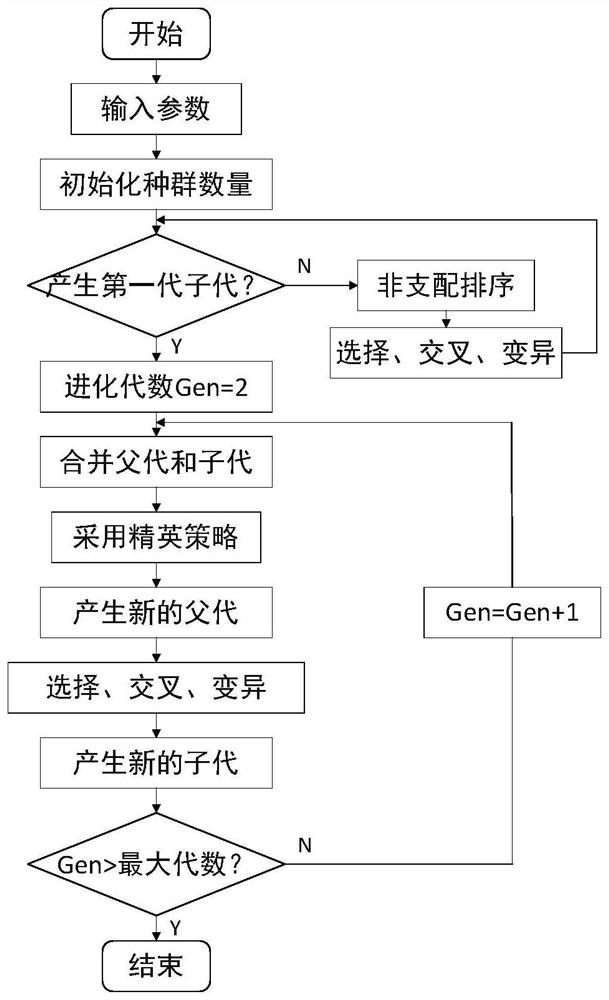
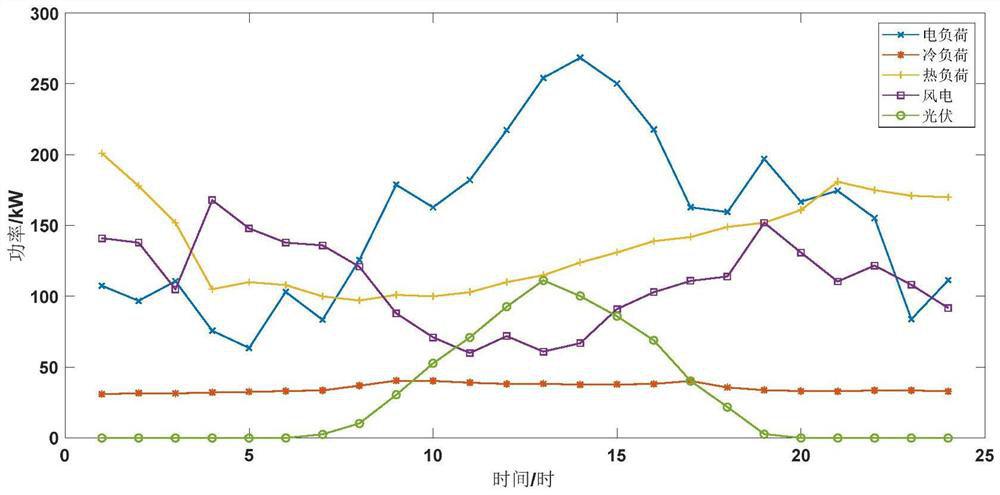
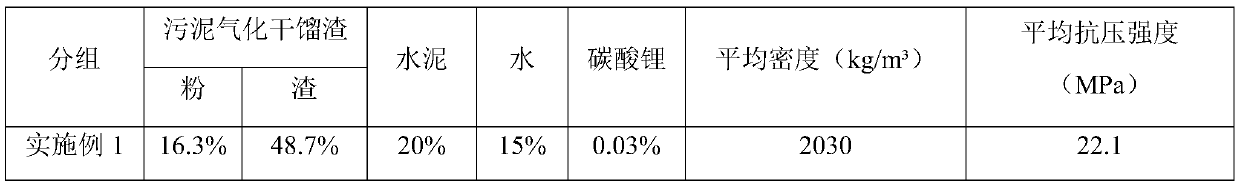
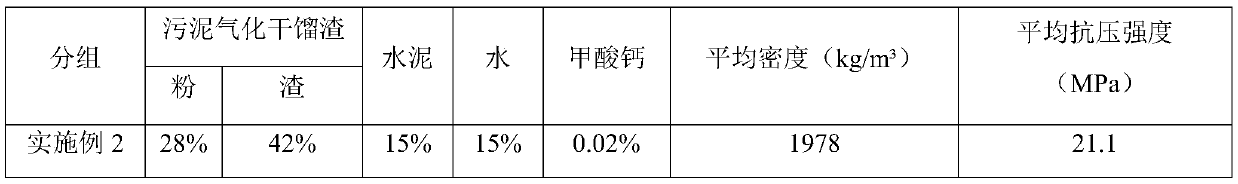
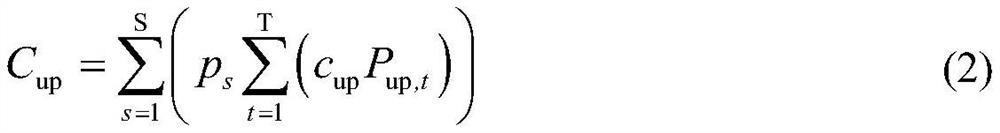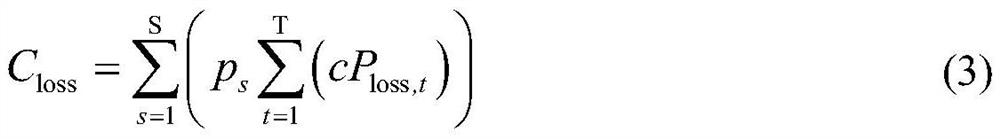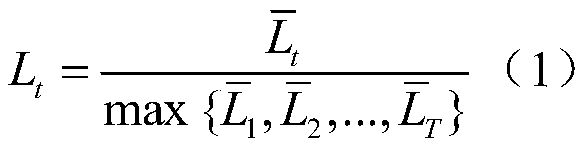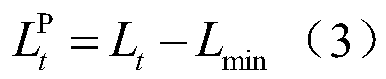Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Full consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low cost and high efficient soundproof material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103897262AImprove heat and aging resistanceExcellent ozone resistanceSound producing devicesRelaxation effectFilling materials
The invention relates to a low cost and high efficient soundproof material and a manufacturing method thereof, relates to the field of soundproof materials, solves the problems that in the prior art, soundproof materials do not have a prominent soundproofing effect, generate harmful gas, which can harm the human health, and have a high cost; and provides a low cost and high efficient soundproof material. The soundproof material comprises thermoplastic resin and an inorganic filling material, wherein the surface of the inorganic filling material has been processed by a coupling agent processing liquid, the inorganic filling material accounts for 15 to 80 wt% of the total weight of the soundproof material, and the balance being thermoplastic resin. In the soundproof material, the connections among the particles are abnormal, thus the internal friction of the incident sound waves is increased by the structure of the soundproof material, and a relaxation effect is generated to absorb the sound waves. Filling materials with different particle sizes are corresponding to waves in different wavelengths or frequencies, so the soundproof material can reduce sounds in different frequencies. Moreover the soundproof material has a good soundproof effect and is suitable for being promoted and used.
Owner:浙江艾迪雅科技有限责任公司
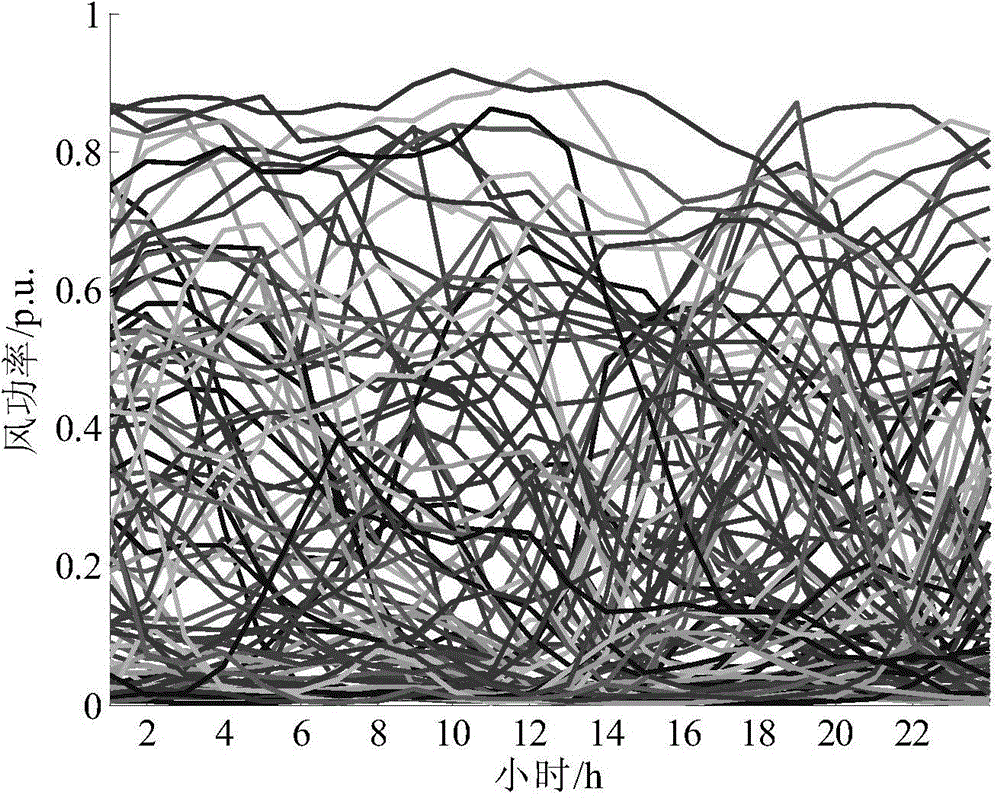
Operation optimizing method capable of coordinating operation risk and wind energy consumption of power system
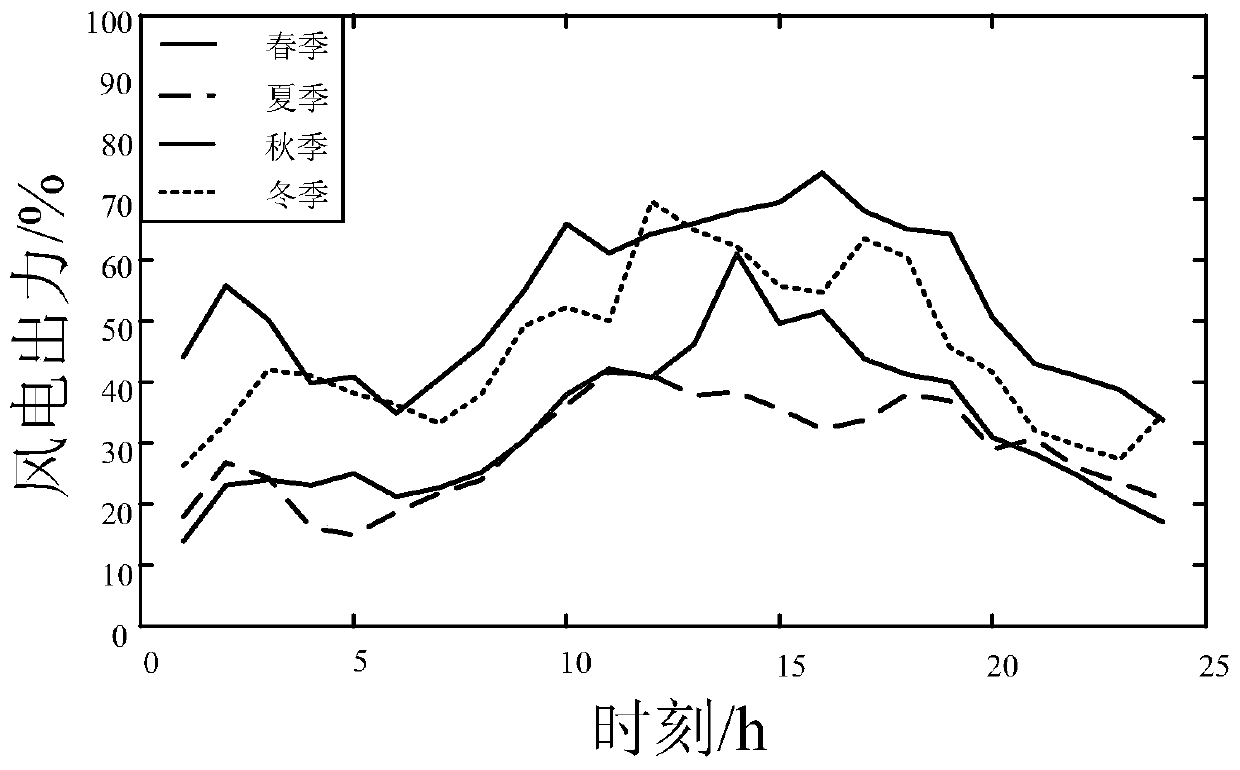
ActiveCN104600747AFull consumptionGuaranteed damageClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAutomotive engineeringWeighting coefficient
The invention discloses an operation optimizing method capable of coordinating operation risk and wind energy consumption of a power system. The method comprises the steps of 1) predicating a load model of the power system, building a wind power model, and forming a net load power model according to the determined load model and the wind power model; 2) building a right end tail part risk related net load sample and a clockwise rotating backup model, determining that the power does not meet the expected value, building a left end tail part risk related net load sample and an anticlockwise rotating backup model, and determining to remove expected wind quantity value; 3) providing weight coefficients according to step 2), substituting into penalty terms, and building an economic dispatch model; 4) solving the economic dispatch model of the step 3) to obtain the primary dispatch operation mode of the power system; 5) predictably improving the wind speed, enabling the wind power predication model to reach accuracy, modifying the dispatch operation mode obtained in step 4) so as to obtain the optimal operation mode through which the wind power predication information can be fully utilized and the risk can be resisted.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +2
Multimode organic filler/polymer composite damping material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103897287AImprove shock absorptionImprove heat and aging resistanceSound energyRelaxation effect
The invention relates to a multimode organic filter / polymer composite damping material and a manufacturing method thereof, relates to the field of soundproof materials, aims to solve the problems that in the prior art high efficient soundproof materials do not have a prominent effect, and generate harmful gas, which harms the human health; and provides a multimode inorganic filler / polymer composite damping material. The damping material comprises the following materials: thermoplastic resin and an inorganic filler, which has been subjected to a surface treatment with a coupling agent processing fluid; wherein the inorganic filter accounts for 15 to 80 wt% of the total weight of the damping material, and the balance being thermoplastic resin. In the damping material, the binding between each particle is abnormal, thus the internal friction between incident sound waves in this structure is effectively increased, thus a relaxation effect is generated, and the sound is absorbed. Fillers with different particle sizes are corresponding to sound waves in different bandwidths or frequencies, so sounds in different frequencies can all be absorbed by the damping material, and moreover the damping material has a good soundproof effect, and is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:浙江艾迪雅科技有限责任公司
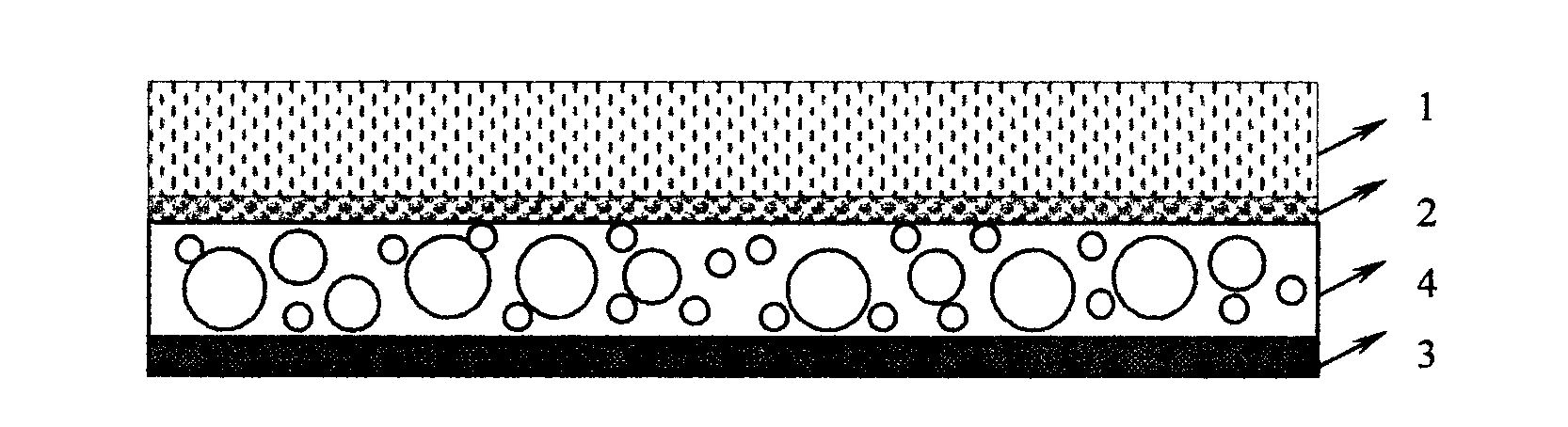
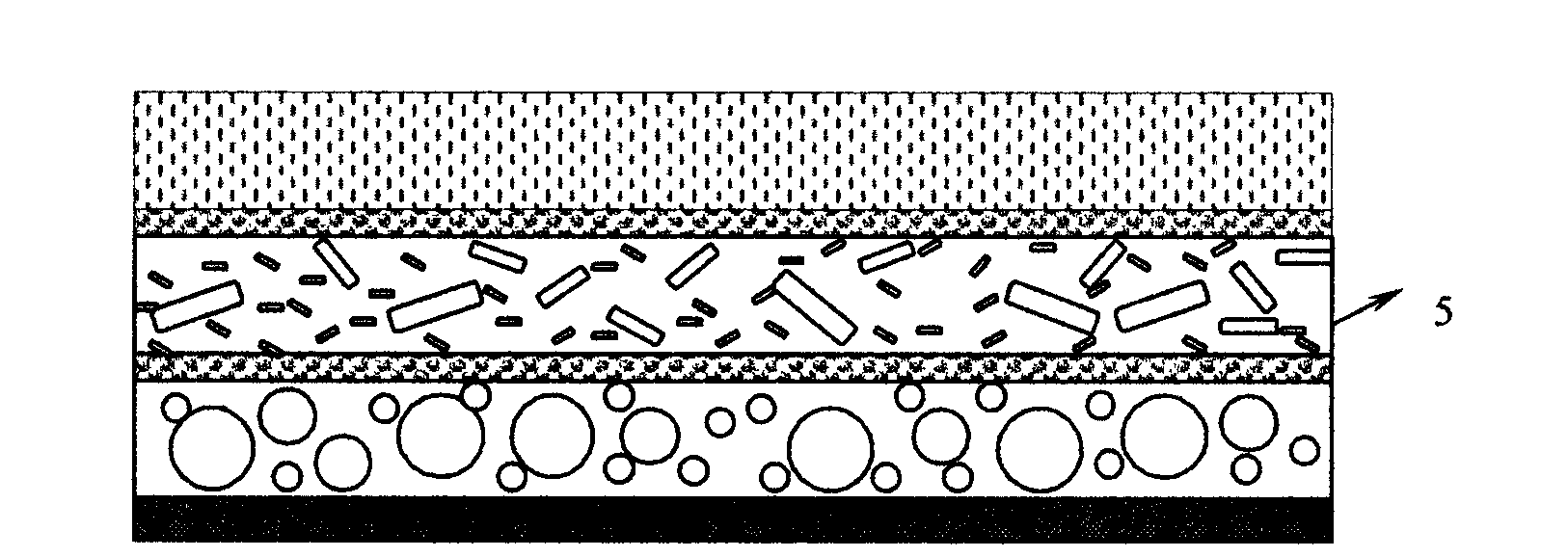
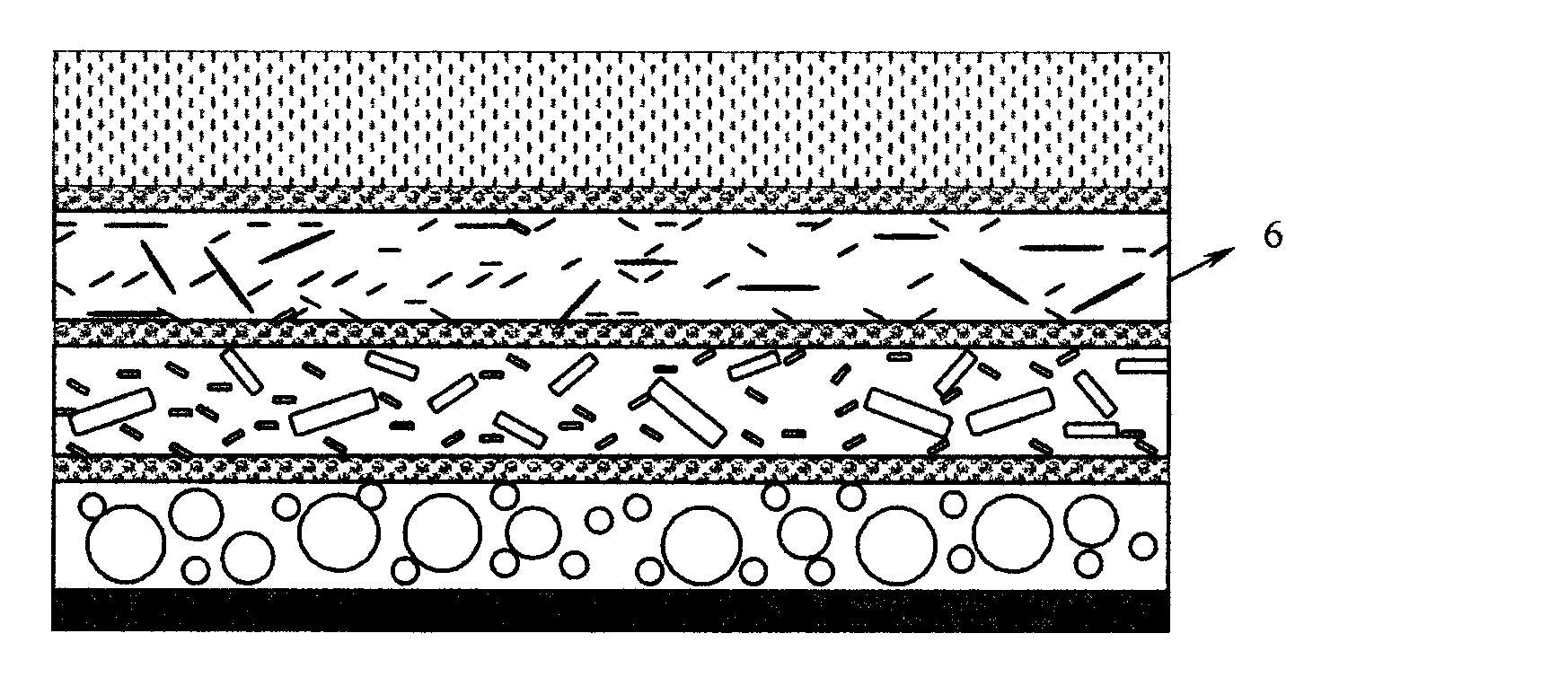
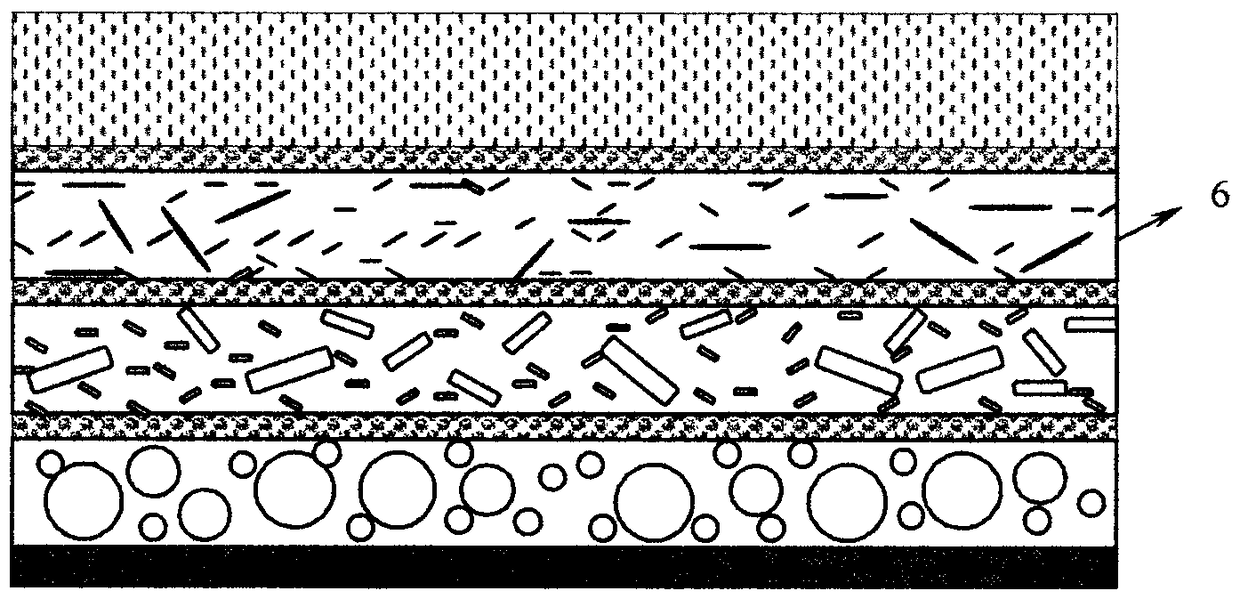
Efficient sound insulation material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103903608AImprove heat and aging resistanceExcellent ozone resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsSound producing devicesInsulation layerFoaming agent
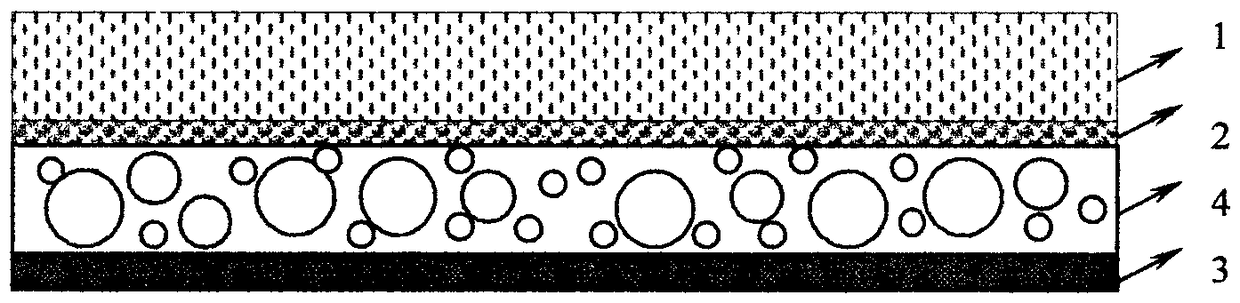
The invention relates to the field of products of sound insulation material, solves the problems in the prior art that the sound insulation material is poor in sound insulation effect, is incomprehensive in high and low frequency sound insulation, causes pollution and is easy to age, and provides an efficient sound insulation material and a manufacturing method thereof. The efficient sound insulation material includes a sound insulation layer, a sound absorption layer, and a bubble layer, wherein the bubble layer is located between the sound insulation layer and the sound absorption layer. The sound absorption layer is made of a sound insulation compound, and the sound insulation compound is prepared by raw materials of the following substances: a thermoplastic resin, inorganic fillers, and a foaming agent, wherein the inorganic fillers account for 15-80wt%, the foaming agent accounts for 5-15wt%, and the rest is the thermoplastic resin. In the efficient sound insulation material, the fillers with different particle diameters correspond to sound waves of different wave bands or frequencies, and thus consumption of sound energy of different frequencies is relatively comprehensive, and the sound insulation effect is good, so the sound insulation material is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:浙江艾迪雅汽车部件新材料有限公司
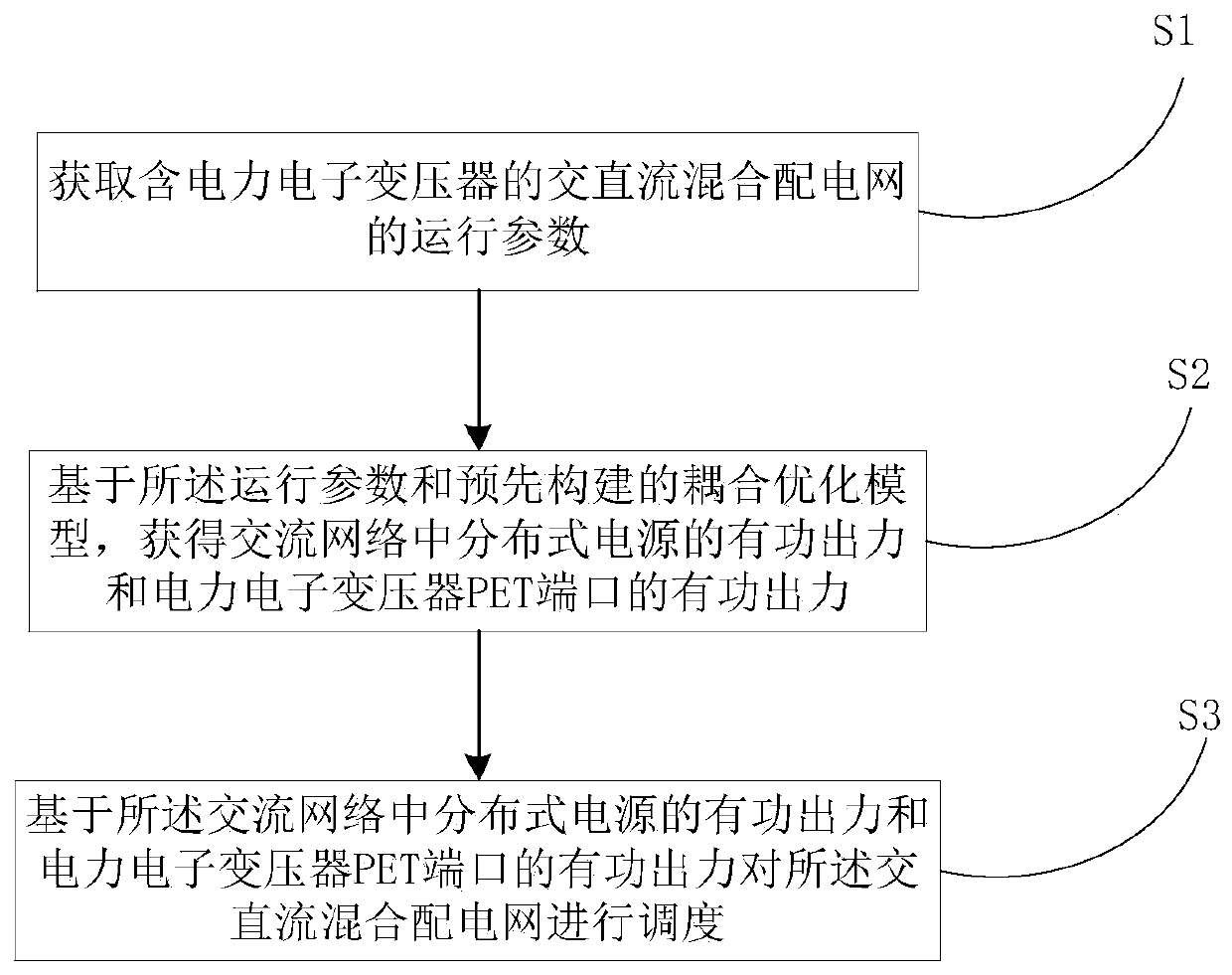
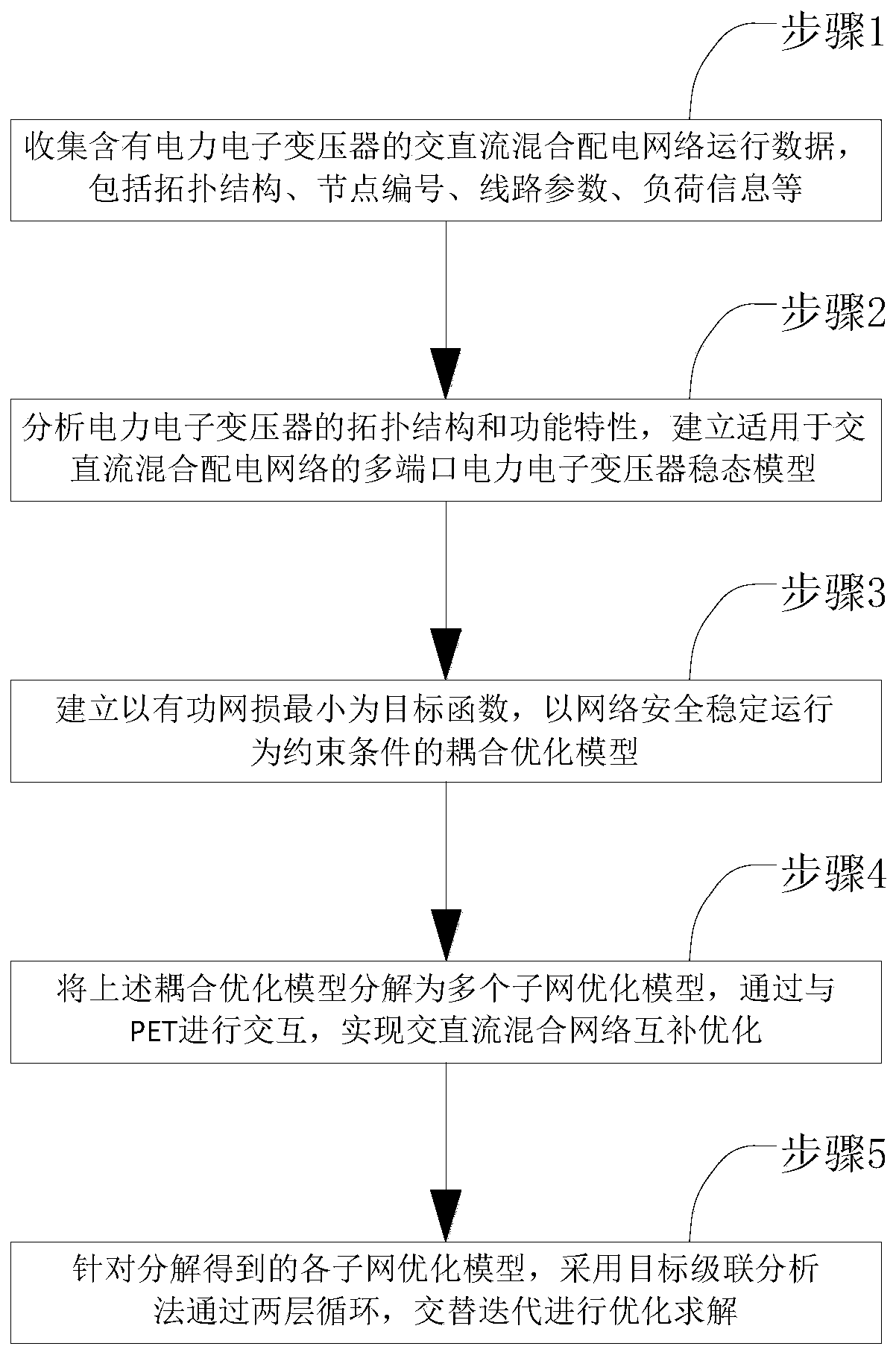
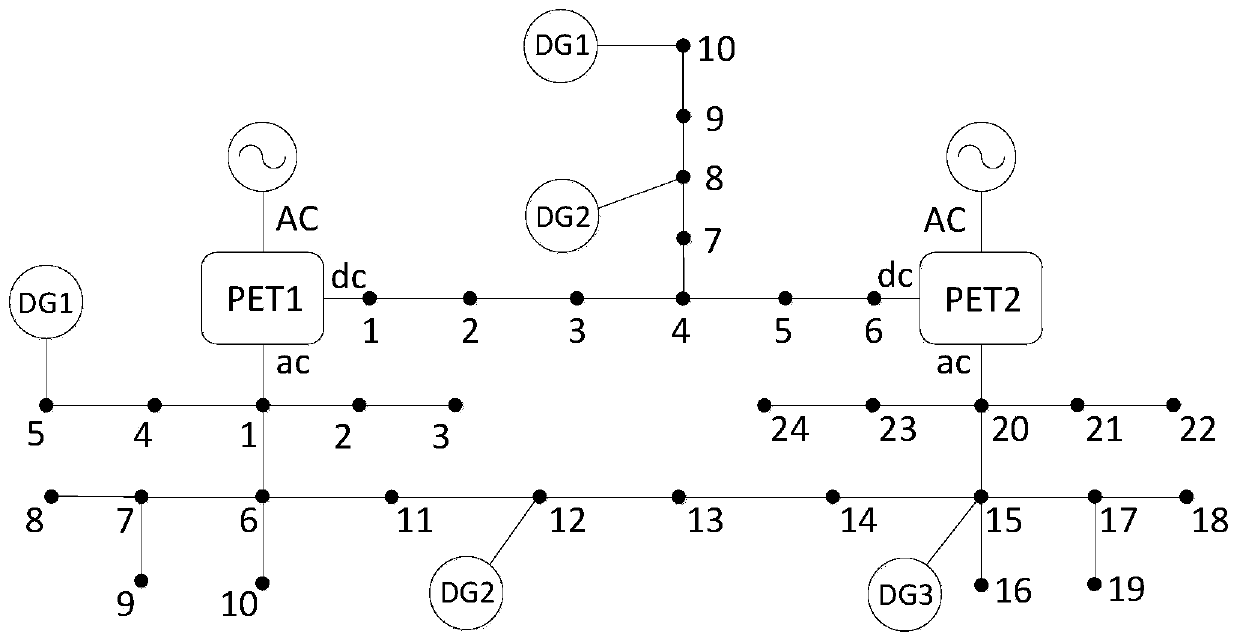
Dispatching method and system for AC/DC hybrid distribution network comprising power electronic transformer
ActiveCN109950907AGive full play to flexible control abilityAchieve mutual coordinationAc networks with different sources same frequencyTransformerEngineering
The invention provides a dispatching method and system for an AC / DC hybrid distribution network comprising a power electronic transformer. The dispatching method comprises steps of: acquiring the operating parameters of the AC / DC hybrid distribution network comprising the power electronic transformer; based on the operating parameters and a pre-established coupling optimization model, obtaining the active output of a distributed power source in the AC network and the active output of the PET port of the power electronic transformer; based on the active output of the distributed power source inthe AC network and the active output of the PET port of the power electronic transformer, dispatching the AC / DC hybrid distribution network. The dispatching method and system realize the sufficient consumption and efficient utilization of the renewable energy source, comprehensively exert the flexible regulation capability of the PET, realize the mutual coordination and complementary optimizationof the AC / DC network, and improve the power interaction capability of the controllable distributed energy between regions.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
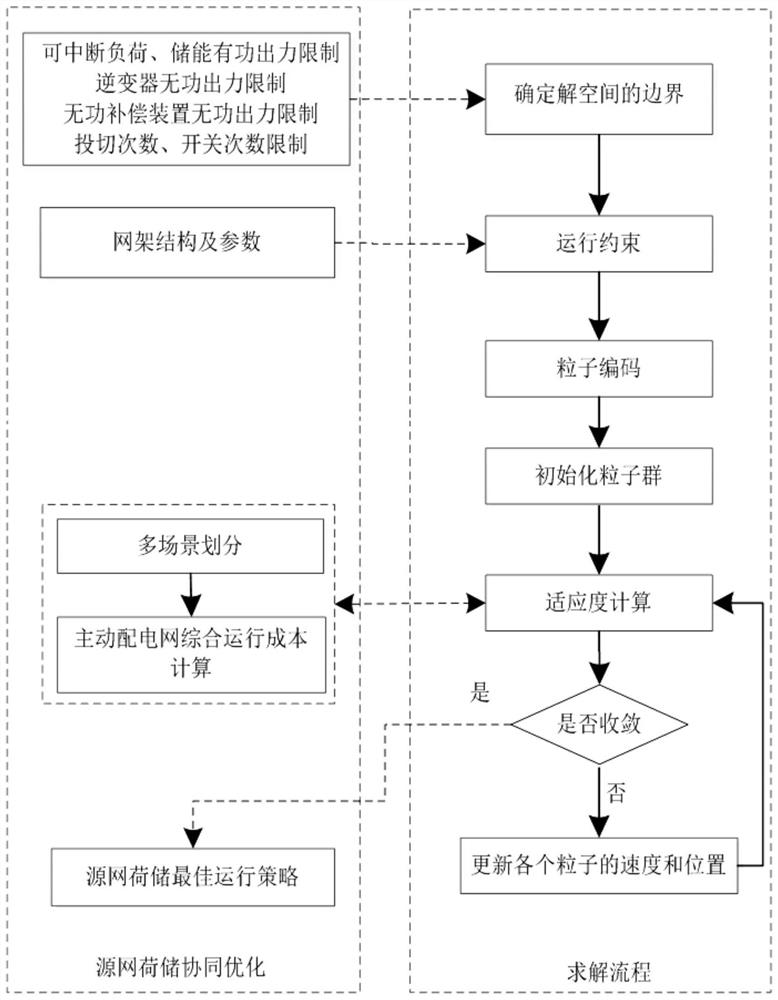
Active power distribution network source network load storage collaborative optimization operation method based on multi-scene technology
ActiveCN112713618AImprove economyFull consumptionPower network operation systems integrationForecastingControl engineeringRenewable power generation
The invention discloses an active power distribution network source network load storage collaborative optimization operation method based on a multi-scene technology. The method comprises steps of firstly carrying out scene division of the active output of distributed renewable energy power generation based on the multi-scene technology, and considering the uncertainty of the active output of the distributed renewable energy power generation; secondly, an active power distribution network source network load storage collaborative optimization model being established with the lowest intra-day comprehensive operation cost of the active power distribution network as the target, and on the basis that only the source load storage collaborative optimization operation model is considered, the load storage collaborative optimization model being established; network reconstruction, reactive power output of a distributed renewable energy power generation inverter and an energy storage inverter and collaborative optimization operation of active power output of distributed renewable energy power generation being also considered, and collaborative optimization operation of active power distribution network source network load storage being realized; and finally, for the active power distribution network source network load storage collaborative optimization model, combining with a particle swarm optimization algorithm to solve a mixed integer programming problem.
Owner:THE ACAD OF TIANJIN UNIV HEFEI
Multi-time-scale active-reactive control method for multi-source coordinated active distribution network
ActiveCN109873447ASolve overvoltageSolve abandoned windSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationScheduling instructionsLoad following power plant
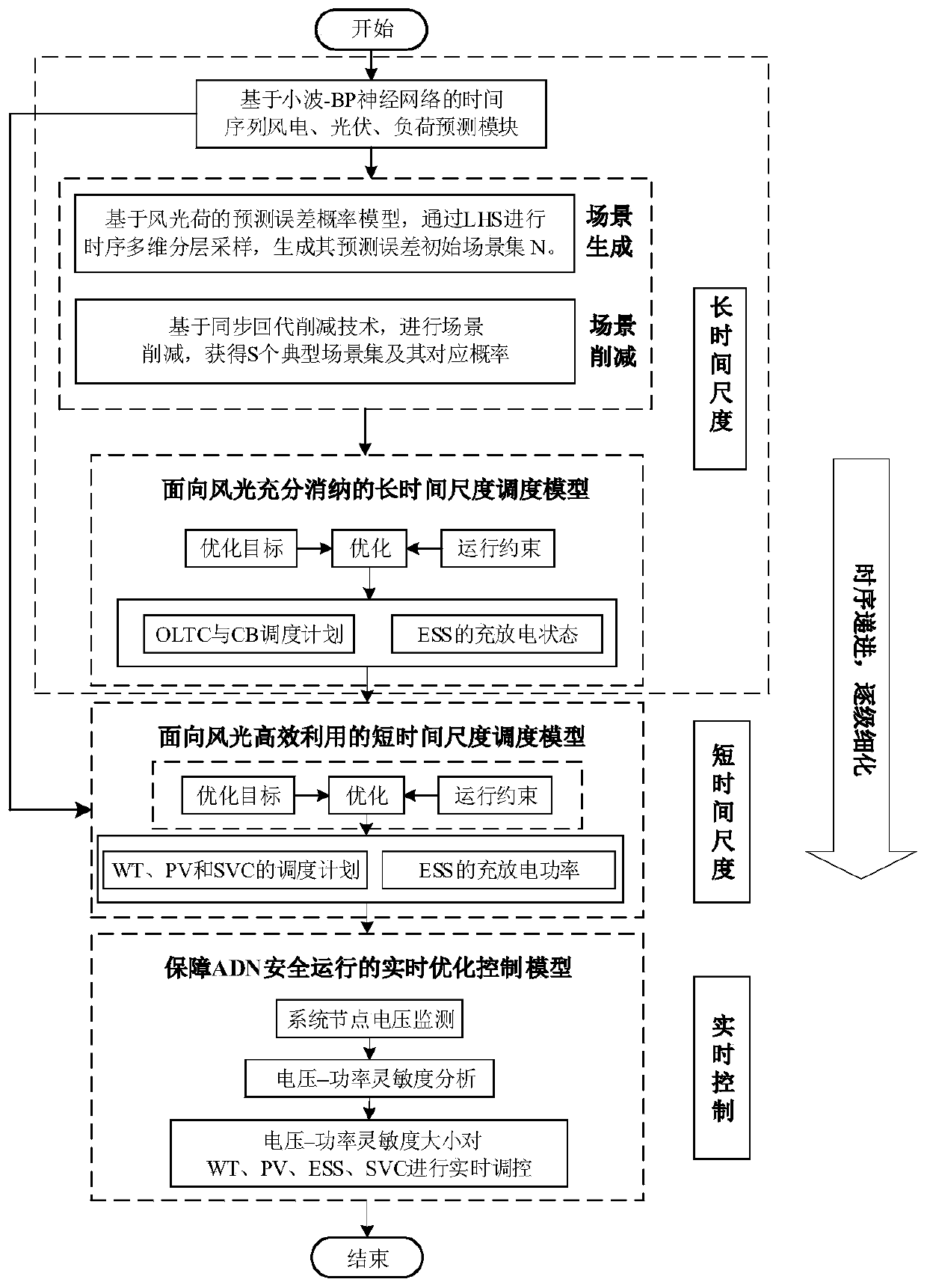
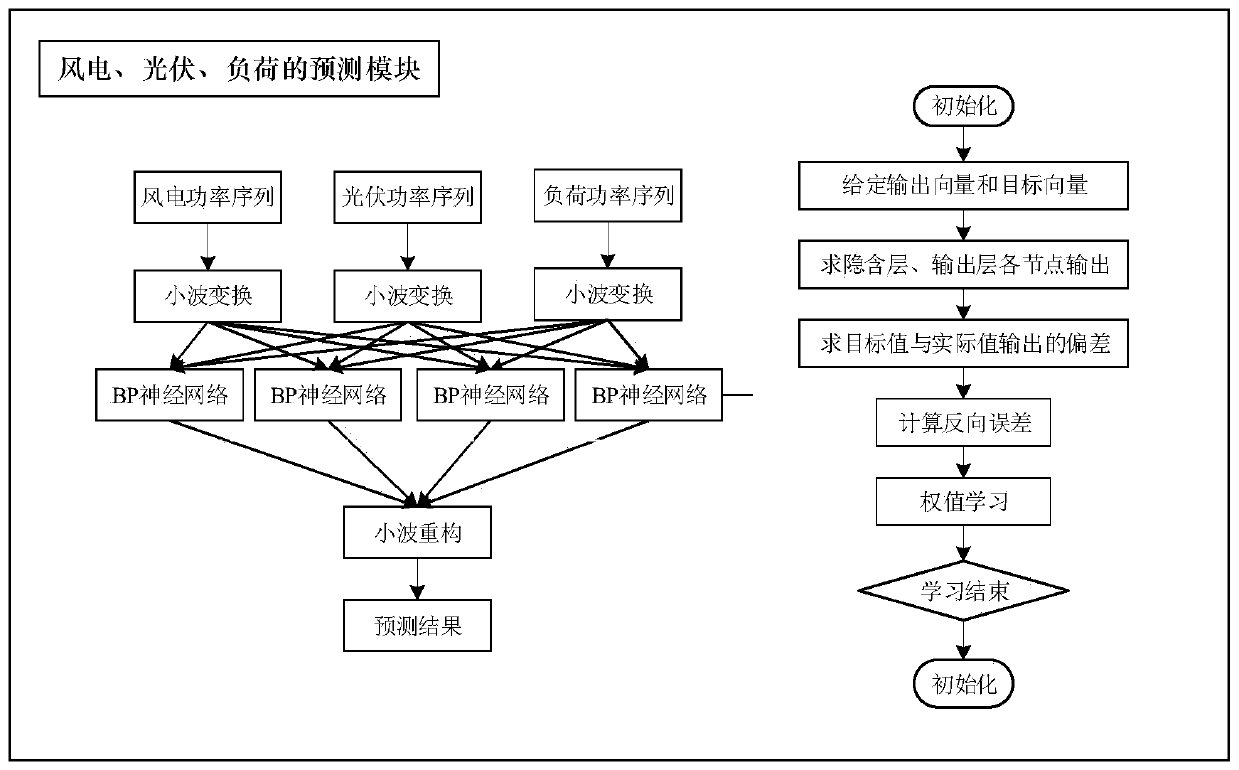
The present invention discloses a multi-time-scale active-reactive control method for a multi-source coordinated active distribution network. The method comprises the following steps: (1) wind power,photovoltaic and load power sequences are predicted; (2) uncertain sampling of the source-load prediction error is performed to obtain a scene set covering the entire sampling space; (3) the scene isreduced by the synchronous back substitution reduction technology and a typical scene set is obtained; (4) in a long-time-scale scheduling phase, a control solution for adjusting the device with a limited adjustment times and the charge and discharge state of energy storage are obtained; (5) in a short-time-scale scheduling phase, scheduling instructions for quickly continuously adjusting devicesare solved; (6) in a real-time control phase, the adjustable devices are sequentially adjusted based on the sensitivity analysis of the node voltage so that the safe and stable operation of the powernetwork is ensured. By using the method of the present invention, the coordinated optimization operation of the adjustable devices in the active distribution network and full consumption and efficientutilization of the renewable energy can be realized.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
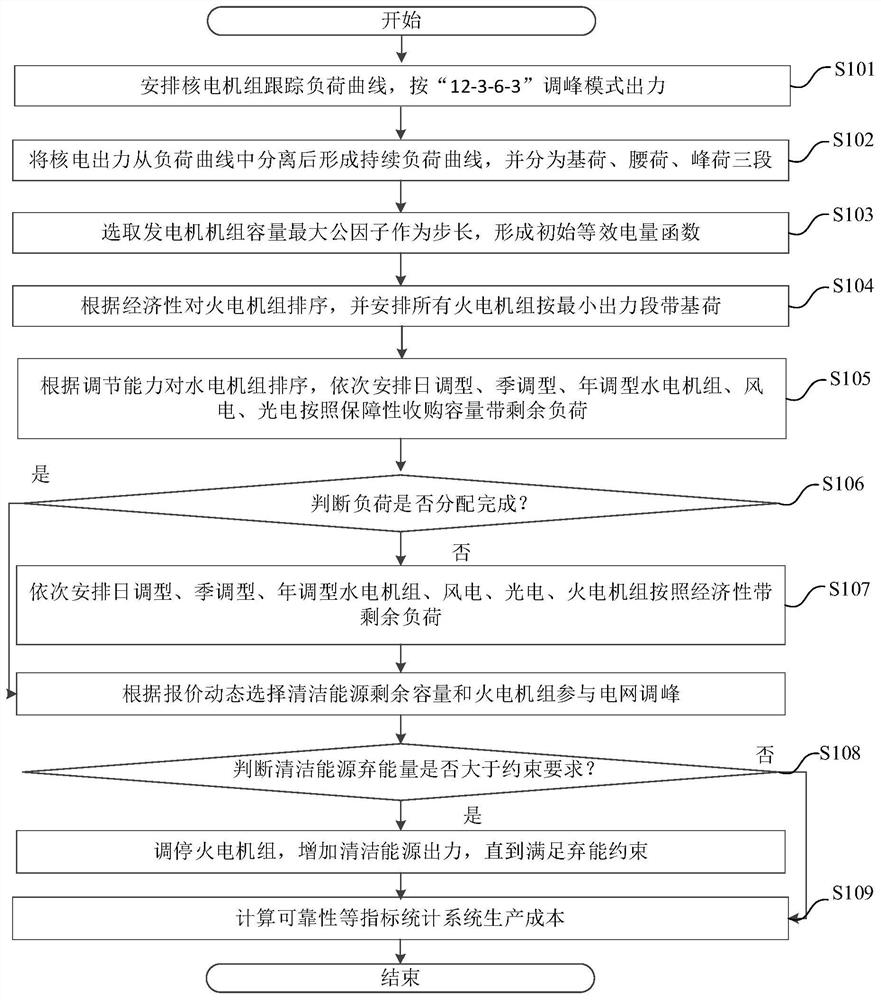
Random production simulation method taking participation of various power supplies in peak load regulation and application thereof
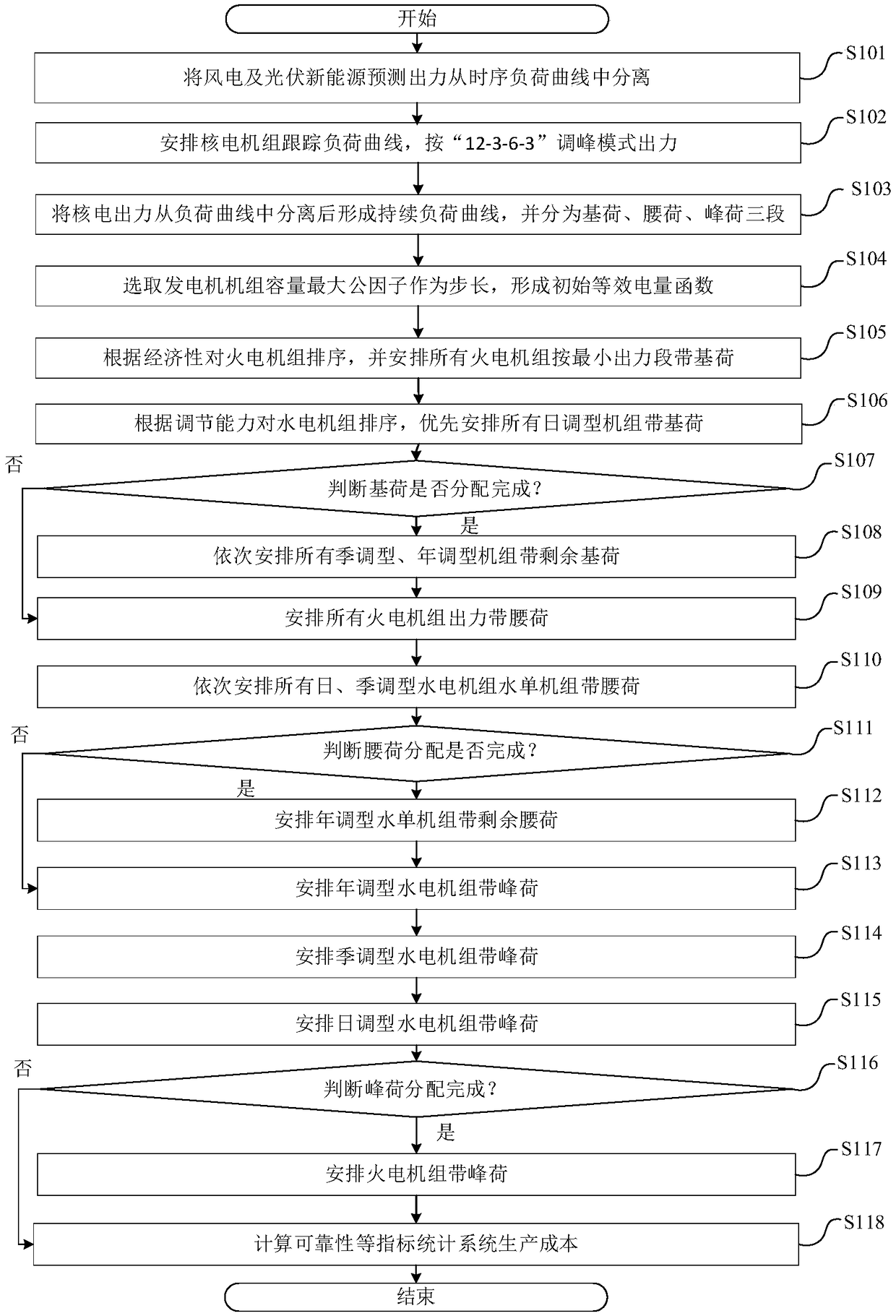
ActiveCN109347152ASmoothing fluctuationsImprove peak shaving performanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectric power systemNuclear power
The invention discloses a random production simulation method taking participation of various power supplies in peak load regulation and application thereof. The random production simulation method comprises the following steps: 1) acquiring an annual load curve; 2) removing annular output of wind power, photovoltaic power and nuclear power from the annular load curve to obtain a continuous load curve, and partitioning the continuous load curve into a base load, a shoulder load and a peak load according to an annual load level; 3) building an equivalent electric quantity function according tothe continuous load curve; and 4) realizing output of a thermal power unit and a hydropower unit at different stages according to the equivalent electric quantity of the base load, shoulder load and peak load to obtain random production simulation data of a power system. Compared with the prior art, the random production simulation method has the advantage of improving the peak load regulation capability of a regional power grid.
Owner:国家电网有限公司西南分部 +2
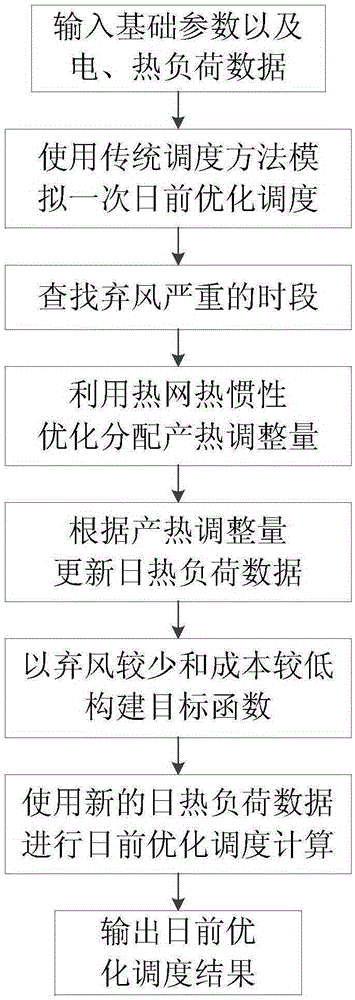
Power grid day-ahead optimization scheduling method based on thermal inertia of hot water network
InactiveCN105279709AFull consumptionIncrease profitData processing applicationsEnergy industryWind drivenCogeneration
The invention discloses a power grid day-ahead optimization scheduling method based on thermal inertia of a hot water network. The power grid day-ahead optimization scheduling method based on thermal inertia of a hot water network utilizes a traditional power grid day-ahead optimization scheduling model which does not consider the thermal inertia of a hot water network to simulate scheduling and search the serious period that a wind driven generator stops working, and then utilizes the thermal inertia of a hot water network to reasonably adjust the quantity of heat production for scheduling simulation under the premise that the indoor temperature of a heat consumer is satisfied, and can reduce the heat supply power of a cogeneration unit during the serious period that a wind driven generator stops working, and can optimize and adjust the reduced heat supply power to the no-serious period that a wind driven generator stops working, so the adjustable scope of the power supply power of the cogeneration unit during the serious period that a wind driven generator stops working can be increased so that more wind power can access the network; and according to the adjusted quantity of heat production, power grid day-ahead optimization scheduling is performed again. Compared with the prior art, the power grid day-ahead optimization scheduling method based on thermal inertia of a hot water network can improve the utilization rate of wind energy resources and reduce the generating cost under the premise that the indoor temperature requirement of the heat consumer is satisfied.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
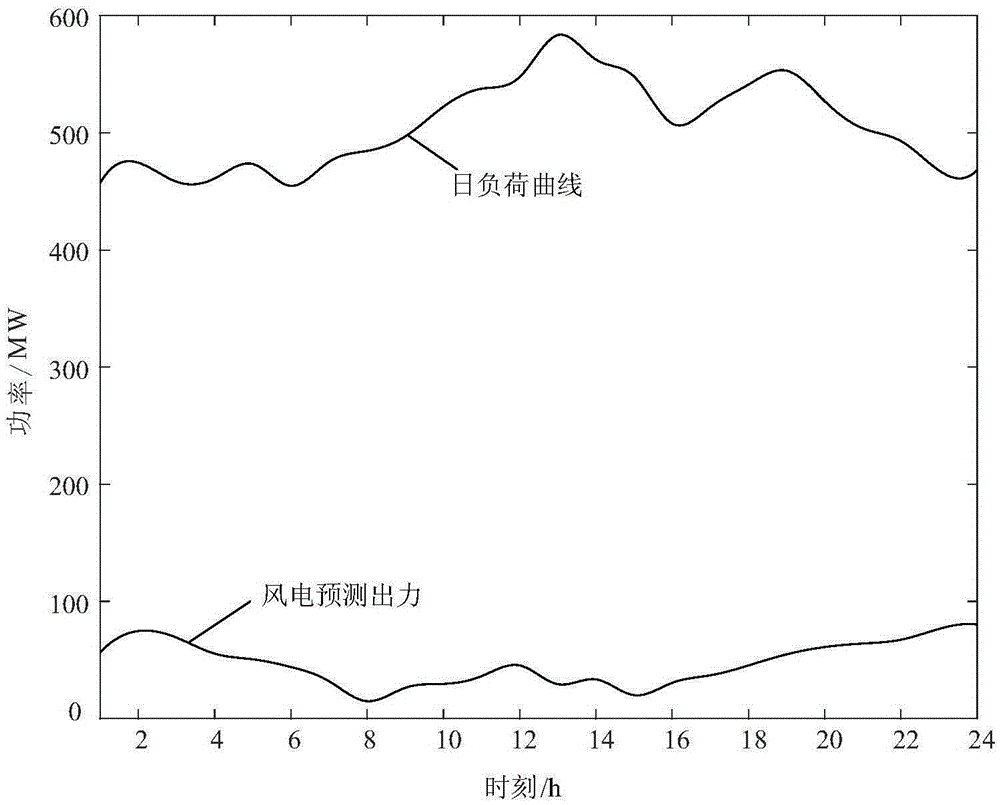
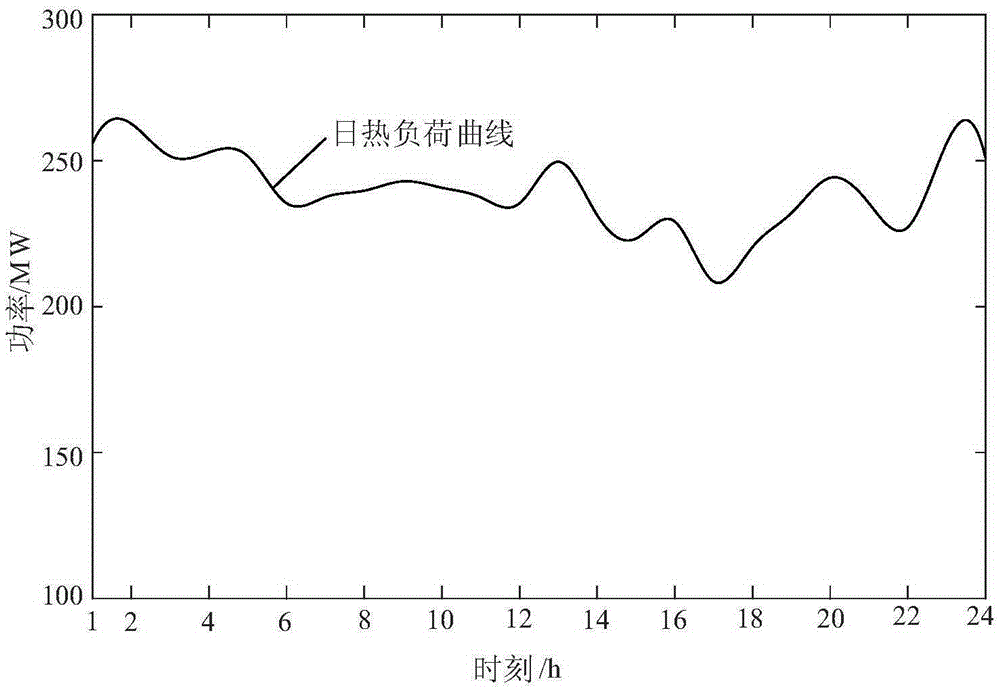
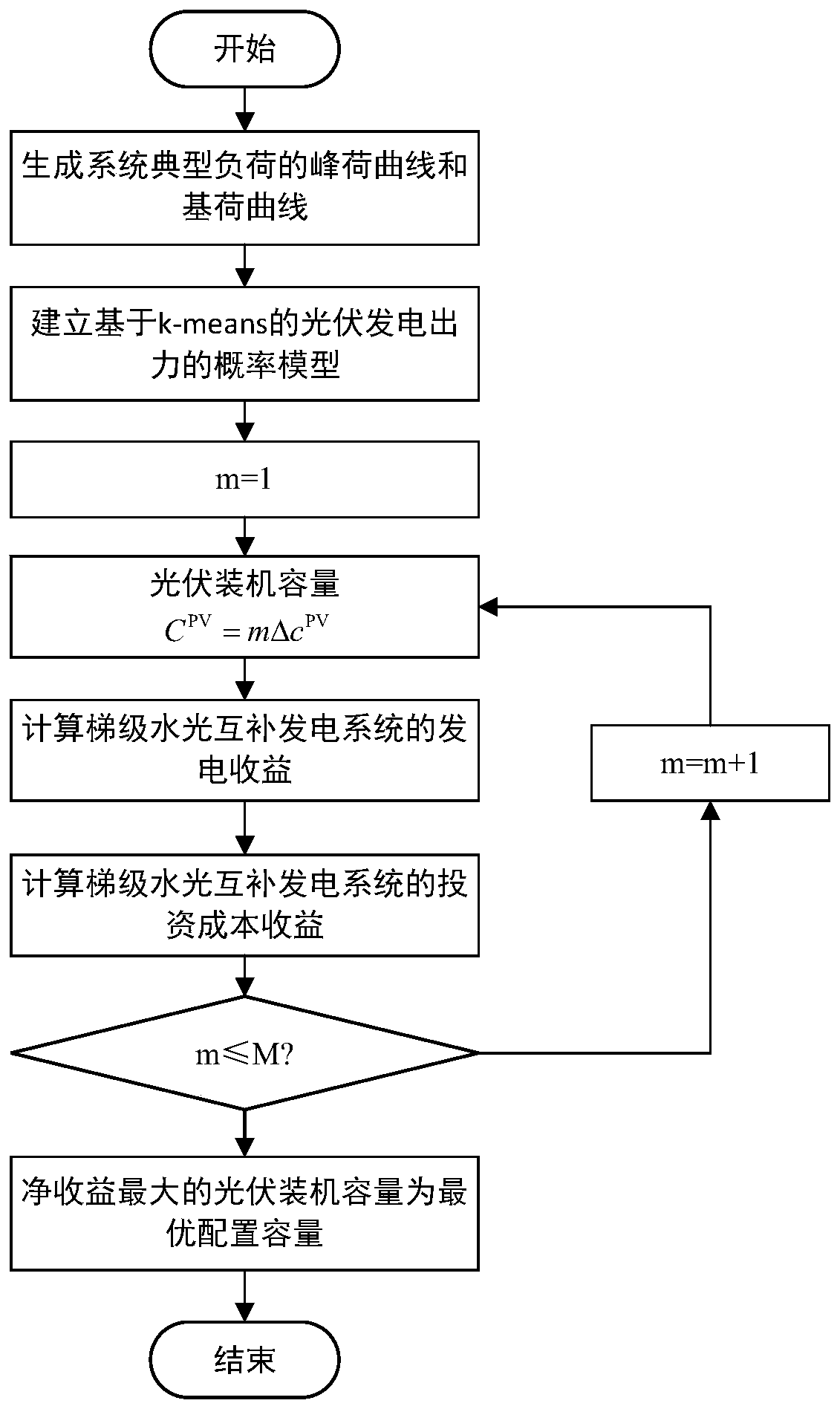
Photovoltaic capacity configuration method suitable for cascade water-light complementary energy power generation system
ActiveCN110838733AFull consumptionMake full use of peak shaving potentialSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationThermodynamicsHydro energy
The invention discloses a photovoltaic capacity configuration method suitable for a cascade water-light complementary energy power generation system. The photovoltaic capacity configuration method comprises the steps: a peak load curve and a base load curve of a typical load of the power generation system is generated; a photovoltaic power generation output probability model based on k-means is established; based on the peak load curve, the base load curve and the photovoltaic power generation output probability model and through establishing an operation simulation model of the cascade water-light complementary energy power generation system, the power generation income of the complementary energy power generation system can be calculated; based on the calculated power generation income and through establishing an investment cost income of the complementary energy power generation system, the photovoltaic installed capacity with the maximum net income is selected as the optimal configuration capacity of the power generation system. Thus, configuration of photovoltaic capacity of a cascade hydropower energy base can be achieved, resource waste caused by excessive photovoltaic investment is avoided, and meanwhile the investment income of a cascade water-light complementary energy power generation system is maximized.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Multi-stage scene generation electric heating system optimal scheduling method based on wind power consumption
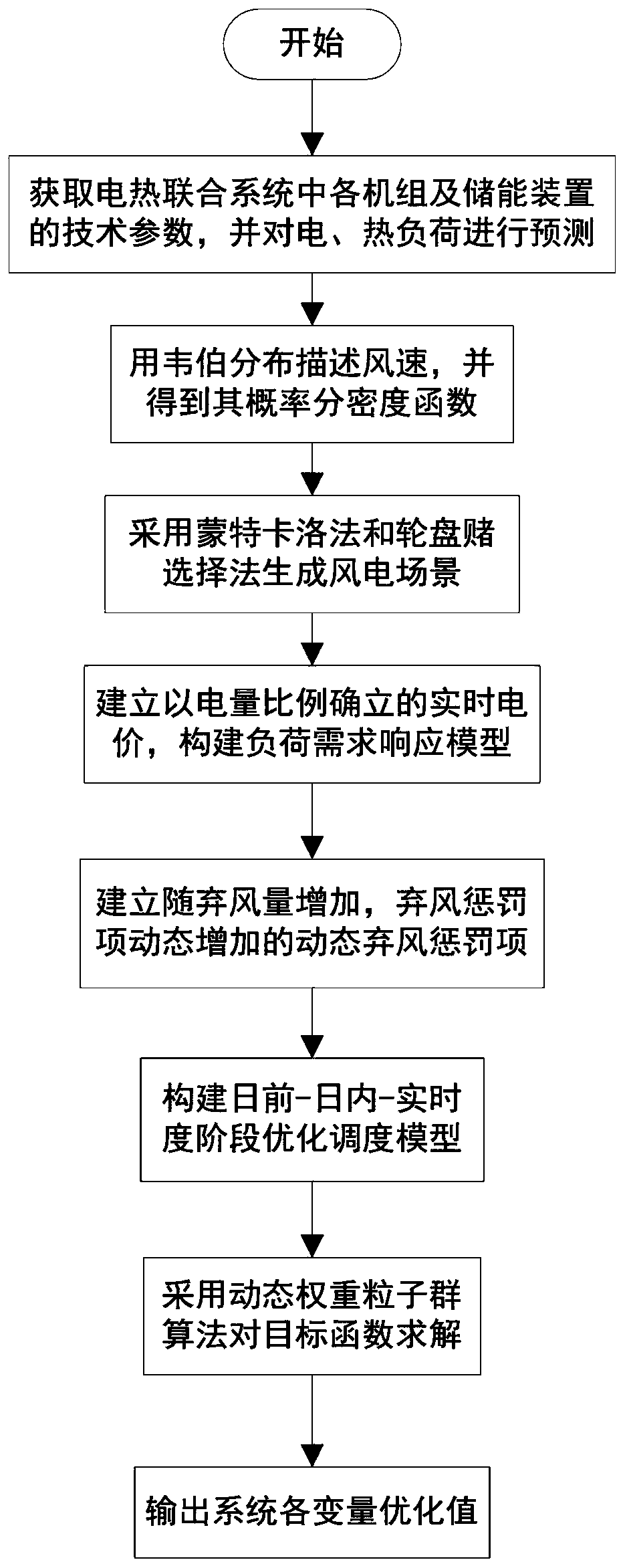
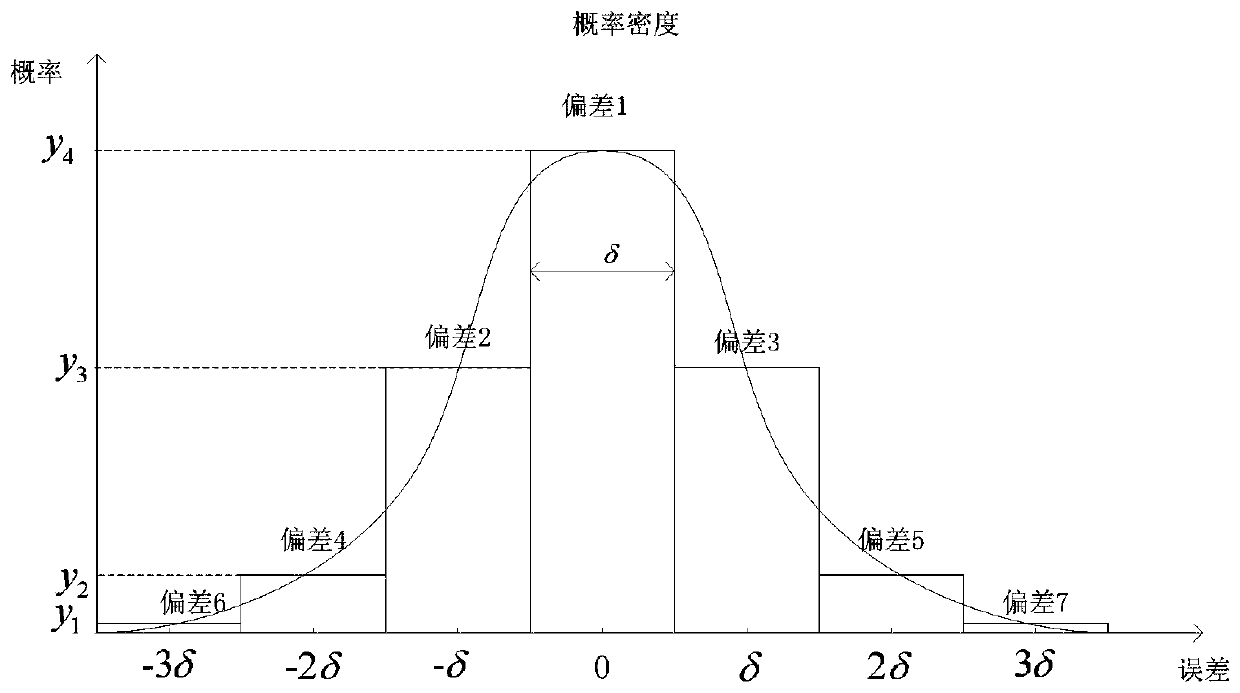
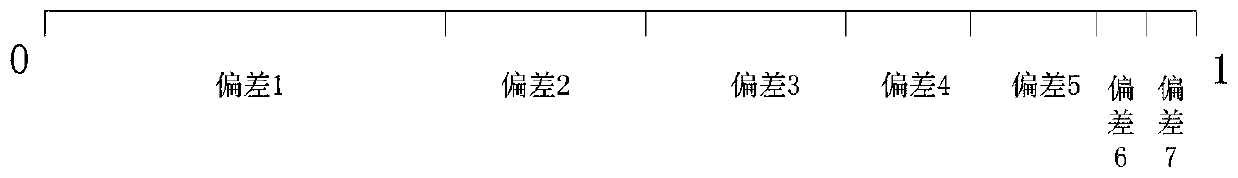
ActiveCN110796373AFlexible and economical operationFully mobilize the enthusiasm of load responseResourcesInformation technology support systemThermodynamicsOptimal scheduling
The invention discloses a multi-stage scene generation electric heating system optimization scheduling method based on wind power consumption, and belongs to the technical field of economic dispatch of an electric heating combined system. The multi-stage scene generation electric heating system optimization scheduling method comprises the steps of generating day-ahead wind power prediction and intra-day and real-time wind power prediction containing prediction errors through a Monte Carlo and roulette selection mechanism on the basis of considering uncertainty of wind power output, determiningreal-time electricity price according to an electric quantity proportion, and constructing an intra-day demand response model. In order to effectively promote the system to consume wind power, a windcurtailment penalty term with the cost dynamically increased along with the wind curtailment amount is constructed. The minimum system cost is used as a target function; and scheduling is carried outby adjusting a conventional unit and a CHP unit before the day; and intra-day scheduling is implemented through a heat accumulating type electric boiler and an intra-day demand response model set based on electric quantity, and unbalanced electric quantity of the real-time market is adjusted through an electric storage device and a unit, and the model is solved through a particle swarm algorithmof dynamic weight, and a reasonable electric-heat joint optimization scheme is obtained.
Owner:FUXIN POWER SUPPLY COMPANY STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER +2
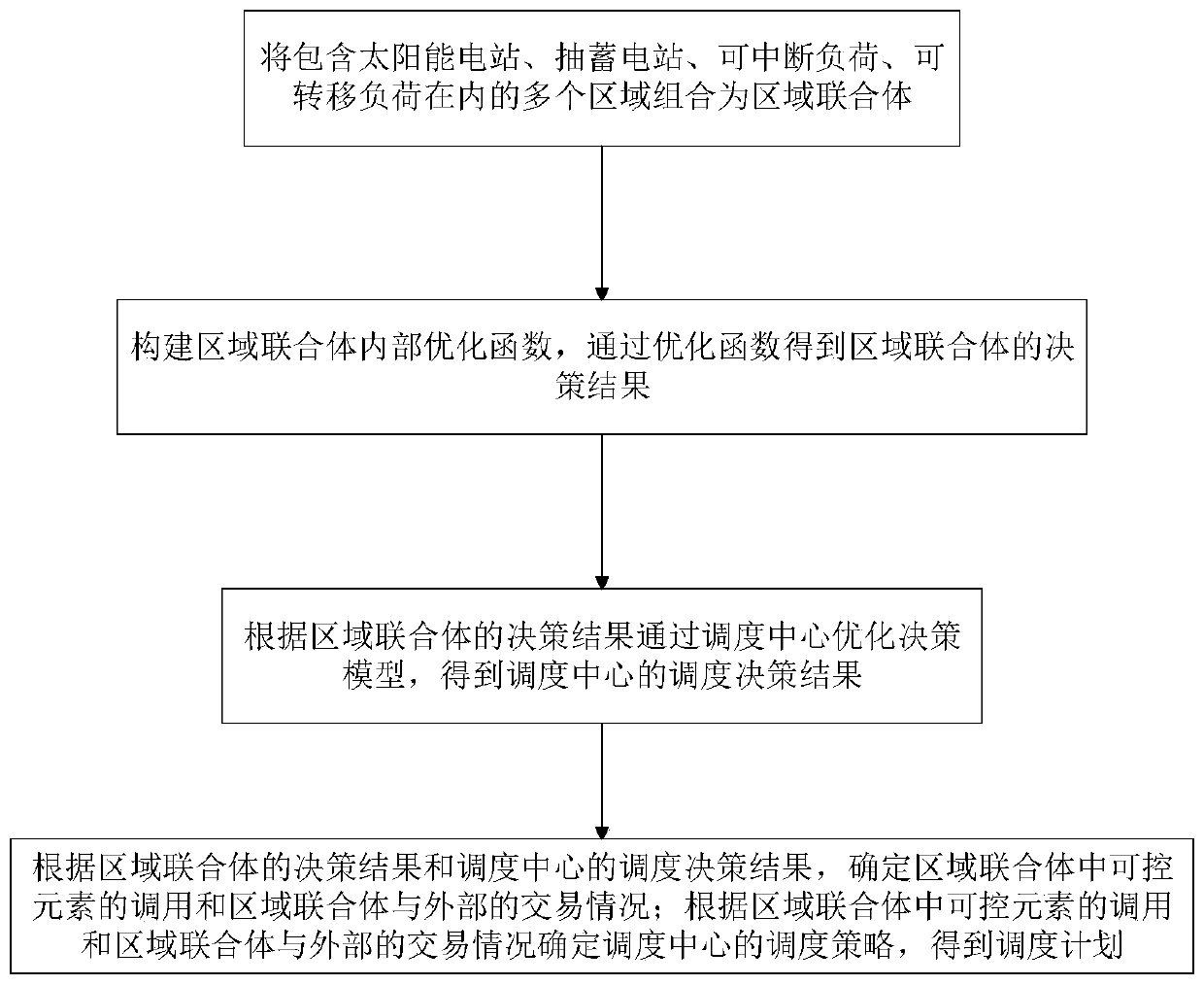
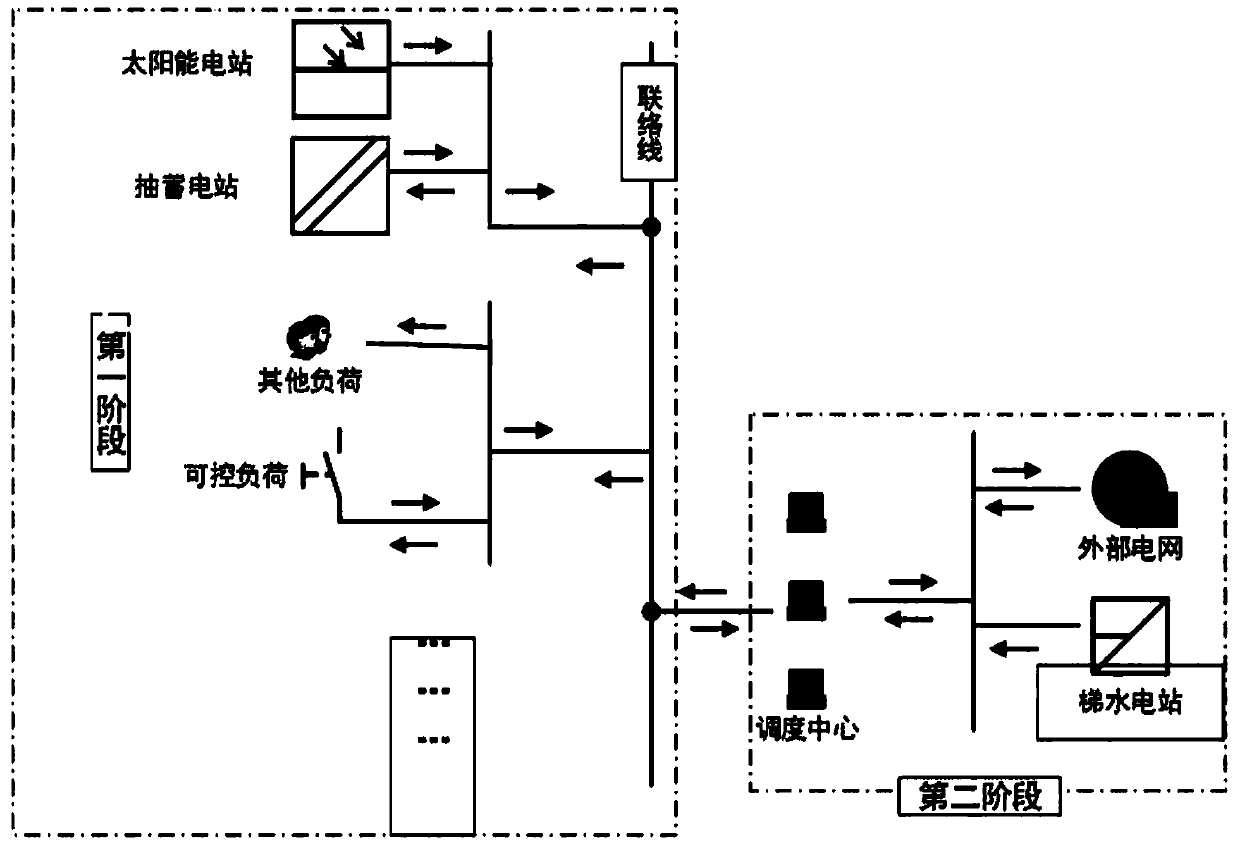
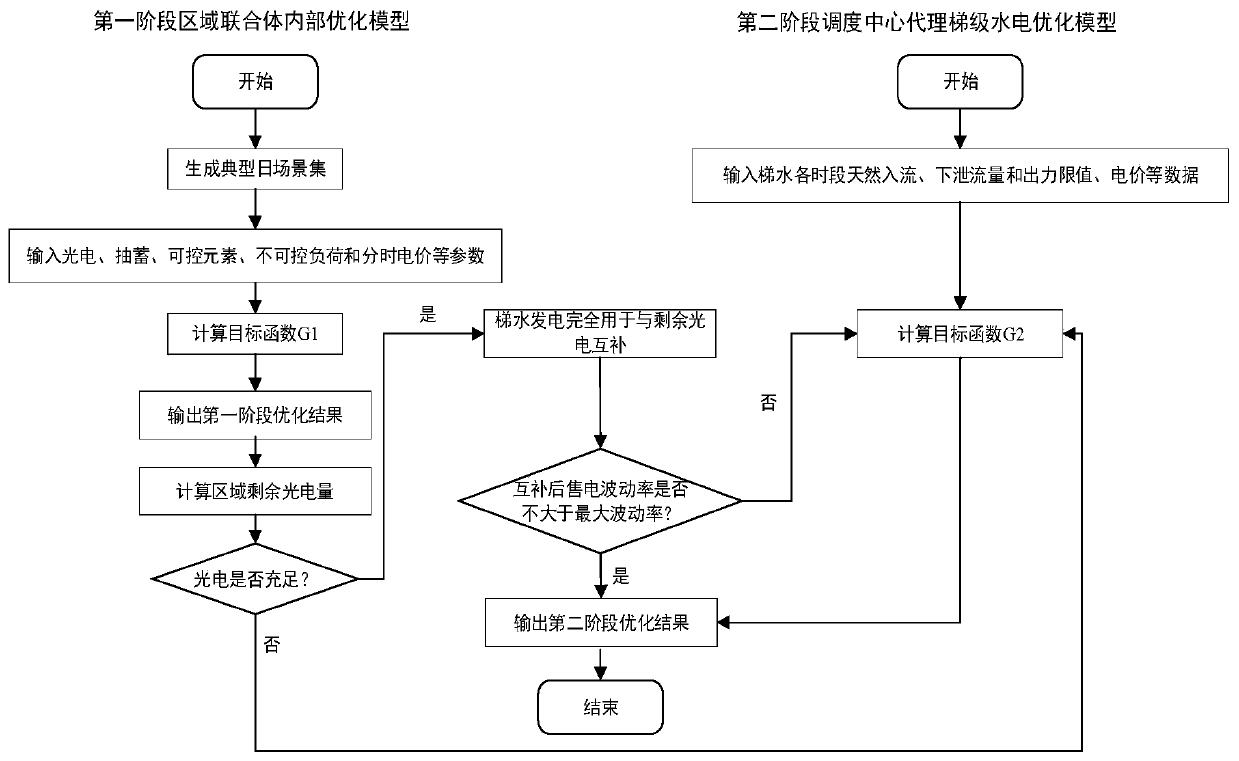
Regional complex two-stage economic dispatching method considering water-light-storage complementation
The invention discloses a regional complex two-stage economic dispatching method considering water-light-storage complementation. The method comprises the following steps: combining a plurality of regions which comprises a solar power station, a pumped storage power station, an interruptible load and a transferable load into a regional complex; constructing an internal optimization function of theregional complex, and obtaining a decision result of the regional complex through the optimization function; optimizing the decision model through the scheduling center according to the decision result of the regional complex to obtain a scheduling decision result of the scheduling center; according to the decision result of the regional complex and the scheduling decision result of the scheduling center, determining the calling of controllable elements in the regional complex and the transaction condition between the regional complex and the outside; and determining a scheduling strategy ofthe scheduling center according to the calling of the controllable elements in the regional combination body and the transaction condition of the regional combination body and the outside to obtain ascheduling plan. According to the invention, the cost of the regional combination body is reduced, the absorption capability of the water-light storage system for new energy is improved, and the source electricity quality is improved at the same time.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
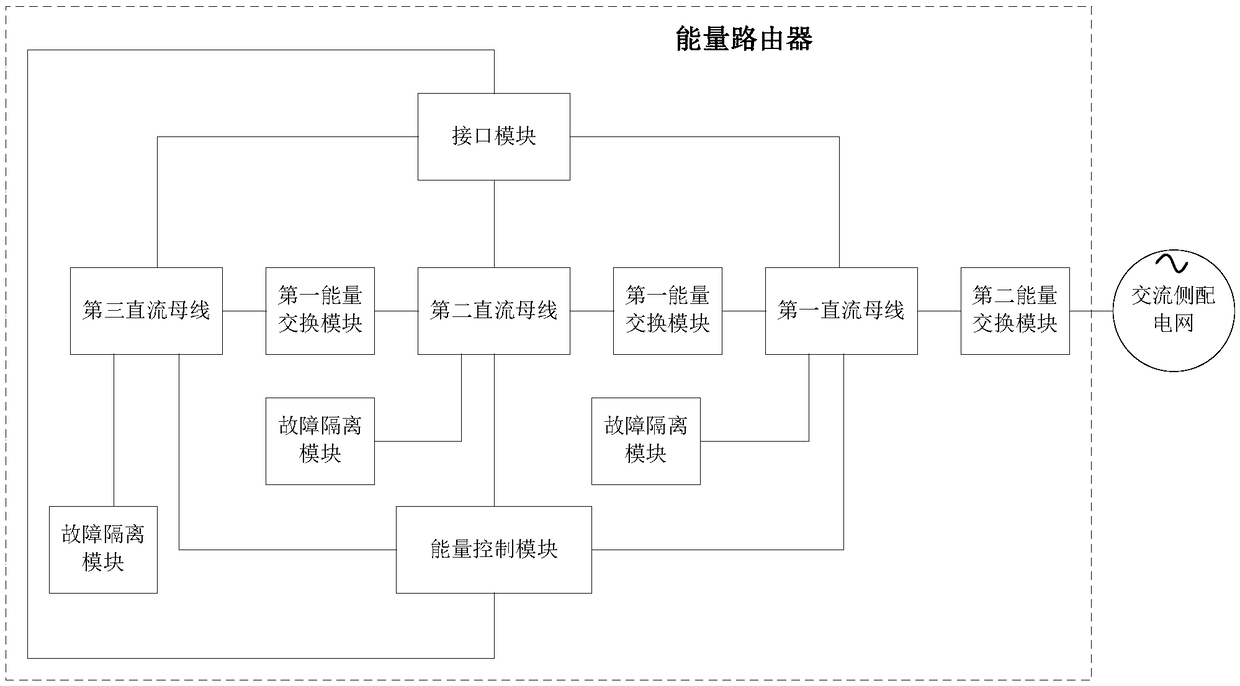
Energy router, and method for controlling energy flow of alternating current/direct current hybrid power distribution network
InactiveCN109378866AIncrease flexibilityImprove accuracyElectrical apparatusEnergy controlAC - Alternating current
The invention discloses an energy router, and a method for controlling energy flow of an alternating current / direct current hybrid power distribution network. The energy router includes a first directcurrent bus, a second direct current bus, a third direct current bus, a first energy exchange module, a second energy exchange module, an energy control module, a fault isolation module, and a powerinterface module. The different direct current buses are connected by the first energy exchange module; the direct current buses are connected to an alternating current power distribution network through the second energy exchange module; the power interface module is connected to external devices. The method includes the following steps of performing state monitoring on internal and external devices of the energy router; and judging whether a first power interface or / and a connected external device is faulty according to state monitoring data, and separately starting the first power interfaceor a second power interface for processing. Through the energy router and the control method, the flexibility of energy flowing of the alternating current / direct current power distribution network can be improved, alternating current / direct current energy can be fully coordinated, and the energy utilization rate and the grid stability can be improved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Power generation cost constraint-based multi-domain scheduling method considering energy storage power system
ActiveCN110829408AFull consumptionIncrease profitSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storagePower system schedulingFlexible scheduling
The invention discloses a power generation cost constraint-based multi-domain scheduling method considering an energy storage power system and belongs to the technical field of power system scheduling. By utilizing the scheduling characteristic of a transferable load of the energy storage system, an important role of flexible scheduling can be played in the actual scheduling of the power system. The multi-domain scheduling method is provided from the perspective of flexible scheduling of source storage, influence of factors such as load, wind power output random fluctuation and system regulation capability is comprehensively considered, and all regulation capacities in the system are uniformly scheduled and redistributed into three control domains, namely a normal domain taking complete wind power consumption as a target, an abnormal domain needing to call an energy storage system to consume wind power, and an emergency domain without regulation capability and forced wind curtailment.Under different domains, through reasonable matching of a conventional thermal power generating unit and an energy storage system, multi-domain economic dispatching is achieved with maximum clean energy consumption as the target.
Owner:ANSHAN POWER SUPPLY COMPANY OF STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +3
Black-odor riverway ecological transformation method utilizing building rubbish reclaimed materials and sludge
PendingCN111472320AReduce governance costsImprove processing efficiencyWater resource protectionCoastlines protectionEnvironmental resource managementRiver routing
The invention provides a black-odor riverway ecological transformation method utilizing building rubbish reclaimed materials and sludge. Building rubbish fine aggregates and solidified sludge are combined to manufacture riverway tunnel bottom composite seepage-proofing materials to be paved at a riverway protection slope and the tunnel bottom; building rubbish rough aggregates are used for manufacturing prefabricated porous vegetation concrete blocks; after being solidified, building rubbish fine aggregates and riverway sludge are combined to manufacture green planting soil to serve as planting base materials; building rubbish fine aggregates and riverway sludge are used for prepaing unfired landscape / water purification ceramsite; building rubbish recovery steel is used for manufacturing prefabricated porous vegetation concrete block fixing parts; and large building rubbish is screened to be shaped to serve as building block materials of a side slope platform or protection feet. By means of the method, building rubbish reclaimed materials and riverway sludge are fully utilized, ecological reasonable transformation is carried out on black-odor riverway side slopes, riverway tunnelbottoms and other positions, the water quality of black-odor riverways is improved, meanwhile, the usage level of stone, cement and other traditional building materials is reduced, solid-waste resource utilization is completed, and remarkable economic and ecological benefits are achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
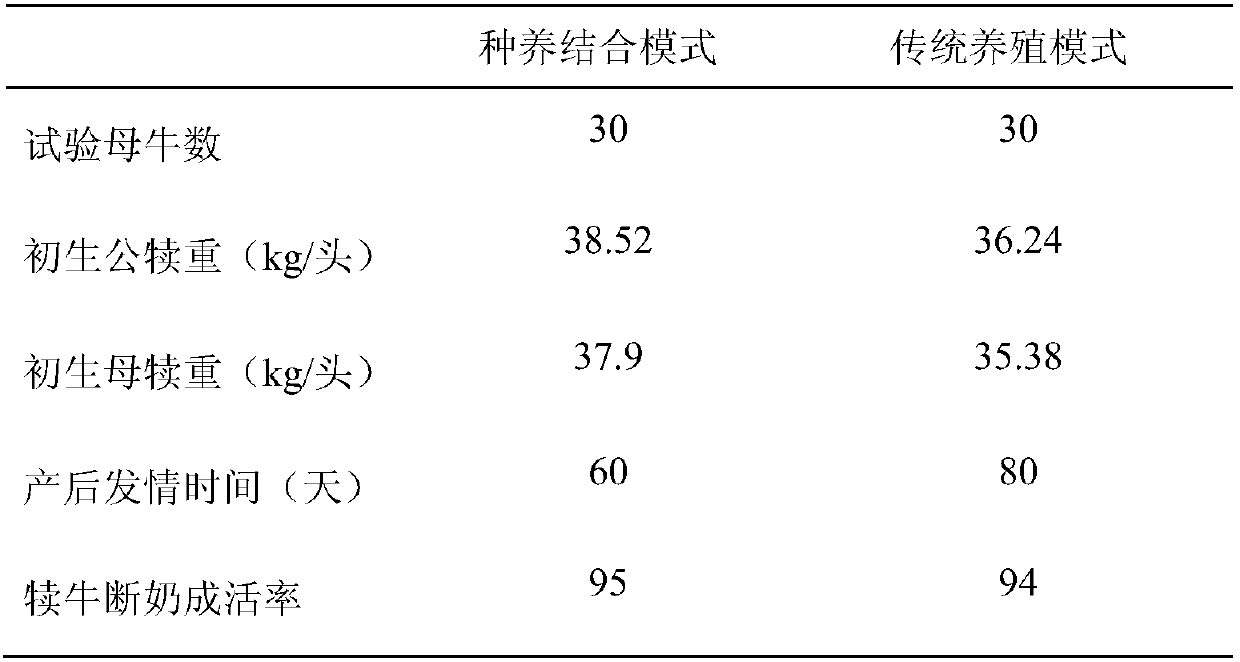
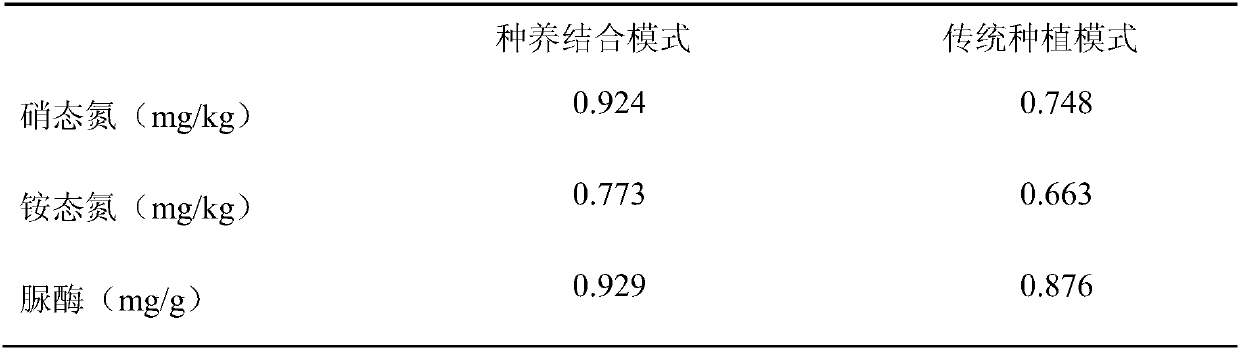
Cow breeding method combining farming and grazing
ActiveCN107691371AReduce demandReduce cleanupFood processingExcrement fertilisersSupplementary FeedingsFertilizer
The invention discloses a cow breeding method with combining farming and grazing. According to the cow breeding method, the land is divided into a grazing area, a repairing area and a supplementary feeding area; in the grazing area, ryegrass, festuca and white clover are mixedly sowed in late September each year, cows are grazed for 5-7 days in each zone block from March to April in the next yearaccording to the growth condition of forage grass, and then cow manure is sprayed with liquid preparation (EM bacteria solution and compound enzymes); in the repairing area, wheat is planted in October in each year, and corn is planted after the wheat is harvested the next year; the grazing area and the repairing area are alternated the next year, after alternation, the wheat is not applied with chemical fertilizer any more; in the non-grazing period, supplementary feeding is carried out on the cows in the supplementary feeding area. Compared with an existing cow breeding mode, cow manure canbe effectively treated by adopting the cow breeding method, and the grazing and rotation grazing method is beneficial for improvement of production performance of beef cattle. Compared with the commonfield for producing grain, the cow breeding method can improve the fertility of soil and save usage of the chemical fertilizer.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
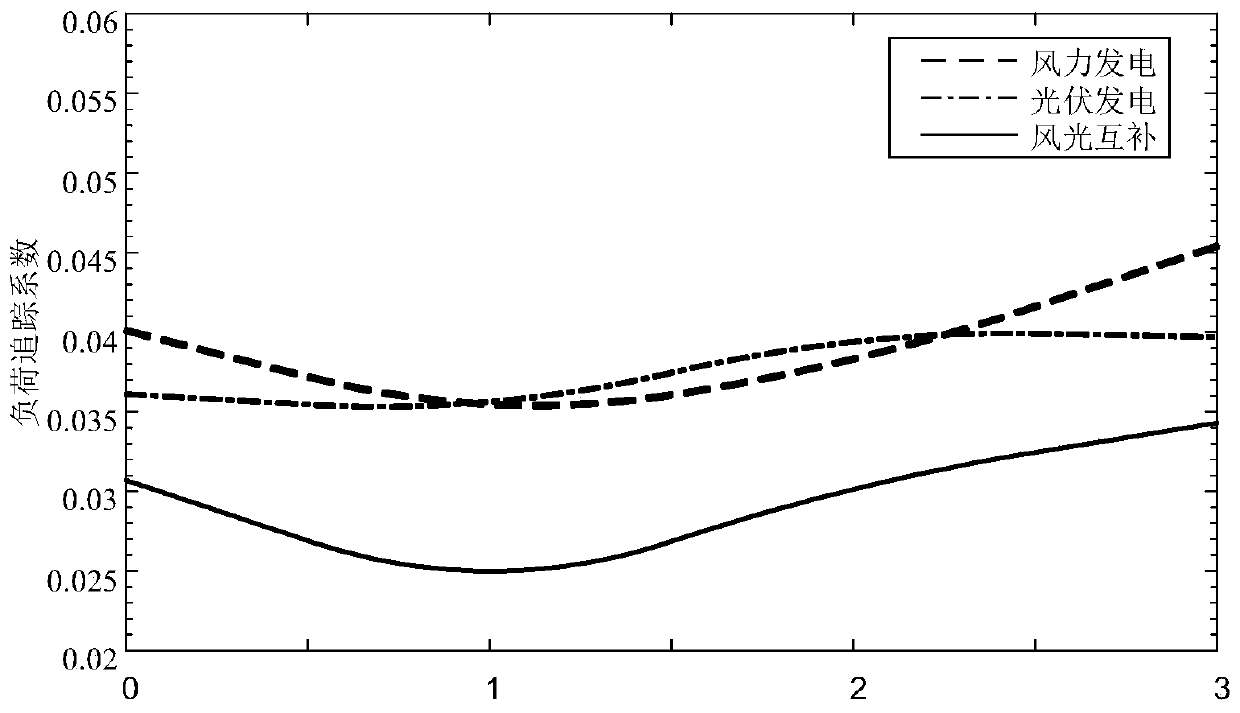
Wind-solar-storage complementary system demand response strategy based on correlation analysis
InactiveCN111404205AFull consumptionReduce load peak-to-valley differenceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageNew energyEngineering
A wind-solar-storage complementary system demand response strategy based on correlation analysis comprises the following steps: selecting a load tracking coefficient to analyze the correlation betweenvarious power supply signals and loads in a wind-solar-storage complementary system; establishing a demand response basic theoretical model based on a demand price elasticity theory; establishing a wind-solar-storage complementary demand response optimization model based on correlation analysis; and solving the established wind-solar-storage complementary demand response optimization model by adopting a particle swarm algorithm. An electricity price strategy is used as a random particle, and an optimal real-time electricity price strategy is solved by continuously optimizing the indexes including the load peak-valley difference, the average electricity price difference and the load tracking coefficient after the demand response, so that a load curve is matched with a wind-solar-storage complementary power generation curve to the maximum extent, and the purpose of fully consuming the output of the wind power on the power generation side is achieved. According to the invention, full consumption of new energy on the power generation side can be realized.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
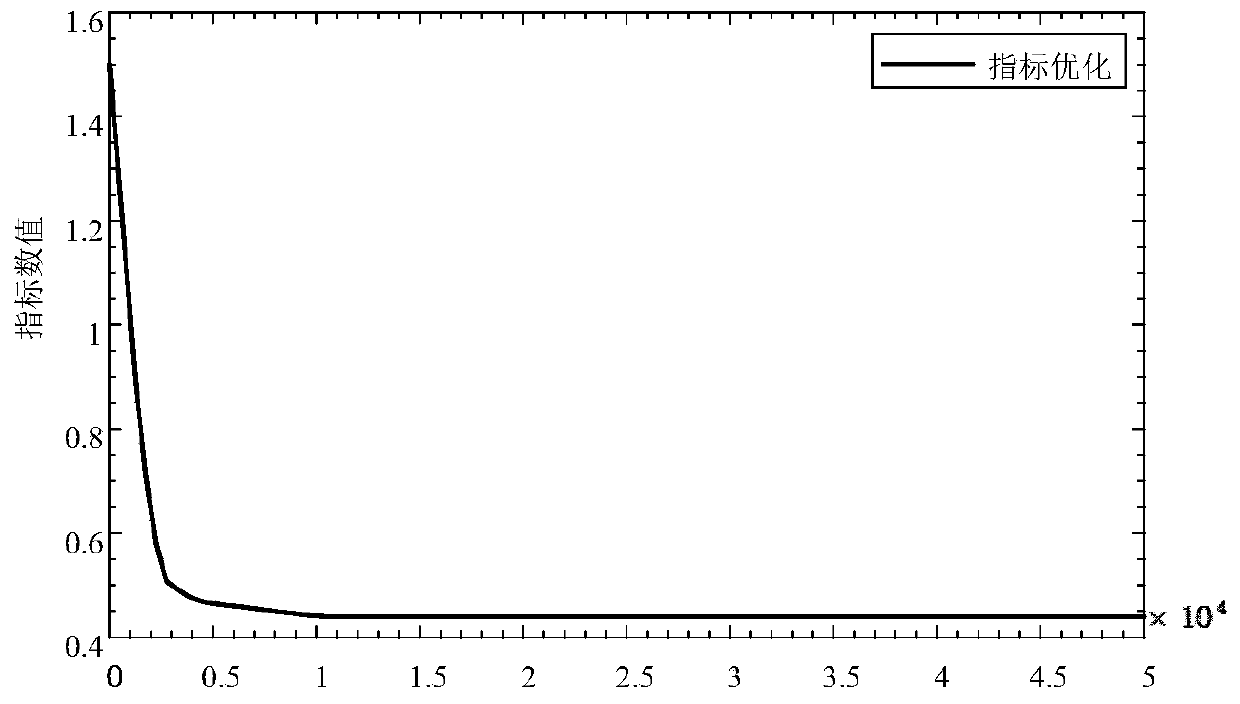
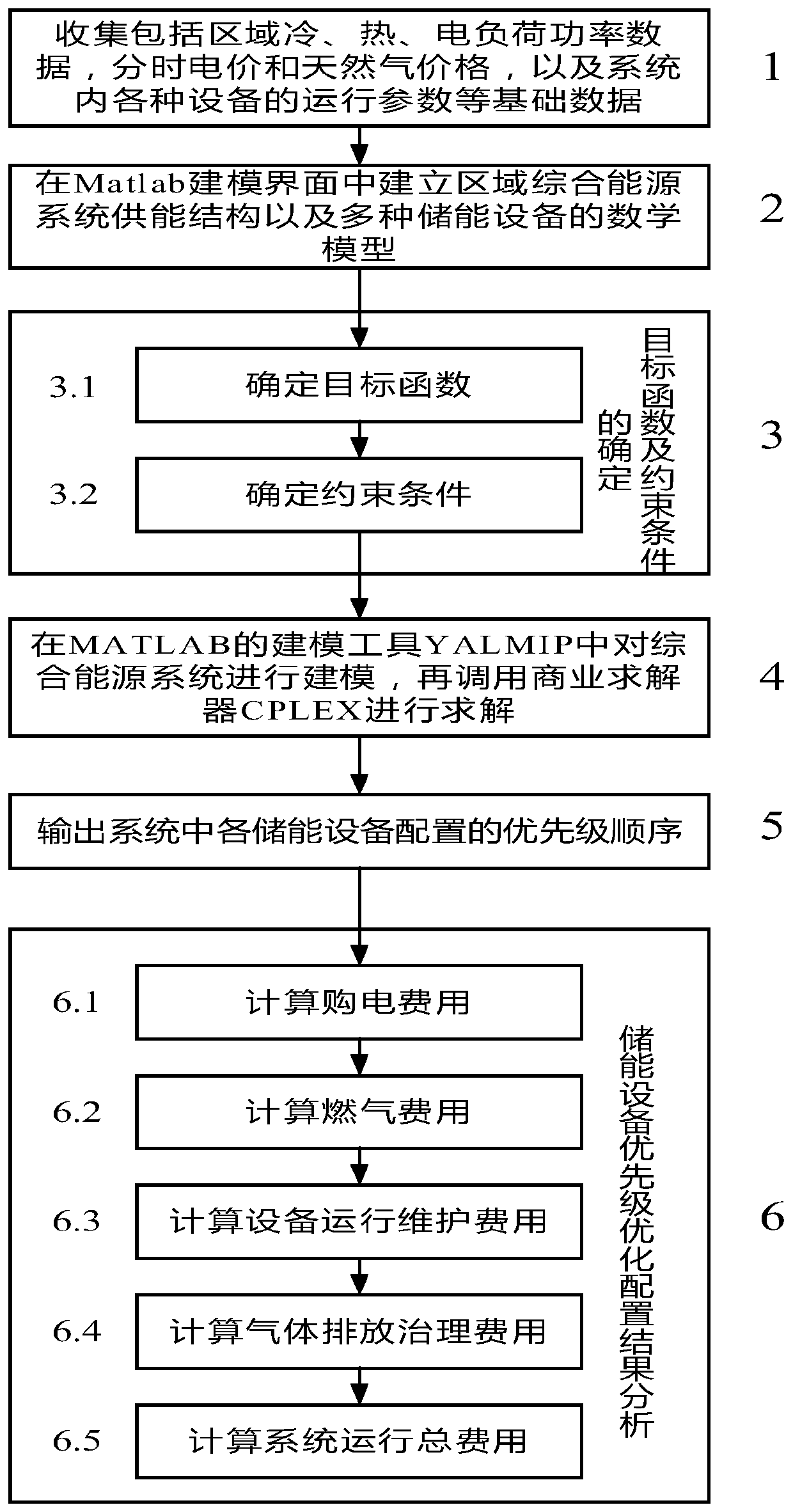
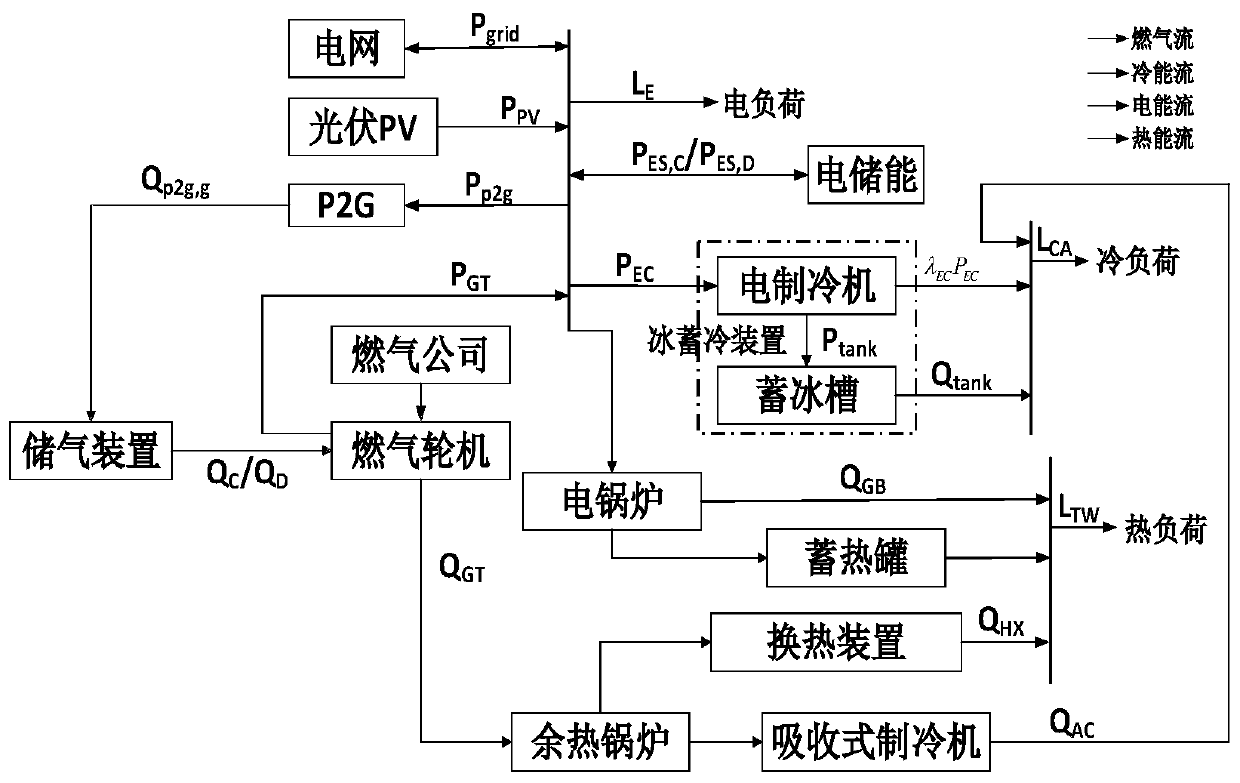
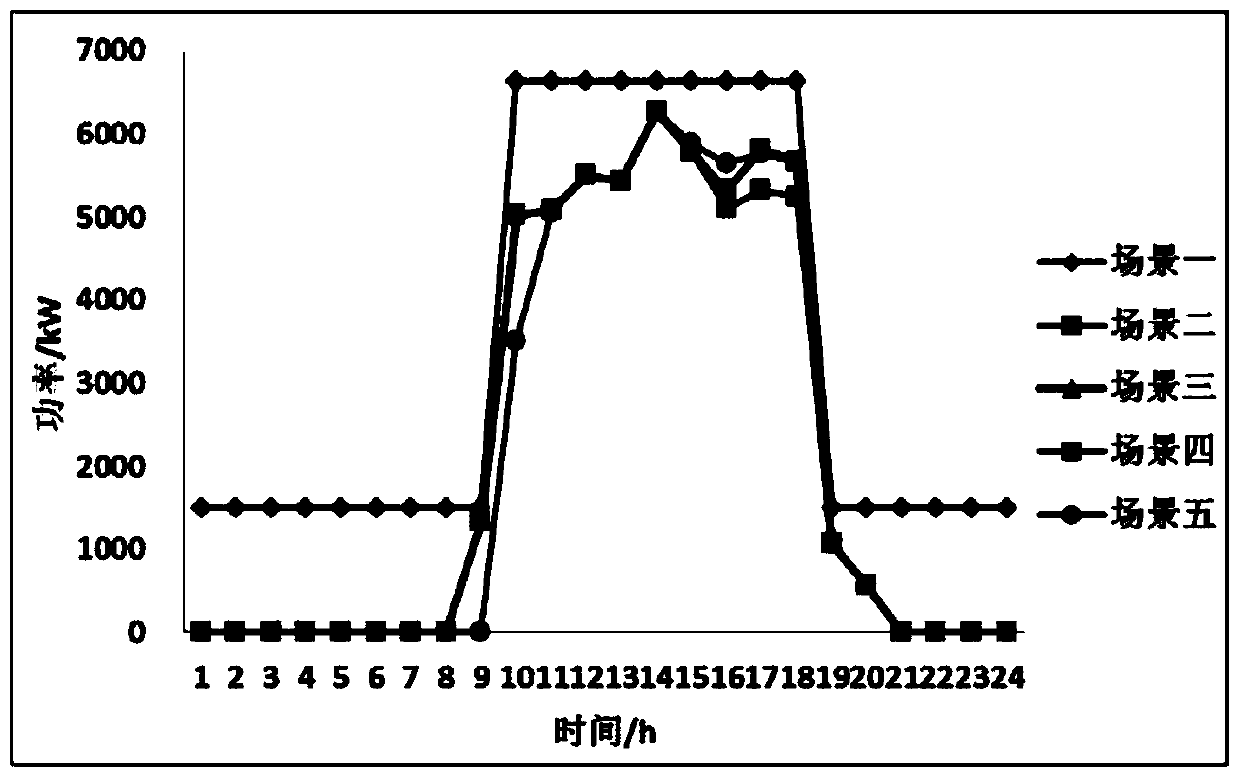
Regional comprehensive energy system energy storage optimal configuration method based on operation benefit increment
The invention discloses a regional comprehensive energy system energy storage optimal configuration method based on operation benefit increment. The regional comprehensive energy system energy storageoptimal configuration method comprises the steps of: collecting basic data; constructing an energy storage equipment mathematical model of a regional comprehensive energy system in a Matlab modelinginterface; determining a constraint condition and an objective function; modeling the regional comprehensive energy system in YALMIP, and calling a commercial solver CPLEX to solve the model; outputting a priority sequence configured by energy storage equipment; and acquiring energy storage equipment configuration scheme suggestions and the like steps. The regional comprehensive energy system energy storage optimal configuration method has the advantages that: operation of the system can completely meet the requirements of electric, cooling and heating loads in a region and fully consume the output of renewable new energy, the operation economy index of the regional comprehensive energy system containing the energy storage equipment is calculated based on the output conditions of the equipment, the economical efficiency and feasibility of configuring different energy storage equipment by the system are analyzed, the energy storage mode suitable for configuration of the region can be specifically solved, and the method has guiding significance for the planning problem of the regional comprehensive energy system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for conveniently judging hydraulic-solar complementary integrated photovoltaic scale under complex power grid
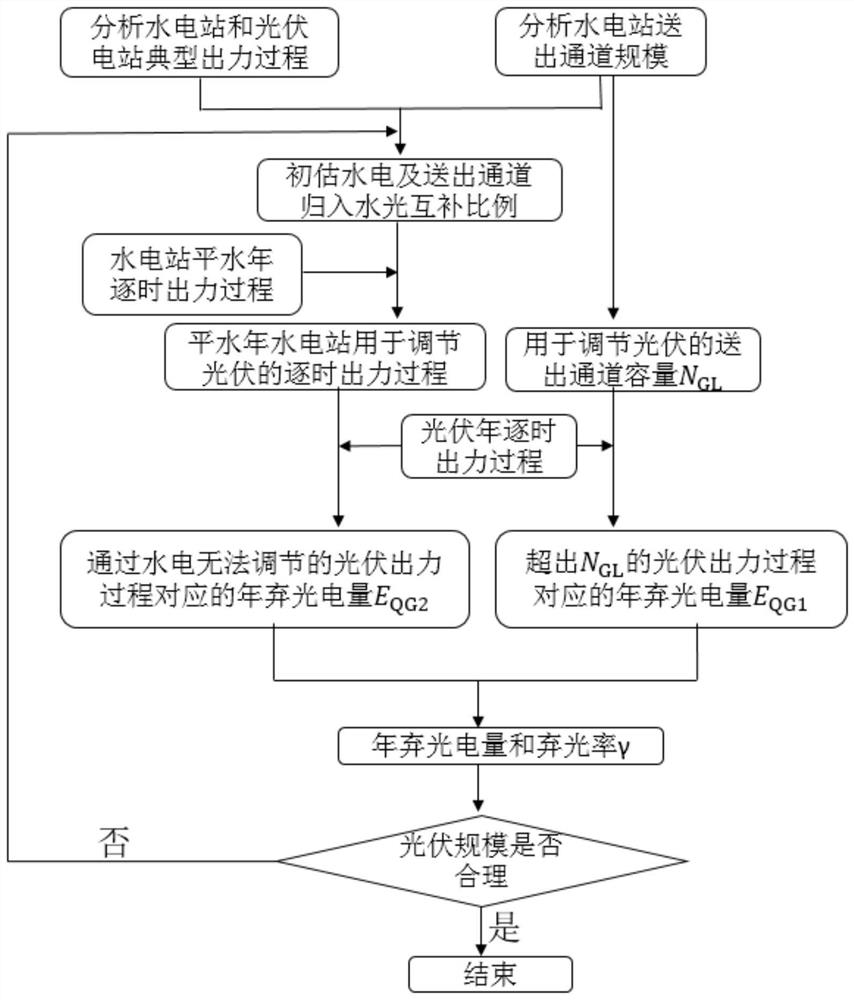
The invention discloses a method for conveniently judging a hydraulic-solar complementary integrated photovoltaic scale under a complex power grid. The method comprises the following steps: S1, analyzing or collecting hourly output processes of a hydropower station and a photovoltaic power station in each typical year; S2, collecting and analyzing the sending-out channel scale of the hydropower station; S3, in combination with the water-electricity and sending-out channel attribution hydraulic-solar complementation situation, a hydraulic-solar attribution complementation proportion scheme is formulated to calculate complementary water-electricity and channel capacity used for complementation; S 4, calculating a light abandoning rate; and S5, calculating the photovoltaic absorption rates ofthe photovoltaic installation scale schemes of different scales under the condition of different hydropower incorporation complementation proportions based on the hydropower incorporation complementation proportions and the light abandonment rates until an optimal solution is obtained. The invention provides a method capable of quickly judging whether the hydraulic-solar complementary integratedphotovoltaic scale is proper or not for the condition that whether the photovoltaic scale is reasonable or not is difficult to quickly judge due to many analysis data, various target functions and complex constraint conditions during large-scale photovoltaic grid-connected consumption of a complex power system.
Owner:CHINA POWER CONSRTUCTION GRP GUIYANG SURVEY & DESIGN INST CO LTD
Multi-level control method for high-proportion photovoltaic access alternating-current and direct-current hybrid microgrid
ActiveCN112542835AEnough flexibility marginLow running costSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsEnergy storageMicrogridPower flow
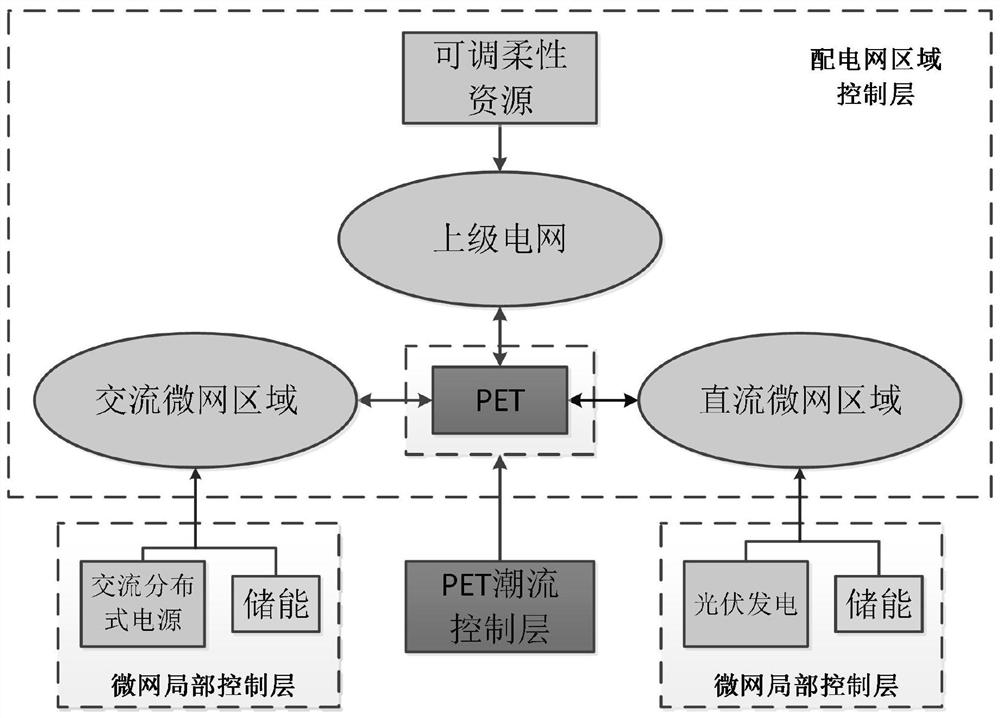
The invention discloses a multi-level control method for a high-proportion photovoltaic access alternating-current and direct-current hybrid microgrid. A system is sequentially divided into three levels, namely a microgrid local control layer, a PET power flow control layer and a power distribution network area control layer. A typical scene set is generated according to the uncertainty of photovoltaic output, and photovoltaic and energy storage devices are bundled to serve as a control main body to complete the control of the level 1; a PET control mode is set according to the network type connected with the PET port, and a PET port control variable is adjusted to complete the control of a layer 2; and other flexible controllable resources in the superior power grid area are adjusted according to the control result of the level 1 to complete the control of the level 3. The method has high flexibility and practicability, photovoltaic output uncertainty, system voltage quality and operation economy are considered, different control targets are set for different levels in the AC-DC hybrid microgrid, the autonomous operation capability of each microgrid area is utilized, the control difficulty is simplified, and interconnection interaction and coordination control among the micro-grid areas are realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
A Smart System for Prevention and Control of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loss in Shallow Water Wetlands
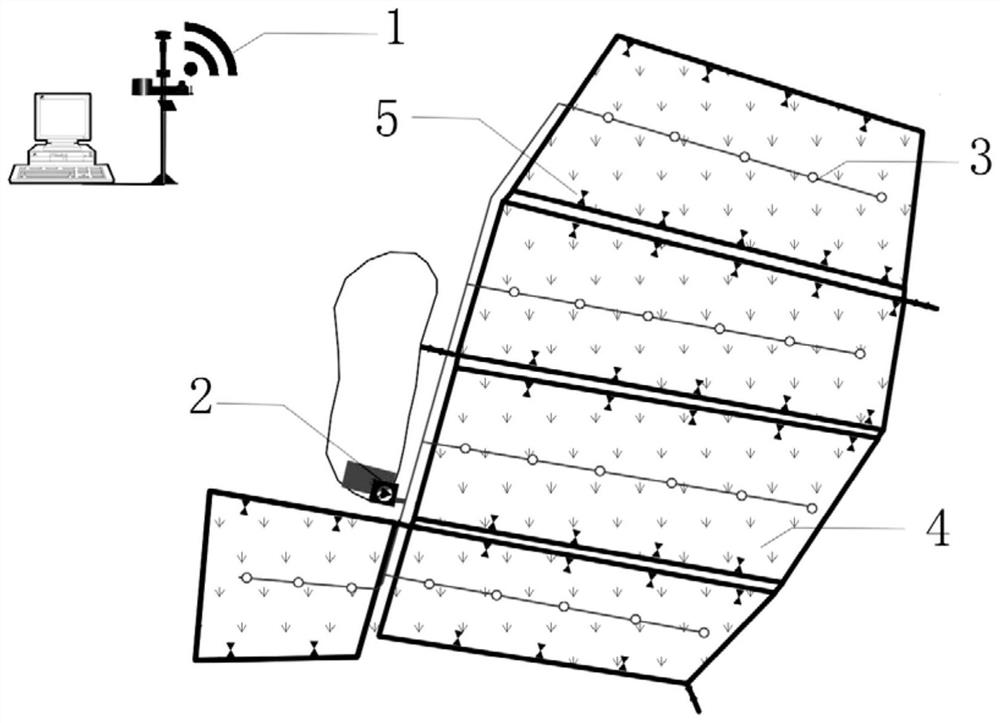
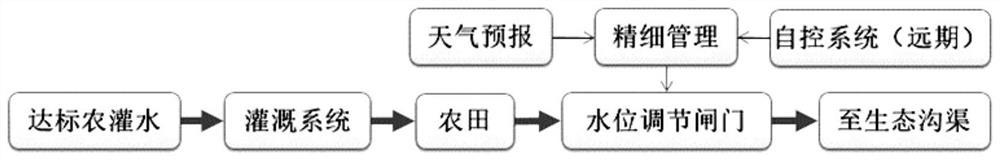
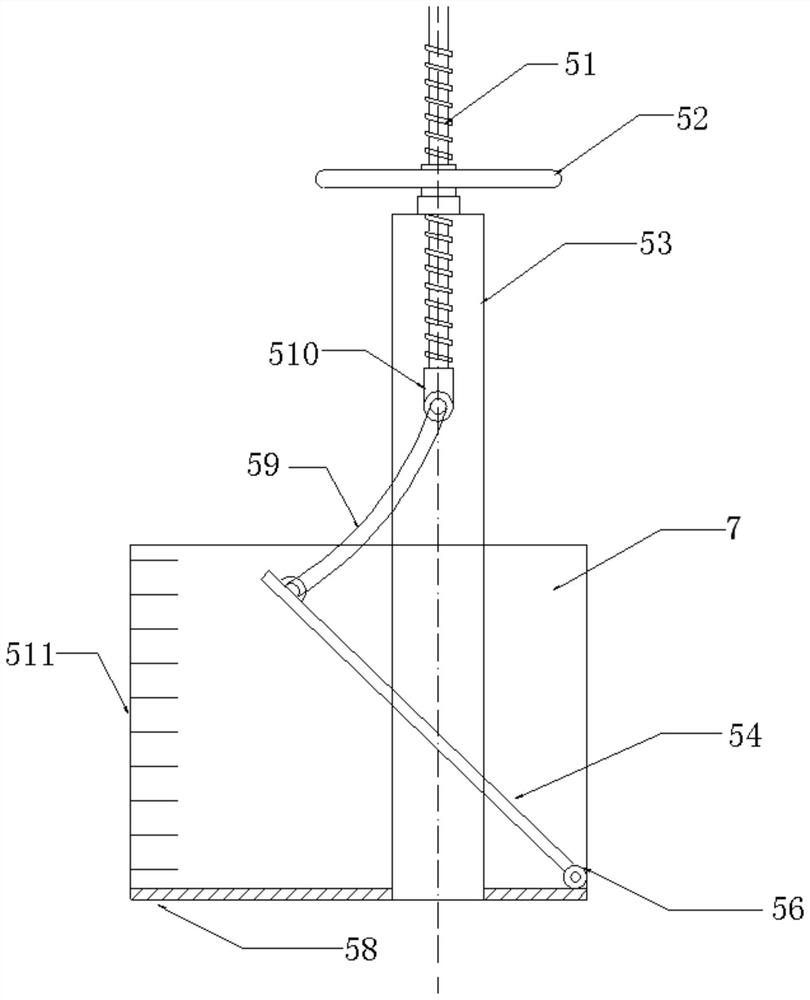
ActiveCN106258814BDoes not occupy arable land resourcesSave engineering investmentConstructionsWatering devicesData acquisitionSurface water
The invention provides an intelligent paddy field surface shallow-water wetland system capable of preventing and controlling nitrogen and phosphorus loss. The system comprises a central control system, a pump station, an irrigation system, a paddy field and a water level regulating gate, wherein the central control system comprises a data acquisition and analysis module, a control base station and a signal receiver; the data acquisition and analysis module comprehensively analyzes water and fertilizer management and a growth stage of aquatic crops determines field surface water level, transmits the information to the pump station and the water level regulating gate, controls start and stop of a water pump at the pump station and regulates the water level of the water level regulating gate; the data acquisition and analysis module reduce the water level of the paddy field in advance before rainfall through combination with weather forecast, and the system produces passive drainage as little as possible; when active drainage is required, water retention time in the field is ensured not to be shorter than required time, so that flow out of a large amount of tail water containing high-concentration nitrogen and phosphorus can be avoided. By means of absorption and purification of nitrogen and phosphorus by the field, agricultural non-point pollutants are discharged out of the area to the smallest extent on the premise that stable and high yield of crops is guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
ORC-containing park integrated energy system multi-objective optimization scheduling method considering efficiency
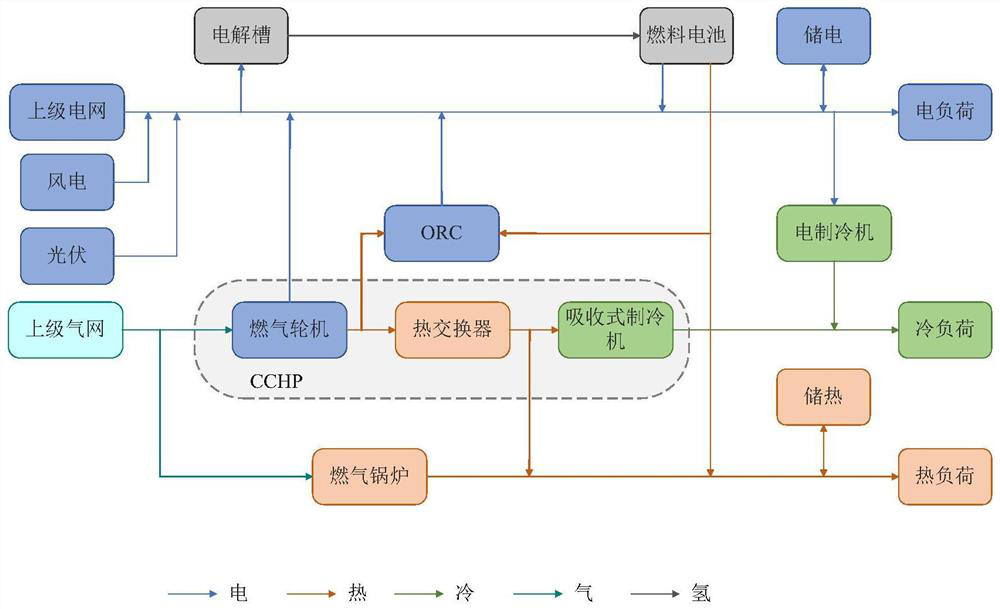
InactiveCN114742276AEmission reductionLow running costForecastingResourcesIntegrated energy systemPower grid
The invention discloses an efficiency-considered multi-objective optimization scheduling method for an ORC-containing park integrated energy system. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing the park integrated energy system; step 2, constructing a multi-objective optimization scheduling model; and step 3, aiming at the multi-objective optimization scheduling model in the step 2, solving by adopting an NSGA-II algorithm. According to the dispatching method, bidirectional coupling between the power grid and the heat supply network is achieved, the economic cost and carbon emission of the system are reduced, and the wind power and photovoltaic absorption capacity is effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
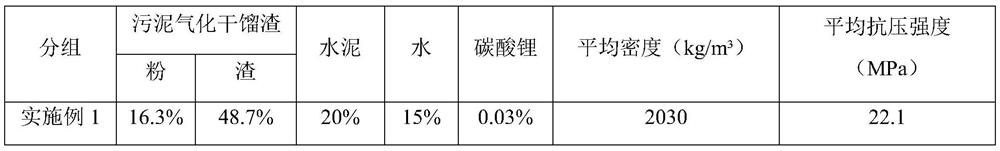
Modified concrete brick containing sludge gasification dry distillation slag and preparation method thereof
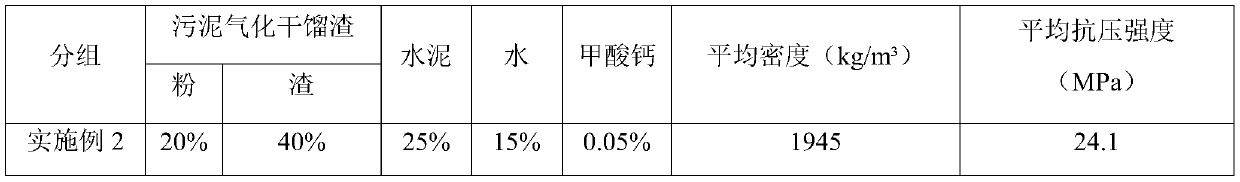
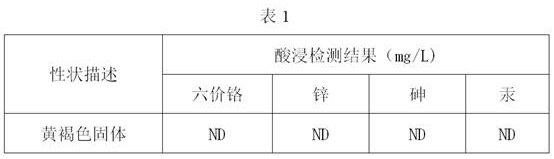
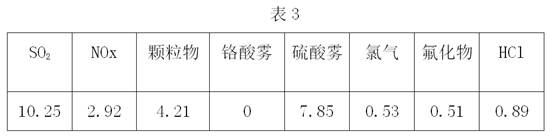
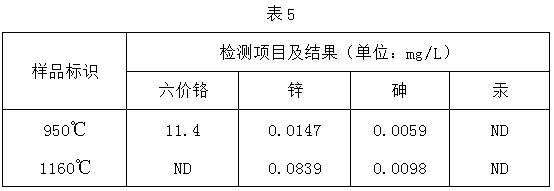
ActiveCN111268971ARealize resource utilizationFull consumptionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSpecific water treatment objectivesBrickSludge
The invention belongs to the field of recycling of urban and industrial waste resources, and particularly relates to a modified concrete brick containing sludge gasification dry distillation slag anda preparation method thereof. The modified concrete brick is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 50%-70% of the gasification dry distillation slag, 15%-25% of cement, 10%-15% of water and 0.01%-0.05% of an accelerant, wherein the ratio of powder to slag in the gasification dry distillation slag is (1-2): 3. The preparation method comprises the following steps: airing the gasification dry distillation slag until the moisture content is less than or equal to 10%, passing through a double-roll crusher, controlling the particle size of coarse particles to be 5-15mm, screening out powder by virtue of a 3mm sieve, weighing cement, the gasification dry distillation slag, the accelerant and water, and uniformly mixing the cement, the gasification dry distillation slag,the accelerant and water; and pouring the mixture into a mold, performing compression molding, demolding, and performing natural curing. The municipal sludge is dried, granulated and gasified to obtain the sludge gasification dry distillation slag, and the sludge gasification dry distillation slag is used as a raw material for preparing the modified concrete brick, thereby being beneficial to environmental protection and lowering the production cost of factories.
Owner:郑州市格沃环保开发有限公司
Sound isolation material and preparation method thereof
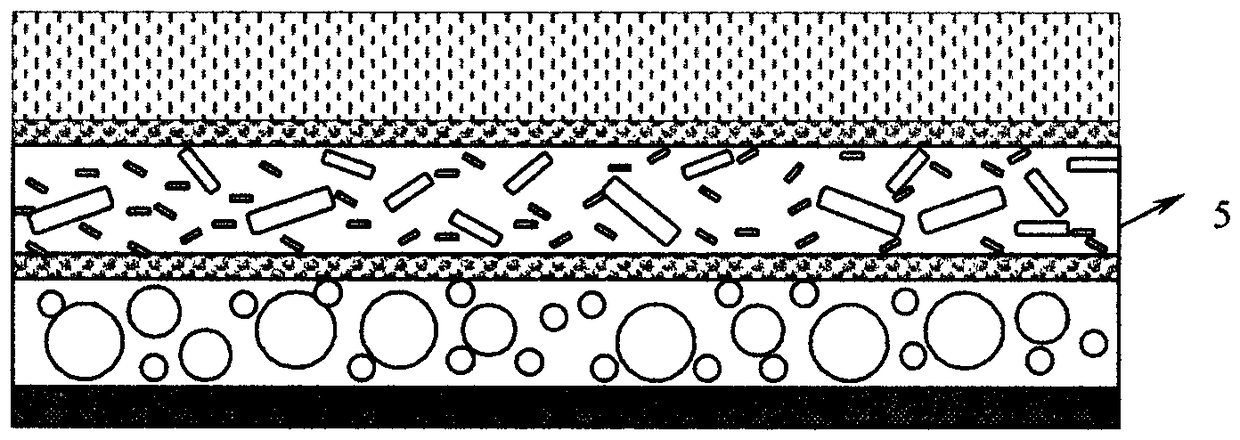
The invention provides a sound isolation material, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40 to 50 parts of poly1,3-adamantane benzylidene diformyl chloride malononitrile dihydroxyethyl amine ester, 5 to 10 parts of 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorostyrene, 5 to 10 parts of 2-adamantil acrylate, 5 to 10 parts of polymerization monomers, 0.3 to 0.5 part of initiators, 2 to 5 parts of cubic aluminum oxide, 2 to 5 parts of flaky aluminum oxide, 2 to 5 parts of leaf type aluminum oxide, 1 to 3 parts of coupling agents and 80 to 100 parts of dimethylsulfoxide. The invention alsodiscloses a preparation method of the sound isolation material. The sound isolation material disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the sound isolation effect is obvious; the preparationcost is low; the use is safe; the environmental-friendly effect is achieved in the use process; the mechanical performance, the weather resistant performance and the fireproof performance are excellent.
Owner:HUNAN CHENLI NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Detoxification formula with high chromium slag amount and process for cooperating with light aggregate production
ActiveCN114349477AFast consumption processingEasy to handleSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalSlagKaolinite
The invention relates to a high-chromium-slag detoxification formula and a synergistic light aggregate production process. The formula comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 60-80% of chromium slag, 15-40% of aluminum-silicon concentrate and 1-5% of a compound additive. The aluminum-silicon concentrate comprises one or more of clay, potassium feldspar, quartz, aluminum oxide, flint clay, mullite and kaolinite. And the compound additive plays a role in reduction and fluxing. The raw materials are dried, metered, crushed, ball-milled, granulated, fired and screened to obtain a fired lightweight aggregate product. Compared with the prior art, the specific gravity of the chromium slag in the formula is increased to 80%, the firing temperature is reduced to 900-1000 DEG C on the basis that hexavalent chromium in the fired lightweight aggregate product is thoroughly reduced and cured by adding the compound additive, and trivalent chromium cannot be oxidized due to temperature reduction under the condition of no cooling process. On one hand, thorough harmlessness of the chromium slag is achieved, and on the other hand, complete recycling of the chromium slag is achieved.
Owner:湖南国发控股有限公司
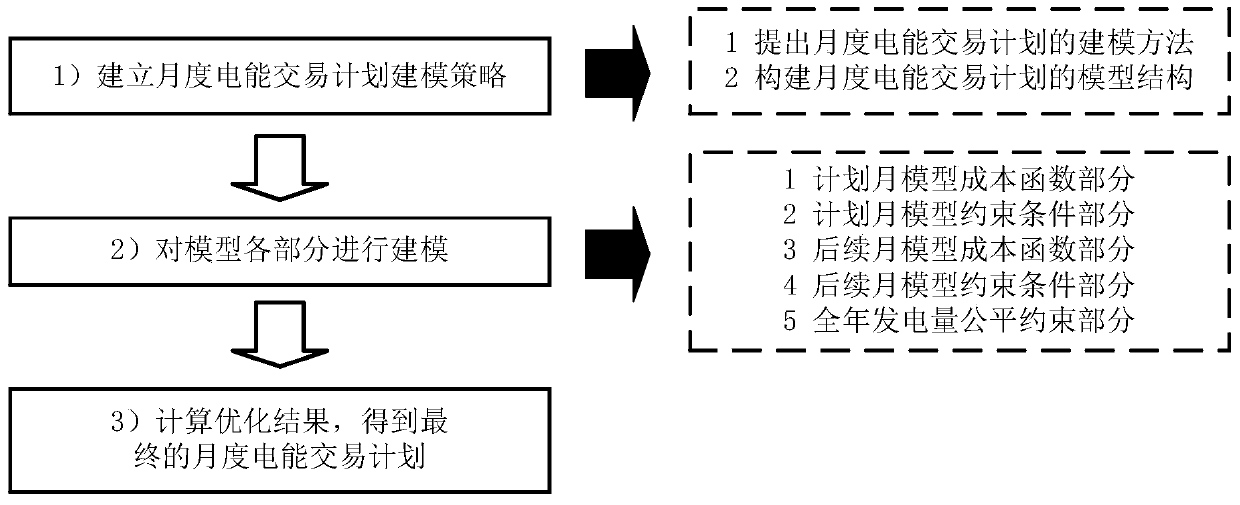
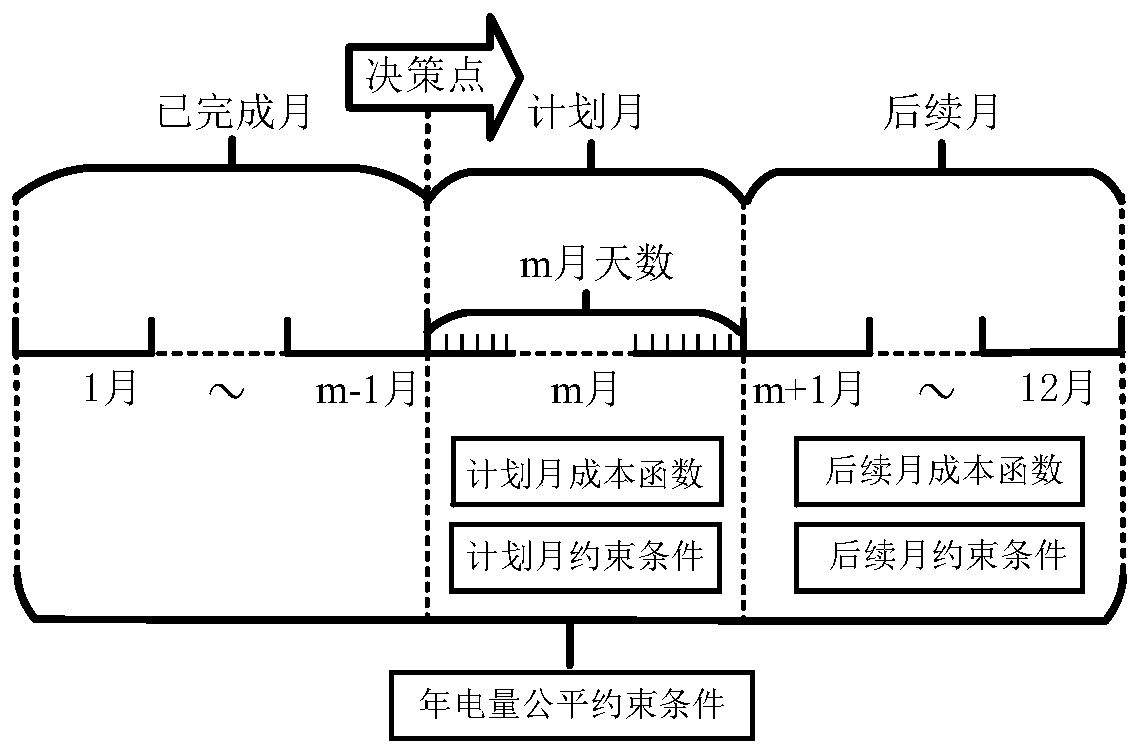
Time sequence simulation method for making monthly electric energy transaction plan in consideration of various energy sources
ActiveCN109961224AFull consumptionImprove energy saving and emission reduction benefitsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsResourcesModel methodElectric power system
The invention discloses a time sequence simulation method for making a monthly electric energy transaction plan in consideration of multiple energy sources, belongs to the technical field of monthly electric energy transaction plan making of an electric power system, and comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a monthly electric energy transaction plan modeling strategy according to the actual demand of the monthly electric energy transaction plan: proposing a monthly electric energy transaction plan modeling method and constructing a monthly electric energy transaction plan model structure; secondly, modeling each part of the model according to an established monthly electric energy transaction plan modeling strategy: a plan monthly model cost function part, a plan monthlymodel constraint condition part, a subsequent monthly model cost function part, a subsequent monthly model constraint condition part and a whole-year electric energy production fair constraint part;and finally, optimizing and solving the model to obtain a final monthly electric energy transaction plan. The time sequence simulation method is introduced into monthly electric energy transaction plan making, staged modeling is carried out according to plan months and subsequent months, and finally a monthly electric energy transaction plan model capable of guaranteeing feasibility and fairness is obtained.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Smart energy management and control system based on cloud platform
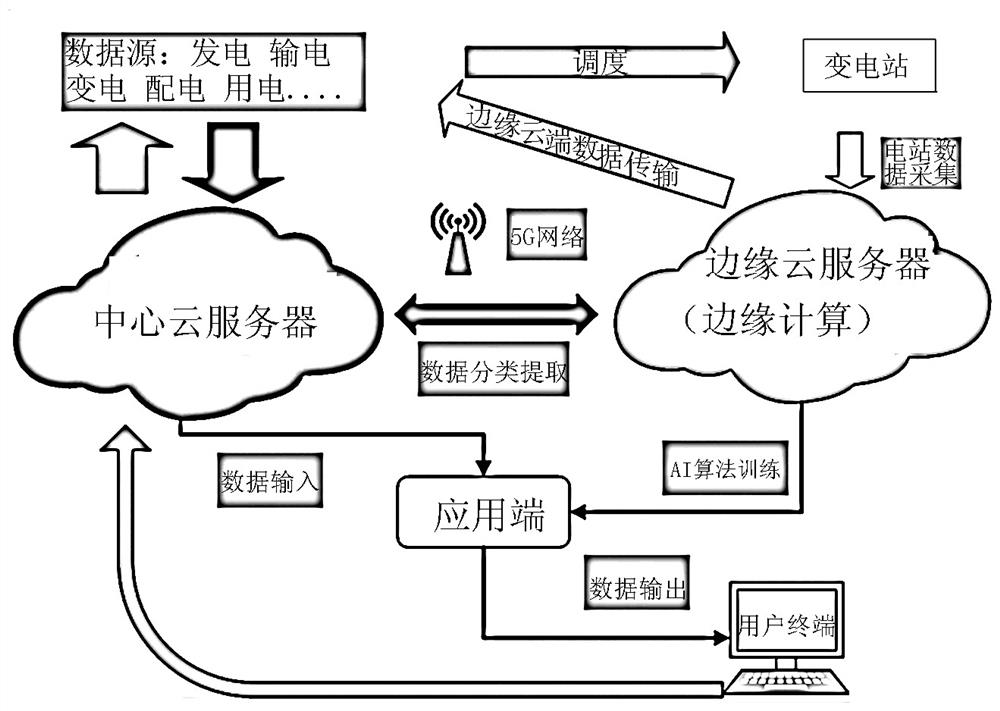
PendingCN112580957AFull consumptionSafe and stable operationDatabase management systemsResourcesData processingGrid connection
The invention relates to a smart energy management and control system based on a cloud platform. The system comprises the following steps: building a Spark platform in a central cloud server, storingreal-time data through employing a NoSQL database, analyzing and processing a real-time data flow based on a cloud computing method, classifying a data source in the Spark platform through employing aTwitter Storm real-time data processing framework, extracting the processed, analyzed and fused data into an edge cloud server through a 5G network, and carrying out training and modeling; and enabling an application end to integrate the algorithm model established in the edge cloud server with the data of the central cloud server, and scheduling the whole new energy power generation system through an AI algorithm to form a closed-loop energy cloud scheduling system. According to the invention, wide interconnection with a power supply terminal, a user terminal and other parties is realized, new energy planning and layout are effectively guided, and positive effects in aspects of promoting new energy scientific development, ordered grid connection, high-efficiency consumption and the likeare achieved.
Owner:SKILLS TRAINING CENT STATE GRID LIAONING ELECTRIC POWER +1
High-efficiency sound-insulating material and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103903608BImprove heat and aging resistanceExcellent ozone resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsSound producing devicesInsulation layerFoaming agent
The invention relates to the field of products of sound insulation material, solves the problems in the prior art that the sound insulation material is poor in sound insulation effect, is incomprehensive in high and low frequency sound insulation, causes pollution and is easy to age, and provides an efficient sound insulation material and a manufacturing method thereof. The efficient sound insulation material includes a sound insulation layer, a sound absorption layer, and a bubble layer, wherein the bubble layer is located between the sound insulation layer and the sound absorption layer. The sound absorption layer is made of a sound insulation compound, and the sound insulation compound is prepared by raw materials of the following substances: a thermoplastic resin, inorganic fillers, and a foaming agent, wherein the inorganic fillers account for 15-80wt%, the foaming agent accounts for 5-15wt%, and the rest is the thermoplastic resin. In the efficient sound insulation material, the fillers with different particle diameters correspond to sound waves of different wave bands or frequencies, and thus consumption of sound energy of different frequencies is relatively comprehensive, and the sound insulation effect is good, so the sound insulation material is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:浙江艾迪雅汽车部件新材料有限公司
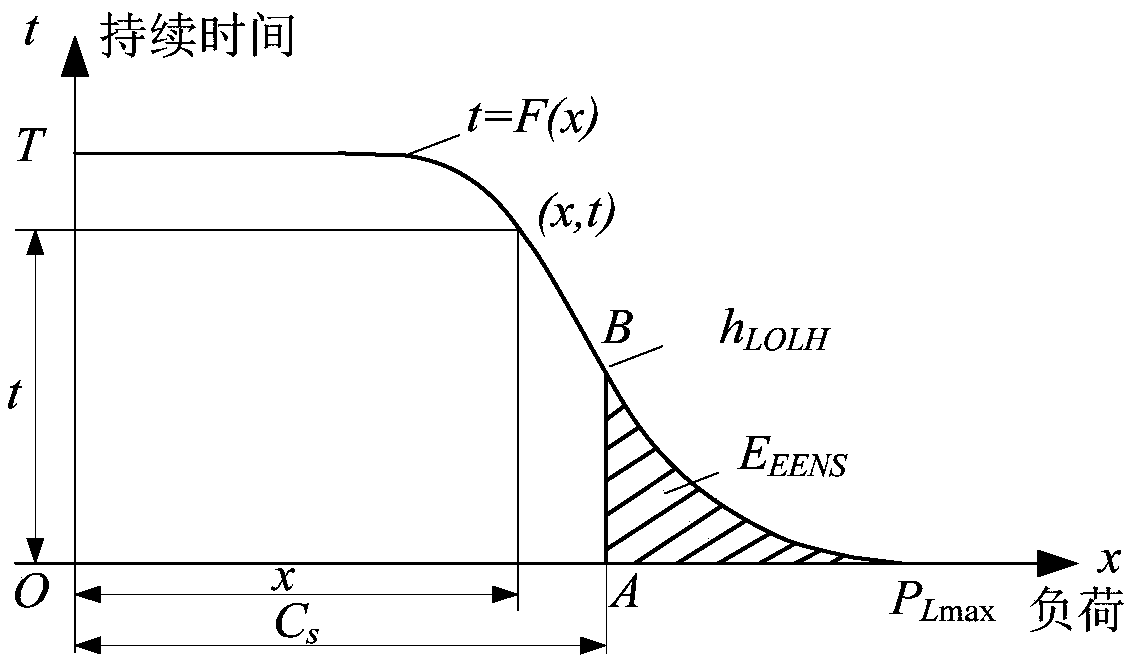
Stochastic production simulation method and application of sending end power system considering energy curtailment constraints
ActiveCN109586284BSmoothing fluctuationsImprove peak shaving performanceData processing applicationsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric power systemNuclear power
The present invention relates to a stochastic production simulation method and application of a sending-end power system considering energy abandonment constraints. The stochastic production simulation method includes the following steps: 1) Obtaining the annual load curve, and removing all nuclear power plants from the annual load curve. Annual output curve to obtain the continuous load curve, and according to the annual load level, the continuous load curve is divided into three stages: base load, waist load and peak load; 2) establish an equivalent power function according to the continuous load curve; 3 ) Realize output control of thermal power units and hydroelectric units at different stages according to equivalent electricity; 4) Consider the quotation of clean energy and its energy abandonment constraints, dynamically adjust the output status of clean energy and thermal power units, and obtain random production simulation data of the power system . Compared with the prior art, the present invention considers that the discardable power generation capacity of clean energy such as solar energy and wind power can be used as a conventional power source to participate in power system peak regulation, so as to ensure the minimum pollution of the system to the environment.
Owner:国家电网有限公司西南分部 +2
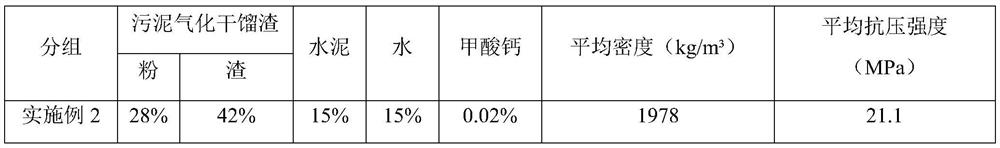
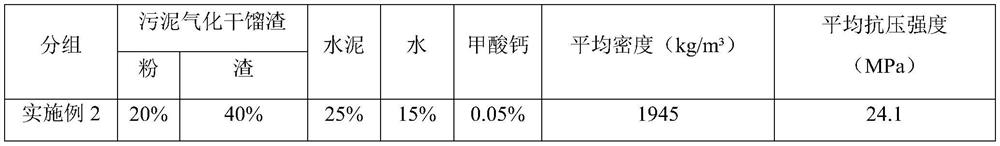
Modified concrete brick containing sludge gasification dry distillation slag and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111268971BRealize resource utilizationFull consumptionSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSpecific water treatment objectivesBrickSludge
The invention belongs to the field of reuse of urban and industrial waste resources, and specifically relates to a modified concrete brick containing sludge gasification and retort slag and a preparation method thereof. 15-25% cement, 10-15% water, 0.01-0.05% accelerator, and the ratio of powder and slag in the gasification and retort slag is (1-2):3. The preparation method is: dry the gasified dry distillation slag until the water content is ≤10%, pass it through a roller crusher, control the coarse particle size to 5-15mm, and then sieve the powder through a 3mm sieve, weigh cement, gas Distillation slag, accelerator and water are mixed uniformly; the mixture is poured into a mold and then pressed into shape, and then naturally cured after demoulding. The invention obtains sludge gasification dry distillation slag by drying, granulating and gasifying urban sludge, and uses it as a raw material for preparing modified concrete bricks, which is beneficial to environmental protection and reduces the production cost of factories.
Owner:郑州市格沃环保开发有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com