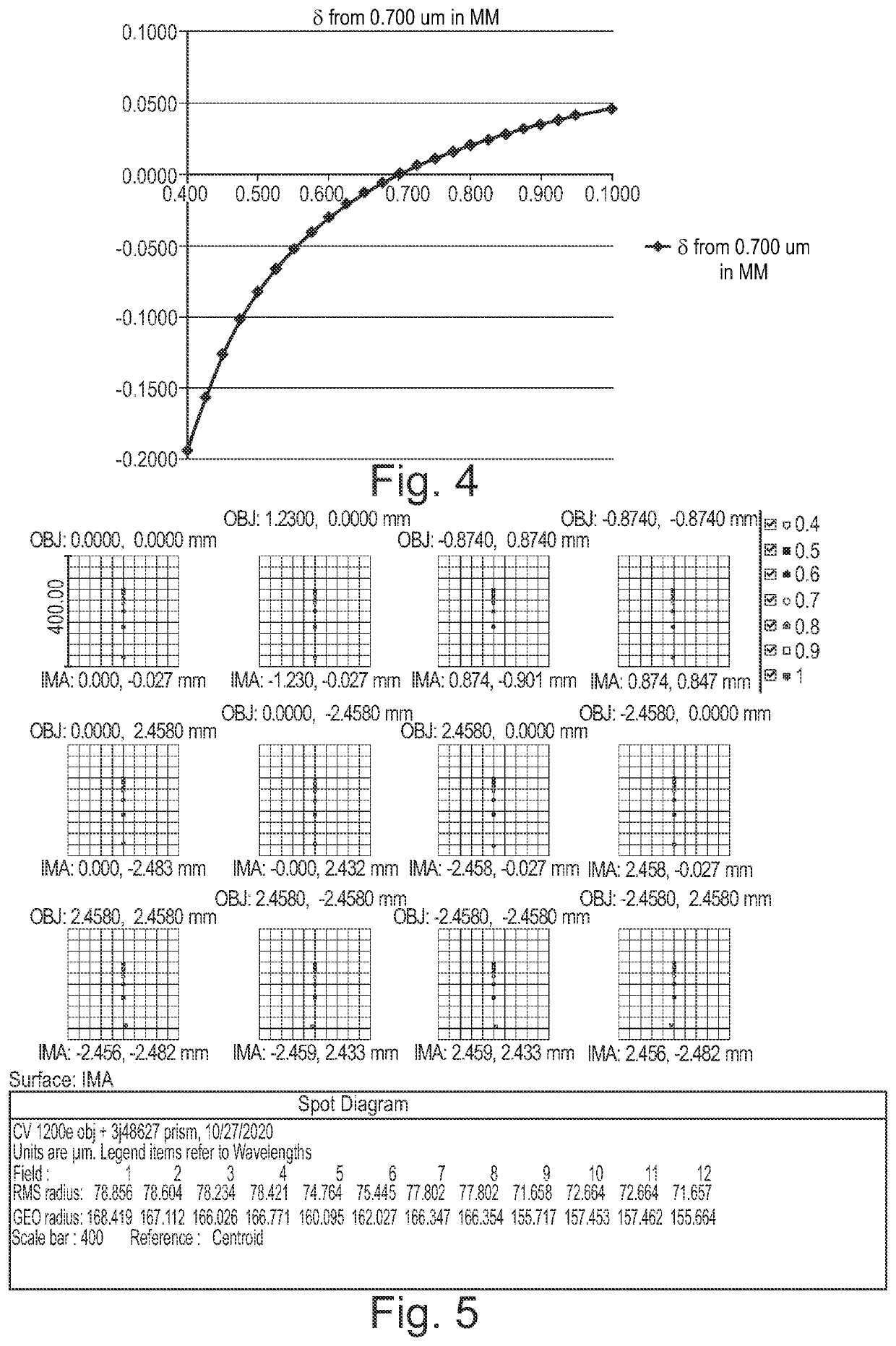
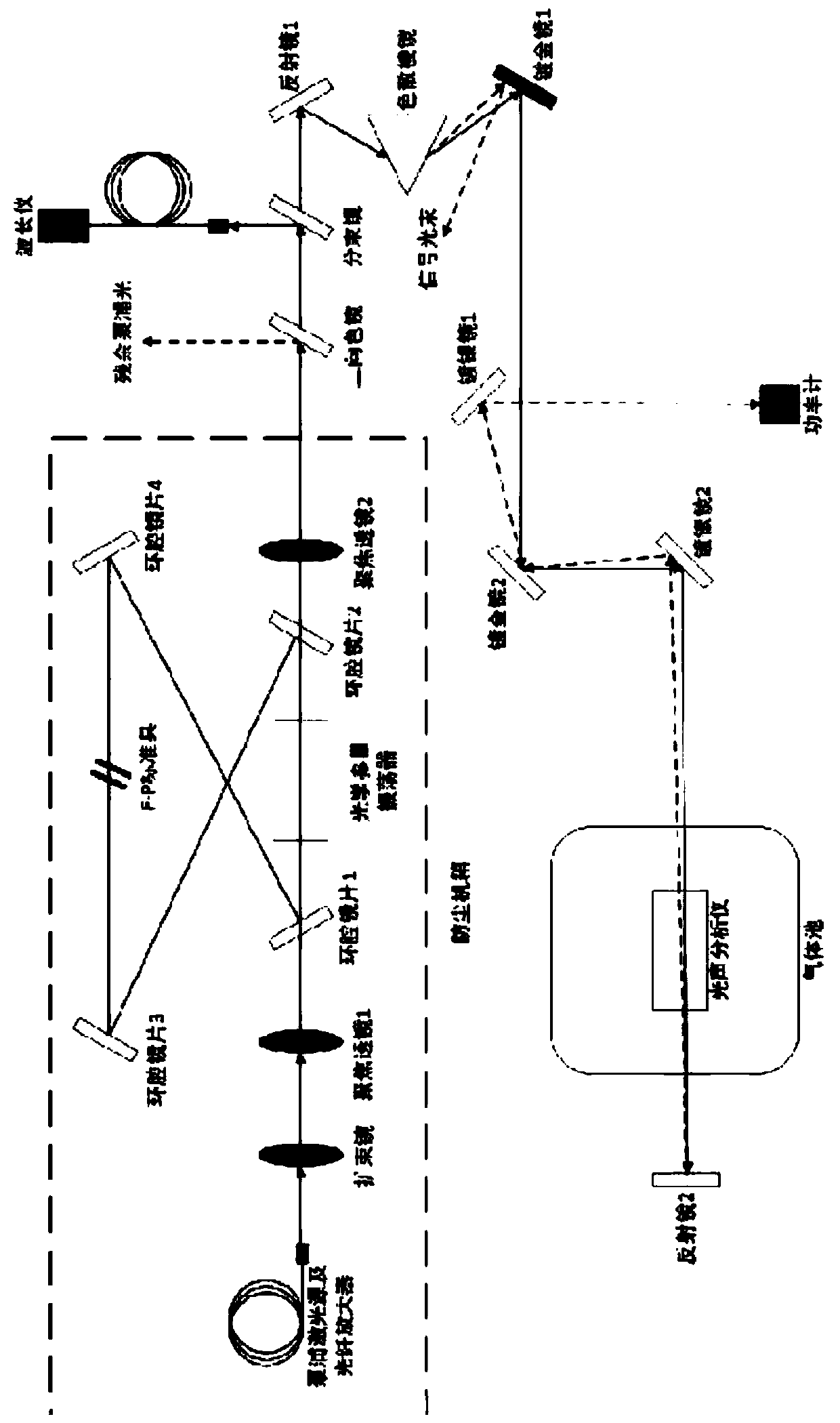
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Dispersive prism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
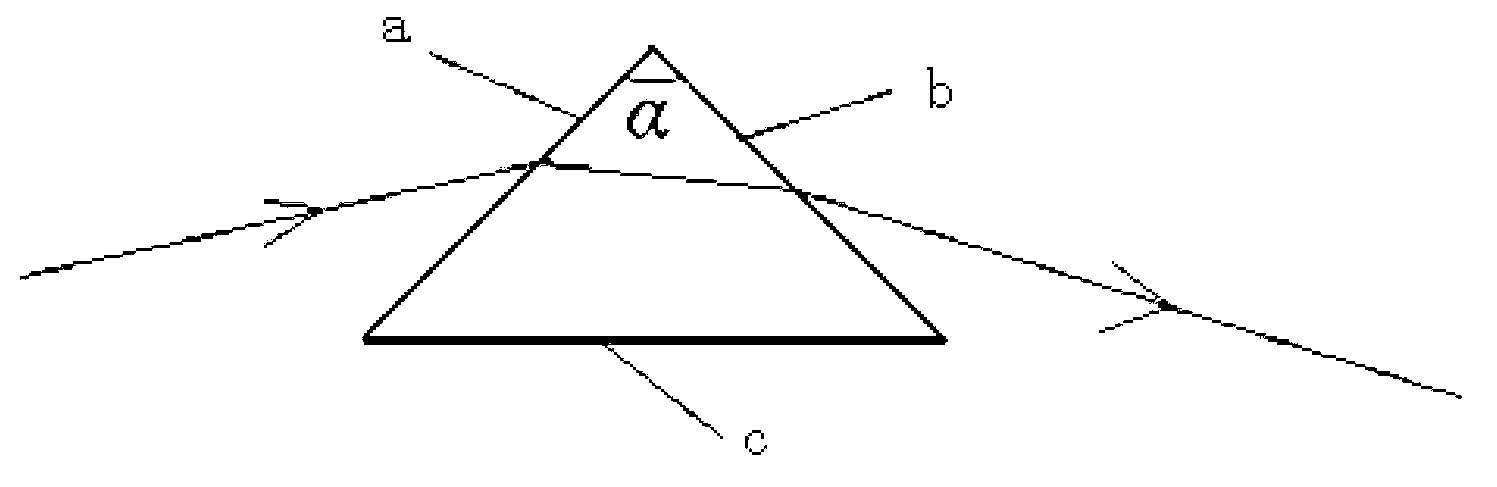
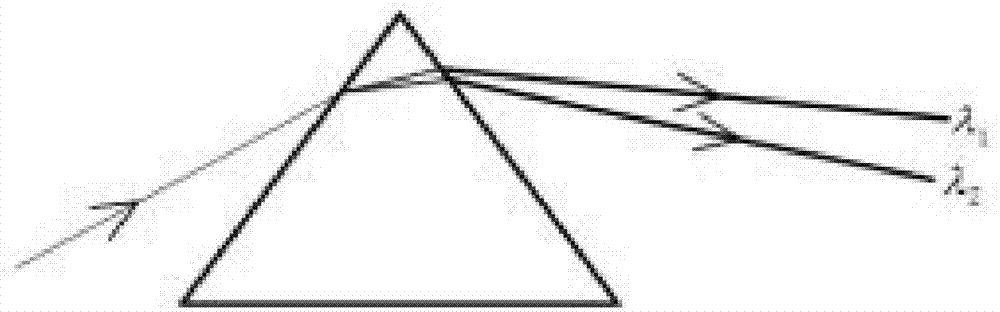
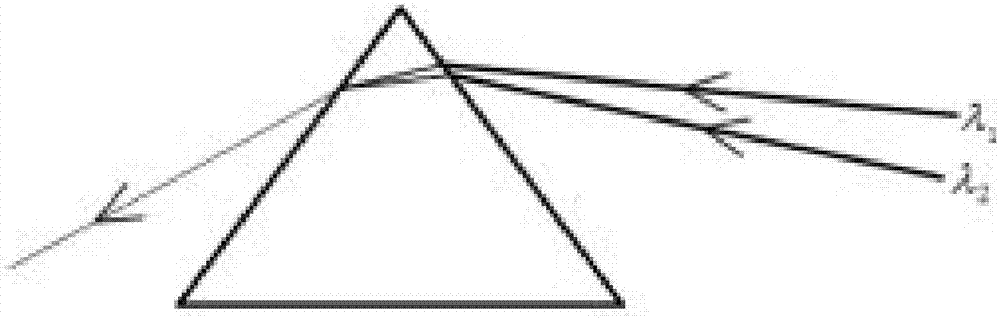
In optics, a dispersive prism is an optical prism, usually having the shape of a geometrical triangular prism, used as a spectroscopic component. Spectral dispersion is the best known property of optical prisms, although not the most frequent purpose of using optical prisms in practice. Triangular prisms are used to disperse light, that is, to break light up into its spectral components (the colors of the rainbow). Different wavelengths (colors) of light will be deflected by the prism at different angles, producing a spectrum on a detector (or seen through an eyepiece). This is a result of the prism's material (often, but not always, a glass) index of refraction varying with wavelength. By application of Snell's law, one can see that as the wavelength changes, and the refractive index changes, the deflection angle of a light beam will change, separating the colors (wavelength components) of the light spatially. Generally, longer wavelengths (red) thereby undergo a smaller deviation than shorter wavelengths (blue) where the refractive index is larger.
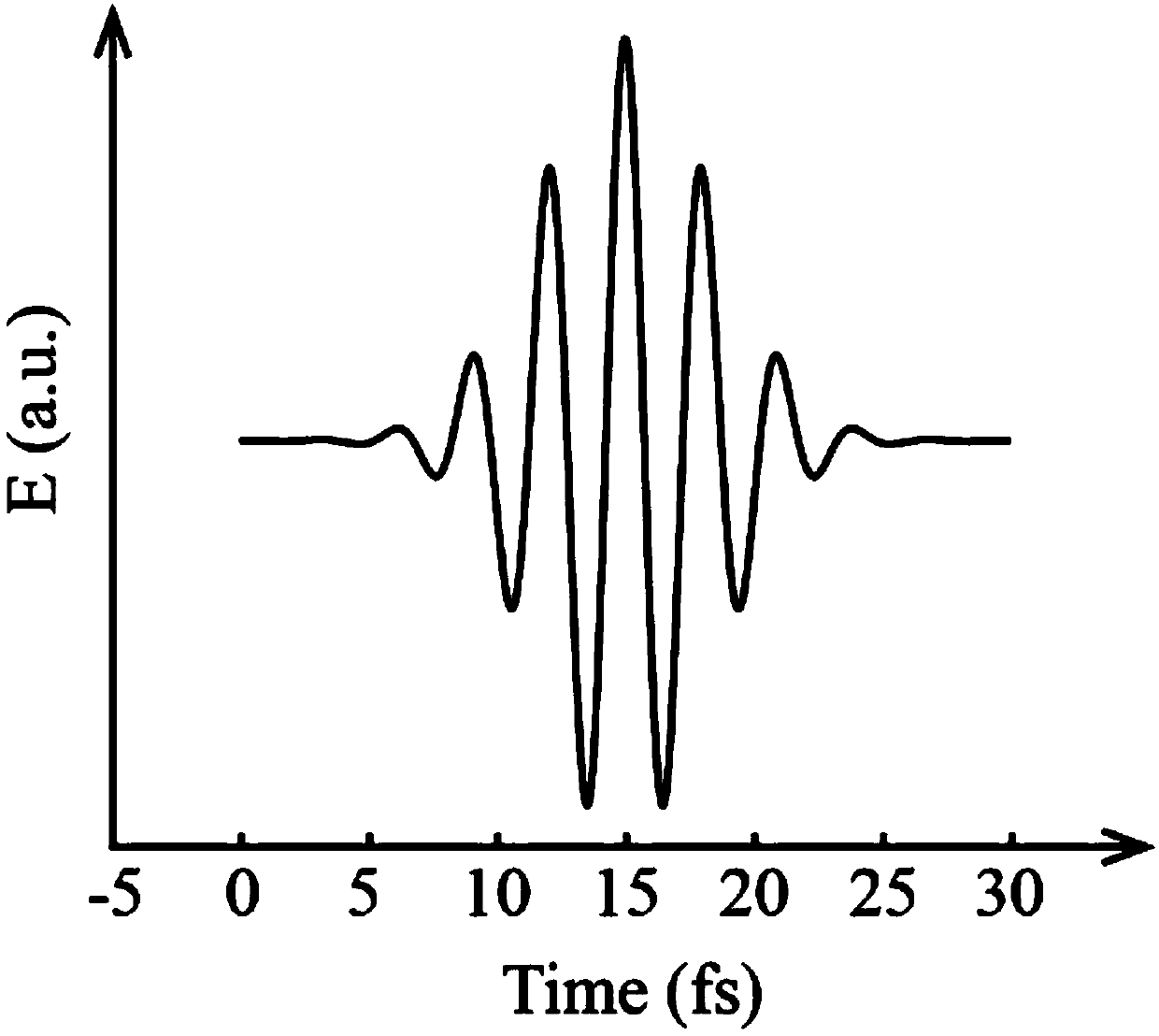
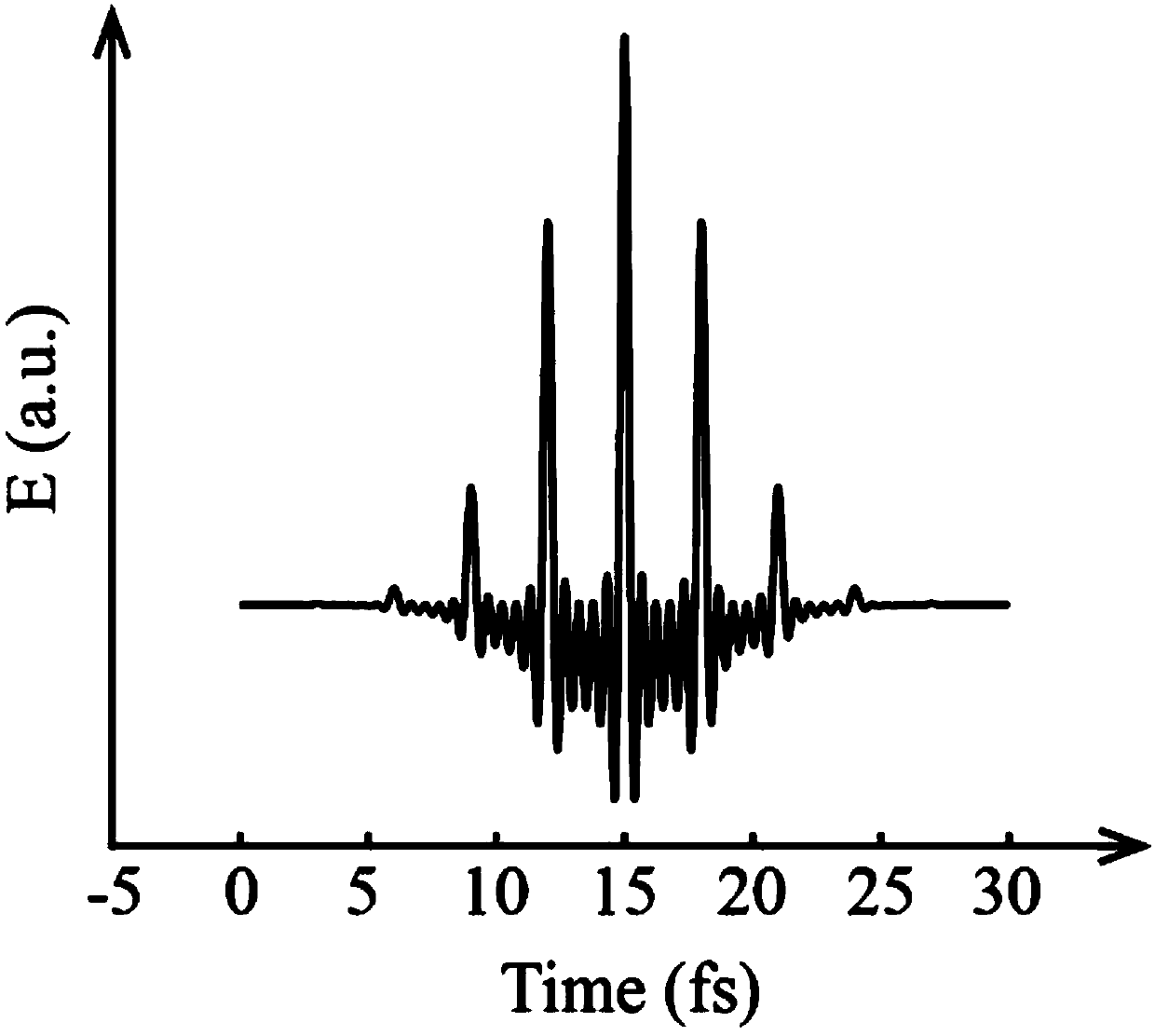
Device for dispersing light pulses of which the spectral amplitude is programmable
InactiveUS20070103778A1Overcome disadvantagesPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLight beamAcoustic wave
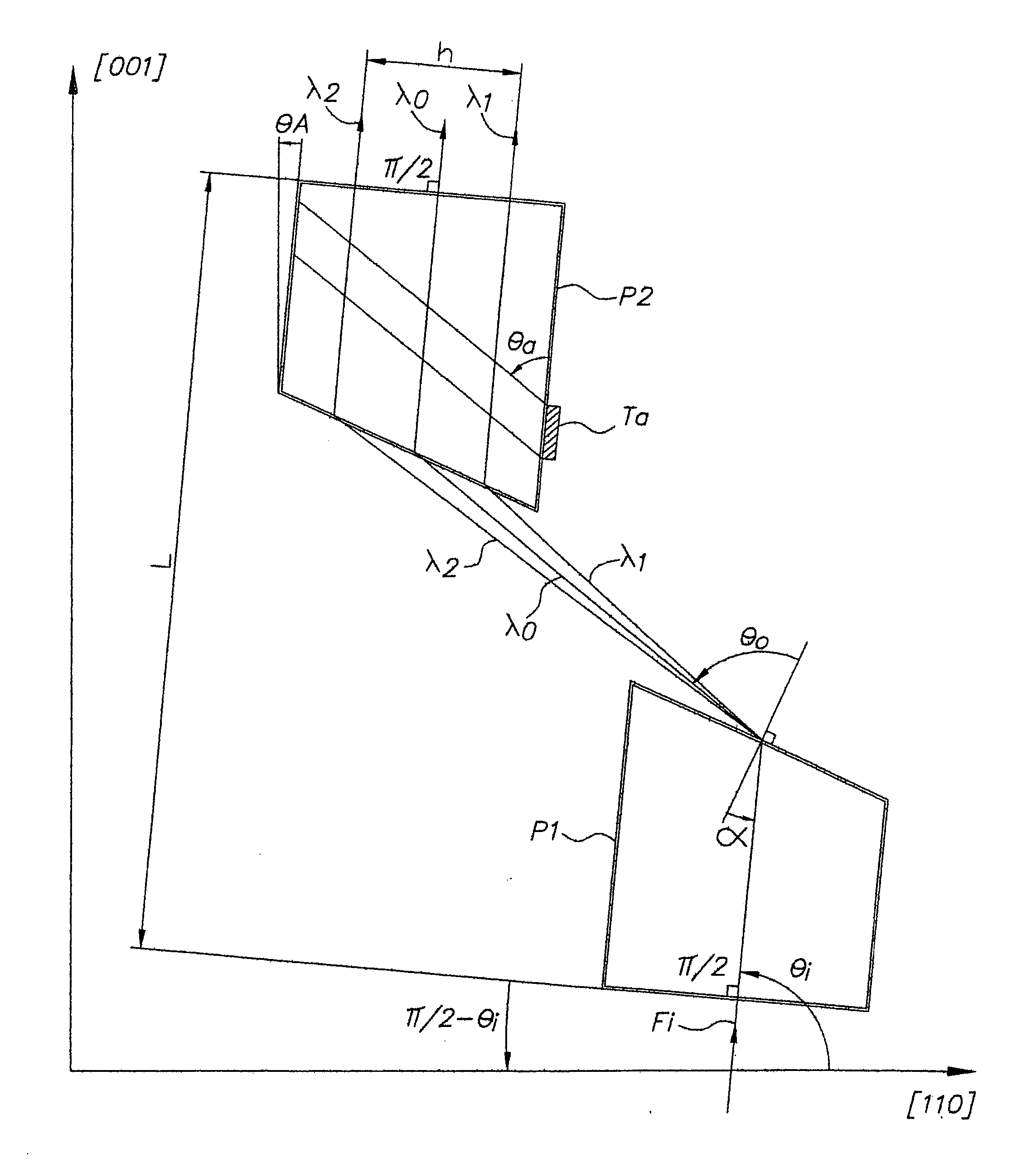
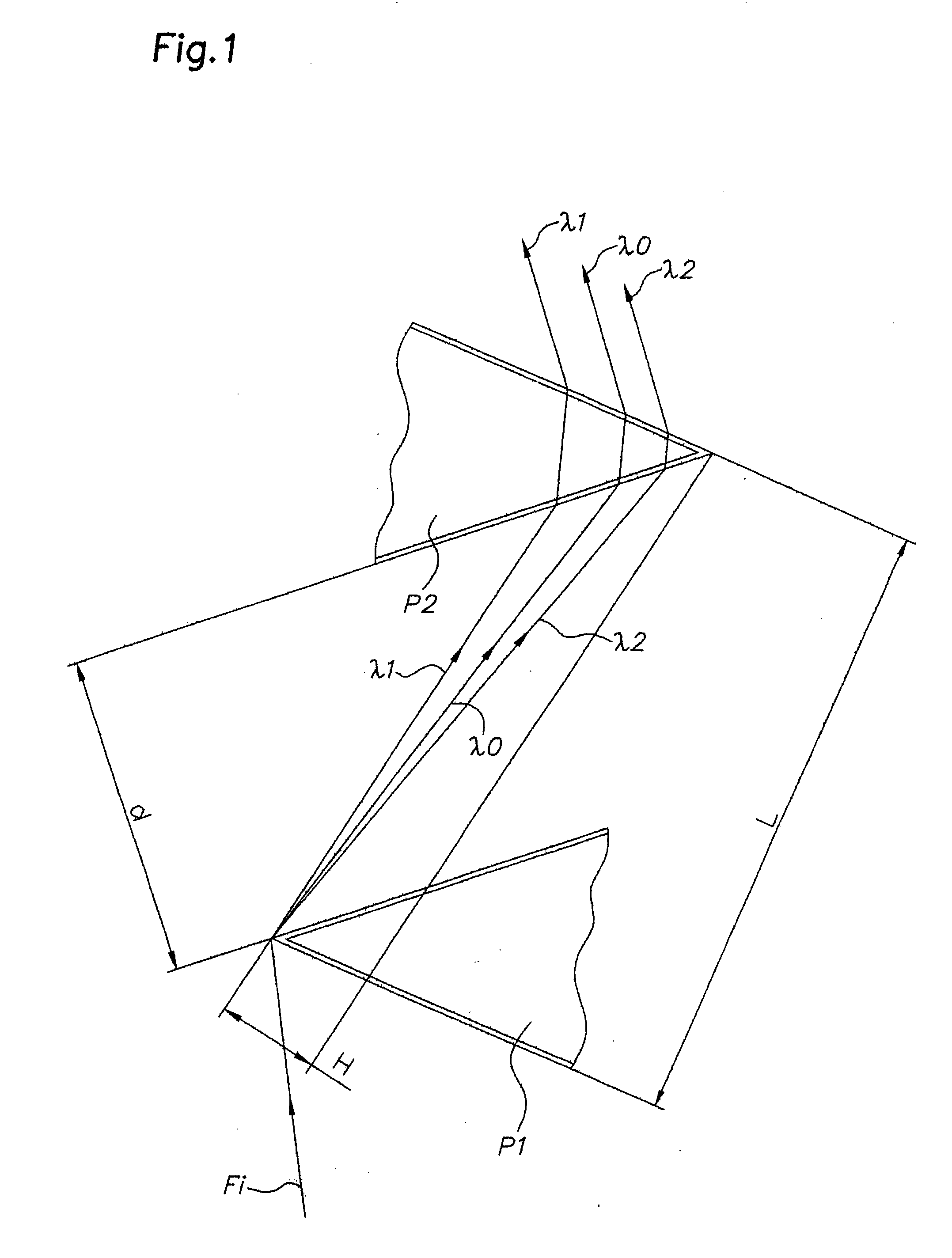
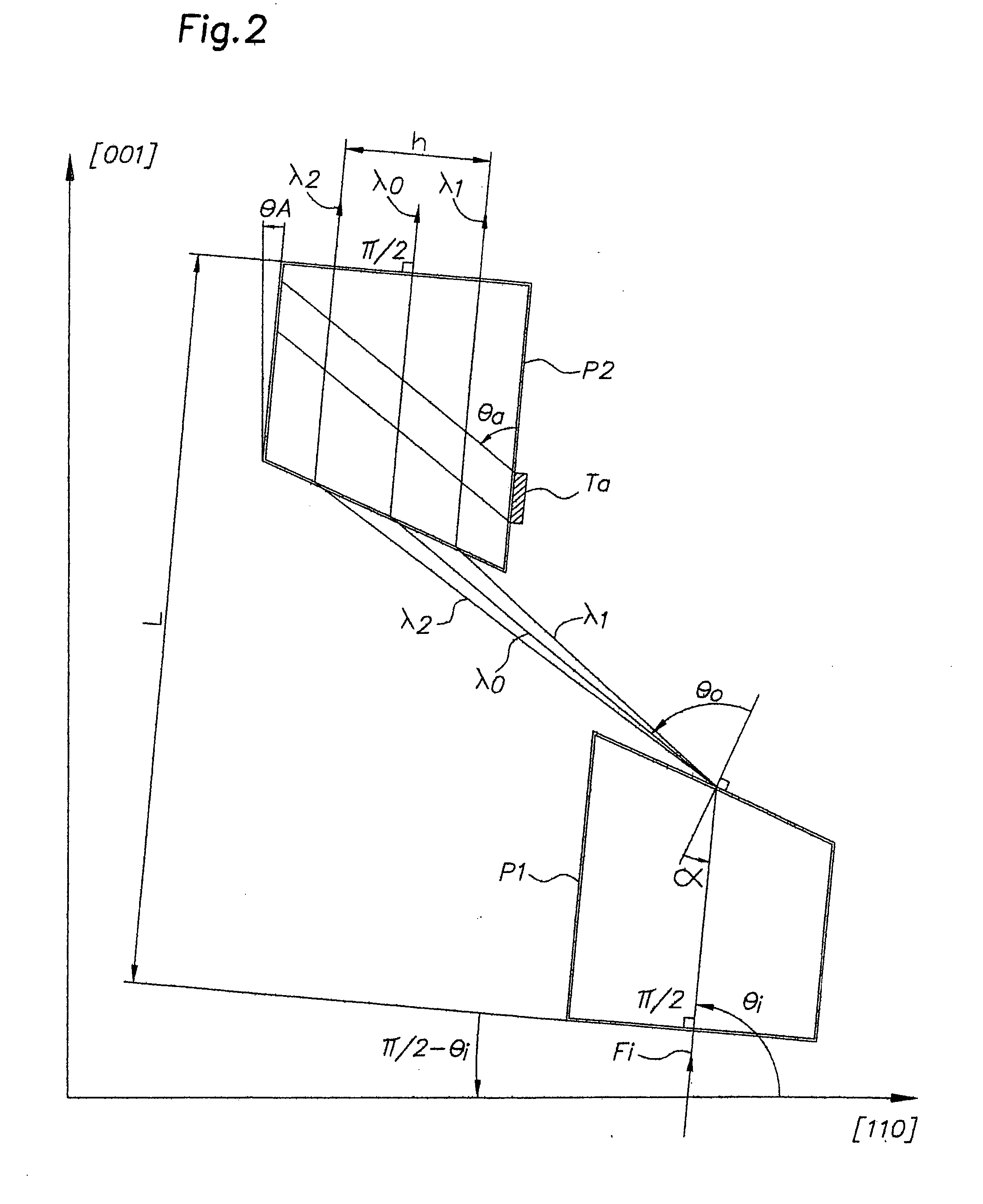
Device for dispersion of light pulses of an optical beam (Fi) constituted by two dispersive prisms (P1, P2), with the same vertex angle (α), mounted head to tail, the optical input surface of the first prism (P1) being parallel to the optical output surface of the second prism (P2), the distance (L) separating said optical input surface of the first prism (P1) and said optical output surface of the second prism (P2) being adjustable, given that the material constituting at least one of said first and second prisms (P1, P2) is an acousto-optic material allowing for acousto-optic interaction between said optical beam and an acoustic beam, the acoustic wave of said acoustic beam generating, in at least one of said first and second prisms (P1, P2), an integrated deflective Bragg cell.
Owner:FASTLITE
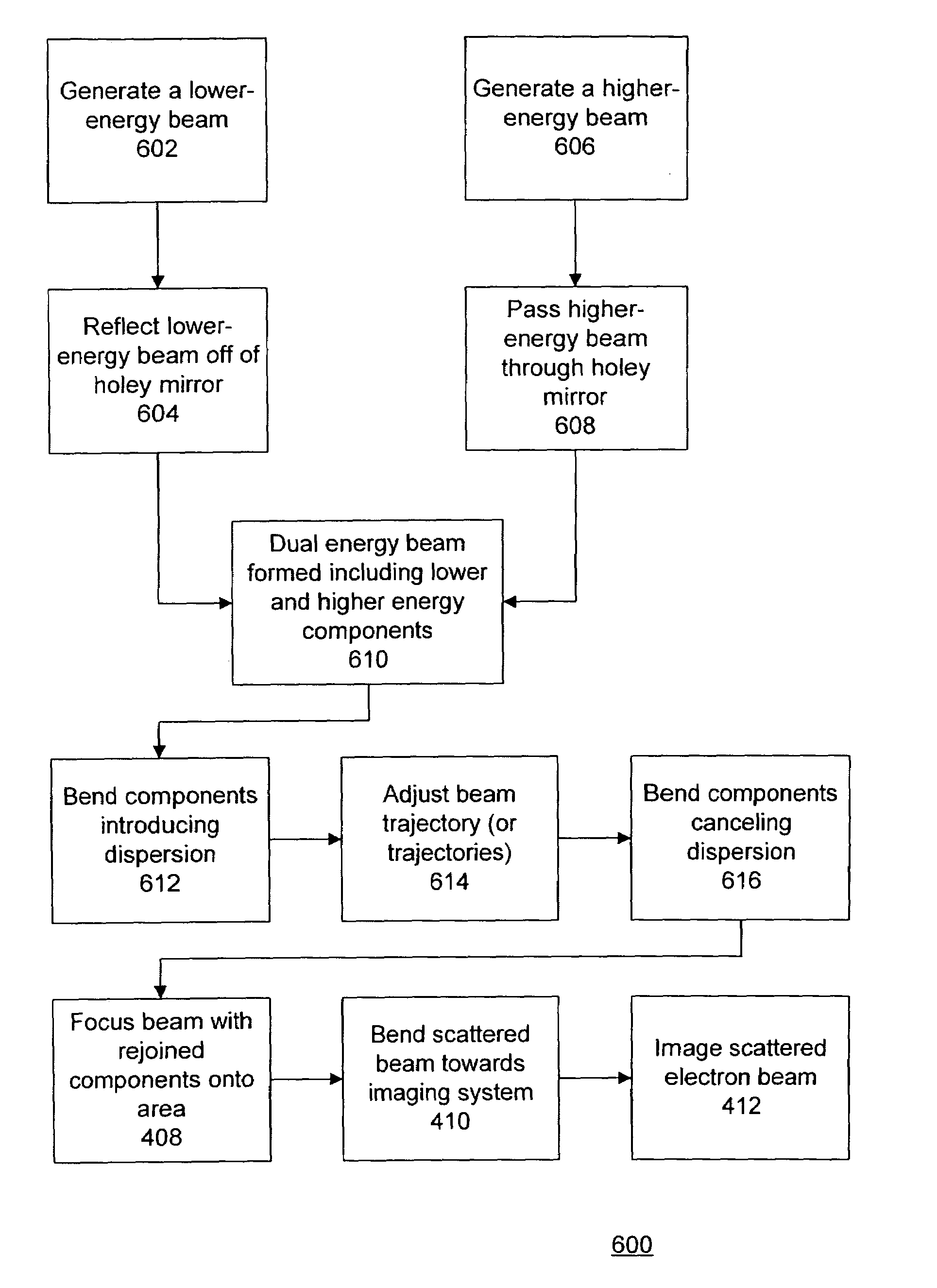
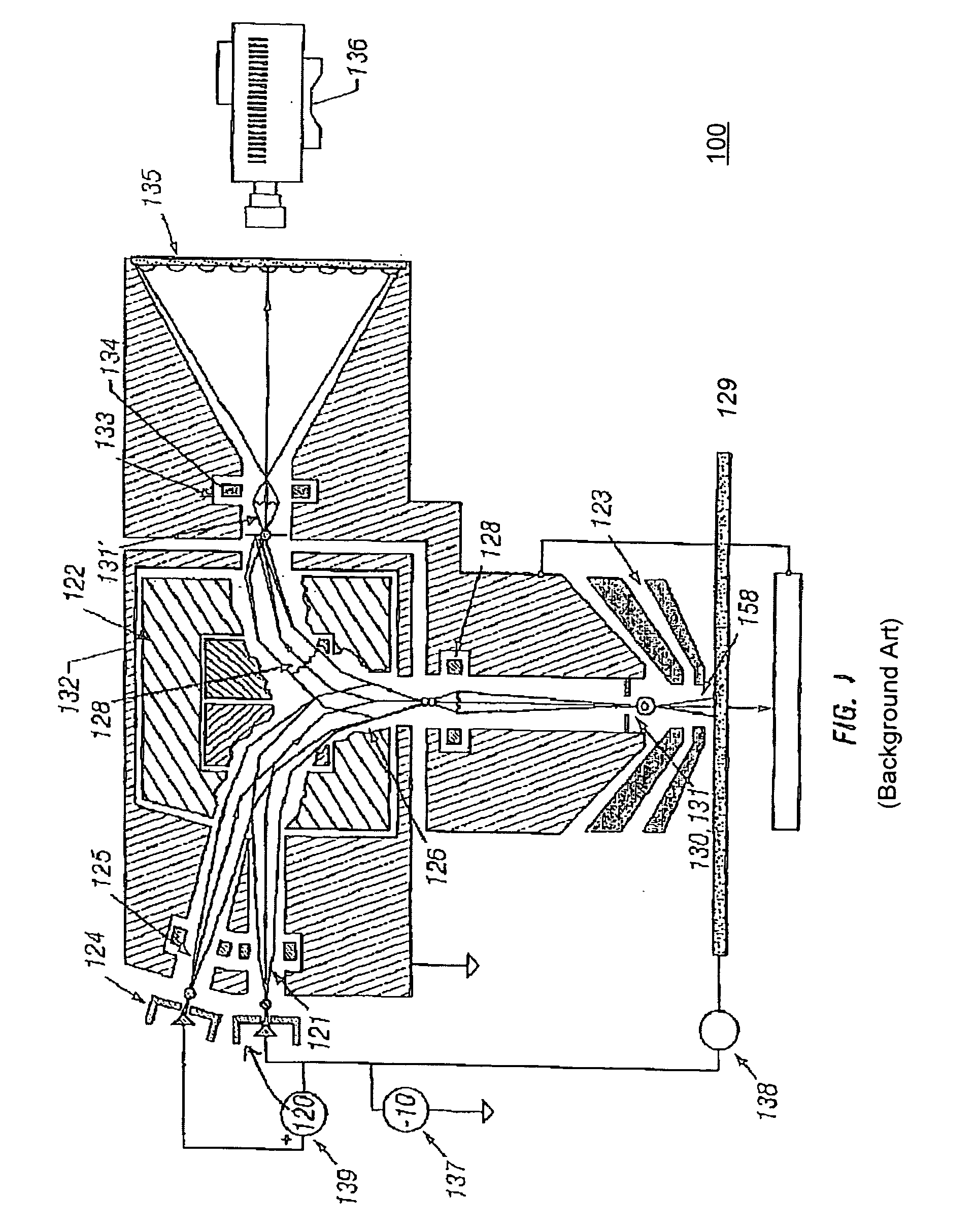
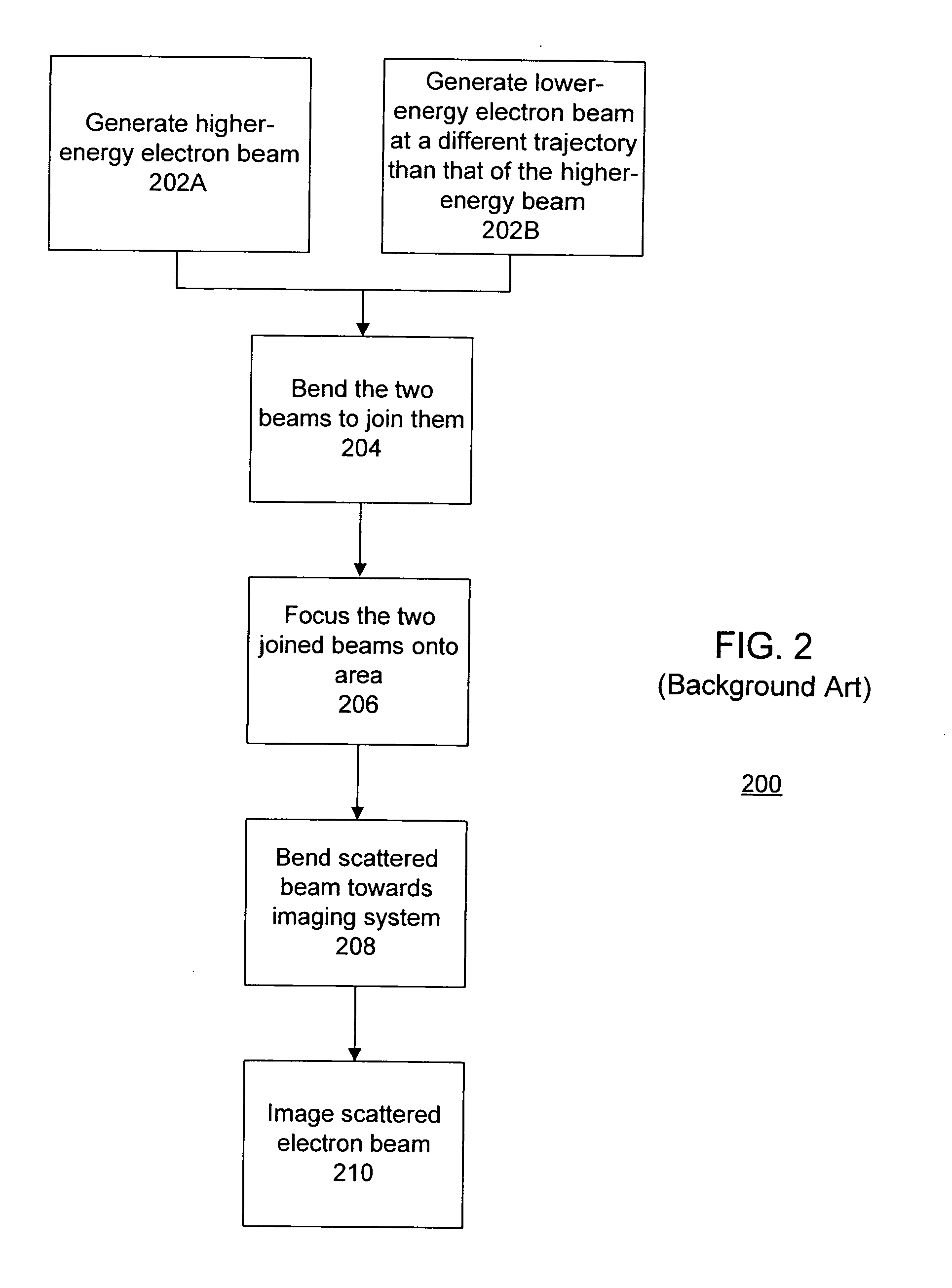
Holey mirror arrangement for dual-energy e-beam inspector
InactiveUS7217924B1Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam sourceDual energy
One embodiment relates to an apparatus for generating a dual-energy electron beam. A first electron beam source is configured to generate a lower-energy electron beam, and a second electron beam source is configured to generate a higher-energy electron beam. A holey mirror is biased to reflect the lower-energy electron beam. The holey mirror also includes an opening therein through which passes the higher-energy electron beam, thereby forming the dual-energy electron beam. A prism array combiner introduces a first dispersion between the lower-energy electron beam and the higher-energy electron beam within the dual-energy electron beam. A prism array separator is configured to separate the dual-energy electron beam traveling to a substrate from a scattered electron beam traveling away from the substrate. The prism array separator introduces a second dispersion which compensates for the dispersion of the prism array combiner. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Prism and grating cascading dispersion two-channel and high-resolution spectrum imaging system
InactiveCN103389159ASuppress stray lightReduce volumeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingDispersion (optics)
The invention discloses a prism and grating cascading dispersion two-channel and high-resolution spectrum imaging system, belongs to the field of aerospace optics, and solves the problem that the high resolution and the broadband spectrum of a conventional single dispersion spectrum imaging system cannot be detected simultaneously. A broadband light beam going out of an entrance slit of the system is sequentially subjected to collimation by a first collimating mirror and pre-dispersion by a dispersion prism and is focused to a color separation film by a focusing reflecting mirror in a wavelength dividing manner; the color separation film performs transmission on a light beam c with a short wavelength and reflects a light beam d with a long wavelength; the transmission light beam is imaged on a focal plane of a first detector by a first focusing lens group in a wavelength dividing manner after sequentially subjected to folding by a plane turning mirror and a first turning prism, collimation by a second collimating mirror and secondary dispersion of a first plane grating; and the reflection light beam is imaged on a focal plane of a second detector by a second focusing lens group in a wavelength dividing manner after sequentially subjected to folding by a second turning prism, collimation by a third collimating mirror and secondary dispersion of a second plane grating. According to the prism and grating cascading dispersion two-channel and high-resolution spectrum imaging system, the broadband and high spectral resolution are simultaneously detected, the spectral resolution is improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
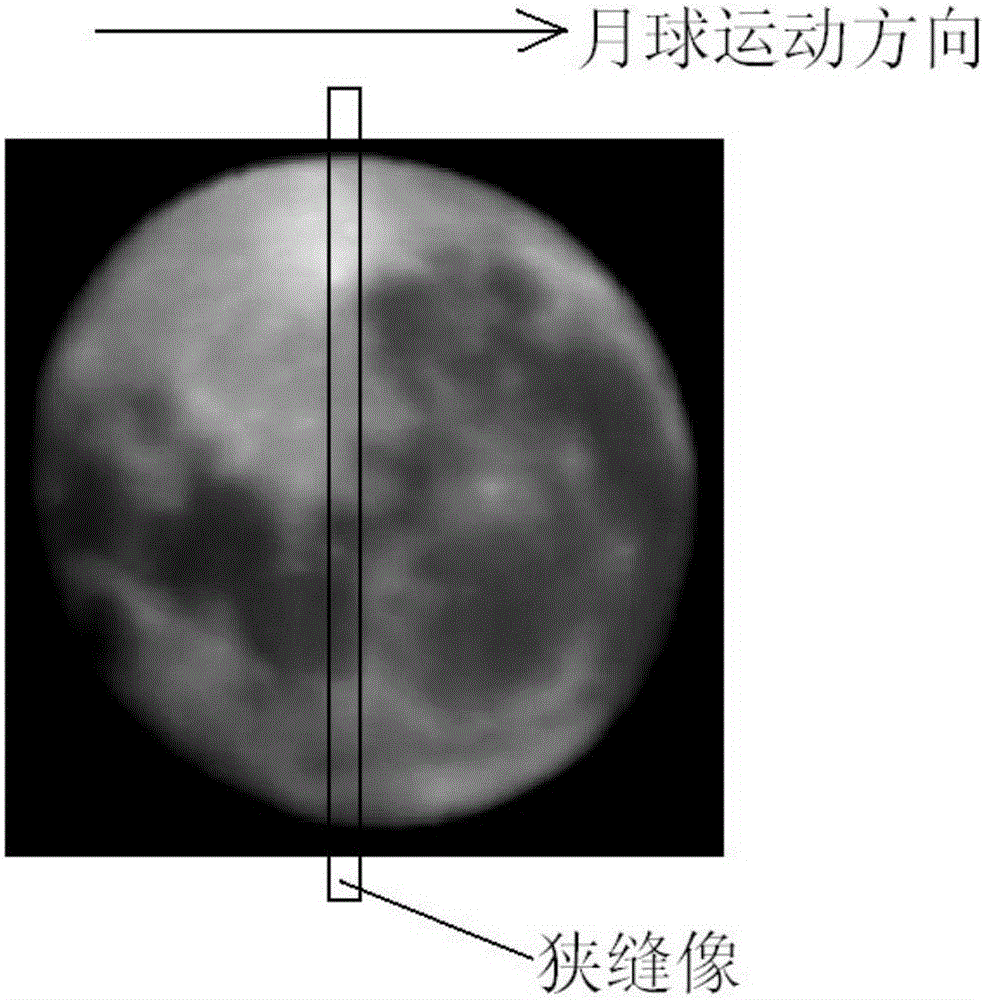
Foundation visible high spectral resolution moon observation system
ActiveCN105136294AHigh spectral resolutionGood spectral imaging qualitySpectrum investigationObservation systemTelescope
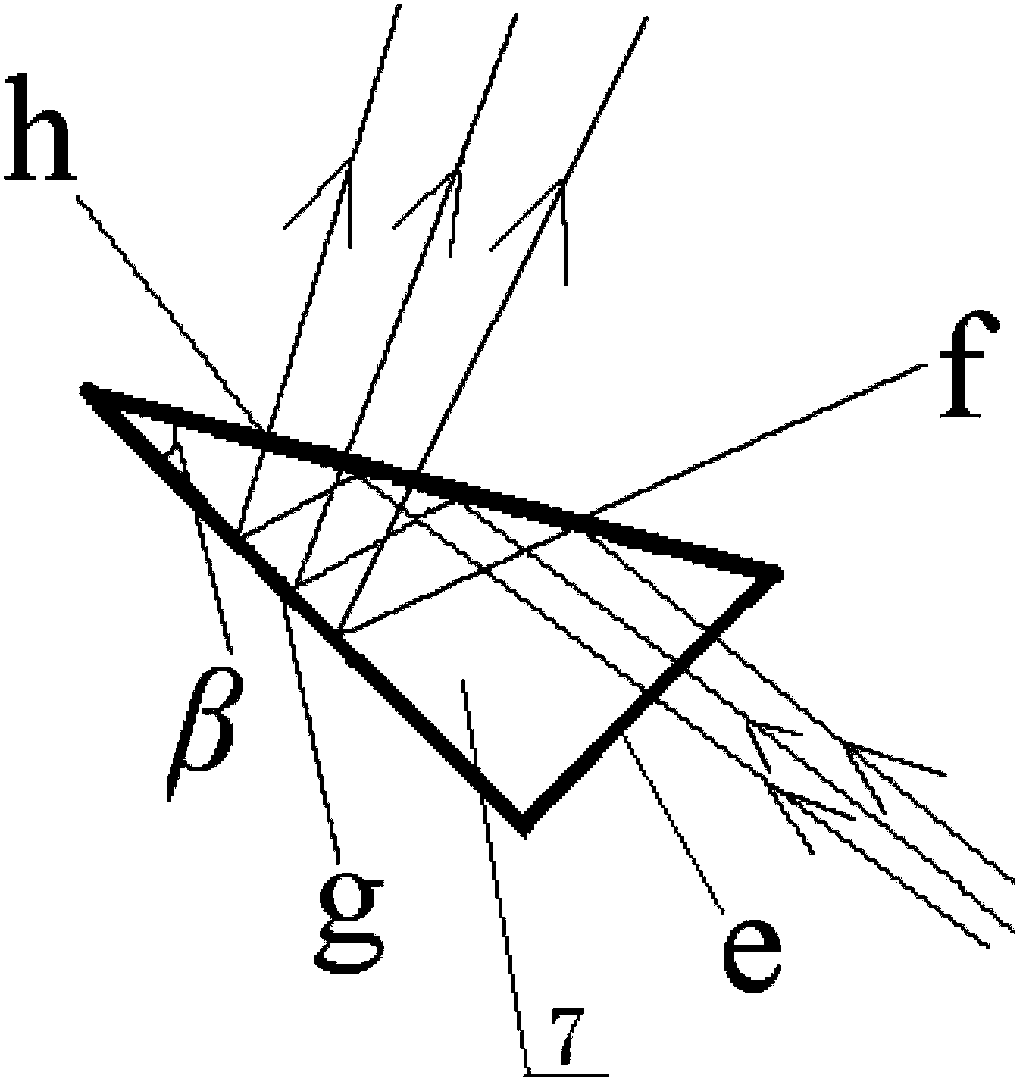
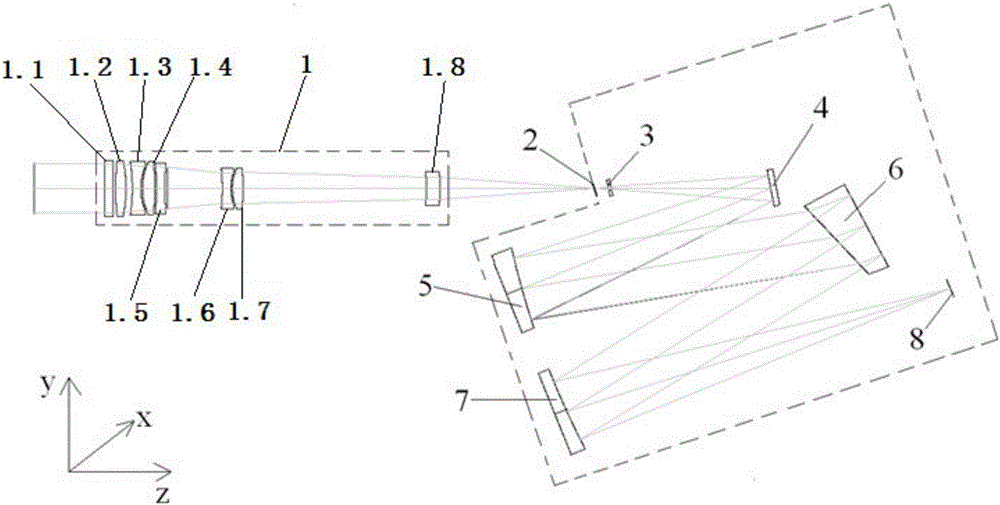
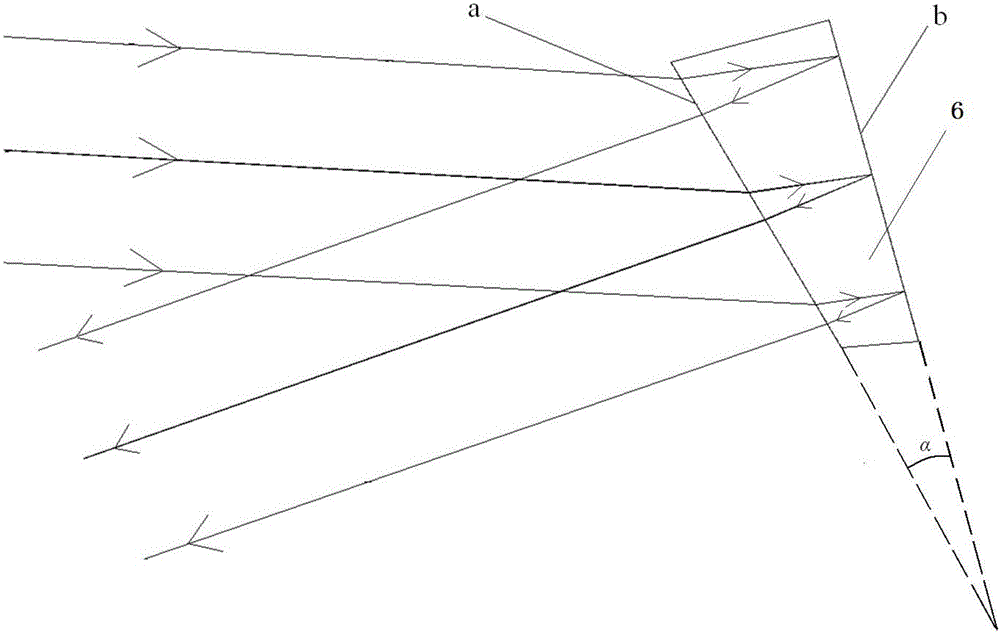
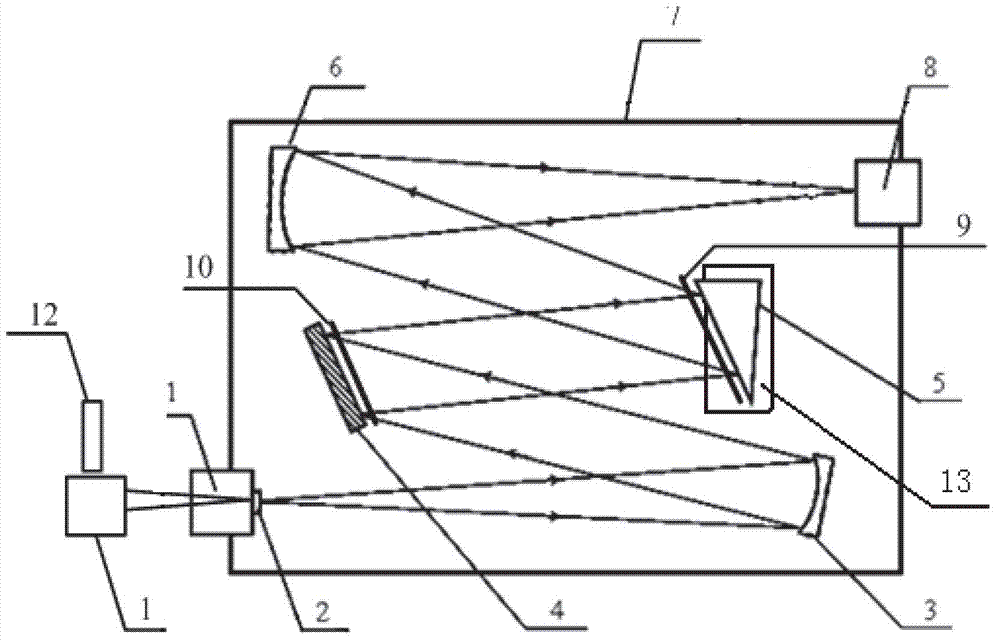
The invention provides a foundation visible high spectral resolution moon observation system, and relates to the technical field of imaging spectrum and radiometric calibration, and can solve the problem that a foundation to moon observation system employing an existing optical filter type spectrum imager is discontinuous in spectral observation and is low in the spectral resolution. The system comprises a moon tracking imager and a visible high spectral imager which are identical in axis, wherein the visible high spectral imager comprises a telescope, an entrance slit in the focal plane of the telescope, a divided wave band attenuation optical filter, a plane turning mirror, an off-axis ellipsoid collimating mirror, a dispersion prism, an off-axis hyperboloid imaging mirror and an area array CCD detector; and the light intensity of beams which eject from the entrance slit is adjusted through the divided wave band attenuation optical filter, and the beams are turned back through the plane turning mirror and are collimated through the off-axis ellipsoid collimating mirror and are dispersed through the dispersion prism, and then the beams are imaged on the area array CCD detector according to different wavelength through focusing of the off-axis hyperboloid imaging mirror successively. The foundation visible high spectral resolution moon observation system is continuous in spectral observation, and is high in the spectral resolution and the spectral imaging quality.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultraviolet, visible and ultraviolet prism chromatic dispersion imaging spectrometer
An ultraviolet, visible and ultraviolet prism chromatic dispersion imaging spectrometer relates to the technical field of the space remote sensing imaging spectrum and solves the problems of short working wavebands and small dynamic scope of detectable signal of the current imaging spectrometer. The ultraviolet, visible and ultraviolet prism chromatic dispersion imaging spectrometer comprises a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector, an electronic system, a telescoping system and a spectrum imaging system; the telescoping system comprises a aperture diaphragm and a telescope; the spectrum imaging system comprises an entrance slit, a planar turning mirror, a collimating mirror, a collimating mirror, an imaging mirror and a sub-waveband attenuation optical filter. The telescoping system images one band of a target into the entrance slit; the spectrum imaging system disperses the entrance slit and images the entrance slit to the CCD detector; and the electronic system acquires and processes the image on the CCD detector. The ultraviolet, visible and ultraviolet prism chromatic dispersion imaging spectrometer has a compact structure, a small volume and a light weight, can carry out imaging spectrum detection for the target of the signal within a big ultraviolet-visible-ultraviolet scope. The ultraviolet, visible and ultraviolet prism chromatic dispersion imaging spectrometer is applied to the field of spaceflight and aerial remote sensing.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dual-channel common-path prism dispersion broadband imaging spectrometer optical system
InactiveCN103017900AHigh spectral transmission efficiencyCompact layoutRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsEarth observationTelescope
The invention discloses a dual-channel common-path prism dispersion broadband imaging spectrometer optical system, and relates to the technical field of space optics, aiming at solving the problems of complex structure, large volume and heavy weight of the existing broadband imaging spectrometer optical system. The dual-channel common-path prism dispersion broadband imaging spectrometer optical system comprises a first aperture diaphragm, a second aperture diaphragm, a telescope, an entrance slit, a first collimating mirror, a second collimating mirror, a dispersion prism, a first imaging mirror, a second imaging mirror and a detector image plane; light beams emitted by a same objective, passing through the first aperture diaphragm and the second aperture diaphragm, are respectively reflected onto the telescope through a first channel and a second channel, imaged on the entrance slit through the telescope, reflected onto the dispersion prism through the first collimating mirror and the second collimating mirror, dispersed by the dispersion prism, and are imaged on the detector image plane through the first imaging mirror and the second imaging mirror. The optical system disclosed by the invention is applicable to aeronautic and astronautic atmospheric remote sensing, earth observation and other fields.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
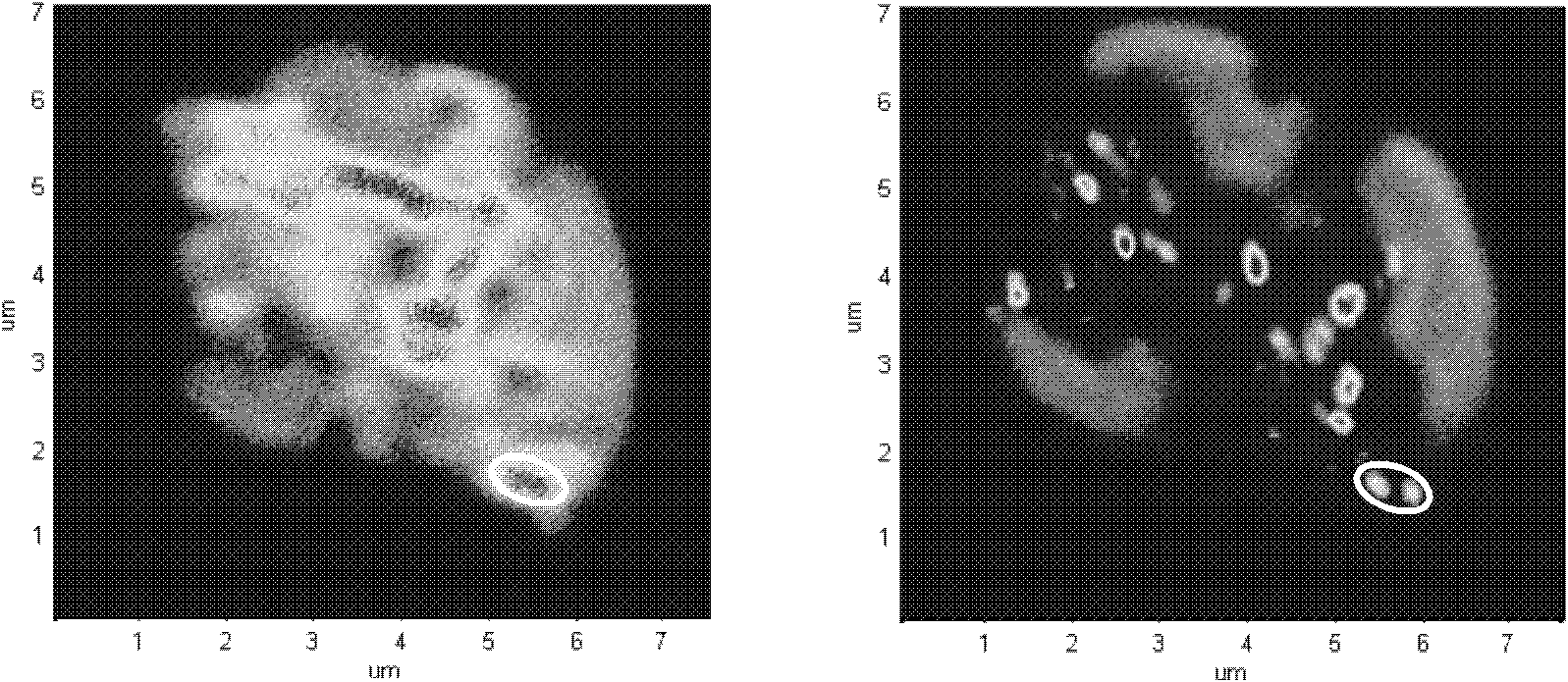
Detection device and detection method for dynamic process of material micro-domain structure change
InactiveCN102262091AAccurate detection positionGood repeatabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splittingLight spot
The invention discloses a detection device and a detection method for dynamics process of structure change of a micro region of a material. The device comprises two paths of laser light, one path of laser light reacts with the material, which results in that the structure of the micro region of the material changes, and the second path of laser light detects the dynamics process of the structure change. In the device and the method, a sample is automatically adjusted to a focal point of the first path of laser light by a CCD (charge coupled device) imaging method and a piezoelectric ceramic, and an objective lens with high numerical aperture is used so as to obtain the structure change of the micro region; the two paths of laser light are coaxial and vertically incident on the surface of the sample, light spots formed on the surface of the sample by the two paths of laser light are simultaneously observed through a CCD, and consequently, and the light spots of the two paths of laser light can be accurately superposed, which facilitates the detection on the dynamics process of the structure change of smaller regions; the utilization rate of the laser light is improved through a polarization beam splitting prism and a quarter wavelength plate, the two coaxial paths of laser light are completely separated by a dispersing prism and a total reflection principle, influence of non-detection light is removed, and detection precision is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-wavelength micro illumination device
ActiveCN102162907AOvercome the disadvantage of low energy densityOvercome the disadvantages of denaturation or even damageMicroscopesNon-linear opticsFluorescenceLasing wavelength
The invention provides a multi-wavelength micro illumination device. In the device, a laser pulse output by a picosecond pulse laser or a femtosecond pulse laser is incident to a nonlinear photonic crystal fiber to obtain a broadband laser source; the pulsed laser beam output by the broadband laser source is incident to an acoustooptical modulator to obtain a laser pulse beam with a repetition frequency; a beam splitter and a plurality of reflectors are arranged on the optical path of the laser pulse beam; the laser pulse beam is divided into n parallel output beams (n is a natural number equal to or larger than 2); a dispersion prism or a diffraction grating, a lens (a), a spatial light modulator and a lens (b) are sequentially arranged on the optical path of each output beam; and (n-1) output beams respectively pass through a right angle prism after passing through the dispersion prism or the diffraction grating, the lens (a), the spatial light modulator and the lens (b) to obtain n parallel output beams with different delay time. The multi-wavelength micro illumination device provided by the invention can provide laser wavelengths with a wide waveband range from near ultraviolet to mid-infrared and high spectral energy density above 1 nJ / nm, and is suitable for excitation of the most of fluorescence and Raman samples. Additionally, the plurality of laser wavelengths are from the same laser source so as to obviate the problem of synchronous time maladjustment, and the apparatus cost can be reduced greatly by using one pulse laser.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SEMICON SUBSTRATE TECH CO LTD
Echelle grating spectrometer, atomic emission spectrometer and spectrum testing method
InactiveCN102879091ARealize spectral line calibrationFulfill performance requirementsEmission spectroscopyAnalysis by thermal excitationImage resolutionDispersive prism
The invention relates to an echelle grating spectrometer, an atomic emission spectrometer based on the echelle grating spectrometer, and a spectrum testing method by virtue of the atomic emission spectrometer. According to the invention, an echelle grating is adopted as a main dispersion element; light rays emitted by a light source are focused at an incident pinhole by a collecting lens, outgoing beams at the incident pinhole are collimated by a collimating lens and then enter the echelle grating for main chromatic dispersion, then enter a cross dispersing prism for crosswise chromatic dispersion, and are finally imaged onto an image surface of a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) by a focus lens after crosswise chromatic dispersion; through changing the incident angle of the cross dispersing prism, rapid measurement of wave bands within 200 nm and 900 nm can be realized, and the advantages of wide wave band, high resolution, high sensitivity, low noise and small size can be achieved. As shown in the testing results, the test is simple and convenient, the sensitivity is high, the sample consumption is low, and the rapid measurement of multiple elements of the wide wave bands can be realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Femtosecond pulse holographic device
InactiveCN1542568AReduced optical path requirementsEasy to operateDigital output to display deviceBeam splitterFemto second laser
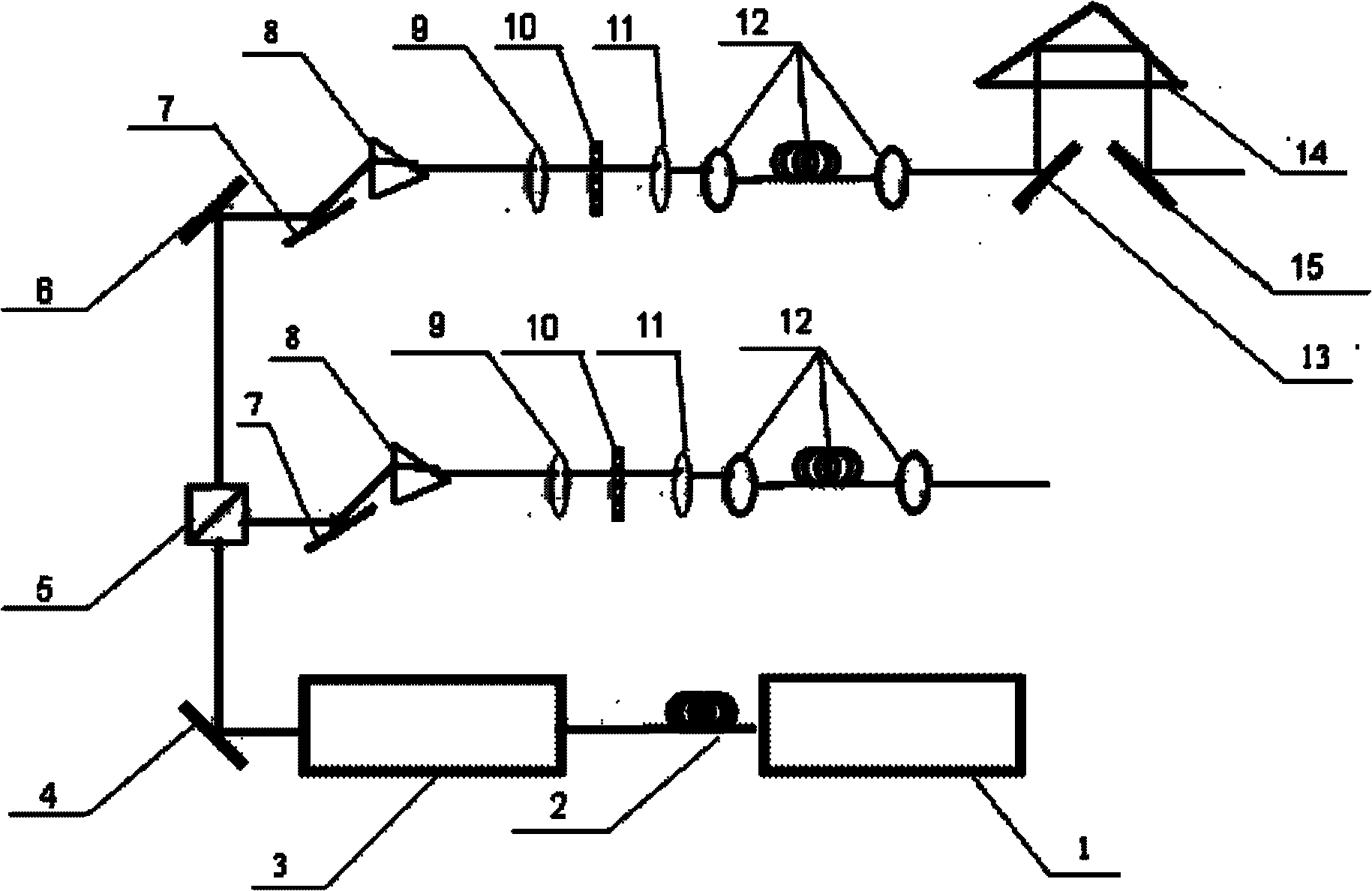
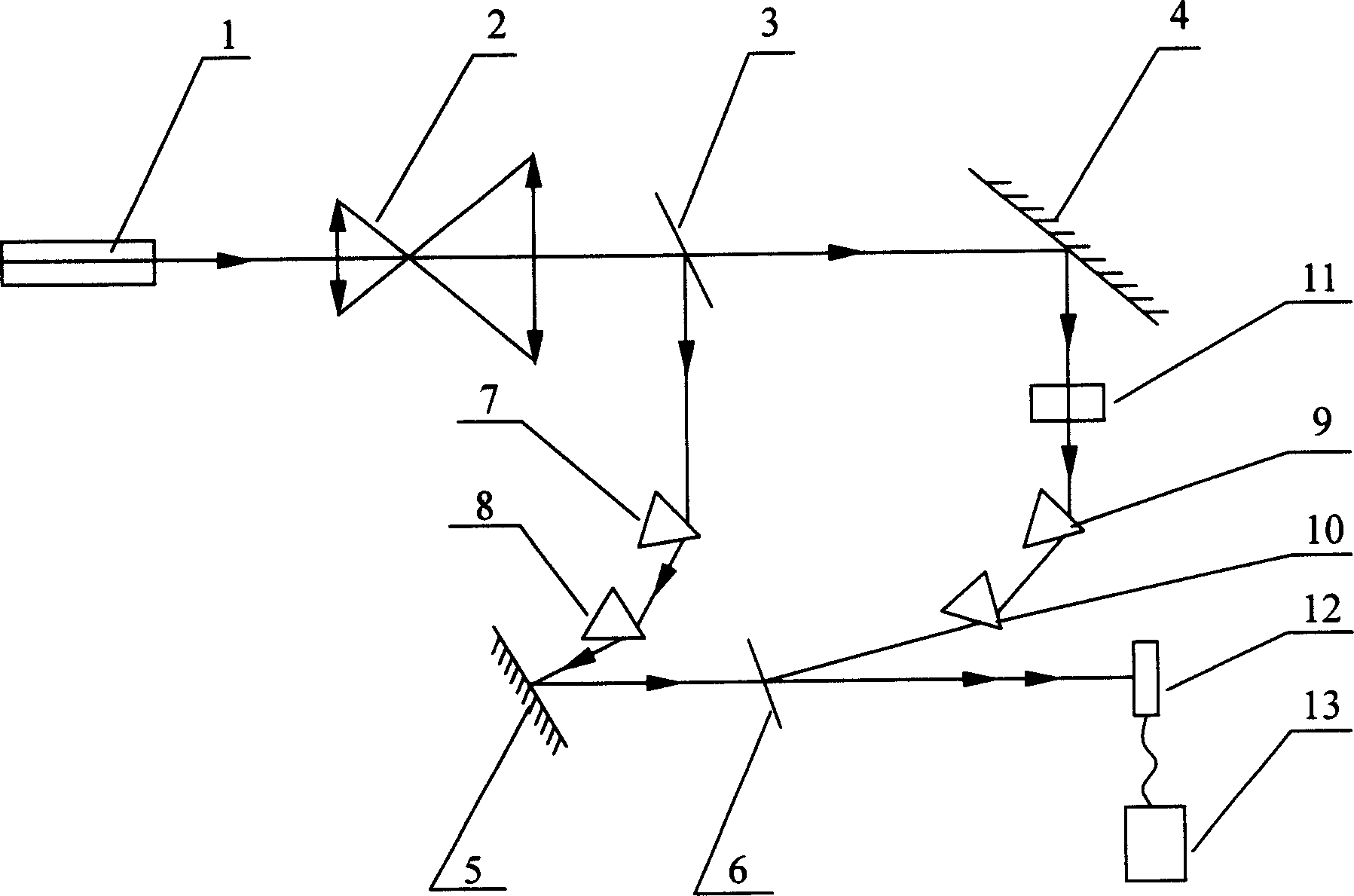
The holographic femtosecond pulse apparatus includes one femtosecond laser as light source, and features that there are beam expanding telescope, the first beam splitter, the transmitting object light path of the first beam splitter, which comprises the first holophote, the first and the second triangular dispersive prisms, the second beam splitter and detector, the reflecting reference light path of the first beam splitter, which comprises the third and the fourth triangular dispersive prisms, the second holophote, the second beam splitter and the detector, successively along the progress direction of the laser beam the laser sends; and the detector is connected to one computer for re-constructing holographic femtosecond image. The apparatus expands the ultrashort pulse of 120 fs into pulse of 1 ns, and this lowers the requirement to object light path and reference light path and facilitates the operation and regulation of holographic femtosecond system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High recurrence rate titanium jewel twitter pulse regeneration amplifier without brodening apparatus
InactiveCN1411112ACompact structureOvercoming Optical Damage ProblemsLaser detailsBeam splitterOptoelectronics
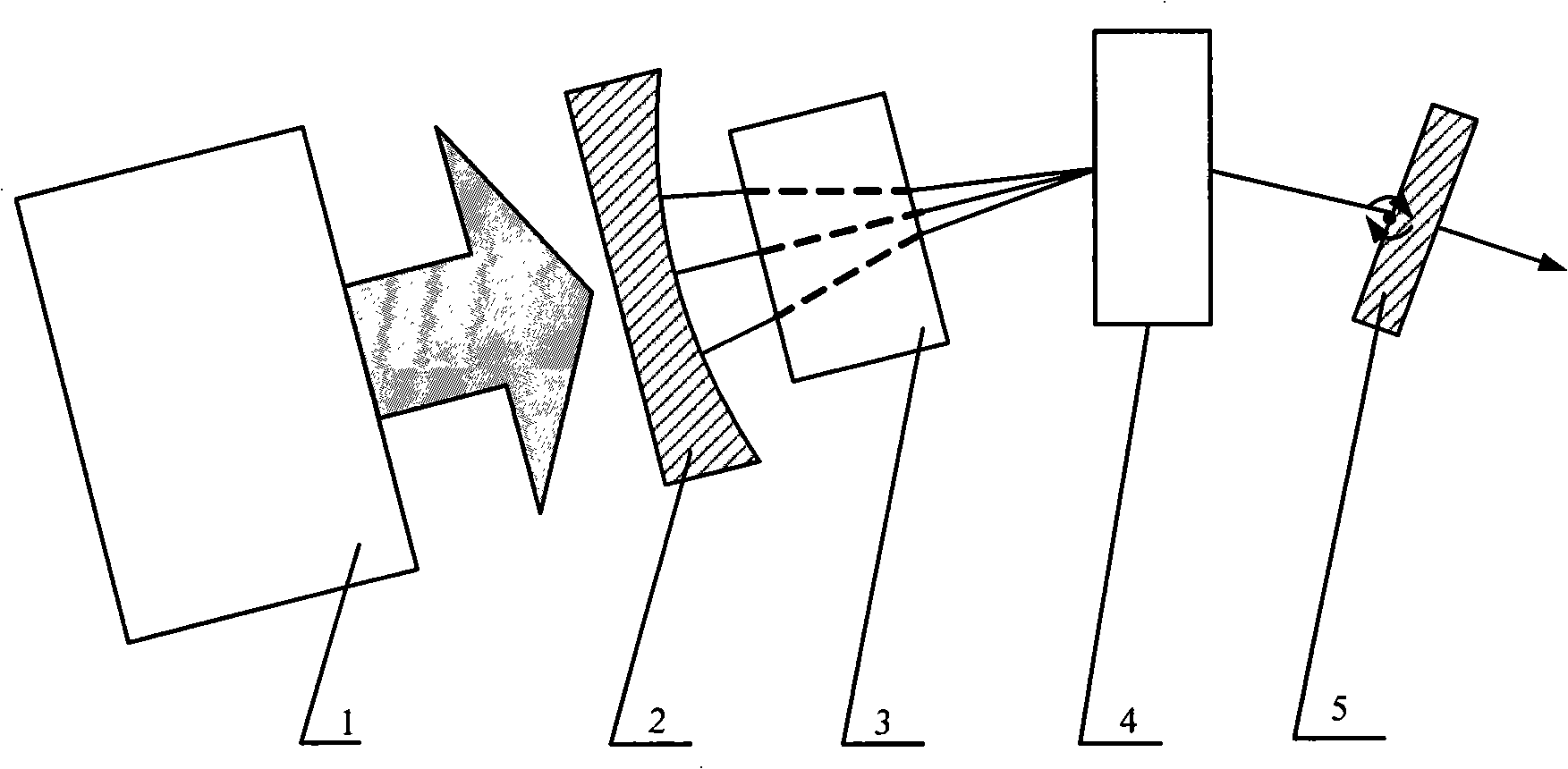
This invention relates to a high-repetition rate Ti precious stone chirped pulse regenerative amplifier without spreader in which a green light pump source, a rear concave mirror, a focusing lens, Tiprecious stone crystal and front concave lens are set along a horizontal shaft direction on the mounting plate, an angle folding plane reflector, low end face plane reflector, thin film polaroid, Puckle box, along the second horizontal optical axis, a light beam lead reflector, light conductive reflector, separator, beam splitter, half wave palte are set along the third horizontal optical axis and upper end face plane reflector, dispersion prism, accumulation prism, aligned dispersion prism, output prism light beam lead reflector, light beam converting reflector, photoelectric converter.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
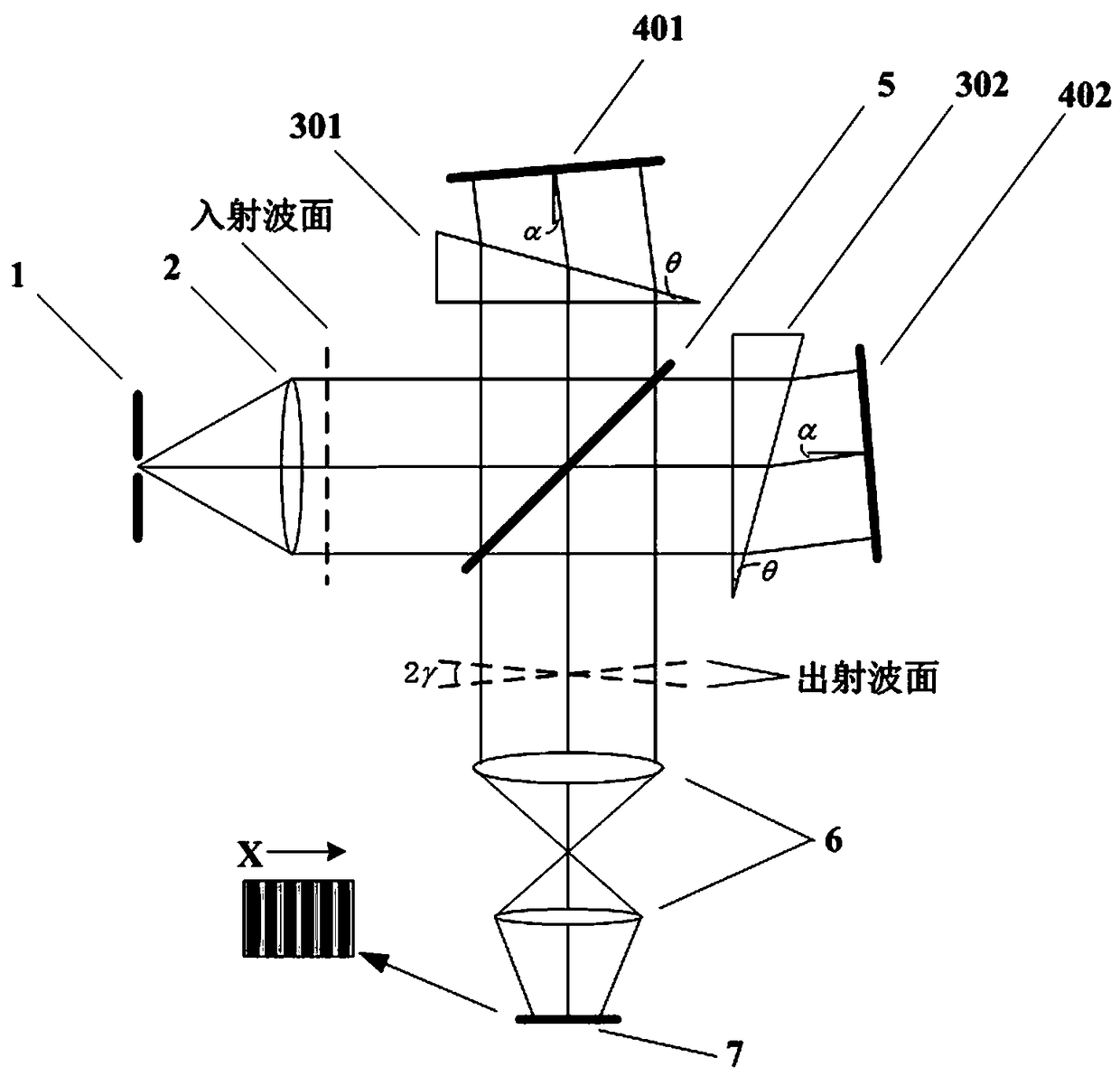
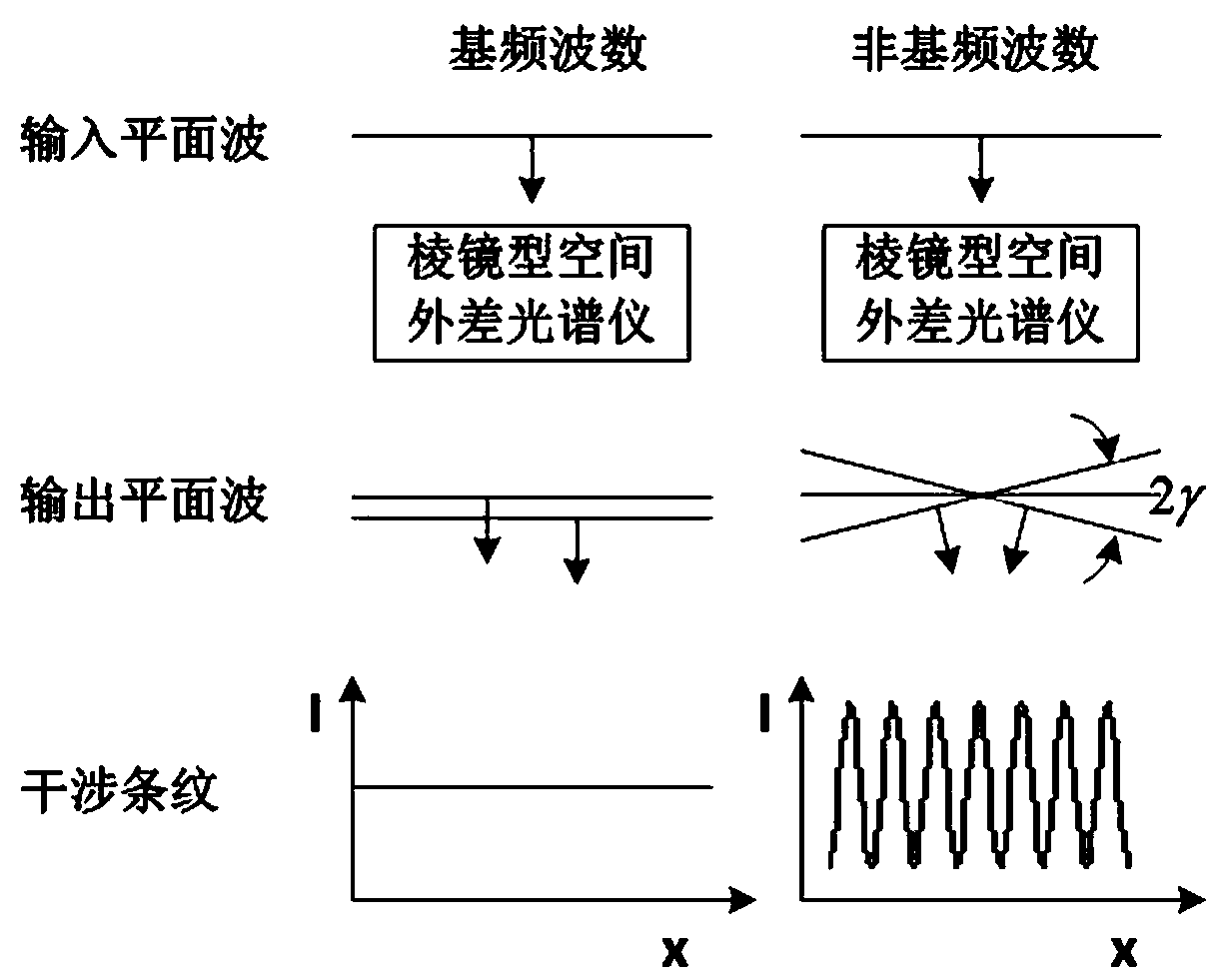
Prism-type spatial heterodyne spectrometer
PendingCN108387317AWith hyperspectral resolutionImprove throughputRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryBeam splitterGrating
The invention discloses a prism-type spatial heterodyne spectrometer, which comprises an incident diaphragm, a collimating lens, a beam splitter, a first dispersion prism, a second dispersion prism, afirst completely reflecting mirror, a second completely reflecting mirror, an imaging unit and a detector, and is characterized in that the rear side of the incident diaphragm is sequentially provided with the collimating lens and the beam splitter, the upper side of the beam splitter is sequentially provided with the first dispersion prism and the first completely reflecting mirror, the rear side of the beam splitter is sequentially provided with the second dispersion prism and the second completely reflecting mirror, and the lower side of the beam splitter is sequentially provided with theimaging unit and the detector. The spectrometer has the advantages of hyperspectral resolution, high throughout and no moving component. Meanwhile, the spectrometer can also avoid the problems of energy loss and interference reduction caused by grating multi-stage diffraction in a grating spatial heterodyne spectrometer.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
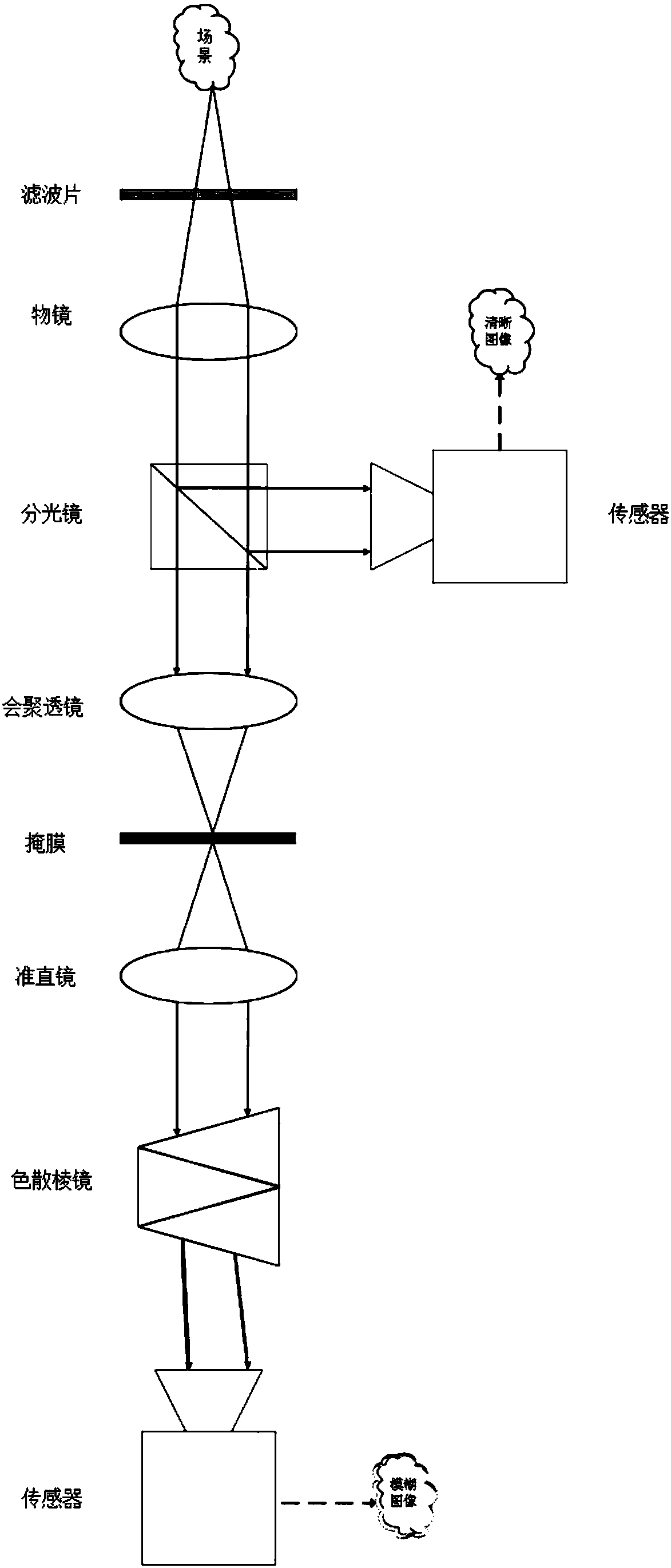
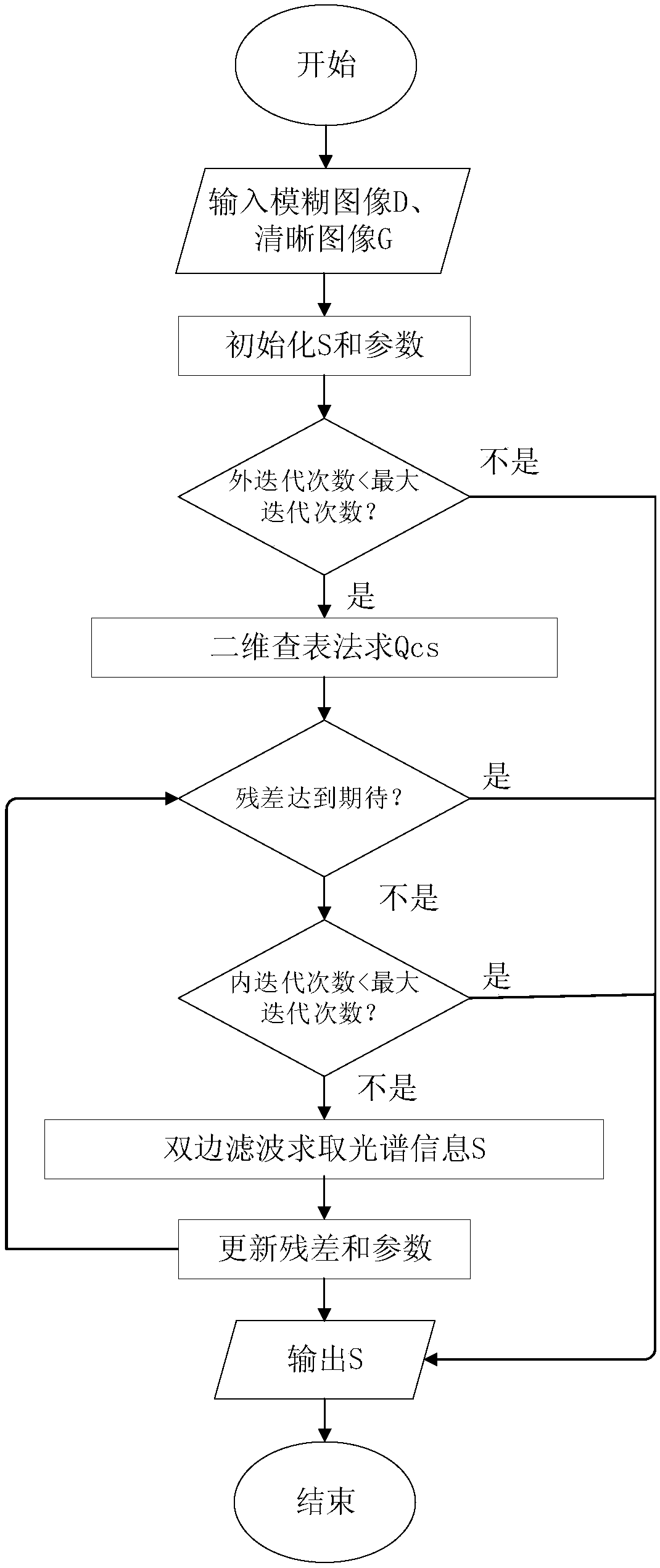
Spectral imaging system based on dispersion fuzziness, and spectral reconstruction method of spectral imaging system
ActiveCN107655571AImprove inherent shortcomingsReduce complexityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFull spectral imagingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a spectral imaging system based on dispersion fuzziness, and a spectral reconstruction method of the spectral imaging system. The specific optical path of the spectral imagingsystem is that the light from a scene sequentially passes through a filter and an objective lens, and is divided into two ways: one way is directly collected by a first sensor, and a clear image is obtained; the other way sequentially passes through a focusing lens, a mask, a collimating mirror and a dispersing prism, and then is collected by a second sensor, and a fuzzy image is obtained. The mask is of an edge blocking type, and is used for carrying out the simple modulation of the fuzzy image, so as to obtain the edge information of the fuzzy image. The system can greatly reduce the calibration complexity, and improves the light transmission quantity, the signal-to-noise ratio and the spatial resolution of the system. The method for spectrum reconstruction through the imaging system canachieve the solving of the full-spatial-resolution spectrum information according to a series of constrain conditions, can achieve the real-time obtaining of the spectrum information of a dynamic scene in principle, and does not need to sacrifice the time and spatial resolution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Realization method of programmable light source system based on DMD
InactiveCN105301769AGood monochromaticityIncrease output strengthOptical elementsContinuous lightUltra-wideband
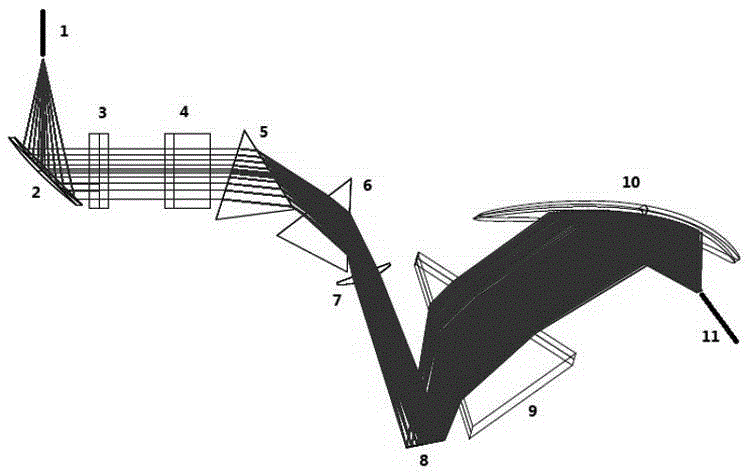
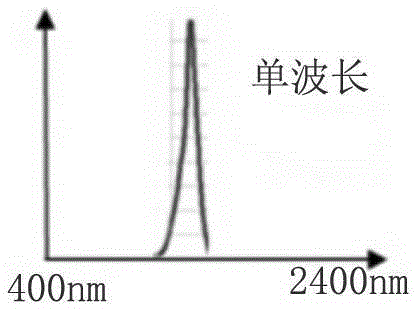
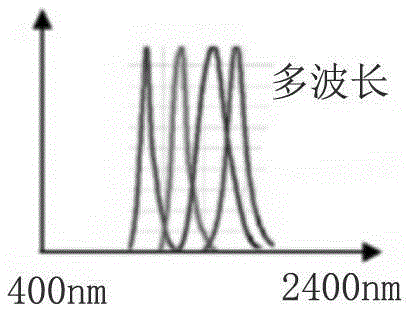
The invention relates to a realization method of a programmable light source system based on a DMD, wherein an ultra wideband output of 400 nm-2400 nm is output by a super-continuous light source at first, and output light is collected by a paraboloid mirror to form parallel light; and the parallel light is split though a dispersing prism combination, the dispersed light is focused by a columnar convex lens, and the light with different wavelengths is projected to the DMD. A DMD control program selects the wavelength by selecting reversal of prisms on different rows. A to-be-output waveband is reflected by a micro mirror to one direction; and unselected wavebands are reflected to other directions. The to-be-collected light reflected by the DMD micro mirror passes through an inverted dispersing prism to offset original dispersing in order to reintegrate the reflected light into the parallel light, and then the parallel light is collected by the paraboloid mirror to an input end of a collection optical fiber. Finally, the whole system realizes rapid programmable outputting by controlling the reversal of the micro mirror on the DMD.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
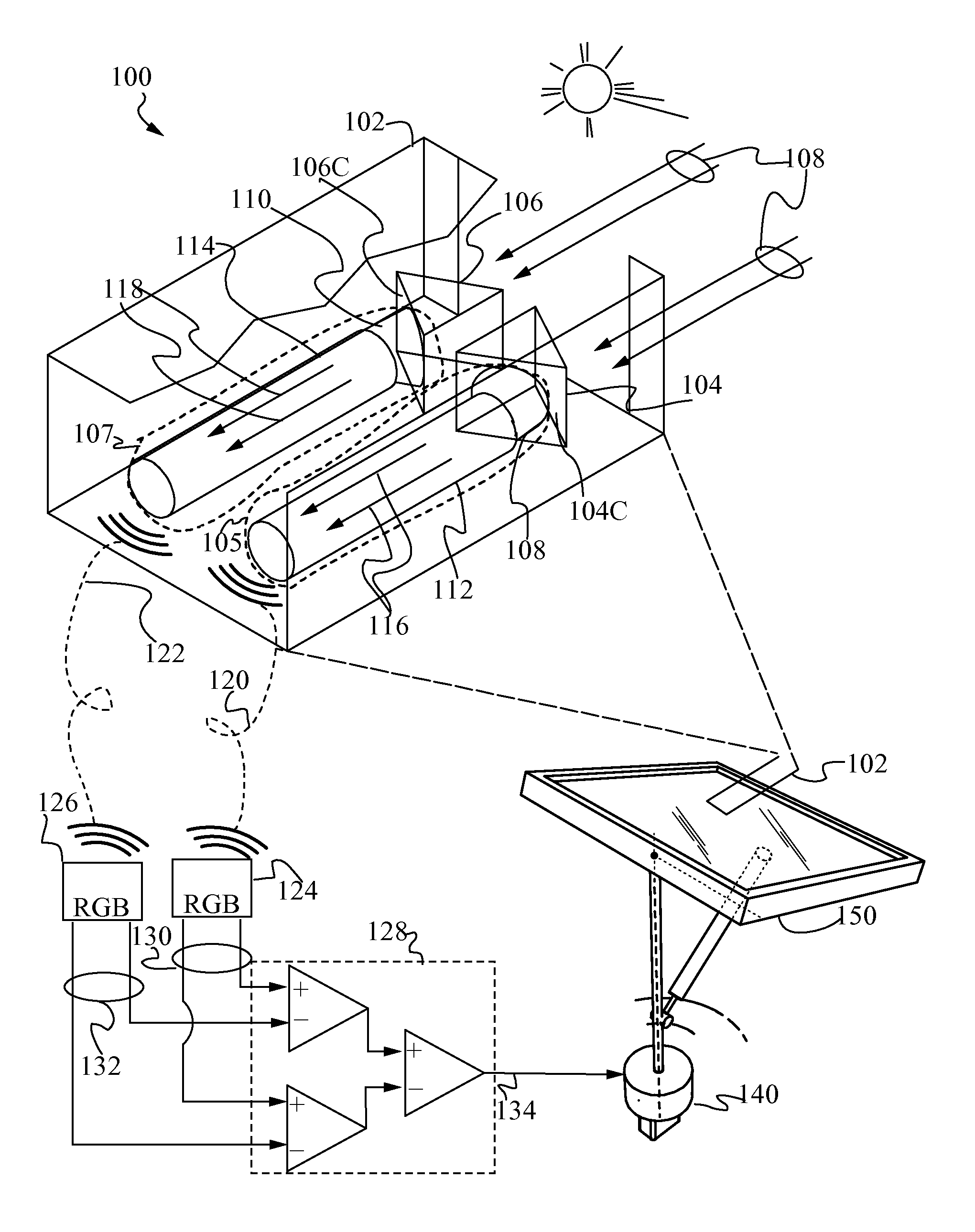
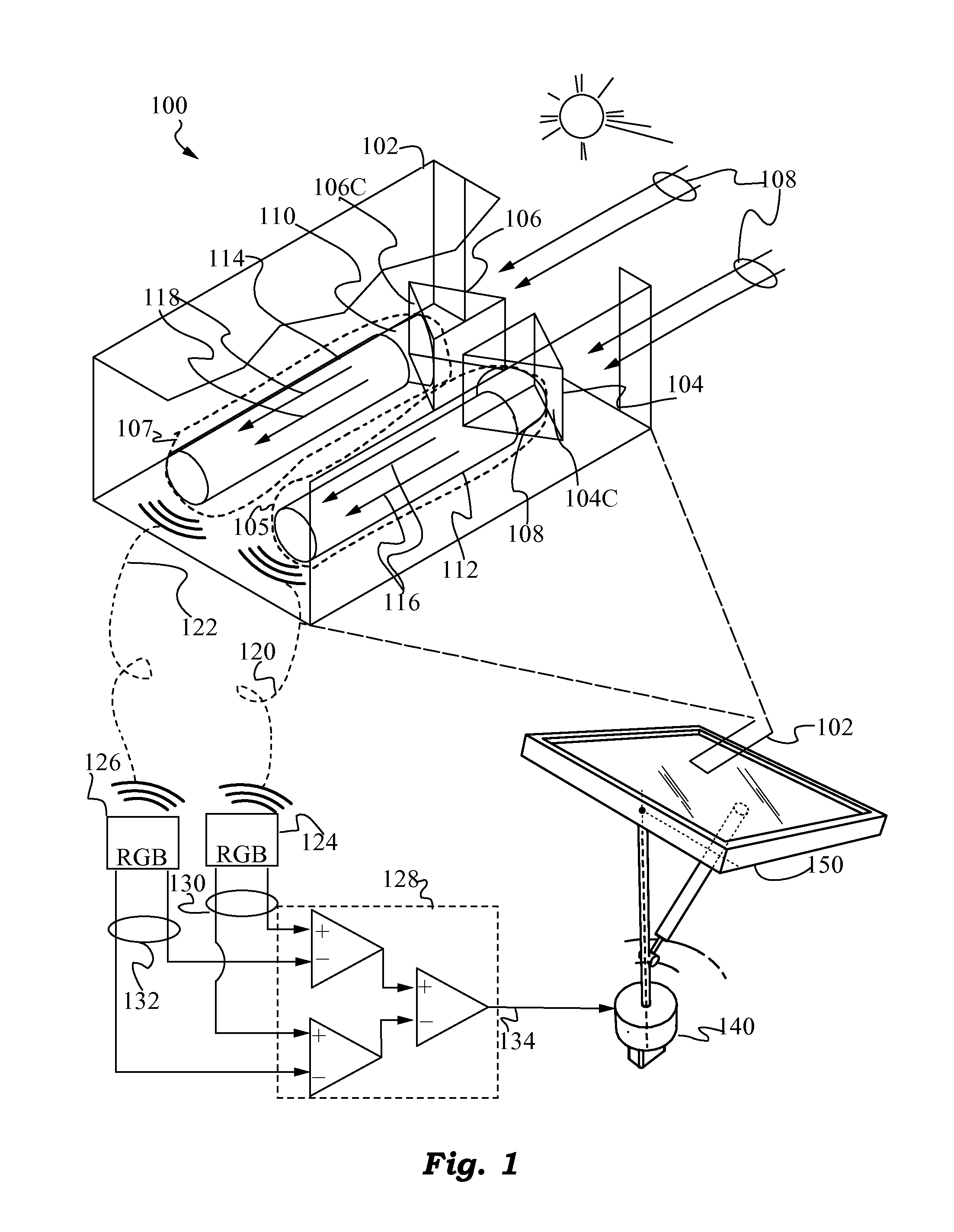
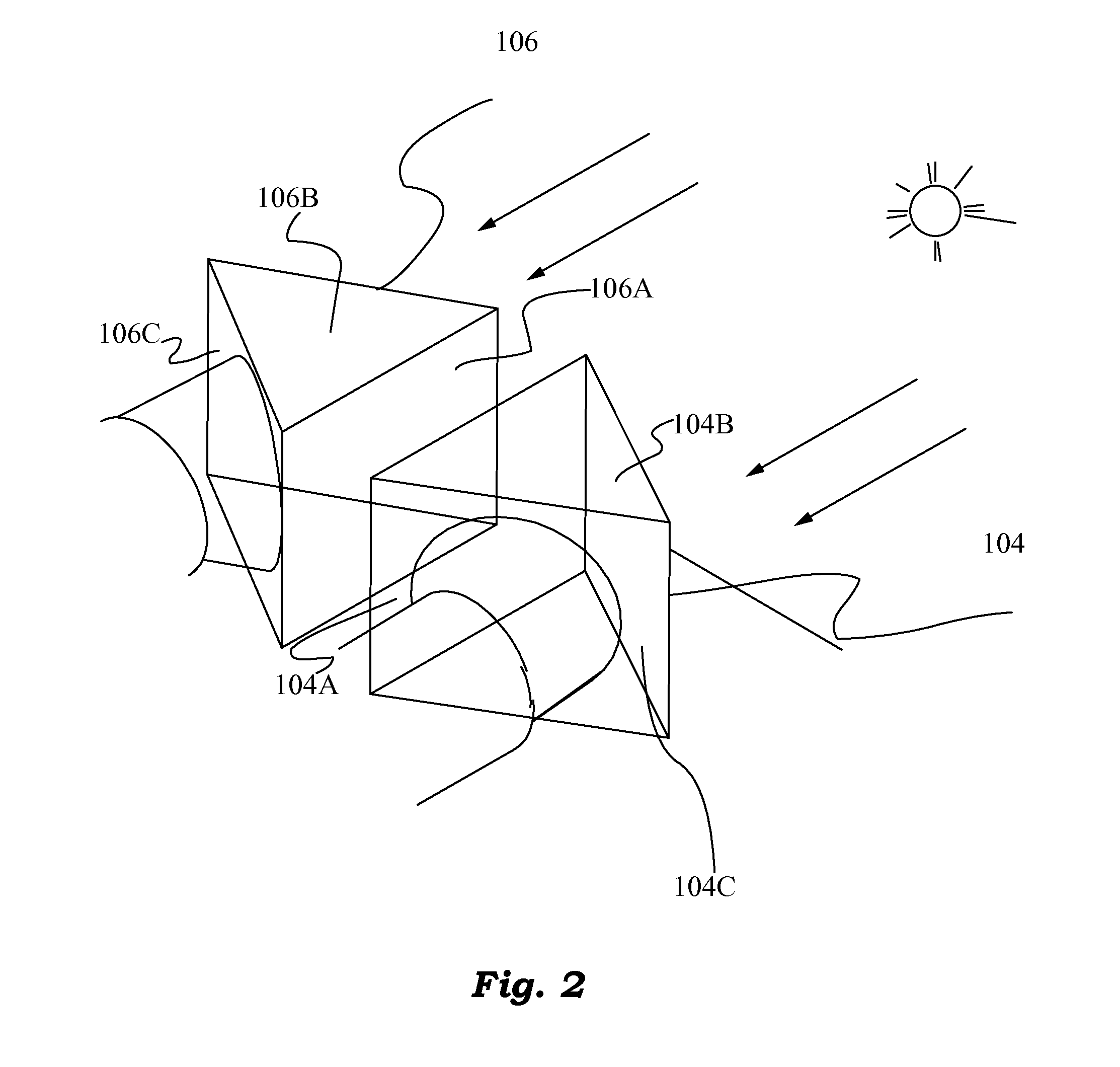
Optical Differential Solar Tracking System
InactiveUS20160047877A1Minimal cost of maintenanceMinimal of operationPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationGratingMonochromatic color
A system and method of using differential optical signals to track the orientation of a solar surface or surfaces is proposed. Two dispersive prisms or gratings arranged in a mirror-symmetric fashion are used to decompose light into its constituent colors, and the gain of a differential amplifier circuit based on the difference of the frequencies of single color collimated light produced by the two prisms or gratings is used to maintain the on-sun orientation of the solar surface or surfaces. The invention provides for a high-precision, low-cost solar tracking system. Preferably, the signal processing and tracking of solar surfaces is performed by a mobile robot that travels to multiple solar surfaces to minimize cost.
Owner:SOLARCITY
Broadband tunable laser parametric oscillator
InactiveCN101304151AOutput line widthCenter wavelength tunableOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingLine width
The invention relates to an oscillator, in particular to a laser parameter oscillator that is tunable in broad band, which belongs to the laser technical field. The tunable laser parameter oscillator of the invention comprises a laser light source, an input spherical mirror, lath nonlinear optical material, dispersion optical elements (like a dispersion prism, a fiber grating, and the like) and an output mirror. The laser parameter oscillator of the invention has the advantages of wide output linewidth, tunable center wavelength and simple structure.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wideband adjustable laser in shape of batten
InactiveCN101291039AOutput line widthCenter wavelength tunableOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionLaser technologyGrating
The invention relates to a laser, in particular to a slab laser with tunable broadband, belonging to the laser technical field. The slab laser with tunable broadband comprises five parts, namely a pumping source, an input mirror, a slab gain medium, a dispersive optical element (such as a dispersing prism, a fiber grating, etc.) and an output mirror. The oscillating light with different wavelengths has different light paths in the laser; all laser nearby a central wavelength can form oscillation and is amplified through the slab gain medium, so as to form wide-line wide-laser output; the central wavelength of the output laser can be changed by regulating the inclination angles of the output mirror, and then the tunable broadband laser output can be realized. The laser of the invention is compact in structure, can change the wavelength of the output laser by regulating the inclination angles of the output mirror, and realizes the tunable broadband laser output.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Device for generating high-efficiency multi-wavelength ultra-short pulse lasers
InactiveCN103490274ASimple structureOptical resonator shape and constructionStimulate raman scatteringLasing wavelength
The invention provides a device for generating high-efficiency multi-wavelength ultra-short pulse lasers to solve the problem that the self-phase modulation process, the self-focusing process and the multiple-photon dissociation process in the transient stimulated raman scattering process under the ultra-short pulse pumping are seriously influenced, and relates to the technical field of non-linear optical equipment. A raman pool is composed of a stainless steel pipe, a fused quartz incidence window without a coating film, and an exit window without a coating film, and pure hydrogen, methane, deuterium gas and the like or mixed gas formed by mixing the pure hydrogen or the methane or the deuterium with inert gas or mixed gas formed by multiple types of raman media can be filled into the raman pool. More stokes wavelength output can be obtained by mixing working gas media, the magnitude of the output stokes wavelength can be adjusted due to the addition of buffer gas, and dense flint materials are selected as materials of an equilateral dispersing prism. The dispersing prism, a fifth focus lens and laser mode selection pinholes are used in cooperation so that different types of laser wavelength output can be selected and energy measurement can be conducted. The device is suitable for the technical field of non-linear optical equipment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optical intelligent perception multidimensional imaging system
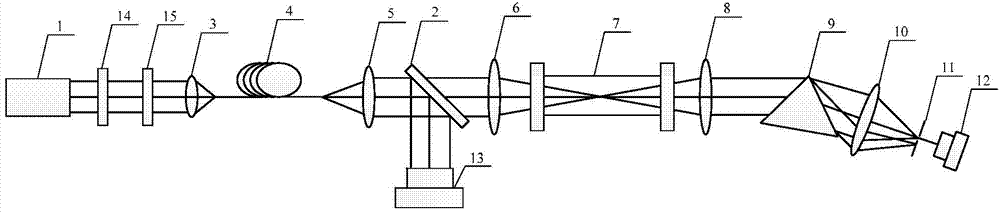
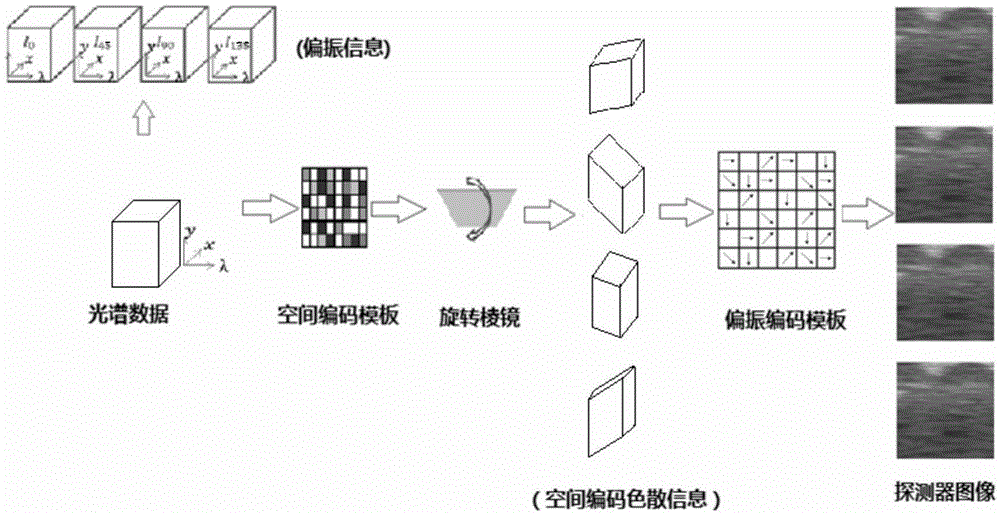
The invention provides an optical intelligent perception multidimensional imaging system comprising a preset lens, a space coding template, a dispersing prism, a polarization coding array and a detector. The units are successively arranged on a same optical axis. The preset lens generates a primary image plane; the space coding template is arranged at the primary image plane; the dispersing prism carries out 0-degree, 90-degree, 180-degree, and 270-degree rotation by being perpendicular to the optical axis; and the polarization coding array is a polarization coding membrane placed on the surface of the detector at a certain distance. With the system, integrated low-data-rate low-limiting intelligent perception imaging and high-quality consensus map reconstruction of multidimensional information containing space, spectrum, and polarization and the like can be realized.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light beam coupling device
The invention discloses a light beam coupling device. The light beam coupling device comprises: at least two emitting mechanisms, wherein the emitting mechanisms are used for emitting light beams, and the different emitting mechanisms are used for emitting light beams with different prescribed wavelengths; an adjusting mechanism, which is arranged in a light beam emitting direction of the emitting mechanisms and is used for adjusting directions of light beams so that light beams emitted from the emitting mechanisms are emitted in a prescribed direction; and a beam combining mechanism, which is a dispersing prism and is arranged in the light beam transmission direction of the adjusting mechanism, wherein the dispersing prism is used for receiving all light beams from the adjusting mechanism and adjusting incoming angles of the light beams different in wavelength so that the light beams are combined to be a whole light beam when being refracted to be sent out. The light beam coupling device, with the structural design, is capable of effectively coupling light beams different in wavelength.
Owner:LIHE TECH (HUNAN) CO LTD
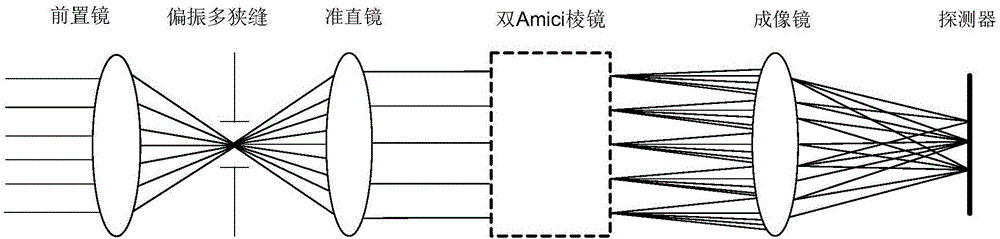
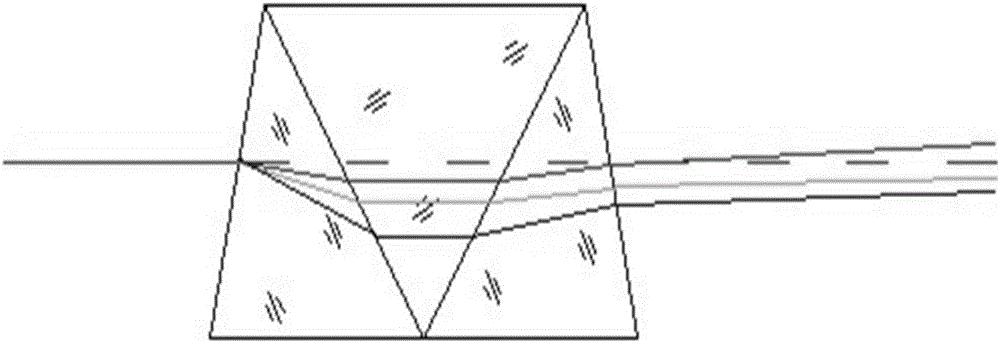
Multi-slit polarization imaging spectrometer based on Amici prism splitting
ActiveCN106840403AAchieve multi-polarization acquisitionImprove energy utilizationPolarisation spectroscopyOptical radiationWide field
The invention discloses a multi-slit polarization imaging spectrometer based on Amici prism splitting. The multi-slit polarization imaging spectrometer consists of a prepositive teleobjective, polarizing multi-slits, a collimating lens, double Amici prisms, an imaging lens and a detector. An infinite target scene is imaged on a single image plane through the prepositive teleobjective by optical radiation, the single image plane is provided with the polarizing multi-slits, beams emit in parallel from the collimating lens for splitting by the double Amici prisms through the polarizing multi-slits, the split beams get through the imaging lens, and polarizing spectral information of the target scene is obtained by the detector. The double Amici prisms are composed of three dispersive prisms in type of symmetric prisms, and the polarizing multi-slits are of three-slit structure. The multi-slit polarization imaging spectrometer achieves a wider field range with the combination of the polarizing multi-slits and the double Amici prisms. A single exposure can directly obtains the three pieces of polarization information of the target scene, and septuple space information of the target scene can be achieved with push-scanning of the whole apparatus.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring nonlinear absorption curve of material
ActiveCN106248636ADoubling the frequencyAchieve laser outputTransmissivity measurementsNonlinear absorptionCcd camera
The invention discloses a method for measuring the nonlinear absorption curve of a material. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining required single-wavelength laser by adopting a crystal frequency multiplication system and a dispersing prism, improving the intensity of incident laser through a long focal length lens, recording the energy and the incident laser and the dimension of light spots through adopting a scientific grade CCD camera, and measuring the energy of emergent laser through an energy meter to obtain the nonlinear absorption curve of a sample to be measured. The method for measuring the nonlinear absorption curve of the material improves the measuring range of the nonlinear absorption curve, simplifies a nonlinear absorption curve measuring system, and realizes multi-wavelength, wide-range and high-precision measurement of the nonlinear absorption curve.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
SPR detection device and SPR detection method using optical dispersion
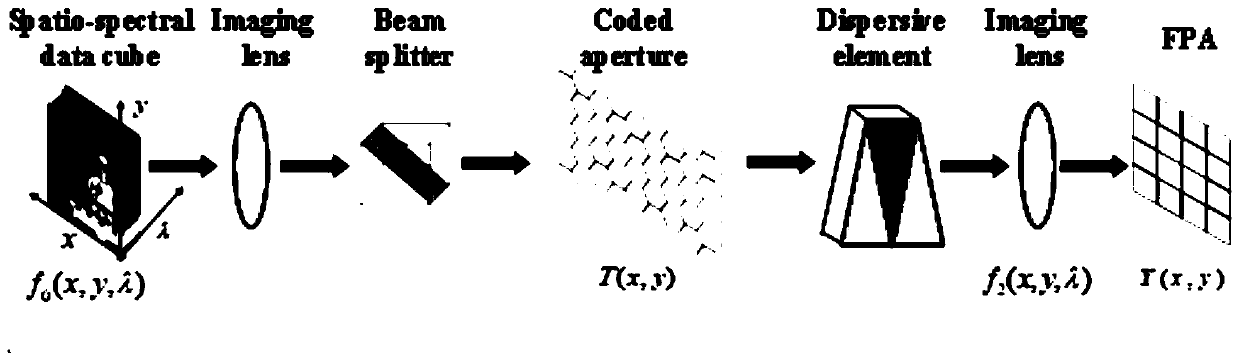
InactiveCN109738395AImprove detection accuracyRealize multi-channel detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansImage detectionMetal
The invention discloses an SPR detection device using optical dispersion. The SPR detection device comprises a wide-spectrum light source, a prism and a detection component, wherein an incident side component is arranged between the wide-spectrum light source and the prism, a correction component is arranged between the prism and the detection component, and a detection chip is arranged on the reflective bottom surface of the prism; the detection chip comprises a gold film and a flow cell, a channel is arranged on one side surface of the flow cell facing the gold film, the gold film covers theflow cell, and the gold film is positioned between the flow cell and the reflective bottom surface of the prism; and the detection component comprises a dispersion prism and a detector, wherein the dispersion prism is used for dispersing the reflected light corrected by the correction component, and the detector is used for recording the spectrum of the reflected light dispersed by the dispersionprism. The invention also discloses a multi-channel SPR detection method using optical dispersion. According to the SPR detection device and the SPR detection method using optical dispersion disclosed by the invention, the wide-spectrum light source is used to perform one-time imaging detection on the complex refractive index of a metal film, so that the requirements of multi-channel detection can be met.
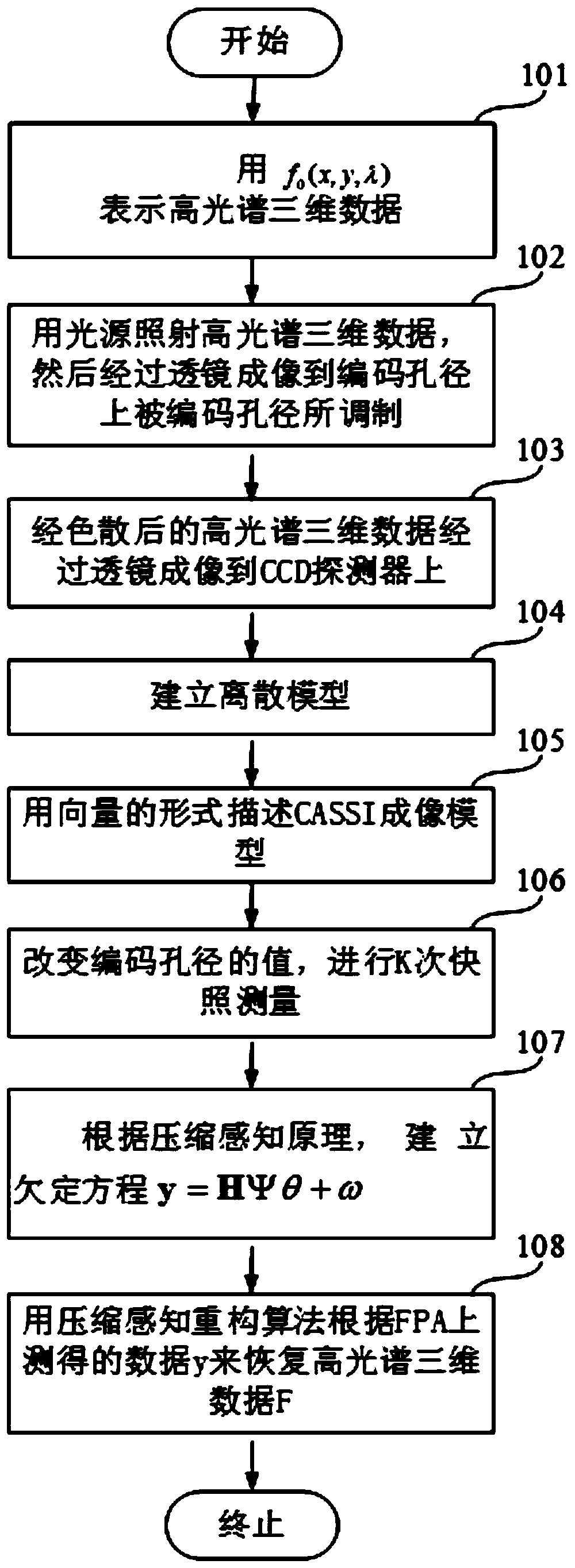
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Spectral imaging method adopting special-shaped blue noise coding aperture
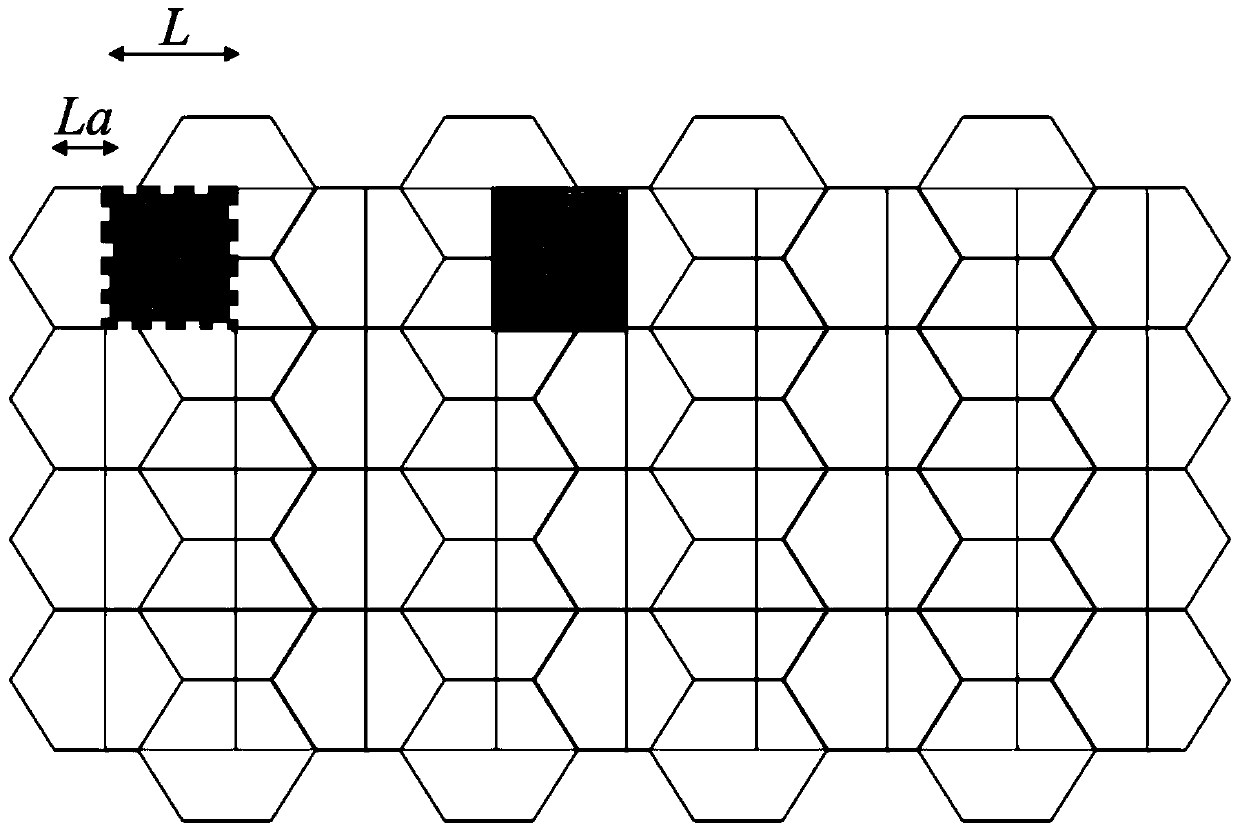
ActiveCN109798978AImprove reconstruction qualityIncrease freedomRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationHoneycombDegrees of freedom
The invention provides a spectral imaging method adopting a special-shaped blue noise coding aperture. The spectral imaging method adopting the special-shaped blue noise coding aperture specifically comprises the following steps: irradiating a target to be imaged with a light source to obtain hyperspectral three-dimensional data, wherein the hyperspectral three-dimensional data are imaged on a hexagonal blue noise coding aperture through a lens and modulated by the coding aperture, and the modulated hyperspectral three-dimensional data are dispersed through a dispersion prism and then imaged on a CCD detector through the lens; and recovering the hyperspectral three-dimensional data of the target to be imaged by utilizing the data detected on the CCD detector. According to the spectral imaging method adopting the special-shaped blue noise coding aperture, in the coding aperture, hexagonal pixels are used for replacing square pixels to form a honeycomb array, because the pixels of the coding aperture are hexagonal, the pixels of a focal plane are rectangular, geometric dislocations exist between the coding aperture and the focal plane, a mathematically equivalent rectangular gray-scale coding aperture is generated by the geometric dislocations, the degree of freedom of modulation is increased, and the reconstruction quality is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for synthesizing femto-second grade ultrashort pulses based on cerenkov radiation
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing femto-second grade ultrashort pulses based on cerenkov radiation. The method includes the steps that 1, a reference light path is established, non-linear crystals are put on a six-dimension rotary horizontal-movement platform, the angle of the non-linear crystals is adjusted by rotating the six-dimension rotary horizontal-movement platform, and therefore non-linear cerenkov radiation occurs on the inner surfaces of the non-linear crystals; 2, according to the reflecting angle of incident laser on the inner surfaces of the non-linear crystals, the non-linear cerenkov radiation angle of each level of frequency doubling light in the crystals is determined; 3, fundamental frequency light, double frequency light, triple frequency light, quadruplicated frequency light, quintuple frequency light and higher-order frequency-doubling light generated by the incident laser emerge at own radiation angles, and are modulated by an amplitude type liquid crystal light modulator and a phase type liquid crystal light modulator, parallel transmission directions of all orders of light waves are changed into converging transmission directions through a second dispersing prism, and the light waves are synthesized into one beam of femto-second grade ultrashort pulses through a third dispersing prism. With the method, the synthesizing process of femto-second grade light wave is achieved, efficiency is high, and fidelity is high.
Owner:中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所
Dispersion photovoltaic power generation system
InactiveCN106887997AHigh outputPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationQuantum efficiencyFull-spectrum light
The invention discloses a dispersion photovoltaic power generation system. The system comprises a dispersion prism used for dispersing the sunlight into the scattered light different in spectral range; and a photovoltaic power generation device used for respectively receiving the scattered light different in spectral range. The solar energy is provided with the full-spectrum light, and the light is dispersed by the dispersion prism. The dispersed light is divided into multiple wave bands. For different wave bands, photovoltaic power generation devices of different maximum quantum efficiencies are selected for power generation. Therefore, the light energy is maximally utilized and converted into electric energy. As a result, the light energy is converted into the electric energy to the maximum extent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINKO SOLAR CO LTD +1
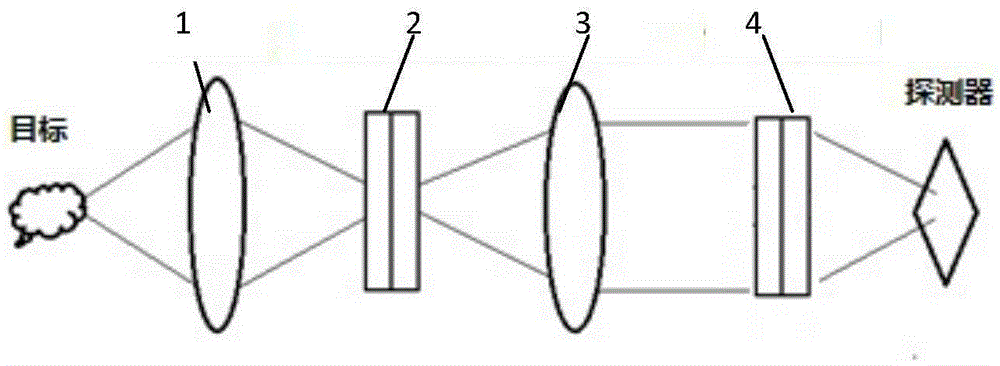
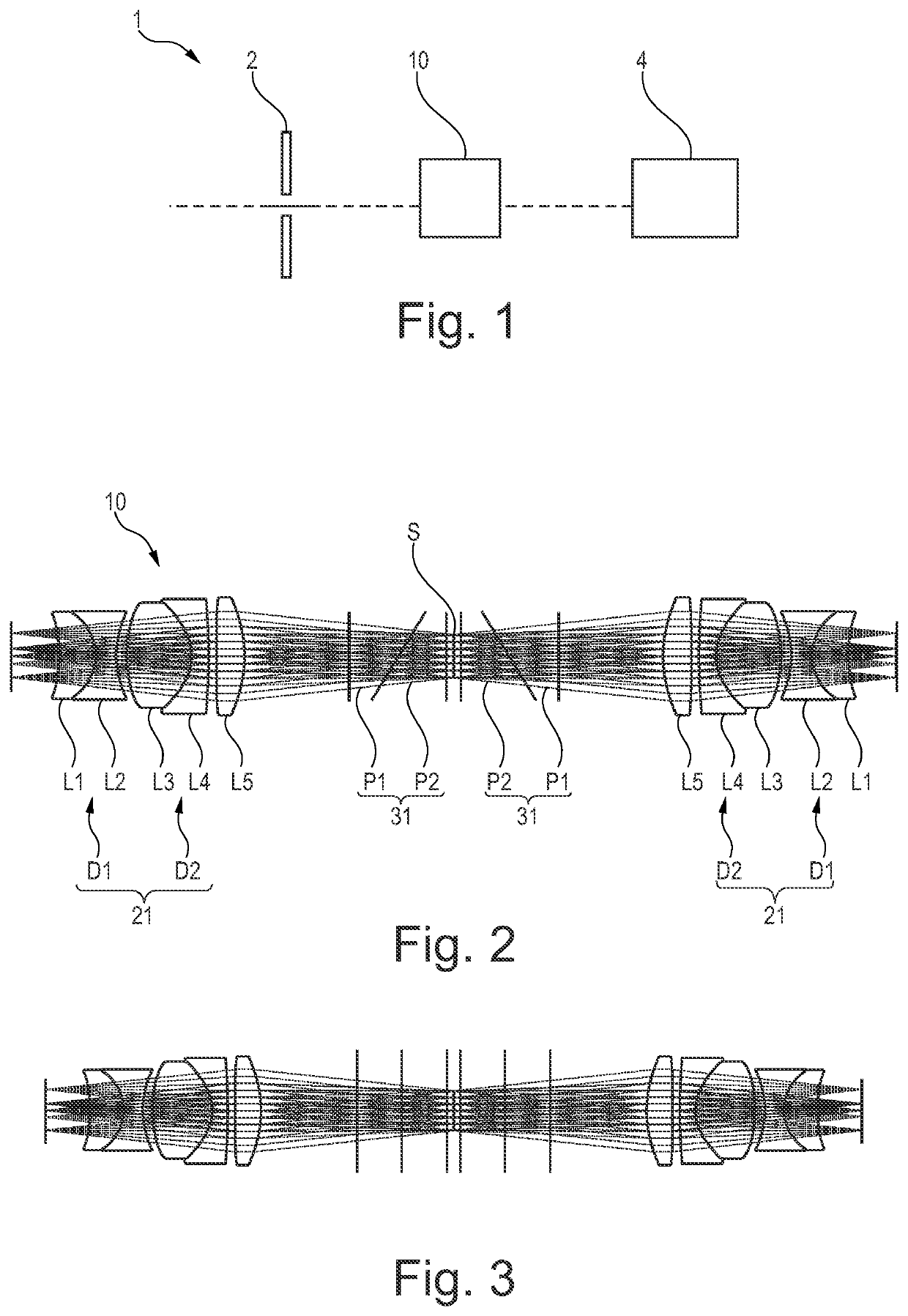
Optical Relay System
PendingUS20220187511A1Improve imaging clarityImprove clarityPrismsSpectrum generation using refracting elementsCompound prismEngineering
A spectrally shearing optical relay system, said relay system being comprised of two halves disposed symmetrically about an aperture stop S, wherein each half comprises a plurality of rotationally symmetric optical elements forming an objective and a com-pound prism comprised of a plurality of dispersing prisms. The compound prisms are located between the objectives and the aperture stop. An imaging device with such an optical relay system is also proposed.
Owner:LIVING OPTICS LTD
Novel high-sensitivity spectrum detection device for detecting GIS characteristic gas
PendingCN111289467AResolve interferenceSolve agingColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterLine width
The invention relates to the electrical field, in particular to a novel high-sensitivity spectrum detection device for detecting GIS characteristic gas. The novel high-sensitivity spectrum detection device comprises a high-power narrow-linewidth optical parametric oscillator assembly, an intermediate light path and dispersion unit assembly and a signal monitoring assembly, wherein the high-power narrow-linewidth optical parametric oscillator assembly is arranged in a case, and comprises an optical fiber amplifier, a beam expander, a focusing lens, a ring cavity lens, an F-P etalon, an opticalparametric oscillator and a pump laser source; the intermediate light path and dispersion unit assembly comprises a dichroscope, a beam splitter, a wavelength meter, two reflectors, two gold-plated mirrors, two silver-plated mirrors and a dispersion prism; and the dispersion prism can be specifically implemented as an equilateral dispersion prism; and the signal monitoring assembly comprises a gaspool and a photoacoustic analyzer, and the photoacoustic analyzer is placed in the gas pool.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Echelle grating spectrometer, atomic emission spectrometer and spectrum testing method
InactiveCN102879091BFulfill performance requirementsQuick measurementEmission spectroscopyAnalysis by thermal excitationLow noiseGrating
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A fast-start mid-infrared laser and corresponding polycrystal switching device
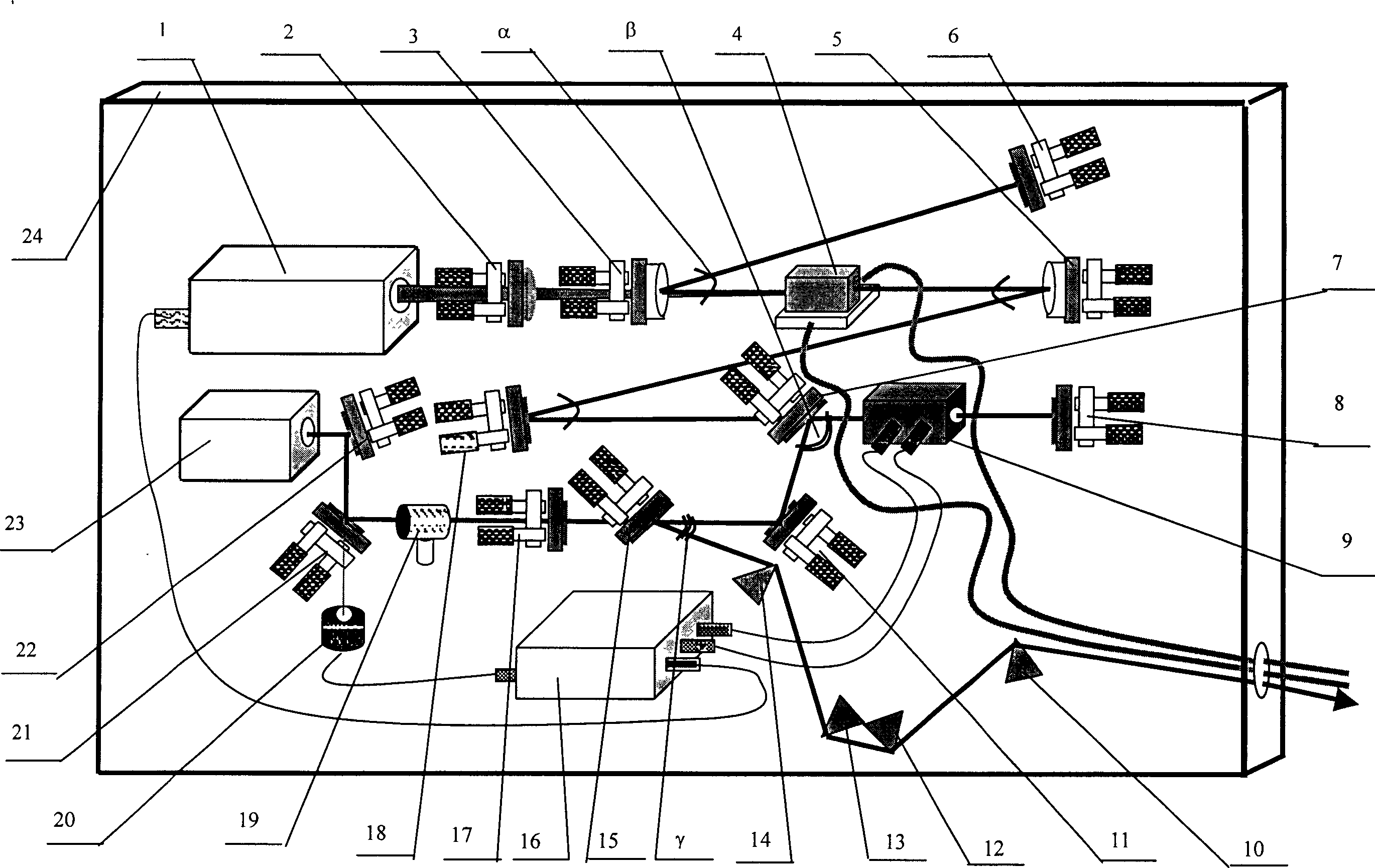
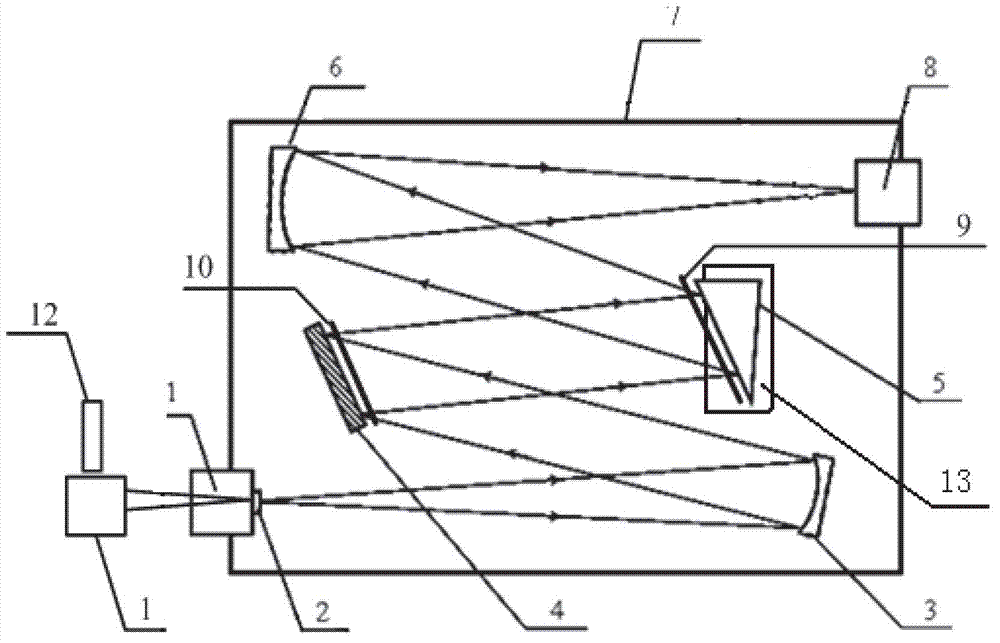
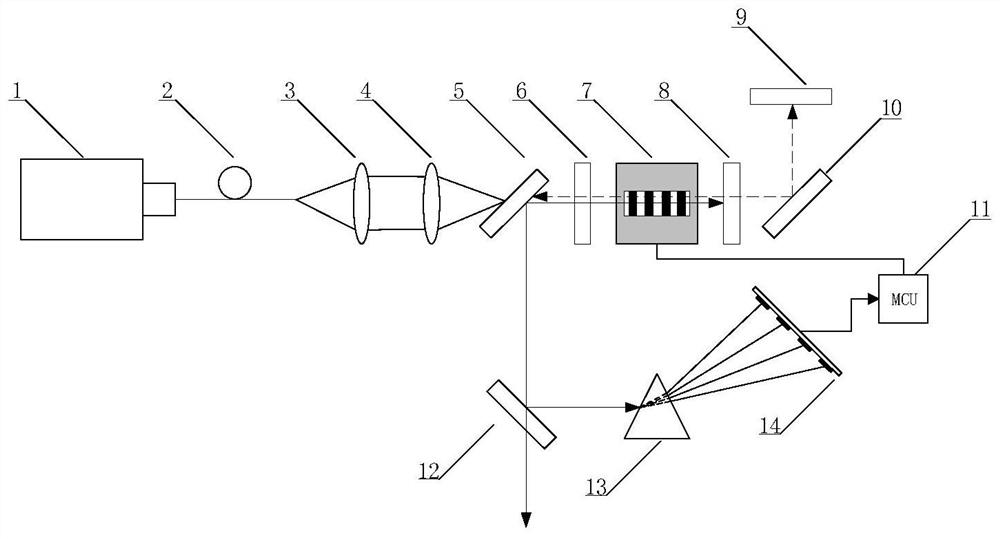
The present disclosure discloses a fast-start mid-infrared laser and a corresponding polycrystal switching device. The laser cavity is provided with an 813nm semiconductor laser, an energy transmission fiber, a first focusing mirror, a second focusing mirror, a third A 45-degree beam splitter, a mid-infrared parametric light output mirror, a polycrystal switching device, a mid-infrared parametric light total reflection mirror, and a second 45-degree beam splitter; the laser refracting cavity is placed with a 1084nm fundamental frequency light total reflection Mirror, third 45-degree beam splitter, dispersive prism, photosensitive element and single-chip microcomputer, 1084nm fundamental frequency light total reflection mirror is opposite to the second 45-degree beam splitter; the third 45-degree beam splitter is separated from the first 45-degree beam The positions of the beam mirrors correspond, the dispersive prism corresponds to the position of the third 45-degree beam splitter; the photosensitive element corresponds to the position of the dispersive prism; the single-chip microcomputer is connected with the photosensitive element and the polycrystal switching device.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com