Patents
Literature
122 results about "Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate mutase promoters for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
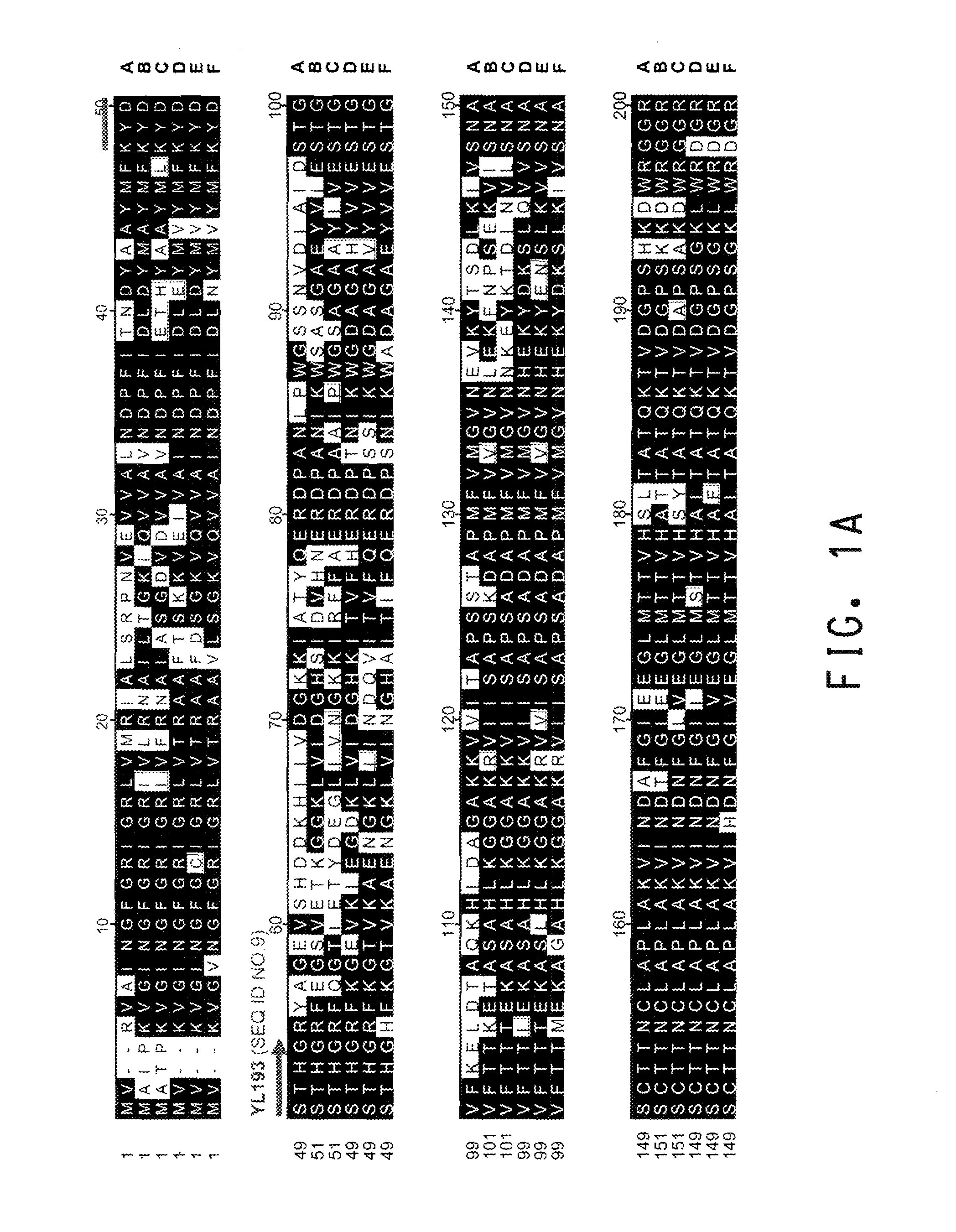
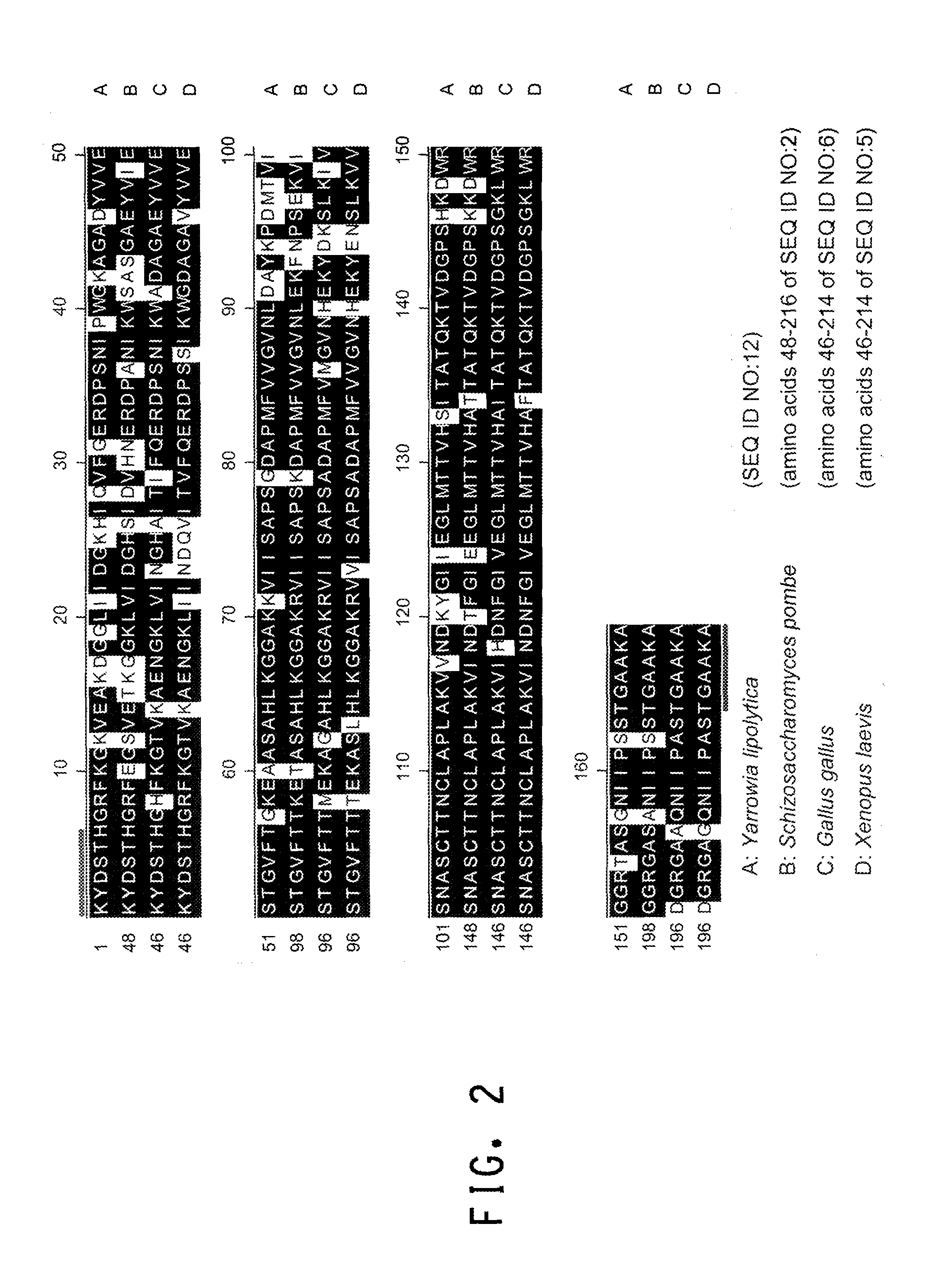
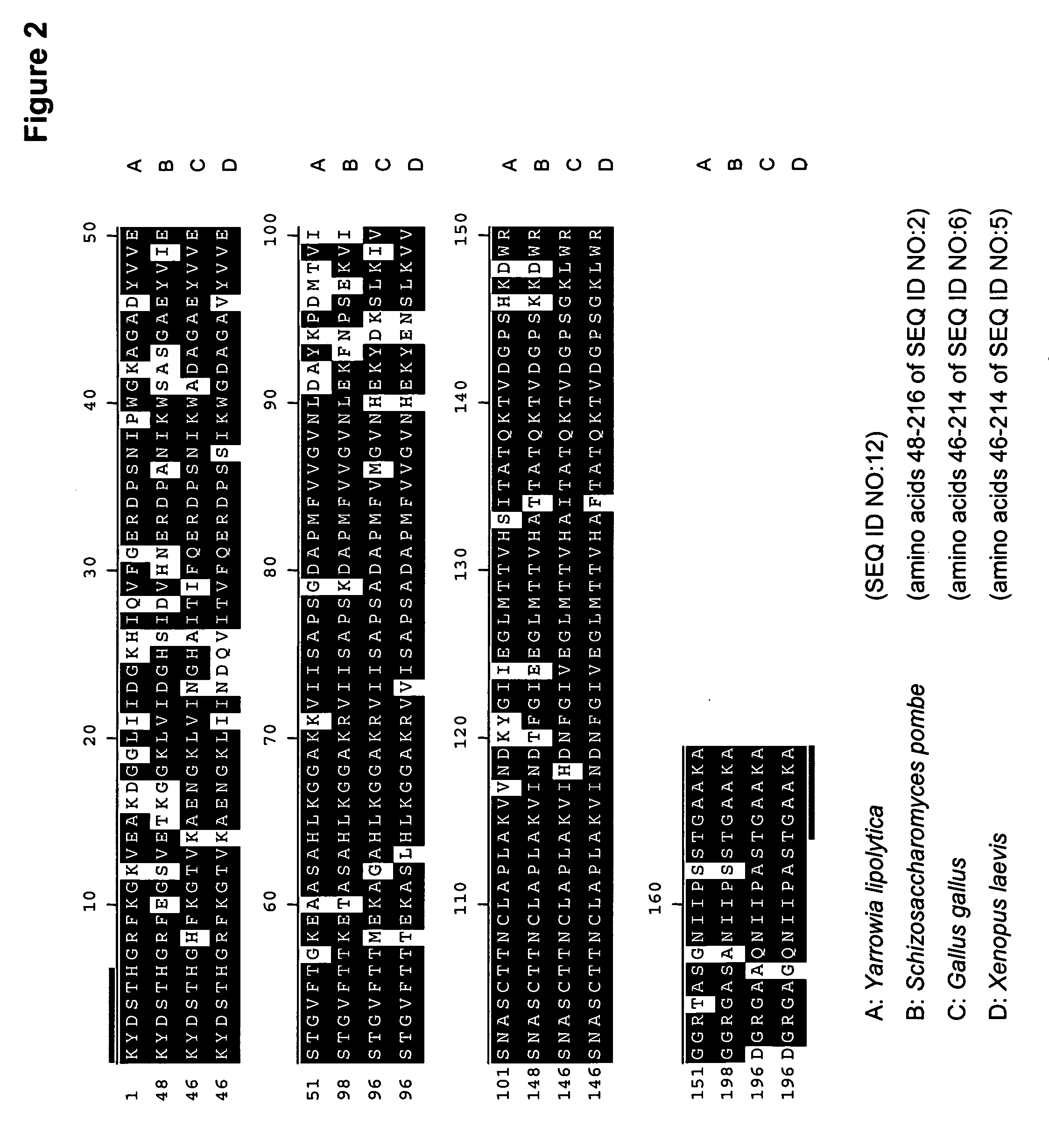
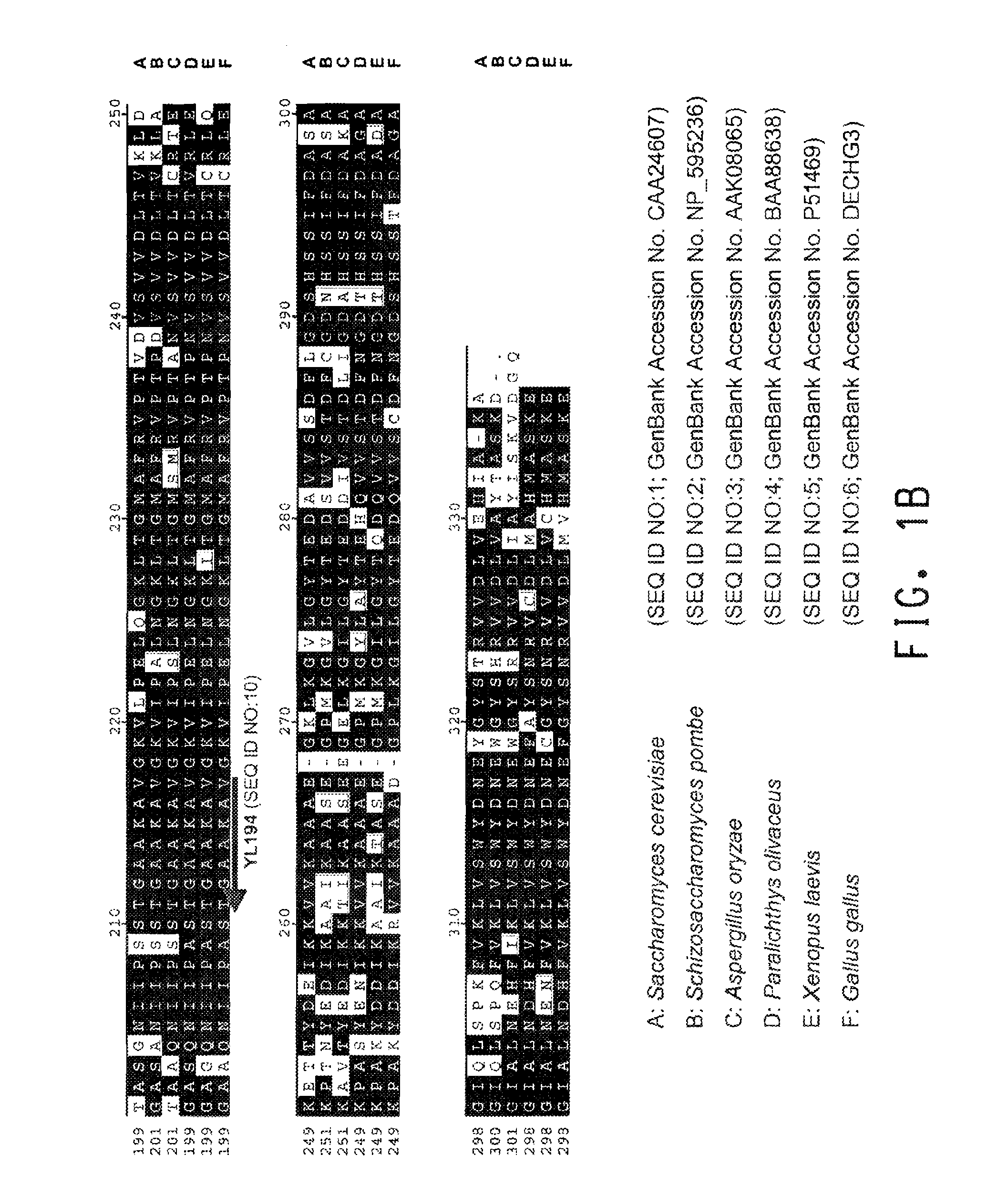
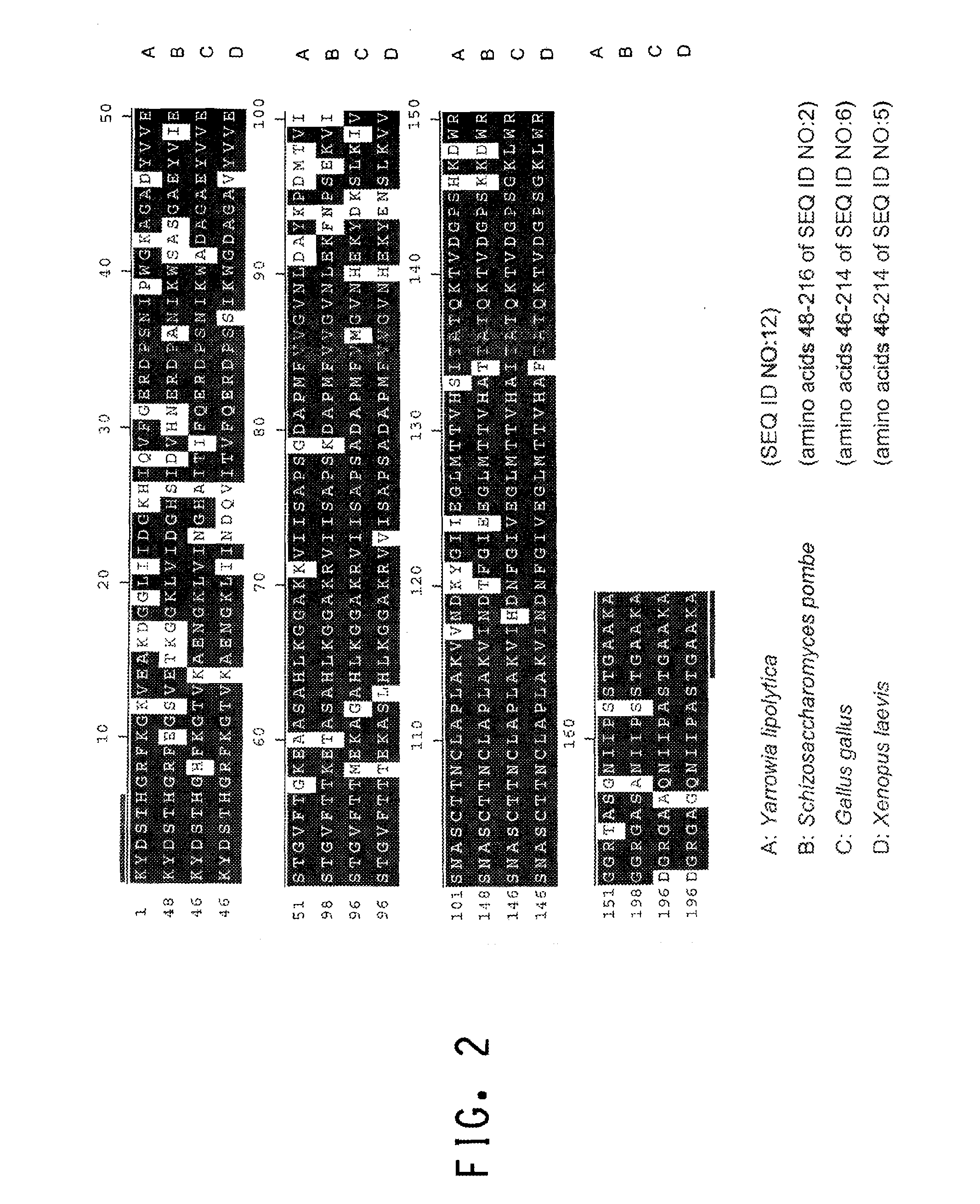
The promoter regions associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) and phosphoglycerate mutase (gpm) genes have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologous genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate mutase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
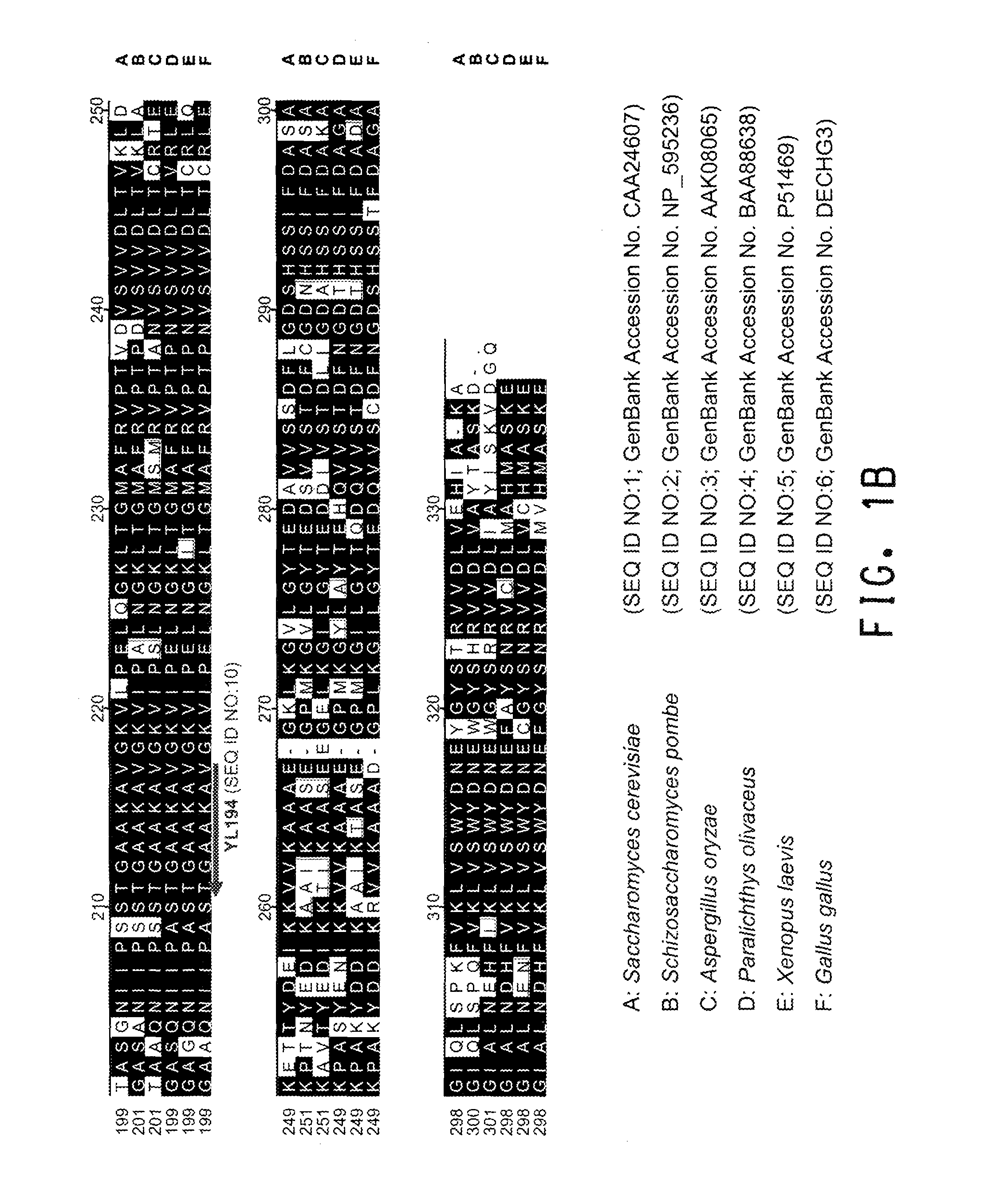
The regulatory sequences associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) and phosphoglycerate mutase (gpm) genes have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologous genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention, intron and enhancer have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
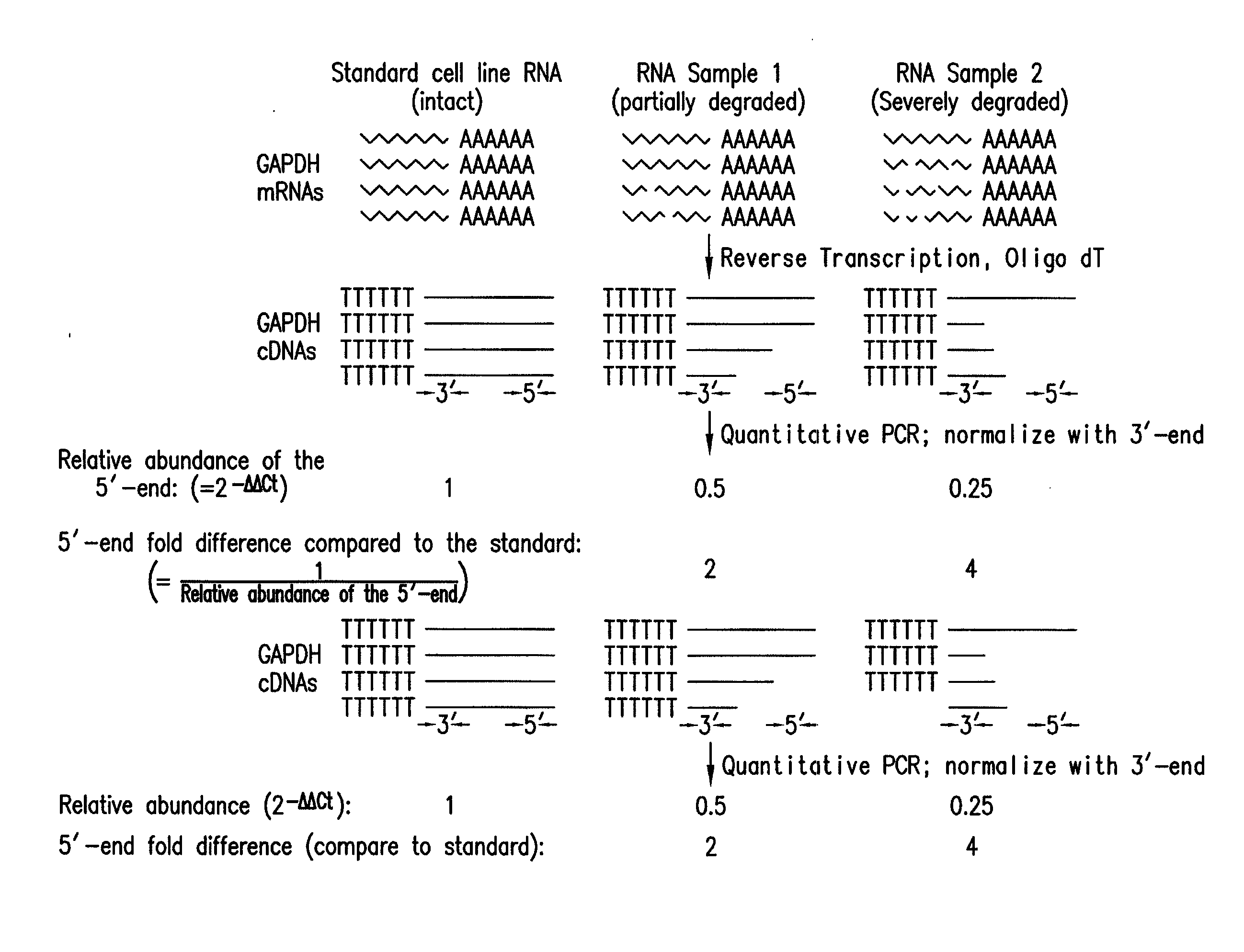
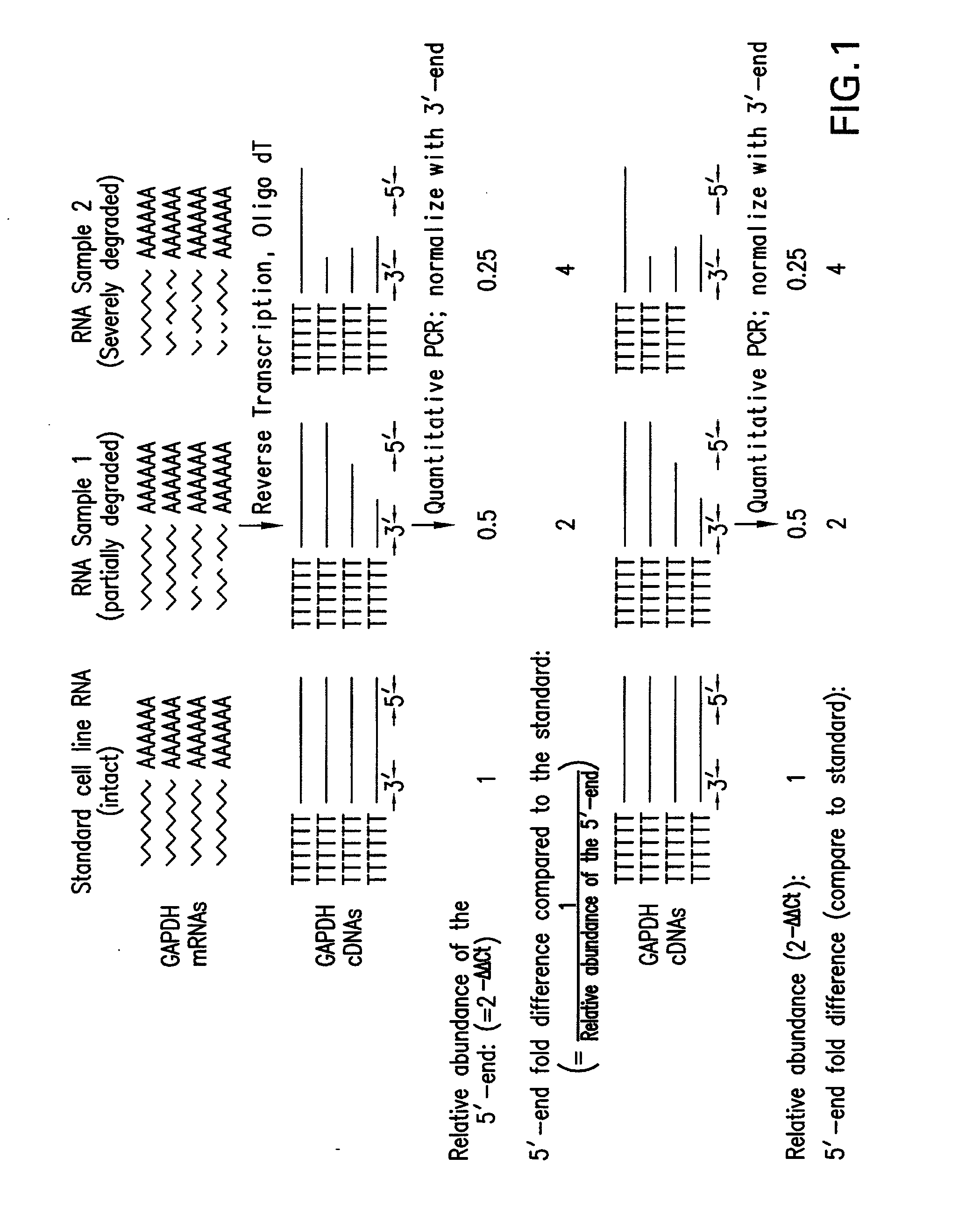
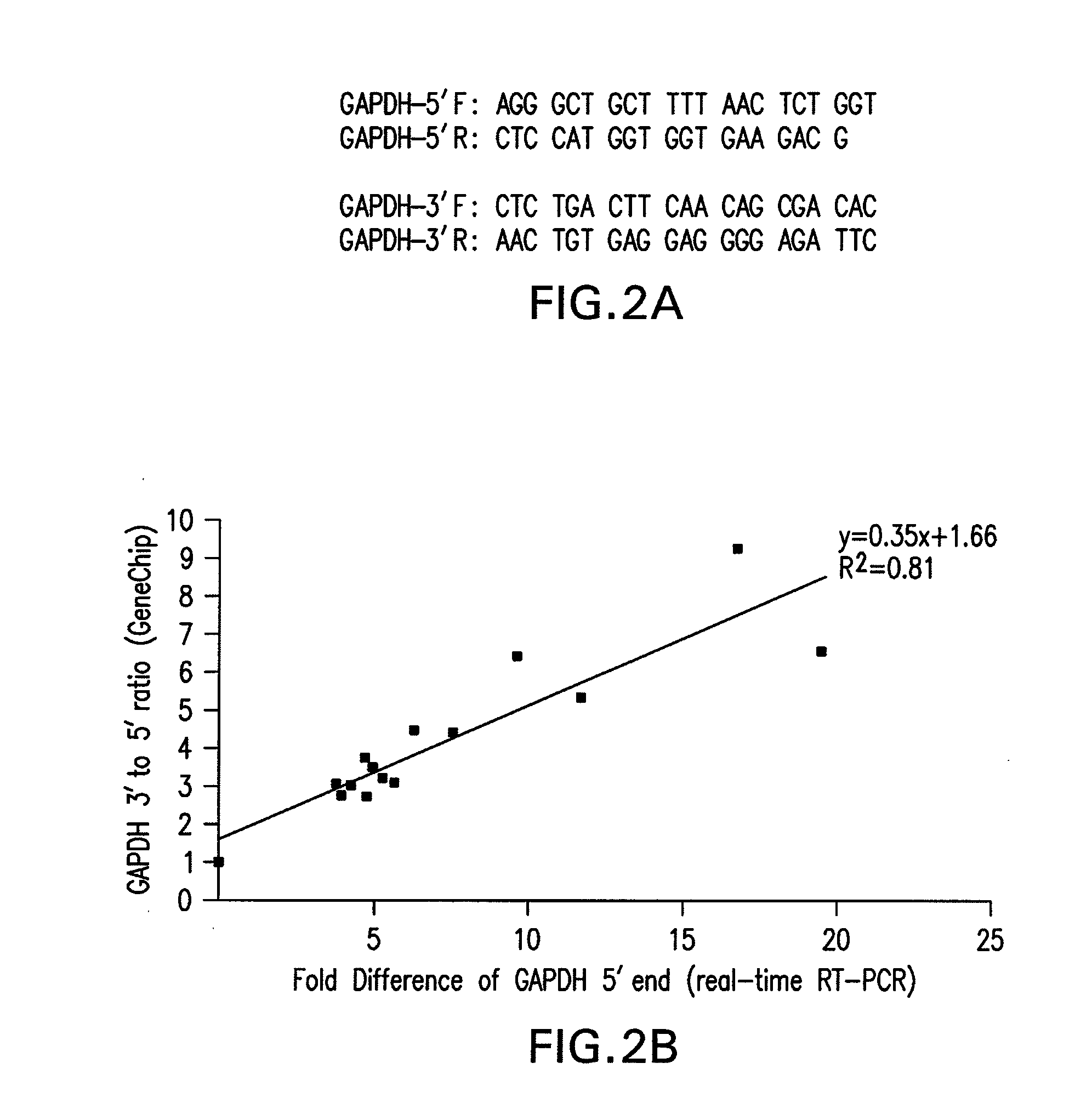
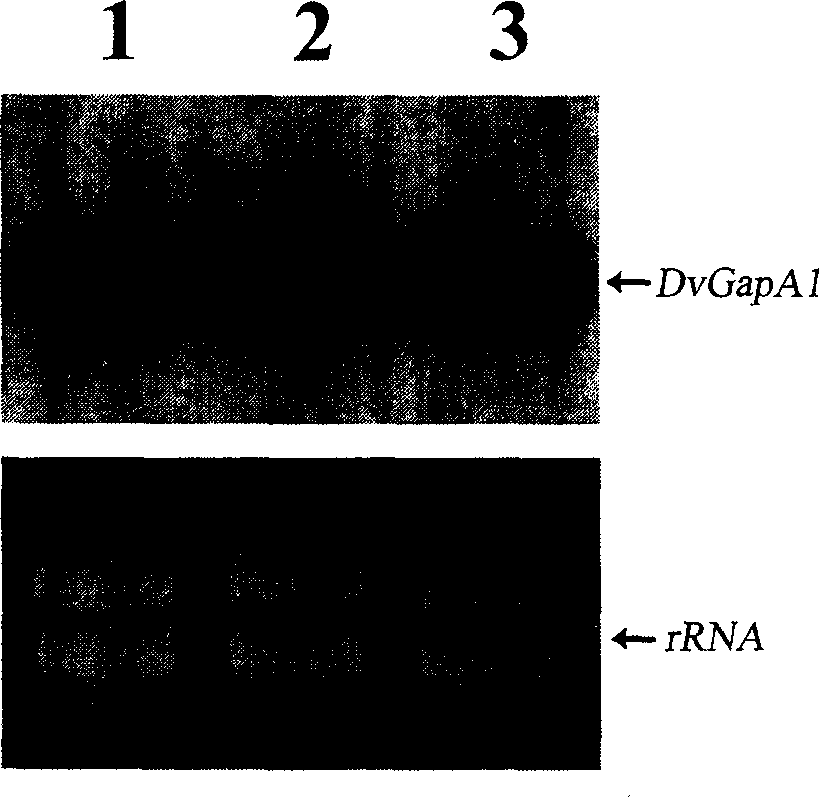
Method and kit for evaluating RNA quality
InactiveUS20080318801A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningReverse transcription polymerase chain reactionBiology
The present invention relates to a method for analyzing and rapidly determining the quality of a test RNA of unknown quality utilizing a novel quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) based method. The present invention is based on normalizing the 3′ end of the house-keeping gene glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) to the relative abundance of the 5′ end of GAPDH MRNA in the test RNA. The present invention is particularly useful in pre-screening postmortem tissue samples for microarray experiments and for evaluating large quantities of samples which would be time consuming and expensive to analyze by methods currently in use.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
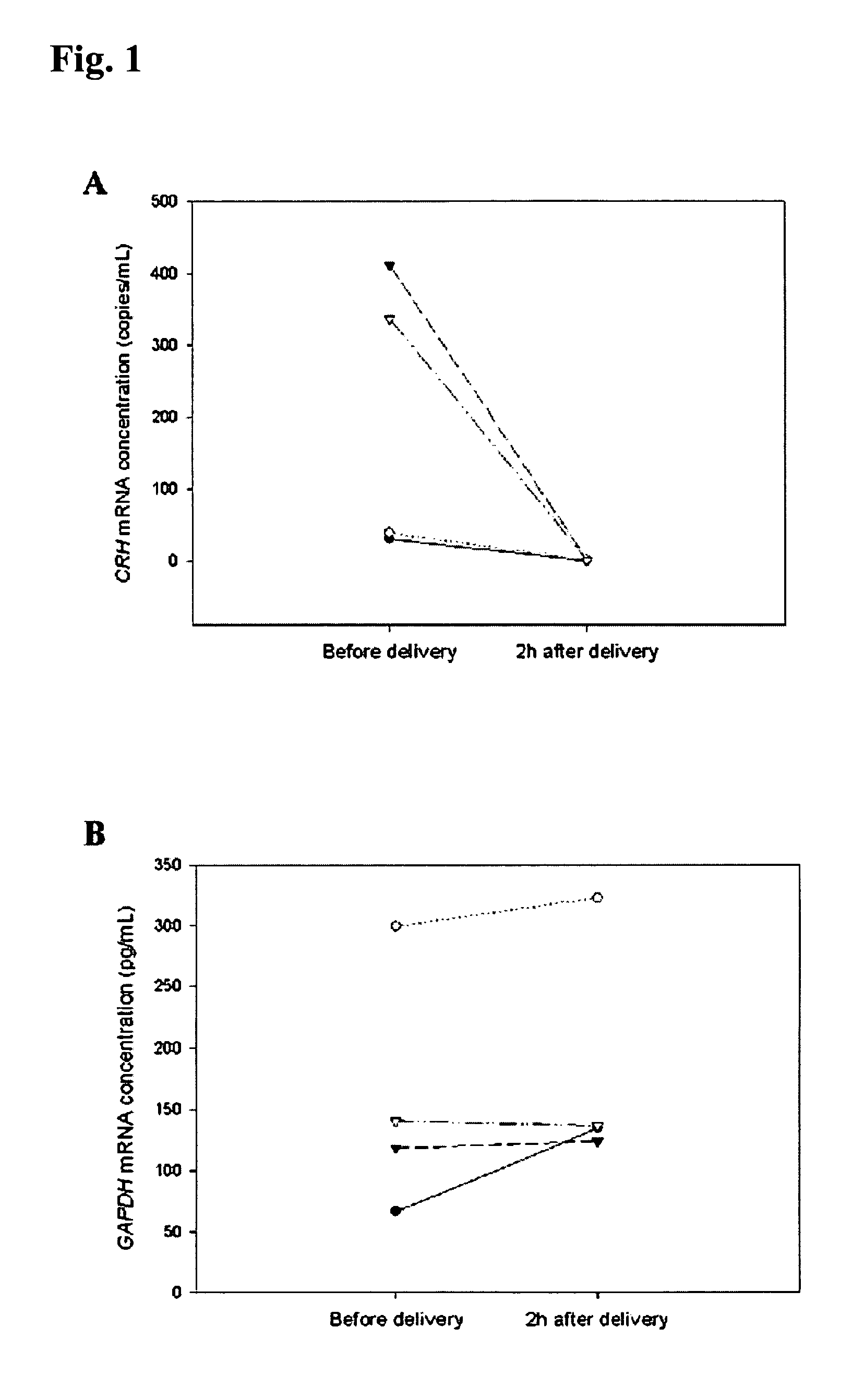
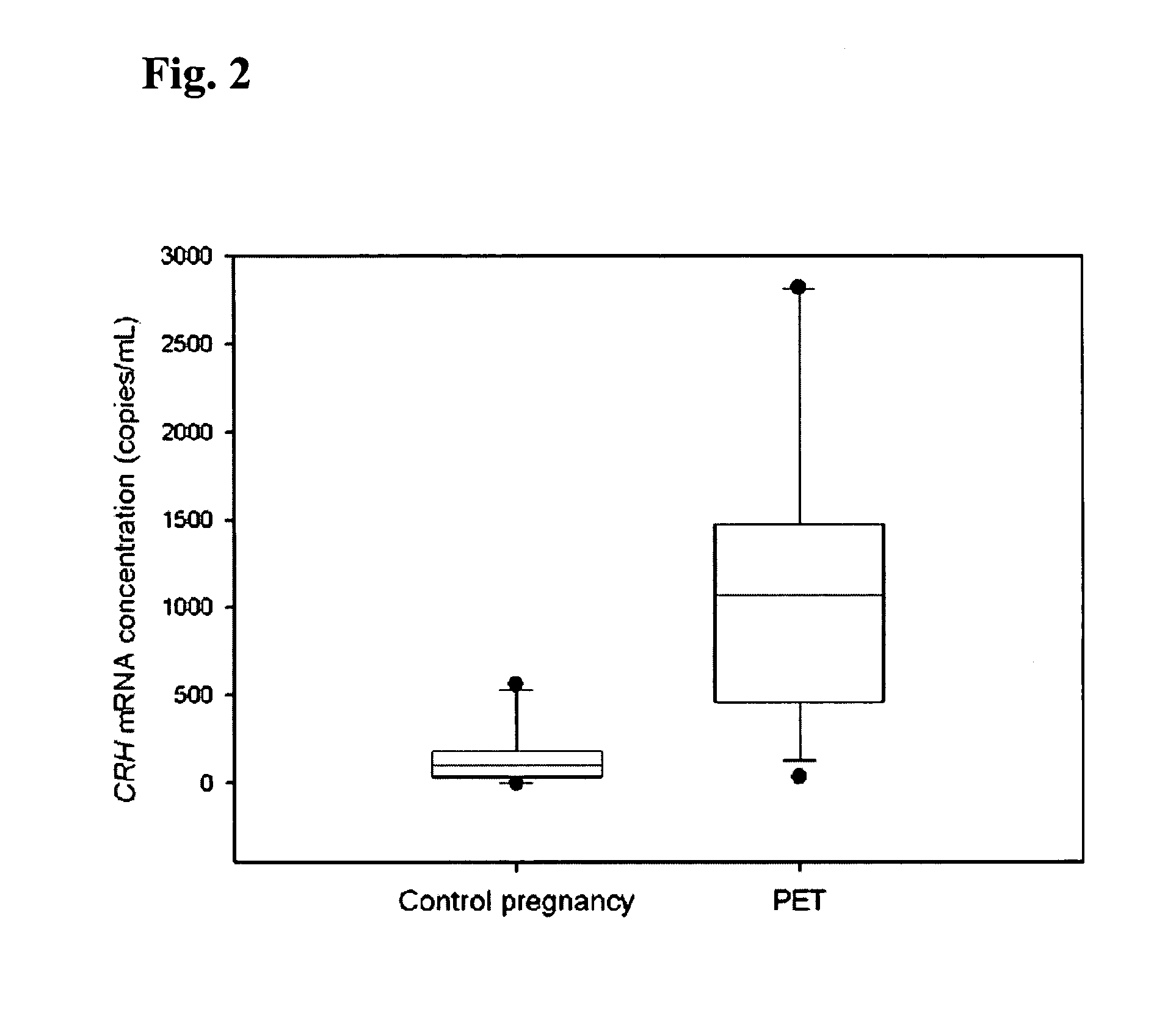
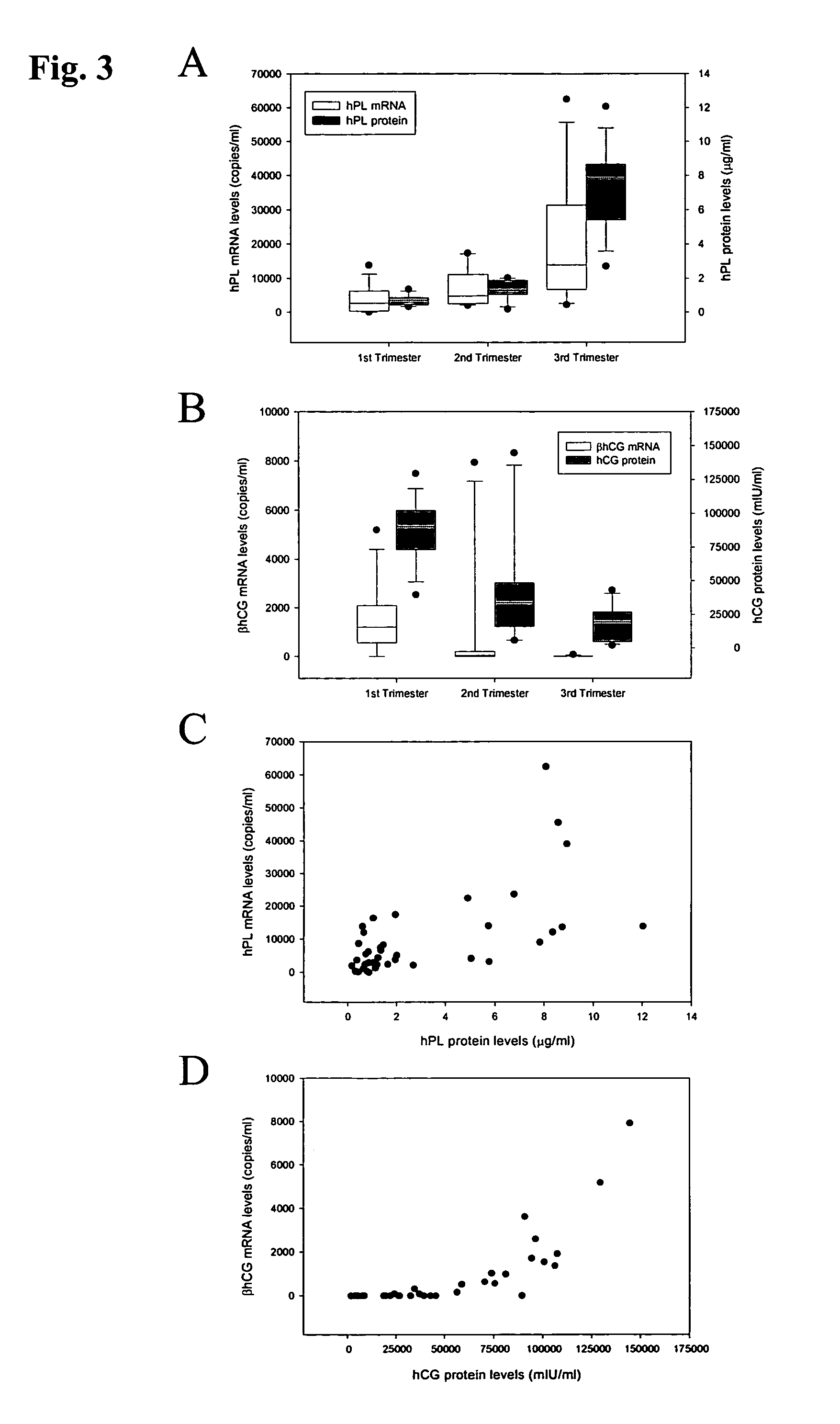
Method for diagnosing preeclampsia by detecting hCRH mRNA
ActiveUS7235359B2Increased risk of developingIncrease volumeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlyceraldehydeMetastasis suppressor
Methods and kits are provided for diagnosing, monitoring, or predicting the conditions of pre-eclaimpsia, fetal chromosomal aneuploidy, and pre-term labor in a pregnant woman, as well as for detecting pregnancy in a woman, by quantitatively measuring in the maternal blood the amount of one or more mRNA species encoding human chorionic gonadotropin β subunit (hCG-β), human placental lactogen (hPL), human corticotropin releasing hormone (hCRH), KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor (KISS1), tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TPFI2), placenta-specific 1 (PLAC1), or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and comparing the amount of the mRNA species with a standard control.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
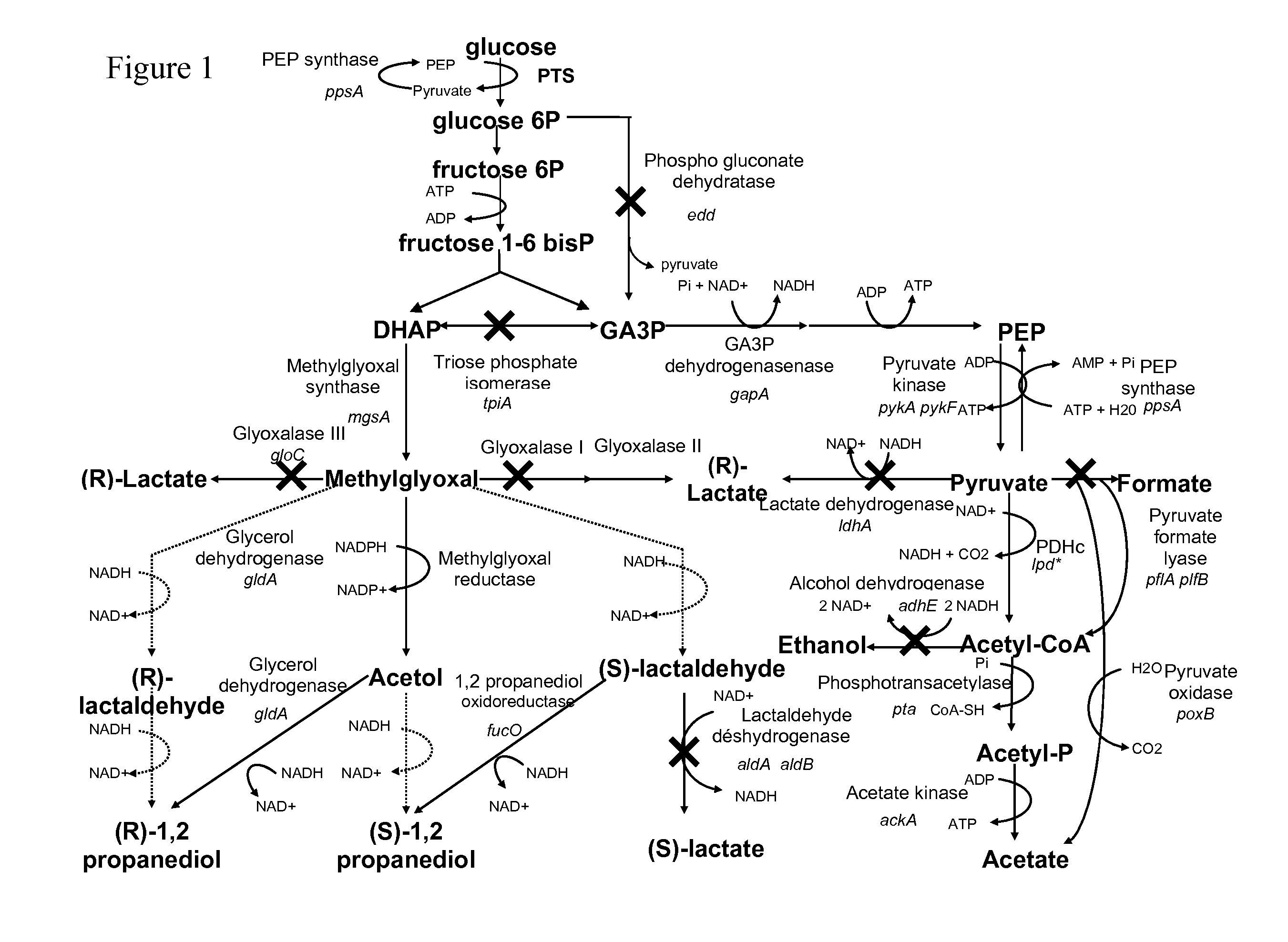
Metabolically engineered microorganism useful for the production of 1,2-propanediol
InactiveUS20100261239A1High activityHigh expressionBacteriaOxidoreductasesMicroorganismGlyceraldehyde
Microorganism useful for the production of 1,2-propanediol from a carbon source, wherein said microorganism is characterized by:an improved activity of the biosynthesis pathway from dihydroxyacetone phosphate to 1,2-propanediol, andan attenuated activity of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenaseThe invention is also related to a method for producing 1,2-propanediol by fermentation with a microorganism according to the invention.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase-S (GAPDHS), a glycolytic anzyme expressed only in male germ cells, is a target for male contraception
Methods for identifying modulators of a male germ cell-specific glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDHS) are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for screening potential modulators for an ability to modulate biological functions of a GAPDHS polypeptide.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +1
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate mutase regulatory sequences for gene expression in oleaginous yeast
The regulatory sequences associated with the Yarrowia lipolytica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) and phosphoglycerate mutase (gpm) genes have been found to be particularly effective for the expression of heterologous genes in oleaginous yeast. The promoter regions of the invention, intron and enhancer have been shown to drive high-level expression of genes involved in the production of ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Production of clavulanic acid by genetic engineering of Streptomyces clavuligerus
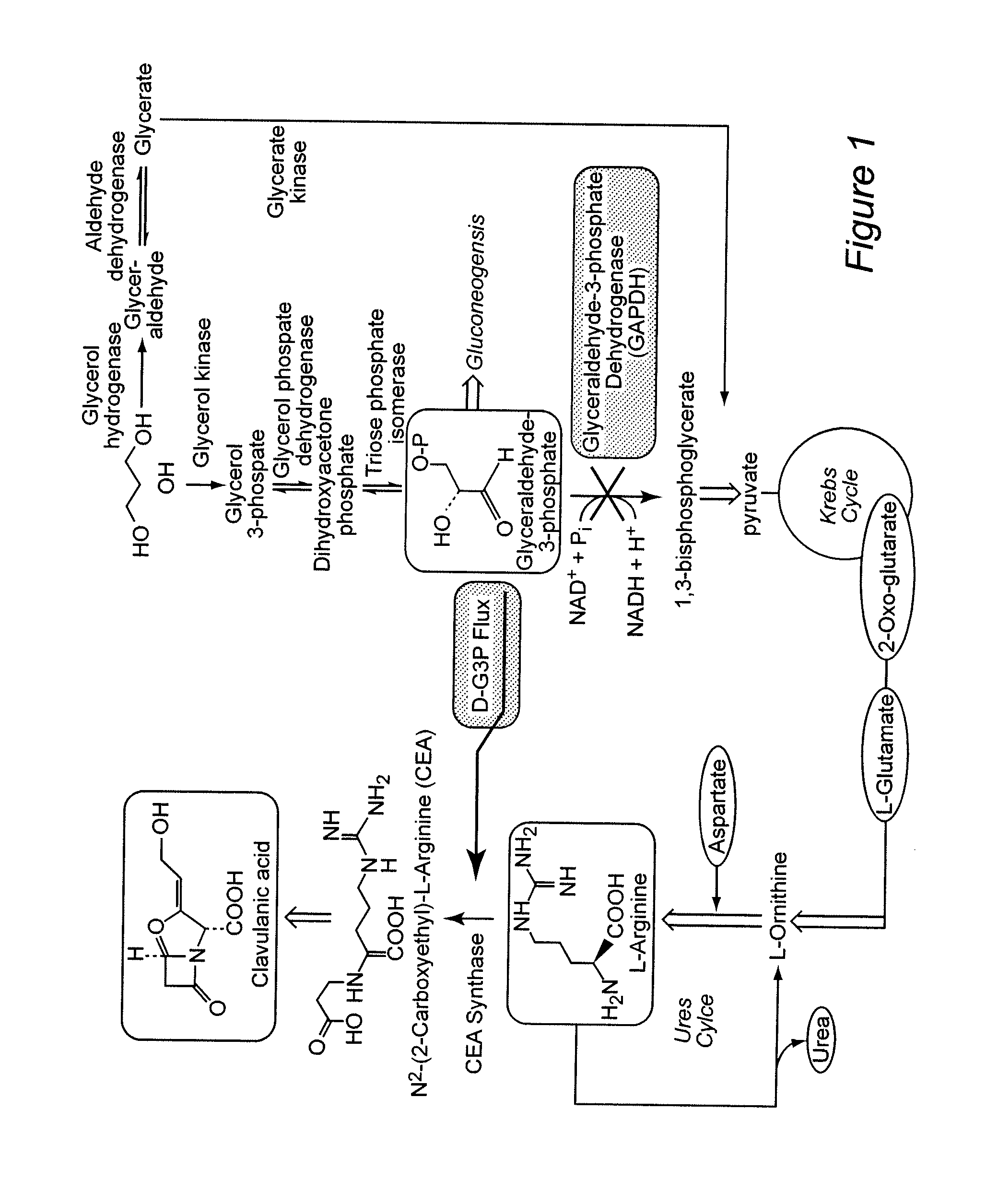
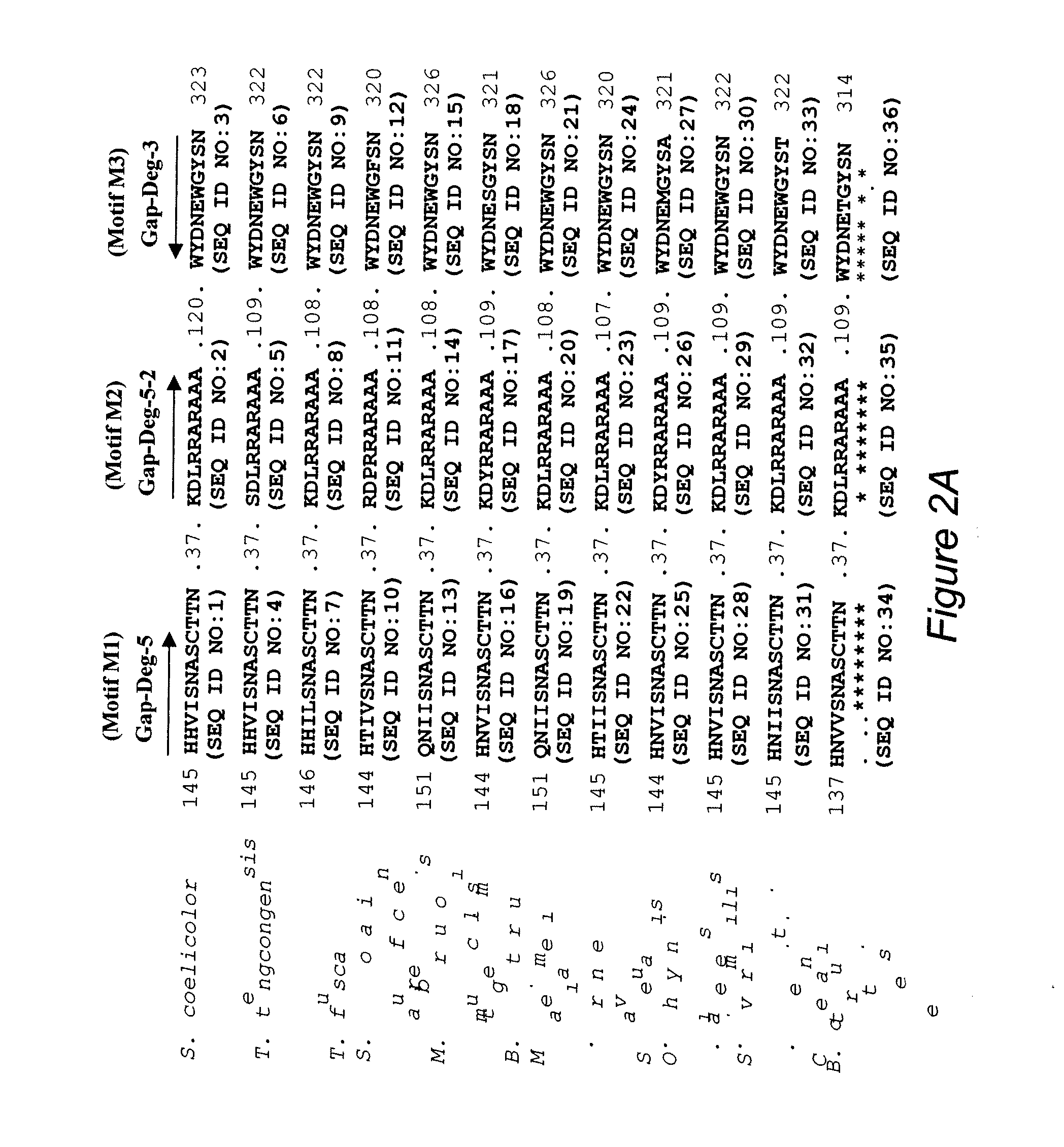
Genetically engineered Streptomyces clavuligerus strains with improved capabilities to produce clavulanic acid are provided. The strains are genetically engineered by disrupting newly identified glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) genes. This results in an increased intracelluar pool of the clavulanic acid precursor D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (D-G3P), and increased clavulanic acid production. Clavulanic acid production may be further increased by supplying arginine to the medium in which the S. clavuligerus is grown.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Fungal micro-organism having an increased ability to carry out biotechnological process(es)
InactiveUS20050106734A1Easy to useDecreasing and eliminating needFungiBiofuelsNucleotideGlyceraldehyde
The present invention relates to fungal microorganism having an increased ability to carry out biotechnological process(es). In particular, the invention relates to improving the regeneration of redox cofactors in biotechnological processes where useful products are produced from biomass containing pentoses. According to the invention, the microorganism is transformed with a DNA sequence encoding an NADP linked glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. The invention can be used to provide useful products for mankind from biological materials, including e.g. agricultural and forestry products, municipal waste. Examples of such useful products are ethanol, lactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates, amino acids, fats, vitamins, nucleotides and a wide variety of enzymes and pharmaceuticals.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
Ammonia diagnosis/determination reagent kit and ammonia concentration determination method
InactiveCN101169411AFast measurementImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementWavelengthGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The invention relates to an ammonia diagnosing / measuring reagent box which utilizes the technique of the enzyme contrasting color method and the enzyme jointing method, and belongs to the technical field of the medicine / food / environment test. The main components of the reagent box of the invention mainly include cushion liquid, coenzyme, glutamic acid, adentosine triphosphoric acid, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, glutamine synthetase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and stabilizing agent; the reagent box generates a series of enzymic reactions through the mixing of the samples and the reagent at a certain cubage rate, and then the reactants are positioned under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer which tests the reducing speed of the absorbency at the main wave length of 340nm, thereby measuring the concentration size of the enzyme. The invention can absolutely get needed measuring result through the ultraviolet / visible light analyzer.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Preparation method of Trichoderma reesei gene engineering bacterium for highly yielding heat stability xylanase
ActiveCN106676126AIncrease productionFungiVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPUC19
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Trichoderma reesei gene engineering bacterium for highly yielding heat stability xylanase. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an expression cassette sequence sequentially comprising a Trichoderma reesei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter, a Trichoderma reesei cbh1 signal peptide sequence, an xylanase xyn-LVK gene sequence and a Trichoderma reesei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase terminator; cloning the expression cassette sequence into pUC19 in order to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid; and lightly uniformly mixing the recombinant expression plasmid with a pAN7-1 vector, co-transforming Trichoderma reesei protoplasts, and screening the Trichoderma reesei protoplasts to obtain the Trichoderma reesei gene engineering bacterium for highly yielding heat stability xylanase xyn-LVK. The content of the xylanase xyn-LVK expressed in the Trichoderma reesei is about 40% higher than the content of the xylanase xyn-LVK expressed in Pichia yeast.
Owner:深圳市鼎宏生物科技有限公司
Methods for transforming Phaffia strains, transformed Phaffia strains so obtained and recombinant DNA in said methods
InactiveUS6329141B1High expressionSuitable for productionFungiBacteriaRibosomal protein E-L30Open reading frame
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the disclosed amino acid sequences. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV +1
Isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on genomic scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN104630250AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSynthetic biologyIsobutanol synthesis
The invention provides an isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding the adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on a genomic scale metabolic network model. Based on the genomic scale metabolic network model, by adopting flow balance analysis and metabolic minimum adjustment analysis, the action law of different reconstruction modes of an intracellular reducing power metabolism to strain growth and isobutanol synthesis is simulated, and according to phenotypic coefficients, a conclusion that glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key target spot of the intracellular reducing power adjustment of an isobutanol synthetic strain is obtained. By using a synthetic biological artificially-regulated element, an NADP+ depended glycerin-3-phosphate dehydrogenase metabolic pathway is built and adjusted so as to match and balance the intracellular reducing power metabolism, thereby obtaining an efficient isobutanol synthetic strain. The intracellular NADPH / NADP ratio of the strain reaches 0.4-0.8, and when 20-50 g / L glucose as a substrate is adopted for carrying out batch fermentation, the yield of isobutanol can reach over 8 g / L in 36 h, which is increased by over 60%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
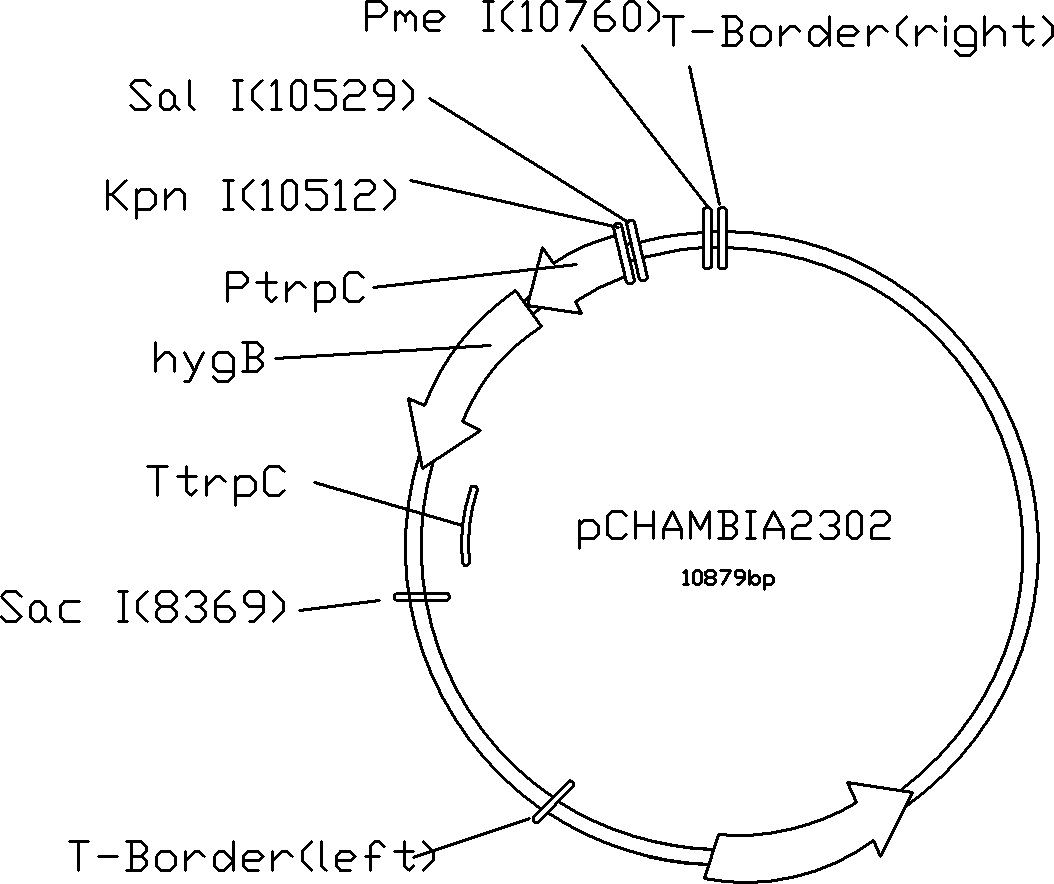
Method for obtaining strain capable of expressing lipase effectively
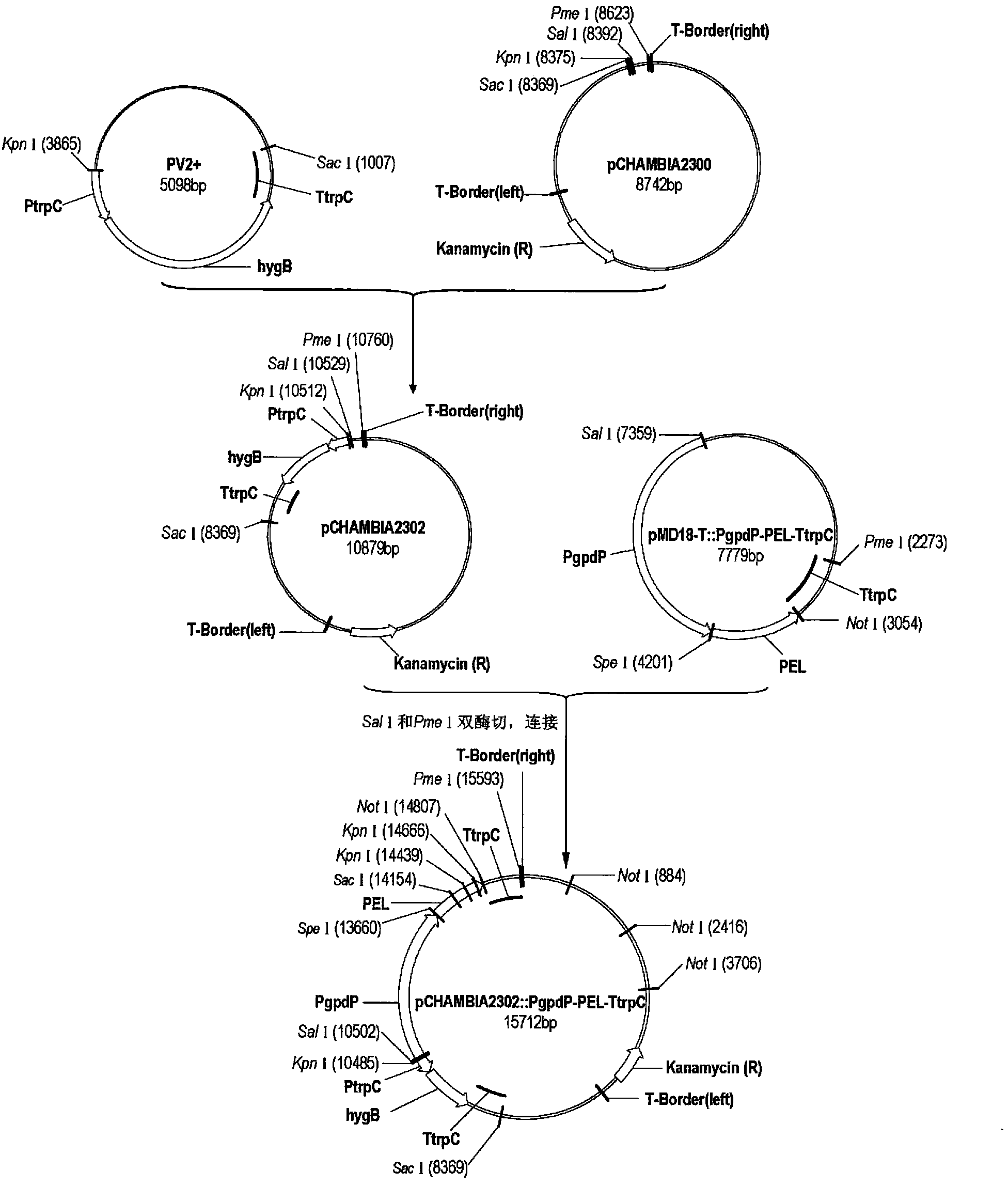
ActiveCN102154340ABreeding goals are clearImprove efficiencyFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyPenicillium cainii
Aiming at the drawbacks of the prior art, the invention applies for providing a method for breeding a penicillium gene engineering bacterium having high lipase synthesis capability. The method comprises: obtaining a hygromycin-resistance expression box and cloning to a target plasmid to obtain a hygromycin-resistance plasmid; amplifying the lipase gene, namely primary effusion lymphoma (PEL), of the penicillium and the strong promoter, namely glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter PgpdA, of Aspergillus nidulans and tryptophan synthetase terminator TtrpC of the Aspergillus nidulans respectively to obtain a PEL gene expression box driven by the strong promoter; inserting the PEL gene expression box into the hygromycin-resistance plasmid to obtain a PEL gene super expression vector containing a hygromycin screening marker; and finally, transferring Agrobacterium rhizogenes by using the PEL gene super expression vector containing the hygromycin screening marker, and transferring the PEL gene expression box into a penicillium strain by using a Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transfer method to obtain the penicillium gene engineering bacterium with high lipase expressing capability.
Owner:ANHUI LEVEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for increasing expression of CP4-EPSPS in Hansenula polymorpha
ActiveCN102559730ASuitable for large-scale productionMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsKnowledge FieldGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, particularly to a method for realizing high expression of CP4 (cysteine proteinase 4)-EPSPS (5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase) fusion protein gene in a constitutive manner in Hansenula polymorpha cells by using a composite enhancer. The method comprises the following steps: (1) improving the yield of codon-optimized CP4-EPSPS fusion protein gene in Hansenula polymorpha by using the composite enhancer; (2) regulating and controlling CP4-EPSPS fusion protein gene to express in a constitutive manner in polytype Hansenula by adopting Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter; (3) fermenting optimized Hansenula polymorpha; and (4) rapidly purifying the recombinant heterologous protein by employing nanofiltration and nickel column affinity chromatography. The CP4-EPSPS recombinant fusion protein prepared by the method can serve as an alternative protein standard substance in the field of study on the origin of protein and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
NADP-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase for therapeutic use
According to the present invention, a series of genes are identified in Group B Streptococcus, the products of which may be located on the outer surface of the organism. The genes, or functional fragments thereof, may be useful in the preparation of therapeutics, e.g. vaccines for the immunization of a patient against microbial infection.
Owner:EMERGENT PROD DEV UK
Salt algae NADP glyceral dehyde-3-phosdehydrogenase gene clone and protein expression method
The present invention relates to a kind of saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, coded protein and its clone and protein expression method. The invented saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene has the base sequence showed by SEQ NO 5, and its coded protein has the amino acid sequence showed by SEQ NO 6. Said invention uses homologous fragment of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene originated from chlamydomonas as probe and firstly clones a glyceraldehydes-3 phosphate dehydrogenase specialized by saline alga. Besides, said invention makes primary analysis for its sequence and coded protein sequence, at the same time makes primary function analysis for said gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
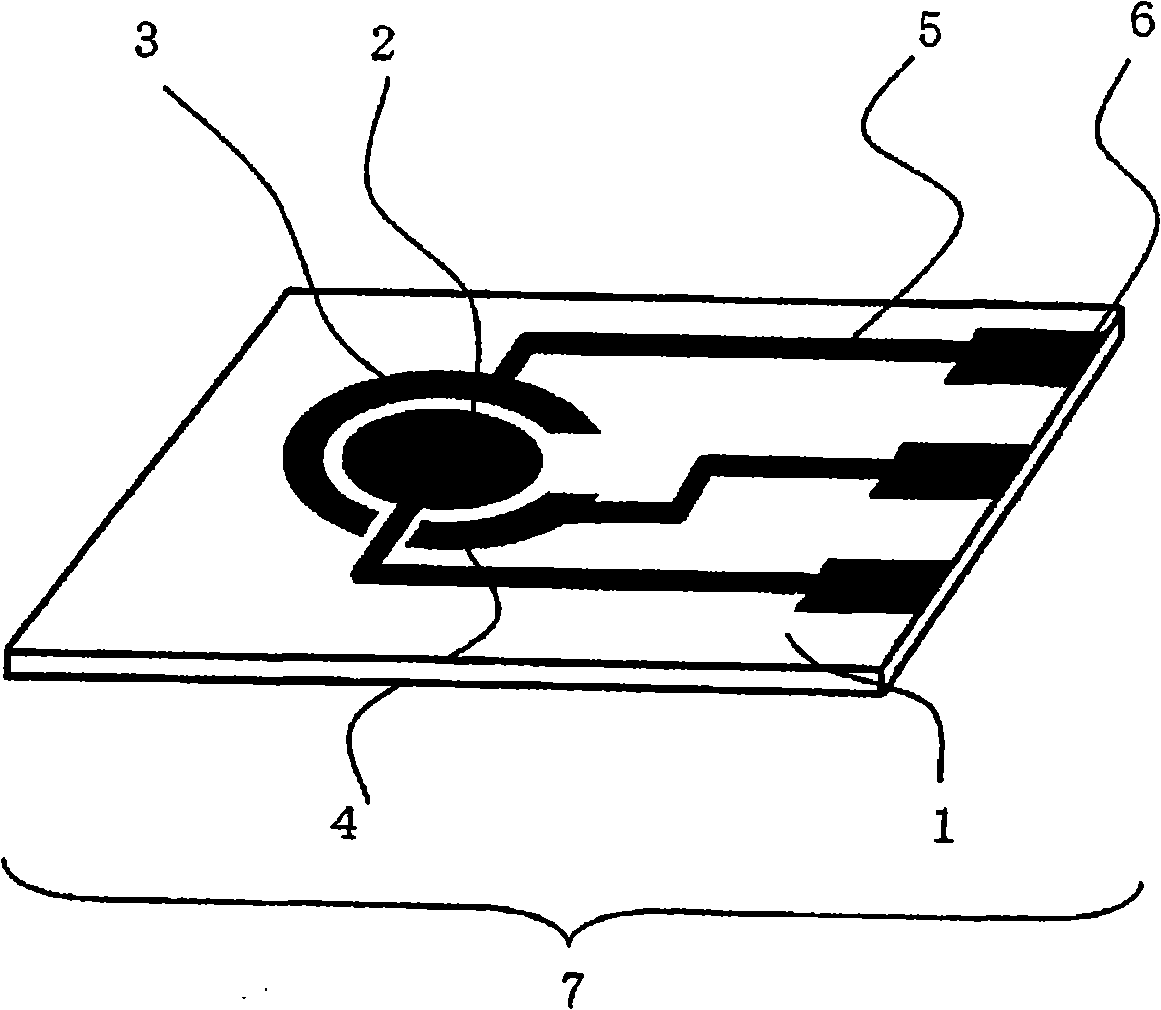
Sensor of pyrophosphate and SNP typing sensor using the same
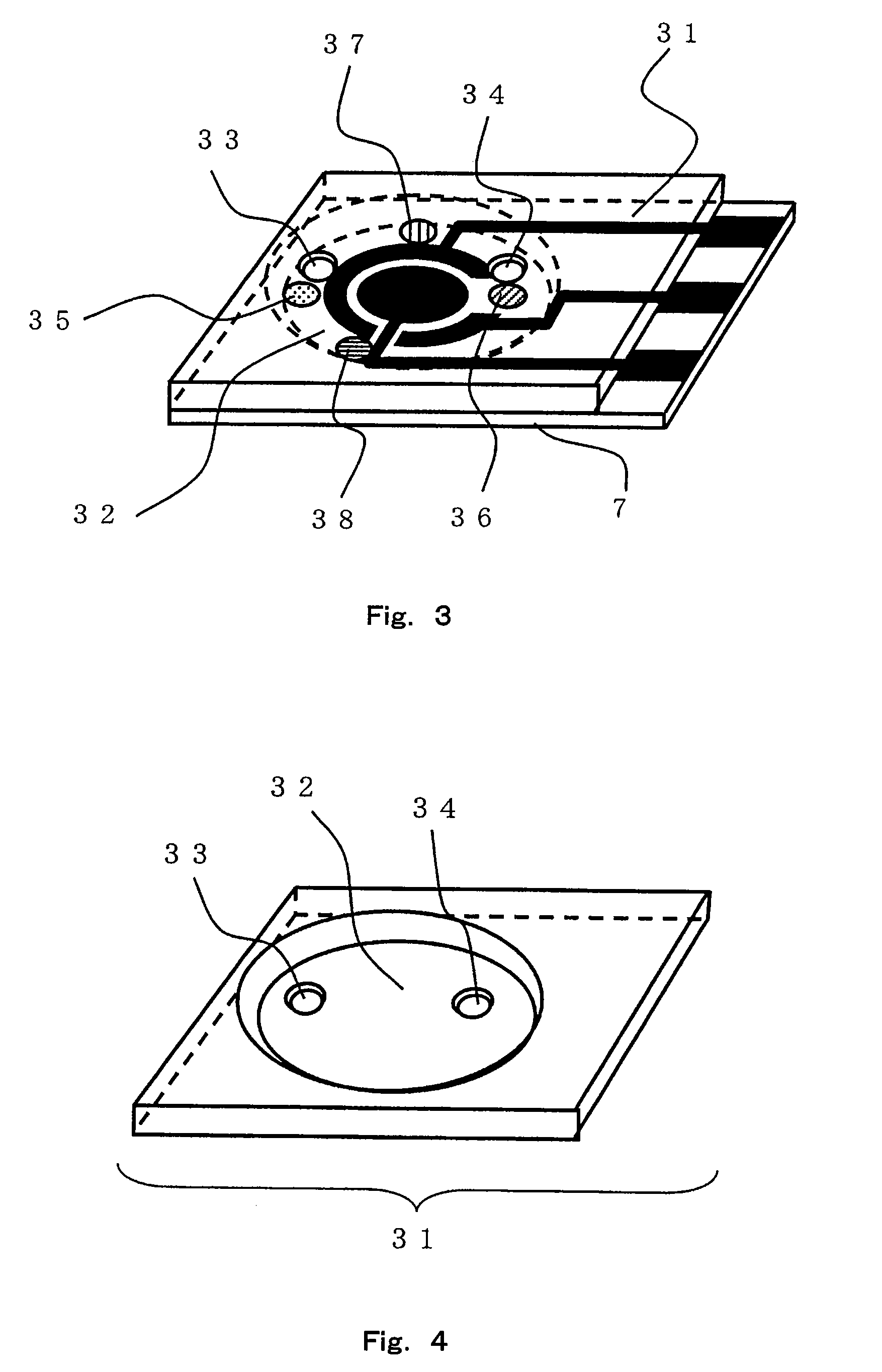
ActiveUS20080293128A1High sensitivityEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMagnesium saltPhosphoric acid
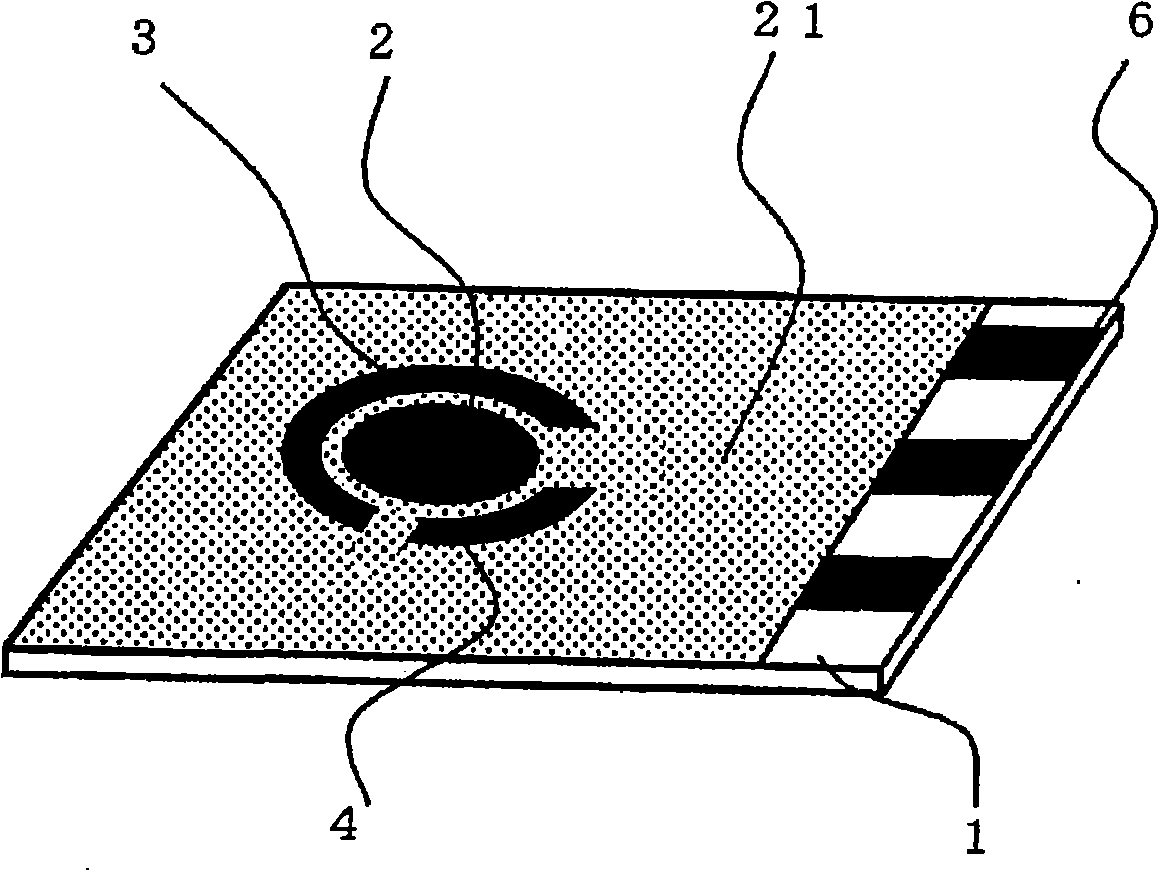
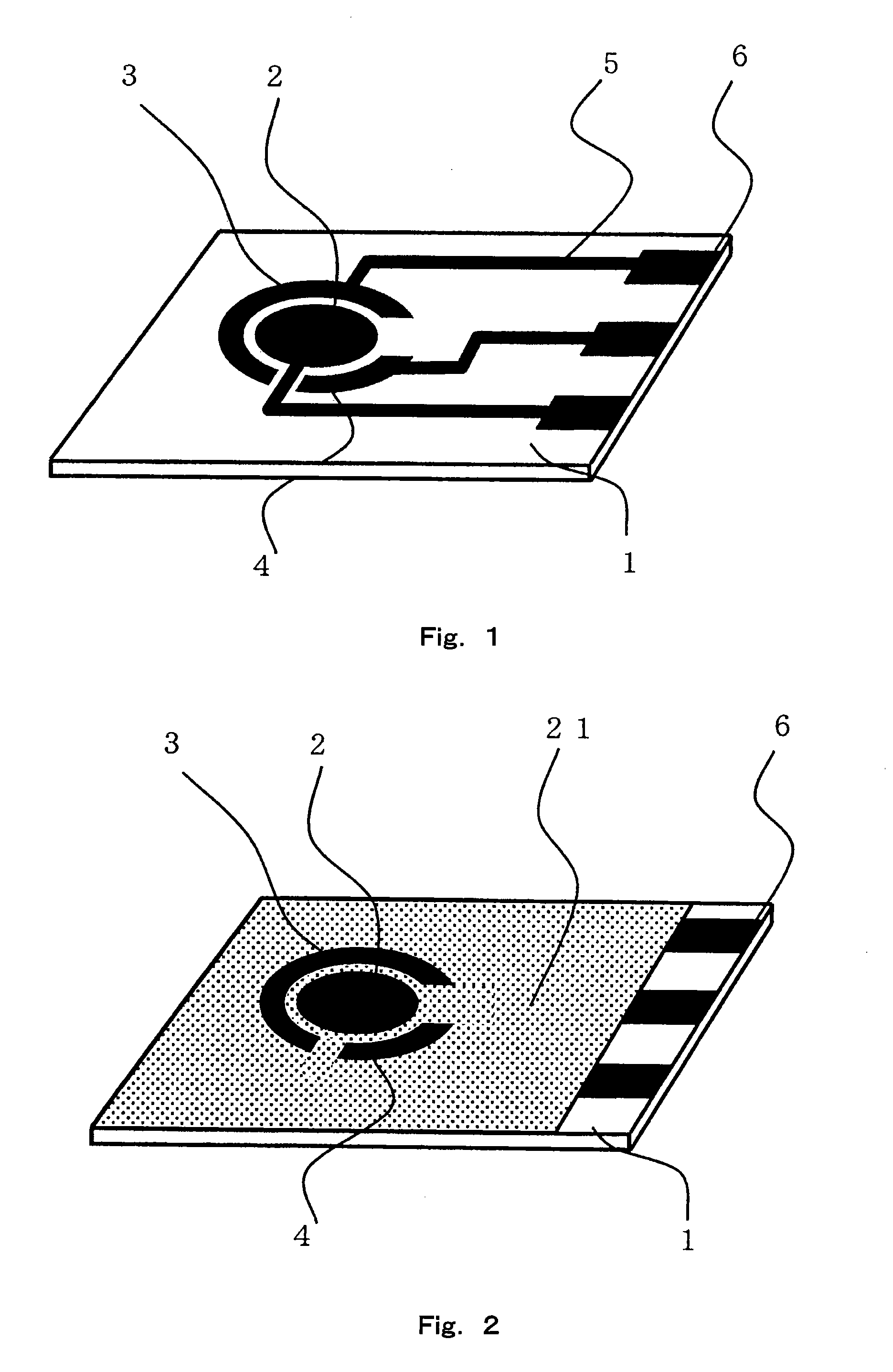
A sensor of pyrophosphate which can detect pyrophosphate conveniently with high sensitivity in a method for measuring pyrophosphate in SNP typing utilizing a primer extension reaction is provided.A sensor of pyrophosphate which is characterized by including: an insulative substrate 1; an electrode system that is formed thereon and has a measurement electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3; and a plurality of reaction reagent layers that are provided on the substrate 1 and include pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide, an electronic mediator, a magnesium salt and a buffer component, reaction reagent layer 36 including the enzyme being separated from reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component, and reaction reagent layer 37 including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate being separated from the reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Edwardsiella tarda subunit oral microencapsule vaccine for aquatic product
InactiveCN105920593AWide variety of sourcesLow priceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseAntigen
The invention relates to an edwardsiella tarda subunit oral microencapsule vaccine for an aquatic product. The edwardsiella tarda subunit oral microencapsule vaccine comprises a calcium alginate-chitosan release-controlled microcapsule and three recombinant protein-lipopolysaccharide conjugates which are encapsulated in the microcapsule, wherein the three recombinant protein-lipopolysaccharide conjugates include edwardsiella tarda glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases, outer membrane protein and flagellin which are mixed with astragalus polysaccharide. The oral microencapsule is characterized in that the encapsulation efficiency is 78%, the protein load is 102mg / g, and the grain size is 150+ / -10 microns. The prepared oral microencapsule vaccine is convenient to use, proper in grain size, high in slow release performance and high in antigen protection performance, and can effectively irritate a fish intestinal immune system to perform immune response so as to enable a fish to gain the specific immunity protection capacity for edwardsiella tarda; and as a result, the edwardsiella tarda subunit oral microencapsule vaccine is applicable to prevention and treatment of fish edwardsiella tarda disease.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
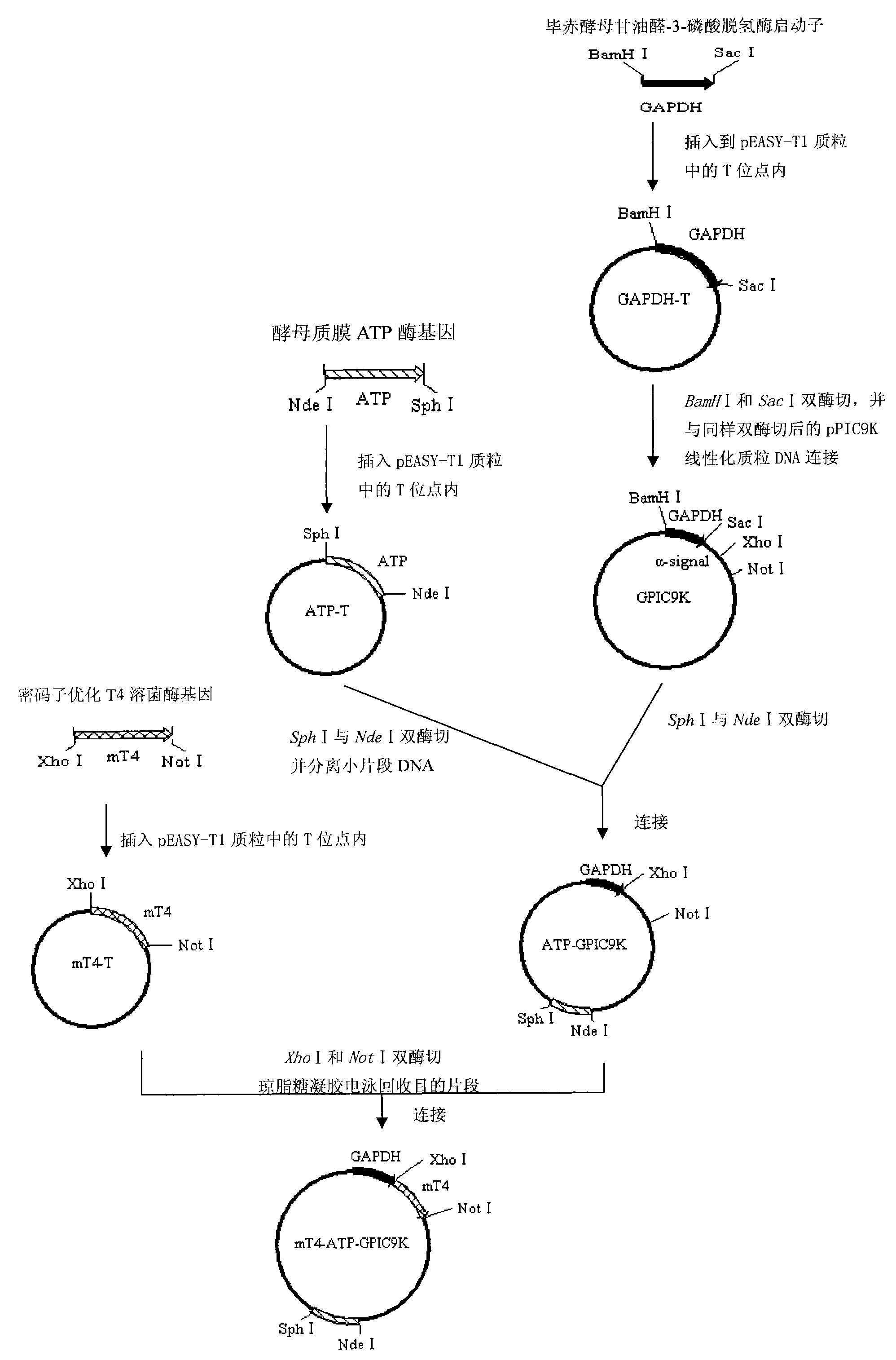
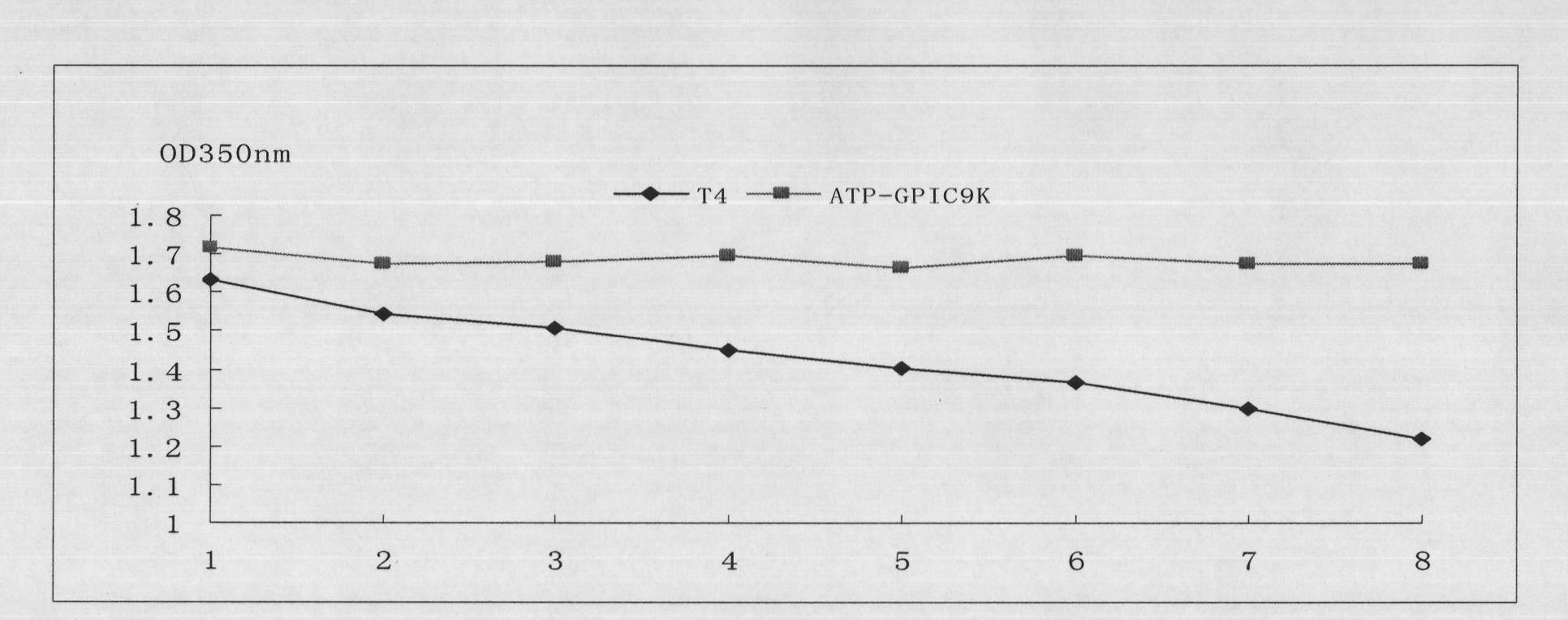
Method for efficiently expressing and producing T4 lysozyme through recombinant hansenula polymorpha in constitutive mode
ActiveCN101831451AExtended shelf lifeHigh antibacterial activityFungiMicroorganism based processesATPaseBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for efficiently expressing and producing recombinant protein of T4 lysozyme in a recombinant hansenula polymorpha cell in a constitutive mode. The method comprises the following steps: 1) increasing the biological output of T4 lysozyme genes in a eukaryotic expression system, namely hansenula polymorpha cells, by using the T4 lysozyme gene with optimized codon; 2) taking a coded sequence of a plasmalemma ATP enzyme nucleotide derived from the hansenula polymorpha as a homologous sequence for completely integrating exogenous plasmid into the hansenula polymorpha genome; 3) adjusting and controlling the high-efficiency expression of the T4 lysozyme gene in the hansenula polymorpha in the constitutive mode by using pichiapastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter; and 4) providing a specific hansenula polymorpha engineering bacteria fermentation culture and growth condition so as to improve the biological output of recombinant protein of T4 lysozyme and quickly extract the recombinant exogenous protein. The recombinant protein of T4 lysozyme finally prepared by the method has biological activity and can be widely applied in fields such as medicinal treatment, foods, feeds, scientific research and the like.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Triple real-time fluorescence PCR method for detecting bovine-derived, sheep-derived and porcine-derived ingredients
ActiveCN107058498AReduce generationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase GenePositive control
The invention relates to a triple fluorescence PCR method for detecting bovine-derived, sheep-derived and porcine-derived ingredients. The method comprises four elements, namely a sample DNA, a pair of universal primers and three probes, fluorescence PCR premixed liquid as well as a positive control. The method comprises the following steps: designing primers and probes according to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes of cows, sheep and goats as well as pigs, amplifying a target sequence, and exciting and quenching a fluorescence signal, wherein a non-target sequence is not amplified and has no fluorescence signal; and preparing a kit according to a formula of a reagent used in fluorescence PCR amplification carried out on a to-be-detected sample DNA and amplification conditions. Concrete actions are as follows: a triple fluorescence PCR primer system used for detecting the bovine-derived, sheep-derived and porcine-derived ingredients is established; a triple fluorescence PCR kit used for detecting the bovine-derived, sheep-derived and porcine-derived ingredients is established; and a triple fluorescence PCR identification method used for detecting the bovine-derived, sheep-derived and porcine-derived ingredients is determined. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the standard error is small, the detection time is short, multiple target genes can be detected at the same time, and the reagent cost is saved; and the method is applicable to true and false identification of an animal product.
Owner:贵州省产品质量检验检测院
Truncated glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter
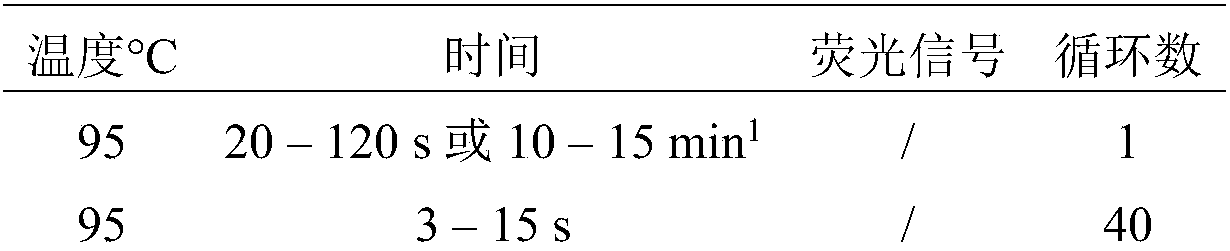
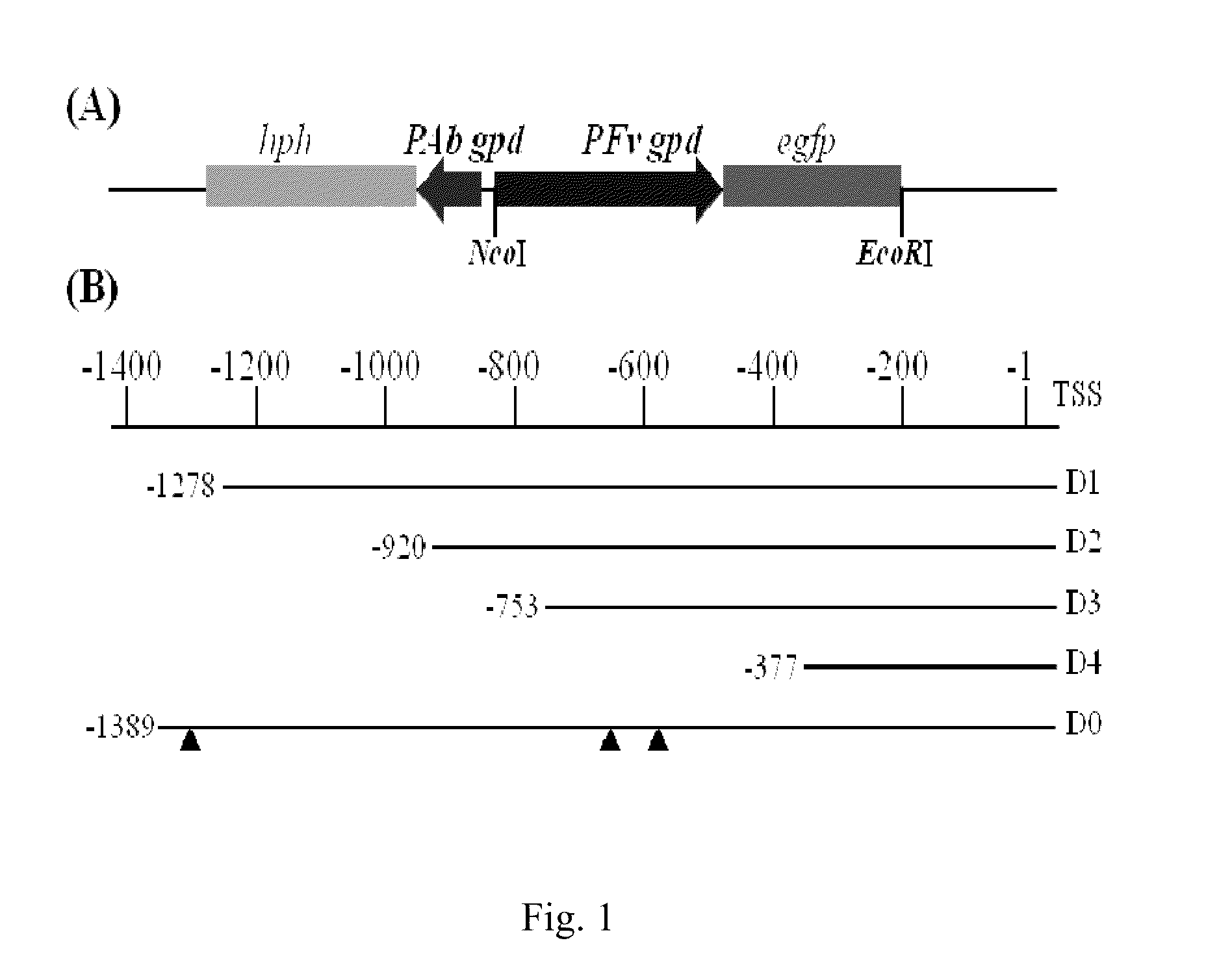
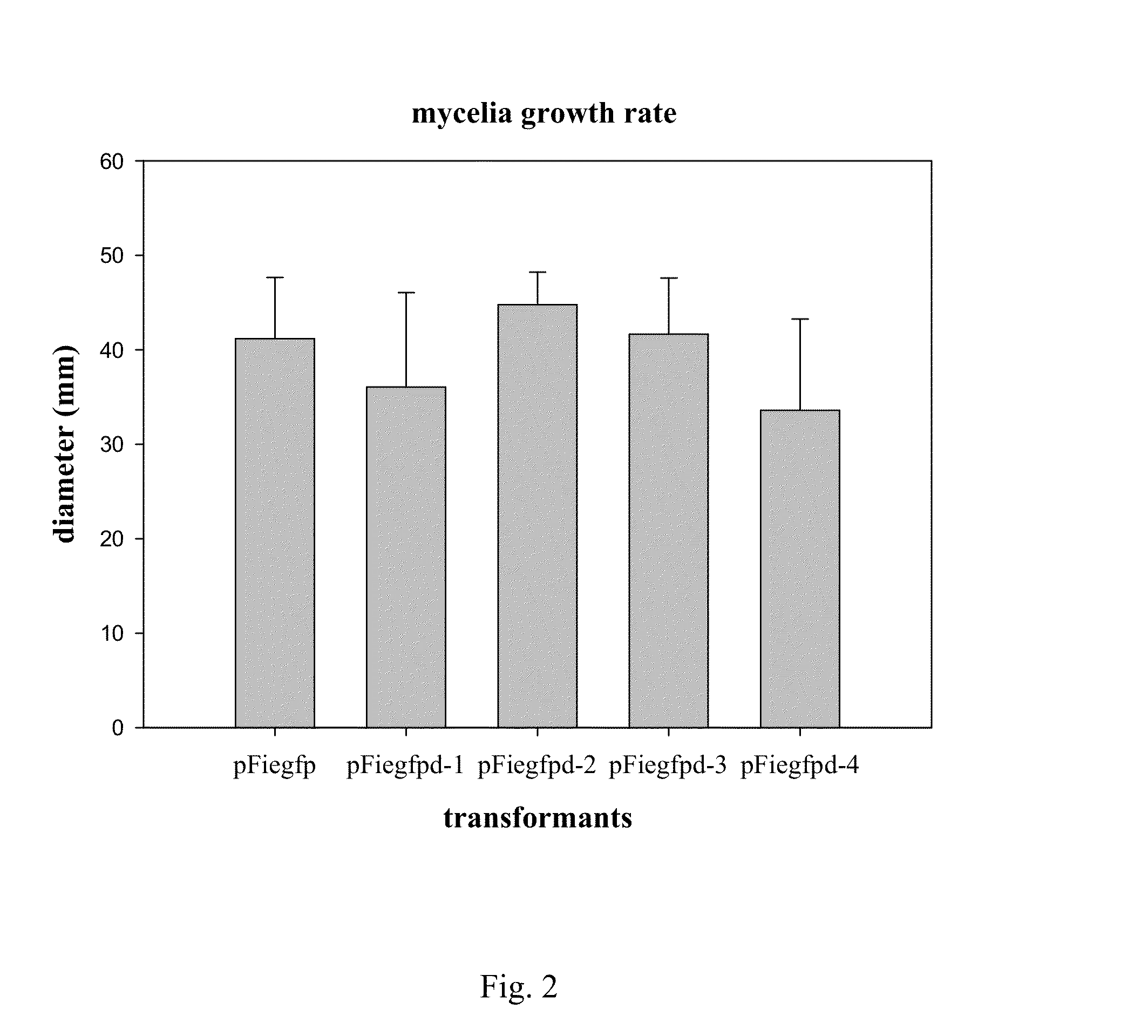
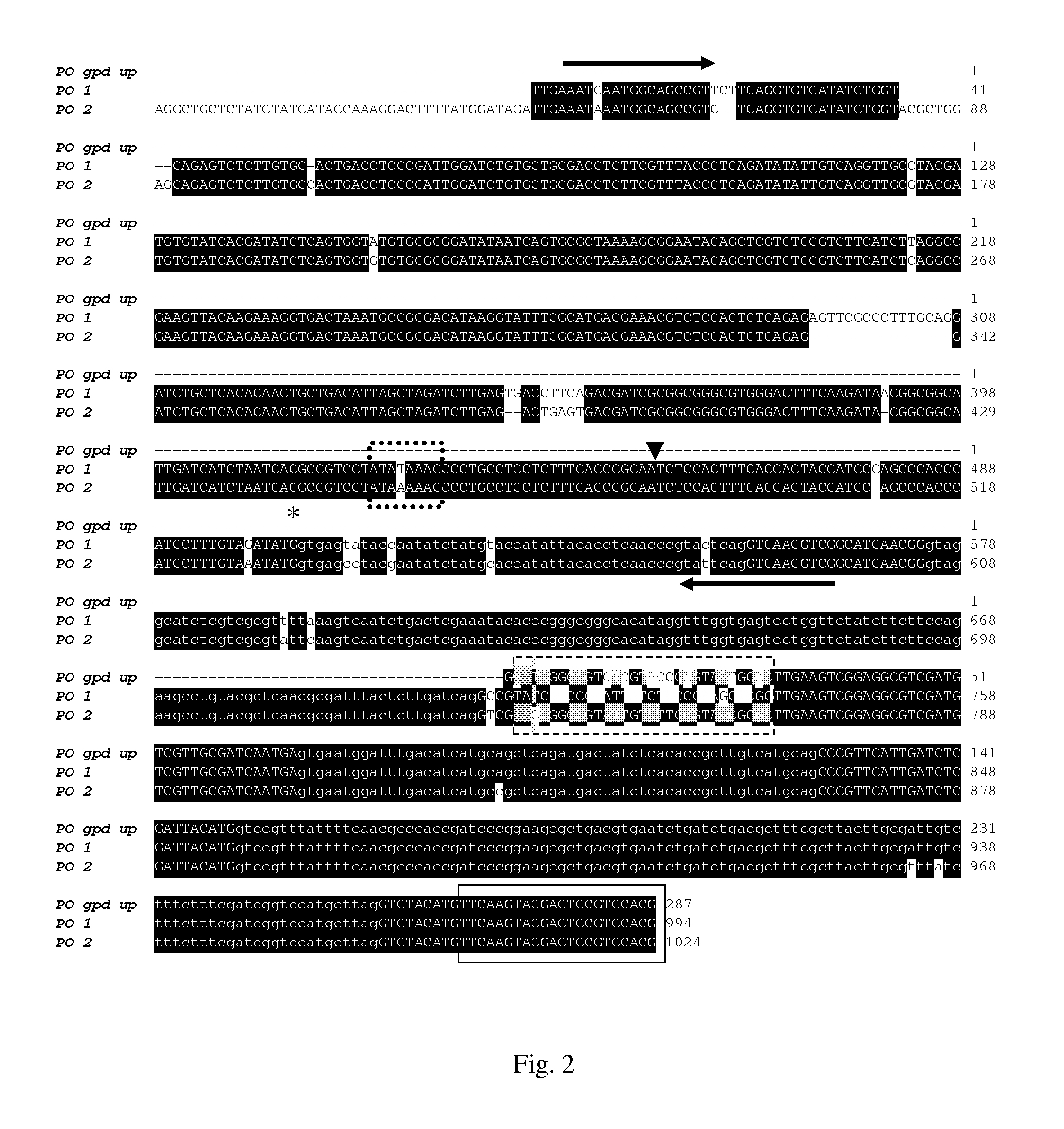
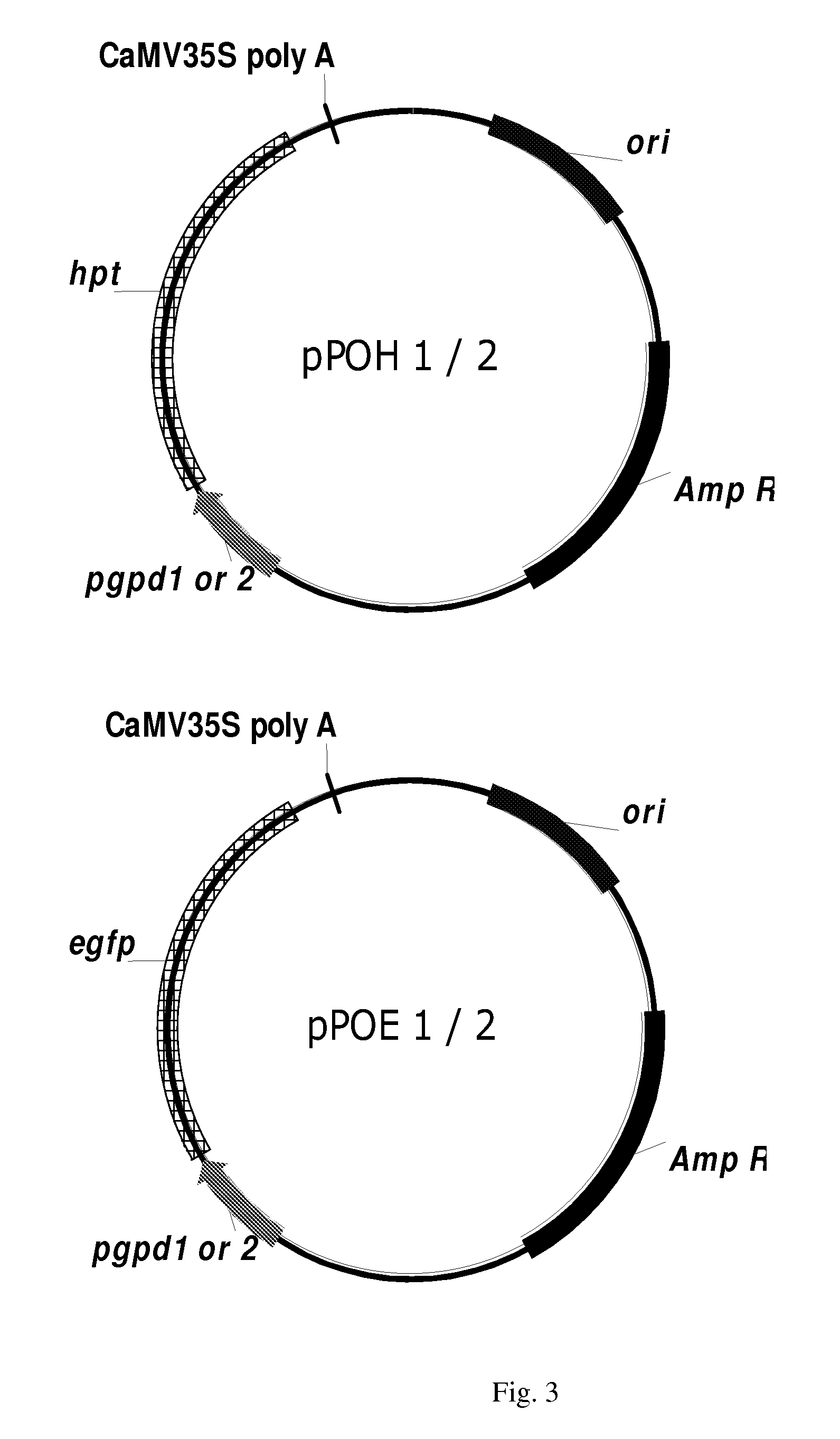
The invention found that partial deletion of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) promoter can enhance gene expression (even heterologous gene expression) in basidiomycetous fungi. With the discovery of these gpd promoters, an expression system can be constructed for the expression of a heterologous gene in mushroom. Accordingly, the invention provides a truncated glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and a construct comprising the promoter of the invention operably linked to a heterologous transcribable polynucleotide molecule and a mushroom comprising the construct.
Owner:MYCOMAGIC BIOTECH
Zinc diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and method for measuring zinc concentration
InactiveCN101173931AFast measurementImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The invention relates to a zinc diagnosis / determination reagent kit which adopts the techniques of enzymatic colorimetric method and enzyme couple reaction, belonging to the technical field of medicine / food / environment test and determination. The invention also relates to the method principle of determining the zinc concentration, and the reagent composition and components. The component of the reagent kit mainly comprises buffer solution, coenzyme, phosphate monoester, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, alkaline phosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. The method for determining the zinc concentration is as follow: mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain volume ratio to perform a series of enzymatic reactions; placing the reactant under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect the ascending speed of the absorbency at the main wavelength of 340 nm; finally determining the zinc concentration. The invention has the advantages that the required determining result is obtained only with the ultraviolet / visible light analyzer.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
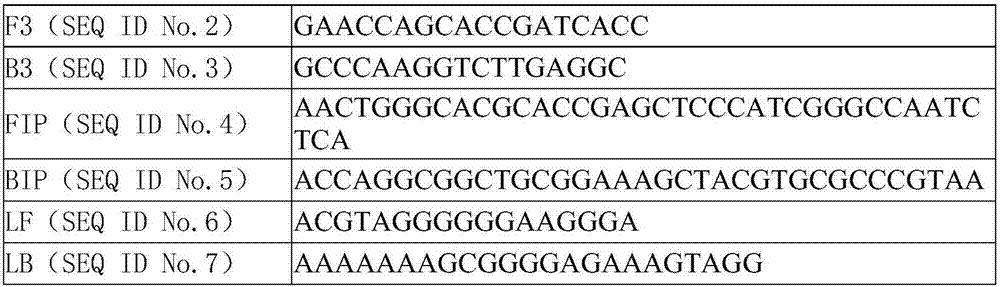
LAMP (loop mediated isothermal amplification) detection primer combination and kit for GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene
InactiveCN107287320AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGAPDH GeneQuality control system
The invention provides a detection primer combination and kit for a GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene. The primer combination is designed in the sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 as a target sequence and comprises F3, B3, FIP, BIP, LF and LB. When the primer combination is applied to an LAMP (loop mediated isothermal amplification) detection kit, results show that nonspecific amplification in primers and nonspecific binding amplification between the primers and a template are avoided for the primer combination, An LAMP amplified internal reference quality control system for a humanized sample is established successfully, and preliminary foundation is laid for widespread clinical use of the LAMP method in future.
Owner:曹国君
Preparation method and application of penicillium genetically engineering bacterium
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a penicillium genetically engineering bacterium. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining a hygromycin resistance expression cassette, cloning the hygromycin resistance expression cassette onto a target plasmid so as to obtain a hygromycin resistance recombinant plasmid; respectively cloning a penicillium lipase gene (PEL), a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter PgpdP of penicillium expansum and a aspergillus nidulans tryptophan synthetase terminator TtrPC so as to obtain a PEL gene expression cassette driven by a strong promoter; cloning the PEL gene expression cassette to the hygromycin resistance recombinant plasmid, thus obtaining a hygromycin selection marker containing a PEL gene over-expression vector; and converting the over-expression vector into an engineering agrobacterium, and converting the PEL gene expression cassette to a penicillium strain by using an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method, thus obtaining the penicillium genetically engineering bacterium. The penicillium genetically engineering bacterium obtained by the method has strong lipase production capacity; the enzyme activity of the lipase prepared by the penicillium genetically engineering bacterium is 100%-150% higher than that of a starting strain penicillium wild fungus.
Owner:ANHUI LEVEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Urine protein marker of ovarian cancer and diagnosis application thereof
InactiveCN109270276AComponent separationBiological testingEster hydrolaseRab GDP dissociation inhibitors
The invention relates to a urine protein marker of ovarian cancer and a diagnosis application thereof, in particular to a urine protein marker obtained by using in-situ injection of ovarian cancer cells in a rat ovary and mass spectrum analysis, and application in the diagnosis and disease course monitoring of human ovarian cancer. The urine protein marker is selected from cystathionine-gamma-lyase, a Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta, an ester hydrolase C11orf54 homolog, neutral and alkaline amino acid translocator rBAT, apolipoprotein A-1, OX-2 membrane glycoprotein, charged multivesicularbody protein 5, beta-amino hexosaminidase subunit beta, monocyte differentiation antigen CD14, glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, cadherin 1, gastricsin, a serine protease inhibitor A3M, alpha-1-asialoglycoprotein and the like. Differential protein obtained from the marker provides a simpler, quicker and non-invasive choice for early diagnosis and disease course monitoring of ovarian cancer.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
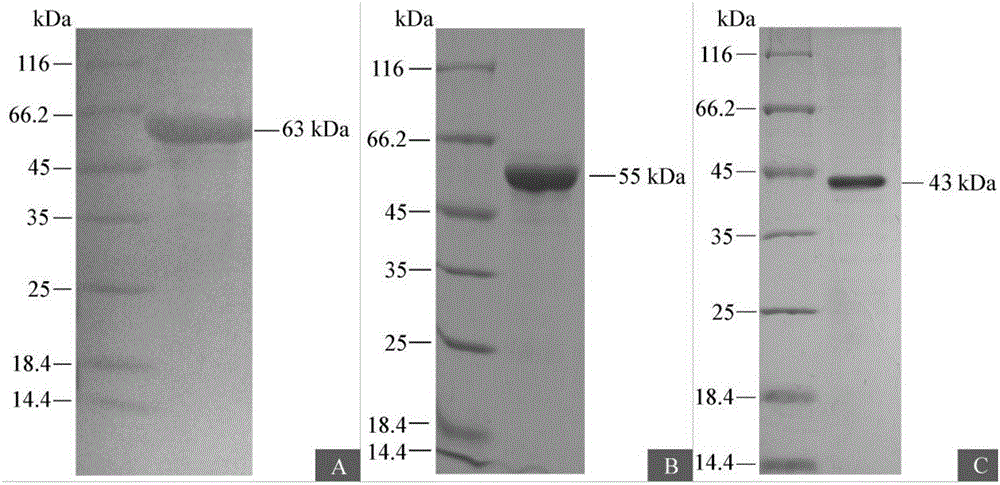
Method for distinguishing back muscles from muscles of three parts of male cyprinus carpio
The invention relates to a method for distinguishing back muscles from muscles of three parts of a male cyprinus carpio. The method comprises the following steps of: first obtaining a high-quality cyprinus carpio bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) 4 antibody; then successfully extracting proteins of the back muscles, belly muscles and tail muscles of the male cyprinus carpio; and finally detecting BMP4 proteins in muscle tissues of a target cyprinus carpio by using the detected cyprinus carpio BMP4 antibody, taking glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a control of target proteins, determining that the muscles belong to the back muscles of the male cyprinus carpio if the proteins of 55KD can be detected, and determining that the muscles belong to the muscles of the other parts of the male cyprinus carpio if the proteins of the 55KD cannot be detected. The method has the advantages that: the back muscles can be distinguished from the belly muscles and tail muscles of the male cyprinus carpio; a breakthrough can be provided for researches on pectoral muscle distinguishing and the other muscles; and simultaneously, a way and a method for the breeding of the back muscles of the male cyprinus carpio can be sought according to a molecular marker.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Gylceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter and heterologous gene expression
Owner:MYCOMAGIC BIOTECH
Pyrophosphoric acid sensor and snp typing sensor utilizing the same
ActiveCN101360993ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnesium saltGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
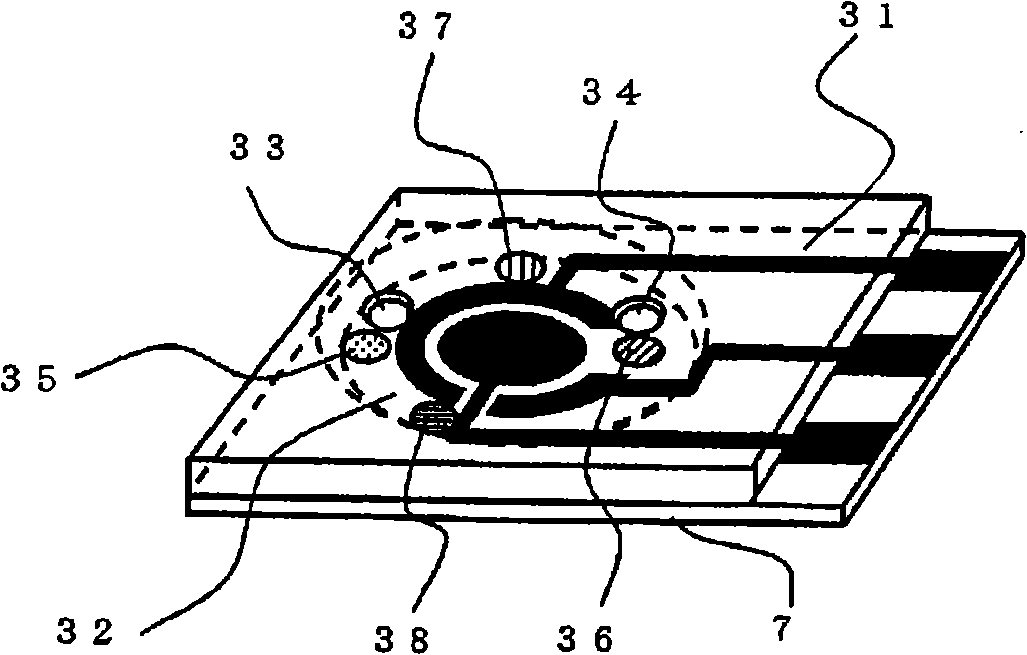
A pyrophosphoric acid sensor that in the method of measuring pyrophosphoric acid in SNP typing making use of primer extension reaction, realizes convenient detection of pyrophosphoric acid with high sensitivity. There is provided a pyrophosphoric acid sensor composed of insulating substrate (1); formed thereon, an electrode group consisting of measuring electrode (2) and counter electrode (3); and superimposed on the substrate (1), multiple reaction reagent layers consisting of pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, electron mediator, magnesium salt and buffer solution components wherein reaction reagent layer (35) containing buffer solution components is separated from enzyme-containing reaction reagent layer (36), characterized in that reaction reagent layer (37) containing glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is separated from the reaction reagent layer (35) containing buffer solution components.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Sensor of pyrophosphate and SNP typing sensor using the same
ActiveUS7632392B2High sensitivityEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMagnesium saltPhosphoric acid
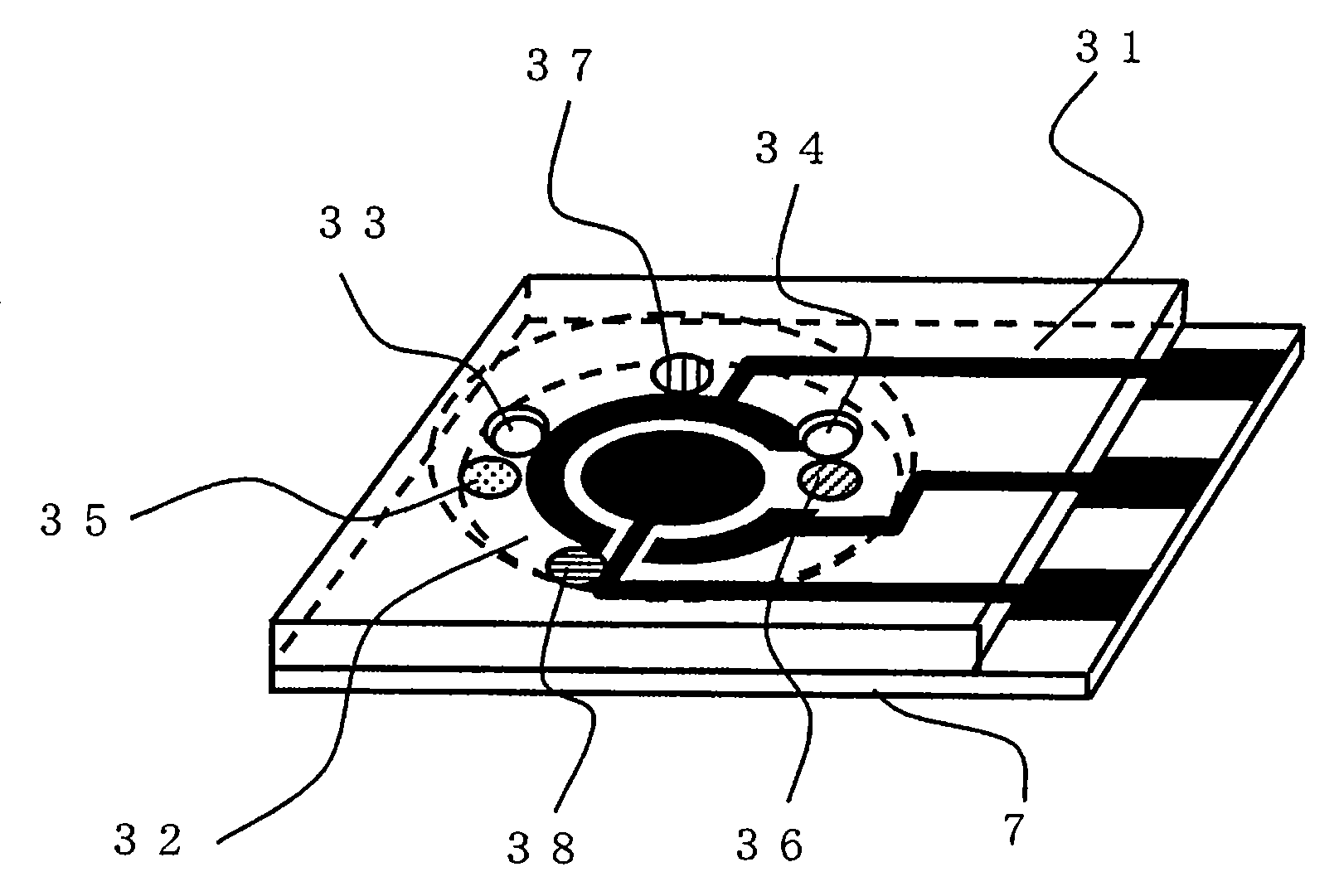
A sensor of pyrophosphate which can detect pyrophosphate conveniently with high sensitivity in a method for measuring pyrophosphate in SNP typing utilizing a primer extension reaction is provided.A sensor of pyrophosphate which is characterized by including: an insulative substrate 1; an electrode system that is formed thereon and has a measurement electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3; and a plurality of reaction reagent layers that are provided on the substrate 1 and include pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide, an electronic mediator, a magnesium salt and a buffer component, reaction reagent layer 36 including the enzyme being separated from reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component, and reaction reagent layer 37 including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate being separated from the reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com