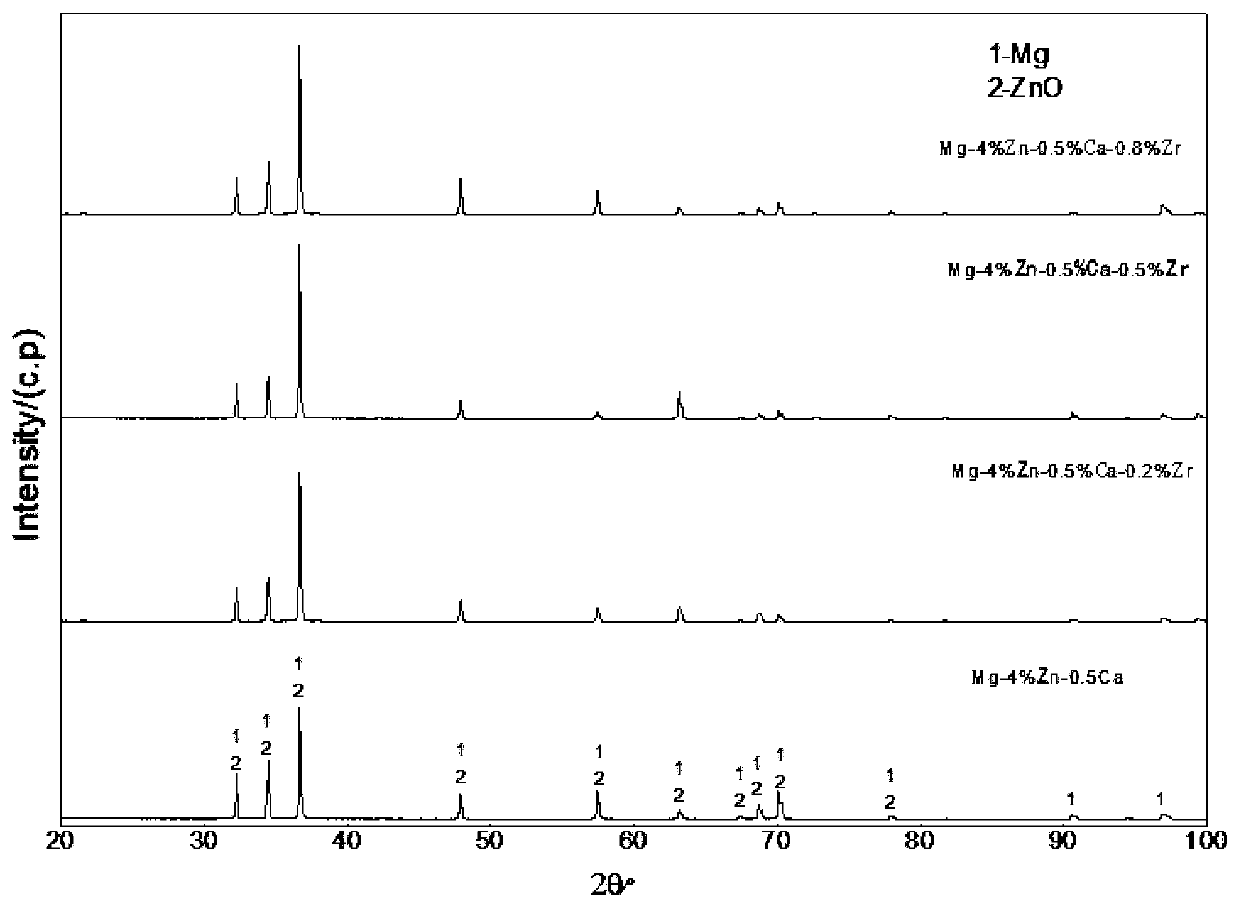
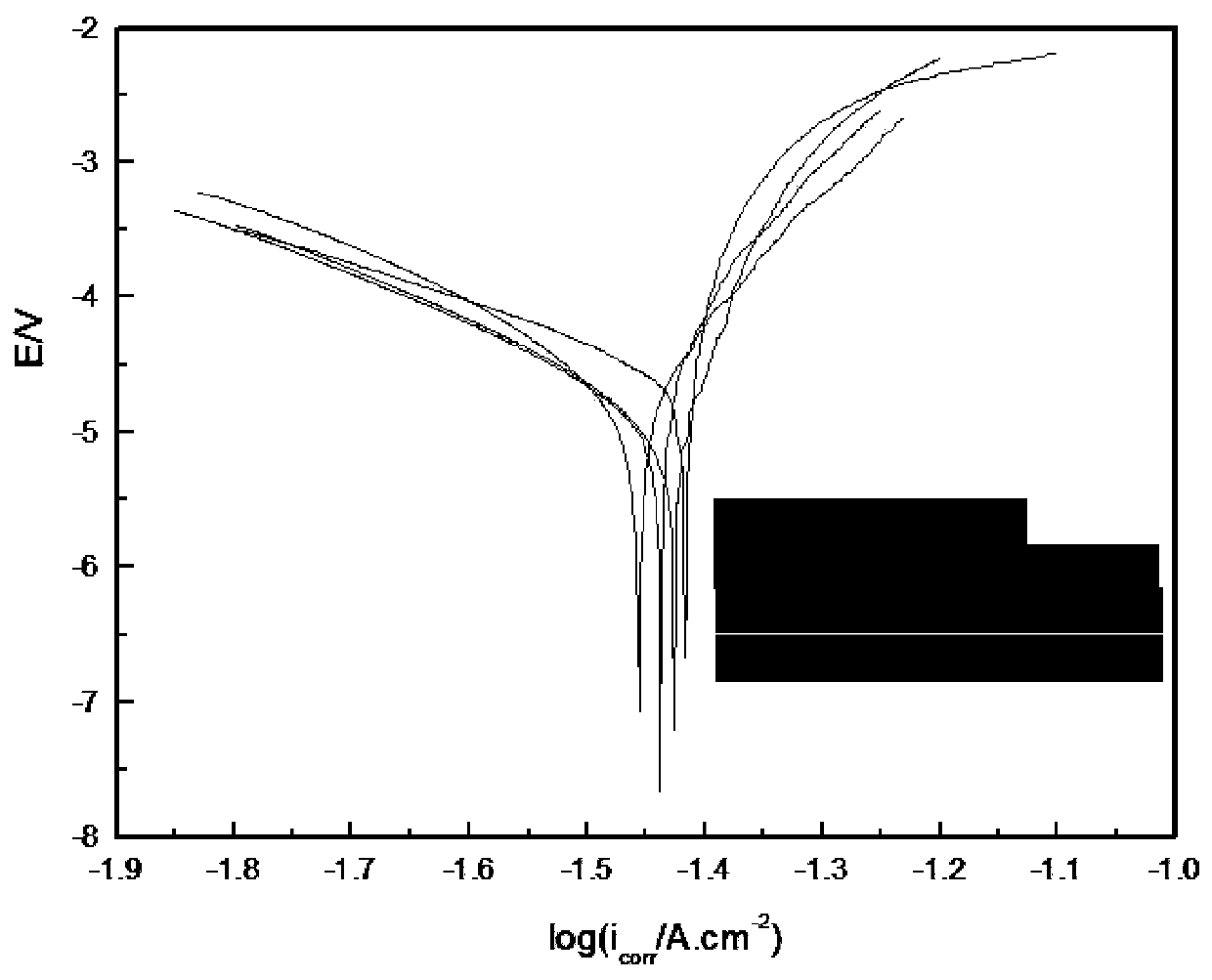
Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Reduce stress shielding effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Beta type Ti Nb Zr alloy with low modulus of elasticity, preparation method and application
This invention discloses a beta-type Ti alloy with low elastic modulus for mrdical application. The Ti alloy comprises: Nb 30-37%, Zr 0-20%, and Ti. The cast structure of the Ti alloy is beta phase. The Ti alloy has moderate strength, and can satisfy the strength requirement for clinical bearing material. The elastic modulus of the Ti alloy is only 45-55% that of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The alloy is a casting alloy, and has no noble metals added such as Ta, thus effectively lowering the cost. Besides, all the added elements have biocompatibility, and toxic elements are avoided. The Ti alloy has high biocompatibility and mechanical compatibility, and can be used to produce bone plates with reduced stress shielding effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
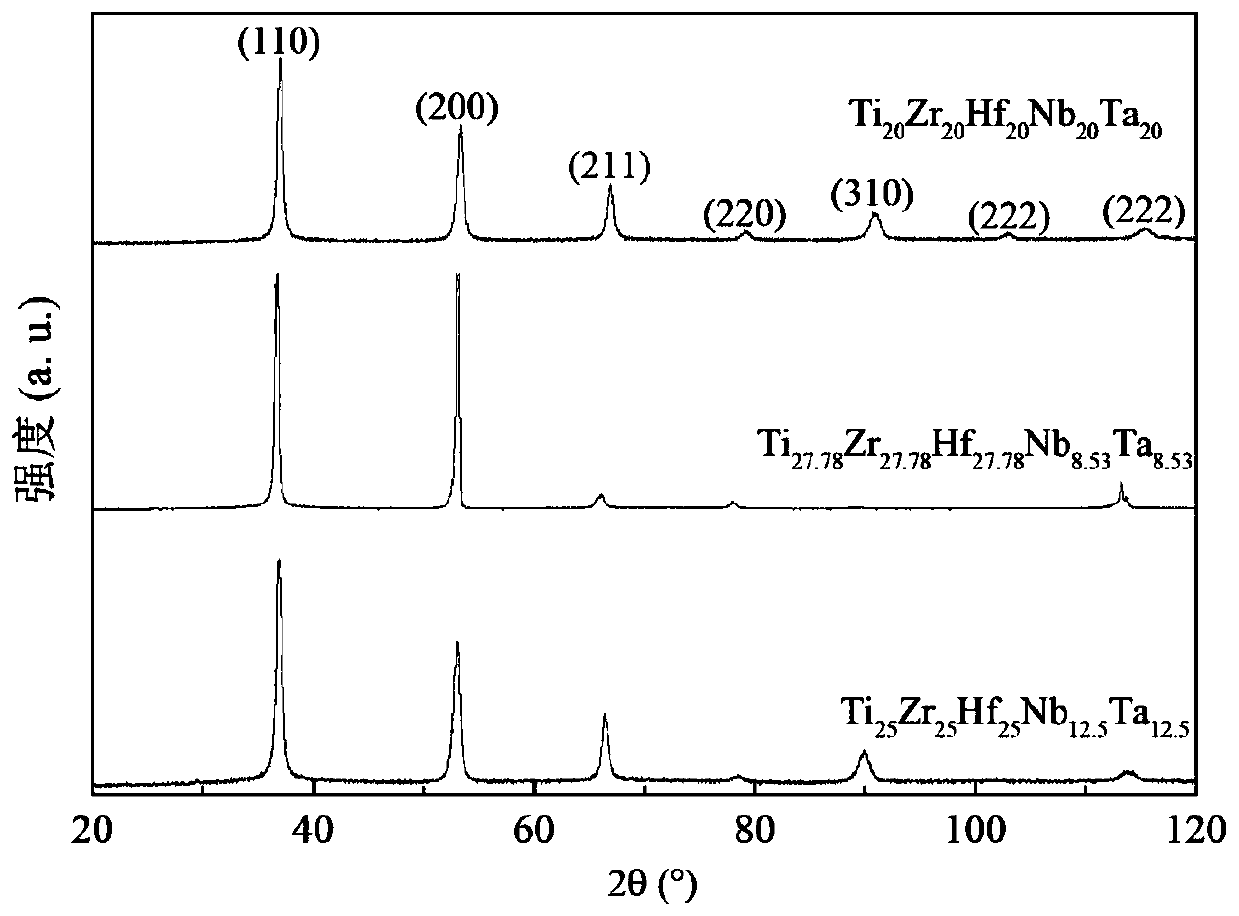
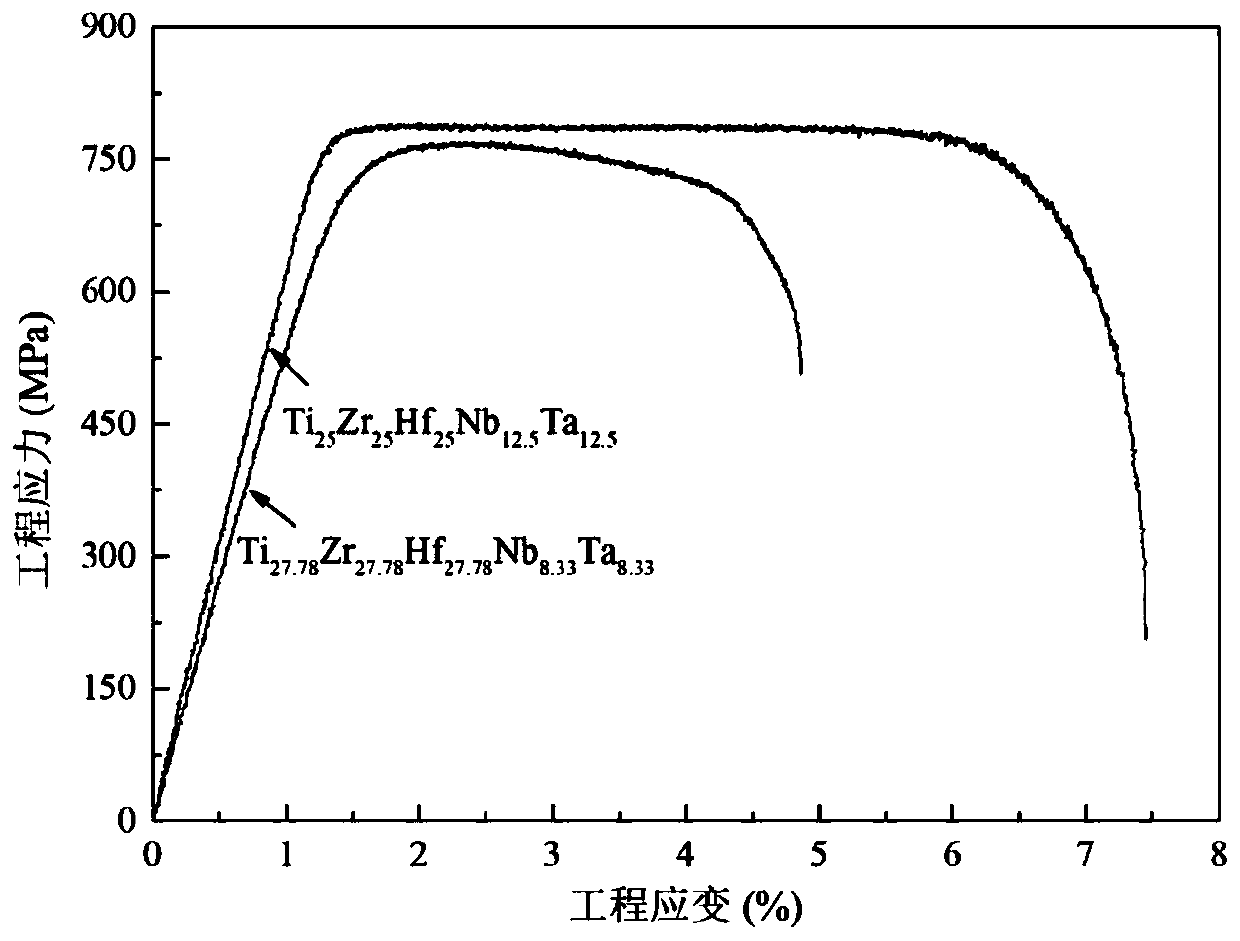
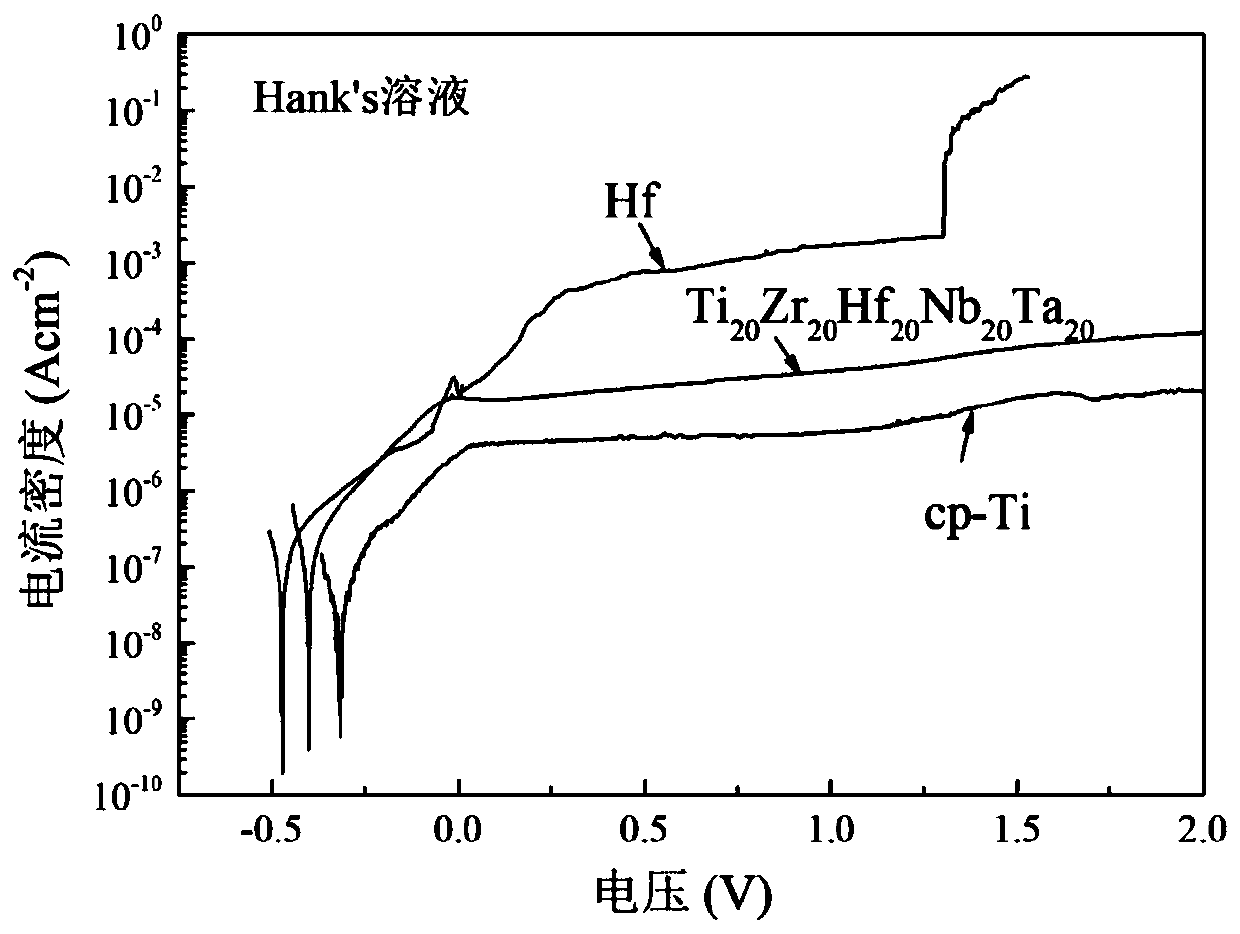
Biomedical Ti-Zr-Hf-Nb-Ta series high-entropy alloy and preparing method
InactiveCN110423933AHigh elastic modulusLow elastic modulusTissue regenerationProsthesisHigh entropy alloysUnit model
The invention relates to a biomedical Ti-Zr-Hf-Nb-Ta series high-entropy alloy. The composition general formula of the high-entropy alloy is TiZrHf<c>Nb<d>Ta<e>, wherein a, b, c, d and e are atomic percents, a is larger than or equal to 5 and smaller than or equal to 40, b is larger than or equal to 5 and smaller than or equal to 40, c is larger than or equal to 5 and smaller than or equal to 40, d is larger than or equal to 5 and smaller than or equal to 40, e is larger than or equal to 5 and smaller than or equal to 40, and the sum of a, b, c, d and e is 100. Starting from a TiZr-transition group high-entropy alloy system, a cluster type structure unit model is combined for component design, a low-modulus and high-corrosion-resistance biomedical TiZr-transition group high-entropy alloy with more excellent comprehensive mechanical performance is prepared, and the elasticity modulus of the Ti-Zr-Hf-Nb-Ta series high-entropy alloy is low to 54GPa.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Prestress-reinforced light high-strength controllable-degradation medical composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103330959AMake full use of the strengthening effectReduce dosageSurgeryAbsorbable polymersProtection layer
The invention relates to a prestress-reinforced light high-strength controllable-degradation medical composite material and a preparation method thereof. The medical composite material is characterized in that a magnesium alloy wire subjected to prestress processing is taken as a reinforced phase to improve strength and stiffness of the composite material, an absorbable high polymer material is taken as a matrix, and meanwhile, the early-stage degradation velocity of the composite material can be further regulated and controlled by regulating the thickness of a shell protection layer formed by the high polymer material of the matrix. According to the composite material, bars or plates are manufactured by utilizing methods of thermal die pressing, extrusion or drawing or the like, and various degradable high-toughness bone repairing and fixing instruments such as bone nails and bone plates can be obtained by carrying out subsequent machining; and compared with the conventional absorbable polymer bone surgery instruments, the composite material has the advantages that the mechanical fixing effect is relatively good, and furthermore, the problems that the degradation speed of the absorbable magnesium alloy bone surgery instruments is difficult to control and the hydrogen release quantity during degradation is large and the like can be overcome.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Magnesium alloy bone surgery internal fixation and implantation material
InactiveCN101264339ADegradation rate regulationPromote healingSurgeryProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingInternal fixation
The invention relates to a magnesium alloy internal fixation and implant material used in orthopedic surgeries, which is characterized in that the pure magnesium is used as the substrate, and calcium and zinc elements are added into the pure magnesium; wherein, the zinc accounts for 2-5%, and the calcium accounts for 1-3%. The magnesium alloy internal fixation and implant material used in orthopedic surgeries has the advantages of enjoying favorable biocompatibility, excellent mechanical property and controllable degradation rate, and meeting the demands for internal fixation and implant materials in orthopedic surgeries, thus being particularly suitable for screw plate systems and intramedullary pin systems.
Owner:BEIJING ALLGENS MEDICAL SCI & TECH +1
Designing and making method of customized 3D printing porous titanium alloy segmental prosthesis for reconstruction of large segmental bone defect
InactiveCN106923936AAvoid surrounding bone resorptionImprove fitAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantReconstruction methodArtificial bone
The invention discloses a designing and making method of a customized 3D printing porous titanium alloy segmental prosthesis for reconstruction of large segmental bone defect. Through preoperative thin-slice CT, a lesion bone area is scanned, obtained data is imported into a computer, and a three-dimensional digital model is reconstructed through computer aided design. Then, in combination with such imageological examination as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and the like, an osteotomy range of the lesion part is determined. The individual porous titanium alloy segmental prosthesis is designed in accordance with the specific osteotomy range and a reconstruction method. Prosthesis data is imported into metal 3D printing equipment so as to print the prosthesis. During an operation, lesion bone can be excised by virtue of such precision operation assisted technologies as navigation, a guide plate and the like. Then, a proper autogenous fibula (or biological ceramic artificial bone and allogeneic bone) is selected for conducting composite bone grafting. Finally, a complex is implanted into a bone defect area and is stably fixed. The method can complete precision making by virtue of a 3D printing technology and can achieve precision excision by virtue of the navigation and guide plate technologies, so that precision reconstruction of the large segmental bone defect is finally achieved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing renewable magnesium-based bone material with Mg/TiO2-HA gradient porous coating
PendingCN108992705AImprove biological activityHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCell adhesionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a method for preparing a renewable magnesium-based bone material with an Mg / TiO2-HA gradient porous coating for bone implantation and belongs to the field of medical materials. The renewable magnesium-based bone material with an Mg / TiO2-HA gradient porous coating comprises a Ti02 / Ag-HA gradient porous coating and a magnesium-based bone material and the Ti02 / Ag-HA gradientporous coating coats the magnesium-based bone material. Printing materials used by the experiment are divided into two groups, the first group comprises Mg particle and Ag powder mixed powder as a metal powder base and the second group comprises multiple gradient coating powder obtained by mixing Mg, TiO2 and HA materials according to a strict ratio. The method comprises: constructing a 3D printing model, carrying out printing and carrying out post-treatment after cladding. The porous coating has high bonding strength, is degradable and antibacterial, greatly improves cell adhesion, proliferation and the production of new blood vessels, significantly improves biological activity and biocompatibility and achieves bone regenerability.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
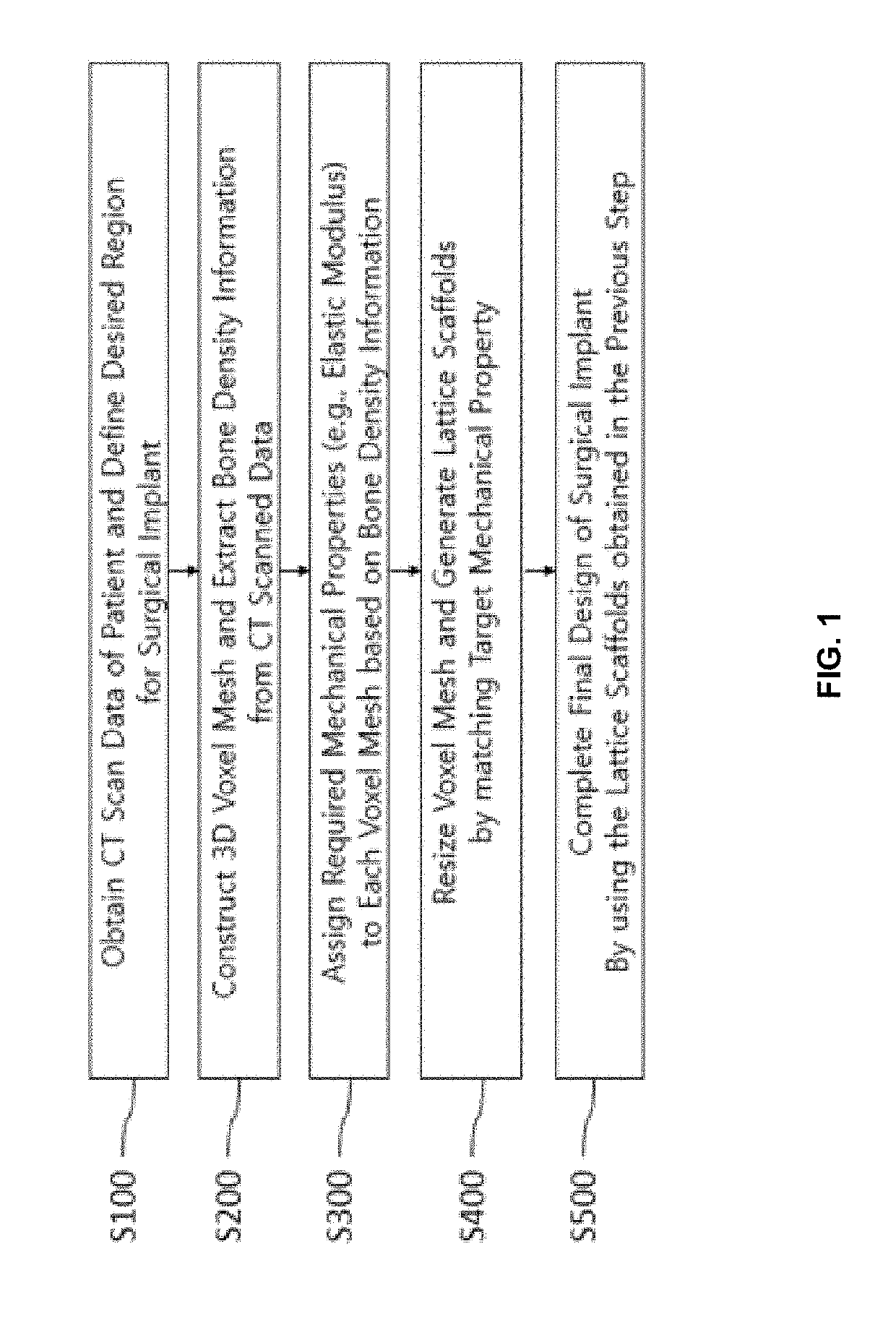
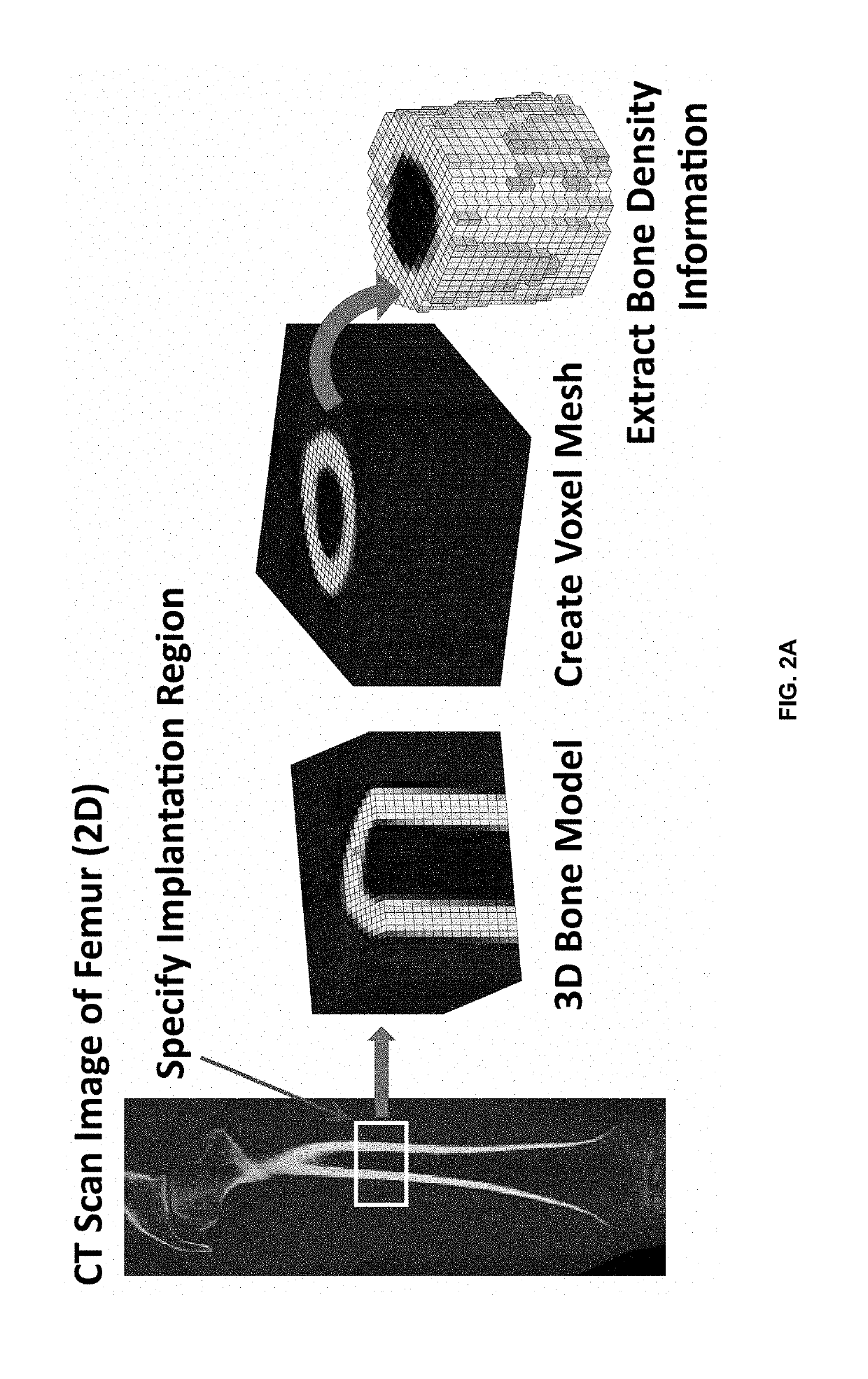
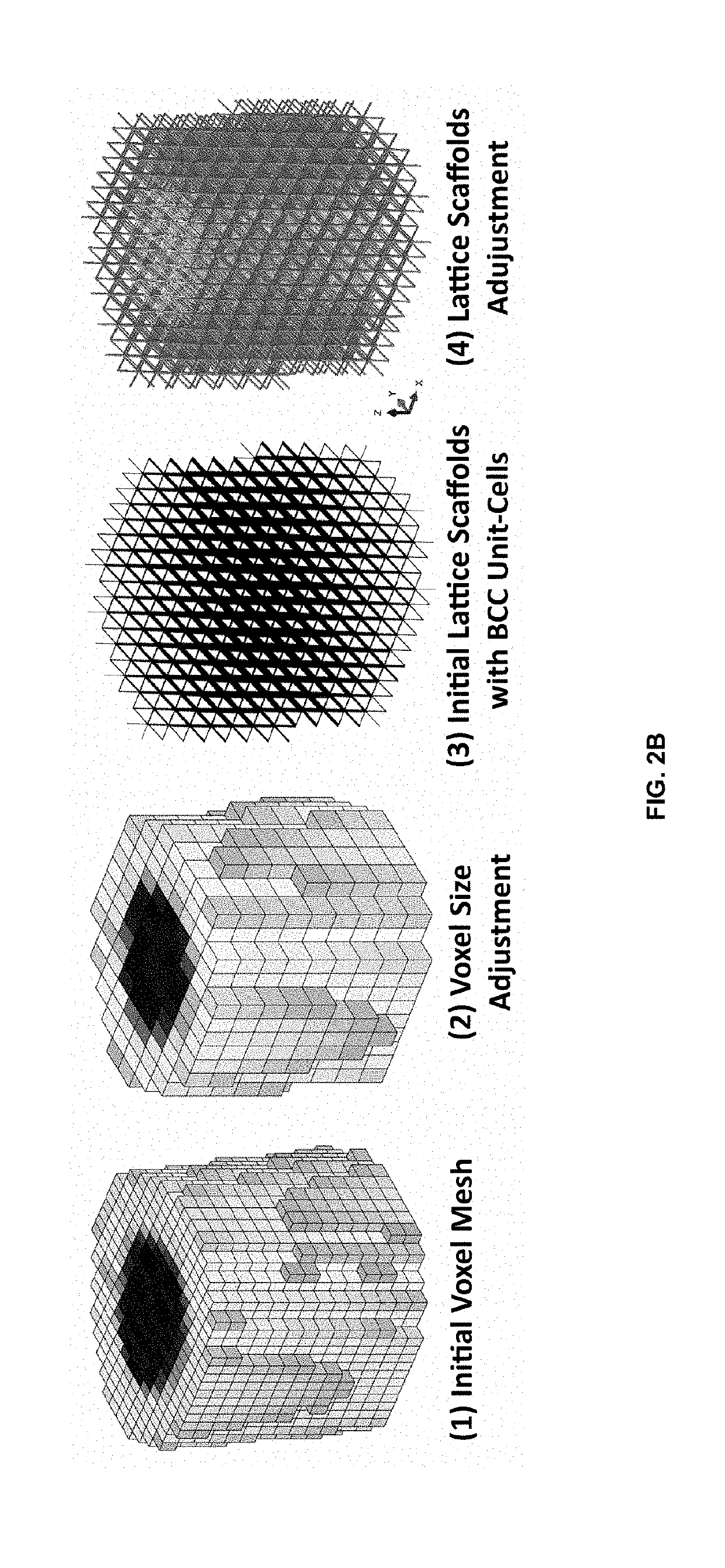
Method for adjusting mechanical properties of implant and patient specific surgical implants
InactiveUS20190240029A1Eliminate side effectsAvoid reoperationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesJoint implantsSide effectBone density
The present invention is for a systematic process of creating patient specific implants by matching target mechanical properties (e.g. elastic modulus of bone) based on a patient's CT scan images. The present invention creates a metamodel that matches the elastic modulus values of lattice scaffolds to desired values by using a homogenization approach to determine the characteristics of the lattice structure at the unit-cell level. This eliminates the computational cost associated with optimizing the lattice structures and works at structural level.The present invention includes the following featured steps to adjust a mechanical property (e.g., the elastic modulus) of the implant: 1) specifying a region requiring the implant operation from the CT scan images of the affected part, 2) determining the implant shape to be inserted into the specified region from the previous step, 3) dividing the implant shape into multiple partitioned three-dimensional regions, 4) assigning target elastic modulus values (Et) for each of the partitioned three-dimensional regions according to the bone density information obtained from the CT scan images, 5) selecting a specific type of unit-cell of lattice scaffolds with respect to the implant shape, 6) selecting a specific implant material, which has the elastic modulus of Eo, and 7) determining the required strut diameter and density of each unit-cell of the lattice scaffolds to minimize the error between the target elastic modulus (Et) and the homogenized elastic modulus (Eh), which is calculated from the implant material's elastic modulus value (Eo) obtained from the selected three-dimensional regions.The present invention creates patient specific surgical implants with precisely designed lattice scaffolds. The implants are designed for long term use because the stress shielding effect can be reduced by matching the elastic modulus of the implant to the elastic modulus of the bone of the affected area. Therefore, the present invention can significantly reduce the side effect of the implant and prevent reoperations.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Orthopedic implanted magnesium alloy material and preparation method thereof
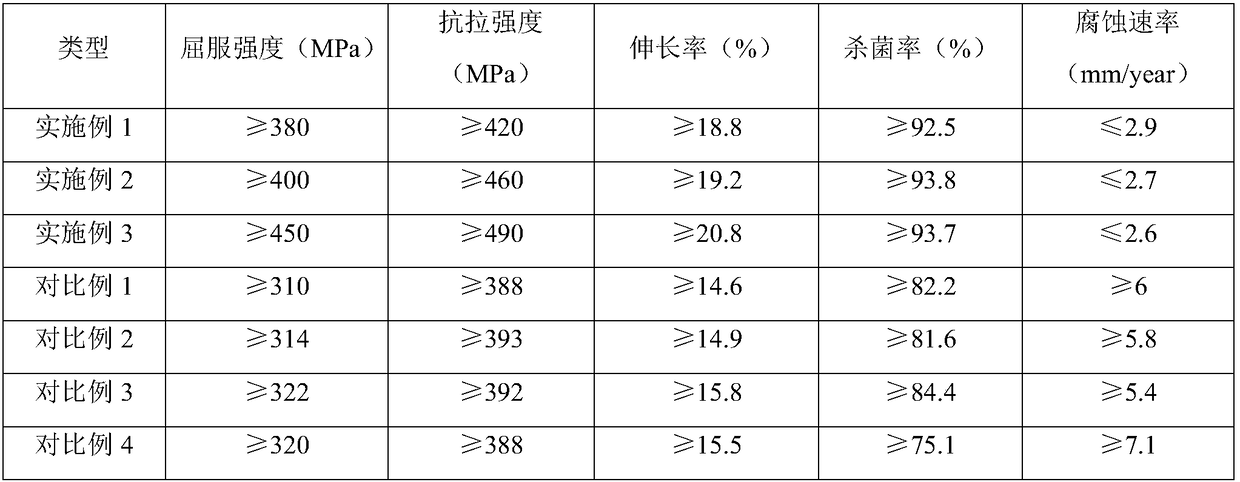
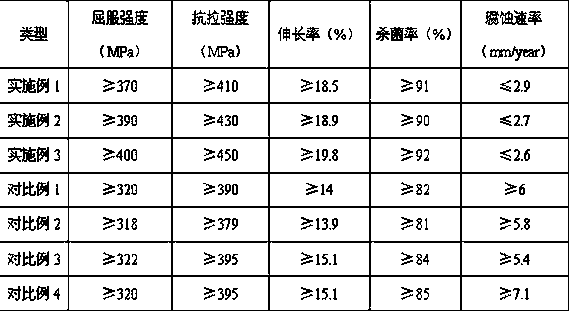
InactiveCN108286003AReduce stress shielding effectHigh strengthSurgeryMetallic material coating processesChemical compositionUltimate tensile strength
An orthopedic implanted magnesium alloy material is characterized by comprising the following chemical components by weight: 1.5-3% of Zn, 0.6-1.1% of Mn, 0.3-0.8% of Ca, 0.3-0.45% of Si, 0.5-0.85% ofSn, 1-1.8% of Li, 2.5-3.5% of Cr, 1.3-1.4% of Mo, 0.01-0.08% of Sc+La+Y, 0.5-0.8% of Ti, and balance of Mg and unavoidable impurity elements. The magnesium alloy has a yield strength equal to or greater than 380 MPa, a tensile strength equal to or greater than 420 MPa, an elongation equal to or greater than 18.8%, and a sterilization rate equal to or greater than 92% which are significantly higher than that of other products lacking alloying elements, and significantly higher than that of similar products without surface coating.
Owner:王甲林
Mg alloy for being implanted in bone and preparation method of Mg alloy
InactiveCN108359868AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceSurgeryMetallic material coating processesImpurityMagnesium alloy
The invention provides a Mg alloy for being implanted in bone. The Mg alloy is characterized by comprising the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 1.5-3% of Zn, 0.6-1.1% of Mn, 0.3-0.8% of Ca, 0.3-0.45% of Si, 0.45-0.8% of Sr, 1-1.8% of Li, 2.5-3.5% of Cr, 1-2% of Cu, 1.3-1.4% of Mo, 0.01-0.08% of Sc, La and Ce, 0.1-0.8% of Nb, and the balance of Mg and inevitable impurity elements. According to the Mg alloy provided by the invention, the yield strength is higher than or equal to 370 MPa, the tensile strength is higher than or equal to 410 MPa, the elongation is higher thanor equal to 8.5%, and the sterilizing rate is higher than or equal to 90%. The above indices of the Mg alloy are obviously higher than those of other products which lack alloy elements and those of similar products which are not subjected to surface coating treatment.
Owner:温州市赢创新材料技术有限公司
Centering joining tooth type coaptation plate
InactiveCN1686057AGood flexural resistanceImprove bending resistanceInternal osteosythesisBone platesTherapeutic effectEngineering
Owner:张荣魁 +1
Preparation method of nickel titanium foam alloy with double pore structure
A preparation method of a nickel titanium foam alloy with a double pore structure relates to a preparation method of a nickel titanium foam alloy. The invention solves the problems that the existing nickel titanium foam alloy used for the replacement and repair of the bone tissue has low pore interconnectivity and uneven pore distribution. The method comprises the following steps: respectively weighting several parts of nickel powder, titanium powder, large-particle sodium chloride and small-particle sodium chloride, evenly spreading large-particle sodium chloride and the mixed powder of nickel powder, titanium powder and small-particle sodium chloride in a mould in a laminated mode successively, and then performing cold compressing and forming, cold isostatic pressing, hot pressing sintering and homogenizing treatment in turn. The porosity of the nickel titanium foam alloy is 59.17%-71.71%; and the elastic modulus of the alloy is effectively reduced, which is close to the modulus of the bone tissue. The pore distribution is uniform, and small pores are distributed around large pores to ensure that the large pores are connected to form interconnected pores. By adopting the nickel titanium foam alloy, the bone tissue is controlled to only grow in the large pores; and the nickel titanium foam alloy can be used as the material used for the replacement and repair of the bone tissue.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
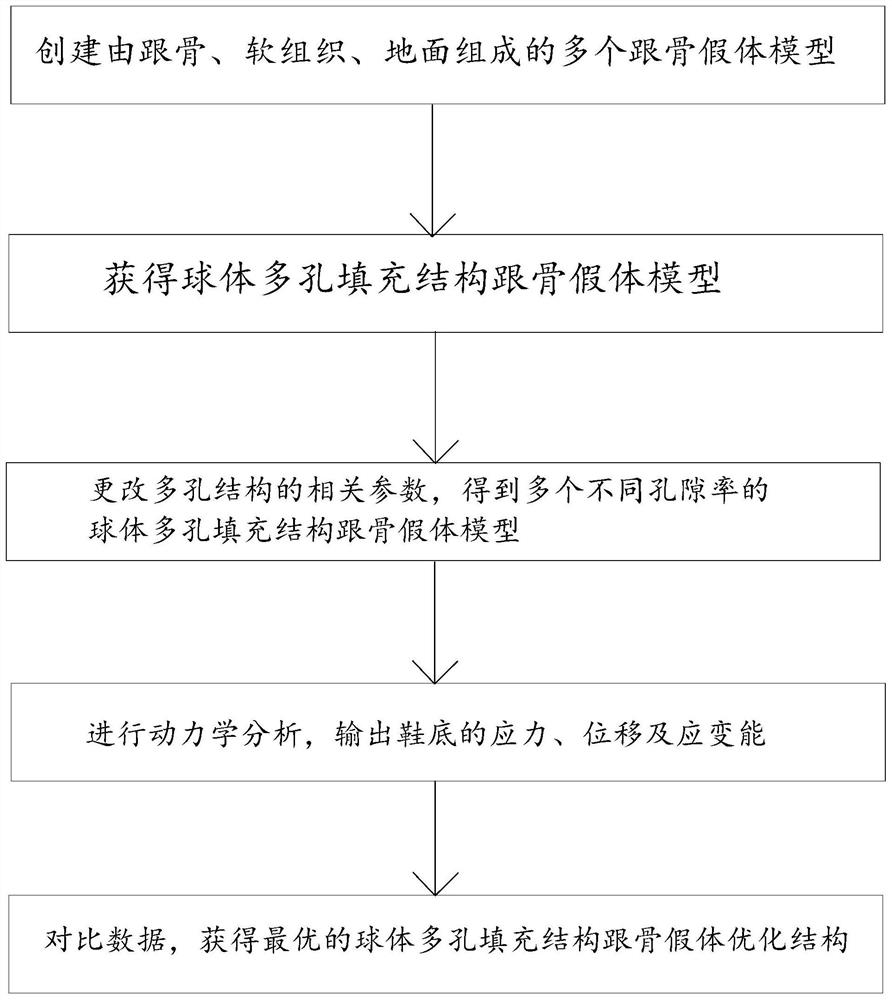
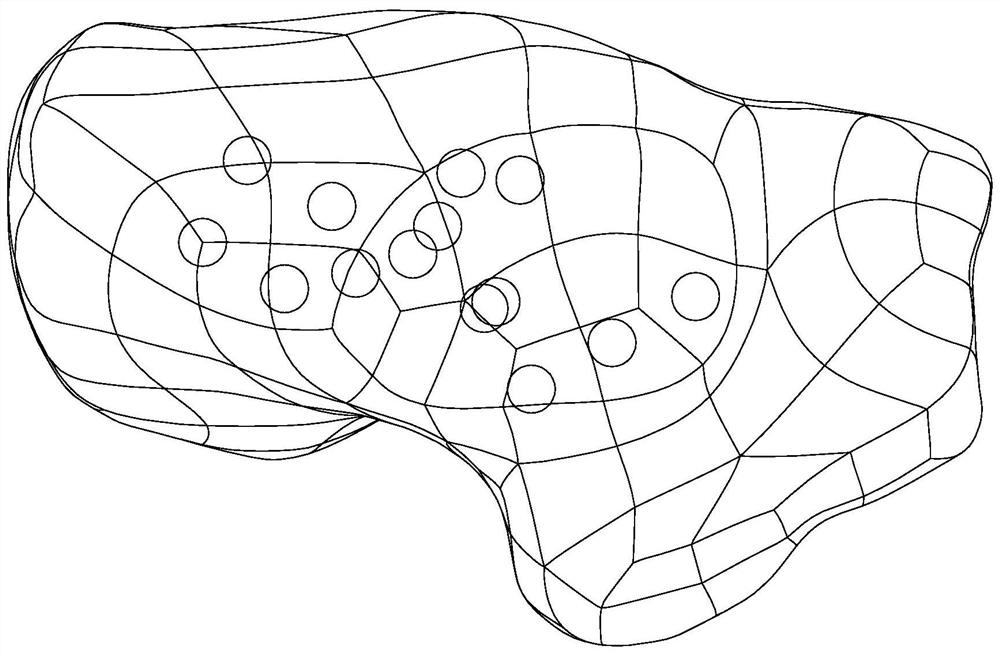
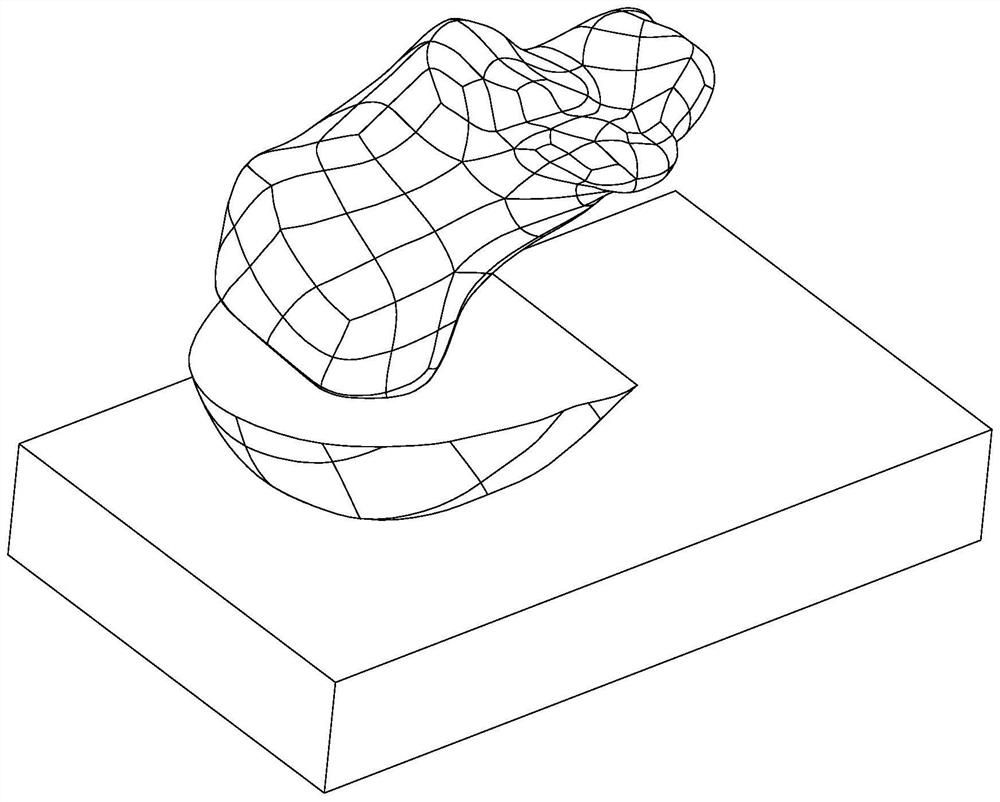
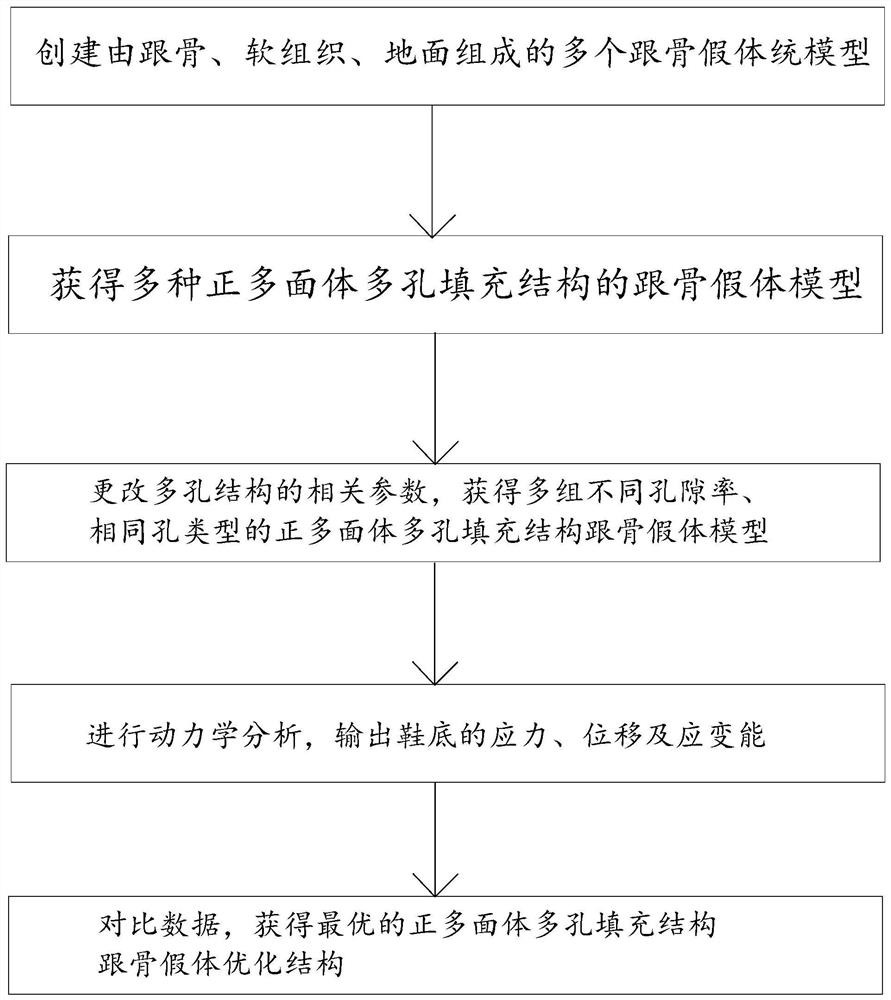
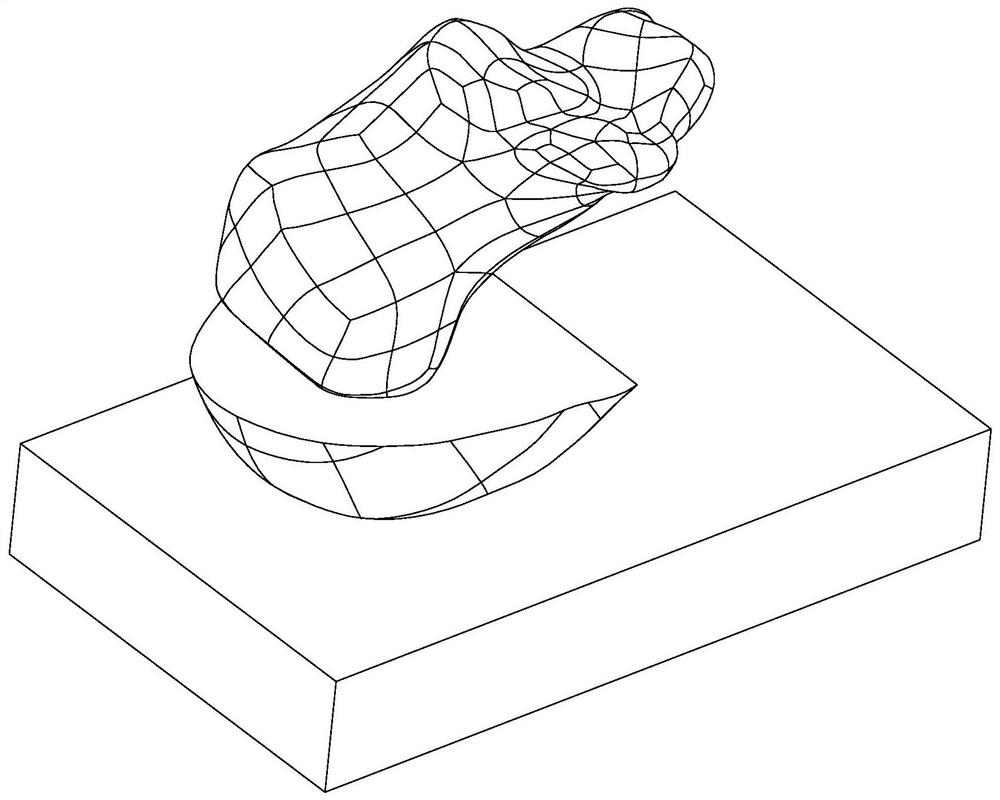
Spherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis and optimization design method thereof
PendingCN112075990AReduce stress shielding effectMaximum strain energyMedical simulationComputer-aided planning/modellingFinite elemente analyseBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a spherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis design method. The method specifically comprises the following steps of S1, obtaining a calcaneus prosthesis model consisting of calcaneus, soft tissues and the ground; S2, performing porous structure modeling on the calcaneus model to obtain spherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis models; S3, makingcombinations of different spherical radiuses r and array spacings a to obtain a plurality of spherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis models; S4, performing finite element analysis on the models consisting of calcaneus prostheses, the soft tissues and the ground in ABAQUS to obtain data of strain energy, stress, displacement and the like of the calcaneus prostheses; and S5, comparing data of maximum strain energy, maximum stress, maximum displacement and the like of the spherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis models with different porosities to obtain an optimalspherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis optimization structure. The invention furthermore provides a spherical porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Medical slight contact type plate screw system
InactiveCN104939900APromote ingrowthEasy to put inInternal osteosythesisFastenersRepair tissueScrew system
The invention relates to a medical slight contact type plate screw system, and aims to solve the problem that as an ordinary steel plate generates a stress shielding effect and the bone contact area is overlarge, local blood supply is impacted in the prior art. The medical slightly contact type plate screw system comprises a steel plate used for fixing a bone, and a bridging screw, wherein a support screw is arranged between the steel plate and the bone to be fixed; the support screw is screwed into the bone to ensure that a clearance is formed between the steel plate and the bone; the bridging screw is used for connecting and fixing the steel plate, the support screw and the bone. Through the adoption of a slight contact biological type fixing manner, the plate screw system has the advantages that the stress shielding effect is reduced to a great extent; due to the clearance between steel plate and the bone, convenience is brought for ingrowth of a blood vessel and a repaired tissue; as the plate screw system can be fixed outside a periosteum, convenience is brought for minimally invasive surgery; as the bridging screw is used for connecting and fixing the steel plate, the support screw and the bone, the fixing effect is enhanced, and the healing process is accelerated; the structure is simple; the operation is convenient.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
Zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula uni-compartment tibial plateau containing oxide layer and preparation method
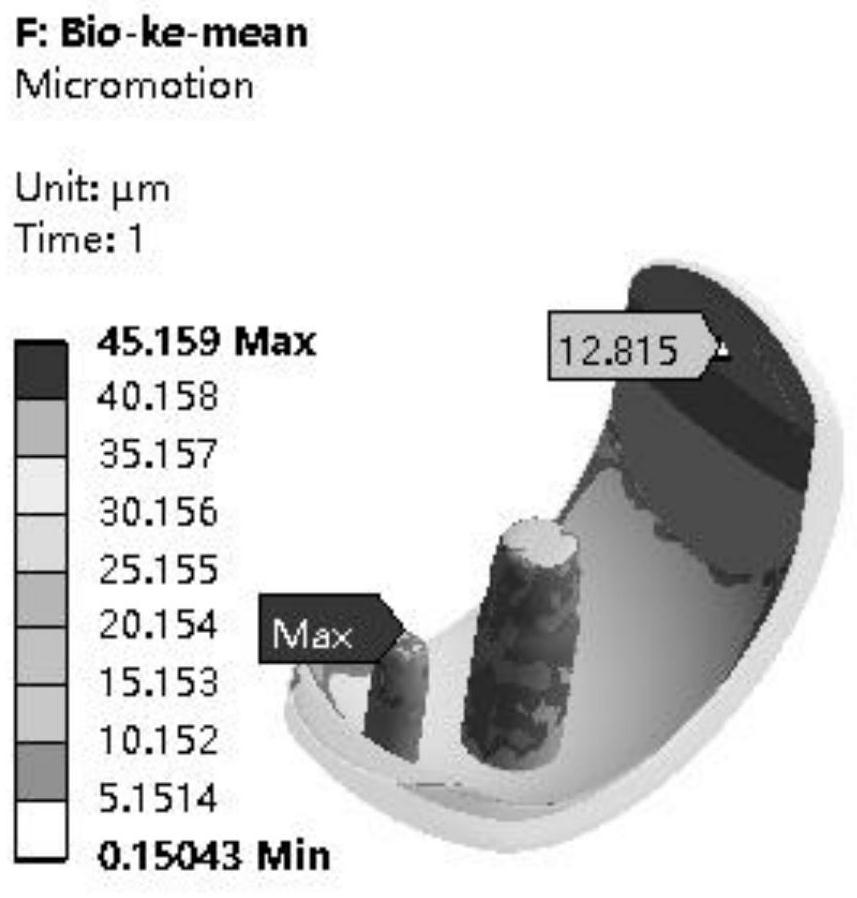
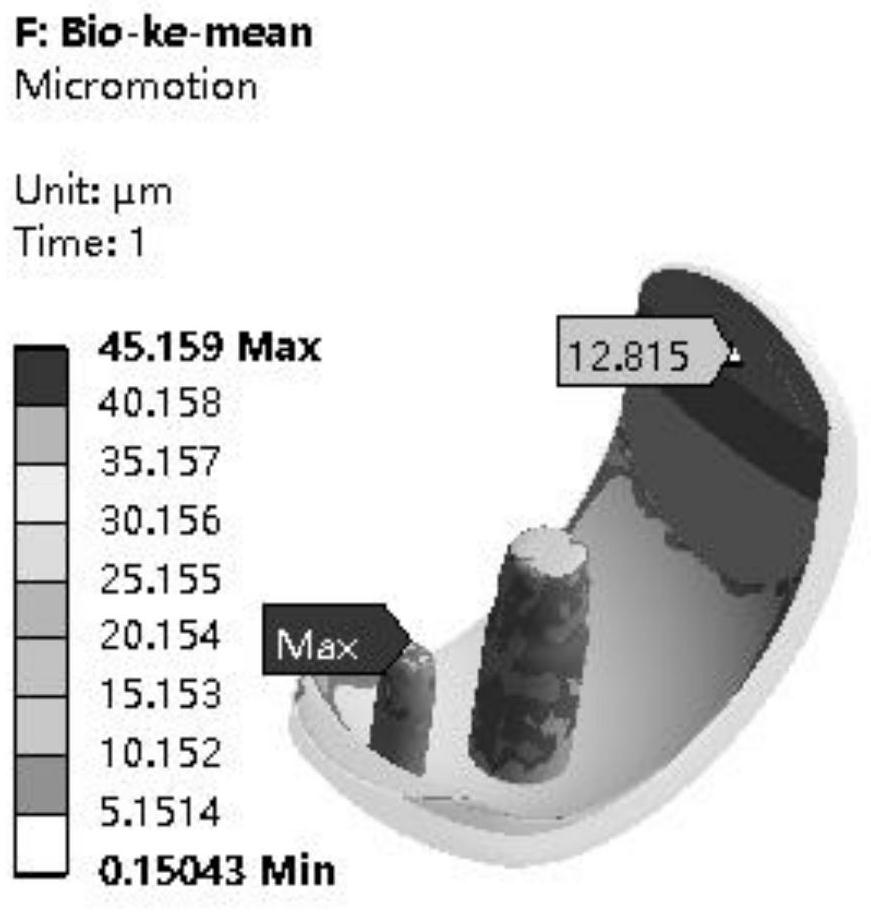
ActiveCN112404433AReduce stress shielding effectUniform stressAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implantsBone ingrowthProsthesis
The invention discloses a zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula uni-compartment tibial plateau containing an oxide layer and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the steps that zirconium-niobium alloy powder serves as a raw material, an intermediate product of the zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula uni-compartment tibial plateau containing the oxide layer is obtained through 3D printing integral forming, and through hot isostatic pressing and cryogenic oxidation, the zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula uni-compartment tibial plateaucontaining the oxide layer is obtained. A bone trabecula is arranged on the lower surface of a semi-tibial plateau support and the surface of a semi-oval keel with a long round hole, a gradient distribution bone trabecula structure is arranged, micro-motion between a prosthesis and a bone interface can be reduced, the stress shielding effect of the prosthesis on a bone tissue is reduced, so thatthe tibial plateau is uniform in bone tissue stress, the bone ingrowth performance is excellent, and the initial stability and the long-term stability are improved. The bone trabecula is integrally formed through 3D printing, the problem that a complex structure cannot be prepared through traditional machining is solved, the bone trabecula and a solid body are high in bonding strength and not prone to falling off, and the service life of the prosthesis is prolonged.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Medical bone fracture plate capable of being sustainably and initiatively pressurized and elastically fixed
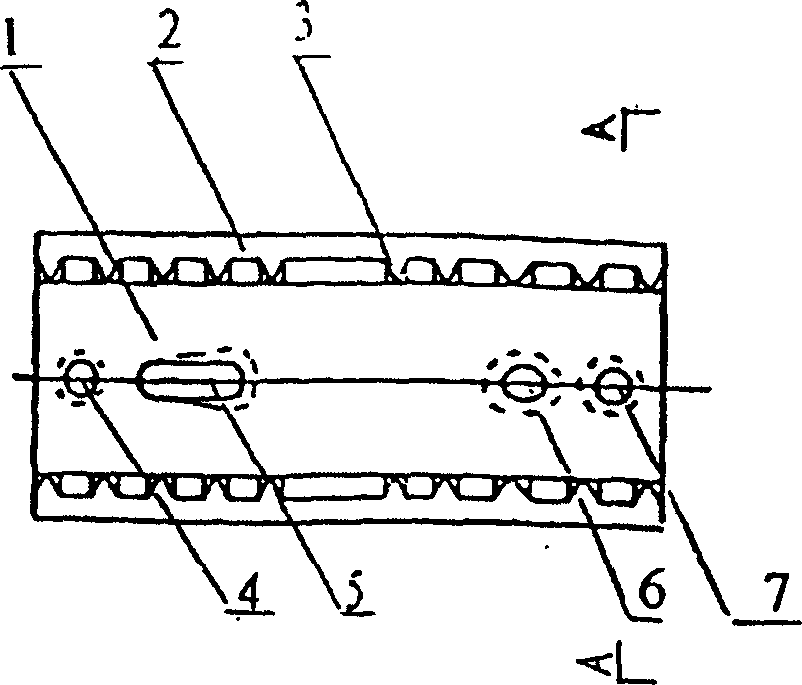
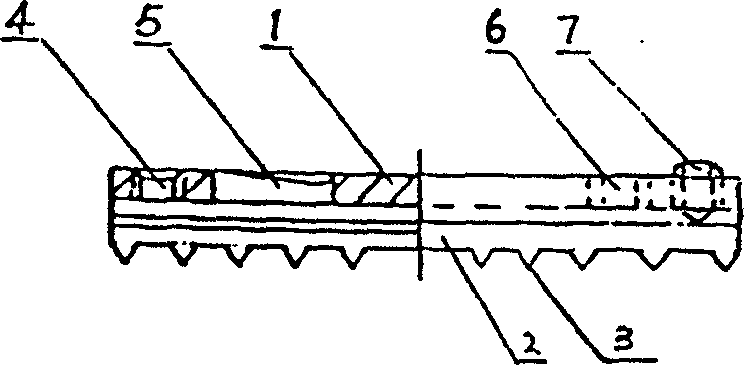
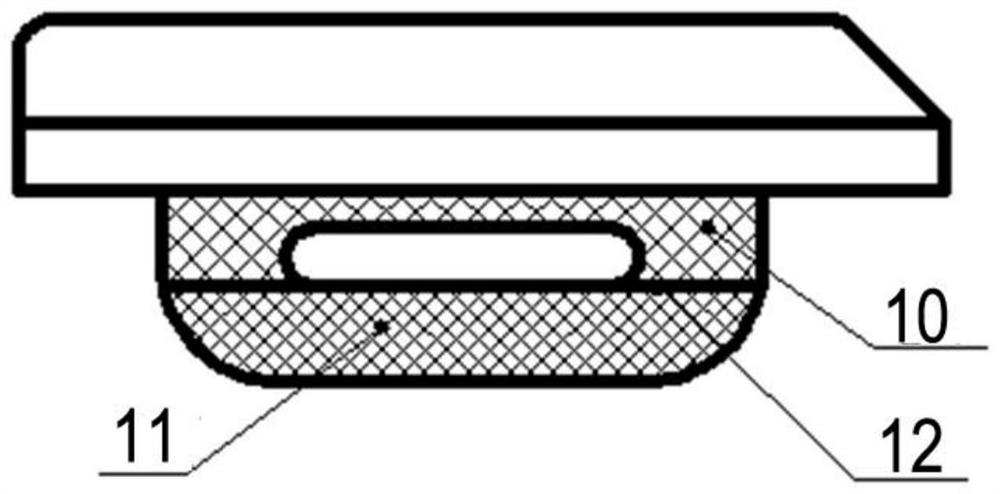
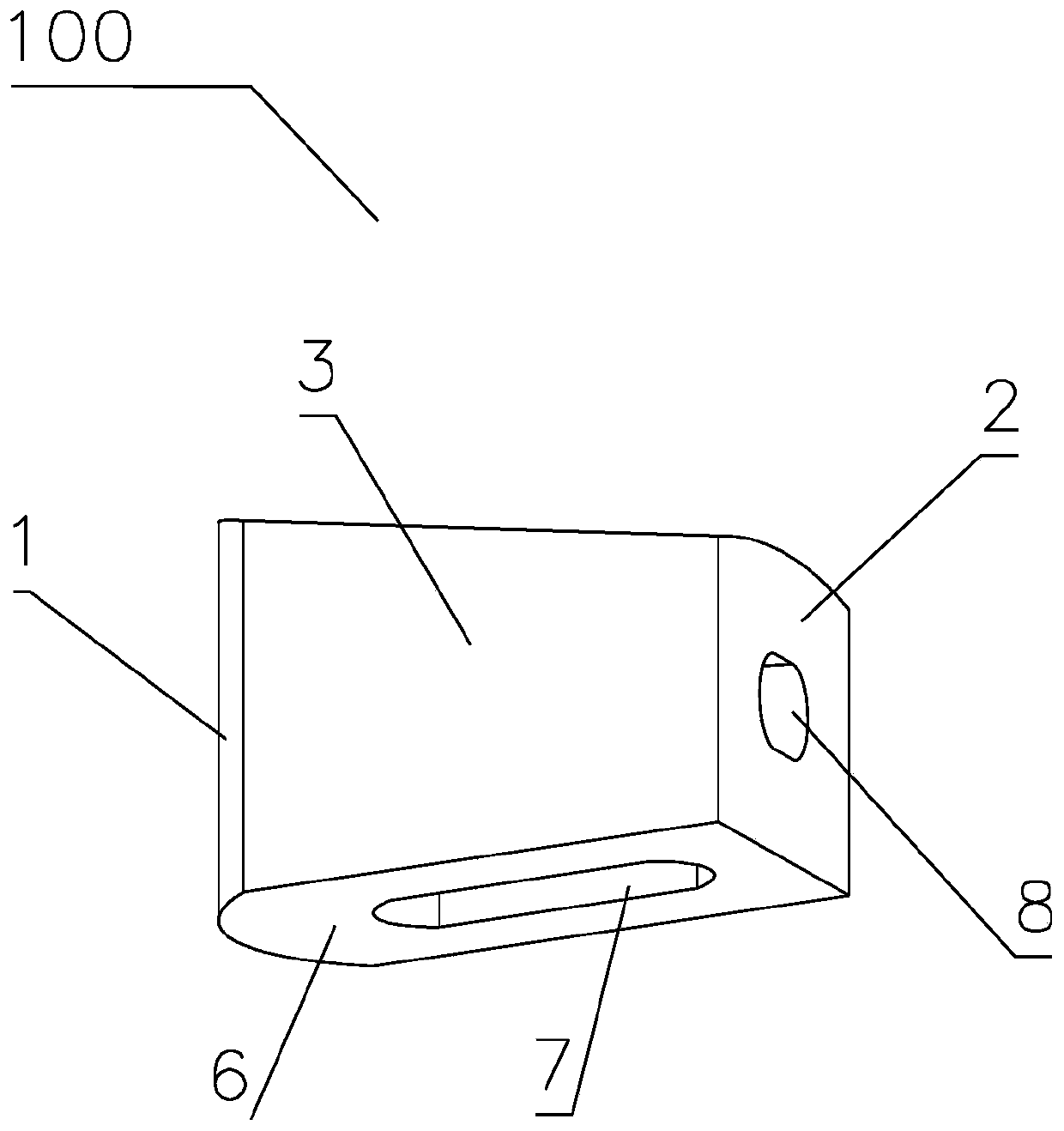
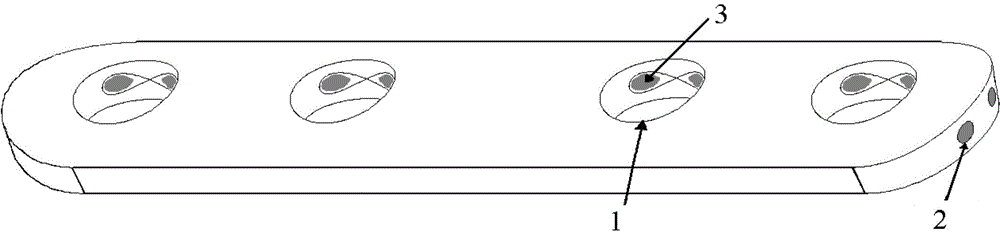
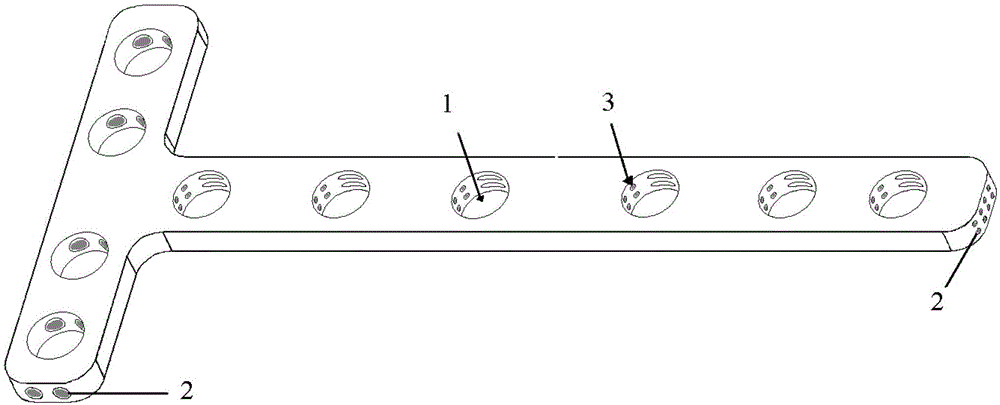
The invention discloses a medical bone fracture plate capable of being sustainably and initiatively pressurized and elastically fixed. The middle of an existing bone fracture plate (usually a fracture portion to be fixed) is designed to be a hollow elastic hole (1), the elastic hole deforms under the action of pressurized screw holes (3) or a pressurizer, and near and far ends of the fracture can be initiatively pressurized. By the design of the hollow elastic hole (1), effect of stress shelter can be reduced by deformation of the elastic hole.
Owner:齐克海
Zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle containing oxide layer and preparation method
ActiveCN112296342ANot easy to fall offInhibit sheddingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyArticular surfacesFacial bone
The invention discloses a zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle containing an oxide layer and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises thesteps that zirconium-niobium alloy powder serves as a raw material, an intermediate product of the zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle containing theoxide layer is obtained through 3D printing integral forming, then the zirconium-niobium alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle containing the oxide layer is obtained through hot isostatic pressing, cryogenic treatment and surface oxidation, the femoral condyle comprises a femoral condyle articular surface and an osseointegration surface, and the osseointegration surface is provided with the bone trabecula in a partitioned manner. Micro-motion of the prosthesis and a bone interface can be reduced, the stress shielding effect of the prosthesis on bone tissue is reduced, the stress of the femoral condyle bone tissue is uniform, and the initial stability and long-term stability of the single-compartment femoral condyle are improved. According to the preparation method, excellent biocompatibility and bone ingrowth of the osseointegration interface and super-strong wear resistance and low wear rate of a friction interface are integrally realized; the femoral condyle bone trabecula has excellent compression resistance; and the compressive yield strength and plasticity of the solid part are enhanced.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
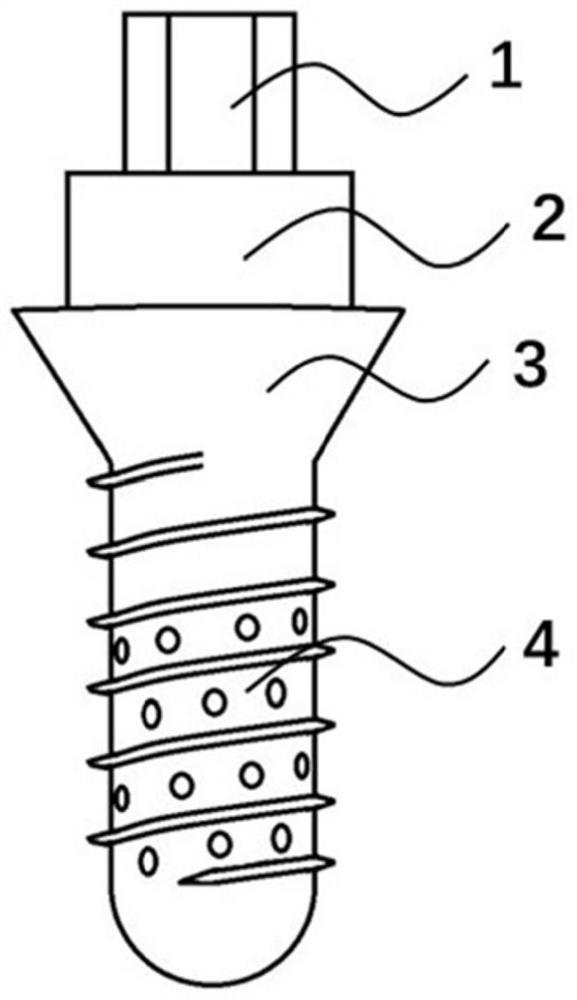
Preparation method of bone screw with double-layered structure
ActiveCN108052774AReduce stress shielding effectGood elastic modulus propertiesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLayered structureElastic modulus
The invention relates to a bone screw with a double-layered structure. The bone screw with the double-layered structure is suitable for broken bone connection of osteoporosis bones, bone lesion and bone deformity correction. By three steps including design and optimization of a prism structure of the inner layer of the bone screw, design and optimization of an outer-layer structure of the bone screw and printing of a whole structure of the bone screw, the bone screw with the double-layered structure is prepared. By the bone screw, while approximate bone elasticity modulus performance is ensured, torque which is large enough is still maintained to meet application requirements. By the provided bone screw, the problem of mechanical properties of the bone screw are not matched is solved, anda stress shielding effect caused by a traditional bone screw is reduced effectively; a method for designing a porous structure of the bone screw is proposed, and a new thought is provided for searching a designing mode and a processing method for the bone screw which promotes rapid recovery of broken bones and avoids secondary injury to the bone after surgery; and the problem that by a traditionalmanufacturing mode, a complicated bone screw cannot be manufactured is solved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Medical magnesium alloy material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110669970AGood biocompatibilityPromote absorptionProsthesisSurface cleaningMetallic materials
The invention discloses a medical magnesium alloy material. The material is composed of the following chemical components by weight percentage: 4 wt% of Zn, 1 wt%-3 wt% of Zr, 0.5wt% of calcium and the balance of magnesium. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the medical magnesium alloy material. The method comprises the steps of surface cleaning, mold preheating, melting and mixing, temperature reduction, and casting molding. The medical magnesium alloy material and the preparation method thereof effectively improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy, improve the uniformity of the metal material structure, and meet the requirements of biomedical metal implant materials.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Cobalt alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle prosthesis and preparation method
PendingCN112168433APrevent looseningReduce frettingAdditive manufacturing apparatusJoint implants3d printArticular surfaces
The invention discloses a cobalt alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle prosthesis and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking cobalt alloy powder as a raw material, performing 3D printing integrated molding to obtain an intermediate product of the cobalt alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle prosthesis, and performing hot isostatic pressing and a deep cooling process to obtain the cobalt alloy partitioned bone trabecula single-compartment femoral condyle prosthesis. The prosthesis comprises a femoral condyle articular surface and an osseointegration surface. Due to the partitioned bone trabecula, micro motion of the prosthesis and a bone interface can be reduced, and the initial stability is achieved; the stress shielding effect of the prosthesis on bone tissues is reduced, the femoral condyle bone tissue stress is uniform, excellent and uniform bone ingrowth performance is achieved, prosthesis looseness caused by osteoporosis after long-term implantation of the prosthesis is avoided, and long-term stability is achieved. Due to 3D printing integrated molding, the bone trabeculaand the entity are high in bonding strength, the bone trabecula does not easily drop, and the service life of the prosthesis is prolonged. The bone trabecula part of the prosthesis has excellent compression resistance; and the entity part releases residual stress, and the plasticity is enhanced.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
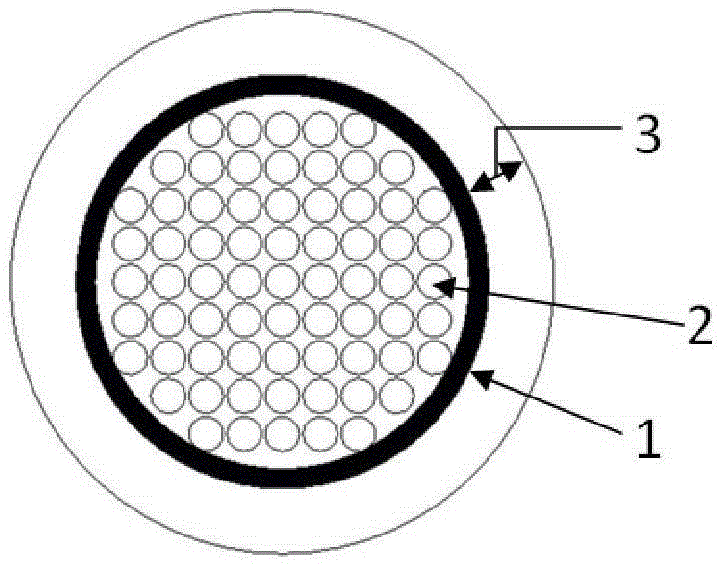
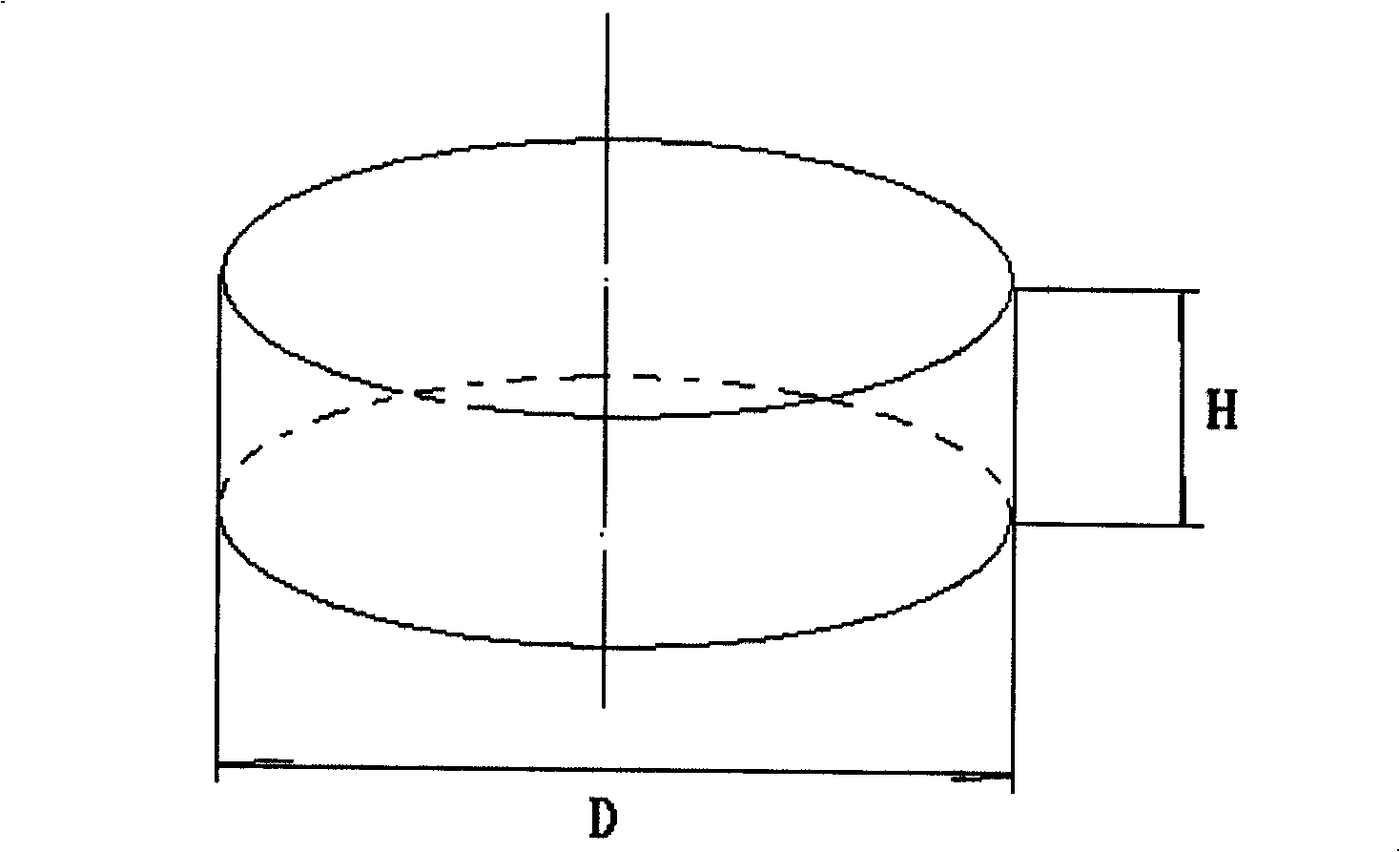
Weight bearing tissue engineering bone porous pure magnesium bracket and bracket imitation human bone material surface coatings
A weight bearing tissue engineering bone porous pure magnesium stent and a surface coating of human bone simulating material of the stent are provided. The stent is made from high pure magnesium powder and pore former into cylinders or round plates with certain diameter (D) and height (H) through powder metallurgy and main holes (1), interlocking pores (2) and blind holes (3) are randomly distributed. The main holes are mutually communicated. The blind holes are enclosed. The total volume of all holes and pores occupies 35-55 percent of the outer contour volume of the stent. The volume of the blind holes occupies 2-5 percent in all holes and pores. The diameter of the main holes and the blind holes is 200-500Mum, and the diameter of communicating holes is 50-100Mum. The formation of the surface coating of the human bone simulating material of the stent (4) is that the stent is immersed in the coating solution with a constant temperature of 37 DEG C, and the coating solution contains Na<+>, K<+>, Ca<2+>, Mg<2+>, HCO3-, Cl<->, HPO4<2->, SO4<2-> and Type I collagen. Finally, the coating of the stent is formed into hydroxyapatite containing magnesium ions and the Type I collagen, and the thickness is 1-3Mum.
Owner:李秉哲 +2
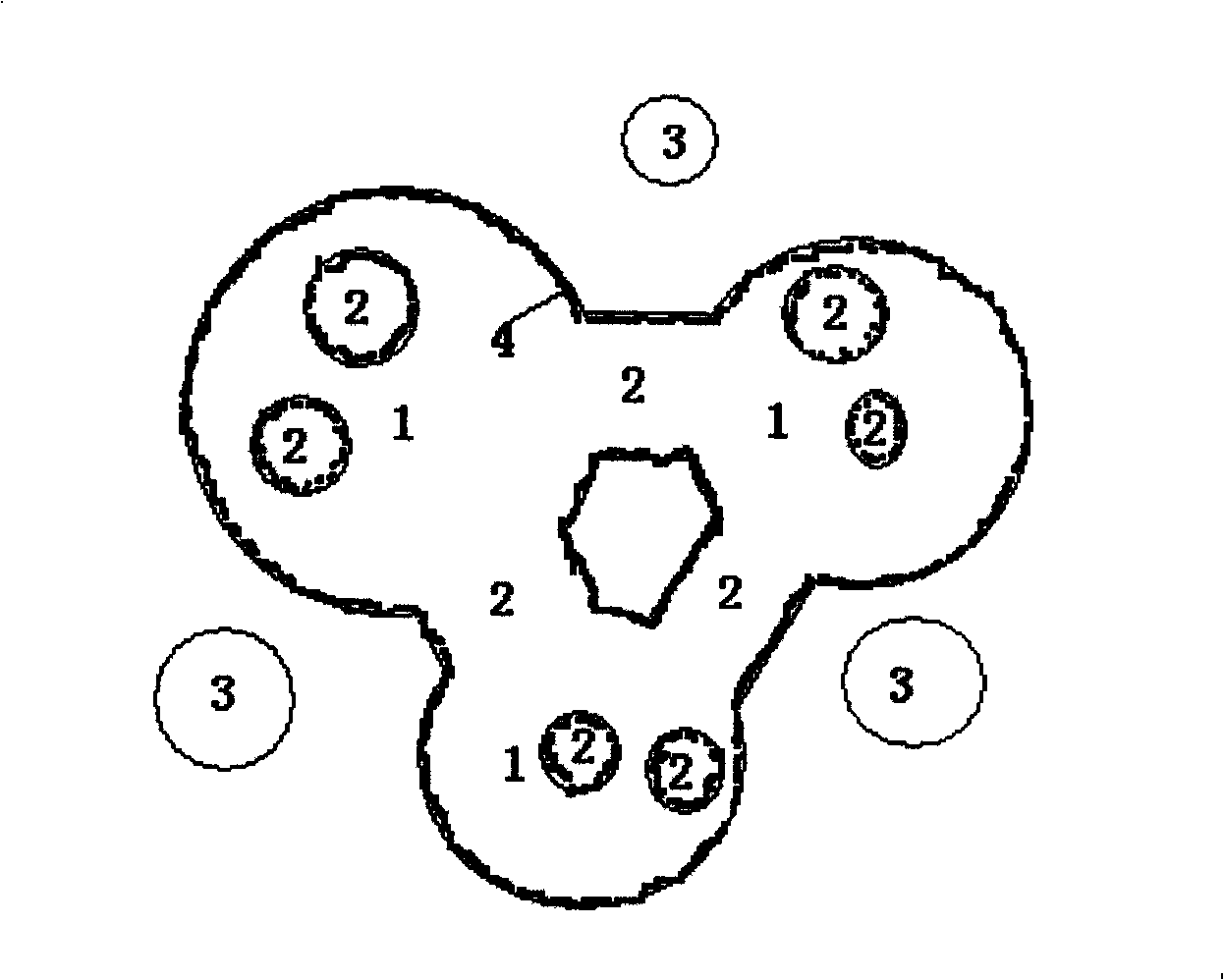
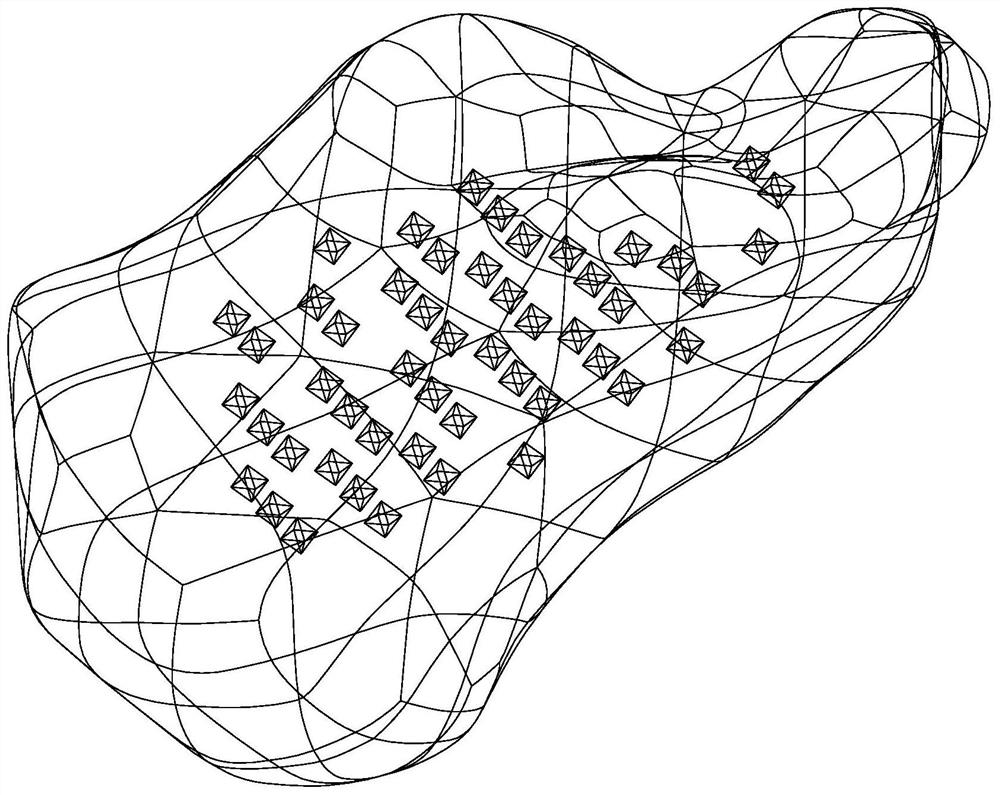
Regular polyhedron porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis and optimization design method thereof
PendingCN112075989AReduce stress shielding effectMaximum strain energyMedical simulationComputer-aided planning/modellingProsthesisElement analysis
The invention discloses a design method of a regular polyhedron porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis. The method specifically comprises the following steps that S1, a system model composed ofthe calcaneus, soft tissue and the ground is built; S2, porous structure modeling is carried out on the calcaneus model, and a calcaneus prosthesis model containing a regular polyhedron porous filling structure is obtained; S3, combinations of different regular polyhedron radiuses r and array distances d are formulated, and a plurality of regular polyhedron porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis models are obtained; S4, finite element analysis is carried out on the models composed of the calcaneus prosthesis, the soft tissue and the ground in ABAQUS, and data such as strain energy, stress and displacement of the calcaneus prosthesis are obtained; and S5, the data such as the maximum strain energy, the maximum stress and the maximum displacement of the regular polyhedron porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis models with different porosities are compared, and the optimal regular polyhedron porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis optimization structure is obtained. The invention further provides the regular polyhedron porous filling structure calcaneus prosthesis.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
In-vivo absorbable lumbar limitation dynamic fixing device
ActiveCN108577954ALess side effectsPromote healingInternal osteosythesisPosterior fusionStress shielding
The invention discloses an in-vivo absorbable lumbar limitation dynamic fixing device. The in-vivo absorbable lumbar limitation dynamic fixing device comprises a first locker, a spacer and a second locker, wherein the first locker, the spacer and the second locker are connected in series through mooring ropes. Buckles are arranged at the front end of the first locker, and locker fixing teeth are arranged at the tail end of the first locker. Spacer fixing teeth are arranged at both ends of the spacer. Locker fixing teeth are arranged at the front end of the second locker, and buckles are arranged at the tail end of the second locker. The locker fixing teeth can mesh with the spacer fixing teeth. The in-vivo absorbable lumbar limitation dynamic fixing device is applied to lumbar posterior fusion surgery on the basis of providing limited micro-motion, so that relatively rigid fixation to fusion segments at the initial stage is provided, and the movement of the fusion segments in all directions is limited; with healing of bone graft and the degradation of magnesium alloys in the fixing device, fixed segments have limited micro-motion in all directions, so that the healing of the bone graft is promoted, and the stress and activity of an adjacent segment are reduced; and finally, the magnesium alloys are completely degraded to reduce stress shielding.
Owner:哈尔滨鸿途远驰科技有限公司
Medical Implant Porous Scaffold Structure Having Low Modulus
InactiveUS20170224491A1Low modulusModulus is reducedBone implantTissue regenerationThree-dimensional spaceBone tissue
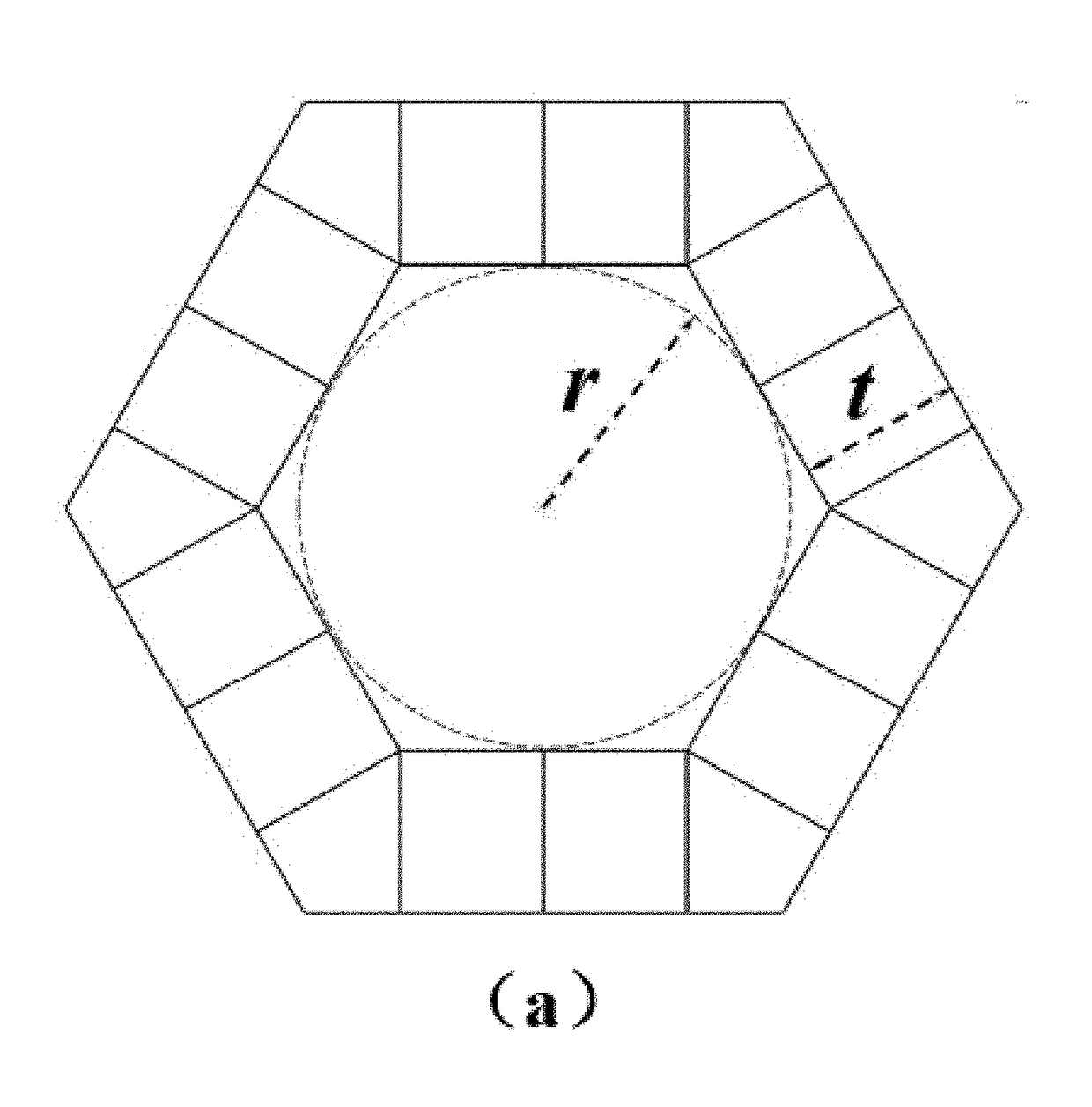
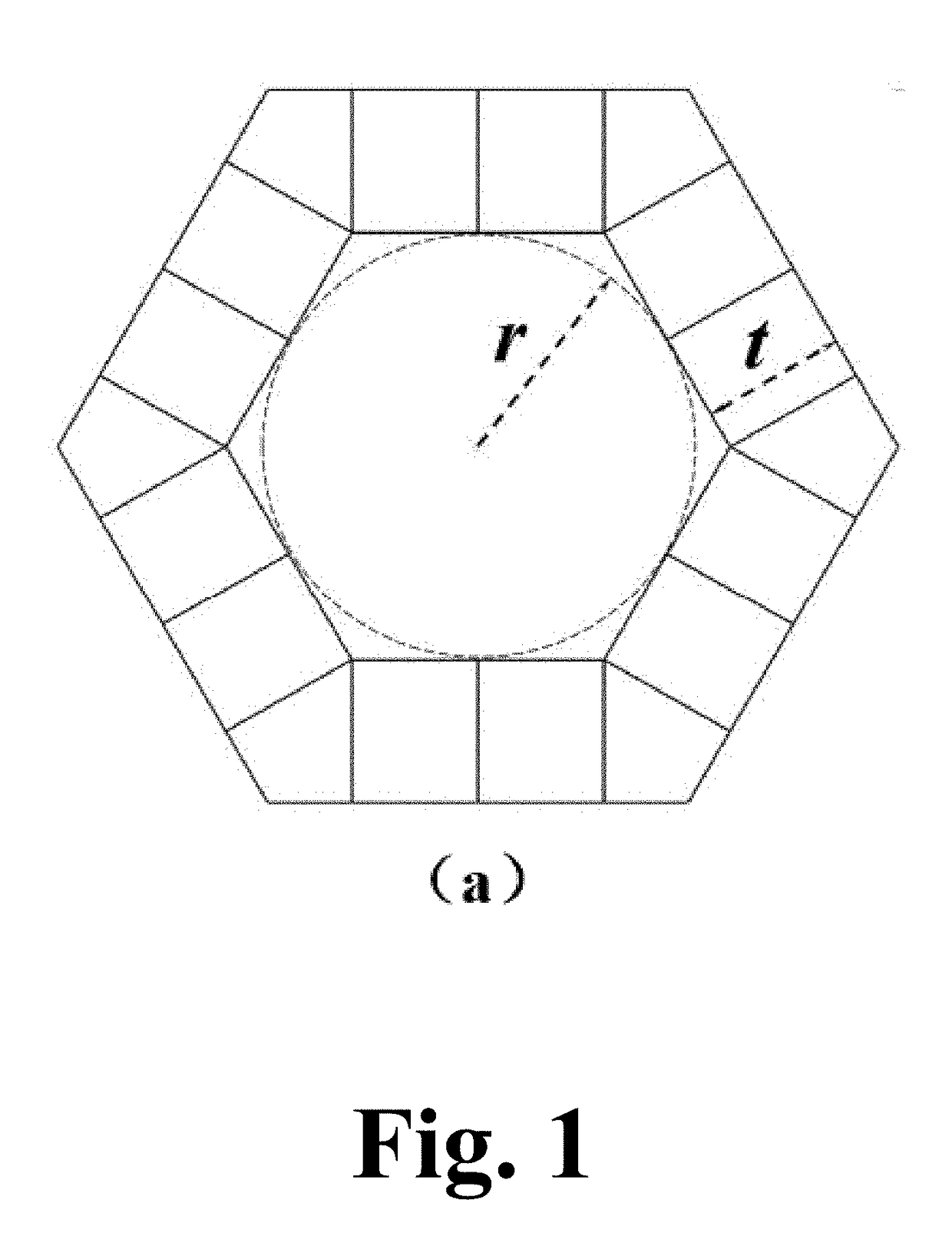
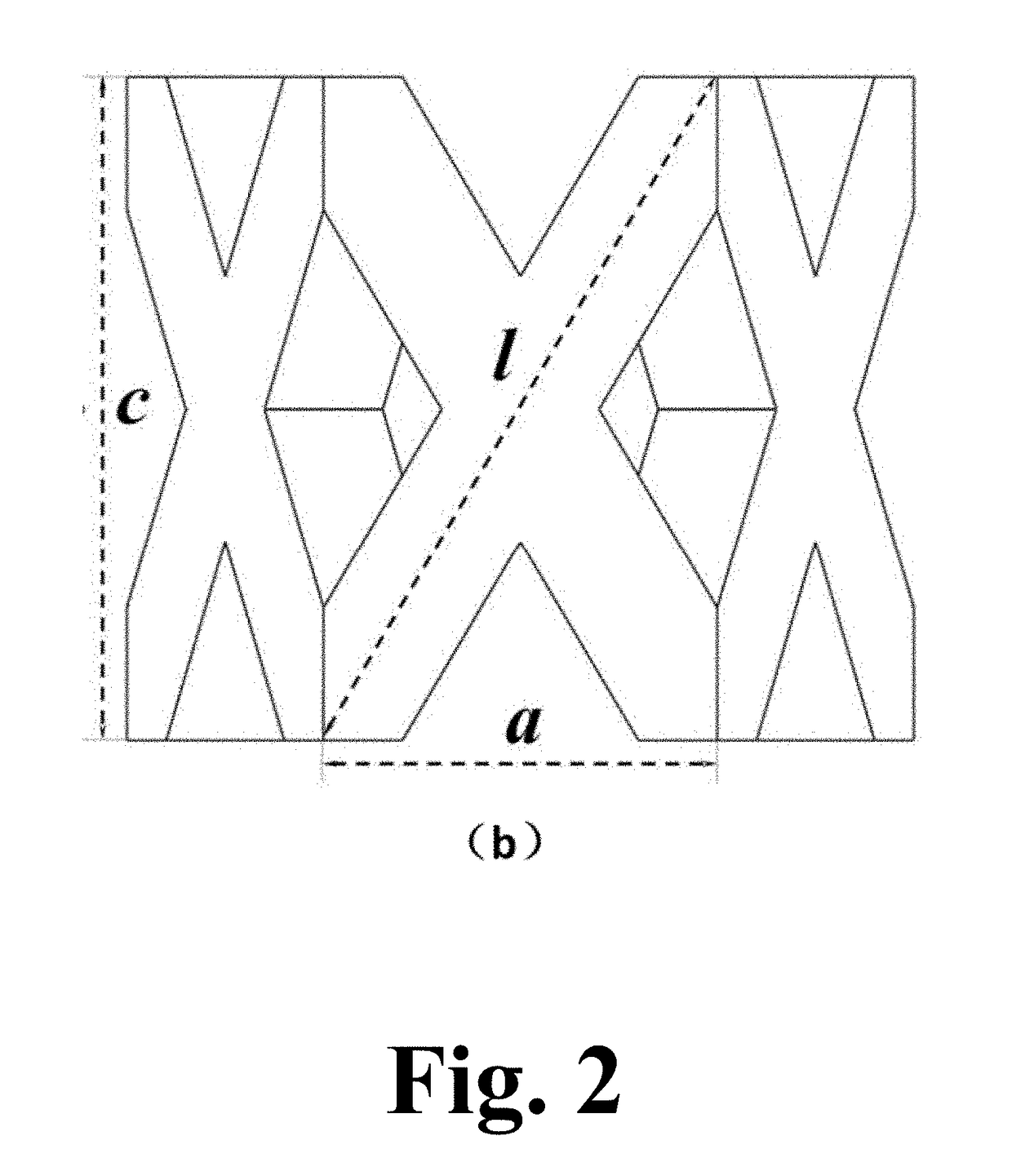
A medical implant porous scaffold structure having low modulus, wherein said structure is formed by multiple basic units superposed sequentially along the three-dimensional directions in three-dimensional space, each of the basic units is composed of a quadrangular prism or hexagonal prism having central interconnected pores encircled by four or six side walls, each of the side walls is composed by a “X-type” frame structure formed by two crossed ribs, and the central interconnected pores of the adjacent basic units arranged along the axis direction of the quadrangular prism or the hexagonal prism are interconnected to each other. The structure could not only reduce the modulus of the implant, make the modulus of the implant and strength achieve an ideal match, improve the configuration of traditional metal implants to optimize the distribution of mechanical and weaken the stress shielding effect; but also has a regular interconnected pores structure which is conducive to bone tissue in-growth, and can increase mutual locking of bone tissue and implant and shorten the recovery time of patients.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Atlantoaxial lateral mass joint fusion appliance
PendingCN110755182AAvoid damageSimple and fast operationSpinal implants3D printingJoint fusionCurative effect
The invention discloses an atlantoaxial lateral mass joint fusion appliance. The atlantoaxial lateral mass joint fusion appliance comprises a first structure of which the temperature is 20 DEG C or above and a second structure of which the temperature is 0-8 DEG C, wherein the second structure is formed by the compressing of the first structure in the same direction; when the temperature is raisedto 20 DEG C or above under the second structural state, the second structure can be restored to the first structure; and the outside outline of the first structure and the outside outline of the second structure adopt a polyhedron-shaped structure or a curved surface body-shaped structure. The atlantoaxial lateral mass joint fusion appliance disclosed by the invention is transplanted from the rear part of an atlantoaxial lateral mass joint, and during transplanting, large operation space is not needed, so that the operation is simple and convenient, damage to joints and surrounding structuresis low, the resetting effect is good, and the surgery curative effects can be notably improved.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
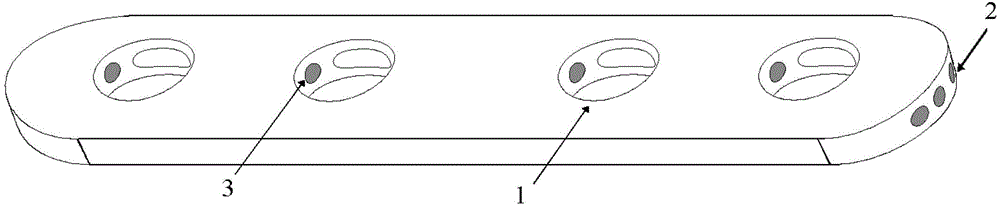
Cervical anterior fixation system and manufacturing method thereof
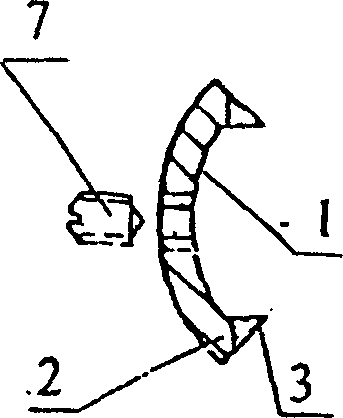
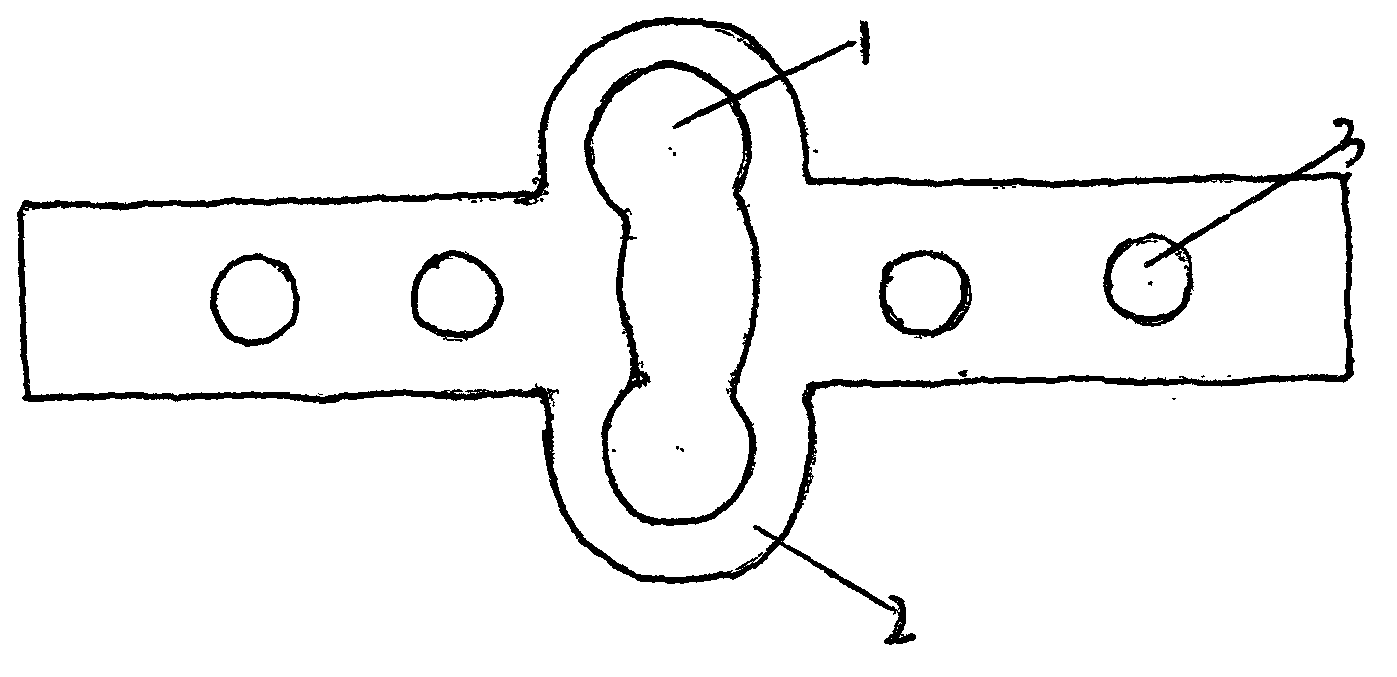
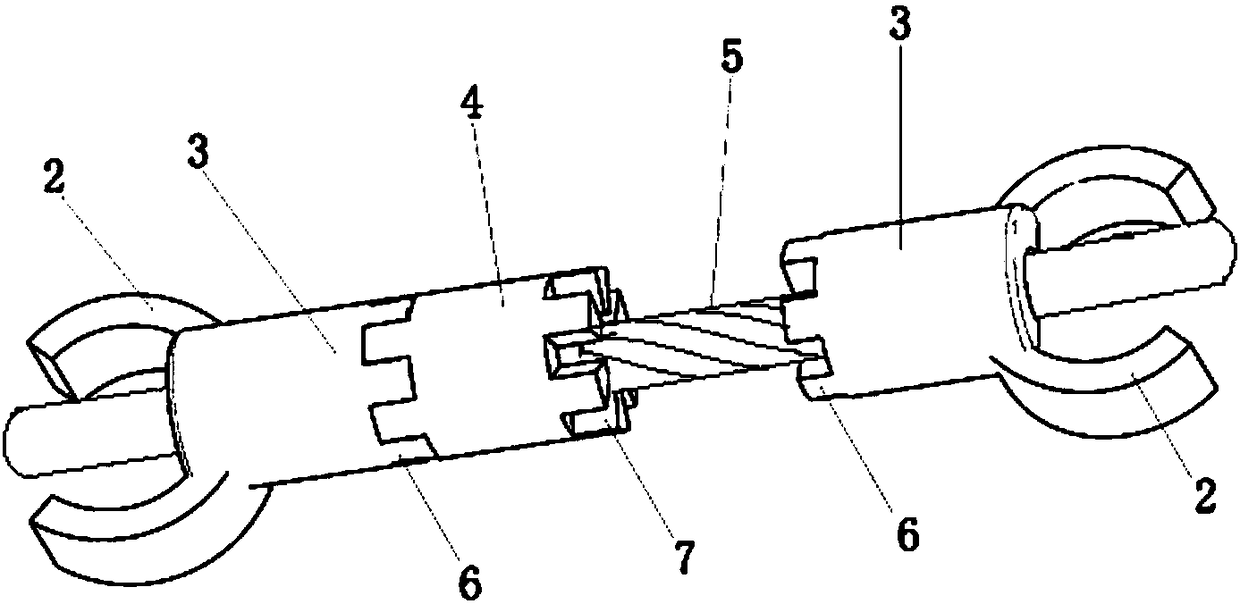
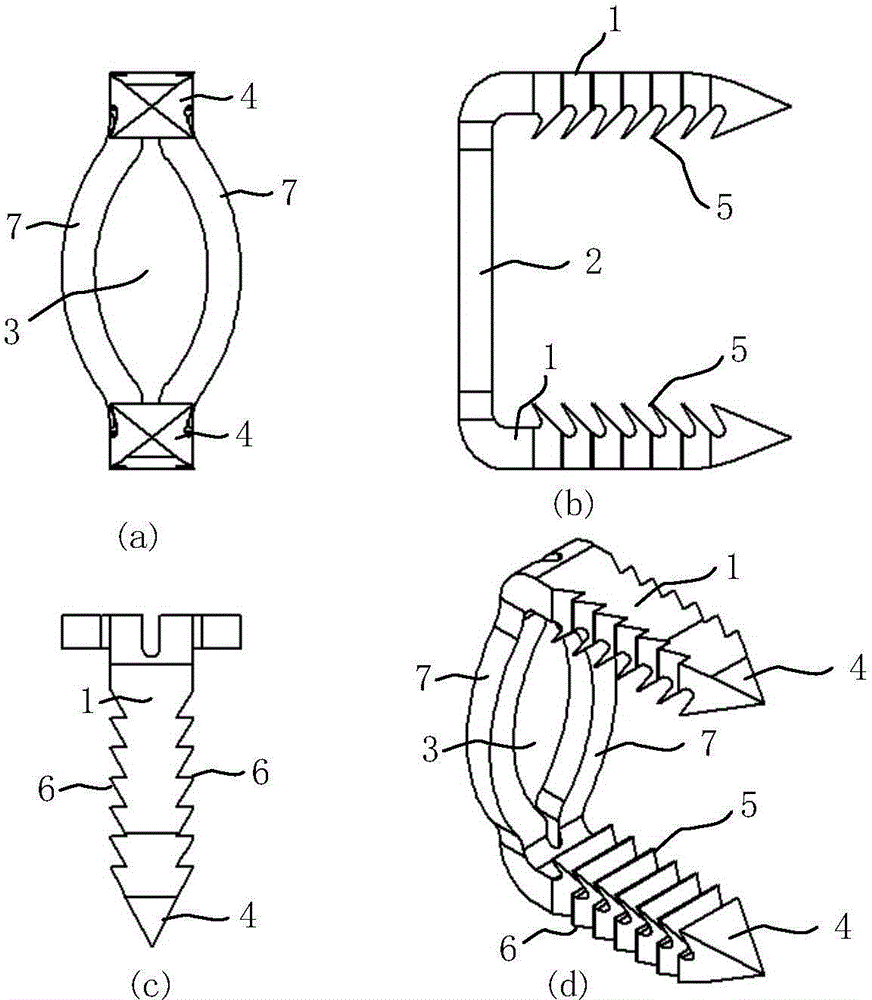
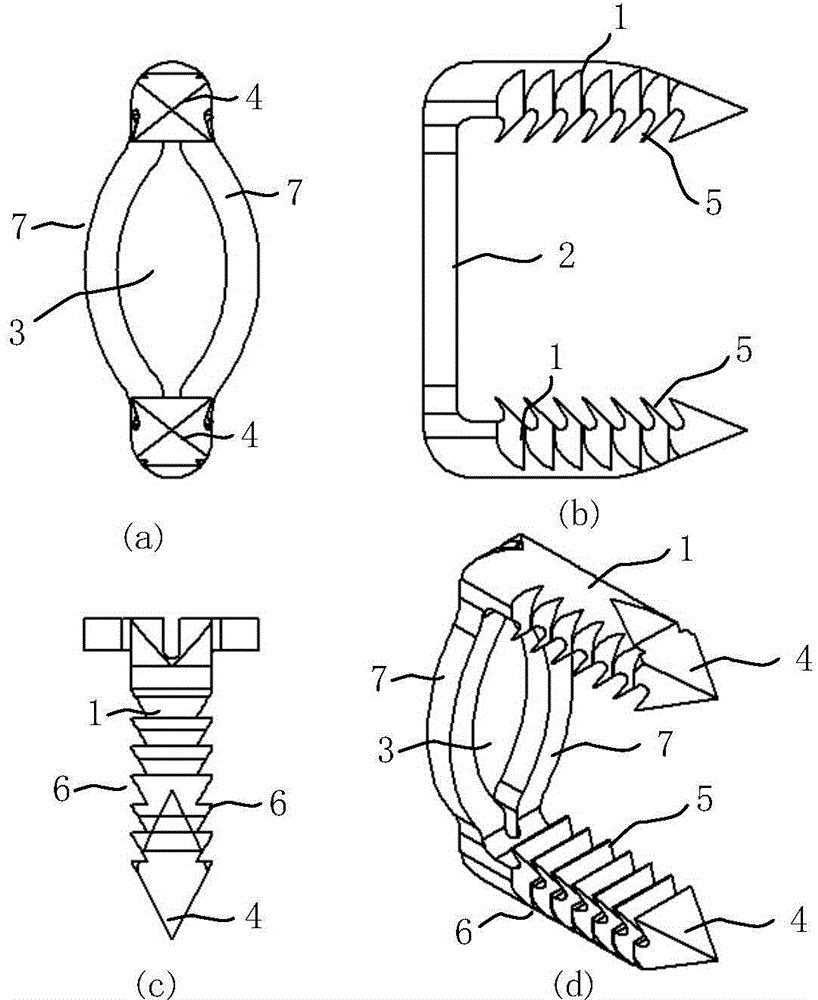
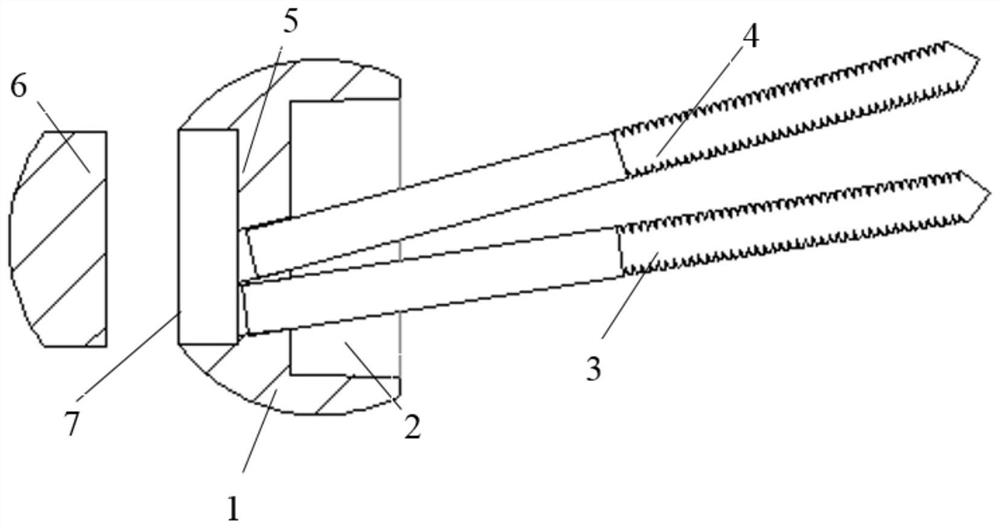
InactiveCN104939901APlay the role of pressure fixationRelieve painInternal osteosythesisSurgical staplesDistractionCervical vertebral body
An internal fixation system for the anterior cervical vertebrae and a preparation method therefor. The system comprises a pair of fixing legs (1) arranged oppositely; the ends of the pair of fixing legs (1) are connected by a legs connection rod (2); the other ends of the fixing legs (1) are conical; saw-tooth barbs (5) are arranged on the inside surface of each fixing foot (1); saw-tooth ridges (6) are arranged on two sides of each saw-tooth barb; the middle of the legs connection rod (2) is pierced to form an observation window (3). While the system exerts a distraction force to the two sides of the middle of the observation window (3) of the legs connection rod (2), the two fixing legs (1) continuously press inwards, thus achieving the effect of pressing and fixing a single segment of cervical spine; the system accords with the physiological structural features of the cervical spine, has good conformability, fastens effectively, is simple in structure and easy to put in place and adjust. The preparation method uses single-piece shaping and a degradable magnesium and magnesium alloy matched bioactivity coating, so that the degrading speed of the magnesium and magnesium alloy can be effectively controlled, and injury caused by separation of a screw from a steel plate or removal in a second operation is fully avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS
3D printing porous surface zirconium oxide dental implant and design and processing method thereof
PendingCN114010349AReduce stress shielding effectHigh mechanical strengthDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatus3d printComputer Aided Design
The invention relates to a 3D printing porous surface zirconium oxide dental implant and a design and processing method thereof. The 3D printing porous surface zirconium oxide dental implant comprises an intraosseous porous implant and a supraosseous abutment, and the porous surface implant is produced and processed by 3D printing; the porous structure of the porous surface implant is adjustable and controllable in pore shape, diameter and porosity; the 3D printing adopts a three-dimensional light curing method or a digital light processing method. The method comprises the following steps: forming a dental implant structure with high surface porosity and high core density by using a computer-aided design technology, and processing by using a 3D printing technology to obtain the porous surface zirconium oxide implant with a controllable pore structure, so that the surface design and processing of the zirconium oxide implant can be optimized, and the bone bonding performance can be improved; the individuation degree of planting restoration treatment is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY
A New Multifunctional Bone Plate and Its Application
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A biomimetic surface hip prosthesis for easy replacement
ActiveCN113397767BEasy to replaceHigh strengthJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral head prosthesisBone ingrowth
The invention relates to the technical field of medical device design, in particular to a bionic surface hip joint prosthesis that is convenient for replacement, which comprises an acetabular cup prosthesis, a femoral head prosthesis, a pressure main nail and a tension auxiliary nail, and an acetabular cup prosthesis. The inner surface of the femoral head prosthesis is a hemispherical sliding friction fit with the outer surface of the femoral head prosthesis. The contact surface between the acetabular cup prosthesis and the femoral head prosthesis and the bone is a 3D printed bone trabecular structure. A head groove and a tail groove are formed in the femoral head prosthesis, and a spherical cover is installed at the head groove. The rear ends of the pressure main nail and the tension auxiliary nail are respectively provided with external threads, and the front ends of the pressure main nail and the tension auxiliary nail are respectively connected to the partitions respectively. The device provided by the invention has simple structure, convenient replacement, low cost, low friction coefficient and metal ion precipitation, good long-term bone ingrowth performance and can reconstruct the physiological fulcrum of the hip joint.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
femoral head support prosthesis
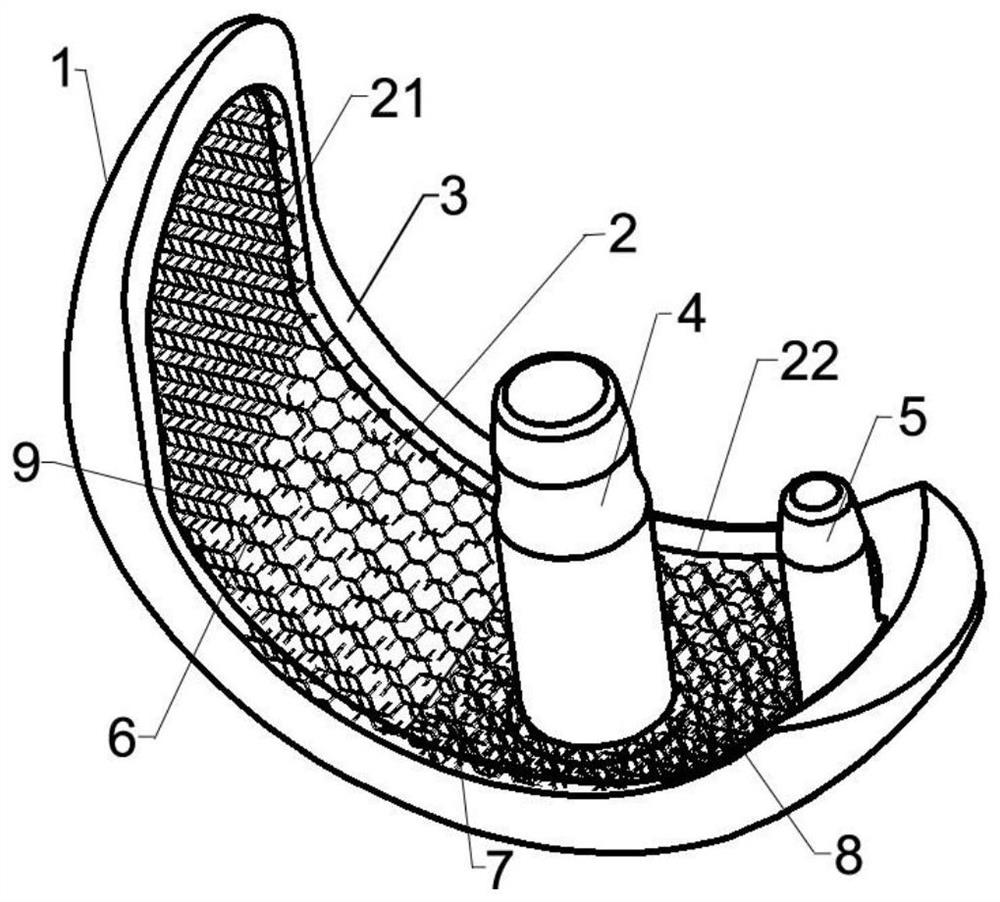
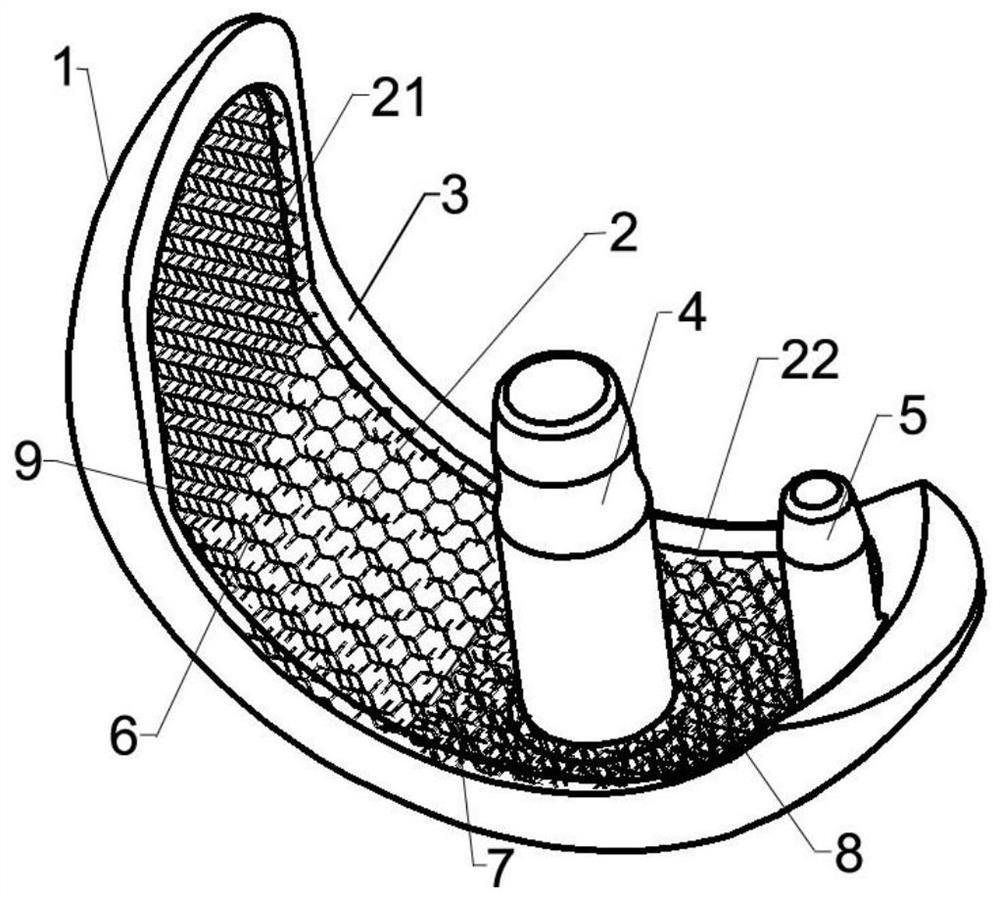
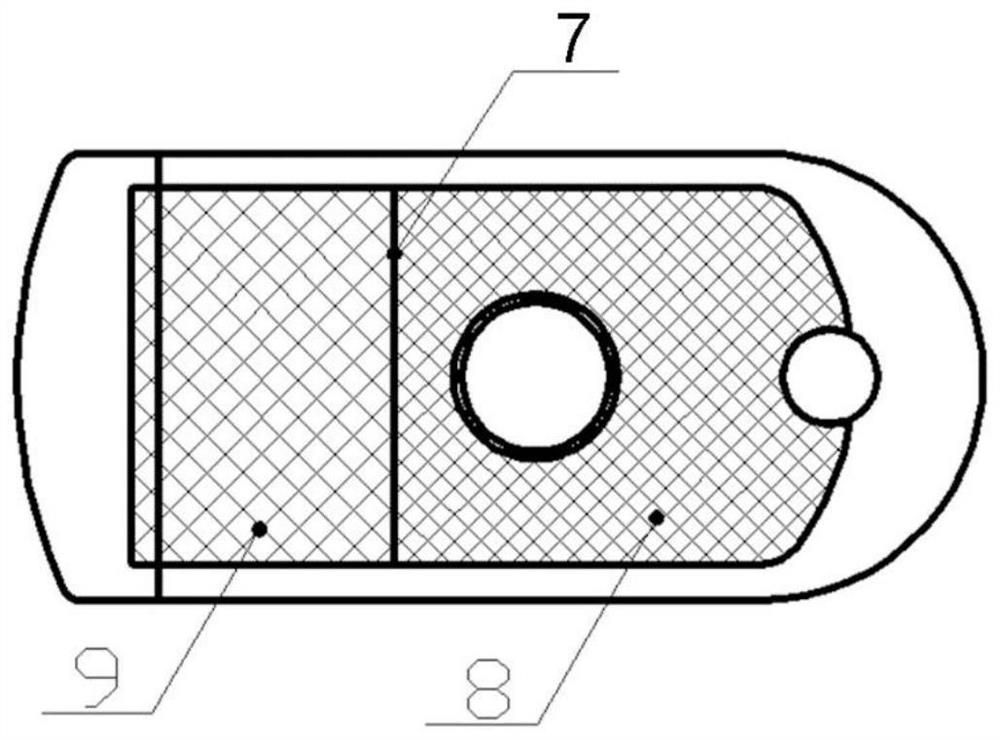
ActiveCN112773573BImprove mechanical propertiesImprove support strengthJoint implantsFemurRight femoral headStress shielding
The invention provides a femoral head internal support prosthesis, comprising: a tubular porous outer layer with an inner cavity; a reinforcing beam arranged on the inner wall of the tubular porous outer layer, the reinforcing beam includes a head and a main body, and the head includes an elastic The deformation section; the operating part is arranged at the end of the tubular porous outer layer; the fastening structure is arranged on the outer wall of the tubular porous outer layer. The technical solution of the present application effectively solves the problem in the related art that bone loss of the femoral head is prone to occur due to the stress shielding effect produced by the prosthesis.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
A kind of preparation method of double-layer structure bone screw
ActiveCN108052774BSolve the problem of mechanical property mismatchReduce stress shielding effectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOsteoporotic boneBone lesion
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com