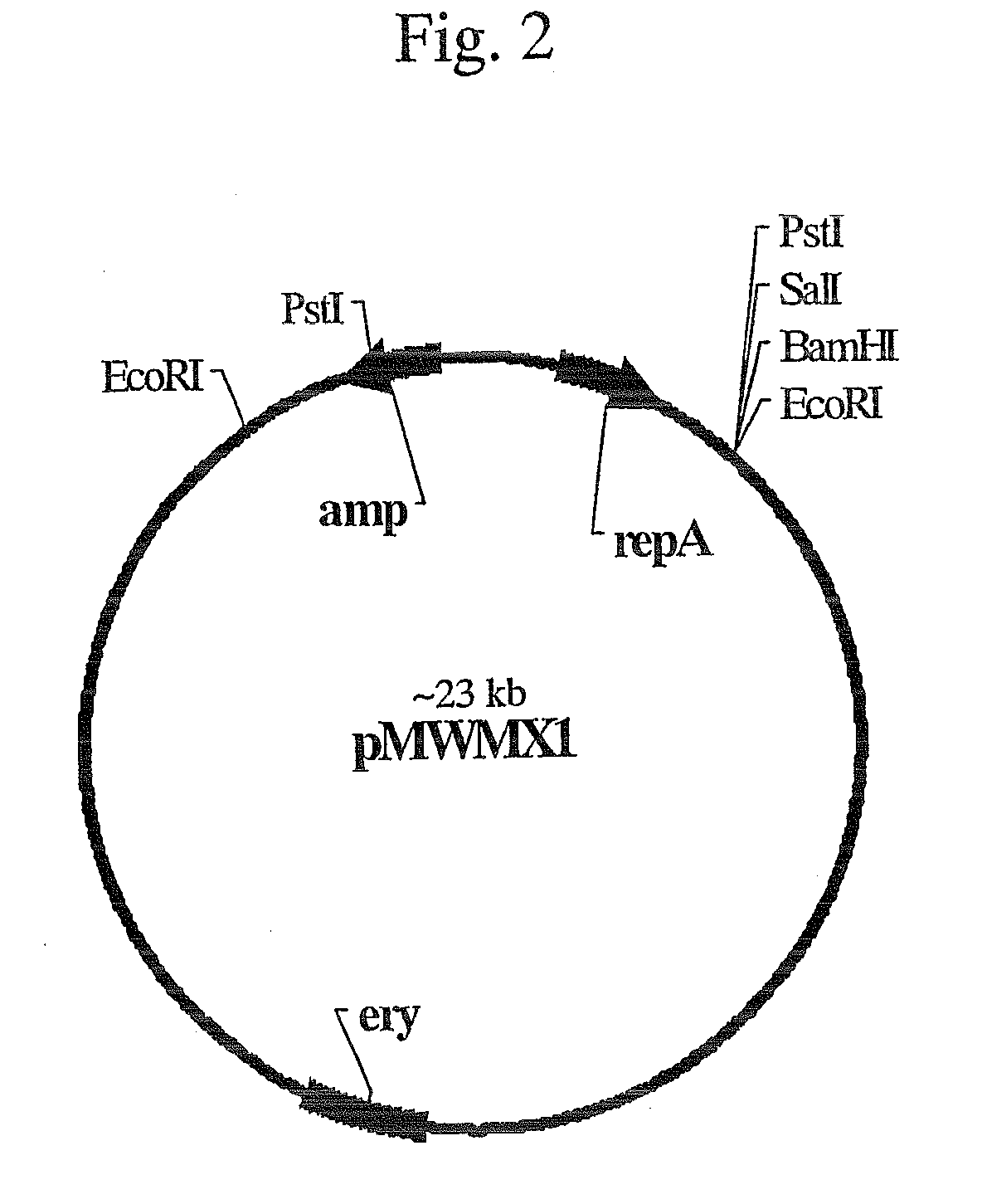
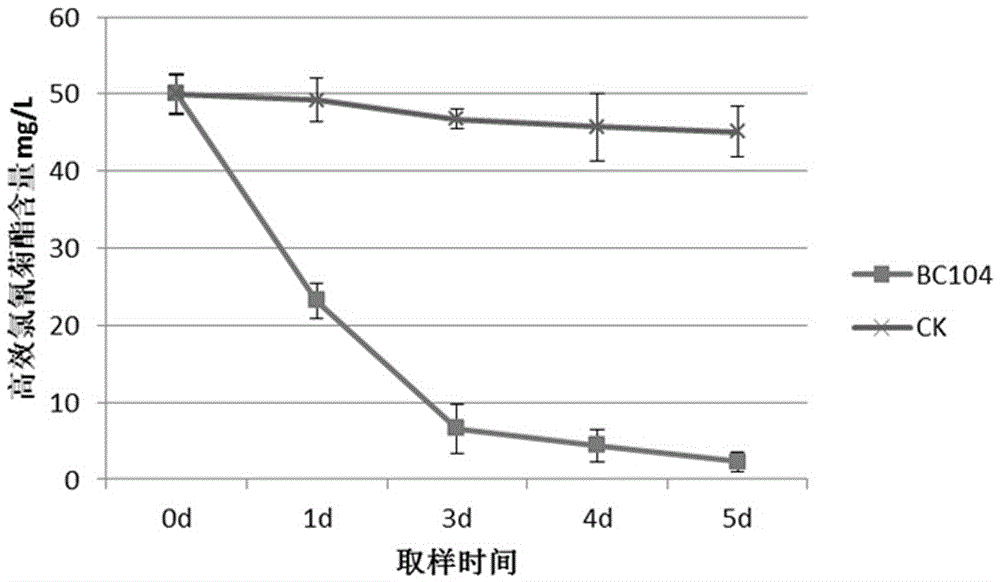
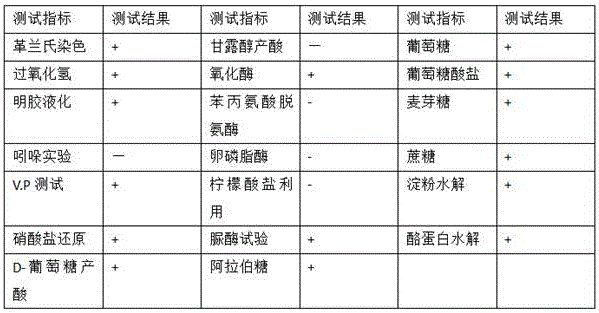
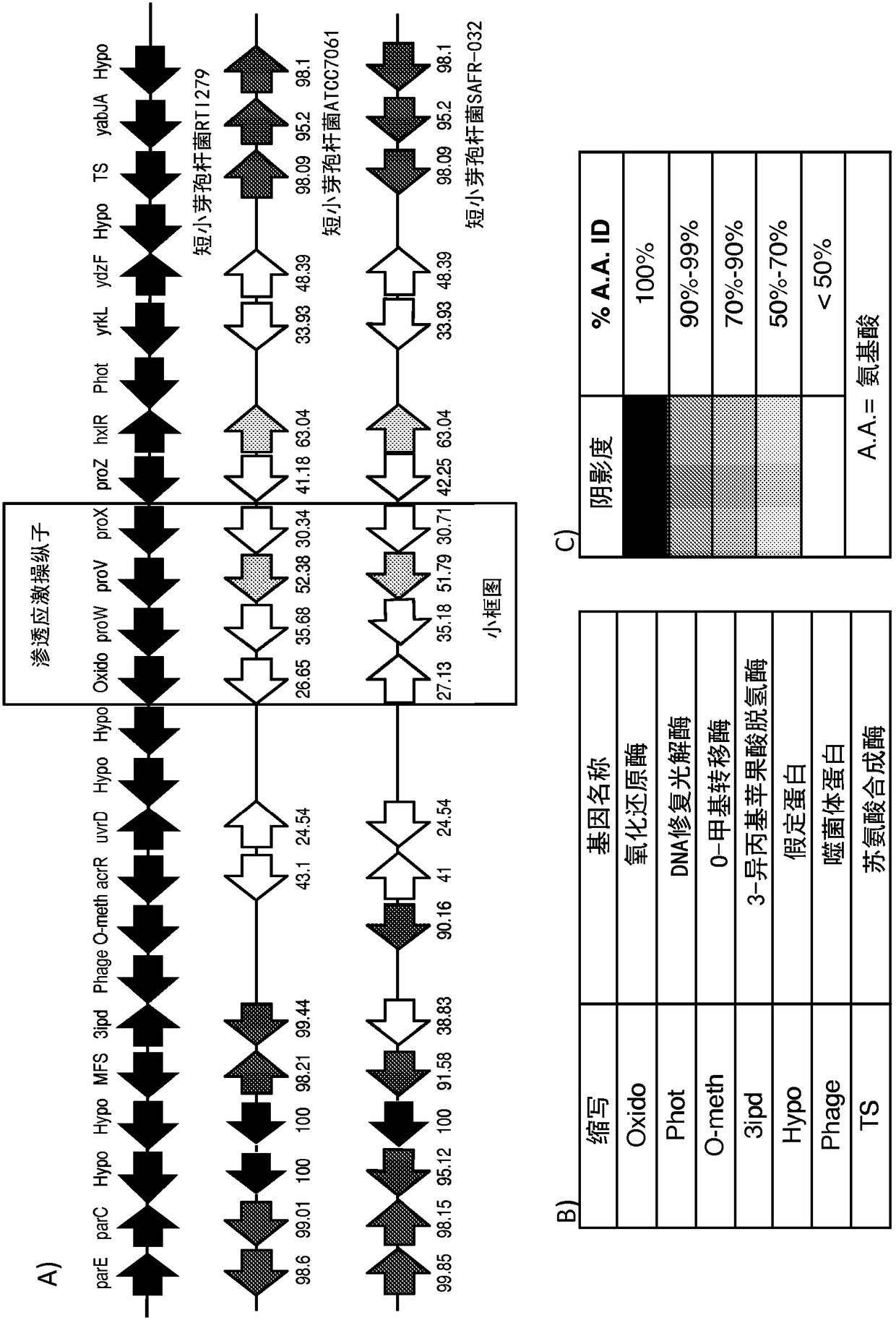
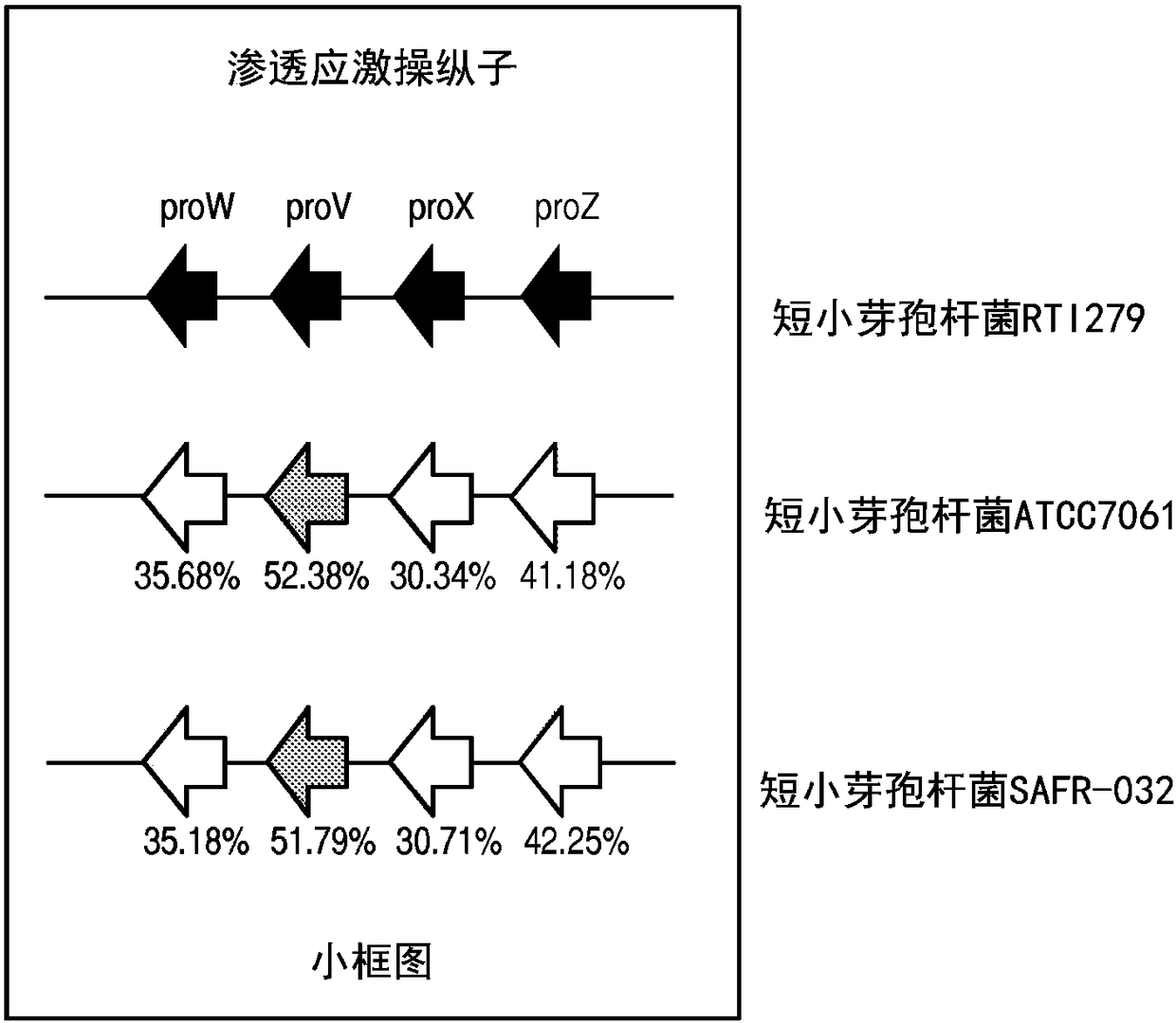
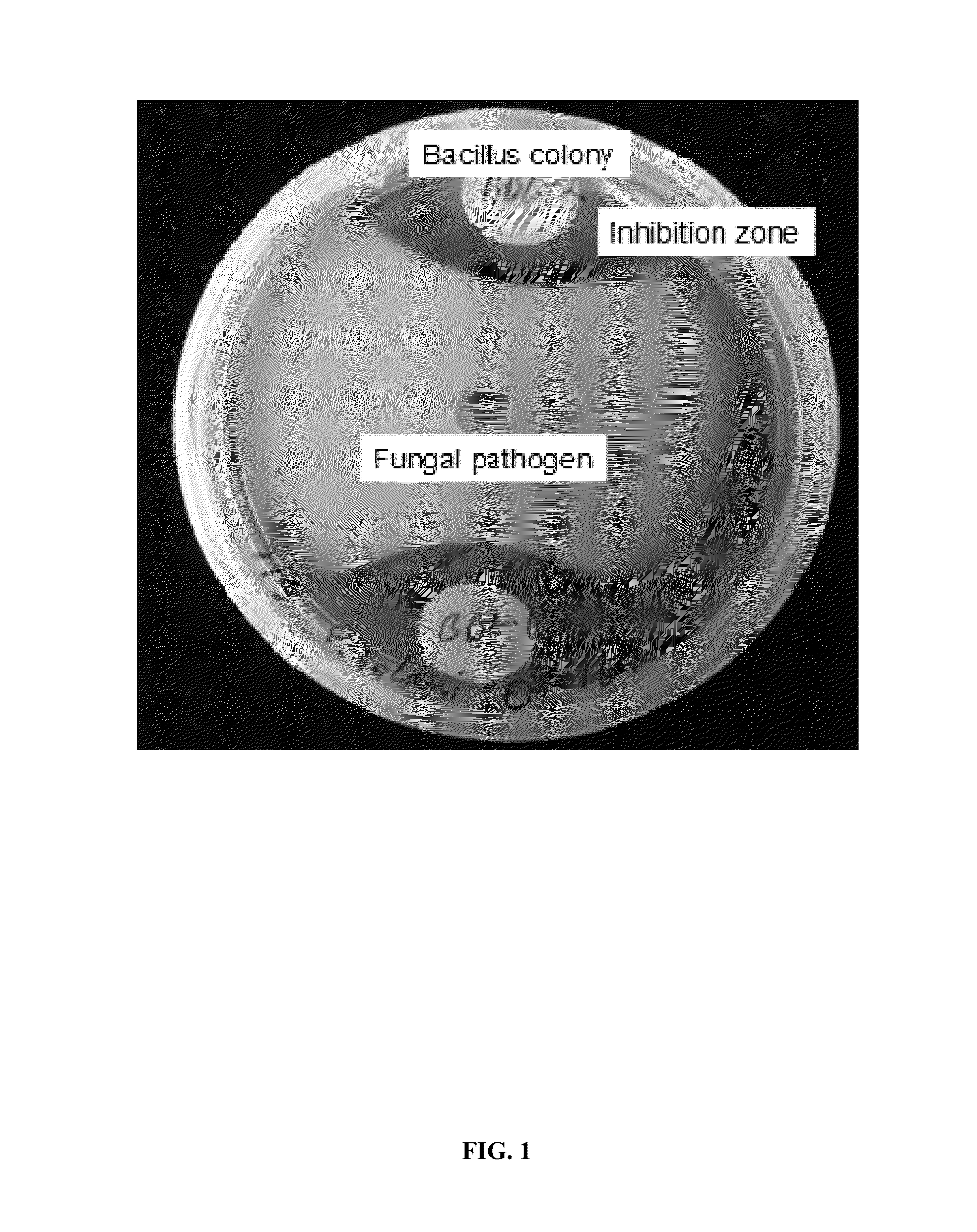
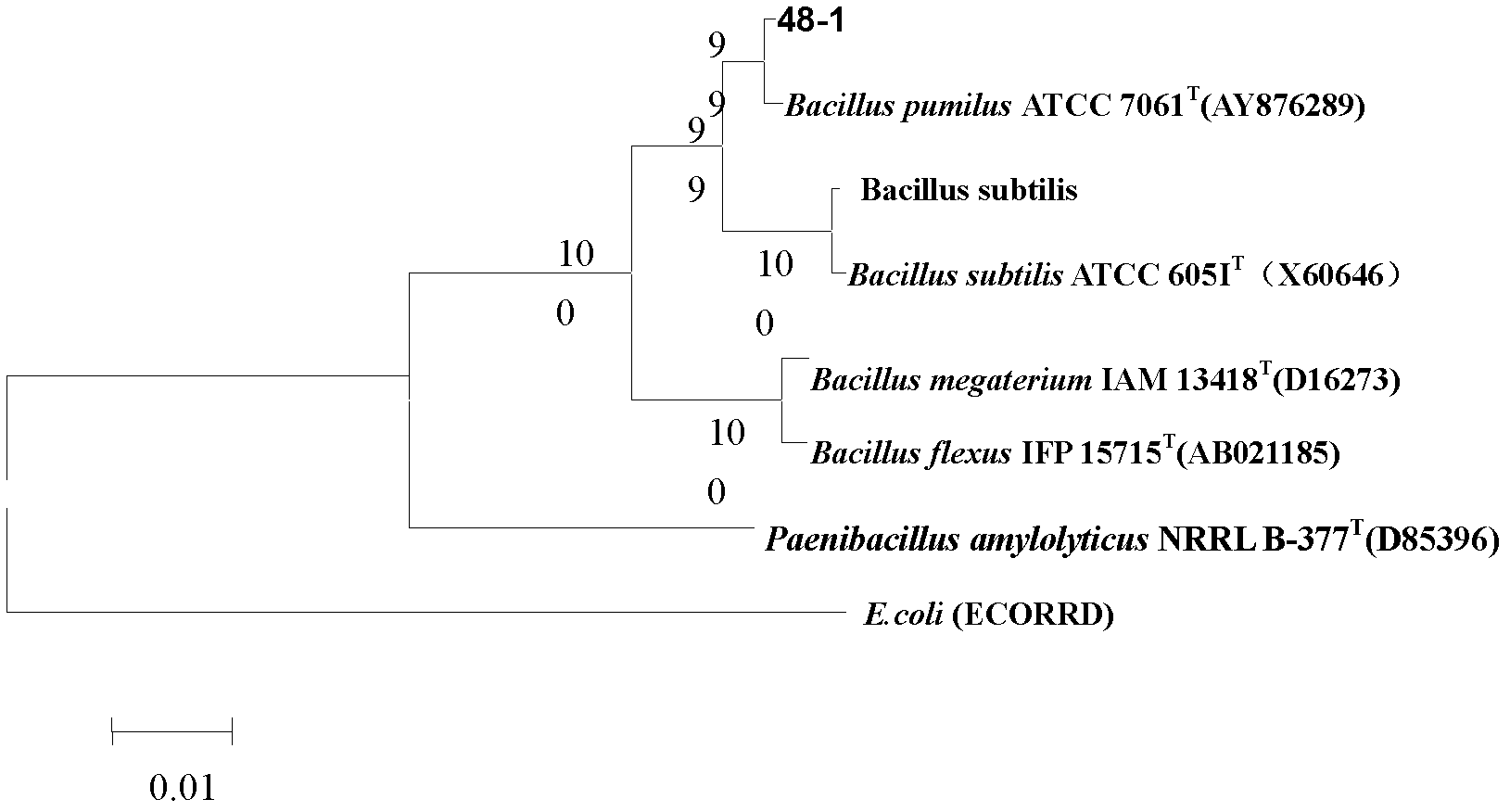
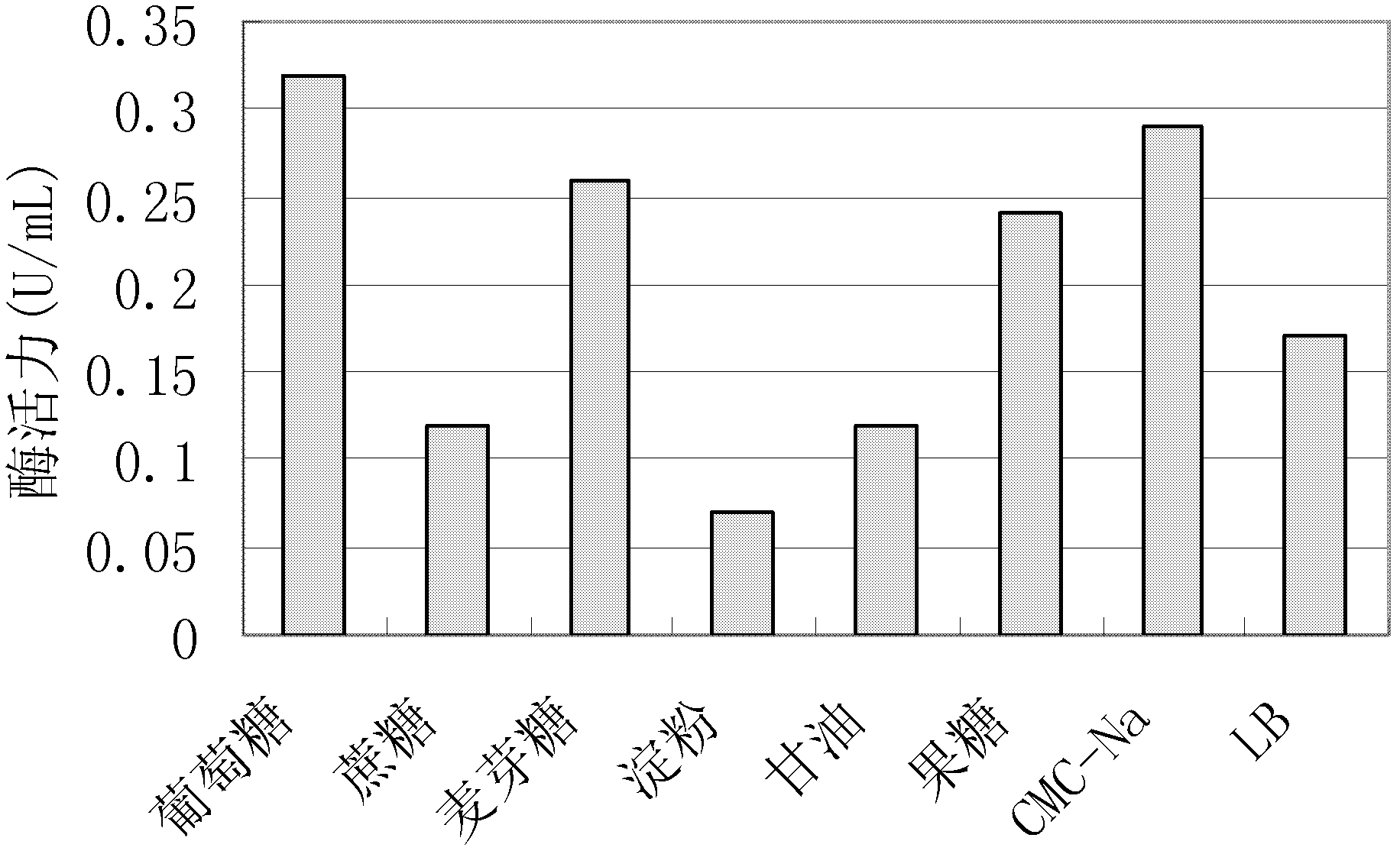
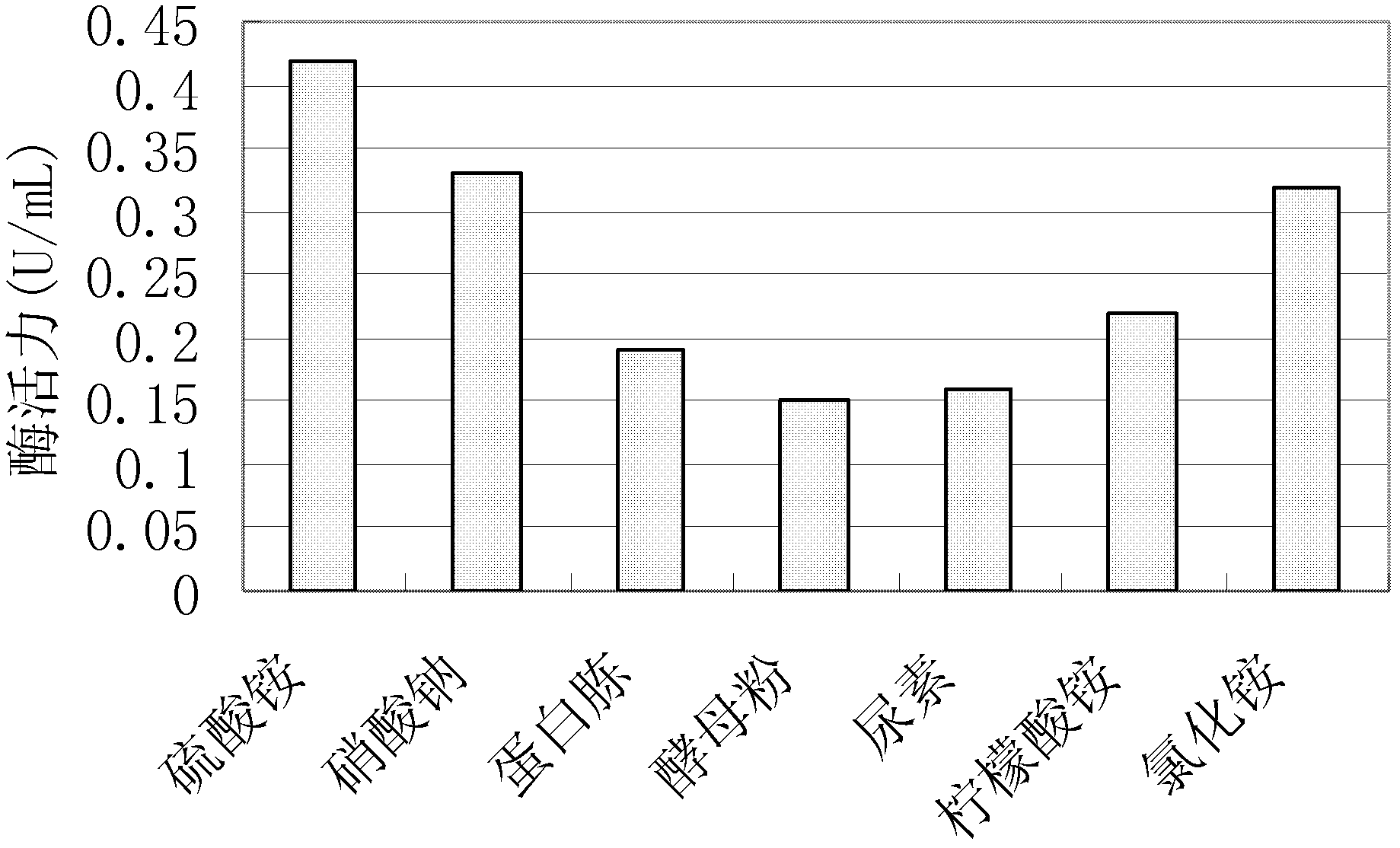
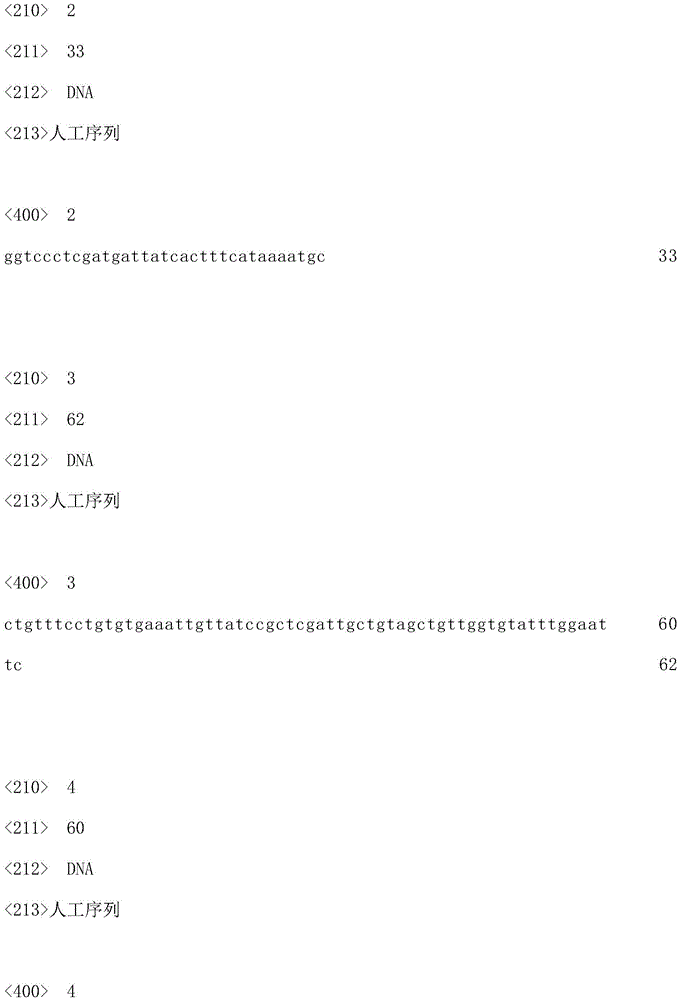
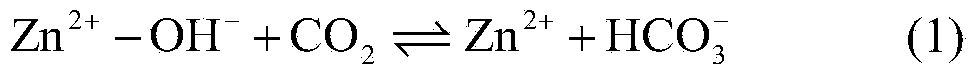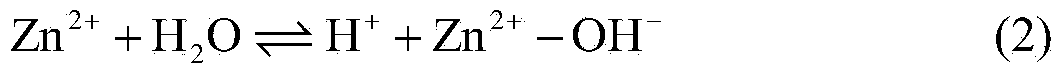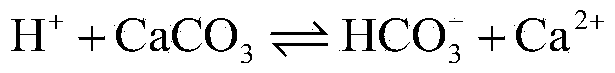Patents
Literature
211 results about "Genus Bacillus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
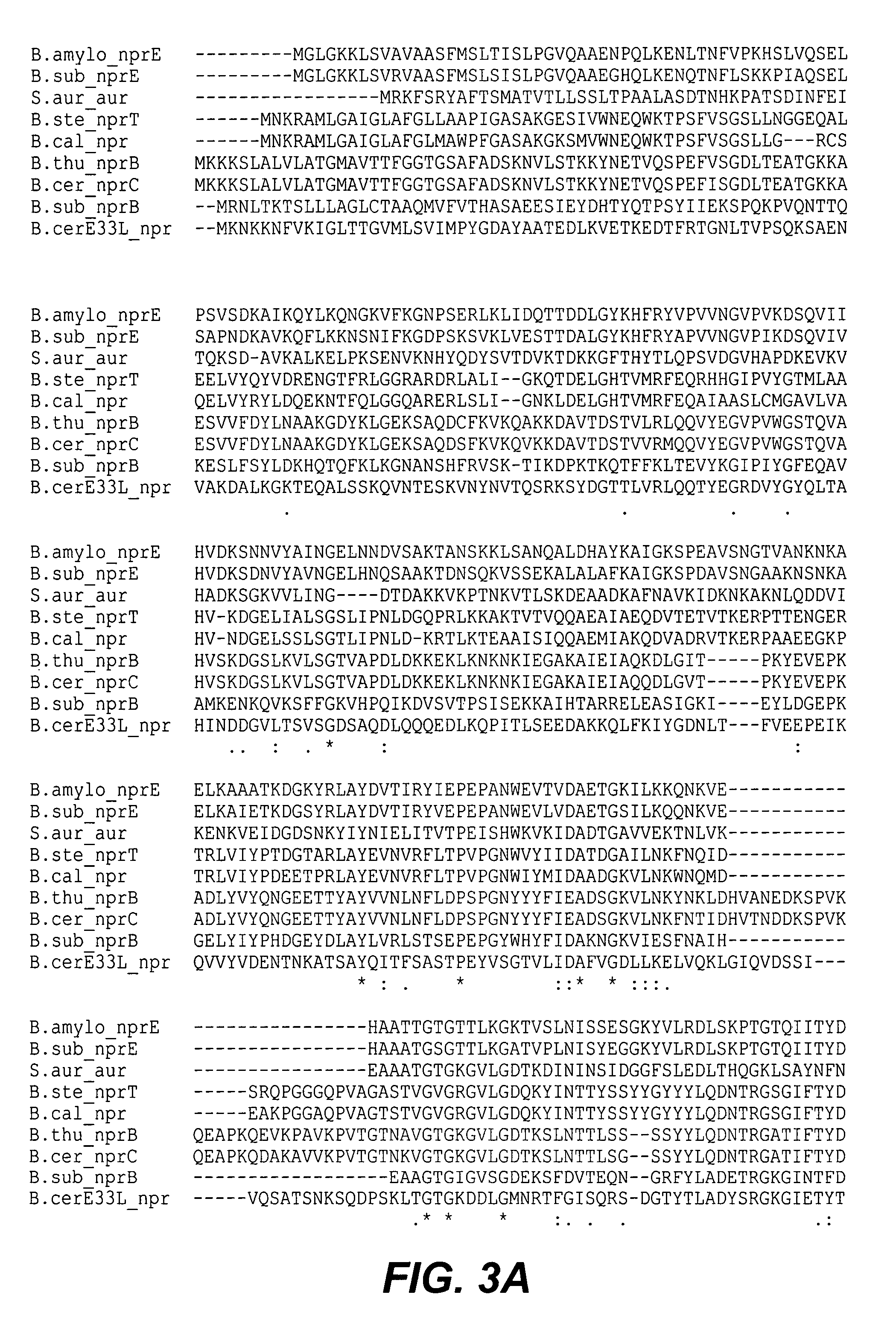
Use and production of storage-stable neutral metalloprotease
InactiveUS20080293610A1Good storage stabilityImprove performanceBacteriaFermentationBiologyGenus Bacillus
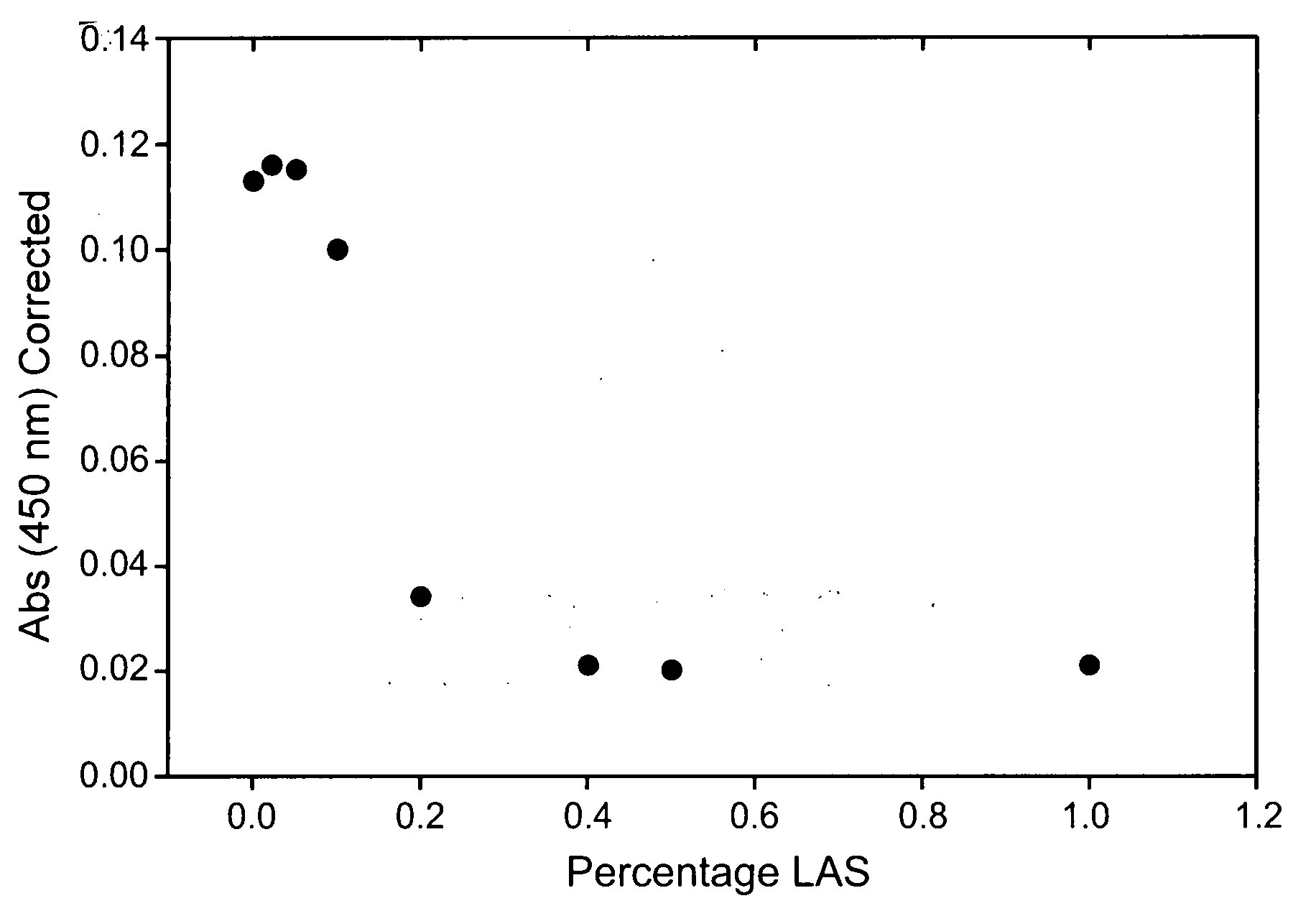
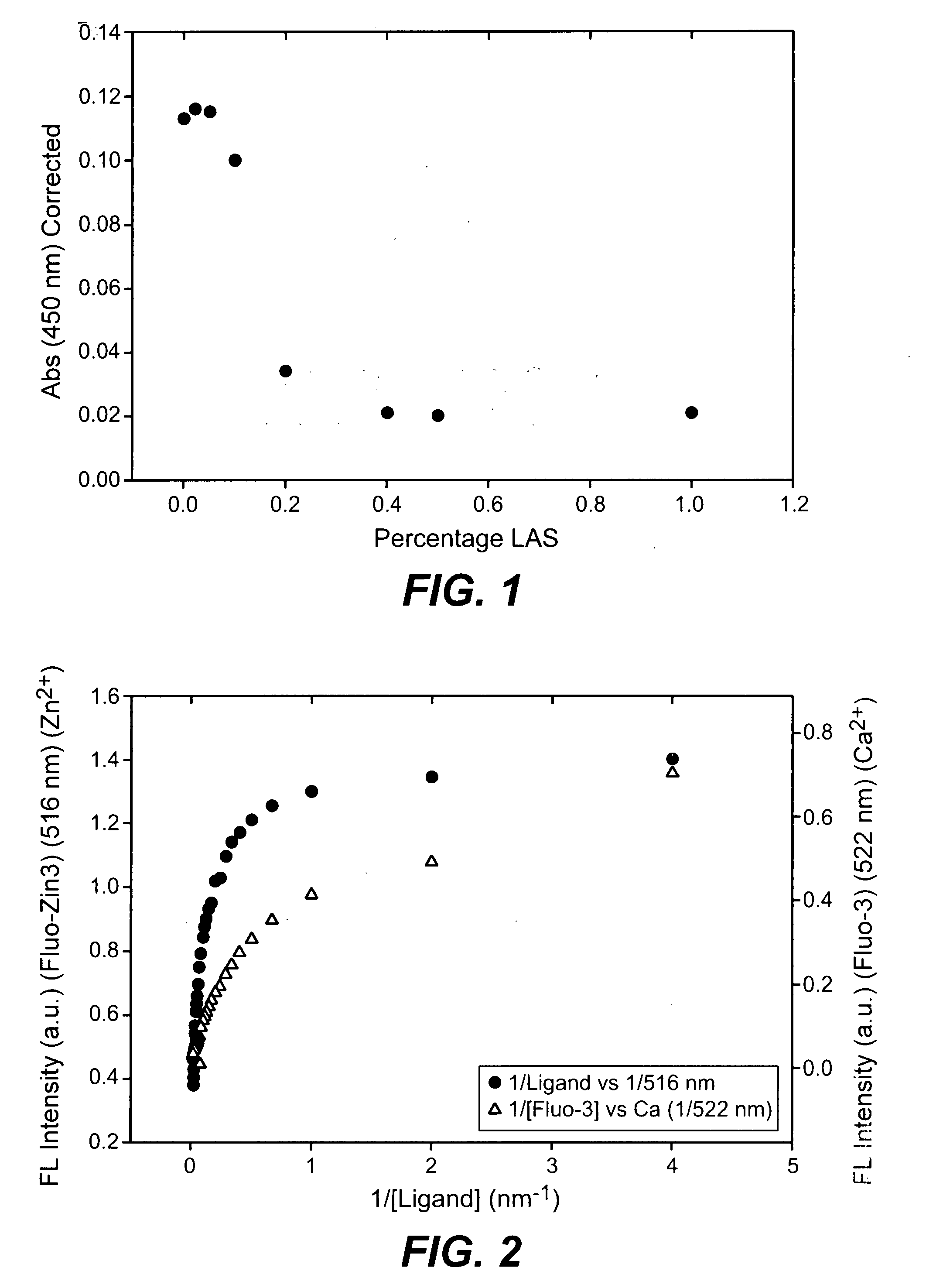
The present invention provides methods and compositions comprising at least one neutral metalloprotease enzyme that has improved storage stability. In some embodiments, the neutral metalloprotease finds use in cleaning and other applications. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions comprising neutral metalloprotease(s) obtained from Bacillus sp. In some more particularly preferred embodiments, the neutral metalloprotease is obtained from B. amyloliquefaciens. In still further preferred embodiments, the neutral metalloprotease is a variant of the B. amyloliquefaciens neutral metalloprotease. In yet additional embodiments, the neutral metalloprotease is a homolog of the B. amyloliquefaciens neutral metalloprotease. The present invention finds particular use in applications including, but not limited to cleaning, bleaching and disinfecting.
Owner:DANISCO US INC +1
Microbial fermenting agent
InactiveCN1624100APromote growthImprove disease resistanceFungiBacteriaPenicillium bilaiaeStreptomyces
A microbial leaven used for preparing organic or microbial fertilizer from organic waste is prepared from at least two of nine microbes. Aspergillus, Sporotrichun, Mucoraceae, Penicillium sp, Ceotrichum sp., Neurospora, Bacillus, Saccharomyces and Streptomyces sp.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of biogas residue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103848698AWon't burnDecompose thoroughlyBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelMicrobial agentPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological organic fertilizer prepared by aerobic fermentation of a biogas residue and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing the biogas residue and a swelling agent to form a fermentation raw material, inoculating a compound microbial agent in the fermentation raw material, uniformly mixing for fermenting, and adding urea, diammonium phosphate, a potassium chloride inorganic salt, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhiza fungi, silicate bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria acetic bacteria, bifidobacterium, and saccharomycetes after the fermentation is completed to prepare the biological organic fertilizer, wherein the compound microbial agent comprises strains of bacillus, pseudomonas, staphylococcus, streptomyces, penicillium, aspergillus and trichoderma. The compound microbial agent prepared by using the biological organic fertilizer has a pertinence to aerobic fermentation of the biogas residue, and is capable of effectively increasing the fermentation rate of the biogas residue, shortening the fermentation time and realizing high-additional value production, innocent treatment and recycling of the biogas residue; and the problem of resources and environment of villages and small towns is solved, and the rapid development of construction of new countryside and towns and cities can be promoted.
Owner:青岛福瑞斯生物能源科技开发有限公司
Method and agent for controlling plant disease using bacteria of genus bacillus
This invention provides a control agent or material for biologically controlling plant diseases caused by plant pathogenic bacteria, fungi, or viruses, a method for controlling plant diseases using the same, and bacteria that can be used therefor. Also, this invention relates to a control agent or material for plant diseases comprising bacteria of the genus Bacillus capable of inhibiting infection with or proliferation of plant pathogenic bacteria, fungi, or viruses, the method for applying the same to plants, and bacteria that can be used therefor.
Owner:ITSUKI
Method of controlling plant disease damage by using bacillus and controlling agent
It is intended to provide a controlling agent or a controlling material for biologically controlling plant disease damage caused by a phytopathogenic bacterium, a fungus or a virus; a method of controlling plant disease damage by using the same; and a bacterium usable therein. Namely, a controlling agent or a controlling material for plant disease damage containing a bacterium which belongs to the genus Bacillus and is capable of inhibiting the infection with phytopathogenic bacterium, a fungus or a virus or growth thereof; a method of applying the same to a plant; and a bacterium usable therein.
Owner:株式会社树
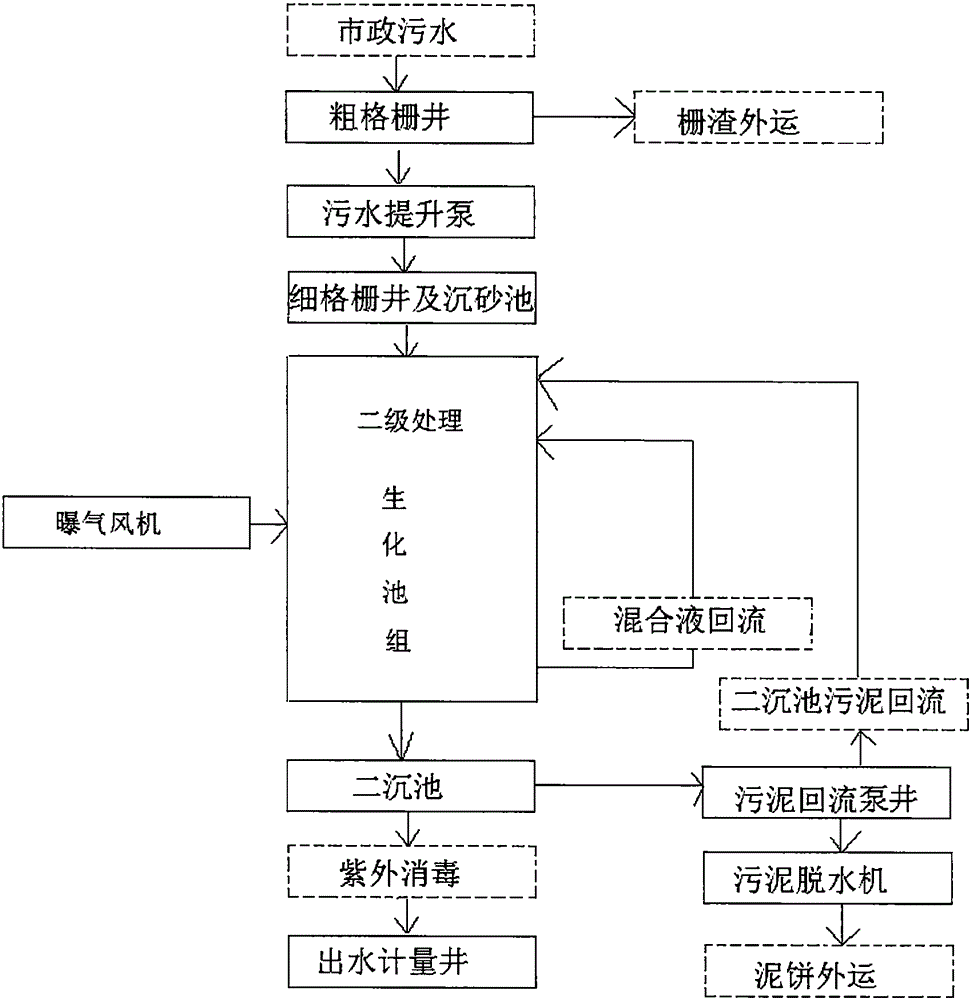
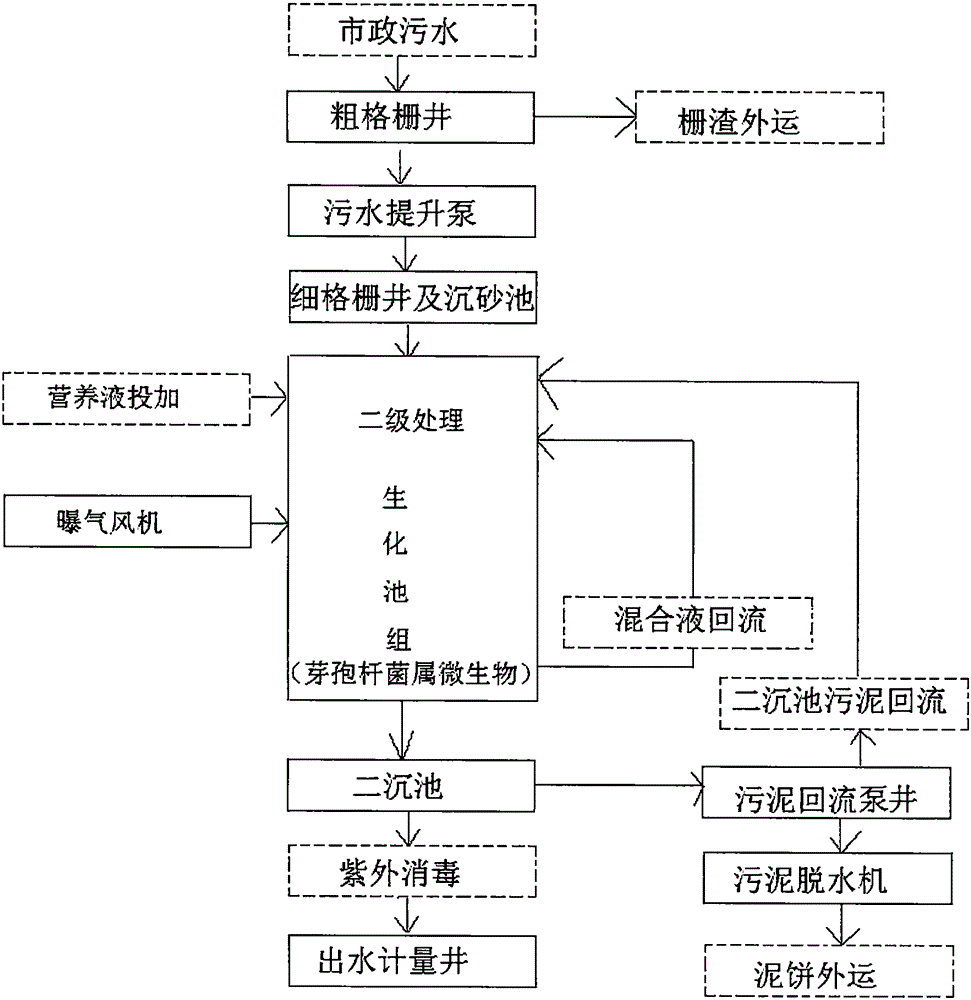
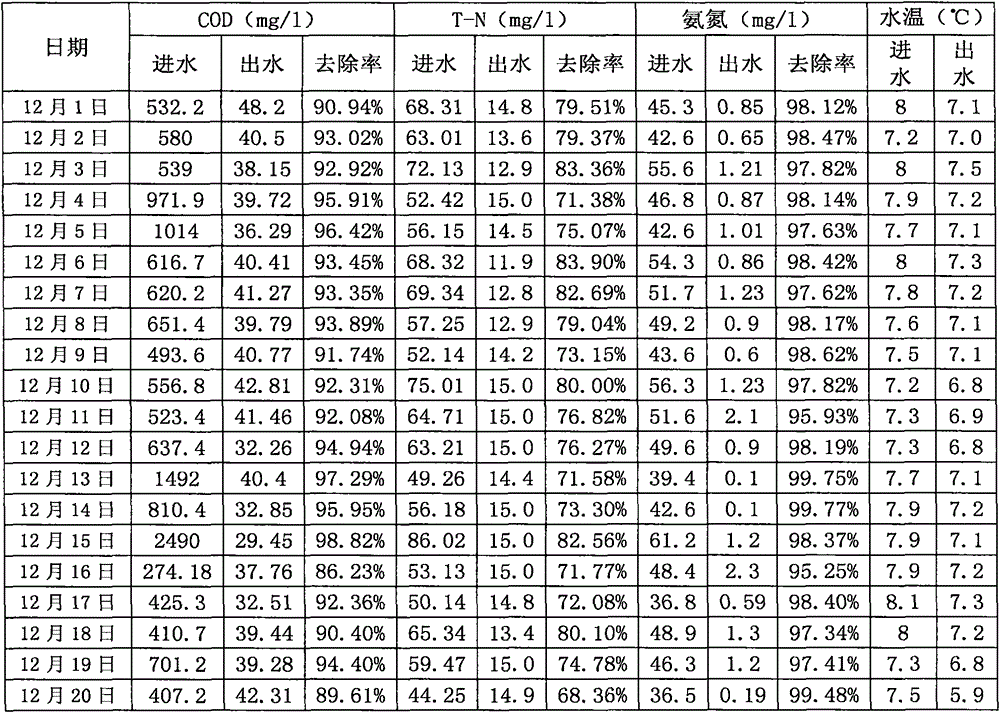
New method of urban sewage treatment
InactiveCN105130126AEfficient nitrogen and phosphorus removal capacityLow investment costMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesWater quality
The invention discloses a new method of urban sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps: 1, sewage enters into a coarse screen well to remove a large volume of pollutants; 2, fine screens of a fine screen well intercept impurities and large particulate matters in the sewage; 3, sediments in the sewage are deposited by a grit chamber; 4, sludge in a secondary sedimentation tank flows backs to the front end of a biochemical pool group, and bacterial flora taking genus bacillus microorganisms as dominant bacteria is added into the biochemical pool group; 5, effluent water of the biochemical pool group flows into the secondary sedimentation tank, and sludge-water separation is performed in the secondary sedimentation tank; 6, effluent water of the secondary sedimentation tank flows into a disinfection system and is discharged by a water metering tank. By adopting the technical scheme of the invention, due to the fact that the bacterial flora taking the genus bacillus microorganisms as the dominant bacteria is added into the biochemical pool group so as to achieve the following beneficial effects that the capability of nitrogen and phosphorus removal is efficient, no extra deodorization system is needed, the cost of investment is greatly reduced, energy conservation and space saving are realized, and the discharged water quality is good.
Owner:柴建中
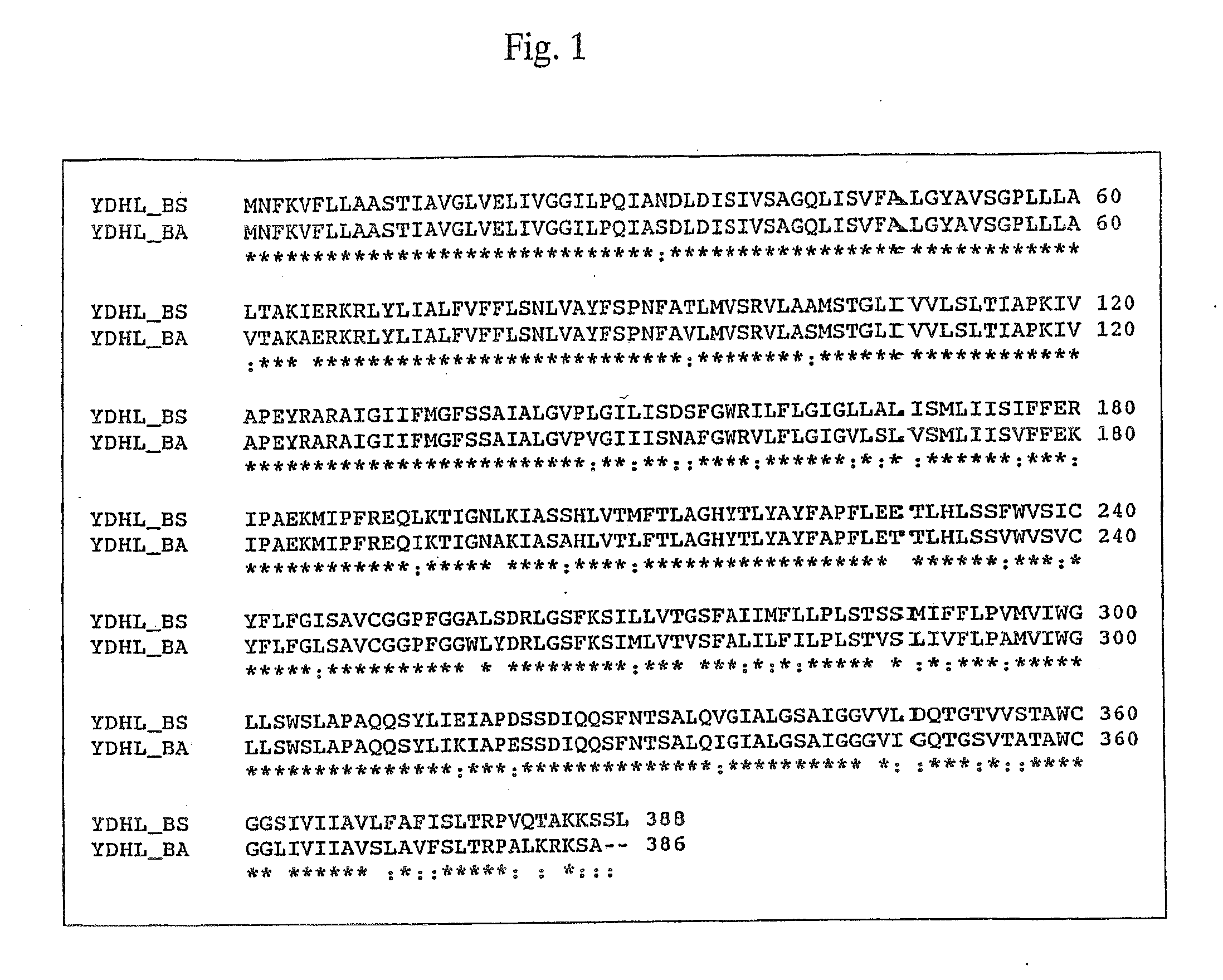
Method for Producing Purine Nucleosides and Nucleotides by Fermentation Using Bacterium Belonging to the Genus Bacillus or Escherichia
Methods for producing purine nucleosides, and purine nucleotides, such as inosine and 5′-inosinic acid are provided which include using a bacterium belonging to the genus Bacillus or to the genus Escherichia wherein the purine nucleoside productivity of said bacterium is enhanced by increasing an activity of the YdhL protein. Also disclosed is the amino acid sequence of the YdhL protein from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and the gene encoding it.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bacillus aryabhattai, microbial inoculums thereof, preparation method and application
The invention discloses bacillus aryabhattai, microbial inoculum thereof, a preparation method and application. The bacillus aryabhattai BC104 is beta-cypermethrin degrading bacteria, and the preservation unit is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection center (CGMCC), the preservation date is 15th, Dec, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11664; the bacillus aryabhattai belongs to mycomonera, phylum firmicutes, bacillus class, bacilli bacteria, bacillaceae and bacillus. The microbial inoculum with the bacillus aryabhattai as an active ingredient is the microbial inoculum obtained by preforming activation culture and fermentation culture on the bacillus aryabhattai BC104. The preparation method comprises the steps of activation culture and fermentation culture; the application of the microbial inoculum is to prepare a medicine for degrading beta-cypermethrin. The strain disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process of the microbial inoculum, low cost, convenience in use and good application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Production process of surfactin
A process for producing Surfactin, comprising culturing a microorganism of the genus Bacillus in a liquid culture medium containing flour of beans such as soybean or an extract thereof as a nitrogen source and accumulating Surfactin in the culture broth, and a microorganism of the genus Bacillus which have an activity to produce a crude Surfactin in a concentration of from 8 to 50 g / L on culturing for 20 to 90 hours.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Bacillus subtilis takemi and compositions thereof
InactiveUS6812022B1Reduce nitratePreferable propertyBiocideBio-organic fraction processingFood additiveNitrate
Microorganisms of the genus Bacillus that are capable of reducing nitrates and contain chitin and / or chitosan in their cell walls are provided. The microorganism of the invention can be used for improving soil, for treating organic waste by fermentation, for fermenting soybeans, and for reducing bitterness. The microorganism of the invention can also be used as a feed additive or a good additive. Further, the microorganism of the invention has an anti-microbial effect.
Owner:GOLD KOSAN
Novel Strains Belonging to the Genus Paenibacillus and Method of Controlling Plant Disease by Using These Strains or Culture Thereof
Novel strains Paenibacillus sp. BS-0048, Paenibacillus sp. BS-0074, Paenibacillus polymyxa BS-0105 and Paenibacillus sp. BS-0277 and Fusaricidin A, Fusaricidin B and novel compounds 3 and 4 produced thereby have an activity of inducing resistance to plant diseases. Thus, they can protect plants from infections with fungi, bacteria, viruses and so on and, as a result, effectively control plant diseases.
Owner:KAKEN PHARMA CO LTD
Method and agent for controlling plant disease using bacteria of genus bacillus
This invention provides a control agent or material for biologically controlling plant diseases caused by plant pathogenic bacteria, fungi, or viruses, a method for controlling plant diseases using the same, and bacteria that can be used therefor. Also, this invention relates to a control agent or material for plant diseases comprising bacteria of the genus Bacillus capable of inhibiting infection with or proliferation of plant pathogenic bacteria, fungi, or viruses, the method for applying the same to plants, and bacteria that can be used therefor.
Owner:YUKI DAIJU +1
Process for increasing biomass and spores production of plant growth promoting bacteria of the bacillus genus
ActiveUS20160058016A1Increased biomass productionAppropriate and affordable for large scale productionBiocideProductsBacteroidesBacillus cereus
The present invention refers to a process designed to increase the production of plant growth-promoting microorganisms of the Bacillus genus, using a culture medium poor in nutrients and with specific environmental conditions, allowing to obtain a greater amount of biomass and / or spores, which can be used to prepare solid or liquid compositions to be applied to plants, aiming to promote their growth and / or counteract the effect of phytopathogenic agents.
Owner:UNIV EAFIT +1
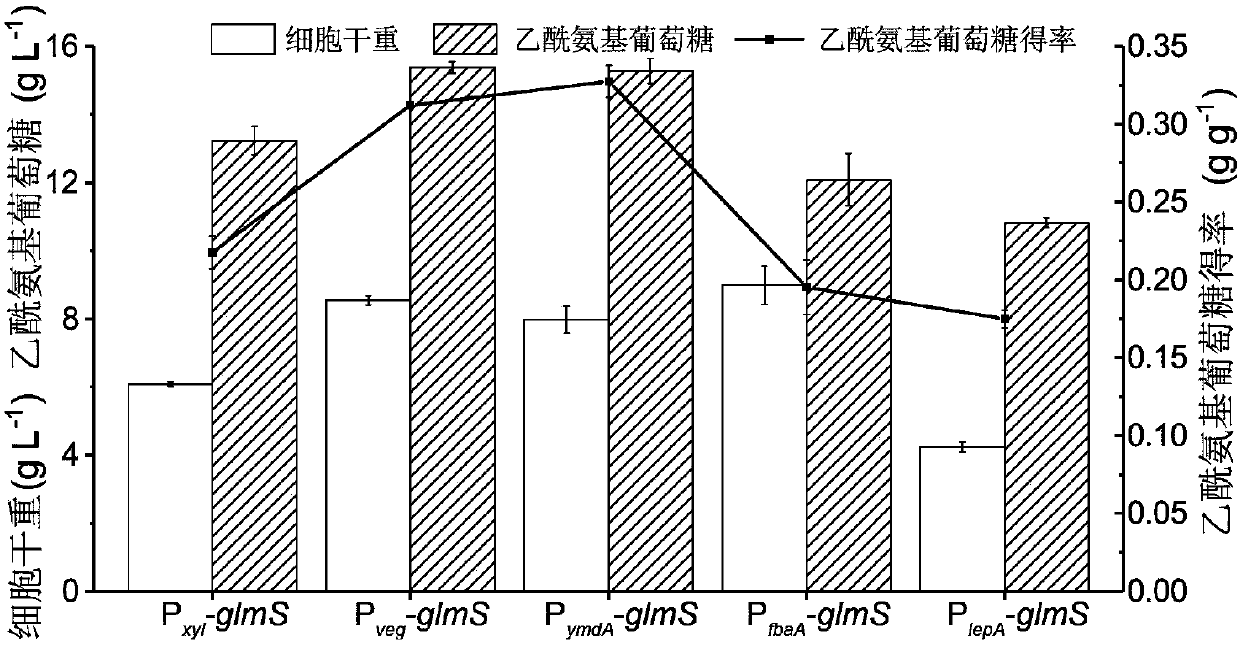
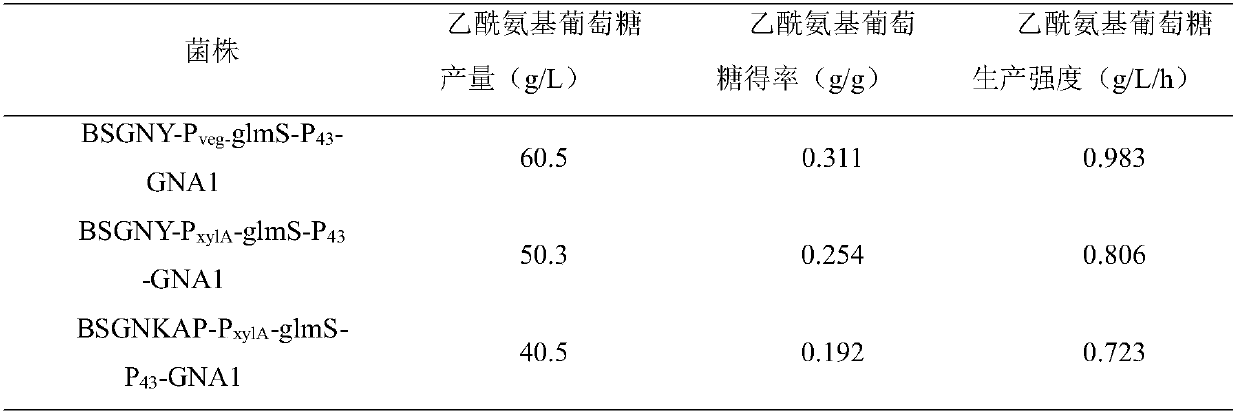
Recombinant bacillus subtitles capable of increasing yield of acetylglucosamine
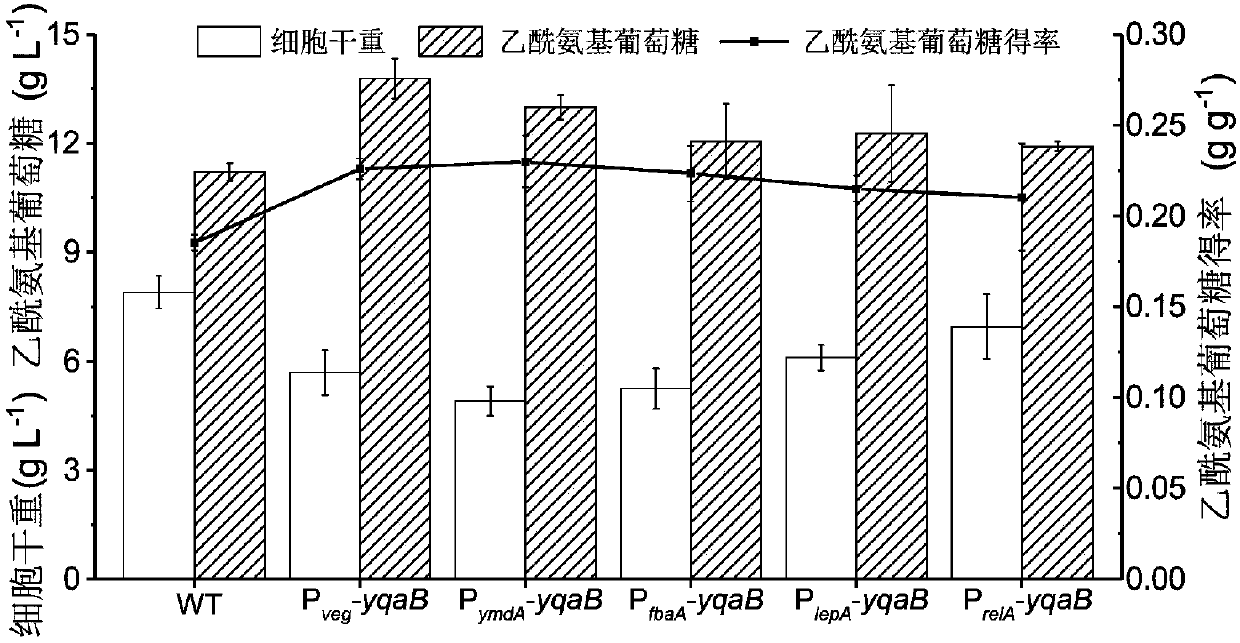
InactiveCN107699533AReturn to normal growthIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesPhosphateAcetylglucosamine
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtitles capable of increasing the yield of acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The recombinant bacillus subtitles is characterized in that bacillus subtitles BSGNKAP-Pxy1A-glmS-P43-GNA1 is used as the original strain, a phosphatase yqaB gene controlled by a strong constitutive promoter Pveg is integrated to the genome, and the promoter of 6-phosphate glucosamine synthase is replaced by the strong constitutive promoter Pveg to obtain genetically engineered bacillus subtitles BSGNY-Pveg-glmS-P43-GNA1 accumulating the acetylglucosamine. The recombinant bacillus subtitles has the advantages that the yield of the acetylglucosamine of a 3L fermentation tank reaches 60.5g / L, the yield of the acetylglucosamine is 0.311g / g glucose, production intensity is 0.983g / L / h, the yield of the acetylglucosamine outside the cells of the recombinant bacillus subtitles is increased, and a foundation is laid for glucosamine production using metabolic engineering modified bacillus subtitles.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria bacillus cereus H-hrb01 and screening method and application
ActiveCN102827787AEasy to waterExcellent water indicatorsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChemical oxygen demand
Owner:HIT YIXING ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improvedresistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including speciessuch as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
Compositions Comprising Bacillus Strains and Methods of Use to Suppress the Activities and Growth of Fungal Plant Pathogens
This invention provides compositions of Bacillus strains and methods for using such compositions to inhibit the activity and / or growth of fungal pathogens of plants. In one embodiment, this invention provides a composition comprising Bacillus bacteria selected from the group consisting of Brevibacillus laterosporus strain CM-3, Brevibacillus laterosporus strain CM-33, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BCM-CM5, Bacillus licheniformis ATCC-11946, Bacillus mojavensis BCM-01, Bacillus pumilus NRRL-1875, Bacillus subtilis 10 DSM-10, Bacillus subtilis NRRL-1650, Bacillus megaterium BCM-07, Paenibacillus polymyxa DSM-36, Paenibacillus chitinolyticus DSM-11030, and combinations thereof. In another embodiment, this invention provides a method for preparing a bacterial composition comprising one or more Bacillus strains by growing Bacillus strain bacteria until the bacteria form spores, collecting said spores, and formulating said composition.
Owner:BIO CAT MICROBIALS
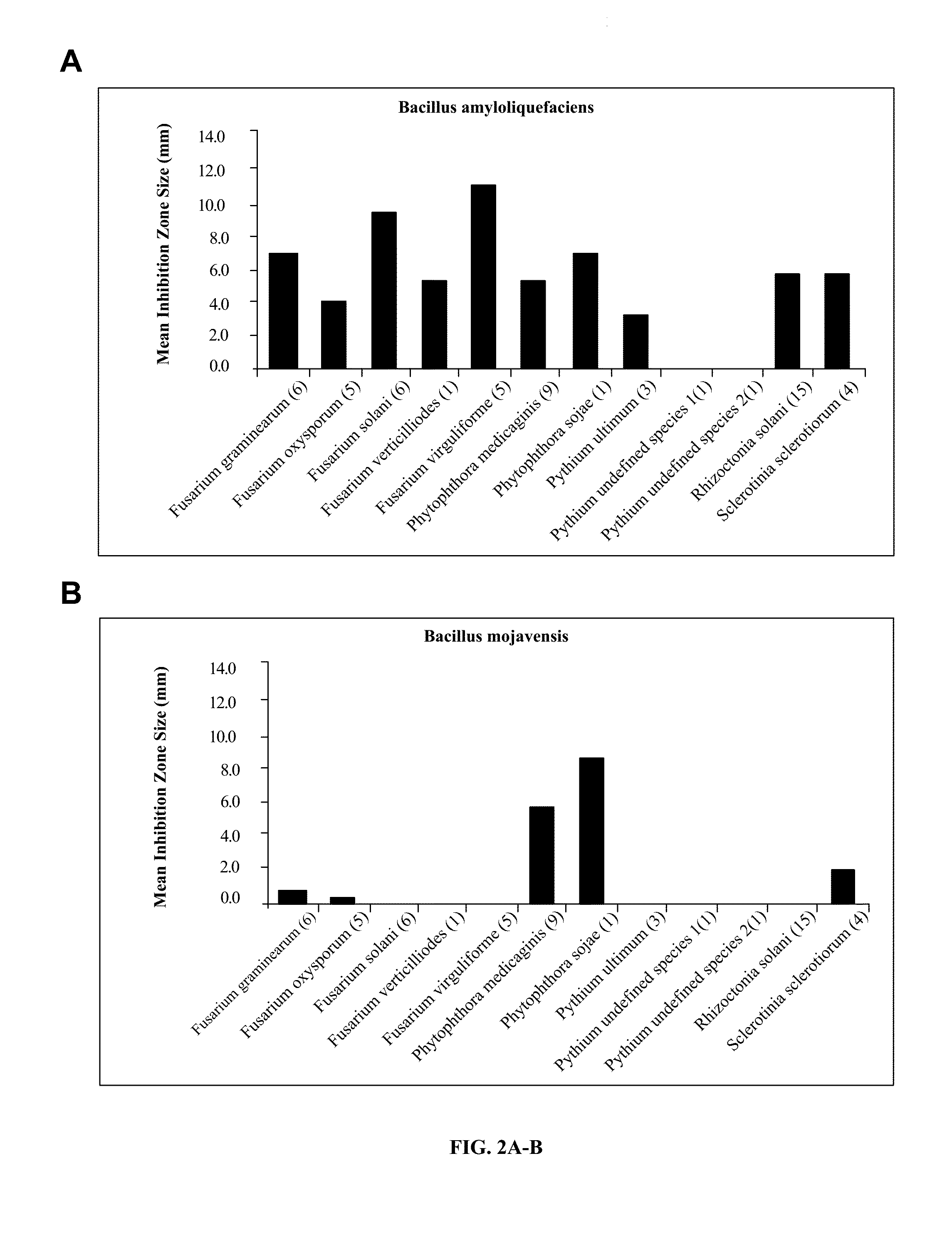
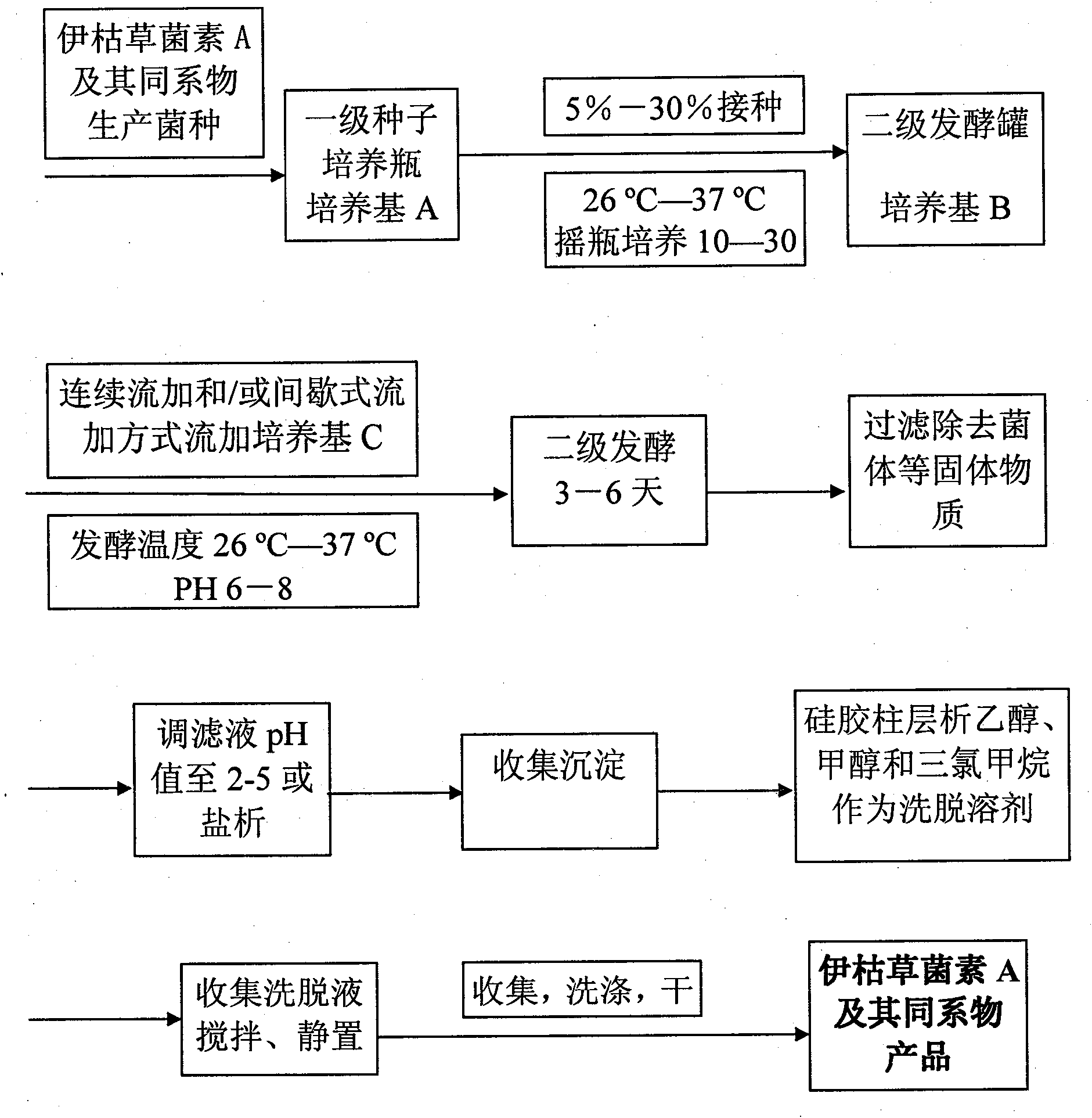
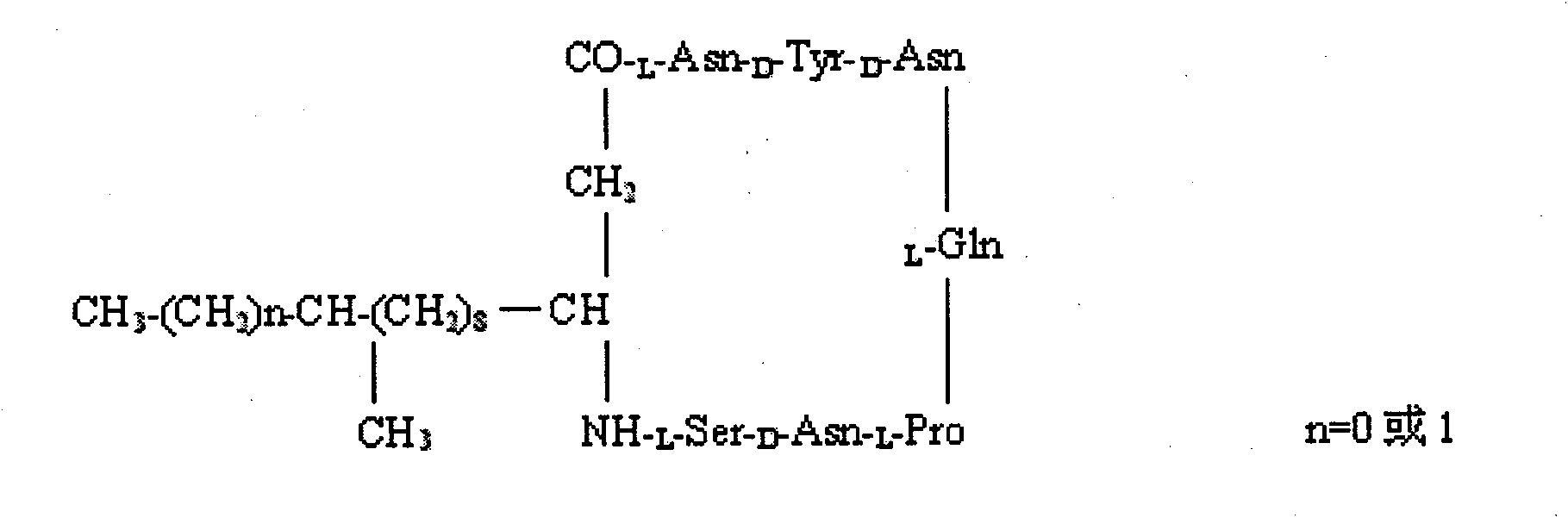
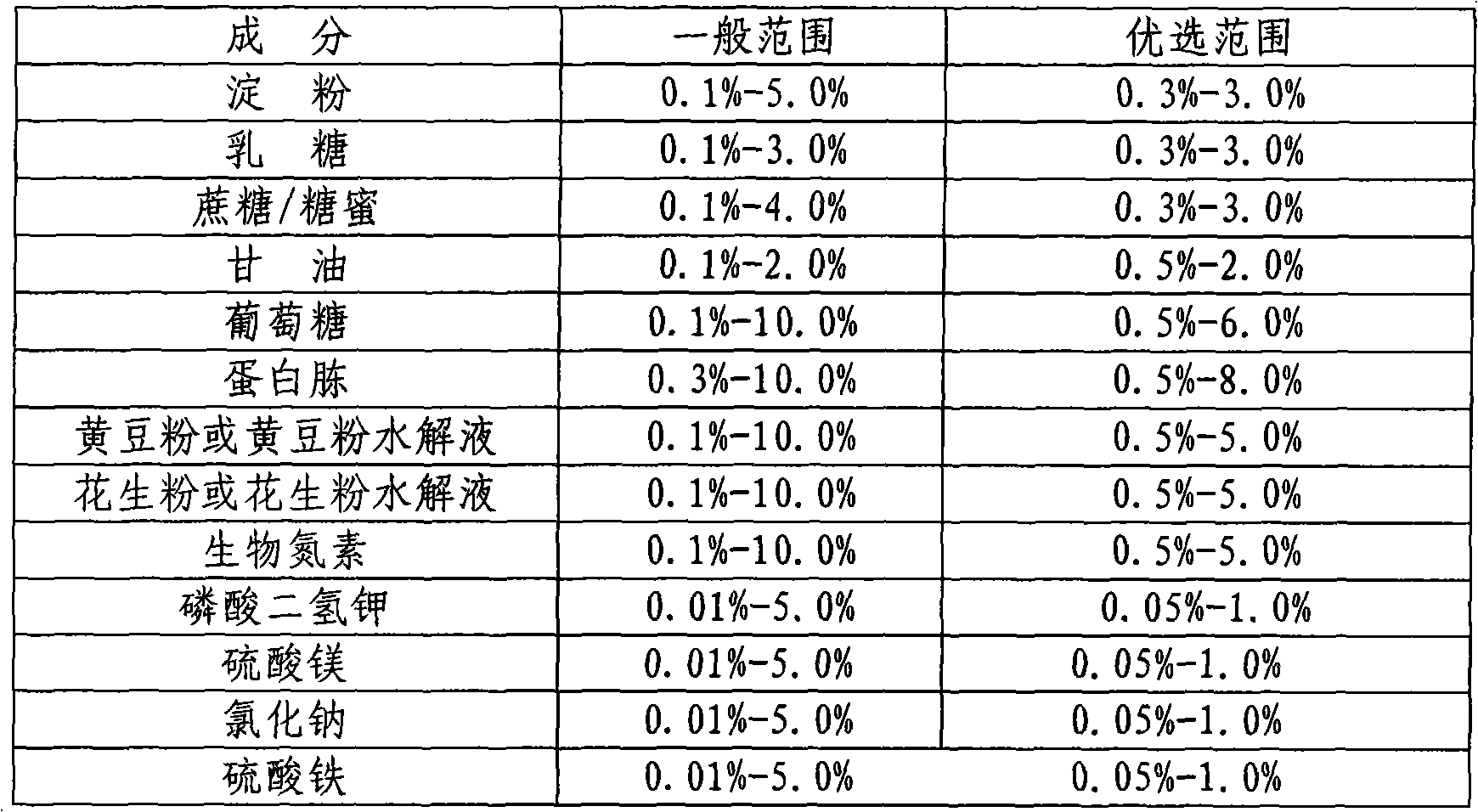
New method for preparing Iturin A and homolugues thereof
InactiveCN101831481AIncrease concentrationIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyCulture fluid
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms, particularly relates to a method for preparing Iturin A and homolugues thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing bacillus strains and genetic improved strains thereof into a first-stage liquid culture medium, wherein the bacillus strains and genetic improved strains thereof are capable of producing the Iturin A and homolugues thereof; then, using as seed liquid and inoculating into a second-stage liquid culture medium; adding a certain proportion of adsorption and fixing cell material and thickening agent into the second-stage liquid culture medium before inoculating the seed liquid; and carrying out fermentation culture and feeding and supplying culture on the second-stage liquid culture medium after inoculating the seed liquid; and finally collecting the Iturin A and homolugues thereof from the fermentation culture liquid after the fermentation is finished. The invention has the advantages of simple process, convenient operation, high yield, easy industrialization, and the like.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Agricultural compositions containing bacteria
An agriculturally effective active ingredient is applied to plant foliage before, after, or simultaneously with an enhancer component containing a substantially pure bacterial culture, suspension, spores, or cells of a bacteria selected from the genus Bacillus or a soil bacteria.
Owner:MICRO FLO
Bacillus strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and screening and application thereof
ActiveCN108102963APromote degradationNo pollution in the processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus strainCell culture media
The invention discloses a bacillus strain for degrading aflatoxin B1 and screening and application thereof. The class of the strain is named bacillus aryabhattai DT and perserved in the China GeneralMicrobiological Culture Collection Center, with a perservation number of CGMCC 14949. A treatment method comprises: strain screening and separation by using a medium taking coumarin as a unique carbonsource, and 16S rDNA authentication. Meanwhile, the degradation effect of the fermentation culture solution of the strain on aflatoxin B1 is explored. A single colony of bacillus aryabhattai on a solid medium is picked and inoculated in 50mL of growth medium and then vibration is performed for 12-24h on a shaking table at 30-40 DEG C; the fermentation culture solution of the bacillus aryabhattaireacts with 2mu g / mL aflatoxin B1 for 3-4d in a dark place to realize a degradation rate of 82.98%. The screened bacillus aryabhattai realizes an obvious degradation effect on aflatoxin B1 and has thecharacteristics of high efficiency, energy saving, environmental friendliness and the like, and can be applied to the preparation of relevant aflatoxin detoxification agents.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
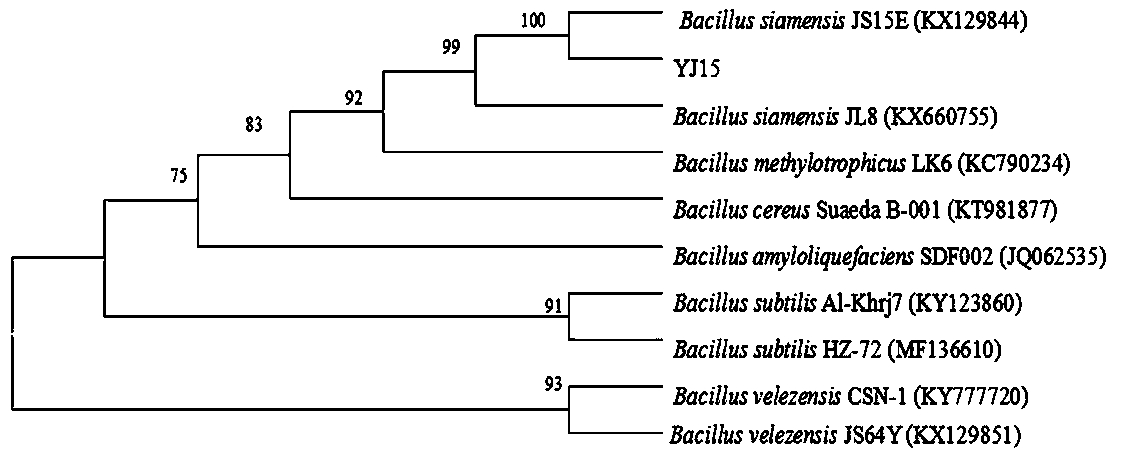
Bacillus siamensis YJ15 and application thereof
ActiveCN109207404ANo pollution in the processGood control effectBiocideBacteriaMicrobial agentCollection management
The invention relates to a Bacillus siamensis YJ15 and an application thereof in biological control of blueberry gray mold. Bacillus siamensis strain YJ15 of that invention belong to the genus Bacillus sp., Deposited in the Common Microorganism Center of China Microorganism Culture Collection Management Committee (CGMCC), strain collection No. CGMCC No. 15952. Bacillus siamensis YJ15 is inoculatedin LB liquid culture medium to obtain fermentation seed liquid, and then the fermentation seed liquid is inoculated in fermentation culture liquid to obtain fermentation broth or supernatant of fermentation broth to obtain biological microbial agent. The biological bacterial agent prepared by the invention can control the blueberry gray mold and has good control effect equivalent to carbendazim.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Microbial Strains and Their Use in Animals
InactiveUS20150216915A1Improve survivalIncrease body weightBiocideBacteriaAquatic animalLactobacillus gasseri
Bacillus and Lactobacillus strains and methods that are useful for improving the performance of aquatic animals. The invention also discloses Bacillus and Lactobacillus strains and methods that are useful for inhibiting or slowing the growth of a pathogenic agent in an aquatic animal.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Cellulose-producing strain, cellulose and method for producing and fermenting cellulose
ActiveCN102586133AIncrease enzyme activityProduction method is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyScreening cultures
Owner:HONGTA TOBACCO GRP
Bacterium agent for renovation of organic pollution aquifer, producing and using method of the same
InactiveCN101153271AContinuously strengthen the purification effectCutting costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationNutrition
The invention relates to the microbial field, in particular to a microorganism agent for recovering the organic polluted water and preparation process and using method. The microorganism agent consists of facultative anaerobics including Pseudomonas, Alcaligenes, Bacillus and Enterbacter with the weight ratio of 1:1-3:1-4:2-7, and the residual is the culture liquid containing nitrobenzene; the degradation rate can reach between 97.7 percent and 99.6 percent when the invention is implemented in the polluted water containing nitrobenzene. The microorganism agent of the invention is made by that the nitryl aromatic hydrocarbon compound and the nutrition compound with relatively high concentration are acclimatized and sorted, and has strong growing and reproductive ability as well as adaptability; in addition, the invention can assure a higher biomass in the environment at low cost, and does not cause the secondary pollution, and has the effect of continuously strengthening the purification of the water, thereby having good social, economic and ecological benefits.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant Bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN106479945AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCandida famataGenetic engineering
The invention discloses recombinant Bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Recombinant Bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS is used as a starting strain, glucosamine synthetic route is enhanced by overexpressing glucosamine acetylase coding gene (CaGNA1) from Candida albicans SC5314 or knocking out unnecessary area skin at the same time, and accumulated acetylglucosamine Bacillus subtilis genetically-engineered bacteria are obtained; the yield is 21% or 94% higher than that of CaGNA1 genetically-engineered bacteria from overexpressed Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the basis is laid for the further metabolic engineering modification of Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:SHANDONG RUNDE BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for removing calcium carbonate scales by using microbial extracellular carbonic anhydrase
ActiveCN104071890AAchieve emission reductionDoes not cause dischargeTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsBiological water/sewage treatmentIndustrial water treatmentChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of industrial water treatment, and particularly relates to a method for removing calcium carbonate scales by using microbial extracellular carbonic anhydrase. The invention aims to provide a method for relieving the phenomenon of carbonate scales in an industrial circulating water system. The method can reduce the phosphorus-containing wastewater which enters the ambient water body. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a bacillus microbial inoculant for secreting extracellular carbonic anhydrase; 2) carrying out refrigerated centrifugation, and salting out to extract a crude enzyme solution containing the carbonic anhydrase; and 3) adding the crude enzyme solution into industrial circulating water with carbonate scales. The method can be used for removing the calcium carbonate scales in the industrial circulating water system, and has the advantages of low cost and no environment pollution.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Bacterial polyphenol oxidase from bacillus for use in oxidation of colored substances
InactiveUS6184014B1Efficient of substanceEfficient oxidationOrganic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaBacteroidesFiltration
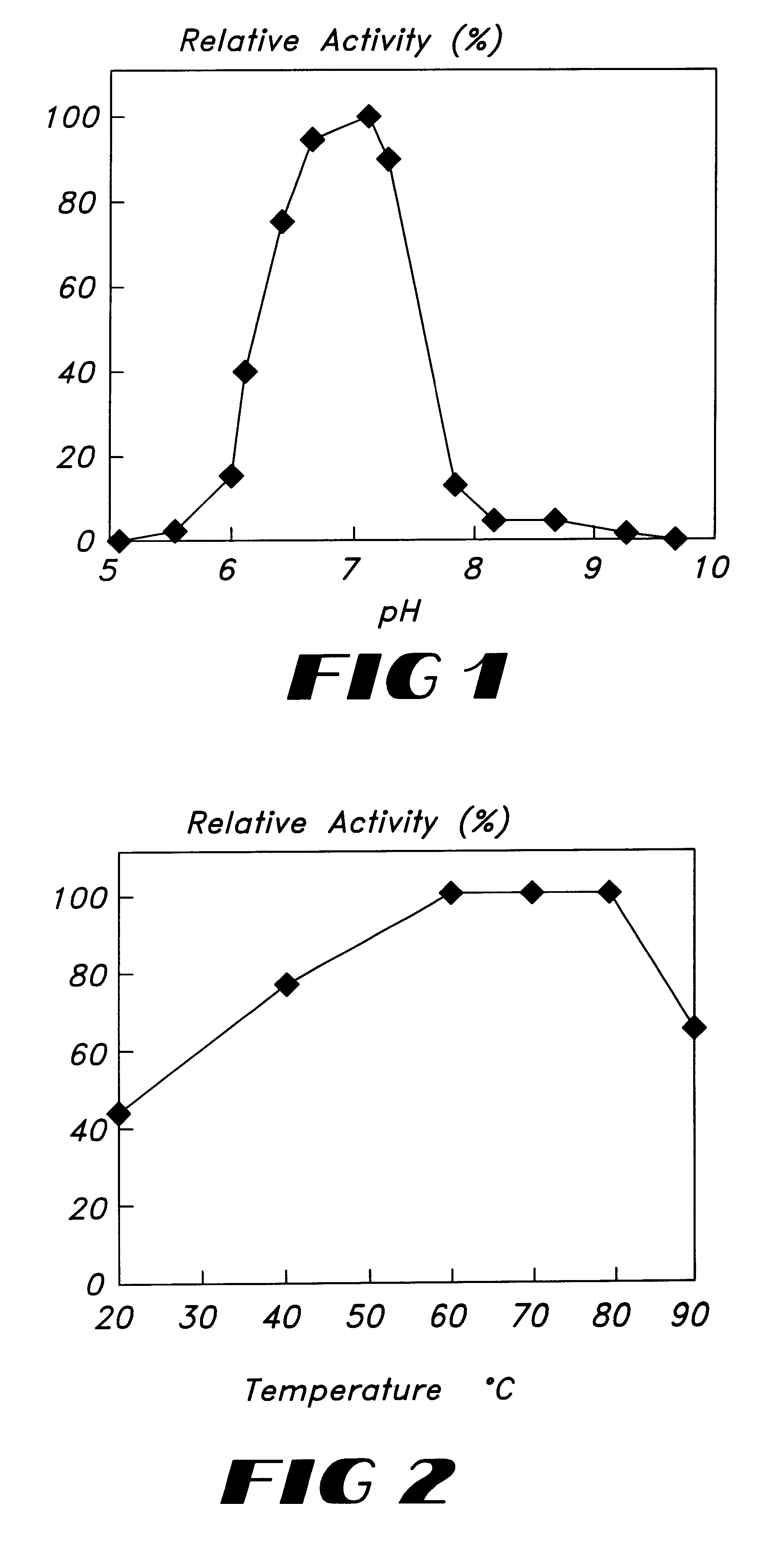
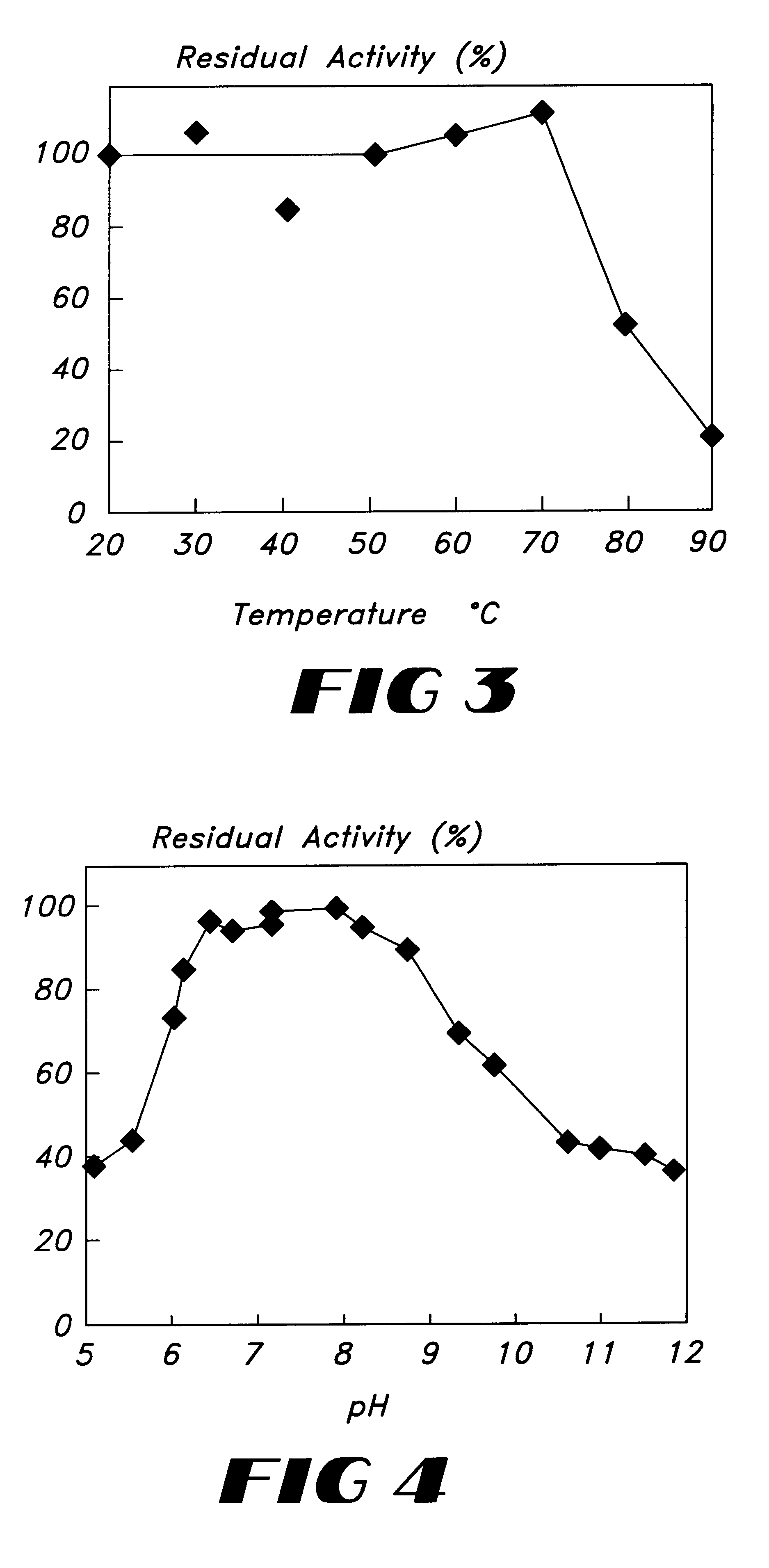
The present invention provides polyphenol oxidases from bacteria, particularly from the genus Bacillus including, without limitation, B. licheniformis, B. natto, and B. sphaericus, In some embodiments, the polyphenol oxidase has an optimum reaction pH of about 7; an optimum reaction temperature between 60° C. and 80° C.; and a molecular weight of 51,000 measured by gel filtration chromatography. The enzymes of the invention are useful for oxidizing and / or bleaching a variety of substrates.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Microbial fermenting agent
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
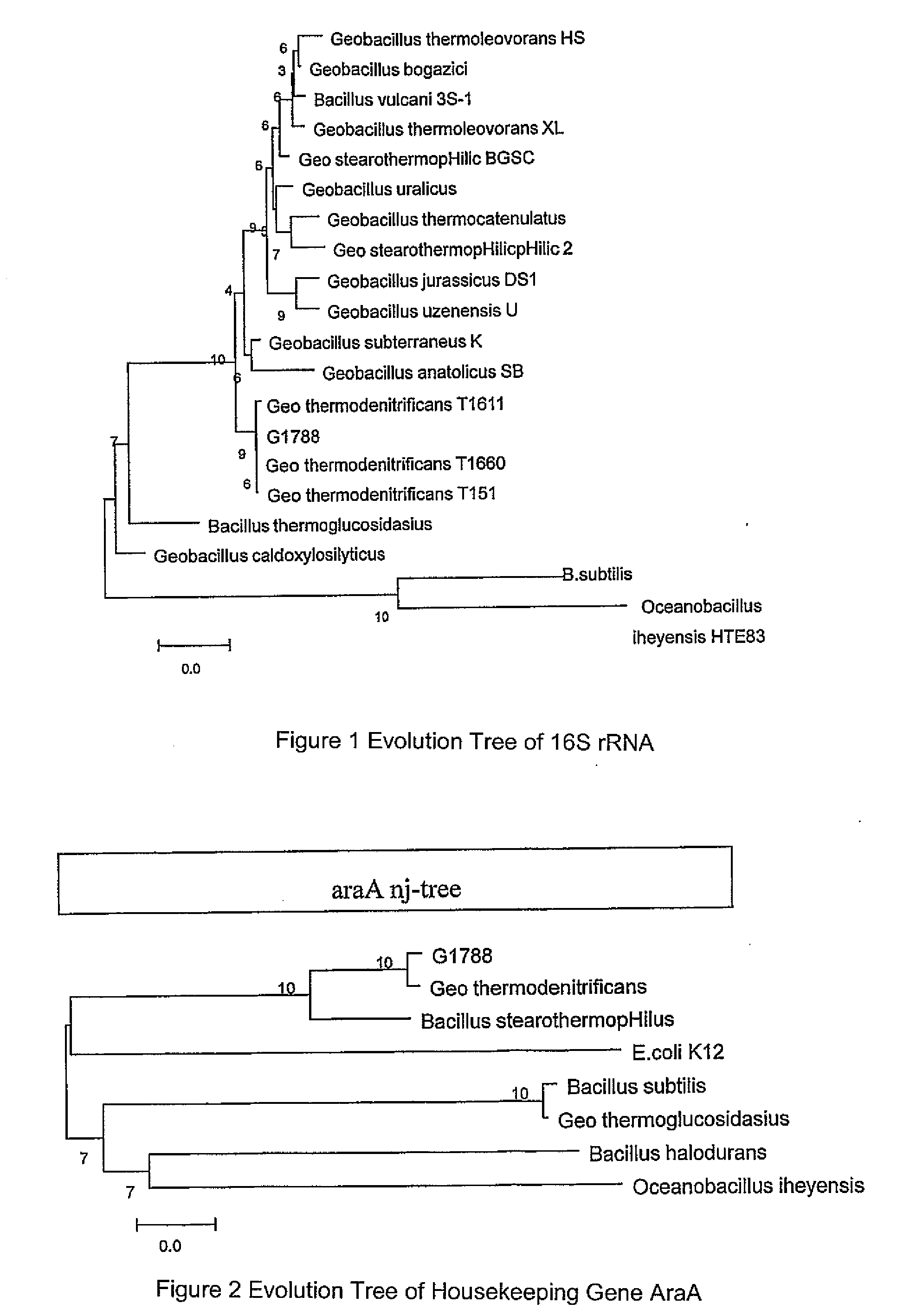
Geobacillus thermodenitrificans as well as the screening method and the uses thereof
InactiveUS20090148881A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove featuresOrganic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaAlkaneScreening method
The invention provides a strain of Geobacillus thermodenitrificans as well as the screening method and the uses thereof. The strain was deposited as the number CGMCC-1228 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of the China Committee of Culture Collection for Microorganisms. The strain was obtained by primary screening, re-screening, inoculation, domestication and propagation using the bacteria in the aqueous samples from the strata of oil field as the original screening strain. The strain screened in the invention belongs to the genus Geobacillus, which can tolerate a high temperature, and has good thermostability, which can be applied to the industrial production which need the condition of thermostable enzymes, such as fermentation, etc. With its ability of growing well in the oil-reservoir environment, degrading alkanes, decreasing viscosity and increasing fluidity of crude oil, the strain is able to remarkably enhance the yield of oil and improve the transporting efficiency of oil. Additionally, with its good ability of degrading oil, it can be developed for the treatment and clearing of the material such as the oil contaminated water, etc., so it can be useful in protection of the environment. This strain also has the ability of decreasing the surface tension of substances, which can be applied to the industry of biosurfactants preparation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com