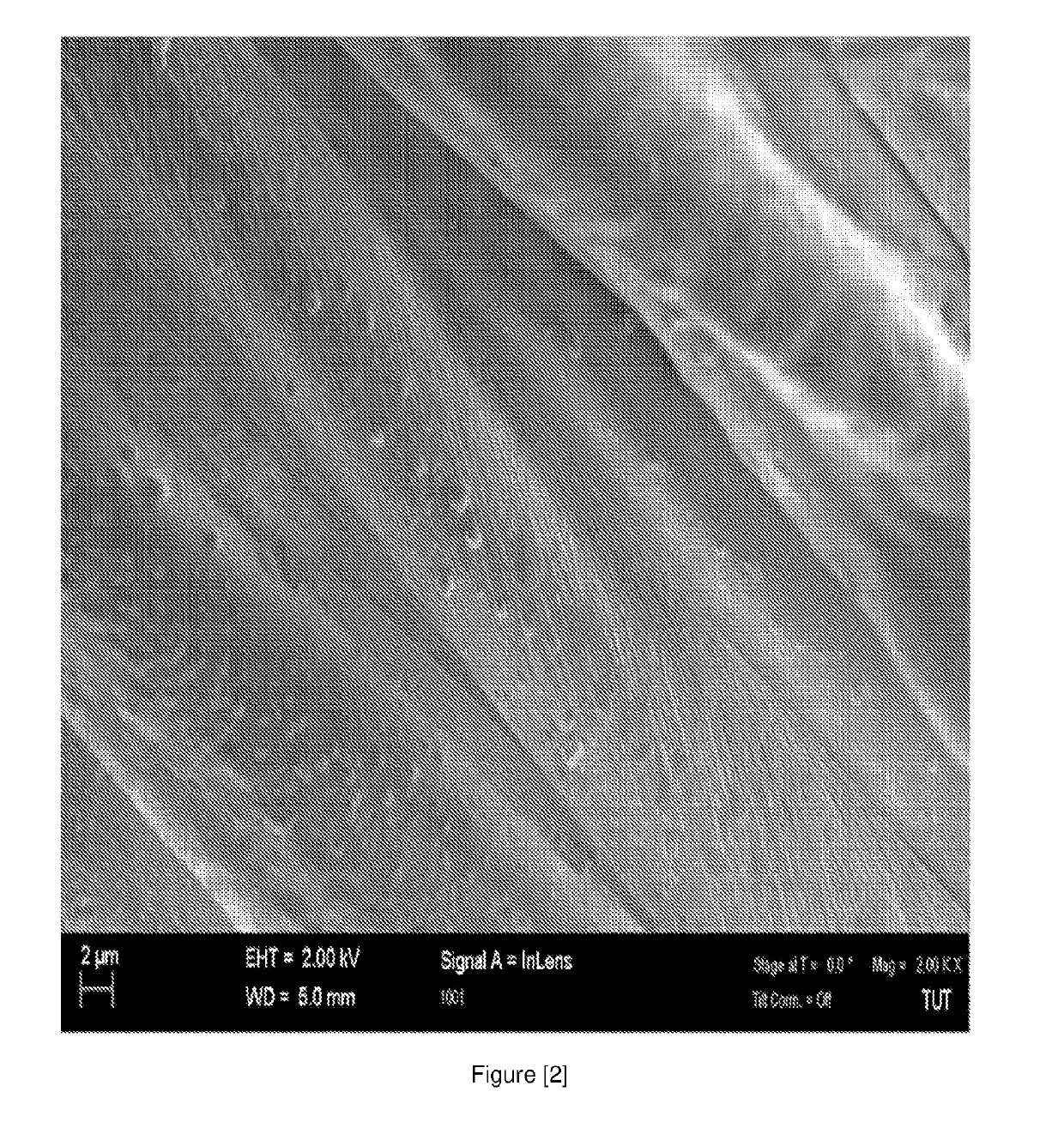
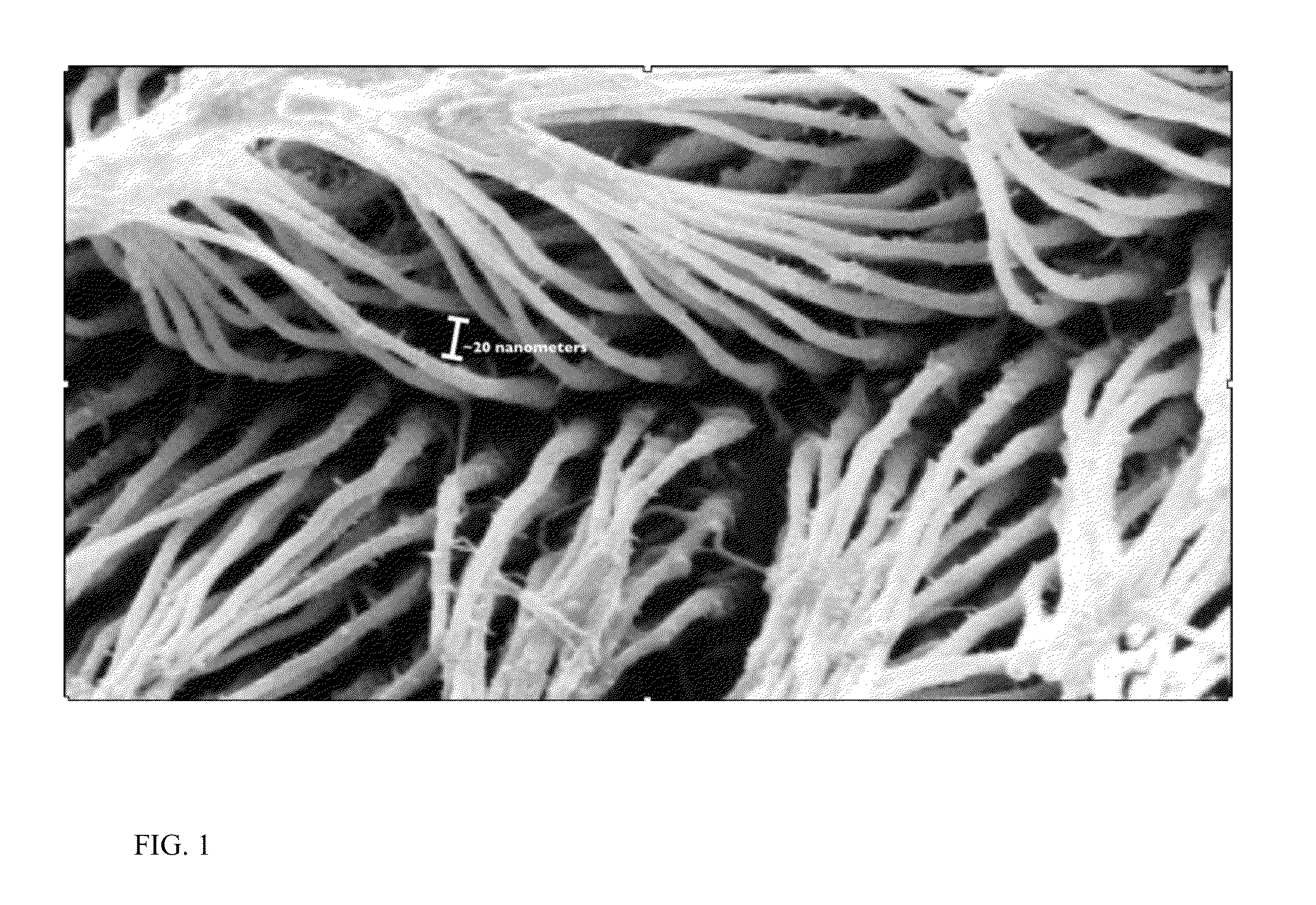
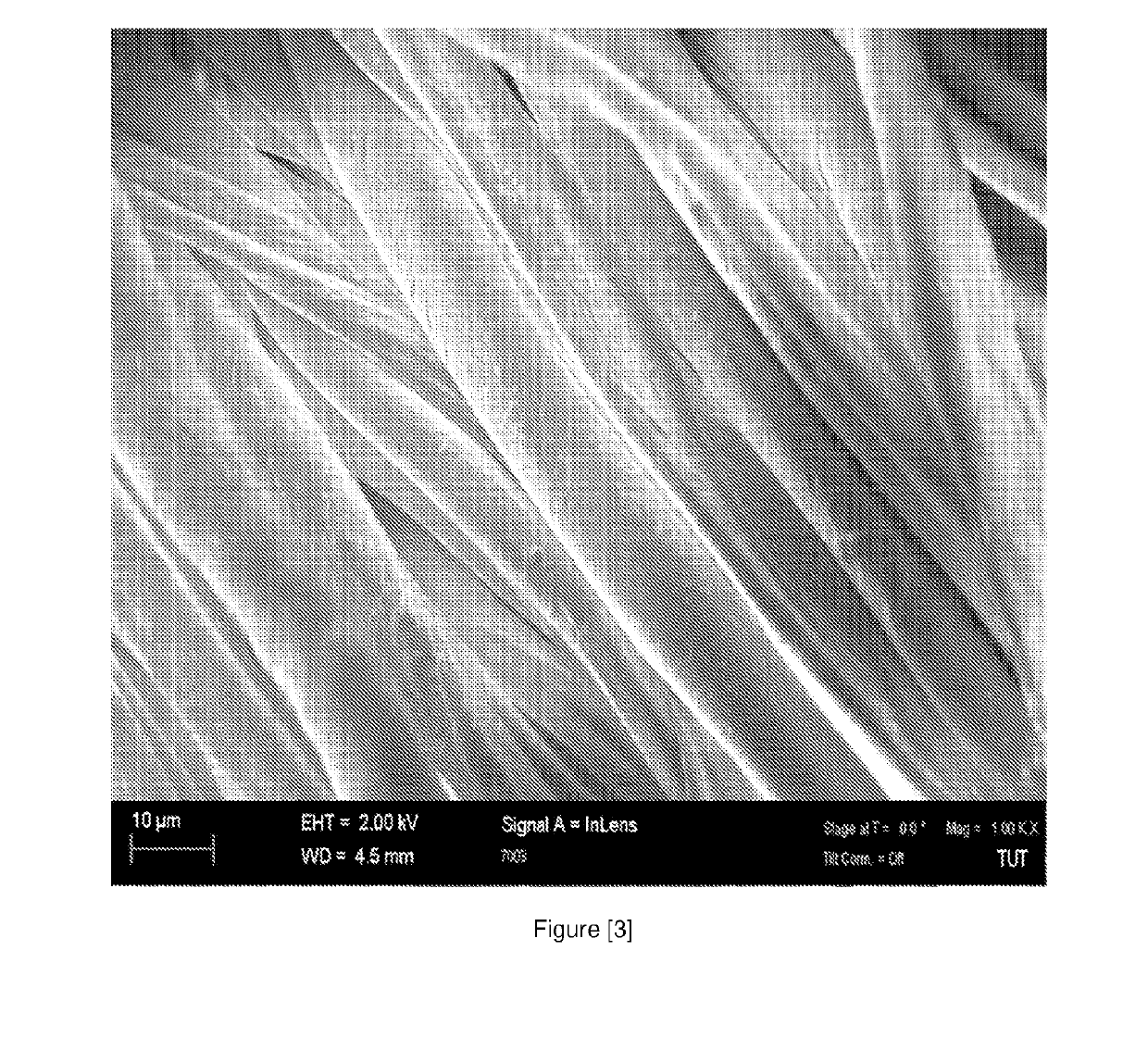
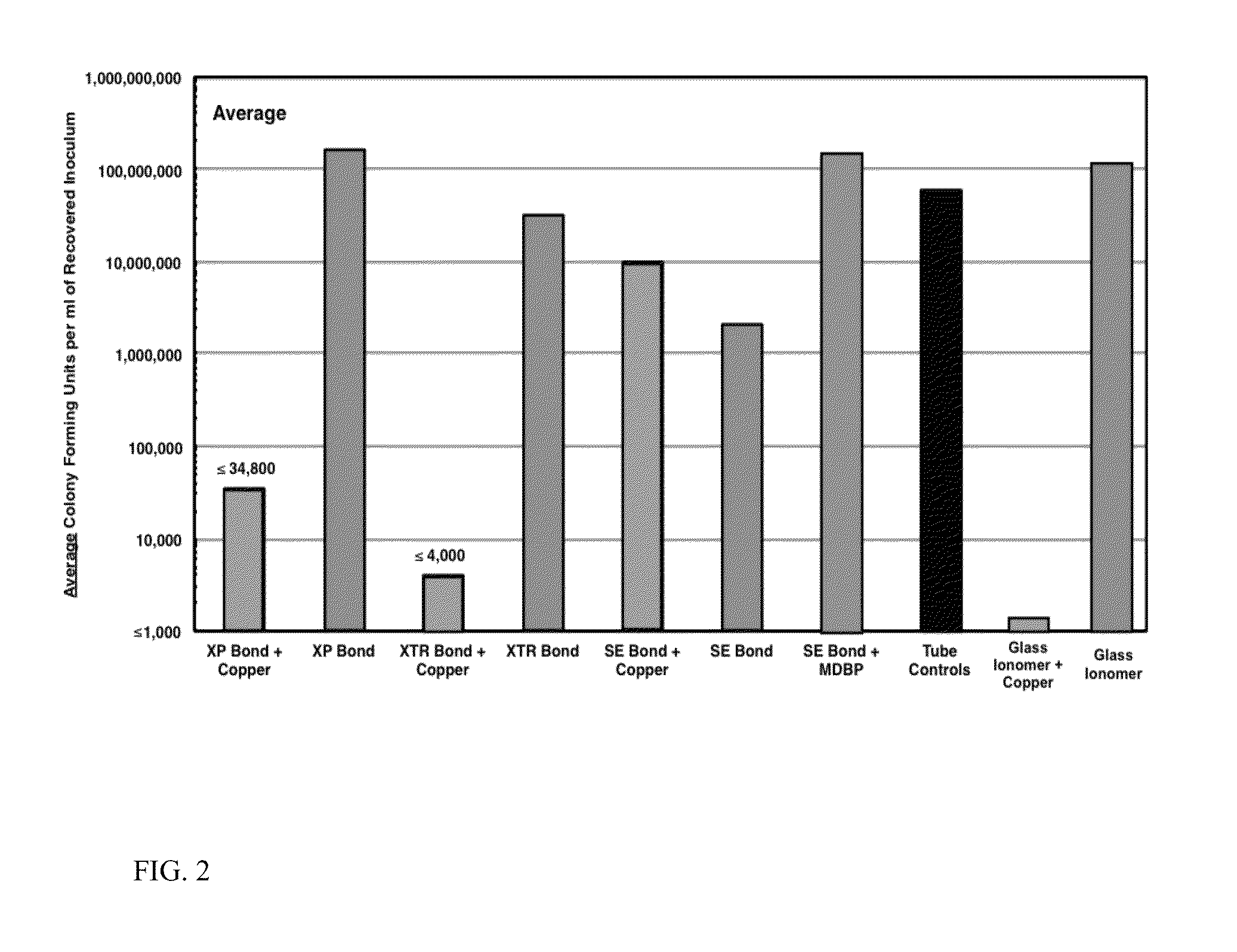
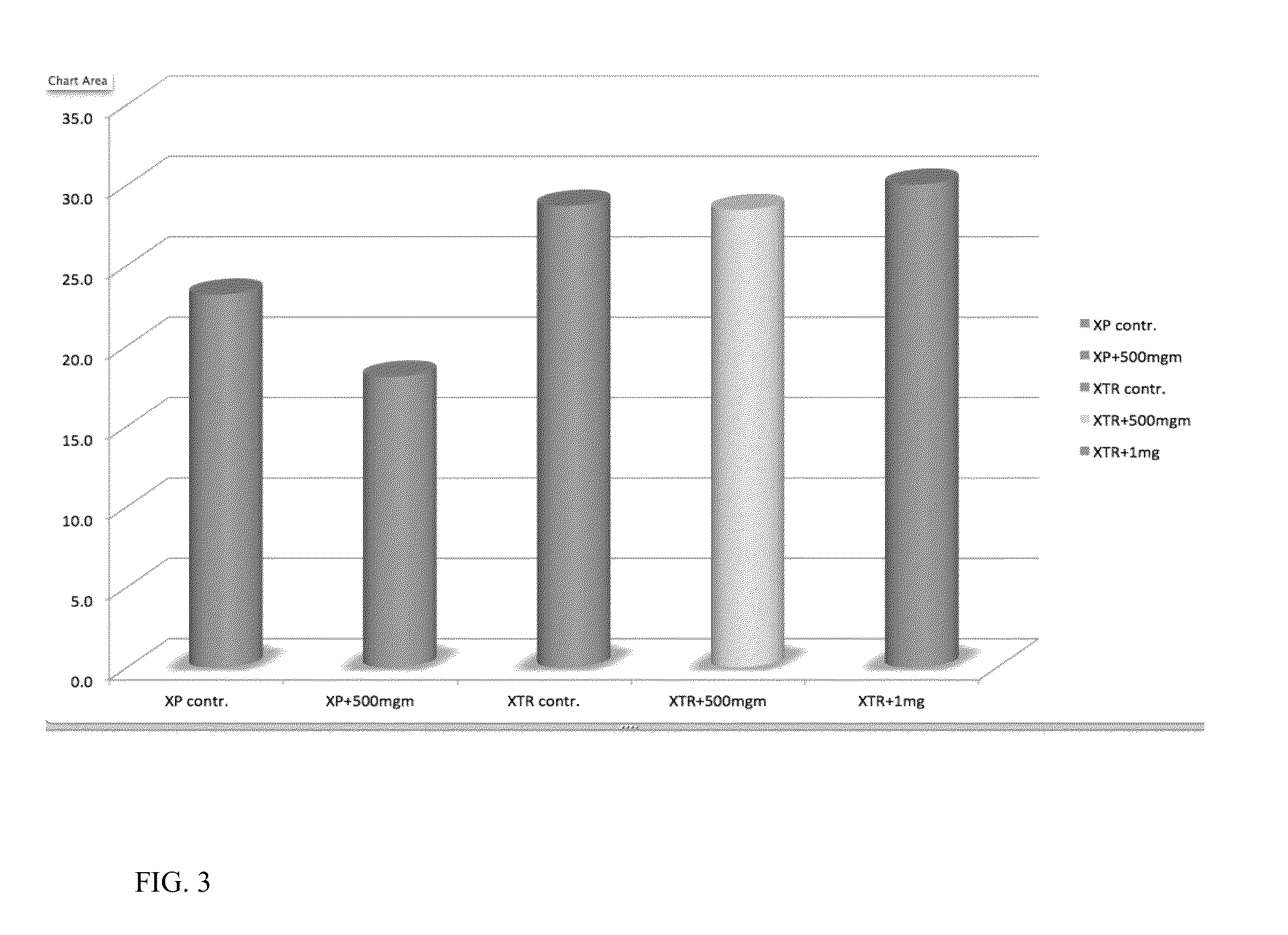
Patents
Literature
60 results about "Antimicrobial properties of copper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
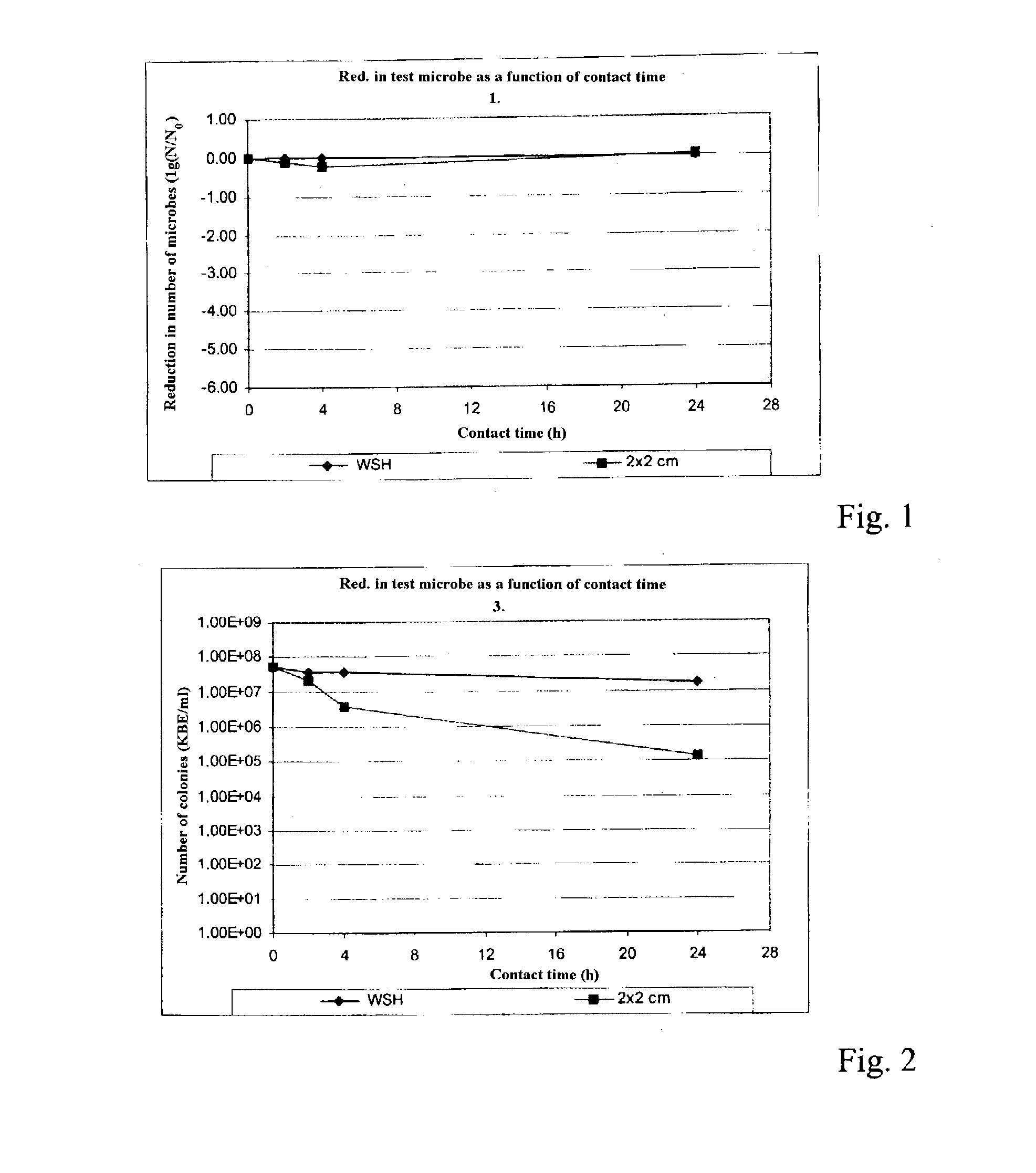
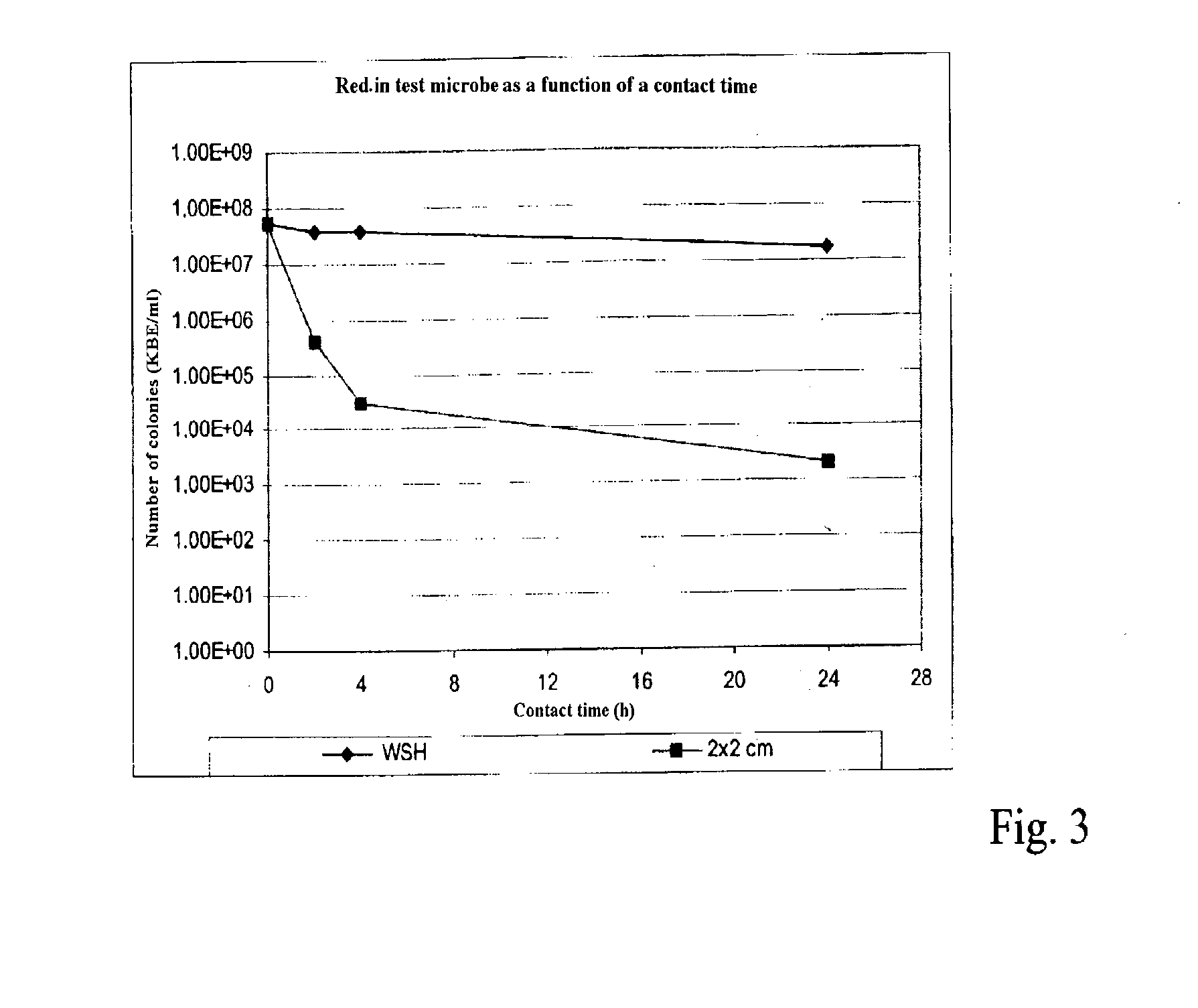
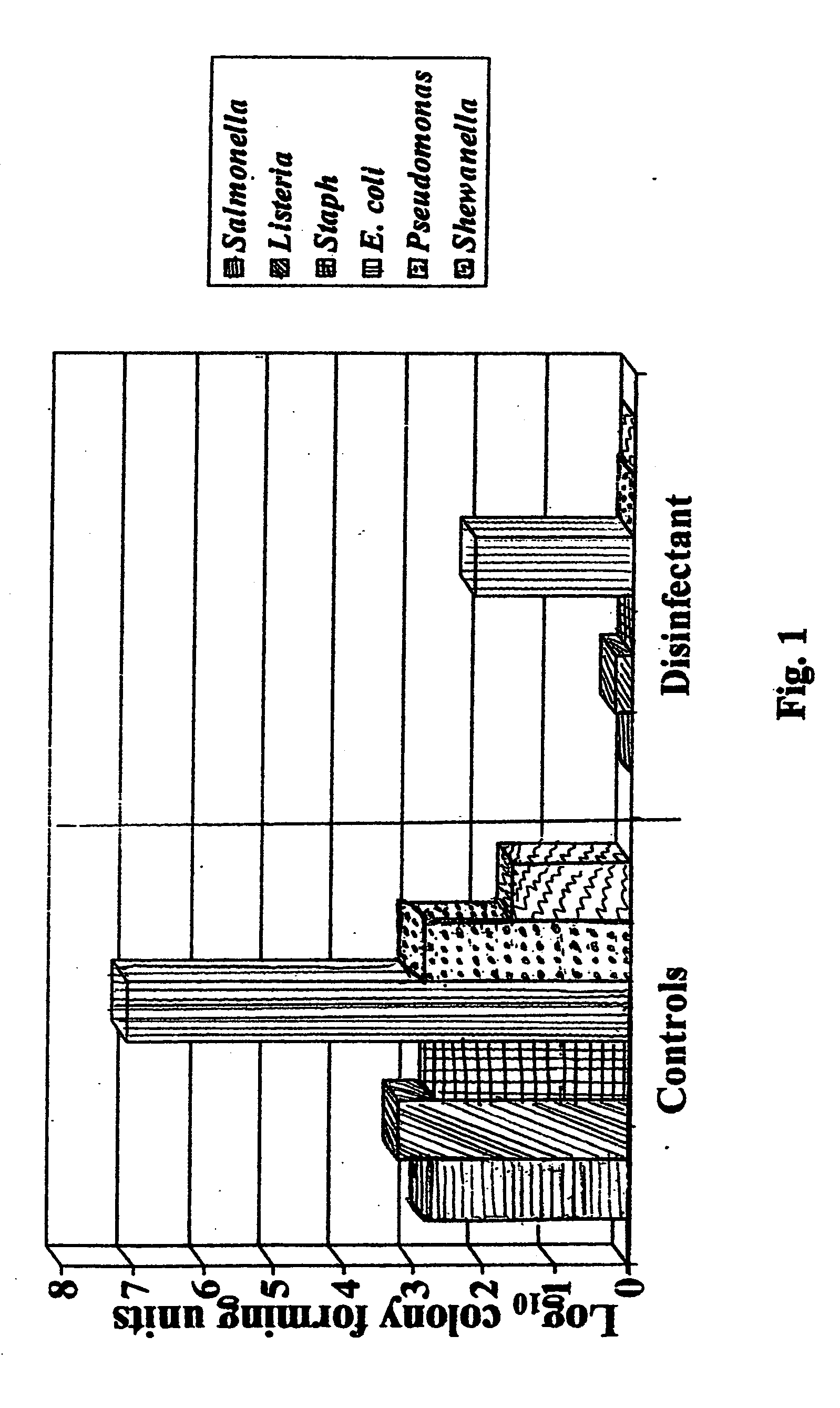
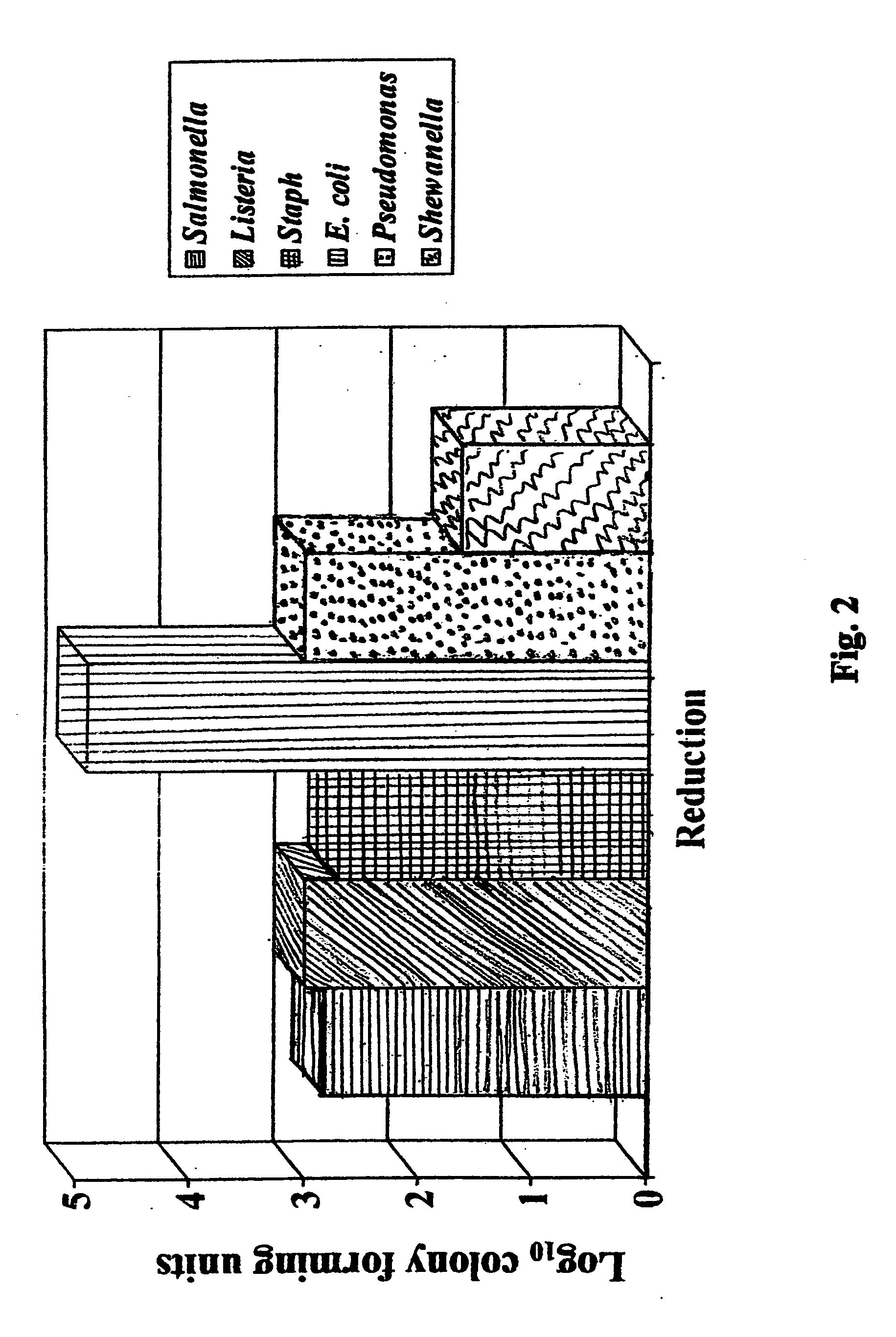
Copper and its alloys (brasses, bronzes, cupronickel, copper-nickel-zinc, and others) are natural antimicrobial materials. Ancient civilizations exploited the antimicrobial properties of copper long before the concept of microbes became understood in the nineteenth century. In addition to several copper medicinal preparations, it was also observed centuries ago that water contained in copper vessels or transported in copper conveyance systems was of better quality (i.e., no or little visible slime or biofouling formation) than water contained or transported in other materials.
Self-cleaning lotus effect surfaces having antimicrobial properties
A self-cleaning or lotus-effect surface that has antimicrobial properties, commercial products comprising such a surface, and uses thereof. A process for the production of an antimicrobial self-cleaning or lotus-effect surface in which one or more antimicrobial polymer(s) is secured to a surface-coating system for securing structure-formers to generate a self-cleaning surface. This method lastingly binds antimicrobial polymers to the self-cleaning surface. Commercial products comprising an antimicrobial self-cleaning or lotus-effect surface.
Owner:CREAVIS GES FUER TECH
Topical application of solid antimicrobials to carpet pile fibers during carpet manufacture
InactiveUS6641829B1Good light fastnessShampoo durabilityBiocideBiochemical fibre treatmentFiberLiquid medium
Carpeted floor covering articles comprising carpet pile fibers to which a topical antimicrobial application of solid particles has been applied either during or after product manufacture (such as part of a cleaning or treatment process) are provided. Such a topical treatment includes specific inorganic antimicrobial metal ion-based solid compounds, such as silver ion-exchange compounds, silver zeolites, and / or silver glasses, which may or may not be dispersed within a liquid medium for ease in handling and application. Such treatments also optionally include compositions of stain resistant agents, anti soil-redeposition compounds and liquids, surfactants, antistatic agents, and the like, to impart other characteristics to the target carpeted products. Such carpeted products thus exhibit excellent antimicrobial characteristics at both the surface of the carpet pile, as well as within the pile itself. Furthermore, it has been found that application of such solid metal-ion based antimicrobials permits the ability to increase antimicrobial activity for the target carpet product after vacuuming.
Owner:SAGE AUTOMOTIVE INTERIORS INC
Bi-laminar, hyaluronan coatings with silver-based anti-microbial properties
InactiveUS6866859B2Improve securityProlonged and sustained releaseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideMetallurgySilver ion
An article including a surface having a coating thereon, in which the coating includes a base coat, firmly adhered to the surface, and a hydrophilic, biocompatible top-coat. An antibiotic ceramic component is dispersed in one or both of the base coat and top-coat. Preferably, the ceramic component is dispersed in the base coat. In a preferred embodiment, the ceramic component is a zeolite with silver ions exchanged onto internal acidic sites of the zeolite, and the top-coat includes a polysaccharide, such as hyaluronan. The zeolite is highly effective in imparting anti-microbial character to the coating.
Owner:SCIESSENT LLC +1
Antimicrobial food additive and treatment for cooked food, water and wastewater
A composition of matter with antimicrobial and antibacterial properties for treatment of water, wastewater, processed food and for use as a food additive is provided. The antimicrobial composition inhibits cellular growth of known pathogenic, indicator and spoilage organisms, such as salmonella, stahphylococcus, listeria, E-coli, aerobic and anerobic organisms in wastewater and the like. The antimicrobial composition of the present invention is useful in many situations and conditions in need of disinfectants and sanitizers. One of the primary benefits of the antimicrobial agent is that it inhibits the growth of bacteria that have become antibiotic resistant. In addition, the antimicrobial composition herein does not have any known toxicity to man or the environment.
Owner:TASKER PRODS IP HLDG CORP
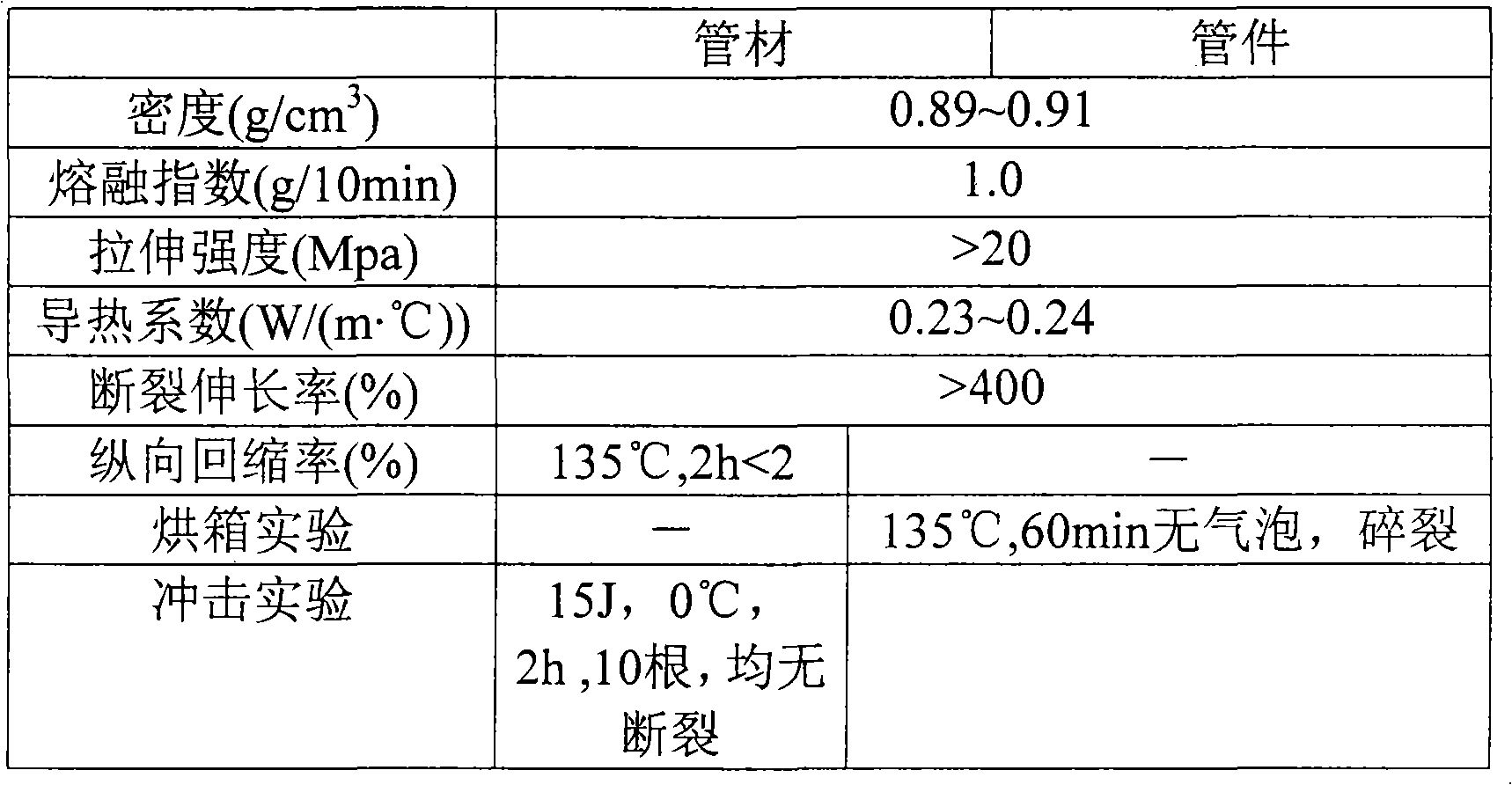
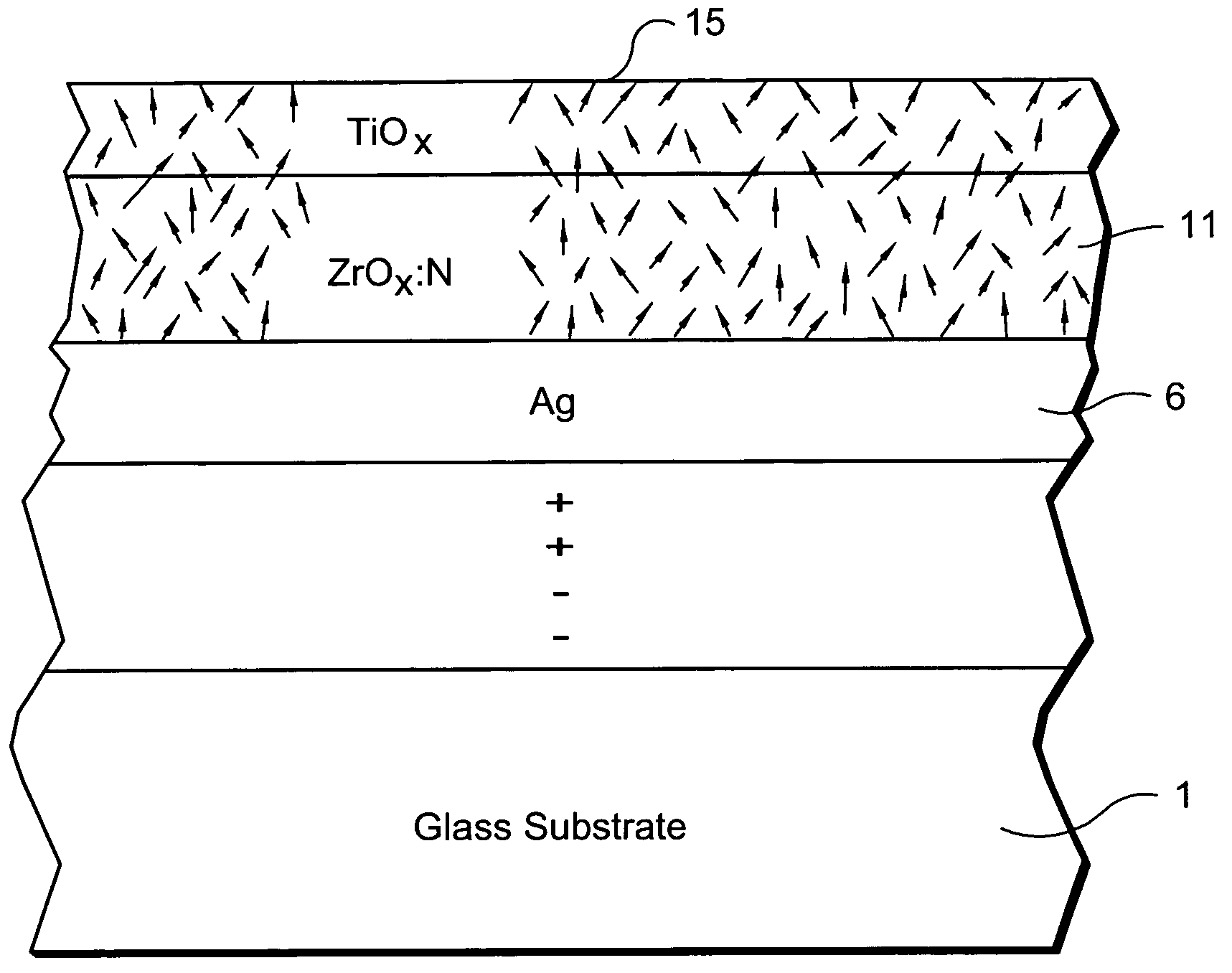
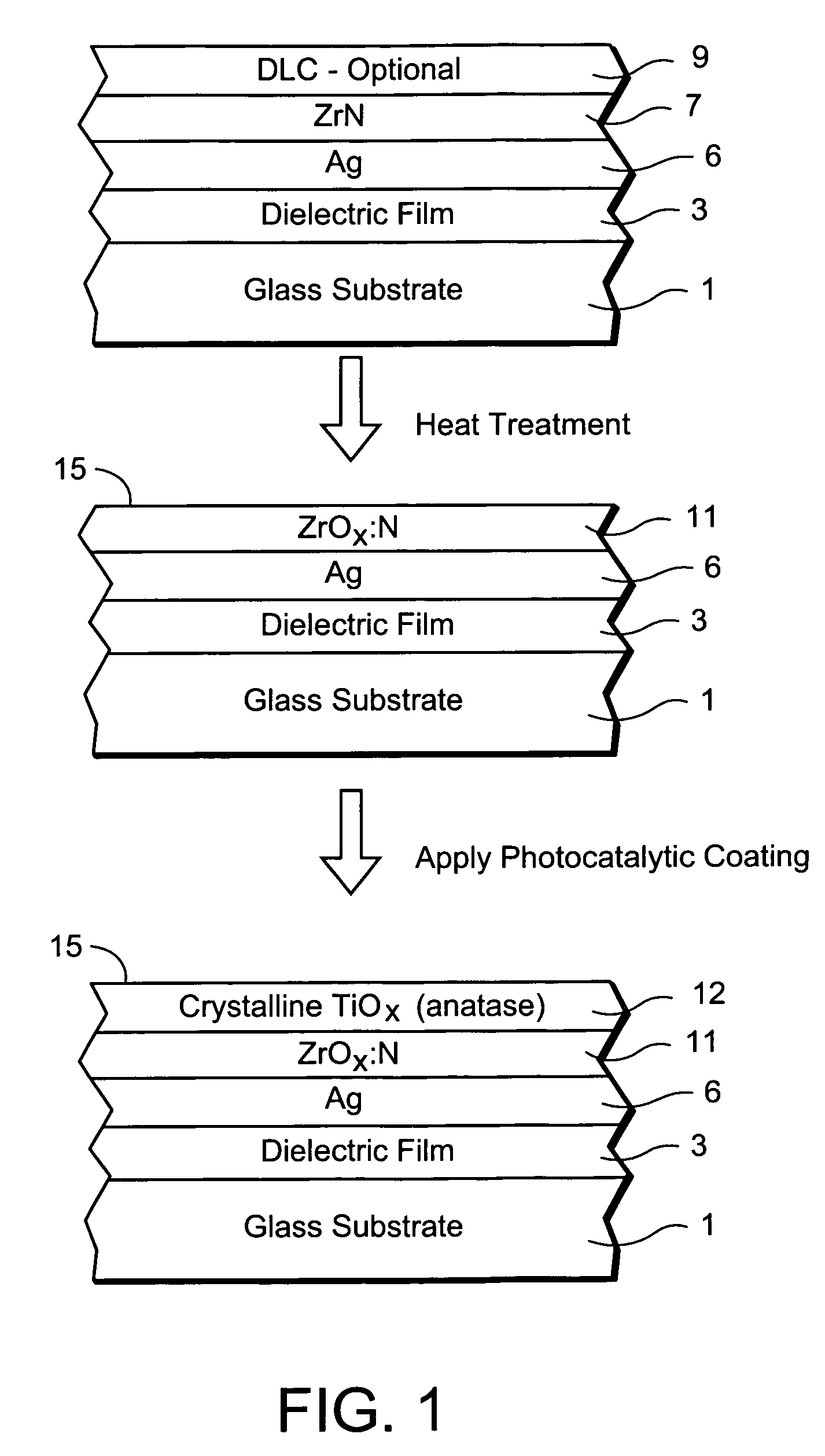
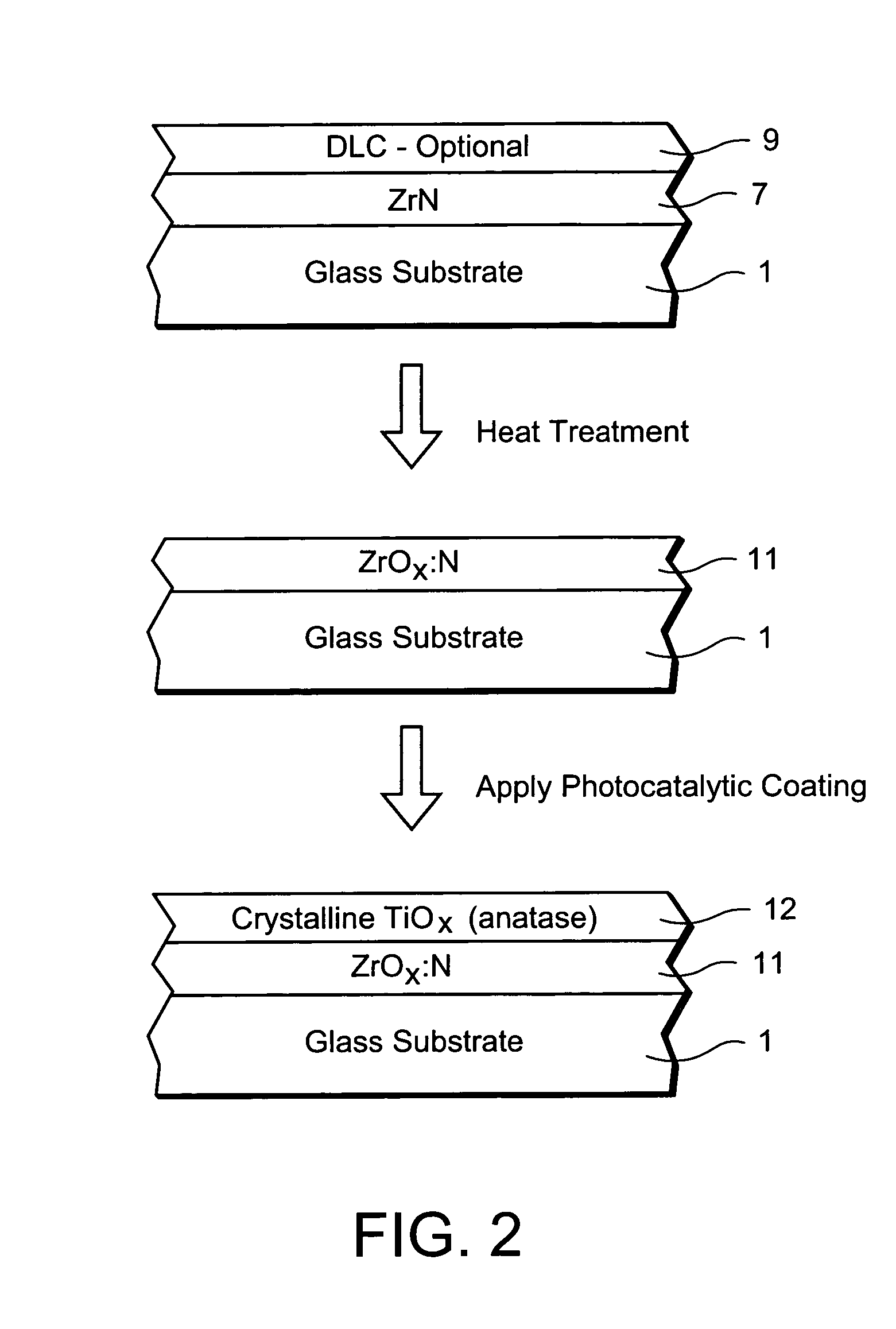
Window with anti-bacterial and/or anti-fungal feature and method of making same
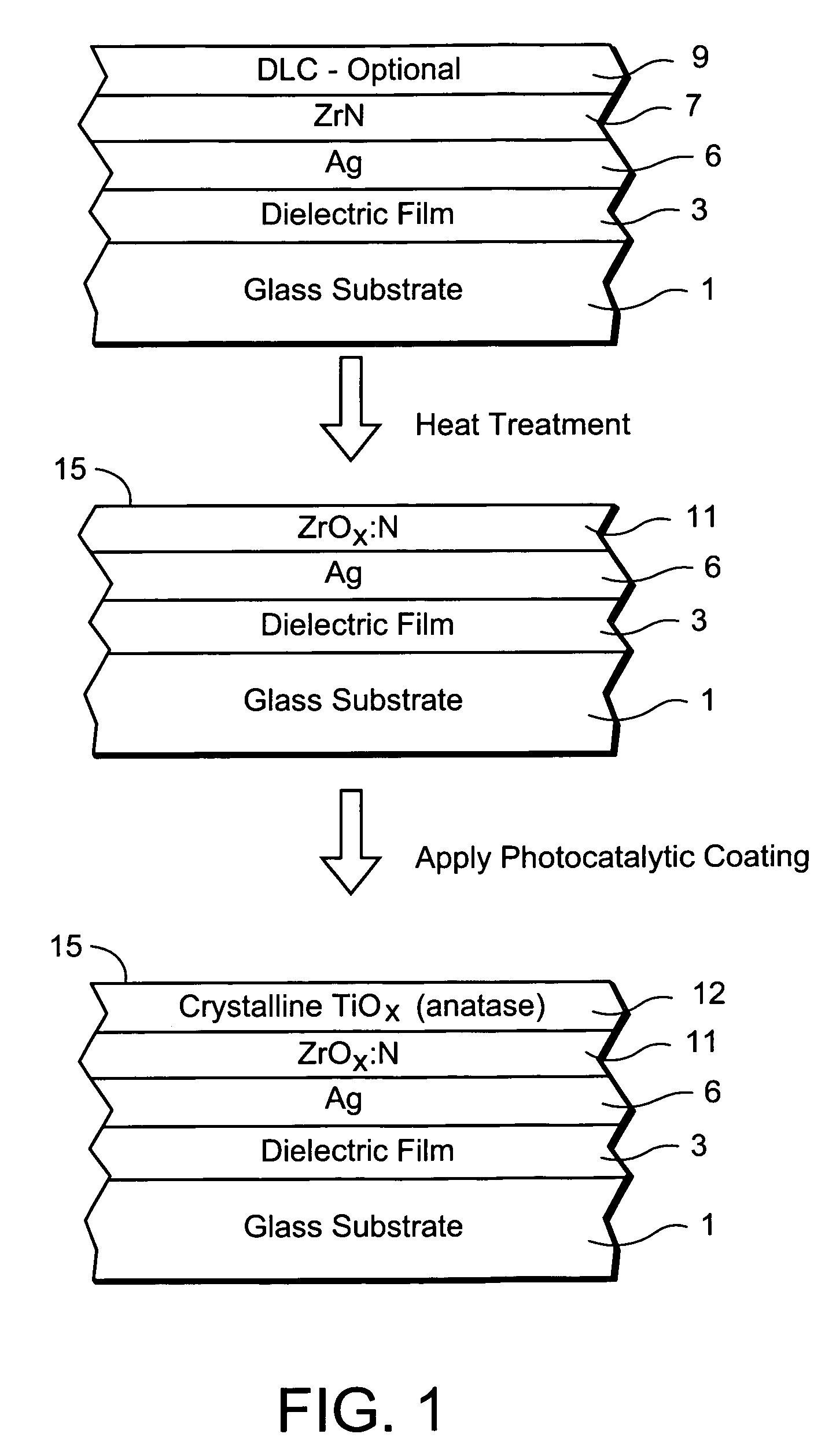
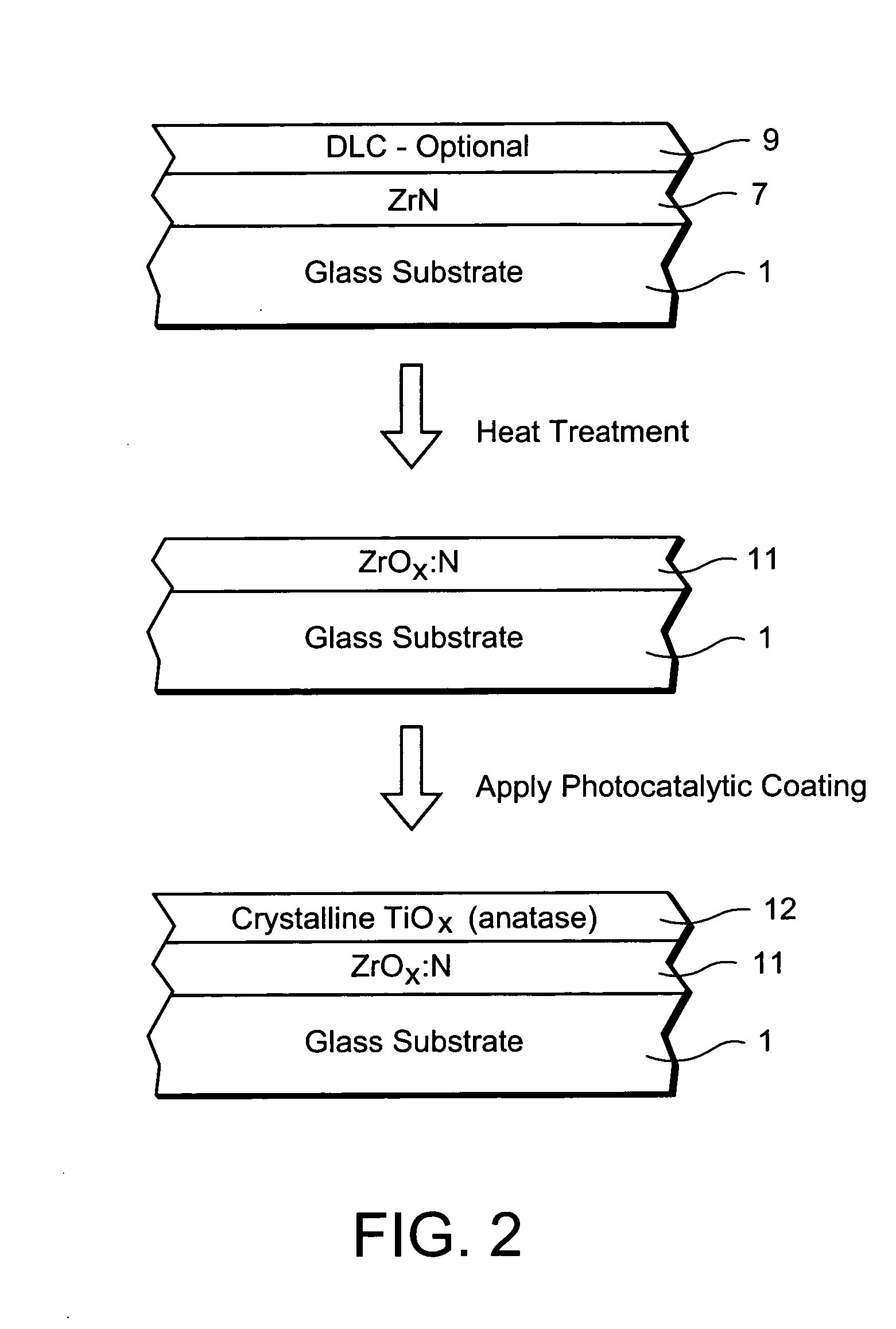
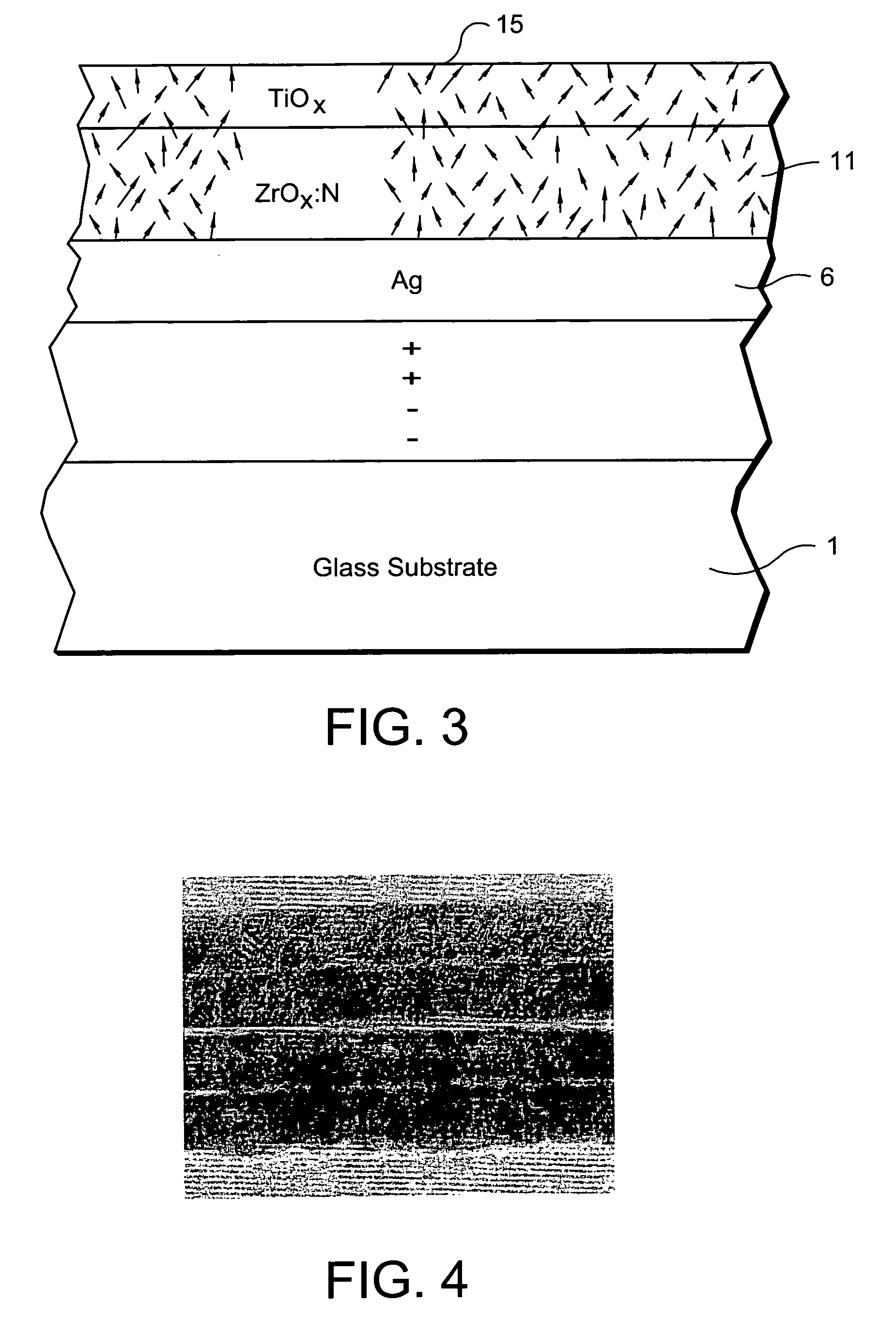
InactiveUS20070254163A1Increase visible transmissionIncreased durabilityLiquid surface applicatorsGlass/slag layered productsAnti fungalSilver particles
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to a window having anti-fungal / anti-bacterial properties and / or self-cleaning properties, and a method of making the same. In certain example embodiments, a silver based layer is be provided and the layer(s) located thereover (e.g., the zirconium oxide inclusive layer) are designed to permit silver particles to migrate / diffuse to the surface over time to kill bacteria / germs at the surface of the coated article thereby creating an anti-bacterial / anti-fungal effect. In certain example embodiments, silver may also or instead be mixed in with other material as the top layer of the anti-bacterial coating.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Ag-carrying nano antibiotic material and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN101305735AAging resistantHigh temperature resistantBiocideDisinfectantsAntibiotic YSilver ion
The invention discloses an silver-supported antibacterial nano-material and the preparation method and the application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding surfactant to a water solution of NH4H2PO4 and ZrOCl2*8H2O, co-precipitating, filtering, rinsing, dewatering, drying and pulverizing to obtain a nano-scale mesoporous zirconium phosphate carrier; and (2) adding dispersant and water to the carrier prepared in the step (1) to obtain a suspension A; mixing AgNO3, NH3*H2O and water to obtain a sliver-ammine complex ion water solution B; mixing the suspension A and the sliver-ammine complex ion water solution B, adding acid to inhibit the hydrolysis so that the generated nano-scale silver ions cluster is adhered to the carrier; and filtering, rinsing, dewatering, drying, sintering and pulverizing to obtain nano-scale silver ion antibacterial powder. The antibacterial nano-material has excellent antibacterial performances such as persistent effect, stability, high temperature resistance, etc. and can be applied in the fields such as building materials, public facilities, medical facilities and appliance, daily products, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI SONGMING COMML CONSULTANT & SERVICE
Low-temperature method of producing an antimicrobial, durable coating for hard surface substrates
Broadly defined sol-gel films for the coating of solid substrates, wherein such sol-gel films provide effective and durable antimicrobial properties, are provided. The utilization of such films permits relatively low-temperature production of antimicrobial substrates, such as ceramics, metals (e.g., stainless steel, brass, and the like), plastics (e.g., polyimides), glass (e.g., borosilicates, and the like), as compared with typical glazes for ceramics and the like. The inventive films comprise, as the primary antimicrobial active ingredients, certain inorganic antimicrobial compounds, such as, preferably, metal-containing ion-exchange, oxide, and / or zeolite compounds (most preferably, including silver therein as the metal component). Preferably, also, the particular solid substrate to which such films are applied should exhibit substantially high melting and / or heat distortion temperatures to permit high temperature curing of the films to the solid substrate surface (in the range of 300-800° C., for example). If the solid substrate melts or distorts, the antimicrobial activity of the ultimate composite is drastically reduced. End uses for such film-coated articles include bathroom fixtures, furniture, and any other surface that exhibits the high melt and / or heat distortion temperatures noted above and requires antimicrobial characteristics. The specific method of producing such films is also encompassed within this invention.
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Window with anti-bacterial and/or anti-fungal feature and method of making same
InactiveUS7892662B2Increased durabilityFacilitate transmissionGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsAnti fungalSilver particles
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to a window having anti-fungal / anti-bacterial properties and / or self-cleaning properties, and a method of making the same. In certain example embodiments, a silver based layer is be provided and the layer(s) located thereover (e.g., the zirconium oxide inclusive layer) are designed to permit silver particles to migrate / diffuse to the surface over time to kill bacteria / germs at the surface of the coated article thereby creating an anti-bacterial / anti-fungal effect. In certain example embodiments, silver may also or instead be mixed in with other material as the top layer of the anti-bacterial coating.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Wipe Coated with a Botanical Emulsion having Antimicrobial Properties
An oil-in-water emulsion that is environmentally friendly and also exhibits antimicrobial activity is provided. More specifically, the oil phase of the emulsion includes a botanical oil derived from a plant (e.g., thymol, carvacrol, etc.). Because the botanical oil tends to leach out of the emulsion during storage and before it is used in the desired application, a water-dispersible polymer is also employed in the aqueous phase of the emulsion to enhance long term stability of the oil and, in turn, antimicrobial efficacy. Without intending to be limited by theory, it is believed that the water-dispersible polymer can effectively encapsulate the botanical oil within the emulsion and inhibit its premature release. Once the emulsion is formed, water can then be removed so that it becomes a substantially anhydrous concentrate. In this manner, the water-dispersible polymer will not generally disperse before use and prematurely release the botanical oil. When it is desired, moisture may simply be re-applied to the concentrate to disperse the polymer and activate the release of the botanical oil. Of course, to provide the optimum degree of biocompatibility, the water-dispersible polymer is also a “biopolymer” that is biodegradable and / or renewable.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method and substance for obtaining surfaces with antimicrobial properties
InactiveUS20030035750A1Reduce the possibilityInhibit microbial growthBiocideLavatory sanitoryDispensarySinglet oxygen
The present invention involves the use of photosensitizers to provide antibacterial surfaces on consumer and industrial items. This approach avoids the used of chemicals and solutions that may be toxic. The inventions also avoids the use of chemical compositions that might form degradation products which may be unacceptable to healthy persons or irritating to persons who may have allergies or are otherwise sensitized. According to the invention, photosensitizers with specific properties and specific design features are selected to make practical use of photosensitizers in the consumer and industrial market place. It is important to select a photosensitizer with an activation spectrum that is matched to the environmental conditions under which the surface to be protected is required to exhibit its antimicrobial properties. This means that the illumination energy and intensity levels expected need to yield enough singlet oxygen to destroy the targeted microbes. It is also possible to select photosensitizers that are activated only by wavelengths prominently present in certain illumination lamps, such as those lamps commonly present in a laboratories, medical offices, pharmacies and food service areas, thereby making the surfaces antimicrobial only on demand when the illumination lamps are turned on.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG
Treatment of humans with colloidal silver composition
InactiveUS20050061678A1Effective antimicrobial agentAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryColloidSilver particles
We disclose a colorless composition comprising silver particles and water, wherein said particles comprise an interior of elemental silver and an exterior of ionic silver oxide, wherein the silver particles are present in the water at a level of about 5-40 ppm, and wherein the composition manifests significant antimicrobial properties. Methods of use of the composition are described.
Owner:AMERICAN SILVER LLC
Wound dressings
A wound dressing that provides galvanic current and has antimicrobial properties. The dressing comprises a pliable base material, along with a pattern of deposited metal flakes. The metal flakes include at least two different metal types which are deposited in patterns which touch or overlap, typically in a repeating pattern. The two metals create a galvanic current in the wound area. The metals are deposited in mounds so that the wound dressing continues to work over extended periods of time.
Owner:ENVITA II
Production method of Ag-HA and applications used as anti-bacteria agent
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydroxyapatite loading Ag (HAP-Ag) and an application as an antimicrobial. The preparation method thereof mainly includes the following steps: hydrothermal reaction step, that is adding the hydroxyapatite to the mixed solution of the silver nitrate and the cerous nitrate, wherein the concentration of both the silver nitrate and the cerous nitrate is 0.01mol / L-0.2mol / L, the reaction temperature is 30 DEG C - 60 DEG C and the reaction time is 2-5 hours; the steps of depositing, sucking and filtrating, drying, and grinding. The novel preparation method of the HAP-Ag and the application as the antimicrobial have remarkable antimicrobial products with high durability, long-term antimicrobial effect, convenient usage, no toxin and harmlessness, so as to be applicable to pregnant women and babies.
Owner:朱鹏播
Advanced Electrolytic Device--Bimetallic Wound Dressing
InactiveUS20140107740A1Guaranteed current efficiencyMore currentPlastersSanitary towelsPower flowWound dressing
An Advanced Electrolytic Device-Bimetallic Wound Dressing that provides galvanic current and has antimicrobial properties. The dressing comprises a pliable base material, along with a pattern of deposited metal powder and flakes. The metal powder and flakes include at least two different metal types. The two different metals create a galvanic current in the wound area.
Owner:ENVITA II
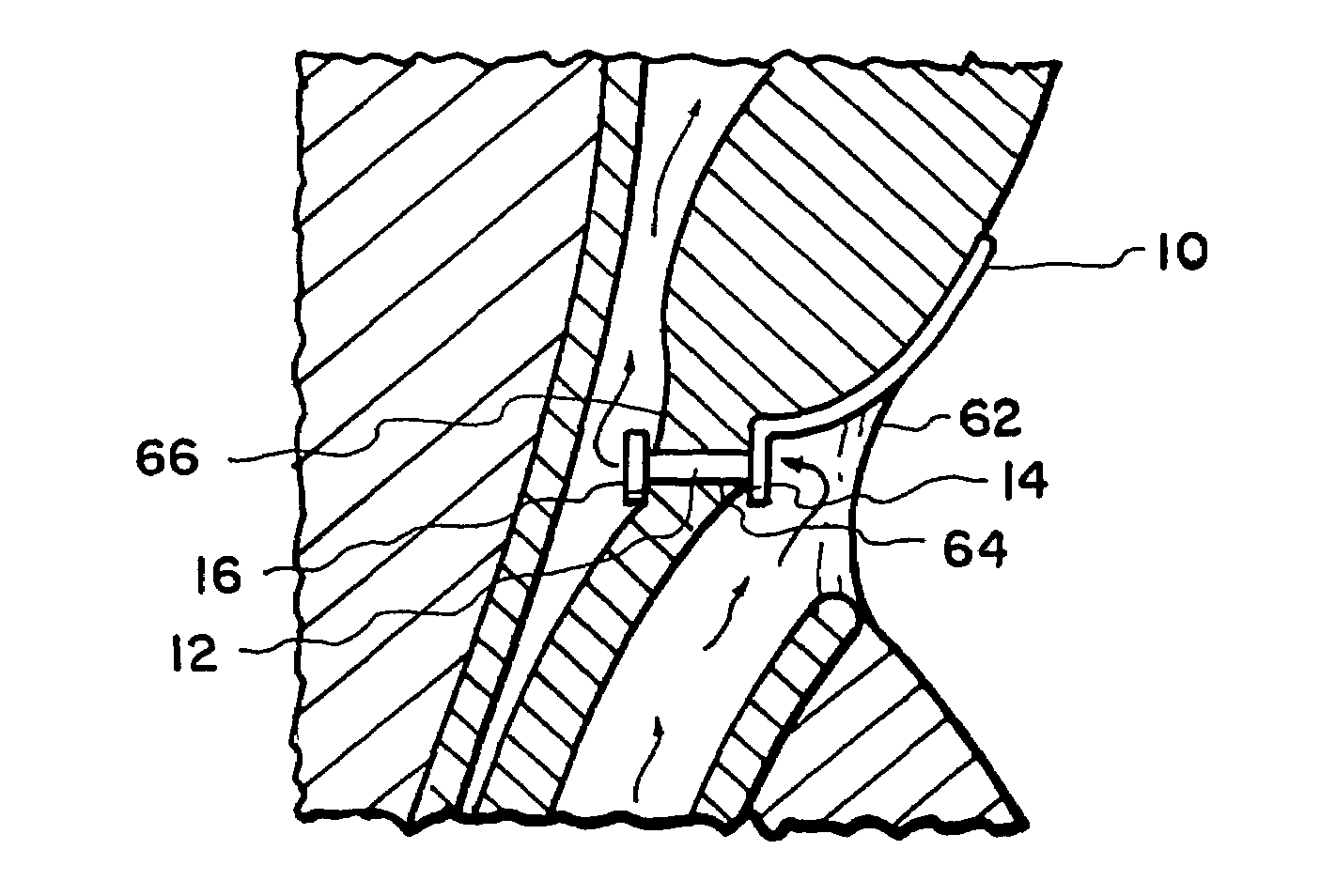
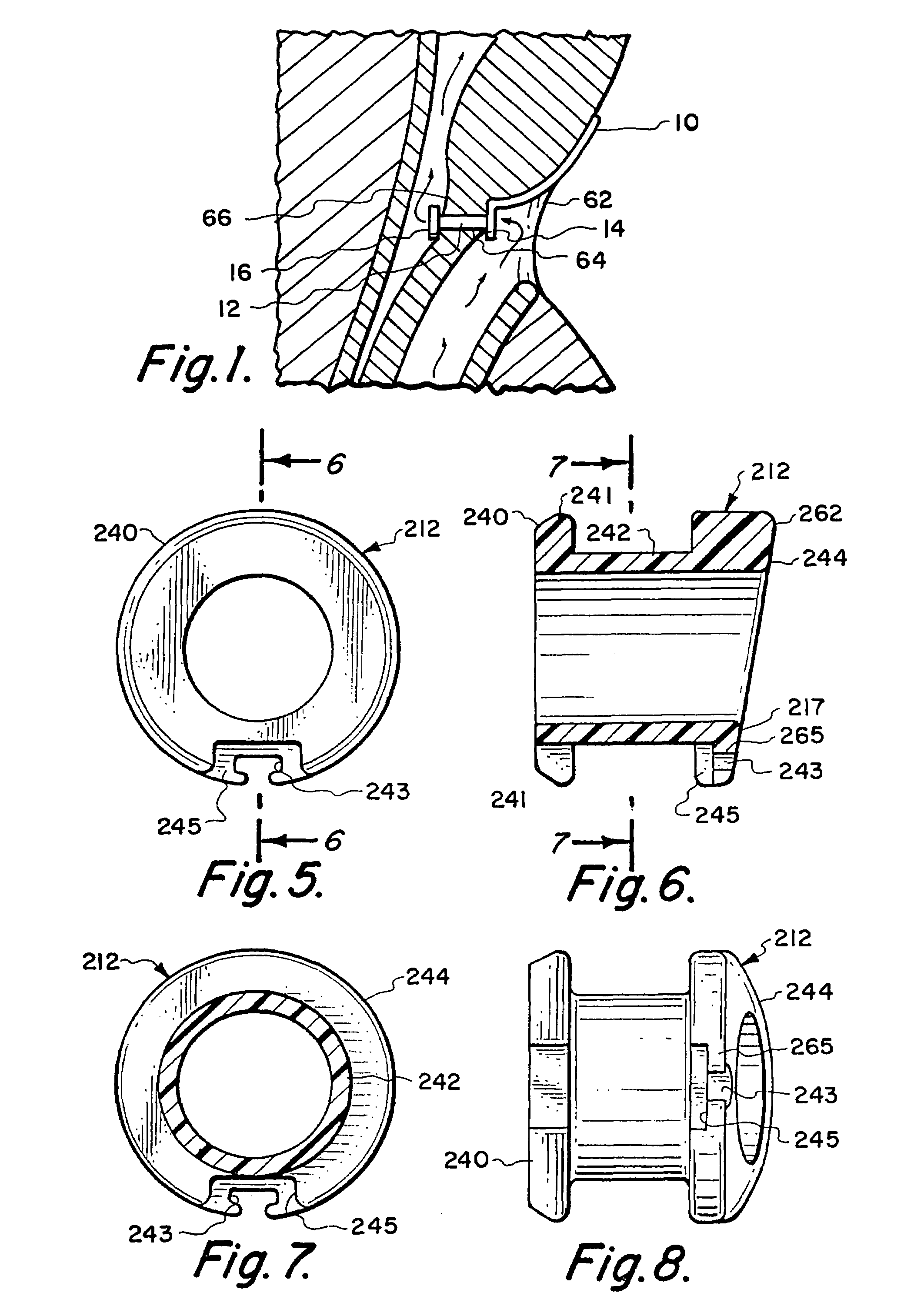
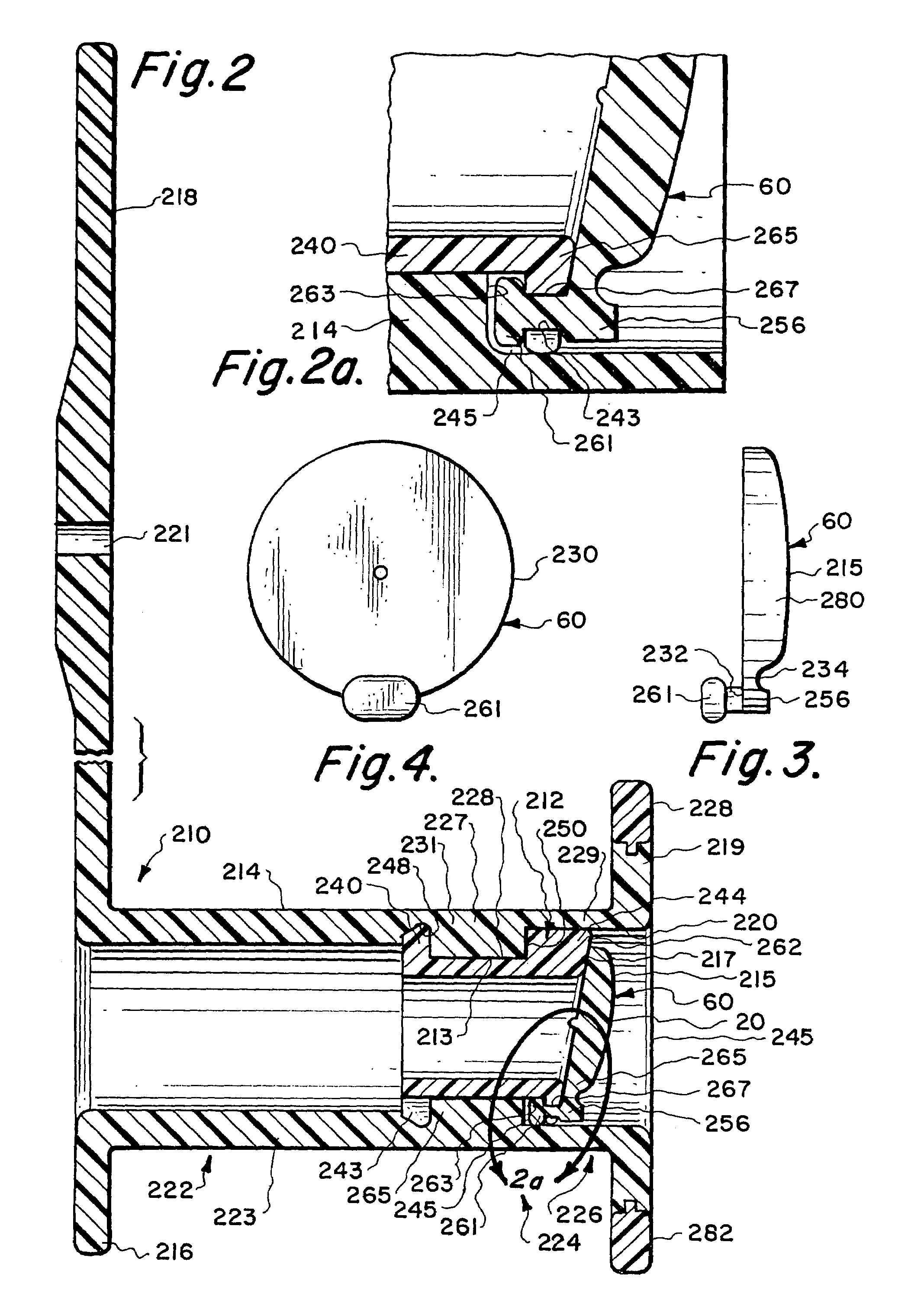
Medical devices having antimicrobial properties
Microbial growth on the surface of a valve of a voice prosthesis and optionally the cartridge or ring supporting the valve, is inhibited by providing antimicrobial activity at a level sufficient to retard growth of a microbial film by dispersing an inorganic antimicrobial agent such as silver oxide or an organic antimicrobial agent such as triclosan or butyl paraben dispersed in a medical grade silicone elastomer. The valve, ring or cartridge is in contact with body fluids containing microorganisms and nutrients therefor. The antimicrobial surface can interfere with or inhibit the growth of a biofilm, bacterial layer or a yeast layer. The body of the prosthesis may also contain an antimicrobial surface as long as it is non-toxic to the tissue it contacts.
Owner:FREUDENBERG MEDICAL
Preparation and application of green tea polyphenol microcapsules taking whey protein isolate (WPI) and maltodextrin (MD) as wall materials
InactiveCN109497161AThe processing technology is cumbersomeFull of nutritionOther dairy technologyCheese manufactureGreen Tea PolyphenolsAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a preparation method of green tea extract microcapsules and application of the green tea extract microcapsules to fresh cheese. Whey protein isolate (WPI) and maltodextrin (MD) are mixed according to the ratio ranging from (1 to 1) to (4 to 1) to obtain a wall material; green tea extract green tea polyphenol (accounting for 5 percent (w / w) of the adding amount of the wallmaterial) is used as a core material; green tea polyphenol microcapsules are prepared by adopting two methods including freeze drying and spray drying, and are applied to the fresh cheese. Raw materials of the wall material comprise the WPI and MD, and have the characteristics of nutritional and functional properties, high covering rate, wide application range and the like. By adopting the preparation method provided by the invention, the problems that the green tea polyphenol has bitter and astringent tastes, low bioavailability and the like are successfully solved; the WPI and MD are effective wall materials for preparing the microcapsules, and anti-oxidization and antibacterial properties of the green tea polyphenol can be sufficiently expressed, so that the cheese has an anti-oxidization functional effect and the shelf life of the fresh cheese can be prolonged by about 10 days. The green tea extract microcapsules prepared by the preparation method can be used as a functional ingredient to be applied to dairy products and other baked products, the shelf life of the products is prolonged and the safety is high.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Calcium sulfite skin beautifying ball and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101921084APrevent agingIncrease the content of negative ionsWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationAntibiosisAlkaline water
The invention relates to a calcium sulfite skin beautifying ball and a manufacturing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing calcium sulfite powder, organic acid and anion powder; pouring into a ball forming mill; spraying mist adhesive liquid; and then rolling to form balls to obtain the calcium sulfite skin beautifying balls which maintain the function of removing chlorine. The added organic acid can transfer alkaline water quality of tap water to faintly acid water quality to ensure that the water quality has antibiosis property and antimicrobial property, can promote shrinkage of skin pores and can supplement water for skin, thereby achieving the effects of moisturizing skin, preventing skin from aging, whitening and protecting skin. The added anion powder can effectively increase the content of anions in water; and after the anions are absorbed by a human body, the excitatory state of a nerve centre can be adjusted preferably, the ventilation function of lung can be improved, metabolism is promoted, fatigue is removed and sleeping is improved.
Owner:林洪臻
Method for treating pipelines
InactiveUS20060018967A1Evenly distributedInhibition formationPowder deliveryAntifouling/underwater paintsBiological bodyEngineering
A method for treating and sanitizing a pipeline, such as a drinking water line, wherein the pipeline is freed from internal deposits, if any, and then internally covered with a coating material. The coating material may be easily applied to the interior of the pipeline by the disclosed methods, and to insure easy hygienic conditions in the interior of the pipeline on a long-term basis, the coating material is mixed with an agent that is harmful to lesser developed organisms and harmless to higher developed organisms, i.e., an agent with antimicrobial properties.
Owner:SCHILDHAUER OTTO
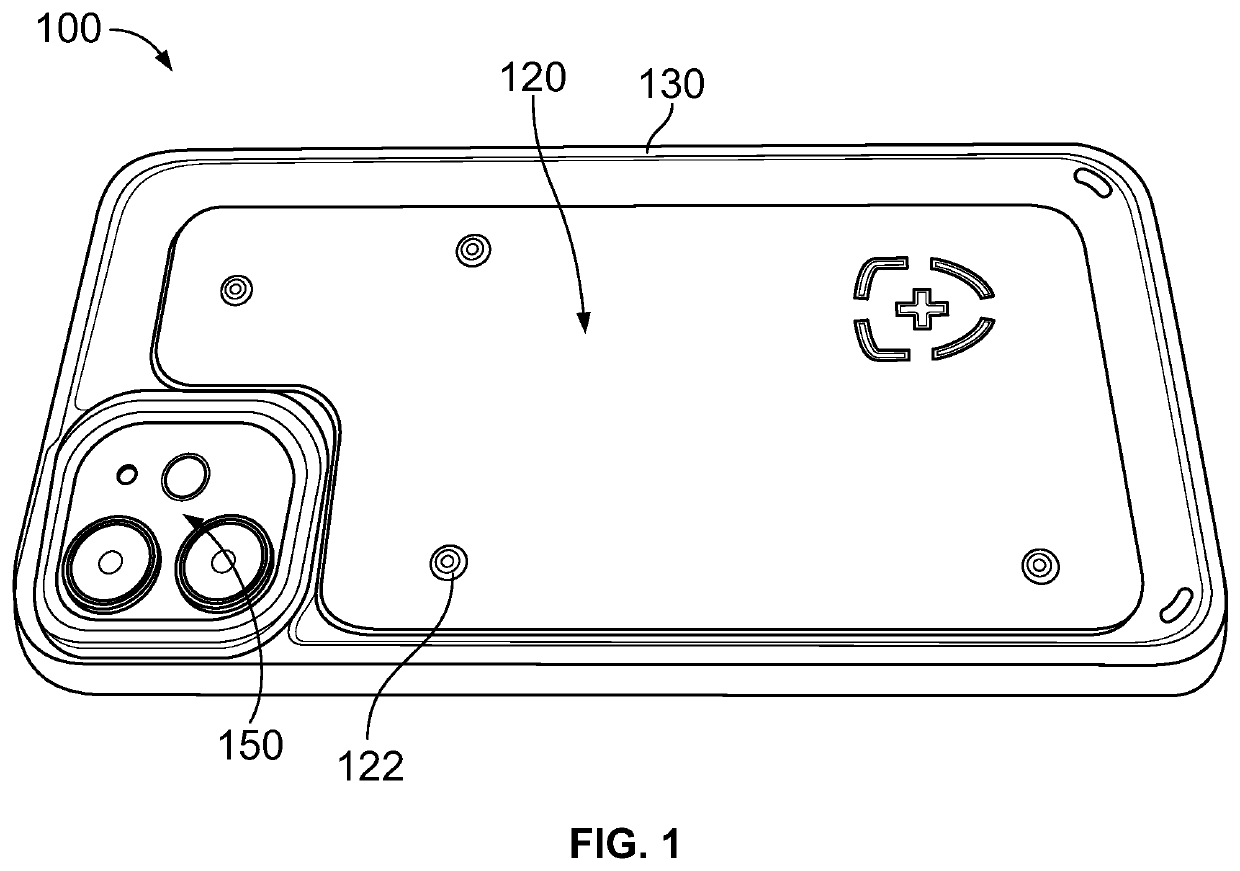
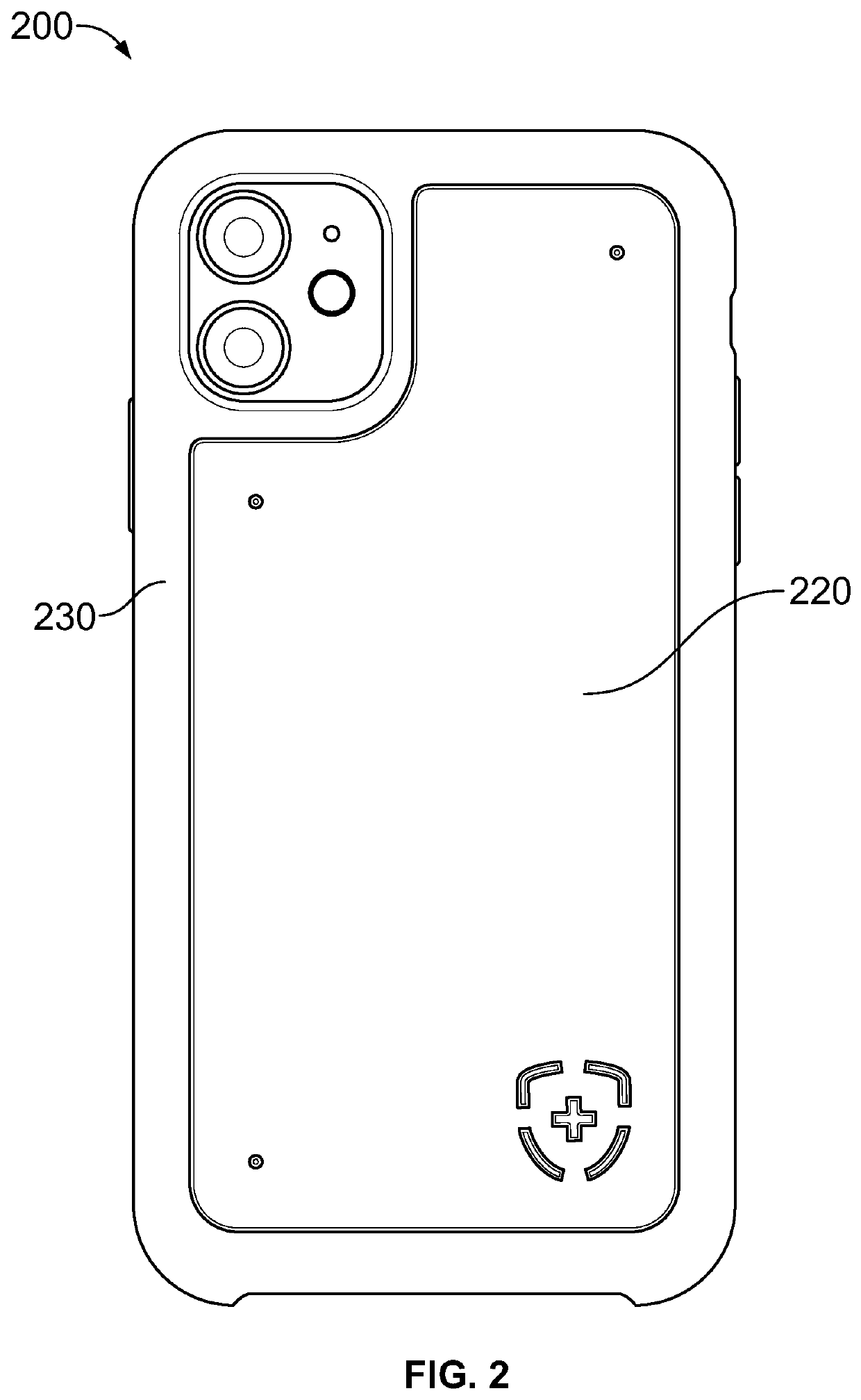
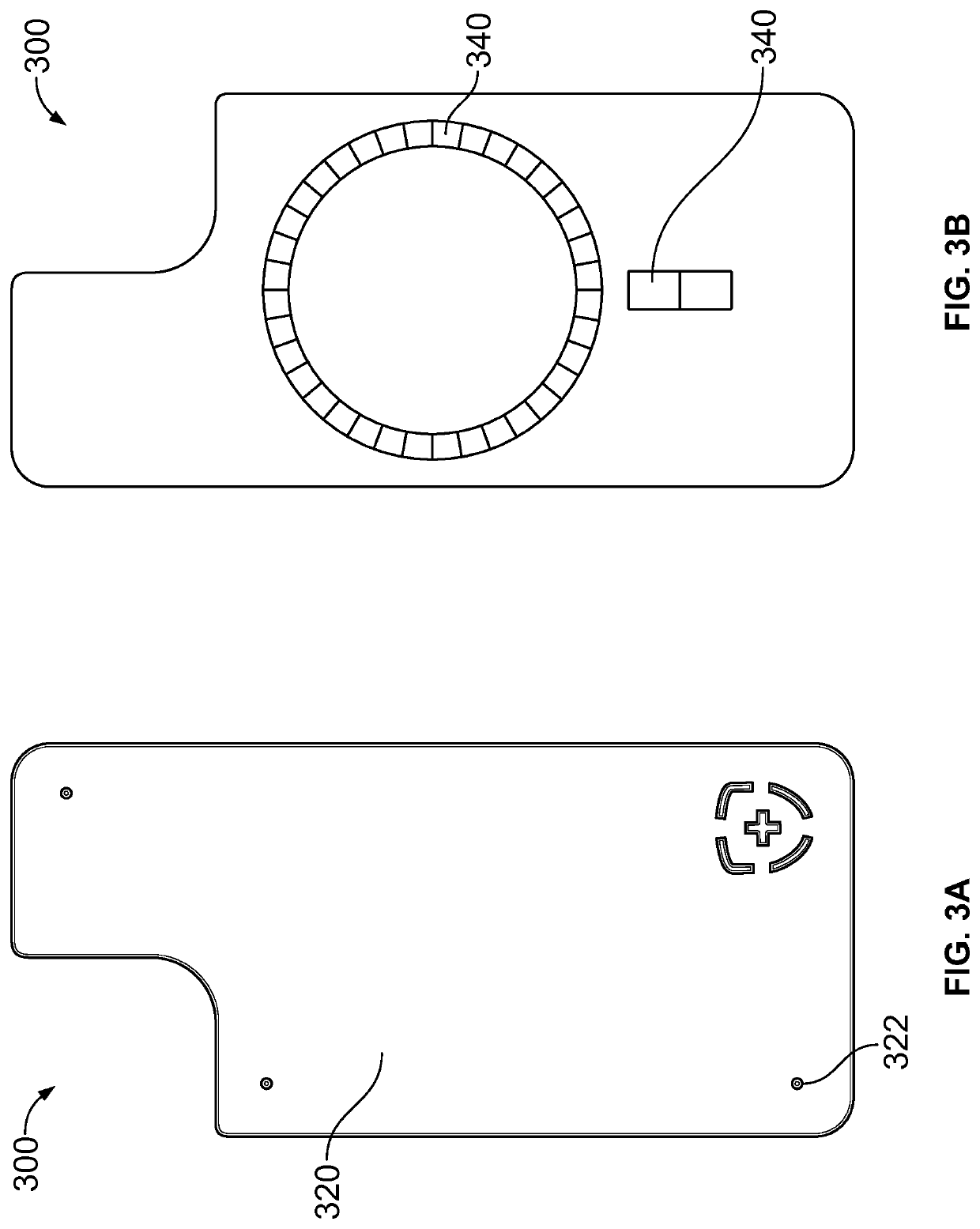
Antimicrobial phone case
A cover for a device that can provide antimicrobial protection is provided. The cover includes a case for enveloping an external device, an antimicrobial plate coupled to the case, and one or more protrusions provided on the antimicrobial plate for creating a physical separation between the antimicrobial plate and an external surface. The antimicrobial plate can be made of copper or a copper alloy that exhibit antimicrobial properties. Moreover, one or more magnets can be provided on the underside of the case to removably attach the case onto the external device. In certain embodiments, the case can be omitted and the antimicrobial plate can be directly coupled to the external device.
Owner:JOHNSON COPPER LLC
Antibacterial ceramic glaze and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106746652AImprove stabilityStability, so that it can be better dispersedBiocideDead animal preservationCalcitePotassium
The invention discloses antibacterial ceramic glaze and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing antibacterial glaze slip, and then glazing and sintering to obtain the antibacterial ceramic glaze. The preparation method of the antibacterial glaze slip comprises the following steps: mixing the following materials in percentage by mass: 25 to 35 percent of low temperature frit, 30 to 40 percent of potassium feldspar, 10 to 20 percent of quartz, 3 to 6 percent of calcite, 3 to 6 percent oftalc, 2 to 5 percent of calcium phosphate, 1 to 5 percent of kaolin and 5 to 10 percent of calcined clay to obtain mixed powder; adding antibacterial powder into mixed powder, and uniformly mixing, wherein the adding amount of the antibacterial powder is 0.1 to 1 percent of the mass of the mixed powder; finely grinding to be 300 to 350 meshes, then adding water to obtain the glaze slip, and regulating the specific weight of the glaze slip to be 1.6 to 1.7g / cm<3>, thus obtaining the antibacterial ceramic glaze. Compared with existing ceramic glaze, the ceramic glaze prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is scientific in material burdening, reasonable in preparation and stable in performance; in addition, the antibacterial ceramic glaze does not contain extremely toxic substances such as lead and cadmium; meanwhile, the antibacterial ceramic glaze also has uniform and persistent antibacterial characteristic, and further the application range of the ceramic glaze is widened.
Owner:FOSHAN GAOMING DISTRICT MINGCHENG TOWN NEW ENERGYNEW MATERIAL IND TECH INNOVATION CENT
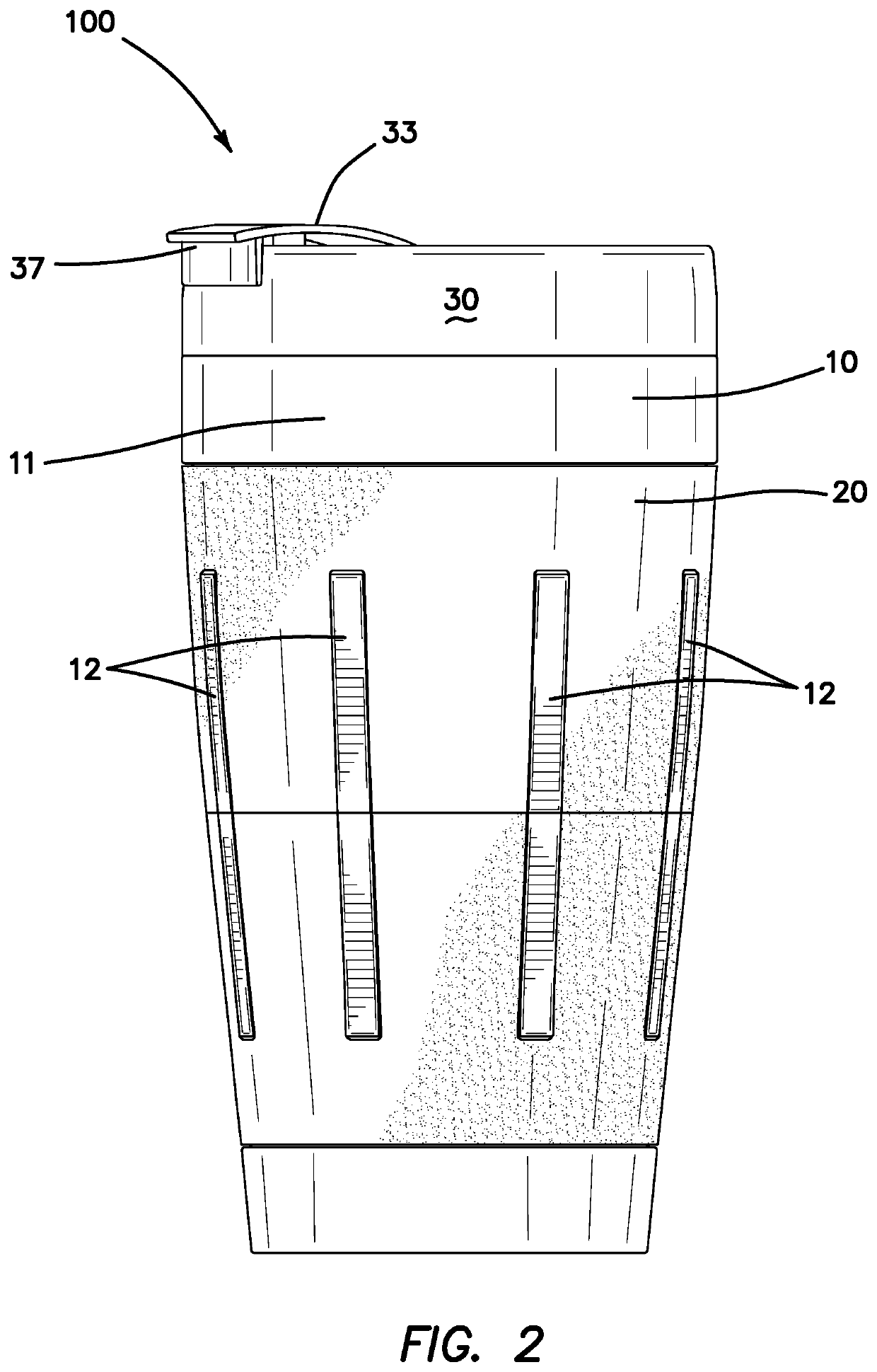
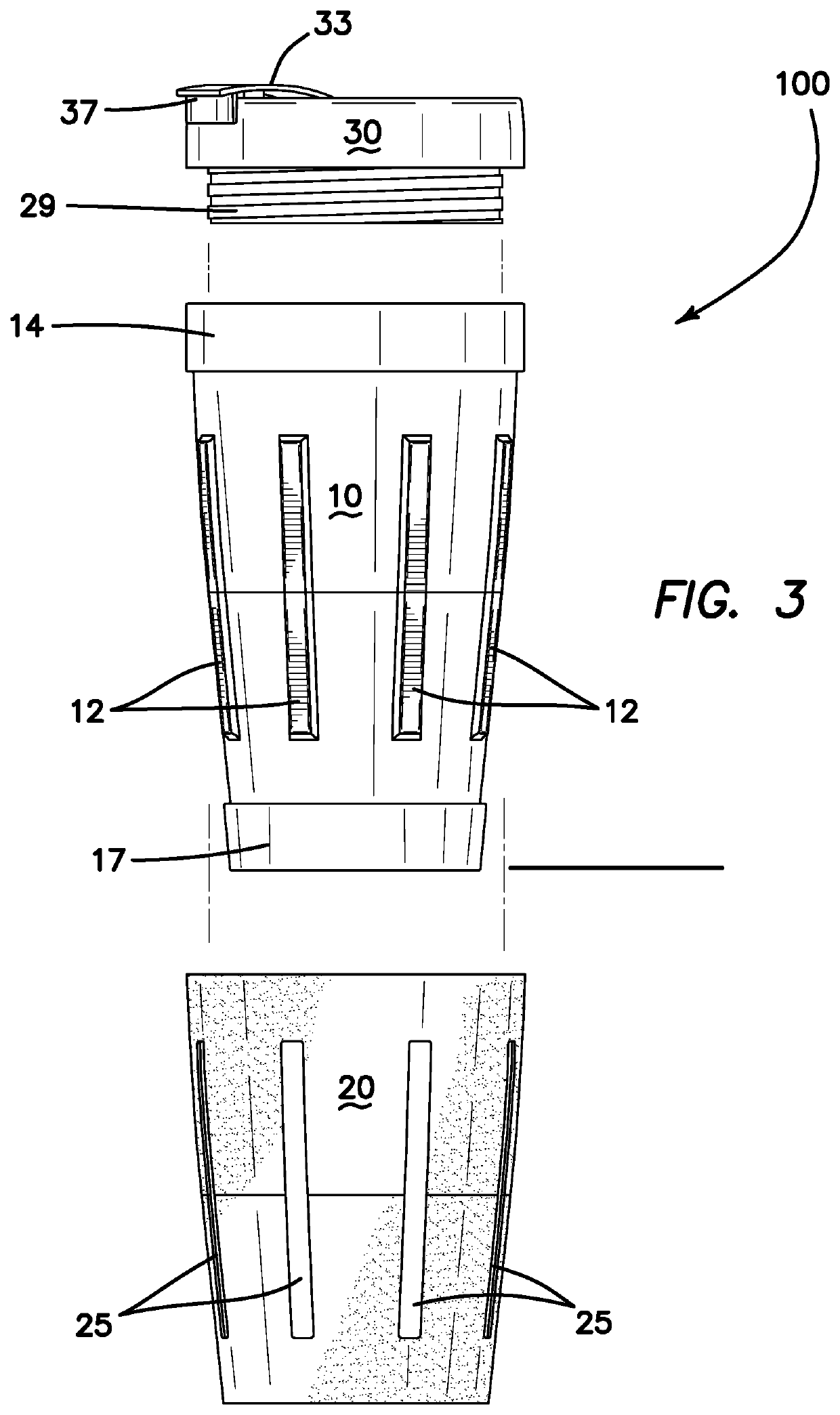
Easily cleanable drinking assembly
ActiveUS10524598B2Easy to cleanClean thoroughlyDwelling equipmentDrinking vesselsEngineeringWater drinking
An easily cleanable drinking assembly having a receptacle, a lid, and a coating with hydrophobic, oleophobic, and antimicrobial properties. The receptacle has an inner curved surface having a geometry with no edges, corners, or distinctly angled connections between sections, preventing any fluid or particles from remaining in these areas. The receptacle further has a wider opening and narrower end, allowing for ease of cleaning, so that a cleaning instrument can easily be inserted and easily reach all parts of the interior of the receptacle. Both the interior of the receptacle and the lid are coated with a coating with hydrophobic, oleophobic, and antimicrobial properties, repelling common fluids and particles, maintaining the cleanliness of the interior surfaces and improving the ease of cleaning.
Owner:GREEN BENNY
Vapour of a Citrus Essential Oil Blend and Its Antimicrobial Properties
InactiveUS20110136761A1Reduce pollutionBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationMicroorganismOrganoleptic
A vapour of a blend comprising the oil of orange and the oil of bergamot, a process for its preparation and its use as an antimicrobial. The vapour has been found to be particularly useful on food contaminated with microorganisms without affecting the sensory properties of the food.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTHAMPTON
Noctilucent deodorant ceramic glaze and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a noctilucent deodorant ceramic glaze and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly preparing a noctilucent deodorant glaze slurry, and then conducting glazing and sintering to obtain ceramic glaze. Specifically, the preparation method of the noctilucent deodorant glaze slurry consists of: by mass percentage, mixing 25-35% of low temperature frit, 30-40% of potassium feldspar, 10-20% of quartz, 3-6% of calcite, 3-6% of talc, 2-5% of calcium phosphate, 1-5% of kaolin, and 5-10% calcined soil to obtain mixed powder, adding a functional agent accounting for 3-10% of the mass of the mixed powder into the mixed powder and mixing the substances evenly, performing fine grinding, and adding water to obtain the glaze slurry, i.e. noctilucent deodorant ceramic glaze slurry. Compared with existing ceramic glazes, the ceramic glaze prepared by the invention has the characteristics of scientific compounding, reasonable preparation, stable performance, and no lead, cadmium or other extremely toxic substances, also has uniform and lasting spectral antibacterial properties, deodorizing properties and noctilucent function, thus further broadening the application scope of ceramic glaze.
Owner:FOSHAN GAOMING DISTRICT MINGCHENG TOWN NEW ENERGYNEW MATERIAL IND TECH INNOVATION CENT
Process for producing fibrous material with antimicrobial properties
ActiveUS20190271111A1Process is simple and time-savingLong processing timeBiocideBiochemical fibre treatmentEmulsionBuilding material
The application relates to a process for producing fibrous material with antimicrobial properties, wherein in the first step coniferous resin acid composition is emulsified into aqueous solution with emulsifier and wetting agent, and in the second step thus formed emulsion is transferred into fibrous material by impregnation. Further, the application relates to an aqueous antimicrobial composition for use as a water-soluble concentrate in the treatment of fibrous materials, and to a fibrous material with antimicrobial properties, and to its use in e.g. fabrics, fur, leather, clothes, canvas, tissues, plastics, webs, accessories, packaging materials, wallpapers, food-related products, household products, footwear, construction materials, insulating materials and medical products.
Owner:NORDIC BIOTECH GRP OY
Bacteriostatic and anti-collagenolytic dental materials through the incorporation of polyacrylic acid modified CuI nanoparticles
InactiveUS9034354B2Preventing and inhibiting growth of bacteriaComprehensive bactericidal effectBiocideNanotechHigh surfaceOxygen
Owner:CLEMSON UNIVERSITY +1
Copper-doped plastic anti-microbial master batch
The invention discloses a copper-doped plastic anti-microbial master batch and belongs to the technical field of the anti-microbial master batch. The copper-doped plastic anti-microbial master batch comprises the following components in parts by weight: 80-96 parts of polyethylene glycol terephthalate (PET), 0.3-20 parts of nanometer copper, 0.1-5 parts of nanometer zinc, 0.3-10 parts of nanometer silver and 0.01-3 parts of modifier. The bronze powder which is formed by mixing nanometer copper with the zinc powder has the characteristics of abundant layer, bright color and golden metallic luster; after the bronze powder is mixed with the nanometer silver at a certain ratio, the mixture has a toning function and can be used as a metal pigment with an anti-microbial effect; besides, the nanometer copper, zinc and silver have an anti-microbial characteristic; after the nanometer copper, zinc and silver are mixed, a synergistic effect is promoted and the anti-microbial effect is further enhanced.
Owner:苏州申久高新纤维有限公司
Antibacterial material additive material, preparation method and application
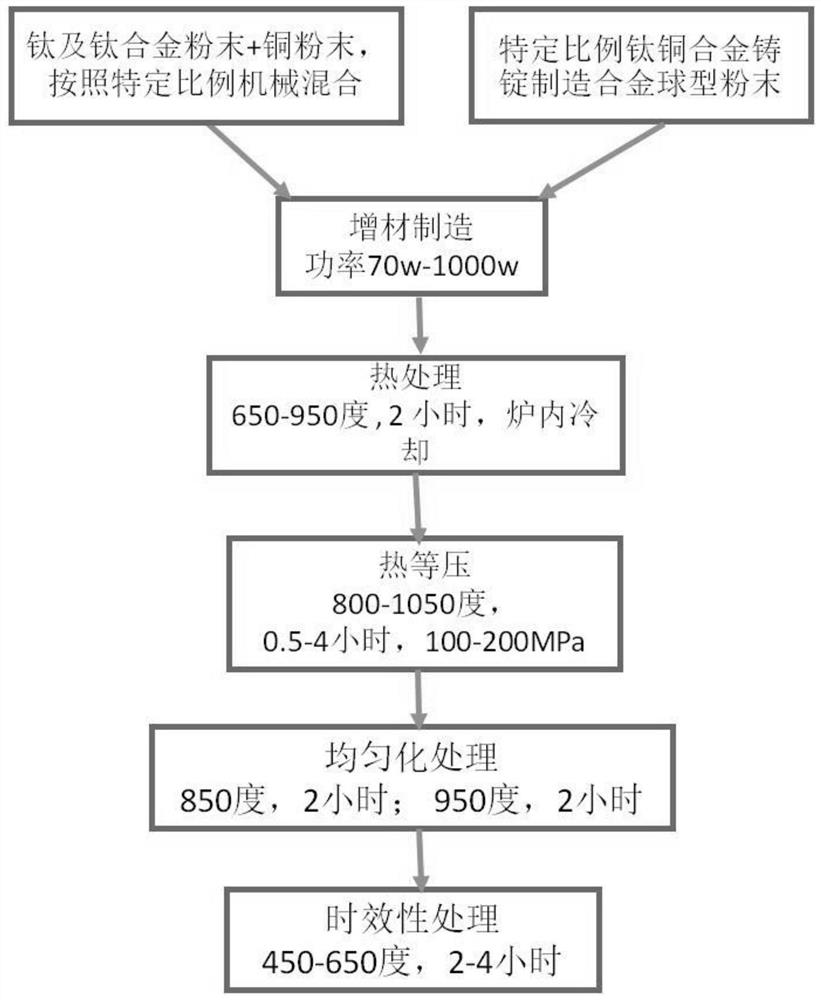
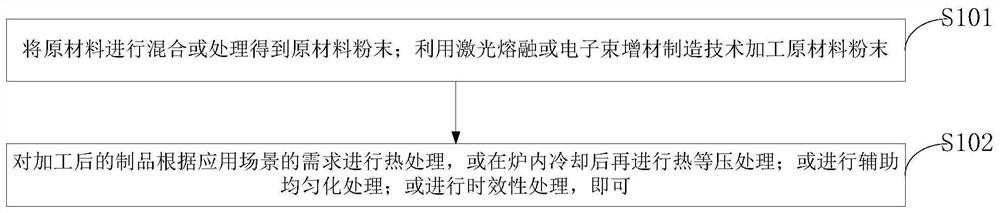
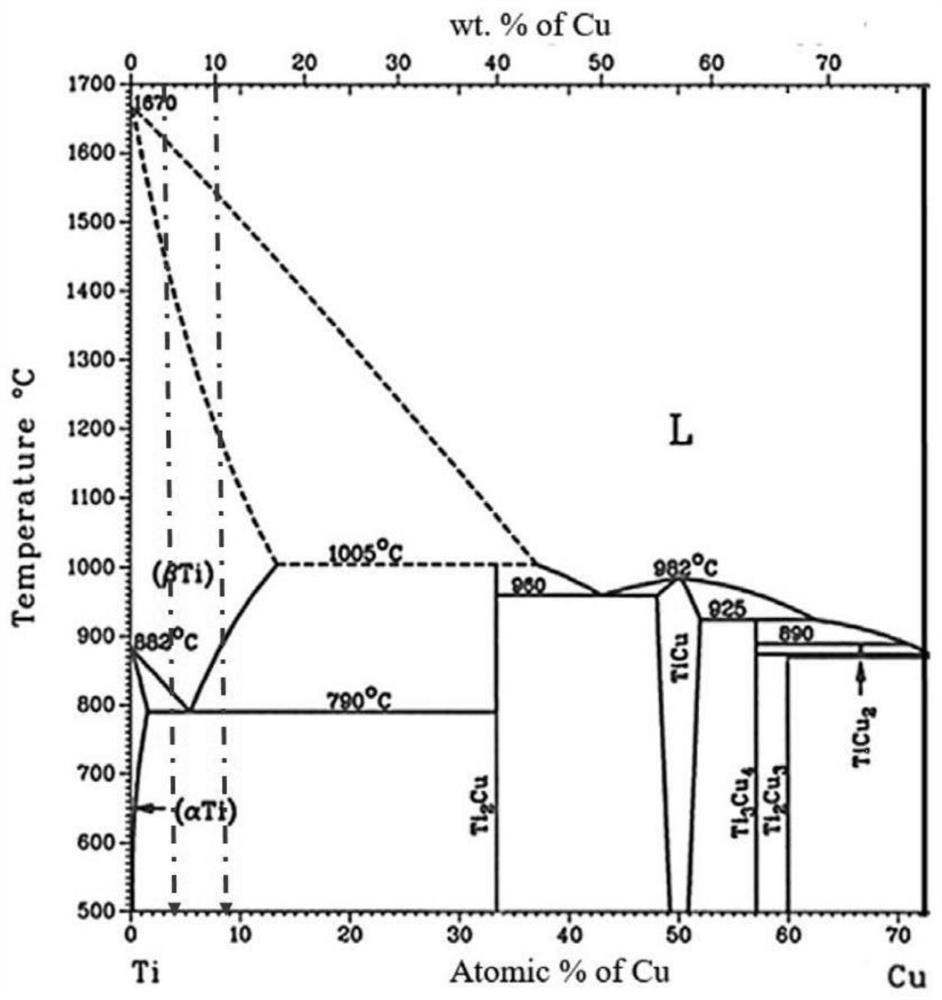
InactiveCN113172237ALong-acting antibacterialBalance of Mechanical PropertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMetallic materialsTi-Cu alloy
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal materials, and discloses an antibacterial material additive material, a preparation method and application. Titanium or titanium alloy spherical powder and copper spherical powder are mixed according to a specific proportion, or a titanium-copper alloy ingot in a specific proportion is utilized, and spherical alloy powder is prepared through a plasma rotating electrode and a plasma atomization or gas atomization method; raw material powder is processed by using a laser melting or electron beam additive manufacturing technology; heat treatment is carried out on a processed product, the product is cooled in a furnace, and then hot isobaric treatment is carried out; homogenization treatment is carried out; and timeliness processing is carried out. According to the alloy additive manufacturing production method and a post-treatment process, compared with an antibacterial coating, common titanium and titanium alloy can have a long-acting antibacterial effect. A mixed material in a specific proportion can be processed by utilizing the advantages of additive manufacturing, a traditional titanium-based material is endowed with the antibacterial characteristic, and the mechanical property and the antibacterial effect of a part can be balanced through the post-treatment process.
Owner:广州柔岩科技有限公司
Antibiotic martensitic stainless steel and use thereof in hardware industry
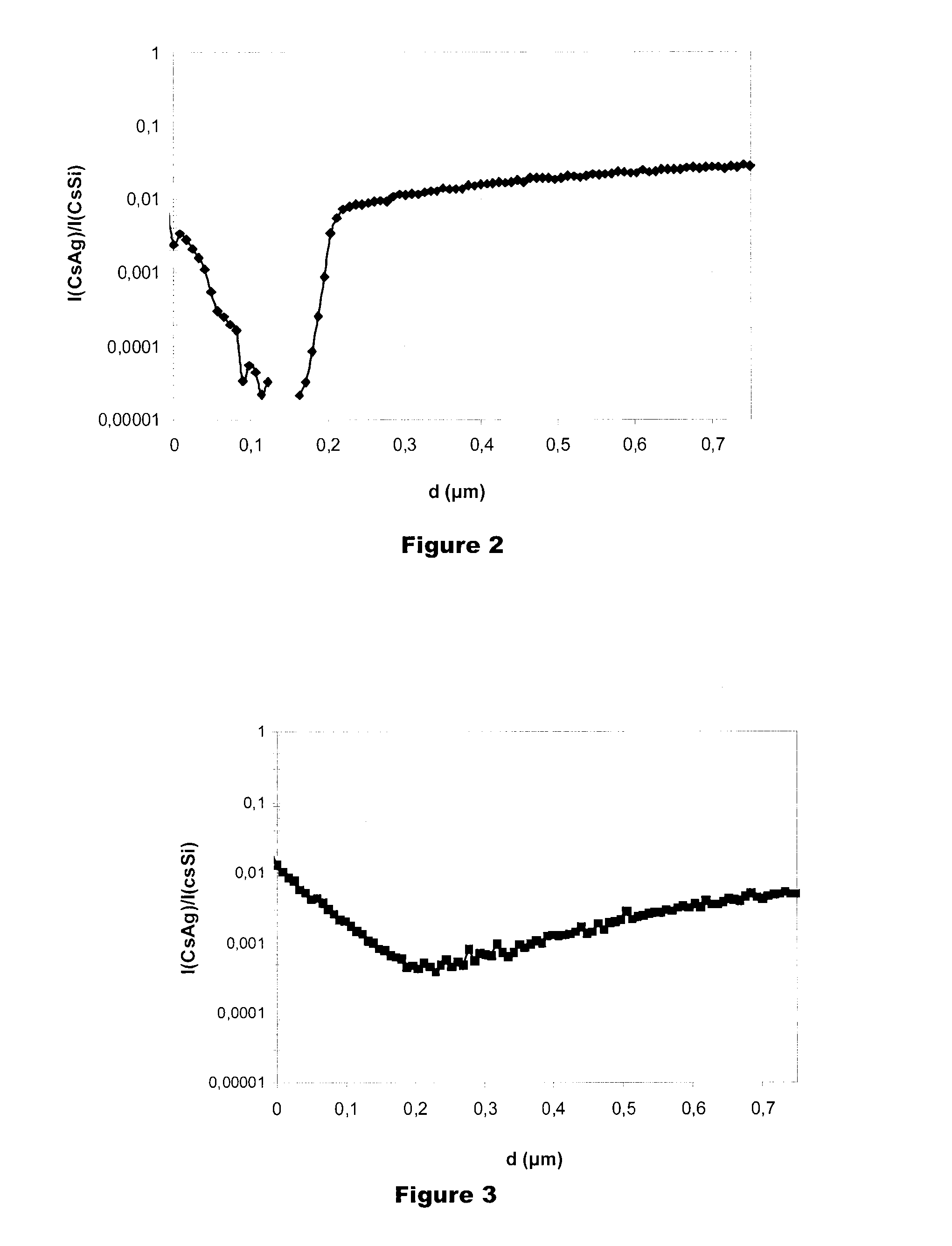
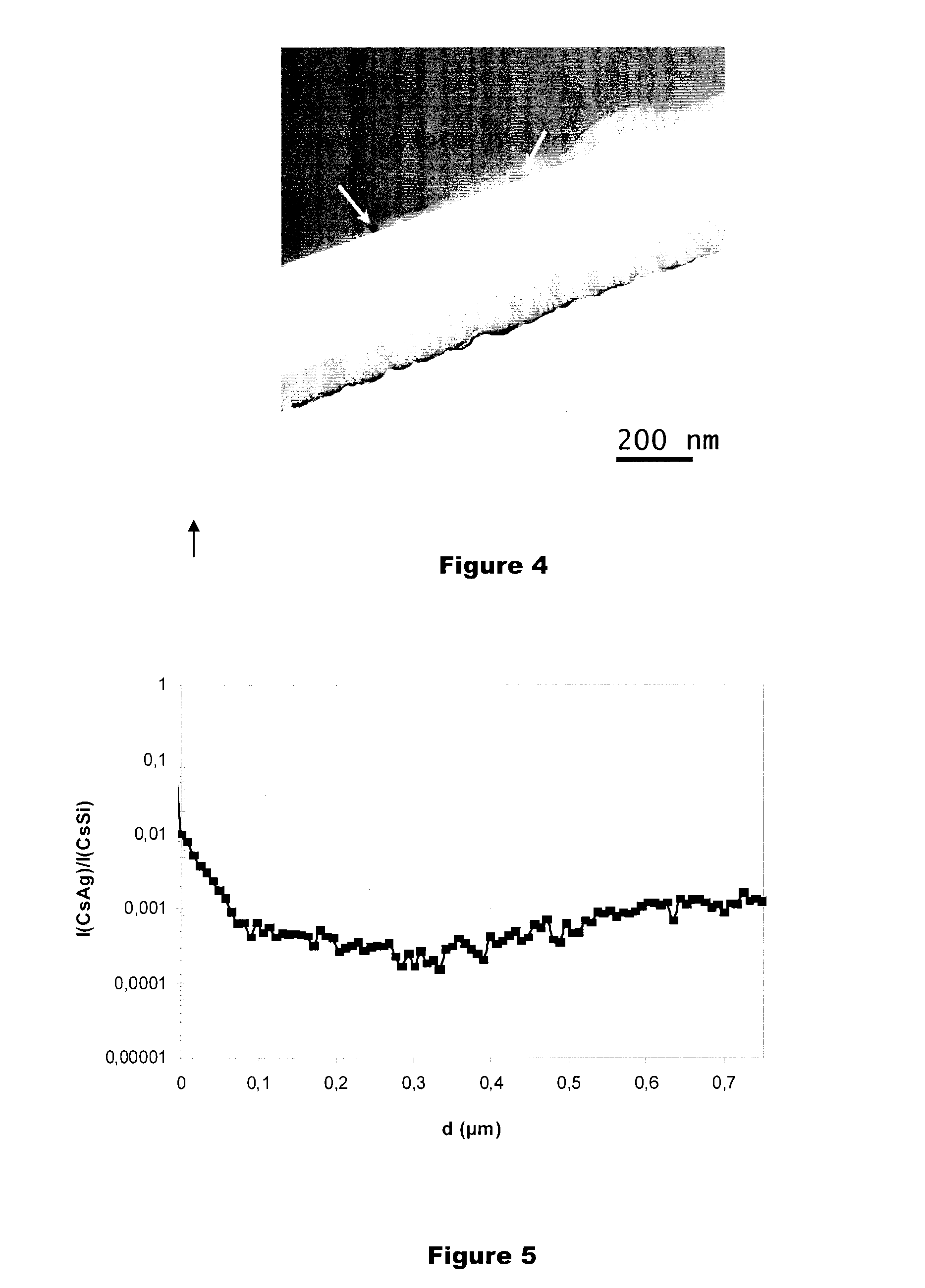
InactiveCN101323930AGrain refinementHigh strengthLavatory sanitoryDisinfectionMartensitic stainless steelAntimicrobial properties of copper
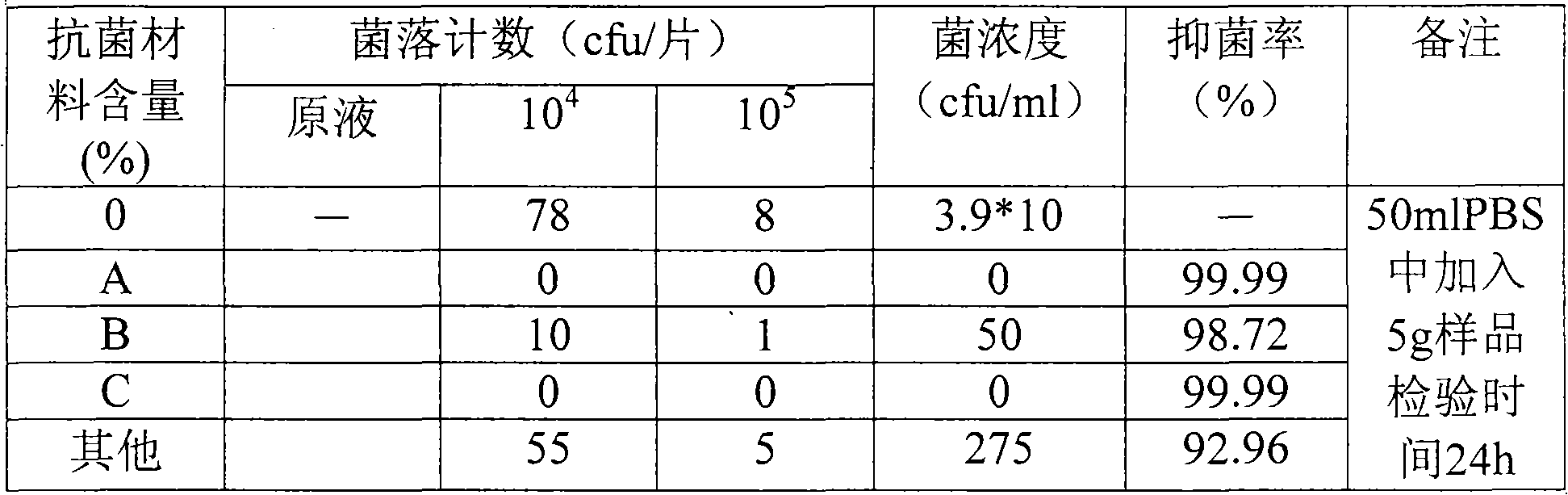
The invention discloses a martensite stainless steel with antibacterial property and an application thereof in the industry of hardware. Through researches on the aspect of stainless steel material and how to make use of antibacterial property and how to add Cu into stainless steel material and through adding appropriate Cu into martensitic stainless steel as well as through special thermal treatment (high-temperature tempering is adopted so as to obtain relatively good organizational structure, endowing material with the properties of relatively high intensity, good toughness, corrosion resistance and antibacteria), Epsilon-Cu phase can be precipitated dispersedly from stainless steel and then coppor ion can be dissolved out in water; therefore, the obtained stainless steel has good antibacterial property. The addition of Cu can cause grain of stainless steel to be thinned, have relatively high intensity and hardness, reduce passivation range and increase corrosion rate slightly. The antibacterial effect of the martensite antibacterial stainless steel on staphylococcus aureus is more than 99 percent, and the effect on escherichia coli reaches 97 percent; therefore, the stainless steel of the invention can not only improve the performance of the stainless steel material, but also effectively inhibit the breeding of bacteria. The martensite stainless steel with antibacterial property is mainly applied to hardware products.
Owner:上海张小泉刀剪制造有限公司
Electrolytic bath for producing antibacterial metal composite coatings of antibacterial zinc metal particles (zn/pma)
ActiveUS20180195190A1Avoid allergiesMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic coatingsEscherichia coliBenzylideneacetone
The invention relates to the use of an electrolytic bath for electroplating zinc-particles metal composite coatings of metals with antibacterial ability, which inhibits bacteria growth such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, at least by 87% over its surface.The method of formulating an electrolytic bath that allows the production of antibacterial coatings involves the following steps: a) adding metal particles with antibacterial ability suspended in a cationic surfactant to an electrolytic bath containing boric acid, chlorides, polyethylene glycol, benzylideneacetone, sodium benzonate, triethanolamine and dissolved Zn2+ salts, adding; b) electroplating the metal composite coating of zinc-antibacterial metal particles by applying direct current density. The occlusion of metal nanoparticles with antibacterial ability in the coating matrix provides said coating with antibacterial characteristics.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO TECH & ELECTROQUIMICA SC (CIDETEQ SC)
Glass article with antimicrobial properties
InactiveUS20130123091A1The process is simple and fastOvercome disadvantagesNanoparticleAntimicrobial properties of copper
The invention relates to a glass item, at least one of the surfaces thereof having antimicrobial properties that are resistant to a temperature treatment, especially a temperature treatment in preparation of the subsequent tempering thereof. The glass item especially comprises an antimicrobial agent beneath the surface of the glass, and nanoparticles that are partially and / or totally incorporated into the mass of the glass close to said surface and consist of at least one inorganic component.
Owner:AGC GLASS EUROPE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com